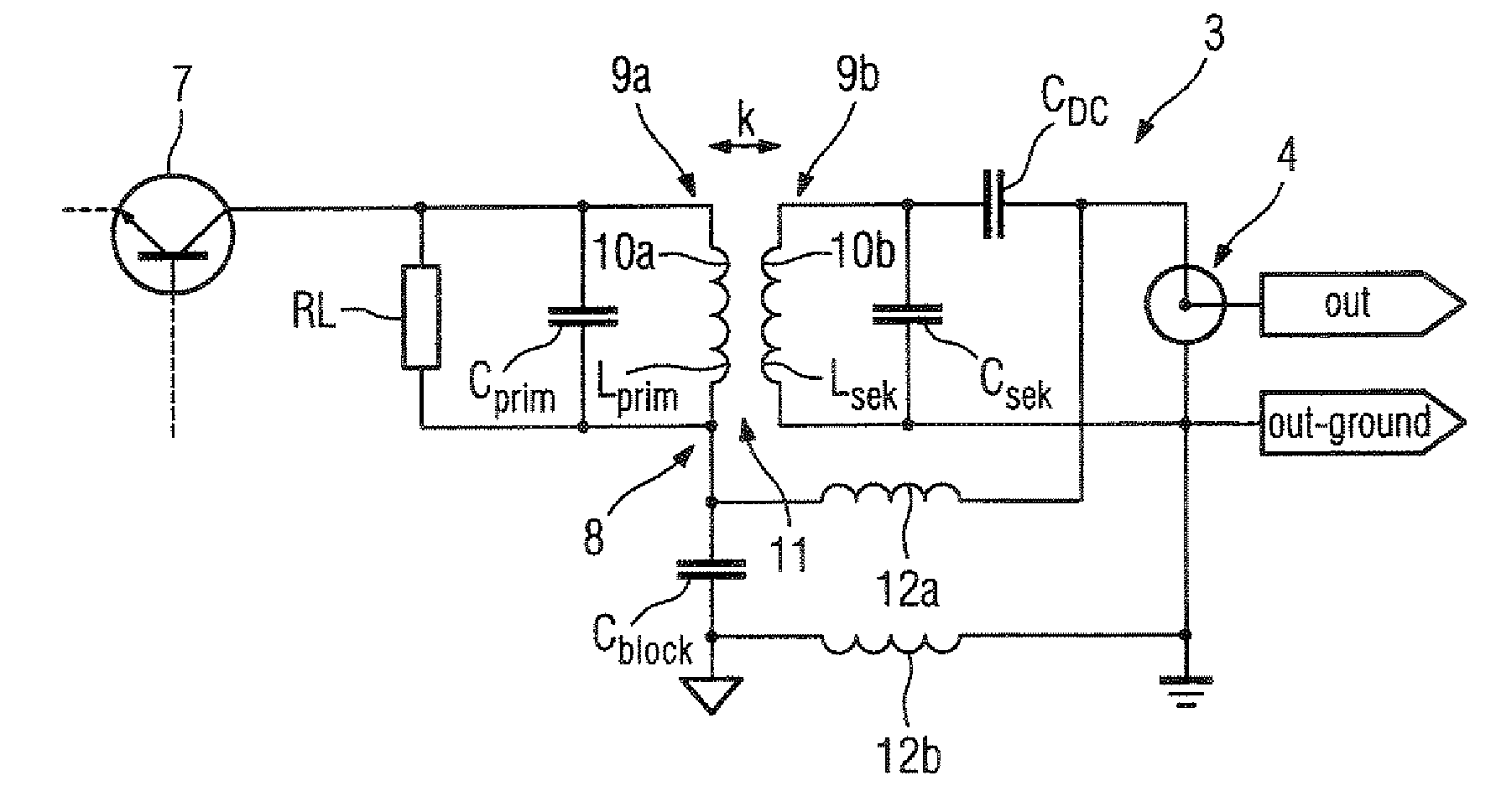
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
102 results about "Antenna amplifier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In electronics, an antenna amplifier (also: aerial eamplifier (booster), Am antennefier) is a device that amplifies an antenna signal, usually into an output with the same impedance as the input impedance. Typically 75 ohm for coaxial cable and 300 ohm for twin-lead cable.
Radio frequency network
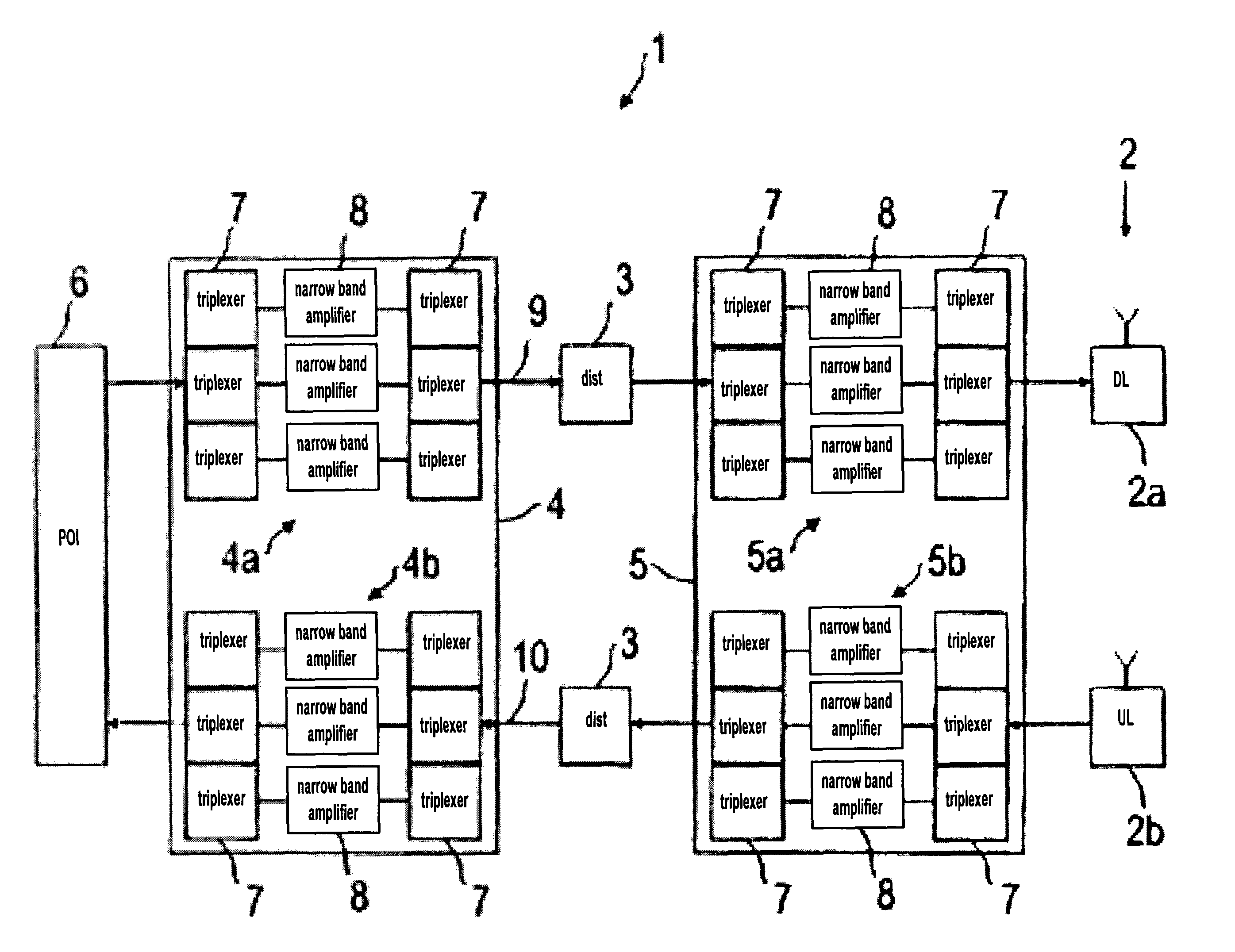
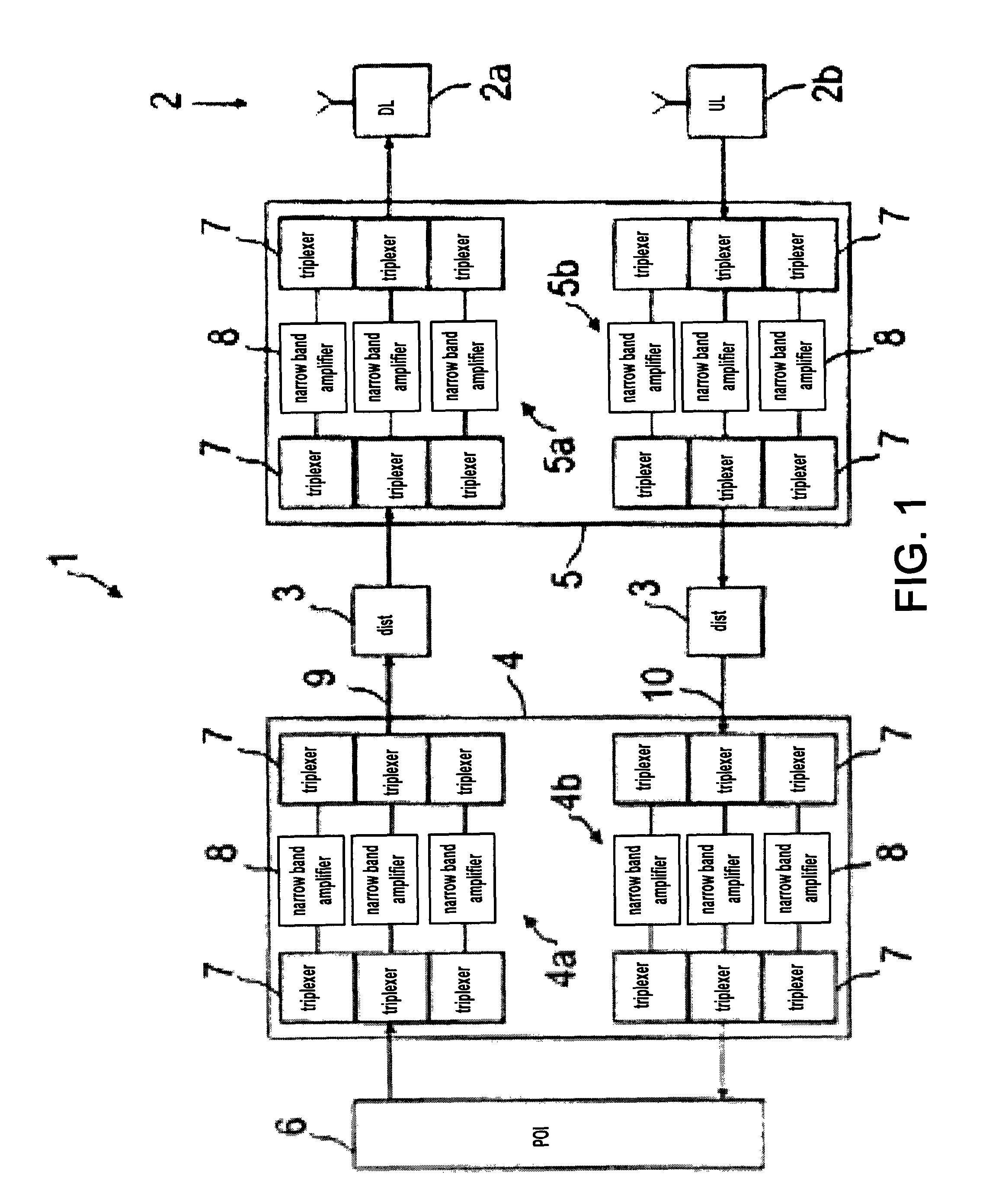
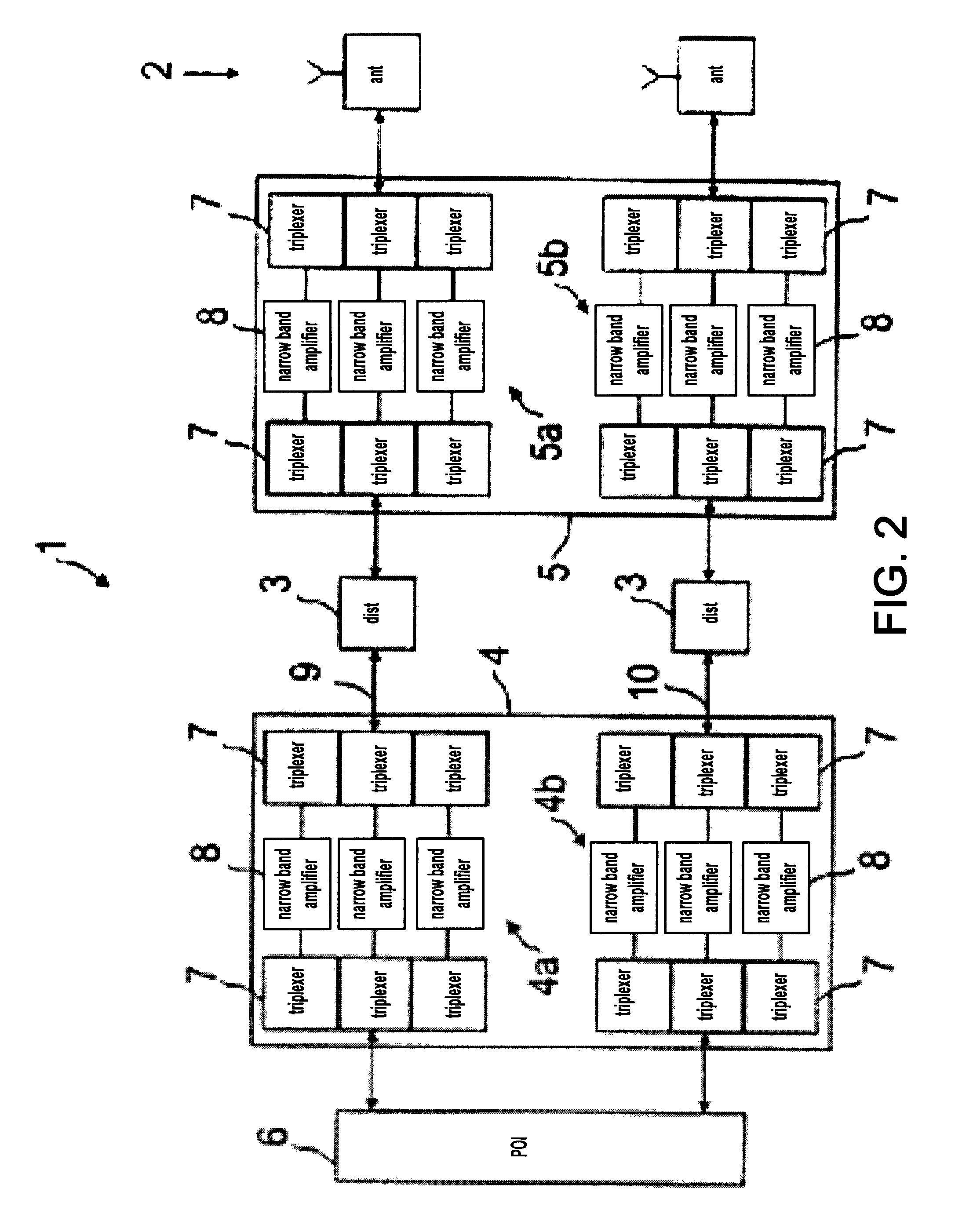
ActiveUS8428033B2Avoid intermodulationsReduce sizeFrequency-division multiplexWireless commuication servicesAudio power amplifierDistributed antenna system
Owner:RFS TECH INC
Radio integrated circuit with integrated power amplifier
InactiveUS20060128347A1Increase power consumptionMinimizes digital signal processingTransmission control/equalisingDigital dataDigital signal processing
A radio system includes a radio frequency (RF) integrated circuit (IC), a baseband digital signal processing (DSP) IC, and a serial digital interface coupling data there-between. In one embodiment of the invention, the RF IC has an input receiver to receive a serial digital transmission bit stream from a digital signal processing integrated circuit; a data recoverer coupled to the input receiver to recover digital data bits from the serial digital transmission bit stream; a low pass filter coupled to the data recoverer convert the digital data bits into an analog transmission signal; a mixer coupled to the low pass filter to up-convert the analog transmission signal from a baseband frequency to a second selectable carrier frequency as a transmit radio frequency signal; and an amplifier coupled to the mixer and an antenna, the amplifier to amplify the transmit radio frequency signal for broadcast over the antenna.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
Shark fin type antenna
InactiveCN101000977AReasonable designSimple structureAntenna supports/mountingsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesCoaxial cableAudio power amplifier
The invention of shark fins antenna relates to a radio receiver antenna for vehicle and marine, especially for AM / FM, GSM, GPS, and ETV. The structure has the antenna shell. The upper of shell inner sets a radio receiver antenna. One side of the antenna sets the output end of antenna signals. The output end connects the component and the signal input end of antenna amplifier through the antenna, or matching connects the coaxial cable directly. The antennas shell bottom installs the floor. The type of shell sets to be the shark fins. The radio receiver antenna uses the spiral spring antenna or metal antenna. The installed floor sets up the antenna fixed screw and nut. The floor can be installed with AM / FM antenna amplifiers, GPS receiver, GSM receiver, and ETV receivers.
Owner:蒋小平 +1
Radio frequency network
ActiveUS20100054227A1Addressing Insufficient CoverageImprove dynamic rangeFrequency-division multiplexWireless commuication servicesAudio power amplifierDistributed antenna system
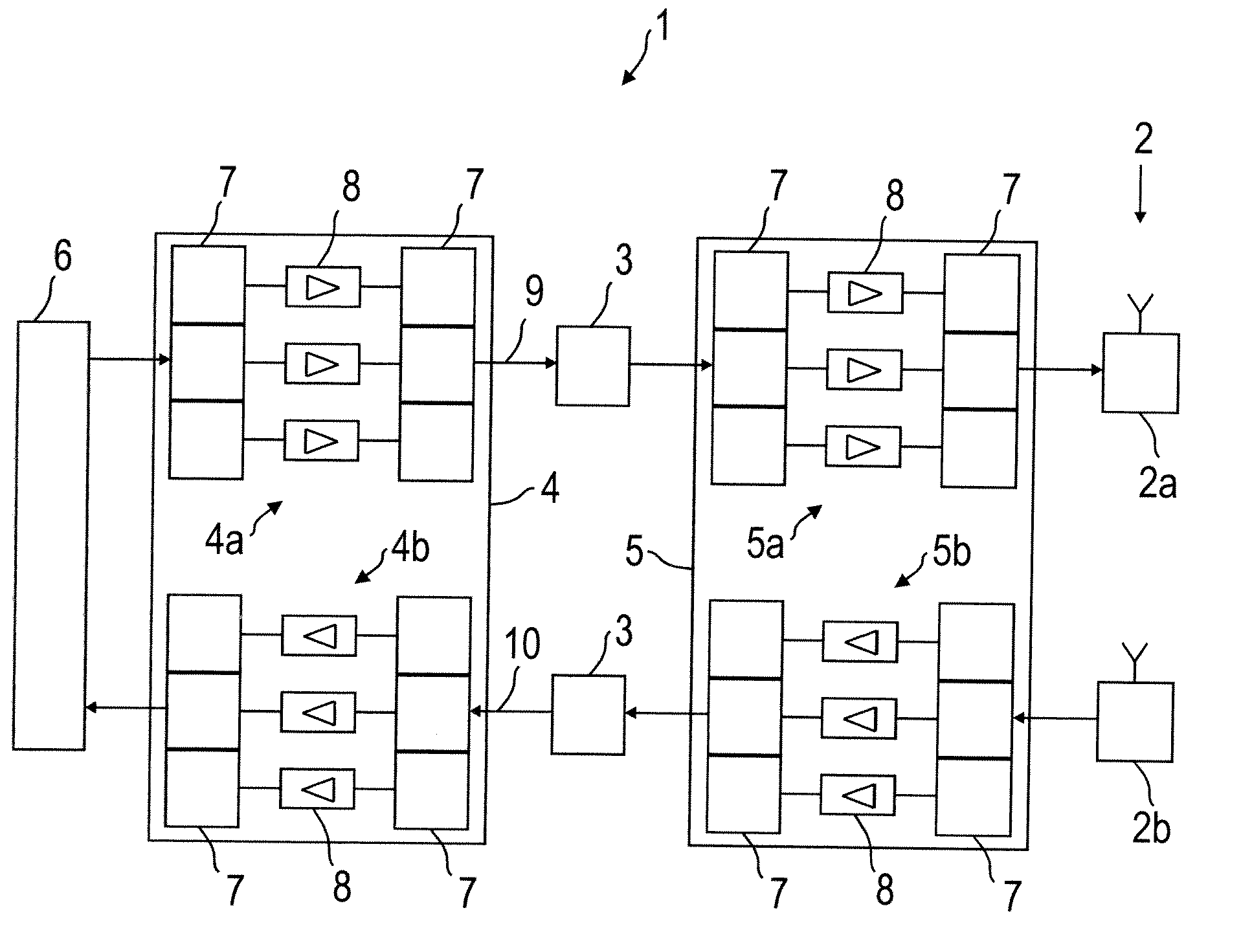
The present invention relates to radio frequency (RF) distribution systems for mobile communications. In particular, the present invention relates to a radio frequency network facilitating radio communication where the usual free space propagation of electromagnetic waves is hampered, undesired or impossible, for example in tunnels, mines, and buildings and in large complexes like exhibition grounds, shopping malls, and airports. The radio frequency network (1) comprises a distributed antenna system (2) having radiating elements, a wired distribution system (3) feeding the distributed antenna system (2), at least one antenna amplifier (5) between one end of the wired distribution system (3) and the distributed antenna system (2), at least one line amplifier (4) at the other end of the wired distribution system (3), and automatic self-leveling units included in the antenna and line amplifiers (4, 5).
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Digital UHF/VHF antenna
InactiveUS20070229379A1Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsAudio power amplifierAntenna amplifier
The invention comprises a Digital UHF / VHF (DUV) Antenna with a driven DUV antenna preferably boosted by an amplifier mounted close to the DUV dipole and a DUV signal line with antenna, amplifier, and signal line contacts being conductively bonded. The DUV dipole is preferably enhanced by a VHF enhancer and / or by a UHF enhancer comprising one of a reflective and a directive element. The UHF / VHF enhancer preferably includes an RF booster with a reflective element displaced from the longitudinal axis and near the driven antenna to enhance VHF signals. The DUV antenna is preferably configured for DTV reception in the VHF high band range of 174 MHz to 216 MHz, and in the UHF range of 470 MHz to 698 MHz.
Owner:ECKWIELEN BRADLEY L
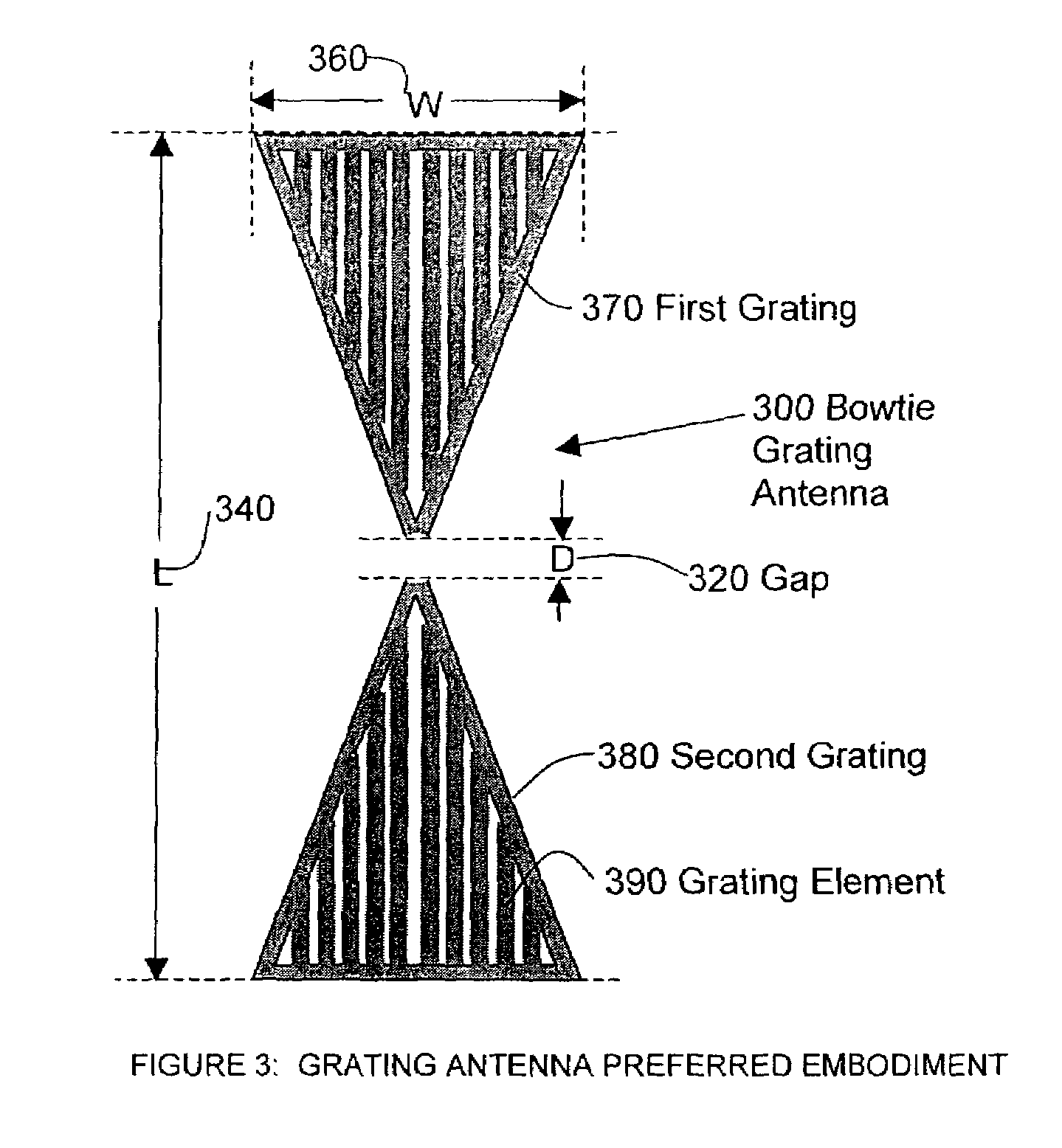
Optical disc head including a bowtie grating antenna and slider for optical focusing, and method for making
InactiveUS7177236B2Maintain positionReduce manufacturing costCombination recordingOptical flying-type headsGratingAudio power amplifier
A slider system have been developed to aid in the spacing between read / write heads and the storage medium, and a grating antenna amplifier has been developed to improve illumination spot size and polarization characteristics. The grating antenna can be attached to a grayscale slider to obtain a distance between the illumination spot and antenna that lies in the near field region.
Owner:MEMS OPTICAL
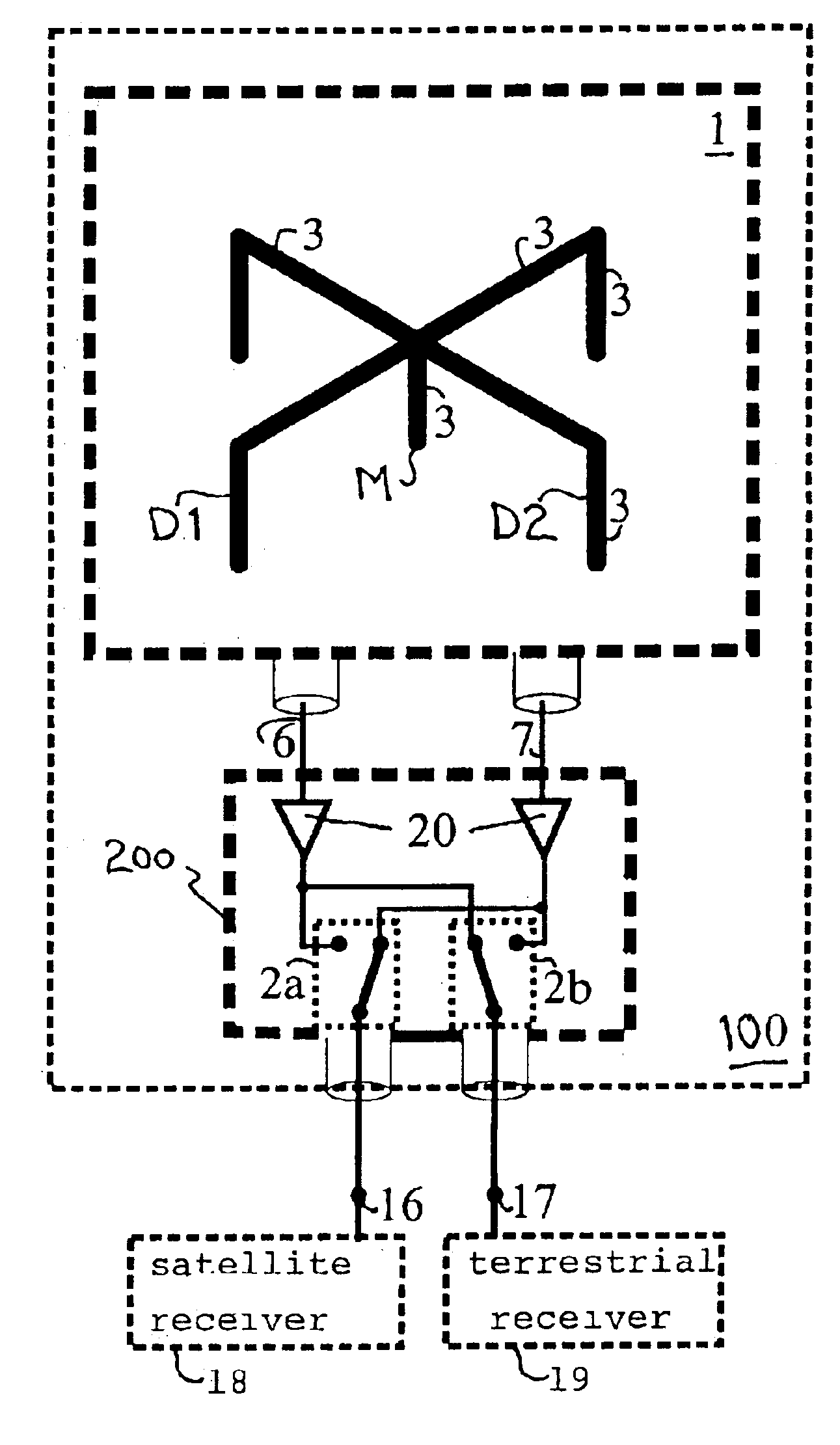
Antenna arrangement for satellite and/or terrestrial radio signals for motor vehicles
InactiveUS6911946B2Reduce the probability of interferenceQuality improvementSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityMobile vehicleAudio power amplifier
A reception antenna arrangement for motor vehicles for the GHz frequency range that is formed as a combined system for the reception of circularly polarized waves and / or vertically polarized waves by a plurality of dipole antennas. Their length is not greater than ¾ of the wavelength. To form a diversity function, at least one switching or reversing device (2) is provided so that at least two signals that are different in terms of diversity and received from the dipole antennas are alternatively supplied to at least one antenna connection point for diversity reception so that one or several more favorable reception signals can be selected and provided to the antenna amplifiers.
Owner:DELPHI DELCO ELECTRONICS EUROPE GMBH
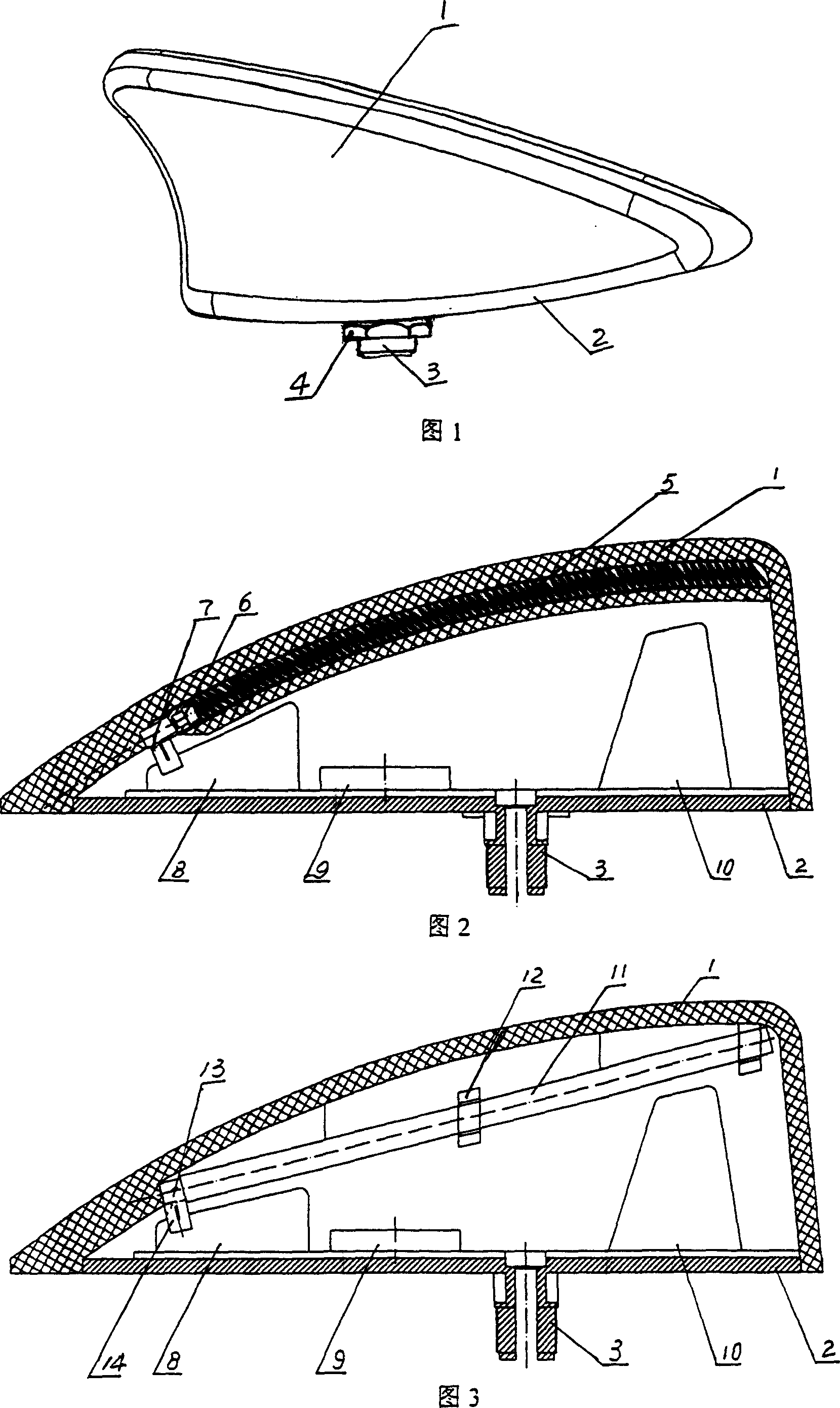
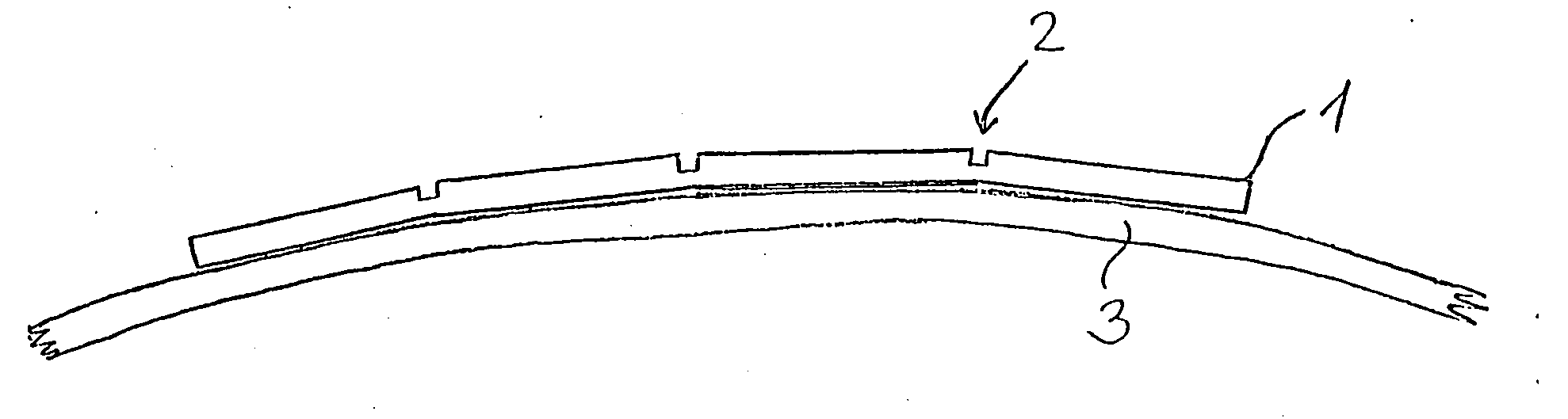
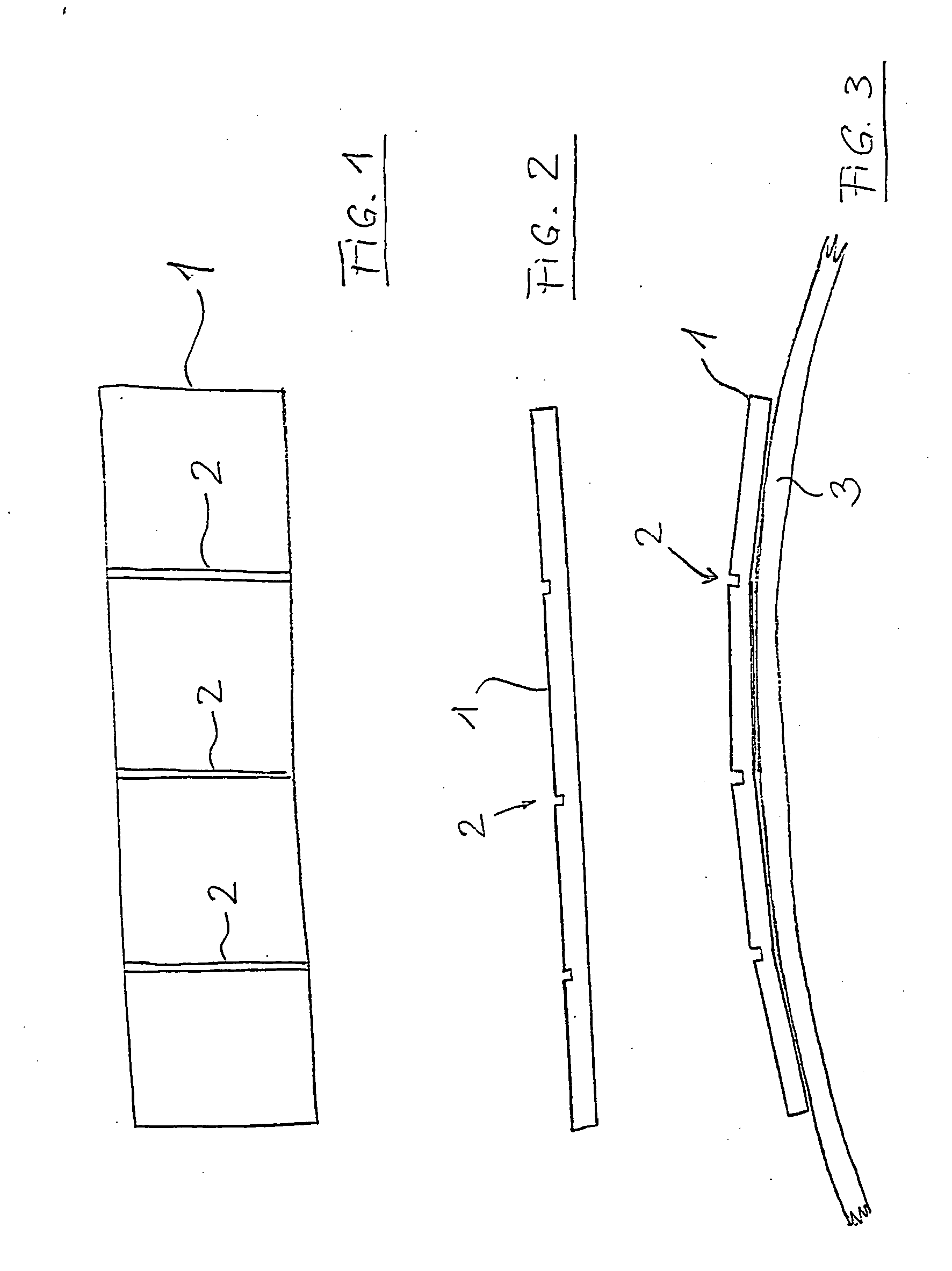
Domed circuit board of an antenna amplifier for a vehicle antenna device
InactiveUS20060238428A1Circuit bendability/stretchabilityAntenna supports/mountingsElectrical conductorAudio power amplifier
A high-frequency device for a vehicle antenna device which can be mounted on a surface of the vehicle, comprising a circuit board (1) with strip conductors and circuit components, in addition to feed means such as lines or connectors or the like. According to the invention, the circuit board (1) has at least one recess (2) extending crosswise in relation to a domed surface (3) for approximate equalization of said dome-shape.
Owner:HIRSCHMANN ELECTRONICS GMBH & CO KG
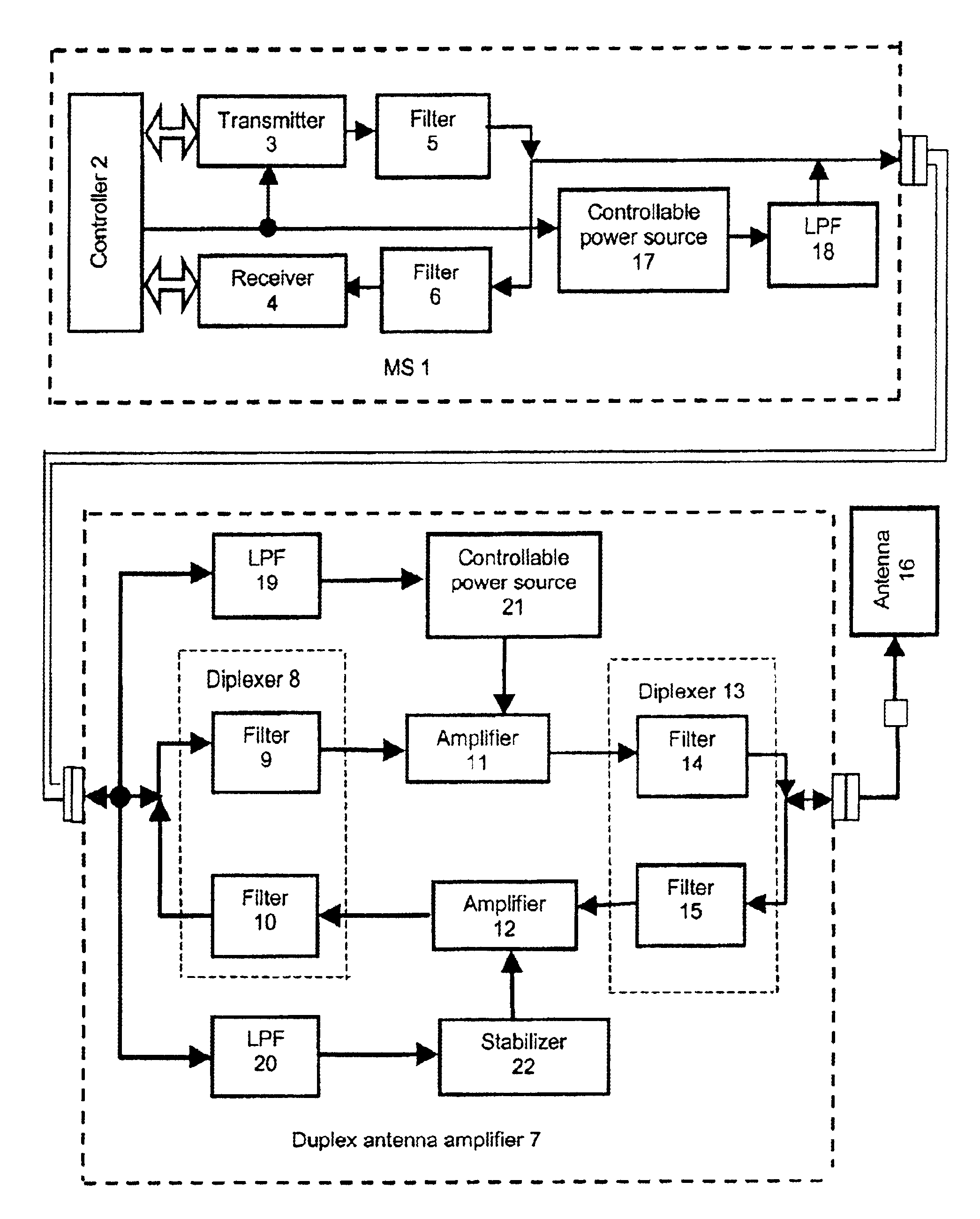
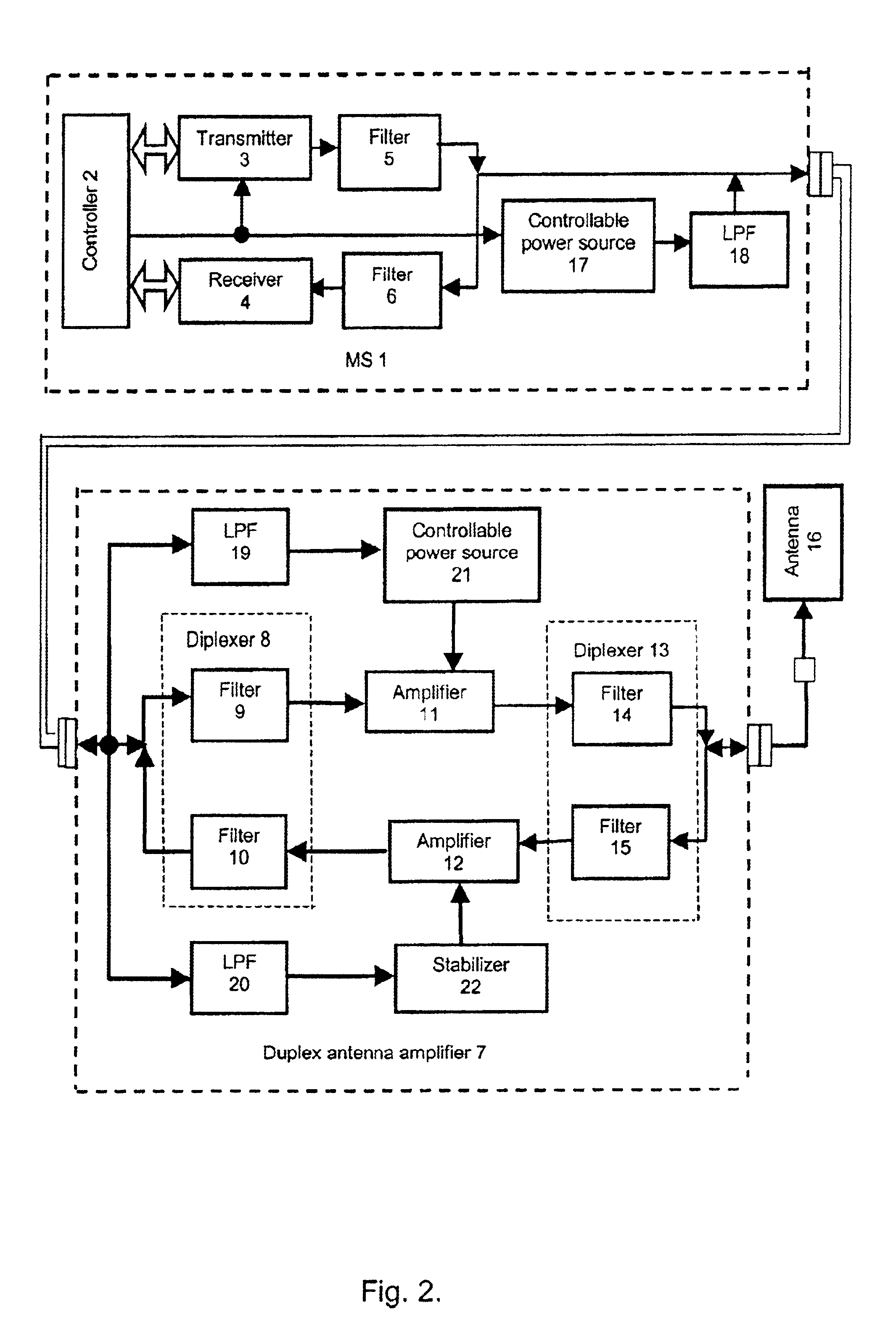
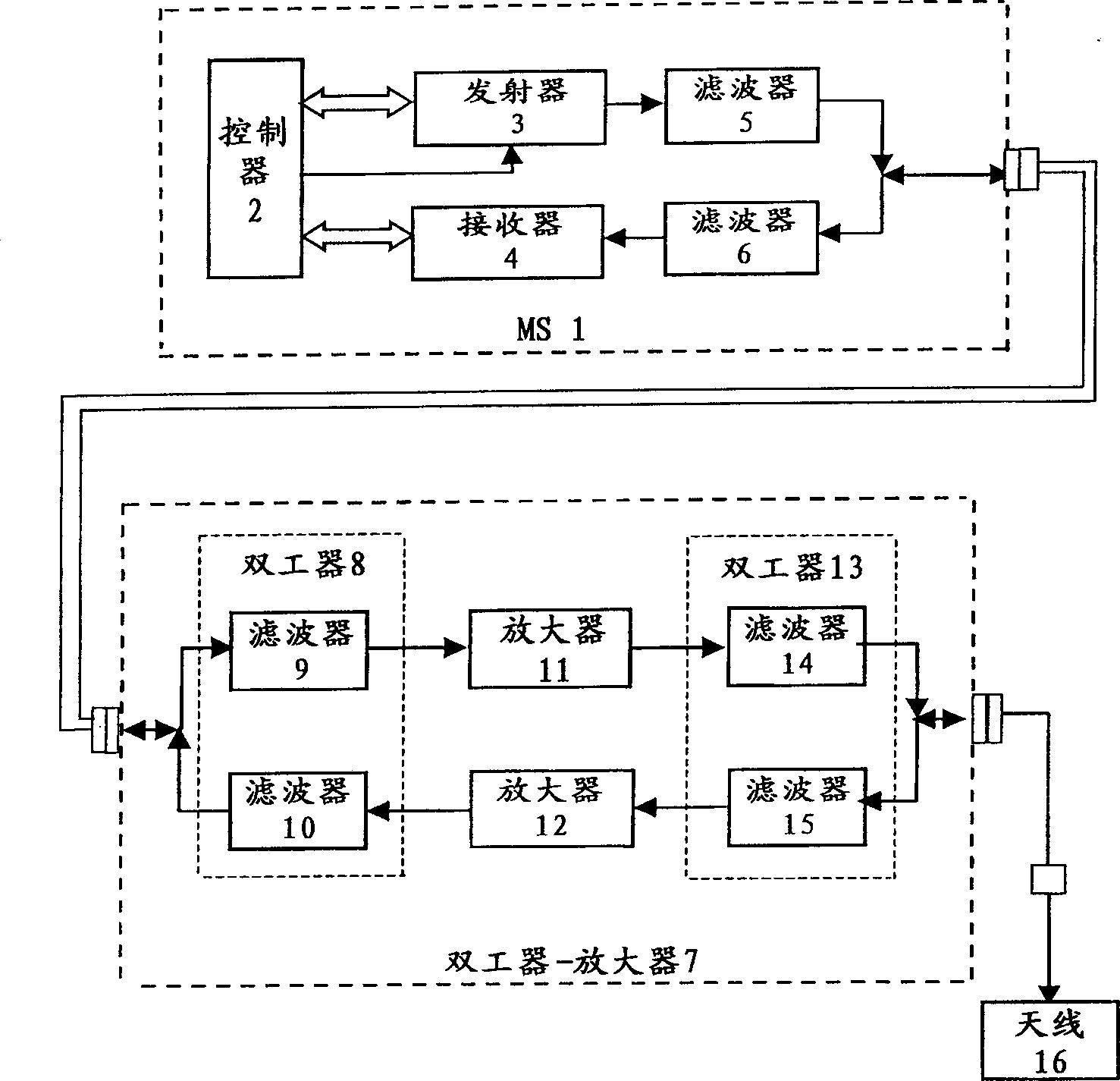
Subscriber station with duplex antenna amplifier
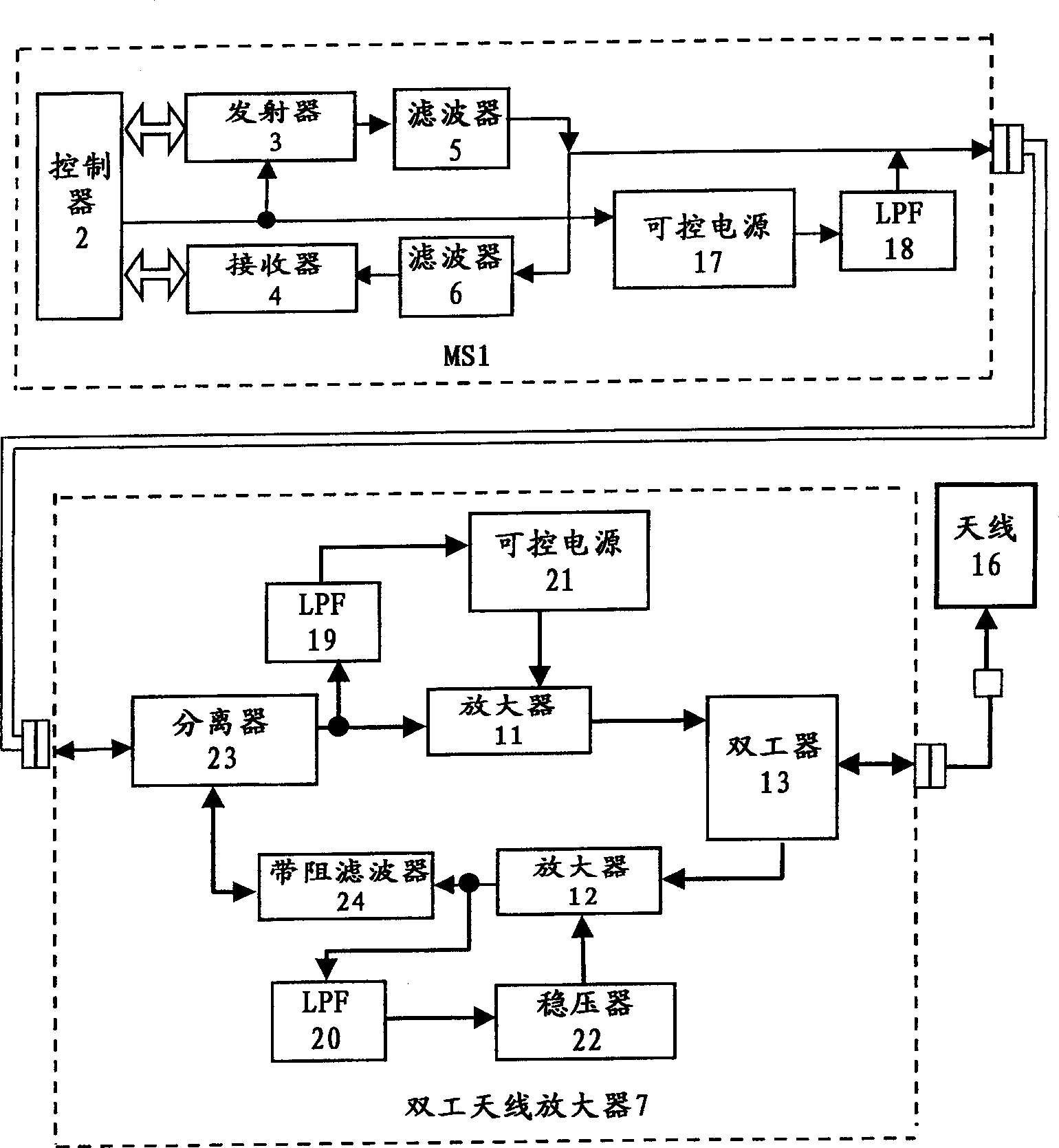
InactiveUS6892056B1Improve system power consumption economyImprove economyTransmission control/equlisationRepeater circuitsUltrasound attenuationAudio power amplifier
For the purpose of making the system more economic, given full compensation of transmitter and receiver signal attenuation in the communication cable, the circuit controlling transmitter enable / disable status, including a controllable power source (control command converter) and a low pass filter separating a receive / transmit UHF signal from a lower frequency up to direct voltage) signal, a number of control commands, is introduced into mobile station, mobile station having autonomous power supply.According to the first variant of the device, the control command, having passed the low pass filter (19), enables the power source (21) control from which power is supplied to the power amplifier (11) whose amplification is selected so as to compensate attenuation of the transmitter signal traveling from mobile station (1) to antenna (16). The voltage supplied from the mobile station (1) via the communication cable is applied to a stabilizer (22) via the other low pass filter (20) isolating the supply circuit from radio frequency receive and transmit signals.According to the second variant of the device, a splitter (23) and rejector (24) are used in the duplex antenna amplifier (7). This makes implementation of antenna amplifier simpler and cheaper.
Owner:ALEXANDR VASILIEVICH GARMONOV +1
Micro-wave extension method and device of the time division duplex mobile communication system
InactiveCN101035323AFrequency-division multiplex detailsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless controlCommunications system
The invention discloses a methode and device of microwave zooming out with time division duplex in the mobile communication system. It has solved the problem of radio frequency zoom out with cable or optical fiber connection bwteen base station and antenna in TD-SCDMA system. The microwave transmission equipment is composed of cable and wireless base stations connected by group of separation remote microwave machine and microwave cables using the antenna amplifier. Microwave antenna amplifier synchronization is controlled by wireless base station through the cable control. Remote microwave machine and antenna amplifier synchronization and controlling is abtained by wireless control unit through the medium of space communication. Using three electric control decliners, outself-adapting control can be achieved. The invention solves the problem of TD-SCDMA super base station radio frequency zooming out.
Owner:NTS TECH CHENGDU
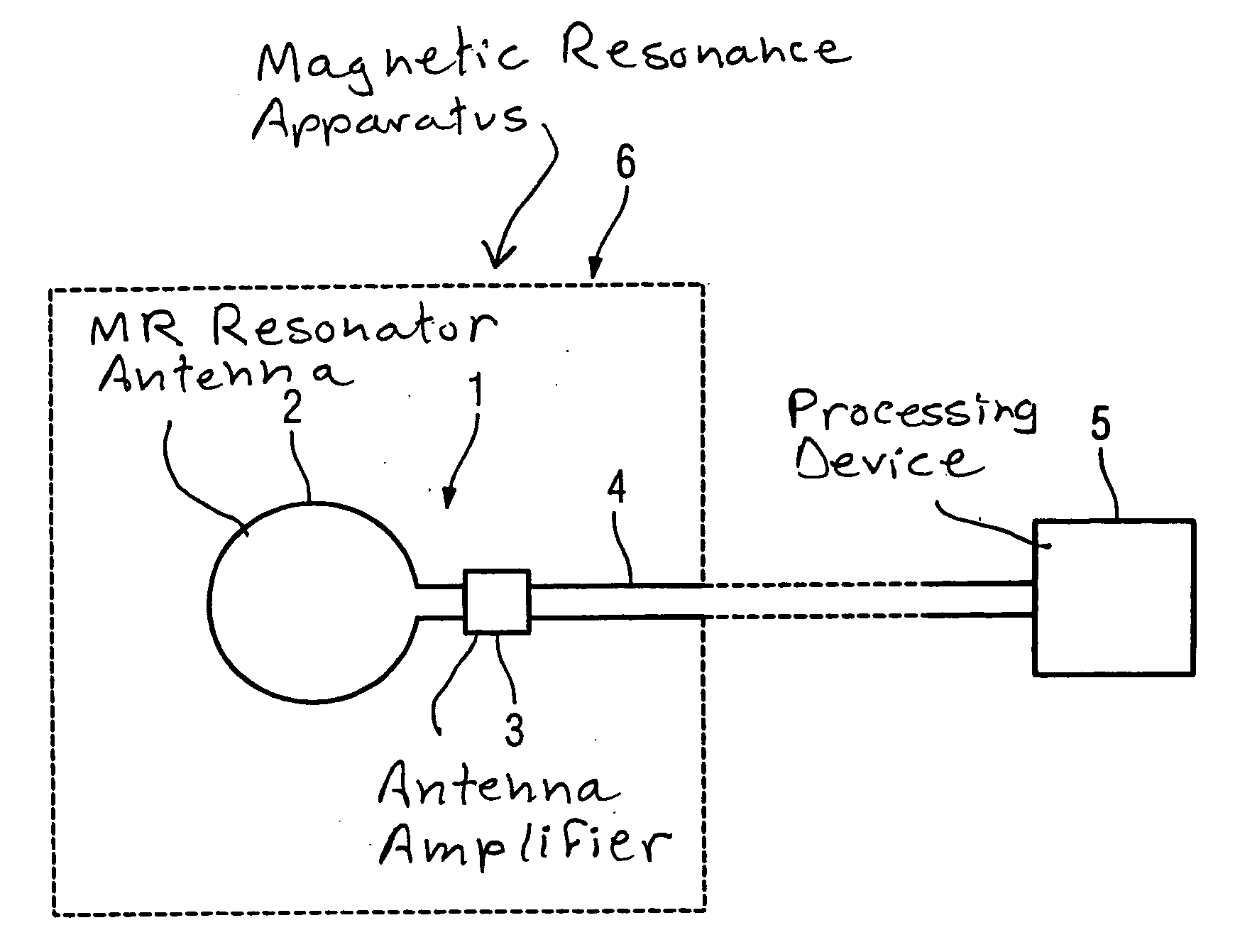
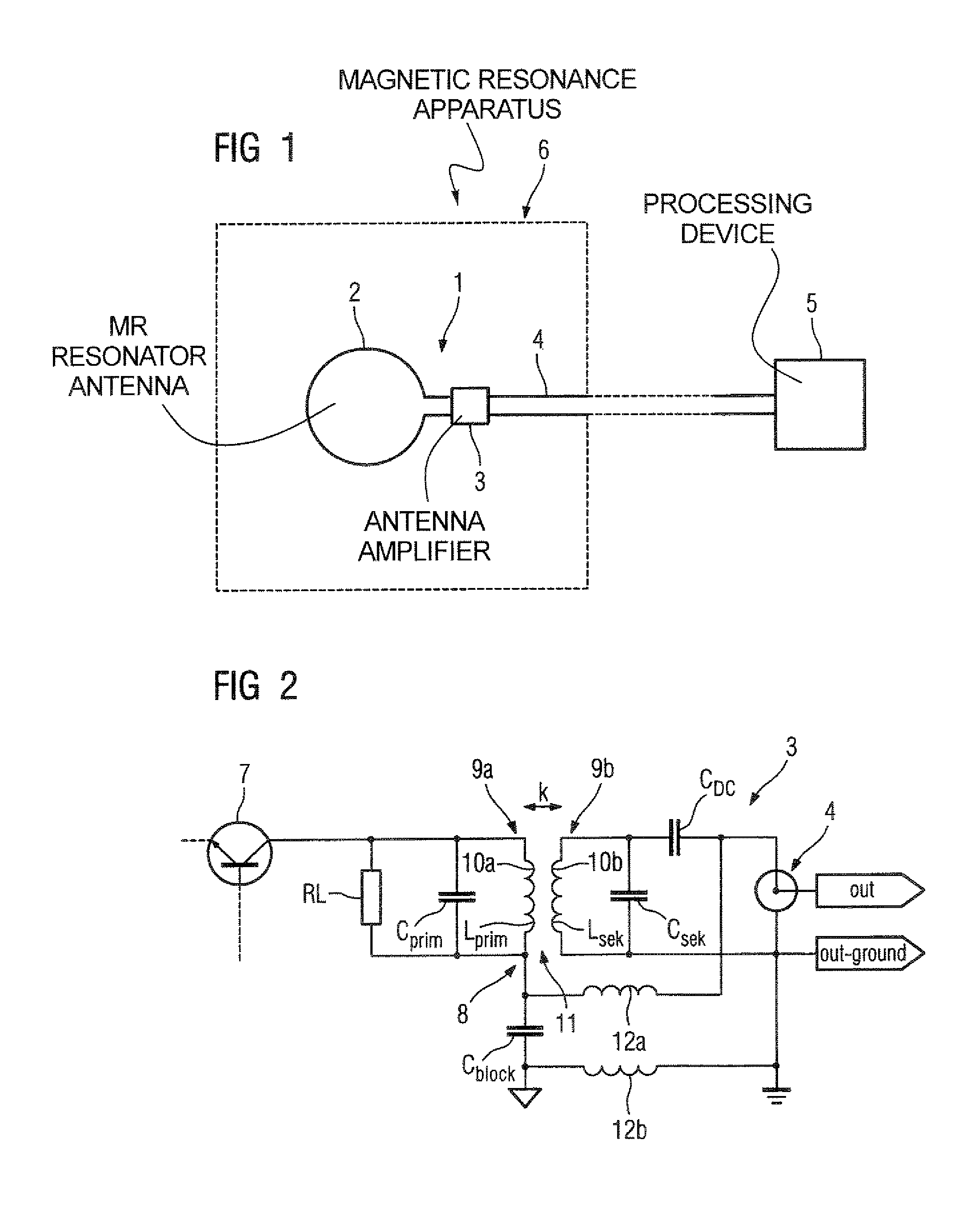
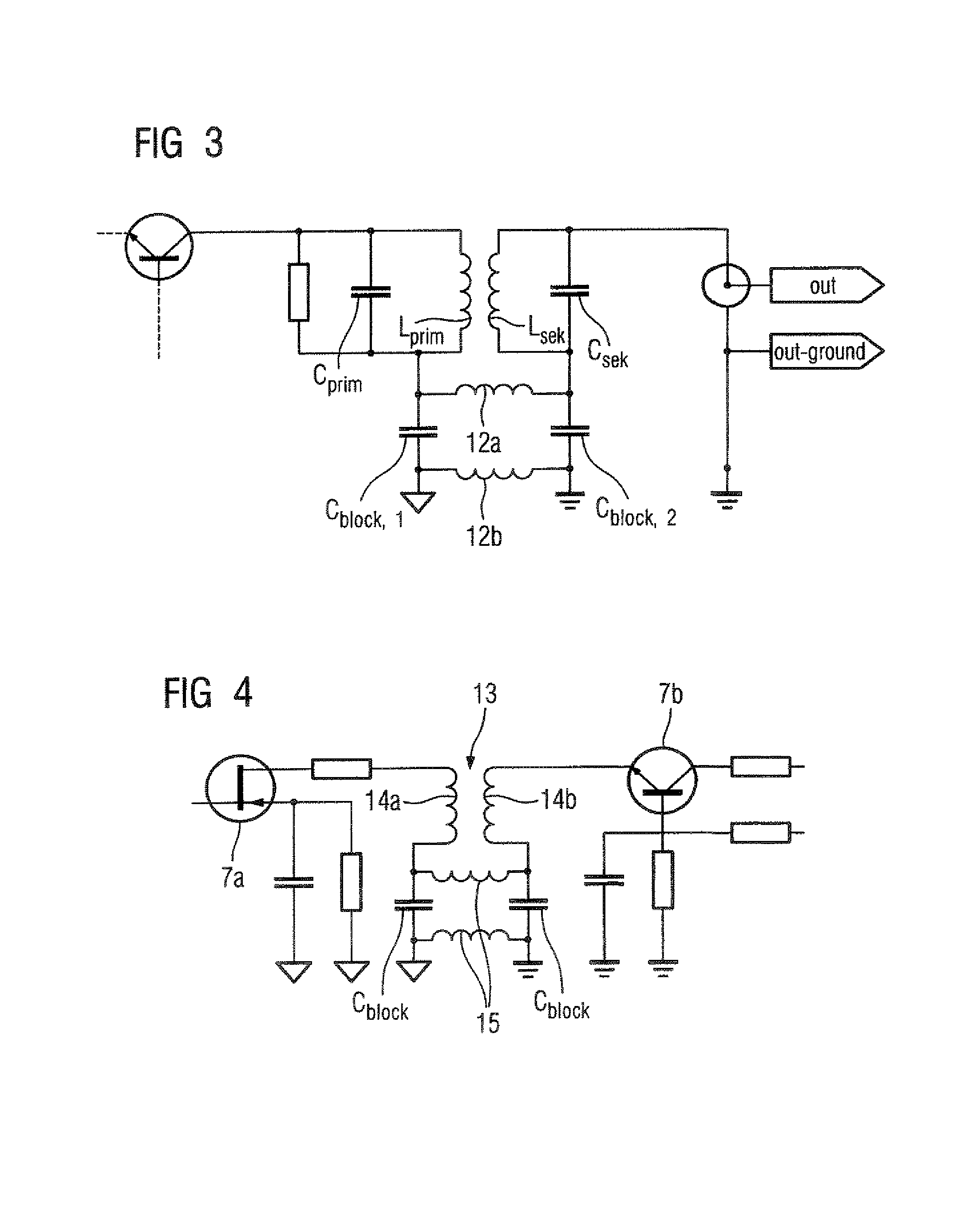
Antenna Amplifier, in particular for a magnetic resonance antenna
ActiveUS20050270031A1Reduce the inductance valueElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceAudio power amplifierResonance
An antenna amplifier, in particular for a magnetic resonance antenna, has a sheath wave barrier integrated into the signal path of the antenna amplifier in the form of a component designed exclusively for transfer of a differential signal.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
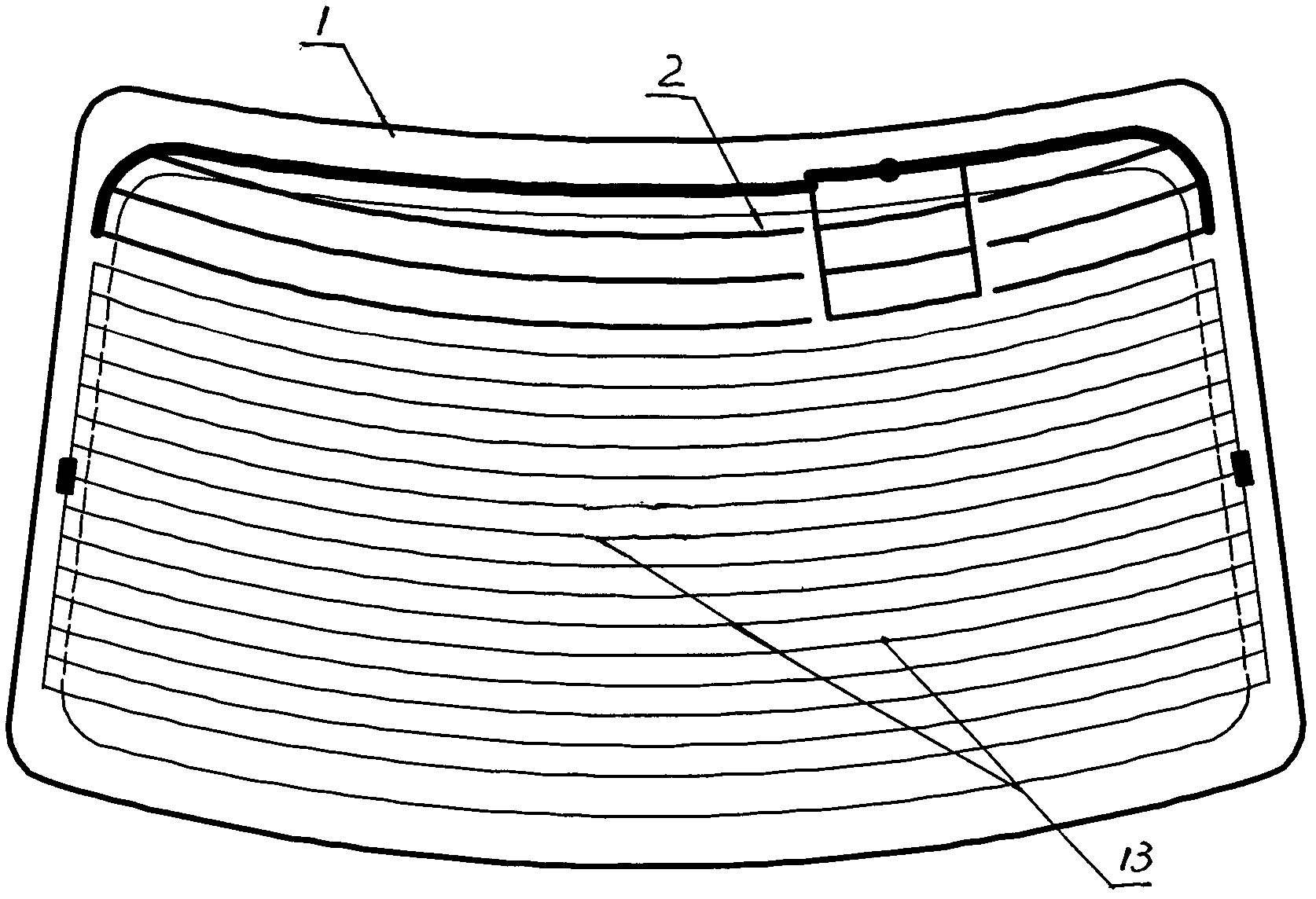
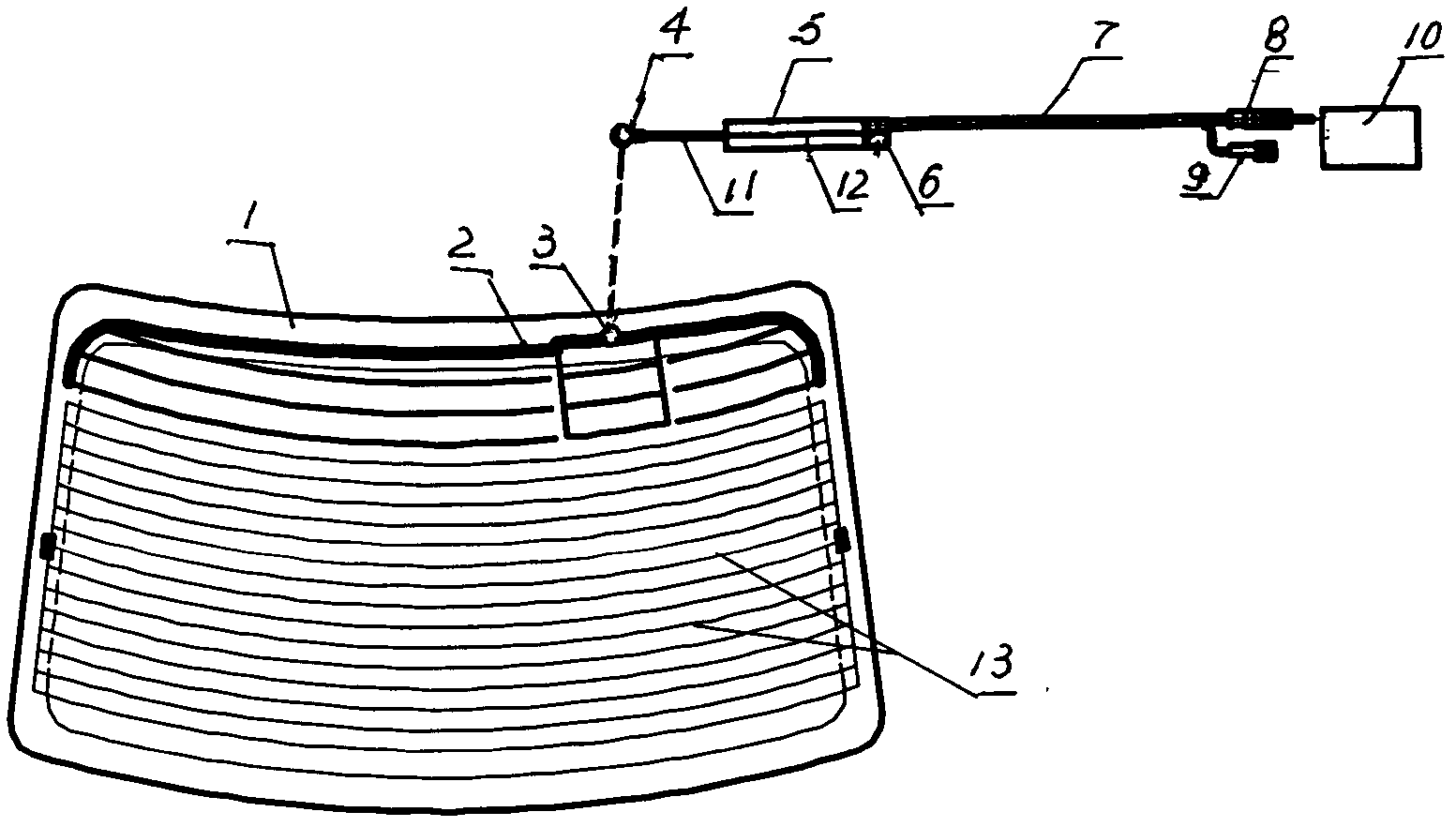
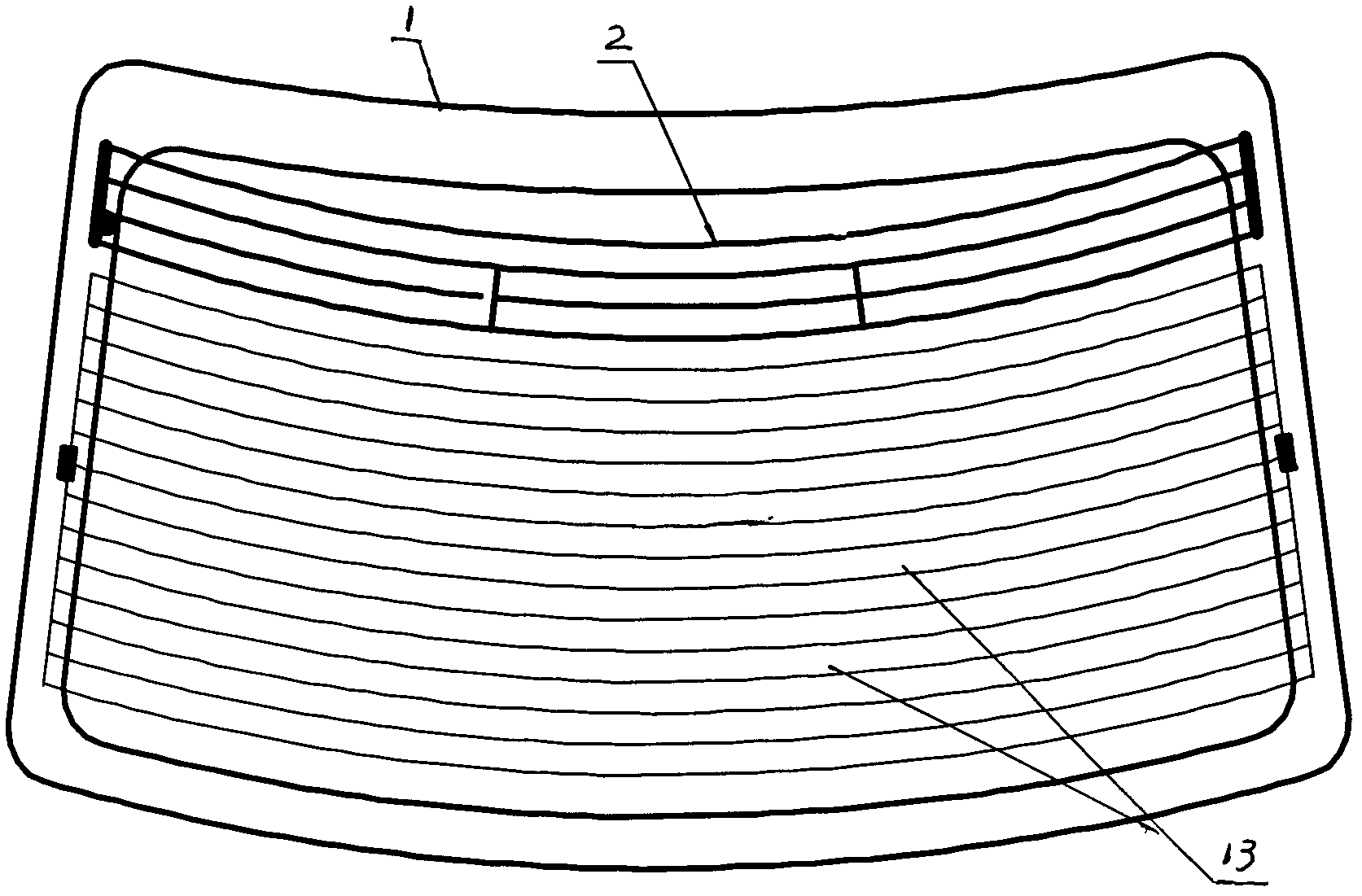
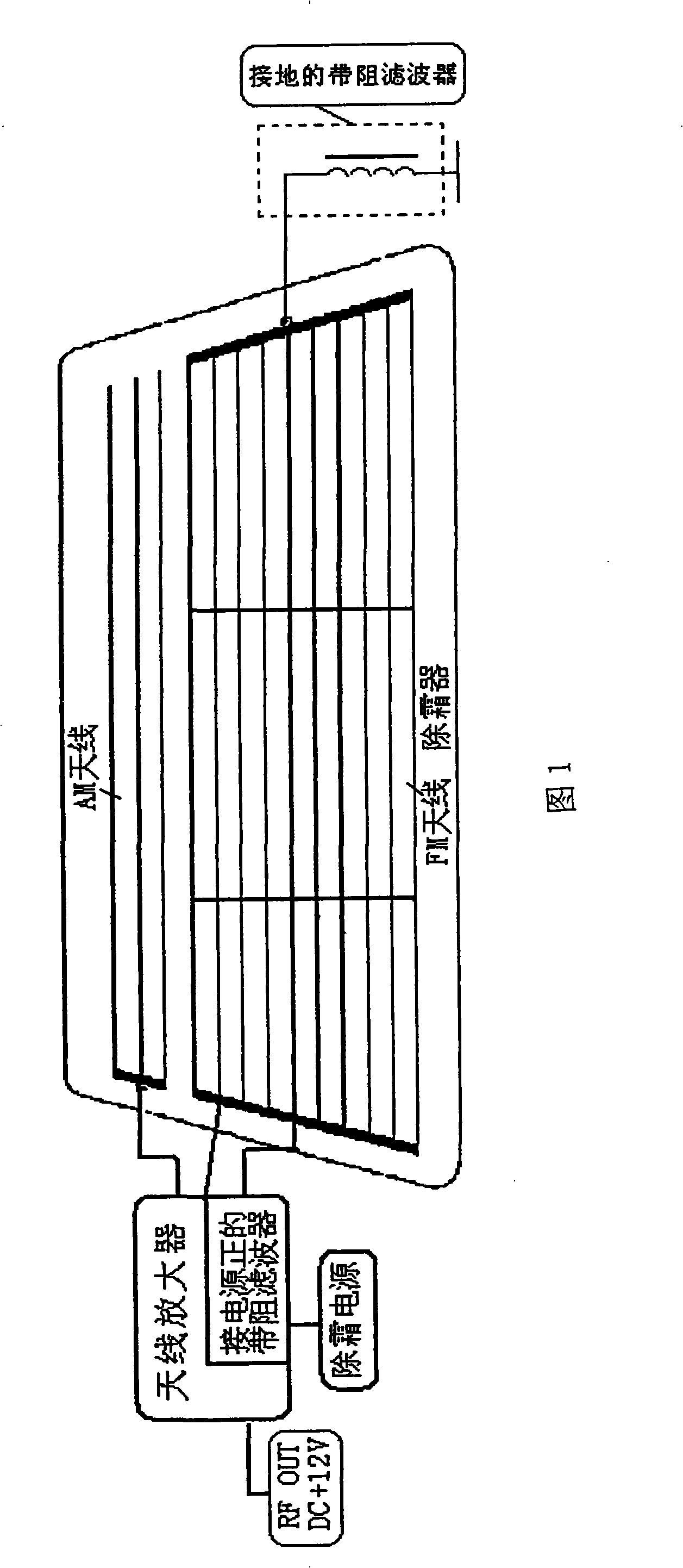
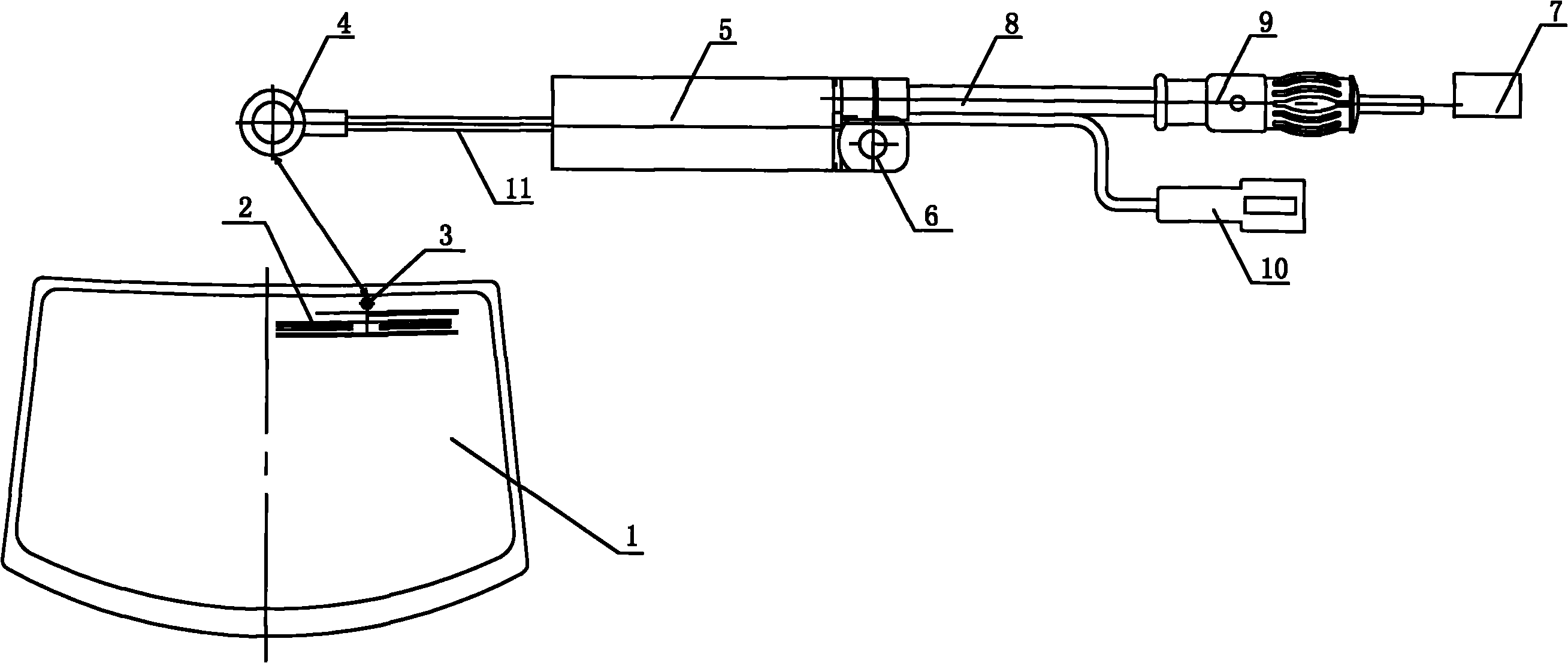
Automobile window glass amplitude modulation and frequency modulation shared printed antenna system
InactiveCN102064378AOverall small sizeReduce volumeWindowsAntenna arraysAudio power amplifierCoaxial cable
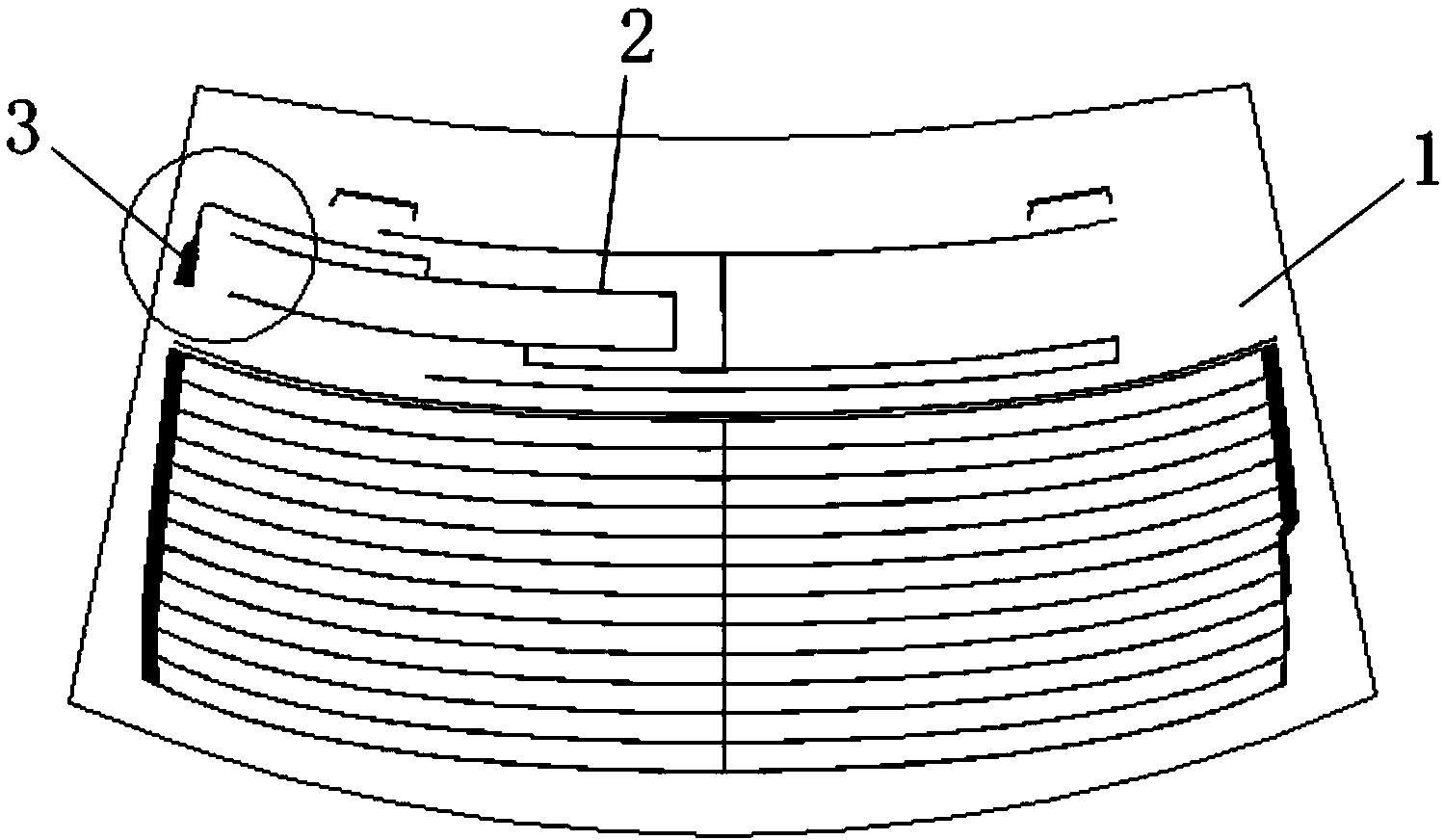
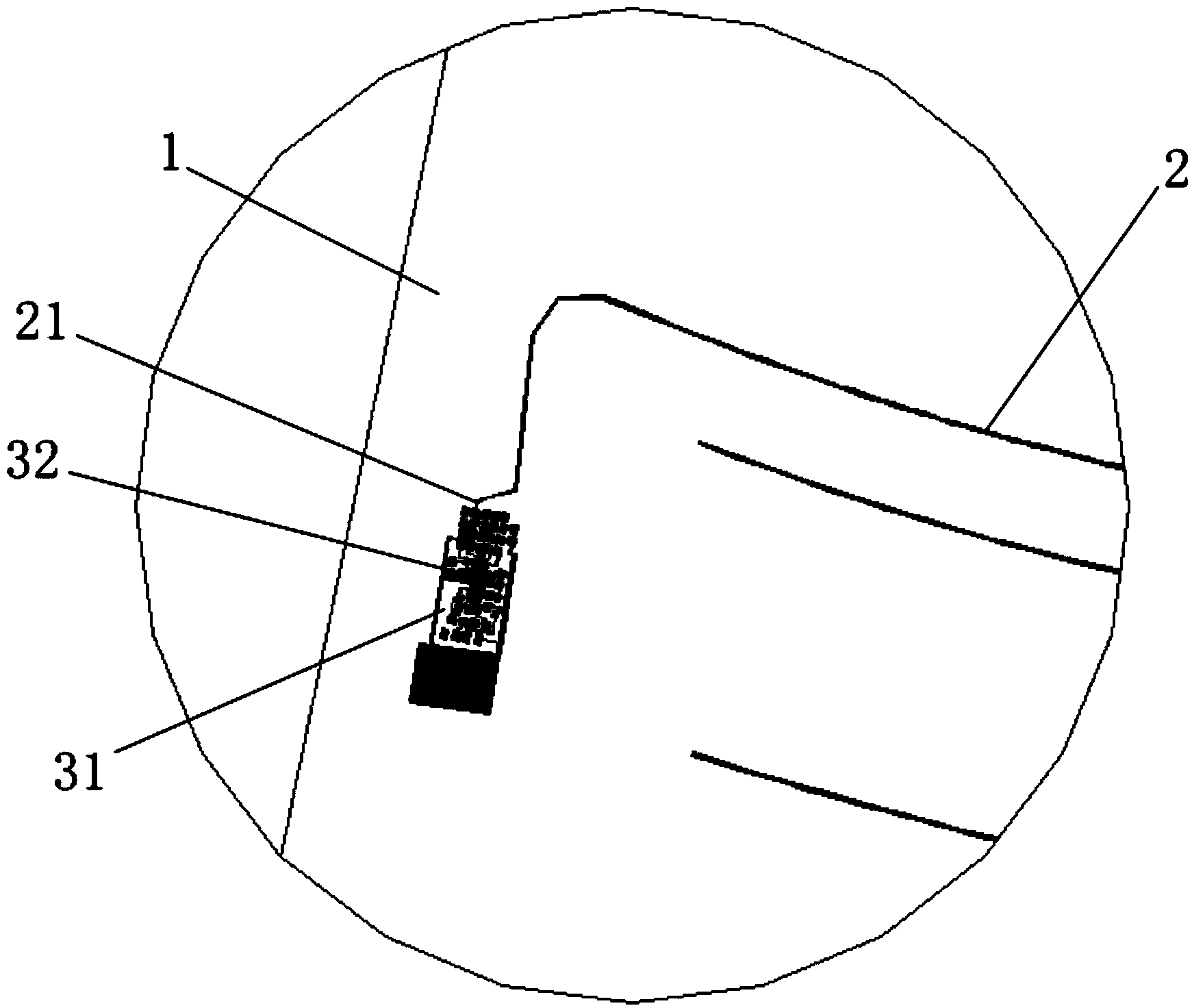
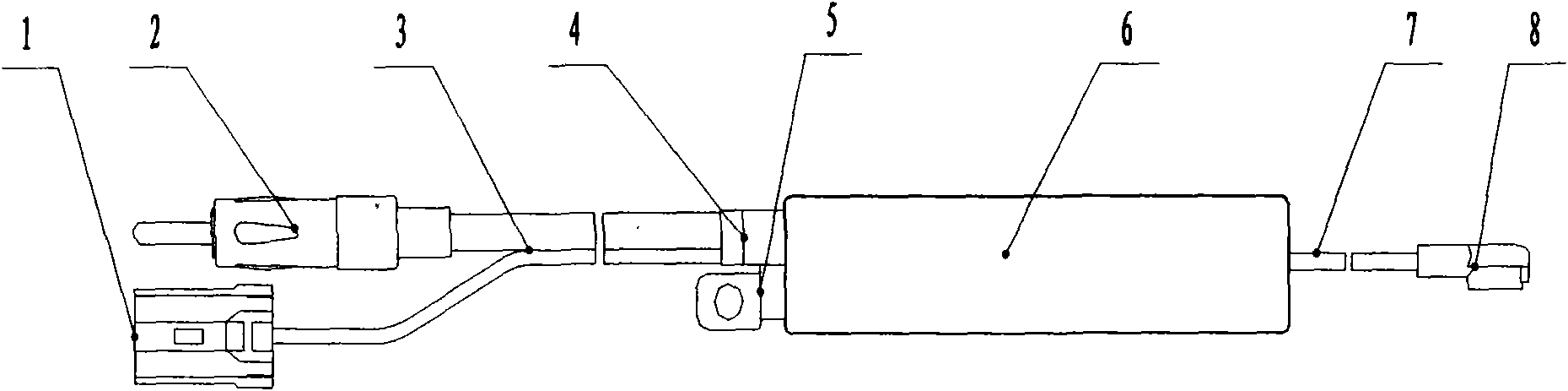
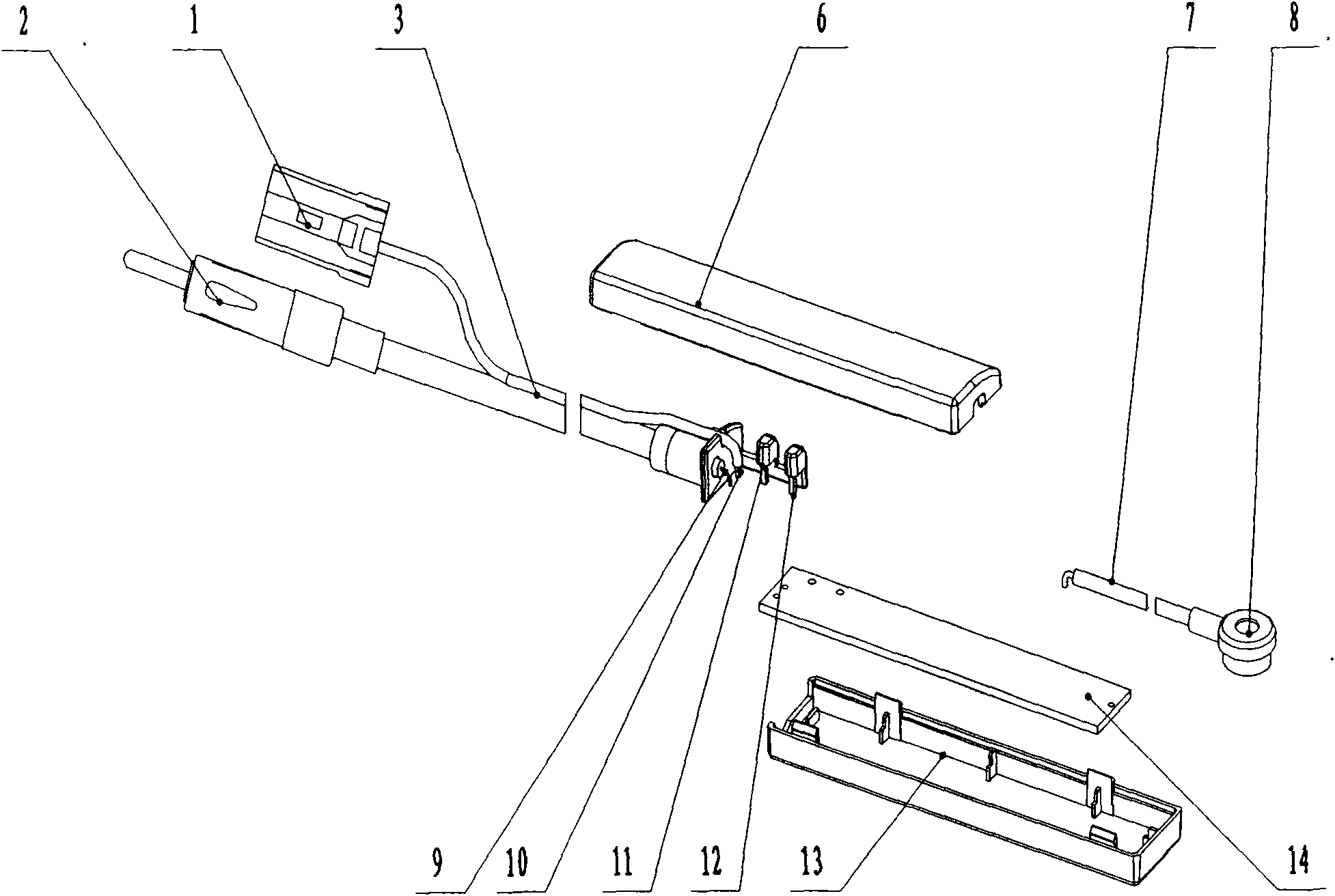
The invention discloses an automobile window glass amplitude modulation and frequency modulation (AM / FM) shared printed antenna system, which relates to an automobile front window, rear window and side window windscreen AM / FM shared printed antenna system. The system consists of a window glass printed antenna part and an antenna amplifier part and is characterized in that: the automobile window glass printed antenna part is provided with an automobile window windscreen; the automobile window windscreen is printed with an AM / FM shared printed antenna and is provided with an antenna signal output terminal; the AM / FM shared printed antenna is connected with the antenna signal output terminal through a lead; the antenna amplifier part comprises an antenna amplifier shell, a bracket, an electronic circuit board, a signal output plug, a power supply input socket, parallel coaxial cable output lines, an antenna signal input terminal and a high-frequency signal connection line; the electronic circuit board is arranged on the bracket; a mounting hole is formed on the bracket; and the shell is sleeved on the bracket.
Owner:蒋小平
Printing antenna system of vehicle rear window glass
ActiveCN101345334AReasonable designCompact structureWindowsHigh frequency amplifiersAudio power amplifierEngineering
The invention relates to an automobile rear window glass printing antenna system, in particular to a frequency-modulation and amplitude-modulation printing antenna which is arranged on the rear window glass and connected with an antenna amplifier; the automobile rear window glass printing antenna system which is connected with a demisting and defrosting power supply is especially suitable for being used as acoustic antennas of middle-class and high-class cars. The automobile rear window glass printing antenna system is characterized in that the automobile rear window glass is provided with a frequency-modulation and amplitude-modulation printing antenna; the frequency-modulation printing antenna is provided with a plurality of antennas; the amplitude-modulation printing antenna is provided with a plurality of antennas; the frequency-modulation printing antenna and the amplitude-modulation printing antenna are respectively provided with printing antenna output terminals; the printing antenna output terminals of the frequency-modulation printing antenna and the amplitude-modulation printing antenna are respectively connected with the antenna amplifier by an over-bridge wire; the antenna amplifier is internally provided with a band stop filter which is connected with the anode of the power supply; the band stop filter of the frequency-modulation printing antenna connected with the anode of the power supply is connected with an elastic contact sheet; and one end of the band stop filter which is grounded at the other side of the frequency-modulation printing antenna is connected with the elastic contact sheet and the other end thereof is grounded.
Owner:TAIZHOU SUZHONG ANTENNA GROUP
Antenna amplifier and shared antenna amplifier
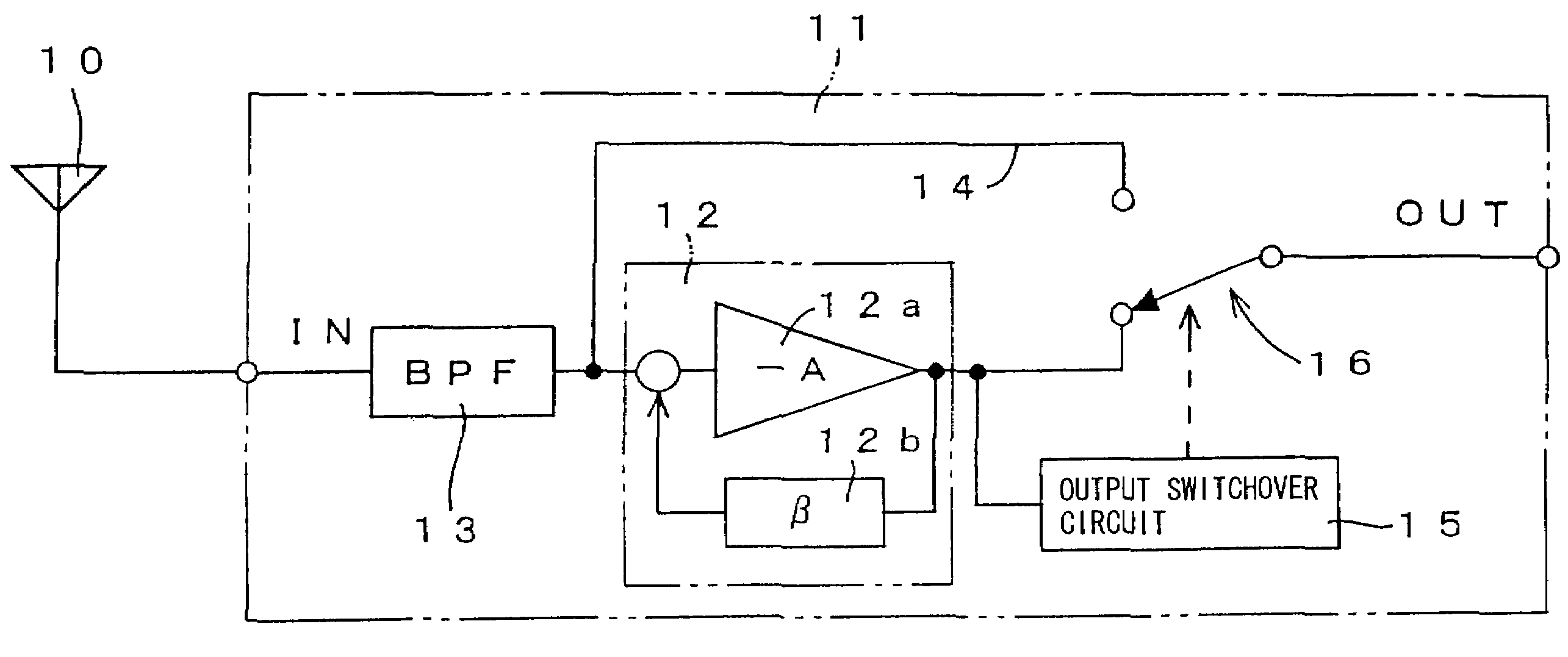
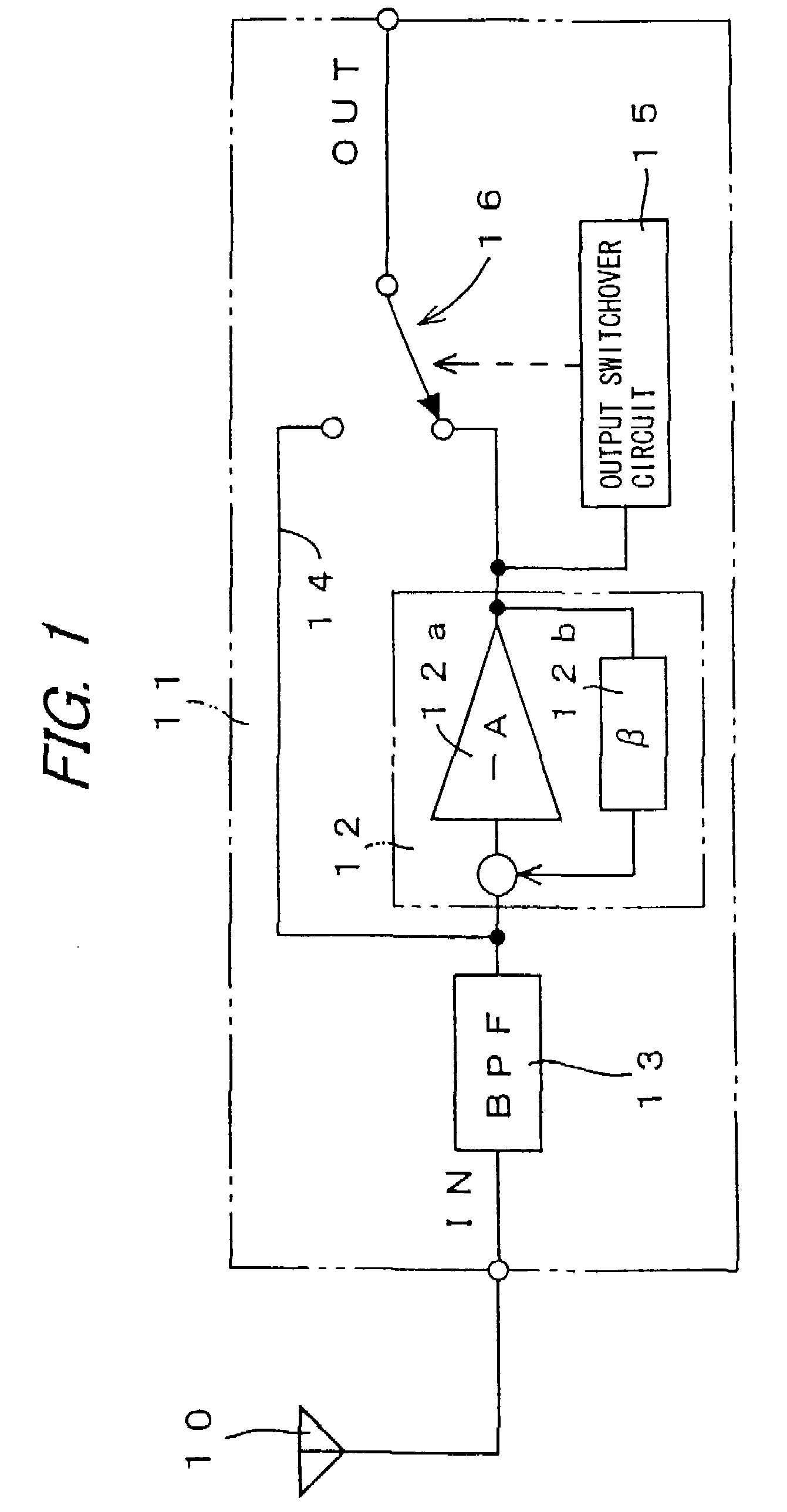
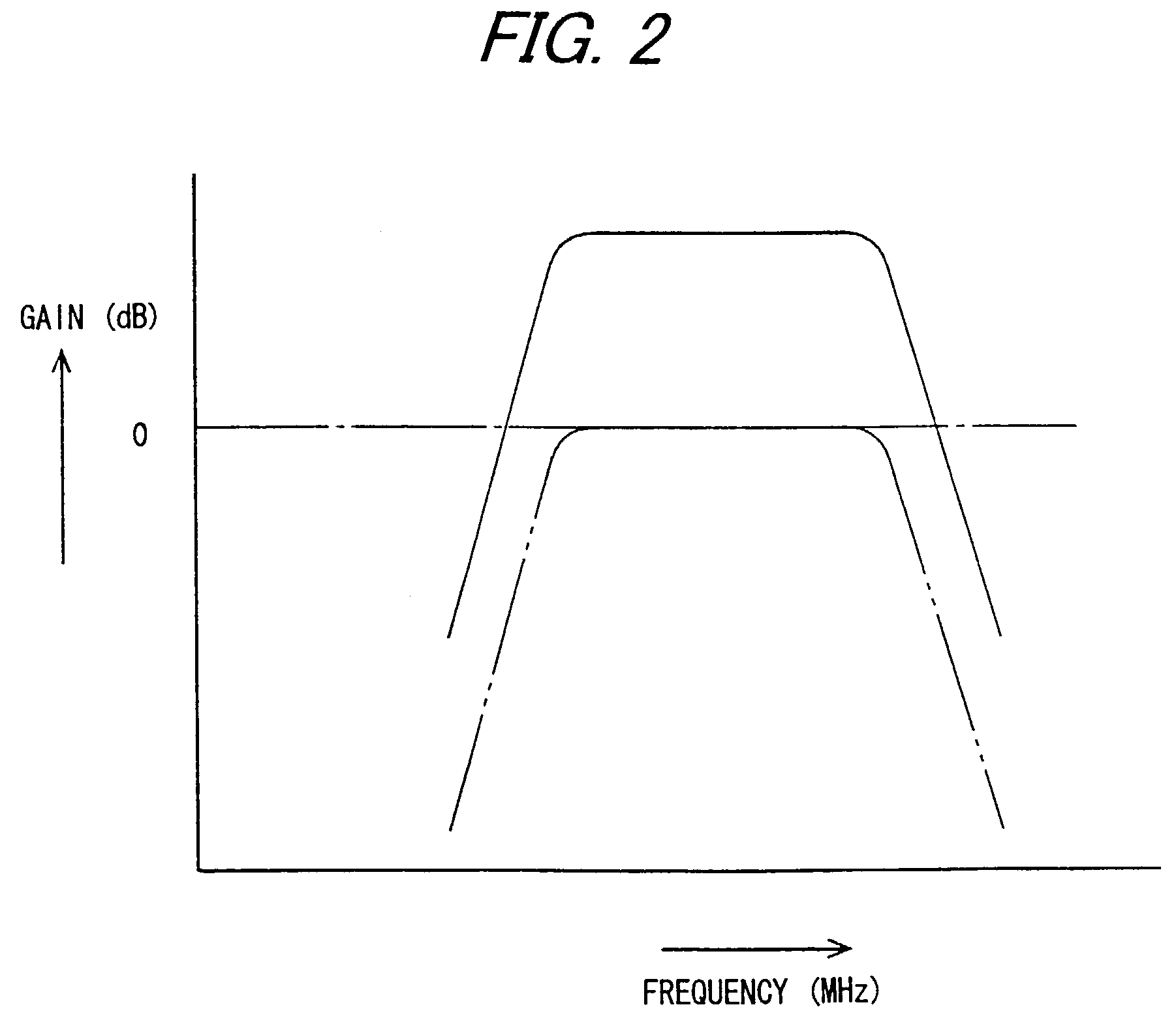
InactiveUS7277684B2Reduce distortionReduce signal suppressionGain controlRadio transmissionAudio power amplifierDistortion reduction
An object of the invention is to receive a weak signal with high sensitivity and reduce distortion and signal suppression when a strong interference signal exists. When a high-frequency signal received by an antenna is to be amplified by an antenna amplifier and when an interference wave of high field strength exists, a switch circuit is switched by an output switchover circuit from the output of an amplifier to a through-circuit. The through-circuit guides the high-frequency signal, directly to the output side without passing through the amplifier. When the switching operation of the switch circuit is performed based on low-frequency components which are highly correlated with distortion components due to intermodulation, the switching operation can be performed more adequately. Noises can be reduced by performing a smoothing process on the switching operation, and the use of an inverting amplifier can prevent occurrence of oscillation.
Owner:FUJITSU GENERAL LTD
Car top-set wireless device and its wireless amplifier
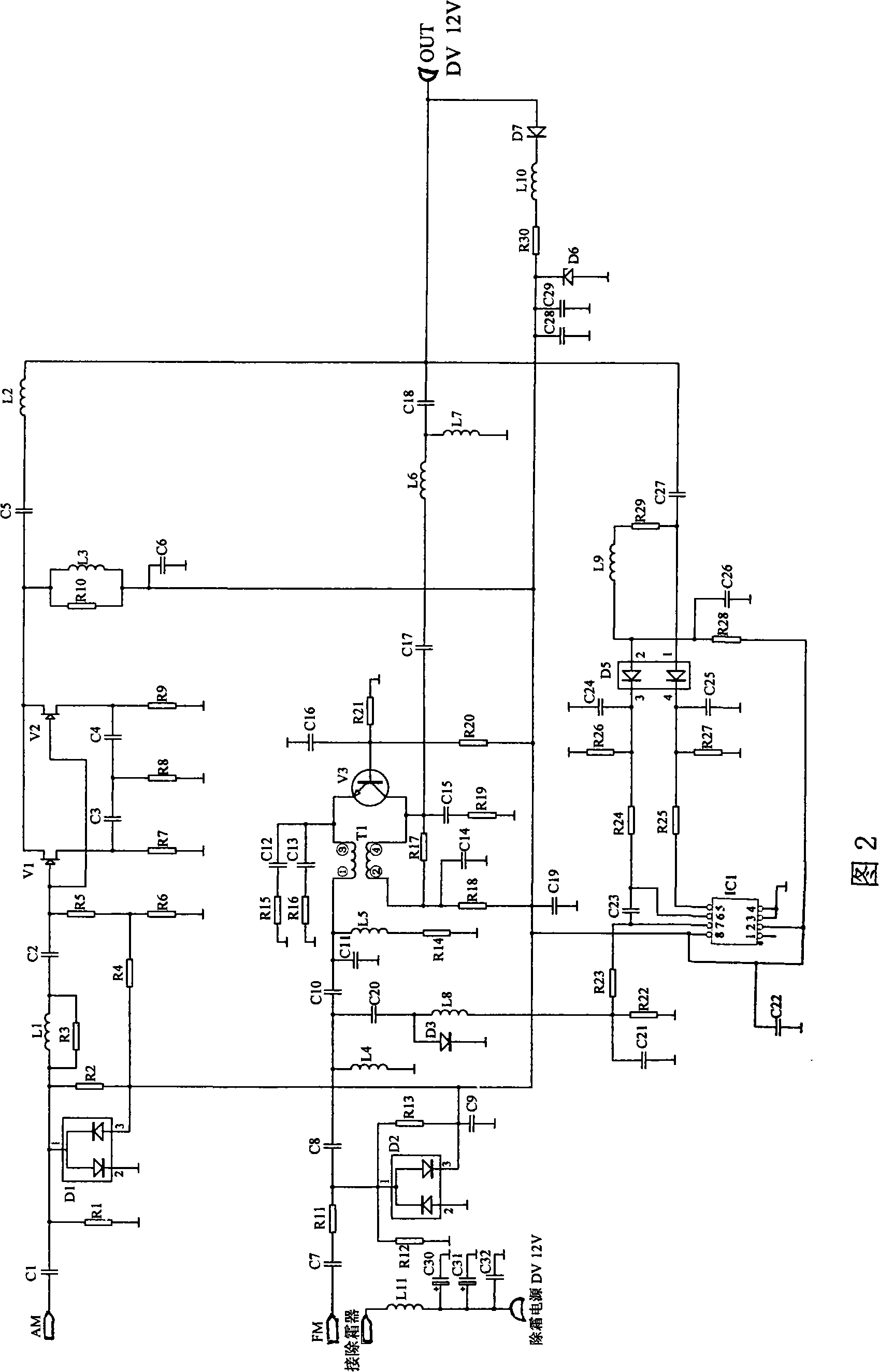
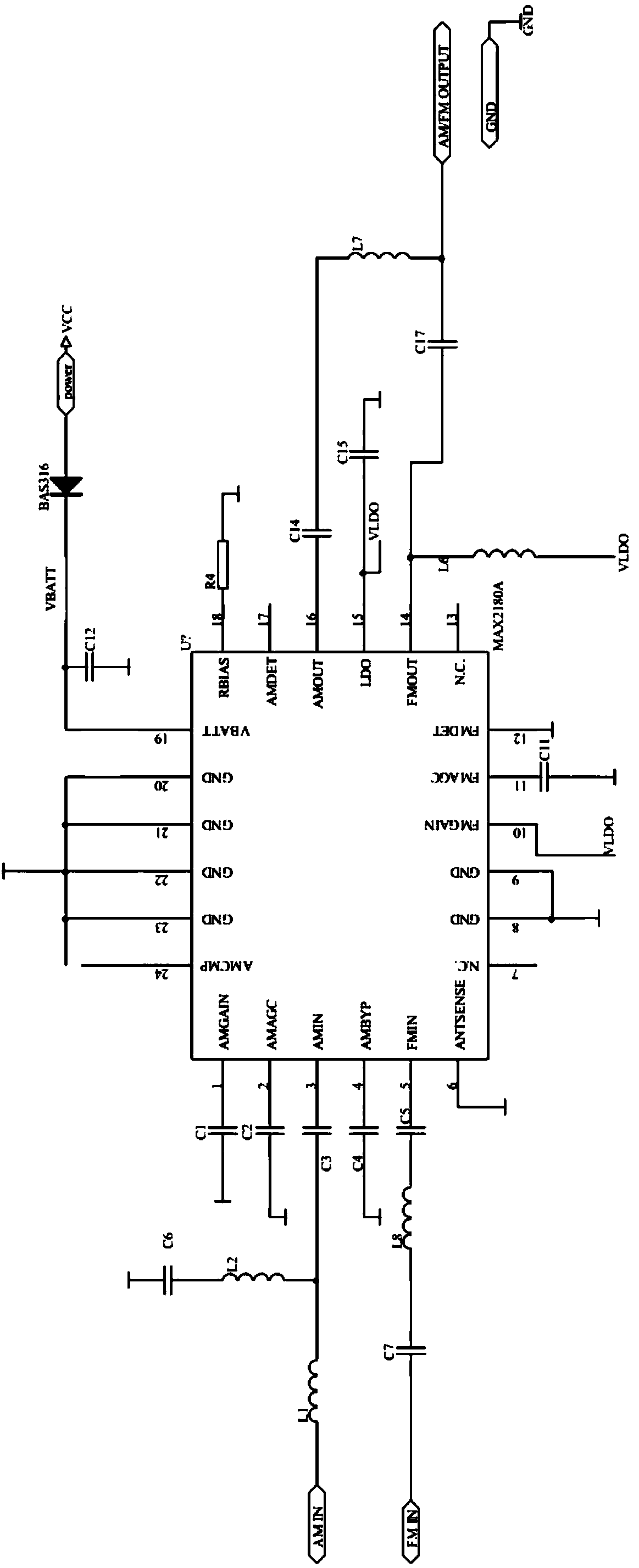
ActiveCN101262235ARaise the potentialImprove reception performanceAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesRadiating elements structural formsAudio power amplifierRadio reception
The invention relates to a vehicle overhead aerial system and an aerial amplifier thereof. The aerial amplifier comprises an AM frequency selection circuit, an AM signal amplifying circuit, an FM frequency selection circuit, an FM signal amplifying circuit and a power supply circuit, wherein, the aerial amplifier is further provided with a trapping circuit, one end of the trapping circuit is connected with the ground terminal of the aerial amplifier, and the other end thereof is connected with a metal aerial mounting base at the top of the vehicle. The aerial system is provided with a shark fin type aerial shell, a metal mounting base, an aerial frame and a wireless reception aerial; the aerial shell is arranged at the metal mounting base, which forms an internal accommodation space; the accommodation space is internally provided with the aerial frame, the wireless reception aerial and a circuit board which is provided with the aerial amplifier. The vehicle overhead aerial system and an aerial amplifier thereof increase the ground electric potential of the aerial amplifier at a printed circuit board, which is equal to increasing the height of the aerial amplifier to the metal mounting base, thus reducing the high frequency signals absorbed by the vehicle top, and increasing the receiving effect of the amplifier.
Owner:TAIZHOU SUZHONG ANTENNA GROUP
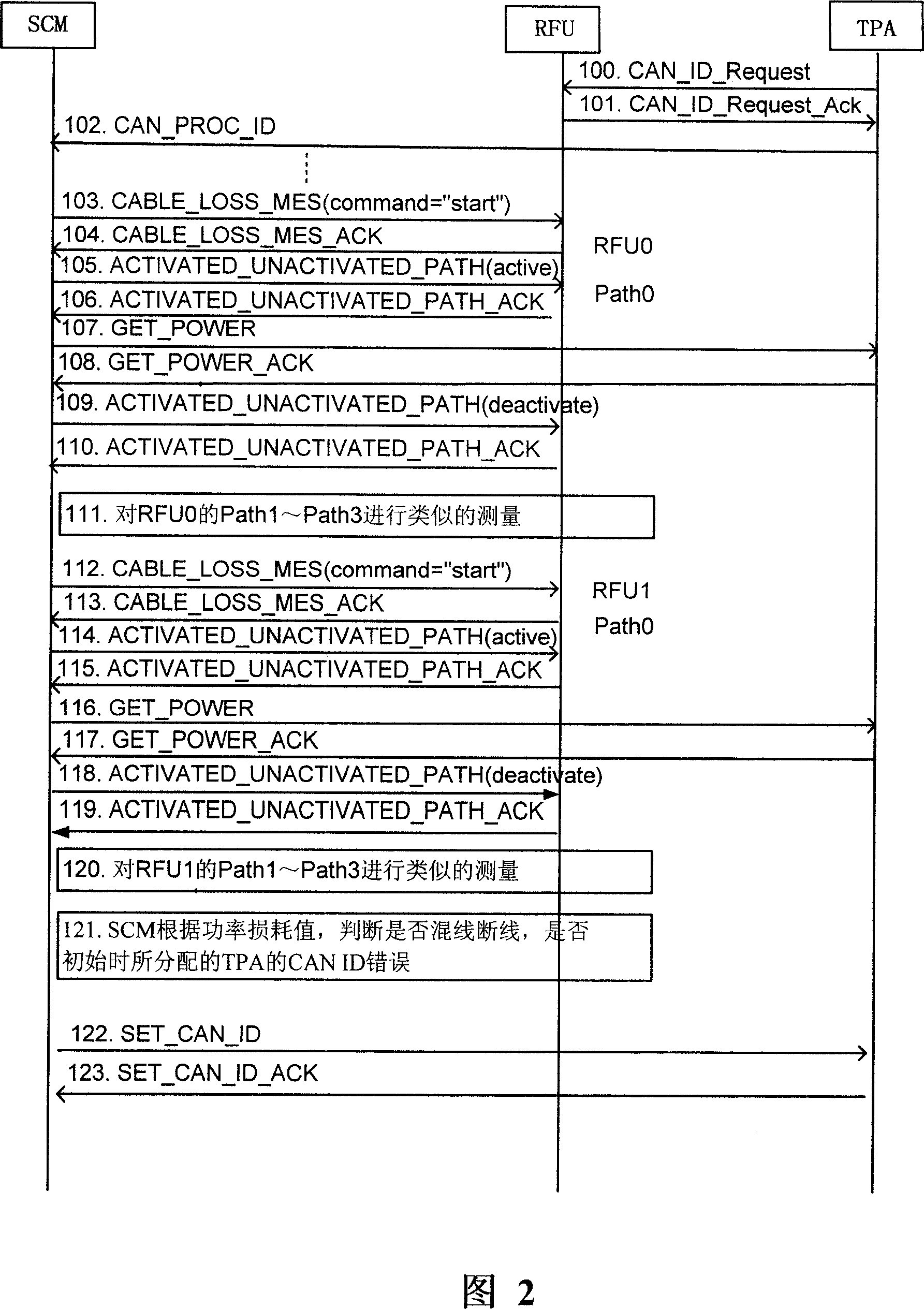
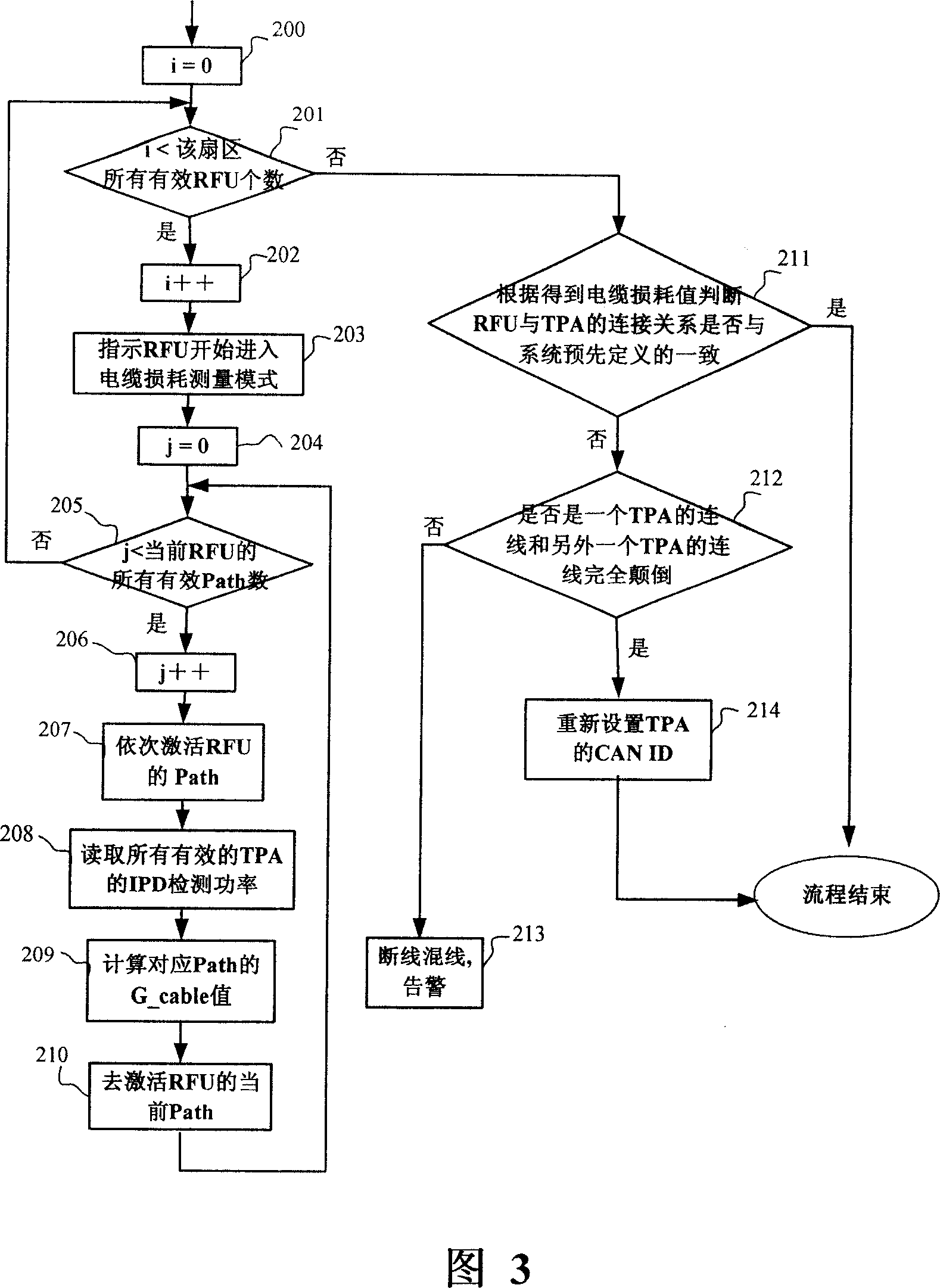
Method for setting controller local network identification of antennafier unit and macro base station
ActiveCN101119141AAvoid errors of judgmentEasy to installSpatial transmit diversityTransmission control/equalisingAudio power amplifierMacro base stations
The invention discloses a method for setting amplifier unit CAN ID of antenna and a micro base station. The micro base station of the invention comprises a SCM unit, a RFU unit and a TPA unit, and every unit is communicated with each other through CAN assembly. The method for setting amplifier unit CAN ID of antenna includes the procedures as follows: the RFU assigns a CAN ID for TPA; a Path of RFU is used for sending signal with certain power, and the power detection is carried out at the input port of Path of TPA; the power loss value is calculated, thus, the connection condition of the TPA and RFU is judged and the CAN ID is regulated. The invention provides a method to automatically set the CAN ID of the TPA, which is used for setting the CAN ID of the TPA wireless base station; the dial-up switch component is taken off and the manual judge and the manual dial-up during the setting of the CAN ID in the prior art are prevented; therefore, the installation and maintenance of the base station is convenient.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
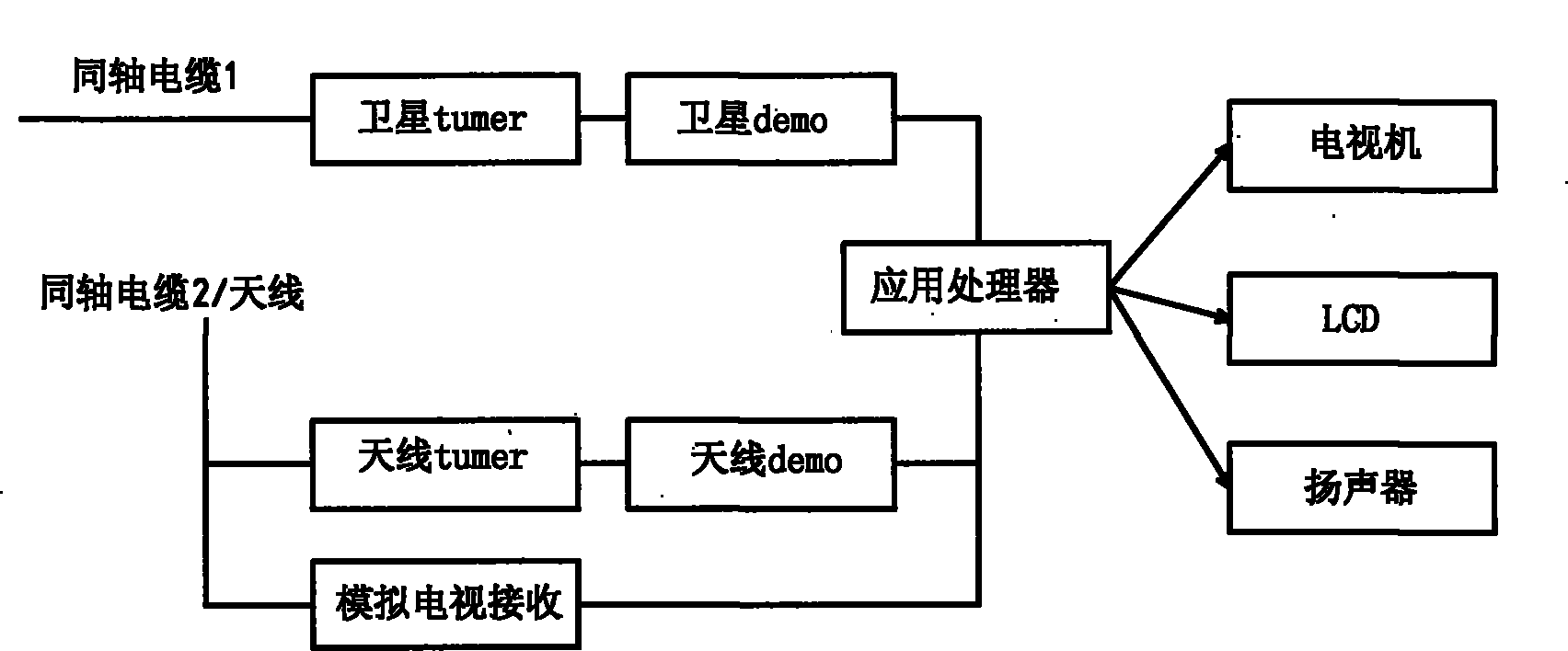
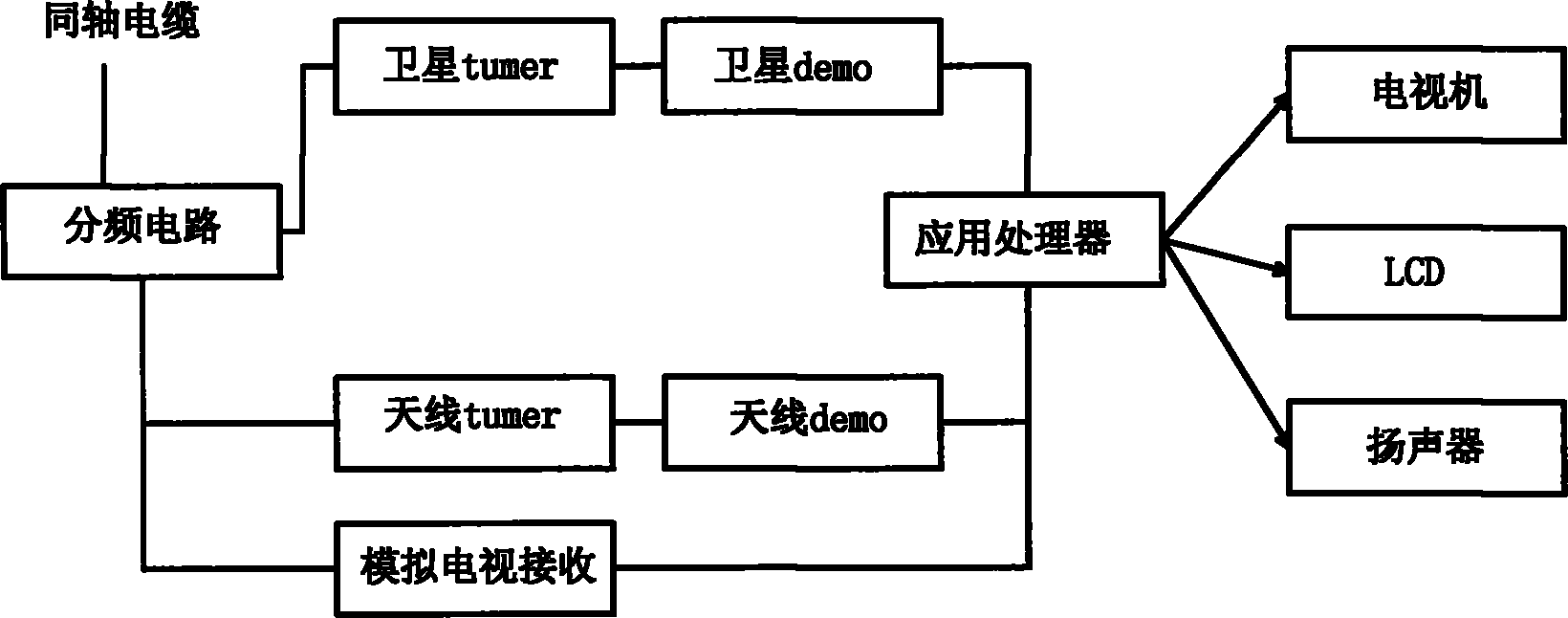
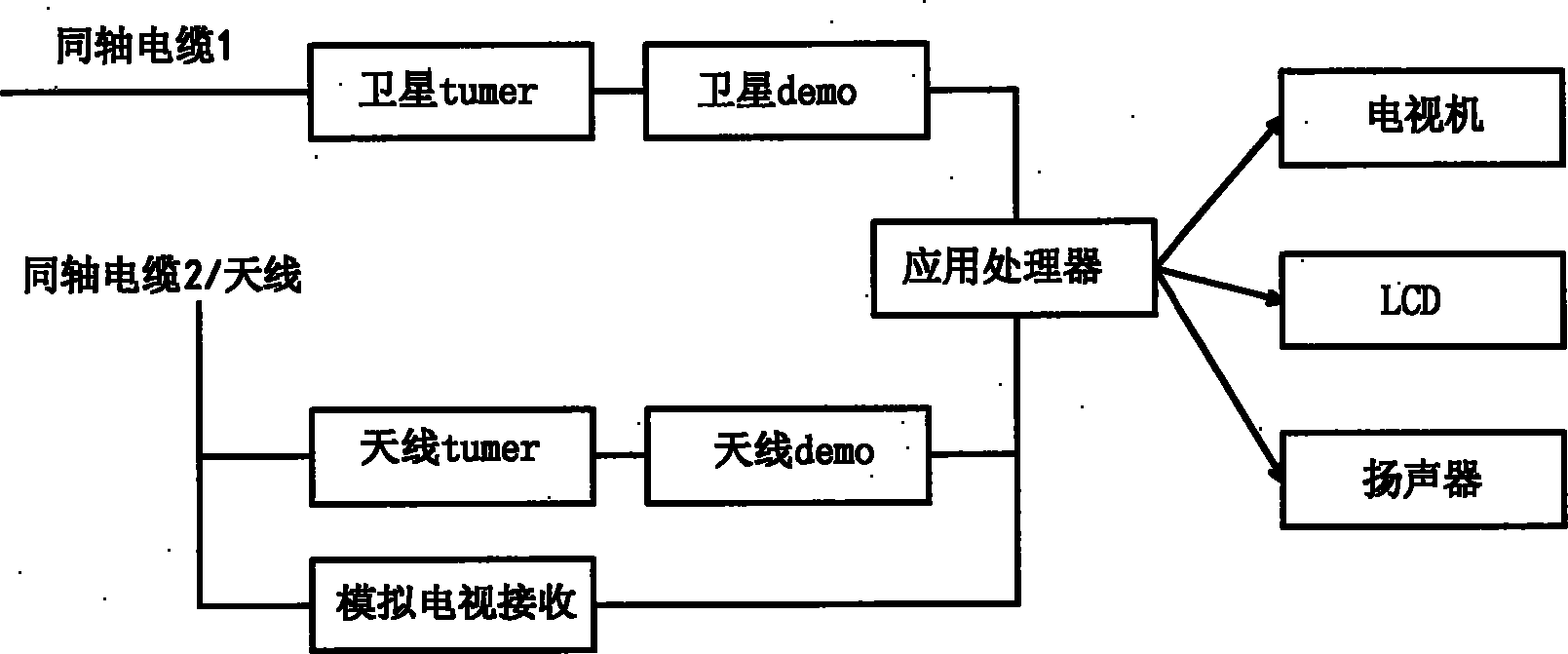
Ground and satellite combined television receiving system
InactiveCN102036029AEfficient receptionAccelerate the digitization processTelevision system detailsColor television detailsHuman–machine interfaceAudio power amplifier
The invention relates to a ground and satellite combined television receiving system. The system mainly comprises two parts, namely a fused antenna and a fused receiver, wherein the fused antenna is a mixed antenna integrating a satellite antenna with a wireless broadcasting antenna physically; the fused receiver is provided with two demodulators and two interfaces which receive satellite television signals by using a coaxial cable; the fused antenna transmits the satellite television signals and wireless broadcasting signals through one coaxial cable; and the fused receiver is used for supplying power to a satellite tuner, a wireless antenna amplifier, and the remote control steering and steering automatic positioning of the antenna simultaneously. The ground and satellite combined television receiving system is easy to operate and use, has a friendly man-machine interface, and can effectively receive cable digital television broadcasting programs, and satellite and ground digital television broadcasting programs.
Owner:郴州希典科技有限公司
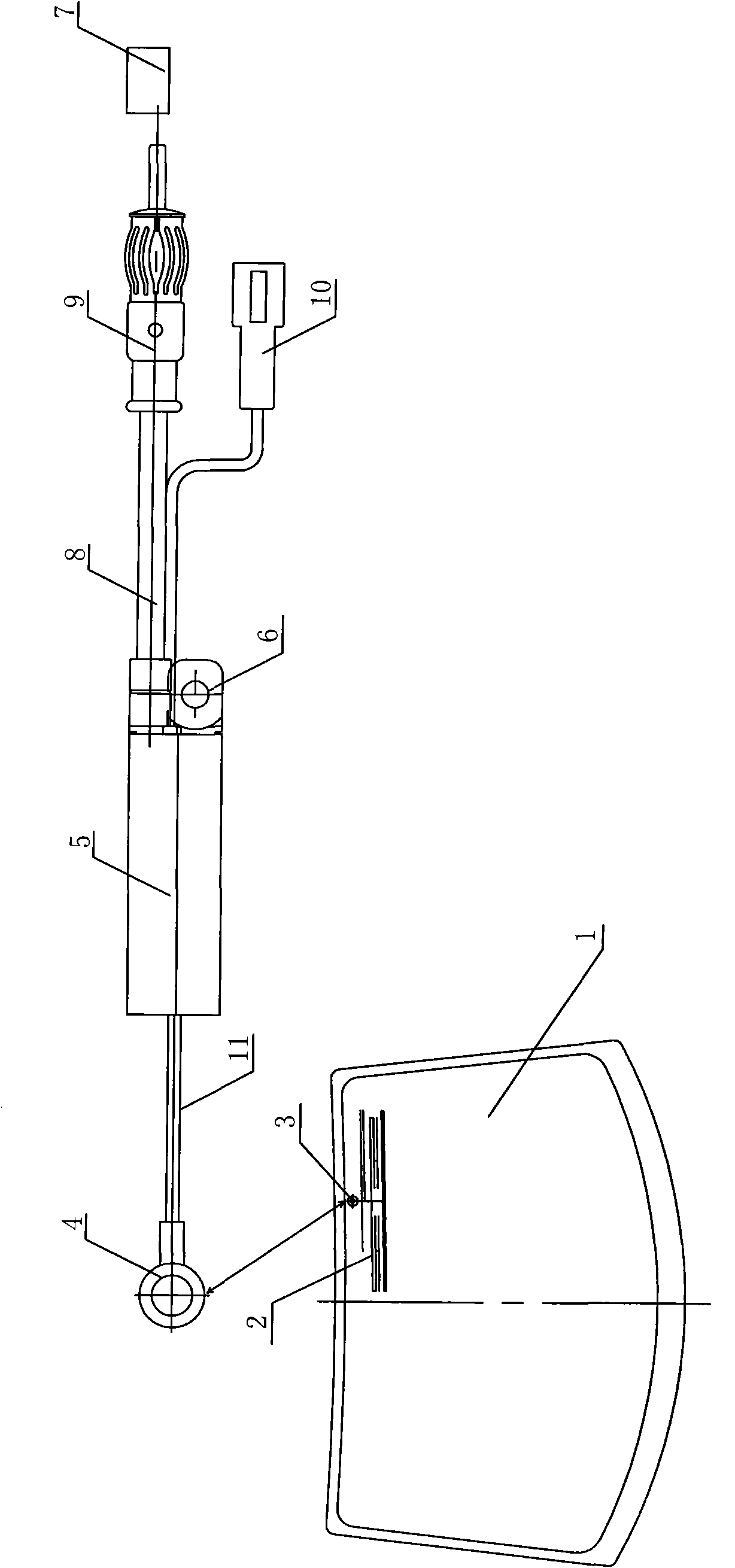
Amplifier system of front screen printed antenna for automobiles
The invention provides an amplifier of a front screen printed antenna for automobiles, which relates to a front windshield printed antenna for the automobiles and a small antenna amplifier system thereof and is suitable for a on-board antenna receiving system of a transceiver for the automobiles. The system of the invention comprises a front screen printed antenna part and an antenna amplifier part, wherein the front screen printed antenna part comprises a front windshield, and a frequency modulation (FM) and amplitude modulation (AM) combined printed antenna are printed on the front windshield; the antenna amplifier part comprises an antenna amplifier shell, a bracket, an electronic circuit board, a signal output plug, a power input socket, parallel coaxial cable output lines, an antennasignal input terminal and high-frequency signal connecting lines; the electronic circuit board is connected with the antenna signal input terminal, and the antenna signal input terminal is connected with an antenna signal output terminal; and electronic circuits comprise an AM input frequency selection circuit, an AM amplifying circuit, an AM output frequency selection circuit, an FM input frequency selection circuit, an FM amplifying circuit, an FM output circuit, a power circuit and an electrostatic protection circuit.
Owner:TAIZHOU SUZHONG ANTENNA GROUP
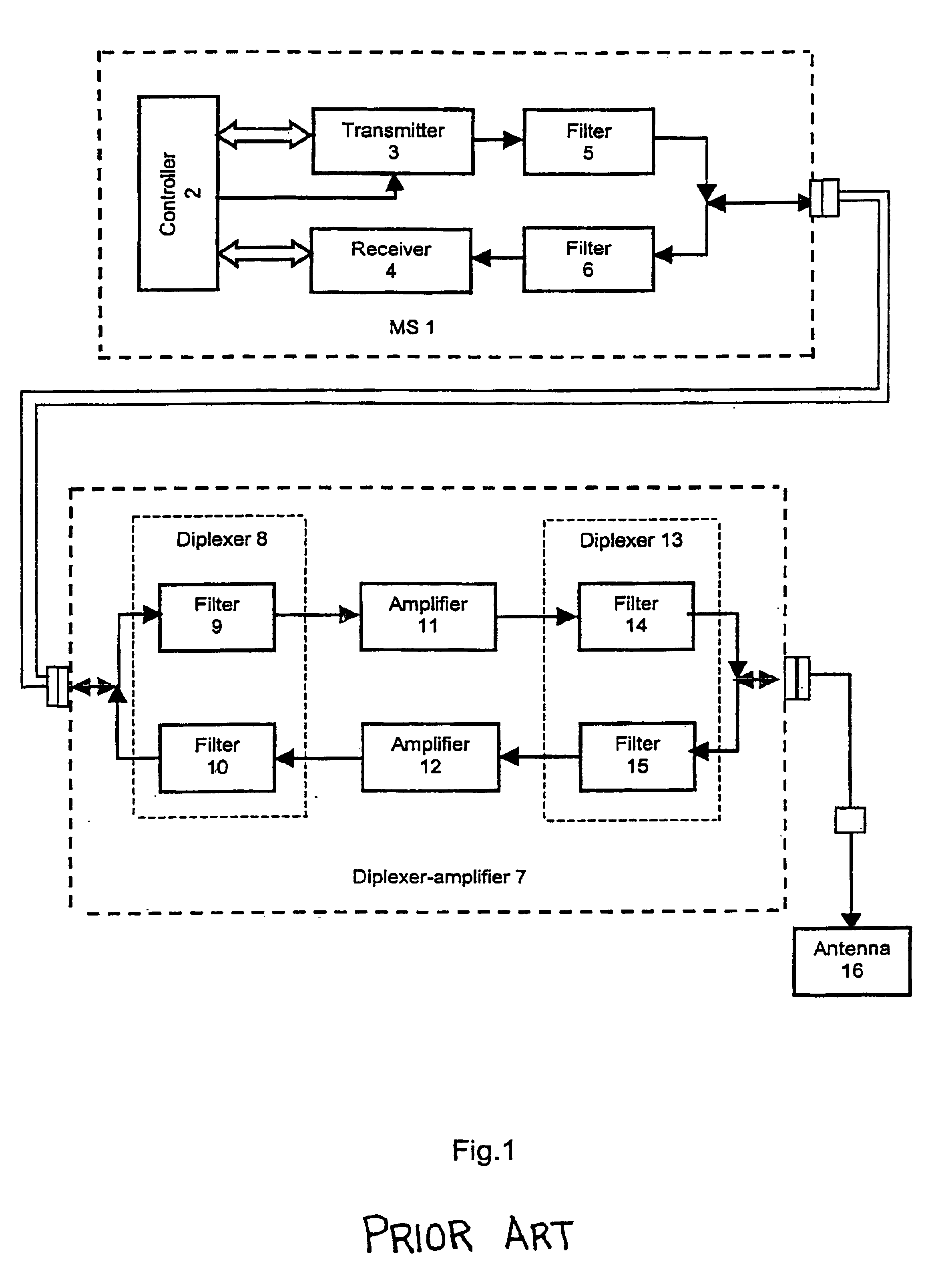
Subscriber station with duplex antenna amplifier
InactiveCN1365582AReduce manufacturing costReduce radiation levelsTransmission control/equlisationRepeater circuitsControl signalSignal on
According to the invention, in order to make a system more economical during full compensation of the attenuation of a transmitter and receiver signal in a communication cable, a subscriber station includes a transmitter on / off control circuit with a controlled power source (a control command converter) and a low-pass filter used to separate a transmission / reception VHF signal from a lower frequency (up to a D.C. level) control signal / command, whereby the power supply of the subscriber station is autonomous. In the first variant of the inventive device, a control command passing through the low-pass filter 19 turns on the control of the power source 21 supplying the power amplifier 11. The amplification is selected to compensate for the attenuation of the transmitter signal on its way from the subscriber station 1 to the antenna 16. By means of an interconnect cable, the supply voltage from the subscriber station is fed into a stabilizer 22 through another low-pass filter 20 which performs decoupling of the supply circuit from the transmission and reception radiofrequency signals. In the second variant of the device, the duplex antenna amplifier 7 includes a splitter and a rejector filter 24, which enables the simplification of the design of the antenna amplifier and makes it less expensive.
Owner:JSC KODOFON
Carrier for Holding an Antenna Amplifier of a Vehicle
InactiveUS20090206219A1Reduce stepsAvoid radiationCoupling device connectionsFurniture partsAudio power amplifierCarrier signal
The invention relates to a carrier (1) for holding an electronic device, in particular an antenna amplifier of a vehicle, having at least one printed circuit board (9), the electronic device being able to be attached to a vehicle component, in particular a vehicle window (12), by means of the carrier (1) which is composed of an electrically nonconductive material, there being provision according to the invention for the carrier (1) to be embodied in a planar fashion and to have latching means as well as spring means which interact therewith and have the purpose of securing the printed circuit board (9) to the carrier (1), as well as at least one recess for holding a contact element in order to make electrical contact with a contact face of the printed circuit board (9) by means of a corresponding contact face (13) on the vehicle component.
Owner:HIRSCHMANN CAR COMMUNICATION
Vehicle-mounted active glass antenna and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103872465AReduce distanceStable receptionRadiating elements structural formsAudio power amplifierSignal amplifier
The invention relates to the field of glass antennas, particularly provides a vehicle-mounted active glass antenna integrating an antenna amplifier and glass, and also provides a manufacturing of the vehicle-mounted active glass antenna. The vehicle-mounted active glass antenna comprises the glass, an antenna element and an antenna signal amplifier, wherein an antenna signal amplifying circuit is integrally printed on the surface of the glass, the input end of the antenna signal amplifying circuit is at least partially coincided with the feeding end of the antenna element, and an antenna signal amplifying element is welded on the antenna signal amplifying circuit. The vehicle-mounted active glass antenna has the advantages that by integrally printing the antenna signal amplifying circuit on the surface of the glass, the number of antenna parts is reduced, and the manufacturing cost is correspondingly reduced; the distance between the antenna signal amplifier and the antenna element is minimized, and the problem of instable signals is obviously reduced; the position is very firm, the poor contact with the antenna element is avoided, the receiving stability of communication signals is guaranteed, and the integral performance is improved.
Owner:FUYAO GLASS IND GROUP CO LTD
Series fed amplified antenna reflect array
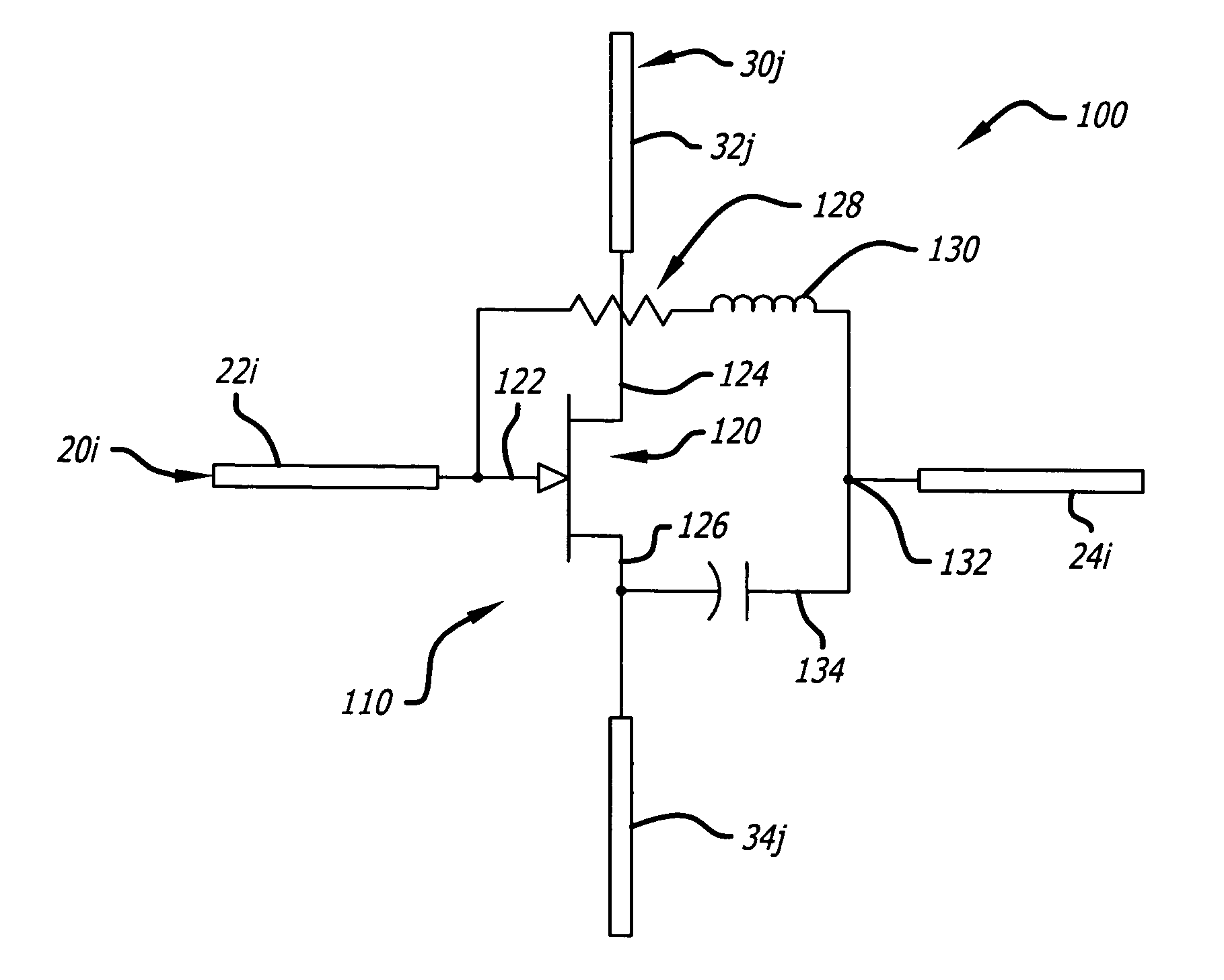
InactiveUS20060279470A1Amplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesRF amplifierDipole antennaVoltage divider
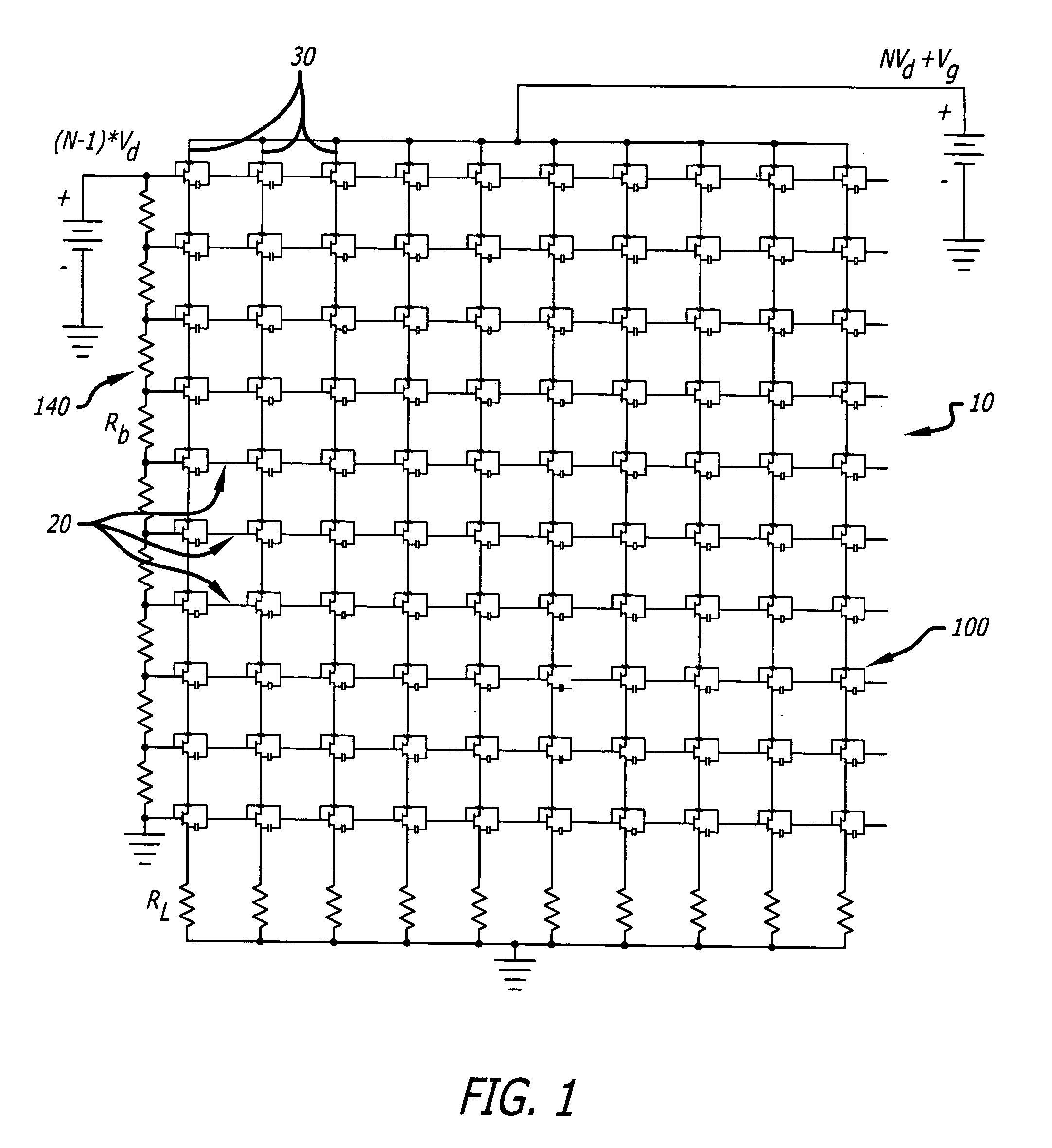
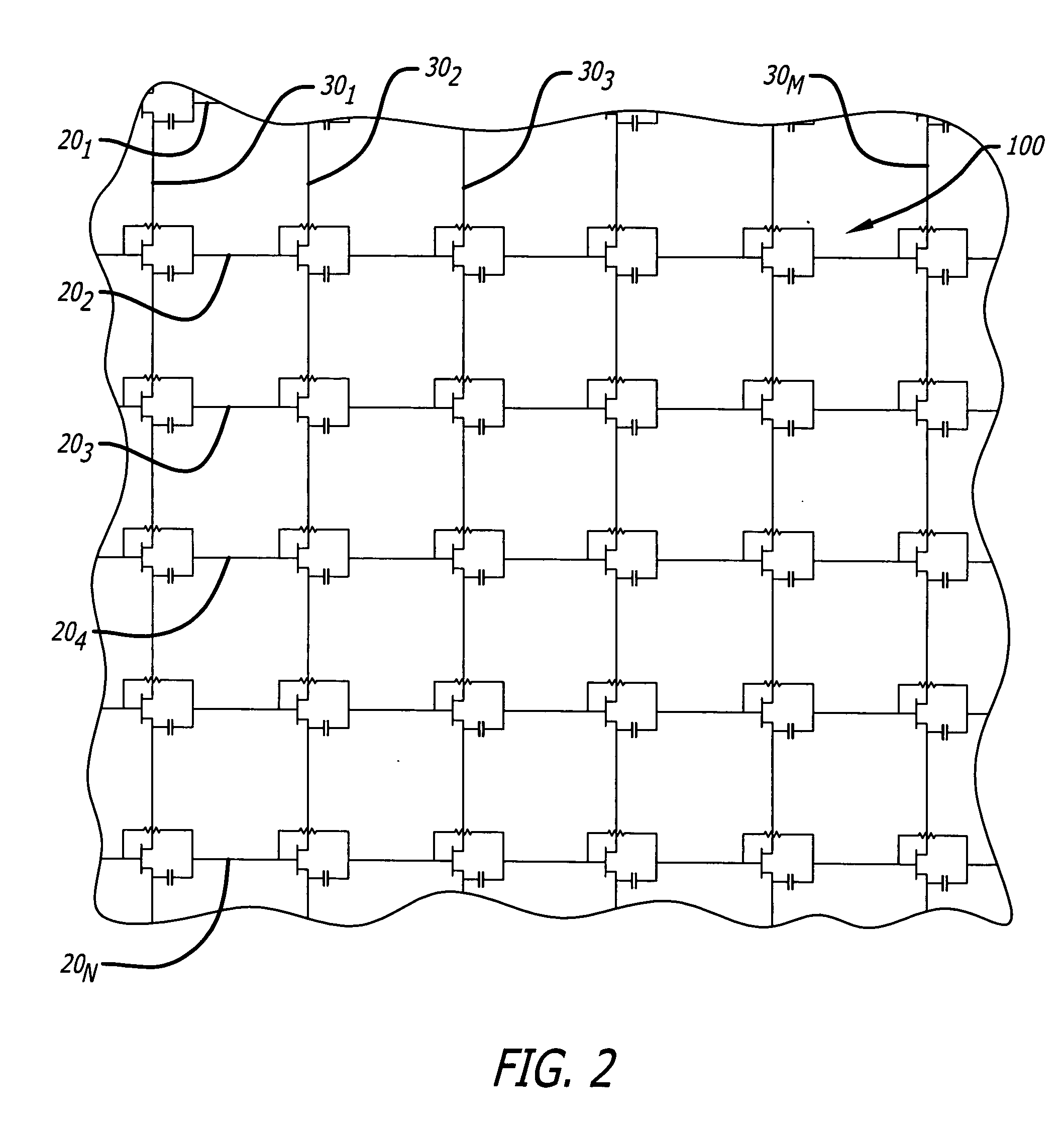
A reflect array antenna. The array includes a plurality of unit cells. Each cell includes a first dipole antenna having a first orientation and a first polarization; a second dipole antenna having a second orientation and a second polarization; and an amplifier input coupled inline to said first dipole antenna and output coupled inline to said second dipole antenna. The array further includes N first dipole antennas having a first orientation and a first polarization; M second dipole antennas having a second orientation and a second polarization; and a plurality of unit cells, each cell including an amplifier input coupled inline to a first dipole antenna and output coupled inline to a second dipole antenna. The second orientation and the second polarization are orthogonal to the first orientation and the first polarization. Each amplifier includes a transistor with an input terminal and first and second output terminals. Each input terminal is connected to the first dipole antenna and the output terminals are coupled to the second dipole antenna. The first and second terminals are adapted to be coupled to second and first terminals respectively of a neighboring cell in the array. A direct current bias for the array is applied via the second dipole antenna. Input bias for the transistors is applied via the first dipole antenna. A unique gate bias voltage for each transistor in the array is provided on a row-by-row basis via a voltage divider network. The voltage divider network includes (N−1) first resistors Rb connected in series to a first source of supply potential, where N is the number of rows in the array. Each of the resistors is connected to provide an input voltage to one of the transistors in the array. The resistive network further includes M second resistors RL connected to a respective one of the second dipoles antennas, where M is the number of columns in the array. The array is fabricated by via a metallization pattern which is disposed on a first substrate to provide a chip. The chip is secured to a second substrate with a bonding agent. In the best mode, the bonding agent is an anisotropic electrically conductive bonding film that allows current to flow along a path orthogonal to a surface of the array while blocking current flow parallel to the surface of the array.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Antenna amplifier device and antenna device provided in mobile object
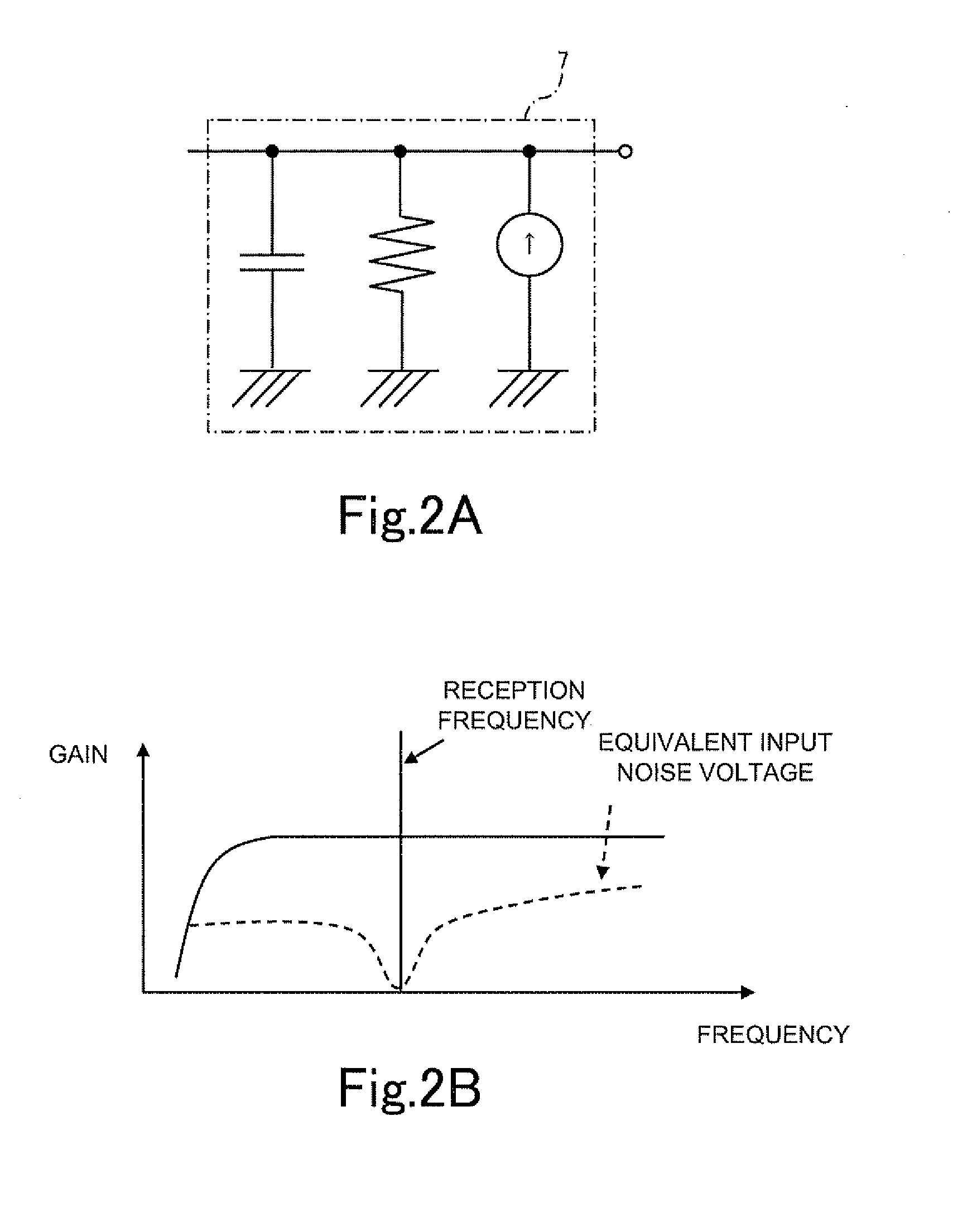
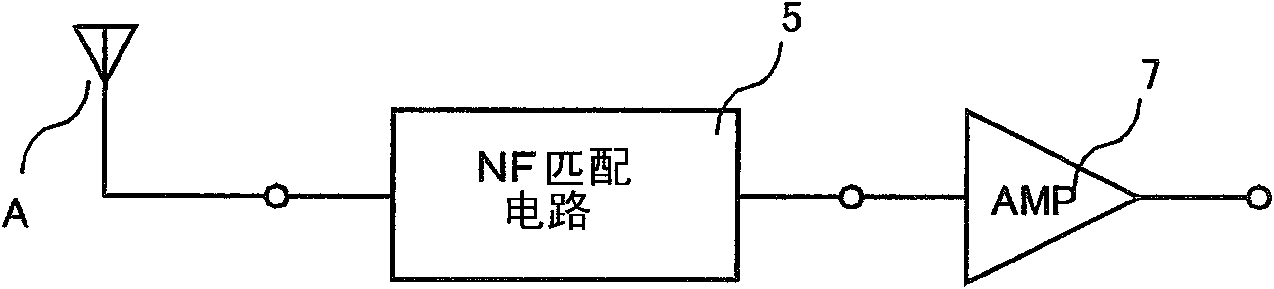
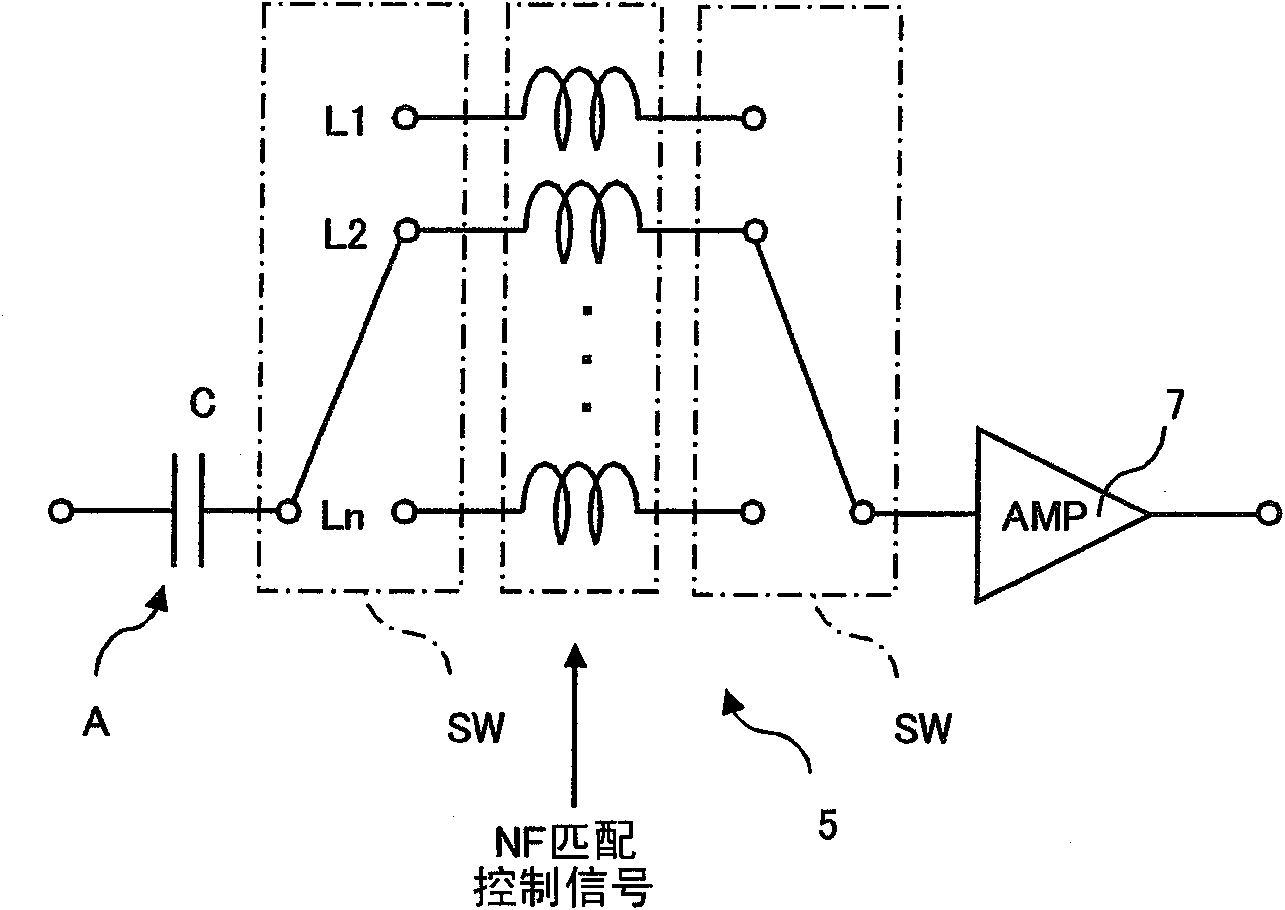
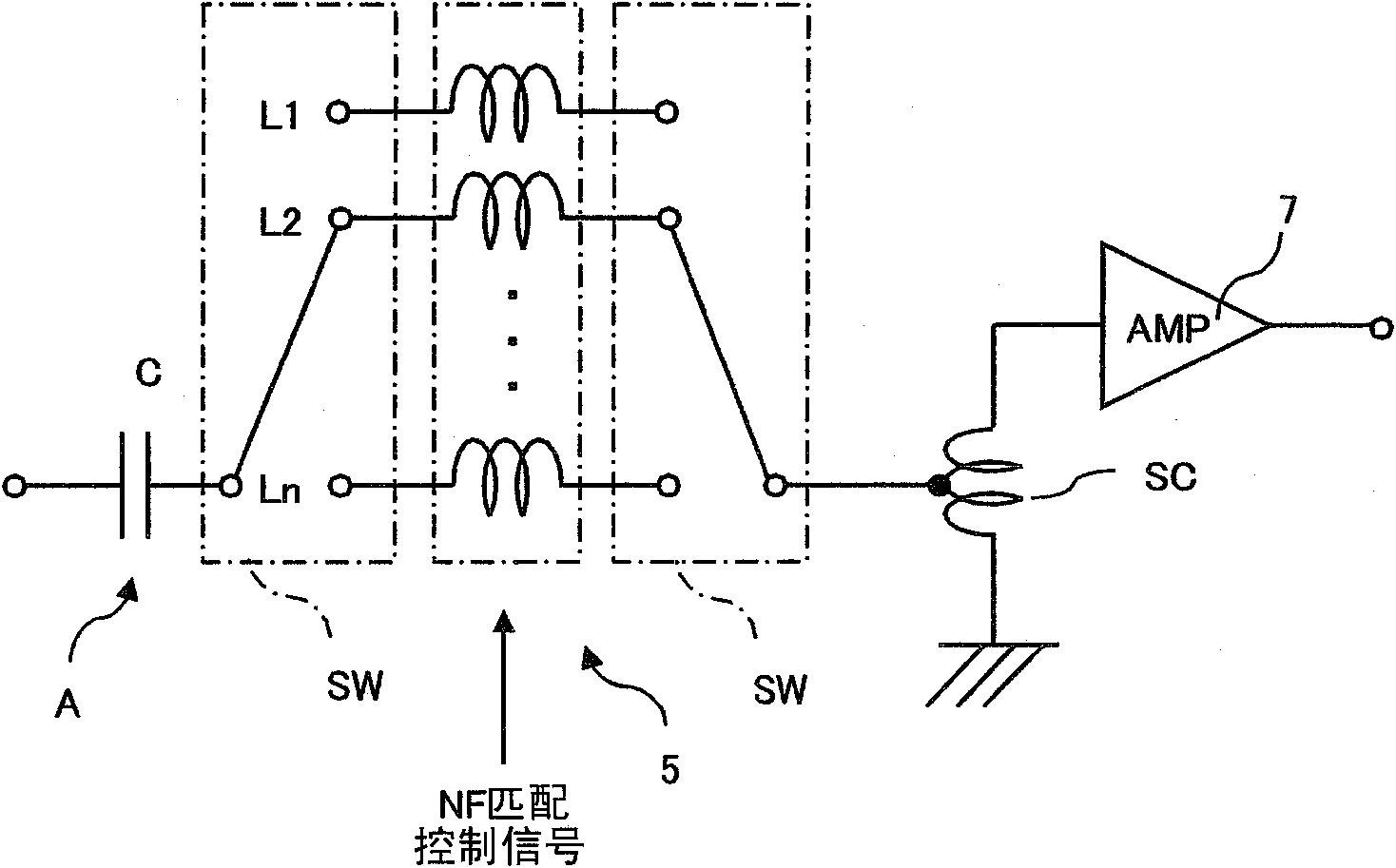
InactiveUS20110294452A1Low costImprove performanceAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
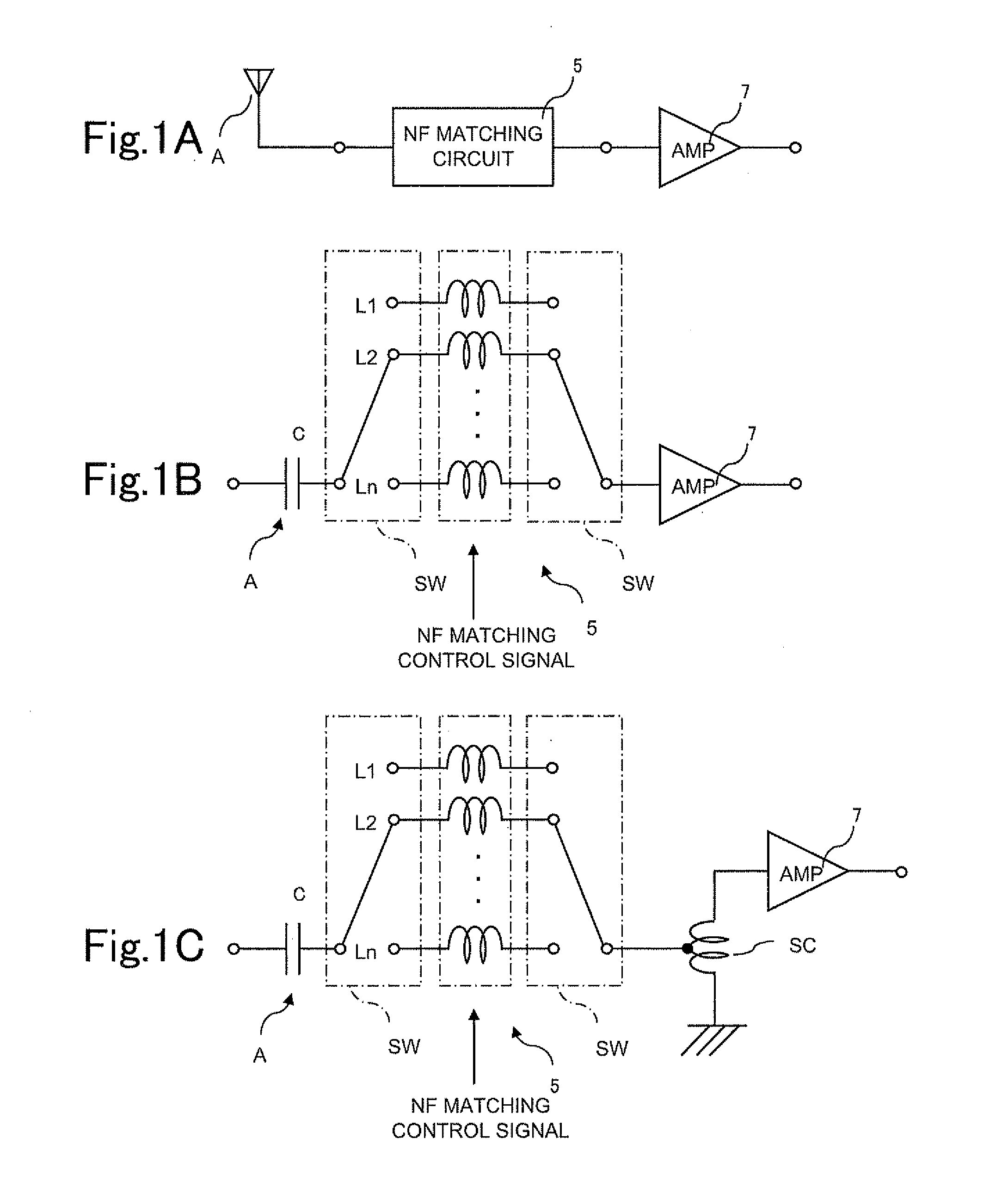
Even when an input is weak, an antenna amplifier device may achieve a high sensitivity while reducing a noise factor (NF). The antenna amplifier device includes an amplification circuit 7 for amplifying a high frequency signal received by an antenna A, and an NF matching circuit 5 provided between the amplification circuit 7 and the antenna A of which input impedance has a capacitance, the NF matching circuit 5 for switching the input impedance to the amplification circuit7 in accordance with a reception frequency. The NF matching circuit 5 includes a plurality of coils having different inductances, and at least one switch SW for connecting one of the coils, selected in accordance with the reception frequency, between the antenna A and the amplification circuit 7. A step-up coil SC is interposed between the NF matching circuit 5 and the amplification circuit 7.
Owner:FUJITSU GENERAL LTD
Antenna amplifier device and antenna device provided in mobile object
InactiveCN102315857AImprove performanceReduce the numberAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
Even when an input is weak, an antenna amplifier device may achieve a high sensitivity while reducing a noise factor (NF). The antenna amplifier device includes an amplification circuit 7 for amplifying a high frequency signal received by an antenna A, and an NF matching circuit 5 provided between the amplification circuit 7 and the antenna A of which input impedance has a capacitance, the NF matching circuit 5 for switching the input impedance to the amplification circuit 7 in accordance with a reception frequency. The NF matching circuit 5 includes a plurality of coils having different inductances, and at least one switch SW for connecting one of the coils, selected in accordance with the reception frequency, between the antenna A and the amplification circuit 7. A step-up coil SC is interposed between the NF matching circuit 5 and the amplification circuit 7.
Owner:FUJITSU GENERAL LTD
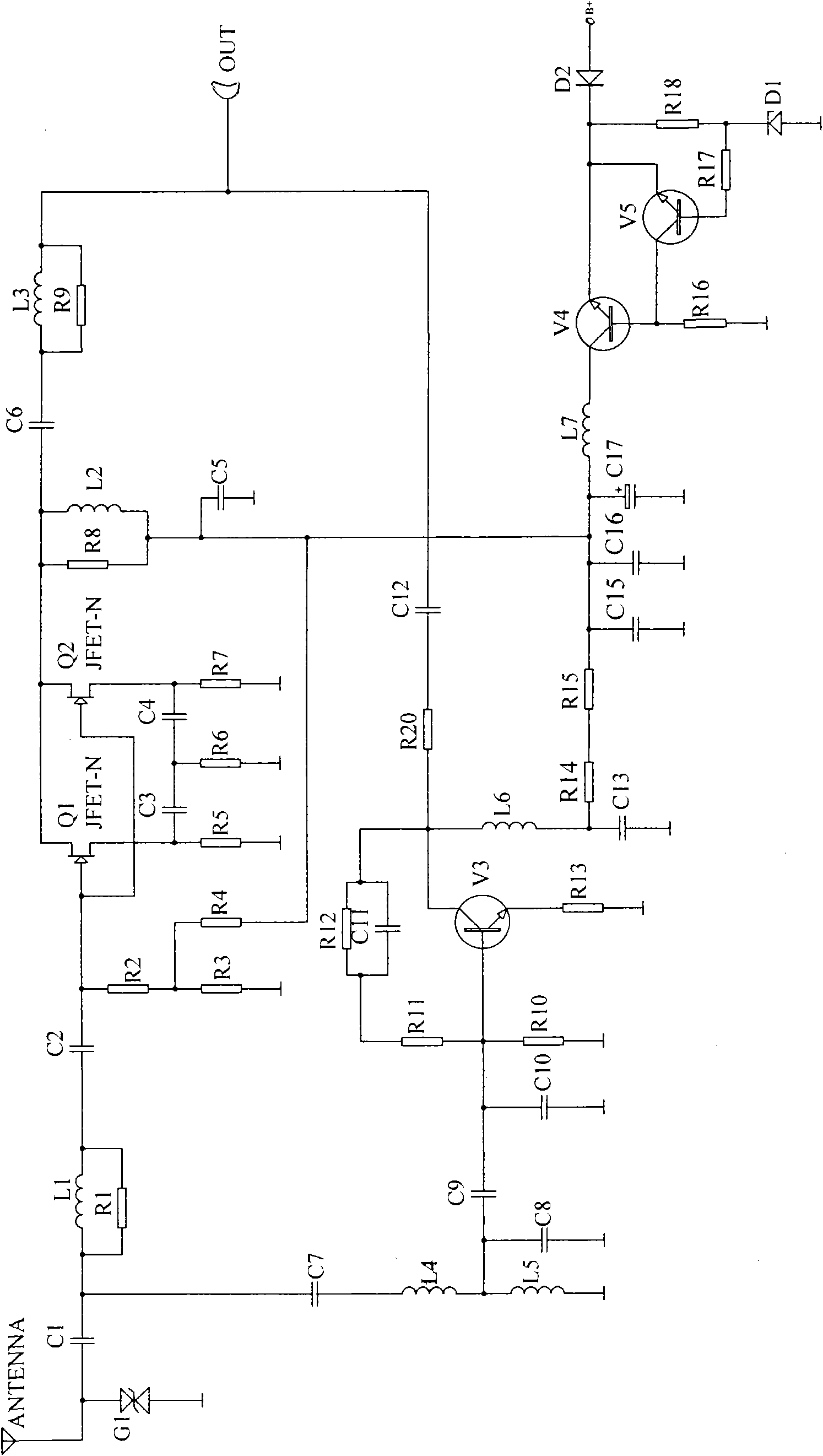
Automatic gain vehicle active antenna amplifier
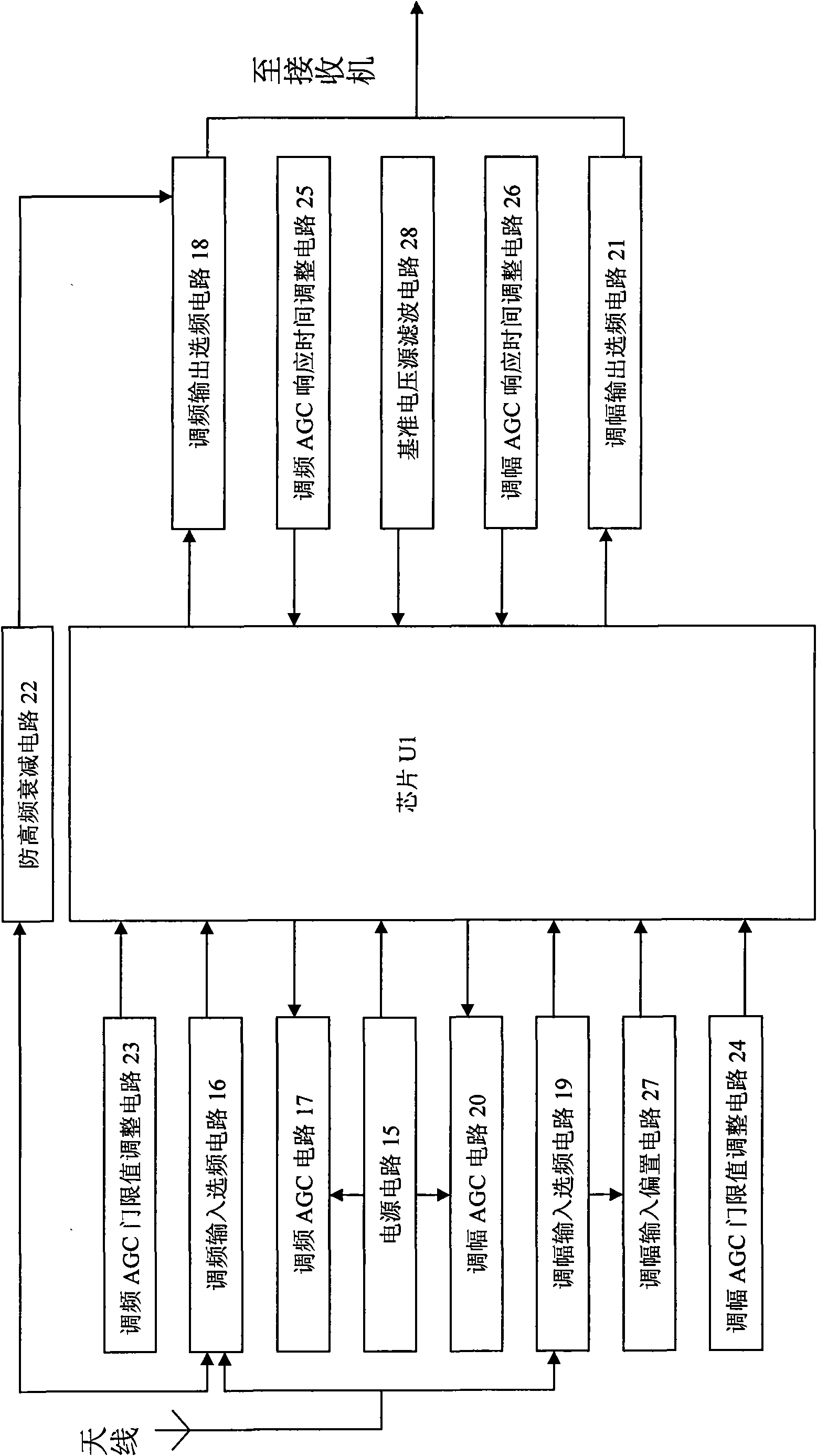
InactiveCN101604959AImprove dynamic rangeClear radioHigh frequency amplifiersGain controlAutomatic controlEngineering
The invention relates to an automobile antenna amplifier, in particular to an automatic gain vehicle active antenna amplifier. The amplifier comprises a chip for realizing the automatic gain control logical operation of a signal, a frequency selection circuit for processing a frequency modulation signal and an amplitude modulation signal respectively, an AGC circuit, an AGC threshold value adjusting circuit and an AGC response time adjusting circuit; and the automatic gain vehicle active antenna amplifier utilizes automatic gain control to eliminate voltage error between the output signal amplitude of the antenna amplifier and the needed output signal amplitude, improves the dynamic range of the amplifier to make the output signal stable and reception clear, overcomes the disadvantages of the unstable signal of the prior art and is free from distorting even if the amplifier is in extreme environment with rapidly-changed signal strength.
Owner:HEFEI BANGLI ELECTRONICS
Fin-style vehicular antenna and method for producing same
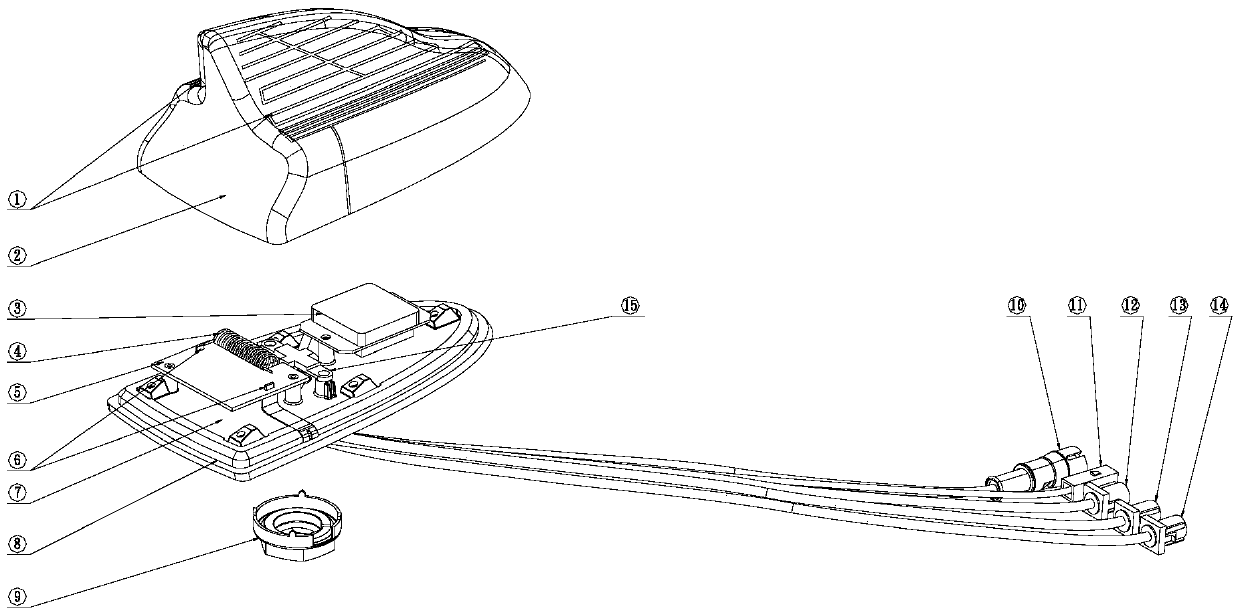
InactiveCN105514601AGuaranteed reception performanceEfficient use ofRadiating elements structural formsRadiating element housingsAudio power amplifierPlastic materials
The invention discloses a fin-style vehicular antenna and a method for producing the same. The fin-style vehicular antenna comprises a top cover and a base which are connected to form an enclosed receiving space. A connection element, an antenna amplifier, a tuning element, a GPS antenna, and multiple socket connectors are disposed in the receiving space. A receiving antenna is disposed on the outer surface of the top cover. The feed line of the receiving antenna is connected with the antenna amplifier through the connection element and the tuning element. The top cover is prepared from a modified plastic material containing LDS laser powders. After the top cover is formed, three-dimensional layout is easily achieved by means of LDS (laser direct structuring) technology and convenient processes according to a designed antenna pattern. Injection molding is carried out by using laser inducing material and selective metallization is carried out after laser activation in order that a high-precision circuit intersection structure is formed. The receiving performance of the antenna is guaranteed and space is effectively utilized.
Owner:JIANGSU HUASHENG AUTOMOTIVE ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Vehicle mounted antenna
ActiveCN103715494AWith FM receptionHigh gainAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesRadiating elements structural formsAudio power amplifierRadio receiver
The invention discloses a vehicle mounted antenna which comprises a housing, an installing base plate and a radio oscillator arranged outside the housing. The housing and the installing base are matched. The vehicle mounted antenna further comprises an amplifier circuit module, a satellite antenna amplifier and a wireless communication oscillator which are arranged on the installing base plate, wherein the amplifier circuit module is connected with the radio oscillator and outputs a radio signal received by the radio oscillator to an in-vehicle radio receiver device. The satellite antenna amplifier outputs a received satellite signal to an in-vehicle satellite positioning device. The wireless communication oscillator is provided with a sleeve loading structure, connected with an in-vehicle wireless communication device and used for transmitting / receiving a wireless communication signal wirelessly. By adopting the technical scheme, the vehicle mounted antenna has the capacities of frequency modulation receiving, satellite positioning and wireless network connection, achieves high gain and wide frequency band by adopting the wireless communication oscillator with the sleeve antenna loading structure and can be suitable for various wireless network types.
Owner:AMPHENOL SUNPOOL (LIAONING) AUTOMOTIVE ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Antenna amplifier, in particular for a magnetic resonance antenna
ActiveUS7239144B2Reduce the inductance valueElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceAudio power amplifierResonance
An antenna amplifier, in particular for a magnetic resonance antenna, has a sheath wave barrier integrated into the signal path of the antenna amplifier in the form of a component designed exclusively for transfer of a differential signal.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
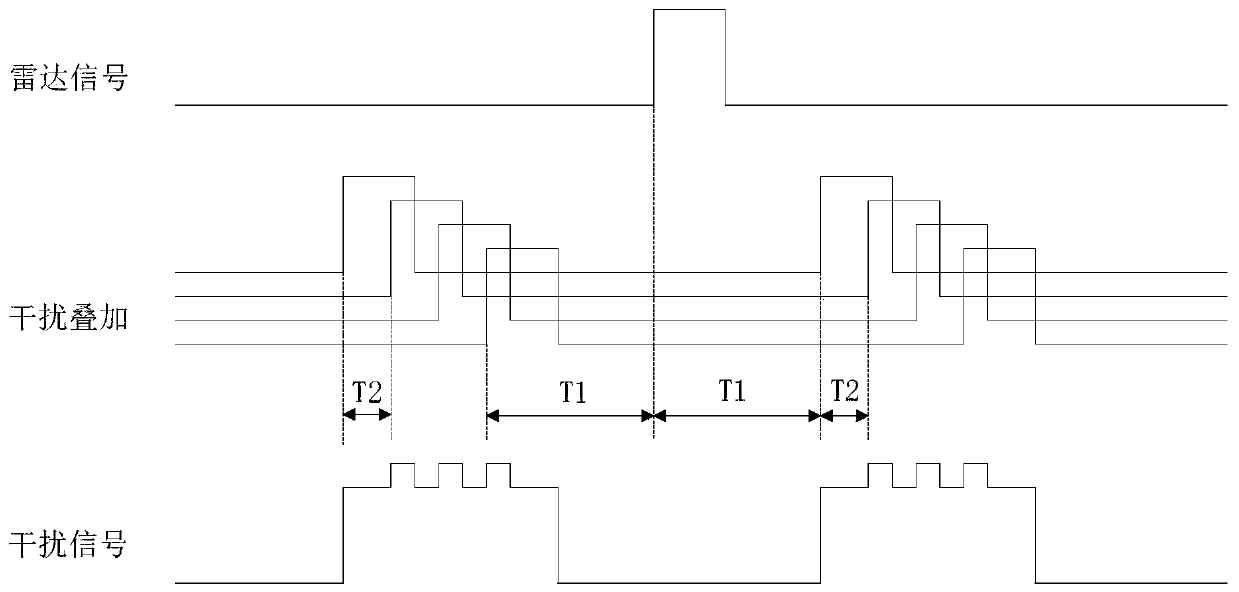
Track deception jamming system and method for airborne early-warning PD radar
PendingCN111123218AImprove realismLittle prior knowledgeWave based measurement systemsSquare waveformAirborne early warning
The invention discloses a track deception jamming system and a track deception jamming method for an airborne early-warning PD radar. The track deception jamming system comprises a receiving antenna,a transmitting antenna, an amplifier, a high-frequency shunt circuit, a radio frequency storage broadening module, a high-sensitivity receiving branch circuit, a pulse delay module, a low-sensitivityreceiving branch circuit, a square wave delay module, a square wave shaping module, a pulse gating module, a pulse modulation module, a microwave signal power amplification module and a power supply module. Through the design of two groups of track false targets related to radar signal repetition frequency, false tracks can be generated in front, back, left and right directions of a jammer and a shield target, and the purpose of supporting jamming is achieved.
Owner:扬州船用电子仪器研究所
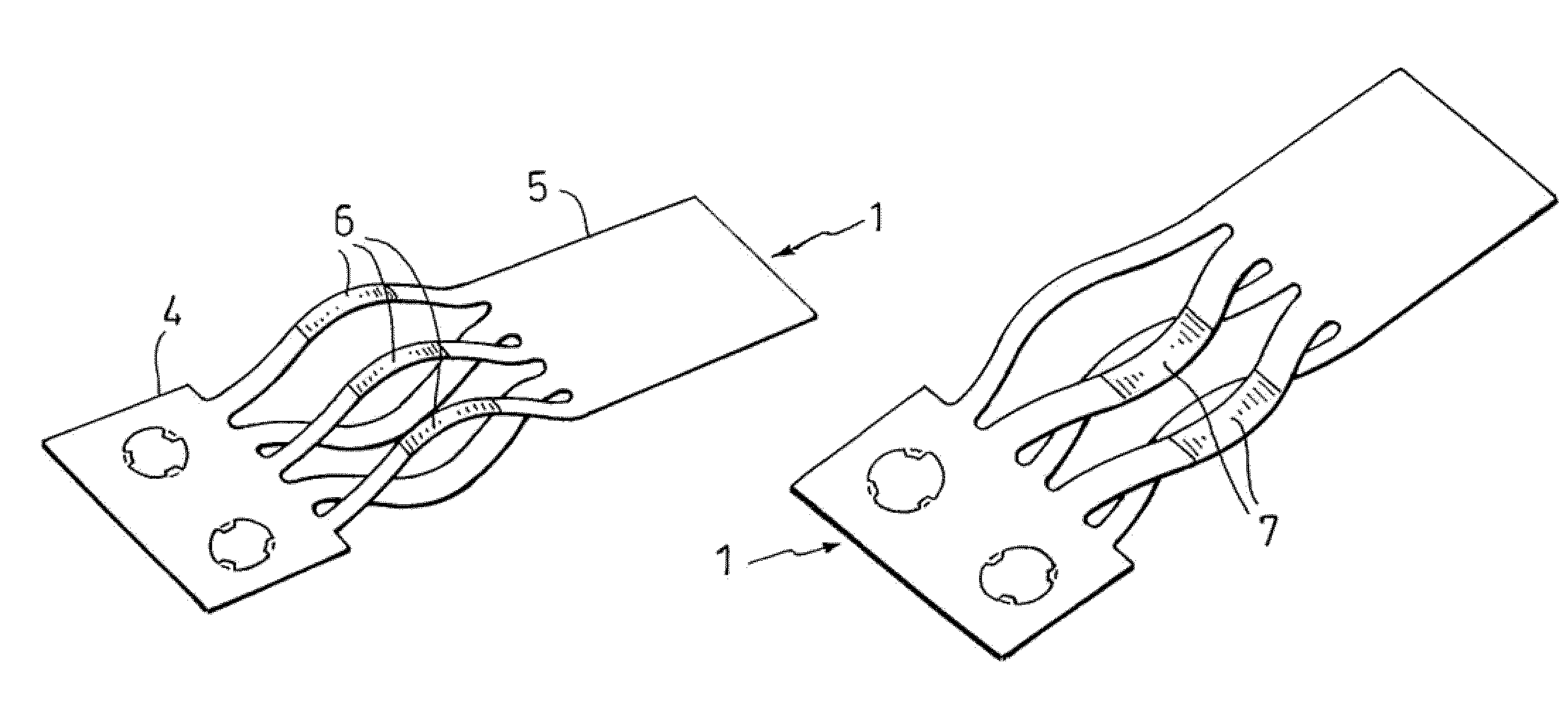
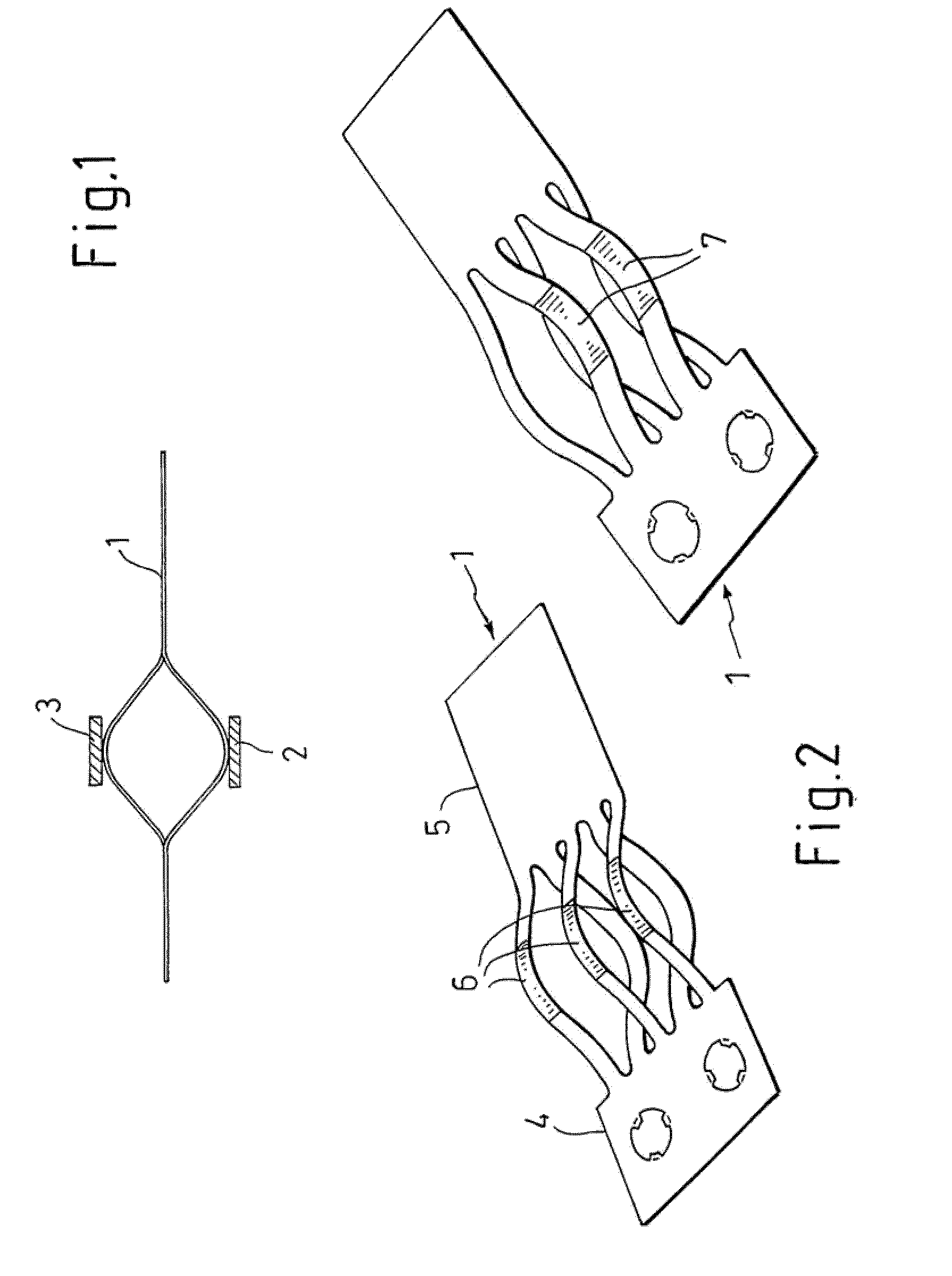
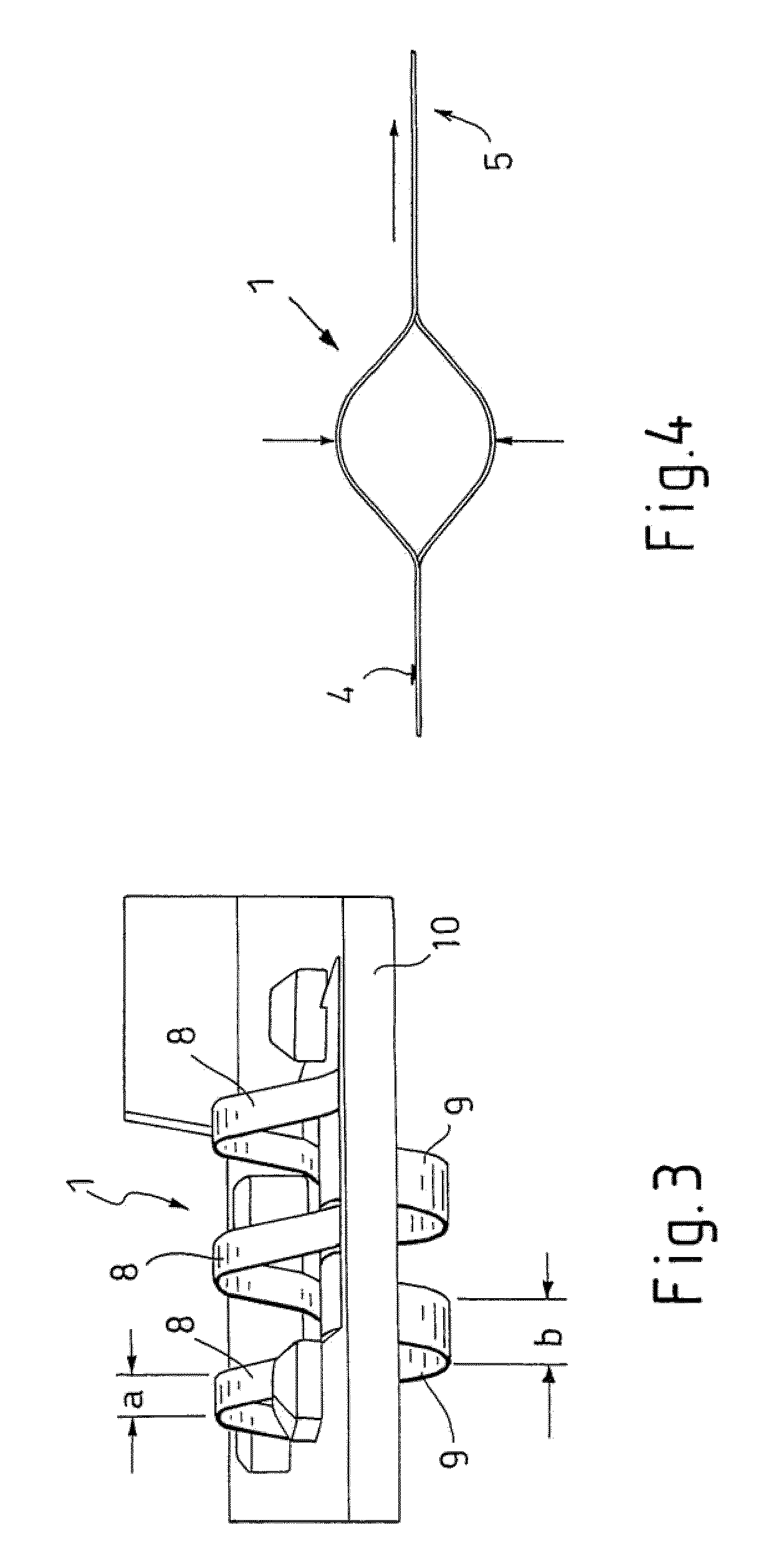
Contact Spring in a Support Frame of an Antenna Amplifier of a Vehicle
ActiveUS20090305579A1Reduce contact forceReduce abrasive wearAntenna connectorsCoupling contact membersAudio power amplifierBiomedical engineering
The invention relates to a contact spring (1) which has lamellae (8, 9) in the direction of a respective contact area (2, 3), it being possible to bring the lamellae (8, 9) into contact with the contact areas (2, 3) by means of contact points (6, 7), wherein the invention provides that at least one of the contact points (6, 7) has a coating, with the respective material of the coating being matched to the material of the contact area (2, 3).
Owner:HIRSCHMANN CAR COMMUNICATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com