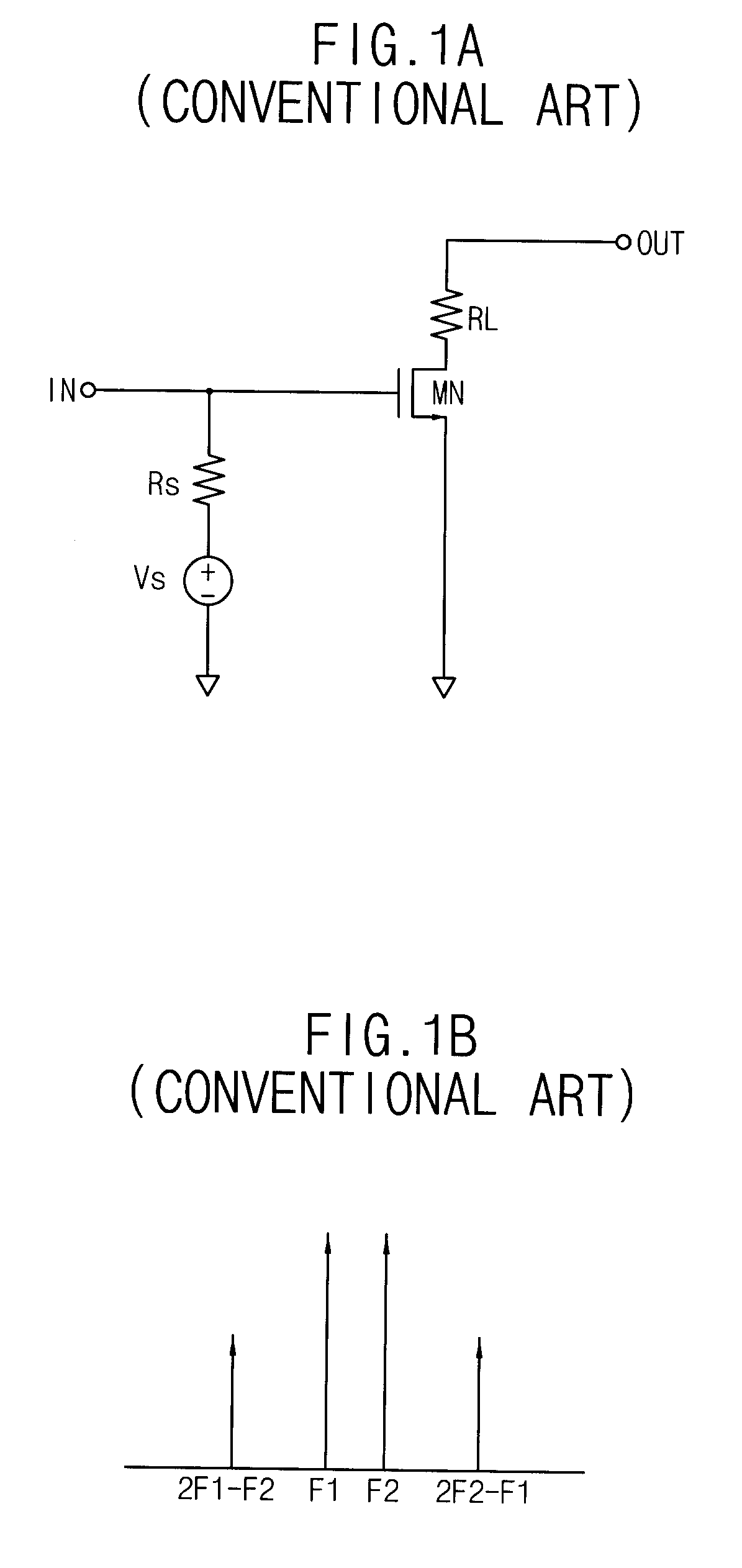
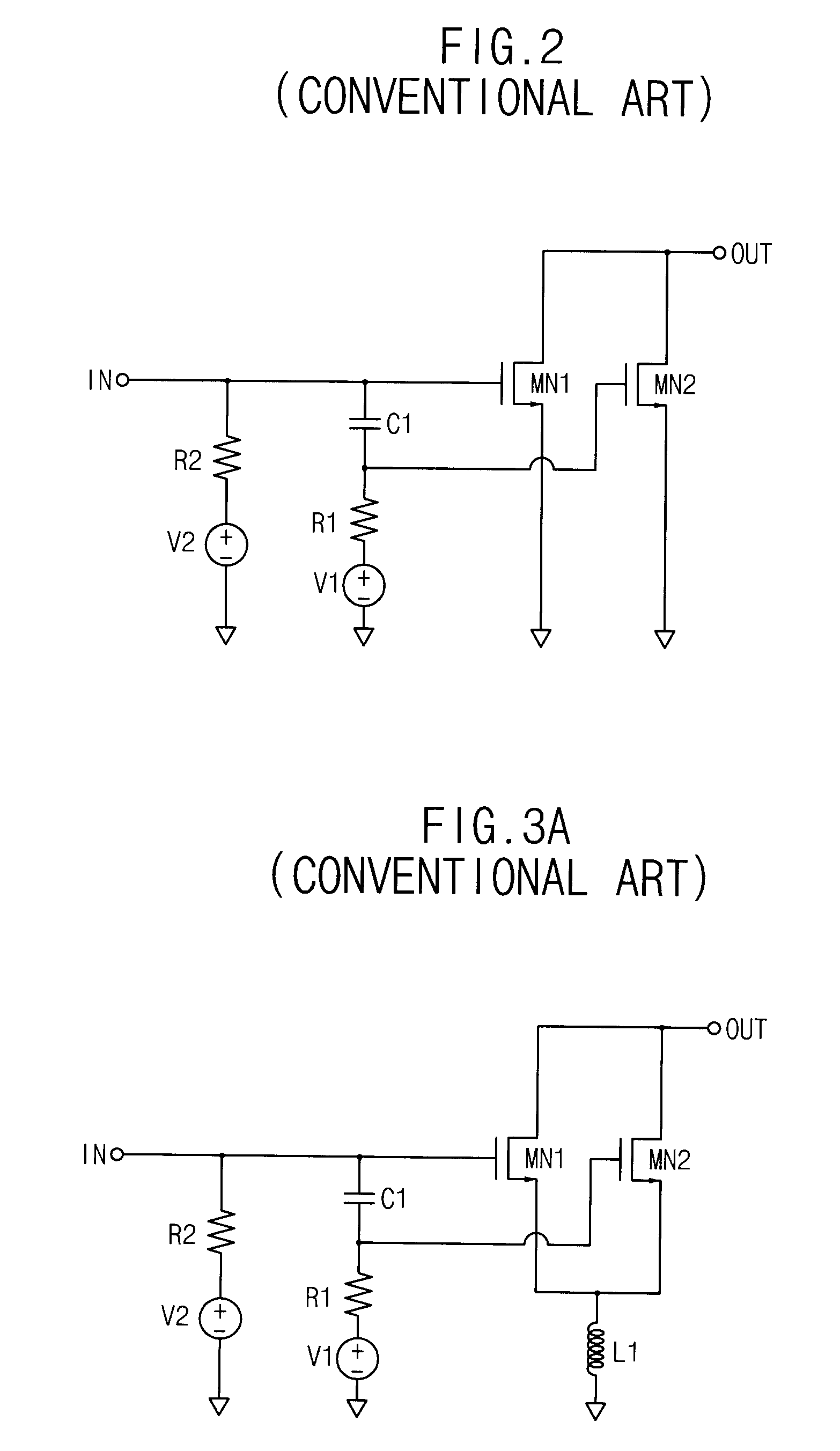
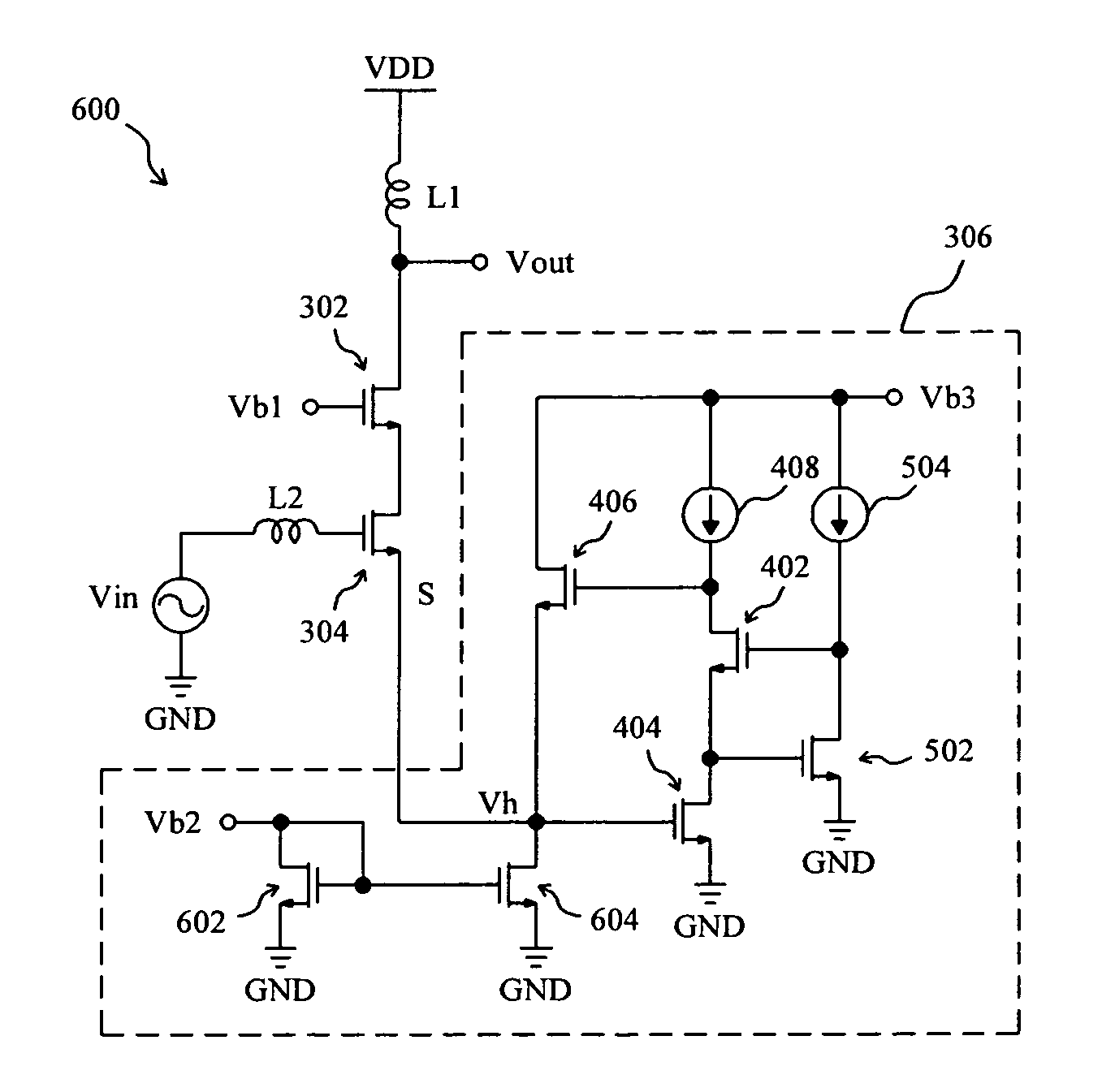
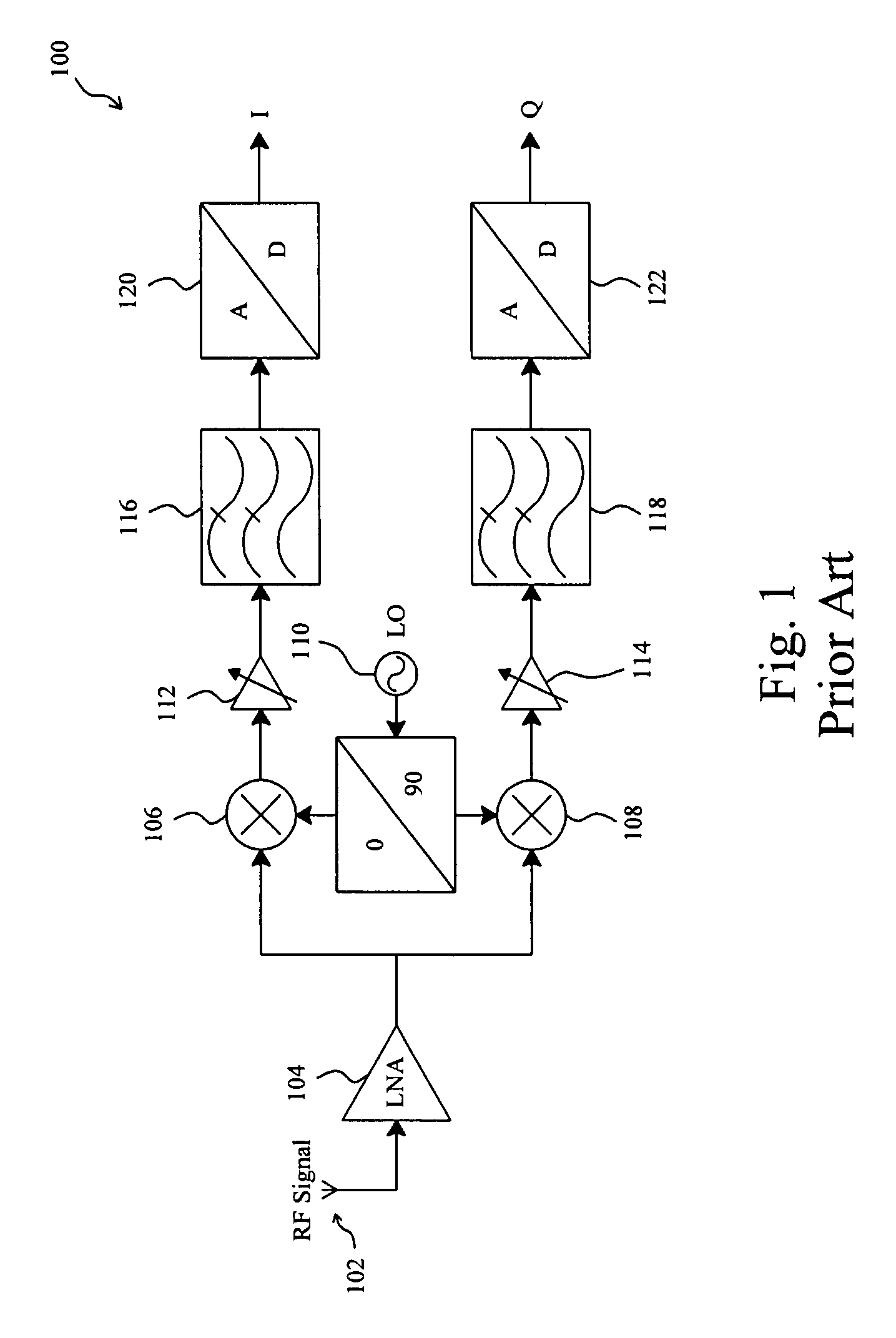
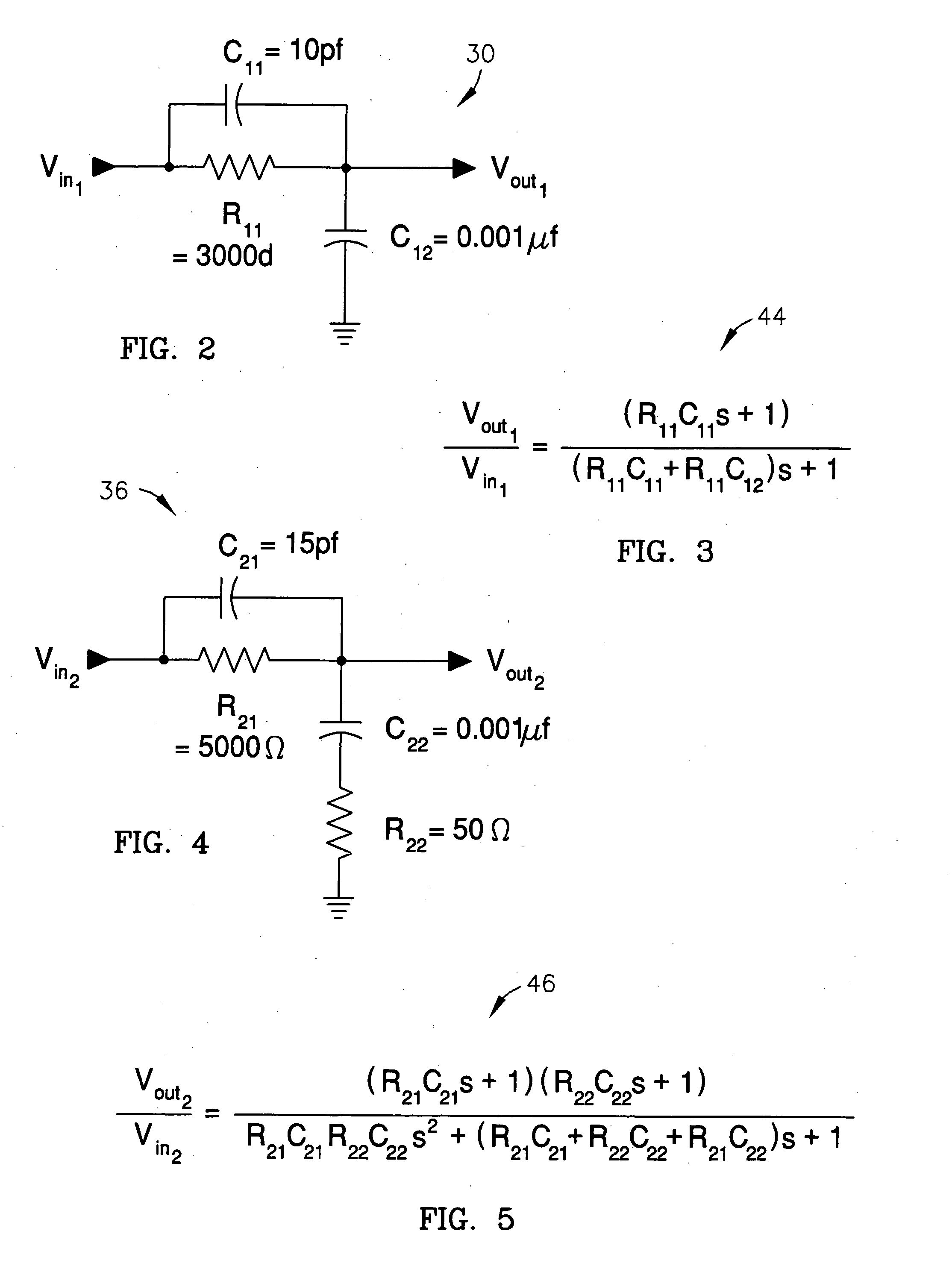
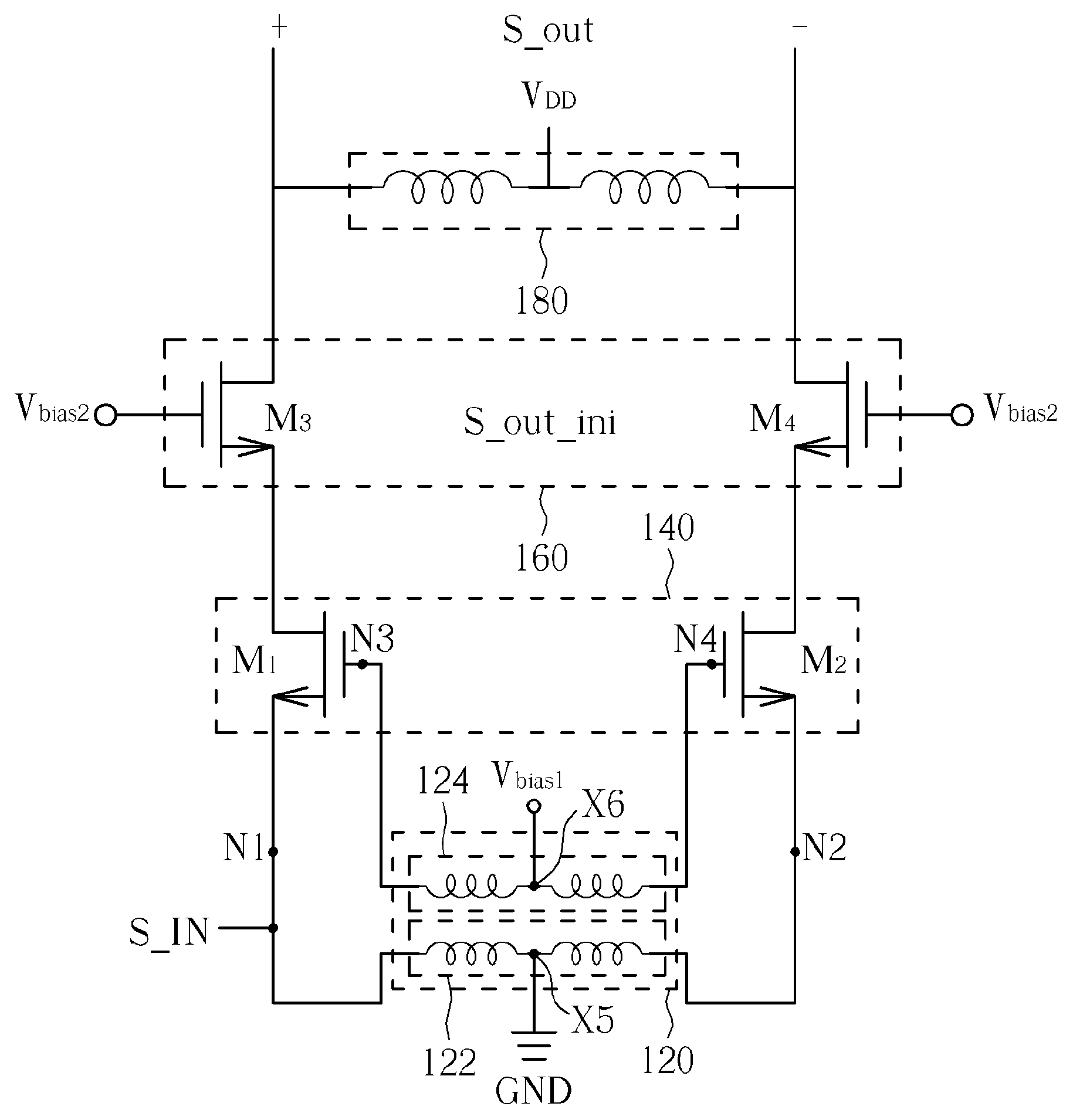
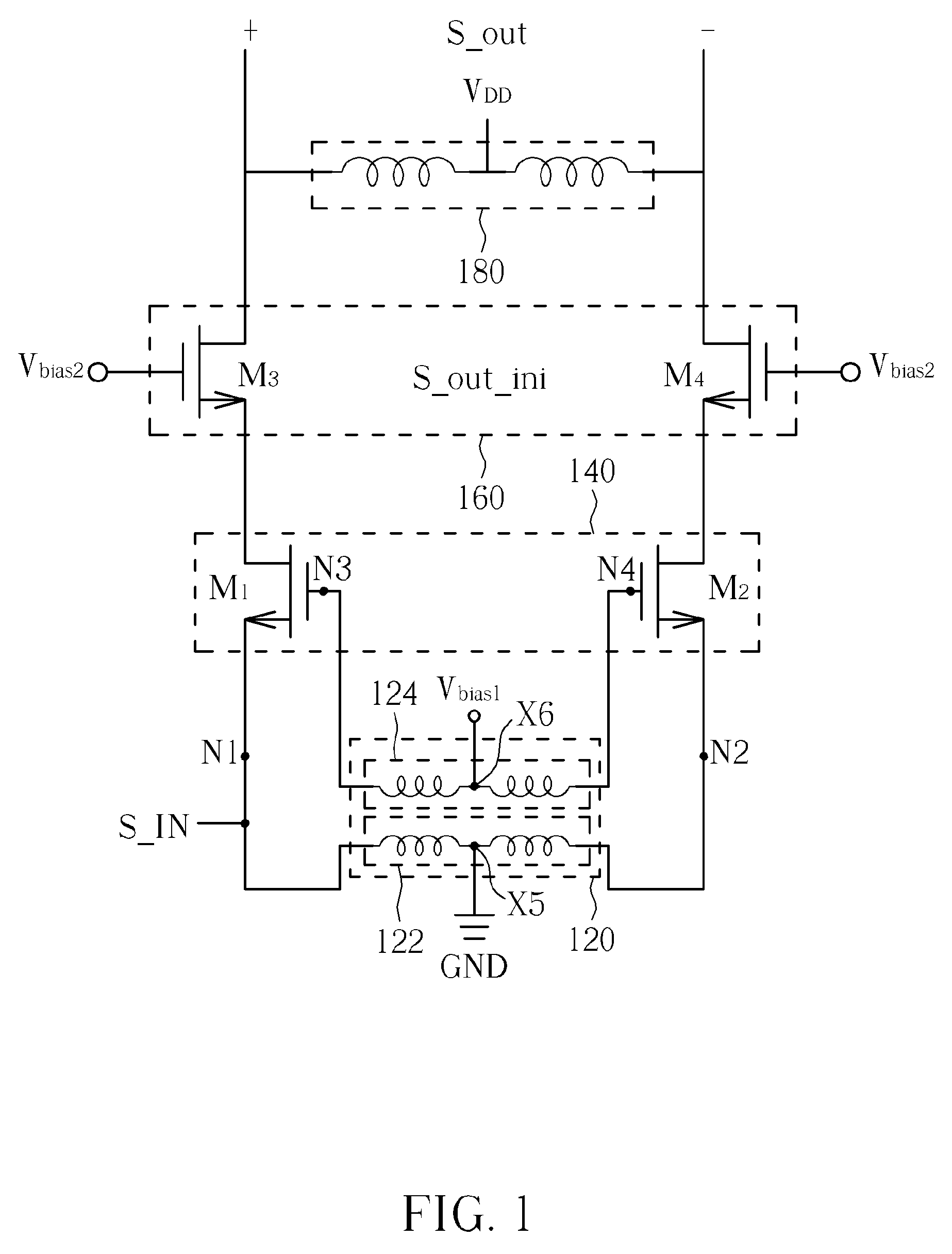
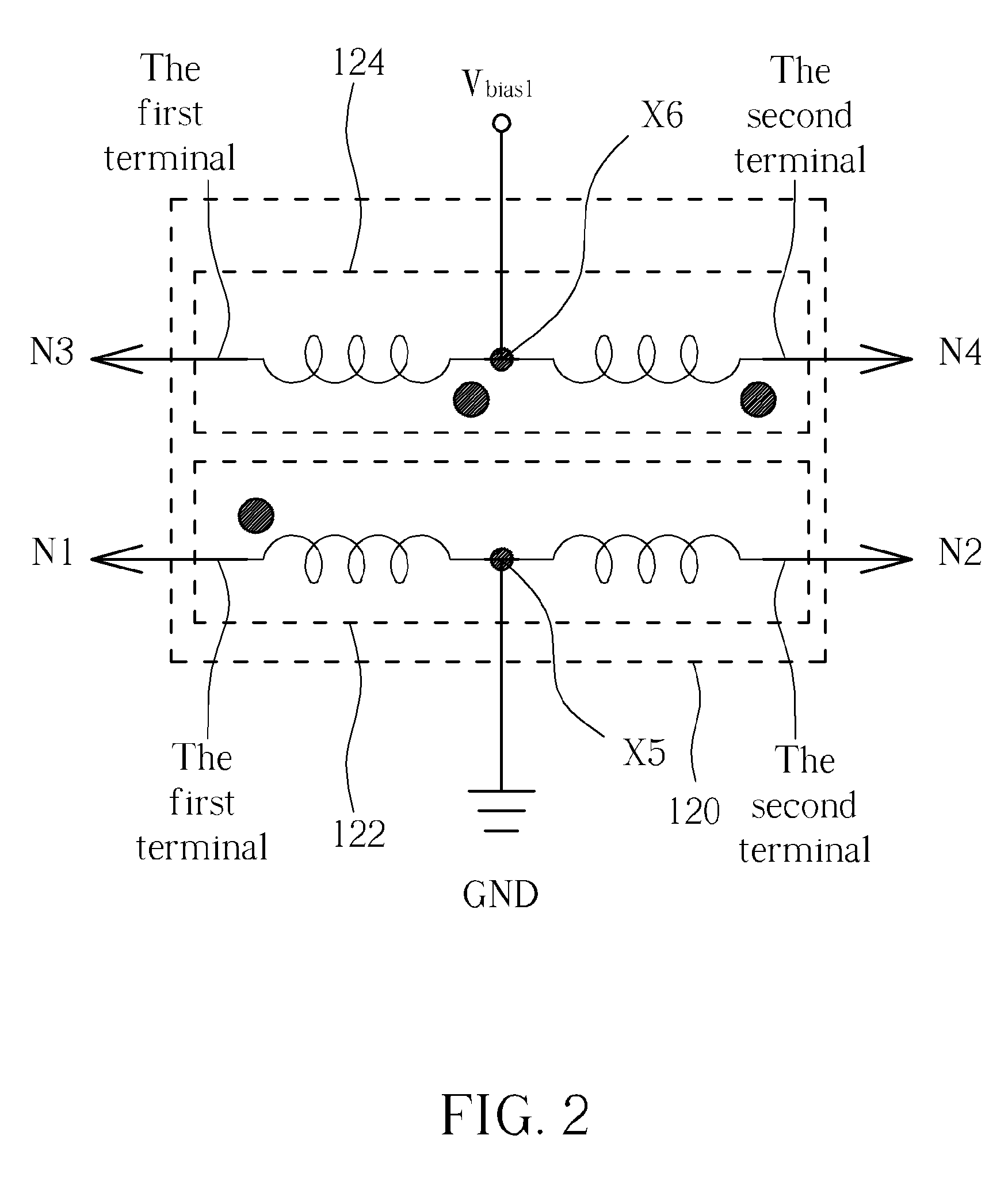
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
45results about How to "Low noise amplifier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
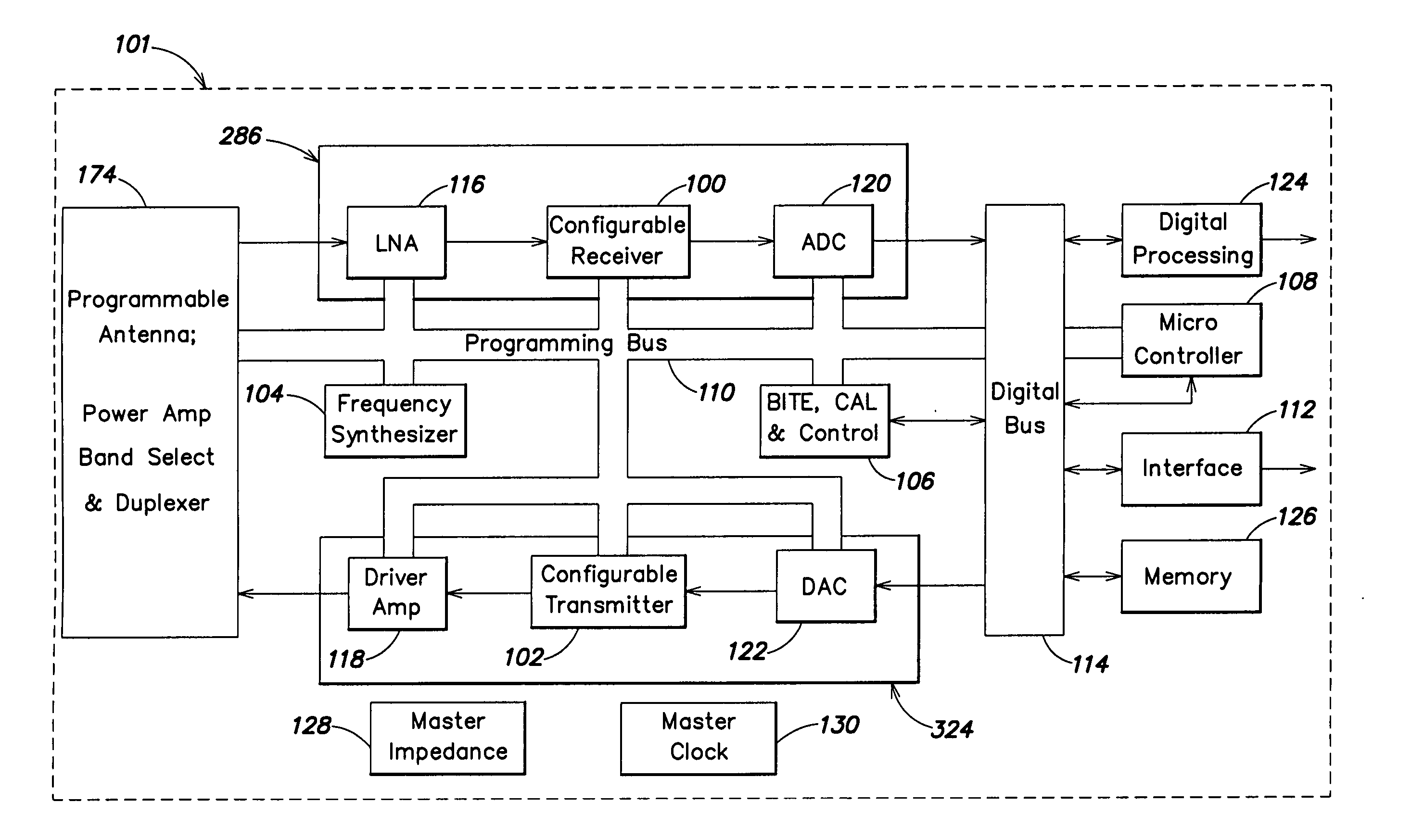
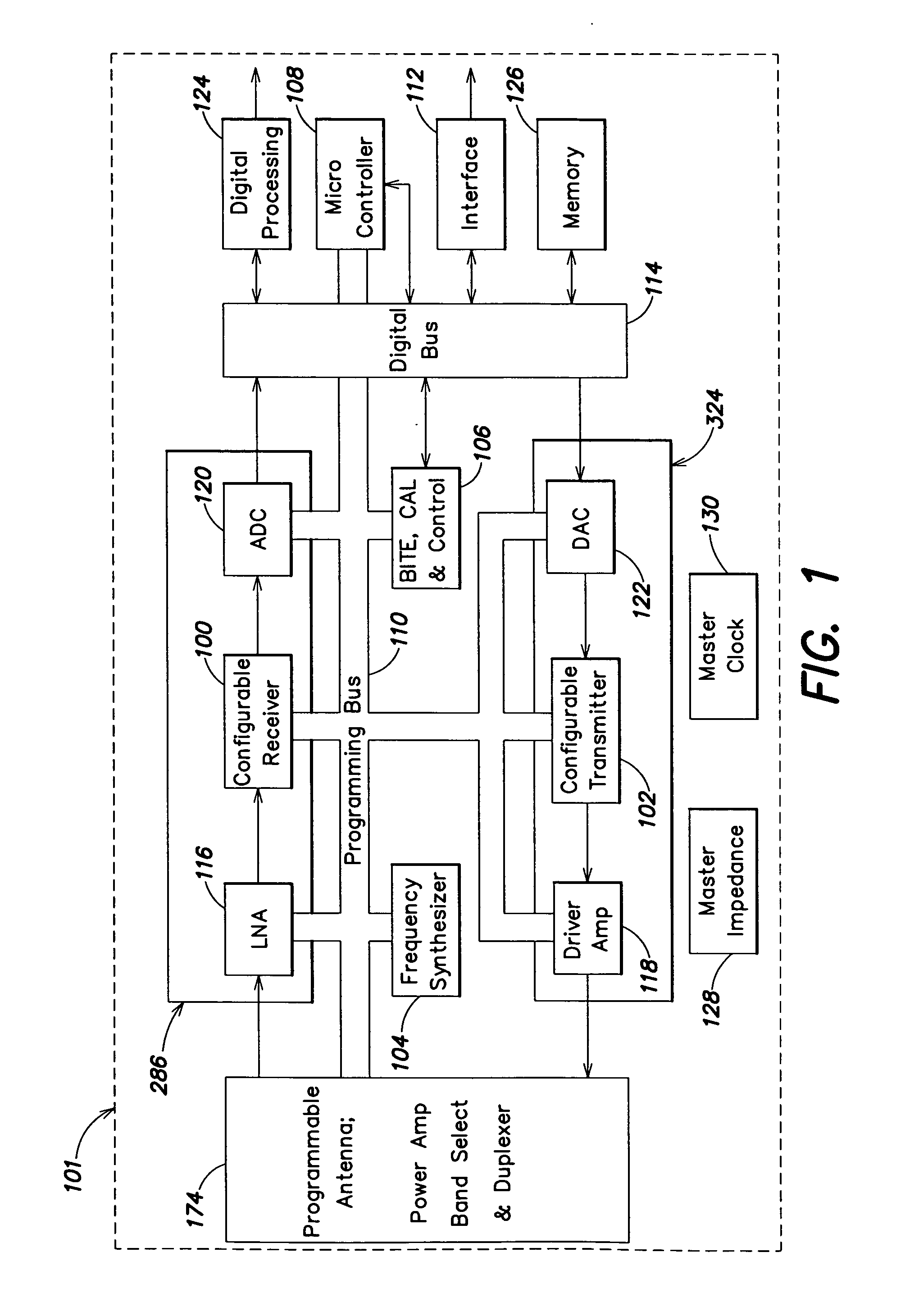
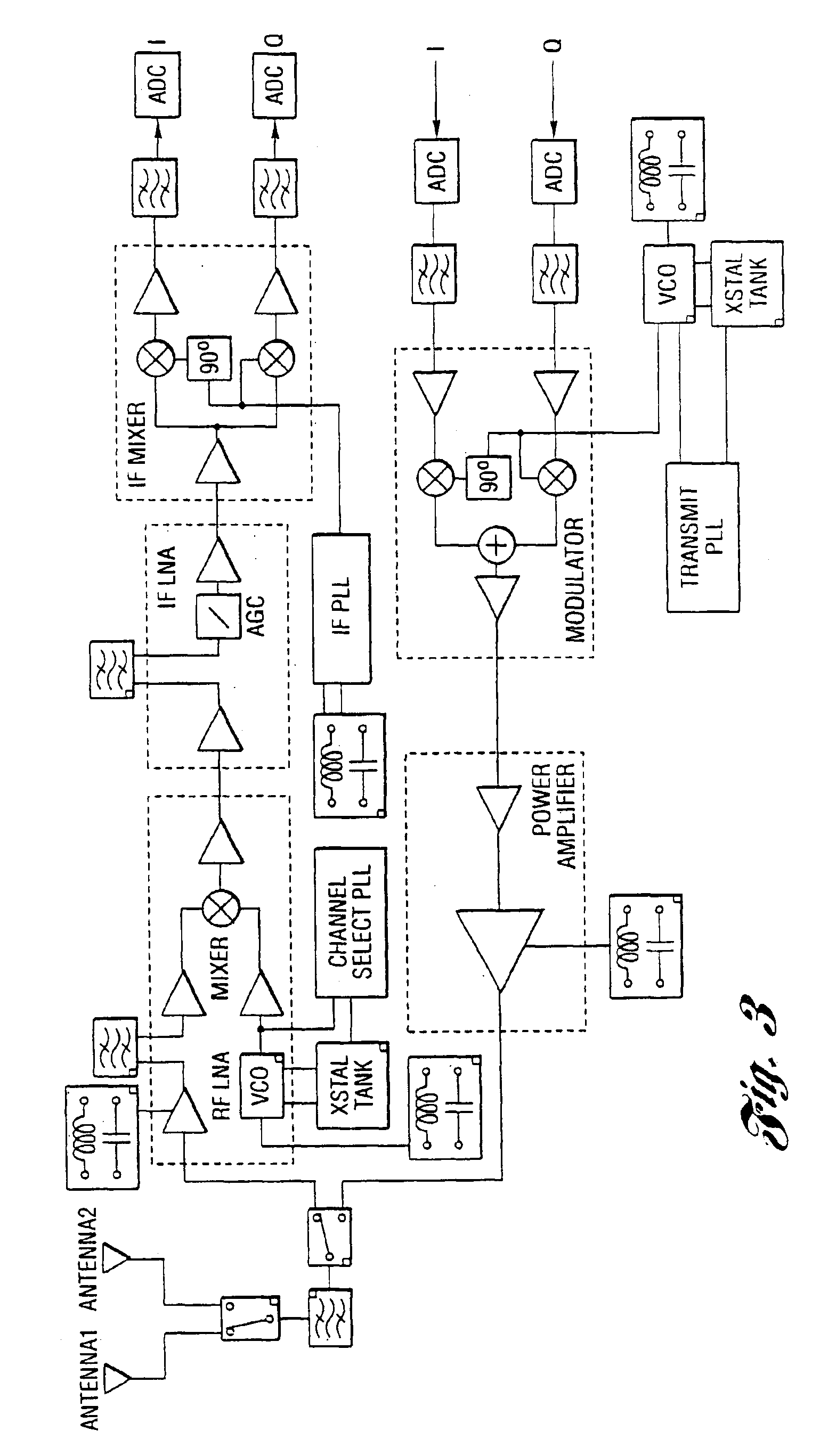
Programmable radio transceiver
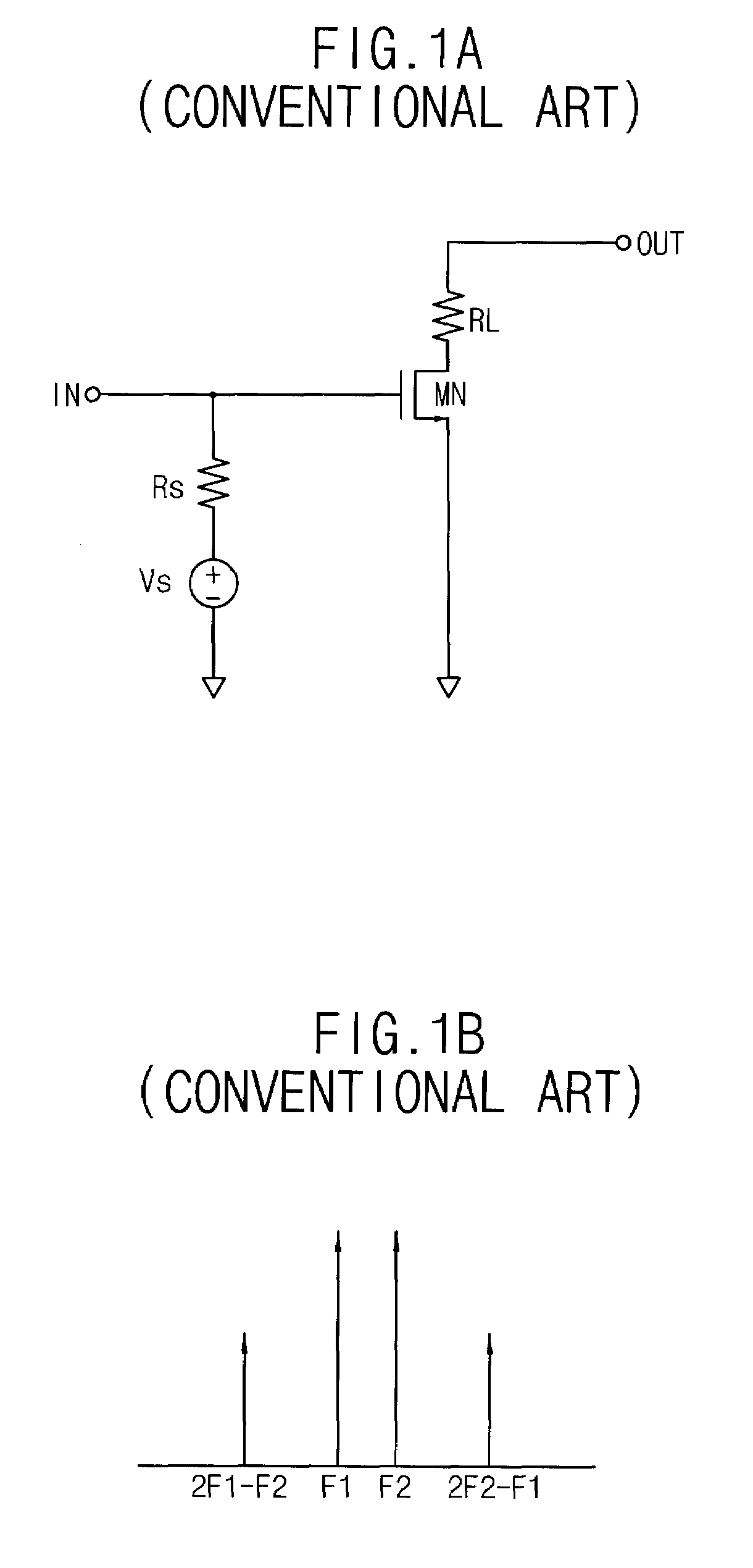
ActiveUS20060030277A1Prevent leakageLow noise amplifierSolid-state devicesAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesExtensibilityTransceiver
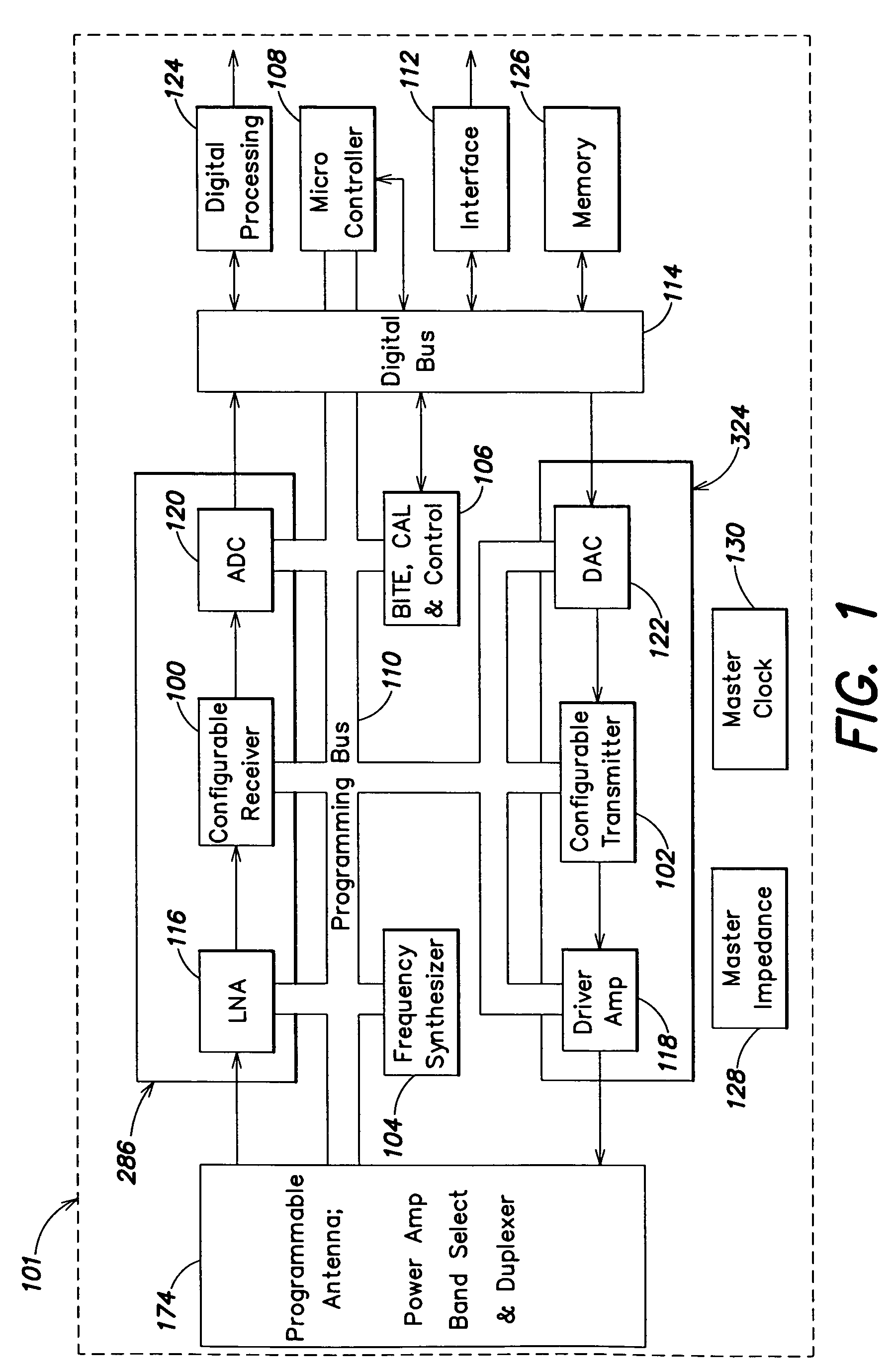
A fully integrated, programmable mixed-signal transceiver comprising a radio frequency integrated circuit (RFIC) which is frequency and protocol agnostic with digital inputs and outputs, the transceiver being programmable and configurable for multiple radio frequency bands and standards and being capable of connecting to many networks and service providers. The RFIC does not use spiral inductors and instead includes transmission line inductors allowing for improved scalability. Components of the transceiver are programmable to allow the transceiver to switch between different frequency bands of operating. Frequency switching can be accomplished though the content of digital registers coupled to the components.
Owner:GULA CONSULTING LLC
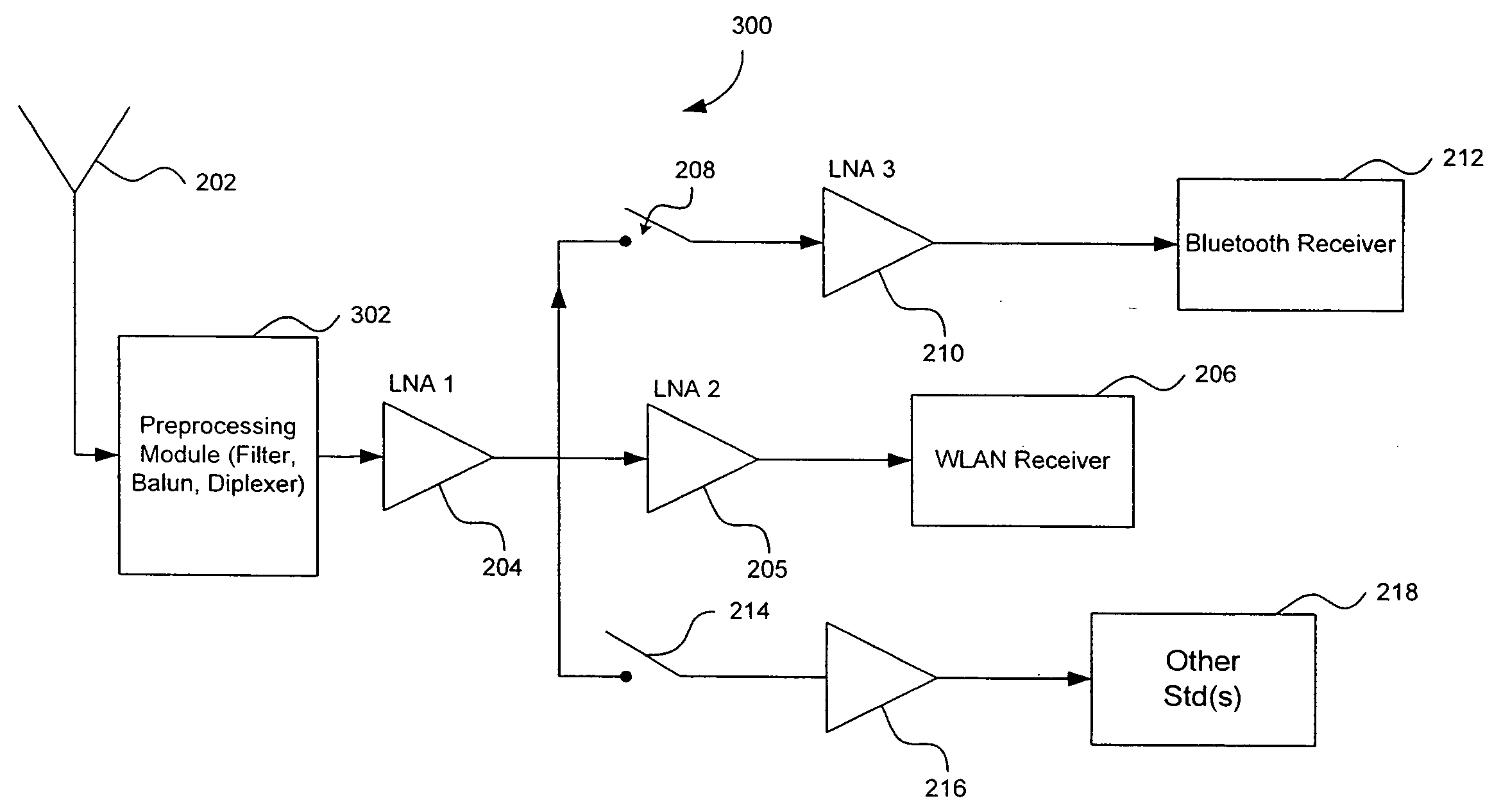
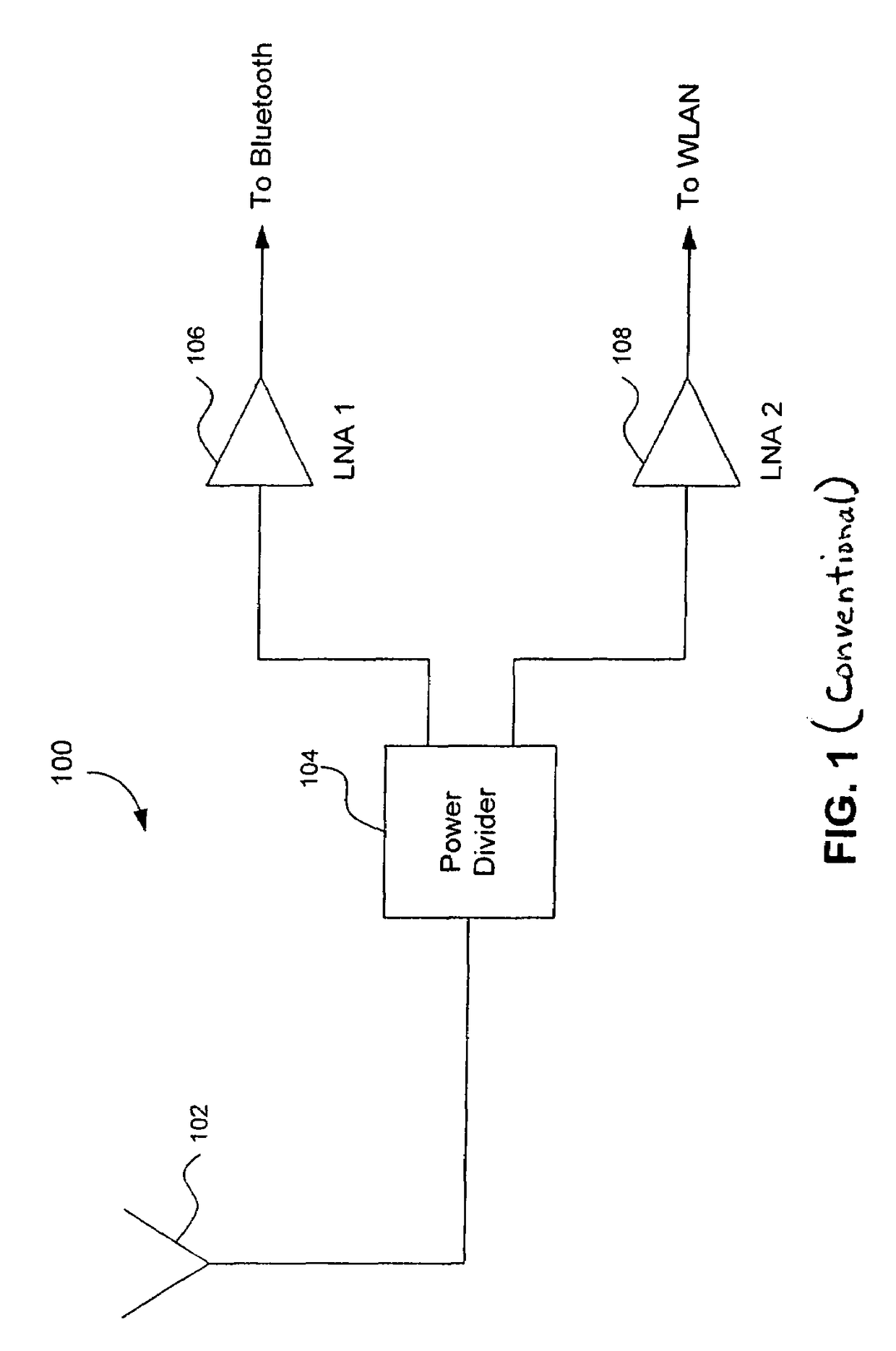
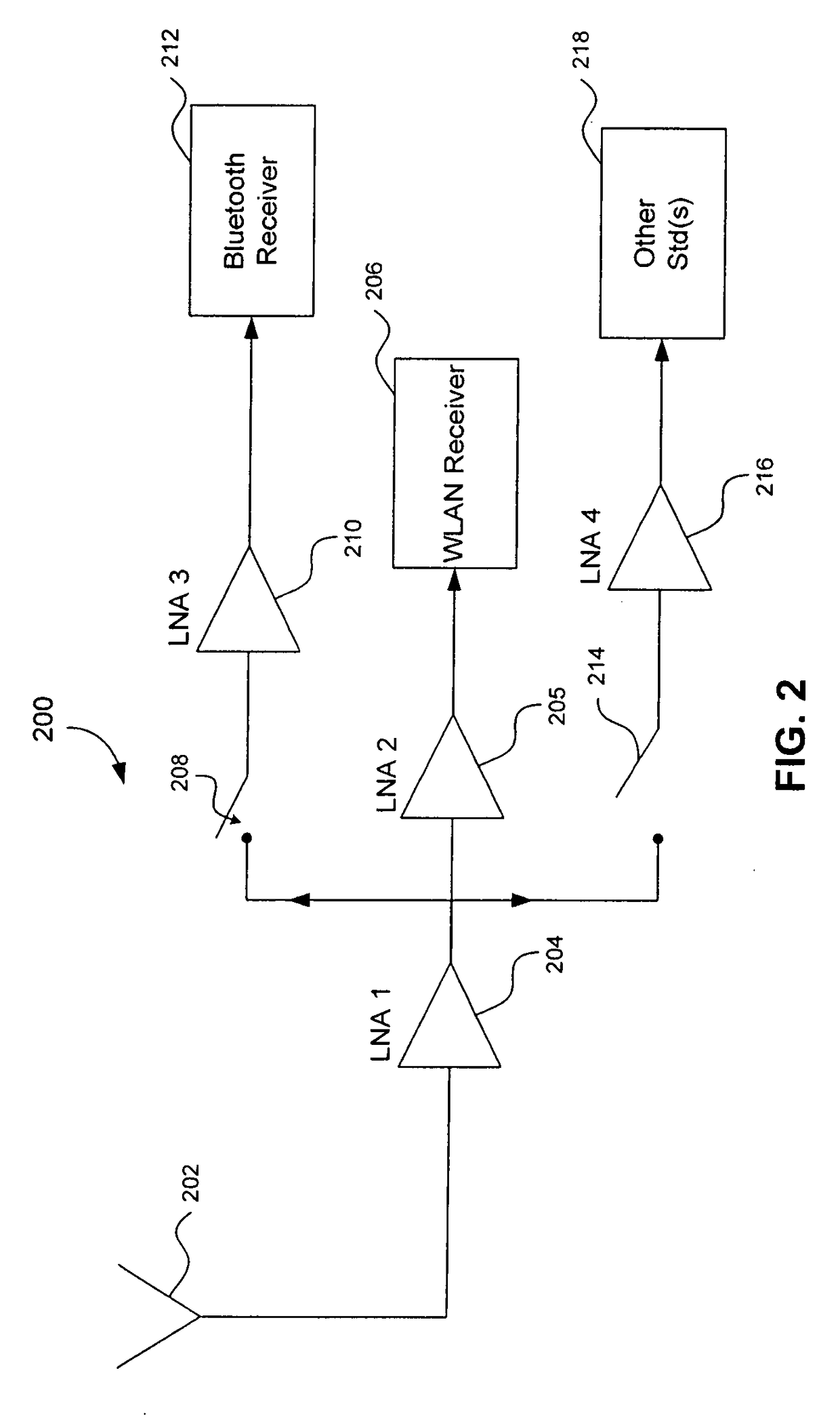
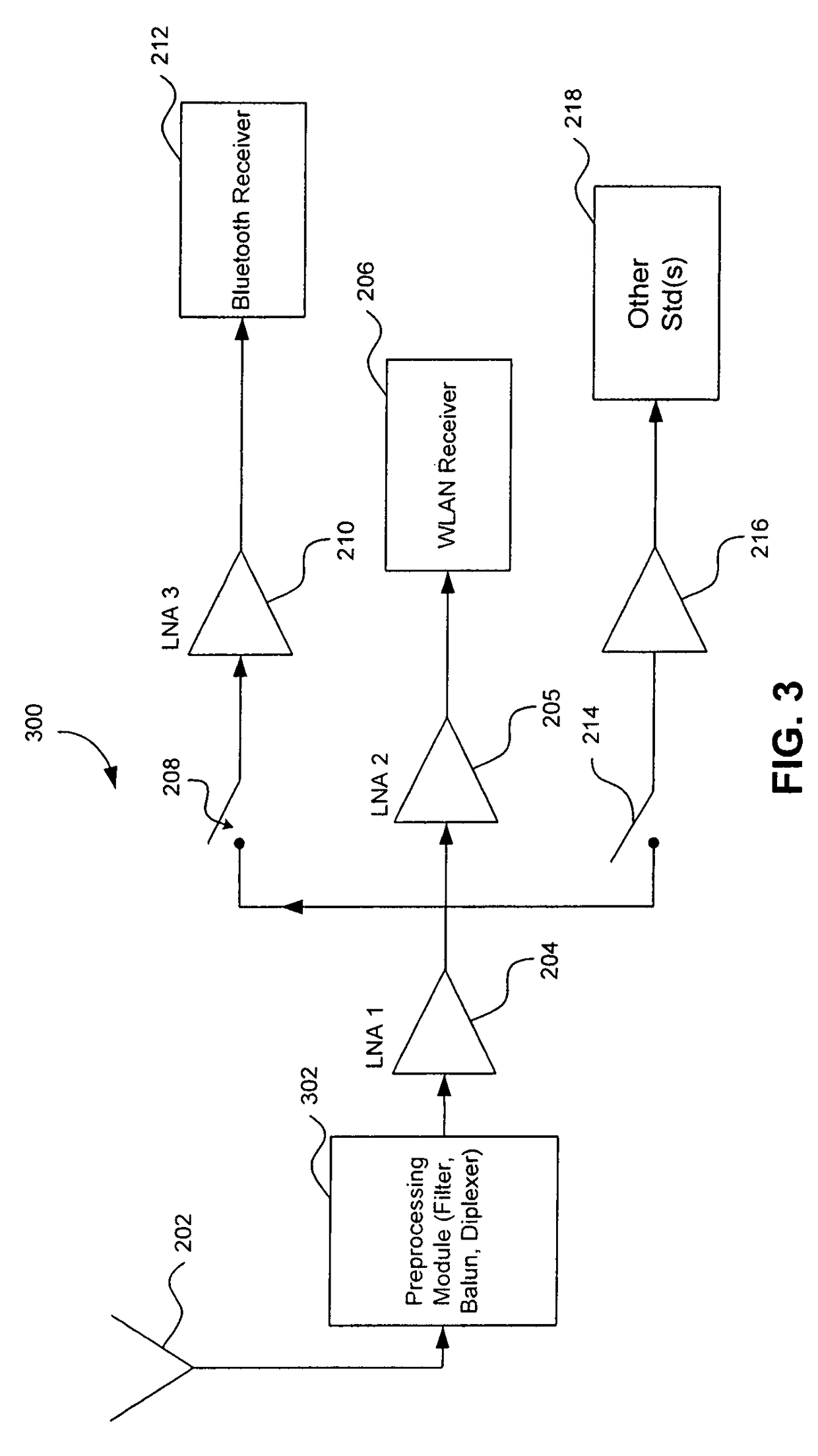
Radio Receiver with shared low noise amplifier for multi-standard operation in a single antenna system with loft isolation and flexible gain control
ActiveUS20070207752A1Improve reverse isolationReduce noiseSpatial transmit diversitySubstation equipmentAudio power amplifierRadio reception
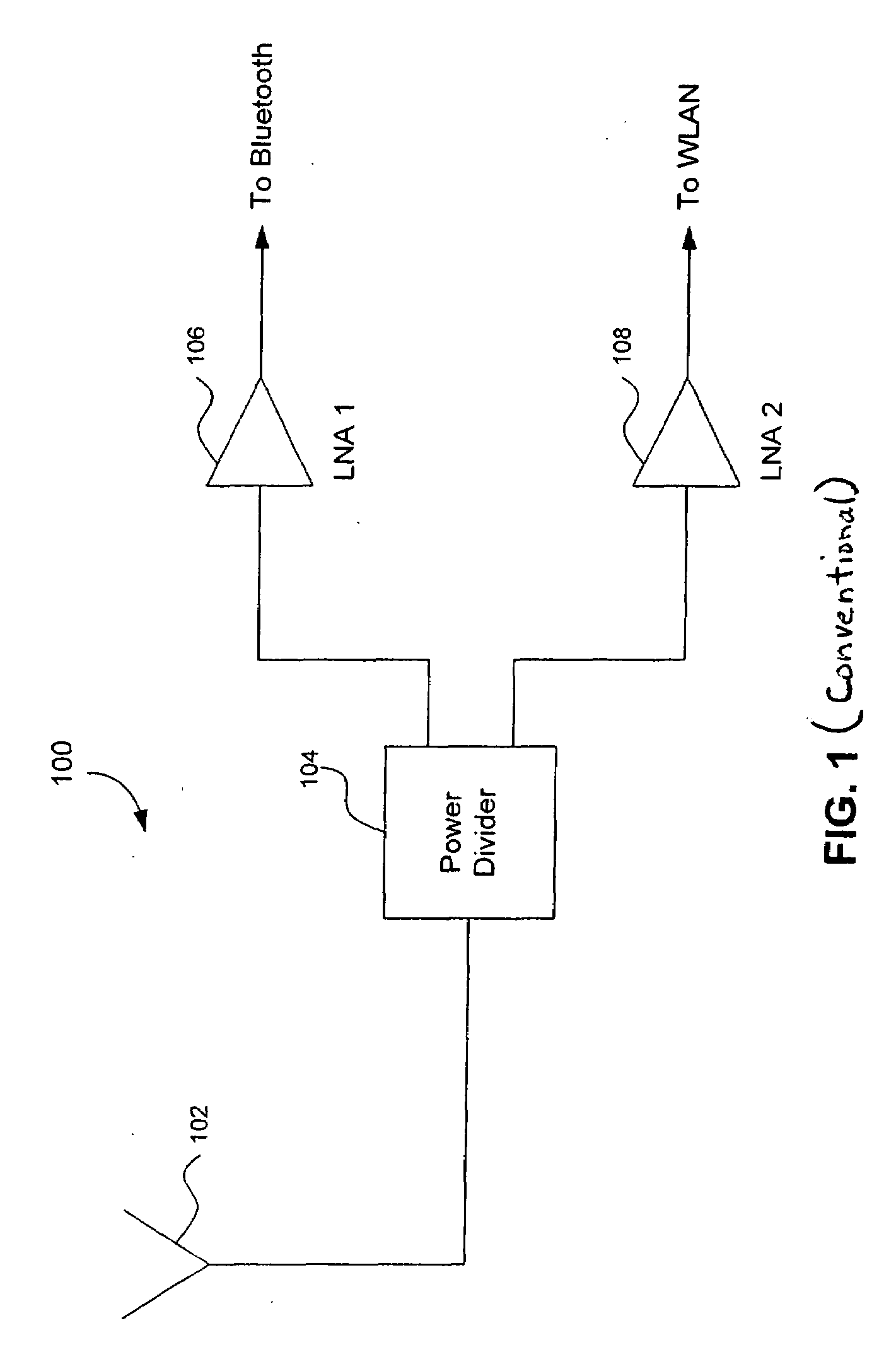
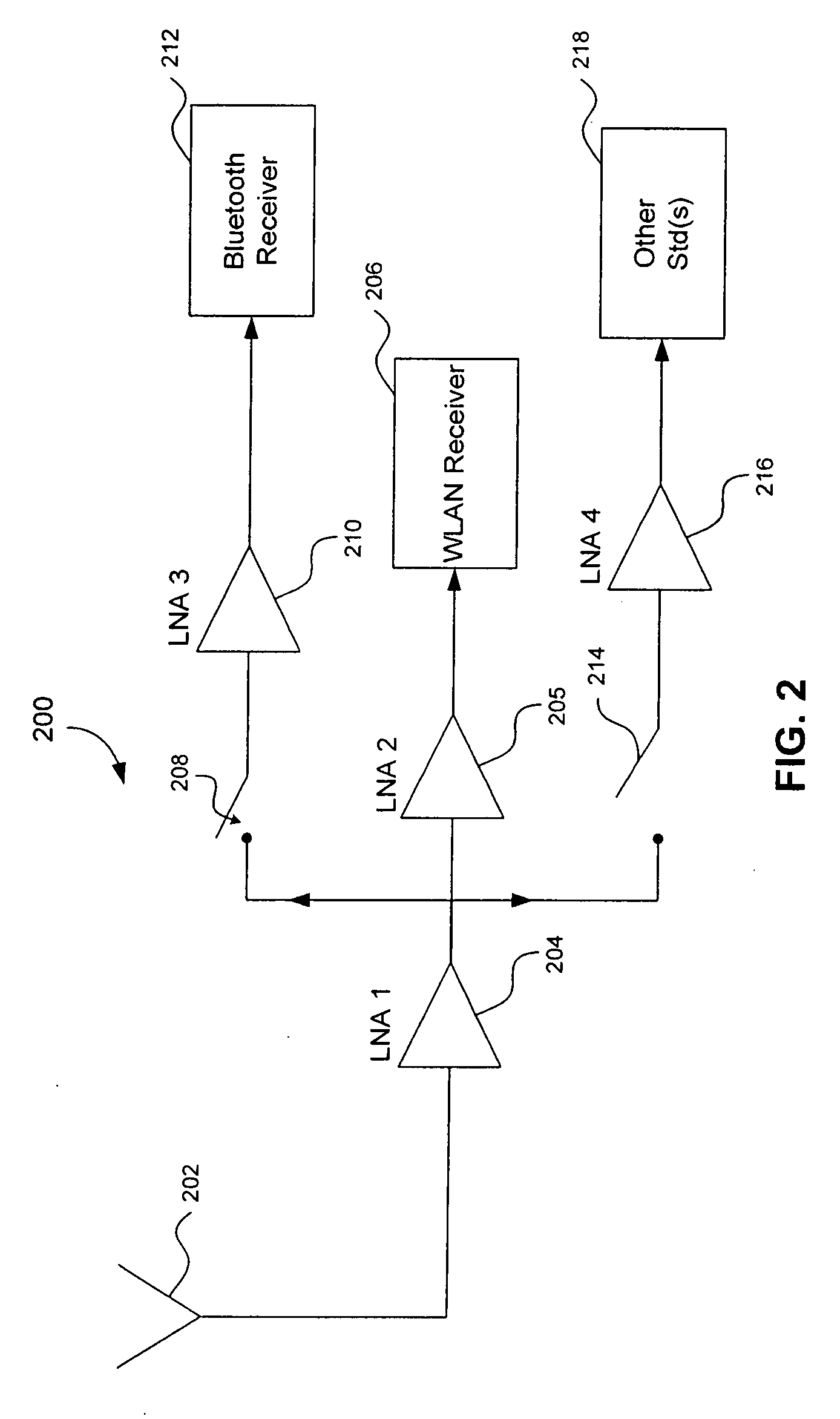
A radio receiver is described that processes multiple wireless standards using a single antenna according to embodiments of the invention. The radio receiver includes a single antenna, and a low noise amplifier that is connected to the antenna, without an intervening power divider or power splitter. The output of the low noise amplifier feeds multiple wireless receivers in a parallel arrangement that are operating according to different communications standards, including for example a Bluetooth and a WLAN 802.11. Additional wireless standards and their corresponding receivers could be added as well. The input impedance of the low noise amplifier defines the impedance seen by the antenna, regardless of which operational standard is actually in use. Each signal path includes an additional low noise amplifier having a gain that can be customized for the particular signal path and receiver in use, and which also improves the reverse isolation between signal paths. Further, a switch can be added to one or more of the signal paths so as to further improve isolation when a particular path is not being used.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Programmable radio transceiver
ActiveUS7508898B2Prevent leakageLow noise amplifierSolid-state devicesAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesTransceiverRFIC
A fully integrated, programmable mixed-signal transceiver comprising a radio frequency integrated circuit (RFIC) which is frequency and protocol agnostic with digital inputs and outputs, the transceiver being programmable and configurable for multiple radio frequency bands and standards and being capable of connecting to many networks and service providers. The RFIC does not use spiral inductors and instead includes transmission line inductors allowing for improved scalability. Components of the transceiver are programmable to allow the transceiver to switch between different frequency bands of operating. Frequency switching can be accomplished though the content of digital registers coupled to the components.
Owner:GULA CONSULTING LLC
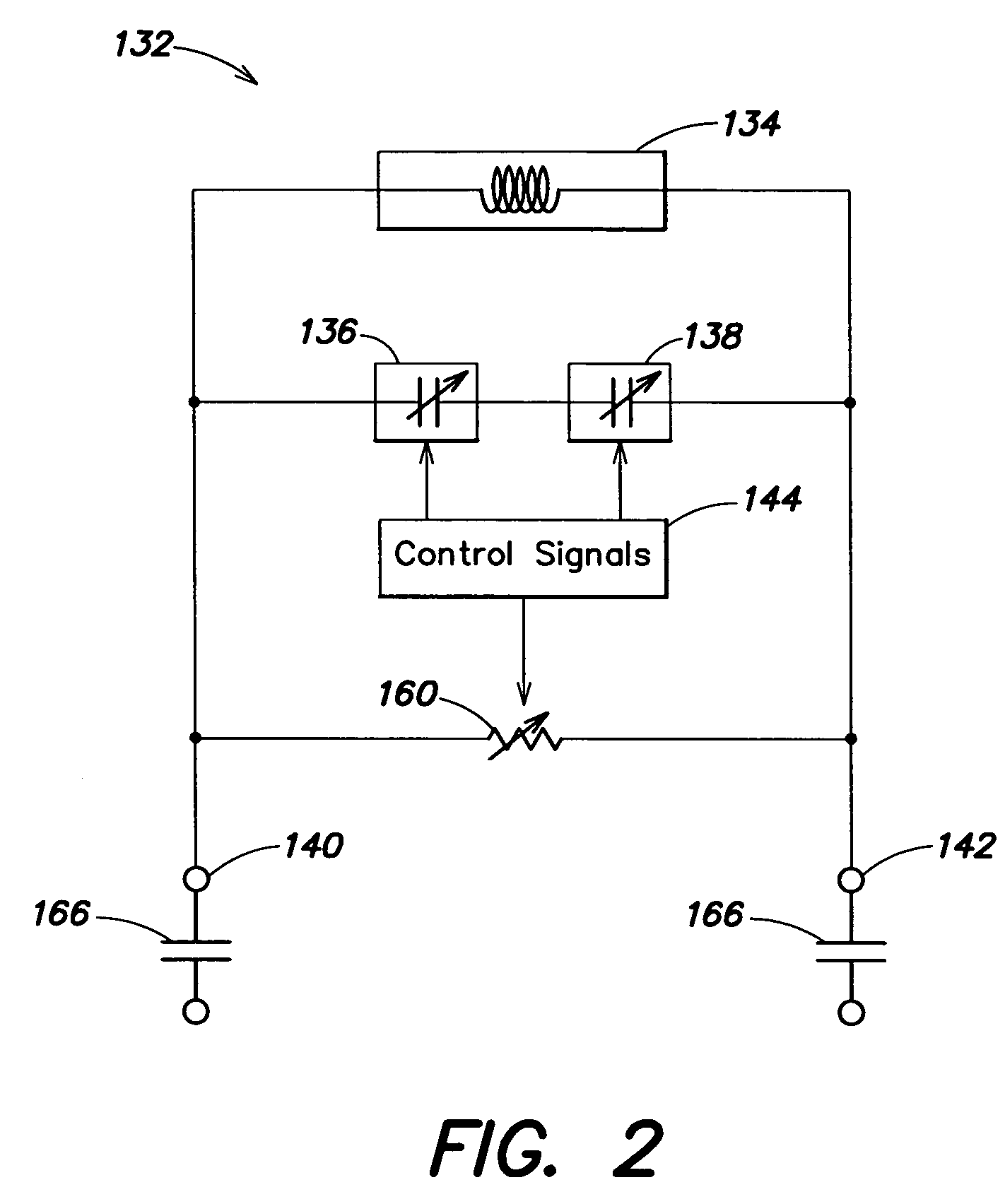
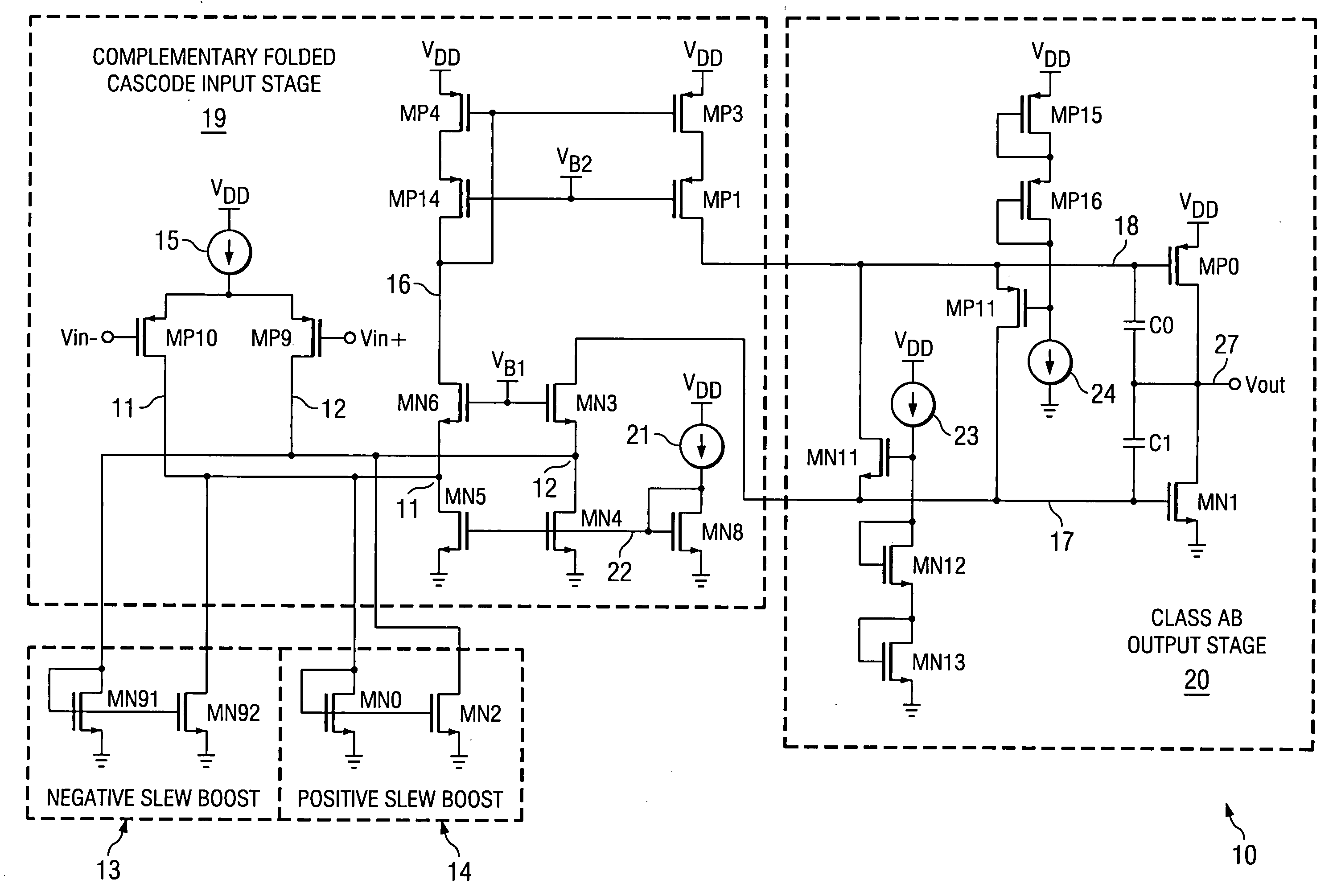
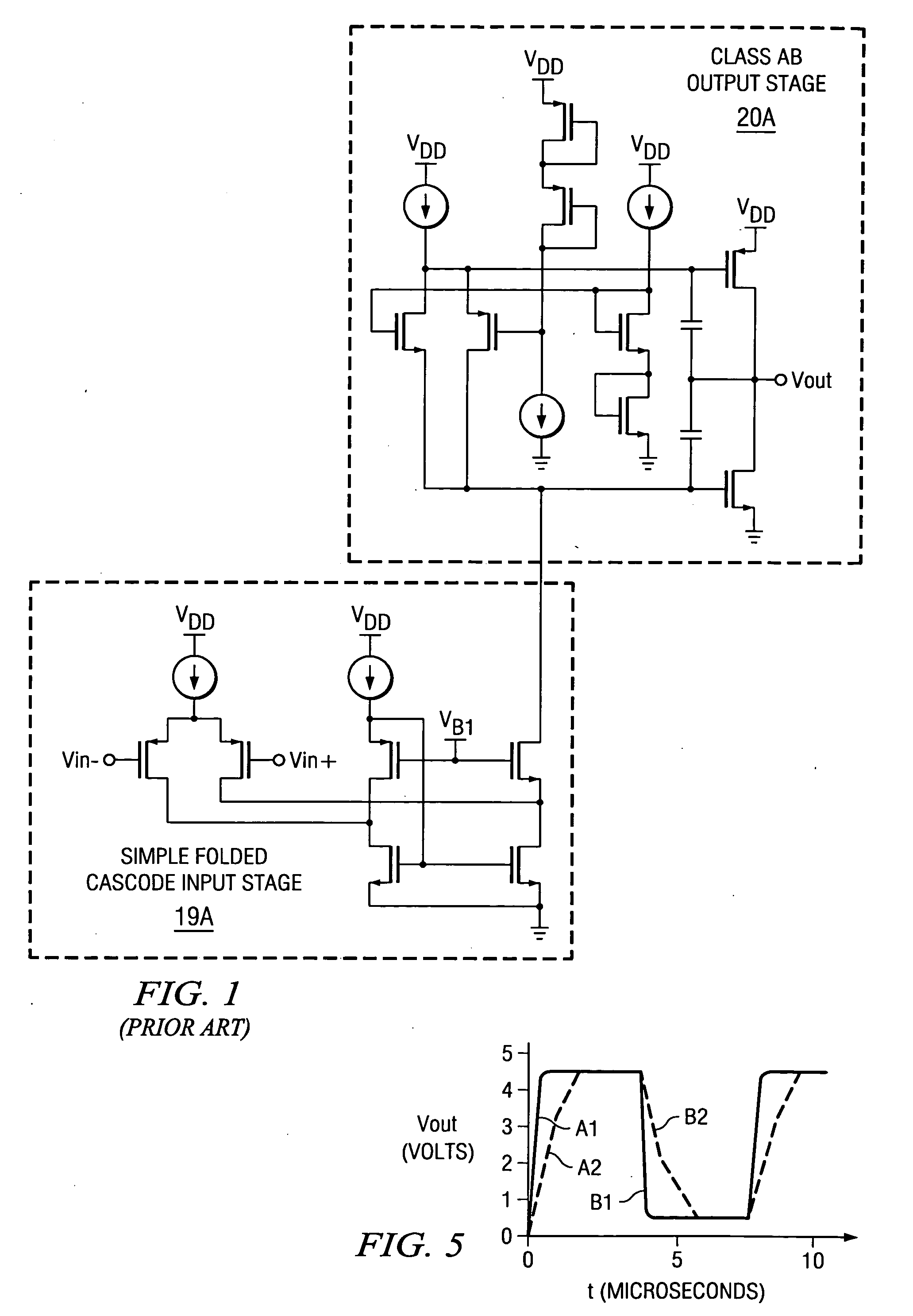
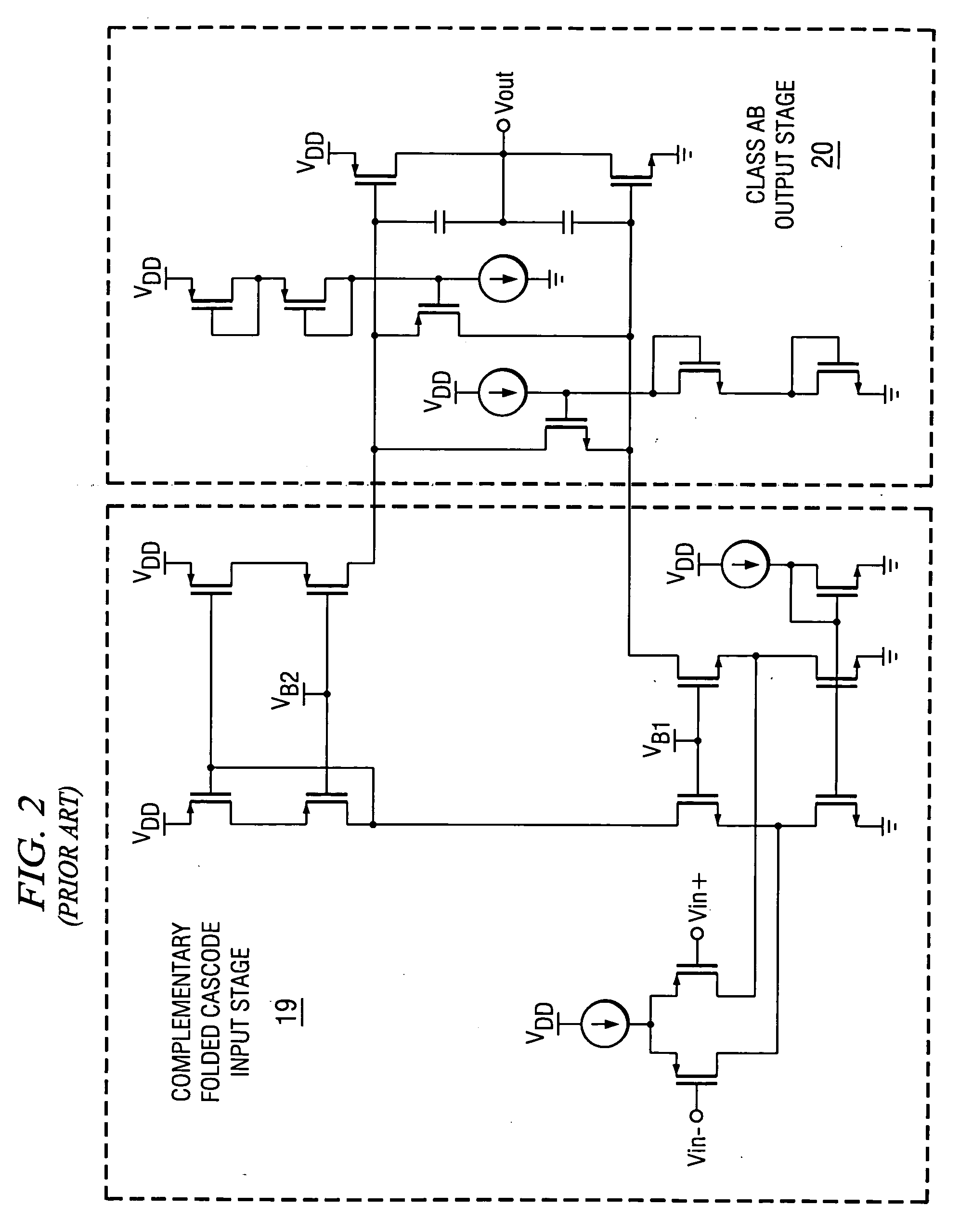
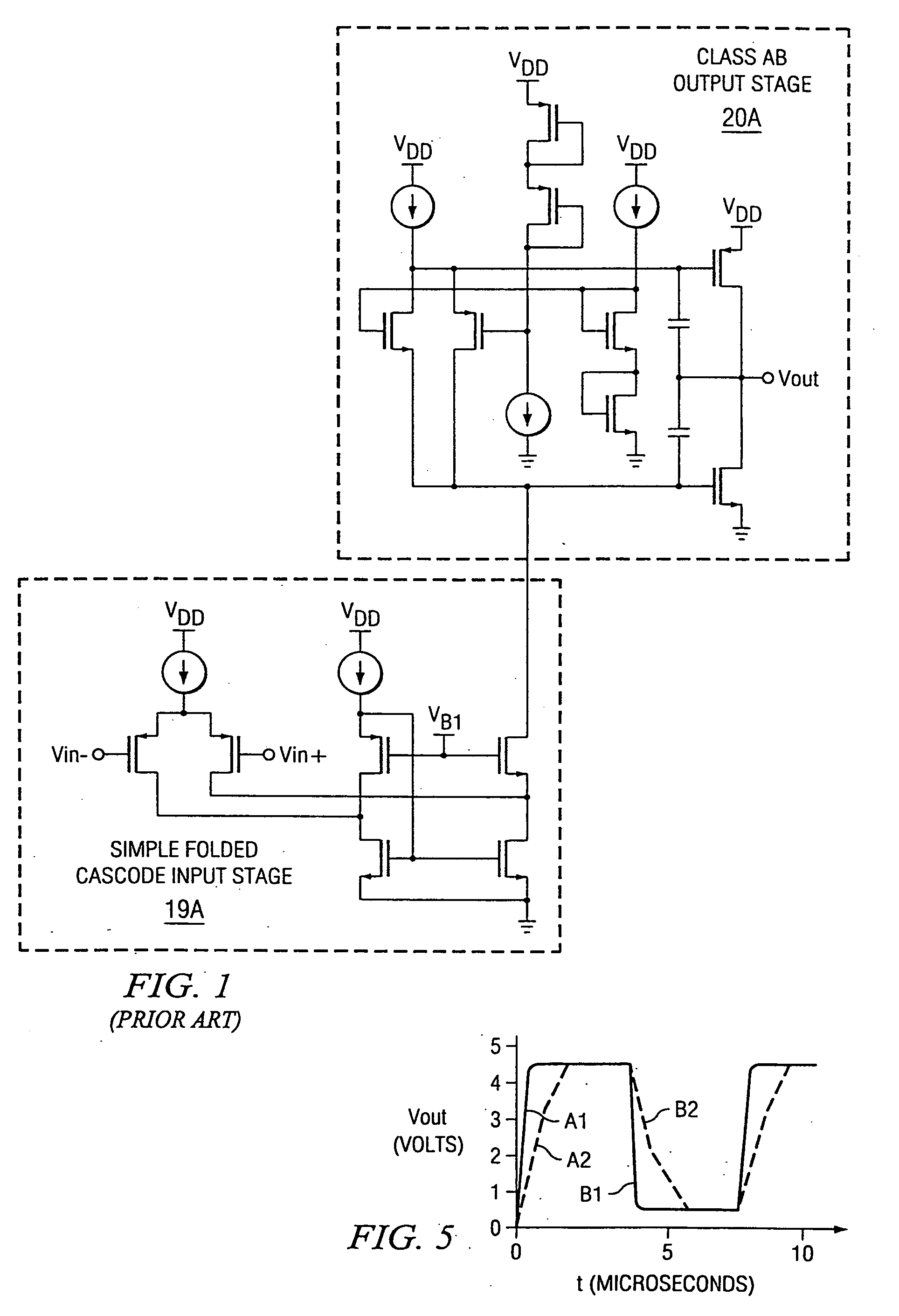
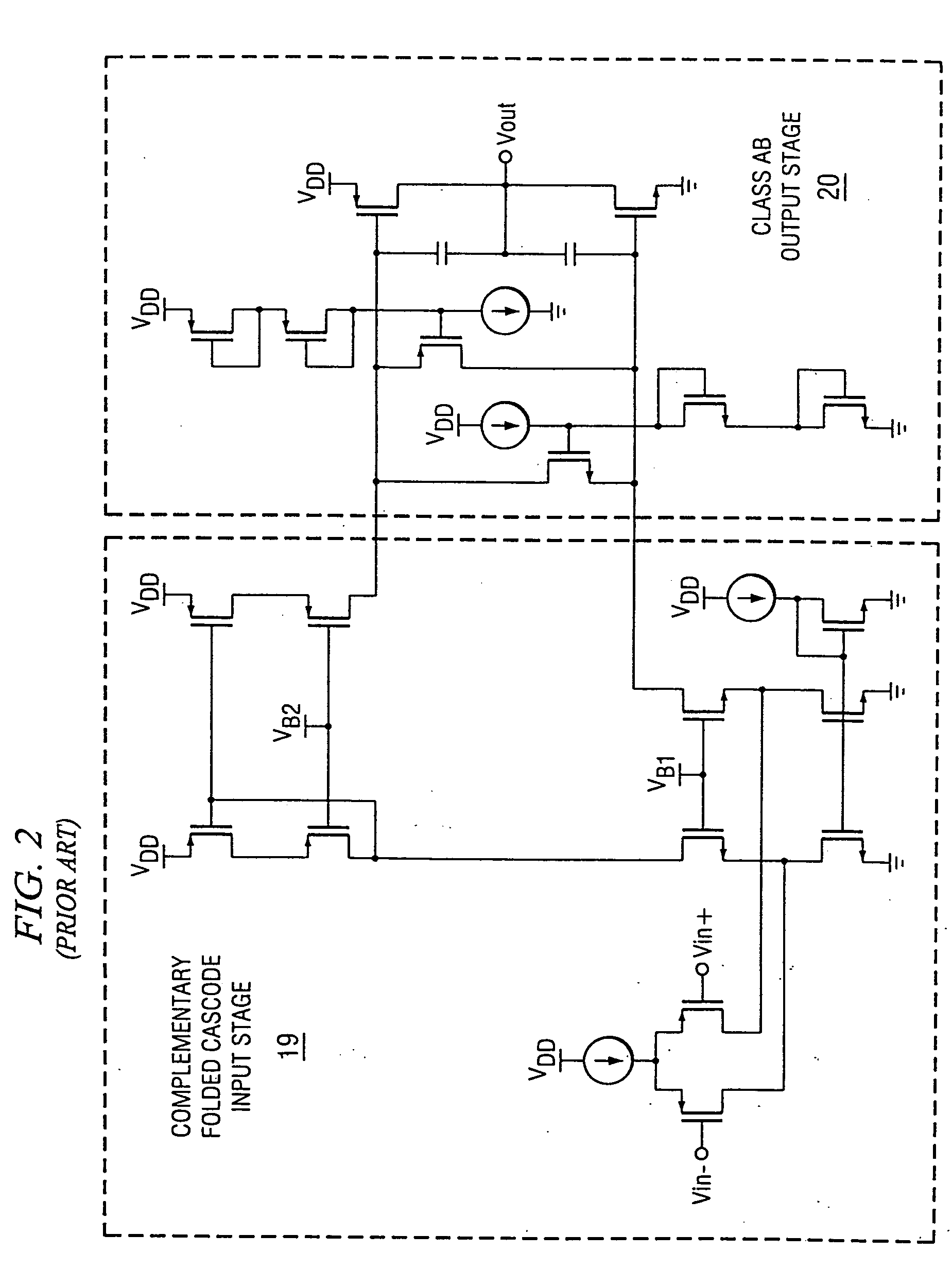
Slew rate enhancement circuitry for folded cascode amplifier
InactiveUS20050285676A1Low costIncrease conversion rateDifferential amplifiersSingle-ended push-pull amplifiersAudio power amplifierSlew rate
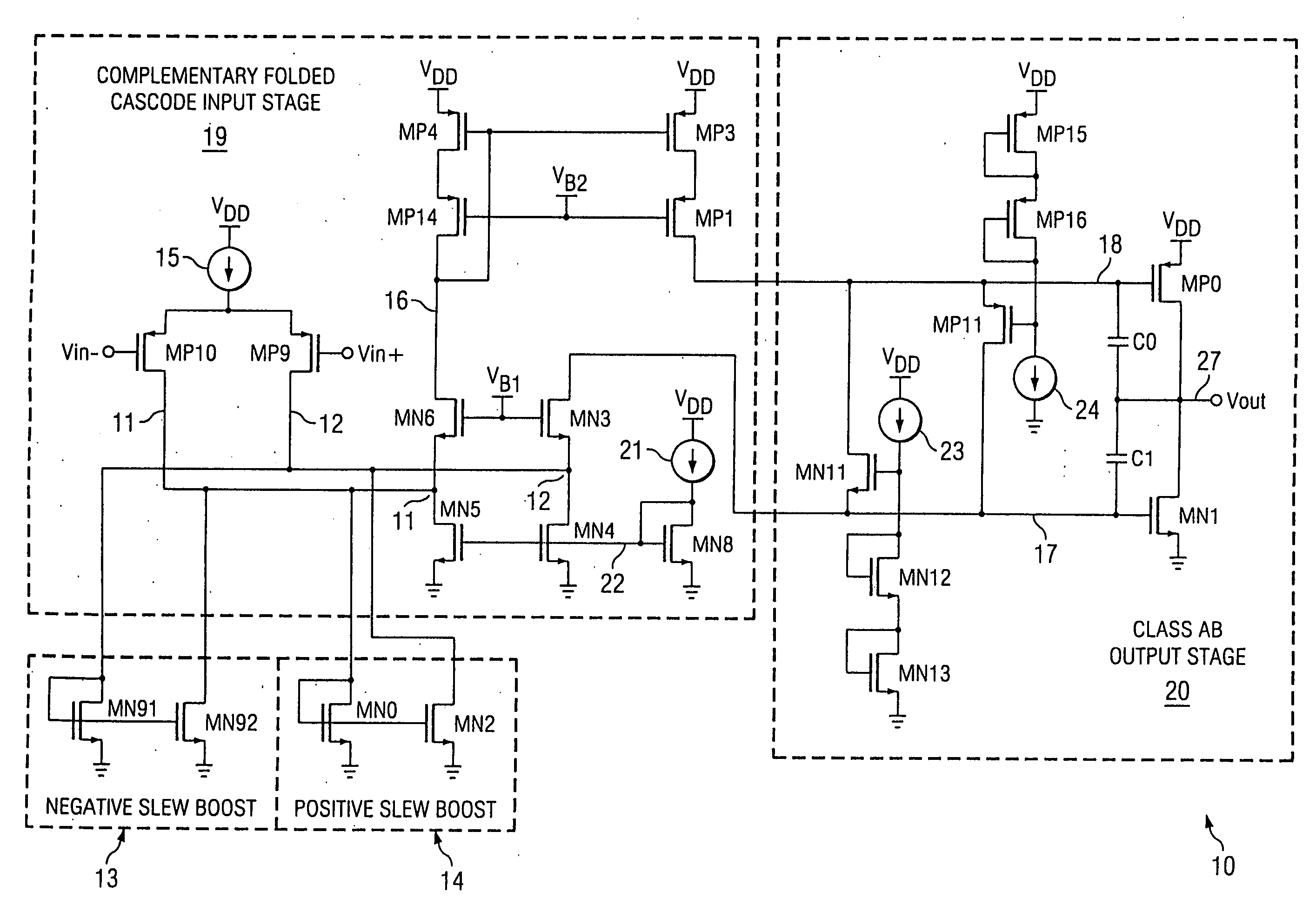
A folded-cascode operational amplifier including a differential input stage (19) and a class AB output stage (20) includes a first slew boost current mirror (13) and a second slew boost current mirror (14) having inputs connected to drains of the input transistors, respectively. Each current mirror amplifies excess tail current steered into it as a result of a large, rapid input signal transition. The amplified excess tail current is used to boost the slew rate of the class AB output stage. in accordance with a first polarity of the difference between the first (Vin+) and second (Vin−) input voltages. The drains of the input transistors are maintained at a voltage less than a transistor threshold voltage above the ground except during slewing operation of the operational amplifier to effectively isolate the current mirrors except during slewing operation.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
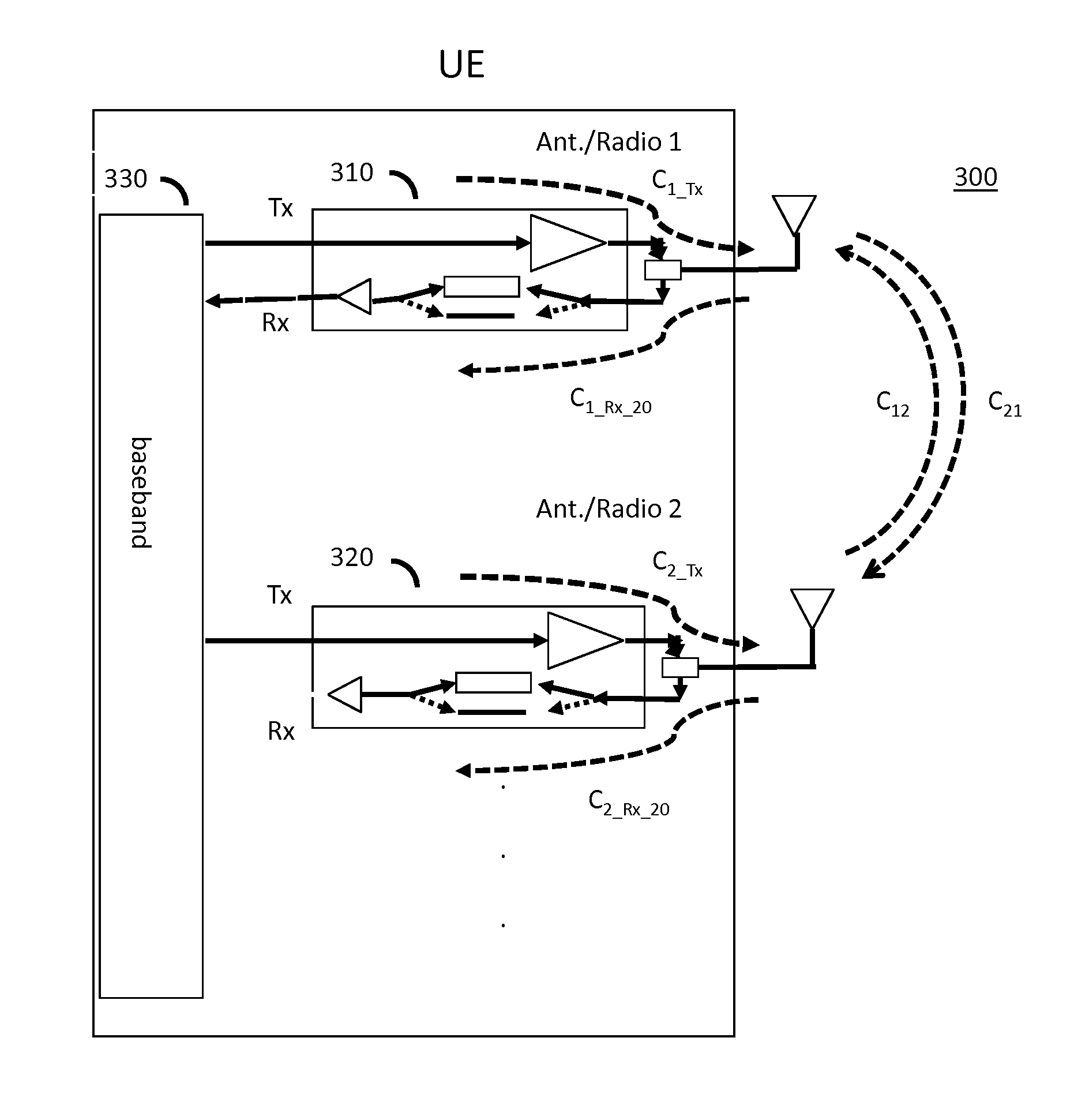
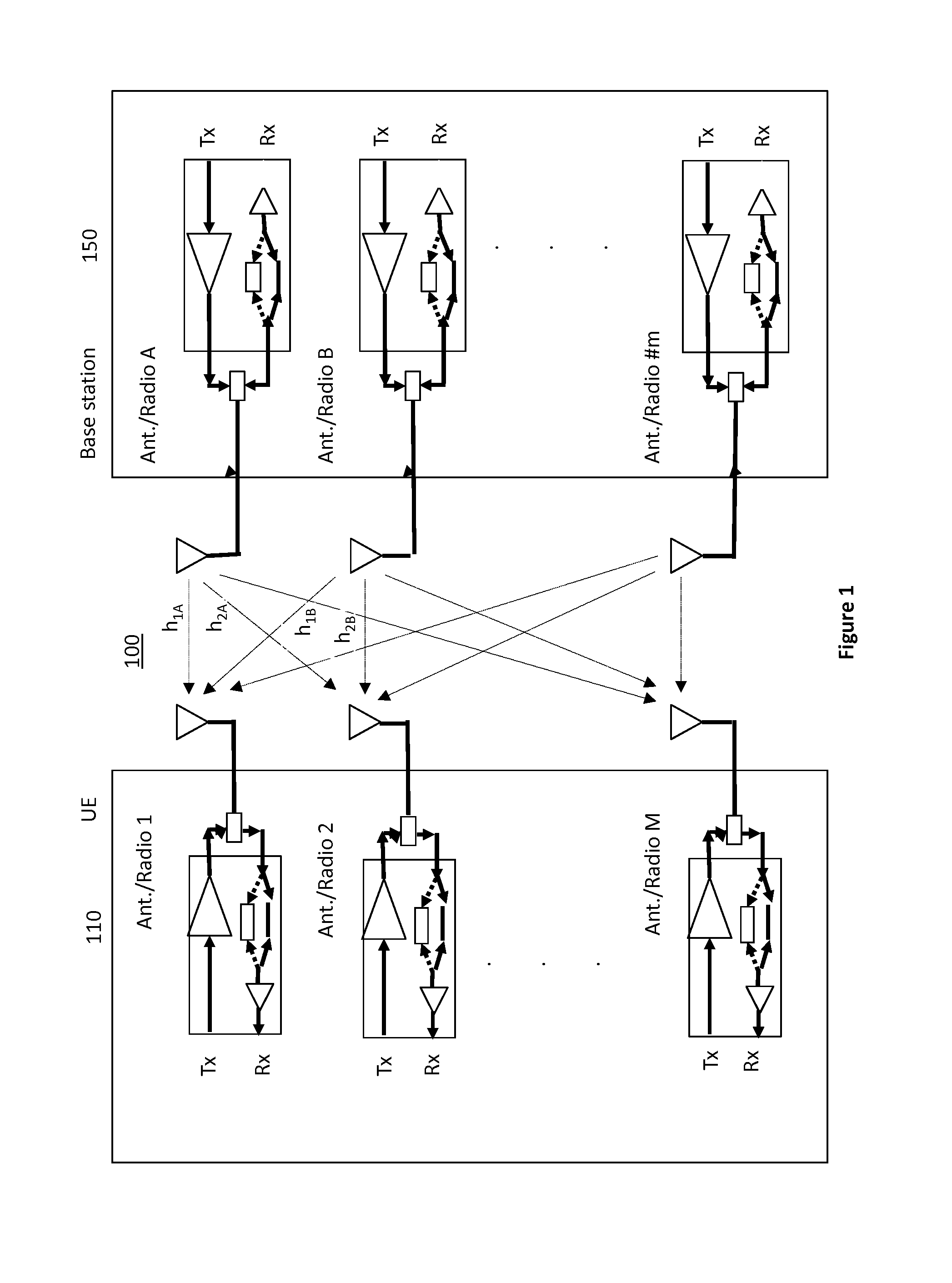
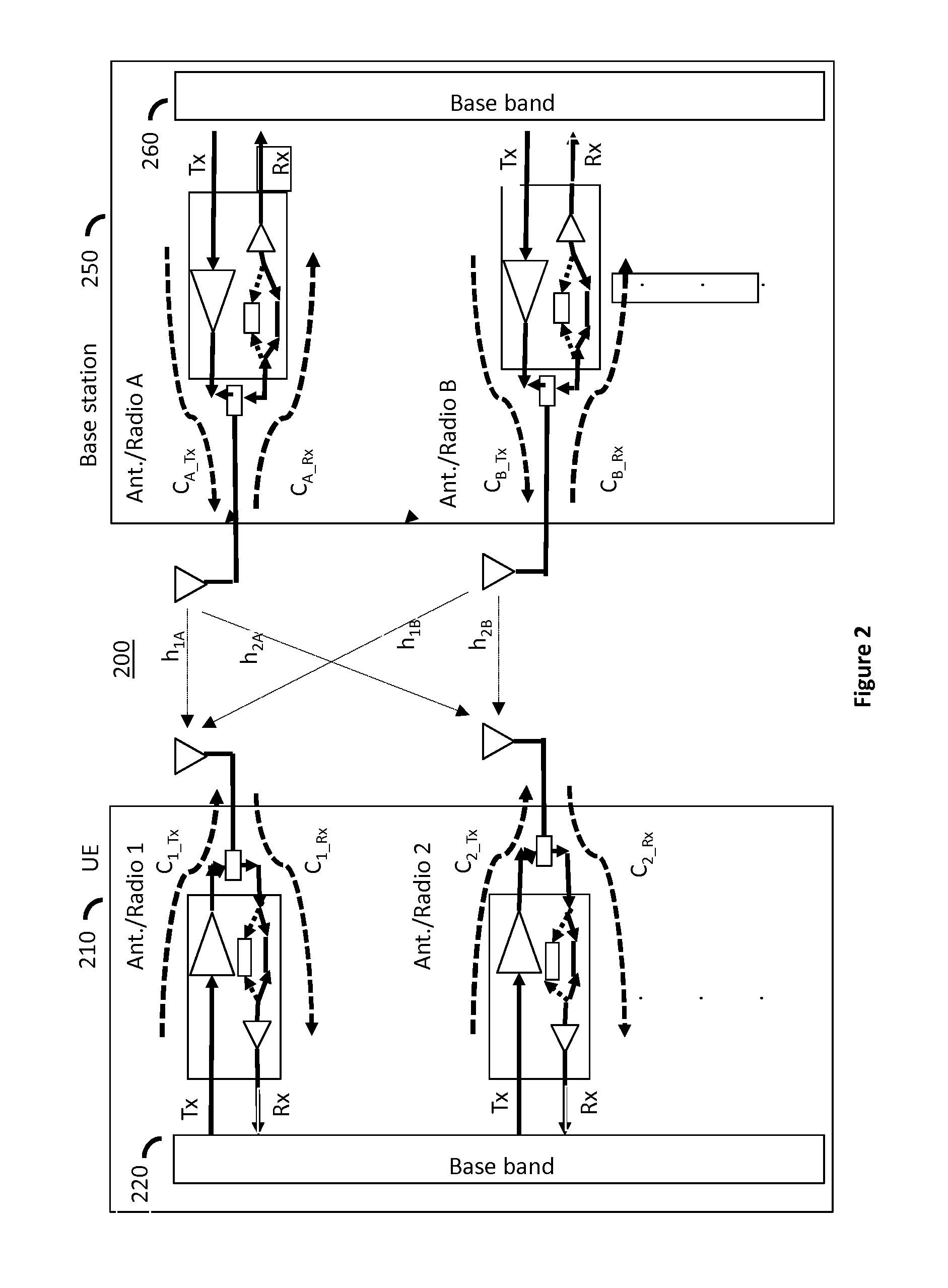
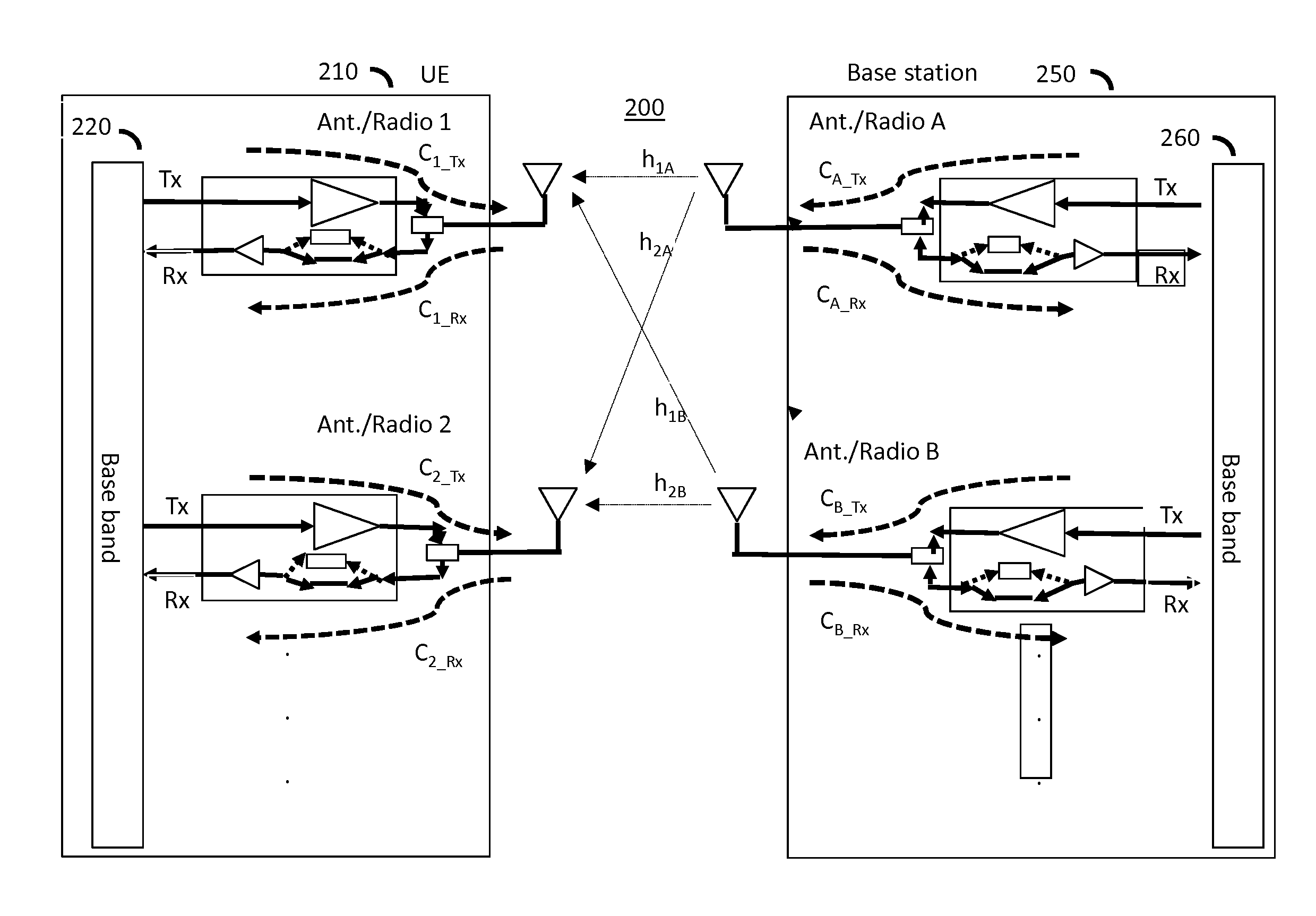
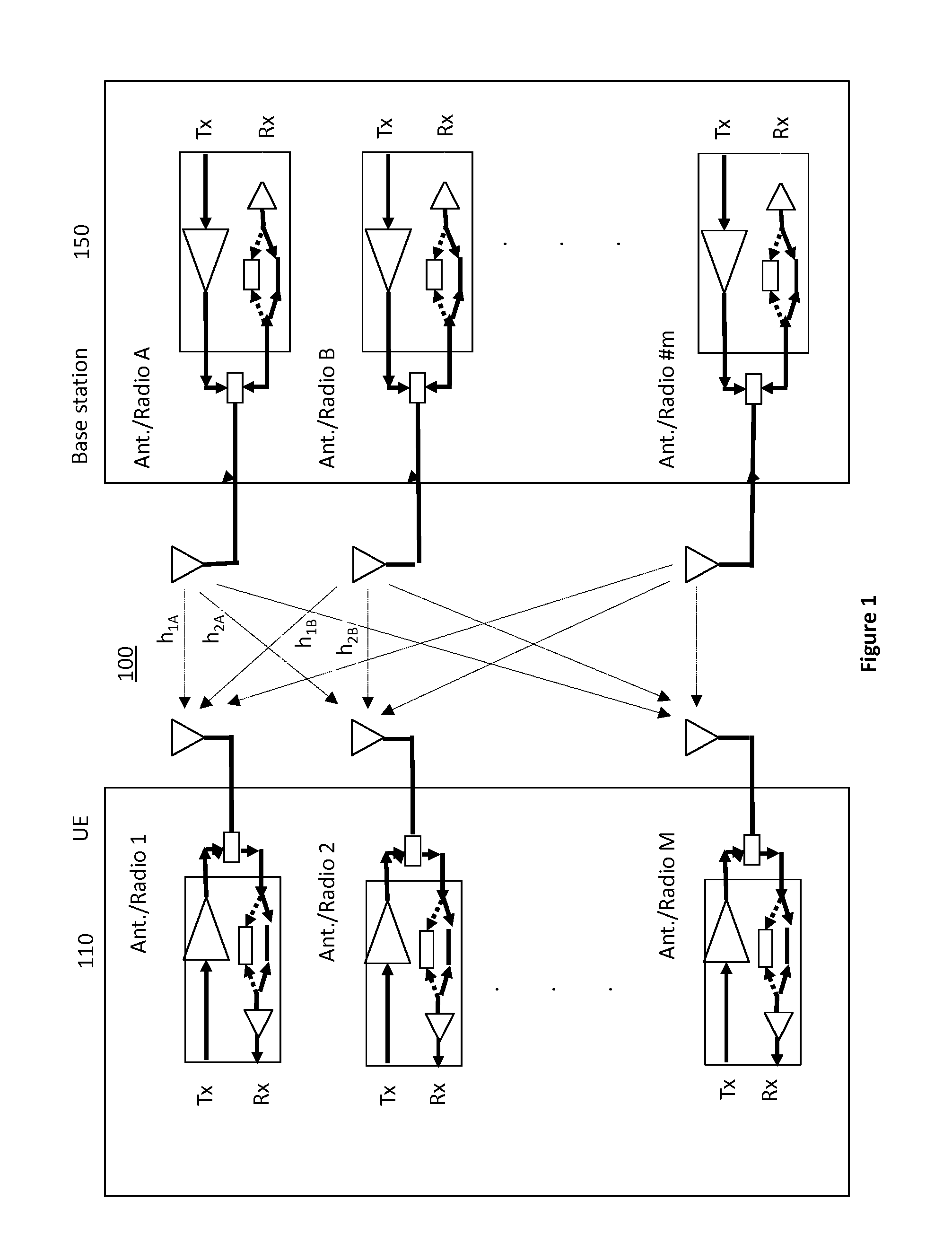
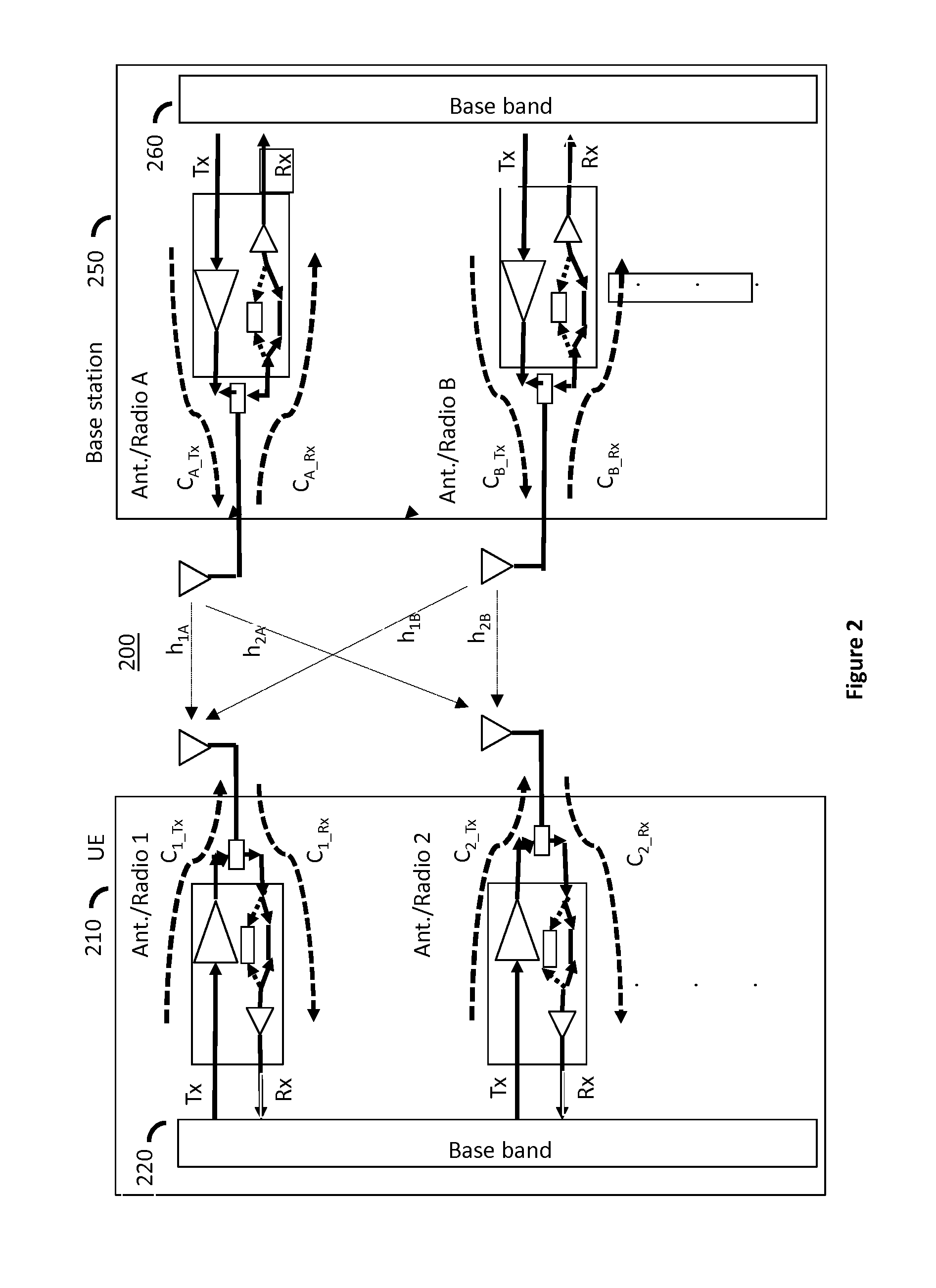
Transmitter and receiver calibration for obtaining the channel reciprocity for time division duplex MIMO systems
InactiveUS8891598B1Low Noise AmplifierTransmitters monitoringReceivers monitoringMimo systemsMultiple input
A communication device operating in time division duplex (TDD) mode using multiple antennas is provided herein. The communication device uses receive channel estimation measurements to perform transmit beamforming and multiple input multiple output (MIMO) transmission, based on self-calibration of the various up / down paths via a method of transmission and reception between its own antennas, thus achieving reciprocity mapping between up and down links. Either user equipment (UE) or a base station may routinely perform this self-calibration to obtain the most current correction factor for the channel reciprocity to reflect the most current operating conditions present during TDD MIMO operation.
Owner:MAGNOLIA BROADLAND INC
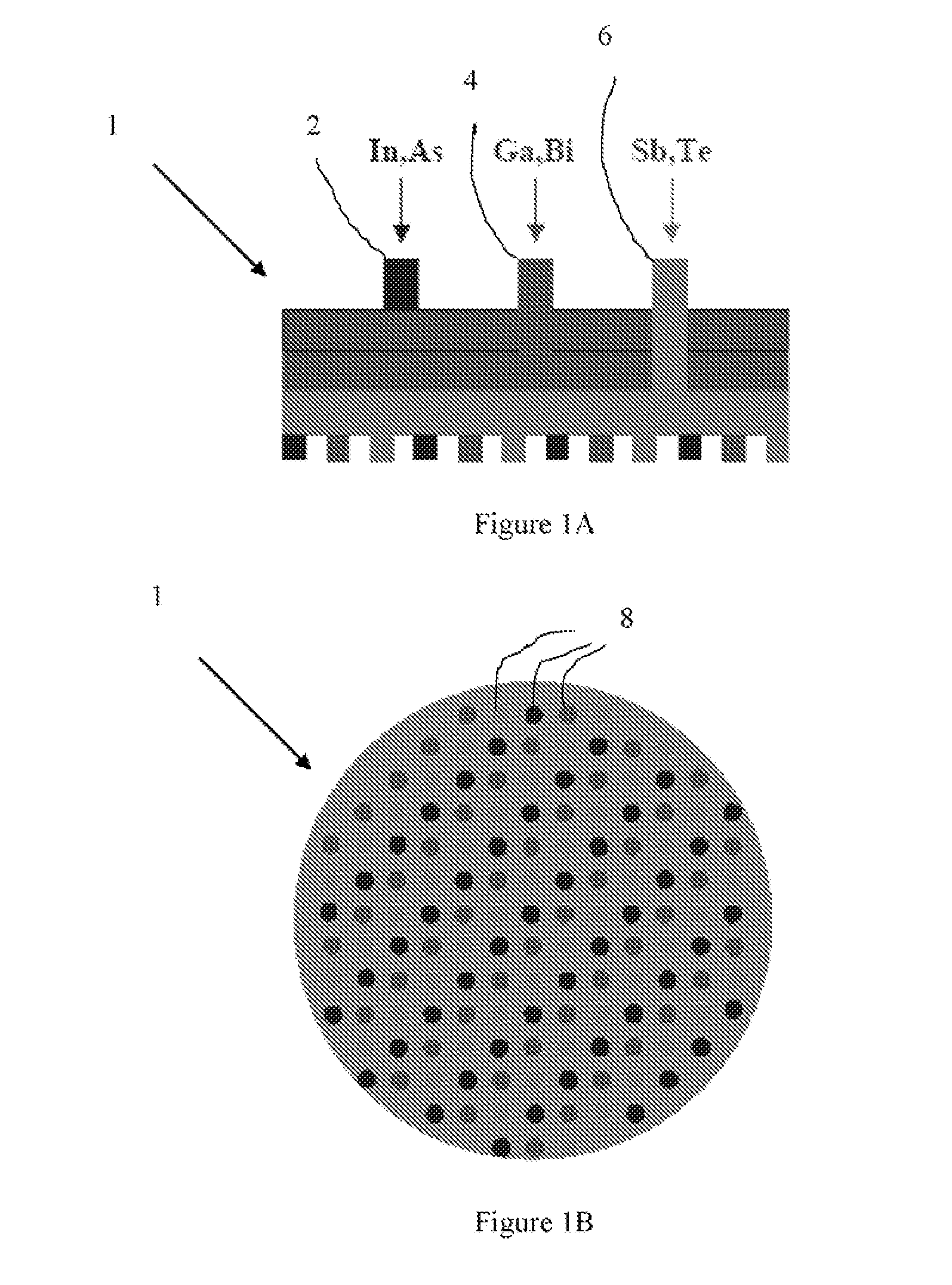
Thermoelectric nanowire composites
InactiveUS20080178921A1Improve reliabilityImproved thermal managementThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentContact padNanowire array
An MOCVD process provides aligned p- and n- type nanowire arrays which are then filled with p- and n-type thermoelectric films to form the respective p-leg and n-leg of a thermoelectric device. The thermoelectric nanowire synthesis process is integrated with a photolithographic microfabrication process. The locations of the p- and n-type nanowire micro arrays are defined by photolithography. Metal contact pads at the bottom and top of these nanowire arrays which link the p- and n-type nanowires in series are defined and aligned by photolithography.
Owner:ELORET CORP
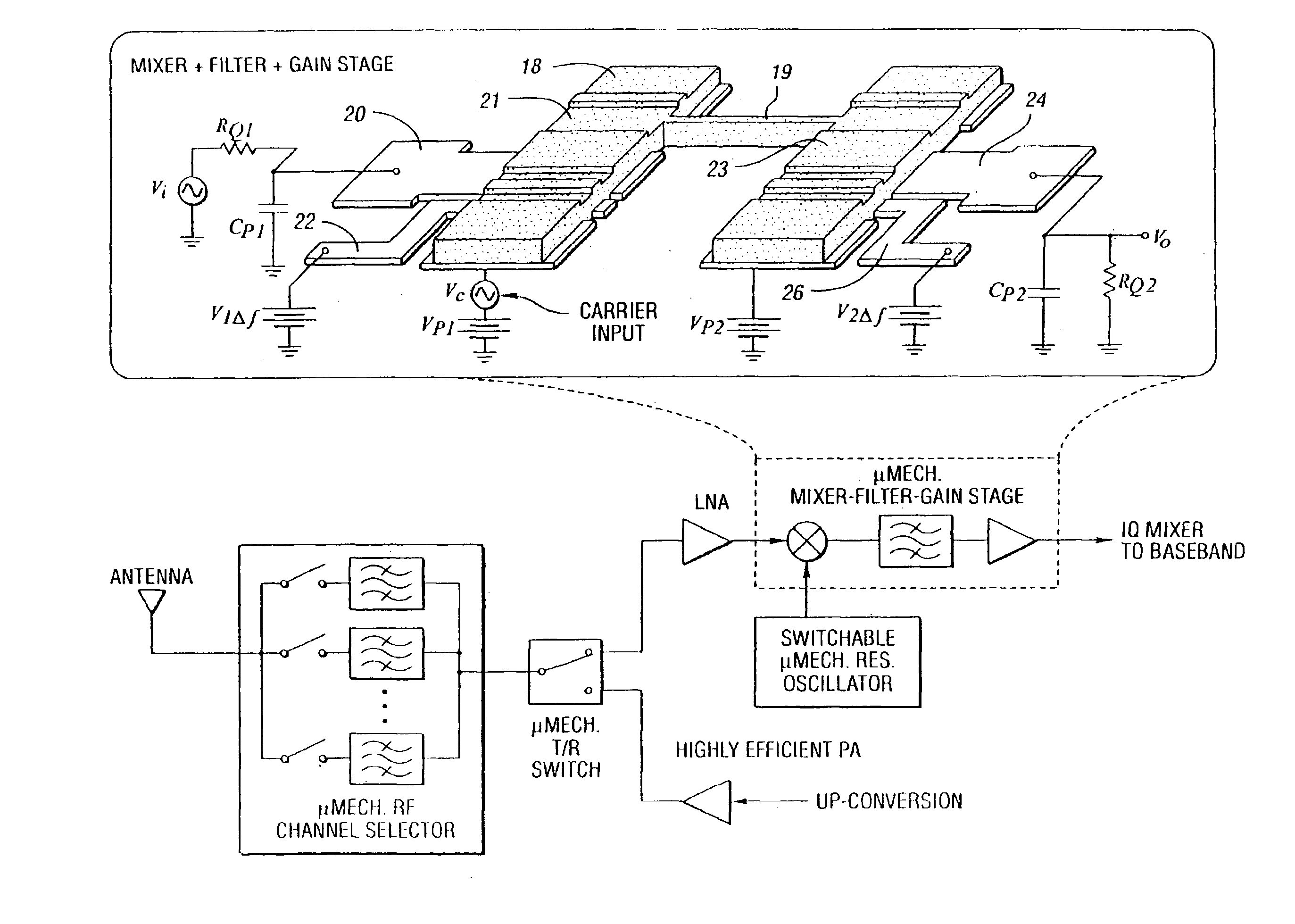
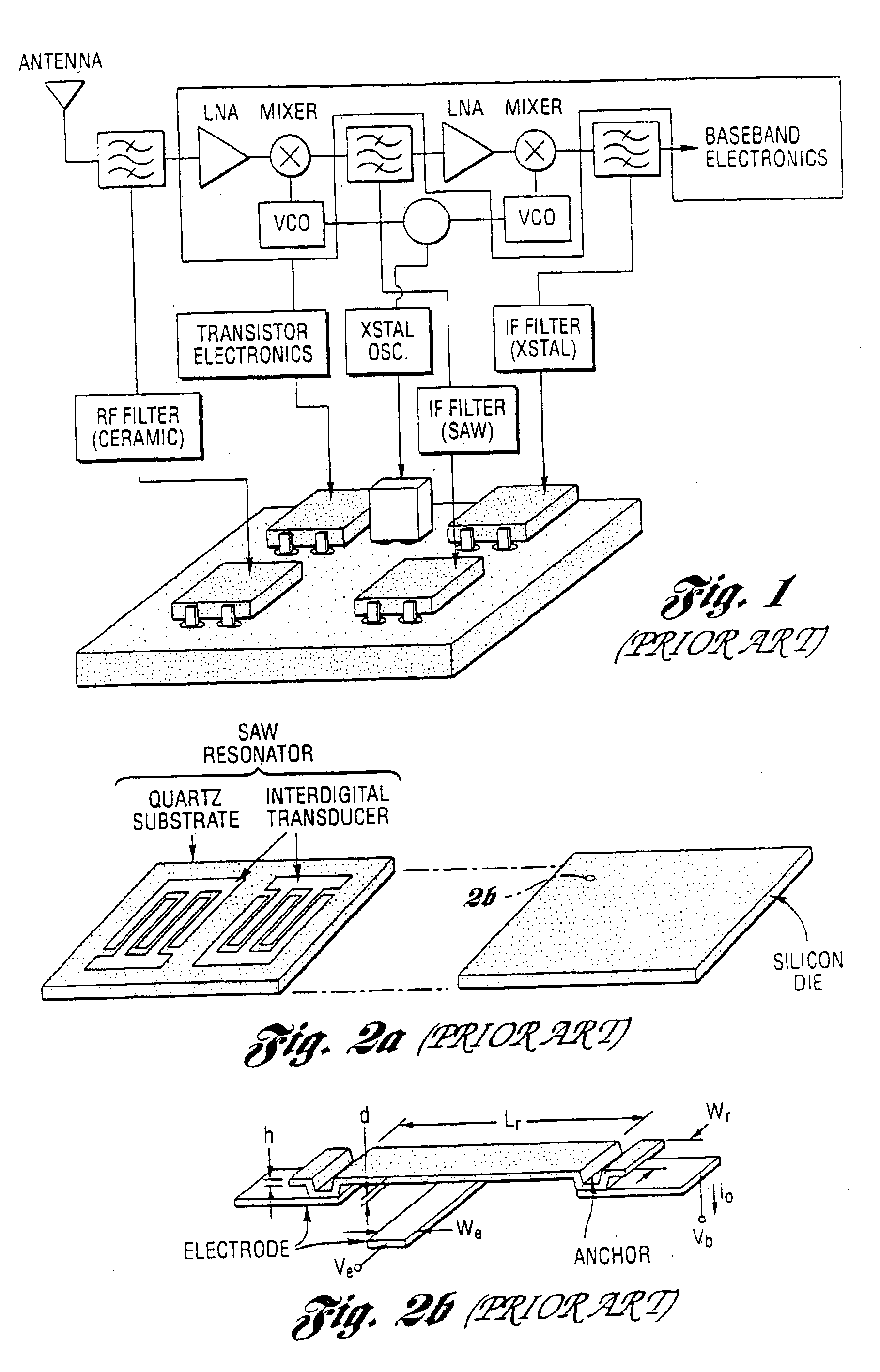
Method and subsystem for processing signals utilizing a plurality of vibrating micromechanical devices
InactiveUS6917138B2Reduce needLow noise amplifierElectrostatic/electro-adhesion relaysImpedence networksAudio power amplifierTransceiver
Several MEMS-based methods and architectures which utilize vibrating micromechanical resonators in circuits to implement filtering, mixing, frequency reference and amplifying functions are provided. A method and subsystem are provided for processing RF signals utilizing a plurality of vibrating micromechanical devices typically in the form of an IF mixer-filter and an RF channel selector or an image-reject RF filter. One of the primary benefits of the use of such architectures is a savings in power consumption by trading power for high selectivity (i.e., high Q). Also, such methods and circuits can eliminate the need for a low noise amplifier in a receiver or transceiver subsystem. Consequently, the present invention relies on the use of a large number of micromechanical links in SSI networks to implement signal processing functions with basically zero DC power consumption.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
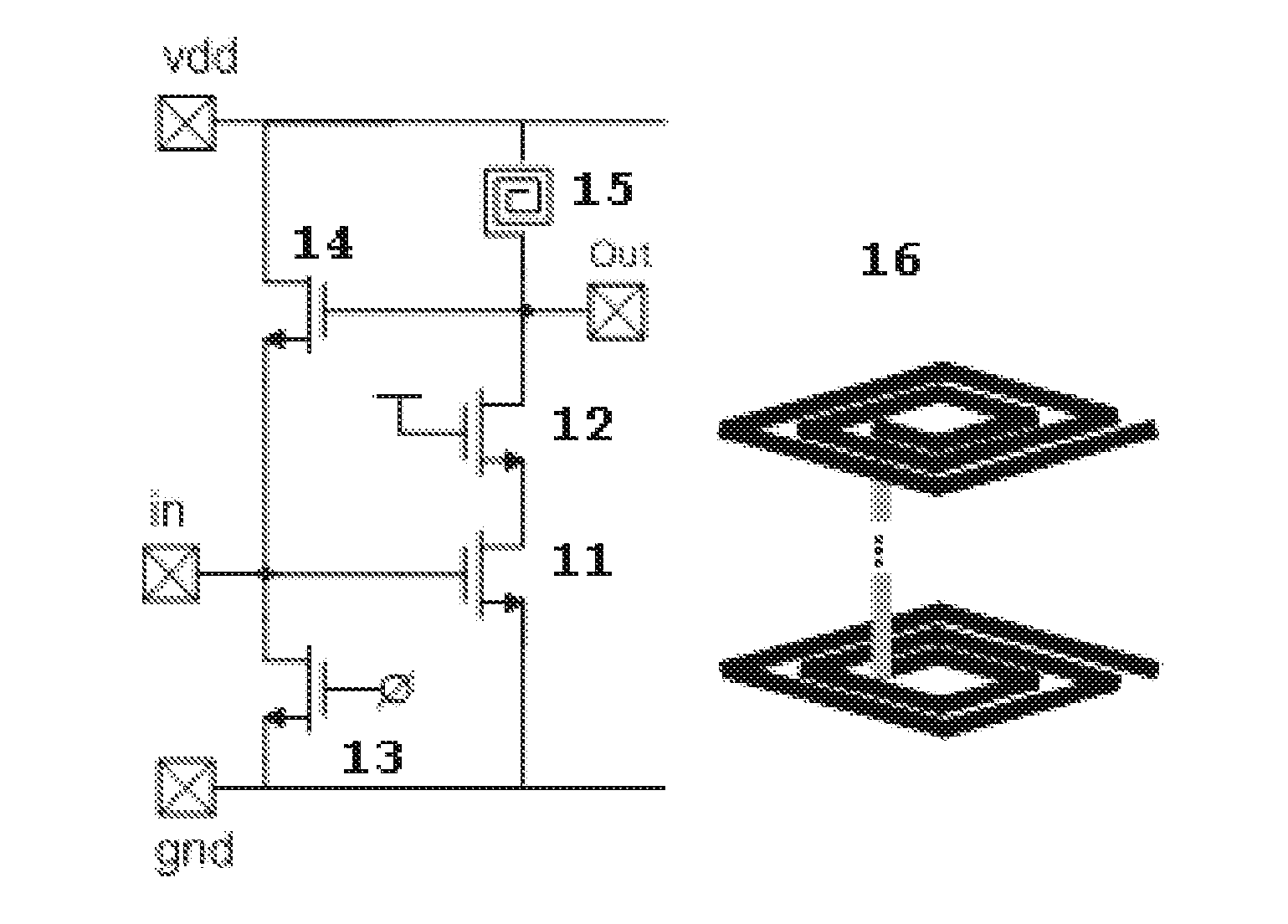
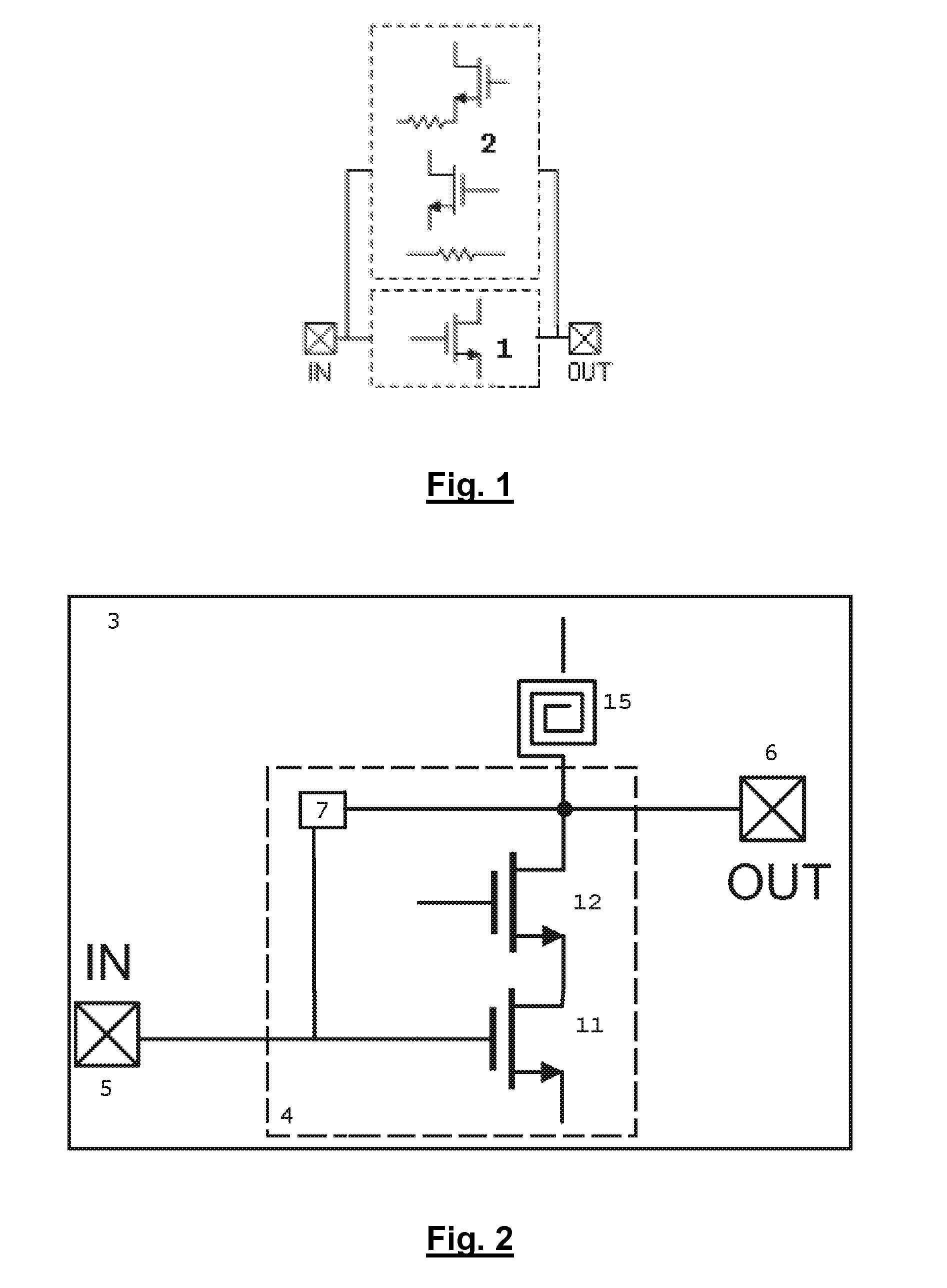
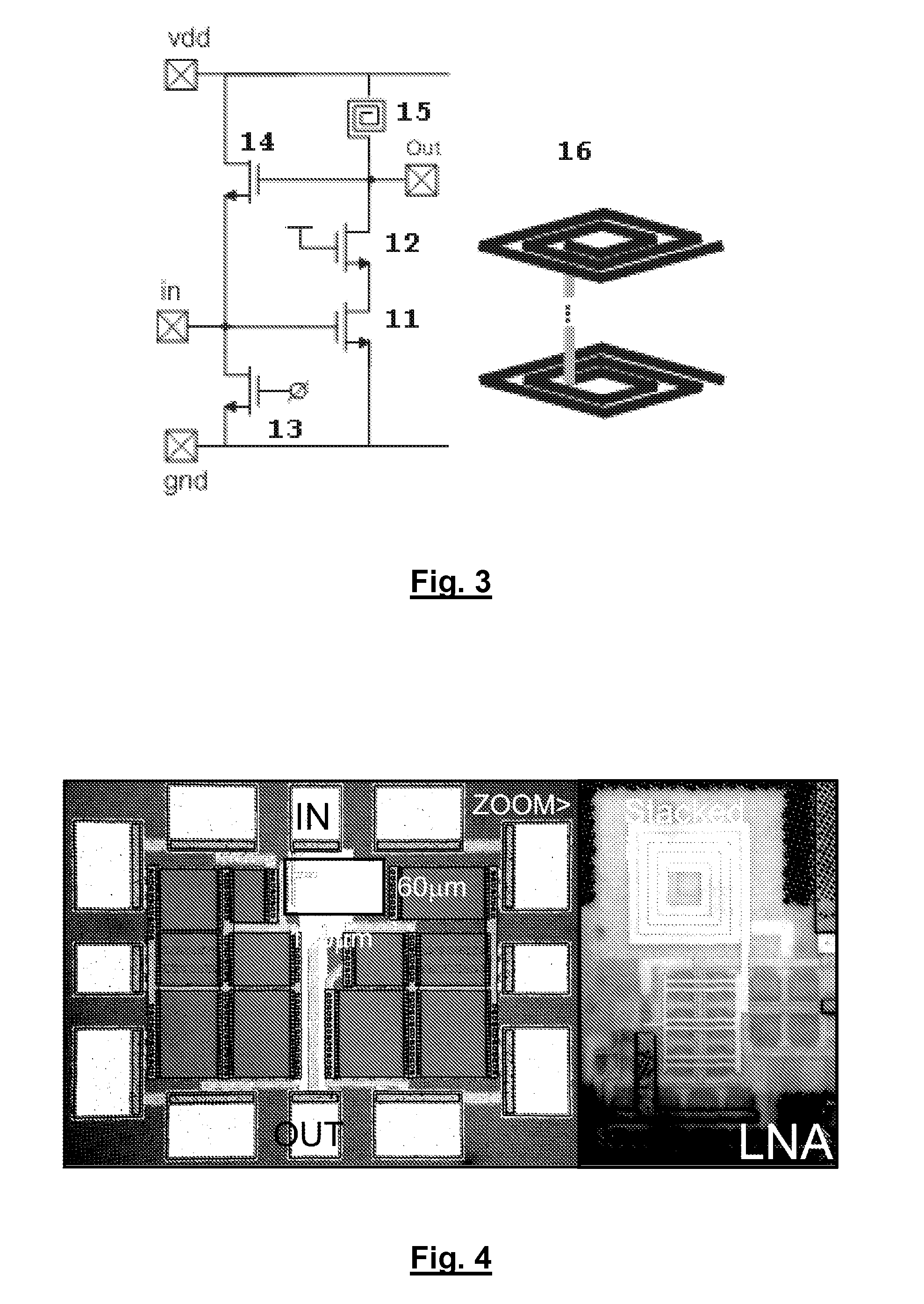
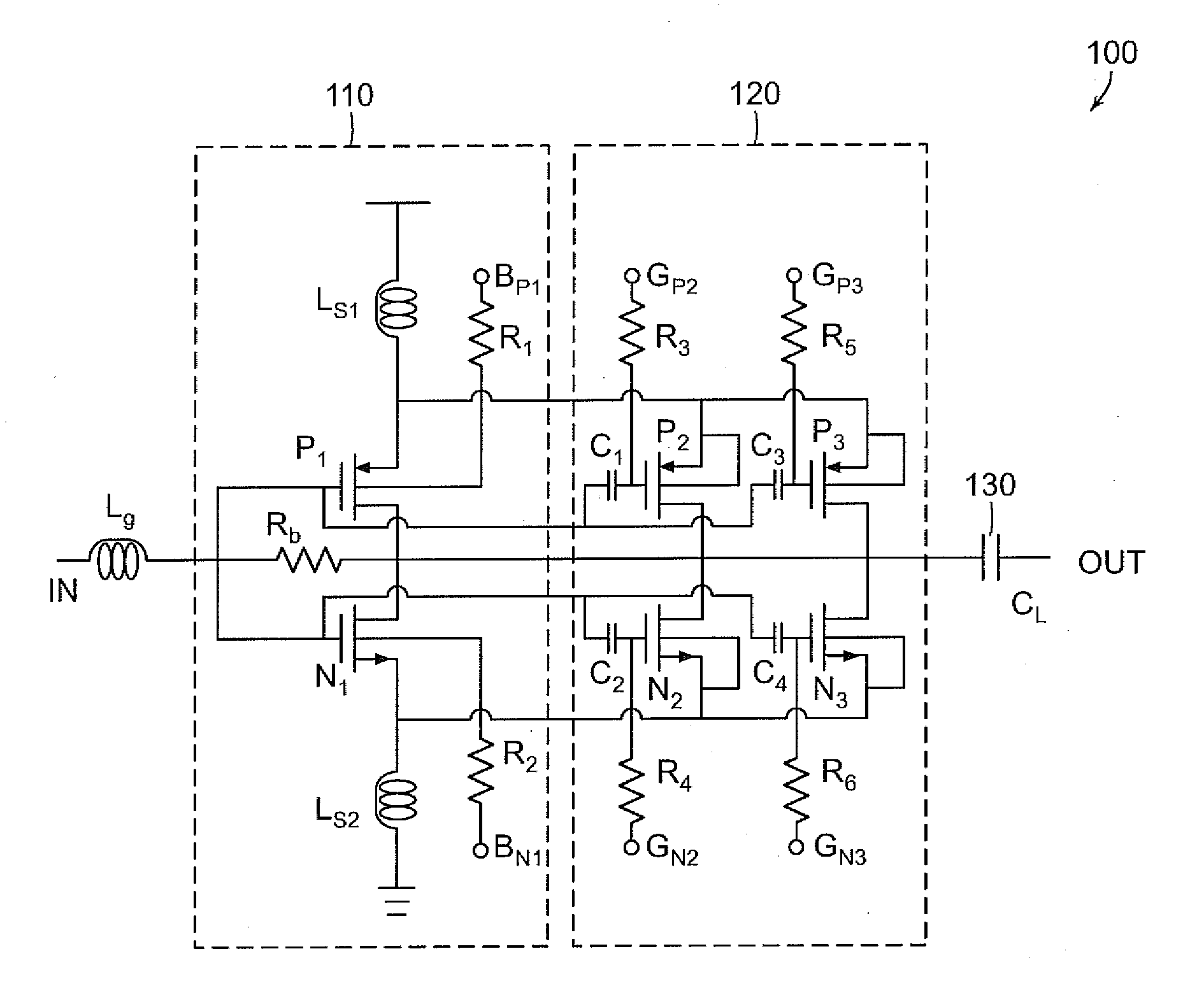
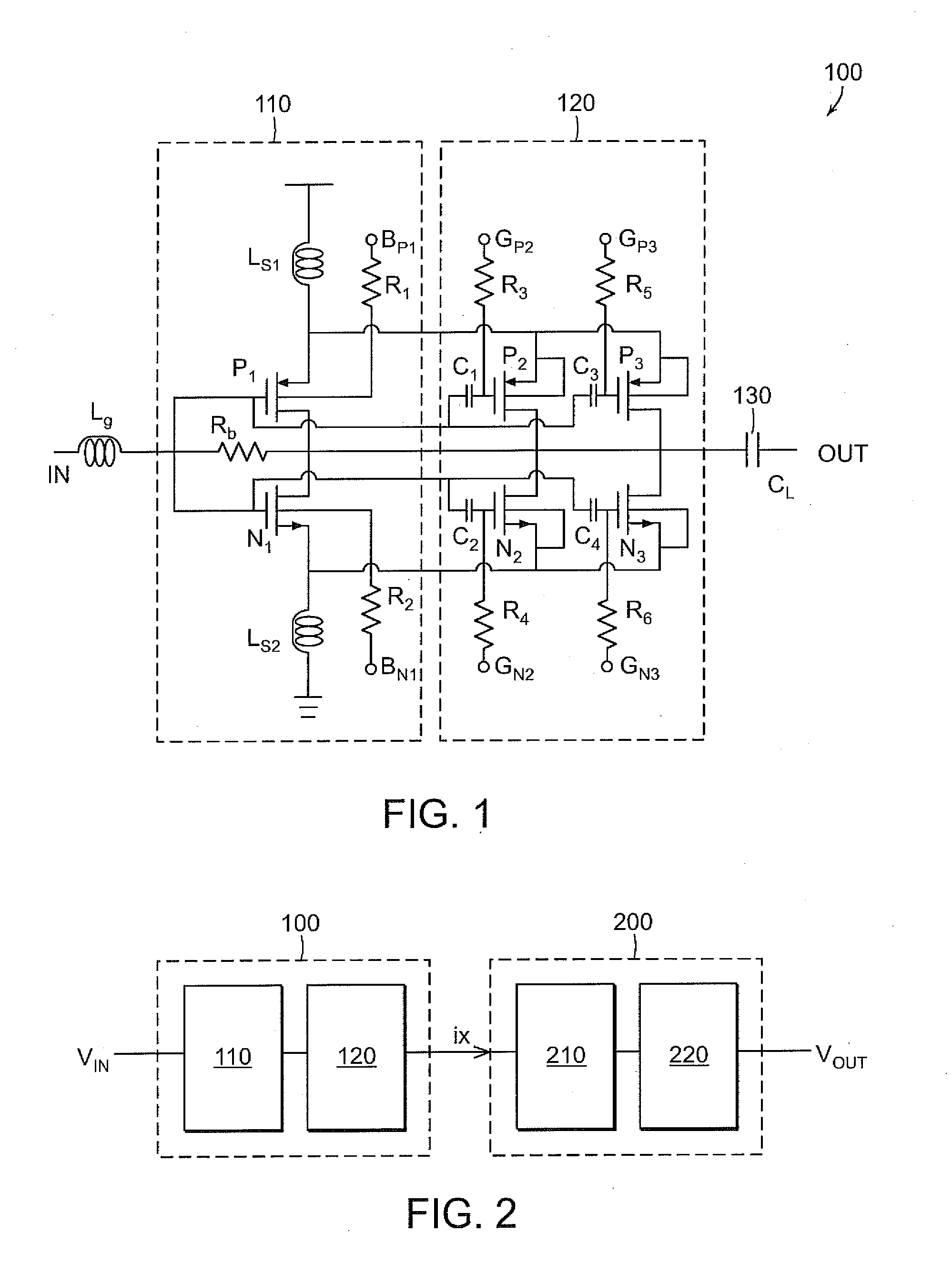
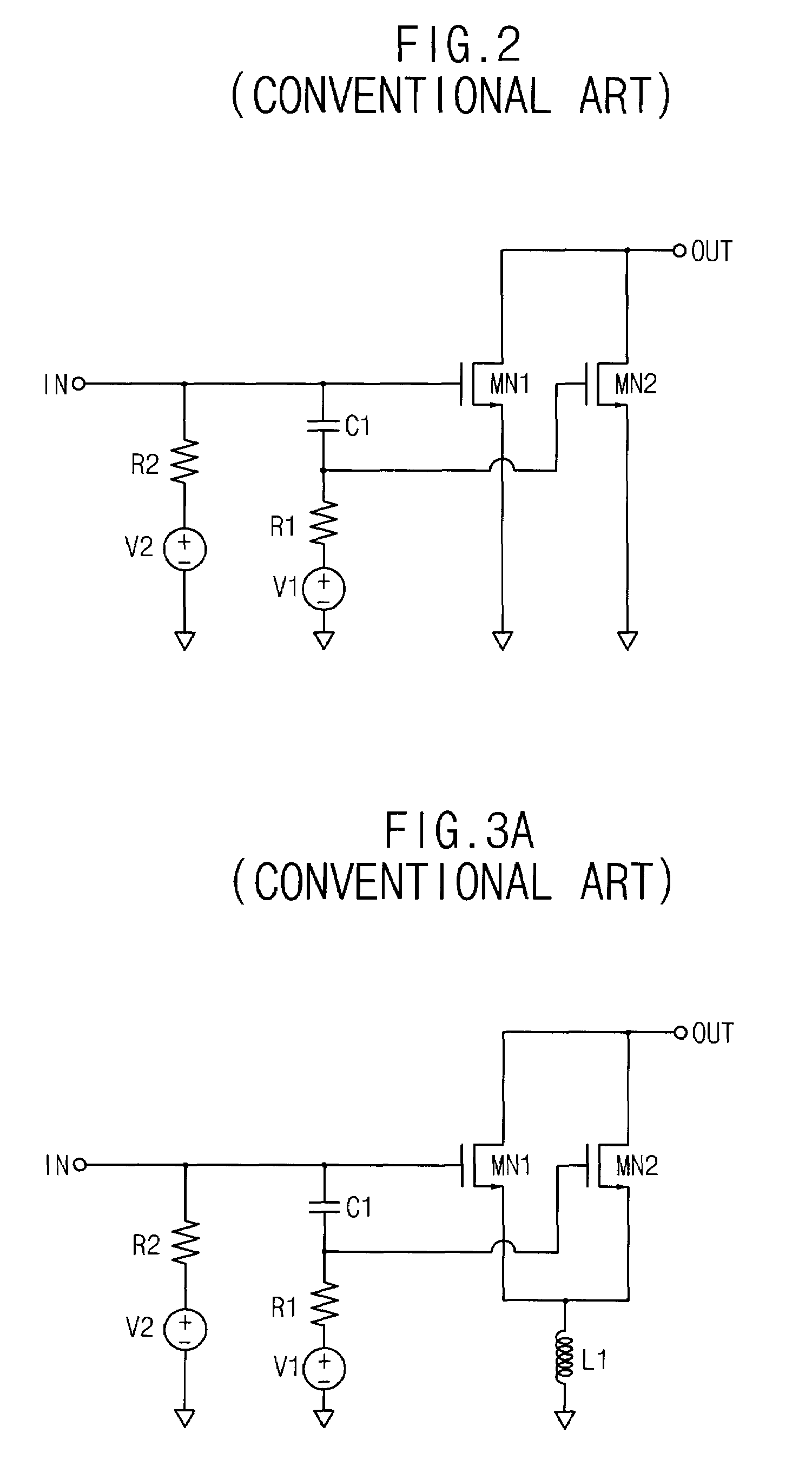
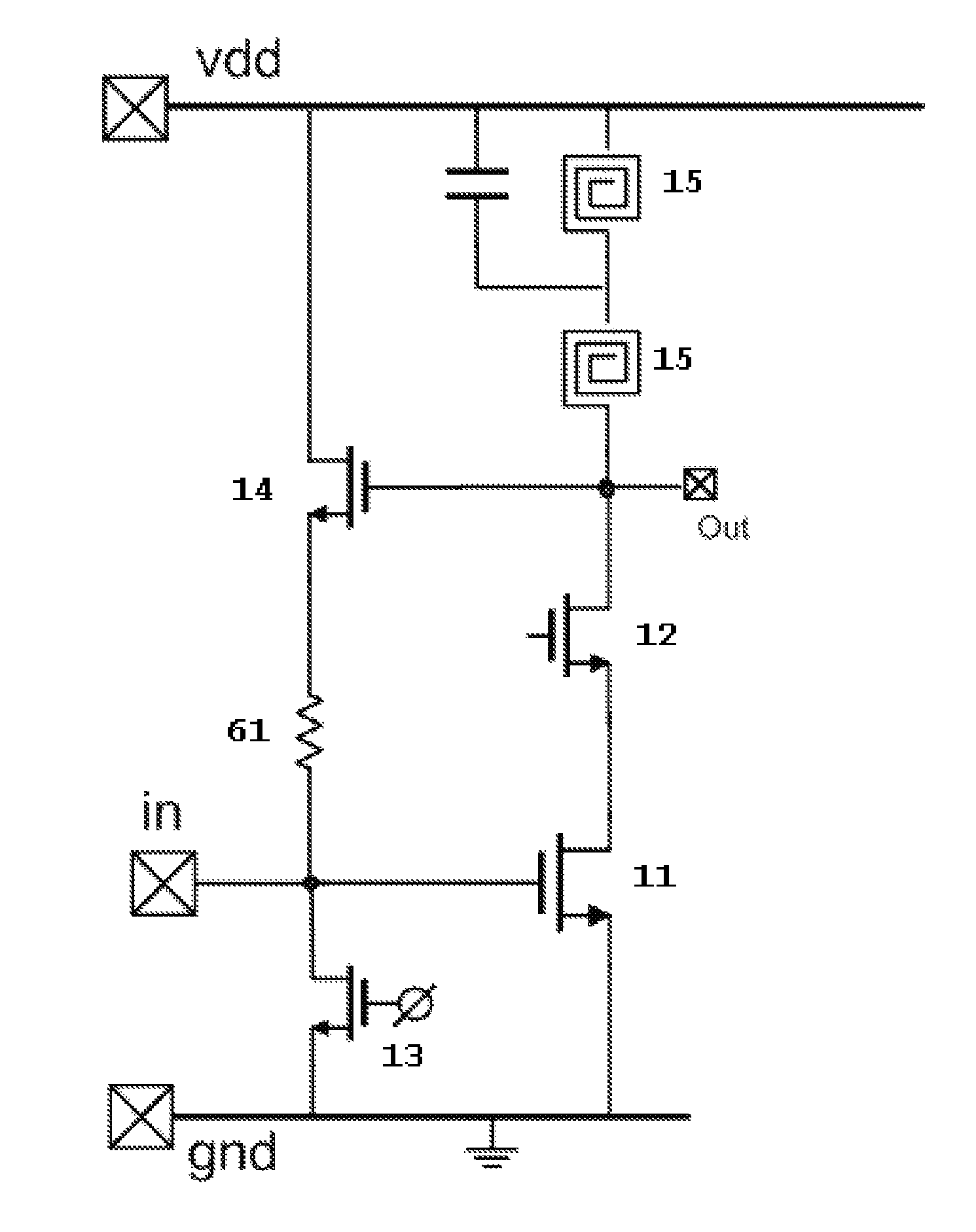
Switchable Multiband LNA Design
ActiveUS20100301946A1Consumes less design areaReduce noiseNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsGated amplifiersLow noiseResonance
A low noise amplifying (LNA) circuit comprising an amplifying section (11, 12) and a feedback means (14) arranged for providing input matching from the output to the input. The LNA circuit further comprises at least one frequency band determining inductor (15) having a predetermined resonance frequency for influencing at least one frequency band in which the amplifying section operates. The at least one inductor is directly connected to the output of the circuit and the feedback means (14) provides a feedback connection for the section (s) to the input. In this way, the at least one frequency band in which the amplifying section operates is substantially completely determined by the at least one frequency band determining inductor (15).
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW) +1
GNSS antennas
InactiveUS20140247194A1Moderate bandwidthReduce lossAntenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsPhased arrayRadiation pattern
A global navigation satellite system (GNSS) antenna system includes interference mitigation and multipath canceling. Multiple ports or phased arrays of antennas can be provided. Antennas can comprise controlled radiation pattern antennas (CRPA). Crossed dipole and patch antenna configurations can be utilized.
Owner:HEMISPHERE GNSS
Transmitter and receiver calibration for obtaining the channel reciprocity for time division duplex MIMO systems
ActiveUS20150139046A1Low Noise AmplifierTransmitters monitoringSpatial transmit diversityMimo systemsUser equipment
A communication device operating in time division duplex (TDD) mode using multiple antennas is provided herein. The communication device uses receive channel estimation measurements to perform transmit beamforming and multiple input multiple output (MIMO) transmission, based on self-calibration of the various up / down paths via a method of transmission and reception between its own antennas, thus achieving reciprocity mapping between up and down links. Either user equipment (UE) or a base station may routinely perform this self-calibration to obtain the most current correction factor for the channel reciprocity to reflect the most current operating conditions present during TDD MIMO operation.
Owner:MAGNOLIA BROADLAND INC
Low noise amplifier having both ultra-high linearity and low noise characteristic and radio receiver including the same
ActiveUS20120064852A1Improve linearityReduce noiseHigh frequency amplifiersGated amplifiersLow noiseAudio power amplifier
Disclosed herein is a low noise amplifier having both ultra-high linearity and a low noise characteristic and a radio receiver including the low noise amplifier. The low noise amplifier includes a first main transistor unit, a first auxiliary transistor unit, and an optimum noise and input impedance matching capacitor. The first main transistor unit includes a first NMOS transistor and a first PMOS transistor configured to form a complementary common source amplifier, a feedback-type resistor connected between drains of the first NMOS transistor and the first PMOS transistor and configured to generate biases to the two transistors, and bias resistors connected to bodies of the first PMOS transistor and the first NMOS transistor. The first auxiliary transistor unit includes transistors connected to the two transistors. The optimum noise and input impedance matching capacitor is connected to output terminals of the first main transistor unit and the first auxiliary transistor unit.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Low noise amplifier and receiver
ActiveUS20150280672A1High linearity low noise amplifierHigh P1dBHigh frequency amplifiersGain controlPower flowAudio power amplifier
A low noise amplifier is disclosed. The low noise amplifier comprises a current mirror circuit, a bias circuit, a cascode amplifying circuit and a power gain compensating circuit. The current mirror circuit is used for providing a first current and third current. The bias circuit is used for receiving a first current and third current and outputting a first bias voltage and a second bias voltage according to the first current and third current. The cascode amplifying circuit respectively receives the first bias voltage and the second bias voltage, and accordingly to work at an operation bias point. The power gain compensating circuit is used for receiving a RF output signal and accordingly outputs a gain compensating signal to the current mirror circuit so as to dynamically adjust current value of the first current and third current and further to compensates power gain of the low noise amplifier in order to increase 1 dB gain compression point (P1dB).
Owner:ADVANCED SEMICON ENG INC
Low noise amplifier having both ultra-high linearity and low noise characteristic and radio receiver including the same
ActiveUS8577325B2Reduce noiseUltra-high linearityHigh frequency amplifiersGated amplifiersLow noiseRadio reception
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
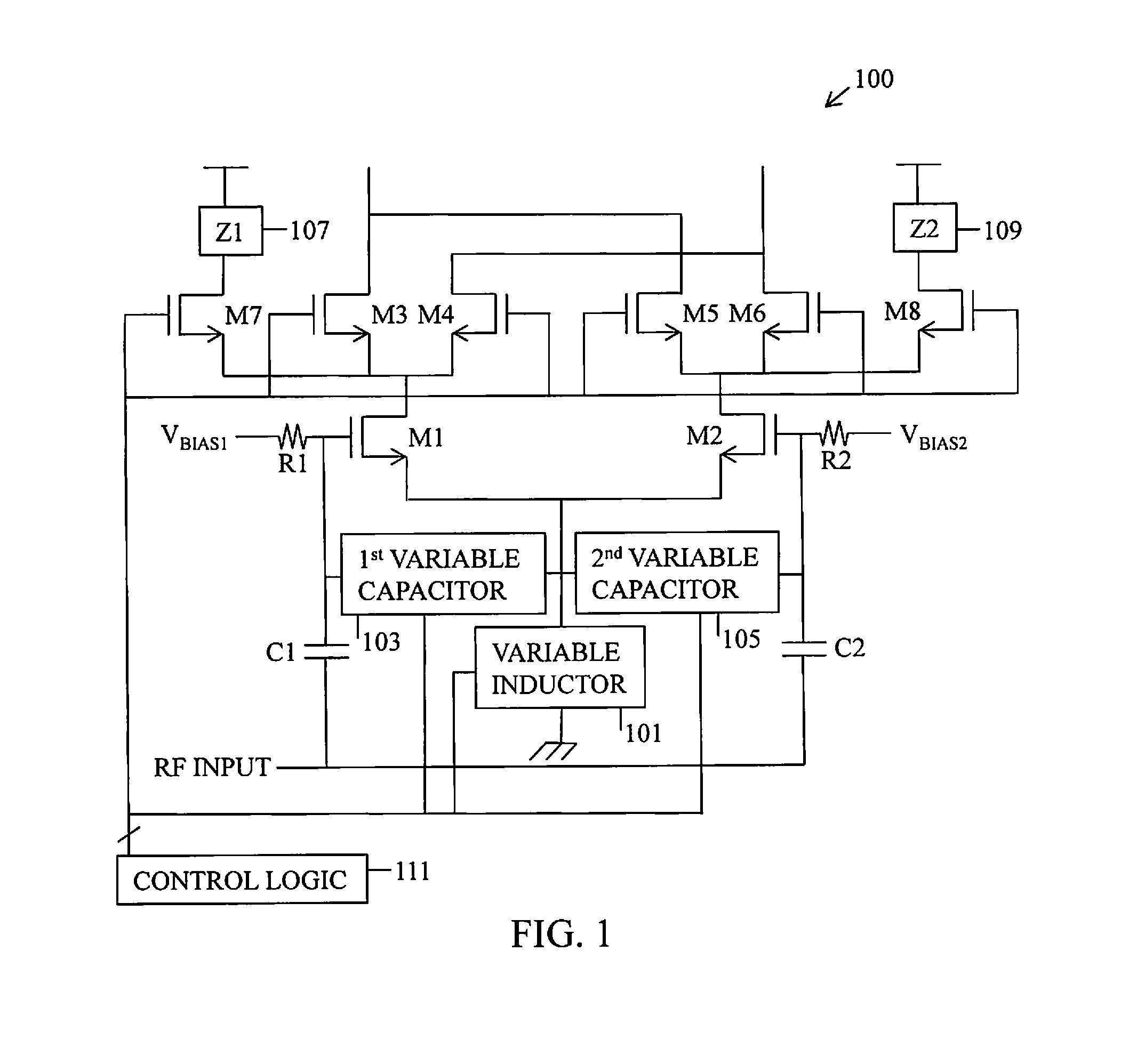
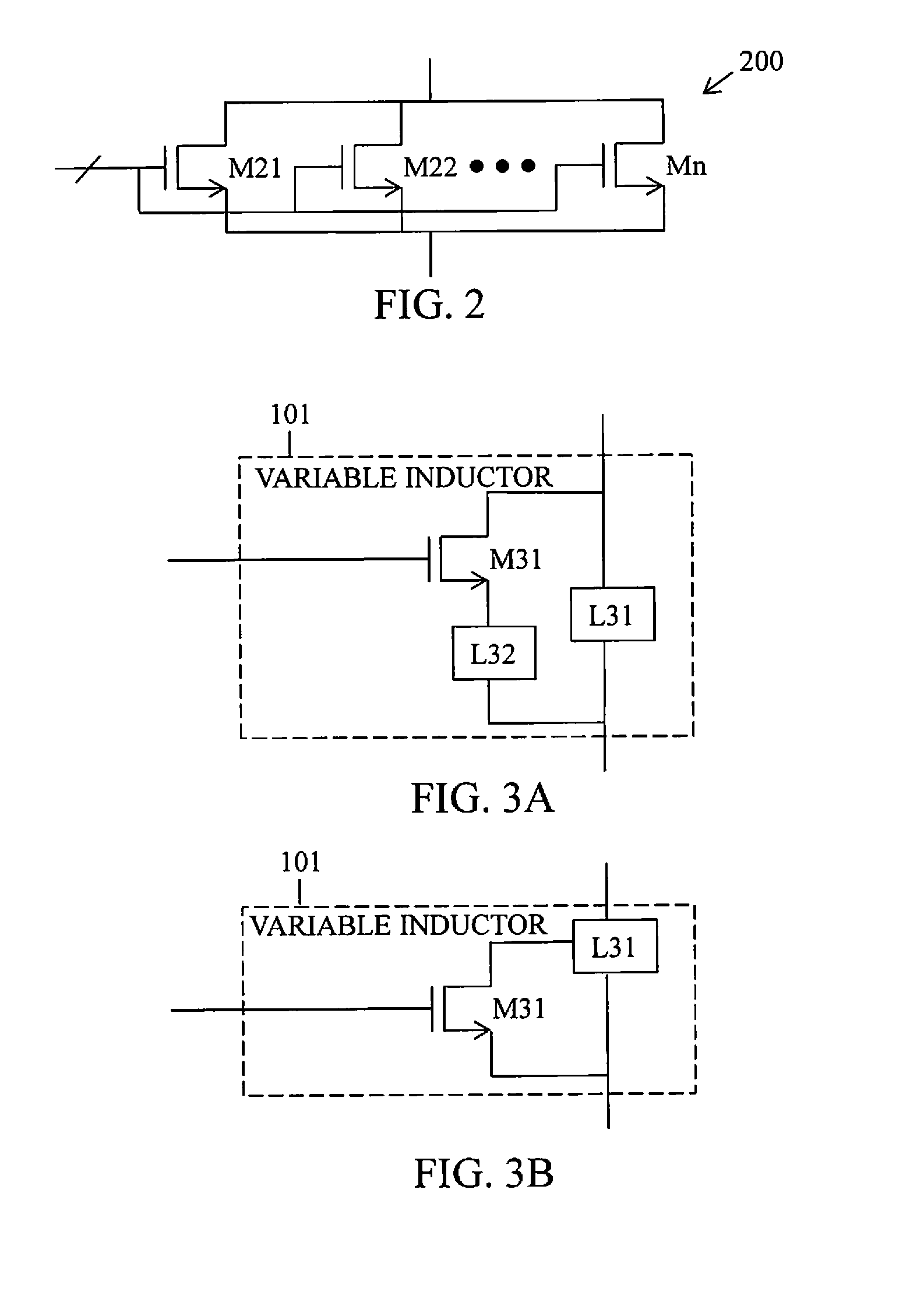
Low noise amplifier and method for carrier aggregation and non-carrier aggregation
ActiveUS20160065264A1Low noiseLow noise amplifierAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesSubstation equipmentCarrier signalTelecommunications
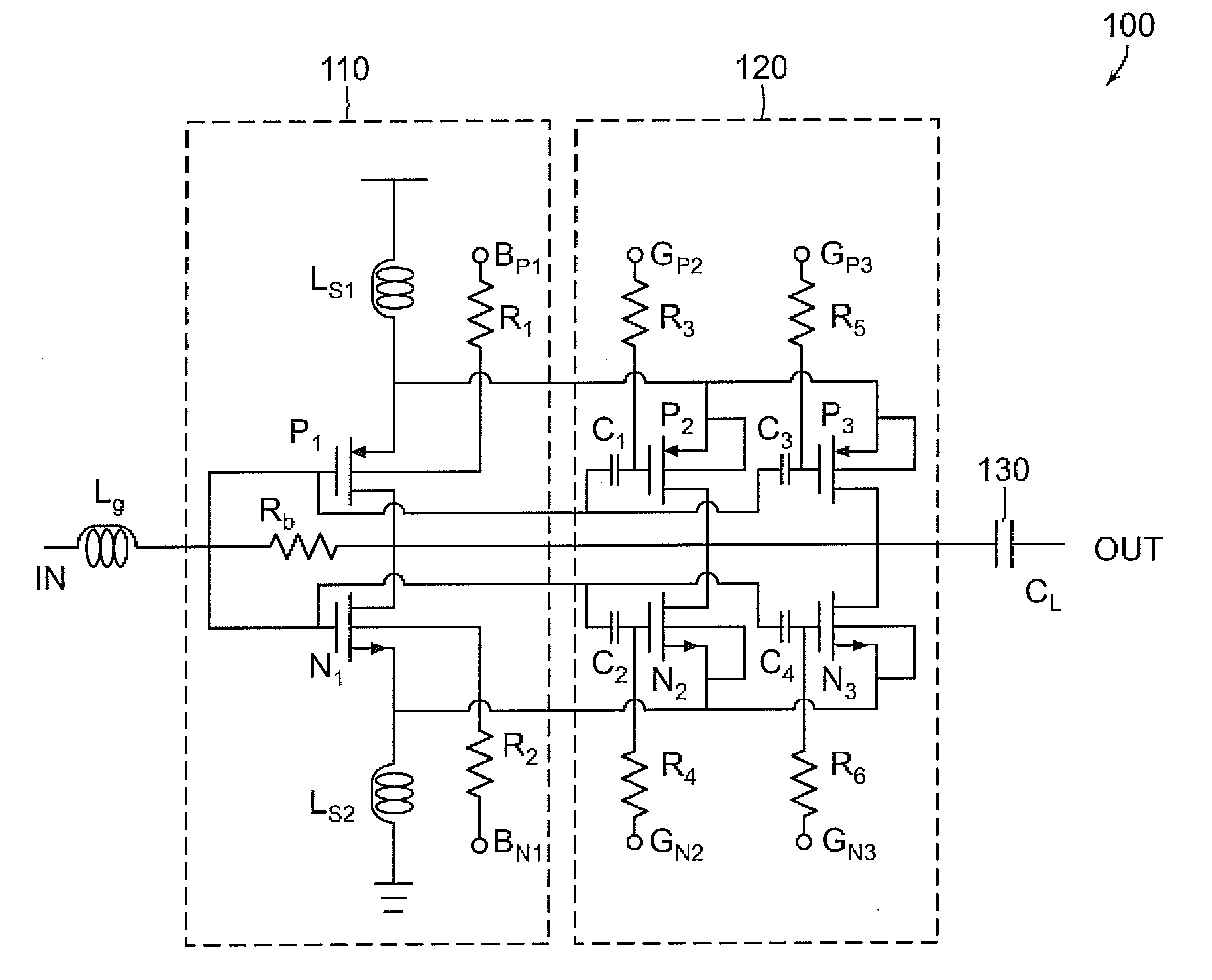
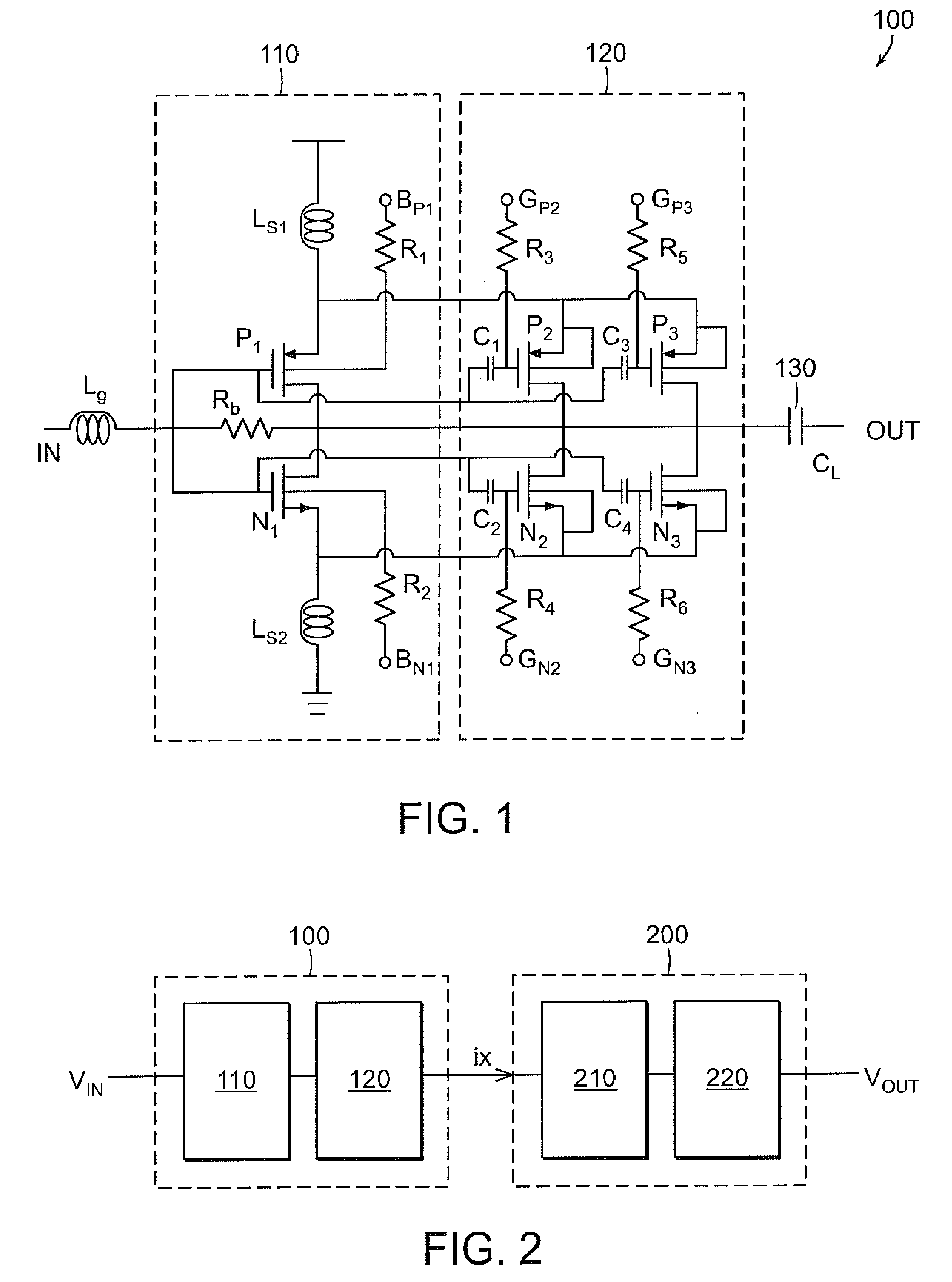
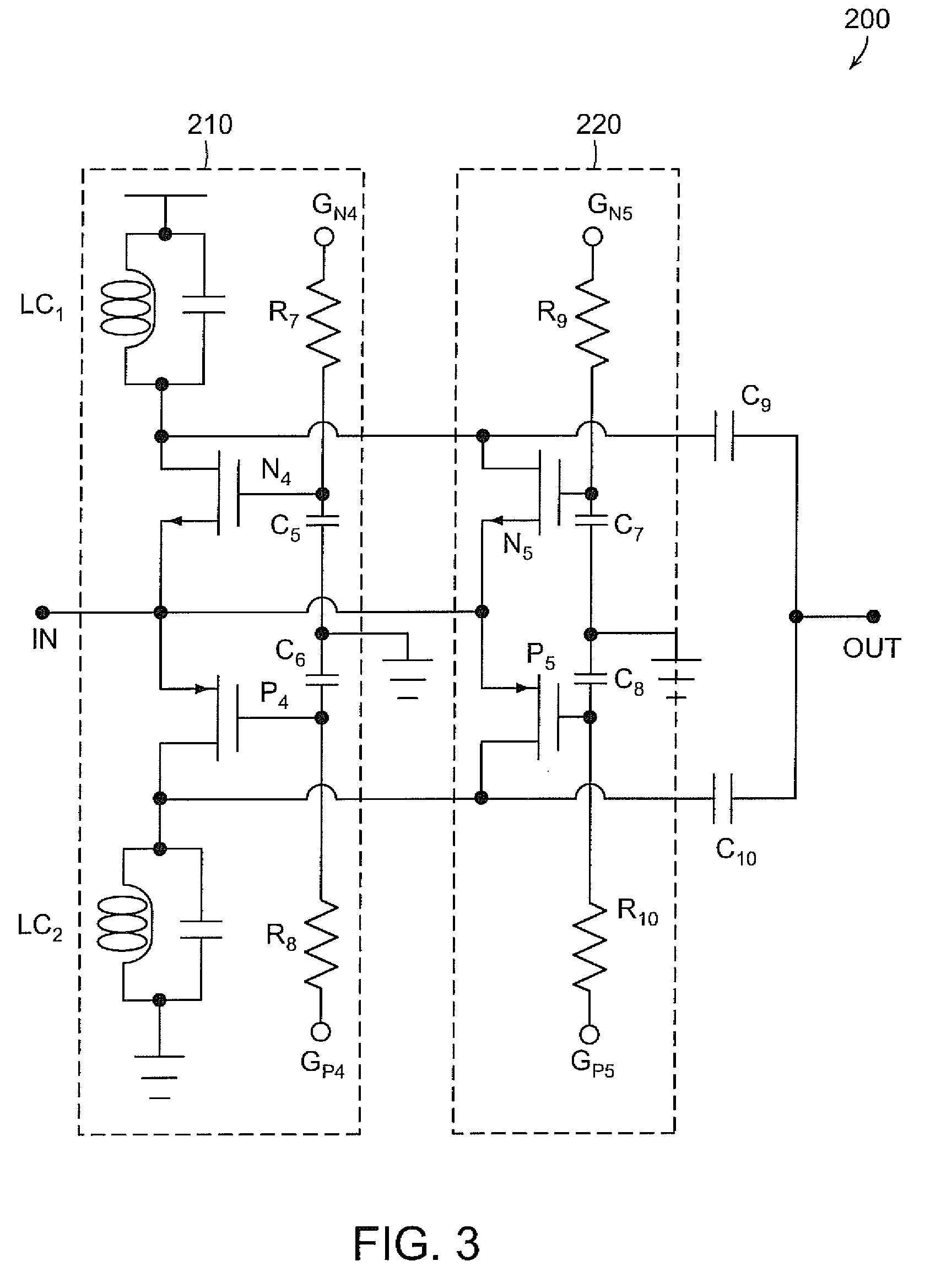
A low noise amplifier for carrier aggregation and non-carrier aggregation is provided. The low noise amplifier includes a plurality of symmetrical half circuits, a plurality of bias circuits, where each of the plurality of bias circuits is connected to one of the plurality of symmetrical half circuits, a plurality of capacitors, where each of the plurality of capacitors is connected to one of the plurality of symmetrical half circuits for Alternating Current (AC) coupling an RF signal containing at least one component carrier, and a control logic circuit connected to each of the plurality of symmetrical half circuits for configuring the low noise amplifier to process one component carrier or a plurality of component carriers.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
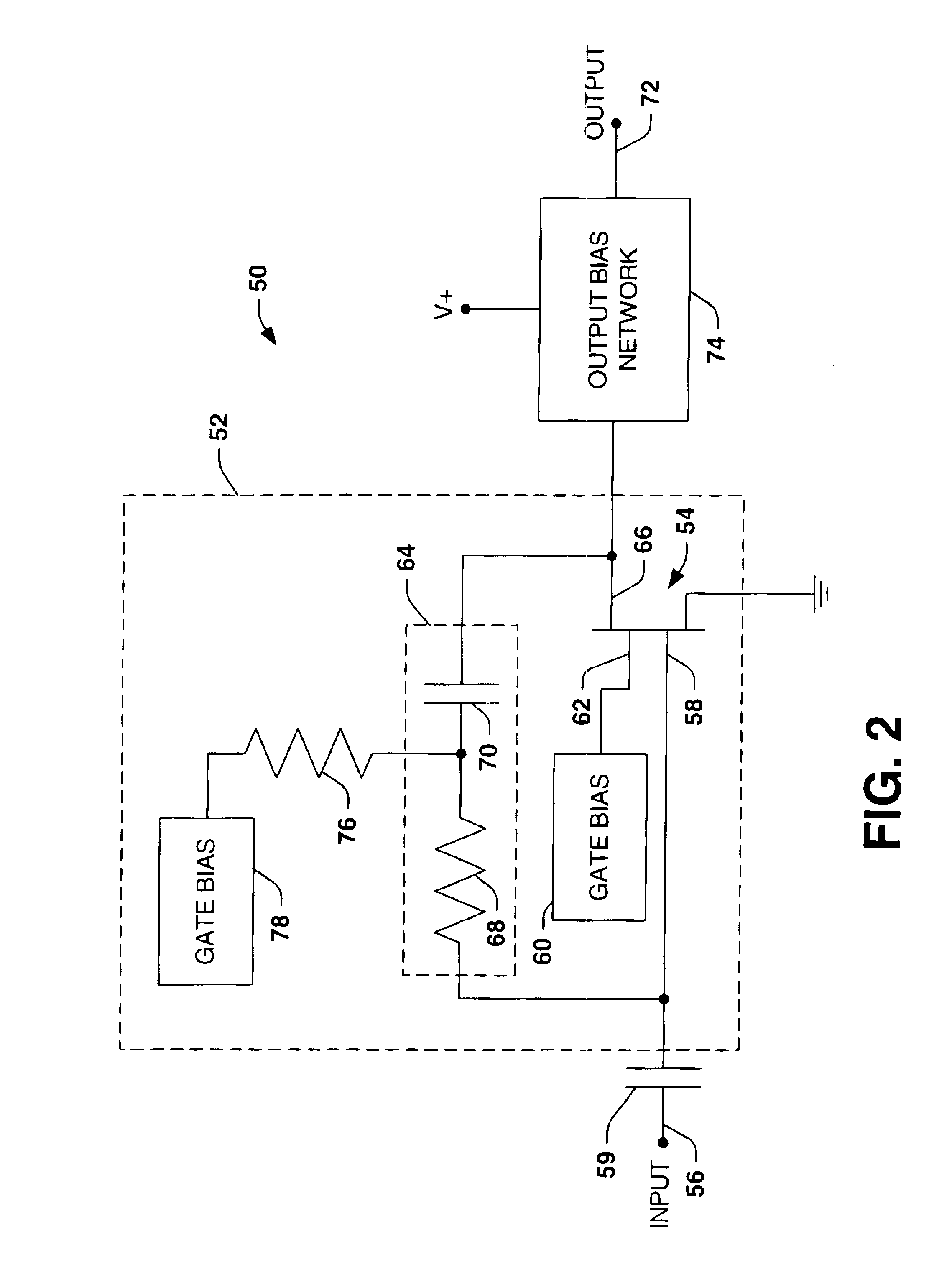
Dual gate low noise amplifier
InactiveUS6801088B2Occupying less real estateImprove performanceNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceLow noiseAudio power amplifier
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
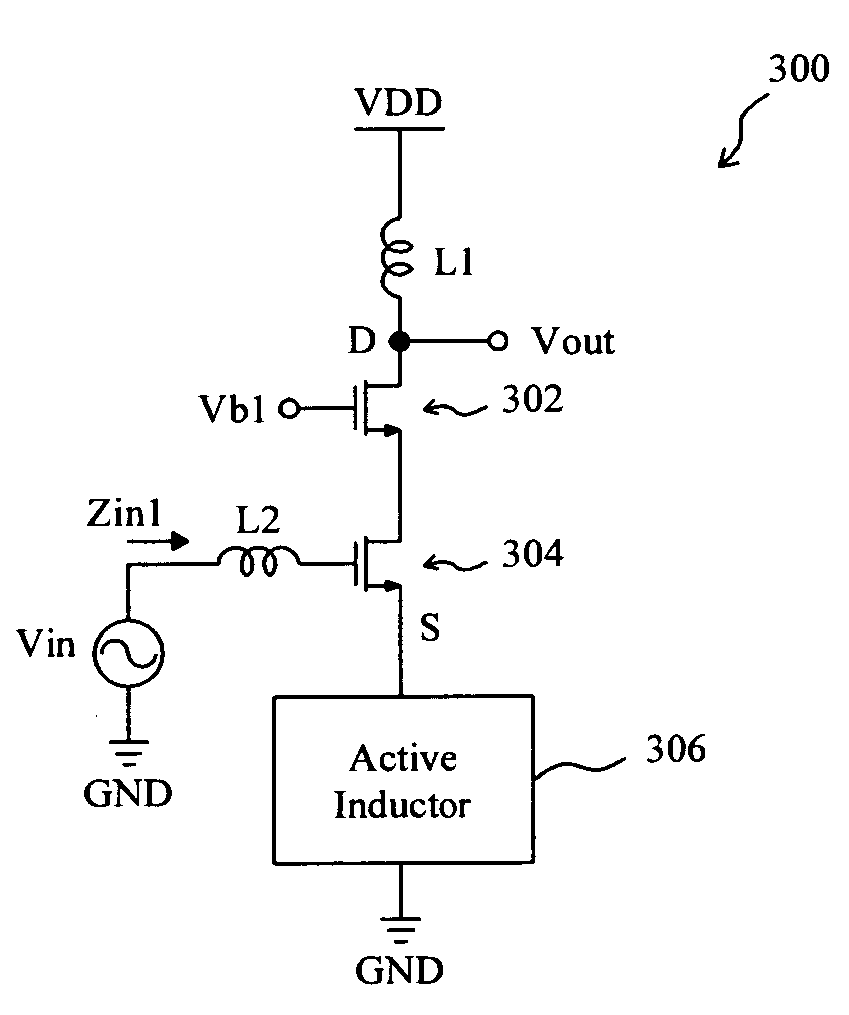
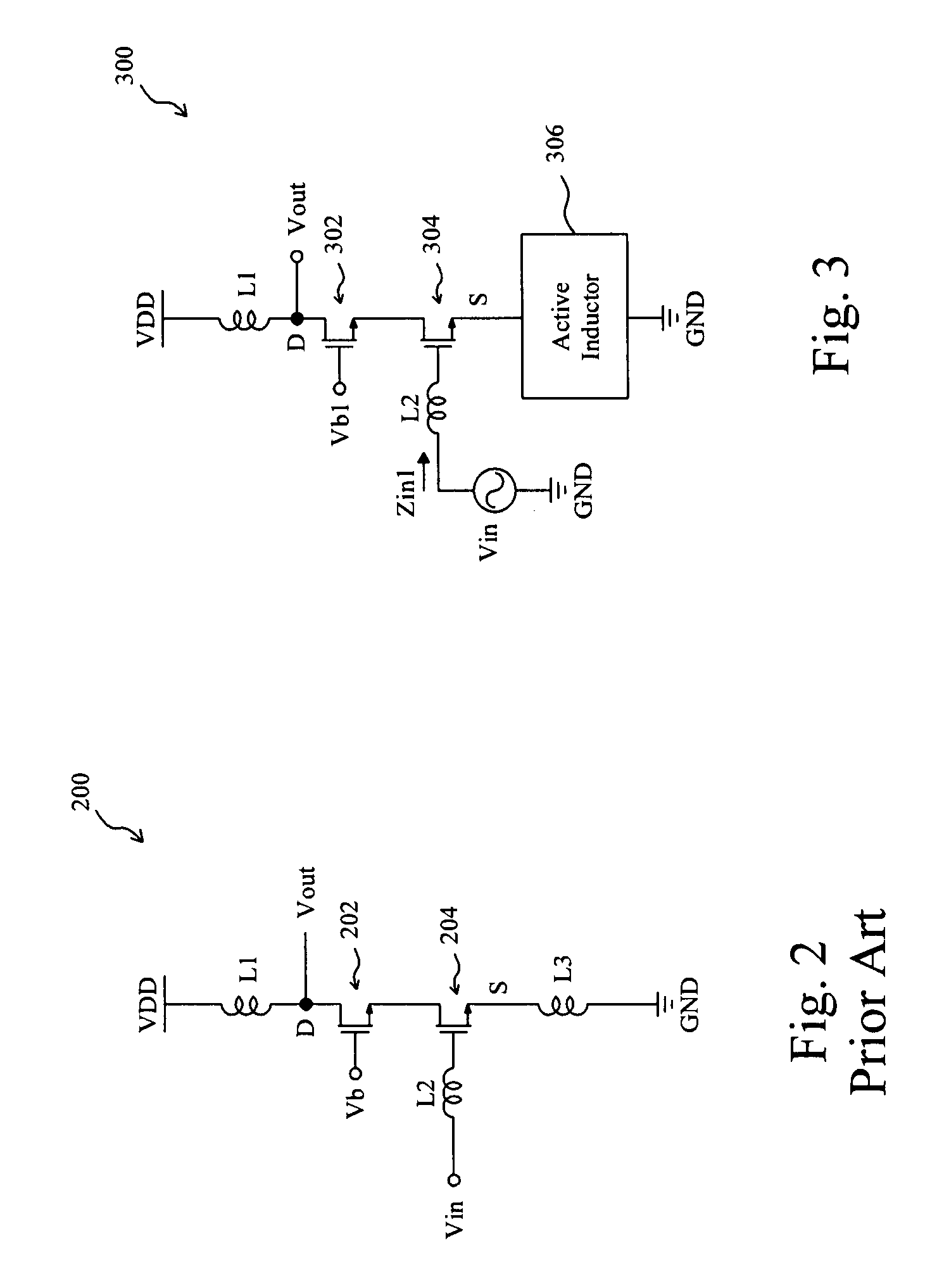
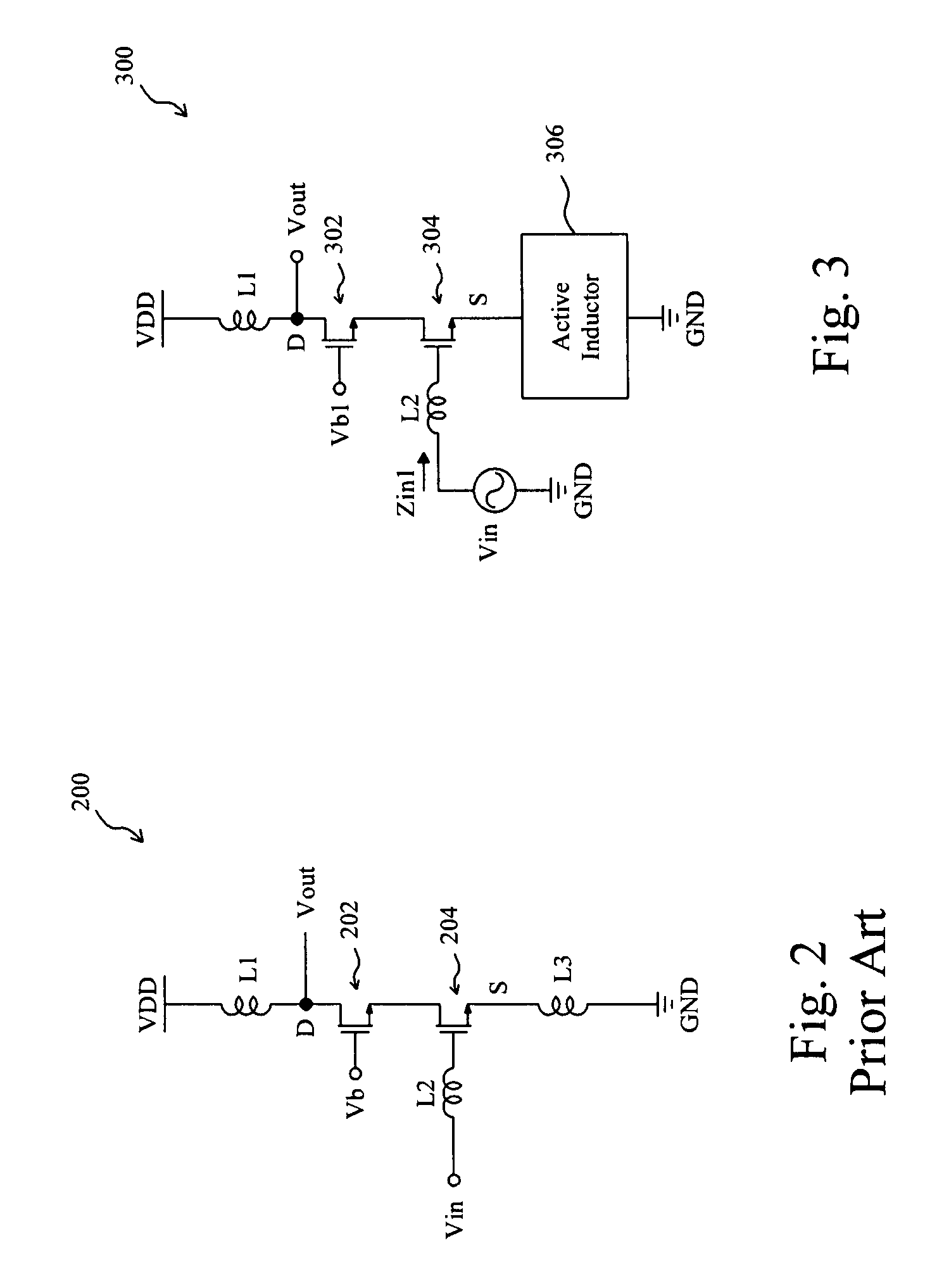
Cascode low noise amplifier with a source coupled active inductor
InactiveUS20080111632A1Reduce chip sizeLow noise amplifierHigh frequency amplifiersAmplifier combinationsLow noiseAudio power amplifier
A cascode low noise amplifier includes an input transistor and an output transistor cascode together, the input transistor has a source coupled to an active inductor, and the output transistor has a drain to provide an output signal. By using the active inductor, the low noise amplifier has smaller size, lower noise figure, and higher gain. The active inductor also provides input impedance matching for the low noise amplifier.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
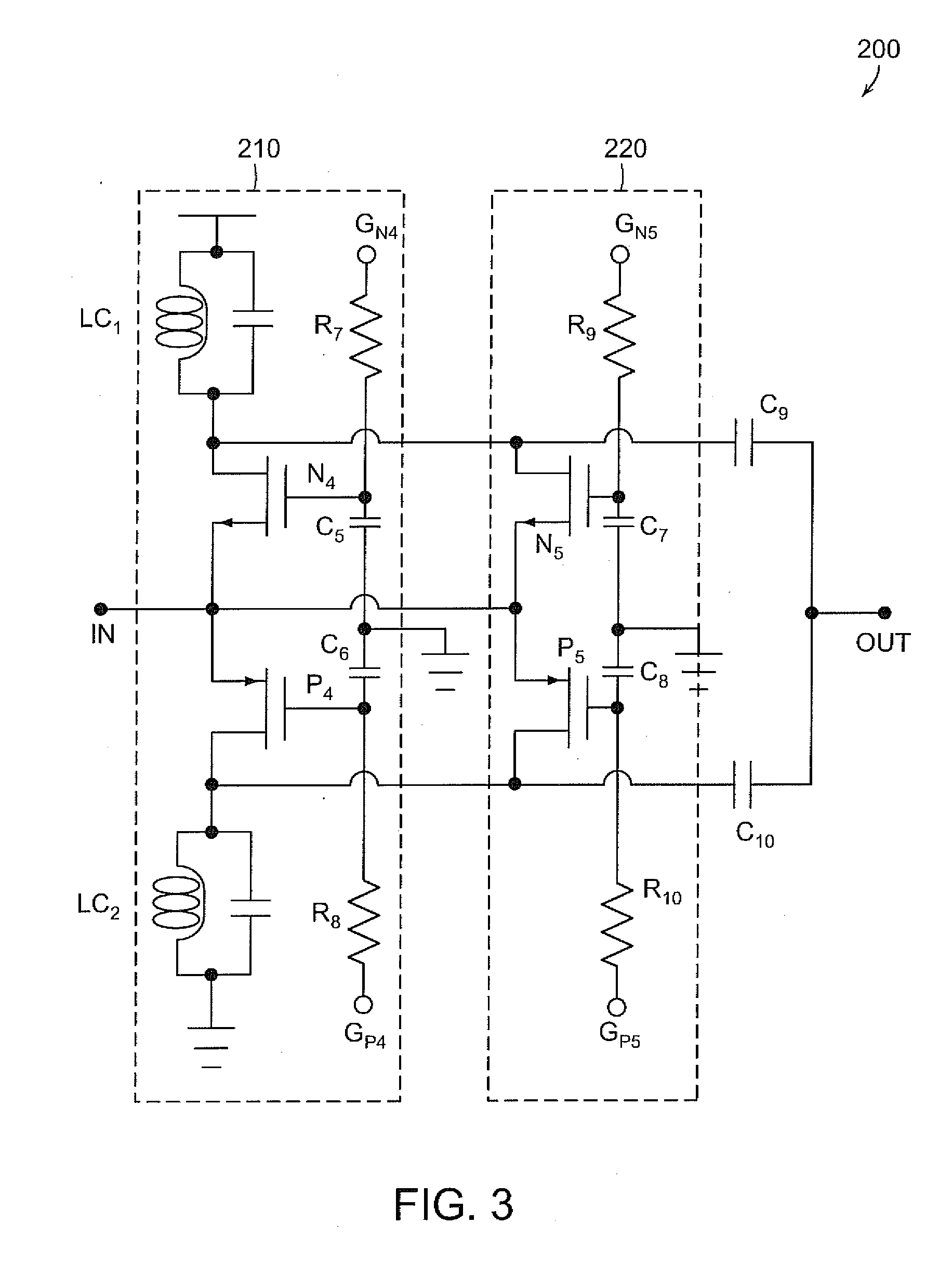
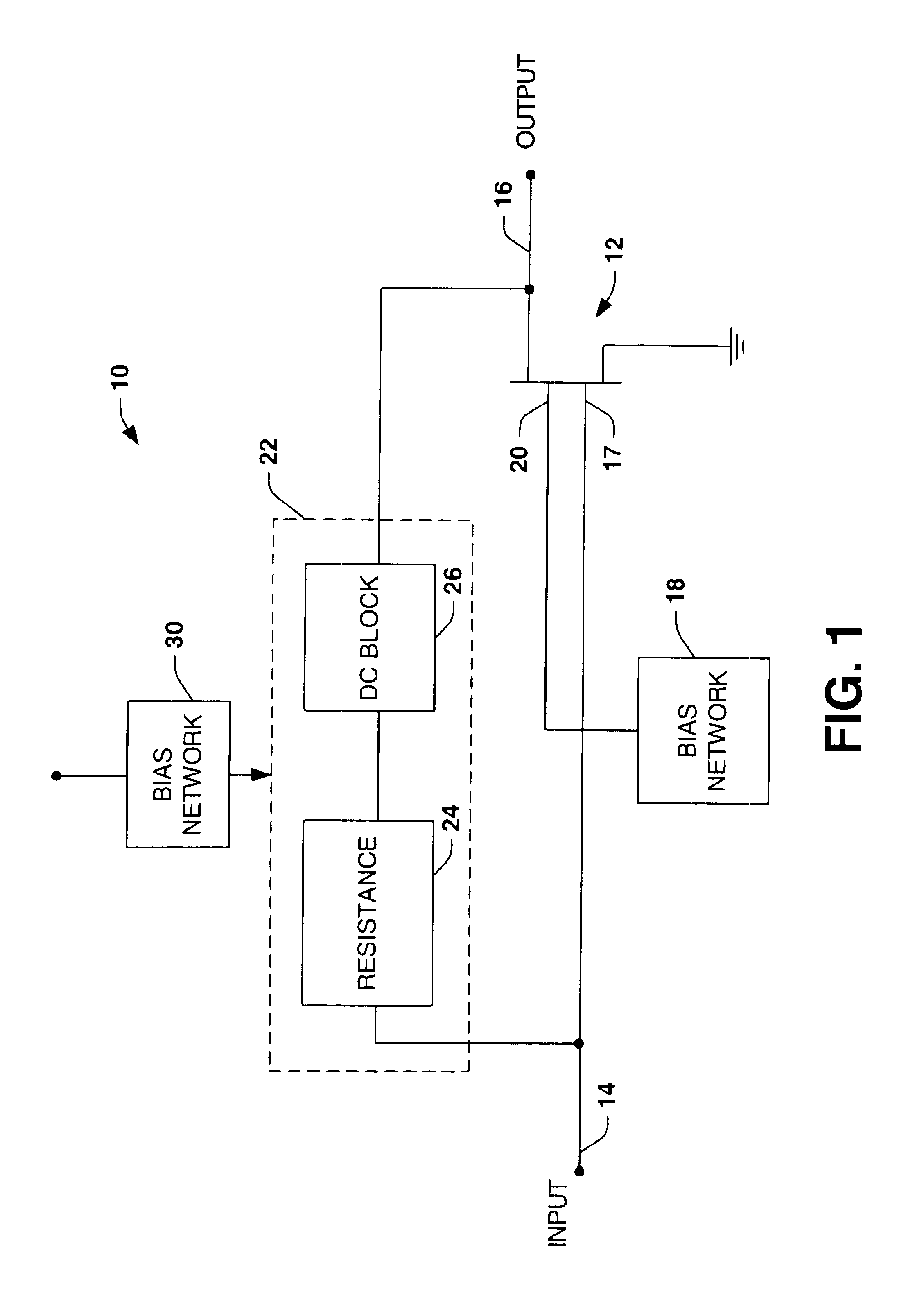
Low noise amplifier
InactiveUS20080204142A1Reduce third order intermodulation distortionReduce distortion problemsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceHigh frequency amplifiersTime constantSignal production
A low noise amplifier includes a main amplifier configured to amplify a first input signal to generate a first output signal and an auxiliary amplifier configured to amplify a second input signal to generate a second output signal. The auxiliary amplifier is coupled to the main amplifier for superposing the second output signal and the first output signal. The low noise amplifier also includes an adjusting unit configured to adjust a time constant for reducing a third order intermodulation distortion of the superposed signal in response to a control signal. The adjusting unit is configured to generate the second input signal based on the time constant and the first input signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Cascode low noise amplifier with a source coupled active inductor
InactiveUS7714663B2Reduce chip sizeLow noise amplifierHigh frequency amplifiersAmplifier combinationsLow noiseAudio power amplifier
A cascode low noise amplifier includes an input transistor and an output transistor cascode together, the input transistor has a source coupled to an active inductor, and the output transistor has a drain to provide an output signal. By using the active inductor, the low noise amplifier has smaller size, lower noise figure, and higher gain. The active inductor also provides input impedance matching for the low noise amplifier.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Radio receiver with shared low noise amplifier for multi-standard operation in a single antenna system with loft isolation and flexible gain control
ActiveUS8121564B2Improve reverse isolationLow noise amplifierSpatial transmit diversitySubstation equipmentAudio power amplifierRadio reception
A radio receiver is described that processes multiple wireless standards using a single antenna according to embodiments of the invention. The radio receiver includes a single antenna, and a low noise amplifier that is connected to the antenna, without an intervening power divider or power splitter. The output of the low noise amplifier feeds multiple wireless receivers in a parallel arrangement that are operating according to different communications standards, including for example a Bluetooth and a WLAN 802.11. Additional wireless standards and their corresponding receivers could be added as well. The input impedance of the low noise amplifier defines the impedance seen by the antenna, regardless of which operational standard is actually in use. Each signal path includes an additional low noise amplifier having a gain that can be customized for the particular signal path and receiver in use, and which also improves the reverse isolation between signal paths. Further, a switch can be added to one or more of the signal paths so as to further improve isolation when a particular path is not being used.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Low-power-consumption bidirectional noise-reducing low-noise amplifier
ActiveCN105281682AGood input matchChannel noise cancellationAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDifferential amplifiersLow noiseChannel thermal noise
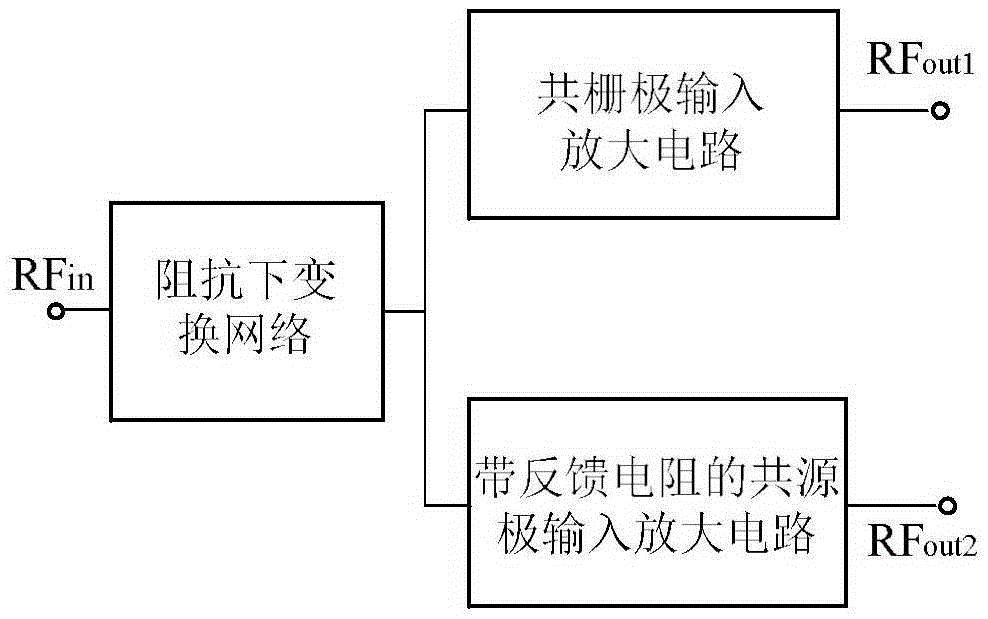
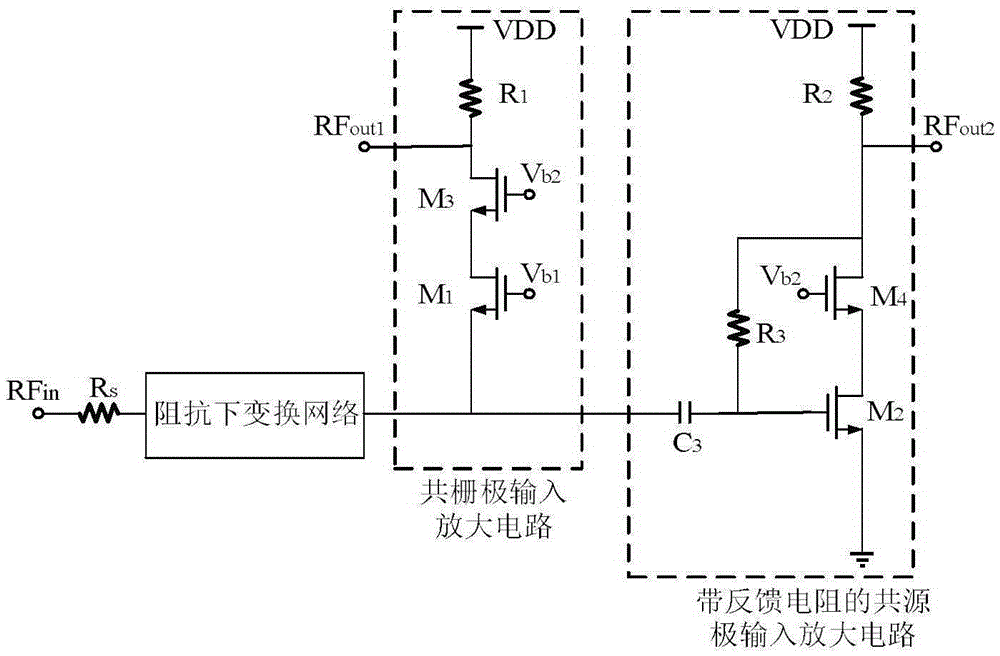
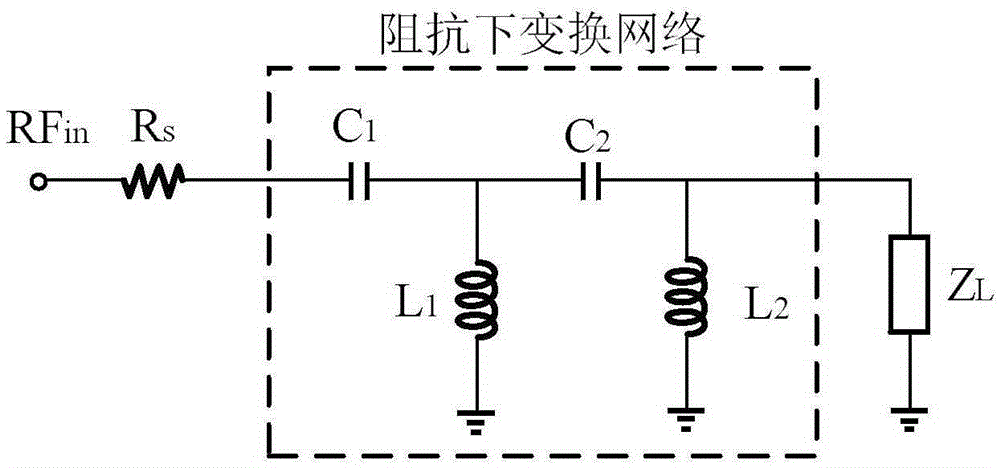
The invention provides a low-power-consumption bidirectional noise-reducing low-noise amplifier and aims to provide the low-power-consumption bidirectional noise-reducing low-noise amplifier which has advantages of low noise coefficient, high reliability and stable gain, wherein the low-power-consumption bidirectional noise-reducing low-noise amplifier can eliminate a common-gate-tube channel thermal noise and reduce a common-source-tube channel thermal noise and a common-source-end load resistor thermal noise. The low-power-consumption bidirectional noise-reducing low-noise amplifier is realized through a technical solution which is characterized in that an impedance down-conversion network is parallelly connected with a common-source-electrode amplifying circuit with a feedback resistor through a common-gate-electrode amplifying circuit, thereby forming a single-end-input double-end-output low-noise amplifying circuit, wherein a common-gate-electrode input amplifying circuit is composed of an MOS tube M1, a serially connected MOS tube M3, and a load resistor R1 which is serially connected between the drain electrode of the MOS tube M3 and a power supply VDD. A common-source-electrode input amplifier circuit is composed of a capacitor C3 which is connected with the source electrode of an MOS tube M2, an MOS tube M4 which is serially connected with the MOS tube M2, a feedback resistor R3 which is parallelly connected between the gate electrode of the MOS tube M2 and the drain electrode of the MOS tube M4, and a load resistor R2 which is serially connected between the drain electrode of the MOS tube M4 and the power supply VDD.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
Slew rate enhancement circuitry for folded cascode amplifier
ActiveUS20060181350A1Low costIncrease conversion rateDifferential amplifiersArbitary function generatorsAudio power amplifierSlew rate
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
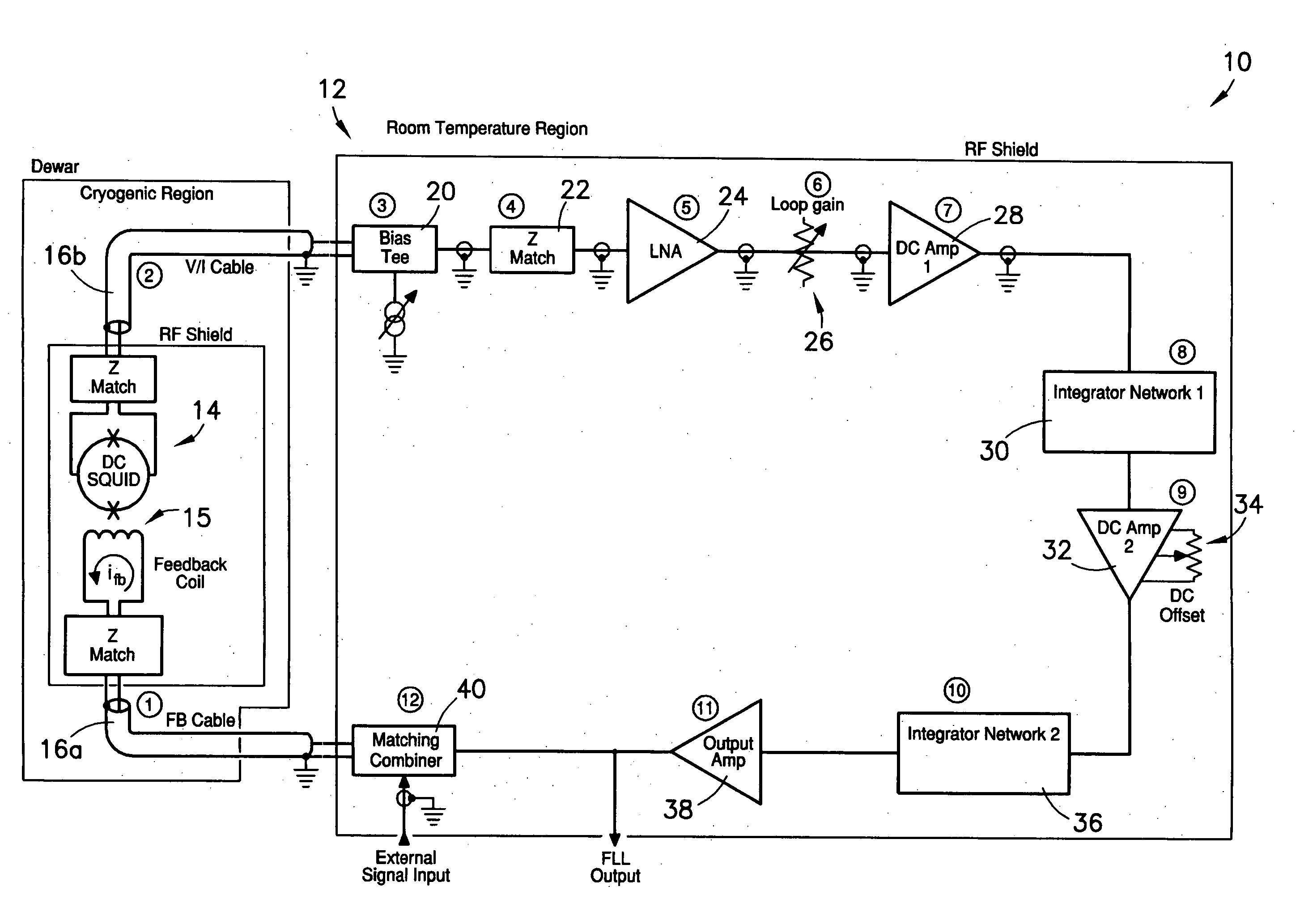
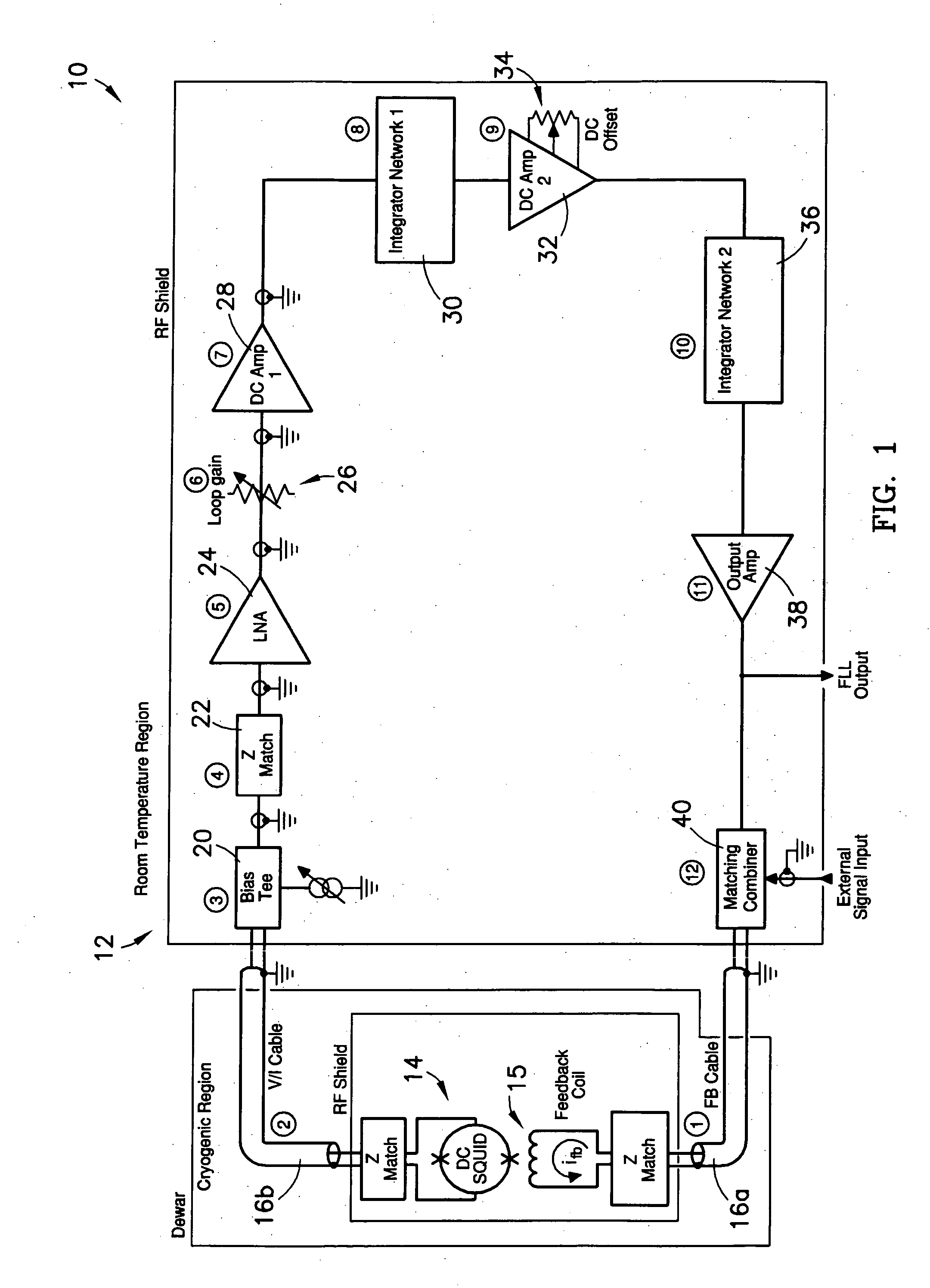
System having unmodulated flux locked loop for measuring magnetic fields
ActiveUS20060164081A1Few and small and less-expensiveEasy to adjustSuperconductors/hyperconductorsMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsDirect feedbackRoom temperature
A system (10) for measuring magnetic fields, wherein the system (10) comprises an unmodulated or direct-feedback flux locked loop (12) connected by first and second unbalanced RF coaxial transmission lines (16a,16b) to a superconducting quantum interface device (14). The FLL (12) operates for the most part in a room-temperature or non-cryogenic environment, while the SQUID (14) operates in a cryogenic environment, with the first and second lines (16a,16b) extending between these two operating environments.
Owner:HONEYWELL FED MFG & TECHNOLOGI
Amplifier with gain circuit coupeld to primary coil of transformer
ActiveUS8860507B2Reduce areaLow noise amplifierPush-pull amplifiersPhase-splittersAudio power amplifierTransformer
An amplifier includes a transformer and a first stage gain circuit. The transformer includes a primary coil and a secondary coil. The primary coil is utilized for receiving an input signal. The first stage gain circuit has a first input port, which is coupled to the primary coil. The first stage gain circuit is utilized for gaining the input signal so as to generate a first output.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
Radar receiver, and radar device equipped with same
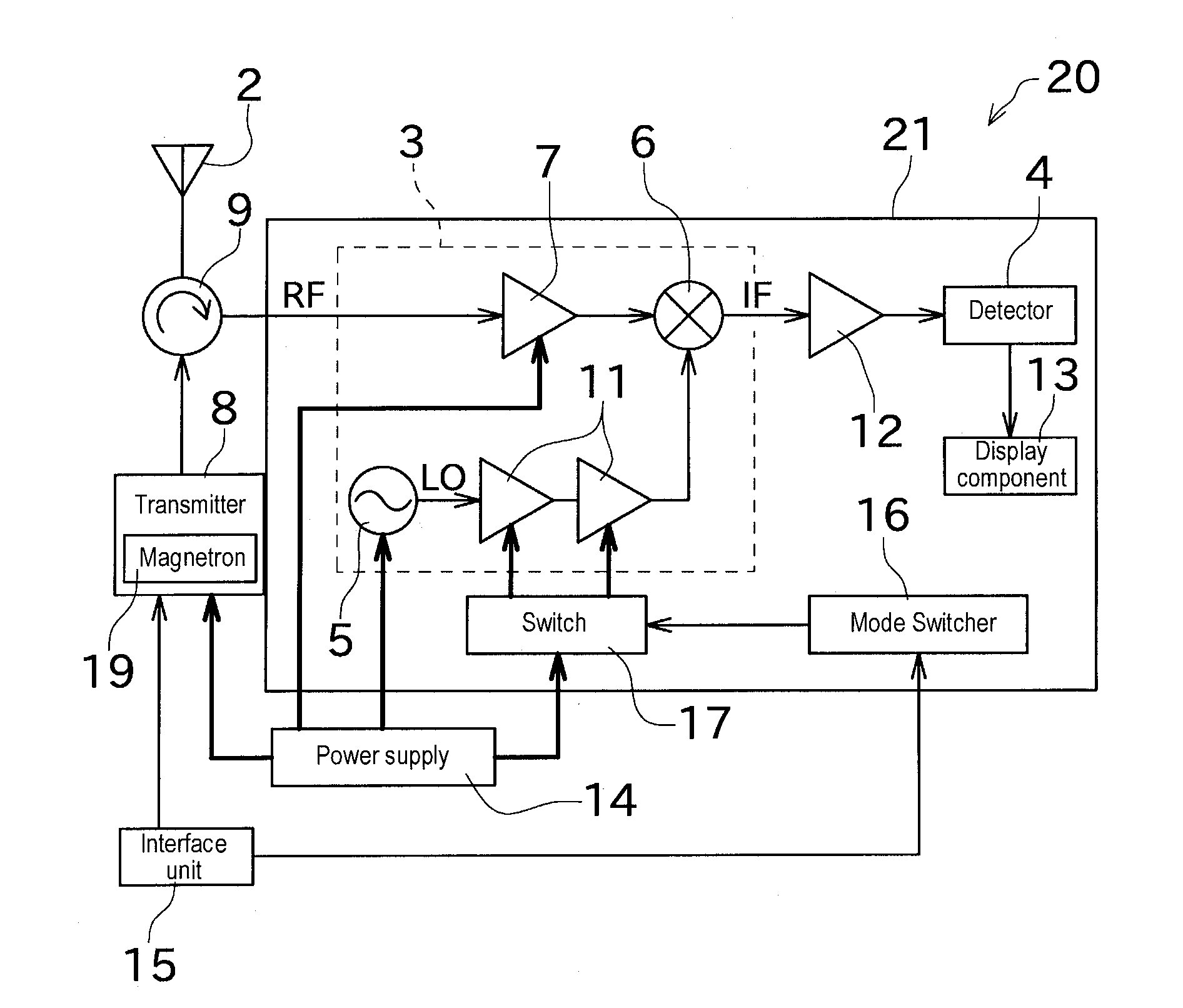
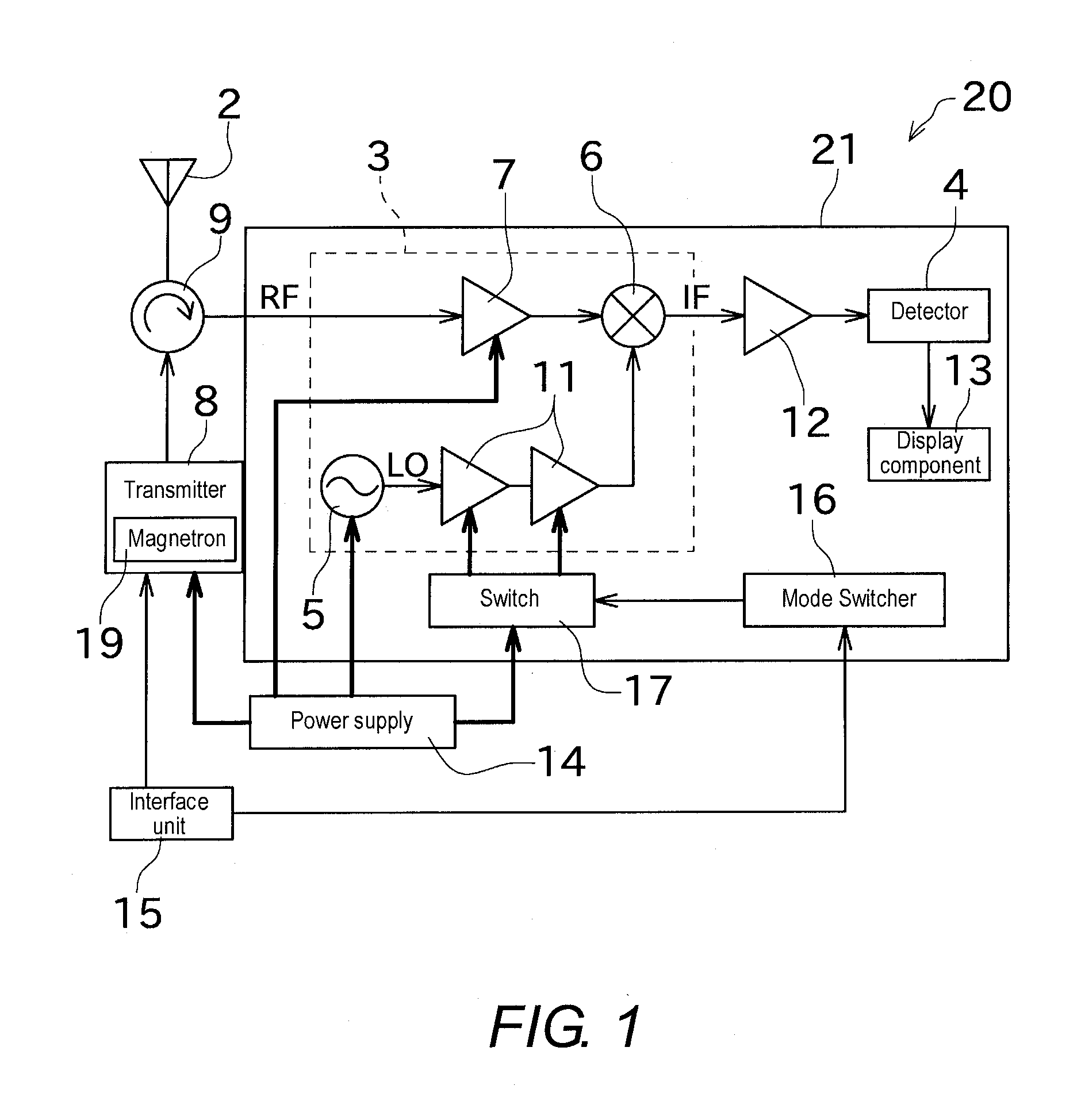
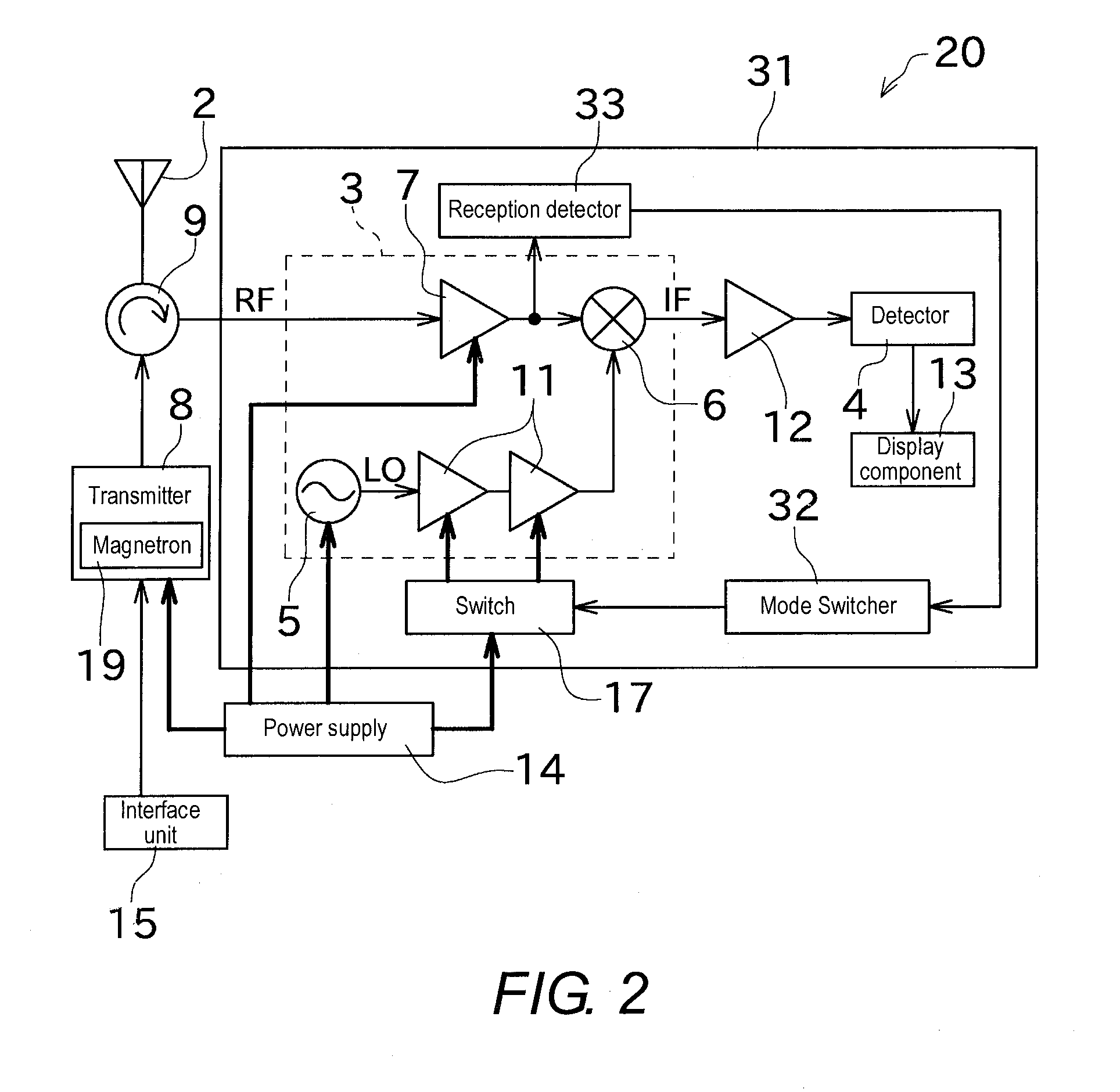
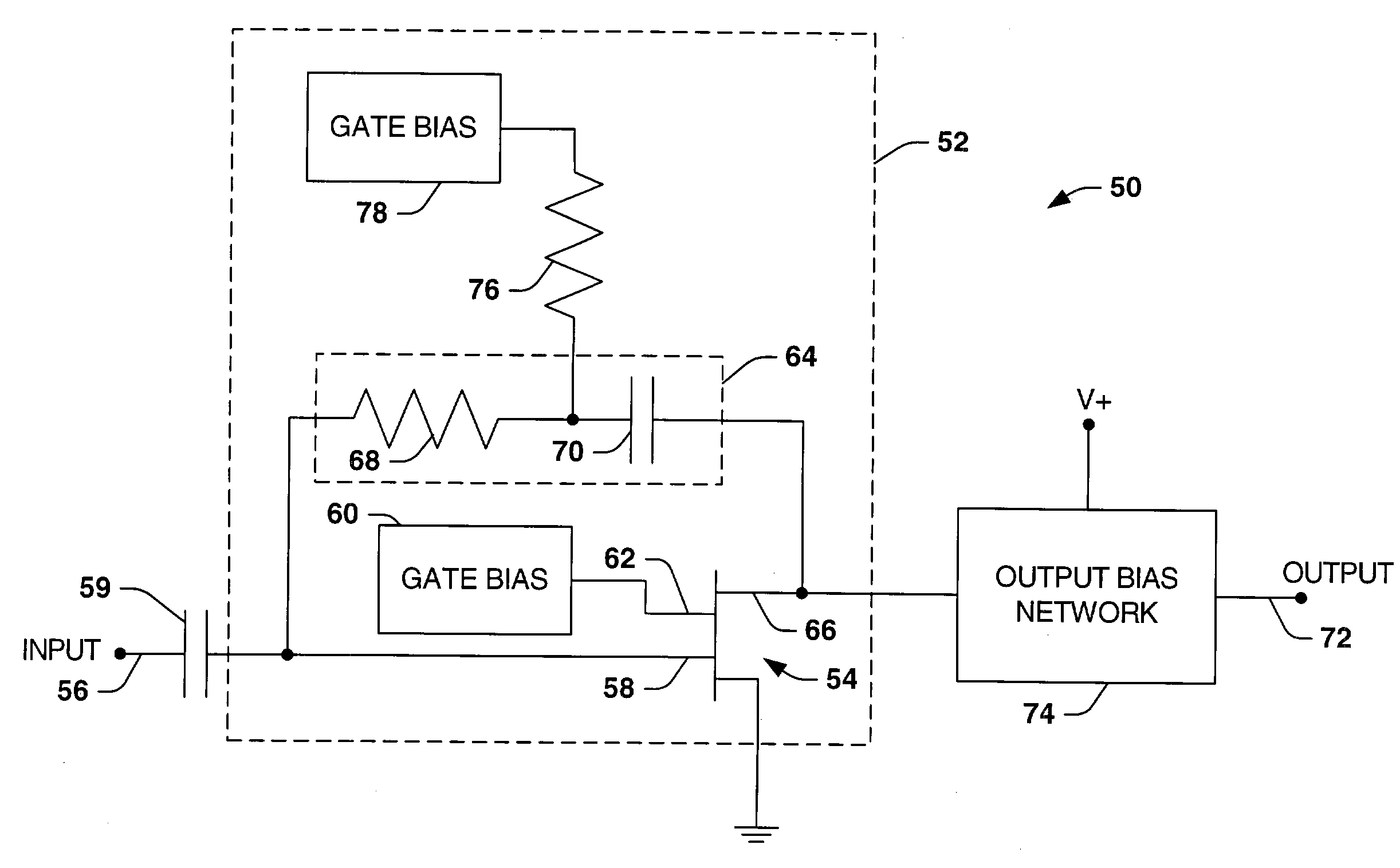
ActiveUS20140002298A1Stable receptionAvoid temperature changesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionLocal oscillator signalRadar
There is provided a radar receiver that effectively prevents local oscillator signals from leaking out from an antenna. A receiver 21 includes a local oscillator 5, a mixer 6, a buffer amplifier 11, and a mode switcher 16. The local oscillator 5 outputs a local oscillation signal LO. The mixer 6 mixes a high-frequency signal RF received by a radar antenna 2 with the local oscillation signal LO. The buffer amplifier 11 is disposed between the local oscillator 5 and the mixer 6. The mode switcher 16 switches at least between a standby mode in which power is supplied to the local oscillator 5 and no power is supplied to the buffer amplifier 11 and a reception mode in which power is supplied to both the local oscillator 5 and the buffer amplifier 11.
Owner:FURUNO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Low noise amplifier
InactiveUS7663441B2Reduce distortion problemsLow noise amplifierAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceHigh frequency amplifiersAudio power amplifierControl signal
A low noise amplifier includes a main amplifier configured to amplify a first input signal to generate a first output signal and an auxiliary amplifier configured to amplify a second input signal to generate a second output signal. The auxiliary amplifier is coupled to the main amplifier for superposing the second output signal and the first output signal. The low noise amplifier also includes an adjusting unit configured to adjust a time constant for reducing a third order intermodulation distortion of the superposed signal in response to a control signal. The adjusting unit is configured to generate the second input signal based on the time constant and the first input signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Switchable multiband LNA design
ActiveUS8294520B2Consumes less design areaLow noise amplifierNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsGated amplifiersLow noiseResonance
A low noise amplifying (LNA) circuit comprising an amplifying section (11, 12) and a feedback means (14) arranged for providing input matching from the output to the input. The LNA circuit further comprises at least one frequency band determining inductor (15) having a predetermined resonance frequency for influencing at least one frequency band in which the amplifying section operates. The at least one inductor is directly connected to the output of the circuit and the feedback means (14) provides a feedback connection for the section (s) to the input. In this way, the at least one frequency band in which the amplifying section operates is substantially completely determined by the at least one frequency band determining inductor (15).
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW) +1
Signal processing apparatus
InactiveUS20170257165A1Low powerLighterRadio-over-fibreAircraft components testingAudio power amplifierComputer module
Signal processing apparatus located in and / or mounted on an entity (e.g. an aircraft), the signal processing apparatus comprising: a first module; a second module connected to the first module such that signals may be sent between those modules; one or more amplifiers configured to amplify signals sent between the modules; and one or more optical fibres. The first module is located at a first location in / on the entity. The second module and the one or more amplifiers are located at a second location in / on the entity. The first location and the second location are spatially separate, i.e. remote from one another. The optical fibre(s) couple together the first and the second locations such that a signal sent between those locations is sent via the optical fibre(s).
Owner:BAE SYSTEMS PLC
Low noise amplifier and method for carrier aggregation and non-carrier aggregation
A low noise amplifier for carrier aggregation and non-carrier aggregation is provided. The low noise amplifier includes a plurality of symmetrical half circuits, a plurality of bias circuits, where each of the plurality of bias circuits is connected to one of the plurality of symmetrical half circuits, a plurality of capacitors, where each of the plurality of capacitors is connected to one of the plurality of symmetrical half circuits for Alternating Current (AC) coupling an RF signal containing at least one component carrier, and a control logic circuit connected to each of the plurality of symmetrical half circuits for configuring the low noise amplifier to process one component carrier or a plurality of component carriers.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Low noise amplifier with switch gain control
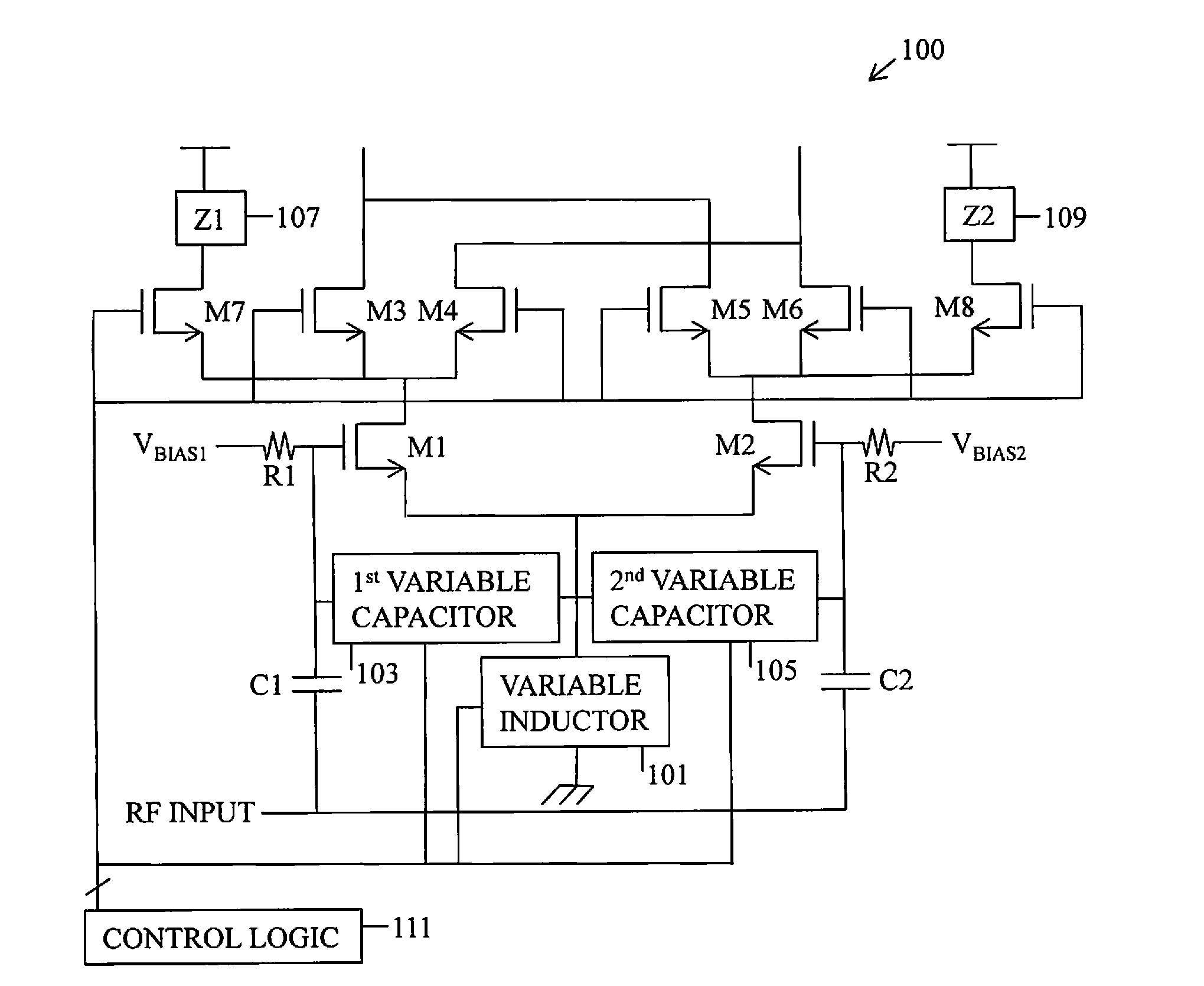
ActiveUS20070057733A1Improve dynamic rangeLow noise amplifierAmplifier combinationsAmplifier modifications to reduce detrimental impedenceLow noiseControl signal
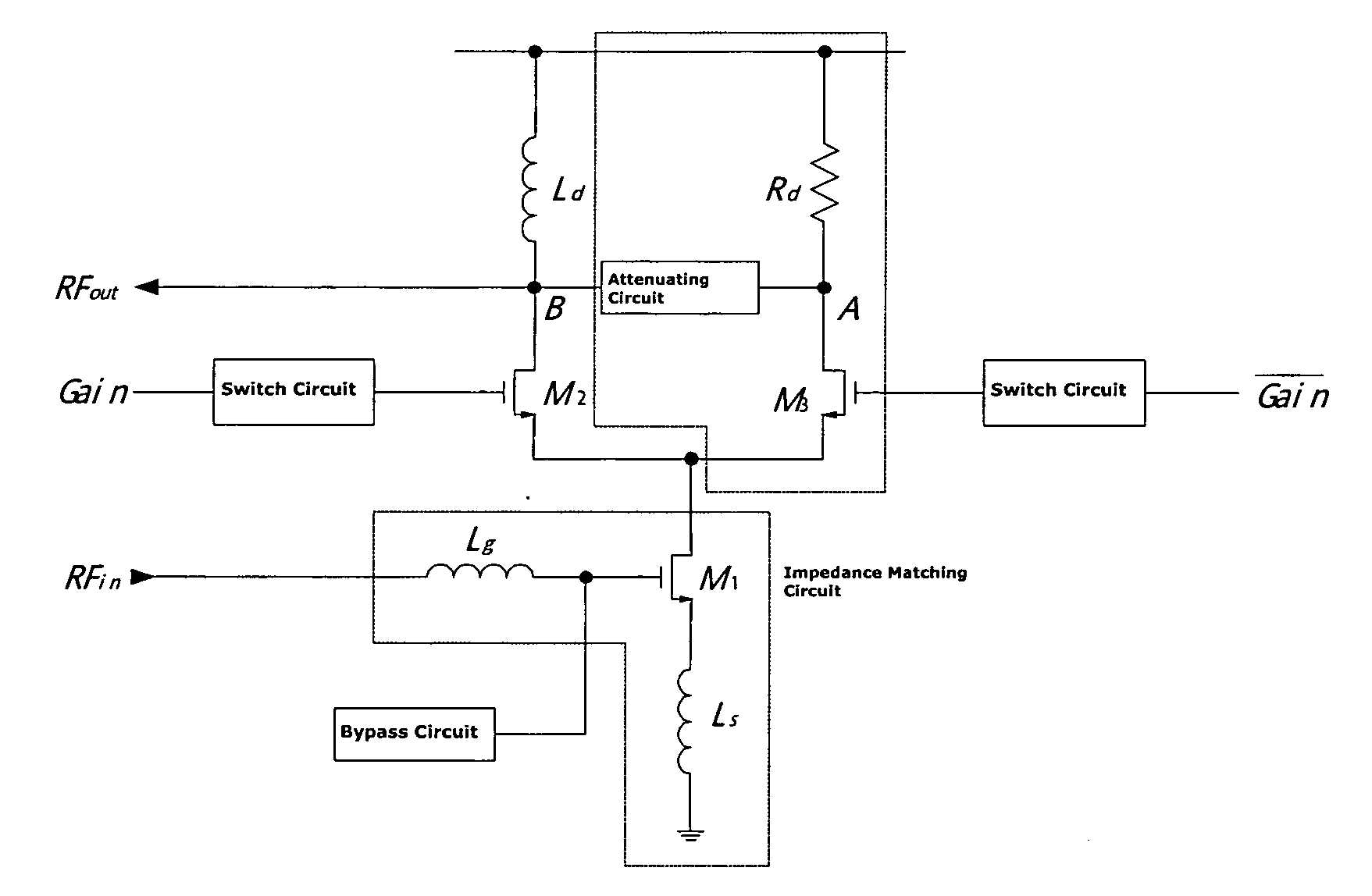
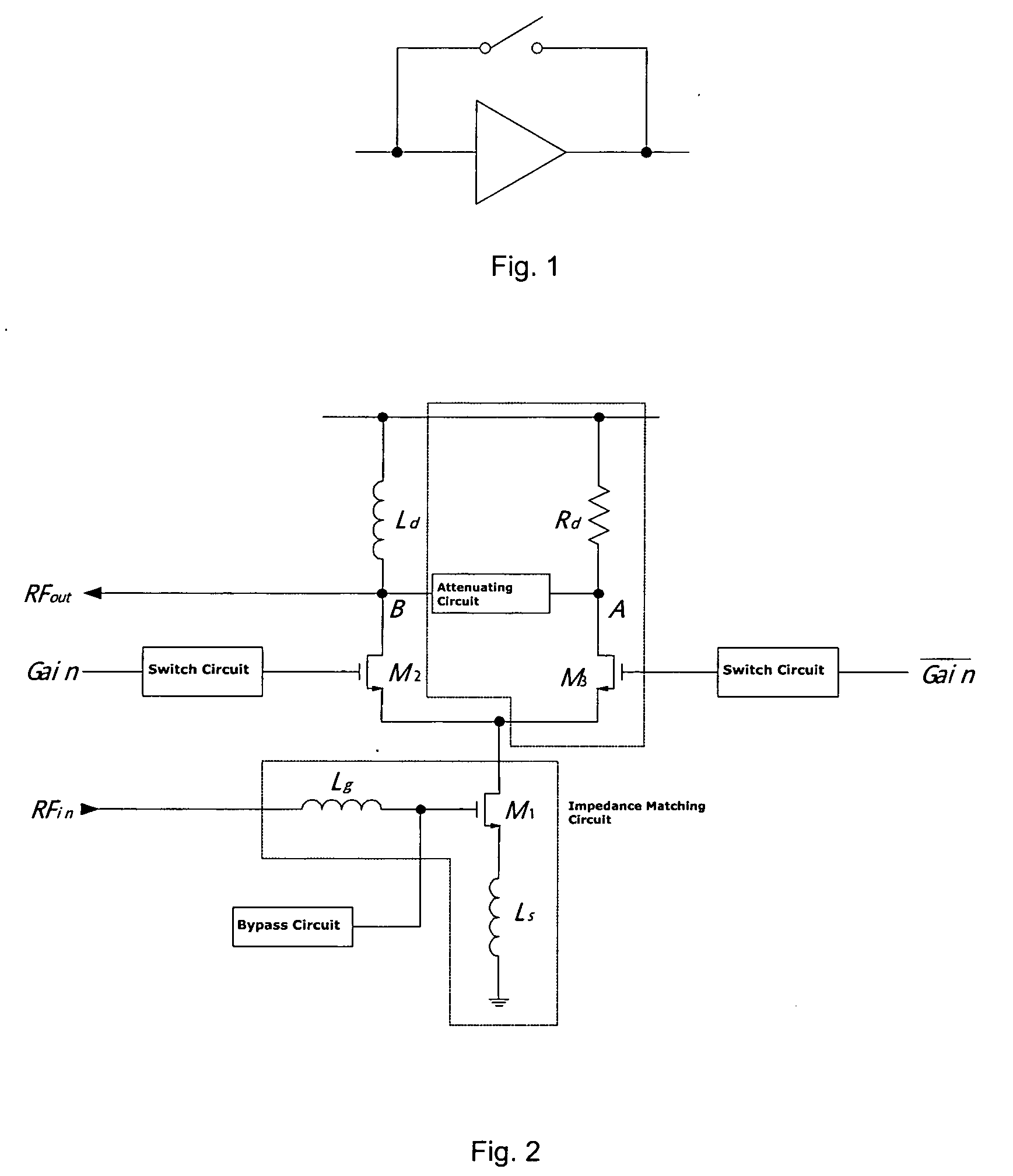
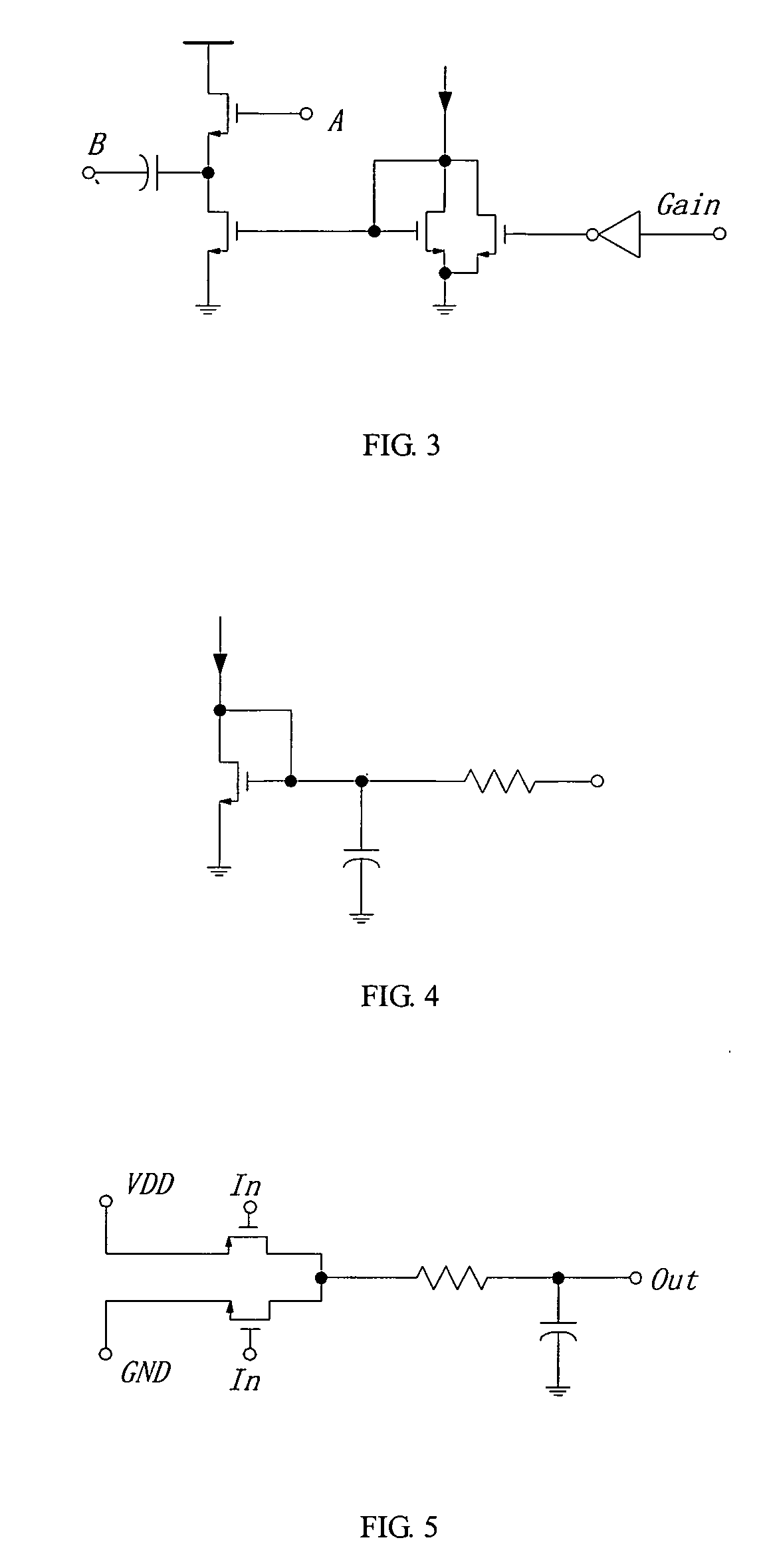
This invention presents a low noise amplifier with switching gain control, comprising an amplifier having an impedance matching circuit a switch circuit, a signal amplifying branch circuit, a switch control circuit, a signal attenuating circuit and a current bias circuit, wherein the switch circuit controls signal amplifying or attenuating based on the high or low of an input signal level. This invention provides low noise, great dynamic range, increased system integration, and low power consumption. This invention is used for integrated circuit wireless communication system and RF preamplifiers for receiver.
Owner:SPREADTRUM COMM (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Dual gate low noise amplifier
InactiveUS20040155710A1Improve performanceHigh gainNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceLow noiseAudio power amplifier
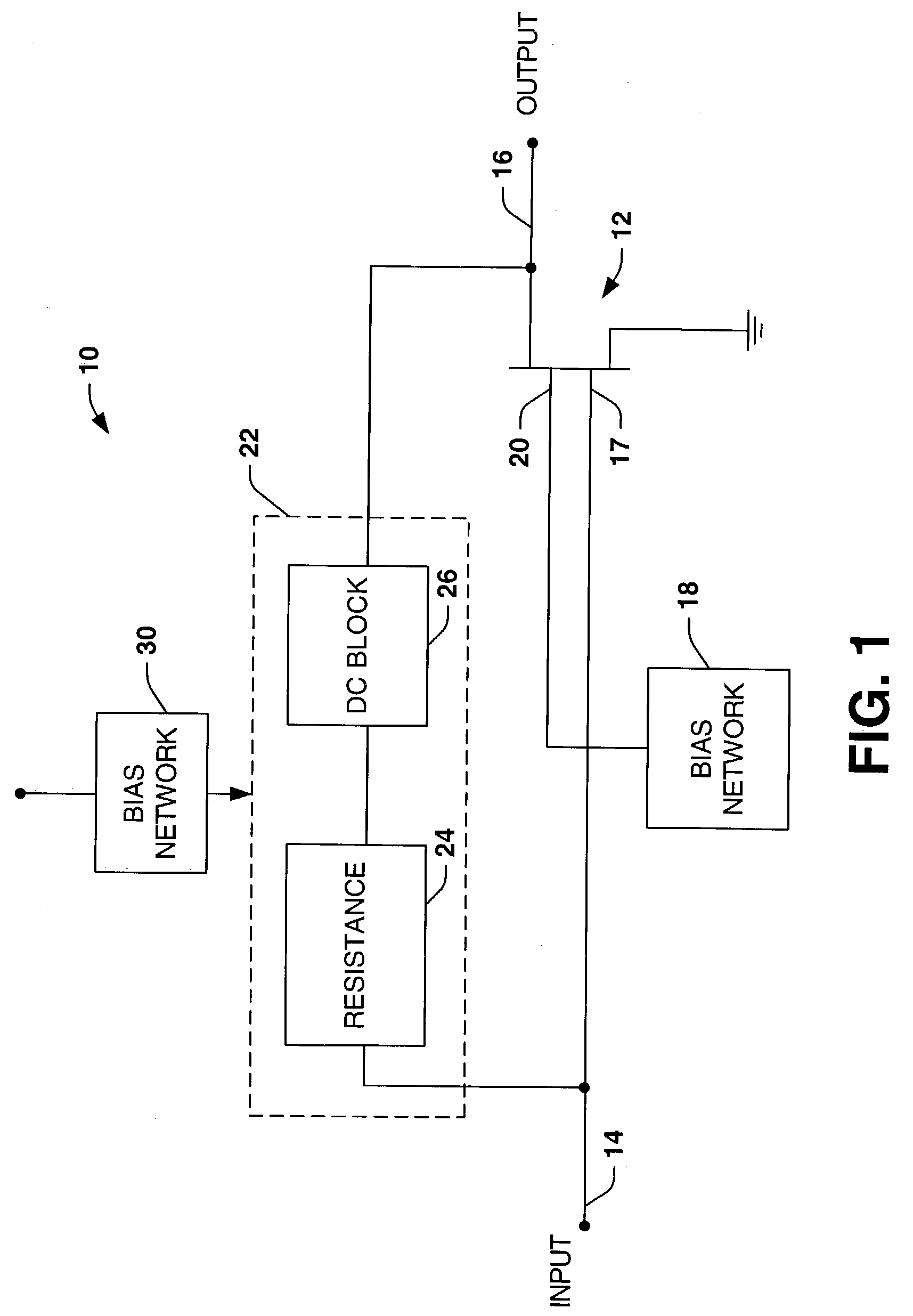
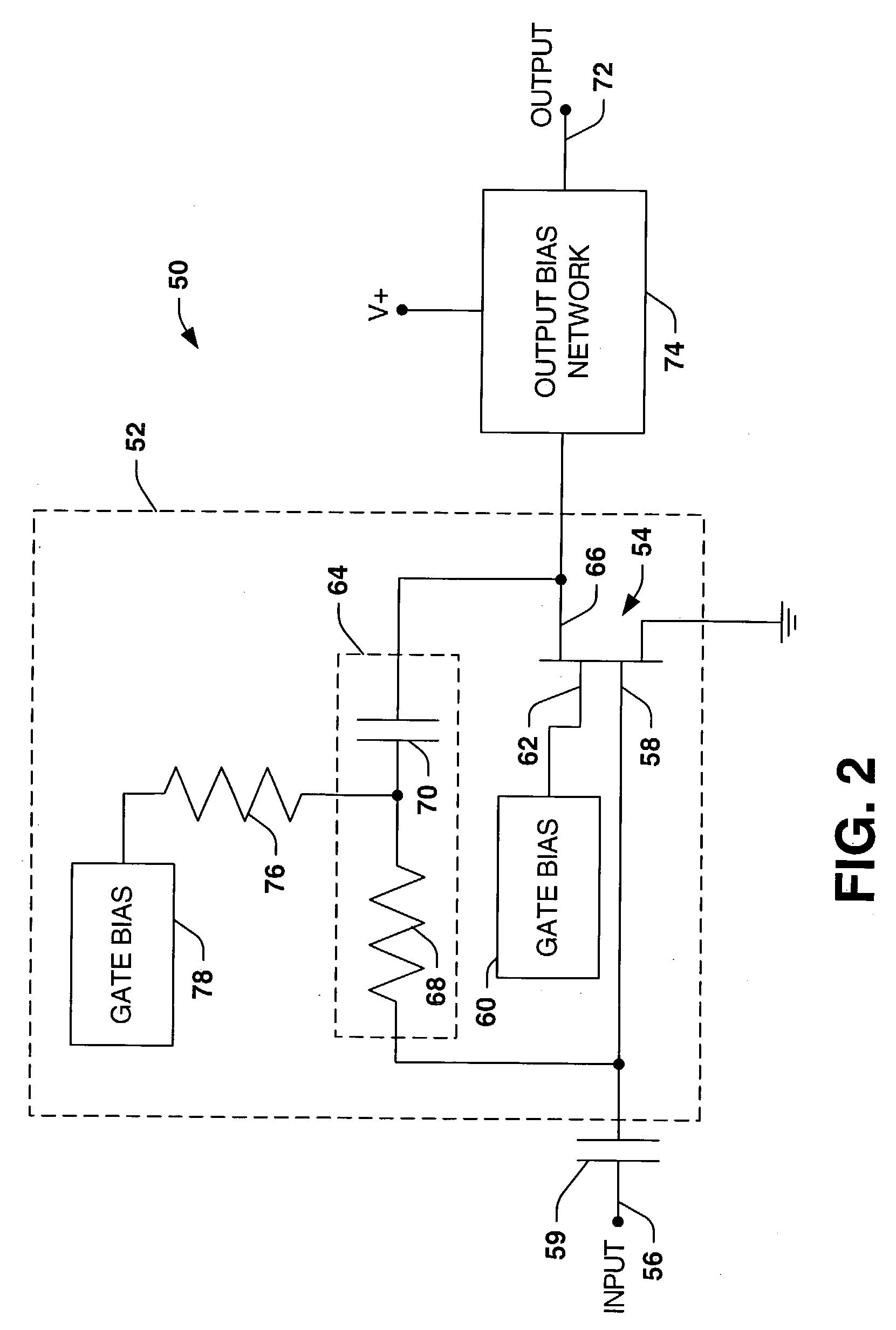
A low noise amplifier topology includes a dual gate transistor device, such as a HEMT device and employs resistive feedback with a DC block associated with the amplifier output to provide a desired high voltage gain and a low noise figure over a desired range of frequencies.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com