Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1912results about "Turbine/propulsion lubrication" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
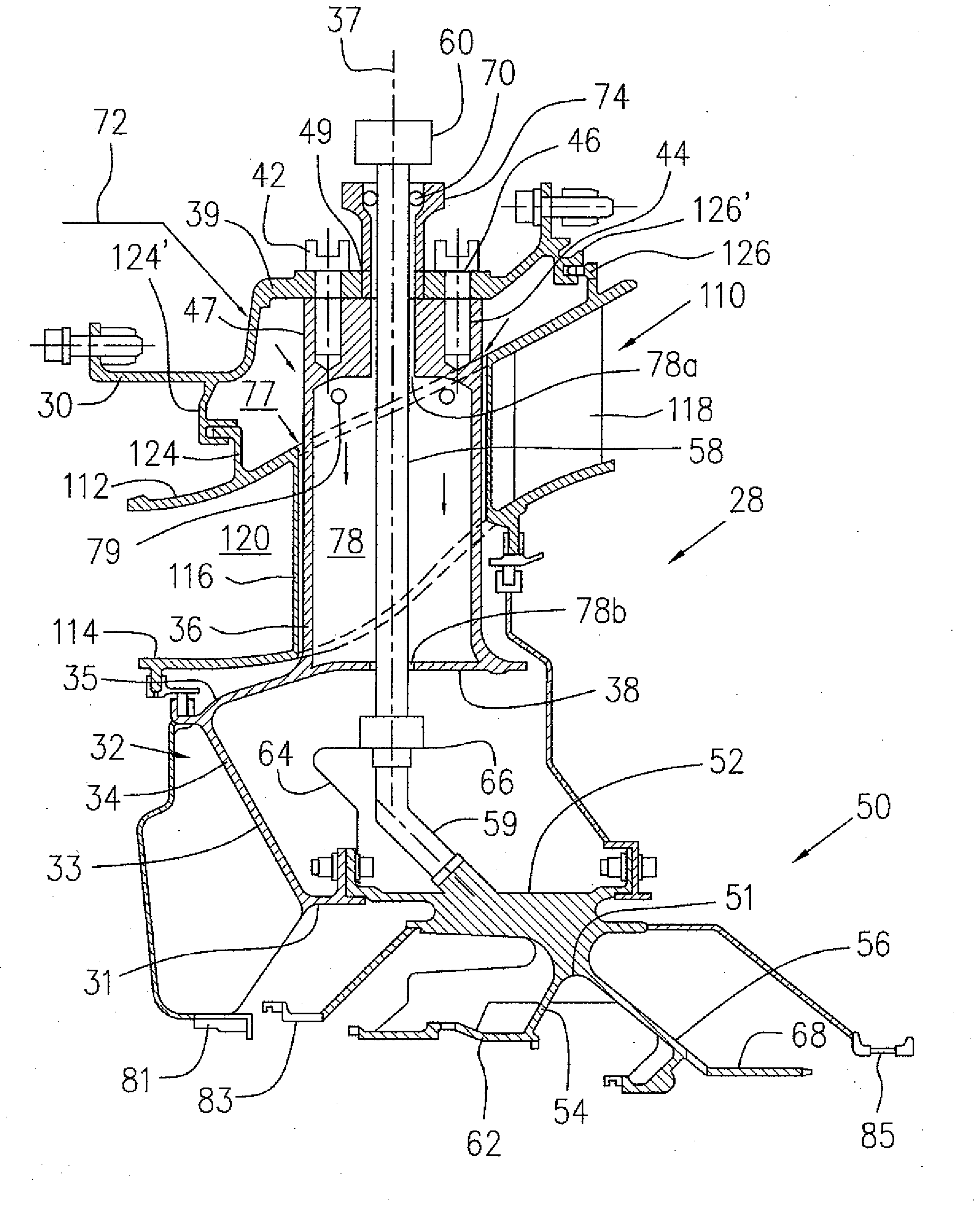
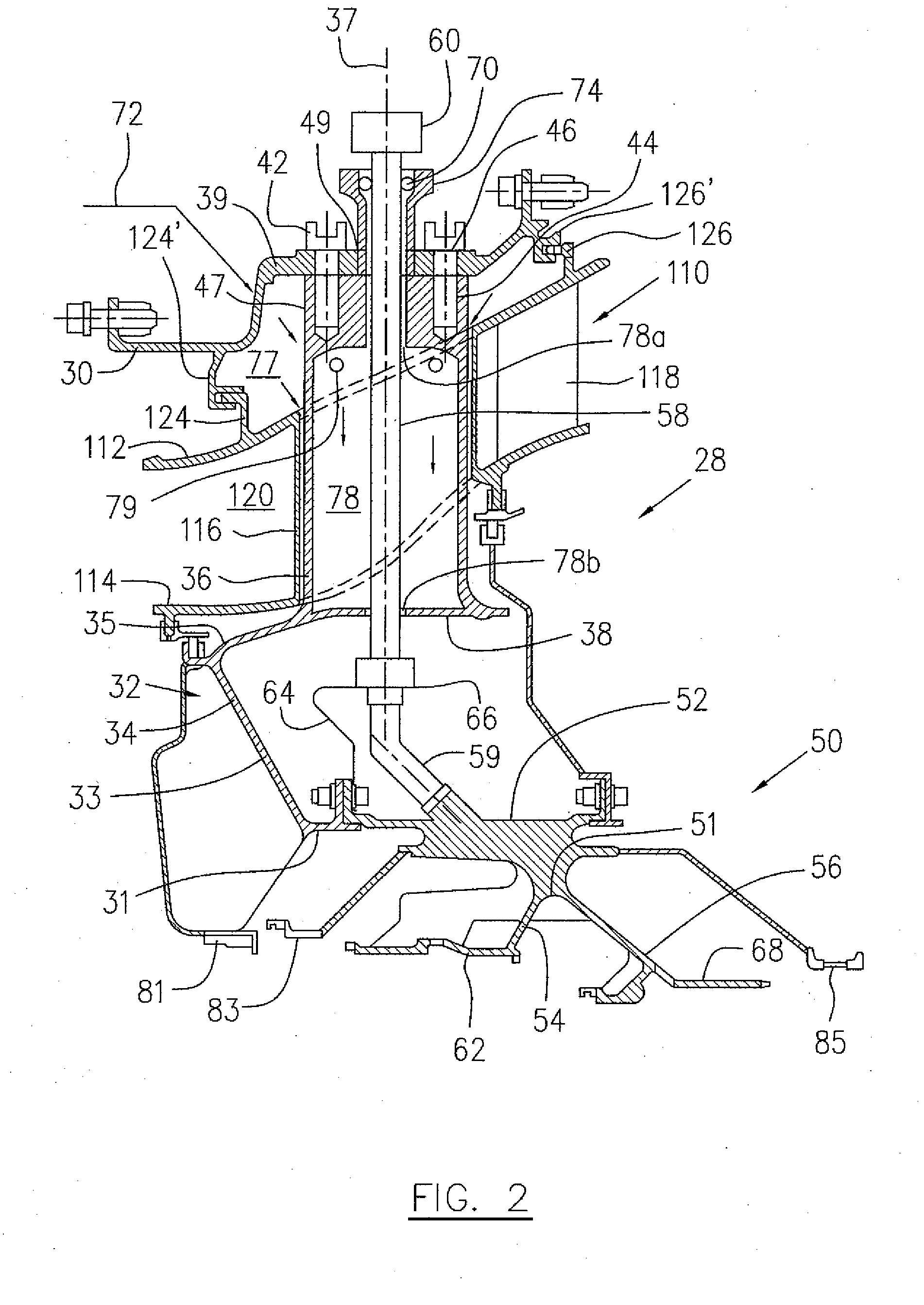
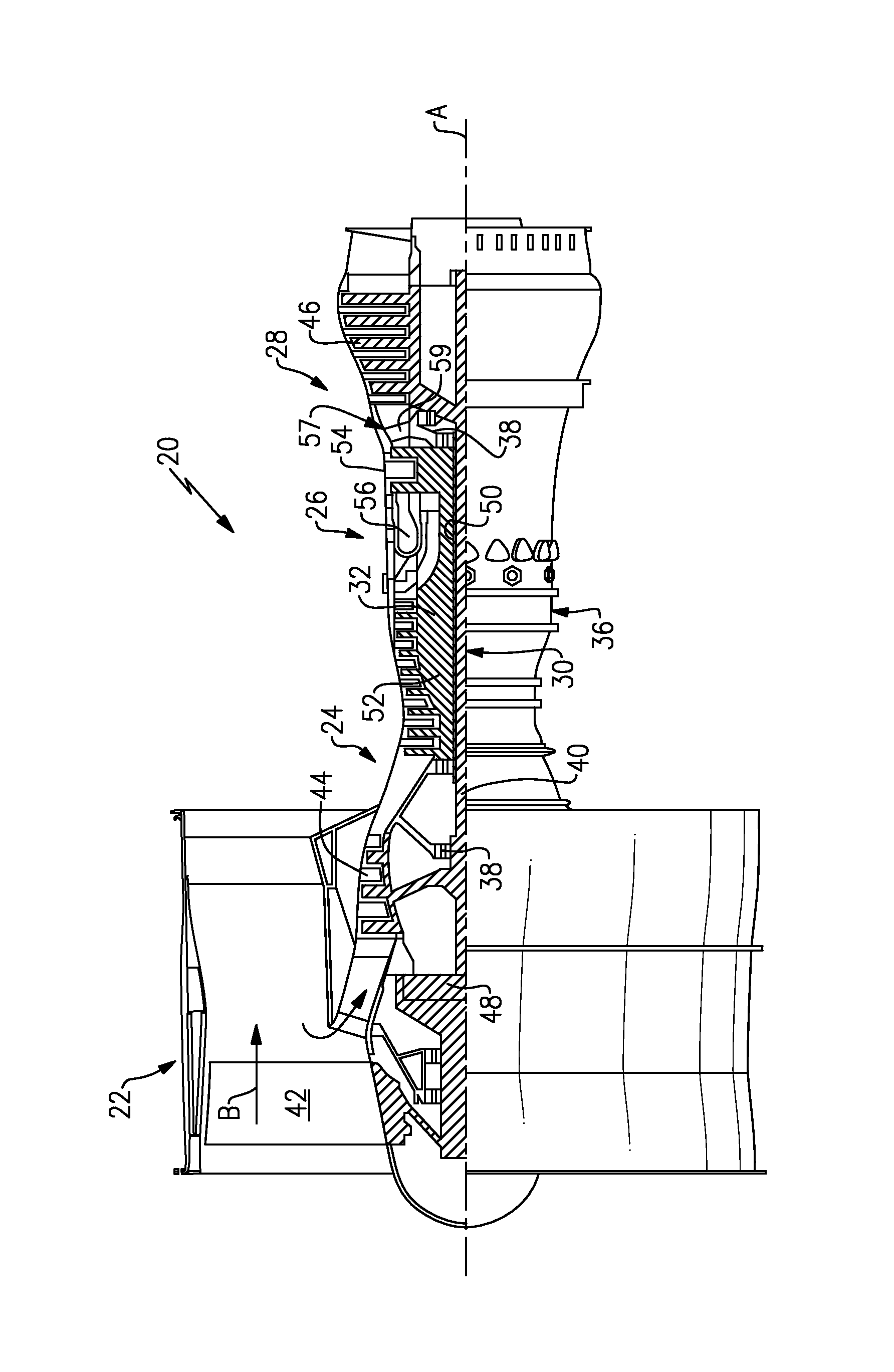
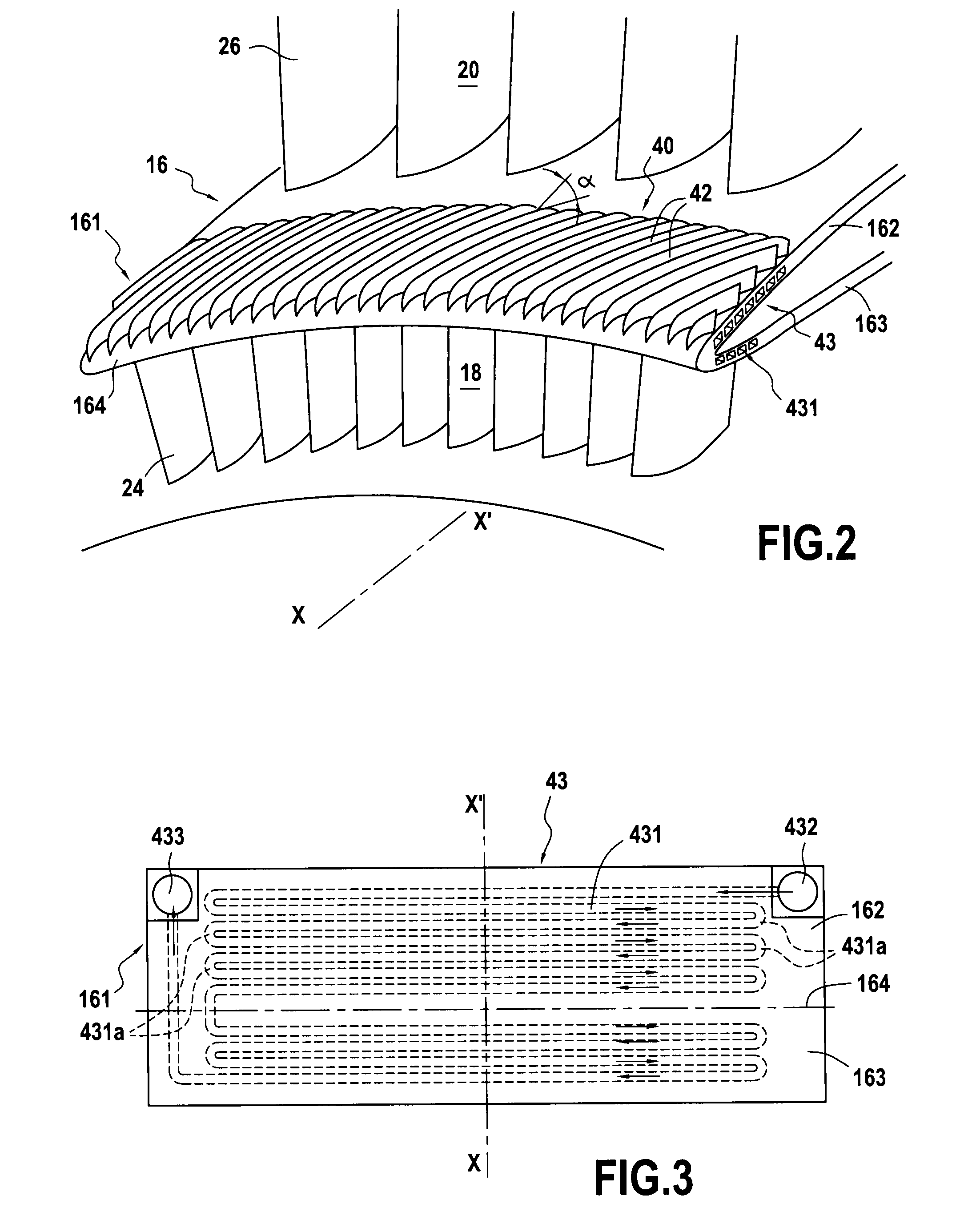
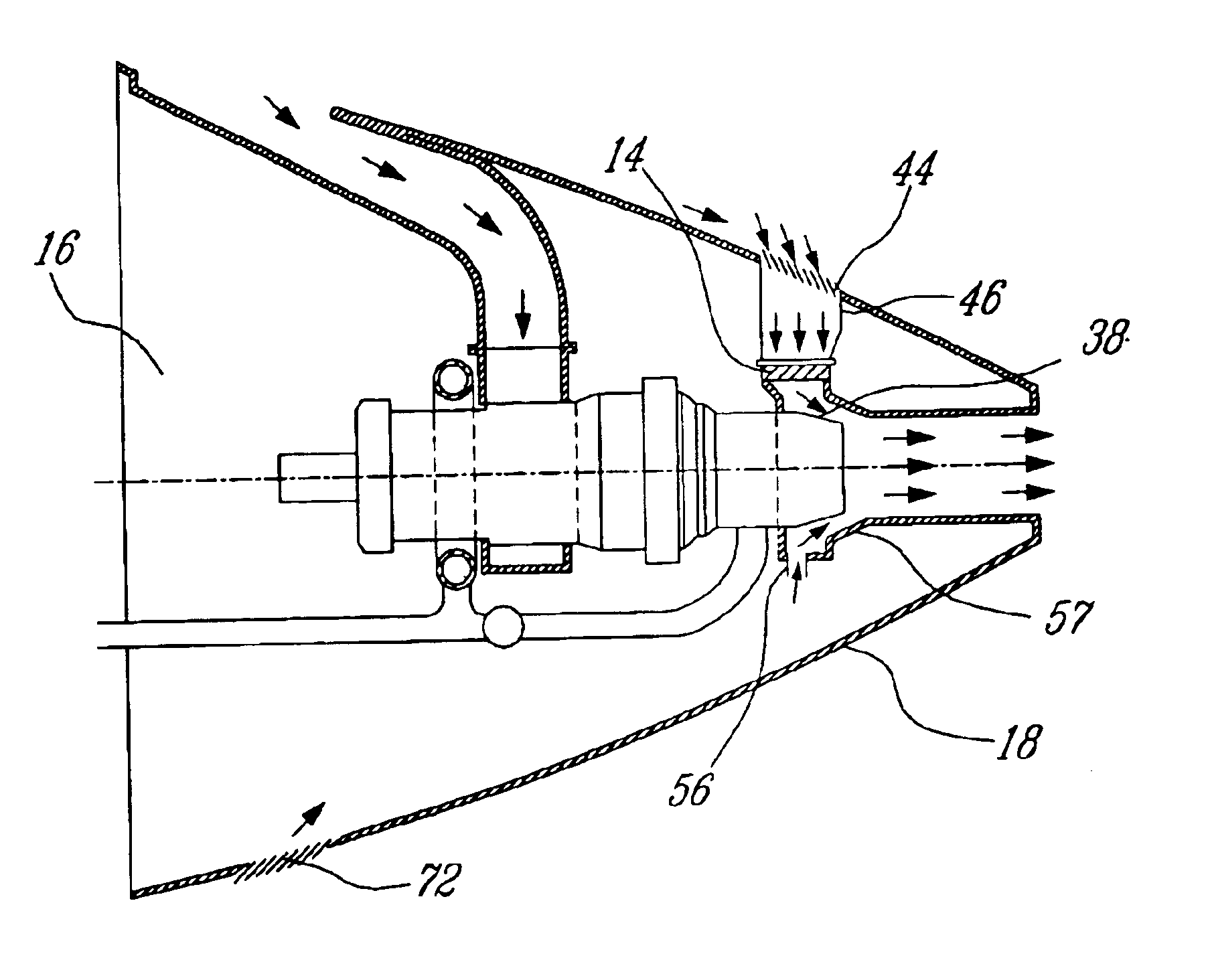
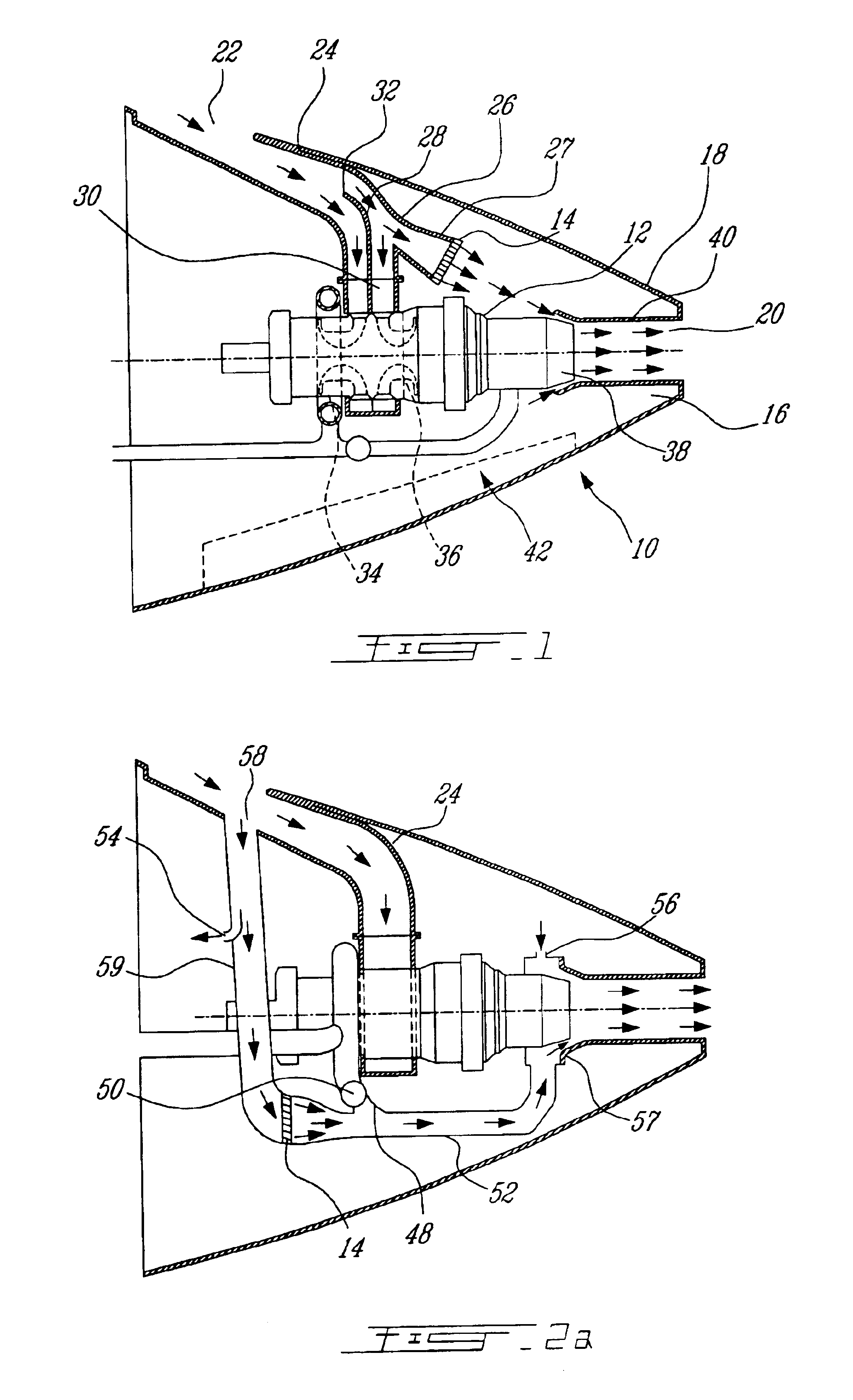
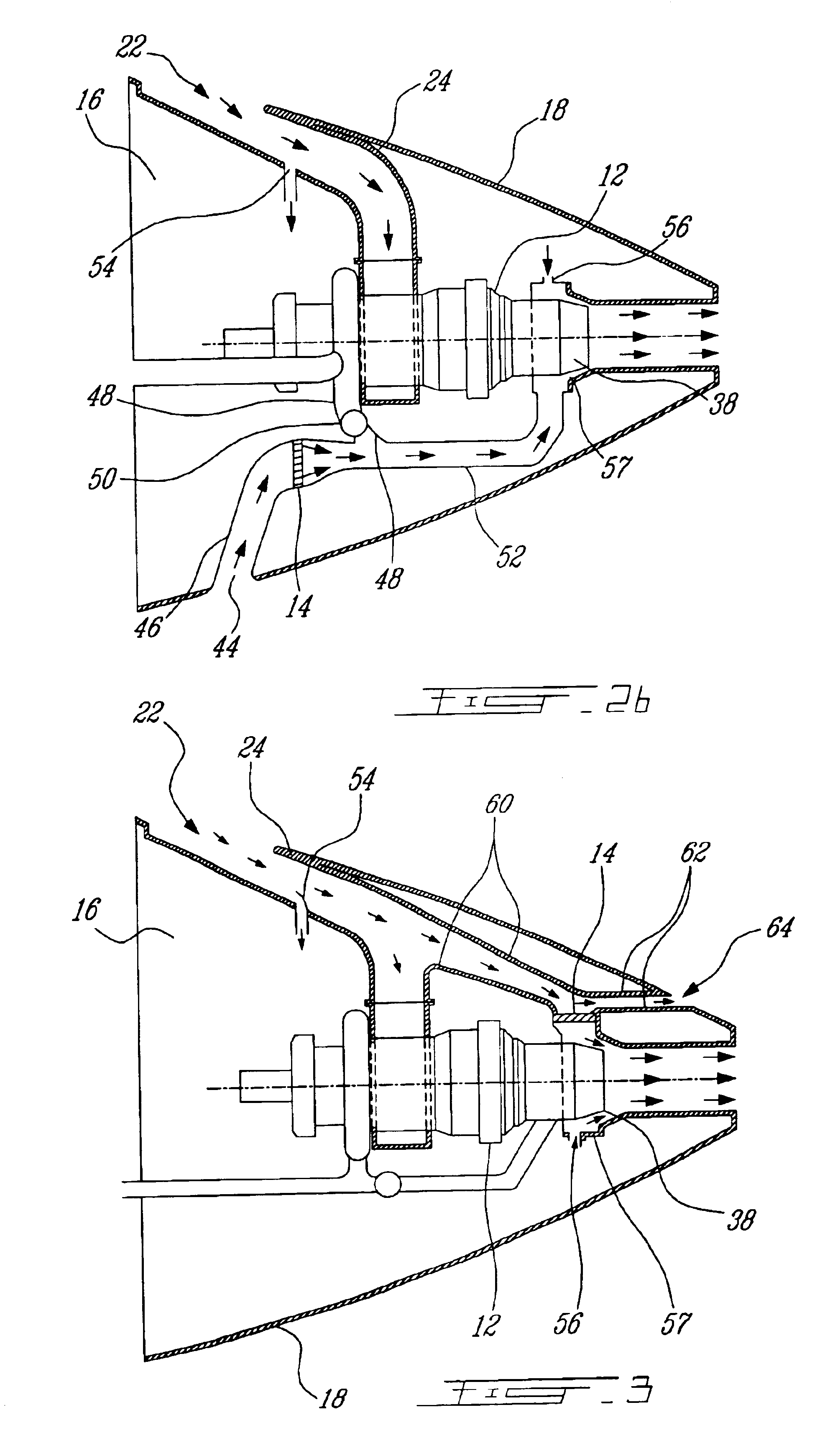
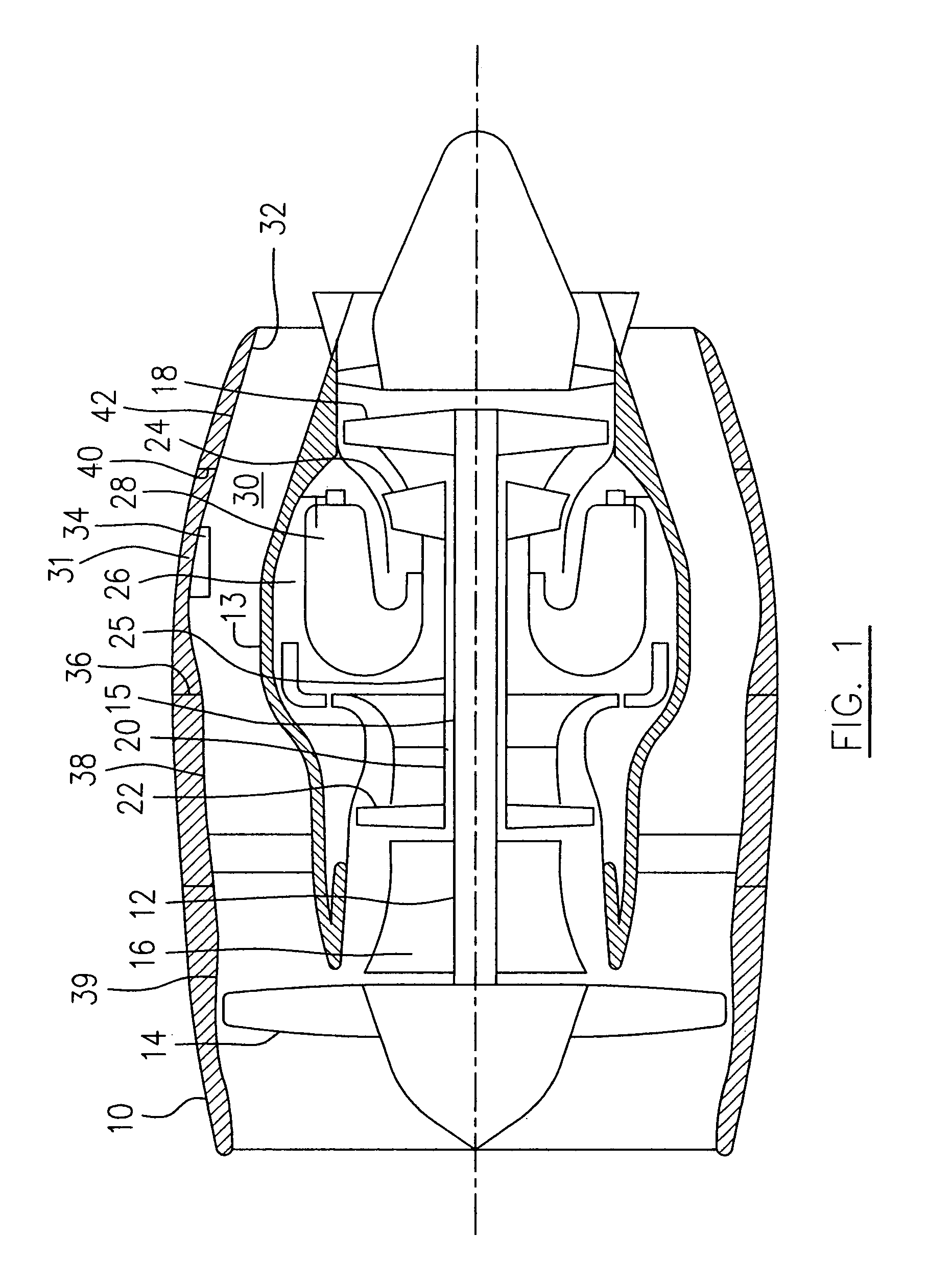
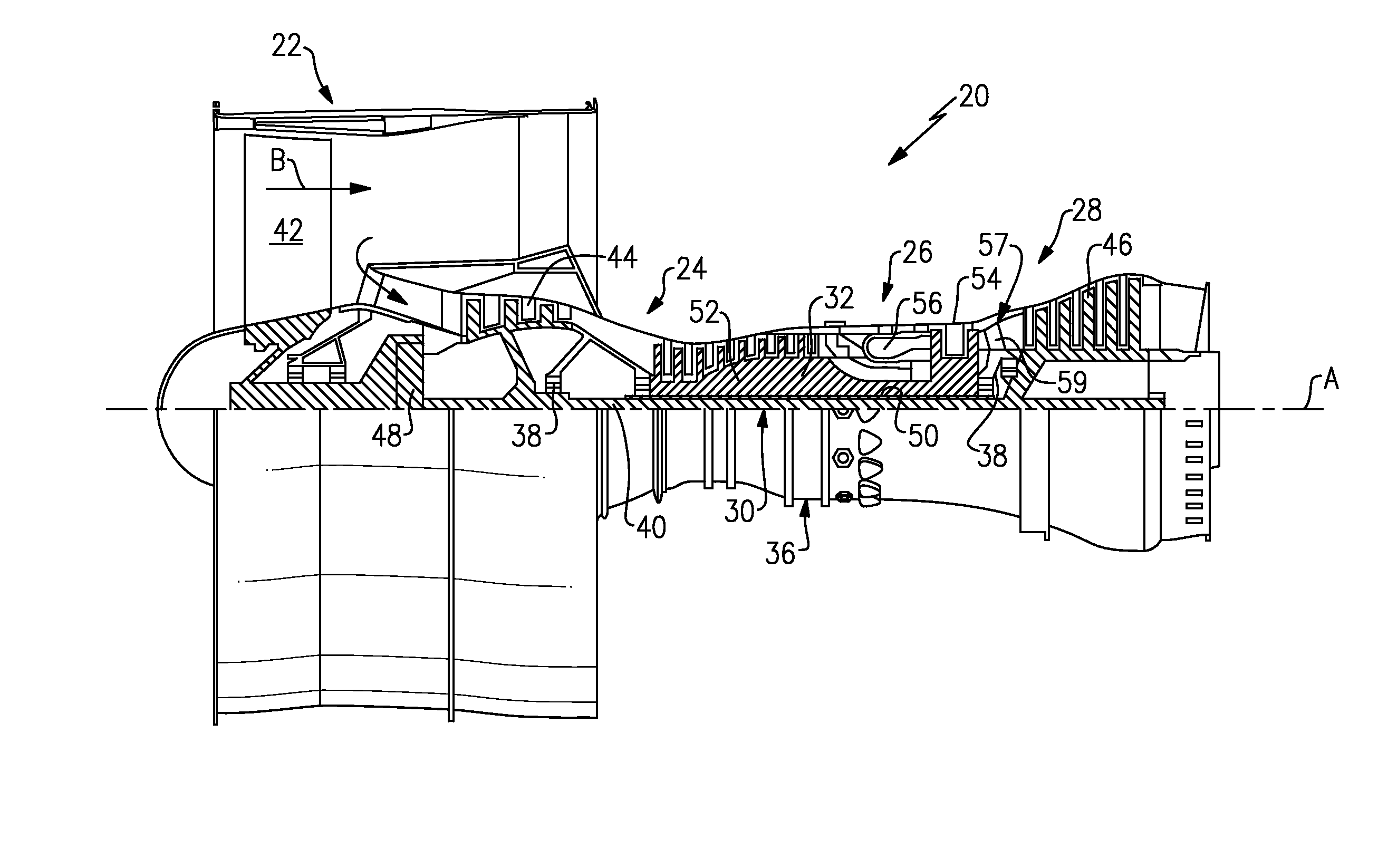
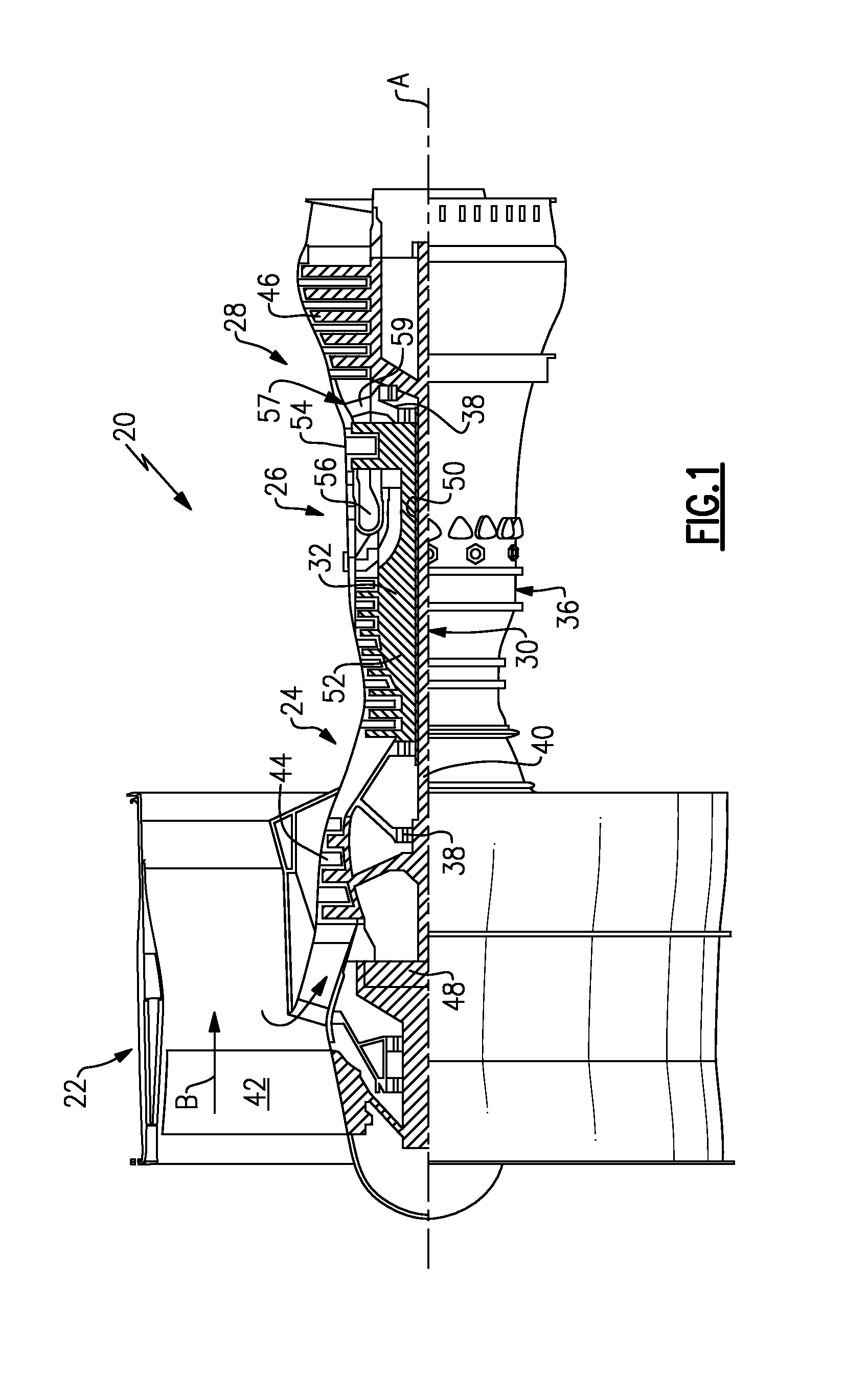
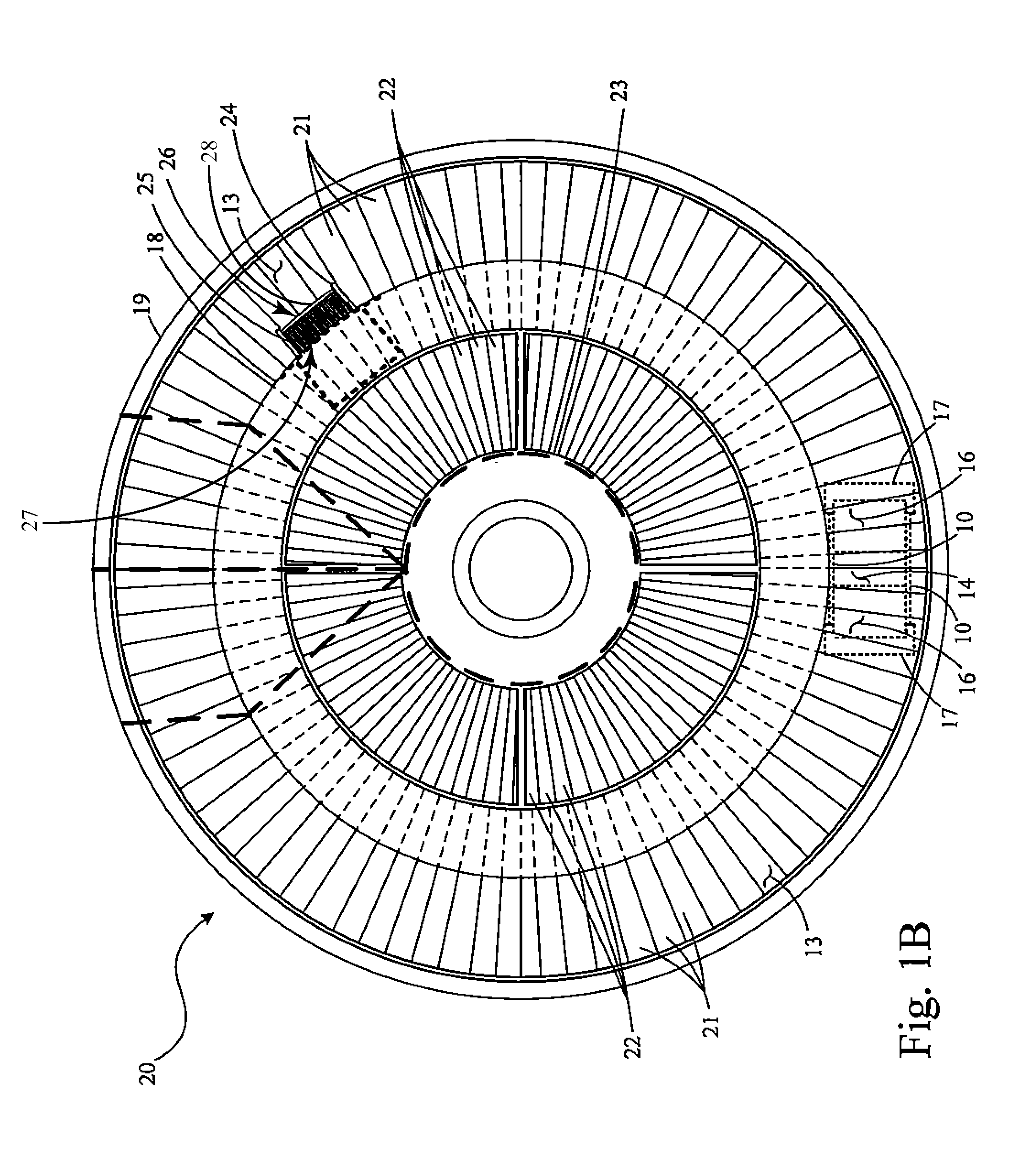
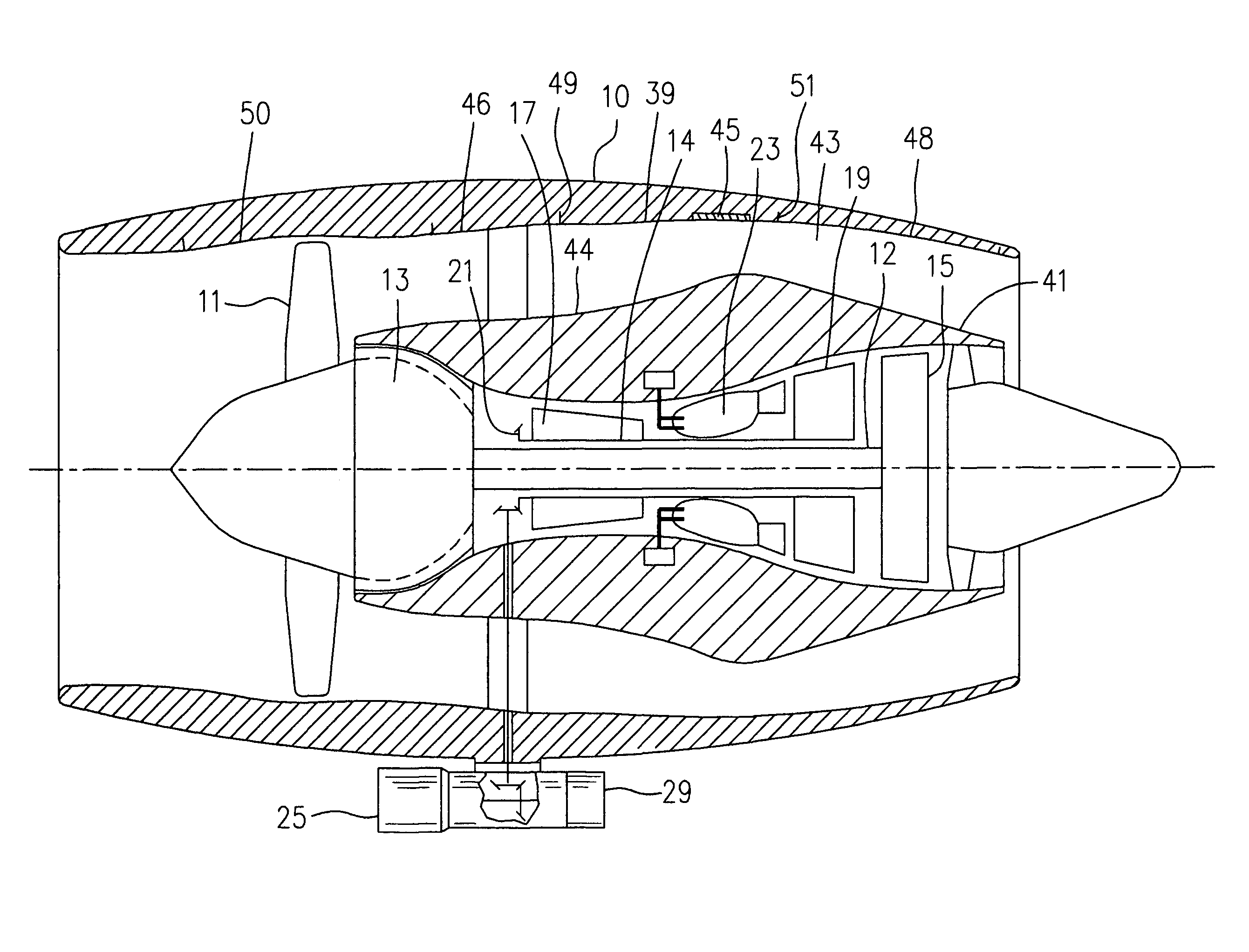
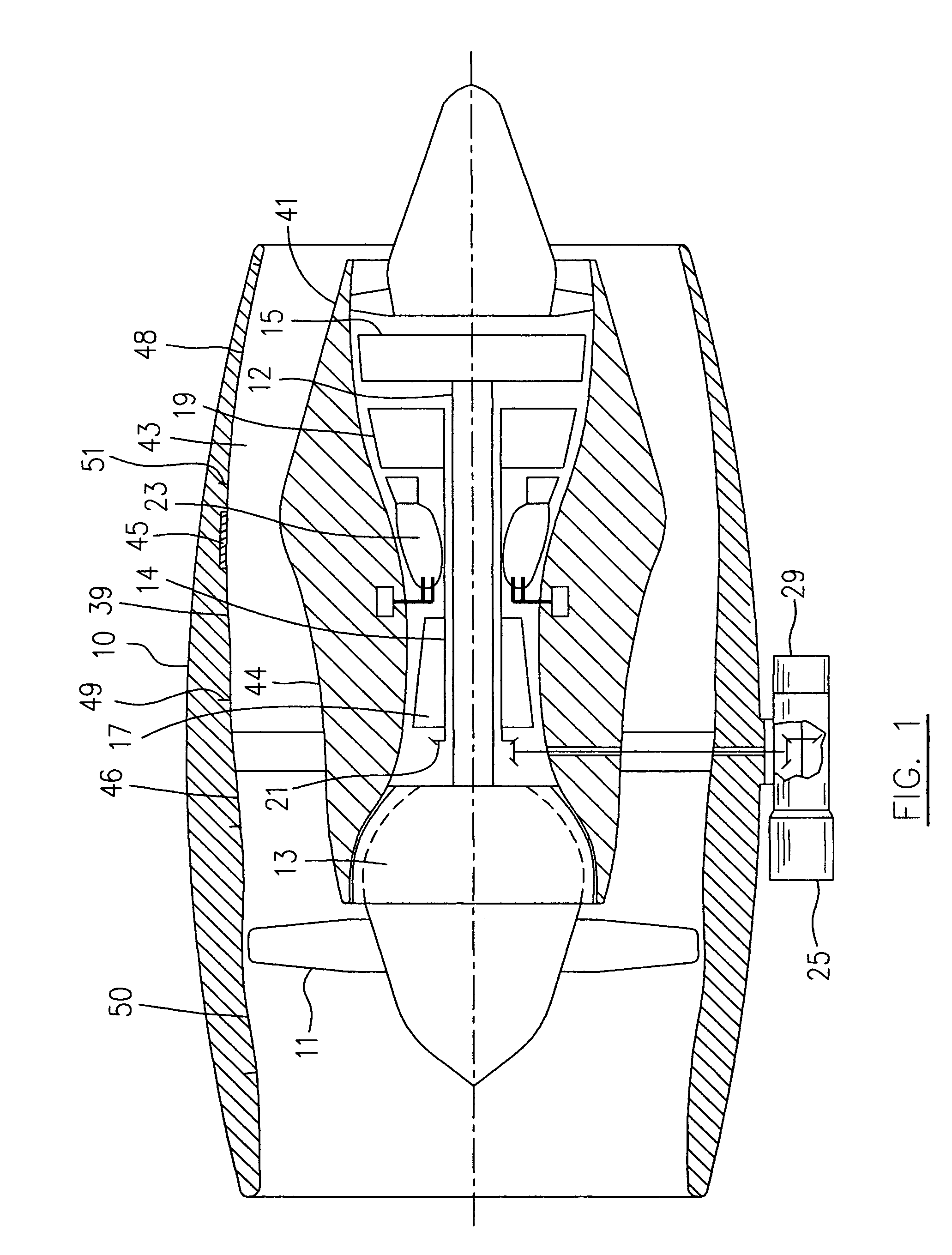
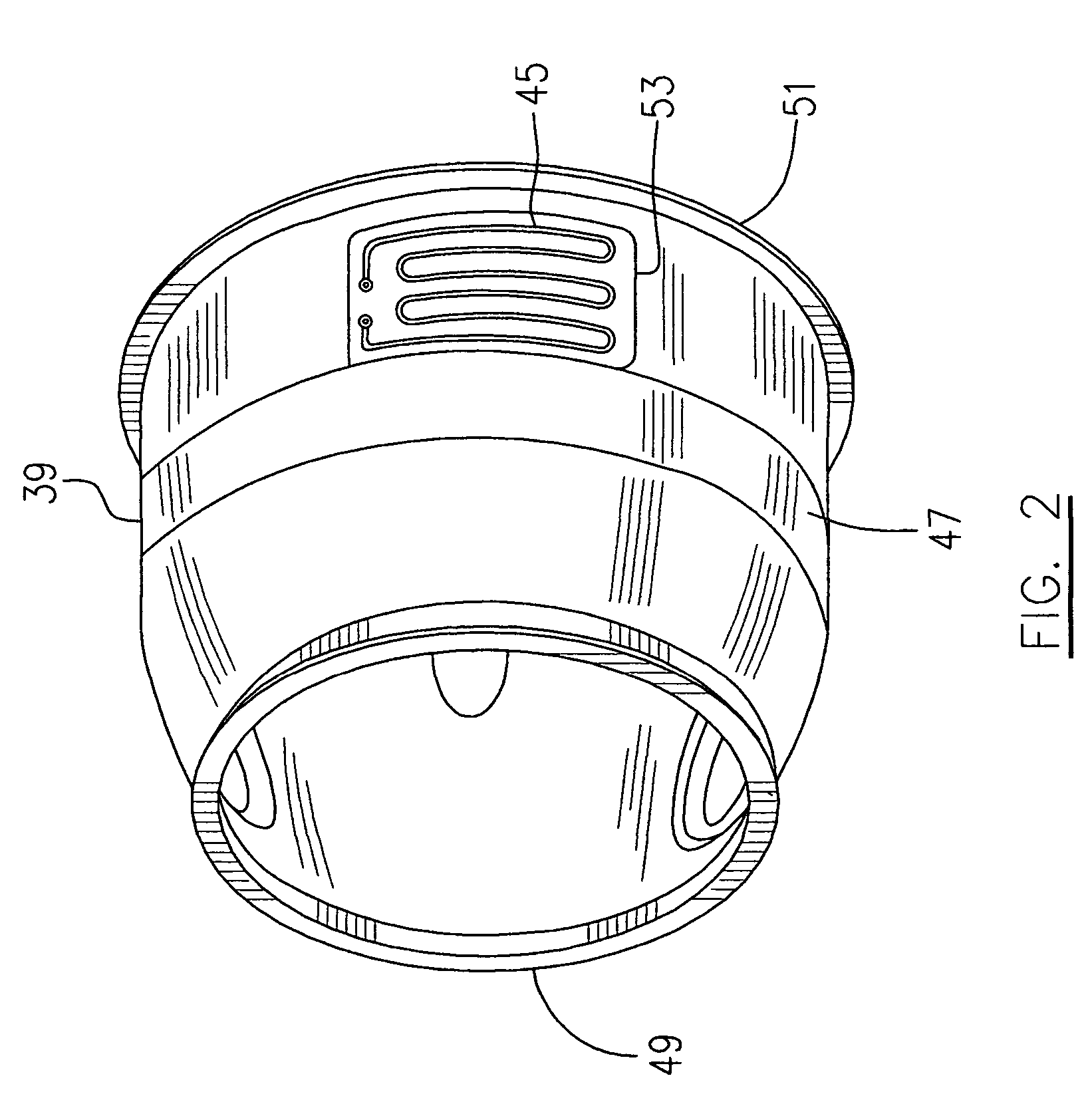
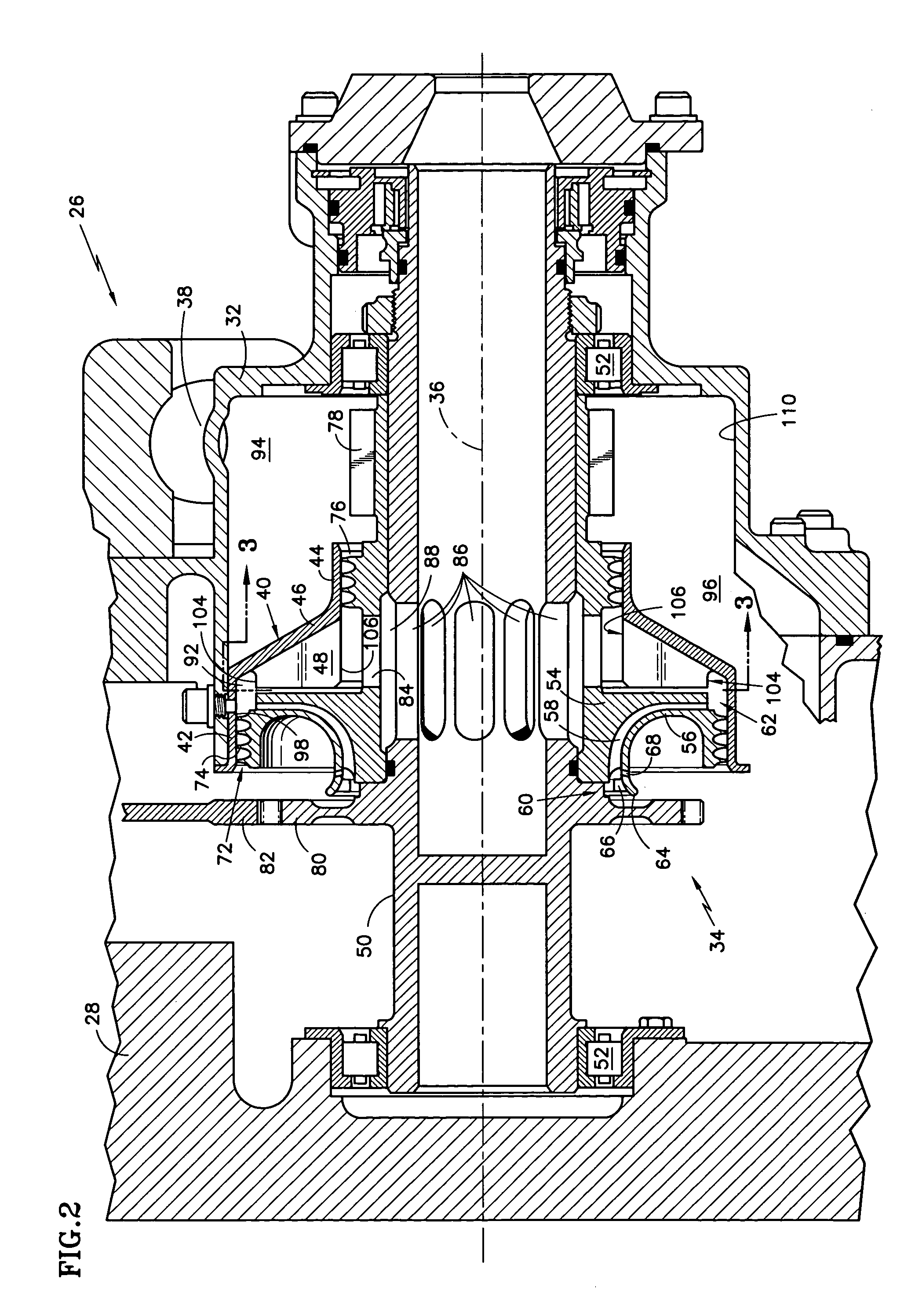
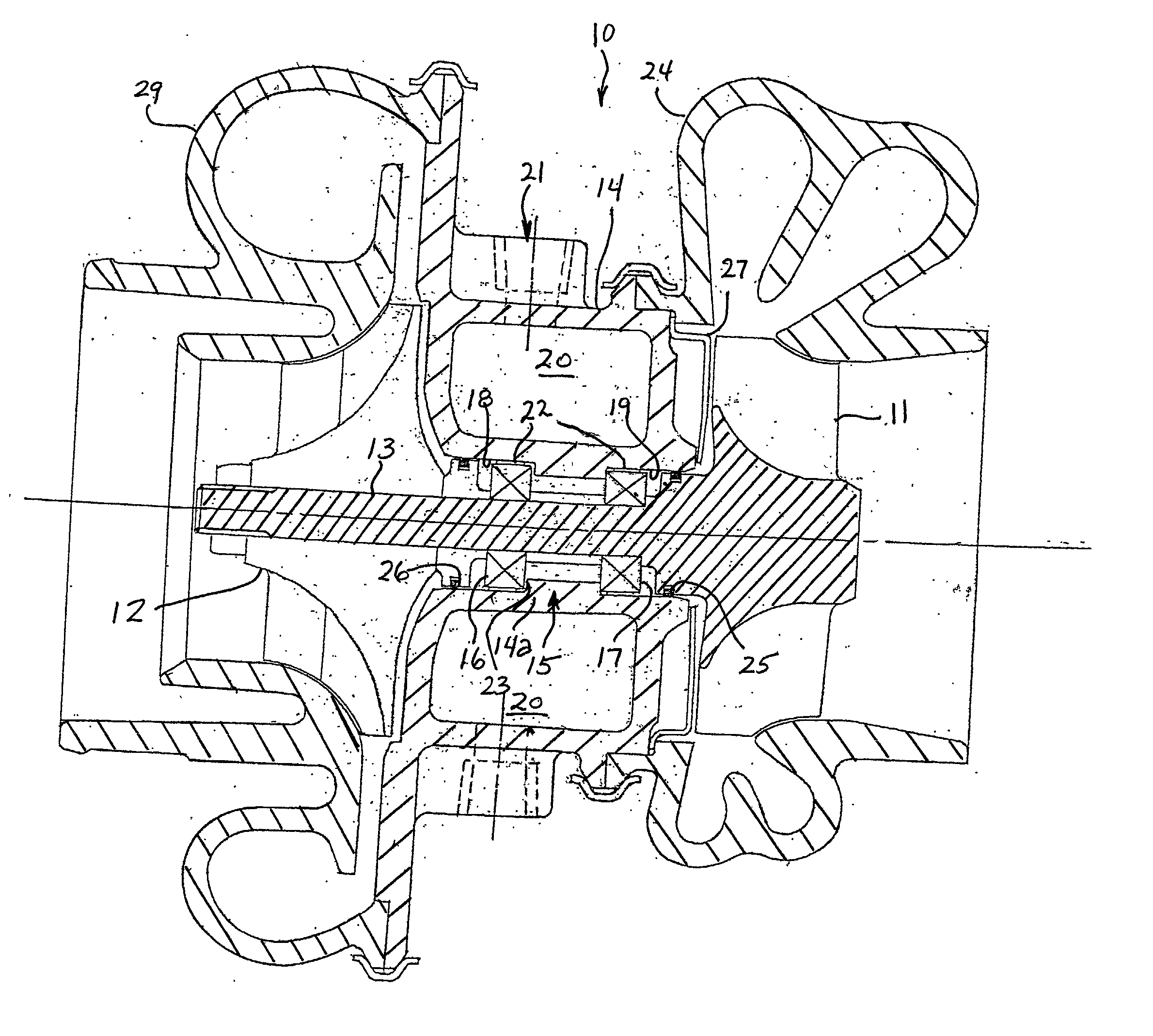
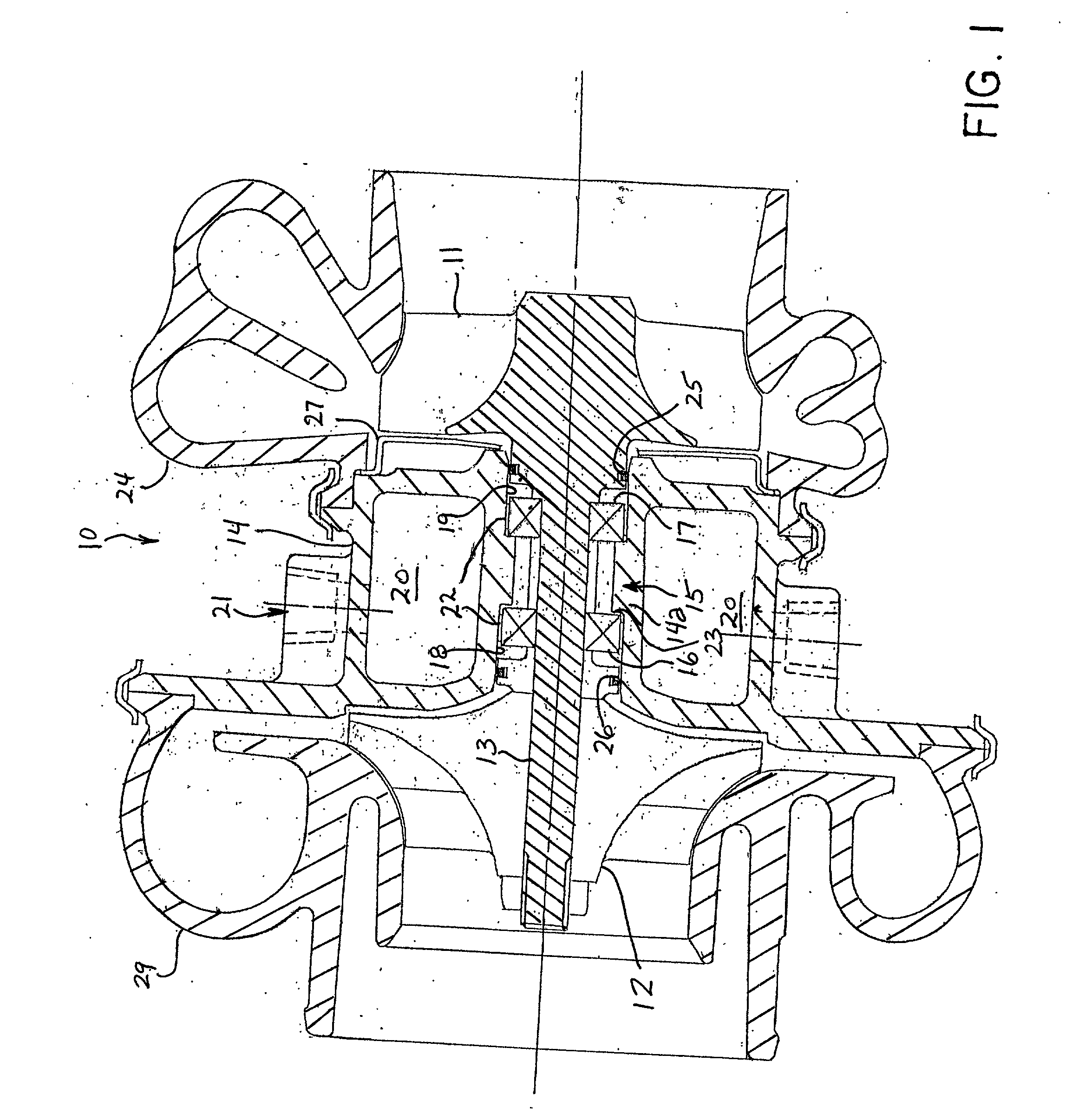
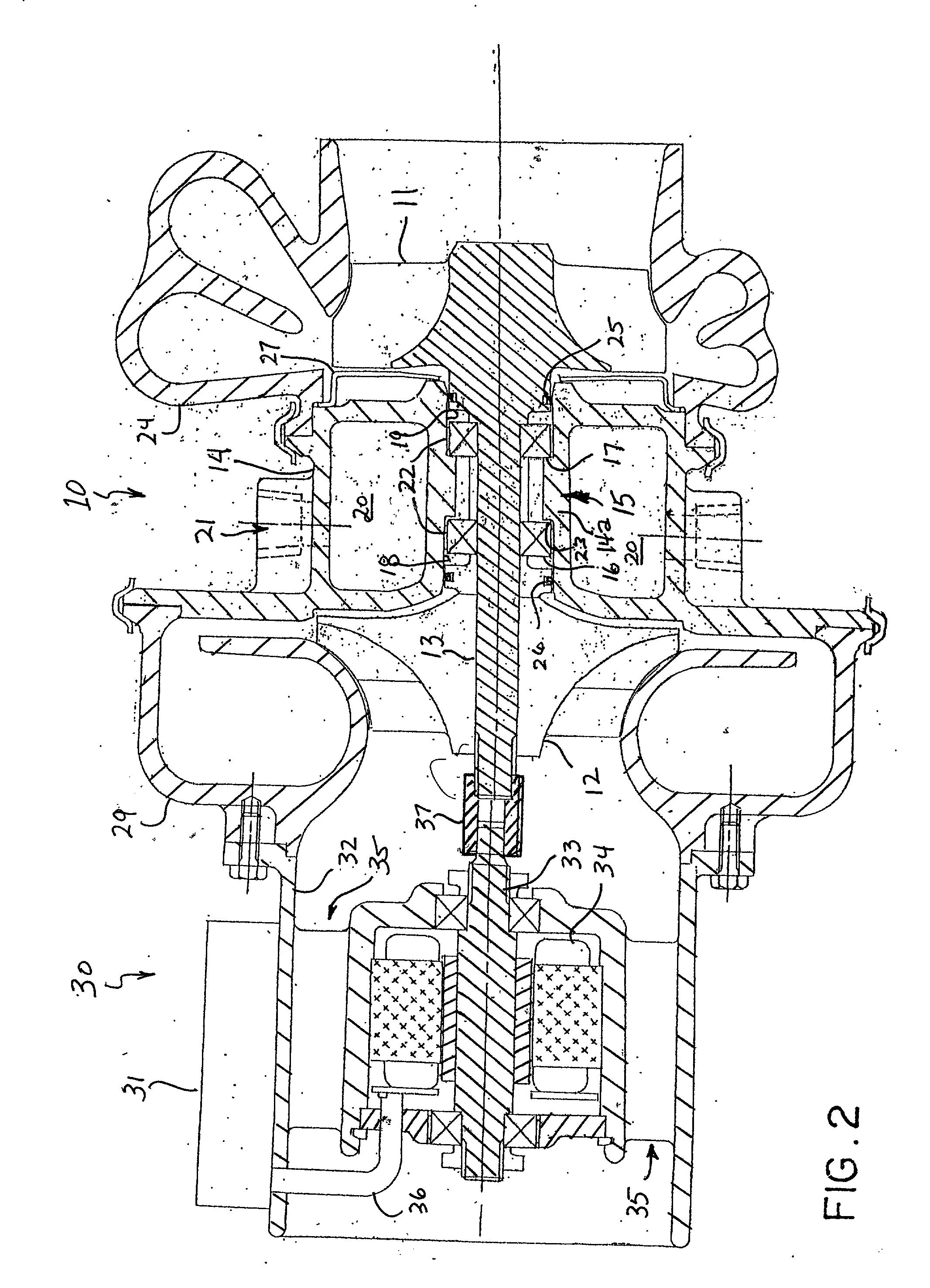
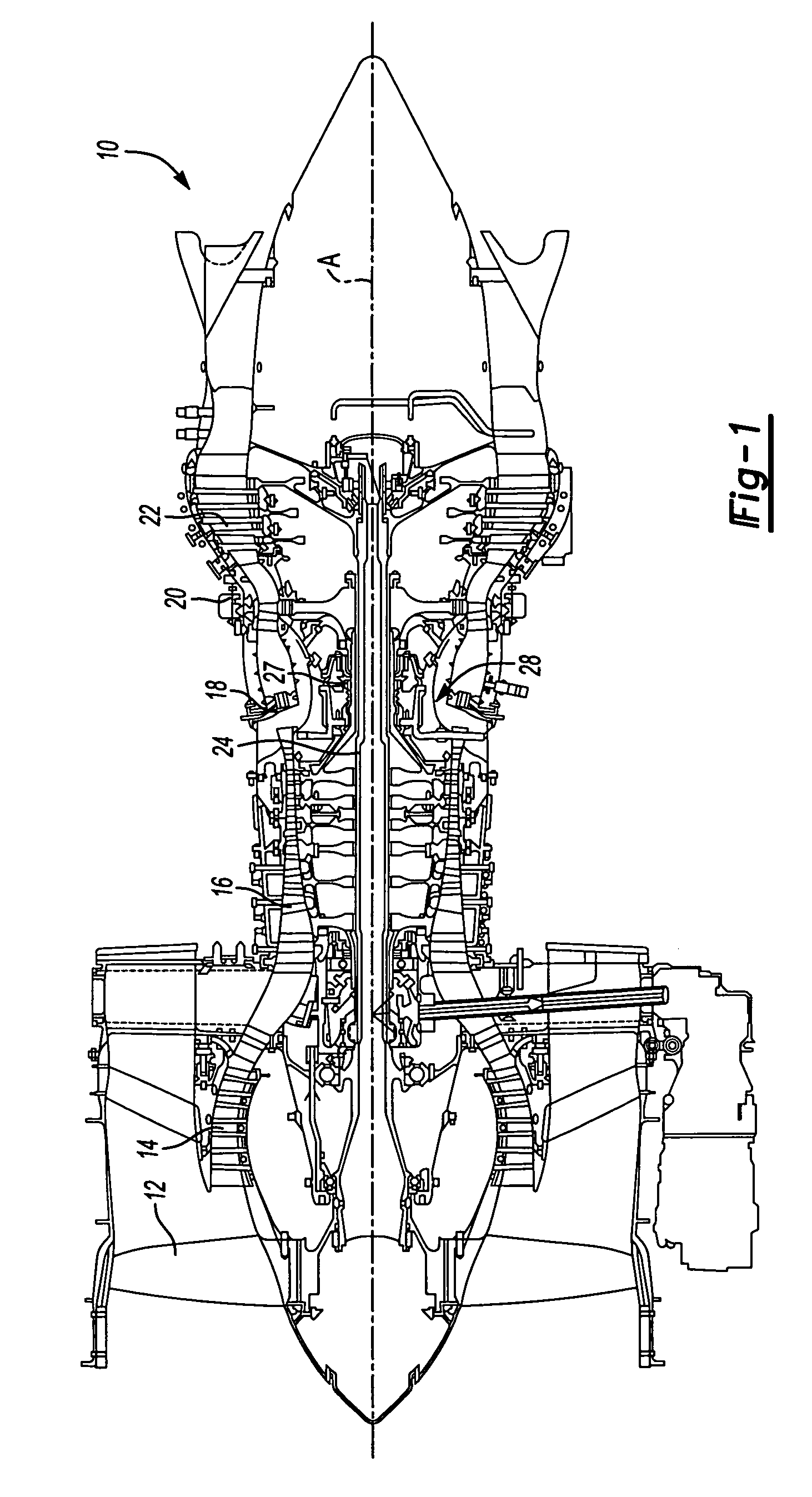
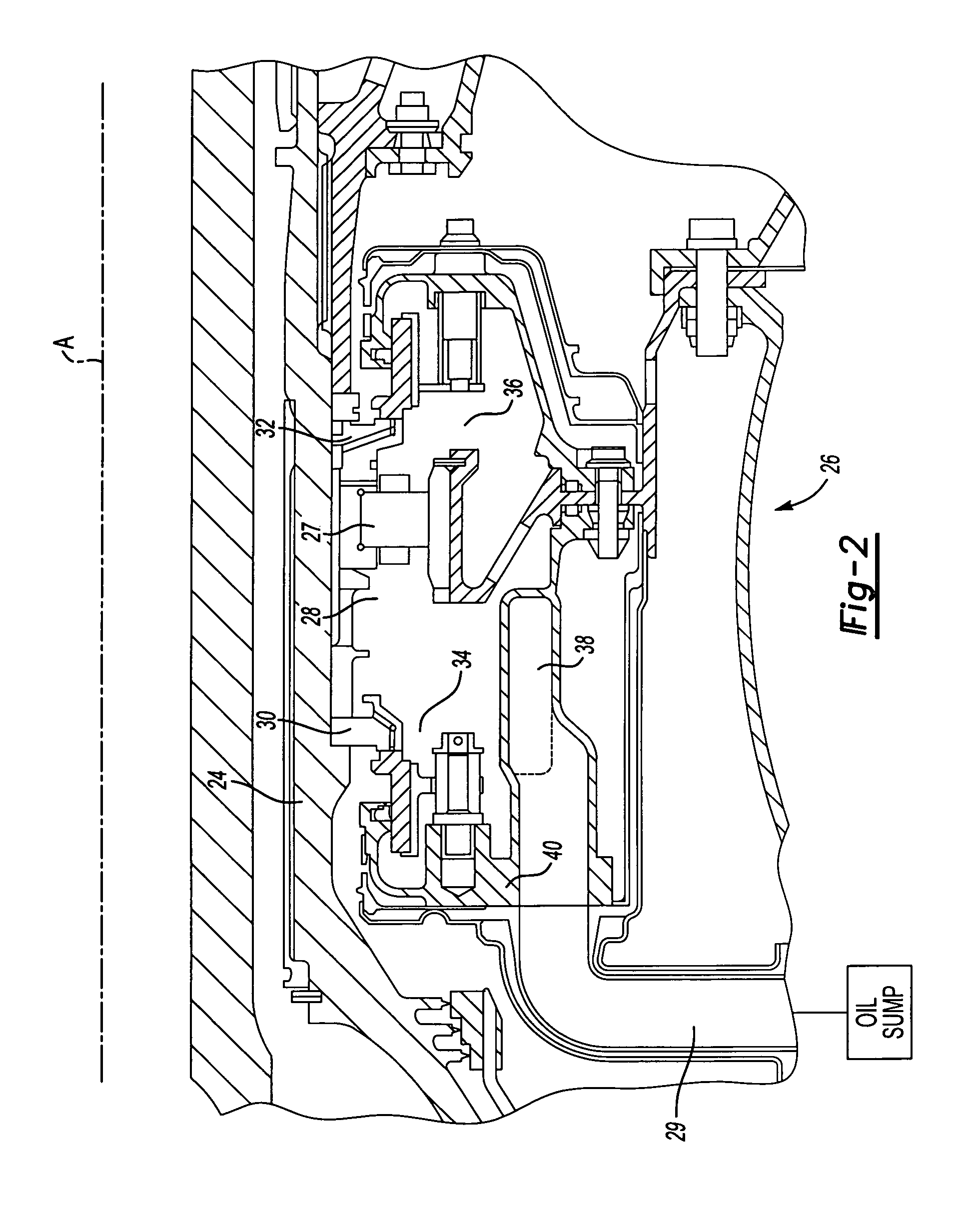
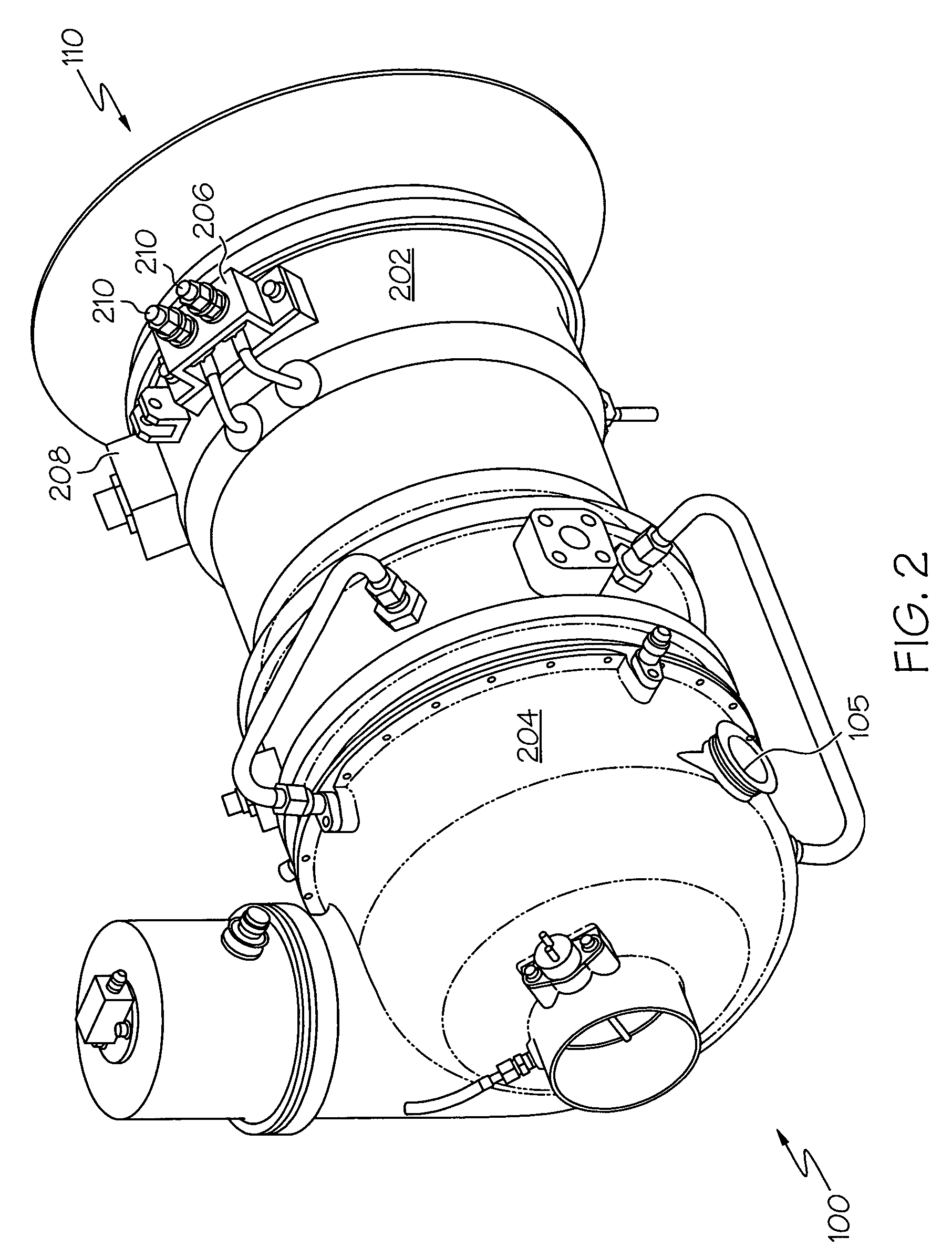
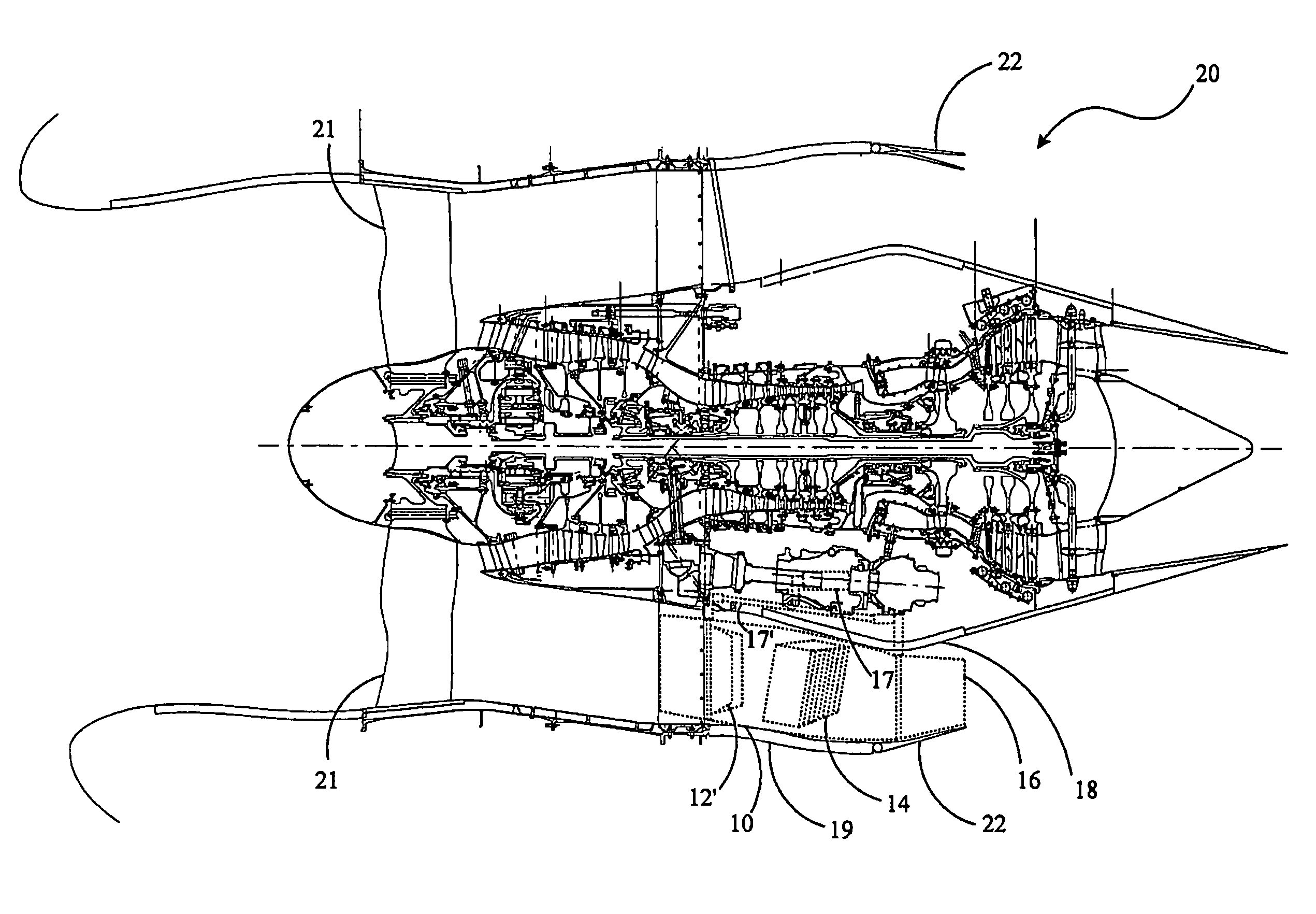
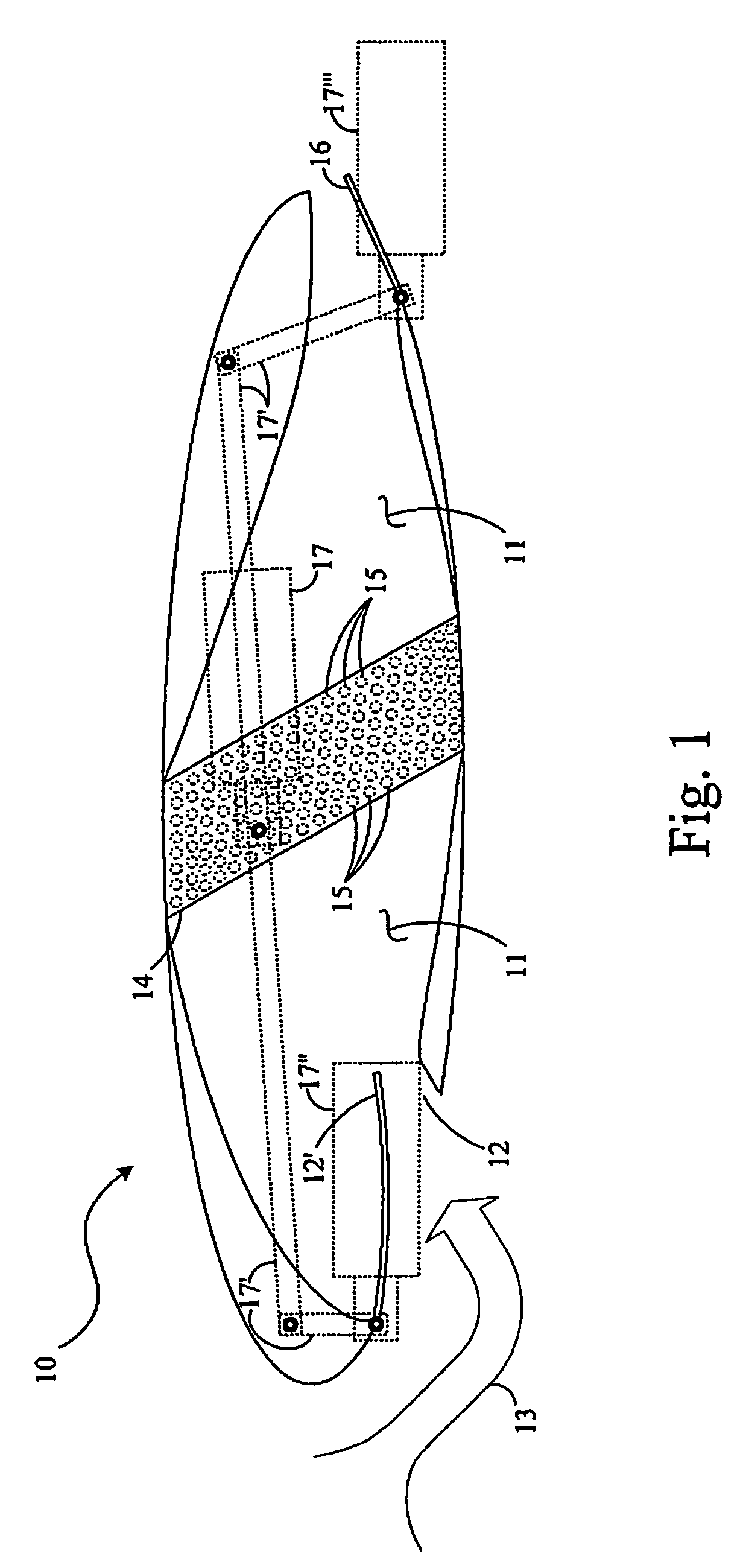
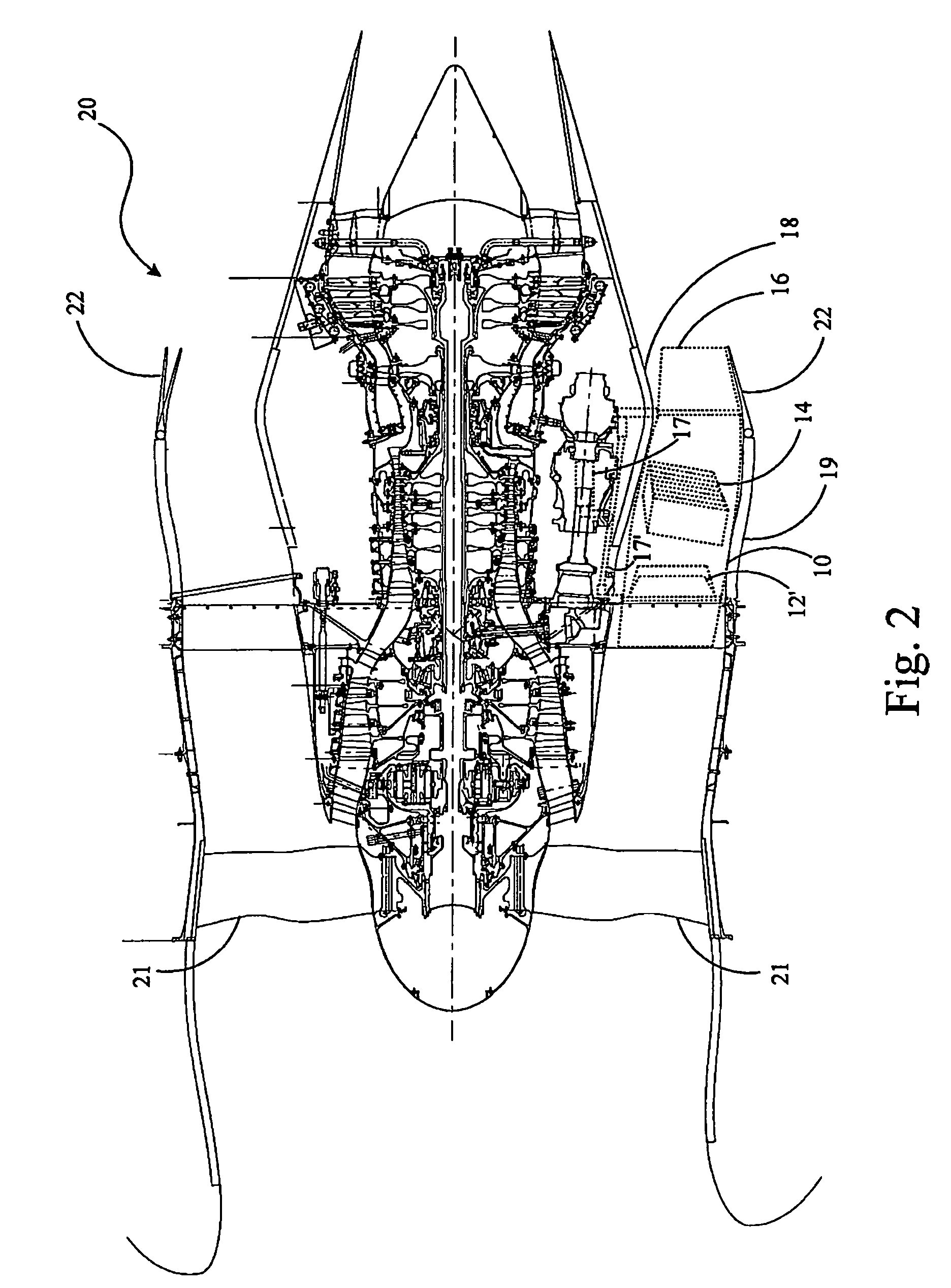
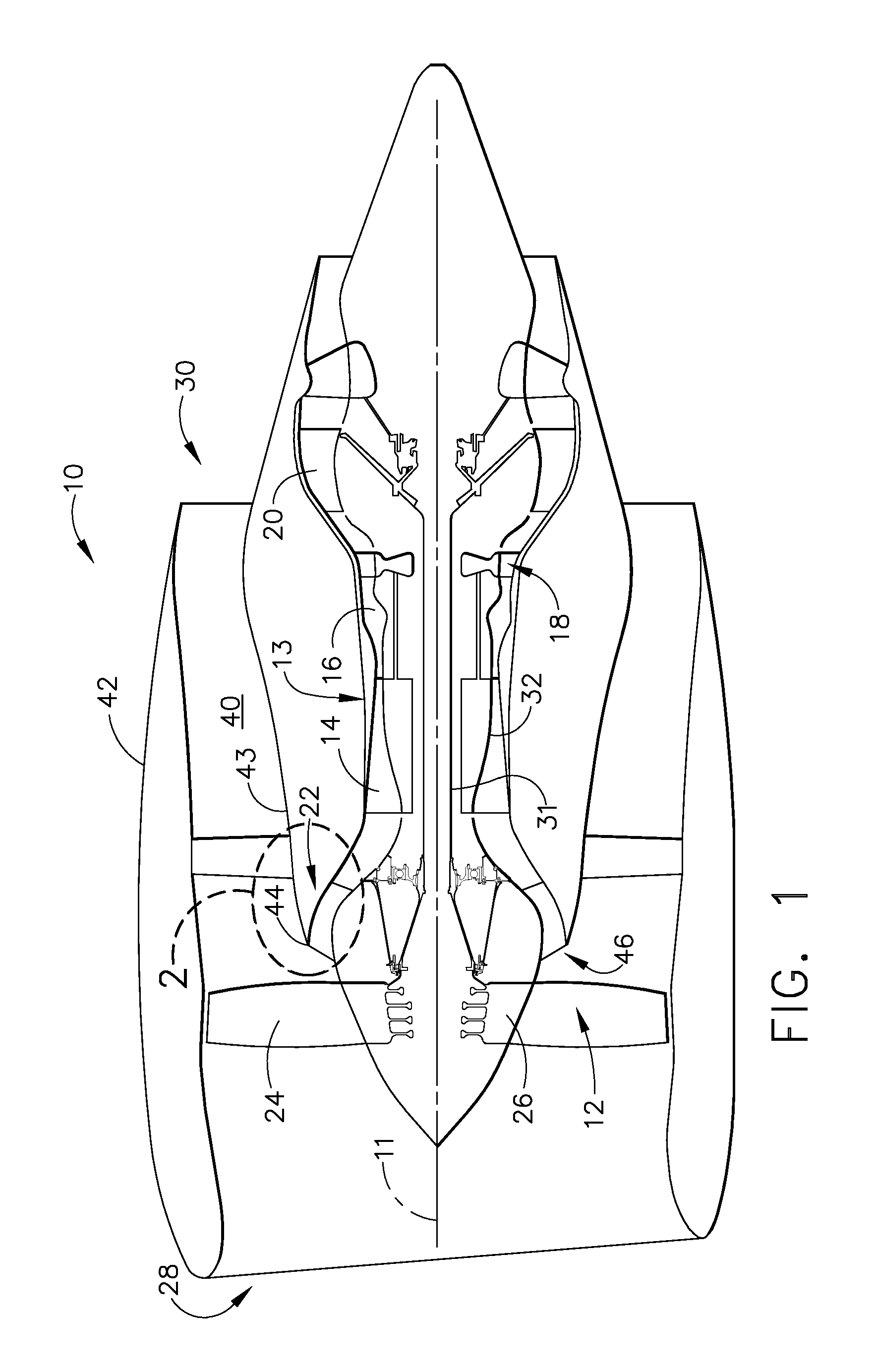
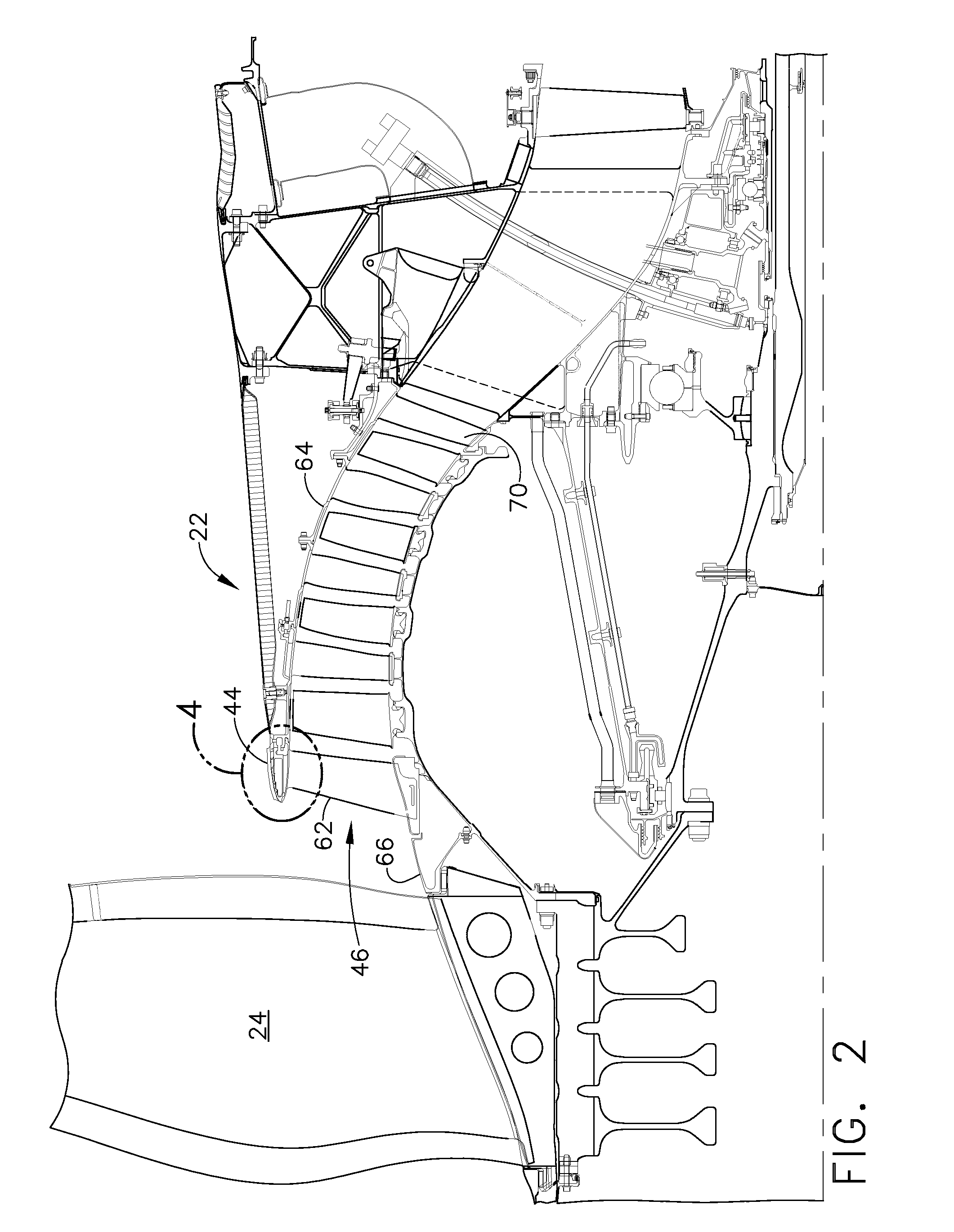
Oil line insulation system for mid turbine frame
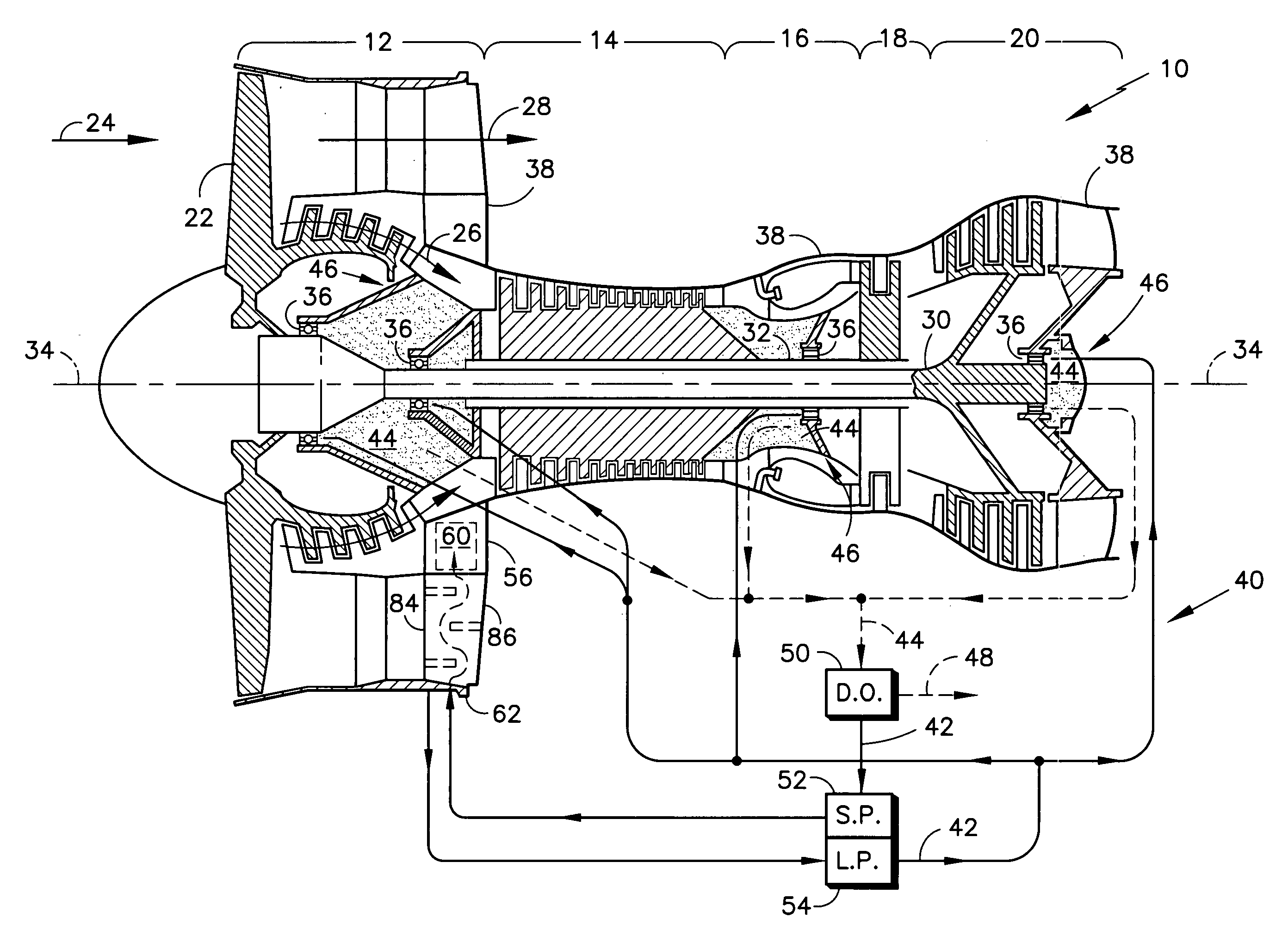
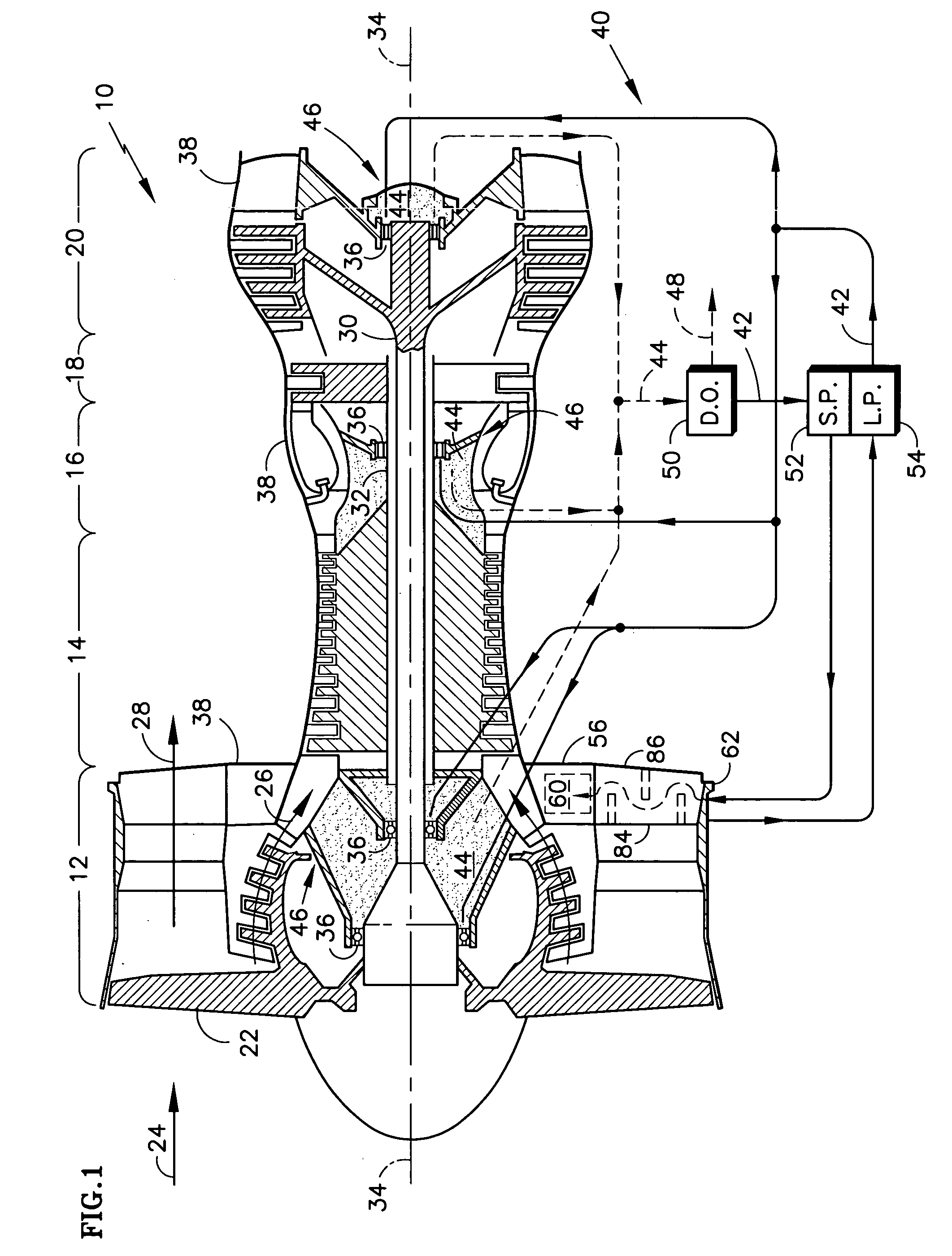
A gas turbine engine having a mid turbine frame comprising an annular outer case providing a portion of an engine casing; an interturbine duct (ITD) disposed within the outer case, the ITD including outer and inner rings radially spaced apart one from another and being interconnected by a plurality of radially extending and circumferentially spaced hollow strut fairings, the inner and outer rings co-operating to provide a portion of a hot gas path through the engine; a tube for delivering or discharging a lubricant fluid to or from a bearing housing, the tube extending radially through one of the hollow struts; and an insulation structure radially extending through one said hollow strut fairing, the insulation structure surrounding the tube and being spaced apart from the tube and from a hot internal surface of the one hollow strut fairing for shielding the tube from heat radiated from the hot internal surface of the one hollow strut fairing and for preventing the lubricant fluid from contacting the hot internal surface of said one hollow strut fairing when lubricant fluid leakage occurs.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
Low noise turbine for geared turbofan engine
A gas turbine engine is utilized in combination with a gear reduction to reduce the speed of a fan relative to a low pressure turbine speed. The gas turbine engine is designed such that a blade count in the low pressure turbine multiplied by the speed of the low pressure turbine will result in operational noise that is above a sensitive range for human hearing. A method and turbine module are also disclosed.
Owner:MTU AERO ENGINES GMBH +1
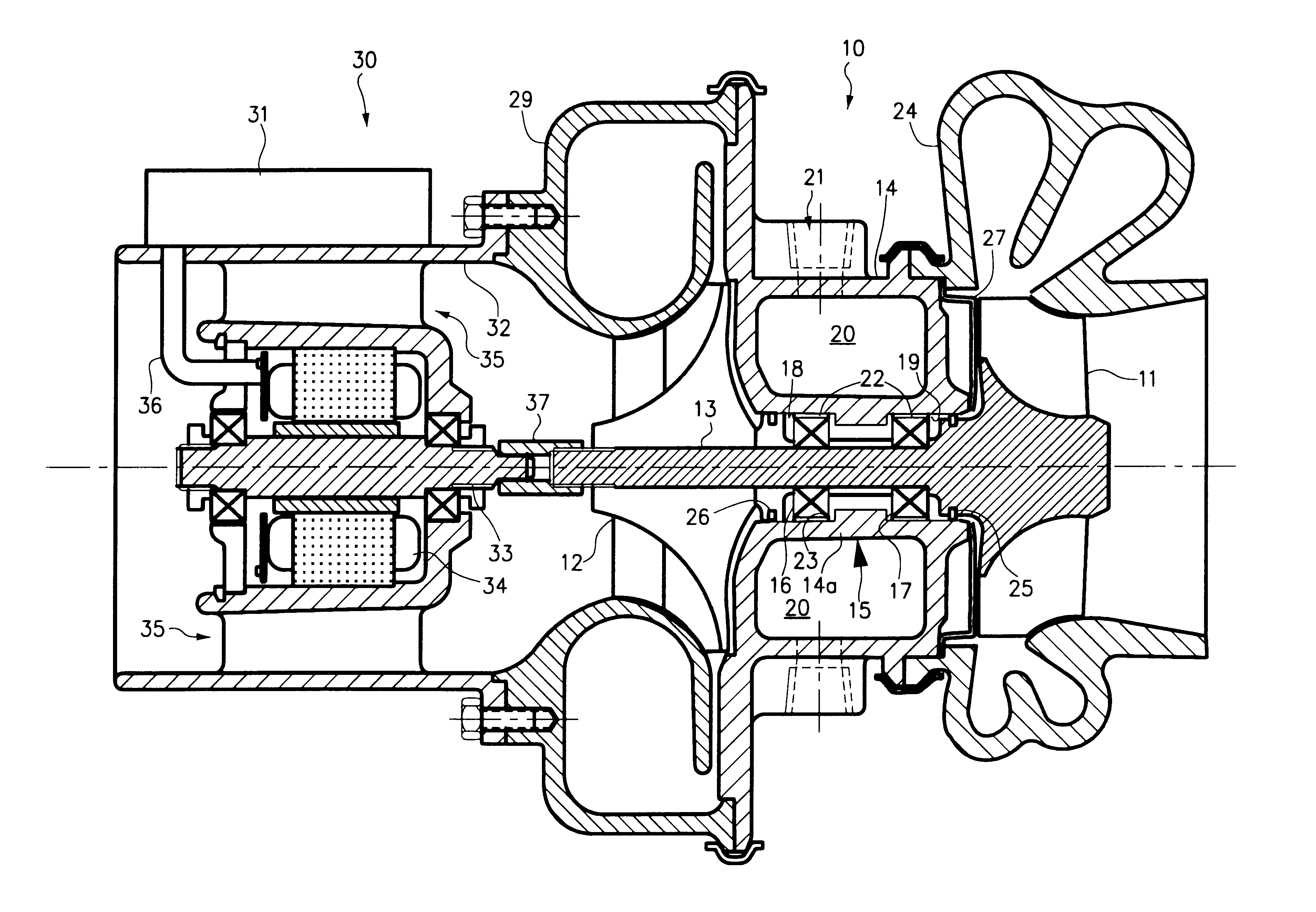
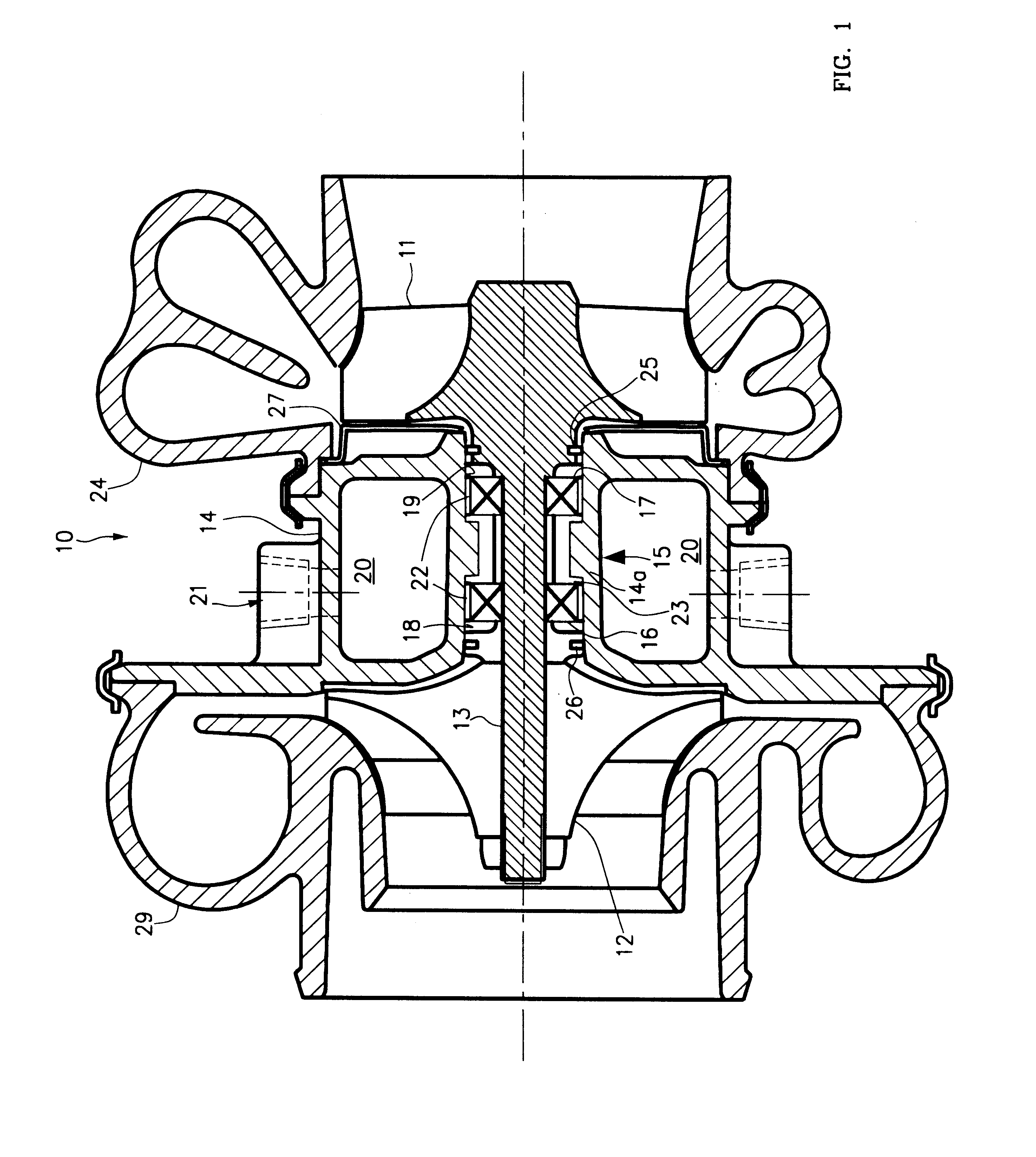
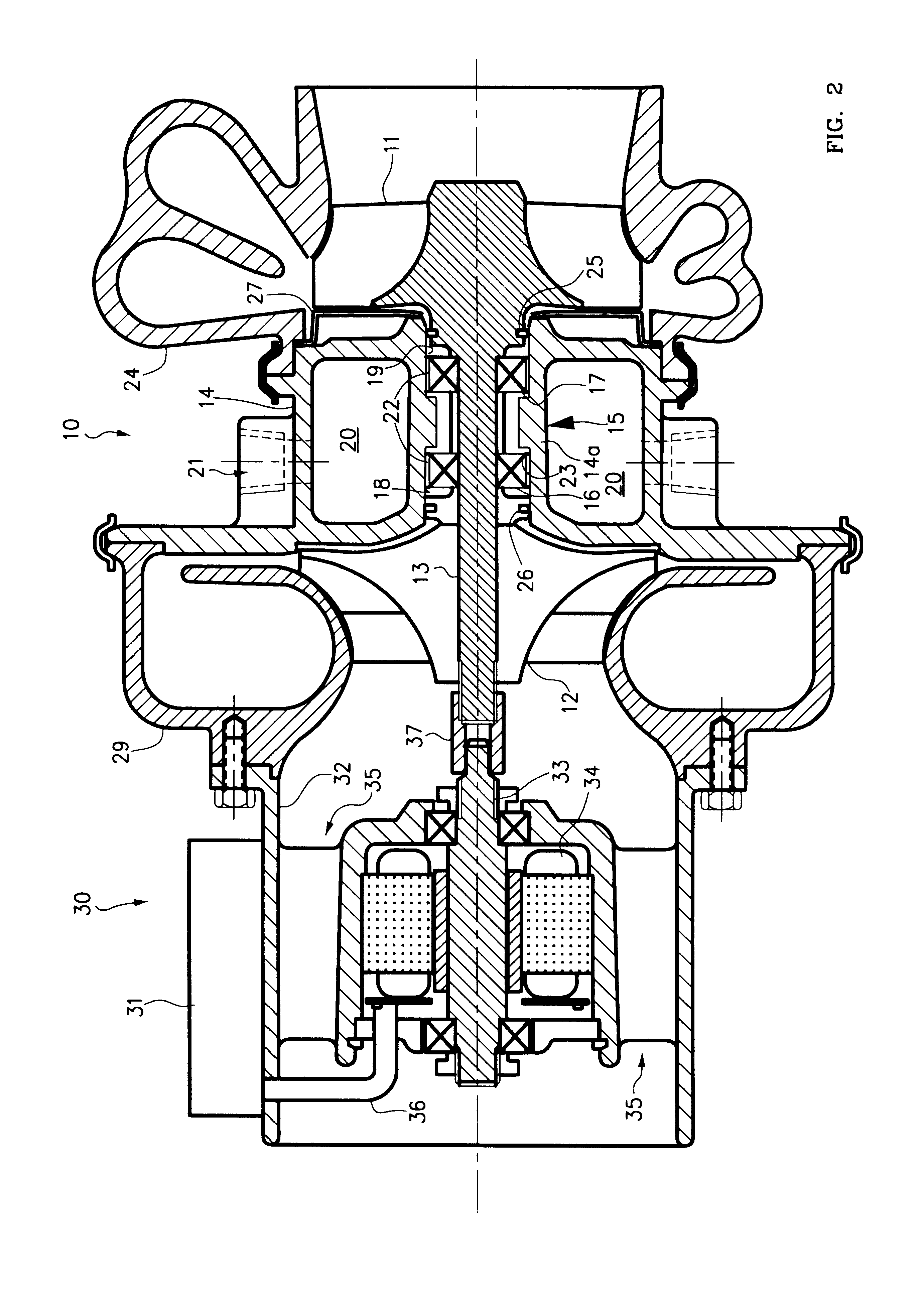
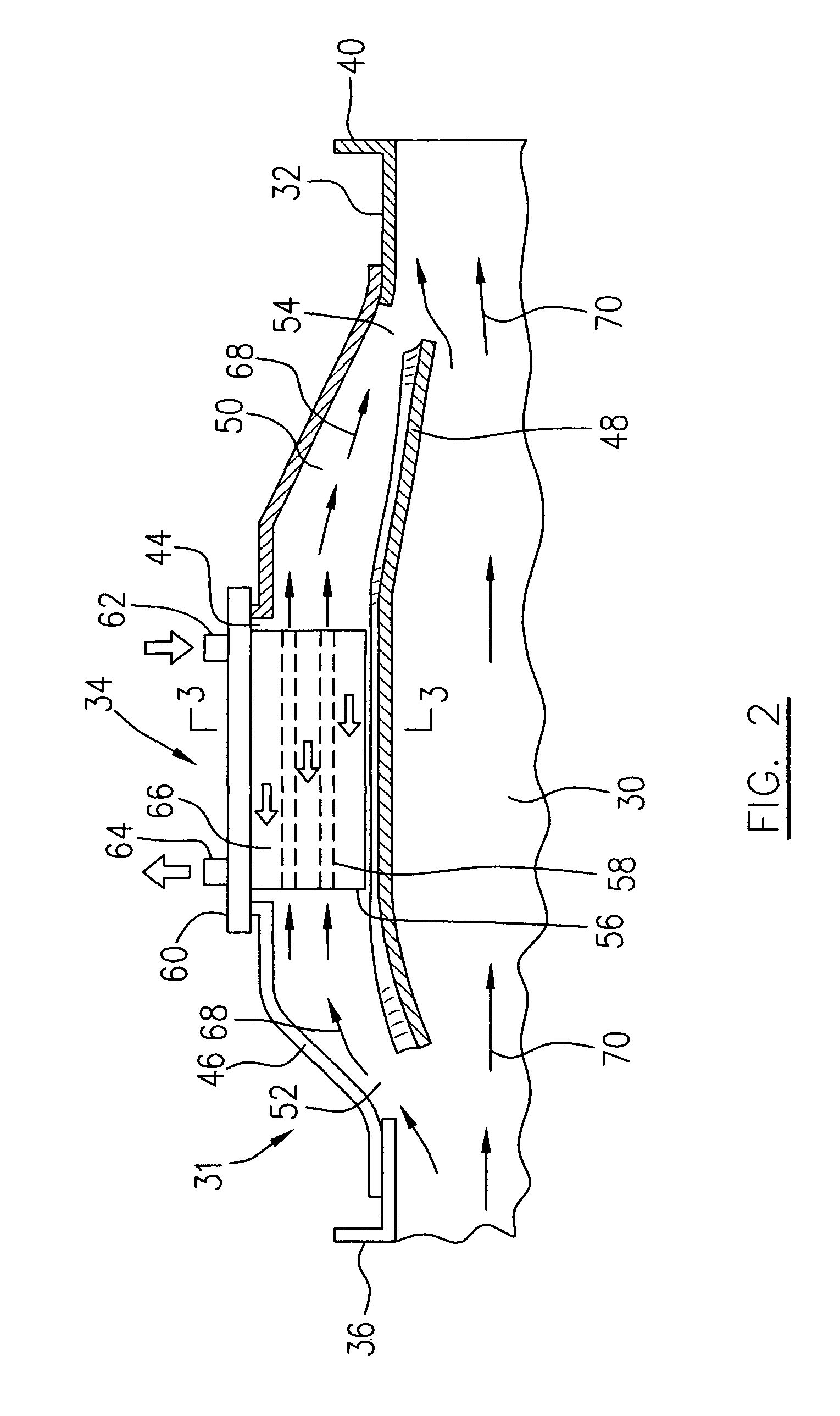
Gas turbine engine frame with an integral fluid reservoir and air/fluid heat exchanger
ActiveUS7377098B2Reduce riskEasy maintenanceTurbine/propulsion engine coolingEfficient propulsion technologiesPlate heat exchangerEngineering
Owner:RTX CORP
Gas turbine engine frame with an integral fluid reservoir and air/fluid heat exchanger
ActiveUS20060042223A1Reduce riskEasy maintenanceTurbine/propulsion engine coolingEfficient propulsion technologiesEngineeringGas turbines
Disclosed is a structural frame for a gas turbine engine comprising an integral fluid reservoir and air / fluid heat exchanger. A central hub includes a reservoir for storing a fluid and an outer rim circumscribes the hub. A heat exchanger is fluidly coupled to the reservoir and is in simultaneous communication with the fluid and an air stream.
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP
Continuous large-power turbine fracturing equipment
PendingCN111206992AStable and efficient transmissionStable working platformPositive displacement pump componentsGear lubrication/coolingDrive shaftControl engineering
The invention discloses continuous large-power turbine fracturing equipment. The large-power turbine fracturing equipment comprises a turbine engine, a reduction box, a transmission shaft and a plunger pump, wherein the turbine engine and the reduction box are arranged on the same straight line; the reduction box is connected to the plunger pump through a transmission shaft; and an angle of the transmission shaft ranges from 2 degrees to 4 degrees. The continuous large-power turbine fracturing equipment has the beneficial effects that: a chassis T1 material is selected, so that a stable working platform is provided for the equipment; the turbine engine and the reduction box are on the same straight line, the transmission shaft is arranged between the reduction box and the plunger pump, andthe angle of the transmission shaft ranges from 2 degrees to 4 degrees, so that stable and efficient transmission of the turbine engine is guaranteed, and a fault occurrence rate is reduced; a lubricating system driven by an auxiliary power system guarantees that the turbine engine, the reduction box and the plunger pump work under a proper environment; dual lubricating systems guarantee that theplunger pump realizes continuous operation under power of 5000 HP or higher; and the technical means finally can meet continuous large-power operation requirements of the fracturing equipment.
Owner:美国杰瑞国际有限公司
Air-oil heat exchanger placed at the location of the air separator nose of a turbojet, and a turbojet including such an air-oil heat exchanger
InactiveUS20090165995A1Prevent freezingWithout significantly disturbing the air streamExhaust apparatusTurbine/propulsion engine coolingLeading edgeJet engine
The invention relates to an air-oil heat exchanger located at the inner shroud of the secondary duct of a turbojet. In characteristic manner, it comprises an oil circuit placed inside the separator nose and fins placed outside the top wall of the separator nose, between the leading edge of the separator nose and the outlet guide vanes.
Owner:TECHSPACE AERO
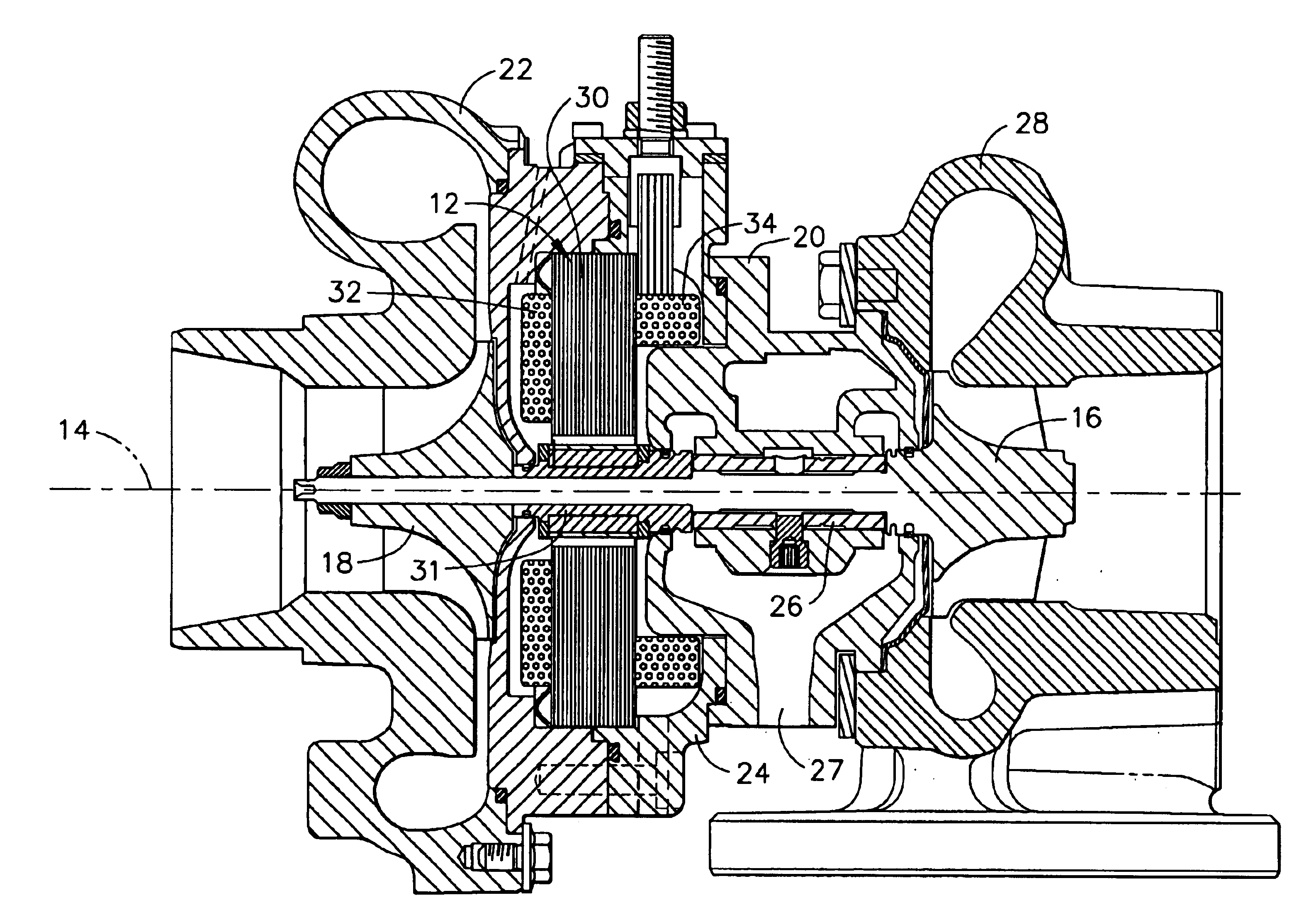
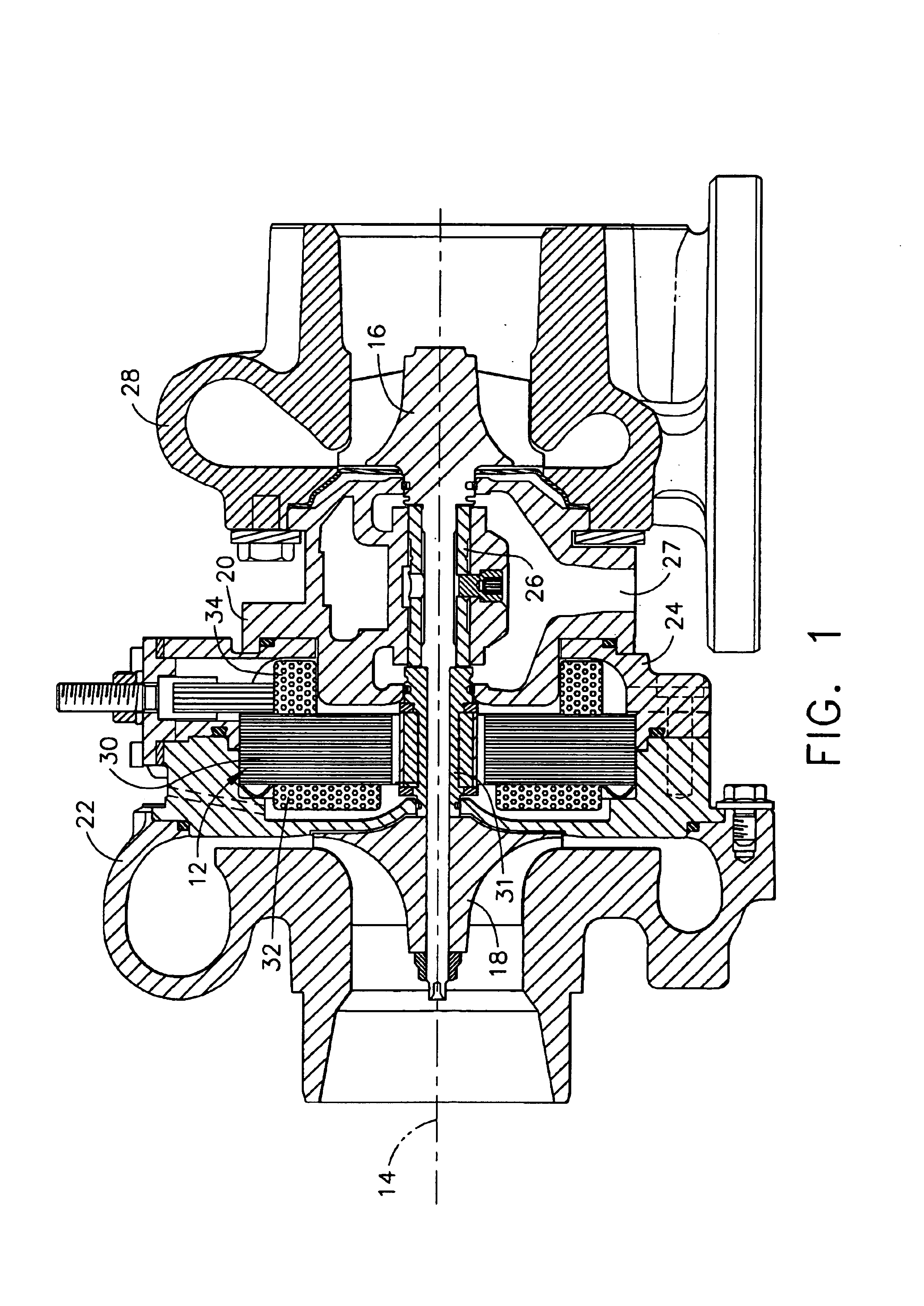
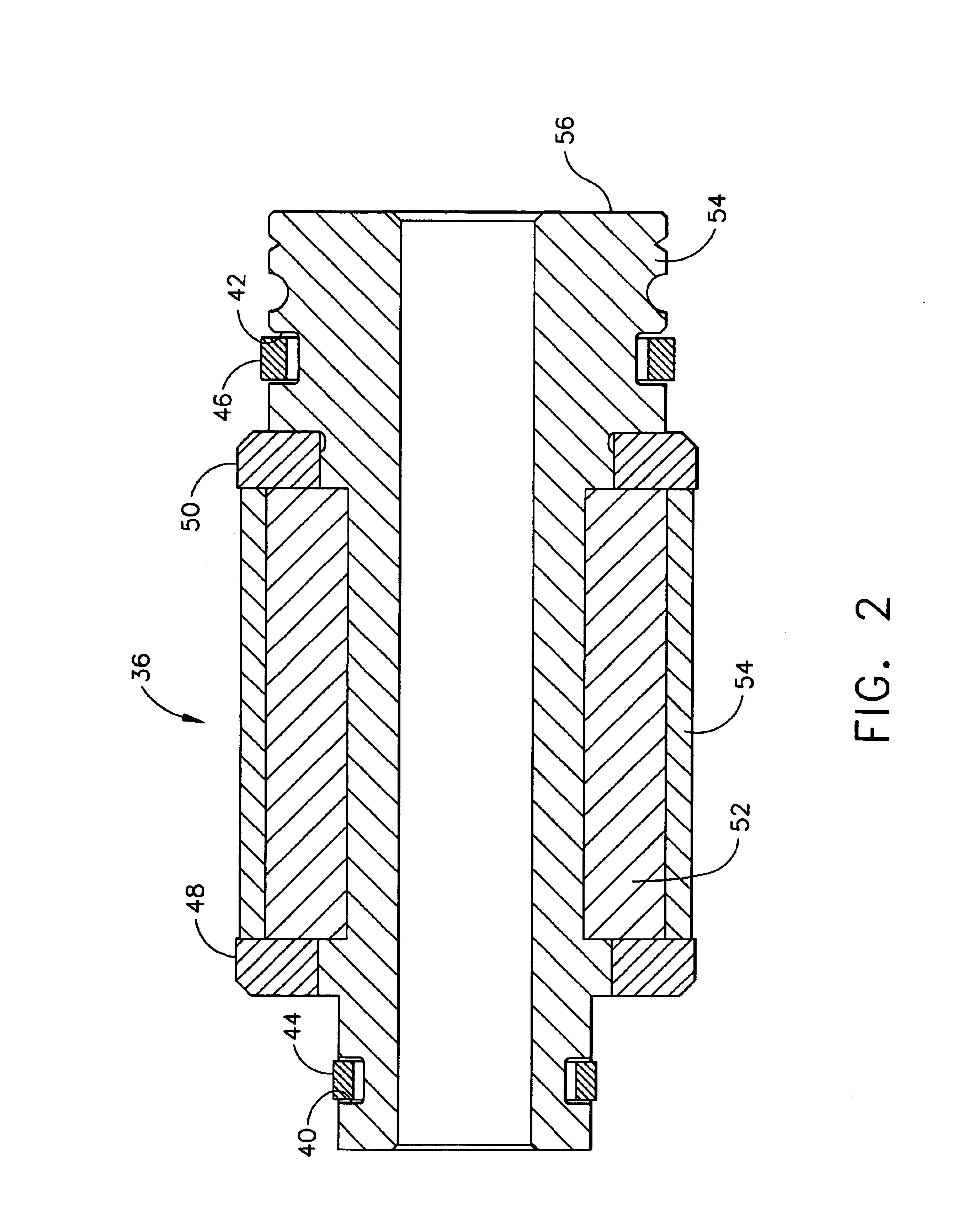
Compact turbocharger
InactiveUS6739845B2Minimal lengthLow thermal expansionInternal combustion piston enginesPump componentsTurbochargerControl theory
A turbocharger comprising two closely spaced ball bearings that does not require lubricating oil from an engine. The bearing housing forms a cooling jacket with two bearing engagement surfaces engaged with the outer races of the ball bearings through an intermediate radial spring. Closely spacing the ball bearings provides a rotor shaft of minimal length. In addition, an external motor-generator may be by mounted on the turbocharger, with the motor rotor solidly connected to the turbocharger rotor. In such an assembly, an electronic control is energizes the motor from battery power during acceleration up to approximately torque peak speed; thereafter, the control changes to a generator mode when there is excess energy in the engine exhaust gas.
Owner:WOOLLENWEBER WILLIAM E
Passive cooling system for auxiliary power unit installation
InactiveUS6942181B2Improve cooling effectEnhanced cooling airflowPower plant cooling arrangmentsAir-treating devicesAuxiliary power unitOil cooling
A passive cooling system for an auxiliary power unit (APU) installation on an aircraft is provided. The system is for an auxiliary power unit having at least a compressor portion of a gas turbine engine and an oil cooler contained separately within a nacelle. The system includes the auxiliary power unit housed within the nacelle of the aircraft, an engine exhaust opening defined in the aft portion of the nacelle and communicating with the gas turbine engine, at least a first air inlet duct communicating with a second opening defined in said nacelle and with said compressor portion and the oil cooler is located within a second duct communicating with an opening other than the engine exhaust opening of said nacelle and with the engine exhaust opening. Exterior cooling air and engine exhaust ejected through said engine exhaust opening entrain cooling air through said second duct to said oil cooler, and thus provide engine oil cooling. An exhaust eductor is also provided.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
Turbofan bypass duct air cooled fluid cooler installation
ActiveUS7861512B2Facilitate heat exchangeTurbine/propulsion engine coolingEngine fuctionsCooling fluidTurbofan
A cooling apparatus for cooling a fluid in a bypass gas turbine engine comprises a heat exchanger disposed within a bypass duct and accommodated by a sub-passage defined by a flow divider affixed to an annular wall of the bypass duct. The sub-passage defines an open upstream end and an open downstream end to direct a portion of the bypass air flow to pass therethrough.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
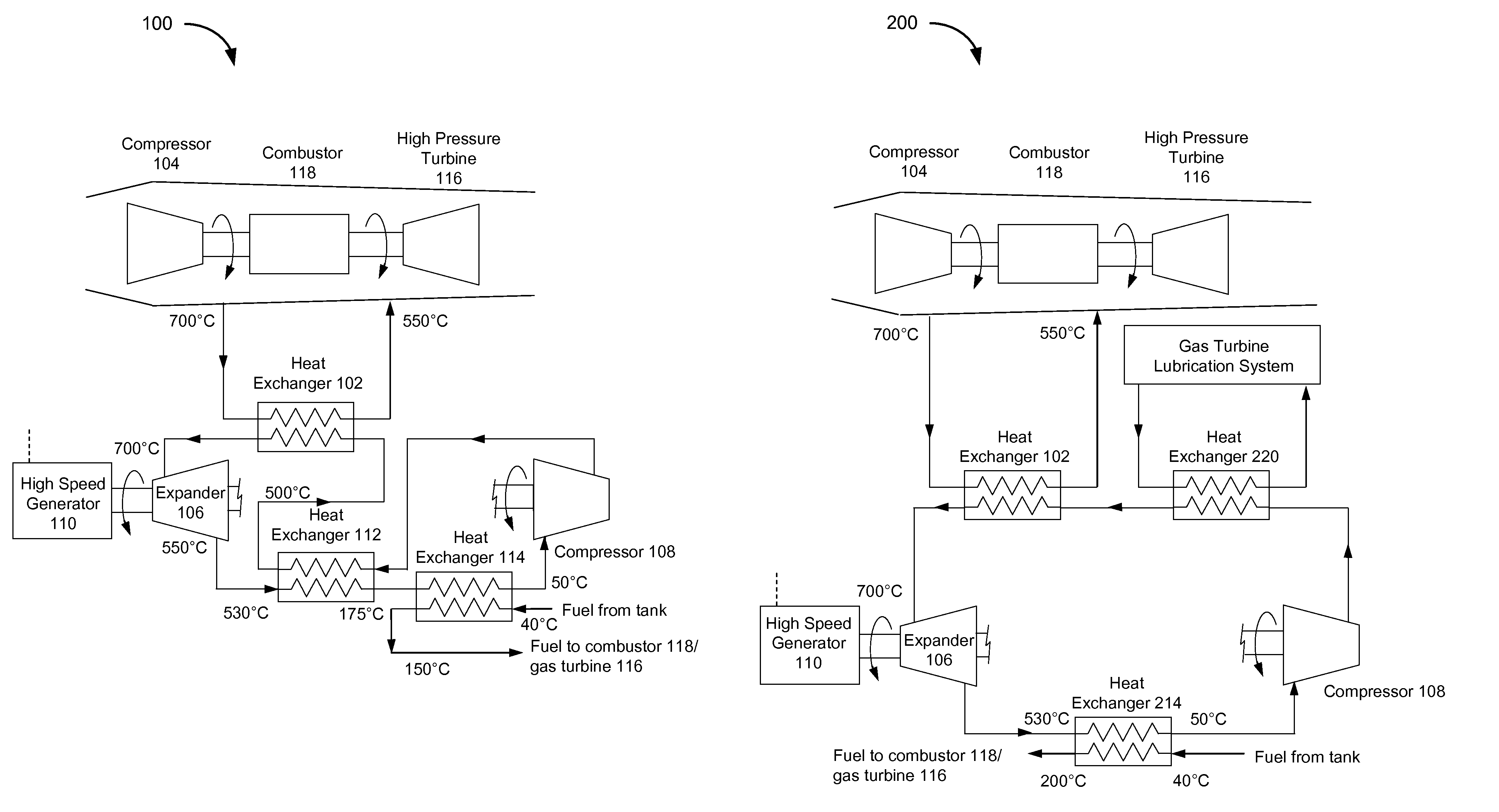
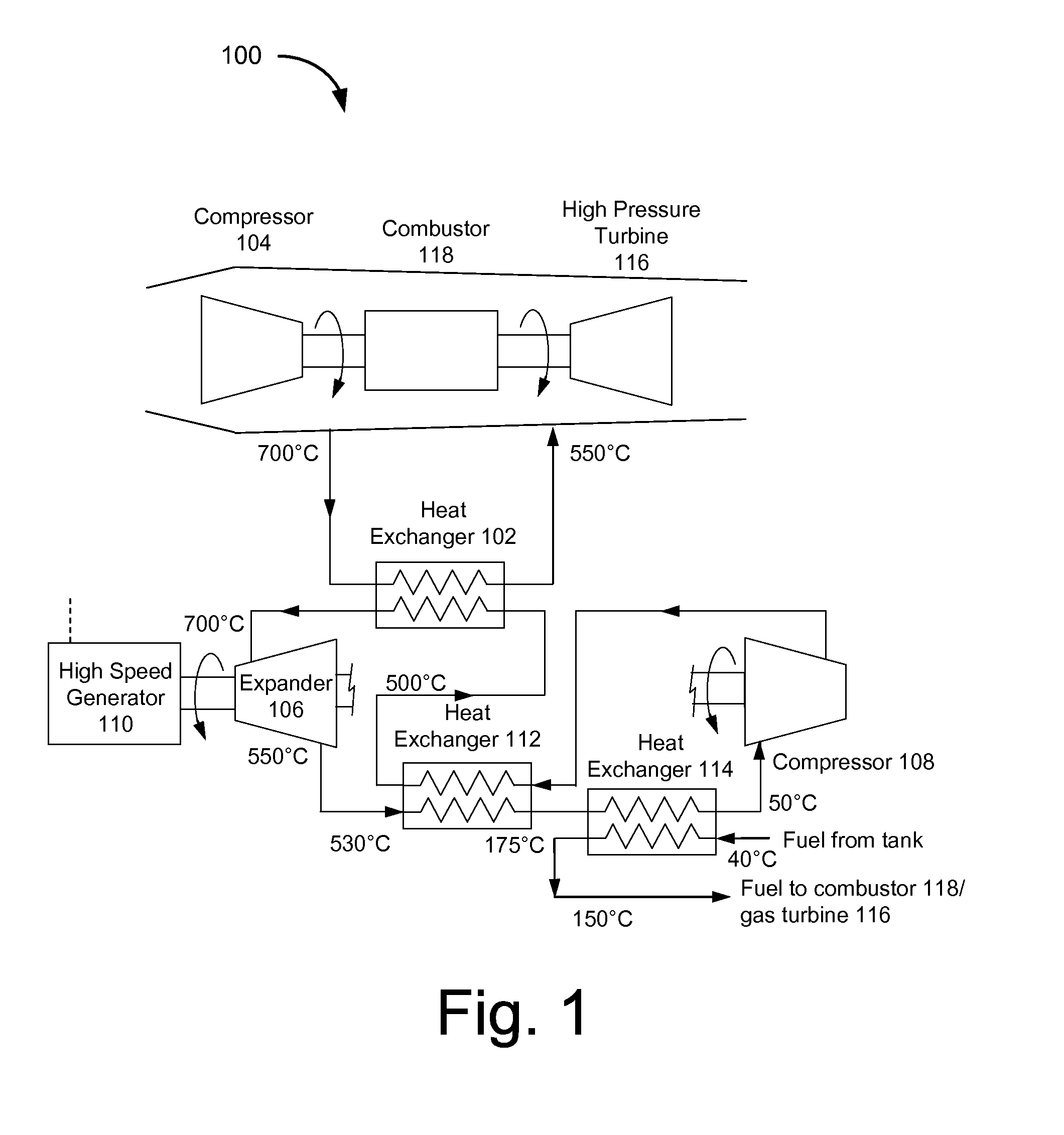
System and method for managing thermal issues in gas turbine engines
ActiveUS9014791B2Turbine/propulsion engine coolingTurbine/propulsion fuel heatingOn boardEngineering
The present invention generally relates to a system that enables one to address various thermal management issues in advanced gas turbine engines. In one embodiment, the present invention relates to a method to extract heat from an air stream, utilize a significant fraction for on-board power generation, and reject a small quantity of heat to the fuel stream safely at, for example, a lower temperature. In another embodiment, the present invention relates to a method to extract heat from an air stream, utilize a significant fraction for on-board power generation, and reject a small quantity of heat to the fuel stream safely at, for example, a lower temperature with no potential air / fuel contact is disclosed.
Owner:ECHOGEN POWER SYST LLC
Gas turbine engine architecture
A gas turbine engine having an oil cavity architecture and bearing placement which reduce heat rejection and oil system complexity by enclosing the reduction gearbox bearings and at least the shaft bearings supporting the high pressure shaft in the same oil cavity.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
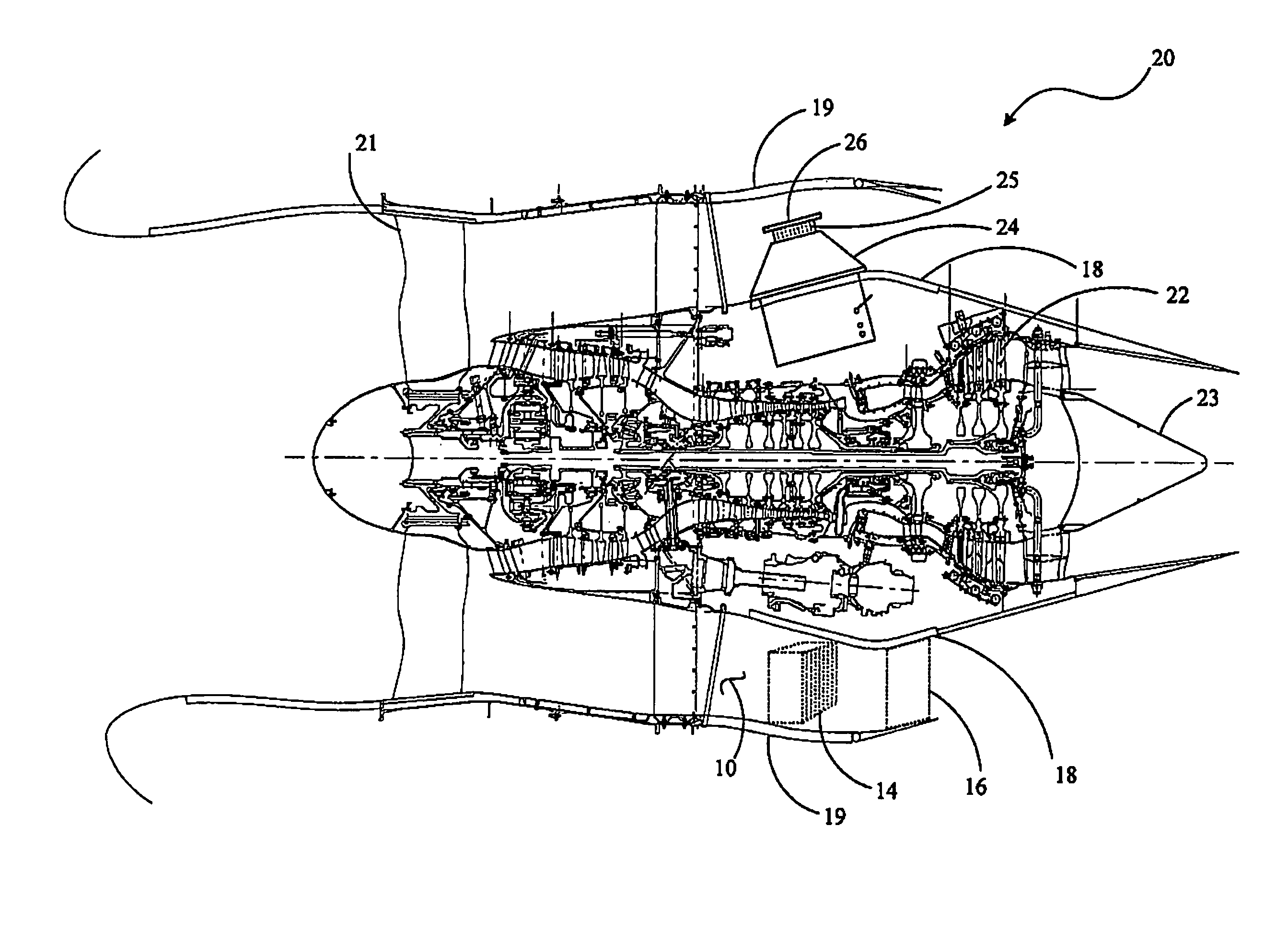
Gas turbine engine assembly and methods of assembling same
InactiveUS7490460B2Cosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusEngineeringGas turbines
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Thermal management system for an aircraft
ActiveUS7260926B2Minimizes air-to-liquid heat exchangersEngine fuctionsTurbine/propulsion fuel deliveryThermal management systemProcess engineering
A fuel based thermal management system includes a fuel stabilization system which permits the fuel to exceed the traditional coking temperatures. High temperature components are arranged along the fuel flow path such that even at the higher operating temperatures the fuel operates as a heat sink to transfer heat from high temperature components to the fuel. An optimal high temperature ester-based oil permits an oil-loop to exceed current oil temperature limits and achieve a high temperature to permit efficient rejection of heat to the fuel late in the fuel flow path.
Owner:RTX CORP
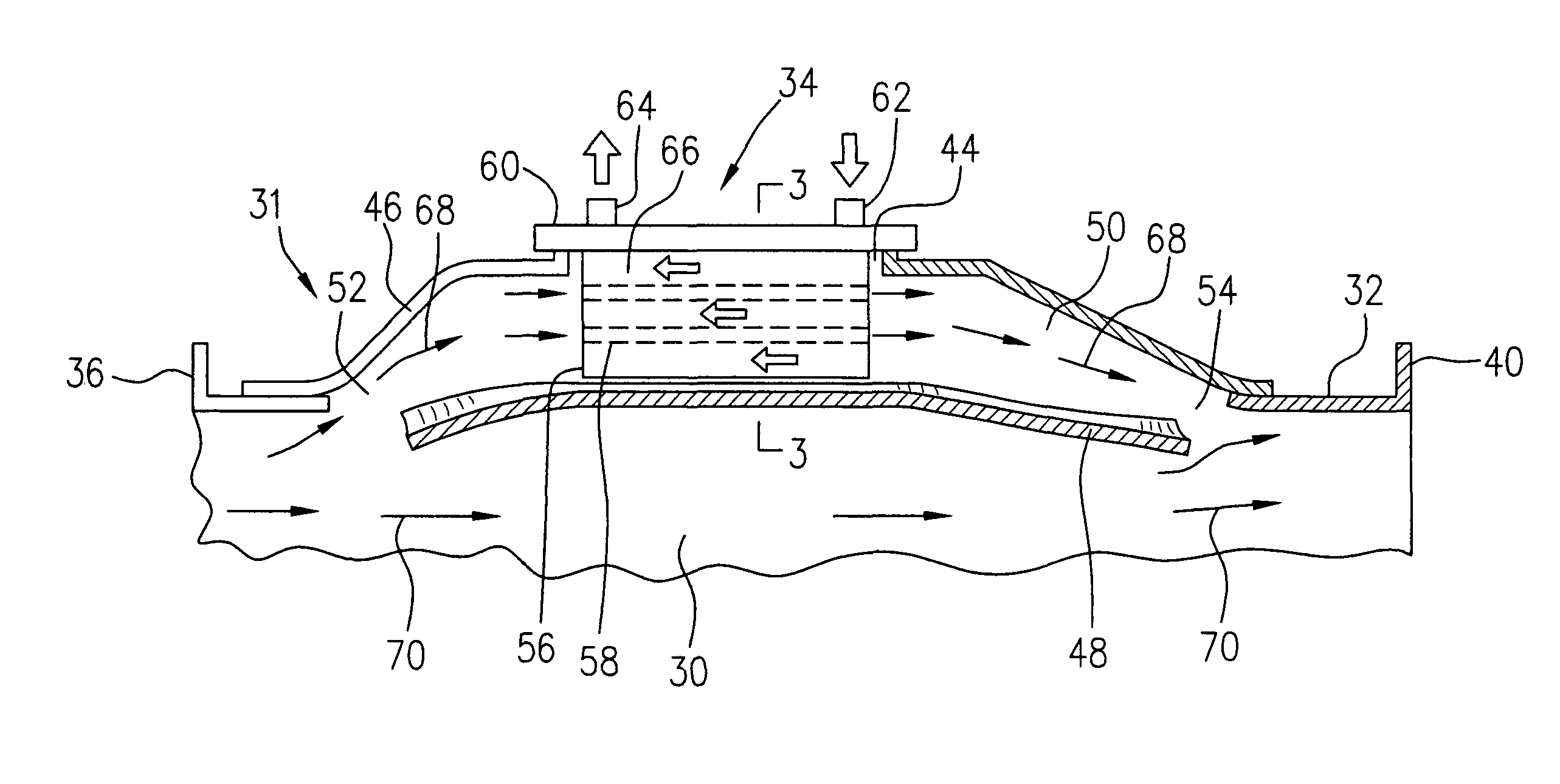
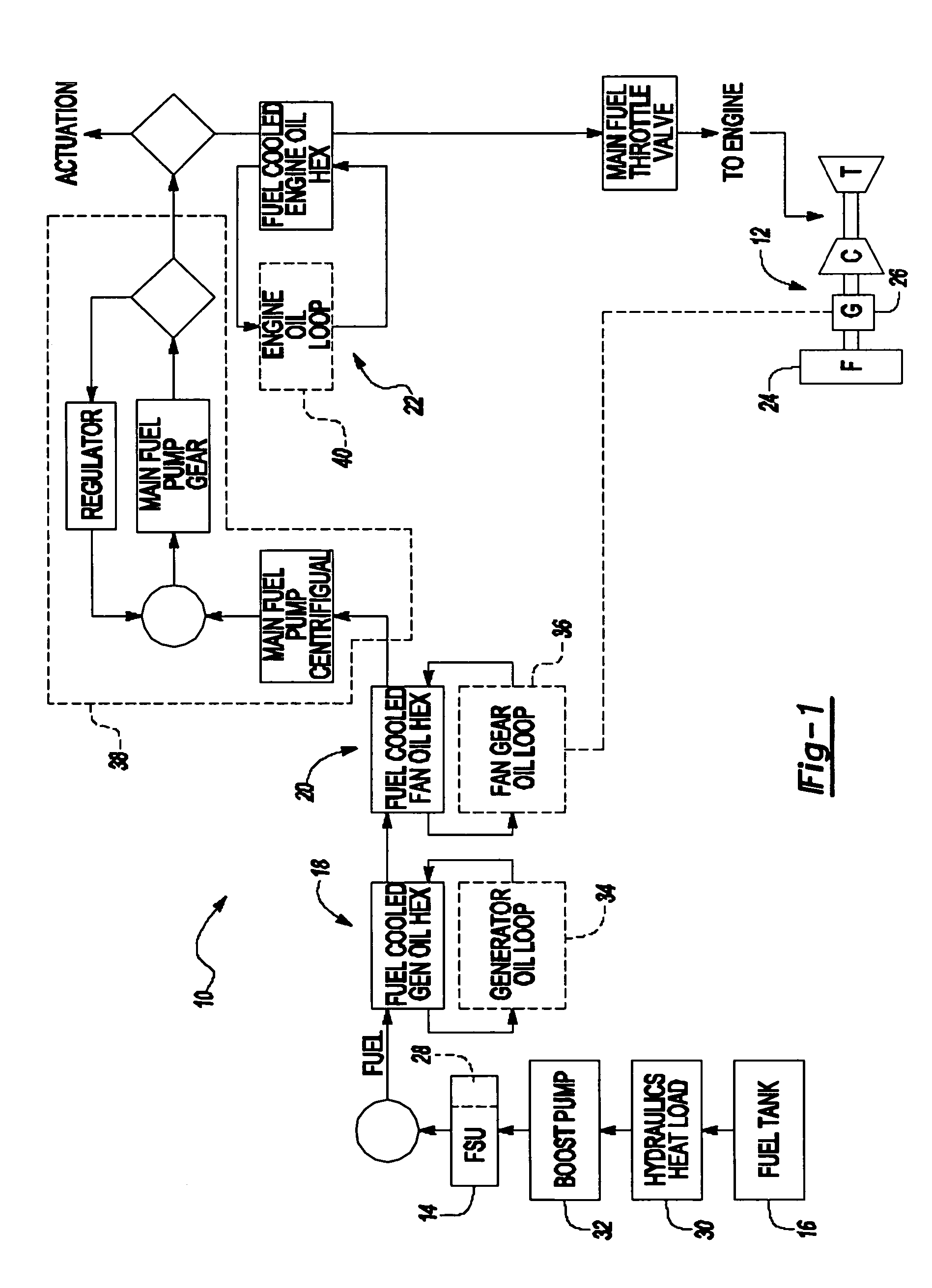
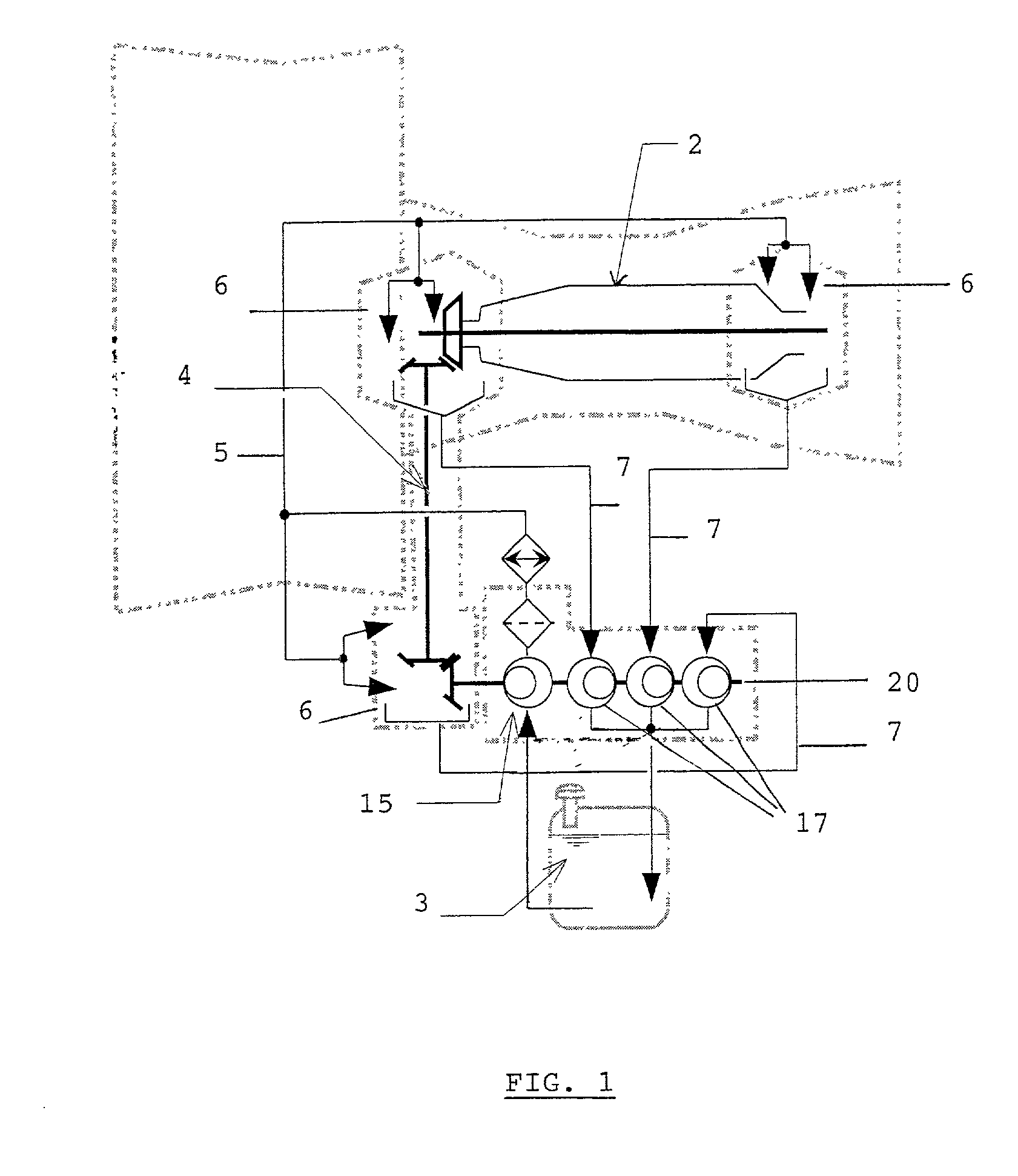
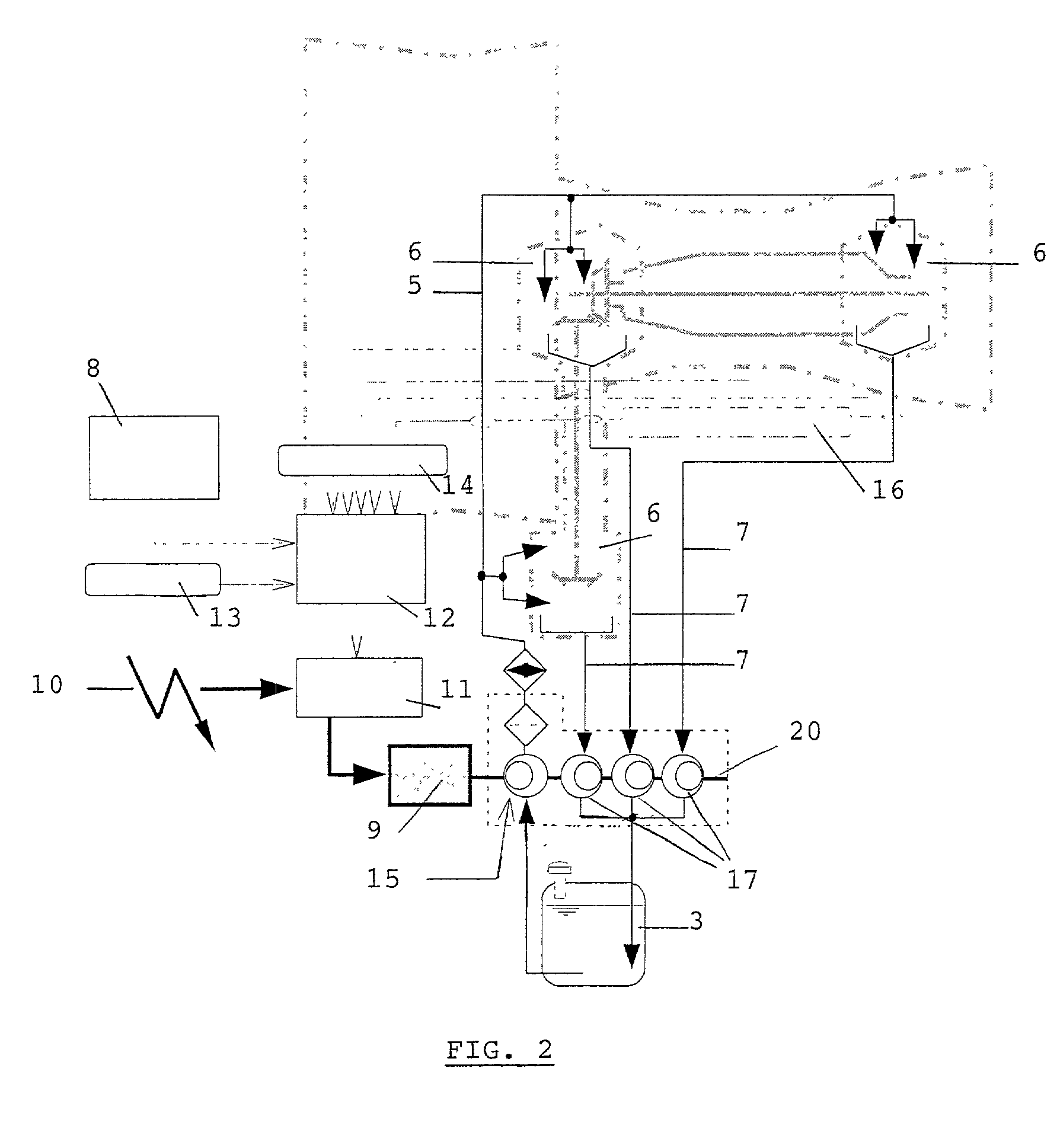
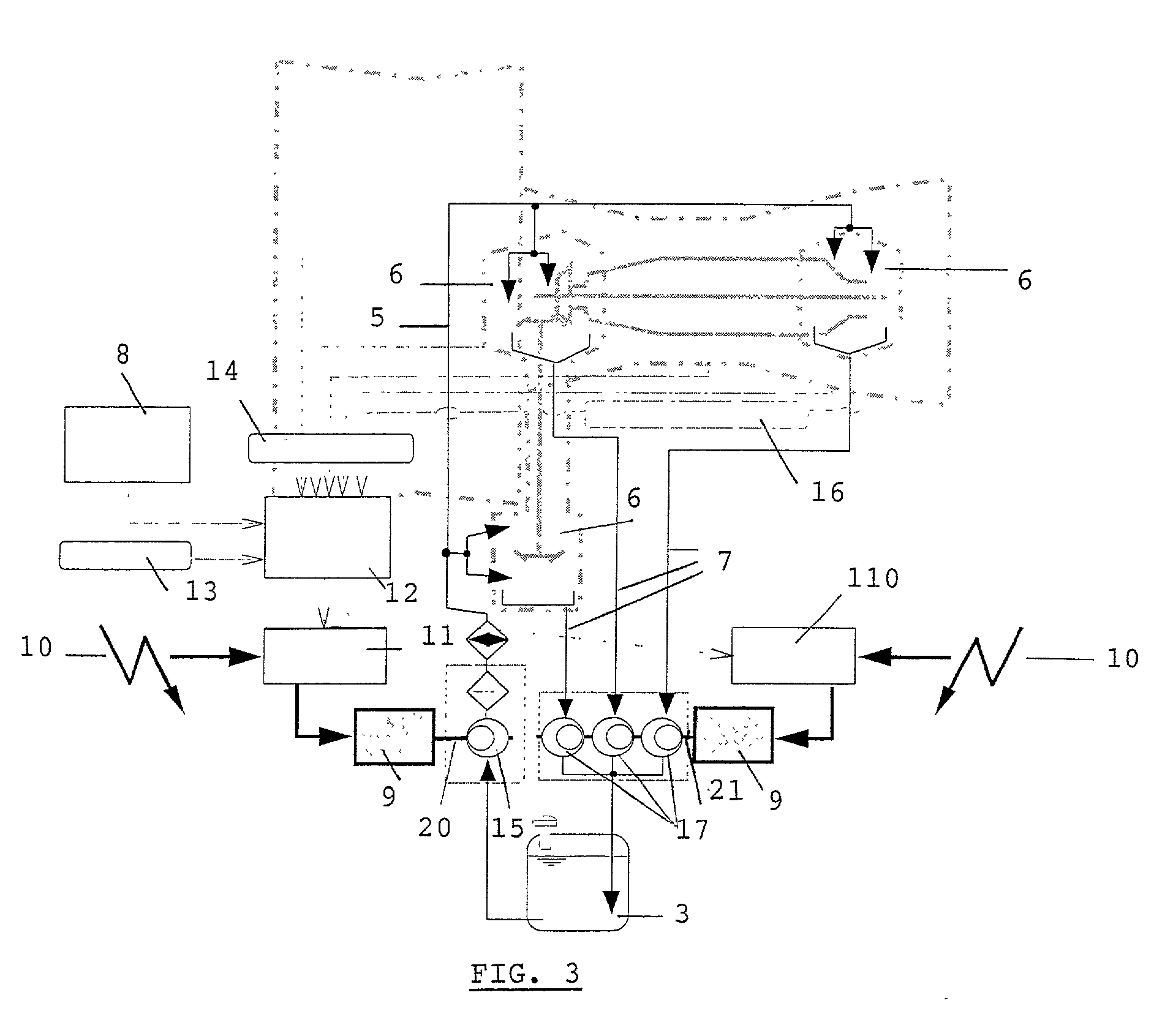
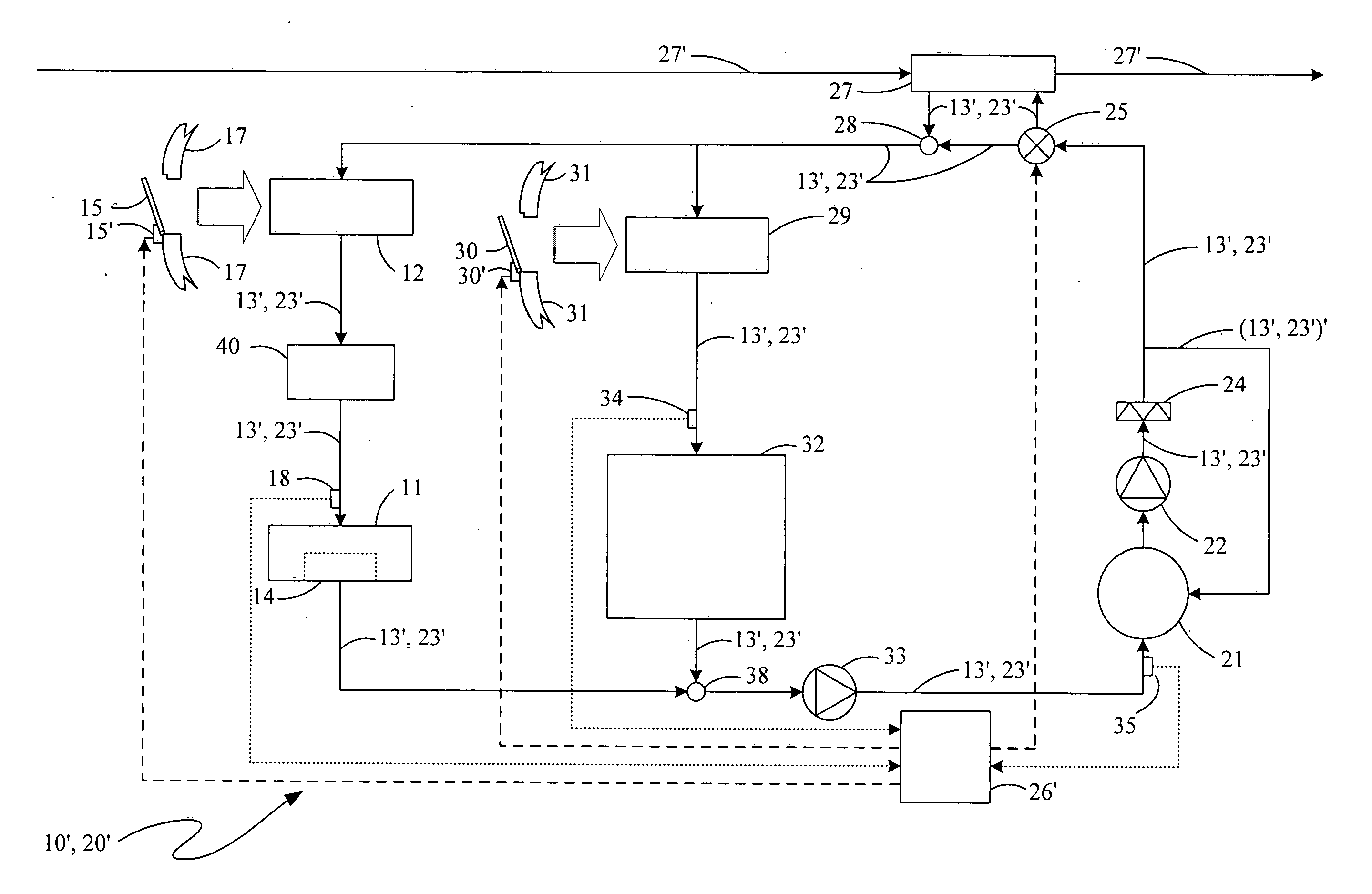
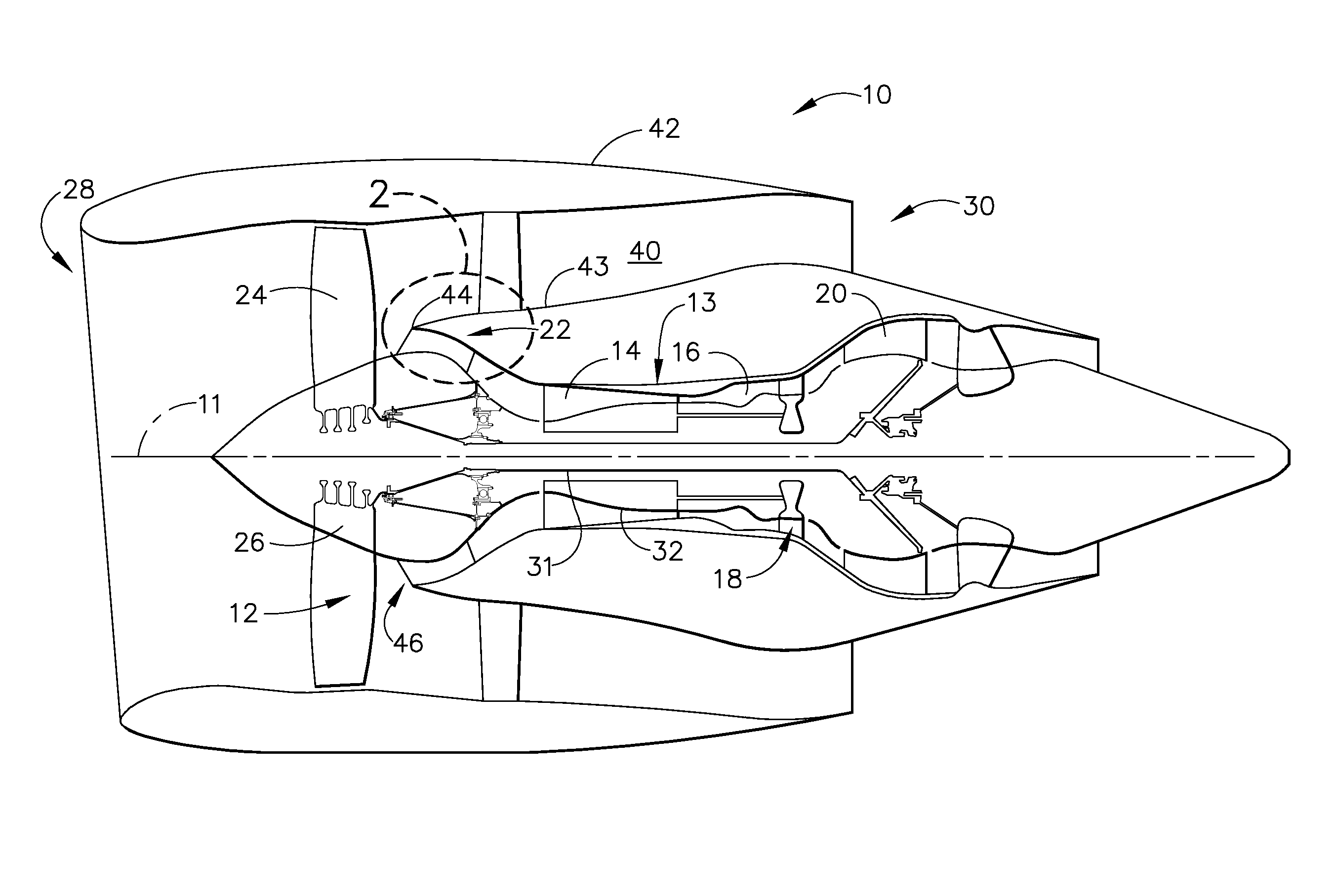
Process and device for lubricating an aircraft engine
The present invention relates to a process for lubricating an aircraft engine, and preferably a turboreactor engine, comprising at least one shaft (2), in which the pressurization of oil taken from a reservoir (3), the distribution of the oil via a downstream circuit (5) to elements (6) of said engine, and the return of the oil via an upstream circuit (7) to the reservoir (3) are ensured by means of a pump (1, 15, 17), the rotational speed of said pump (1, 15, 17) being variable and adjustable, characterized in that this rotational speed of said pump (1, 15, 17) is preferably regulated by a predetermined law in order to adapt to the actual lubrication needs of said engine.
Owner:TECHSPACE AERO
Low noise turbine for geared turbofan engine
A gas turbine engine is utilized in combination with a gear reduction to reduce the speed of a fan relative to a low pressure turbine speed. The gas turbine engine is designed such that a blade count in the low pressure turbine multiplied by the speed of the low pressure turbine will result in operational noise that is above a sensitive range for human hearing. A method and turbine module are also disclosed.
Owner:MTU AERO ENGINES GMBH
Thermal management system for turbofan engines
A heat exchange system for use in operating equipment in which a working fluid is utilized needing a heat exchange system to provide air and working fluid heat exchanges to cool the working fluid at selectively variable rates in airstreams. The system comprises a plurality of heat exchangers including a first heat exchanger in the plurality of heat exchangers that is mounted with respect to the equipment so as to permit corresponding portions of the airstreams to pass through the core thereof during at least some such uses of the equipment. Also, a second heat exchanger is mounted with respect to the equipment so as to selectively permit corresponding portions of the airstreams to pass through the core thereof during such uses of the equipment. A core actuator is mounted with respect to the second heat exchanger to selectively increase or reduce the passing of those corresponding portions of the airstreams through the core.
Owner:RTX CORP
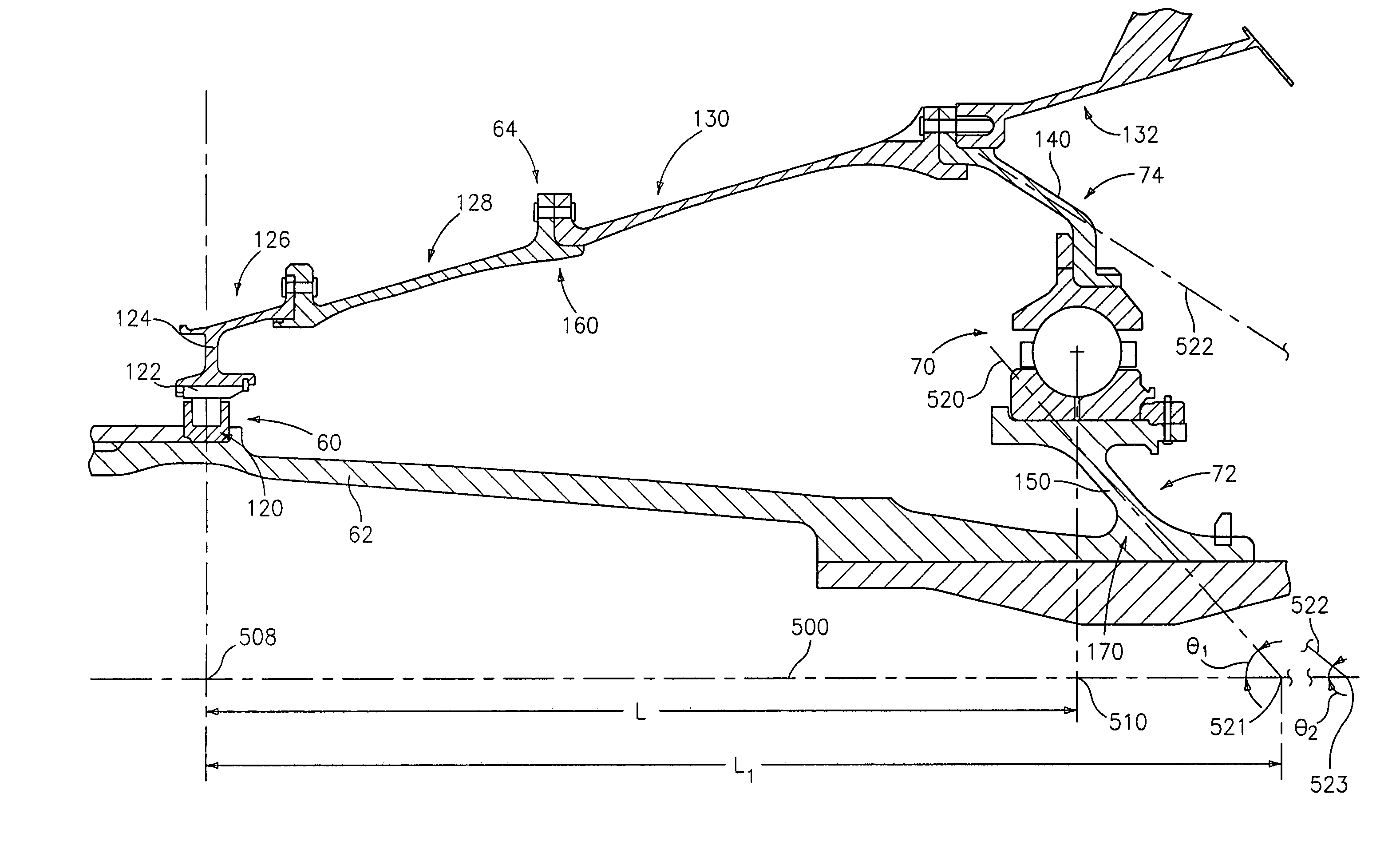
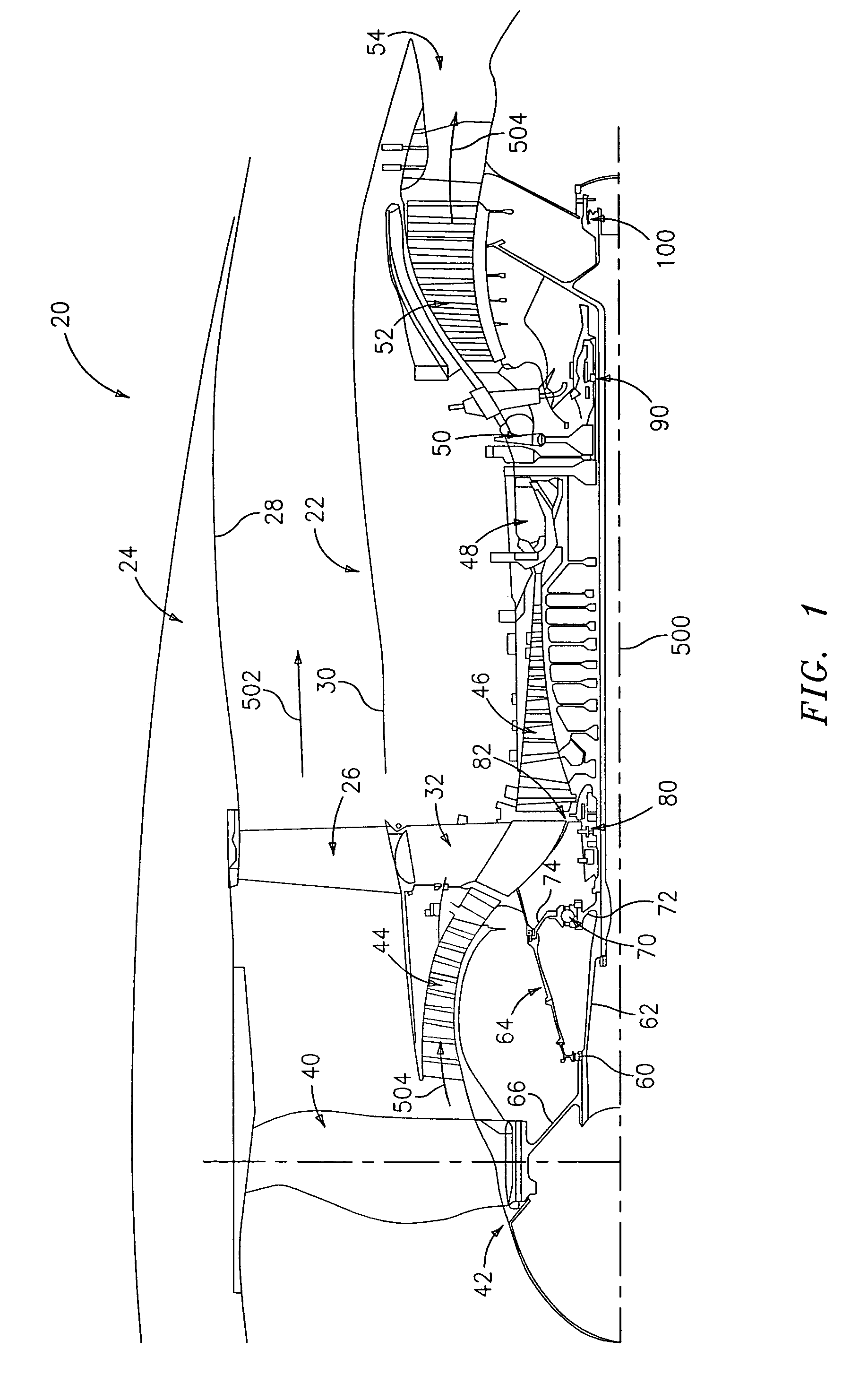
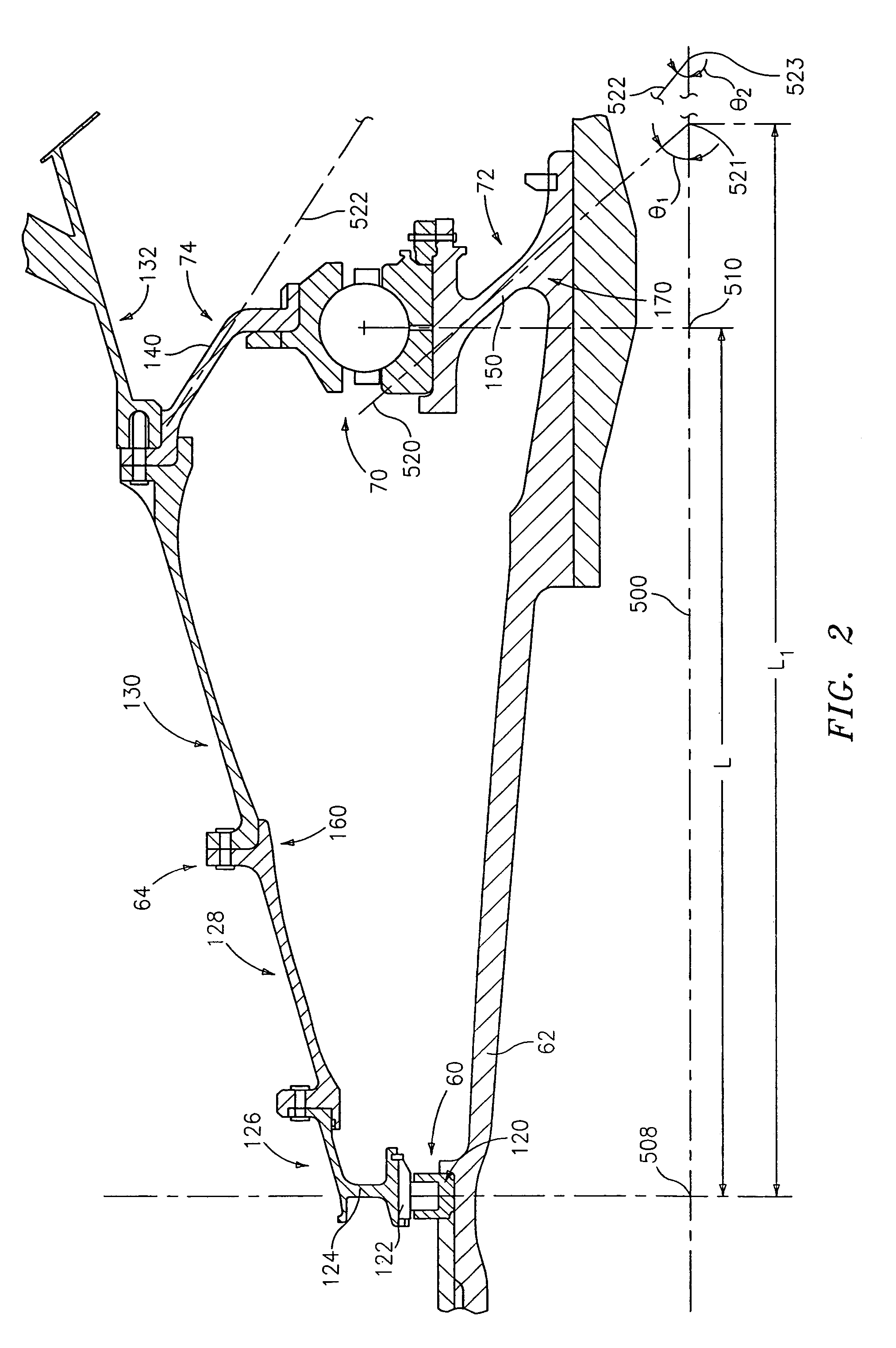
Bearing support
To further isolate imbalances in a rotating structure such as a gas turbine engine, an effective length between two bearings may exceed an actual length. This may be achieved via one or more tapering bearing supports associated with at least one of the bearings.
Owner:RTX CORP
Bypass duct fluid cooler
ActiveUS7377100B2Light weightCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusEngineeringGas turbines
A method and apparatus for cooling a fluid in a bypass gas turbine engine involves directing the fluid to the bypass duct of the engine to allow for heat exchange from the fluid to bypass air passing through the bypass air duct.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
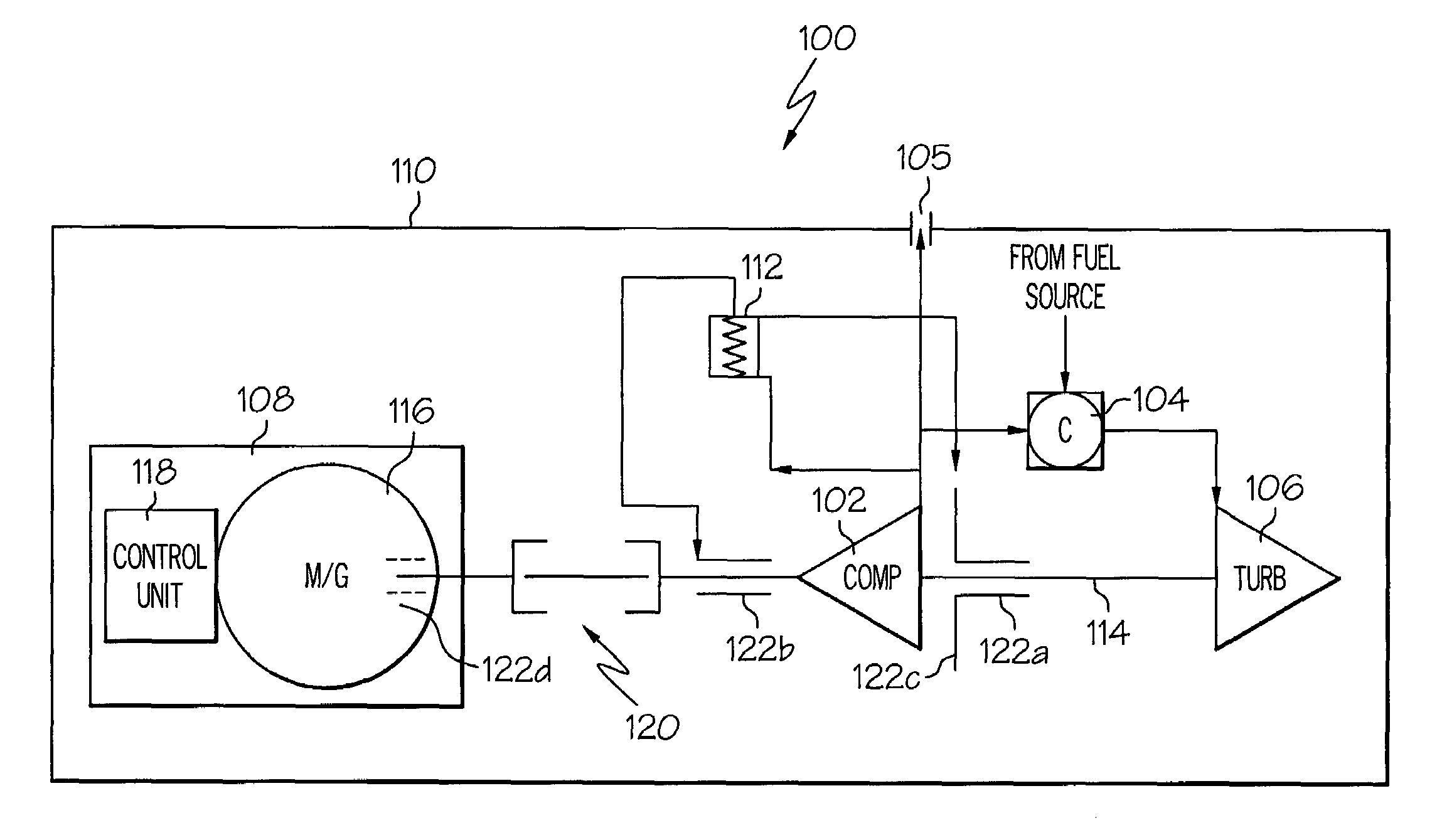
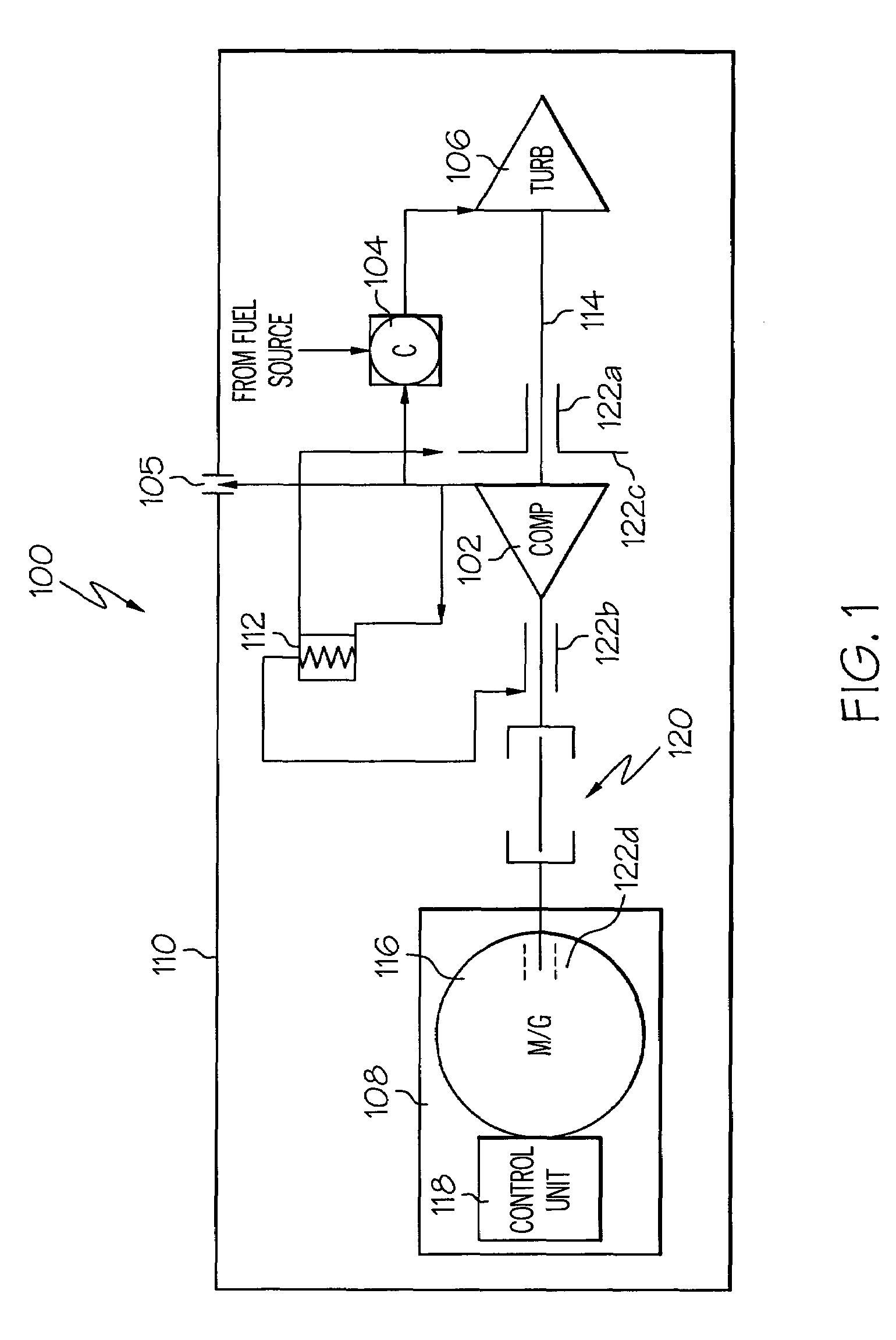
Turbine engine with integrated generator having shared lubrication system
ActiveUS20080121376A1Engine fuctionsEfficient propulsion technologiesWorking fluidProcess engineering
A heat exchange system for use in operating equipment having a plurality of subsystems in each of which a common working fluid is utilized to provide selected operations in that subsystem with a reservoir containing at least some of the common working fluid and has both a supply system and a return system connected between the reservoir and each of the plurality of subsystems through which any common working fluid in the reservoir can be conveyed. An airstream heat exchanger is provided connected in one of the supply and return systems so as to have the common working fluid conveyed therethrough cooled at selectively variable rates in the airstreams passing thereby during at least some such uses of the operating equipment.
Owner:RTX CORP
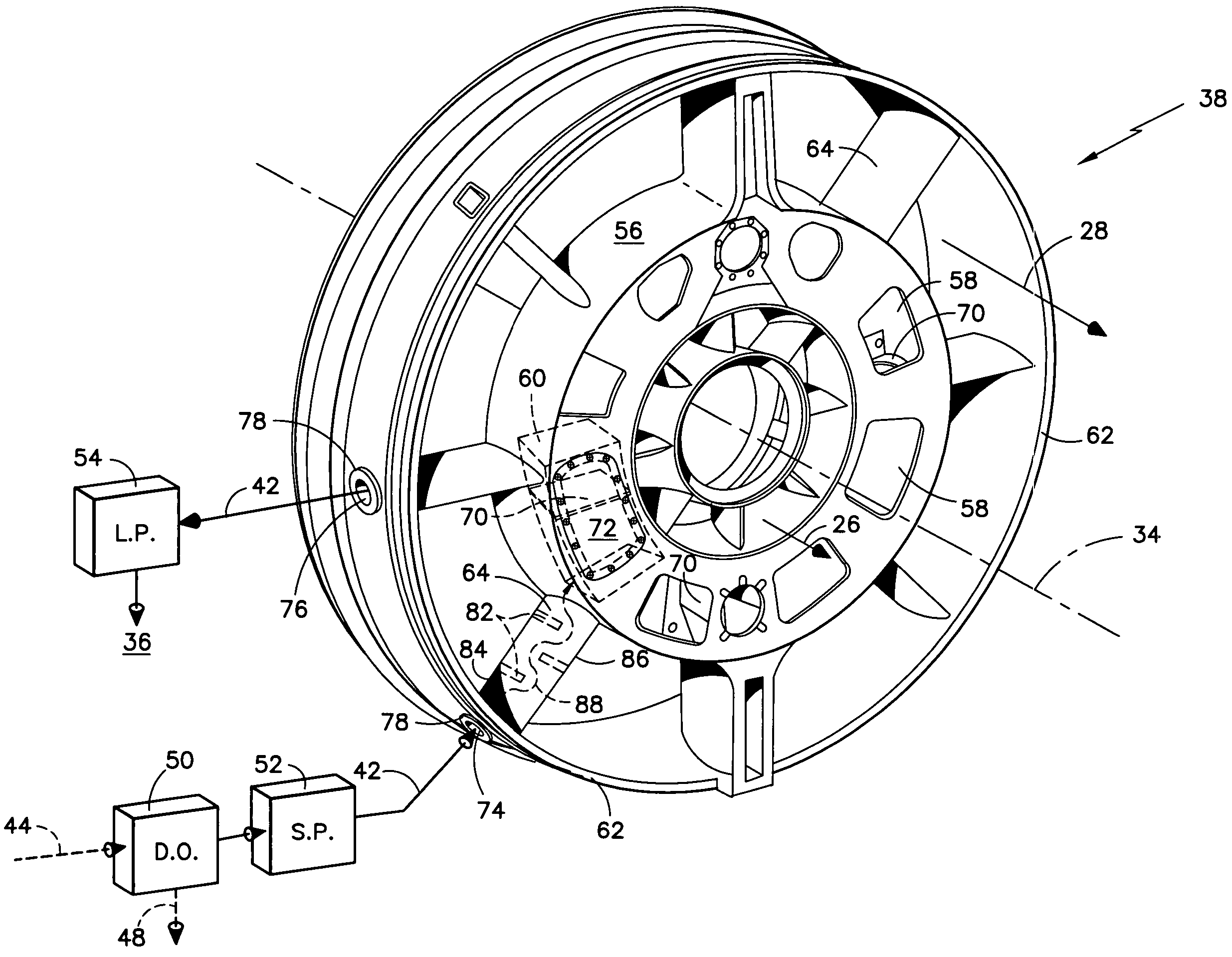
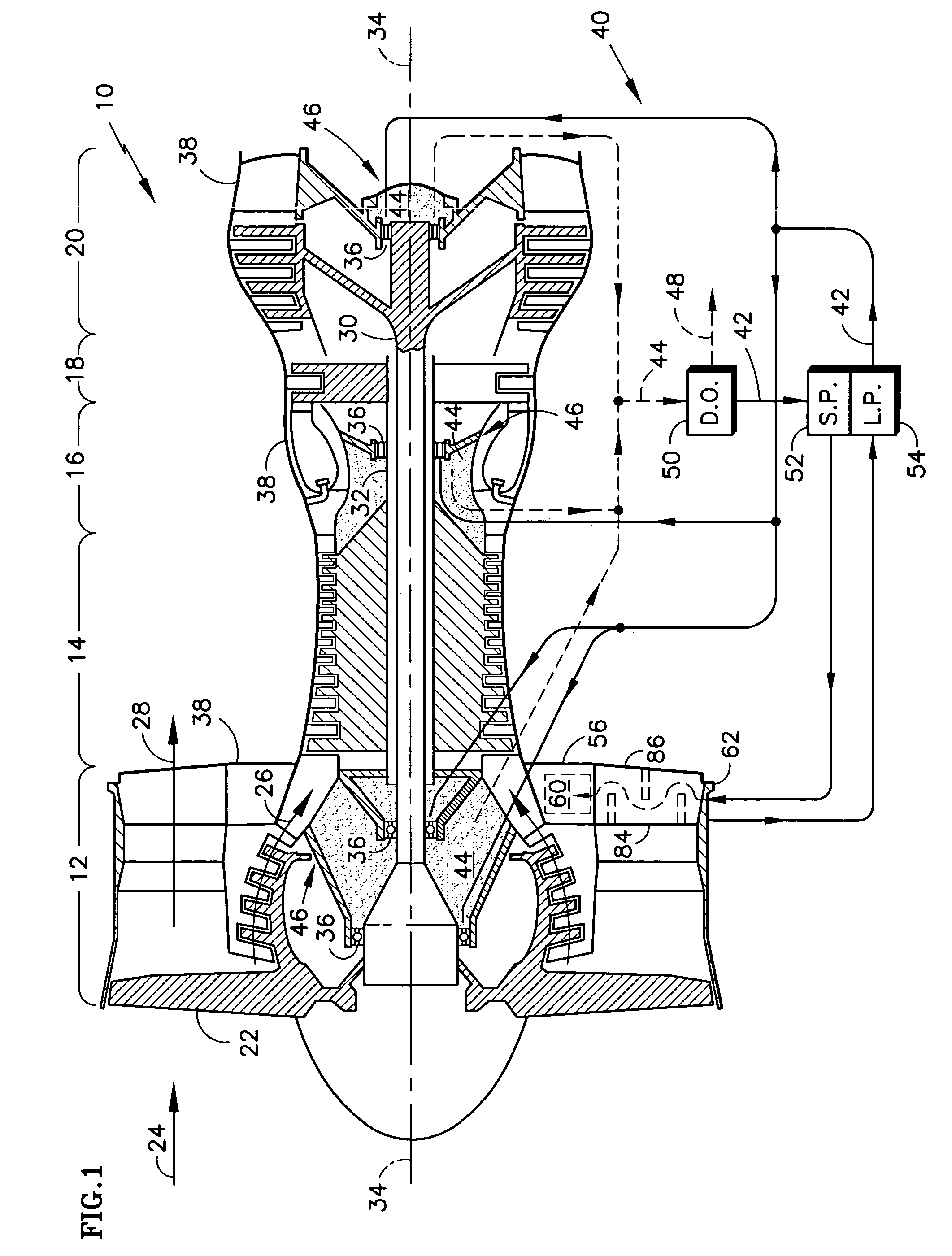
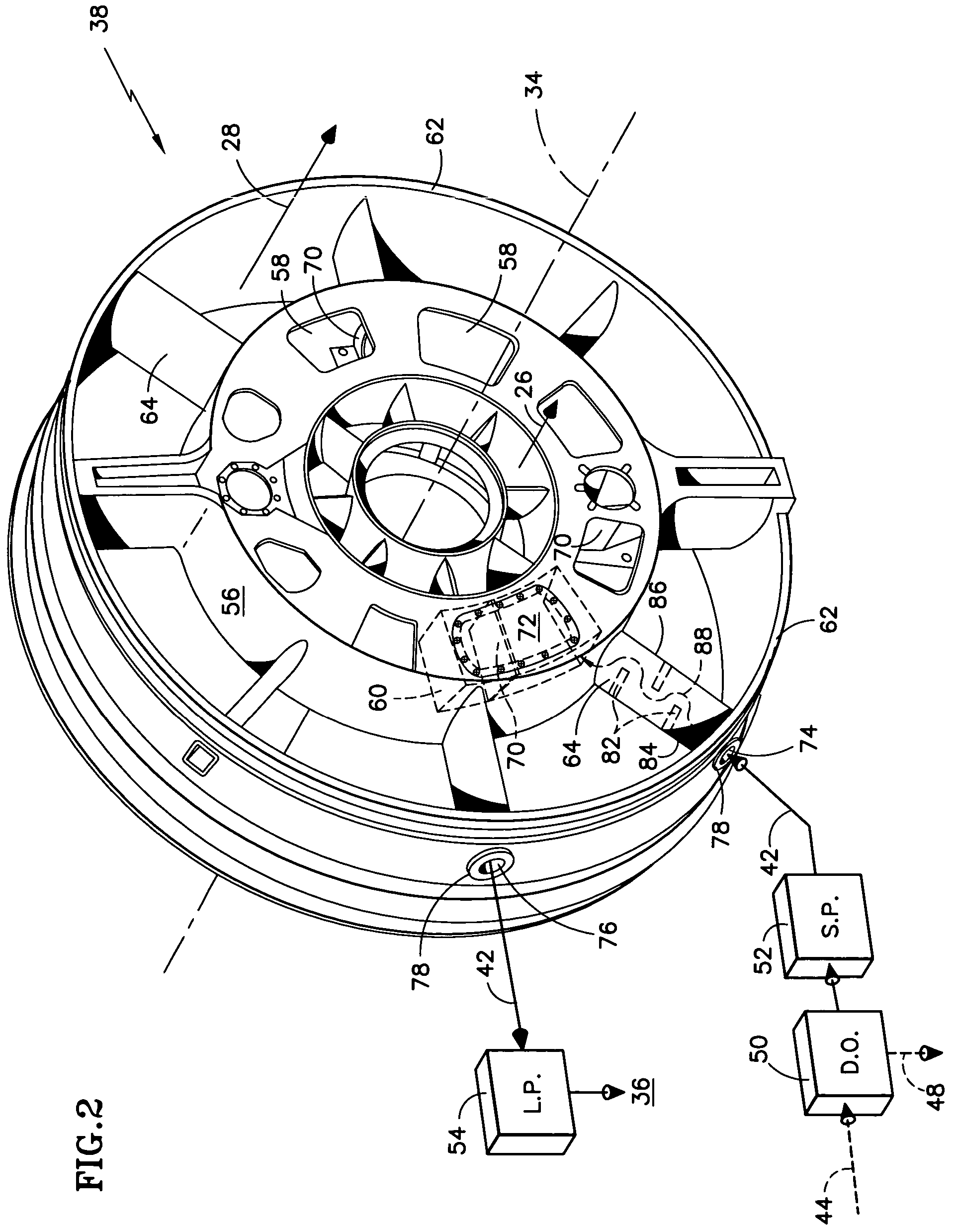
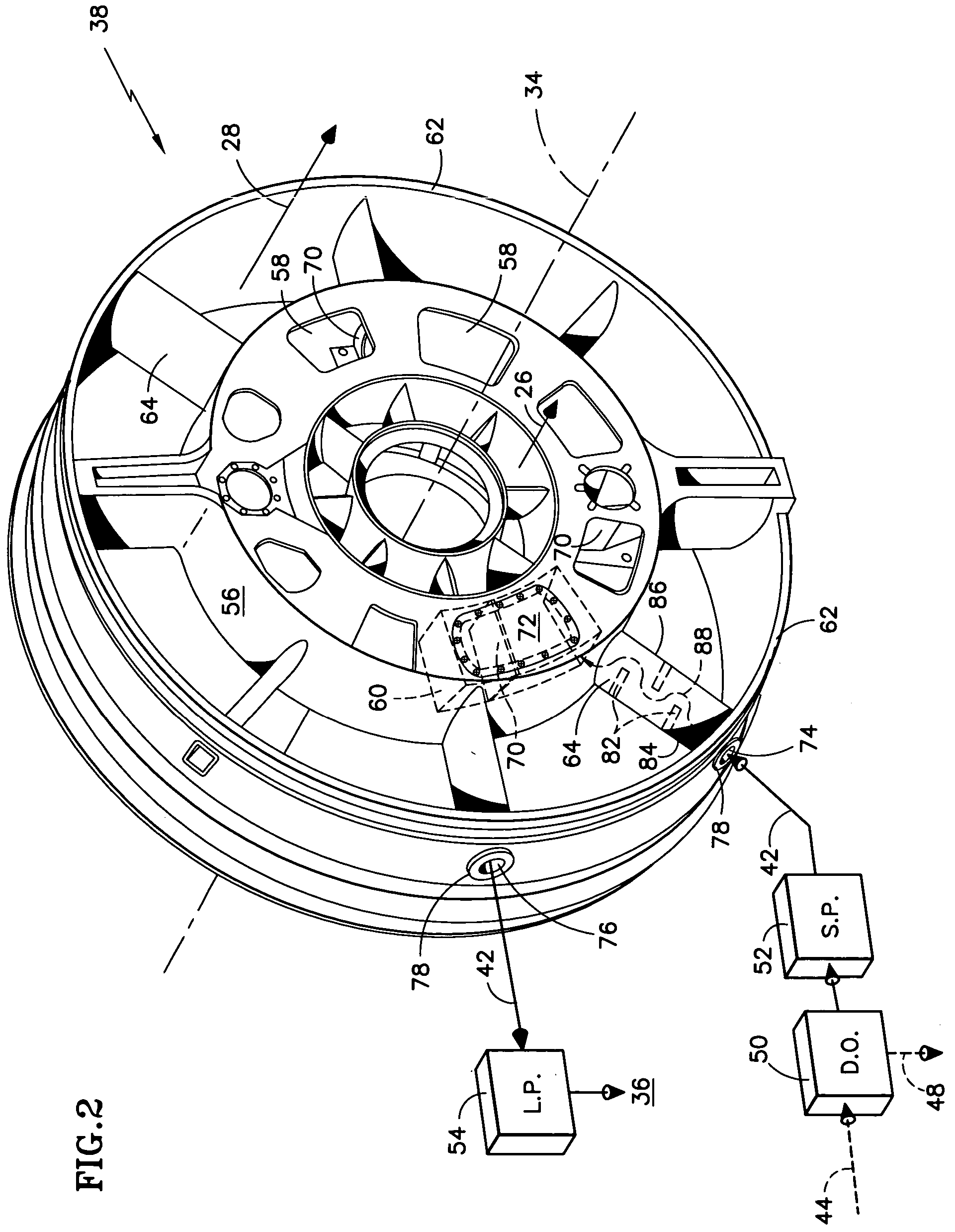
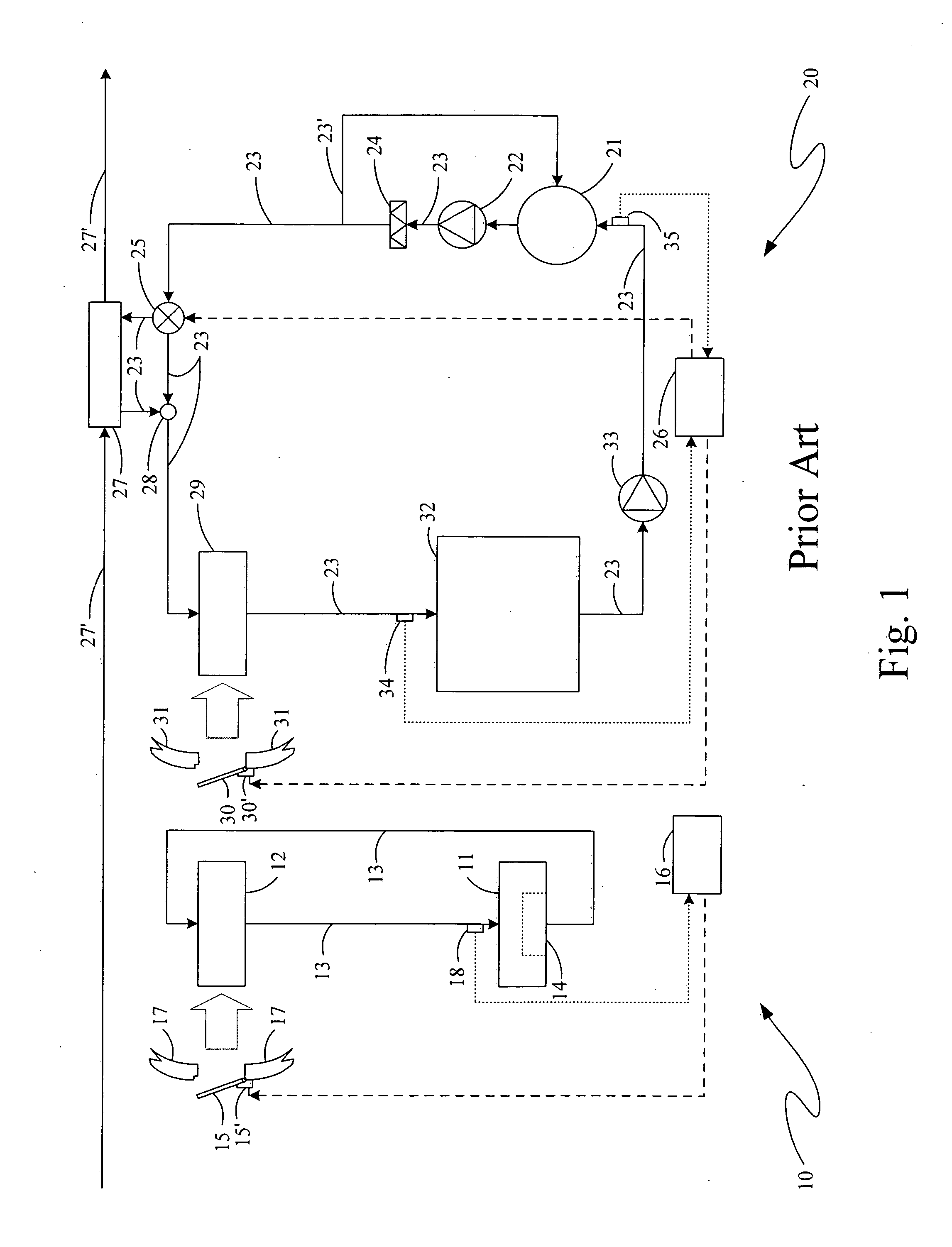
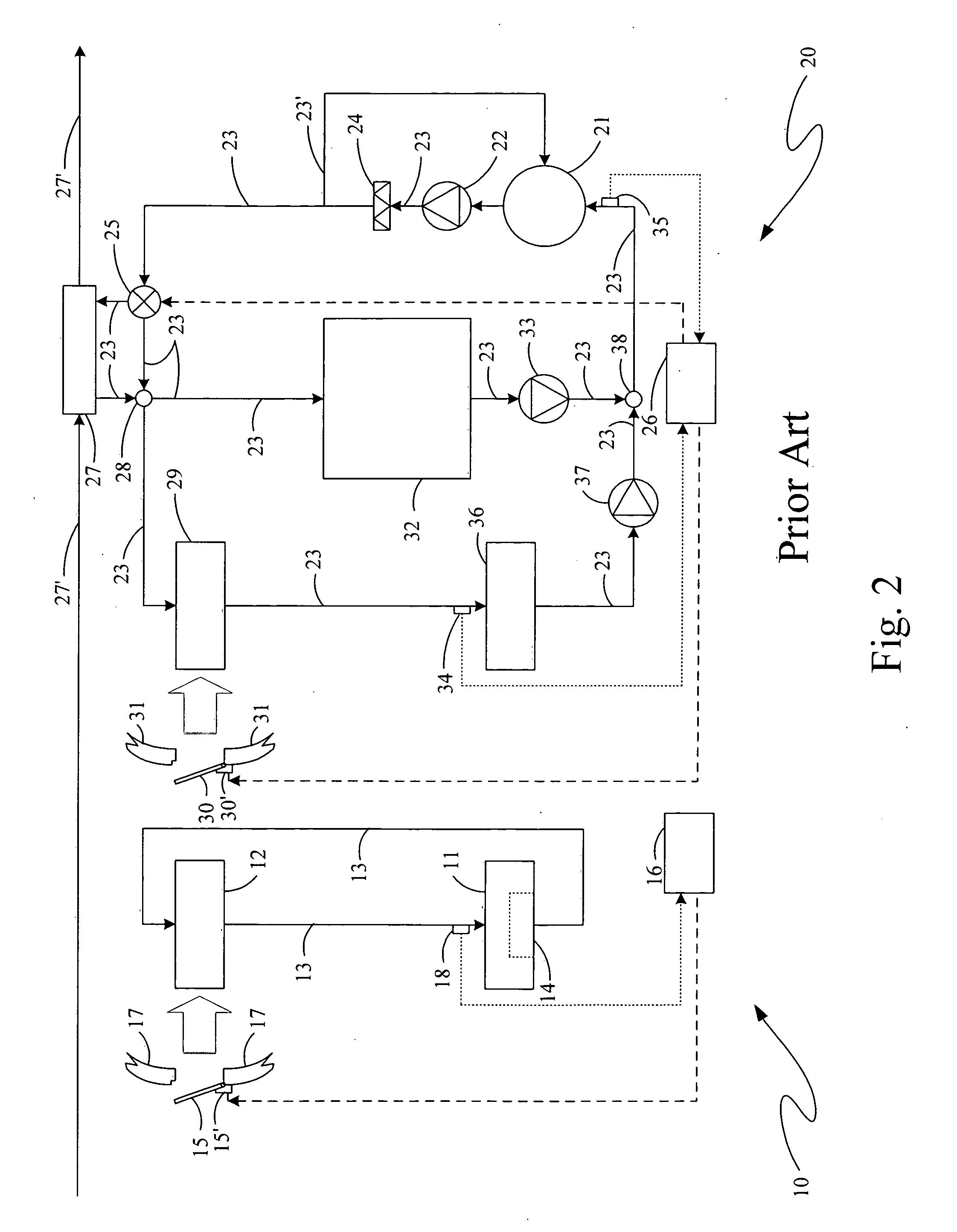
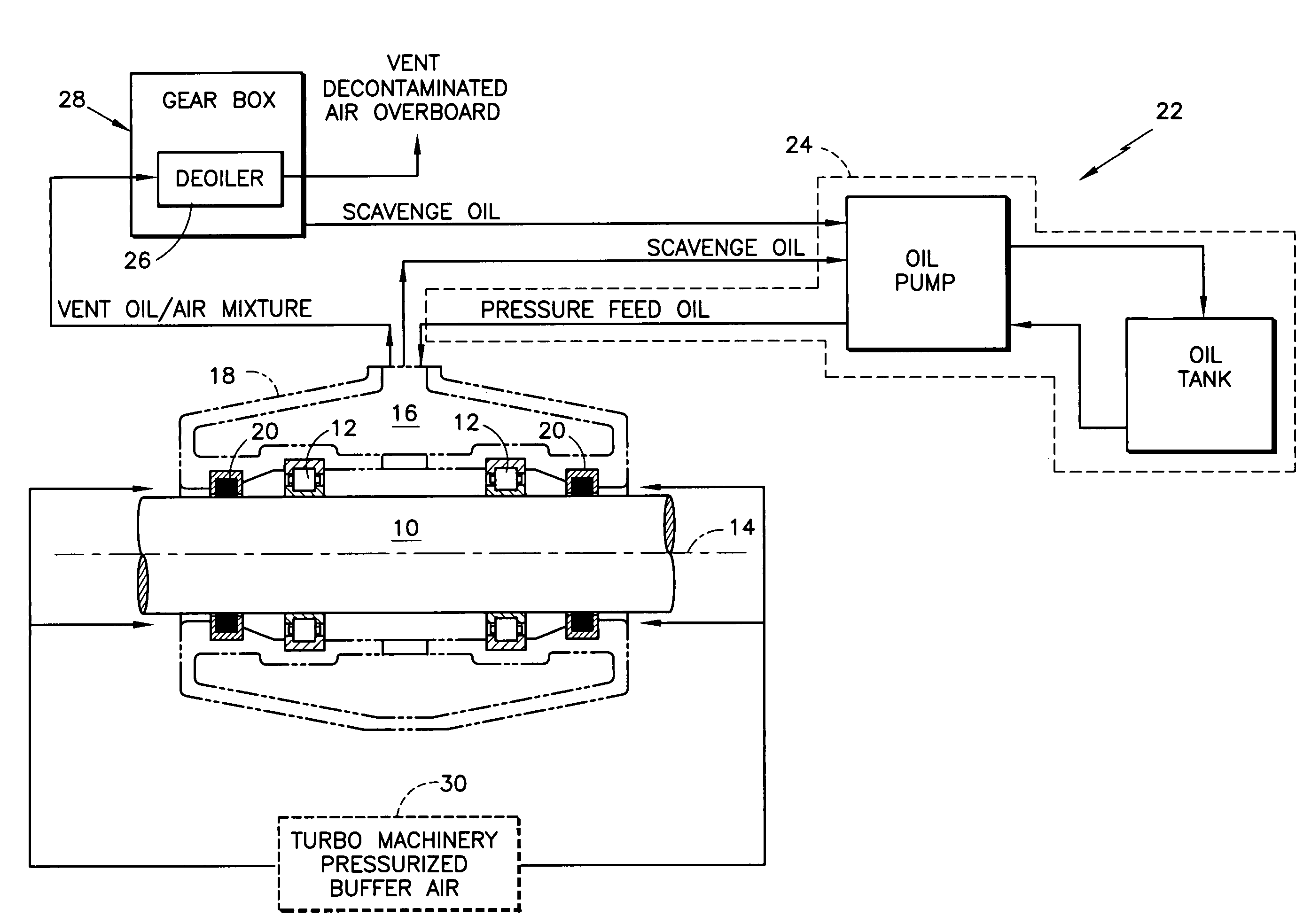
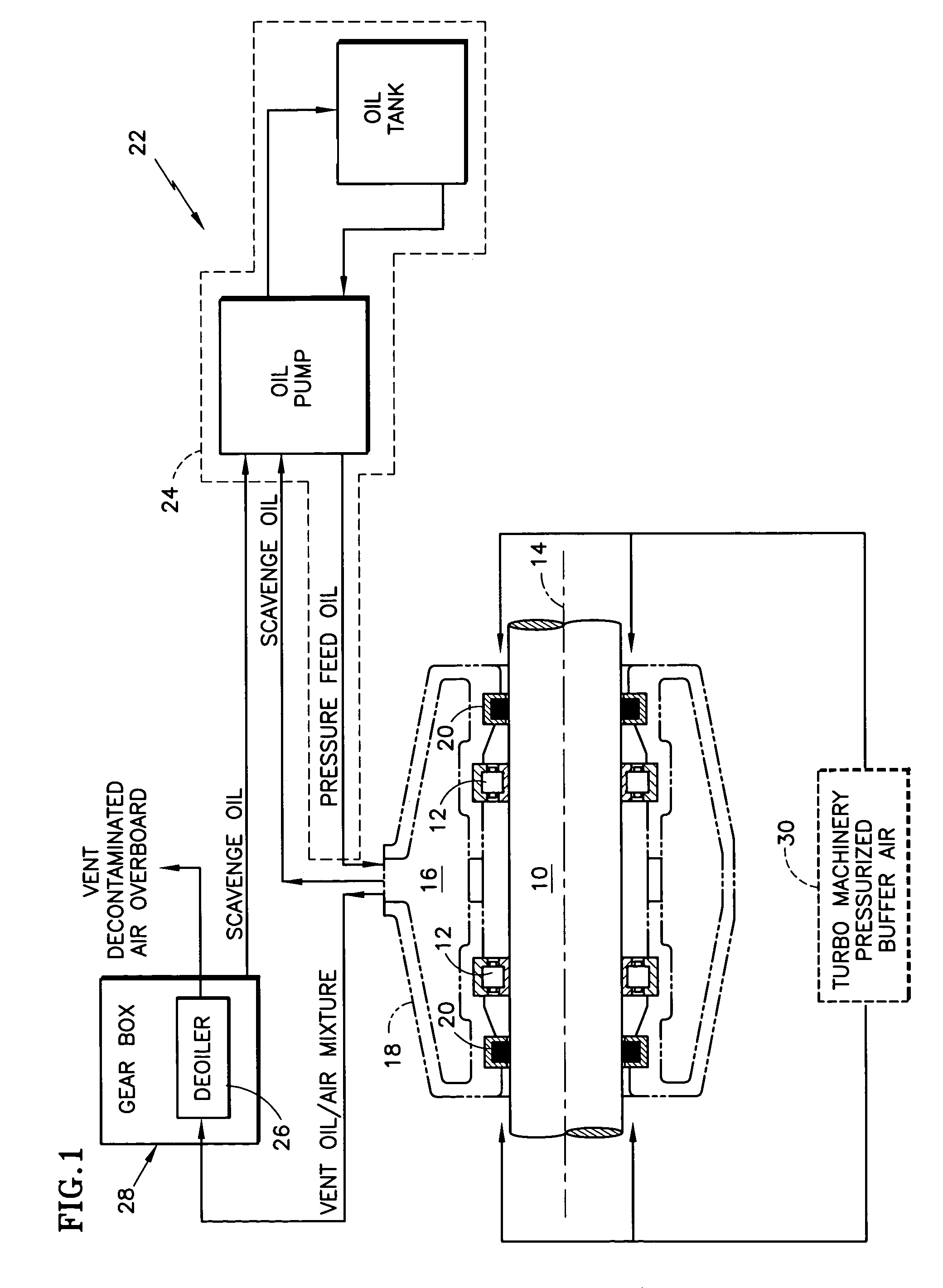
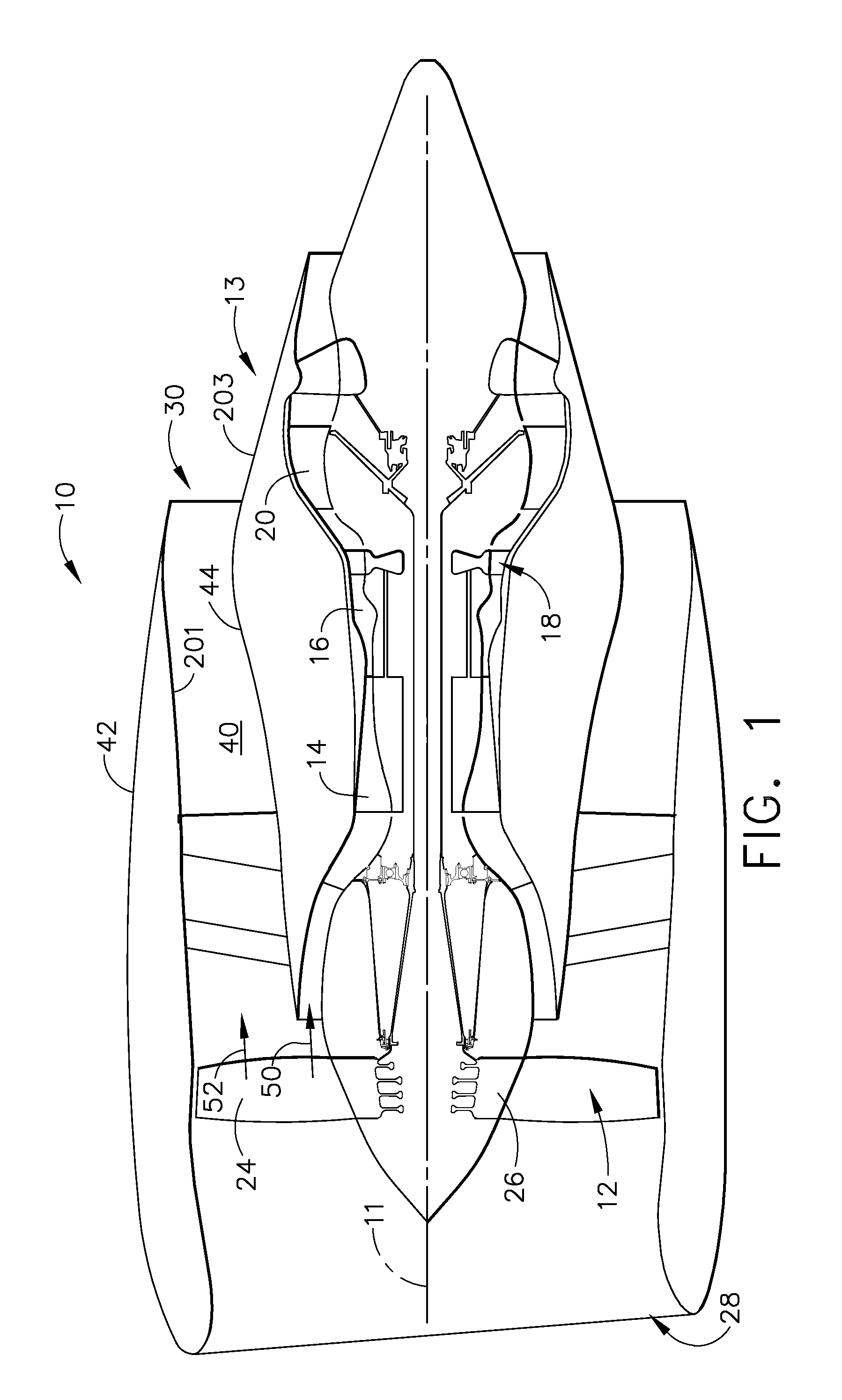
Deoiler for a lubrication system
ActiveUS7377110B2Reduce pressureHigh power settingPump componentsEngine fuctionsPositive pressureEngineering
A deoiler 26 for separating oil from air contaminated with the oil has at least one separator for separating the oil from the air and also has a source of suction for reducing air pressure at the source of the air. In an exemplary embodiment, the deoiler 26 creates the suction at a first operating condition, but acts as a restrictor at a second operating condition. A deoiling method according to the invention creates suction at a first operating condition to reduce the air pressure at the source of the oil-contaminated air, establishes a flow restriction at a second operating condition to pressurize the air source, and encourages oil to separate from the air at both operating conditions. When used as a component of a turbine engine lubrication system 22, the source of contaminated air may be a buffered bearing compartment 16. The inventive deoiler ensures a positive pressure difference across the bearing compartment seals 20 at the engine's idle power setting without requiring the idle setting to be undesirably high, and without requiring the use of buffer air whose pressure at higher engine power is high enough to be detrimental. In an exemplary embodiment, the deoiler pressurizes the bearing compartment at higher power settings to resist excessive buffer air infiltration into the bearing compartment.
Owner:RTX CORP
Center housing design for electric assisted turbocharger
InactiveUS6845617B1Shorten the axial lengthInhibit migrationInternal combustion piston enginesGas turbine plantsTurbochargerDynamic balance
An electric assisted turbocharger has an electric motor with a stator and a rotor that is coupled to a turbocharger shaft carried by a bearing assembly. The stator has a left-hand winding and a right hand-winding each projecting axially outwardly therefrom. The winds each extend a different distance radially along the motor (and are thus asymmetrical with respect to one another), thereby forming a radial gap along an axial end of the stator. The so-formed stator is disposed within a motor housing and together, the stator and motor housing, facilitate placement center housing axial end therein to minimize turbocharger axial length. The rotor is configured to prevent migration of oil into the motor housing, to improve dynamic balance, and comprises an integral thrust washer for placement against the bearing assembly.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Compact turbocharger
InactiveUS20030223892A1Minimal lengthLow thermal expansionInternal combustion piston enginesPump componentsClose couplingBall bearing
The use of anti-friction ball bearings in a unique arrangement does not require the use of lubricating oil from the internal combustion engine lubricating system and permits close coupling of the bearings and a compact turbocharger. A turbocharger bearing housing forms a coolant jacket with an inner bearing engaging portion that has two bearing engagement surfaces engaged with the outer races of two anti-friction bearings whose inner races carry rotating shaft, turbine and compressor of the turbocharger. The anti-friction bearings are, preferably, angular contact ball bearings, and the two bearing engagement surfaces of the bearing housing are closely spaced, providing a turbocharger shaft of minimal length and substantially reducing the thermal expansion of the shaft. The coolant jacket protects the anti-friction bearings from exposure to the extreme heat of the exhaust gas driven turbine, notwithstanding their increased proximity due to the shortened turbocharger shaft. In addition, an external motor-generator may be carried by the compact turbocharger, and its motor may be connected to the turbocharger rotor assembly by a permanent, solid connector and stay connected throughout the entire operating range of the turbocharger. In such assembly, the electronic motor-generator control is mounted on the motor housing and energizes the motor from battery power during the engine acceleration period up to approximately the torque peak speed; thereafter, the control changes to a generator mode when excess energy is available in the engine exhaust gas.
Owner:WOOLLENWEBER WILLIAM E
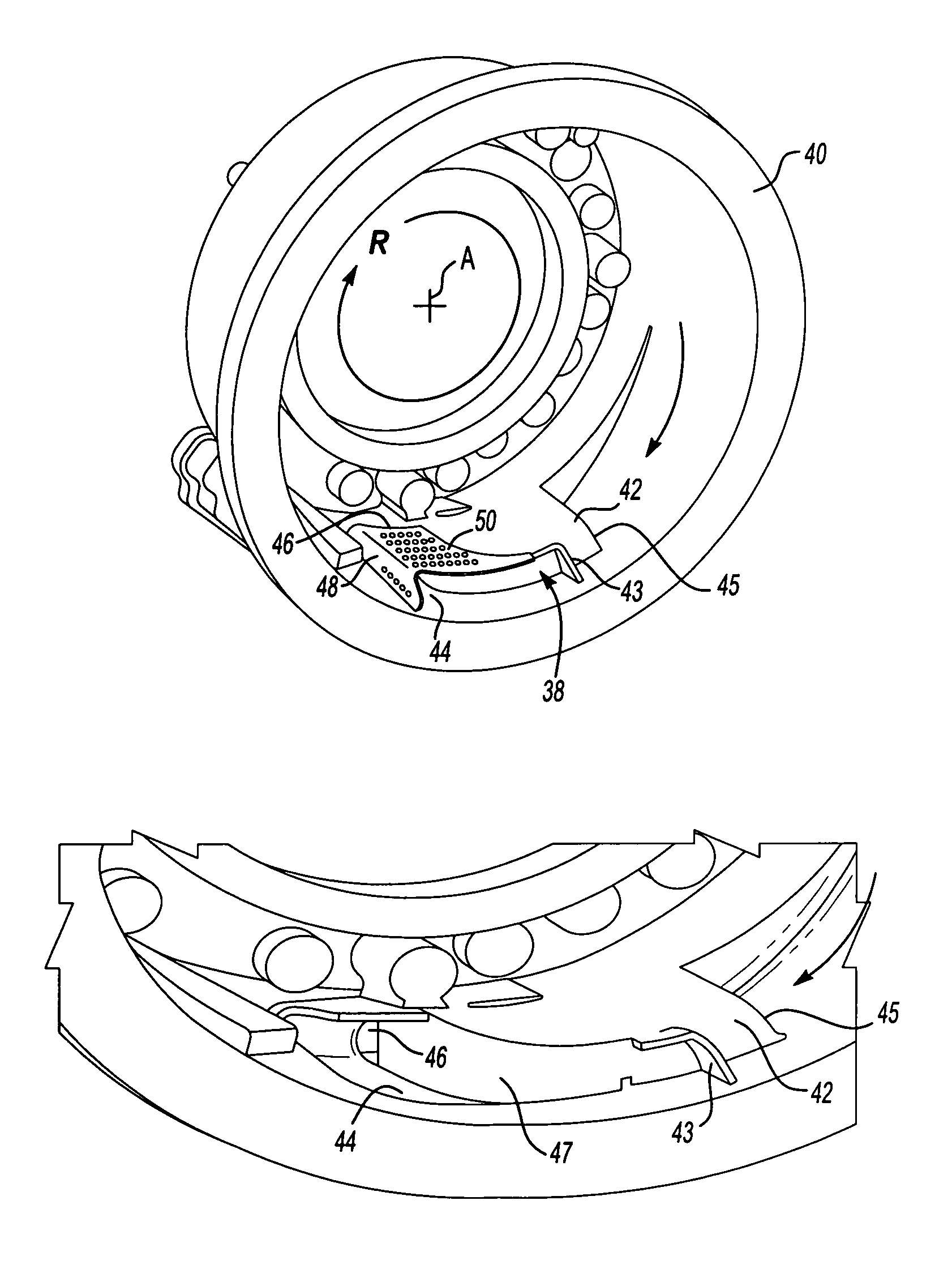
Bifurcated oil scavenge system for a gas turbine engine
An oil scavenge system includes a tangential scavenge scoop and a settling area adjacent thereto which separately communicate with a duct which feeds oil into an oil flow path and back to an oil sump. A shield is mounted over the settling area to at least partially shield the collecting liquid oil from interfacial shear. A multiple of apertures are located through the shield to permit oil flow through the shield and into the duct. The scavenge scoop forms a partition which separates the duct into a first portion and a second portion. The first portion processes upstream air / oil mixture that is captured by the tangential scoop while the second portion receives the oil collected in the settling area.
Owner:RTX CORP
Method and apparatus for controlling fuel in a gas turbine engine
InactiveUS20090313999A1Solution value is not highTurbine/propulsion engine coolingTurbine/propulsion fuel valvesWorking fluidCombustor
A method and system for controlling fuel in a gas turbine engine including a fuel supply system channeling fuel to a combustor are provided. The system includes a first heat exchanger configured to transfer heat between a working fluid and a first cooling medium. The system also includes a second heat exchanger in series flow communication with the first heat exchanger wherein the second heat exchanger is configured to transfer heat between the working fluid and a second cooling medium. The system further includes a modulating valve configured to control the flow of at least one of the first and the second cooling media to maintain a temperature of the first or second cooling medium substantially equal to a predetermined limit.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Gas Turbine and Method of Operating a Gas Turbine
ActiveUS20090301053A1Cool evenlyUniform cooling of the rotorGas turbine plantsSafety/regulatory devicesCombustion chamberTurbine
A gas turbine including at least one compressor, one combustion chamber, and at least one turbine including at least one rotor and at least one generator coupled to the at least one rotor is provided. The at least one turbine is coupled to the at least one compressor. Once the gas turbine is shut down, the at least one generator can be used as a motor in order to drive the at least one rotor for a predetermined time period following shutdown of the gas turbine and thereby effect a uniform cooling of the rotor. A method of operating a gas turbine is also provided.
Owner:MTU AERO ENGINES GMBH
Method and apparatus for varying the critical speed of a shaft
A system is provided for changing the critical speed of a shaft that includes: a first shaft supported for relative rotational movement with respect to a stationary structure, a forward bearing disposed at the forward end of the shaft, an aft bearing disposed at the aft end of the shaft, at least one active bearing disposed between the forward bearing and the aft bearing, and means for changing the support stiffness of the active bearing.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Integrated gearless and nonlubricated auxiliary power unit
An auxiliary power unit (APU) includes a compressor, a turbine, a combustor, and a starter-generator unit all integrated within a single containment housing. The turbine has an output shaft on which the compressor is mounted, and the starter-generator unit is coupled to the turbine output shaft without any intervening gears. The rotating components are all rotationally supported within the containment housing using bearings that do not receive a flow of lubricating fluid.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
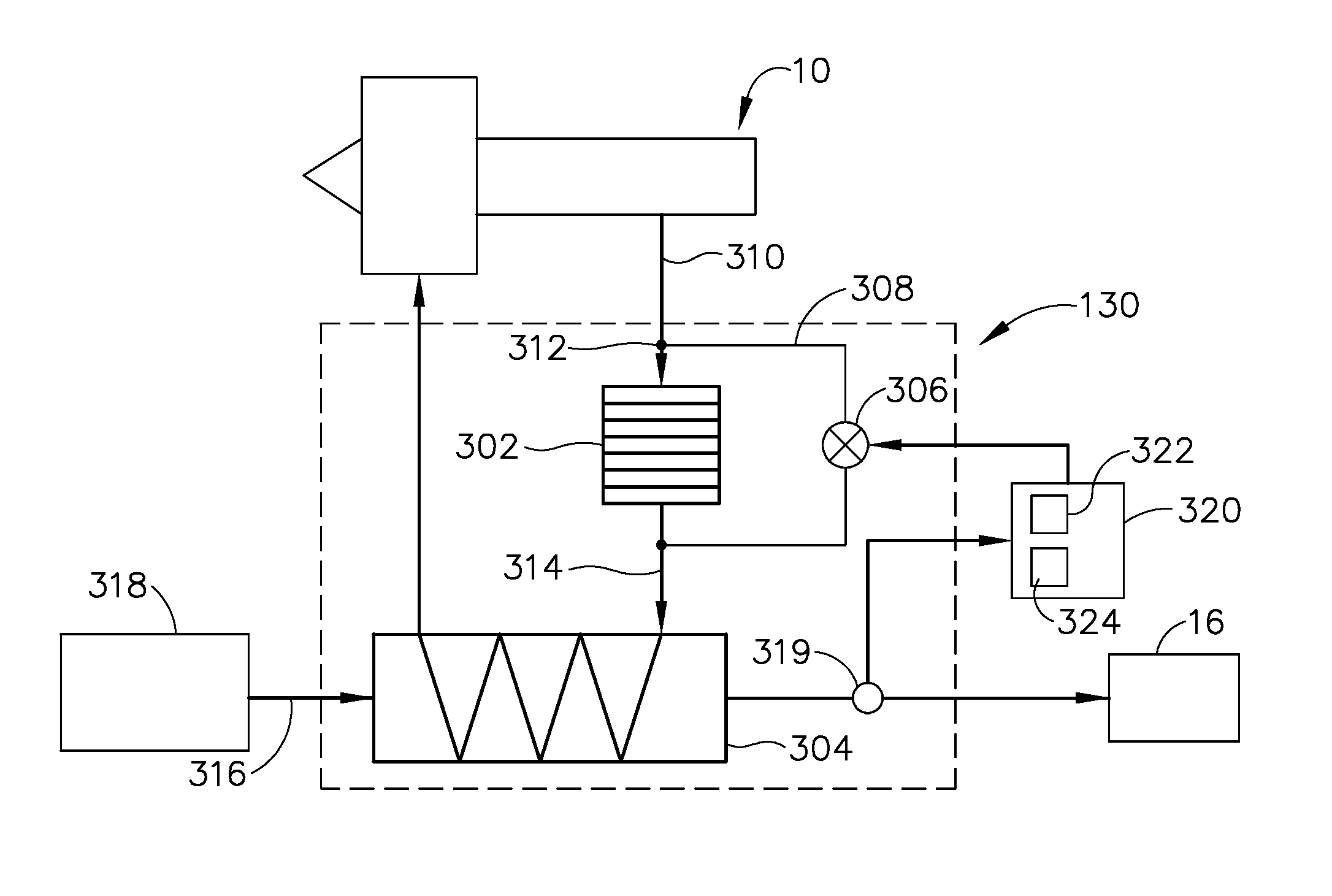
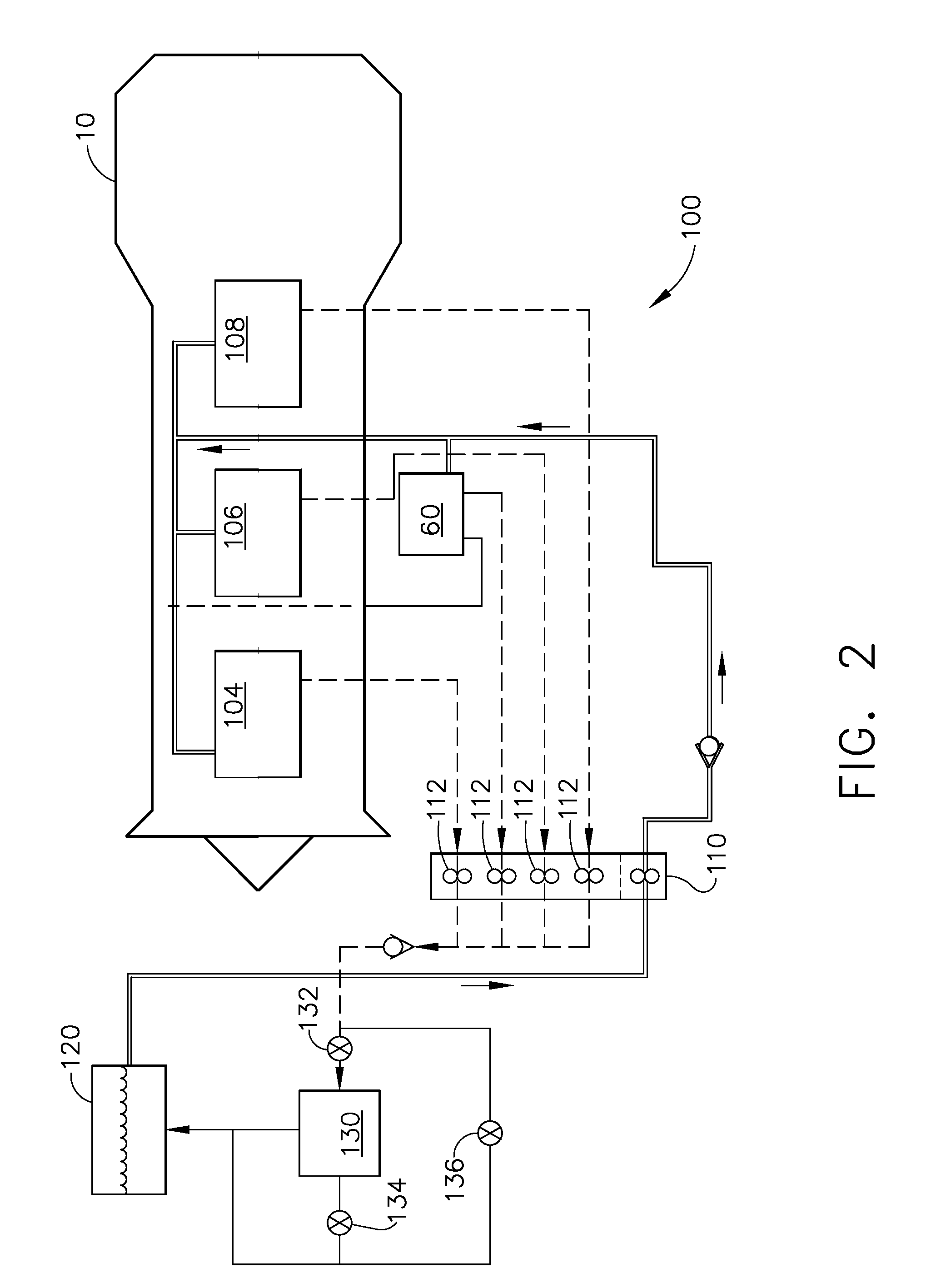
Systems and methods for thermal management in a gas turbine powerplant
InactiveUS20100107603A1Minimize impactReduce coke depositionAnalogue computers for vehiclesTurbine/propulsion engine coolingWorking fluidThermal management system
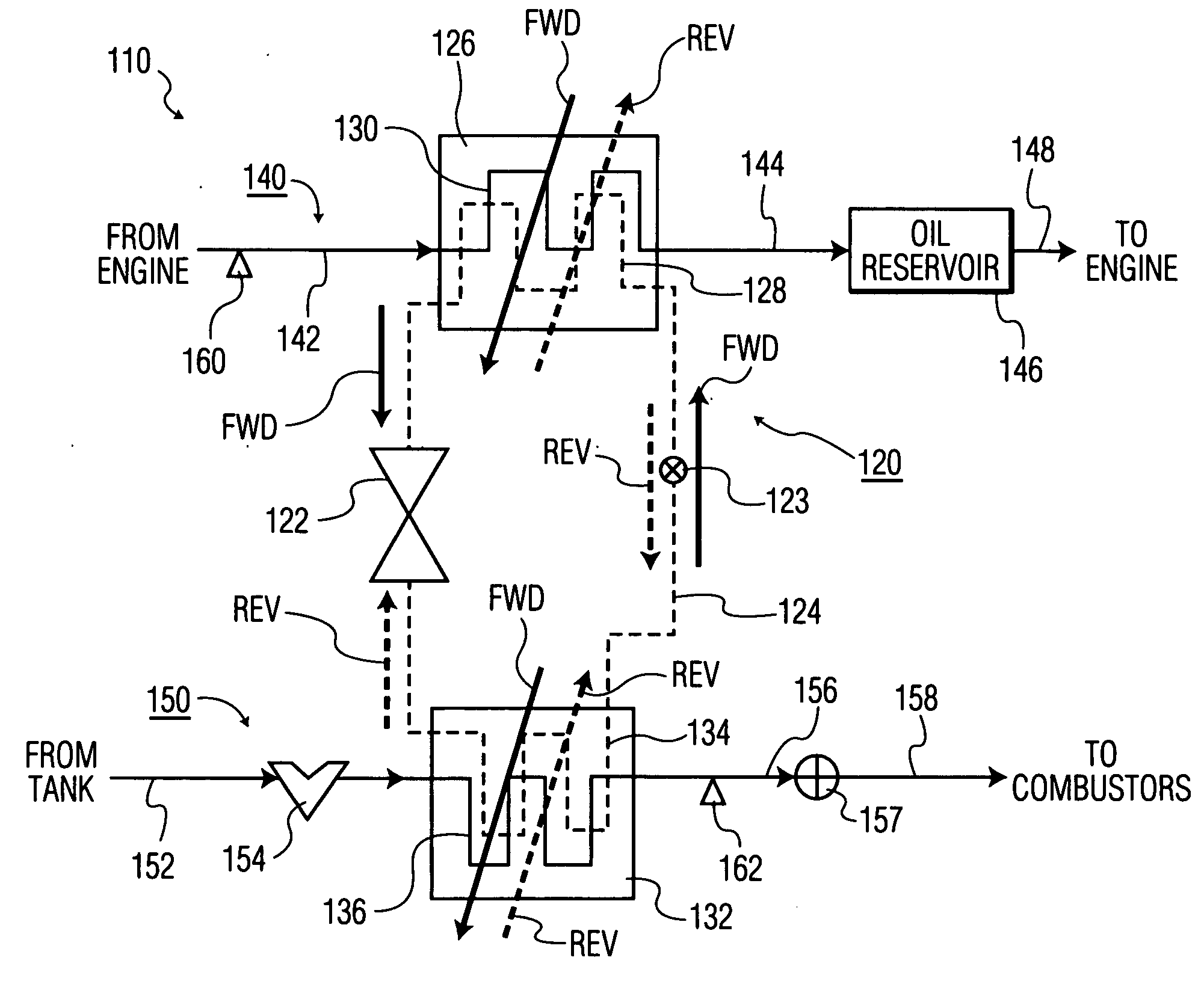
A thermal management system for a gas turbine powerplant with an engine oil line and an engine fuel line incorporates a heat transfer control module that includes a reversible heat pump with a heat pump compressor for circulating working fluid in forward and reverse directions through a working fluid line of the heat pump. The heat control module also includes a first heat exchanger having a heat exchange path for the working fluid between the compressor and a heat pump expansion valve and another heat exchange path for the engine oil. A second heat exchanger has a heat exchange path for the working fluid between the compressor and the expansion valve and another heat exchange path for the engine fuel. The heat pump can be operated in forward or reverse directions depending on whether heat is to be transferred from the engine oil or the fuel to the heat pump working fluid. In another embodiment an engine oil reservoir located between the first heat exchanger and the engine collects the oil before it is introduced to the engine and thus acts as a heat capacitor for the system.
Owner:PROPULSION GAS TURBINE & ENERGY EVALUATIONS
Cooling exchanger duct
InactiveUS7765788B2Cosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusWorking fluidEngineering
A heat exchange system for use in operating equipment in which a working fluid is utilized in providing selected operations thereof, including for use in lubricating systems for aircraft turbofan engine equipment, the heat exchange system for providing air and working fluid heat exchanges to cool the working fluid at selectively variable rates in the operating equipment developed airstreams. A heat exchanger core is provided in a controlled air flow duct system opening at its entrance to those airstreams and having its outlet end opening downstream in those airstreams.
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP
Method and apparatus for operating gas turbine engines
ActiveUS20100236213A1Outer walls isReduce the temperatureTurbine/propulsion engine coolingEfficient propulsion technologiesLeading edgeEngineering
A method for assembling a turbine engine to facilitate reducing an operating temperature of a lubrication fluid during engine operation, the gas turbine engine including a fan assembly, a booster downstream from the fan assembly, and a splitter circumscribing the booster. The method includes coupling a radially inner wall and a radially outer wall at a leading edge to form a splitter body, and coupling an inner support structure within the splitter body such that a cooling circuit is defined between at least a portion of the inner support structure and the inner and outer walls, said cooling circuit configured to circulate lubrication fluid therethrough such that as a temperature of the lubrication fluid is reduced and a temperature of at least a portion of the inner and outer walls is increased.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com