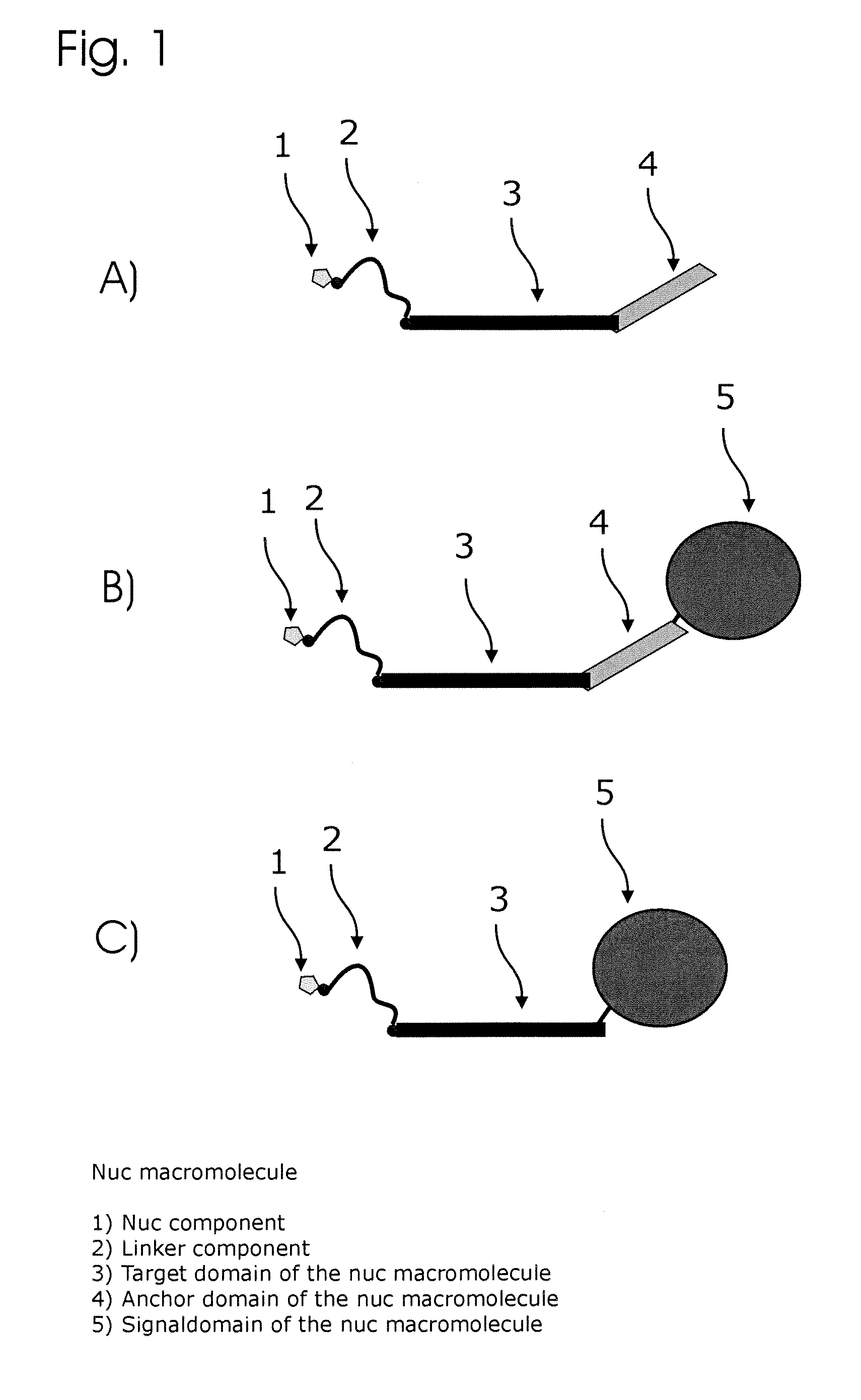
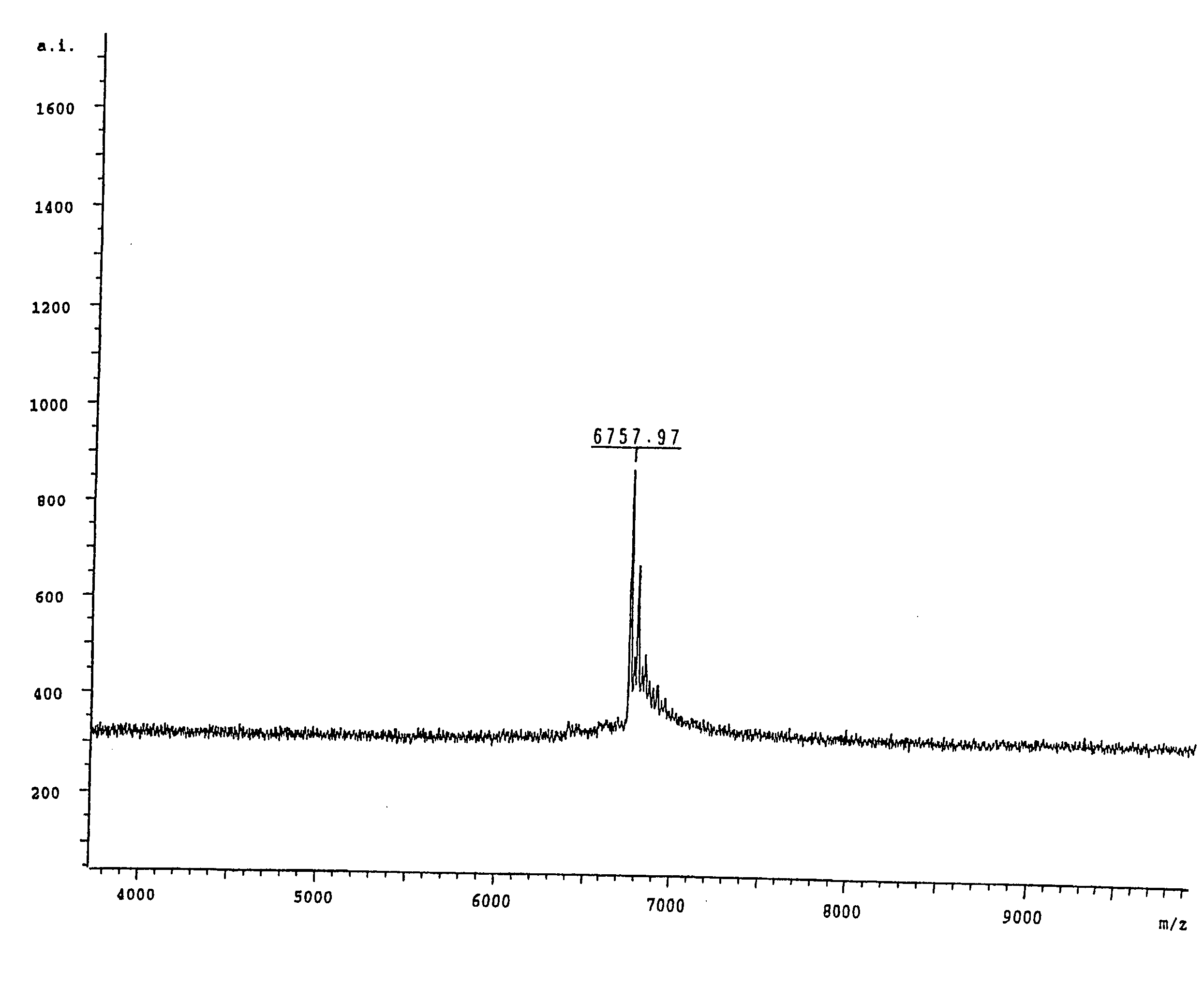
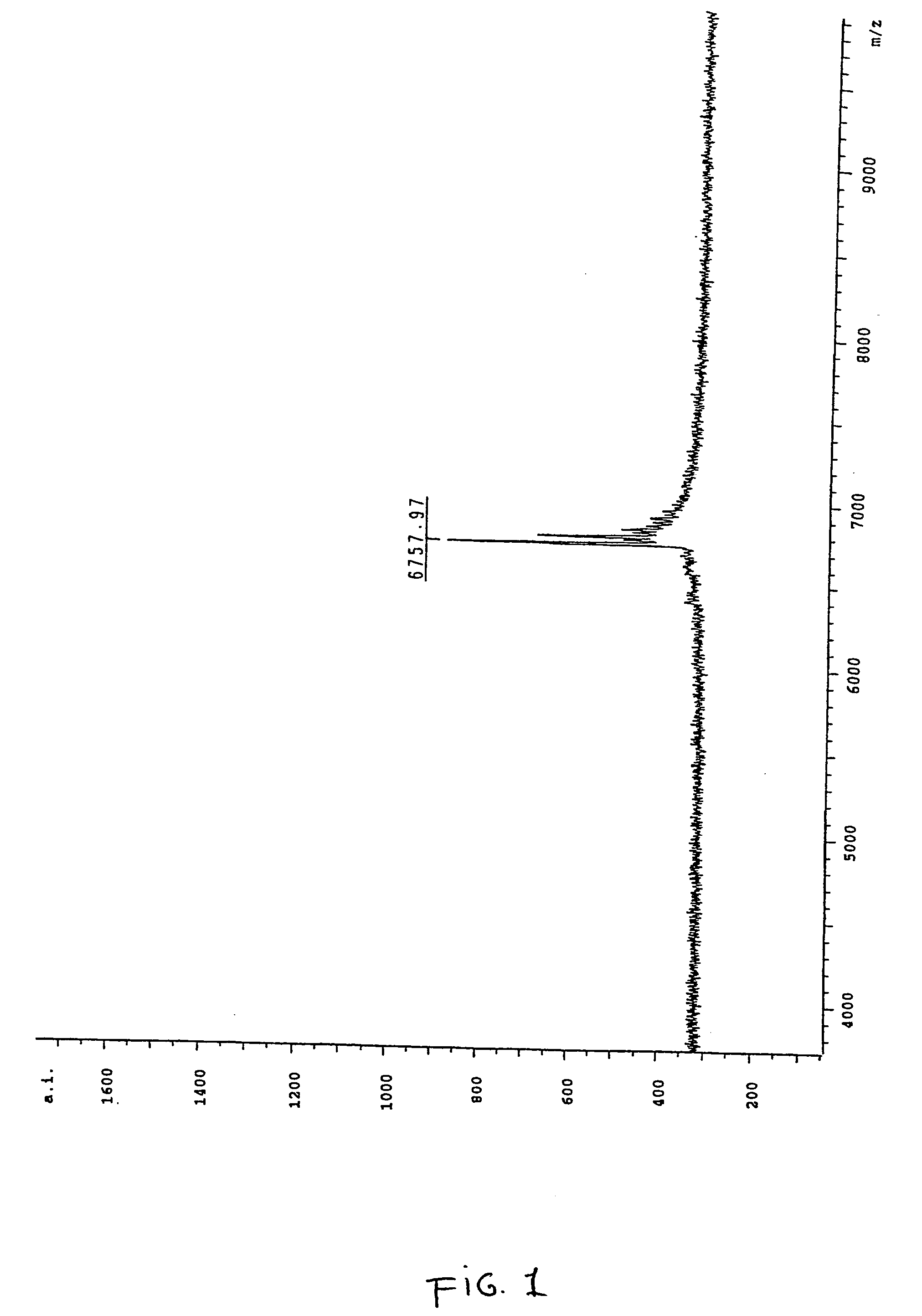
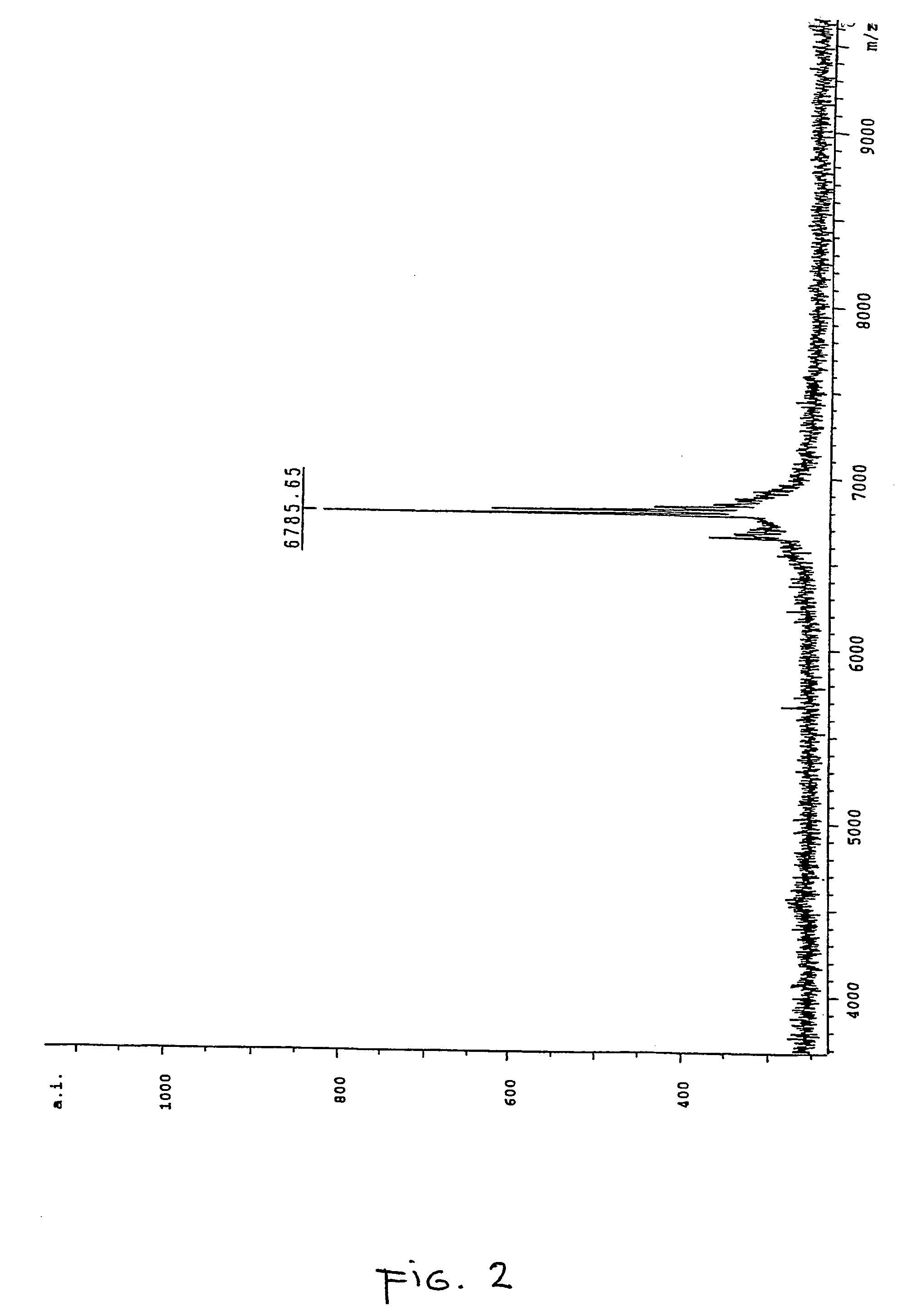
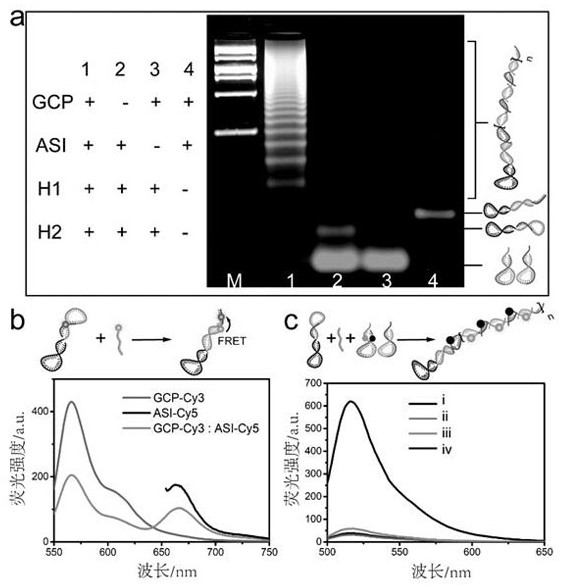
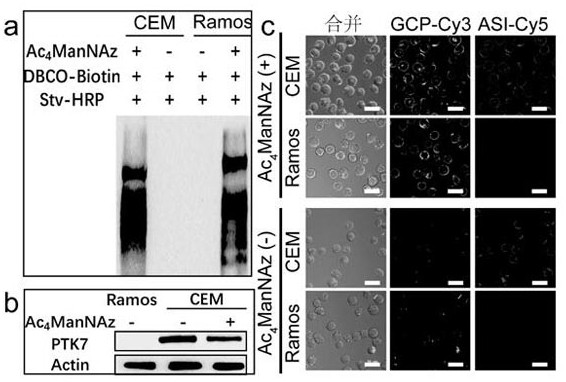
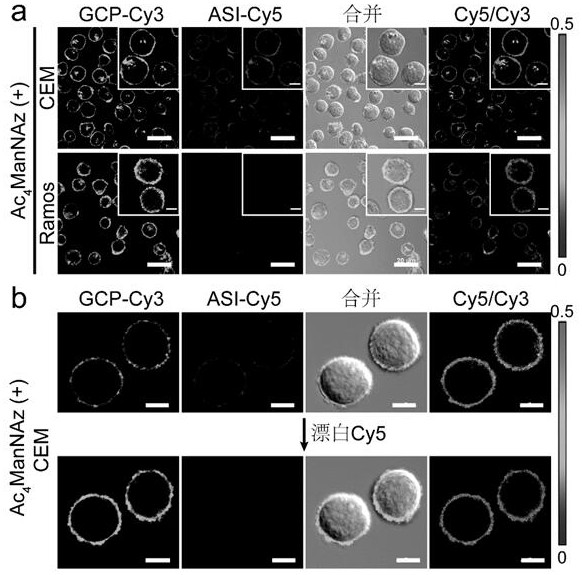
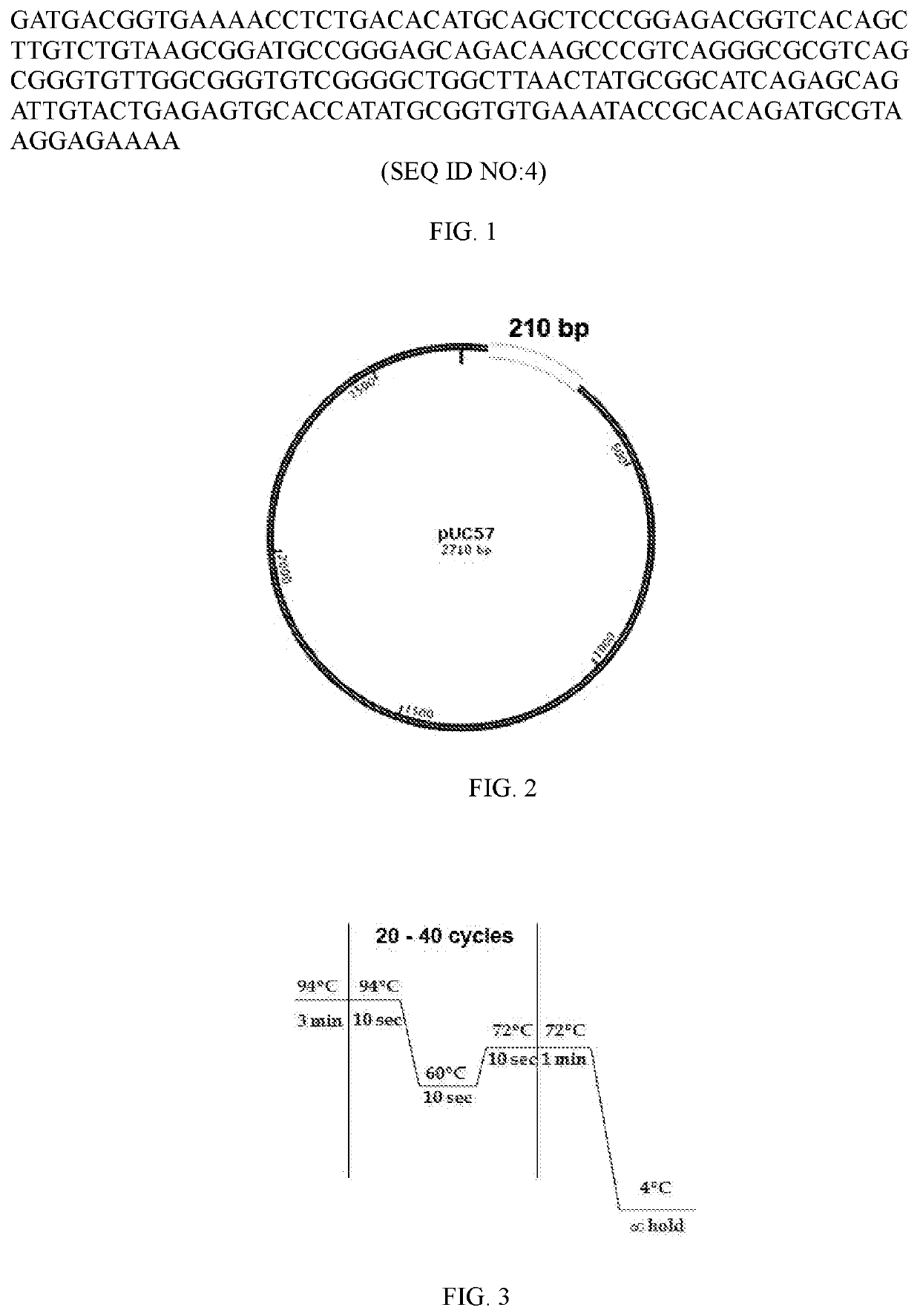
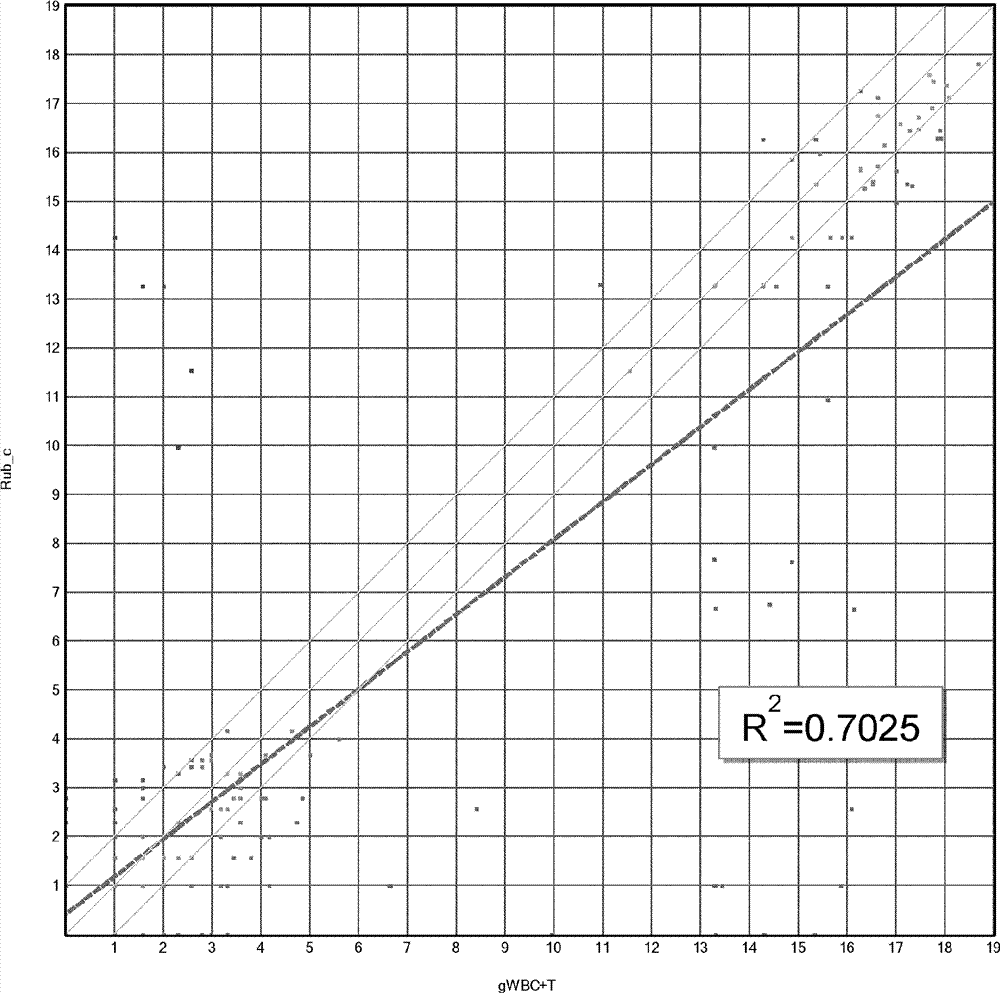
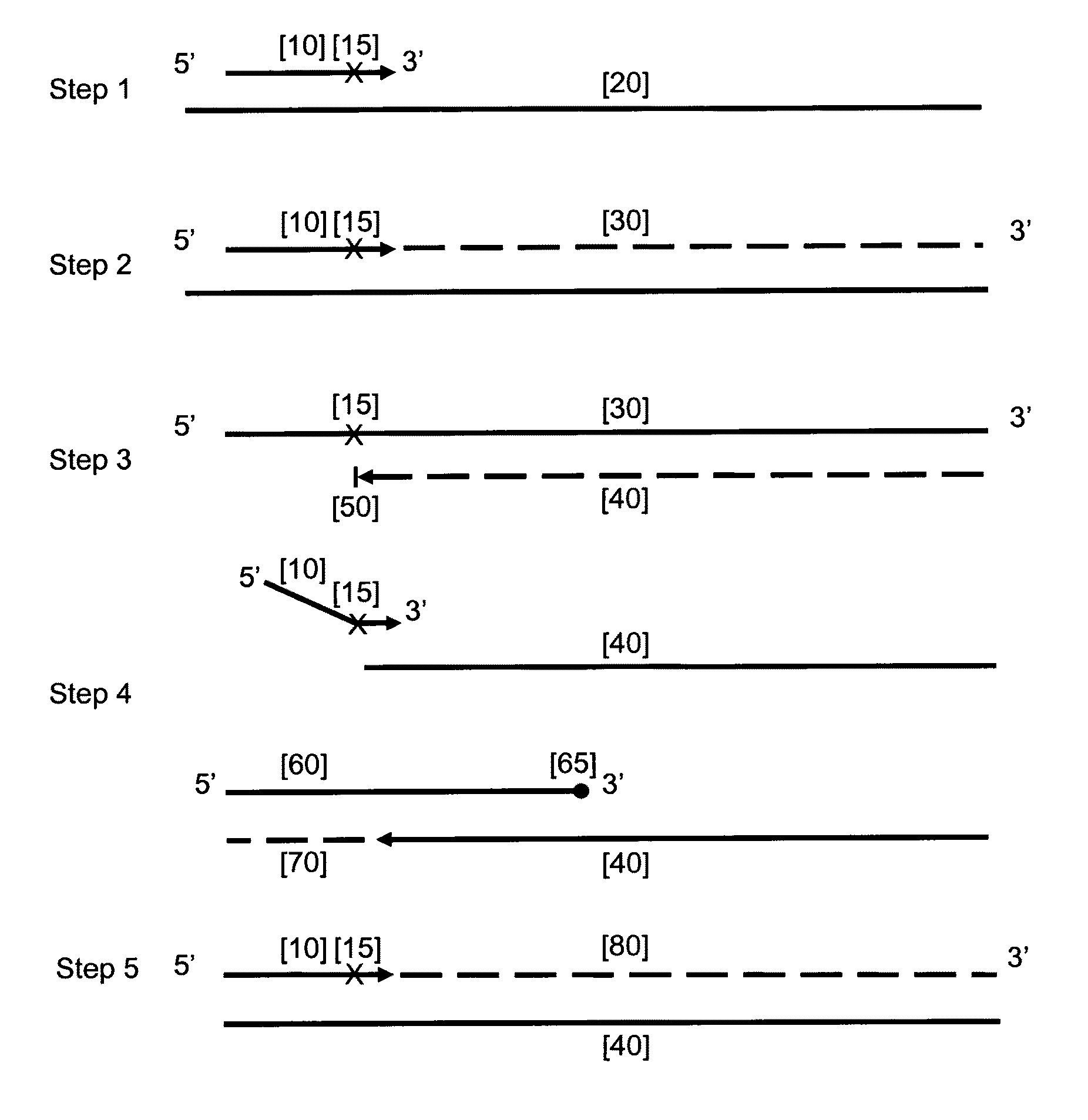
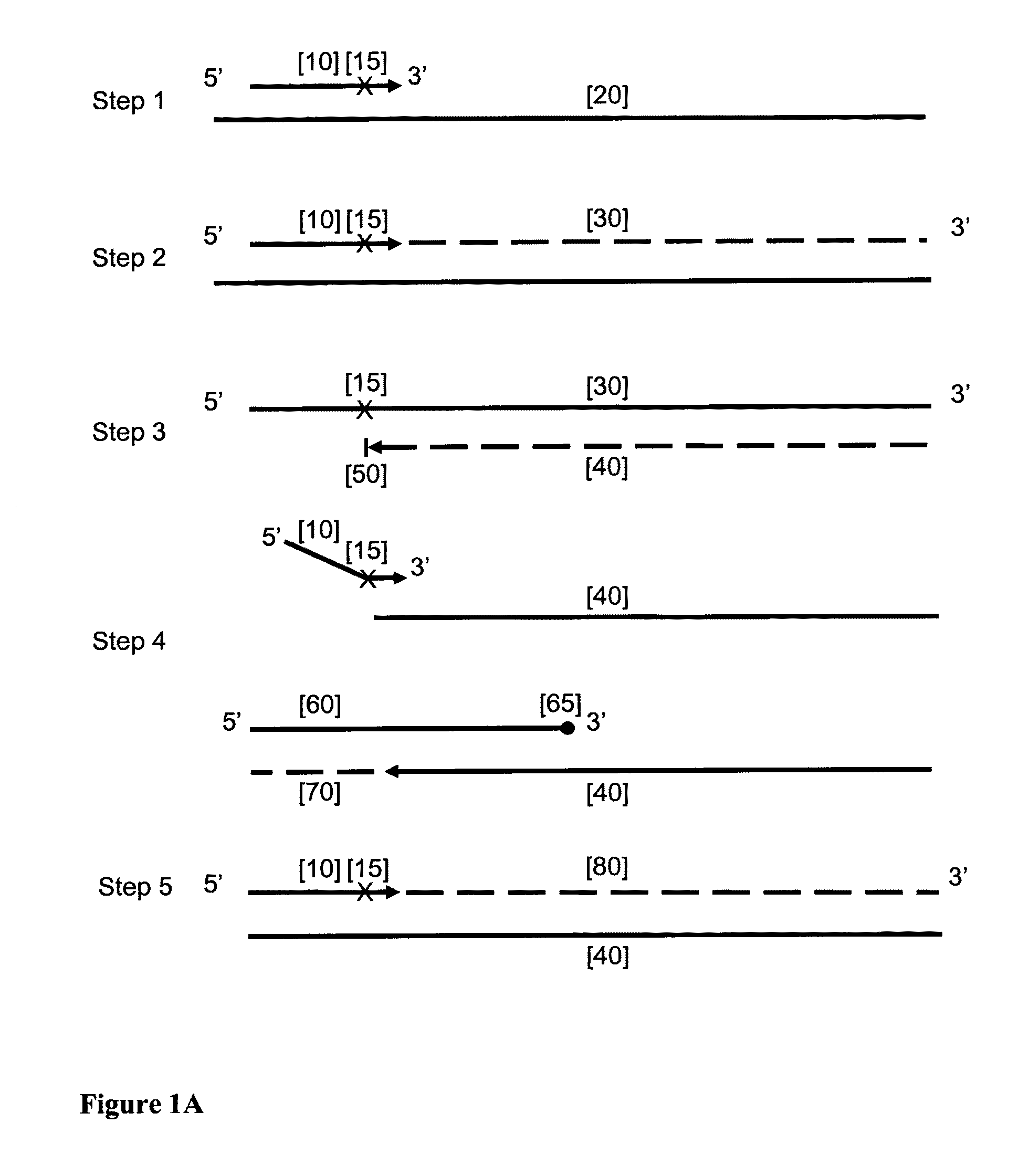
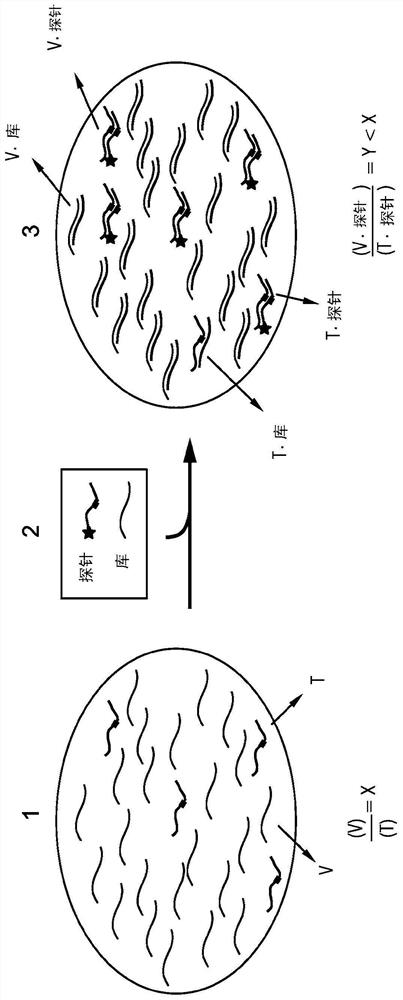
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Enzymatic amplification" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nucleic acid amplification
ActiveUS20110033851A1Strong specificityReducing and eliminating amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationOligonucleotide PrimerNucleotide sequencing
Provided herein is a method for the selective amplification of a target nucleotide sequence located within a nucleic acid molecule, the method comprising contacting the nucleic acid molecule (“template” molecule) with (i) at least one facilitator oligonucleotide, wherein the facilitator oligonucleotide includes at least one modification at or near its 3′ terminus such that 3′ extension from the facilitator oligonucleotide is blocked, and (ii) two or more oligonucleotide primers, at least one of which is an initiator primer modified such that the presence of the modification prematurely terminates complementary strand synthesis, wherein the facilitator oligonucleotide and the initiator primer bind to substantially the same or adjacent regions of the template nucleic acid molecule and the facilitator oligonucleotide further comprises sequences complementary to the target sequence 3′ to the binding location of the initiator primer; and carrying out thermocyclic, enzymatic amplification such that the specific target sequence is selectively amplified.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Method for detection and multiple, simultaneous quantification of pathogens by means of real-time polymerase chain reaction
Owner:SIGMA ALIMENTOS S A DE
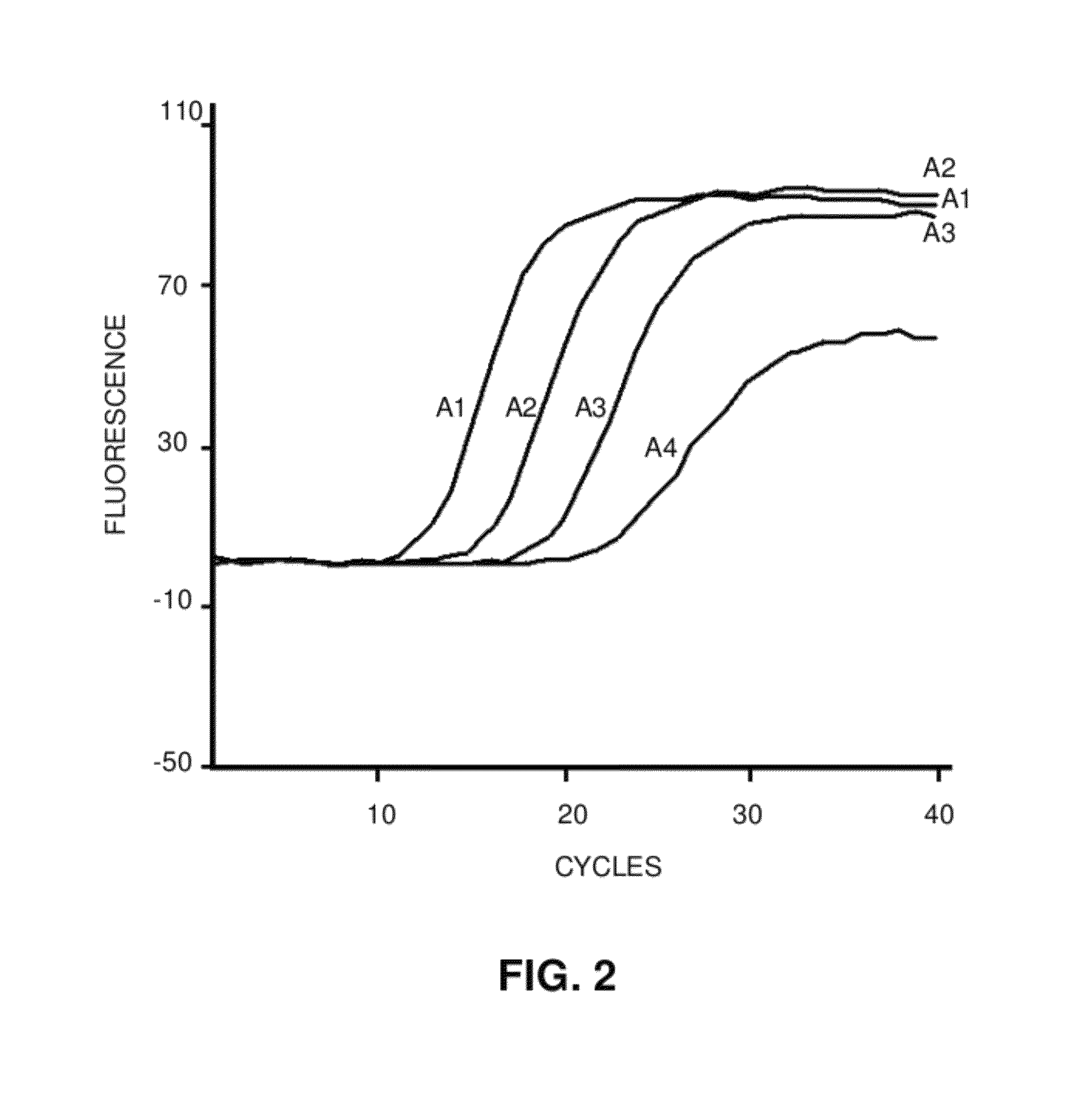
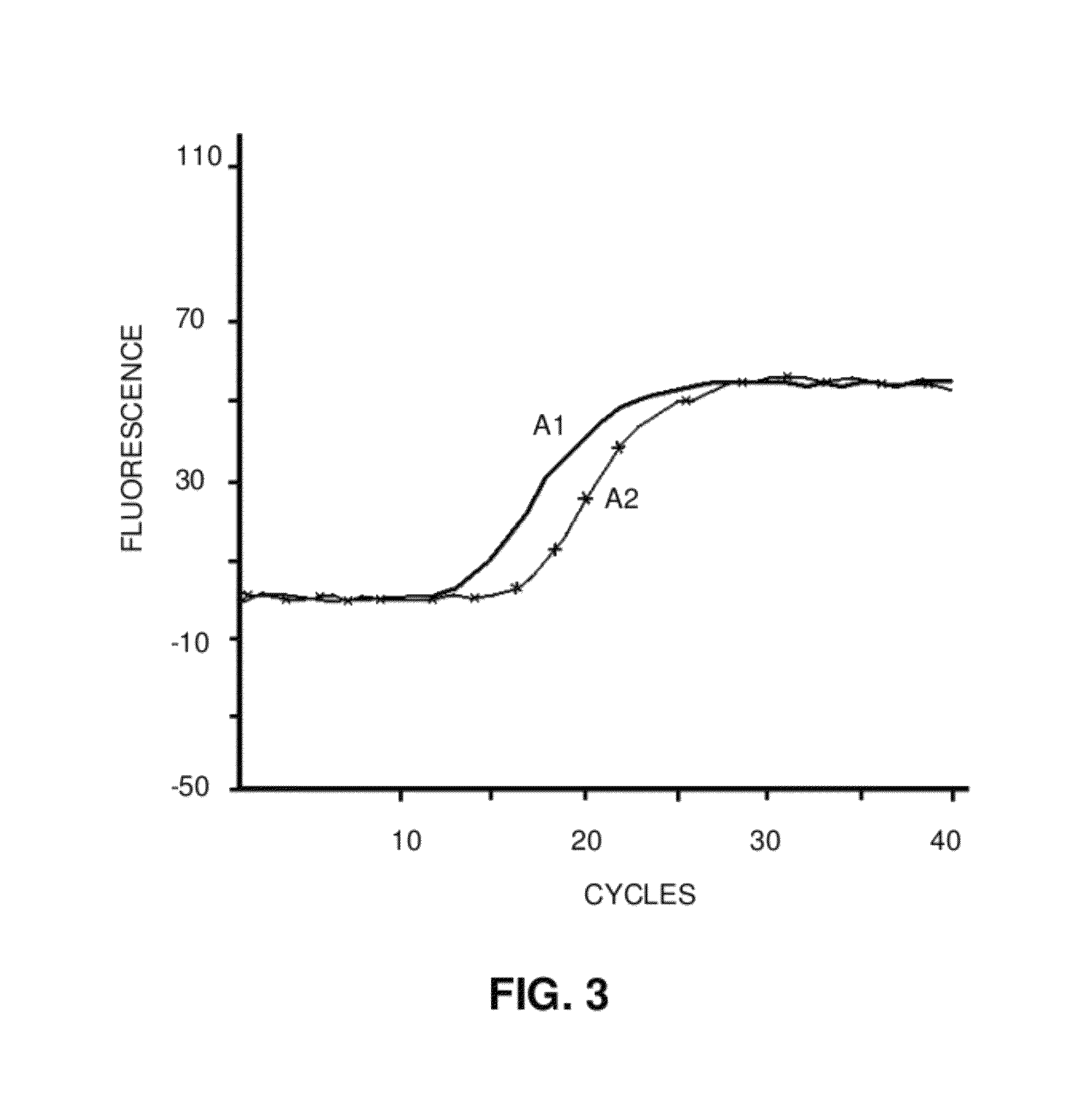
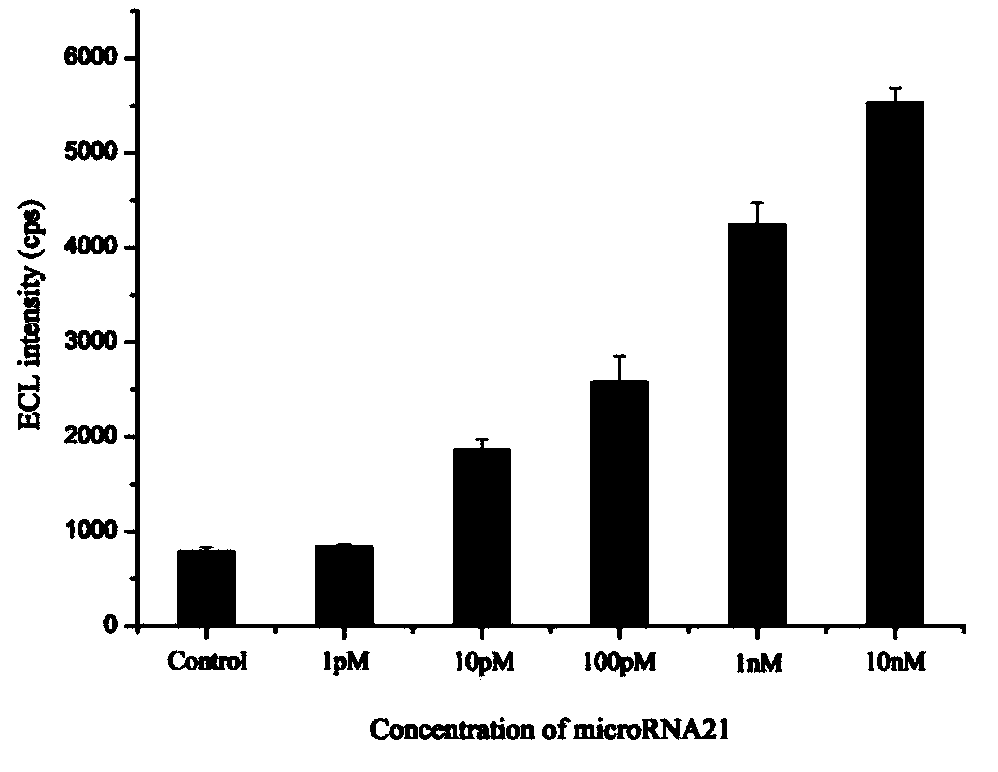
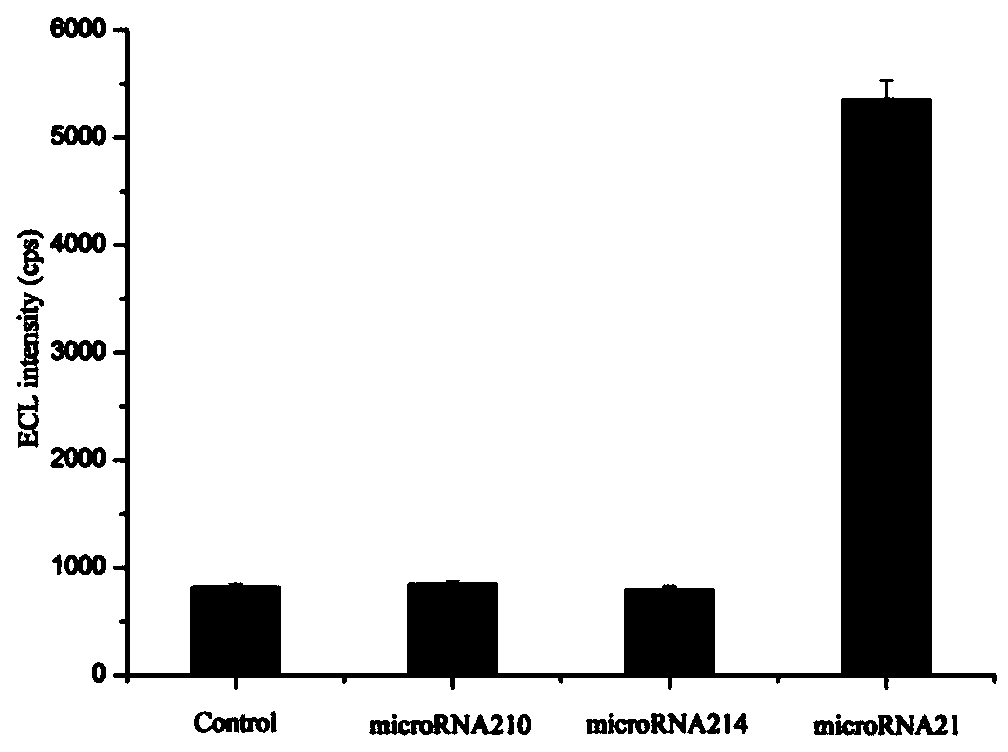
MicroRNA detection method based on non-enzymatic amplification and electrochemiluminescence principles
InactiveCN103383355AThe principle is simpleLow costChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceNucleic acid detectionMicroRNA
The invention relates to the technical field of nucleic acid detection, in particular to a microRNA detection method based on non-enzymatic amplification and electrochemiluminescence principles. The detection method comprises the steps of: 1) designing DNA hairpin probes, i.e. designing the hairpin H1 and hairpin H2 sequences required by a non-enzymatic amplification system according to a non-enzymatic amplification principle and a detected microRNA sequence; 2) conducting electrochemiluminescence group marking; 3) performing hairpin probe pretreatment; 4) constructing a non-enzymatic amplification detection system; 5) carrying out product cleaning and separation; and 6) conducting signal detection. The method has the characteristics of high sensitivity, accuracy, fastness and simple operation, and the whole amplification process does not involve enzyme, so that the detection cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
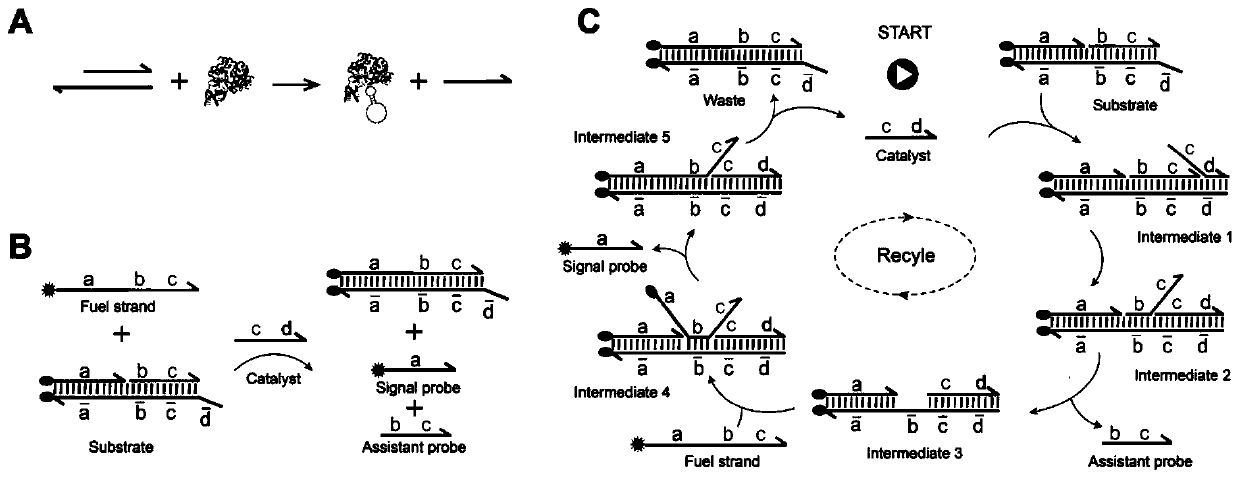
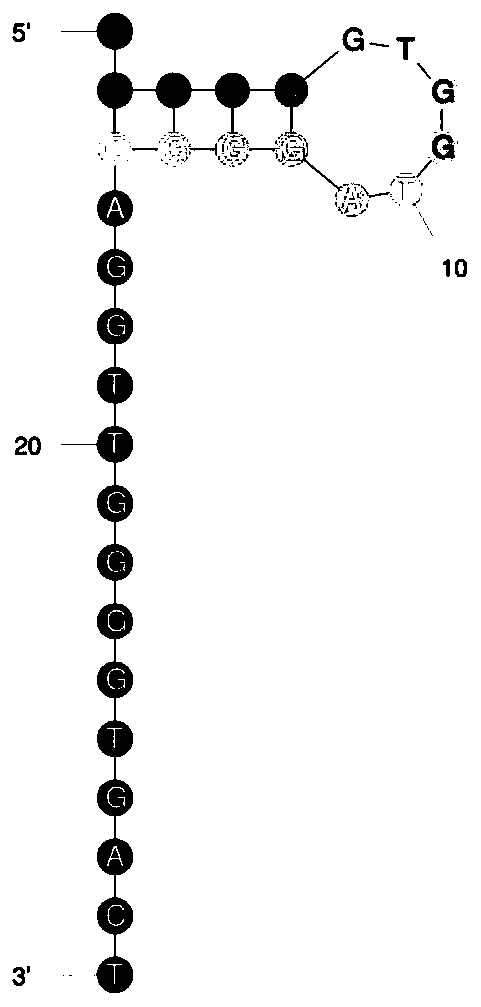
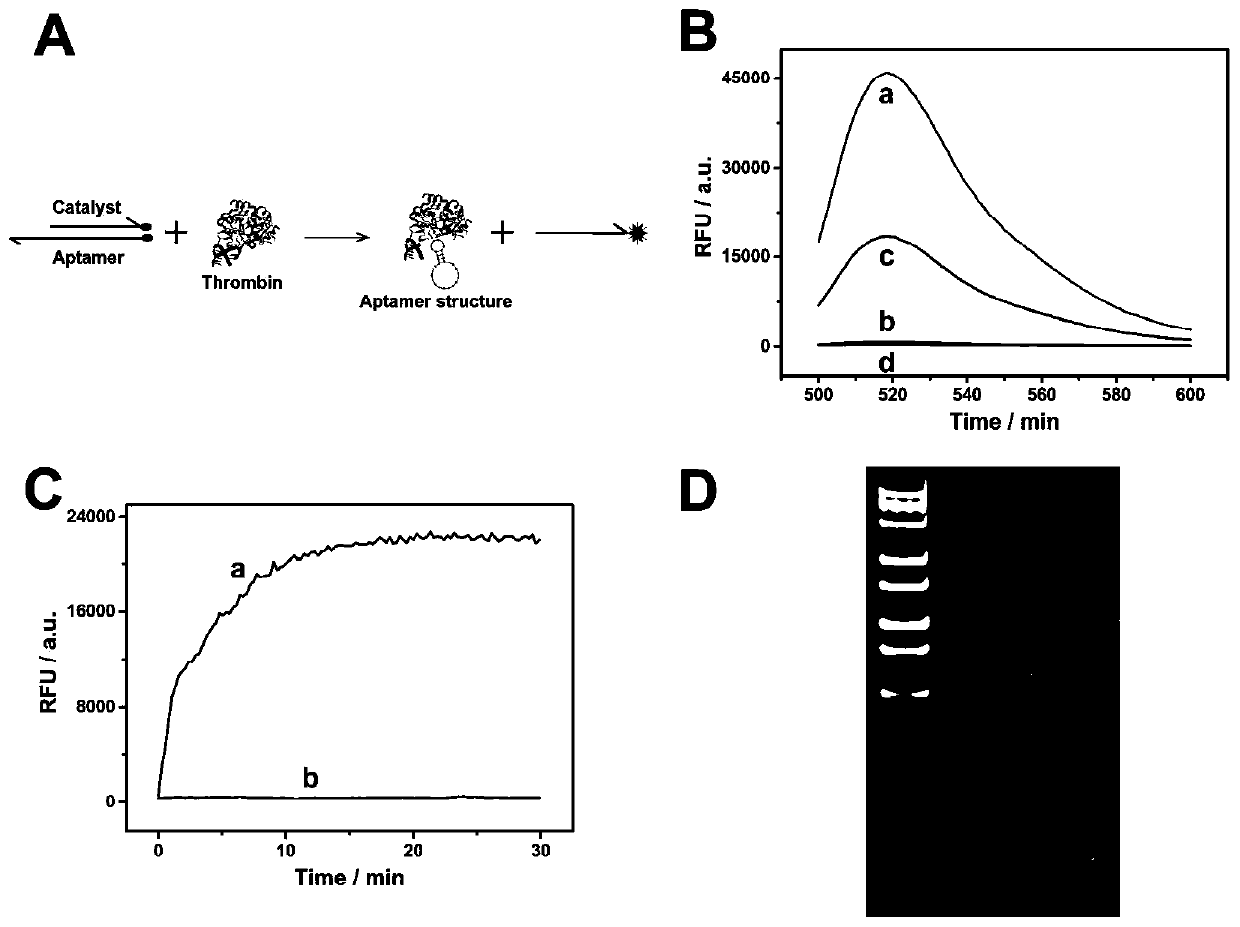
Method for detecting thrombin based on fluorescent dual-signal non-enzymatic amplification strategy of aptamer and application of method
PendingCN111455026AStrong specificityLow detection limitMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingAptamerPtru catalyst
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomedicine, and particularly discloses a method for detecting thrombin based on a fluorescent dual-signal non-enzymatic amplification strategy of an aptamer and application of the method. The method comprises the following steps: reacting an auxiliary probe, a signal probe and a Linker chain to form a three-chain DNA reaction substrate, then mixingthe three-chain DNA reaction substrate, a fuel chain and the aptamer / catalyst chain for reaction to form a reaction solution, thus obtaining a thrombin fluorescent detection system, and after the thrombin is added, detecting the thrombin by monitoring the change of a fluorescent signal FAM and ROX. According to the method, the release of the catalyst chain is induced through the specific combination of the thrombin and the aptamer; the catalyst chain triggers and starts a DNA cyclic amplification reaction through nucleic acid hybridization and branch migration, so that the recycling and cyclic utilization and dual-signal amplification of the catalyst chain are realized; the whole reaction process of the method does not need any protease, and the whole reaction can be completed in one reaction system in one step; and the selectivity is good, the sensitivity is high, the linear range is 1fM-1nM, and the lowest detection lower limit is 0.45fM.
Owner:THE AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICAL TO SOUTHWEST MEDICAL UNIV
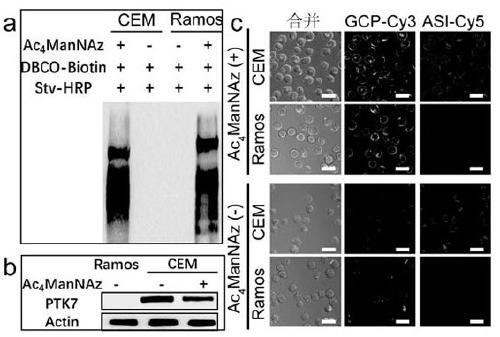
Protein glycosylation detection kit and detection method, and application
ActiveCN109307773AImprove label stabilityGood biocompatibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingCell membraneIn vivo
The invention discloses a protein glycosylation detection kit and a detection method, and an application. Specific protein targeting, an HCR-based non-enzymatic amplification strategy, and the proteinglycosylation detection kit and detection method for detecting and imaging specific protein glycosylation on a cell membrane surface in living cells and living bodies by using the HCR-based non-enzymatic amplification strategy, and detection applications in various application occasions such as an in vitro application occasion and an in vivo application occasion are achieved by using technical means such as modification of azido glycosyl on the surface of a protein by a glycosyl-labelled nucleic acid sequence, introduction of a protein probe nucleic acid sequence, and introduction of a hybridization chain reaction reagent.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
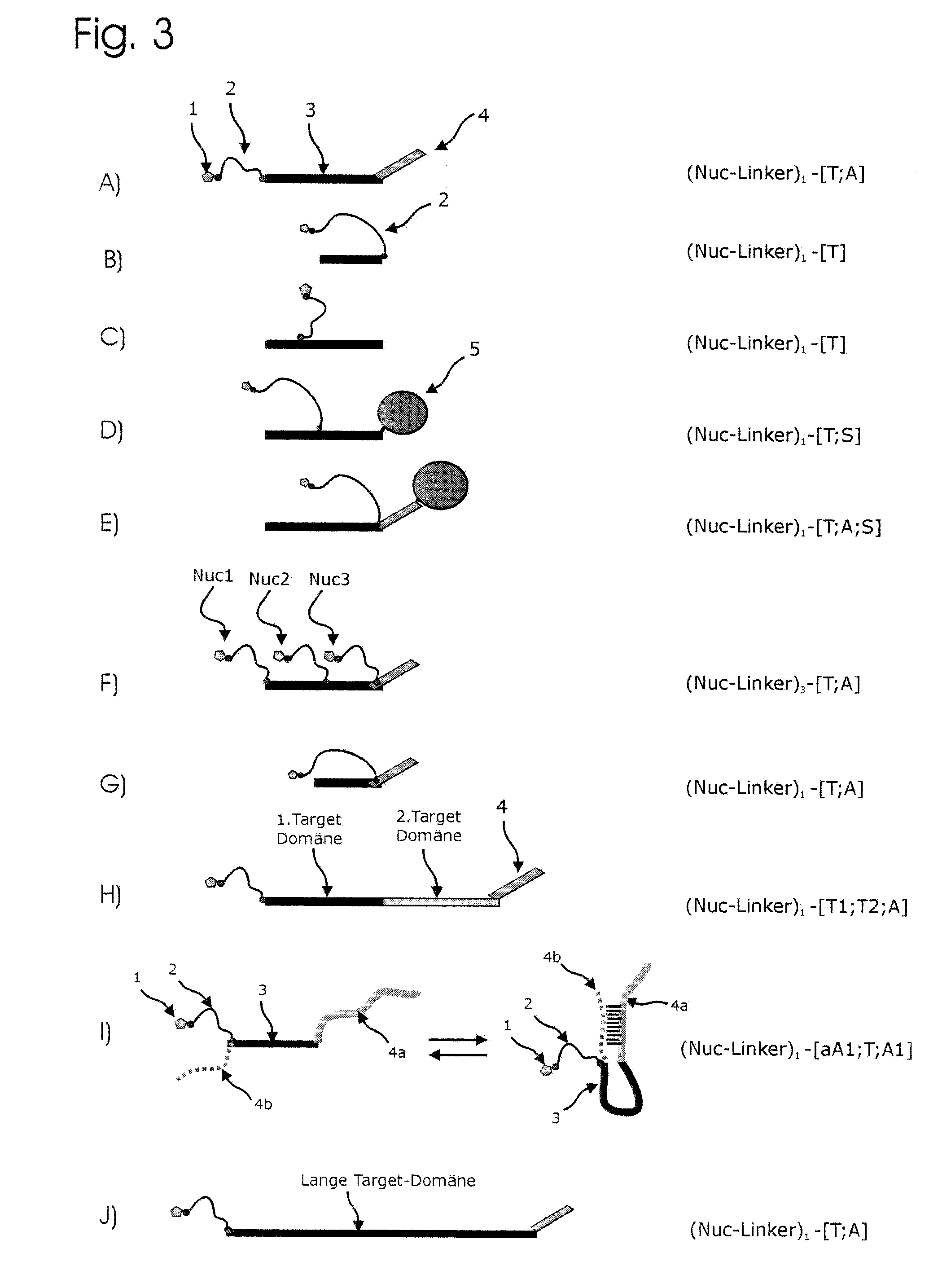
Conjugates of nucleotides and method for the application thereof
ActiveUS20130171631A1Much robustUseful in detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationPolymerase LEnzymatic amplification
The invention relates to a novel method for enzymatically marking nucleic acid chains (target sequences) by using nucleotide conjugates. Said nucleotide conjugates are capable of binding specifically to the target sequence under reaction conditions and of being incorporated in the complementary growing strand by means of a polymerase. The nucleic acid chains marked with such conjugates can be bound to the solid phase. The marking can be carried out in parallel with the enzymatic amplification of target sequences.
Owner:GENOVOXX
Method for detection and multiple, simultaneous quantification of pathogens by means of real-time polymerase chain reaction
InactiveUS20100159448A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliFluorescence
A method for the detection and multiple, simultaneous quantification of any combination of Listeria sp., Staphylococcus aureus, Campylobacter jejuni and / or Escherichia coli O157.-H7, in one or more test samples, by multiplex amplification reaction, using real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The steps in the method are: (a) extracting DNA from the test sample or samples; (b) preparing a reaction mixture specific for the pathogens to be detected and quantified, such that the reaction mixture contains the necessary reagents for enzymatic amplification of the extracted DNA and identification of the pathogens to be detected and quantified; (c) amplifying the reaction mixture by means of multiplex amplification reaction using PCR; and (d) simultaneously determining the presence or absence of and quantification of the pathogens in the test sample or samples. The method has the special feature that (i) the reaction mixture for enzymatic amplification of the DNA has sets of pairs of oligonucleotide primers identified as SEQ ID No. 1 and SEQ ID No. 2, SEQ ID No. 4 and SEQ ID No. 5, SEQ ID No. 7 and SEQ ID No. 8, and SEQ ID No. 10 and SEQ ID No. 11, and probes with oligonucleotide sequences identified as SEQ ID No. 3, SEQ ID No. 6, SEQ ID No. 9 and SEQ ID No. 12; (ii) the presence or absence of and quantification of said pathogens in any combination is determined by means of a fluorescent signal or fluorescence emission specific for each pathogen.
Owner:SIGMA ALIMENTOS S A DE
Method for the analysis of methylation patterns within nucleic acids by means of mass spectrometry
The present invention describes a method for the analysis of methylation patterns comprising the following steps: a) isolation of genomic nucleic acids from a biological sample, b) amplification of one or more target nucleic acids of said genomic nucleic acids in a manner whereby the methylation patterns of said genomic nucleic acids are maintained in the amplificate nucleic acid, c) performing mass spectrometry on said amplified nucleic acid or fragments thereof to obtain mass spectra; d) evaluating the obtained mass spectra and e) determining the methylation pattern and / or methylation status of the sample. The disclosed invention provides novel methods for the analysis of cytosine methylation patterns within genomic DNA samples. Said method comprises a methylation retaining enzymatic amplification of a test nucleic acid sample, followed by mass spectrometric analysis of the amplificate nucleic acids.
Owner:EPIGENOMICS AG
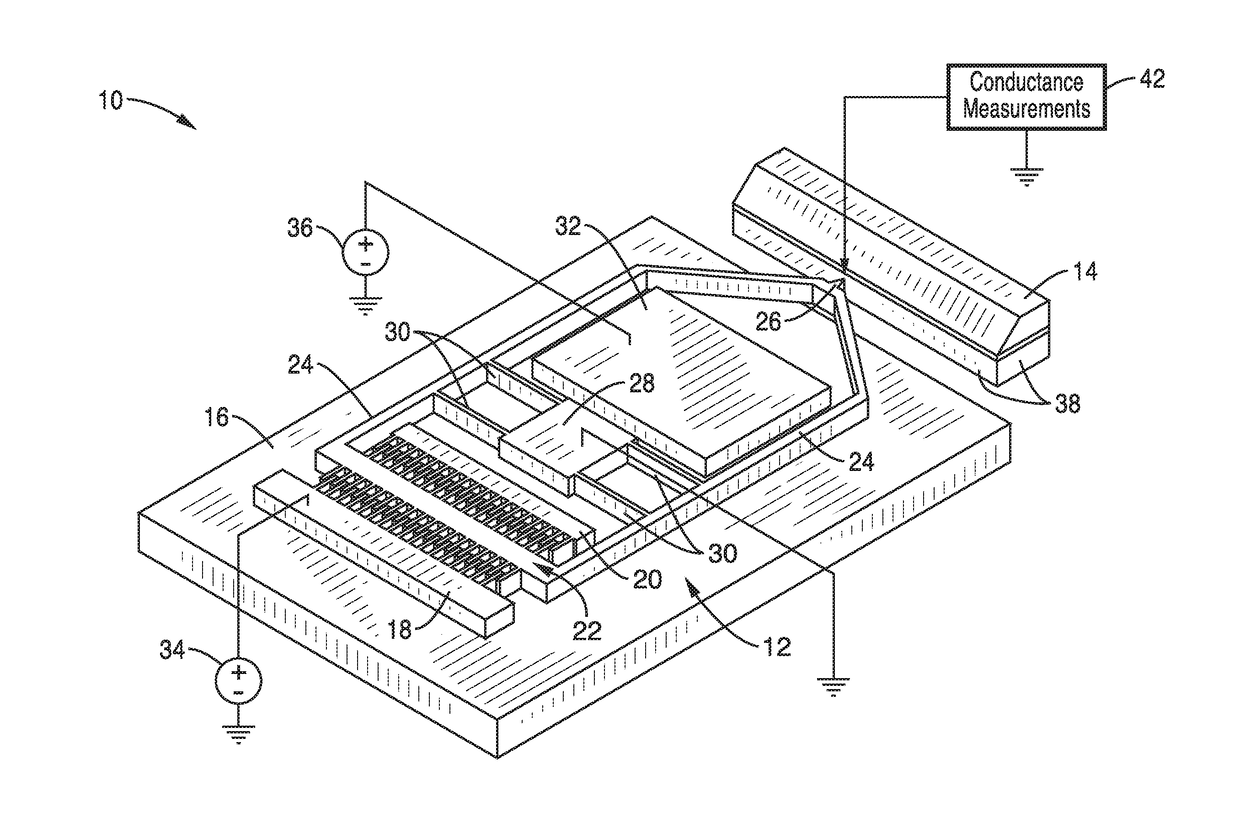
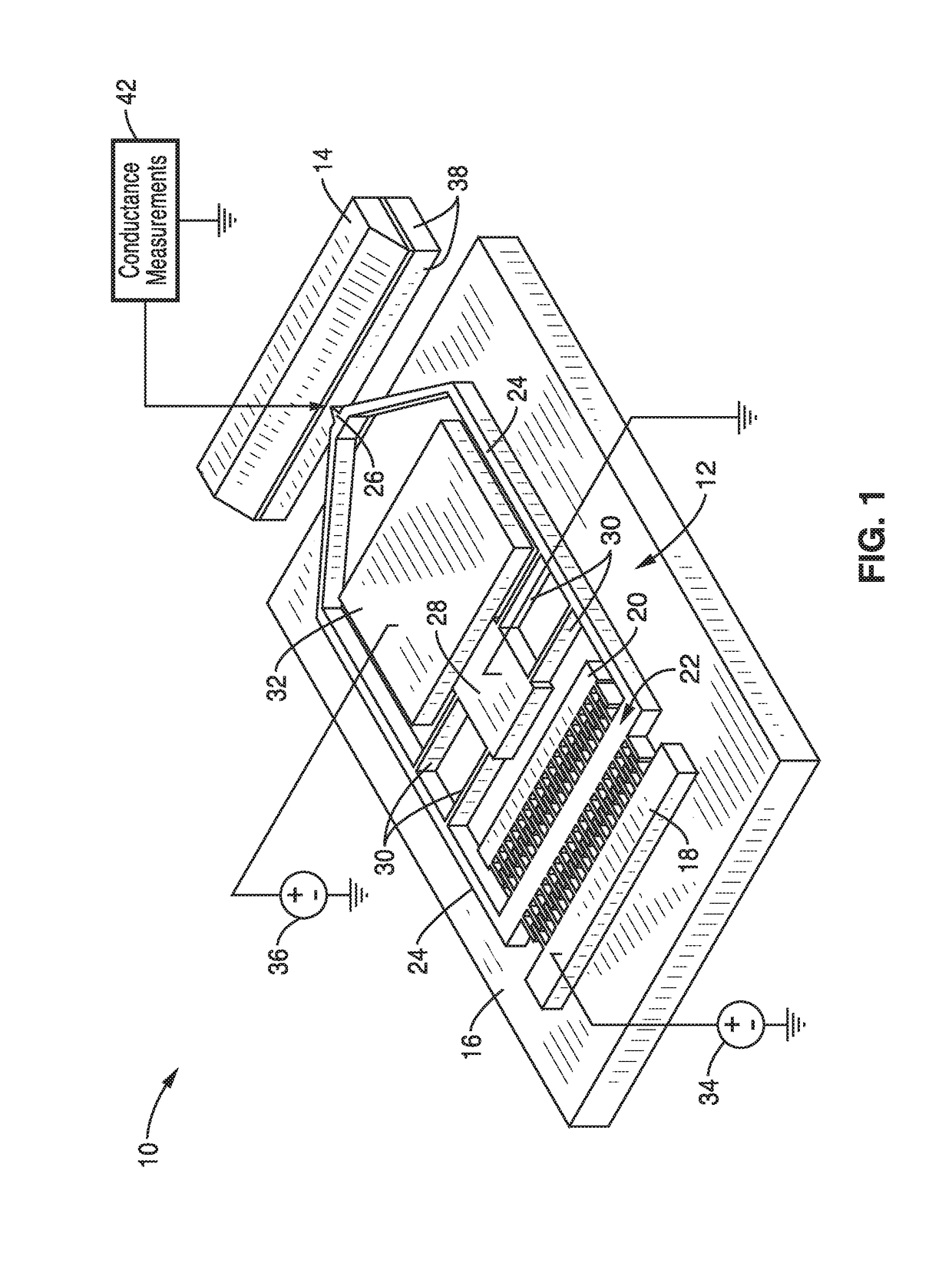
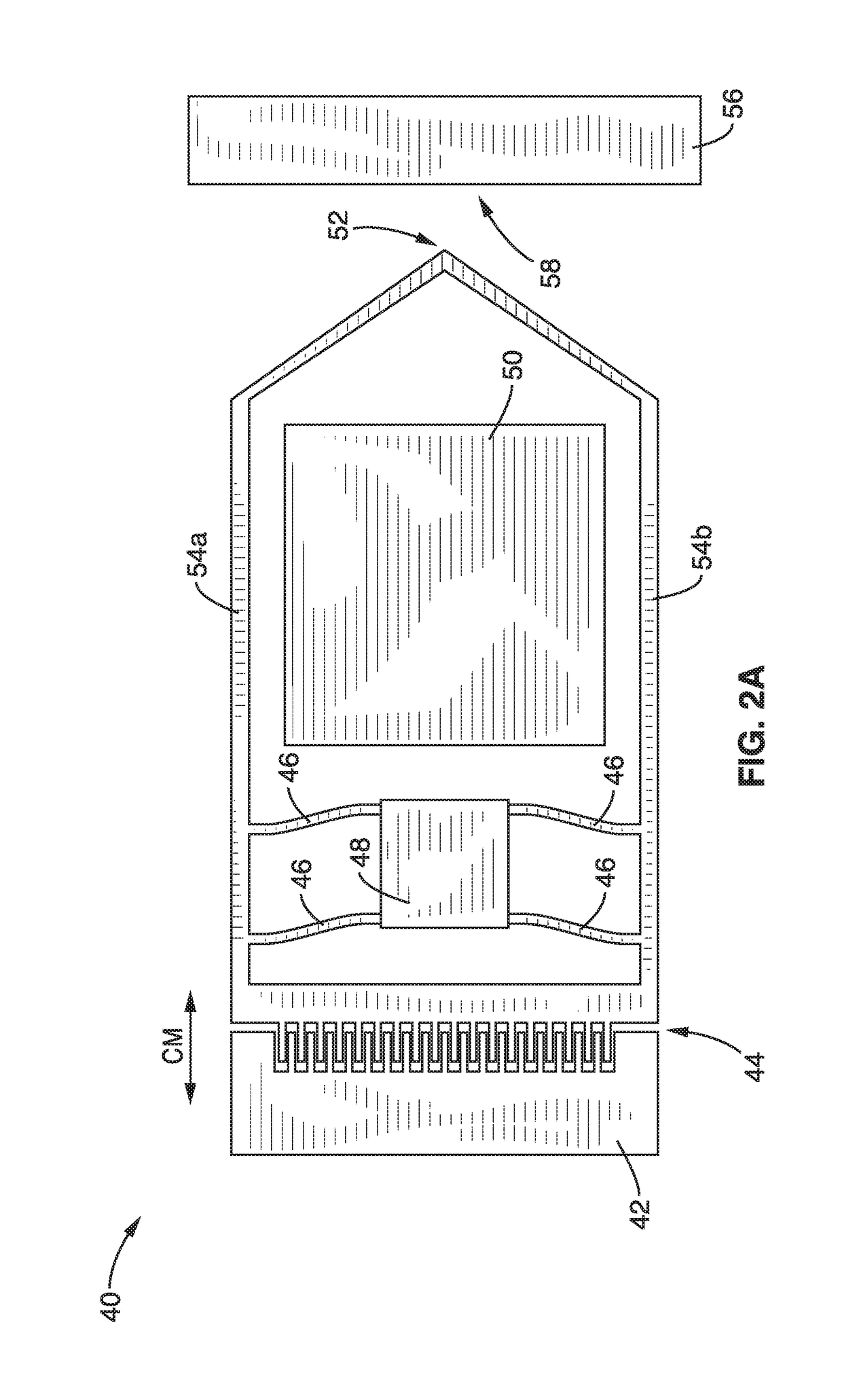
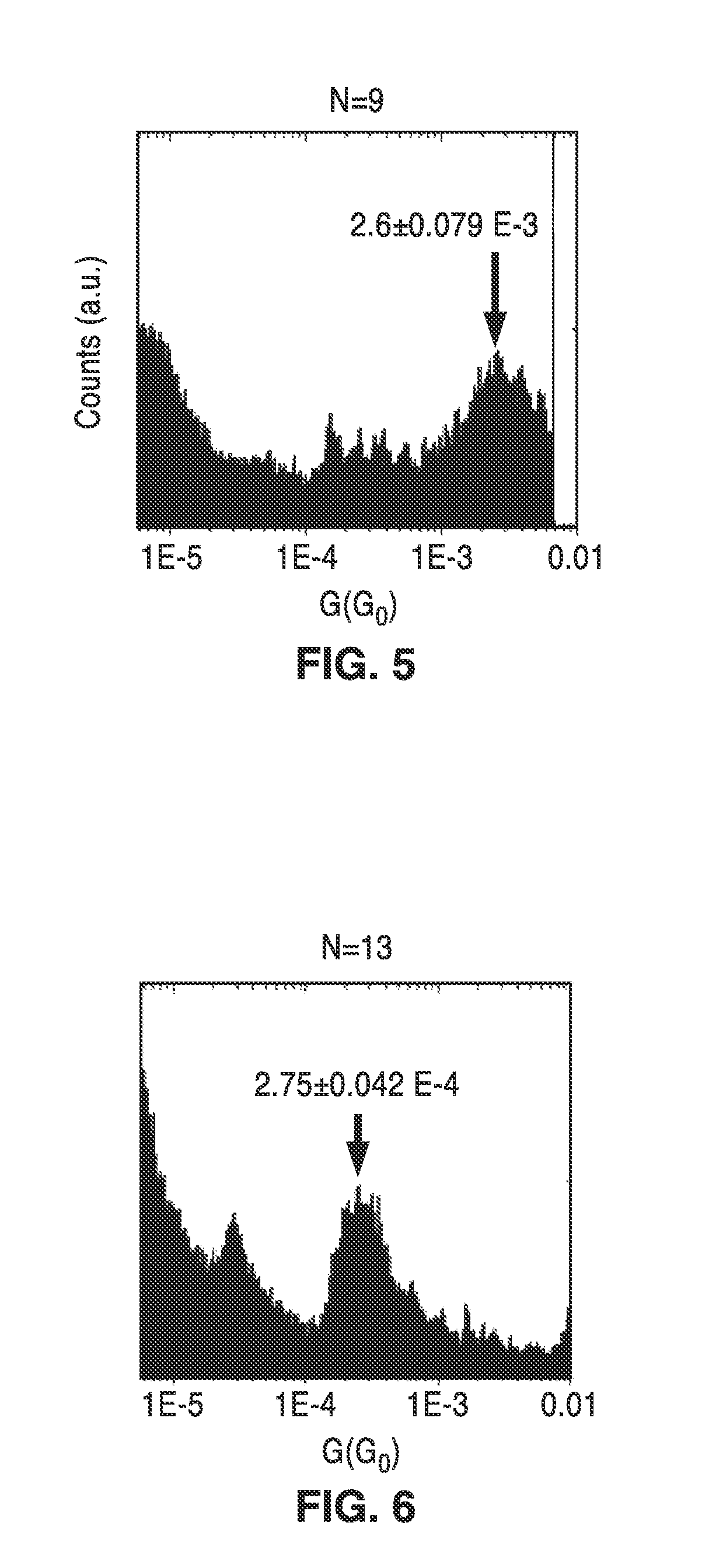
On-chip platform for single-molecule electrical conductance measurements
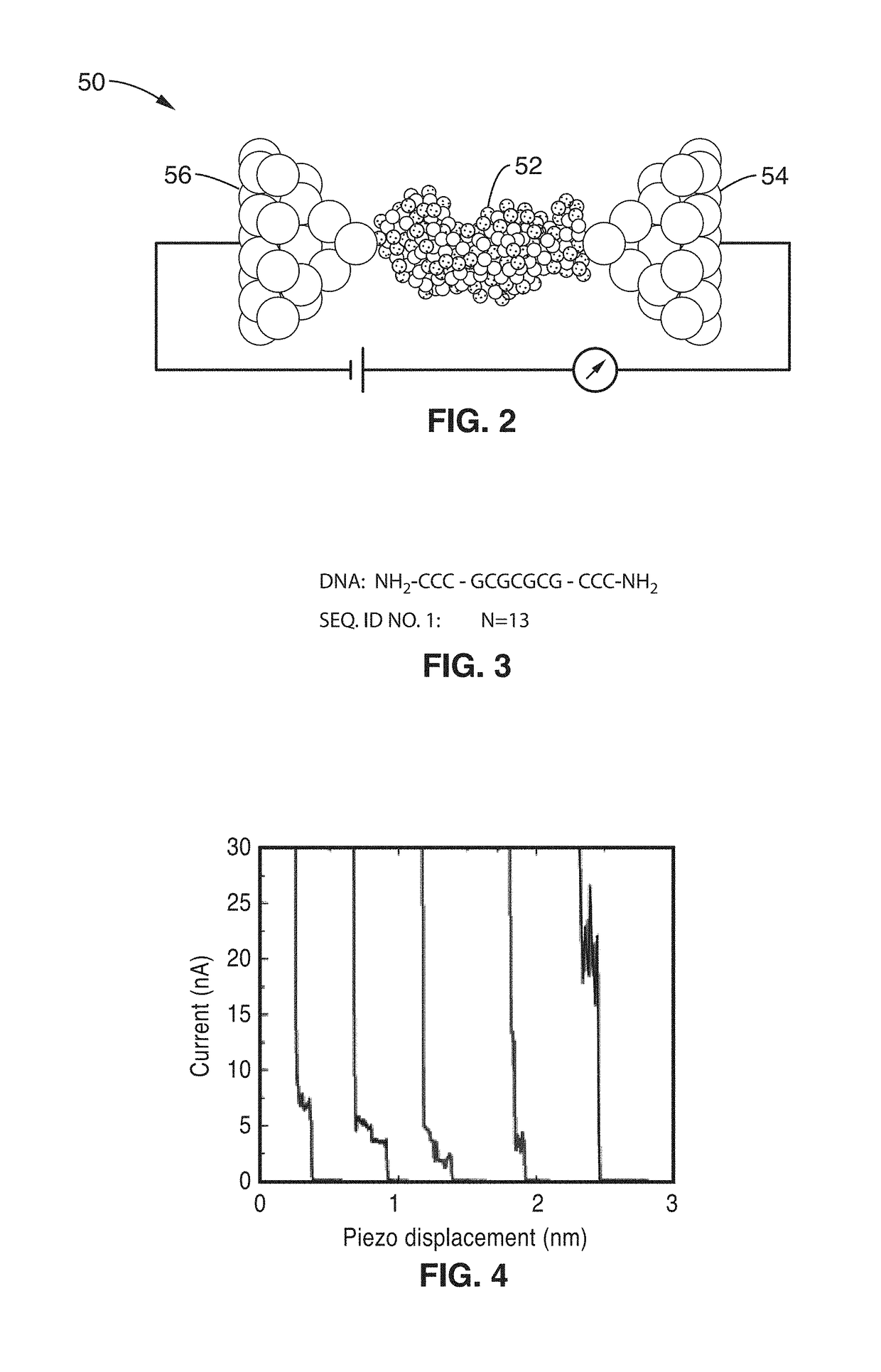
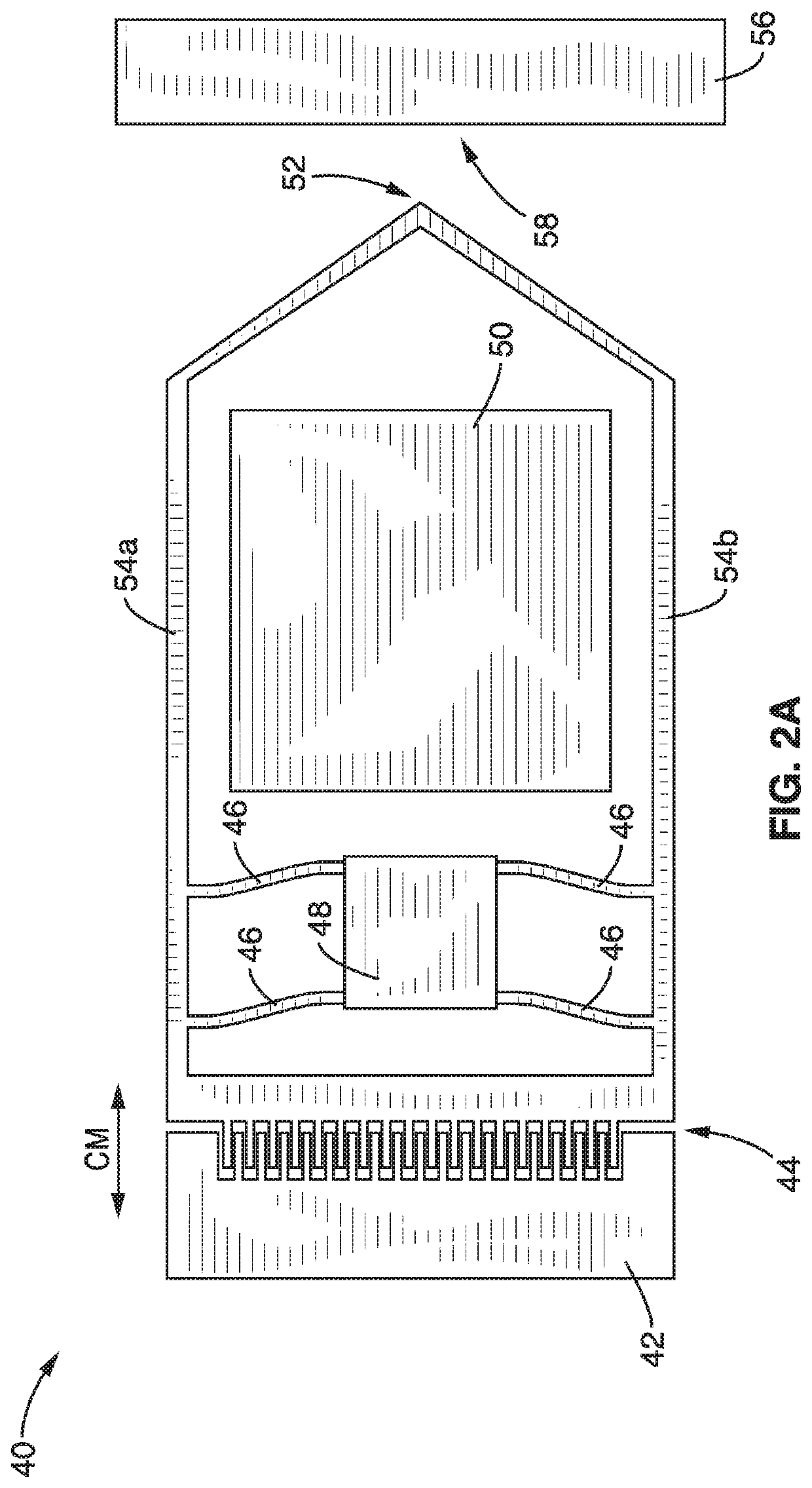
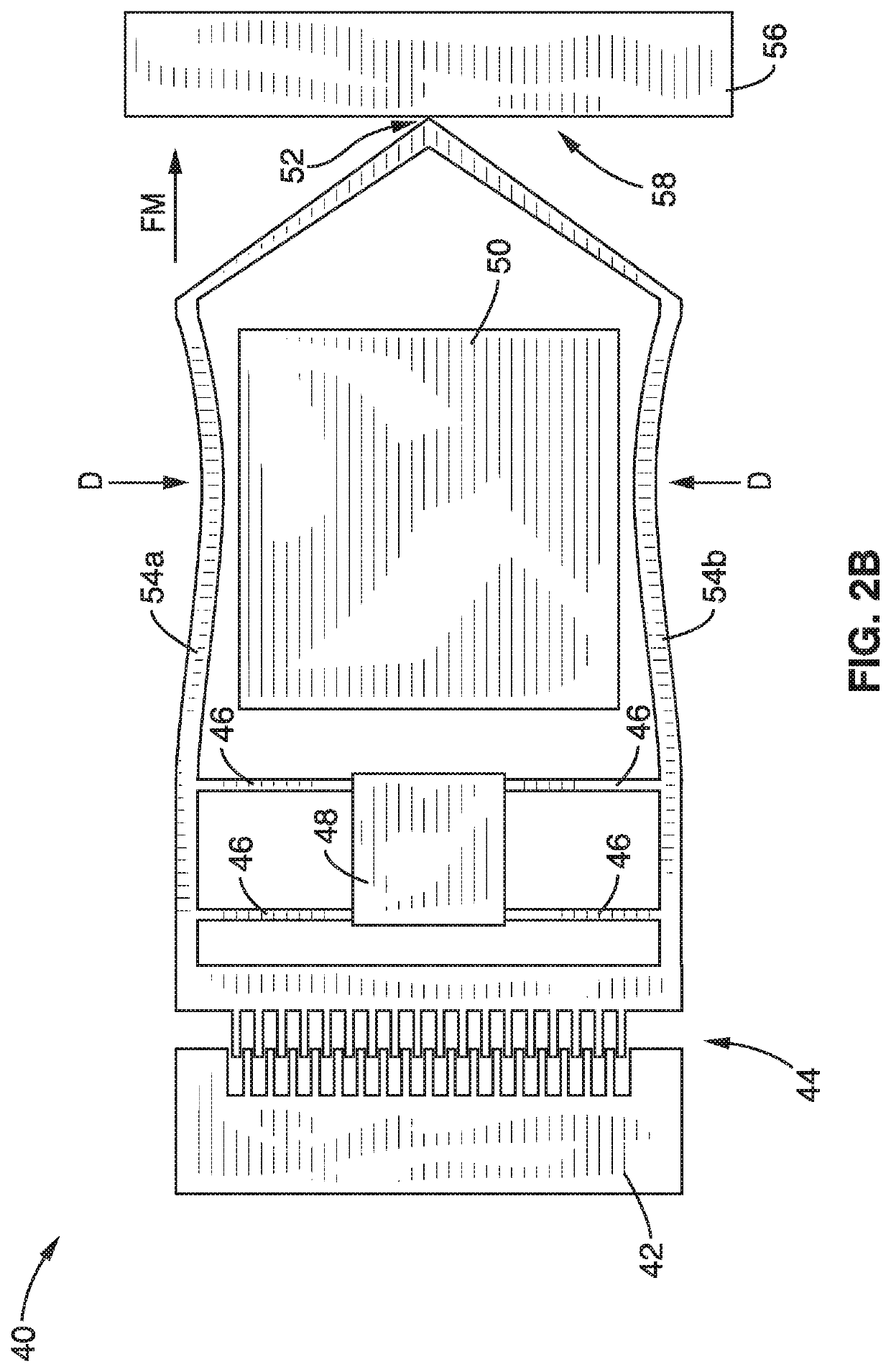
ActiveUS20170343531A1Easy to integrateAmenable to multiplexingMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisIn planeStatistical analysis
A micro-electromechanical platform and array system and methods for identifying microbial species with single molecule electrical conductance measurements are provided. The electromechanical platform has a two-tier actuation mechanism with a long stroke provided by a comb drive and a fine stroke provided by an in-plane flexural actuator. The platform is capable of making contact with a single-molecule, applying a bias, measuring the current, and performing a large number of measurements for statistical analysis. The system is capable of detecting any microbial species without requiring enzymatic amplification by detecting specific RNA sequences, for example. With oligonucleotide target molecules, the conductance is extremely sensitive to the sequence so even single-nucleotide polymorphisms can be identified. The system can also discern between subspecies using the same DNA probe. The system provides reliable, efficient, and inexpensive detection and species-level identification of microorganisms in complex detecting environments.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Field mouse babesia RPA molecular detection method
ActiveCN108486224ARapid Molecular Detection MethodsSensitive Molecular Detection MethodsMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
The invention discloses a field mouse babesia RPA molecular detection method. The field mouse babesia RPA molecular detection method comprises the following steps: designing a pair of specific primersand probes according to field mouse babesia mitochondria COX I gene sequence, wherein the nucleotide sequences of the primer pair is shown as SEQ ID NO: 2 to SEQ ID NO: 4 respectively; then extracting total DNA inside a dog blood sample to carry out recombinase combined enzymatic amplification reaction; and finally adopting a lateral flow analysis test paper strip to carry out detection on an amplification product. The method is high in sensitivity and high in specification, and field mouse babesia can be identified rapidly.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for amplification of nucleic acids of low complexity
InactiveUS20070178453A1Easy to identifyReduce complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingOligonucleotide PrimerBisulfite
The invention describes a method for amplifying nucleic acids, such as DNA with means of an enzymatic amplification step, such as a polymerase chain reaction, specified for template nucleic acids of low complexity, e.g. pre-treated DNA, like but not limited to DNA pre-treated with bisulfite is disclosed. The invention is based on the use of specific oligo-nucleotide primer molecules to solely amplify specific pieces of DNA. It is disclosed how to optimize the primer design for a PCR if the template DNA is of low complexity.
Owner:EPIGENOMICS AG
Method and components for detecting nucleic acid chains
InactiveUS20140295438A1Easy to separateStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideOrganic chemistry
The invention relates to a novel method for the enzymatic marking of nucleic acid chains (target sequences) by means of nucleotide conjugates. Said nucleotide conjugates are able, under reaction conditions, to specifically bind to the target sequence and integrate into the complementary growing strand by means of a polymerase. The nucleic acid chains marked by such conjugates can be bound to the solid phase. The marking can be carried out parallel to the enzymatic amplification of target sequences.
Owner:GENOVOXX
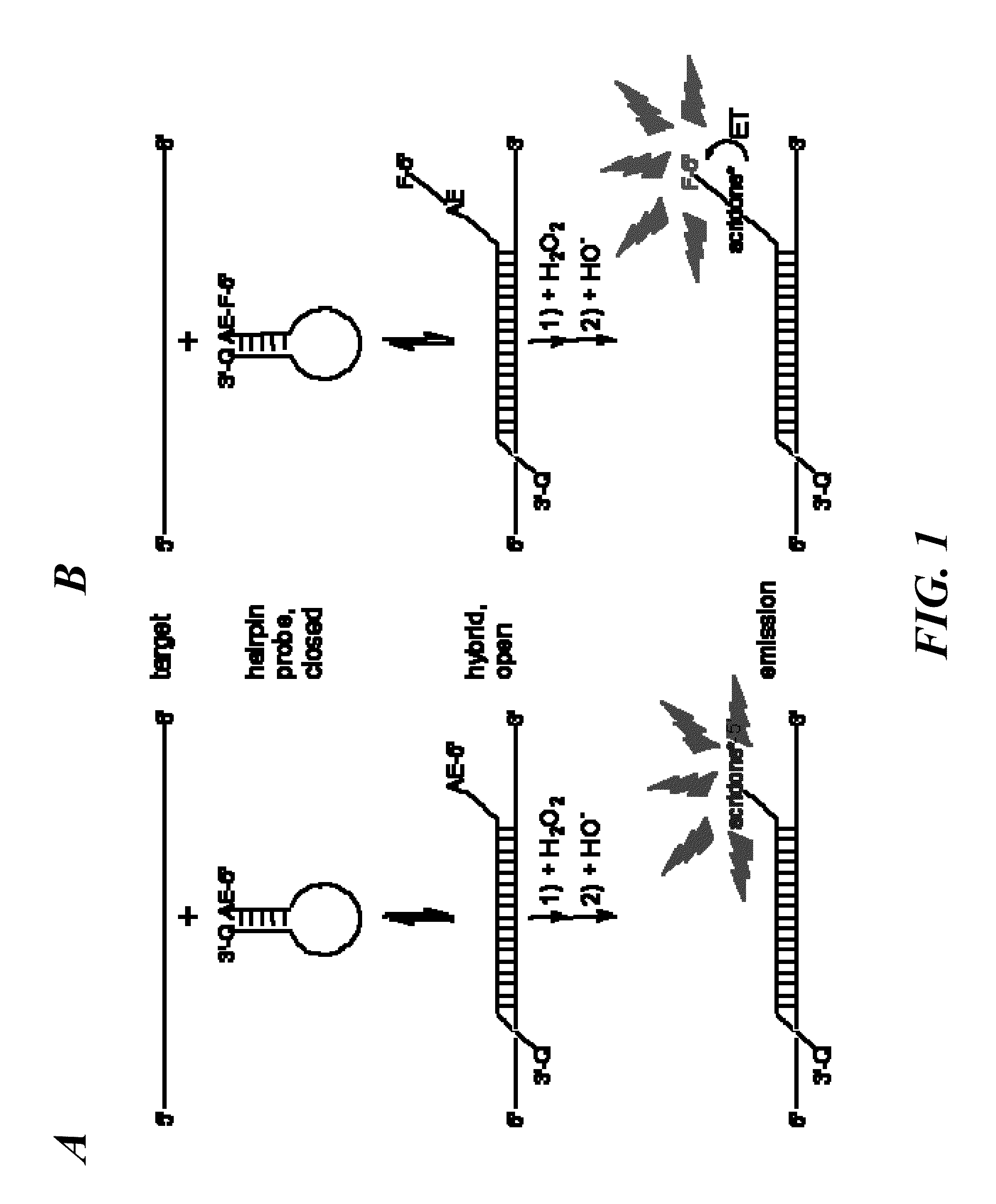
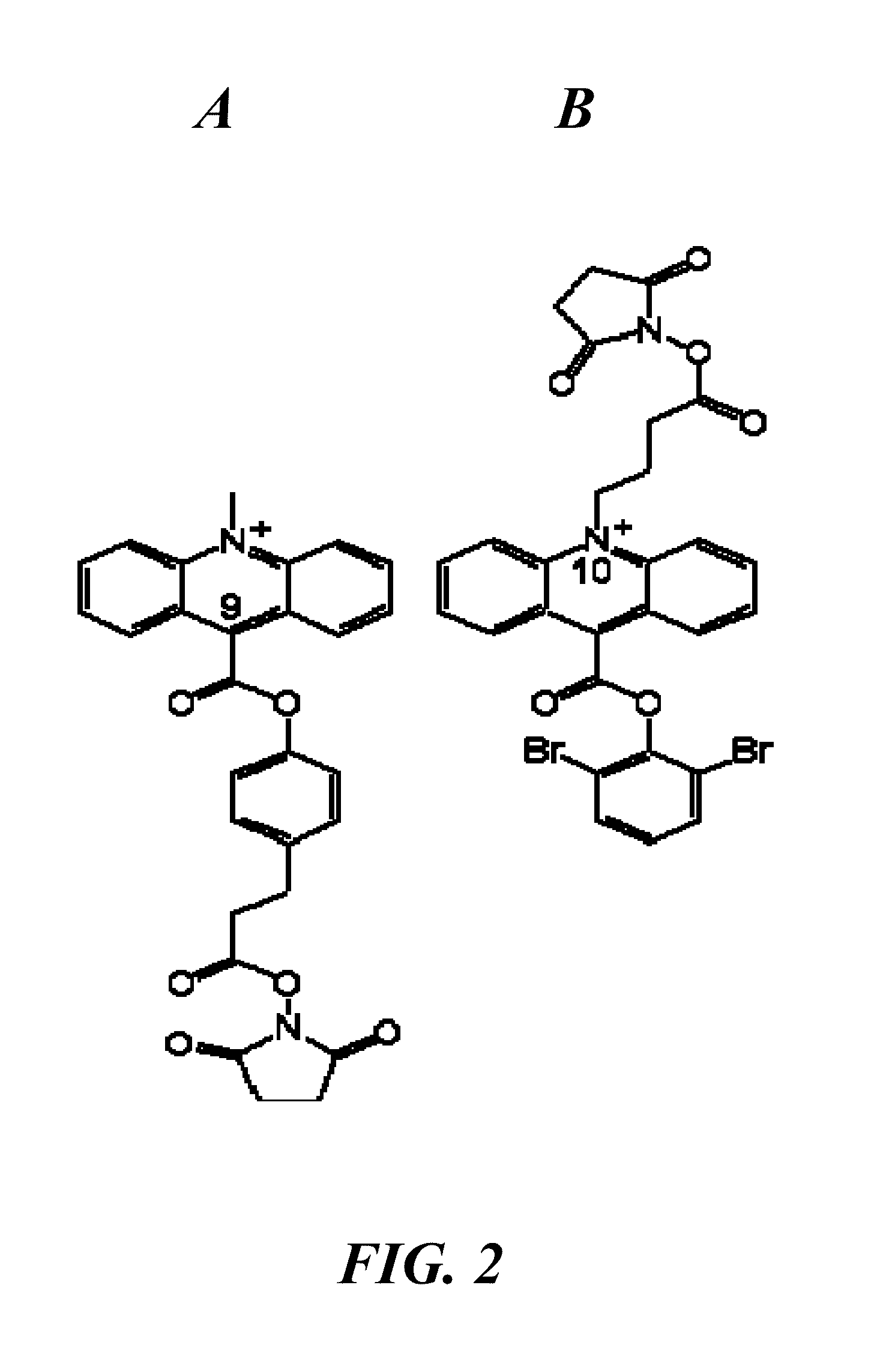
Spectrally-resolved chemiluminescent probes for sensitive multiplex molecular quantification
InactiveUS20130040859A1Avoid emissionsSugar derivativesNucleotide librariesEnergy transferLuminophore
Hybrid luminescent probes emit light of distinct wavelength ranges and intensities upon energy transfer from an in-common, acridinium ester chemiluminophore to a coupled luminophore. The probes include: (1) a target binding region with a base sequence that is substantially complementary to a portion of the target nucleic acid sequence; (2) an acridinium ester (AE) moiety attached to a first region flanking the target binding region; (3) a luminophore coupled to the AE moiety to allow energy transfer from an acridone moiety, produced by a chemical triggering of the AE moiety, to the luminophore; and (4) a quencher moiety attached to a second region flanking the target binding region, such that the first and second flanking regions are on the opposite sides of the target binding region. The probes are particularly useful in homogeneous assays for sensitive, multiplex quantification of nucleic acid target sequences without prior enzymatic amplification.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
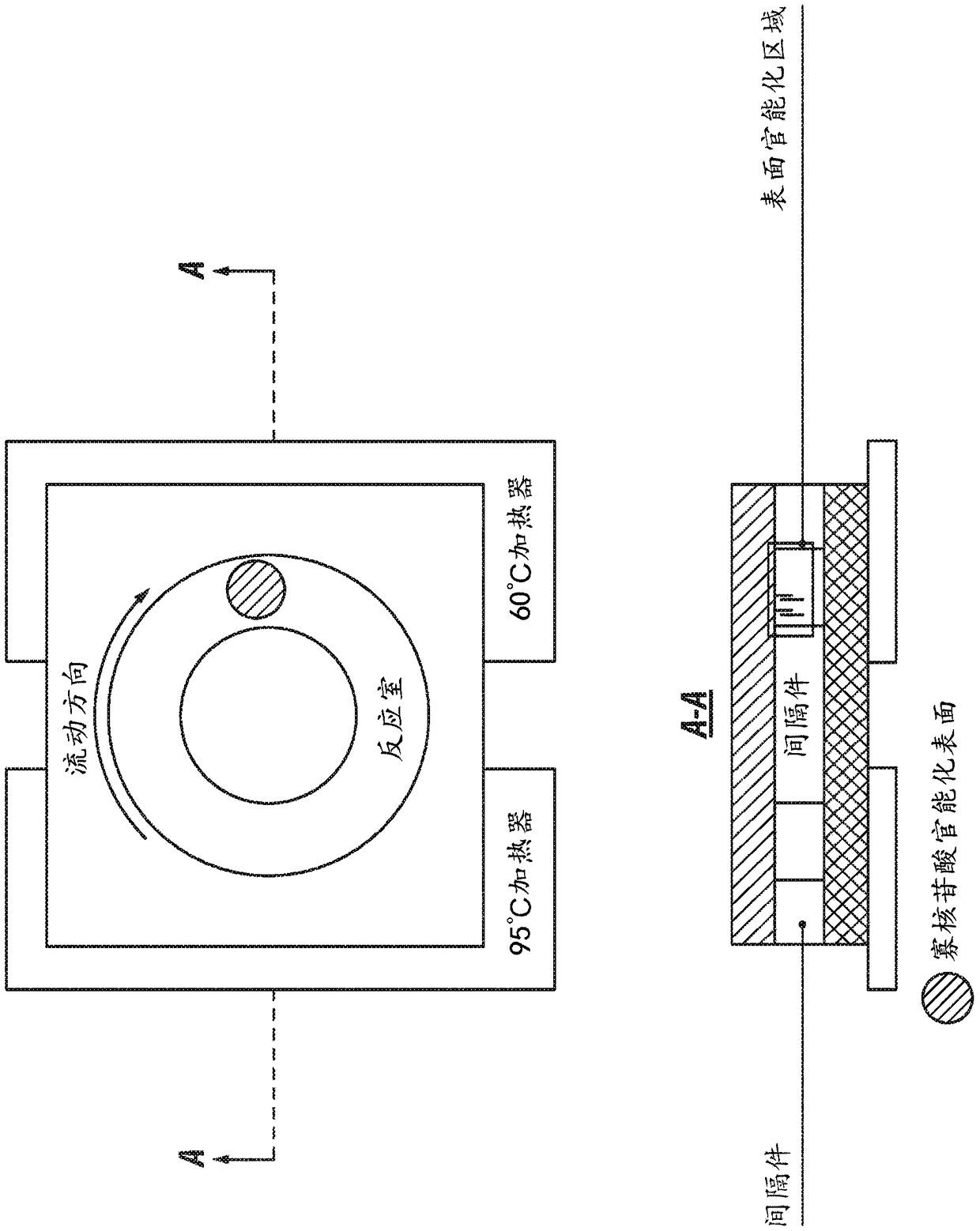
Surface-based detection of nucleic acid in a convection flow fluidic device
PendingCN109477136ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusAssayNucleic acid test
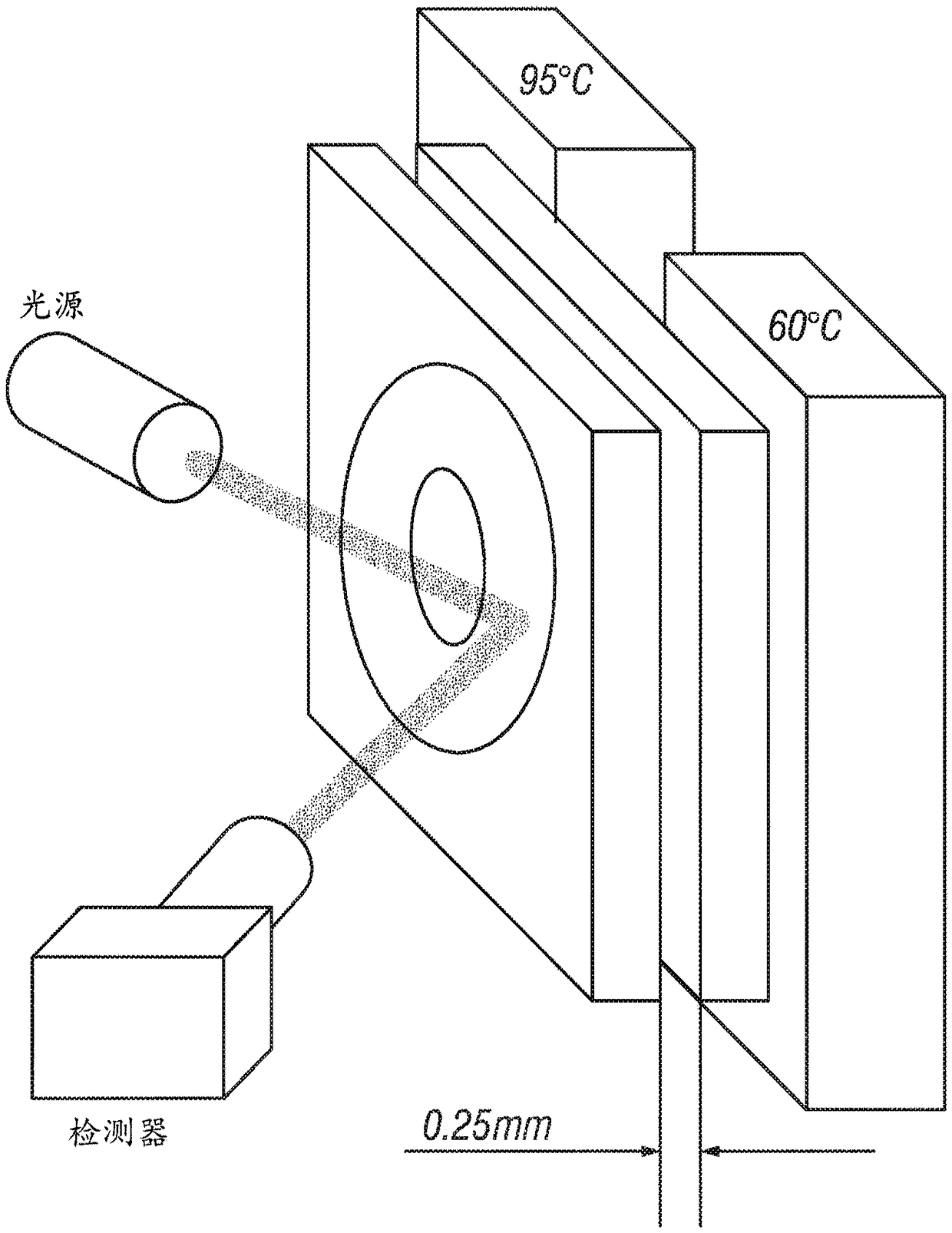
The present disclosure provides methods, composition and devices for performing convection-based PCR and non-enzymatic amplification of nucleic acid sequences. Techniques and reagents employed in these methods include toehold probes, strand displacement reactions, Rayleigh-Benard convection, temperature gradients, multiplexed amplification, multiplexed detection, and DNA functionalization, in openand closed systems, for use in nucleic tests and assays.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Competitive compositions of nucleic acid molecules for enrichment of rare-allele-bearing species
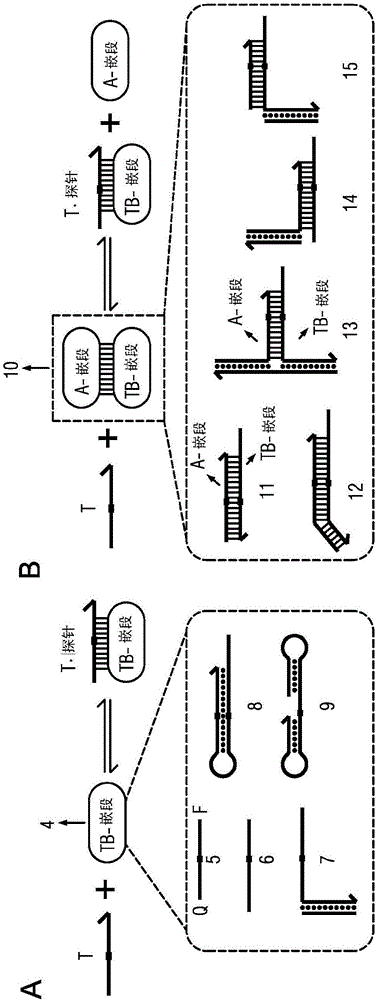
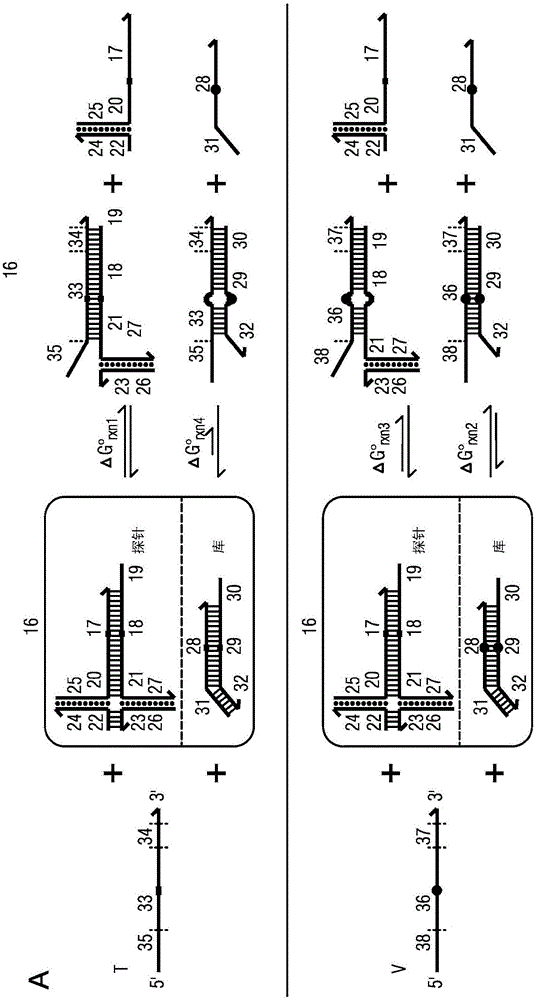
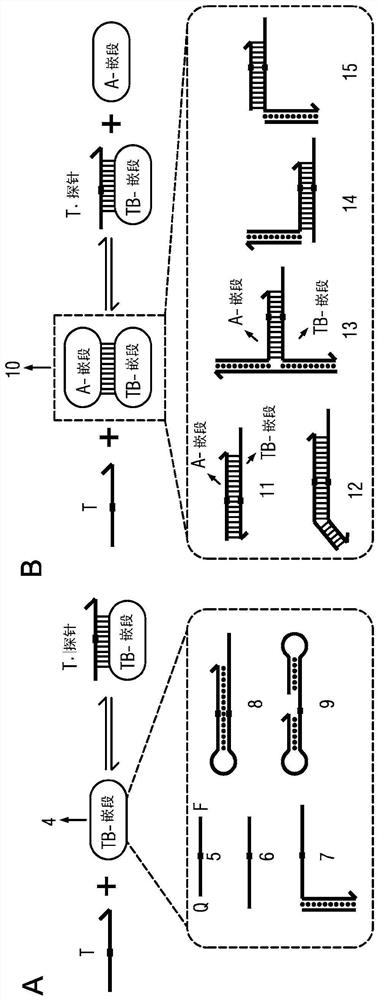
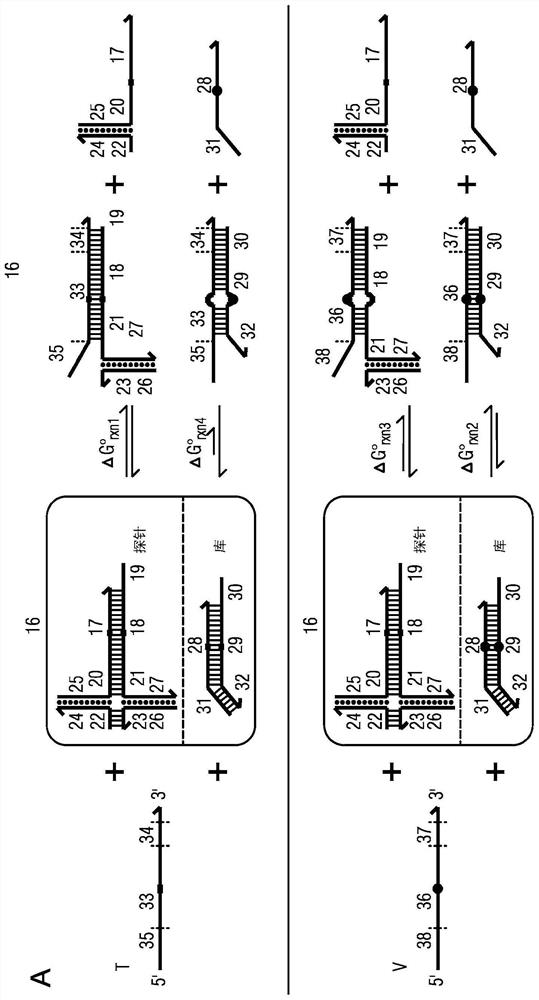
The present disclosure describes the thermodynamic design and concentrations necessary to design probe compositions with desired optimal specificity that enable enrichment, detection, quantitation, purification, imaging, and amplification of rare-allele-bearing species of nucleic acids (prevalence<1%) in a large stoichiometric excess of a dominant-allele-bearing species (wildtype). Being an enzyme-free and homogeneous nucleic acid enrichment composition, this technology is broadly compatible with nearly all nucleic acid-based biotechnology, including plate reader and fluorimeter readout of nucleic acids, microarrays, PCR and other enzymatic amplification reactions, fluorescence barcoding, nanoparticle-based purification and quantitation, and in situ hybridization imaging technologies.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Method for detecting, locating and monitoring seepage and leakage of hydraulic structures
InactiveCN108699596AReduce usageHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementSoil scienceWater flow
The disclosure relates to an improved method for detecting, locating and monitoring fluid seepage and leakage from a hydraulic work with superior sensitivity. The method includes using a DNA sequenceas the probe to trace the fluid seepage and leakage from a hydraulic work. The probe can be captured and then amplified more than a millionfold by an enzymatic method such as the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to give a detection signal. Even a single molecule of the DNA probe can be detected by an enzymatic amplification, thus to give superior sensitivity. The improved detection method is applicable to detecting, locating and monitoring fluid seepage and leakage from hydraulic works, the improved method can also be used, for example, to trace the groundwater flow, underground water flow andother liquid flow. Other related methods are also described.
Owner:HUNAN ZONSEN PEPLIB BIOTECH CO LTD
A protein glycosylation detection kit, detection method and application
ActiveCN109307773BImprove label stabilityGood biocompatibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingCell membraneNucleic acid sequence
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Method and components for detecting nucleic acid chains
InactiveUS9994894B2Easy to separateAvoid interactionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideEnzyme
The invention relates to a novel method for the enzymatic marking of nucleic acid chains (target sequences) by means of nucleotide conjugates. Said nucleotide conjugates are able, under reaction conditions, to specifically bind to the target sequence and integrate into the complementary growing strand by means of a polymerase. The nucleic acid chains marked by such conjugates can be bound to the solid phase. The marking can be carried out parallel to the enzymatic amplification of target sequences.
Owner:GENOVOXX
Conjugates of nucleotides and method for the application thereof
ActiveUS9315860B2Quick checkIncrease productionMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleotideOrganic chemistry
The invention relates to a novel method for enzymatically marking nucleic acid chains (target sequences) by using nucleotide conjugates. Said nucleotide conjugates are capable of binding specifically to the target sequence under reaction conditions and of being incorporated in the complementary growing strand by means of a polymerase. The nucleic acid chains marked with such conjugates can be bound to the solid phase. The marking can be carried out in parallel with the enzymatic amplification of target sequences.
Owner:GENOVOXX
A pcr-sbt method and reagent for genotyping of human platelet alloantigen system
ActiveCN105296601BSolve the problem of accurate typingThe result is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh throughput genotypingAntigen
The invention provides a PCR-SBT method for genotyping human platelet alloantigen system, the method comprising the following steps: preparing human genome DNA; amplifying the gene sequence of the antigen system in human genome DNA; performing double-enzyme synthesis on the amplified product The purified product was subjected to sequencing PCR reaction; the sequencing product was purified by sodium acetate-ethanol precipitation method, followed by capillary electrophoresis sequencing; the obtained sequence was analyzed by software to determine its genotype. The present invention also provides reagents used in the above typing method. The present invention can be used as an independent and widely used identification method, solves the problem of accurate typing of 28 antigen systems of HPA, utilizes the characteristics of high-throughput and accurate results of PCR-SBT for HPA gene typing operation, and can be used in clinical blood transfusion medicine research The related applications in fields such as genetics and genetics will be highly valued, and it has important practical significance for medical research units, pharmaceutical research and reagent development units.
Owner:浙江省血液中心
Method for detecting, locating and monitoring seepage and leakage of hydraulic structures
InactiveUS20210214788A1Ensure efficient flowHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementSoil scienceStream flow
The disclosure relates to an improved method for detecting, locating and monitoring fluid seepage and leakage from a hydraulic work with superior sensitivity. The method includes using a DNA sequence as the probe to trace the fluid seepage and leakage from a hydraulic work. The probe can be captured and then amplified more than a millionfold by an enzymatic method such as the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to give a high detection signal. Even a single molecule of the DNA probe can be detected by an enzymatic amplification, thus to give superior sensitivity. The improved detection method is applicable to detecting, locating and monitoring fluid seepage and leakage from hydraulic works, the improved method can also be used, for example, to trace the groundwater flow, underground water flow and other liquid flow. Other related methods are also described.
Owner:HUNAN ZONSEN PEPLIB BIOTECH CO LTD
Rna-based, amplification-free, organism identification using nano-enabled electronic detection
ActiveUS20150275279A1Eliminate needQuick and efficient and inexpensiveBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectricityRNA Sequence
A technique that uses nanotechnology to electrically detect and identify RNA sequences without the need for using enzymatic amplification methods or fluorescent labels. The technique may be scaled into large multiplexed arrays for high-throughput and rapid screening. The technique is further able to differentiate closely related variants of a given bacterial or viral species or strain. This technique addresses the need for a quick, efficient, and inexpensive bacterial and viral detection and identification system.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
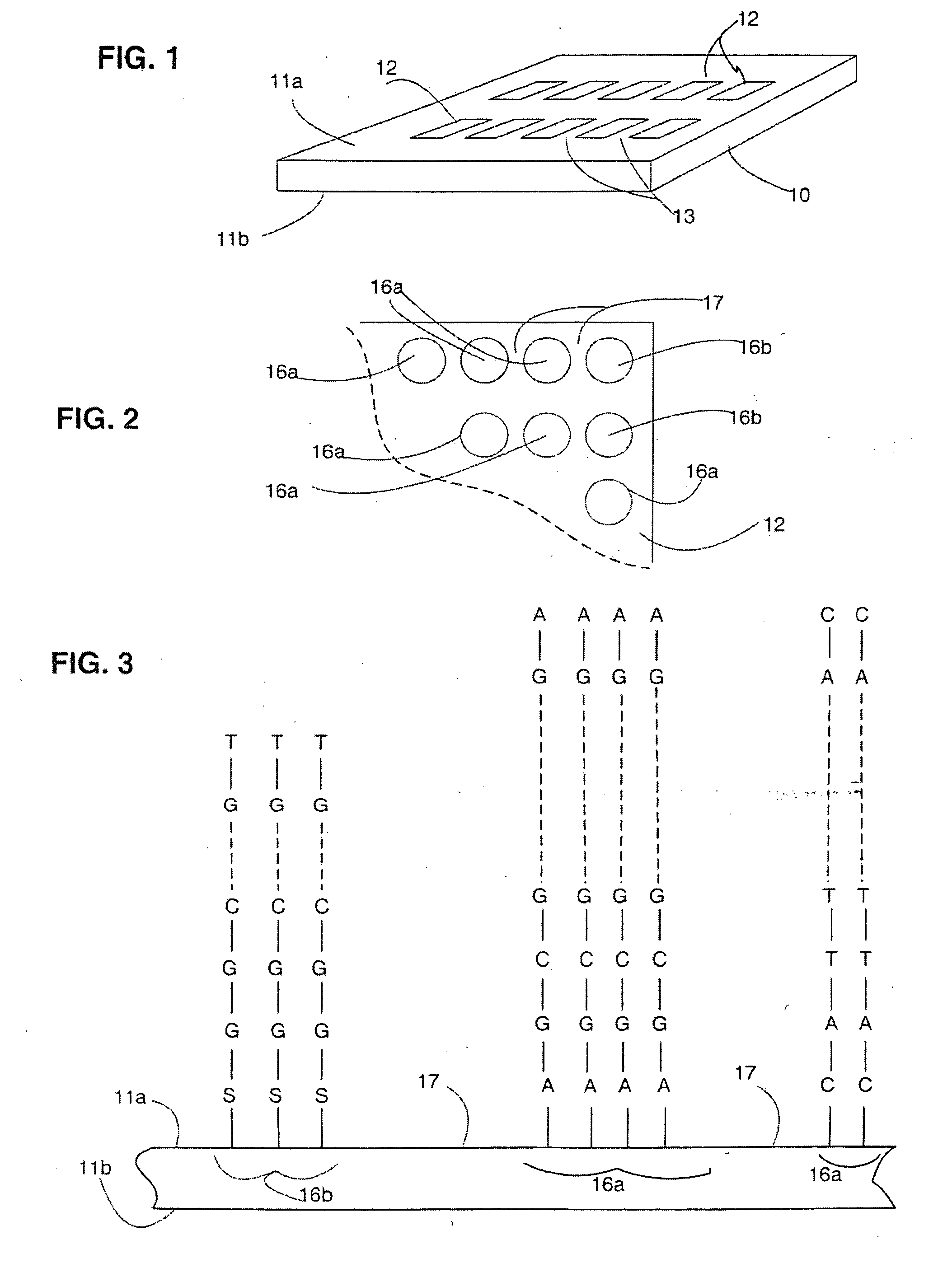
Composite arrays
InactiveUS20060008836A1Easy to useBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyPolynucleotideEnzyme
A polynucleotide array, and methods of making and using such arrays. The array may include a first set of multiple features each of which has first polynucleotide molecules of at least 400 nucleotides in length, and a second set of features each of which has second polynucleotide molecules of no more than 100 nucleotides in length. The second set of features can be used as control features, or to replace failed sequences in an enzymatic amplification to produce first polynucleotides, or to detect polymorphisms or splice variants which may not be detected by a particular first polynucleotide.
Owner:AMORESE DOUGLAS A +3
MicroRNA detection method based on the principle of non-enzyme amplification and electrochemiluminescence
InactiveCN103383355BThe principle is simpleLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid detectionMicroRNA
The invention relates to the technical field of nucleic acid detection, in particular to a microRNA detection method based on non-enzymatic amplification and electrochemiluminescence principles. The detection method comprises the steps of: 1) designing DNA hairpin probes, i.e. designing the hairpin H1 and hairpin H2 sequences required by a non-enzymatic amplification system according to a non-enzymatic amplification principle and a detected microRNA sequence; 2) conducting electrochemiluminescence group marking; 3) performing hairpin probe pretreatment; 4) constructing a non-enzymatic amplification detection system; 5) carrying out product cleaning and separation; and 6) conducting signal detection. The method has the characteristics of high sensitivity, accuracy, fastness and simple operation, and the whole amplification process does not involve enzyme, so that the detection cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Dual enzymatic amplification
InactiveUS20150167070A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationGenomic mutationGenome
Provided are methods for validating the presence and character of genomic mutations, particularly single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), by parallel amplification of a portion or the whole genome with at least two different DNA polymerases.
Owner:CYNVENIO BIOSYST
RNA-based, amplification-free, organism identification using nano-enabled electronic detection
ActiveUS9803234B2Quick and efficient and inexpensiveQuick filterBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological bodyElectricity
A technique that uses nanotechnology to electrically detect and identify RNA sequences without the need for using enzymatic amplification methods or fluorescent labels. The technique may be scaled into large multiplexed arrays for high-throughput and rapid screening. The technique is further able to differentiate closely related variants of a given bacterial or viral species or strain. This technique addresses the need for a quick, efficient, and inexpensive bacterial and viral detection and identification system.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
On-chip platform for single-molecule electrical conductance measurements
ActiveUS10989705B2Easy to integrateAmenable to multiplexingMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisMicroorganismStatistical analysis
A micro-electromechanical platform and array system and methods for identifying microbial species with single molecule electrical conductance measurements are provided. The electromechanical platform has a two-tier actuation mechanism with a long stroke provided by a comb drive and a fine stroke provided by an in-plane flexural actuator. The platform is capable of making contact with a single-molecule, applying a bias, measuring the current, and performing a large number of measurements for statistical analysis. The system is capable of detecting any microbial species without requiring enzymatic amplification by detecting specific RNA sequences, for example. With oligonucleotide target molecules, the conductance is extremely sensitive to the sequence so even single-nucleotide polymorphisms can be identified. The system can also discern between subspecies using the same DNA probe. The system provides reliable, efficient, and inexpensive detection and species-level identification of microorganisms in complex detecting environments.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Dual enzymatic amplification
Provided are methods for validating the presence and character of genomic mutations, particularly single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), by parallel amplification of a portion or the whole genome with at least two different DNA polymerases.
Owner:ZHUHAI LIVZON CYNVENIO DIAGNOSTICS
Nucleic acid amplification
ActiveUS8455197B2Strong specificityOptimization orderMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationOligonucleotide PrimerNucleotide sequencing
Provided herein is a method for the selective amplification of a target nucleotide sequence located within a nucleic acid molecule, the method comprising contacting the nucleic acid molecule (“template” molecule) with (i) at least one facilitator oligonucleotide, wherein the facilitator oligonucleotide includes at least one modification at or near its 3′ terminus such that 3′ extension from the facilitator oligonucleotide is blocked, and (ii) two or more oligonucleotide primers, at least one of which is an initiator primer modified such that the presence of the modification prematurely terminates complementary strand synthesis, wherein the facilitator oligonucleotide and the initiator primer bind to substantially the same or adjacent regions of the template nucleic acid molecule and the facilitator oligonucleotide further comprises sequences complementary to the target sequence 3′ to the binding location of the initiator primer; and carrying out thermocyclic, enzymatic amplification such that the specific target sequence is selectively amplified.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Competitive composition of nucleic acid molecules for enrichment of rare allele-containing species
ActiveCN106460069BMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationWild typeNucleic acid molecule
The present invention discloses the thermodynamic design and concentrations required to design probe compositions with the desired optimal specificity that enables the major allele-containing species (wild-type) to be detected in large stoichiometric excess Enrich, detect, quantify, purify, image and amplify material containing rare alleles of nucleic acids (prevalence < 1%). As an enzyme-free and uniform nucleic acid enrichment composition, this technique is broadly compatible with virtually all nucleic acid-based biotechnologies, including plate readers and fluorometer readouts of nucleic acids, microarrays, PCR and other enzymatic amplification reactions, Fluorescent barcoding, nanoparticle-based purification and quantification, and in situ hybridization imaging.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com