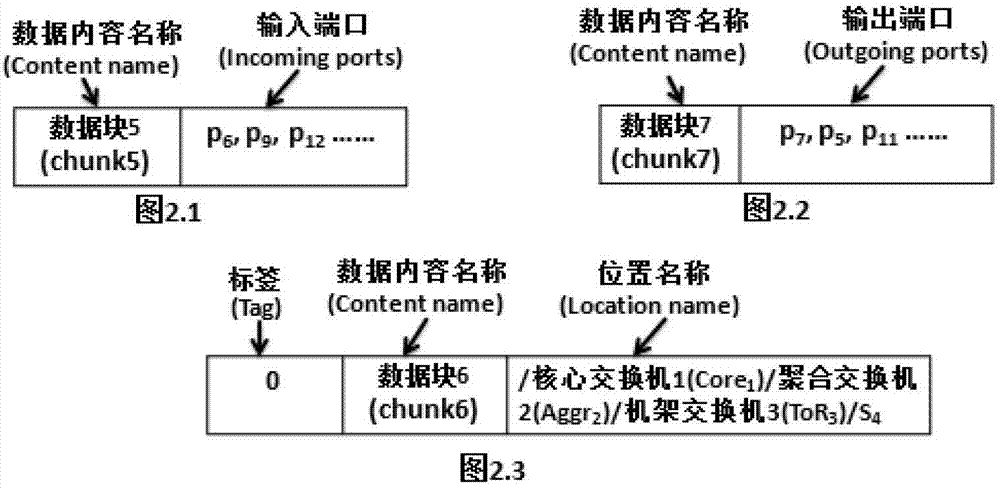
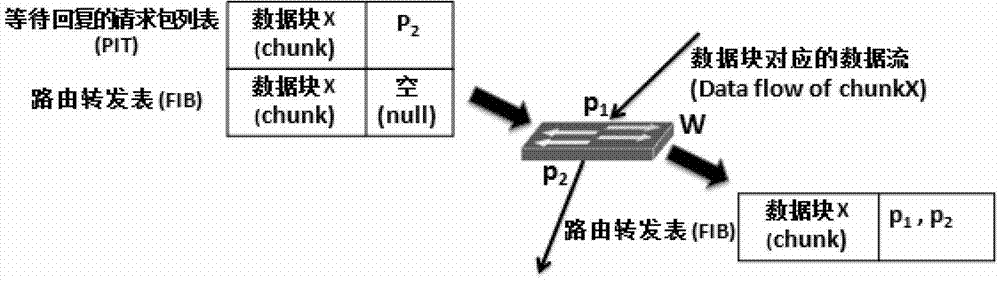
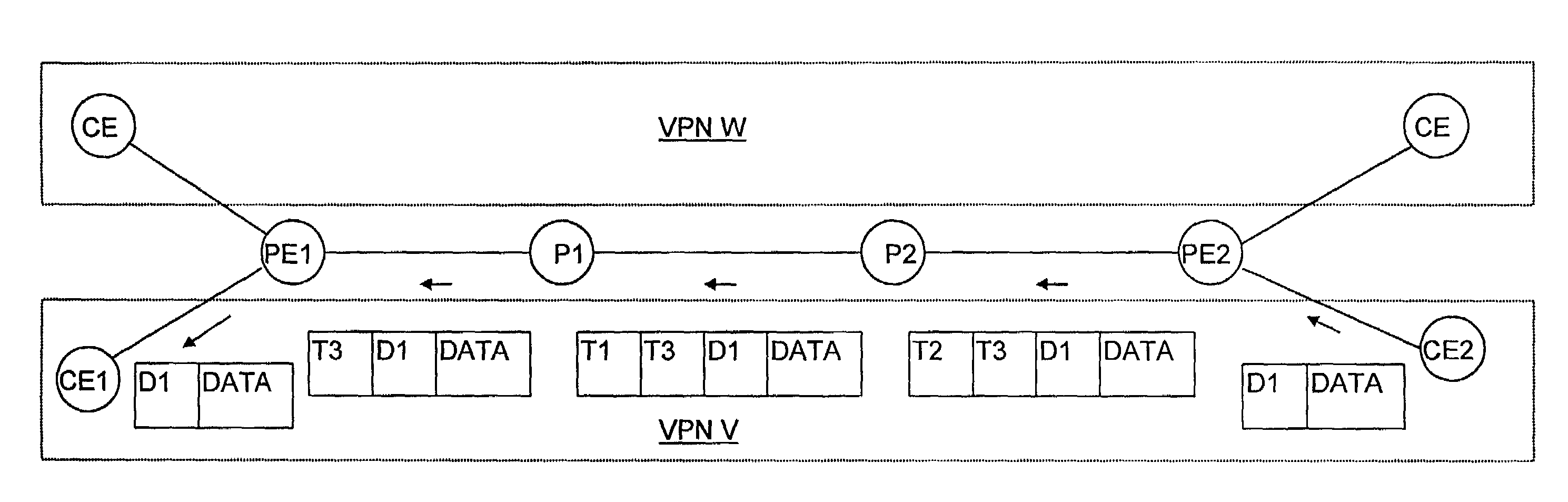
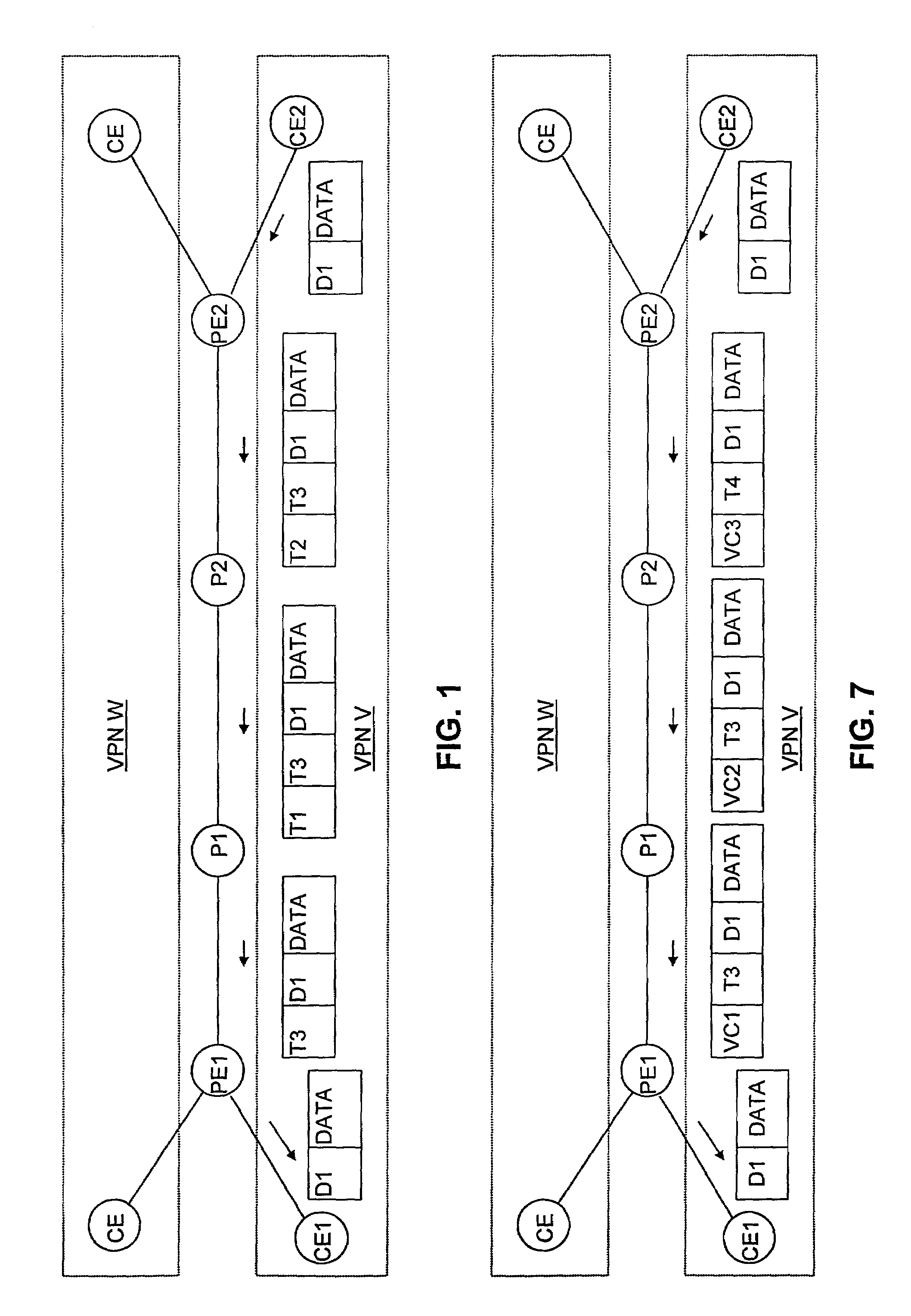
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
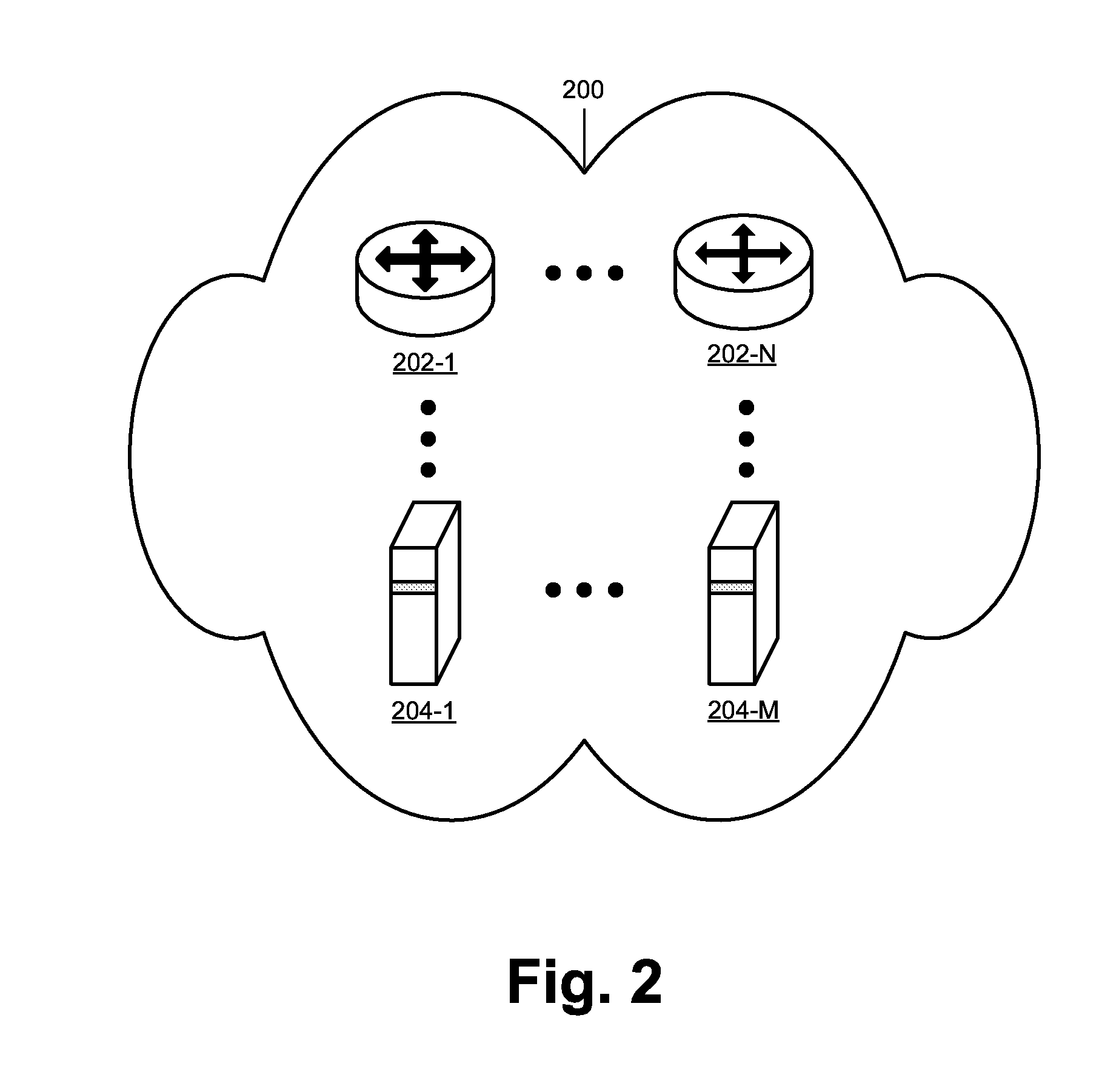
199 results about "Forwarding information base" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
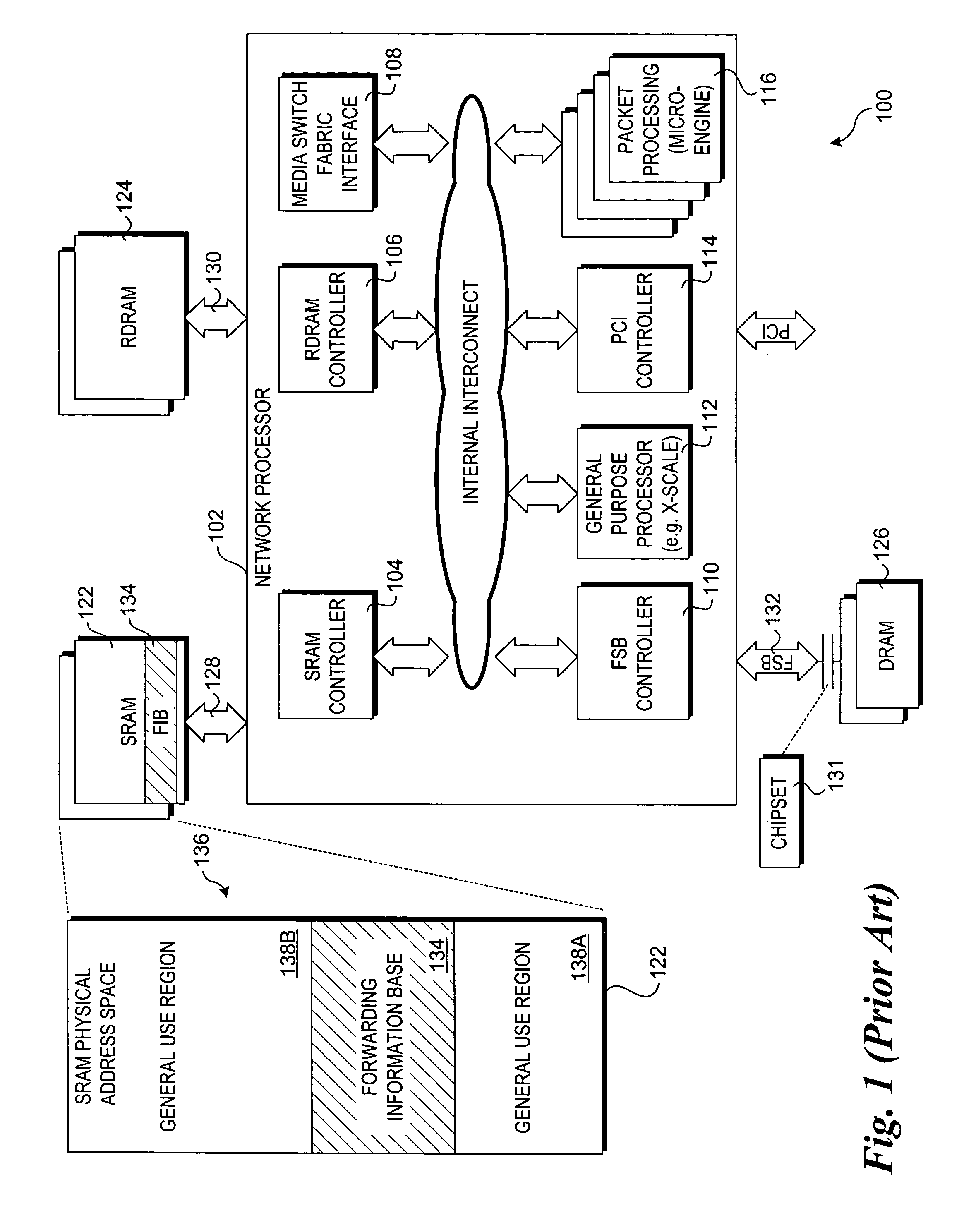
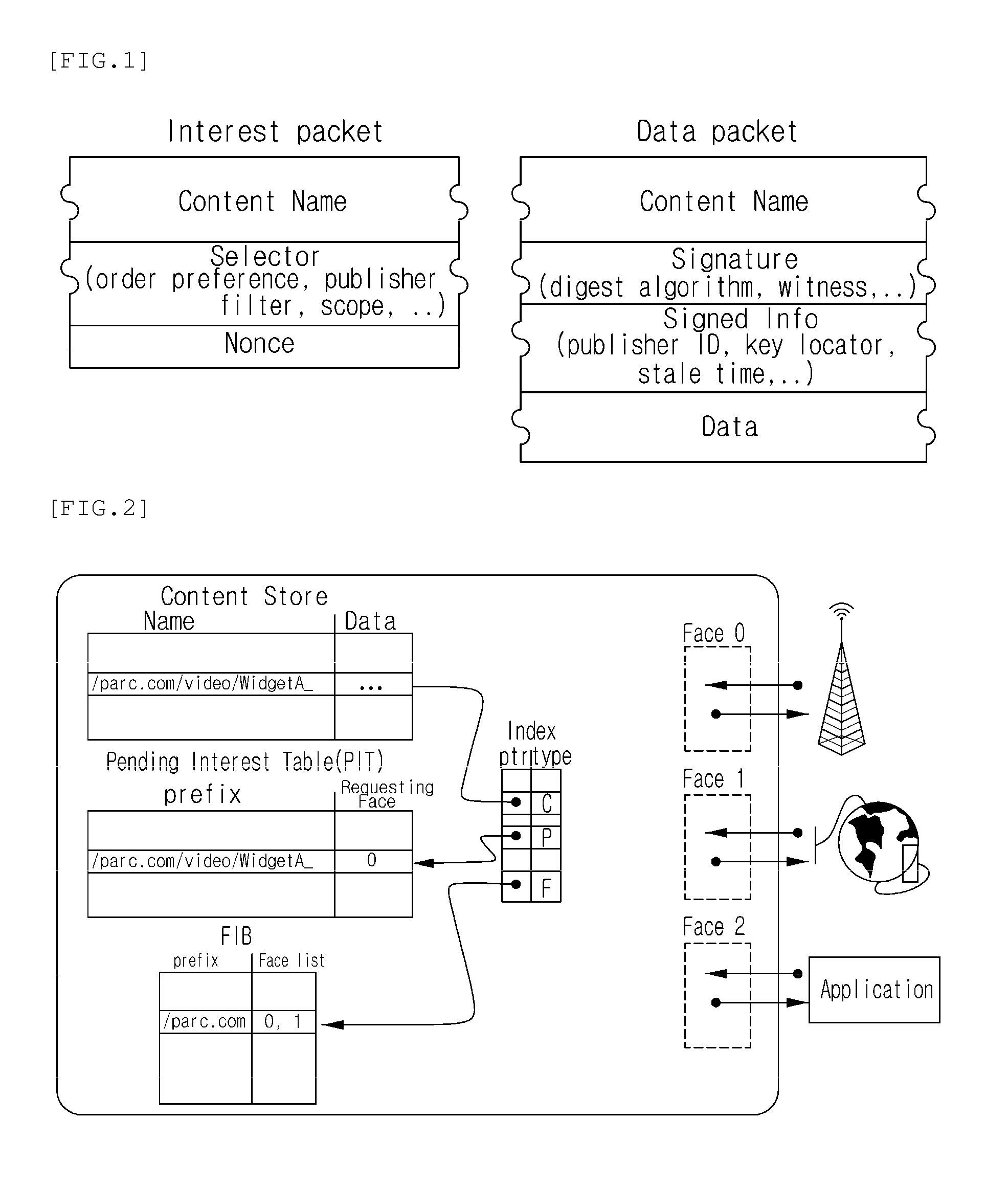
A forwarding information base (FIB), also known as a forwarding table or MAC table, is most commonly used in network bridging, routing, and similar functions to find the proper output network interface to which the input interface should forward a packet. It is a dynamic table that maps MAC addresses to ports. It is the essential mechanism that separates network switches from Ethernet hubs. Content-addressable memory (CAM) is typically used to efficiently implement the FIB, thus it is sometimes called a CAM table.
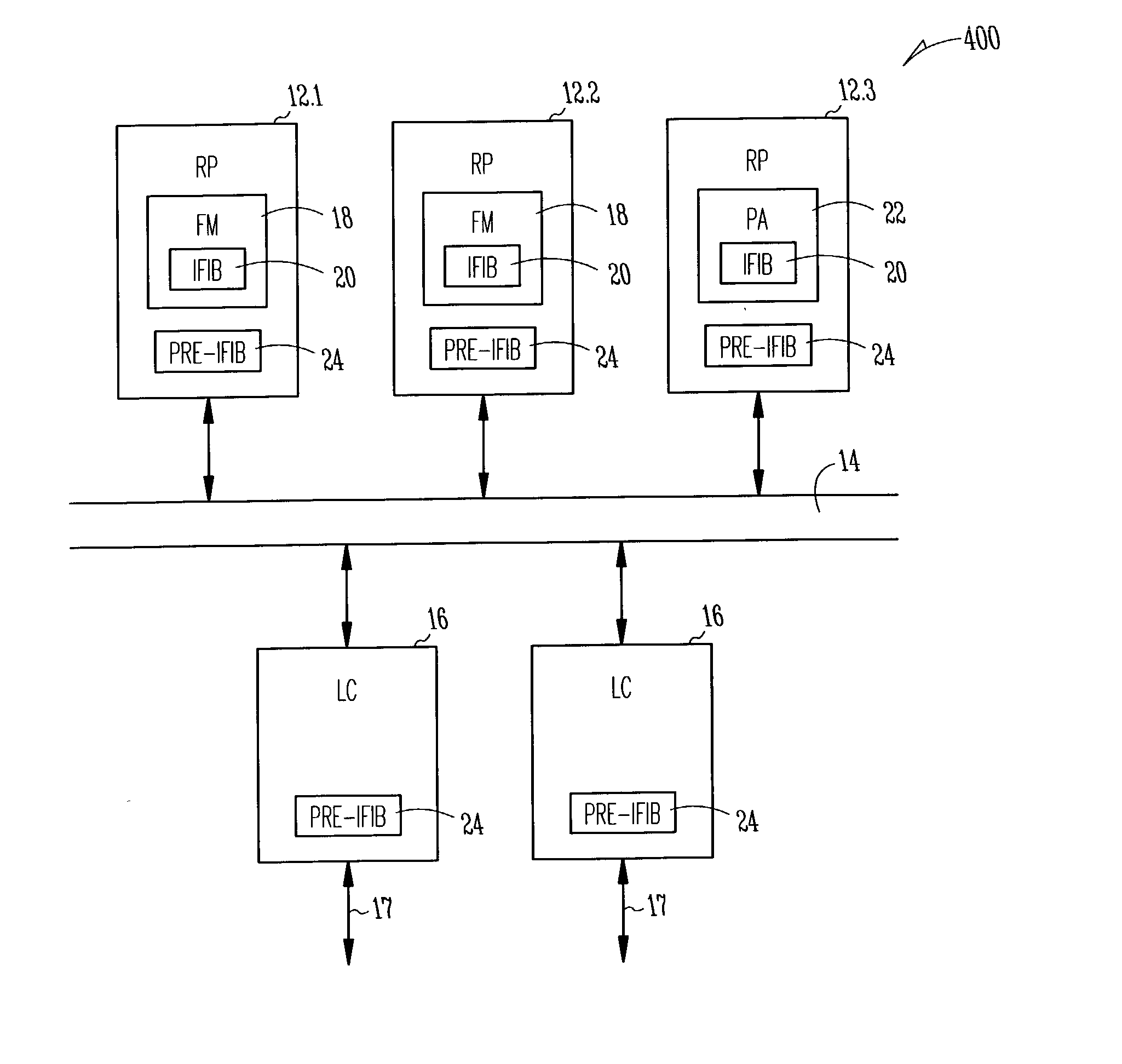
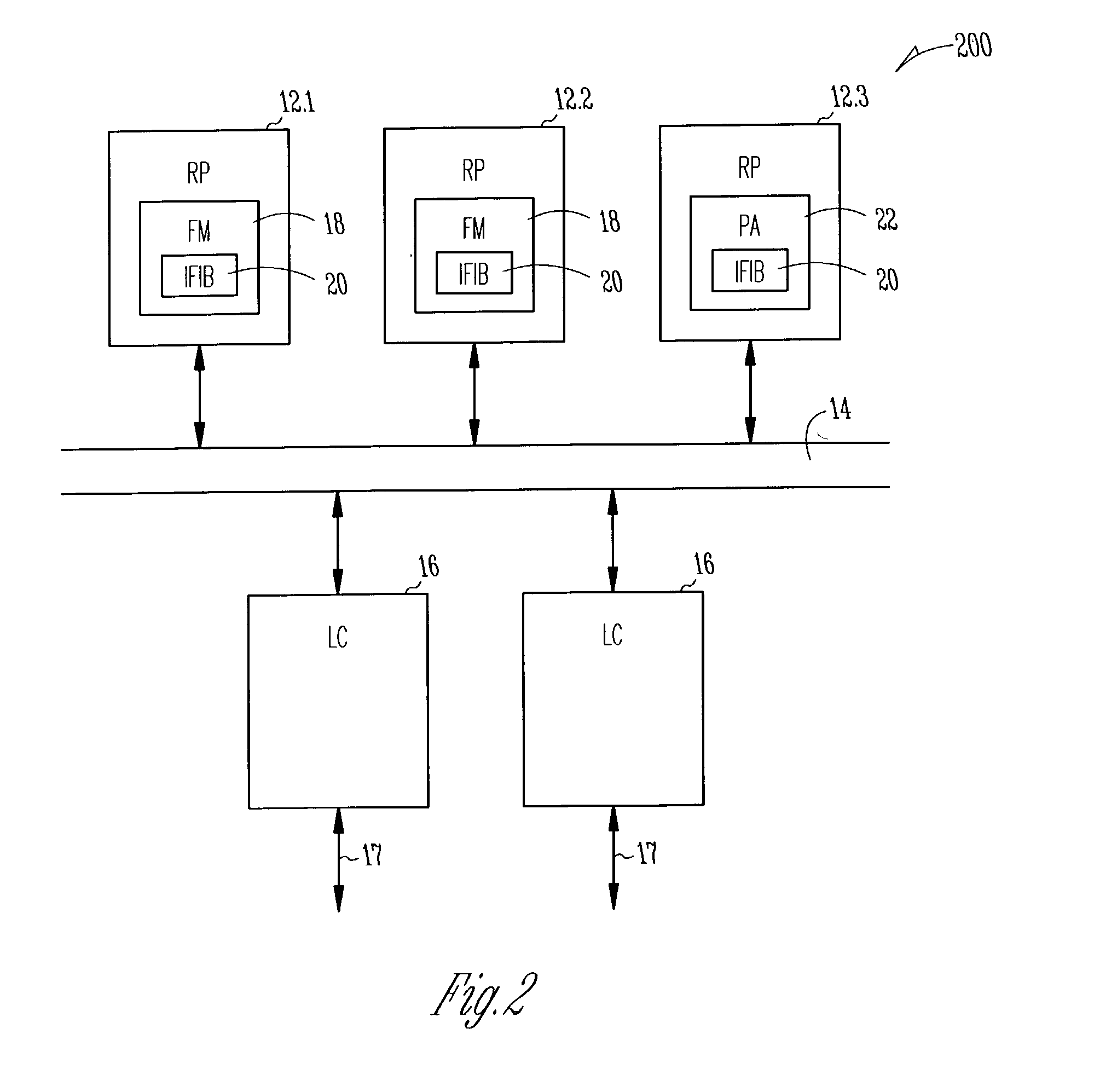
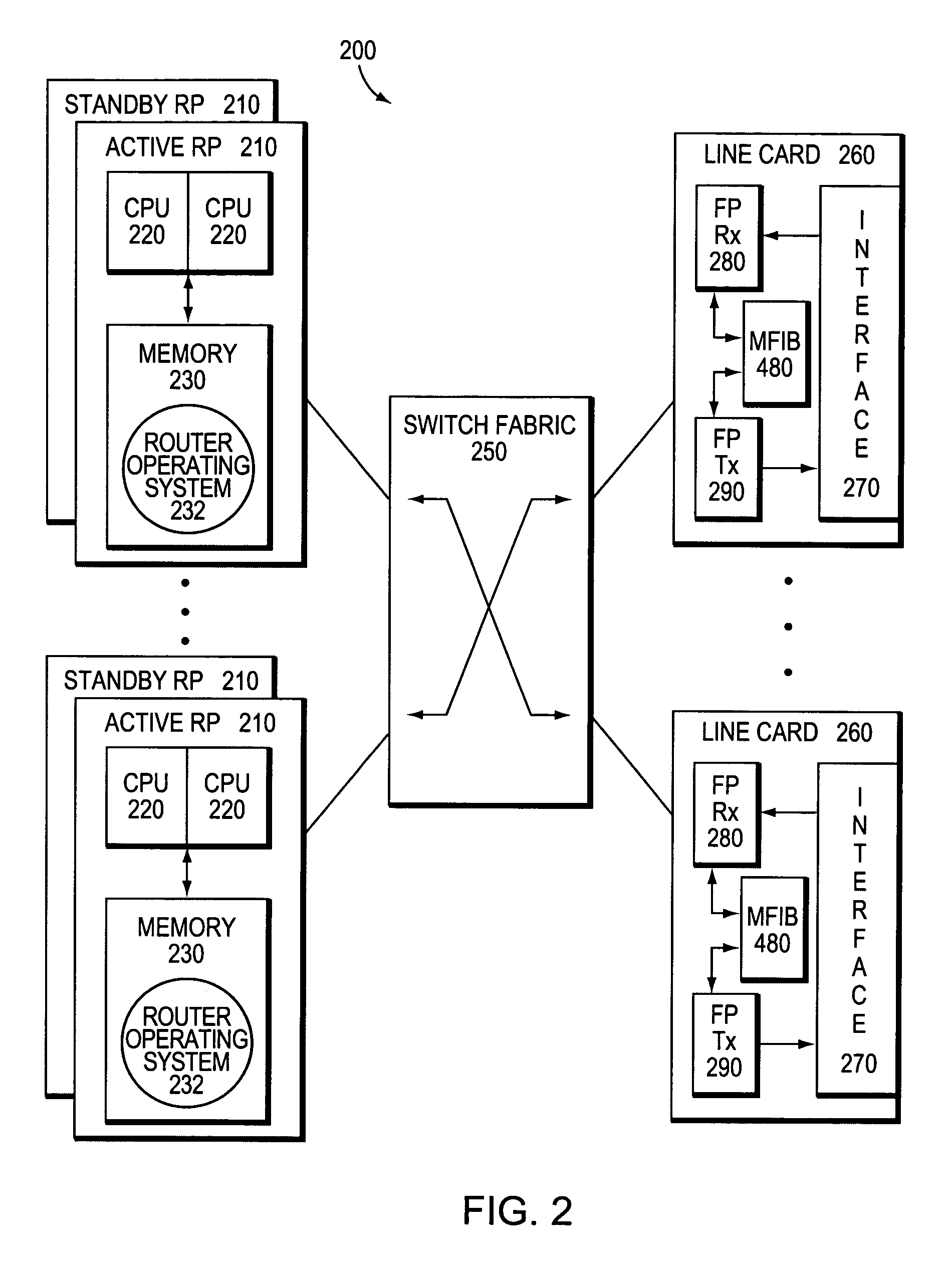
System and method for local packet transport services within distributed routers
A system and method for routing packets within a router having a plurality of loosely-coupled route processors, including a first route processor, and a line card operably coupled to the plurality of distributed-route-processors. Each route processor includes an internal forwarding information base (IFIB). Each IFIB includes information that is used to route packets addressed to elements within the router.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
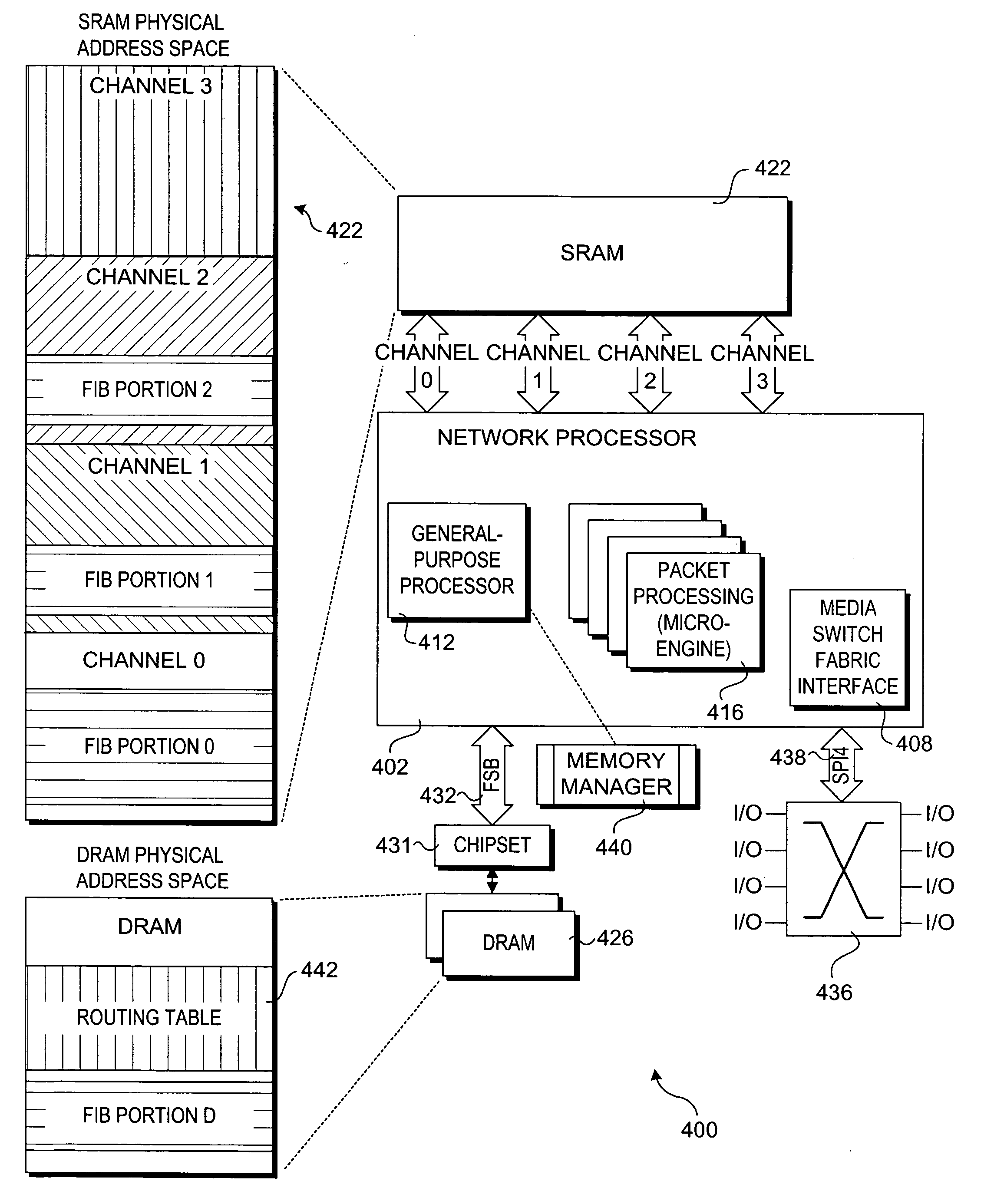
Method to improve forwarding information base lookup performance
InactiveUS20050259672A1Multiprogramming arrangementsData switching by path configurationInformation repositoryDepth level
A method and apparatus for improving forwarding information base (FIB) lookup performance. An FIB is partitioned into a multiple portions that are distributed across segments of a multi-channel SRAM store to form a distributed FIB that is accessible to a network processor. Primary entries corresponding to a linked list of FIB entries are stored in a designated FIB portion. Secondary FIB entries are stored in other FIB portions (a portion of the secondary FIB entries may also be stored in the designated primary entry portion), enabling multiple FIB entries to be concurrently accessed via respective channels. A portion of the secondary FIB entries may also be stored in a secondary (e.g., DRAM) store. A depth level threshold is set to limit the number of accesses to a linked list of FIB entries by a network processor micro-engine thread, wherein an access depth that would exceed the threshold generates an exception that is handled by a separate execution thread to maintain line-rate throughput.
Owner:INTEL CORP
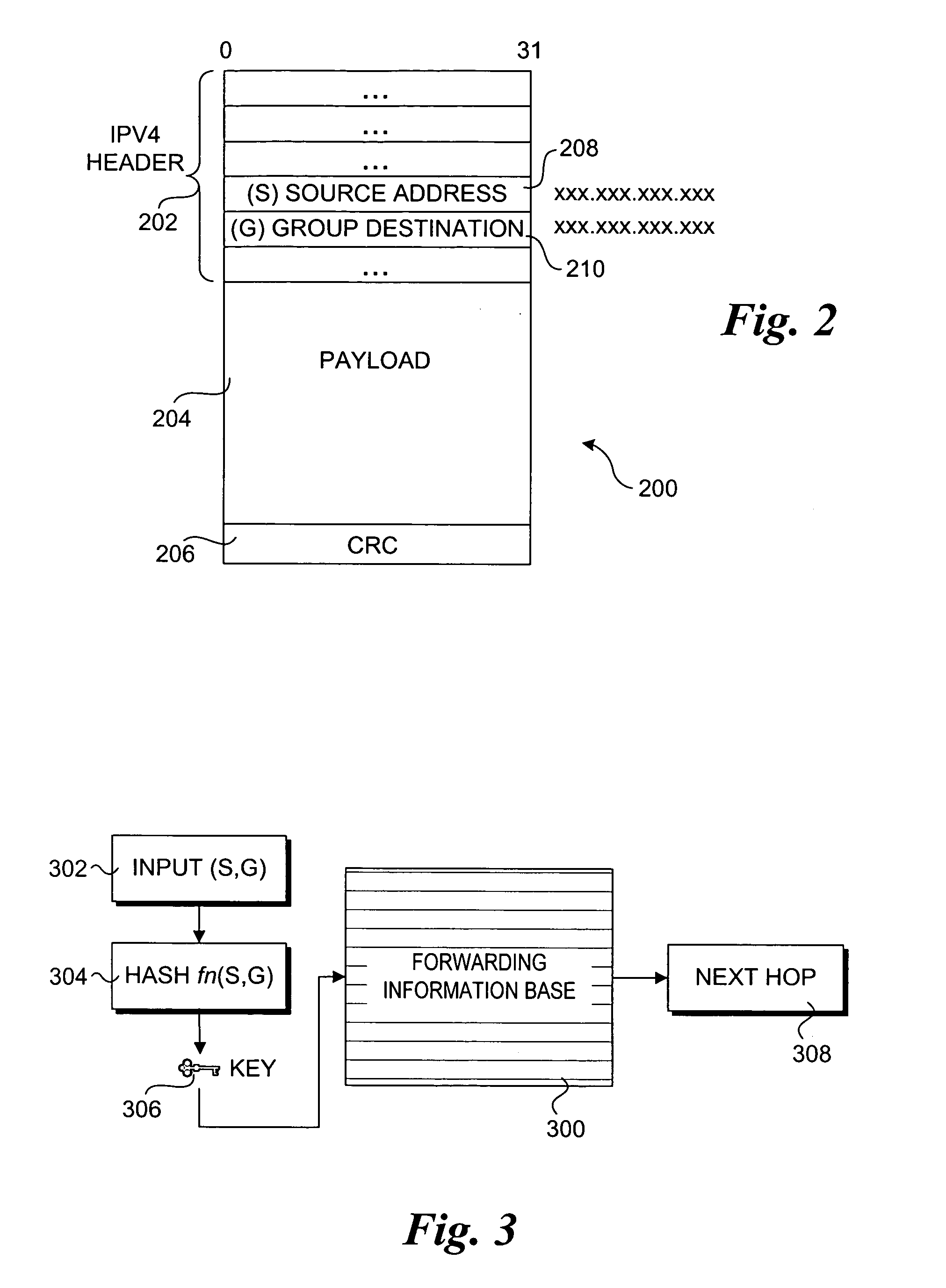
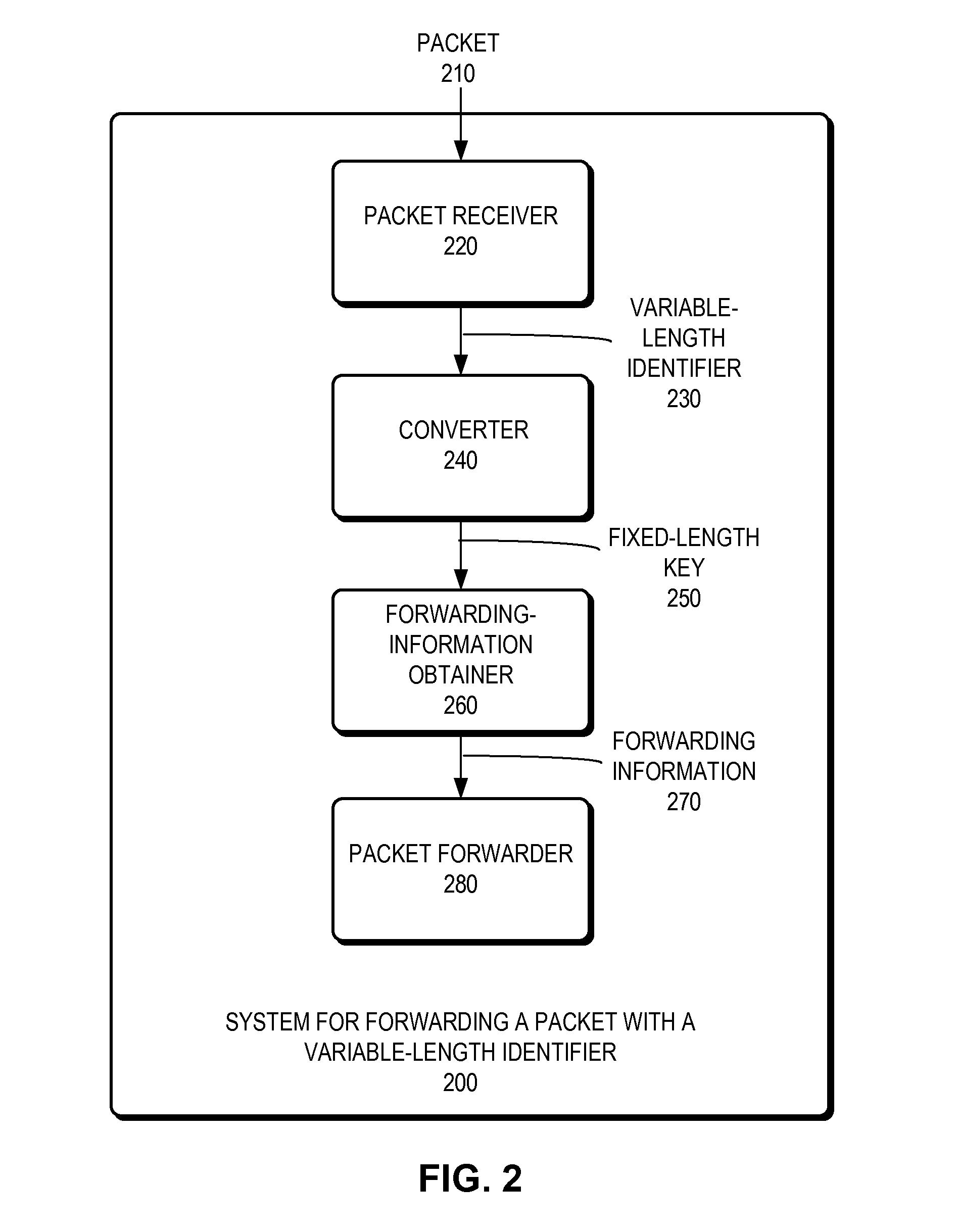
System for forwarding a packet with a hierarchically structured variable-length identifier
ActiveUS8160069B2Data switching by path configurationStructure of Management InformationLongest prefix match
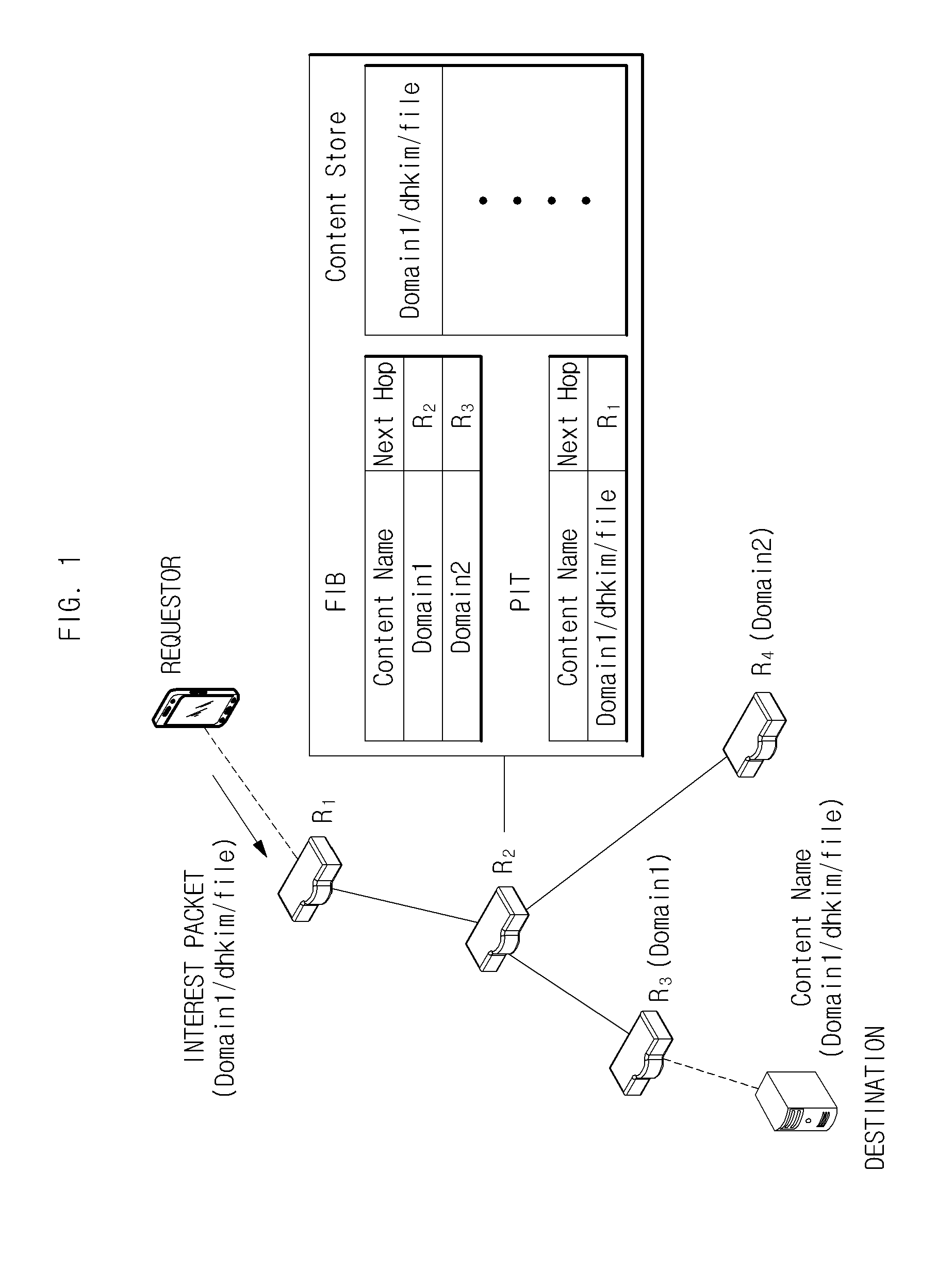
One embodiment provides a system that receives a packet with a hierarchically structured variable-length identifier (HSVLI). An HSVLI indicates a piece or collection of content and may be hierarchically structured, comprising contiguous components ordered from a most general level to a most specific level. The length of a respective identifier is not fixed. During operation, the system converts the HSVLI into a fixed-length key. Subsequently, the system obtains forwarding information based on one or more longest-prefix matches with a longest-prefix-match lookup engine using the fixed-length key. Next, the system forwards the packet to an output port based on the forwarding information.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for distributing routing instructions over multiple interfaces of a data router
InactiveUS20020126671A1Special service provision for substationError preventionCommunication interfaceInformation repository
A software application in a multi-processor data router in which a forwarding information base for the router is maintained is provided with a server module and one or more client modules, each client module associated with one or more communication interfaces of the data router. The application is characterized in that the server module sends to each client module only that portion of the forwarding information base specific to the communication interfaces associated with the client module.
Owner:PLURIS
Routing method in content-centric network
InactiveUS20130111063A1Avoid network bottlenecksFlexibly solving network congestionDigital computer detailsData switching by path configurationInformation repositoryTraffic capacity
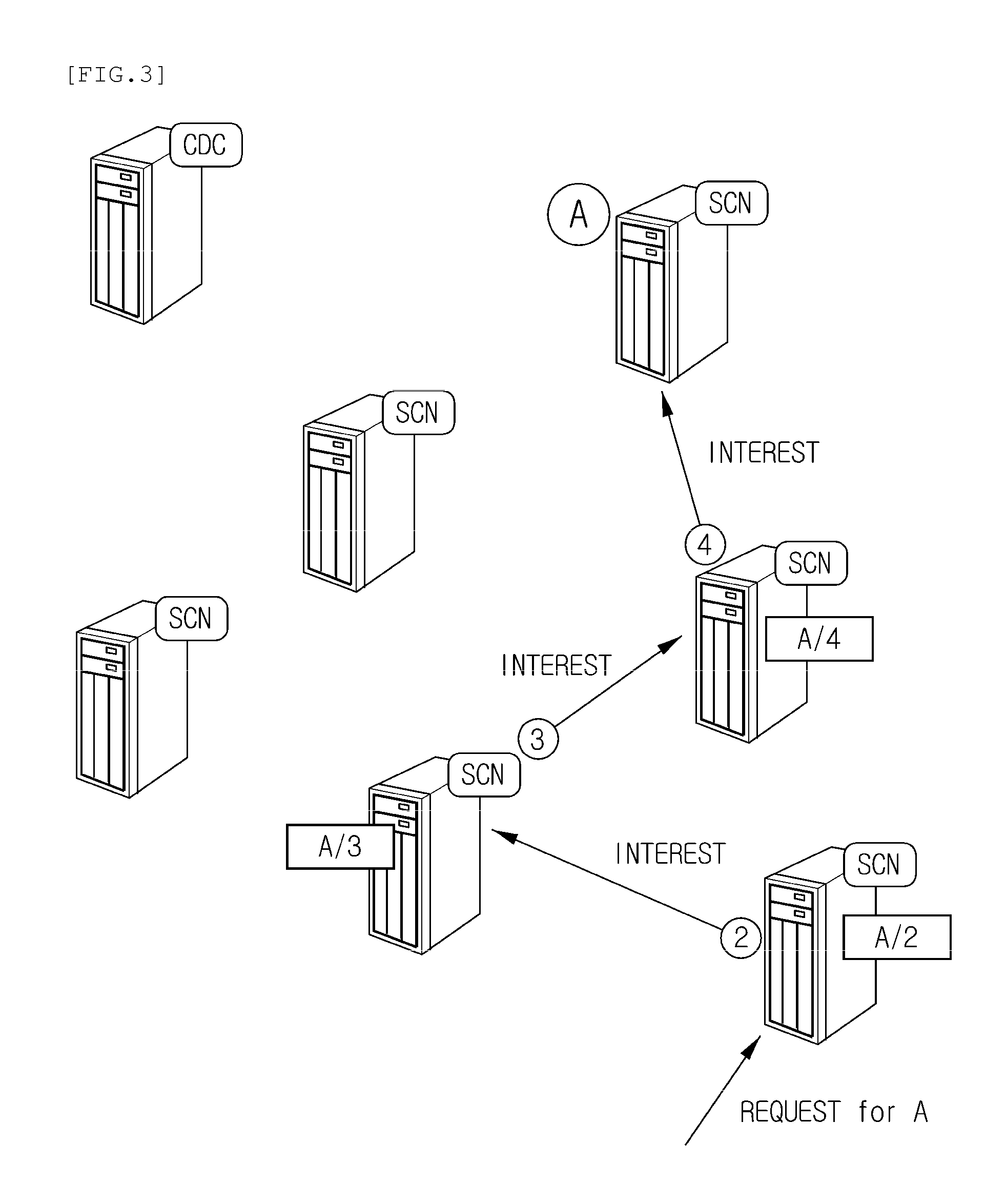
Disclosed is a centralized controlling method of the process of delivering a routing packet for content transmission in a content-centric network (CCN). The routing method in a content centric network according to the present invention includes: a content distribution controller in the content centric network receiving a request for specific-content distribution from a user, determining locations of routers storing the content, and finding one of the routers to which the request from the user will be transmitted; and the content distribution controller finding an optimal path in consideration of a traffic distribution status and then transmitting a forwarding information base (FIB) to routers included in the optimal path.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
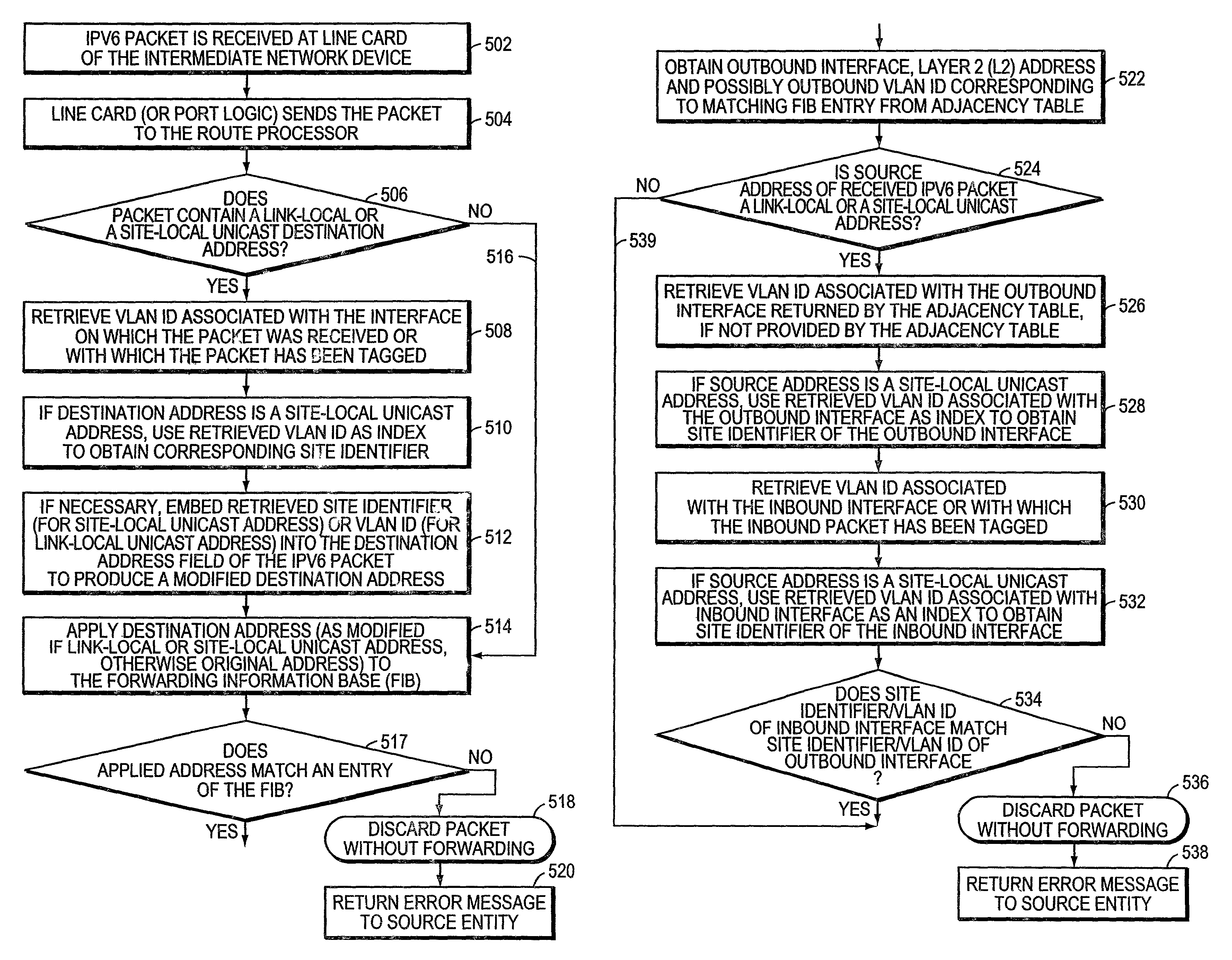
System and method for deriving IPv6 scope identifiers and for mapping the identifiers into IPv6 addresses
InactiveUS7095738B1Efficient and high-speedSpecial service provision for substationDigital computer detailsInformation repositoryVirtual LAN
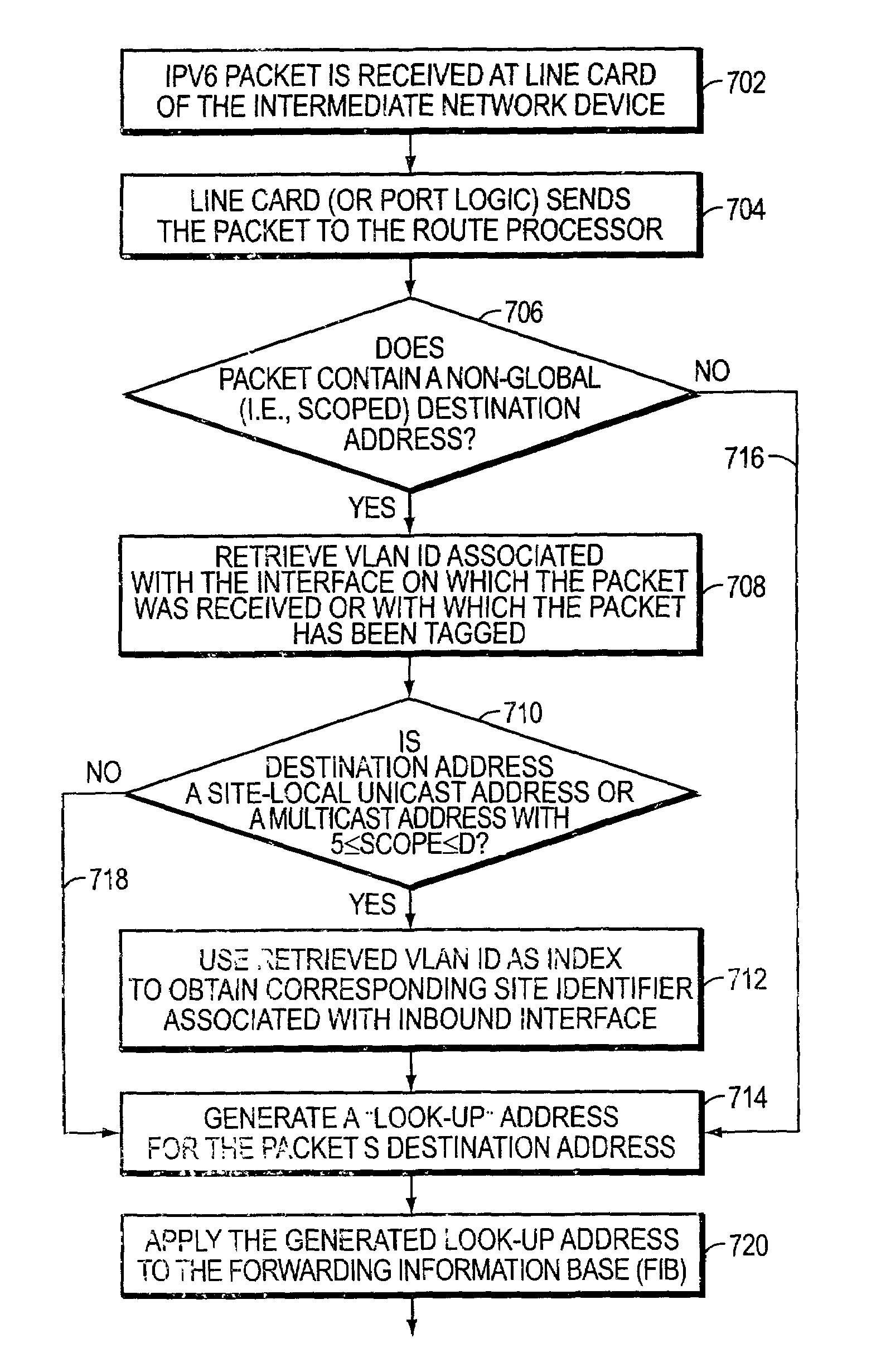
A system and method for use at an intermediate network device employs Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) designations as Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) link identifiers, and maps VLAN designations to IPv6 site identifiers (IDs). The system also generates a compacted look-up address based on the destination address specified within a received network message, such as an IPv6 packet. For a network message having a link-local unicast destination address, the VLAN ID associated with the port on which the message was received is encoded within the corresponding look-up address. For a network message having a site-local unicast address, the VLAN ID associated with the port on which the message was received is used to derive a site ID which is then encoded within the corresponding look-up address. For a network message having a multicast destination address, if the address's scope value is between hexadecimal “2” and “4” inclusive, the VLAN ID associated with the port on which the message was received is encoded within the corresponding look-up address. If the scope value is between hexadecimal “5” and “D”, inclusive, the VLAN ID associated with the port on which the message was received is used to derive a site ID which is then encoded within the corresponding look-up address. The look-up addresses are applied to a forwarding information base (FIB) to derive the outbound interface(s) from which the message is to be forwarded.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
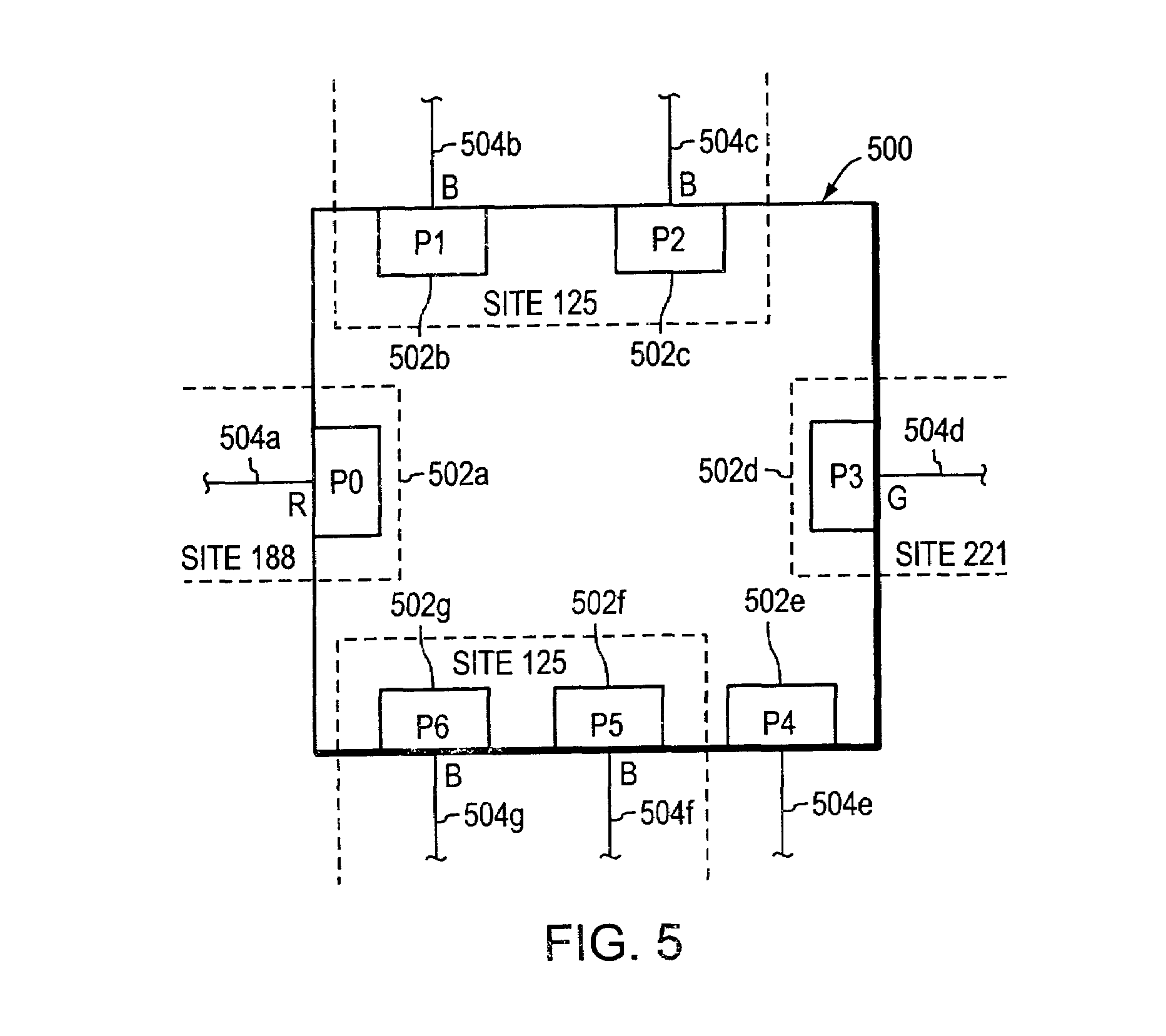
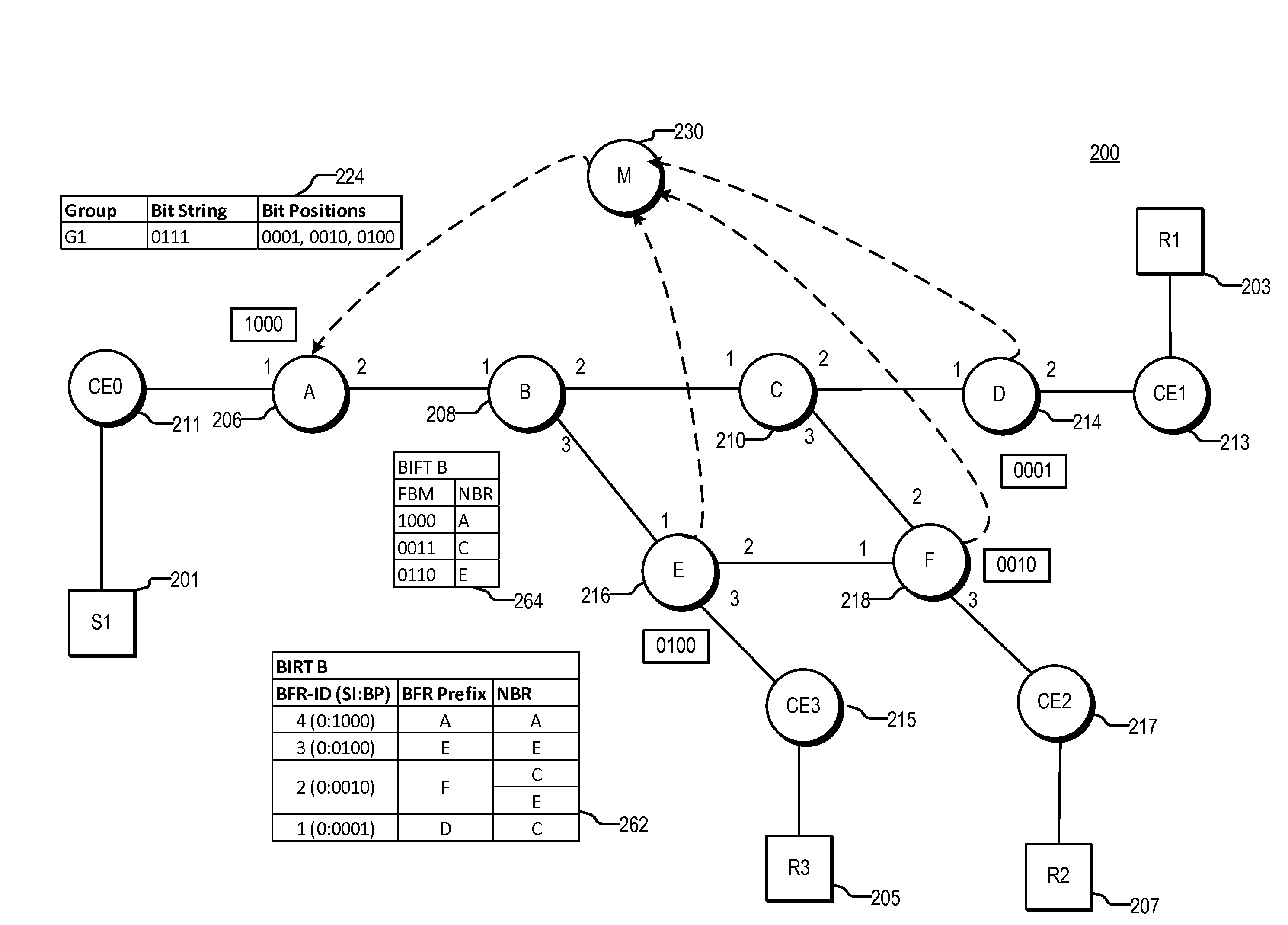
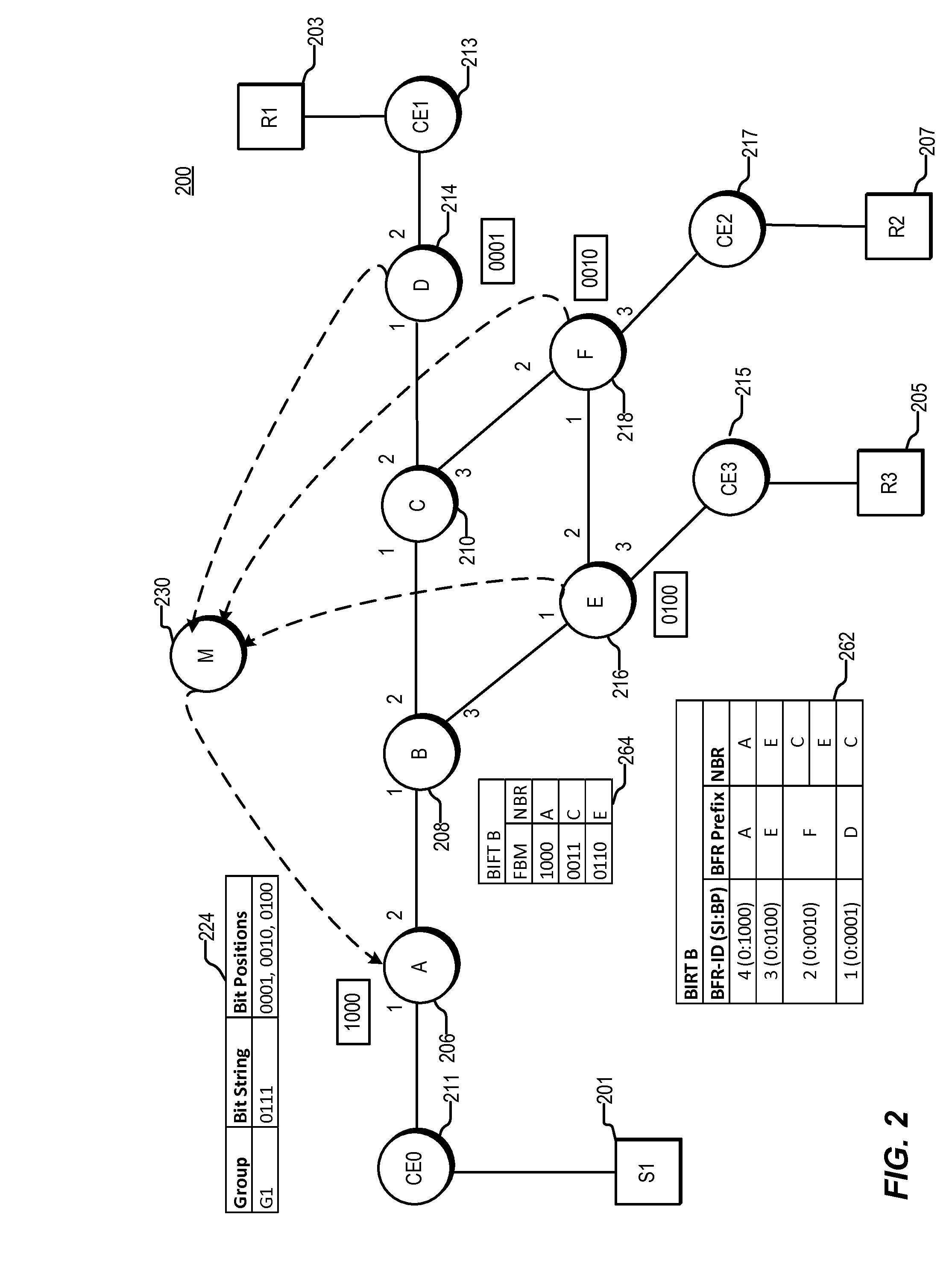
Equal Cost Multi-path With Bit Indexed Explicit Replication
ActiveUS20150131658A1Special service provision for substationData switching by path configurationMulti pathDistributed computing
Various systems and methods for performing bit indexed explicit replication (BIER). For example, one method involves receiving a packet at a node. The packet includes a bit string. The node selects forwarding information based on a flow value associated with the packet. The forwarding information includes a forwarding bit mask. The node then forwards the packet based on the bit string and the forwarding information.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
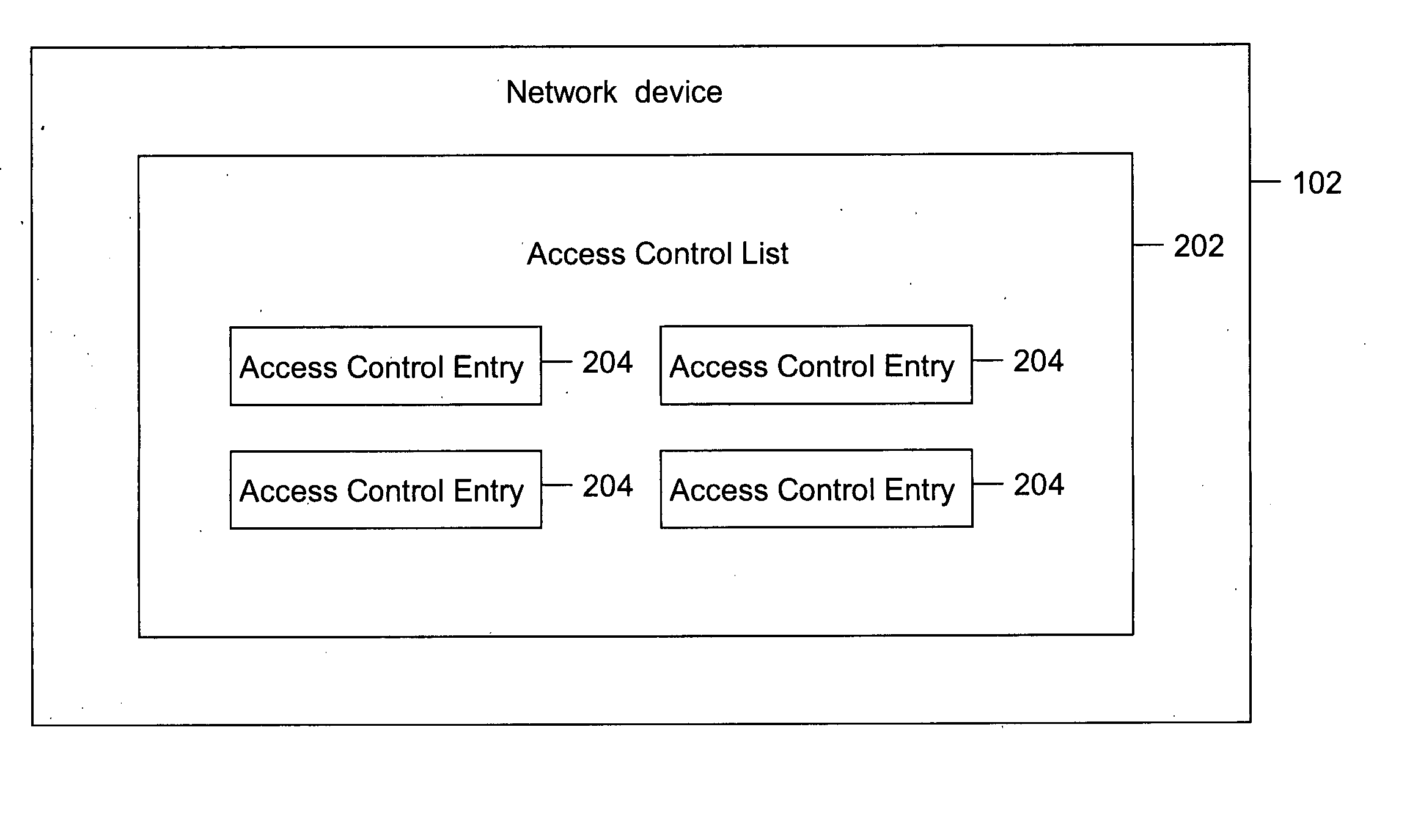
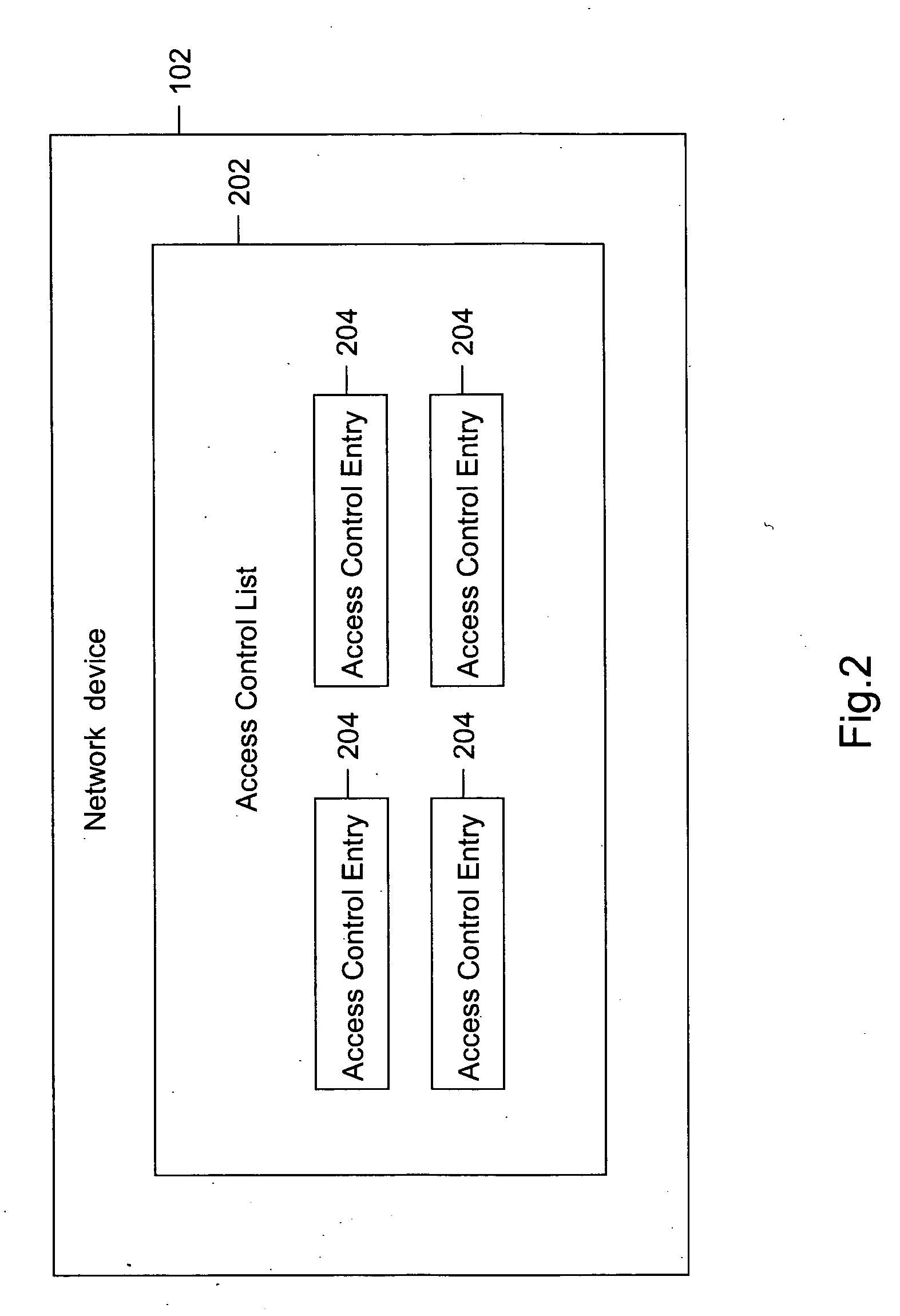
Method and system for removing dead access control entries (ACEs)
ActiveUS20070223487A1Improve manageabilitySave processing timeData switching by path configurationInformation repositoryTime limit
Methods and systems have been provided for removing dead Access Control Entries (ACEs) in an Access Control List (ACL). In one embodiment, the dead ACEs can be detected for an egress as well as an ingress ACL. The ACEs that have a hit count above a user-specified hit count are checked for their validity. The validity of the ACE is checked, using the information based on a Forwarding Information Base (FIB). If an ACE is found to be invalid, it is considered dead. The dead ACEs are referred as candidates for removal from the ACL. If the ACE is found to be a candidate for removal, a system administrator can either warn the network administrator about the candidate for removal or delete the ACE from the ACL after a pre-defined time limit.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
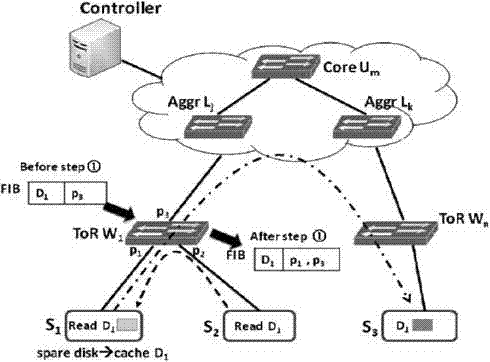
Data transmission method of content-centric datacenter network
InactiveCN103179037AMultiple available bandwidthImprove throughputData switching networksExtensibilityContent centric
The invention belongs to a content data network technology, and discloses a data transmission method of a content-centric datacenter network. The method is characterized in that an NDN (Named Data Network) based content-centric routing and forwarding strategy is used; multicast characteristics and expandability of the CCDN (content-centric datacenter network) are guaranteed only by storing a complete PIT (Pending Interest Table) and part of an FIB (forwarding information base), by adopting a Hybrid Content and Location routing strategy and by taking limited storage resources and datacenter network topology of a datacenter switch into consideration; and different from an on-path caching strategy of the NDN, an off-path mechanism that a host provides data caching is adopted by taking large data volume characteristic of the datacenter network and host storage capacity of redundancy into consideration. According to multistage topological characteristics, of the datacenter network, such as Fat-Tree, the CCDN guarantees Distance-aware Content based Forwarding through FIB learning, average path length of data transmission is decreased, and network throughput is improved. By the aid of the adaptive forwarding strategy, the CCDN can still provide accurate and efficient data forwarding in network failure.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Peer-model support for virtual private networks having potentially overlapping addresses
InactiveUS7154889B1Reduce loadReduce decreaseNetworks interconnectionInformation repositoryData pack
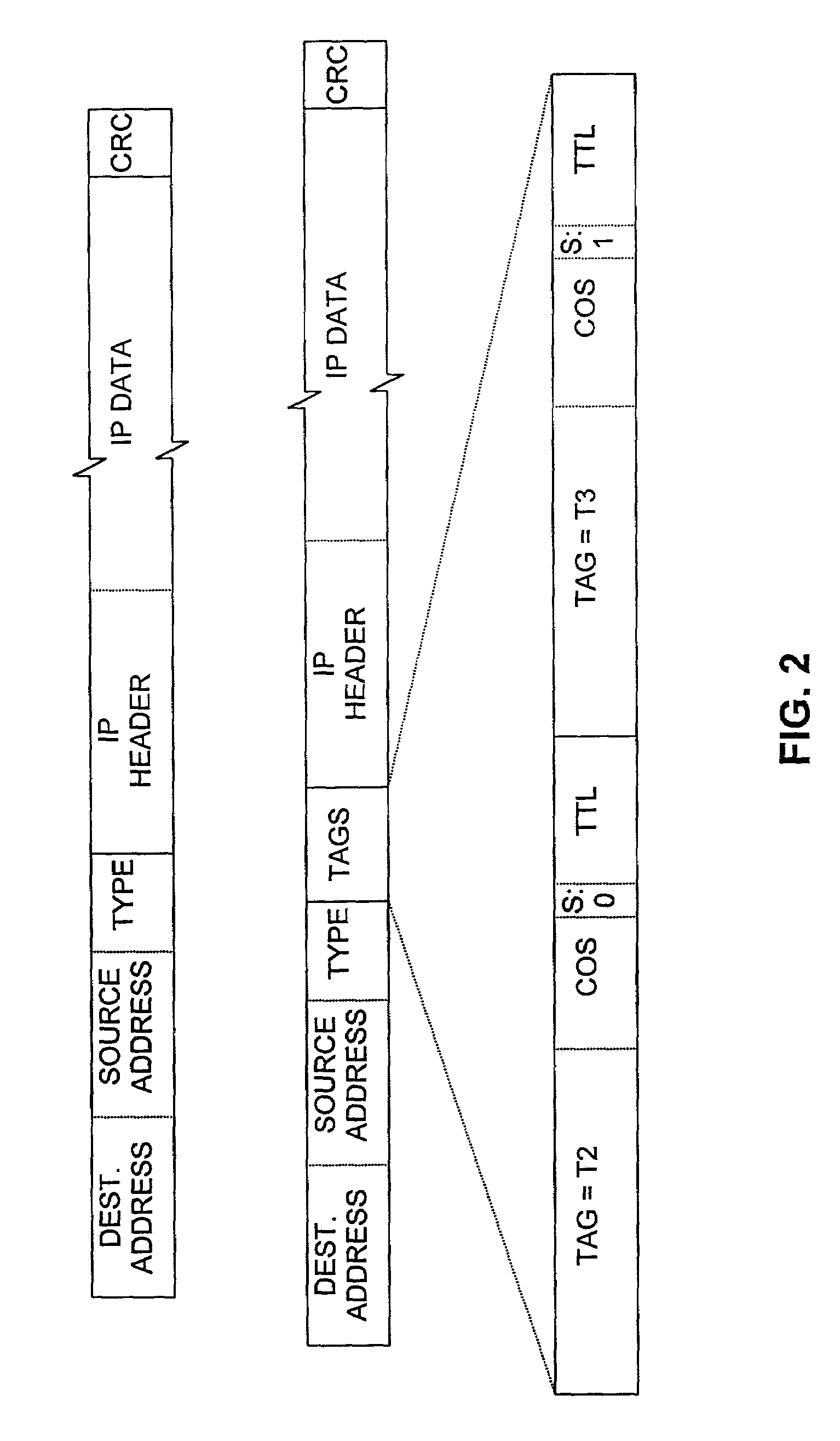
A service provider's routers (PE1, P1, P2, PE2) provide connections between and share routing information with routers (CE1, CE2) of a customer virtual private network (VPN) as well as routers of other customers' VPNs, which may have overlapping address spaces. A service provider's edge router (PE1) informed by the customer's router (CE1) that it will forward packets to a given prefix notifies the other edge router (PE2) that PE1 can forward packets to that address prefix if the destination is in the VPN to which CE1 belongs. PE1 also tells PE2 to tag any thus-destined packets with a particular tag T3. PE2 stores this information in a forwarding information base that it separately keeps for that VPN so that when PE2 receives from a router CE2 in the same VPN a packet whose destination address has that prefix, it tags the packet as requested. But PE2 also tags it with a tag T2 that the router P2 to which PE2 first sends it has asked PE2 to apply to packets to be sent to PE1. P2 routes the packet in accordance with T2, sending it to P1 after replacing T2 with a tag T1 that P1 has similarly asked P2 to use. P1 removes T1 from the packet and forwards it in accordance with T1 to PE1, which in turn removes T3 from the packet and forwards it in accordance with T3 to CE1. In this manner, only the edge routers need to maintain separate routing information for separate VPNs.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Technique for graceful shutdown of a routing protocol in a network
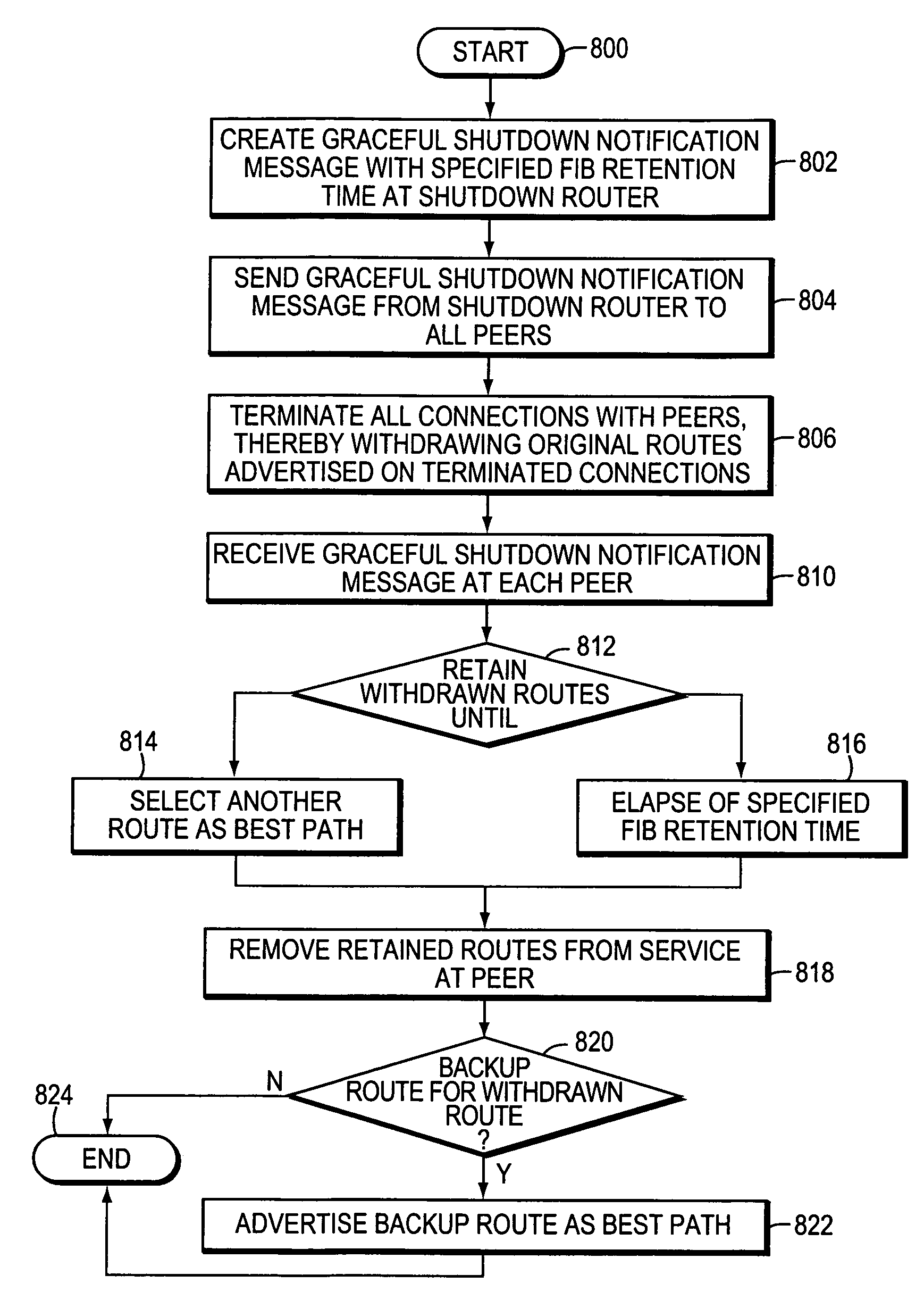
ActiveUS20050177634A1Reduce lossesOvercome disadvantagesMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksInformation repositoryBackup path
A graceful shutdown technique modifies a routing protocol to allow an intermediate node, such as a router, to announce to its peer routers (peers) its intention to be gracefully shutdown and removed from service in a network. By announcing its intention to be removed from service, the shutdown router closes (terminates) all connections with its peers and all original routes advertised on those connections are removed (withdrawn) from service. According to the inventive technique, the shutdown router may continue forwarding packets over the network for a “grace” period of time, i.e., the router maintains the validity of those original routes so that packets mapped to the routes are not dropped (at least during the grace period). The grace period also allows backup paths to be propagated to each peer and put into service prior to a final withdrawal of the shutdown router's paths from a forwarding information base of the peer. Thus, the grace period enables the network to continue using the shutdown router as a next hop as it re-converges to use the alternate, backup paths.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Technique for graceful shutdown of a routing protocol in a network
ActiveUS7355983B2Overcome disadvantagesMaintain validityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsInformation repositoryBackup path
A graceful shutdown technique modifies a routing protocol to allow an intermediate node, such as a router, to announce to its peer routers (peers) its intention to be gracefully shutdown and removed from service in a network. By announcing its intention to be removed from service, the shutdown router closes (terminates) all connections with its peers and all original routes advertised on those connections are removed (withdrawn) from service. According to the inventive technique, the shutdown router may continue forwarding packets over the network for a “grace” period of time, i.e., the router maintains the validity of those original routes so that packets mapped to the routes are not dropped (at least during the grace period). The grace period also allows backup paths to be propagated to each peer and put into service prior to a final withdrawal of the shutdown router's paths from a forwarding information base of the peer. Thus, the grace period enables the network to continue using the shutdown router as a next hop as it re-converges to use the alternate, backup paths.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
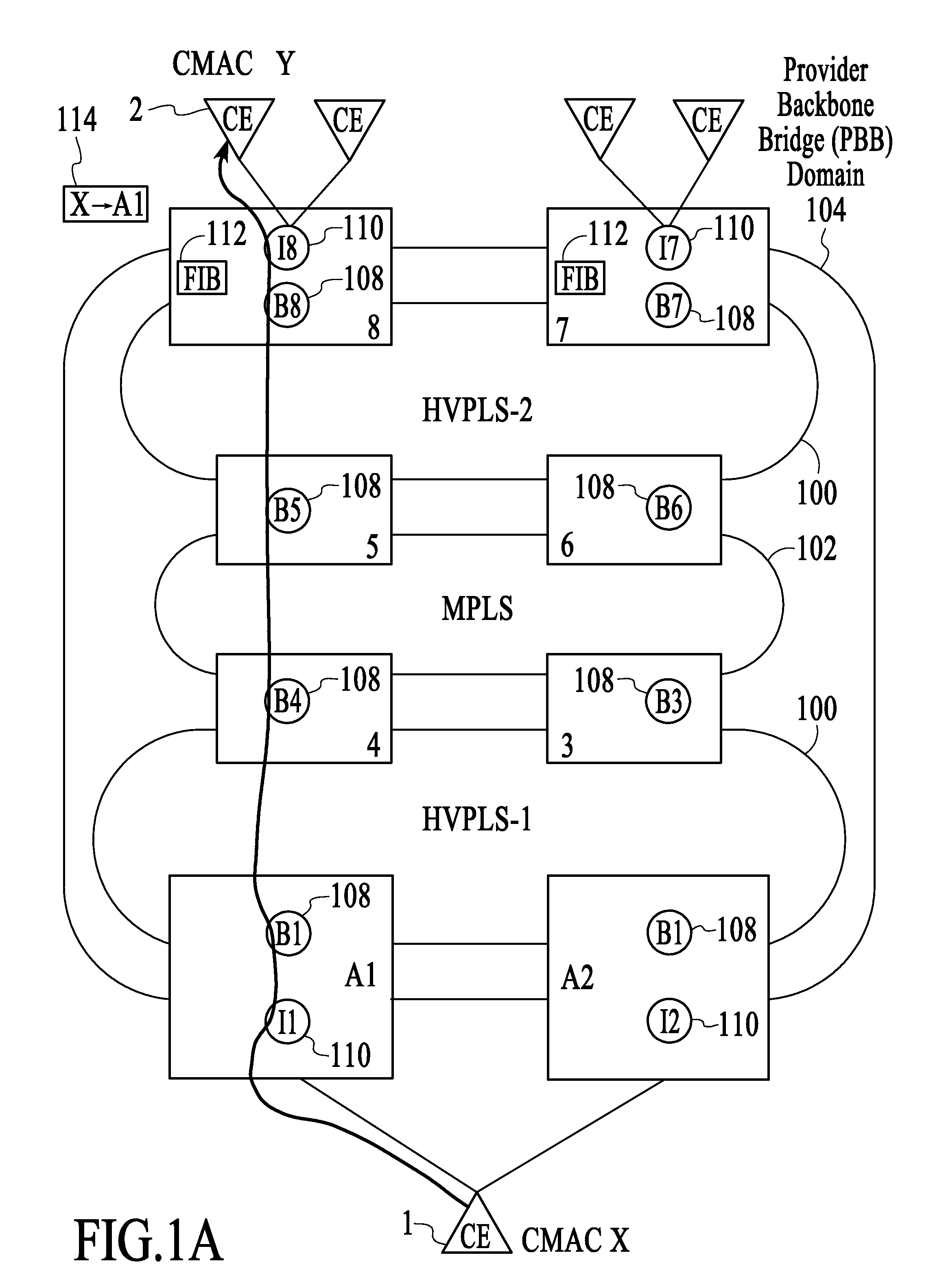
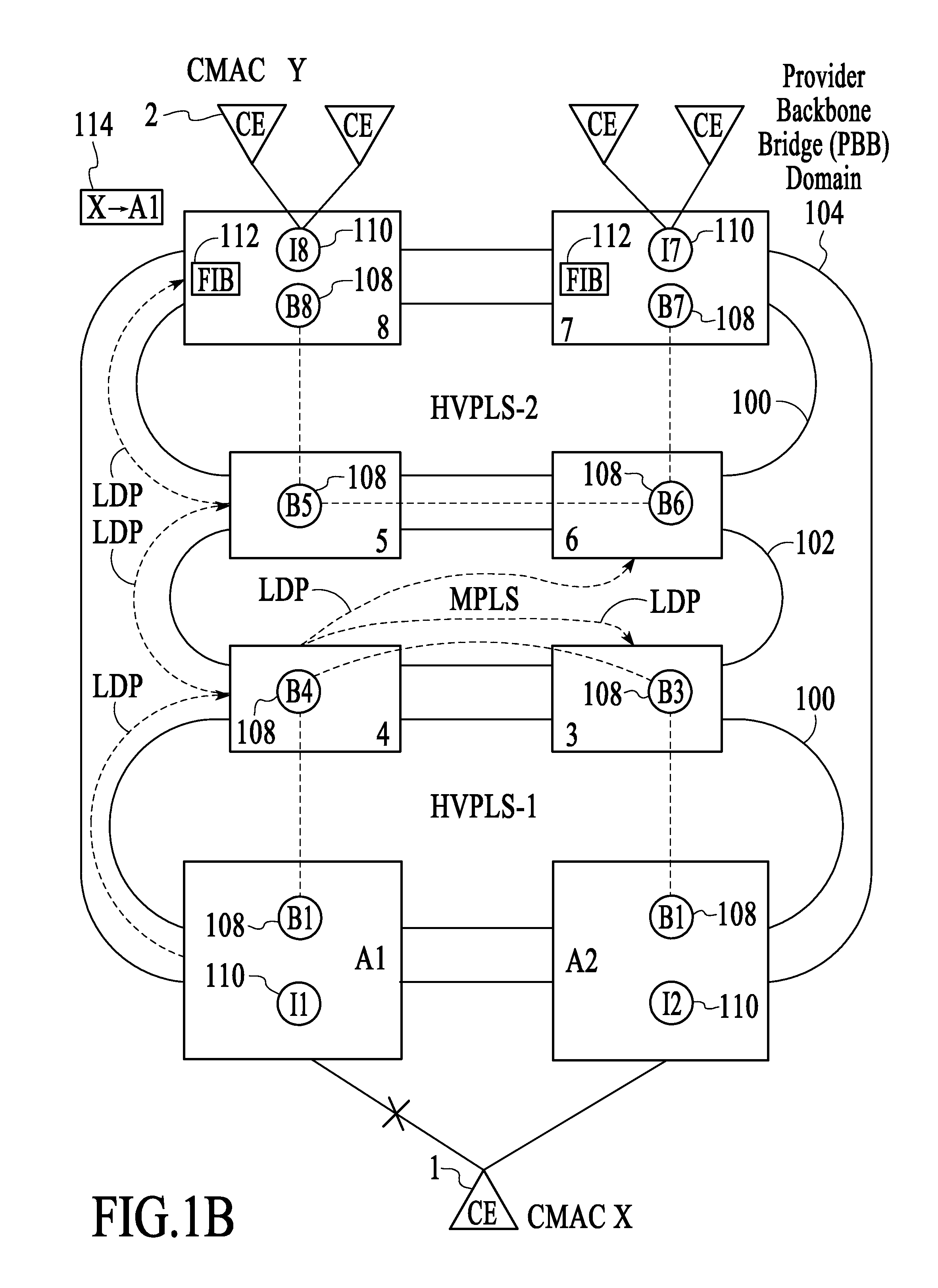
Failure protection in a provider backbone bridge network using forced mac flushing
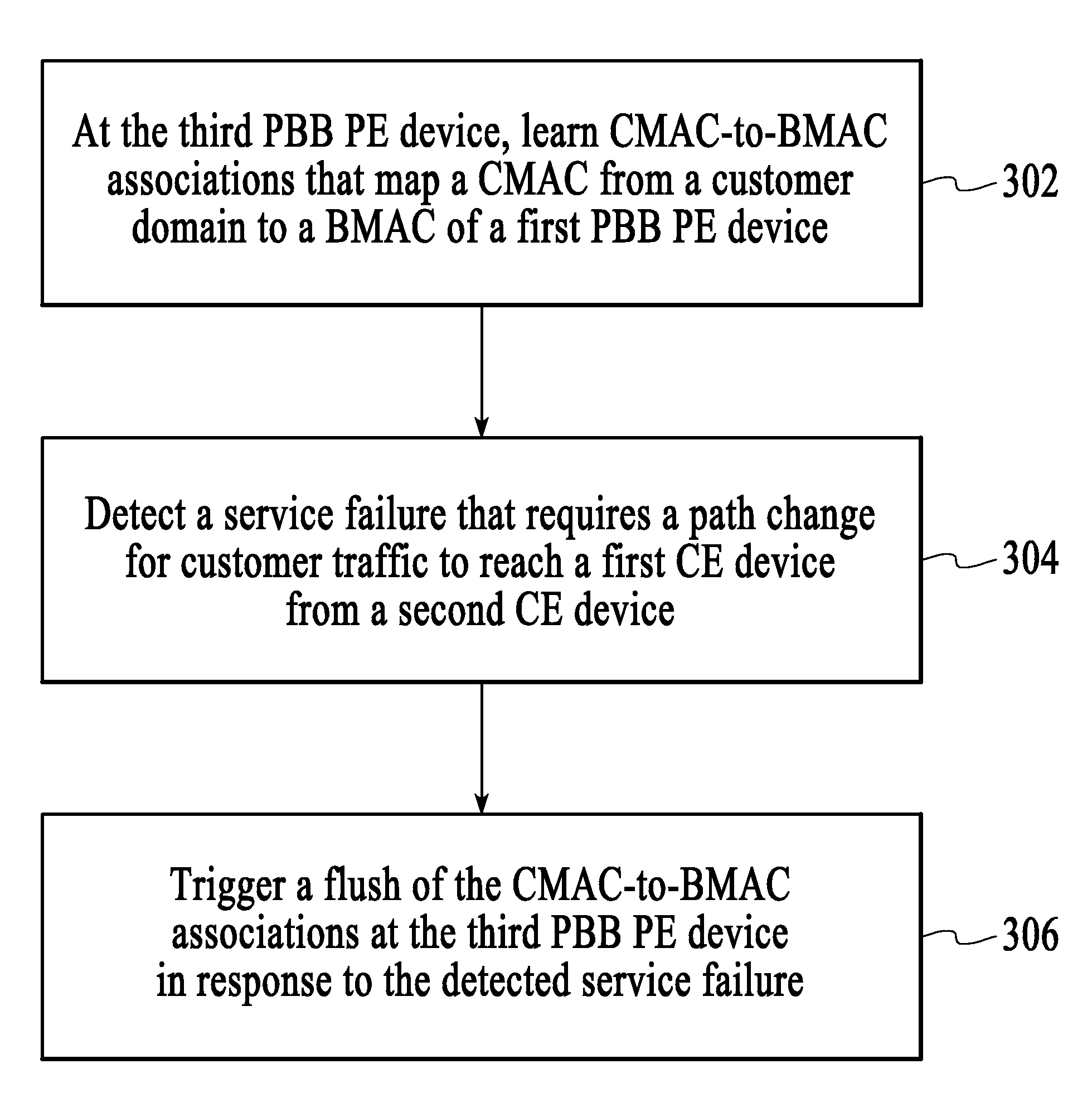
ActiveUS20080225695A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsInformation repositoryTraffic capacity
A technique for operating a network involves controlling the black-holing of traffic by forcing customer source MAC address (CMAC)-to-backbone source MAC address (BMAC) associations at provider backbone bridge (PBB) provider edge (PE) devices to be flushed from their corresponding forwarding information bases (FIBs) in response to a service failure so that new CMAC-to-BMAC associations, which are reflective of a secondary traffic path, are learned faster than they would otherwise be learned if the network had relied on native functionality to learn new CMAC-to-BMAC associations that are reflective of the secondary traffic path.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
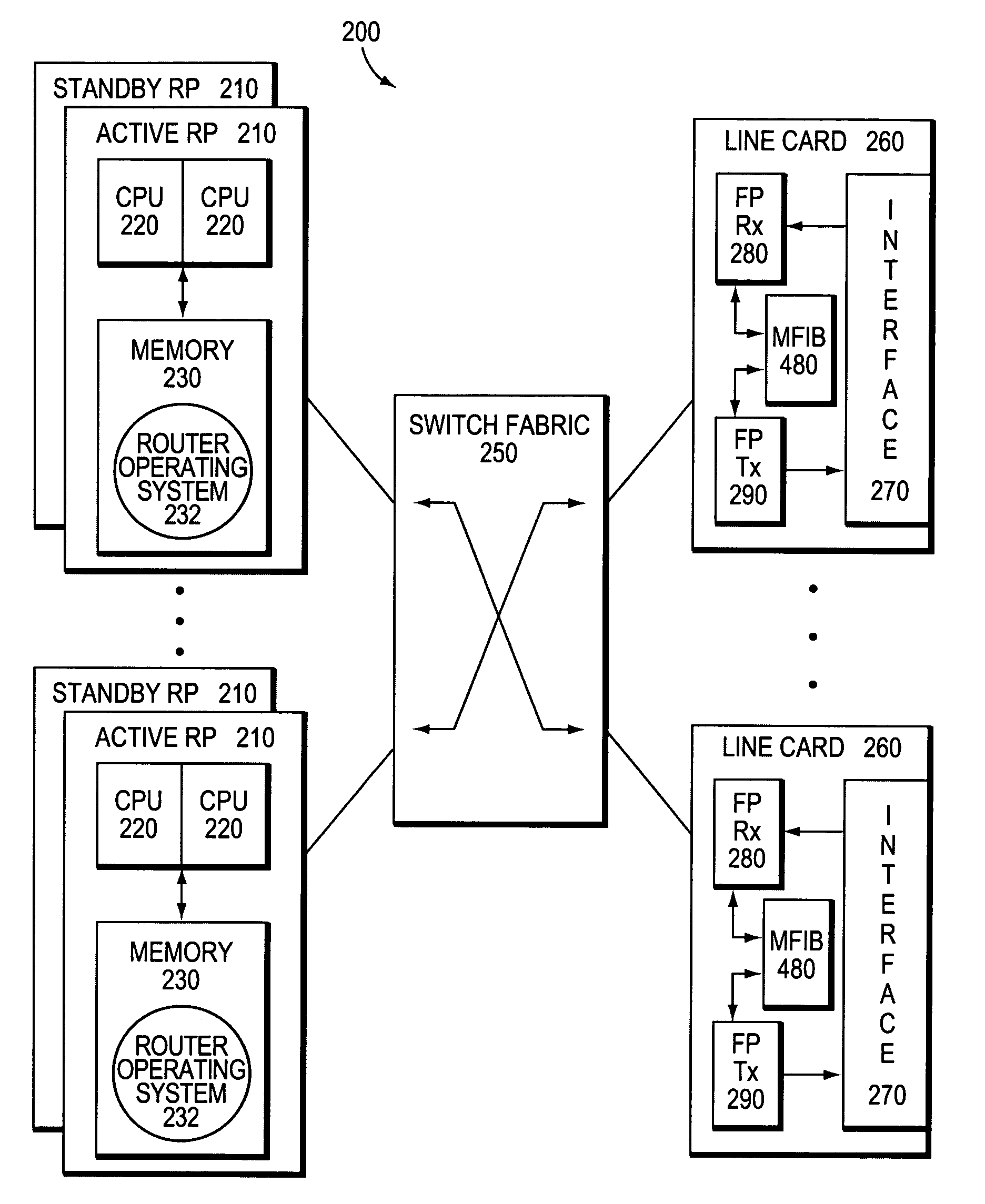
Multiple multicast forwarder prevention during NSF recovery of control failures in a router
ActiveUS7447225B2Time-division multiplexStore-and-forward switching systemsInformation repositoryTraffic capacity
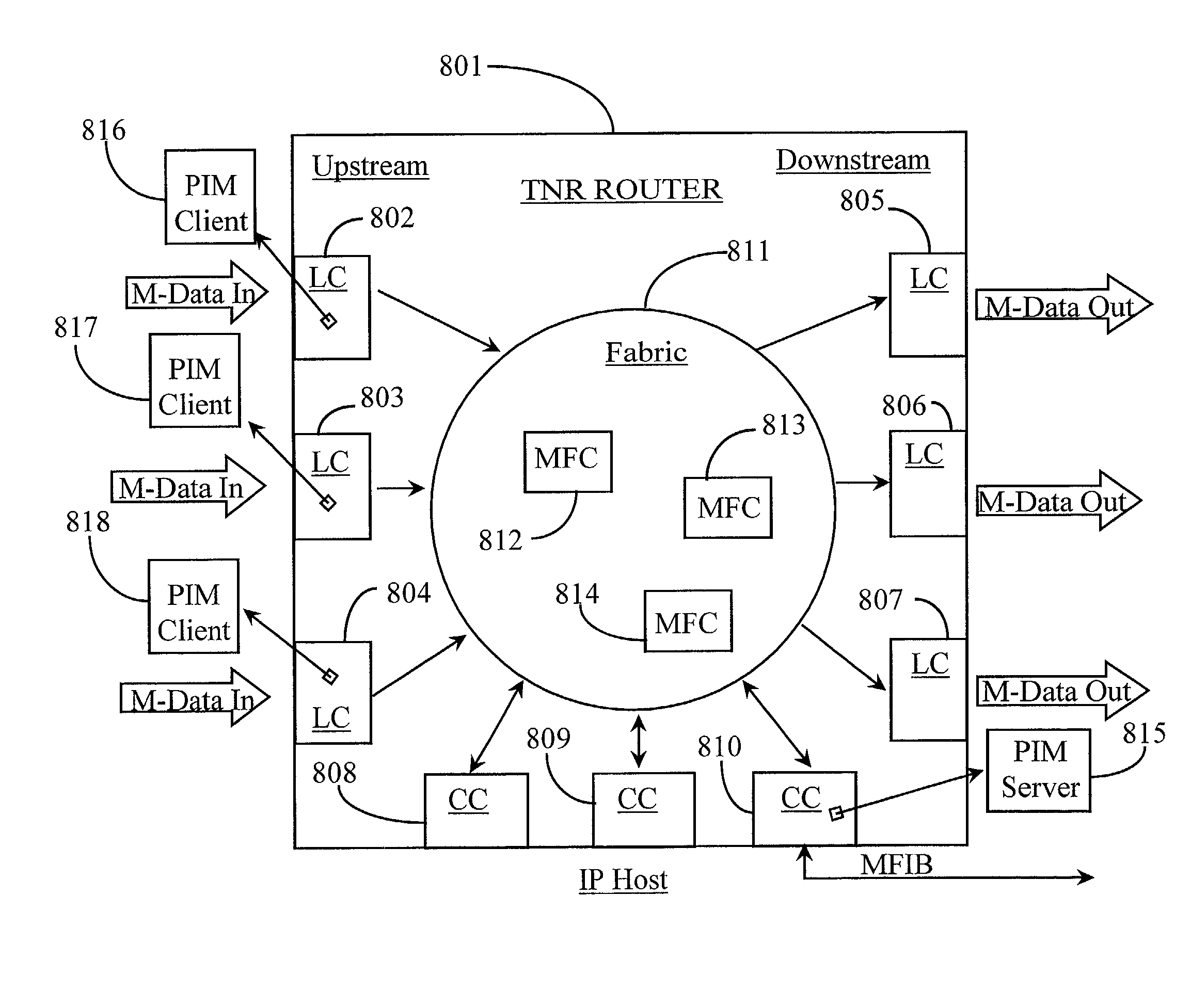
A technique prevents multiple multicast forwarders from forwarding multicast packets for a route over a link in a computer network during non-stop forwarding (NSF) recovery of one or more failures in a control plane of a multicast router. The multicast router has a functional infrastructure that allows data traffic forwarding operations to continue throughout a data plane of the router in the presence of a failure and / or software restart to a multicast component, e.g., a protocol independent multicast (PIM) routing protocol, executing in the control plane. Another multicast component, e.g., a multicast forwarding information base (MFIB) executing in the data plane, is configured to prevent multiple multicast forwarders due to routing changes in the network that arise during NSF recovery.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and system of virtue cluster route
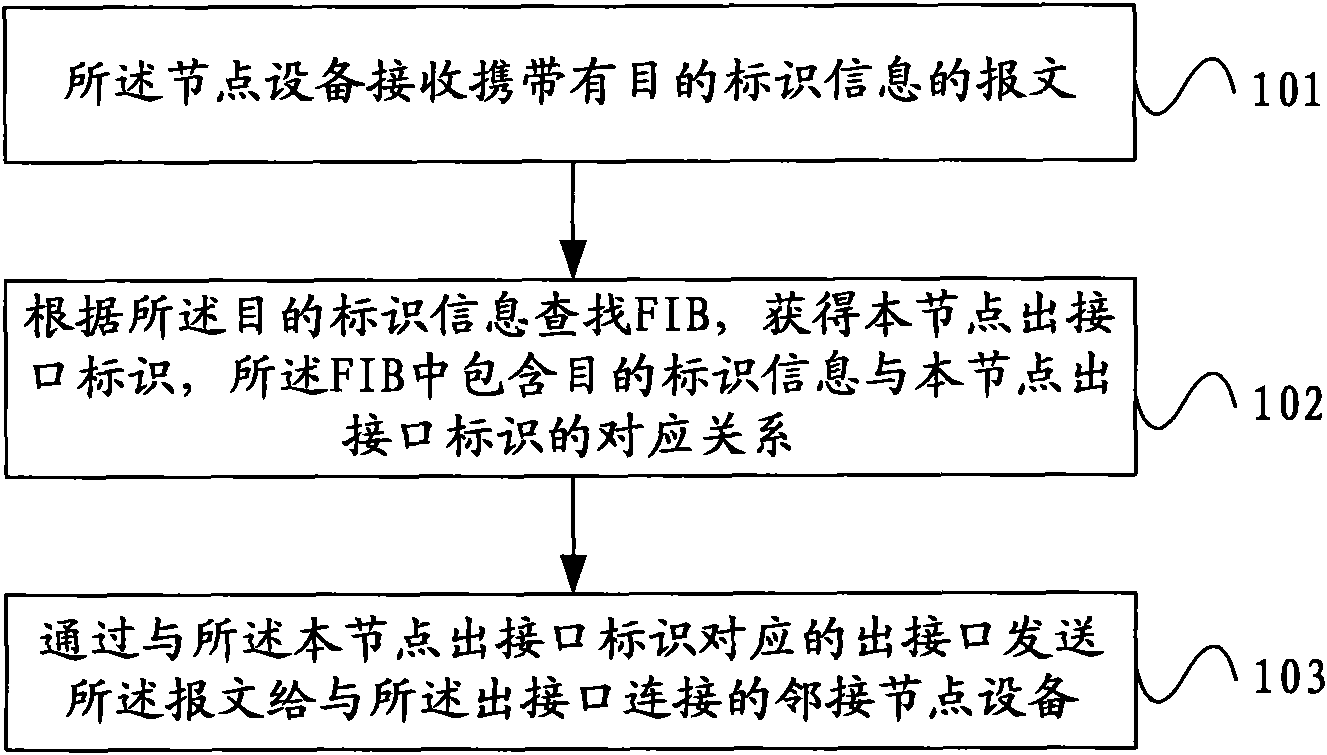
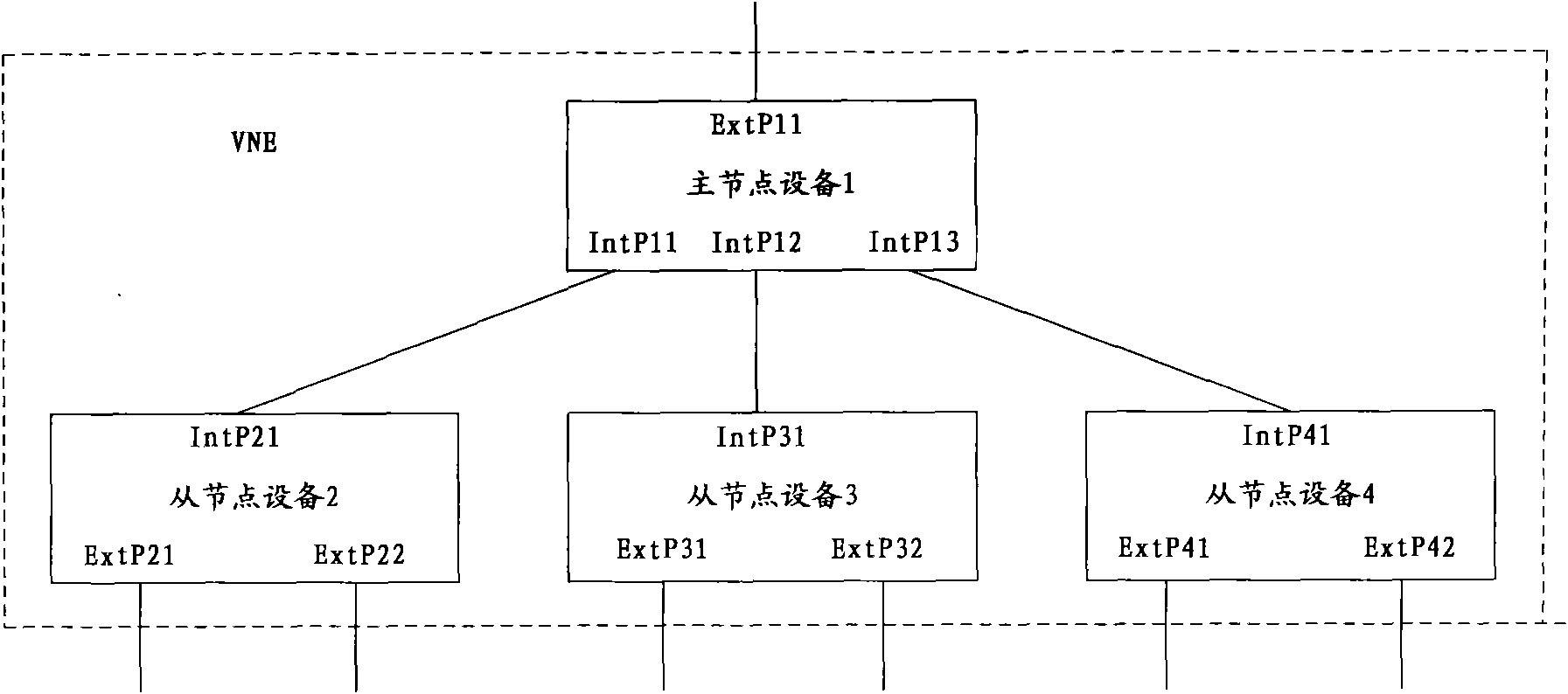
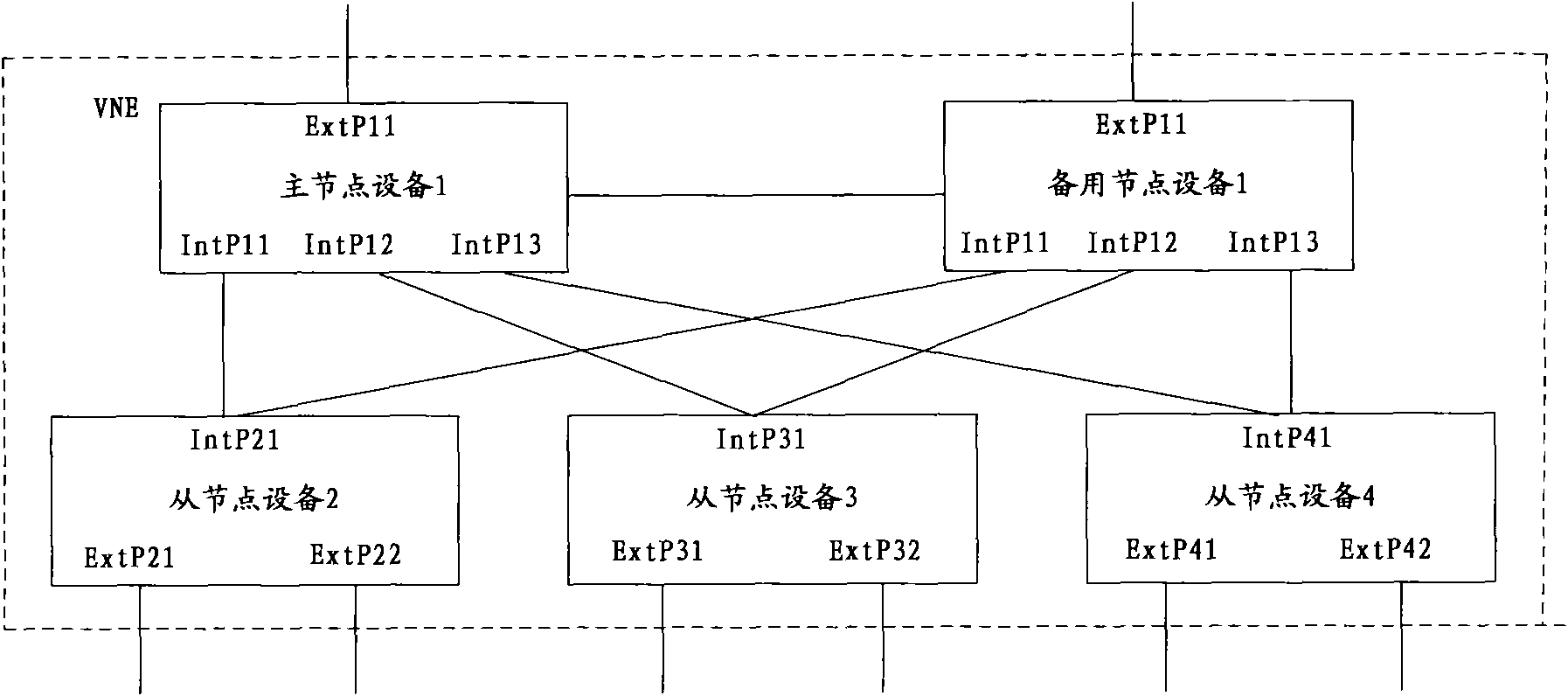
InactiveCN101931587ASimple topologySimple operation and maintenance managementError preventionData switching networksInformation repositoryInformation finding
The embodiment of the invention relates to a method and system of virtue cluster route. The method is applied to the virtue cluster route system which comprises multiple node devices connected mutually through ports. The method comprises the following steps: a node device receives a message carrying goal identification information; a forwarding information base FIB is searched according to the goal identification information to obtain output interface identification of the node, wherein the FIB contains the corresponding relationship between the goal identification information and the output interface identification of the node; and the message is transmitted to an adjacent node device connected to the output interface through the output interface corresponding to the output interface identification of the node. The embodiment of the invention merges the goal identification information and the output interface identification of multiple mutually connected router devices into the FIB, thus the multiple mutually connected router devices are merged into one virtue cluster routing system.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Apparatus and method for dispersively processing QoS supported IP packet forwarding
InactiveUS20020078196A1Multiple digital computer combinationsNetworks interconnectionQos quality of serviceInformation repository
In an apparatus and method for dispersively processing an IP packet forwarding for supporting a quality of service(QoS), an IP forwarding information base gotten by processing and extracting a routing protocol is dispersed to all input ports of a router on the basis of the QoS in a private network processor for performing a routing protocol process function, so as to dispersively process the IP packet forwarding. The method for dispersively processing the IP packet forwarding for supporting the QoS includes the steps of: a) classifying reception IP packets according to the QoS and storing them at an input-side class queue; b) searching the forwarding information base by using an exact matching table and an LPM (Longest Prefix Matching) search table according to an IP header value of the IP packet stored at the input-side class queue, and gaining forwarding information; c) transferring the IP packet according to the gained forwarding information; d) classifying the transferred IP packets according to the QoS, and storing them at an output-side class queue; and e) outputting the IP packet stored at the output-side class queue according to the QoS, whereby being used in the IP packet forwarding dispersion processing apparatus for supporting the quality of service, etc.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method of communicating content in mobile ad-hoc network and communication node included in mobile ad-hoc network
InactiveUS20150222479A1Increase valueReduce wasteError preventionTransmission systemsInformation repositoryInformation-centric networking
Provided are a method of communicating content in a mobile ad-hoc network and a communication node included in a mobile ad-hoc network, the method and communication node intended to efficiently perform communication based on information centric networking (ICN) in a mobile ad-hoc network and reduce the waste of energy resulting from frequent reconfiguration of communication caused by the mobility of a terminal. The method includes receiving an interest packet or a response packet for content; determining a next node to which the received packet will be relayed based on a forwarding information base (FIB) or a pending interest table (PIT), and relaying the packet using a unicast scheme; and when the relay of the packet to the next node fails, restoring a routing path by storing the packet in a relay candidate buffer and broadcasting the packet.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method and system for optimizing routing table changes due to ARP cache invalidation in routers with split plane architecture
ActiveUS7415028B1Data switching by path configurationAddress Resolution ProtocolInformation repository
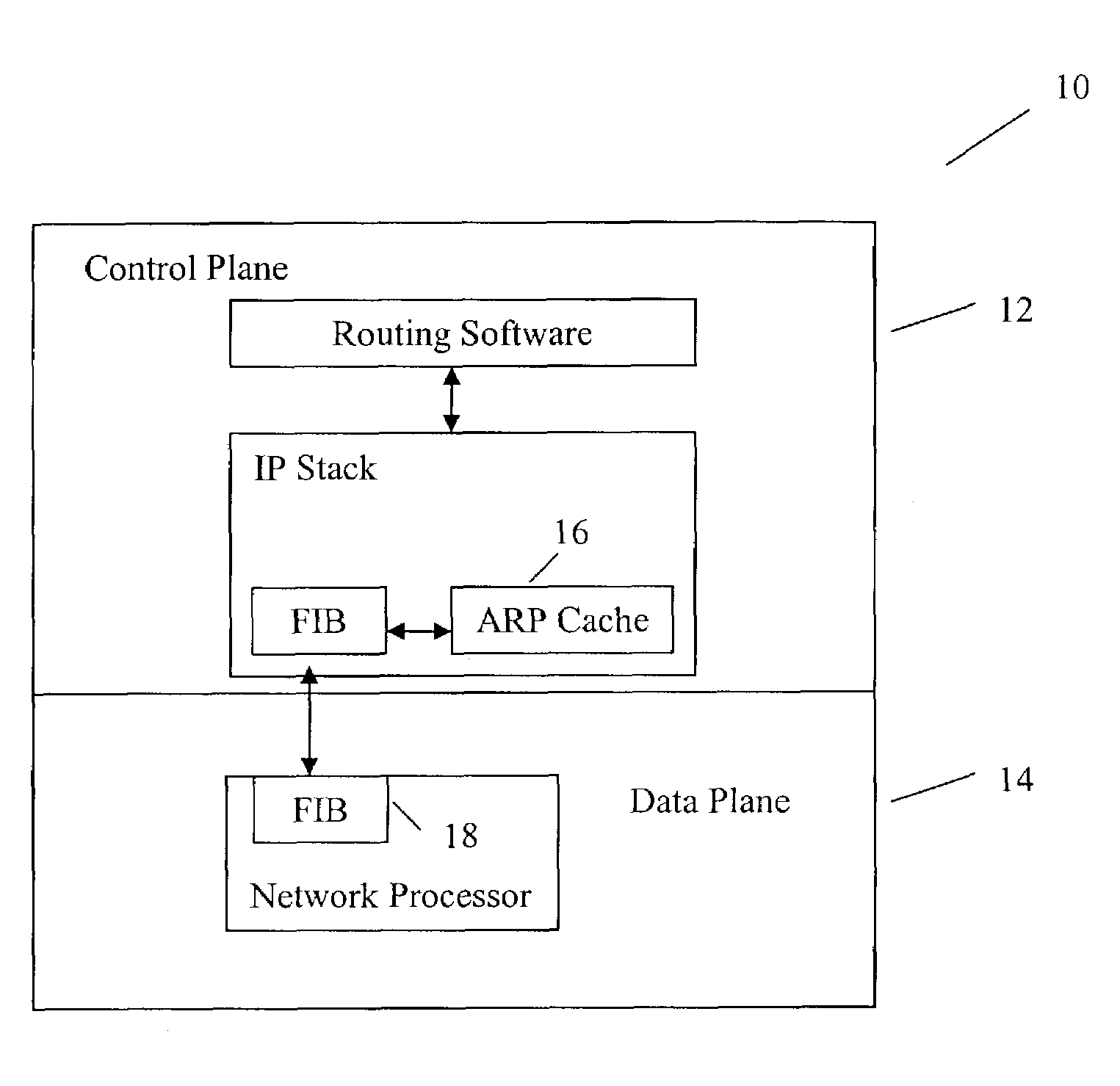
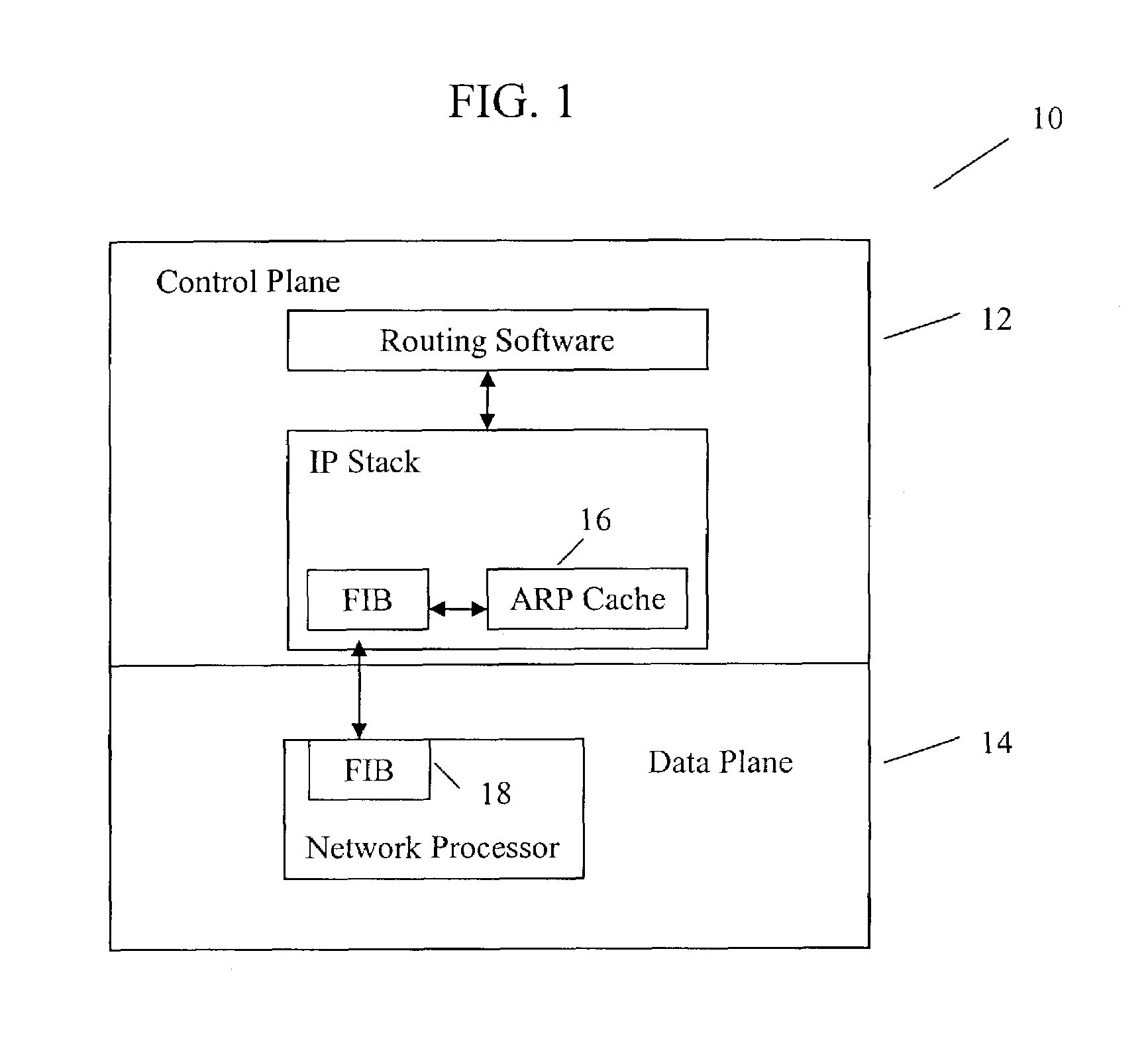
A method for optimizing routing functions in a router is provided. The router has a split plane architecture including a control plane and a data plane. The control plane includes an Address Resolution Protocol cache and the data plane includes a programmable forwarding information base. According to one aspect, when the control plane obtains information about a route, it evaluates the obtained information about the route to determine if address resolution is needed. If it is determined that address resolution is needed for the route, the control plane performs the needed address resolution to derive additional information about the route. The control plane programs the forwarding information base to incorporate the obtained and additional information. The determination as to whether address resolution is needed for the route is performed regardless of whether packets are to be delivered on the route.
Owner:RIBBON COMM OPERATING CO INC
Label switching method, apparatus and system
ActiveUS20110188857A1Easy networkingHybrid transportOptical multiplexInformation repositoryTransmission channel
A label switching method is provided. When a Passive Optical Network (PON)-based Label Switching Path (LSP) is established, a PON logical service transmission channel is established between an Optical Line Terminal (OLT) and an Optical Network Unit (ONU). According to an identifier (ID) of the PON logical service transmission channel as a PON label, a PON-based Forwarding Information Base (FIB) table on the ONU is updated, and a PON-based Label Forwarding Information Base (LFIB) table on the OLT is updated, where the PON-based LFIB table records a forwarding relationship between an ingress port plus an ingress label and an egress port plus an egress label, and the PON-based FIB table records a forwarding relationship between the ingress port plus a destination address and the egress port plus the egress label. Therefore, the problems between network segments of different forwarding characteristics, protocol variation, inter-segment conversion, and mapping and control complexity are avoided.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Network equipment and forwarded information updating method
ActiveCN102347905AReduce congestionImprove reliabilityData switching networksTraffic capacityDistributed computing
The invention discloses a network equipment and a forwarded information updating method. The application is used in upper link equipment connected to a stacking system, and the upper link equipment can update a forward information base locally saved according to the failure of a down link chain of member equipment of the stacking system, so that a message forwarding path selecting scheme in the existing converged network is optimized. When the down link chain has failure, load sharing can be better carried out for flow in the member equipment of the stacking system, the forwarding load of a converged link is reduced, the link congestion of the member equipment is avoided, and the reliability of the link is improved.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
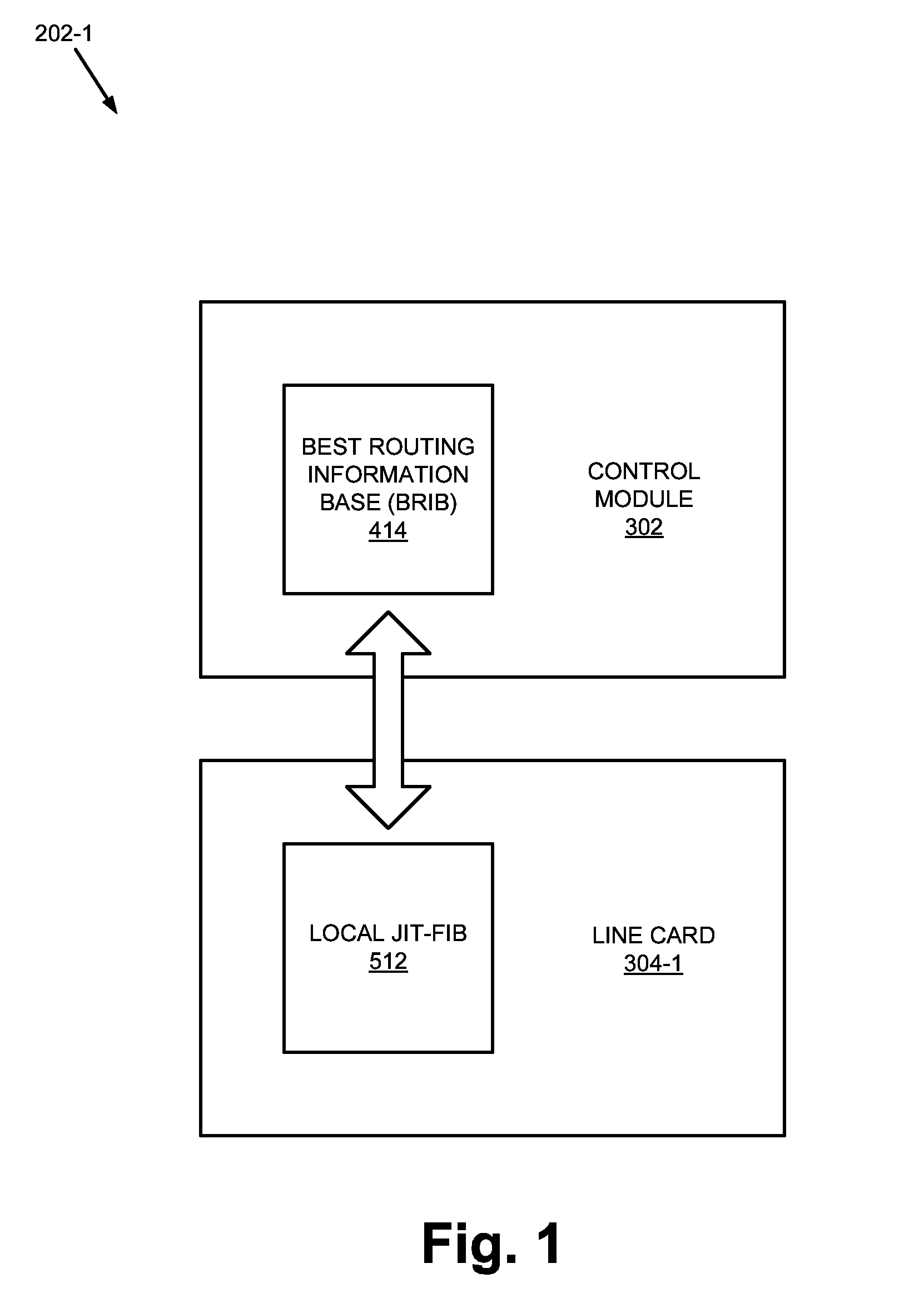
Just-in-time forwarding information base
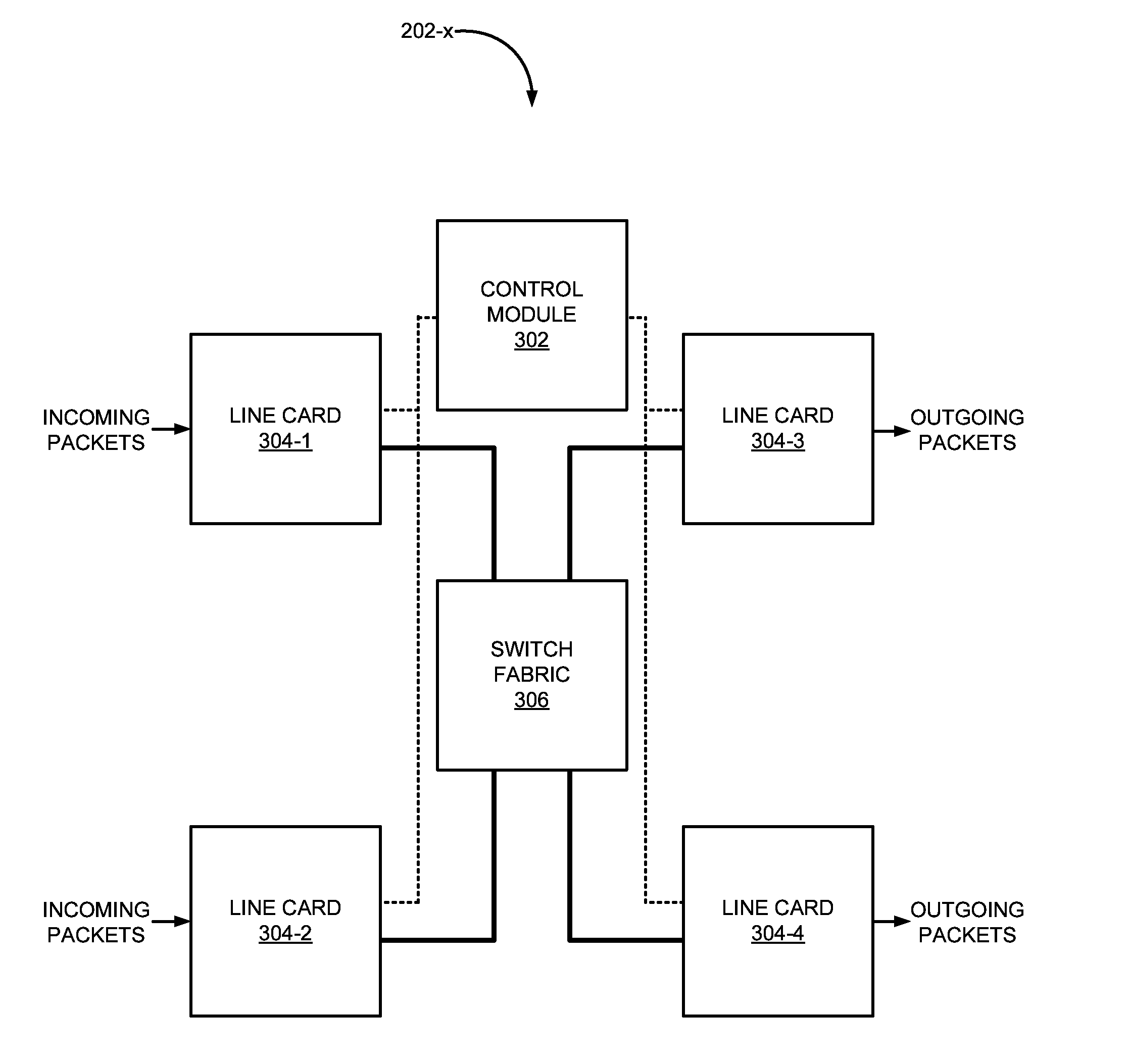
ActiveUS20110122889A1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionInformation repositoryComputer module
A device may include a line card and a control module. The line card may include a memory that stores a local routing table. The line card may request a routing entry from a routing table, receive the routing entry, insert the routing entry in the local routing table, and age out stale routing entries from the local routing table. The control module may include the routing table. The control module may distribute the routing entry in the routing table to the line card.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
Label switching method, apparatus and system
ActiveUS8565597B2Easy networkingHybrid transportOptical multiplexInformation repositoryTransmission channel
A label switching method is provided. When a Passive Optical Network (PON)-based Label Switching Path (LSP) is established, a PON logical service transmission channel is established between an Optical Line Terminal (OLT) and an Optical Network Unit (ONU). According to an identifier (ID) of the PON logical service transmission channel as a PON label, a PON-based Forwarding Information Base (FIB) table on the ONU is updated, and a PON-based Label Forwarding Information Base (LFIB) table on the OLT is updated, where the PON-based LFIB table records a forwarding relationship between an ingress port plus an ingress label and an egress port plus an egress label, and the PON-based FIB table records a forwarding relationship between the ingress port plus a destination address and the egress port plus the egress label. Therefore, the problems between network segments of different forwarding characteristics, protocol variation, inter-segment conversion, and mapping and control complexity are avoided.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
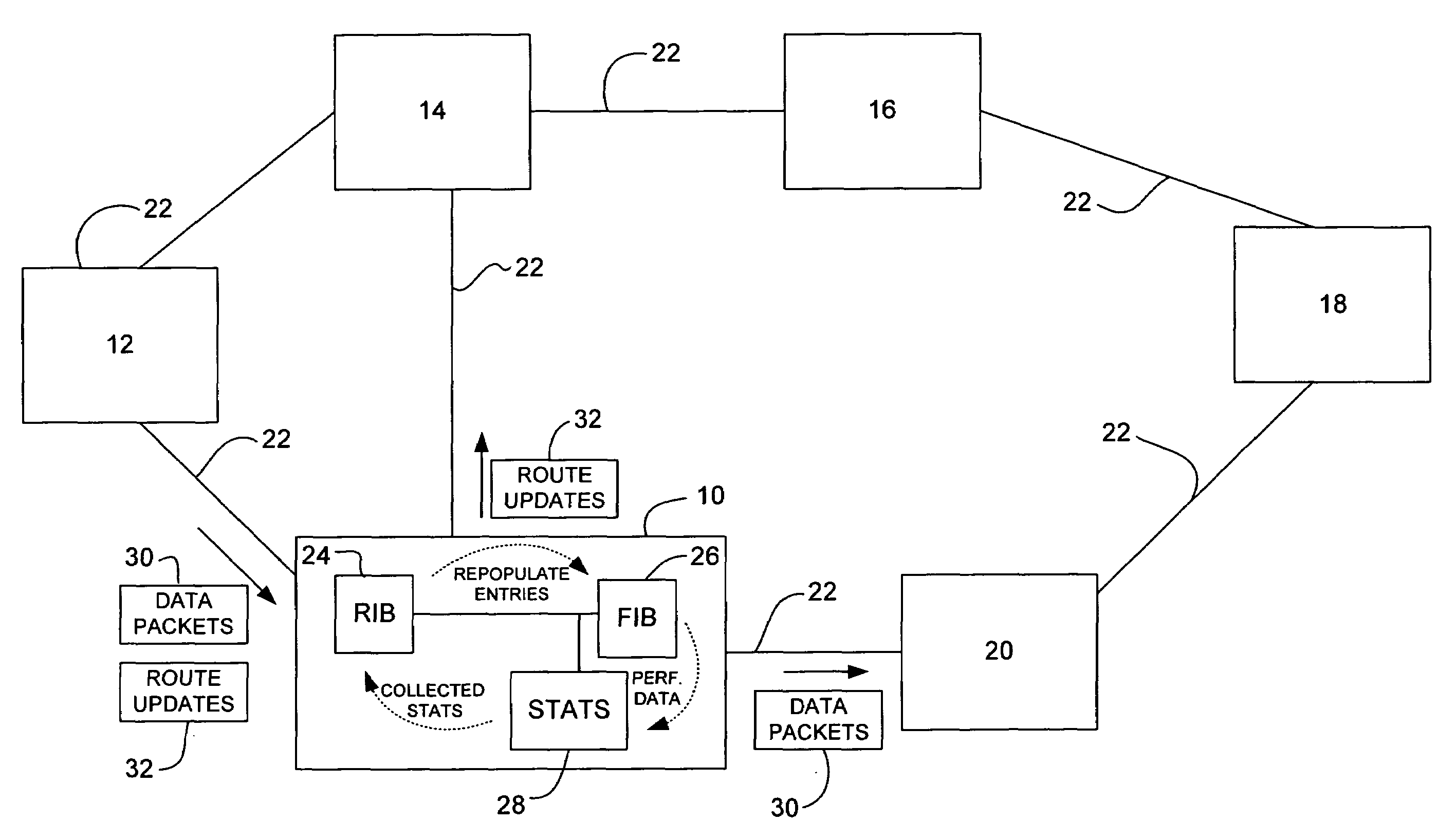
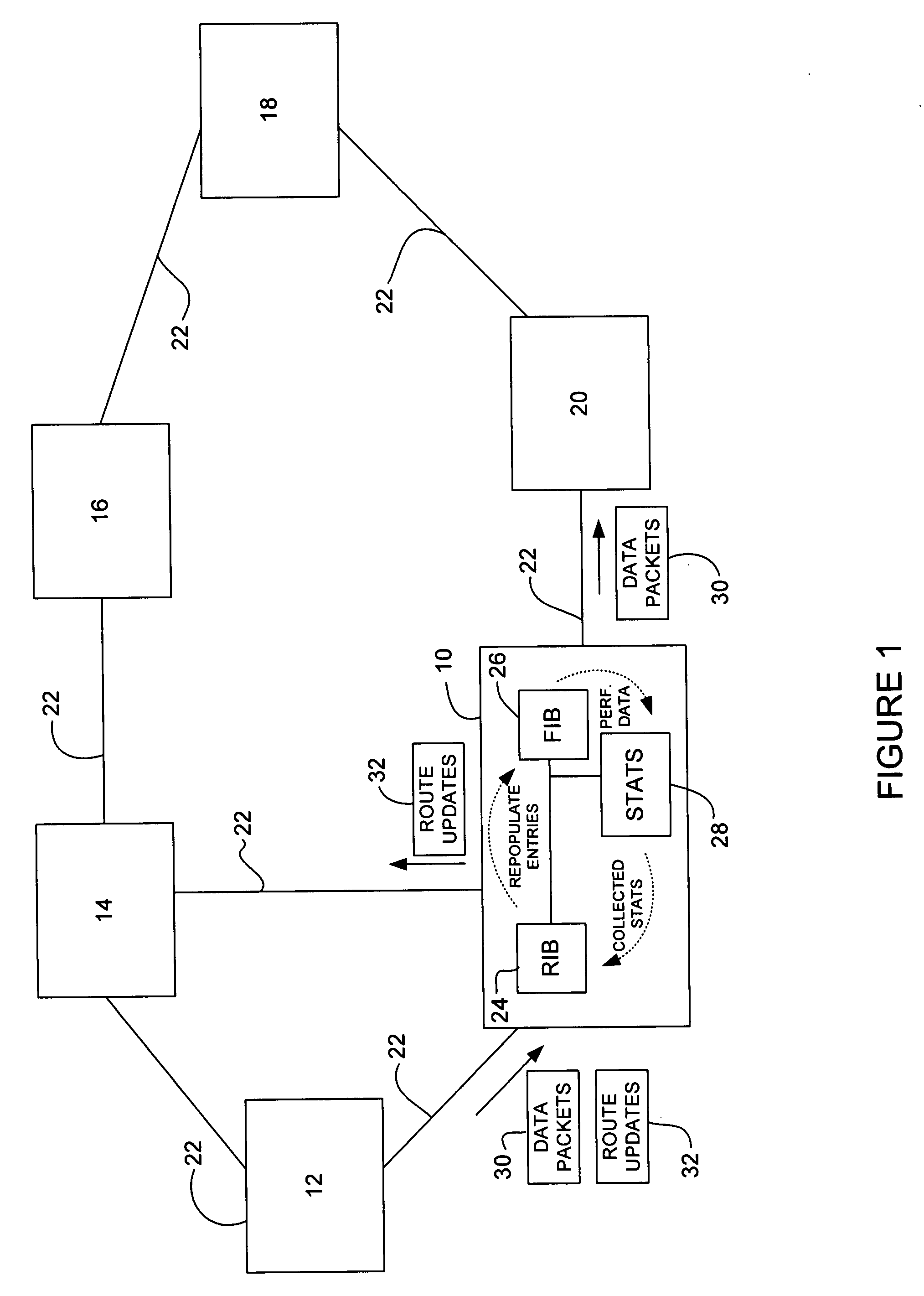
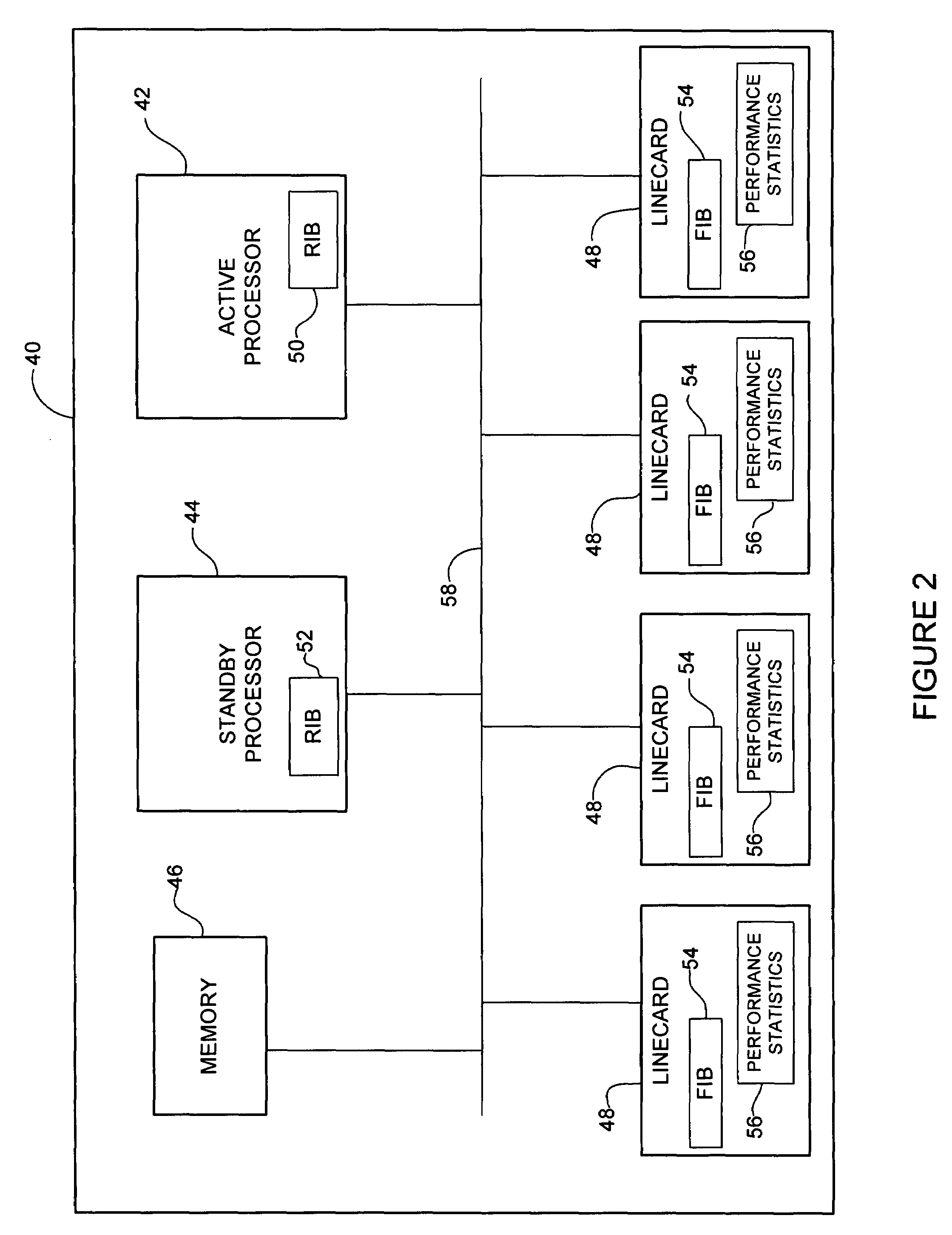
Statistics based forwarding information base repopulation
ActiveUS20090109852A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsForwarding information baseReal-time computing
A method and apparatus for repopulating a forwarding information base at a network device are disclosed. In one embodiment, the apparatus includes a routing information base, forwarding information base, memory for storing performance data based on packets forwarded from the network device, and a processor configured to prioritize routes stored in the routing information base based on the performance data, propagate the routes from the routing information base to the forwarding information base in an order based at least in part on the route priorities.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Communication arrangement between virtual routers of a physical router
ActiveUS20060106934A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionInformation repositoryNetworking protocol
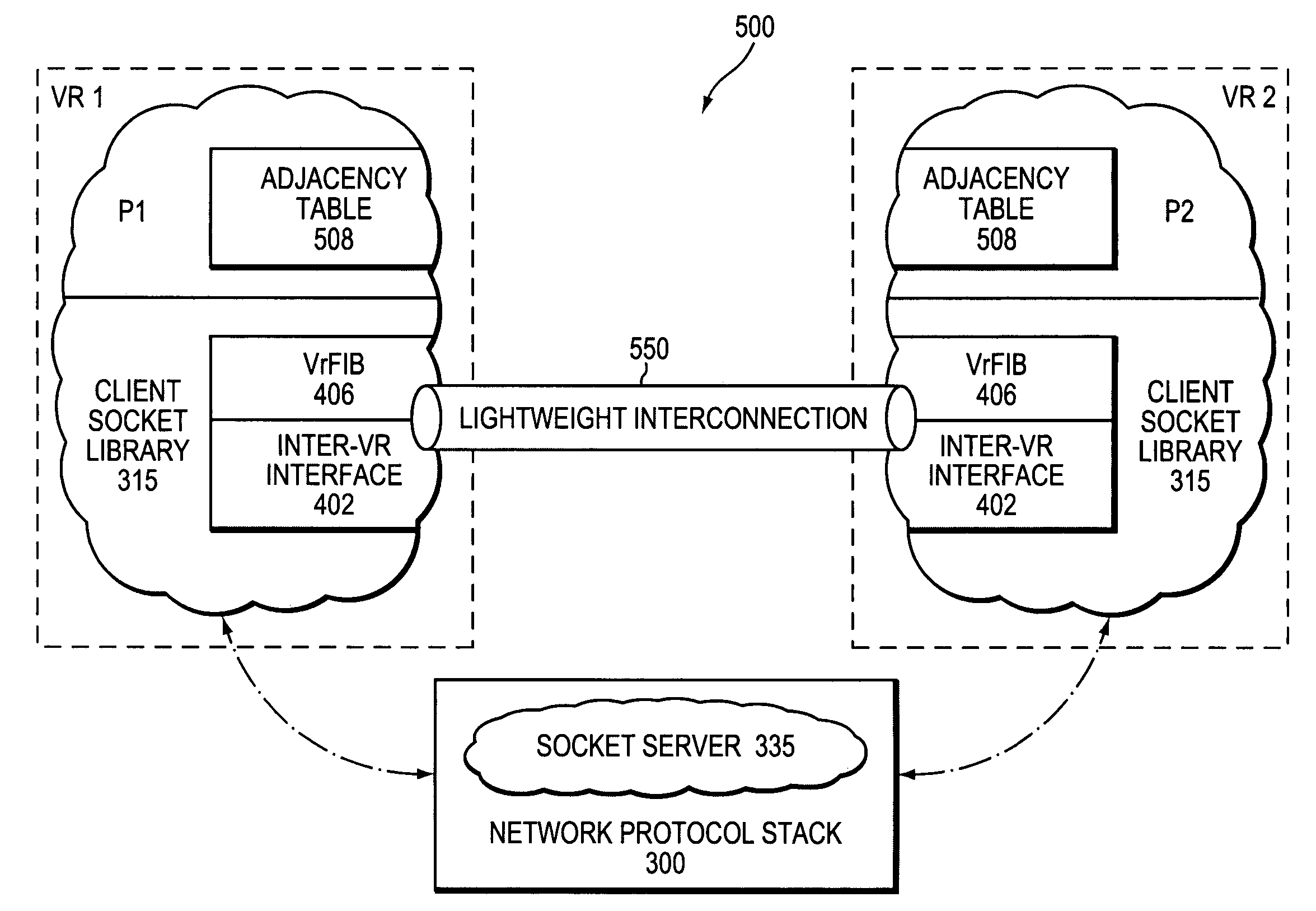
A virtual router (VR) communication arrangement enables services on different VRs executing on the same physical router to communicate without utilizing or substantially consuming communication resources, such as a network protocol stack and physical interfaces, of the physical router. The services are illustratively implemented as separately-scheduled VR processes executing on the physical router. A virtual router forwarding information base (vrFIB) is provided within a client socket library of each VR process and is used to determine whether the services are on the same physical router. If so, a lightweight interconnection is created between the services and a message (“packet”) is forwarded over that interconnection to effectuate communication. If the services are not on the same physical router, the packet is sent over the network protocol stack and communication is established using the communication resources of the router.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
System and method for mapping an index into an IPv6 address
InactiveUS7609689B1Easy to processData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsInformation repositoryInternet Protocol
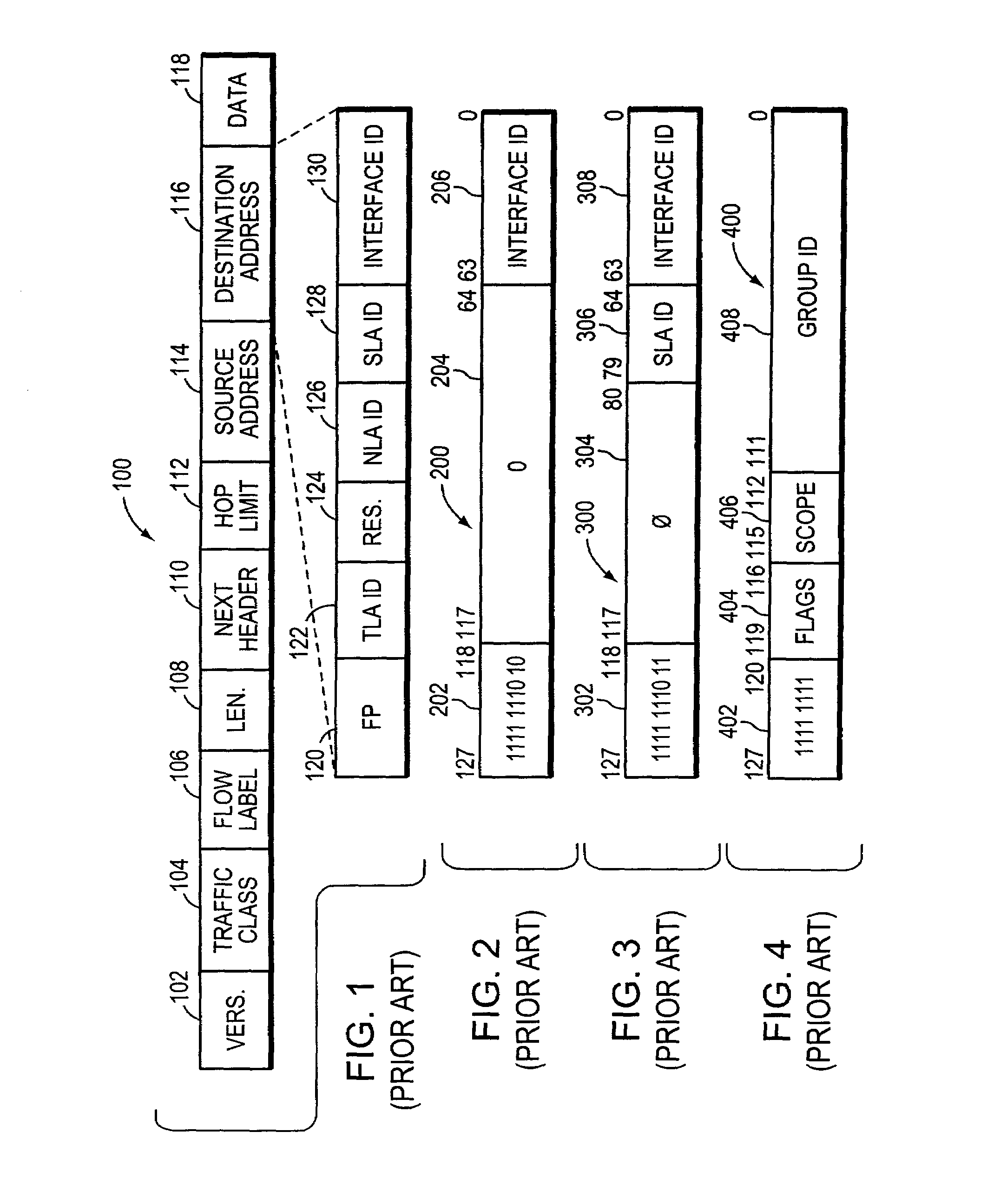
A system and method maps Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) designations to Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) site identifiers (IDs), and embeds site IDs into scoped internet addresses in such a way as to facilitate processing by primarily hardware-oriented forwarding tables. A router has a plurality of interfaces for receiving and forwarding packets, and a route processor for making forwarding decisions for received packets. The route processor includes a routing engine, a routing table, a forwarding information base (FIB), a VLAN store and a site ID store. At least some of the router's interfaces are associated with corresponding VLAN IDs, and the site ID store is preconfigured with a mapping of VLAN IDs to site IDs. For IPv6 packets with link-local unicast destination addresses, embedding the VLAN ID associated with the inbound interface into the address, while for packets with site-local unicast destination addresses, using the retrieved VLAN ID as an index to obtain the corresponding site ID, which is then embedded into the address. The modified destination address is then applied to the FIB, which is a forwarding table optimized to permit fast lookups, to derive the outbound interface from which the packet is to be forwarded to reach the destination entity.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
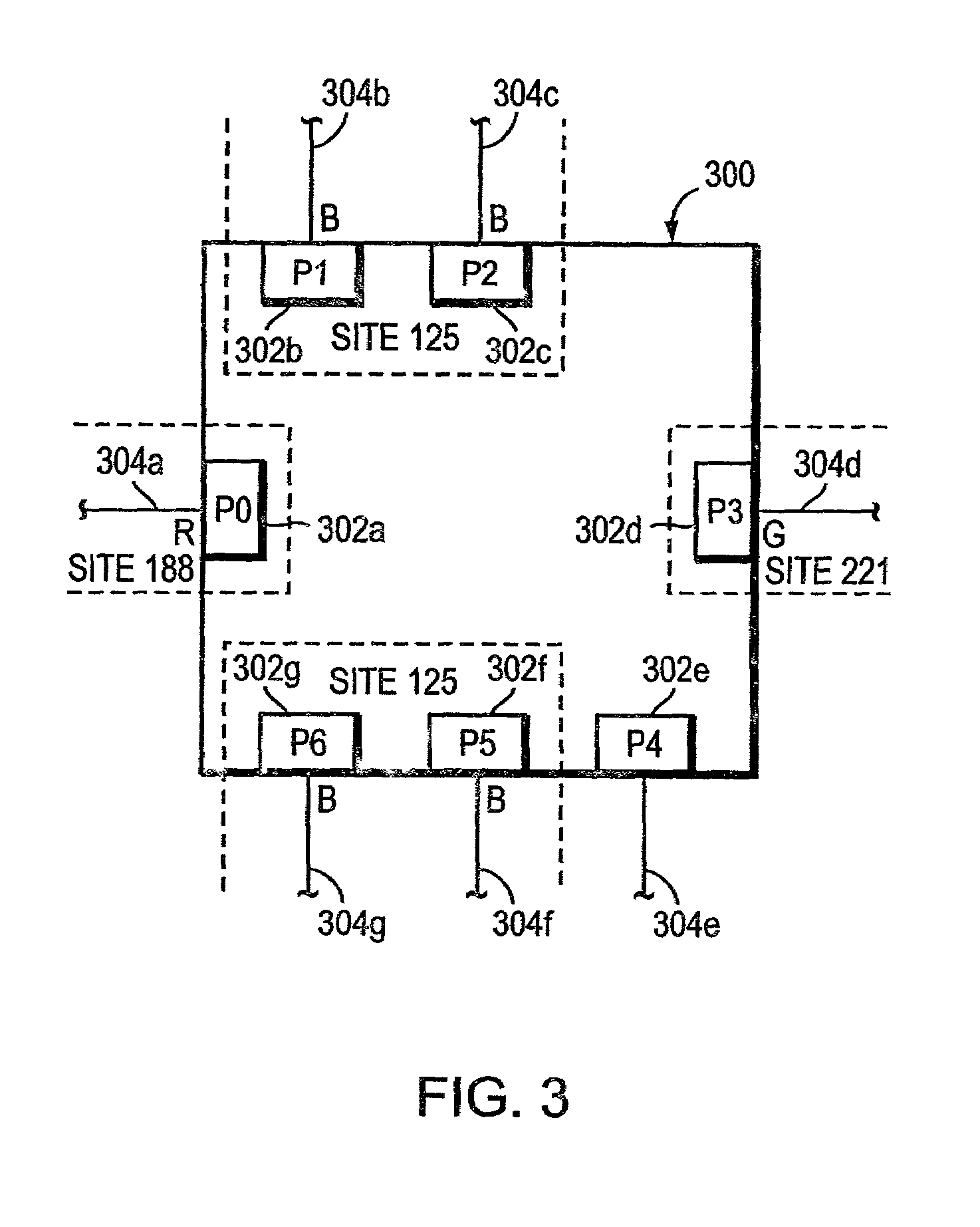
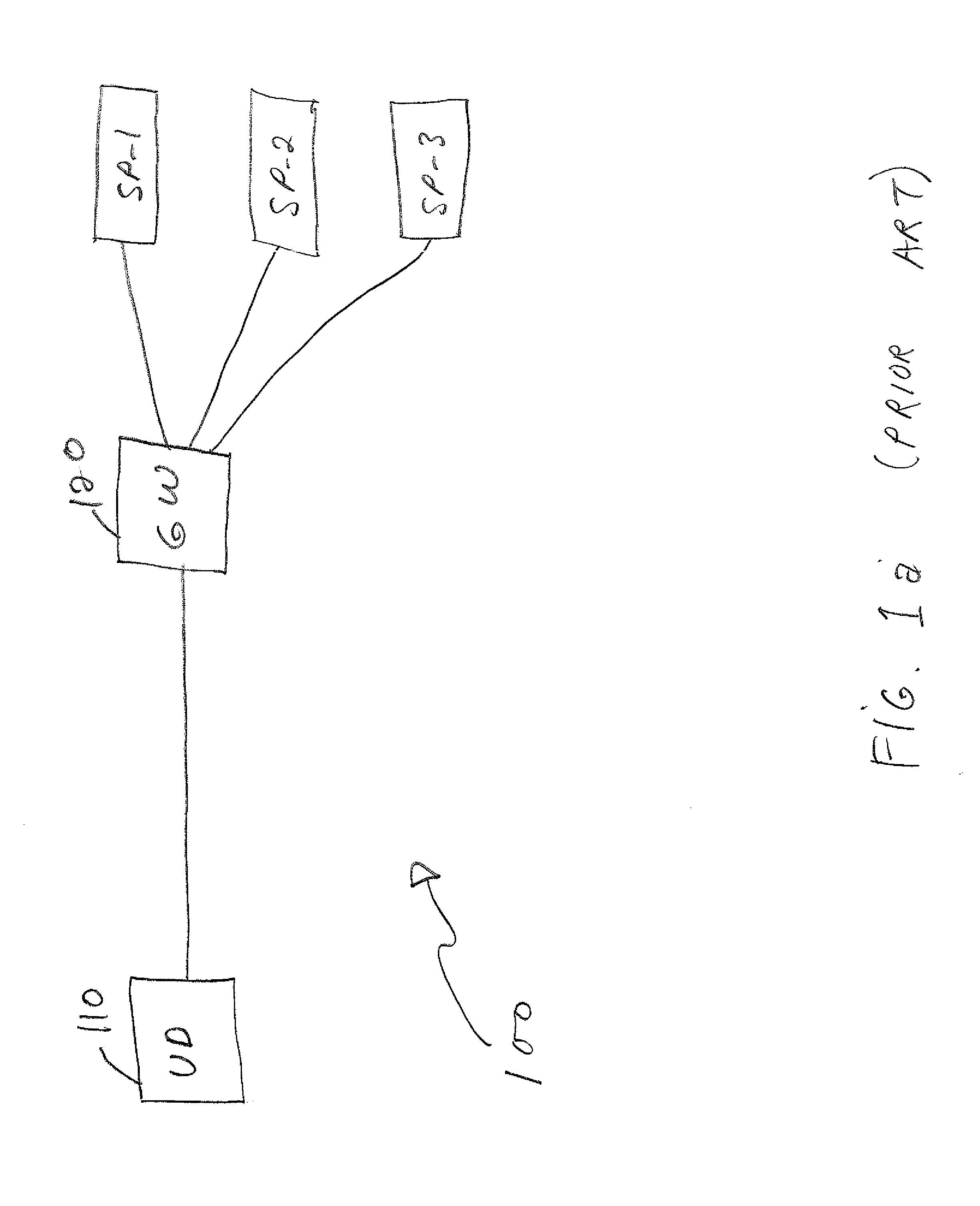
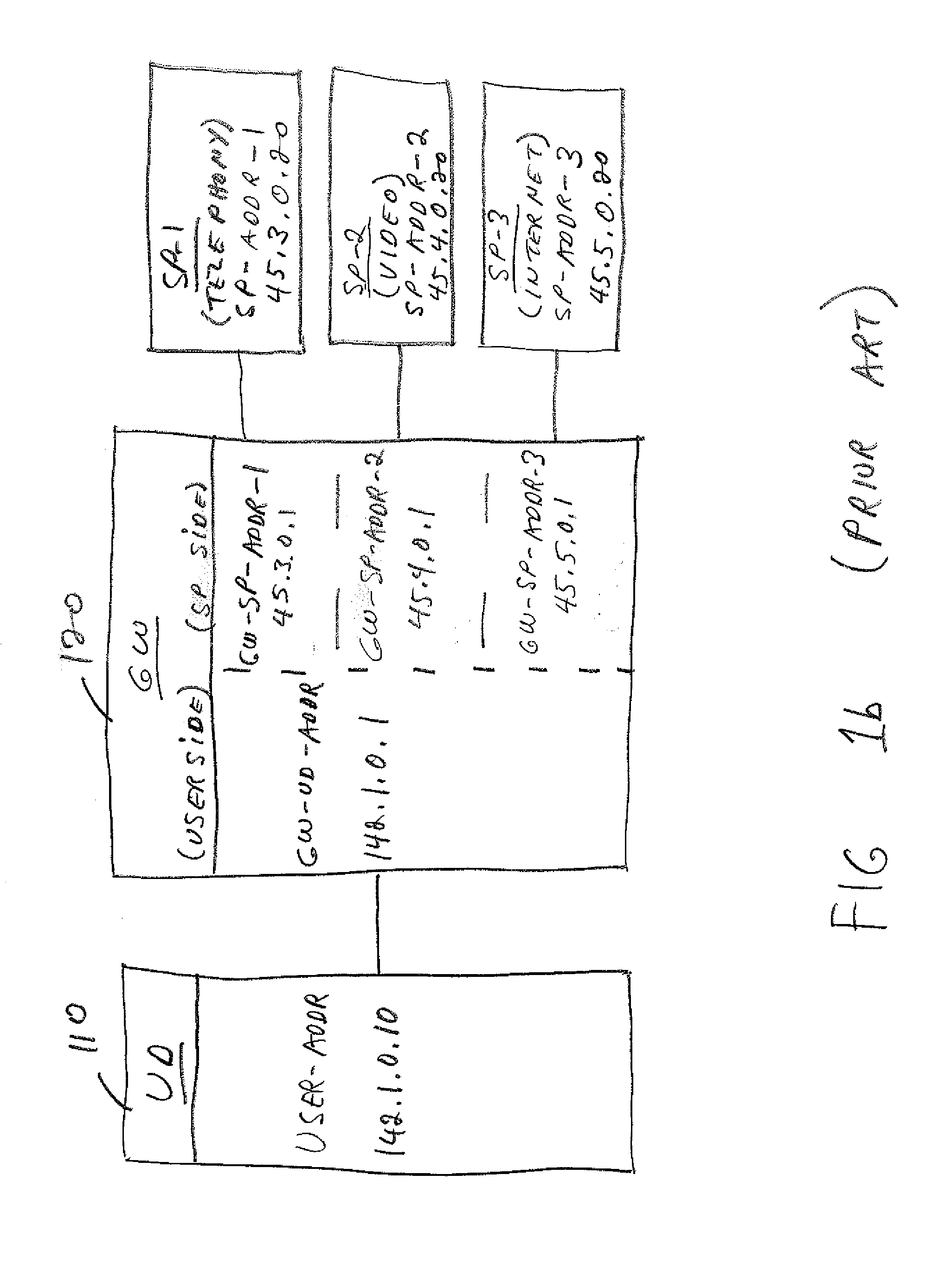
Support of triple play services in user devices
Several services offered by distinct service providers can be accessed from a single user device, through one or more gateways. To ensure quality of service control, each service provider allocates a distinct address to the user device. Distinct forwarding information bases and service mappings are defined at the user device, comprising one such forwarding information base for each service provider and one service mapping for each service type offered by a given service provider. The separate addresses allocated to the user device are related to the separate service mappings. Distinct virtual local area networks (VLANs) are defined, each containing one of the forwarding information base and one of the service mappings. Tags added to packets by the gateways and arriving at the user device are used to link the packets to the proper service provider and to the proper service type.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method for realizing rapid path switching and apparatus thereof
ActiveCN102201964AReduce switching speedShorten the timeNetworks interconnectionInformation repositoryPath switching
The invention provides a method for realizing rapid path switching and an apparatus thereof. Next hop information and next hop state, which are main / standby paths for each other, are maintained through forming a virtual next hop (VN) table which aims at destination. Prefix information corresponding to the destination in a forwarding information base (FIB) is pointed to the VN table so that when there are changes in the next hop information, the prefix information in the FIB does not need to be modified point by point because there is no change in the point of the prefix information. The next hop information in the updated VN table only needs to be sent to a drive so that the drive can update the next hop information which is written-in hardware. Even if there are a plurality of equal-cost multipath routings (ECMP), the VN table only needs to be updated once and then sends the information so as to realize switching of a plurality of paths. The prefix information in the FIB does not need to be modified point by point. Therefore, speed of switching paths is substantially raised and interruption time in traffic can be reduced.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
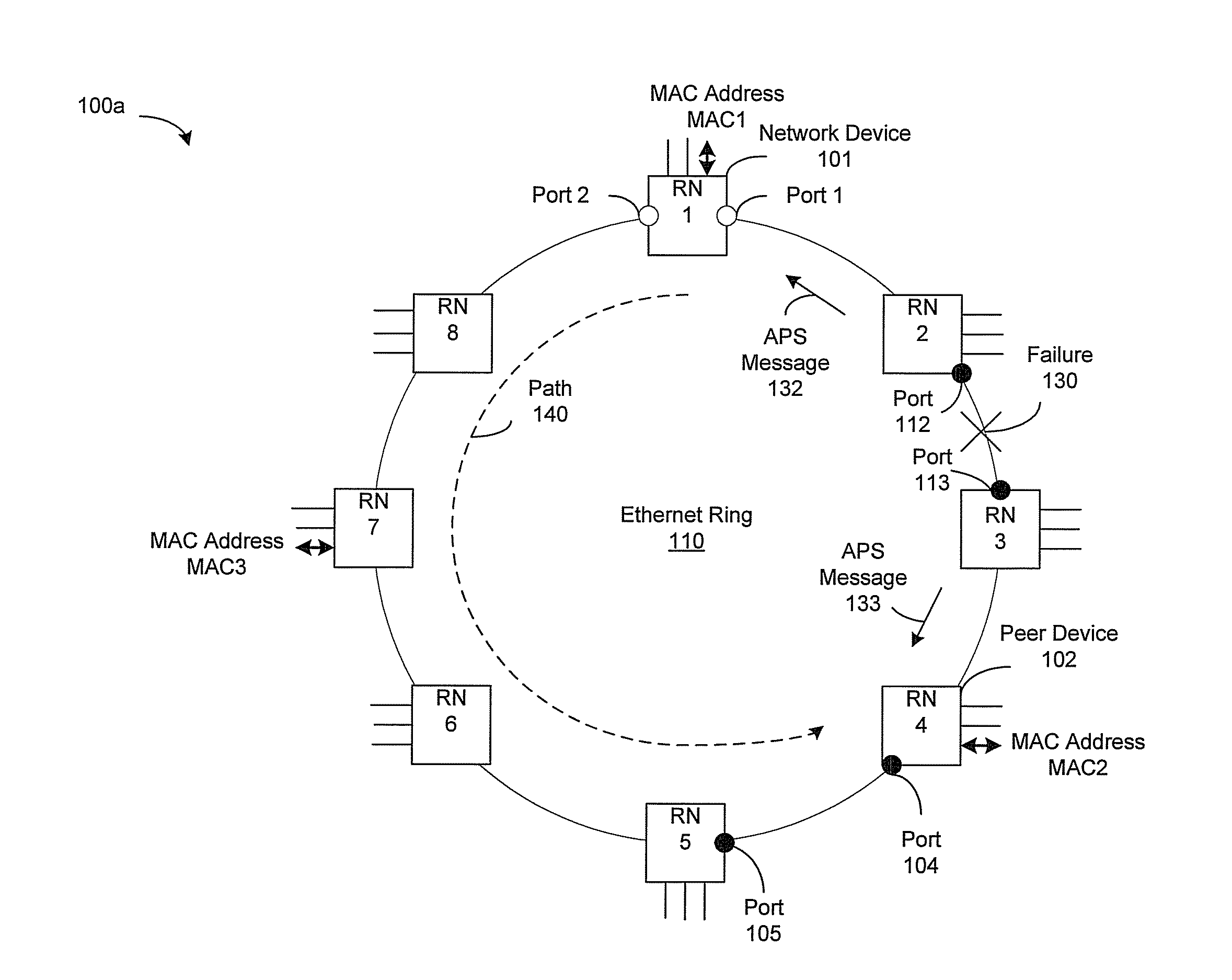
Ethernet Ring Protection without MAC Table Flushing
A network device located in an Ethernet ring may be operable to determine binding between a MAC address and a peer device in the Ethernet ring. The binding may indicate that the MAC address is behind the peer device. When an Ethernet ring failure occurs, the network device may be operable to update forwarding information based on a ring topology of the Ethernet ring, a position of the failure on the Ethernet ring and the binding. The forwarding information may indicate which ring port that is used on the network device to forward MAC frames to a destination corresponding to the MAC address. The network device may then forward the MAC frames based on the updated forwarding information. The Ethernet ring may utilize a VLAN frame format, a Q-in-Q frame format or a MAC-in-MAC frame format. The forwarding information may comprise a MAC table and / or a protection table.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
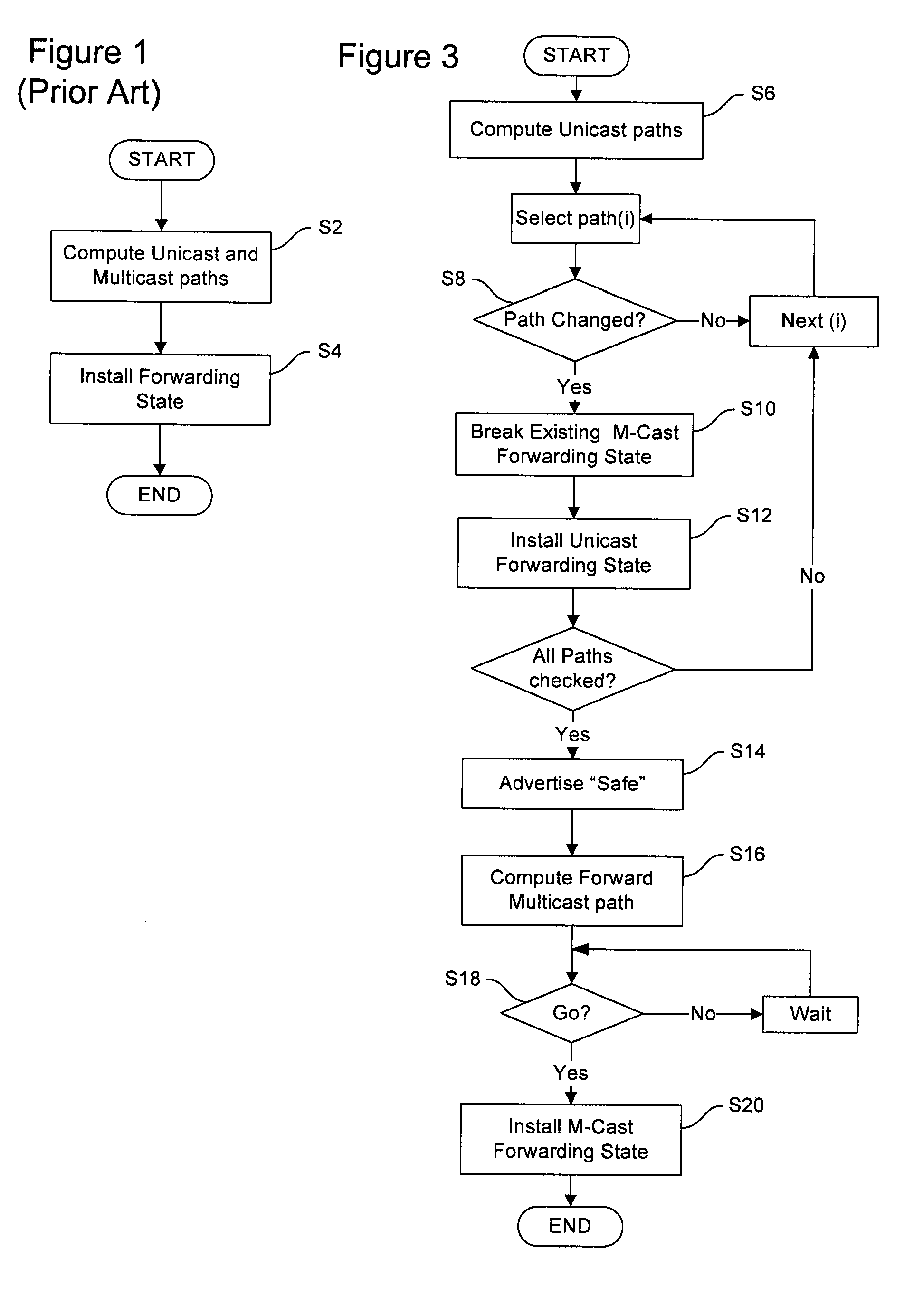
Break before make forwarding information base (FIB) population for multicast
InactiveUS20090180400A1Degree of parallelismSpecial service provision for substationData switching by path configurationInformation repositoryUnsafe condition
A method of installing forwarding state in a link state protocol controlled network node having a topology database representing a known topology of the network, and at least two ports for communication with corresponding peers of the network node. A unicast path is computed from the node to a second node in the network, using the topology database, and unicast forwarding state associated with the computed unicast path installed in a filtering database (FDB) of the node. Multicast forwarding state is removed for multicast trees originating at the second node if an unsafe condition is detected. Subsequently, a “safe” indication signal is advertised to each of the peers of the network node. The “safe” indication signal comprises a digest of the topology database. A multicast path is then computed from the network node to at least one destination node of a multicast tree originating at the second node. Finally, multicast forwarding state associated with the computed multicast path is installed in the filtering database (FDB) of the network node, when predetermined safe condition is satisfied.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
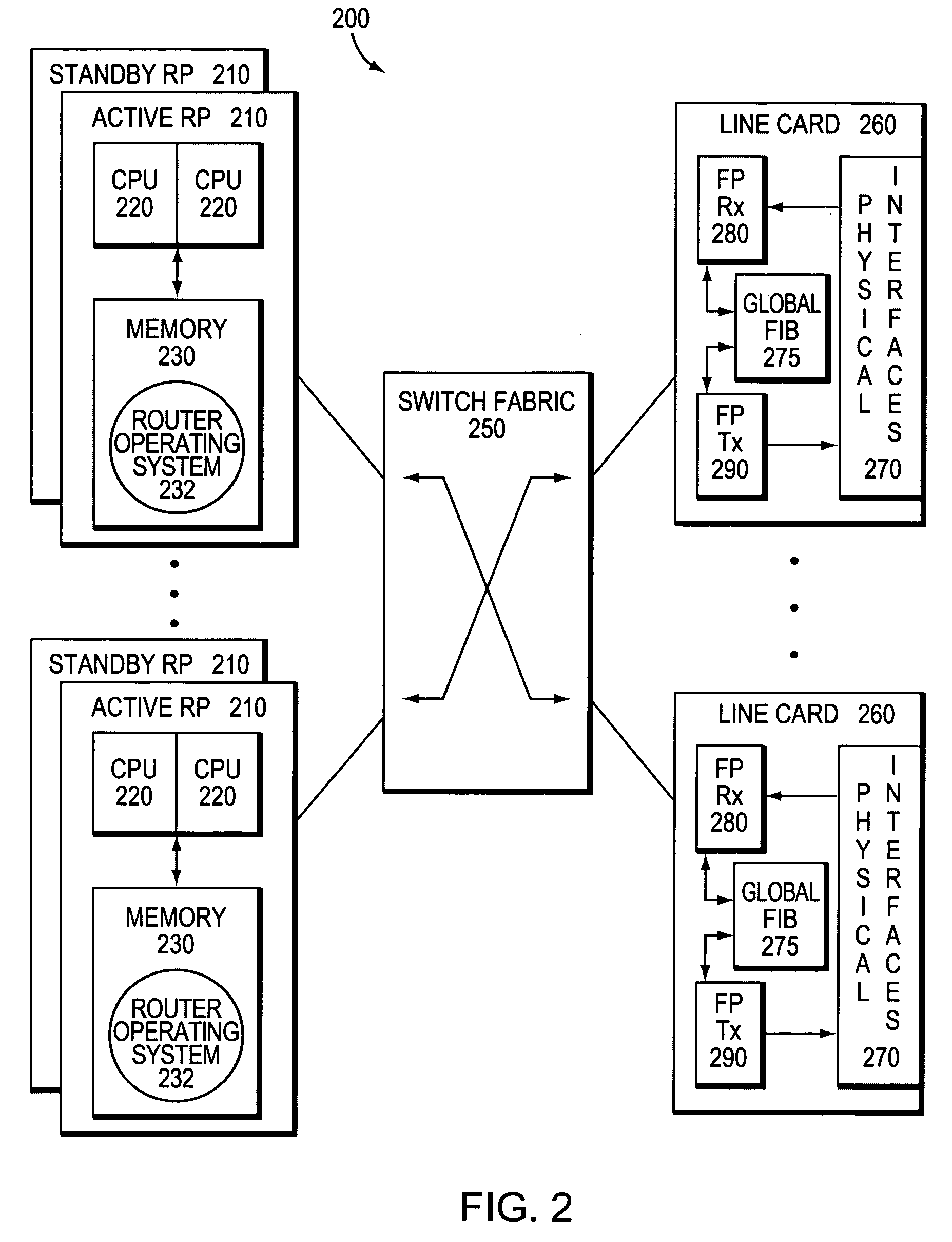
High availability packet forward apparatus and method
ActiveUS7206309B2Improve usabilityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsInformation repositoryFailover
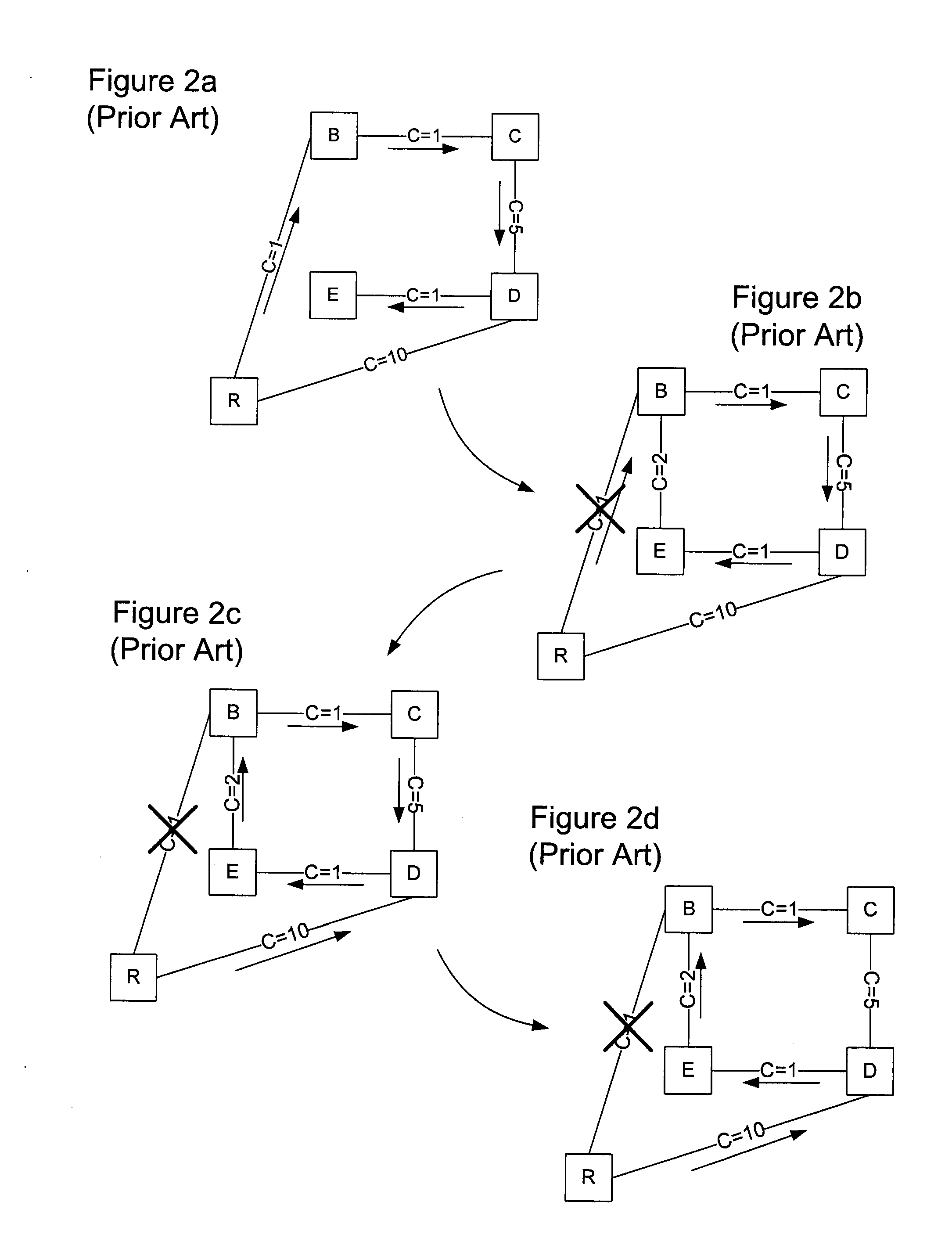
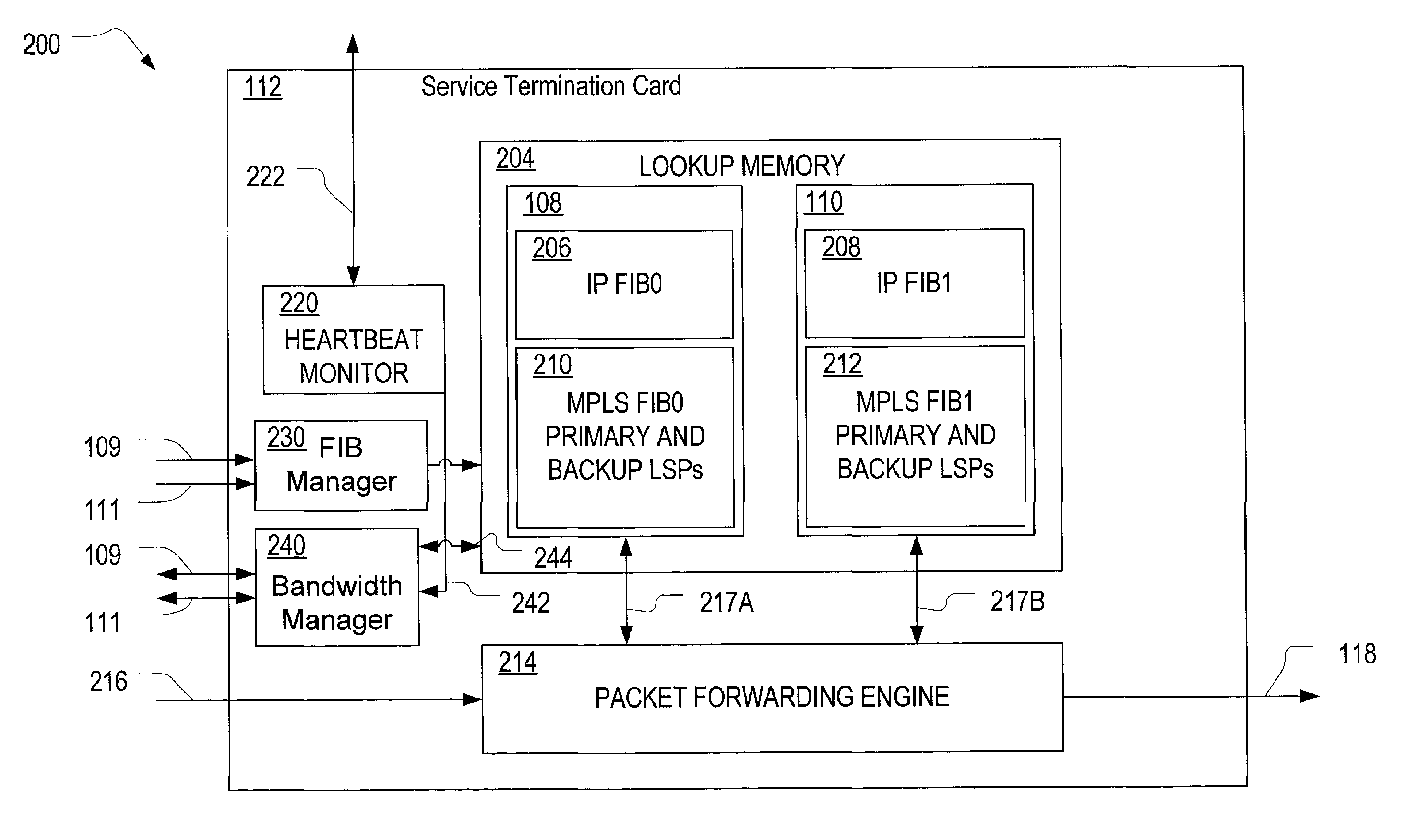
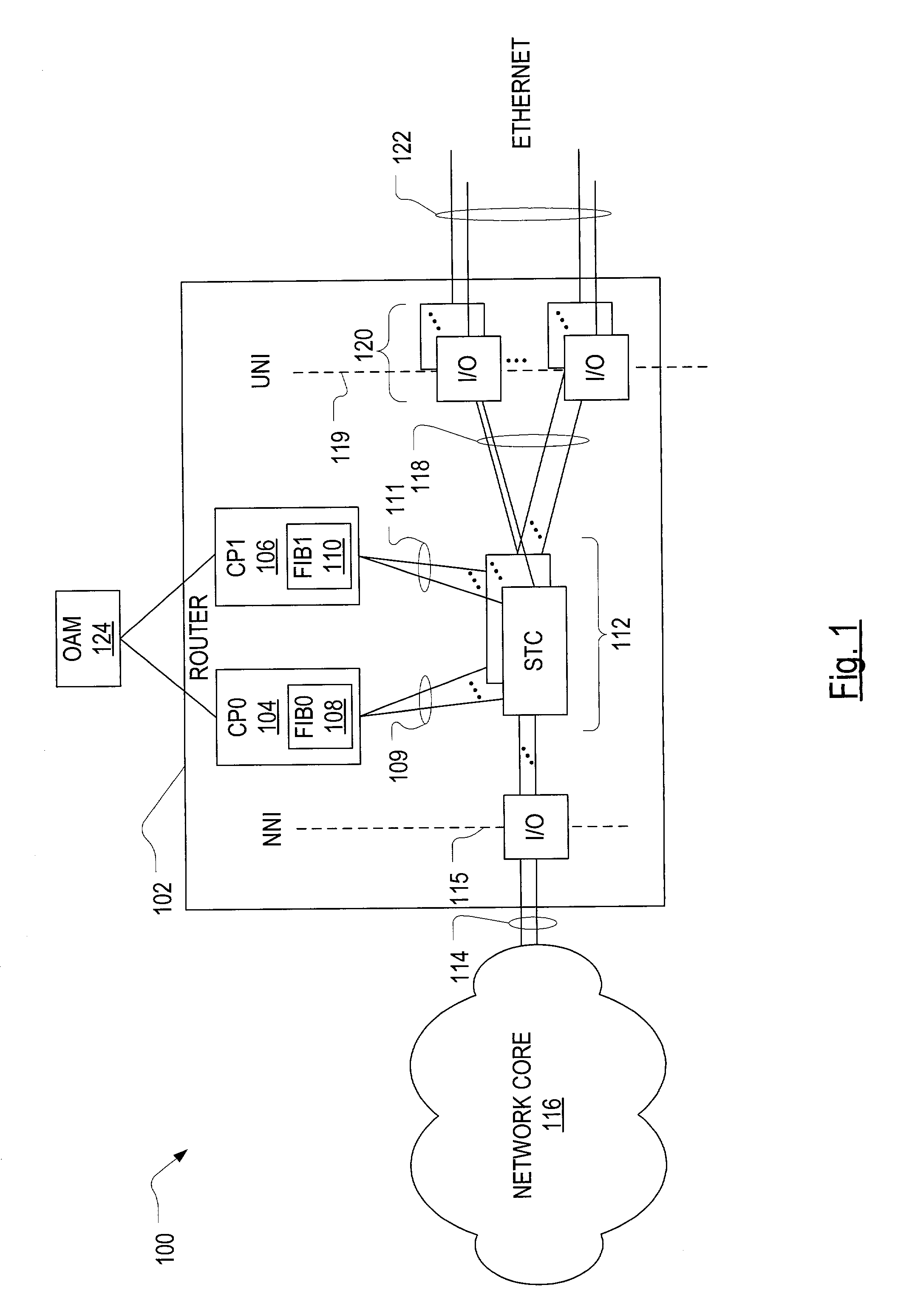
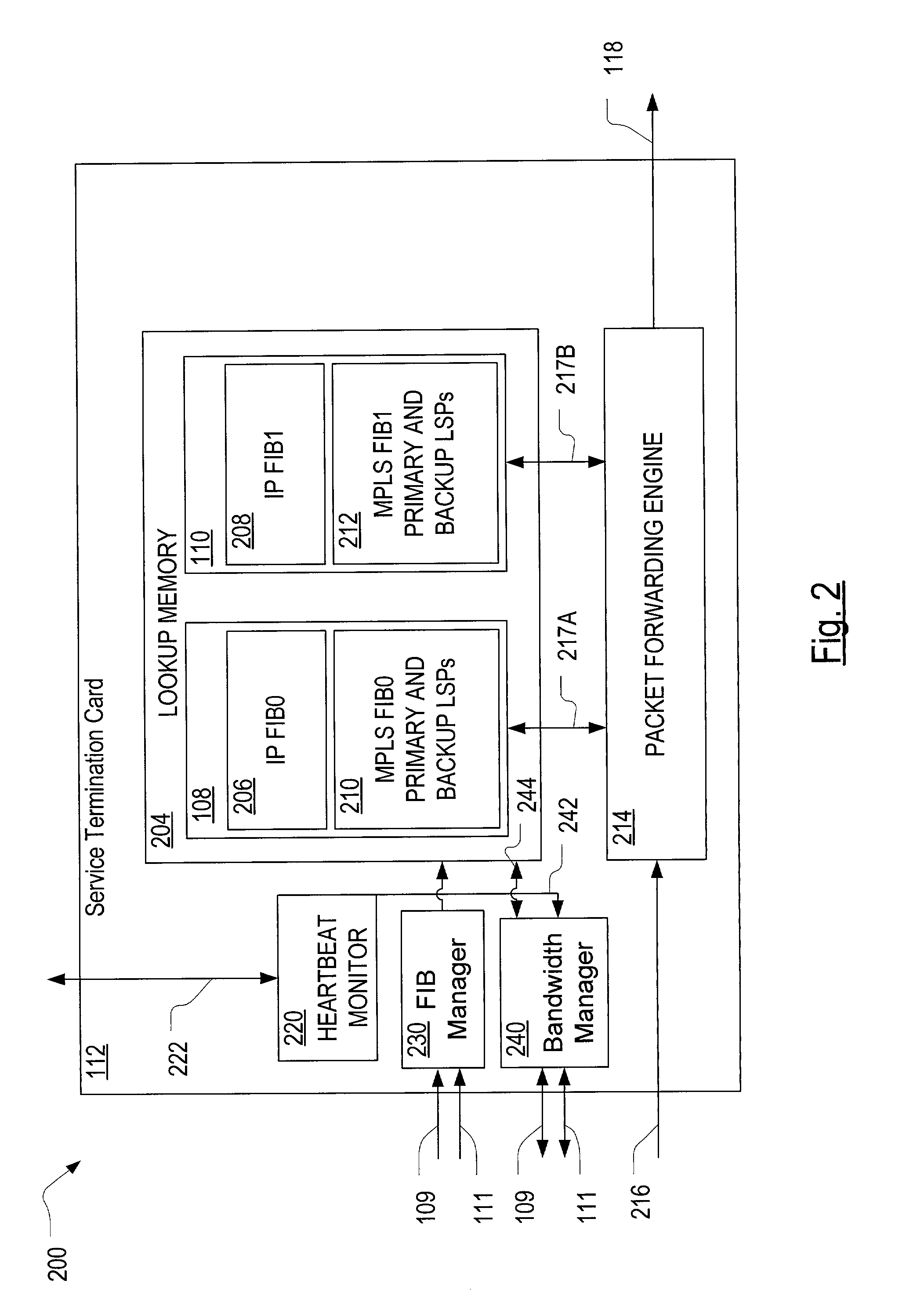
A high availability packet forwarding router for an internet protocol (IP) network, includes two control processors, one or more service termination cards (STCs) with forwarding information bases (FIBs), and a packet forwarding engine. The two processors run asynchronously in a master / standby relationship. Integrity of processes running on the control processors is monitored and the forwarding engine forwards packets according to a FIB maintained by an in-service one of the control processors. Hitless failover and hitless software upgrades are supported.
Owner:CIENA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com