Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
142 results about "Elevation map" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
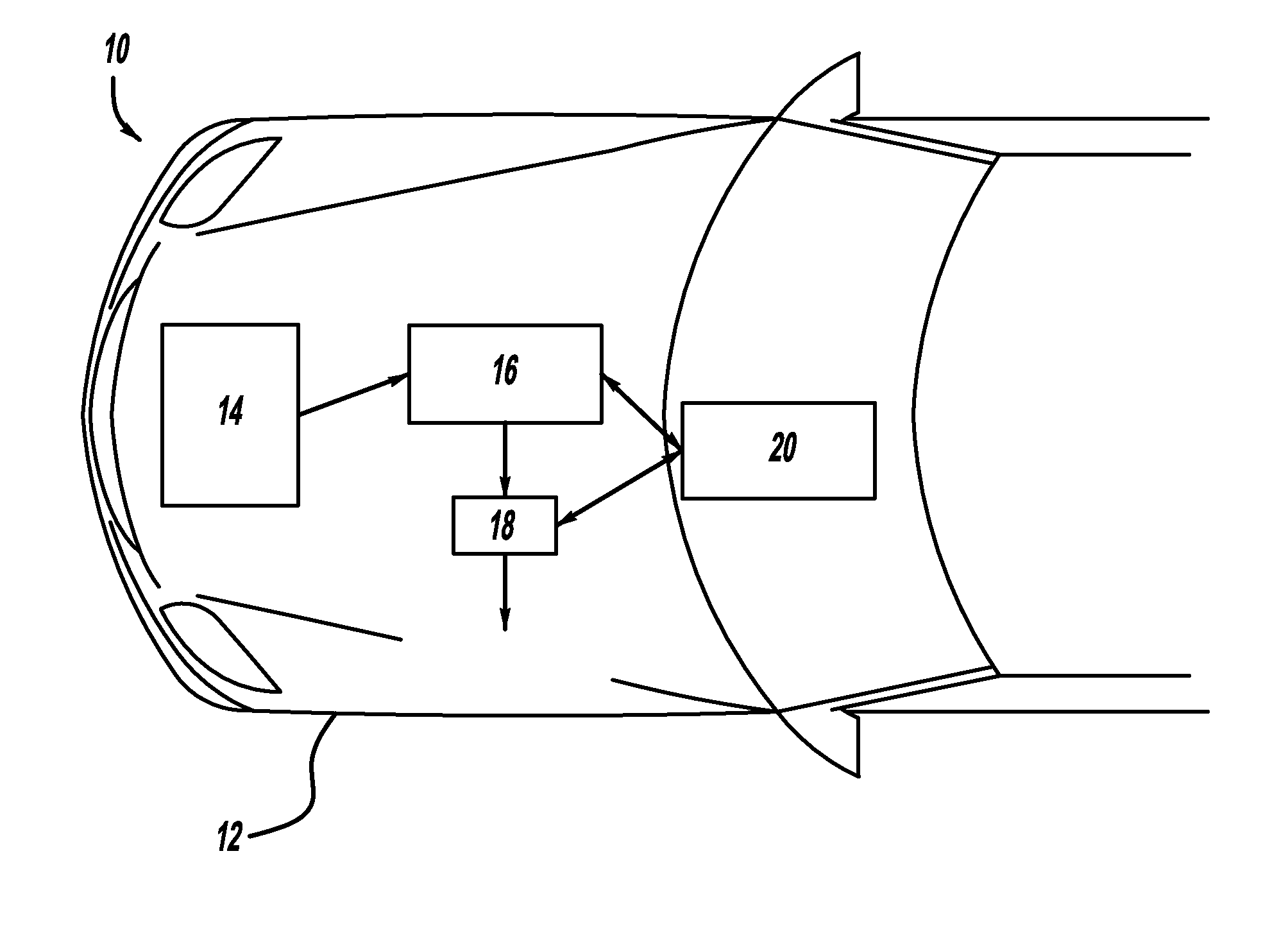
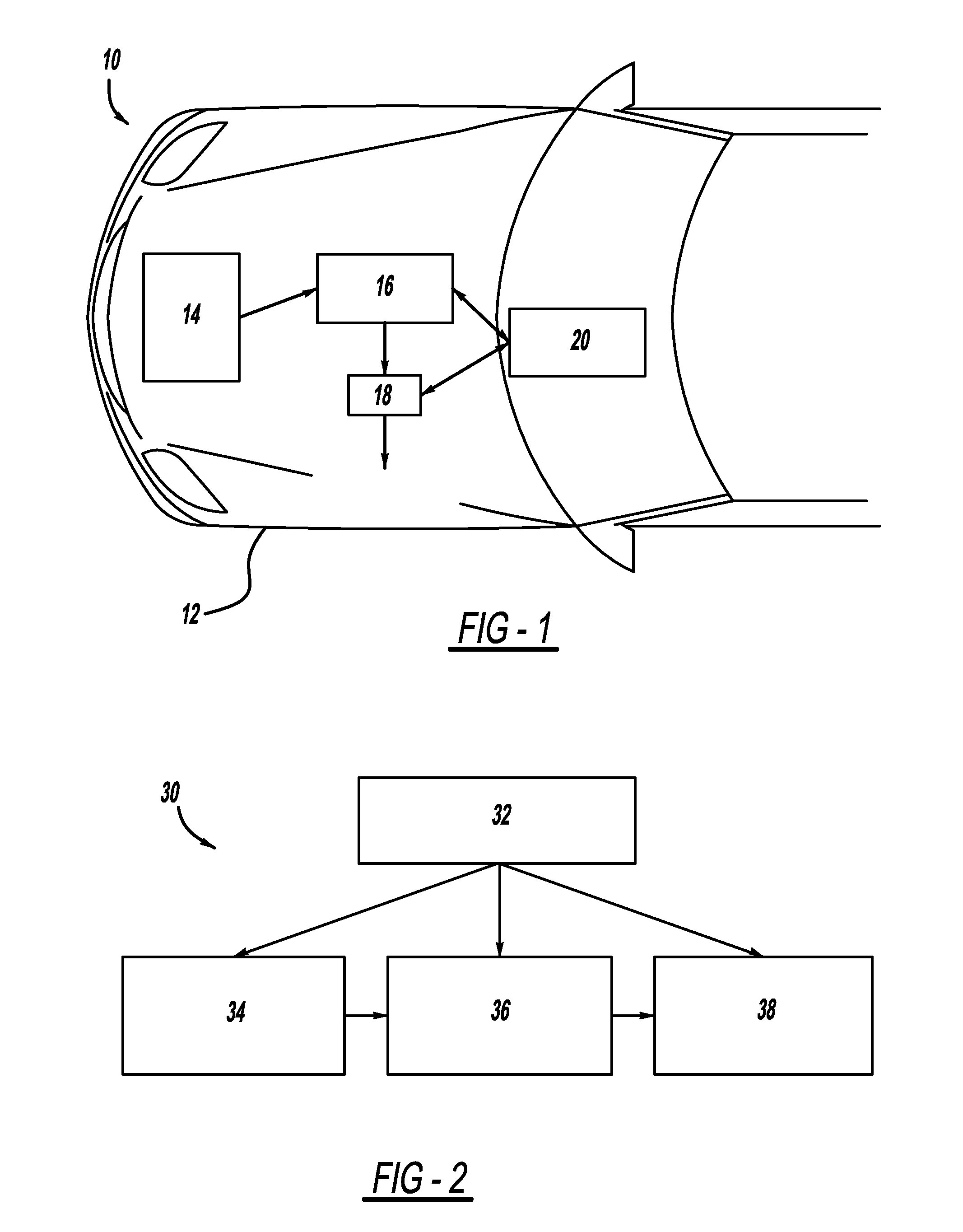
Object and vehicle detection and tracking using 3-d laser rangefinder
ActiveUS20110282581A1Anti-collision systemsElectromagnetic wave reradiationVehicle detectionGround plane
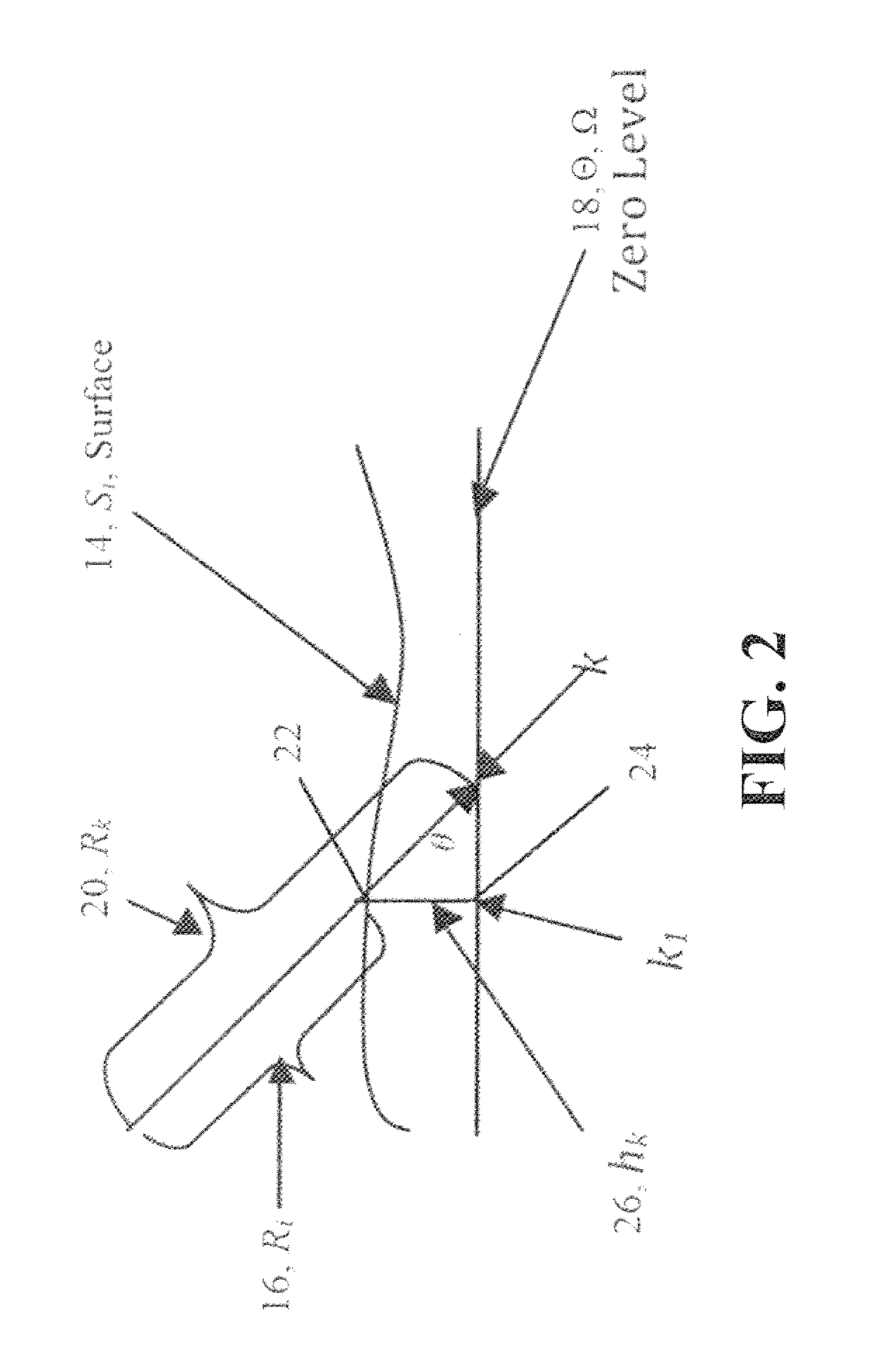
A method and system for detecting and tracking objects near a vehicle using a three dimensional laser rangefinder. The method receives points from the laser rangefinder, where the points represent locations in space where the rangefinder senses that some object exists. An algorithm first estimates the location of a ground plane, based on a previous ground plane location, data from onboard sensors, and an eigenvector calculation applied to the point data. Next, a plan view occupancy map and elevation map are computed for stationary objects, based on point data in relation to the ground plane. Finally, dynamic objects are detected and tracked, sensing objects which are moving, such as other vehicles, pedestrians, and animals. The output of the method is a set of stationary and dynamic objects, including their shape, range, and velocity. This output can be used by downstream applications.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Apparatus and method for automatic airborne LiDAR data processing and mapping using data obtained thereby
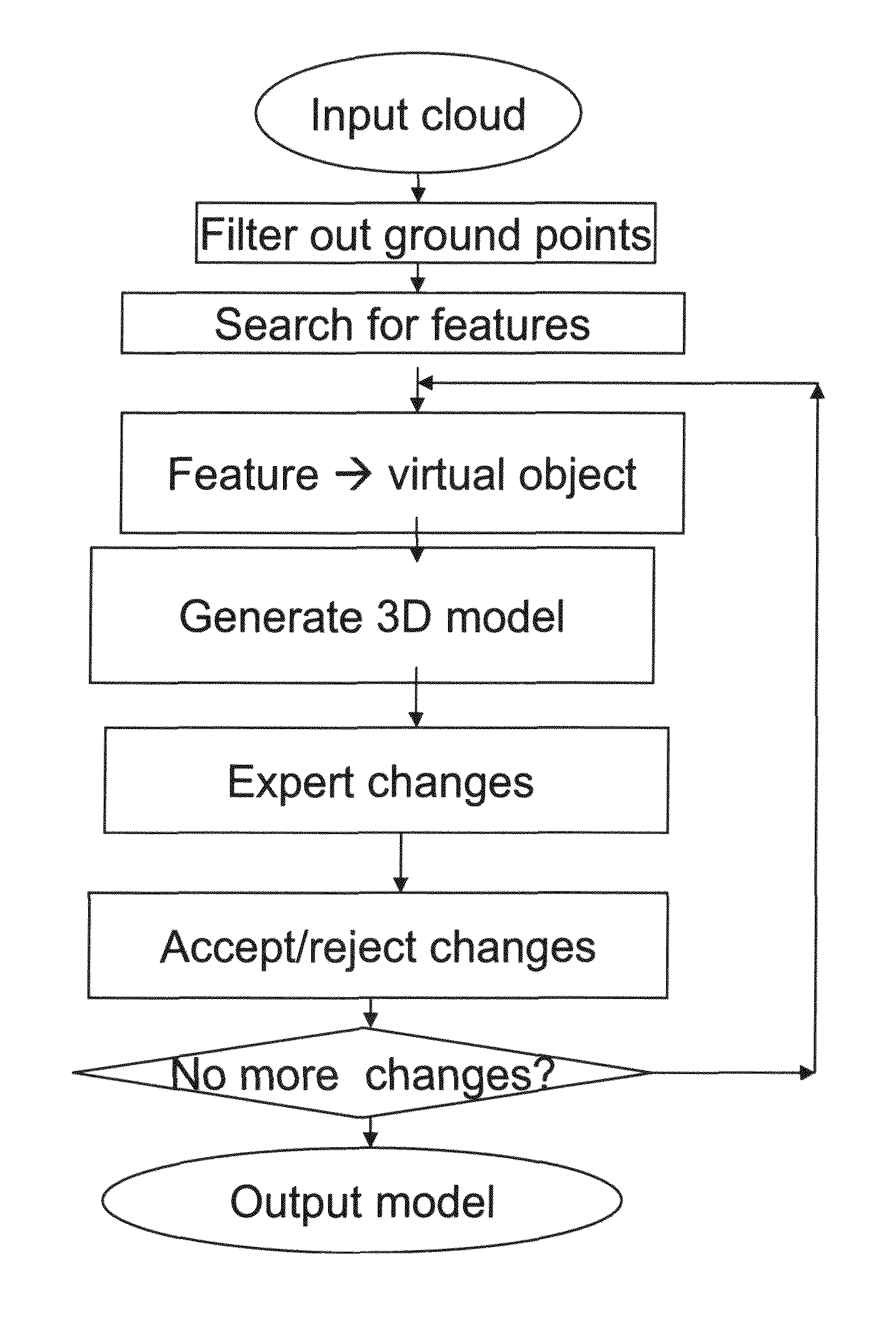
Apparatus for processing of a LiDAR point cloud of a ground scan, comprises: a point cloud input for receiving said LiDAR point cloud, a ground filter for filtering out points that belong to the ground from said point cloud, thereby to generate an elevation map showing features extending from the ground, an automatic feature search and recognition unit associated with said three dimensional graphical engine for searching said elevation map of said three-dimensional model to identify features therein and to replace points associated with said feature with a virtual object representing said feature, thereby to provide objects within said data; and a three-dimensional graphical renderer supporting three-dimensional graphics, to generate a three-dimensional rendering of said ground scan.
Owner:TILTAN SYST ENG
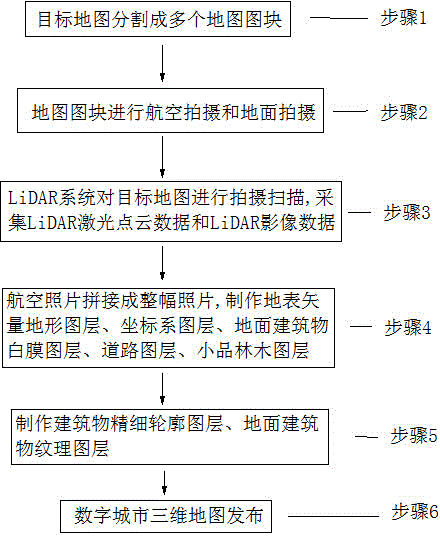
Urban digital map three-dimensional modeling manufacturing method
The invention discloses an urban digital map three-dimensional modeling manufacturing method which comprises the following steps: encoding and identifying map blocks divided from a target map; acquiring aerial images and ground shot images of the map blocks; shooting and scanning the target map by using a LiDAR system, so as to acquire LiDAR laser point cloud and LiDAR image data; splicing the aerial images so as to generate a whole image of the target map; performing vectorization processing on the whole image so as to obtain an earth surface vectorization topographic map layer of the target map; manufacturing a coordinate system map layer and an earth surface elevation map layer reflecting the earth surface height by using LiDAR laser point cloud data; respectively manufacturing map layers of roads, small items, forests, ground building elevation and ground building texture according to the ground images, and finally fusing the map layers on a map publication platform so as to establish a three-dimensional digital map of the target map. The urban map manufactured by using the method comprises urban ground elevation, ground building texture, urban road surface texture, road materials, small urban items and urban gardening, and a user can conveniently check and use the urban map.
Owner:南京市测绘勘察研究院股份有限公司
Object and vehicle detection and tracking using 3-D laser rangefinder
ActiveUS8260539B2Anti-collision systemsElectromagnetic wave reradiationGround planeVehicle detection
A method and system for detecting and tracking objects near a vehicle using a three dimensional laser rangefinder. The method receives points from the laser rangefinder, where the points represent locations in space where the rangefinder senses that some object exists. An algorithm first estimates the location of a ground plane, based on a previous ground plane location, data from onboard sensors, and an eigenvector calculation applied to the point data. Next, a plan view occupancy map and elevation map are computed for stationary objects, based on point data in relation to the ground plane. Finally, dynamic objects are detected and tracked, sensing objects which are moving, such as other vehicles, pedestrians, and animals. The output of the method is a set of stationary and dynamic objects, including their shape, range, and velocity. This output can be used by downstream applications, such as collision avoidance or semi-autonomous driving systems.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
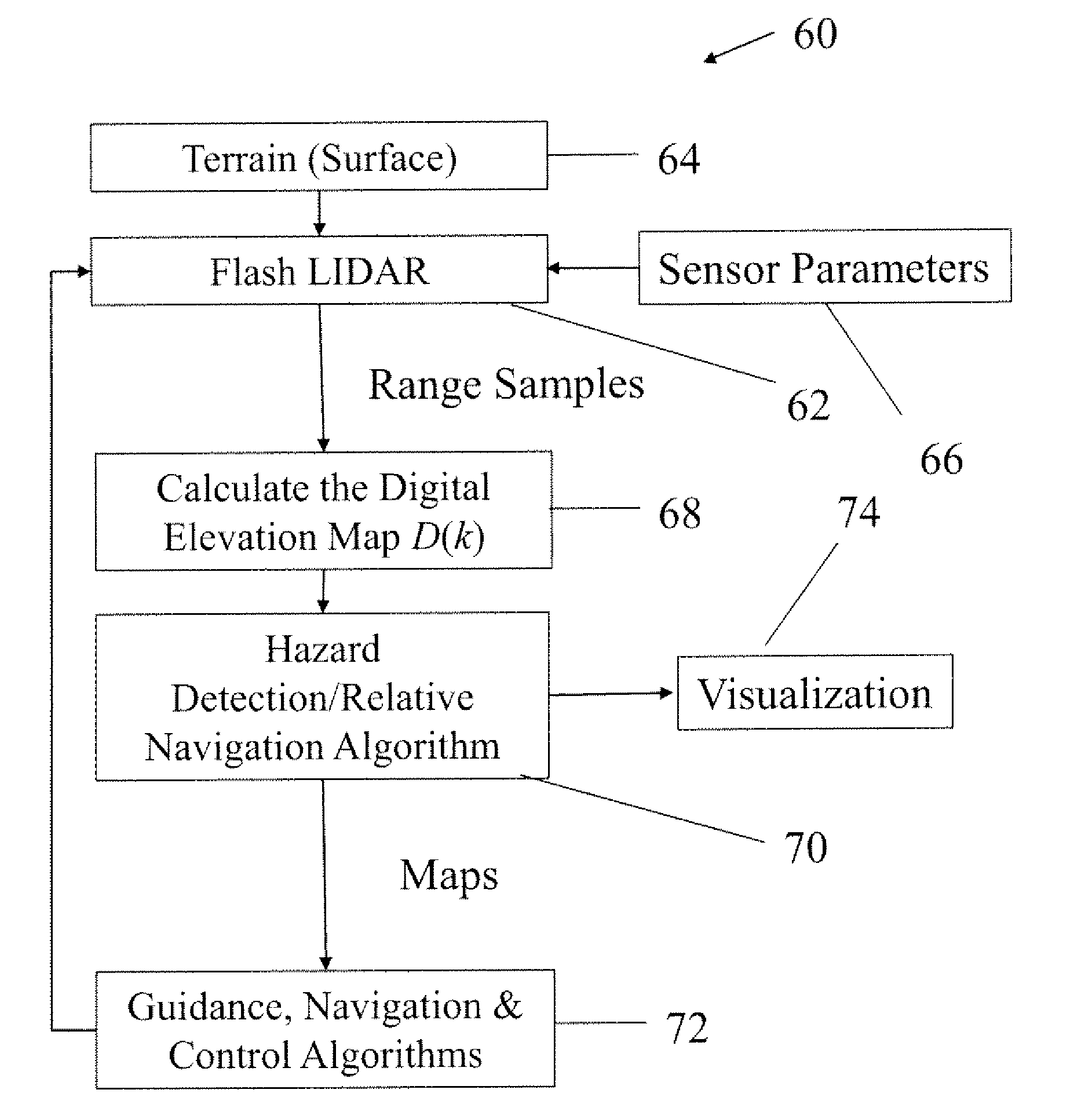
Method for Enhancing a Three Dimensional Image from a Plurality of Frames of Flash Lidar Data
ActiveUS20120033196A1Increase heightSafe preciseOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationConsecutive frameDigital elevation map
Owner:NASA
Vertical graph identification method for converting architectural drawing into three-dimensional BIM model
ActiveCN109993827AImprove integrityImprove accuracyGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsVisibilitySize measurement
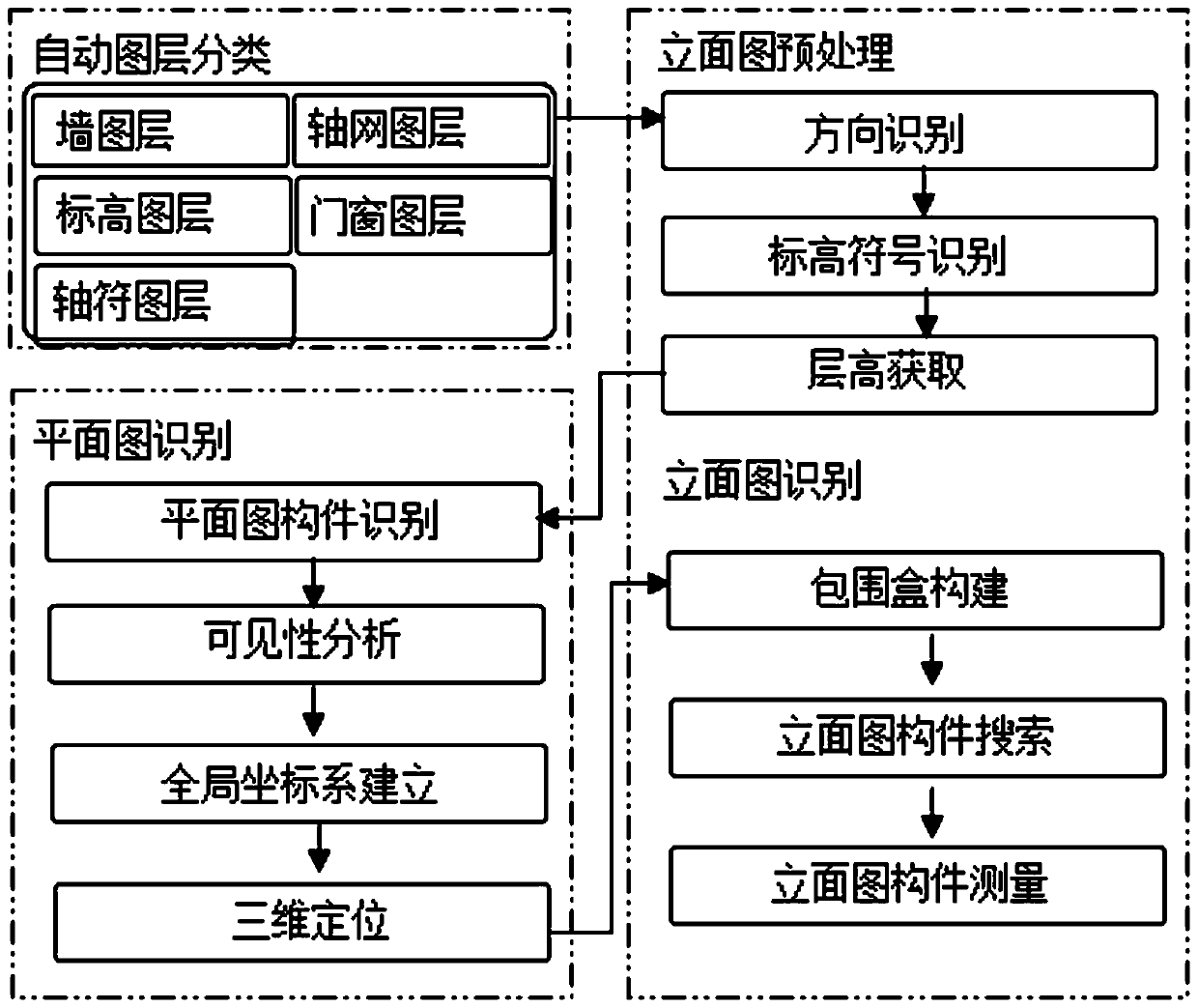
The invention discloses a vertical graph recognition method for converting a building drawing into a three-dimensional BIM model, and the method comprises the following steps: a, obtaining a target graph layer of the CAD building drawing, and obtaining a wall graph layer, a door and window graph layer, an elevation graph layer, an axis symbol graph layer, and an axis network graph layer; b, performing direction identification, elevation symbol identification and story height acquisition on each vertical drawing of the CAD building drawings; c, performing building component recognition, visibility analysis and three-dimensional positioning on each layer of plane drawing of the CAD building drawing; d, carrying out bounding box construction on the elevation drawing paper in each direction ofthe CAD building drawing paper, and carrying out search and size measurement on the elevation drawing component; according to the method, when the CAD building drawing is converted into the three-dimensional BIM model, the components of the elevation map of the CAD building drawing are recognized, the size numerical value of the components is obtained, and the CAD building drawing recognition andthree-dimensional BIM model reconstruction efficiency is improved.
Owner:宁波睿峰信息科技有限公司
Object and vehicle detecting and tracking using a 3-D laser rangefinder
ActiveCN102248947ARoad vehicles traffic controlElectromagnetic wave reradiationGround planeStationary object
Provided are a method and system for detecting and tracking objects near a vehicle using a three dimensional laser rangefinder. The method receives points from the laser rangefinder, where the points represent locations in space where the rangefinder senses that some object exists. An algorithm first estimates the location of a ground plane, based on a previous ground plane location, data from onboard sensors, and an eigenvector calculation applied to the point data. Next, a plan view occupancy map and elevation map are computed for stationary objects, based on point data in relation to the ground plane. Finally, dynamic objects are detected and tracked, sensing objects which are moving, such as other vehicles, pedestrians, and animals. The output of the method is a set of stationary and dynamic objects, including their shape, range, and velocity. This output can be used by downstream applications, such as collision avoidance or half autonomous driving systems.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method of bioimage data processing for revealing more meaningful anatomic features of diseased tissues
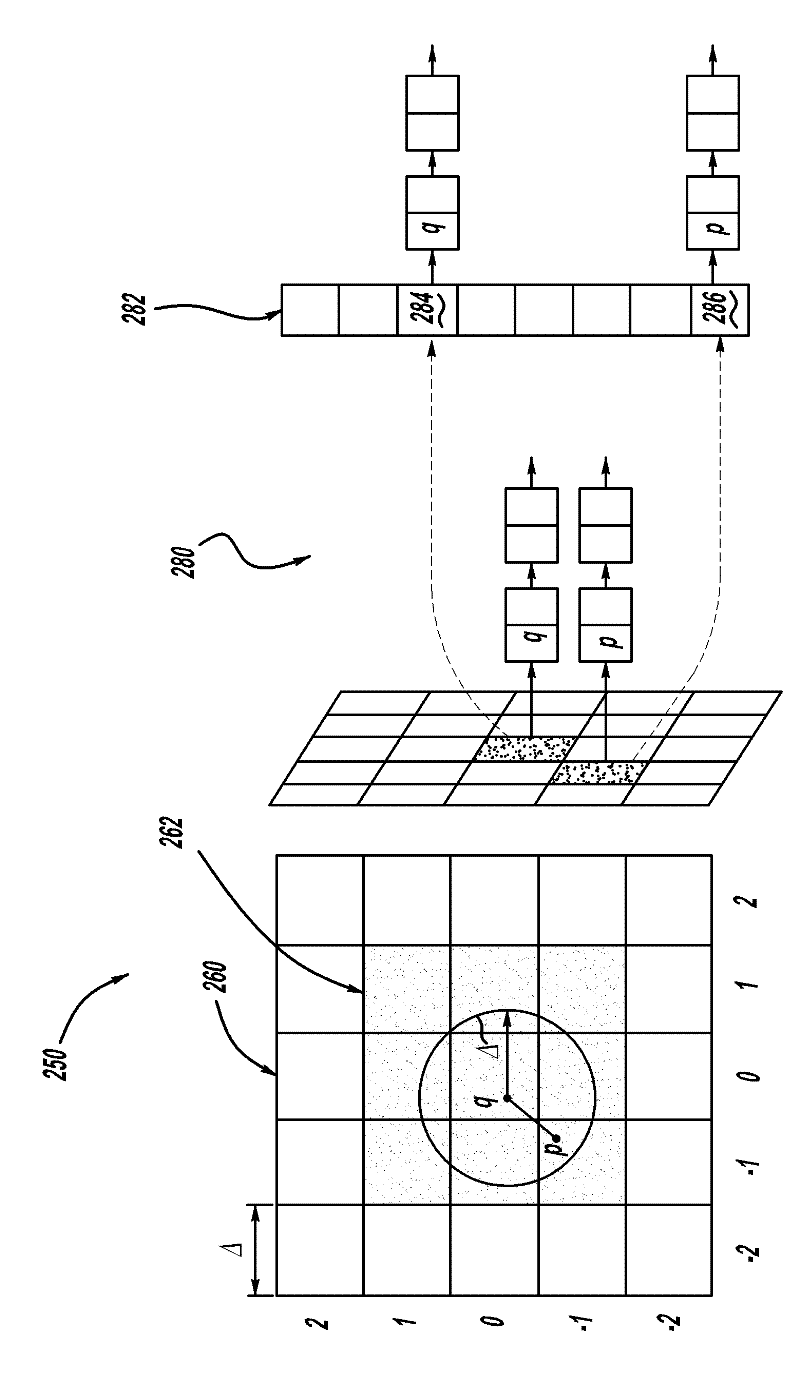
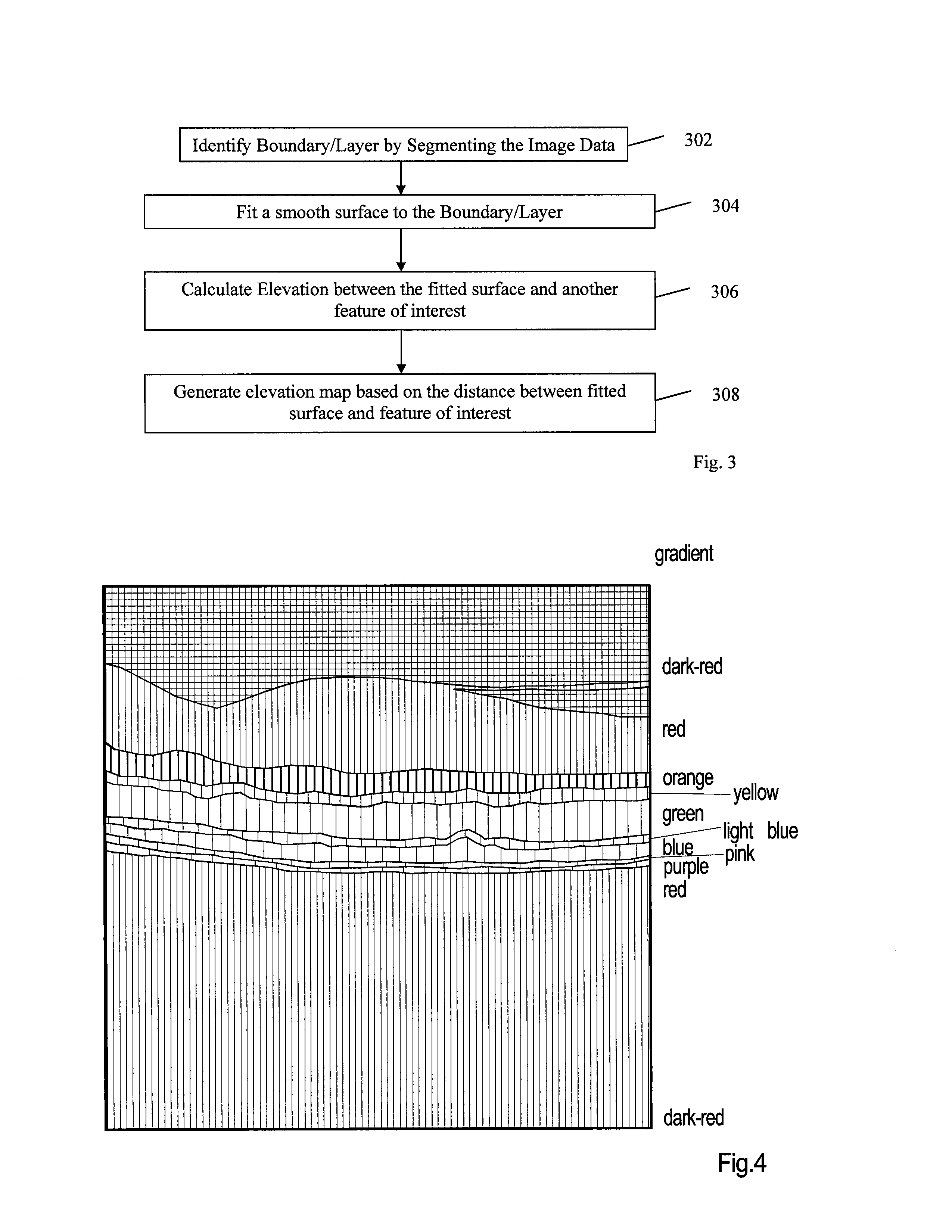
The present invention discloses a method for generating elevation maps or images of a tissue layer / boundary with respect to a fitted reference surface, comprising the steps of finding and segmenting a desired tissue layer / boundary; fitting a smooth reference surface to the segmented tissue layer / boundary; calculating elevations of the same or other tissue layer / boundary relative to the fitted reference surface; and generating maps of elevation relative to the fitted surface. The elevation can be displayed in various ways including three-dimensional surface renderings, topographical contour maps, contour maps, en-face color maps, and en-face grayscale maps. The elevation can also be combined and simultaneously displayed with another tissue layer / boundary dependent set of image data to provide additional information for diagnostics.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC INC
Wavefront reconstruction using fourier transformation and direct integration
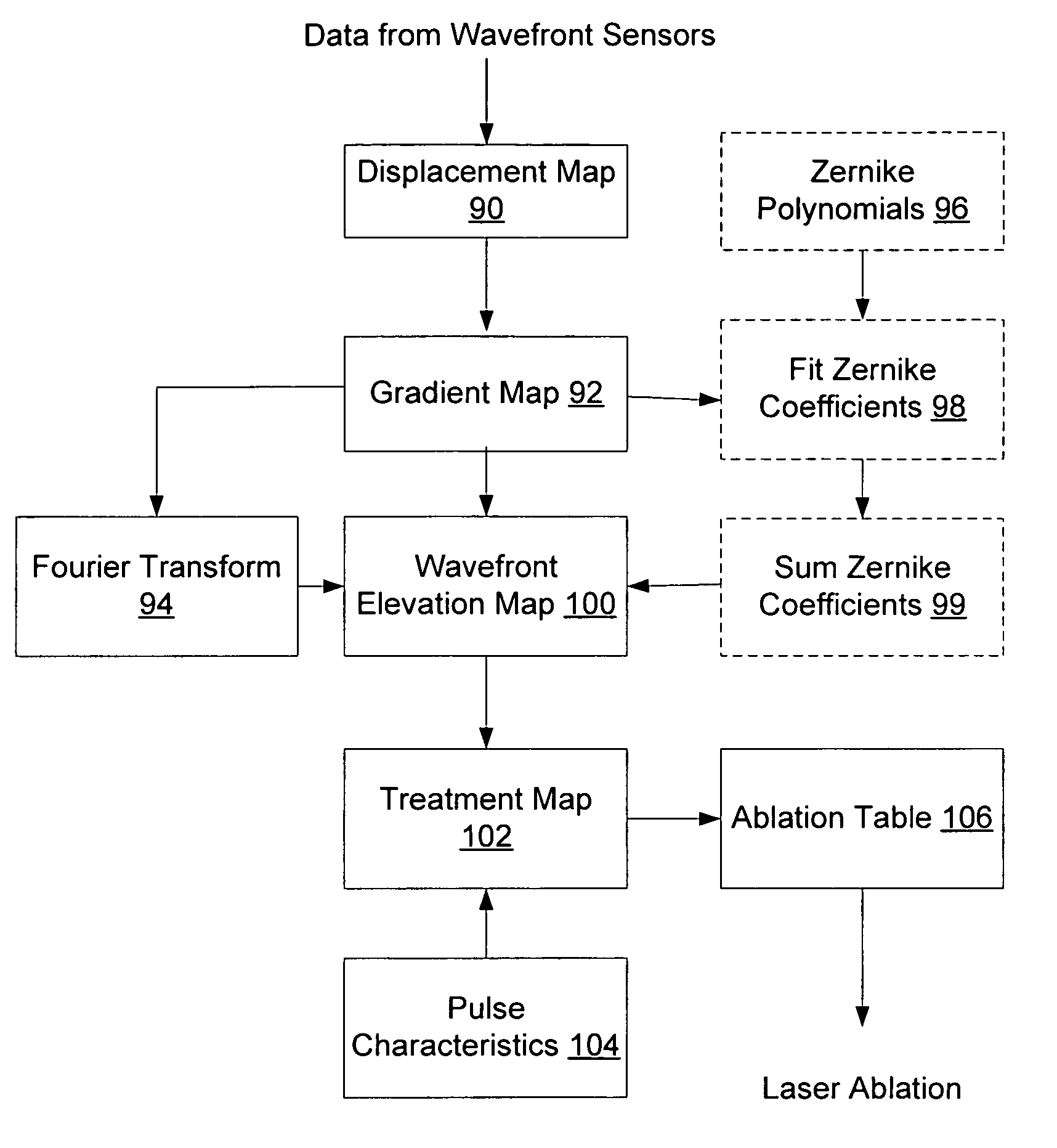
The present invention provides methods, systems and software for generating a wavefront elevation map using Fourier transformation algorithms. In one embodiment, the present invention provides a method of reconstructing optical tissues of an eye. The method comprises transmitting an image through the optical tissues of the eye. The surface gradients from the transmitted image are measured across the optical tissues of the eye. A Fourier transform algorithm is applied to the surface gradients to reconstruct a surface that corresponds to the optical tissues of the eye.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
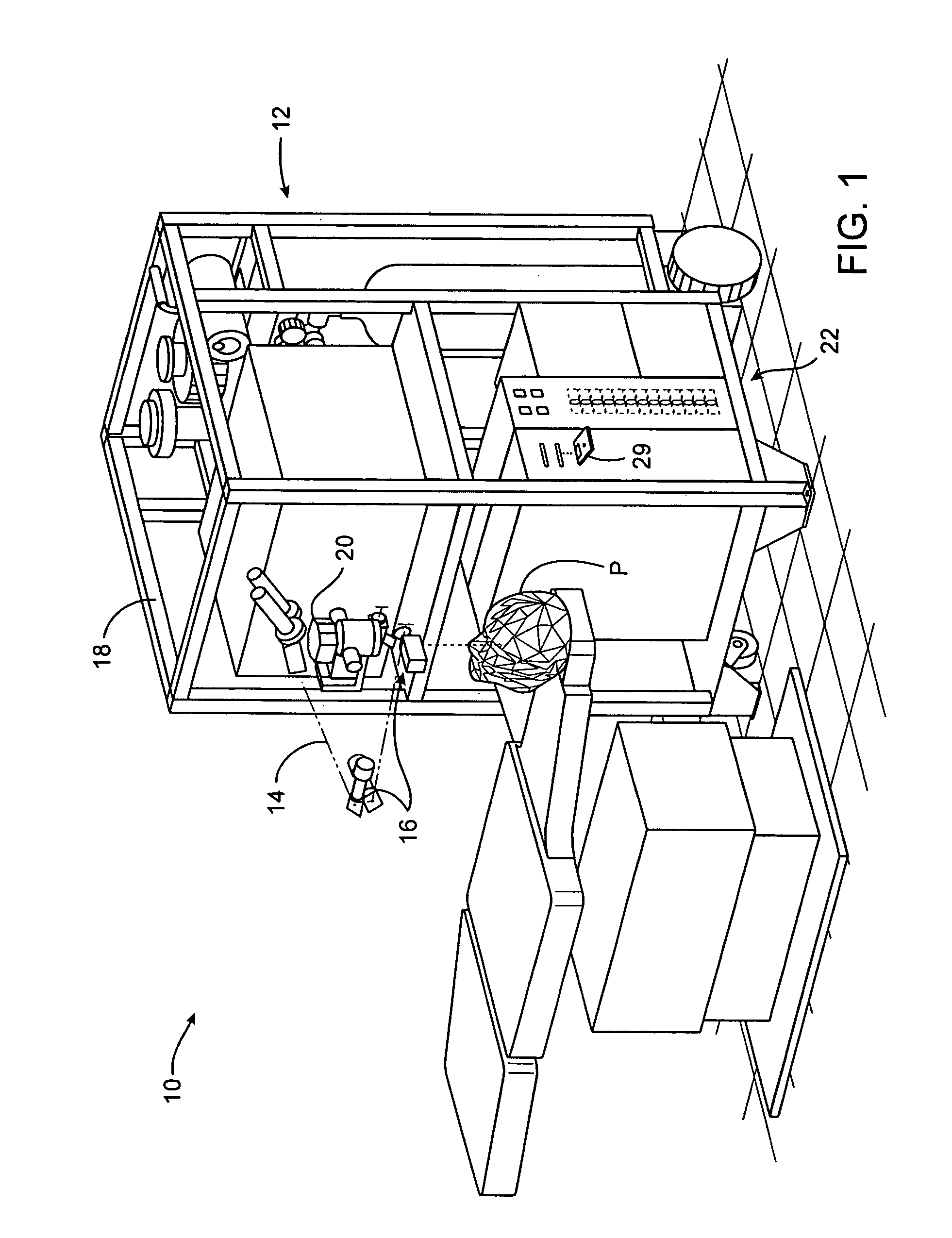
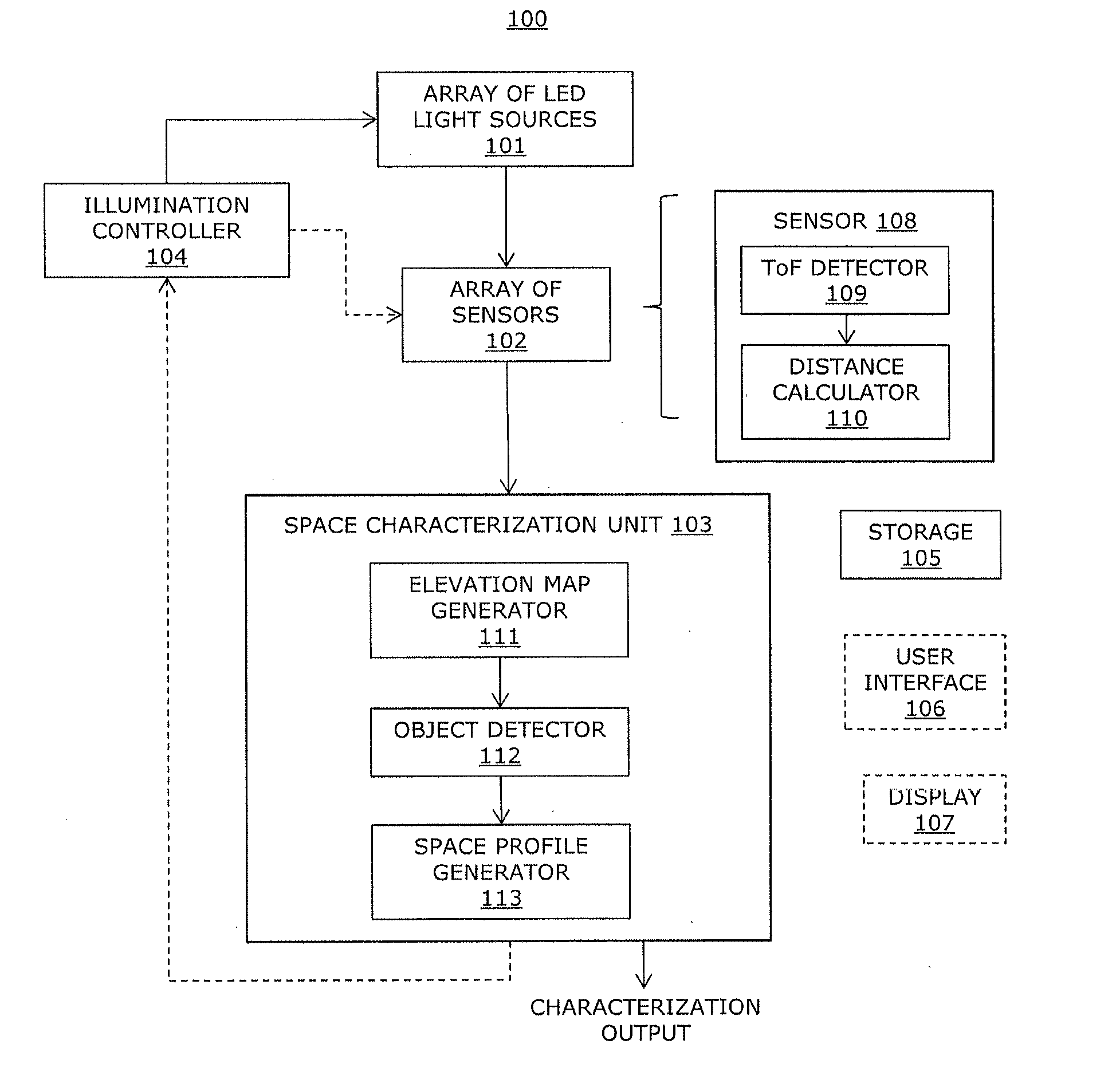
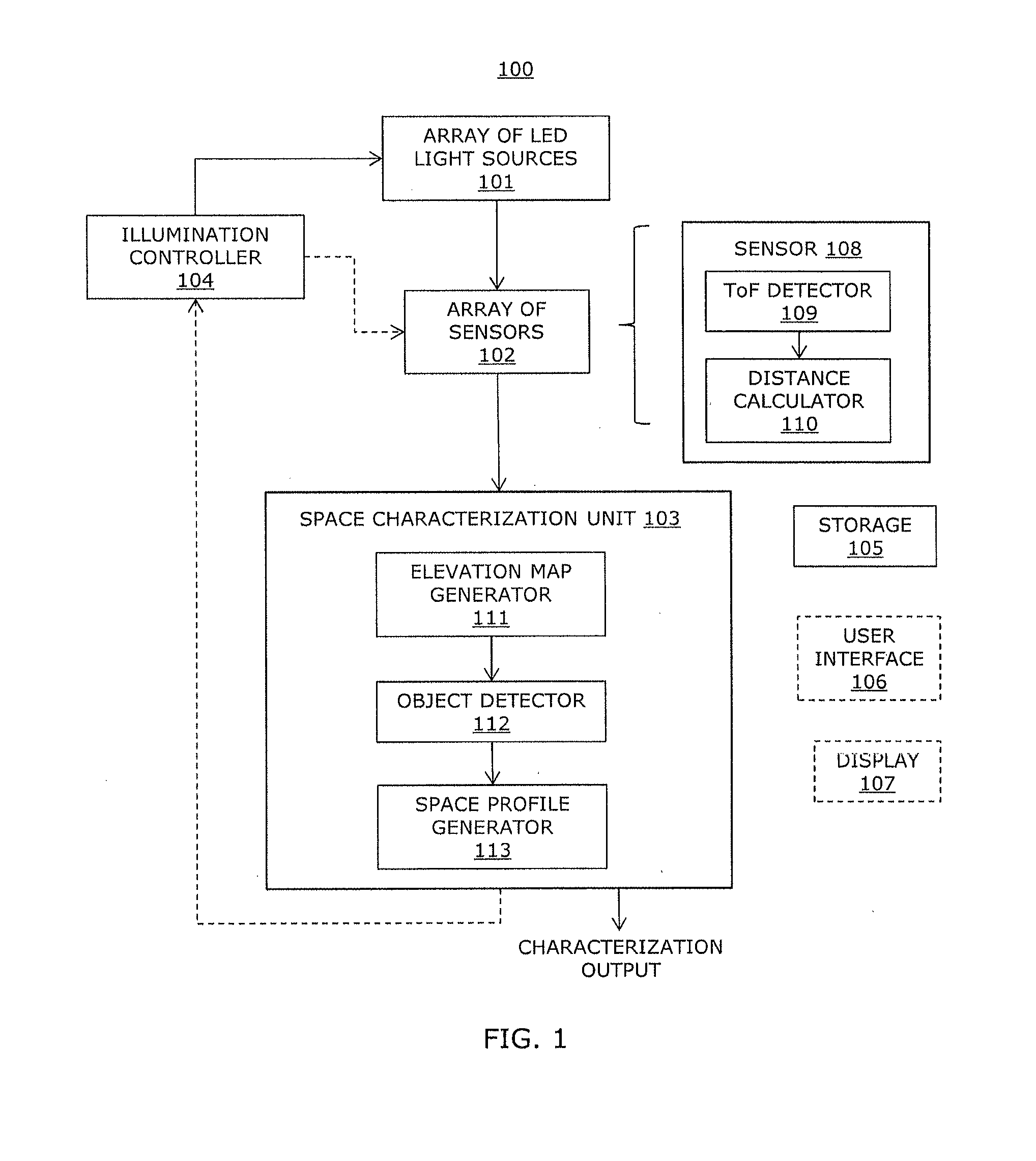
Sensory lighting system and method for characterizing an illumination space
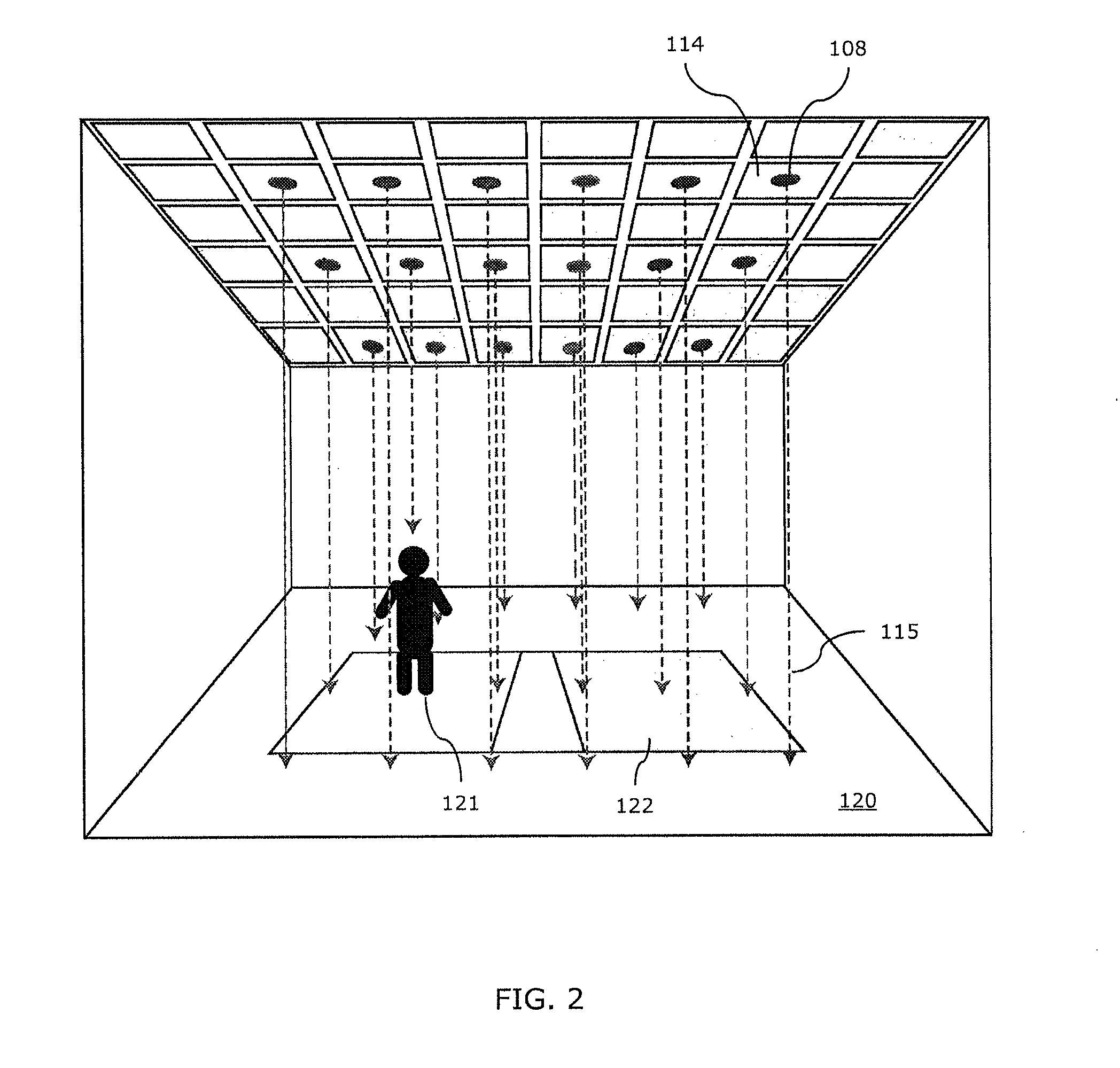
Disclosed herein is an illumination system including an array of LED light sources for emitting light encoded with a modulation pattern, an array of sensors and a space characterization unit. The array of sensors receives emitted light scattered by an object. Each sensor determines a distance between the corresponding light source and the object using the modulation pattern. The space characterization unit uses the distance from each sensor to generate an elevation map indicating a presence of the object.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST +1
Self-adaptive three-dimensional space path planning method based on particle swarm algorithm
InactiveCN102722749AImprove adaptabilityFreedom of movementBiological models3D modellingAlgorithmThree-dimensional space
The invention provides a self-adaptive three-dimensional space path planning method based on a particle swarm algorithm and direct at a submarine topography elevation model. The method comprises firstly initializing space position and displacement of particles, conducting dimensional reconstruction while space position is initialized, initializing the best position where a first generation of particles pass and the best position found by a group currently, then updating the next generation displacement and the space position of particles, introducing an attraction operator and an exclusion operator during the updating, updating the best position where the next generation of particles pass and the best position found by the group by calculating the adaptability of the particles, and updating the displacement and the space positions of the particles repeatedly until the required number of iterations is fulfilled. The method has no special requirements on a pathing environment, the convergence rate, the convergence accuracy and the self-adaptability are all improved in the path planning process, the free movement of particle nodes in the space becomes possible, the success rate of pathing is increased, and the calculated amount of path planning is reduced.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Apparatus and method for automatic airborne LiDAR data processing and mapping using data obtained thereby
Apparatus for processing of a LiDAR point cloud of a ground scan, comprises: a point cloud input for receiving said LiDAR point cloud, a ground filter for filtering out points that belong to the ground from said point cloud, thereby to generate an elevation map showing features extending from the ground, an automatic feature search and recognition unit associated with said three dimensional graphical engine for searching said elevation map of said three-dimensional model to identify features therein and to replace points associated with said feature with a virtual object representing said feature, thereby to provide objects within said data; and a three-dimensional graphical renderer supporting three-dimensional graphics, to generate a three-dimensional rendering of said ground scan.
Owner:TILTAN SYST ENG
Spatial Frequency Wavefront Sensor System and Method
ActiveUS20080073525A1Easy searchMore accuratePhotometry using reference valueMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPoint spreadWavefront sensor
Devices systems, and methods can characterize an optical surface of an object. A wavefront sensor system focuses light energy propagating from the object to form a pattern on a detector. The system maps the pattern to an array with a transform function such as a Fourier transform. The values of array correspond to characteristic locations and signals in a transform space, for example an intensity of spatial frequency signals in frequency space. The characteristic location and intensity of these signals in transform space are used to measure the optical surface. For example, a characteristic frequency of a spatial frequency intensity peak in Fourier transform space can be used to estimate the location of spots on the detector. Alternatively, the characteristics can be used to the measure sphere, cylinder and axis of a wavefront, wavefront elevation maps and point spread functions, often without locating positions of individual spots on the detector.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
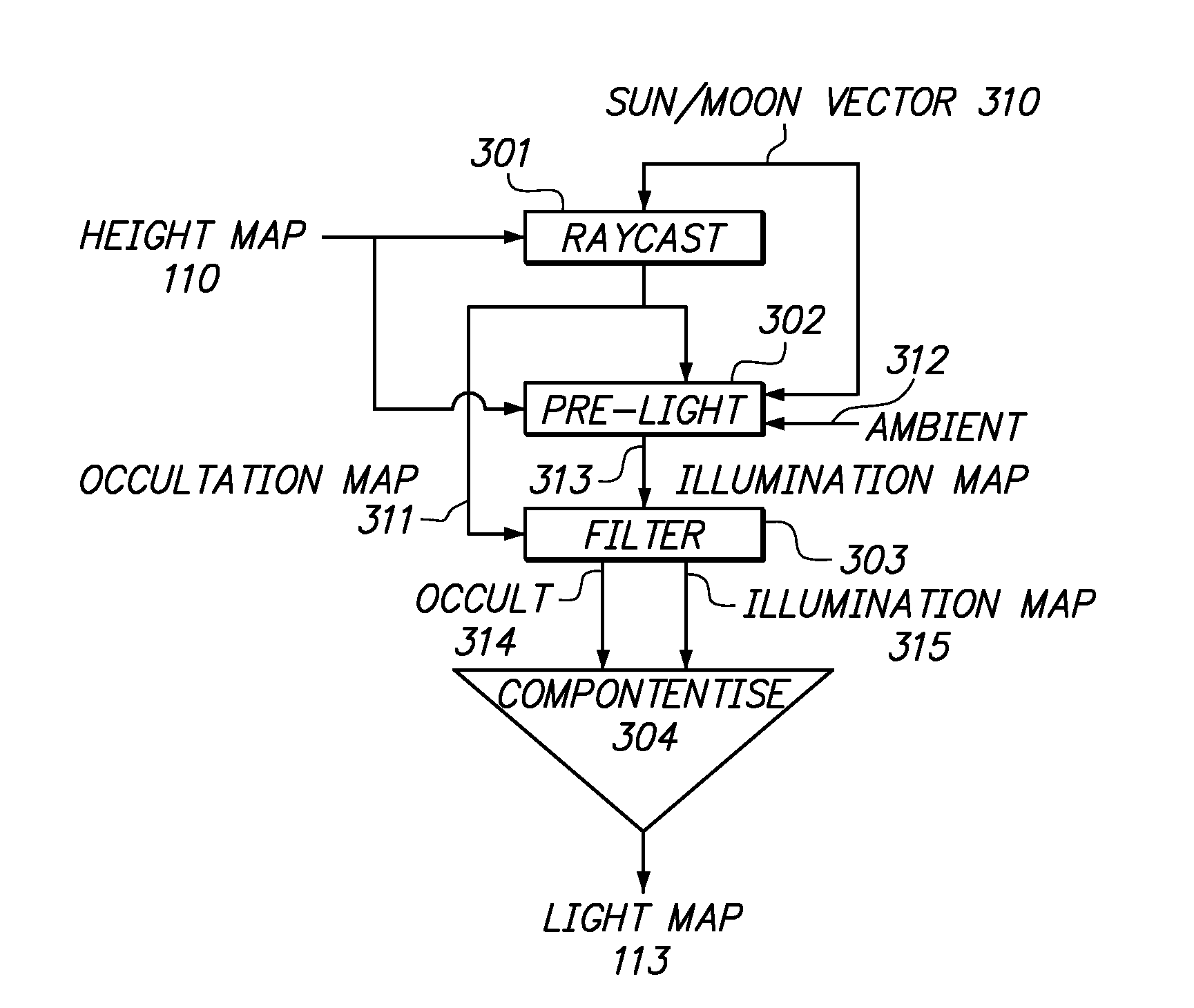
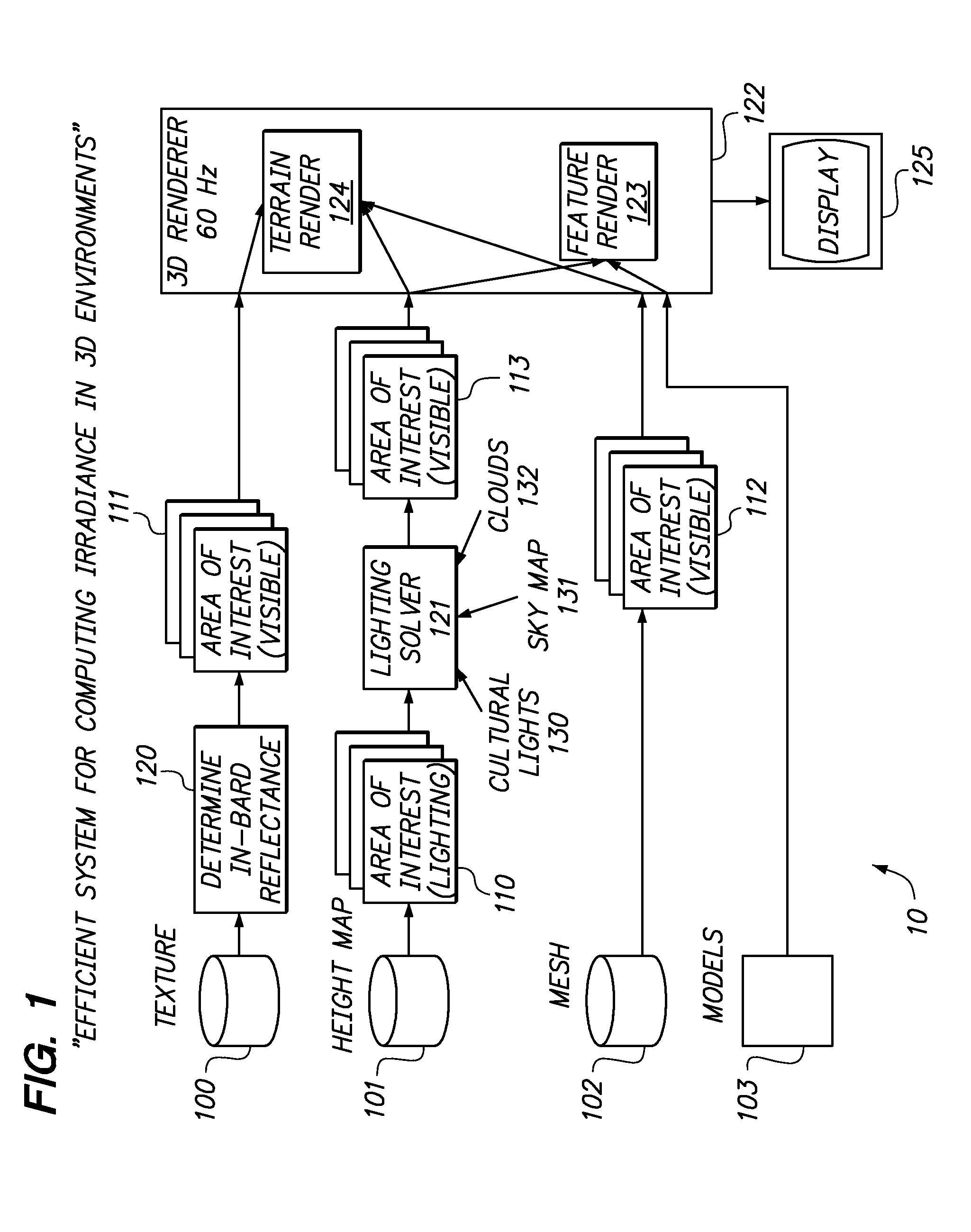
Efficient illumination of large three dimensional environments
Efficient determination of illumination over large 3D environments, including shadowing, is provided. Illumination, including shadows, is generated using a raster elevation map by a lighting solver. The lighting solver fetches the raster elevation map for an illumination area of interest at the paging rate and produces an illumination map that is applied to terrain and features by a 3D renderer. The lighting solver updates subsets of the illumination map as necessary to reflect changing illumination or movement of the visual area of interest.
Owner:AECHELON TECH
Aerial carrier flight control method and aerial carrier flight control system
InactiveCN105786019AEnsure flight safetyGlobalizationPosition/course control in three dimensionsControl systemLandform
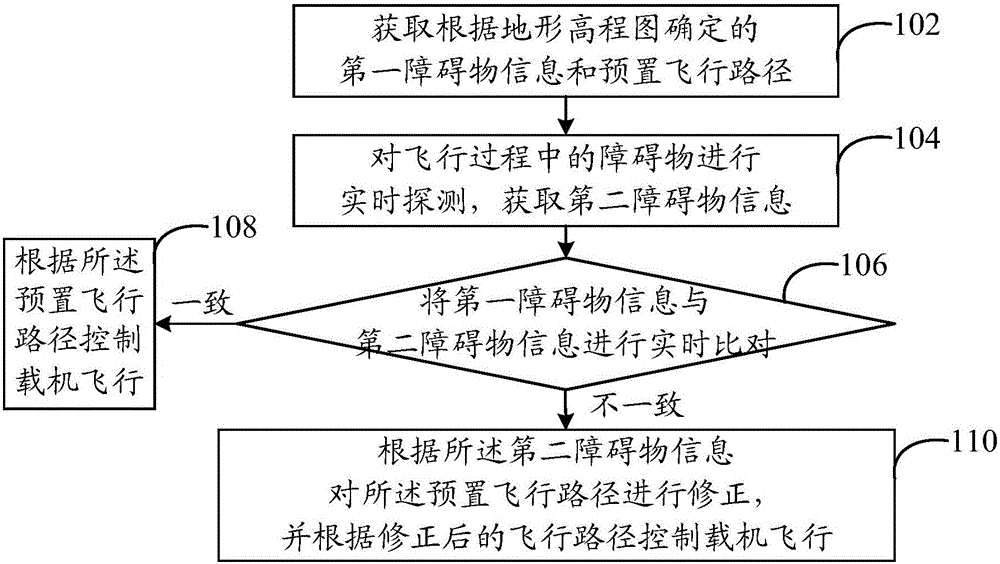
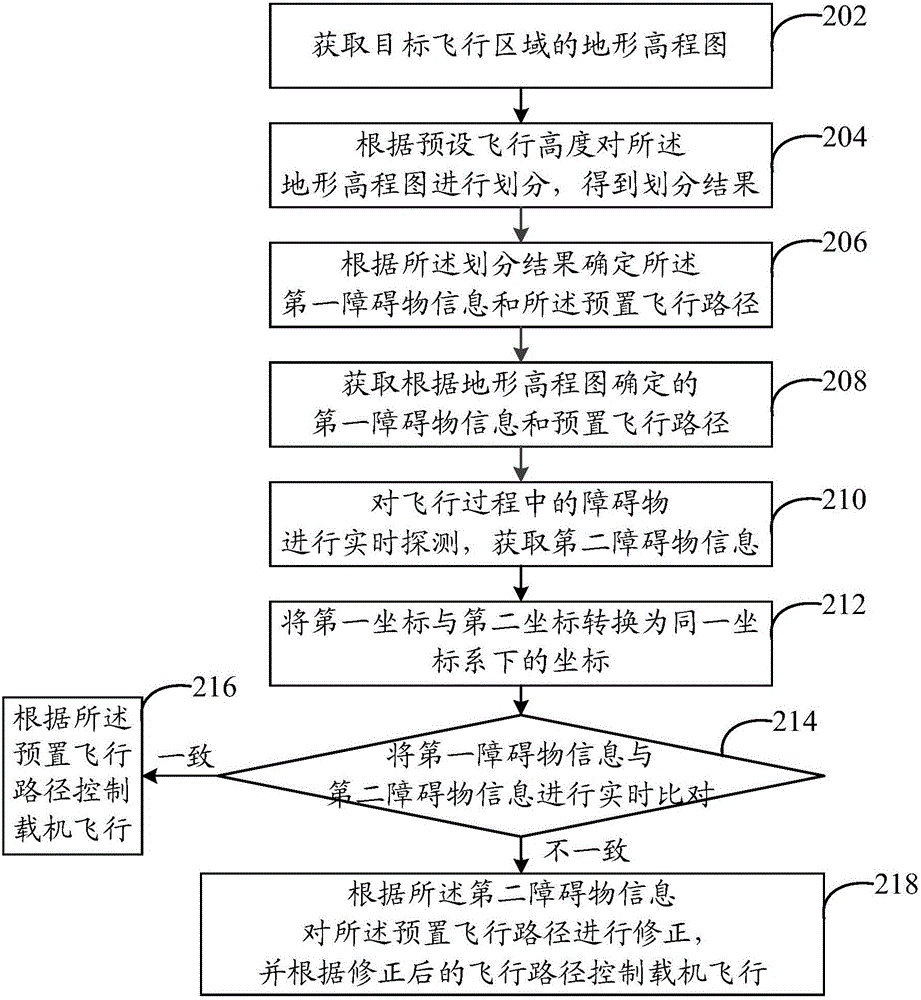
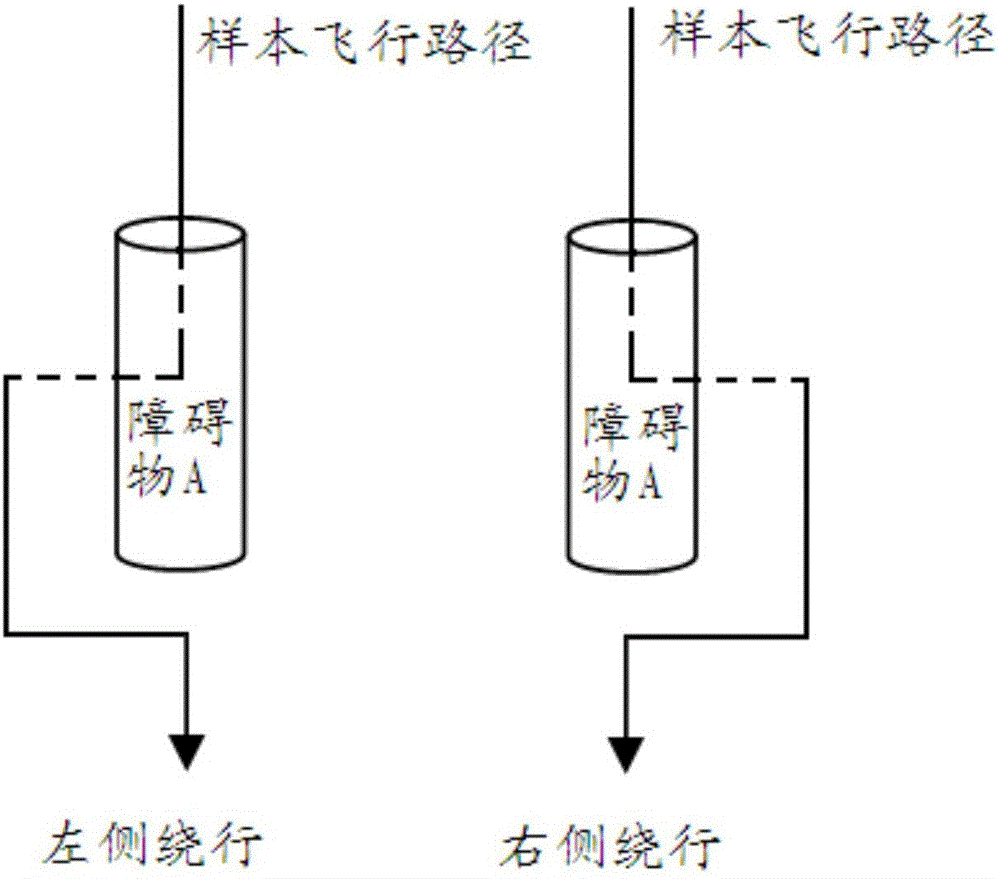
The invention provides an aerial carrier flight control method and an aerial carrier flight control system, wherein the method comprises the steps of acquiring first obstacle information and a preset flight path which are determined according to a landform elevation map; performing real-time detection on obstacles in the flight process, and obtaining second obstacle information; performing real-time comparison on the first obstacle information and the second obstacle information; if the first obstacle information is same with the second obstacle information, making the aerial carrier fly according to the preset flight path; and if the first obstacle information does not accord with the second obstacle information, correcting the preset flight path according to the second obstacle information, and making the aerial carrier fly according to the corrected flight path. The aerial carrier flight control method and the aerial carrier flight control system effectively prevent collision between the aerial carrier and the obstacles and furthermore ensure high flight safety of the aerial carrier.
Owner:GUANGZHOU XAIRCRAFT TECH CO LTD
AUV multi-strategy navigation method based on submarine topography matching
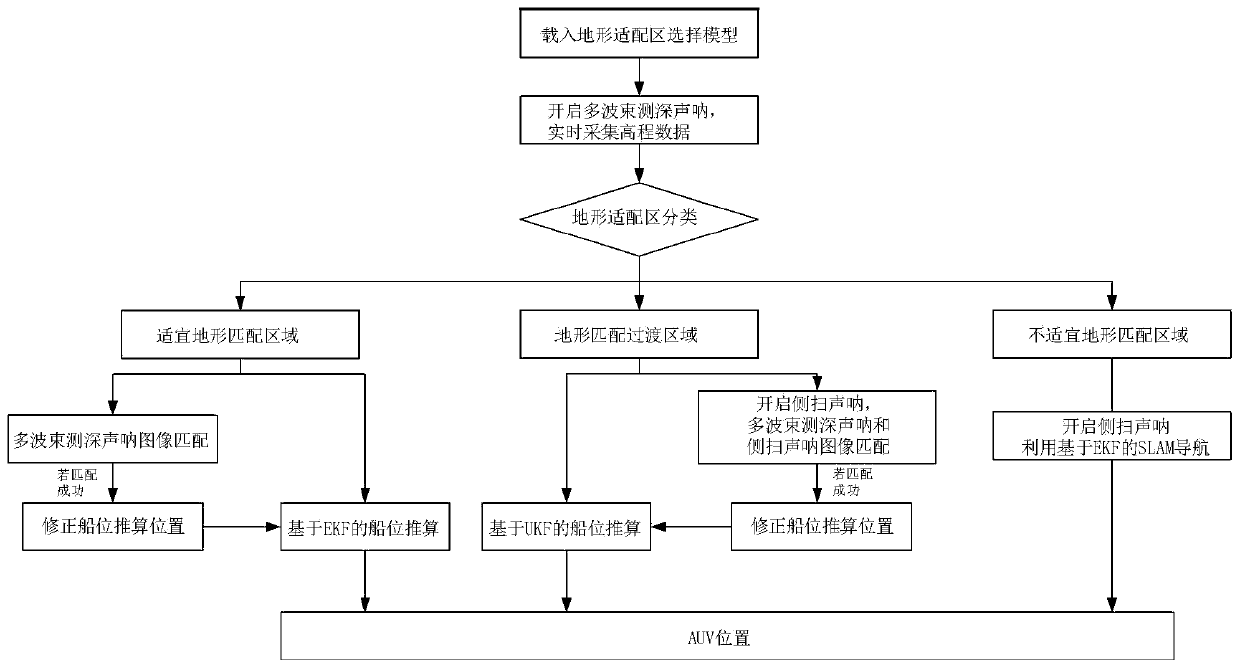
ActiveCN111486845ARectification errorImprove navigation accuracyNavigational calculation instrumentsAcoustic wave reradiationSonarRegion selection
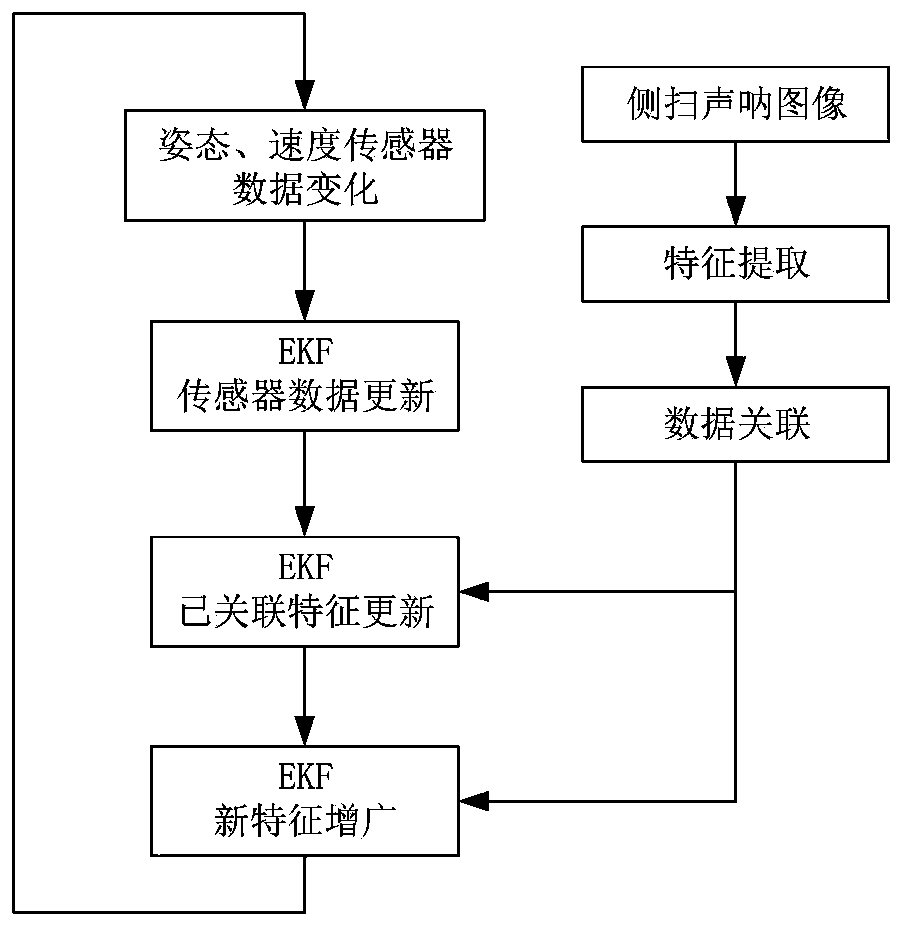
The invention discloses an AUV multi-strategy navigation method based on submarine topography matching. The method comprises the steps: constructing a topography adaptive region selection model basedon a machine learning algorithm, wherein the topography adaptive region selection model includes a suitable topography matching region, a topography matching transition region, and an unsuitable topography matching region; during specific navigation, analyzing a type of a navigation area through collected real-time data, and carrying out navigation based on a multi-beam sonar underwater topographyelevation image matching auxiliary method for the suitable topography matching region; for the topography matching transition region, starting a side-scan sonar, and carrying out underwater side-scansonar image matching by using a multi-beam depth finder and the side-scan sonar data to assist ship position calculation for navigation; and for the unsuitable topography matching region, starting the side-scan sonar, and carrying out navigation based on simultaneous localization and a map construction algorithm. The navigation method has better significance and value in practical application.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Field robot binocular vision navigation method and system
ActiveCN106338989AImprove impactImprove real-time performanceNavigational calculation instrumentsPosition/course control in two dimensionsVisual perceptionRidge
The present invention discloses a field robot binocular vision navigation method and system. A baseline is defined at the middle of an image; a density curve is obtained on the baseline by using sector scanning; an angle constraint relation between a sector scanning density model and ridge lines is designed, and the angle constraint relation is used to search other ridge lines; logistic regression is adopted to identify nearest ridge lines, so that a ridge line spacing parameter can be obtained; the elevation map of crop ridges is obtained, and a height limit is added into the elevation map; the enhanced elevation map and a binary image are fused, so that a crop ridge confidence density map can be generated; and a ridge line extraction algorithm is applied to the crop ridge confidence density map so as to extract a navigation parameter. According to the field robot binocular vision navigation method and system of the invention, the enhanced elevation map is adopted to make up the defect of feature point sparseness; the weight of height information is increased; interference information which does not accord with specified height is filtered out; the concept of the confidence density map is adopted; the information of the enhanced elevation map and the binary image are fused; the sector scanning detection is adopted to detect the reference ridge line; a double-peak method is adopted to detect the adjacent ridge lines; logistic theories are used in combination; and therefore, the accuracy of ridge line detection can be improved.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIVERSITY
Method for compressing elevation maps
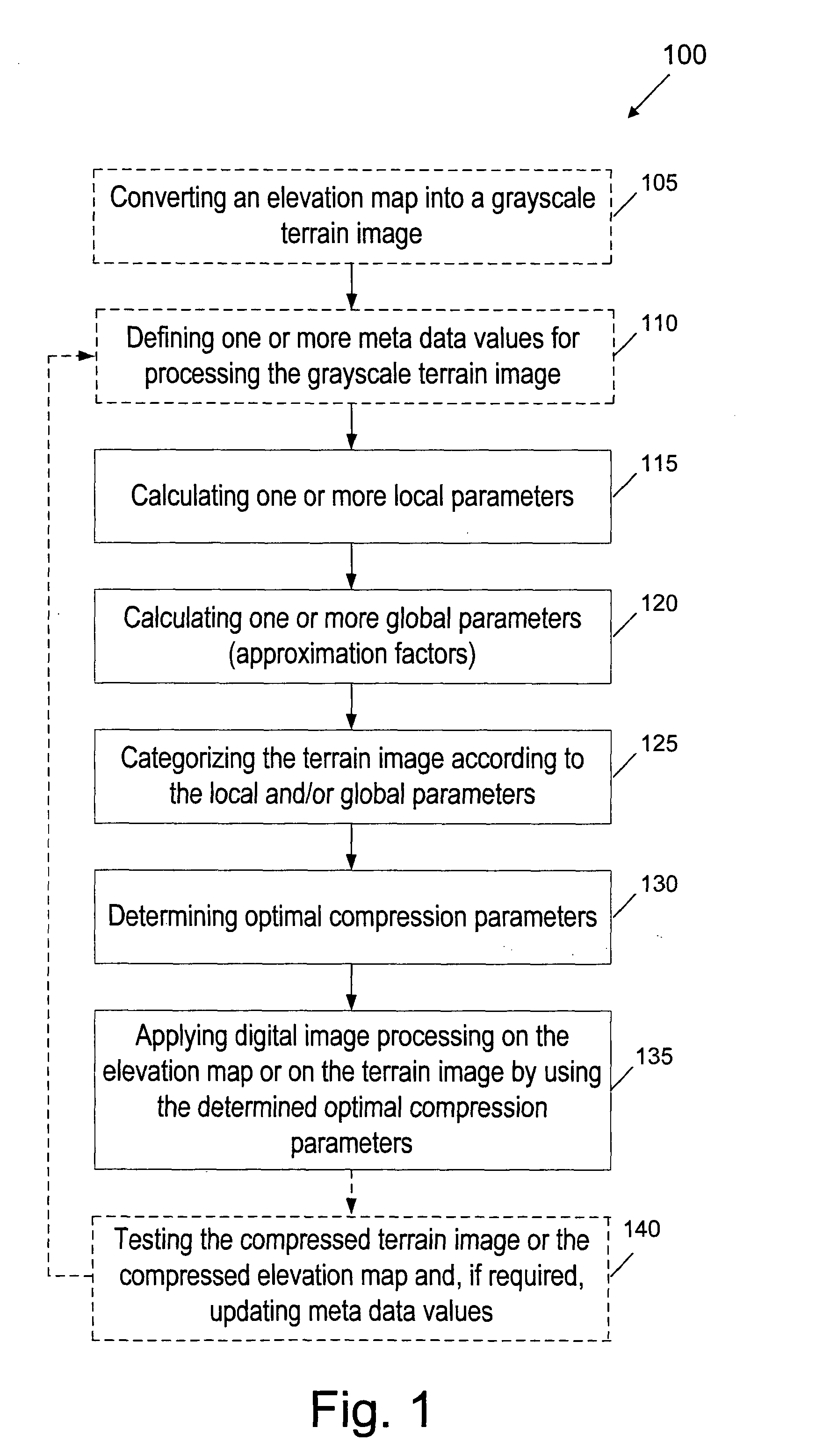
InactiveUS20100061626A1Improve geometry qualityTerrain simplificationCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationComputer scienceDigital image processing
A method for compressing an elevation map by means of digital image processing, according to which local and global parameters of an elevation map are calculated for sorting the elevation map into a corresponding category and the elevation map is categorized according to the calculated local and global parameters. Optimal parameters for compressing the elevation map are determined according to the calculated local and global parameters and according to the corresponding category and then the elevation map is compressed by applying on it digital image processing by using the determined optimal compression parameters.
Owner:ARIEL UNIV RES & DEV
A simulation method for large-scale terrain roam based on rule grid
InactiveCN101261743AFast readAvoid duplicate transmission3D-image rendering3D modellingRegular gridImage resolution
A large scale landform roaming simulation method based on regular gridding is based on the Geometry Clipmap principle and takes VBO as a basic storage mode, thus optimizing the top point updating strategies. The method includes the steps that: (1) a Geometry Clipmap framework is used at the pre-treating stage to form a clipmap pyramid; the landform is taken as a 2D elevation map, the data points of the regular gridding is used to express the ground height and caching the landform data in a group of embedded regular gridding which takes an observation point as the center for the use of drafting; (2) at the protracting stage, the VBO technology that is universally supported in a display card of a newer generation is used to quicken and draft the landform situation that is gradually degressive layer by layer by taking the observation point as the center resolution factor; (3) in the operation process, a new method for updating a top point queue and searching the queue is adopted to real time update the data of the embedded gridding according to the change of the observation point. The large scale landform roaming simulation method based on regular gridding of the invention effectively improves the important problem of speed during large scale landform drafting.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
application method and system of a BIM adaptive model in special-shaped curtain wall construction
The invention discloses an application method and system of a BIM self-adaptive model in special-shaped curtain wall construction. The method comprises the following steps: step S1, establishing a volume model of a support system according to a transverse and vertical elevation map of a design drawing, a curtain wall form, a size and related data, and constructing a self-adaptive family model of acorresponding curtain wall component by referring to the design drawing; Step S2, analyzing three-dimensional model data, reasonably cutting the surface of the volume model of the support system according to the positioning of a curtain wall framework, dividing grids, opening node options of a surface representation form, and sequentially matching the self-adaptive model at the nodes to enable the self-adaptive model to be self-adaptive to a special-shaped surface structure form of the self-adaptive model; And S3, after the self-adaptive family model is matched with the surface form of the supporting system, obtaining a component model in a specific shape, extracting through the self-adaptive family model to obtain corresponding specification data, modeling through the obtained data, anddrawing.
Owner:THE GUANGDONG NO 3 WATER CONSERVANCY & HYDRO ELECTRIC ENG BOARD CO LTD
3S technology based method for returning farmland to forests
The present invention discloses a 3S technology based method for returning farmland to forests. The method comprises the following steps: determining a returning farmland to forest scheme through remote sensing and GIS monitoring; generating a DEM by digitizing contour lines, and performing overlay analysis on an elevation map, a slope map, an aspect map, a land use map, and a map of returned farmland, to obtain a database of land use, slopes, and aspects; grading soil erosion by using a USLE equation; grading soil fertility and land productivity; performing overlay analysis on the database of land use, slopes, and aspects, soil erosion grading data and land productivity grading data, to obtain a grading and distribution map of returning farmland to forests; performing comprehensive analysis to obtain a planning map for returning farmland to forests; and digitizing collected data, to build a database for returning farmland to forests. The method disclosed by the invention is adapts to local conditions, and is suitable for trees and lands, and the human and capital investment is reduced, so as to meet the requirements for rapid returning farmland to forests and sustainable development.
Owner:SICHUAN YUHANG PLANNING DESIGN +1
Interferential circular SAR elevation estimation processing method
The invention discloses an interferential circular SAR elevation estimation processing method. The method comprises the steps that (1) a scene DEM is estimated roughly; (2) on the basis of the roughly estimated scene DEM, BP imaging is carried out on an InSAR platform main antenna and an InSAR platform auxiliary antenna respectively and independently, wherein BP imaging is carried out on circular SAR data obtained by the main antenna and the auxiliary antenna by adopting a molecule aperture mode, one sub aperture is set every n degrees, 360 / n sub aperture image pairs are obtained, and n is a natural number larger than or equal to 1; (3) interference processing is carried out on each sub aperture image pair; (4) weighted average is carried out on the scene elevation, estimated through the interference processing, of all the sub aperture image pairs obtained in the step (3) according to the value of a corresponding interference coefficient, and an elevation map observed under 360 degrees is obtained; (5) the elevation map estimated in the step (4) is used as a reference DEM of the step (2) to be input, and the step (2) to the step (4 )are repeated for several times until the interference coefficient of interference images does not decline any more.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A Positioning Method of Ground Mobile Communication Network Corrected by Map Elevation
InactiveCN102300311AHigh positioning accuracySimple methodWireless communicationNatural satelliteHorizon
The invention relates to a positioning method for correcting and revising a ground mobile communication network by using a map elevation, which relates to positioning technology, and uses an electronic map marked with horizon and building elevation as the elevation constraint, and the high precision of the electronic map is decimeter or centimeter level. When using the ground mobile communication network or broadcasting network to measure the pseudo-range positioning, due to the non-line-of-sight error in the pseudo-range measurement, the current positioning accuracy is low. To improve the positioning accuracy of terrestrial mobile networks and broadcasting networks, the influence of non-line-of-sight errors must be corrected. This method utilizes the initial positioning solution and the elevation constraint to verify the accuracy of the pseudo-range measurement, judges whether the measured pseudo-range has non-line-of-sight transmission error, and corrects the pseudo-range error to improve the positioning accuracy of the mobile station. The method of the invention is simple and easy, can distinguish, estimate and eliminate non-line-of-sight propagation errors, and improves the positioning accuracy of the mobile phone to the order of meters, which has practical significance. It is suitable for radiolocation of terrestrial mobile communication network, radiolocation of terrestrial broadcasting network and radiolocation of satellite transmission network.
Owner:NAT ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORIES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Detection of an open area
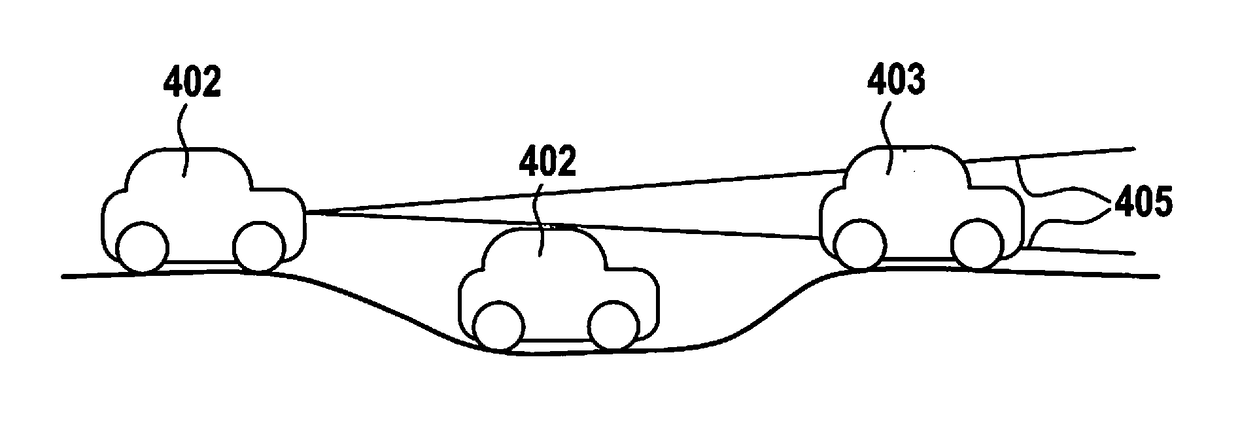
InactiveUS20170162056A1Reliable conclusionImprove securityRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesDetection of traffic movementEngineeringTrafficability
A method for a vehicle equipped with a surroundings sensor system for generating an evaluation signal representing the trafficability of at least one route section to be traveled by the vehicle, the evaluation signal being ascertained as a function of surroundings data which are gathered with the aid of the surroundings sensor system, the evaluation signal being further ascertained as a function of at least one piece of surroundings information from an elevation map representing the topology of the at least one route section and / or at least one movement value of the vehicle representing a pitch and / or roll angle.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Example based editing of virtual terrain maps
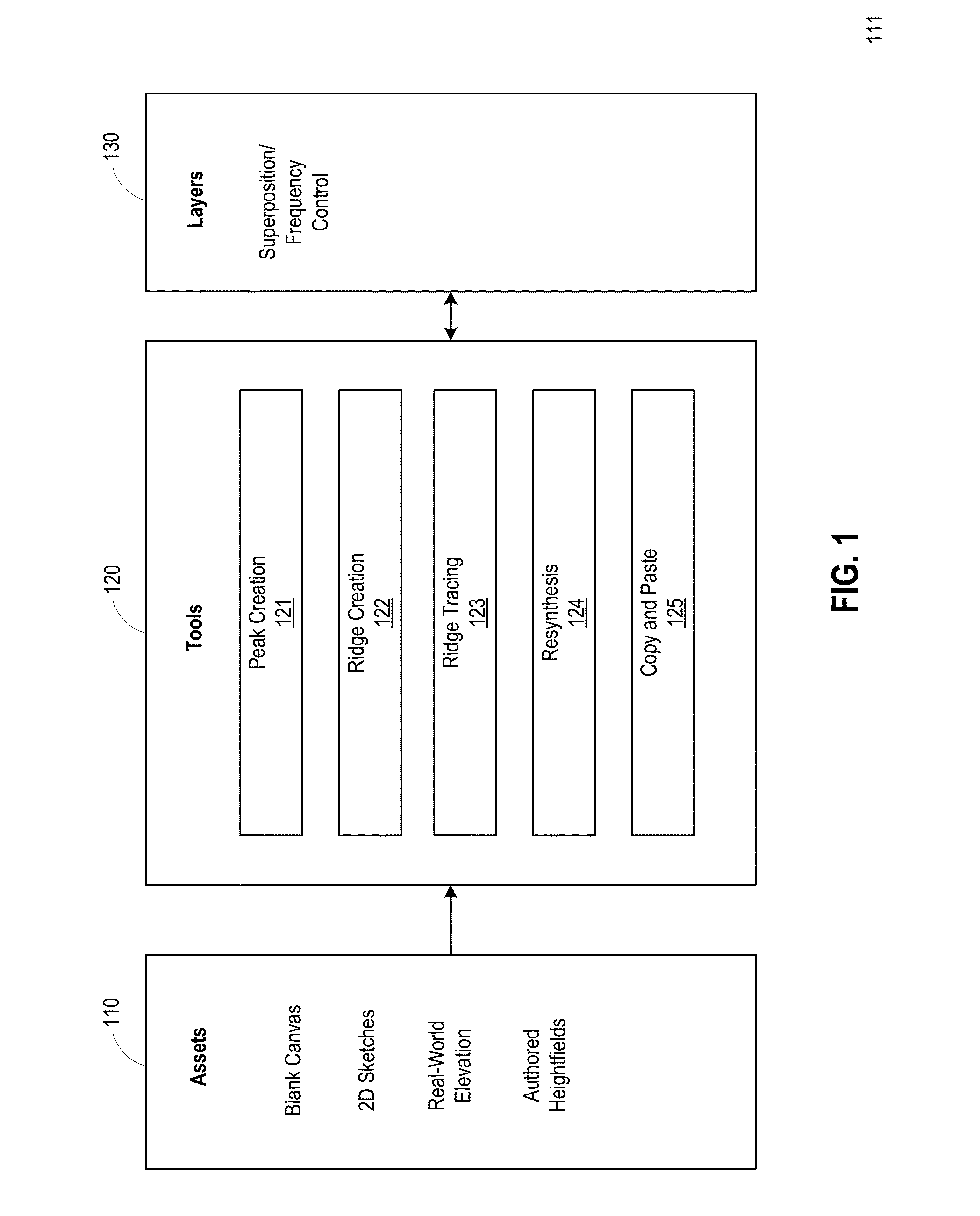
ActiveUS20150348284A1Texturing/coloringCathode-ray tube indicatorsDecompositionComputer graphics (images)
The disclosure provides an approach for generating virtual terrains. A terrain editing application is configured to receive assets of various types, including a blank canvas, two-dimensional (2D) sketches, real-world elevation maps, authored heightfields, etc. The assets specify characteristics of a terrain, and provide starting points for creating the virtual terrain. The editing application further provides a set of tools allowing a user to modify the virtual terrain. In one embodiment, the set of tools may include a copy-and-paste tool, a peak creation tool, a ridge creation tool, a ridge tracing tool, and a resynthesis tool. The editing application generates a new layer for each edit, as well as 2D and three-dimensional (3D) previews of the edited terrain. The editing application also provides a user-adjustable frequency decomposition of each layer. The editing application combines layers using Laplacian blending to produce the final virtual terrain.
Owner:UNIV COLLEGE OF LONDON
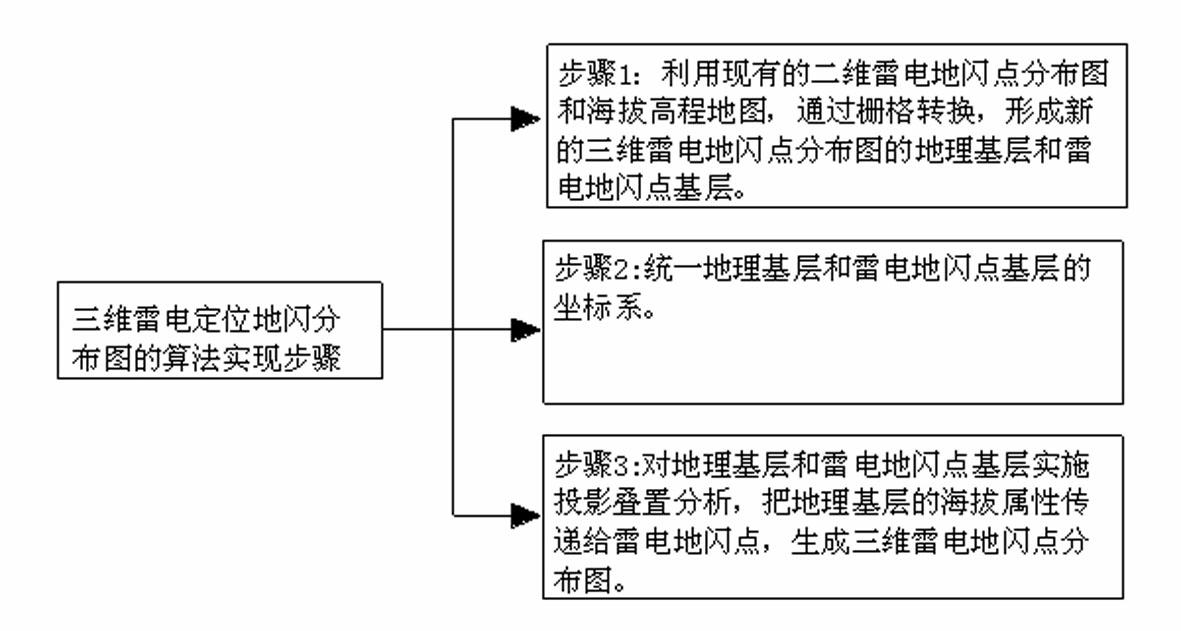
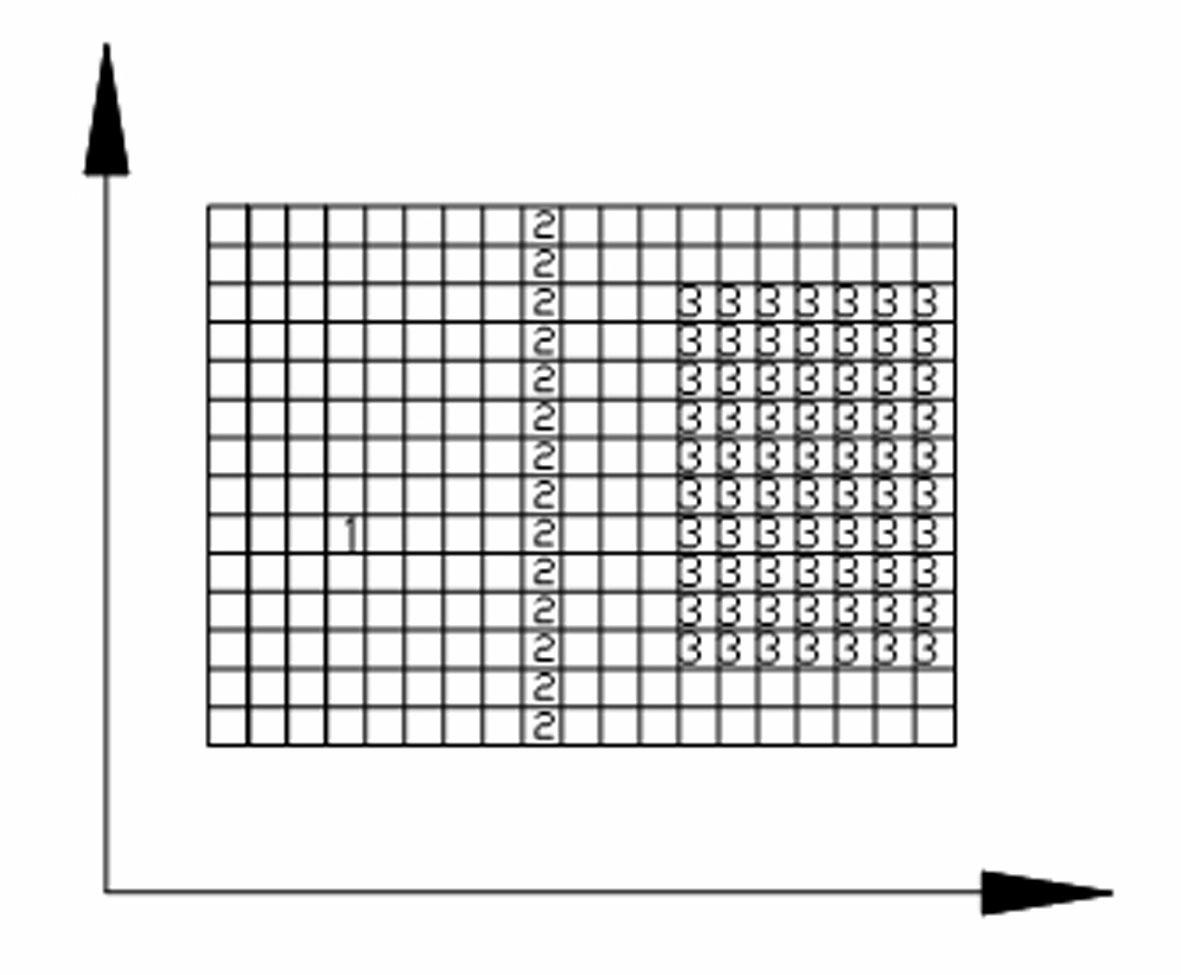
Method for generating three-dimensional lightning positioned place flash point distribution map
ActiveCN102565554AAdd altitude informationThe calculated value is accurateElectromagentic field characteristicsEngineeringAtmospheric sciences
The invention discloses a method for generating a three-dimensional lightning positioned place flash point distribution map. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, generating a geographical basic layer and a lightning place flash point basic layer of the novel three-dimensional lightning positioned place flash point distribution map by utilizing the existing two-dimensional lightning positioned place flash point distribution map and a sea-level elevation map and carrying out grid conversion; then unifying coordinate systems of the geographical basic layer and the lightning place flash point basic layer; and finally, implementing projection overlay analysis on the geographical basic layer and the lightning place flash point basic layer and transmitting sea-level elevation data of corresponding positions of the geographical basic layer to lightning place flash points to generate the three-dimensional lightning positioned place flash point distribution map. According to the method, the defects of the existing conventional two-dimensional lightning positioned place flash point distribution map are improved, so that the lightning place flash points obtain three-dimensional elevation attributes and a foundation is laid for further analyzing the lightning activity rule and improving a lightning parameter algorithm.
Owner:云南电力试验研究院(集团)有限公司
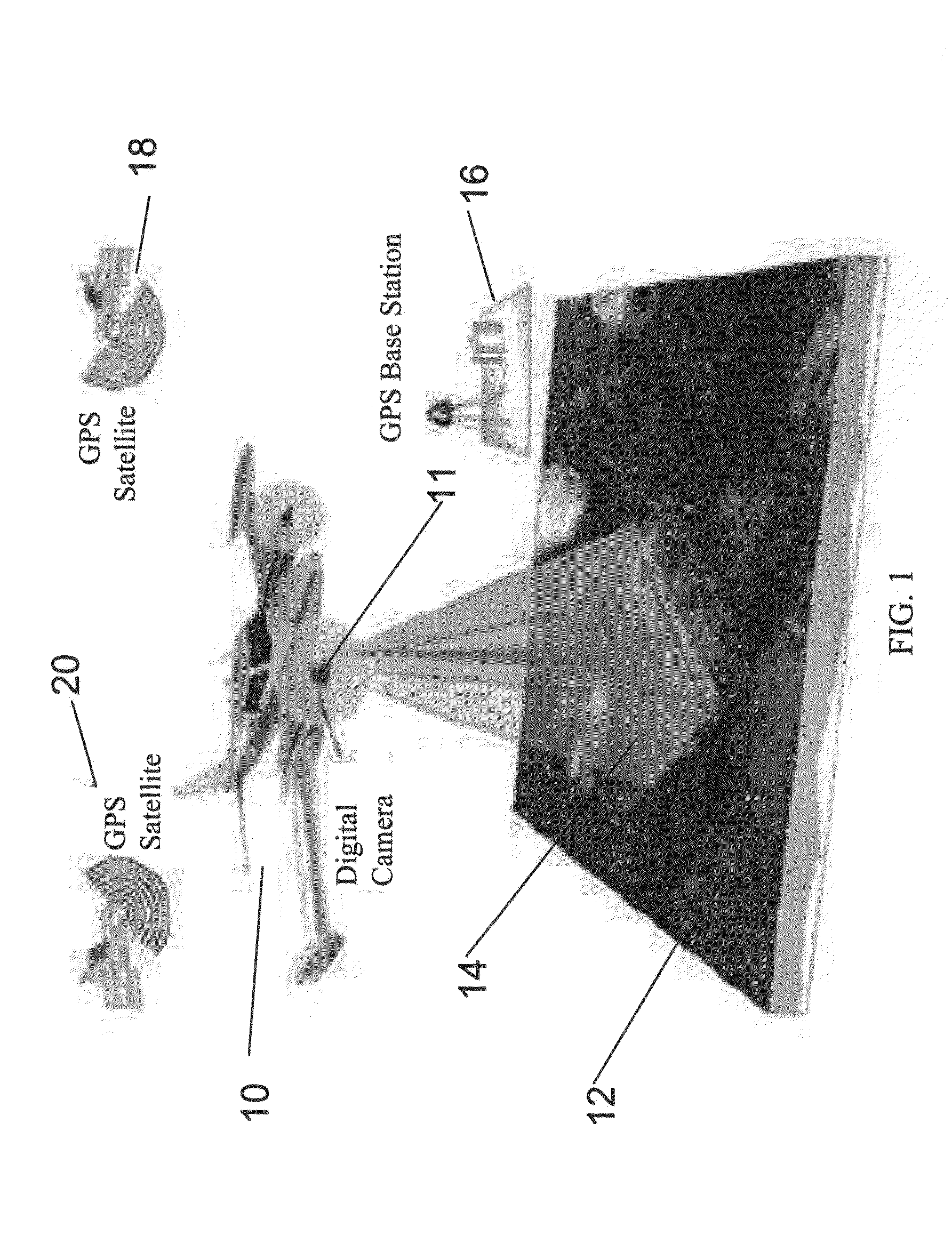
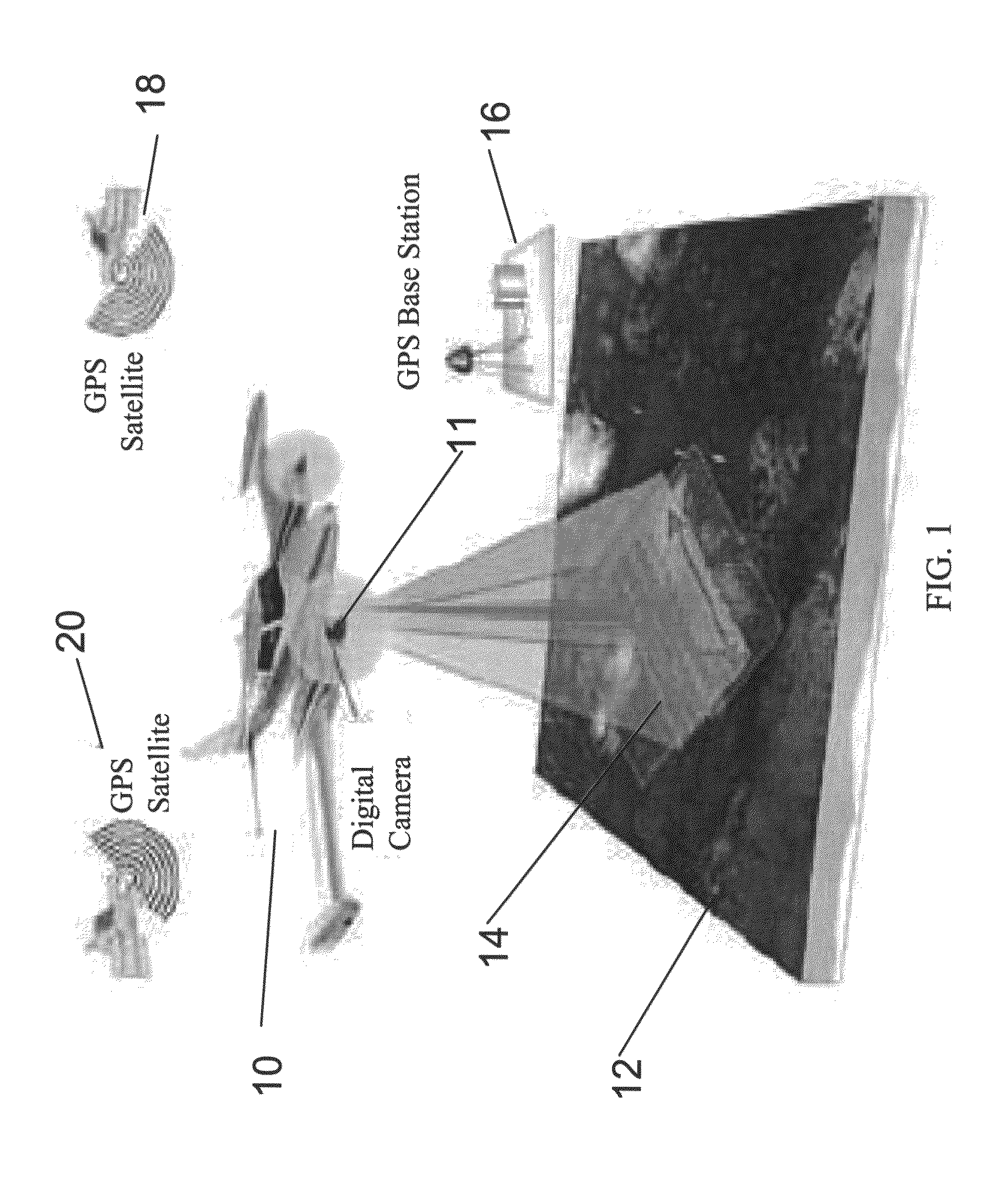
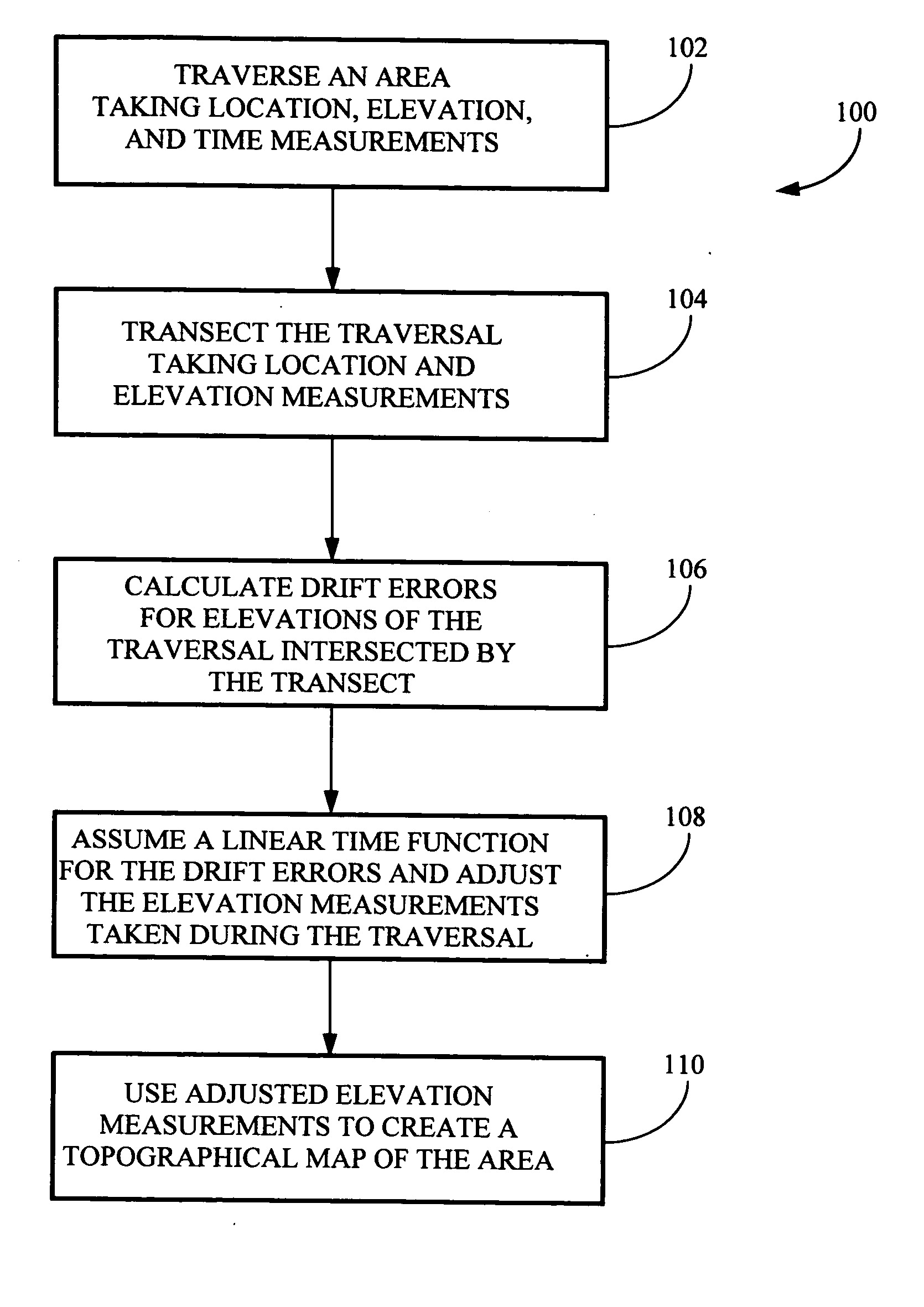
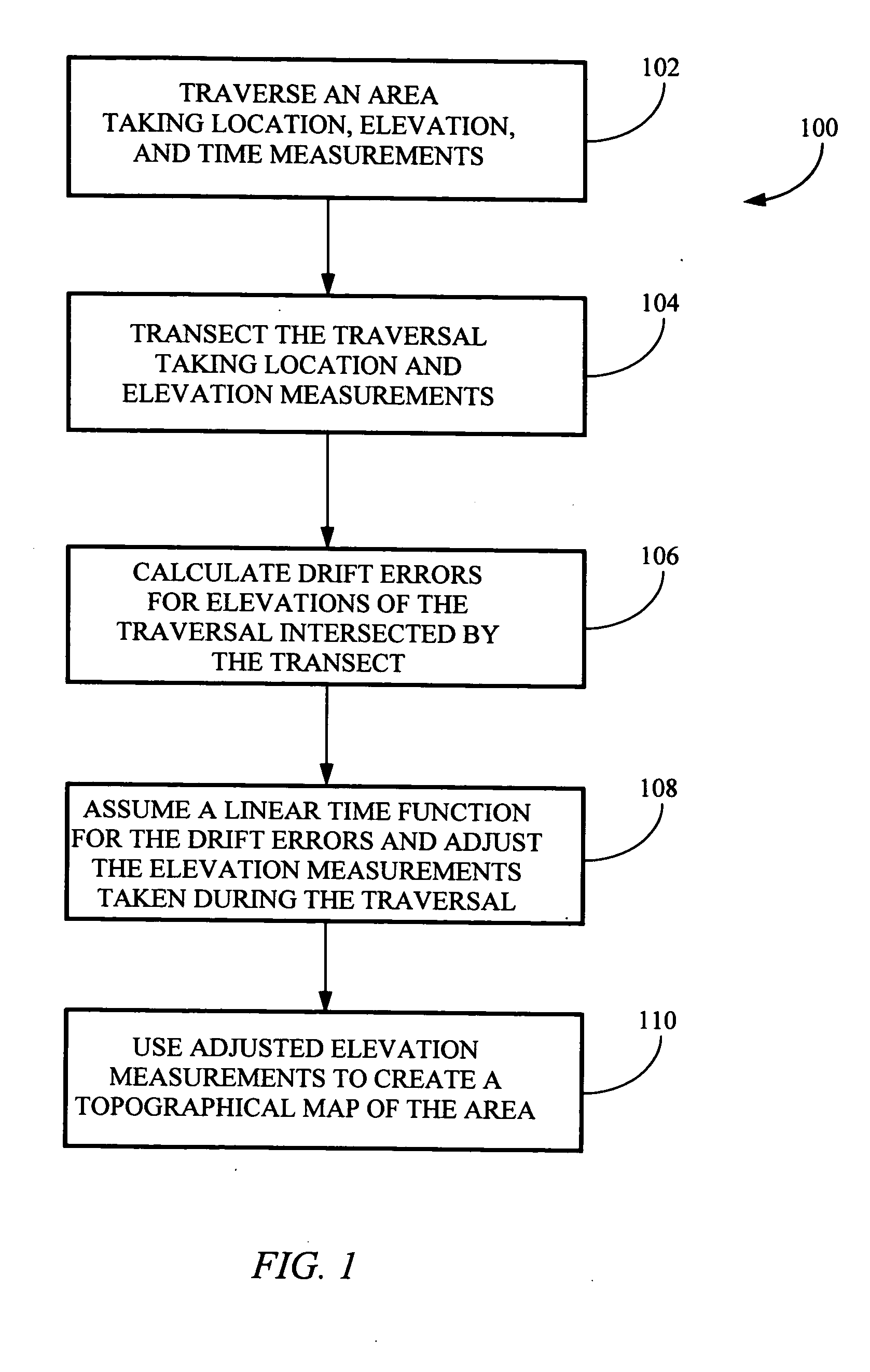
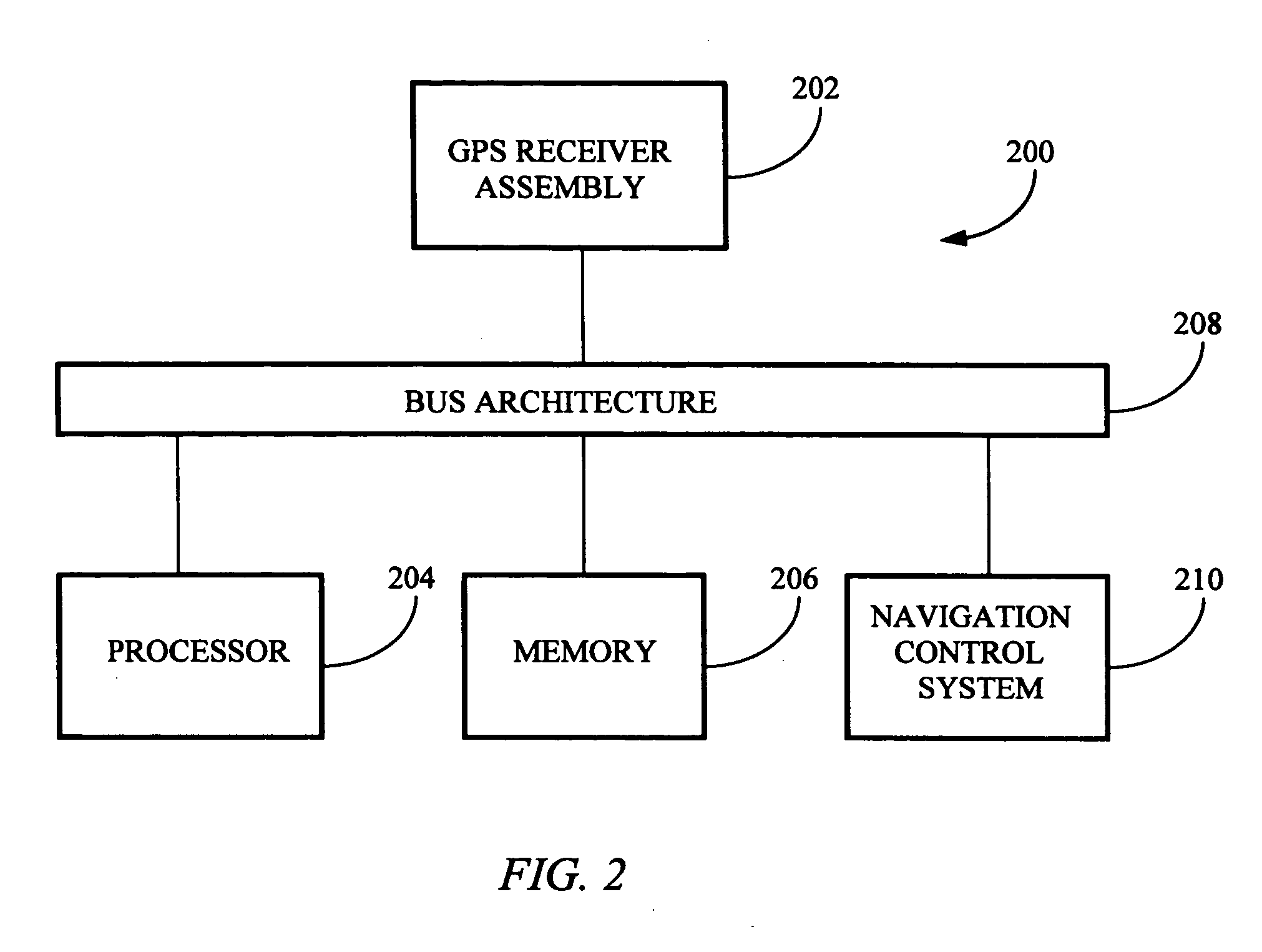
System and method for creating accurate topographical maps using low-drift DGPS
InactiveUS20050228585A1Low drift rateTracking time is shortInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlGps receiverTopographical mapping
The present invention is directed to a method for acquiring elevation data for an area. The method includes using a GPS receiver to map ground elevations while driving back and forth over an area and periodically recording position, elevation, and time. Then, at least one track is made across the parallel tracks so that the cross track intersects the parallel tracks. The data obtained is processed and elevation data from the cross track is used to adjust elevation data for the parallel tracks, compensating for elevation drift in measurements recorded by the GPS receiver. The adjusted data for the entire area is processed using the method of the present invention to obtain an elevation map for the area.
Owner:DEERE & CO
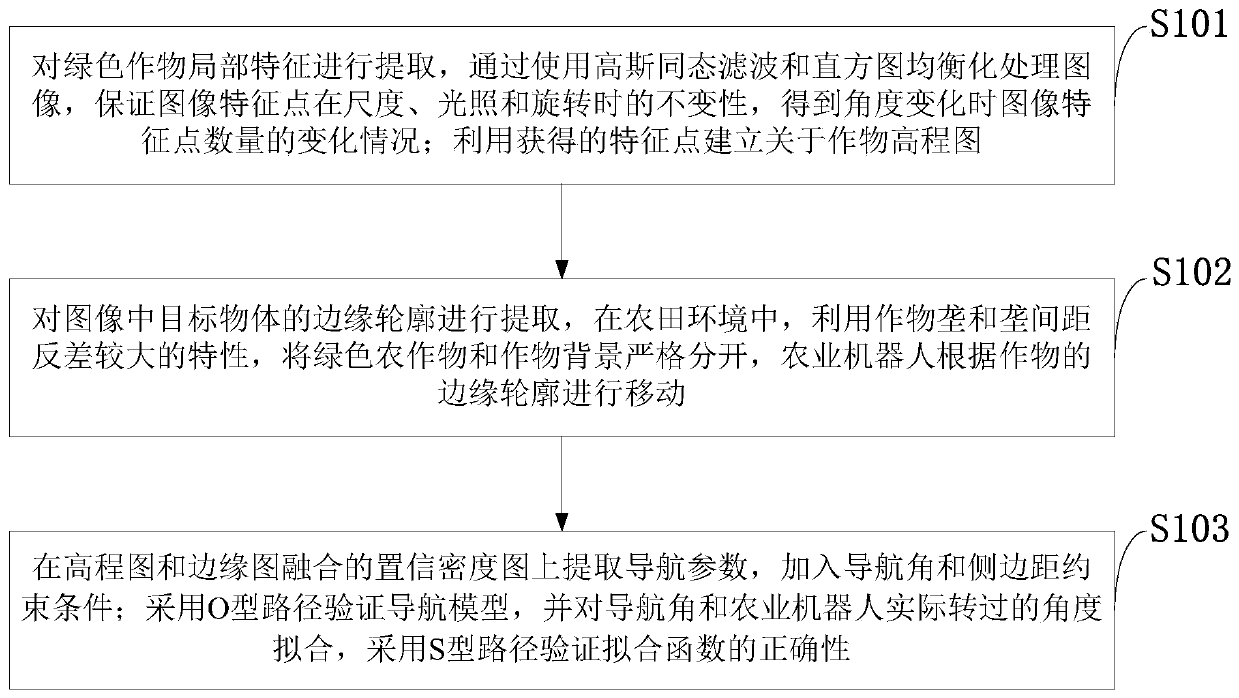
Stereoscopic vision navigation method based on green crop feature extraction invariance
ActiveCN110232389AKeep Feature ScaleUniform gray scaleNavigational calculation instrumentsCharacter and pattern recognitionAcquired characteristicEdge maps
The invention belongs to the technical field of visual navigation, and discloses a stereoscopic visual navigation method based on green crop feature extraction invariance, which is used for extractinglocal features of green crops, and obtaining the change condition of the number of image feature points during angle change by using Gaussian homomorphic filtering and histogram equalization to process an image; establishing a crop elevation map by using the obtained feature points; extracting the edge contour of the target object in the image, and separating the green crop from the crop background; extracting navigation parameters from the confidence density map fused by the elevation map and the edge map, and adding navigation angle and side edge distance constraint conditions; and fittingthe navigation angle and the angle actually rotated by the agricultural robot, and verifying the correctness of a fitting function by adopting an S-shaped path. The agricultural robot platform is built, agricultural crop image information collected by the binocular camera is processed, parameters of the navigation process are extracted, and automatic navigation control over the agricultural robotis achieved.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIVERSITY
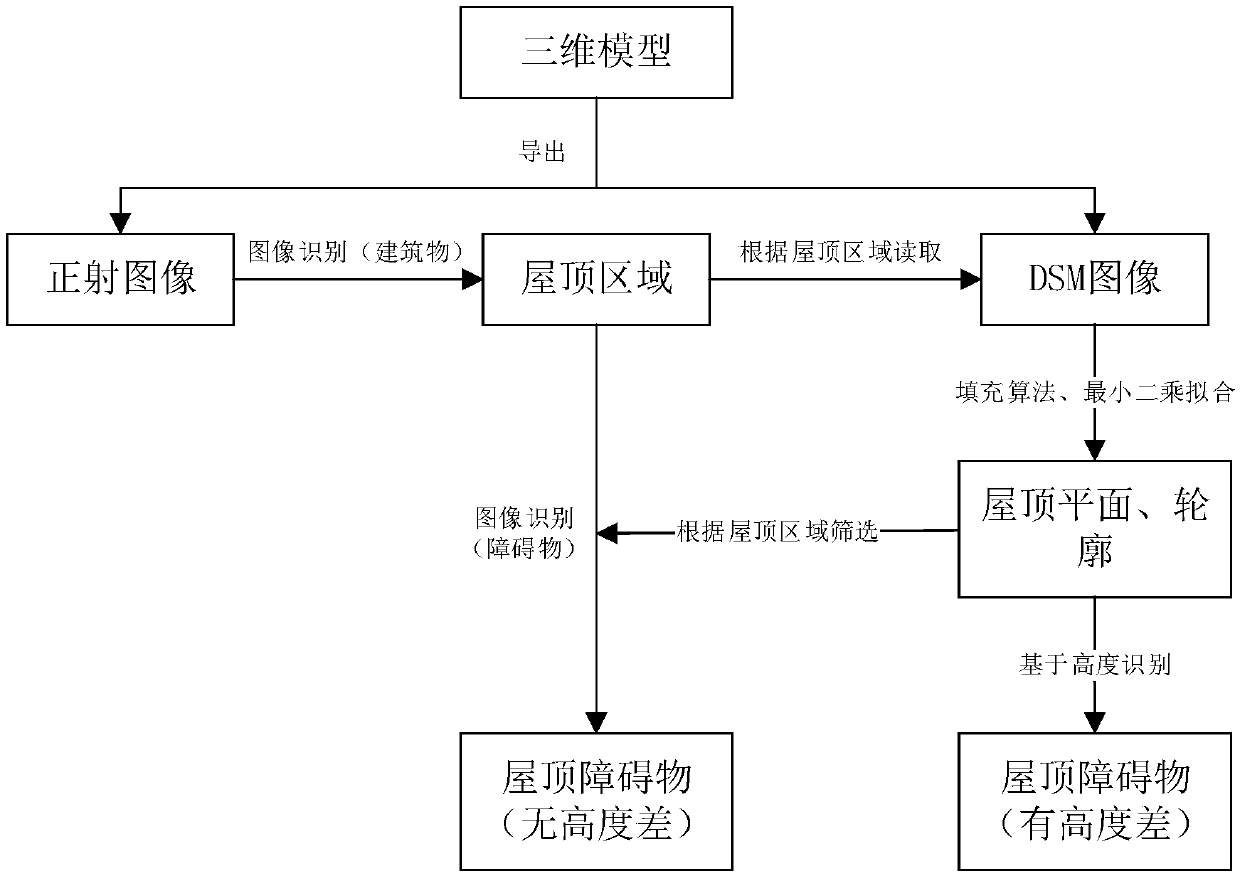
Photovoltaic roof and photovoltaic obstacle automatic identification algorithm
ActiveCN109614871AImprove efficiencyImprove recognition accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmProjection image
The invention relates to a photovoltaic roof and photovoltaic obstacle automatic identification algorithm. The method includes steps of by combining the information of the elevation image and the information of the orthographic projection image, locating a roof profile, within the contour of each roof identified by the image, finding points in a roof plane by adopting least square fitting and a seed filling algorithm, fitting to obtain a plane, solving a corresponding plane equation, correcting a roof contour range, identifying a full-image roof, searching and identifying obstacle informationin the roof on the basis of roof identification, and identifying various photovoltaic obstacles while automatically identifying the roof. The design work efficiency and the recognition precision are greatly improved, and the time and effort spent on manual operation are reduced.
Owner:远景能源(南京)软件技术有限公司 +1
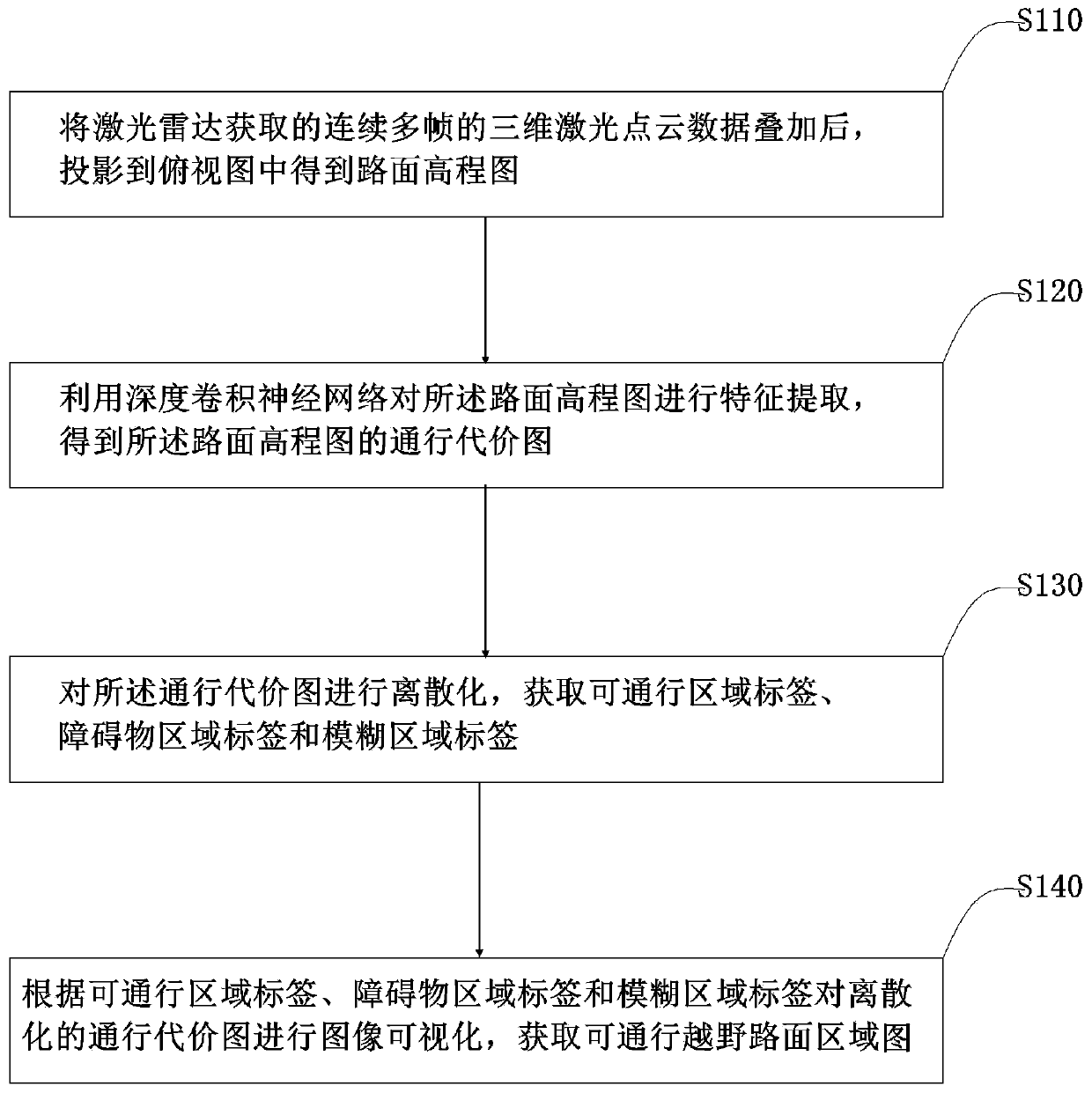
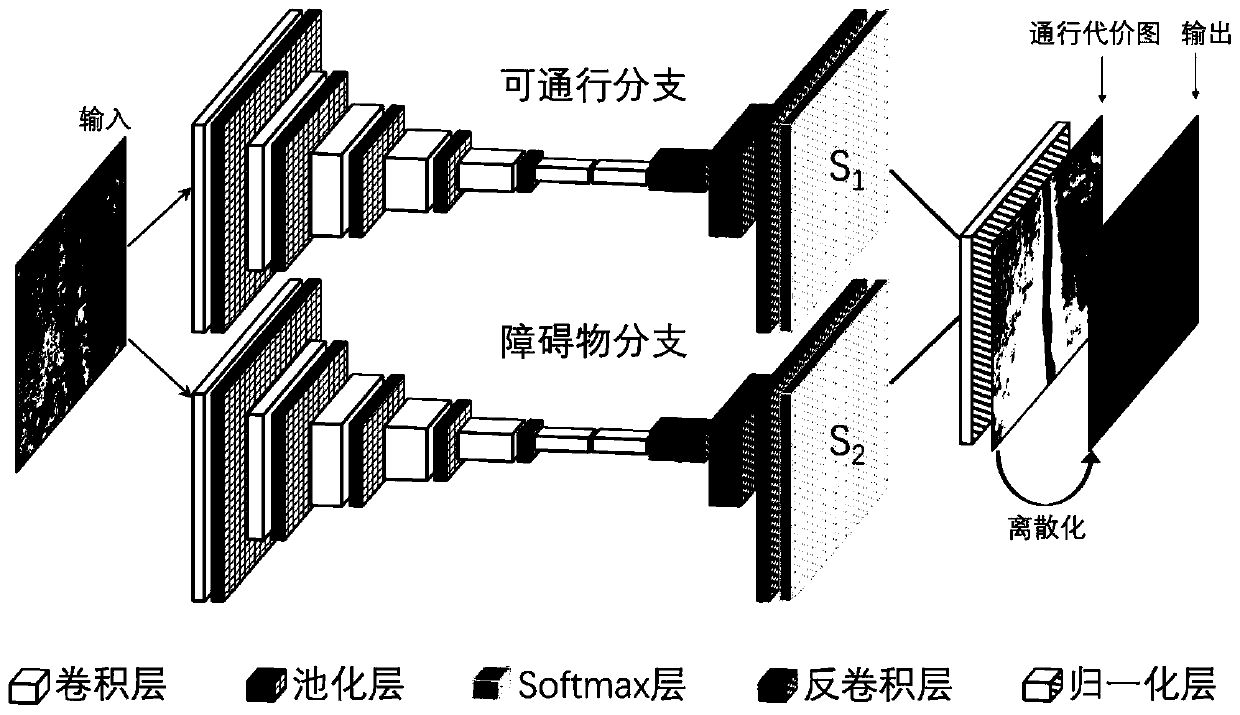
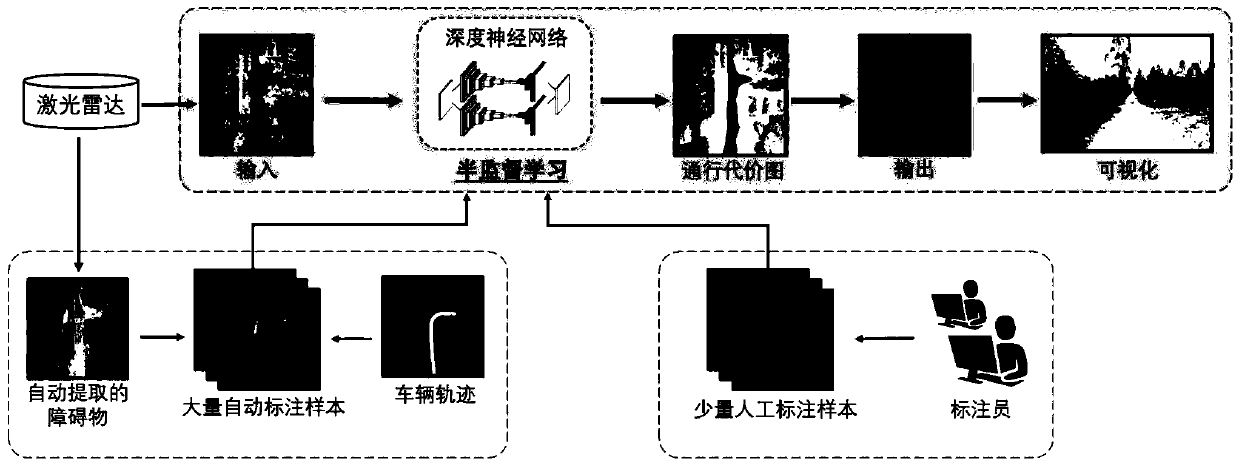
Cross-country road surface extraction method based on a three-dimensional laser radar
ActiveCN109800773AEffective trainingReduce demandCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesAdaptive learningRoad surface
The invention provides a cross-country road surface extraction method based on a three-dimensional laser radar, and belongs to the technical field of image recognition. The method comprises the stepsof superposing continuous multi-frame three-dimensional laser point cloud data acquired by a laser radar, and projecting the superposed three-dimensional laser point cloud data to a top view to obtaina pavement elevation map; performing feature extraction on the pavement elevation map by using a deep convolutional neural network to obtain a traffic cost map of the pavement elevation map; discretizing the passing cost map to obtain a passable area label, an obstacle area label and a fuzzy area label; and according to the passable area label, the obstacle area label and the fuzzy area label, carrying out image visualization on the discretized passable cost map to obtain a passable cross-country road surface area map. The method is not influenced by illumination and weather, and a passable cross-country road surface can be extracted; the feature extraction method based on deep learning can adaptively learn environmental features, and is higher in adaptability in different scenes; According to the provided automatic data labeling scheme, the requirement for manually labeling samples is effectively reduced.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com