Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
47results about How to "Variation in brightness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
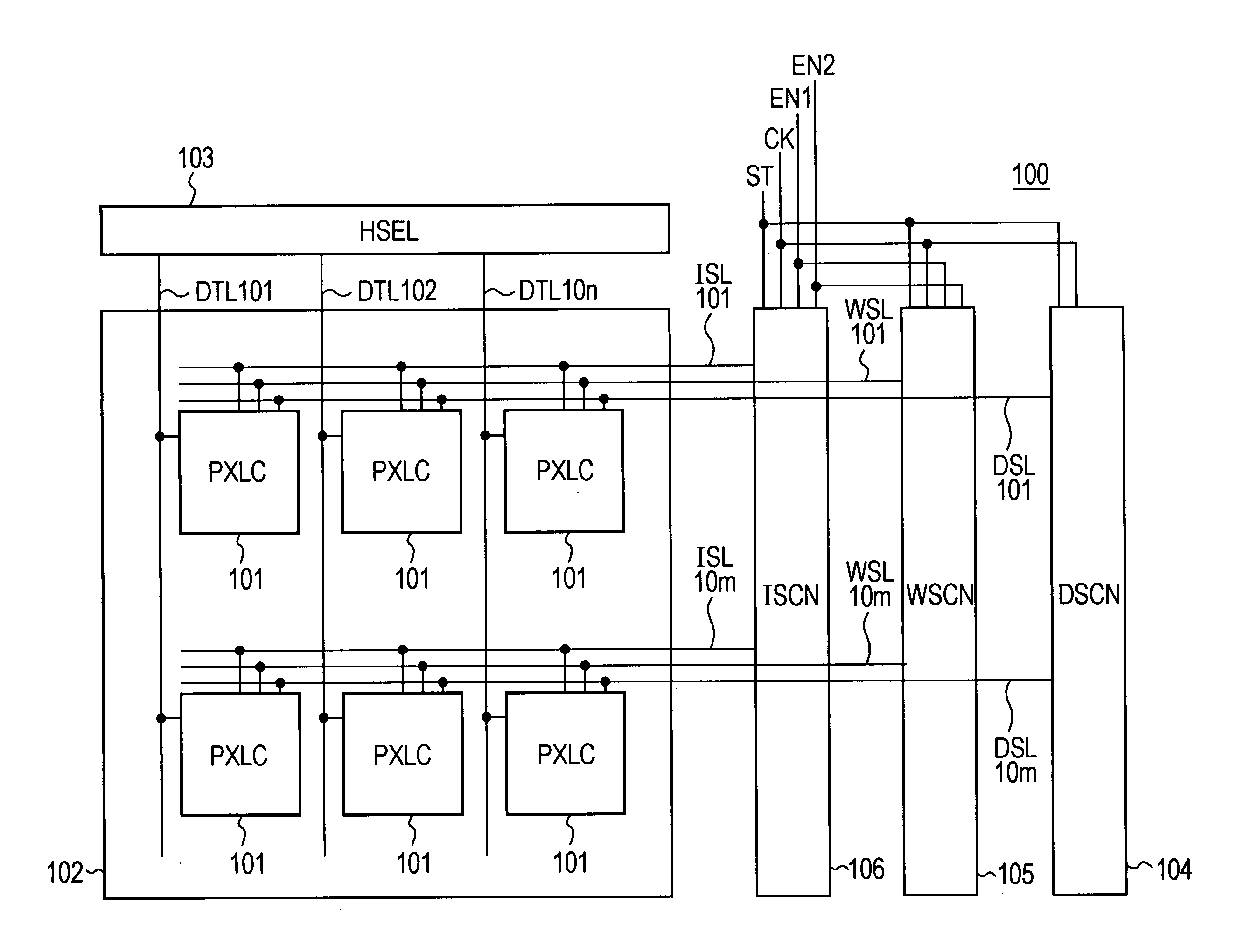
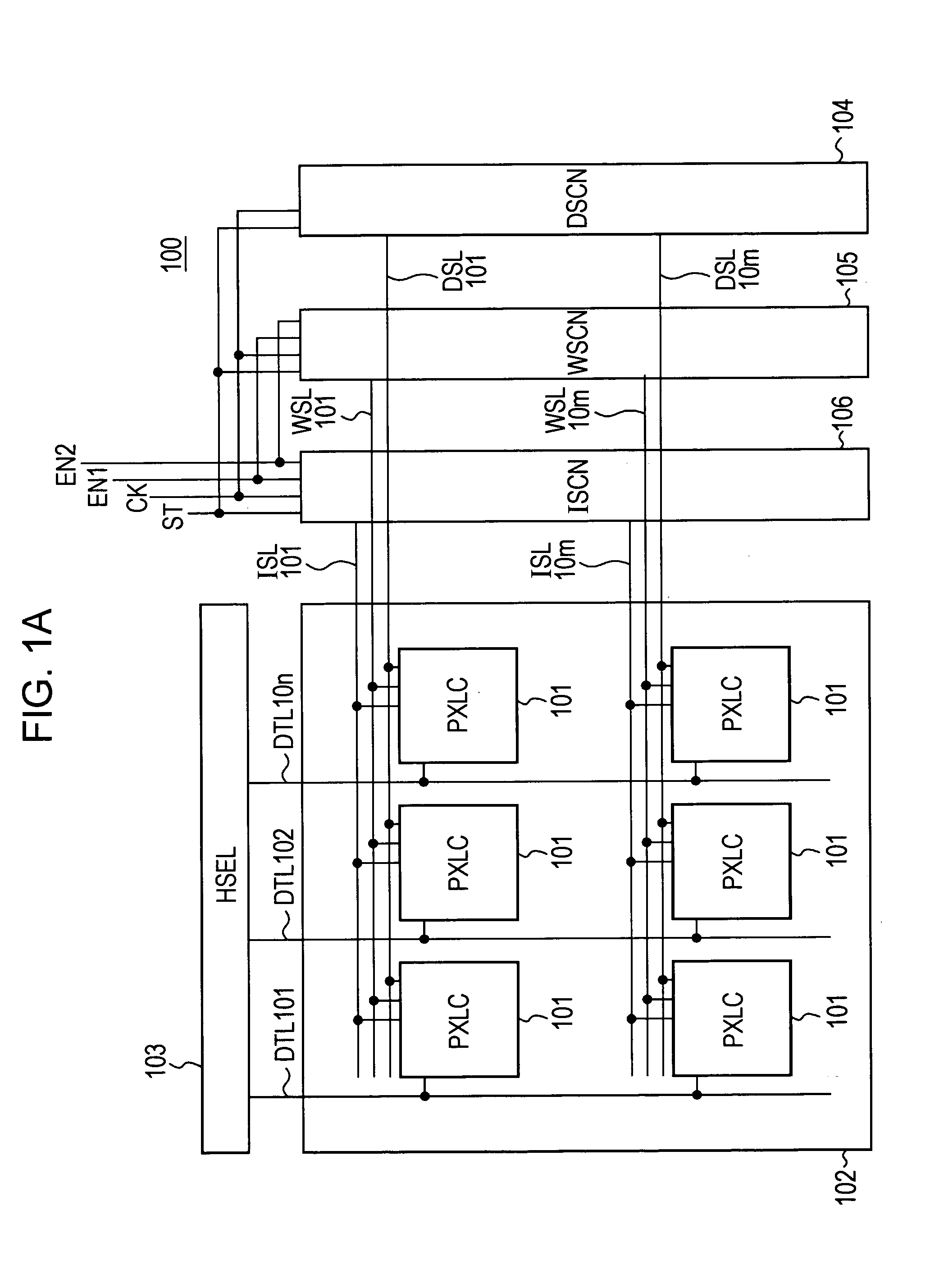
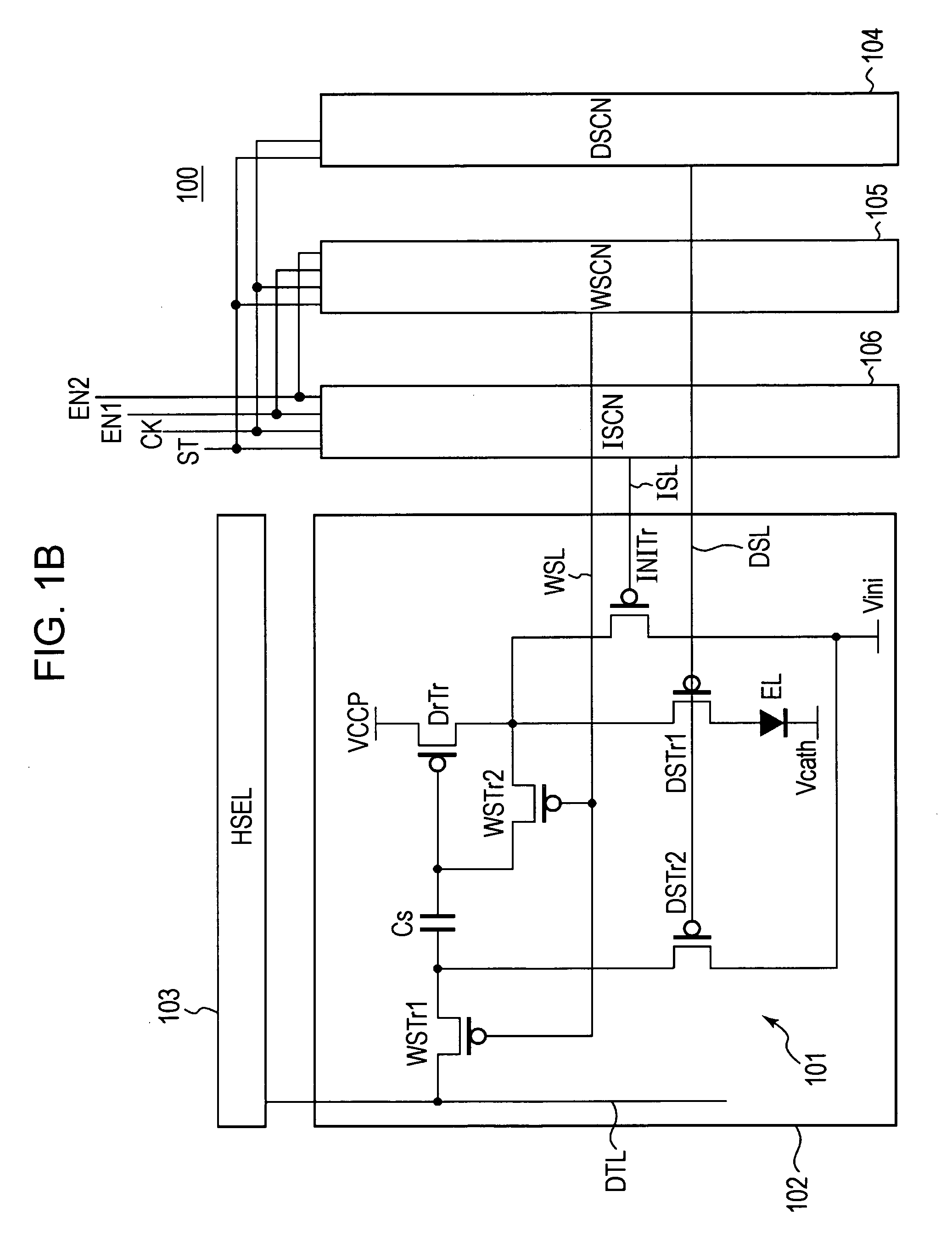
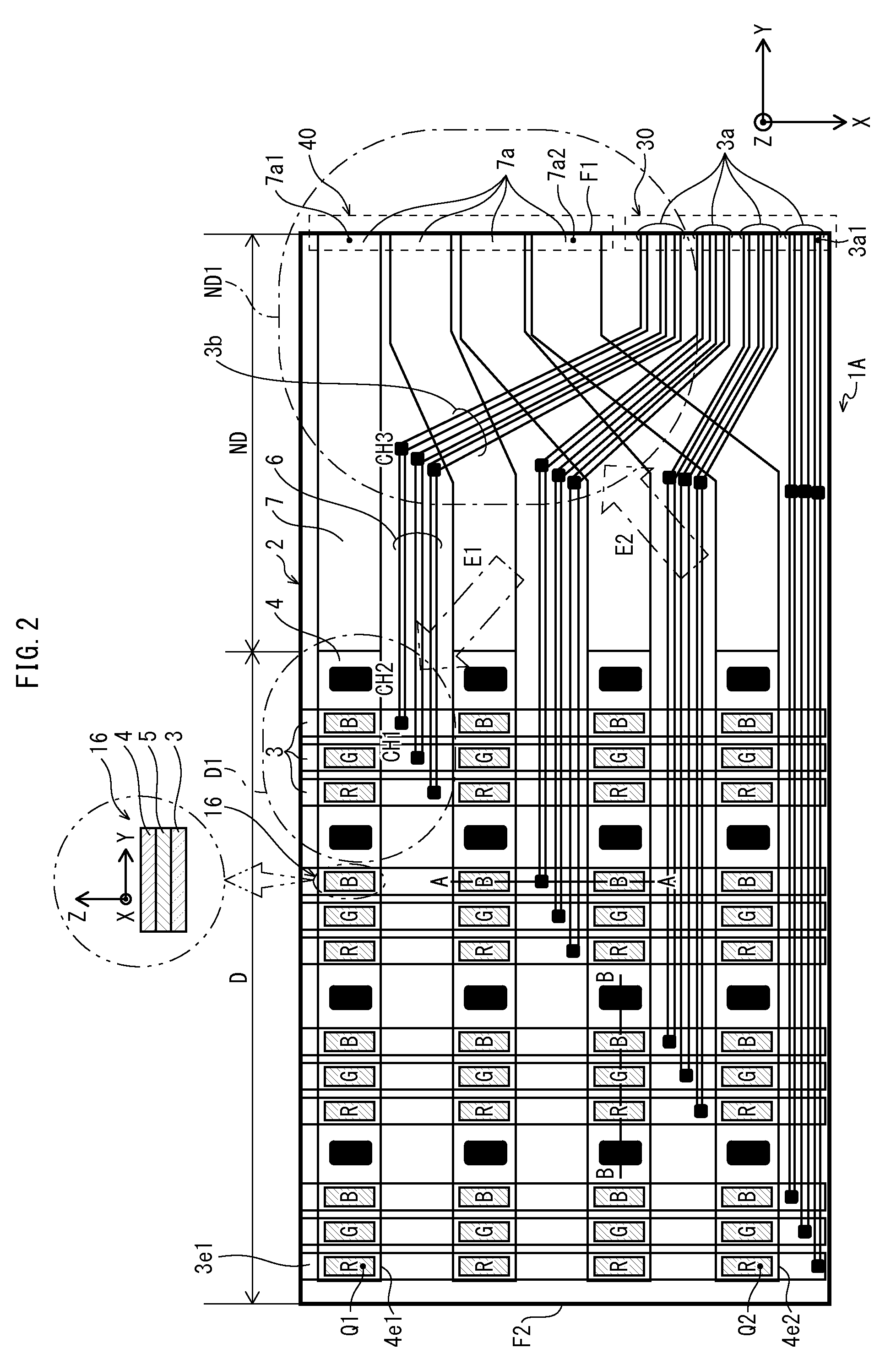
Pixel circuit, display device, driving method of pixel circuit, and driving method of display device
InactiveUS20060022907A1Increase brightnessLow mobilityStatic indicating devicesCapacitanceDriving current
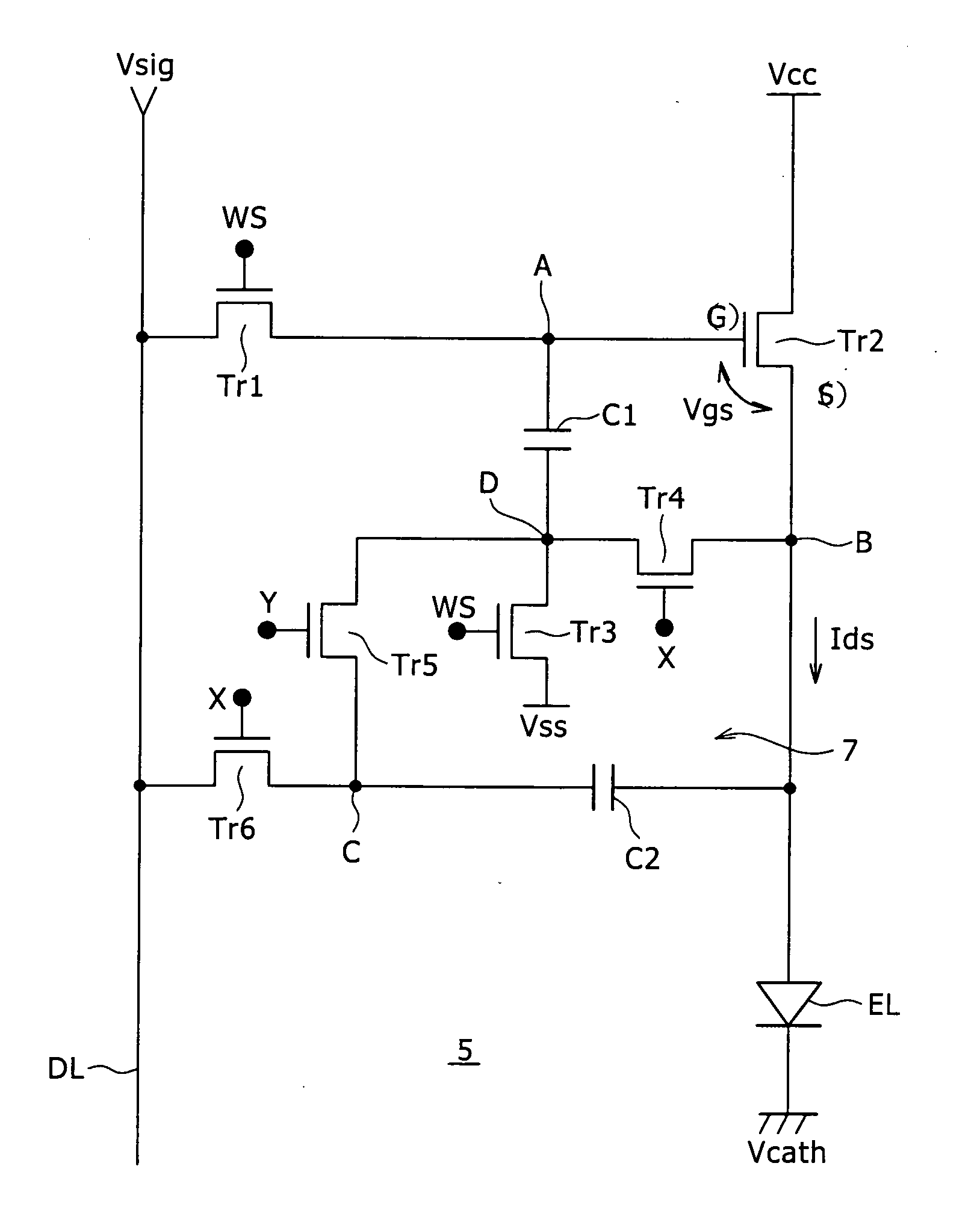
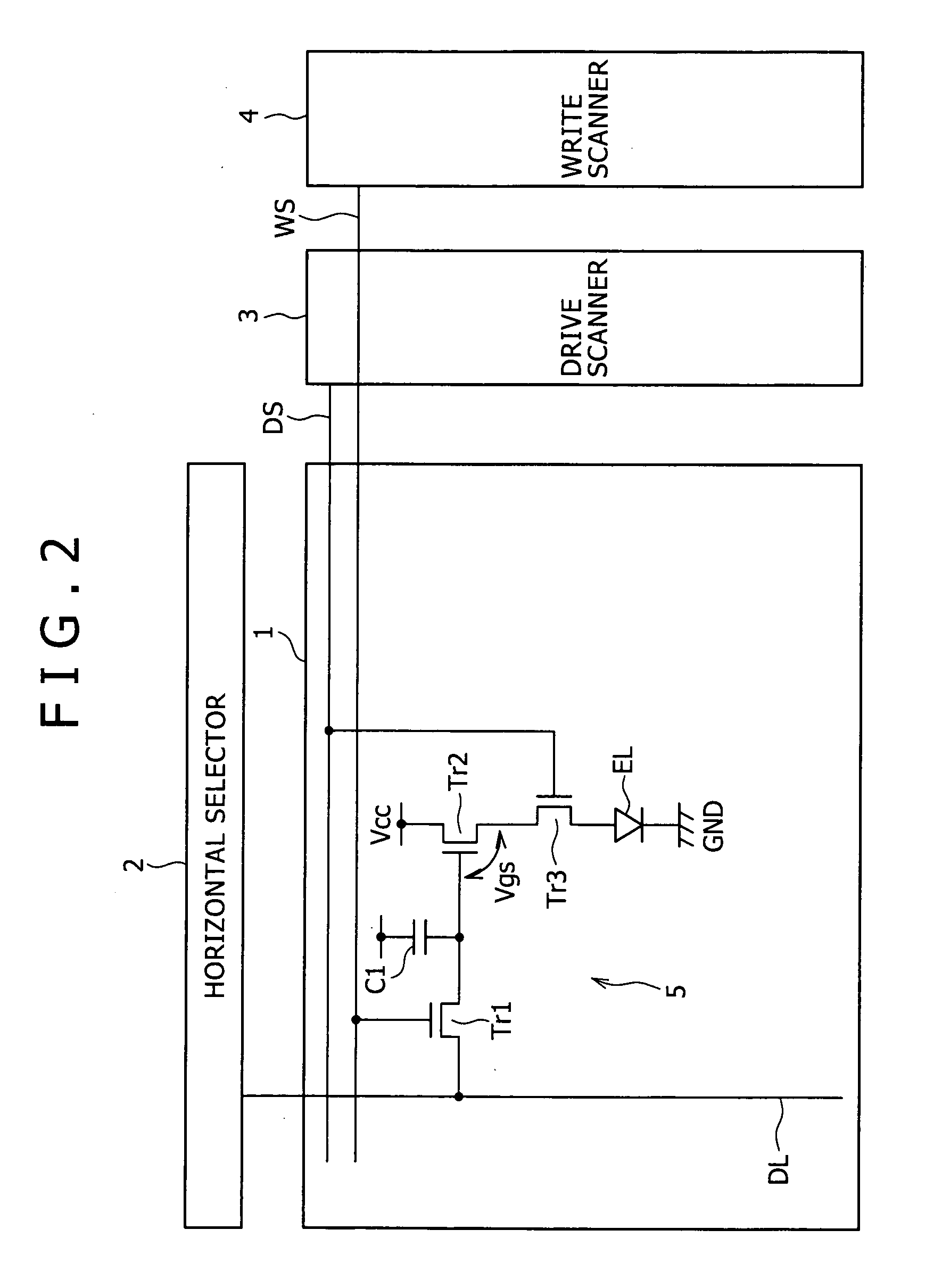
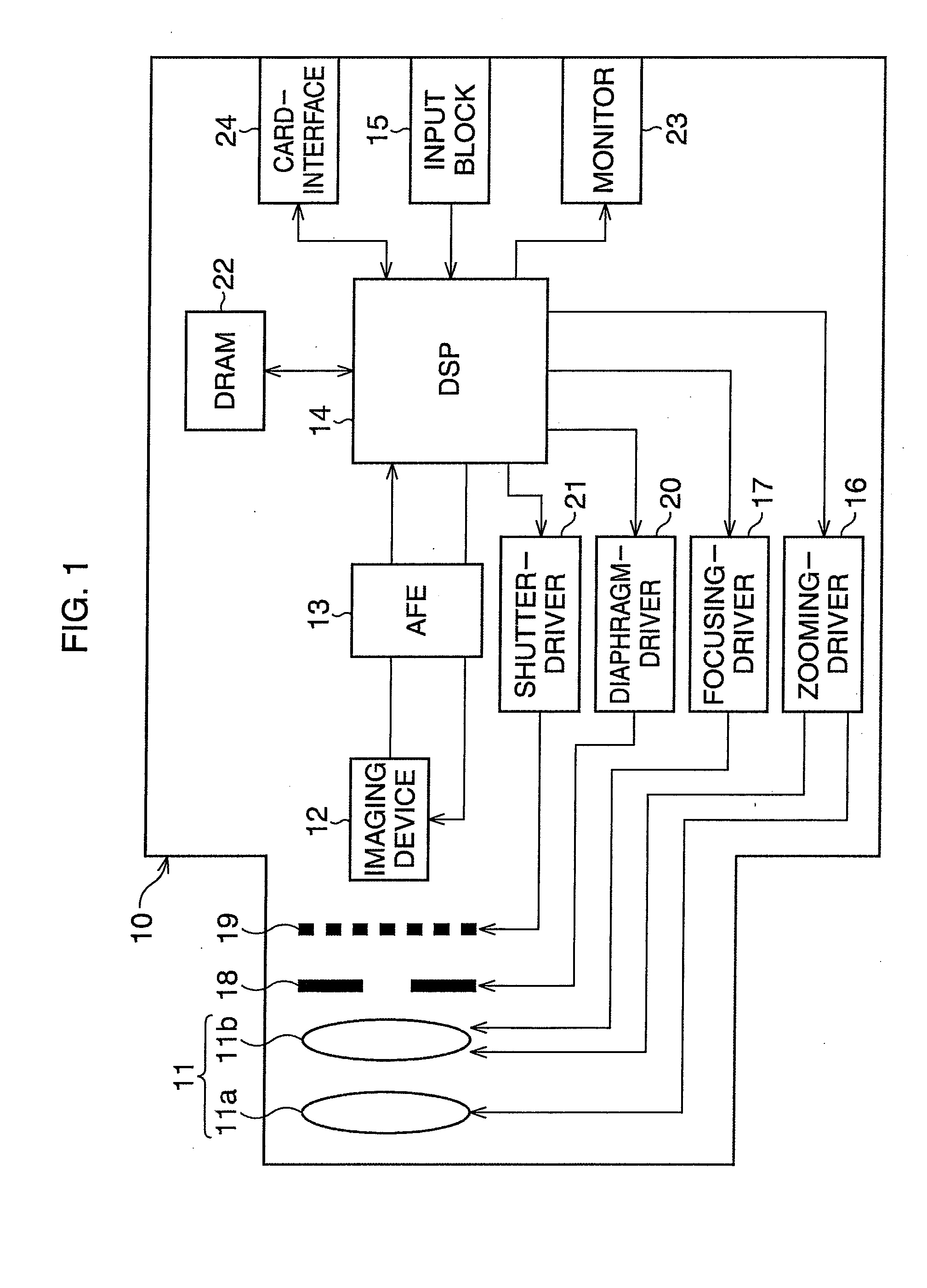
A pixel circuit disposed at a part where a scanning line and a signal line intersect each other includes at least an electrooptic element, a drive transistor, a sampling transistor, and a retaining capacitance. The drive transistor has a gate connected to an input node, a source connected to an output node, and a drain connected to a predetermined power supply potential and supplies a driving current to the electrooptic element according to a signal potential retained in the retaining capacitance. The electrooptic element has one terminal connected to the output node and another terminal connected to a predetermined potential. The sampling transistor is connected between the input node and the signal line and operates when selected by the scanning line, samples an input signal from the signal line, and retains the input signal in the retaining capacitance. The retaining capacitance is connected to the input node. The pixel circuit further includes a compensating circuit which detects a decrease in the driving current from a side of the output node, and feeds back a result of detection to a side of the input node, for compensating for a decrease in the driving current which decrease is attendant on a secular change of the drive transistor.
Owner:SONY CORP
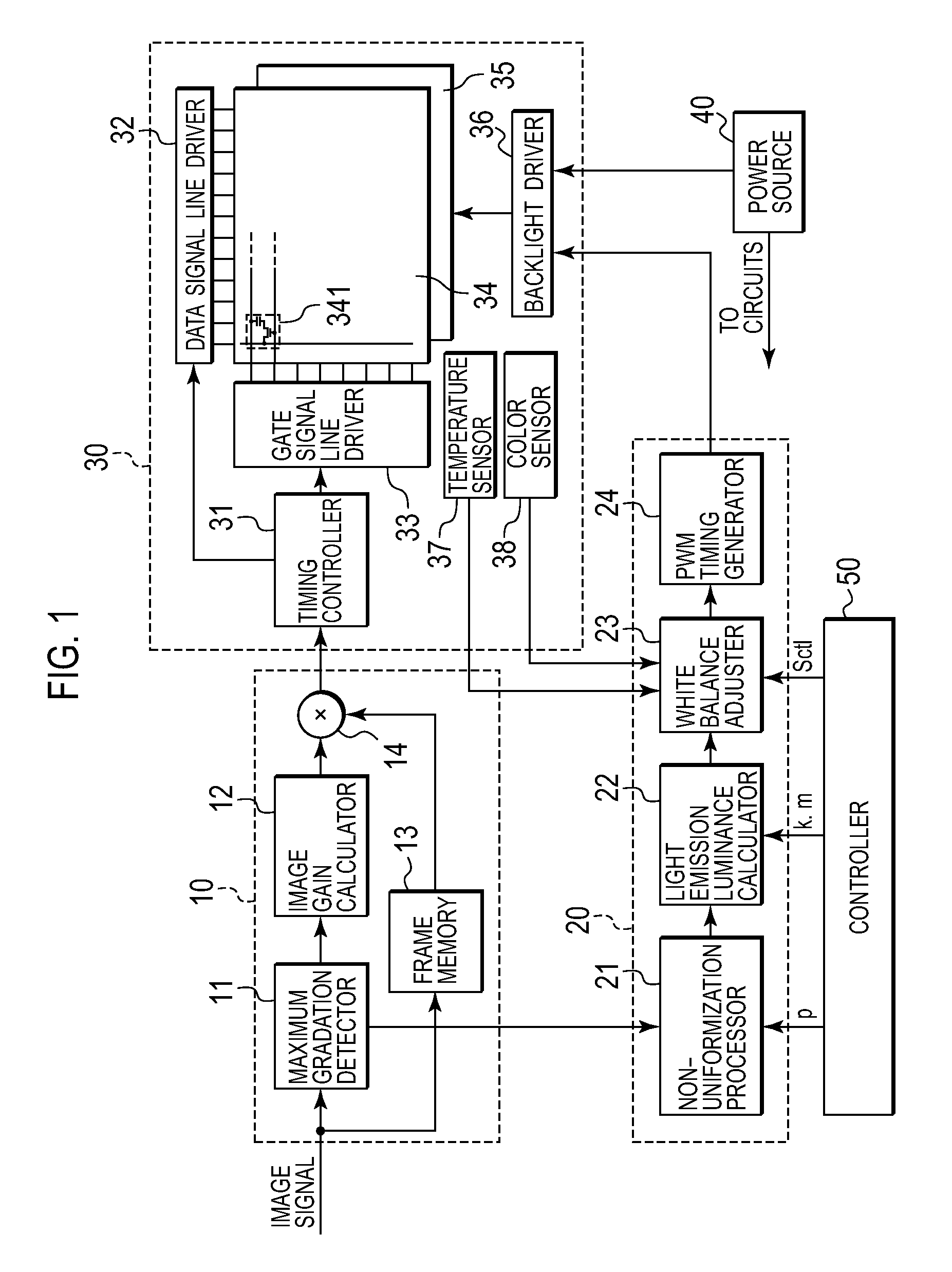
Liquid crystal display device and image display method thereof
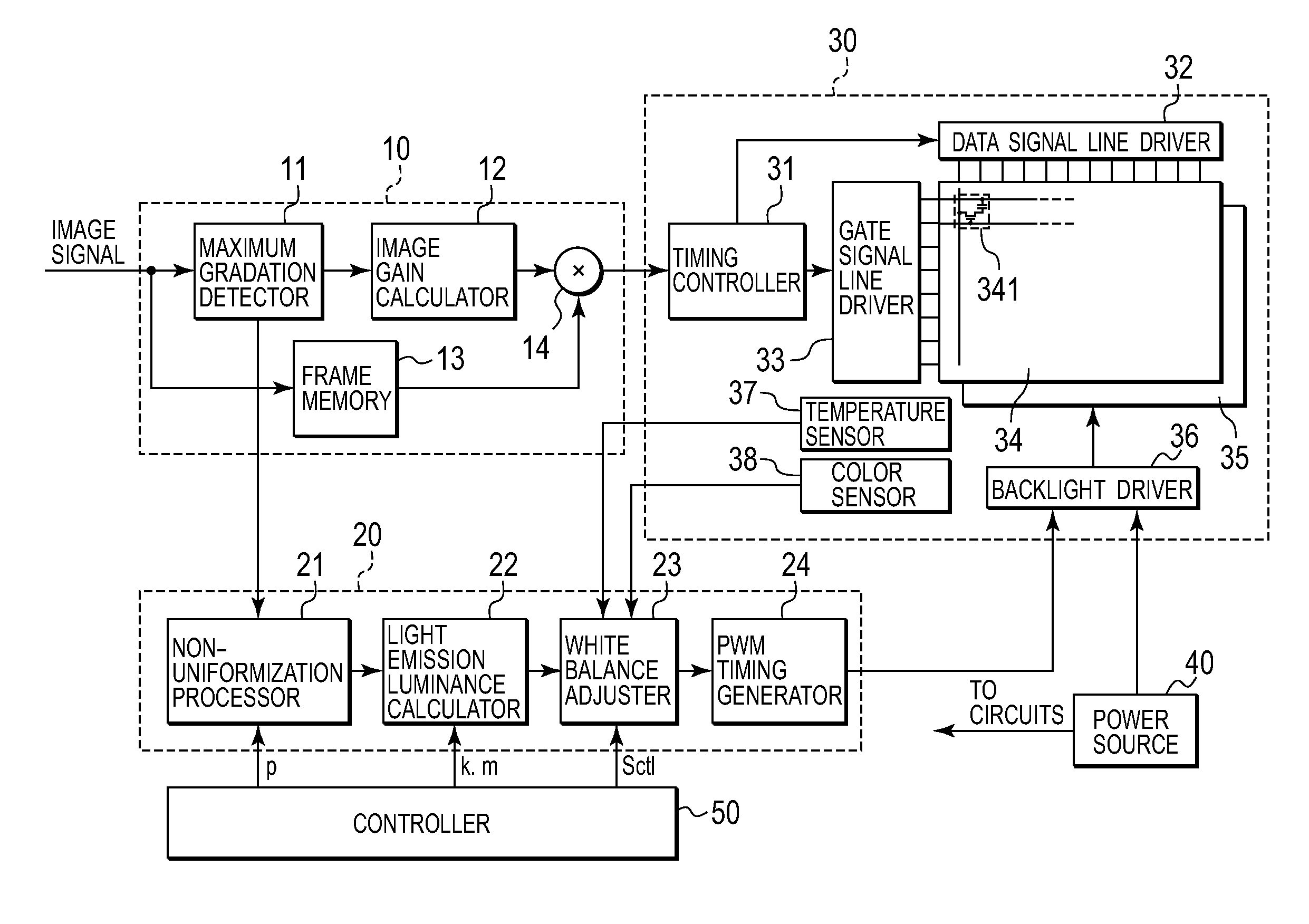
ActiveUS20080278432A1Improve image display qualityReduce power consumptionStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayLiquid crystal
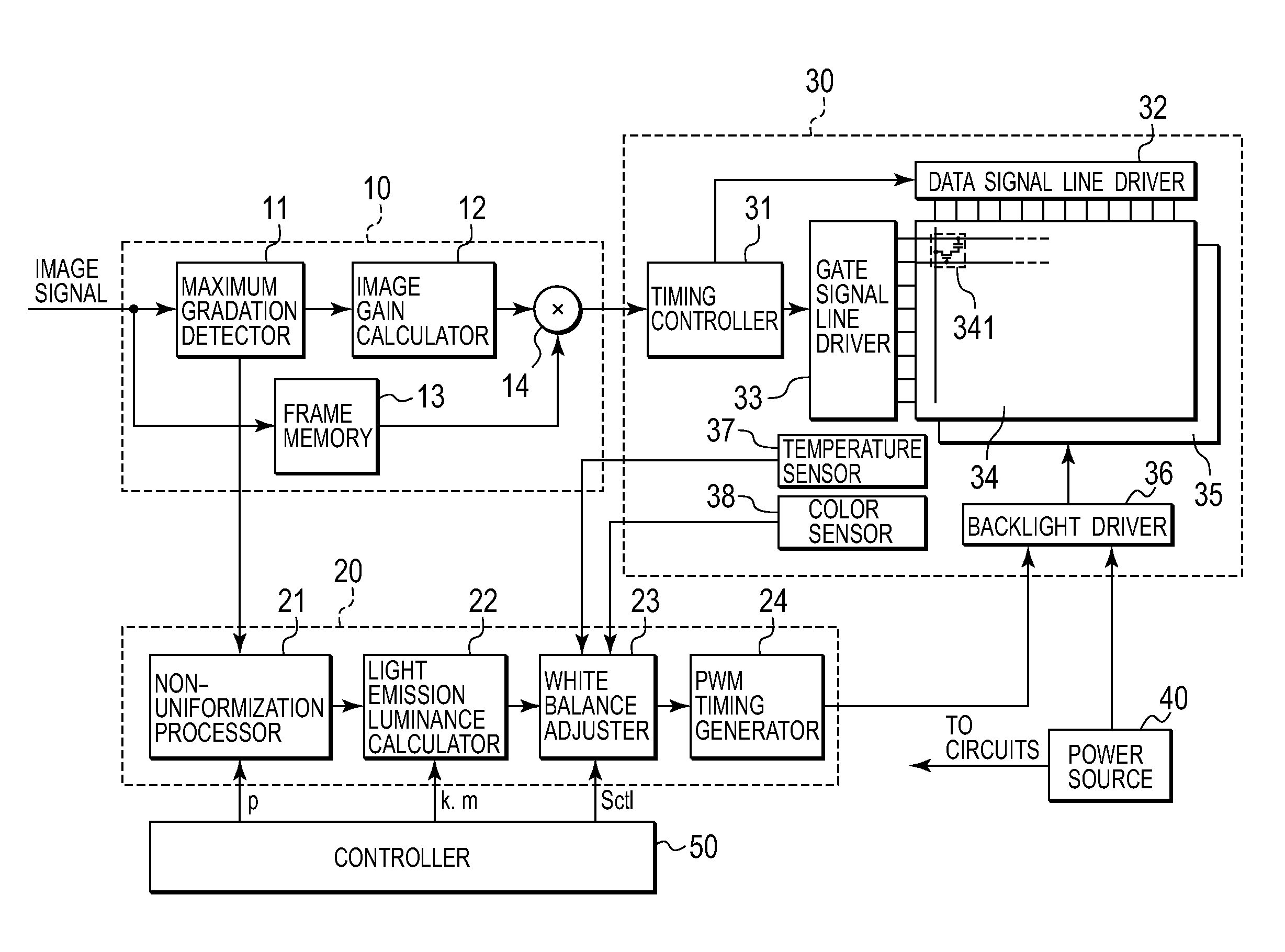
A backlight device is divided into multiple regions, and has a configuration in which light emitted from a light source of each of the regions is allowed to leak to other regions. A maximum gradation detector detects a maximum gradation of a regional image signal displayed on each of the regions of the liquid crystal panel. An image gain calculator obtains a gain to be multiplied to each regional image signal. An emission luminance calculator obtains an emission luminance of light to be emitted by each light source, by using an operation expression according to the emission luminance of light to be emitted by the backlight device. At this time, if the emission luminance takes a negative value as a result of calculation, the emission luminance calculator makes a correction so that the emission luminance can take a value equal to or greater than 0.
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP A CORP OF JAPAN
Light source module and optical member
InactiveUS20120218752A1Good shading effectSufficiently blockNon-electric lightingMirrorsEffect lightReflective layer
A light source module includes: a light source; a lighting curtain that partially blocks light from the light source; and a reflective layer that is provided on the lighting curtain and that has a planar shape smaller than the lighting curtain.
Owner:SHARP KK
Organic light-emitting display device
InactiveUS6864638B2Variations in brightness due to the resistance of wiring connected to an electrodeVariation in brightnessDischarge tube luminescnet screensStatic indicating devicesDisplay deviceOrganic layer
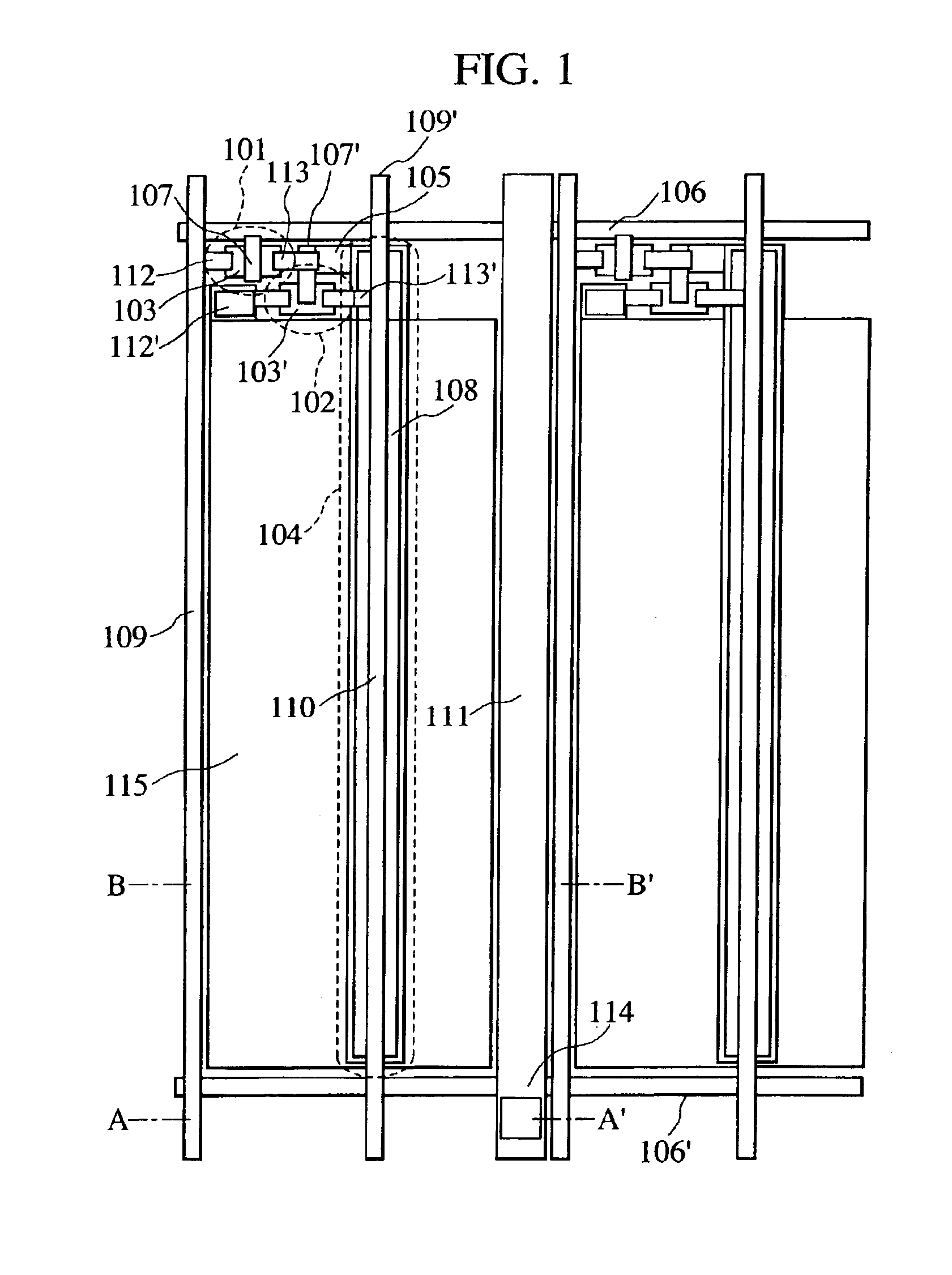
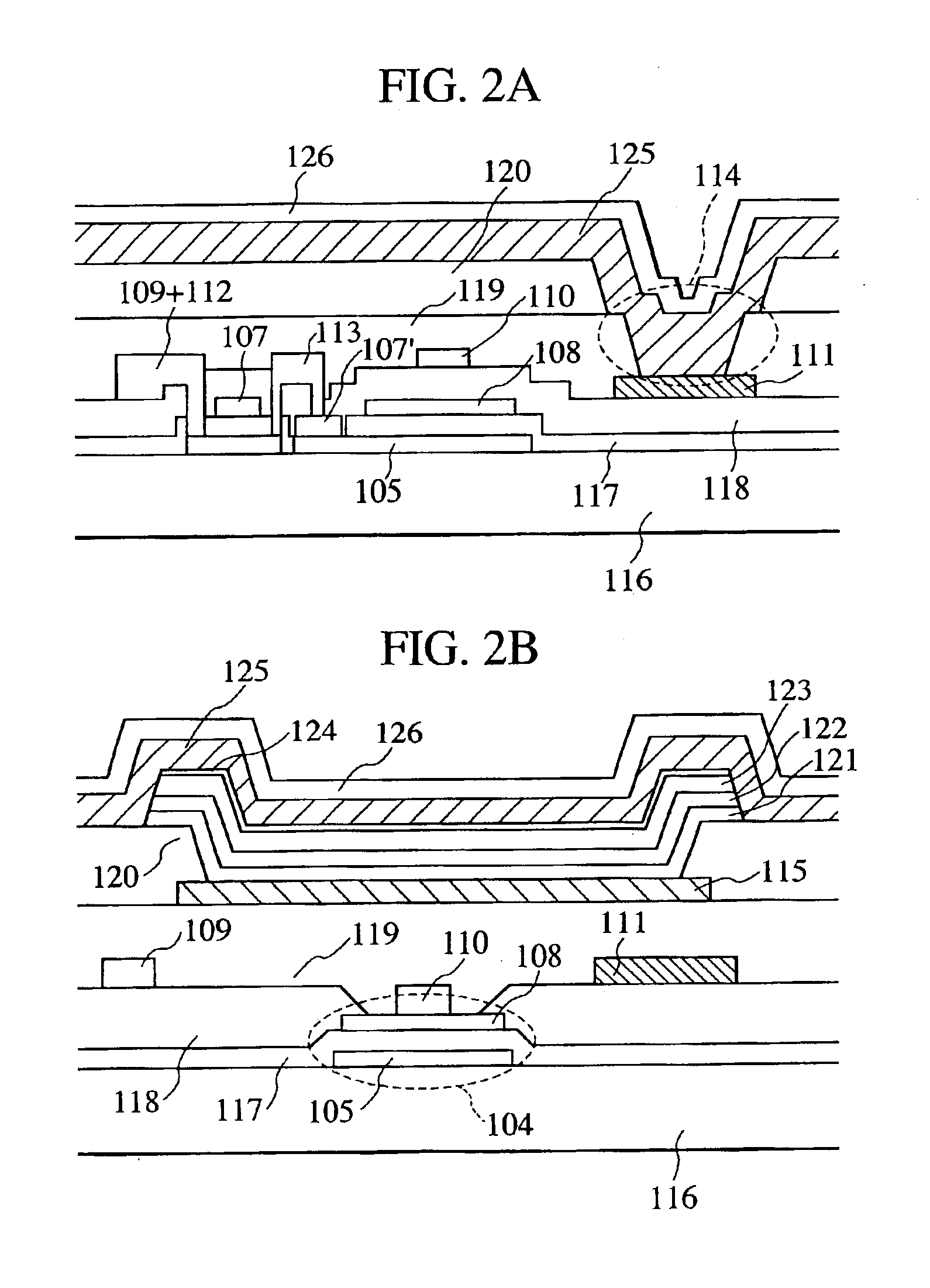
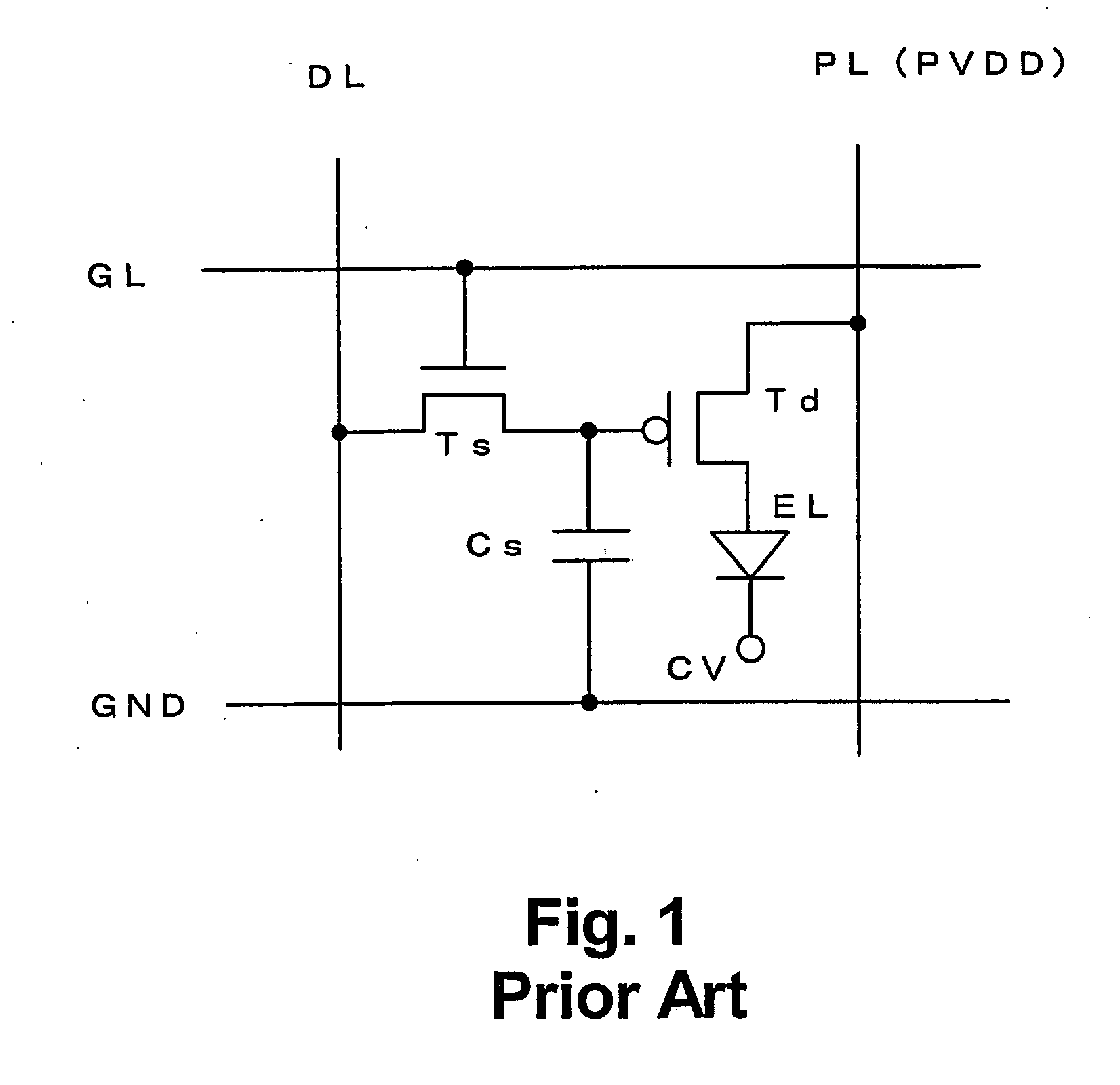
A scanning line, signal line, first current supply line, and second current supply line are formed on a glass substrate. A first electrode is formed thereon; and, an organic layer, including a hole transport layer, light-emitting layer, electron transport layer, and electron injection layer is formed on the first electrode. A second electrode is formed as a cathode on the electron injection layer. The first electrode, serving as an anode, is connected to a plus terminal of a power source through driving devices and first current supply line, whereas the second electrode is connected to a minus terminal of the power source and is connected to the second current supply line in the display region of each pixel, with a contact hole serving as a feeding point, whereby the wiring resistance of the second electrode is reduced, and variations in the brightness of the panel is reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD +1
LED package, and illumination device and liquid crystal display device provided therewith
InactiveUS20090135592A1Variation in brightnessVariation in colorMechanical apparatusLighting support devicesLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
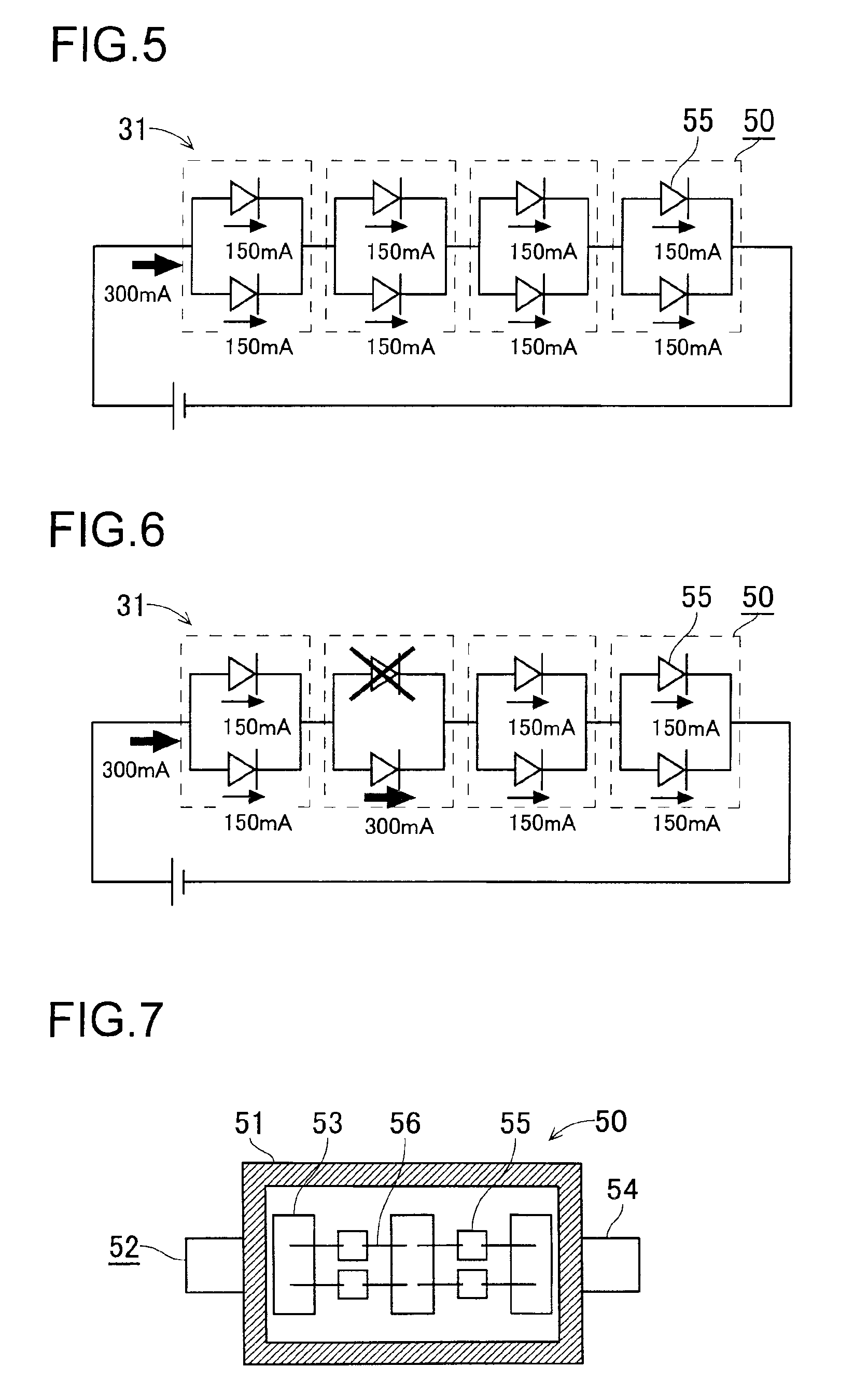
In an LED package, LED chips are connected in parallel by wires between lead frames connected to terminals. When an open circuit failure such as the coming off of the wire occurs in one of the LED chips in the LED package that is being energized, a current twice as high as that flowing through the other LED chip prior to the open circuit failure is passed through the other LED chip, and thus the amount of light emitted therefrom is increased about two-fold. Consequently, the amount of light emitted from the LED package does not change significantly.
Owner:SHARP KK
Liquid crystal display device
ActiveUS20100253897A1High quality displayAbnormal alignmentNon-linear opticsVertical alignmentEngineering
There is provided a liquid crystal display device of high picture quality with high brightness and small display unevenness.A vertical alignment type liquid crystal display device which has a plurality of pixels includes: a first electrode which includes, in each of the plurality of pixels, a plurality of first branch portions extending in a first direction and a plurality of second branch portions extending in a second direction that is different from the first direction; a second electrode disposed so as to oppose the first electrode; and a liquid crystal layer interposed between the first electrode and the second electrode, wherein a width of each of the plurality of first branch portions and the plurality of second branch portions is in a range not less than 1.4 μm and not more than 8.0 μm.
Owner:SHARP KK
Backlight Device and Liquid Crystal Display Device
ActiveUS20080192174A1Variation in brightnessVariation in colorElongate light sourcesElectric lightingLiquid-crystal displayLight source
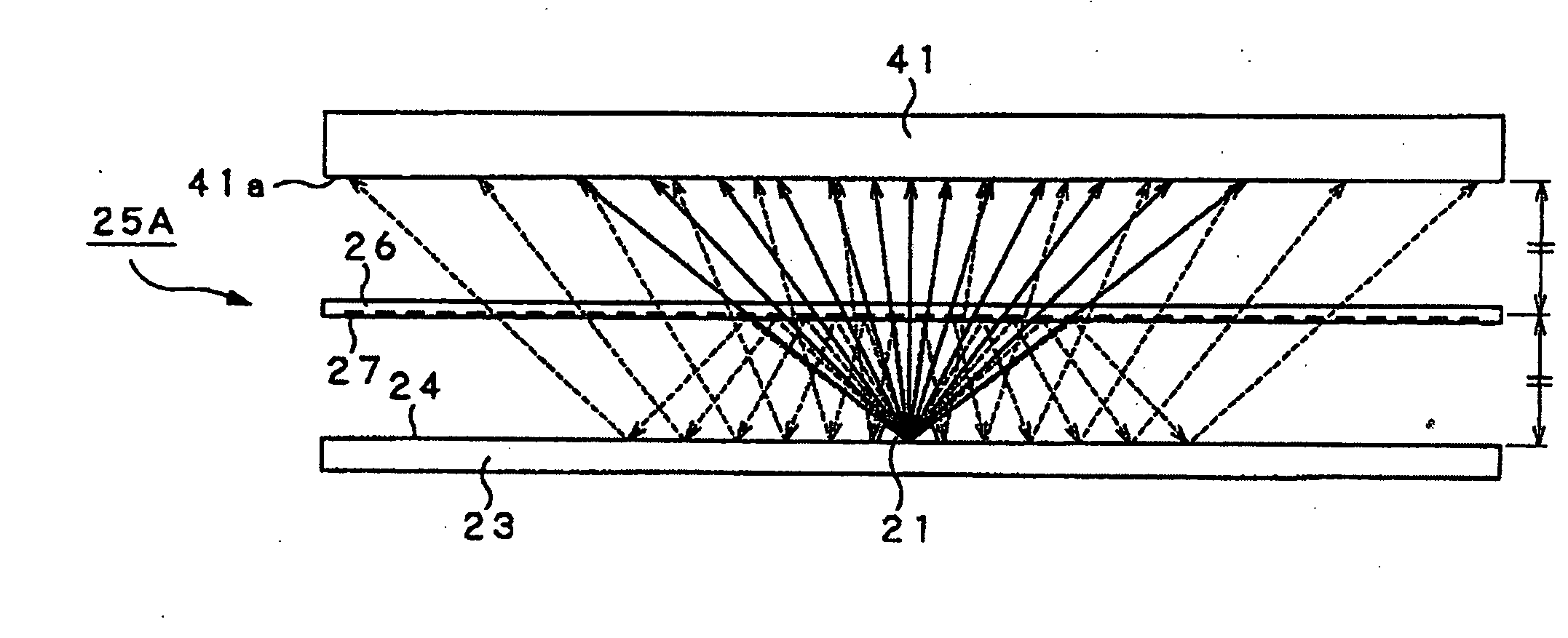
A backlight device includes a light source (21) arranged in a casing (23) opened in a light radiating surface (20a), so that the light source faces the light radiating surface (20a) and radiates light towards the light radiating surface (20a), a light transmitting reflecting plate (25) arranged in the casing for delimiting a space inclusive of the light source (21) and adapted for transmitting a fraction of the incident light and for reflecting another fraction of the incident light, and a light transmitting diffusing plate (41) arranged on the light radiating surface (20a) of the casing (23) for diffusing the light transmitted through the light transmitting reflecting plate (25) and for causing surface light radiation. A light reflecting surface (24) is formed on the inner surface of the casing (23). A portion of light radiated by the light source (21) is internally reflected by the light transmitting reflecting plate (25) and by the light reflecting surface (24), in a space delimited in the casing (23) by the light transmitting reflecting plate (25), after which the light portion is transmitted through the light transmitting reflecting plate (25).
Owner:SATURN LICENSING LLC
Electroluminescence display device
ActiveUS20060284803A1Deterioration and variationExacerbate differenceDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesDriving currentDisplay device
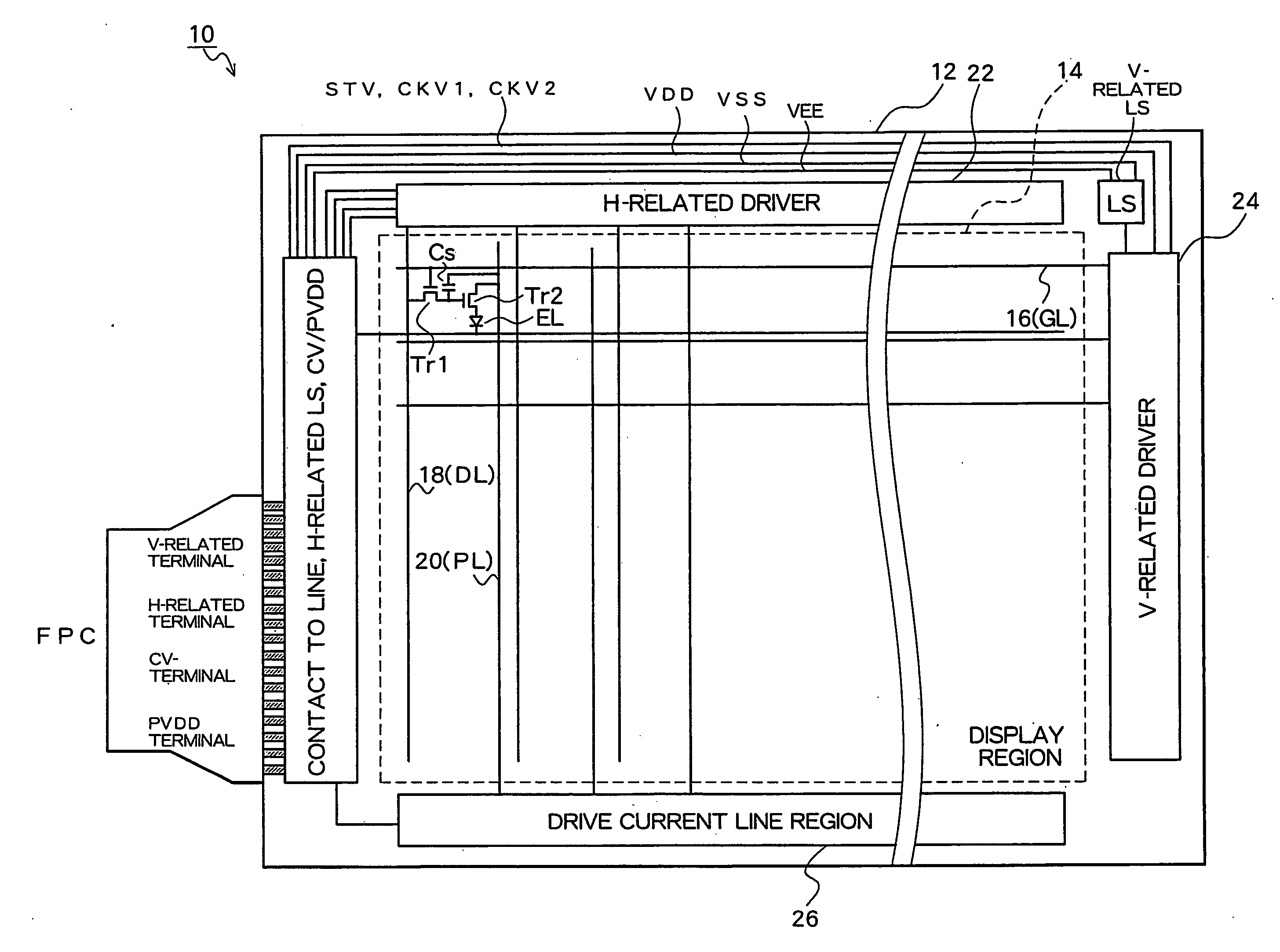
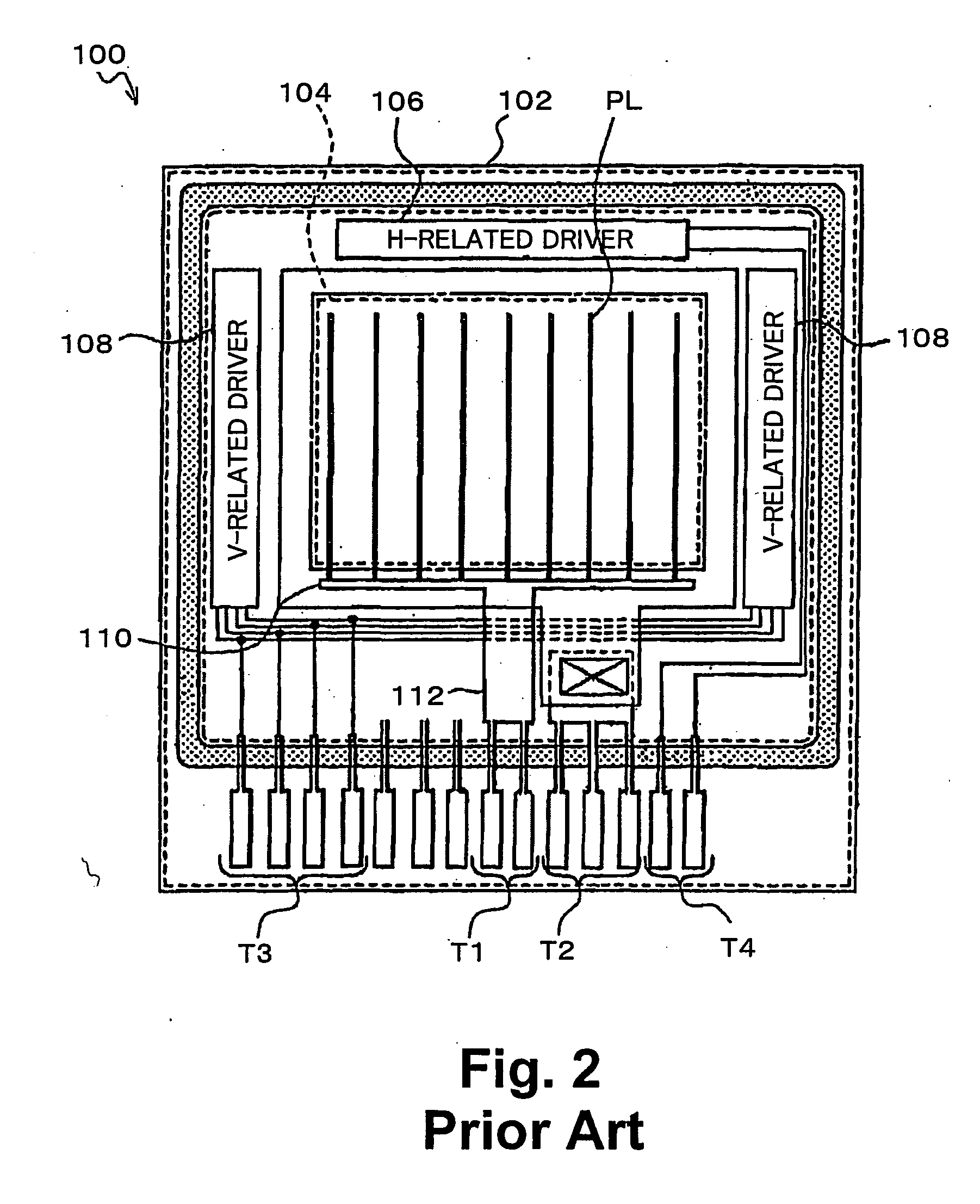
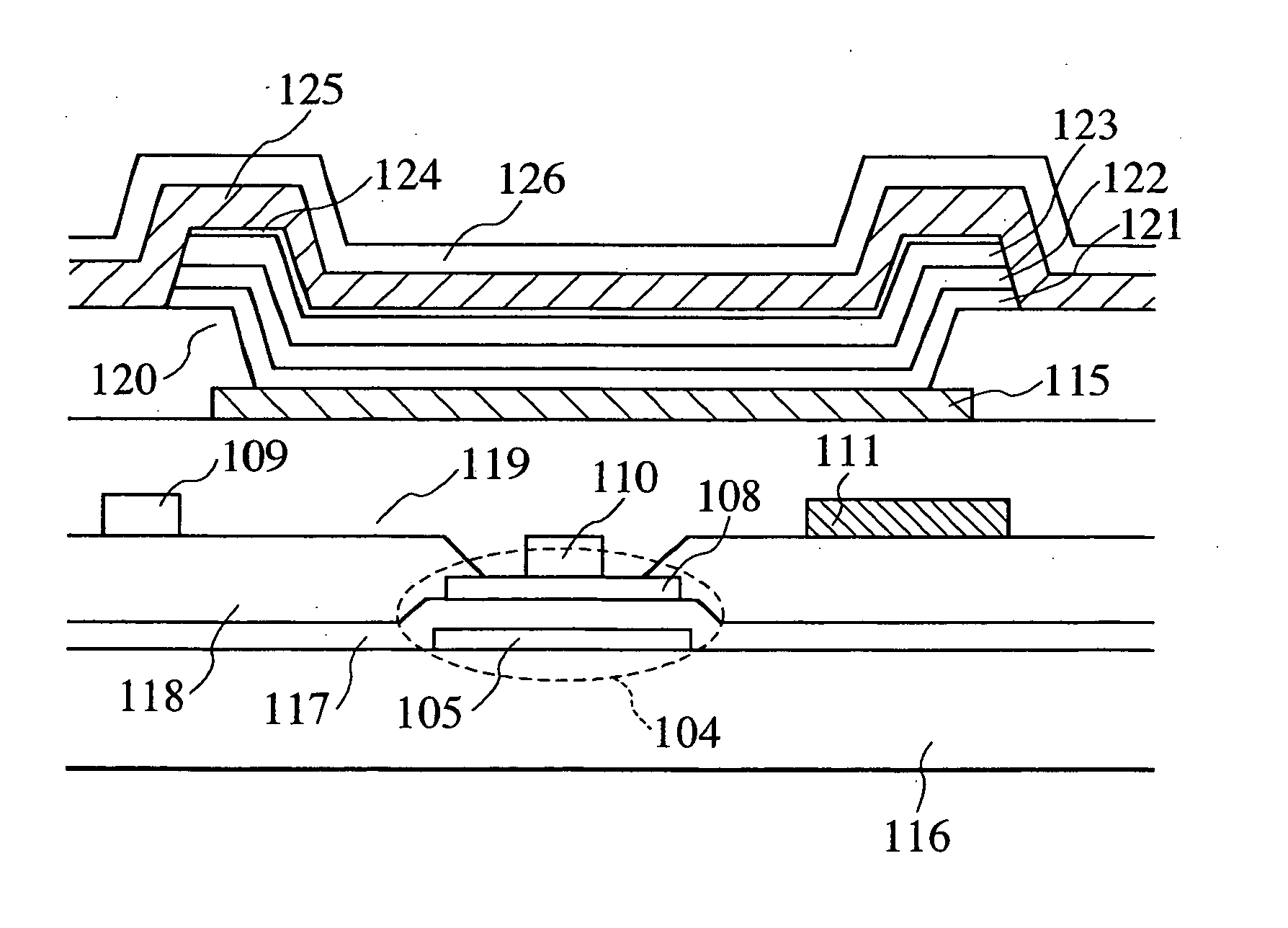
A display portion in which pixels are arranged in a matrix is formed on a display panel and a drive current line, which supplies a drive current from a terminal formed at a side along a column direction to a display element in each pixel, includes a branch line provided for each column of the display portion and along each column of the display portion; a trunk line to which the branch line is connected and which extends along a row direction at a peripheral portion at a lower side of the display portion; and a connection line which connects the trunk line and the terminal. The connection line is separated from a region of the trunk line near the terminal by a slit provided from a side of the trunk line near the terminal to a side of the trunk line distanced from the terminal and extends in parallel to the region of the trunk line near the terminal at the peripheral portion at the lower side of the display portion from a region in which the terminal is formed. The connection line is connected to the trunk line at an intermediate position of the peripheral portion at the lower side of the display portion along the row direction. A length of the slit and a width of the region of the trunk line near the terminal are optimized to inhibit brightness variation within the display portion.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Organic light-emitting display device
InactiveUS20050127372A1Variation in brightnessDeterioration of image qualityElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesOrganic layerDisplay device
A scanning line, a signal line, a first current supply line, and a second current supply line are formed on a glass substrate, a first electrode is formed on the wiring layer comprising the above members, an organic layer comprising a hole transport layer, a light-emitting layer, an electron transport layer, and an electron injection layer is formed on the first electrode, a second electrode is formed as cathode on the electron injection layer, the first electrode as anode is connected to a plus terminal of a power source through the driving devices and the first current supply line, whereas the second electrode as cathode is connected to a minus terminal of the power source, and is connected to the second current supply line in the display region of each pixel, with a contact hole serving as a feeding point, whereby wiring resistance due to the second electrode is reduced, and variations in the brightness of a panel is reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD +1
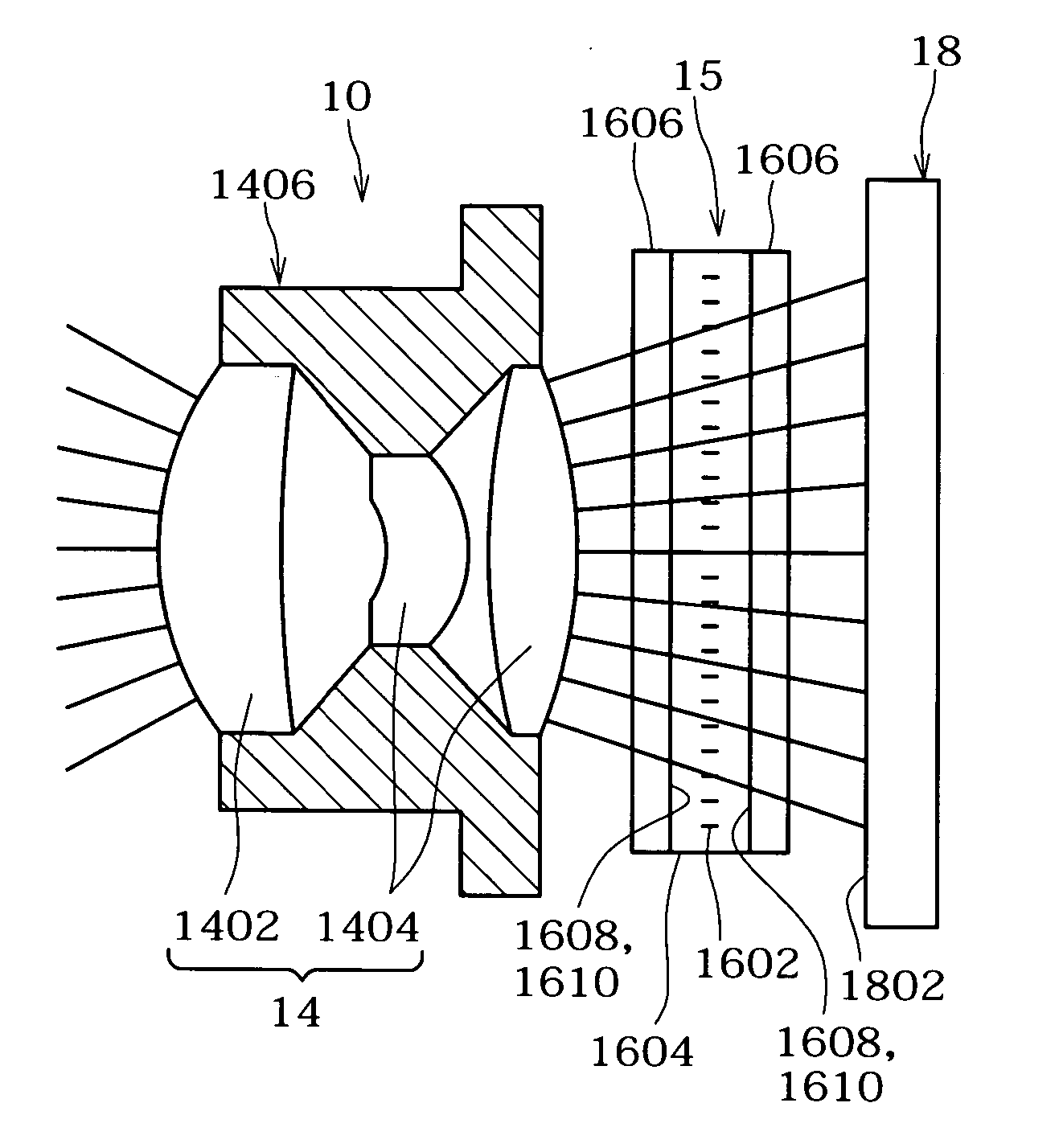
Infrared zooming lens
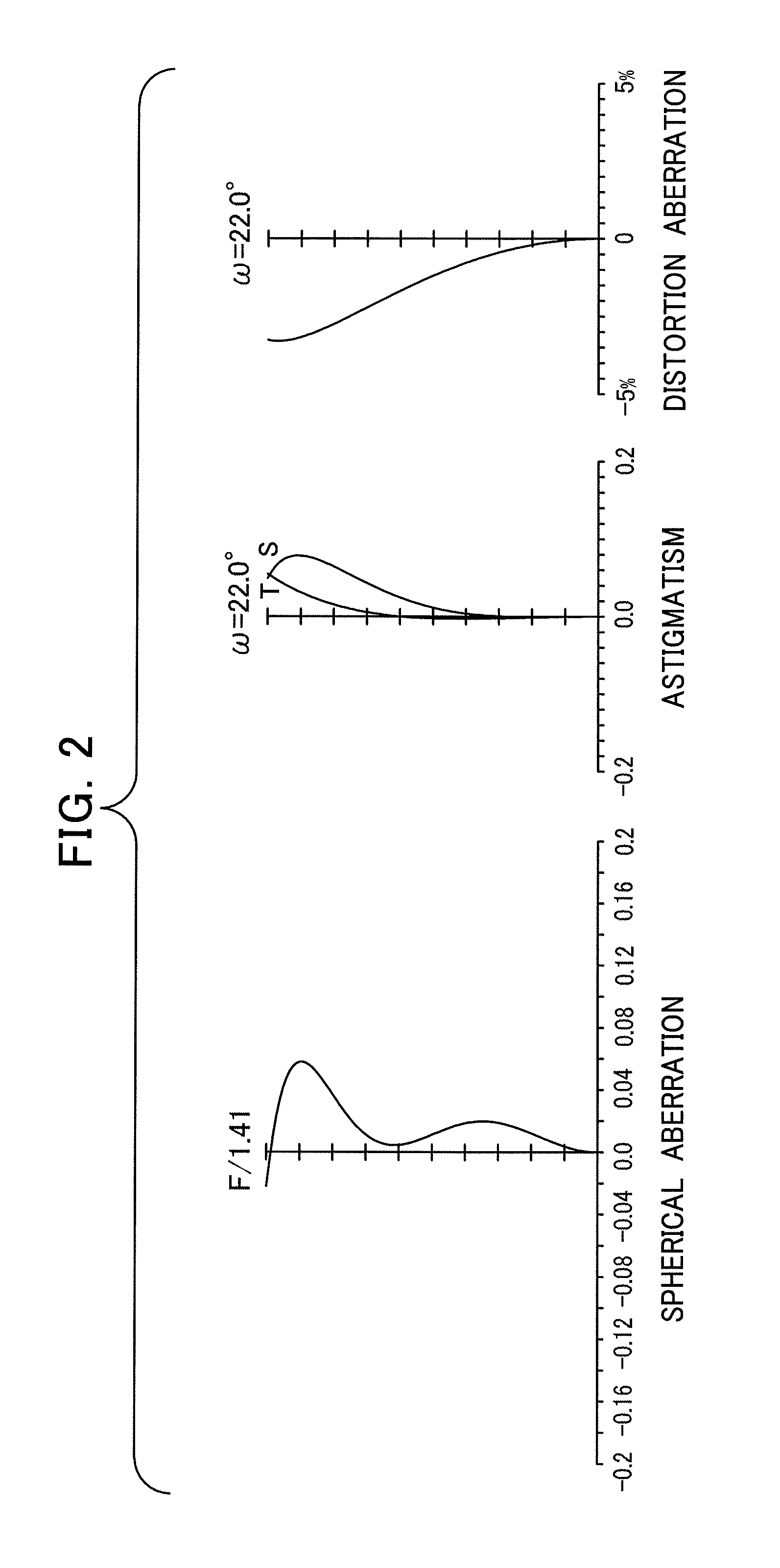
ActiveUS20110216398A1Good compensationEffectively inhibits variation in aberrationOptical elementsCamera lensMagnification
The present invention is directed to an infrared zoom lens that consists merely of optical components of germanium so as to implement an optical system that is capable of reducing variation in brightness during varying a magnification rate and is quite bright and that facilitates compensating for aberration, especially spherical aberration that is generally hard to do, thereby producing a clear and vivid image. The infrared zoom lens comprises first to fourth groups of lens pieces arranged in series from the foremost position closest to the object; each of the lens groups having all the lens pieces made of germanium, and at least one of the lens groups consisting simply of a single lens piece.
Owner:TAMRON
Display device
InactiveUS8207024B2Variation in brightness of light emitting elements between pixelsImprove reliabilityTransistorStatic indicating devicesPower flowDisplay device
At least two TFTs which are connected with a light emitting element are provided, crystallinities of semiconductor regions composing active layers of the respective TFTs are made different from each other. As the semiconductor region, a region obtained by crystallizing an amorphous semiconductor film by laser annealing is applied. In order to change the crystallinity, a method of changing a scan direction of a continuous oscillating laser beam so that crystal growth directions are made different from each other is applied. Alternatively, a method of changing a channel length direction of TFT between the respective semiconductor regions without changing the scan direction of the continuous oscillating laser beam so that a crystal growth direction and a current flowing direction are different from each other is applied.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
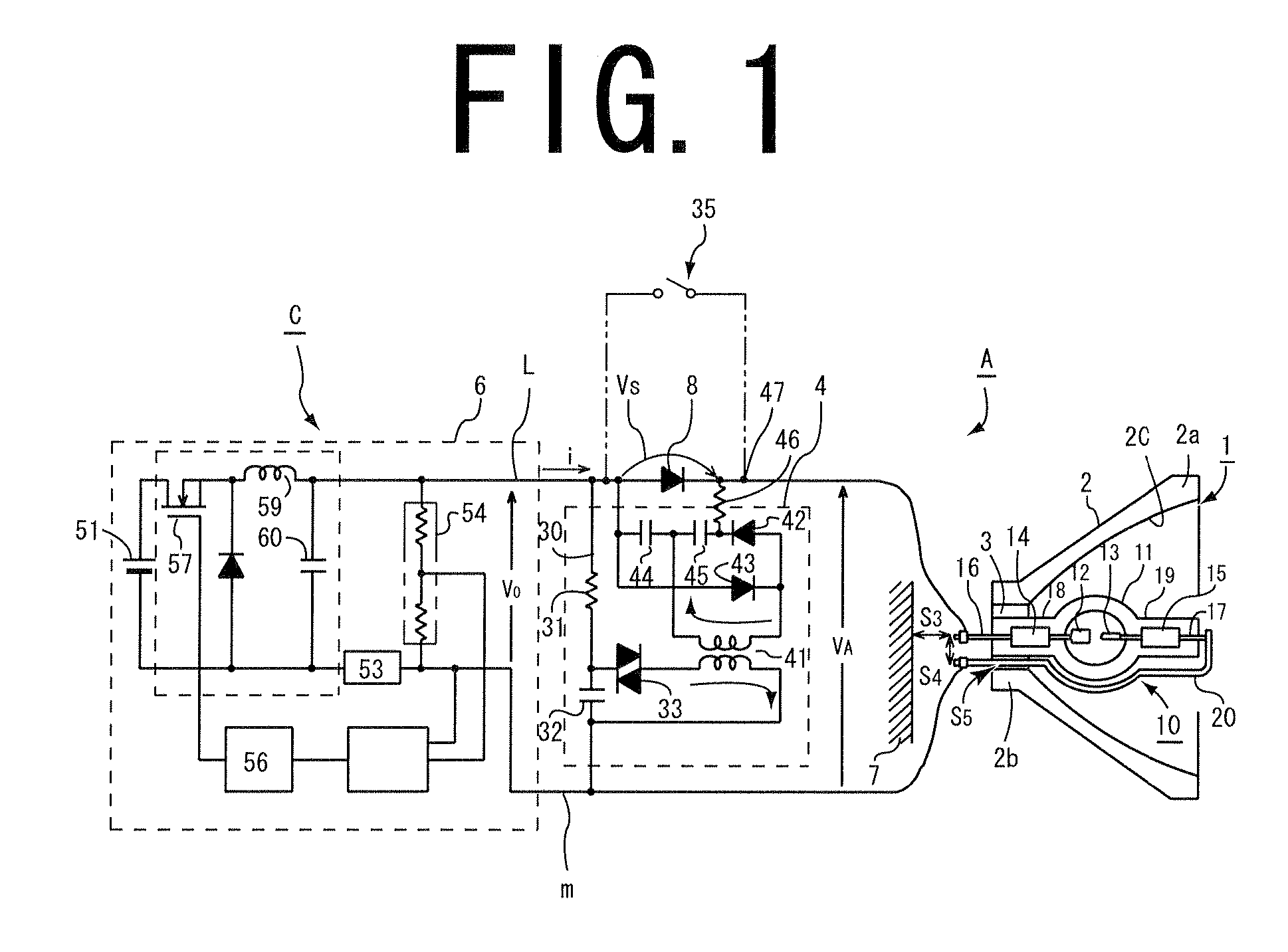
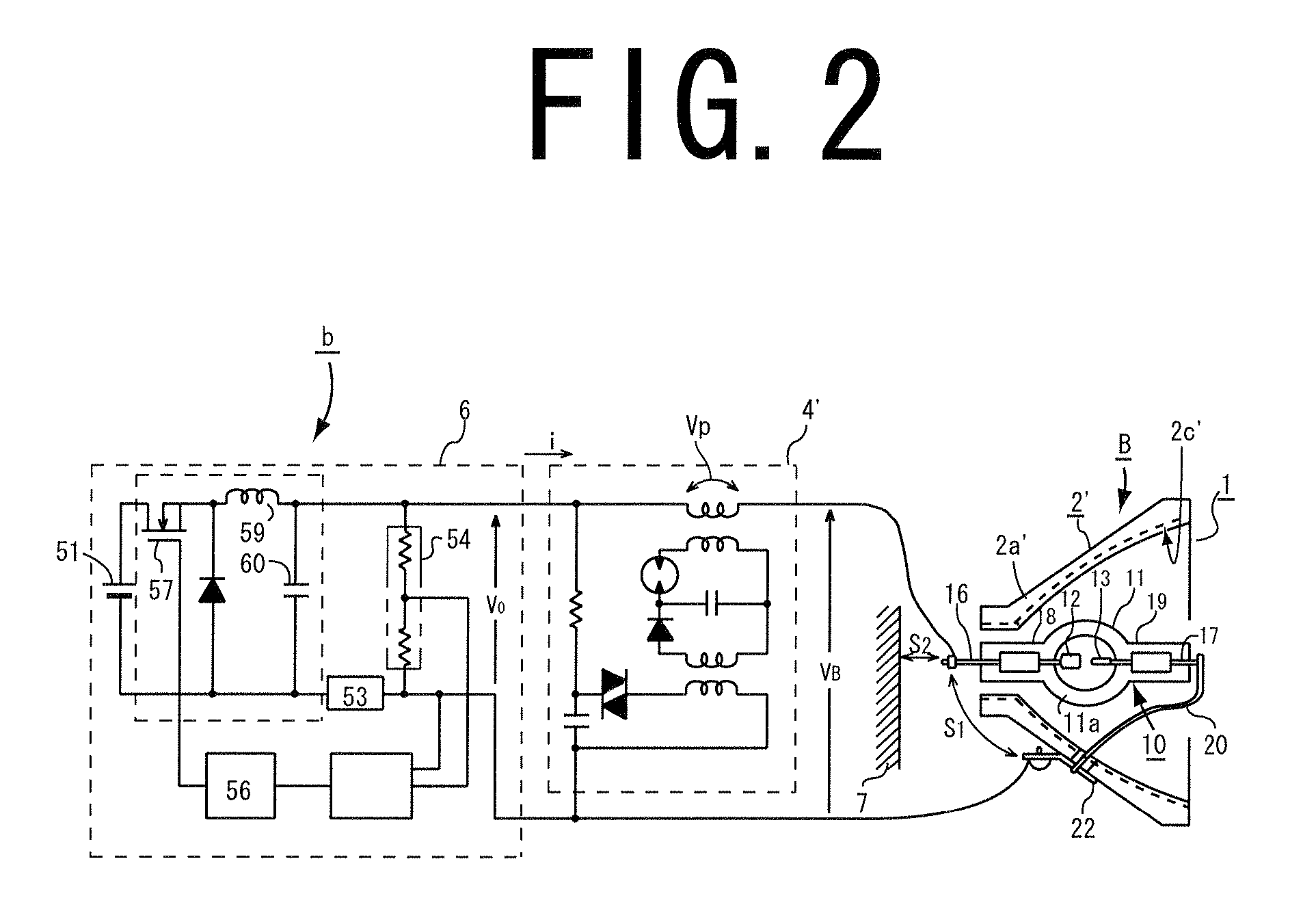
Lens barrel and imaging device
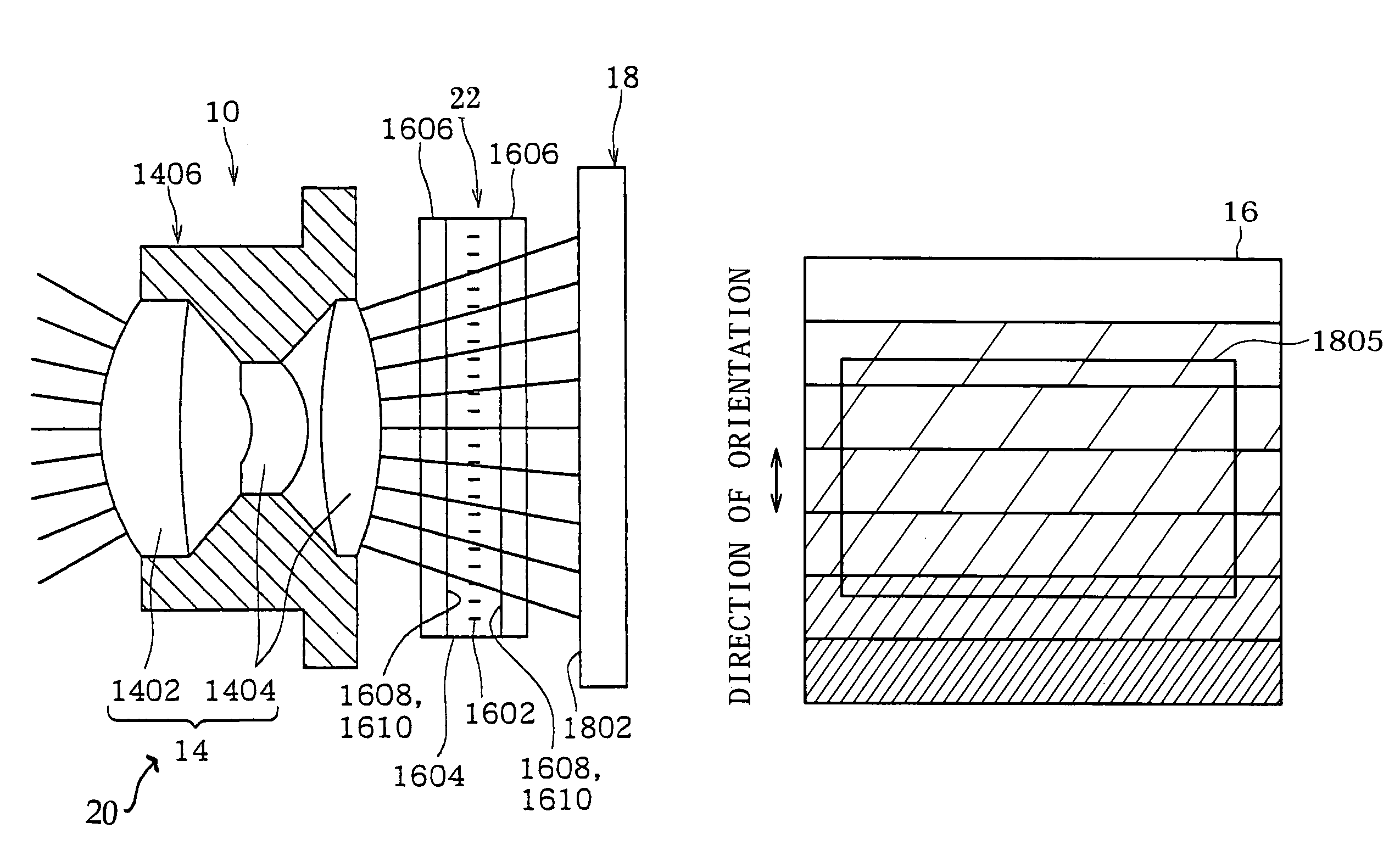
InactiveUS7339649B2Small sizeVariation in brightnessTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptical axisOptic system
Owner:SONY CORP
Pattern matching system
InactiveUS20070223819A1Variation in brightnessExact matchTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern matchingImage signal
A pattern matching system, comprising a receiver, a comparison block, a calculation block, an output block, a ratio reading block, and a controller, is provided. A likeness value indicates how much a first and second image accords to each other. The receiver receives first and second image signal corresponding to the first and second images as an area signal. The comparison block compares the signal levels of the area signals corresponding to the pattern areas at the relatively same location of the first and second images. The calculation block calculates the likeness value. The ratio reading block reads a amplification ratio by which the first and second image signals are amplified. The controller changes the type of the signal components of the area signal used for the comparison by the comparison block and the calculation of the likeness value by the calculation block.
Owner:RICOH IMAGING COMPANY
Pixel circuit, display device, driving method of pixel circuit, and driving method of display device
InactiveUS7893895B2Increase brightnessLow mobilityStatic indicating devicesDriving currentCapacitance
A pixel circuit, disposed at a part where a scanning line and a signal line intersect each other, includes at least an electrooptic element, a drive transistor, a sampling transistor, and a retaining capacitance. The drive transistor has a gate connected to an input node, a source connected to an output node, and a drain connected to a predetermined power supply potential and supplies a driving current to the electrooptic element according to a signal potential retained in the retaining capacitance. The electrooptic element has one terminal connected to the output node and another terminal connected to a predetermined potential. The sampling transistor is connected between the input node and the signal line and operates when selected by the scanning line, samples an input signal from the signal line, and retains the input signal in the retaining capacitance. The retaining capacitance is connected to the input node. The pixel circuit further includes a compensating circuit which detects a decrease in the driving current from a side of the output node and feeds back a result of detection to a side of the input node to compensate for a decrease in the driving current, which decrease is attendant on a secular change of the drive transistor.
Owner:SONY CORP
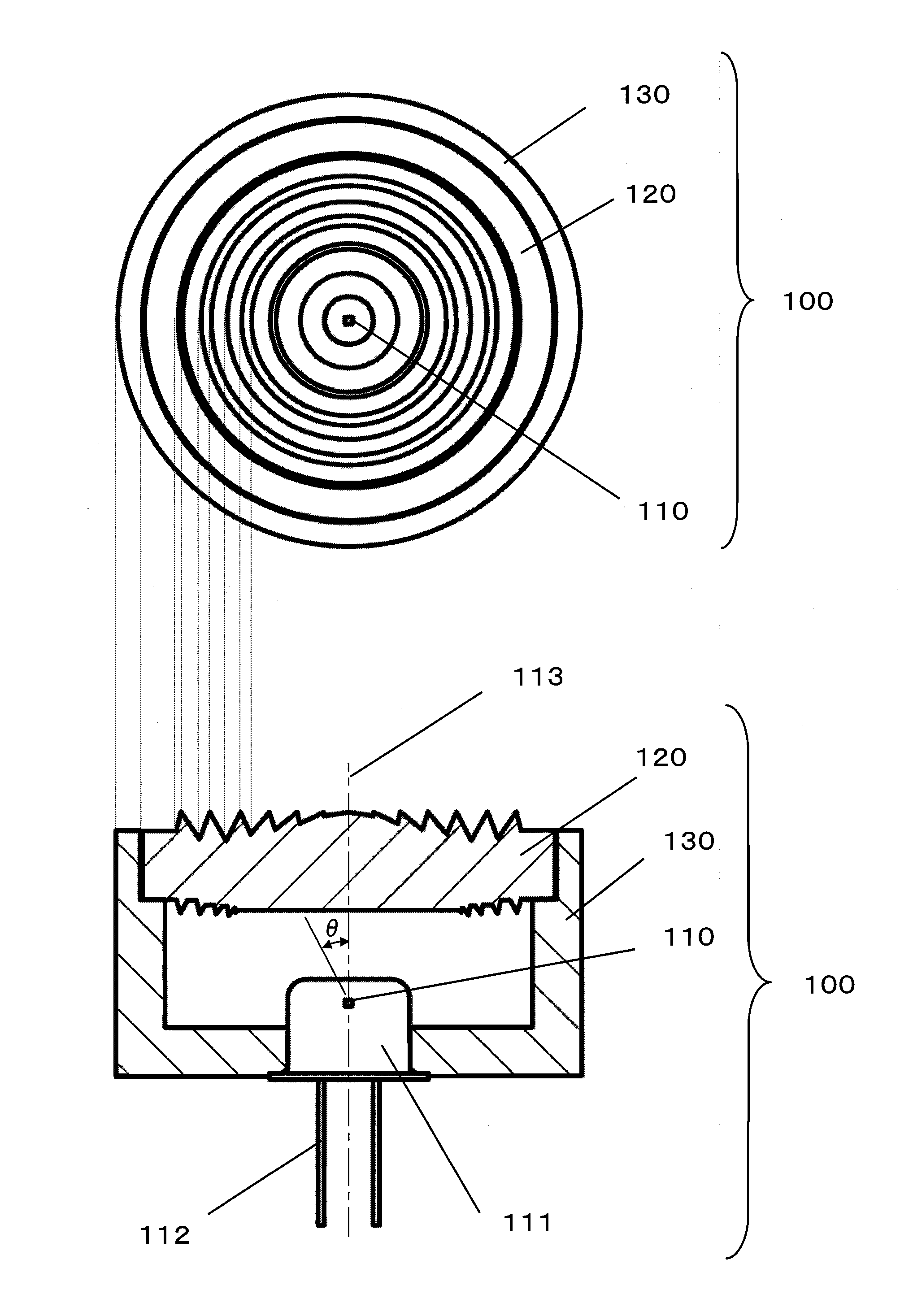
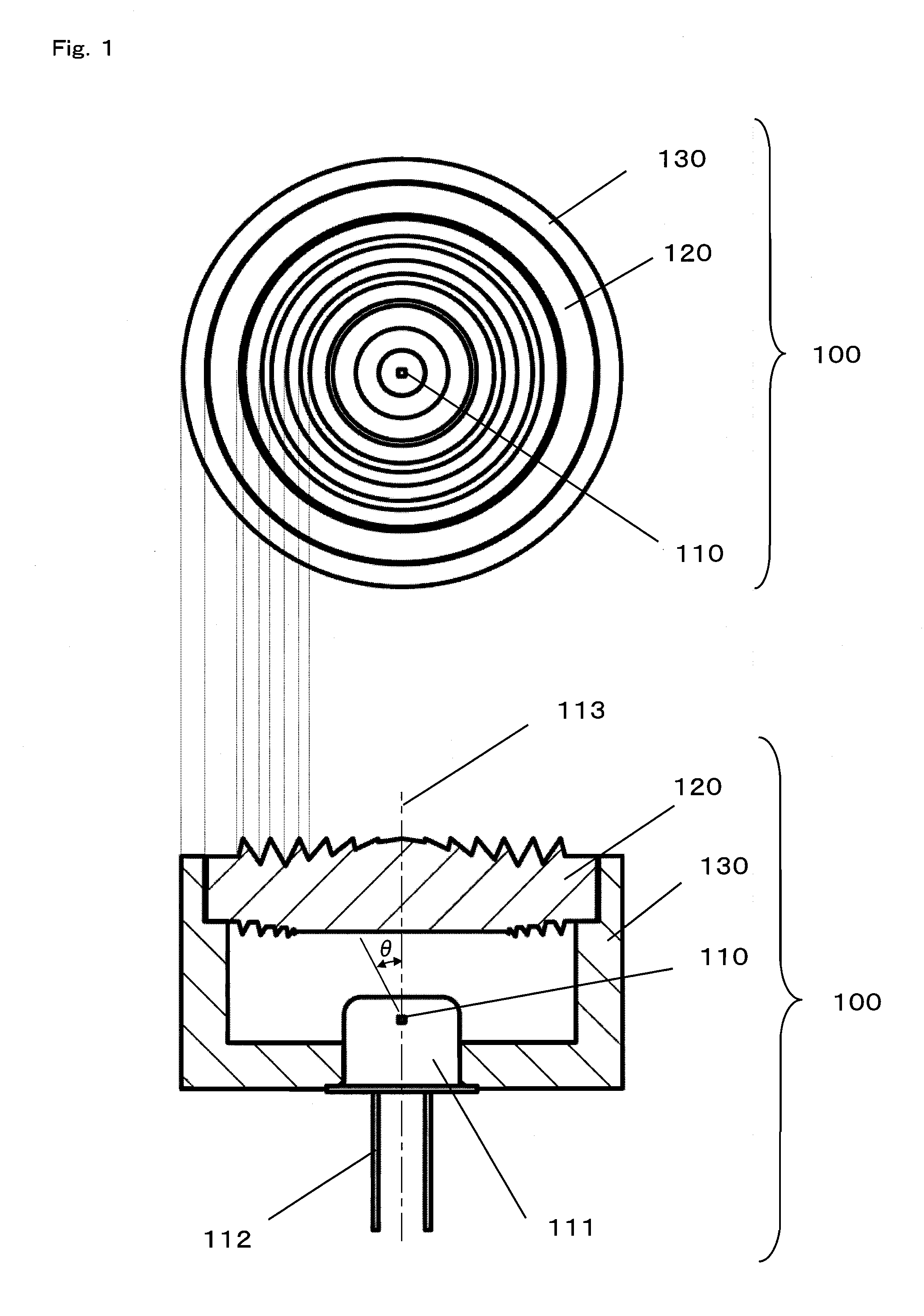
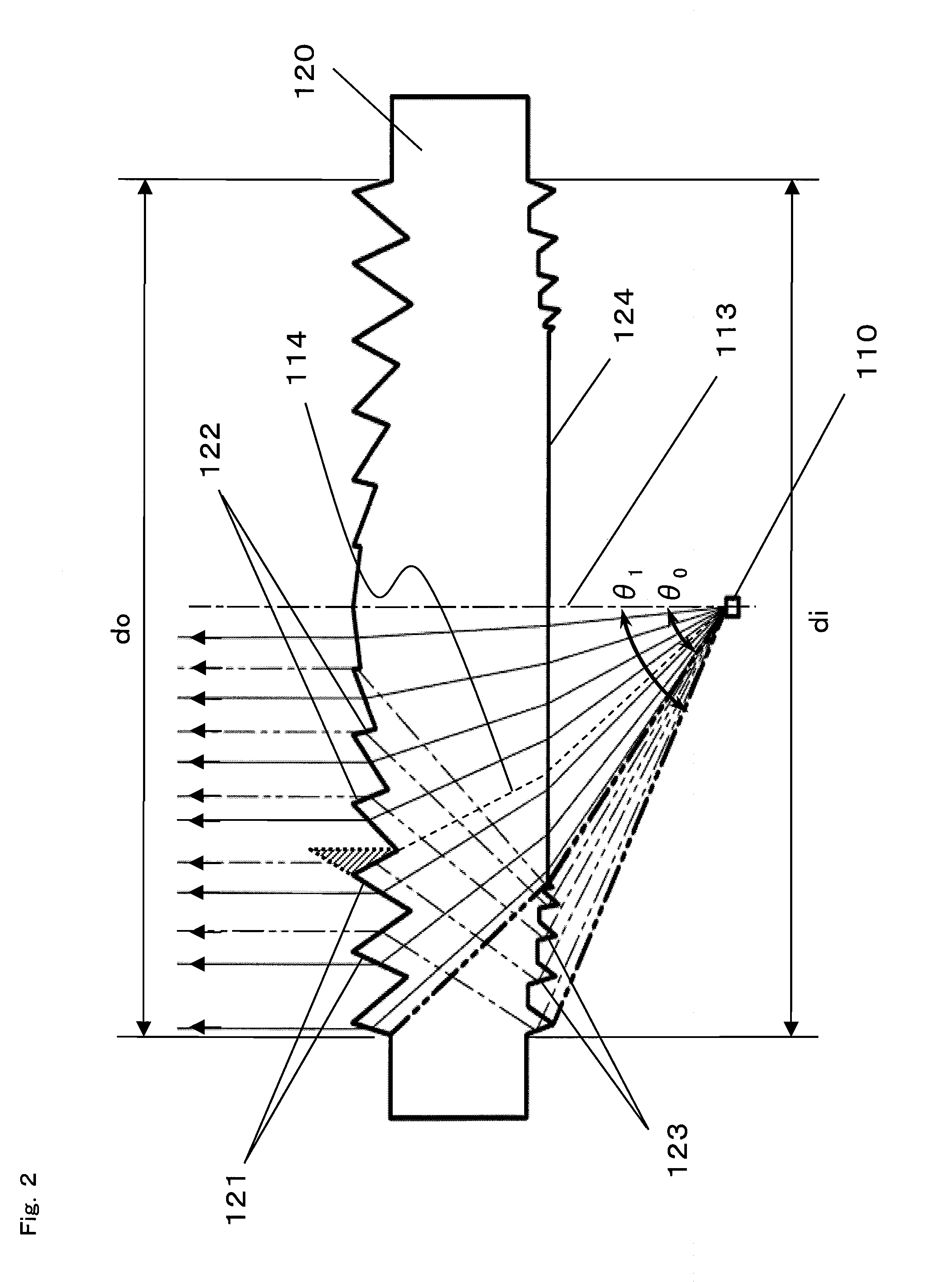
Light emitting module and light receiving module
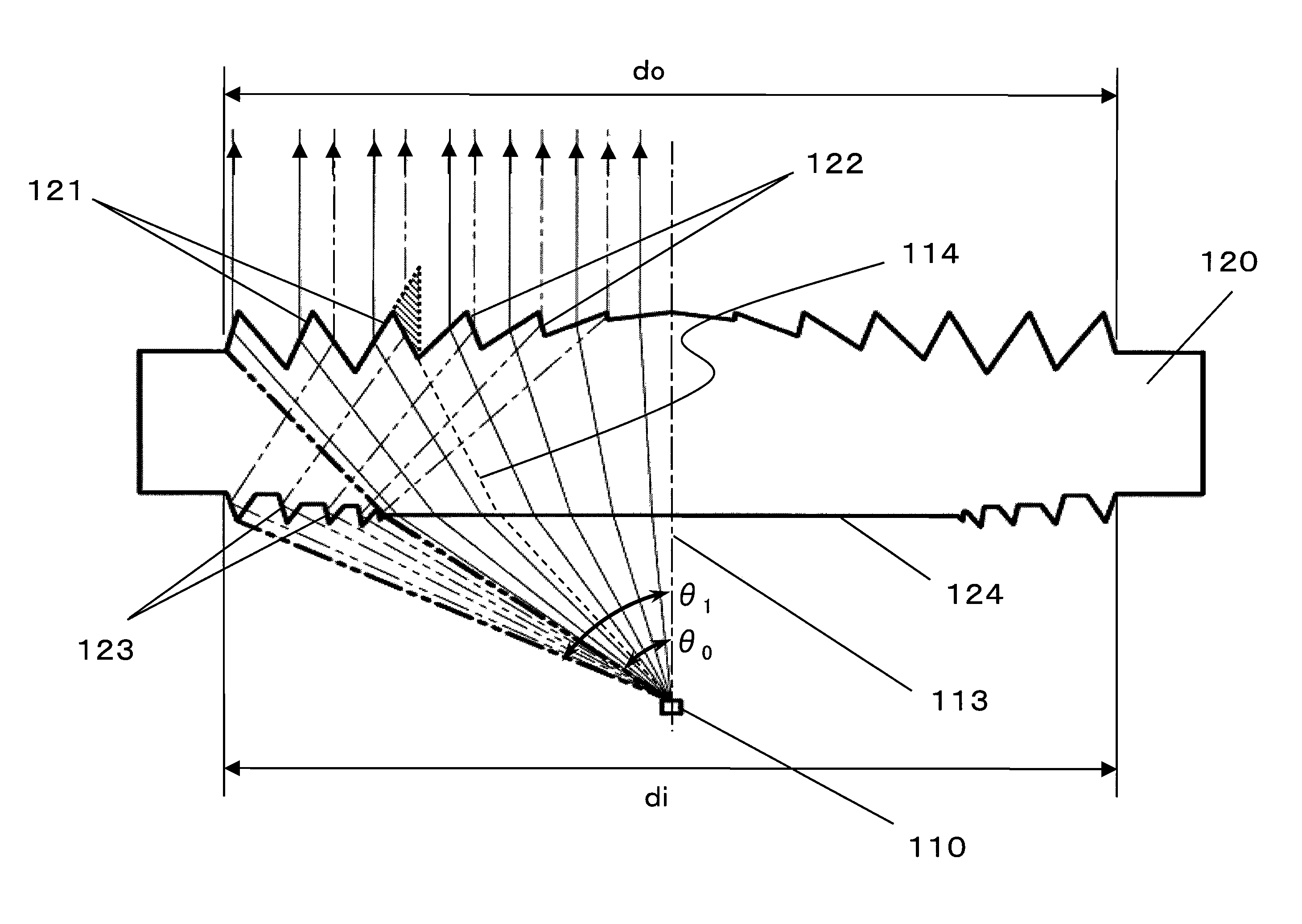
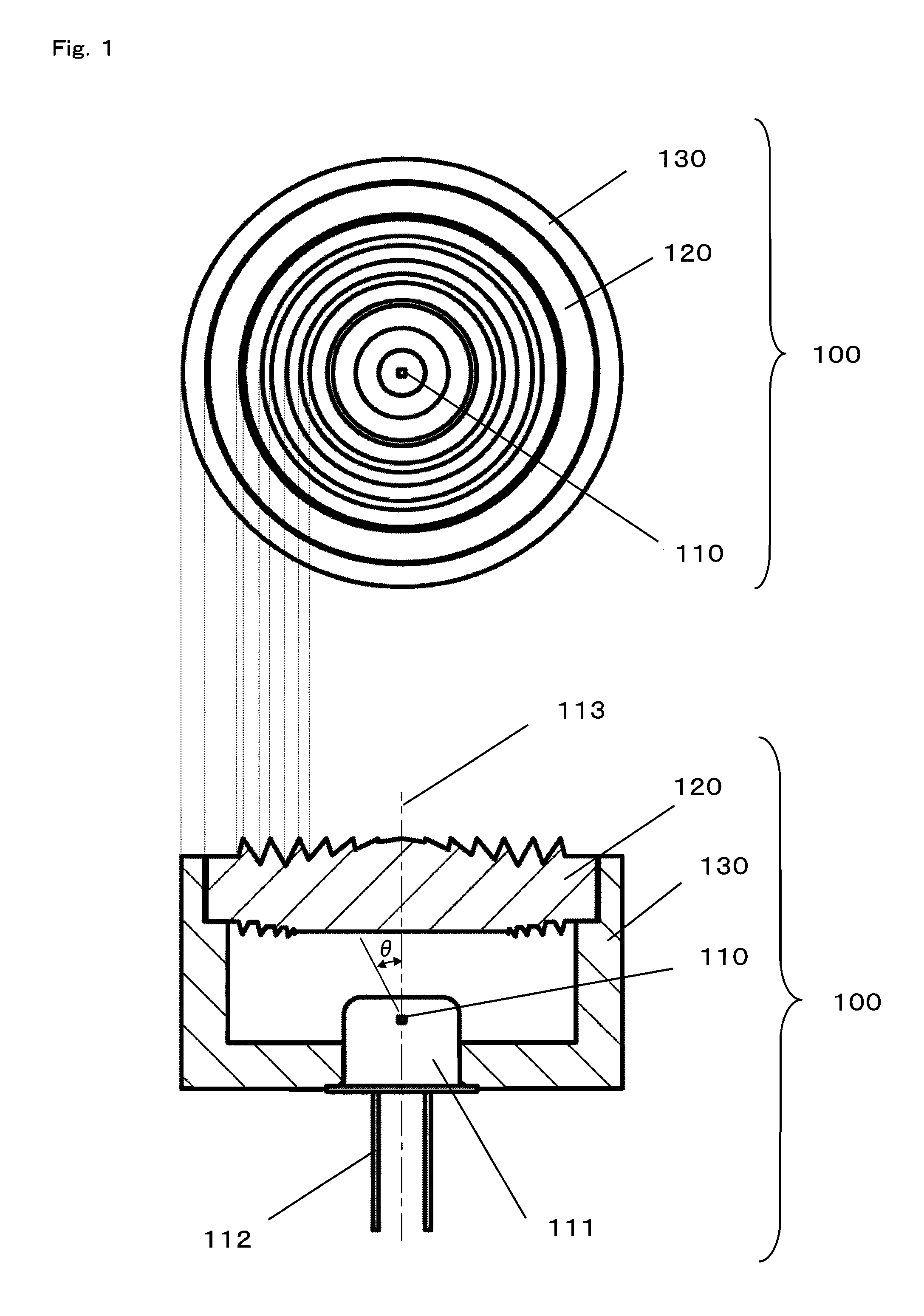
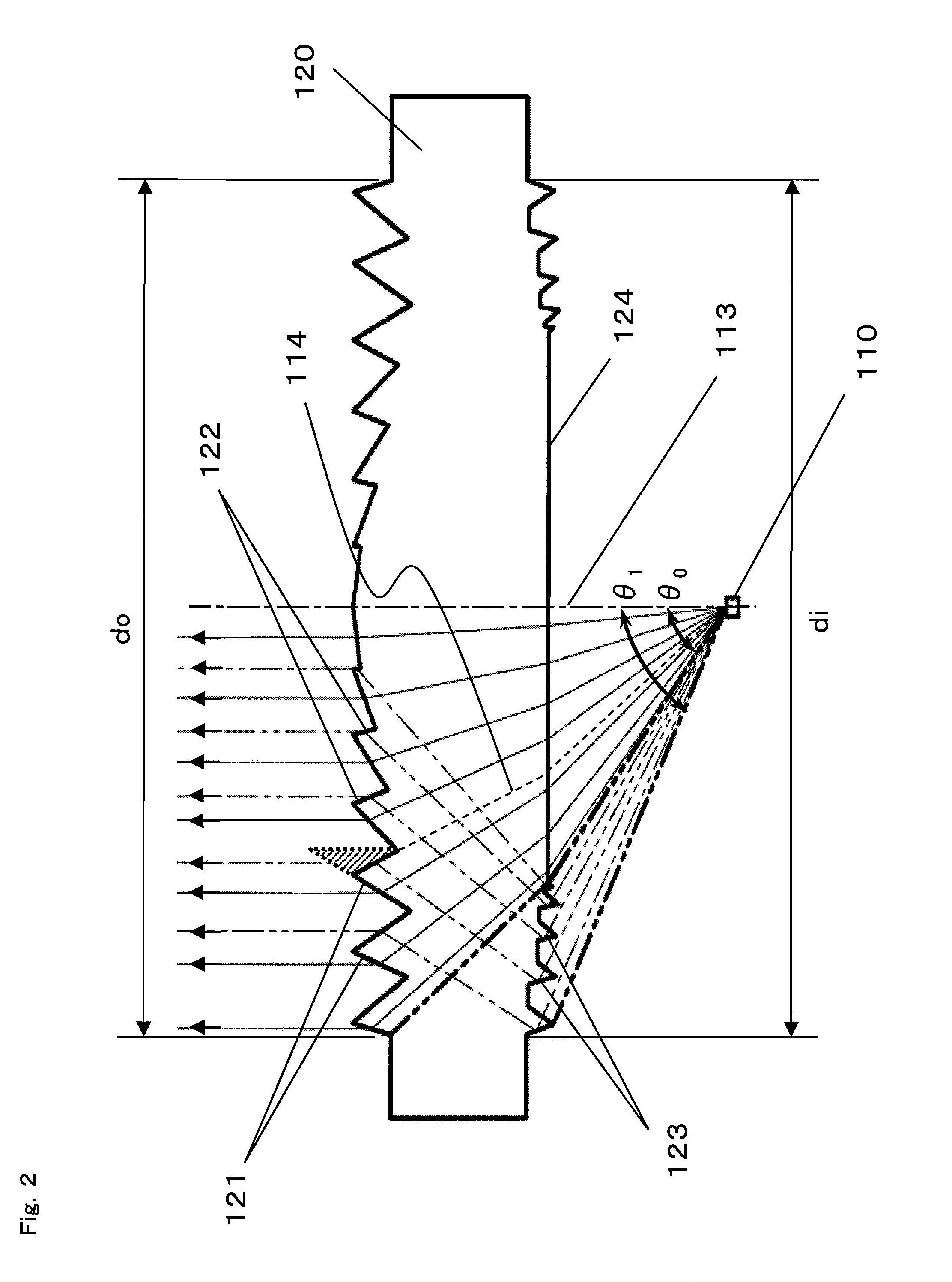
InactiveUS20080106804A1Variation in brightnessDiameter minimizationLensLuminous intensityOptical axis
A plurality of first refraction surfaces 121 and a plurality of second refraction surfaces 122 are alternately provided on an emission surface of a lens element 120 so as to form concentric circles each having an optical axis 113 at the center thereof, and having diameters different from each other, and a light reflected by a plurality of reflection surfaces 123 provided on an incident surface of the lens element so as to form concentric circuits each having the optical axis 113 at the center thereof and having diameters different from each other, is refracted and emitted by the plurality of second refraction surfaces 122 at desired angles. Therefore, it is possible to enhance efficiency and an emission intensity, and reduce variations in brightness of an emitted light without increasing the diameter of the lens element 120, thereby realizing a light emitting module 100 enabling advantageous performance.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Light emitting module and light receiving module
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Liquid crystal display device and image display method thereof
ActiveUS8139020B2Reduce brightnessReduce colorStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayImage signal
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP
Lens barrel and imaging device
InactiveUS20050134776A1Less variationReduce brightnessTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptical axisOptic system
A lens barrel and imaging device advantageous for making unnatural brightness variation in an image, due to a liquid-crystal light control element, less noticeable, while reducing the size of an optical system, are disclosed. A lens barrel comprises an optical system, a rectangular planar liquid-crystal light control element, and an imaging element. An object image captured by the optical system is guided to the imaging element through the control element comprising a liquid crystal layer sealed in between a pair of alignment layers and containing rod-shaped liquid crystal molecules. A sensor unit of the imaging element has a rectangular imaging area. Light rays guided from the optical system to the imaging element diverge away from an optical axis. An orientational direction of the control element is substantially parallel to the shorter sides of the imaging area.
Owner:SONY CORP
Light emitting device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20110278602A1Reducing variation in brightnessReducing in emission colorSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThermal radiationLight emitting device
A light emitting device includes a substrate having an element mounting area in a principal surface thereof. The light emitting device also includes at least one light emitting element mounted in the element mounting area of the substrate. The light emitting device also includes a heat transfer member provided on the substrate. The heat transfer member has a thermal conductivity different from thermal conductivity of the substrate so as to form uneven thermal resistance distribution in the element mounting area. Thermal resistance in a heat radiation path through the substrate for release of heat emitted from the light emitting element changes with the mounting position of the light emitting element.
Owner:STANLEY ELECTRIC CO LTD
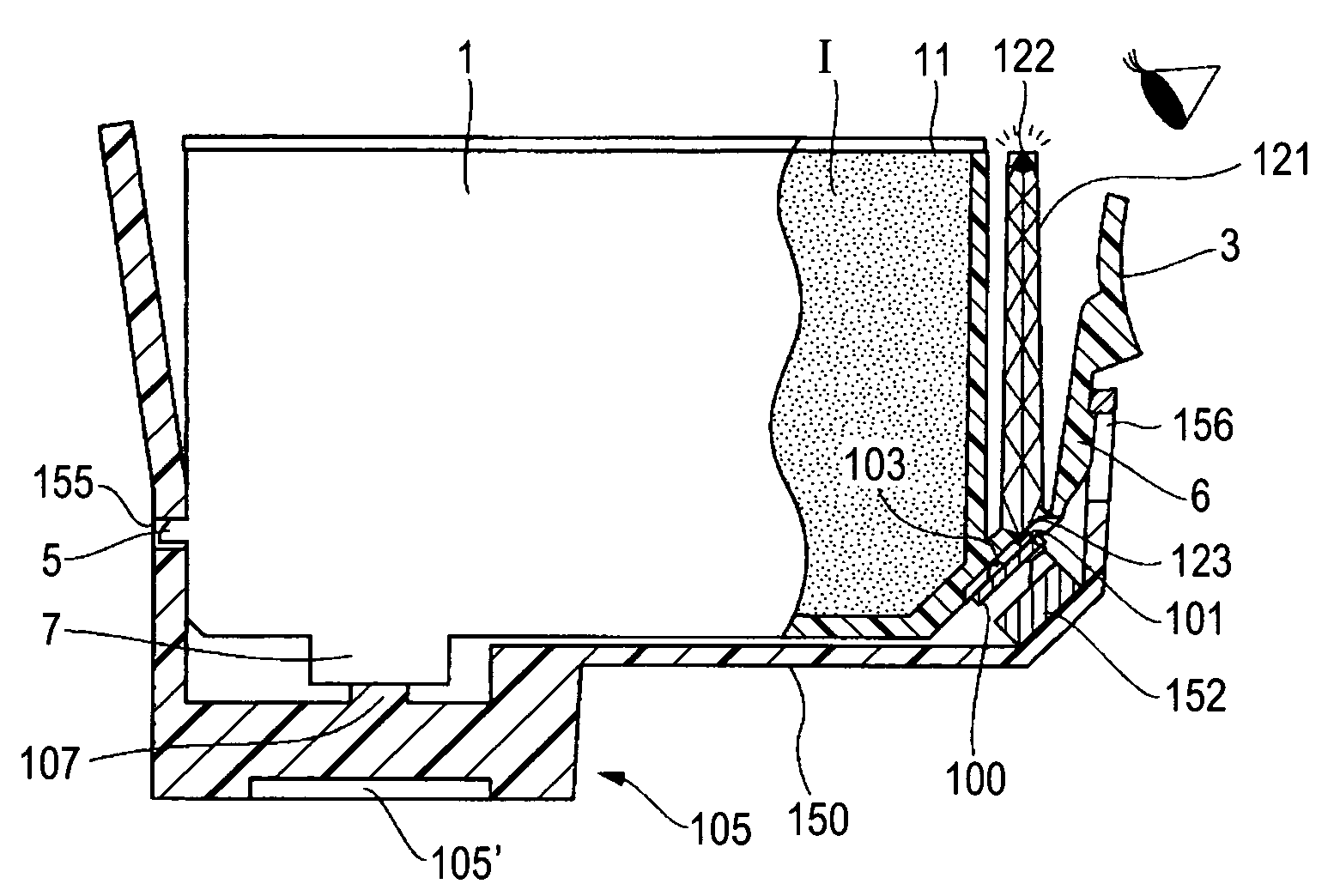
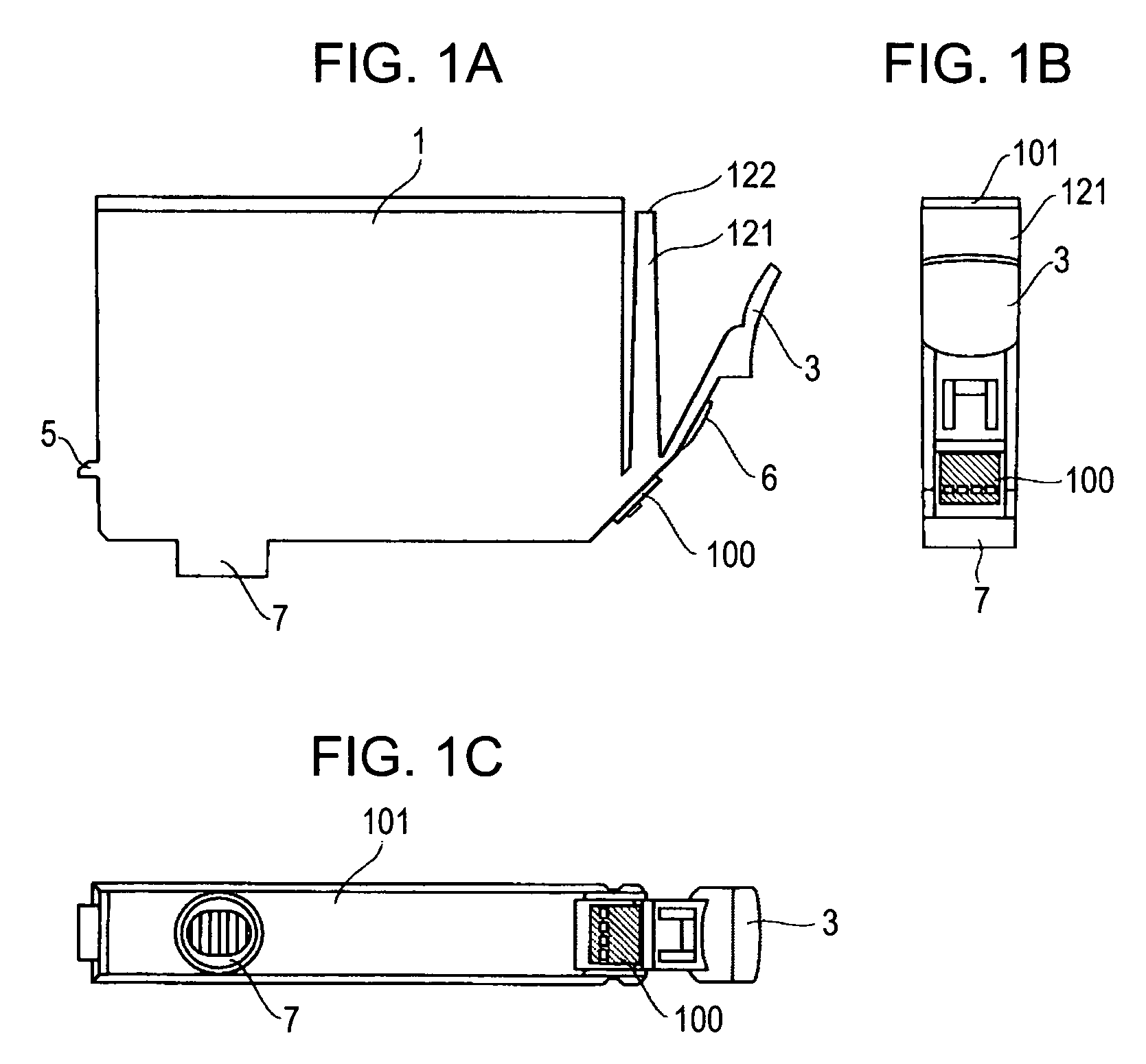
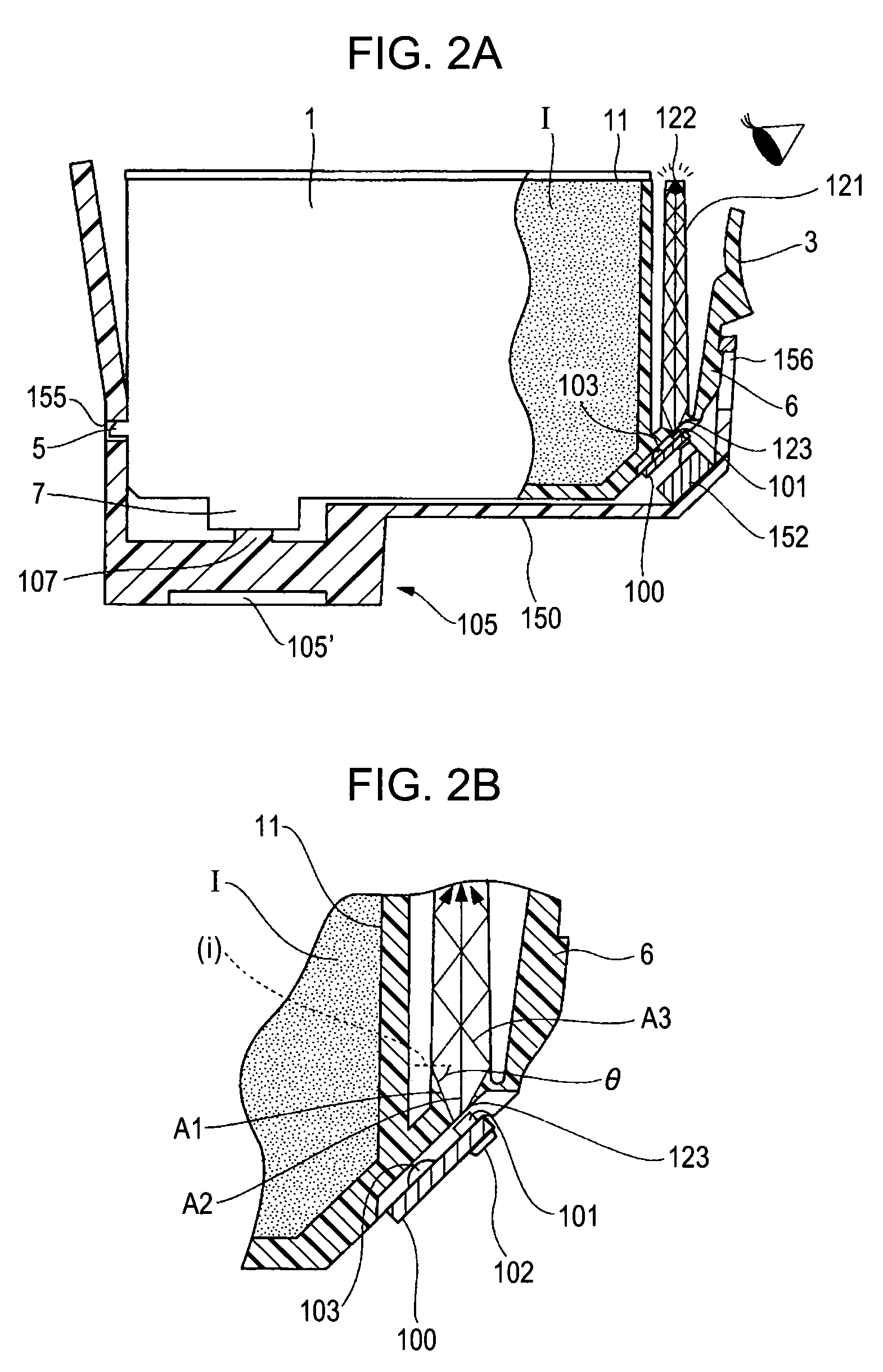
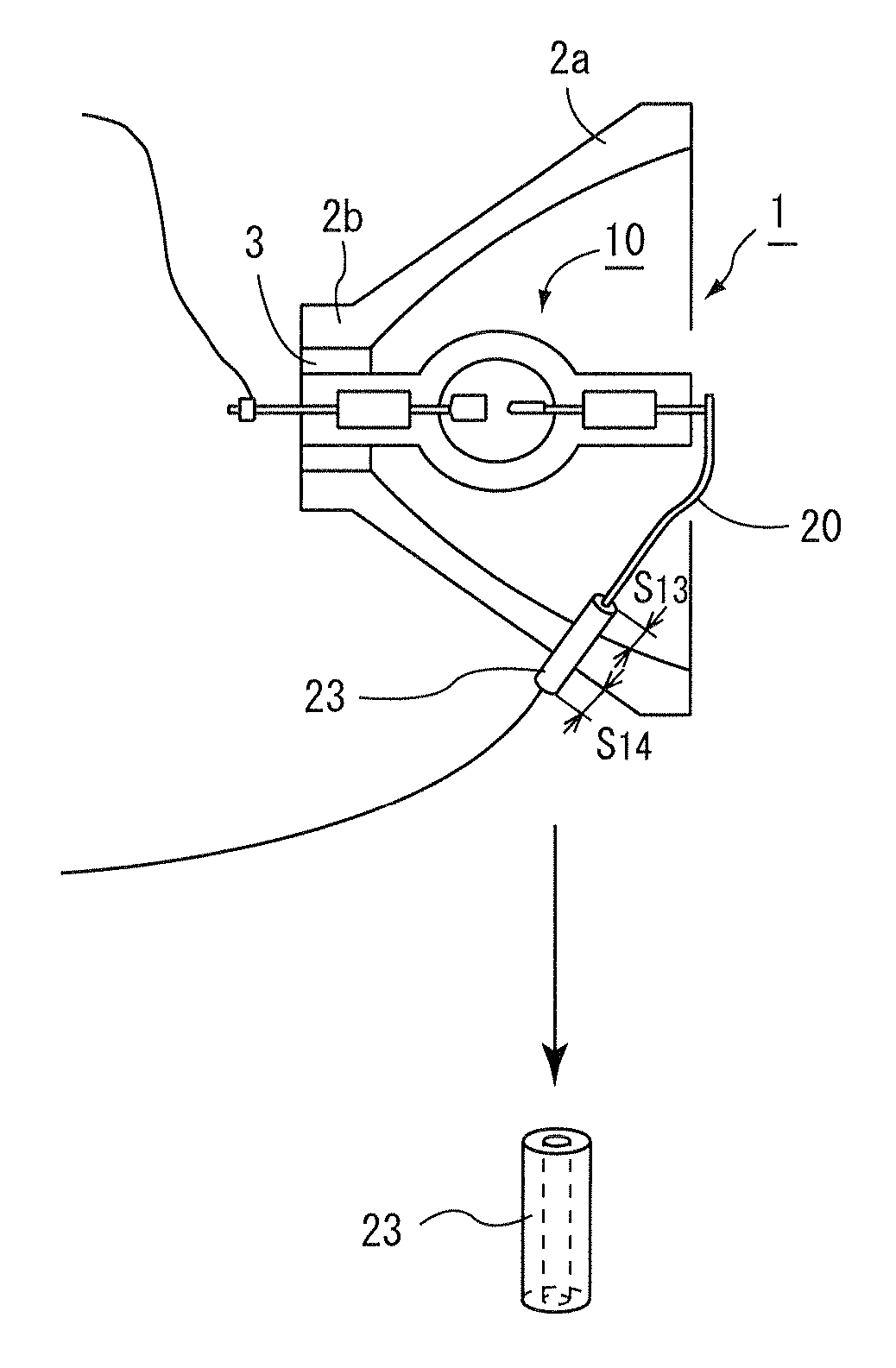
Ink container with light-emitting unit to convey information
ActiveUS7458667B2Reduce variation brightnessVariation in brightnessOther printing apparatusEngineeringBrightness perception
A liquid container that can present various information using illumination of a light-emitting unit includes an IC package having a storage element and the light-emitting unit. The storage element stores information used for controlling the amount of light emitted from an LED included in the light-emitting unit, so that variation in brightness of the light-emitting unit can be reduced and the information can be adequately presented.
Owner:CANON KK
Pixel circuit, display device, and electroinc appliance
ActiveUS20100117938A1Uniform imagingReduce uniformityElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesCapacitanceDisplay device
A pixel circuit provided on a substrate on which a signal line, first and second scanning lines supplying first and second control pulse signals, a fixed power line, and a variable power line are arranged includes a capacitance element, a sampling transistor connected between the signal line and one of ends of the capacitance element, where the gate of the sampling transistor is connected to the first scanning line, a drive transistor of which gate is connected to the other end, where one of a drain and a source of the drive transistor is connected to the fixed power line, an initializing transistor of which gate is connected to the second scanning line, which is connected between the other end and the other of the drain and the source, and a light emitting element connected between the variable power line and the other of the drain and the source.
Owner:JOLED INC
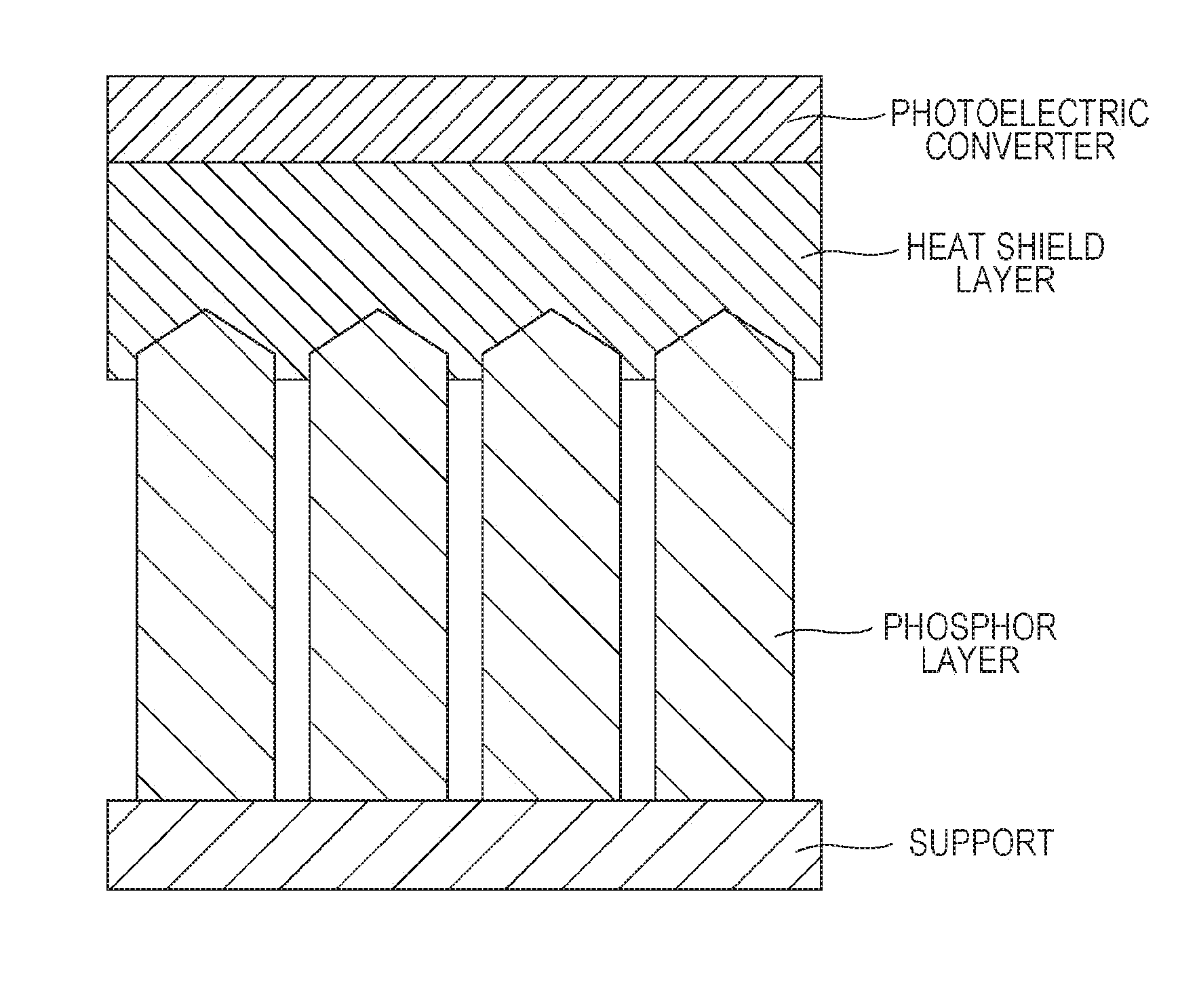
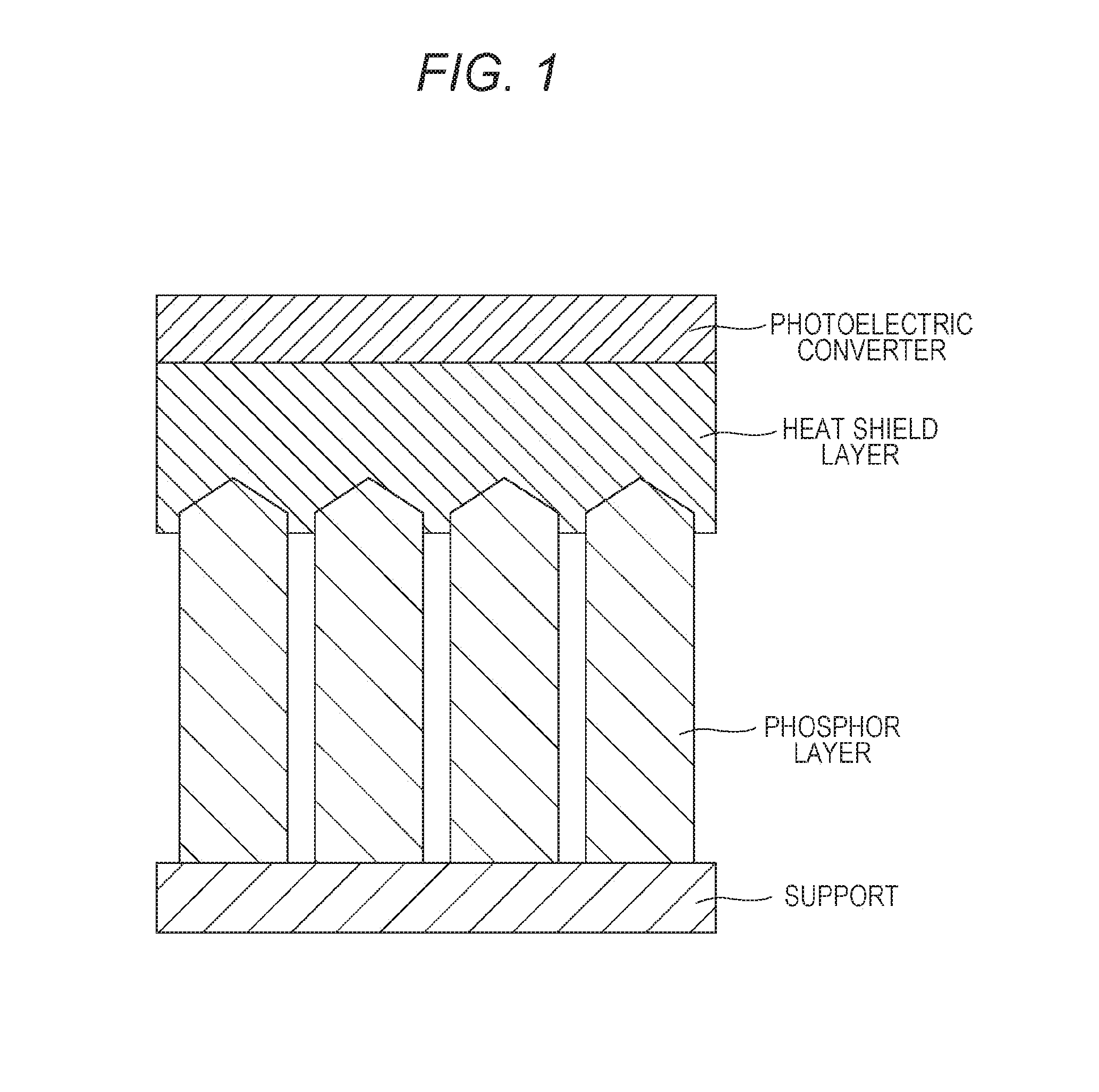
Radiographic image detector
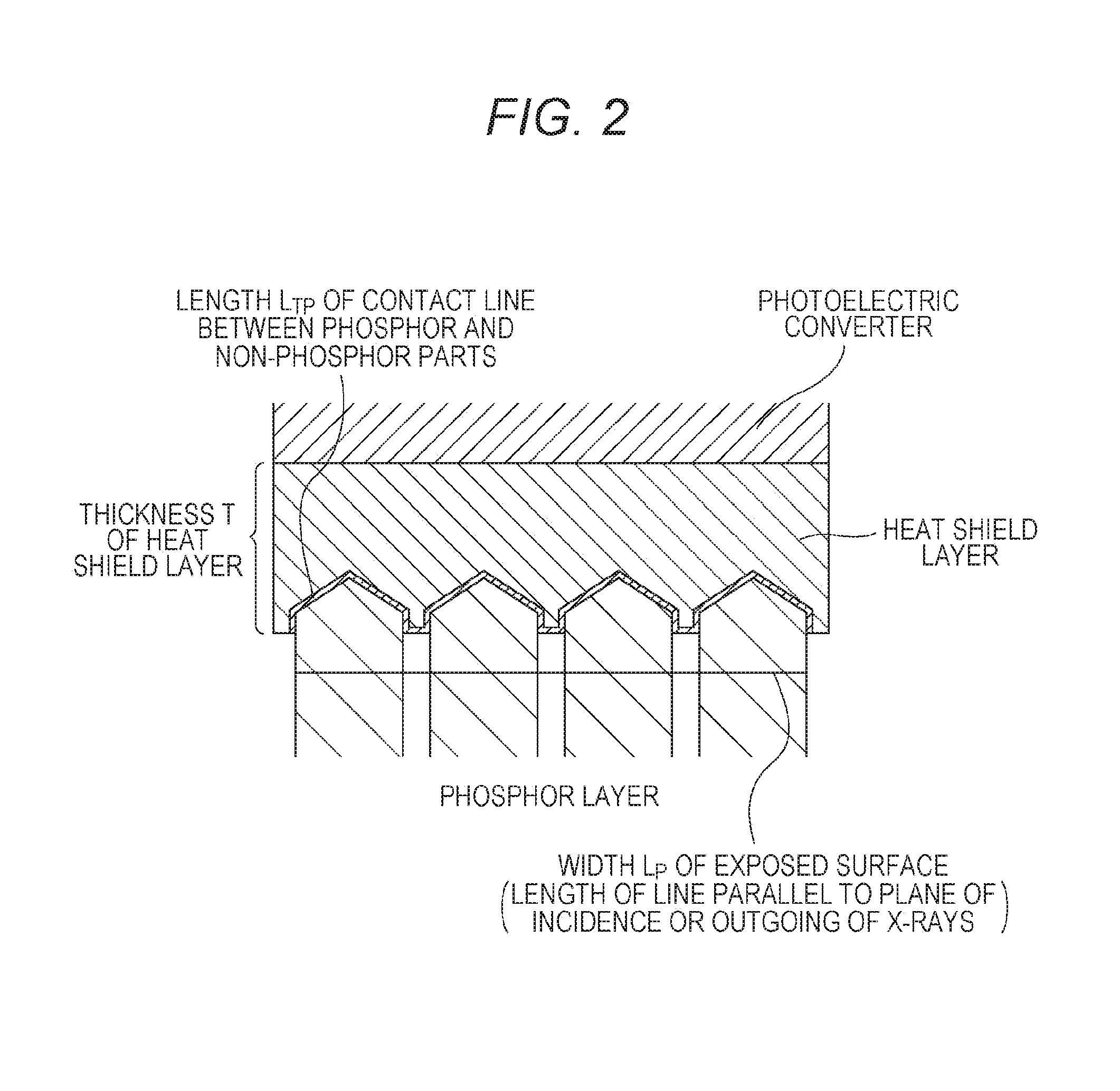
ActiveUS20160372611A1Suppress temperature quenchIncrease temperatureSolid-state devicesX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentImage detectorThermal conductivity
A radiographic image detector includes a phosphor layer, a heat shield layer, and a photoelectric converter in this order, wherein the heat shield layer has a thickness T (μm) and a thermal conductivity C (W / m·K) satisfying that C / T is from 0.004 to 5.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Display Device
InactiveUS20100151634A1Improve image qualityVariation in brightnessTransistorStatic indicating devicesAmorphous semiconductorsLaser annealing
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Backlight device and liquid crystal display device
ActiveUS7508467B2Variation in brightnessVariation in colorElongate light sourcesElectric lightingLiquid-crystal displayLight source
Owner:SATURN LICENSING LLC
Liquid container and recording apparatus
ActiveUS20060139421A1Reduce variation brightnessVariation in brightnessOther printing apparatusEngineeringBrightness perception
A liquid container that can present various information using illumination of a light-emitting unit includes an IC package having a storage element and the light-emitting unit. The storage element stores information used for controlling the amount of light emitted from an LED included in the light-emitting unit, so that variation in brightness of the light-emitting unit can be reduced and the information can be adequately presented.
Owner:CANON KK
Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS20190130838A1Variation in brightnessIncrease in numberStatic indicating devicesOptical elementsHigh potentialElectricity
An electro-optical device includes a scan line, a data line, a pixel circuit provided at an intersection of the scan line and the data line, a first high potential line, a first low potential line, a second high potential line, and a second low potential line. The pixel circuit includes a light emitting device, a memory circuit disposed between the first high potential line and the first low potential line, a first transistor of N-type including a gate electrically connected to the memory circuit, and a second transistor disposed between the memory circuit and the data line. The light emitting device and the first transistor are disposed in series between the second high potential line and the second low potential line.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS10748487B2Variation in characteristicsVariation in voltageStatic indicating devicesOptical elementsScan lineHemt circuits
An electro-optical device includes a scan line, a data line, a pixel circuit provided at an intersection of the scan line and the data line, a first high potential line, a first low potential line, a second high potential line, and a second low potential line. The pixel circuit includes a light emitting device, a memory circuit disposed between the first high potential line and the first low potential line, a first transistor of N-type including a gate electrically connected to the memory circuit, and a second transistor disposed between the memory circuit and the data line. The light emitting device and the first transistor are disposed in series between the second high potential line and the second low potential line.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Metallic Concave Reflection Mirror, Light Source and Light Source Apparatus Using the Same, and Lighting Circuit Thereof
InactiveUS20080042538A1Improve curved surface precision of surfaceImprove integration densityIncadescent screens/filtersMirrorsElectric lightHeat resistance
This invention makes it possible to use a concave reflection mirror using metal in at least a concave reflective portion thereof for discharge lamps. The concave reflection mirror is characterized by including: a metallic concave reflective portion; and a neck portion for receiving therein a high voltage side seal portion of a high-pressure discharge lamp to be continuously applied with a d.c. voltage of 1000 V to 4000 V during an ignition phase, the neck portion protruding rearward from a central portion of the metallic concave reflective portion and being formed partially of an insulating member or entirely of an insulating material. The concave reflection mirror can have a concave reflective surface with improved curved surface precision thereby making it possible to reduce variations in brightness, use a multi-layered deposited film having a low heat resistance, and reduce the required cost considerably.
Owner:PHOENIX ELECTRIC CO
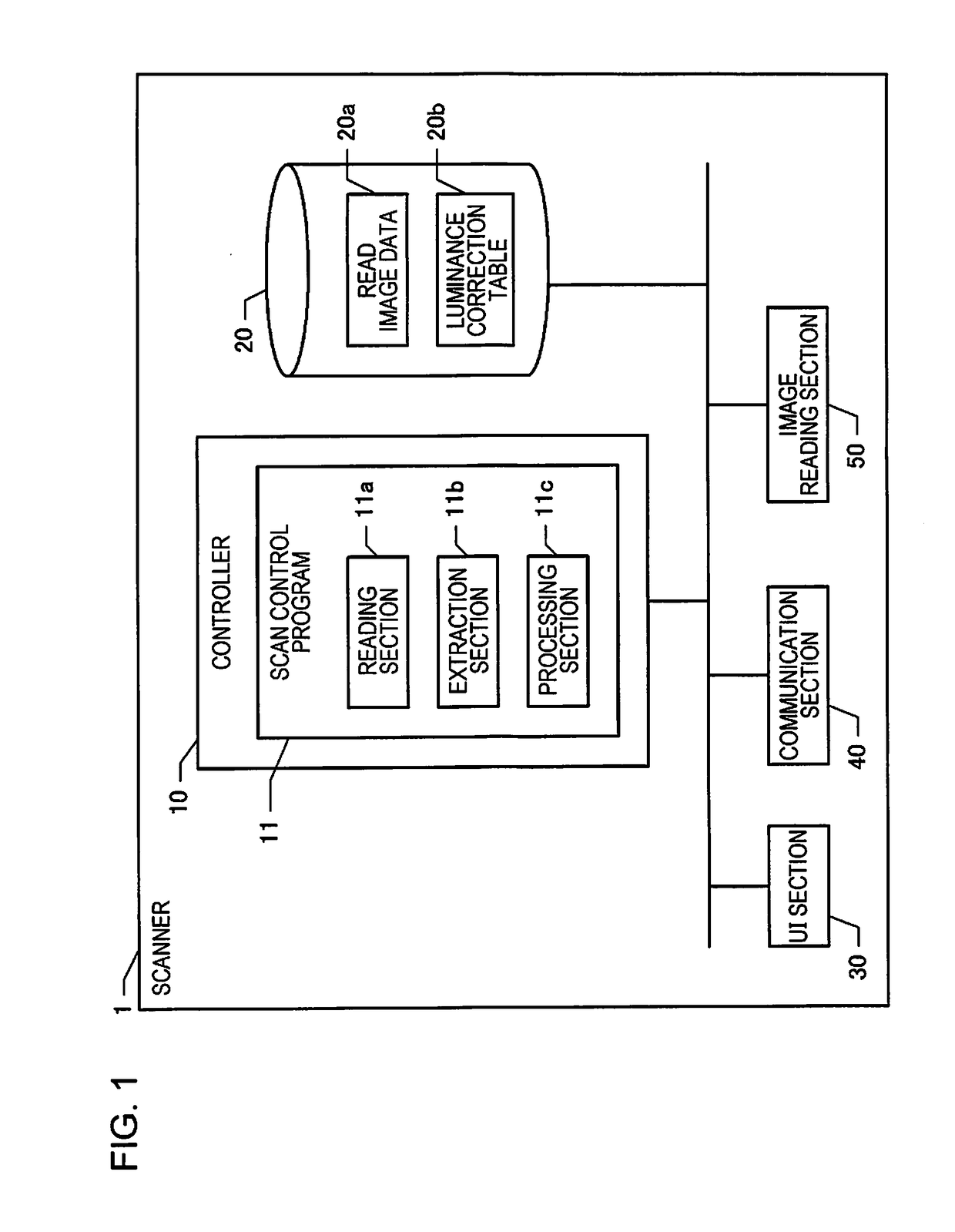
Scanner, method of producing scan data, and scan control program
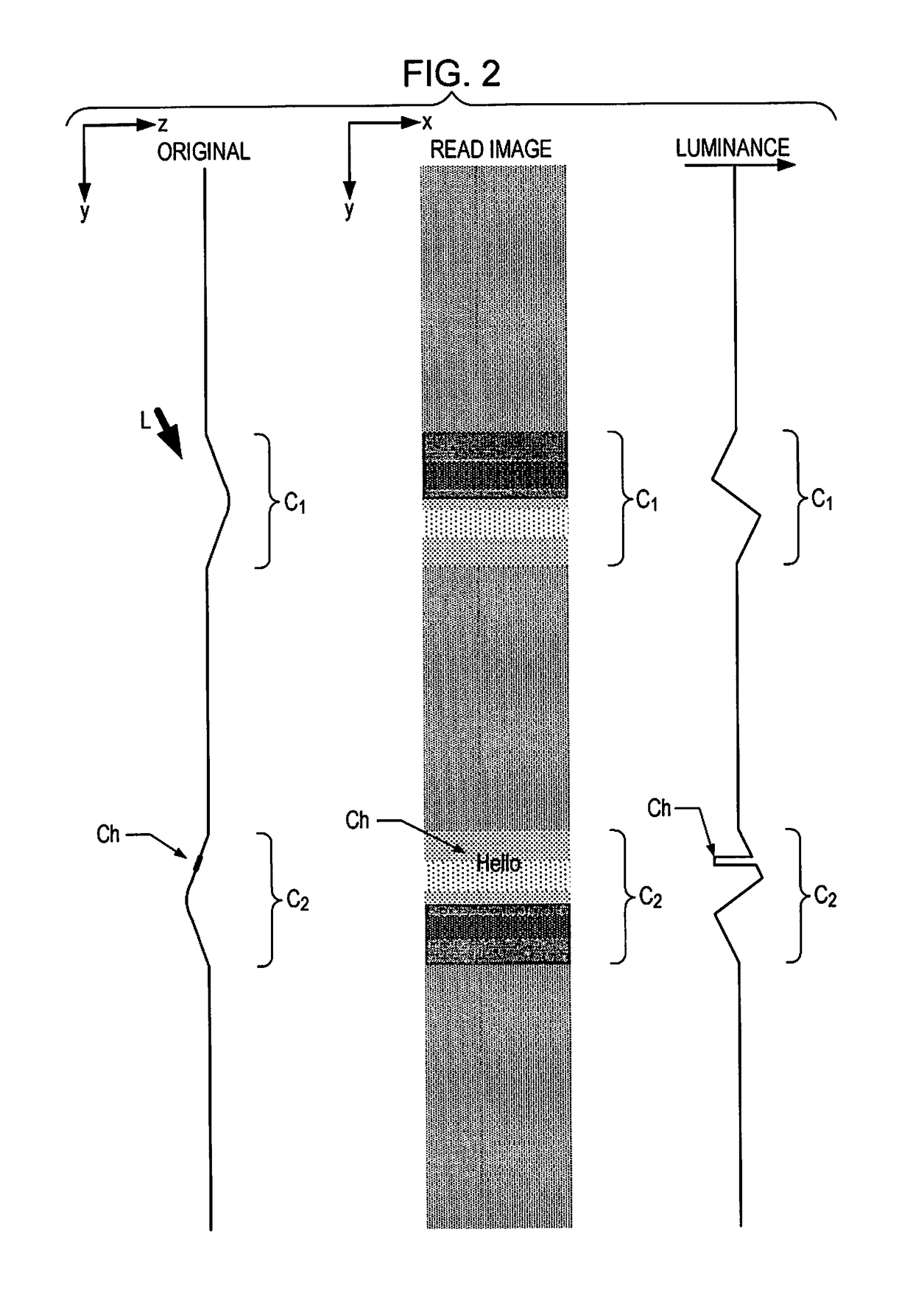
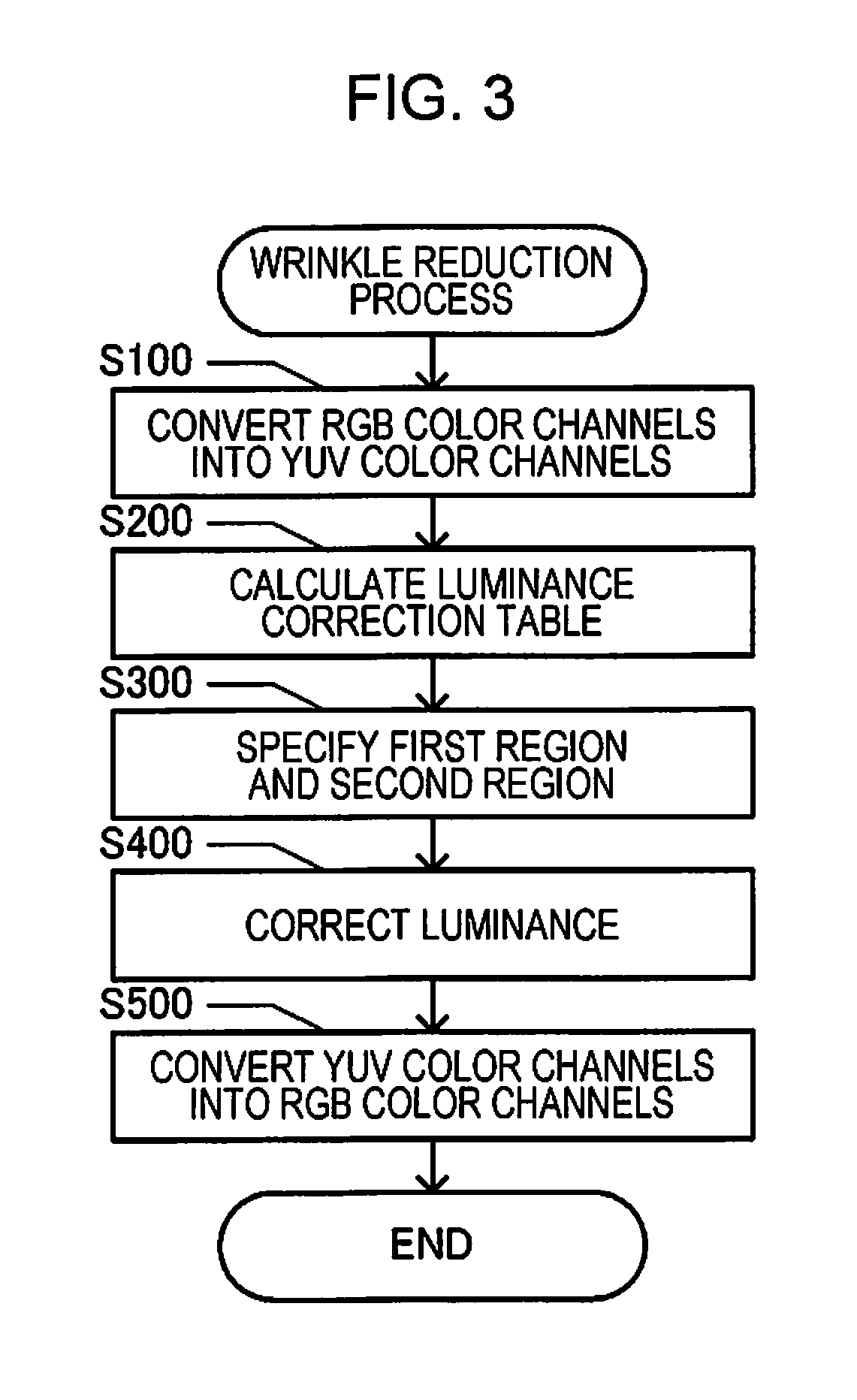
ActiveUS20190082078A1Reduce the impactIncrease brightnessPictoral communicationComputer graphics (images)Wrinkle reduction
A scanner reads an original and generates a read image, specifies a first region having a pattern on a wrinkle and a second region having a wrinkle and no pattern from the read image, and performs a wrinkle reduction process in which the wrinkle is not reduced in the first region and the wrinkle is reduced in the second region, included in the read image.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Passive-matrix display and tiling display
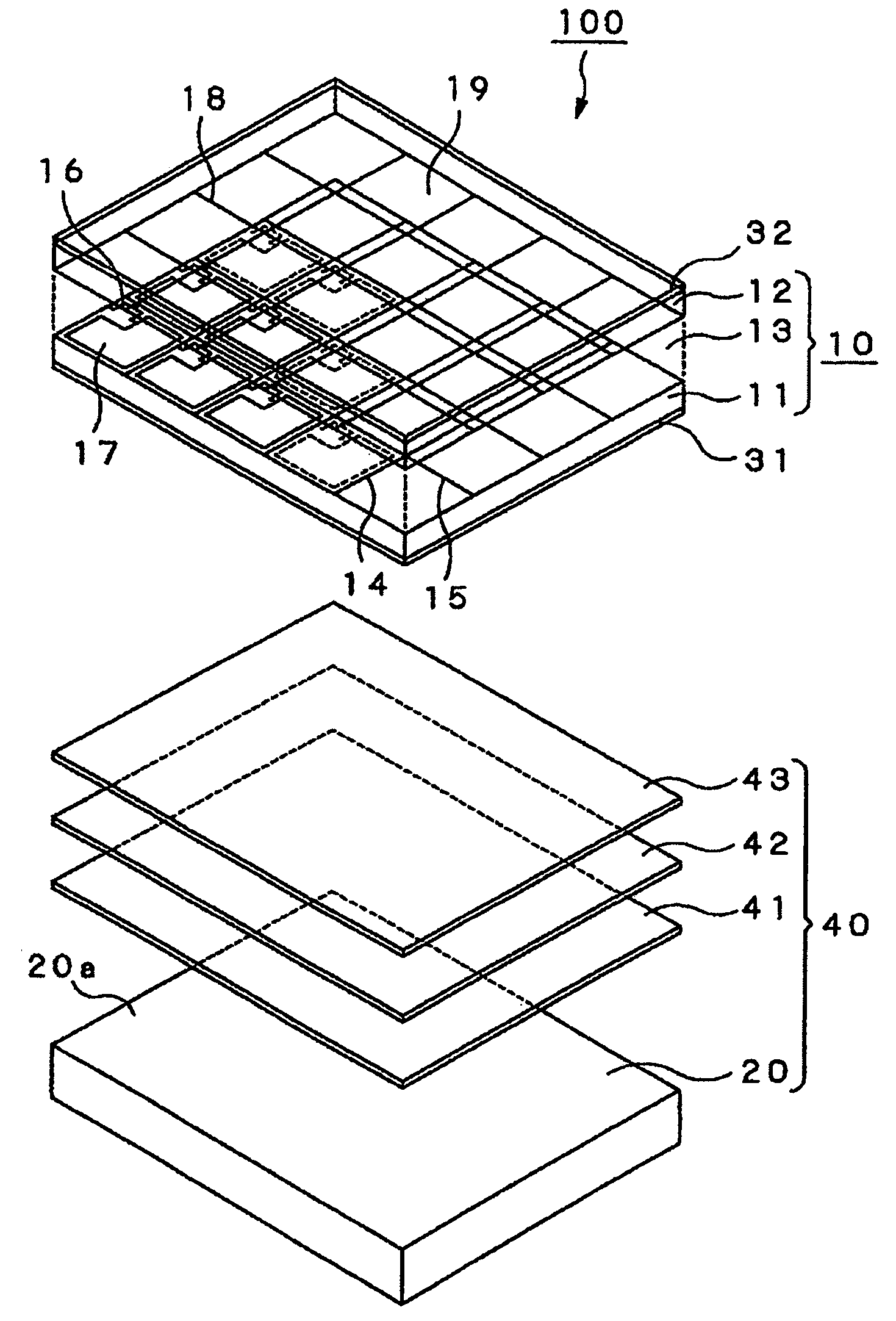
ActiveUS9240438B2Increase the number ofConnection portionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical resistance and conductanceVoltage drop
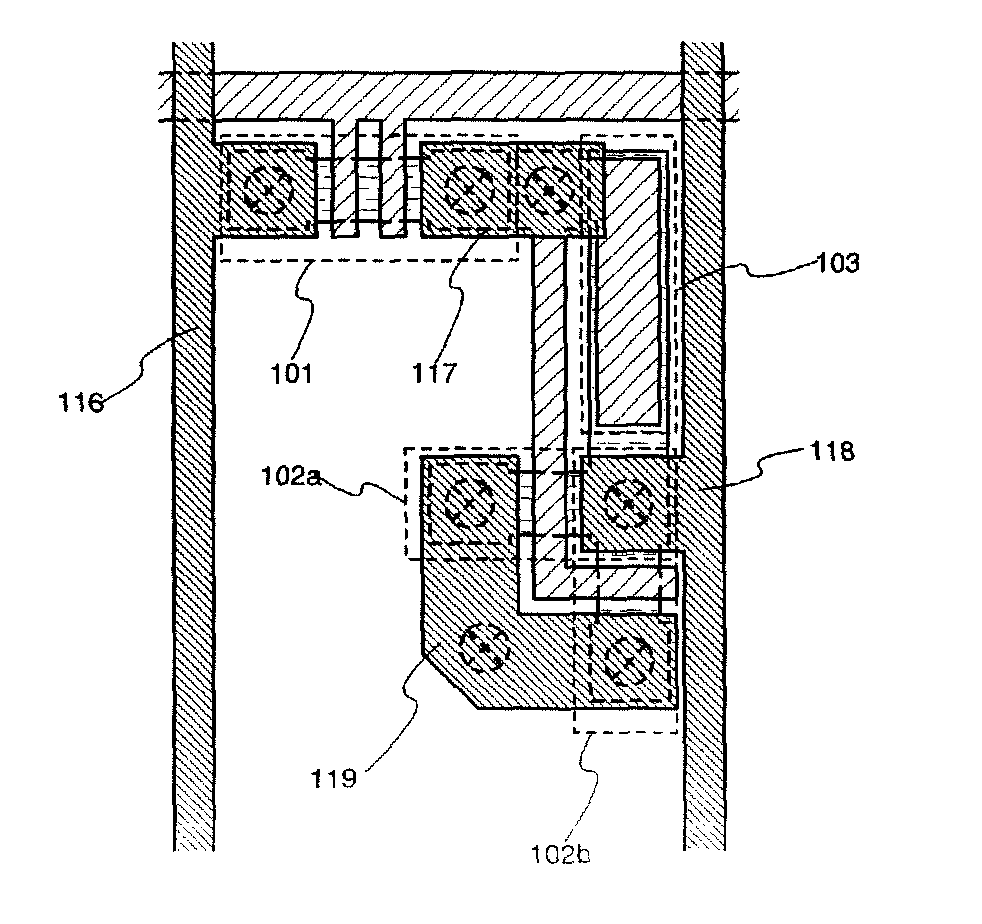
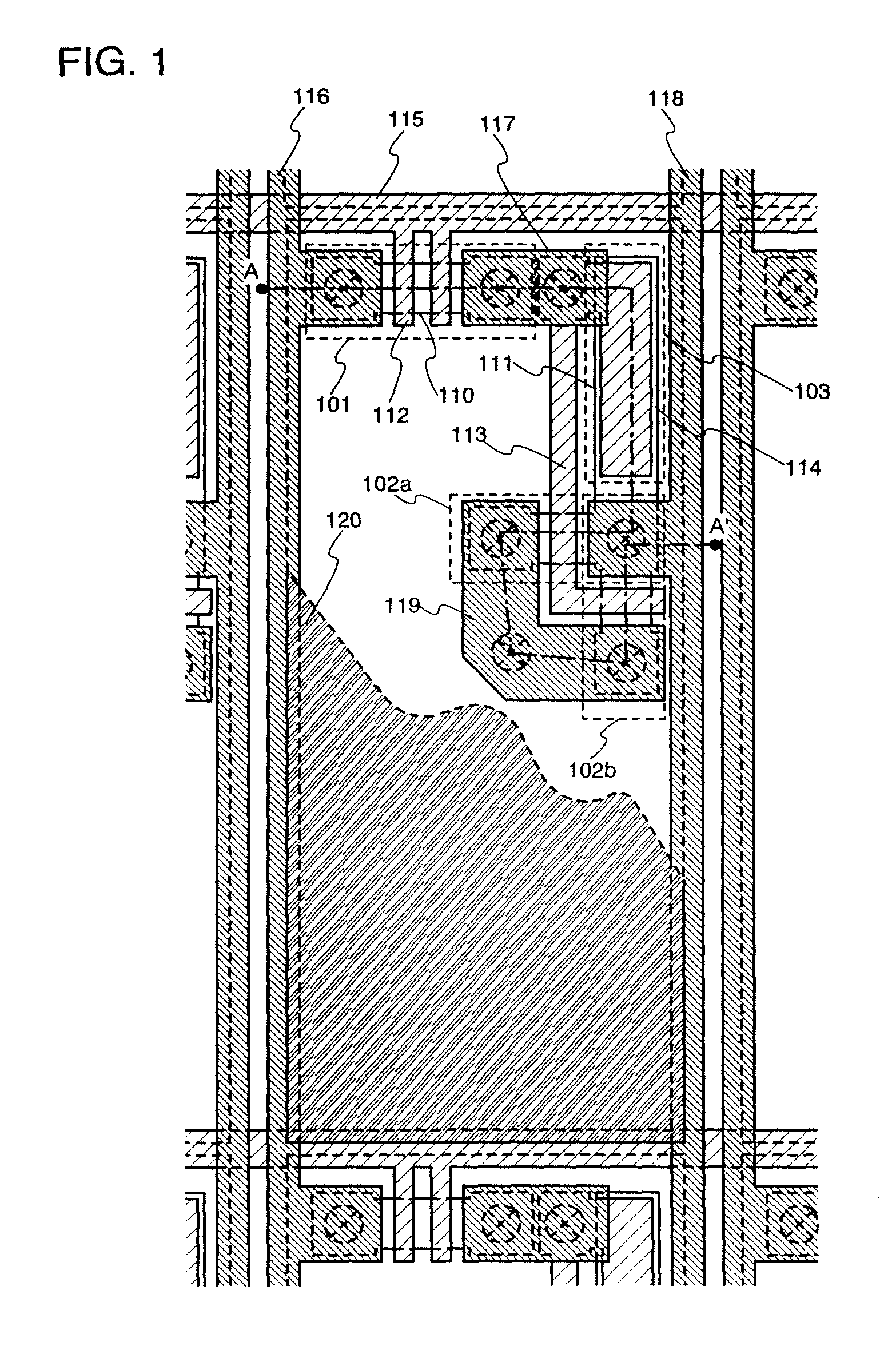
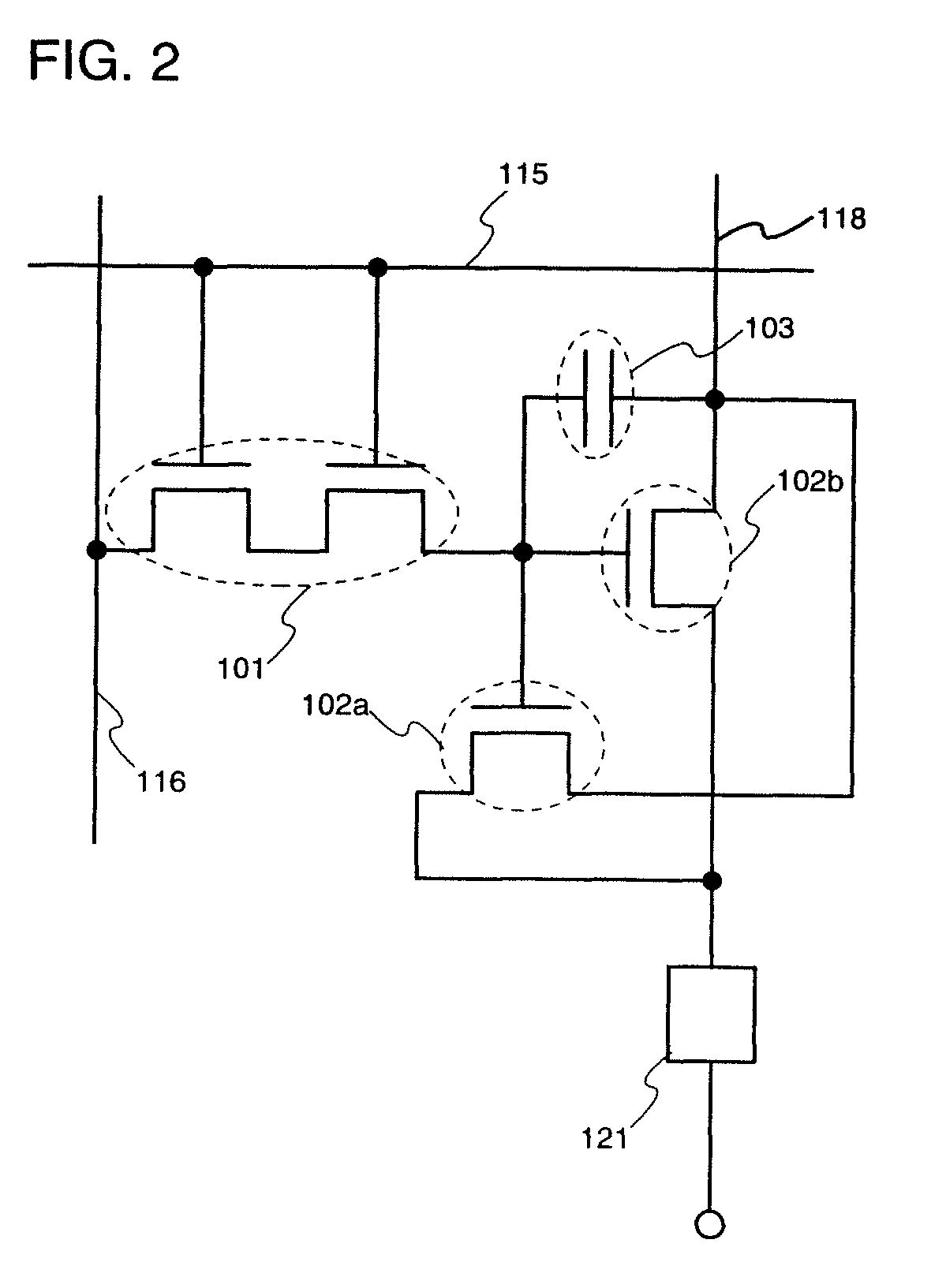
A passive-matrix display of the disclosure includes a first electrode disposed over a substrate, a second electrode disposed over the first electrode and three-dimensionally intersecting the first electrode, a first auxiliary electrode disposed between the substrate and the first electrode, three-dimensionally intersecting the first electrode and being parallel to the second electrode, and a second auxiliary electrode parallel to the first auxiliary electrode and to the second electrode, the first electrode and the first auxiliary electrode being electrically connected by a first connection portion, and the second electrode and the second auxiliary electrode being connected by a plurality of second connection portions each disposed with at least one of the first electrodes therebetween. The passive-matrix display enables voltage drop and variation in brightness to be reduced by lowering the wiring resistance of the second electrode.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com