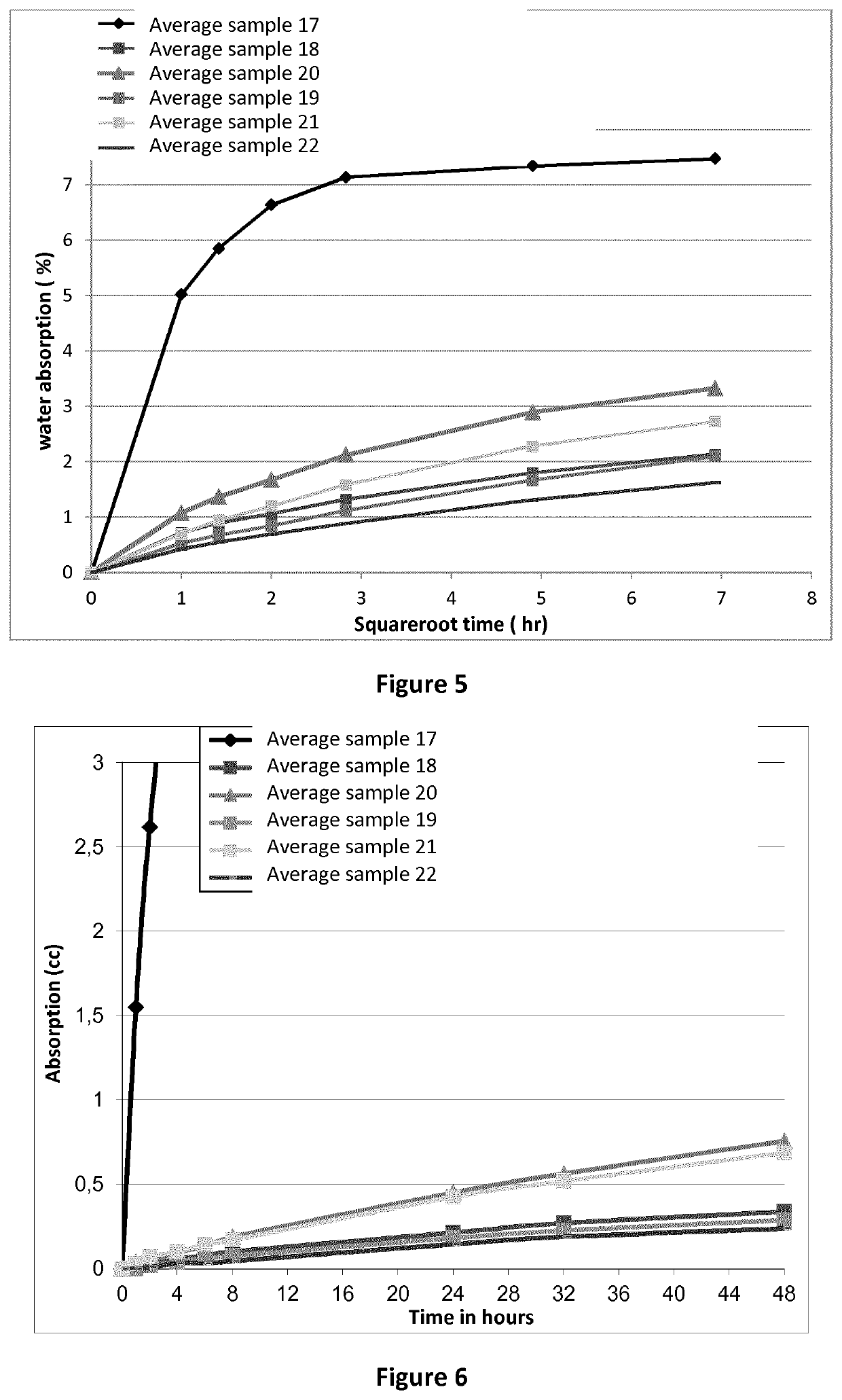
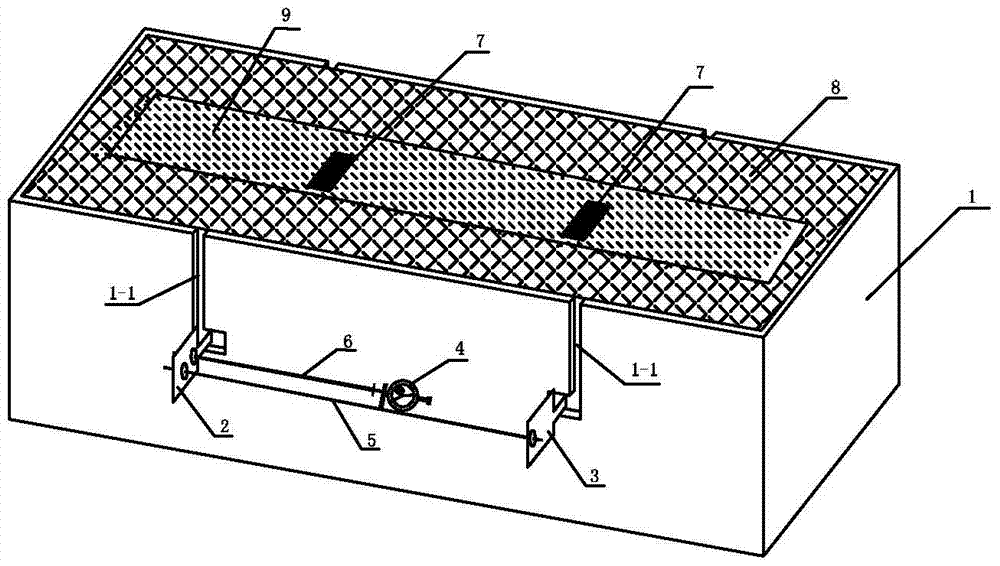
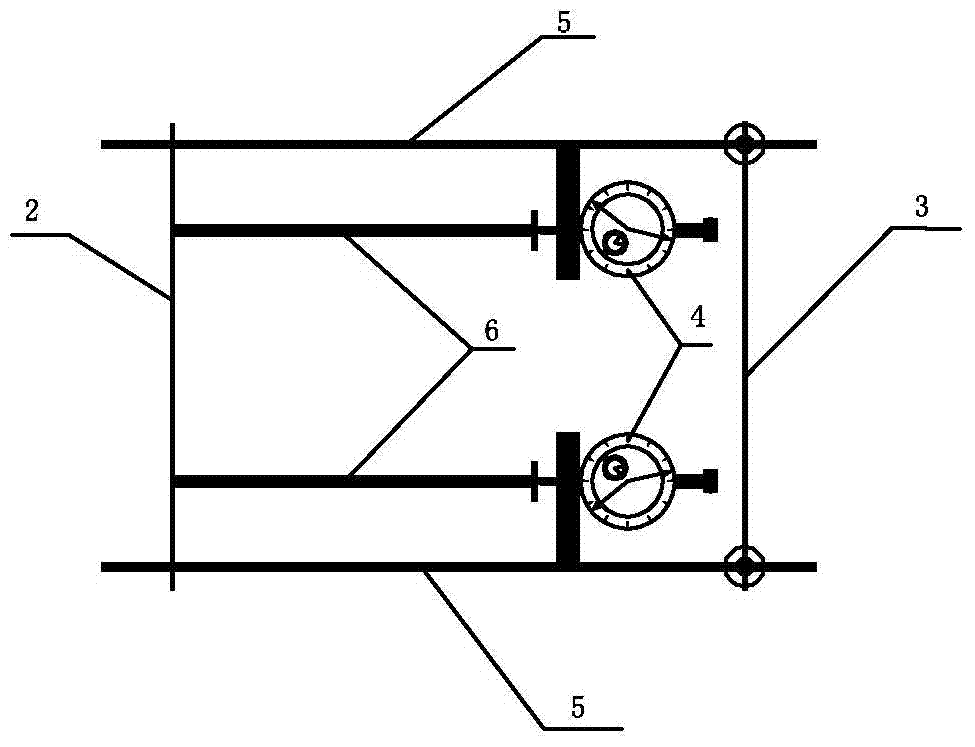
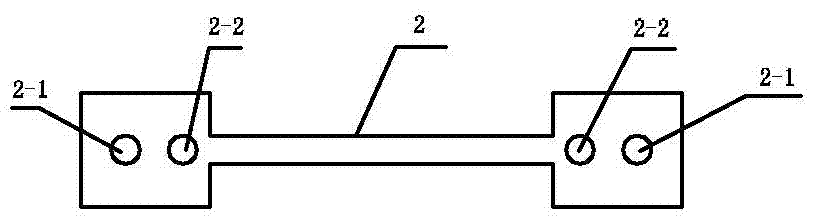
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35 results about "Cementitious matrix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
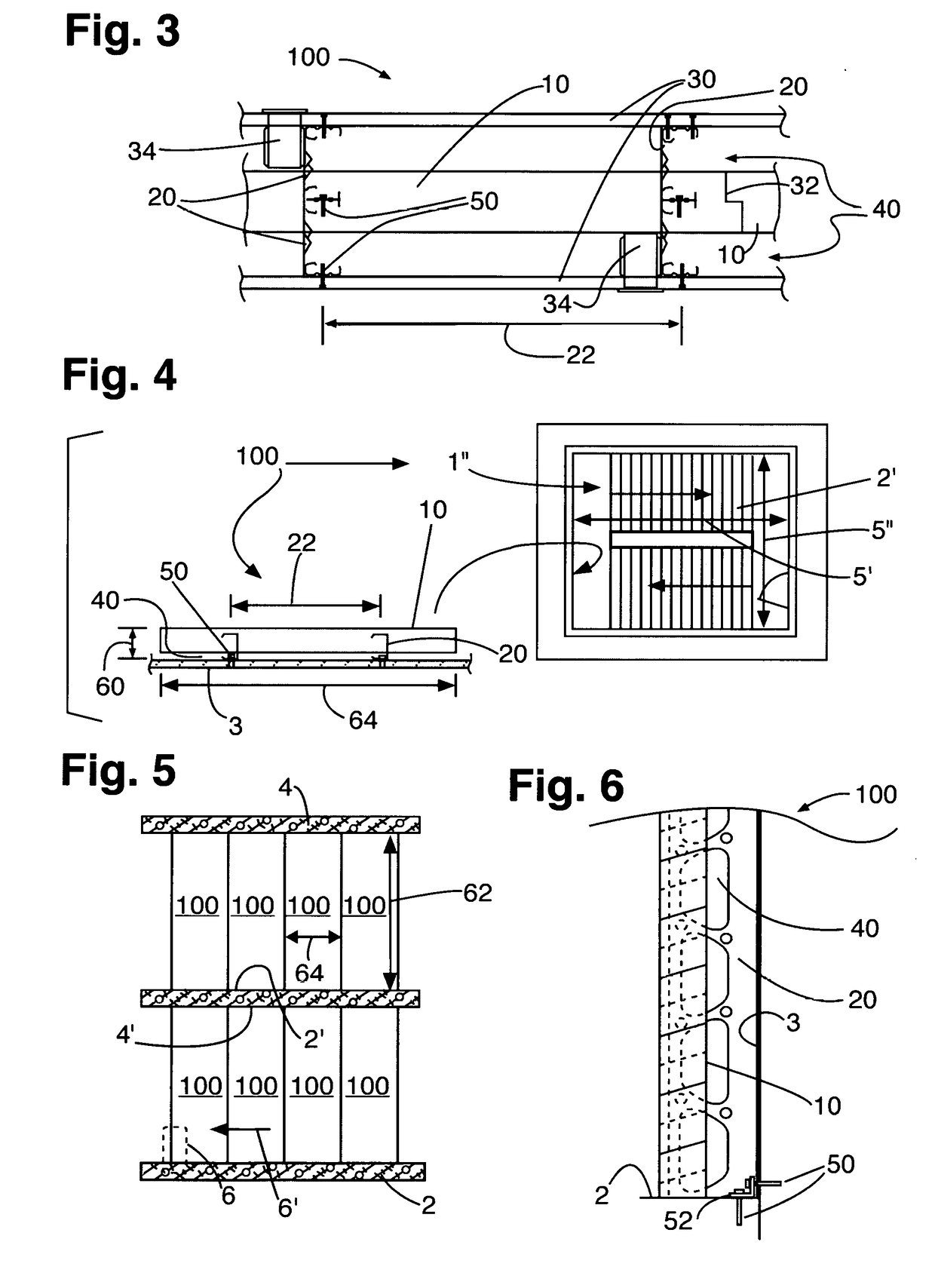
Fireproof insulating cementitious foam comprising phase change materials
ActiveUS8070876B1Improve fire resistanceImprove high temperature resistanceSolid waste managementSynthetic resin layered productsThermal energyThermal energy storage
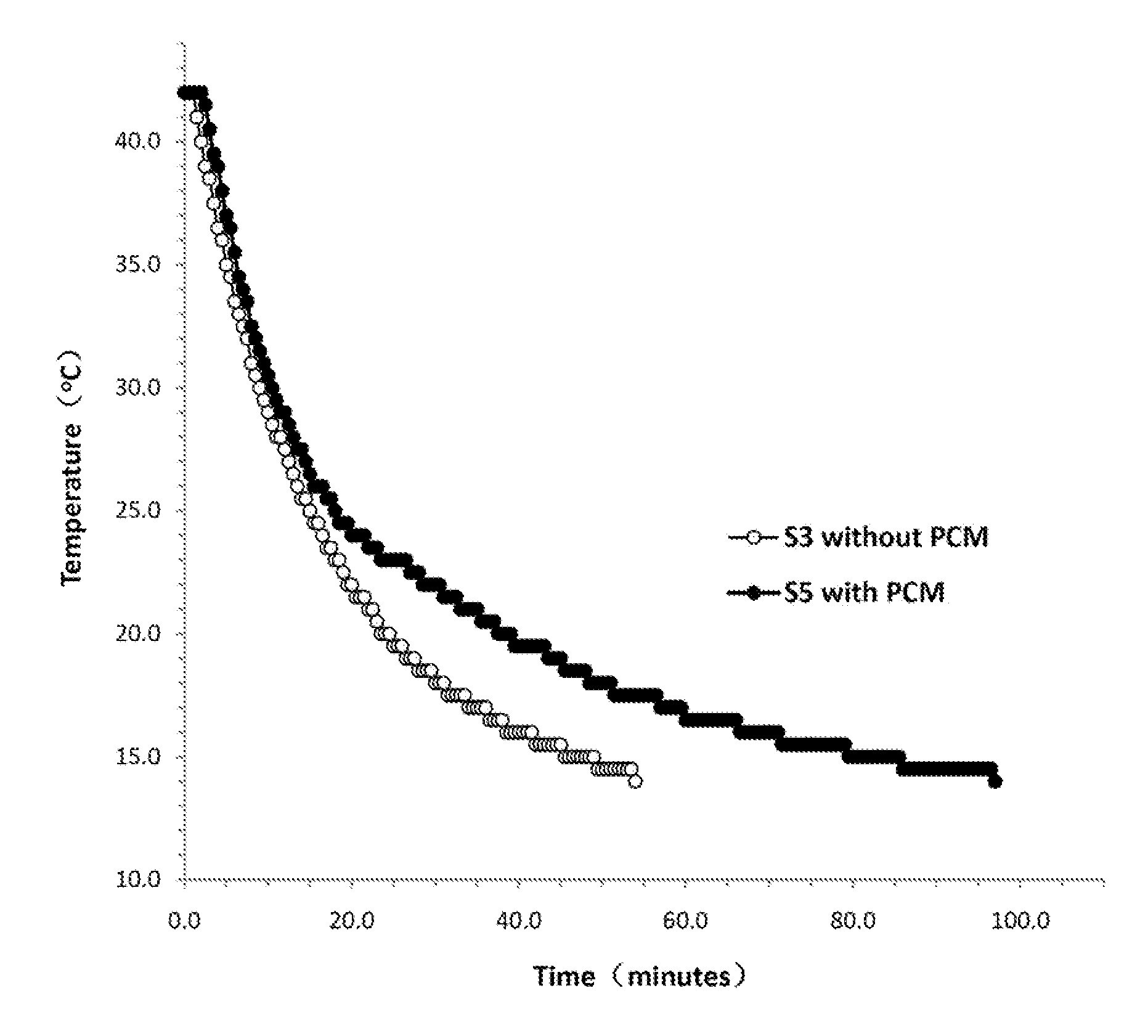
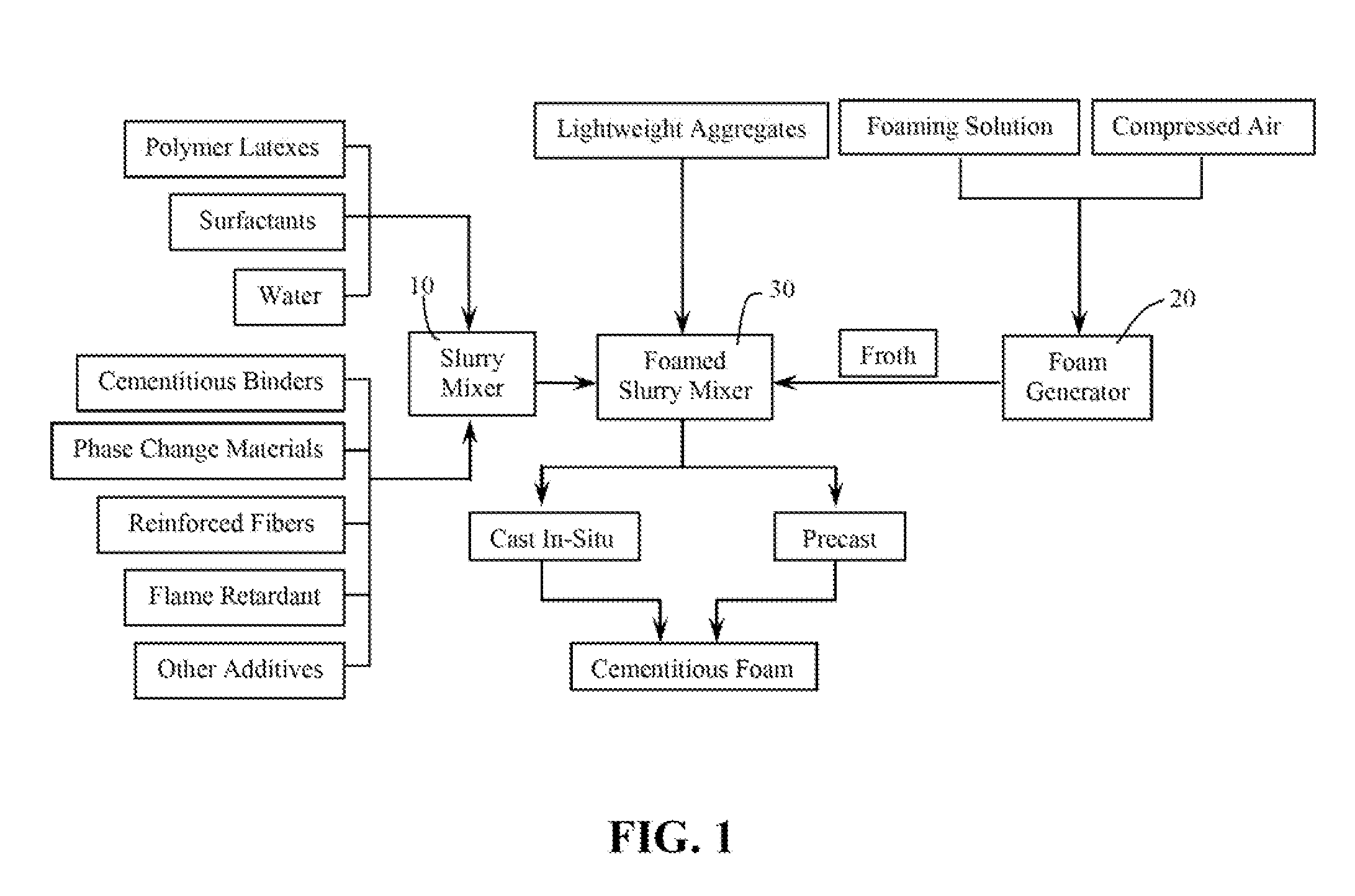
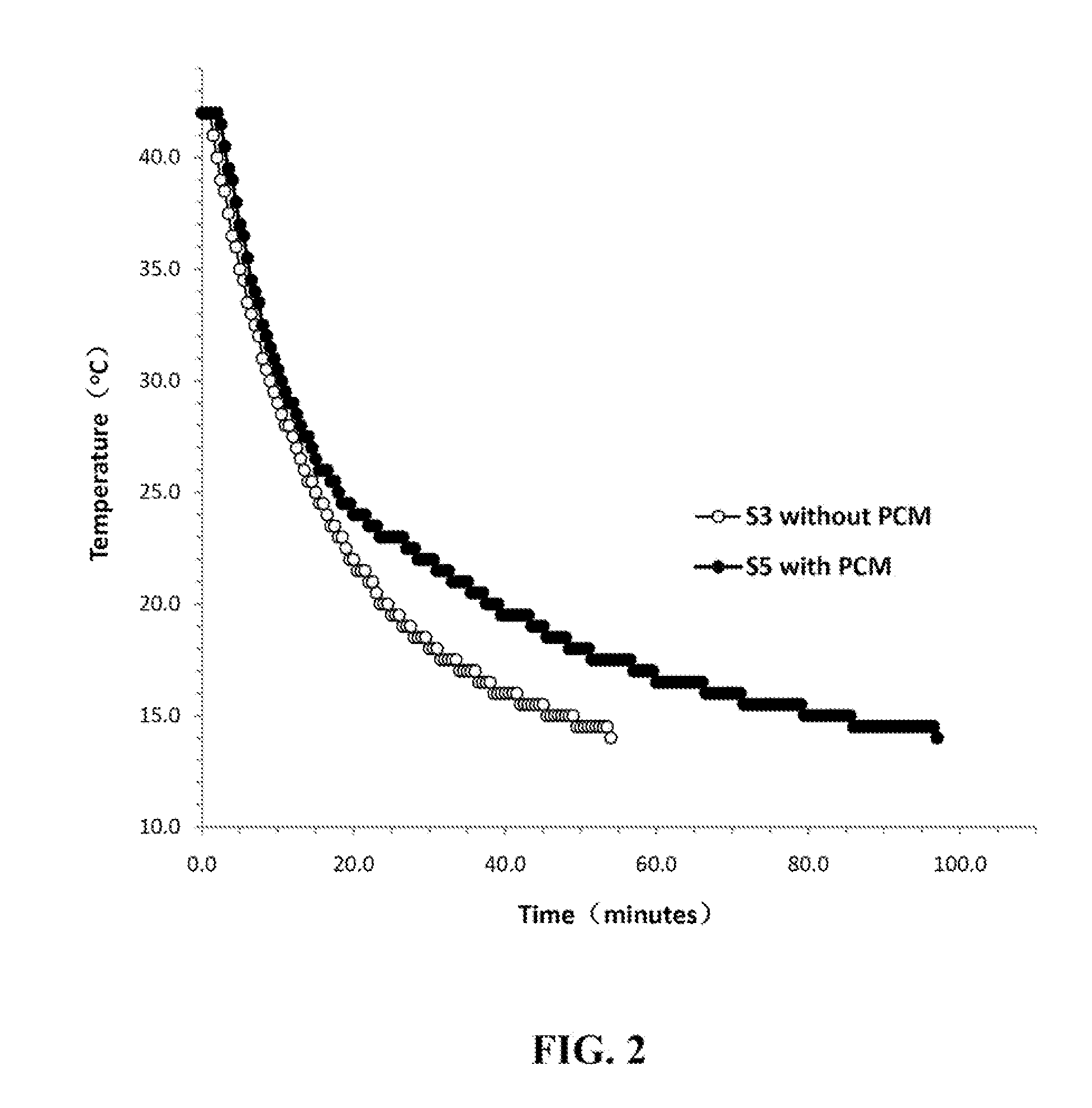
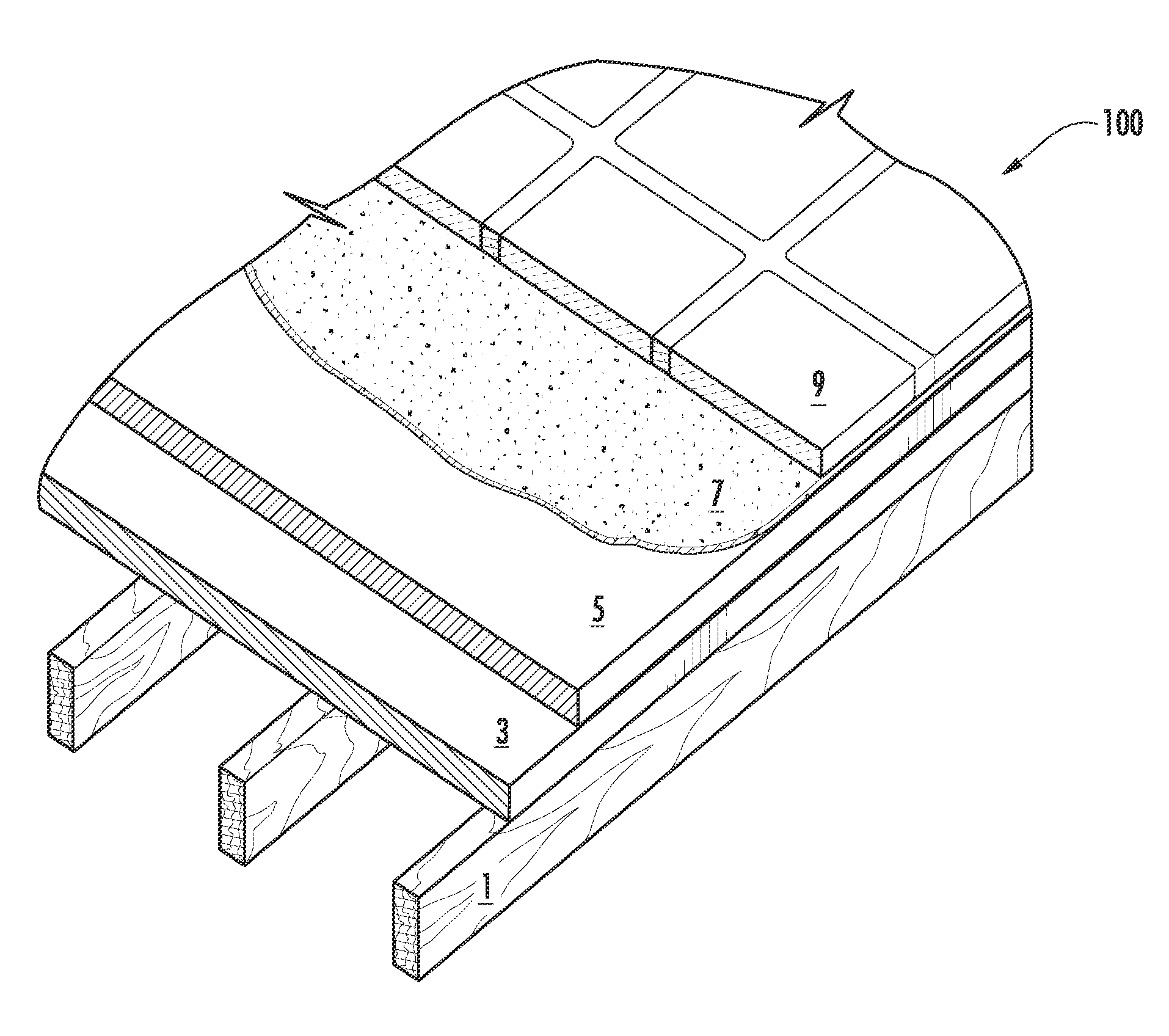
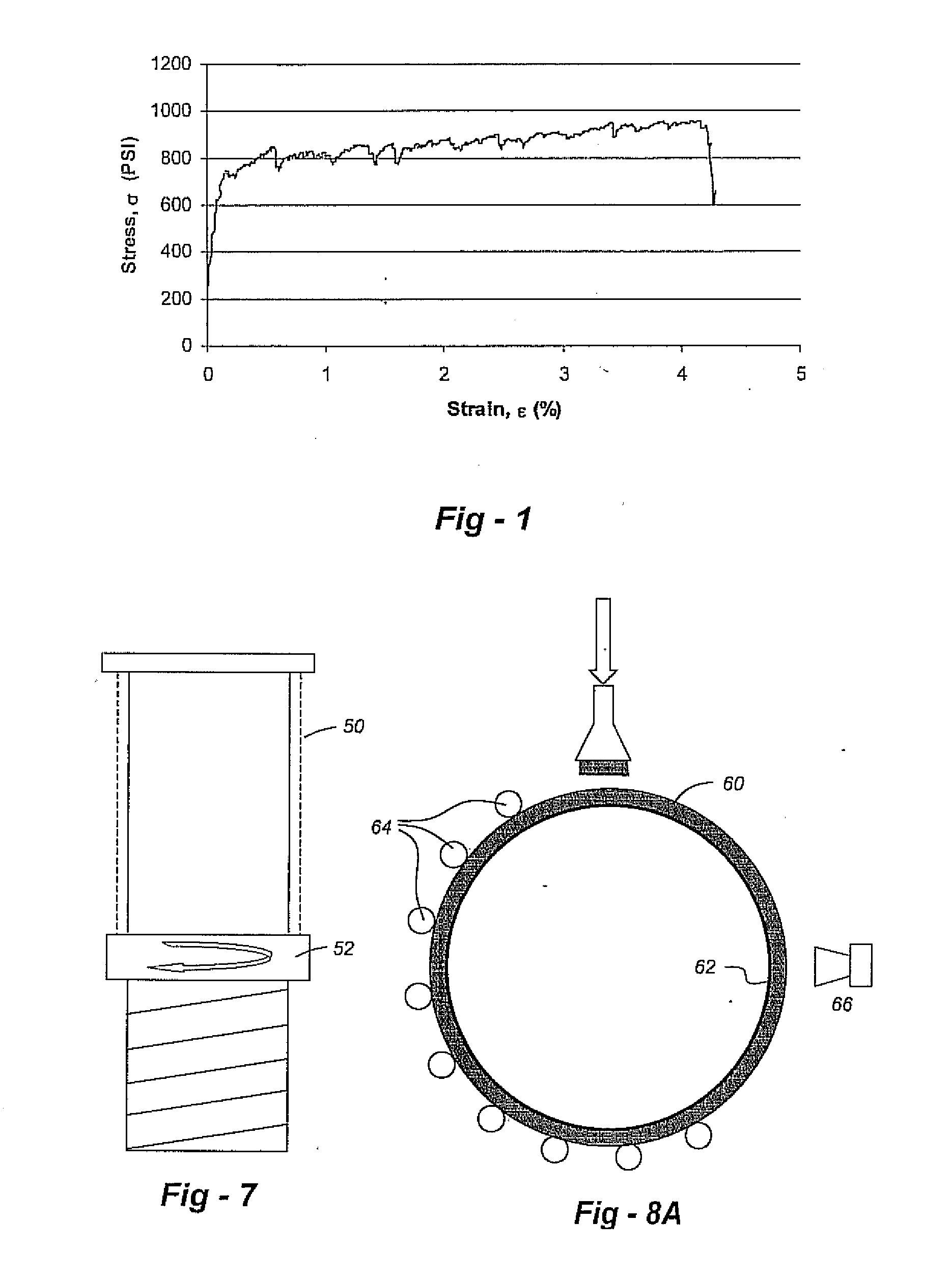
A fireproof insulating foamed cementitious composition with thermal energy storage capacity is provided for use in producing wall insulation boards, fireproof claddings for steel structures, inner cores of fire resistant wall or door panels, and the like. The composition demonstrates improved energy efficiency in which phase change materials, such as microencapsulates, are used in conjunction with a cementitious mixture of calcined gypsum and hydraulic cement, lightweight aggregates, a polymer latex, and a foaming solution to create stable air bubbles inside the cementitious matrix. The calcined gypsum and the hydraulic cement are present in a weight ratio range from about 1:3 to about 3:1. The composition may further include reinforced fibers, surfactants, inorganic flame retardants, and other additives. The presence of the phase change material not only increases energy efficiency of the cured cementitious foam material, but also improves compatibility between calcined gypsum and cement during slurry mixing and hardening.
Owner:JIANG HAIHONG
Structural fiber cement building materials
ActiveUS20090162602A1Suitable for useEliminate needConstruction materialSolid waste managementCellulose fiberCementitious matrix
Owner:JAMES HARDIE TECH LTD
Porous Particulate Material For Fluid Treatment, Cementitious Composition and Method of Manufacture Thereof
InactiveUS20080179253A1Improve machinabilityInhibit initial setting timePhysical/chemical process catalystsOther chemical processesRed mudPorous particle
A porous particulate material for treating a fluid containing a contaminant is disclosed. The particulate material comprises a cementitious matrix or binder and treated bauxite refinery residue or red mud. At least a portion of the pores in the particulate material is open cell or interconnected pores. The invention also relates to the use of a reactive permeable barrier comprising porous material, for treating a contaminated fluid. Also disclosed is a method for producing porous particulate material for treating a contaminated fluid and a method for treating a contaminated fluid, in which the porous material is used. The invention furthermore relates to a cementitious composition comprising partially neutralised red mud and cement, wherein the partially neutralised red mud has been pre-treated by contacting it with water having a total hardness supplied by calcium, magnesium or a combination thereof, of at least 3.5 millimoles per litre calcium carbonate equivalent. The cementitious composition is useful as a building and construction material.
Owner:MT ASPIRING GEOCHEMISTRY CONSULTANTS PTY LTD
Method for producing materials from recycled glass and cement compositions
InactiveUS20050045069A1High porosityEvenly distributedOther chemical processesSolid waste managementCementitious matrixAlkali–silica reaction
A method of producing material from recycled glass comprising: preparing a mixture of glass in a cementitious matrix, and an alkali-silica reaction suppressant; providing a mold of the material and coating said mold with a release agent; casting said mixture into said mold; curing said mold; and removing the material from said mold. The recycled glass and concrete compositions are: 25-79% by weight glass; 8-35% by weight cement and up to 22% by weight of an alkali-silica reaction suppressant.
Owner:ICESTONE
Light-weight, fire-resistant composition and assembly
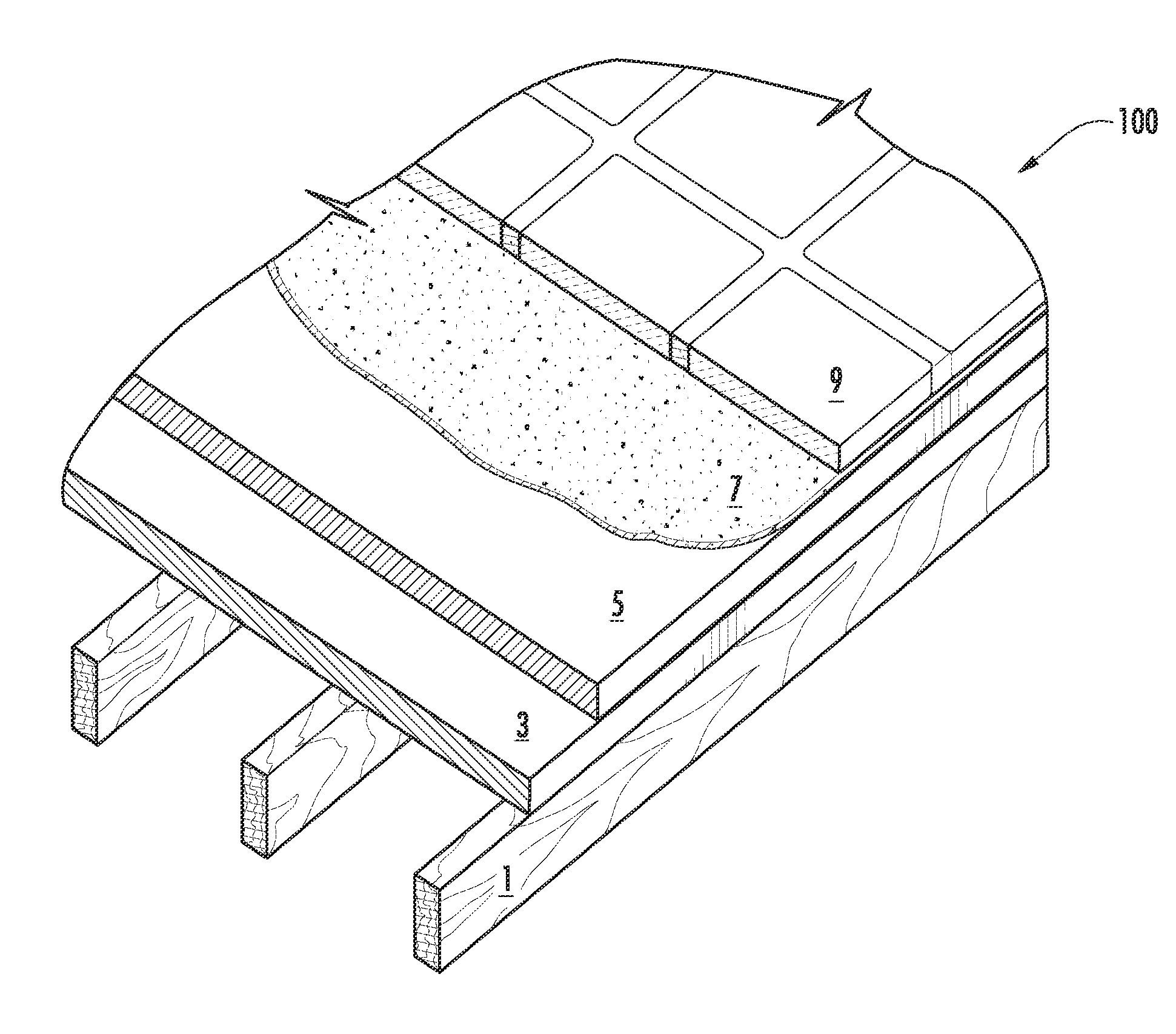
Light-weight, fire-resistant “mineral foam” includes an inorganic cementitious matrix and at least one metal hydrate that is a “super hydrate” substance, in which water is present with the substance in an amount of at least about ten moieties of water of hydration per formula unit of the substance. As a cured solid, that “mineral foam,” or another mineral foam composition including an inorganic cementitious matrix, can be provided as a structural member in part of an assembly that has at least one open web, thermally insulating support member at least partially embedded in the cured solid. Also, the cured “mineral foam” may be a solid foam in a form of a panel, panel block or tile, which may have a tongue provision and / or a groove provision.
Owner:MABEY MICHAEL JOHN
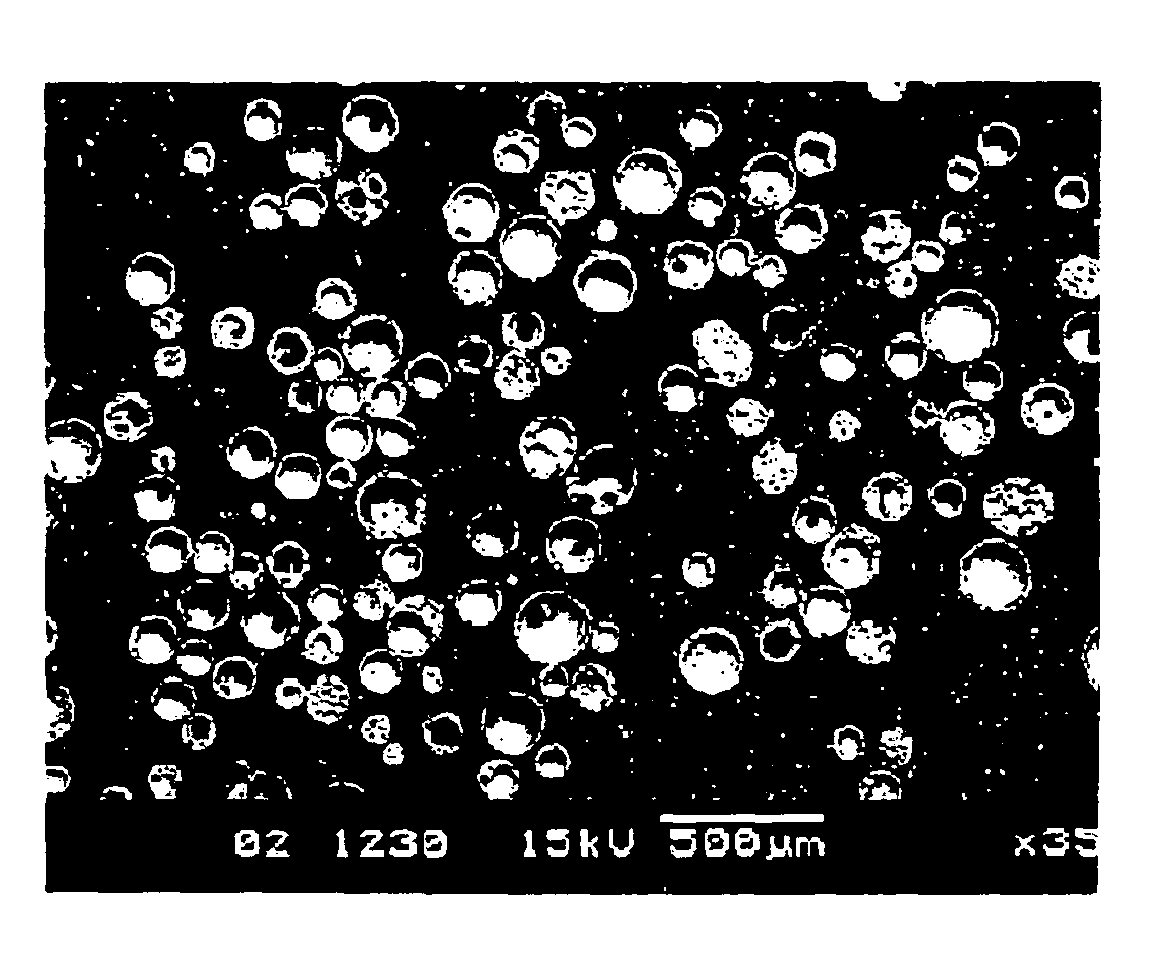
Synthetic microspheres and methods of making same
InactiveUS7651563B2Low-density materialSolid waste managementSolid waste disposalBuilding productCombustion
Owner:JAMES HARDIE TECH LTD
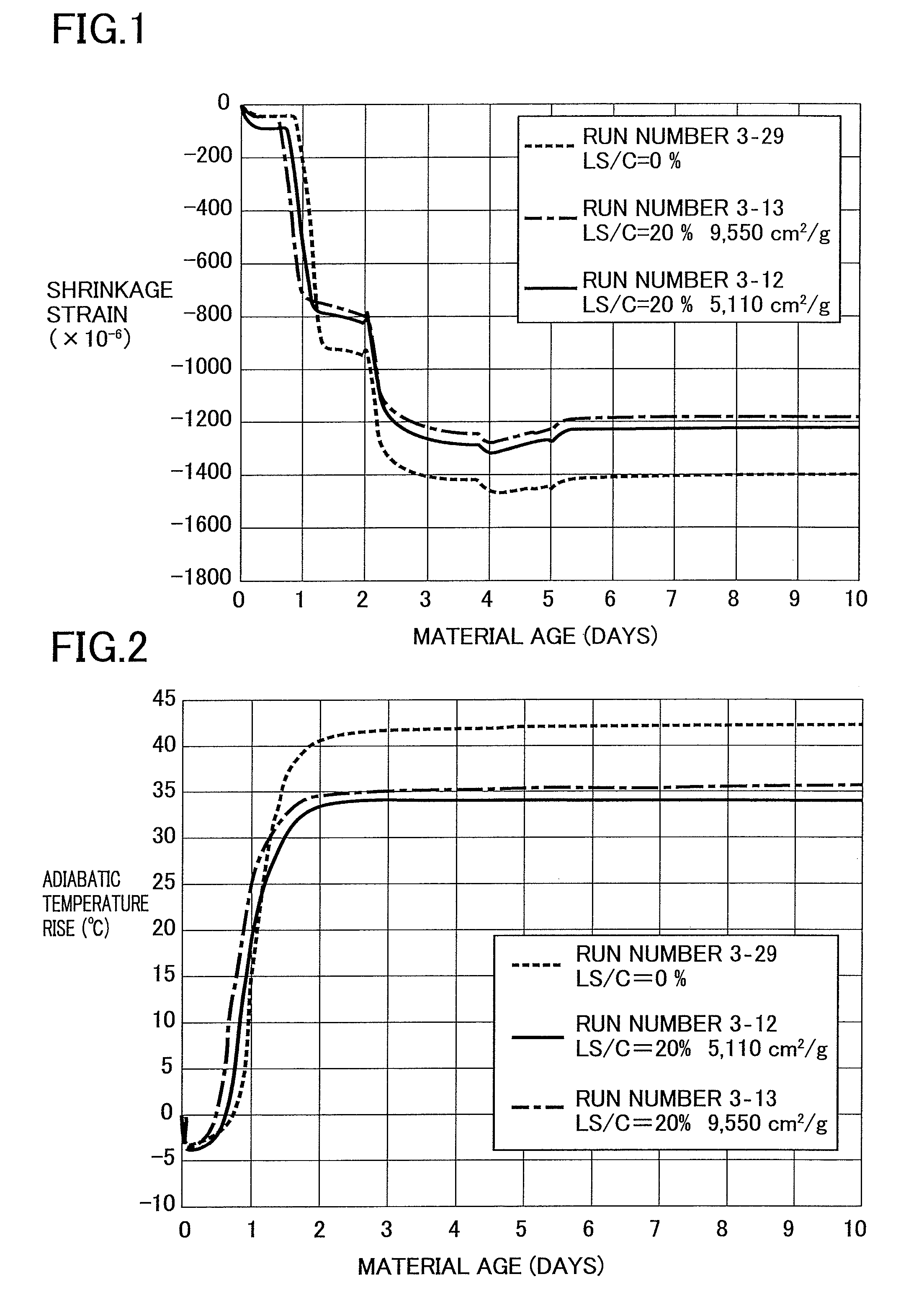
Hydrophobic low shrinkage lightweight cementitious matrix
ActiveUS20150152011A1Reduce Shrinkage ProblemsReduce water consumptionSolid waste managementCeramicwareCementitious matrixLow shrinkage
The present invention provides a composition for forming a lightweight, low shrinkage and hydrophobic cementitious matrix, and a method for preparing thereof. The present cementitious matrix formed by the composition is lightweight, hydrophobic (or water repelling) and with low shrinkage which is useful in building and construction industry as non-structural wall resistant to water, heat and sound entry. The present invention also provides a method of preparing the composition and the cementitious matrix formed from the composition.
Owner:NANO & ADVANCED MATERIALS INST
Method for producing materials from recycled glass and cement compositions
InactiveUS7700017B2High porosityEvenly distributedOther chemical processesSolid waste managementCementitious matrixSilicon dioxide
A method of producing material from recycled glass comprising: preparing a mixture of glass in a cementitious matrix, and an alkali-silica reaction suppressant; providing a mold of the material and coating said mold with a release agent; casting said mixture into said mold; curing said mold; and removing the material from said mold. The recycled glass and concrete compositions are: 25-79% by weight glass; 8-35% by weight cement and up to 22% by weight of an alkali-silica reaction suppressant.
Owner:ICESTONE
Porous particulate material for fluid treatment, cementitious composition and method of manufacture thereof
InactiveCN1926075AImprove permeabilityRich sourcesSolid waste managementWater/sewage treatment by ion-exchangeRed mudMaterials science
A porous particulate material for treating a fluid containing a contaminant is disclosed. The particulate material comprises a cementitious matrix or binder and treated bauxite refinery residue or red mud. At least a portion of the pores in the particulate material is open cell or interconnected pores. The invention also relates to the use of a reactive permeable barrier comprising porous material, for treating a contaminated fluid. Also disclosed is a method for producing porous particulate material for treating a contaminated fluid and a method for treating a contaminated fluid, in which the porous material is used. The invention furthermore relates to a cementitious composition comprising partially neutralised red mud and cement, wherein the partially neutralised red mud has been pre-treated by contacting it with water having a total hardness supplied by calcium, magnesium or a combination thereof, of at least 3.5 millimoles per litre calcium carbonate equivalent. The cementitious composition is useful as a building and construction material.
Owner:MT ASPIRING GEOCHEMISTRY CONSULTANTS PTY LTD
Synthetic Microspheres and Methods of Making Same
InactiveUS20100192808A1Low-density materialSolid waste managementCeramicwareBuilding productAlkali metal oxide
A building product incorporating synthetic microspheres having a low alkali metal oxide content is provided. The synthetic microspheres are substantially chemically inert and thus a suitable replacement for natural cenospheres, particularly in caustic environments such as cementitious mixtures. The building product can have a cementitious matrix such as a fiber cement product. The synthetic microspheres can be incorporated as a low density additive and / or a filler for the building product and / or the like.
Owner:JAMES HARDIE TECH LTD
Matrix for masonry elements and method of manufacture thereof
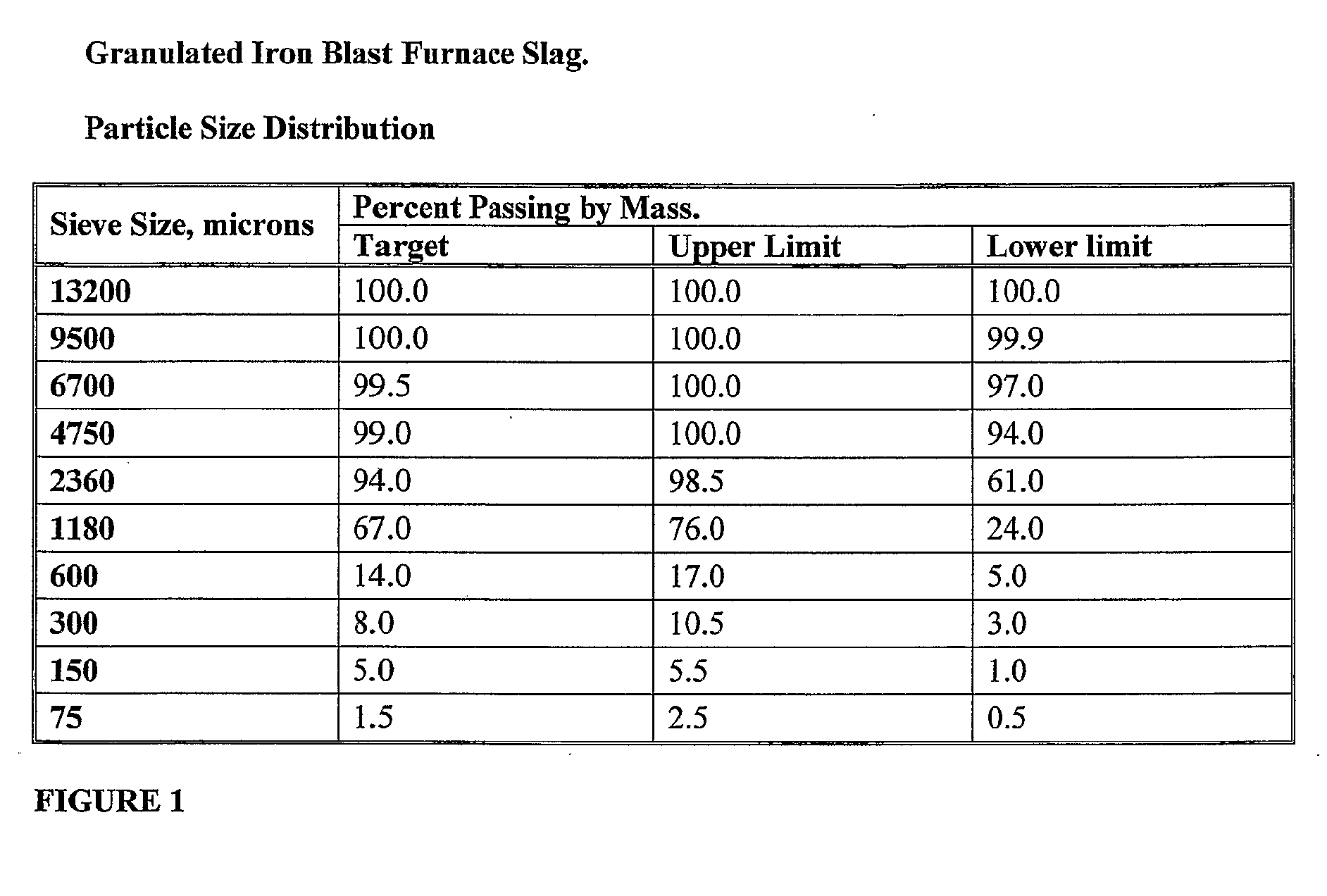
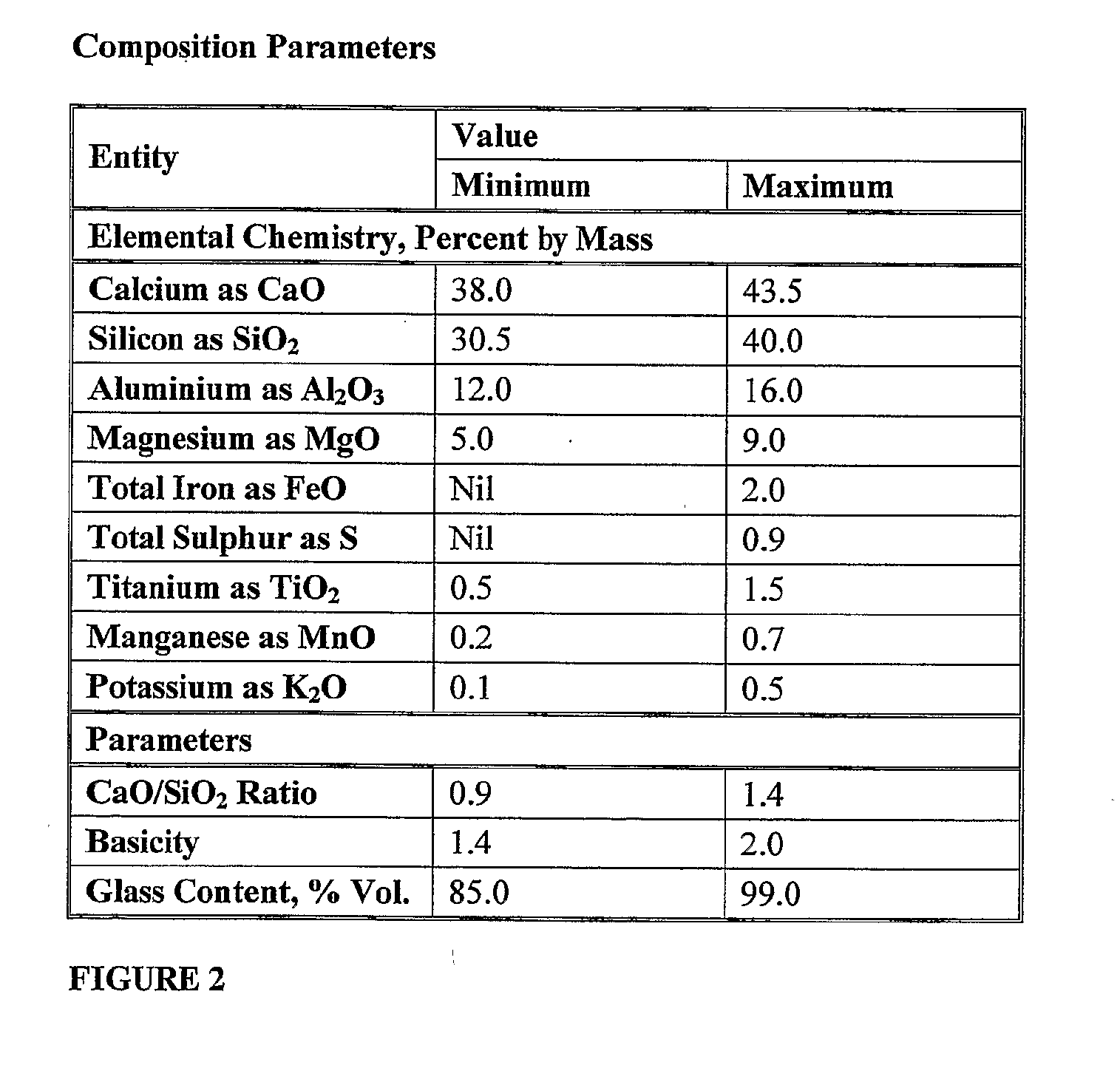
A cementitious matrix for forming a moulded masonry product, the matrix formed from a group of materials comprising; an aggregate comprising granulated iron blast furnace slag; air-cooled iron blast furnace slag, bottom ash, pulverised fuel ash and at least one cementitious binder; and ground granulated iron blast furnace slag acting as binder and aggregate; and water.
Owner:CEMENTECH
Coated pipe and method using strain-hardening brittle matrix composites
InactiveUS20090035459A1Low costReduce material volumeLiquid surface applicatorsCorrosion preventionDamage toleranceCementitious matrix
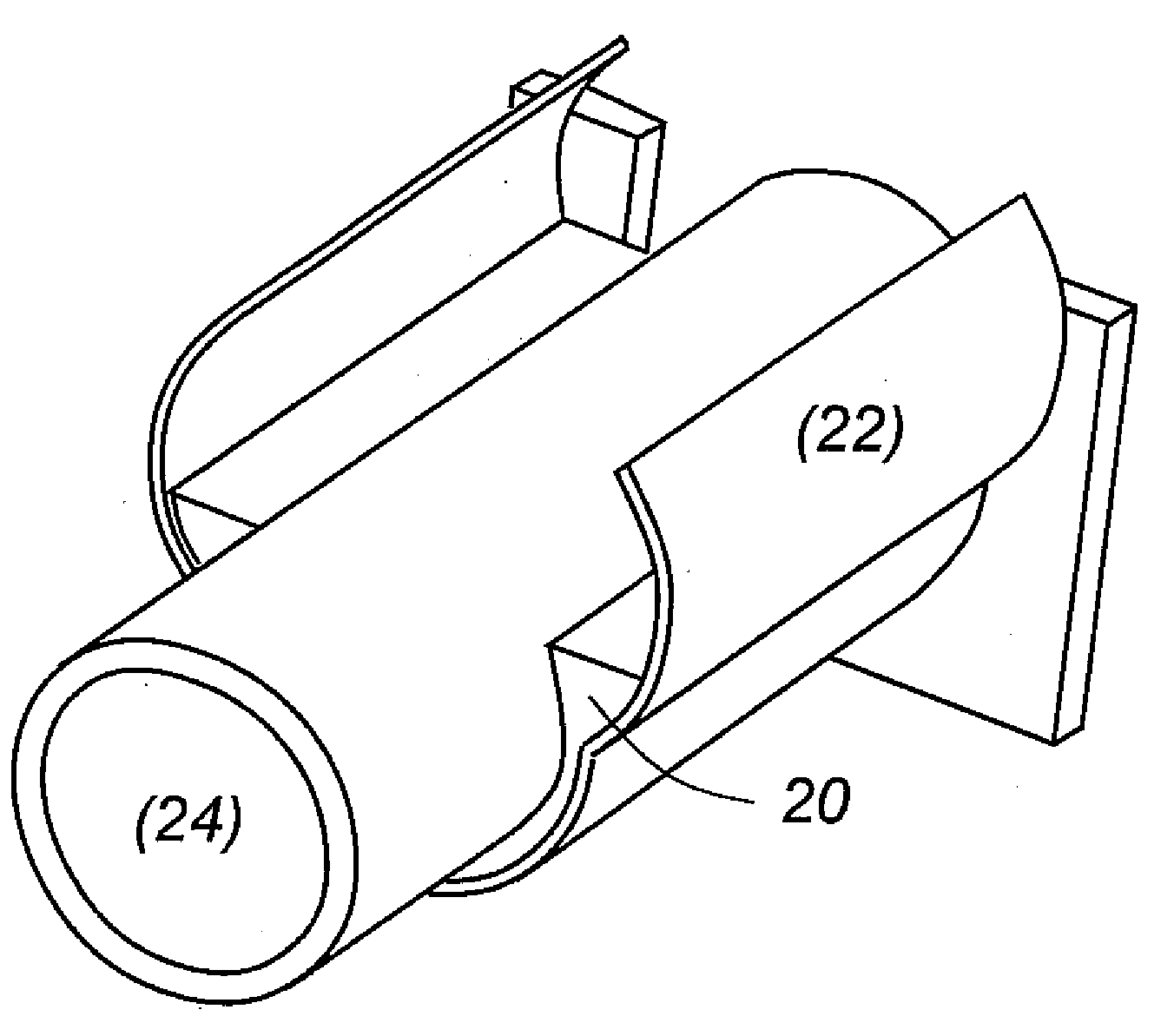
Pipe cladding is based upon a fiber-reinforced brittle matrix composite material. The coating is isotropic, demonstrating pseudo-strain hardening behavior in uniaxial tension, and damage tolerance by design, not relying on stratified layers of reinforcing mesh embedded within concrete or other brittle cementitious matrices for impact resistance, fracture toughness, or crack width control. The fiber reinforced brittle matrix composite cladding protects both the pipe and inner thin, anti-corrosion layer (if present) from impact or abrasion damage while permitting bending of coated and clad pipe. The finished composite clad can be in a simple circular form alone the pipe or in some complex form providing an integrated housing for electrical or optical fiber cables, or optical sensing sensors for continuous or intermittent sensing of pipeline leakage or failure.
Owner:MECC TECH
Structural fiber cement building materials
ActiveUS8209927B2Suitable for useEliminate needConstruction materialSolid waste managementCellulose fiberCementitious matrix
A structural fiber cement sheet containing cementitious matrix and reinforcing cellulose fibers distributed throughout the matrix having a dry density less than 1.25 g / cm3, a thickness less than 0.7500 in, and able to withstand uniform loads of 200 psf or greater according to test method of Section 6.4.2.4 of PS2 and with a deflection of less than 0.067 inches at 60 psf when spaced on a span of 24 inches or less on center.
Owner:JAMES HARDIE TECH LTD
Hydrophobic low shrinkage lightweight cementitious matrix
ActiveCN105036666ALow densityLow hydrophobicitySolid waste managementCeramicwareCementitious matrixLow shrinkage
The present invention provides a composition for forming a lightweight, low shrinkage and hydrophobic cementitious matrix, and a method for preparing thereof. The present cementitious matrix formed by the composition is lightweight, hydrophobic (or water repelling) and with low shrinkage which is useful in building and construction industry as non-structural wall resistant to water, heat and sound entry. The present invention also provides a method of preparing the composition and the cementitious matrix formed from the composition.
Owner:NANO & ADVANCED MATERIALS INST
Cementitious matrix and fiber reinforced cement based mixture
ActiveUS9115026B2Early strengthHigh tensile and flexural strengthSolid waste managementChemical admixtureSlag
Owner:TAISEI CORP
Cementitious matrix and fiber reinforced cement based mixture
ActiveUS20150166414A1Early strengthHigh tensile and flexural strengthSolid waste managementChemical admixtureSlag
A cementitious matrix in which the development of early strength is fast, the hydration heat temperature is small, and the amount of shrinkage during curing is small, while keeping the fluidity when concrete is fresh, is provided. The cementitious matrix is characterized by comprising 100 parts by weight of Portland cement, 5 to 30 parts by weight of silica fume, 5 to 25 parts by weight of limestone powder, 30 to 80 parts by weight of at least one of ground blast furnace slag or fly ash, at least one chemical admixture, water, and 70 to 150 parts by weight of aggregate having a largest aggregate diameter of 1.2 to 3.5 mm.
Owner:TAISEI CORP
Hydrophobic low shrinkage lightweight cementitious matrix
ActiveUS9840440B2Reduce water consumptionImprove distributionSolid waste managementCeramicwareCementitious matrixLow shrinkage
The present invention provides a composition for forming a lightweight, low shrinkage and hydrophobic cementitious matrix, and a method for preparing thereof. The present cementitious matrix formed by the composition is lightweight, hydrophobic (or water repelling) and with low shrinkage which is useful in building and construction industry as non-structural wall resistant to water, heat and sound entry. The present invention also provides a method of preparing the composition and the cementitious matrix formed from the composition.
Owner:NANO & ADVANCED MATERIALS INST
Reinforced structure comprising a cementitious matrix and zinc coated metal elements
The invention relates to a reinforced structure comprising a cementitious matrix and zinc coated metal elements. The structure comprises at least at the interface of the zinc coated metal elements and the cementitious matrix a compound selected from the group consisting of the imidazoles, the triazoles and the tetrazoles. The invention further relates to a zinc coated metal element for the reinforcement of a cementitious matrix and to a method to inhibit hydrogen gas evolution at the interface of zinc coated metal elements embedded in a cementitious matrix.
Owner:NV BEKAERT SA
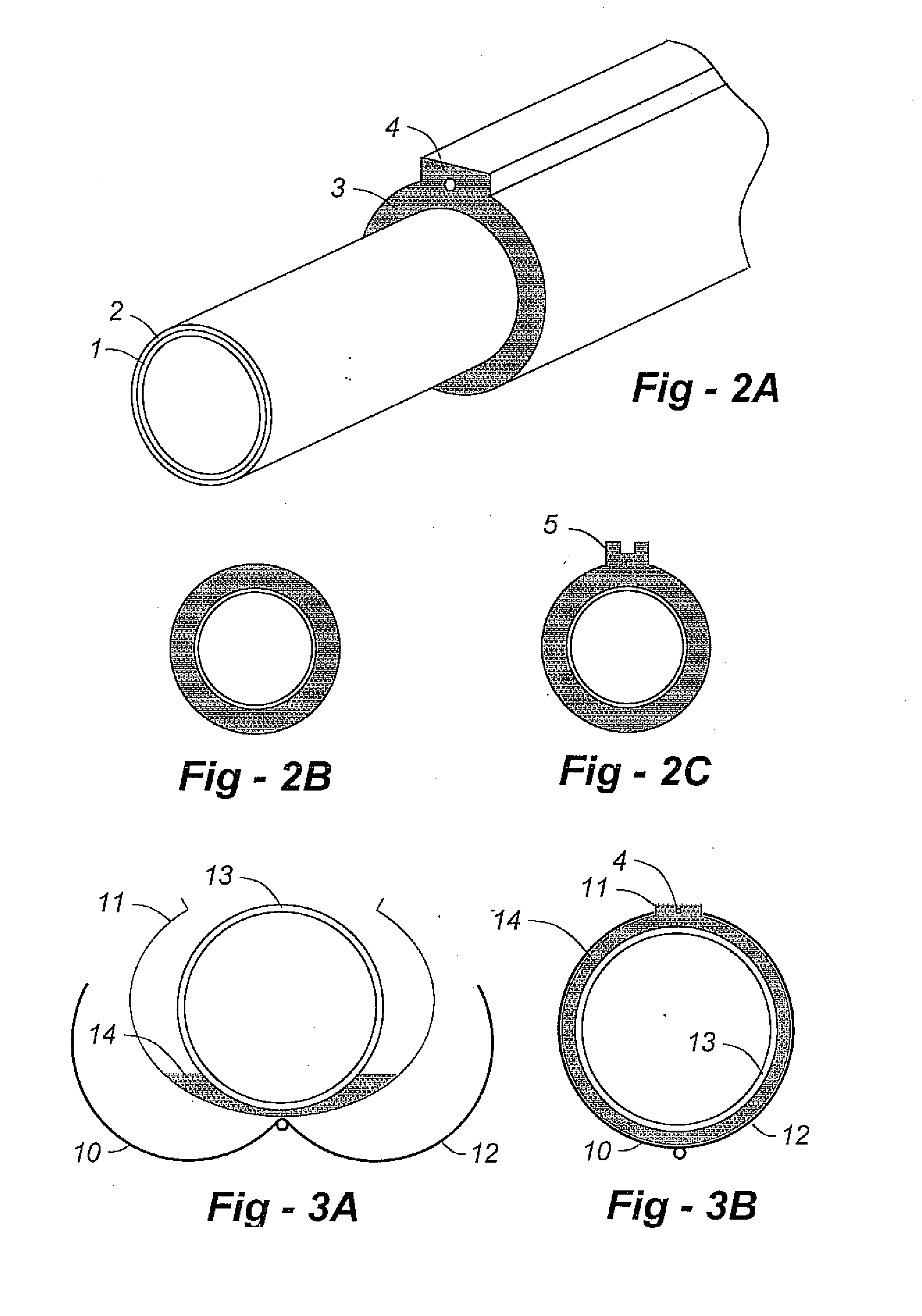
Unitized filamentary concrete reinforcement having circumferential binding element
InactiveUS20050011417A1Improved dispensability and dispersabilityMaintain integrityLaminationLamination apparatusCementitious matrixUltimate tensile strength
The present invention relates to a filamentary film construct which is used in providing cementitious mixtures supplemental and reinforcing strength upon setting, and more particularly, to a unitized filamentary construct which comprises a plurality of oriented reinforcing filamentary film components combined with a circumferential retaining element, said circumferential retaining element providing temporary retention of the oriented reinforcing filamentary components until such point the unitized filamentary substrate is incorporated and subjected to mechanical agitation during preparation of a cementitious blend or mixture. The unitized filamentary film construct is endowed with inherent and improved dispensability and dispersability of the associated reinforcing filamentary component into organic or inorganic cementitious matrixes, such as concrete, mortar, plaster, etc. The oriented reinforcing filamentary film components can comprise fibrillated film components.
Owner:POLYMER GROUP INC
Unitized filamentary concrete reinforcement having circumferential binding element
InactiveUS20060147694A1Improved dispensability and dispersabilityMaintain integrityInorganic adhesivesBuilding reinforcementsCementitious matrixUltimate tensile strength
The present invention relates to a filamentary film construct which is used in providing cementitious mixtures supplemental and reinforcing strength upon setting, and more particularly, to a unitized filamentary construct which comprises a plurality of oriented reinforcing filamentary film components combined with a circumferential retaining element, said circumferential retaining element providing temporary retention of the oriented reinforcing filamentary components until such point the unitized filamentary substrate is incorporated and subjected to mechanical agitation during preparation of a cementitious blend or mixture. The unitized filamentary film construct is endowed with inherent and improved dispensability and dispersability of the associated reinforcing filamentary component into organic or inorganic cementitious matrixes, such as concrete, mortar, plaster, etc. The oriented reinforcing filamentary film components can comprise fibrillated film components.
Owner:FABPRO ORIENTED POLYMERS L L C
Method for producing prestressed concrete structures by means of profiles made of shape memory alloys and structures built according to this method
The invention relates to a method involving placing a profile comprising a shape memory alloy in concrete, or roughening the outside of reinforced concrete, and then fixing the profile (2) comprising a shape memory alloy to the structure ( 6) and apply the cementitious matrix to the rough outer side (9) to cover the profile (2). After the cement matrix has been placed, the profile ( 2 ) develops contraction forces and thus tension due to the heat input. Due to the interlocking of the mortar cover (16) with the rough outer side (9) of the structure (6), the mortar cover (16) acts as a reinforcing layer. The profile (2) extends in the outer mortar as reinforcement layer (16) on the outside of the structure along the outer side of the structure inside the mortar or reinforcement layer (16). The structure can also be prepared for prestressing in the equipped mortar or reinforcement by heat input, since the cable (3) is routed from its end area to the outside of the mortar or reinforcement (16) or the end of the cable (3) The area is accessible by removing the insert (5).
Owner:RE FER +1
Cord for reinforcement of a cementitious matrix
The invention relates a cord for the reinforcement of a cementitious matrix. The cord comprises number of coated metal filaments twisted together to form a cord. The cord shows cross-sections, whereby three or more of the filaments form a closed sub-structure having a void in the middle of the three or more filaments. The cord further comprises a protective compound whereby the protective compound is at least present in said void. The protective compound gives the coated metal element cathodic protection. The invention further relates to a structure comprising a number of cords such as a knitted, a braided, a welded or a glued structure. Furthermore the invention relates to a cementitious matrix reinforced with a cord according to the present invention and to a method to inhibit hydrogen gas evolution at the interface of a cord embedded in a cementitious matrix.
Owner:NV BEKAERT SA
Light-weight, fire-resistant composition and assembly
Light-weight, fire-resistant “mineral foam” includes an inorganic cementitious matrix and at least one metal hydrate that is a “super hydrate” substance, in which water is present with the substance in an amount of at least about ten moieties of water of hydration per formula unit of the substance. As a cured solid, that “mineral foam,” or another mineral foam composition including an inorganic cementitious matrix, can be provided as a structural member in part of an assembly that has at least one open web, thermally insulating support member at least partially embedded in the cured solid. Also, the cured “mineral foam” may be a solid foam in a form of a panel, panel block or tile, which may have a tongue provision and / or a groove provision.
Owner:MABEY MICHAEL JOHN
Hydrogen-trapping material, method of preparation and uses
InactiveCN102245292AHydrogen separation by selective and reversible uptakeReversible hydrogen uptakeHydrogenTrapping
The present invention relates to a material capable of trapping an inflammable gas, such as hydrogen, comprising at least one metal oxide in a cementitious matrix. The present invention also relates to the preparation of such a material and to its various uses.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Producing cementitious materials with improved hydrophobicity and strength using reclaimed waste substances
ActiveUS10590038B1Improve surface propertiesHigh mechanical strengthSolid waste managementHydration reactionVegetable oil
A hydrophobic admixture, for cementitious materials such as cement paste, mortar, and concrete, includes solid polymer particles with a coating of hydrophobic agent and surfactant. The solid polymer particles adhere to exterior surfaces of hydrated cement particles in the cement matrix. The solid polymer particles deliver the hydrophobic agent into the cement matrix which is hydrophilic. The hydrophobic agents are distributed uniformly throughout the cement matrix. The solid polymer particles can be crumb rubber particles derived from waste rubber tires, recycled plastics and similar solid materials. The hydrophobic liquid agent is derived from waste lubricant oil, spent motor oil, base oil, esters of fatty acids, vegetable oil and the like. Fine particles such as activated carbon, silica fume and spent catalyst can be employed to fill the large pores or cracks that develop in the cementitious matrix. The cured cementitious materials exhibit high contact angles and high compressive strengths.
Owner:SHIN CHUANG TECH CO LTD
Coated steel fiber for reinforcement of a cementitious matrix
PendingCN113939489AIncreased risk of hydrogen formationReduced drawabilityCementitious matrixAlloy coating
A steel fiber adapted for the reinforcement of a cementitious matrix is provided with a zinc aluminium alloy coating. The coating includes 0.05-0.5 wt% of aluminium, with the remainder being zinc and unavoidable impurities. The small amount of aluminium delays the growth of the alloy layer and delays the appearance of brown rust stains on the surface.
Owner:NV BEKAERT SA
Hydrophobized fiber cement products, methods for production, and uses thereof
InactiveUS20200031716A1Avoid VOC emissionsImprove adsorption capacityConstruction materialMolecular networkPolymer science
The present invention relates hydrophobized fiber cement products and methods for the production thereof as well as uses of such products, in particular in the building industry. In particular, the present invention provides hydrophobized fiber cement product, comprising a fiber cementitious matrix and a hydrophobizing agent uniformly dispersed therein, wherein said hydrophobizing agent comprises at least one hydrophobic silicone resin having a three-dimensional molecular network structure. The present invention further provides processes for producing a hydrophobized fiber cement product with enhanced water impermeability, wherein said process comprises at least the steps of: a) admixing an inorganic curable cementitious matrix with a hydrophobizing agent to form a curable mixture, wherein said hydrophobizing agent comprises at least one hydrophobic silicone resin having a three-dimensional molecular network structure, b) transforming the curable mixture into a shaped body; and c) curing the curable mixture to form a uniformly hydrophobized fiber cement product.
Owner:ETEX SERVICES NV
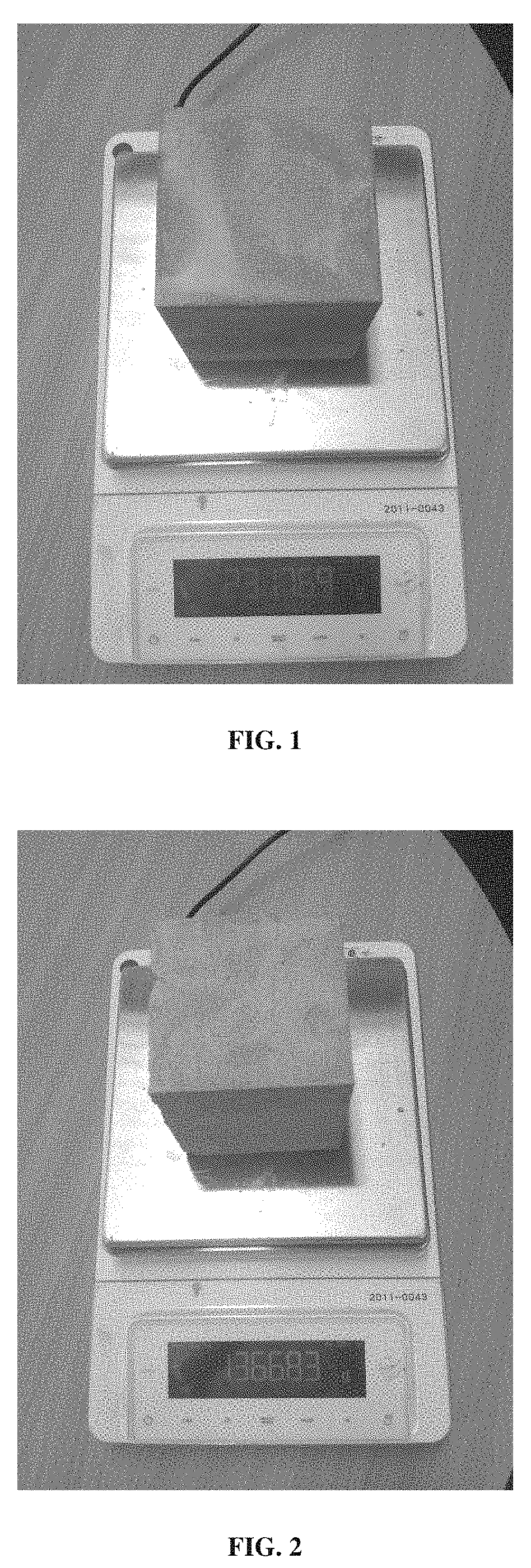
Built-in composite shrinkage measuring instrument for cement-based materials
InactiveCN105044316BHigh precisionEliminate the effects of shrinkage measurementsMaterial testing goodsMeasuring instrumentIsolation layer
The built-in cement-based material composite shrinkage measuring instrument relates to a cement-based material composite shrinkage measuring device. The invention solves the error caused by removing the formwork when the test piece is placed horizontally in the process of measuring the composite shrinkage of the existing cement-based material in the laboratory. And vertical placement measurement also needs to remove the formwork and generally use the bottom of the test mold as the measurement reference point to introduce large deviations in measurement data. The present invention includes metal molds, positioning plates, placement plates, measuring instruments, instrument columns, and instrumentation. There are two transparent L-shaped slots on the metal mold, the top column, the inner wall isolation layer and two matching test pieces. The positioning plate and the placement plate are respectively placed at the bottom of the two L-shaped slots. The instrument column It is fixedly connected with the placement plate and contacted with the positioning plate, the measuring instrument is fixedly connected on the instrument column, and two supporting test pieces are respectively placed on the upper surface of the piece to be tested. The invention is applicable to a composite shrinkage measuring device for cement-based materials.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Coated steel fiber for reinforcement of a cementitious matrix
A steel fiber adapted for the reinforcement of a cementitious matrix is provided with a zinc aluminium alloy coating. The amount of aluminium ranges from 0.05 wt % to 0.5 wt %. The remainder of the coating being zinc and unavoidable impurities. The small amount of aluminium delays the growth of the alloy layer and delays the appearance of brown rust stains on the surface.
Owner:NV BEKAERT SA
Producing cementitious materials with improved hydrophobicity and strength using reclaimed waste substances
ActiveUS10882785B1High strengthImprove surface propertiesPigmenting treatmentSolid waste managementHydration reactionVegetable oil
A hydrophobic admixture, for cementitious materials such as cement paste, mortar, and concrete, includes solid polymer particles with a coating of hydrophobic agent and surfactant. The solid polymer particles adhere to exterior surfaces of hydrated cement particles in the cement matrix. The solid polymer particles deliver the hydrophobic agent into the cement matrix which is hydrophilic. The hydrophobic agents are distributed uniformly throughout the cement matrix. The solid polymer particles can be crumb rubber particles derived from waste rubber tires, recycled plastics and similar solid materials. The hydrophobic liquid agent is derived from waste lubricant oil, spent motor oil, base oil, esters of fatty acids, vegetable oil and the like. Fine particles such as activated carbon, silica fume and spent catalyst can be employed to fill the large pores or cracks that develop in the cementitious matrix. The cured cementitious materials exhibit high contact angles and high compressive strengths.
Owner:SHIN CHUANG TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com