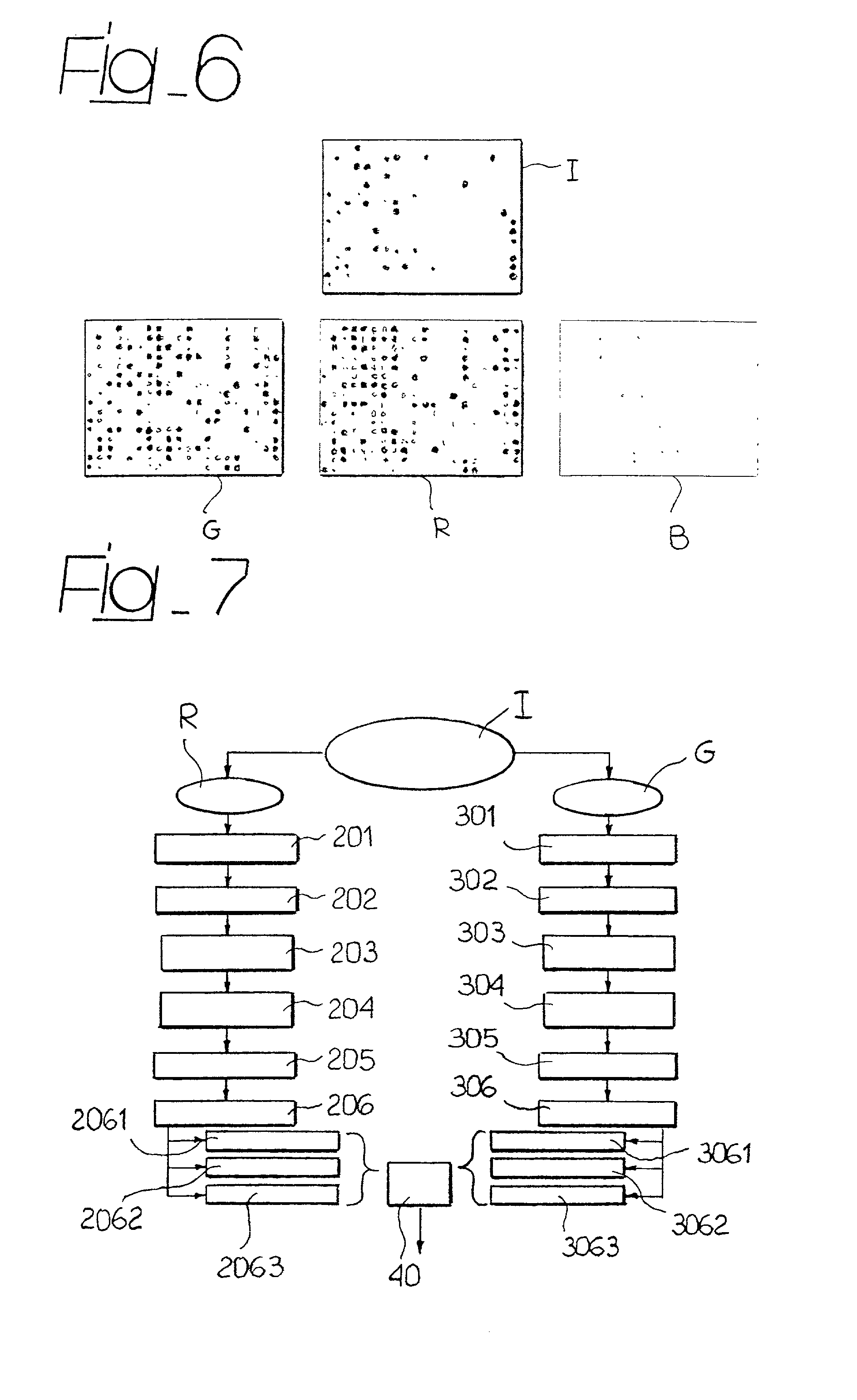
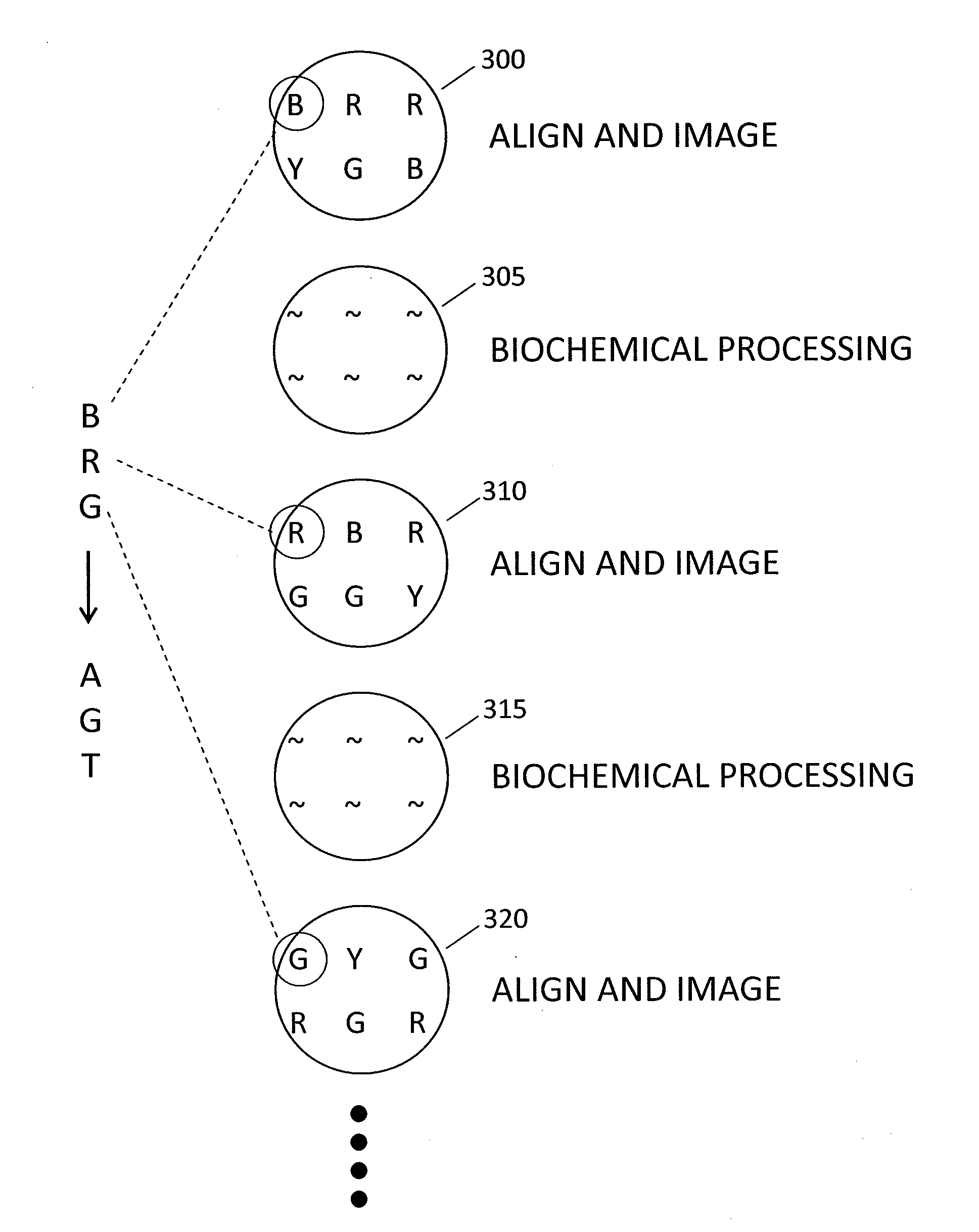
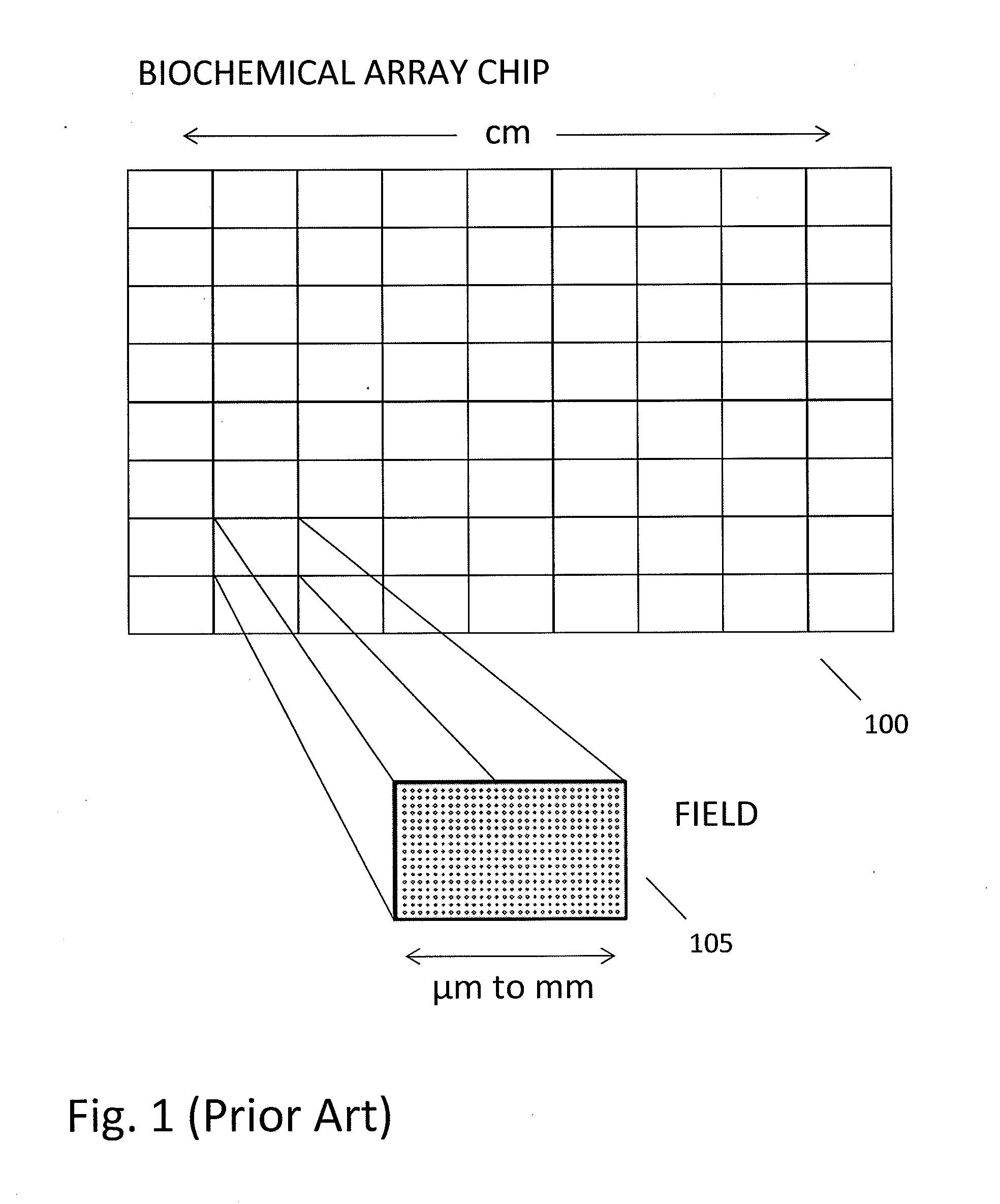
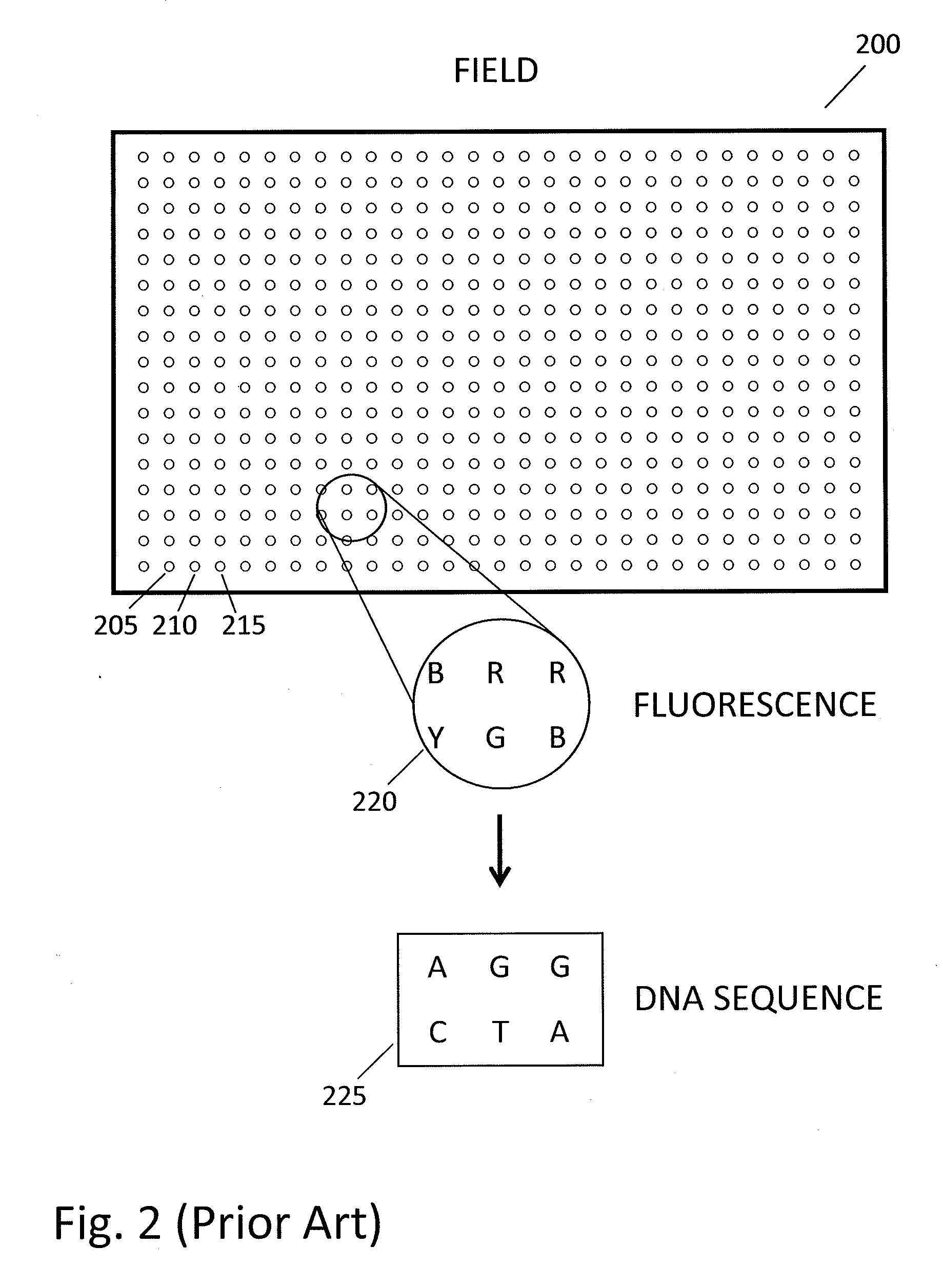
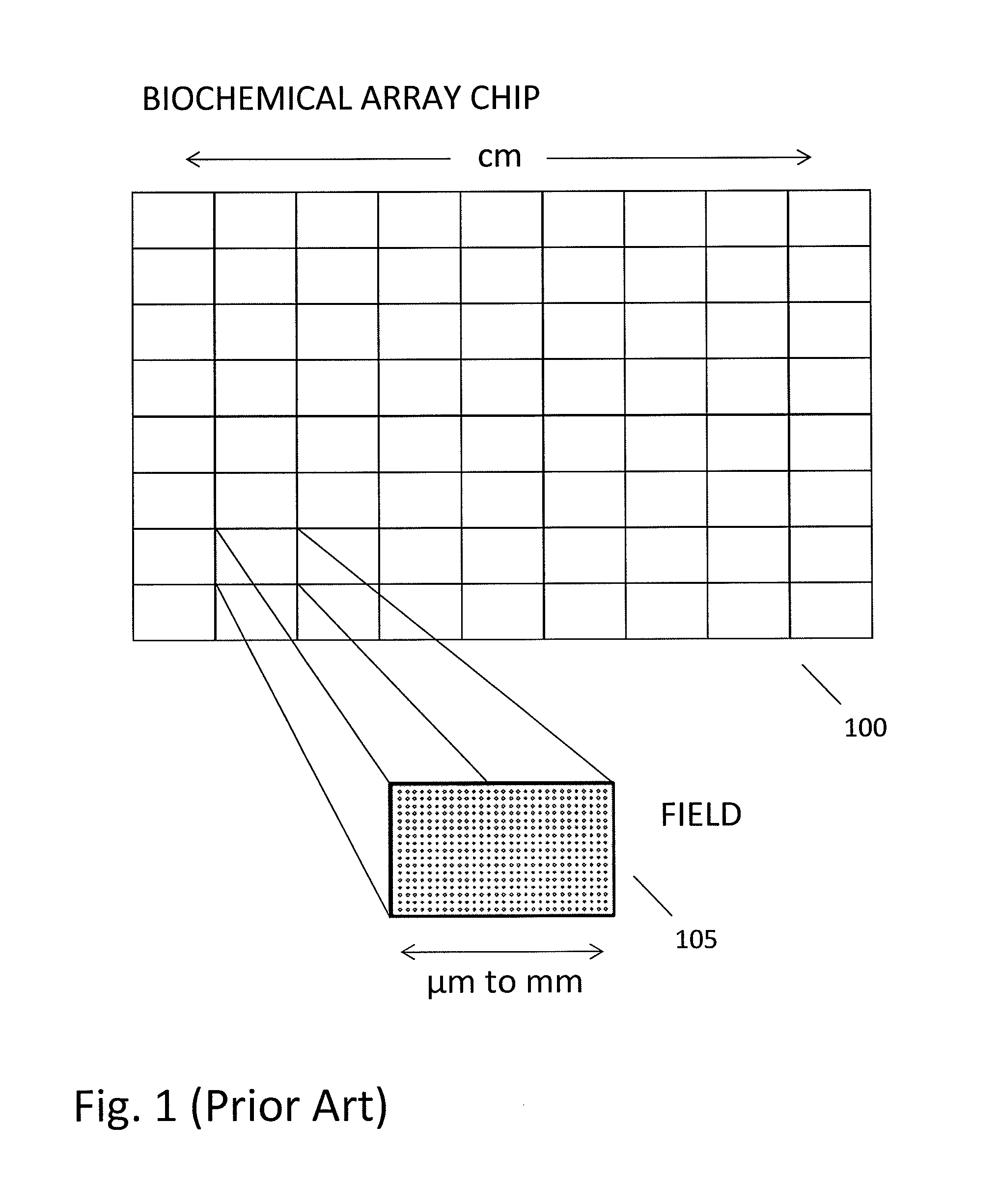
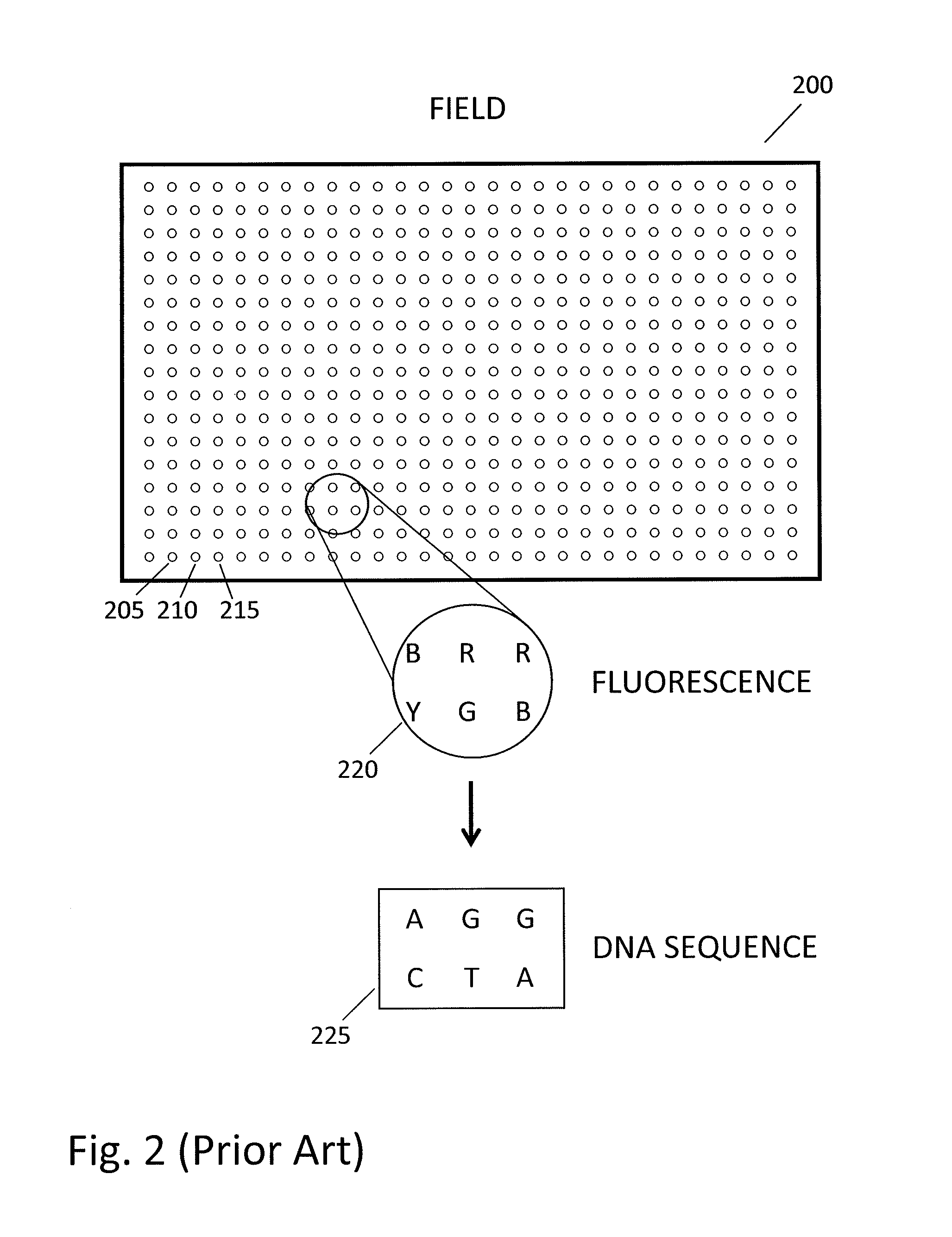
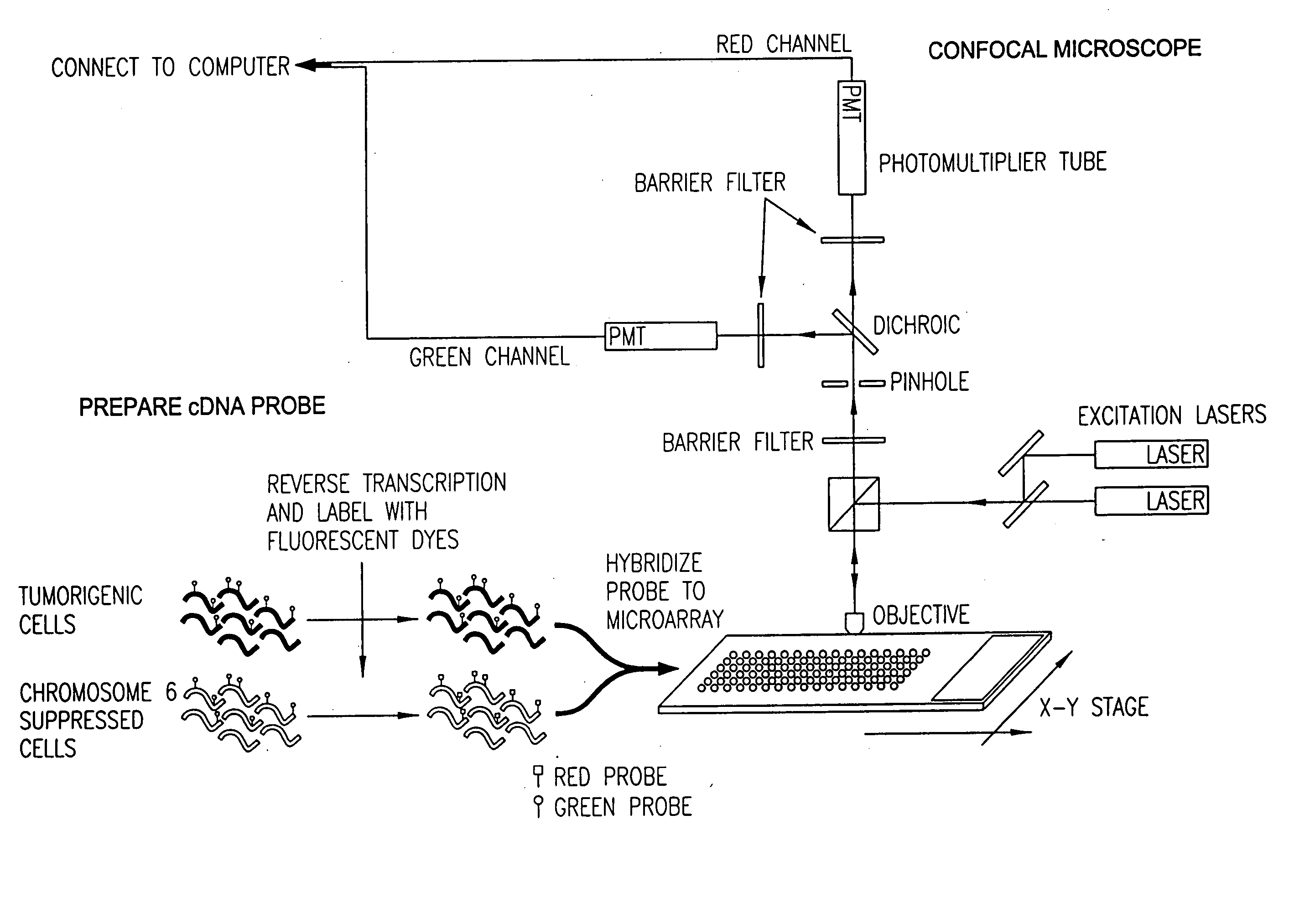
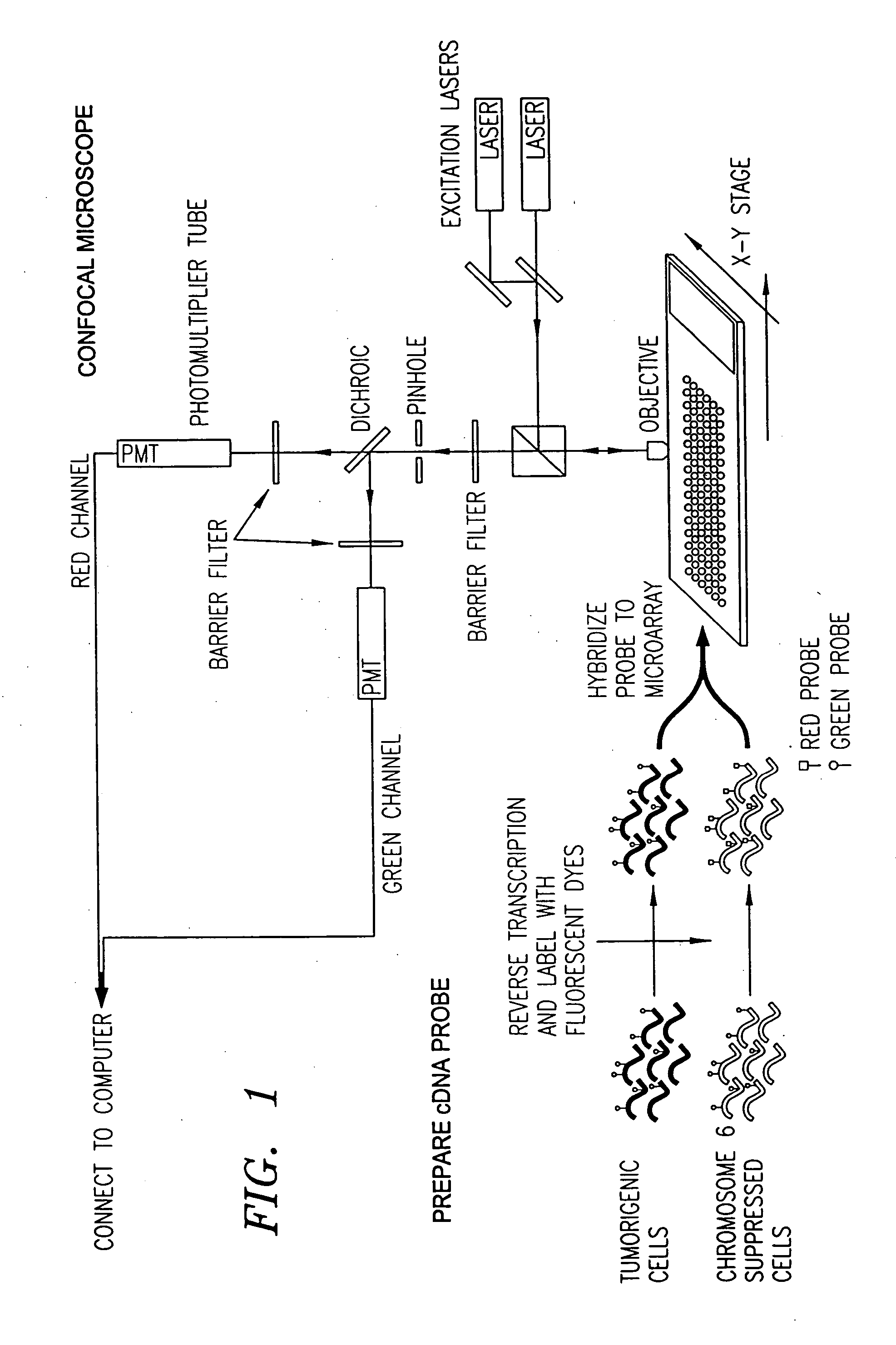
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
63results about "Recognition of DNA microarray pattern" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Apparatus and method for automatic detection of pathogens
ActiveUS20120169863A1Considerable expenseSimplifies and expedites diagnostic procedureMaterial analysis by optical meansBiological particle analysisPattern recognitionData acquisition
The invention discloses an apparatus and method for automatic detection of pathogens within a sample. The apparatus and method are especially useful for high-throughput and / or low-cost detection of parasites with minimal need for trained personnel. The invention entails automated microscopic data acquisition, and performing image processing of images captured from a sample using classification algorithms. Visual classification features of structures are extracted from the image and compared to visual classification features associated with known pathogens. A determination is reached whether a pathogen is present in the sample; and if present, the pathogen may be identified to a pathogen species. Diagnosis is rapid and does not require medically trained personnel.
Owner:S D SIGHT DIAGNOSTICS LTD
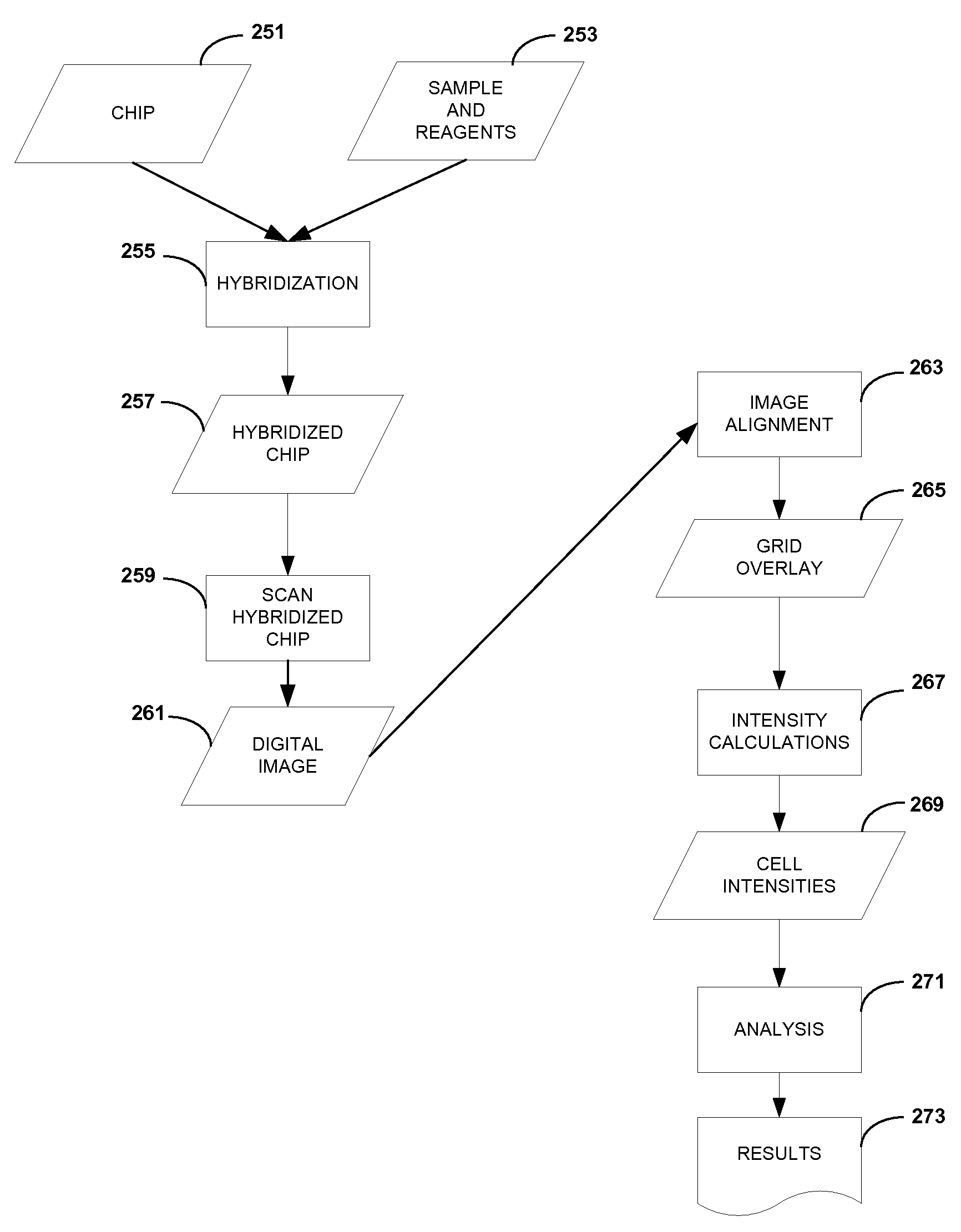
Apparatus and Method for Analyzing a Bodily Sample
ActiveUS20160279633A1Diagnosis considerableExpense of considerableBiological particle analysisLaboratory glasswaresImaging processingDigital image
Apparatus and methods are described for use with a digital camera that is configured to acquire images of a bodily sample. Two or more stains are configured to stain the bodily sample. A computer processor drives the digital camera to acquire, for each of a plurality of imaging fields of the bodily sample, two or more digital images, at least one of the images being acquired under brightfield lighting conditions, and at least one of the images being acquired under fluorescent lighting conditions. The computer processor performs image processing on the digital images, by extracting visual classification features from the digital images and analyzing the extracted visual classification features. The computer processor outputs a result of the image processing that includes an indication of one or more entities that are contained within the sample. Other applications are also described.
Owner:S D SIGHT DIAGNOSTICS LTD
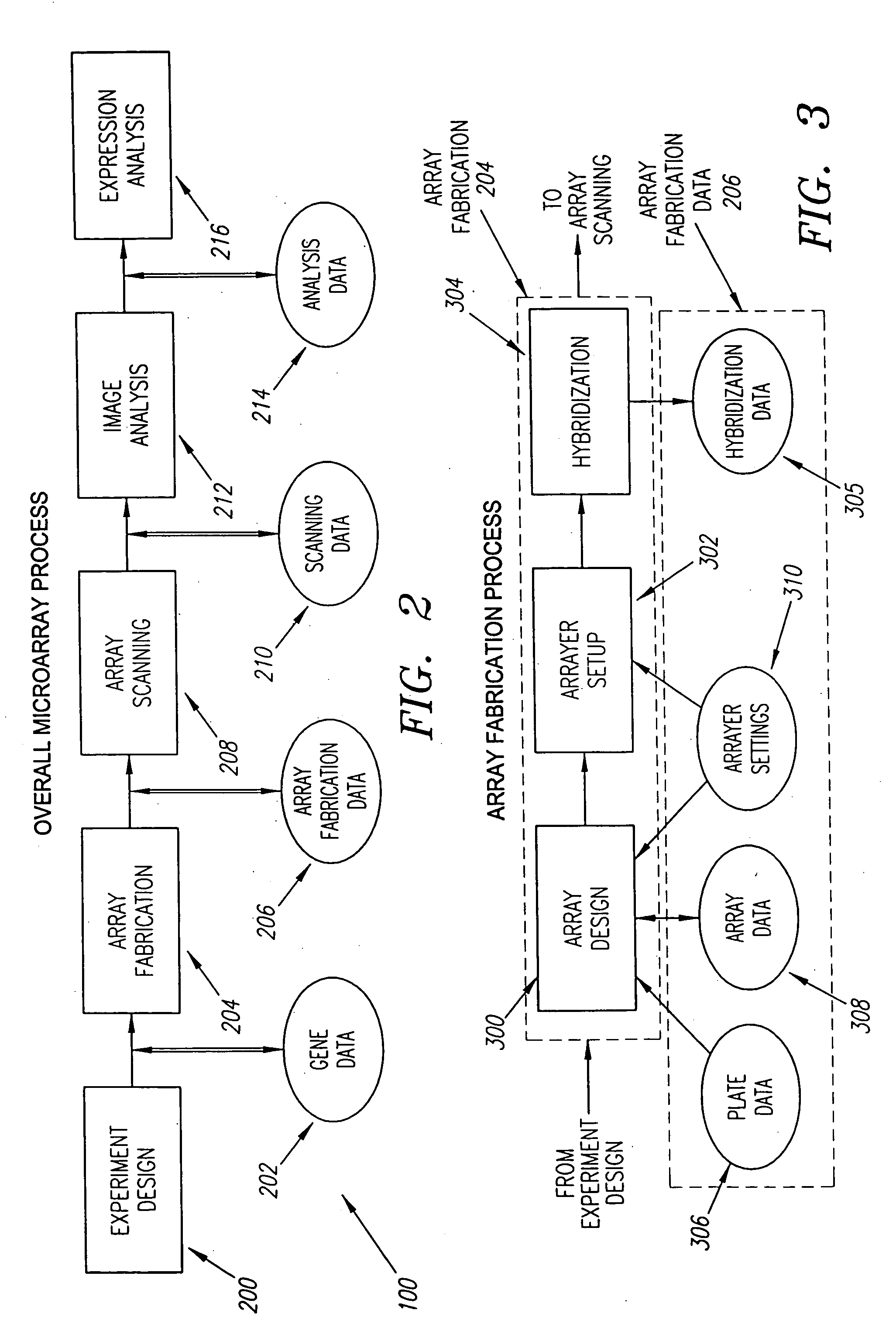
Feature locations in array reading
InactiveUS7206439B2Precise positioningImage enhancementImage analysisArray data structureDisplay device
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
System and method for automatically identifying sub-grids in a microarray
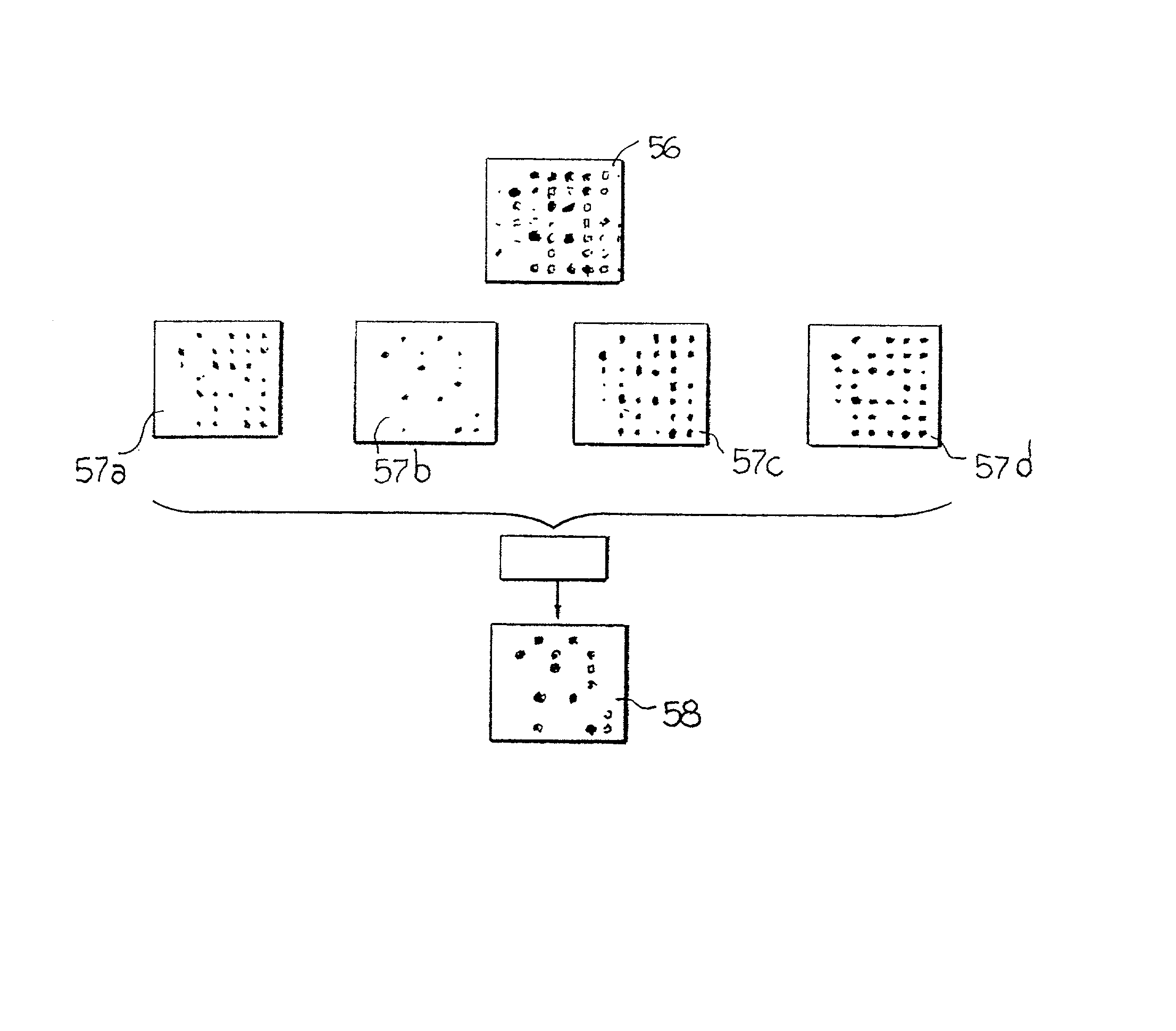
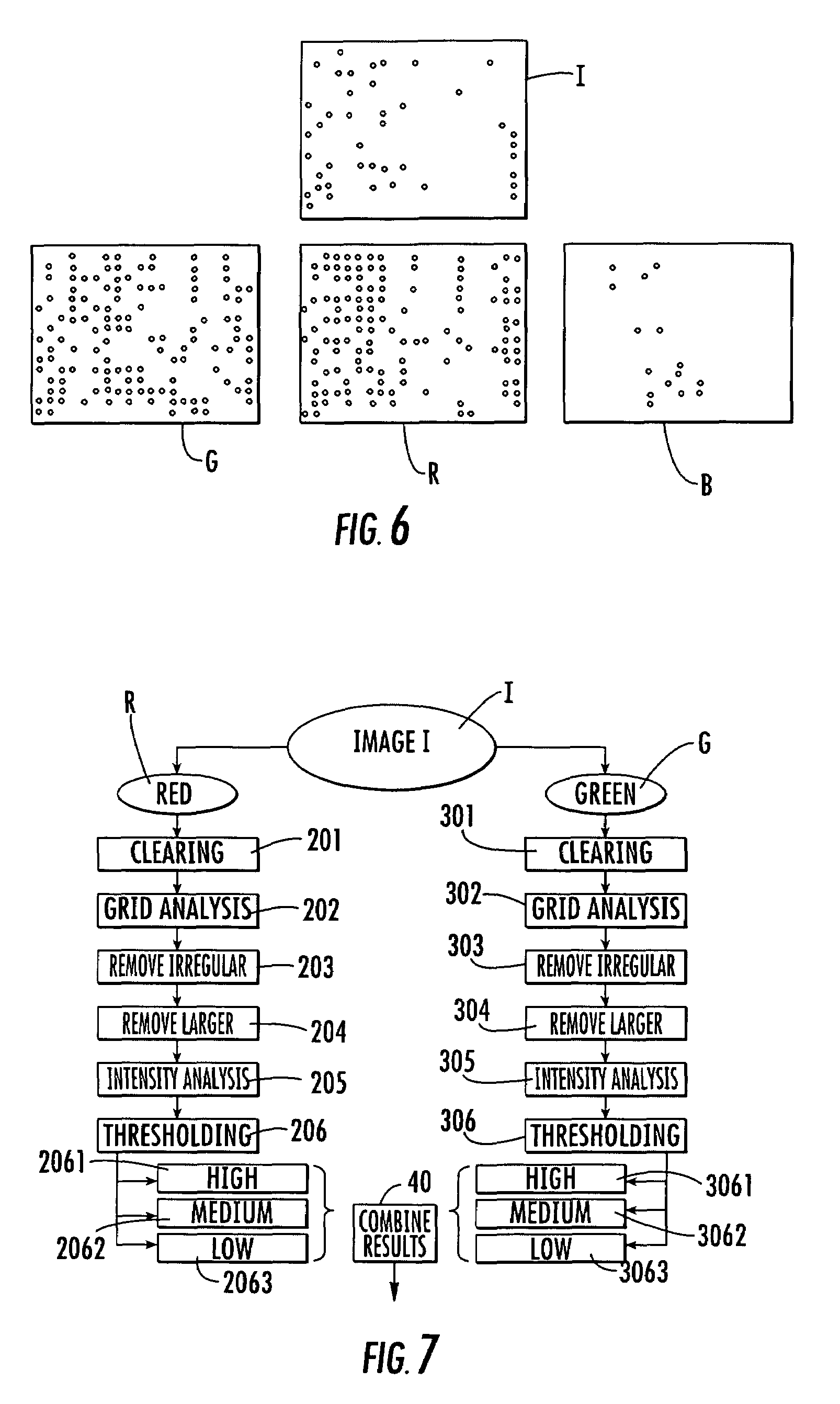
A digital image processing-based system and method for quantitatively processing a plurality of nucleic acid species expressed in a microarray are disclosed. The microarray is a grid of a plurality of sub-grids of the nucleic acid species. The system includes a scanner that has a digital scanning sensor that scans the microarray and transmits from an output a digital image of the microarray, and a computer that receives the digital image of the microarray from the scanner and then processes the digital image, identifying each of the microarray's sub-grids. The computer identifies the position of each of the sub-grids by (a) identifying regions in the digital image that each contains one of the sub-grids, (b) identifying rows and columns in each region where nucleic acid species are expressed to form a set of candidate sub-grids in each region, (c) selecting for each region a probable sub-grid from the set of candidate sub-grids in each region, and (d) comparing the positions of the probable sub-grids from each region to finalize the sub-grid positions.
Owner:BIODISCOVERY
Method, system, and computer code for finding spots defined in biological microarrays
InactiveUS6980677B2Wide rangeEnhance the imageImage enhancementImage analysisMathematical ComputingFrequency filtering
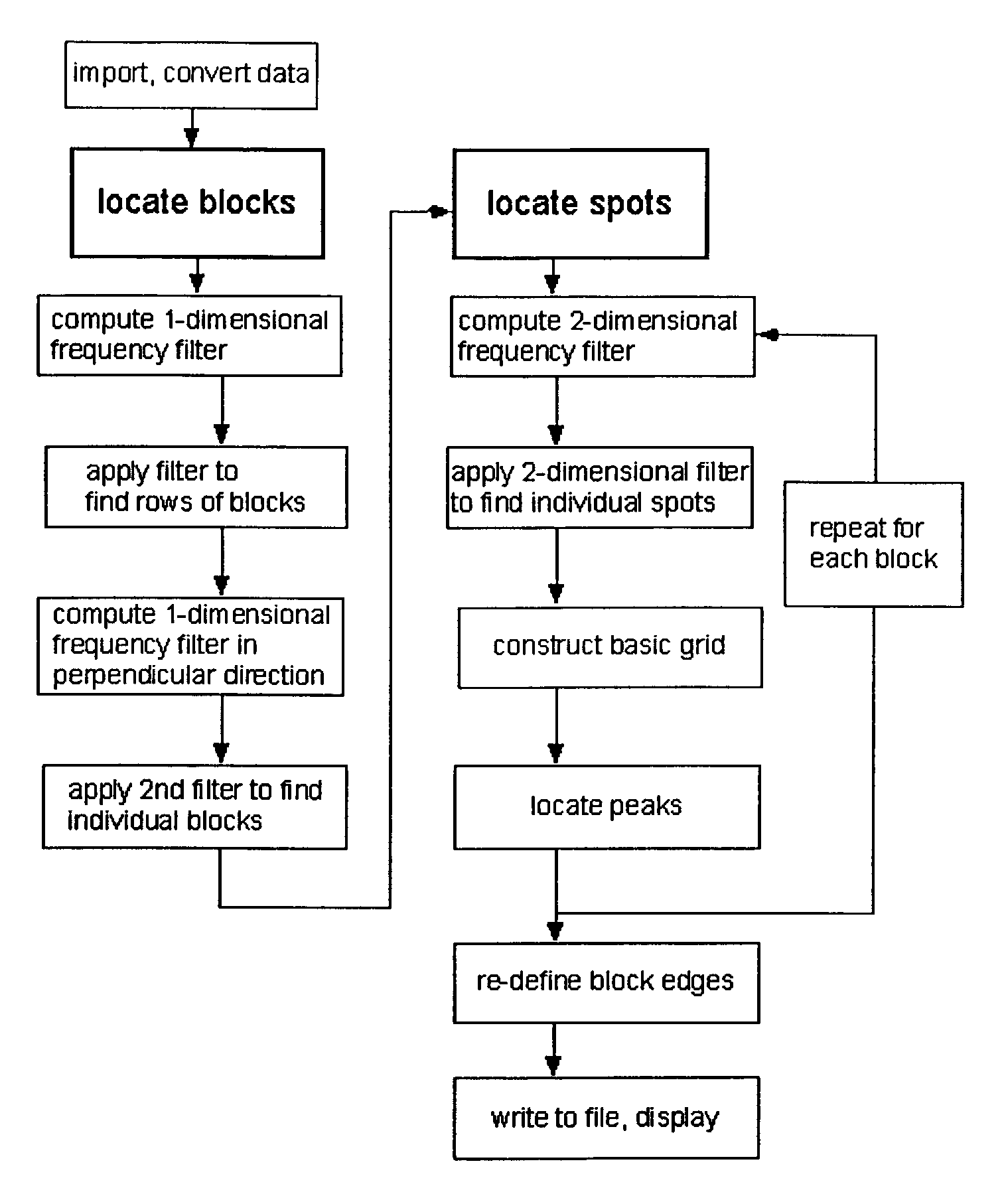
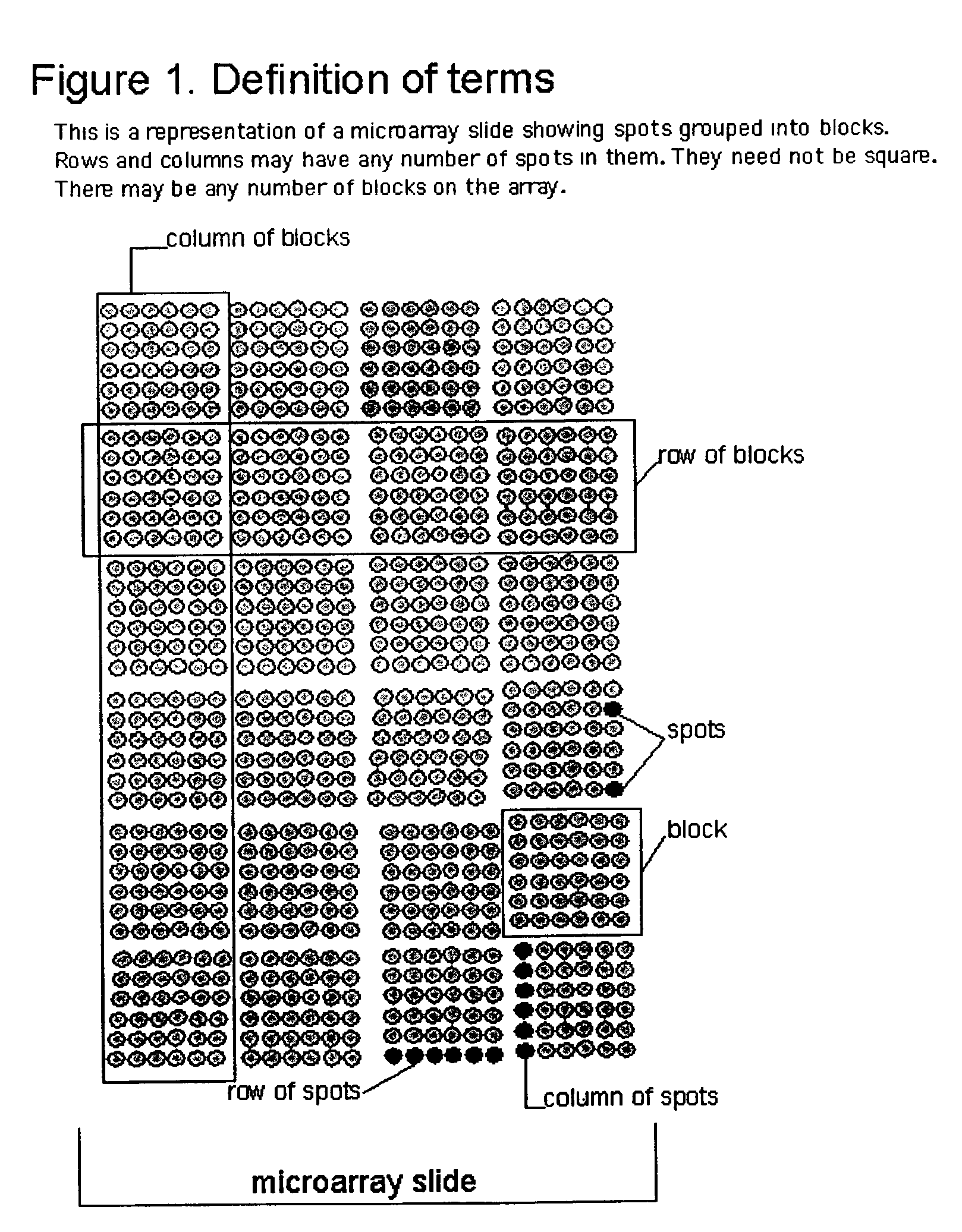
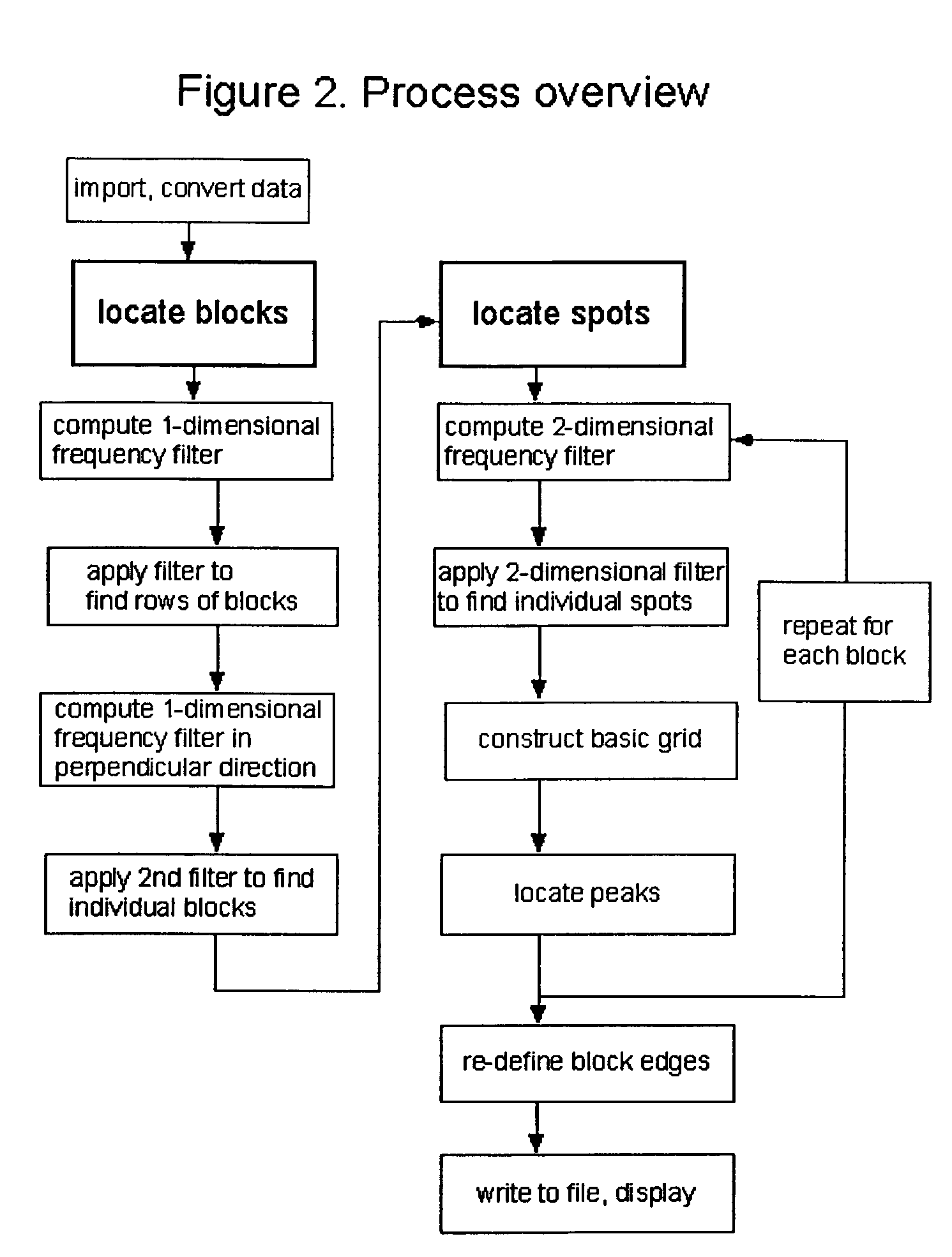
A method (and system) for using information contained within the scanned image to create, in an automated (or semi-automated) process, an accurate data grid. The process has steps: enhance the image; locate blocks of spots; and find each individual spot in each of the blocks. Preferably, the method makes use of image filtering using a“Principal Frequency Filter” based on a mathematical determination of major periodic elements in the image to eliminate noisy, non-periodic signals, and of smoothed intensity profiles of the filtered image data. Here, the term Principal Frequency Filter is used to indicate an image-enhancing filter based upon a mathematical operation which identifies the major periodic components of the image.
Owner:NILES SCI
System for the automatic analysis of images such as DNA microarray images
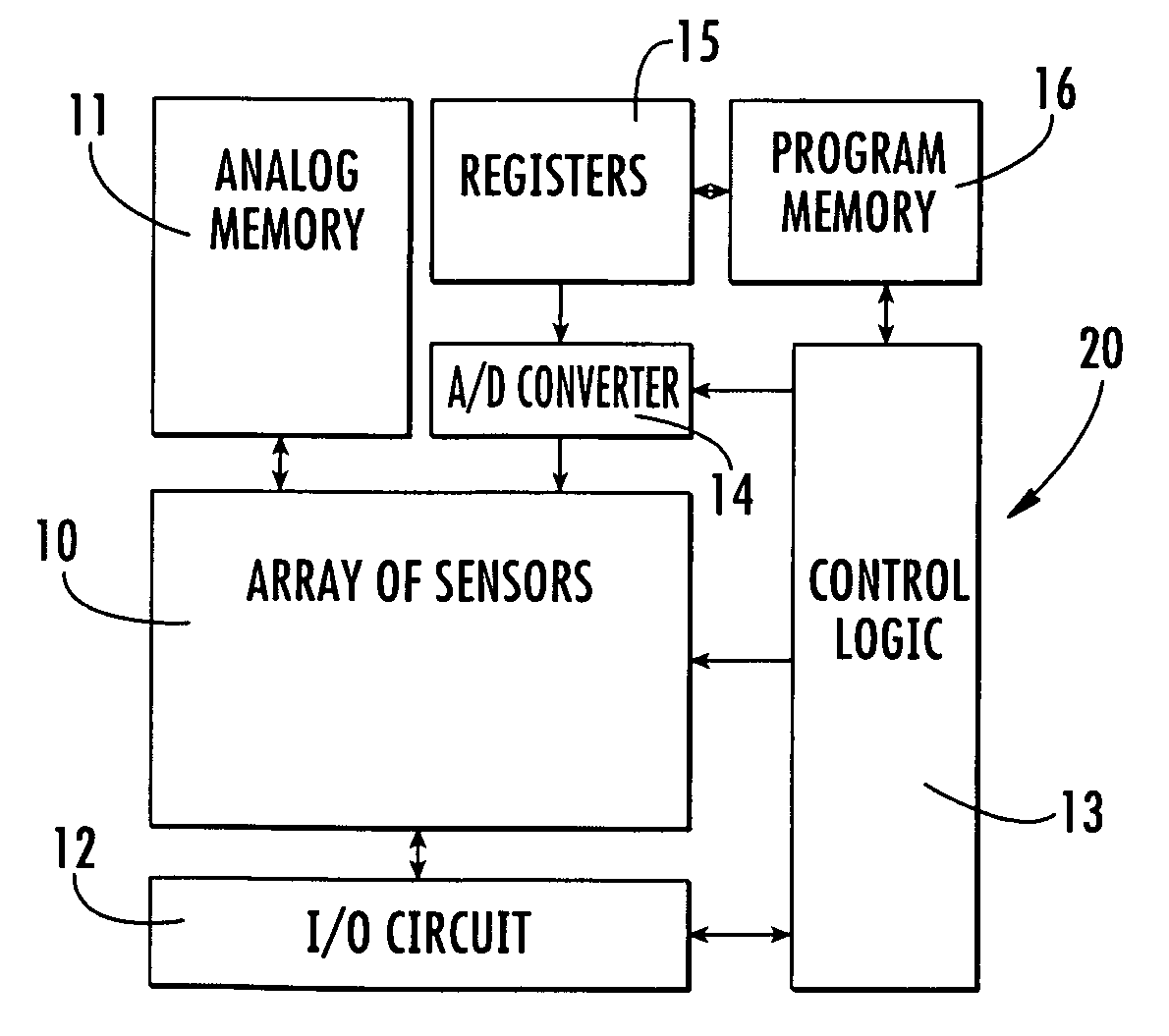
InactiveUS20020097900A1Efficient and rapid automatic analysis of imageImage enhancementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCMOSDNA microarray
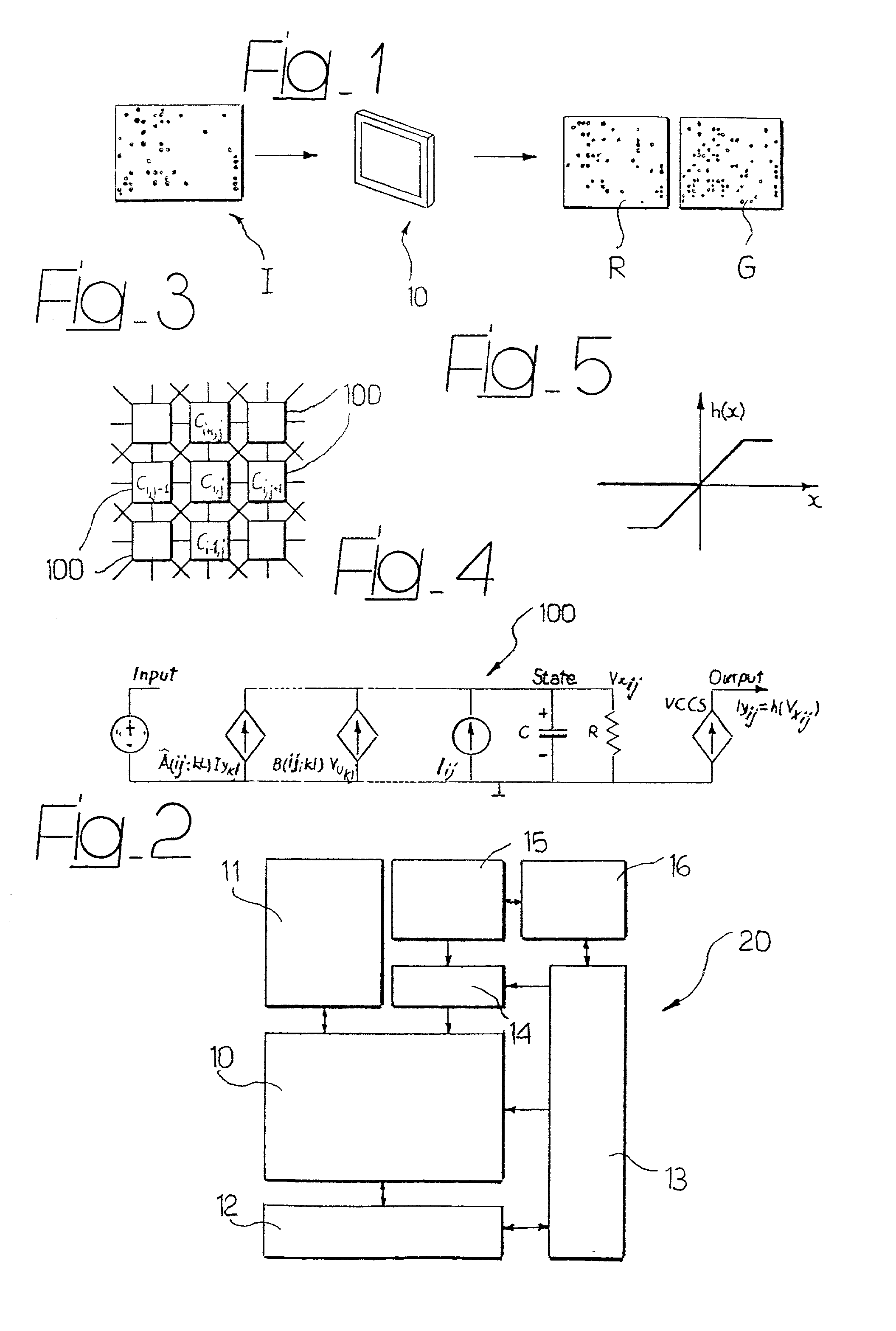
The system can be used for the automatic analysis of images (I), comprising a matrix of spots, such as images of DNA microarrays after hybridisation. The system can be associated-and preferably integrated in a single monolithic component implementing VLSI CMOS technology-to a sensor (10) for acquiring said images (I). The system comprises a circuit (20) for processing the signals corresponding to the images (I), configured according to a cellular neural network (CNN) architecture for the parallel analogue processing of signals.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
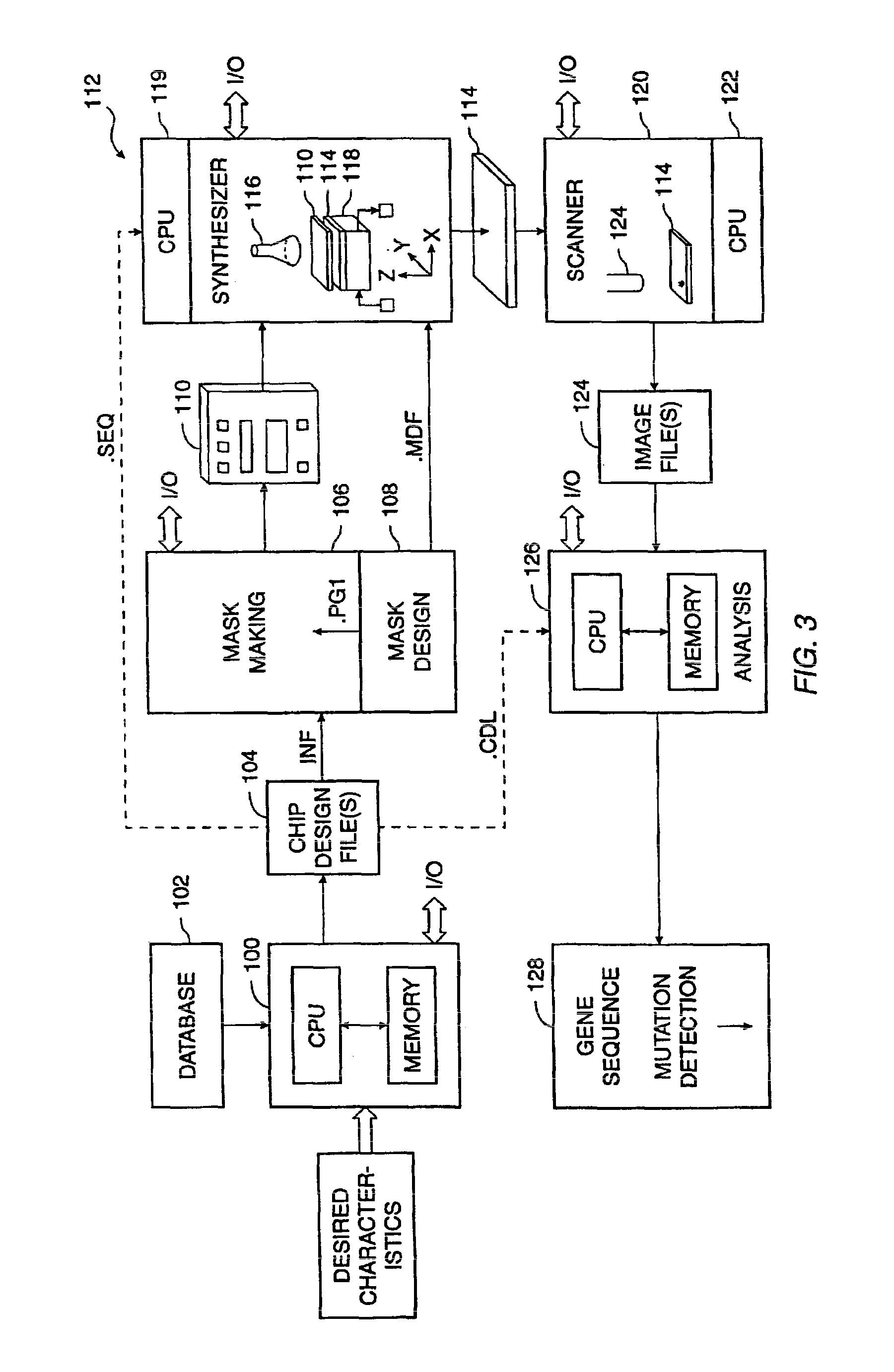
Method and system for accurate alignment and registration of array for DNA sequencing
ActiveUS20110268347A1High precisionImprove trustImage enhancementImage analysisGenomic sequencingPattern matching
In a genome sequencing system and methodology, a protocol is provided to achieve precise alignment and accurate registration of an image of a planar array of nanoballs subject to optical analysis. Precise alignment correcting for fractional offsets is achieved by correcting for errors in subperiod x-y offset, scale and rotation by use of minimization techniques and Moiré averaging. In Moiré averaging, magnification is intentionally set so that the pixel period of the imaging element is a noninteger multiple of the site period. Accurate registration is achieved by providing for pre-defined pseudo-random sets of sites, herein deletion or reserved sites, where nanoballs are prevented from attachment to the substrate so that the sites of the array can be used in a pattern matching scheme as registration markers for absolute location identification. Information can be extracted with a high degree of confidence that it is correlated to a known location, while at the same time the amount of information that can be packed on a chip is maximized.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
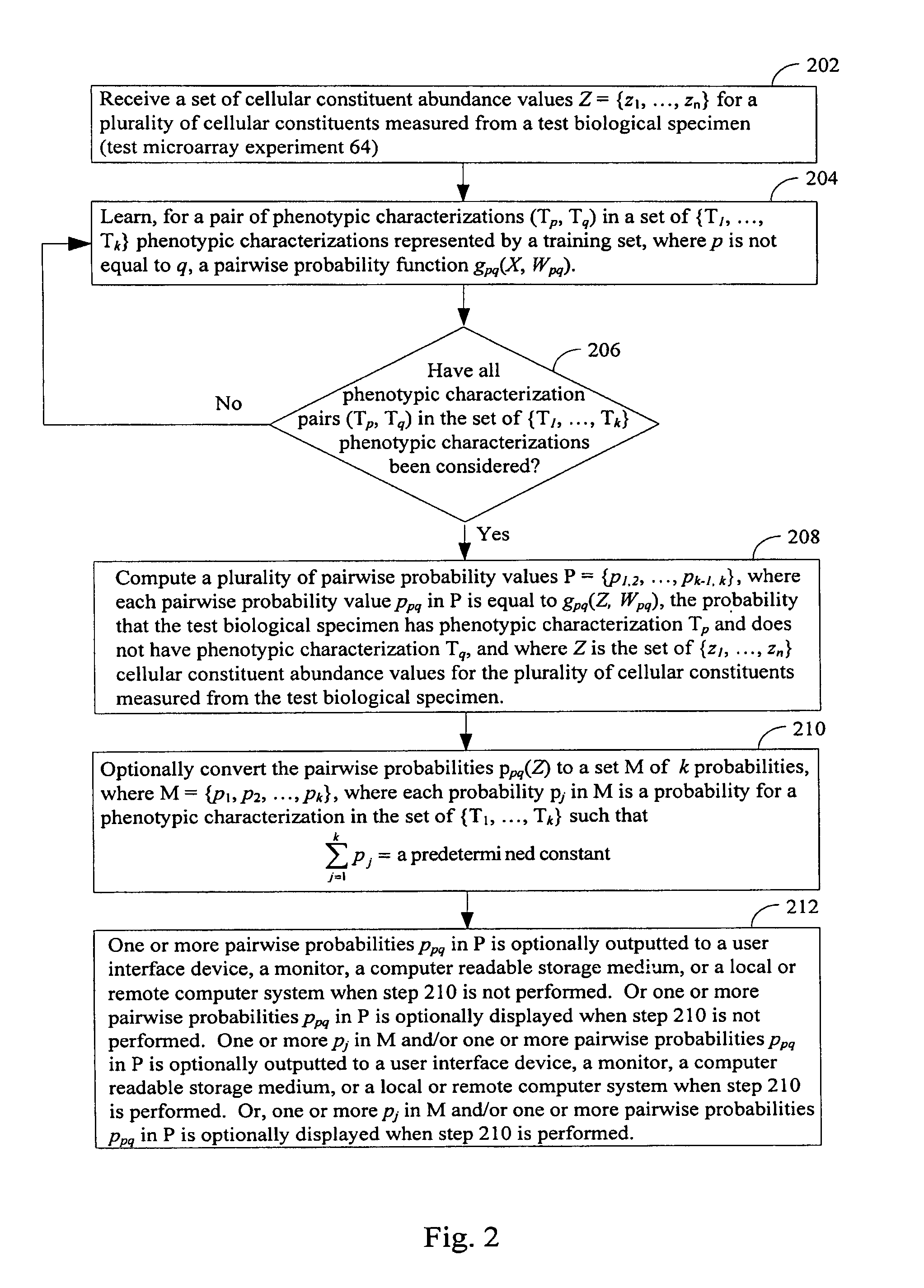
Systems and methods for diagnosing a biological specimen using probabilities
InactiveUS7747547B1Microbiological testing/measurementDigital computer detailsComputer scienceBiological specimen
Apparatus, systems and methods for determining, for each respective phenotypic characterization in a set of {T1, . . . , Tk} characterizations, that a test specimen has the respective characterization are provided. A pairwise probability function gpq(X, Wpq), for a phenotypic pair (Tp, Tq) in {T1, . . . , Tk} is learned using a training population. Wpq is a set of parameters derived from Y for (Tp, Tq) by substituting each Y1 in Y into gpq(X, Wpq), as X, where Yi is the set of cellular constituent abundance values from sample i in the training population exhibiting Tp or Tq. The learning step is repeated for each (Tp, Tq) in {T1 . . . , Tk}, thereby deriving pairwise probability functions G={g1,2(X, W1,2), . . . , gk-1, k(X, Wk-1, k)}. Pairwise probability values P={p1,2, . . . , pk-1, k} are computed, where each ppq is equal to gpq(Z, Wpq) in G, the probability that the test specimen has Tp and not Tq, where Z is cellular constituent abundance values of the test specimen.
Owner:CANCER GENETICS
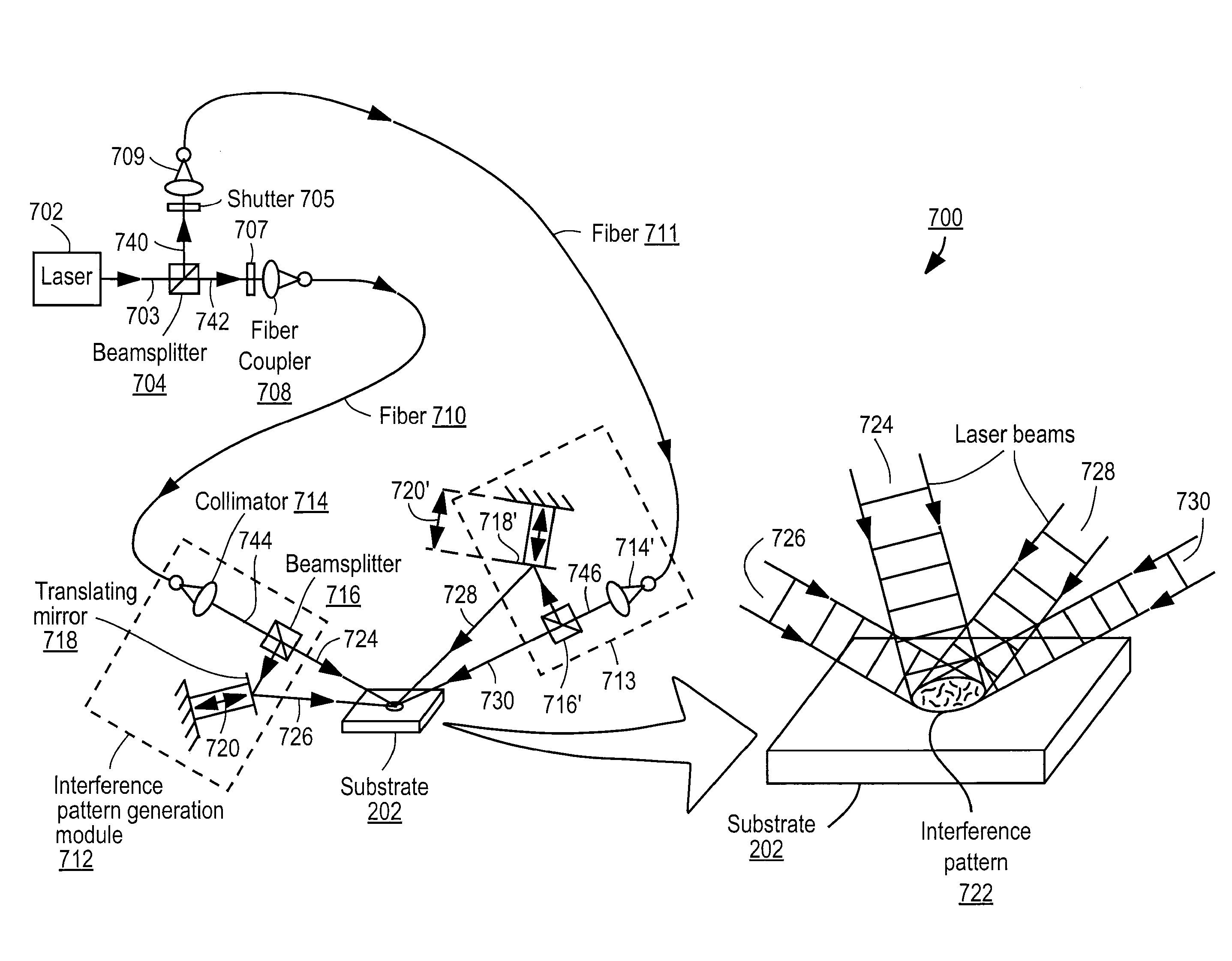
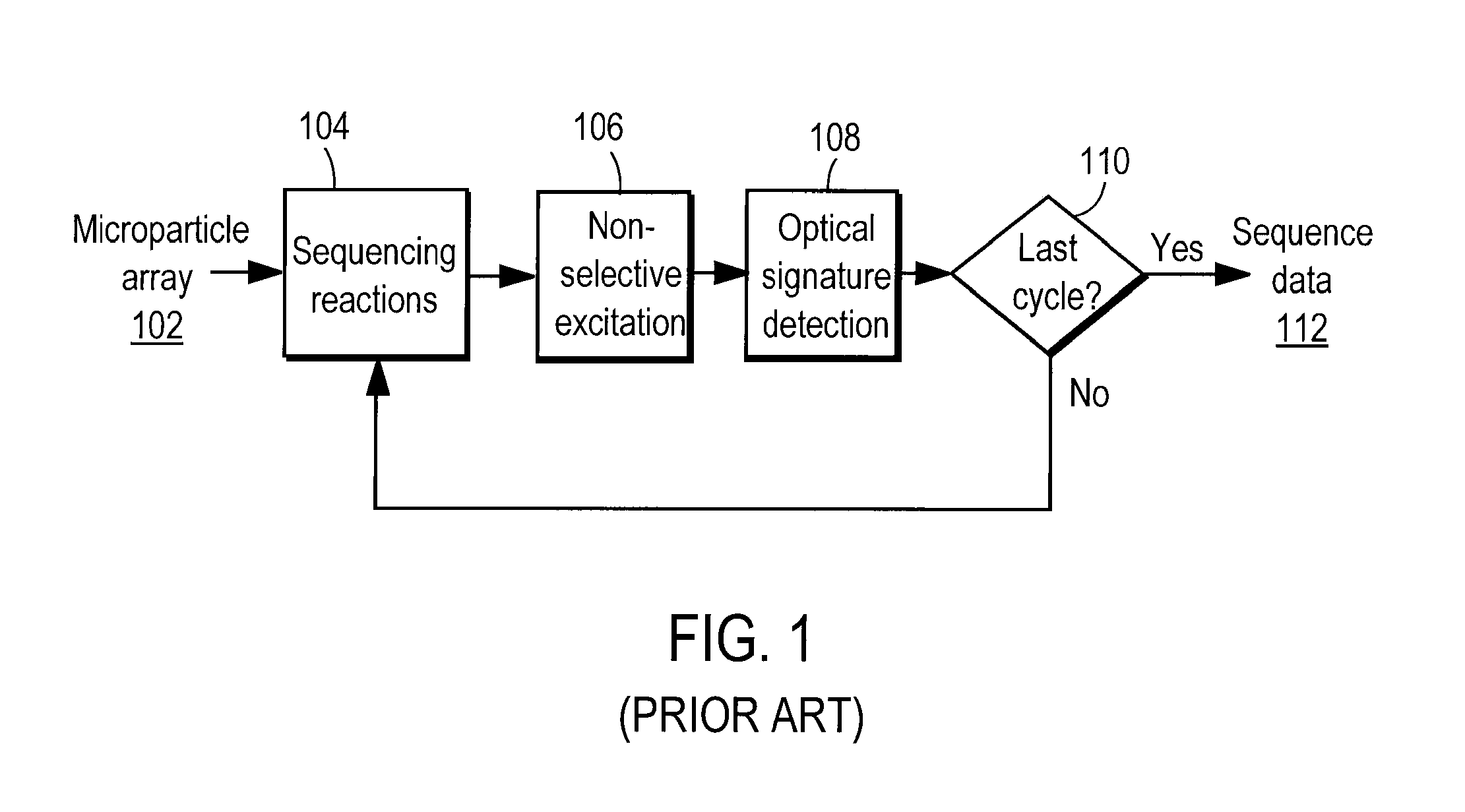
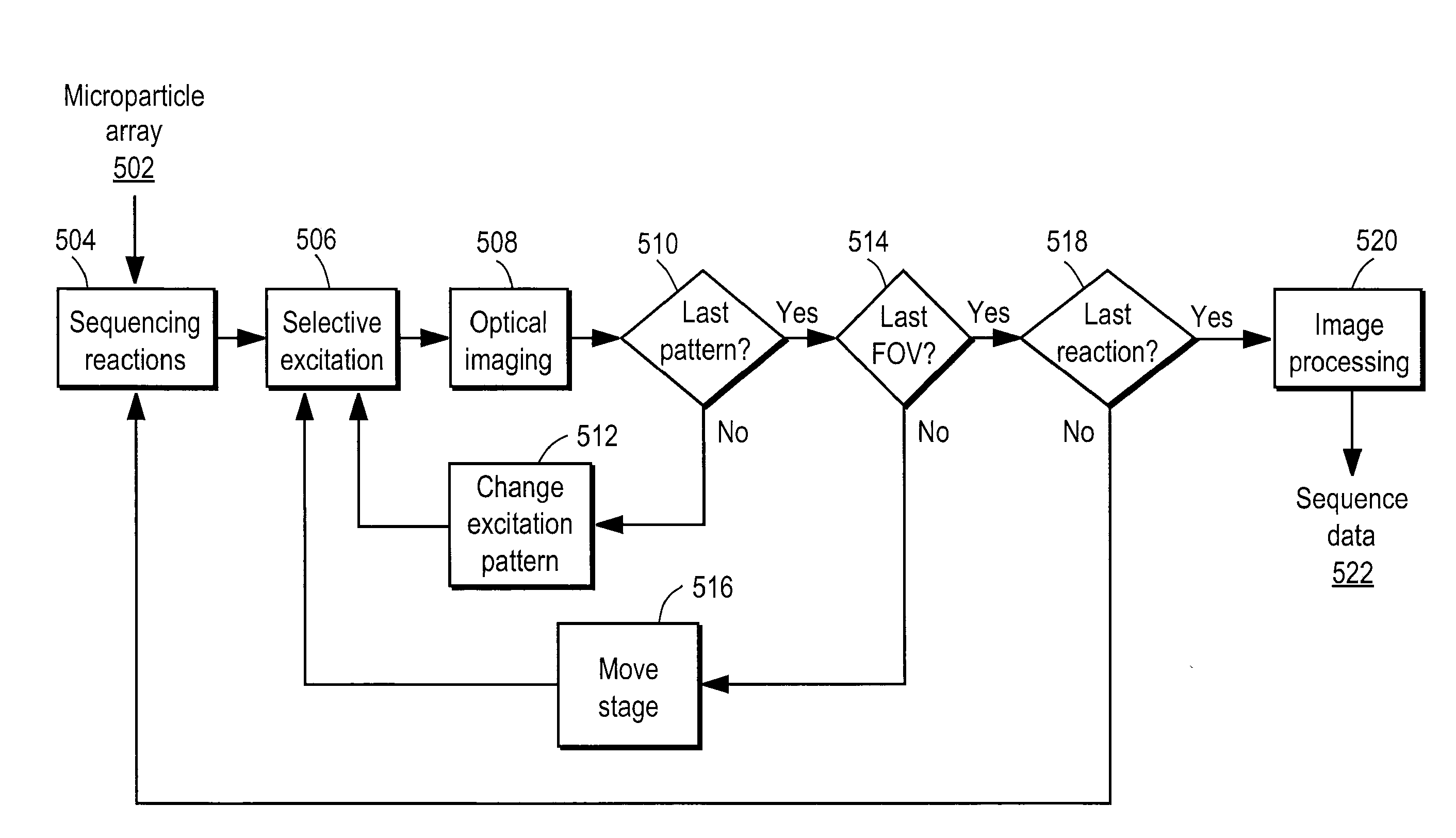
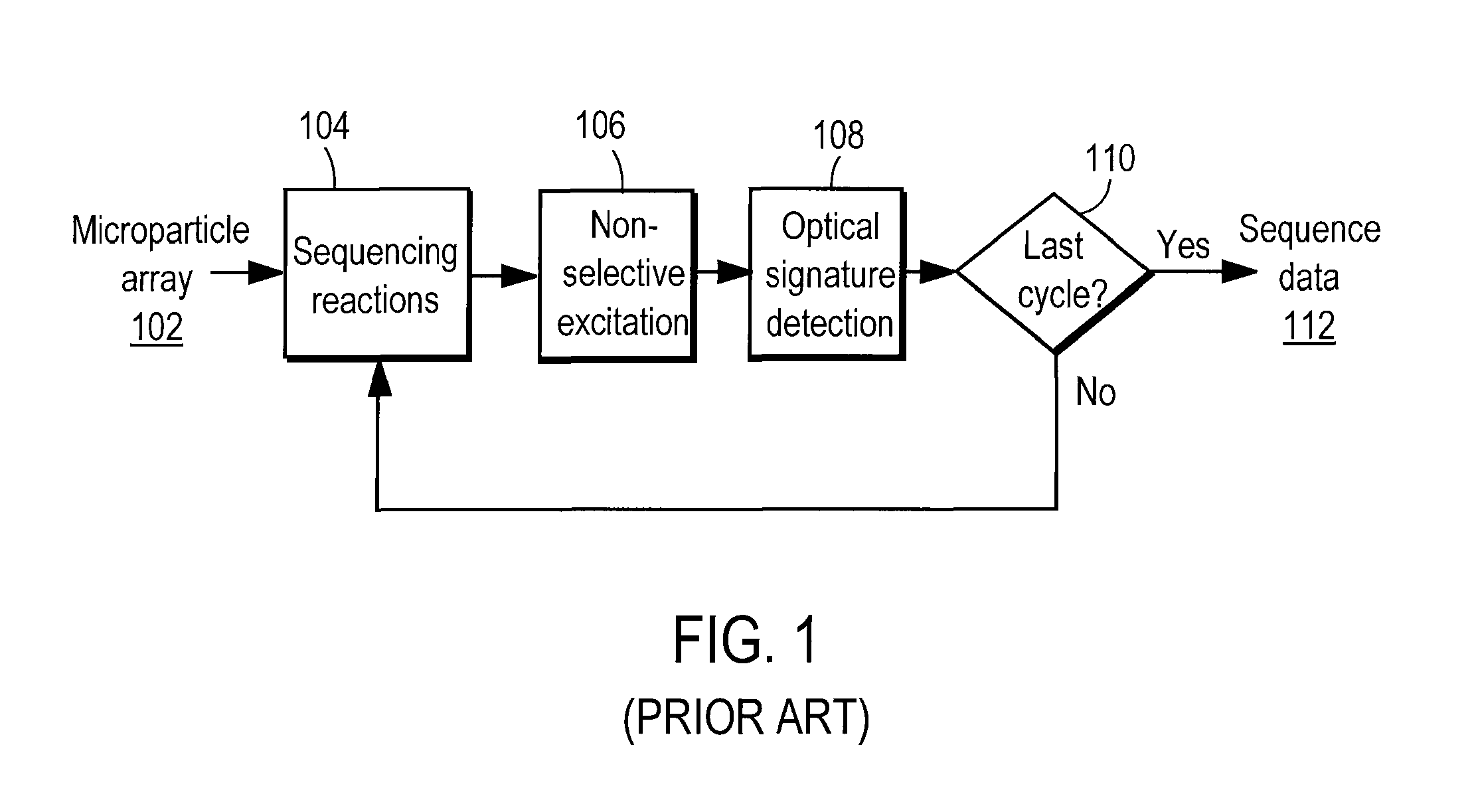
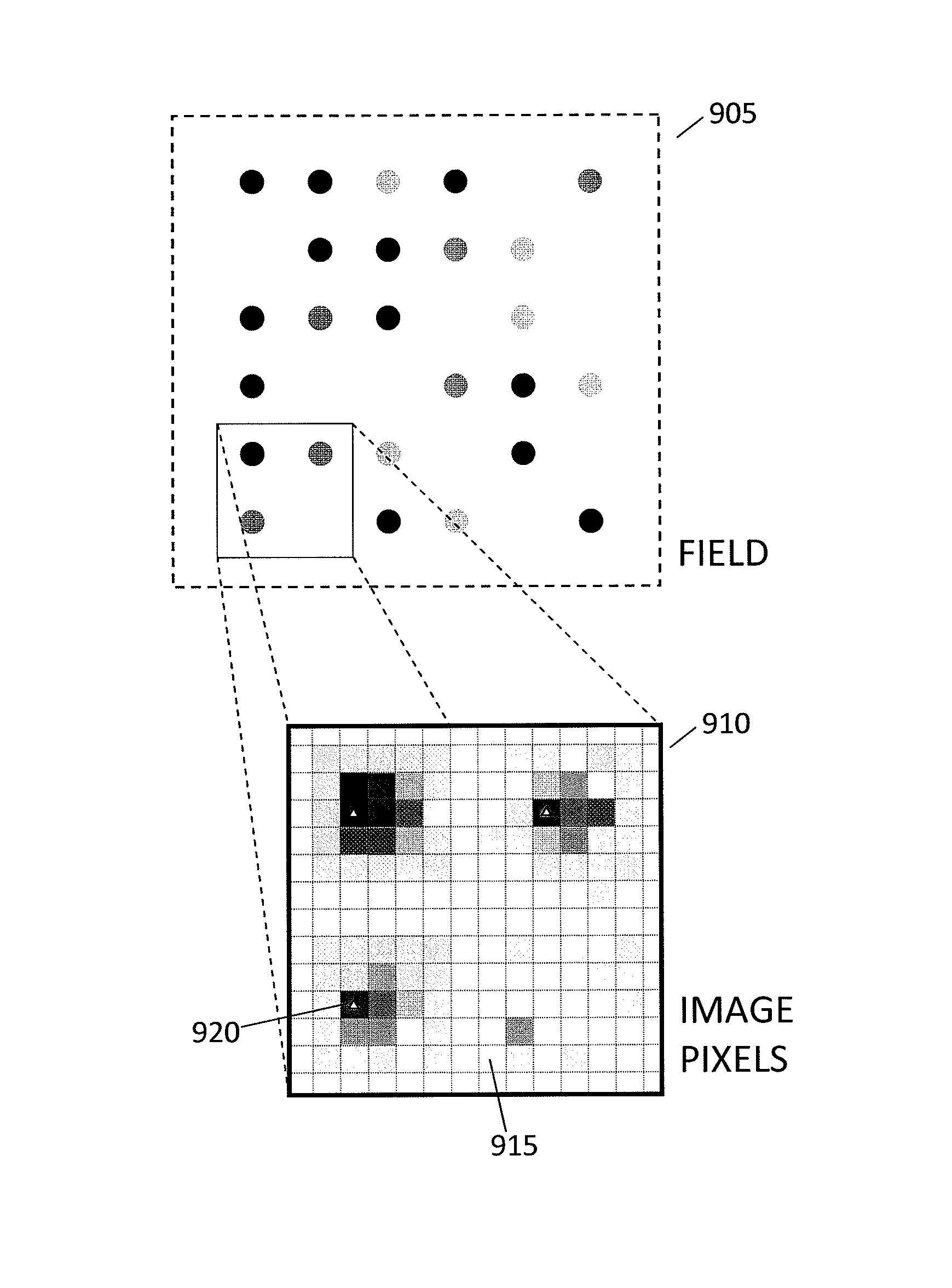
Nucleic acid sequencing by selective excitation of microparticles
ActiveUS20090061526A1High speedData efficientBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSelective excitationImage resolution
Nucleic acid microparticles are sequenced by performing a sequencing reaction on the microparticles using one or more reagents, selectively exciting the microparticles in an excitation pattern, optically imaging the microparticles at a resolution insufficient to resolve individual microparticles, and processing the optical images of the microparticles using information on the excitation pattern to determine the presence or absence of the optical signature, which indicates the sequence information of the nucleic acid. An apparatus for optical excitation of the microparticles comprises an optical fiber delivering a first laser beam, and an interference pattern generation module coupled to the optical fiber. The interference pattern generation module splits the first laser beam into second and third laser beams and generates the excitation pattern for selectively exciting the microparticles by interference between the second and third laser beams.
Owner:REBUS BIOSYSTEMS INC
Nucleic acid sequencing by selective excitation of microparticles
ActiveUS8222040B2High speedData efficientBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSelective excitationMicroparticle
Owner:REBUS BIOSYSTEMS INC
Method and system for accurate alignment and registration of array for DNA sequencing
ActiveUS8774494B2High precisionImprove trustImage enhancementImage analysisGenomic sequencingPattern matching
In a genome sequencing system and methodology, a protocol is provided to achieve precise alignment and accurate registration of an image of a planar array of nanoballs subject to optical analysis. Precise alignment correcting for fractional offsets is achieved by correcting for errors in subperiod x-y offset, scale and rotation by use of minimization techniques and Moiré averaging. In Moiré averaging, magnification is intentionally set so that the pixel period of the imaging element is a noninteger multiple of the site period. Accurate registration is achieved by providing for pre-defined pseudo-random sets of sites, herein deletion or reserved sites, where nanoballs are prevented from attachment to the substrate so that the sites of the array can be used in a pattern matching scheme as registration markers for absolute location identification. Information can be extracted with a high degree of confidence that it is correlated to a known location, while at the same time the amount of information that can be packed on a chip is maximized.
Owner:COMPLETE GENOMICS INC
System and method for automatically identifying sub-grids in a microarray
A digital image processing-based system and method for quantitatively processing a plurality of nucleic acid species expressed in a microarray are disclosed. The microarray is a grid of a plurality of sub-grids of the nucleic acid species. The system includes a scanner that has a digital scanning sensor that scans the microarray and transmits from an output a digital image of the microarray, and a computer that receives the digital image of the microarray from the scanner and then processes the digital image, identifying each of the microarray's sub-grids. The computer identifies the position of each of the sub-grids by (a) identifying regions in the digital image that each contains one of the sub-grids, (b) identifying rows and columns in each region where nucleic acid species are expressed to form a set of candidate sub-grids in each region, (c) selecting for each region a probable sub-grid from the set of candidate sub-grids in each region, and (d) comparing the positions of the probable sub-grids from each region to finalize the sub-grid positions.
Owner:BIODISCOVERY INC
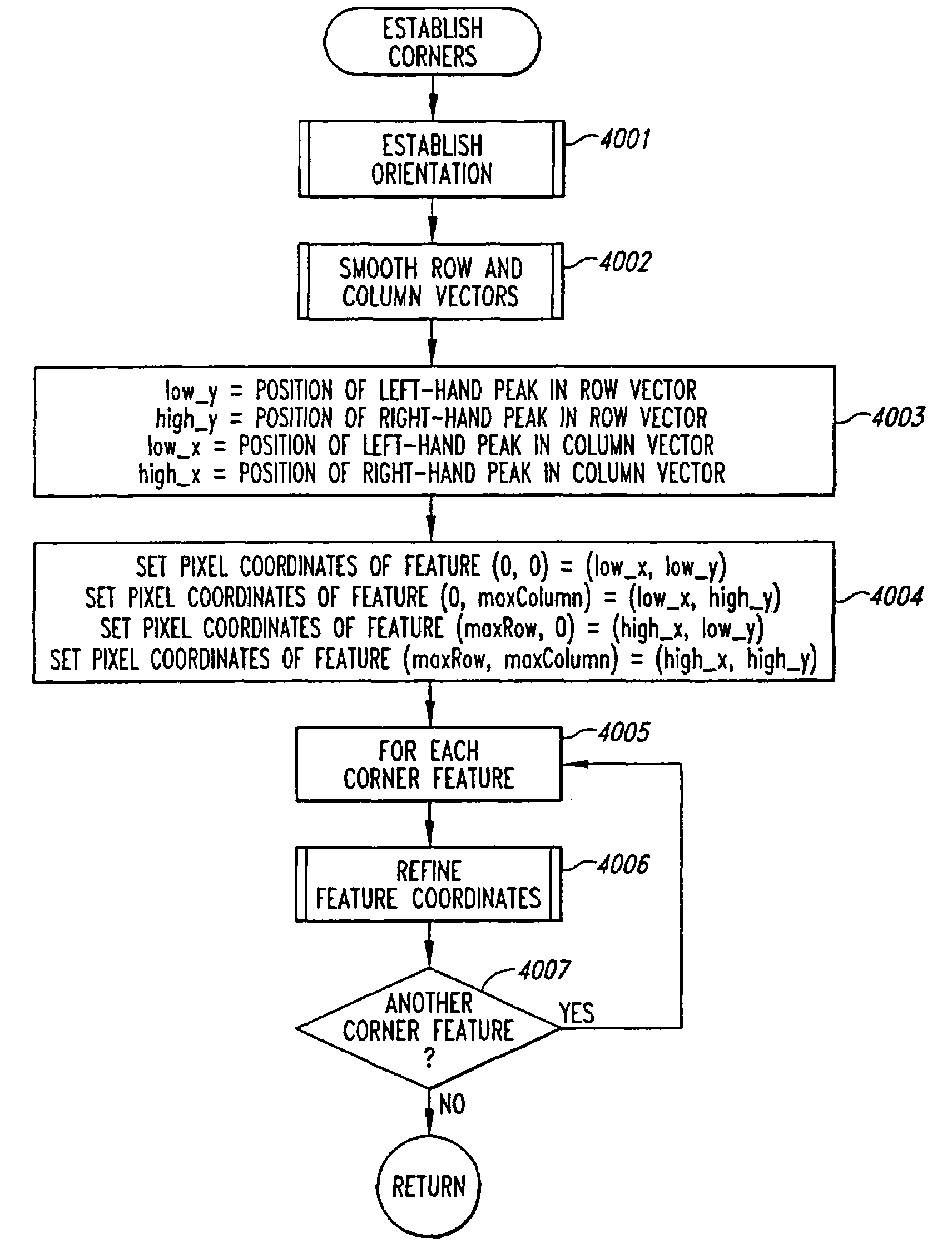
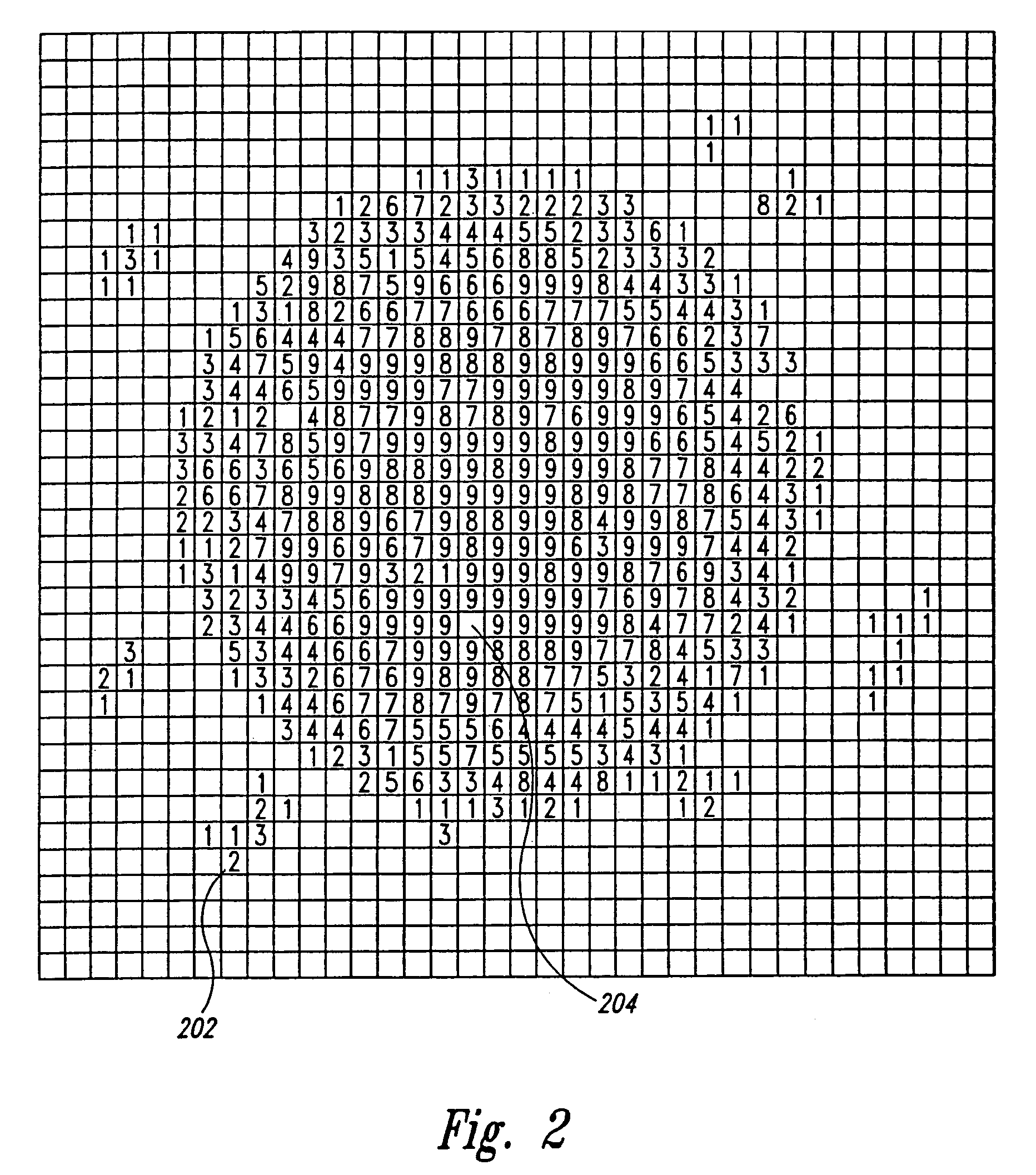
Method and system for extracting data from surface array deposited features
InactiveUS7330606B2Superior in pointHigh positioning accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisMolecular arrayData signal
A method for evaluating an orientation of a molecular array having features arranged in a pattern. An image of the molecular array is obtained by scanning the molecular array to determine data signals emanating from discrete positions on a surface of the molecular array. An actual result of a function on pixels of the image which pixels lie in a second pattern, is calculated. This actual result is compared with an expected result which would be obtained if the second pattern had a predetermined orientation on the array. Array orientation can then be evaluated based on the result.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
System for the automatic analysis of images such as DNA microarray images
InactiveUS7013033B2Efficient and rapid automatic analysis of imageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsImage enhancementCMOSDNA microarray
The system can be used for the automatic analysis of images, including a matrix of spots, such as images of DNA microarrays after hybridization. The system can be associated—and preferably integrated in a single monolithic component implementing VLSI CMOS technology—to a sensor for acquiring the images. The system includes a circuit for processing the signals corresponding to the images, configured according to a cellular neural network (CNN) architecture for the parallel analogue processing of signals.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Cell image recognition method and cell image recognition device
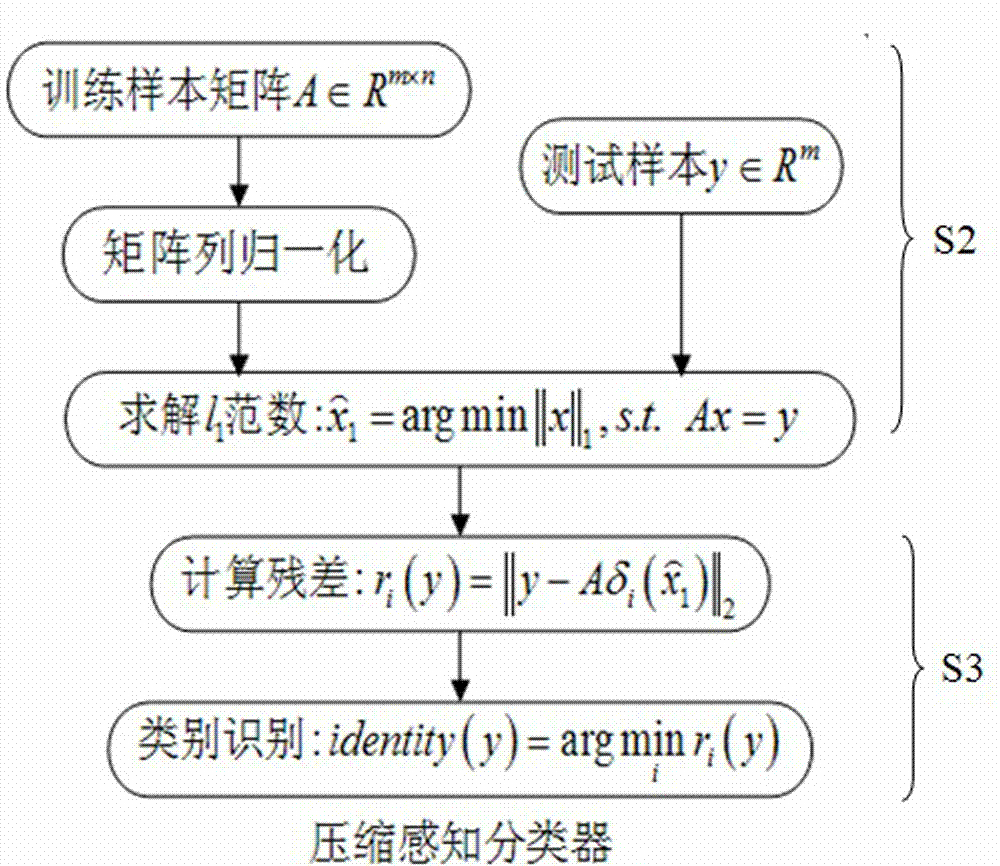
InactiveCN104850860AQuick category statusHigh precisionRecognition of DNA microarray patternPattern recognitionImage denoising
The invention provides a cell image recognition method and a cell image recognition device. In the cell image recognition method, cells are divided into to-be-tested cells and various kinds of training cells. The cell image recognition process comprises the following steps: S1, preprocessing a cell image, specifically including cell image gray processing, image denoising processing, image gray histogram equalization processing, and image segmentation processing; S2, using a compressed sensing technology to establish sparse coefficient representation on the preprocessed cell image; S3, recognizing cells, calculating difference value of linear weighting of the to-be-tested cells and each kind of training sample cells ri(y), and selecting the classification the training sample with the lowest difference value belongs to as the classification of a test sample. Through using the compressed sensing technology in cell recognition, operand is reduced, and the method and the device has self-adaptive capability, so influence of external factors is reduced, and cell image recognition precision and speed are improved.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Simultaneous acquisition of biometric data and nucleic acid
InactiveUS20130106568A1Surgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsBiometric dataRapid processing
Disclosed are devices and methods for collection and analyzing biological samples containing nucleic acid in conjunction with collecting at least one ridge and valley signature of a test subject, while keeping the sample and signature associated with each other. Such devices and methods are used in forensic, human identification, screening, and access control technologies to rapidly process an individual's identity or determine the identity of an individual.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
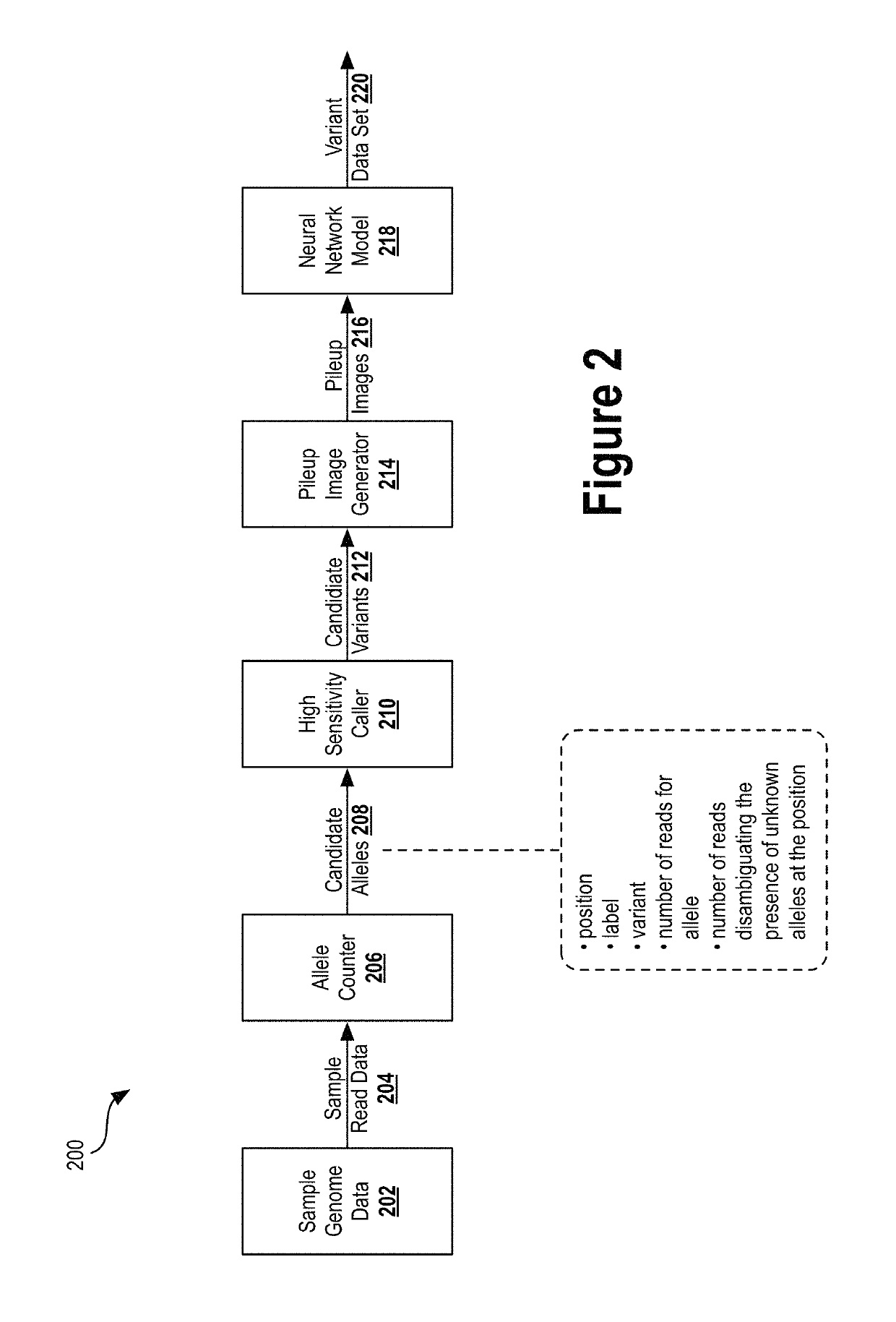
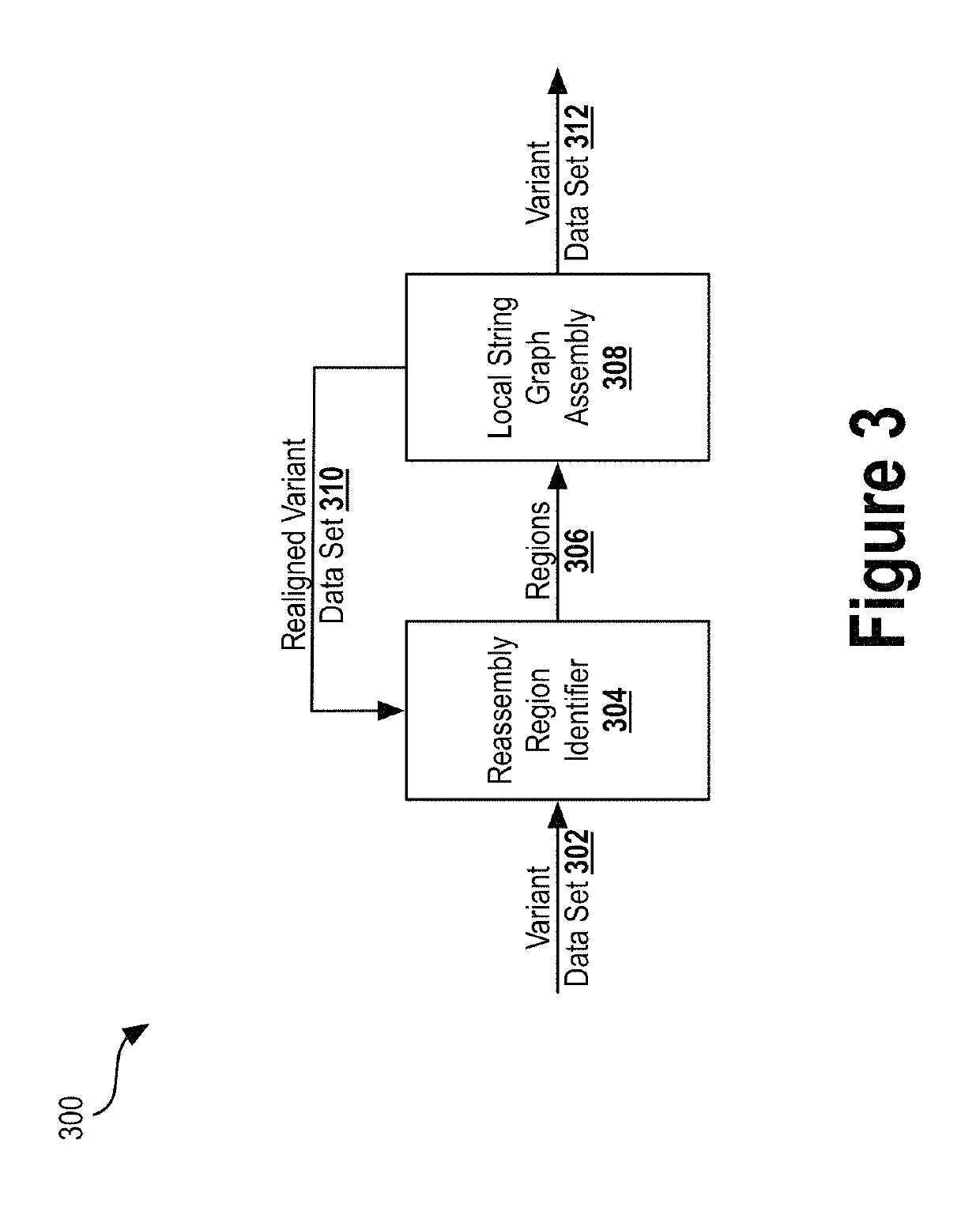
Deep learning analysis pipeline for next generation sequencing
A method for variant calling in a next generation sequencing analysis pipeline involves obtaining a plurality of sequence reads that each include a nucleotide aligned at a nucleotide position within a sample genome. The method also involves obtaining a plurality of alleles associated with the nucleotide position. The method further involves determining that a particular allele of the plurality of alleles matches one or more sequence reads of the plurality of sequence reads, wherein the particular allele is located at the nucleotide position. Additionally, the method involves generating an image based on information associated with the plurality of sequence reads. Further, the method involves determining, by providing the generated image to a trained neural network, a likelihood that the sample genome contains the particular allele. The method may also involves providing an output signal indicative of the determined likelihood.
Owner:VERILY LIFE SCI LLC
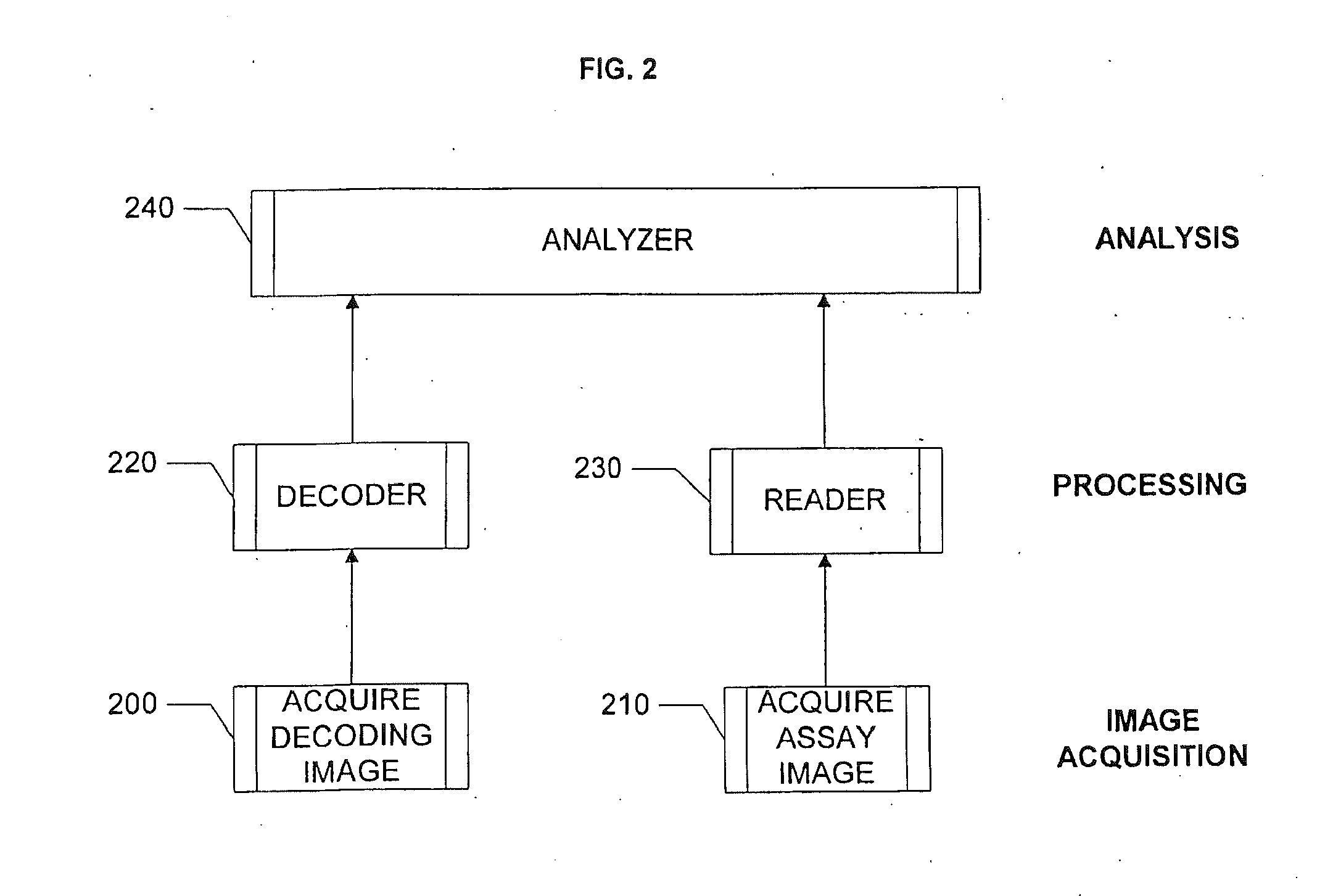
Analysis, secure access to, and transmission of array images
ActiveUS20110251093A1ConfidenceRapid and automated decoding of encoded arraysImage enhancementImage analysisConfidentialityMicroparticle
Systems and methods are provided the autocentering, autofocusing, acquiring, decoding, aligning, analyzing and exchanging among various parties, images, where the images are of arrays of signals associated with ligand-receptor interactions, and more particularly, ligand-receptor interactions where a multitude of receptors are associated with microparticles or microbeads. The beads are encoded to indicate the identity of the receptor attached, and therefore, an assay image and a decoding image are aligned to effect the decoding. The images or data extracted from such images can be exchanged between de-centralized assay locations and a centralized location where the data are analyzed to indicate assay results. Access to data can be restricted to authorized parties in possession of certain coding information, so as to preserve confidentiality.
Owner:BIOARRAY SOLUTIONS
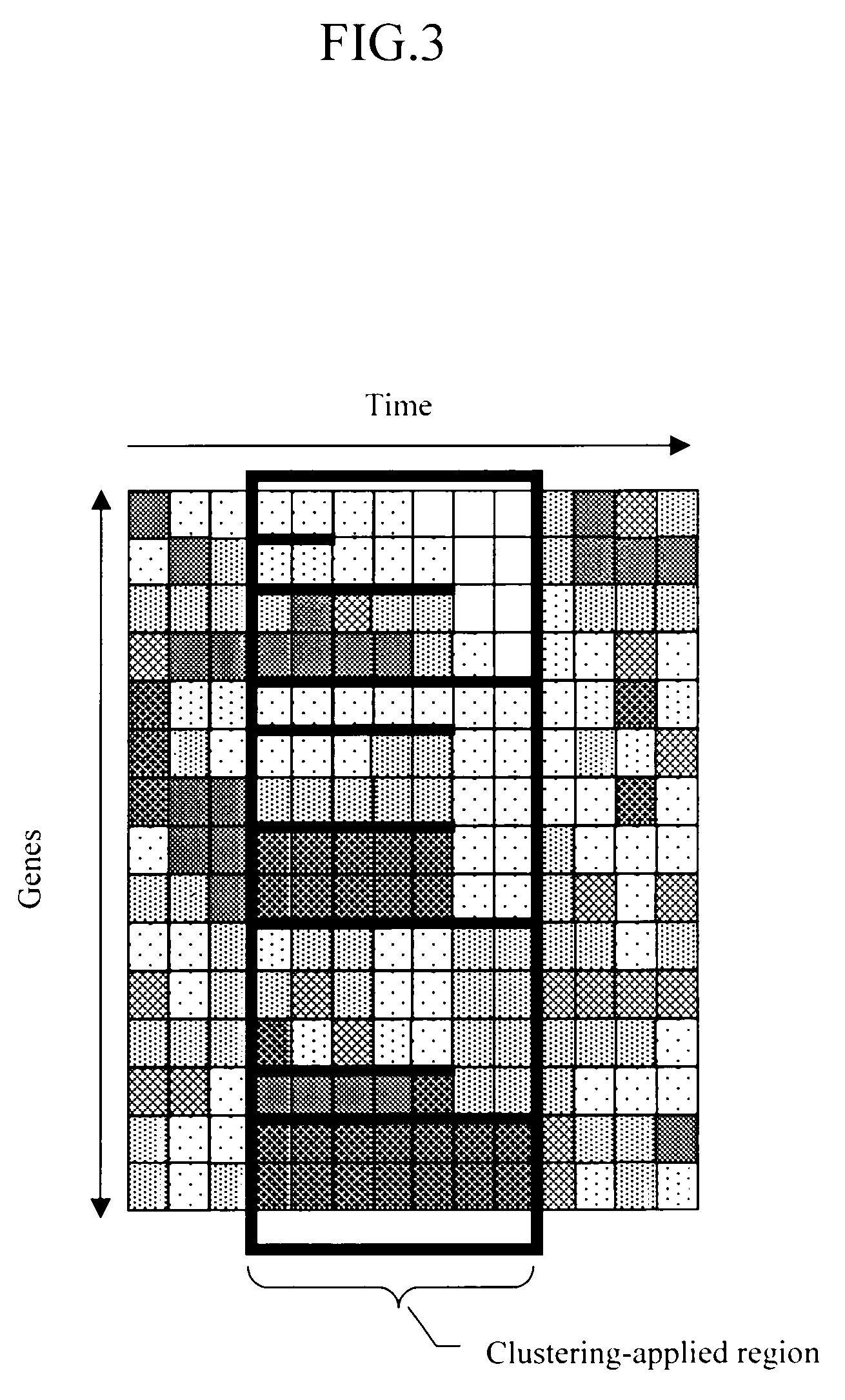
Method and apparatus for displaying gene expression patterns
The present invention discloses a method for displaying gene expression patterns of multiple genes that change according to the experiment cases, where a first axis represents the genes and a second axis represents the experiment cases. The method comprises two steps. The first step consists of designating a segment along the second axis in the expression pattern data of the multiple genes. The second step comprises clustering the expression pattern data within the designated segment along the second axis based on a predetermined reference value, repeating clustering within the same cluster in a forward or reverse direction along the second axis while changing the reference value, and displaying the results according to a predetermined display format.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
System and method for automatically identifying sub-grids in a microarray
A digital image processing-based system and method for quantitatively processing a plurality of nucleic acid species expressed in a microarray are disclosed. The microarray is a grid of a plurality of sub-grids of the nucleic acid species. The system includes a scanner that has a digital scanning sensor that scans the microarray and transmits from an output a digital image of the microarray, and a computer that receives the digital image of the microarray from the scanner and then processes the digital image, identifying each of the microarray's sub-grids. The computer identifies the position of each of the sub-grids by (a) identifying regions in the digital image that each contains one of the sub-grids, (b) identifying rows and columns in each region where nucleic acid species are expressed to form a set of candidate sub-grids in each region, (c) selecting for each region a probable sub-grid from the set of candidate sub-grids in each region, and (d) comparing the positions of the probable sub-grids from each region to finalize the sub-grid positions.
Owner:BIODISCOVERY INC
Tumor image marker extraction method based on gene imaging
The invention relates to a tumor image marker extraction method based on gene imaging. The invention provides a non-intrusive biomarker extraction method with high interpretability by adoption of the gene imaging and in combination with the advantages of the imaging and the molecular technology. According to the method, high-dimensional quantitative image features of a tumor CT are extracted and are associated with a corresponding tumor gene expression pattern; and it is assumed that some quantitative image features can reflect a specific gene expression pattern of a tumor and can be used as prognosis markers of the tumor. The ultimate goal is to extract a non-invasive and biologically interpretable imaging marker.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
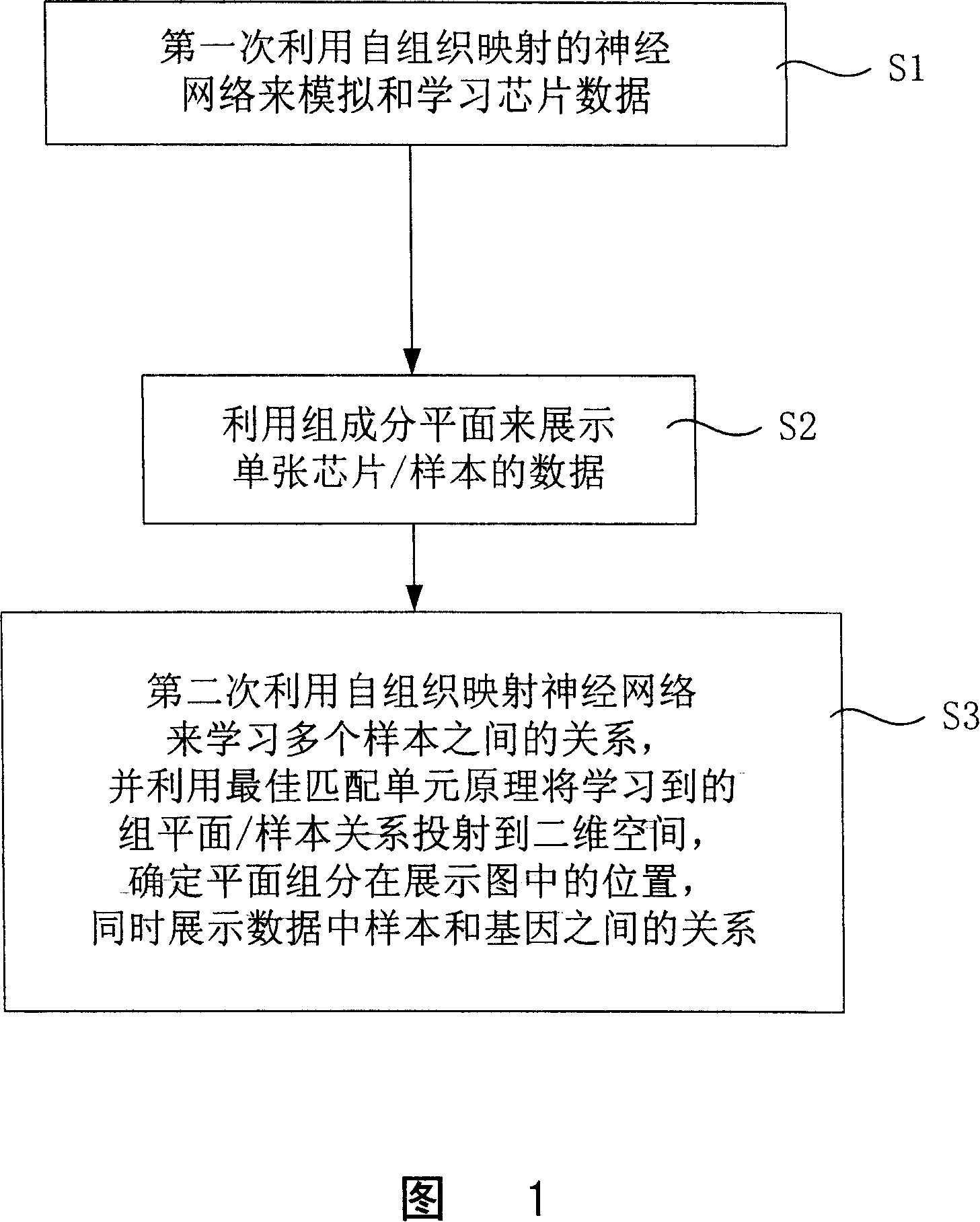
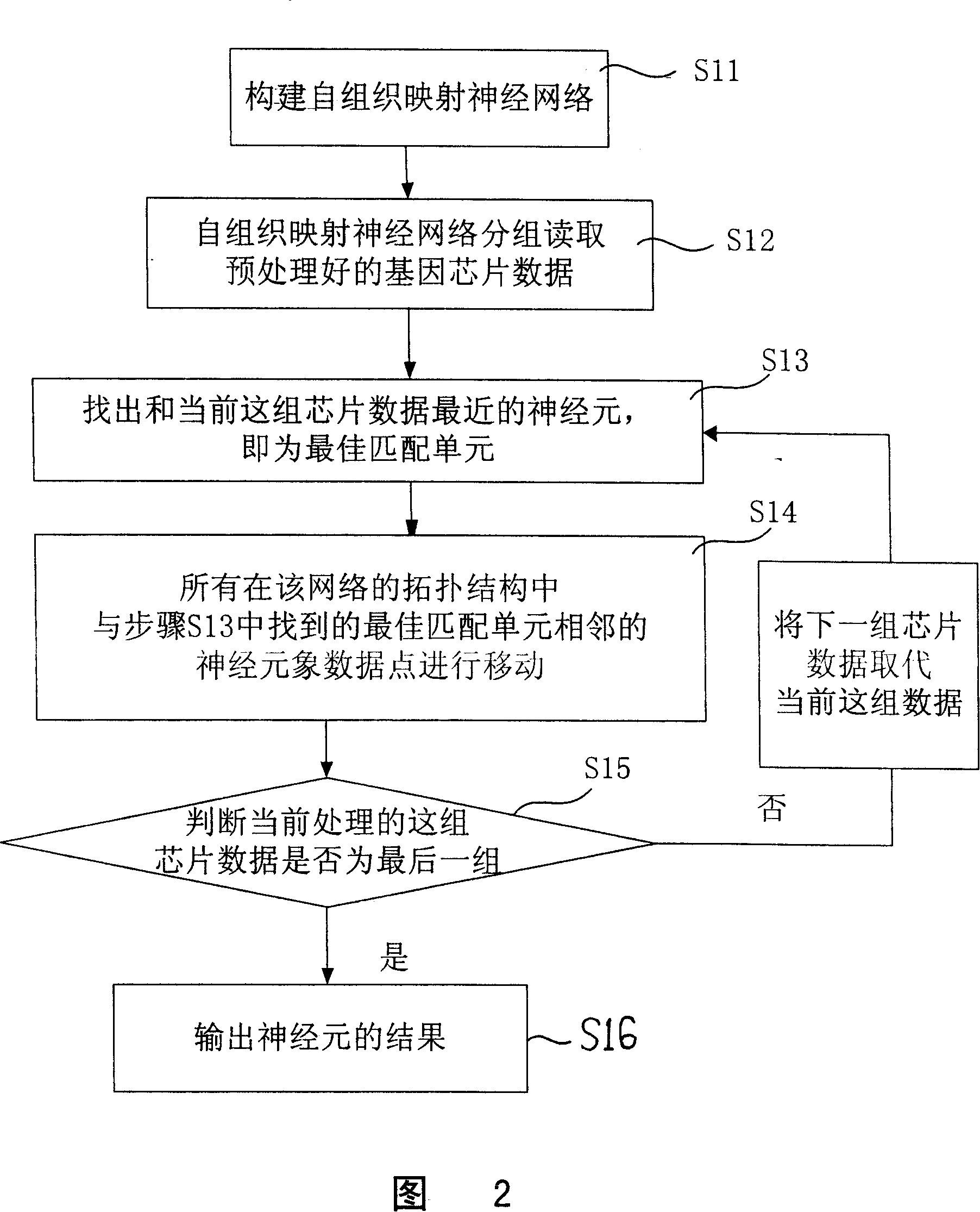
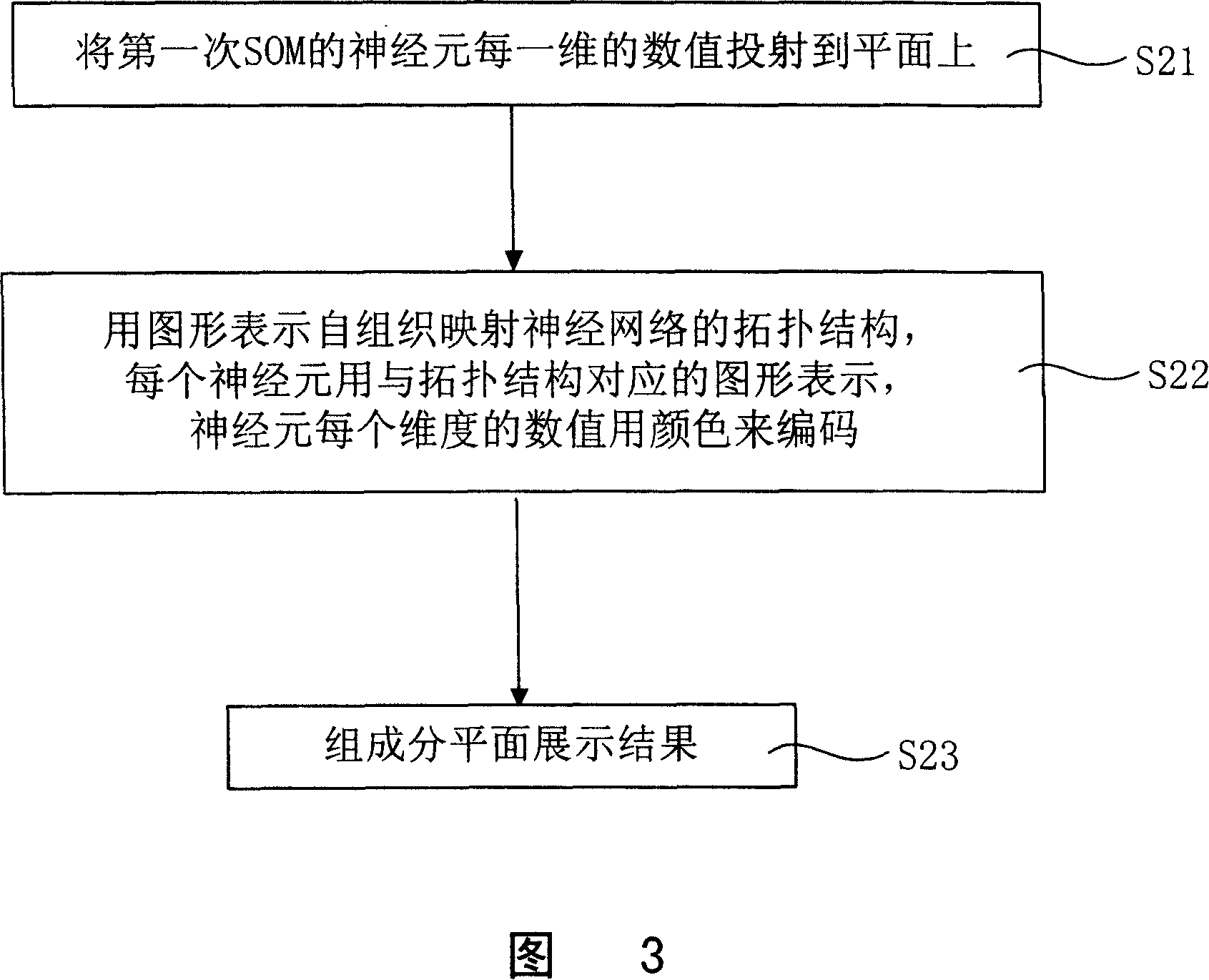
Visual analyzing and displaying method used for chip data analysis
InactiveCN101097585ASolve bottlenecksRecognition of DNA microarray patternSpecial data processing applicationsNerve networkData science
The invention discloses a kind of visual analysis and exhibition method for gene chip data, and it can provide intuitionistic visual method for chip, and it can exhibit large chip data. The technical project is: the method includes: (1)using the self-organized mapping NN to stimulate and study the chip data at first time; (2)using the composing planes to exhibit the data of single chip / sample obtained at step (1), the single component of multi-dimensional nerve carrier is separated, and at the same time, it uses the two-dimensional plane to exhibit the data structure obtained at step (1); (3)it uses the self-organized nerve network to study the relationship between several samples, and projects the relationship of group planes / samples to two-dimensional space using the optimized matching principle, and exhibit the relationship between the samples and the genes. The invention can be used in the data analysis technical field of large gene chip.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
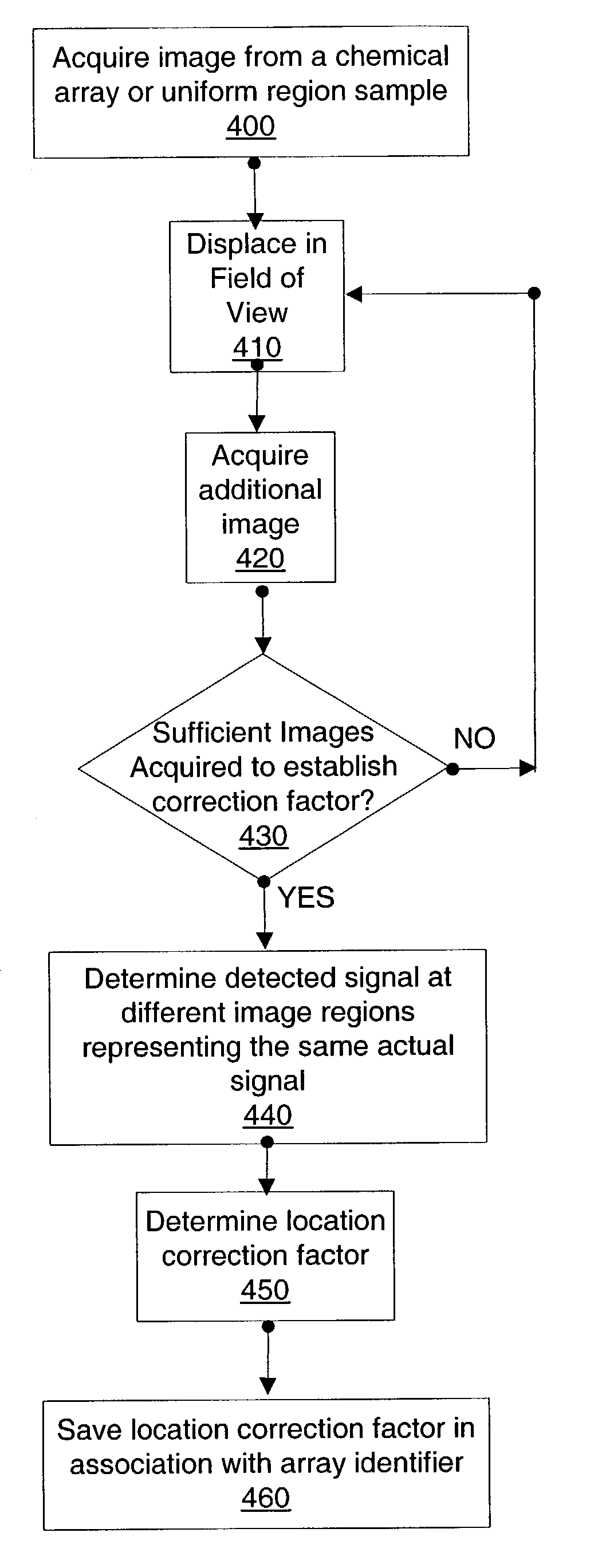
Feature locations in array reading
InactiveUS7206438B2Diminish read signalReduce the differenceImage enhancementImage analysisArray data structureField of view
A method of processing one or more detected signal images each acquired from a field of view of a chemical array reader. A location correction is determined based on different detected signals at different image regions which represent regions in the field of view having the same actual signal. Alternatively or additionally, a location correction is applied to a detected signal at an image region. The location correction reduces detected signal discrepancy between different regions in an acquired image which represent different regions in the field of view having the same actual signal. An array reading system and computer program products are also provided.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Method and system for displacement-vector-based detection of zone misalignment in microarray data
A method and system for detecting block and zone misalignment of feature positions within a microarray-data set and for correcting feature positions for block or zone misalignment. In one embodiment of the present invention, displacement vectors representing the vector differences between observed positions of features and expected positions for the features of a microarray are calculated, based on an initially determined coordinate system. Features within a microarray data set are then partitioned with respect to the calculated vector displacements, so that features misaligned by a common rotation or translation are partitioned into a separate partition. A correction for each common misalignment can then be calculated and applied to the features of each partition.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Feature intensity reconstruction of biological probe array
ActiveUS8009889B2Guaranteed uptimeBiological testingRecognition of DNA microarray patternPattern recognitionComputer vision
The invention provides methods and systems for reconstructing feature intensities from pixel level data. In certain embodiments, the invention uses an empirically determined transfer function to construct a theoretical estimate of pixel level data and then iteratively updates feature intensities based on a minimum multiplicative error between the pixel level data and the theoretical estimate of the pixel level data.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Method for locating the edge of an object
InactiveUS20050053268A1Image analysisMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGel basedEdge based
A method for accurately determining the boundaries of an object, particularly a gel slab includes the steps of creating a binary image of the object, the binary image having a central region a boundary region and an outside region with the boundary region encompassing the gel boundary; and performing a homotopic thinning of the binary image, iteratively until no more pixels can be removed. For optimum results, the homotopic thinning iteration is based on a grey scale image of the gel edge and surrounding area, and is most preferably based on an edge threshold image. This involves producing a grey scale edge image of the gel having high response values or intensity where local intensity changes are highest within the image and performing a grey scale controlled homotopic thinning of the binary image in which the pixels which can be removed homotopicaly from the binary image are ordered and the pixel which is removed is that which corresponds in location to the pixel which has the smallest edge / intensity value in the grey scale edge image of the gel. This process is continued iteratively until no more pixels can be removed.
Owner:PROTEOME SYSTEMS INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY PTY LTD
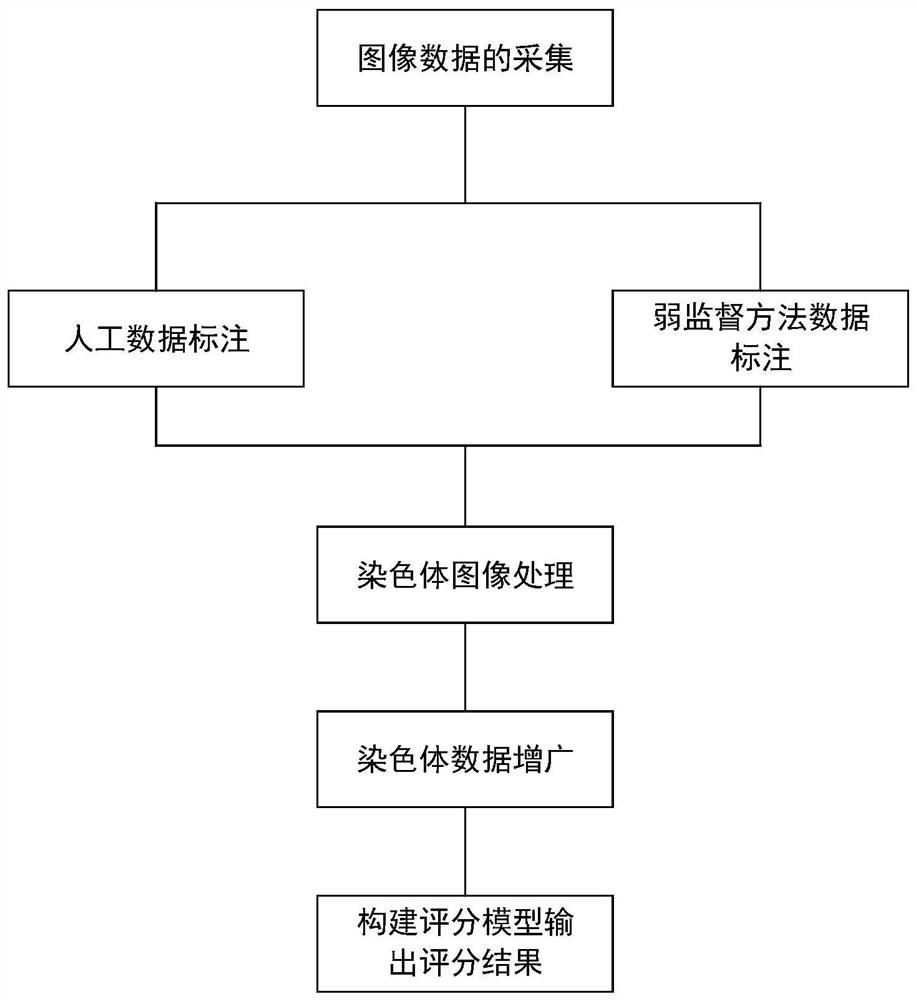
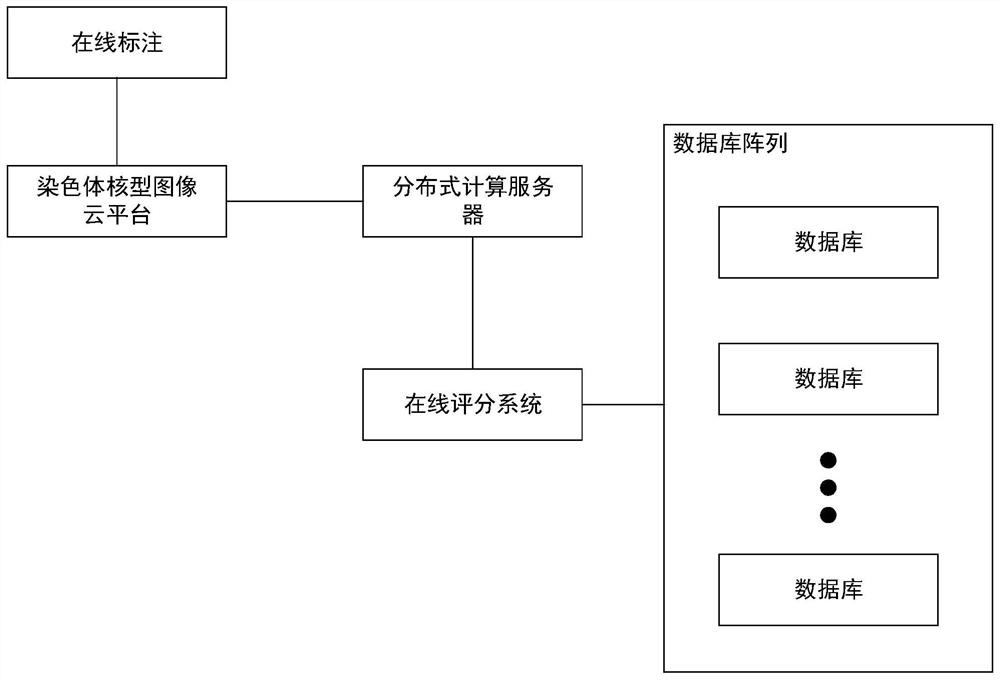
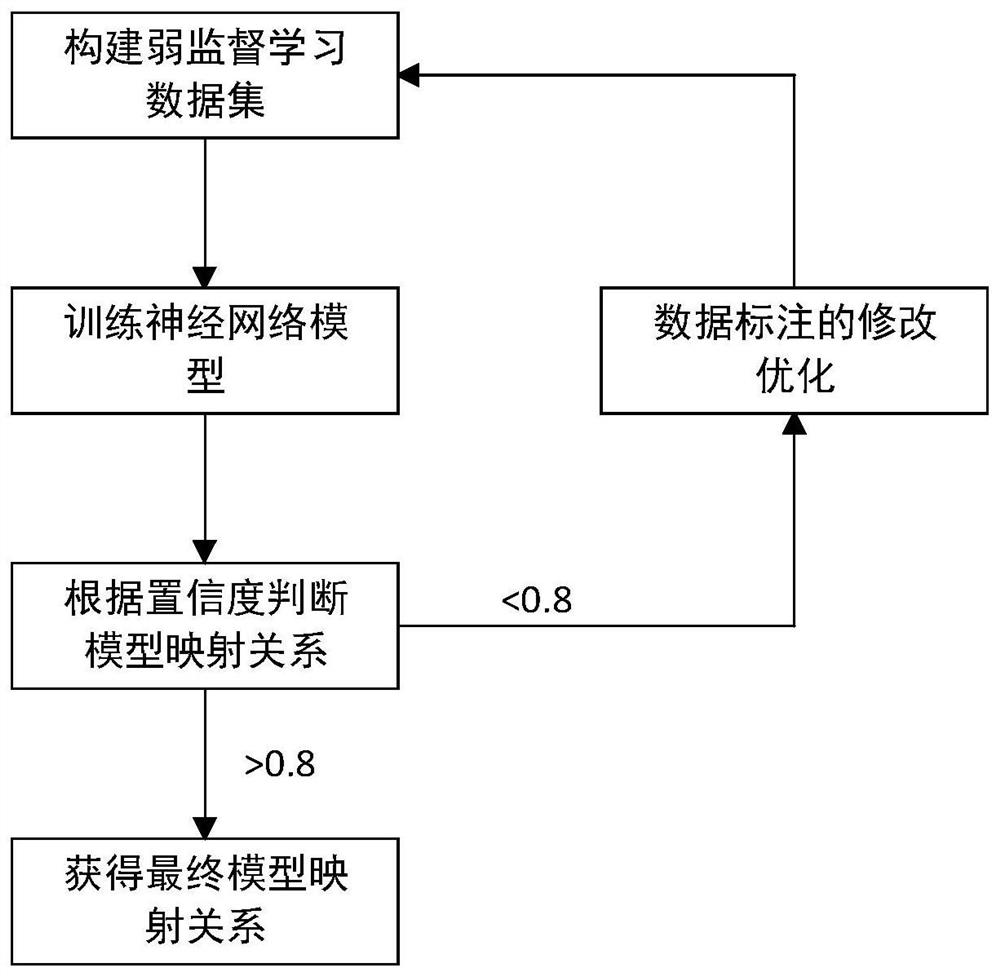
Chromosome karyotype image intelligent evaluation method and system
InactiveCN111652167ALow costImprove labeling efficiencyNeural architecturesRecognition of DNA microarray patternImaging processingImaging analysis
The invention provides a chromosome karyotype image intelligent evaluation method and system. The method relates to the technical field of image processing, and is characterized in that automatic labeling of chromosome image data is carried out through a weak supervised learning model; annotation costs is reduced, labeling efficiency is improved, extension modes such as random projection transformation are adopted for chromosome image data; an optimized residual network model is adopted to build a scoring network model, detail differences of chromosome images are better reserved, the accuracyof the scoring network model is improved, meanwhile, a scoring system is established by adopting a micro-service distributed frame through a cloud platform technology, cross-cloud image analysis is achieved, and the efficiency of the system is improved.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV +1
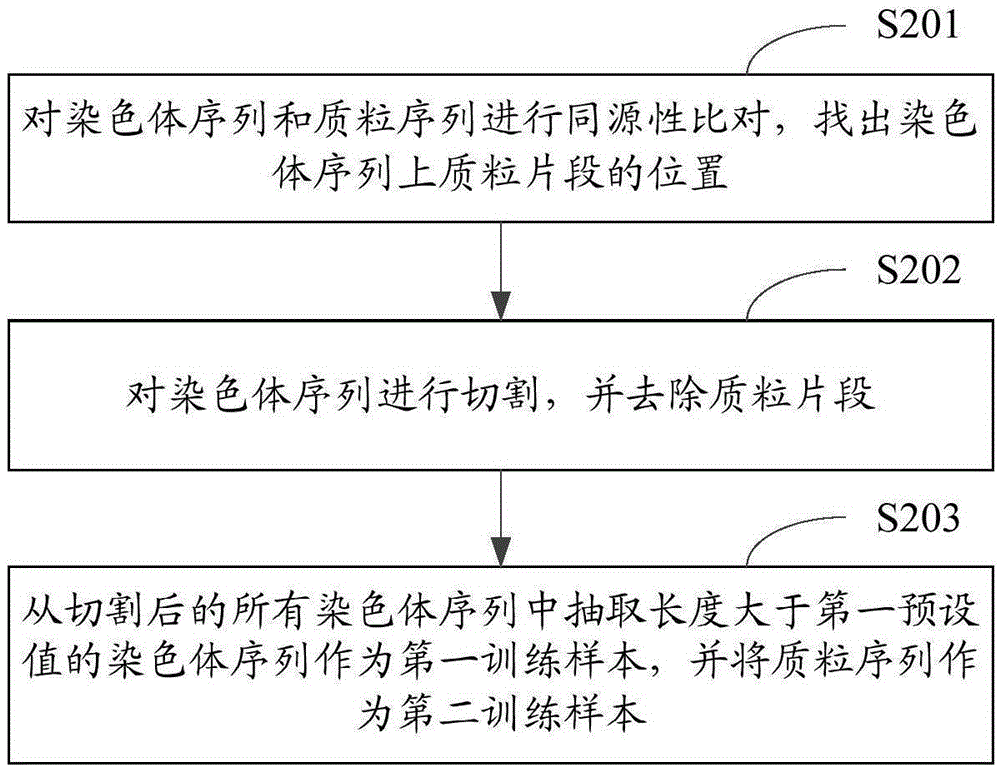
Method and device for classifying chromosome sequences and plasmid sequences
ActiveCN105631464AImprove accuracyImprove training efficiencyRecognition of DNA microarray patternAlgorithmShort string
The invention is applicable to the technical field of data mining and provides a method and a device for classifying chromosome sequences and plasmid sequences. The method comprises steps: chromosome sequences and plasmid sequences are acquired, and a first training sample and a second training sample are obtained; frequency characteristics of all k character short strings and reverse complementary sequence pairs thereof are extracted and a first frequency characteristic table and a second frequency characteristic table are generated, wherein k is no less than 2 but no more than 5; a training set and a test set are extracted from the first frequency characteristic table and the second frequency characteristic table, and a chi-square test algorithm is adopted to calculate weight values of all characteristic data in the training set; a random forests algorithm is adopted and according to the characteristic data whose weight values meet preset conditions, a classification model is trained; and according to the classification model, the chromosome sequences and the plasmid sequences are classified. Thus, the training efficiency and the training effects of the classification model are improved, and accuracy on classification on the chromosome sequences and the plasmid sequences is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
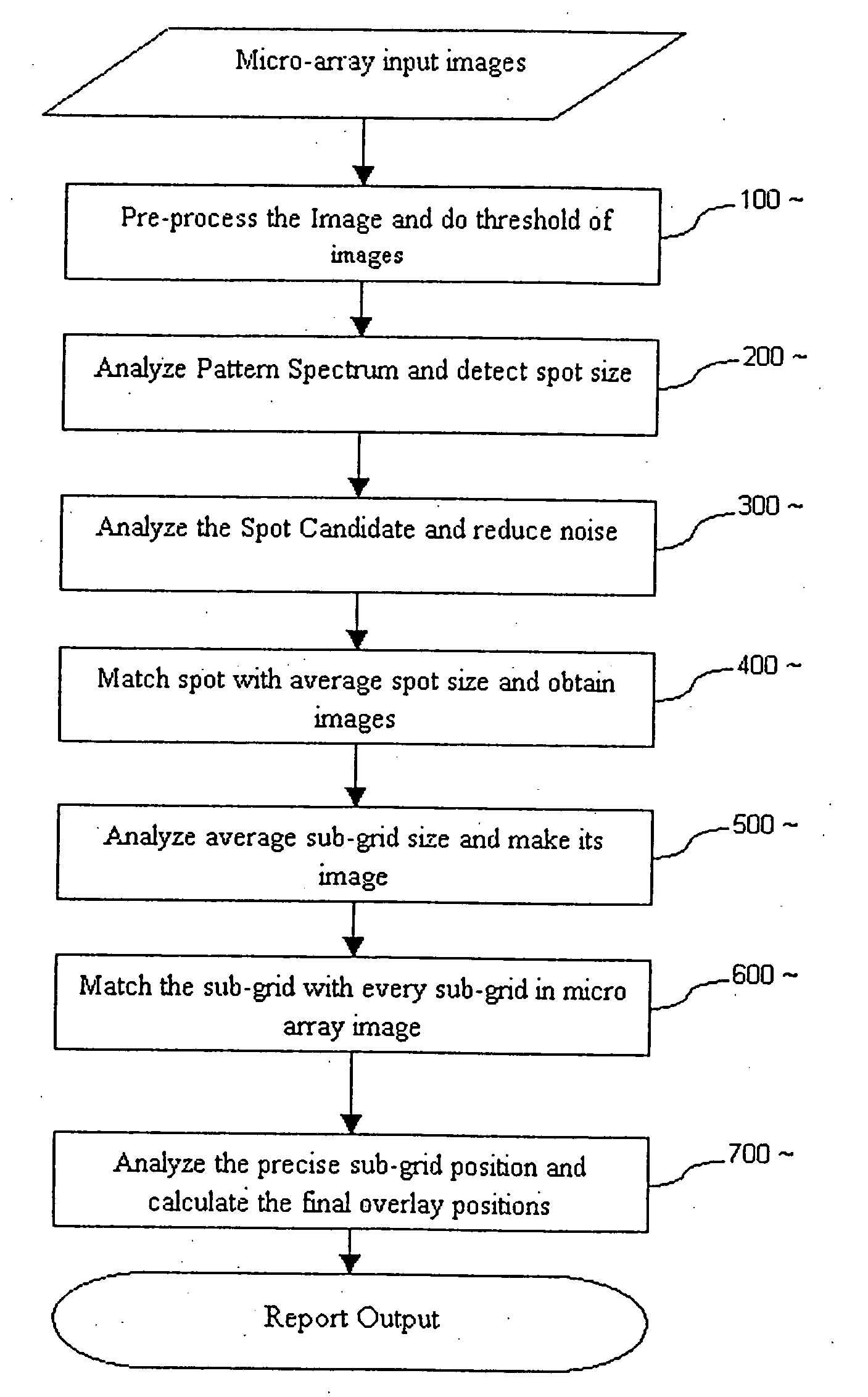
Fully automated segmentation of genetic micro-array images
InactiveUS20050201602A1Automate analysisSugar derivativesRecognition of DNA microarray patternComputer visionSystem usage
A method and system for automatically processing images from a micro-array uses an image processor that is controlled by software. The software controls the microprocessor to process images to ensure that the images meet a predetermined threshold. The microprocessor automatically calculates a size of spot image, a spacing between adjacent spot images, generates a first grid and adjusts the first grid to fit the spot images being processed.
Owner:HURON TECH INT
Method and system for automatic vision inspection and classification of microarray slides
InactiveUS20070071300A1Automatic detectionImage enhancementImage analysisVision inspectionVisual perception
The present invention provides a unique low cost vision inspection and classification system and methods for automatic inspection and classification of a microarray slide without manual intervention. The method first performs morphological dilation operation several times such that internal microarray spots are merged as a big connected component; then, the orientation of the merged spots, with respect to the X-axis and Y-axis is computed by computing the angle of the external boundaries of the connected component using Sobel XY operators for both edges and orientation determination, or using the moment-based algorithm for direct orientation determination; and the translational offset is determined by finding the X and Y centroids of the connected component. Moreover, the present invention provides threshold methods for classifying spots into normal spots, weak spots, missing spots, or overlapping spots.
Owner:NANYANG POLYTECHNIC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com