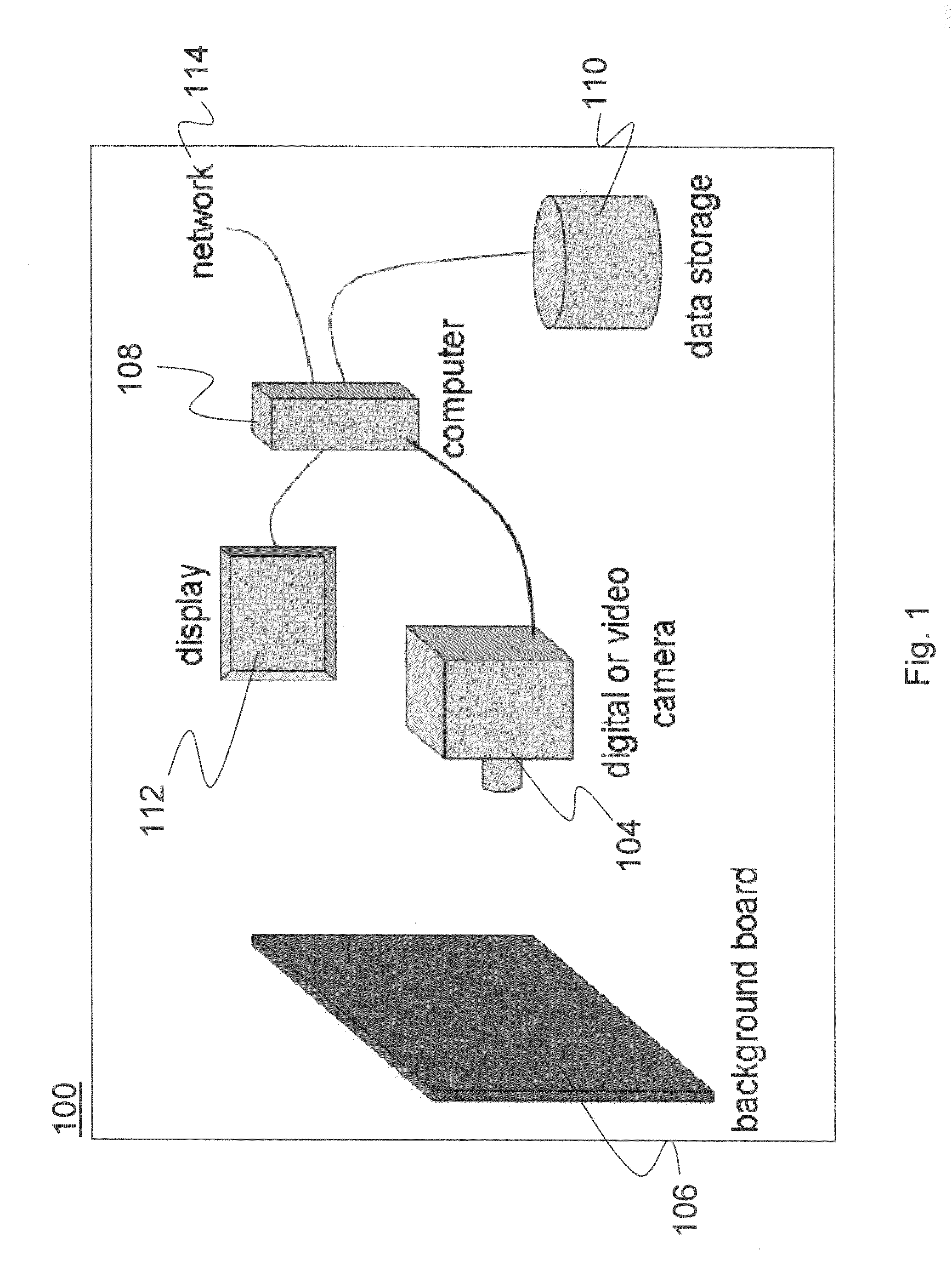
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
119results about How to "Taking image" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
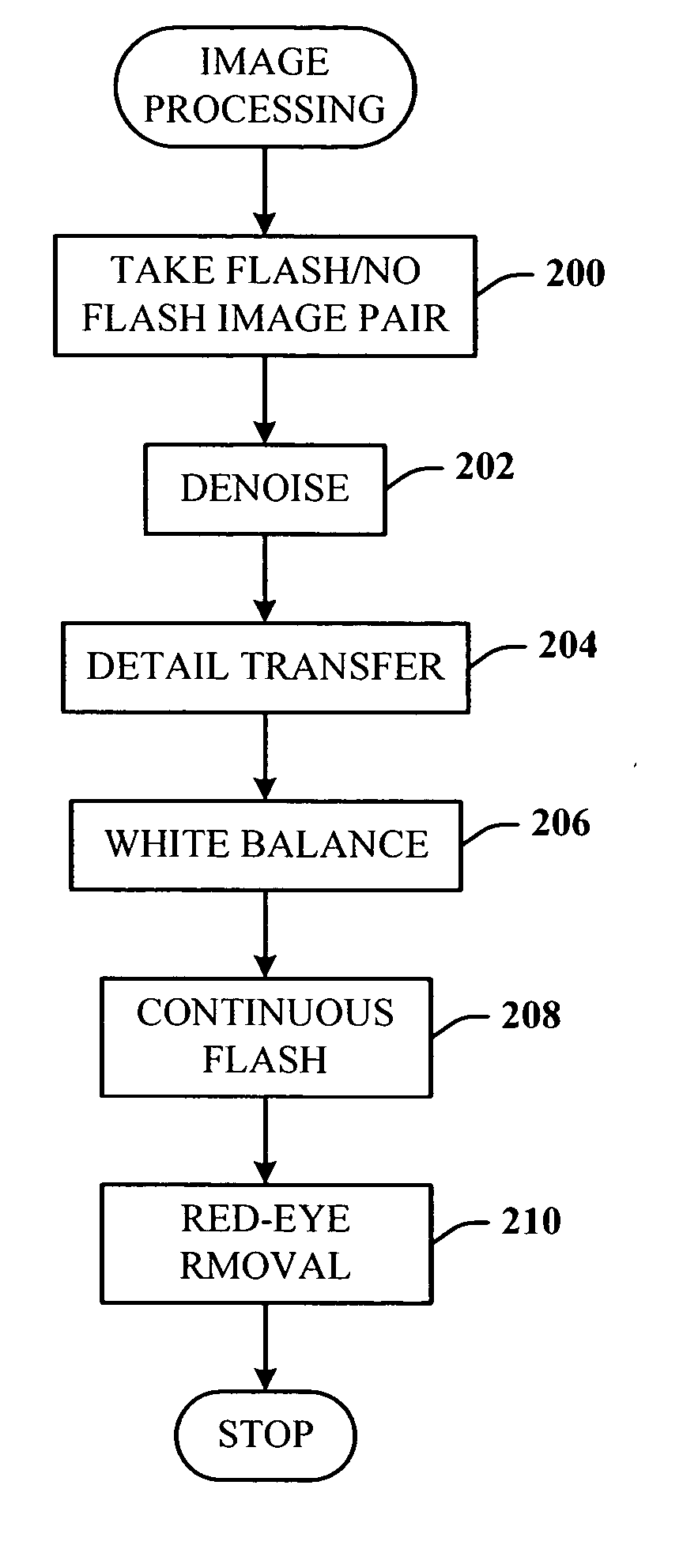
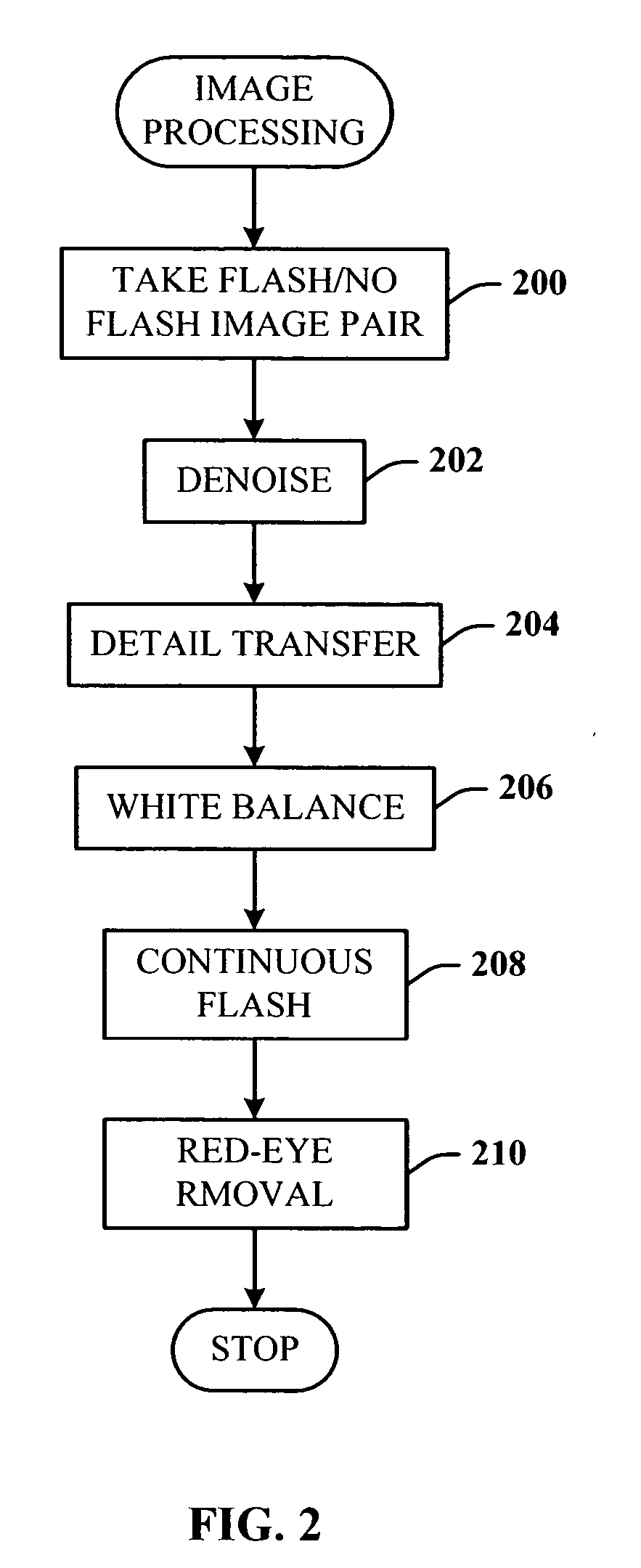
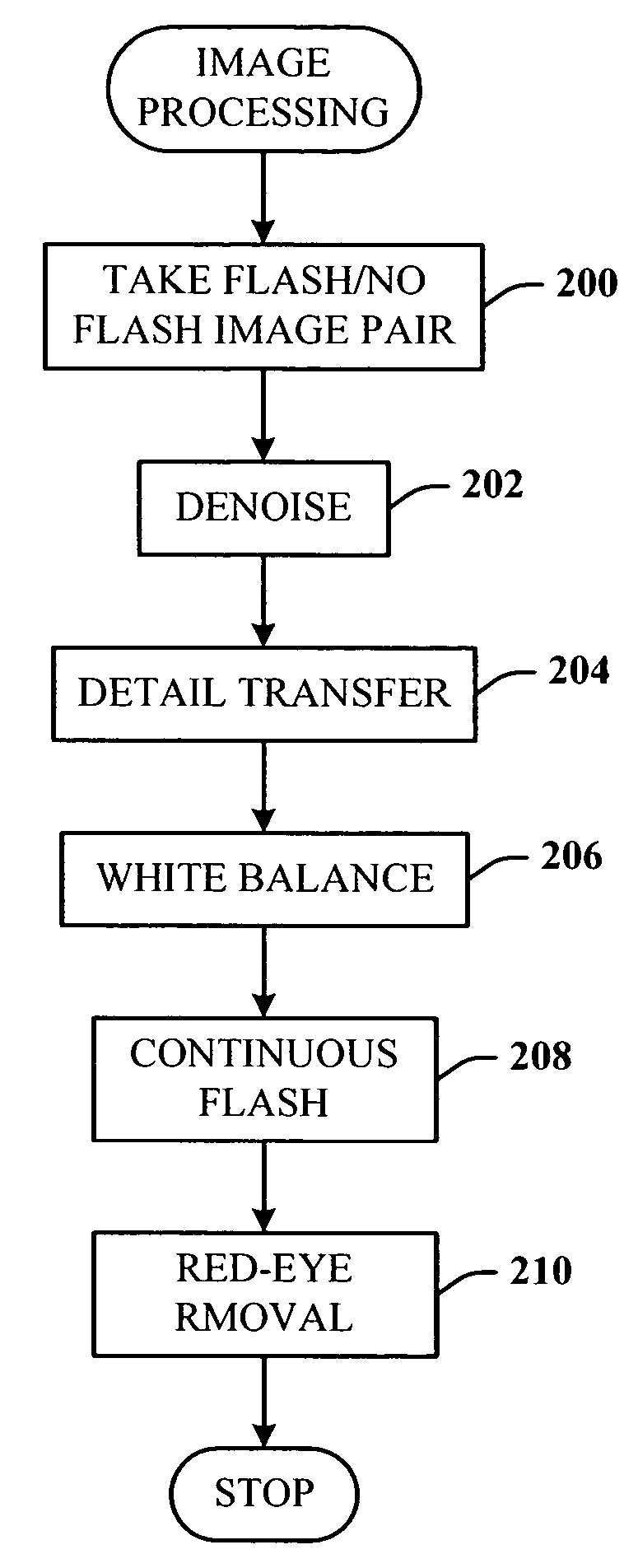
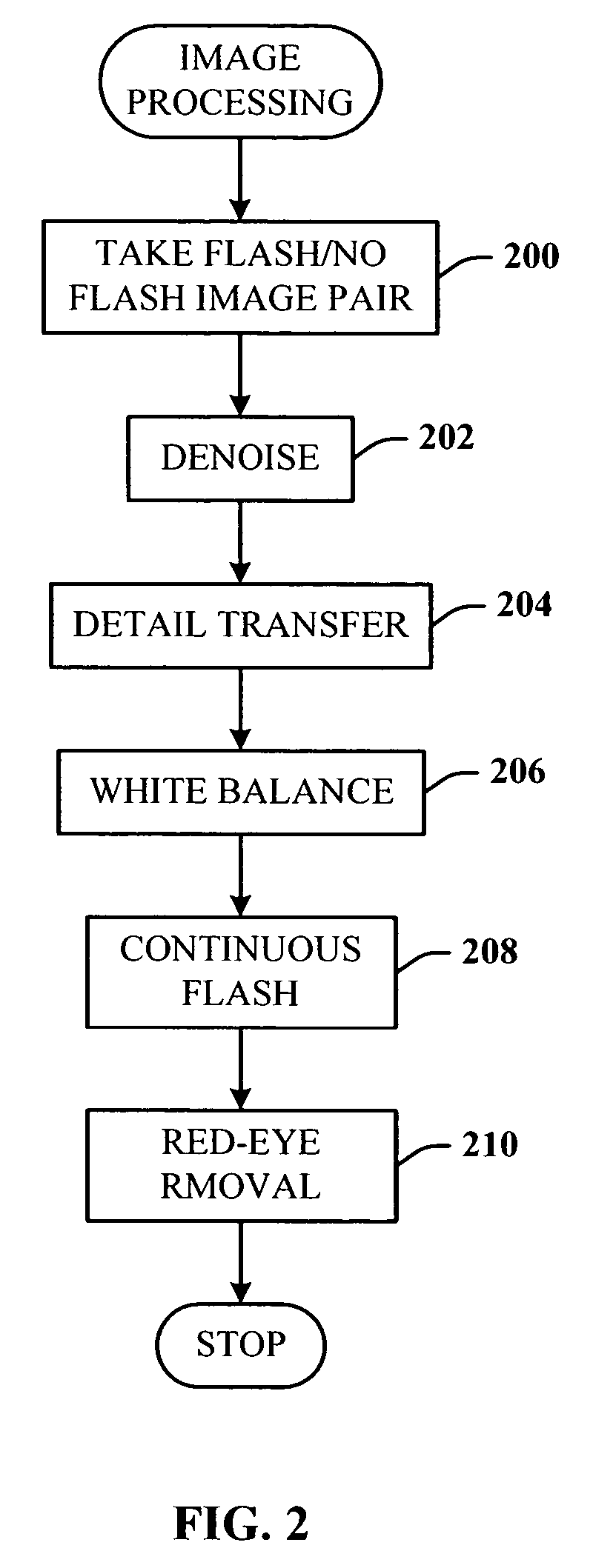
Digital photography with flash/no flash extension
InactiveUS20060008171A1Easy to optimizeTaking imageTelevision system detailsImage enhancementImage pairFlash light
A system and method for improving digital flash photographs. The present invention is a technique that significantly improves low-light imaging by giving the end-user all the advantages of flash photography without producing the jarring look. The invention uses an image pair—one taken with flash the other without—to remove noise from the ambient image, sharpen the ambient image using detail from the flash image, correct for color, and remove red-eye.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
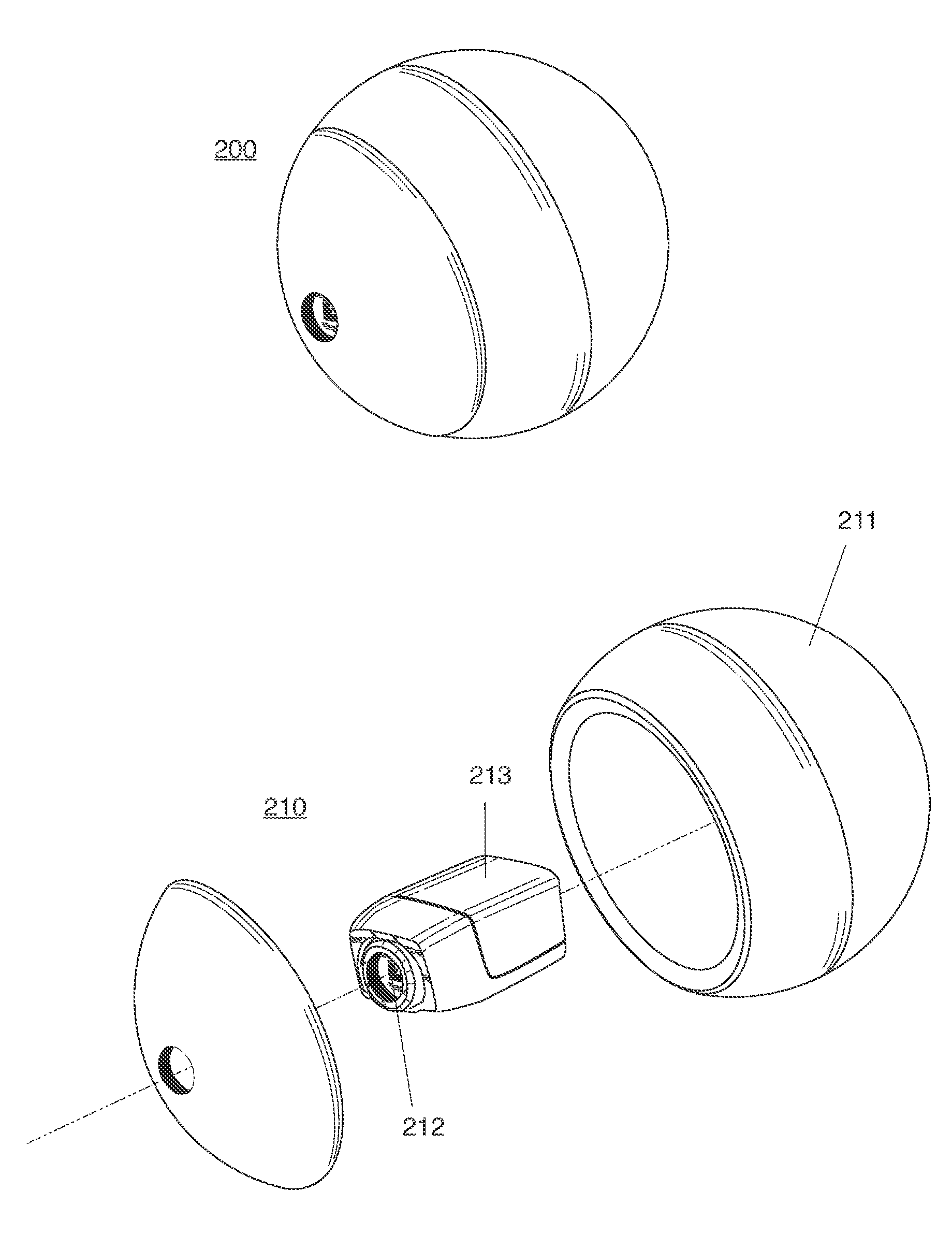
Ball with camera for reconnaissance or recreation and network for operating the same
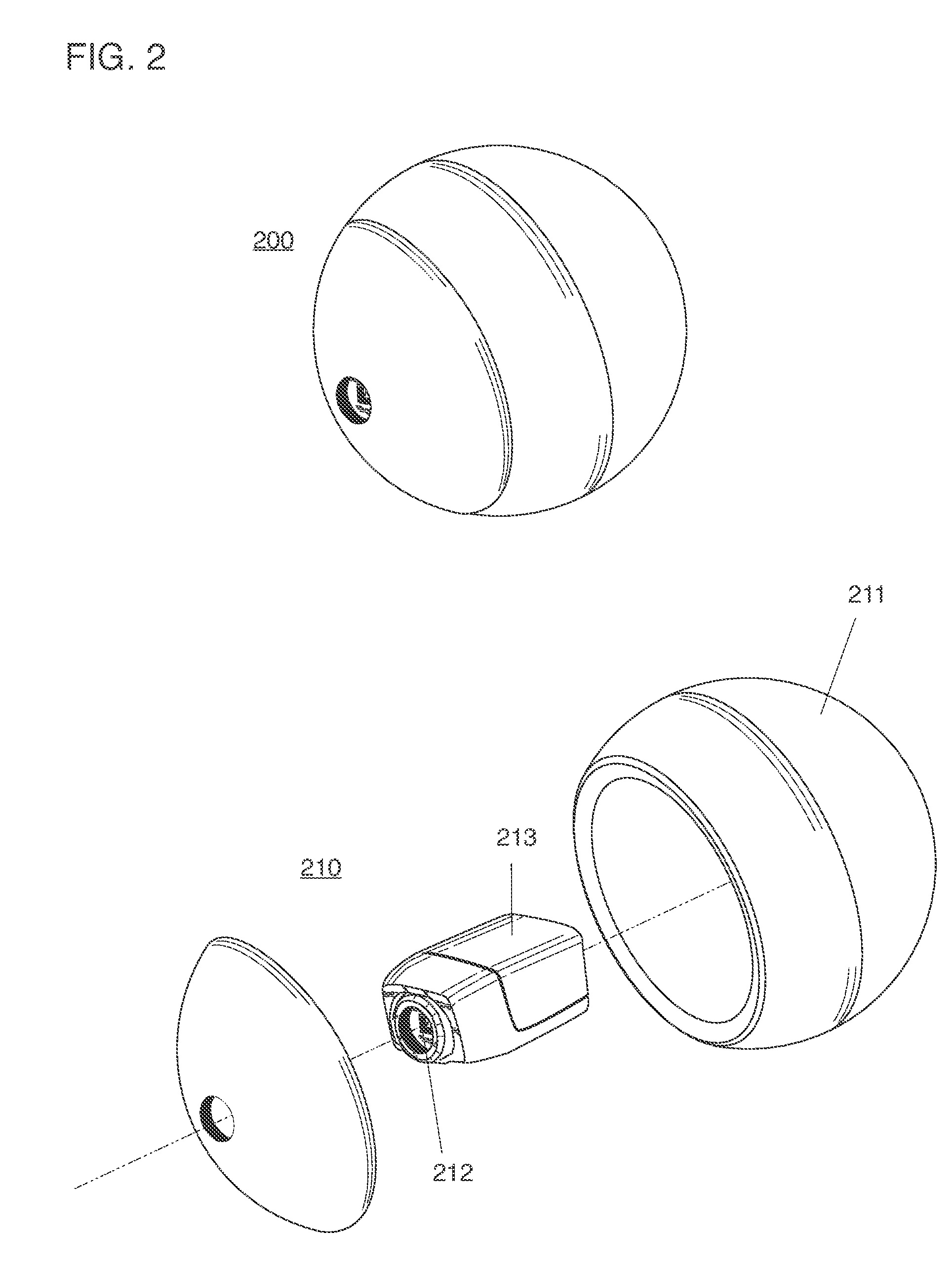
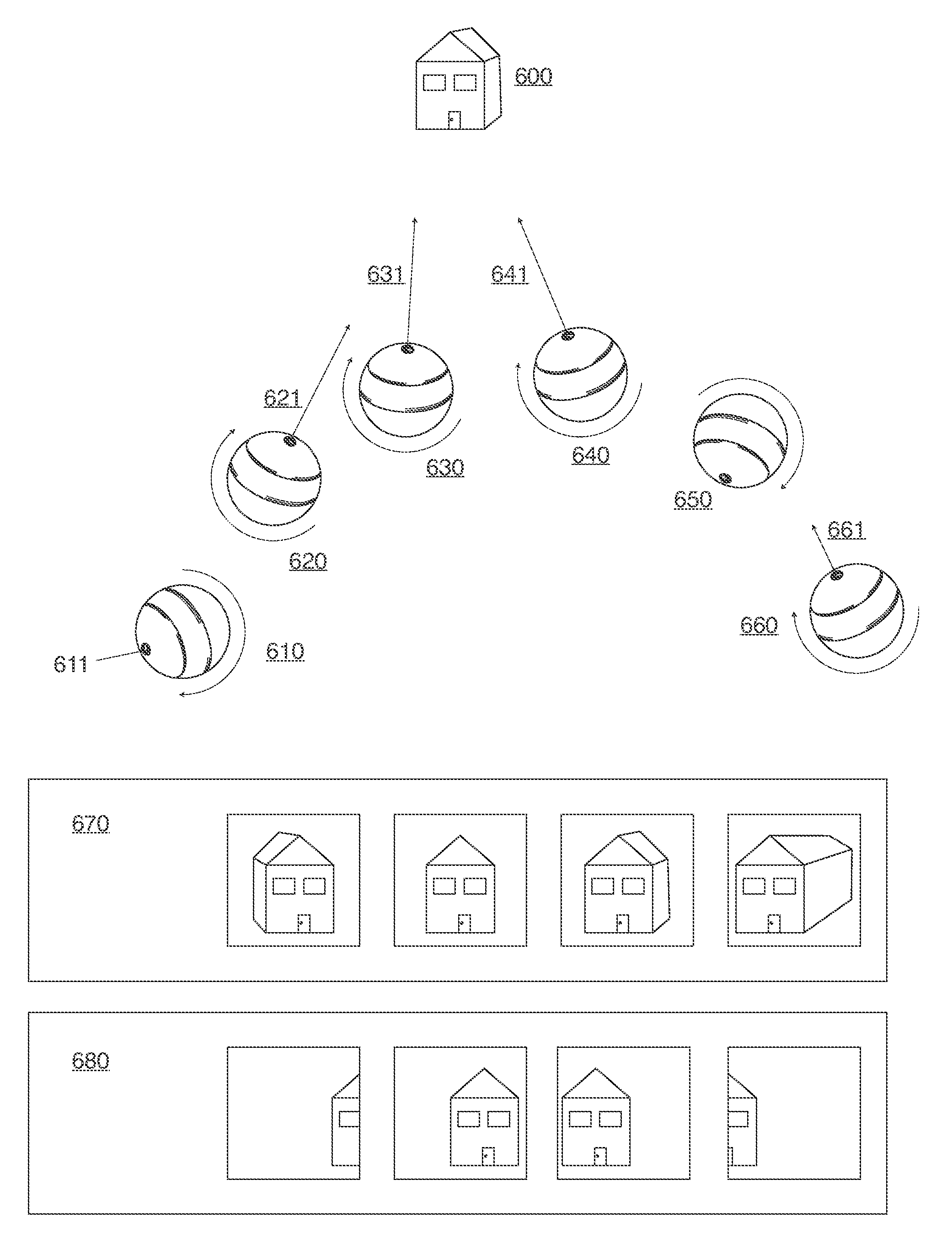
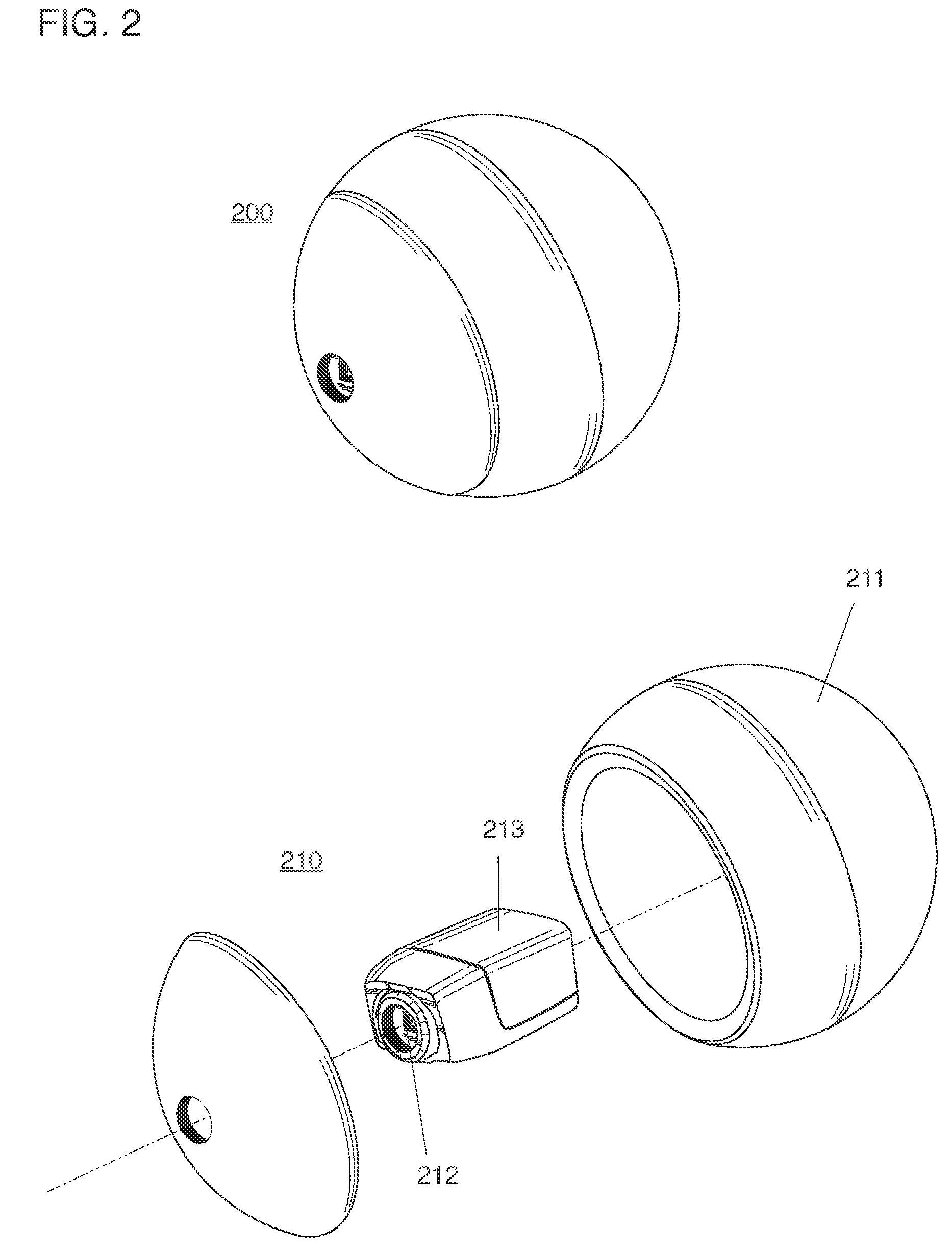
ActiveUS20130210563A1Taking imageEasy to trackTelevision system detailsHollow inflatable ballsRecreationImage capture
A ball-shaped camera thrown or projected into an airborne trajectory, and an image capture system with network devices collaborating for the purpose of generating panoramic images and video sourced from network ball cameras, and ball cameras capable of capturing stable image and video while spinning, spiraling or precessing through a trajectory.
Owner:HOLLINGER STEVEN J
Systems and methods for centering a photograph without viewing a preview of the photograph
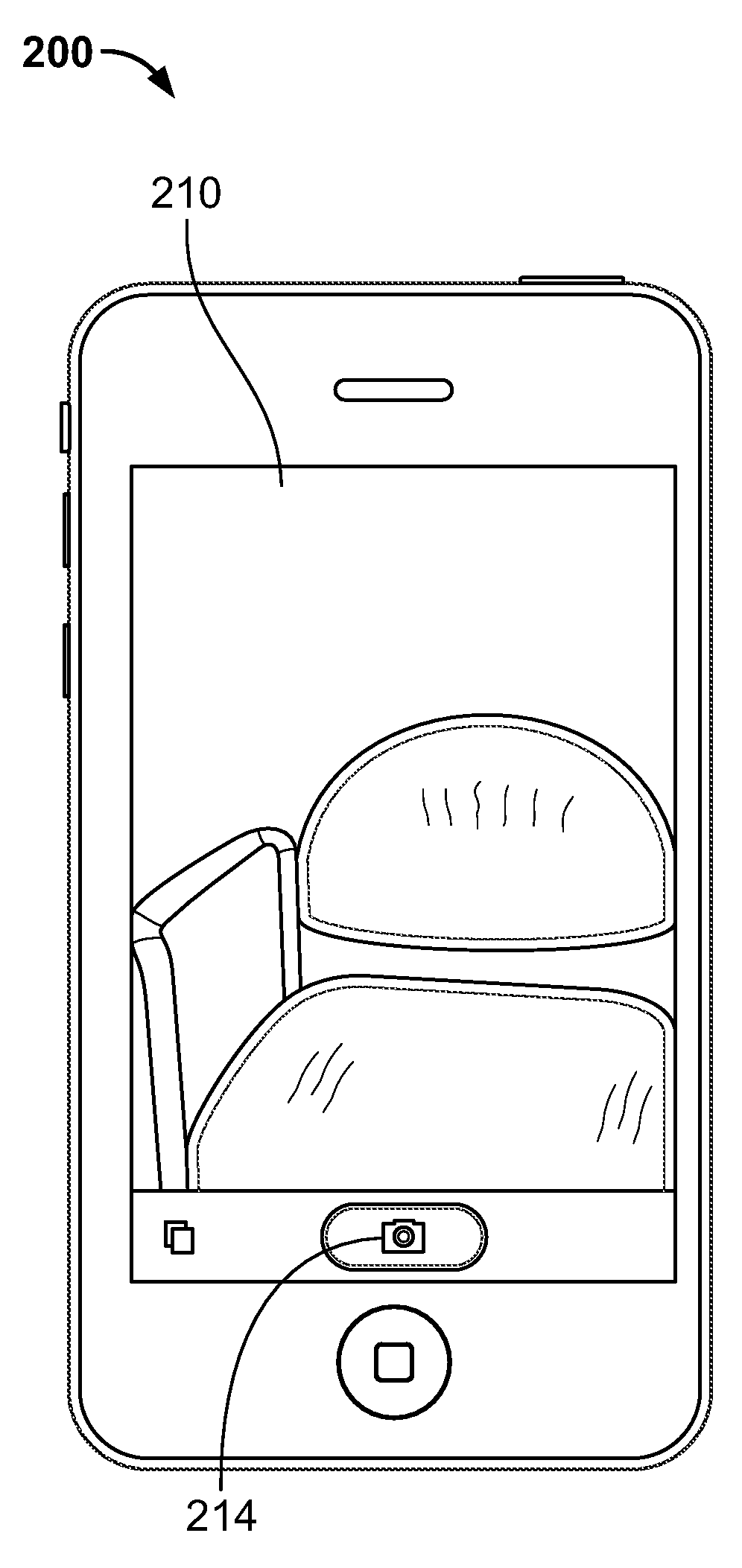
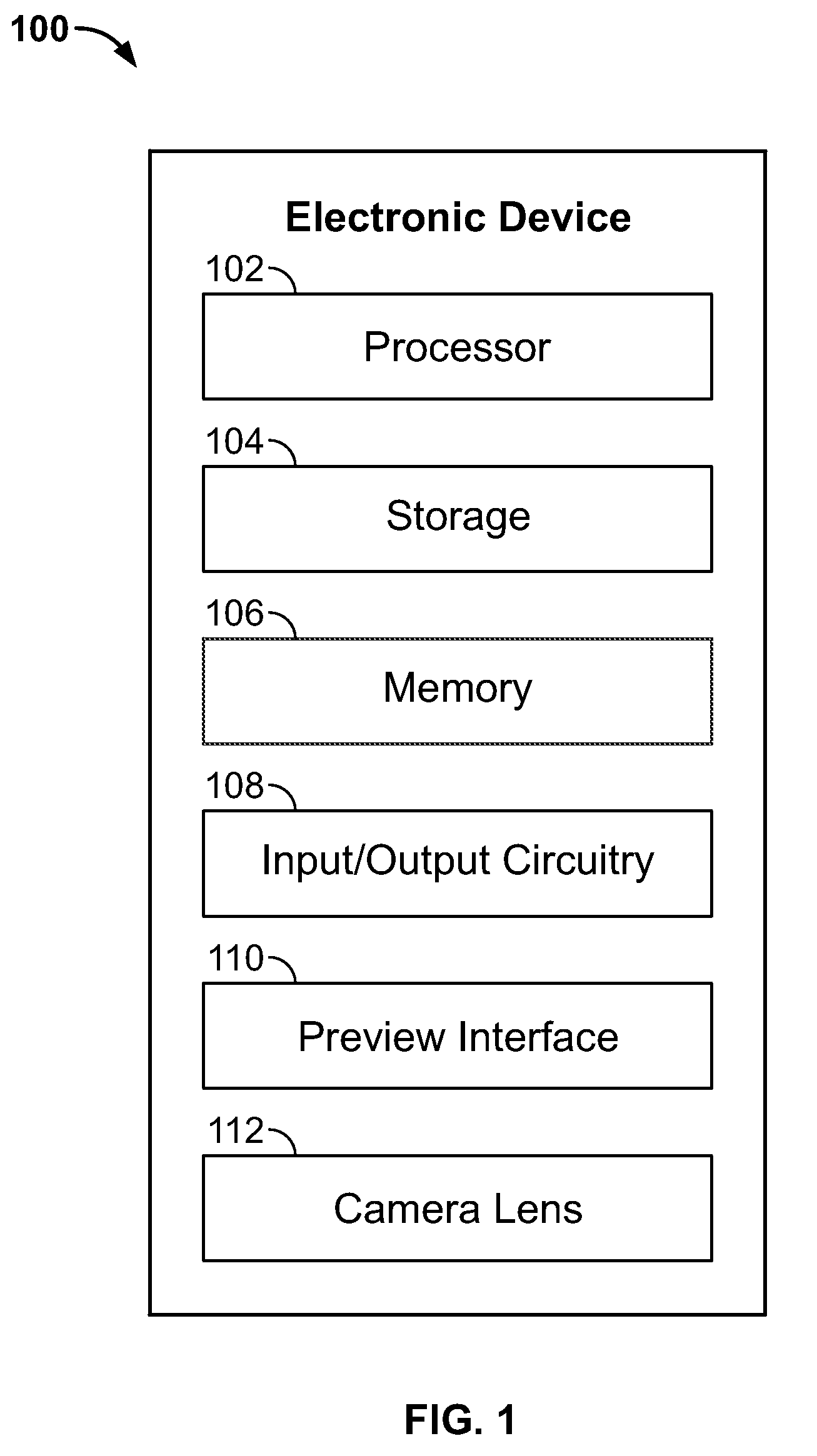
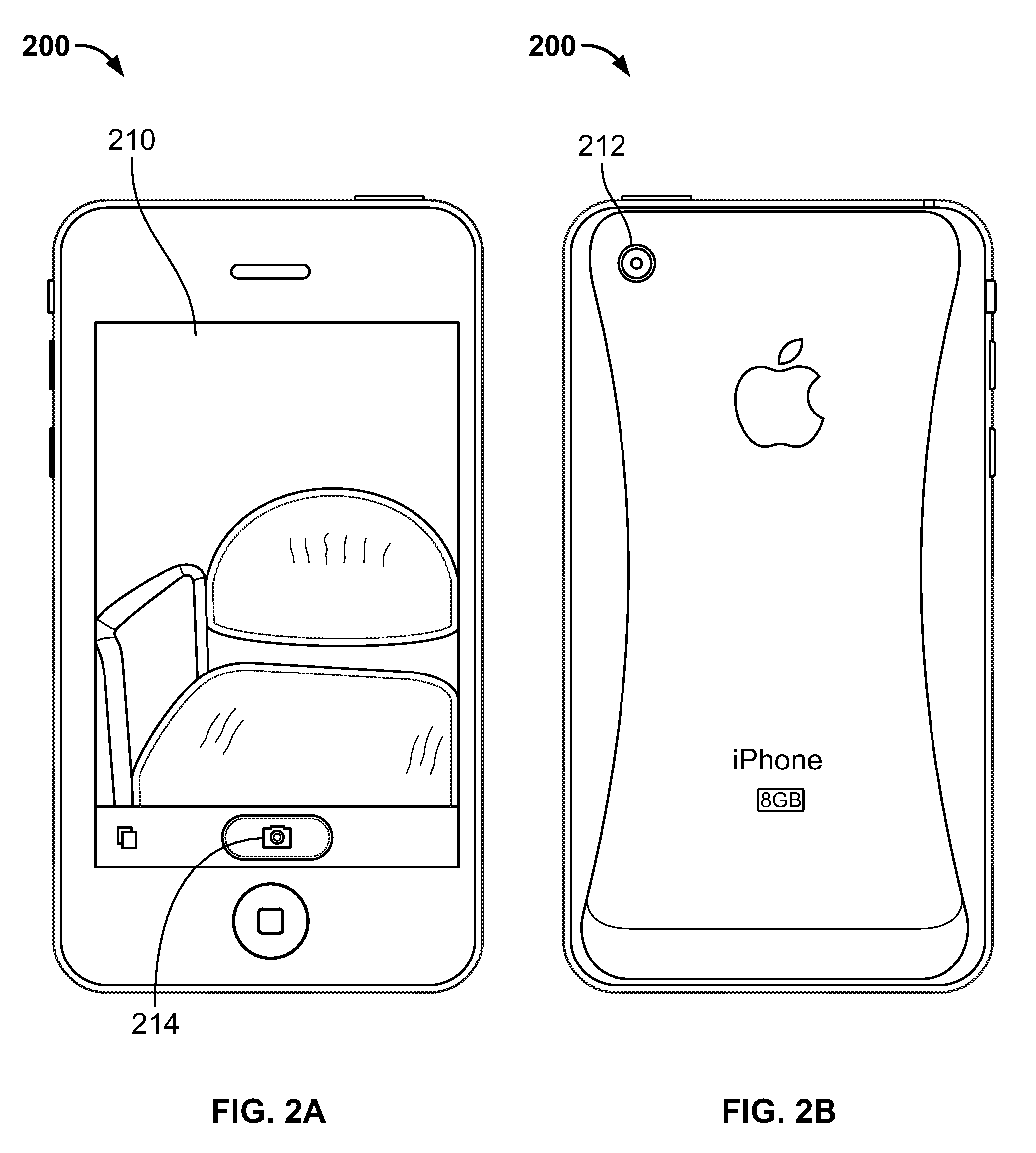
InactiveUS20100225773A1Enhance photographTaking imageTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionCamera lensMotion sensing
Systems and methods are providing for capturing images of objects or faces without previewing the image to be captured. In particular, systems and methods are provided for using a detection algorithm to determine when a camera lens of an electronic device is properly oriented to capture an item (e.g., a face in a self-portrait). The detection algorithm can be configured to identify specific faces or objects, and can direct the electronic device to automatically store a captured image in response to detecting objects or faces of interest. In some embodiments, a motion-sensing component can be used to help align the lens.
Owner:APPLE INC
Liquid crystal display
ActiveUS20100156825A1Improve accuracyIncrease ratingsStatic indicating devicesInput/output processes for data processingLiquid-crystal displayComputer science
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
3D medical anatomical image system using 2d images
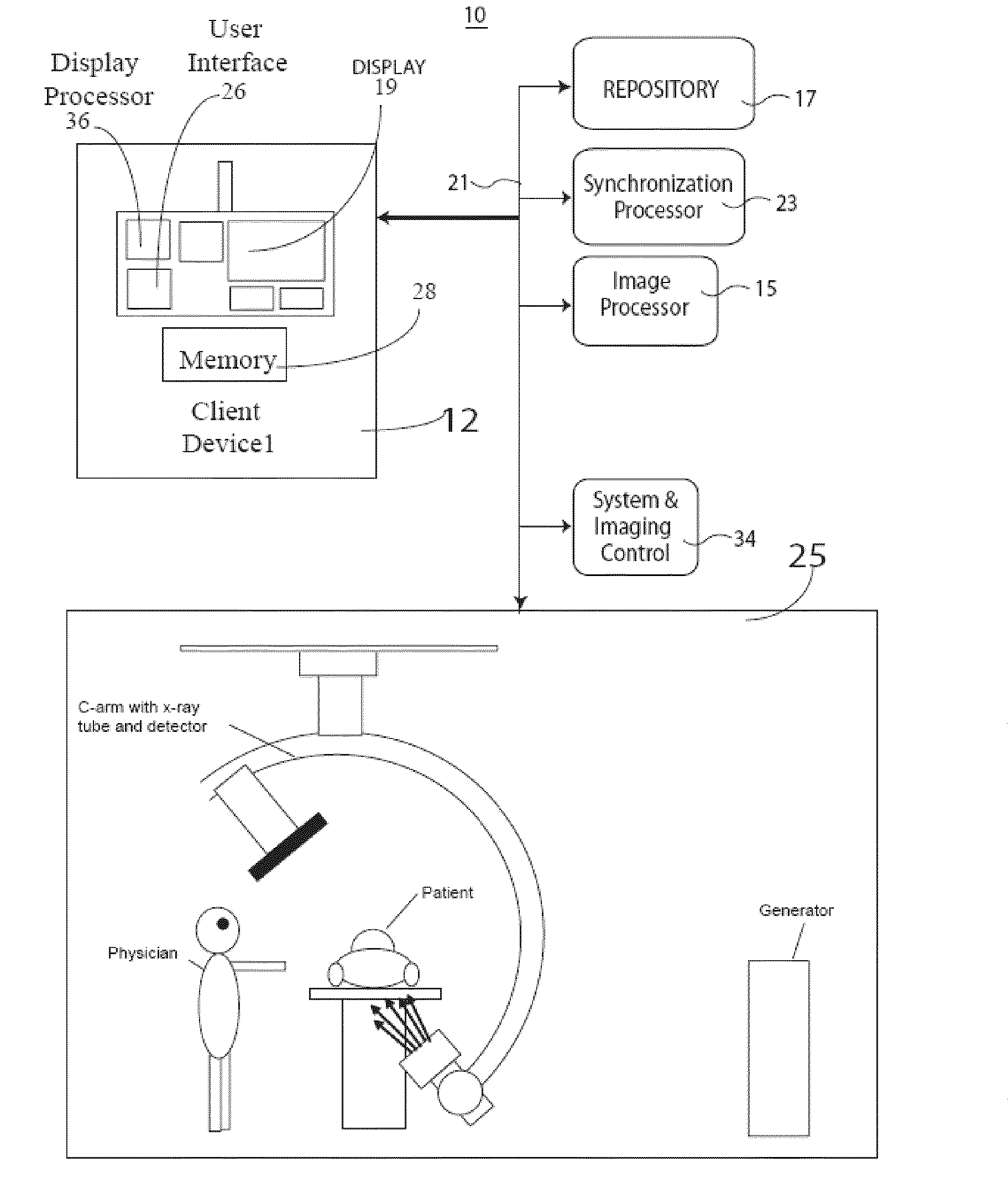
ActiveUS20100086099A1Reduce x-ray exposureIncrease quality of imageReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation exposureMedical imaging
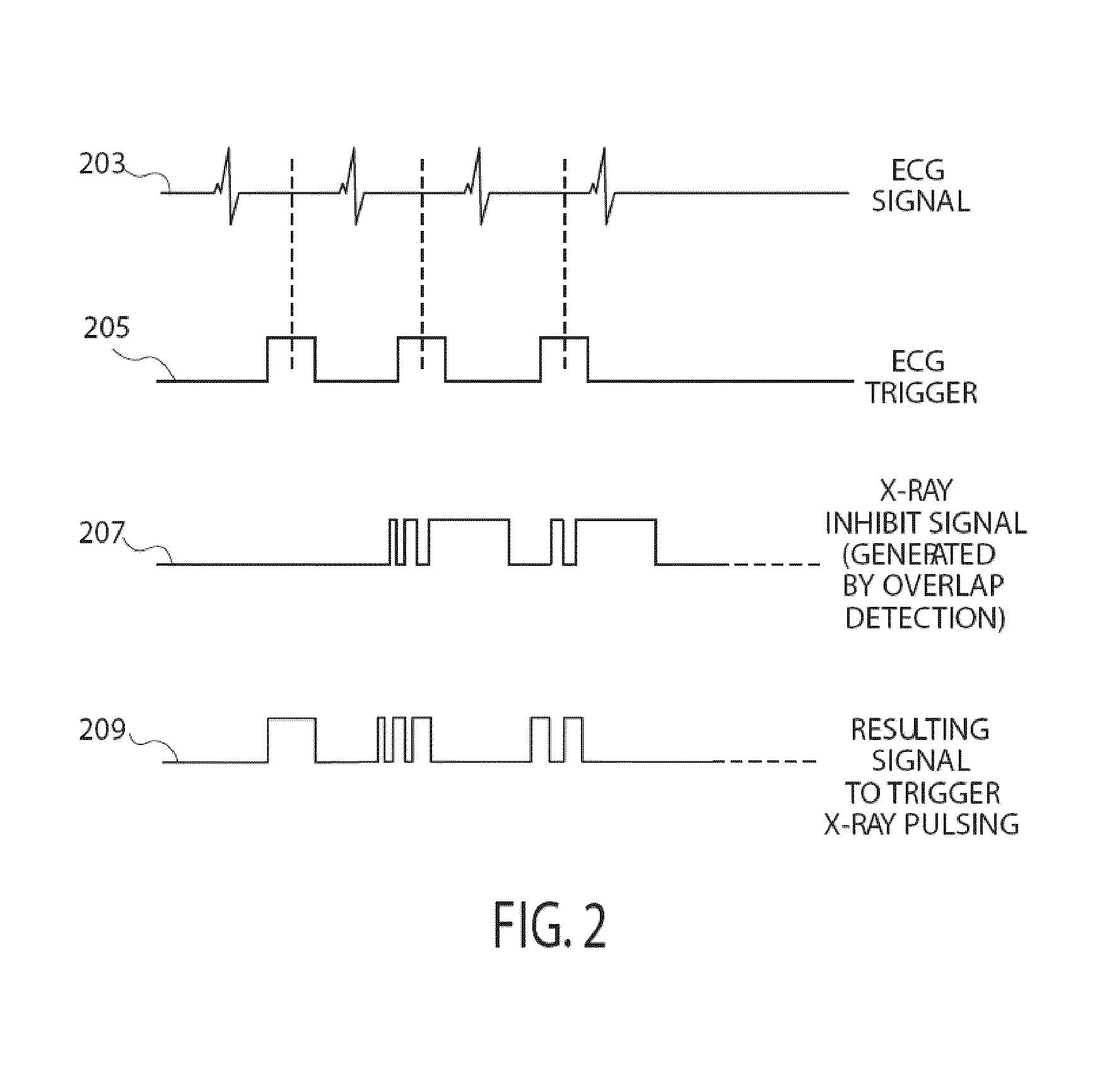
A medical imaging system generates 3D anatomical images from acquired 2D anatomical images. The system includes a synchronization processor for providing a synchronization signal identifying a particular phase of heart operation of a particular patient. An image acquisition device acquires 2D anatomical images of a patient heart in angularly variable imaging planes over multiple different heart cycles at the particular phase of heart operation in response to the synchronization signal and in response to recorded data indicating imaging previously being performed at particular imaging plane angles. An image processor stores the recorded data to prevent imaging overlap at the particular imaging plane angles and to prevent unnecessary radiation exposure of the patient. The image processor processes 2D images acquired by the image acquisition device of the patient heart in multiple different imaging planes having relative angular separation, to provide a 3D image reconstruction of the patient heart
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method for generating a focused image of an object
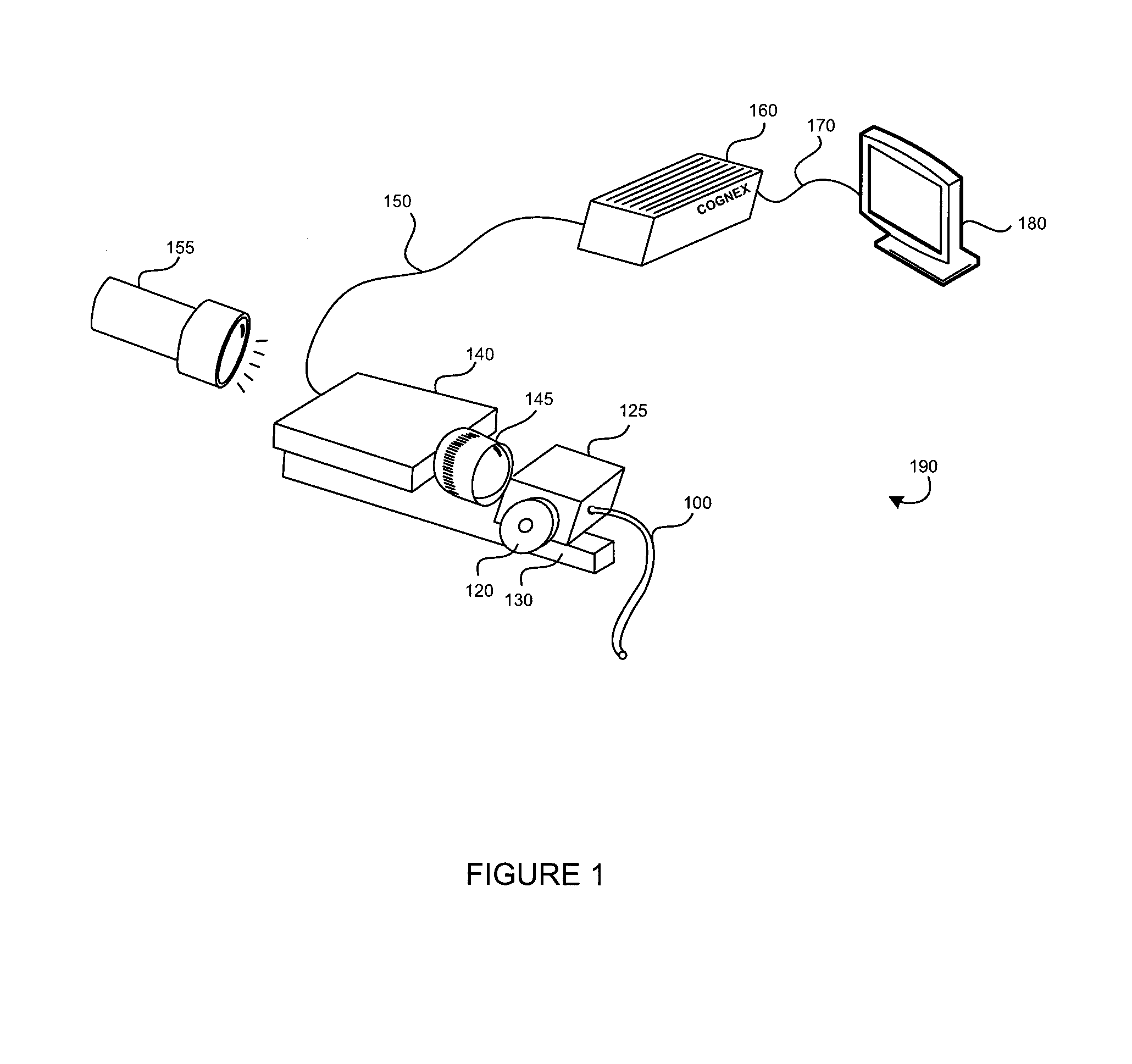
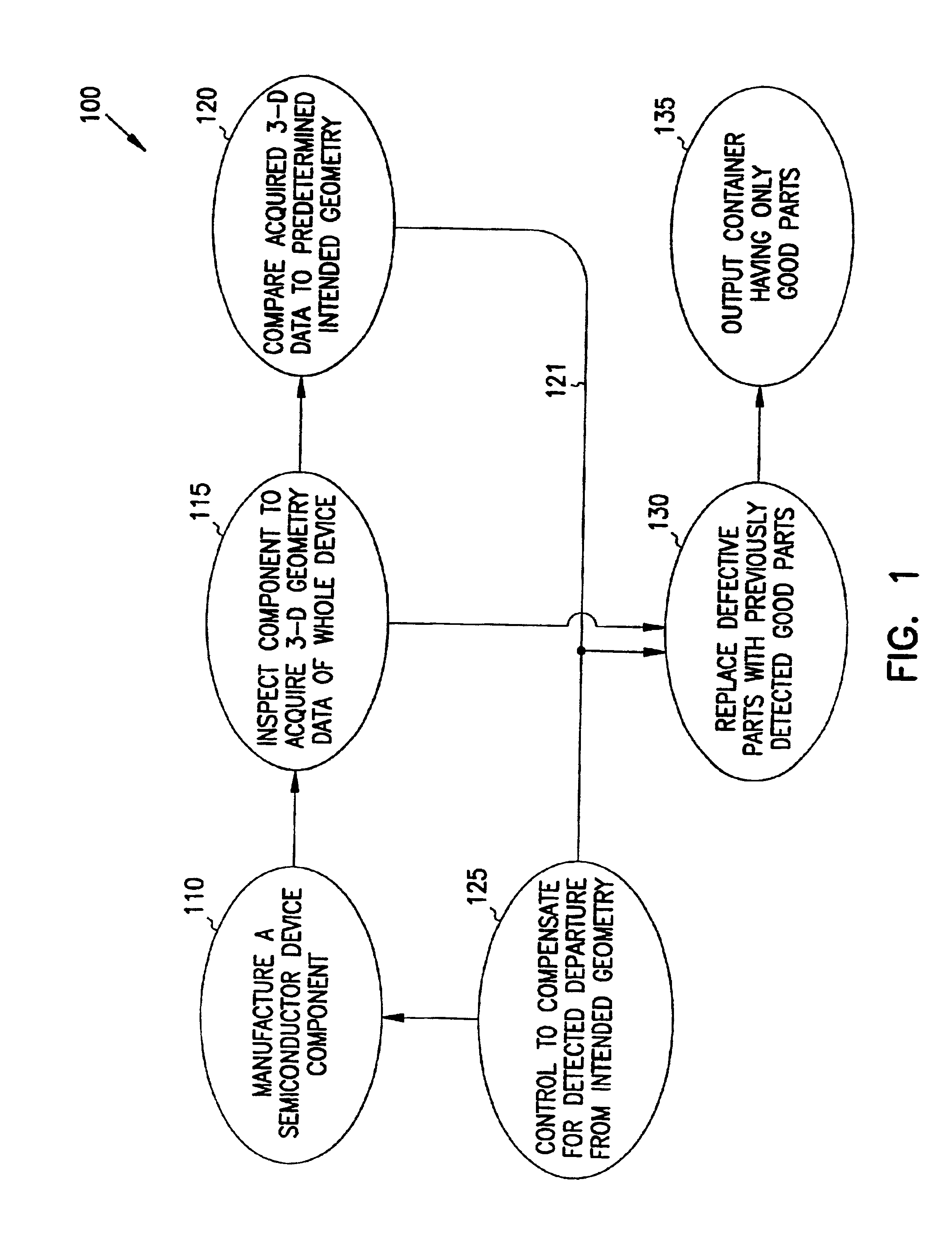
InactiveUS7221805B1Reduce measurementTaking imageTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionMachine visionAcutance
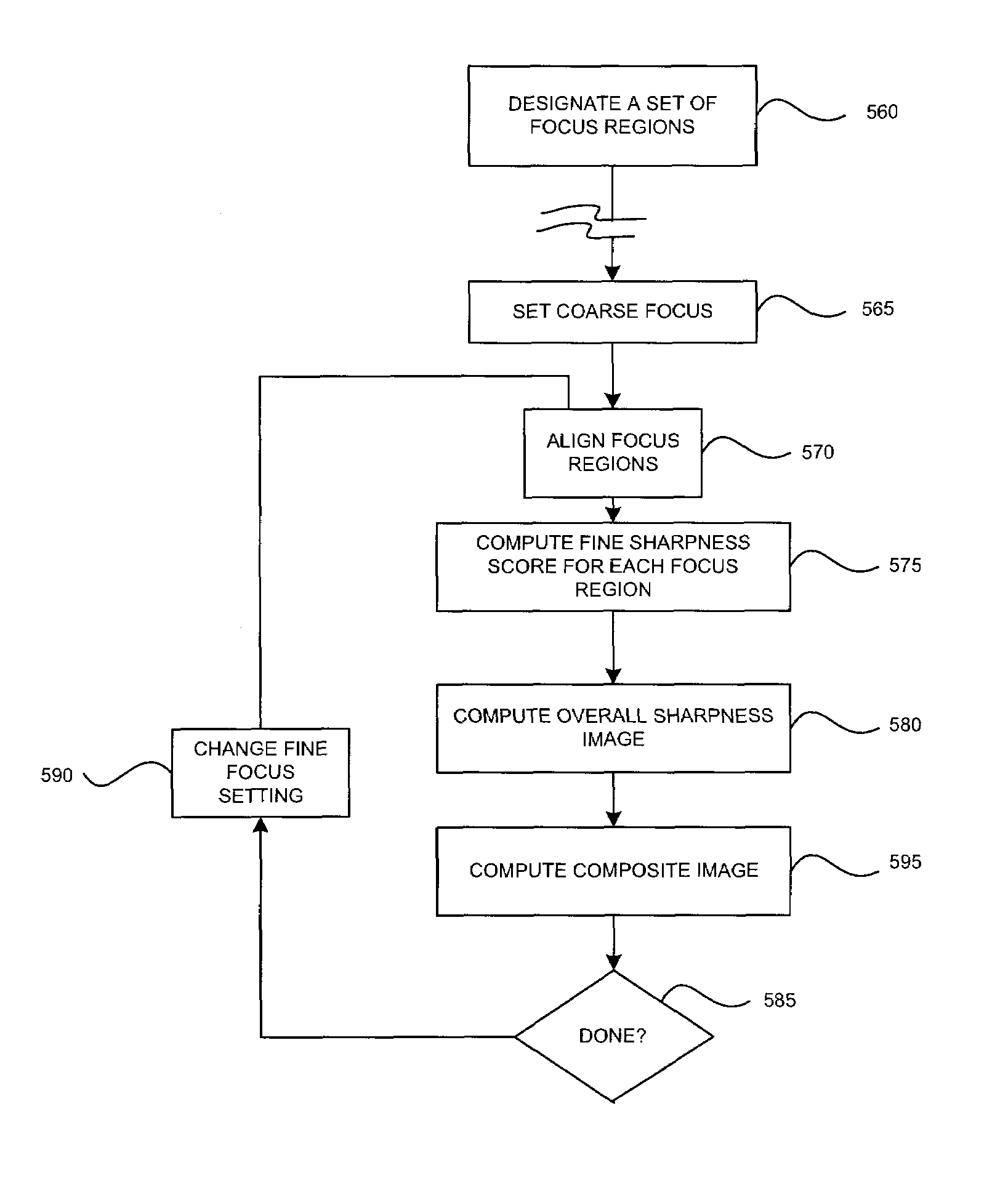
A method is provided for computing a composite image representing a focused image of an object in an application of machine vision in an optical inspection system. An image tessellated into focus regions is evaluated by region for fine feature sharpness. A sharpness image is computed for each focused region using a fine feature sharpness measurement. A focused composite image is computed by combining as a weighted average, the images at several focus settings, using the sharpness image at each focus setting as the weight. The focused composite image can be further analyzed, inspected, or otherwise processed.
Owner:COGNEX TECH & INVESTMENT
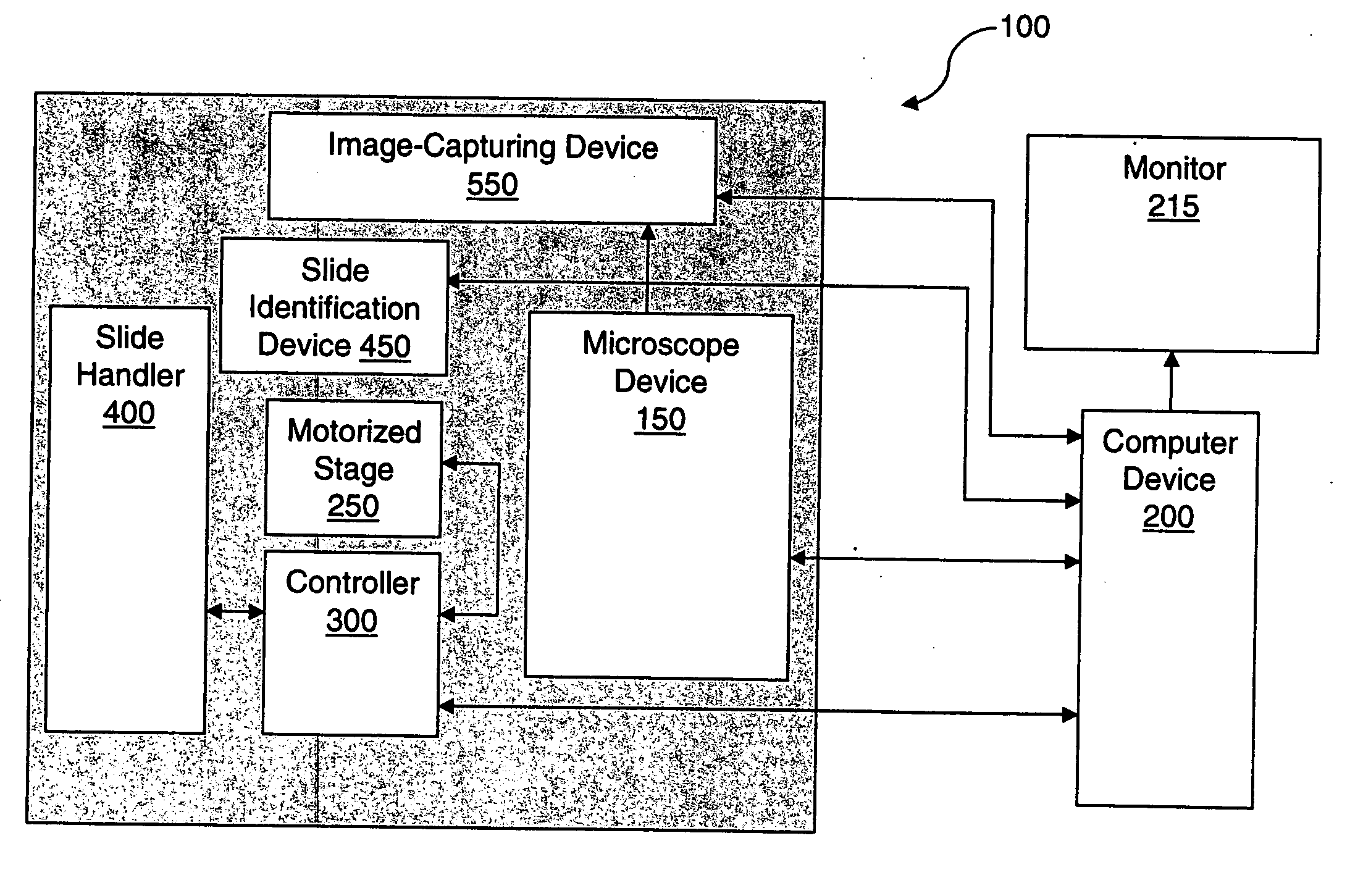
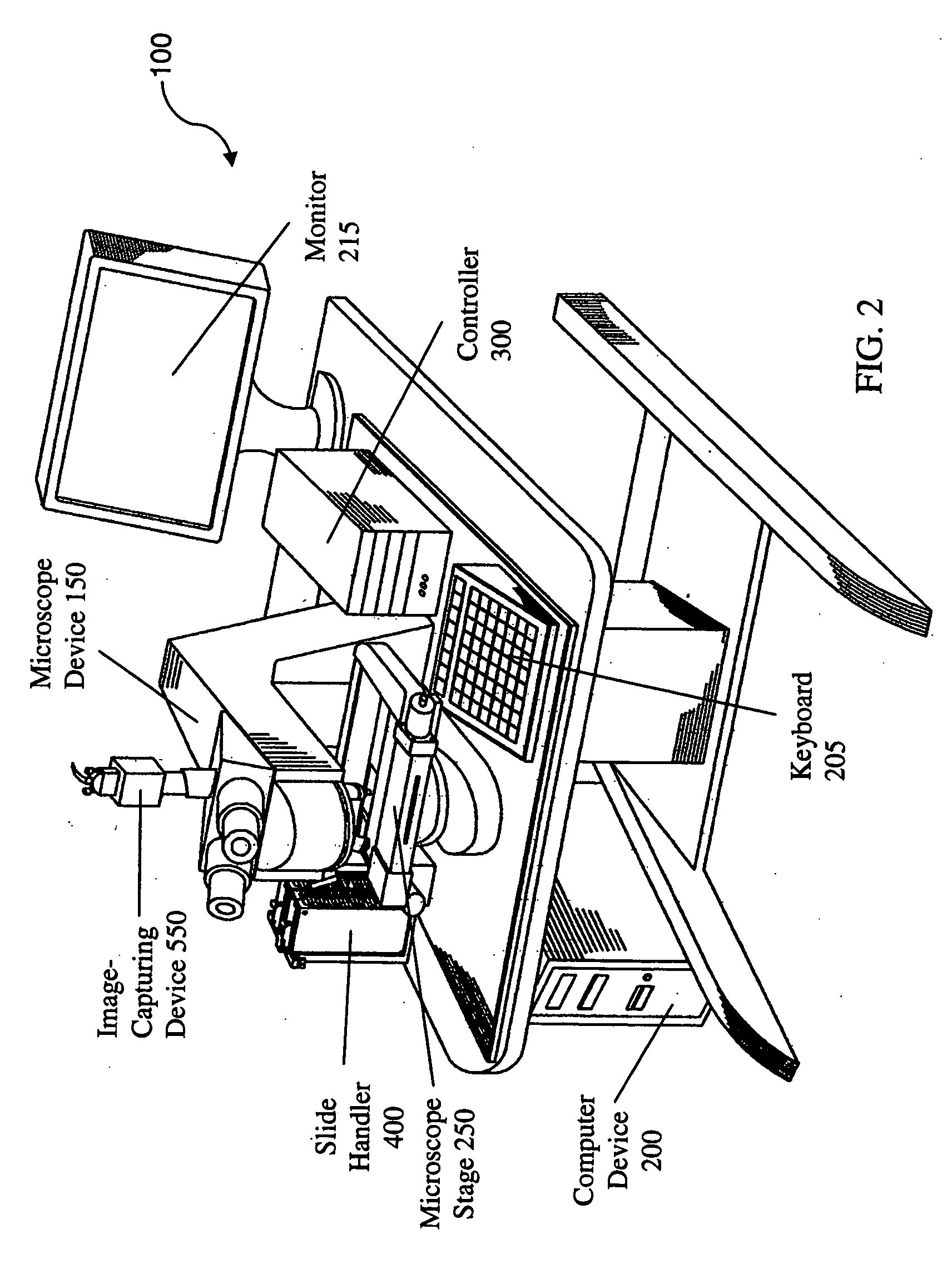
Microscopy system having automatic and interactive modes for forming a magnified mosaic image and associated method
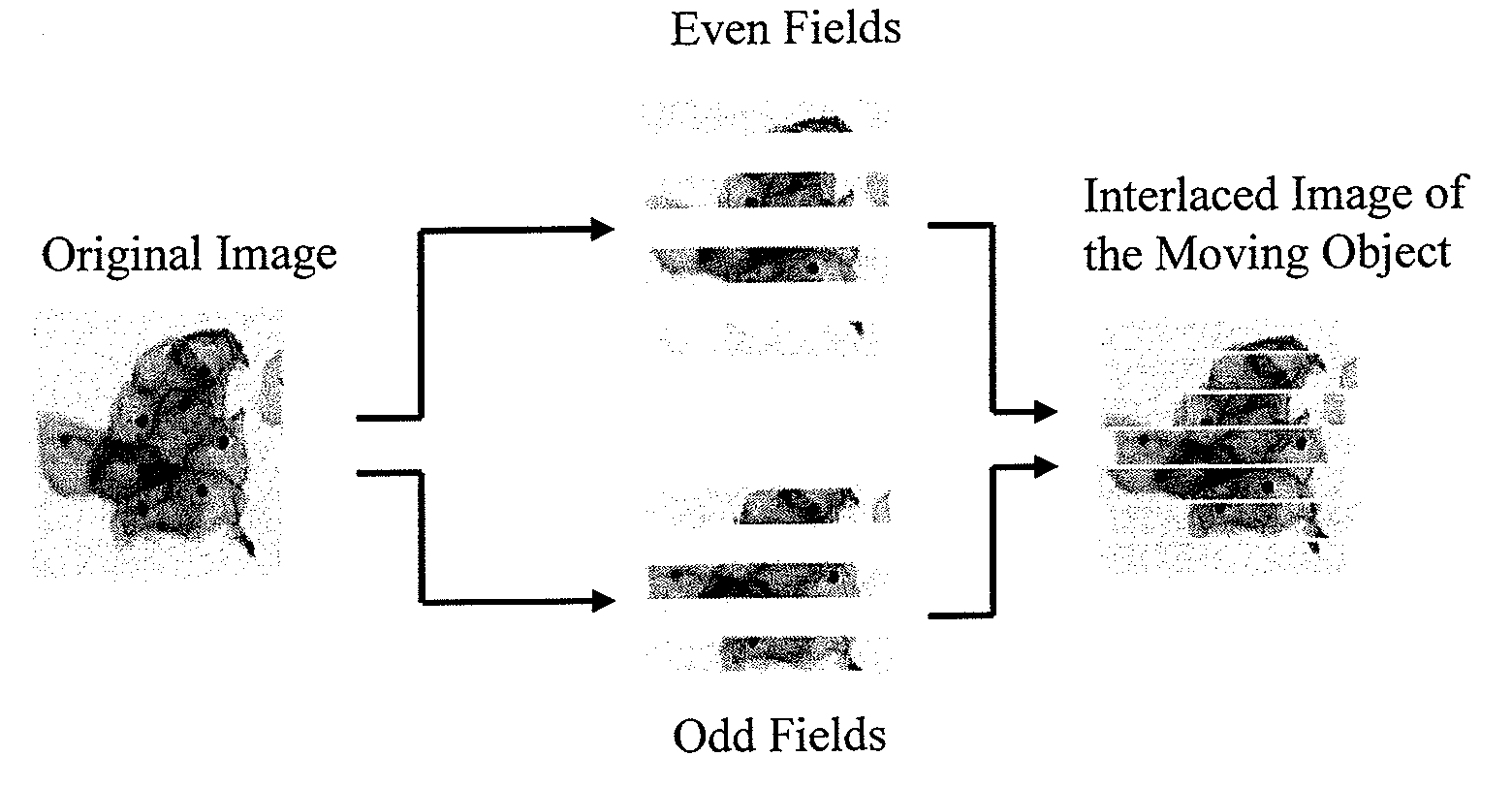
InactiveUS20060133657A1Quality improvementMeet needsAcquiring/recognising microscopic objectsMicroscopesInterlaced videoComputer graphics (images)
A scanning device for biological slides is provided, which can be operated in an interactive routine mode as well as in an unsupervised high speed automatic mode. In the first case, typical components, which the pathologist is used to operating manually, such as the microscope, the stage and the focus, and which have to be motorized for the automatic unsupervised system mode, are configured to simulate manual use, operation, and response. A non-interlaced area scan camera supports the interactive selection and acquisition of individual images in the manual mode, as well as the continuous high-speed scan motion for the rare event detection and virtual slide scan applications of the system. Due to the particular requirements to accommodate both operational modes, methods are described for constructing the virtual slide out of image tiles with varying overlap areas in the x- and y-directions.
Owner:TRIPATH IMAGING INC
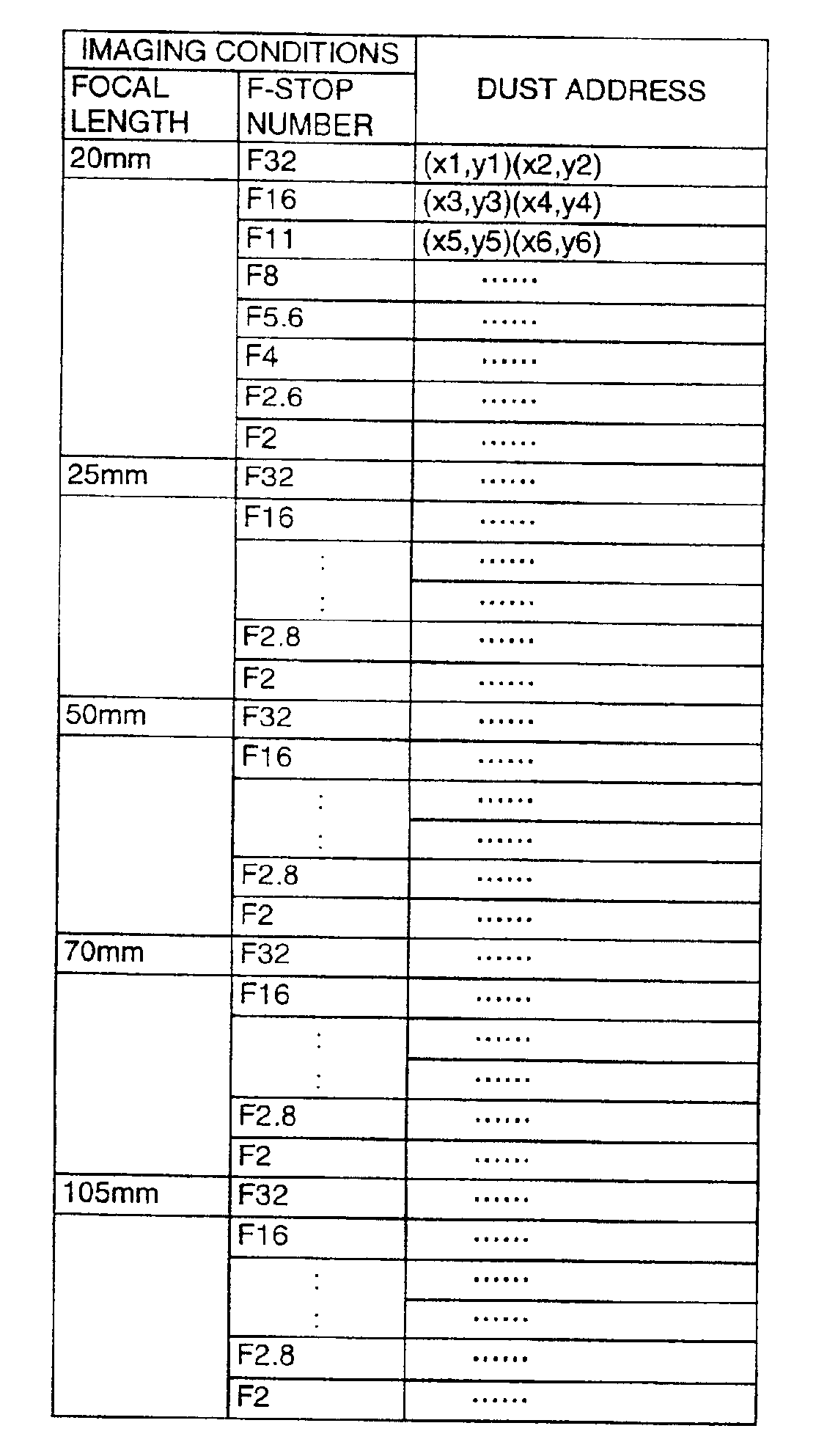
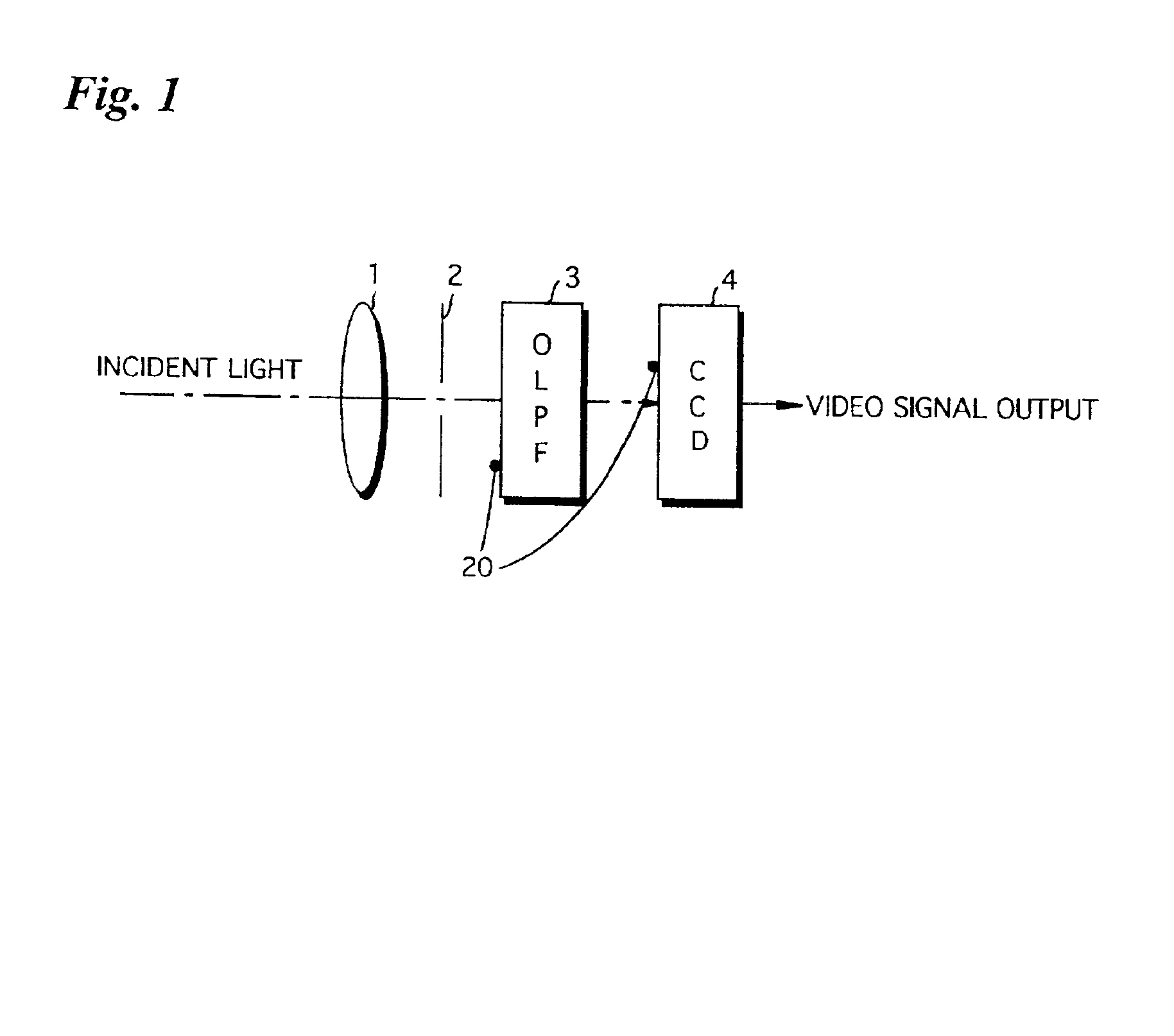
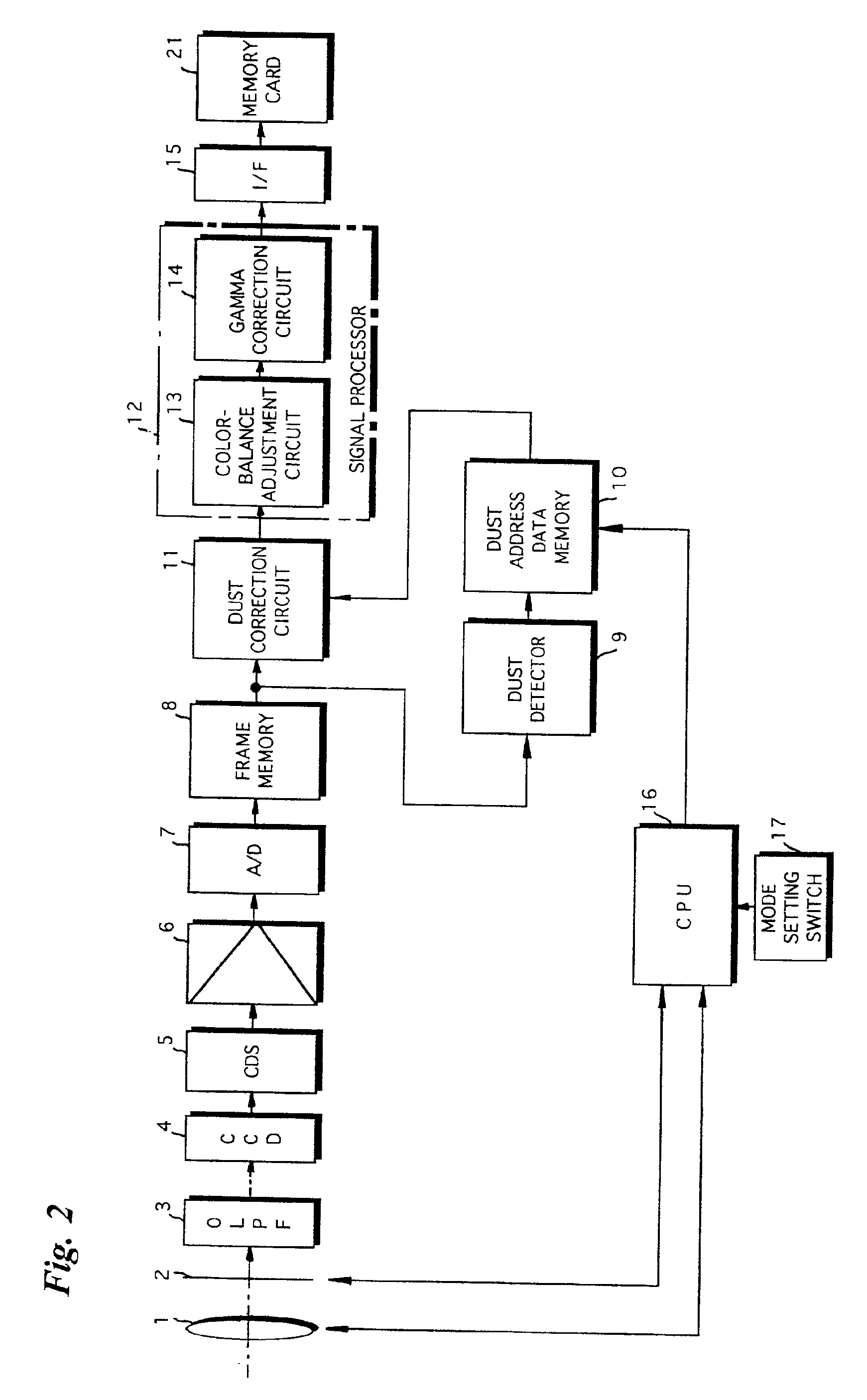
Digital camera and a method for correcting dust images in the camera
ActiveUS6940550B2EliminateClean attractiveTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsComputer scienceImaging data
An all-white reference subject is imaged by a CCD and image data representing the reference subject is obtained. The position of any dust on the reference subject represented by the reference-subject image data is detected by a dust position detector. Address data representing the position of the dust is stored in a memory that stores dust address data. When the user images a subject, image data obtained by such imaging is input to a dust correction circuit. The dust address data is read from the memory and the image at the position represented by this dust address data is eliminated from the image of the subject by reason of the fact that the image at this position is that of dust.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Anti-reflection film, polarizing plate, and liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20090135356A1Eliminates white blurringRemove image blurProjectorsPolarising elementsLiquid-crystal displayRefractive index
An anti-reflection film comprising: a transparent support; at least one high refractive index hard coat layer; and a low refractive index layer disposed as an outermost layer, in this order, wherein (i) the high refractive index hard coat layer has a refractive index of 1.55 or more and a thickness of 4 to 15 μm; (ii) the anti-reflection film has a surface roughness Ra (center line average roughness) of 0.10 μm or less; and (iii) the low refractive index layer comprises a hollow silica microparticle having an average particle diameter of 5 to 200 nm and a refractive index of 1.17 to 1.40.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Imaging for a machine-vision system
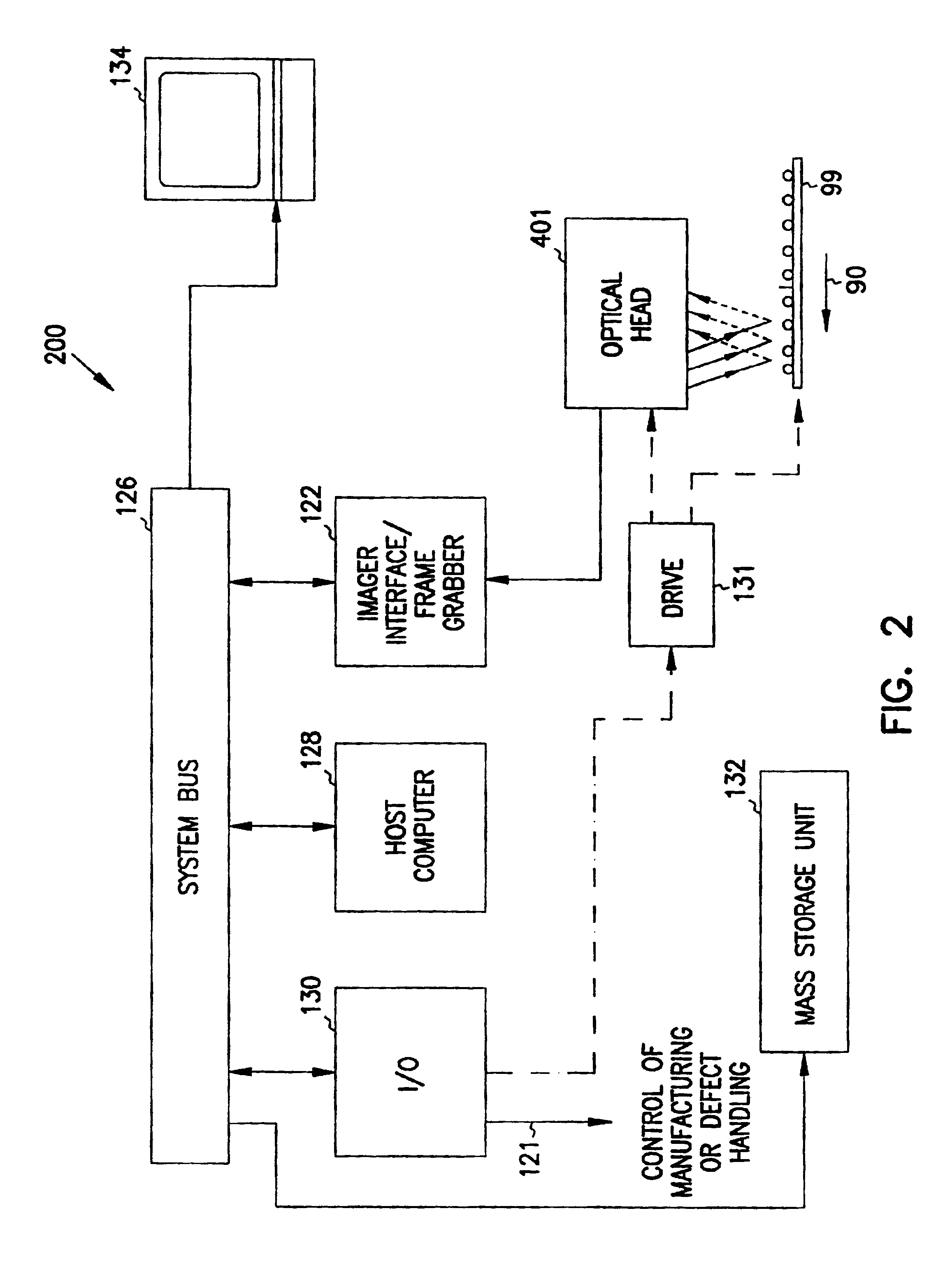
InactiveUS6956963B2Prevents thermal driftLow variabilityImage analysisSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingImage detectionSemiconductor fab
Manufacturing lines include inspection systems for monitoring the quality of parts produced. Manufacturing lines for making semiconductor devices generally inspect each fabricated part. The information obtained is used to fix manufacturing problems in the semiconductor fab plant. A machine-vision system for inspecting devices includes a light source for propagating light to the device and an image detector that receives light from the device. Also included is a light sensor assembly for receiving a portion of the light from the light source. The light sensor assembly produces an output signal responsive to the intensity of the light received at the light sensor assembly. A controller controls the amount of light received by the image detector to a desired intensity range in response to the output from the light sensor. The image detector may include an array of imaging pixels. The imaging system may also include a memory device which stores correction values for at least one of the pixels in the array of imaging pixels. To minimize or control thermal drift of signals output from an array of imaging pixels, the machine-vision system may also include a cooling element attached to the imaging device. The light source for propagating light to the device may be strobed. The image detector that receives light from the device remains in a fixed position with respect to the strobed light source. A translation element moves the strobed light source and image detector with respect to the device. The strobed light may be alternated between a first and second level.
Owner:ISMECA SEMICONDUCTOR HOLDING SA
Digital photography with flash/no flash extension
InactiveUS7457477B2Improving digital flash photographsEnhance the imageImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImage pairFlash light
A system and method for improving digital flash photographs. The present invention is a technique that significantly improves low-light imaging by giving the end-user all the advantages of flash photography without producing the jarring look. The invention uses an image pair—one taken with flash the other without—to remove noise from the ambient image, sharpen the ambient image using detail from the flash image, correct for color, and remove red-eye.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
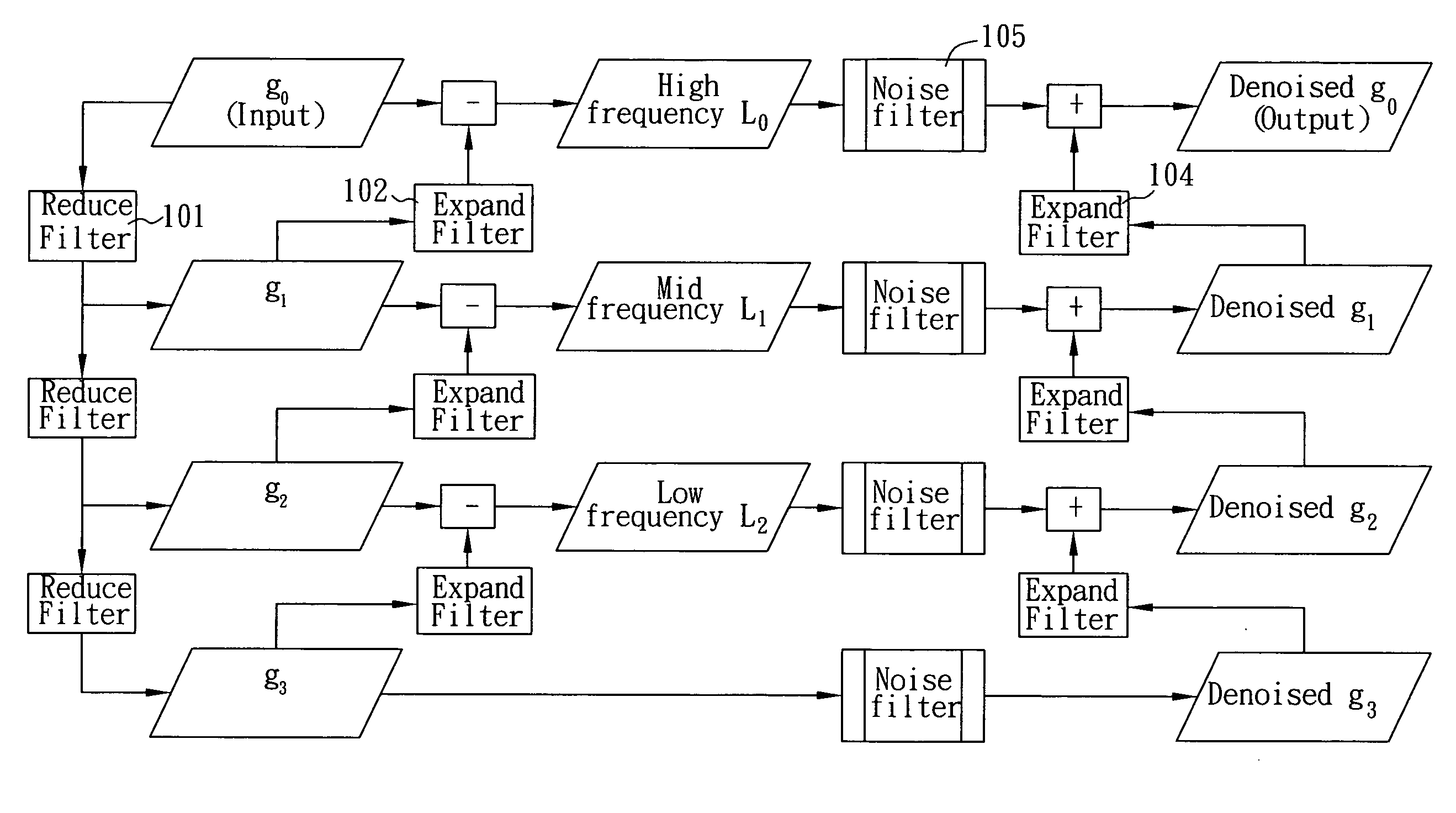
Denoise method on image pyramid
ActiveUS20080253678A1Easy to embedAvoid quality lossImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionNoise level
The present invention is to provide a denoise method on Gaussian / Laplacian image pyramid, which integrates Pyramid analysis / synthesis algorithm, MMSE (minimum mean square error) filter and NL (non local) filter on the image pyramid to reconstruct and output a denoised image of an original input image through a plurality of iterative procedures, and utilizes an auto-adaptive noise estimation algorithm to find parameter of noise level used by the NL filter, so as to be easily embedded in mobile or handheld devices for obtaining better noise removing and anti-shaking results and remove noise much faster than the conventional denoise method, but only with less quality loss.
Owner:ARCSOFT
Method and Apparatus for Removal of The Double Indication of Defects in Remote Eddy Current Inspection of Pipes
InactiveUS20120095686A1Reduce signal noiseTaking imageElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingConstructionsEngineeringEddy current
The apparatus employs the remote field eddy-current (RFEC) inspection technique to electromagnetically measure physical parameters of a metallic pipe. RFEC devices inserted into and displaced along a cylindrical pipes may be used to measure the ratio of pipe thickness to electromagnetic skin-depth and thus allow for the non-invasive detection of flaws or metal loss. Typically these RFEC thickness measurements exhibit a so-called double-indication of flaws, an undesired artifact due to a double-peaked geometrical sensitivity function of the device. The method describes a means by which this double indication artifact may be removed by an appropriate processing of RFEC measurements performed by an apparatus specifically designed for this purpose. The invention is particularly well designed for applications in the oilfield industry.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Parts manipulation and inspection system and method
InactiveUS20050111726A1Low variabilityLighten the taskImage analysisMaterial analysis by optical meansImage detectorFixed position
Manufacturing lines include inspection systems for monitoring the quality of parts produced. Manufacturing lines for making semiconductor devices generally inspect each fabricated part. The information obtained is used to fix manufacturing problems in the semiconductor fab plant. A machine-vision system for inspecting devices includes a light source for propagating light to the device and an image detector that receives light from the device. Also included is a light sensor assembly for receiving a portion of the light from the light source. The light sensor assembly produces an output signal responsive to the intensity of the light received at the light sensor assembly. A controller controls the amount of light received by the image detector to a desired intensity range in response to the output from the light sensor. The image detector may include an array of imaging pixels. The imaging system may also include a memory device which stores correction values for at least one of the pixels in the array of imaging pixels. To minimize or control thermal drift of signals output from an array of imaging pixels, the machine-vision system may also include a cooling element attached to the imaging device. The light source for propagating light to the device may be strobed. The image detector that receives light from the device remains in a fixed position with respect to the strobed light source. A translation element moves the strobed light source and image detector with respect to the device. The strobed light may be alternated between a fit and second level.
Owner:LEMAIRE CHARLES A
Ball with camera for reconnaissance or recreation and network for operating the same
InactiveUS9144714B2Taking imageEasy to trackTelevision system detailsHollow inflatable ballsRecreationImage capture
A ball-shaped camera thrown or projected into an airborne trajectory, and an image capture system with network devices collaborating for the purpose of generating panoramic images and video sourced from network ball cameras, and ball cameras capable of capturing stable image and video while spinning, spiraling or precessing through a trajectory.
Owner:HOLLINGER STEVEN J
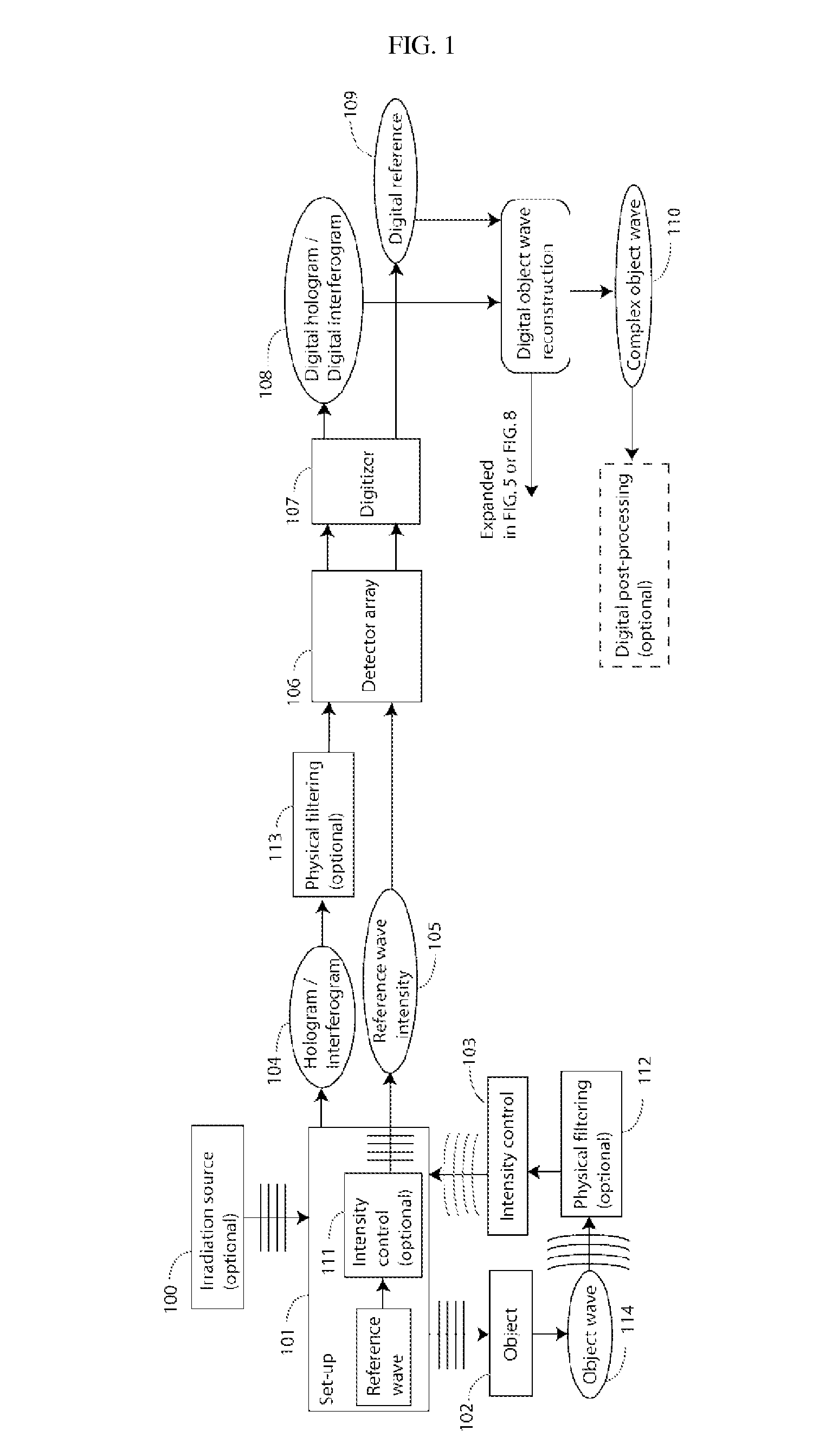
Method and apparatus for enhanced spatial bandwidth wavefronts reconstructed from digital interferograms or holograms
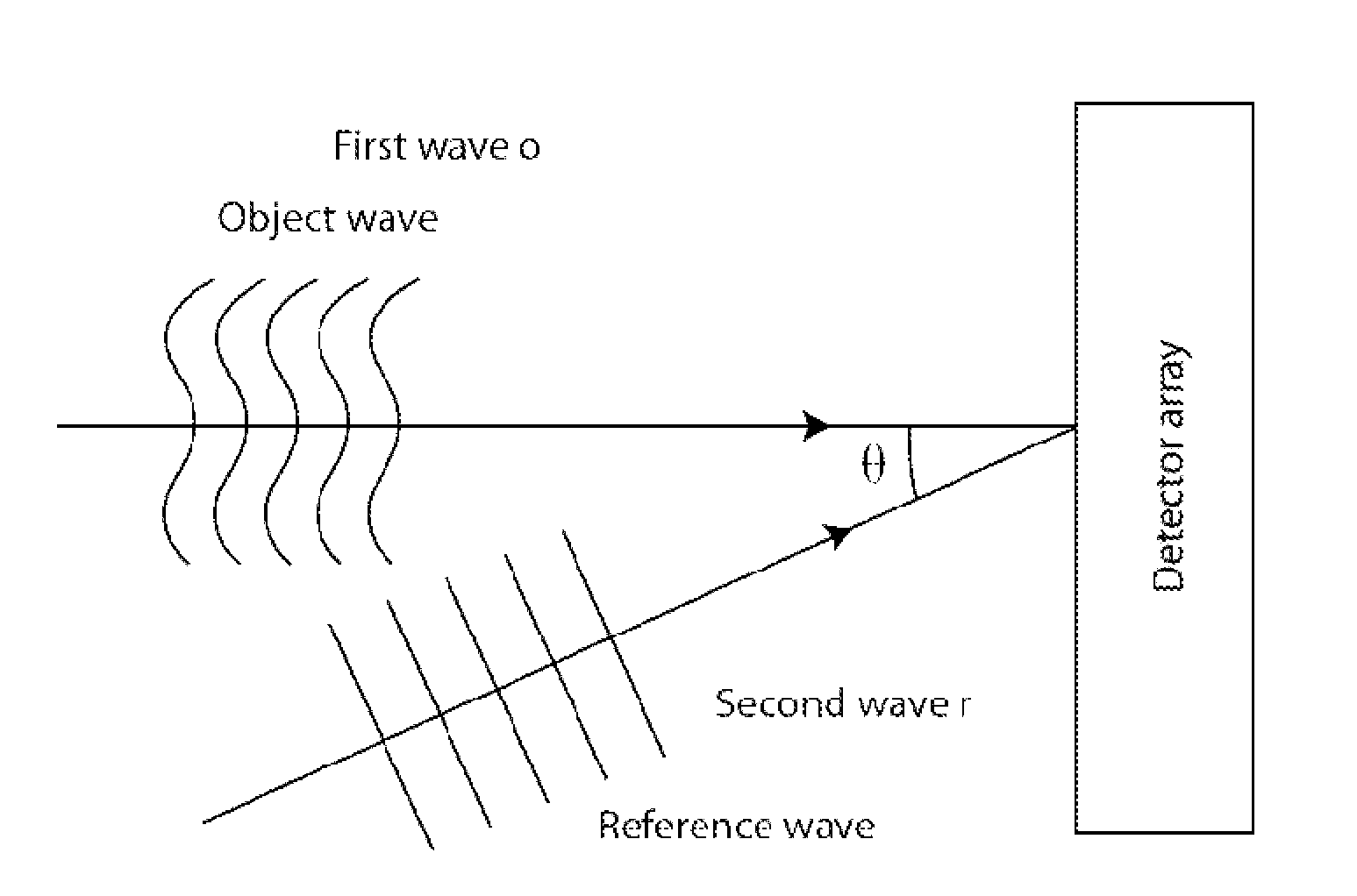
InactiveUS20120116703A1Improve efficiencyIncrease of spatial bandwidthNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementDigital variable/waveform displayWavefrontImage resolution
The present invention discloses a method and an apparatus to compute a complex wavefield, referred to as the object wave o, by means of measuring the intensity signal resulting from the interference of the said object wave with a second wave termed the reference wave. The second wave r is assumed to have some non-vanishing mutual coherence with the said object wave o. The reference wave can be obtained from a source or from the object wave itself. The wave may be emitted from sources of variable degree of coherence and can be scattered waves, but also light-emitting molecules, matter waves such as electron beams or acoustical sources. The disclosed method relates to the said “non-linear method” (NLM). The innovation resides in the fact that the NLM improves considerably the bandwidth of the wavefront reconstructed from off-axis interferograms and holograms obtained in a single shot. The advantage is the significant improvement of the resolution of the images obtained from the reconstructed wavefront, i.e. amplitude and phase images. The said method also suppresses the artifacts resulting from the intensity recording of interferograms and holograms. The method is general in the sense that it can be used for any interferometric measurement, provided that it satisfies the simple requirement that the intensity of the reference wave is larger than the intensity of the object wave, and that the object wave modulated by the reference is confined to at least a quadrant of the spectrum. The disclosed method applies to interferometry, holography in optics, electron waves and acoustics. In particular, it can be implemented in phase, fluorescence, luminescence, electron and acoustic microscopy.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
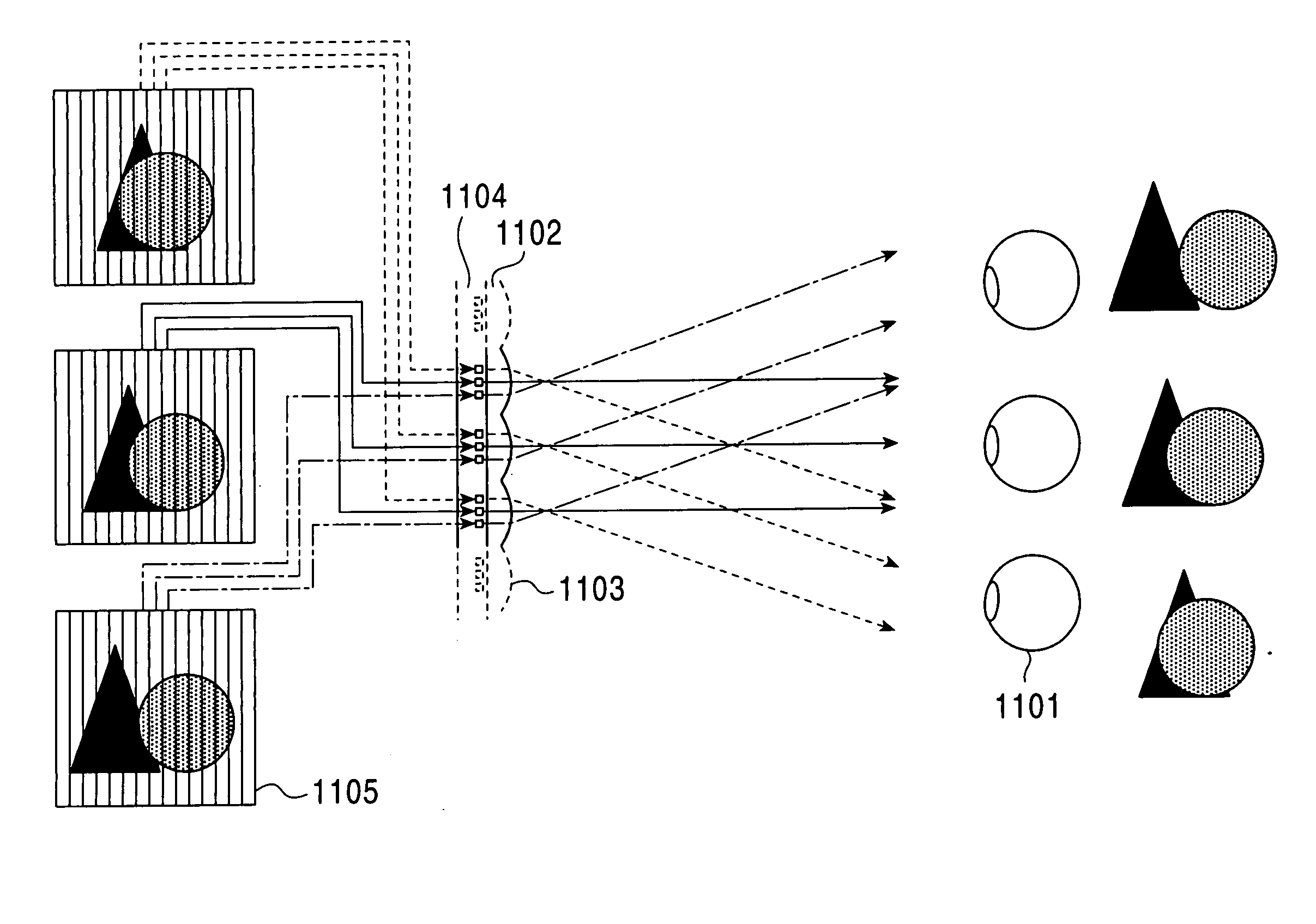
Three-dimensional display method and device therefor
InactiveUS20050030308A1Taking imageSmooth switchingStereoscopic photographySteroscopic systemsAngular rangeThree dimensional display
A three-dimensional display method and a device therefor are provided in which a number of images can be displayed in the horizontal directions while image skips can be eliminated by providing overlaps of display angular ranges between adjacent images having horizontal display directions. A number of images are displayed in horizontal and vertical directions so that the display directions do not agree with each other, and by expanding vertical display angular ranges of entire images with a vertical-direction diffusion plate (17), a vertical display angular range common to the entire images is generated. In this common vertical display angular range, the entire images have different horizontal display directions. Thereby, a number of images can be displayed because image generating sources can be arranged also in the vertical direction in addition to the horizontal directions.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for improving quality of depth image
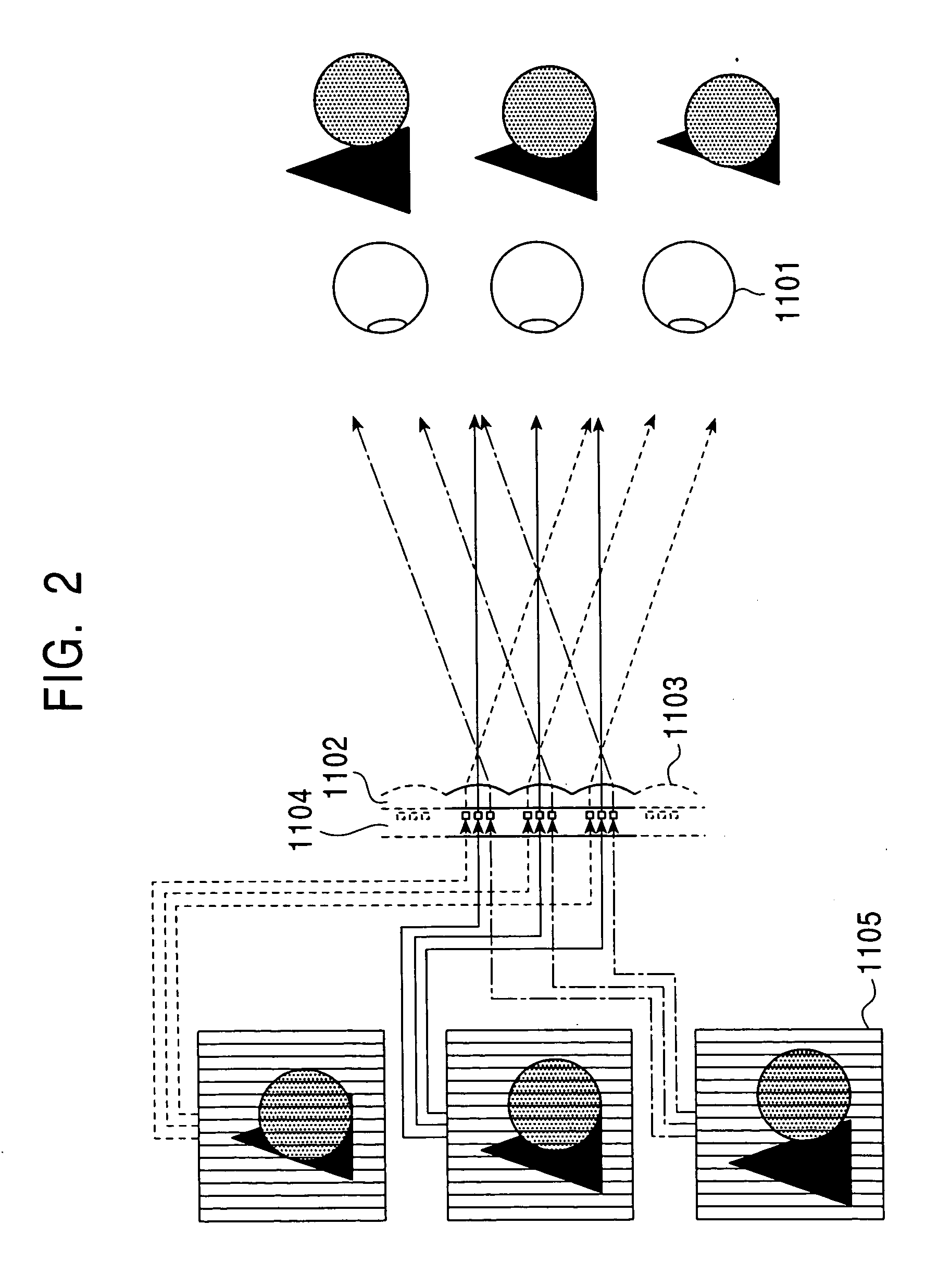
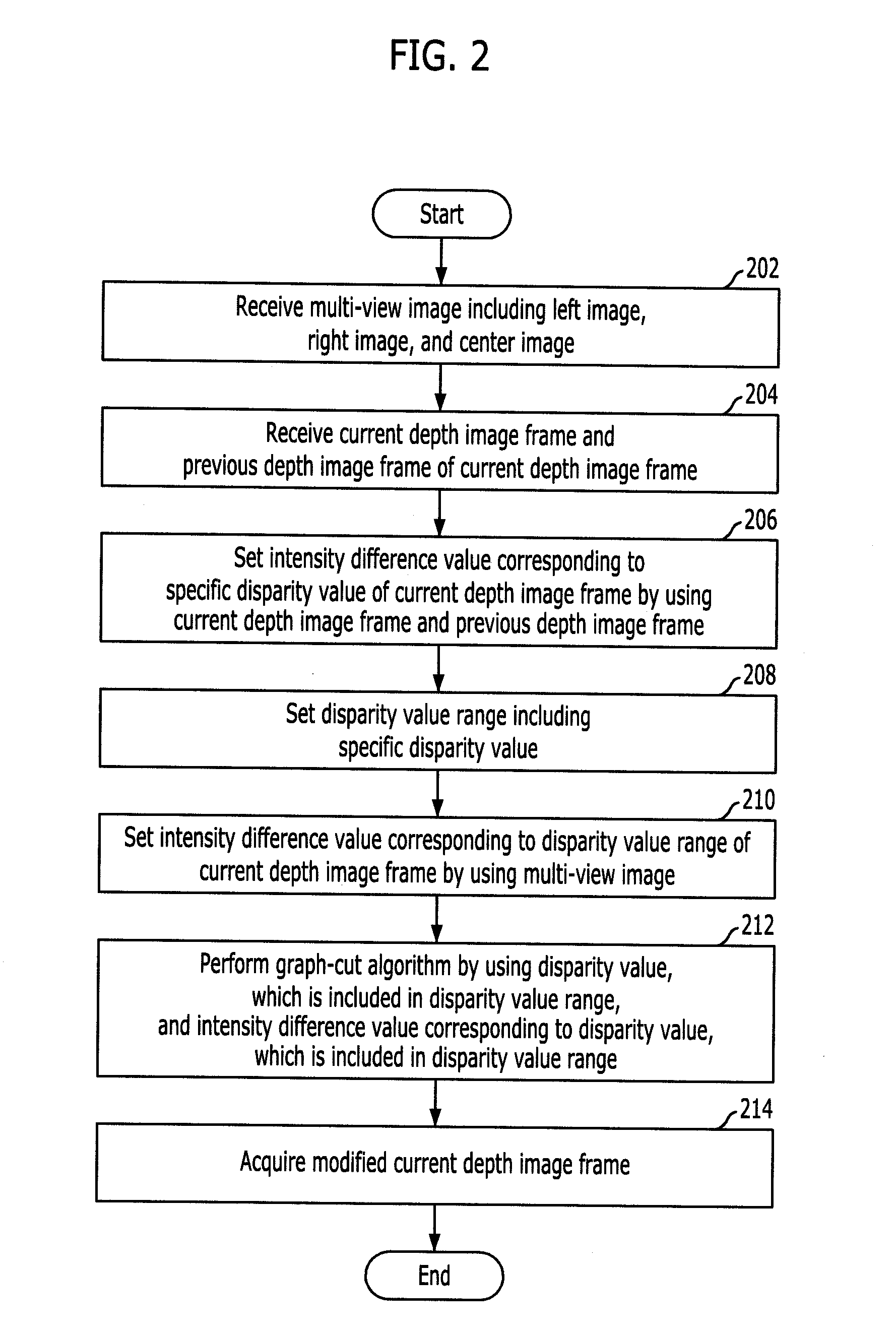
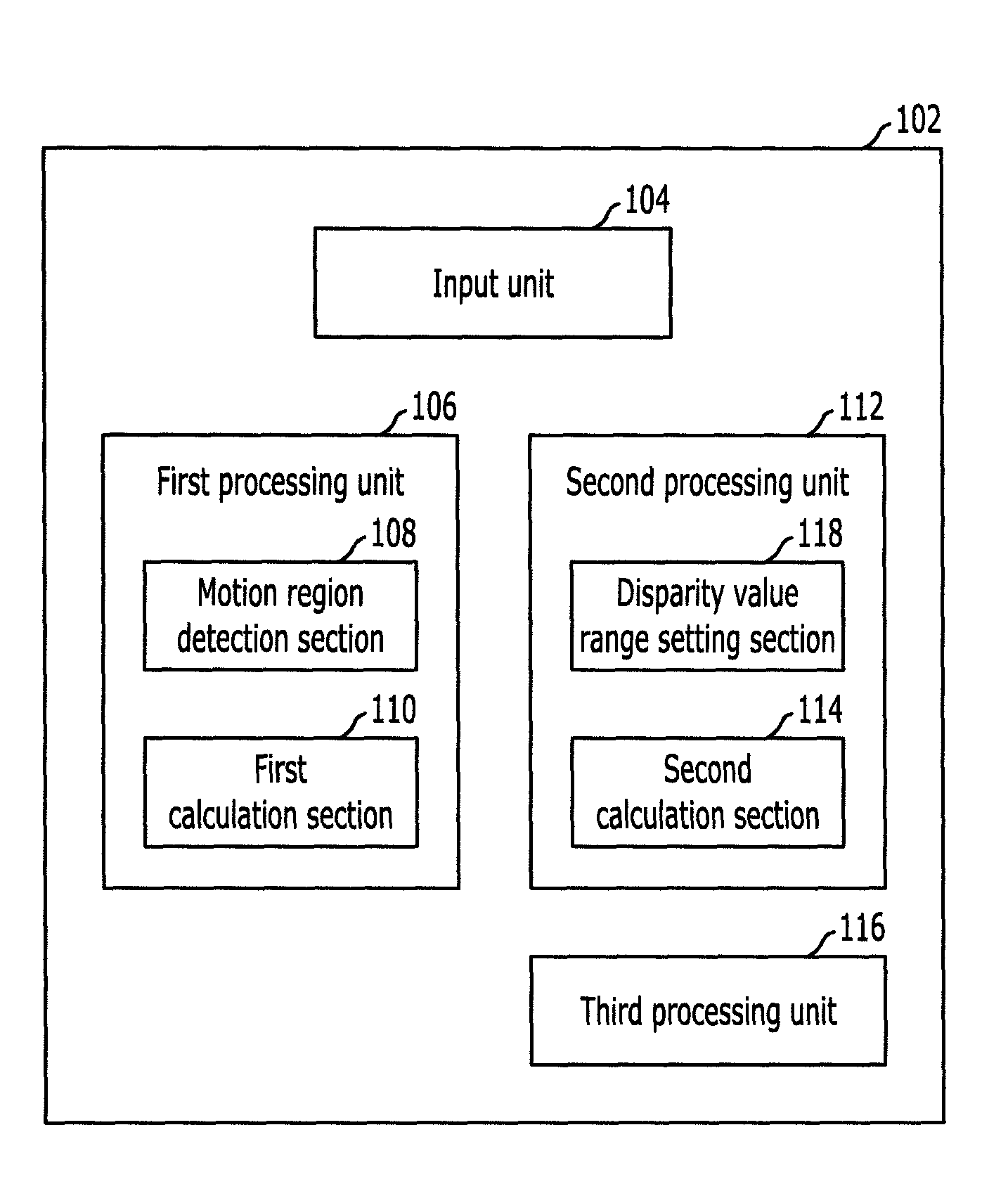
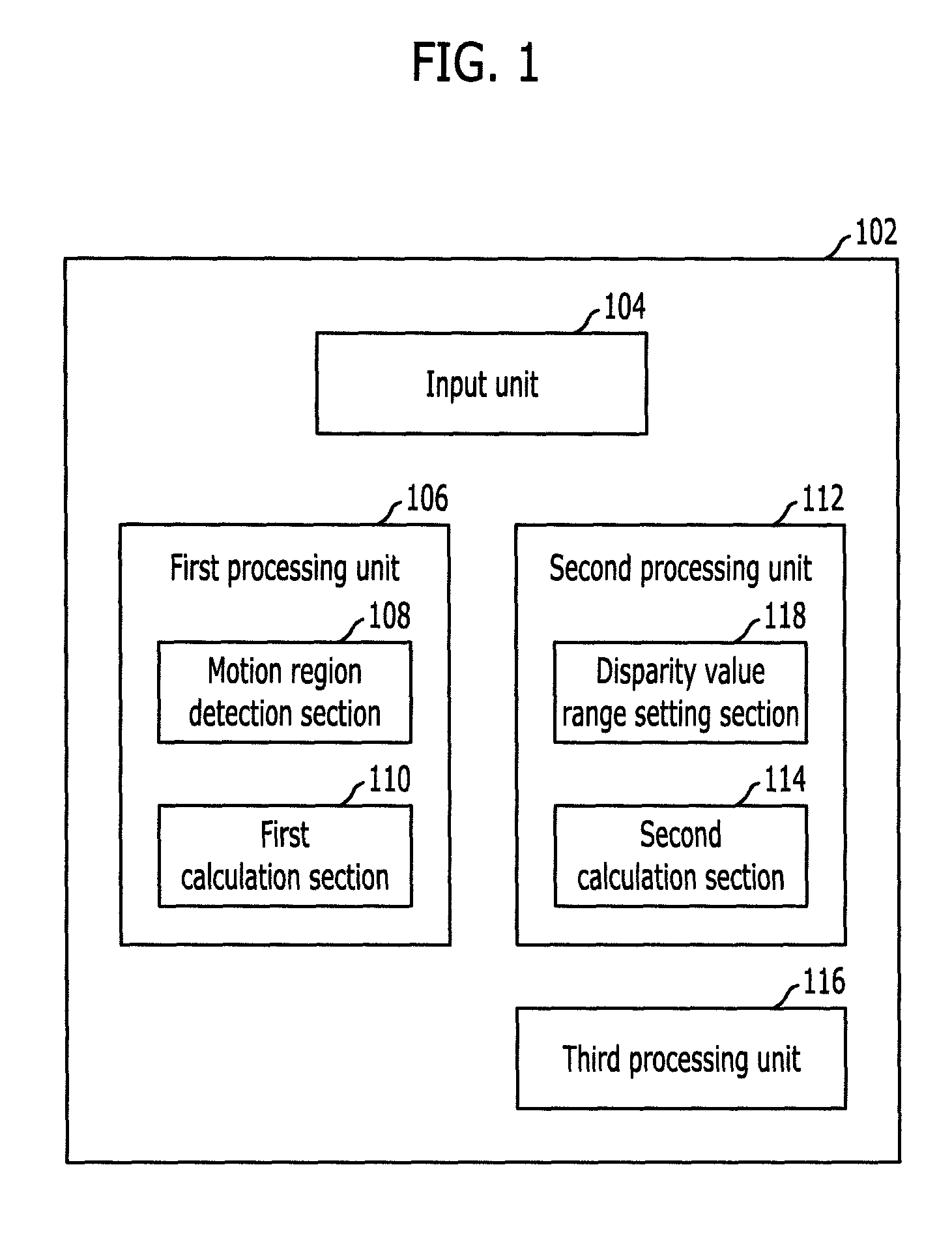
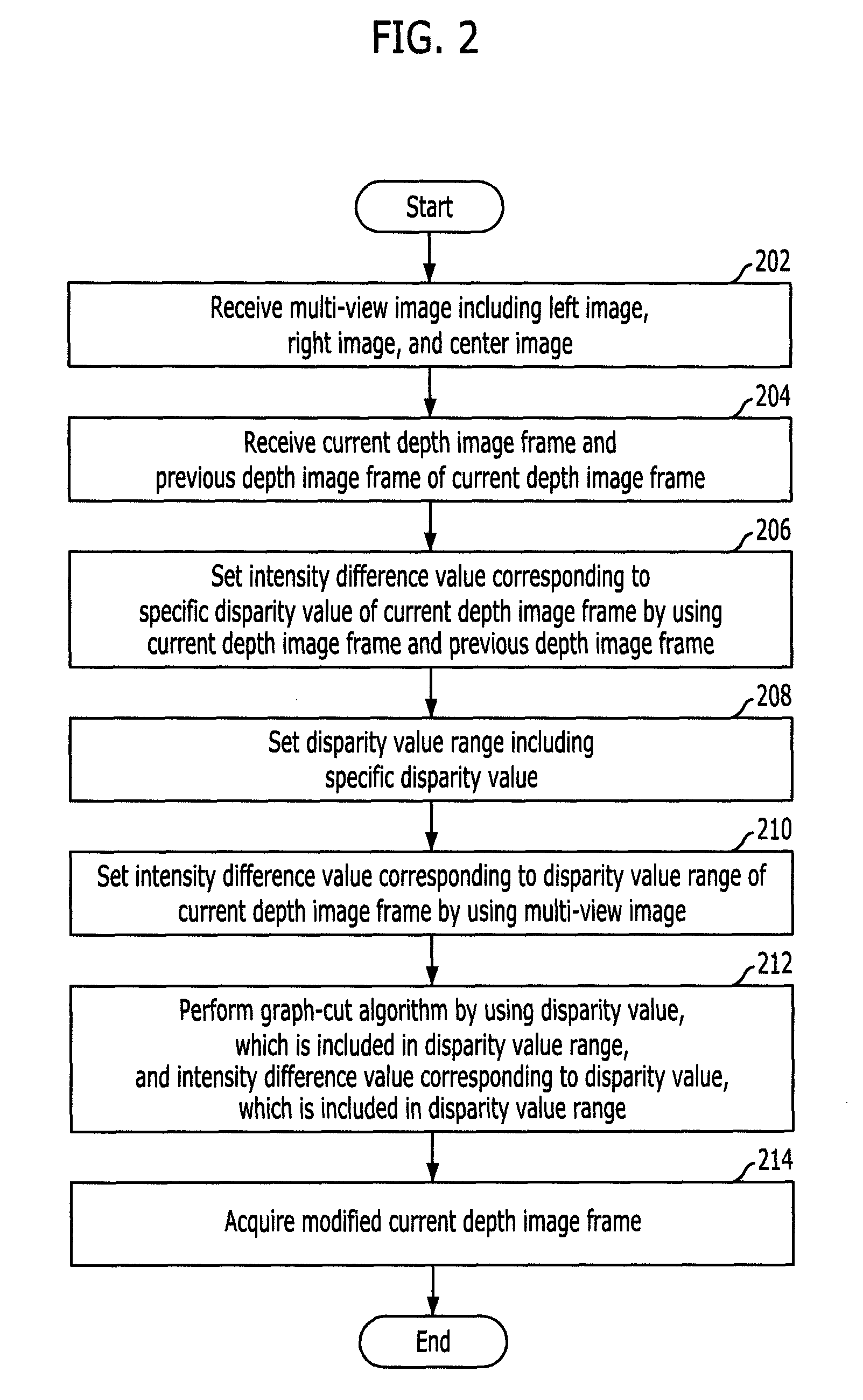
InactiveUS20100195898A1Quality improvementTaking imageImage enhancementImage analysisParallaxComputer science
A method and apparatus for enhancing quality of a depth image are provided. A method for enhancing quality of a depth image includes: receiving a multi-view image including a left image, a right image, and a center image; receiving a current depth image frame and a previous depth image frame of the current depth image frame; setting an intensity difference value corresponding to a specific disparity value of the current depth image frame by using the current depth image frame and the previous depth image frame; setting a disparity value range including the specific disparity value; and setting an intensity difference value corresponding to the disparity value range of the current depth image frame by using the multi-viewpoint image.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
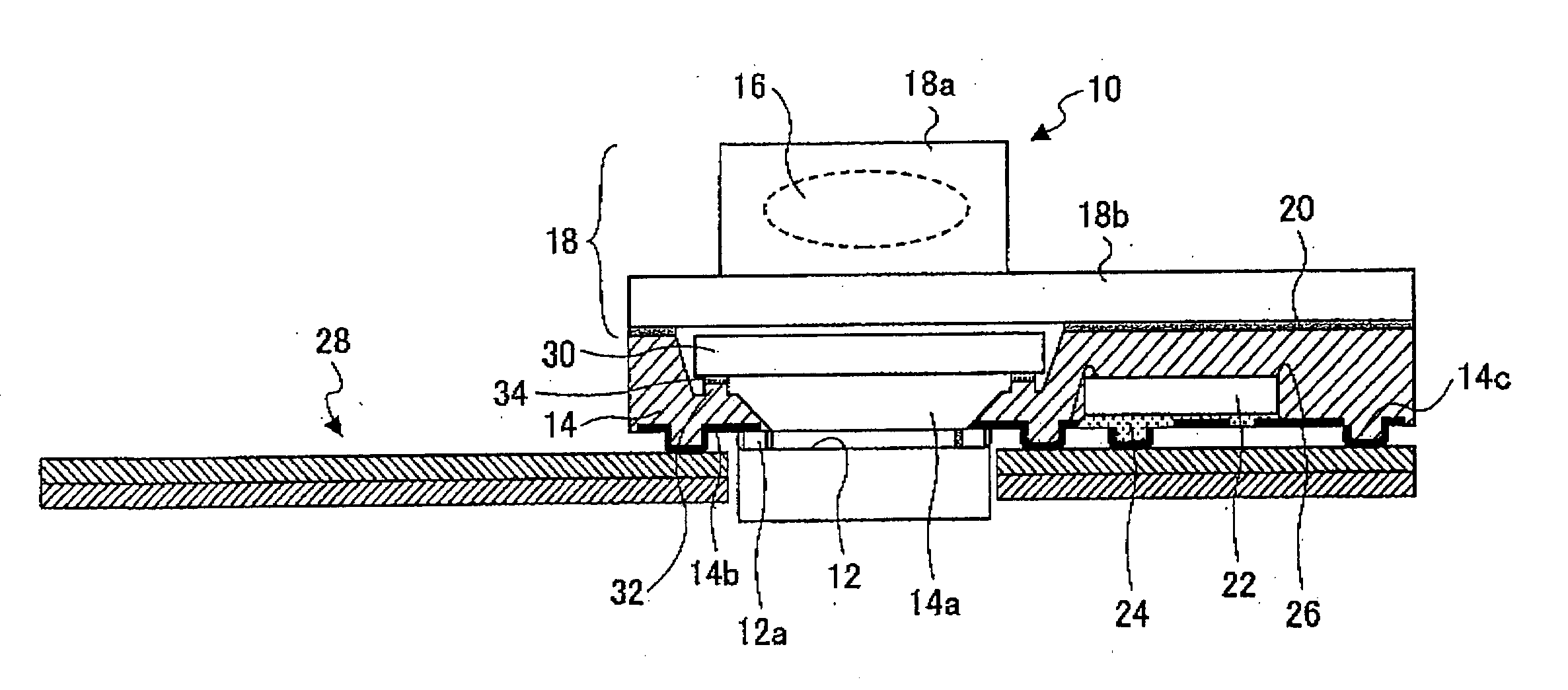
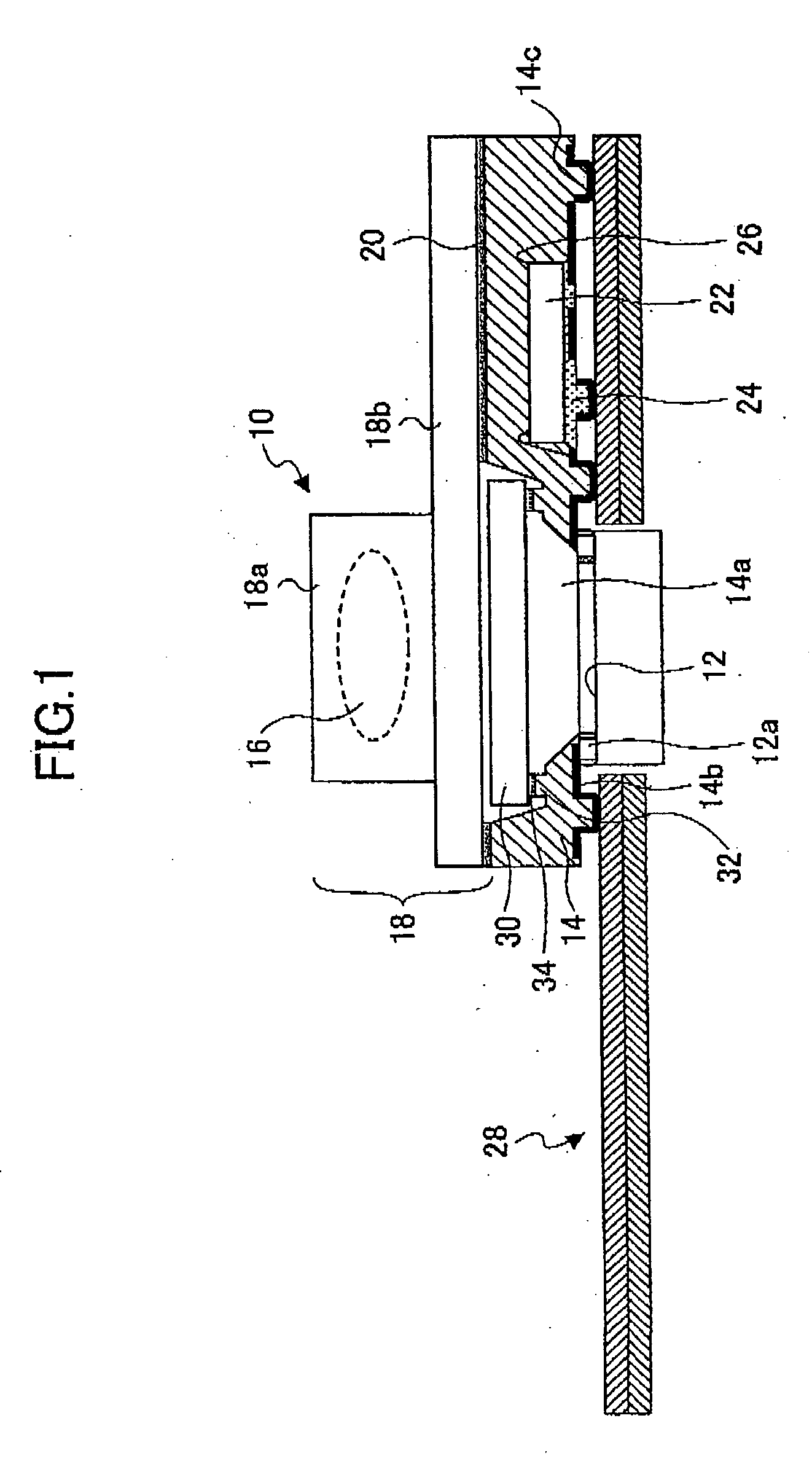
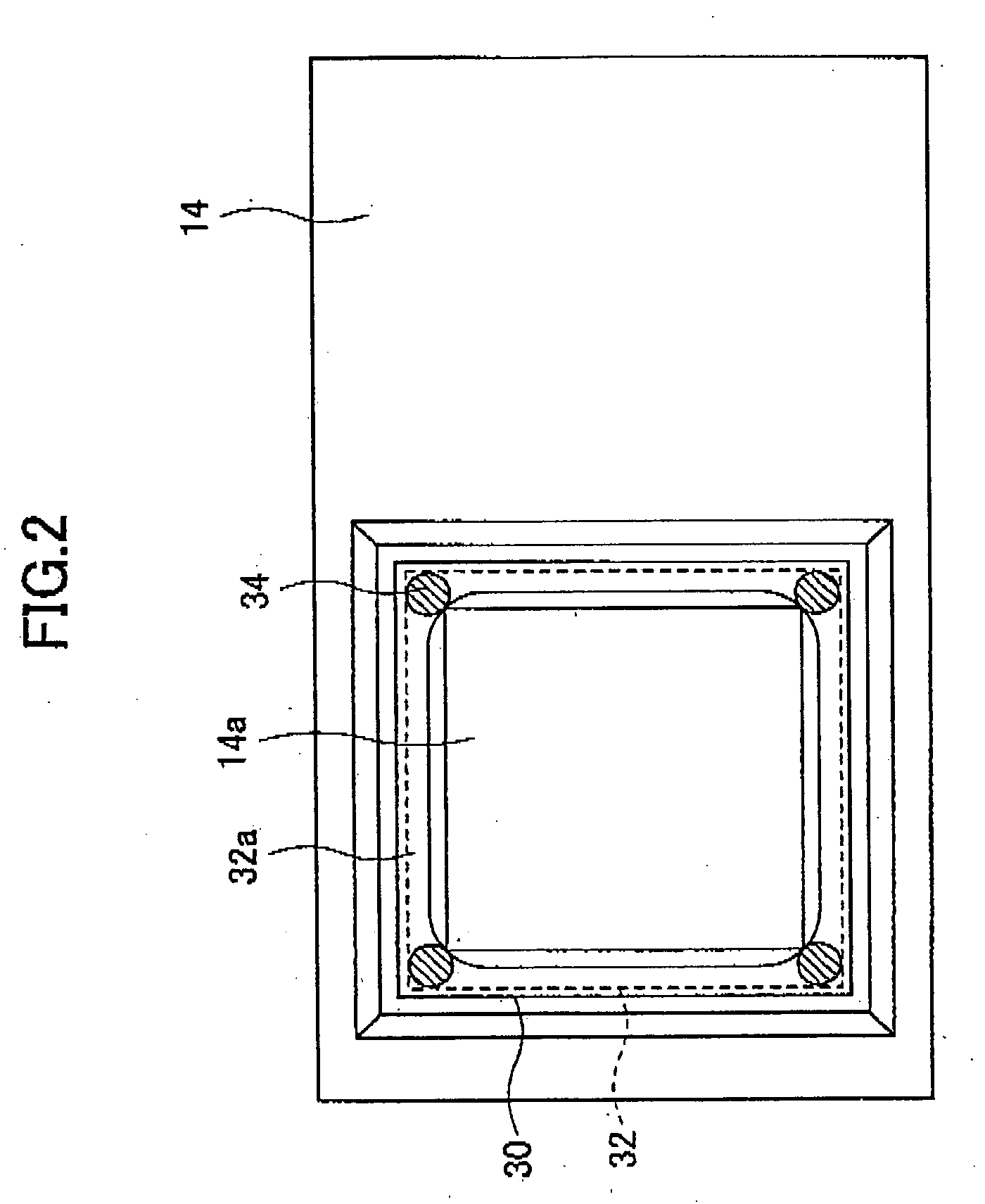
Camera module
InactiveUS20060243884A1Eliminate the problemPrevent of image outputTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesAdhesiveEngineering
A camera module includes a module structure constituted by a lens unit to which an image pickup lens is attached and a package to which an imaging element is attached so as to be opposite to the image pickup lens. An optical filter is arranged between the imaging element and the image pickup lens. A portion of a flat surface of the optical filter is fixed to a filter fixing portion via an adhesive. The optical filter is adhered to the filter fixing portion in a state in which an end portion formed by a side surface of the optical filter and the flat surface is in noncontact with the filter fixing portion or the adhesive. Minute particles generated from a cut surface of the optical filter fall outside the filer fixing portion.
Owner:FUJITSU SEMICON LTD
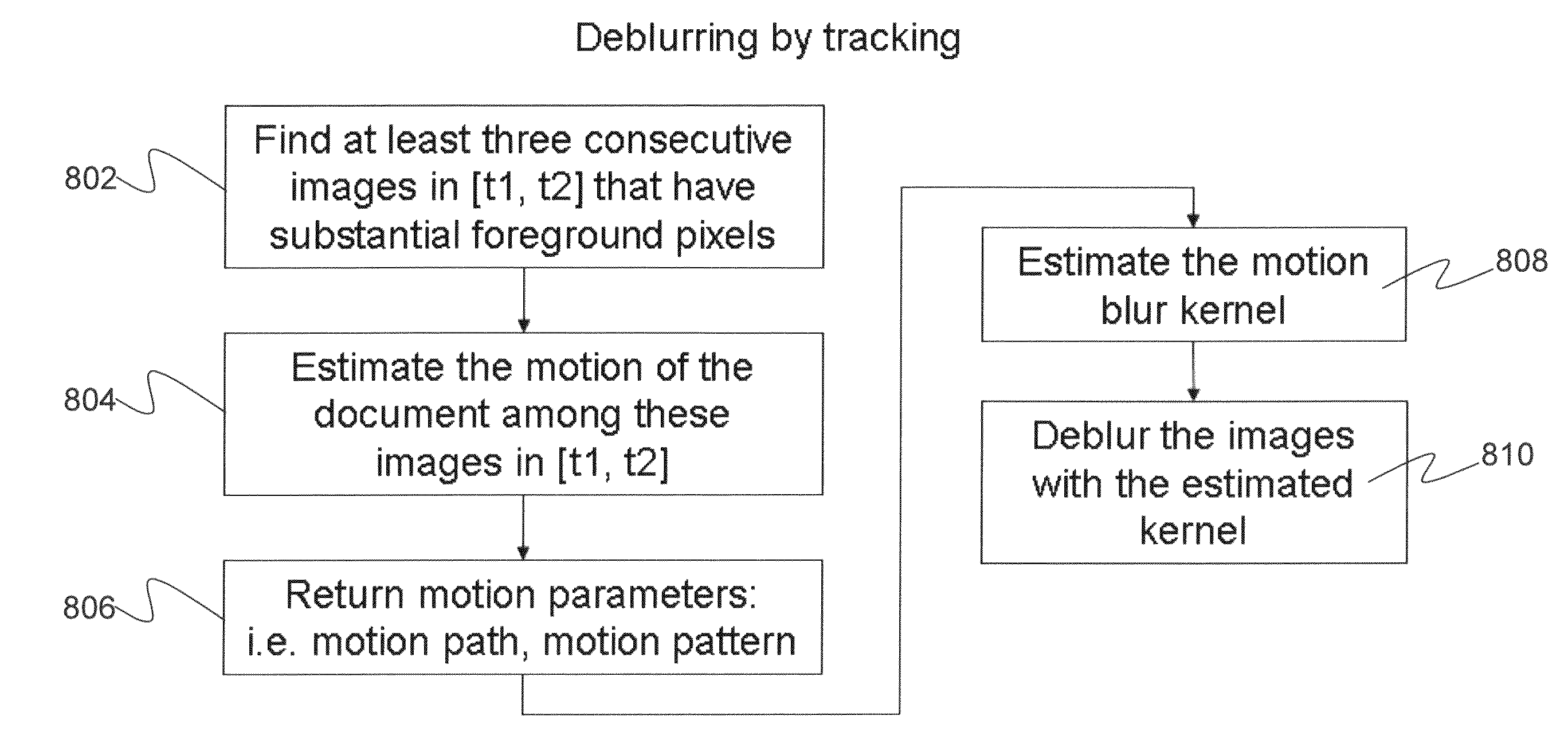
Systems and methods for interactive semi-automatic document scanning
InactiveUS20100202026A1Remove blurEnhance the imageDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
A semi-automatic system for scanning a document includes an image capture device, such as a digital or video camera, which records a sequence of images while a user waves a document in front of the device. The user can present multiple pages of a document to the image capture device, after which the total sequence of images are processed to identify a clear image of each page from the sequence of images. The system further includes image processing techniques to correct for motion blurring, acceleration and perspective errors. The system is capable of processing any size or shape of document without destroying the organization or format of the original.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Ultrasound imaging apparatus and method for acquiring ultrasound image
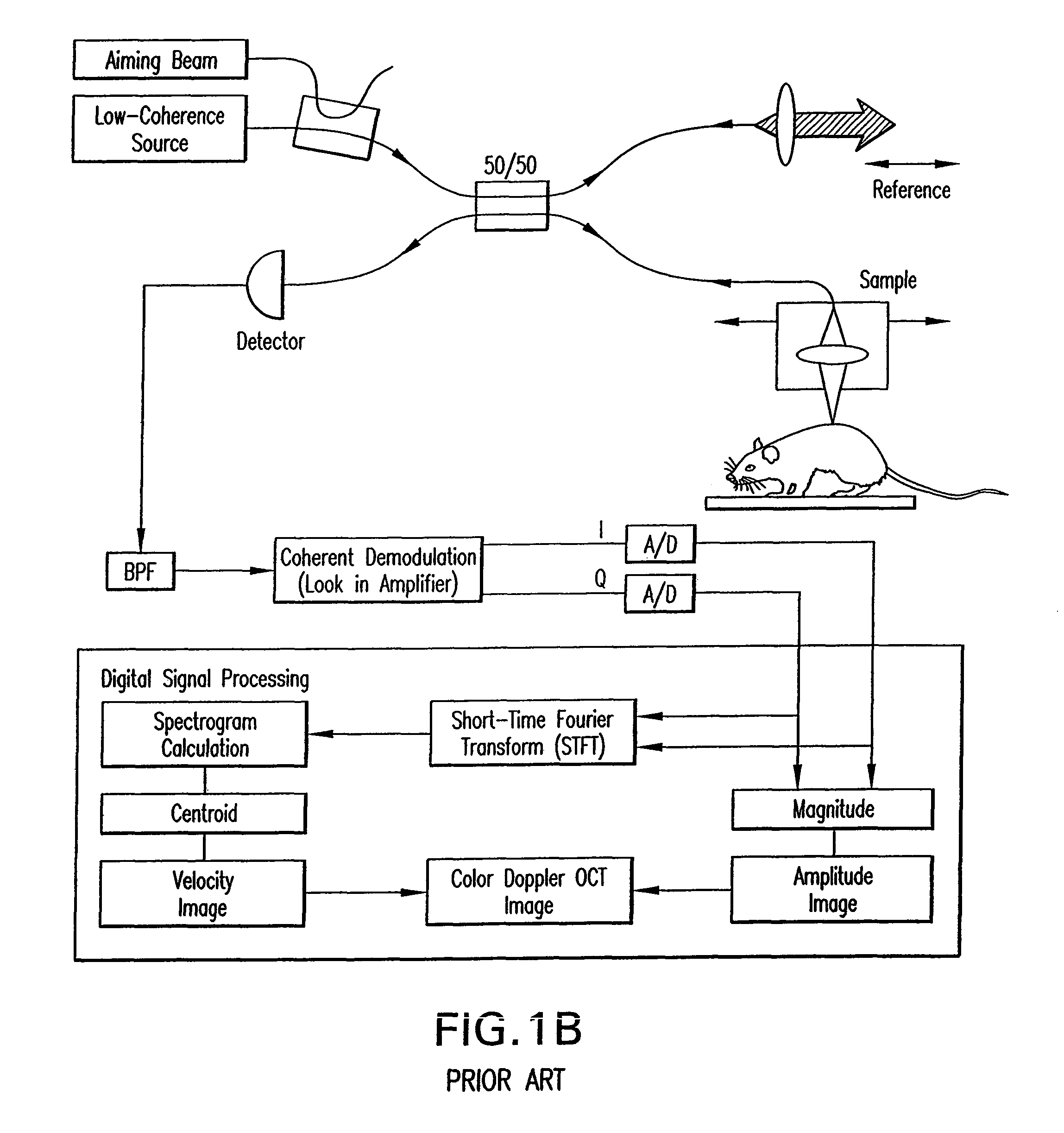
ActiveUS20100030079A1Taking imageDiagnosis moreUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound imagingSonification
An ultrasound imaging apparatus capable of easily displaying a three-dimensional image included in a region of interest (ROI) is provided.A display controller 9 causes a display 10 to display a tomographic image, and further causes the display 10 to display a first marker indicating a three-dimensional scan range and a second marker indicating a range to generate three-dimensional image data (a range subjected to rendering) so as to be superimposed on a tomographic image. The second marker is rotatable on the tomographic image in accordance with an instruction by an operator. A transceiver 3 causes an ultrasound probe 2 to scan the three-dimensional scan range specified based on the first marker. An image processor 7 executes rendering on, of data acquired in the scan, data included in the range specified based on the second marker, thereby generating three-dimensional image data.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Method for editing three-dimensional image and mobile terminal using the same
InactiveUS20120038626A1Taking imageNatural imageSubstation equipmentTransmissionParallaxComputer graphics (images)
A method for controlling a mobile terminal image includes providing a first image and a second image via a controller on the mobile terminal, the first and second images reflecting a binocular disparity to form a three dimensional image, identifying an editing target from the three dimensional image, editing a first image of the identified editing target, and applying the edited first image and a second image corresponding to the edited first image to the three dimensional image.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
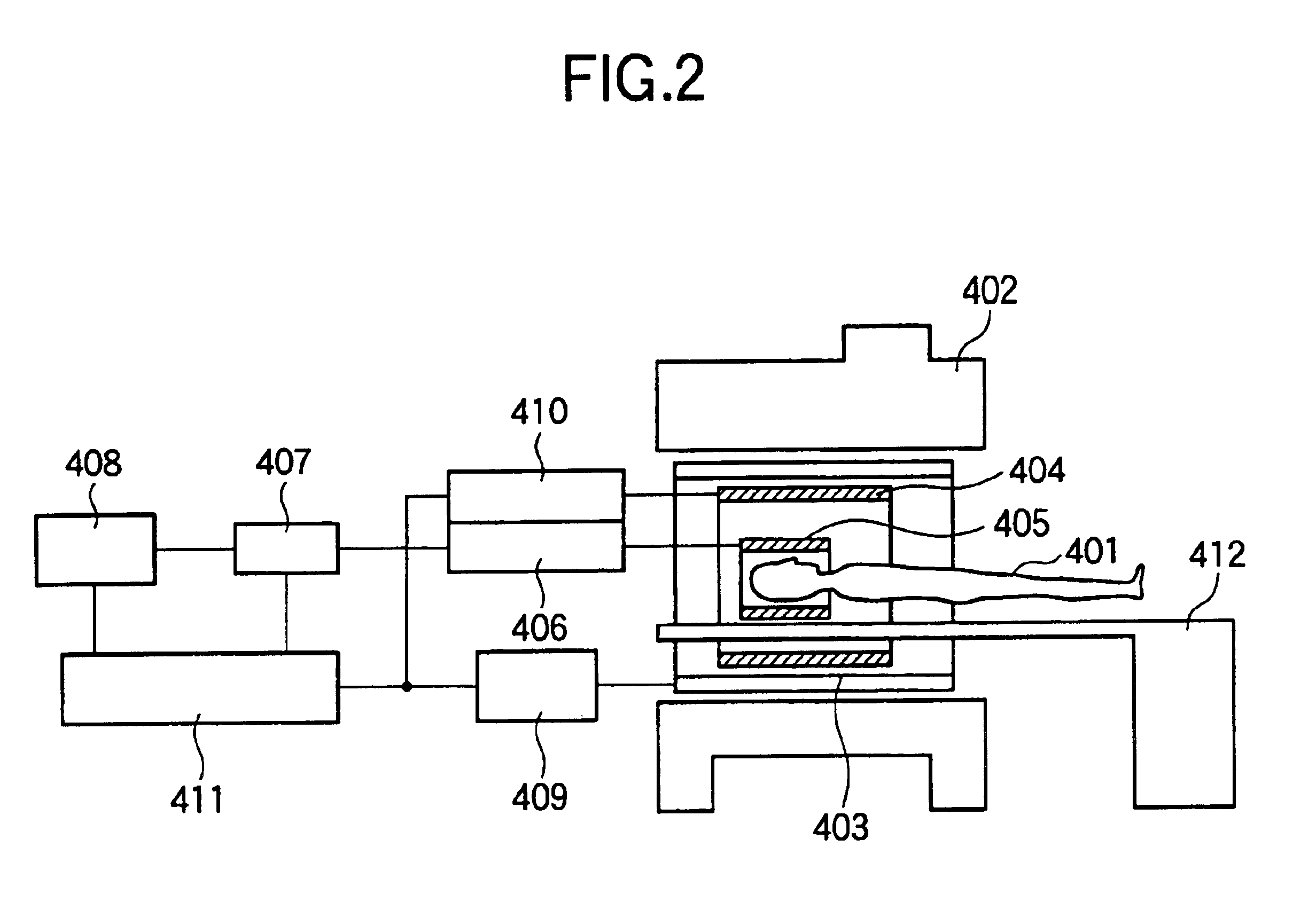
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and method
InactiveUS6876201B2Reduce artifactsImprove image qualityMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceImaging condition
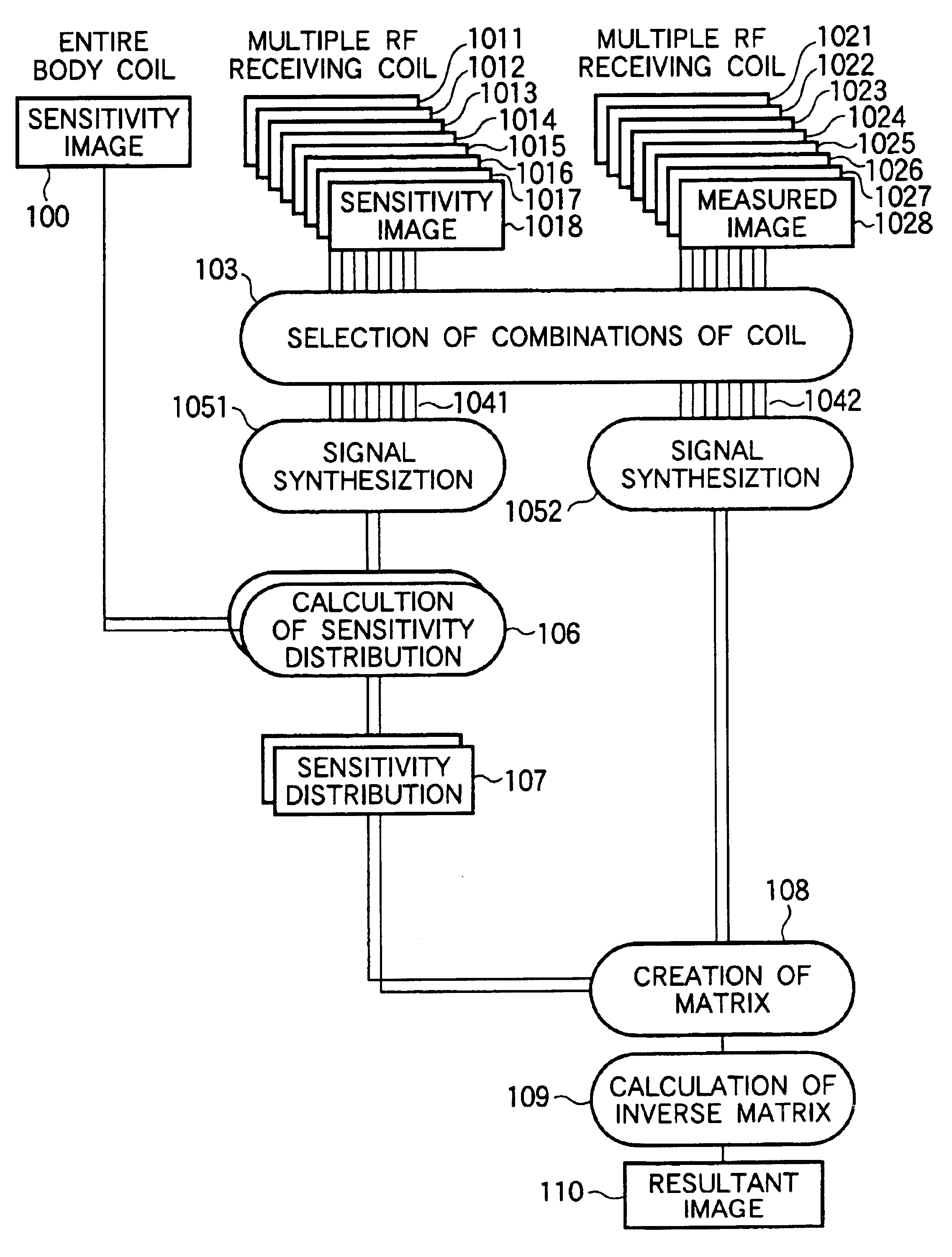
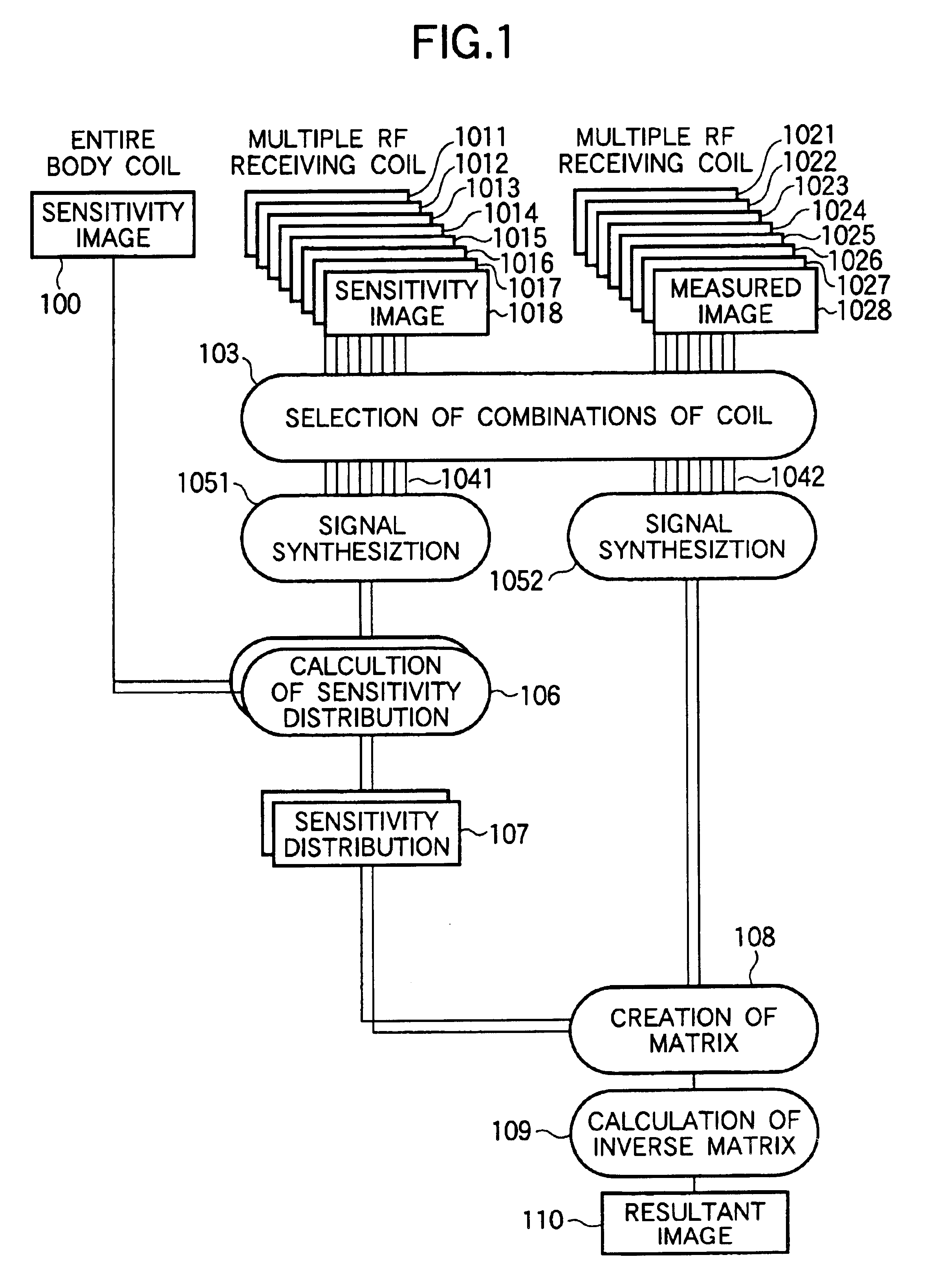
A magnetic resonance imaging apparatus includes a magnetic field generation means for applying gradient magnetic fields and a radio-frequency magnetic field to a patient placed in a static magnetic field in a predetermined pulse sequence; a multiple RF receiving coil comprising at least three RF receiving coils for receiving the nuclear magnetic resonance signals generated from the patient; and an image reconstruction means for reconstructing an image by processing the received nuclear magnetic resonance signals, wherein the image reconstruction means includes a coil selection means for selecting a plurality of RF receiving coil groups that are preset by combining the plurality of RF receiving coils according to imaging conditions, a synthesization means for synthesizing the measured data received by the respective RF receiving coils of each of the plurality of selected RF receiving coil groups, and a calculation means for eliminating aliasing artifacts by executing a matrix calculation as to the synthesized data.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP
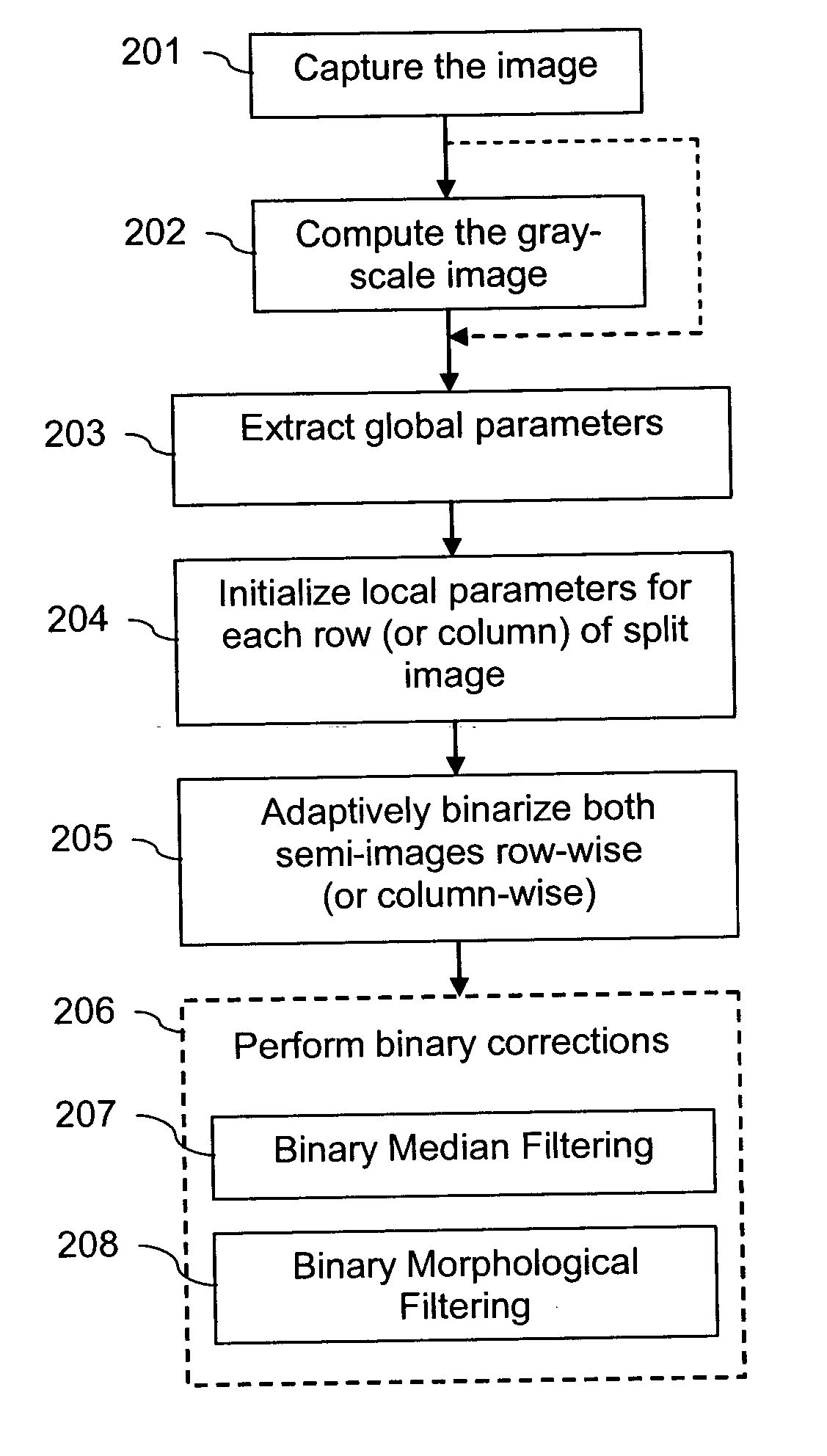
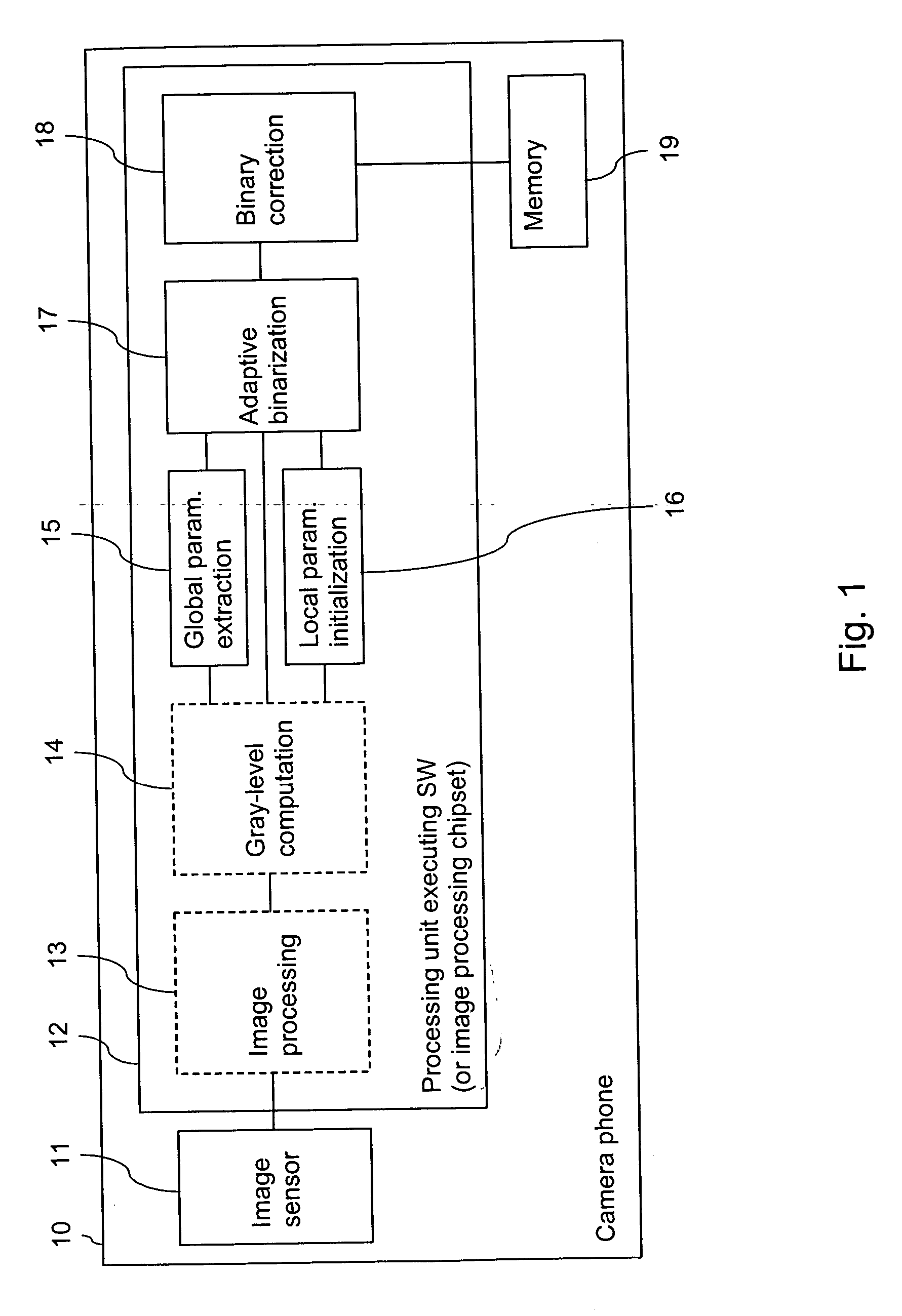
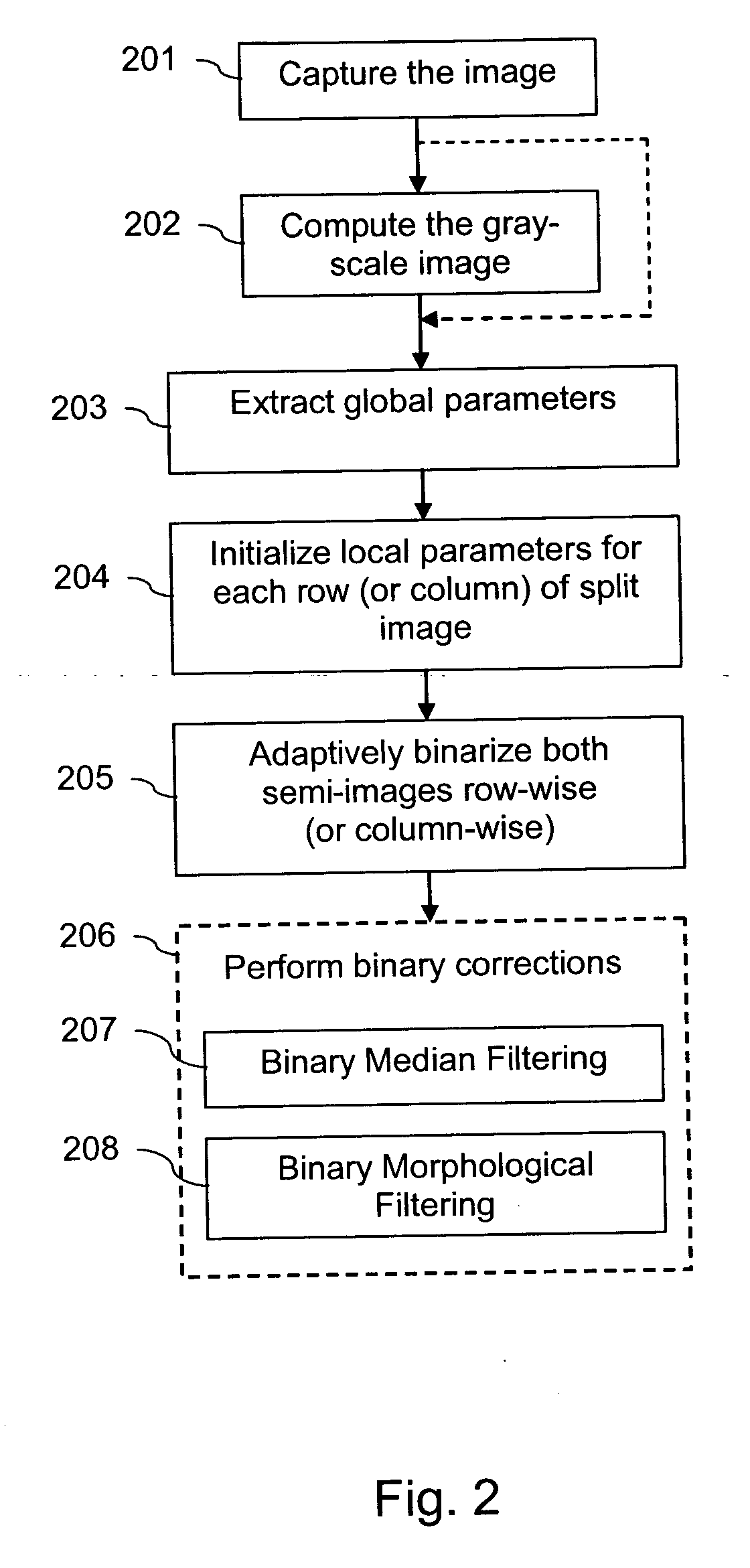
Binarization of an image
InactiveUS20070025625A1Eliminate vignettingComplicated processImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognition
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Method of frequency planning in an ultra wide band system
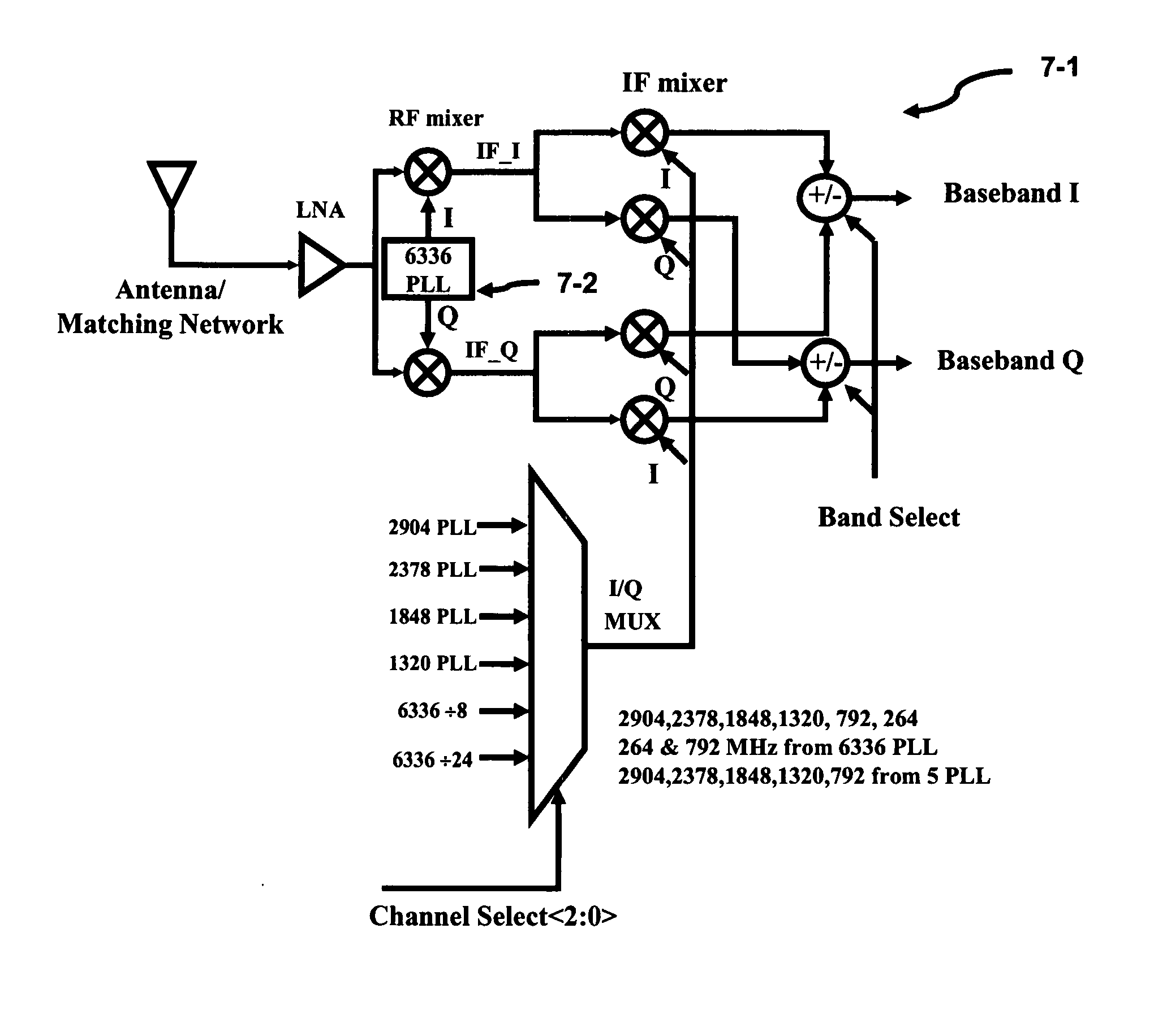
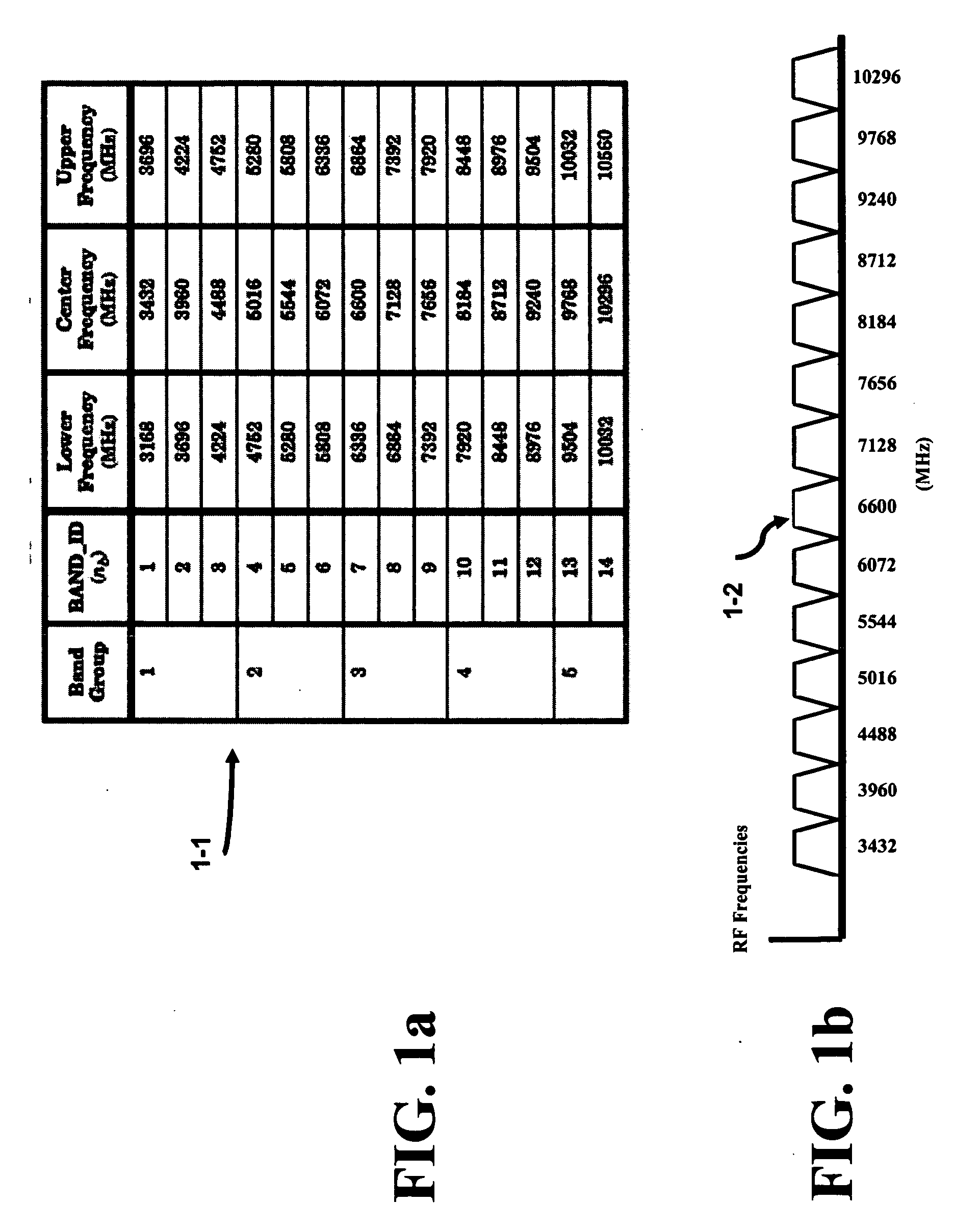
InactiveUS20070155350A1Simple technologyReduce in quantityAutomatic scanning with simultaneous frequency displayModulation transferenceOperational systemOperating frequency
The present invention provides reduces the number of required synthesizers thereby reducing the area and power concerns to extract / insert a signal from / to a multi-channel communication system and is also known as frequency planning. The highest frequency of operation required for the synthesizers or oscillators is approximately the midpoint of the entire signal frequency range. Two superimposed Weaver architectures are used to form the architecture. The receiver extracts the baseband I and Q signals from the multi-channel communication system, while the transmitter upconverts the baseband I and Q signals to the multi-channel communication system. The Weaver architecture, depending on the select bit, can enhance the image signal and reduce the desired signal or the image signal can be reduced while the desired signal is enhanced. Because the image and signal components are symmetrically displaced from the RF LO, less IF LO frequencies or synthesizers are required to operate the system.
Owner:WINONICS RES
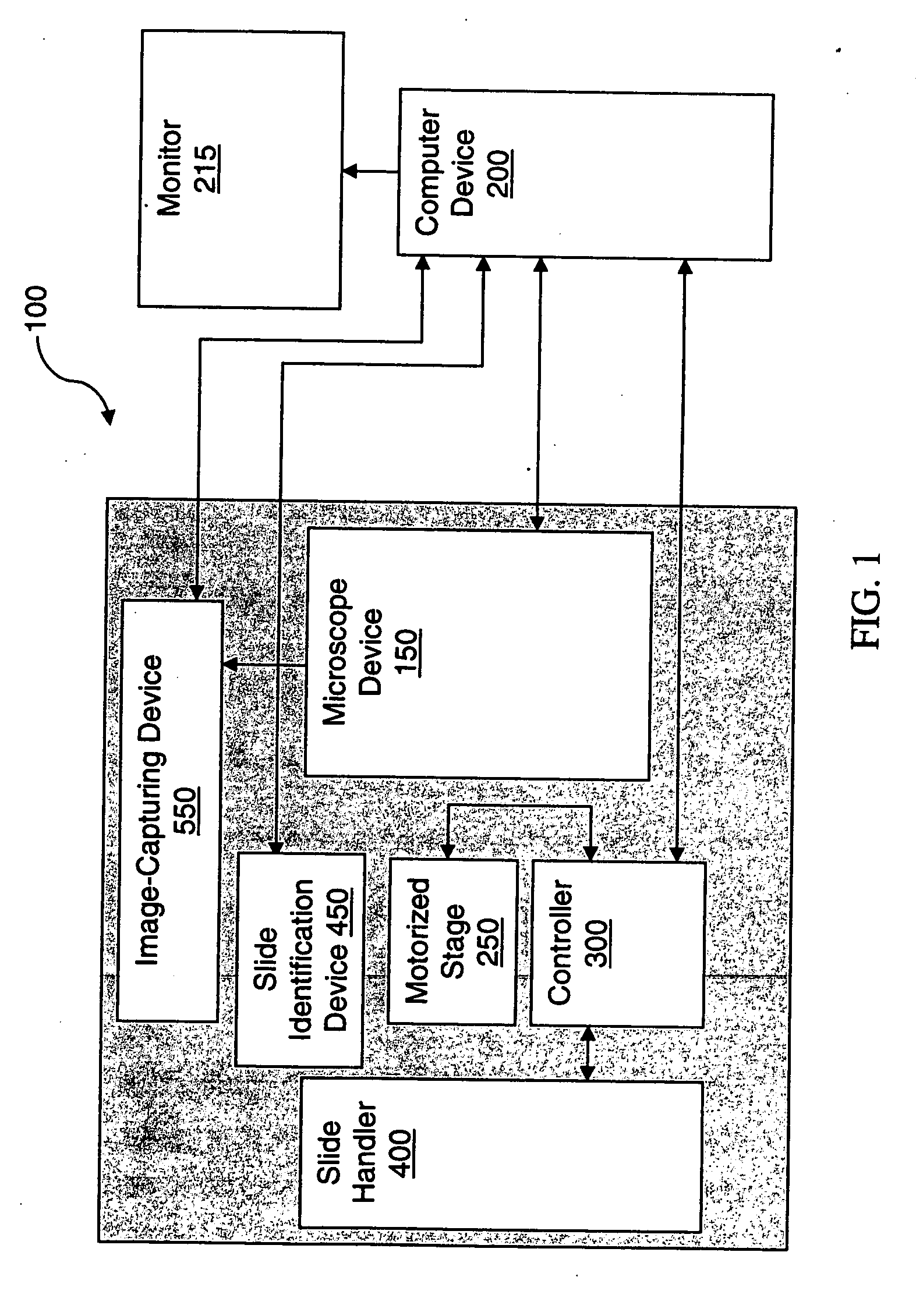
Microscopy system having automatic and interactive modes for forming a magnified mosaic image and associated method
InactiveUS20090196526A1Easy to handleWell equipped with system memoryAcquiring/recognising microscopic objectsSedimentation analysisInterlaced videoComputer graphics (images)
A scanning device for biological slides is provided, which can be operated in an interactive routine mode as well as in an unsupervised high speed automatic mode. In the first case, typical components, which the pathologist is used to operating manually, such as the microscope, the stage and the focus, and which have to be motorized for the automatic unsupervised system mode, are configured to simulate manual use, operation, and response. A non-interlaced area scan camera supports the interactive selection and acquisition of individual images in the manual mode, as well as the continuous high-speed scan motion for the rare event detection and virtual slide scan applications of the system. Due to the particular requirements to accommodate both operational modes, methods are described for constructing the virtual slide out of image tiles with varying overlap areas in the x- and y-directions.
Owner:TRIPATH IMAGING INC
Apparatus, method and system for performing phase-resolved optical frequency domain imaging
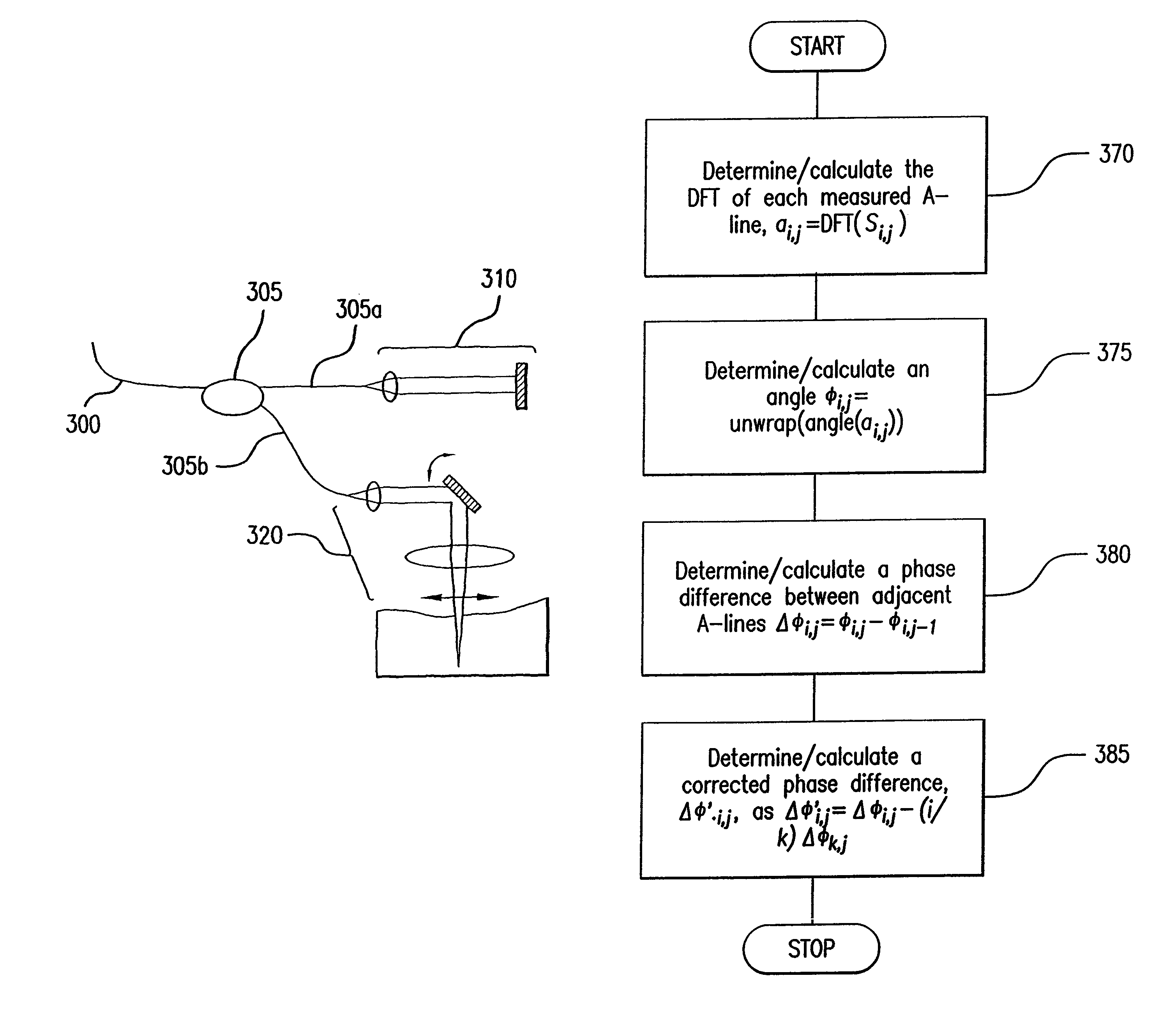
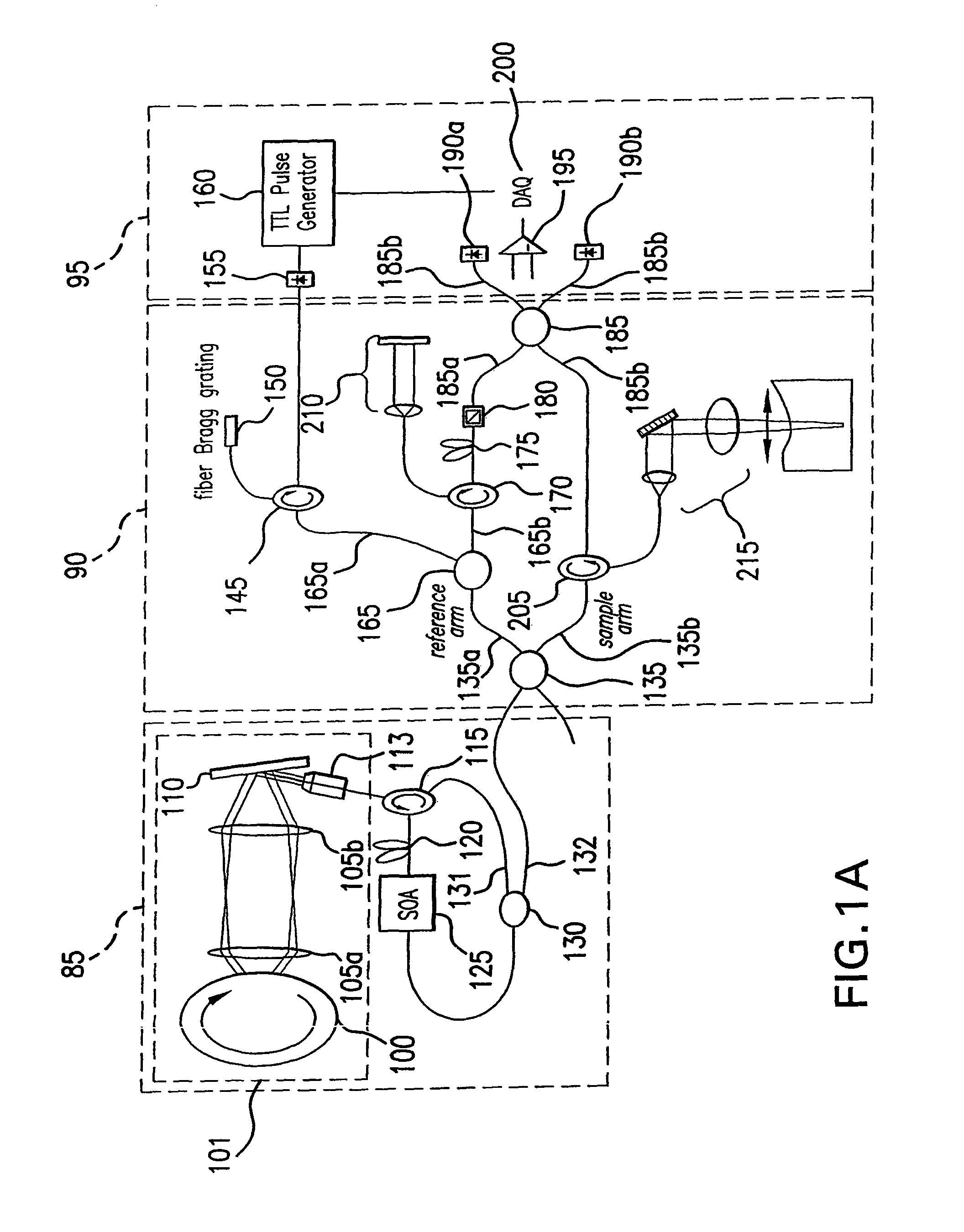
ActiveUS9060689B2Reduce impactWeakening rangePhase-affecting property measurementsScattering properties measurementsPhase correlationTime changes
Apparatus, system and method are provided which utilize signals received from a reference and a sample. In particular, a radiation is provided which includes at least one first electro-magnetic radiation directed to the sample and at least one second electro-magnetic radiation directed to the reference. A frequency of the radiation varies over time. An interference can be detected between at least one third radiation associated with the first radiation and at least one fourth radiation associated with the second radiation. It is possible to obtain a particular signal associated with at least one phase of at least one frequency component of the interference, and compare the particular signal to at least one particular information. Further, it is possible to receive at least one portion of the radiation and provide a further radiation, such that the particular signal can be calibrated based on the further signal.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Method and apparatus for improving quality of depth image
InactiveUS8588515B2Quality improvementTaking imageImage enhancementImage analysisParallaxComputer science
A method and apparatus for enhancing quality of a depth image are provided. A method for enhancing quality of a depth image includes: receiving a multi-view image including a left image, a right image, and a center image; receiving a current depth image frame and a previous depth image frame of the current depth image frame; setting an intensity difference value corresponding to a specific disparity value of the current depth image frame by using the current depth image frame and the previous depth image frame; setting a disparity value range including the specific disparity value; and setting an intensity difference value corresponding to the disparity value range of the current depth image frame by using the multi-viewpoint image.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Light-diffusing film and apparatus provided with the same
InactiveUS20100195313A1Improve heat resistanceAvoid changeDiffusing elementsSynthetic resin layered productsPolypropylenePolycarbonate
A light-diffusing film comprises a light-diffusing layer (e.g., an anisotropic light-diffusing layer), and the light-diffusing layer comprises a continuous phase comprising a polycarbonate-series resin (a polycarbonate-series resin having a number average molecular weight of 15000 to 25000) and a dispersed phase comprising a polypropylene-series resin (a metallocene-catalyzed polypropylene-series random copolymer). A transparent layer may be laminated on at least one side of the light-diffusing layer. The light-diffusing layer may substantially be free from a compatibilizing agent. In spite of a use of the polycarbonate-series resin, the dispersed phase can uniformly be formed. Therefore, the film is suitable for a member of a plane light source device or a display apparatus. The light-diffusing film inhibits a change in a light-diffusing characteristic even under a high temperature.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
Liquid crystal display
ActiveUS8269740B2Improve accuracyIncrease ratingsInput/output processes for data processingLiquid-crystal displayComputer science
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com