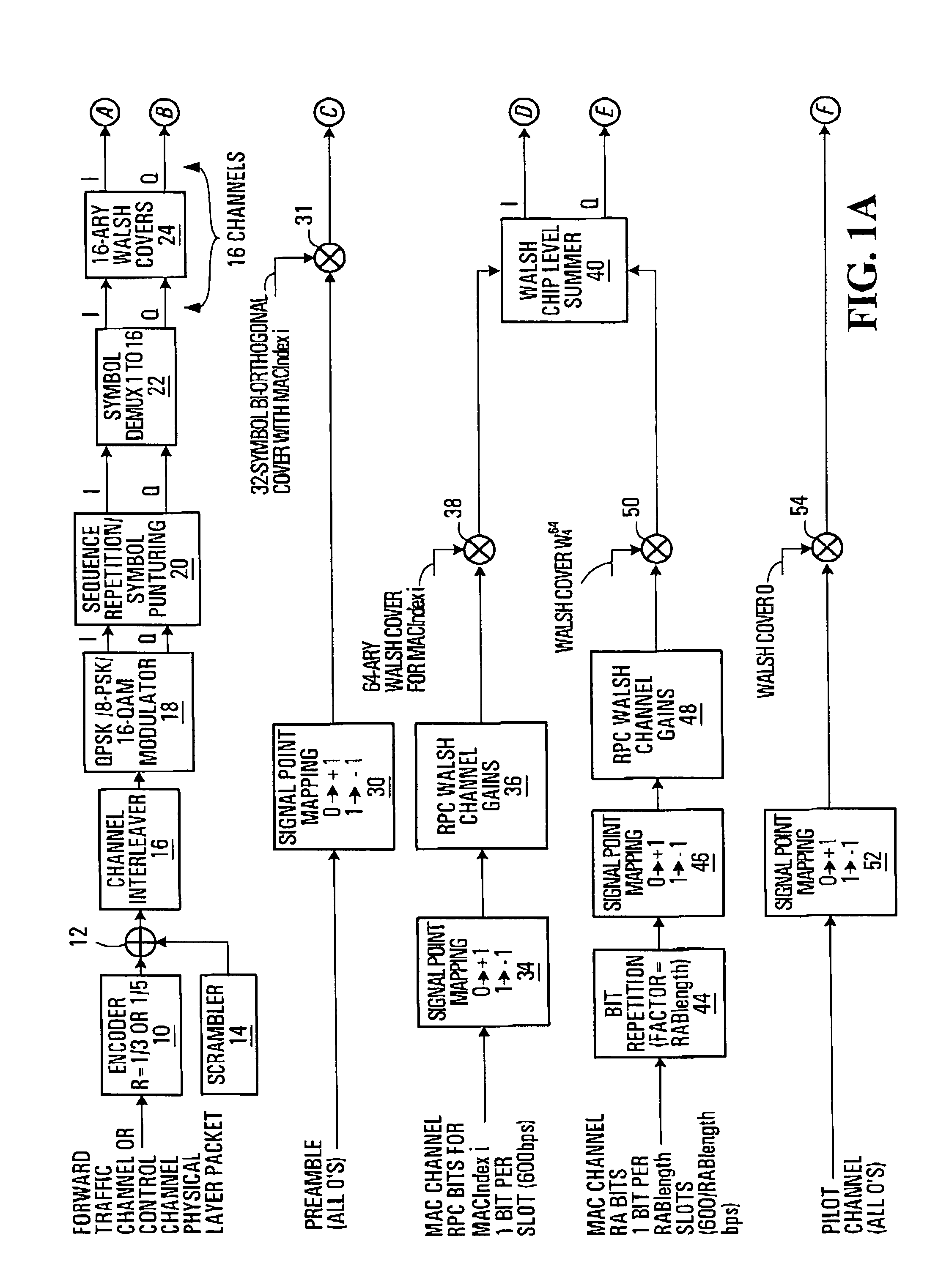
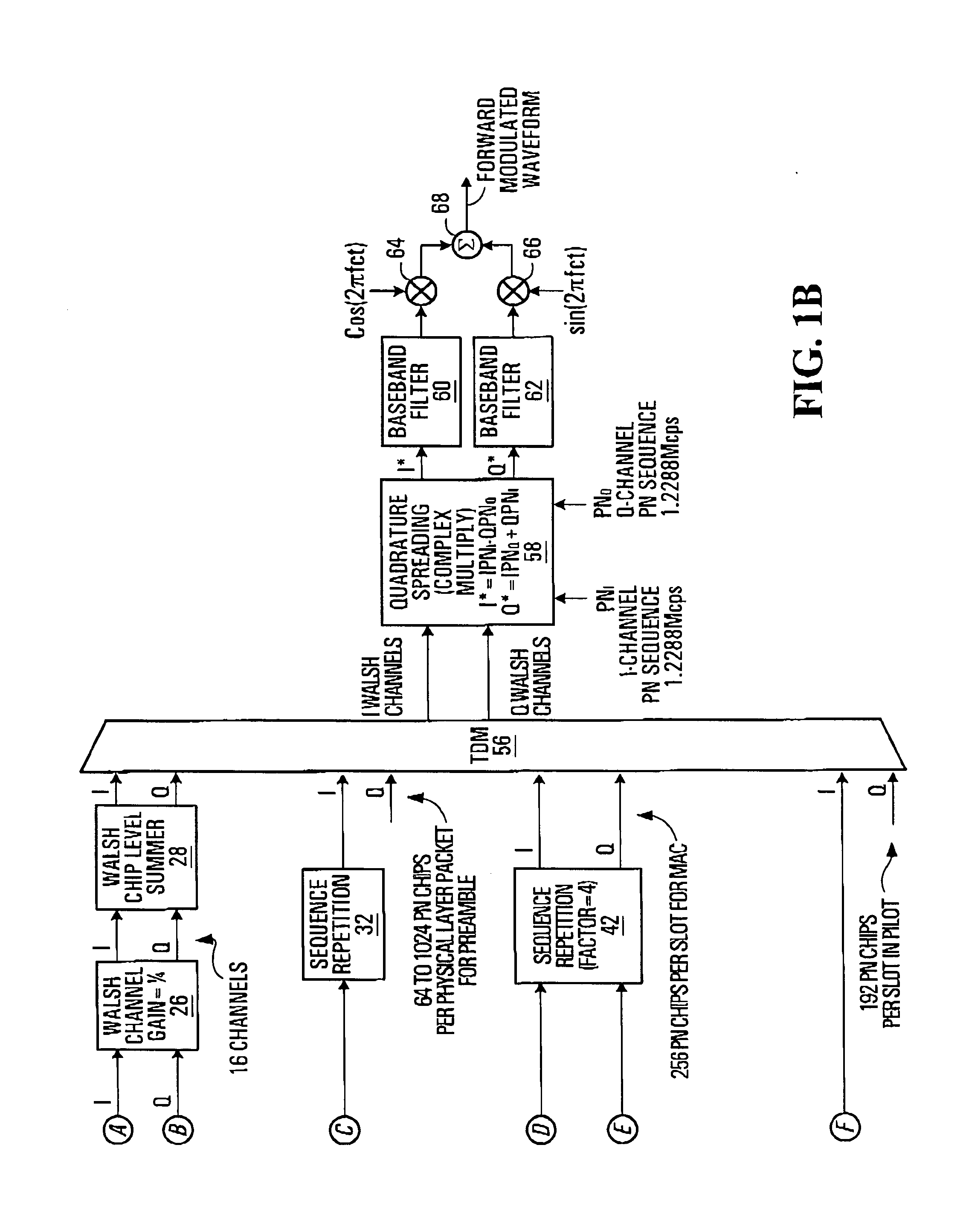
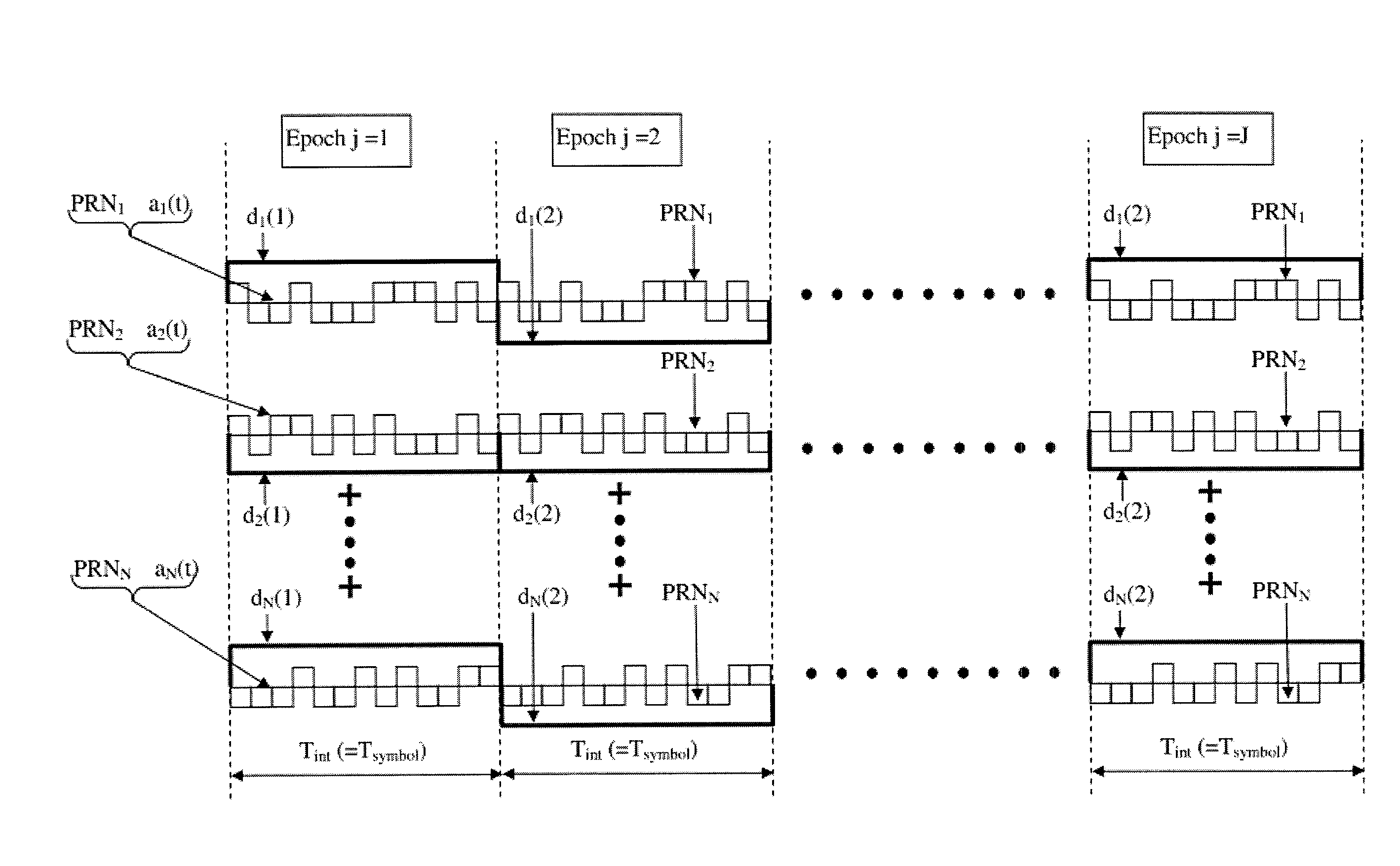
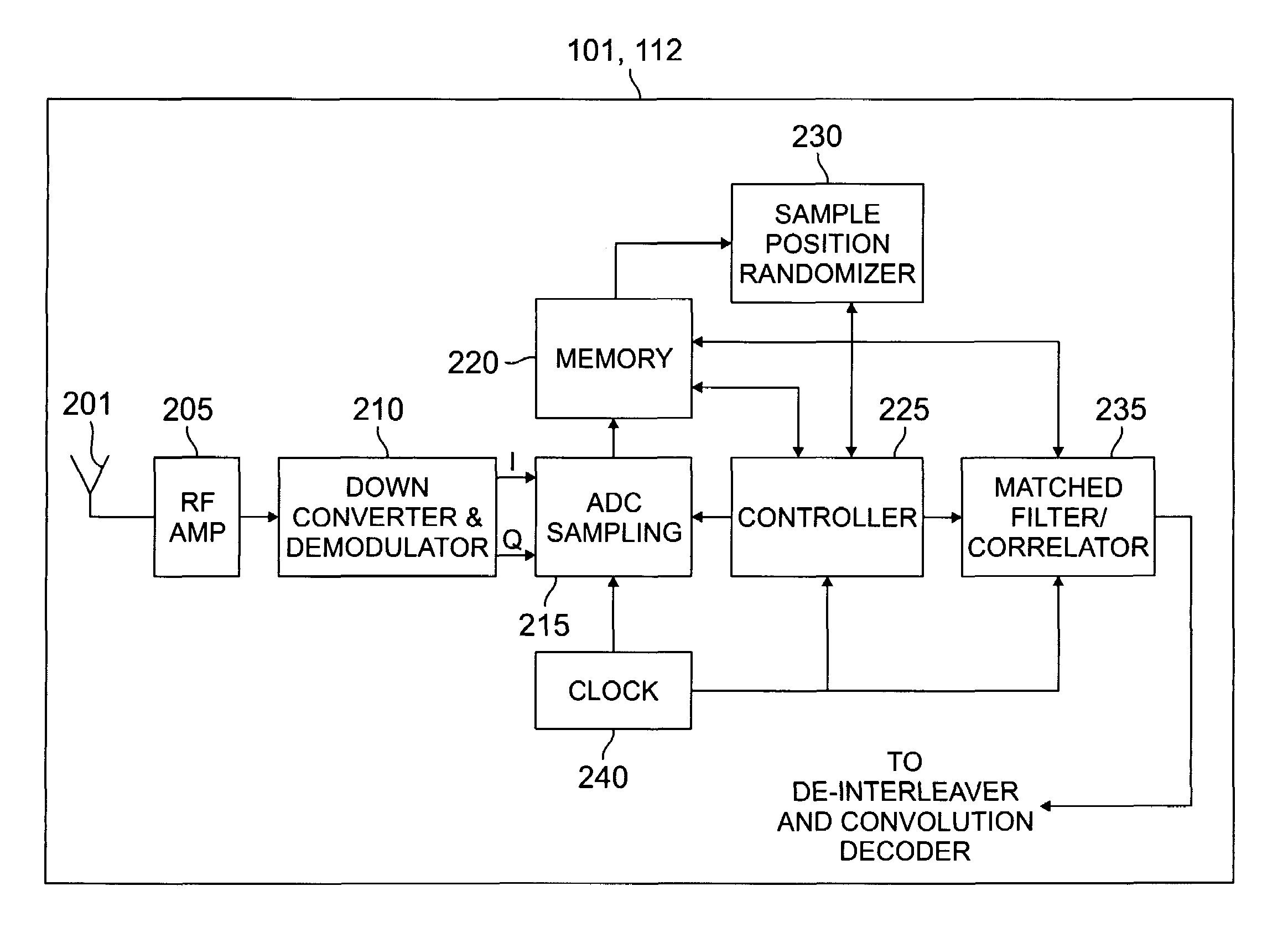
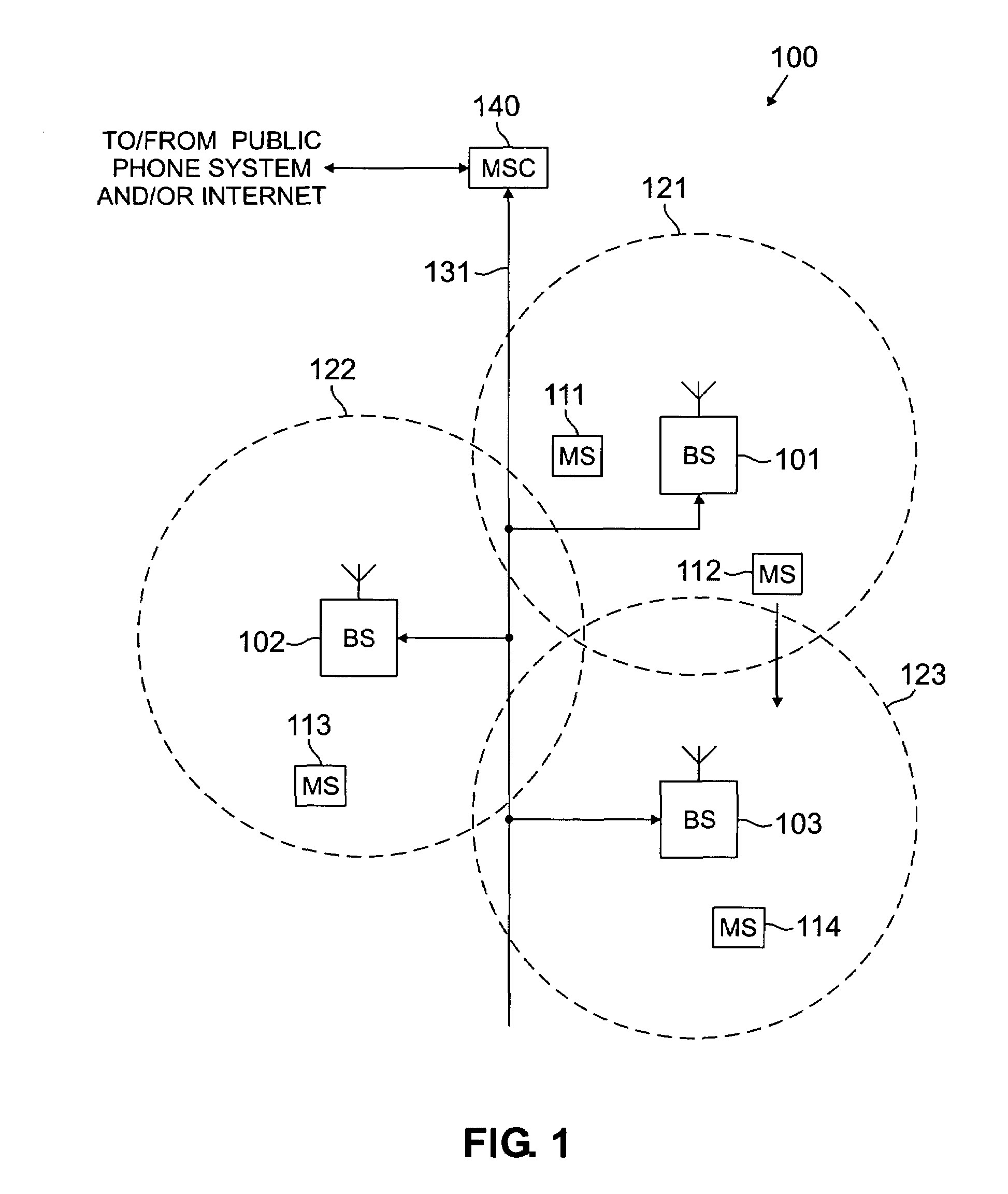
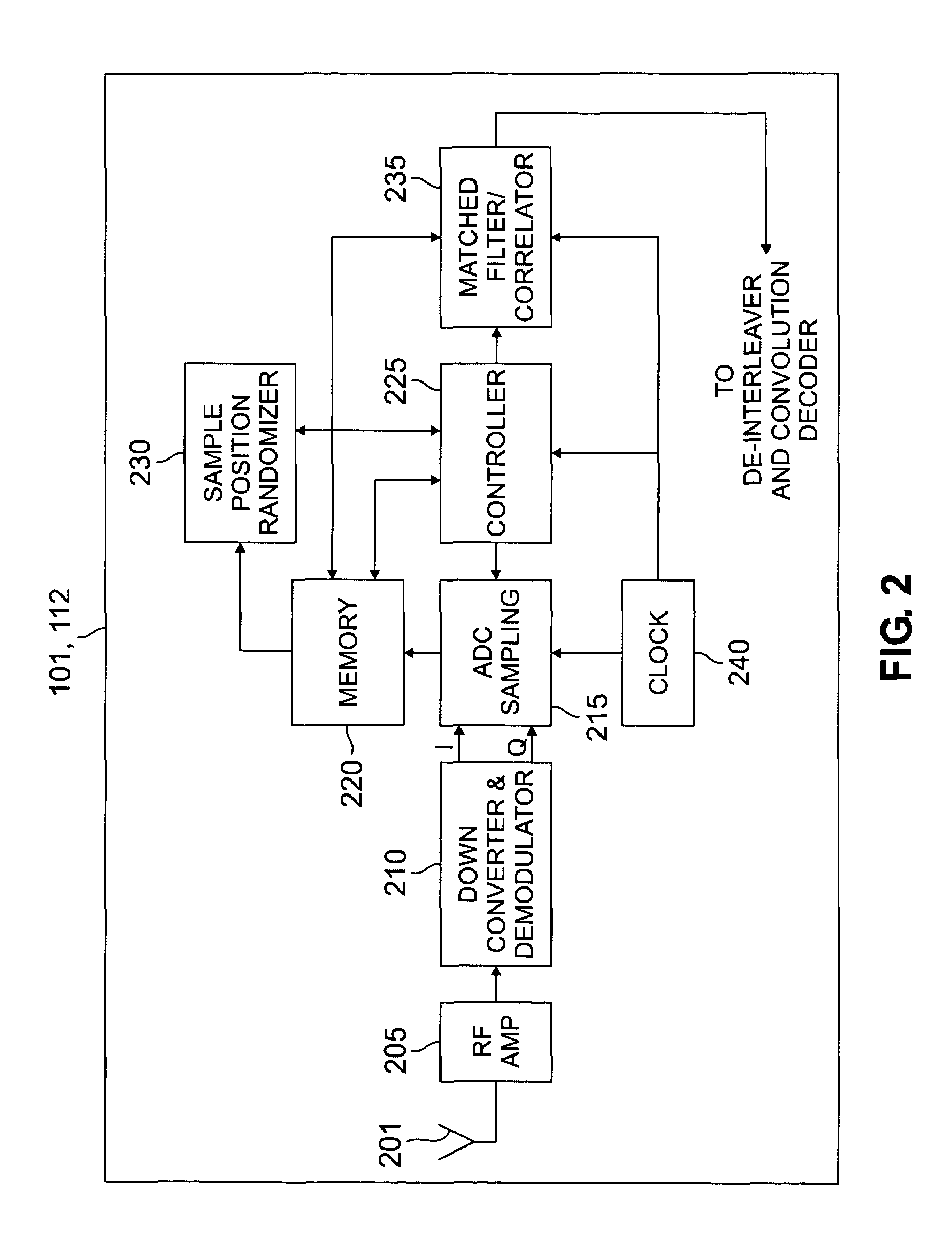
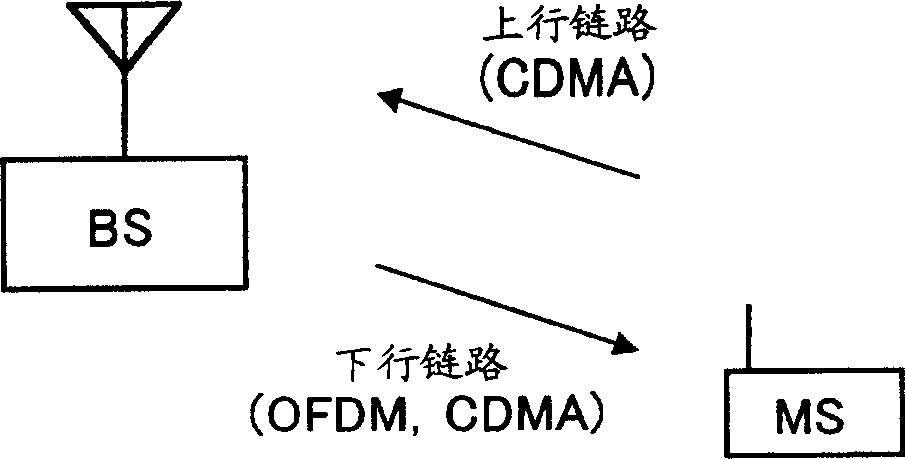
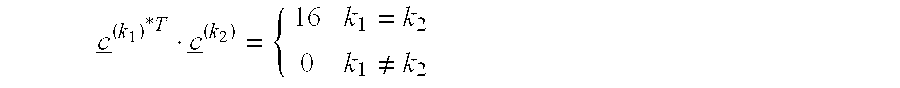Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
270 results about "Cdma signal" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
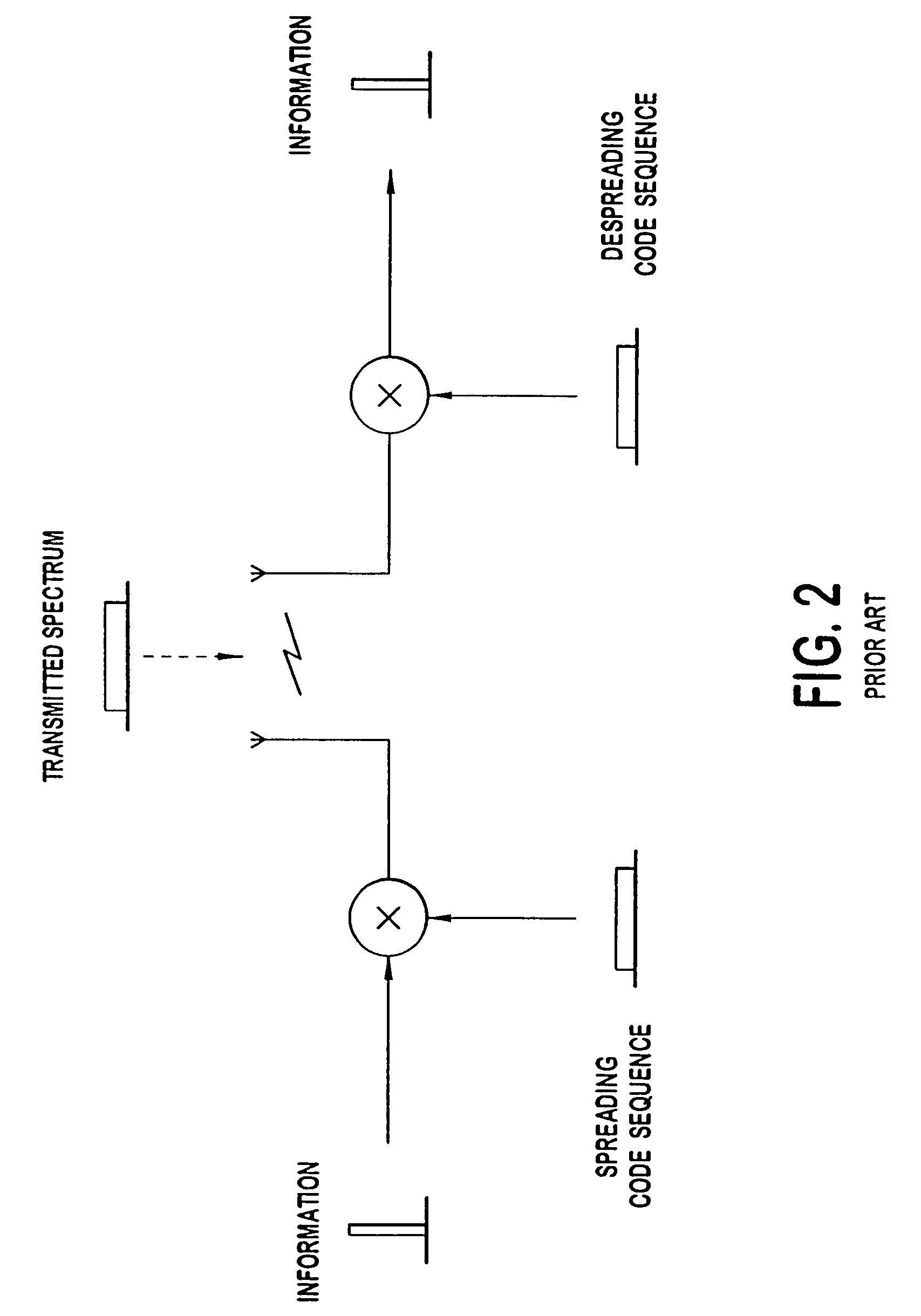
CDMA stands for Code Division Multiple Access. It is a wireless technology used in transmission of signals from places with high Security and noise reduction. The principle of Spread Spectrum is used to work with CDMA. Spread signal is below the noise level and noise has no effect on the signal.
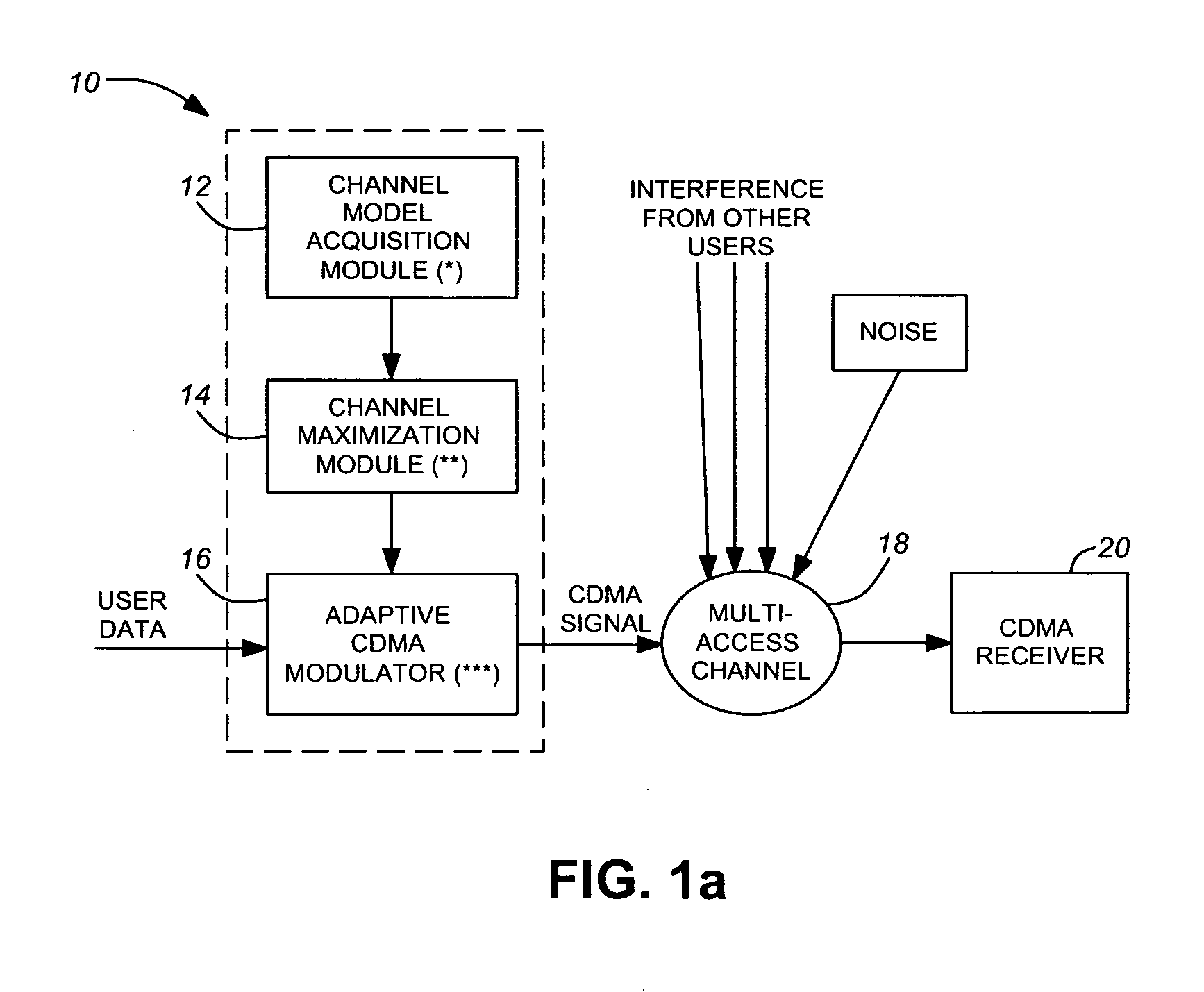
Multiple access method and system
InactiveUS7010048B1Reduce decreaseLower Level RequirementsFrequency diversityWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberPulse envelope
A wireless communication system transmits data on multiple carriers simultaneously to provide frequency diversity. Carrier interference causes a narrow pulse in the time domain when the relative phases of the multiple carriers are zero. Selection of the frequency separation and phases of the carriers controls the timing of the pulses. Both time division of the pulses and frequency division of the carriers achieves multiple access. Carrier interferometry is a basis from which other communication protocols can be derived. Frequency hopping and frequency shifting of the carriers does not change the pulse envelope if the relative frequency separation and phases between the carriers are preserved. Direct sequence CDMA signals are generated in the time domain by a predetermined selection of carrier amplitudes. Each pulse can be sampled in different phase spaces at different times. This enables communication in phase spaces that are not detectable by conventional receivers. The time-dependent phase relationship of the carriers provides automatic scanning of a beam pattern transmitted by an antenna array. In waveguide communications, the carrier frequencies and phase space may be matched to the chromatic dispersion of an optical fiber to increase the capacity of the fiber.
Owner:DEPARTMENT 13 INC
Method and a device for maintaining the performance quality of a code-division multiple access system in the presence of narrow band interference
InactiveUS6807405B1Reduce adverse effectsReducing and eliminating disruptionPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementContinuous scanningTime division multiple access
A method and device which dynamically detects, tracks and filters interfering signals with sufficient speed (i.e. within one IS-95 CDMA data frame period, or 20ms and fidelity to eliminate or greatly reduce the deleterious effects of narrow band interferor signals on a CDMA link. When inserted in an RF signal path an Adaptive Notch Filter (ANF) detects narrow band interferors above a threshold level within the CDMA signal. Detection is accomplished by continuous scanning of a preset excision band, e.g. a specified narrow band associated with an AMPS system. Detected interferors are then automatically acquired and suppressed. This is achieved by electronically placing a rejection notch at the frequency of the interferors. Multiple notch filters may be used to simultaneously suppress multiple interferors. In the absence of interferors a bypass mode is selected allowing the RF signal to bypass the notch. Upon detection of an interferor, a switch is made to a suppression mode where the interferor is steered through a first notch section and suppressed. Alternatively, an external control line may be used to select the bypass mode so that the signal is allowed to pass the notch section, regardless of interferer content.
Owner:ILLINOIS SUPER CONDUCTOR CANADA CORP A CO INC UNDER THE LAWS OF CANADA +1
System and method for positioning in configured environments
ActiveUS7511662B2Easy to useSize moreDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationFrequency spectrumCdma signal
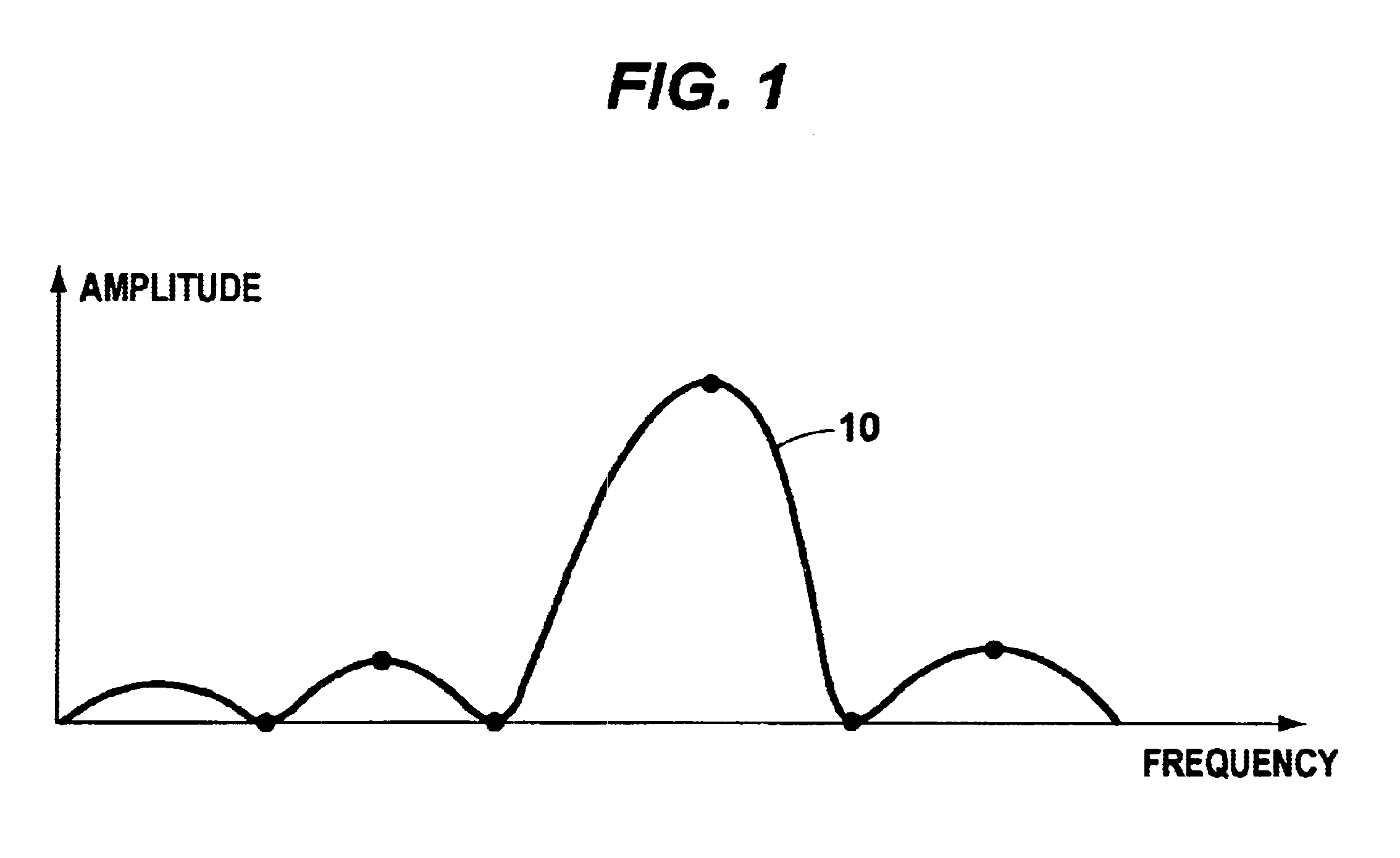
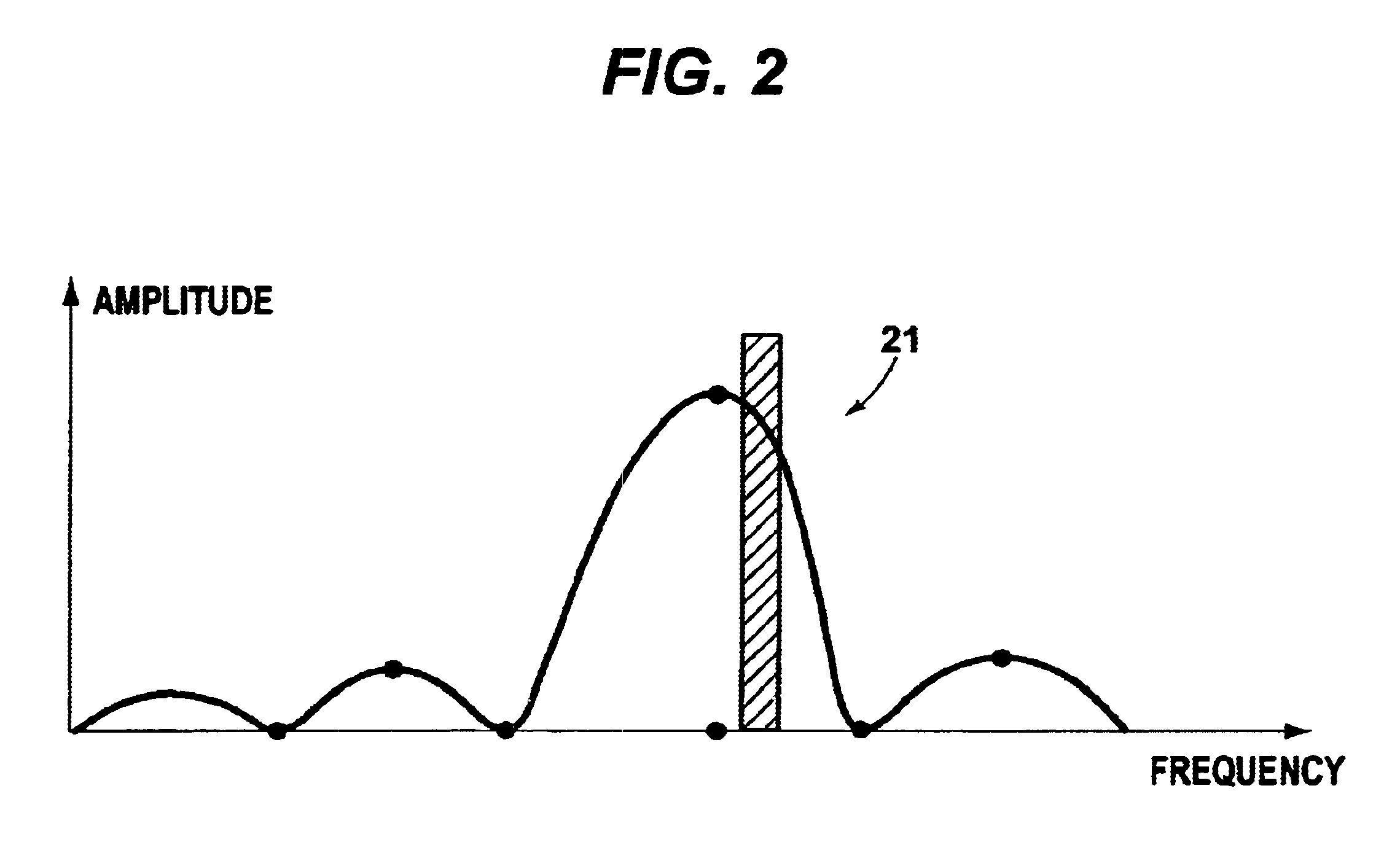
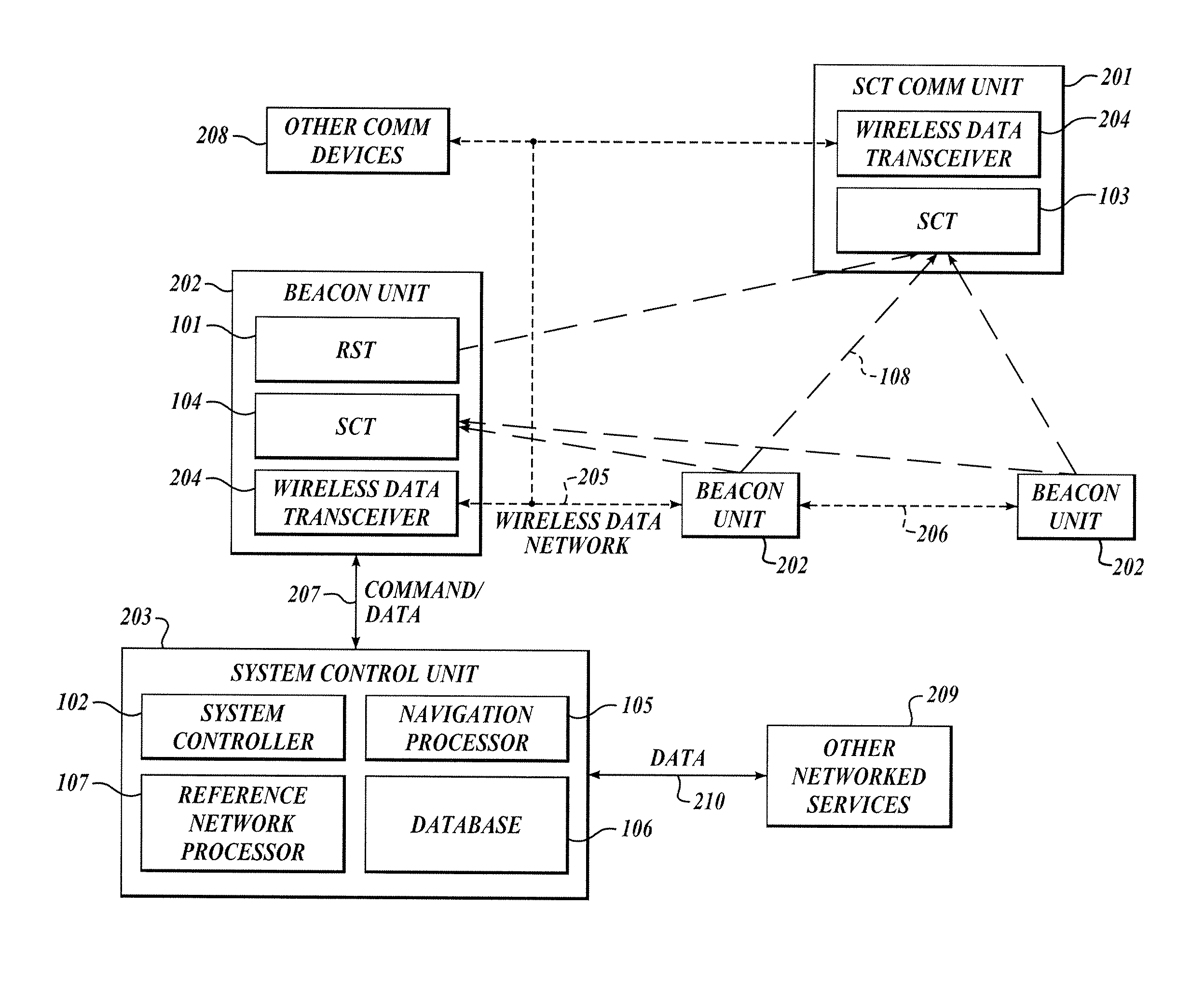
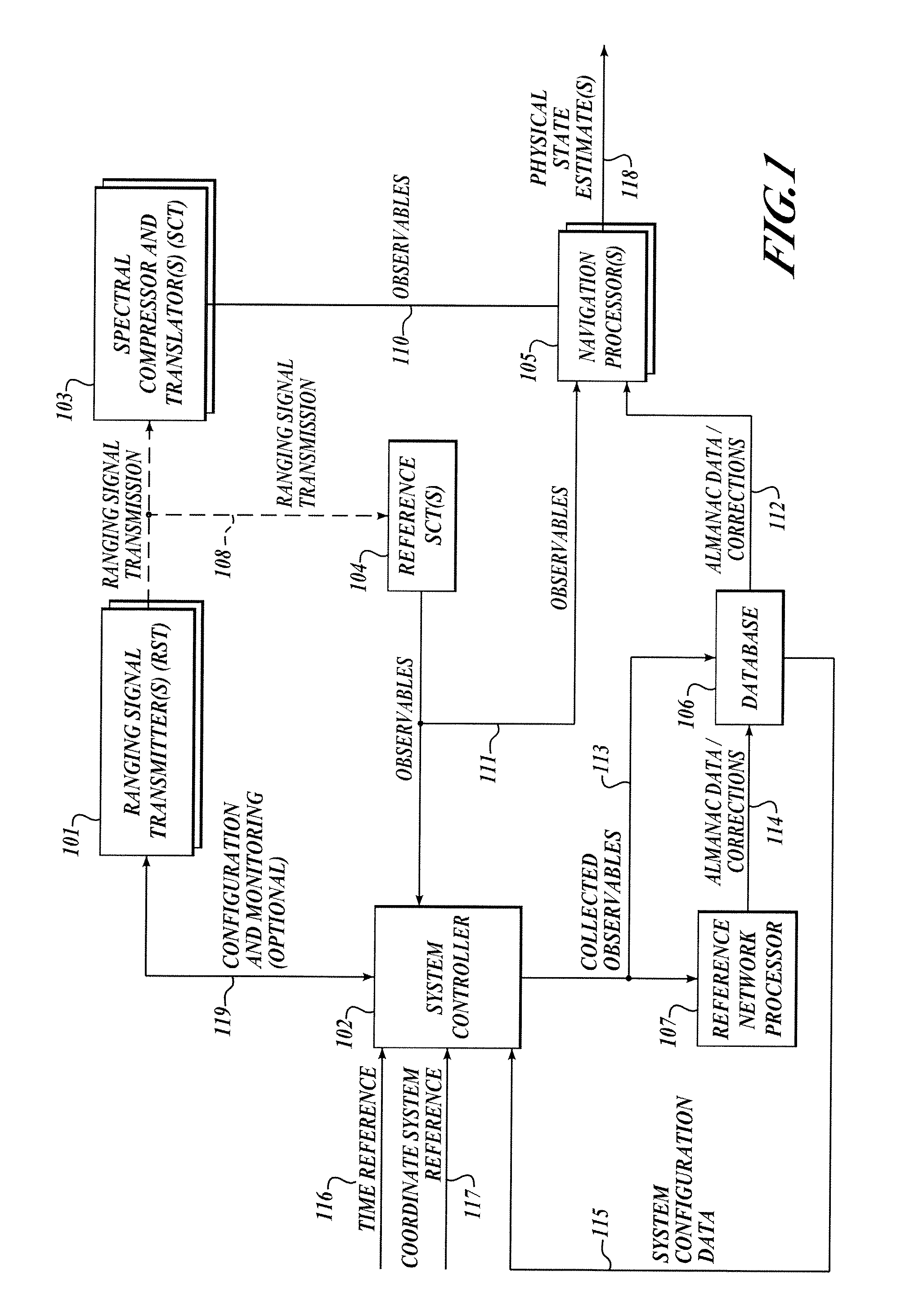
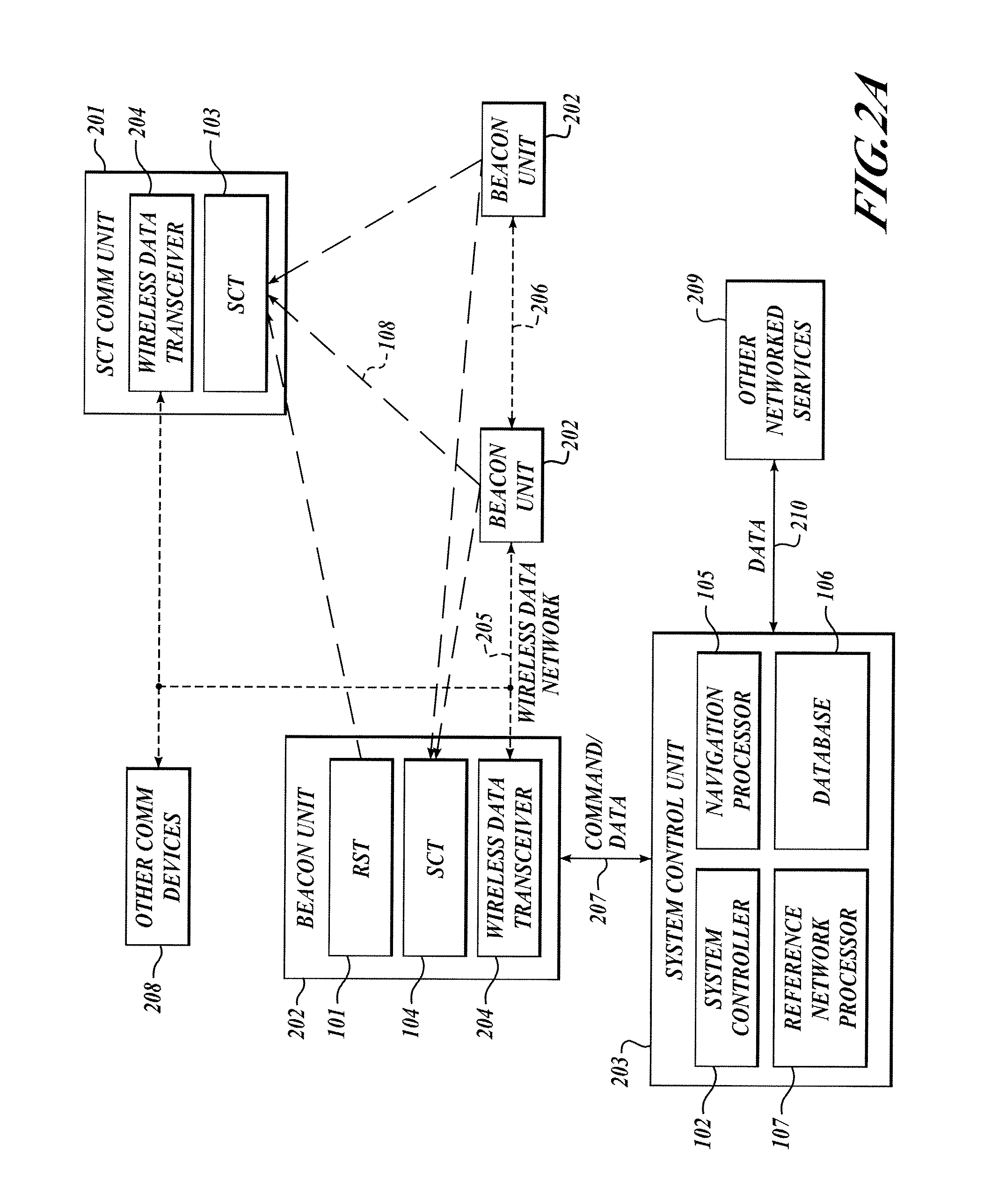
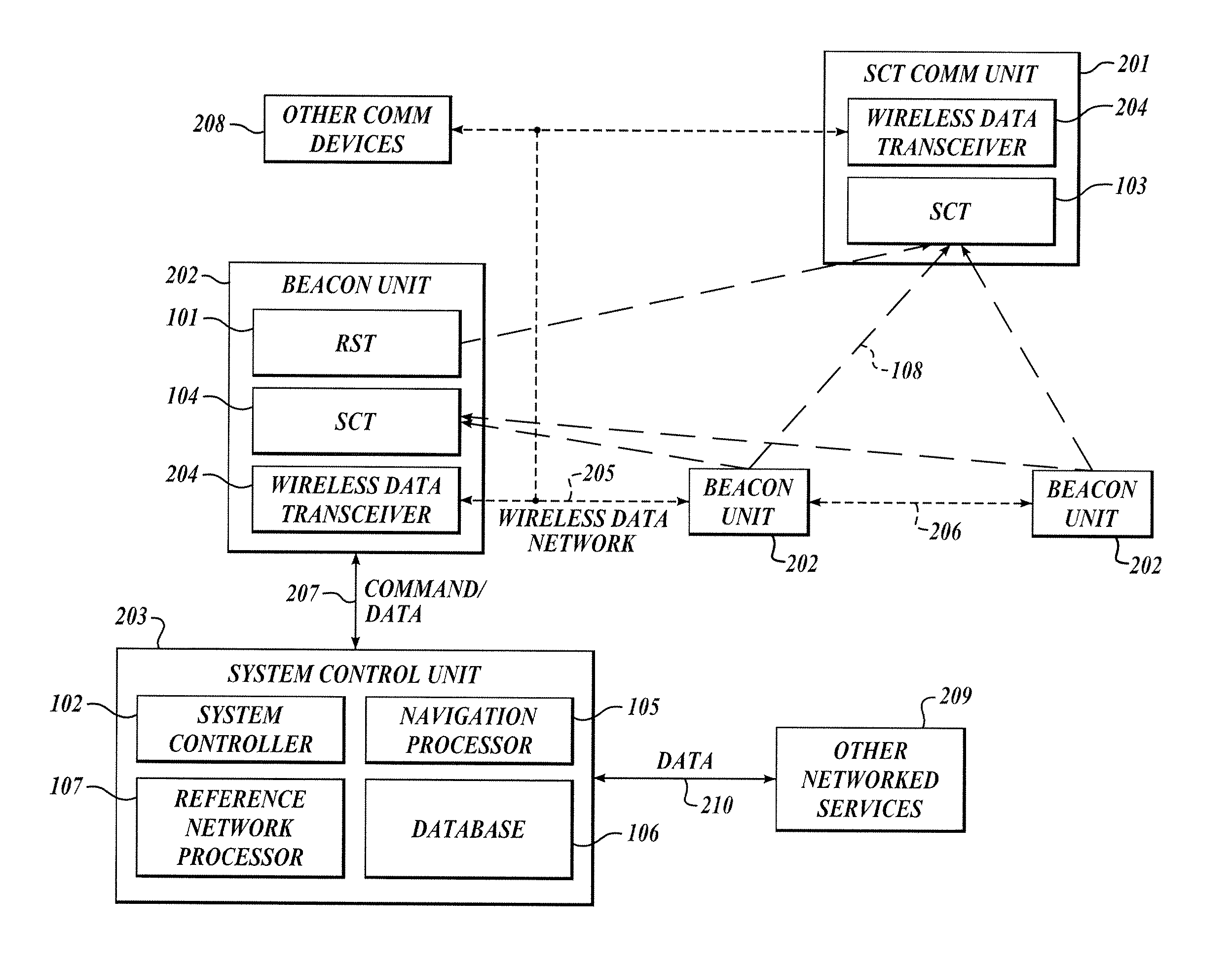
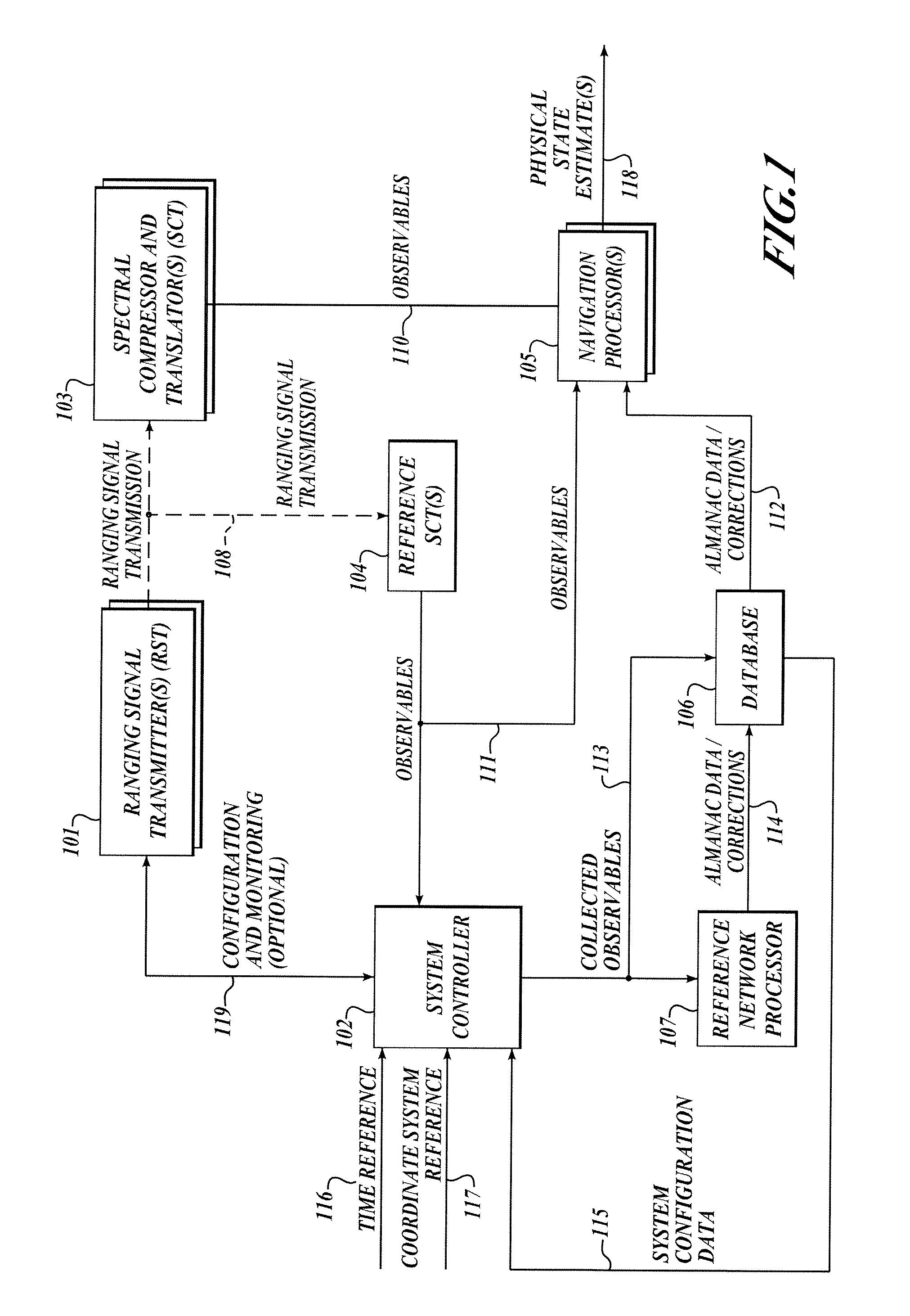
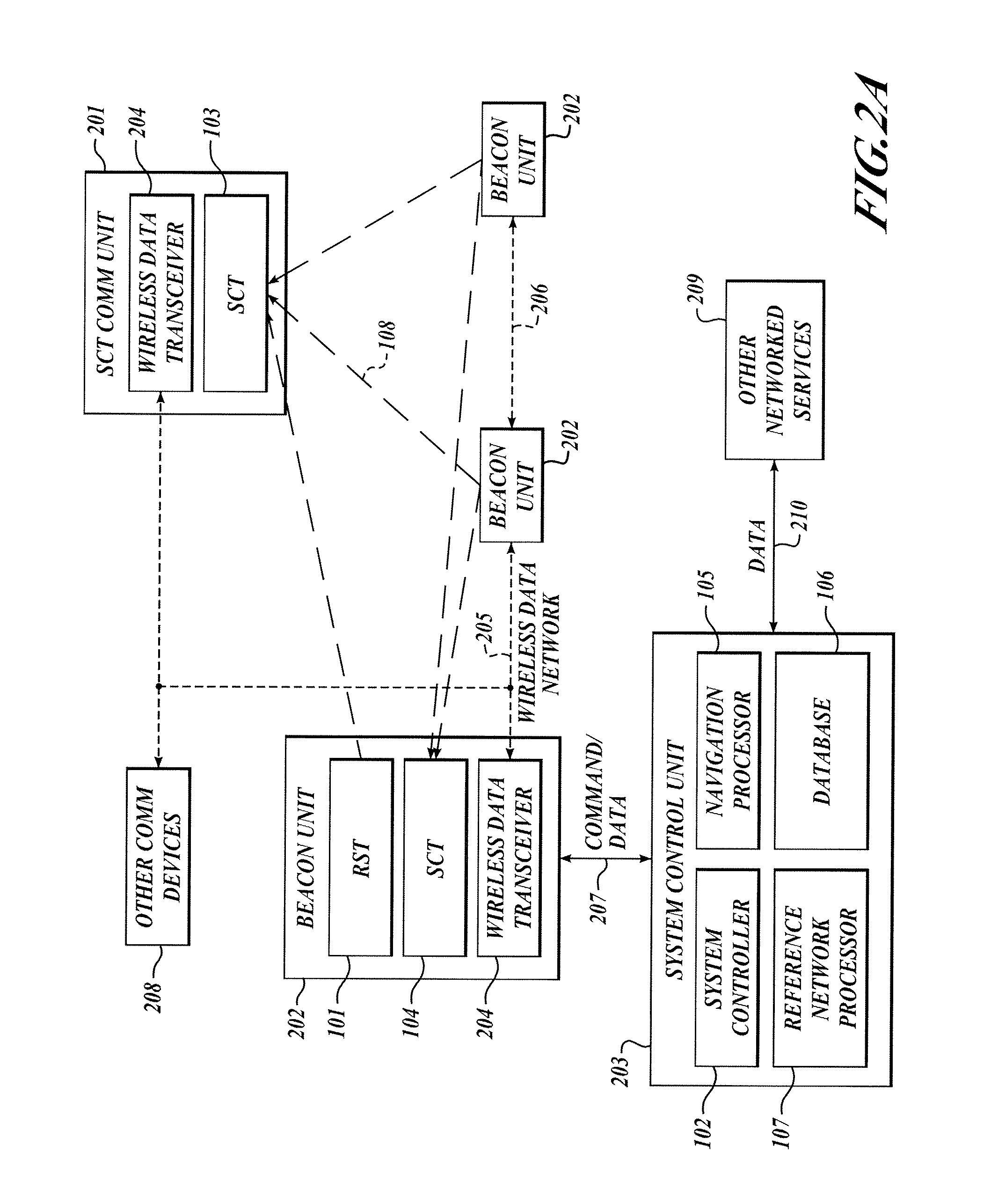
The present invention relates to a system and method for providing location determination in a configured environment in which Global Navigation Satellite System Signals may not be available. In this regard, local beacon systems generate spread spectrum CDMA signals that are received by spectral compression units that derive physically meaningful observations without a requirement for correlation of the intercepted energy by means of the known spreading codes. The invention can coexist with communication assets already in place, and the design allows for self calibration, which simplifies installation and usage. The invention has utility in applications in which GNSS signals are unavailable or limited, for example, in warehouse inventory management, in search and rescue operations and in asset tracking in indoor environments.
Owner:TELECOMM SYST INC
System and method for positioning in configured environments
ActiveUS20070257831A1Easy to implementRapidly deployableDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationFrequency spectrumCdma signal
The present invention relates to a system and method for providing location determination in a configured environment in which Global Navigation Satellite System Signals are not available. In this regard, local beacon systems generate spread spectrum CDMA signals that are received by spectral compression units that derive physically meaningful observations without a requirement for correlation of the intercepted energy by means of the known spreading codes. The invention can coexist with communication assets already in place, and the design allows for self calibration, which simplifies installation and usage. The invention has utility in applications in which GNSS signals are unavailable or limited, for example, in warehouse inventory management, in search and rescue operations and in asset tracking in indoor environments.
Owner:TELECOMM SYST INC
Smart antenna CDMA wireless communication system
InactiveUS6980527B1Increase capacityImprove performanceSynchronisation arrangementSpatial transmit diversityFir systemDownlink beamforming
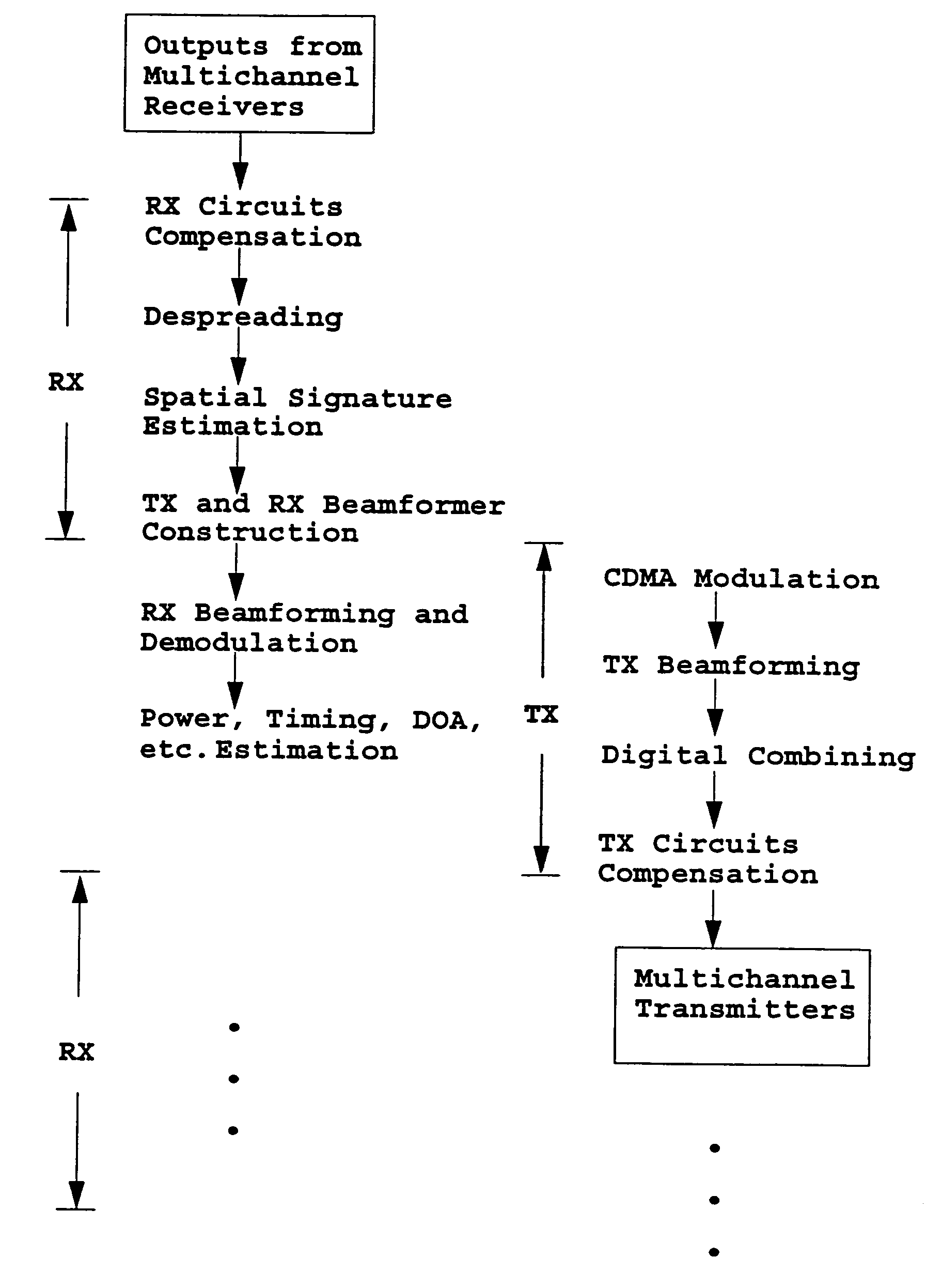
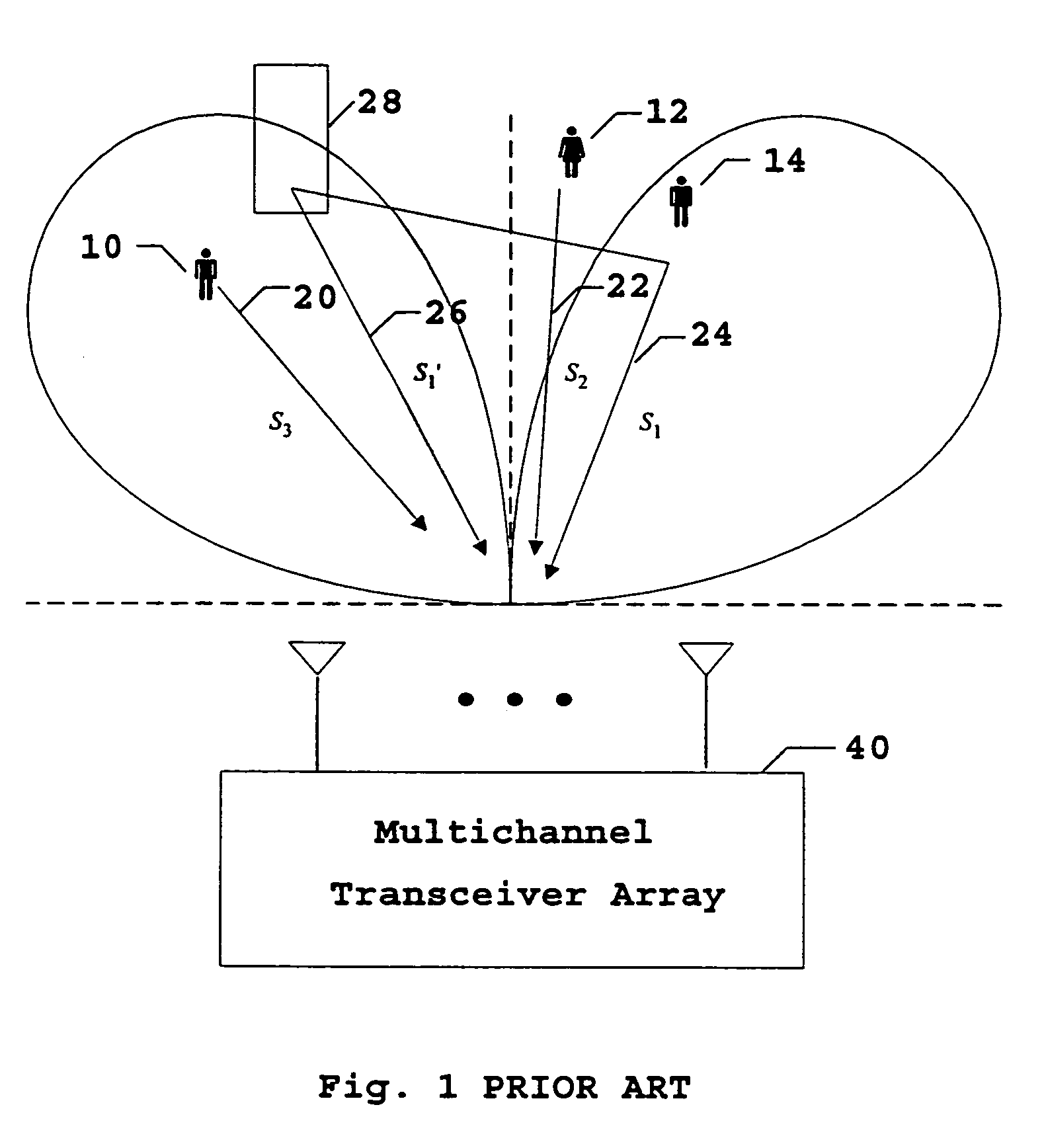
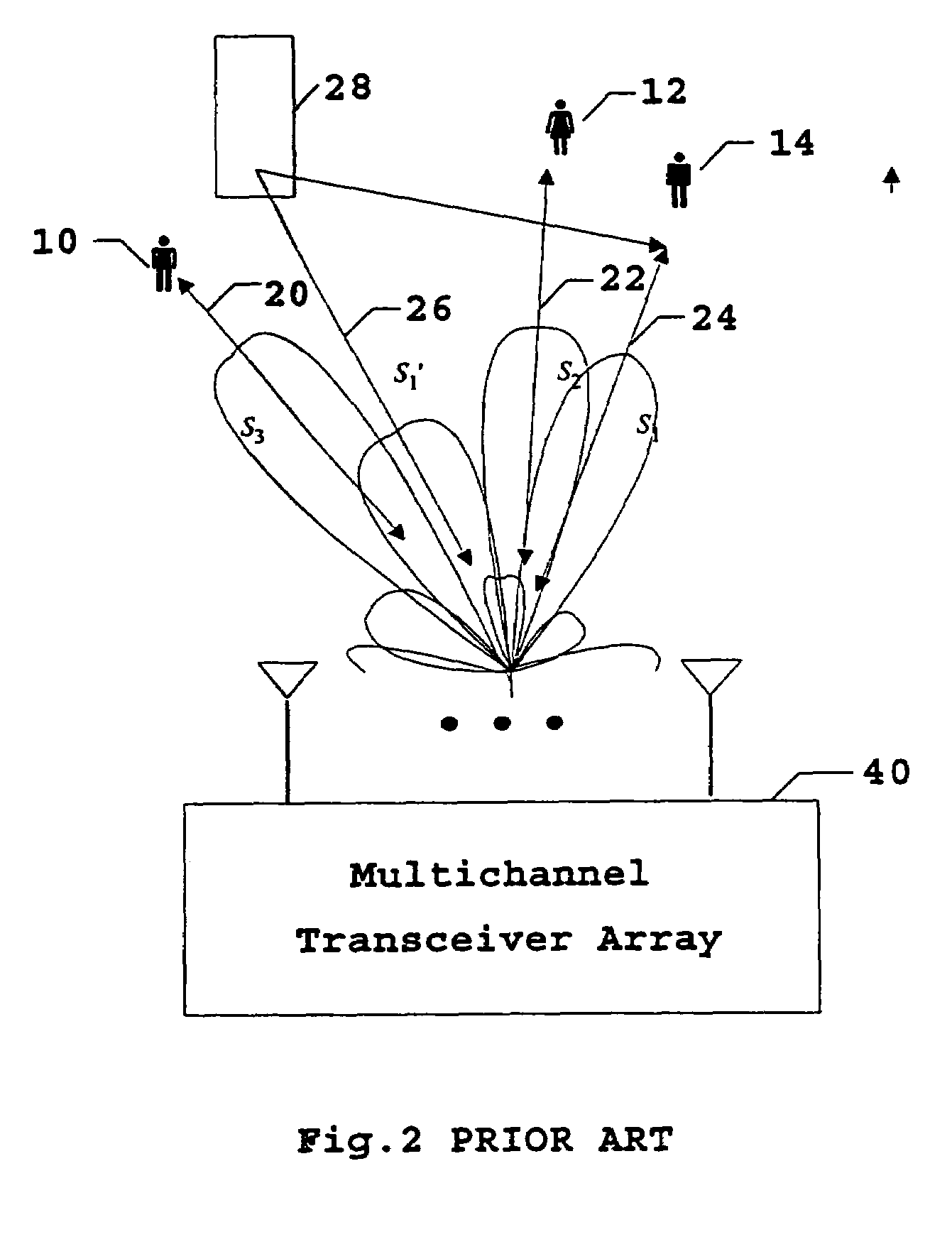
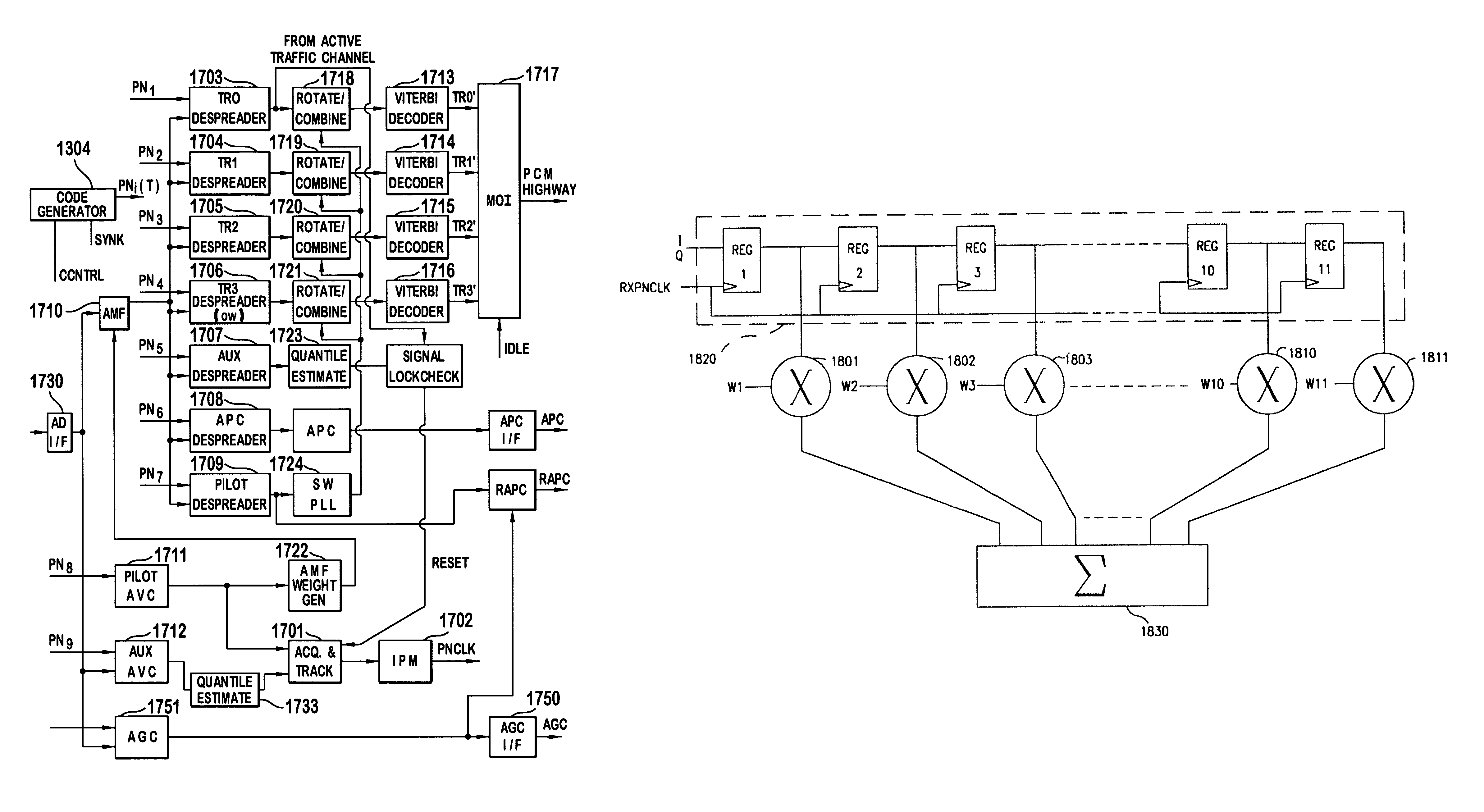
A TDD antenna array S-CDMA system for increasing the capacity and quality of a wireless communications is disclosed. By simultaneous exploiting the spatial and code diversities, high performance communications between a plurality of remote terminals and a base station is achieved without sacrificing system flexibility and robustness. The time-division-duplex mode together with the inherent interference immunity of S-CDMA signals allow the spatial diversity to be exploited using simple and robust beamforming rather than demanding nulling. Measurements from an array of receiving antennas at the base station are utilized to estimate spatial signatures, timing offsets, transmission powers and other propagation parameters associated with a plurality of S-CDMA terminals. Such information is then used for system synchronization, downlink beamforming, as well as handoff management. In an examplary embodiment, the aforementioned processing is accomplished with minimum computations, thereby allowing the disclosed system to be applicable to a rapidly varying environment. Among many other inherent benefits of the present invention are large capacity and power efficiency, strong interference / fading resistance, robustness power control, and easy hand-off.
Owner:BEIJING XINWEI TELECOM TECH
Adaptive forward power control and adaptive reverse power control for spread-spectrum communications
InactiveUS7929498B2Increase profitError preventionRadio transmission for post communicationCommunications systemTransmitted power
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
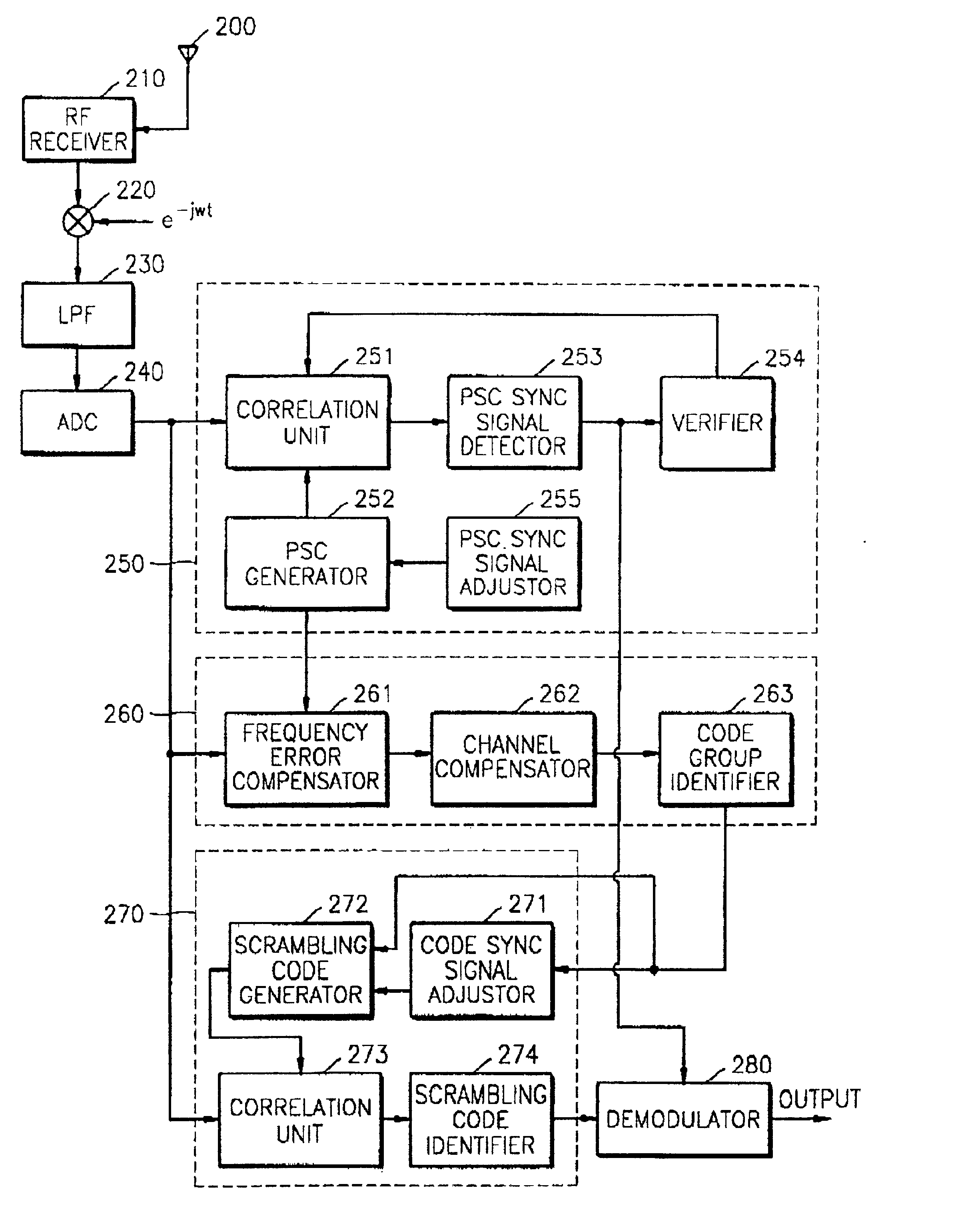
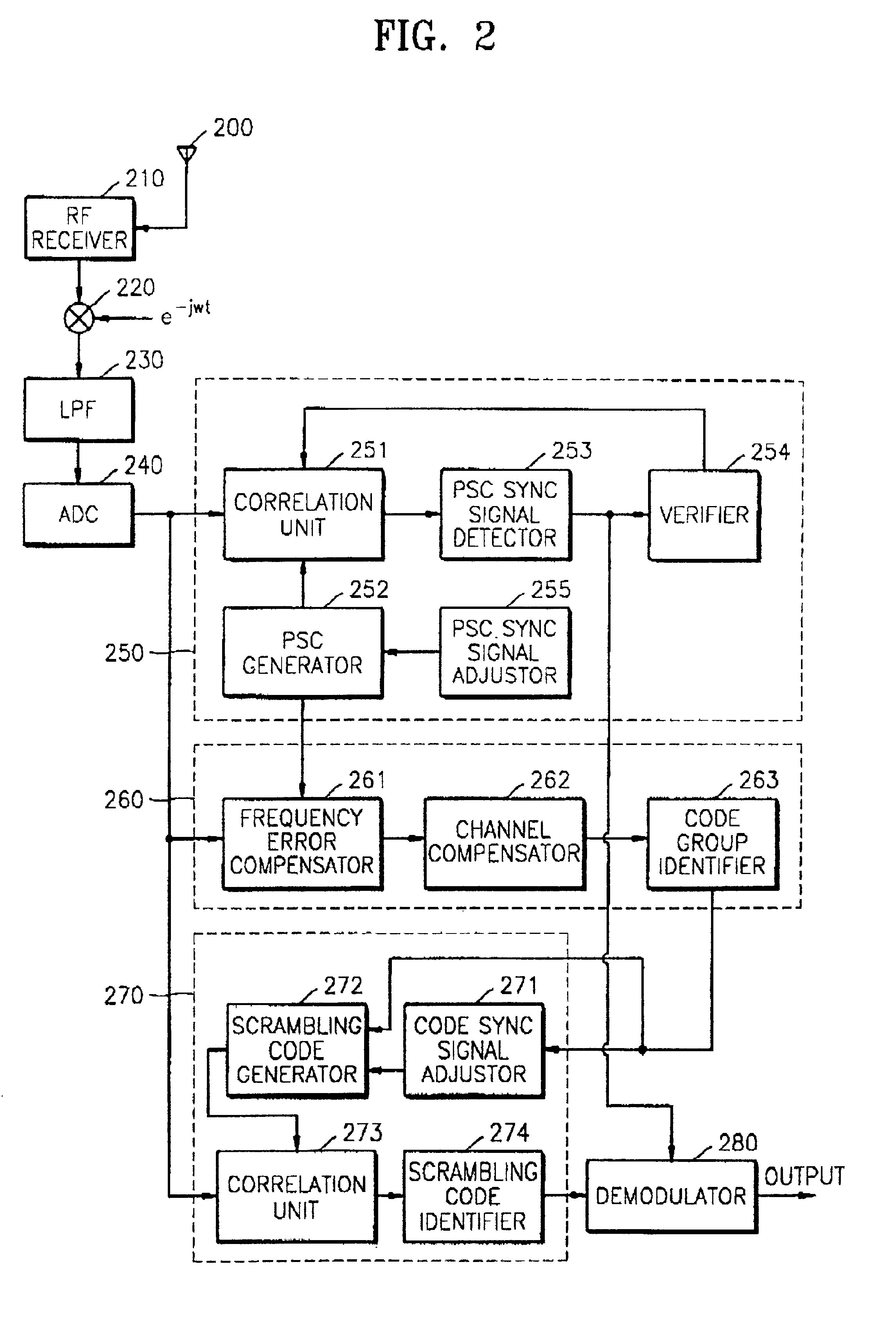
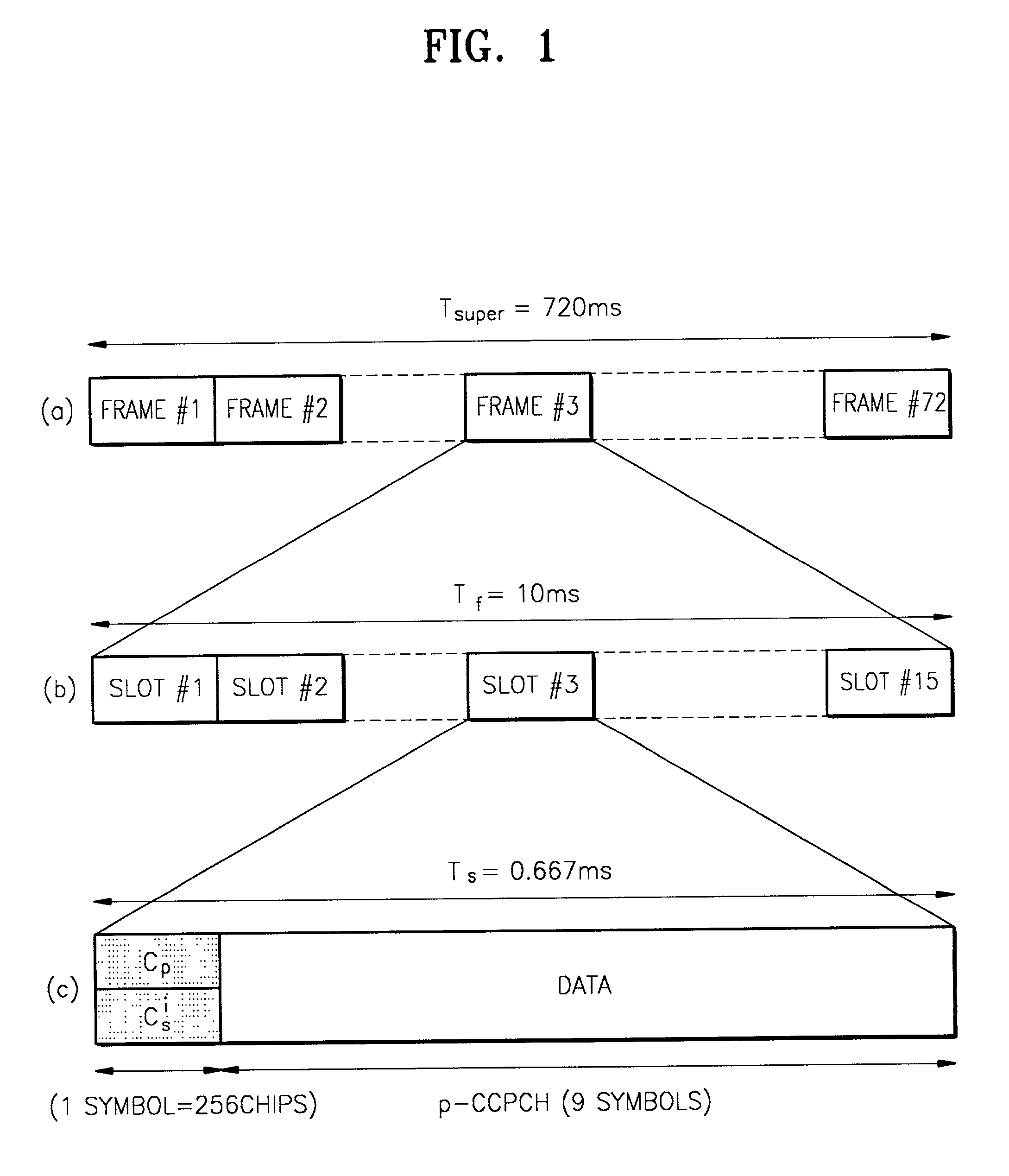
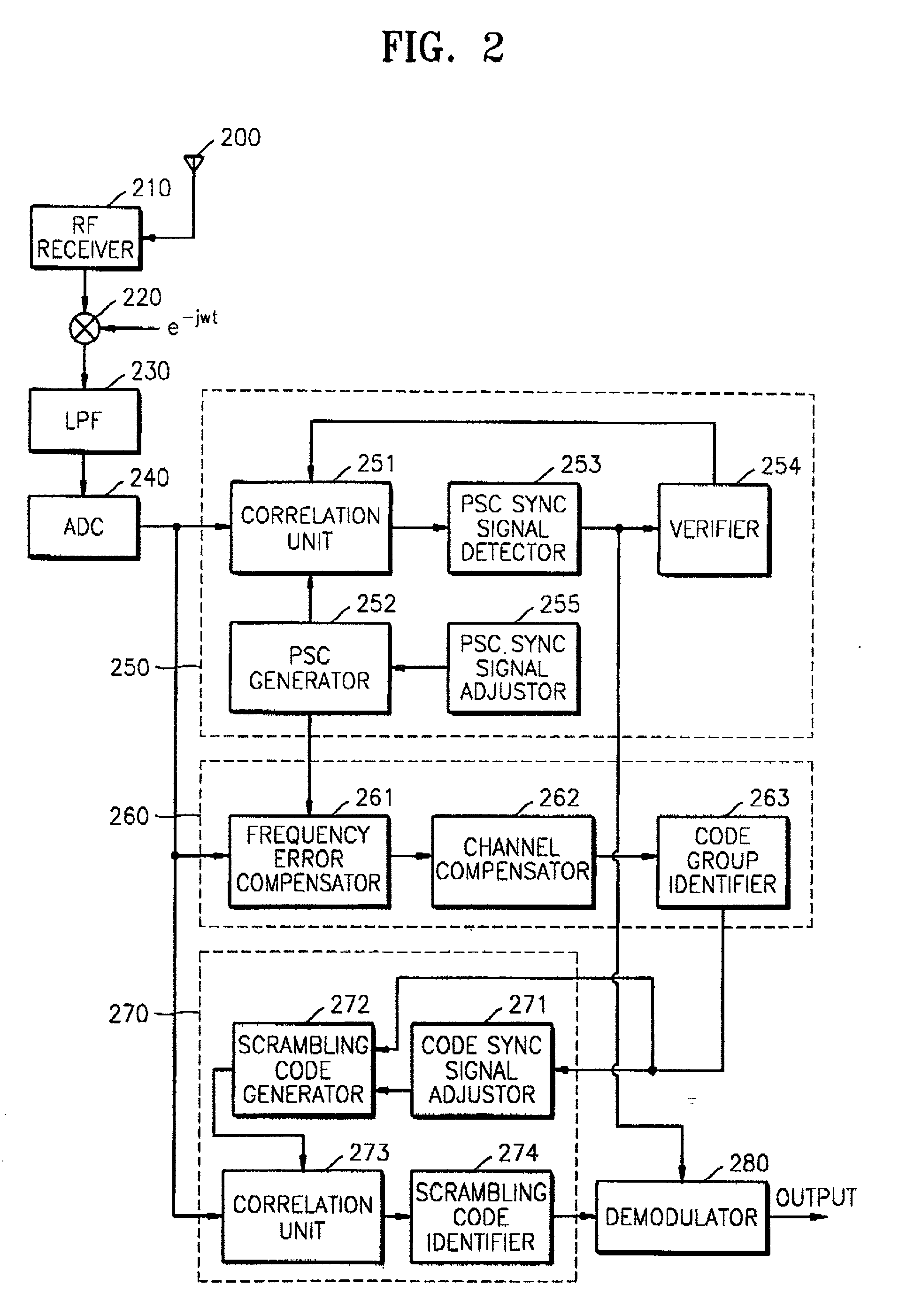
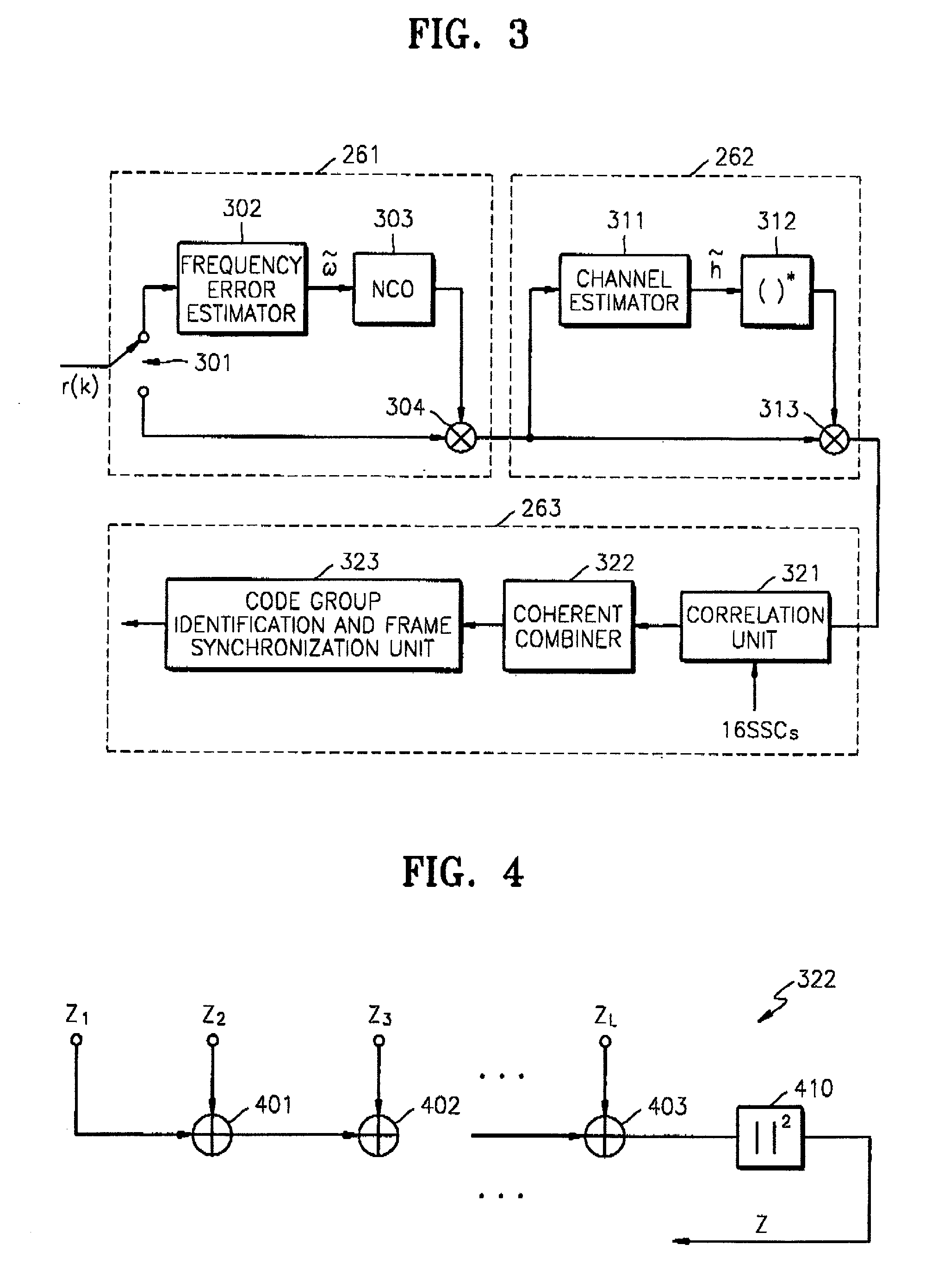
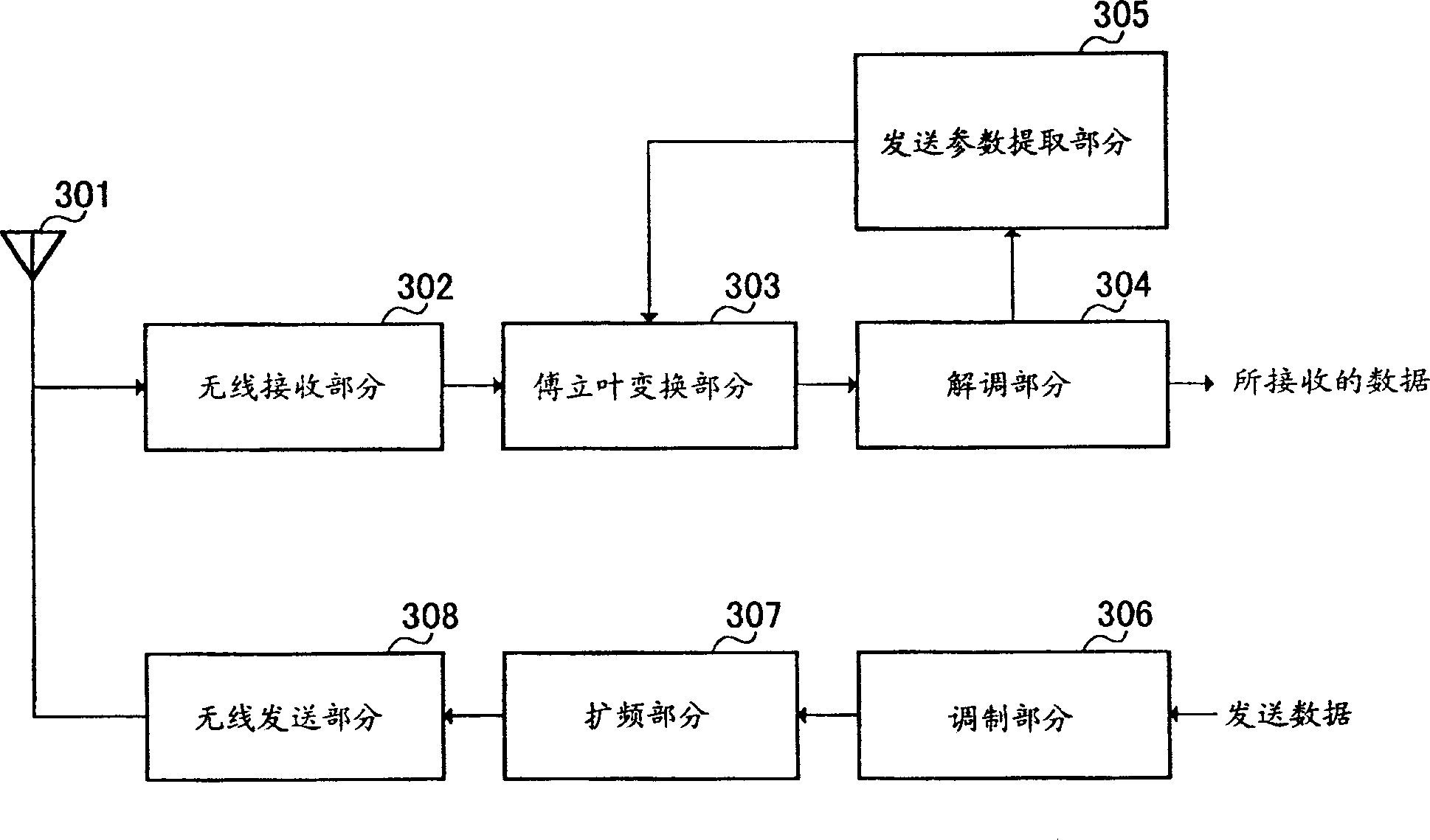
Apparatus for searching for a cell and method of acquiring code unique to each cell in an asynchronous wideband DS/CDMA receiver
InactiveUS6888880B2Assess restrictionRadio transmission for post communicationCdma signalParallel computing
An apparatus for searching for a cell and a method of acquiring a code unique to each cell in an asynchronous wideband Direct-Sequence Code Division Multiple Access (DS / CDMA) receiver, wherein the cell searching apparatus searches for a cell based on a received asynchronous wideband DS / CDMA signal in a receiver, the apparatus including a code group identifying unit for estimating and compensating for a frequency error between the synchronous channel and an internally generated primary synchronization code, estimating and compensating for channel degradation which the synchronous channel has experienced, and performing correlation on the compensated synchronous channel and available secondary synchronization codes, thereby identifying the code group; and a scrambling code identifying unit for performing correlation on a plurality of scrambling codes belonging to the code group, thereby obtaining a scrambling code unique to each cell.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Quick parallel radio frequency test system and test method for mobile terminals
InactiveCN1805313AReduce the number of measuring pointsIncrease profitTransmitters monitoringReceivers monitoringFrequency spectrumSpectrum analyzer
The invention relates to a mobile terminal parallel radio frequency testing device, which comprises a CDMA signal resource, a frequency spectrum analyzer and a switch matrix connected to the CDMA signal resource and the frequency spectrum analyzer; a testing control unit via the GPIB connecting the CDMA signal resource, the frequency spectrum analyzer, and the switch matrix; and a communication direct current power resource connected to the CDMA signal resource, the frequency spectrum analyzer and the tested mobile terminal to supply power for them. The invention uses the dynamic power testing technique based on the single point trigger and the mobile terminal sender, to realize the parallel correction test. The invention can correct and test the radio frequency property of the sender and the receiver of CDMA mobile terminal to improve the testing speed and improve the utilization of device.
Owner:HISENSE +1
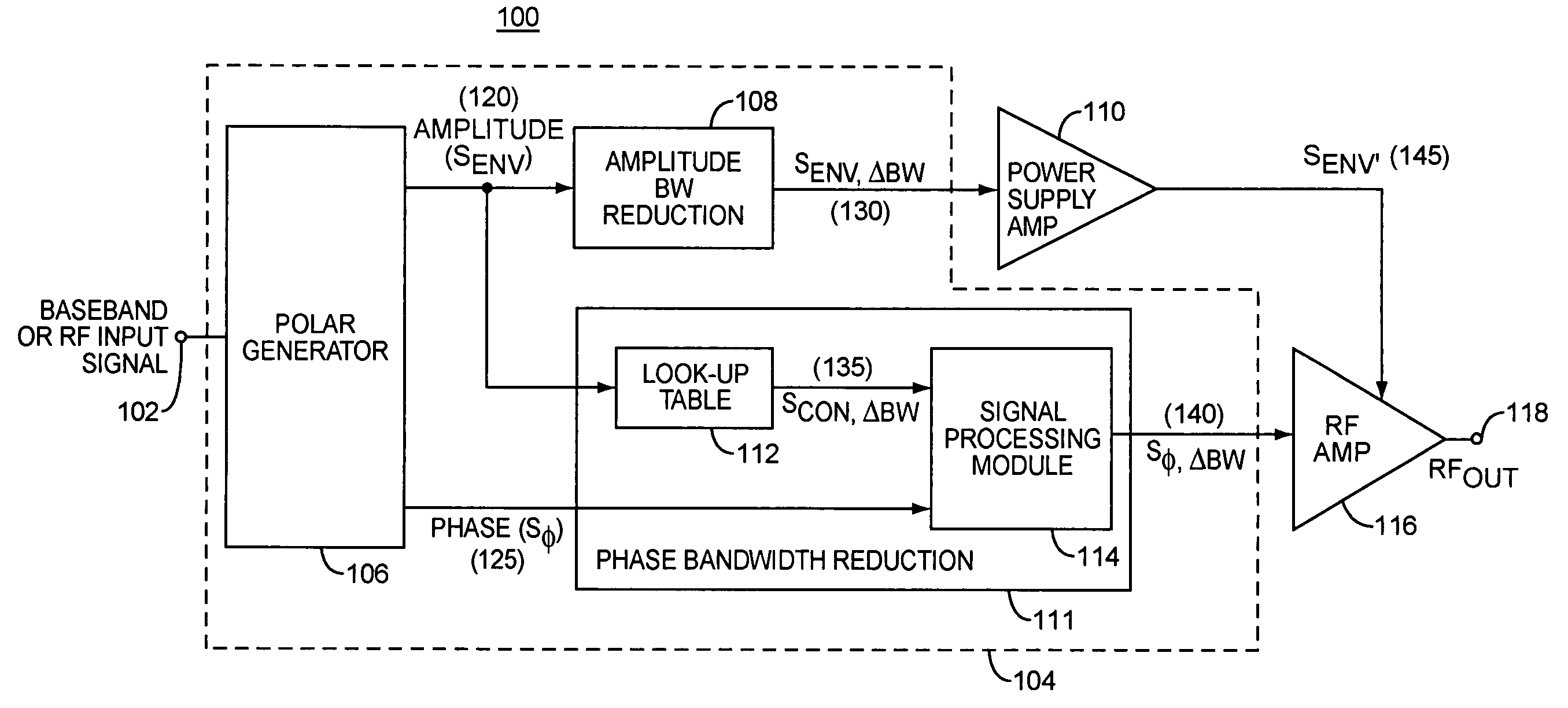
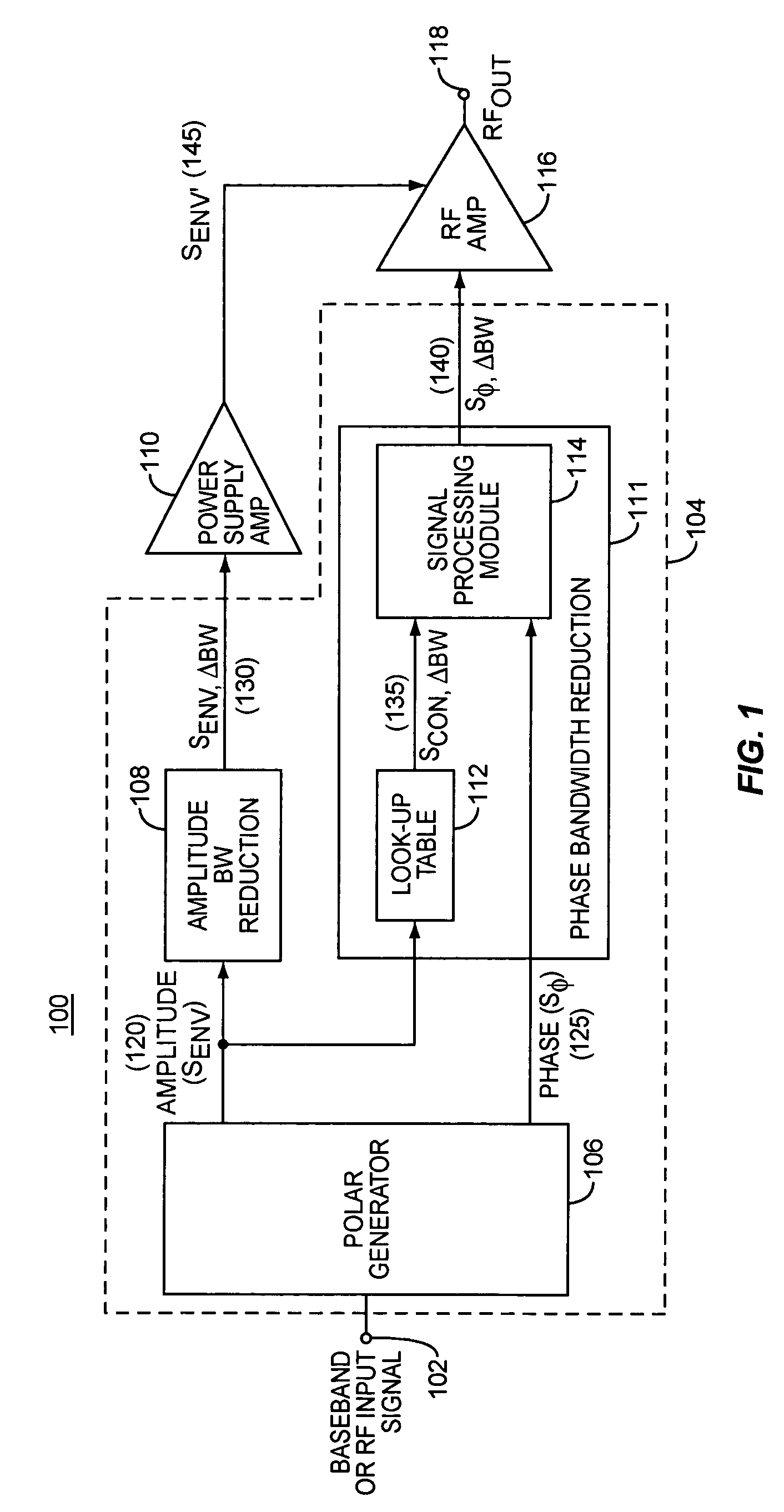
Systems and methods for amplification of a communication signal
ActiveUS7068984B2Efficient amplificationAttenuation bandwidthAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionResonant long antennasPhase bandwidthLinear relationship
Bandwidth reduction of amplitude and / or phase components of relatively wide bandwidth composite signal. In an exemplary embodiment, an EER amplifier system for CDMA signal amplification includes an amplitude bandwidth reduction module included in an amplitude signal component path and a phase bandwidth reduction module is included in a phase signal component path, for controlling an RF amplifier. The phase bandwidth reduction module may reduce the phase component bandwidth of the input signal by, for example, generating a non-linear relationship between phase signal amplitude and input signal amplitude. The amplitude bandwidth reduction module may reduce the amplitude component bandwidth of the input signal by, for example, generating a non-linear relationship between the supply voltage to the RF amplifier and an input signal amplitude.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
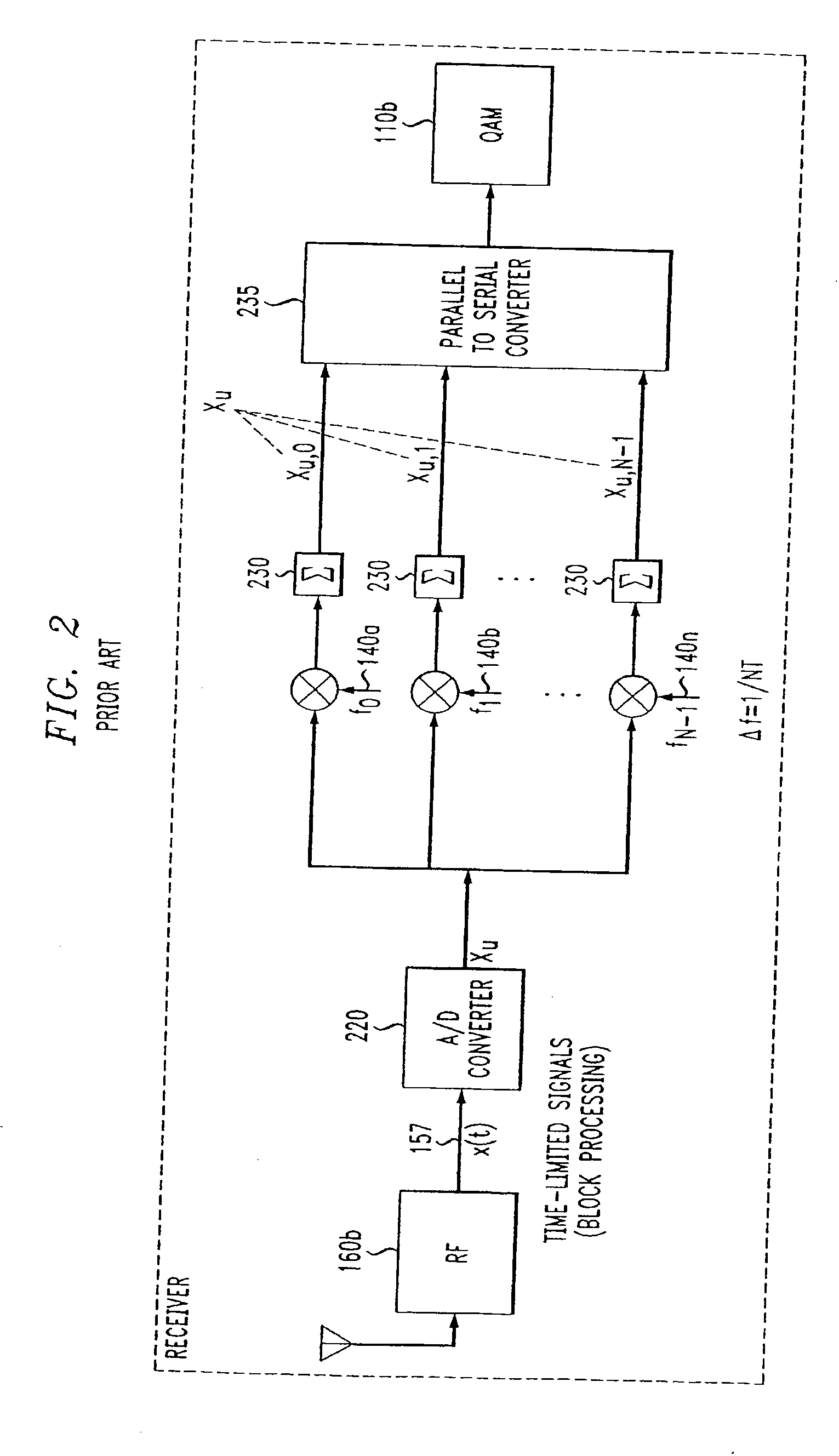
OFDM, CDMA, spread spectrum,TDMA, cross-correlated and filtered modulation
InactiveUS20050175116A1Improve efficiencyImprove performancePolarisation/directional diversityTransmission path divisionTime division multiple accessCdma signal
Modulators for switched or switched and combined Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexed (OFDM), Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA), Spread Spectrum, Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA), cross-correlated and filtered systems. A first modulation circuit for receiving input OFDM baseband signals and a second modulation circuit for receiving input in-phase and quadrature-phase cross-correlated baseband signals, TDMA signals, spread spectrum signals, CDMA signals or other filtered signals. One of the switched or combined modulated Radio Frequency (RF) signals and the other switched or combined modulated RF signals are provided to one or more selected transmitters.
Owner:WI LAN INC
Signal-to-noise ratio estimation of CDMA signals
ActiveUS7313167B2Cancel improvementMinimize timePower managementEnergy efficient ICTSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Deterministic noise
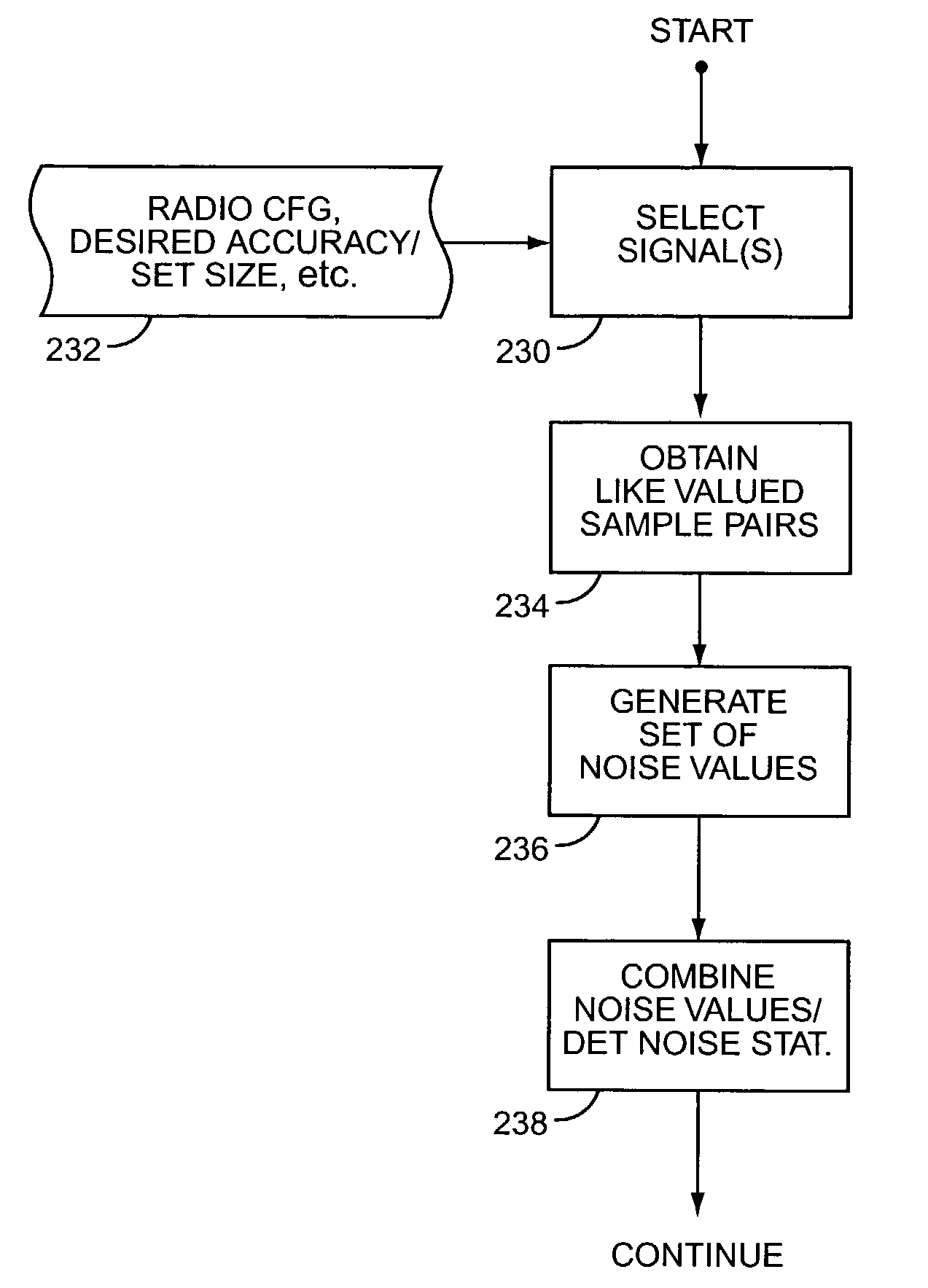
An improved approach to noise estimation permits, for example, tighter closed-loop power control in a wireless communication network with attendant improvements in transmit power efficiency and network capacity. In an exemplary embodiment, the received signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of a data signal is estimated based on noise samples obtained from one or more other signals received in association with the data signal. In general, these associated signals are characterized by the receiver's ability to extract like valued samples from them, such that pairs of these like valued signal samples may be subtracted, thereby canceling their deterministic signal components and leaving only difference values representative of the non-deterministic noise components of the signal samples. Obtaining difference values from more than one associated signal increases the sample size of difference values used in noise estimation, thereby improving the statistical basis for noise estimation and, therefore, the accuracy of SNR estimation.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
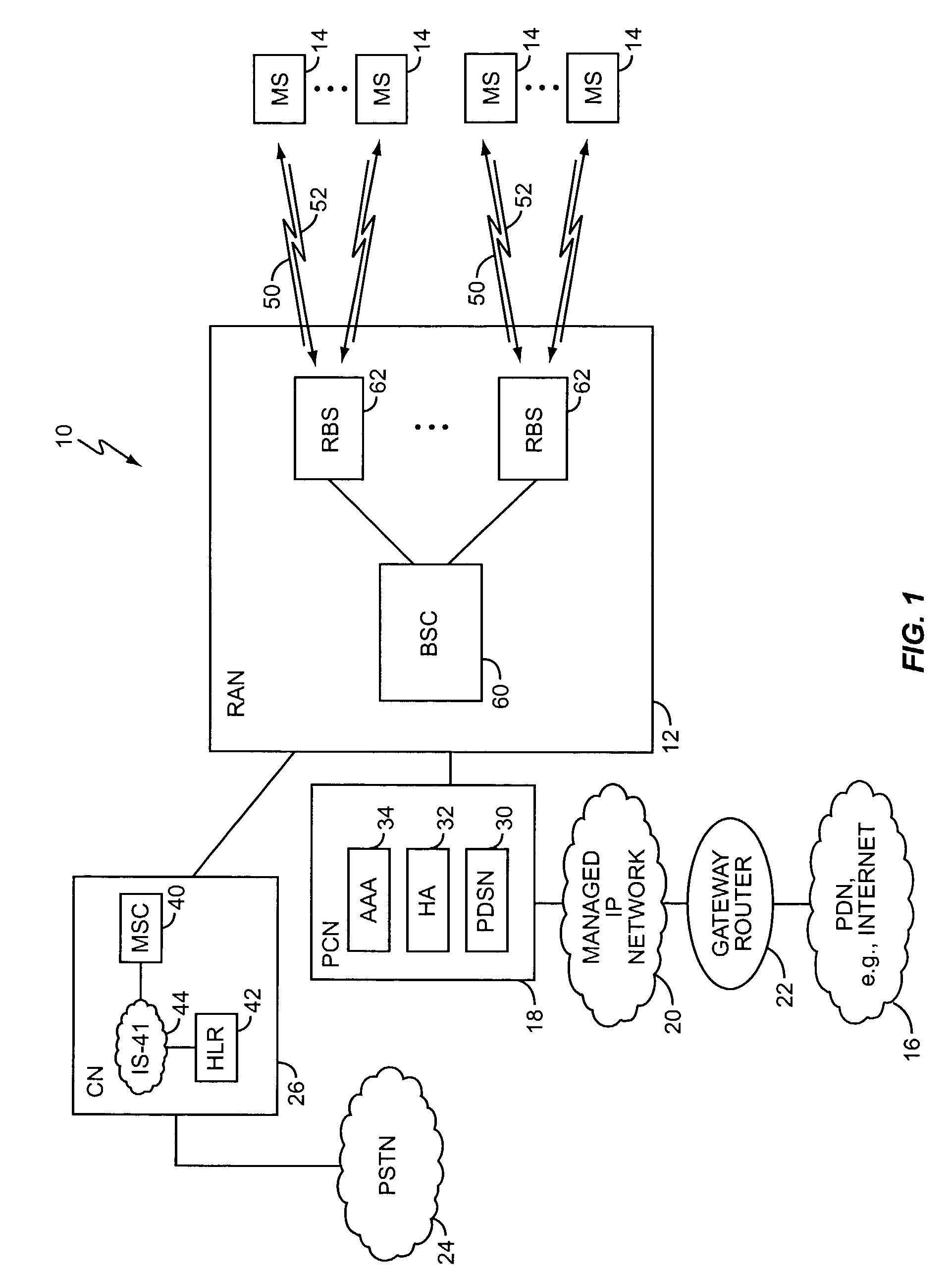
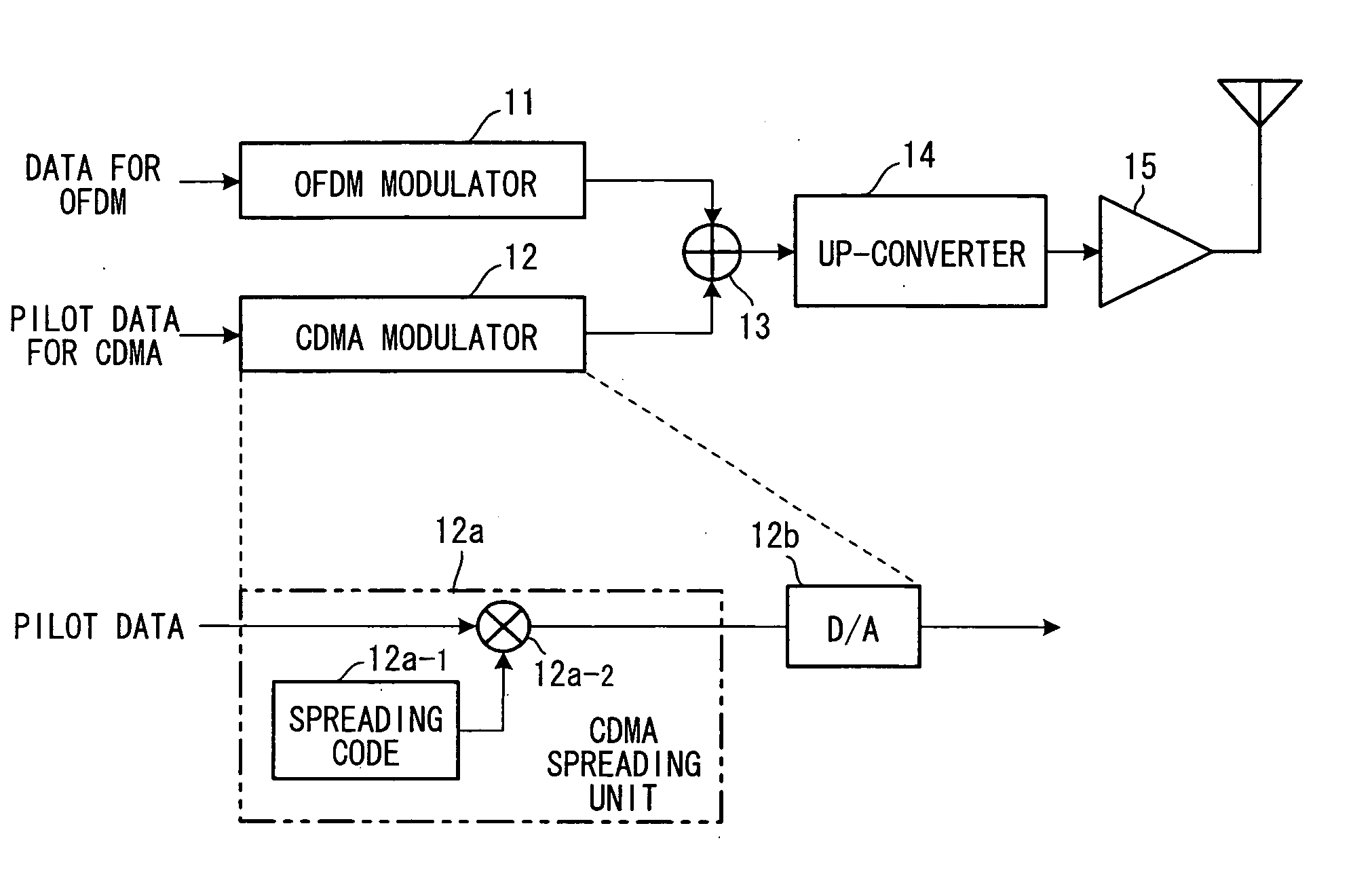
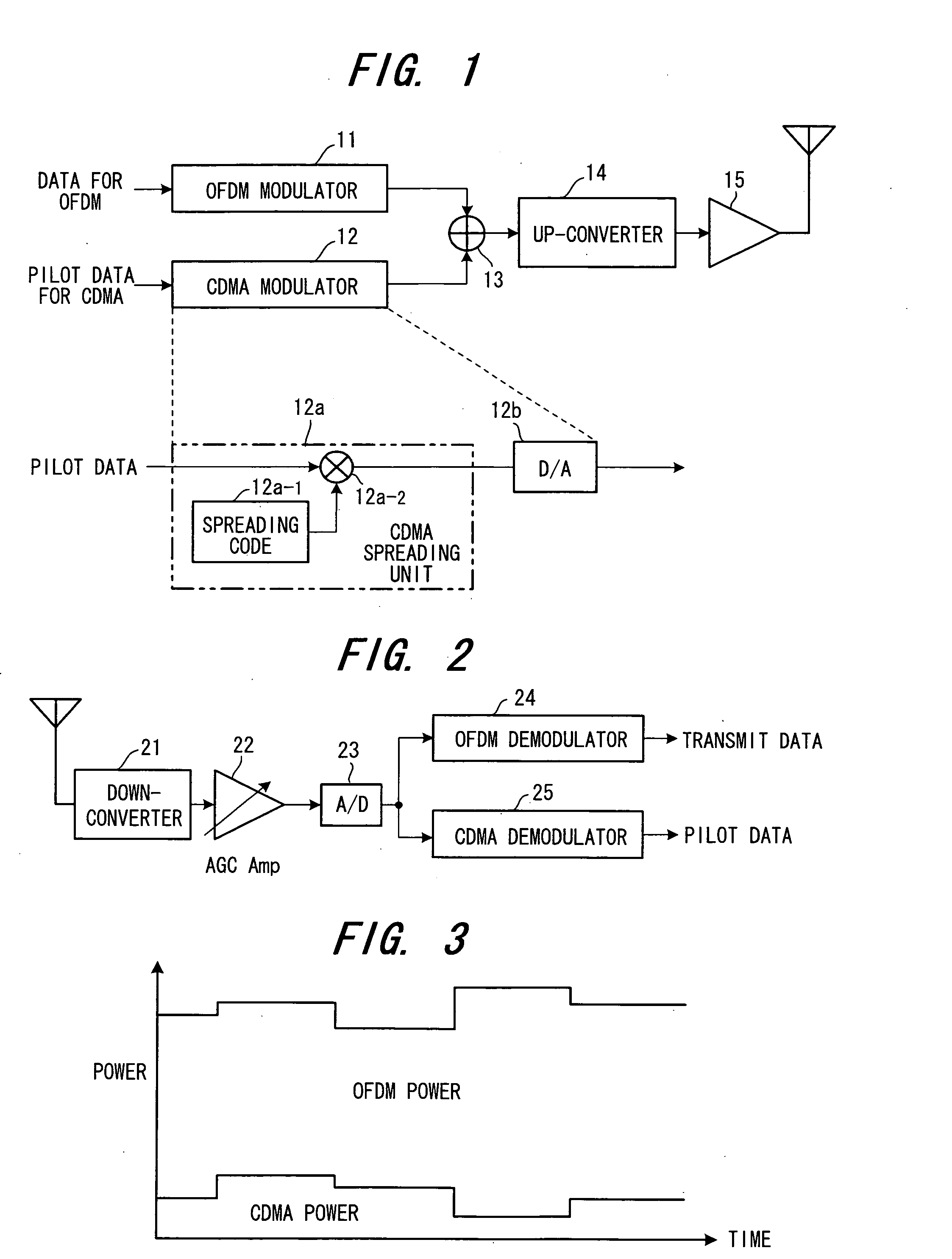
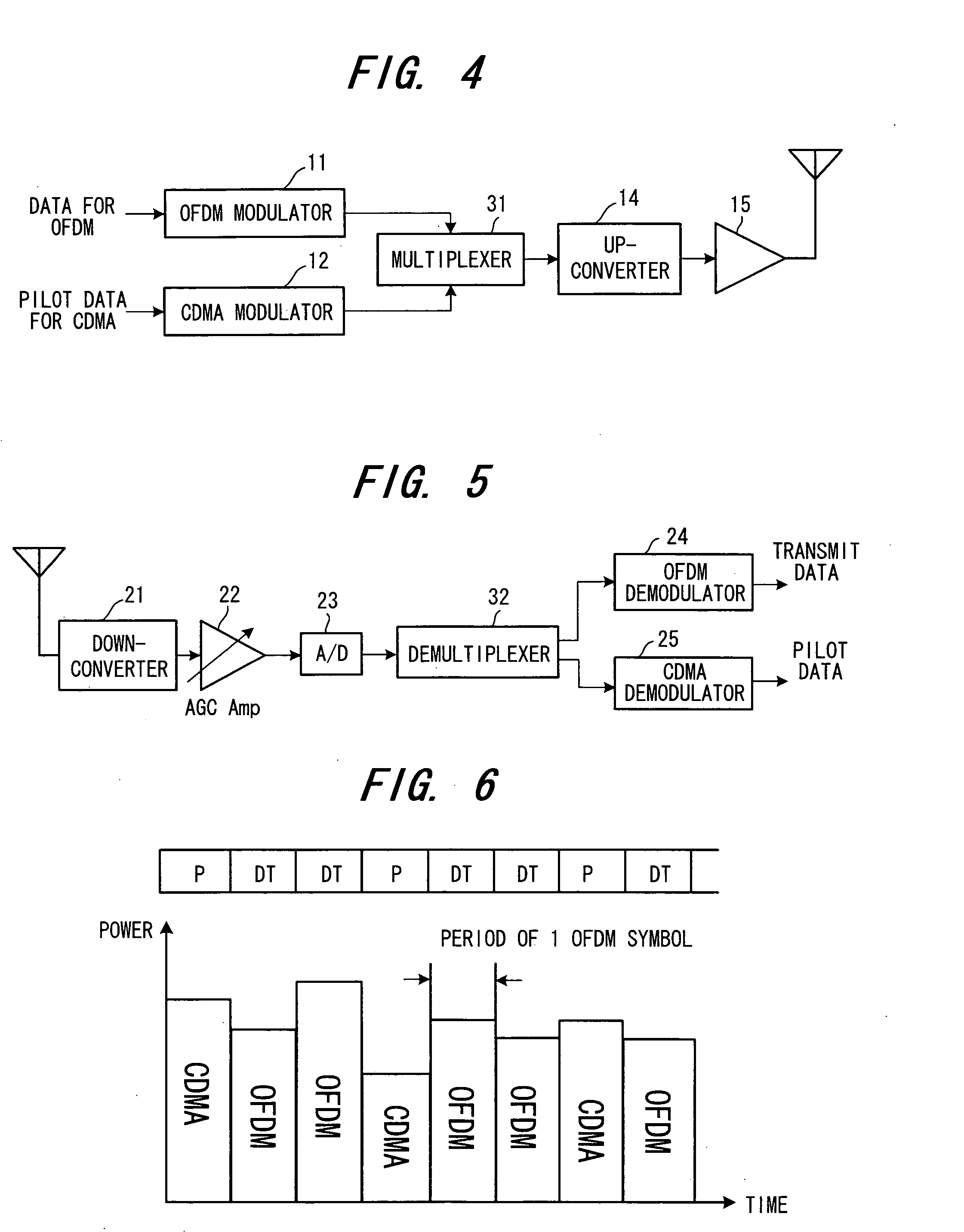
Pilot multiplexing method and OFDM transceiver apparatus in OFDM system
InactiveUS20060114815A1Remove inter-symbol interferenceImprove receiver sensitivityRadio transmissionChannel estimationMultiplexingCdma signal
Disclosed is a pilot multiplexing method in an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) system. Transmit data is transmitted by an OFDM signal through an OFDM scheme, pilot data is directly spread, and a spread-spectrum signal, which has been obtained by spreading, is transmitted in the same frequency band as that of the OFDM signal at the same time in superposition therewith or time-division multiplexed therewith. The spread-spectrum signal is a CDMA signal that has been obtained by spreading the pilot data by a prescribed spreading code.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Apparatus for searching for a cell and method of acquiring code unique to each cell in an asynchronous wideband DS/CDMA receiver
An apparatus for searching for a cell and a method of acquiring a code unique to each cell in an asynchronous wideband Direct-Sequence Code Division Multiple Access (DS / CDMA) receiver, wherein the cell searching apparatus searches for a cell based on a received asynchronous wideband DS / CDMA signal in a receiver, the apparatus including a code group identifying unit for estimating and compensating for a frequency error between the synchronous channel and an internally generated primary synchronization code, estimating and compensating for channel degradation which the synchronous channel has experienced, and performing correlation on the compensated synchronous channel and available secondary synchronization codes, thereby identifying the code group; and a scrambling code identifying unit for performing correlation on a plurality of scrambling codes belonging to the code group, thereby obtaining a scrambling code unique to each cell.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
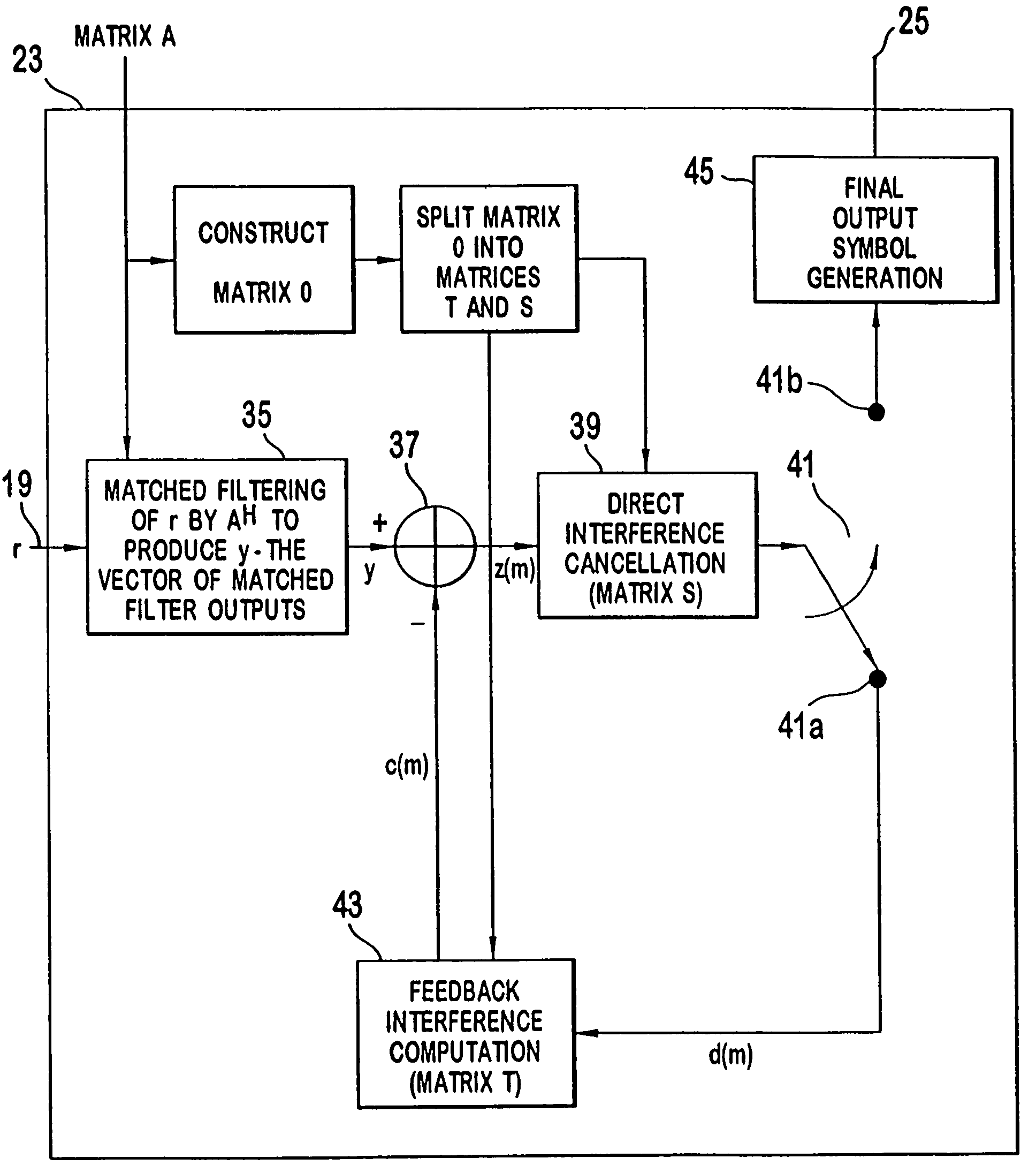
Parallel interference cancellation receiver for multiuser detection CDMA signals
InactiveUS7292623B2Improve accuracyLess required computationTransmission control/equlisationTransmission control/equalisingMultiuser detectionInterference cancelation
A plurality of communications is received. The communications are transmitted in a wireless code division multiple access format. A channel response for each received communication is estimated. A system response matrix is constructed using codes and the channel responses of the received communications. An objective matrix is produced using the system response matrix. The received communications are matched filtered to produce a first input. The first input is processed with an interference cancellation matrix to produce a first set of symbols of the received communications. The first set of produced symbols are processed with a feedback interference construction matrix to produce feedback interference. The feedback matrix added to an inverse of the interference cancellation matrix equals the objective matrix. The feedback interference is subtracted from a result of the match filtering to produce a next input. The next input is processed with the interference cancellation matrix to produce a next set symbols of the received communications.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
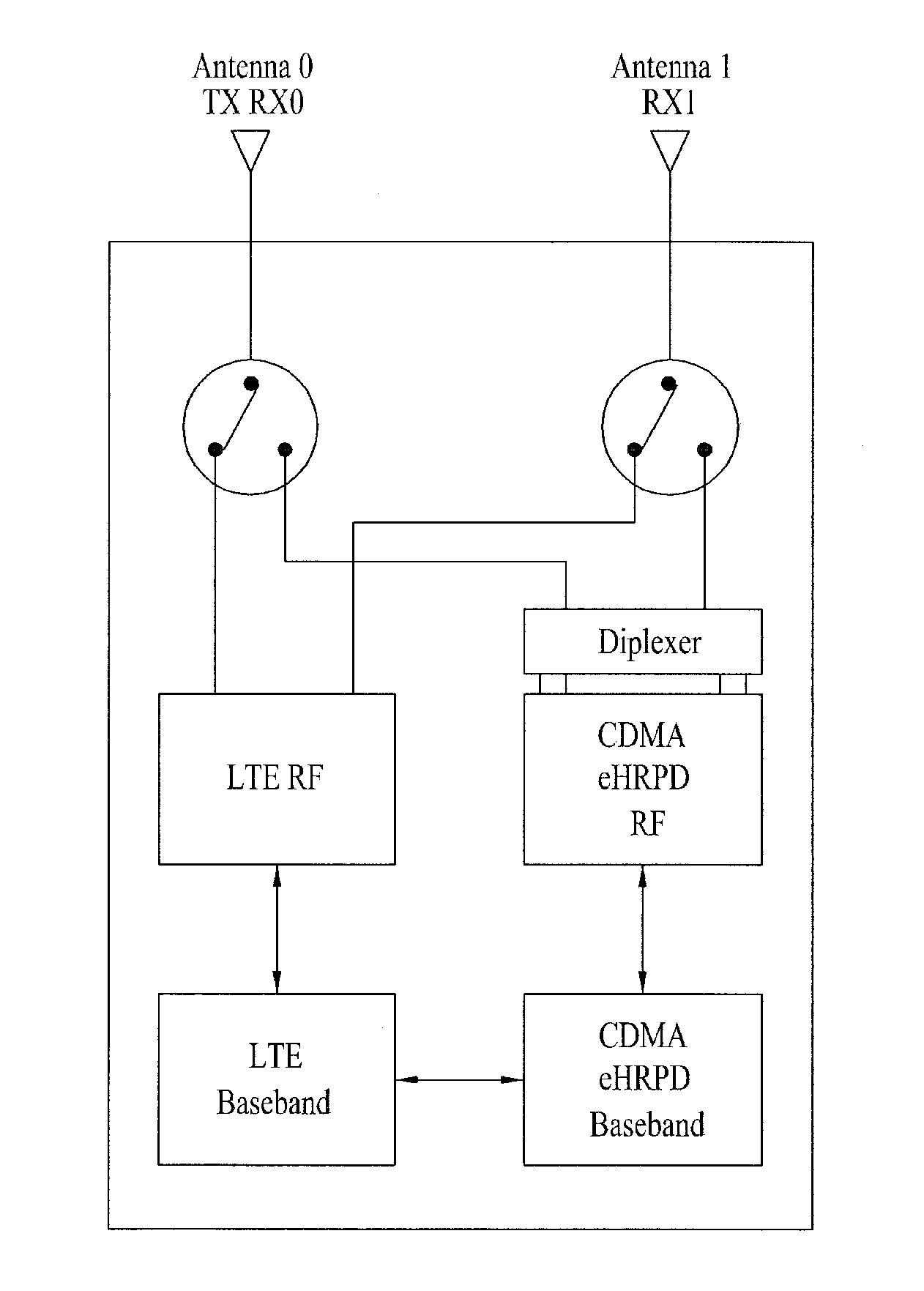
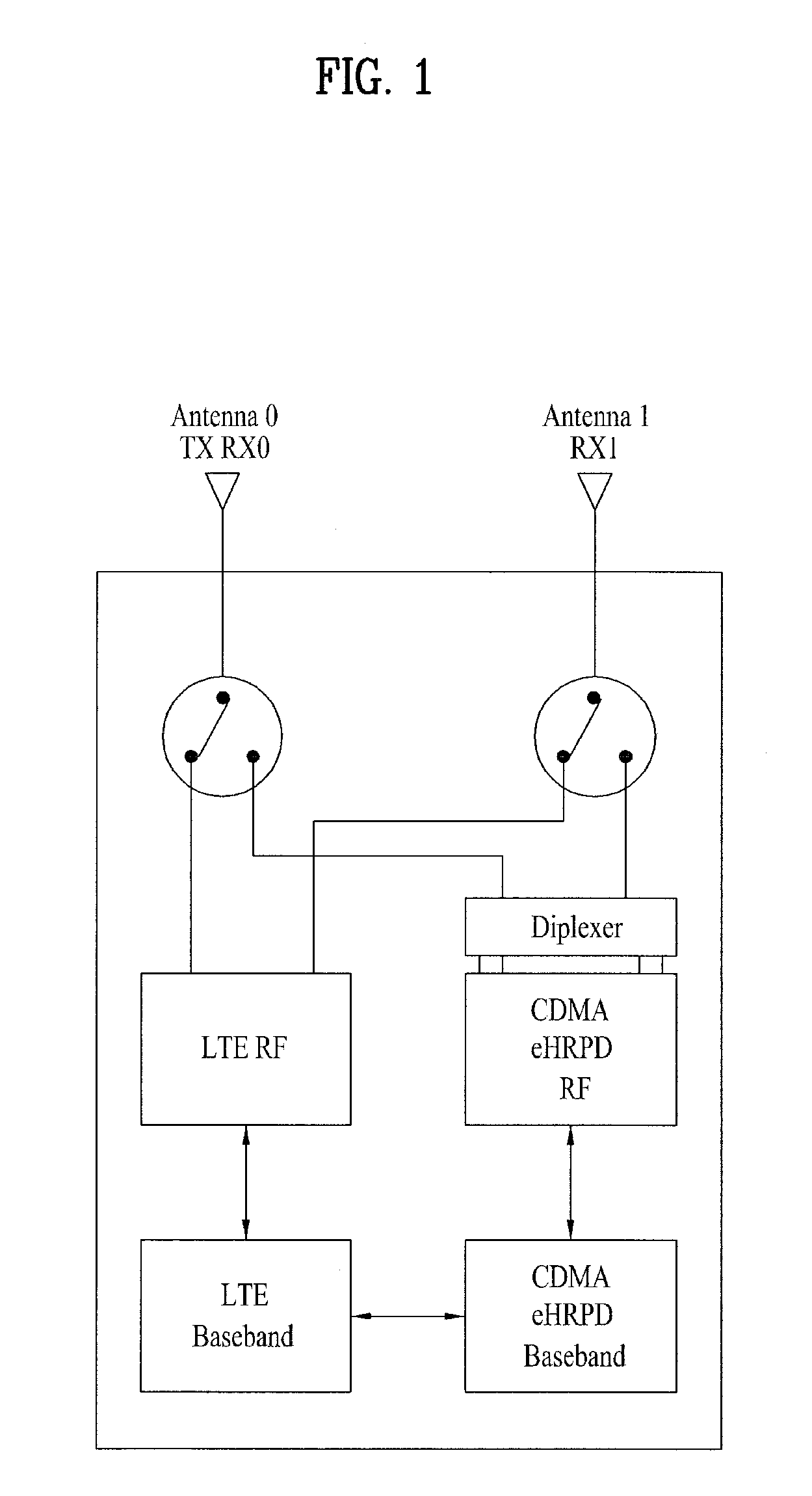
Dual mode mobile terminal in MIMO wireless communication system and controlling method thereof
ActiveUS20100296419A1Improve performanceSite diversityTransmission path multiple useCommunications systemDual mode
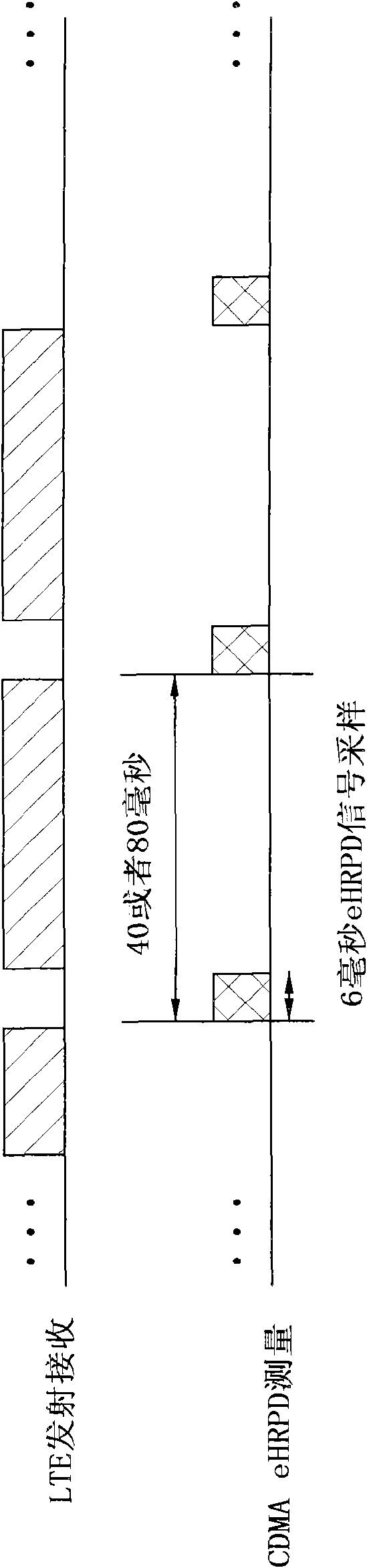
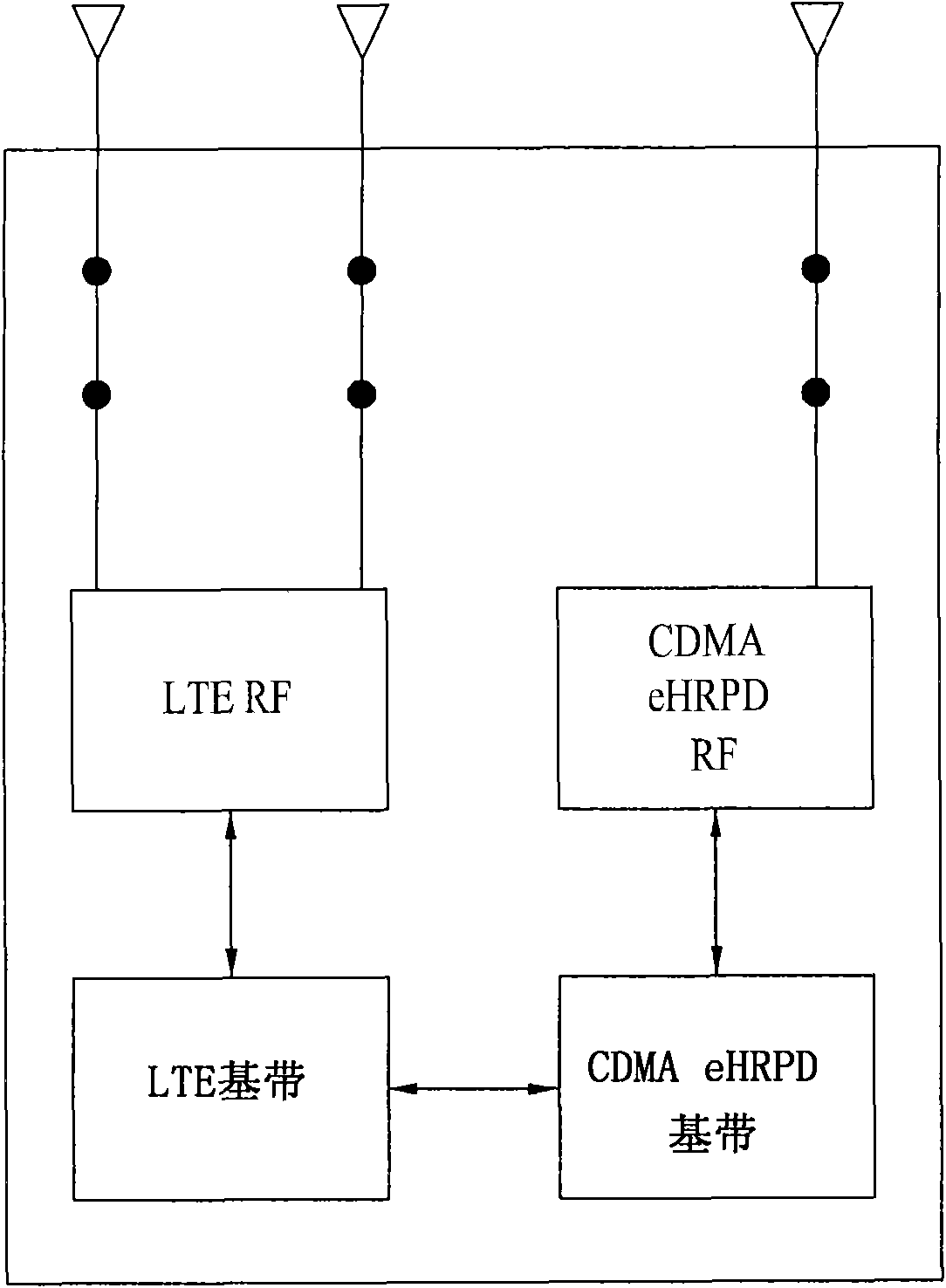
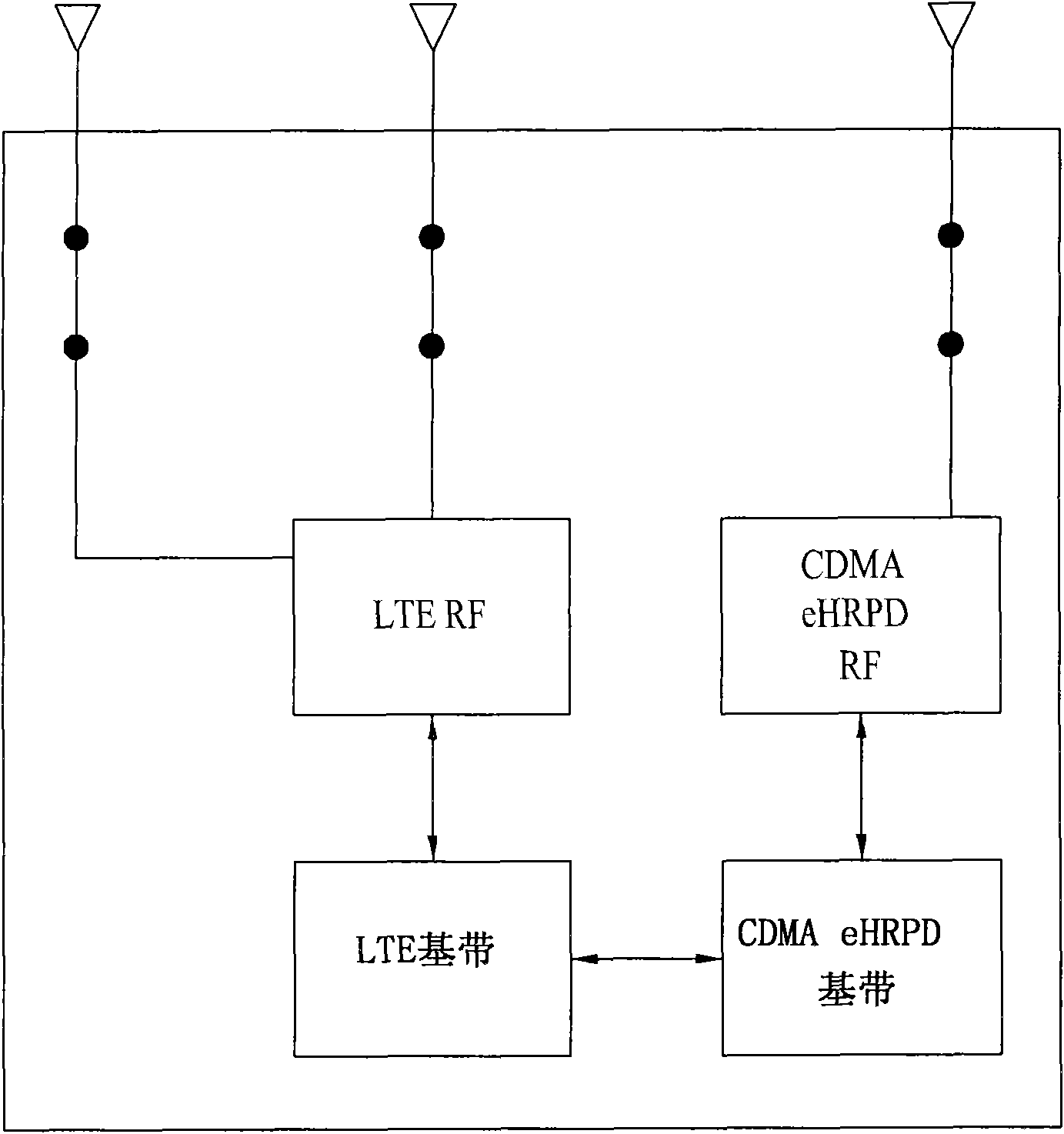
A dual mode terminal and controlling method thereof are disclosed. The present invention includes a first antenna and a second antenna. In particular, a signal received via the second antenna includes a signal generated from multiplexing an LTE downlink signal, a CDMA DCN (data core network) downlink signal and a CDMA PCS (personal communication services) downlink signal. And, the present invention is characterized in including a triplexer for demultiplexing of the downlink signals. Accordingly, a dual mode terminal of the present invention is able to receive an LTE signal without a data rate fall in the course of measuring a quality of a CDMA signal.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
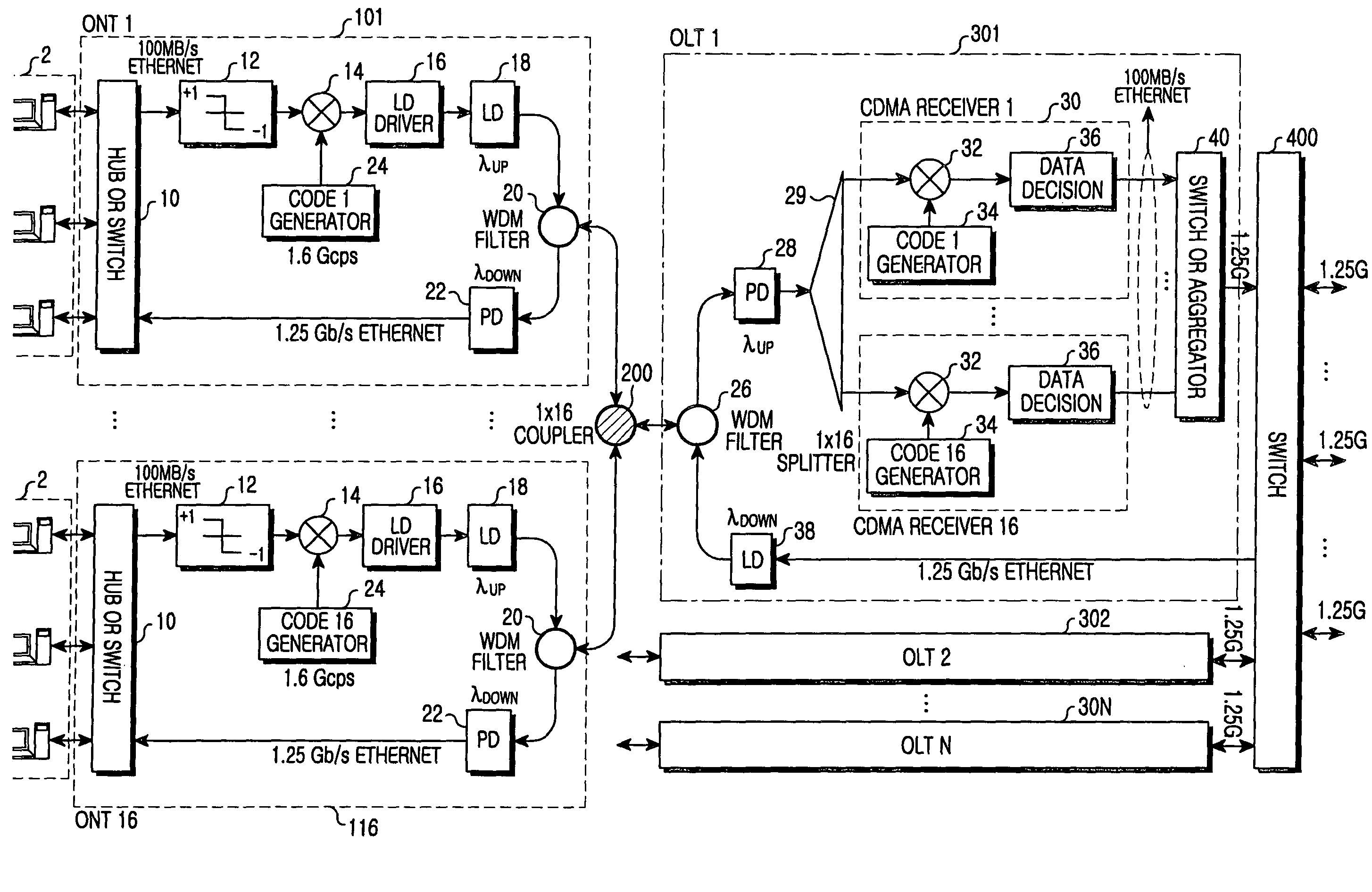
Passive optical network employing code division multiple access
InactiveUS7330656B2Increase speedAvoid small quantitiesMultiplex system selection arrangementsPolarisation multiplex systemsThree levelTransmission protocol
A PON and a method of transmitting data employing different upstream and downstream transmission protocols are disclosed. The PON includes: a plurality of ONTs; WDM filters; an OLT receiving and transmitting optical signals to and from the ONTs and a higher network; and an optical coupler. The ONT includes a first switching unit, a level transformer converting two level Ethernet signals into a three level data signals, a first code generator generating a specific CDMA codes that distinguish the ONT from another ONT, and a first multiplier performing a spread spectrum function with the CDMA codes. The OLT includes an optical receiver, a branching filter branching the upstream CDMA signals, a plurality of second code generators generating codes for despread, a plurality of second multipliers multiplying the received signals by the despread codes, and a plurality of data decider extracting data through correlation calculation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
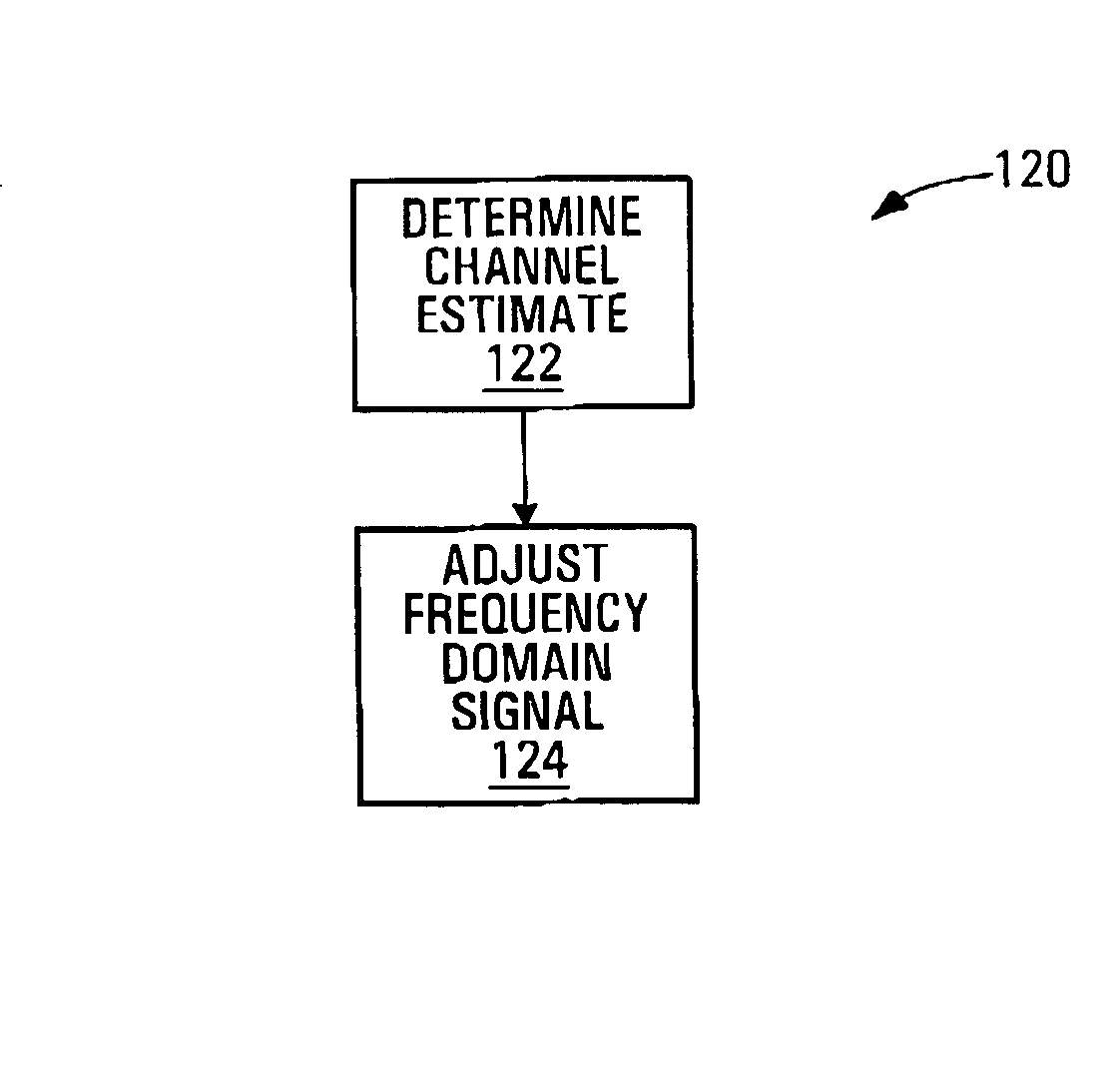
Communication signal equalization systems and methods
InactiveUS20050041574A1Loss of performanceReduce complexityFrequency-division multiplexSecret communicationMultipath channelsCdma signal
Communication signal equalization methods and systems are disclosed. A CDMA signal having a data portion and a known portion including a known or repeated data sequence and received over a multipath communication channel represents a linear convolution between the multipath channel and a transmitted CDMA signal. A channel estimate of the communication channel is determined from the known portion, and the CDMA signal is translated into a new CDMA signal which is a cyclic convolution with the channel estimate. A frequency domain representation of the new CDMA signal is adjusted using the channel estimate to produce a frequency domain representation of an equalized signal.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
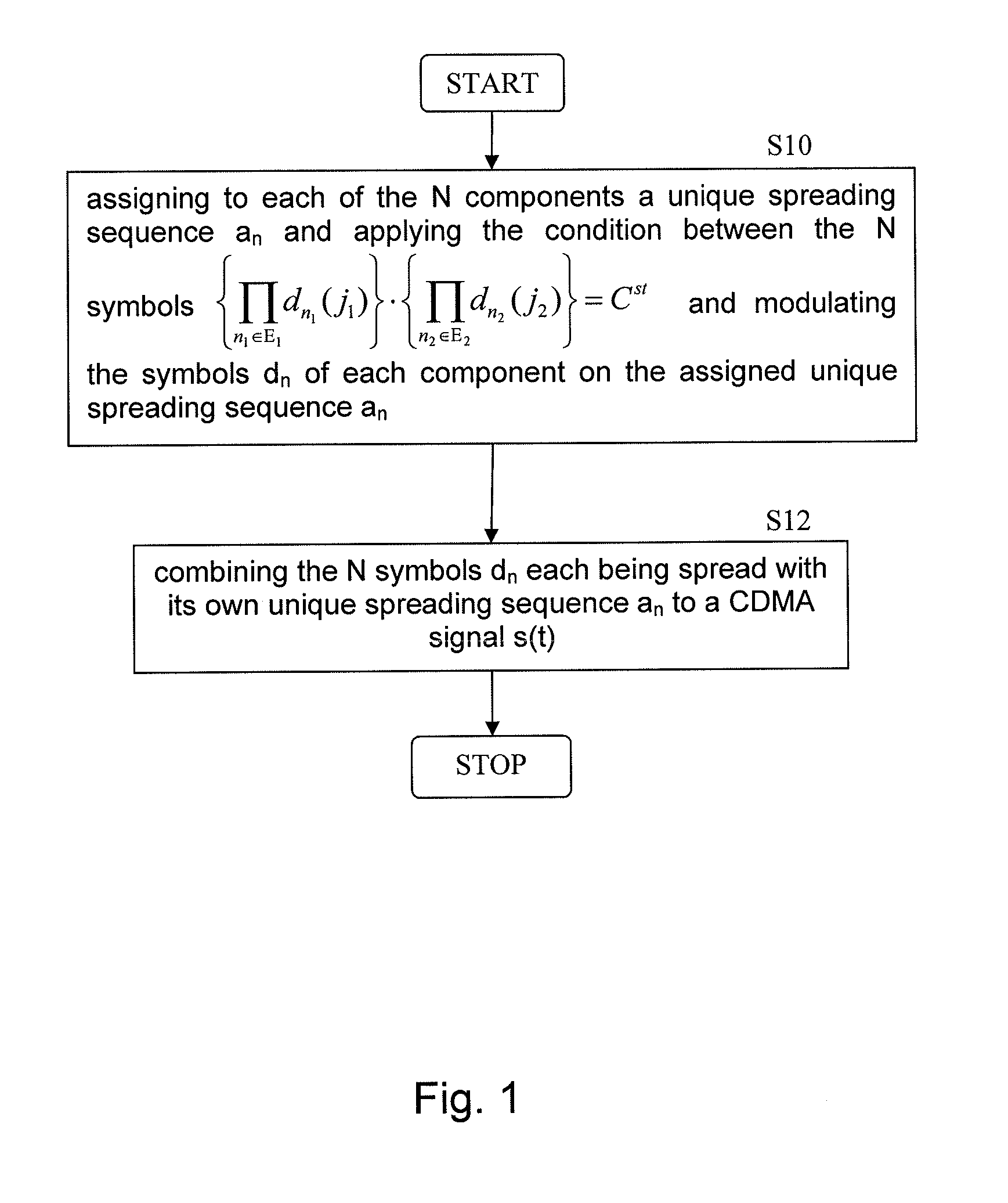
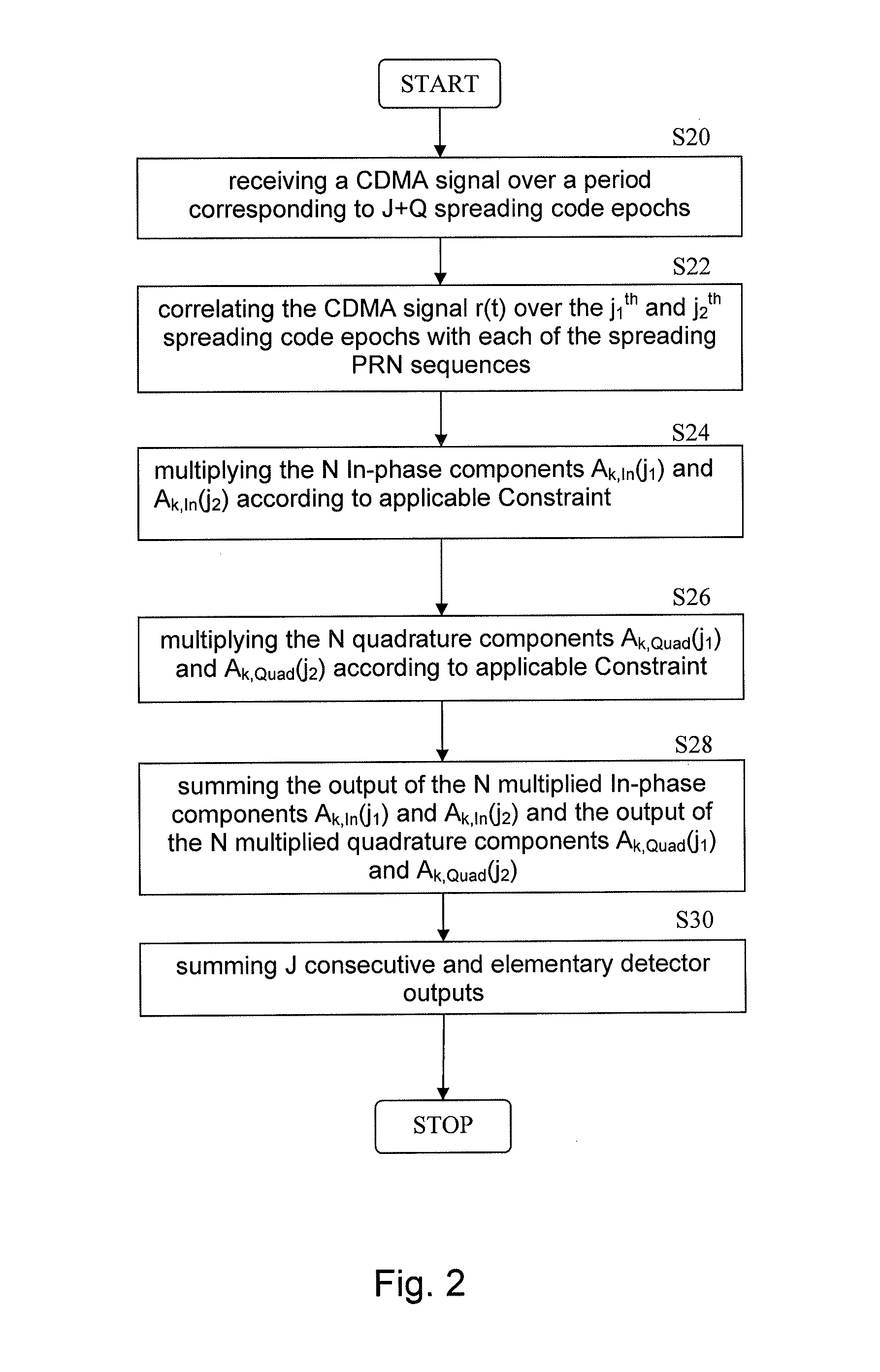
Generating and Processing of CDMA Signals
ActiveUS20140056332A1Improve performanceReduce the impactSatellite radio beaconingMultiplex code allocationCdma signalComputer science
Systems and methods for generating a CDMA signal s(t) comprising N components involves assigning to each of the N components one unique spreading sequence an selected from a set of M spreading sequences with M≧N, modulating the symbols dn of each component on the assigned unique spreading sequence an, and combining the N symbols dn each being spread with its own unique spreading sequence an to a CDMA signal s(t). The assigned spreading sequences an are selected such that all selected pairs within the set of N spreading sequences are orthogonal or very close to be orthogonal so that cross-correlation components between all spreading sequences an are close to zero or zero.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS (RES & DEV) LTD +1
Method and System for Non-Gaussian Code-Division-Multiple-Access Signal Transmission and Reception
InactiveUS20090103568A1Improve spectral efficiencyCode division multiplexForward error control useChannel dataUser input
The present invention relates to a method and system for non-Gaussian code-division-multiple-access signal transmission and reception. Input probability data indicative of a non-equiprobable channel input probability mass function are determined based on received channel data indicative of characteristics of a CDMA transmission channel. The input probability data are determined such that a transmission signal received after transmission has a non-Gaussian distribution. Upon receipt of input user data, a CDMA signal is generated by modulating the received user input data in dependence upon the input probability data and provided for transmission. After transmission a received transmission signal is first processed for determining second channel data and then for determining an estimate indicative of the user input data based on the second channel data.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
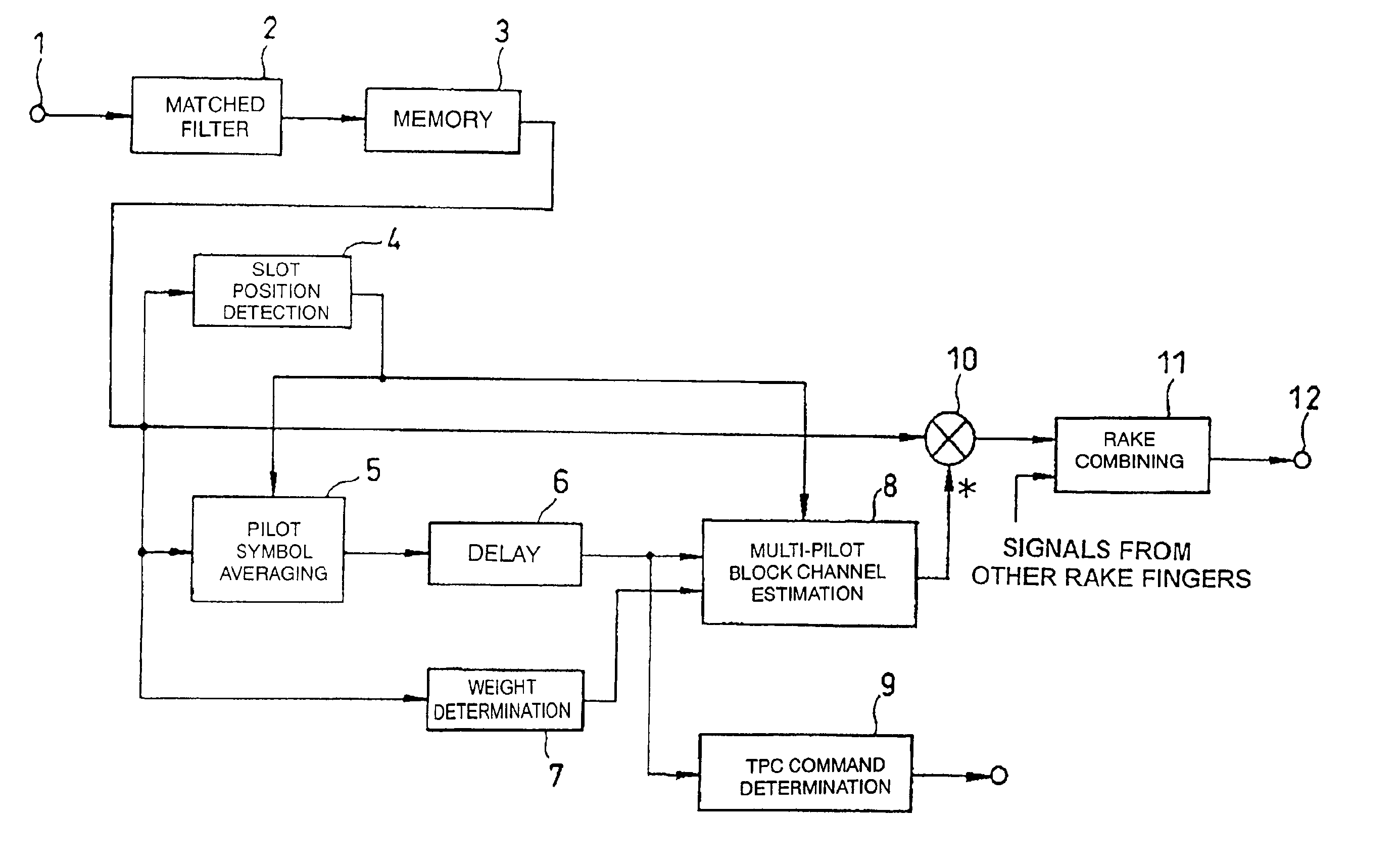
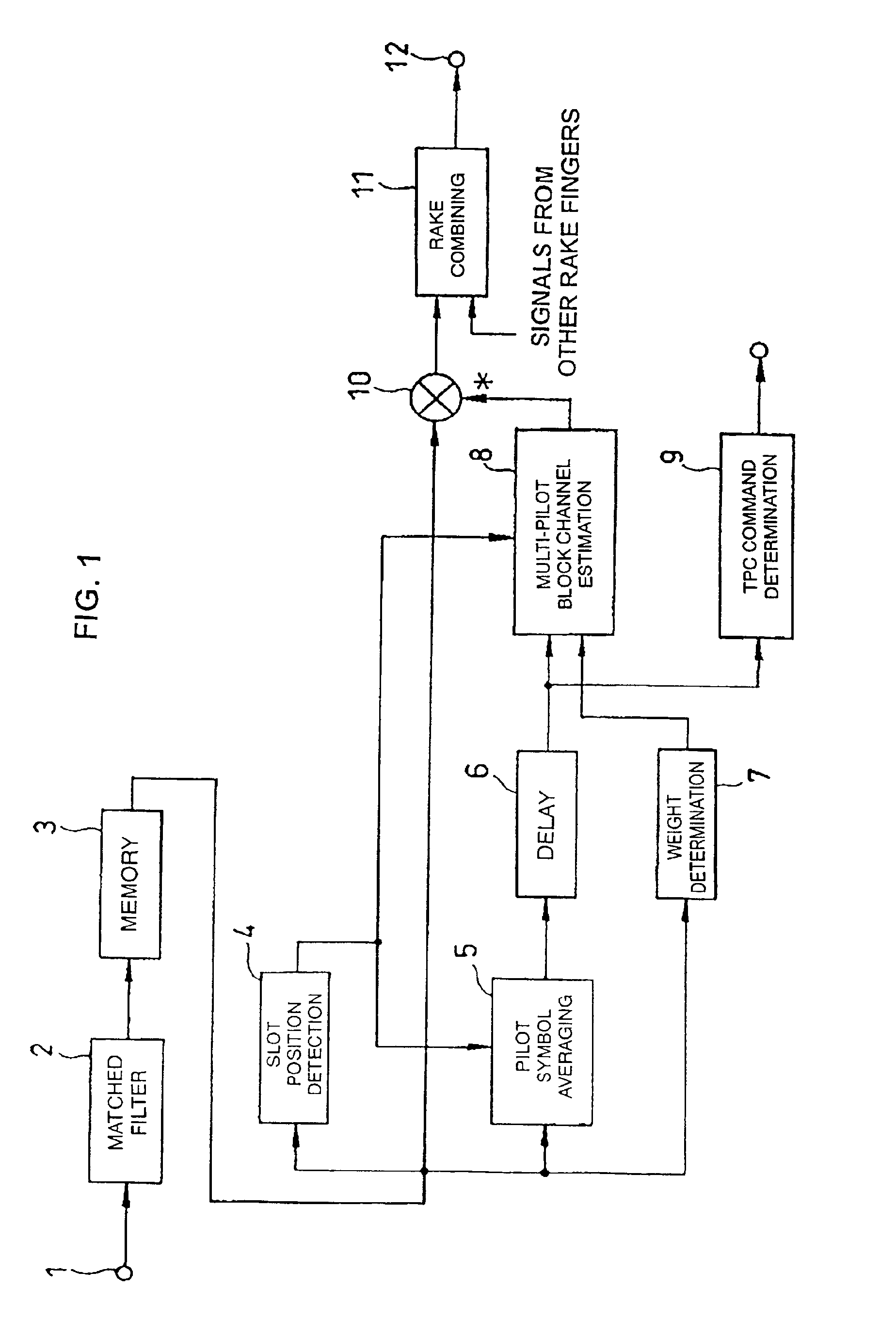
Method and apparatus for QAM demodulation in a generalized rake receiver
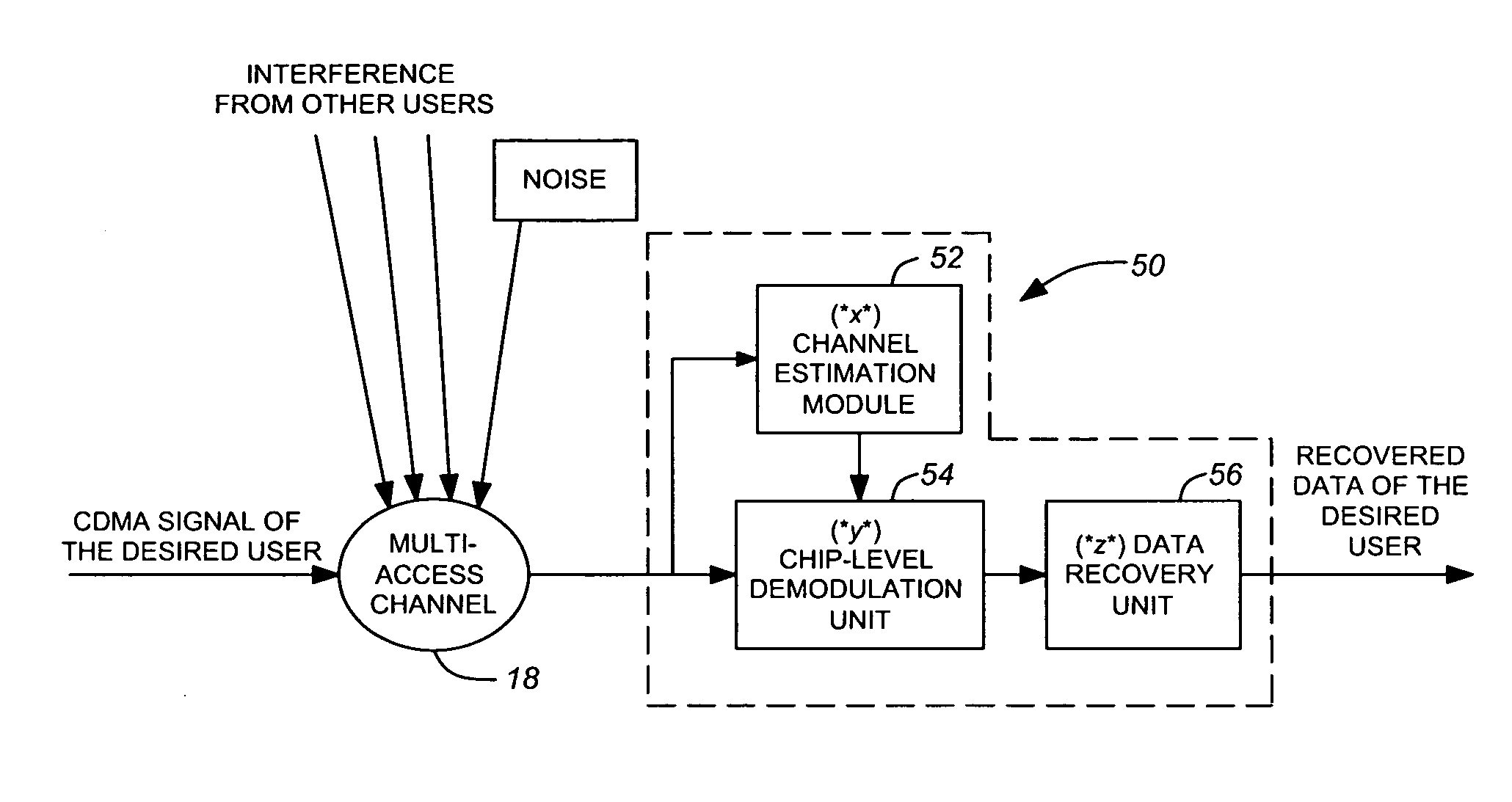
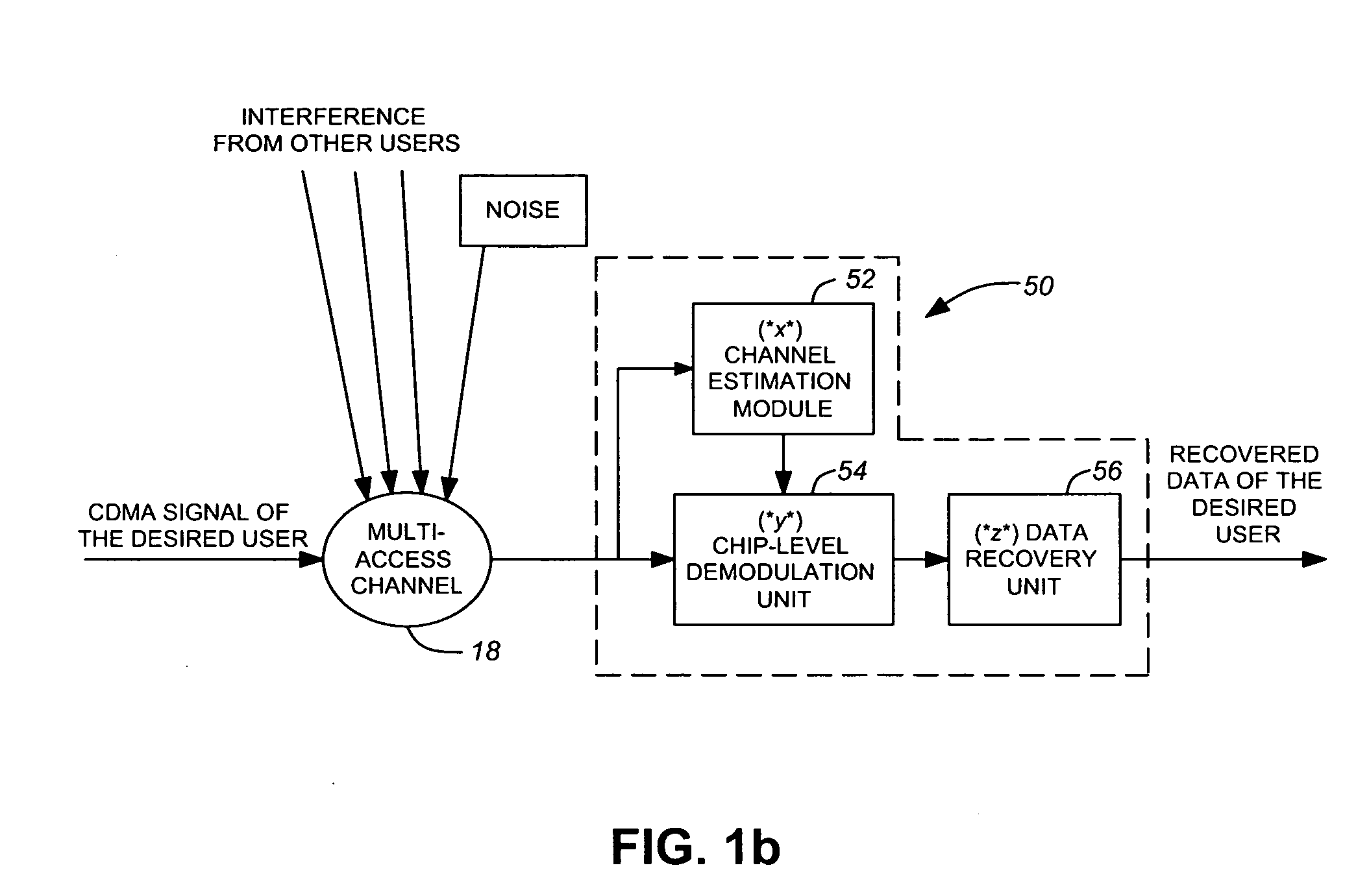
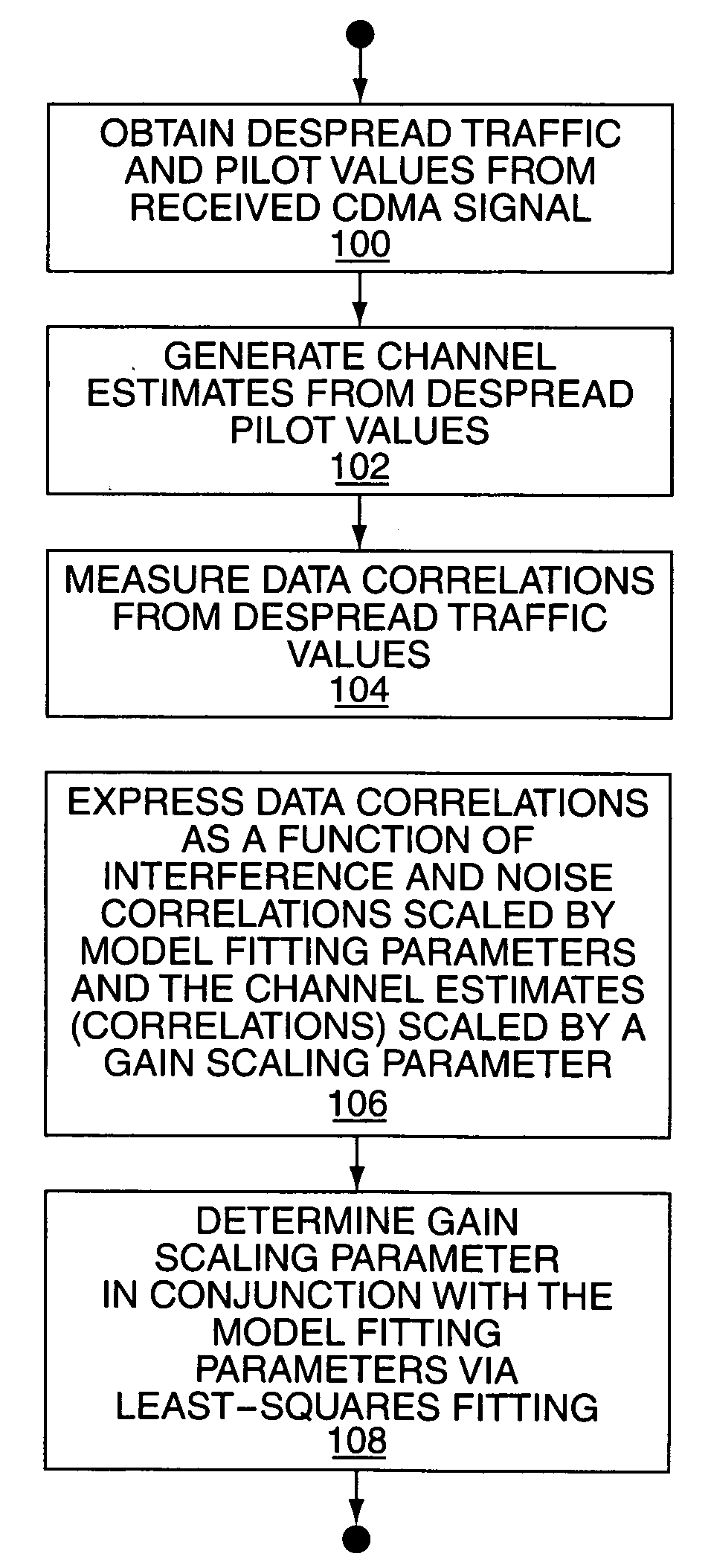
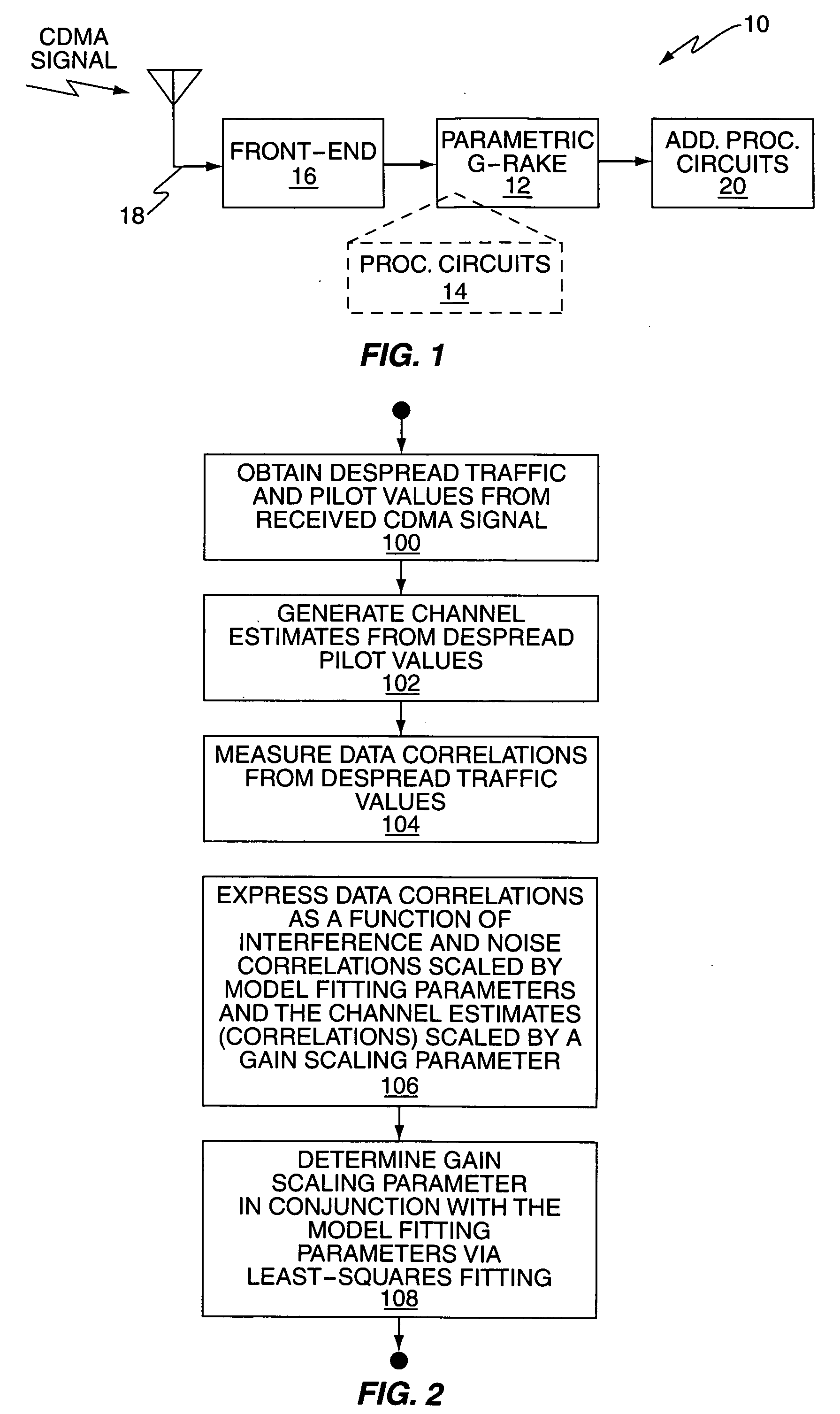
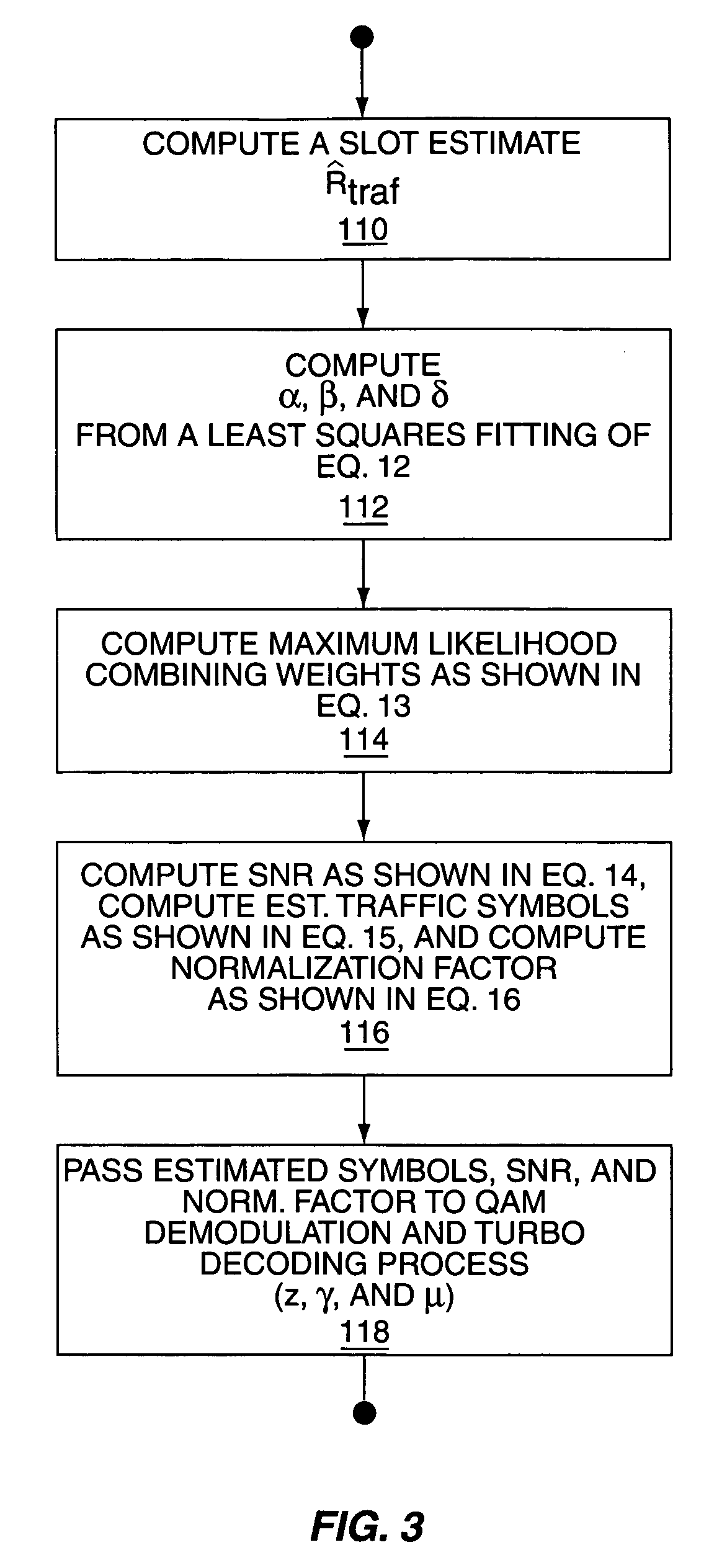
A wireless communication device includes a Generalized RAKE (G-RAKE) receiver circuit that is configured to determine a traffic-to-pilot gain scaling parameter as part of the impairment correlation determination process that underlies (G-RAKE) combining weight generation. In this manner, the receiver circuit conveniently and accurately accounts for gain differences between the pilot channel of a received CDMA signal, as used for channel estimation, and the traffic channel(s) of the CDMA signal, which carry received data to be recovered. The gain difference accounting enables proper demodulation of amplitude-modulated traffic signals. By way of non-limiting example, such gain scaling may be used for demodulating / decoding High Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) signals used in Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (W-CDMA) systems.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Multi-path detection method for CDMA receivers
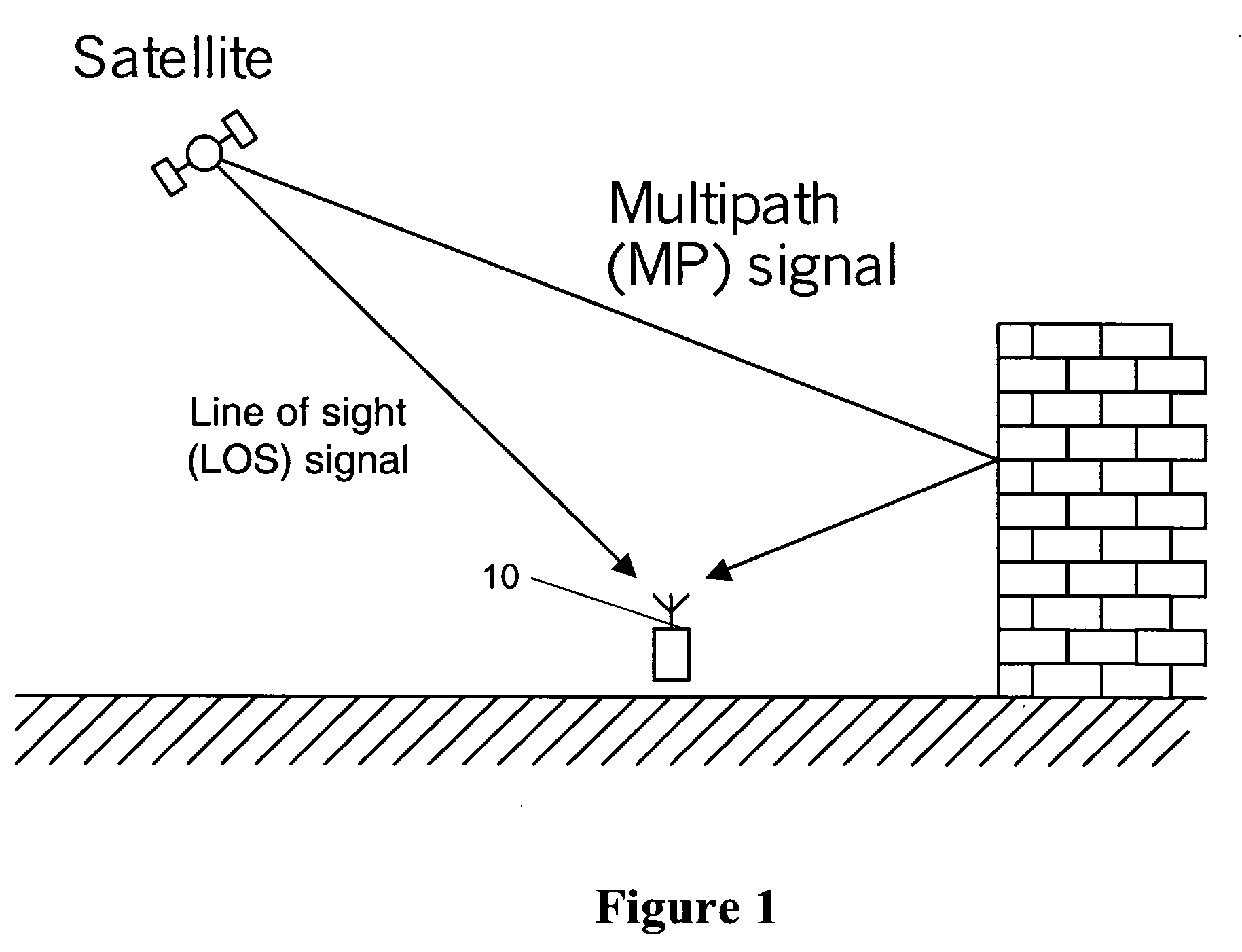
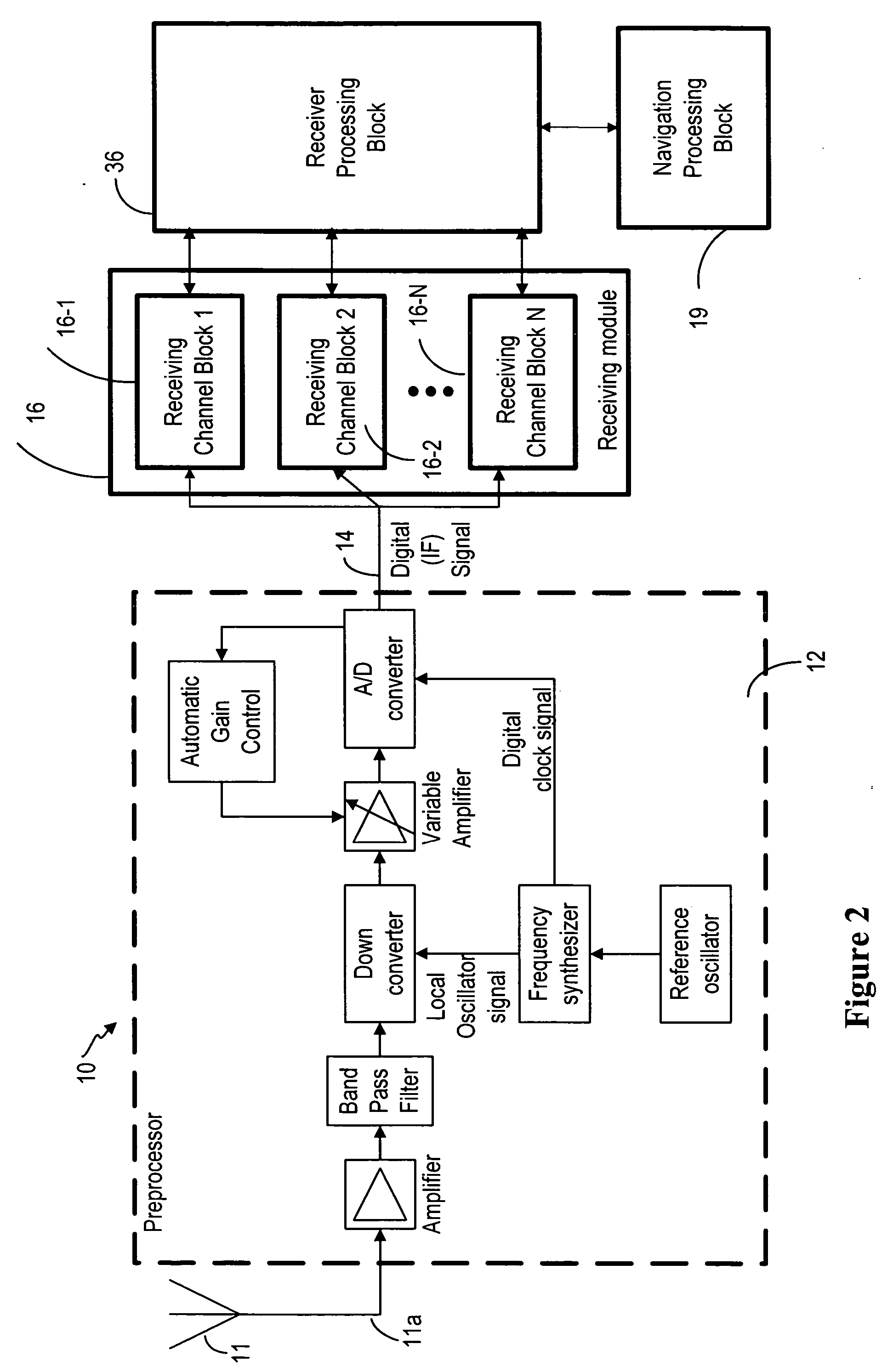
ActiveUS20060140254A1High positioning accuracyReduce weightSatellite radio beaconingTransmissionRadio frequency signalCdma signal
The present invention provides a method for a multi-path detection analysis and selectivity of CDMA signals using spread spectrum receivers using a correlation technique. The invention is based on determining by the spread spectrum receiver whether a distortion of a received radio frequency signal, caused by a multi-path component of said received signal, meets a predetermined condition using a pre-selected correlation analysis of said received signal. This invention is generally applicable to global navigation satellite system (GNSS) receivers and it is particularly useful in GNSS receivers, such as GPS (global positioning system) and Galileo receivers. The important goal of this invention is to provide a simple method for identifying signals that are corrupted by multi-path effects, and can be excluded from position calculation in the GNSS receivers.
Owner:FRANCE BREVETS SAS
Method and apparatus for decoding spread spectrum signal for CDMA
InactiveUS6876694B2Accurate estimateAccurate compensationError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionLocation detectionTransmission channel
Owner:NEC CORP
CDMA receiver
InactiveUS7327775B1Efficient implementationEfficient designSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsFrequency spectrumCdma signal
A signal reception method including method and apparatus for receiving a signal, down converting the received signal through multi-tone down conversion to form an intermediate signal, and decoding the intermediate signal to extract data. In an embodiment, the received signal may include multiple transmission bands of a multi-code (MC)-CDMA signal, each of which occupies a different spectrum. Each of the transmission bands also includes an information channel signal. When the received MC-CDMA signal is down converted through multi-tone down conversion, the intermediate signal is formed. The intermediate signal includes a common spectrum that includes an information channel from a plurality of transmission bands. When the intermediate signal is decoded, data from a plurality of information channel bands is extracted. The method and apparatus may be implemented in a multi-mode MC-CDMA / CDMA receiver.
Owner:NOKIA MOBILE PHONES LTD
RF receiver having improved signal-to-noise ratio and method of operation
InactiveUS7158560B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioReduce signal to noise ratioTransmissionCdma signalNoise reduction
There is disclosed, for use in a CDMA receiver, a noise reduction circuit for improving the signal-to-noise ratio of a received CDMA signal comprising a series of chip sequences. The noise reduction circuit comprises: 1) a sampling circuit for generating an original plurality of samples of the received signal; and 2) a controller for determining a first plurality of time slots containing chip samples equal to Logic 1, and a second plurality of time slots containing chip samples equal to Logic 0. The controller generates a reconstructed plurality of samples by at least one of: a) modifying an order of a first Logic 1 chip sample and a second Logic 1 chip sample; and b) modifying an order of a first Logic 0 chip sample and a second Logic 0 chip sample.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Radio base station and communication terminal
InactiveCN1463563ANetwork traffic/resource managementConnection managementFourier transform on finite groupsCdma signal
Owner:INTERDIGITAL PATENT HLDG INC
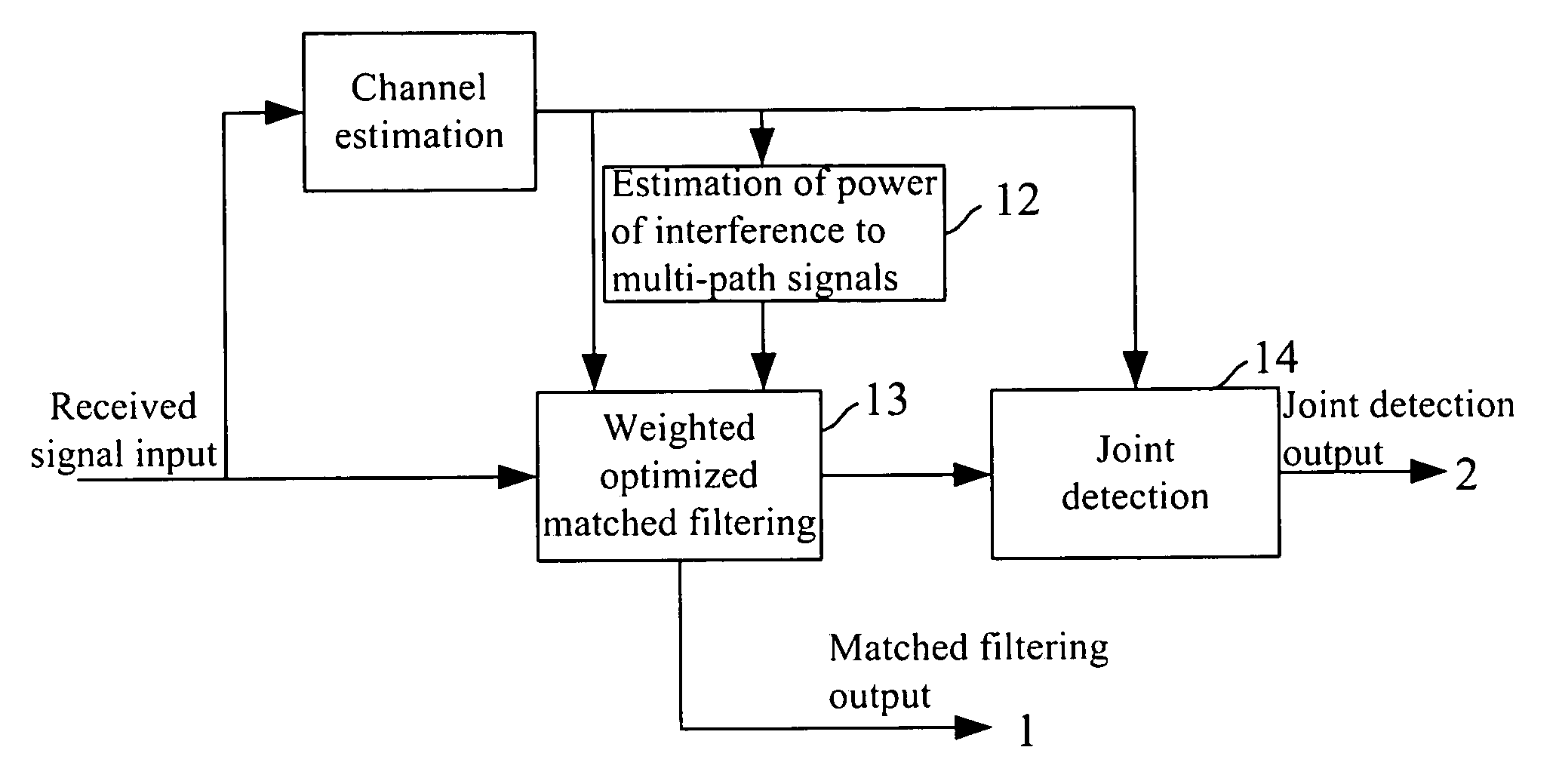
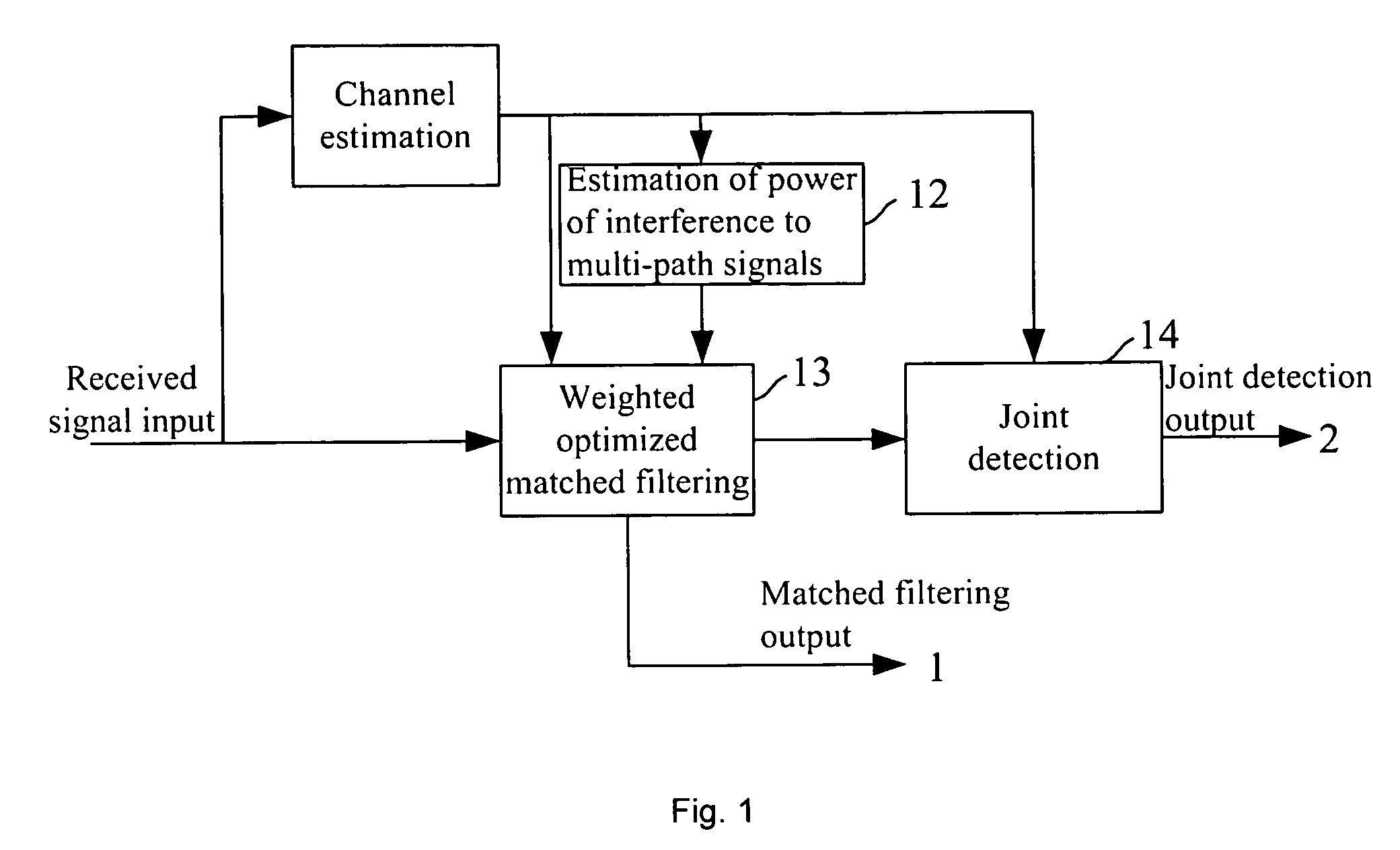
Method for detecting the orthogonal code cdma signal
ActiveUS20070058701A1Simple and improved mannerLow priceSupervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCdma signalTerminal equipment
The present invention discloses a method for detecting orthogonal code CDMA signal implemented mainly through the following steps: estimating the total power of interference to the multi-path signals; performing matched filtering on the multi-path signals and performing maximum ratio combining on the multi-path signals by utilizing the total power of interference to the multi-path signals, to obtain the optimized matched filtering result; and performing joint detection on the optimized matched filtering result. There are two schemes for implementing: if the optimized matched filtering detection scheme is used, only the first two main steps are executed; if the joint detection scheme is used, all of the three steps are executed. In either of above two schemes, the interference code channels involved in the estimation of total power of interference to the multi-path signals are need to be selected, i.e., all of the code channels in the serving cell or the code channels in the serving cell which are not performed joint detection on are selected. As the present invention takes full advantage of the characteristic of orthogonal code as well as the channel estimation result, system performance can be improved at a lower price. The present invention is especially suitable for terminal devices in an orthogonal code Code Division Multiple Access system.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Method and system for reduction of peak-to-average power ratio of transmission signals comprising overlapping waveforms
InactiveUS20100040089A1Reducing PAPReduce signalingResonant long antennasCode division multiplexComputation complexityRound complexity
The present invention provides a method and system for reducing the peak to average power ratio (PAP) of a signal with low computational complexity. According to one embodiment, the present invention is applied to reduce the PAP of an OFDM signal. According to an alternative embodiment, the present invention, is applied to reduce the PAP of a CDMA signal. Rather than seeking the optimum solution, which involves significant computational complexity, the present invention provides for a number of sub-optimal techniques for reducing the PAP of an OFDM signal but with much lower computational complexity. In particular, according to one embodiment utilizing the PTS approach, an iterative technique is used to assign phase factors to each of a set of partial transmit sequences from a set of possible phase factors. Experimental results using the iterative technique showed only a slight degradation (1 dB) from the optimal approach using the same number of subblocks and subcarriers. In an alternative embodiment, which avoids feedback required by the iterative approach, a sequence of phase factors are generated randomly and assigned to each of a set of partial transmit sequences. This procedure is repeated for a pre-determined number of trials and the random sequence generating the lowest PAP is selected. In a third embodiment, a set of phase factors is generated using a structured sequence such as a Walsh sequence.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
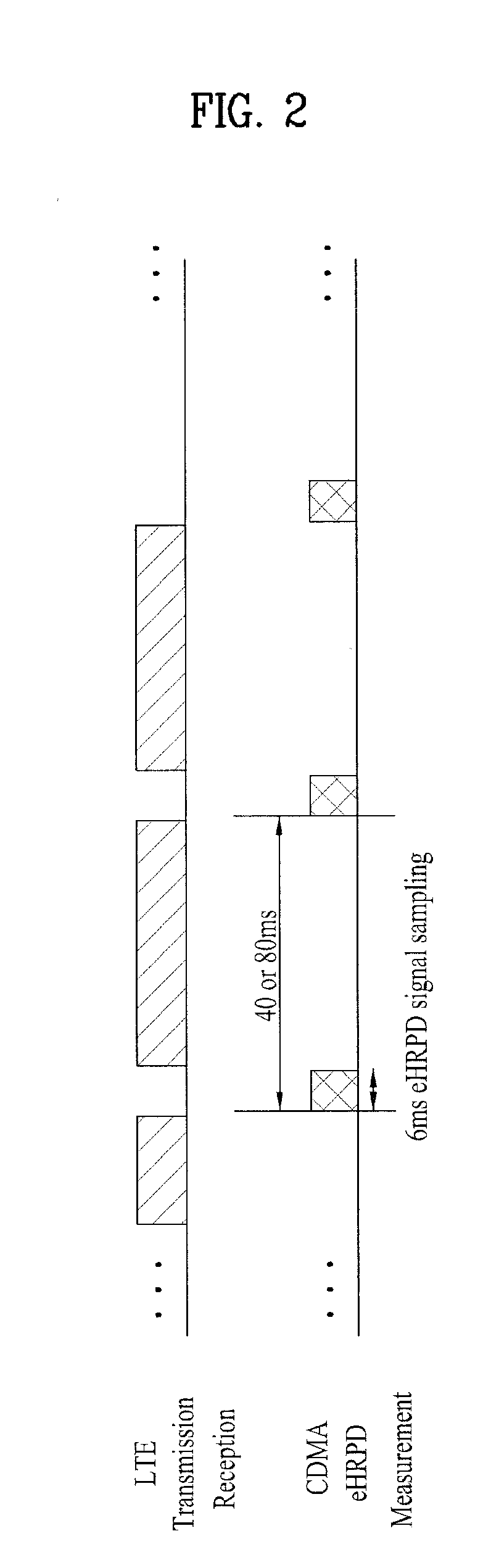
Dual mode mobile terminal in MIMO wireless communication system and control method thereof
InactiveCN101848058AEfficient measurementMaintain Receive Bit Error RateSite diversityWireless communicationSignal qualityCommunications system
The invention relates to a dual mode mobile terminal in a MIMO wireless communication system and a control method thereof and discloses a dual mode terminal and a control method thereof. The terminal comprises a first antenna, a second antenna, a first communication module and a second communication. If the first communication module receives a command for measuring the signal quality of a second base from a LTE base, RI (rank indicator) as 1 is reported to the LTE base. Based on a layer 1 choice and report PMI, the first communication module only uses the first antenna to receive a BLER signal equal to or more than 0.1 from the LTE base. Therefore, the dual module terminal of the invention can efficiently measure the CDMA signal quality by keeping receiving the LTE signal without clearance measurement and can receive the BLER under the condition of a level similar to the normal situation in the process of measuring the CDMA signal quality.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
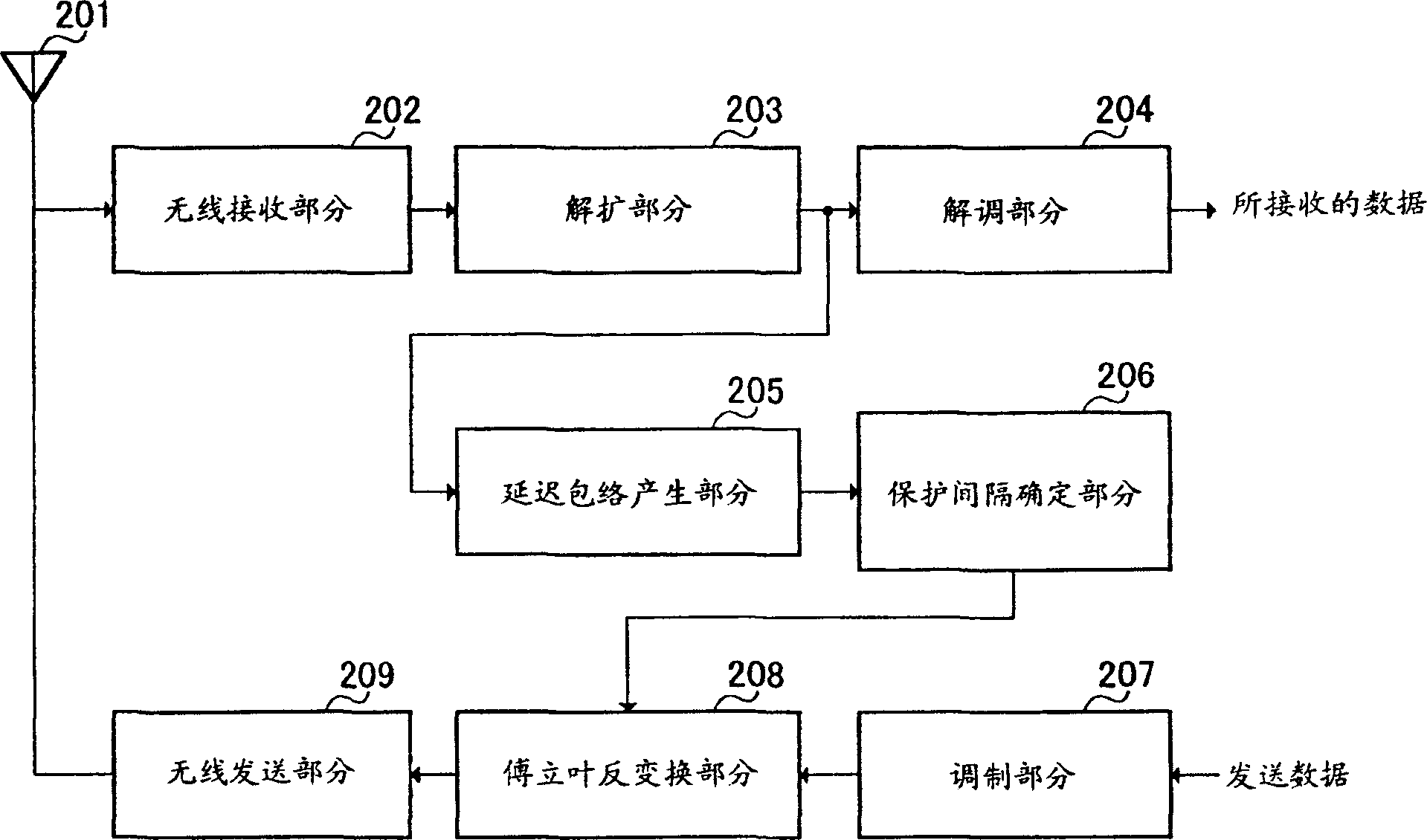
CDMA reception method, device, and wireless communication system
InactiveUS20060245477A1Reduce weight burdenTransmission efficiency loss can be suppressedCode division multiplexSecret communicationCommunications systemTransmission channel
In an arrangement for receiving CDMA signals, insertion of guard intervals is rendered unnecessary and transmission efficiency loss is suppressed, along with greatly reducing the computational burden of weight calculations. Impulse responses of a transmission channel are obtained by time-domain signal processing, the impulse responses are Fourier transformed and converted into frequency domain signals, equalizing filter weights are calculated using the frequency domain impulse responses, the calculated frequency domain weights are converted to time domain weights using an inverse Fourier transform, the received signals are filtered using time-domain signal processing, and data signals are demodulated by despreading the equalized signals.
Owner:NEC CORP
Coherent synchronization of code division multiple access signals
InactiveUS6963548B1Increase signal gainLow costTime-division multiplexRadio transmission for post communicationTime division multiple accessTelecommunications
A novel method and apparatus is described for reducing the number of CDMA codes for a constellation of multiple trasponder platforms serving a number of subscribers in the same service area. A coherent processing technique synchronizes the phase of CDMA signals arriving at a subscriber from multiple trasponder platforms to increase the code capacity and thus the number of possible subscribers for most of the multiple transponder platform systems in current use.
Owner:HUGHES ELECTRONICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com