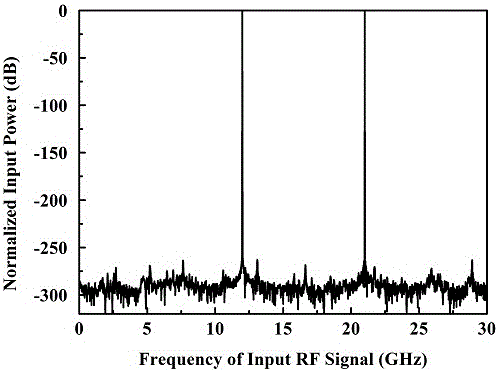
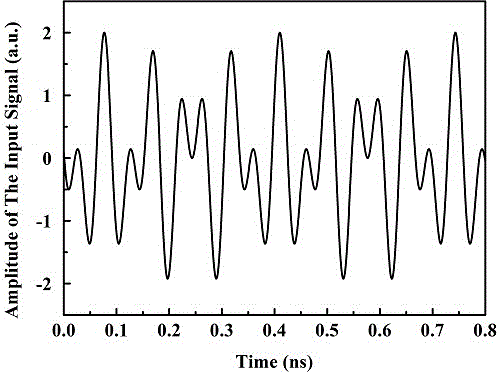
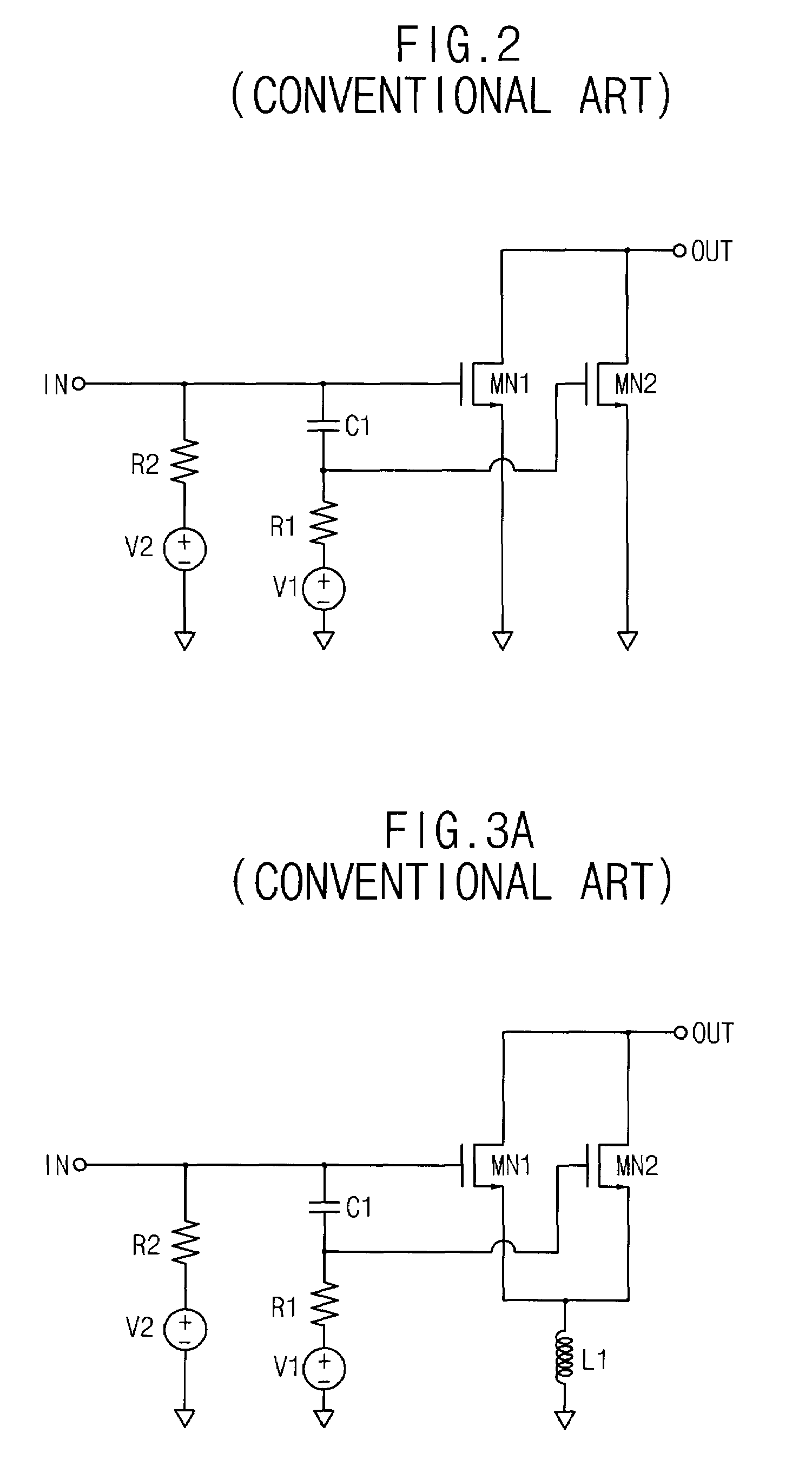
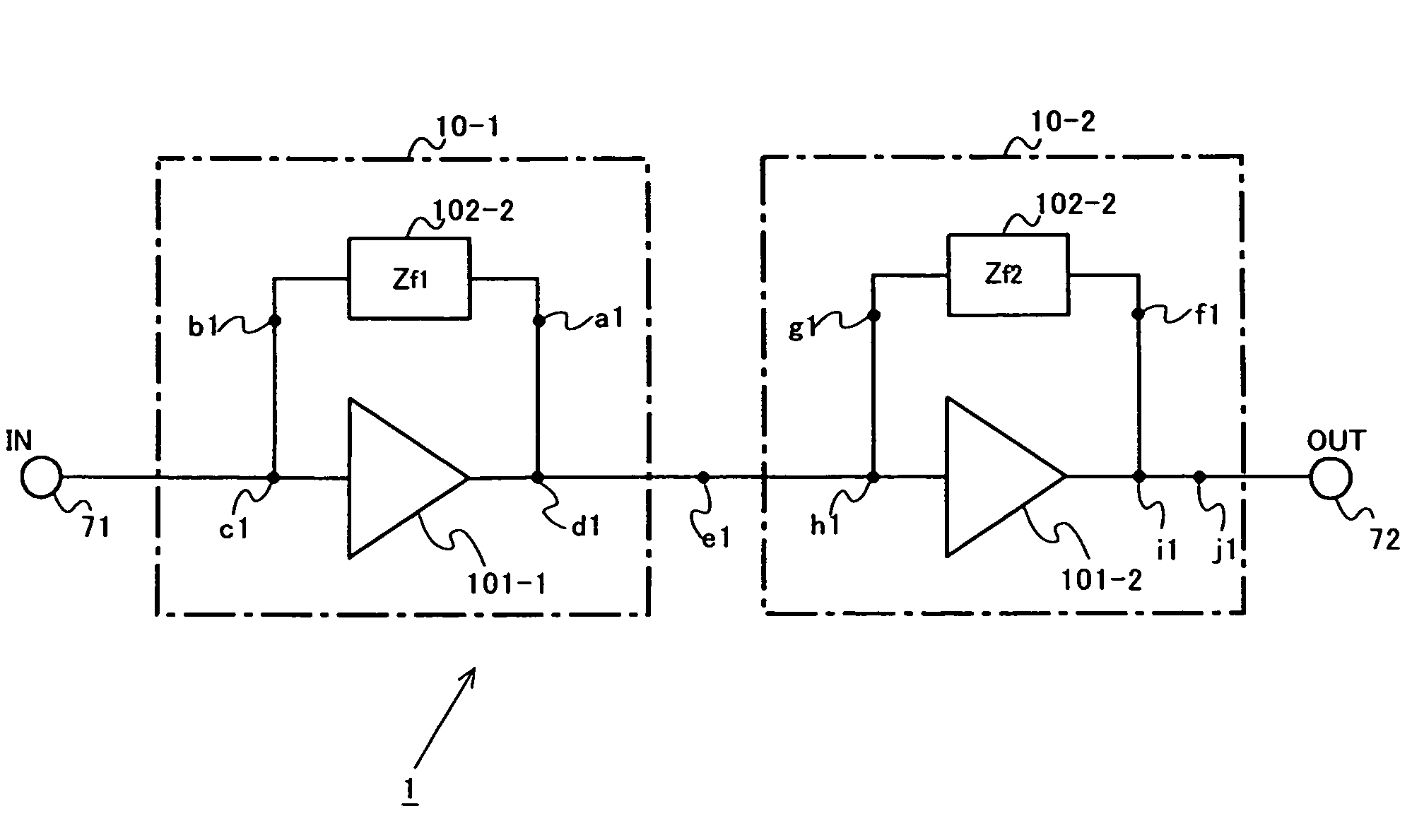
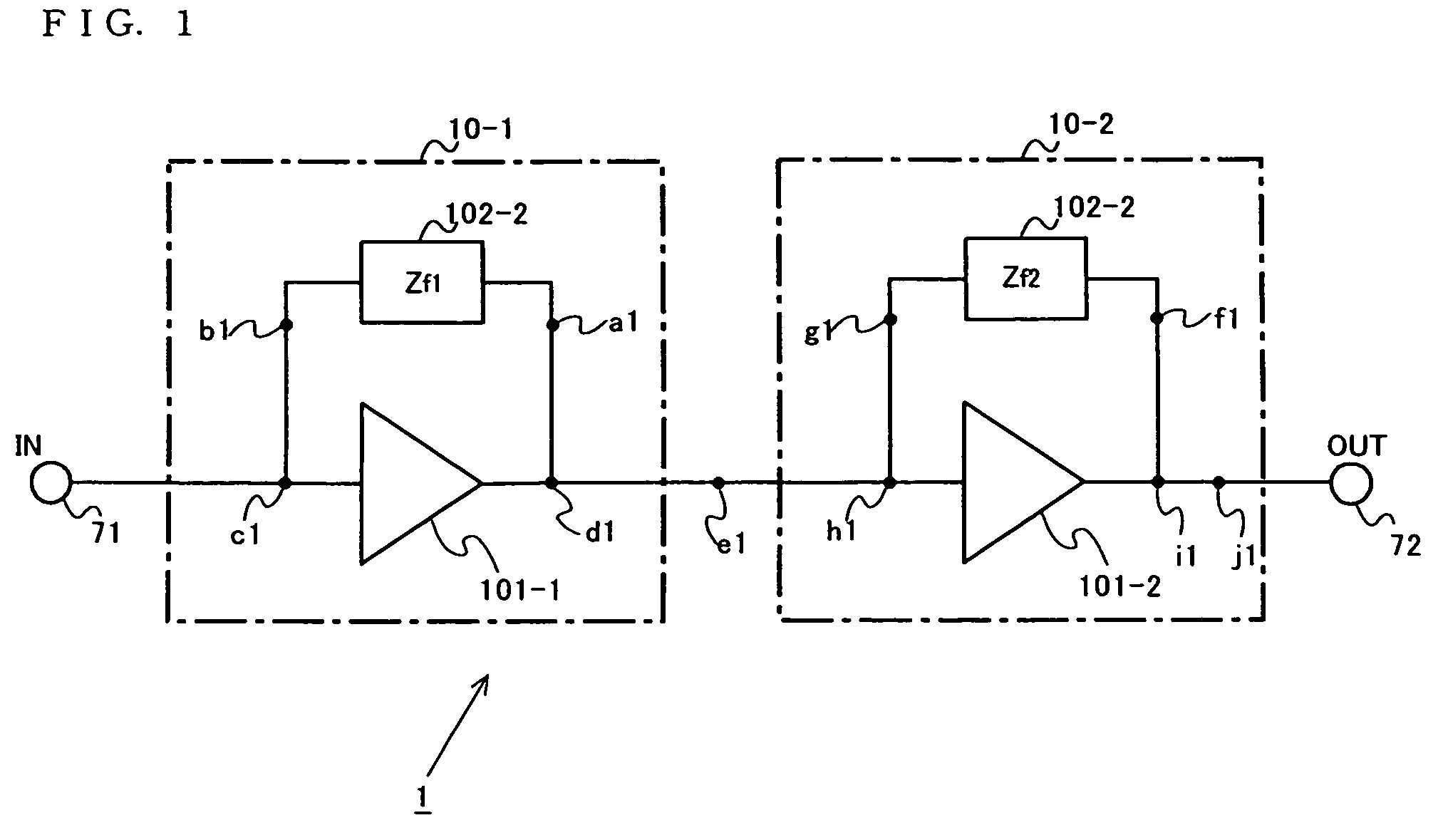
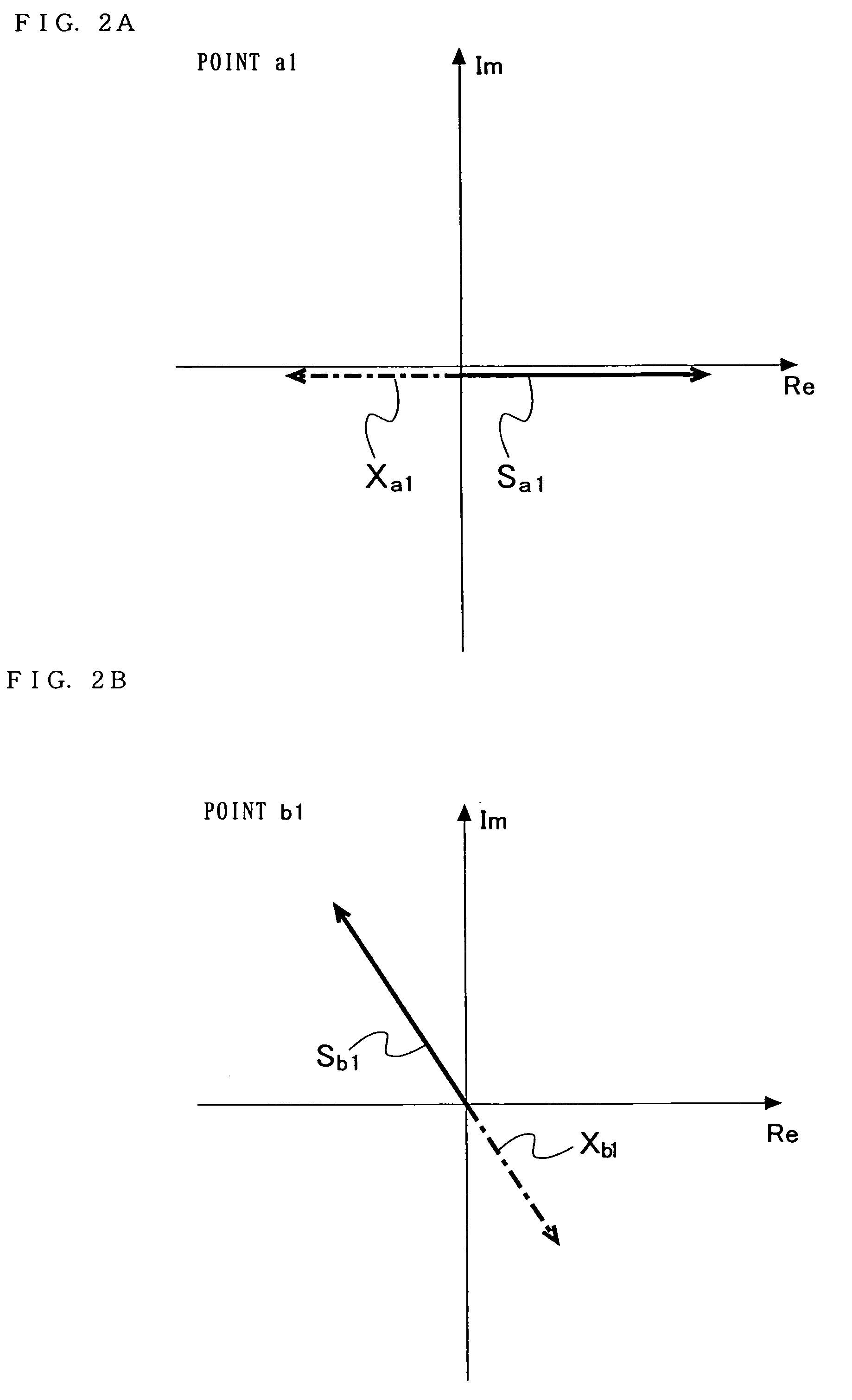
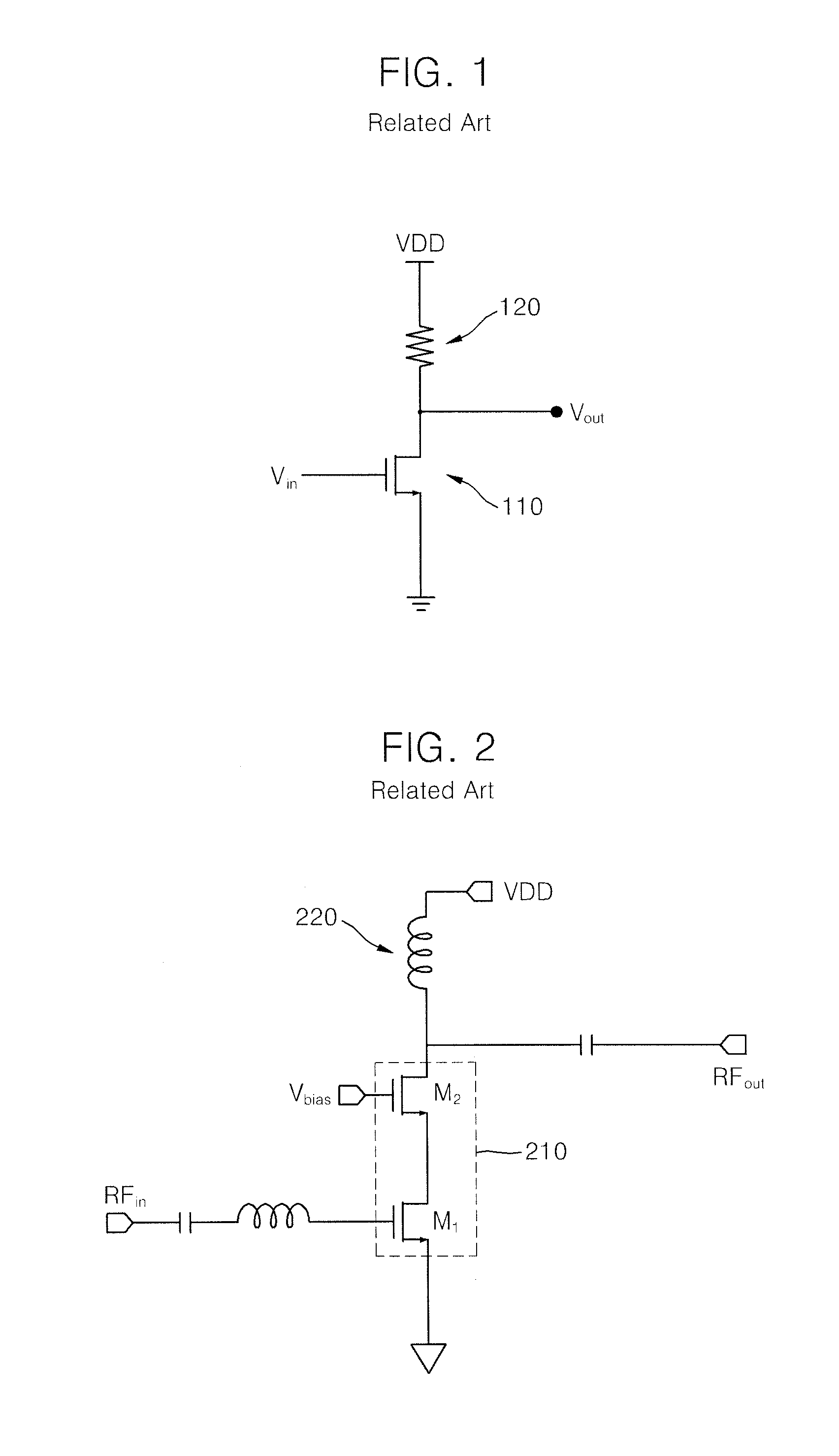
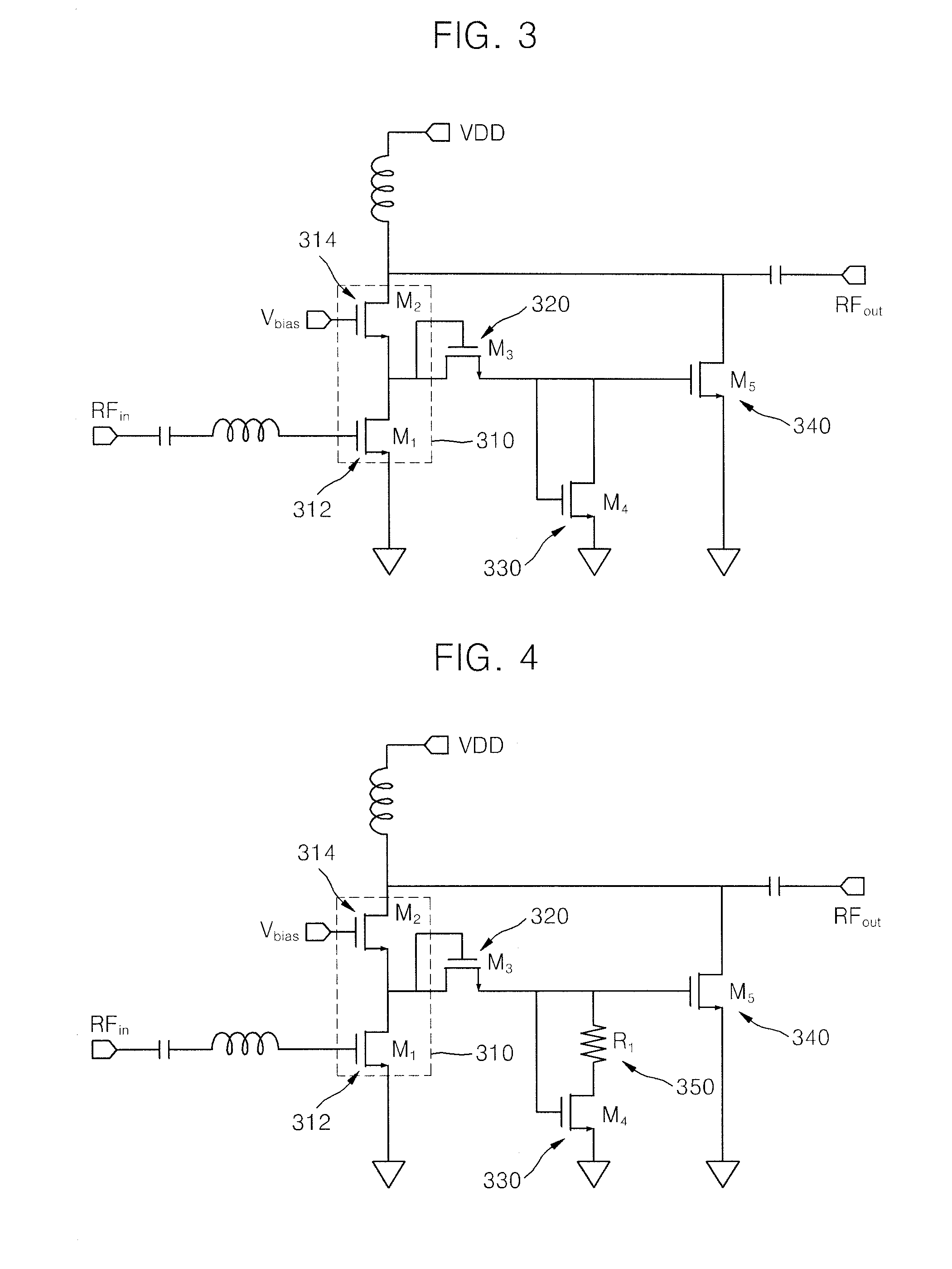
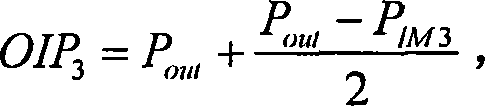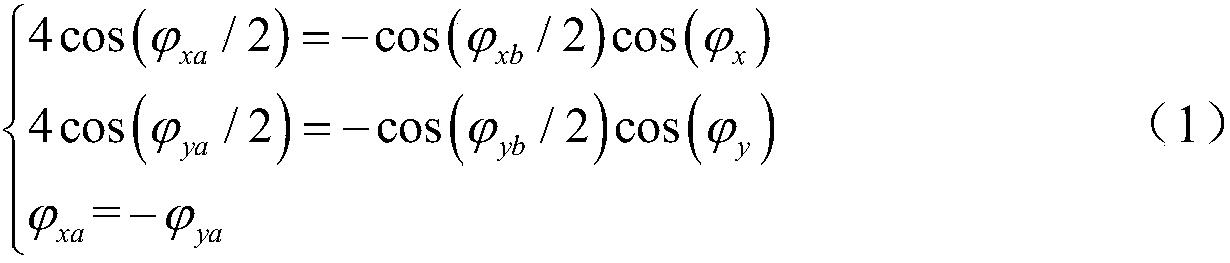Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
44 results about "Third order intermodulation distortion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
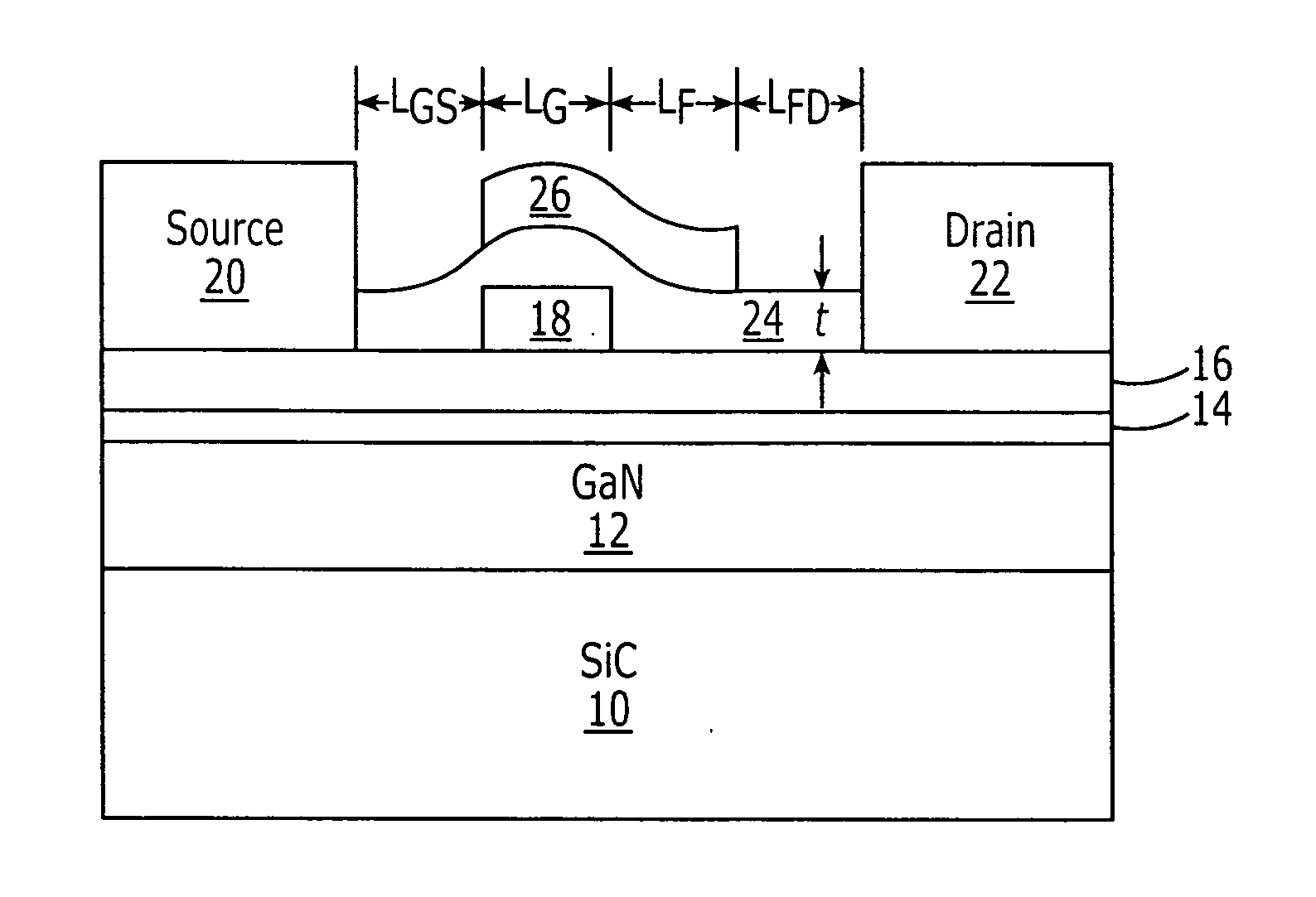
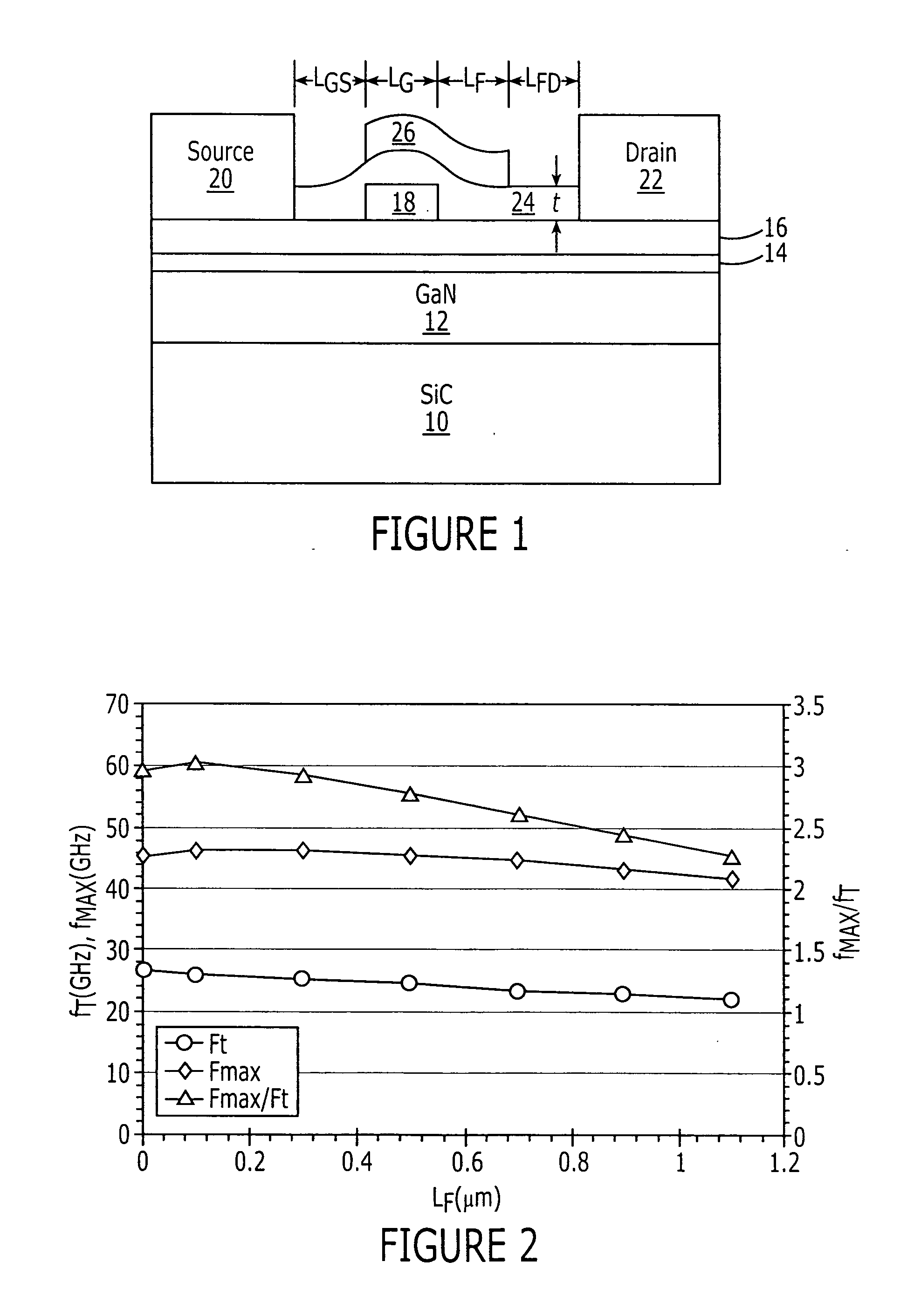
High power density and/or linearity transistors
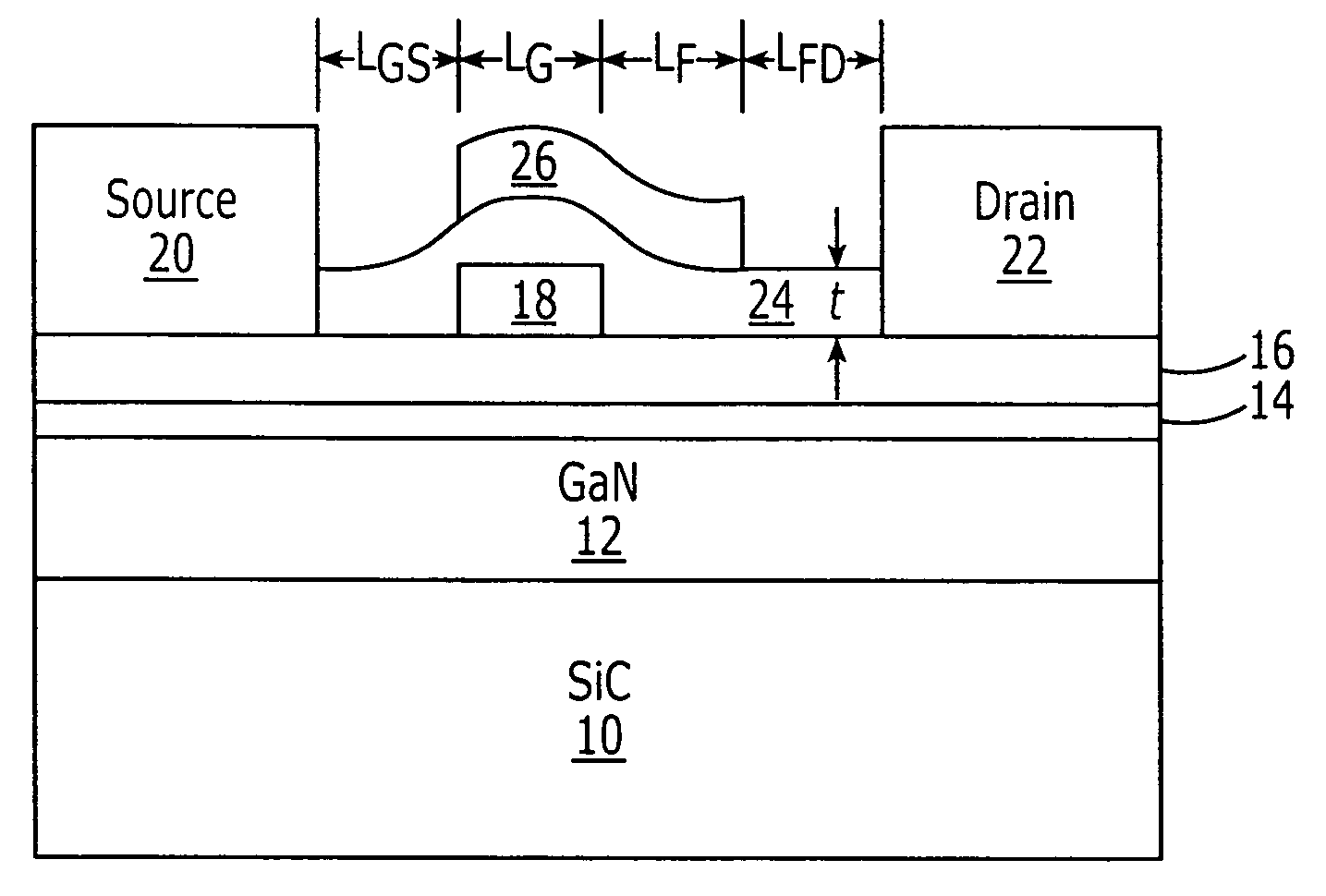
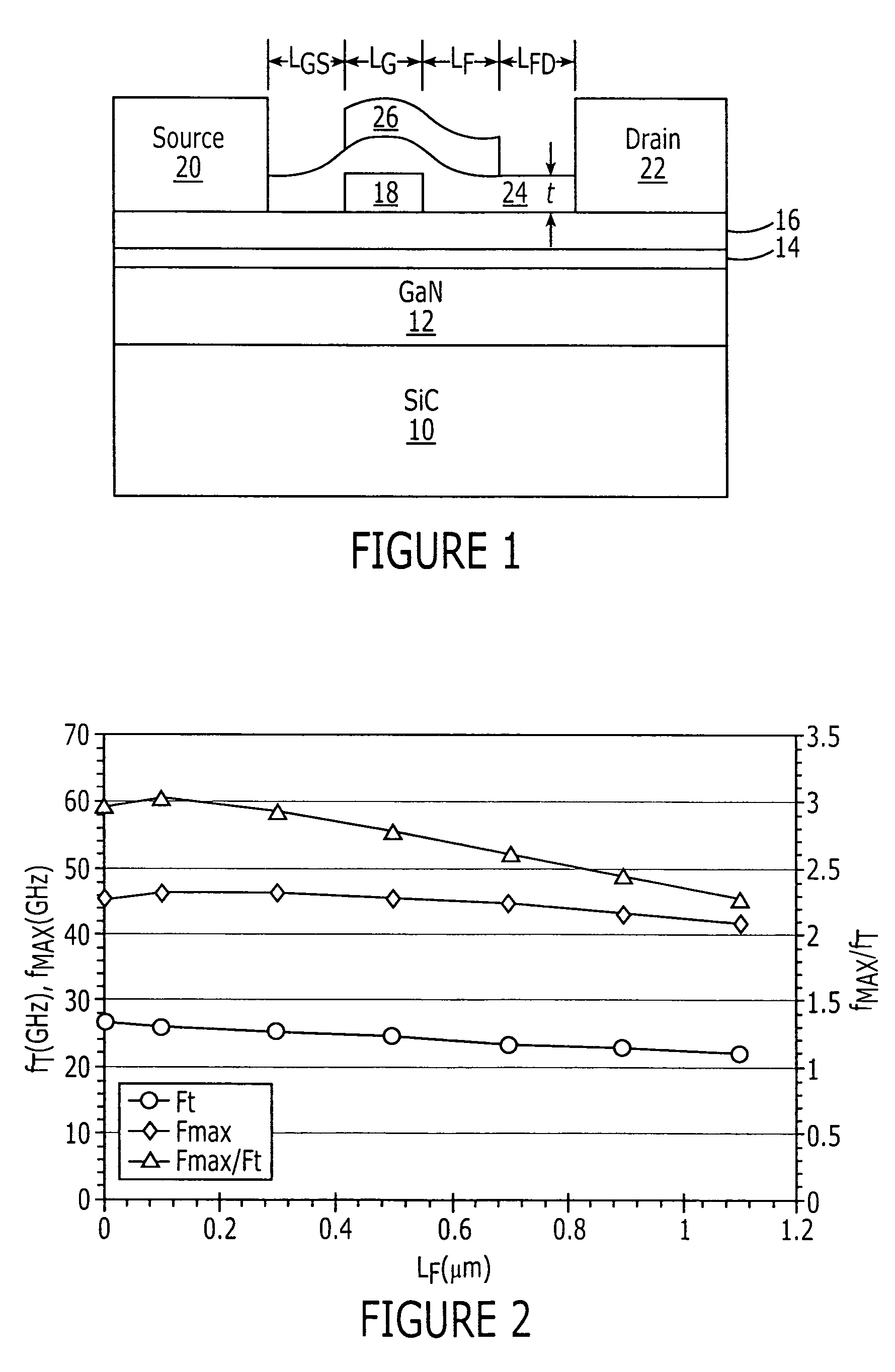
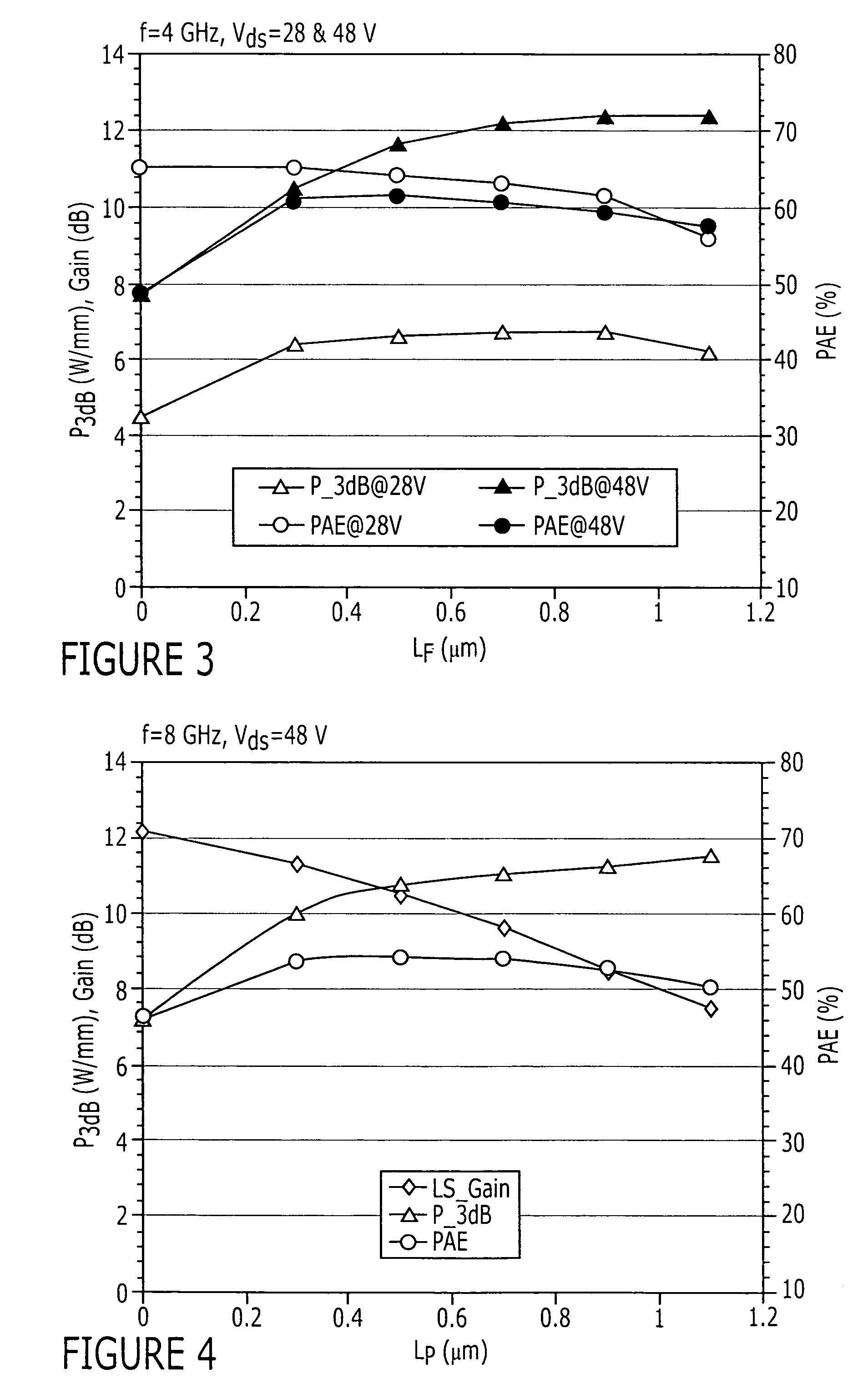
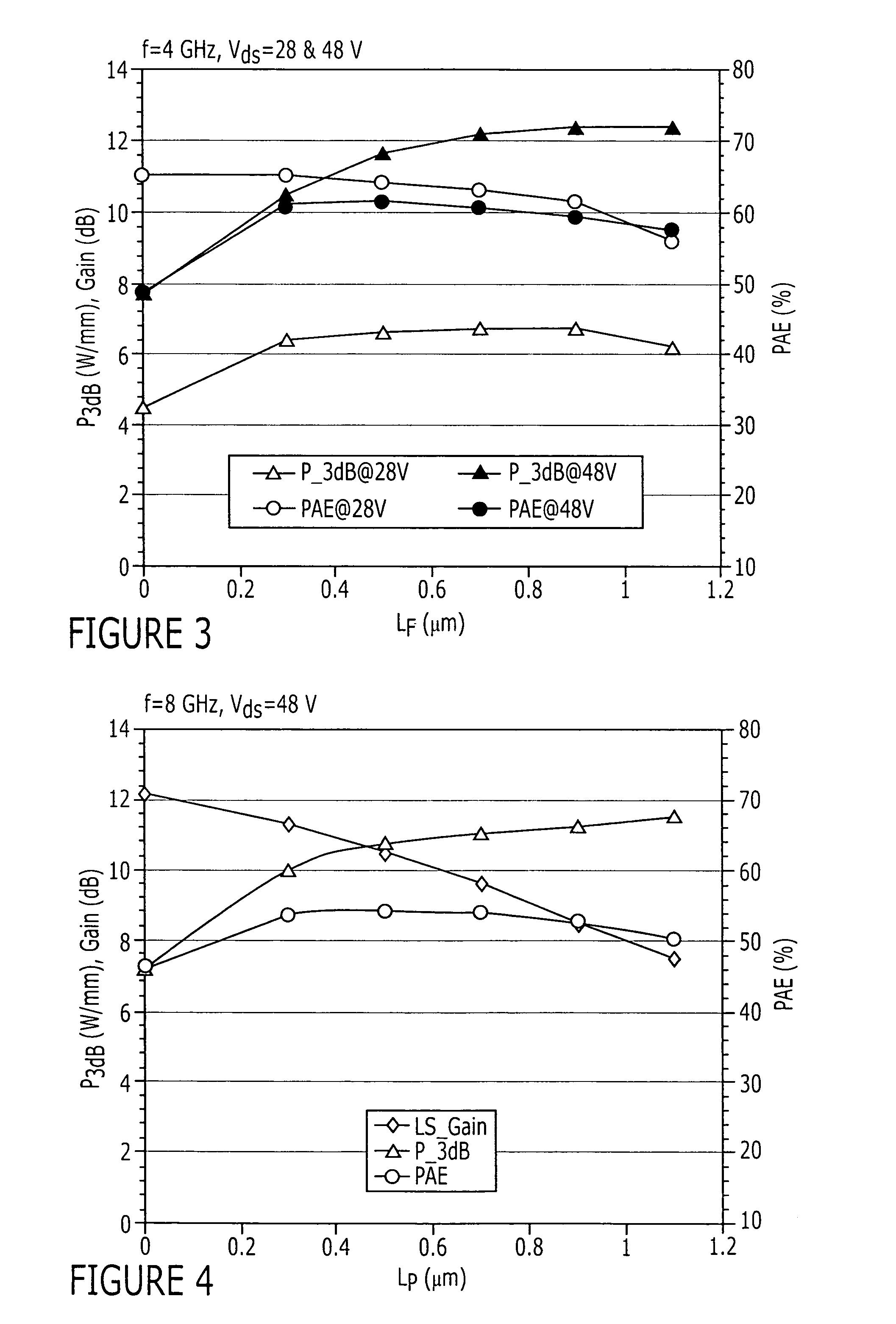
Field effect transistors having a power density of greater than 25 W / mm when operated at a frequency of at least 4 GHz are provided. The power density may be at least 30 W / mm when operated at 4 GHz. The power density of at least 30 W / mm may be provided at a drain voltage of 120 V. Transistors with a power density of at least 30 W / mm when operated at 8 GHz are also provided. The power density of at least 30 W / mm may be provided at a drain voltage of 120 V. Field effect transistors having a power density of greater than 20 W / mm when operated at a frequency of at least 10 GHz are also provided. Field effect transistors having a power density of at least 2.5 W / mm and a two tone linearity of at least −30 dBc of third order intermodulation distortion at a center frequency of at least 4 GHz and a power added efficiency (PAE) of at least 40% are also provided.
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
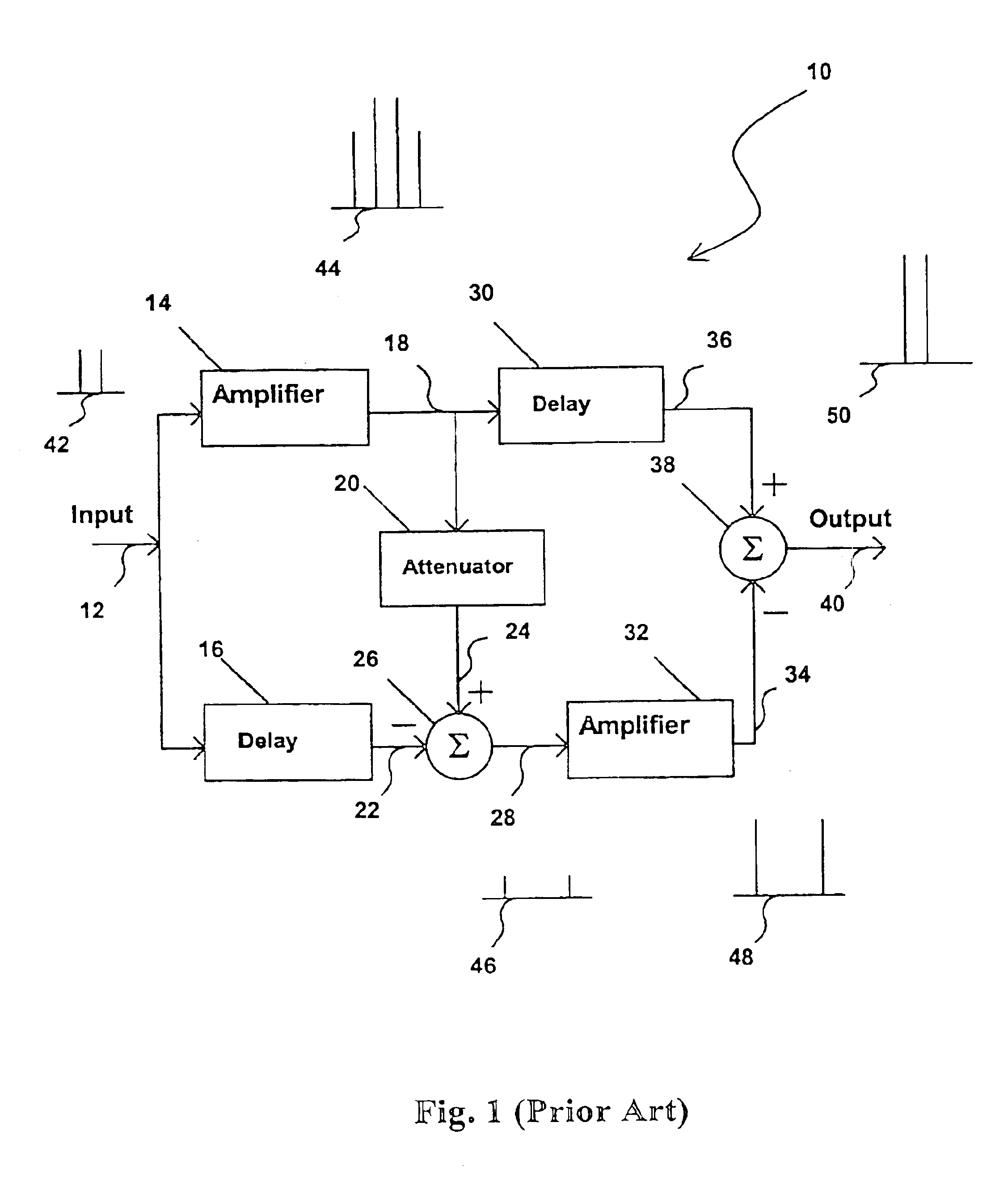
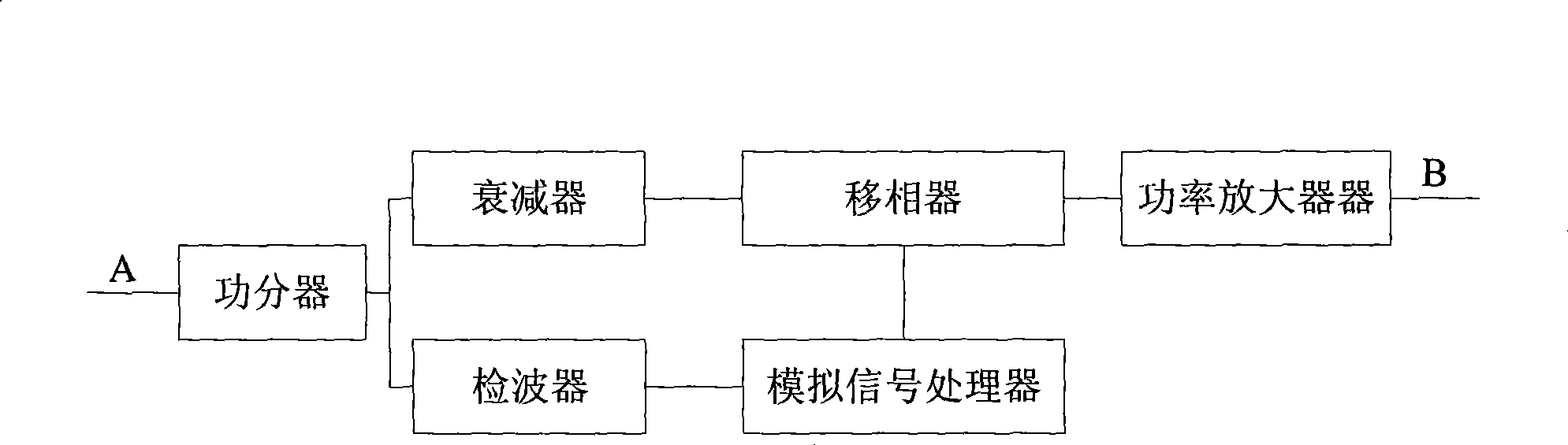
Methods and apparatus for substantially reducing third order intermodulation distortion and other nonlinear distortions
InactiveUS6906585B2Reducing canceling nonlinearitiesReducing and canceling third order nonlinearitiesAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceNonlinear distortionAudio power amplifier
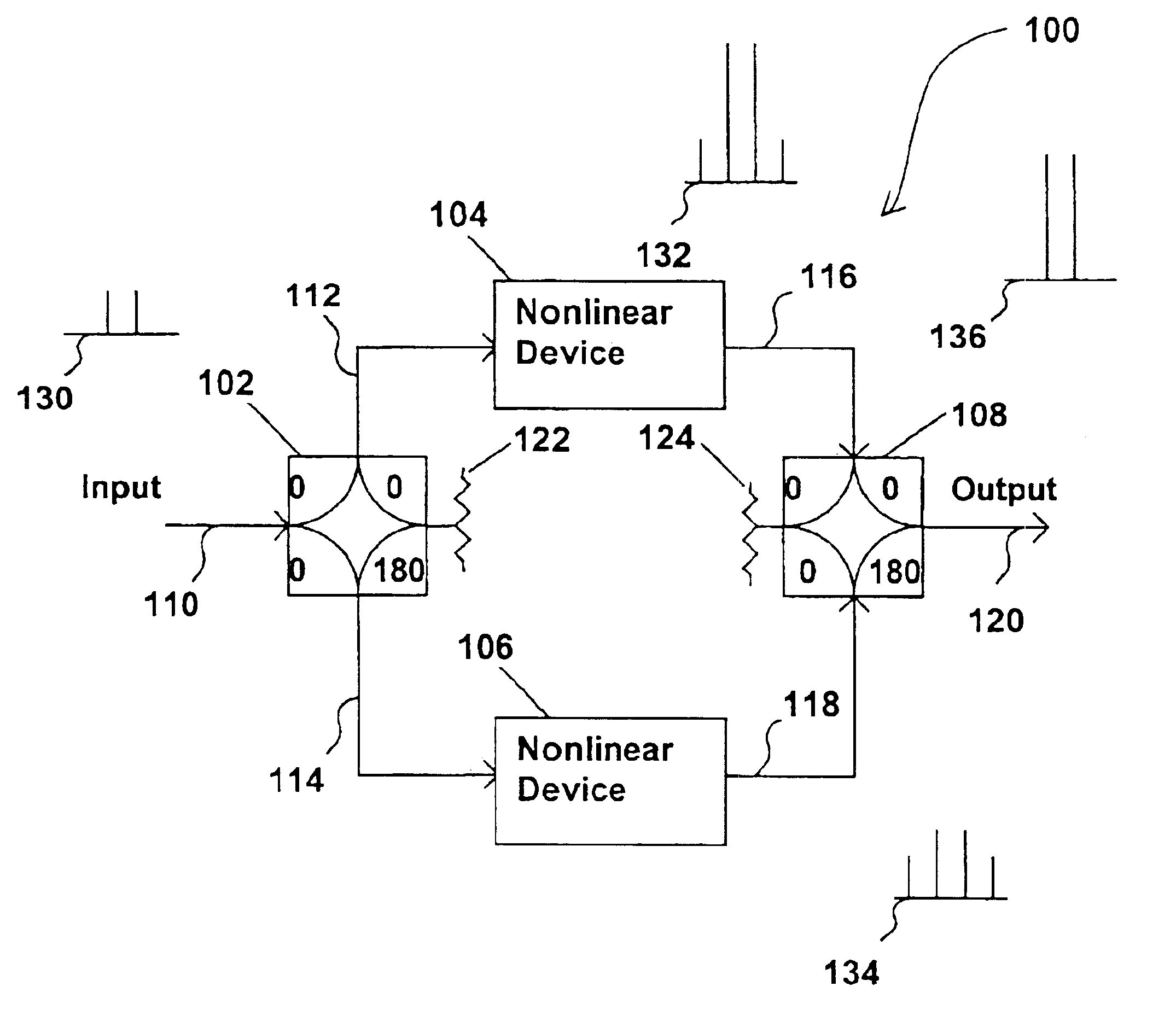
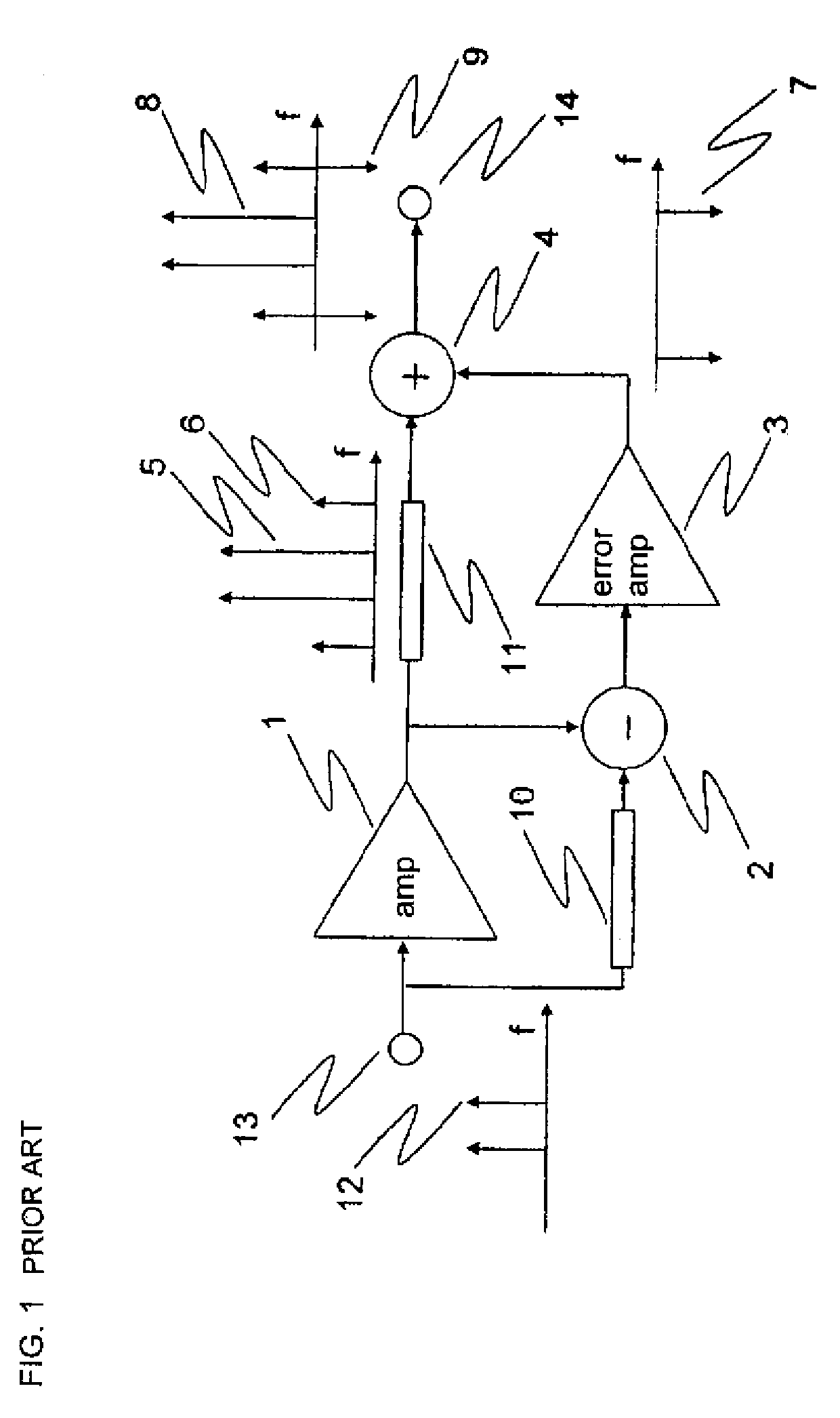
Methods and apparatus are provided for substantially reducing and / or canceling nonlinearities of any order in circuits, devices, and systems such as amplifiers and mixers. In particular, methods and apparatus are provided for substantially reducing and / or canceling third order nonlinearities in circuits, devices, and systems such as amplifiers and mixers. A first coupler is used to split an input signal into two equal-amplitude in-phase components, each component is processed by two nonlinear devices with different nonlinearities, and a final combiner, such as a 180-degree hybrid, recombines the processed signals 180 degrees out of phase and substantially reduces and / or cancels the undesired nonlinear distortion components arising due to nonlinearities in the nonlinear devices.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
High power density and/or linearity transistors
Field effect transistors having a power density of greater than 25 W / mm when operated at a frequency of at least 4 GHz are provided. The power density may be at least 30 W / mm when operated at 4 GHz. The power density of at least 30 W / mm may be provided at a drain voltage of 120 V. Transistors with a power density of at least 30 W / mm when operated at 8 GHz are also provided. The power density of at least 30 W / mm may be provided at a drain voltage of 120 V. Field effect transistors having a power density of greater than 20 W / mm when operated at a frequency of at least 10 GHz are also provided. Field effect transistors having a power density of at least 2.5 W / mm and a two tone linearity of at least −30 dBc of third order intermodulation distortion at a center frequency of at least 4 GHz and a power added efficiency (PAE) of at least 40% are also provided.
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
Highly linear low-noise amplifiers
InactiveUS7554397B2Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationLow noiseTransformer
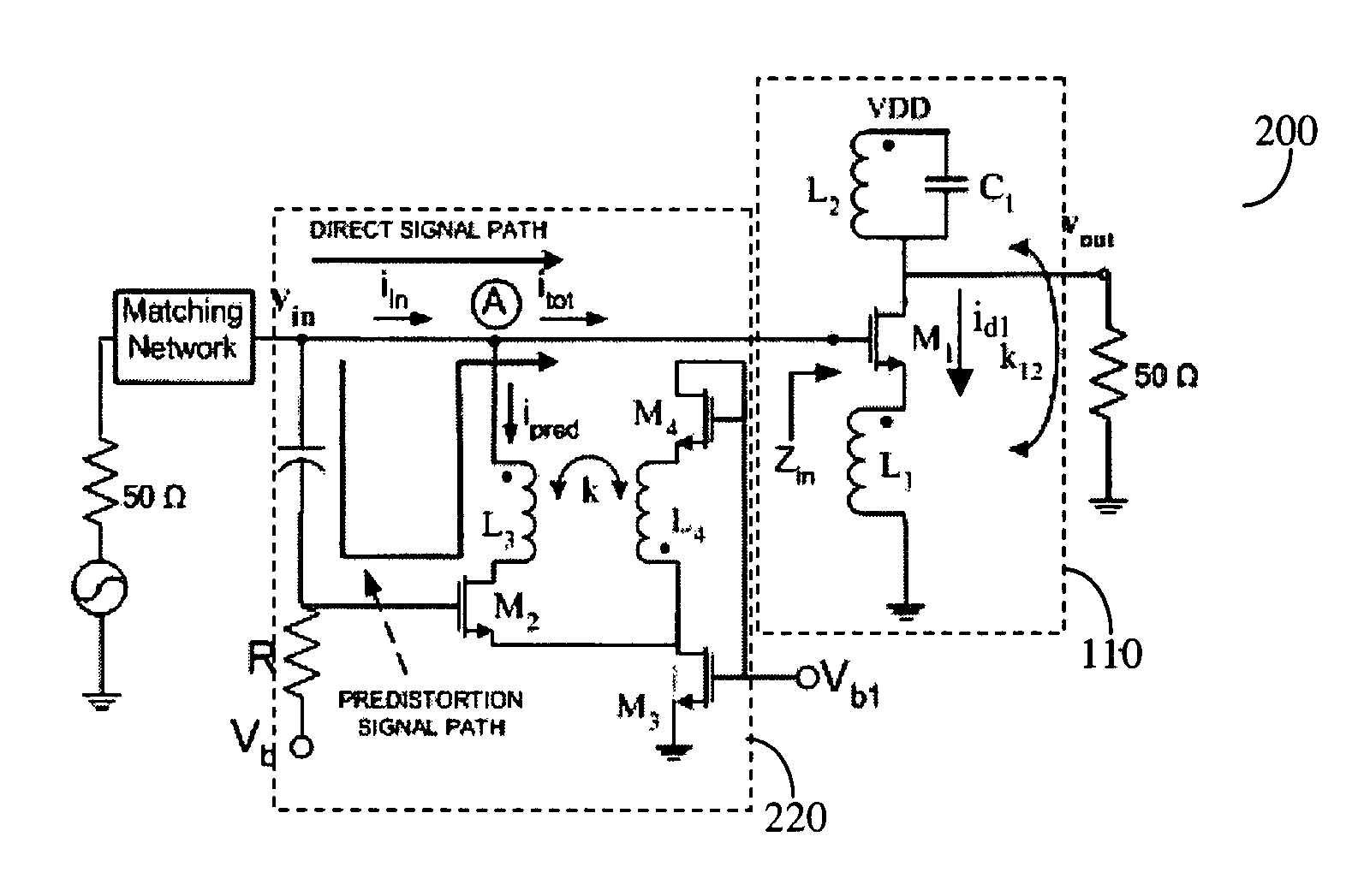
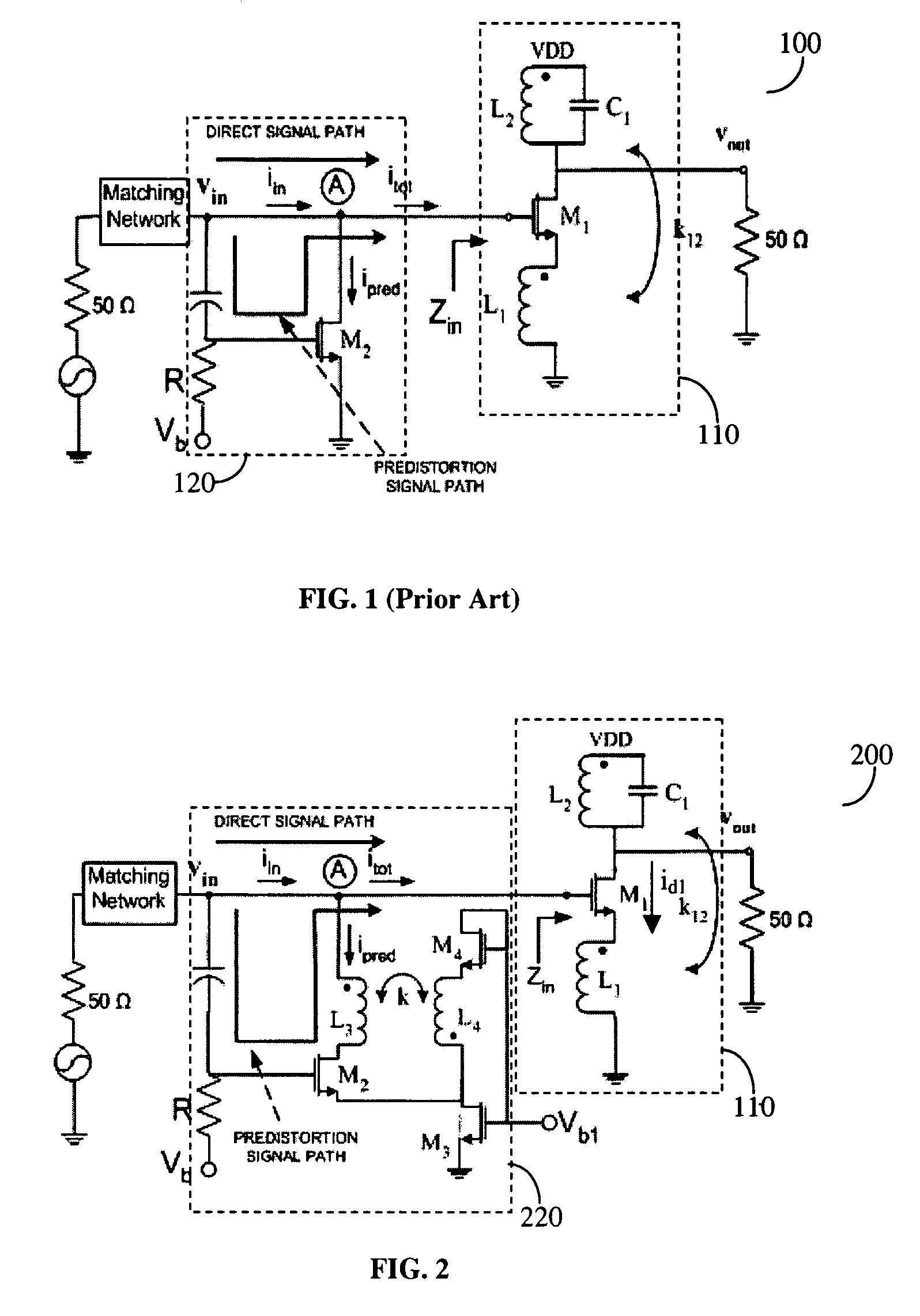
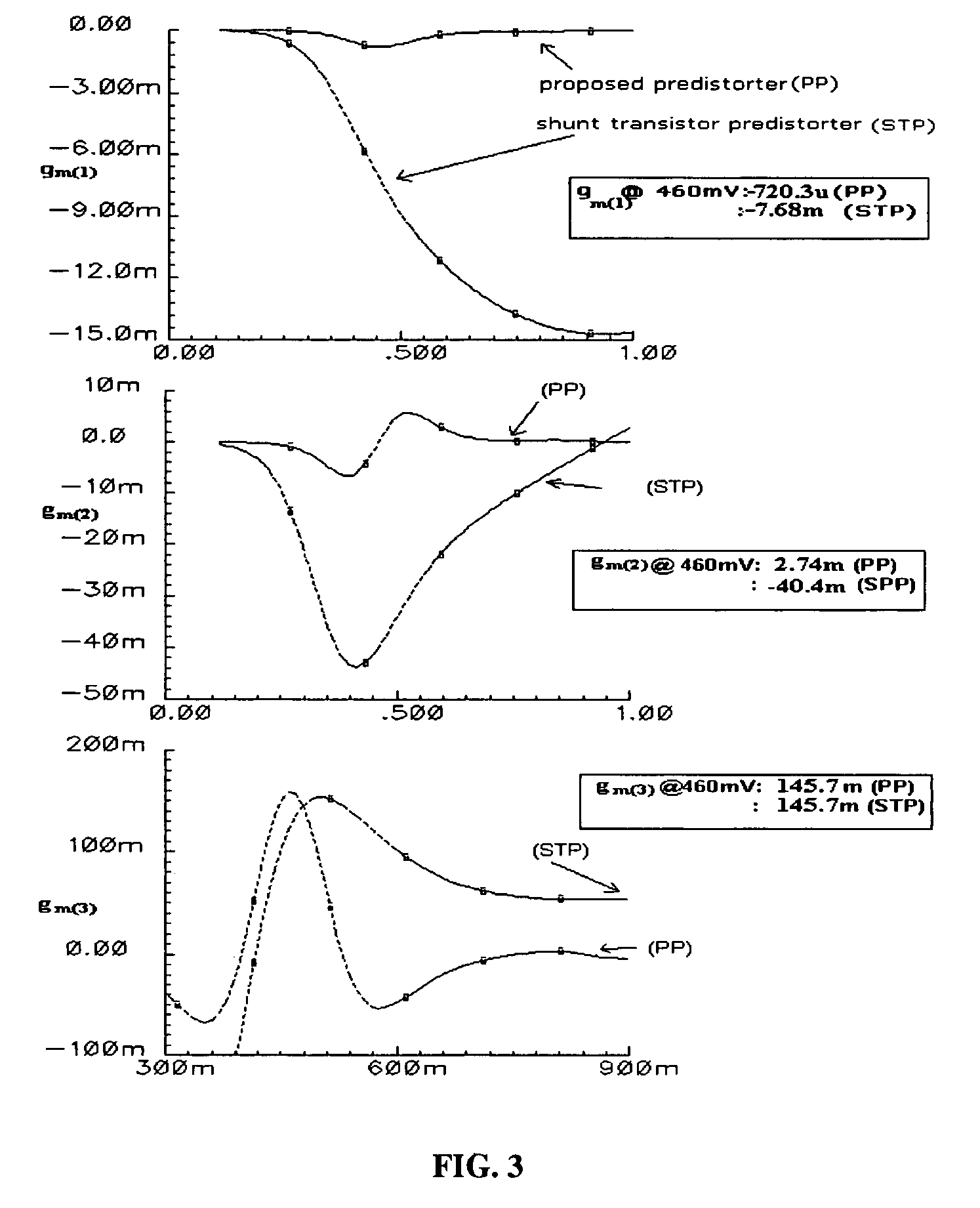
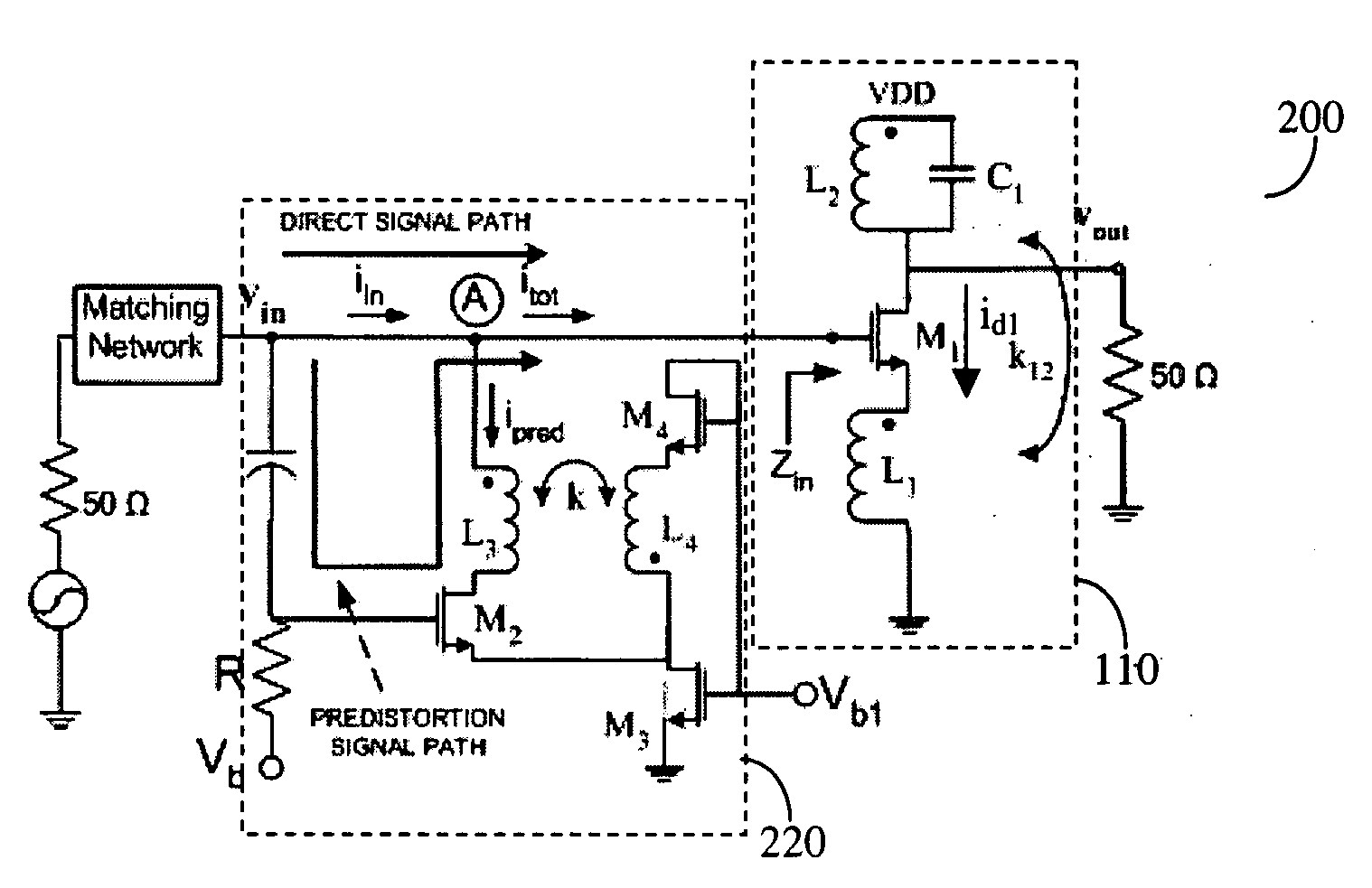
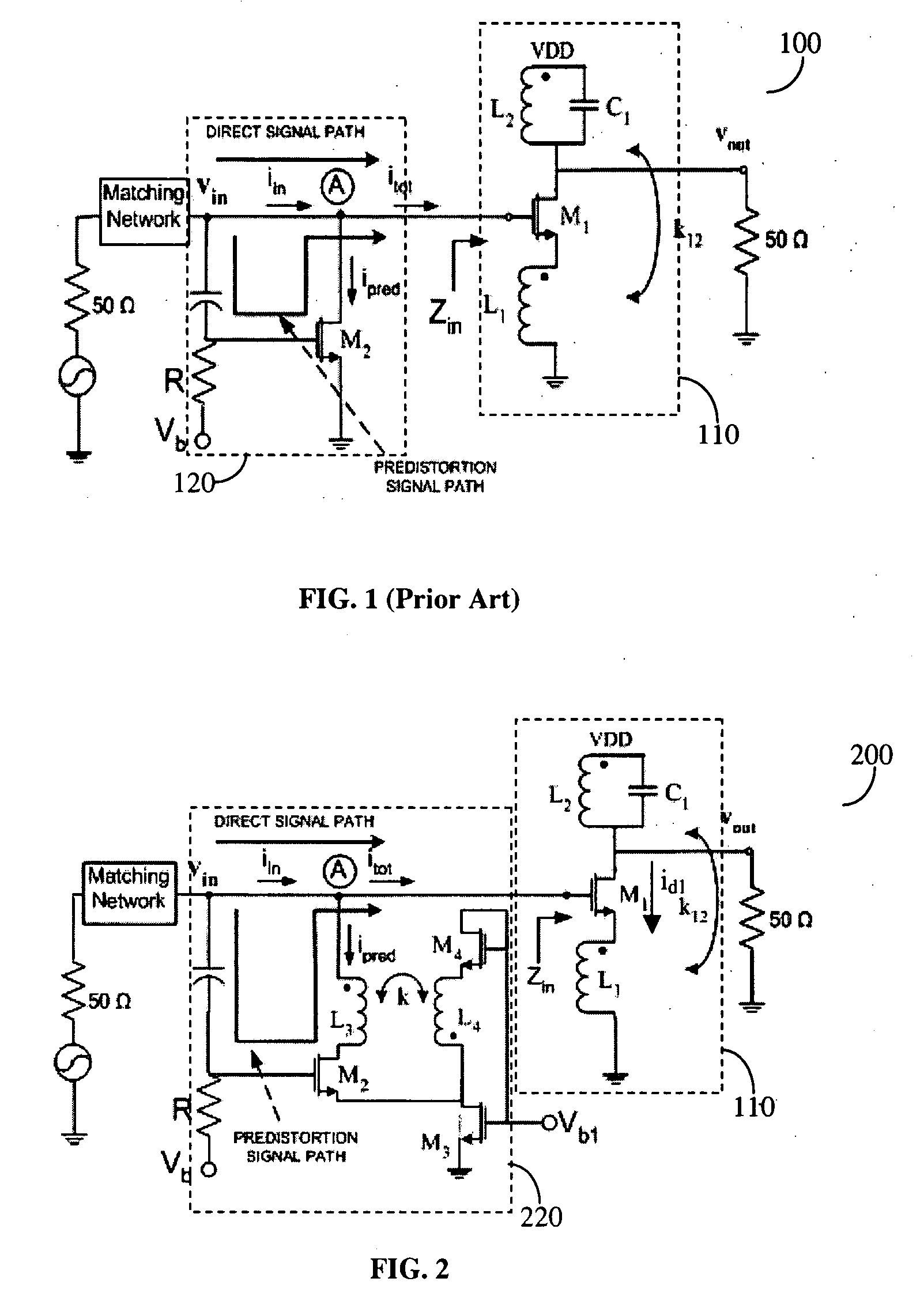
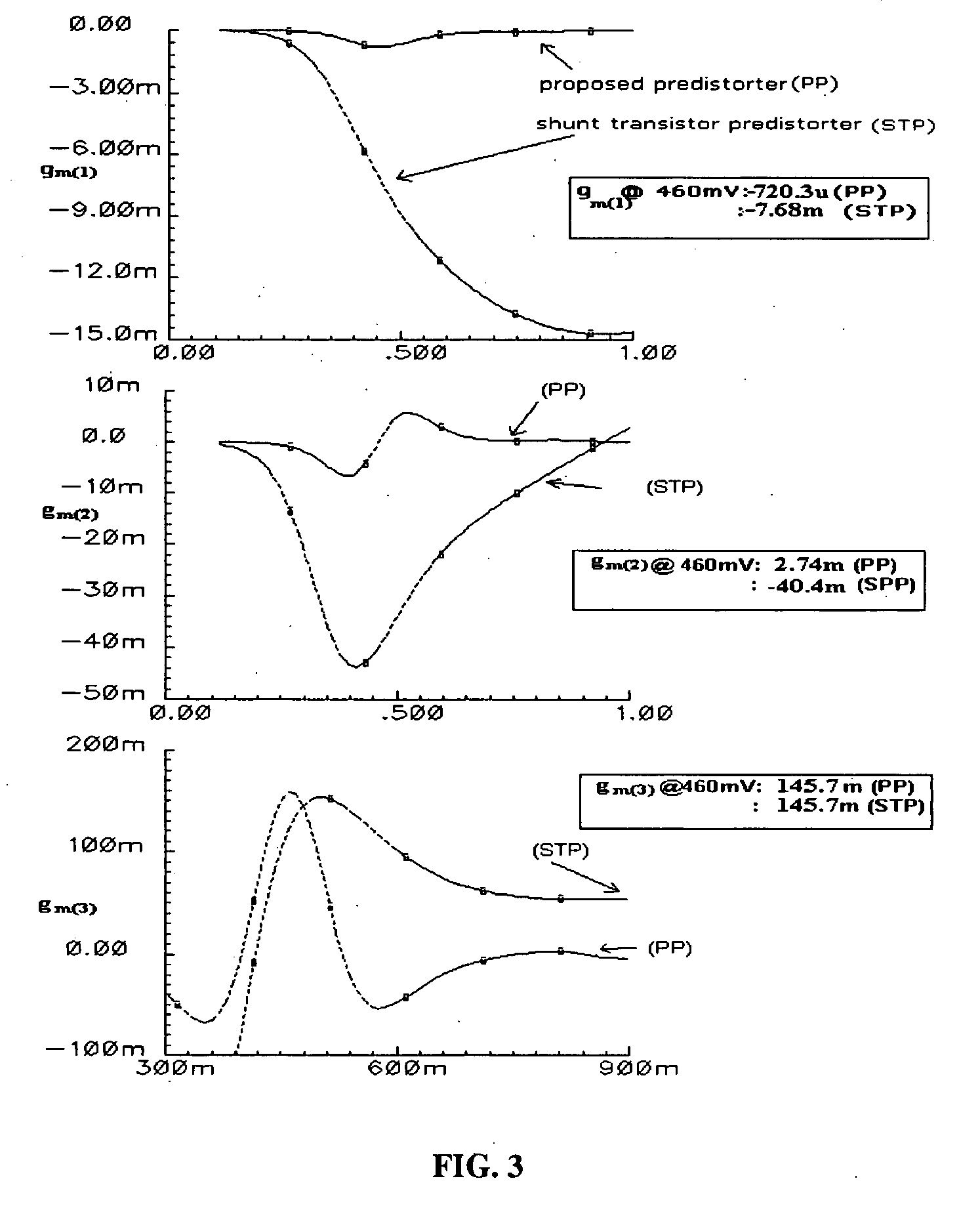
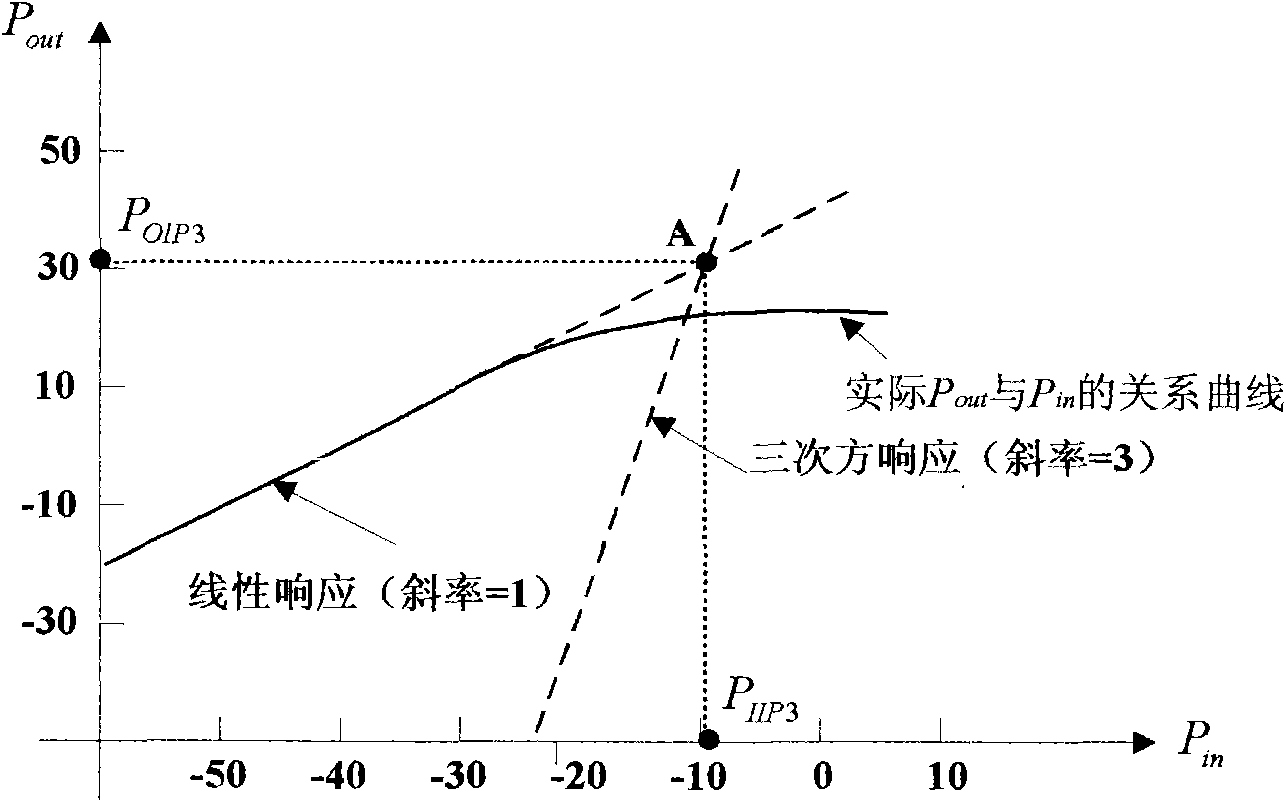
A predistortion method for CMOS Low-Noise-Amplifiers (LNAs) to be used in Broadband Wireless applications is presented. The method is based on the nulling of the third order Intermodulation distortion (IMD3) of the main amplifier by a highly nonlinear predistortion branch. Maximum third order product cancellation is ensured by a transformer feedback method. The technique improves linearity in a wide range of input power without significant gain and Noise Figure (NF) degradation. Simulation results on a 1-V LNA indicate a 10.3 dB improvement in the Input Third-Order Intercept Point (IIP3) with a reduction of only 1 dB and 0.44 dB in amplifier gain and NF respectively.
Owner:THETA IP
Automatic testing method for mixer third order inter-modulation distortion of radio-frequency tuner chip
InactiveCN101251573AIncreased test frequencyGuaranteed test accuracyElectronic circuit testingFrequency analysisSpectrum analyzerEngineering
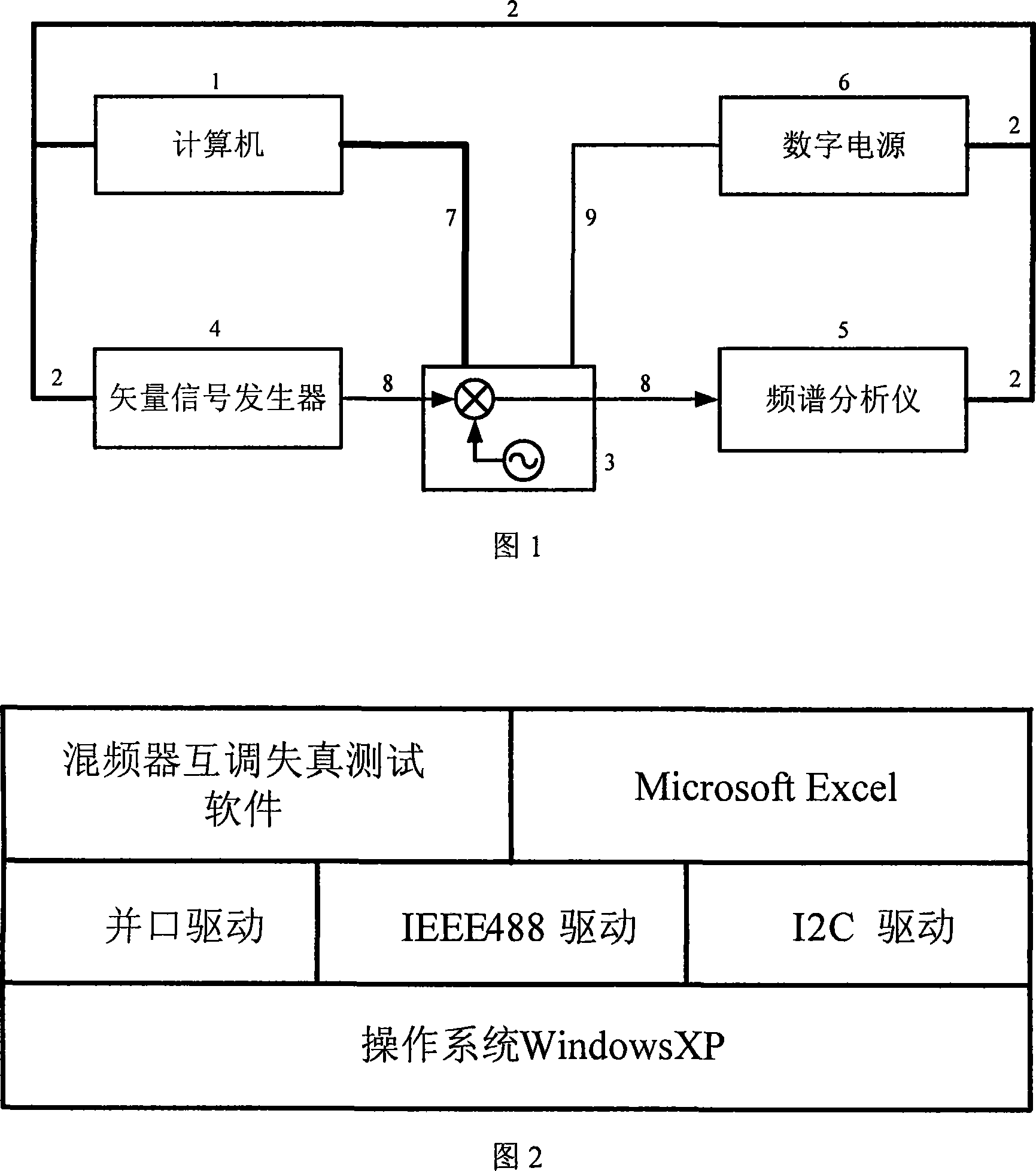
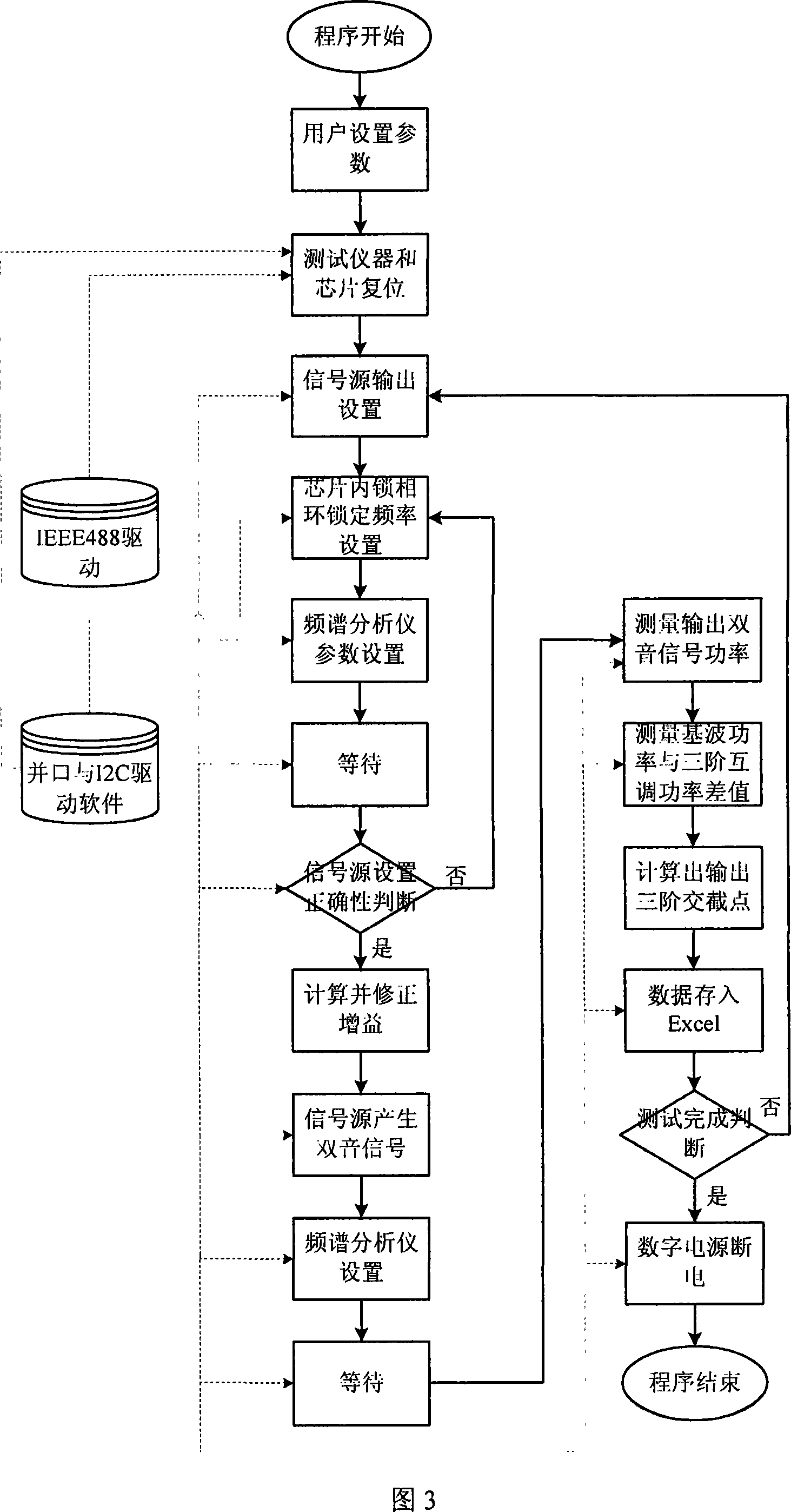
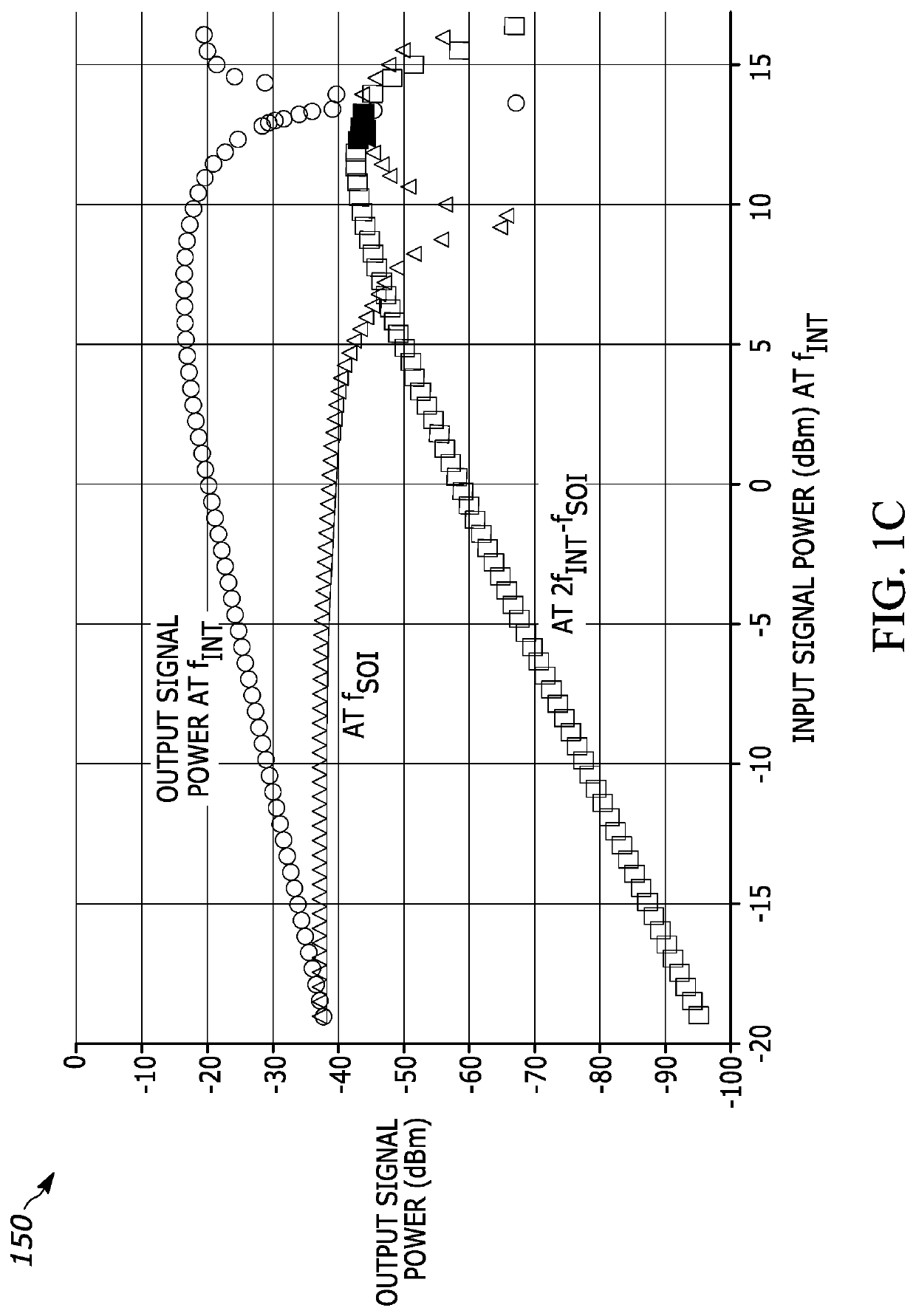
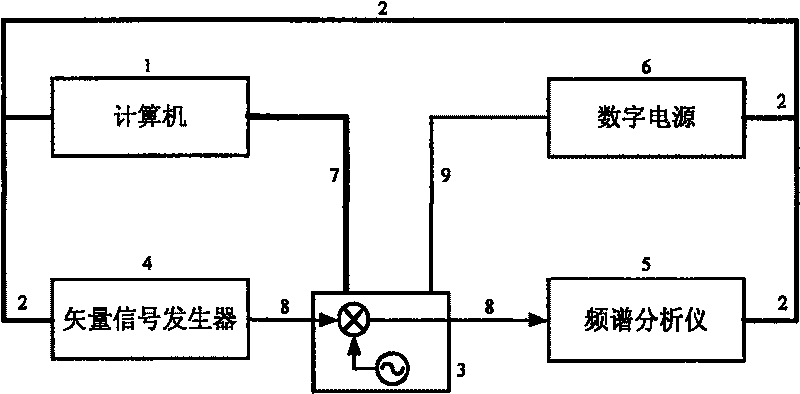
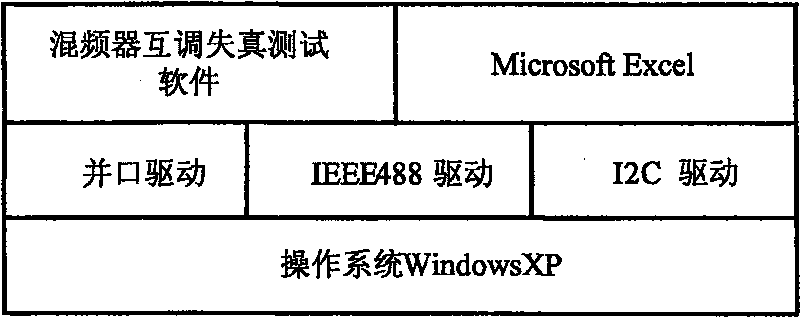
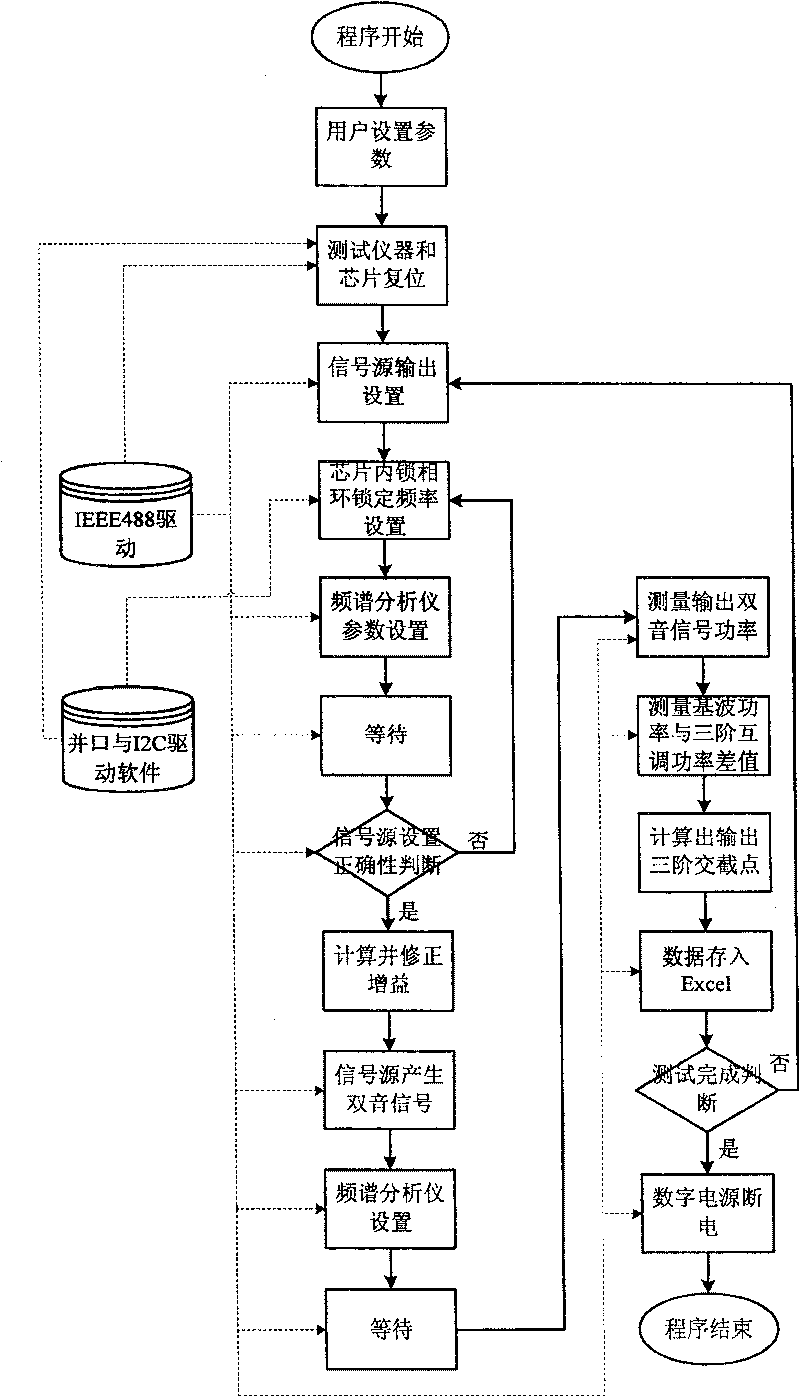
The invention relates to an automatic testing method of mixer third-order intermodulation distortion inside a radio frequency tuner chip, in particular to an automatic testing method of mixer third-order intermodulation distortion inside a DVB-C digital television tuner chip. The automatic testing method adopts the radio frequency apparatus made by Agilent Company as the testing platform. The main equipment of the testing method comprises an Agilent spectrum analyzer E4402B, an Agilent vector signal generator E4438C, an Agilent digital power supply E3649A, an Agilent GPIB link module 82357A and a computer. By means of the IEEE488 communication protocol, the programmable apparatus standard command (SCPI) and chip I<2>C control protocol, test software controls the operating state of the chip and sets and reads relevant parameter of a testing apparatus through the read-write operation of a register arranged inside a tuner chip, thereby realizing automatic radio frequency testing. In addition, the test software consists of an IEEE488 drive module, a parallel port drive module, an I<2>C module and a mixer test module.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
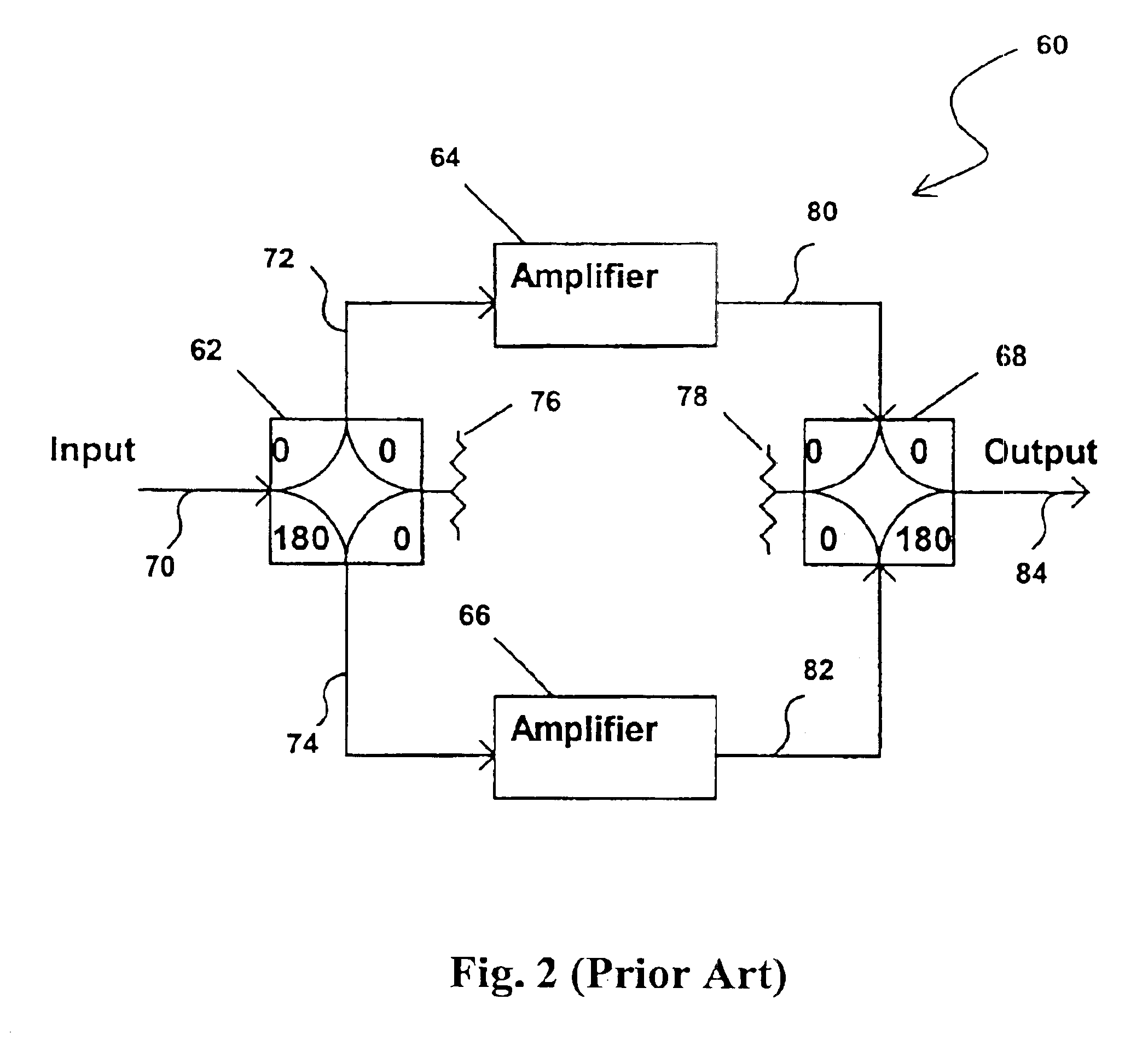
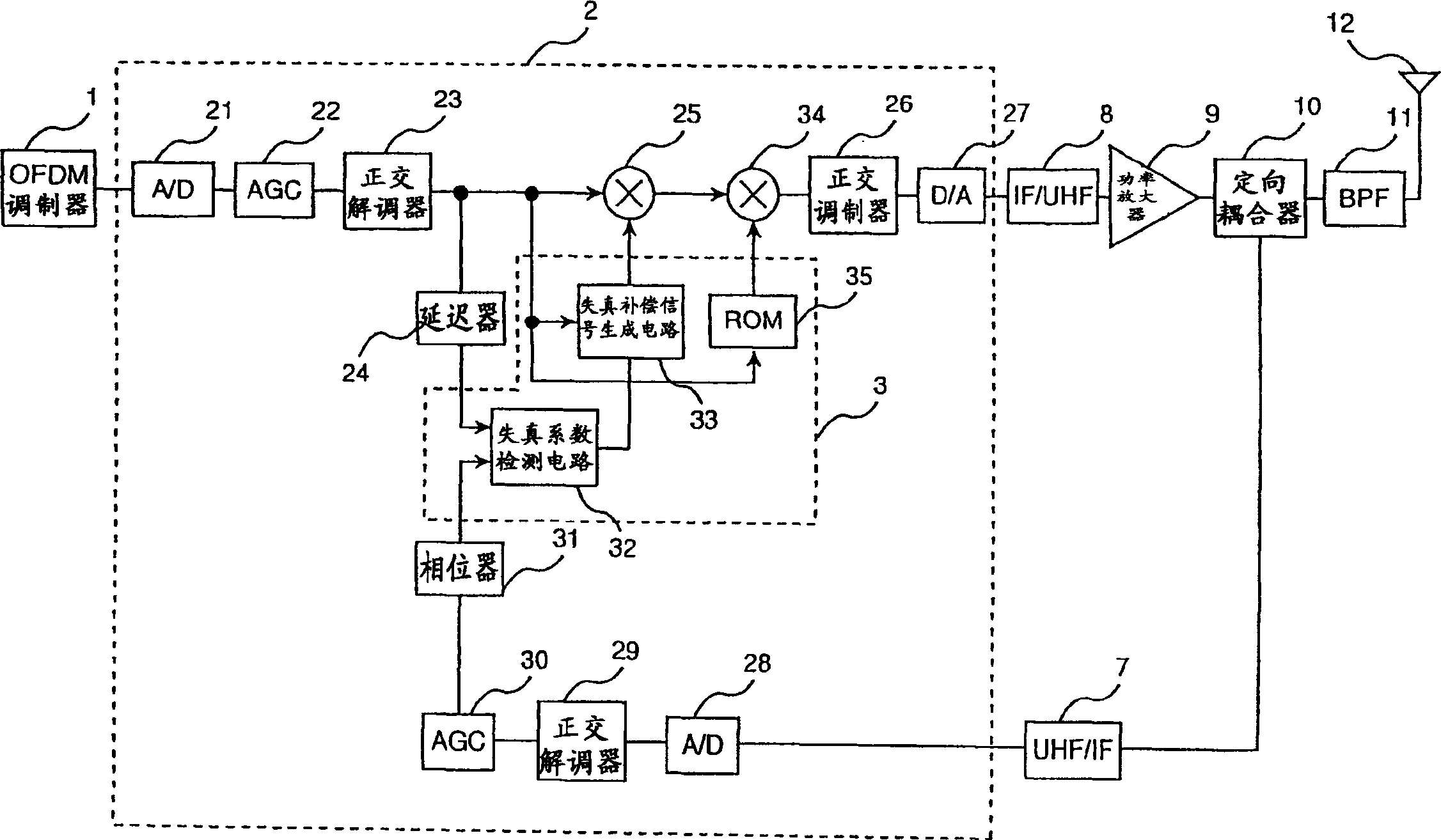
Power amplifier
ActiveUS20090072901A1Reduce distortion problemsImprove efficiencyAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierPhase difference
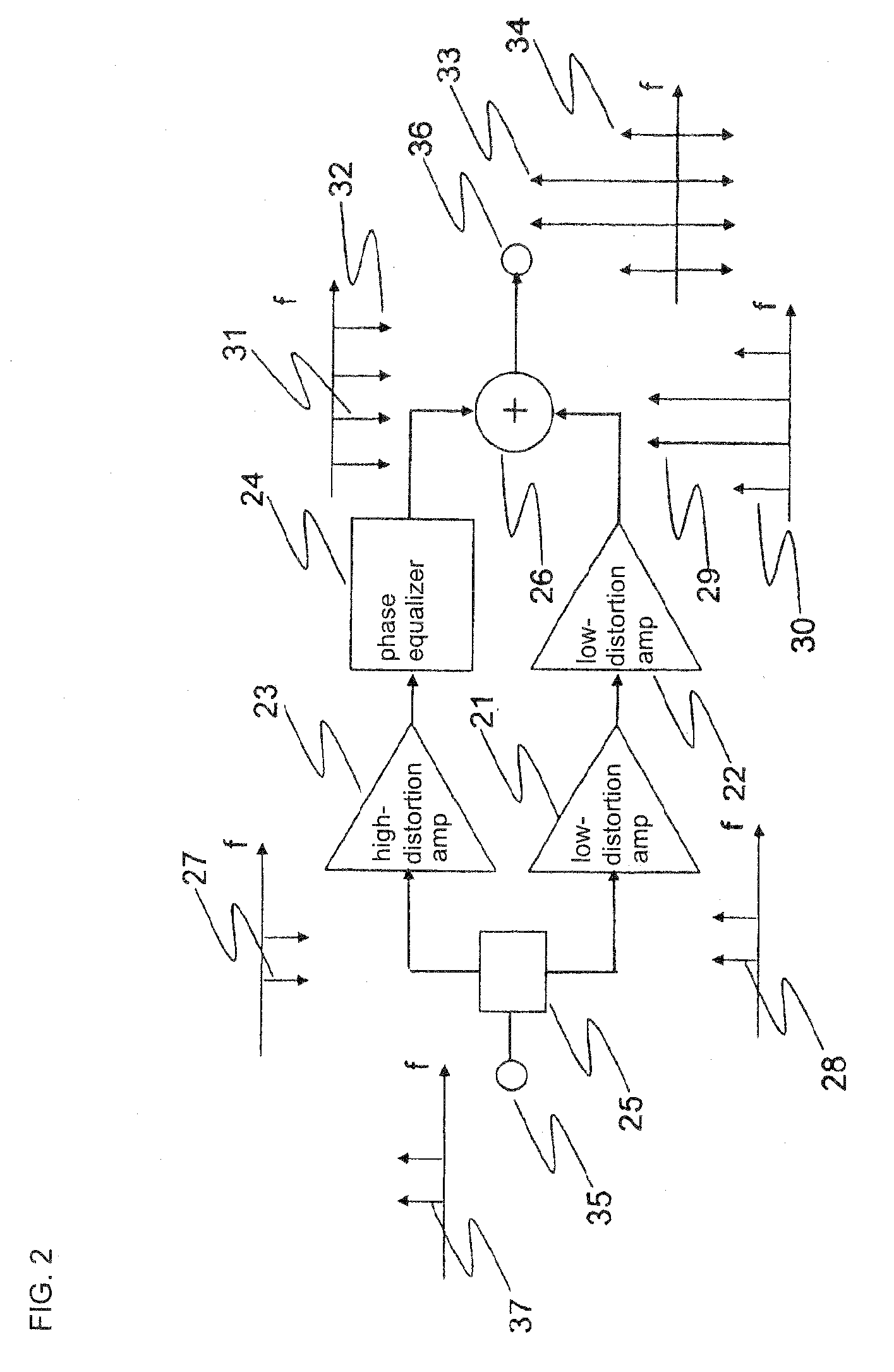
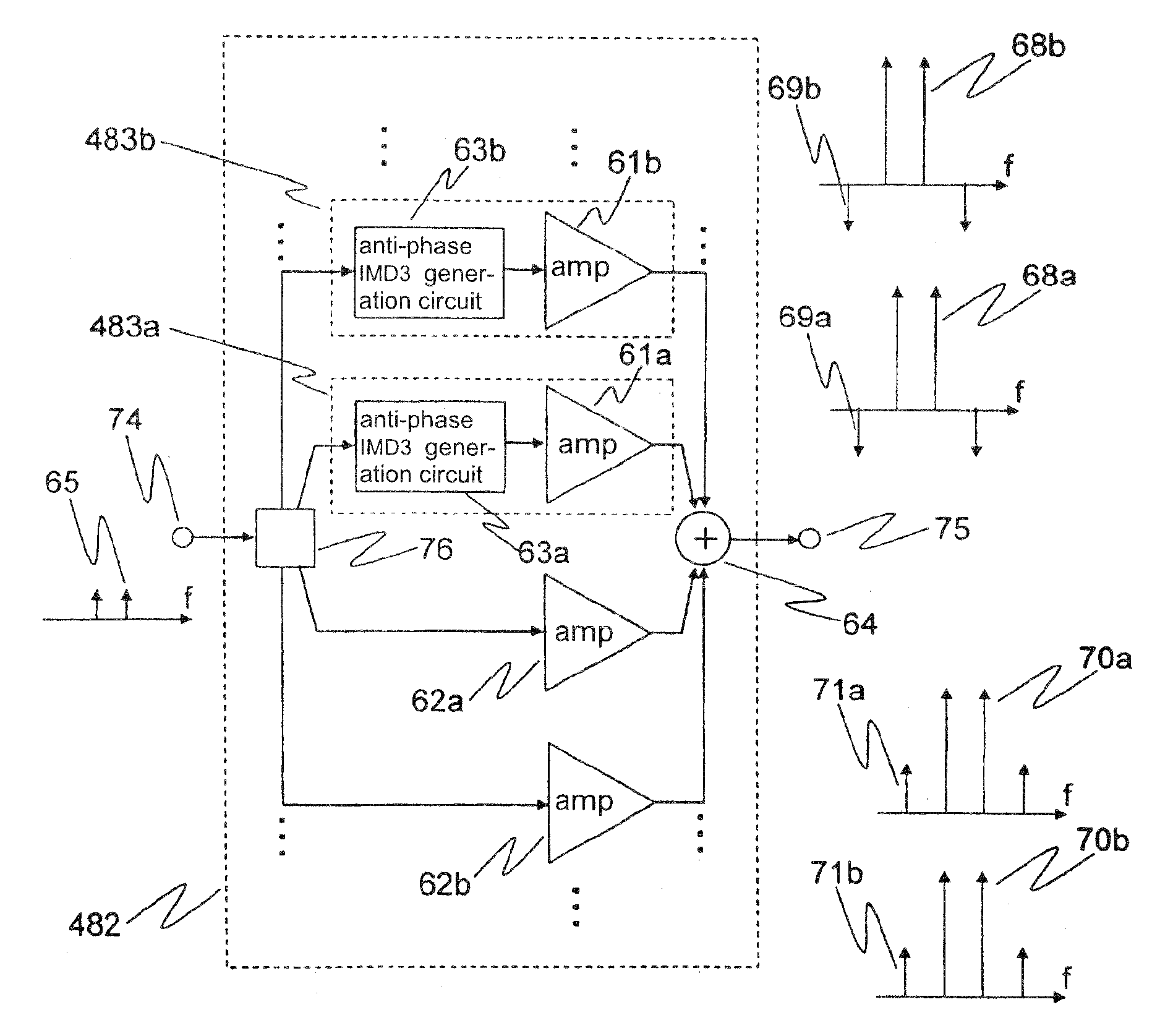
A power amplifier of the present invention includes a distributor (76) for distributing an input signal; an anti-phase third-order intermodulation distortion generation circuit (63) for, upon receiving the input signal that was distributed by the distributor, generating third-order intermodulation distortion for which the phase difference is anti-phase with respect to each of two main signals of different frequencies and supplying the two main signals and the third-order intermodulation distortion; a first amplifier (61) for amplifying the signal received from the anti-phase third-order intermodulation distortion generation circuit and supplying the result; a second amplifier (62) for amplifying the input signal that was distributed by the distributor and supplying the result; and a synthesizer (64) for combining the output signal of the first amplifier and the output signal of the second amplifier.
Owner:NEC CORP
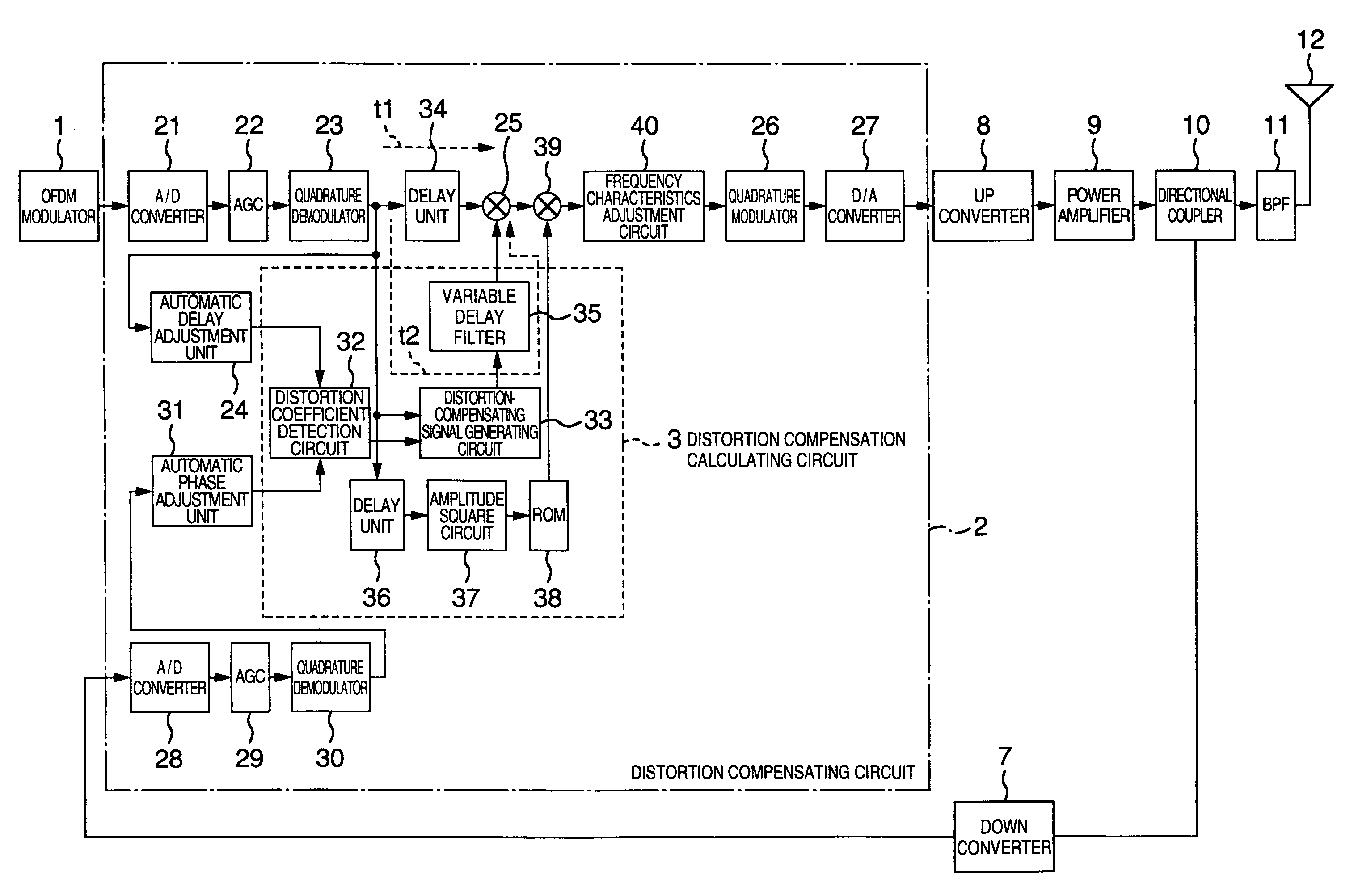
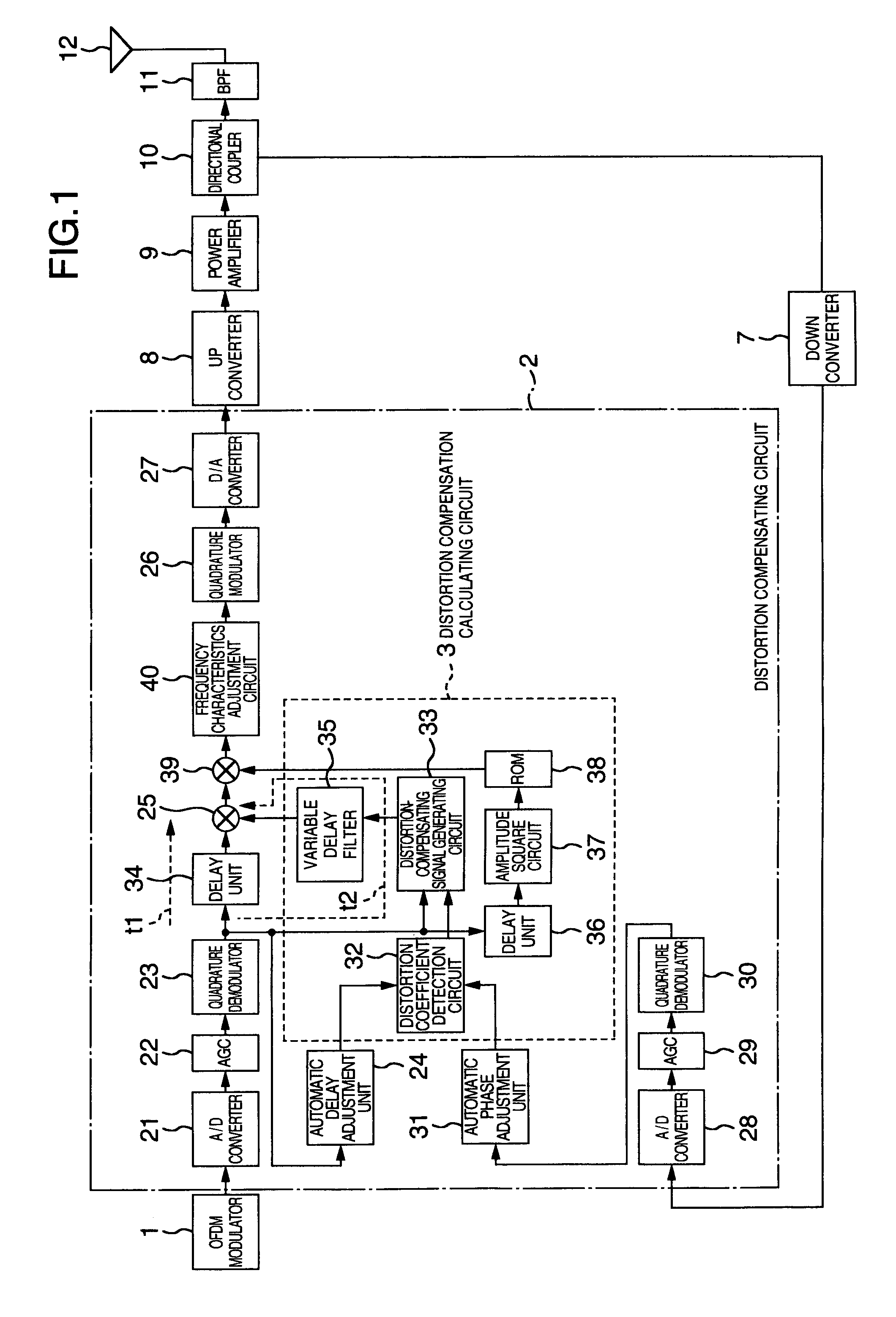
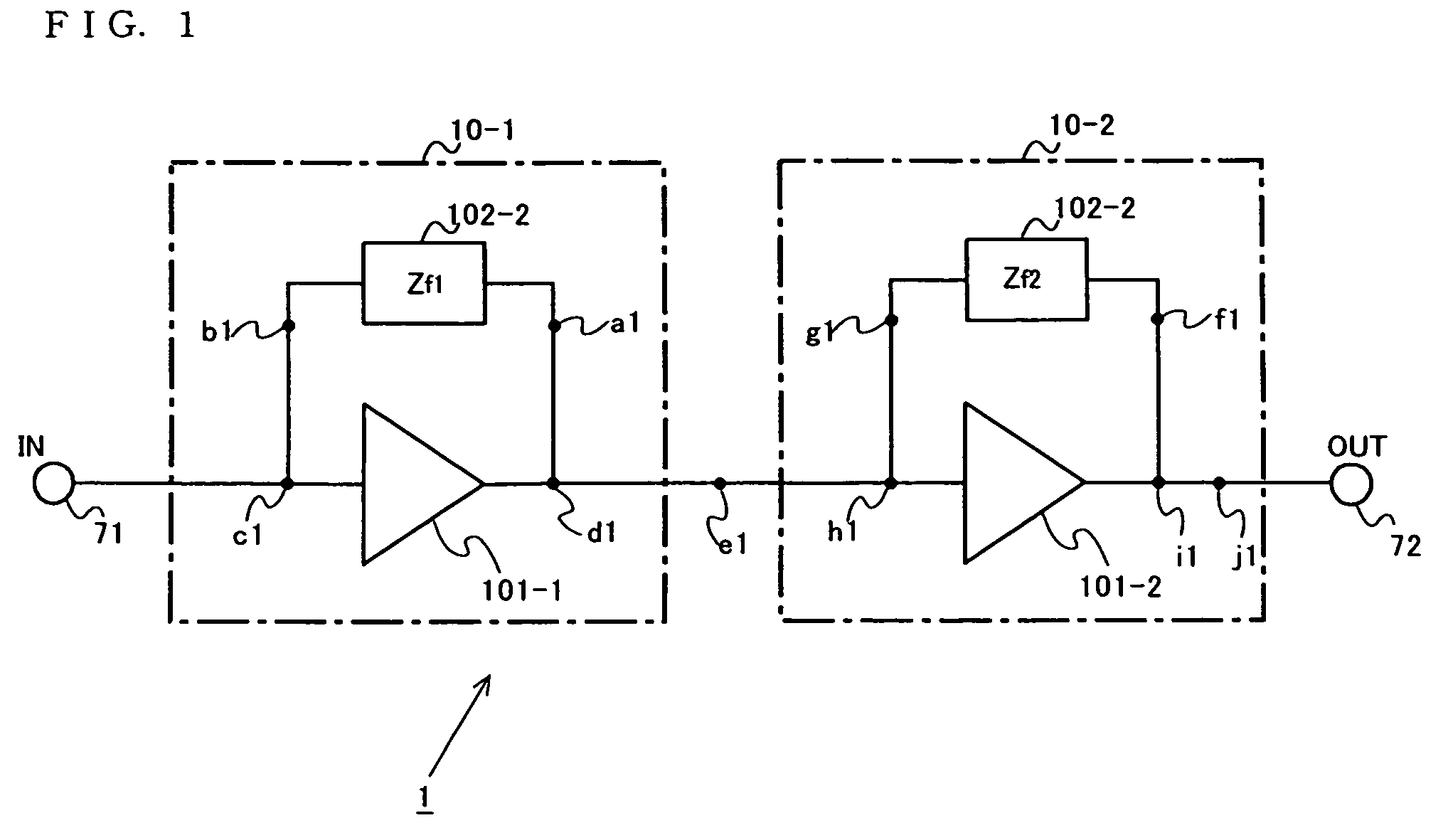
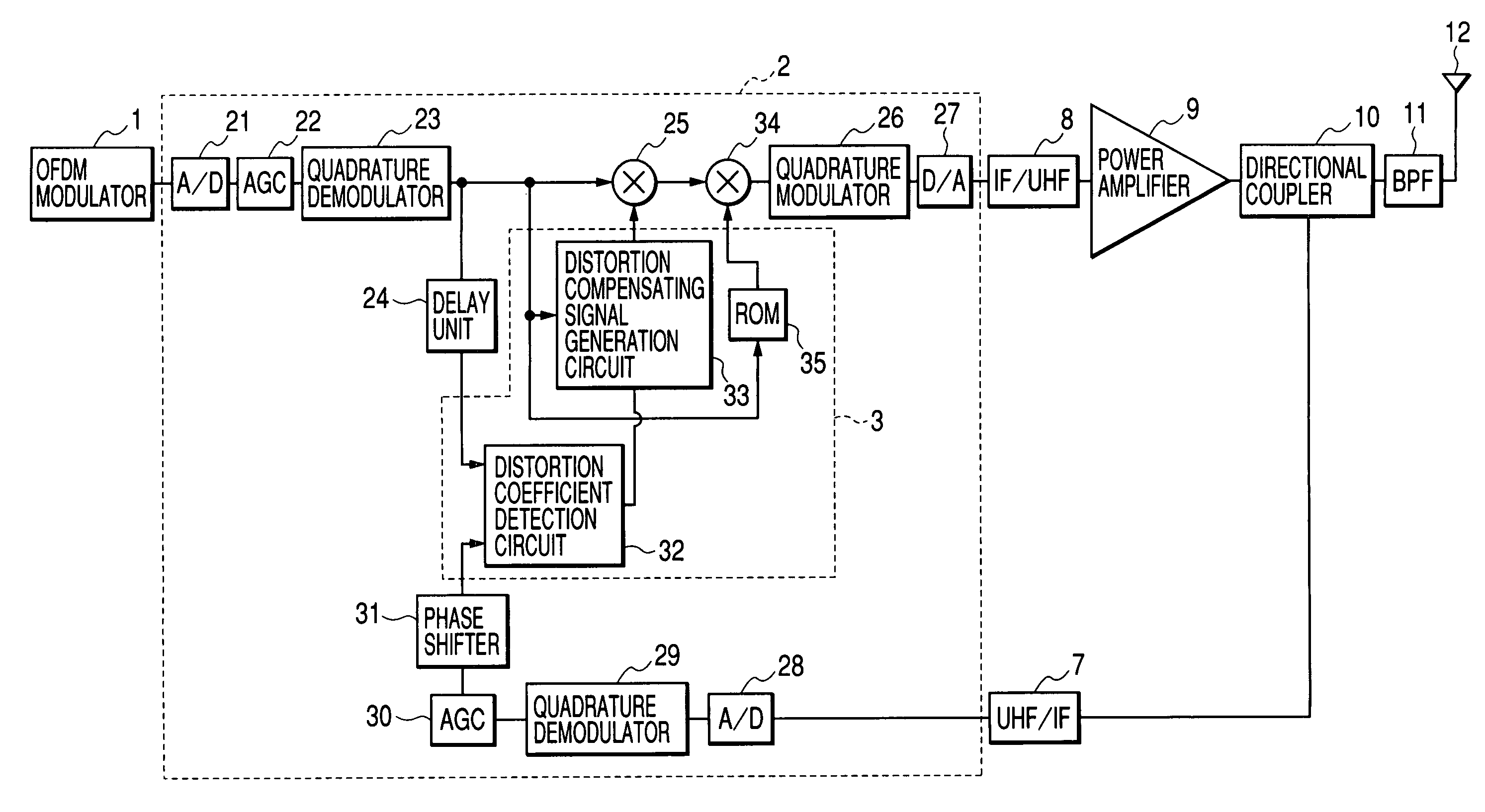
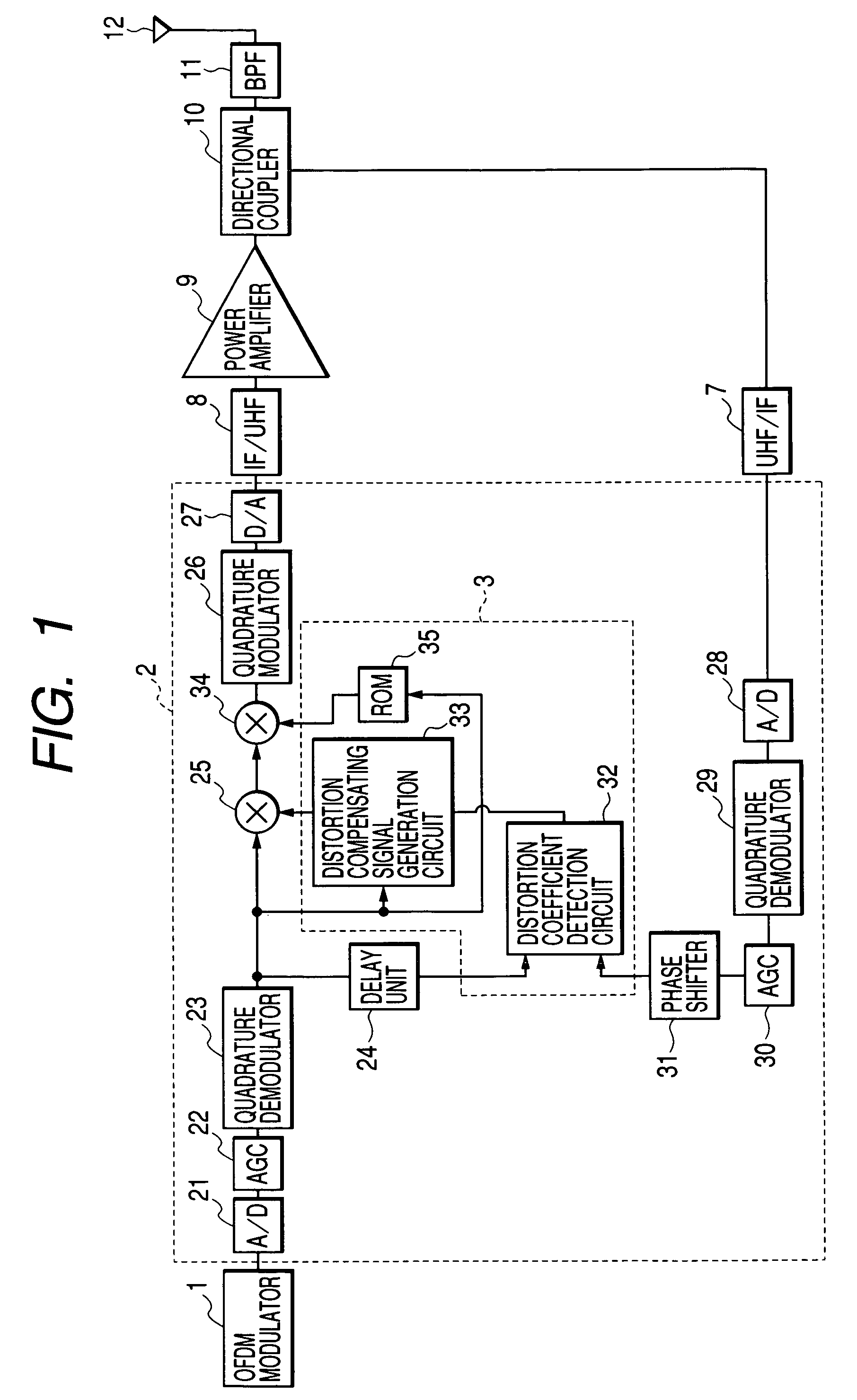
Distortion compensation circuit, power amplifier using distortion compensation circuit, and distortion compensation signal generating method
InactiveUS20050184803A1Improve accuracyIncrease speedAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAudio power amplifierSoftware engineering
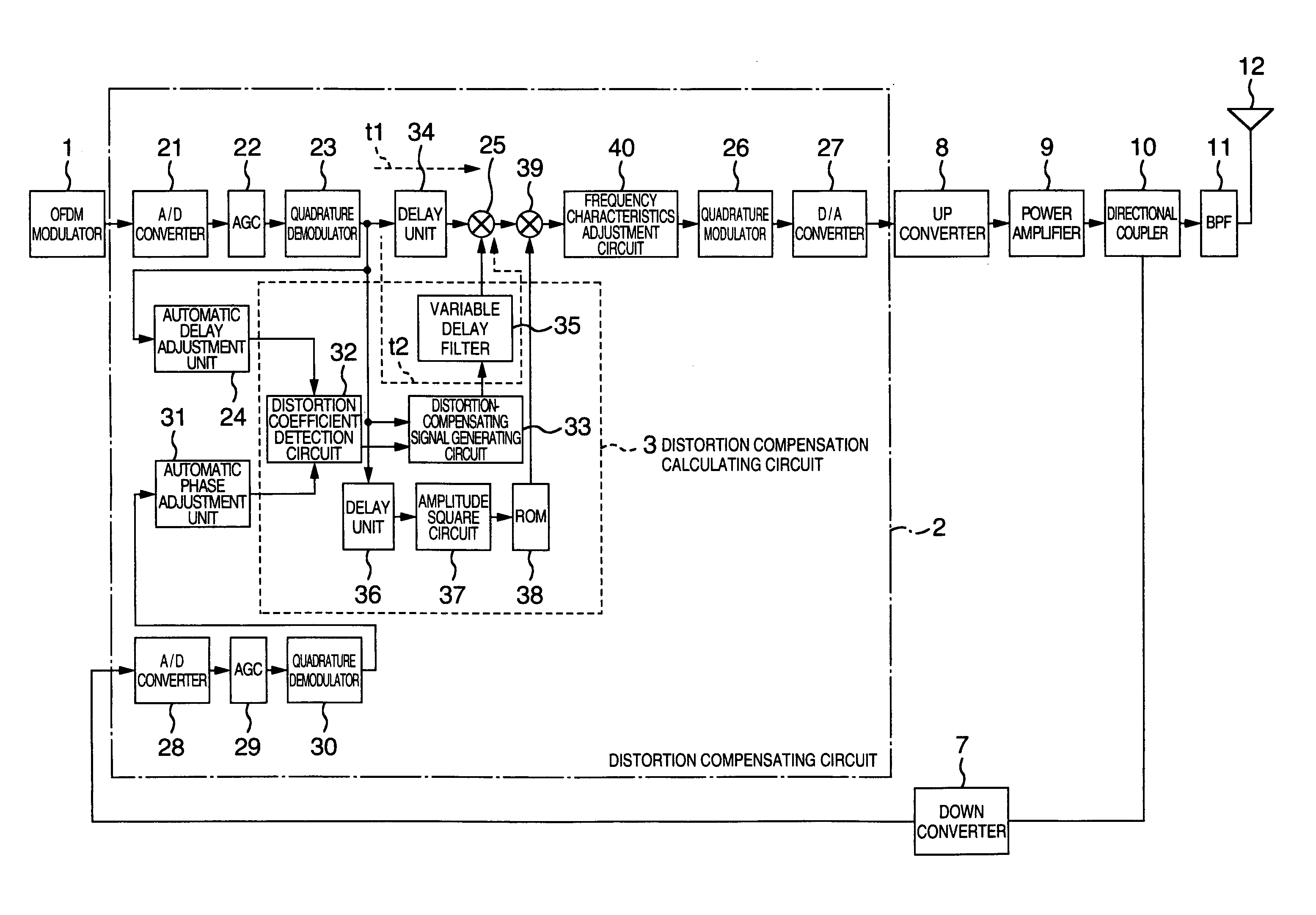
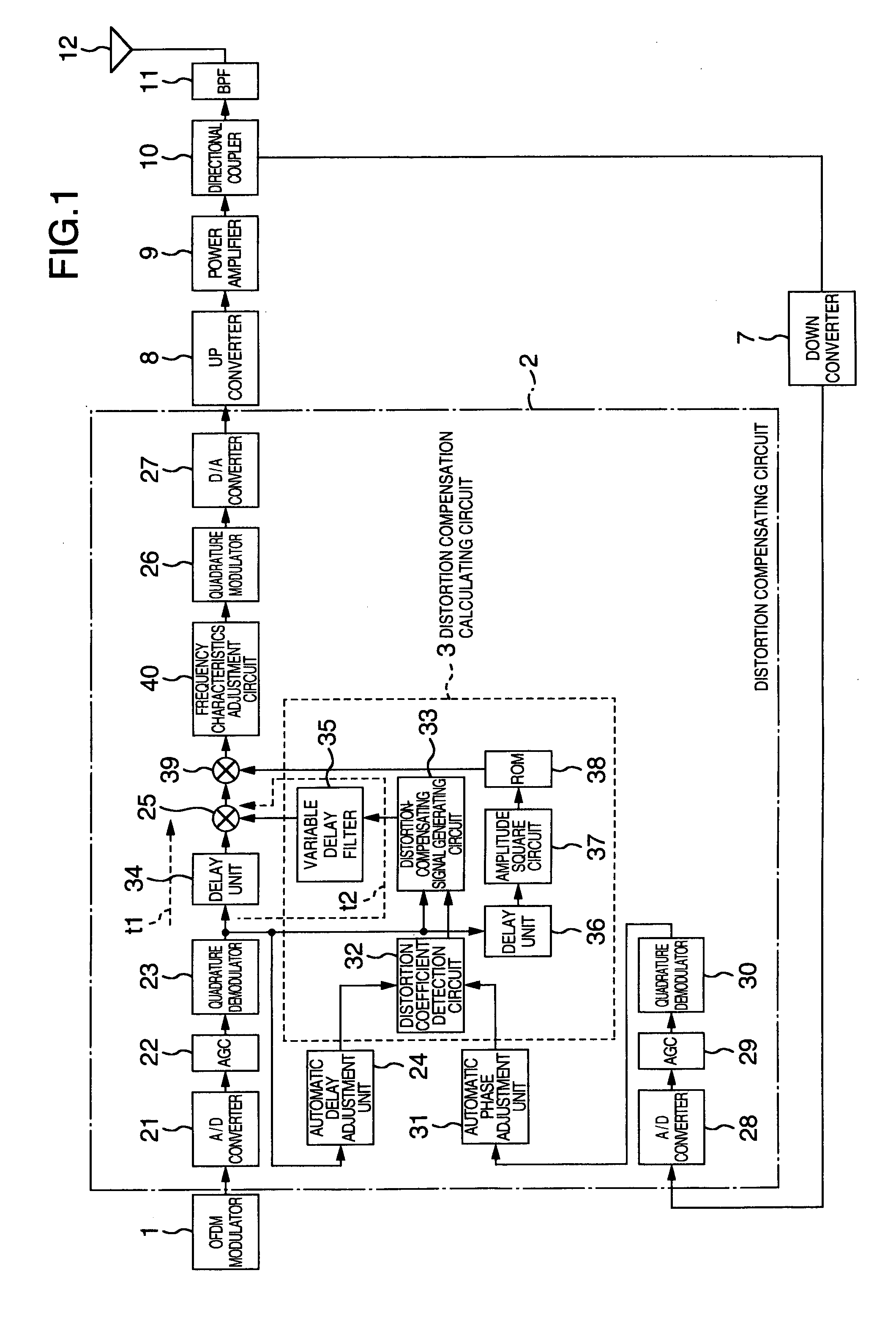
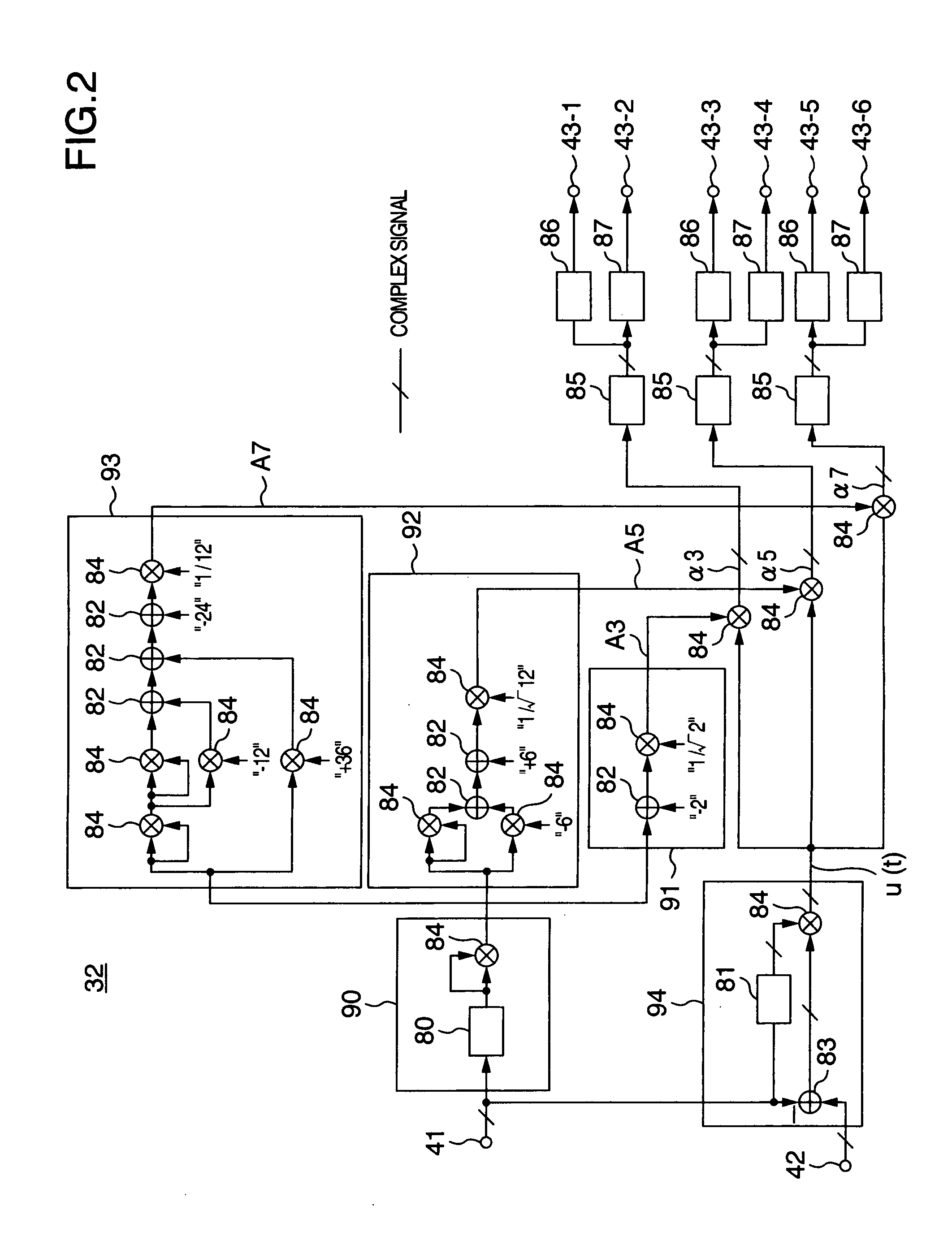
A distortion compensating circuit for a power amplifier attains raised compensating accuracy with shorter convergence time by accurately and quickly generating a distortion compensation signal for predistortion. An error signal representing the difference between the input and output signals of the power amplifier is generated. From the error signal and the input signal, the coefficients of the third-order intermodulation distortion, fifth-order intermodulation distortion and seventh-order intermodulation distortion are calculated. According to these coefficients, a distortion compensating signal which is characteristically opposite in phase and gain to the intermodulation distortions is generated.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Wideband linearization photonic time-stretch analog-to-digital conversion (PTS-ADC) method and device
InactiveCN106226973AEnsure consistencyRemove distortionOptical analogue/digital convertersPhotonicsOpto electronic
The invention belongs to the photoelectric technology field and relates to a wideband linearization photonic time-stretch analog-to-digital conversion (PTS-ADC) method and device. The method has the beneficial effects that single-sideband modulation is achieved by utilizing dual-drive M-Z modulators, thus eliminating baseband signal power attenuation caused by dispersion and achieving improvement of the effective analog bandwidth; distortion caused by dispersion introduction phase shifting is eliminated and timing recovery of zero phase shifting distorted signals is achieved by the phase compensation technology; radio-over-fiber signals with complementary characteristics are obtained by adopting two M-Z modulators respectively biased at linear bias points of a falling edge and a rising edge; envelope removal of the radio-over-fiber signals and suppression of second harmonics and second-order and third-order intermodulation distortion are achieved through difference and arcsine algorithm processing in a digital signal processor, thus achieving the effect of obviously improving the system linearity and quantization precision; besides, synchronous stretch of complementary output signals of the two modulators is achieved by utilizing two circulators, thus reducing the system cost and ensuring the consistency of the stretching ratios.
Owner:成都卓力致远科技有限公司
Power amplifier
ActiveUS7821337B2Reduce distortion problemsImprove efficiencyAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationAudio power amplifierPhase difference
A power amplifier of the present invention includes a distributor (76) for distributing an input signal; an anti-phase third-order intermodulation distortion generation circuit (63) for, upon receiving the input signal that was distributed by the distributor, generating third-order intermodulation distortion for which the phase difference is anti-phase with respect to each of two main signals of different frequencies and supplying the two main signals and the third-order intermodulation distortion; a first amplifier (61) for amplifying the signal received from the anti-phase third-order intermodulation distortion generation circuit and supplying the result; a second amplifier (62) for amplifying the input signal that was distributed by the distributor and supplying the result; and a synthesizer (64) for combining the output signal of the first amplifier and the output signal of the second amplifier.
Owner:NEC CORP
Highly linear Low-noise amplifiers
InactiveUS20070285162A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationLow noiseTransformer
A predistortion method for CMOS Low-Noise-Amplifiers (LNAs) to be used in Broadband Wireless applications is presented. The method is based on the nulling of the third order Intermodulation distortion (IMD3) of the main amplifier by a highly nonlinear predistortion branch. Maximum third order product cancellation is ensured by a transformer feedback method. The technique improves linearity in a wide range of input power without significant gain and Noise Figure. (NF) degradation. Simulation results on a 1-V LNA indicate a 10.3 dB improvement in the Input Third-Order Intercept Point (IIP3) with a reduction of only 1 dB and 0.44dB in amplifier gain and NF respectively.
Owner:THETA IP
Distortion compensation circuit, power amplifier using distortion compensation circuit, and distortion compensation signal generating method
InactiveUS7242247B2Improve accuracyIncrease speedAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAudio power amplifierThird order intermodulation distortion
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Electro-optic modulator, microwave photonic link including an electro-optic modulator, and method of communicating a signal with an electro-optic modulator
InactiveUS20180031946A1Improve linearityHigh spur-free dynamic rangeElectromagnetic transmittersOptical light guidesMicrowaveOptical power
An electro-optic modulator coupled to an optical source providing an optical power and a radio frequency source providing a radio frequency power. The electro-optic modulator includes a waveguide to receive the optical power, a first ring resonator modulator, and a second ring resonator modulator. The first ring resonator modulator and the second ring resonator modulator receives the radio frequency power, and are coupled to the waveguide for modulating the optical power with the radio frequency power. The first ring resonator modulator and the second ring resonator modulator, with the waveguide, substantially suppress third order intermodulation distortion of a combined power. Also disclosed are a microwave photonic link having the electro-optic modulator and a method of communicating a signal with the electro-optic modulator.
Owner:MICHIGAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
Large dynamic range optical carrier radio frequency link system
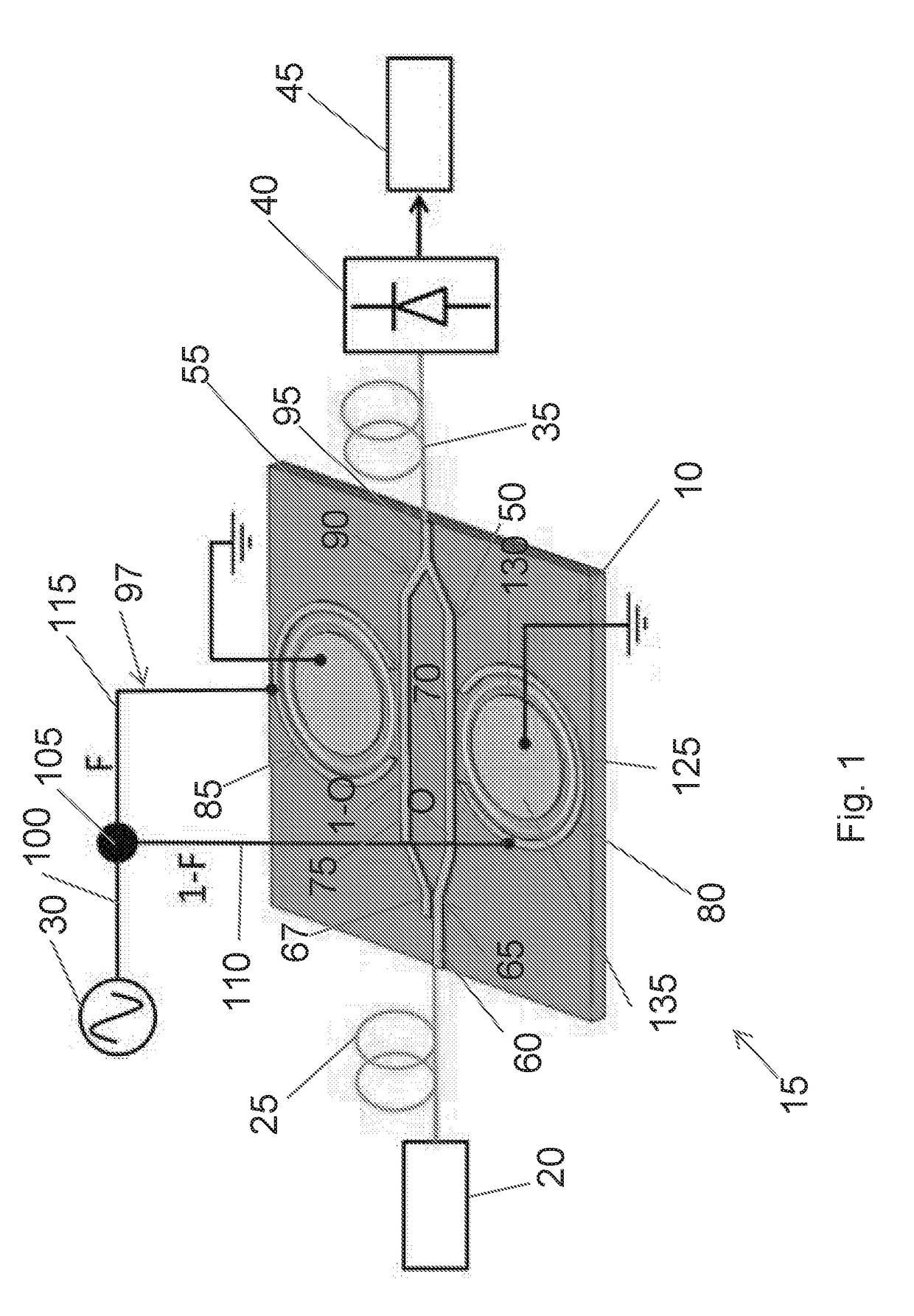
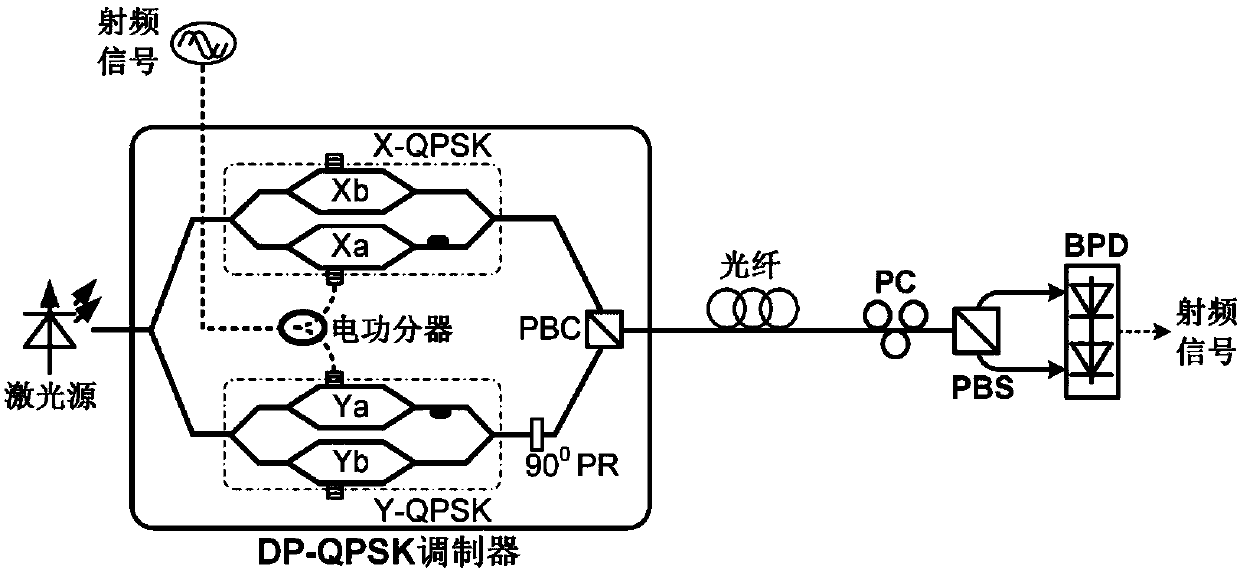
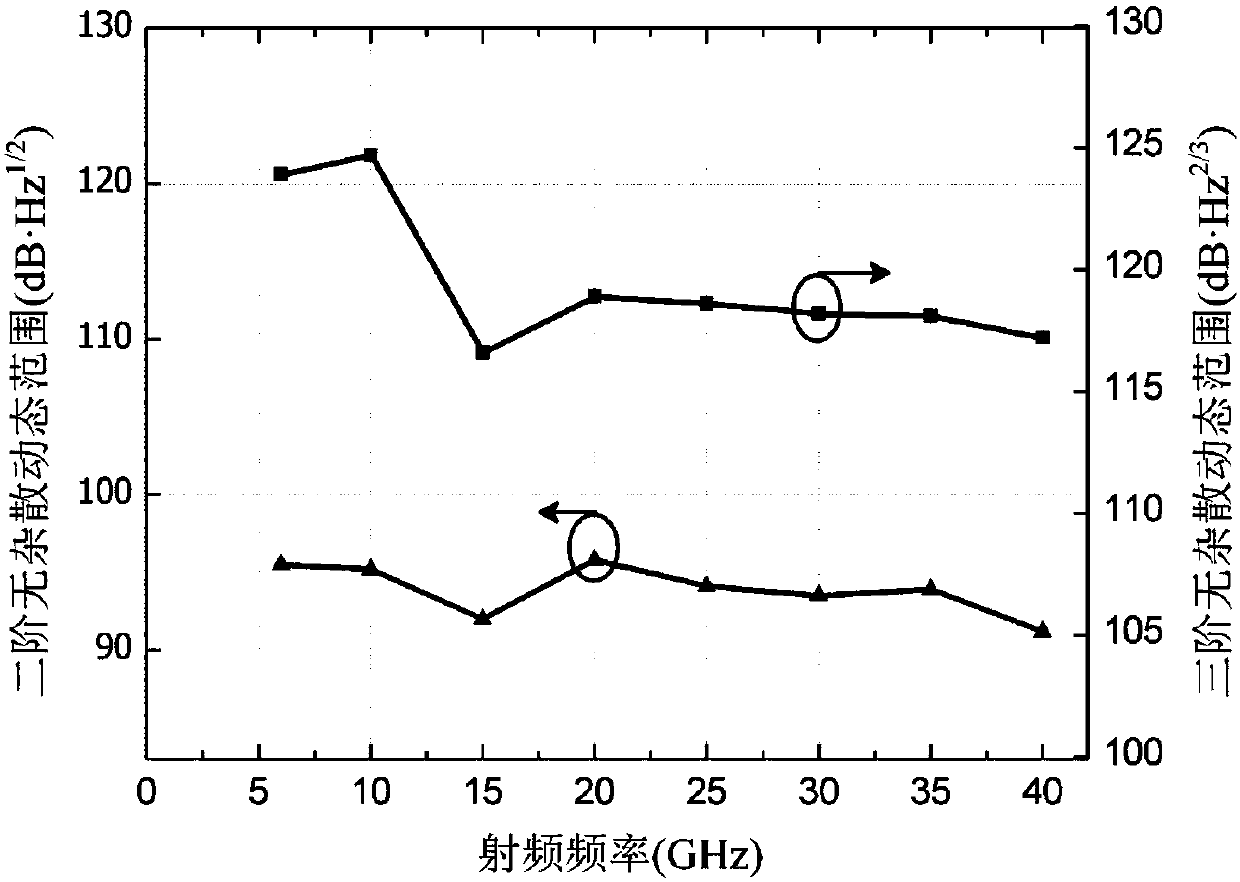
InactiveCN107911174AImprove dynamic rangePrecise Bias ControlRadio-over-fibreElectromagnetic receiversOperating pointPush pull
The invention provides a large dynamic range optical carrier radio frequency link system, and relates to the technical field of optical fiber communication. According to the invention, the optical carrier radio frequency link adopts a dual polarization quadrature phase shift keying modulator to realize electro-optic modulation; a radio frequency signal drives the modulator in a push-pull mode; bias point optimization and balance detection of the modulator are combined to enable simultaneous suppression of second-order and third-order intermodulation distortion in the recovered radio frequencysignal, so as to substantially increase the dynamic range of the link; the DP-QPSK modulator is driven in the push-pull mode; third-order intermodulation distortion is suppressed by adjusting the operating point of each QPSK modulator; second-order intermodulation distortion is suppressed through balance detection; second-order intermodulation distortion and third-order intermodulation distortionare simultaneously suppressed; the suppression effect of second-order intermodulation distortion and third-order intermodulation distortion is improved by using an electrical power divider with a highdegree of balance, high-symmetry modulators, precise bias control and BPD with good responsivity balance and high common-mode rejection ratio; and the dynamic range is increased.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
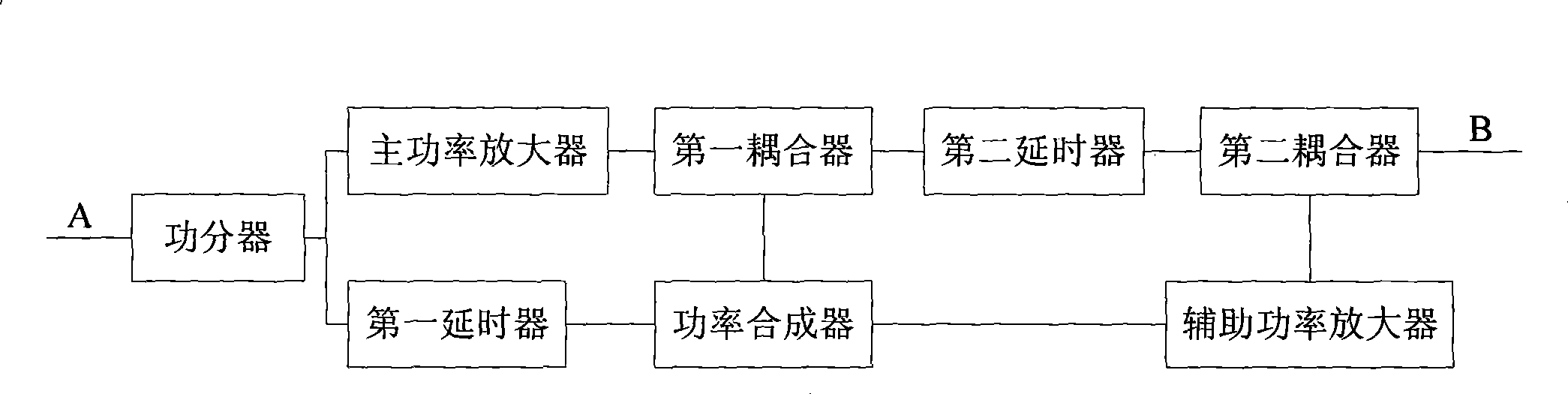
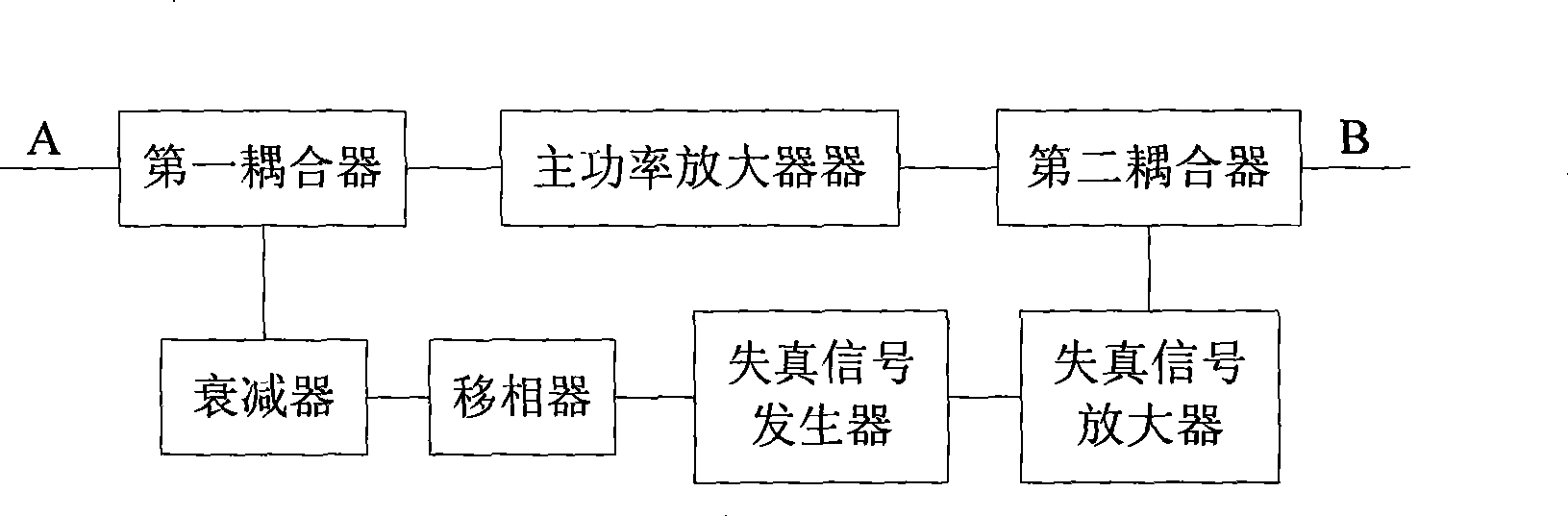
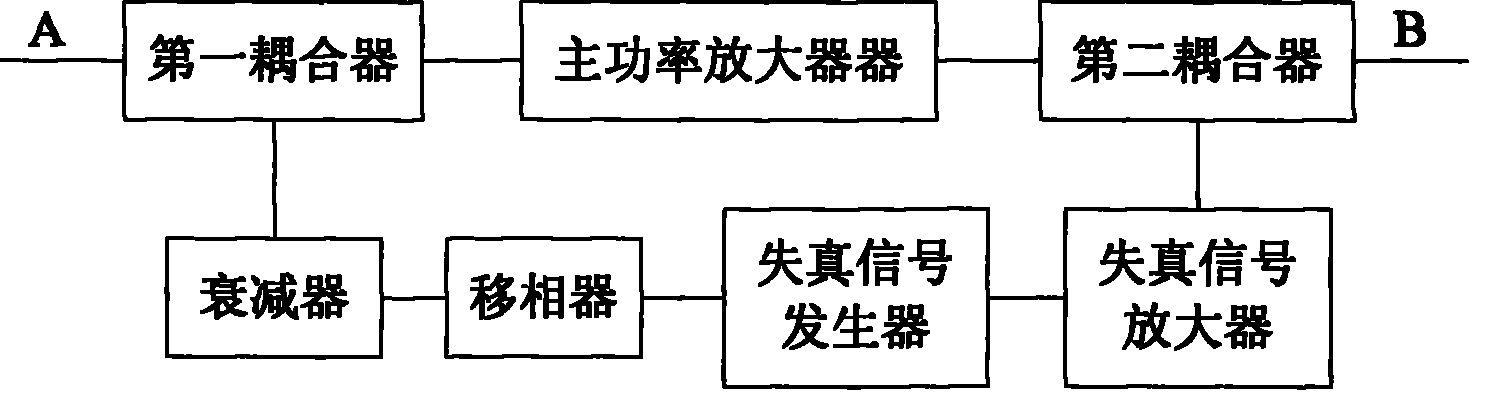
Low non-linear power amplifier
InactiveCN101388649AImprove performanceImprove efficiencyAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionPower amplifiersNonlinear distortionAudio power amplifier
The invention relates to a power amplifier, in particular to a low nonlinear distortion power amplifier. The low nonlinear distortion power amplifier comprises a main power amplifier, a distortion signal generator, a distortion signal amplifier, a first coupling, a second coupling, an attenuator and a phase shifter, wherein the main power amplifier amplifies a radio frequency input signal A, and attenuates and reverses a bypass radio frequency input signal which is coupled simultaneously, a signal which is reversed with a third-order intermodulation distortion signal which is generated by the main power amplifier is generated by the distortion signal generator, the distortion signal which is amplified is coupled with an output signal of the main power amplifier, which enables the third-order intermodulation distortion signal which is generated by the main power amplifier to be counteracted with the distortion signal which is generated by the distortion signal amplifier, and has equiamplitude and is reversed with the third-order intermodulation distortion signal which is generated by the main power amplifier, and finally an ideal radio frequency power amplifying signal is obtained. The invention has the advantages of excellent performance, high efficiency, simple structure and low cost, and can be used in various systems which need to use linearized power amplifiers.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Signal transmission apparatus, electronic device, and signal transmission method
InactiveCN102571269APreventing "Intermodulation Distortion" ProblemsError preventionMulti-frequency code systemsEngineeringFrequency offset
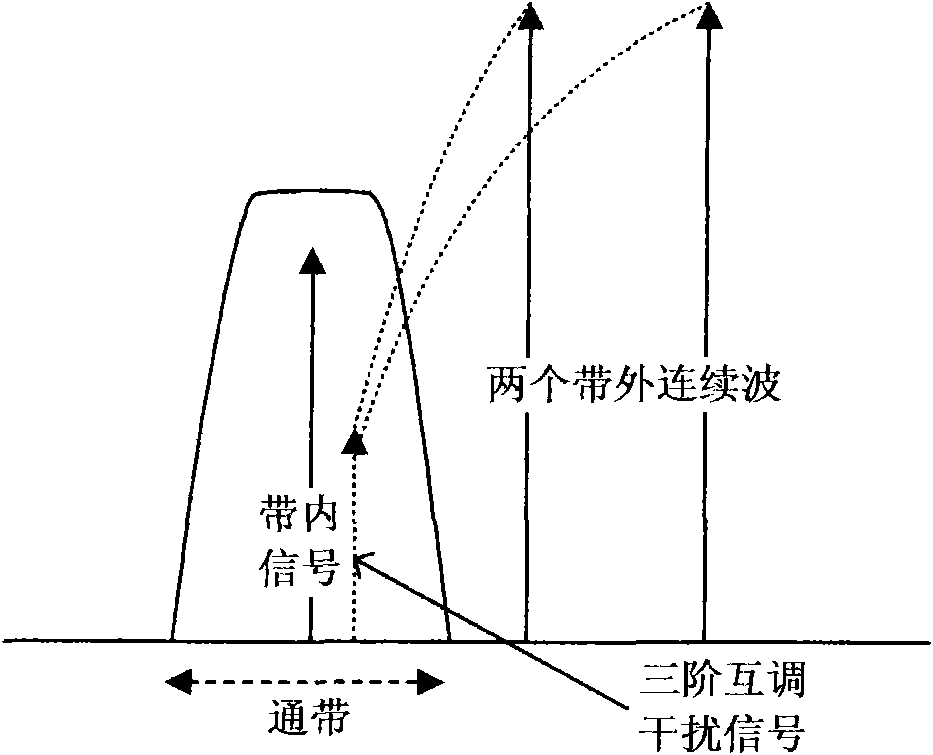
A signal transmission apparatus including: a plurality of modulating sections configured to modulate a transmission object signal; and a plurality of demodulating sections configured to demodulate the modulated signals modulated by the modulating sections, wherein each of carrier frequencies as frequencies different from each other used by respective sets of the modulating sections and the demodulating sections is set such that frequency of a third-order intermodulation distortion component generated on a basis of two carrier frequencies adjacent to each other is not present within any of reception bands of modulated signals based on each of the other carrier frequencies.
Owner:SONY CORP
Multistage amplifying devices, and reception device and transmission device using the same
InactiveUS20050270094A1Reduce power consumptionRemoving white noiseAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAudio power amplifierPhase difference
A multistage amplifying device for amplifying a desired signal comprise first to N-th amplifiers connected in cascade,wherein the k-th (k is 1 to N) amplifier includes a k-th amplification section; and a k-th feedback section which has a reactance component, changes a phase of a signal output from the k-th amplification section. When a phase difference between the desired signal output from the N-th amplifier and a third-order inter-modulation distortion(IM3) output from the (N-1)-th amplifier is referred to as a first phase, and a phase difference between the desired signal output from the N-th amplifier, and a combined IM3 obtained by combining a IM3 occurring in the N-th amplification section and a IM3 fed back from the N-th feedback section is referred to as a second phase, a difference between the first phase and the second phase is 120° or more and 180° or less.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
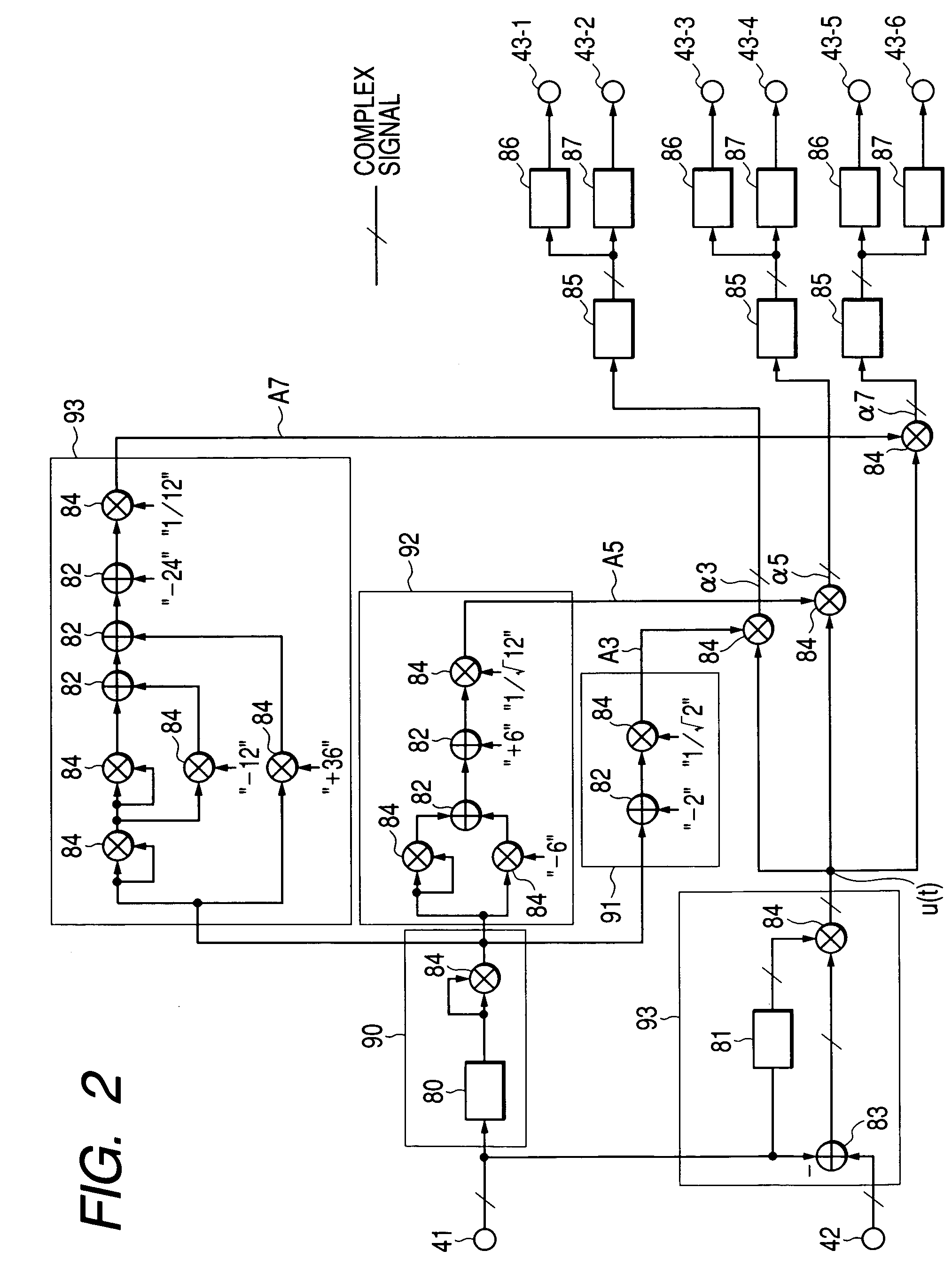
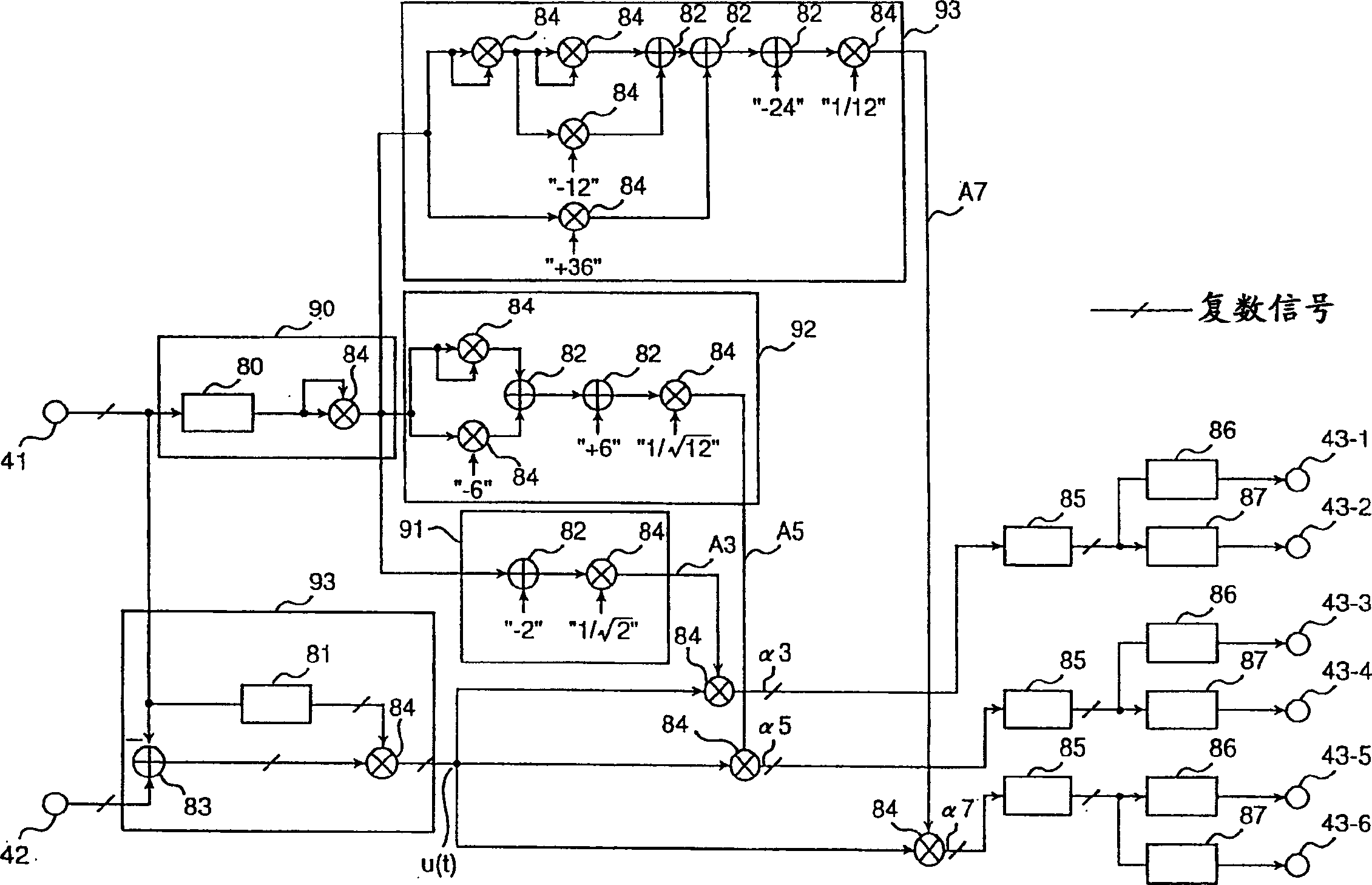
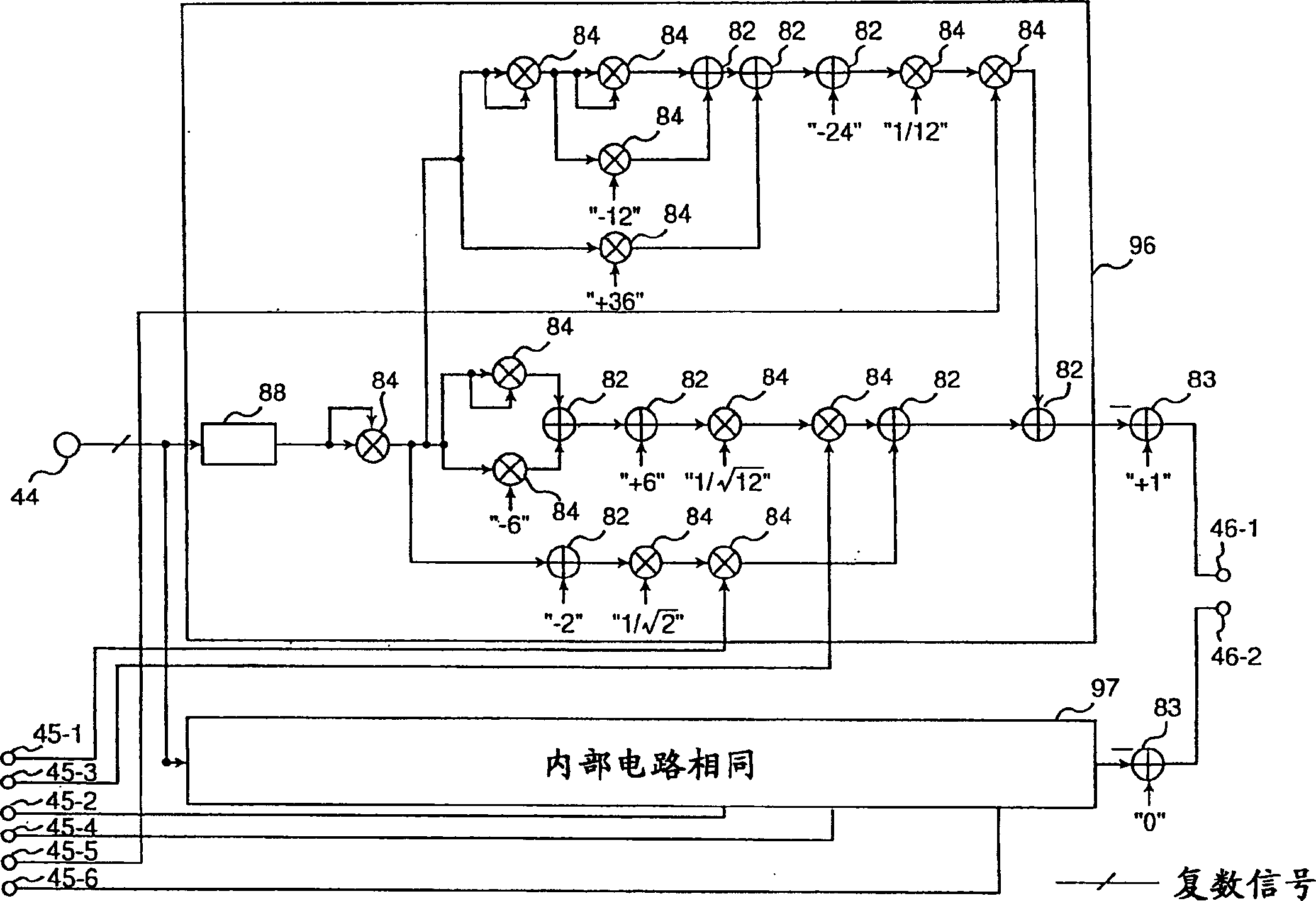
Distortion compensation circuit, distortion compensation signal generating method, and power amplifier
InactiveUS7180368B2Improve accuracyIncrease speedAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAudio power amplifierThird order intermodulation distortion
A distortion compensating circuit for a power amplifier attains raised compensating accuracy with shorter convergence time by accurately and quickly generating a distortion compensation signal for pre-distortion. An error signal representing the difference between the input and output signals of the power amplifier is generated. From the error signal and the input signal, the coefficients of the third-order intermodulation distortion, fifth-order intermodulation distortion and seventh-order intermodulation distortion are calculated. According to these coefficients, a distortion compensating signal which is characteristically opposite in phase and gain to the intermodulation distortions is generated.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
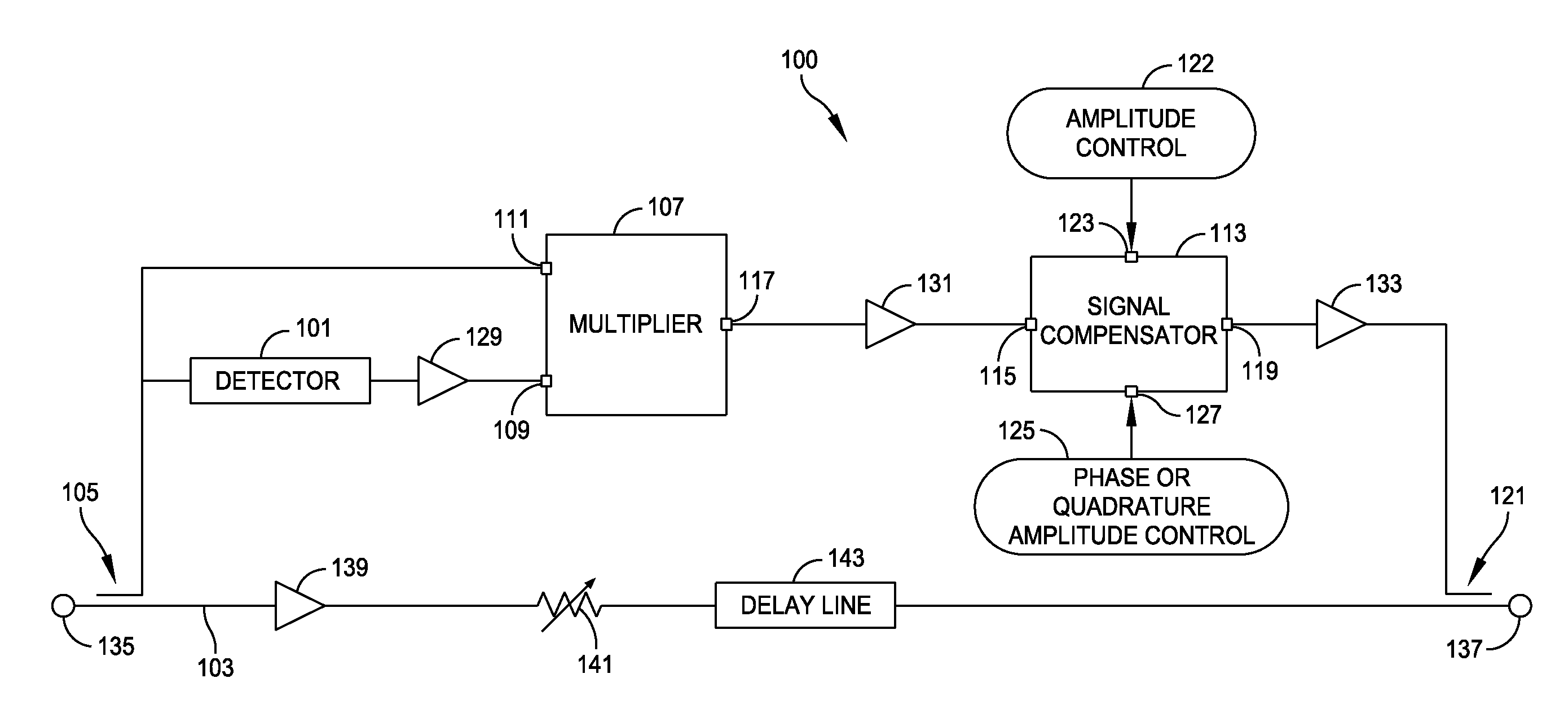
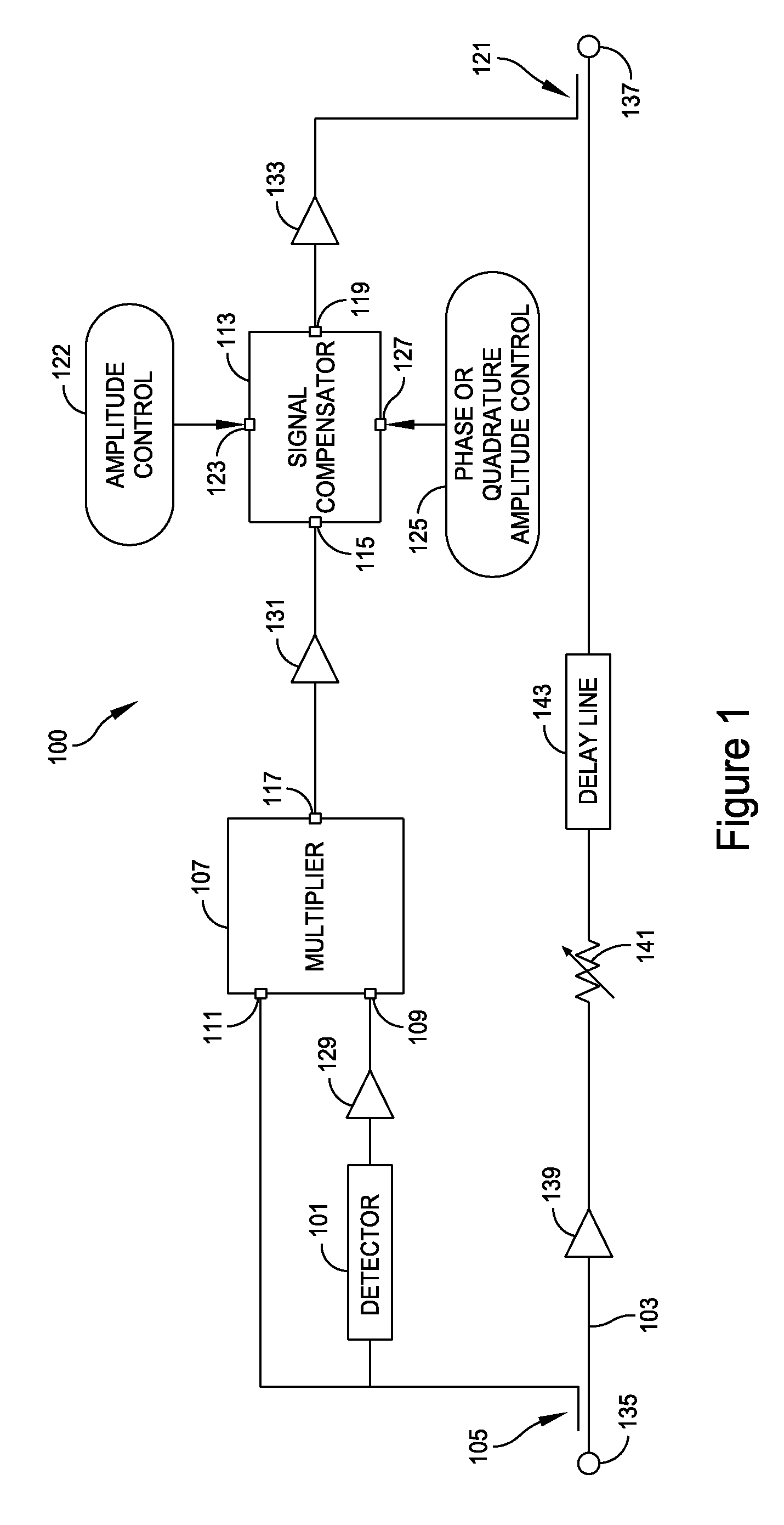
Apparatus and method for reducing third-order intermodulation distortion
ActiveUS20110002428A1Reduce distortion problemsAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionError preventionDistortionVIT signals
A method and apparatus for compensating for third-order intermodulation (IM) distortion in a receiver by passing a received signal through a detector to obtain a second-order difference signal, combining the 2nd-order signal with the received signal in a multiplier to obtain a 3rd-order IM signal, adjusting a parameter such as amplitude, phase or quadrature amplitude of the 3rd-order IM signal, and coupling the 3rd-order IM signal into the received signal.
Owner:KEYSIGHT TECH
Distortion compensation circuit, distortion compensation signal generating method, and power amplifier
InactiveCN1557046AHigh precisionShorten convergence timeAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionTransmissionAudio power amplifierEngineering
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
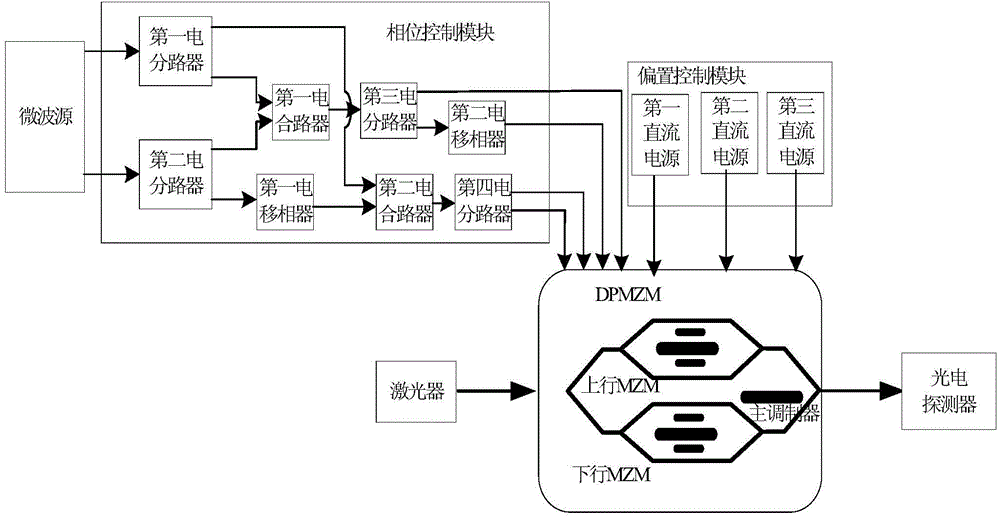
Microwave photonic third-order intermodulation complete suppression system based on double parallel mach-zehnder modulators (DPMZM)
ActiveCN104967488AHigh gain transmissionSuppression of third-order intermodulation interferenceDistortion/dispersion eliminationRadio-over-fibrePhase differenceCommunication link
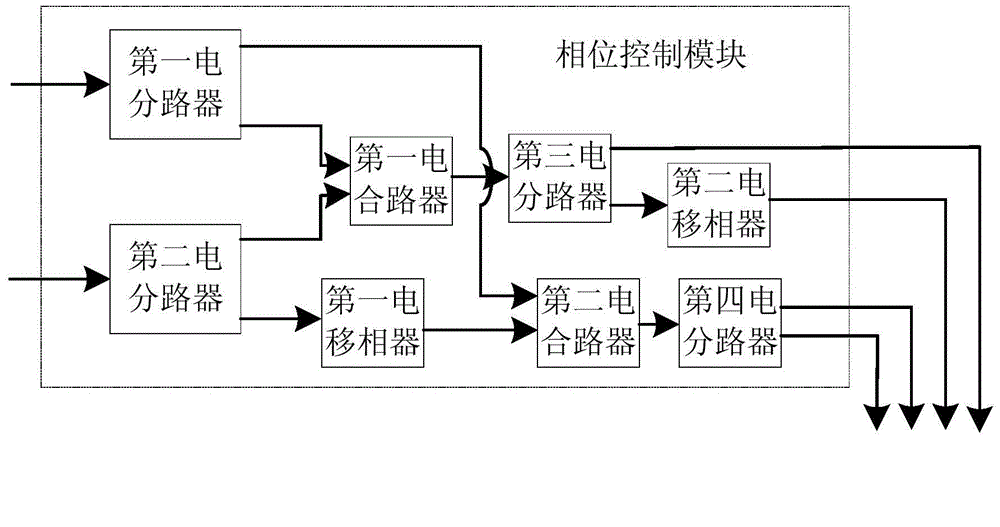
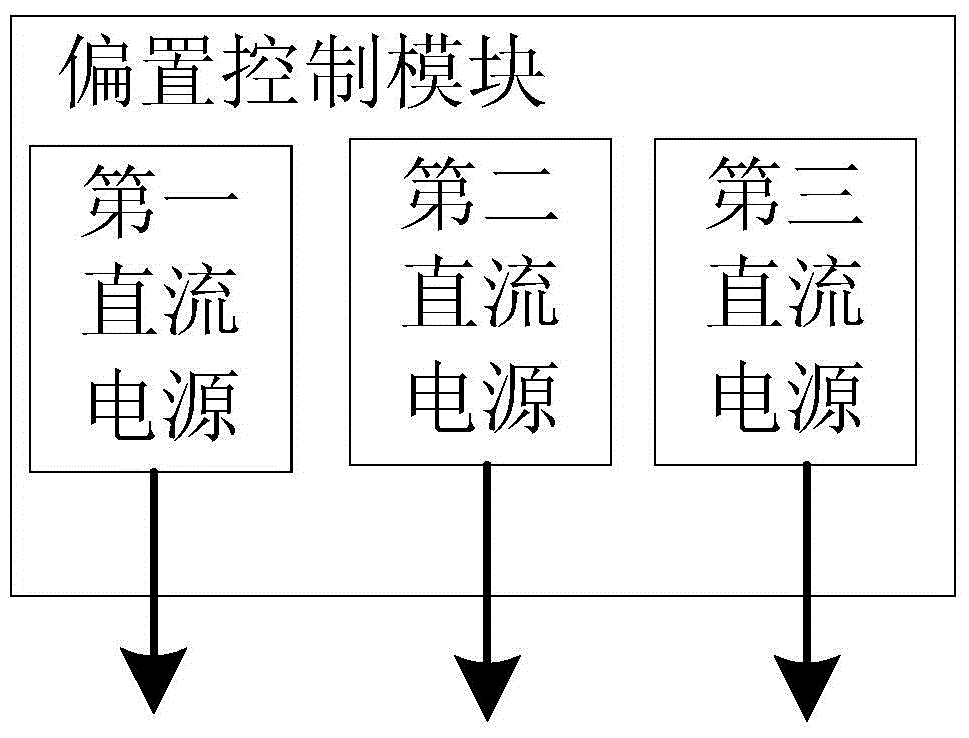
A microwave photonic third-order intermodulation distortion complete suppression system based on the DPMZM comprises a microwave source, a phase control module, a bias control module, a laser, the DPMZM and a photoelectric detector. By the phase control module, the four radio frequency electric signals loaded on the four driving electrodes of the dual driving DPMZM possess the fixed phase difference, a DC bias control unit is combined to carry out the DC bias point control on the uplink MZM and the downlink MZM of the DPMZM, and the phase difference control among the four radiofrequency signals is realized by utilizing two 180-degree phase shifters, thereby realizing the third-order intermodulation complete suppression of a broadband microwave photonic communication link. The microwave photonic third-order intermodulation distortion complete suppression system based on the DPMZM has the characteristics of being low in design complexity, high in stability and good in repeatability and being simple to realize, can solve the broadband microwave photonic communication high linearization demand, and guarantees the high bandwidth and large dynamic range of a broadband microwave photonic communication system.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
Low noise amplifier
InactiveUS7663441B2Reduce distortion problemsLow noise amplifierAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceHigh frequency amplifiersAudio power amplifierControl signal
A low noise amplifier includes a main amplifier configured to amplify a first input signal to generate a first output signal and an auxiliary amplifier configured to amplify a second input signal to generate a second output signal. The auxiliary amplifier is coupled to the main amplifier for superposing the second output signal and the first output signal. The low noise amplifier also includes an adjusting unit configured to adjust a time constant for reducing a third order intermodulation distortion of the superposed signal in response to a control signal. The adjusting unit is configured to generate the second input signal based on the time constant and the first input signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Multistage amplifying devices, and reception device and transmission device using the same
InactiveUS7176757B2Remove noiseAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAudio power amplifierPhase difference
A multistage amplifying device for amplifying a desired signal comprise first to N-th amplifiers connected in cascade,wherein the k-th (k is 1 to N) amplifier includes a k-th amplification section; and a k-th feedback section which has a reactance component, changes a phase of a signal output from the k-th amplification section. When a phase difference between the desired signal output from the N-th amplifier and a third-order inter-modulation distortion(IM3) output from the (N−1)-th amplifier is referred to as a first phase, and a phase difference between the desired signal output from the N-th amplifier, and a combined IM3 obtained by combining a IM3 occurring in the N-th amplification section and a IM3 fed back from the N-th feedback section is referred to as a second phase, a difference between the first phase and the second phase is 120° or more and 180° or less.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Distribution method of third-order intermodulation distortion parameter applied inside receiver radio-frequency system circuit
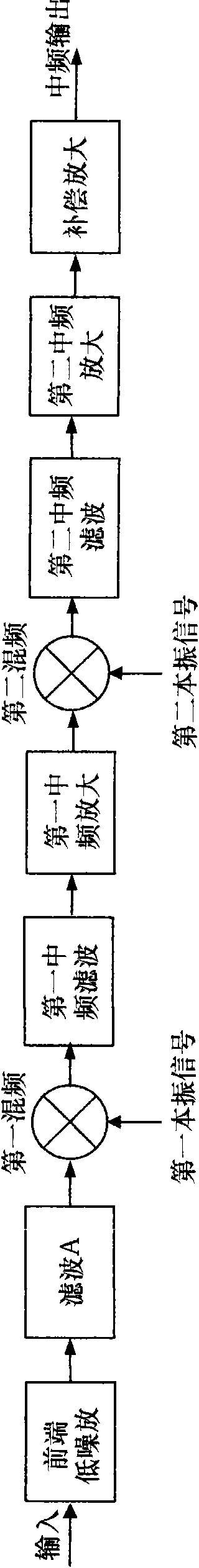
The invention discloses a distribution method of third-order intermodulation distortion parameters applied inside a receiver radio-frequency system circuit, which belongs to the technical field of electromagnetic compatibility. The distribution method comprises the following steps: firstly processing the overall receiving performance index of a receiver radio-frequency system according to nonparasitic response to obtain a threshold voltage; then computing the total distortion voltage of third-order intermodulation distortion in each level of sub circuit, which is about to enter a received passband according to constraint relation; and finally obtaining the third-order cut-off point of each level of sub circuit according to the relation that the total distortion voltage is smaller than and equal to the threshold voltage. The method of the invention realizes the distribution of the third-order intermodulation distortion parameters of each level of sub circuit under the condition of cascade circuit voltage signal in-phase, thereby the problem of poor communication quality caused by overlarge third-order intermodulation distortion signal interference of the receiver radio-frequency system is solved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for improving linearity of directly modulated microwave photonic link based on push-pull structure and compensation algorithm
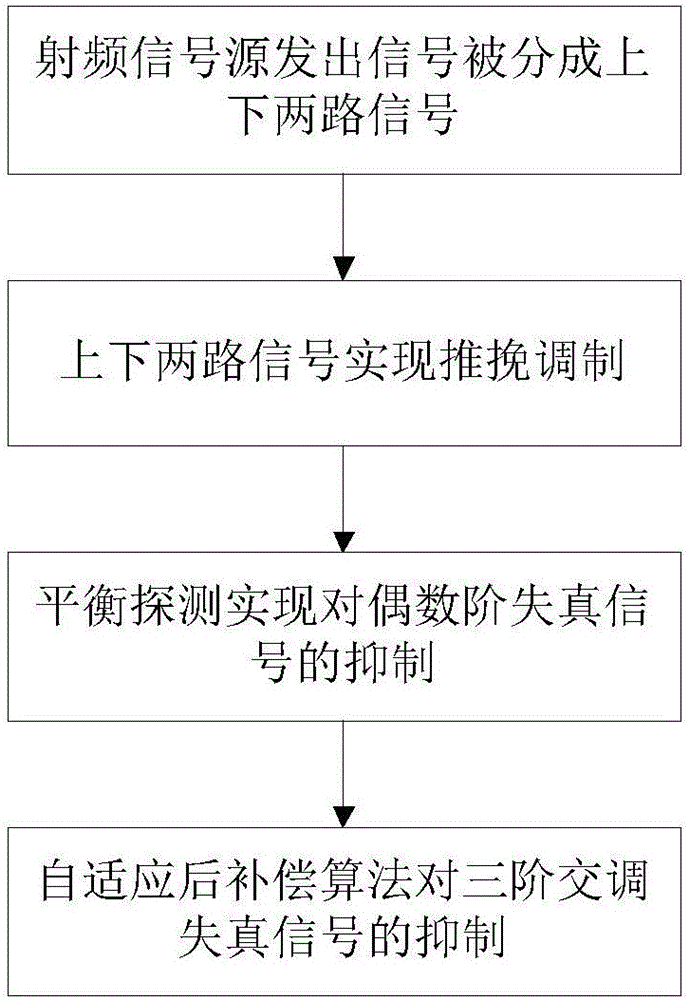
ActiveCN106533566AReduce complexitySuppresses even-order distortionDistortion/dispersion eliminationRadio-over-fibrePush pullEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of microwave photonic signal transmission and processing and discloses a method for improving the linearity of a directly modulated microwave photonic link based on a push-pull structure and an adaptive post-compensation algorithm. The method comprises the following steps: (a) dividing an initial signal into upper and lower signals; (b) performing push-pull modulation on the upper and lower signals; (c) suppressing an even-order distortion signal by using balance detection; (d) suppressing a third-order intermodulation distortion signal (IMD3) by using the adaptive post-compensation algorithm. The method realizes a large-broadband high-linearity directly modulated microwave photonic link in which all even-order distortion signals and the third-order intermodulation distortion signals are suppressed, and the method has the characteristics of low cost, compact structure and high cost performance.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Optical link linearization method
ActiveCN104618023AImprove dynamic rangeAvoid precise estimatesDistortion/dispersion eliminationMultiple carrier systemsCarrier signalLinearization
The invention discloses an optical link linearization method. The optical link linearization method comprises step 1, obtaining an optical signal from an optical link and detecting and recovering a distorted electrical signal from the optical signal; step 2, building a compensation signal according to the distorted electrical signal; step 3, performing compensation on the distorted electrical signal through the compensation signal so as to enable the optical link to be linearized. According to the optical link linearization method, the optical link is an incoherent intensity modulation direct detection link and the simultaneous inhibition of IMD3 (Third-order Intermodulation Distortion) and XMD (Cross-over Modulation Distortion) is implemented by an optical down-conversion and digital post-processing combined nonlinear compensation algorithm; the operation complexity of the existing coherent detection technology experiment is reduced and the system stability is increased; meanwhile the accurate estimation on link parameters or the careful construction on a compensation light path when nonlinear compensation signals are established in a digital domain in the existing technical scheme is avoided and the implementation difficulty of the existing nonlinear inhibition algorithm is simplified.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Signal amplification apparatus with advanced linearization
InactiveUS7940126B2Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier combinationsEngineeringLinearity
Owner:CHUNG ANG UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
Signal amplification apparatus with advanced linearization
InactiveUS20110018636A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier combinationsEngineeringLinearity
Provided is a signal amplification apparatus with advanced linearization, the signal amplification apparatus including: a driving unit having a structure of a cascode amplifier including a first active element and a second active element and outputting an amplification signal in which an input signal is amplified, to an output terminal; a third active element receiving a signal diverged between the first active element and the second active element while gate and drain terminals of the third active element are shorted; a fourth active element of which gate and drain terminals are connected to a source terminal of the third active element; and a fifth active element of which gate terminal is connected to the drain terminal of the fourth active element, outputting a non-linear signal having an opposite phase to the amplification signal to the output terminal so as to cancel a third-order inter-modulation distortion component included in the input signal. An amplification signal in which an input signal is amplified is combined with a non-linear signal having an opposite phase to the amplification signal and a low gain and is output so that a third-order inter-modulation distortion component included in the input signal can be cancelled and a signal with advanced linearity can be output.
Owner:CHUNG ANG UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
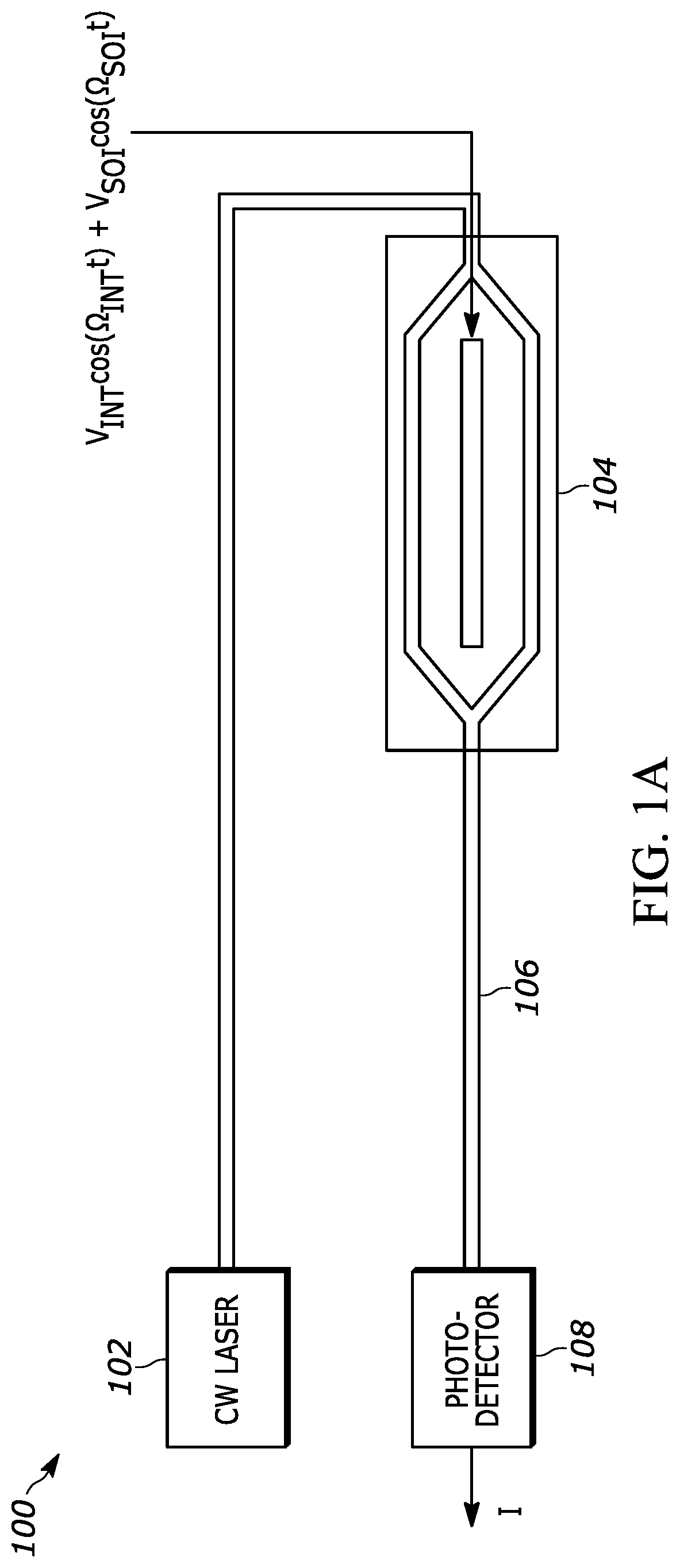
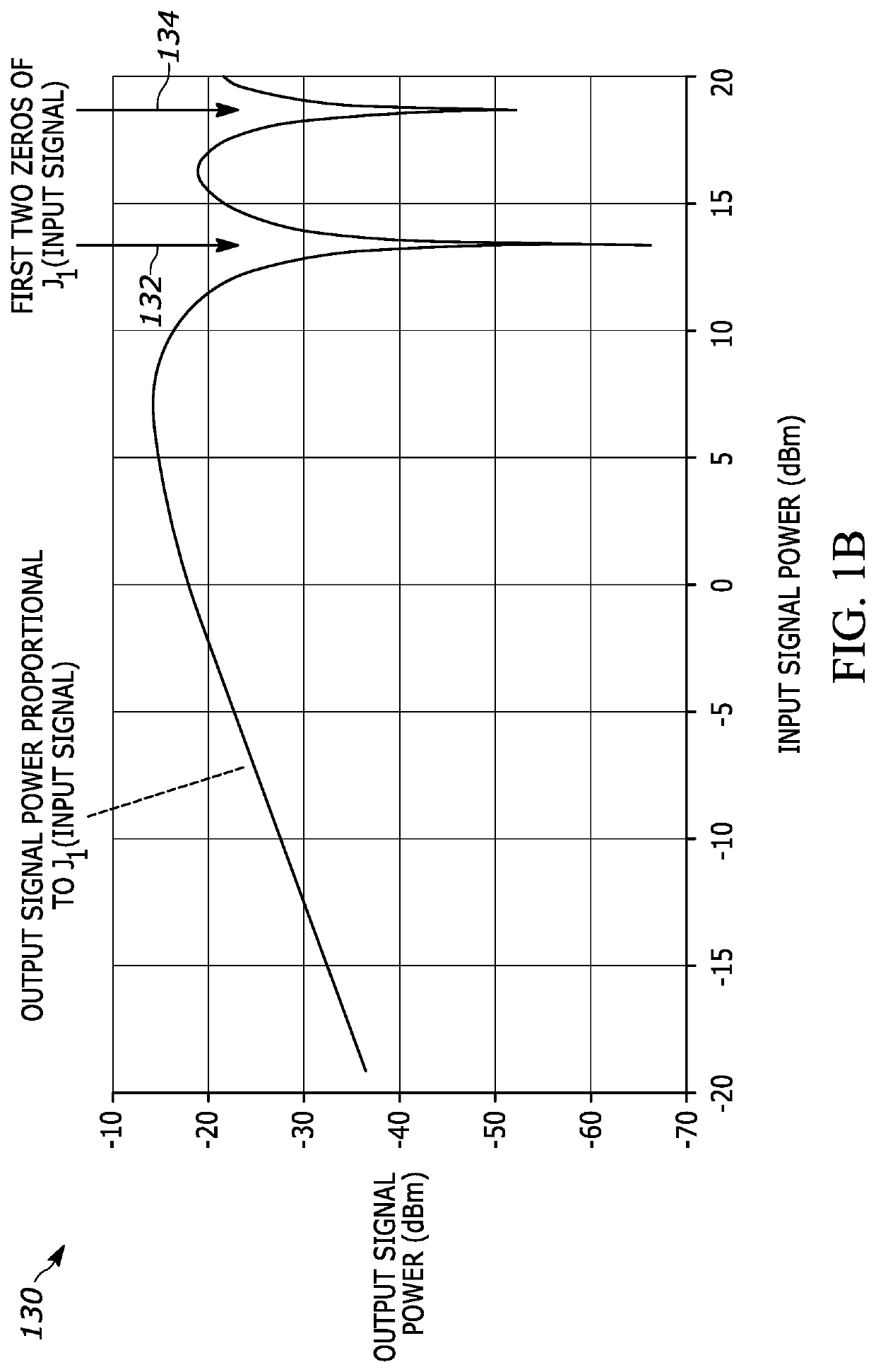
Interference suppression with mitigation of intermodulation distortion
ActiveUS10958344B2Easy to receiveImprove performanceOptical transmission for RF signal generation/processingDistortion/dispersion eliminationSoftware engineeringOptical power
A method of interference suppression with intermodulation distortion mitigation includes processing an RF signal comprising an RF signal of interest and an RF interfering signal to produce a first and second RF drive signal each with a desired RF interference signal power and having a 90 degree relative phase. The first RF drive signal is imposed onto a first optical signal with a modulator to generate a first modulated optical signal so that the modulator has a large-signal behavior that is characterized by a Bessel function of the first kind J1(ϕ), wherein the desired power at a frequency of the interference signal of the first drive signal is chosen to correspond to a zero of the Bessel function of the first kind J1(ϕ). The second RF drive signal is imposed onto a second optical signal with a modulator to generate a second modulated optical signal so that the modulator has a large-signal behavior that is characterized by a Bessel function of the first kind J1(ϕ), wherein the desired power at a frequency of the interference signal of the second drive signal is chosen to correspond to another zero of the Bessel function of the first kind J1(ϕ). The first and second modulated optical signal are combined with an optical power ratio that is selected to suppress third-order intermodulation distortion products in an electrical signal generated by detecting the optically combined first and second modulated optical signals.
Owner:PHOTONICSYST
Automatic testing method for mixer third order inter-modulation distortion of radio-frequency tuner chip
InactiveCN101251573BIncreased test frequencyGuaranteed test accuracyElectronic circuit testingFrequency analysisSpectrum analyzerEngineering
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Low non-linear power amplifier
InactiveCN101388649BImprove performanceImprove efficiencyAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionPower amplifiersNonlinear distortionAudio power amplifier
The invention relates to a power amplifier, in particular to a low nonlinear distortion power amplifier. The low nonlinear distortion power amplifier comprises a main power amplifier, a distortion signal generator, a distortion signal amplifier, a first coupling, a second coupling, an attenuator and a phase shifter, wherein the main power amplifier amplifies a radio frequency input signal A, and attenuates and reverses a bypass radio frequency input signal which is coupled simultaneously, a signal which is reversed with a third-order intermodulation distortion signal which is generated by themain power amplifier is generated by the distortion signal generator, the distortion signal which is amplified is coupled with an output signal of the main power amplifier, which enables the third-order intermodulation distortion signal which is generated by the main power amplifier to be counteracted with the distortion signal which is generated by the distortion signal amplifier, and has equiamplitude and is reversed with the third-order intermodulation distortion signal which is generated by the main power amplifier, and finally an ideal radio frequency power amplifying signal is obtained.The invention has the advantages of excellent performance, high efficiency, simple structure and low cost, and can be used in various systems which need to use linearized power amplifiers.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com