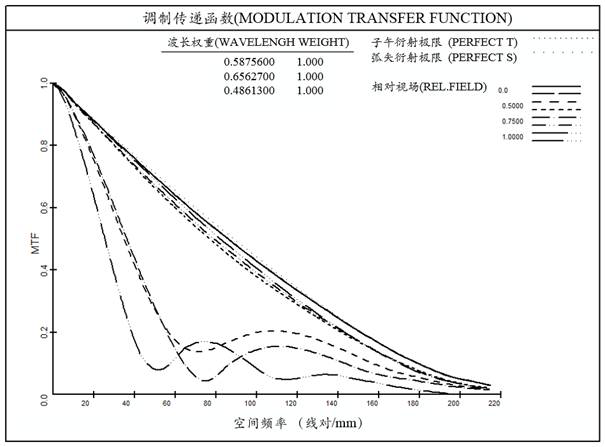
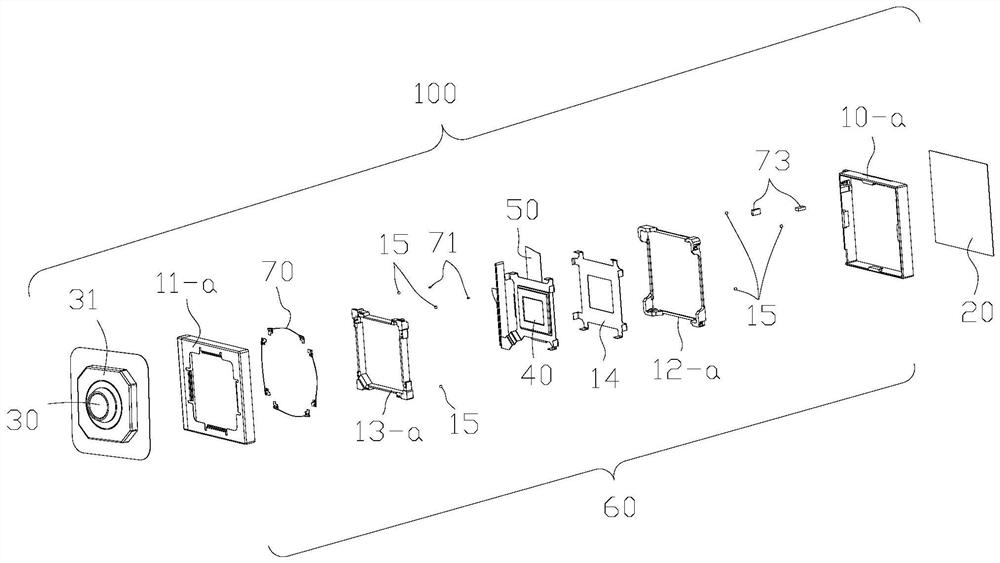
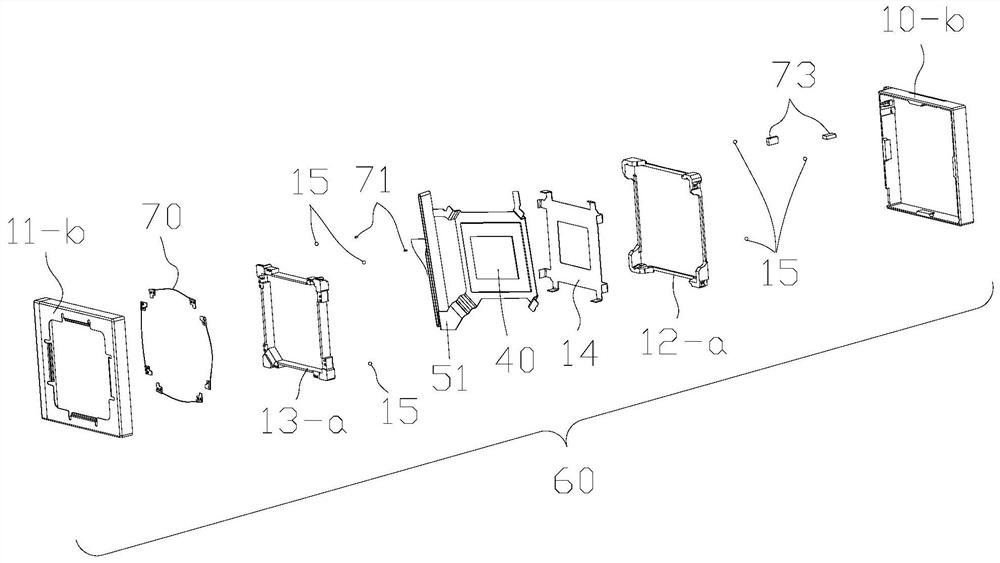
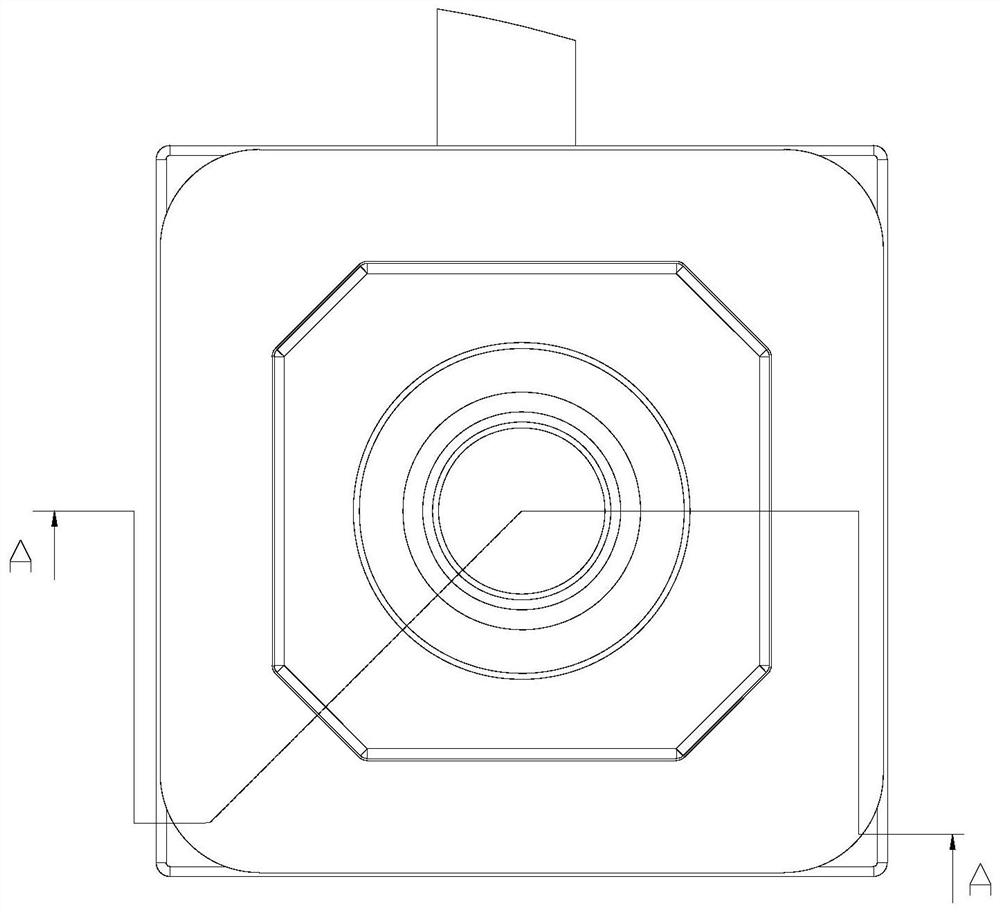
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
72 results about "Cardinal point" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
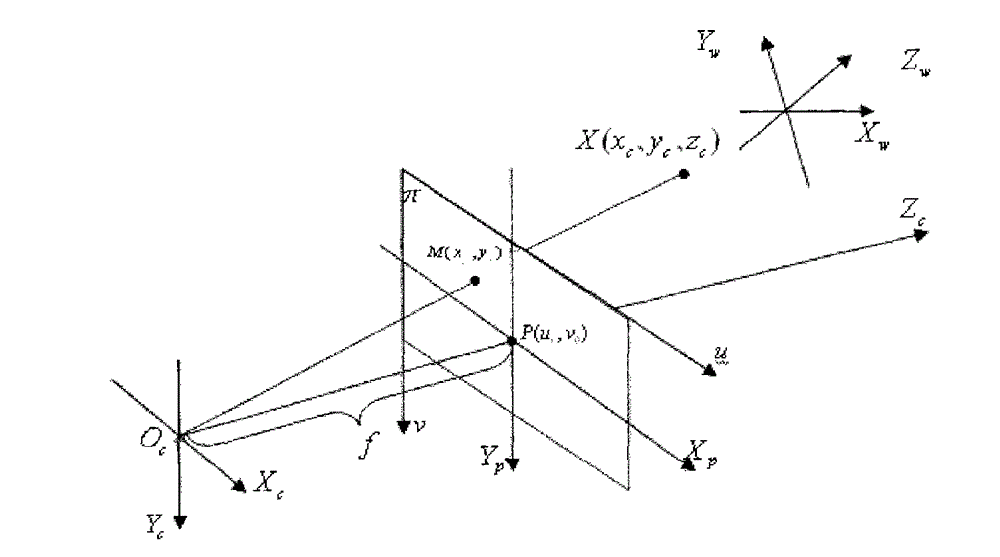
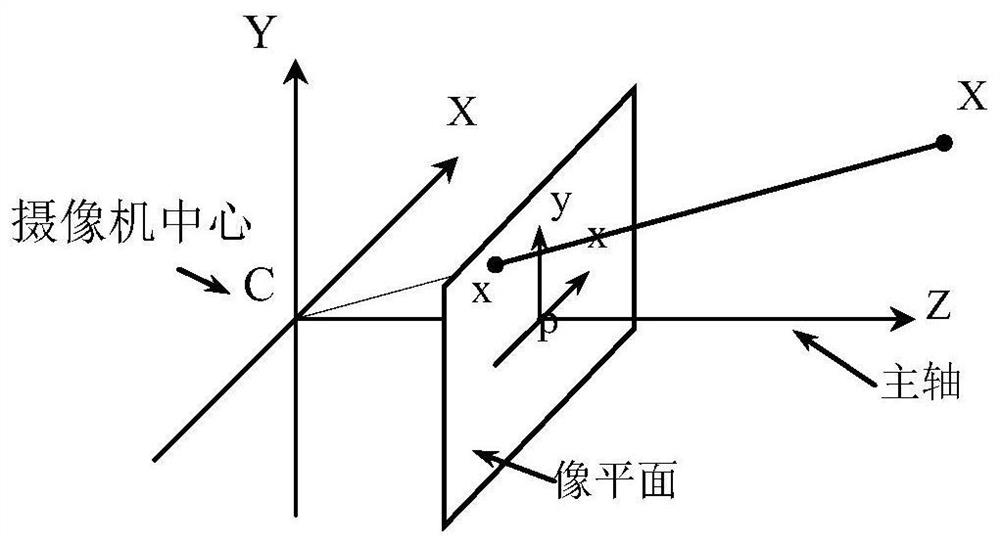
In Gaussian optics, the cardinal points consist of three pairs of points located on the optical axis of a rotationally symmetric, focal, optical system. These are the focal points, the principal points, and the nodal points. For ideal systems, the basic imaging properties such as image size, location, and orientation are completely determined by the locations of the cardinal points; in fact only four points are necessary: the focal points and either the principal or nodal points. The only ideal system that has been achieved in practice is the plane mirror, however the cardinal points are widely used to approximate the behavior of real optical systems. Cardinal points provide a way to analytically simplify a system with many components, allowing the imaging characteristics of the system to be approximately determined with simple calculations.
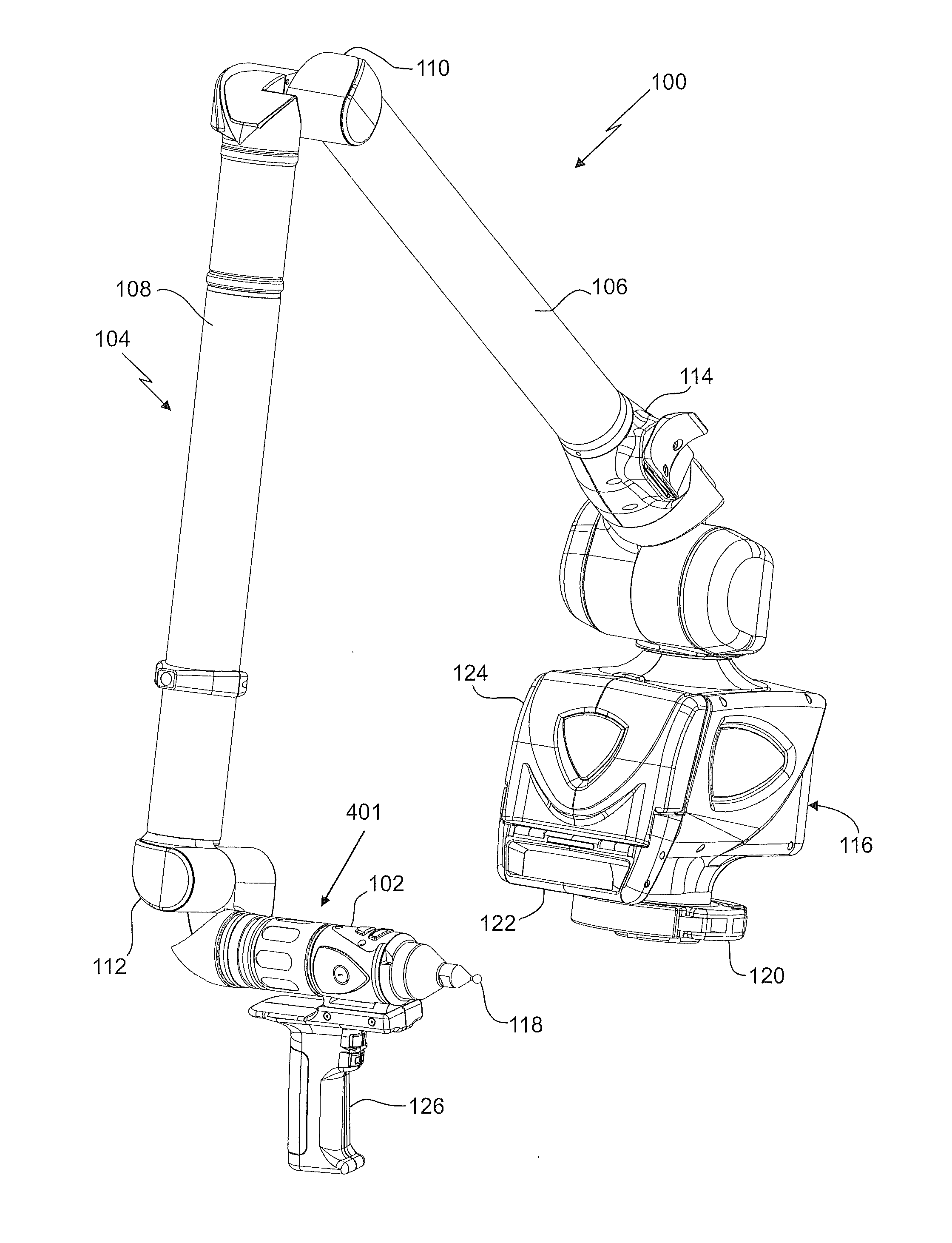
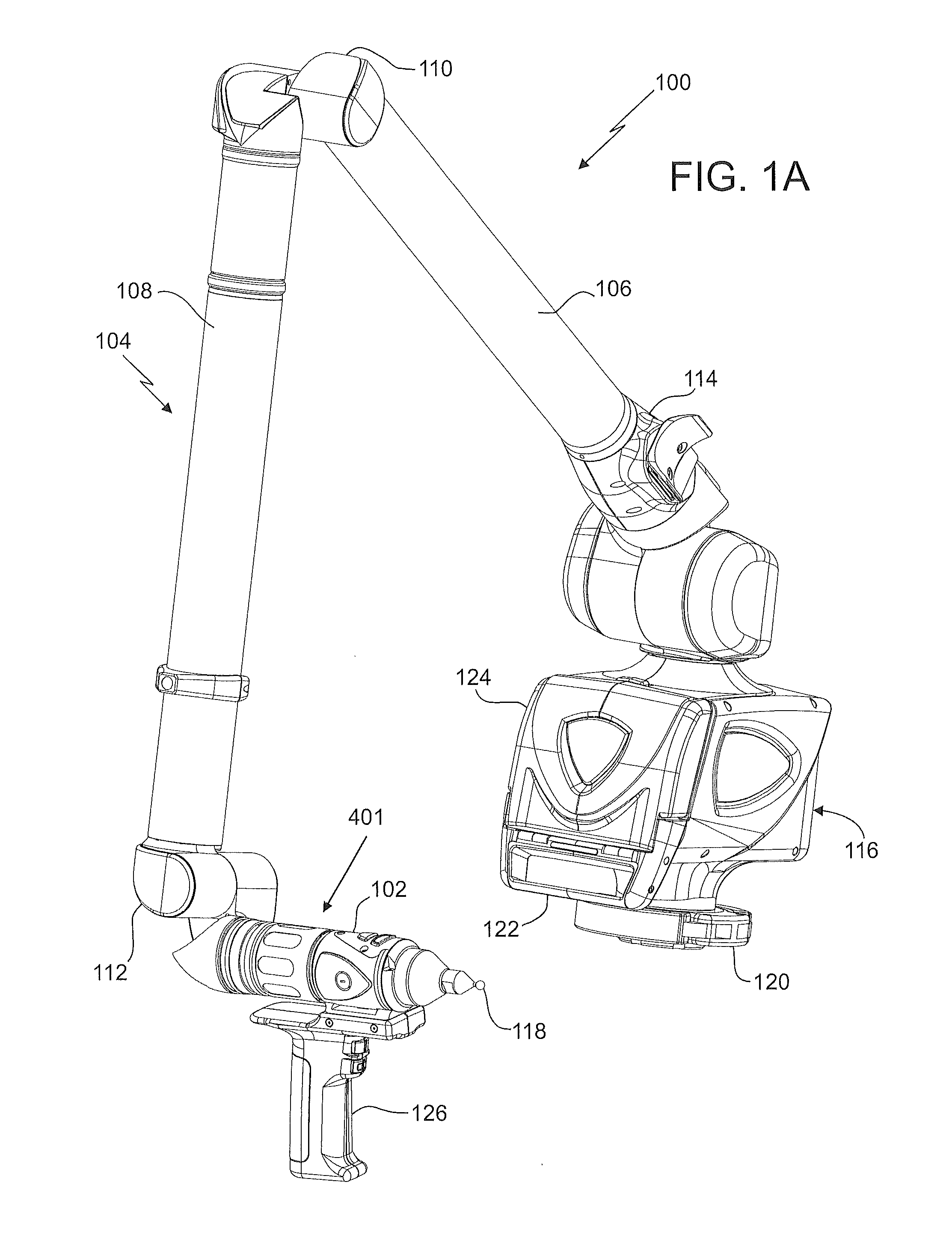
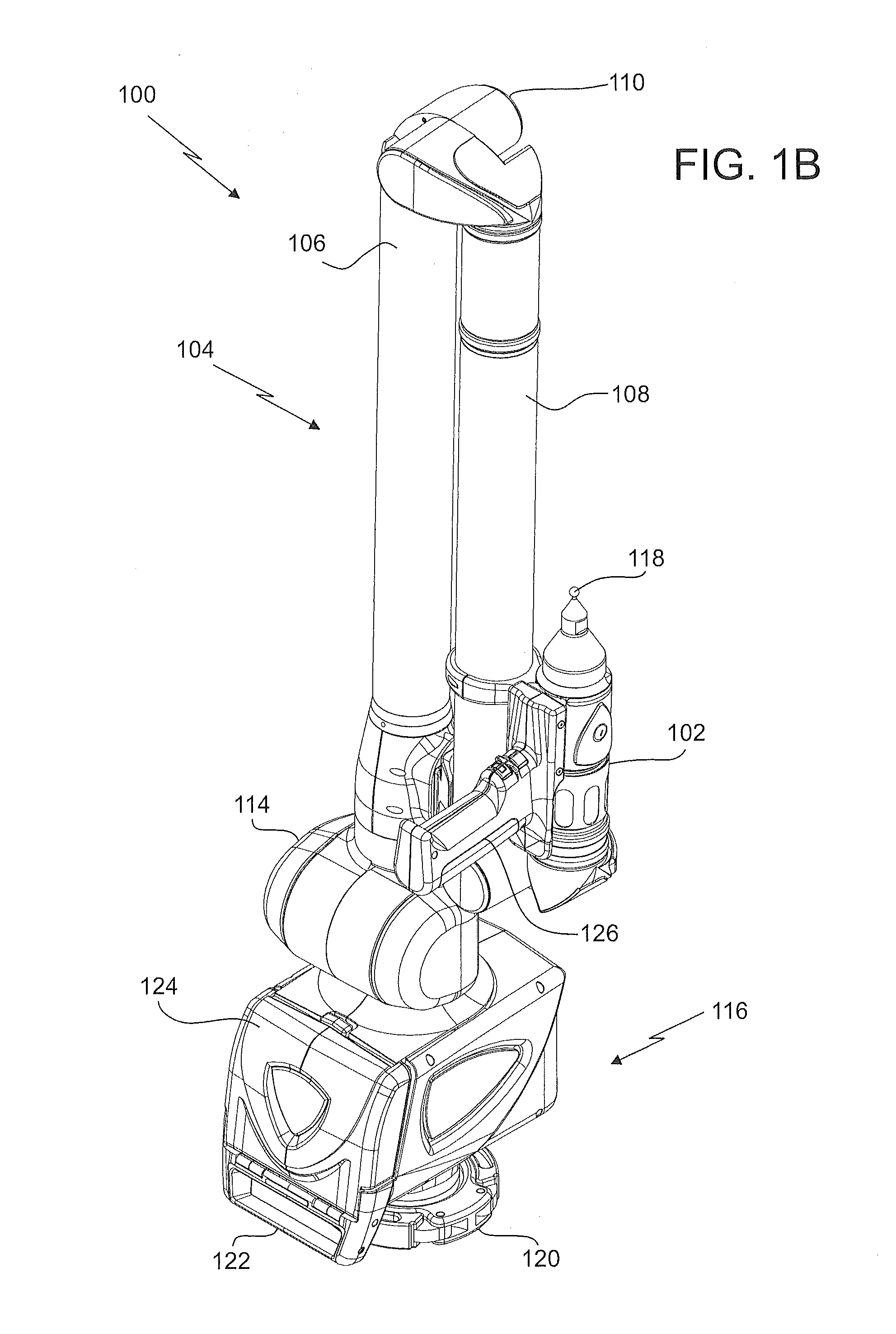
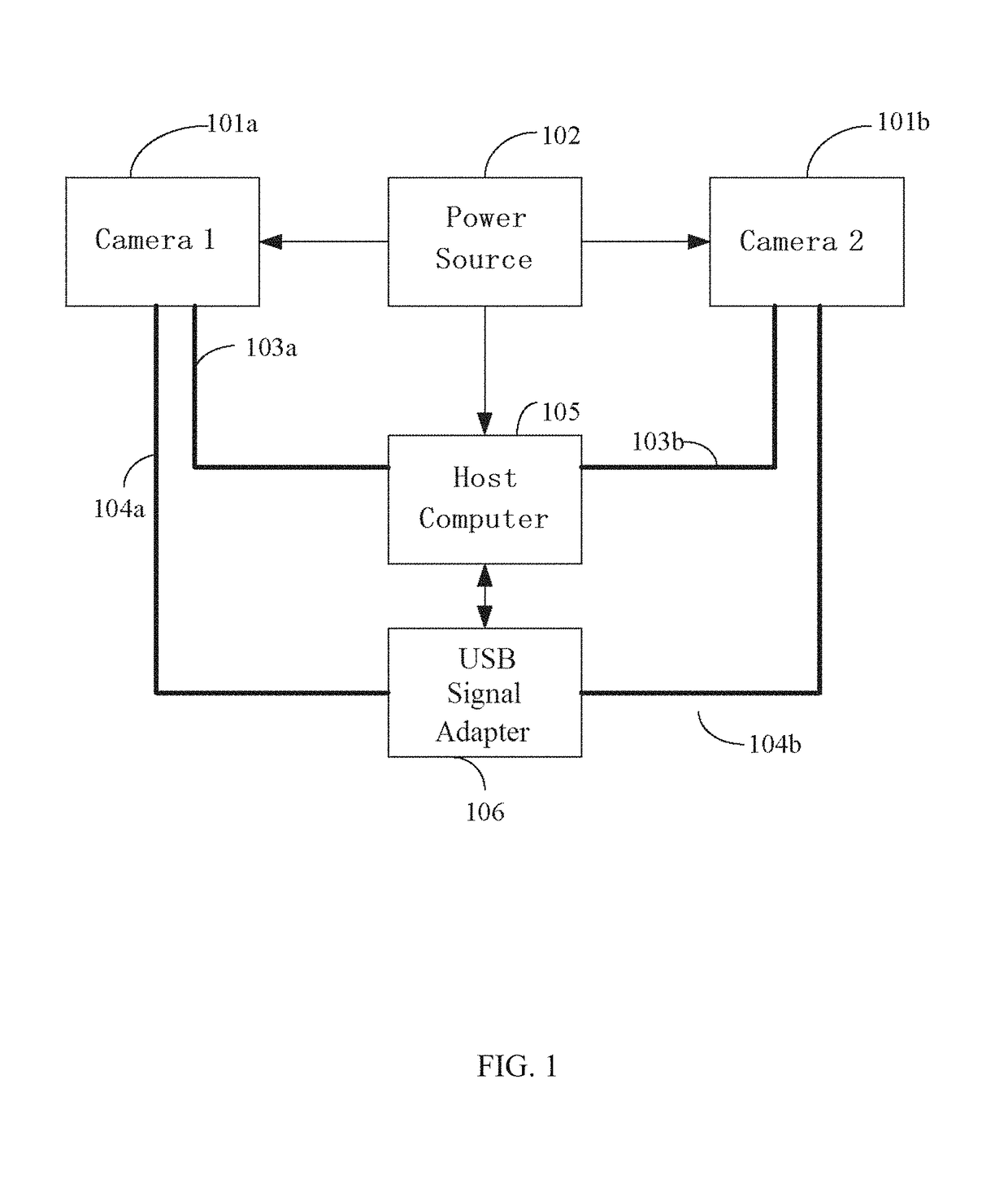
Method for measuring 3D coordinates of a surface with a portable articulated arm coordinate measuring machine having a camera
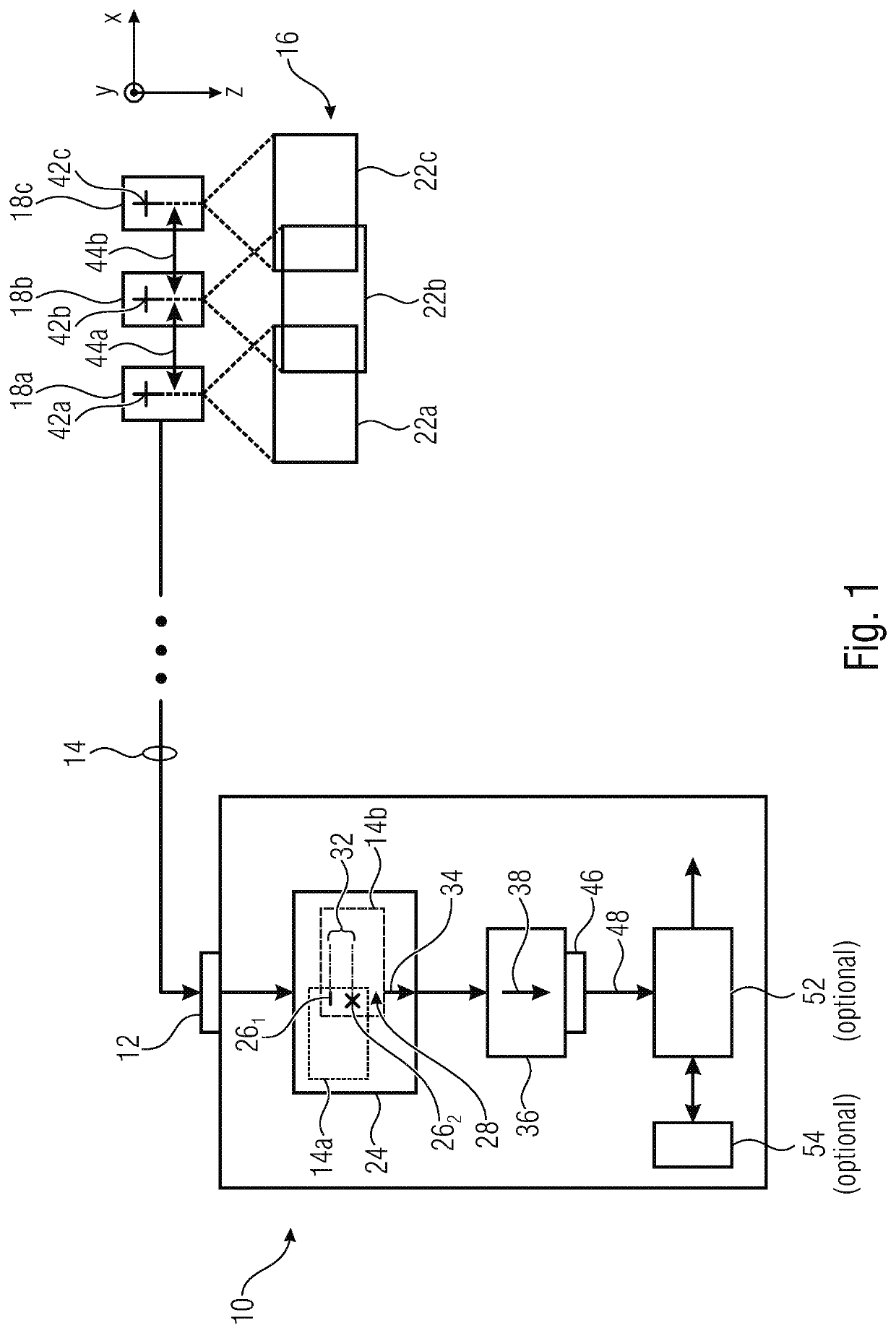
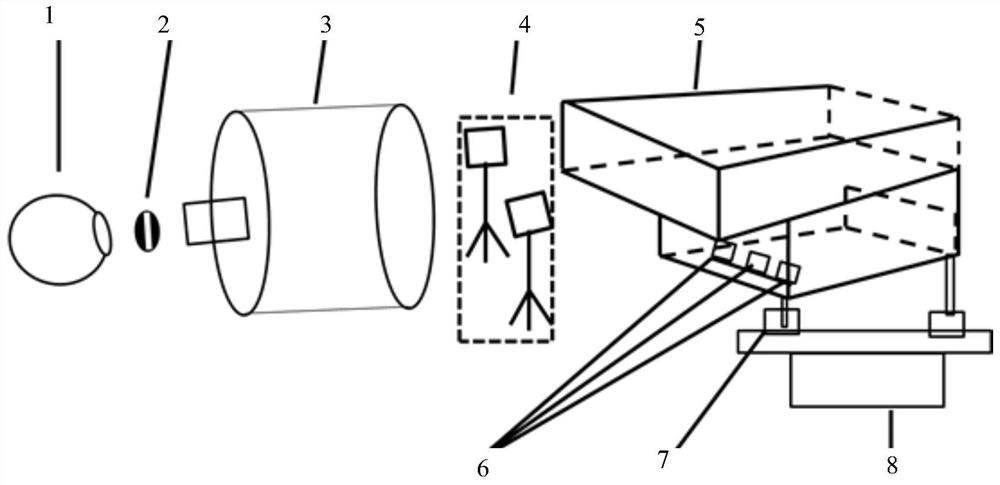
A method for measuring three-dimensional (3D) coordinates of a surface includes providing a manually positionable articulated arm portion having opposed first and second ends, providing a measurement device coupled to the first end, the measurement device including a camera having a lens and a photosensitive array and moving the camera to first and second positions and orientations to capture first and second images. Based on data from the camera, a first set of cardinal points common to the first and images and the second images are used to form a 3D coordinates that describe the surface.
Owner:FARO TECH INC
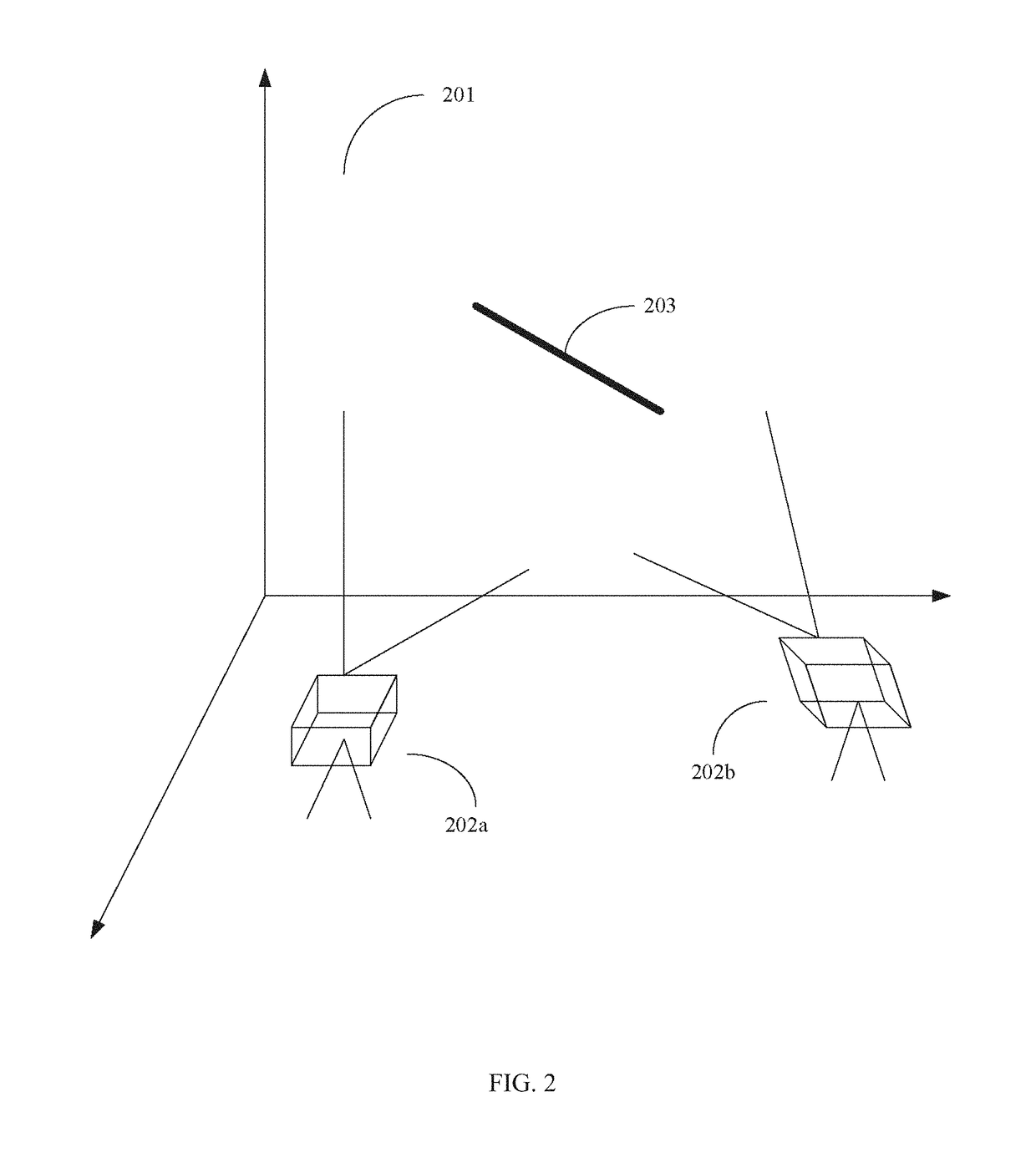
Method for implementing high-precision orientation and evaluating orientation precision of large-scale dynamic photogrammetry system
ActiveUS9857172B1Easy to processEasy to measureImage enhancementImage analysisIn planeKinetic photography
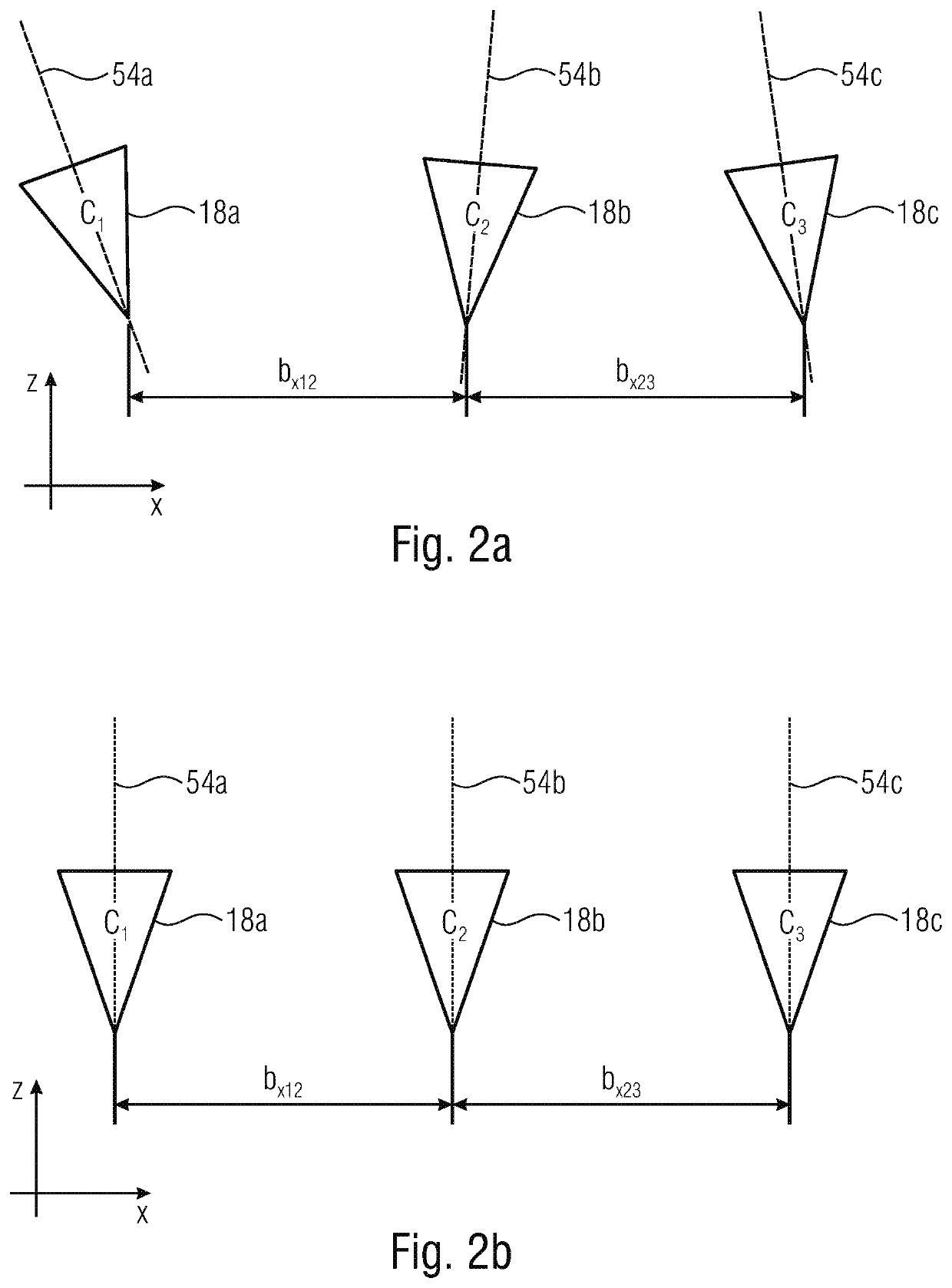
The present invention provides a method for implementing high-precision orientation and evaluating orientation precision of a large-scale dynamic photogrammetry system, including steps: a) selecting a scale bar, arranging code points at two ends of the scale bar, and performing length measurement on the scale bar; b) evenly dividing a measurement space into multiple regions, sequentially placing the scale bar in each region, and photographing the scale bar by using left and right cameras; d) limiting self-calibration bundle adjustment by using multiple length constraints, adjustment parameters including principal point, principal distance, radial distortion, eccentric distortion, in-plane distortion, exterior orientation parameter and spatial point coordinate; and e) performing traceable evaluation of orientation precision of the photogrammetry system. The present invention can effectively reduce the relative error in length measurement.
Owner:BEIJING INFORMATION SCI & TECH UNIV
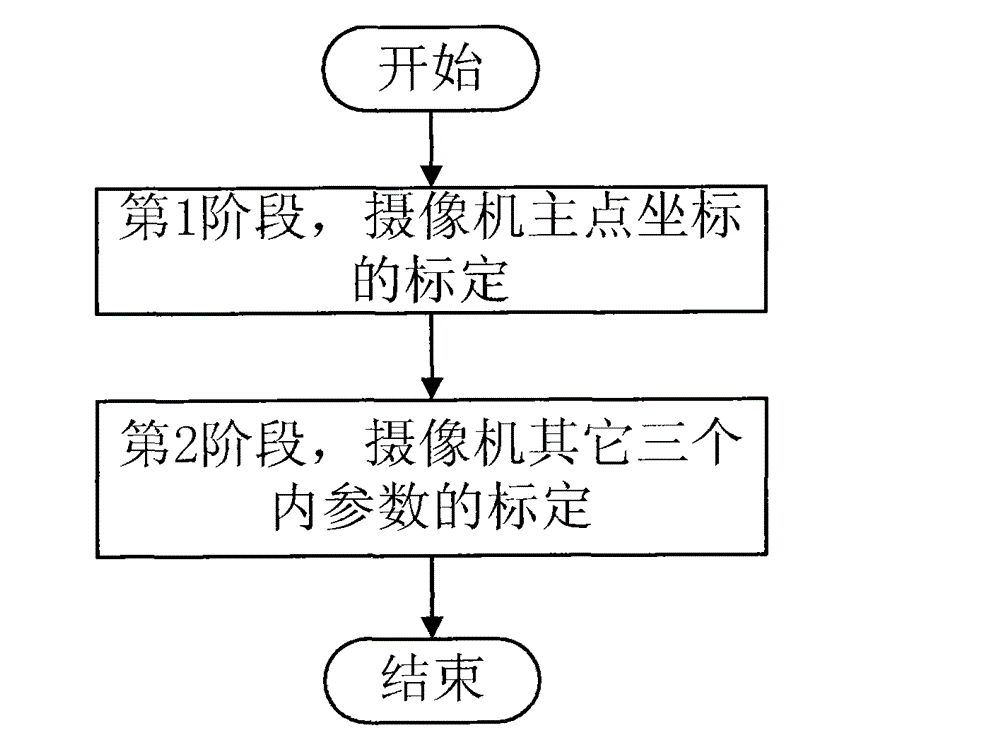
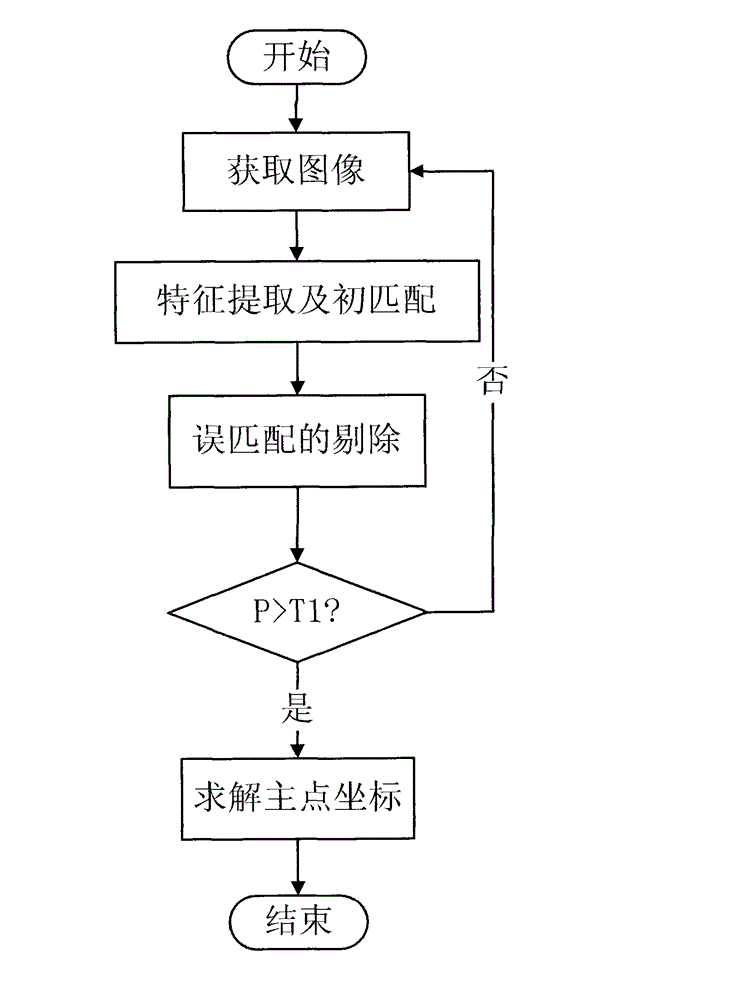
Step-by-step video camera self-calibration method
InactiveCN102750704AImprove calibration accuracyHigh precisionImage analysisFeature extractionThree dimensional measurement
The invention provides a step-by-step video camera self-calibration method, which comprises the following steps: in the first phase, shooting two images of the same scene at different focal lengths, performing feature extraction and matching on the images and eliminating mismatching points, and solving principal point coordinates of the video camera by using matching point pairs; and in the second phase, shooting the same scene from different angles to obtain three images available for matching, and performing feature extraction and matching on the images and eliminating mismatching points, and then based on Kruppa equation, substituting the obtained principal point coordinates into the equation to accomplish solving the three parameters of an obliquity factor, as well as scale factors of the video camera in the directions U and V axes of an imaging plane. By using the method provided by the invention, the calibration accuracy of the principal point coordinates of the video camera is relatively high, and the coefficient matrix size of the Kruppa equation is reduced, the amount of solving computation is reduced, and the method has the characteristic of being real-time. The method is applicable to video camera calibration of a vision system and can be used in the fields of three-dimensional measurement, three-dimensional reconstruction, machine navigation, augment reality and the like.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
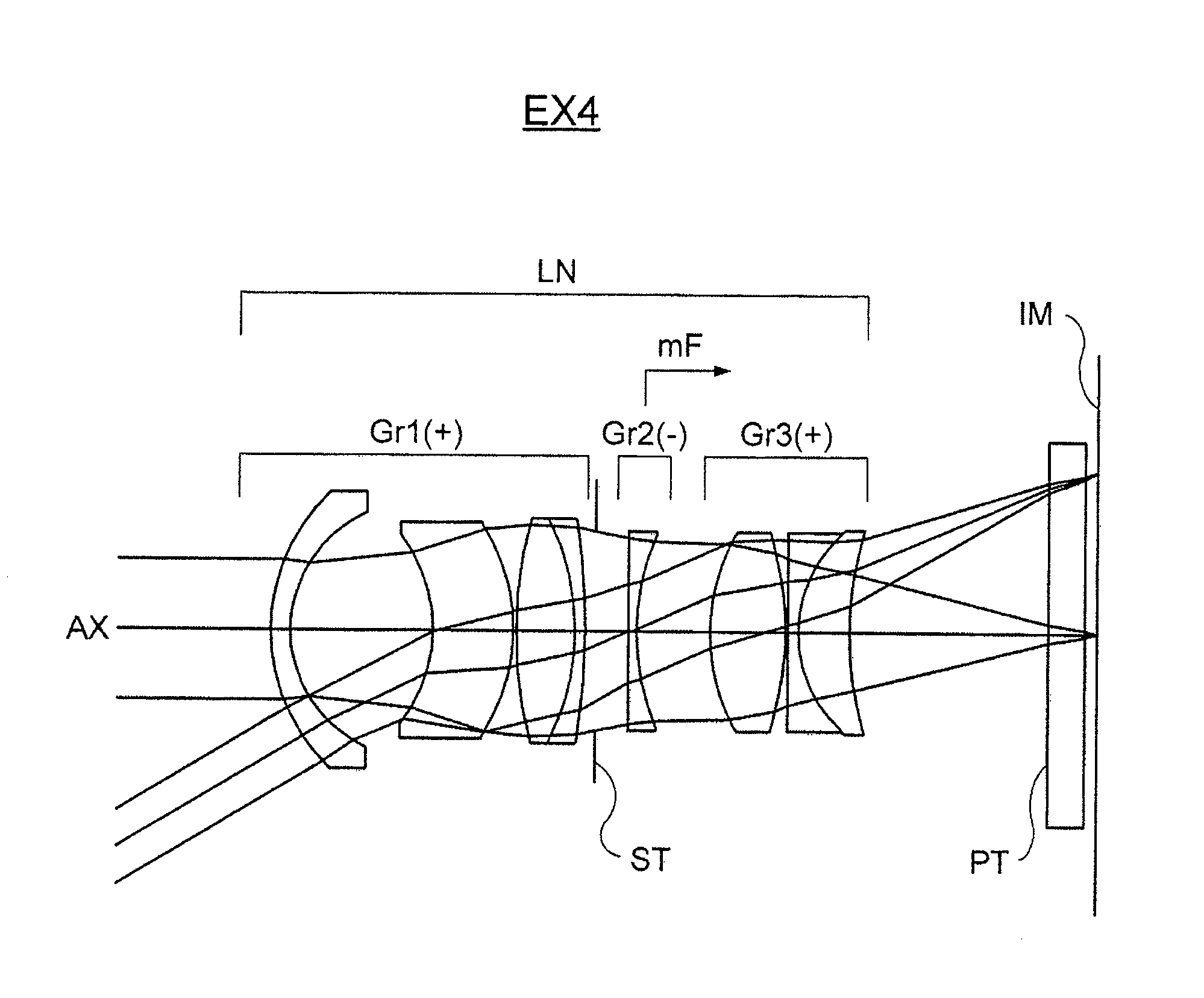
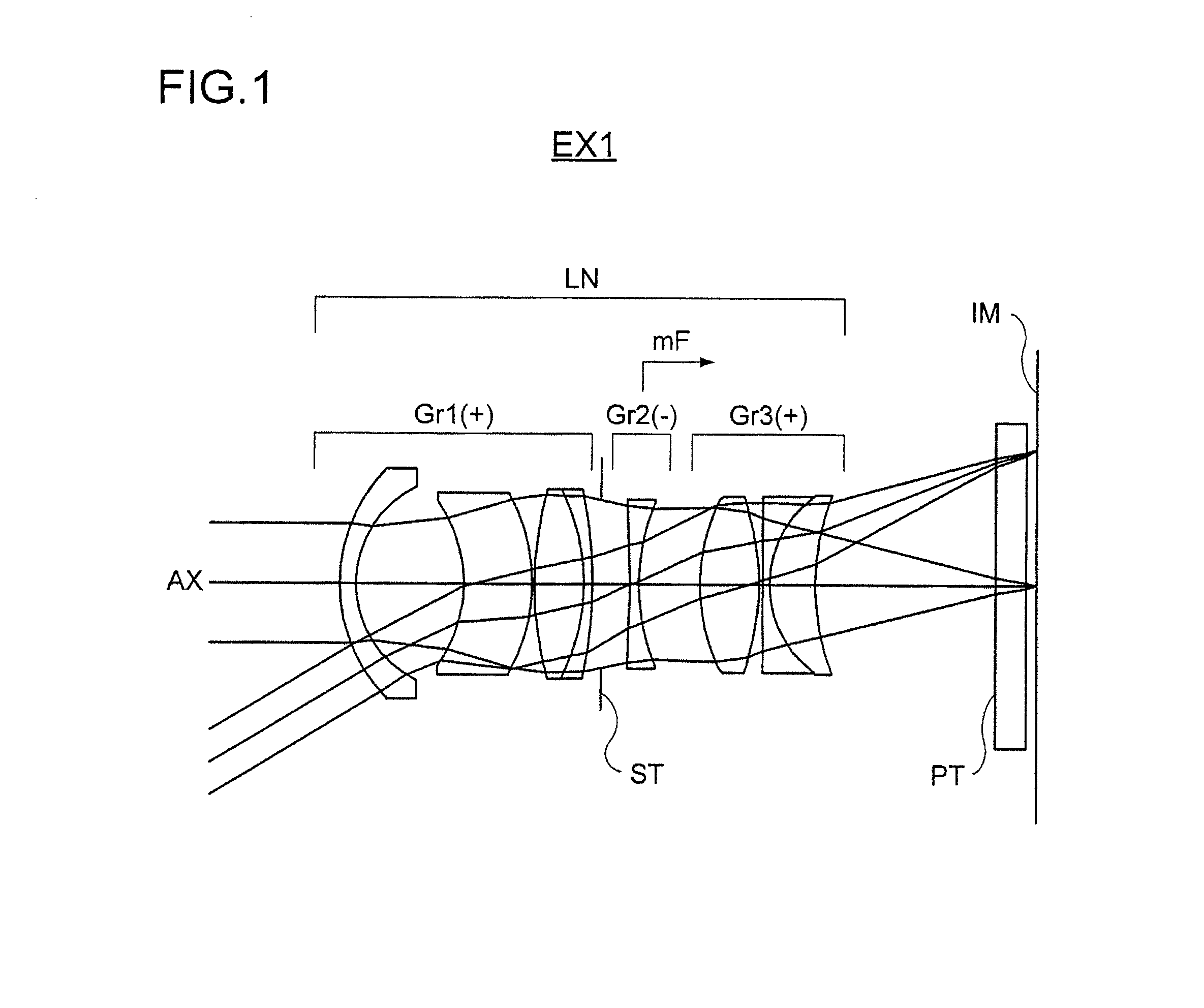
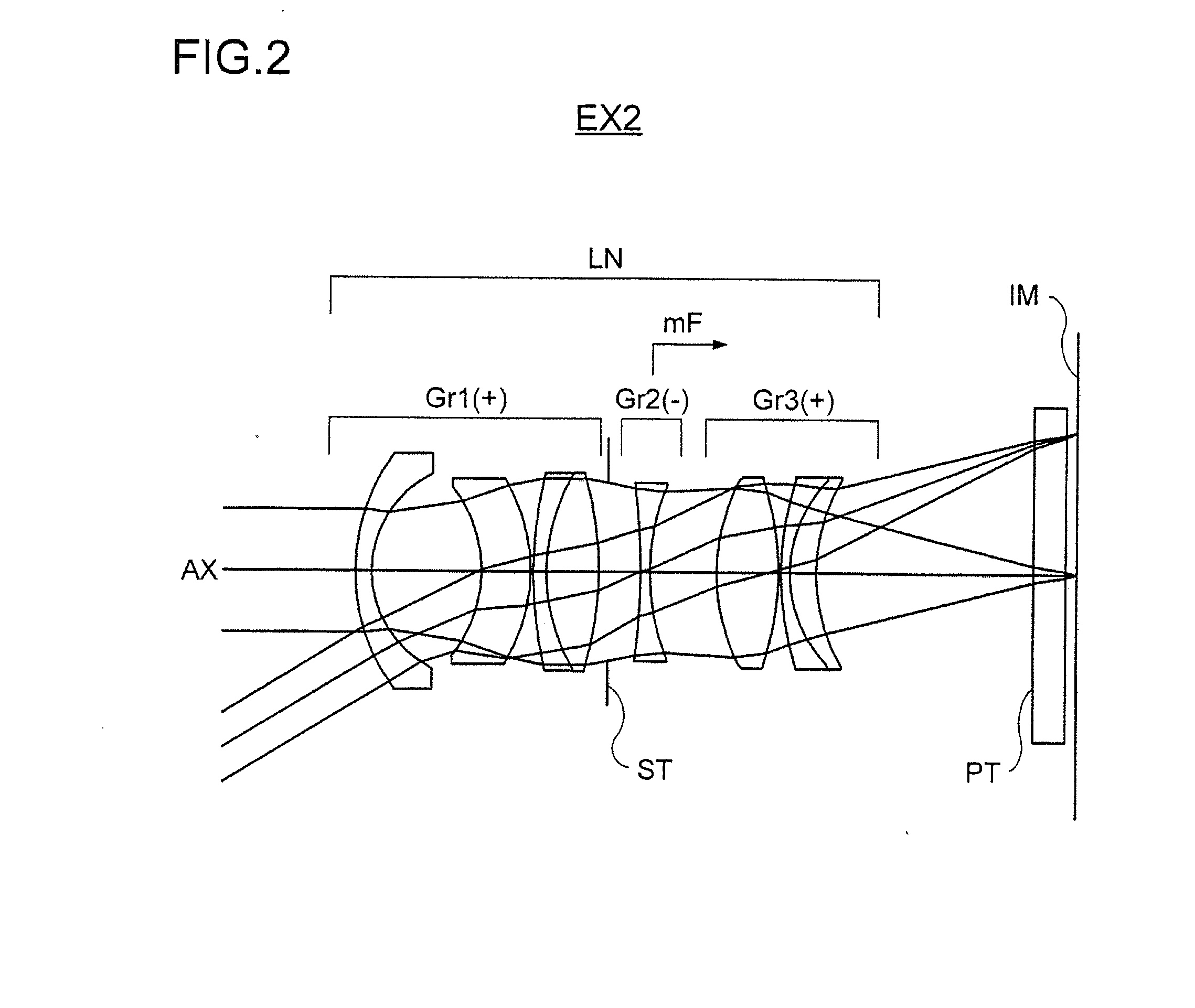
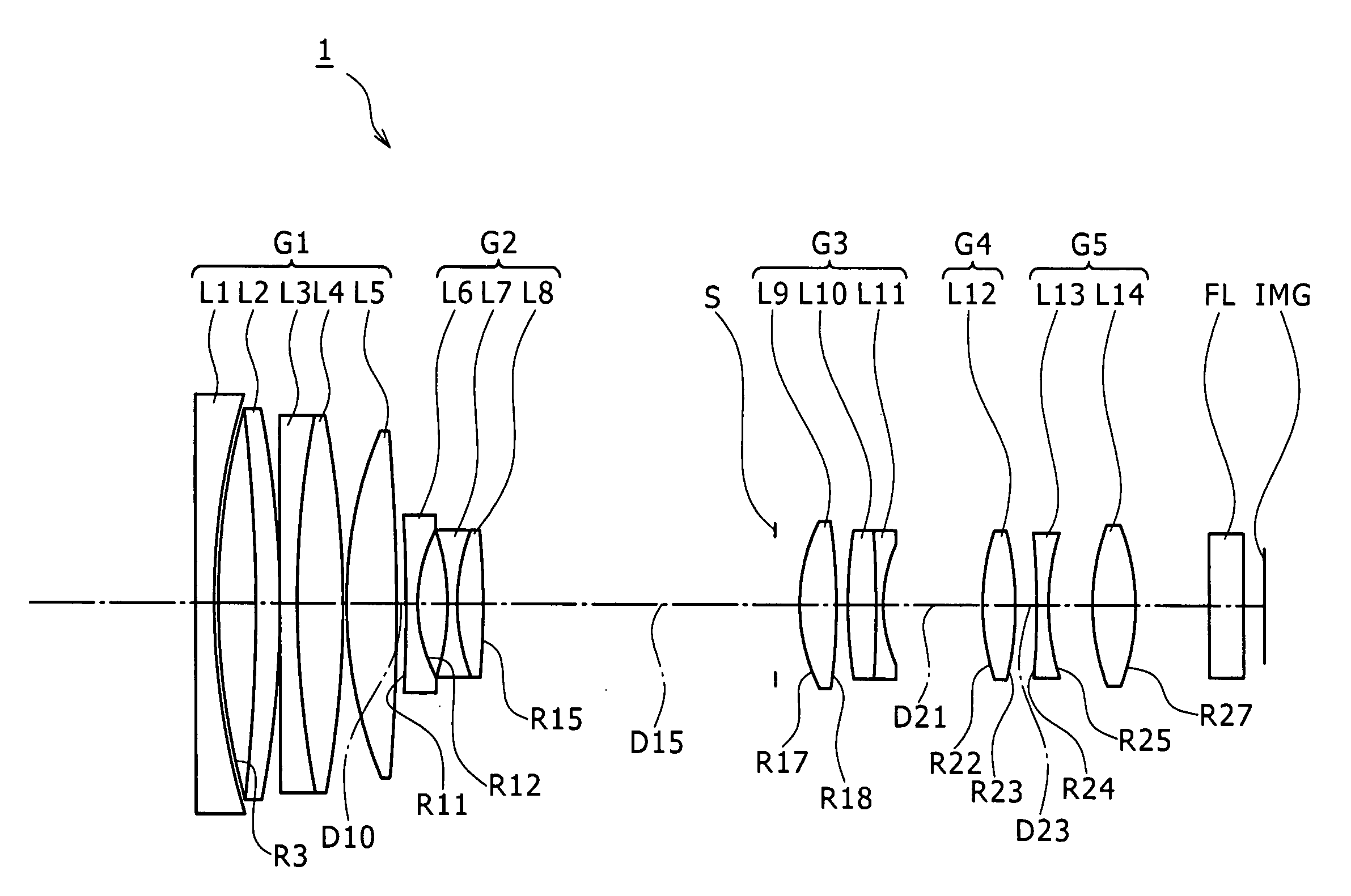
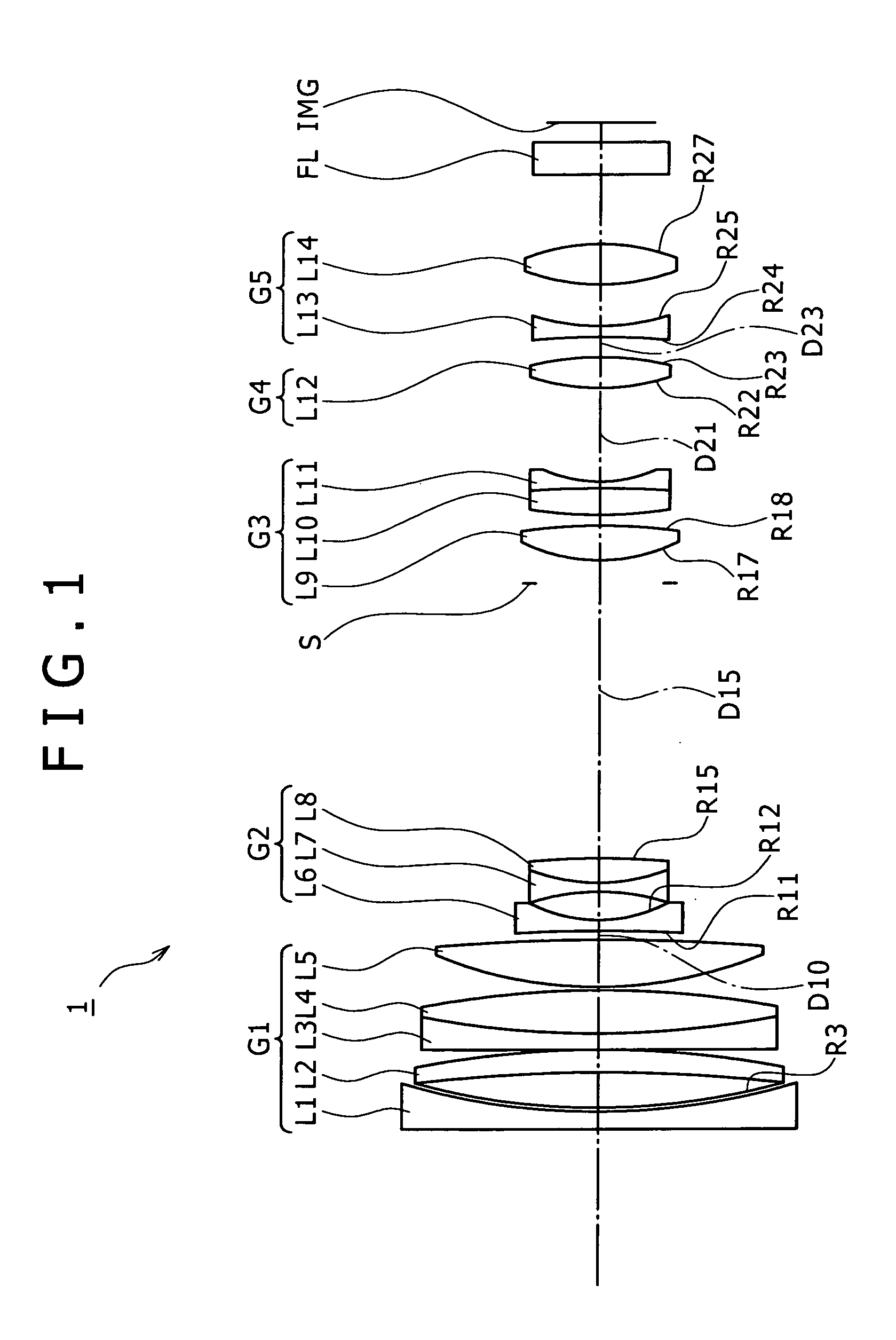
Wide-Angle Lens System, Image Sensing Optical Device and Digital Apparatus
InactiveUS20140055558A1Large apertureReduce focusTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptical axisNegative power
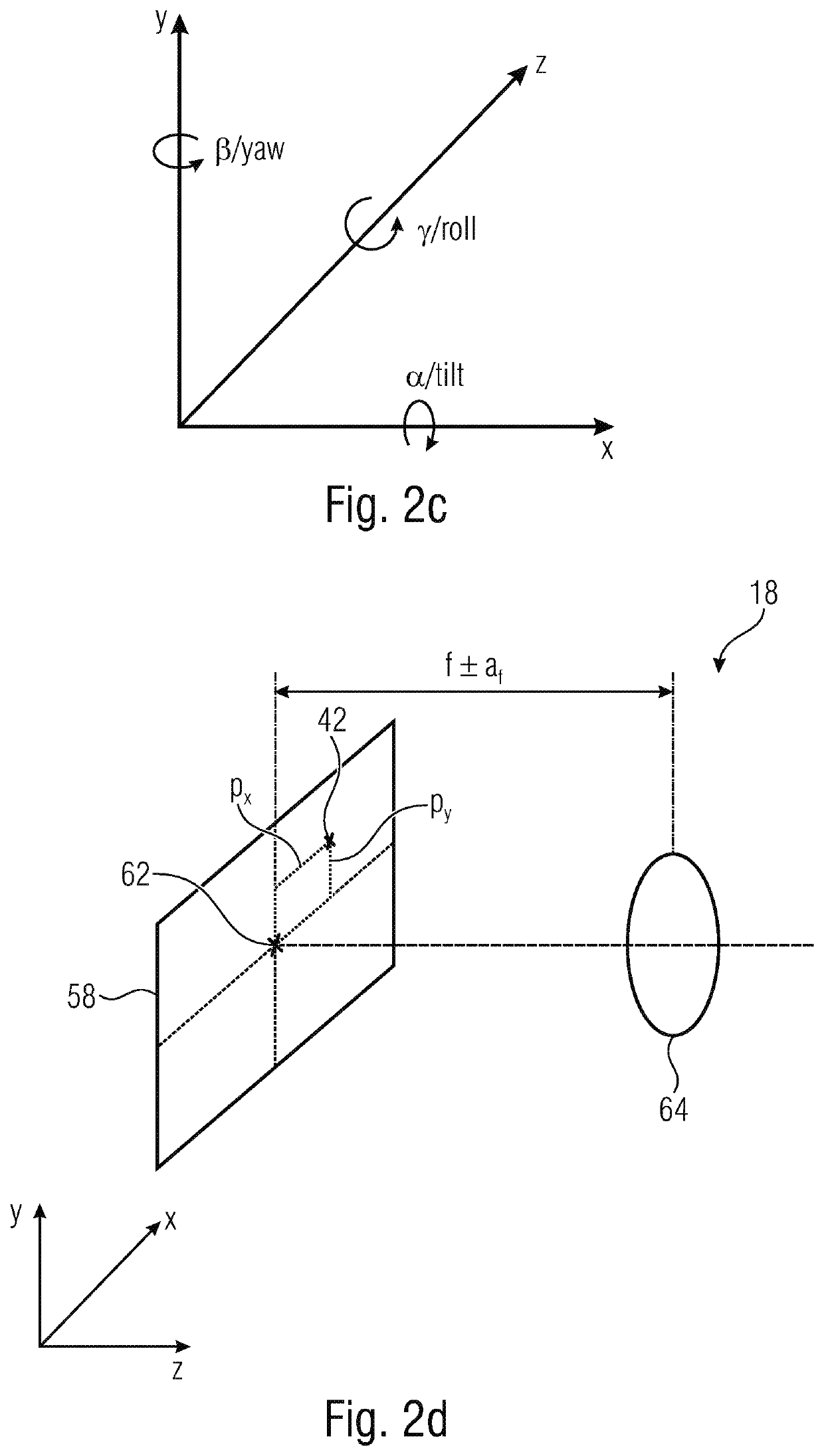
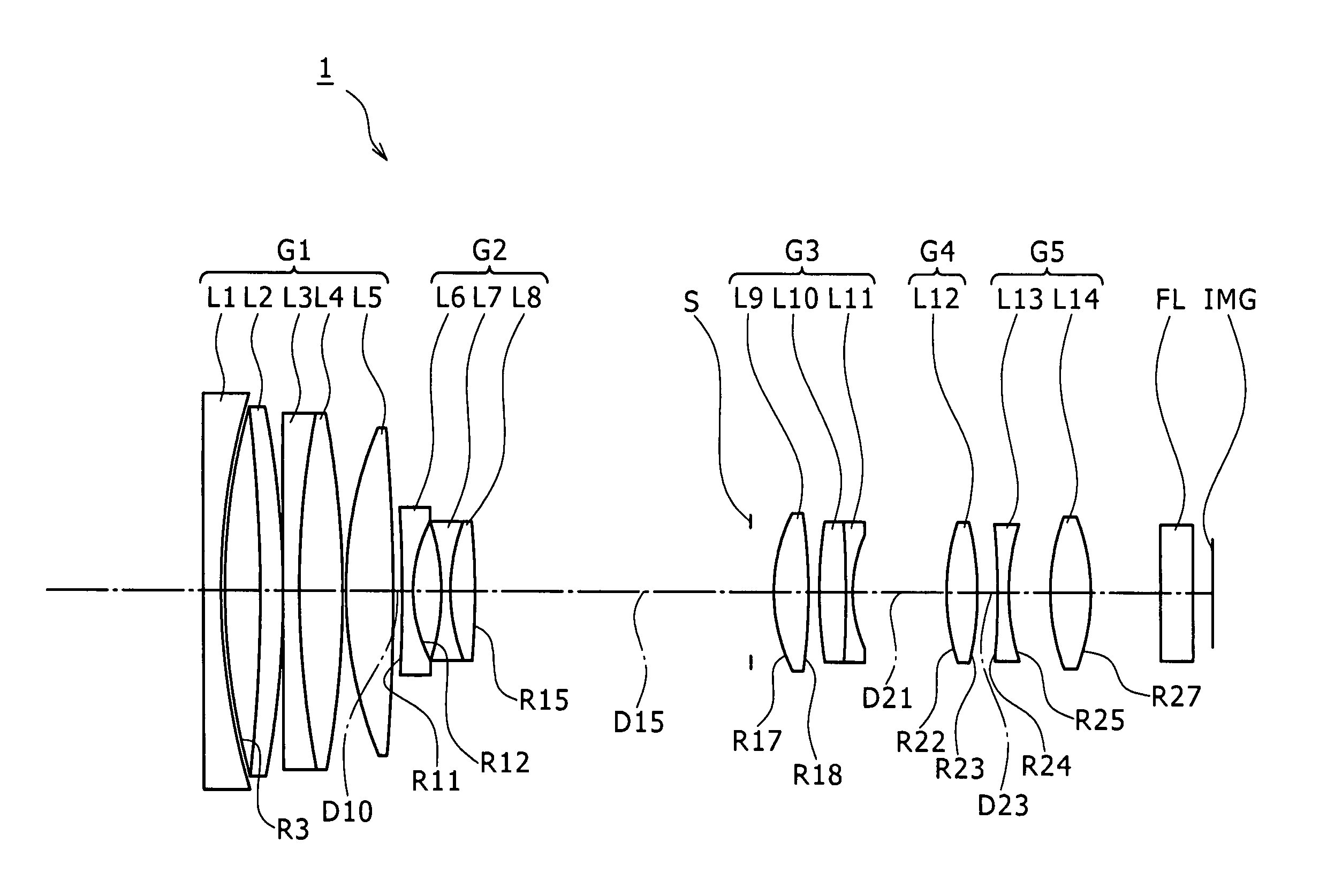
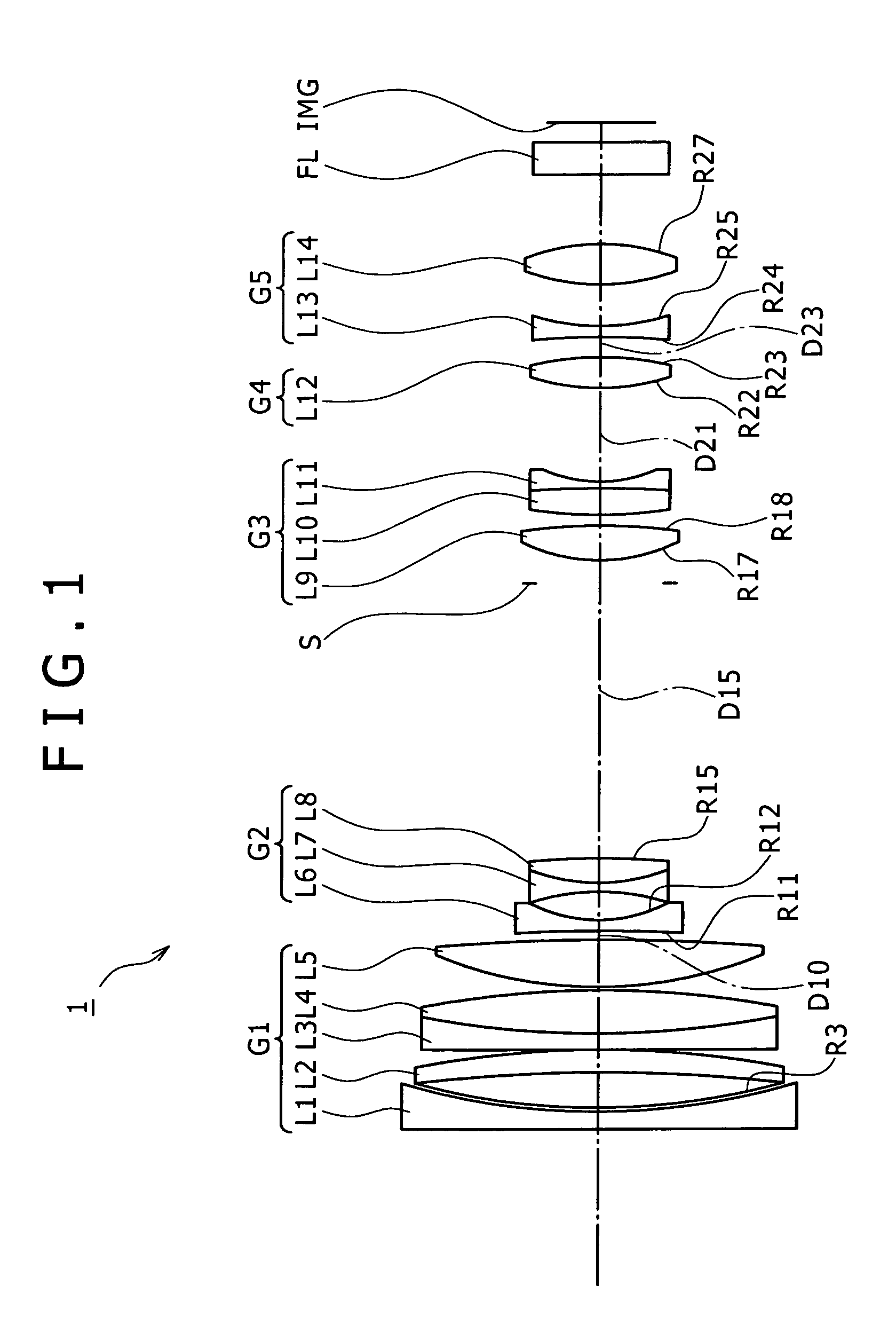
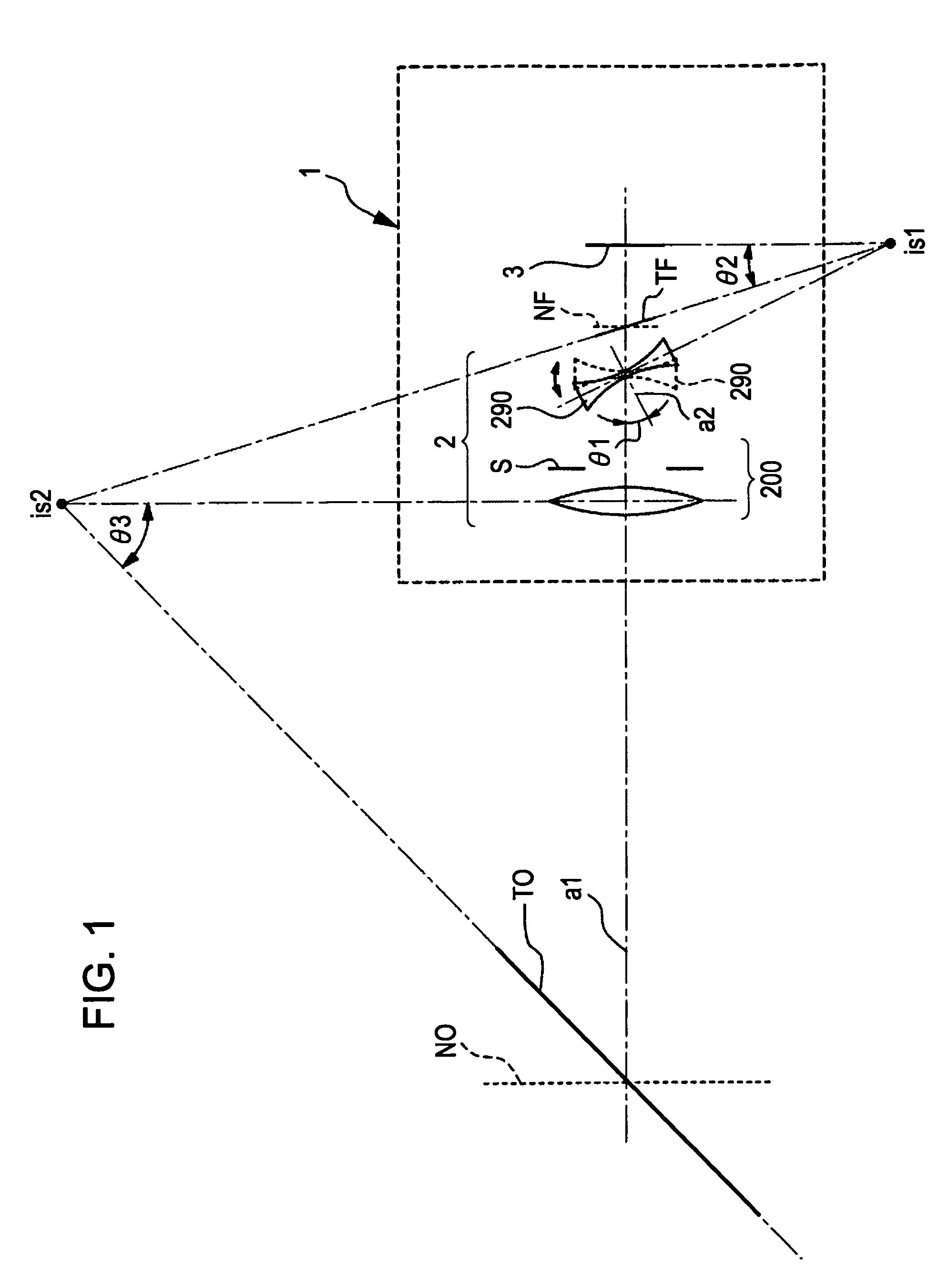
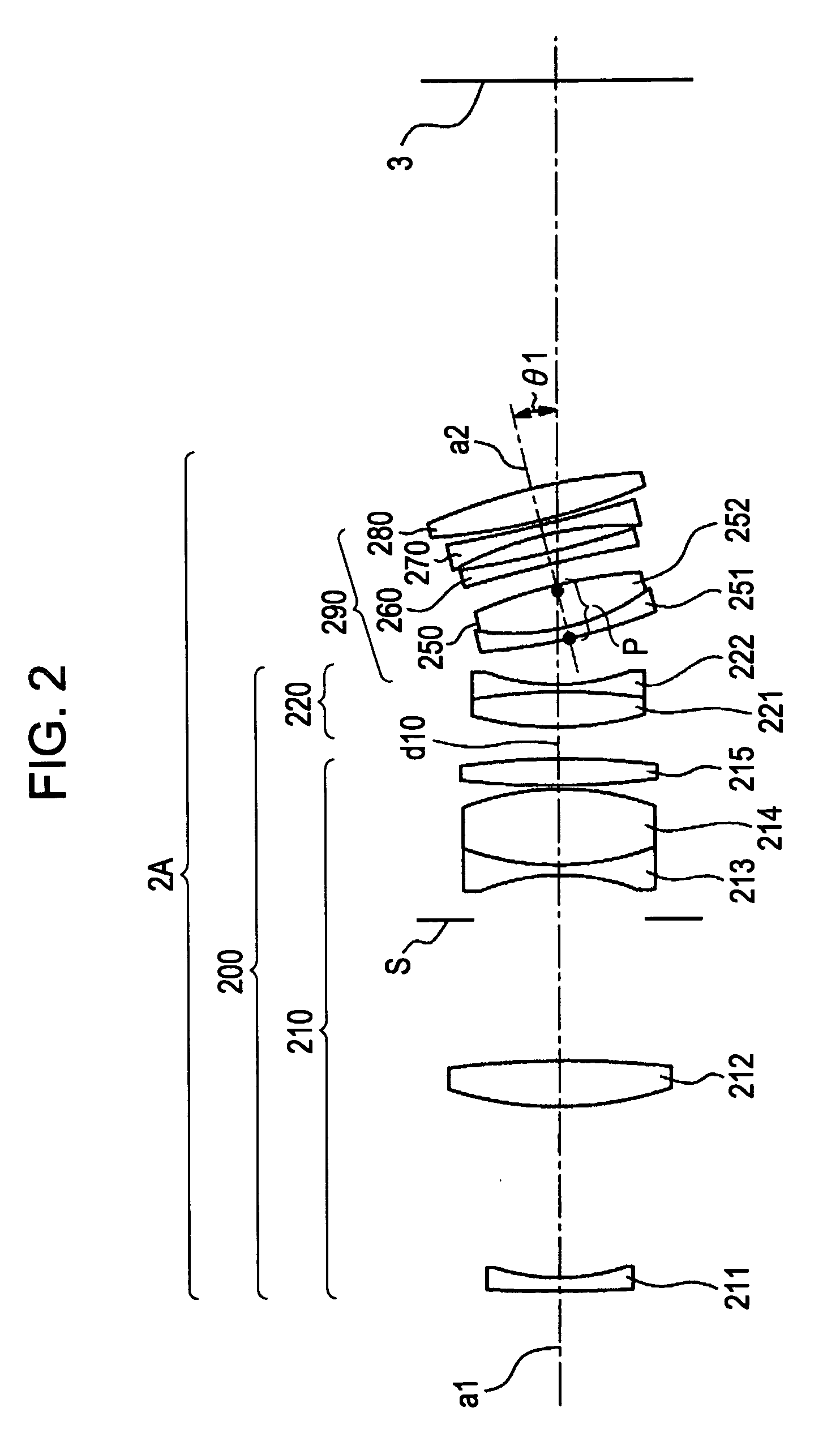
A wide-angle lens system is formed, sequentially from an object side, with a first group having a positive power, a second group having a negative power and a third group having a positive power, and at the time of focusing, only the second group is moved on an optical axis. The lens system satisfies conditional formulas of 0.3<BH1 / T1<0.7 and 0.9<f3 / f<1.8 (where BH1 is a distance from the final surface of the first group to a principal point position on the back side of the first group, T1 is a distance on the optical axis from a lens element surface of the first group closest to the side of the object to a lens element surface closest to the side of the image, f3 is the focal length of the third group and f is the focal length of the entire system).
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Method for calibrating camera measurement system
ActiveUS20140340508A1Easy to manufactureGood adhesionImage enhancementImage analysisOptical axisHorizontal orientation
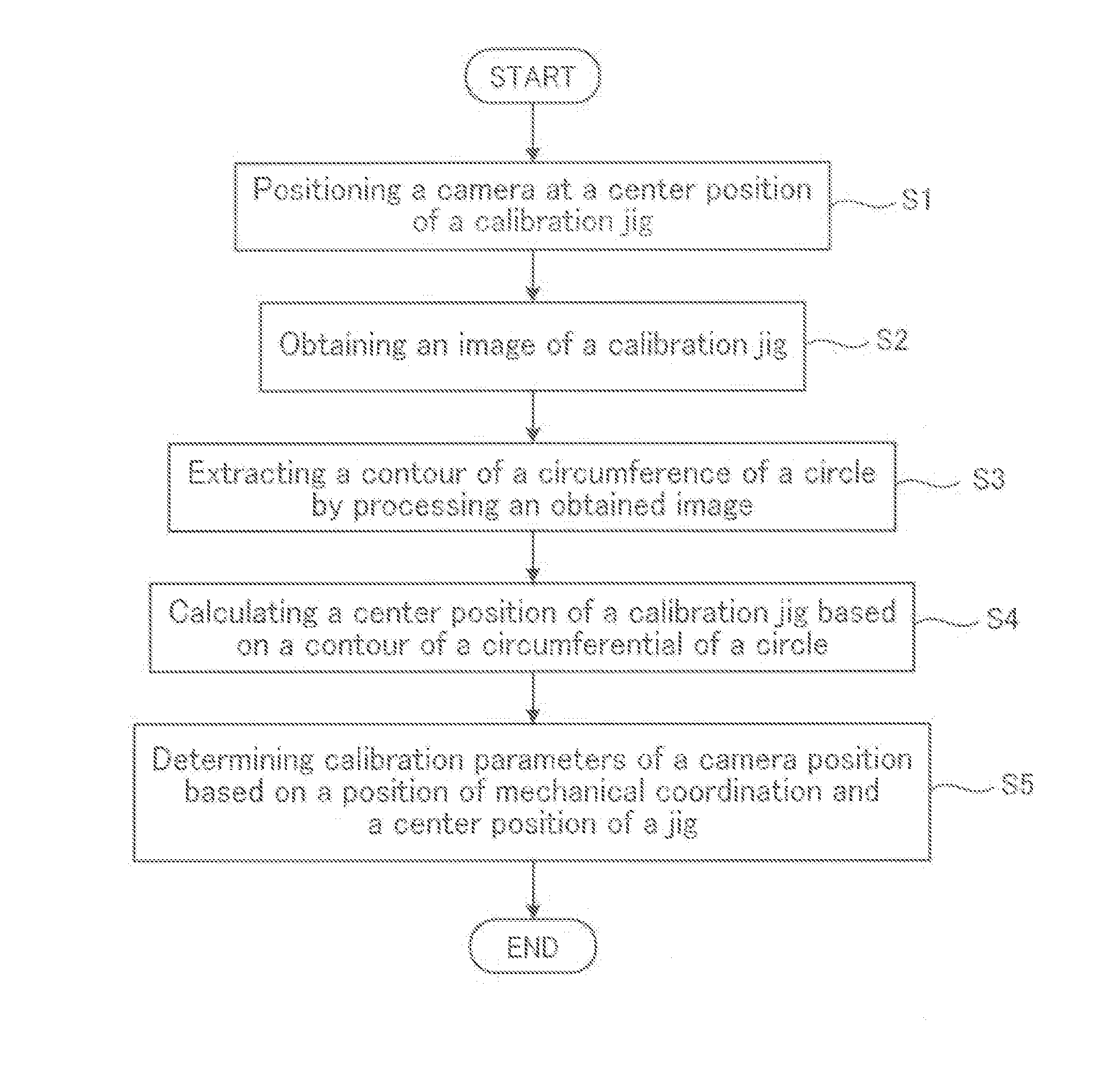
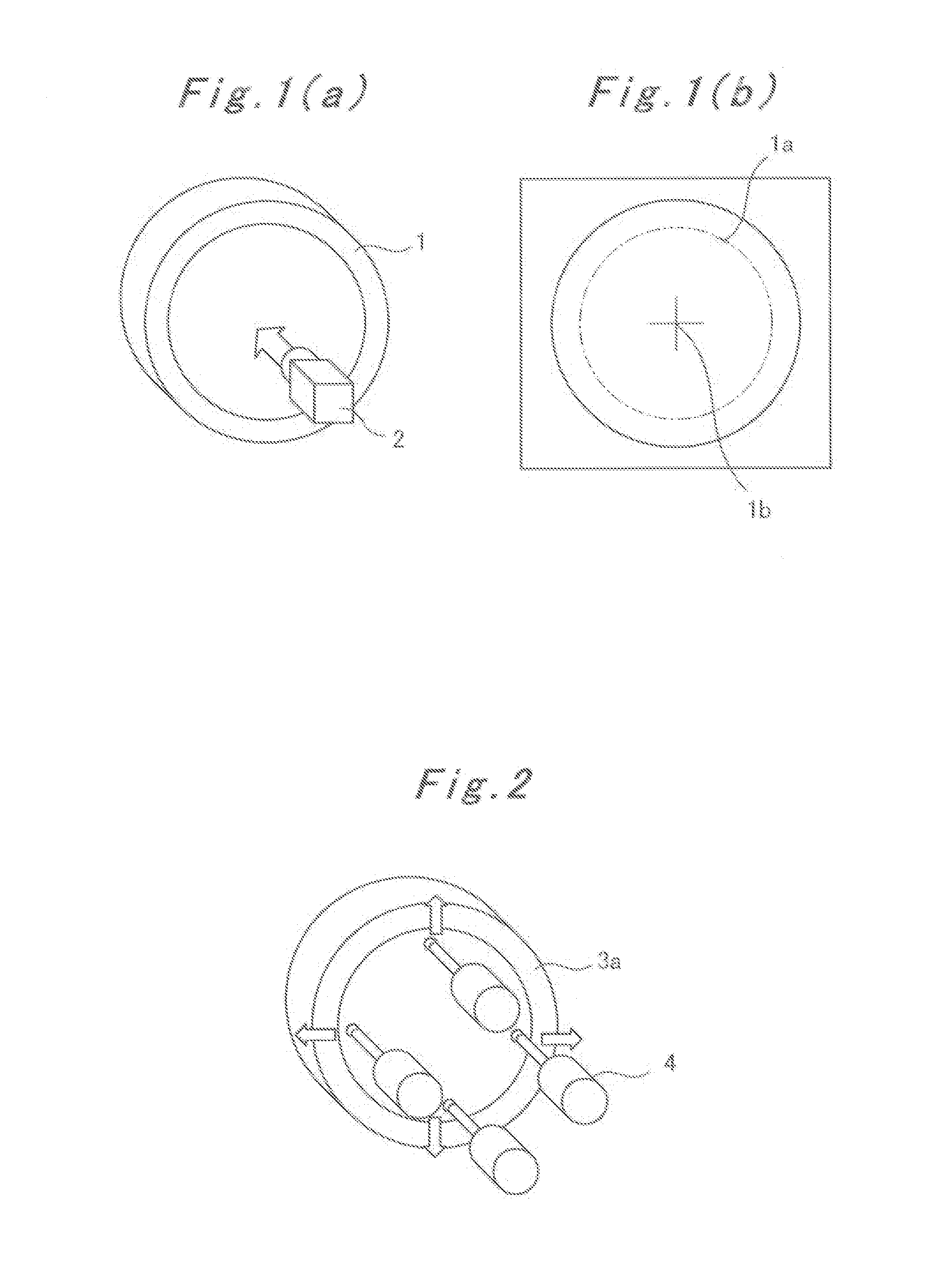
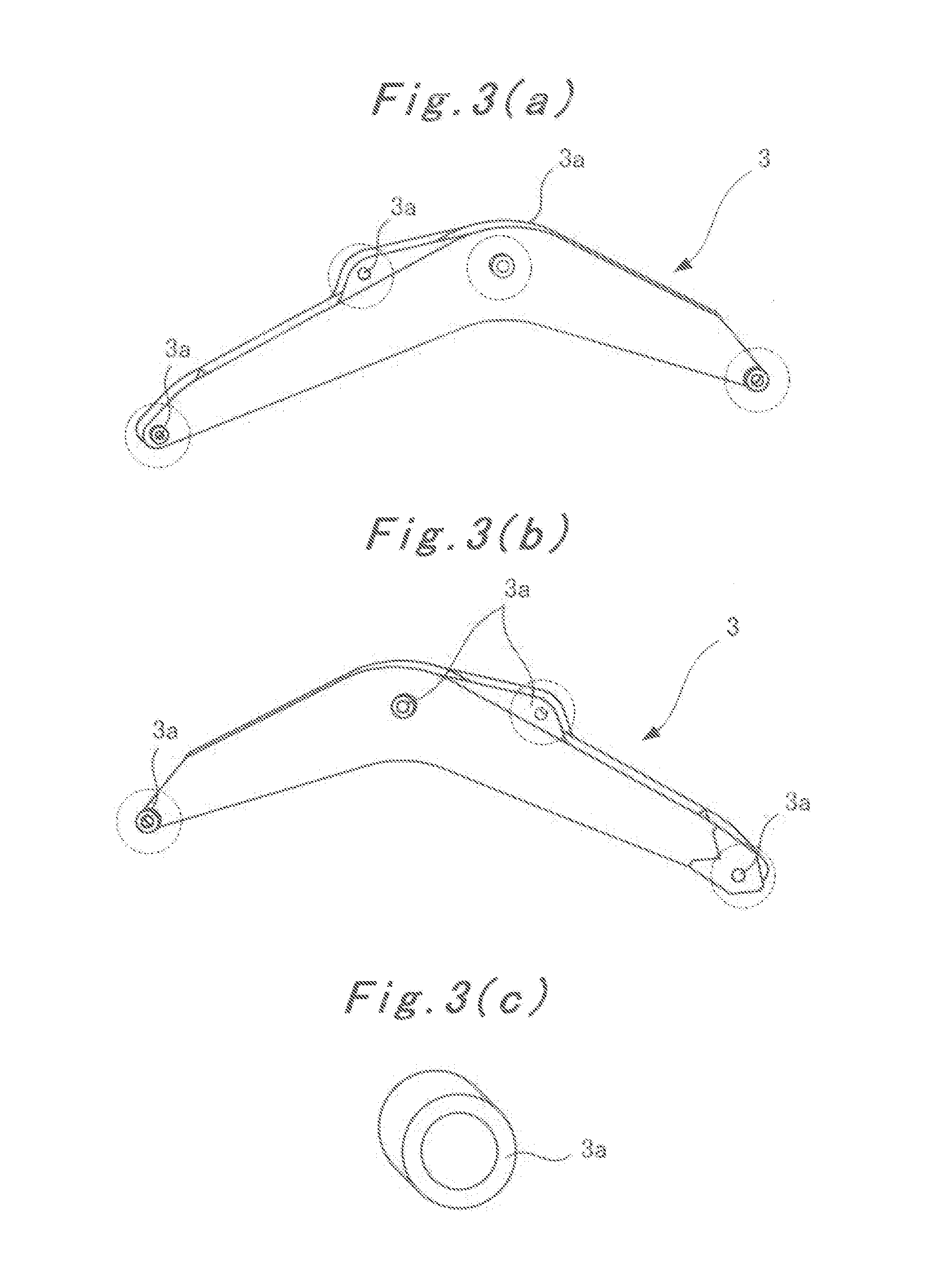
This method is characterized in that a ring-shaped jig is disposed on a workpiece on a machine tool, and the optical axis of a camera is aligned parallel to a single axis of the coordinate system of the machine tool. The jig is photographed using the camera in which the horizontal direction or the vertical direction of the camera is aligned with an axial direction other than the signal direction of the machine tool, and the circumferential shape of the jig in the image photographed by the camera is extracted as a contour. The center position of the jig in the image is calculated from the contour while all the distortion correction coefficients in tangential direction and all the distortion correction coefficients in the radial direction are ignored and set to zero. The displacements of the main point of the camera are all set to zero so as to be included in the translation distance of the camera. The translation distance, which is an external parameter of calibration, is calculated on the basis of the center position of the jig in the image and the known three-dimensional center position of the jig.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND MACHINE TOOL CO LTD
Calibration template, calibration method, calibration operation method and calibration system
PendingCN107330942APracticalFast calibrationImage enhancementImage analysisTemplate matchingComputer graphics (images)
The present invention discloses a calibration template, a calibration method, a calibration operation method and a calibration system. A substrate to be calibrated and a calibration template matching with at least two spherical calibration pieces are subjected to camera calibration, a camera to be calibrated collects a calibration image facing the calibration template, the at least two spherical calibration pieces are projected to an ellipse in the imaging of the camera to be calibrated, the calibration image comprises an array image having a fixed spacing and at least two ellipses, the major axes of the at least two ellipses are interacted, the interaction is employed to calculate the main point coordinate parameters of the camera to be calibrated. The calibration template, the calibration method, the calibration operation method and the calibration system can complete camera calibration based on a calibration image and a calibration template, and is high in practicability, fast in calibration speed and high in precision, etc.
Owner:CHENGDU TOPPLUSVISION TECH CO LTD
Zoom lens and image pickup device
ActiveUS20110157429A1Wide viewing angleSmall sizeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOphthalmologyConditional expression
Disclosed herein is a zoom lens including a first lens group, a second lens group, a third lens group, a fourth lens group, and a fifth lens group. The zoom lens satisfies following conditional expressions (1) and (2),0.03<H1′ / f1<0.3 (1)0.3<|f2| / √(fw·ft)<0.65 (2)where H1′ is an interval from a vertex of a surface nearest to the image side in the first lens group to a principal point on the image side of the first lens group (− denotes the object side, and + denotes the image side), f1 is focal length of the first lens group, f2 is focal length of the second lens group, fw is focal length of an entire lens system at a wide-angle end, and ft is the focal length of the entire lens system at a telephoto end.
Owner:SONY CORP
Macro alignment reticle sight system
ActiveUS20200271419A1Rapid and efficient visual feedbackShorten the timeSighting devicesEngineeringMechanical engineering
An aiming device is provided including an illumination device and an optical element wherein the illumination device projects a primary dot and at least one secondary alignment dot distal from the primary dot to aid a user in obtaining a view of the primary dot when the aiming device is in an aligned mode, the primary dot is visible within a field of view of the user, but the secondary alignment dot is not visible. When the aiming device is in a misaligned mode, the secondary alignment dot is visible to the user, but the primary dot is not. The secondary alignment dot provides instruction to the user to realign the aiming device relative to the field of view of the user so that the aiming device transitions to the aligned mode. A related method of operation is provided.
Owner:GRACE ENG
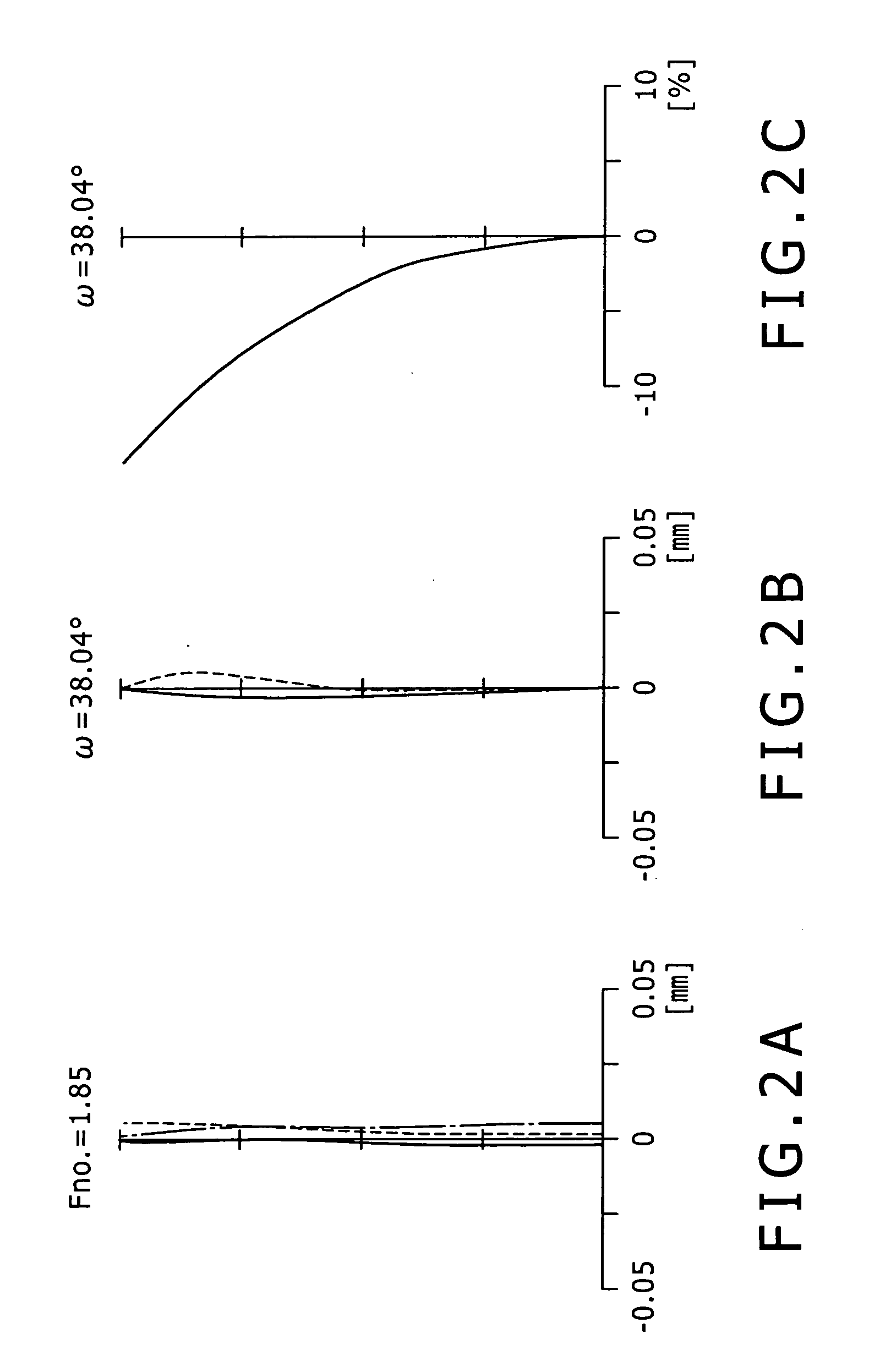
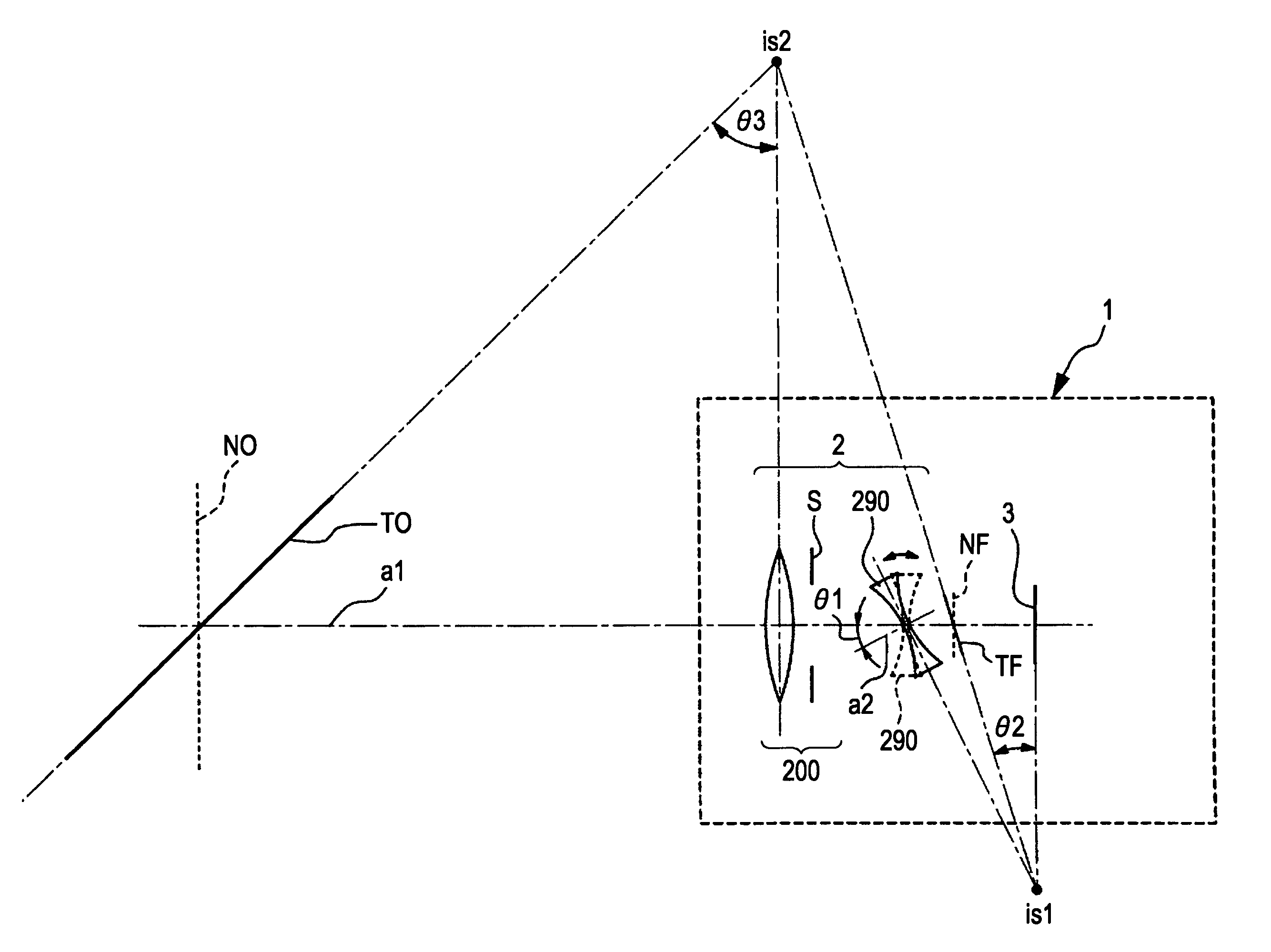
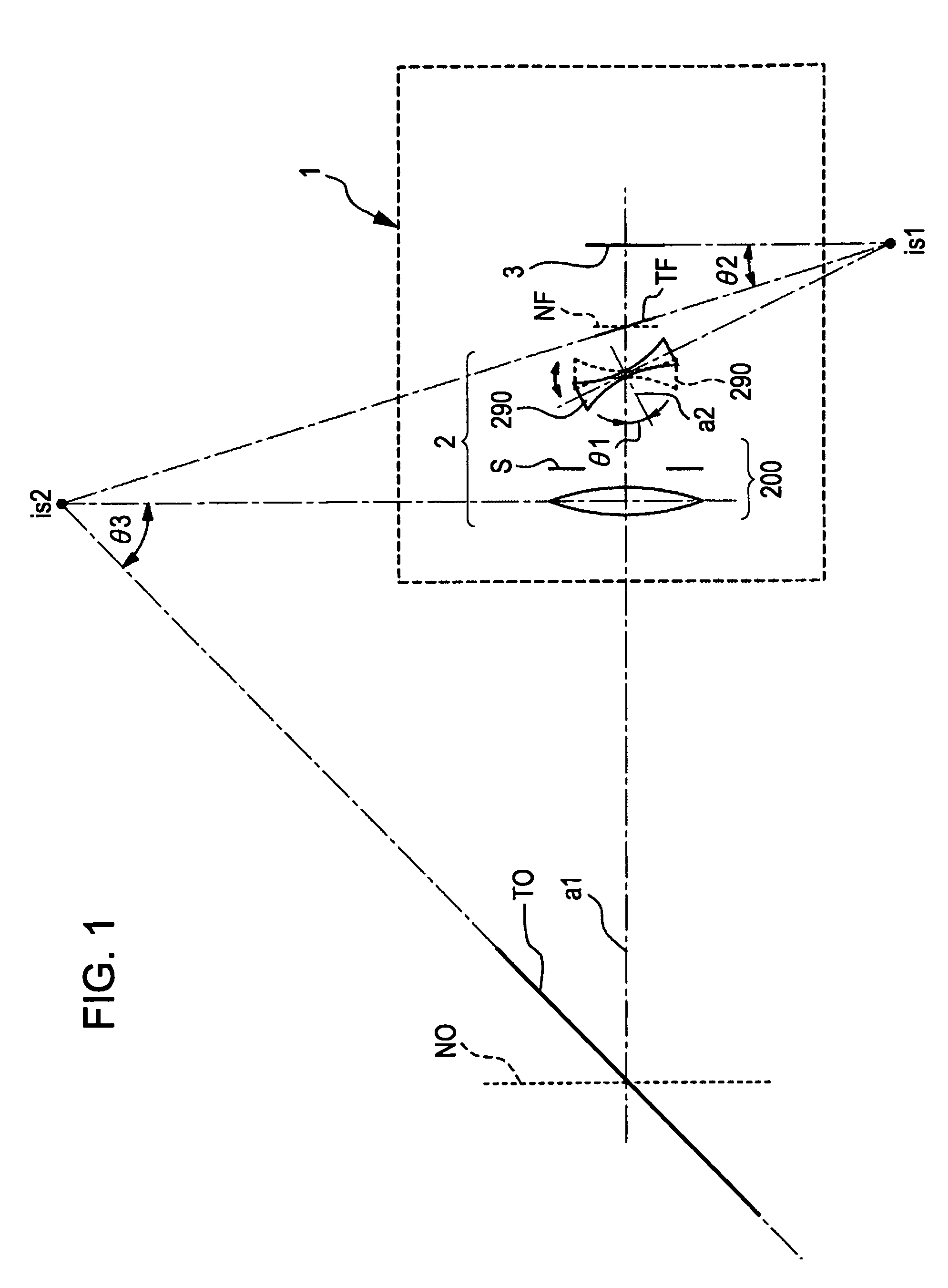
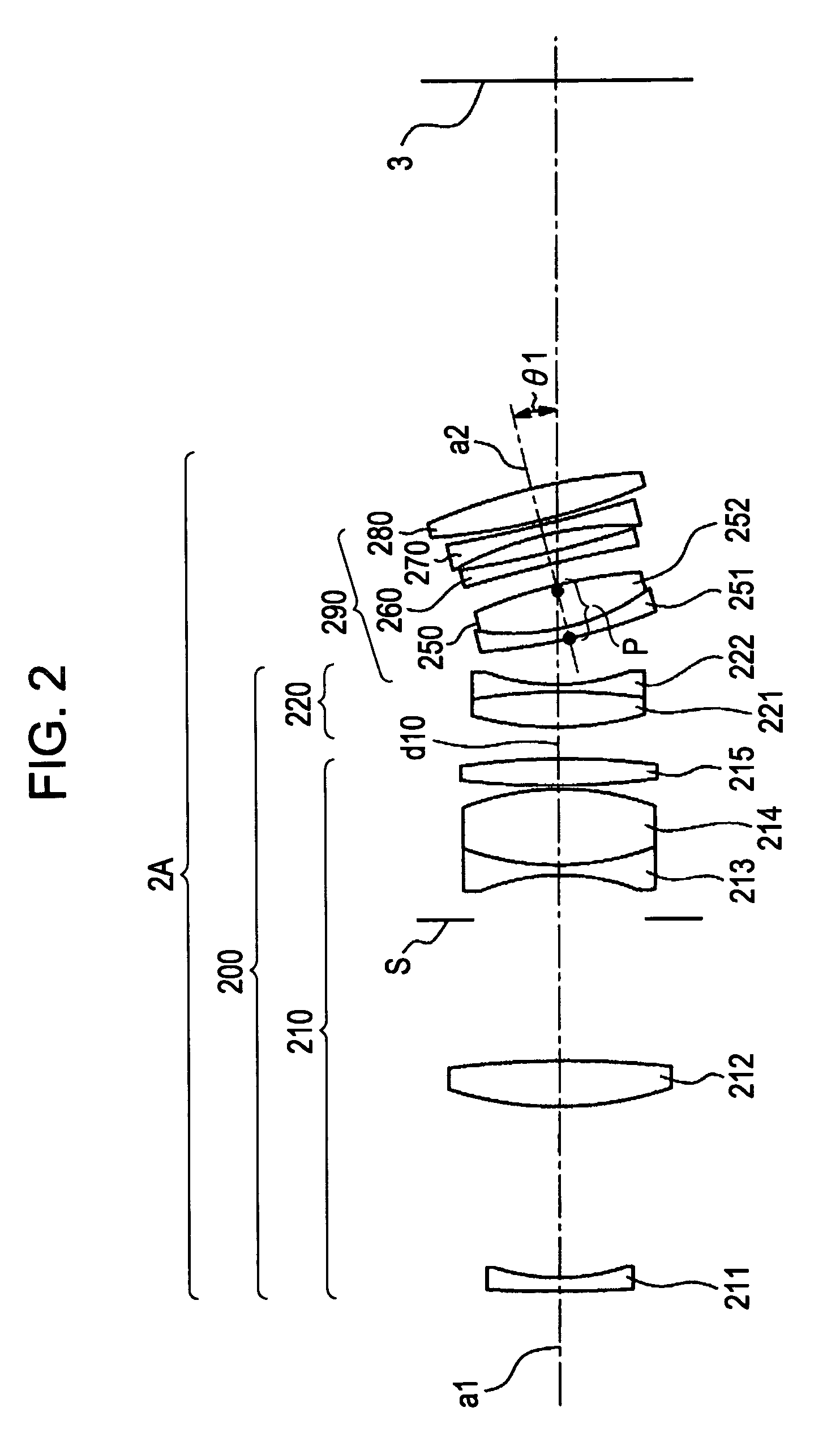
Tilt lens system and image pickup apparatus
InactiveUS7880797B2Easy to operateReduce aberrationTelevision system detailsPrintersOphthalmologyOptical axis
A tilt lens system includes a focus lens unit movable during focusing; a diaphragm sharing a primary optical axis with the focus lens unit; and a tilt lens unit, arranged on an image side of the focus lens unit and the diaphragm, having a negative refractive power and an optical axis tiltable with respect to the primary optical axis. Conditional Expressions (1) and (2) are satisfied as follows,1.3<βt<1.7 (1)0<P<H1 (2)where βt is a lateral magnification of the tilt lens unit in a not tilted state, P is a distance from a most object side surface of the tilt lens unit to a rotating center of the tilt lens unit in a tilted state, and H1 is a distance from the most object side surface of the tilt lens unit to a first principal point of the tilt lens unit.
Owner:SONY CORP
Apparatus for providing calibration data, camera system and method for obtaining calibration data
ActiveUS20200027243A1Improve robustnessLow effortImage enhancementImage analysisComputer graphics (images)Radiology
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Zoom camera calibration method
The invention discloses a zoom camera calibration method, and belongs to the field of camera calibration in machine vision. According to the invention, modeling is carried out on the imaging process and related parameters of the zoom camera, and the constraint condition that the position of the main point of the camera is not changed in the zoom process is provided. Based on the constraint condition, a calibration method based on a zoom image sequence is provided to obtain the accurate position of the main point of the camera. Aiming at a zoom camera focal length calibration problem, a self-calibration method containing additional constraint conditions is provided. Simulation test and actual calibration test results show that the method provided by the invention has high precision and canbe used in actual calibration tasks.
Owner:SHENYANG AIRCRAFT CORP
Zoom lens and image pickup device
ActiveUS8040614B2Decrease the inclinationHinders miniaturizationLensOphthalmologyConditional expression
Disclosed herein is a zoom lens including a first lens group, a second lens group, a third lens group, a fourth lens group, and a fifth lens group. The zoom lens satisfies following conditional expressions (1) and (2), 0.03<H1′ / f1<0.3 (1) 0.3<|f2| / √(fw·ft)<0.65 (2) where H1′ is an interval from a vertex of a surface nearest to the image side in the first lens group to a principal point on the image side of the first lens group (− denotes the object side, and + denotes the image side), f1 is focal length of the first lens group, f2 is focal length of the second lens group, fw is focal length of an entire lens system at a wide-angle end, and ft is the focal length of the entire lens system at a telephoto end.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method for calibrating parabolic catadioptric camera by using separate image of double balls and image of circular point
InactiveCN105321181APhysical scale is not requiredHigh precisionImage analysisMedicineComputer graphics (images)
The present invention relates to a method for calibrating a parabolic catadioptric camera by using a separate image of double balls and an image of a circular point. An image of double balls used as targets is shot by using the parabolic catadioptric camera, and the targets are separated on an image plane. A main point of an intrinsic parameter of the camera is determined by four groups of imaginary antipodal image points, which are correspondingly formed by imaginary intersection points of ball images in the catadioptric image and imaginary intersection points of antipodal ball images; on the basis of obtaining the main point, vanishing lines of planes where two groups of parallel projection small circles of double balls on a unit virtual ball are positioned are solved, so that the image of the circular point on the plane is determined and finally, other intrinsic parameter of the camera are solved by using the constraint of image of the circular point to the intrinsic parameter of the camera. According to the method provided by the present invention, full automatic calibration can be implemented, and errors caused by measurement in the calibration process are reduced. Since all the projection contour lines of the balls in the image can be extracted, thereby improving the calibration accuracy of the camera.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Tilt lens system and image pickup apparatus
InactiveUS20080309815A1Easy to operateReduce aberrationTelevision system detailsPrintersOptical axisCentre of rotation
A tilt lens system includes a focus lens unit movable during focusing; a diaphragm sharing a primary optical axis with the focus lens unit; and a tilt lens unit, arranged on an image side of the focus lens unit and the diaphragm, having a negative refractive power and an optical axis tiltable with respect to the primary optical axis. Conditional Expressions (1) and (2) are satisfied as follows,1.3<βt<1.7 (1)0<P<H1 (2)where βt is a lateral magnification of the tilt lens unit in a not tilted state, P is a distance from a most object side surface of the tilt lens unit to a rotating center of the tilt lens unit in a tilted state, and H1 is a distance from the most object side surface of the tilt lens unit to a first principal point of the tilt lens unit.
Owner:SONY CORP
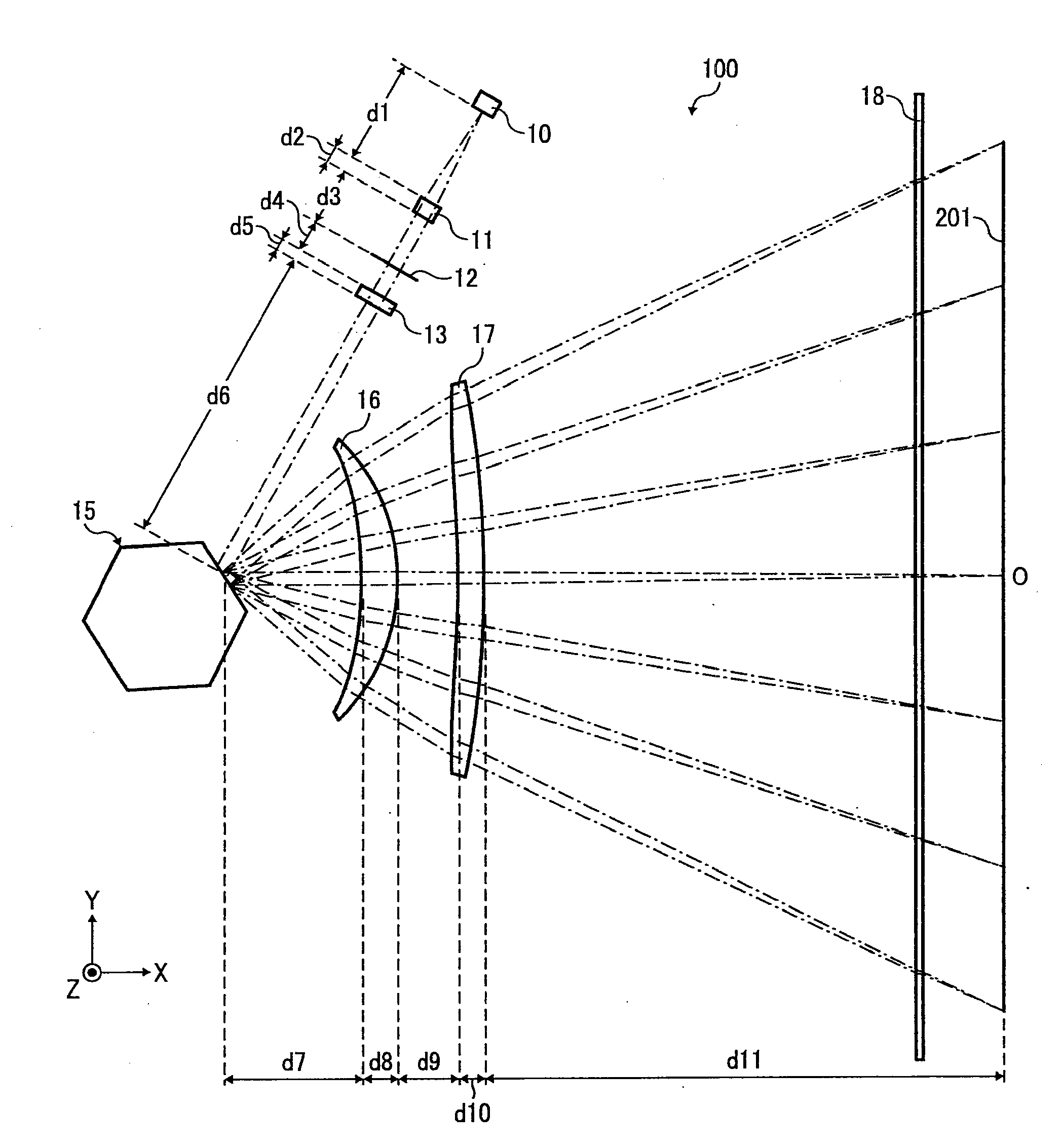
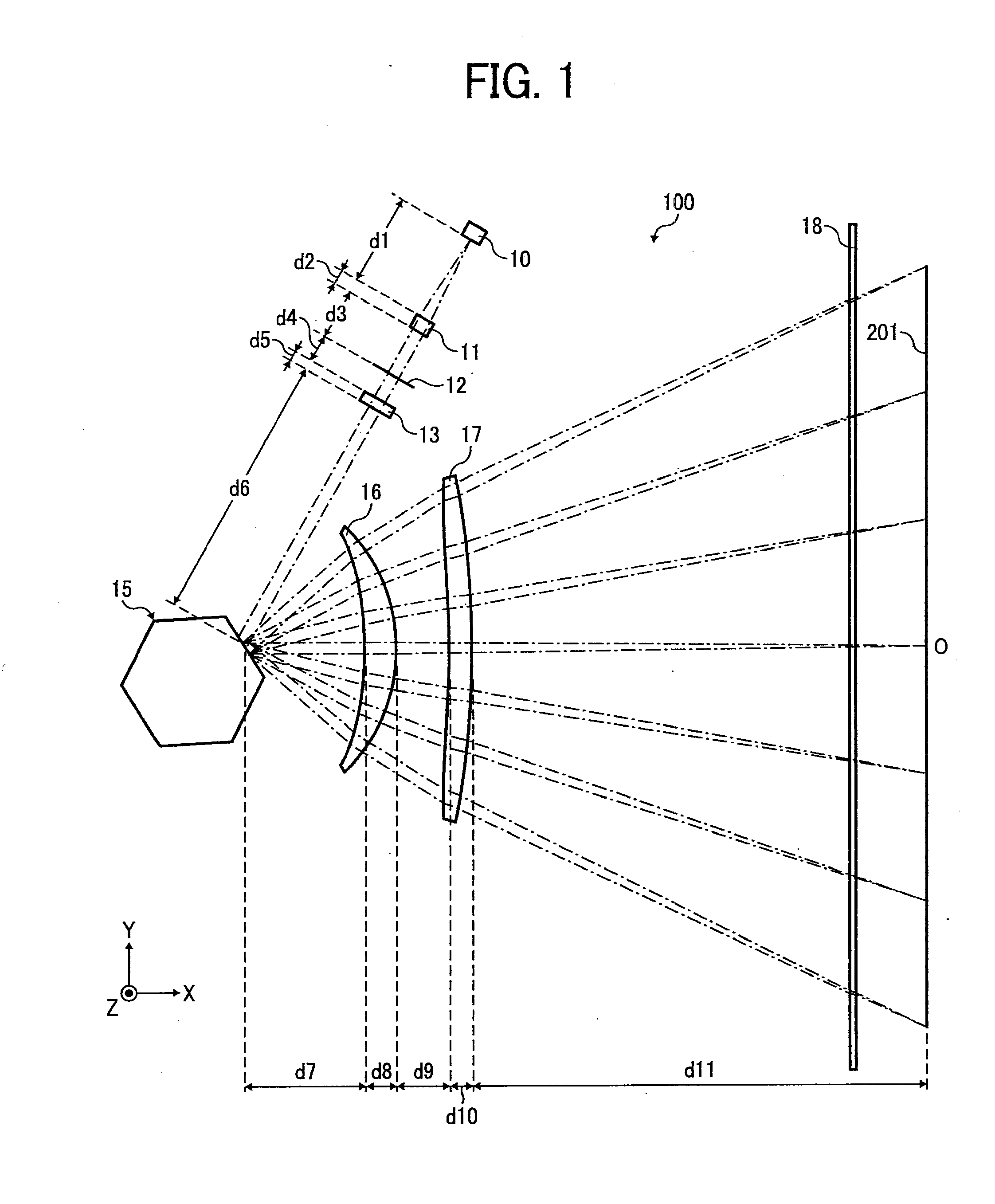
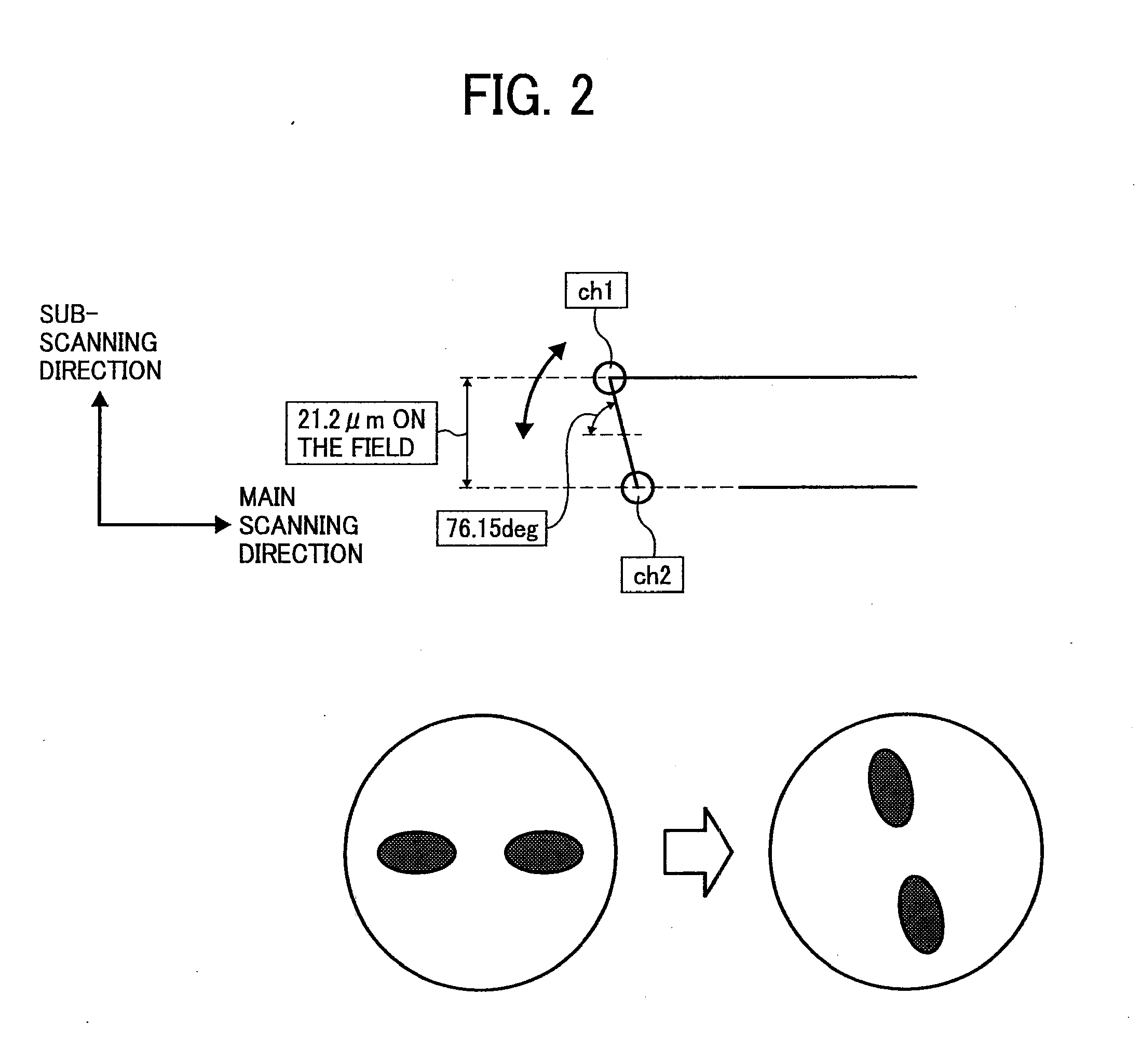
Optical scanning device and image forming apparatus
An optical scanning device includes: a light source; an optical deflecting unit that deflects a light beam emitted from the light source to scan on a scanning surface in main-scanning direction; and a scanning optical system that includes a first scanning lens and a second scanning lens that converge the light beam that is deflected onto the scanning surface. Distance between an exit surface of the first scanning lens and an incident surface of the second scanning lens is shorter than distance between a deflection facet of the optical deflecting unit and an incident surface of the first scanning lens, an exit surface of the second scanning lens is nearer to the deflection facet than a midpoint between the deflection facet and the scanning surface, and an image-surface-side principal point of the scanning optical system in sub-scanning direction is nearer to the scanning surface than the midpoint.
Owner:RICOH KK
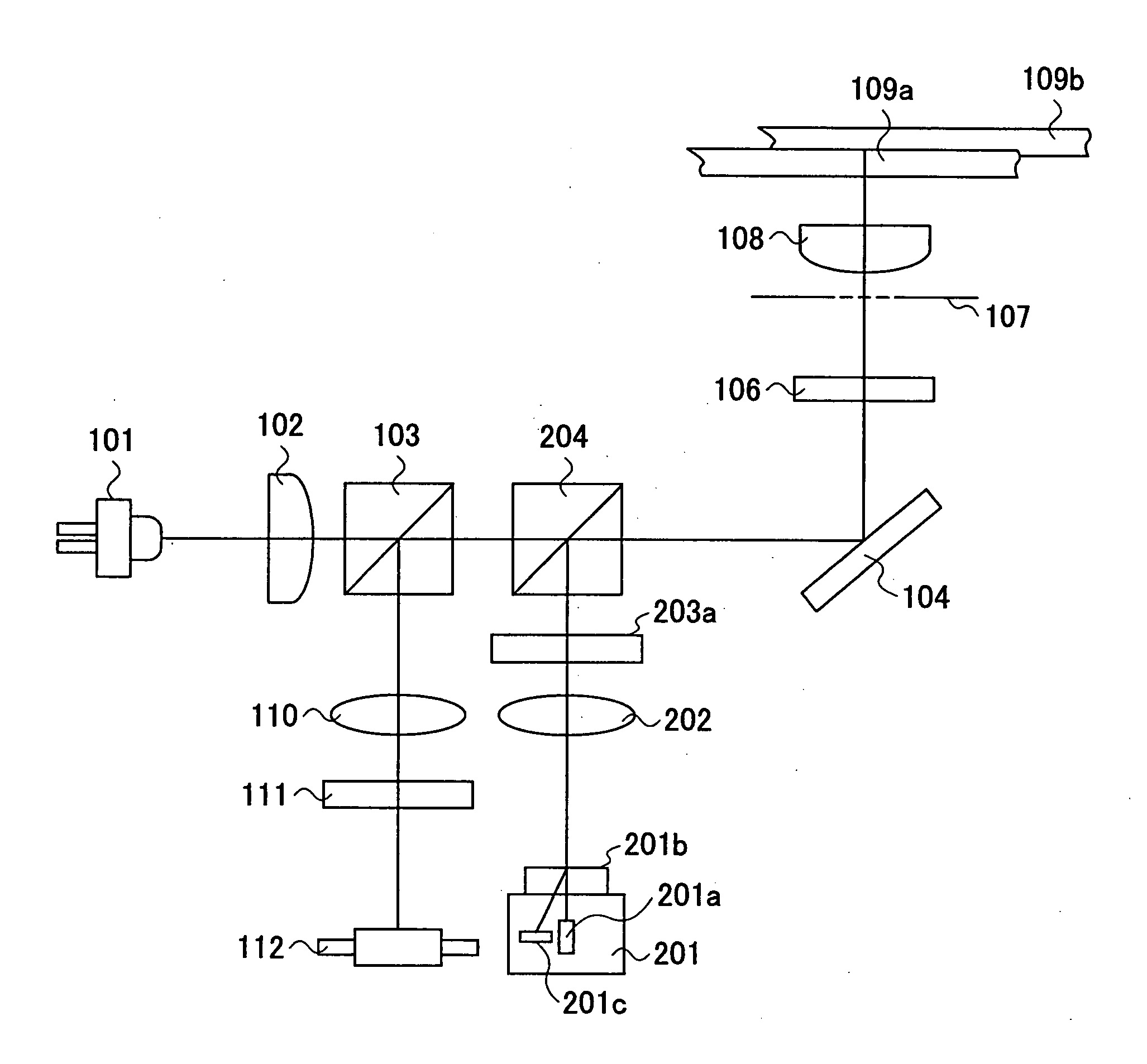
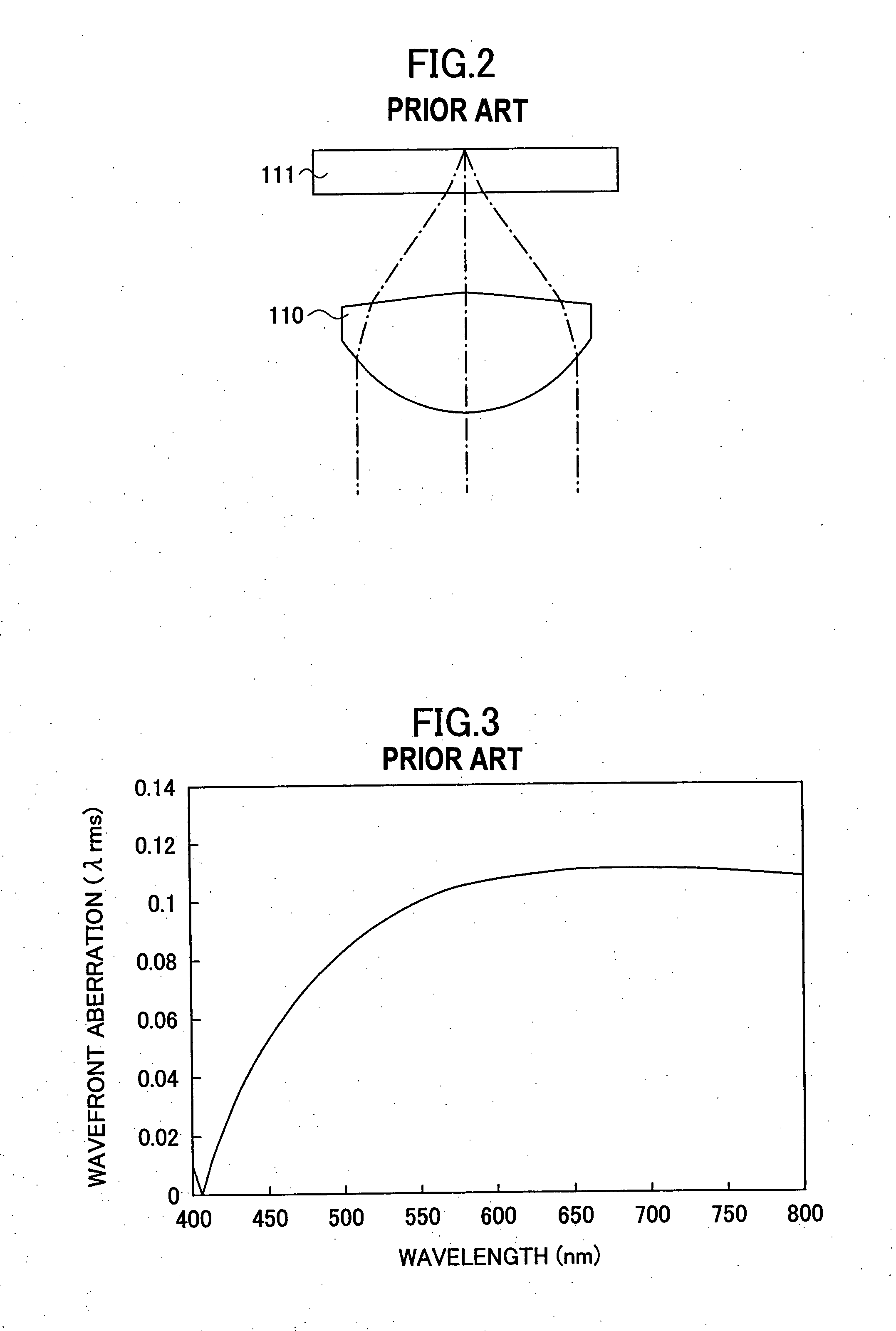
Objective lens, optical pickup, and optical information processing apparatus using the same
InactiveUS20070223350A1Reduce weightSimplify the assembly processOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageOptical pickupInformation processing
An optical pickup includes a first optical source producing a first optical beam having a wavelength λ1, a second optical source producing a second optical beam having a wavelength λ2 (λ1<2), and a single objective lens focusing any of the first and second optical beams to an optical recording medium, the first optical beam is incident to the objective lens as a parallel beam and the second optical beam is incident to the objective lens as a divergent optical, wherein an aperture is provided at a front side of the objective lens with offset from a principal point at the front side by a distance t given by an equationt=L−NA1·f / tan(asin(NA2obj)),wherein f represents a focal distance of the objective lens, NA1 represents the numerical aperture at the side of the image surface when the first optical source is turned on, NA2obj represents the numerical aperture at the front side when the second optical source is turned on, and L represents the object distance at the time when the second optical source is turned on.
Owner:RICOH KK
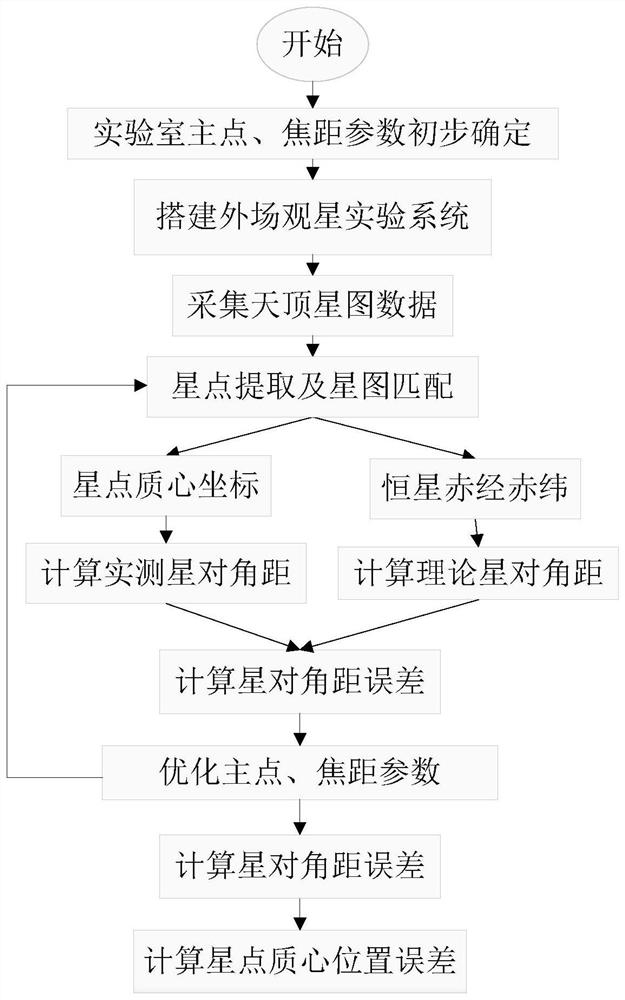
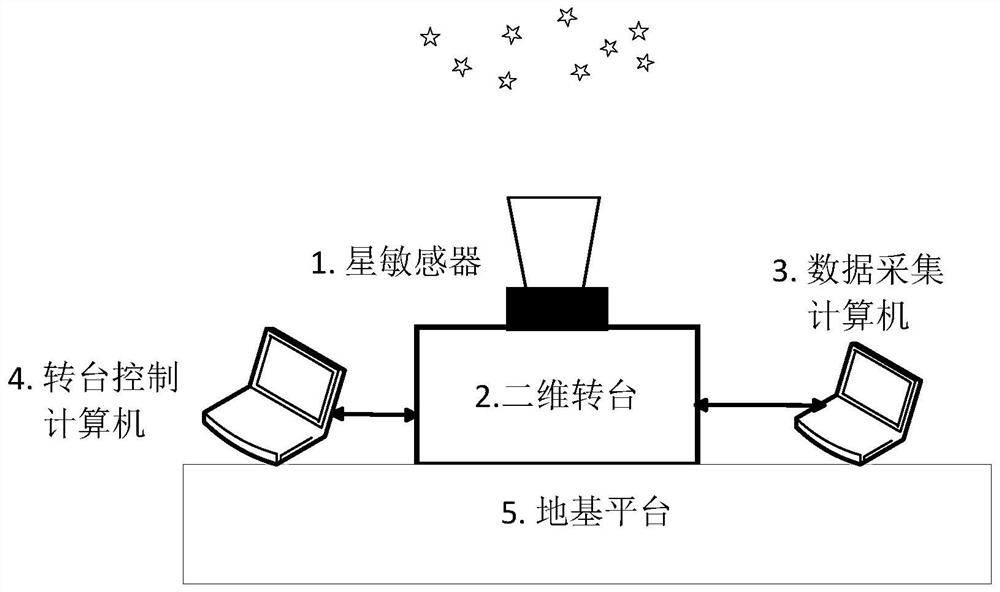
External field measurement method for star point mass center position precision of star sensor
InactiveCN113218577AAccurate measurementAccurate assessmentStatic/dynamic balance measurementNavigation by astronomical meansFixed starsSingle star
The invention discloses an external field measurement method for star point centroid position precision of a star sensor. Matched star point centroid coordinates and corresponding right ascension and declination coordinates are obtained through an external field star observation experiment of the star sensor; the star point centroid coordinates, the optimal principal point and the focal length value are used to calculate a star diagonal distance measurement value; calculating is carried out by using the corresponding right ascension and declination coordinates to obtain a star diagonal distance theoretical value; then, the star diagonal distance error can be calculated; the relationship between a star diagonal distance error and a star point mass center position error is deduced theoretically on the basis; and finally, the position precision of the mass center of the star point is calculated, and a reliable evaluation means is provided for evaluating the position precision of the mass center of the star point of a high-precision matching type star sensor and a small-field-of-view single-star tracker. The error caused by utilizing a single-star simulator and a parallel light tube to simulate the starlight of a fixed star in a laboratory is reduced, so that the measurement and evaluation of the star point mass center position precision of the star sensor are more accurate.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Lens system
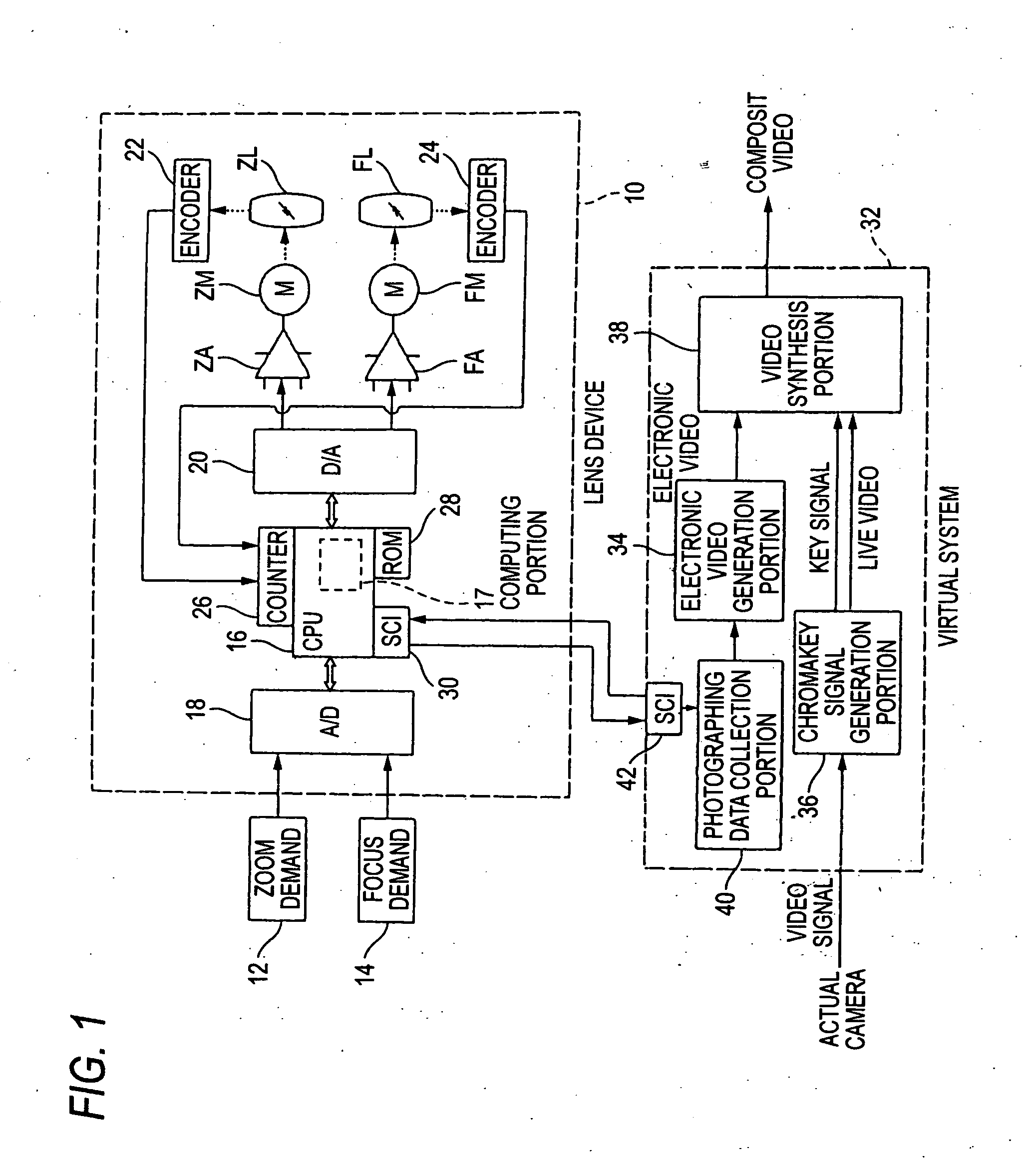
InactiveUS20050195311A1Highly-accurate photographing dataReduce laborTelevision system detailsColor television detailsInformation transmissionOphthalmology
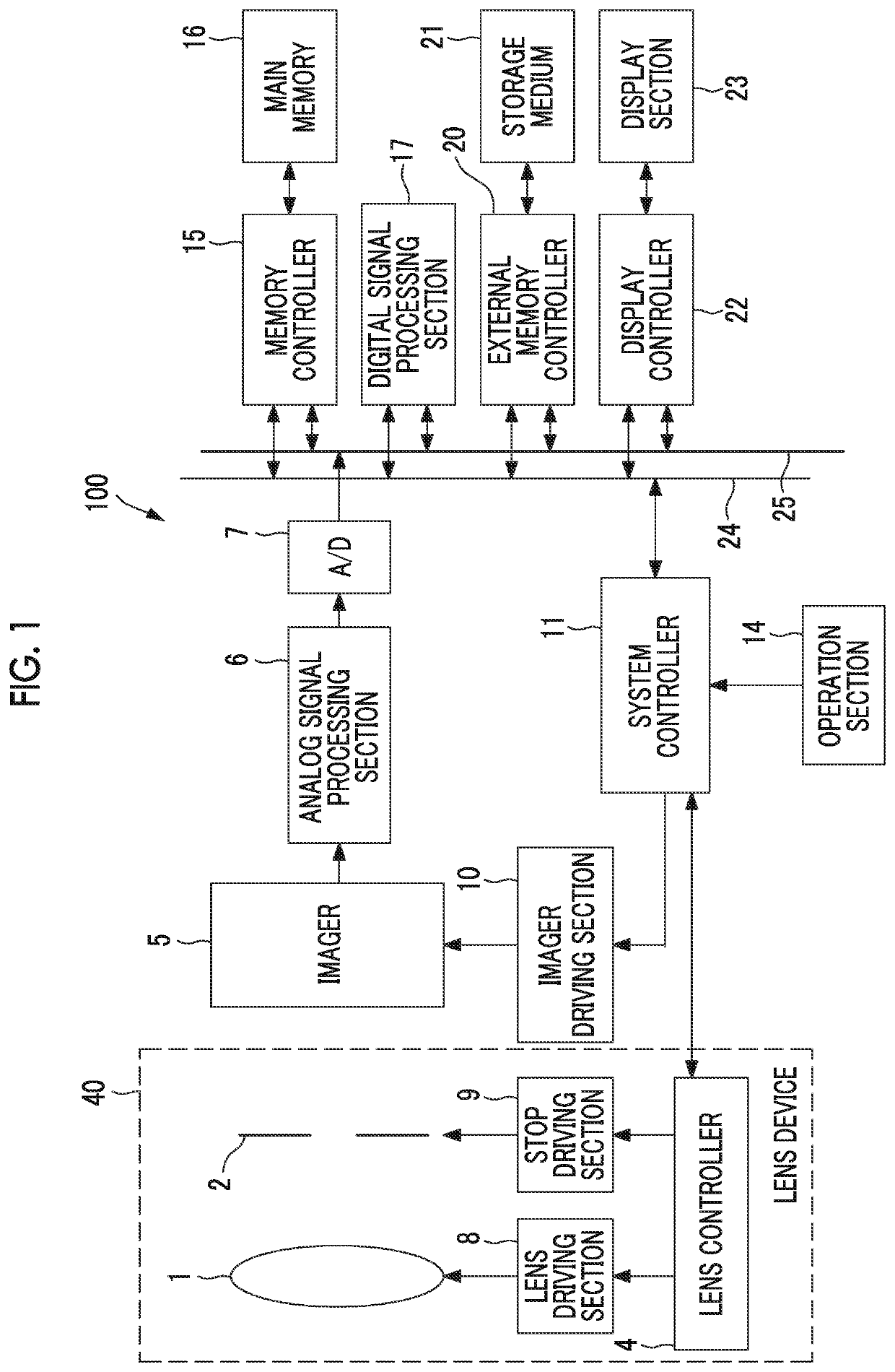
To provide a lens system which is to be used with a virtual system and which can curtail time and labor required by settings of the virtual system by outputting data pertaining to an angle of view, an object distance, and a principal point position, all being required by the virtual system, the lens device of an actual camera used for photographing an actual video to be used by the virtual system includes a CPU determining information about the angle of view, the object distance, and the principal point position, all being required to set a virtual camera in the virtual system, on the basis of a zoom position and a focus position detected by encoders, and transmits the information to the virtual system.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Mobile robot
PendingCN106826749AImprove performanceImprove the success rate of scene recognitionManipulatorData controlComputer graphics (images)
The invention discloses a mobile robot which comprises a robot body, a camera and a central processor, wherein the camera is used for acquiring an image of the surroundings for the mobile robot; the central processor is connected with the robot body and the camera and is used for processing the image data acquired by the camera and controlling a traveling component of the robot body to respond according to the processed image data; wherein, the optic center of the camera is far away from the center of the robot body; and the orthographic projection of the principal optic axis of the camera on the upper surface of the robot body and the orthographic projection of a straight line on the upper surface form a first included angle greater than o degree, and the straight line passes through the center of the robot body and a principal point on an image plane of the camera. When the mobile robot turns, the optical parallax of the camera is larger, and the image acquisition direction greatly varies to improve positioning precision and scene recognition precision. The invention further discloses another mobile robot.
Owner:SHENZHEN XILUO ROBOT CO LTD
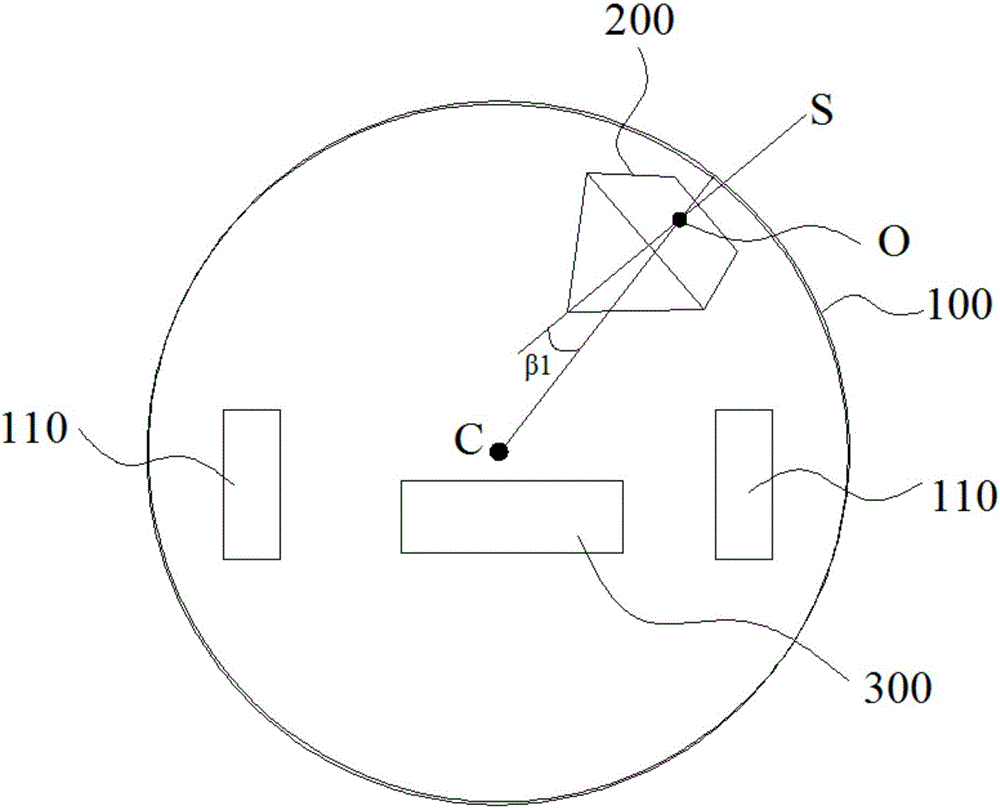
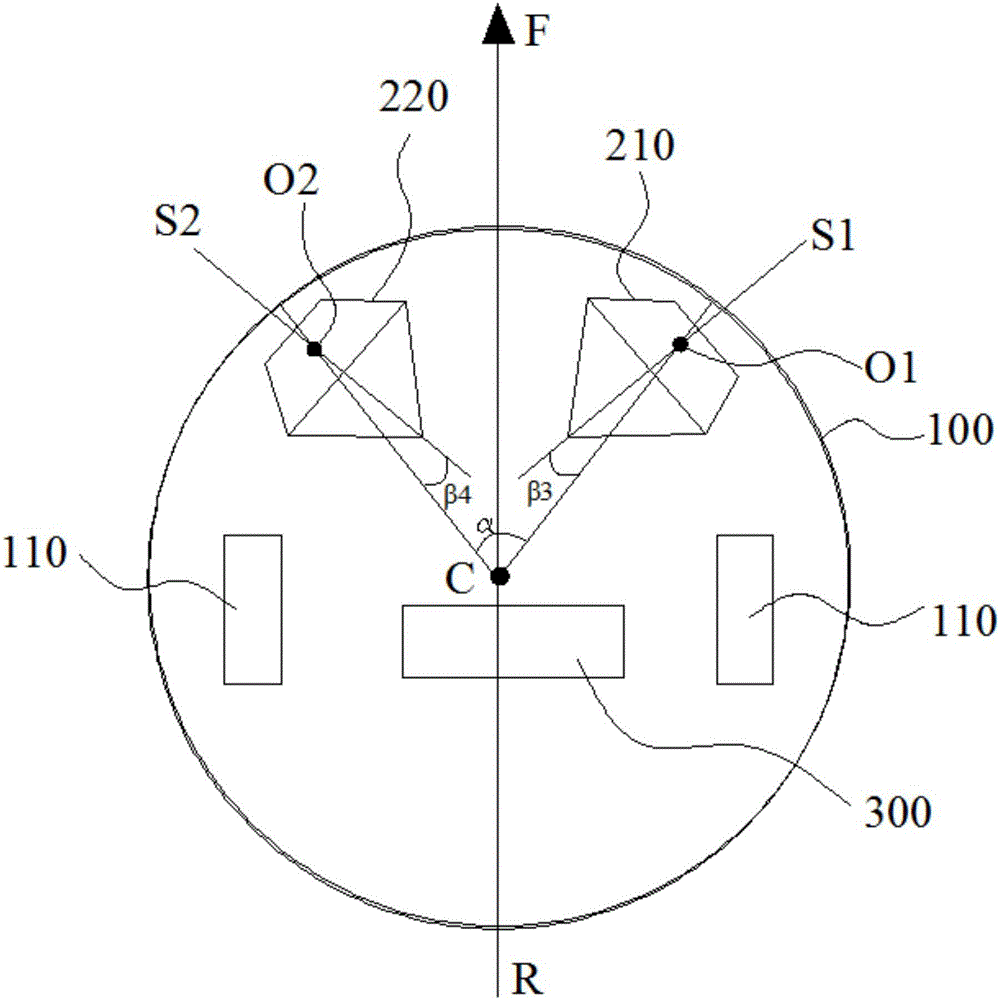
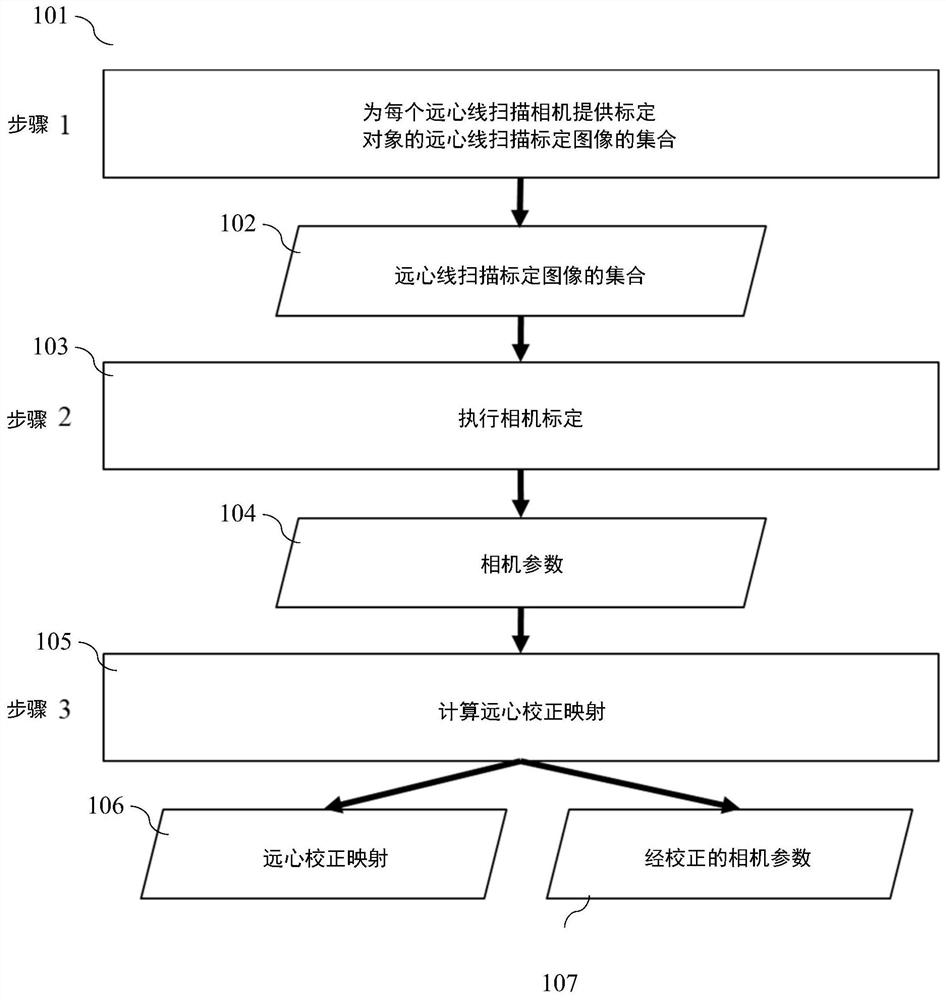
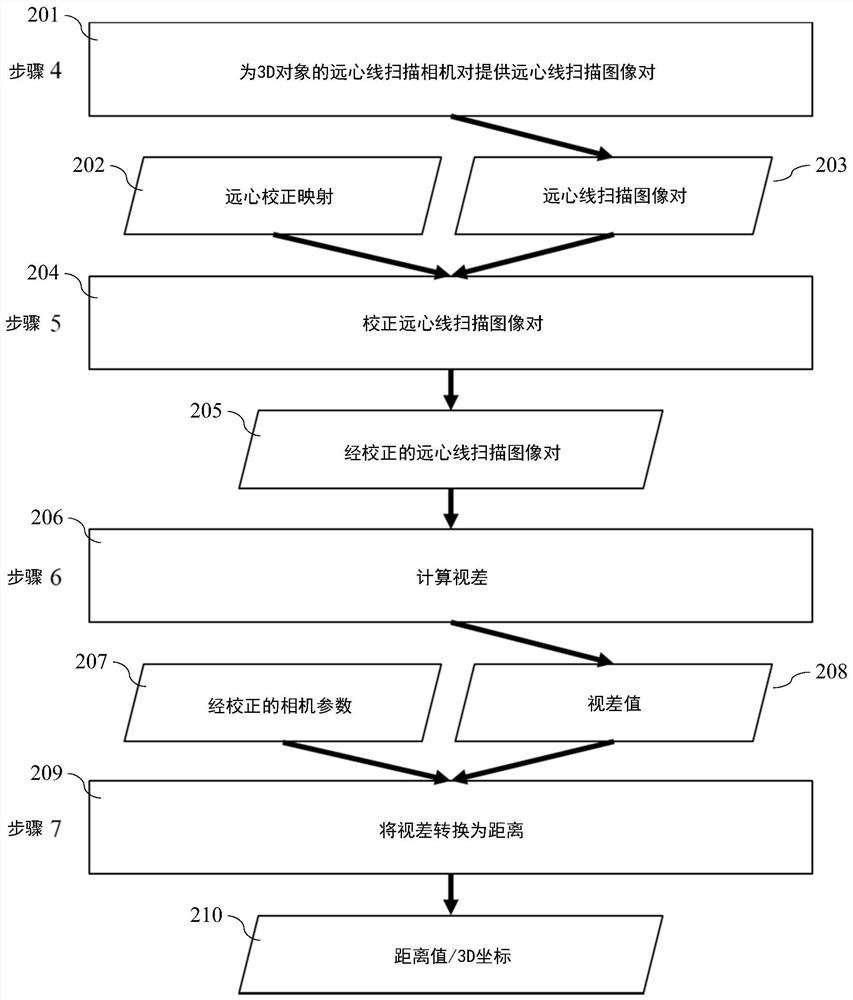
System and method for efficient 3D reconstruction of objects with telecentric line-scan cameras
PendingCN113538589ADetails involving processing stepsImage enhancementStereo matchingComputer graphics (images)
Disclosed are a system and method for efficient 3d reconstruction of objects with telecentric line-scan cameras. In this invention, systems and methods are described that allow performing stereo reconstruction with line-scan cameras in general configurations. Consequently, the cumbersome exact alignment of the sensor lines becomes superfluous. The proposed method requires that telecentric lenses instead of perspective lenses are mounted on the line-scan cameras. In this case, the images can be accurately rectified with stereo rectification. The rectified images can be used to perform an efficient stereo matching. The method comprises a camera model and a calibration procedure that allow to precisely model the imaging process, also including the modelling of lens distortions even if the sensor lines are not exactly mounted behind the principal points. This ensures a high accuracy of the resulting 3D reconstruction.
Owner:MVTEC SOFTWARE
Internal and external parameter calibration method based on known camera position
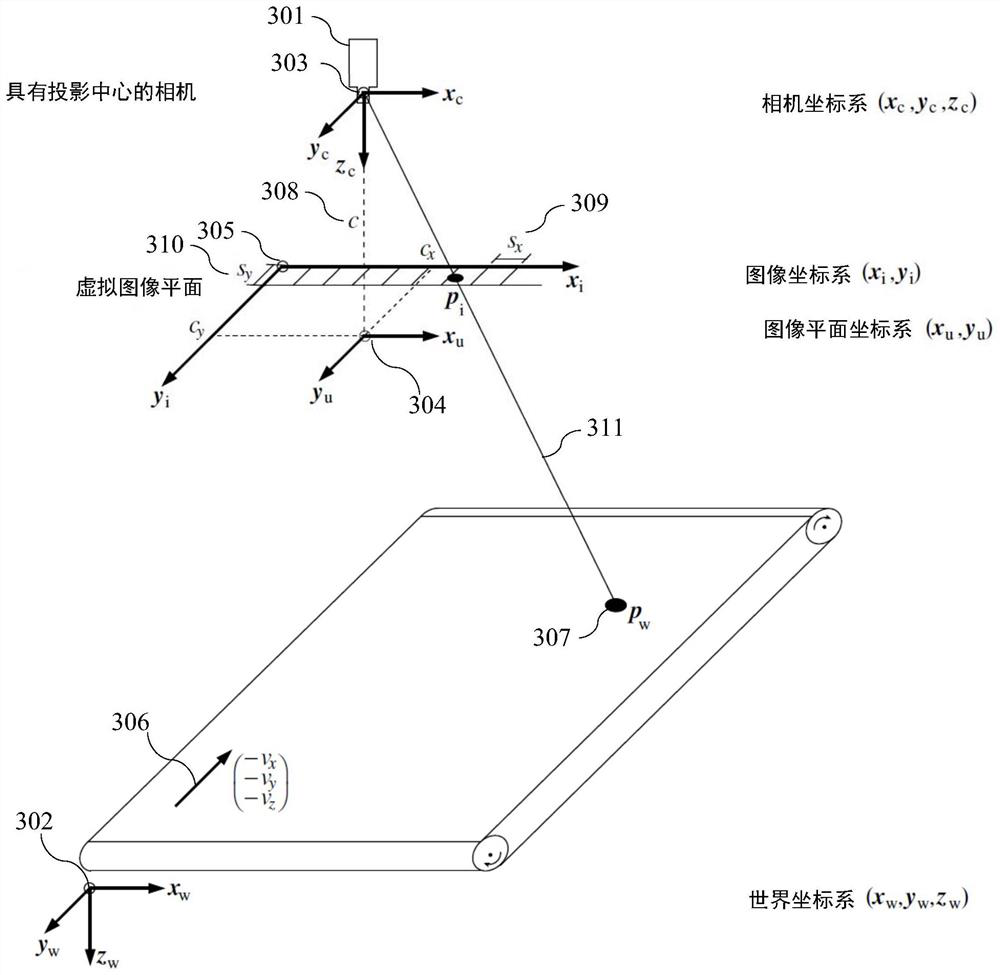
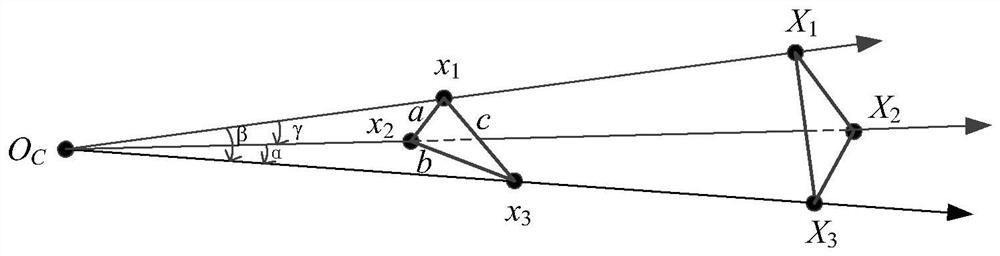
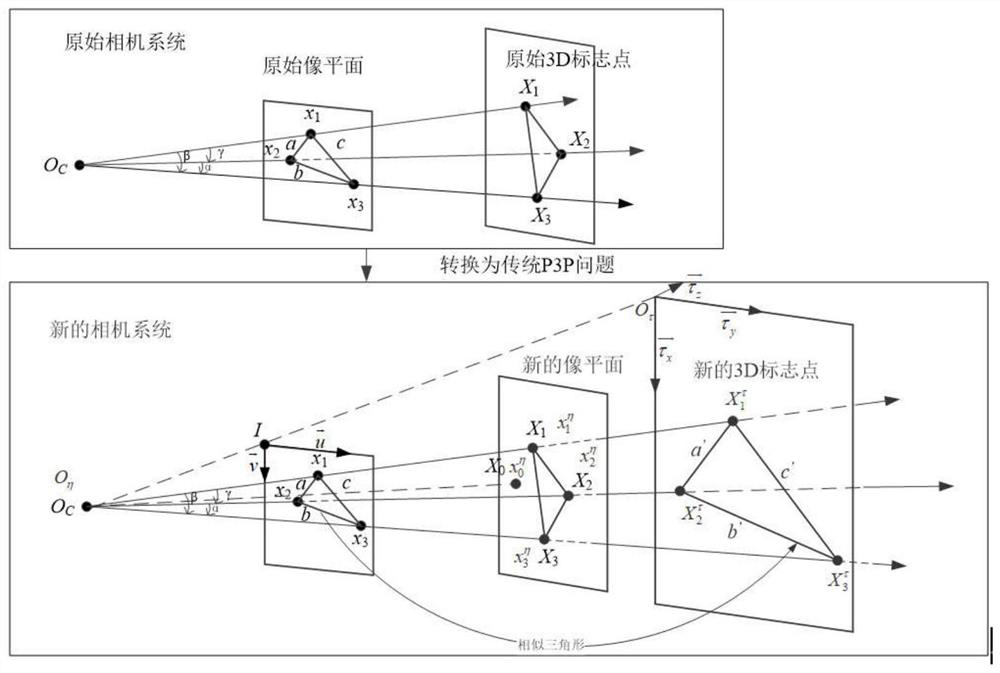
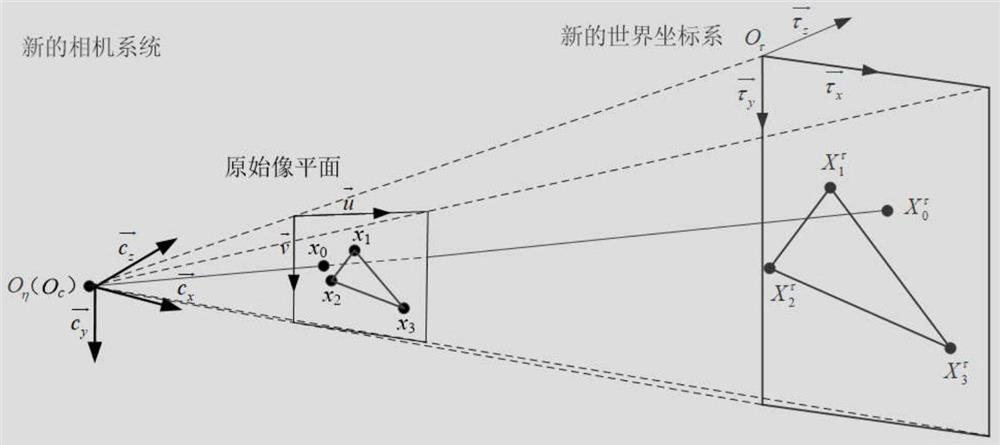
The invention belongs to the technical field of machine vision, photogrammetry, SLAM and the like, and provides an internal and external parameter calibration method based on a camera position, which only needs to arrange three mark points, measure the positions of a camera and the mark points and shoot the image of the mark points to obtain the imaging position of the mark points in the image. Under the condition that a main point and a focal length of a camera are unknown, a new camera system is established, a solving problem is converted into a traditional P3P problem, an intermediate variable and a relation between an intermediate coordinate system and an original coordinate system are solved through a P3P algorithm, and finally, solving of internal and external parameters of the camera is completed according to the relation between the intermediate variable and the coordinate system. The calibration method for the internal and external parameters of the camera does not need to know the internal parameters of the camera, does not increase the number of external mark points, and is suitable for calibration and vision measurement of the internal and external parameters of the camera under the conditions that the internal parameters of the camera are unknown and the position of the camera is fixed.
Owner:中国人民解放军63660部队
System for measuring components of solar radiation
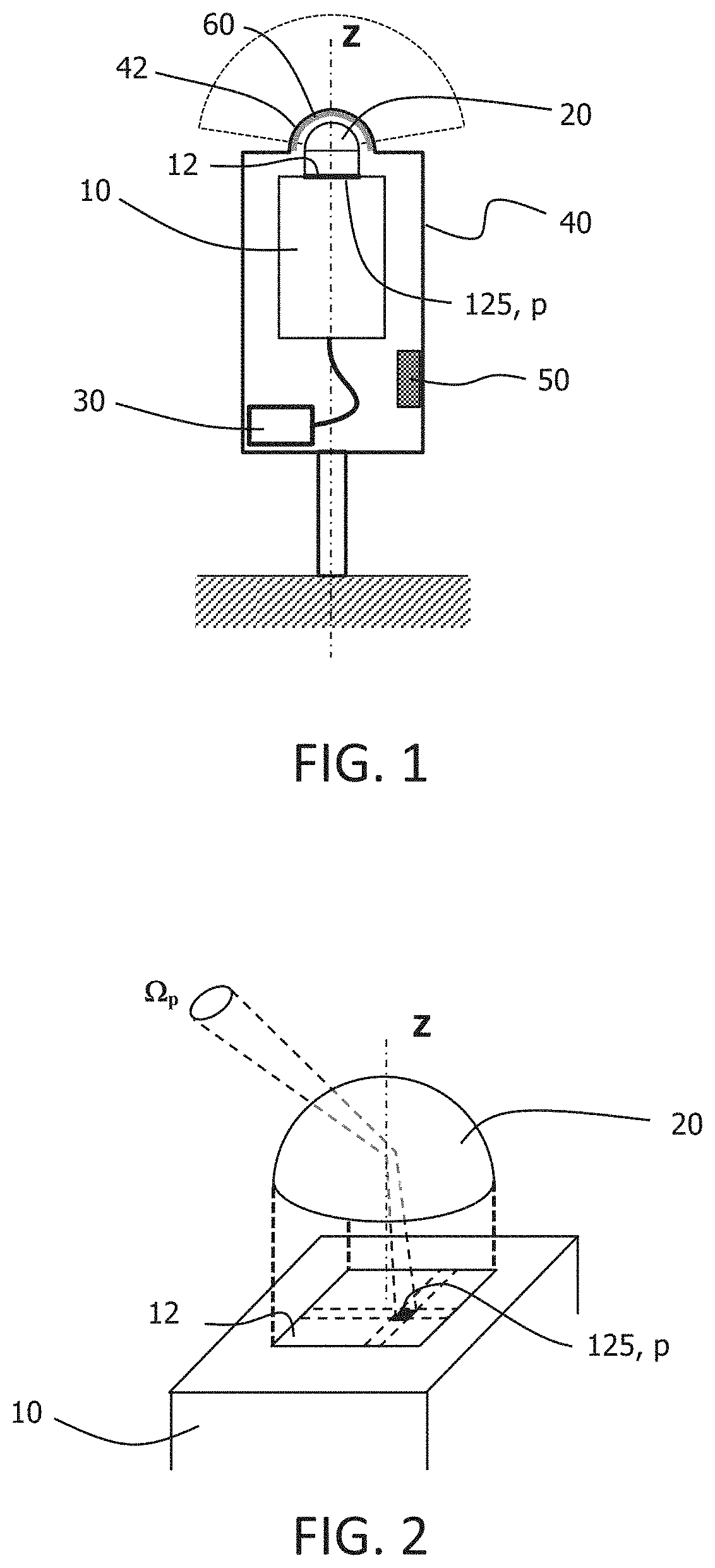
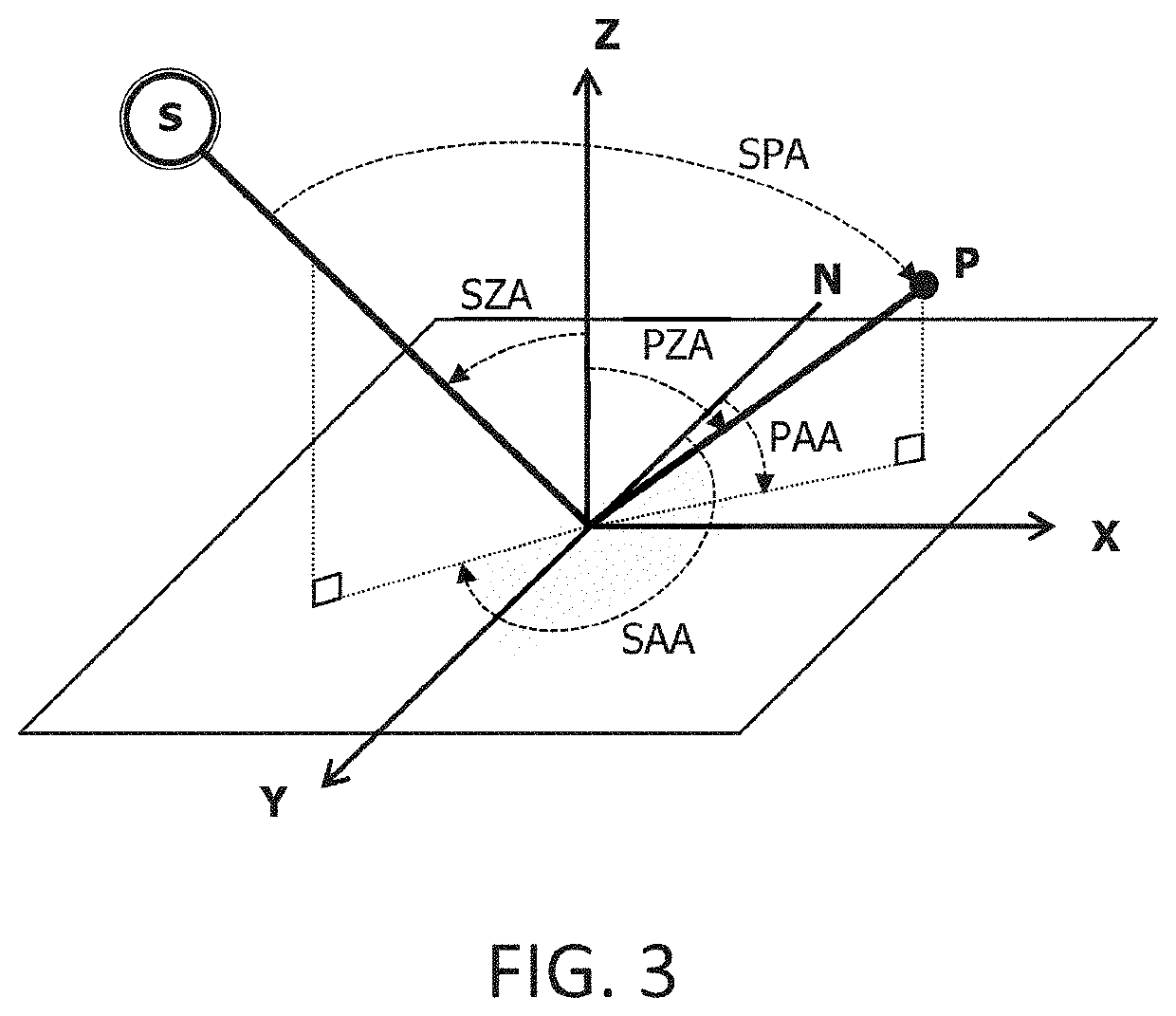
InactiveUS20210123800A1Less complexElimination of maintenance costTelevision system detailsColor television detailsSkyDirect normal irradiance
Disclosed is a system for measuring solar radiation, with a camera having a hemispherical objective and light sensor, and a processor to: perform a geometric calibration of the camera establishing correspondence between coordinate systems of the image pixels and the camera; calculate the solid angle occupied by each pixel; perform a second calibration by comparing the theoretical position of the sun and its position in the image, establishing correspondence between the camera coordinate system and the cardinal points; calculate the angles between: each pixel and the zenith; each pixel and the azimuth; the sun and the zenith; and the sun and the azimuth; then each pixel and the sun. The next steps are: obtain a high-dynamic-range image of the sky; calculate the global horizontal irradiance, the direct normal irradiance, and the diffuse horizontal irradiance; and convert, into global horizontal luminance, direct normal irradiance and diffuse horizontal irradiance, respectively.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
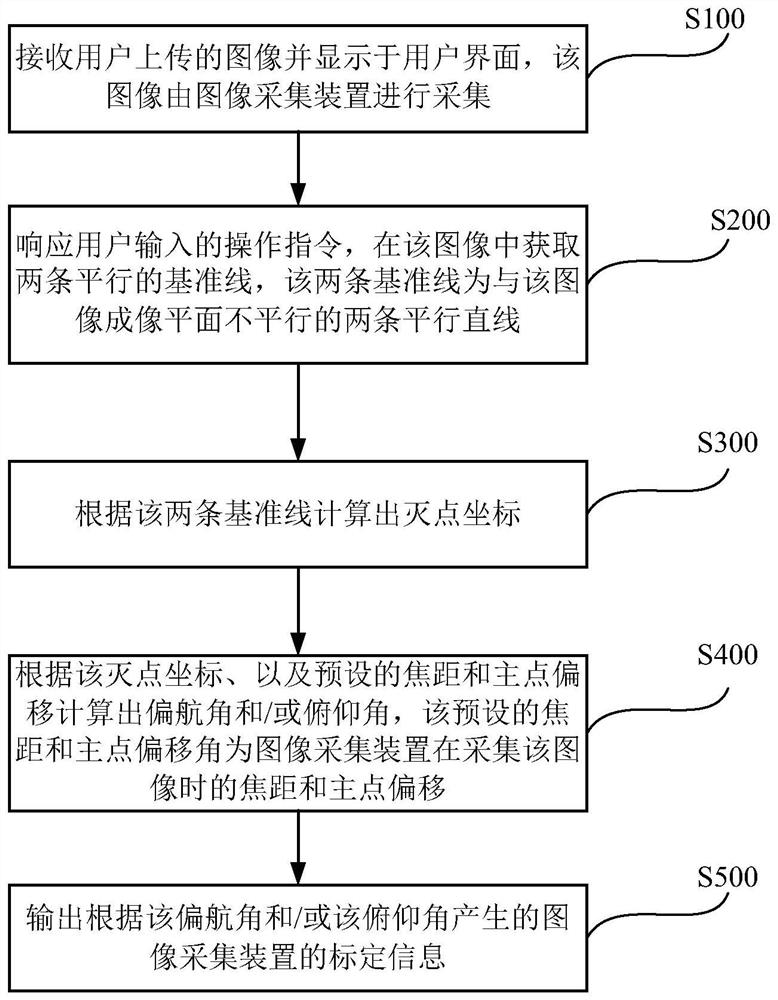
Calibration method of image acquisition device, computer equipment and storage medium
PendingCN112150559AWide user baseSimple and fast operationImage analysisComputer graphics (images)Radiology
The invention provides a calibration method of an image acquisition device. The calibration method of the image acquisition device comprises the following steps: receiving an image uploaded by a userand displaying the image on a user interface, wherein the image is acquired by the image acquisition device; responding to an input operation of a user, and obtaining two parallel datum lines in the image; calculating vanishing point coordinates according to the two parallel datum lines; calculating a yaw angle and / or a pitch angle according to the vanishing point coordinates, a preset focal length and a preset principal point offset, wherein the preset focal length and the preset principal point offset are the focal length and the preset principal point offset of the image acquisition devicewhen the image acquisition device acquires the image; and outputting calibration information of the image acquisition device. In addition, the invention further provides computer equipment and a storage medium. A user only needs to adjust or draw two datum lines which are not parallel to the imaging plane of the image in the image, special professionals are not needed for processing, the application range of user groups is wider, and operation is simpler and more convenient.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINIEYE INNOVATION TECH CO LTD
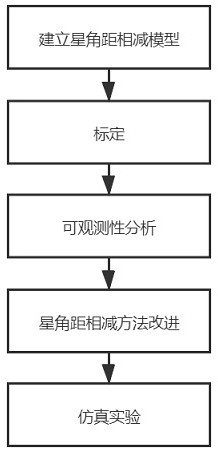
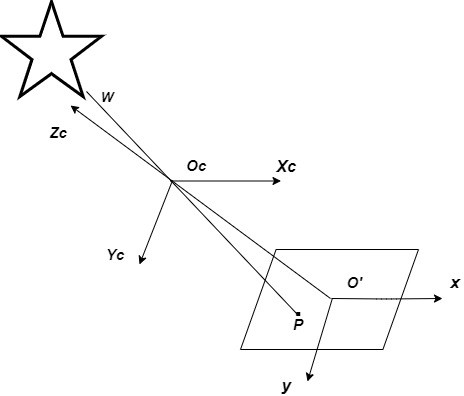
Star sensor on-orbit calibration method based on star angular distance subtraction
The invention relates to a star sensor on-orbit calibration method based on star angular distance subtraction, and belongs to the field of astronomical navigation. The research method comprises the following steps: establishing a pinhole imaging camera model based on a physical process of imaging a scene object to an imaging plane; establishing a star sensor angular distance model; conducting starsensor subtraction; performing observability analysis; improving a star angular distance method; and carrying out simulation experiment. According to the invention, through the improved ADS (adaptivedistance subtraction) algorithm, the precision of u0 and the precision of v0 are respectively improved by 64.0% and 21.7% compared with the traditional AD (angular distance) algorithm, and the main point calibration precision is effectively improved.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF TECH
Geometric calibration method and device for multi-focal-plane spliced large-view-field off-axis camera
ActiveCN112802115AAchieve high-precision geometric calibrationMeet technical requirementsImage analysisTheodoliteCalibration result
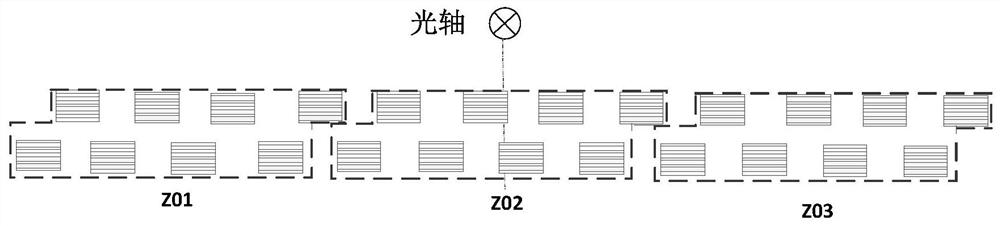
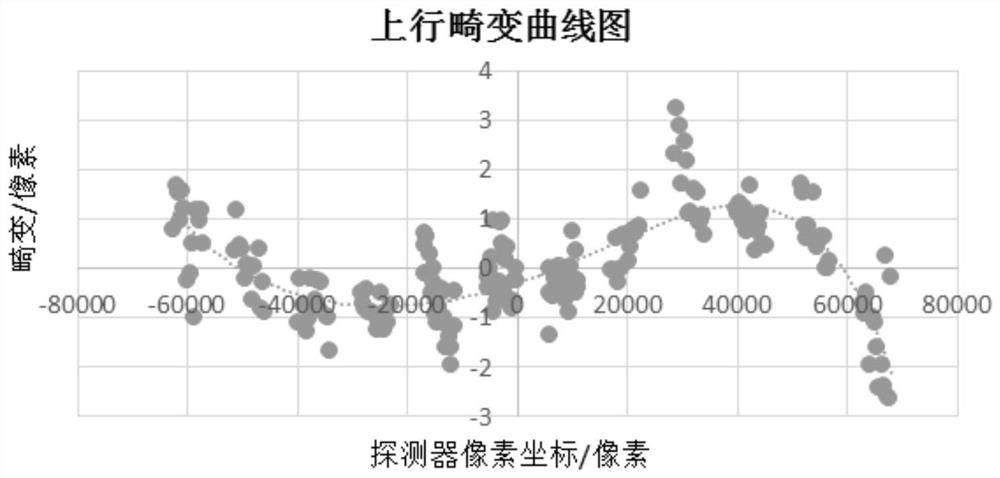
The invention discloses a geometric calibration method and device for a multi-focal-plane spliced large-view-field off-axis camera, relates to the technical field of optical precision measurement, and solves the problem of high-precision ground geometric calibration of a space remote sensing long-focal-length, large-view-field and multi-focal-plane spliced off-axis camera. Firstly, a collimator, slit targets and a theodolite are used for testing splicing areas of all detectors on a focal plane, the relative position relation between the detectors is obtained through calculation, then through a high-precision single-axis rotary table, the slit targets are imaged on all the detectors on the uplink and the downlink of a camera at unequal intervals, collected images are processed, and the detection result is obtained. And extracting a centroid coordinate, converting the centroid coordinate to the same coordinate system through a relative position relation, and calculating through a resolving formula to obtain a principal point, a principal distance and a distortion calibration result of the camera. According to the invention, by selecting a proper collimator, a slit target and a single-axis turntable, high-precision geometric calibration of a camera in any focal plane splicing form is completed.
Owner:CHANGGUANG SATELLITE TECH CO LTD
Imaging apparatus, imaging method, and imaging program
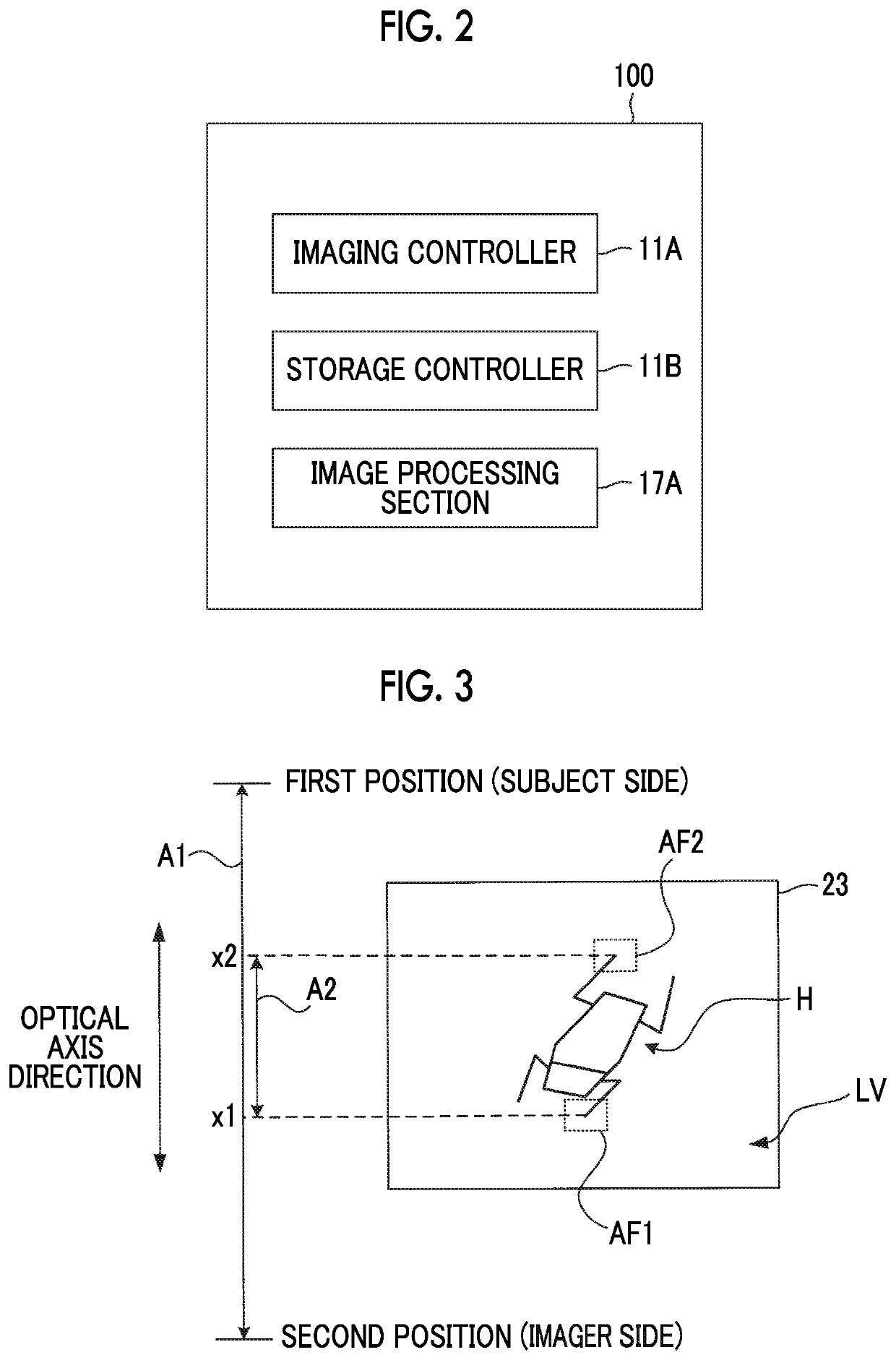
ActiveUS10863095B2Increase the number ofSolve the lack of resolutionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptical axisComputer vision
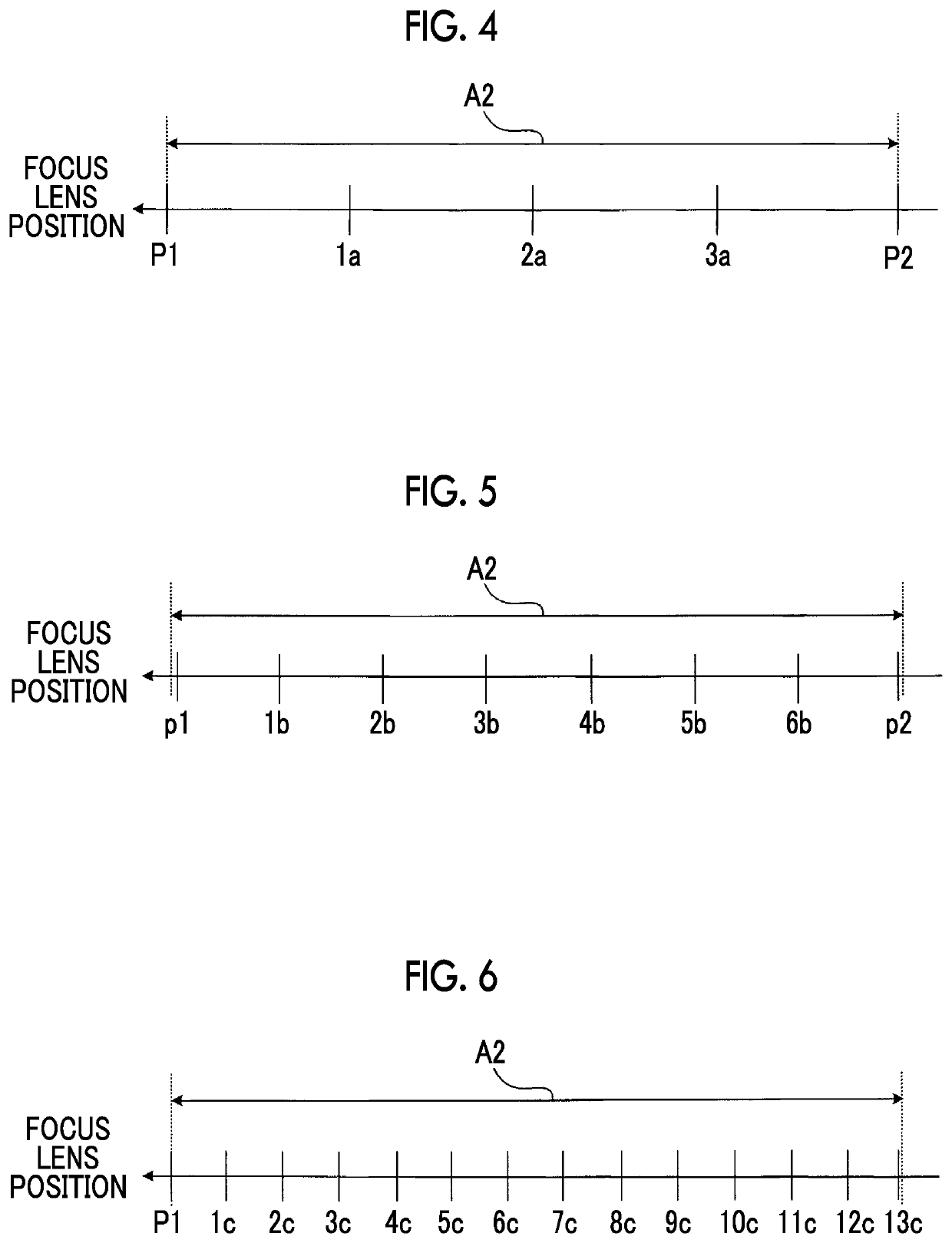
An imaging apparatus includes: an imager that performs imaging of a subject through an imaging optical system including a focus lens capable of changing a position of a principal point in a range between a first position and a second position in a direction of an optical axis; and an imaging controller that continuously performs plural imaging control operations for causing the imager to perform imaging of the subject through the imaging optical system in a state where the principal point of the focus lens is set at each of plural imaging positions which are set in a movement range as at least a partial range of the range, and the imaging controller makes distances between the plural imaging positions narrower and sets a larger number of the plural imaging positions in an imaging control operation performed later in time series among the plural imaging control operations.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Lens assembly, imaging equipment, detection equipment and detection system
ActiveCN112099204AHigh image qualityGood imaging effectPanoramic photographySortingOptical axisImaging equipment
The invention provides a lens assembly, imaging equipment, detection equipment and a detection system. The lens assembly is applied to a lens and comprises a plurality of lens elements which are arranged in a manner of sharing the same optical axis; the entrance pupil position and the front focal point of the lens assembly are both located outside the lens assembly and located at the object side of the lens assembly; the object-side principal point of the lens assembly is farther from the lens assembly than the front focal point; and the peripheral imaging expansion angle corresponding to thelens assembly meets the following formula: alpha=arctanH / 2f, wherein alpha represents the peripheral imaging expansion angle, the alpha is greater than or equal to 18 degrees and less than or equal to25 degrees, H represents the full-view image height corresponding to the lens assembly, f represents the focal length of the lens assembly, and f is less than 0. Therefore, a single imaging device comprising the lens assembly can image the right opposite surfaces of the workpiece and the imaging device and the side peripheral surface of the workpiece at the same time, and a better imaging qualityis achieved.
Owner:BEIJING LEADERTECH INTELLIGENT EQUIP CORP
Anti-vibration mechanism for imaging device, optical system, camera, and electronic equipment
PendingCN112731727AEasy to rest assuredReduce design difficultyTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementOptical axisEngineering
An anti-vibration mechanism for an imaging device is provided in an imaging device including a camera shake correction mechanism. Provided is an optical system which, in an imaging device provided with an optical system that moves in the direction of an optical axis and includes a focus adjustment mechanism, has an anti-vibration mechanism that performs camera shake correction by preventing vibration of an imaging element, and which, in order from the object side, is provided with an imaging lens group, an anti-vibration mechanism, and an imaging element on the anti-vibration mechanism. The image pickup element on the anti-vibration mechanism is rotated with respect to the optical axis of the image pickup lens group, and camera shake correction is performed.
Owner:CHANGZHOU RAYTECH OPTRONICS CO LTD
Anti-vibration mechanism for imaging device, optical system, camera, and electronic equipment
PendingCN112731724AEasy to rest assuredReduce design difficultyTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementOptical axisImaging lens
An anti-vibration mechanism for an imaging device is provided in an imaging device including a camera shake correction mechanism. Provided is an optical system which, in an imaging device provided with an optical system that moves in the direction of an optical axis and includes a focus adjustment mechanism, has an anti-vibration mechanism that performs camera shake correction by preventing vibration of an imaging element, and which, in order from the object side, is provided with an imaging lens group, an anti-vibration mechanism, and an imaging element on the anti-vibration mechanism. The image pickup element on the anti-vibration mechanism is rotated with respect to the optical axis of the image pickup lens group, and camera shake correction is performed.
Owner:CHANGZHOU RAYTECH OPTRONICS CO LTD
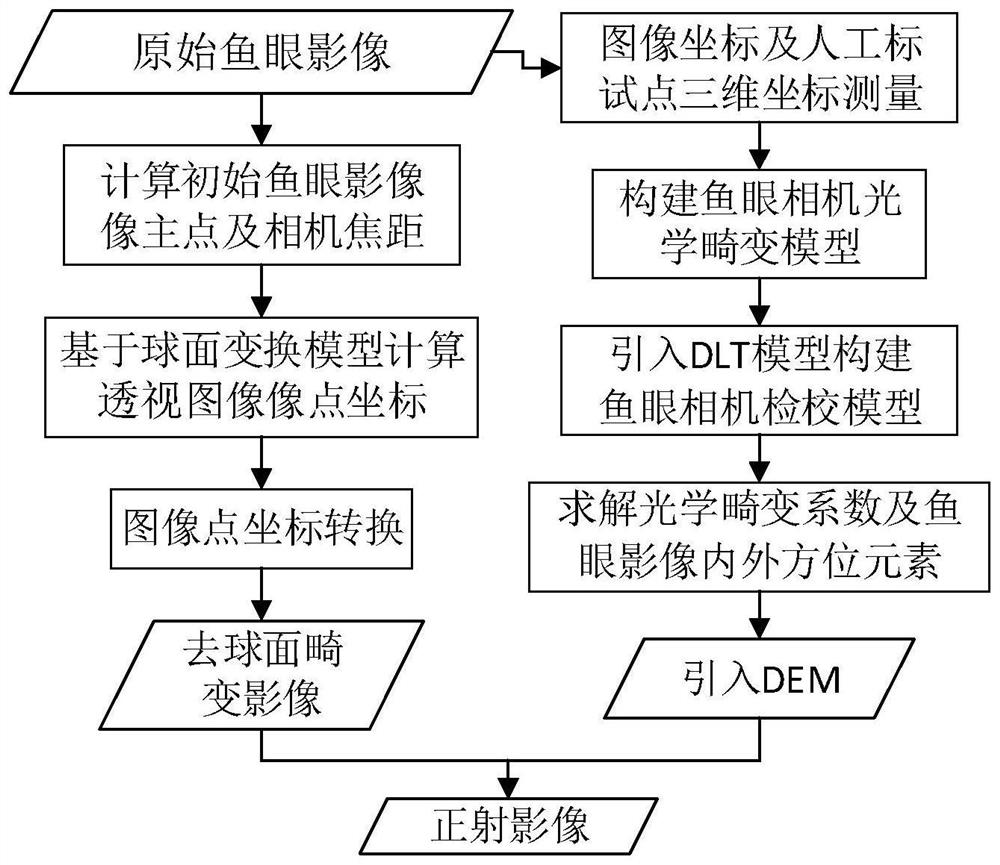
Image orthorectification method for fisheye camera
The invention discloses an image orthorectification method for a fisheye camera. The method comprises the following implementation steps: firstly, establishing an indoor three-dimensional calibration field, establishing a free coordinate system, measuring three-dimensional space coordinates of artificial identification points, and acquiring an original fisheye image; calculating an image principal point and a camera focal length initial value, and performing coordinate transformation on an original image in combination with the spherical perspective model to remove spherical distortion; then constructing a fisheye camera optical distortion model, introducing the model into a direct linear transformation (DLT) model to obtain the fisheye camera optical distortion model, and solving an optical distortion coefficient and internal and external orientation elements of the original image; and finally, starting from a collinear conditional expression, carrying out ortho-rectification on the perspective image without spherical distortion by adopting indirect digital differential rectification to obtain a calibration field ortho-image. According to the method, the original fisheye camera image can be subjected to ortho-rectification, the serious distortion problem of the fisheye camera image is solved, and the large-scale ortho-image can be quickly obtained by adopting the fisheye camera in a narrow space area.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com