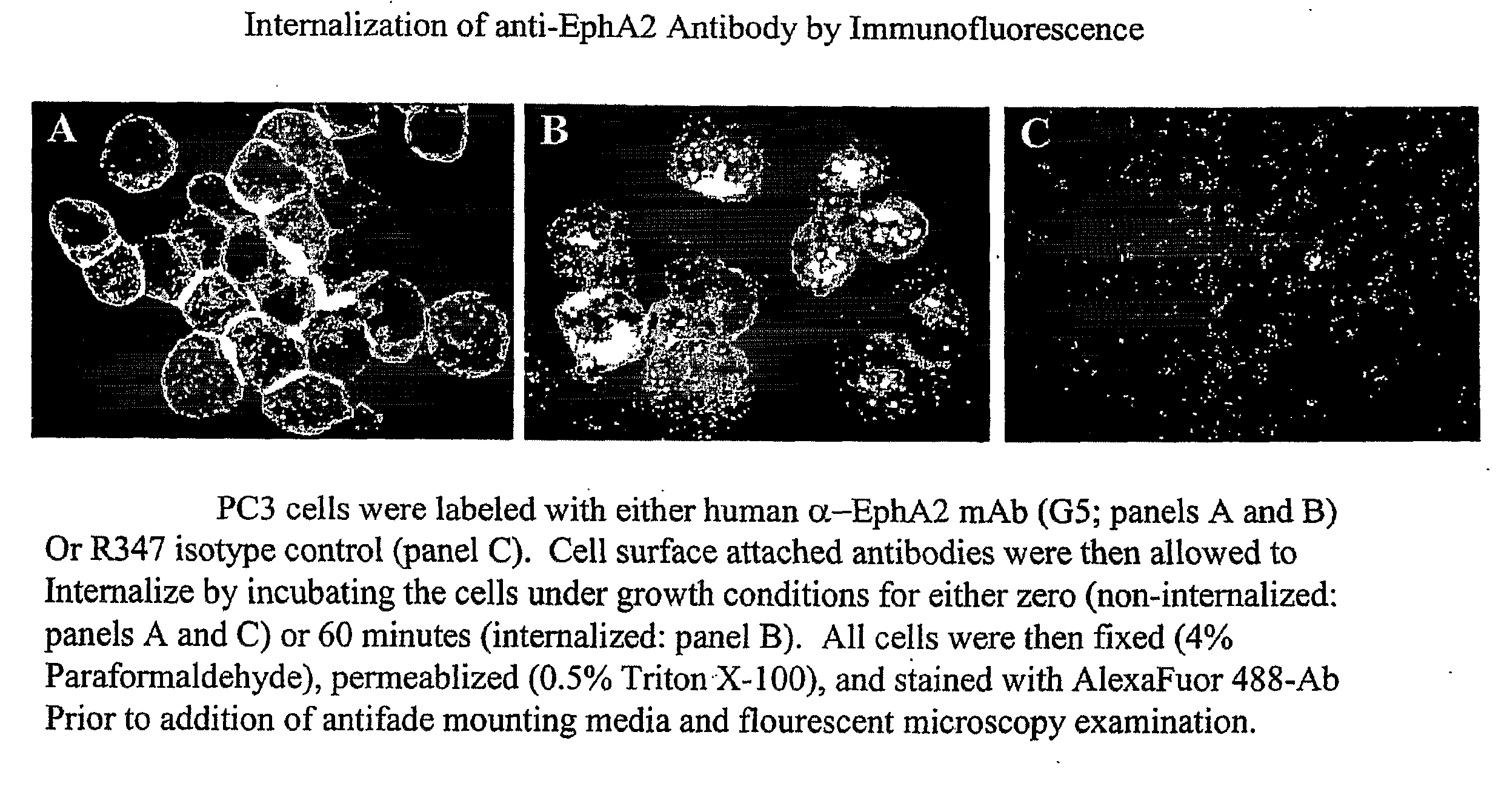
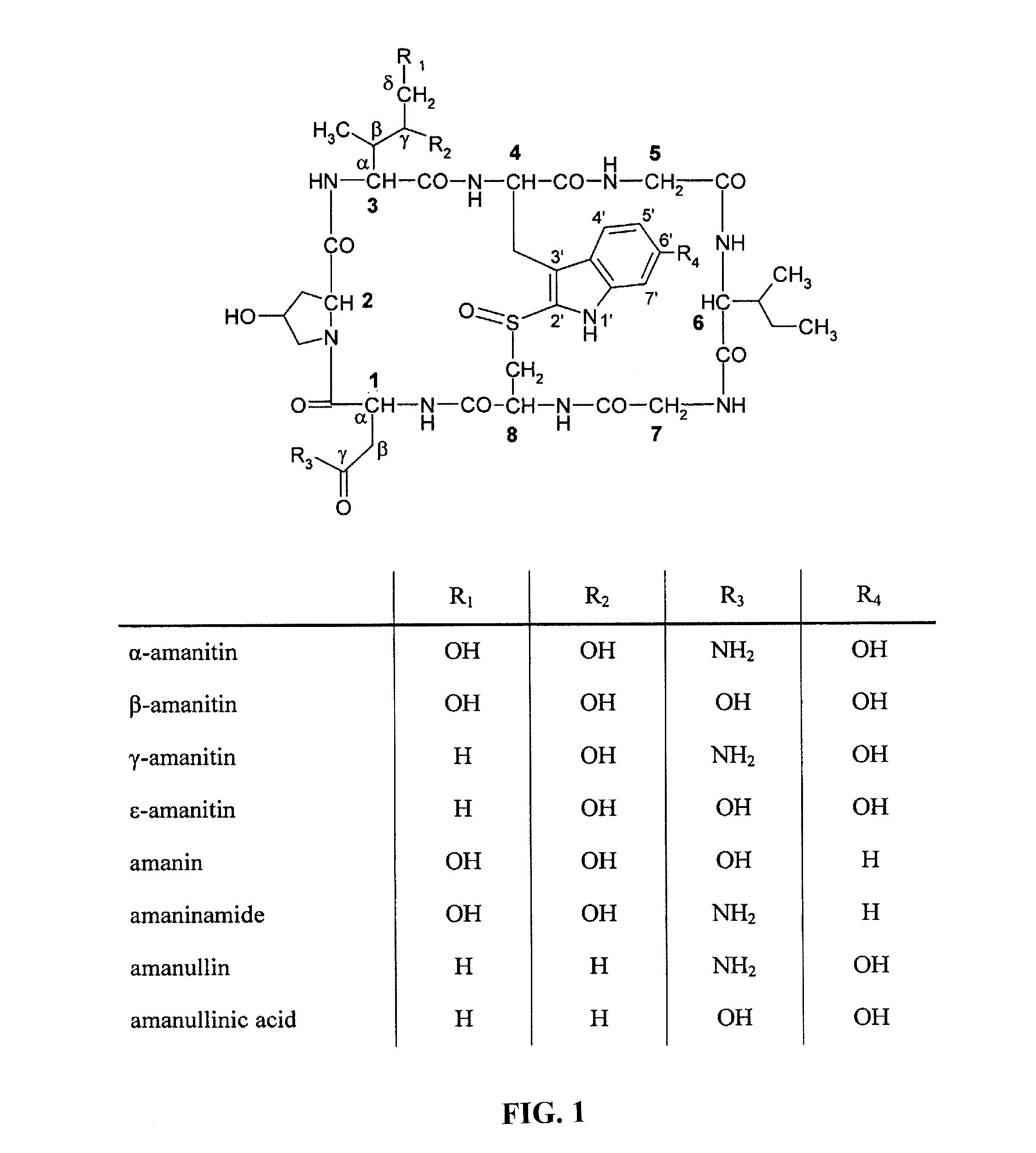
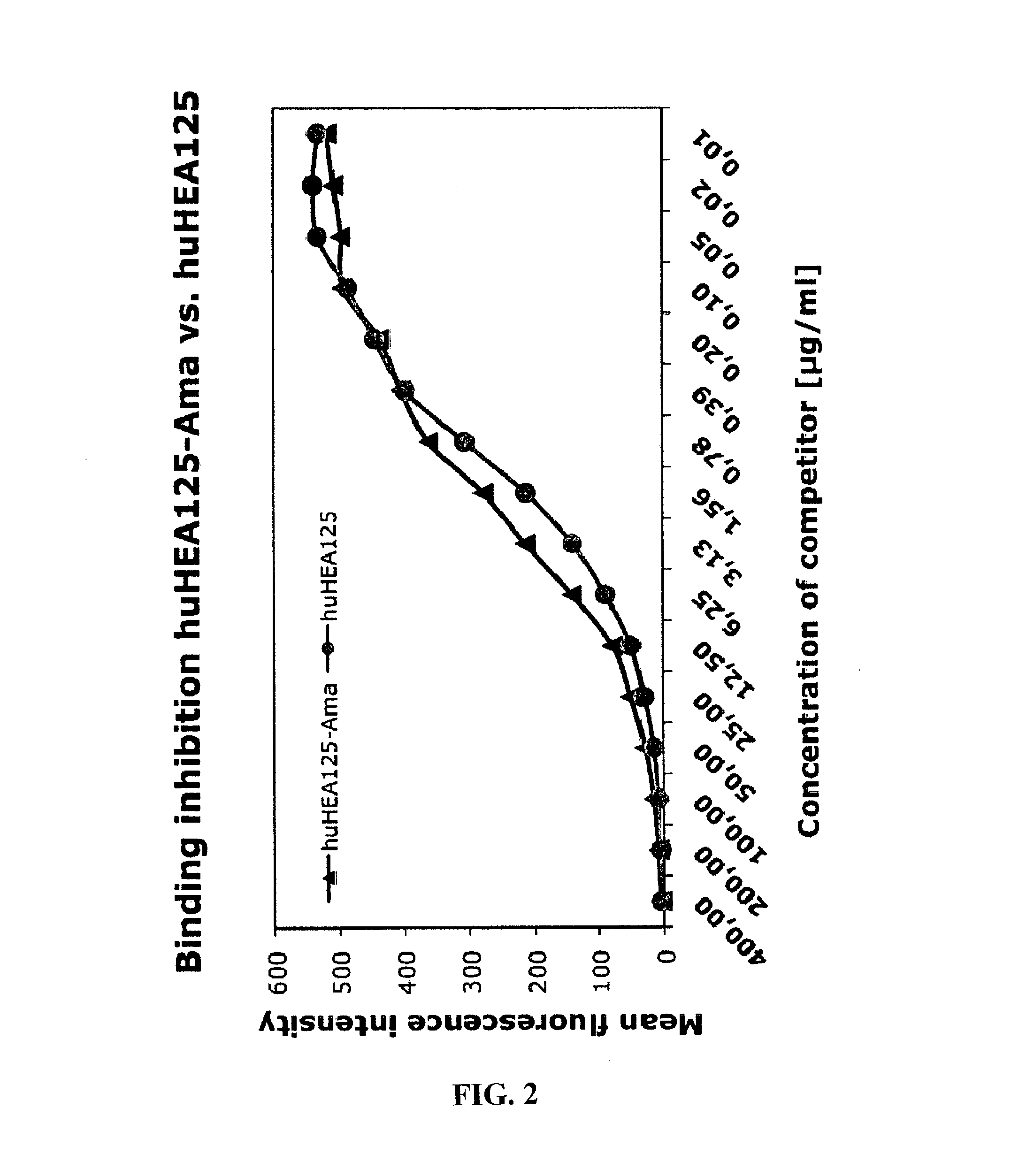
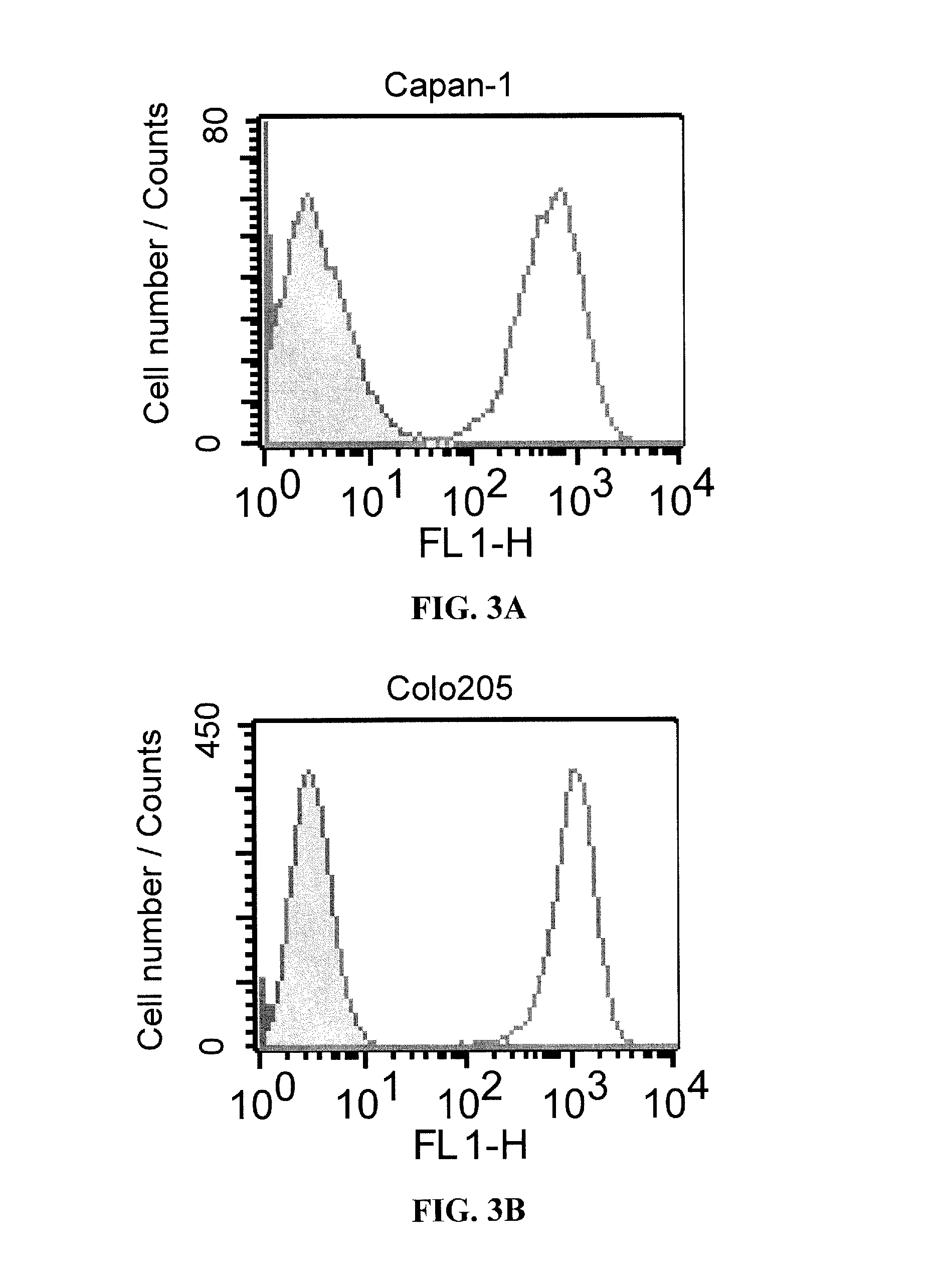
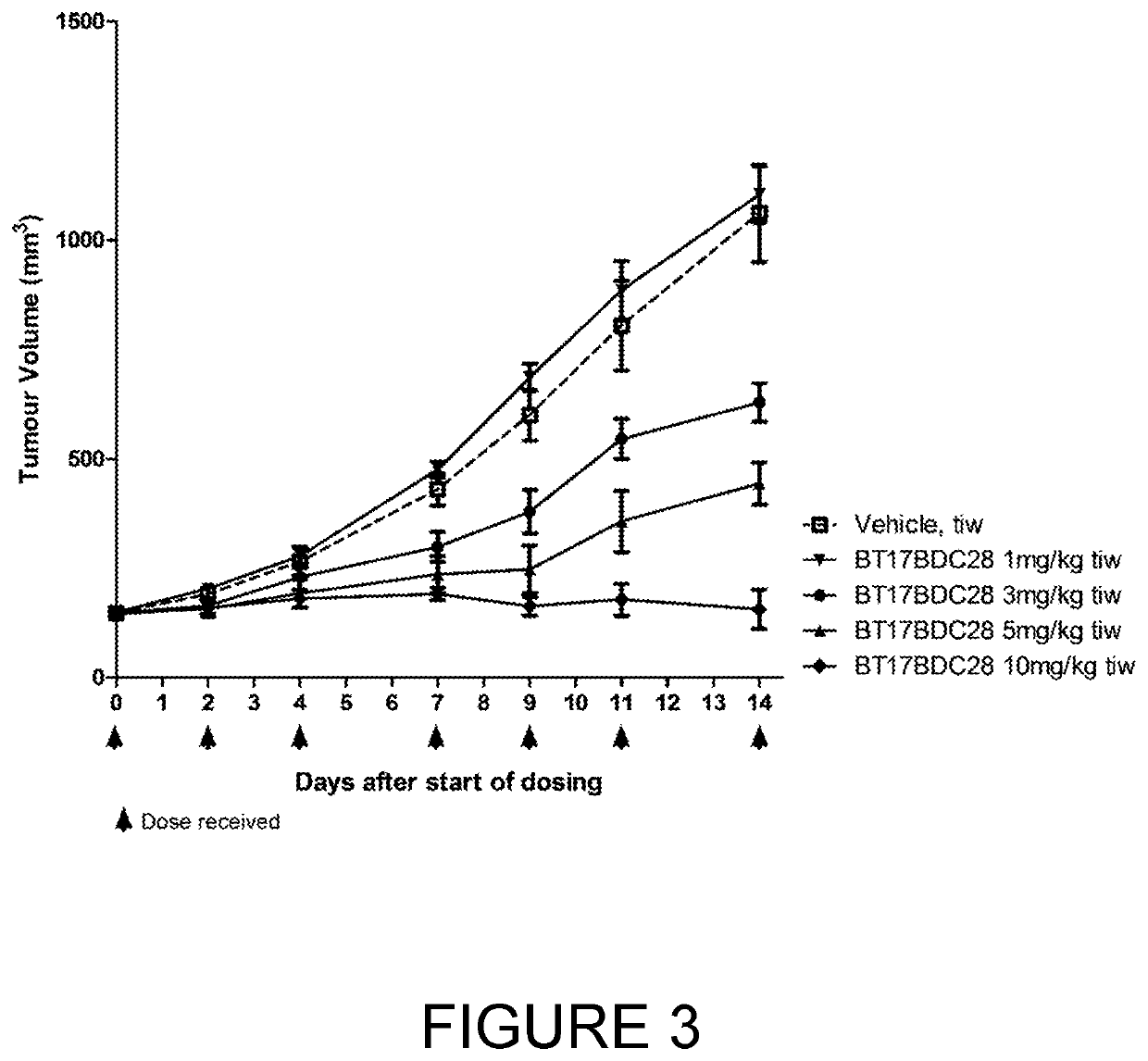
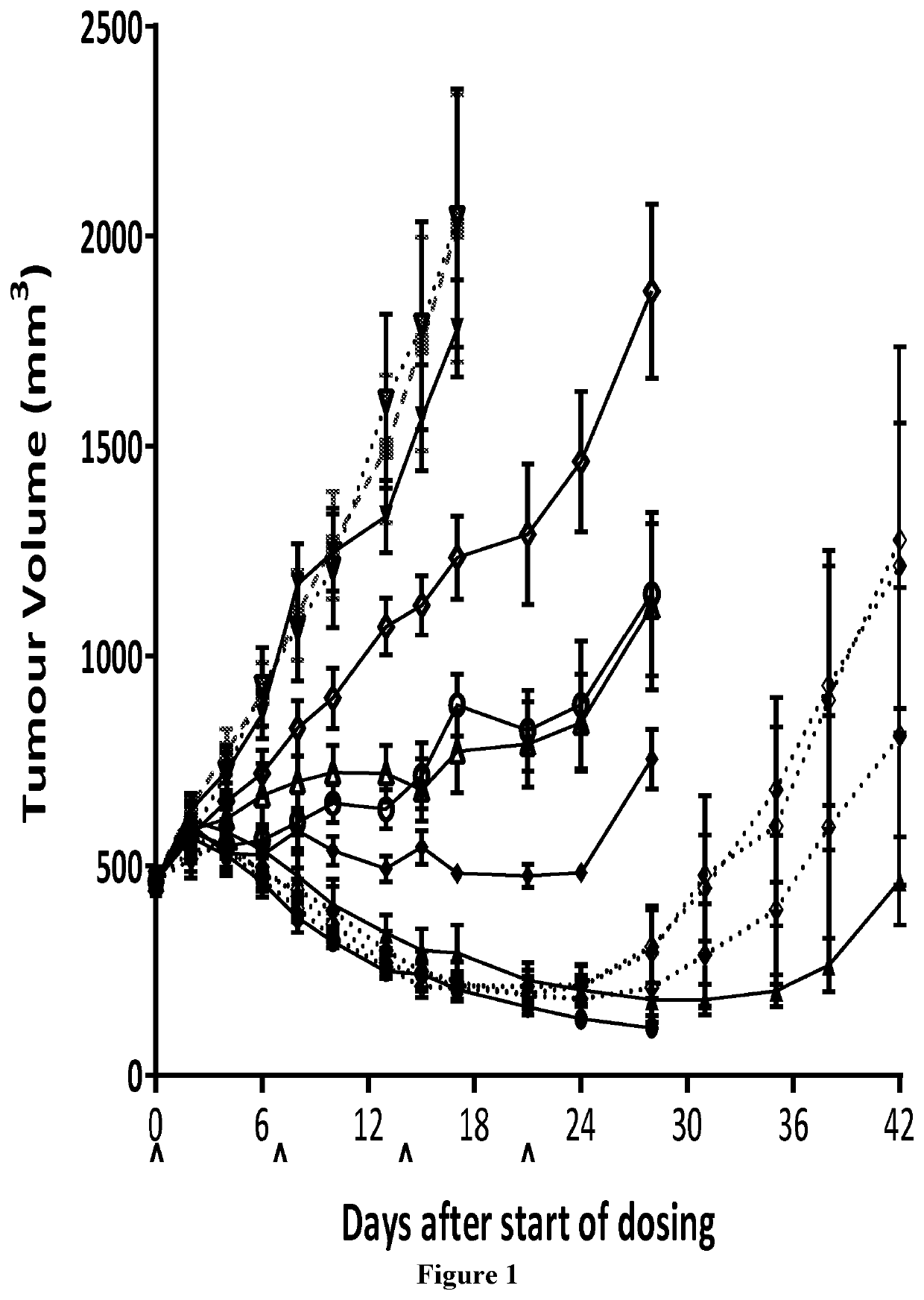
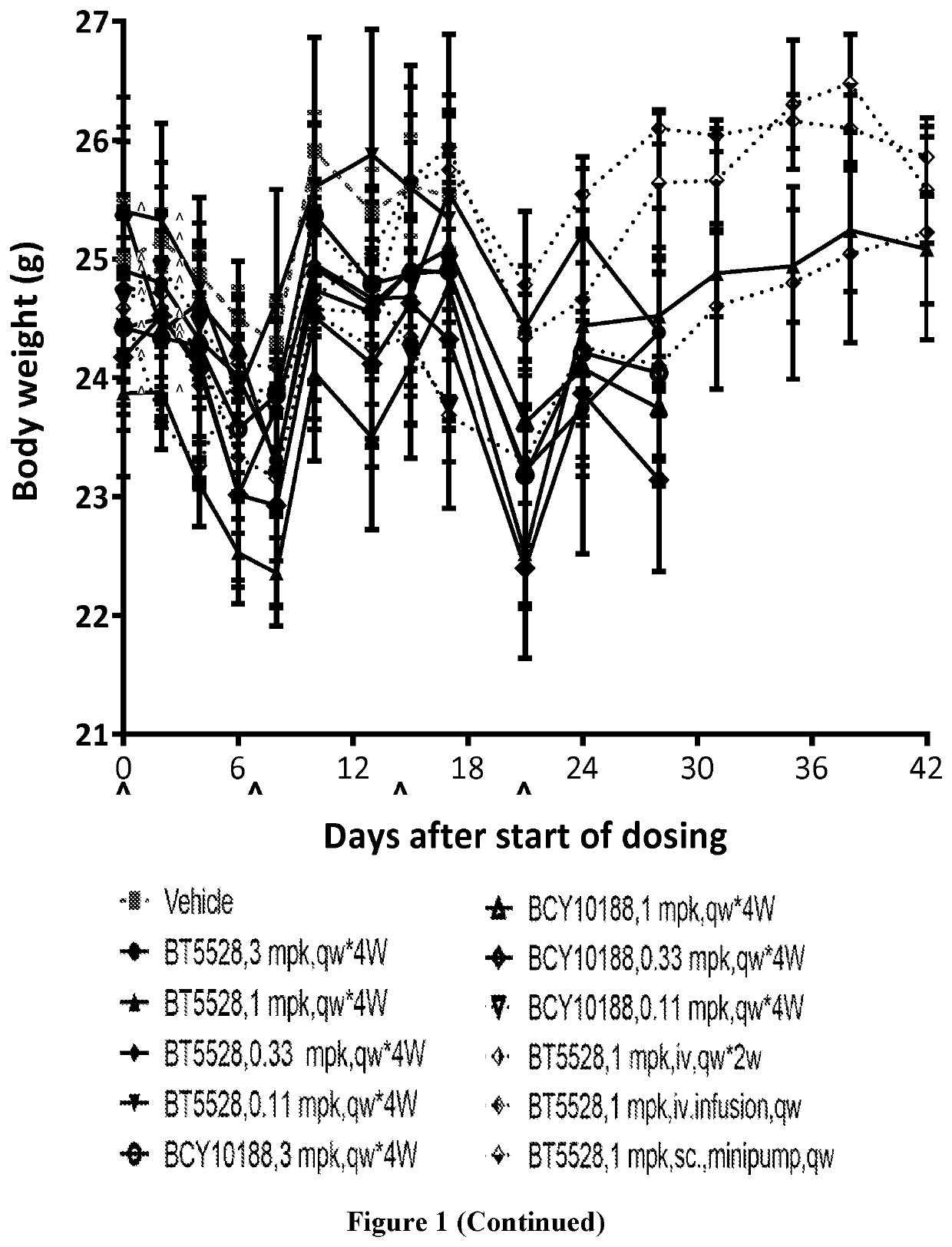
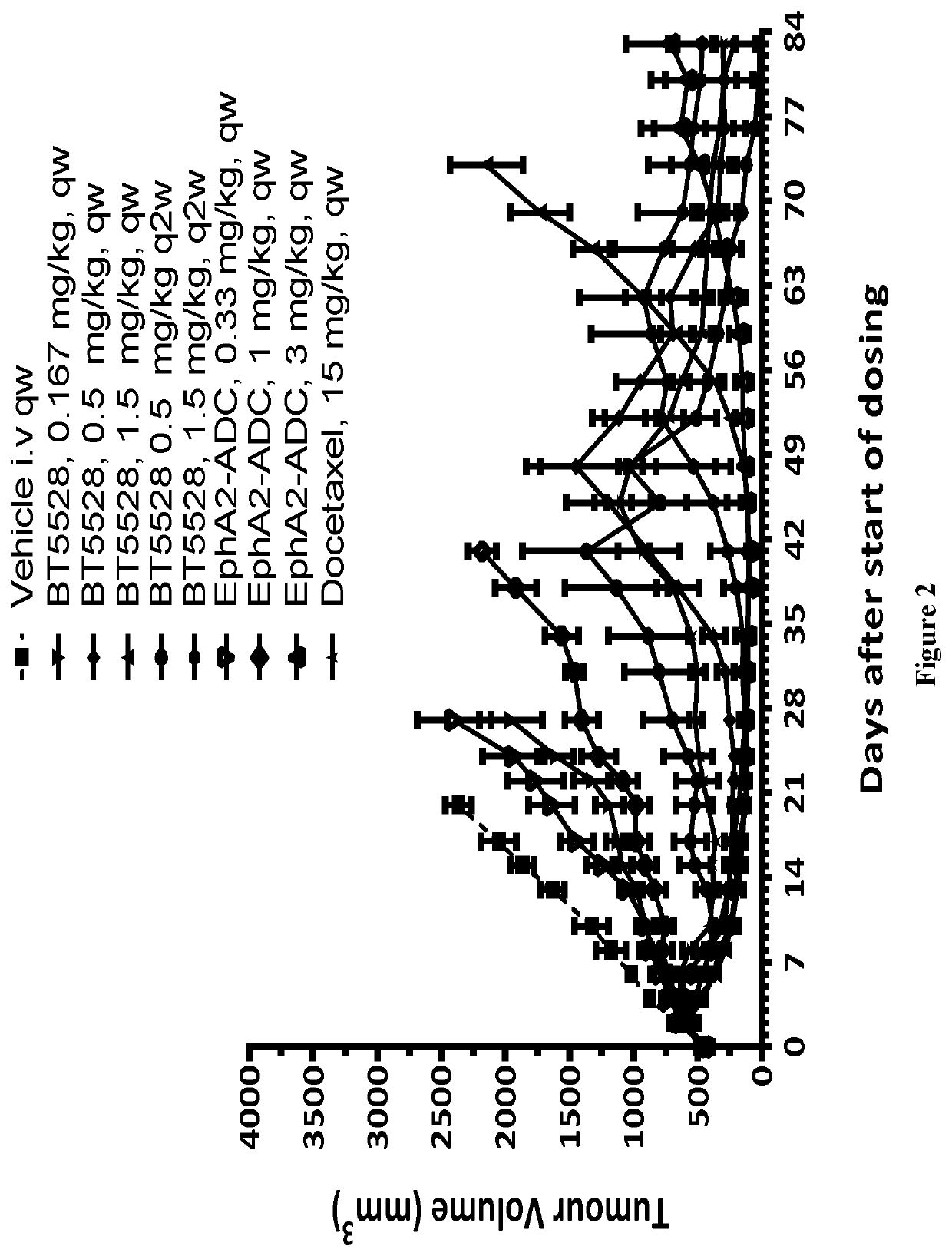
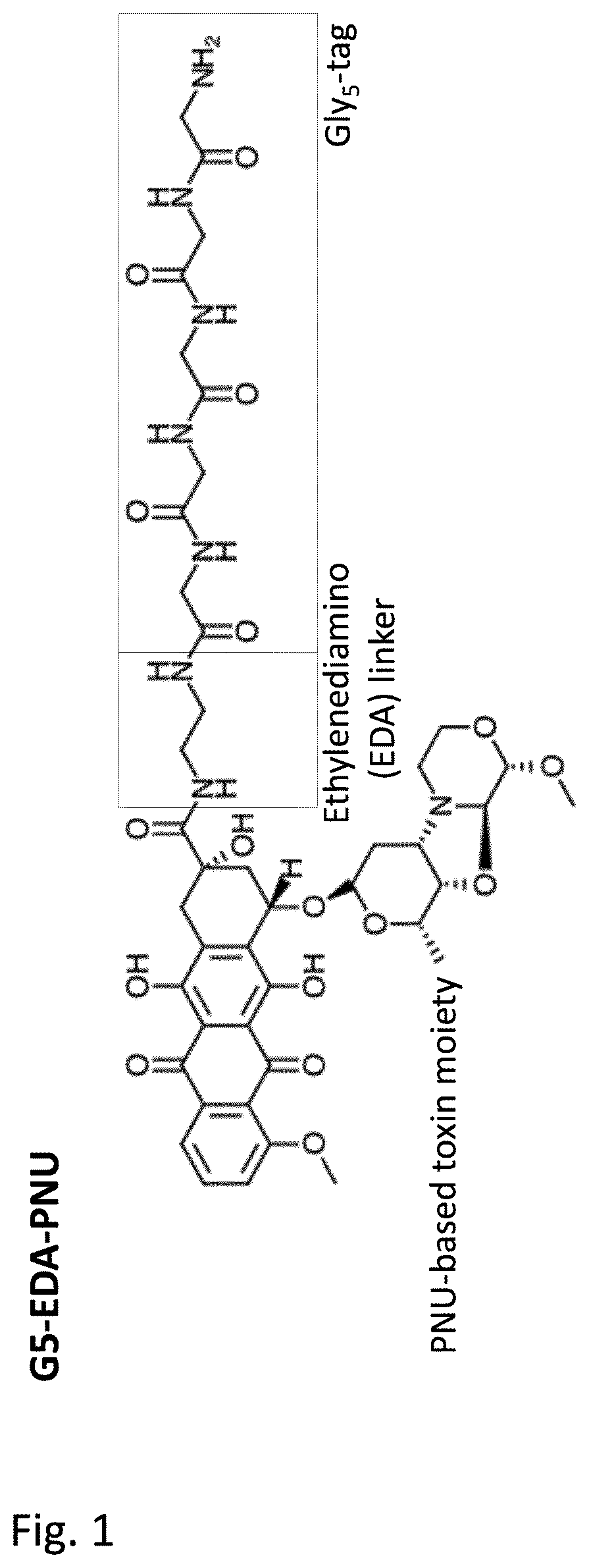
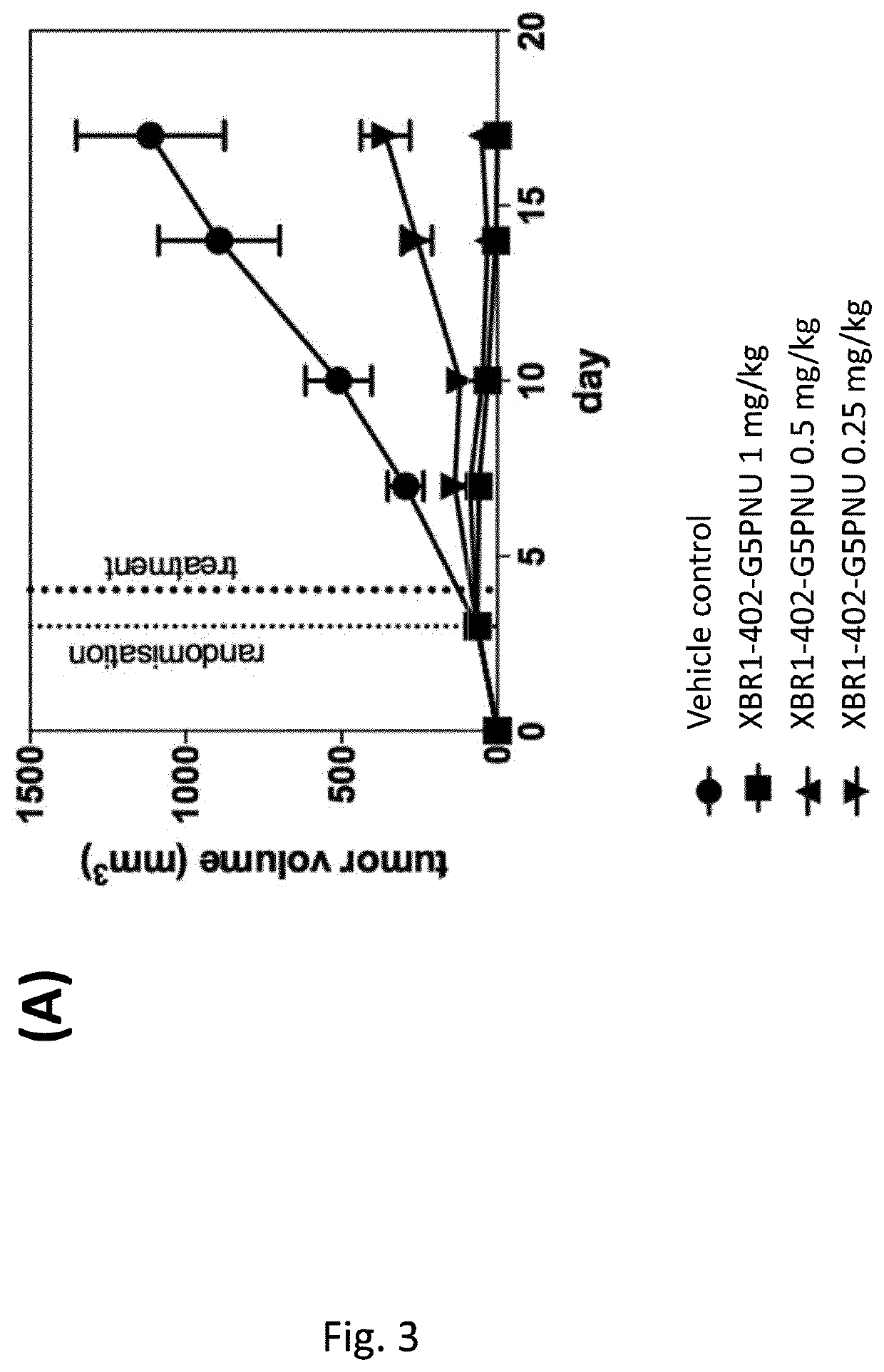
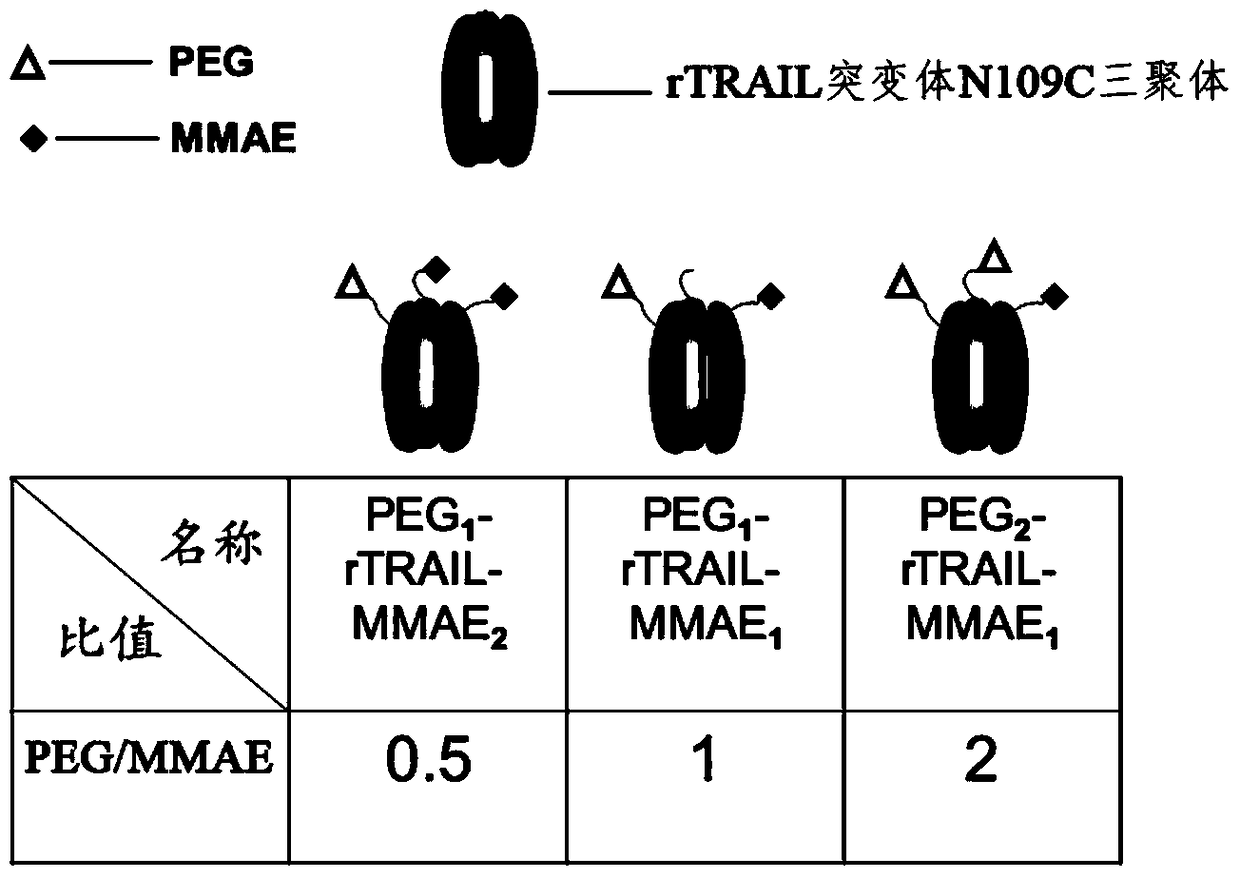
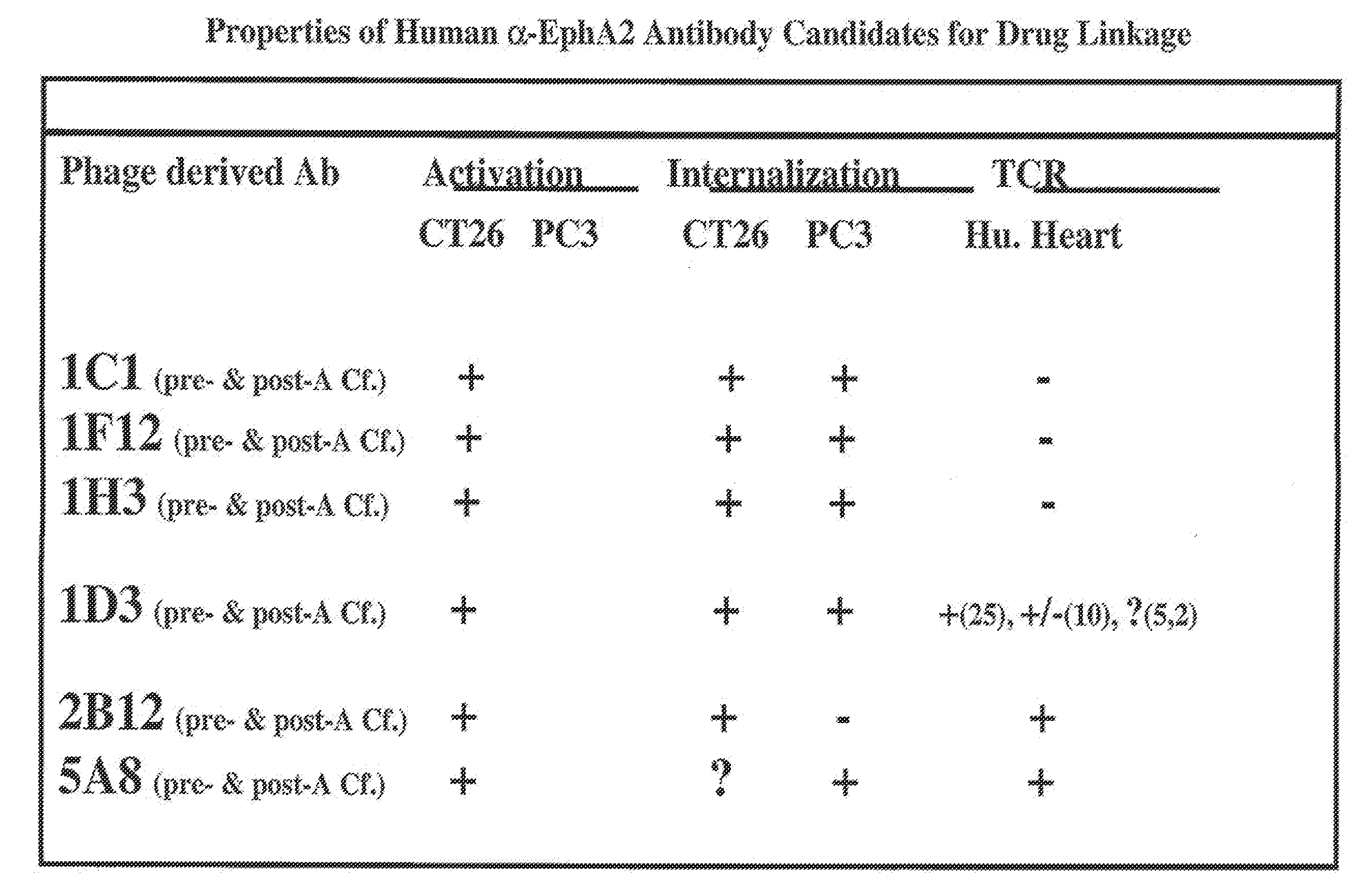Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33 results about "Toxin Conjugates" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
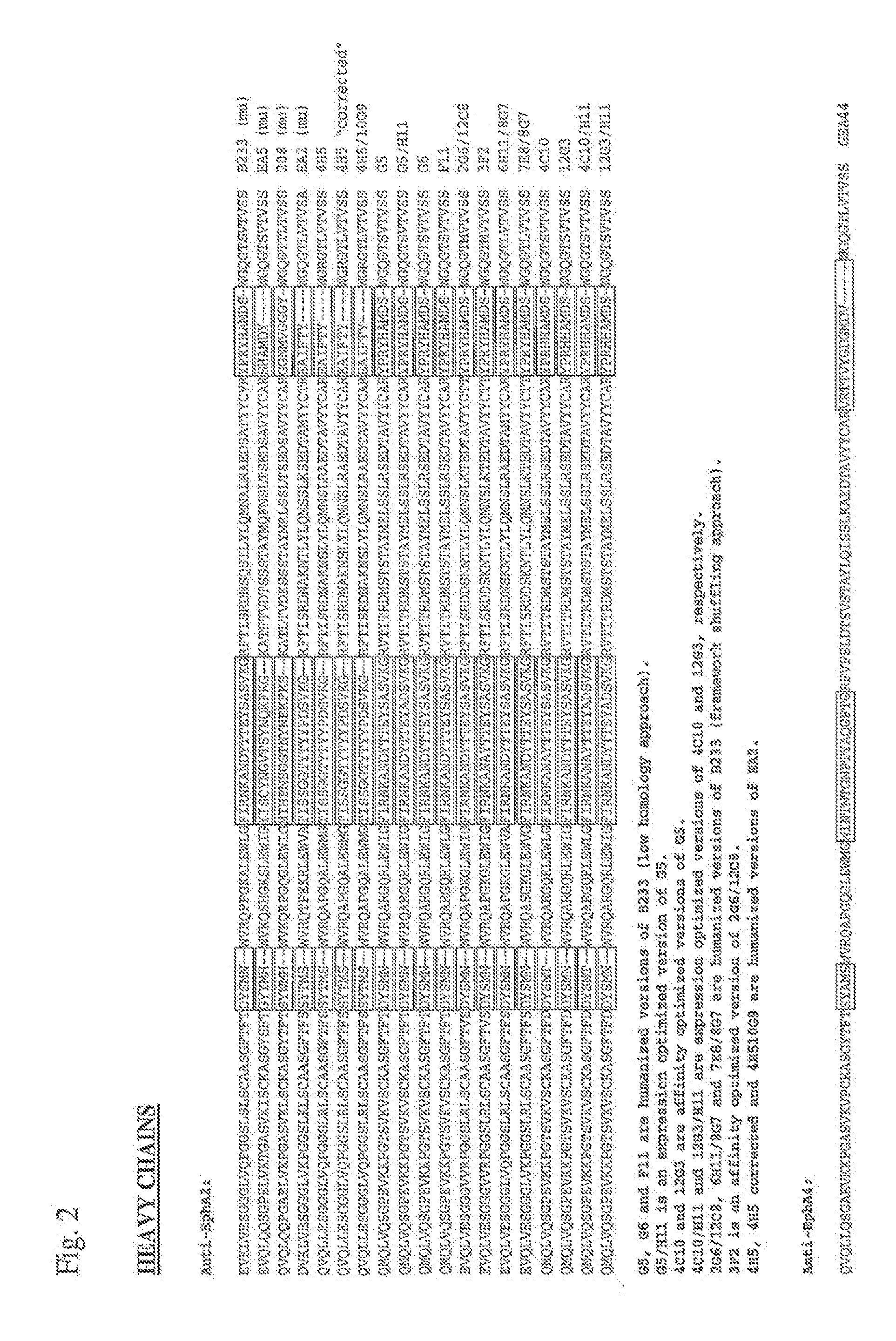
Toxin conjugated eph receptor antibodies
InactiveUS20090304721A1Prolong half-life in vivoIncrease local concentrationAnimal cellsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansCancer cellToxin Conjugates
Owner:SEATTLE GENETICS INC +1
Non-antigenic toxin-conjugate and fusion protein of internalizing receptor system
InactiveUS7033572B2Effective and less toxicIncrease valuePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEphA ReceptorsCytokine
A conjugate of a toxin and a cytokine, and a fusion protein comprising a bispecific antibody that has a first specificity for a cell marker specific to a malignant cell and a second specificity for a region of IL-15α, each optionally further comprising a radionuclide, are useful therapeutic reagents for treating leukemias and lymphomas.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Amatoxin-armed therapeutic cell surface binding components designed for tumour therapy
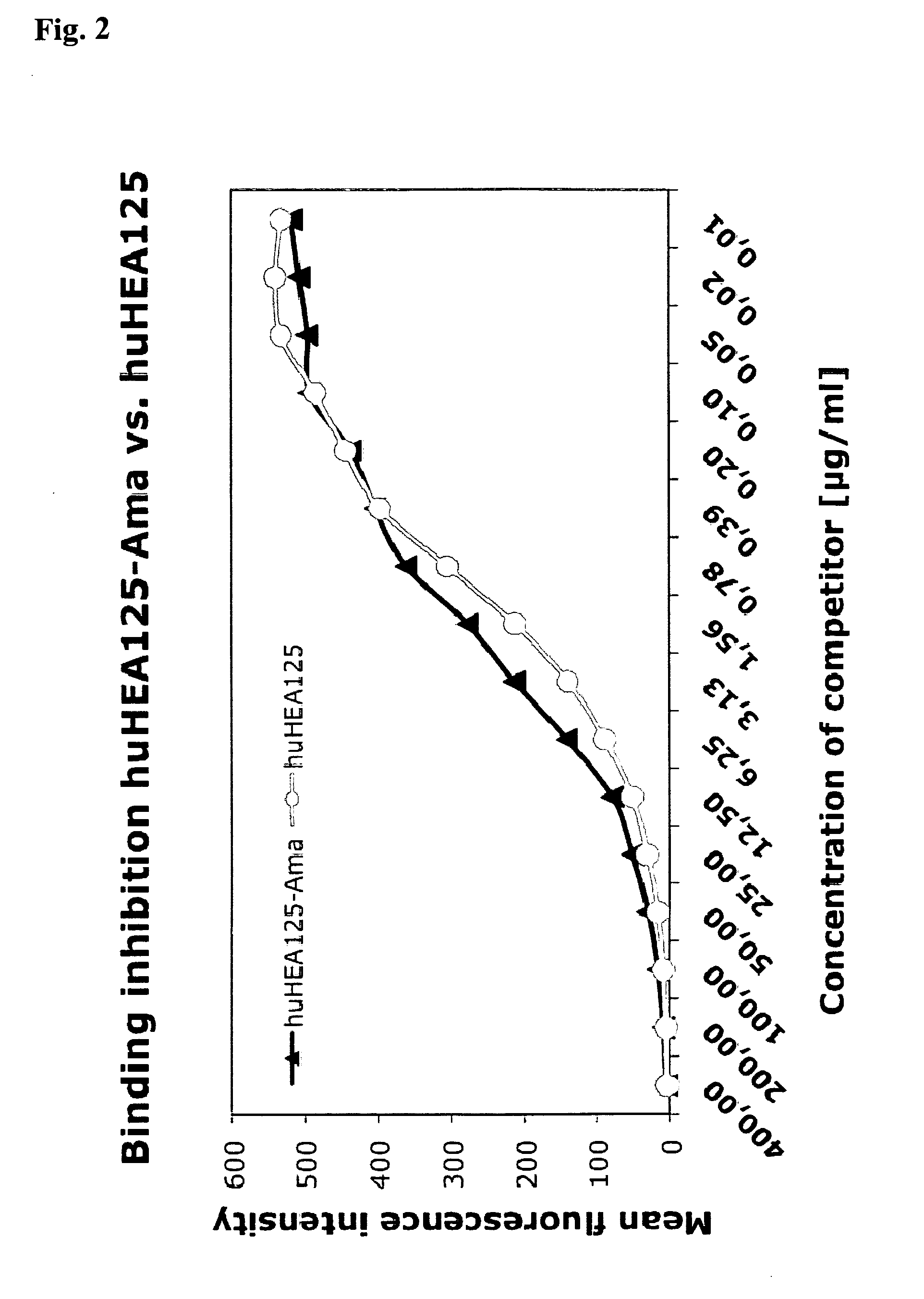
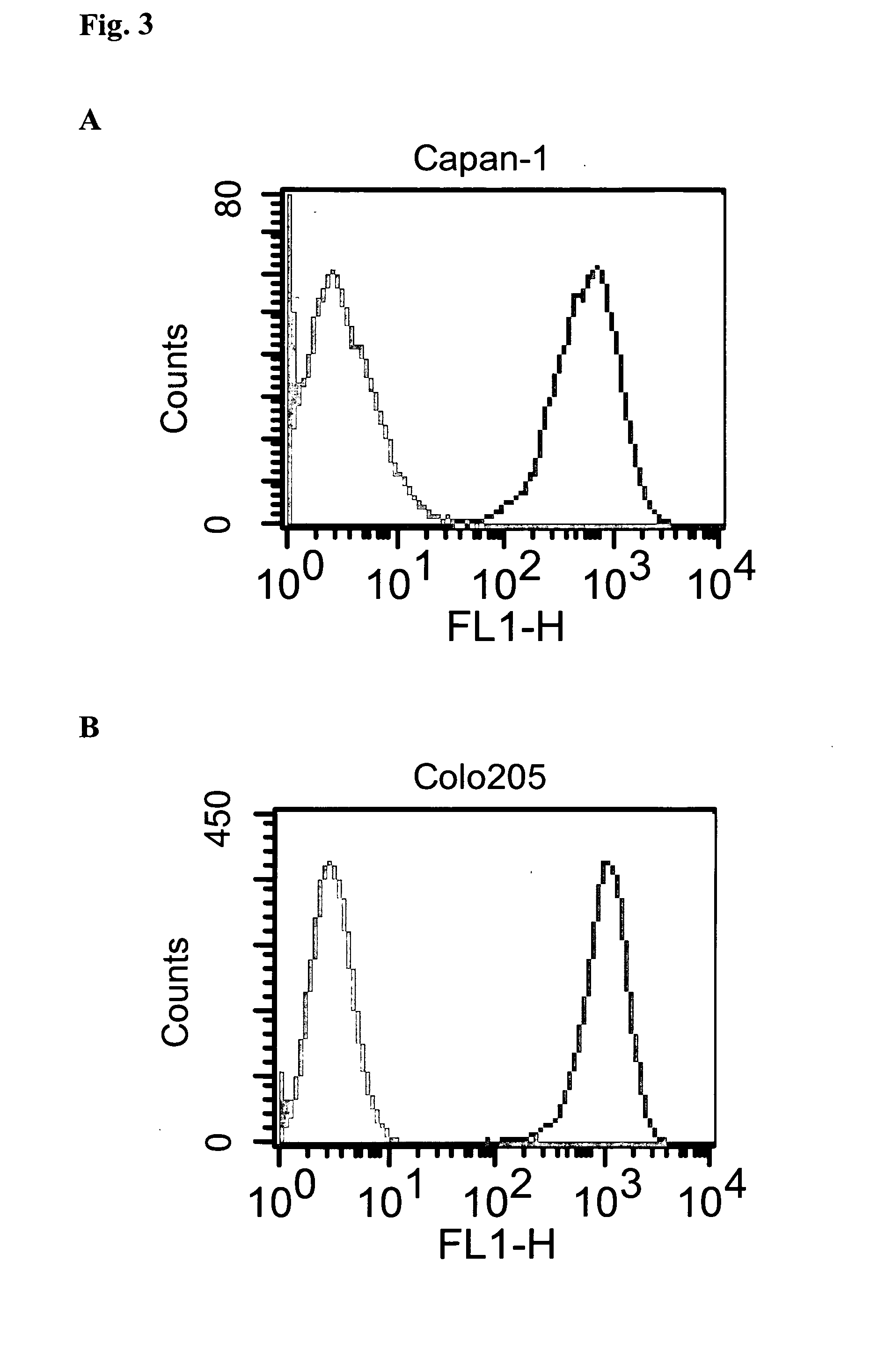
The invention relates to tumour therapy. In one aspect, the present invention relates to conjugates of a toxin and a target-binding moiety, e.g. an antibody, which are useful in the treatment of cancer. In particular, the toxin is an amatoxin, and the target-binding moiety is preferably directed against tumour-associated antigens. In particular, the amatoxin is conjugated to the antibody by linker moieties. In particular the linker moieties are covalently bound to functional groups located in positions of the amatoxin proved as preferred positions for the attachment of linkers with respect to optimum antitumor activity. In a further aspect the invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising such target-binding moiety toxin conjugates and to the use of such target-binding moiety toxin conjugates for the preparation of such pharmaceutical compositions. The target-binding moiety toxin conjugates and pharmaceutical compositions of the invention are useful for the treatment of cancer.
Owner:DEUTES KREBSFORSCHUNGSZENT STIFTUNG DES OFFENTLICHEN RECHTS +1
Toxin conjugated eph receptor antibodies
InactiveUS20110280892A1Prolong half-life in vivoIncrease local concentrationAnimal cellsBacteriaCancer cellAntiendomysial antibodies
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC +1
Therapeutic nucleic acid-3' -conjugates
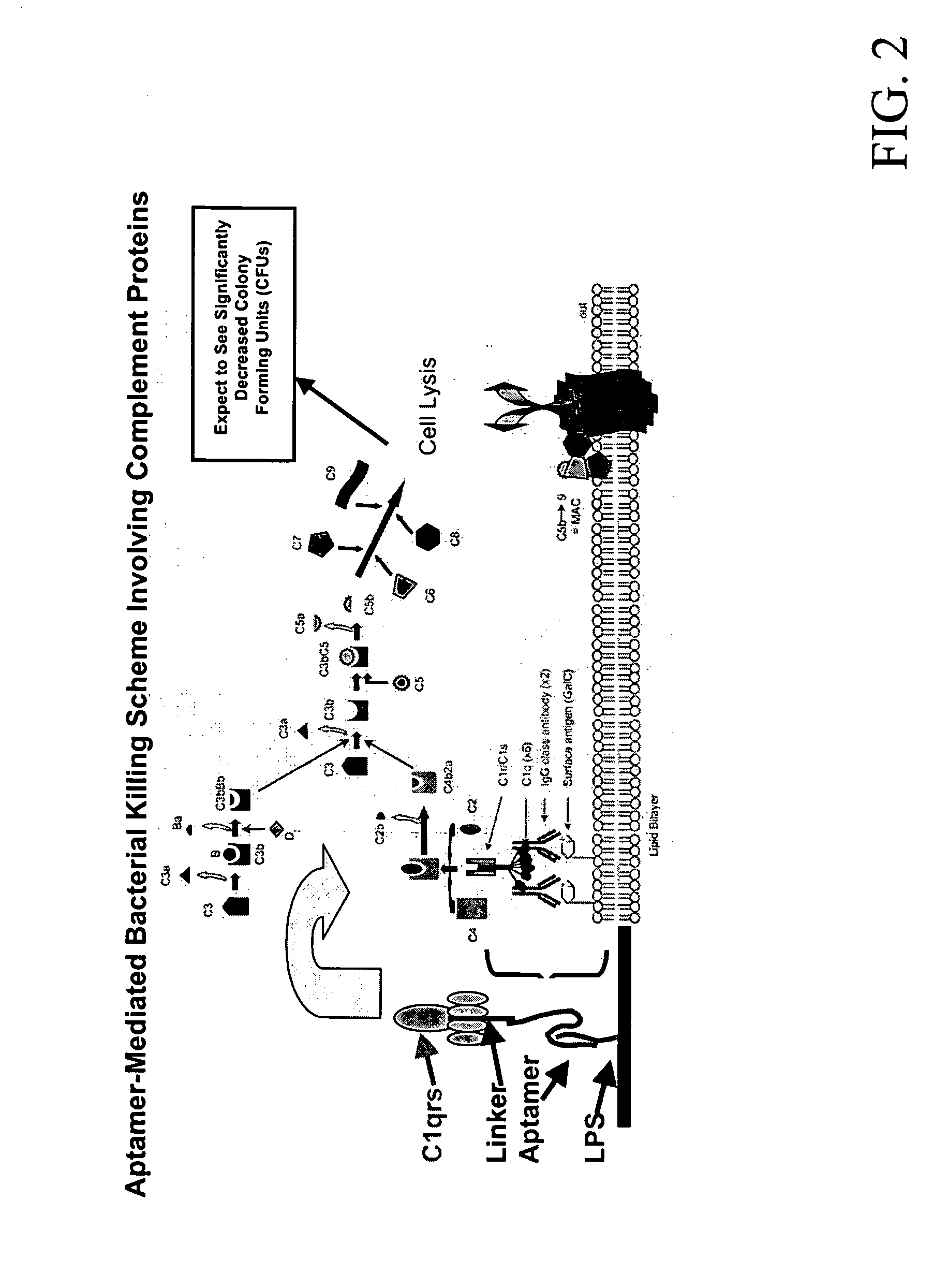
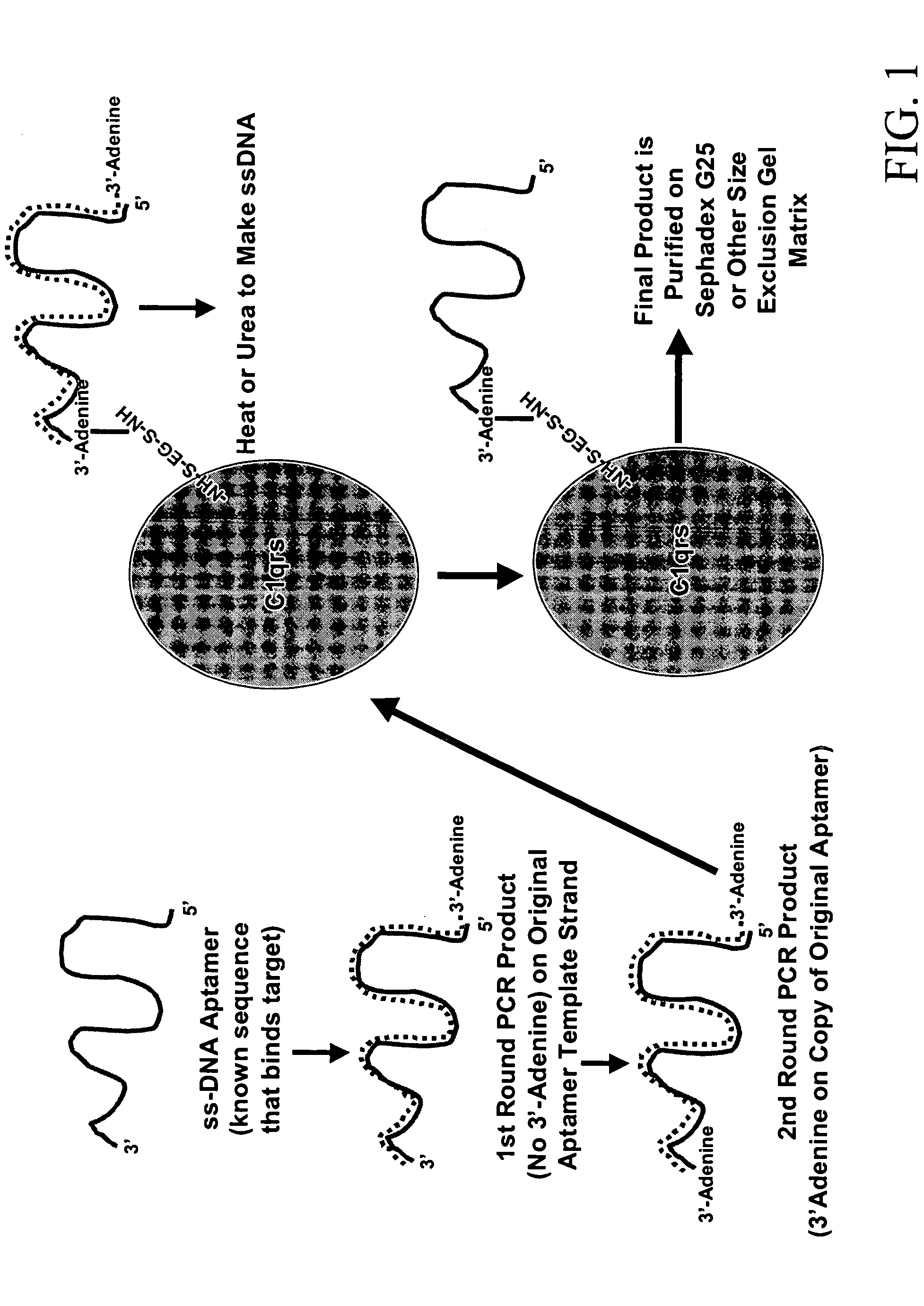
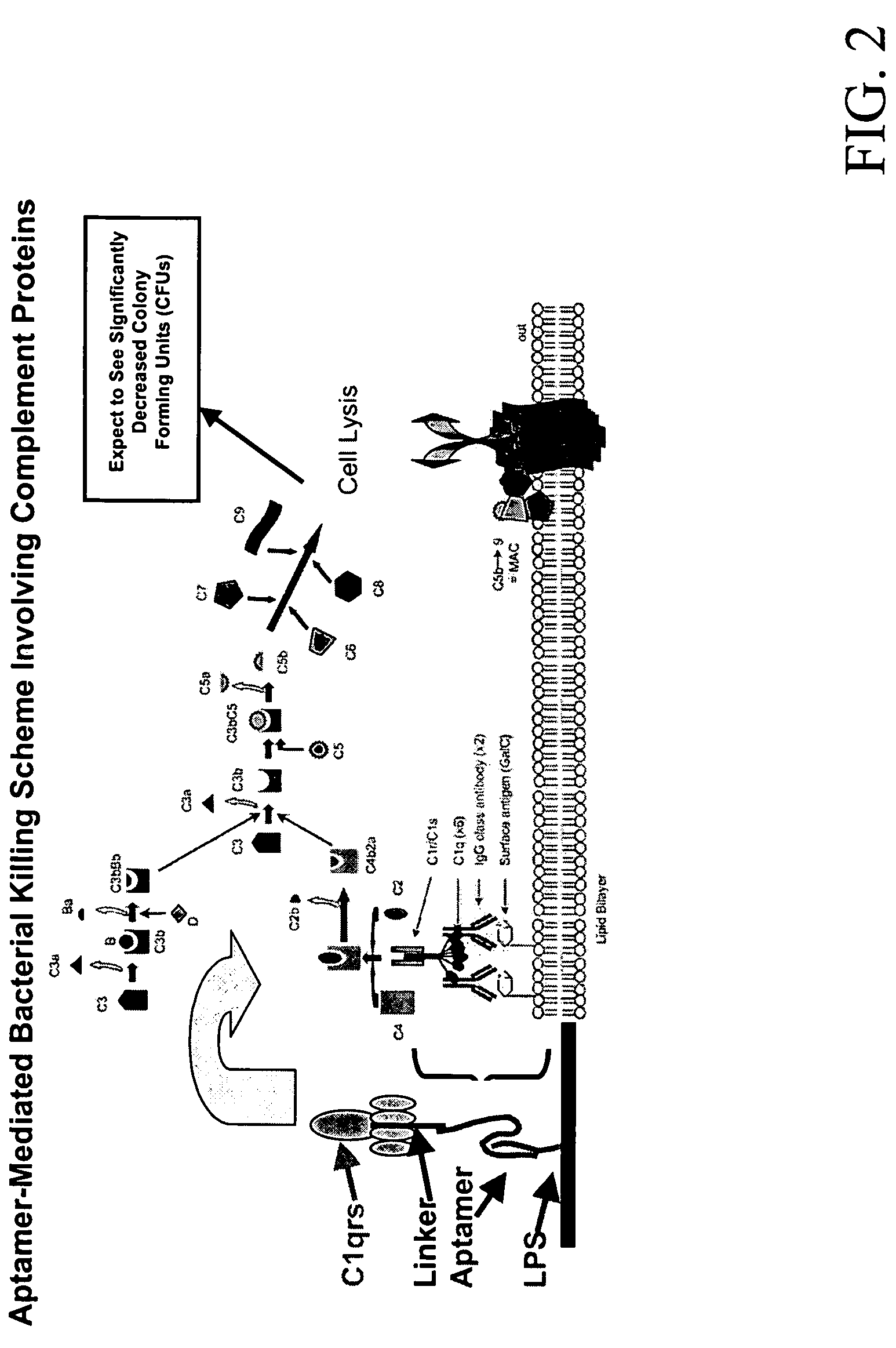
InactiveUS20050191680A1Efficient killingPrevent breakdownMaterial nanotechnologyActivity regulationHalf-lifeWhite blood cell
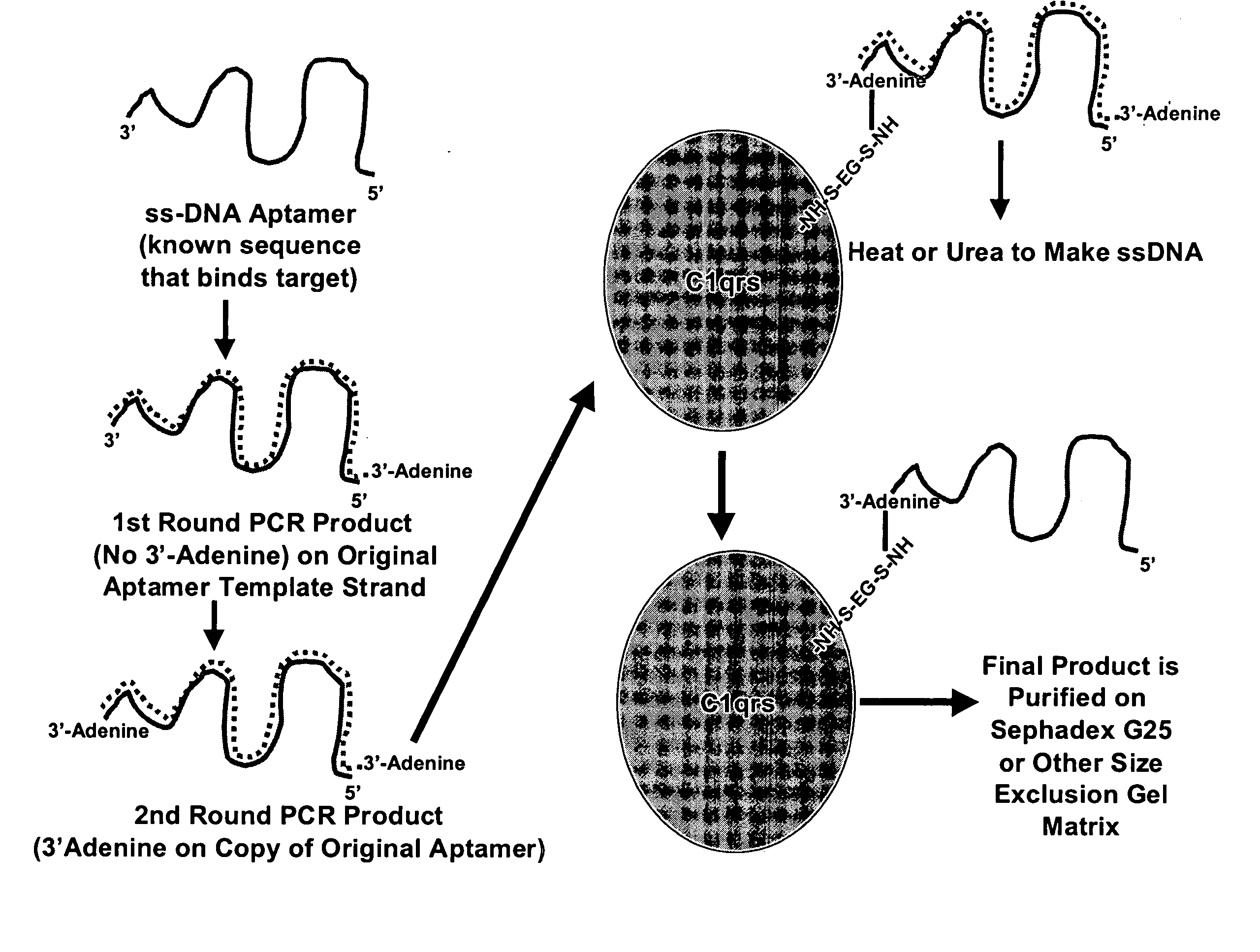
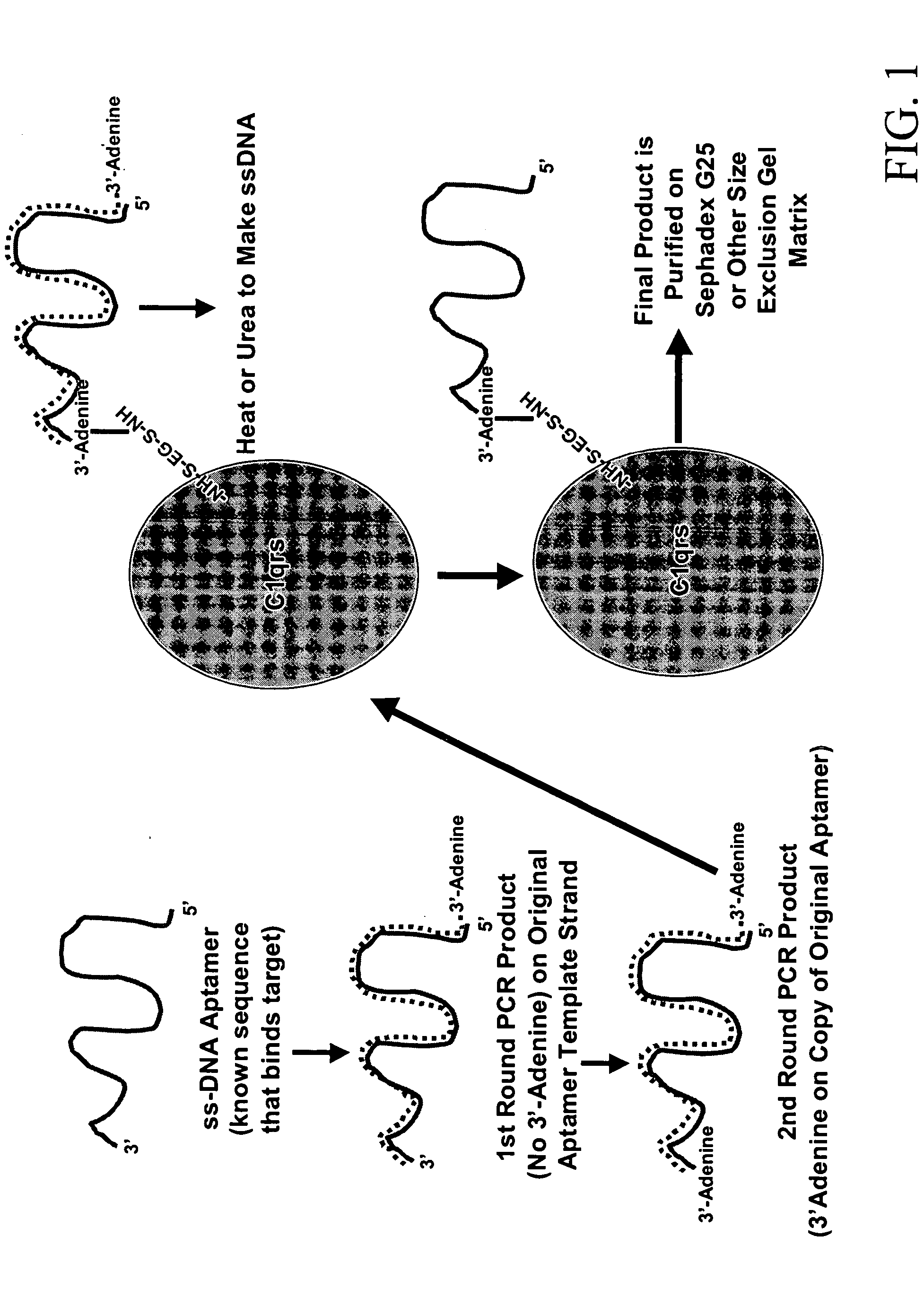
Methods are described for improvement of the serum half life of therapeutic nucleic acids by 3′ conjugation to useful target proteins, or other large molecules with useful function. In one embodiment, a 3′ A, C or G overhang is added to ds-DNA and the primary amines conjugated using biocompatible bifunctional linkers to proteins. The resulting nucleic acid-3′-conjugates are serum nuclease-resistant and retained in vivo for long periods without rapid kidney clearance. Further, the choice of conjugate imparts additional functionality to the nucleic acid-3-conjugate. For example, if the protein in the DNA-protein conjugate is the first component of the complement cascade (Clq or Clqrs) and the DNA aptamer has been developed against surface components of a target cell, it can be used to treat bacterial or parasitic infections and cancers. If the protein is serum albumin or another common (nonimmunogenic) blood protein and the aptamer is directed against a toxin or venom, the aptamer-protein conjugate can be used as an antidote that binds and neutralizes the toxin or venom. Similar DNA (aptamer)-nanotube, -enzyme, and -toxin conjugates could also be used to target and selectively kill bacteria, parasites, and cancer cells in vivo. If the protein is an Fc antibody fragment or C3b protein from the complement system and the aptamer is developed against a bacterial cell capsular material, other cell surface component or viral cell surface component, then the aptamer-3′-protein conjugate can aid in opsonization of the target cells or viruses by phagocytic leukocytes.
Owner:OTC BIOTECH
Amatoxin-Armed Therapeutic Cell Surface Binding Components Designed for Tumour Therapy
The invention relates to tumour therapy. In one aspect, the present invention relates to conjugates of a toxin and a target-binding moiety, e.g. an antibody, which are useful in the treatment of cancer. In particular, the toxin is an amatoxin, and the target-binding moiety is preferably directed against tumour-associated antigens. In particular, the amatoxin is conjugated to the antibody by linker moieties. In particular the linker moieties are covalently bound to functional groups located in positions of the amatoxin proved as preferred positions for the attachment of linkers with respect to optimum antitumor activity. In a further aspect the invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising such target-binding moiety toxin conjugates and to the use of such target-binding moiety toxin conjugates for the preparation of such pharmaceutical compositions. The target-binding moiety toxin conjugates and pharmaceutical compositions of the invention are useful for the treatment of cancer.
Owner:DEUTES KREBSFORSCHUNGSZENT STIFTUNG DES OFFENTLICHEN RECHTS +1
Immunotoxin (mAB-RICIN) for the treatment of focal movement disorders
InactiveUS20050266010A1BiocideImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntigenPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Methods of detecting and treating cancers using autoantibodies
This invention generally relates to a method of identifying pre-neoplastic or neoplastic tissue of a mammal by utilizing autoantibodies that detect the pre-neoplastic or neoplastic tissue. Also described herein are methods of killing pre-neoplastic or neoplastic tissue by either binding toxins to autoantibodies that detect the pre-neoplastic or neoplastic tissue or introducing toxin-conjugated molecules that can in turn recognize the autoantibodies already bound to the pre-neoplastic or neoplastic tissue.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Targeting with firbronectin type iii like domain molecules
InactiveUS20190184028A1Guarantee directionPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsNanoparticle ComplexToxin Conjugates
A fibronectin type III (FN3) domain-nanoparticle or direct conjugate complex containing a polynucleotide molecule, a toxin, polynucleotide molecule or other pharmaceutically active payload is obtained by panning an FN3 domain library with a protein or nucleotide of interest, recovering the FN3 domain and conjugating the FN3 domain with a toxin or nanoparticle containing an active polynucleotide, such as an ASO or siRNA molecule. A fibronectin type III (FN3) domain-nucleic acid conjugate is obtained by panning an FN3 domain library with a protein or nucleotide of interest, recovering the FN3 domain and conjugating the FN3 domain to a nucleic acid (e.g., ASO or siRNA). The nanoparticle complex, nucleic acid conjugate or FN3 domain toxin conjugate may be used in the treatment of diseases and conditions, for example, oncology or auto-immune indications.
Owner:JANSSEN BIOTECH INC
Enzyme linked immunoassay kit for detecting T-2 toxin, and application thereof
The present invention provides an enzyme linked immunoassay kit for detecting T-2 toxin. The kit contains a T-2 toxin conjugated antigen coated enzyme label plate, a T-2 toxin standard substance solution, a concentrated enzyme conjugate, an enzyme conjugate working solution, a substrate coloration solution and a termination solution. The invention further discloses a method for detecting T-2 toxin in a sample by using the enzyme linked immunoassay kit. The method comprises: carrying out a sample pretreatment, detecting by using the kit, and analyzing the detection result. The enzyme linked immunoassay kit can be used for detecting T-2 toxin residue in feed (raw materials, matching materials and concentrated materials) samples, has characteristics of simple operation, low cost, high sensitivity and on-site monitoring, and is suitable for screening of mass samples.
Owner:BEIJING KWINBON BIOTECH
Amatoxin-Armed Tartget-Binding Moieties for the Treatment of Cancer
InactiveUS20120213805A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsAdenocarcinomaToxin Conjugates
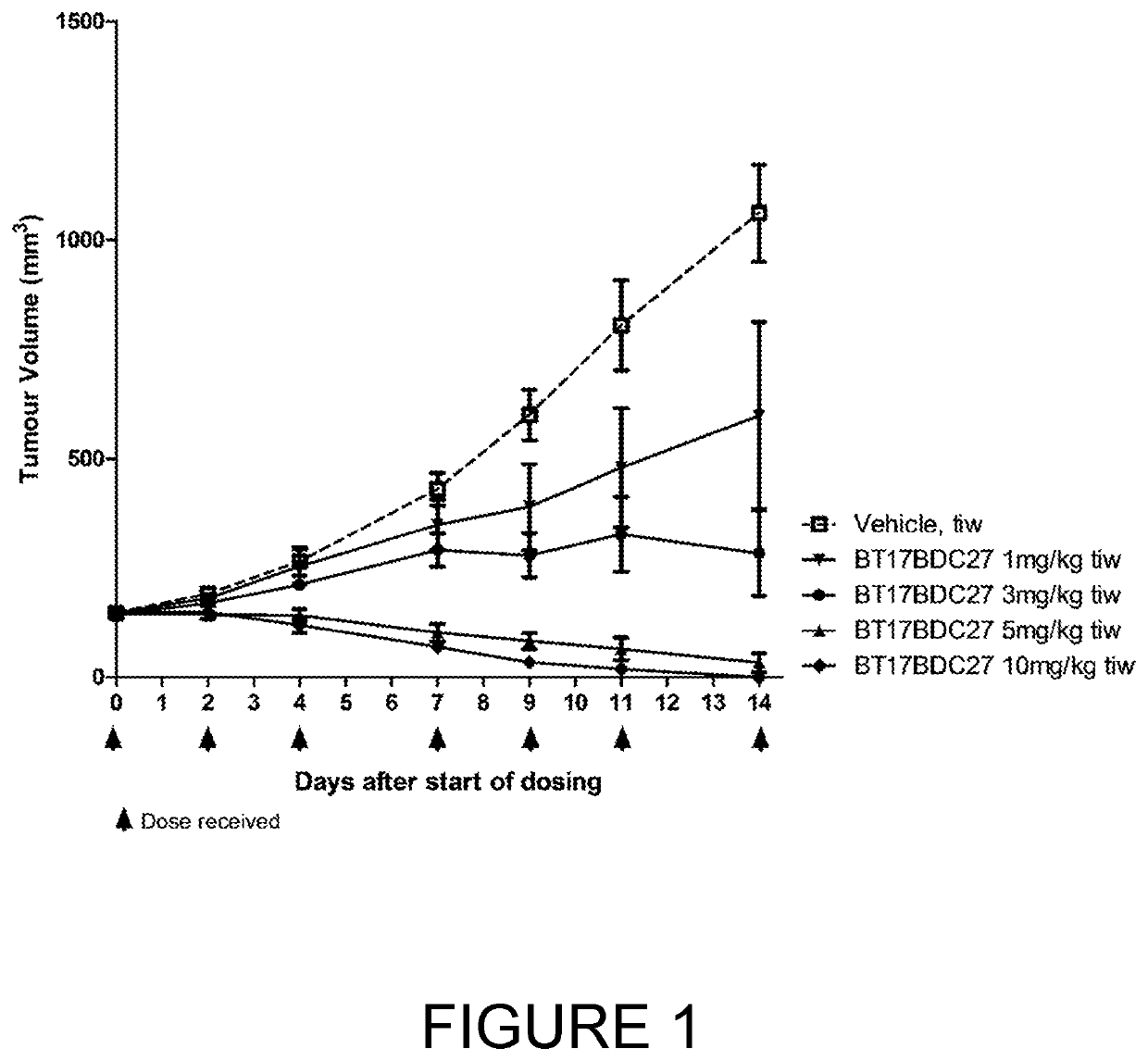
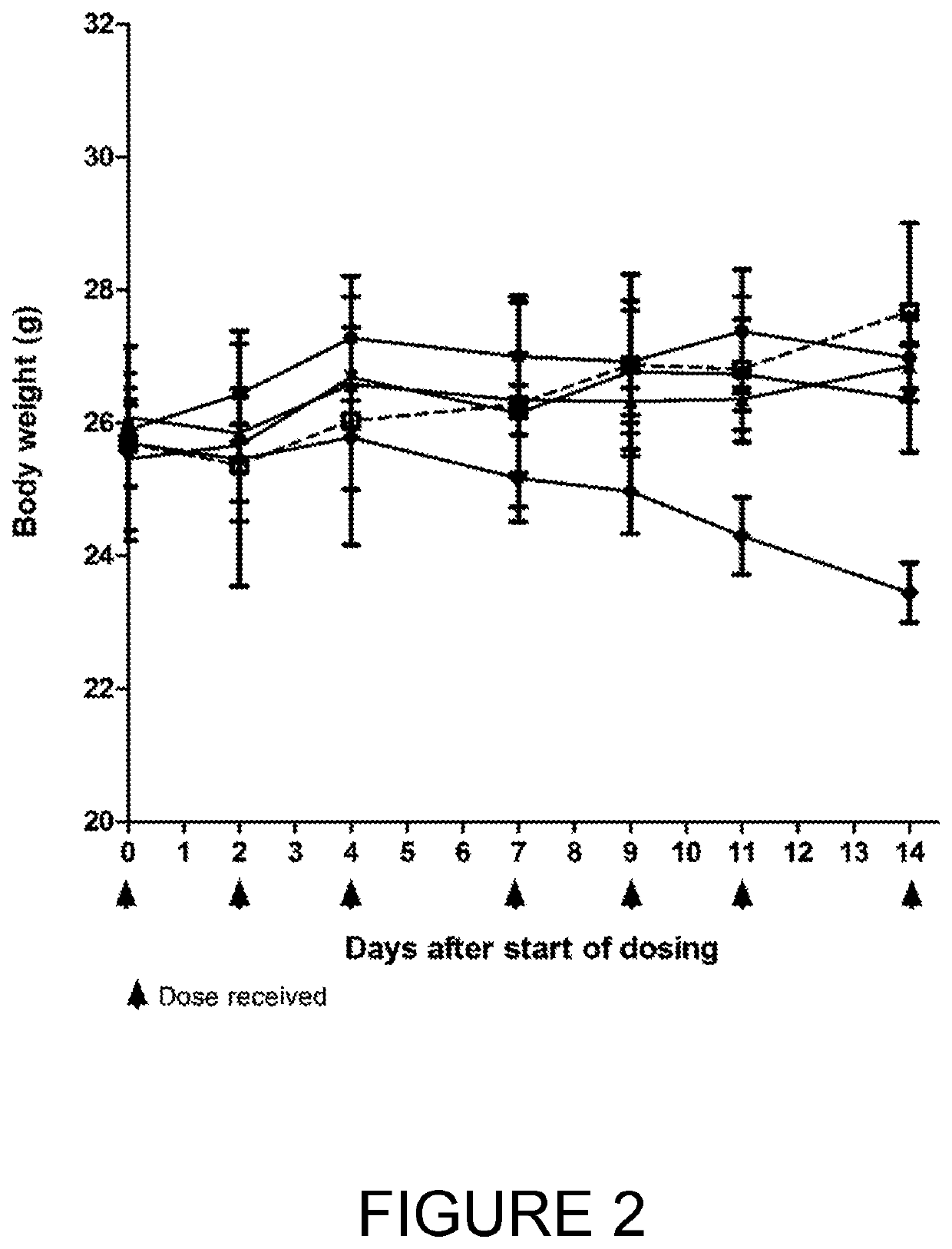
The invention relates to tumour therapy. In one aspect, the present invention relates to conjugates of target-binding moieties and toxins that are useful in the treatment of cancer. In particular, the toxin is an amatoxin, and the target-binding moieties (e.g. antibodies) are directed against tumour-associated antigens, such as epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM). In a further aspect the invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising such target-binding moiety toxin conjugates and to the use of such target-binding moiety toxin conjugates for the preparation of such pharmaceutical compositions. The target-binding moiety toxin conjugates and pharmaceutical compositions of the invention are useful for the treatment of cancer, in particular adenocarcinoma, such as pancreatic cancer, cholangiocarcinoma, breast cancer, and colorectal cancer.
Owner:FAULSTICH HEINZ +3
Monoclonal antibody-antigen binding segment-T-2 toxin conjugate
InactiveCN103330937AReduce toxicityRaise the dose rangeOrganic active ingredientsAntibody ingredientsCross-linkAntigen binding
The invention discloses a monoclonal antibody-antigen binding segment-T-2 toxin conjugate which is formed by connecting a monoclonal antibody-antigen binding segment with T-2 toxin by using one of a peptide chain, 1,4-butanediol diglycidyl ether, N-hydroxy succinimido-3-(2-pyrazolyl dithio)-propionate as a cross-linking agent. The invention further provides a preparation method of the monoclonal antibody-antigen binding segment-T-2 toxin conjugate and application of the monoclonal antibody-antigen binding segment-T-2 toxin conjugate in preparation of a targeted anti-tumor drug. According to the experiments, the conjugate disclosed by the invention has an obvious targeting performance for tumor tissues, and can be used for lowering the toxicity of the T-2 toxin and improving the inhibiting effect of the conjugate on the tumors.
Owner:济南环肽医药科技有限公司
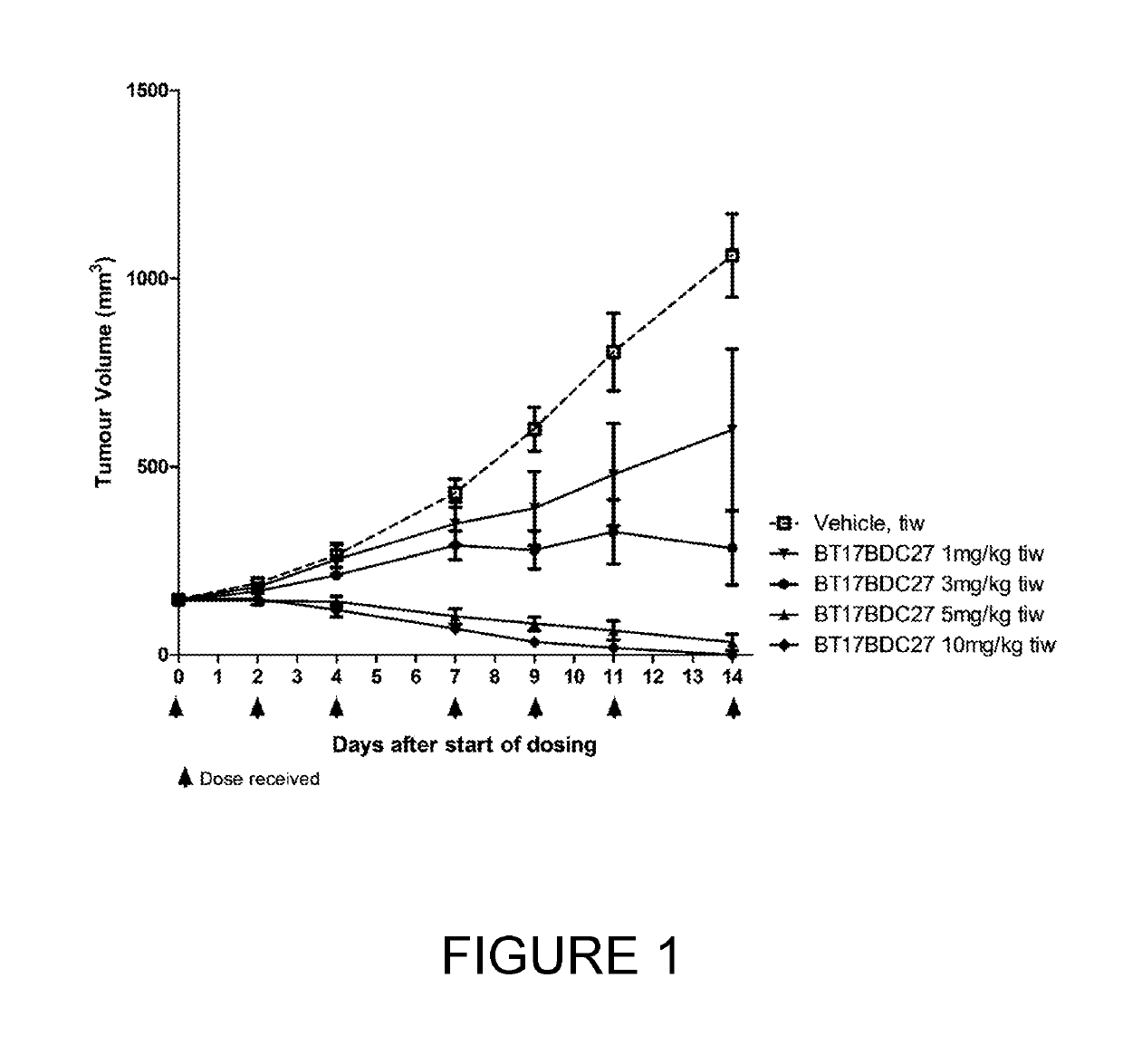
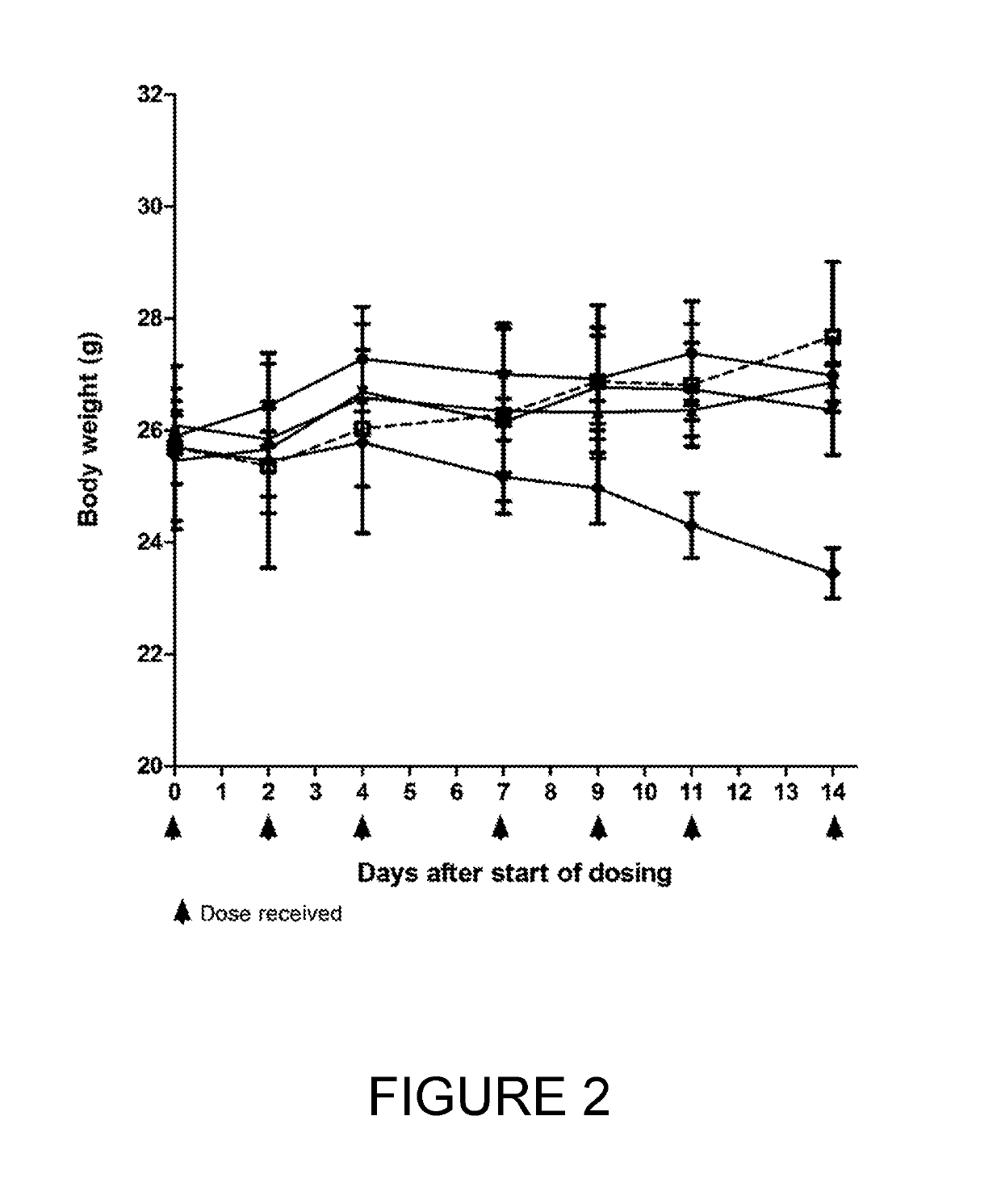
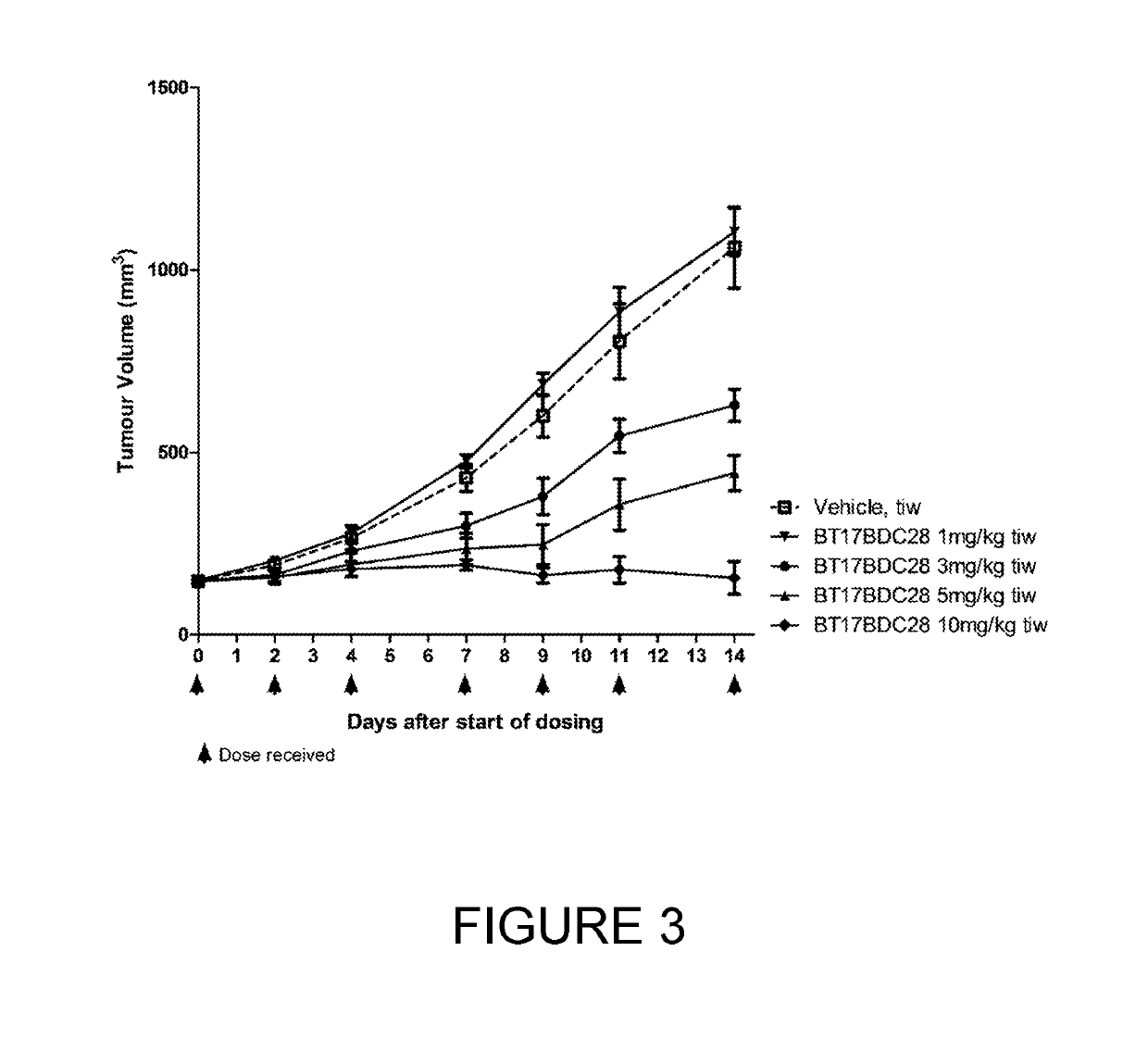
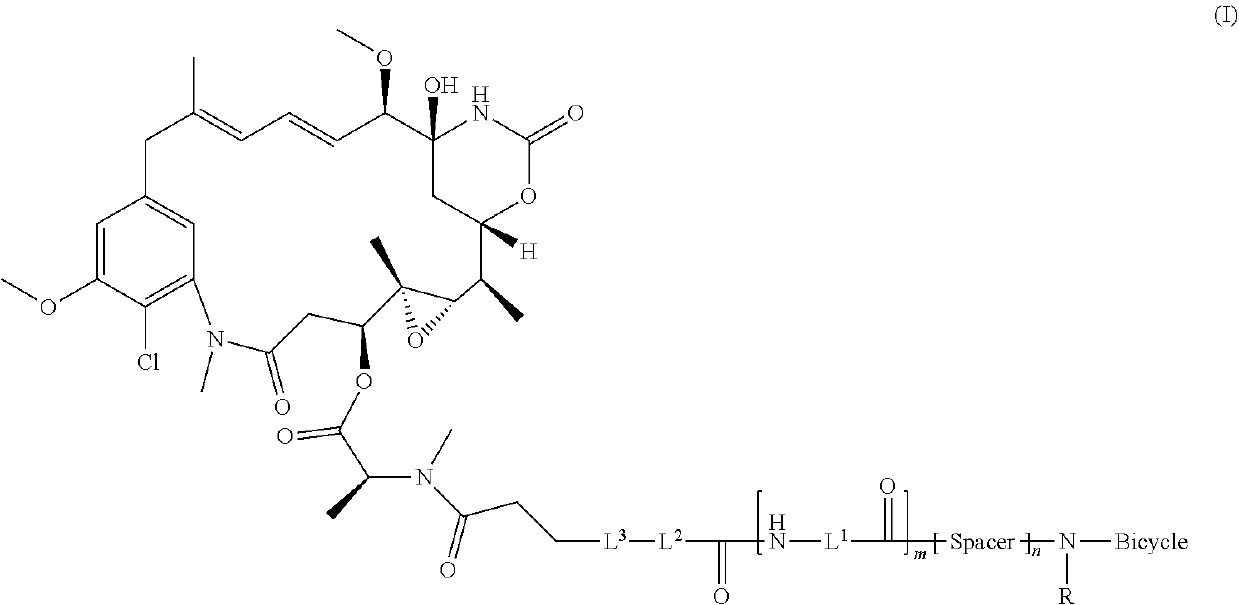
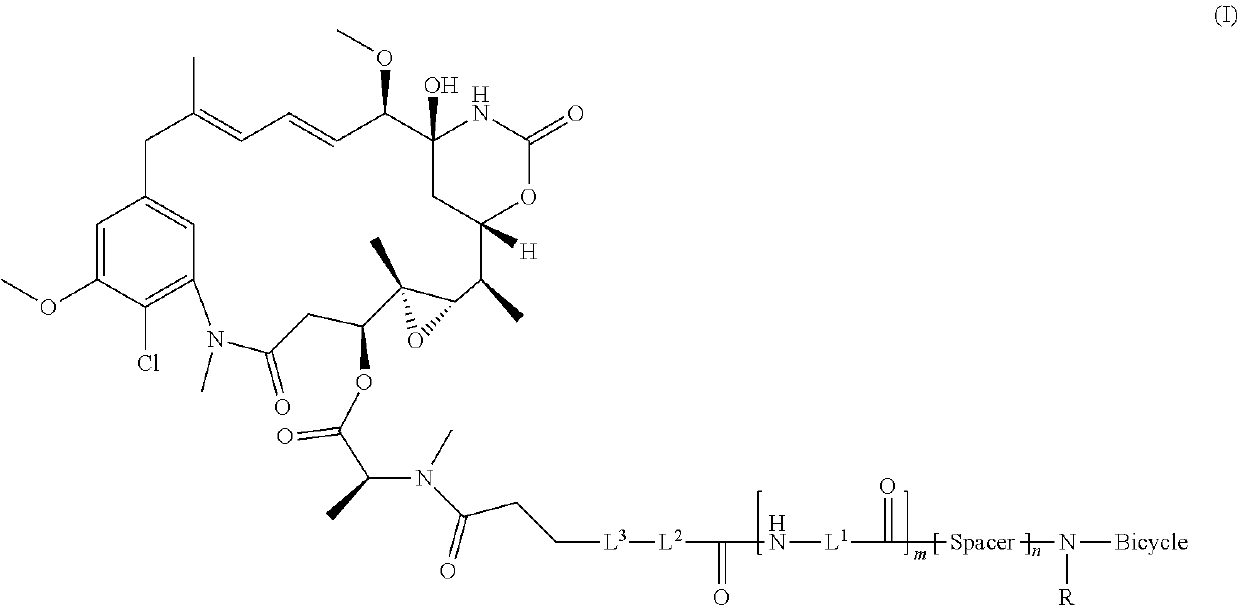
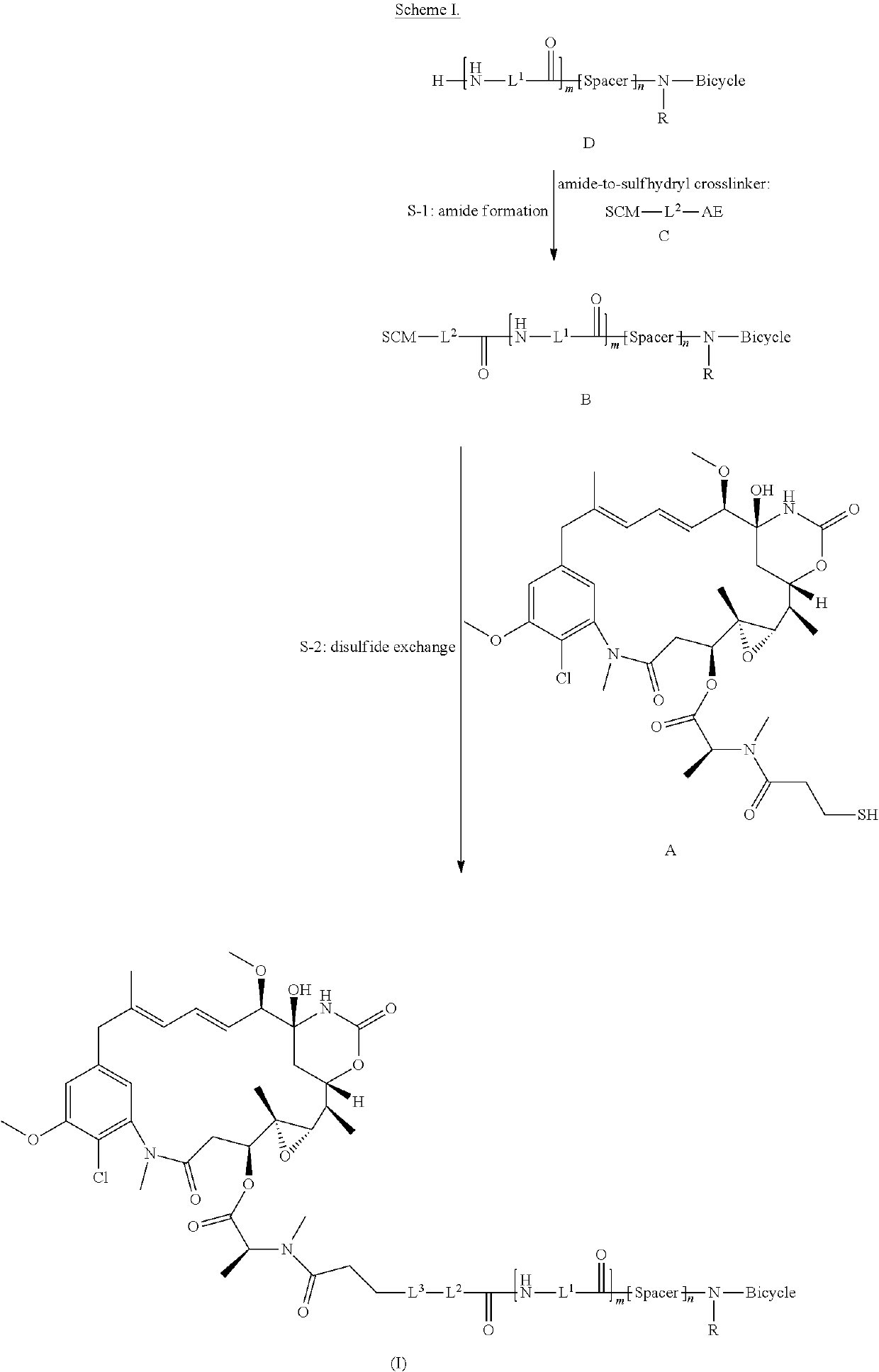
Bicycle toxin conjugates and uses thereof
InactiveUS20220184222A1Pharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsDiseaseToxin Conjugates
Owner:BICYCLETX LTD
Methods and compositions for the preparation and use of toxin conjugates
The present invention relates to methods for the preparation of toxin conjugates that are useful in vaccination and other therapies and diagnostics. In particular, methods are provided that involve a [3+2] cycloaddition between a first reactive unsaturated group on a toxin moiety and a second reactive unsaturated group on a bioactive moiety. Also provided are conjugates that are formed through this conjugation method, pharmaceutical compositions comprising these conjugates, and methods of using these pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment or diagnostic of antigen-related conditions, including tumors and infections.
Owner:INSTITUT CURIE +1
Anti-TRAILR2 antibody-toxin-conjugate and pharmaceutical application thereof in anti-tumor therapy
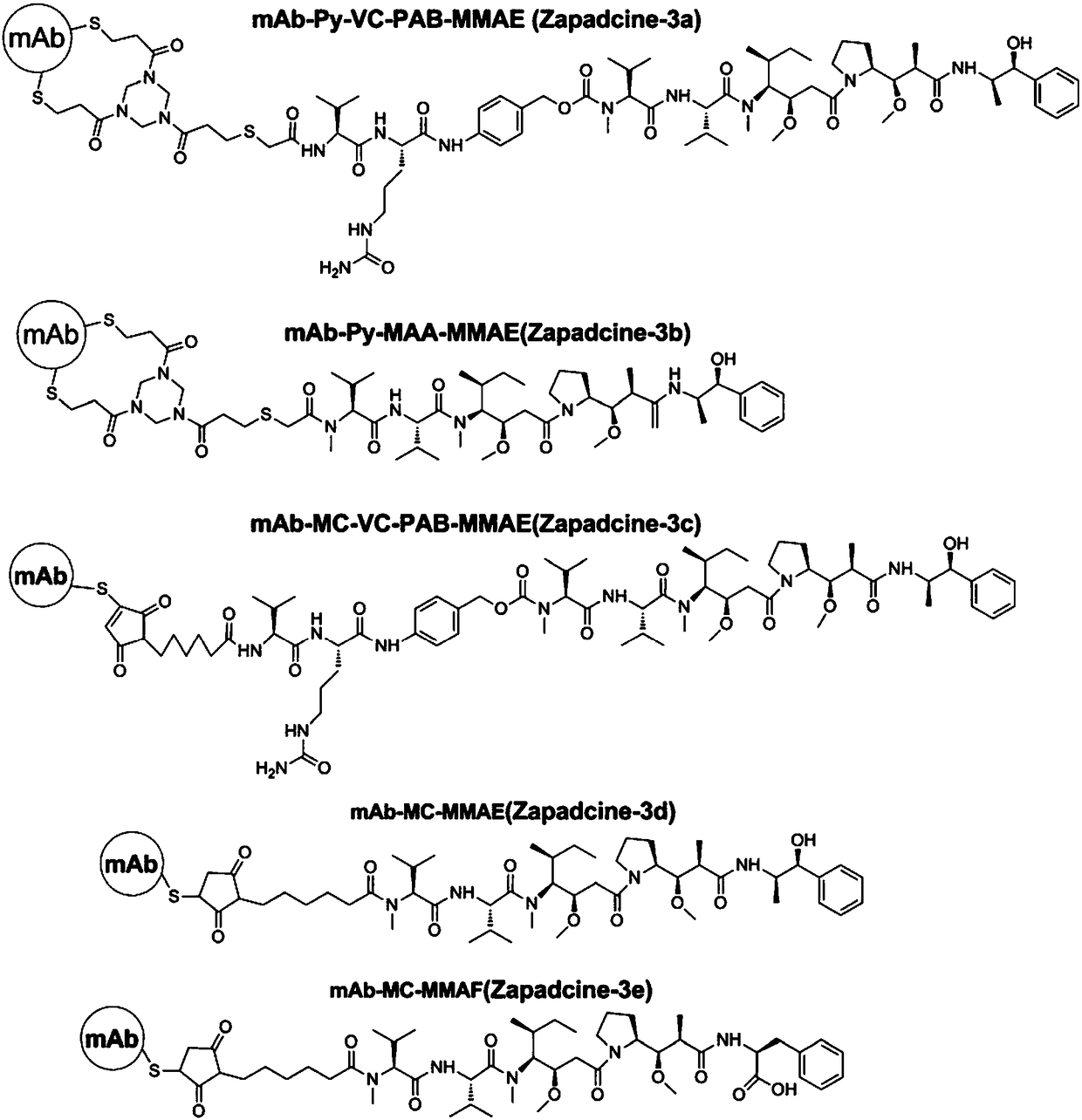
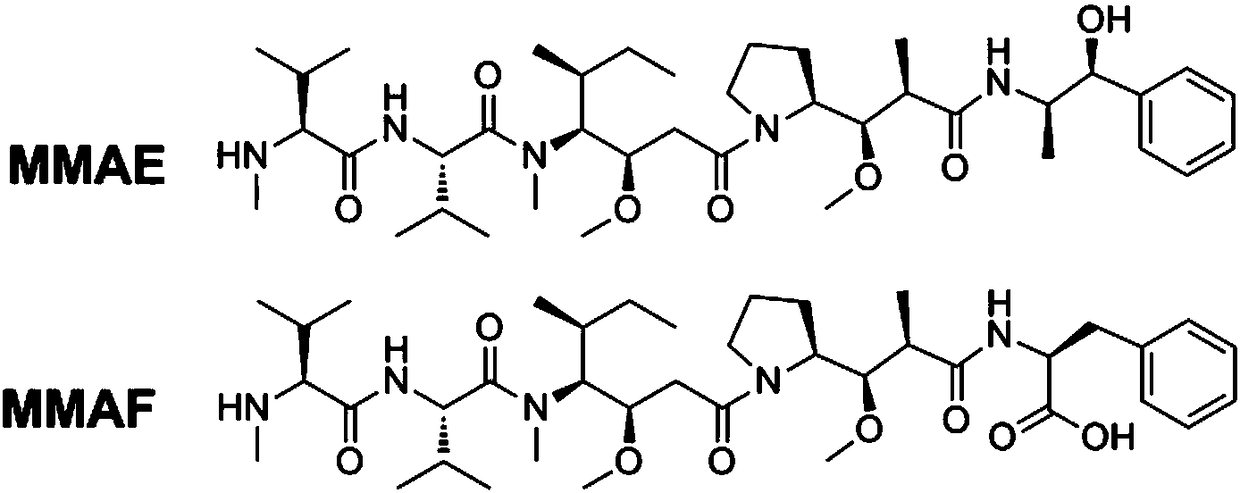
ActiveCN108452320ATetrapeptide ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsLysosomeTumor therapy
The invention provides an broad-spectrum, efficient and anti-tumor anti-TRAILR2 antibody-toxin-conjugate (ADC, called after Zapadcine-3(a,b,c,d,e). Toxin with cytotoxic effect is connected with an anti-TRAILR2 humanized monoclonal antibody through covalent bonds by using disulfide bond bridge connection or conventional coupling technology and chemical linkers, so that the anti-TRAILR2 humanized antibody-toxin-conjugate is formed. The ADC has the specificity of TRAILR2 positive tumors, after the combination with TRAILR2, the positive tumors can be endocytosed and enter into lysosomes of tumor cells, proteases inside the lysosomes are degraded to release free micromolecule urotoxins, so that various TRAILR2 positive tumor cells are killed specifically, the tumor growth is suppressed, the tumor cells are even completely eliminated, and the tumor is cured.
Owner:YANTAI OBIOADC BIOMEDICAL TECH LTD
Synthesis of bicycle toxin conjugates, and intermediates thereof
PendingUS20220135614A1Peptide preparation methodsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsToxin ConjugatesMedicinal chemistry
Owner:BICYCLERD LTD
Therapeutic nucleic acid-3' -conjugates
InactiveUS7910297B2Avoid actionImprove retentionMaterial nanotechnologyPeptide/protein ingredientsAptamerWhite blood cell
Methods are described for improvement of the serum half life of therapeutic nucleic acids by 3′ conjugation to useful target proteins, or other large molecules with useful function. In one embodiment, a 3′ A, C or G overhang is added to ds-DNA and the primary amines conjugated using biocompatible bifunctional linkers to proteins. The resulting nucleic acid-3′-conjugates are serum nuclease-resistant and retained in vivo for long periods without rapid kidney clearance. Further, the choice of conjugate imparts additional functionality to the nucleic acid-3-conjugate.For example, if the protein in the DNA-protein conjugate is the first component of the complement cascade (Clq or Clqrs) and the DNA aptamer has been developed against surface components of a target cell, it can be used to treat bacterial or parasitic infections and cancers. If the protein is serum albumin or another common (nonimmunogenic) blood protein and the aptamer is directed against a toxin or venom, the aptamer-protein conjugate can be used as an antidote that binds and neutralizes the toxin or venom. Similar DNA (aptamer)-nanotube, -enzyme, and -toxin conjugates could also be used to target and selectively kill bacteria, parasites, and cancer cells in vivo. If the protein is an Fc antibody fragment or C3b protein from the complement system and the aptamer is developed against a bacterial cell capsular material, other cell surface component or viral cell surface component, then the aptamer-3′-protein conjugate can aid in opsonization of the target cells or viruses by phagocytic leukocytes.
Owner:OTC BIOTECH
Binding protein-toxin conjugates comprising anthracyclines, and use thereof in immune-oncological applications
PendingUS20210379194A1Tetracycline active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsImmunooncologyToxin Conjugates
The present invention relates to binding protein-toxin conjugates comprising one or more anthracycline toxin moieties, and the use thereof in immunooncological applications.
Owner:NBE THERAPEUTICS
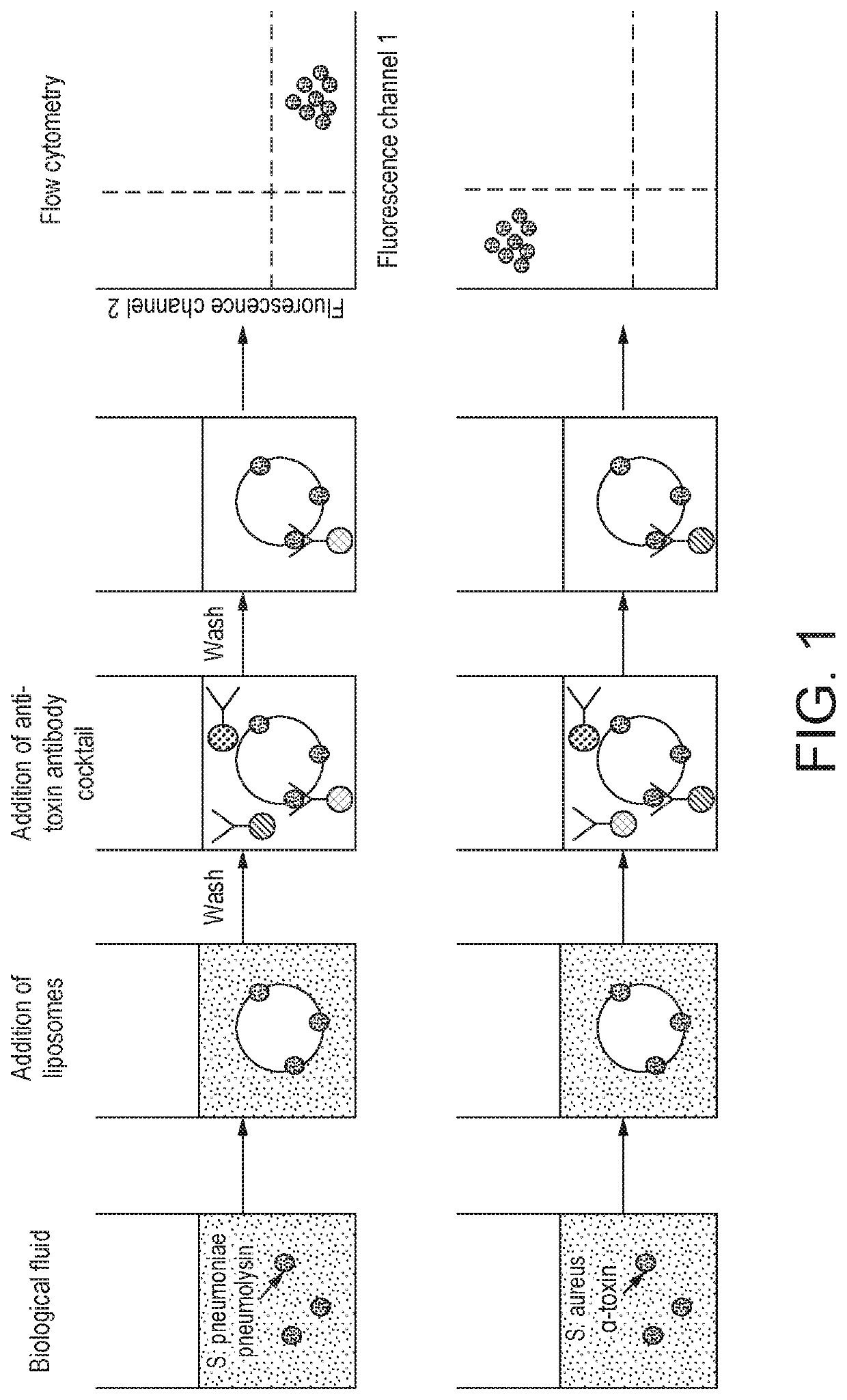
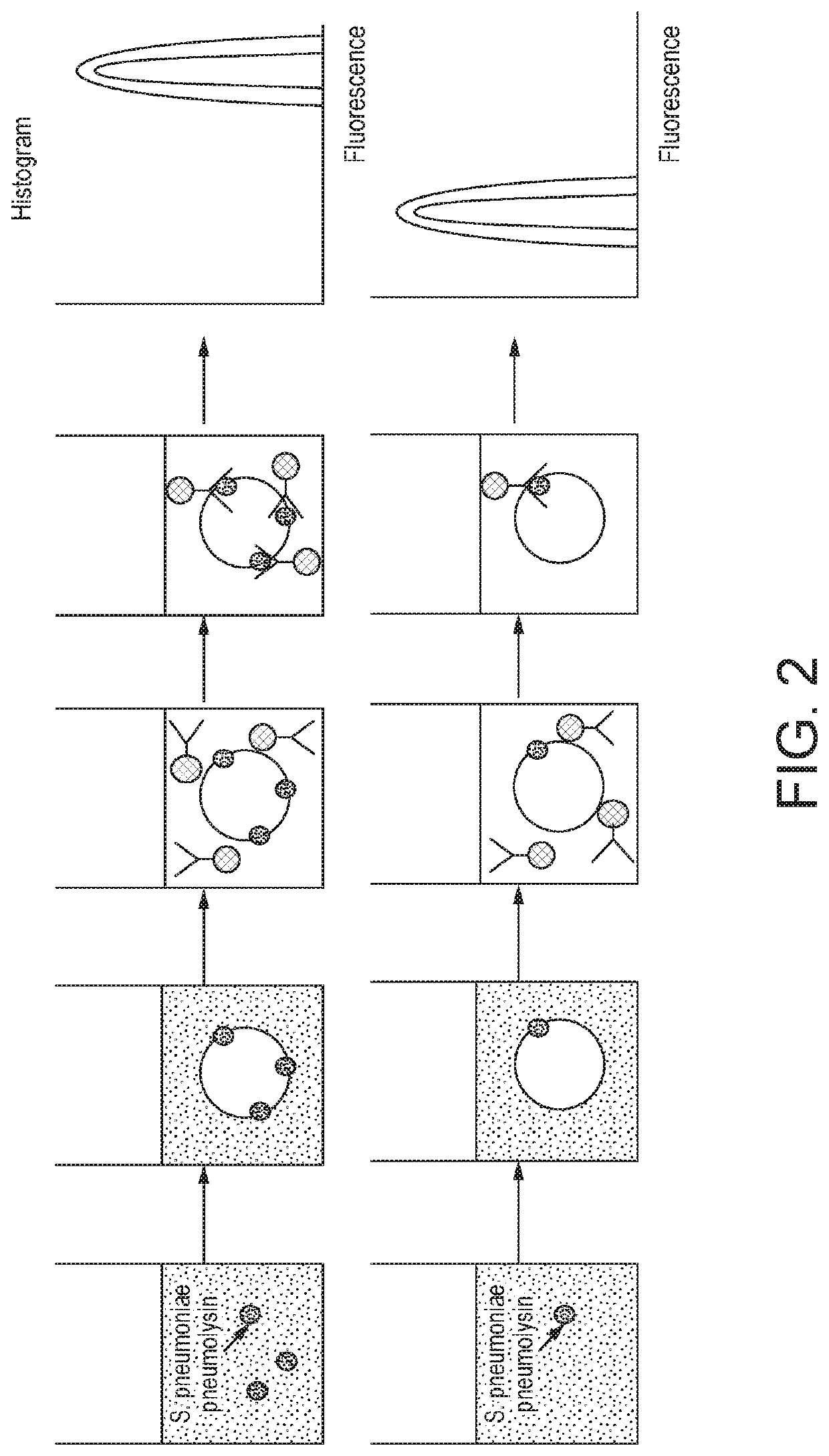
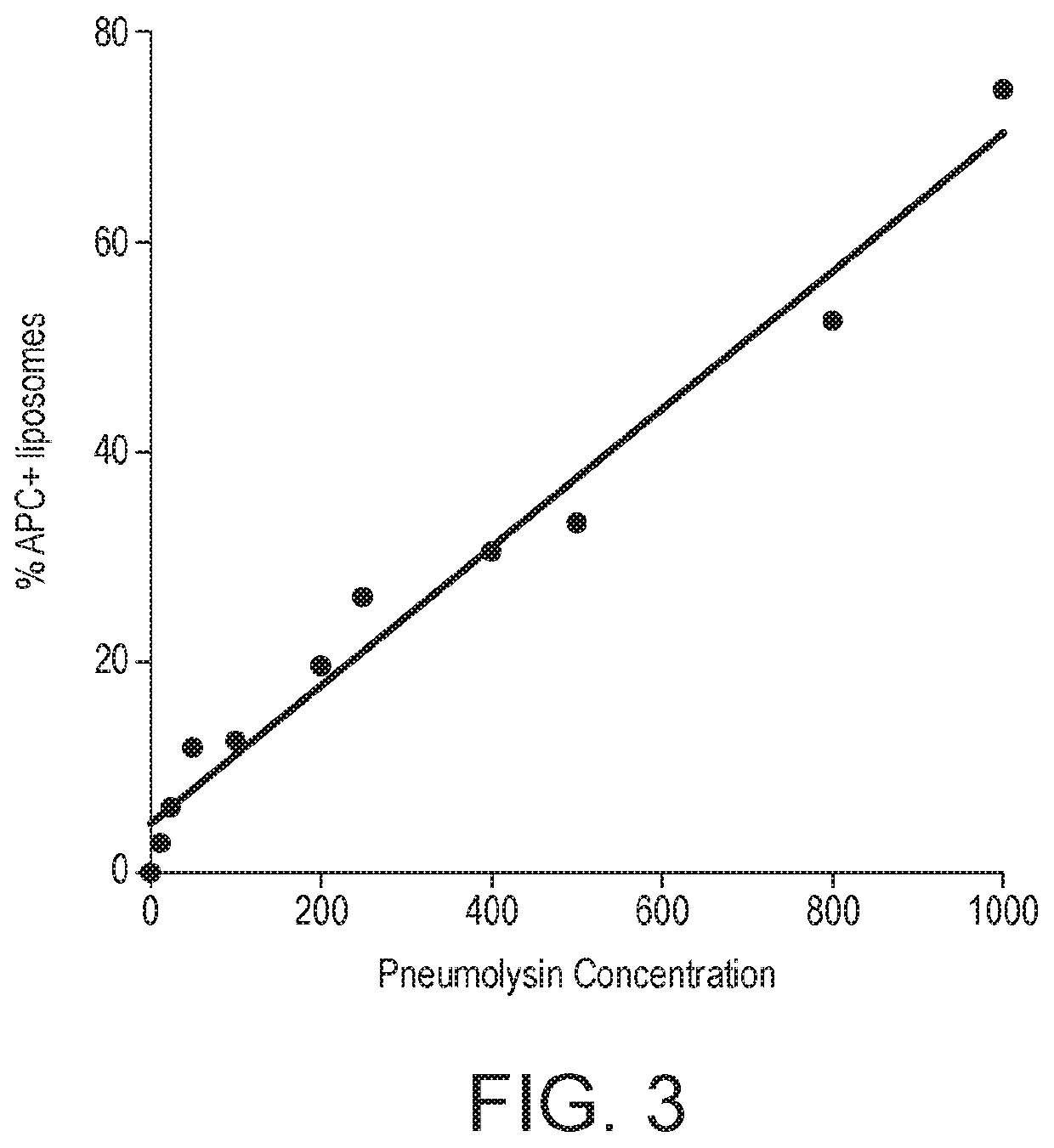
Method for detecting the presence of one or more bacterial toxins in a biological fluid using liposomes
The present invention relates to a method for detecting the presence of one or more bacterial toxins, capable of binding to cell membranes, in biological fluid wherein the method comprises: (i) incubating the biological fluid with a plurality of liposomes, wherein the liposomes comprise a lipid capable of binding to said one or more toxins, to provide one or more liposome-toxin conjugate; (ii) incubating said conjugates with at least one type of antibody bound to a label to provide one or more conjugate-antibody complex; wherein each type of antibody in the mixture is specific for one of the bacterial toxins whose presence is to be detected; and (iii) analysing said complexes in order to detect the presence of one or more bacterial toxins capable of binding to cell membranes. Further aspects of the invention relate to a conjugate-antibody complex useful in the methods of the invention and a kit useful for performing the method of the invention.
Owner:UNIV OF LIVERPOOL
Cysteine engineered antibody-toxin conjugates
ActiveCN108743966BImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAntiendomysial antibodiesValine
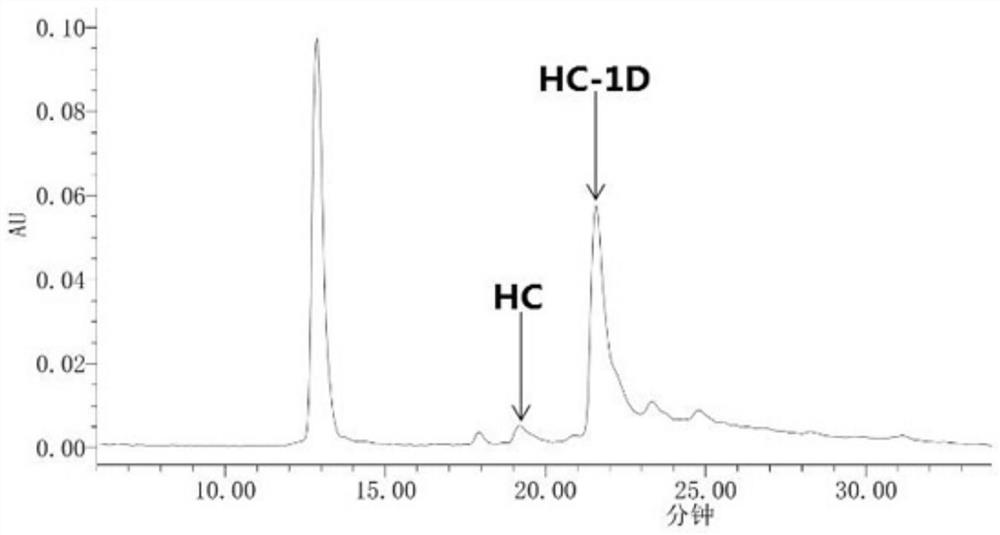
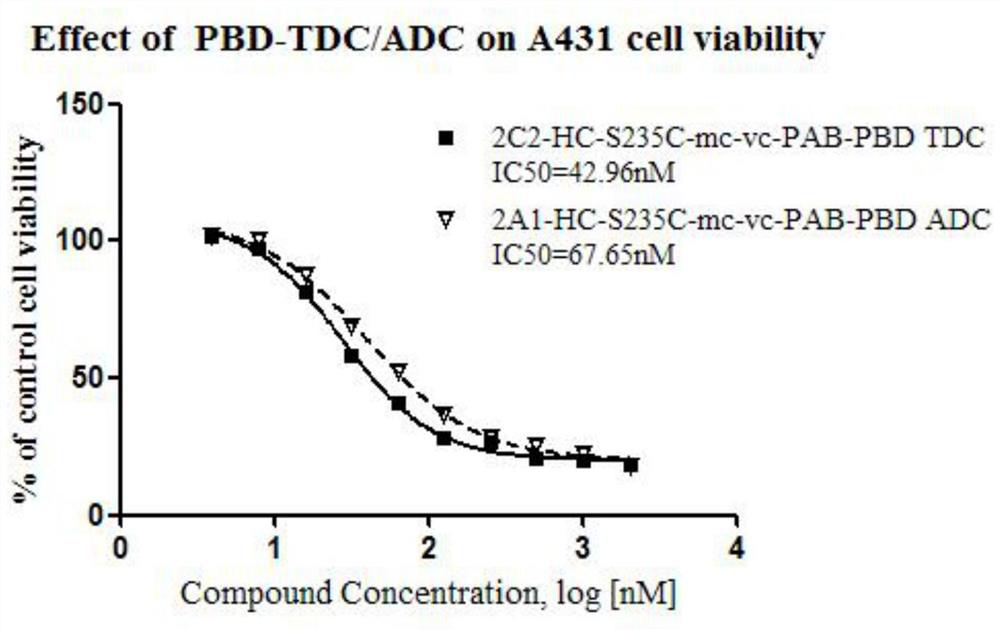
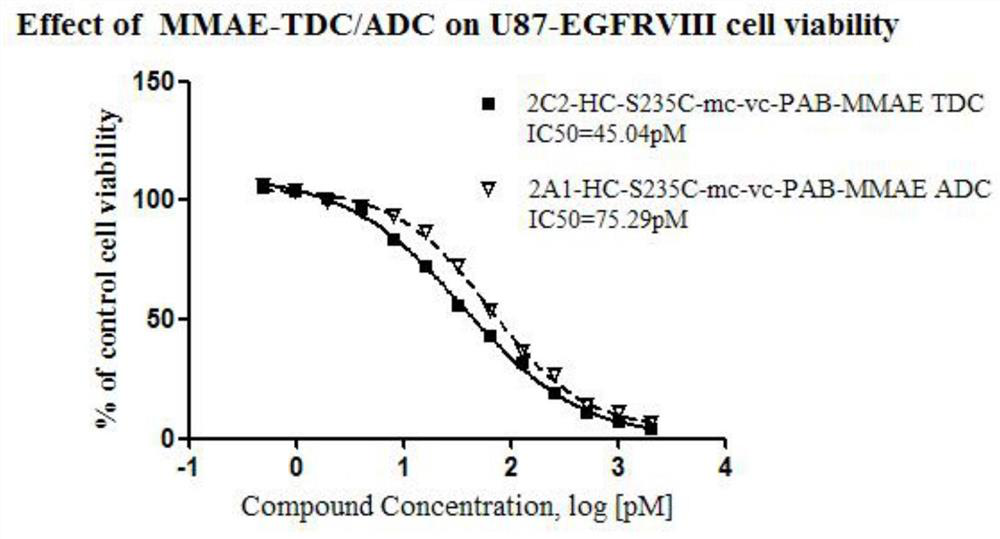
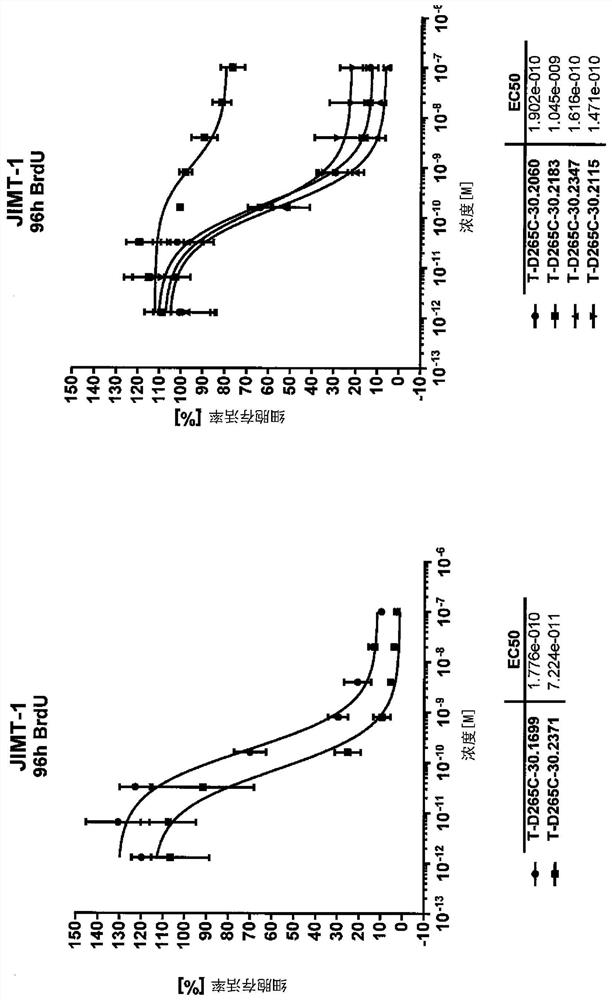
The 235-position serine (S) of the target antibody is transformed into cysteine (C), and the 205-position valine (V) of the light chain is transformed into cysteine (C), and the modified cysteine The free sulfhydryl group (‑SH) of amino acid is coupled with the mc‑vc‑PAB‑OH linker coupled with a small molecule highly active cytotoxin (Payload) to form a cysteine-engineered antibody‑ with excellent homogeneity. Toxin conjugates with a toxin to antibody ratio (DAR) of 3.2-4.0. This antibody-toxin conjugate has the general formula: 2C3-HC-S235C-LC-V205C-mc-vc-PAB-payload. At the same time, the present invention also discloses the preparation and purification method of the TDC medicine, and its application in the treatment of tumors expressing EGFRvIII and overexpressing EGFRwt.
Owner:BAILI-BIO (CHENGDU) PHARM CO LTD
An antibody-dolastatin conjugate and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN107936118BImprove uniformityWiden the optionsPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntiendomysial antibodiesAntibodies monoclonal
The invention discloses a preparation method for an antibody-monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE) conjugate. The method comprises the following steps: (1) a monoclonal antibody with an LPXTG sequence at each C terminus of an anti-MART-1 protein presentation peptide EAAGIGILTV / HLA-A2 composite, and monomethyl auristatin E or a monomethyl auristatin E derivative with an oligo-glycine joint are provided; (2) under the catalysis of a Sortase A enzyme, the LPXTG sequences and the oligo-glycine joint are subjected to a transpeptidation reaction, and the monoclonal antibody is coupled with and the monomethyl auristatin E or the monomethyl auristatin E derivative with the oligo-glycine joint; and (3) after the reaction is completed, separation purification is performed, and therefore the antibody-monomethyl auristatin E conjugate is obtained. Through site-direct coupling, the method provided by the invention makes per molecule of the antibody have four molecules of the MMAE, has good uniformity, andexhibits good tumor killing capacity in vivo experiments; and compared with current target spots of ADCs (antibody-drug conjugates), CLA12-vcMMAE ADCs expand the selection areas of the current targetspots of the ADCs, demonstrate the view that an intracellular protein can also be taken as the target spot of the ADCs through presentation of MHC (major histocompatibility complex) I molecules.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A kind of polyethylene glycol-rtrail mutant trimer-dolastatin conjugate and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN104744584BGood pharmacokinetic propertiesExtended half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMonomethoxypolyethylene glycolToxin Conjugates
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Anti-cd56 antibody and dolastatin coupling complex and its preparation method and use
ActiveCN107744592BImprove utilization efficiencyGood treatment effectNervous disorderTetrapeptide ingredientsAntiendomysial antibodiesSide effect
The invention belongs to the field of preparation of antibody-coupled-medicines, and particularly relates to an anti-CD56-antibody and aplysiatoxin coupled composite, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The anti-CD56-antibody and aplysiatoxin coupled composite includes the anti-CD56-antibody and aplysiatoxin, and a connection molecule which couples the anti-CD56-antibody with theaplysiatoxin, wherein one end of the connection molecule is coupled with a free sulfydryl group on the anti-CD56-antibody via maleimide, while the other end is coupled with a hydroxyl group on the aplysiatoxin via an ester bond. The anti-CD56-antibody coupled composite not only maintains the high-affinity capability of targeted combination between the anti-CD56-antibody and CD56 but also has high-effective cell killing capability of the aplysiatoxin, so that the composite can improve therapy effect of a medicine and also reduces toxic and side effects on human body due to the medicine. The composite can be used for preparing medicines for diagnosing and treating tumors, immunosystem diseases or nervous system diseases, and has great application prospect.
Owner:WEST VAC BIOPHARMA CO LTD
ELISA kit for detecting t-2 toxin and its application
The present invention provides an enzyme linked immunoassay kit for detecting T-2 toxin. The kit contains a T-2 toxin conjugated antigen coated enzyme label plate, a T-2 toxin standard substance solution, a concentrated enzyme conjugate, an enzyme conjugate working solution, a substrate coloration solution and a termination solution. The invention further discloses a method for detecting T-2 toxin in a sample by using the enzyme linked immunoassay kit. The method comprises: carrying out a sample pretreatment, detecting by using the kit, and analyzing the detection result. The enzyme linked immunoassay kit can be used for detecting T-2 toxin residue in feed (raw materials, matching materials and concentrated materials) samples, has characteristics of simple operation, low cost, high sensitivity and on-site monitoring, and is suitable for screening of mass samples.
Owner:BEIJING KWINBON BIOTECH
Cysteine engineered antibody-toxin conjugates
ActiveCN106467575BGood drug uniformityLittle side effectsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsHybrid peptidesAntiendomysial antibodiesToxin Conjugates
According to the invention, light-chain 205-locus valine (V) of a target antibody is modified into cysteine (C); free sulfhydryl group (-SH) of the modified cysteine is subjected to fixed-point conjugation with mc-vc-PAB-OH connexon conjugated with small-molecular high-activity cytotoxin (Payload), such that the cysteine-modified antibody drug conjugate with excellent homogeneity is formed. The drug-antibody ratio (DAR) of the conjugate is 1.6-2.0. The antibody drug conjugate has a general formula 2C1-LC-V205C-mc-vc-PAB-payload. Also, the invention discloses a preparation method and a purification method of the TDC drug, and the application of the drug in treatments of EGFRvIII-expressing and EGFRwt-overexpressing tumors.
Owner:BAILI-BIO (CHENGDU) PHARM CO LTD
Cysteine engineered antibody-toxin conjugates
ActiveCN108727499BOrganic active ingredientsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntiendomysial antibodiesHeavy chain
Owner:BAILI-BIO (CHENGDU) PHARM CO LTD
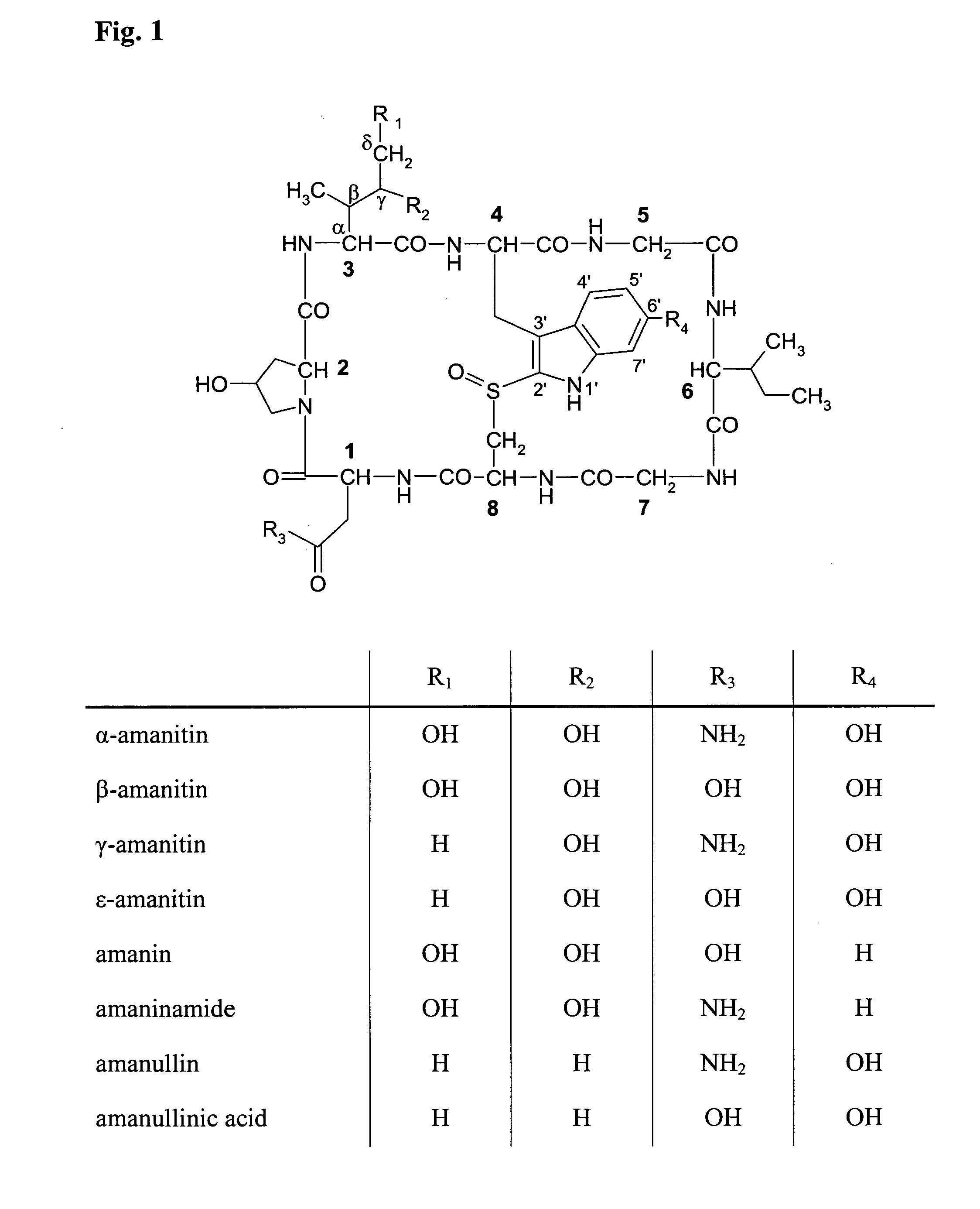
Targeted amatoxin conjugate for the treatment of solid tumors
PendingCN111989122ACyclic peptide ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsToxin ConjugatesOncology
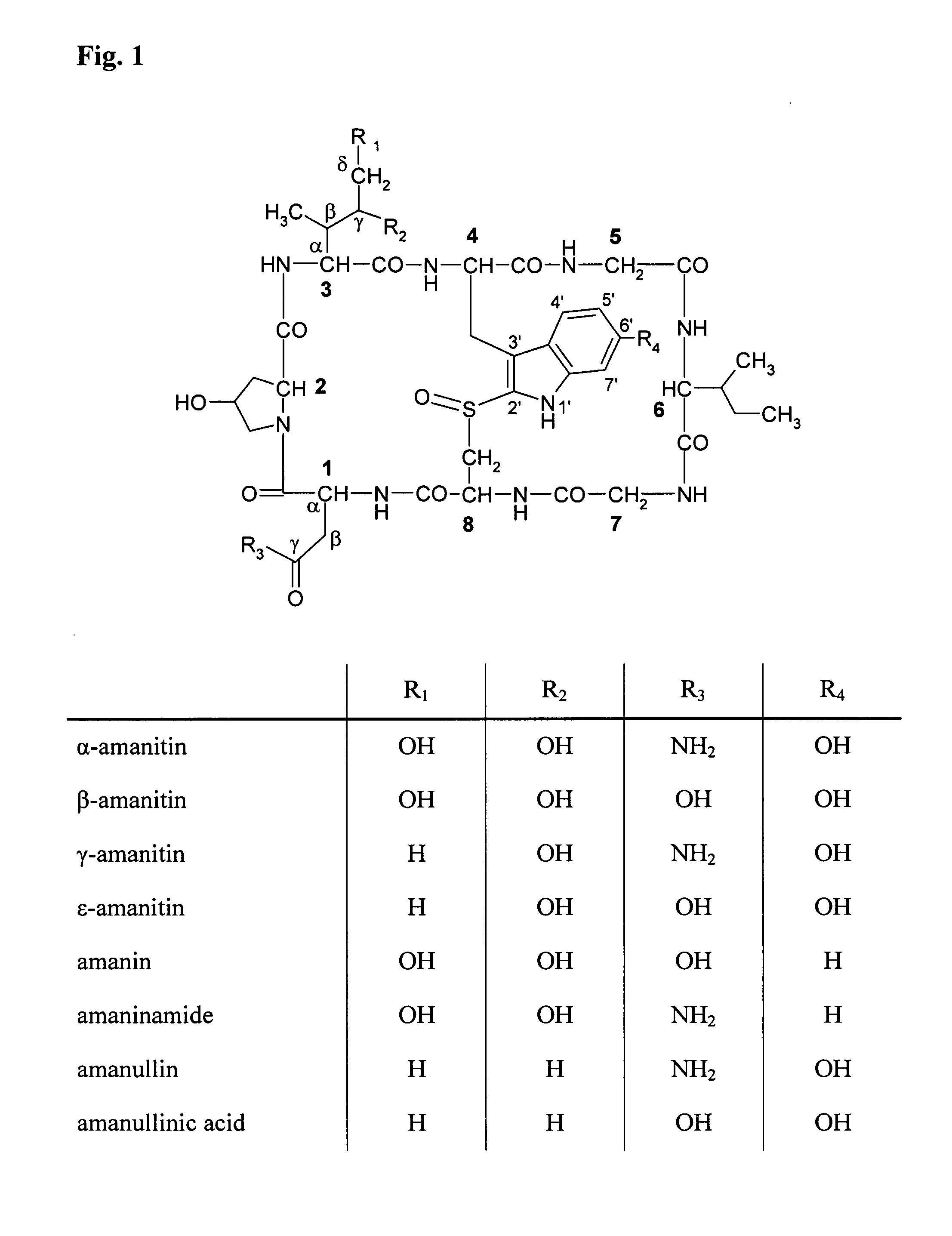
The present invention relates to an amatoxin-linker construct comprising an amatoxin according to formula (I) wherein: R1 and R2 are each -OH, R3 is NH2, or a linker which carries a reactive group Y for linking said amatoxin to a target-binding moiety, R4 is H or a linker which carries a reactive group Y for linking said amatoxin to a target-binding moiety, R5 is absent or =O, wherein R3 and R4 cannot be the same, for use in the manufacture of a binding moiety-toxin conjugate for the treatment of a solid tumor, and a respective binding moiety-toxin conjugate for the treatment of a solid tumor.
Owner:HEIDELBERG PHARMA RES GMBH
Antigen-binding fragment of an antibody-dolastatin conjugate and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN108084267BRetention of lethalityFast tumor penetration rateAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTetrapeptide ingredientsCD20Glycine
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com