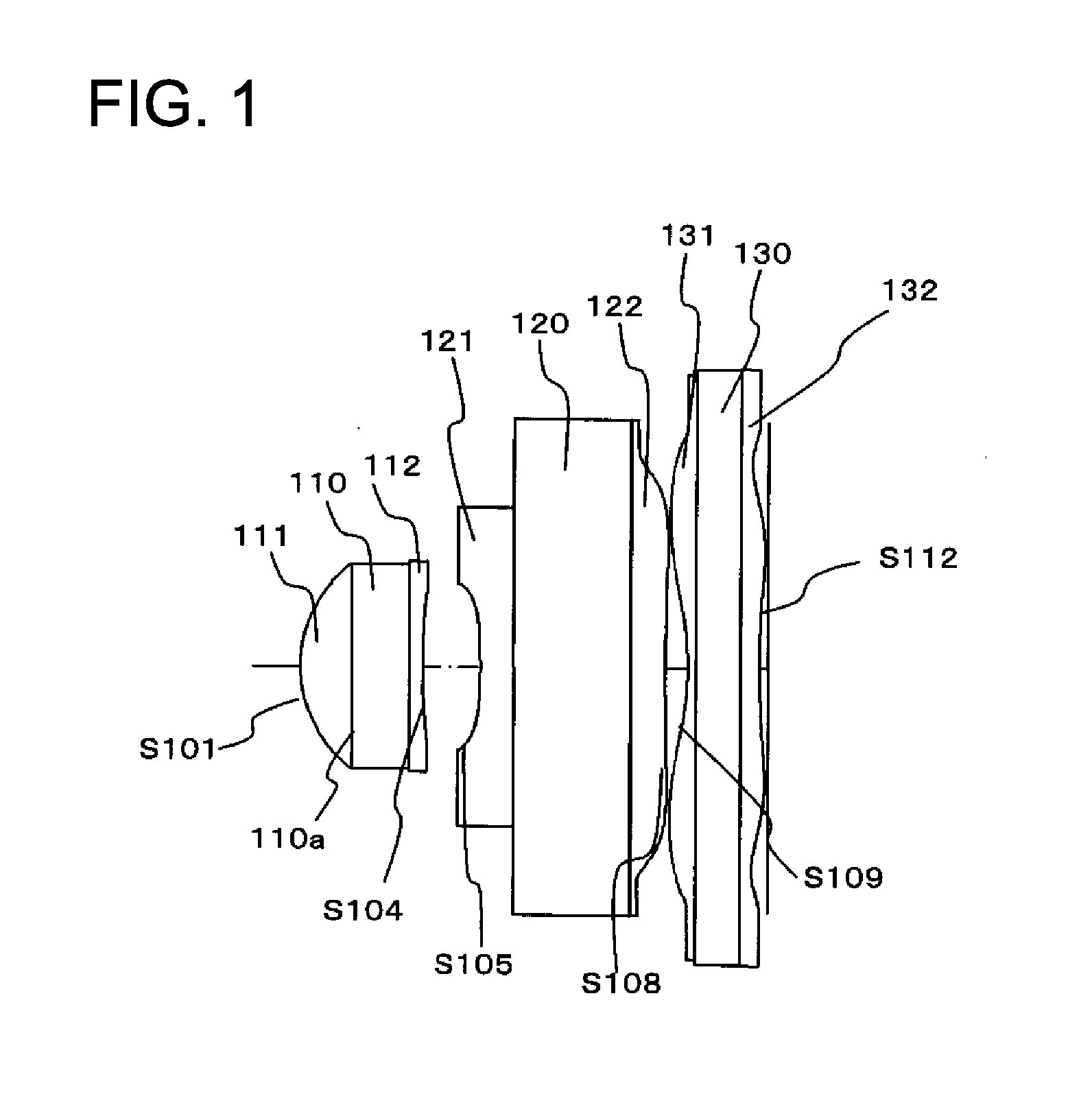
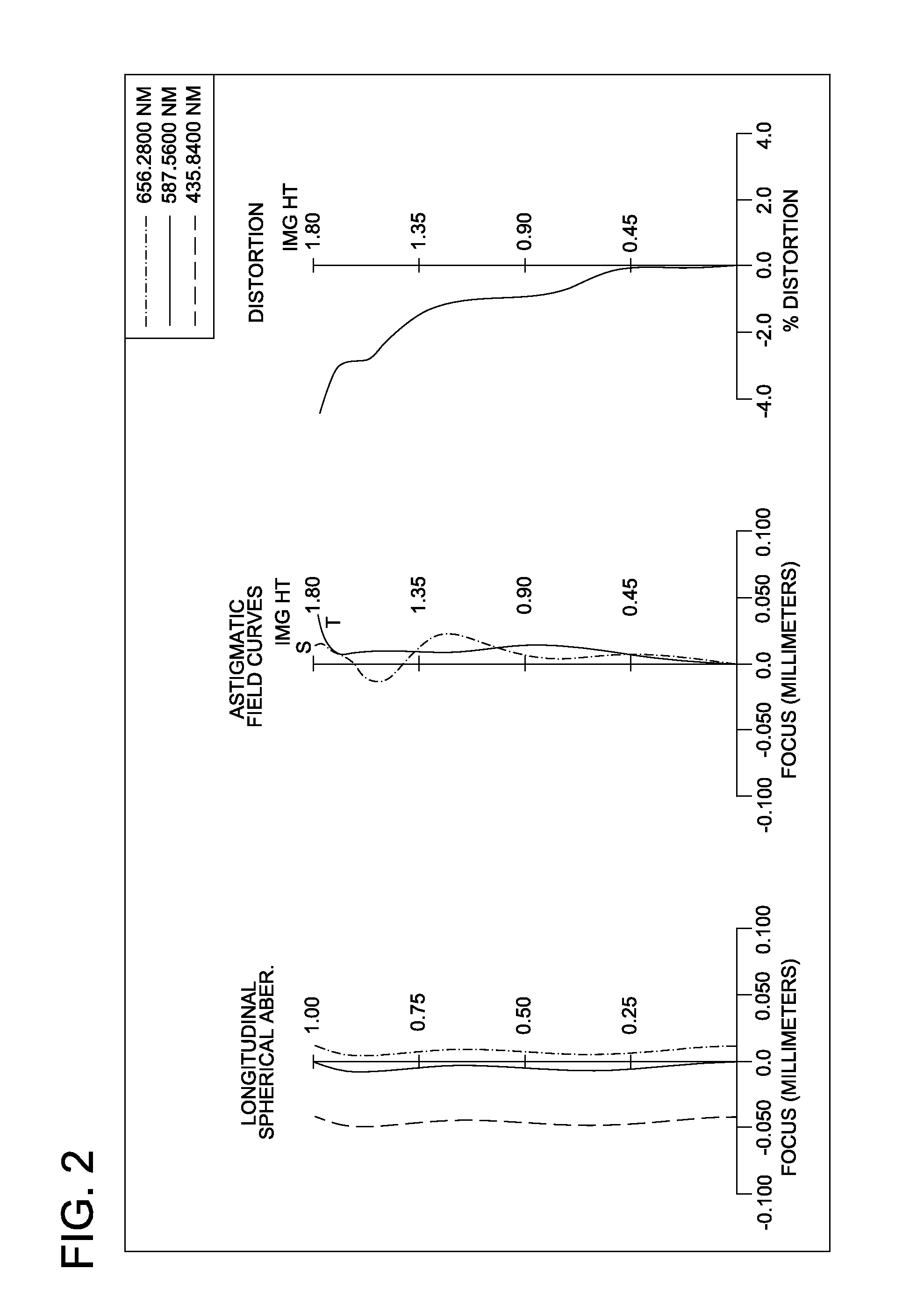
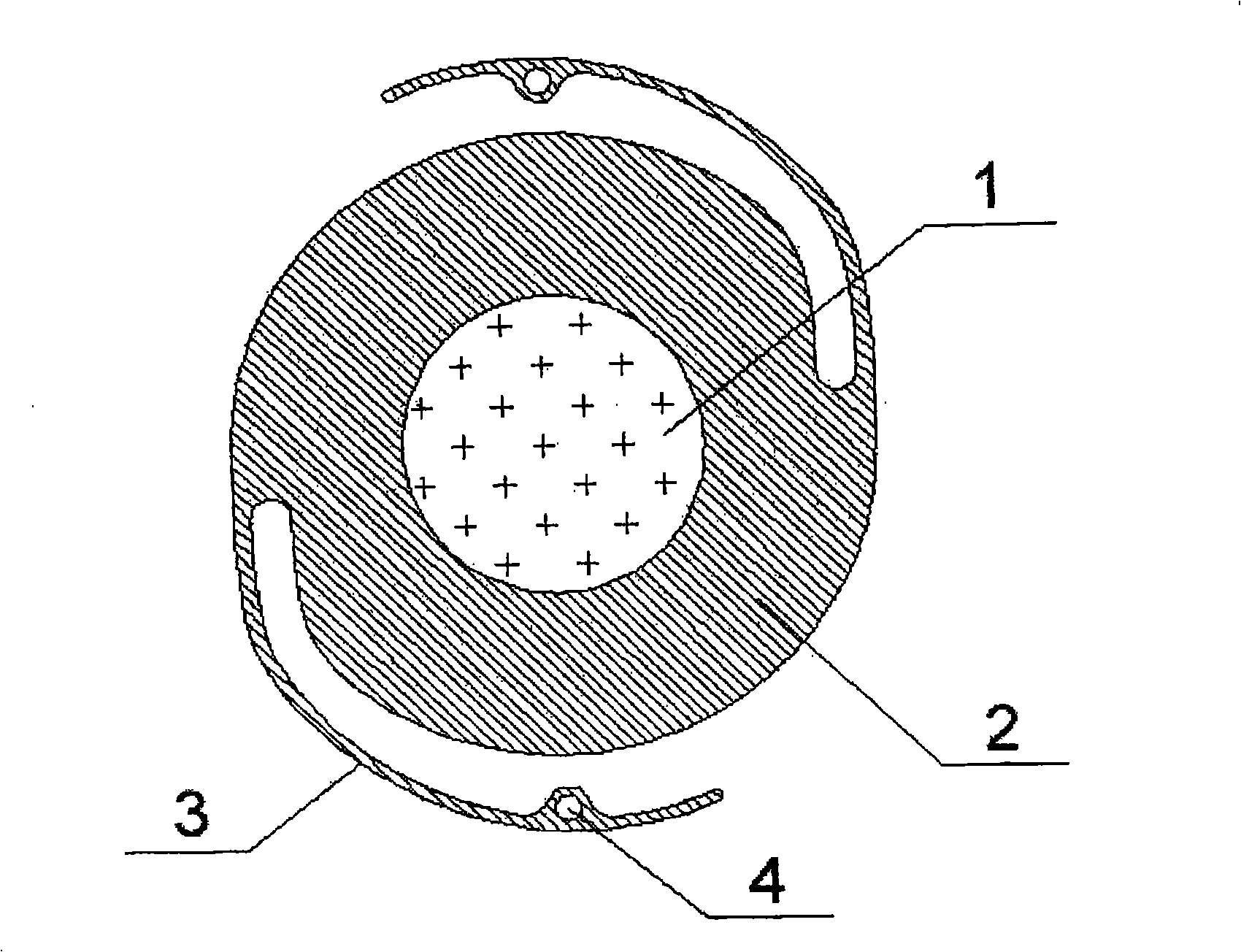
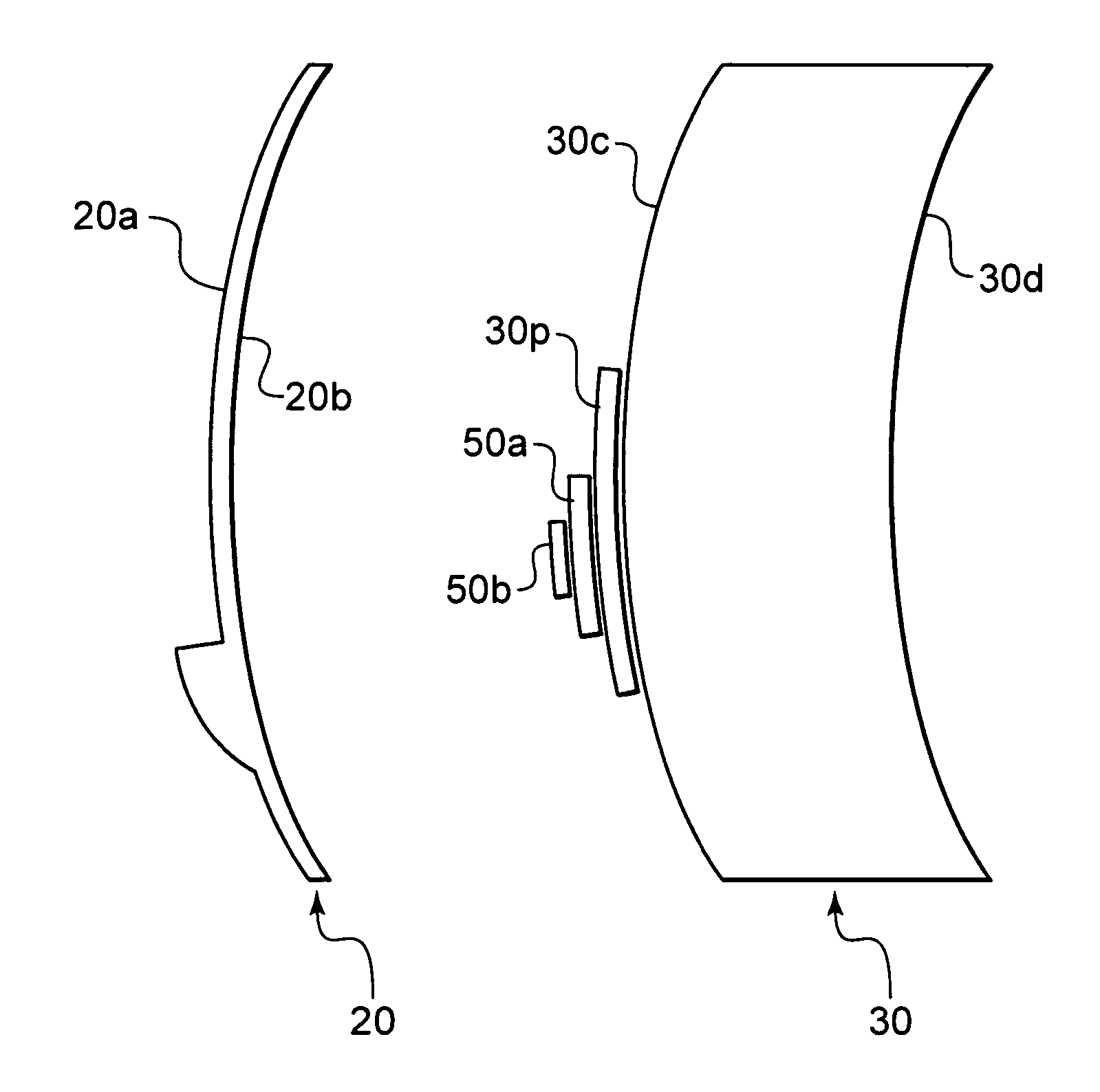
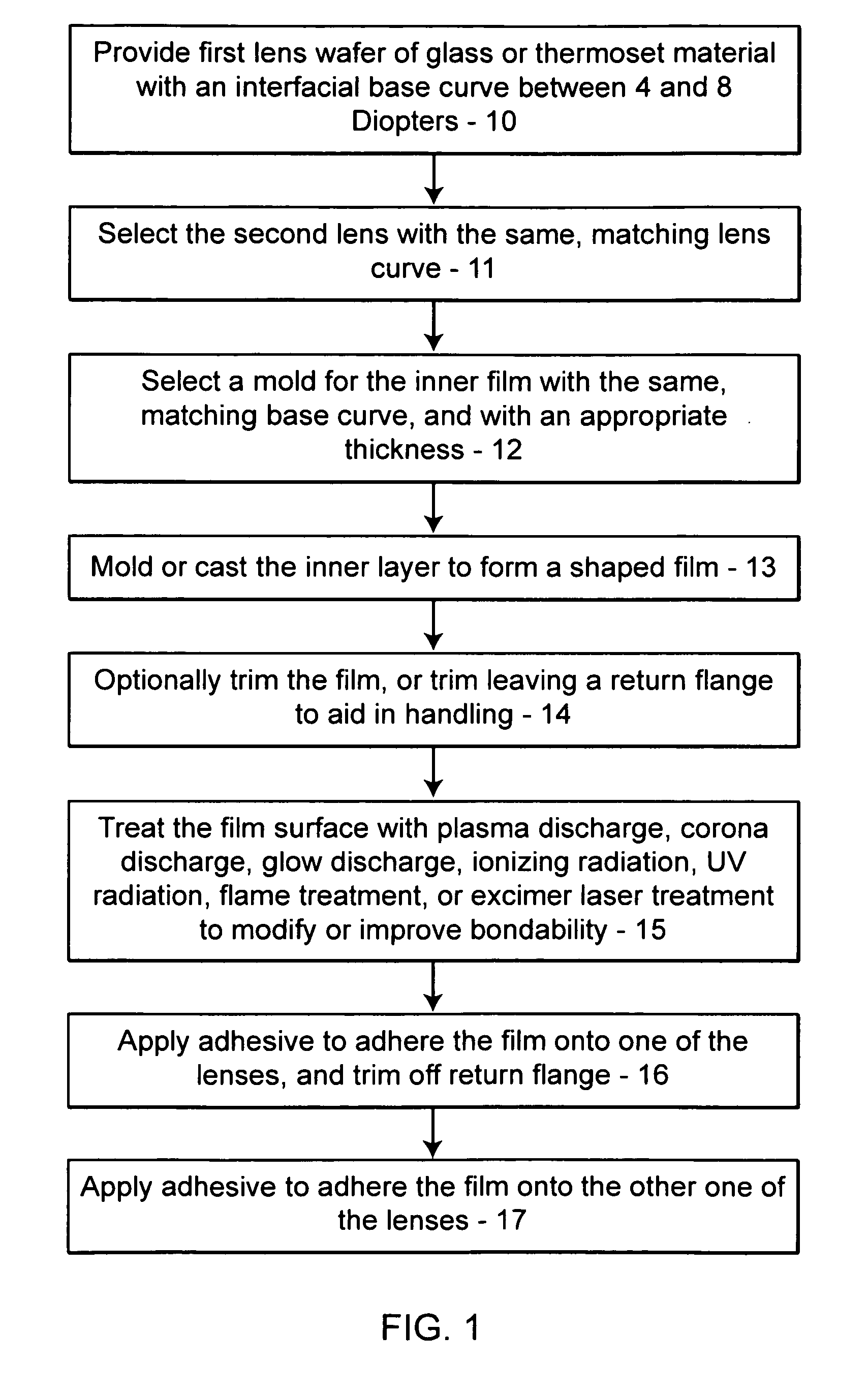
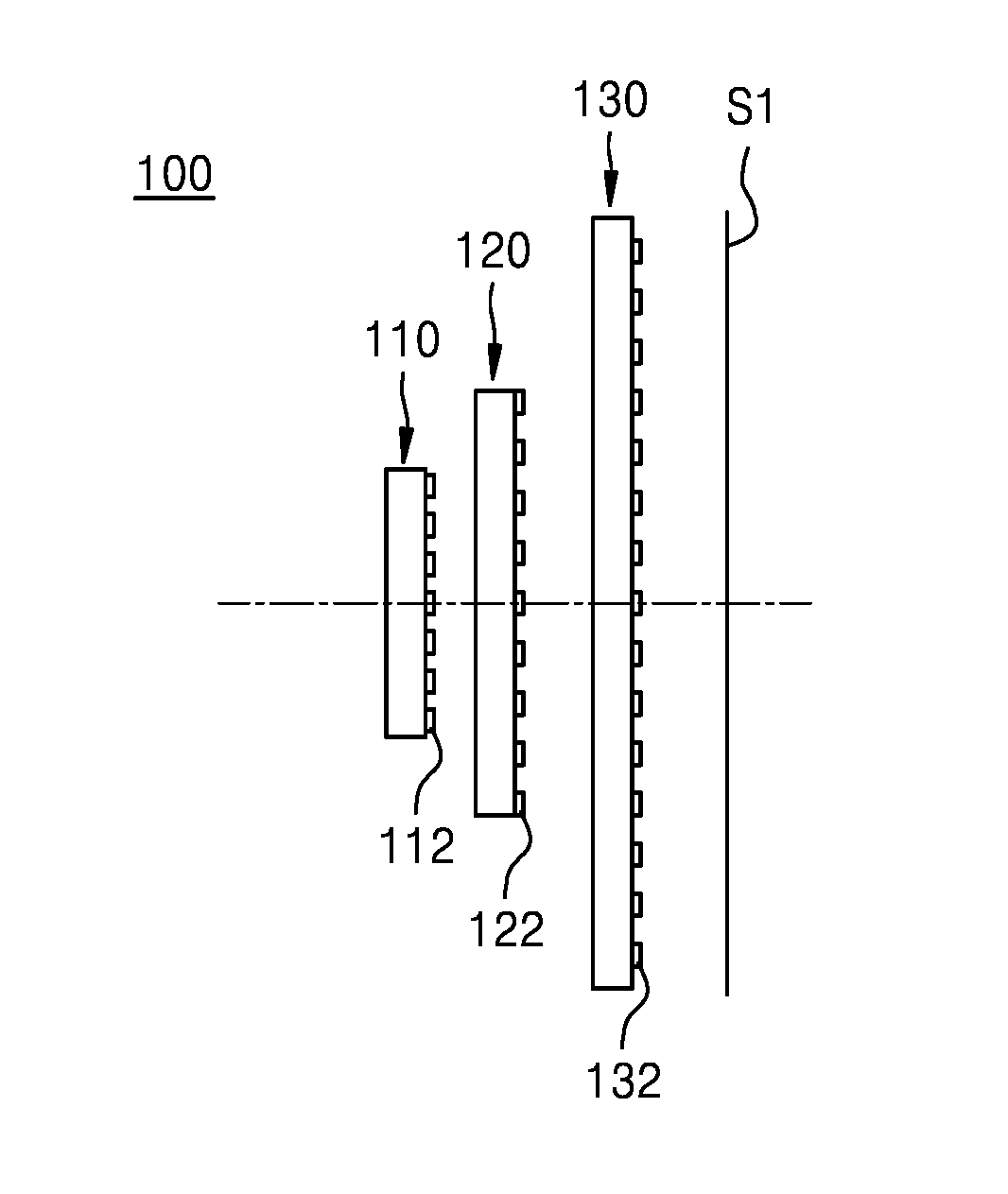
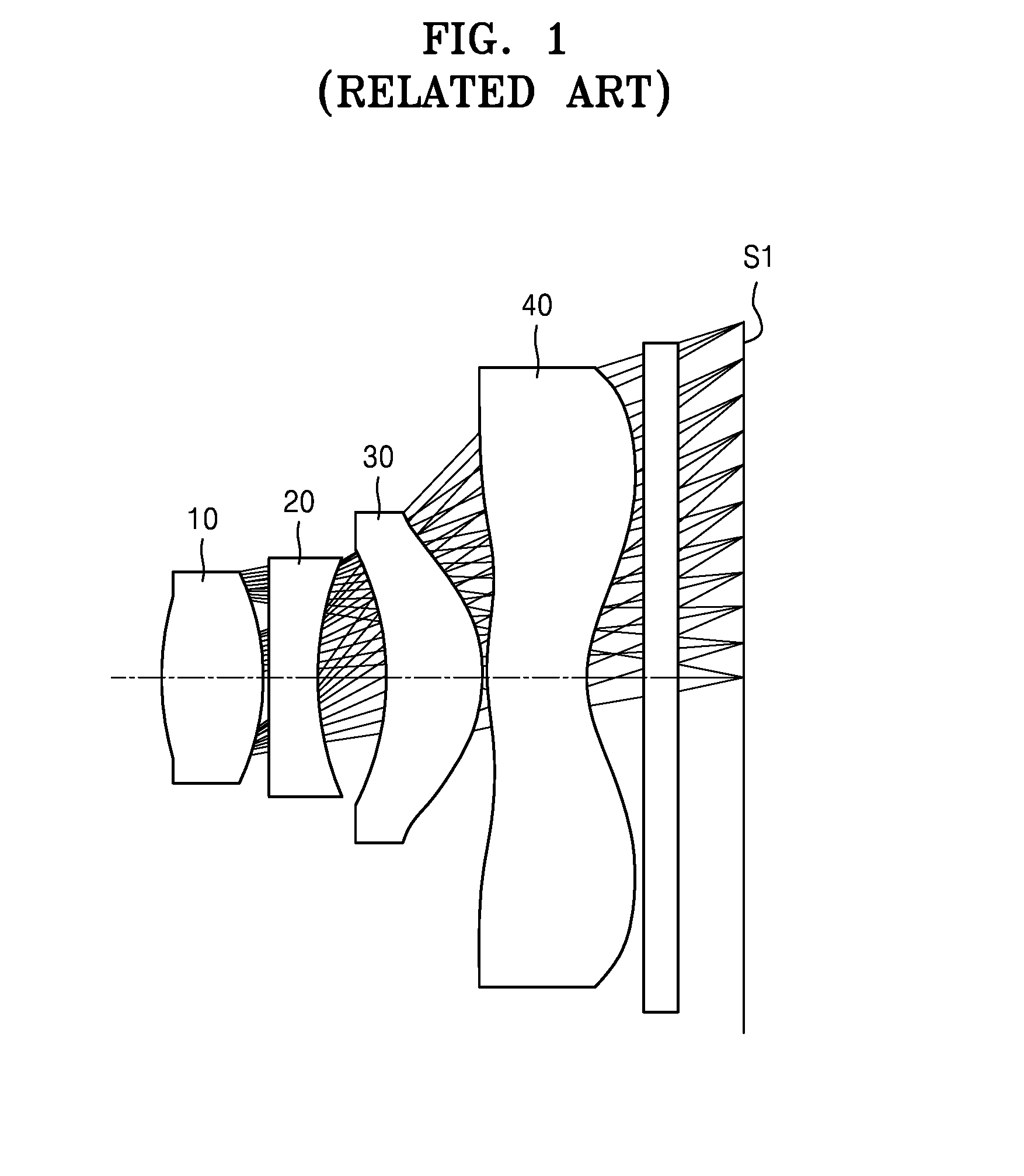
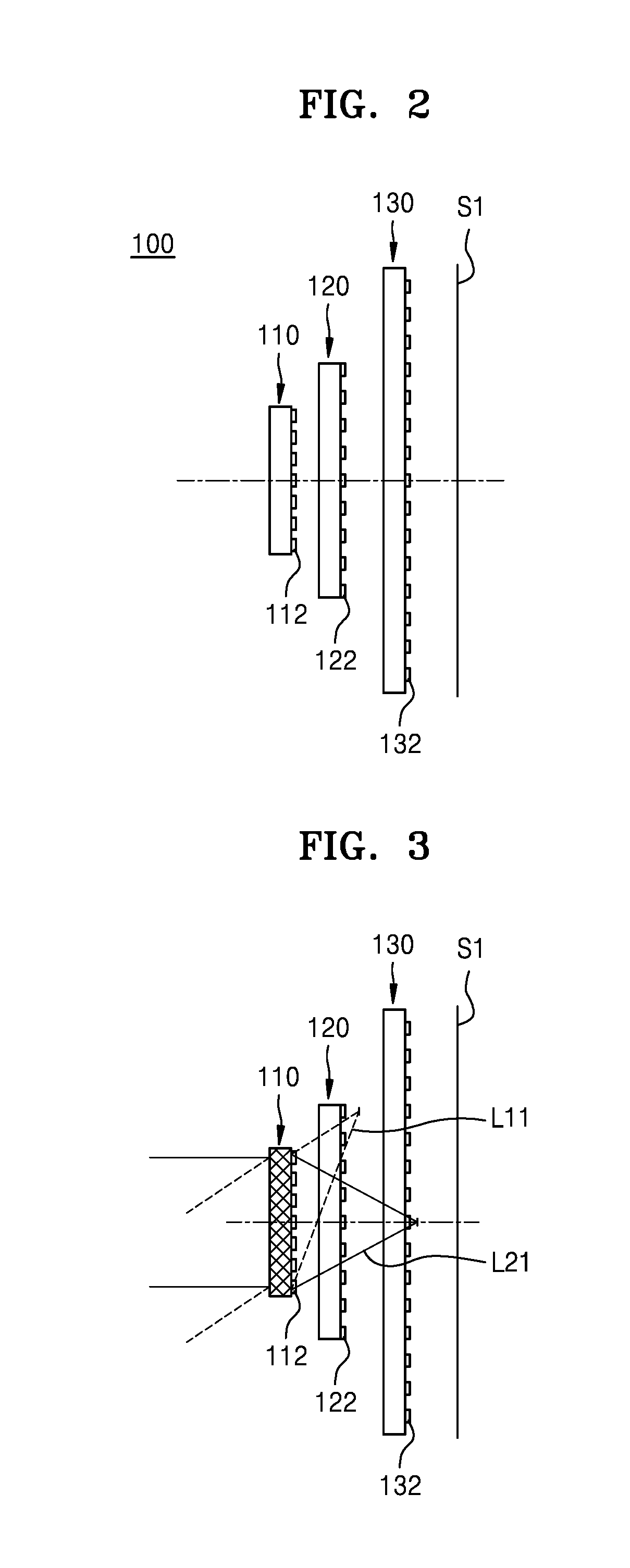
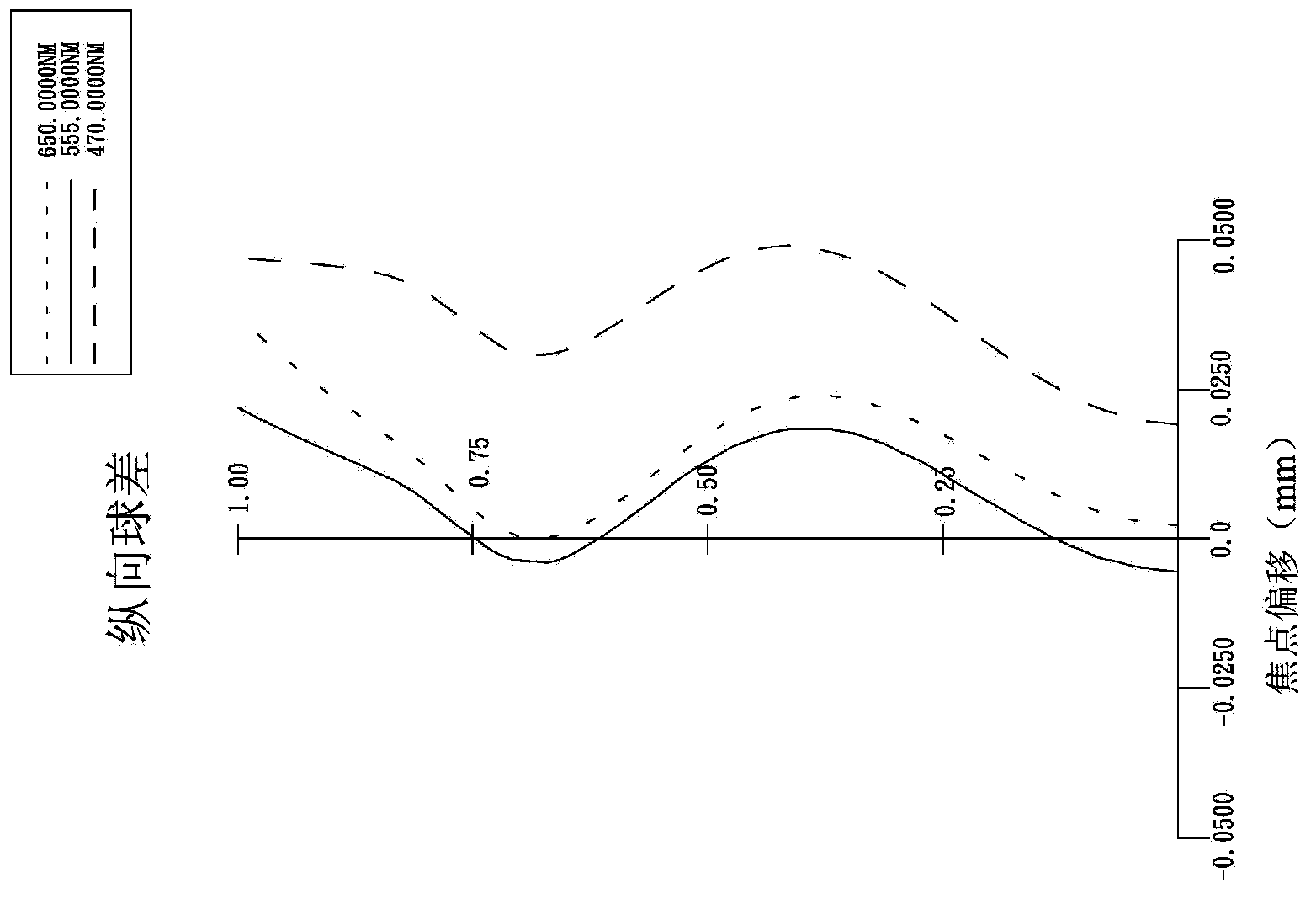
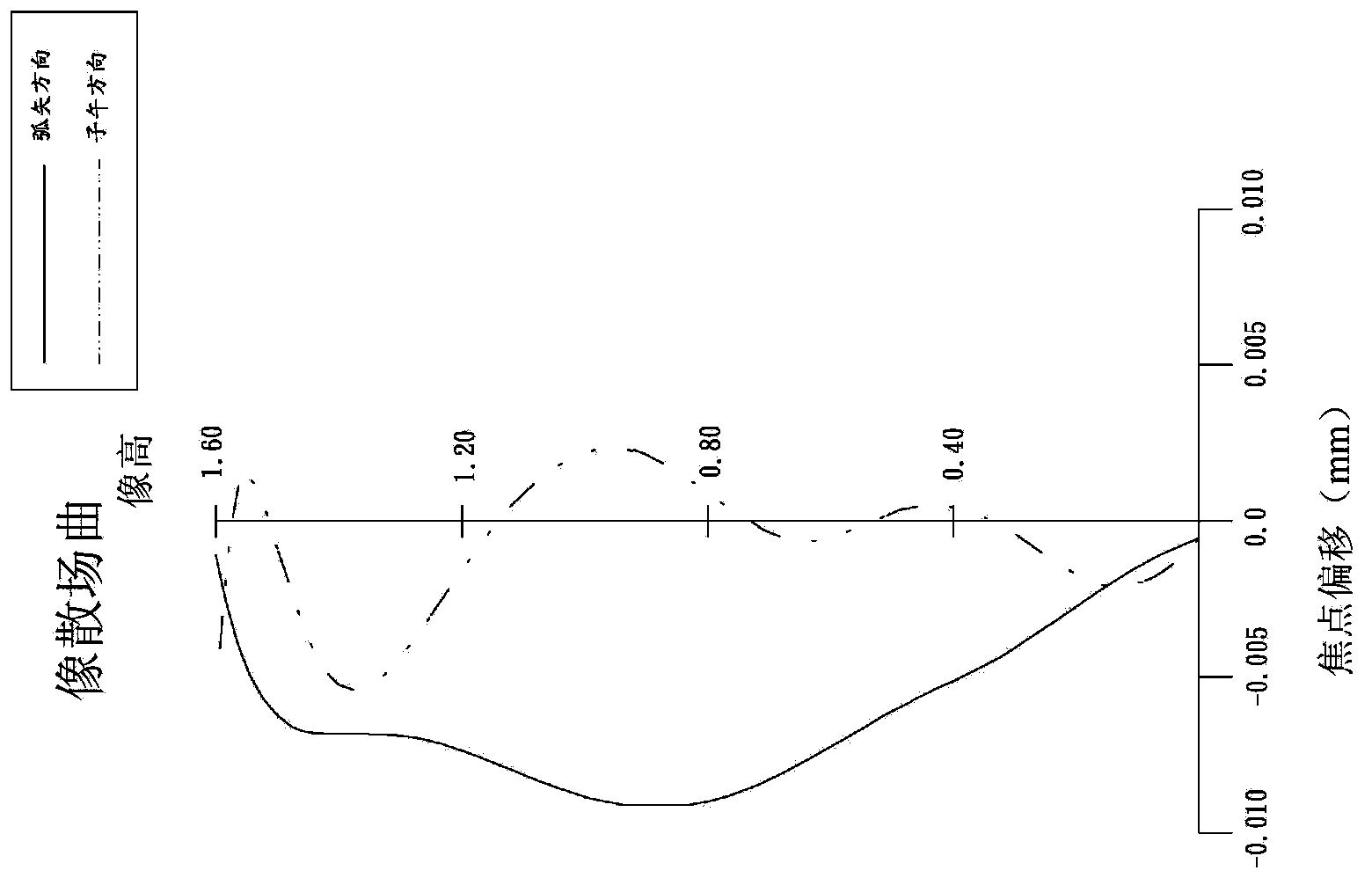
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
95 results about "Thin lens" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In optics, a thin lens is a lens with a thickness (distance along the optical axis between the two surfaces of the lens) that is negligible compared to the radii of curvature of the lens surfaces. Lenses whose thickness is not negligible are sometimes called thick lenses.
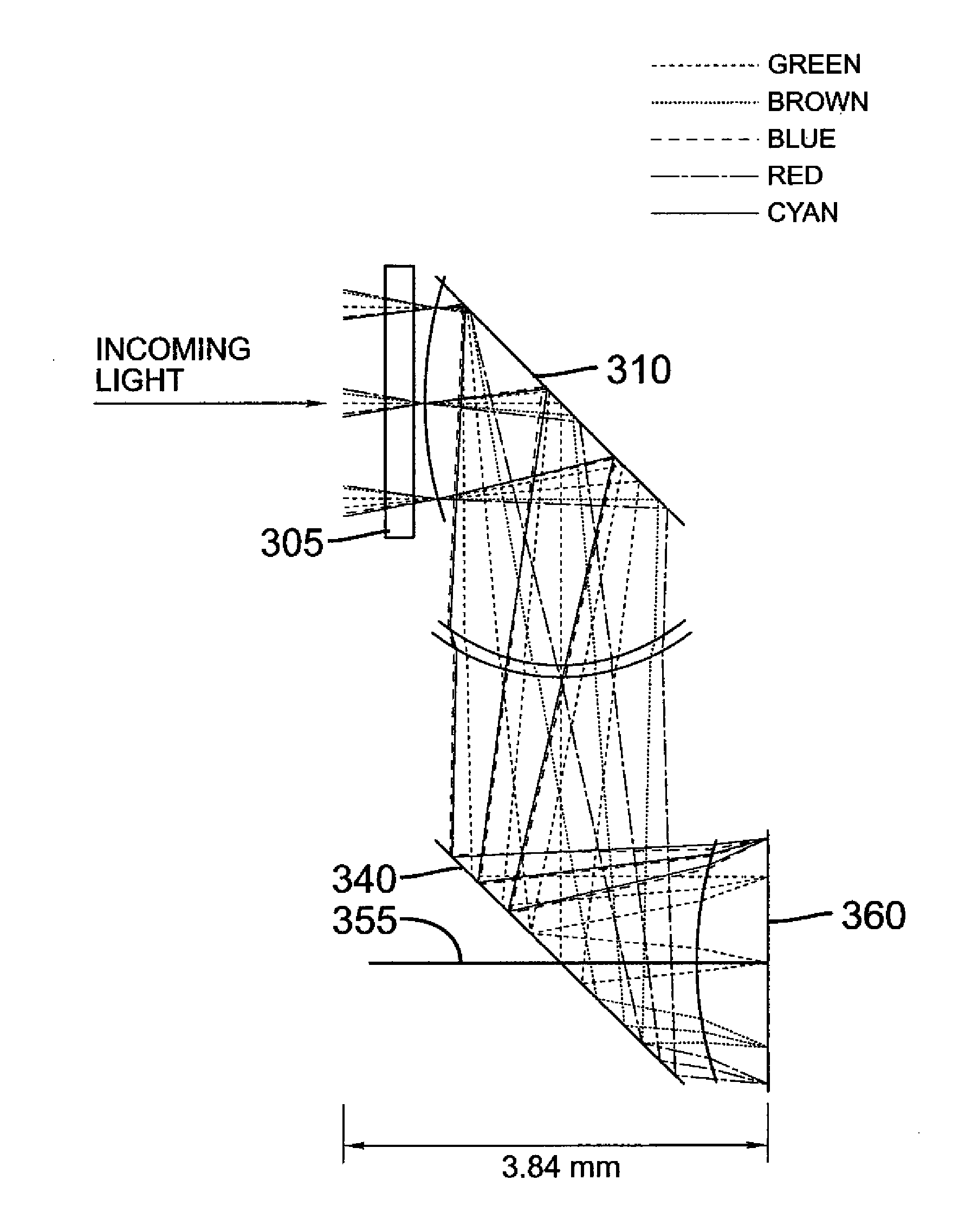
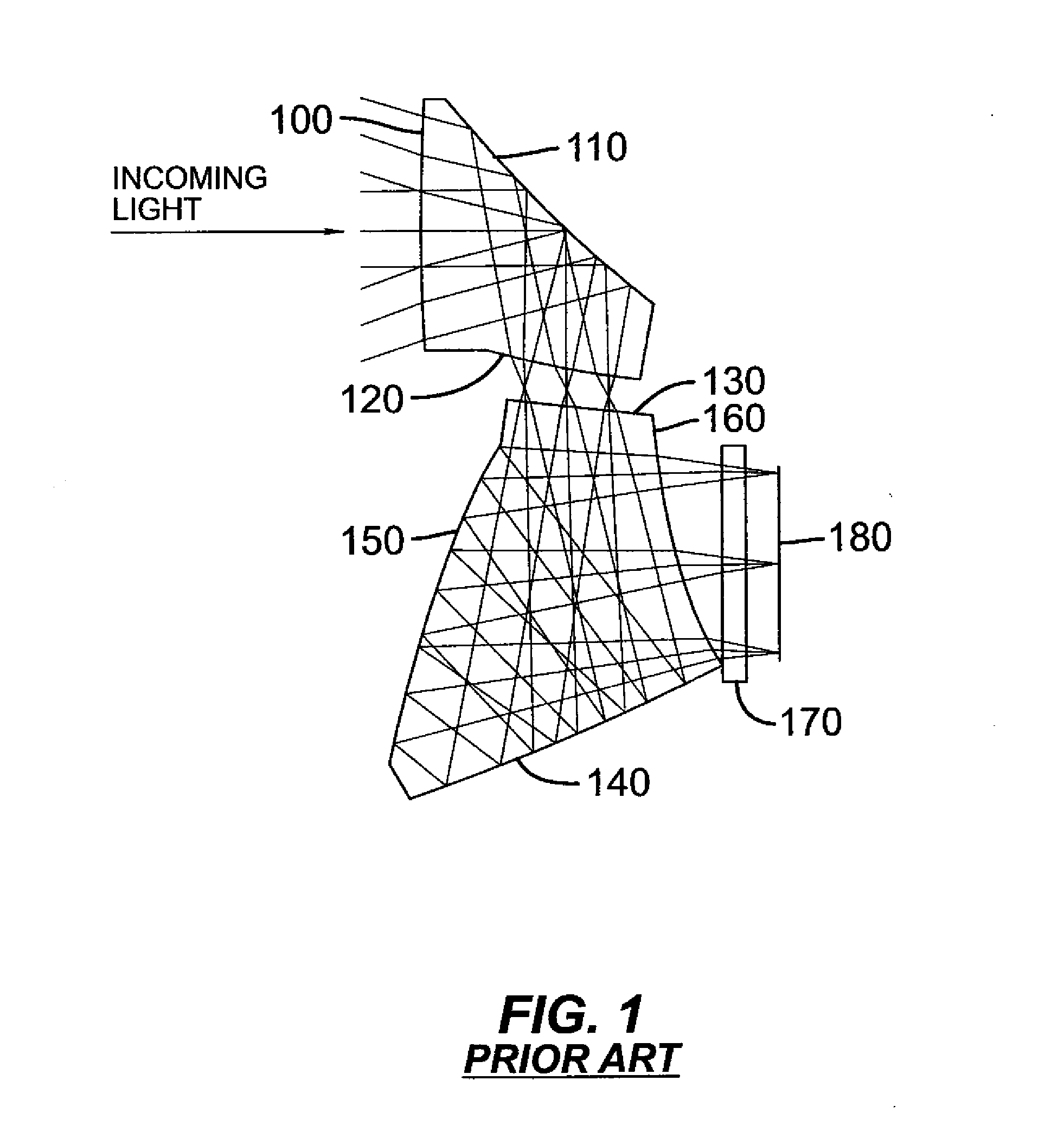
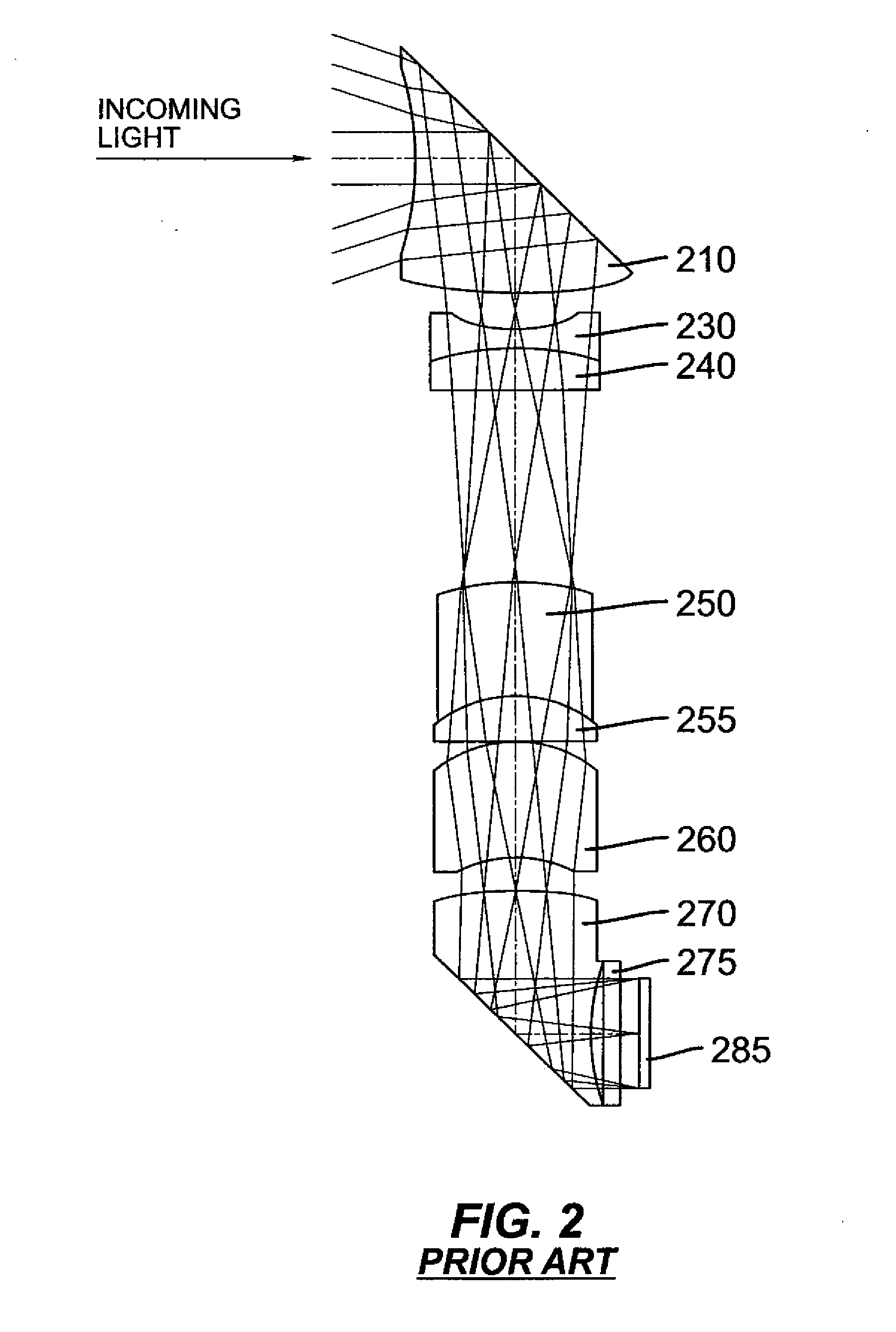
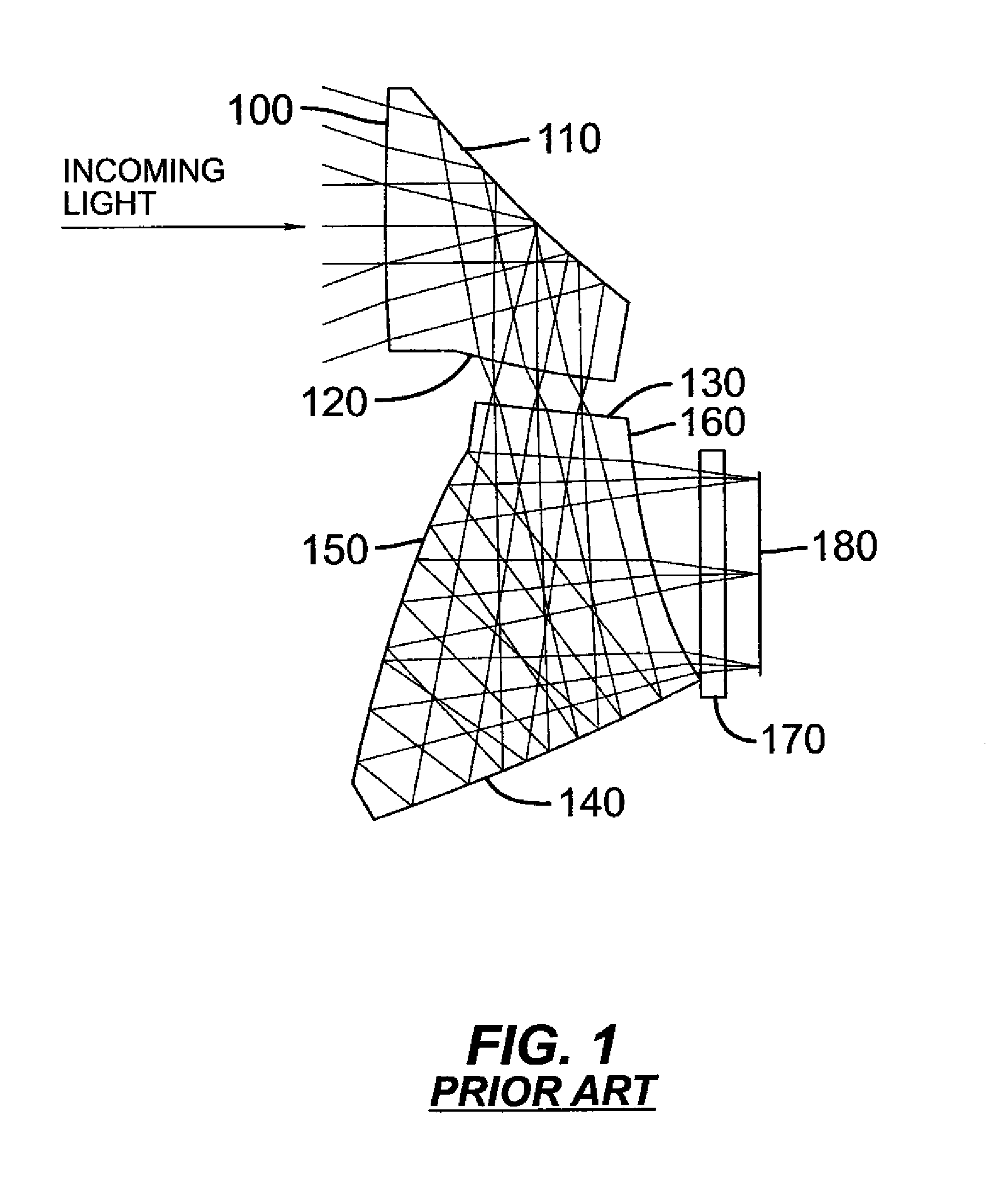
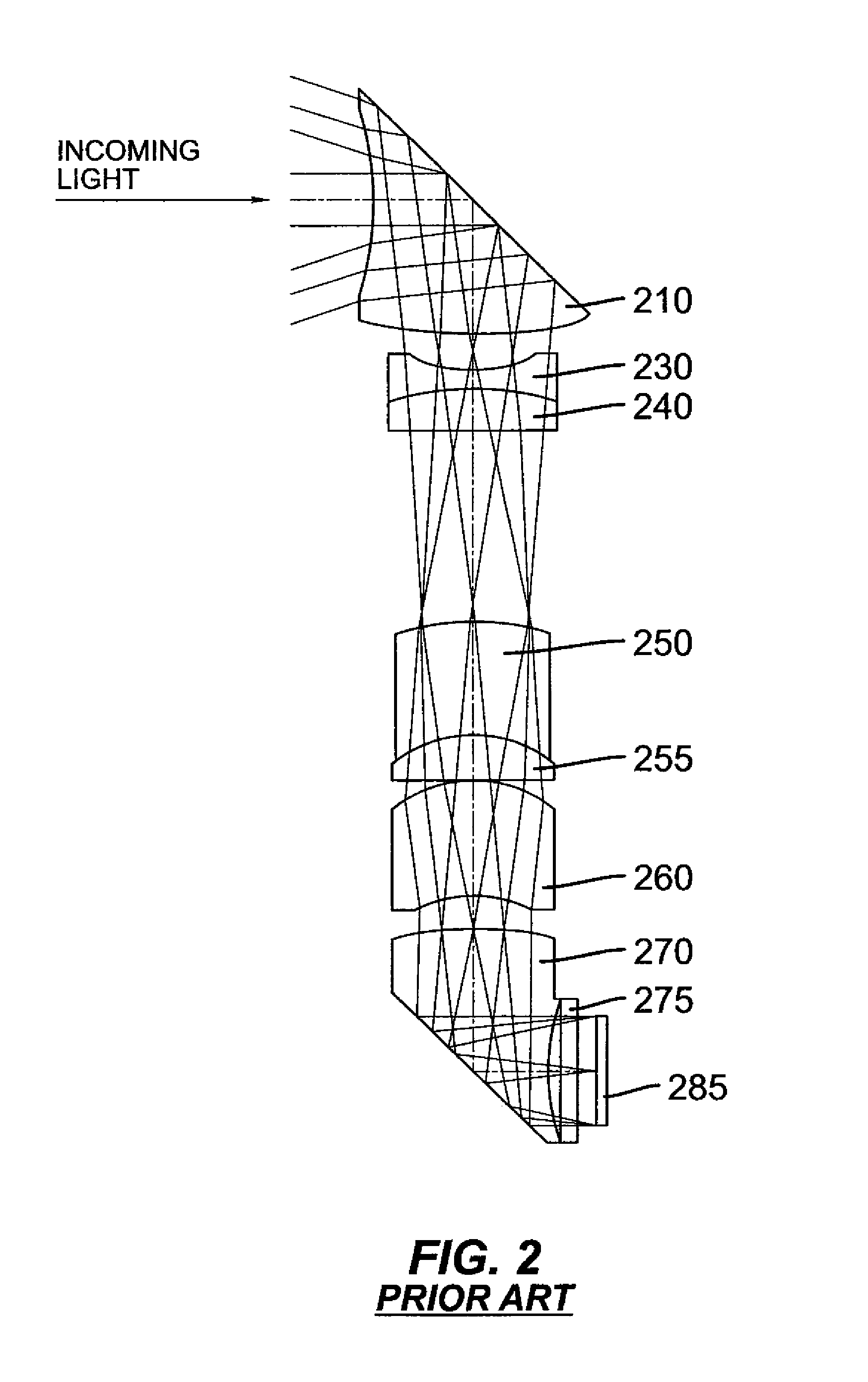
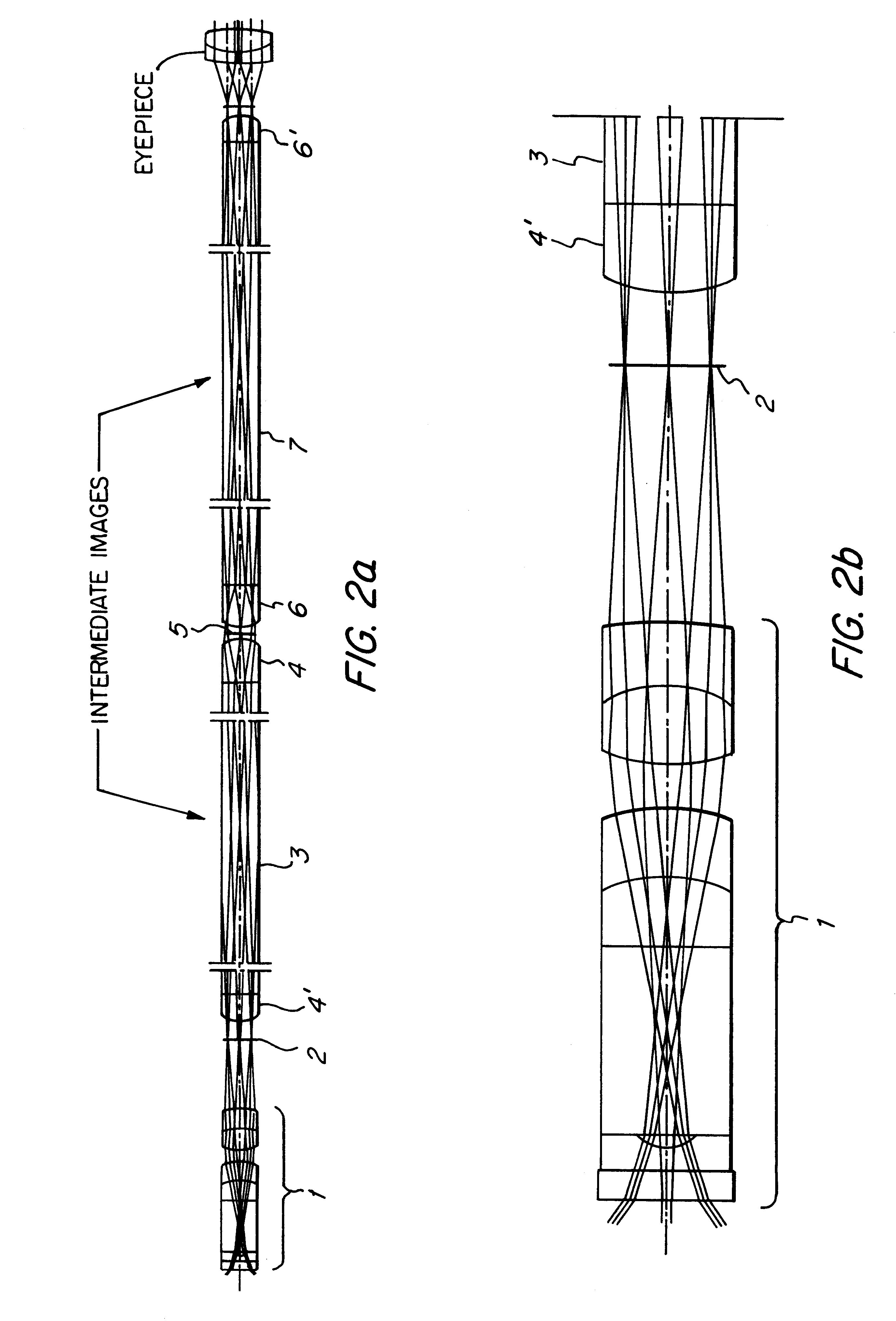
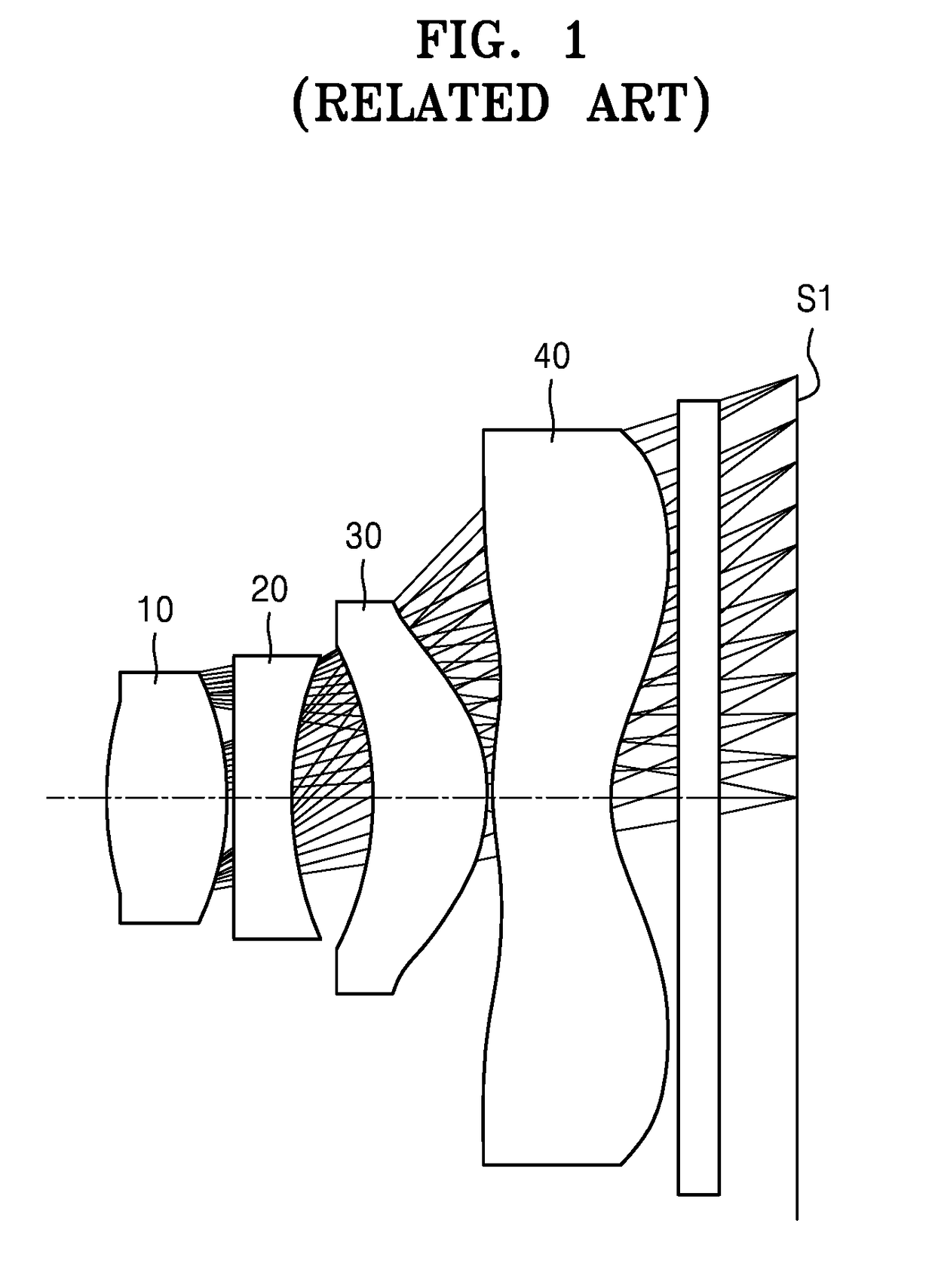
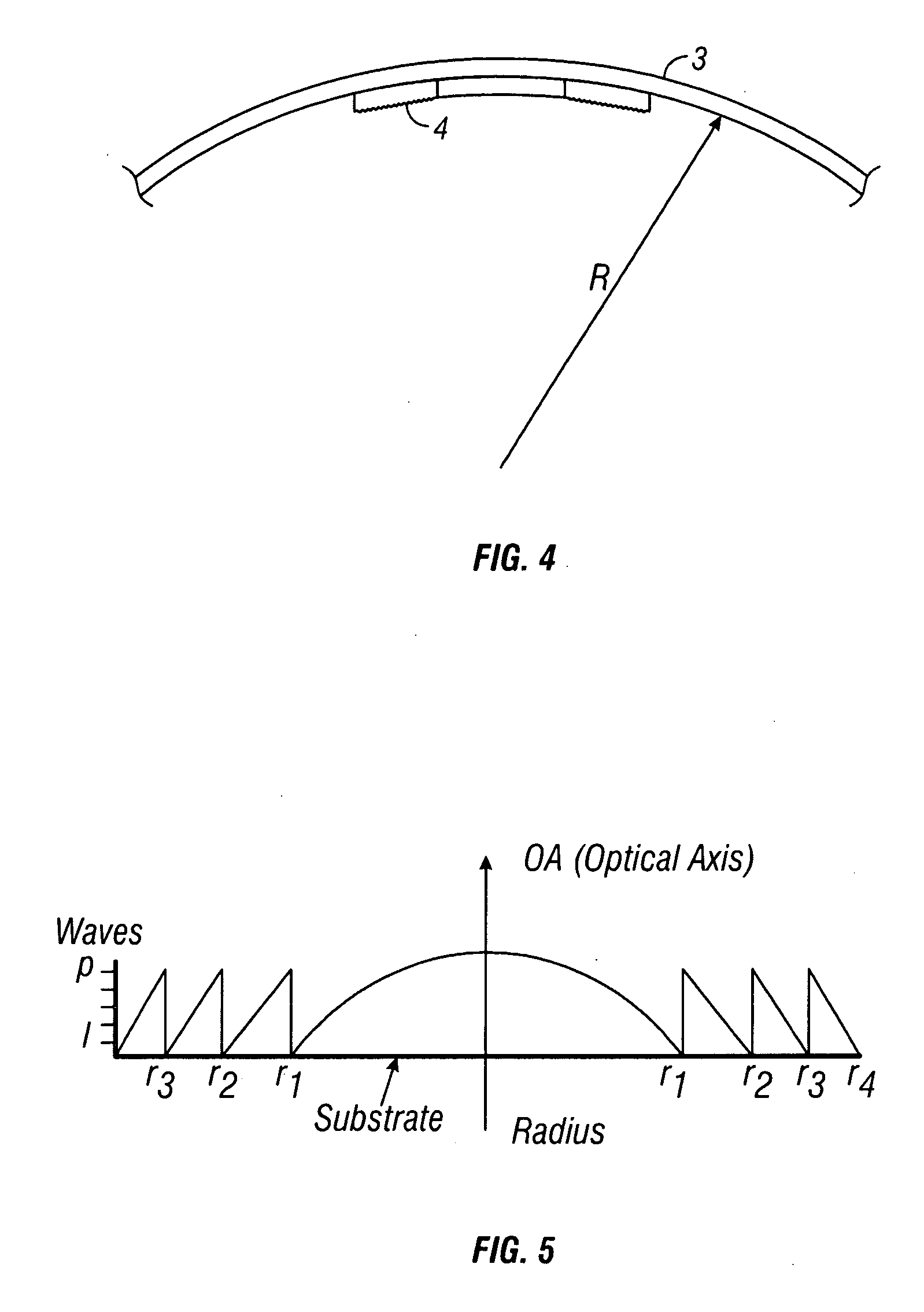
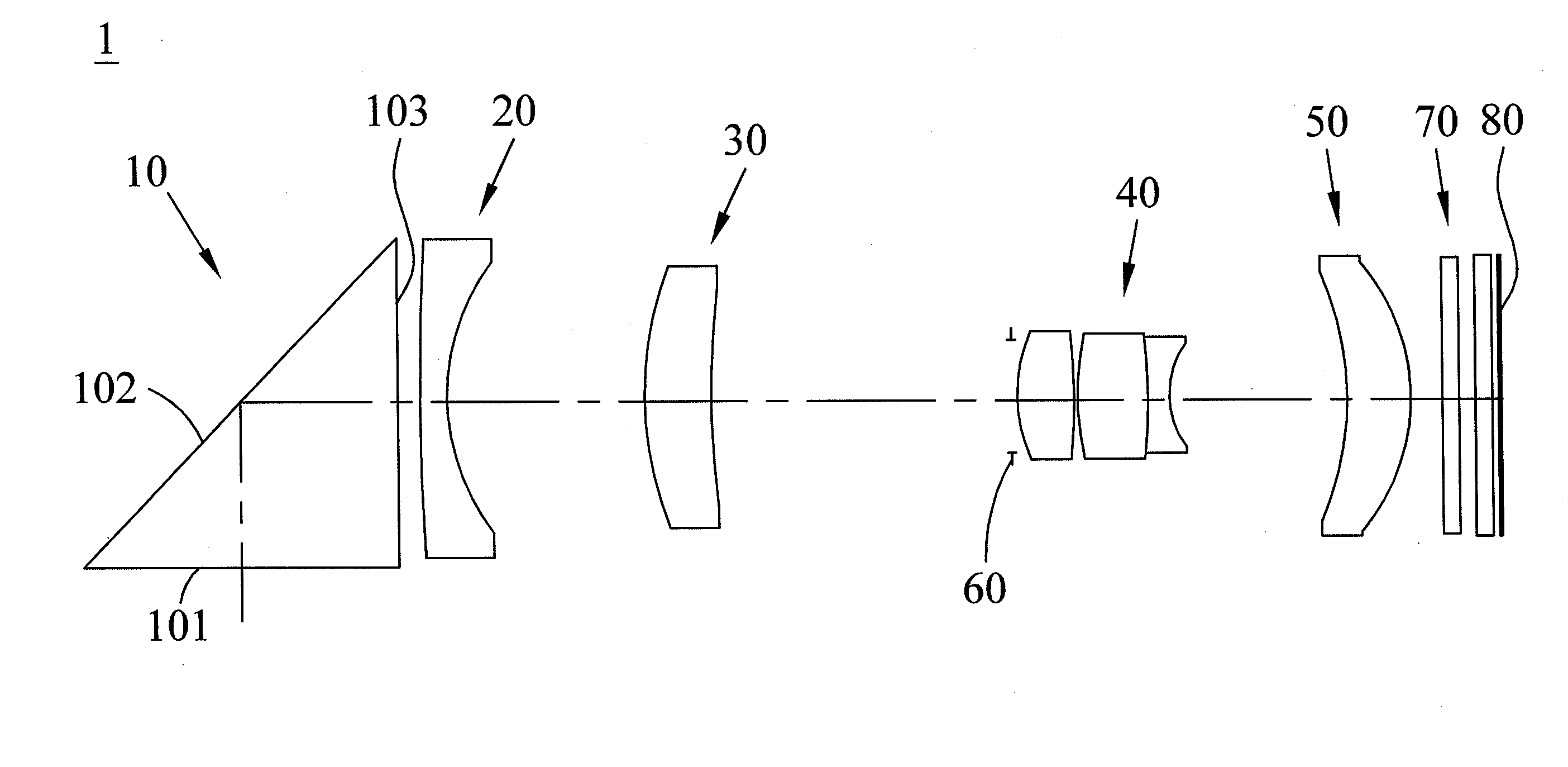
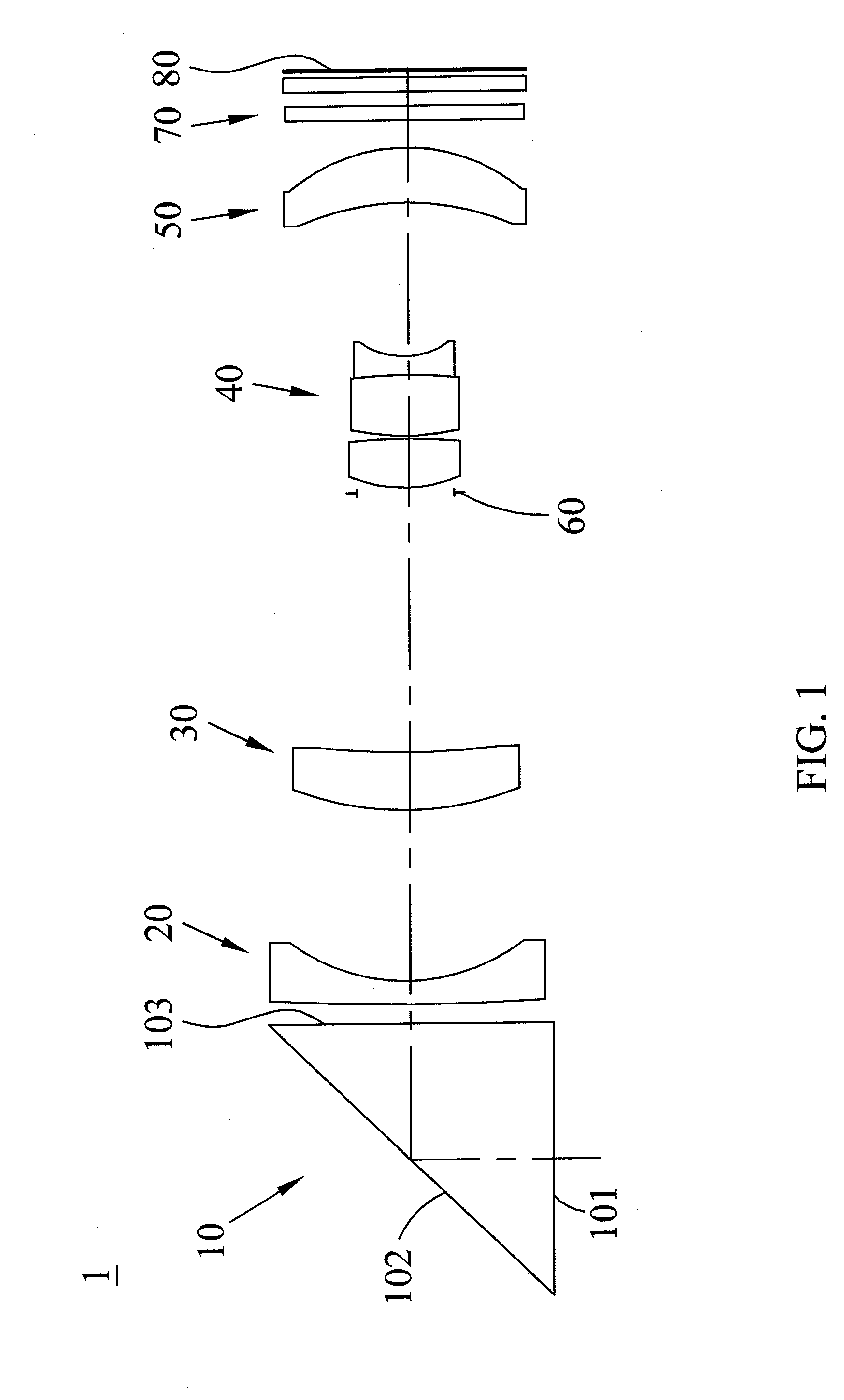
Compact folded thin lens
InactiveUS20090161235A1Low costGood optical performancePrismsOptical elementsOptical axisOptoelectronics
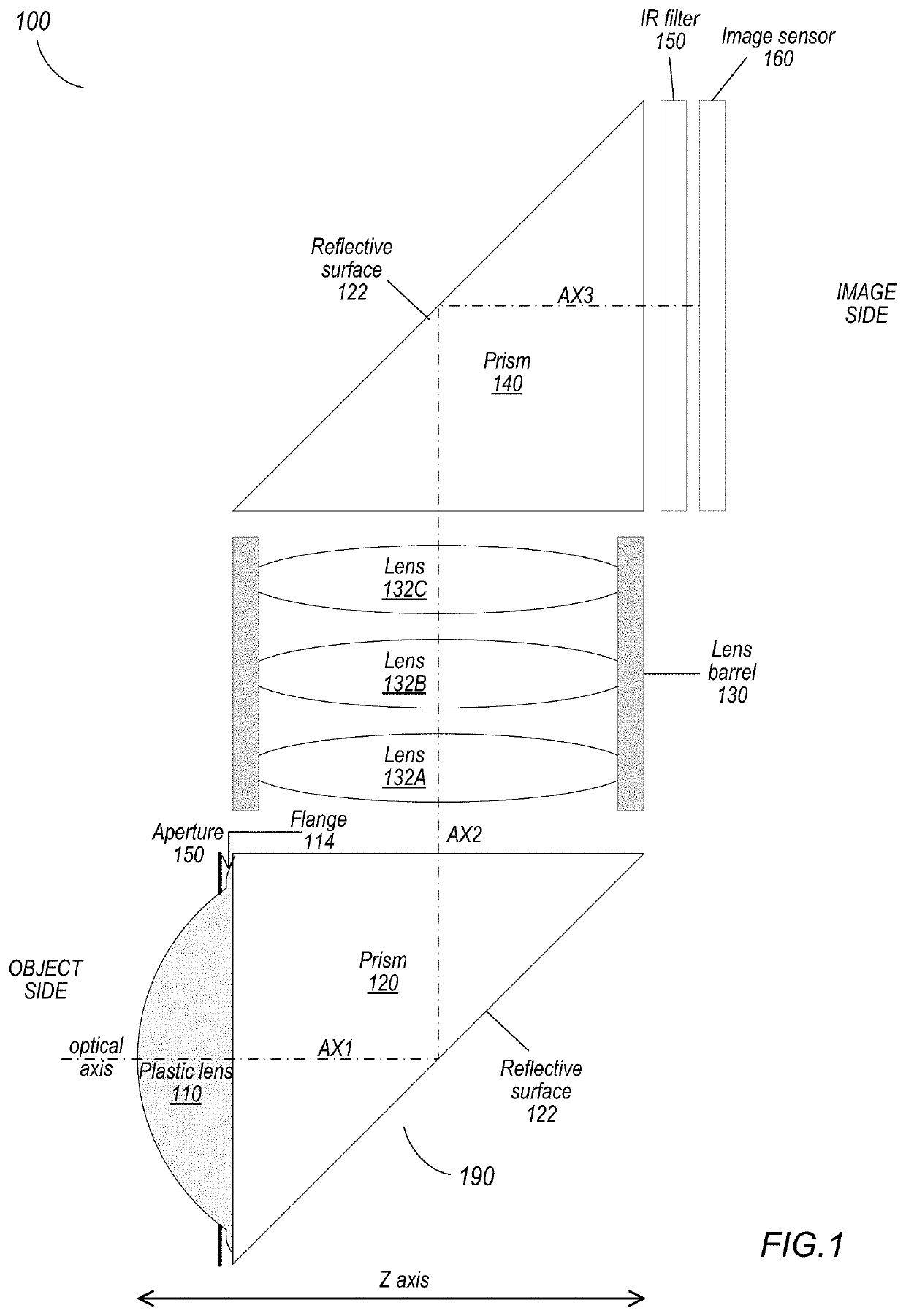
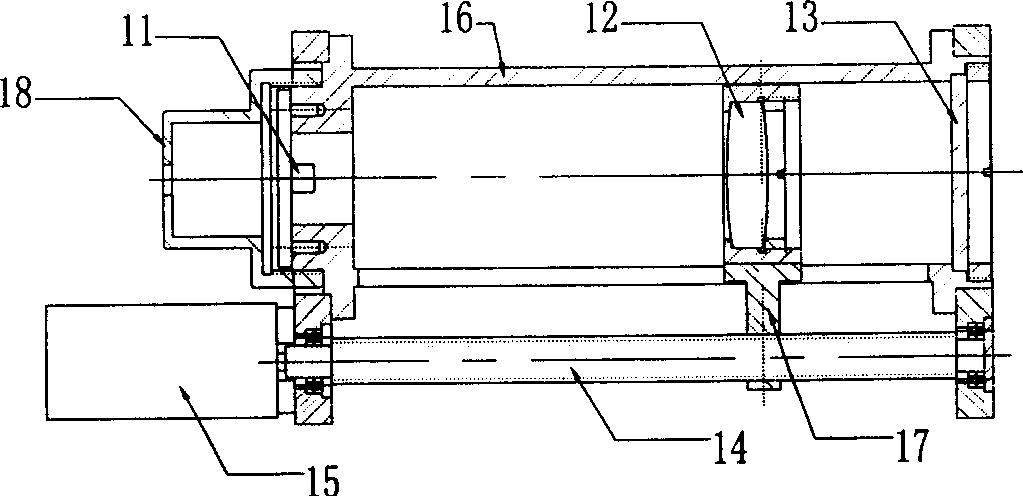
A thin lens consists of a first optical element which comprises a first refracting surface, wherein incoming light passes through the first refracting surface on a first optical axis. A reflecting surface changes a direction of the incoming light from the first optical axis to a second optical axis. Incoming light on the second optical axis passes through a second refracting surface. A second optical element comprises a first refracting surface, wherein incoming light passes through the first refracting surface on the second optical axis. A reflecting surface changes a direction of the incoming light from the second optical axis to a third optical axis. Incoming light on the third optical axis passes through a second refracting surface. The third optical axis is approximately parallel to, and in opposite direction from, the first optical axis.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Imaging lens, imaging device, and mobile terminal
InactiveUS20100188555A1Reduce the amount requiredMaintains telecentricityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptical axisRefractive index
Provided are a wafer scale lens, which is so short in an optical total length with respect to an image height that it can correct an aberration satisfactory, and an optical system including the wafer scale lens and having a thin lens element on the side closest to the image. The optical system includes a first lens having a positive refractive power relative to an object, and a second lens arranged on the side of the image of the first lens and having a recessed shape on the side of the object. At least one lens is arranged on the side of the second lens. When that one of the lenses arranged on the side of the image of the second lens, which is arranged on the side closest to the image, is an i-th lens (i>3), this i-th lens includes an i-th lens flat plate and is formed on the object side of the i-th lens flat plate but has a refractive index different from that of the i-th lens flat plate, and a lens element having a convex shape on the object side where the main light ray of the maximum image height passes. Moreover, the ratio between the optical axial distance (or the lens distance) between a (i−1)-th lens and the i-th lens and the optical axis distance (or the optical total length) from the object side face of the first lens to the image face is 0.01 to 0.15.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
Intraocular lens with iris diaphragm
The invention discloses an artificial lens with an iris diaphragm, comprising an optical zone (1) which is transparent at the center, the iris diaphragm (2) surrounding the optical zone (1) and a loop (3); the artificial lens is in an integrated style and is composed of an entire block of material, the material is selected from foldable materials such as hydrophobic acrylic ester, hydrophilic acrylic ester, silica gel, etc. The artificial lens with the iris diaphragm of the invention has soft texture, can be filled or implanted in the eyes by a small incision after being folded; in addition, the artificial lens has high refractive index, thin lens, small incision and slow formation of after cataract and can slowly restore in 2-30 seconds after being implanted, thus cyst membrane is not easy to be damaged; moreover, the artificial lens has the advantages of little astigmia developed in post-operation, quick healing, fast recovery of visual performance and little postoperative treatment; a brown iris, which is the natural color iris of Chinese, can be adopted, and the eye implanted with such an artificial lens looks more natural.
Owner:苏州六六视觉科技股份有限公司
Method for producing laminated photochromic lenses
A method for laminating an optical assembly and the optical assembly formed thereby. An ultra thin lens is injection molded and may include a bifocal feature. A support lens, e.g. of the single vision type, is provided with a photochromic coating. A flexible two stage compound application process prepares the two lenses for lamination.
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
Imaging apparatus and image sensor including the same
ActiveUS20160316180A1Long focal lengthShort focal lengthTelevision system detailsColor television detailsThin lensNanostructure
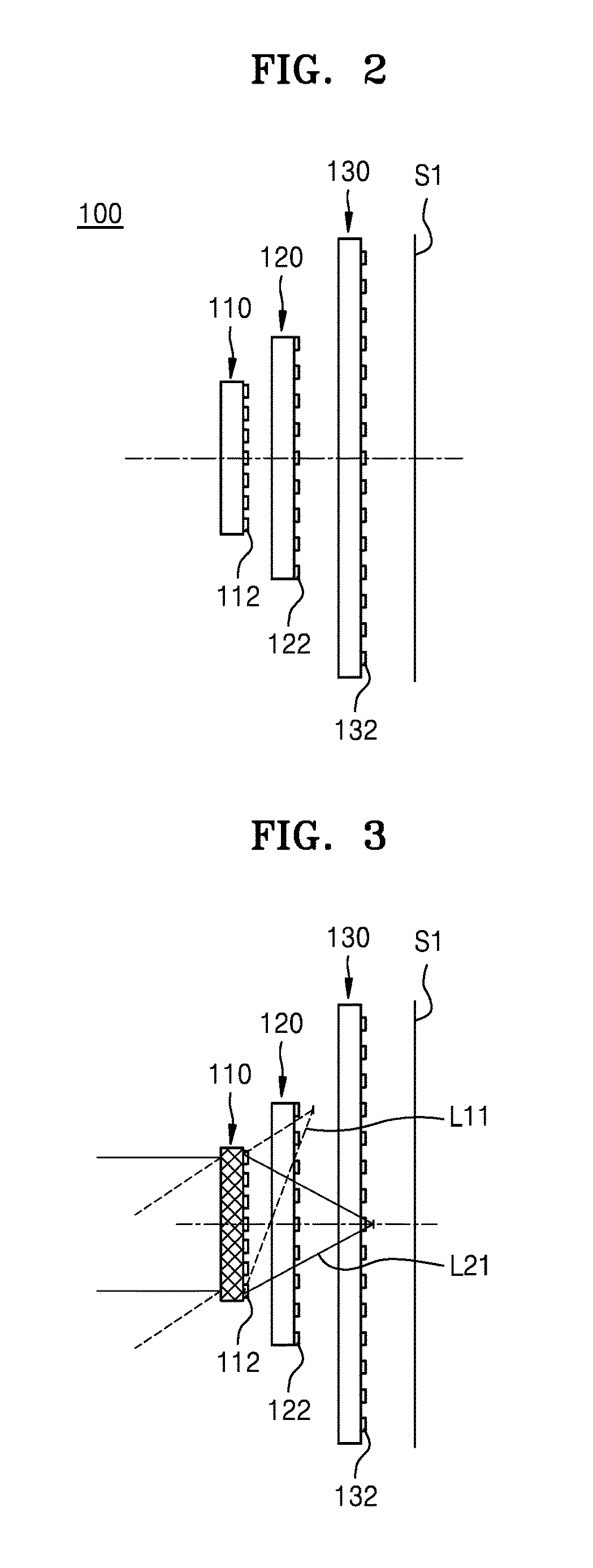
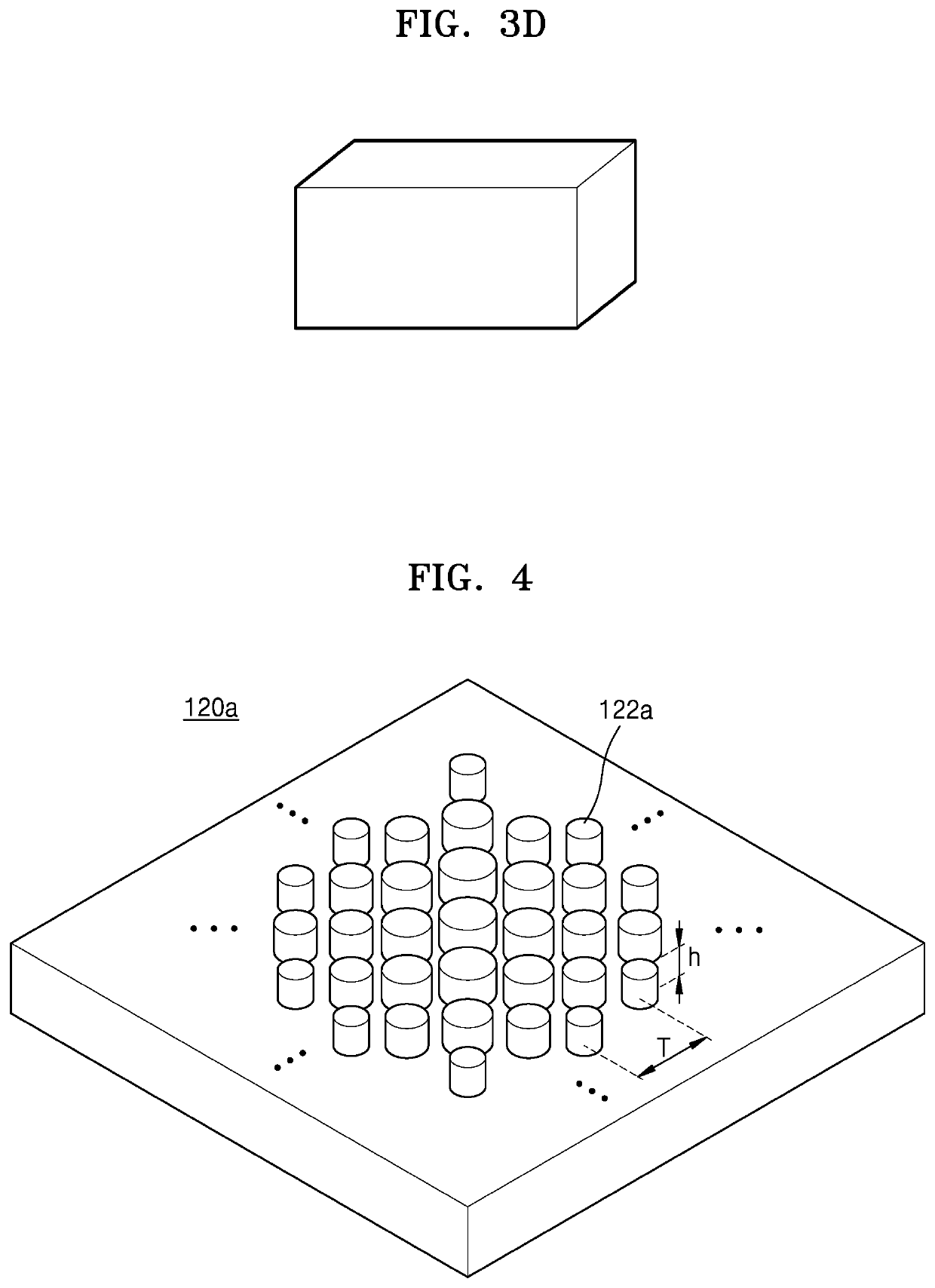
An imaging apparatus and an image sensor including the same are provided. The imaging apparatus includes first, second, and third optical devices. At least one of the first, second, and third optical devices is a thin-lens including nanostructures.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Design method of ultra-thin lens used for LED
ActiveCN101561115AReduce position changesOptical effectsPoint-like light sourceSemiconductor devices for light sourcesOptical axisOptoelectronics
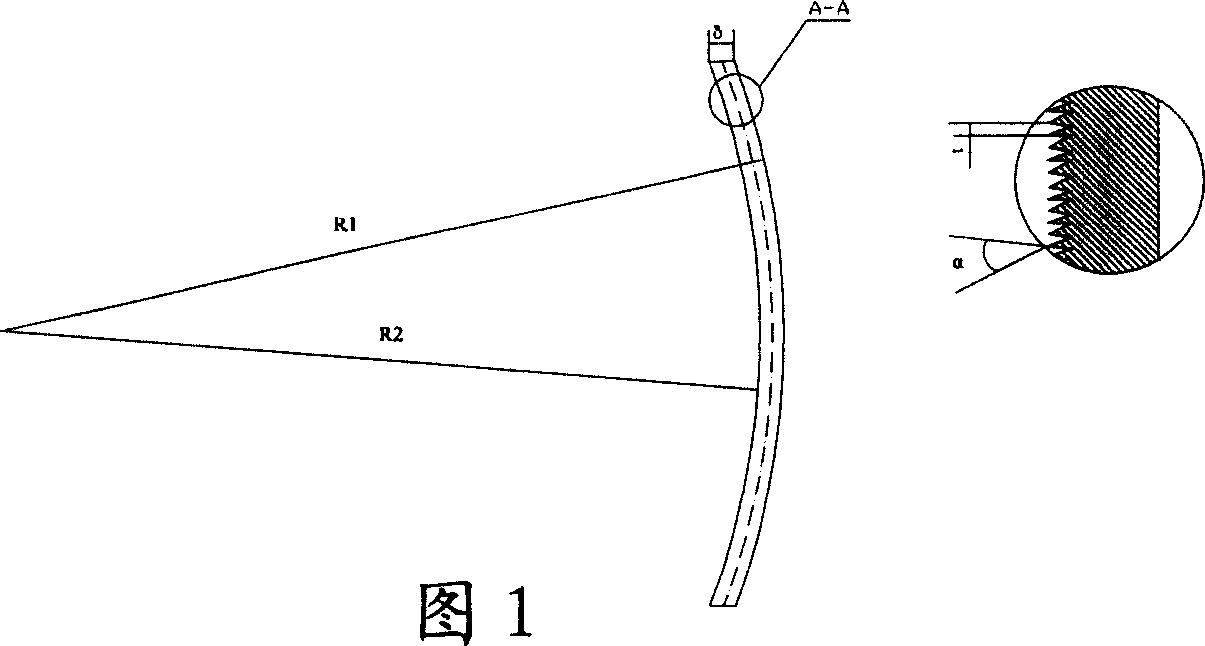
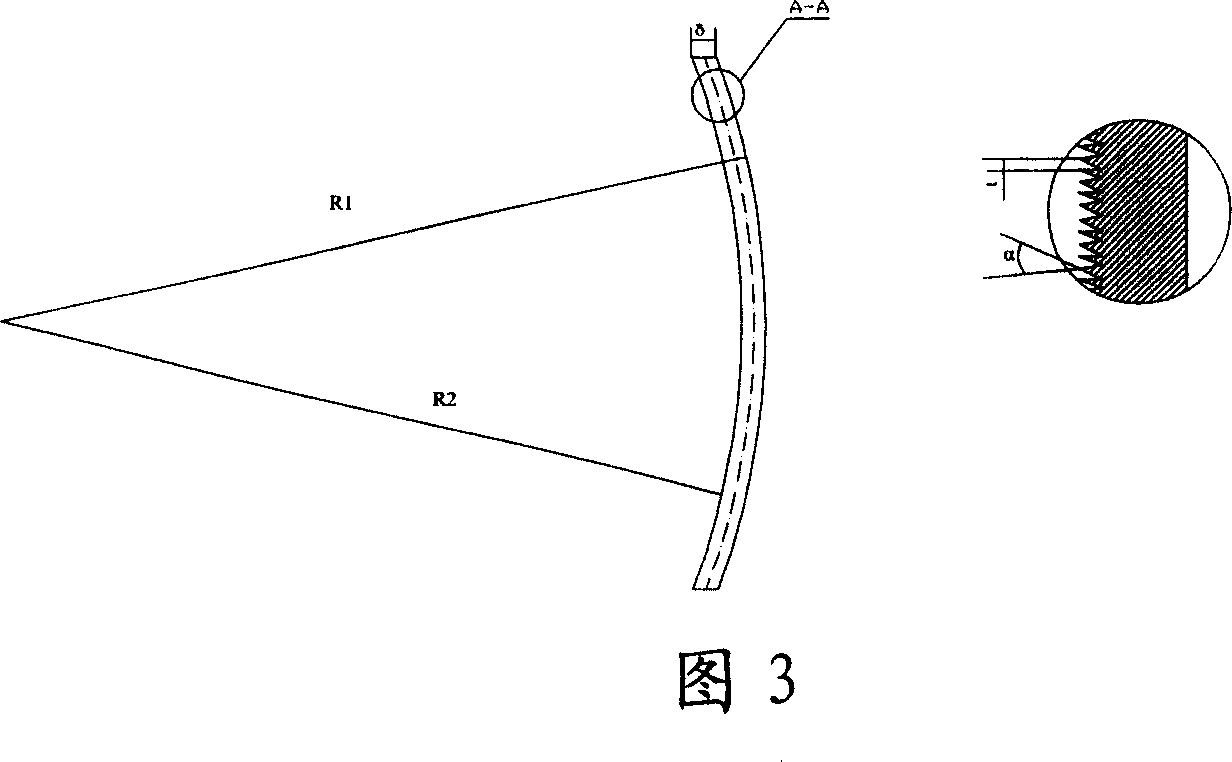
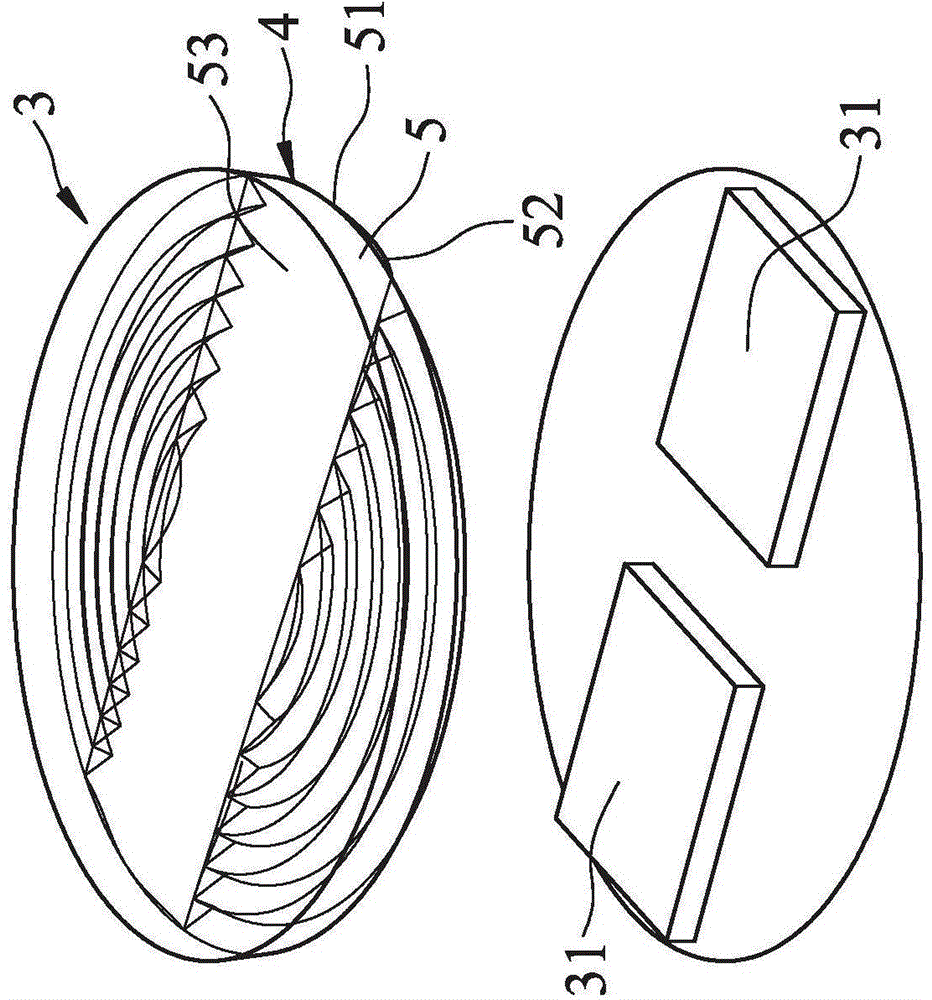
The invention relates to a design method of an ultra-thin lens used for an LED, relates to the optical field and solves the technical problem that the original lens changes from thick to thin. The method divides an incident face into a plurality of small sections of curves according to an opening angle thereof to a light source on the section of a light-passing axis of the original lens by adopting the located point of the LED light source as the center; all the points of the smaller sections of curves are moved along the corresponding incident ray; the length of the original incident ray in the moving process generates amplifying effect by preset proportion; the head part and the tail part of the small sections of adjacent curves after being amplified are connected along the straight line section of the ray direction so as to from a sawteeth section; and the sawteeth section rotates around the optical axis or be drawn along the direction of the normal line of the section so as to form a threaded or sawteeth sheet ultra-thin lens. The method not only can obtain the ultra-thin lens with any thickness and does not have influence on optical effect.
Owner:SHANGHAI SANSI ELECTRONICS ENG +3
Thin lens
The invention relates to a thin lens which comprises a first lens, a second lens, a third lens, a fourth lens, a fifth lens from an object side to an image side along an optical axis. The first lens is a convex-concave lens with negative refractive power, the convex surface of the first lens faces the object side, and the concave surface of the first lens faces the image side. The second lens is a lens with positive refractive power. The third lens is a double-concave lens with negative refractive power. The fourth lens is a double-convex lens with positive refractive power. The fifth lens is a concave-convex lens with negative refractive power, and the convex surface of the fifth lens faces the image side.
Owner:SINTAI OPTICAL SHENZHEN CO LTD +1
Imaging apparatus and image sensor including the same
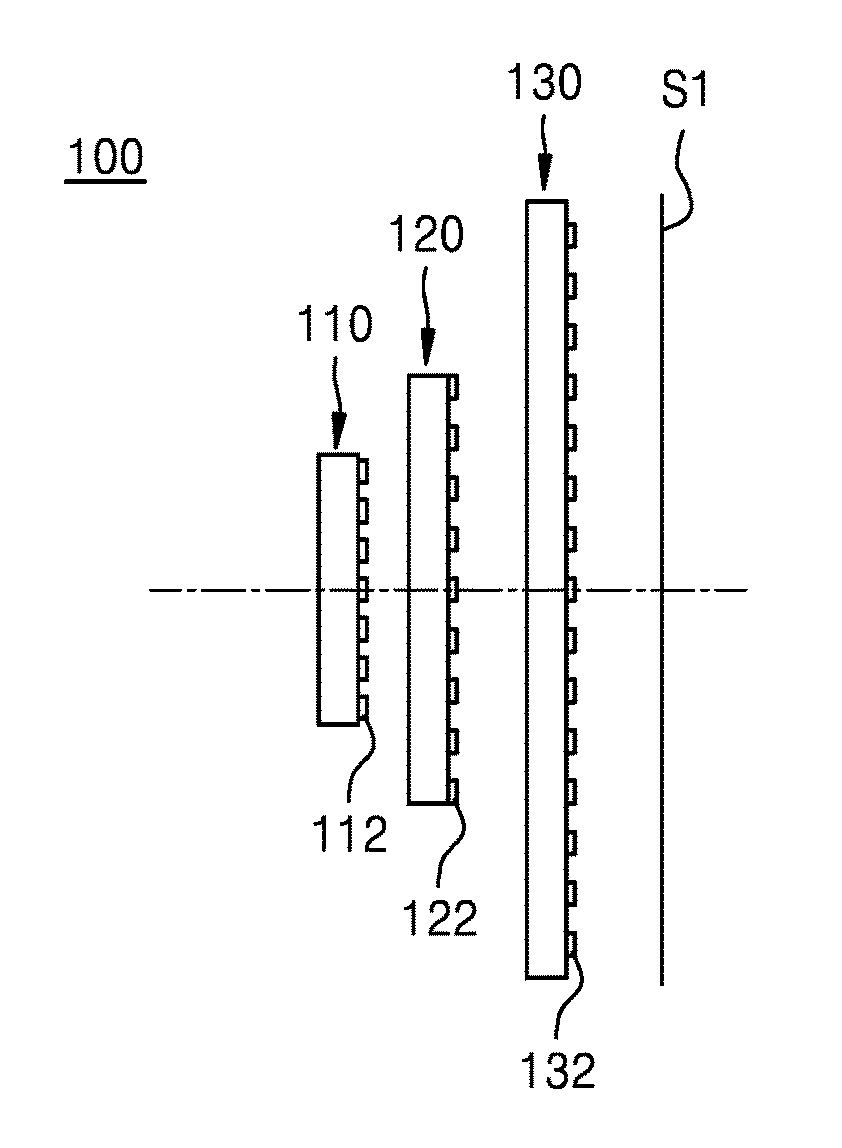
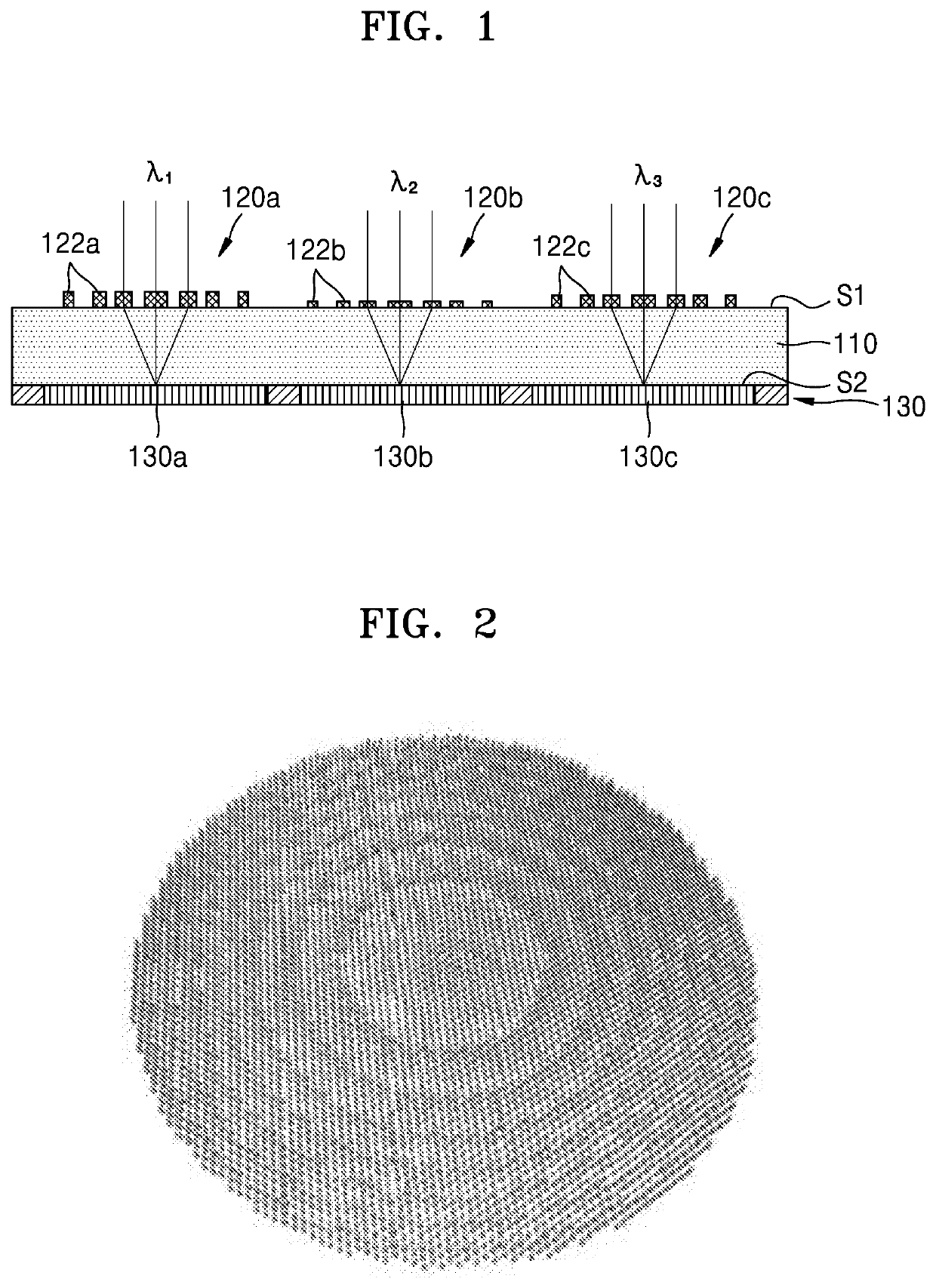
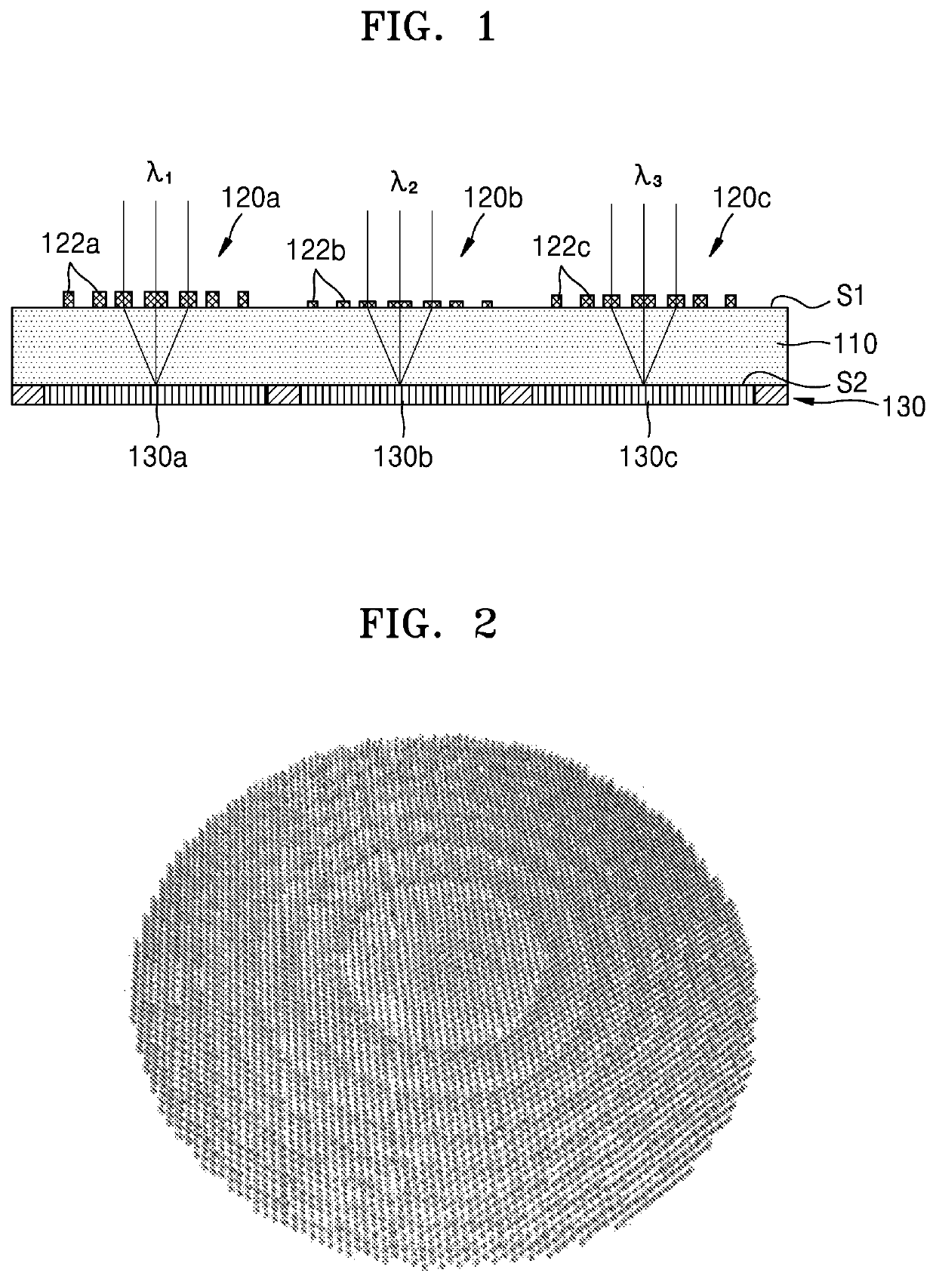
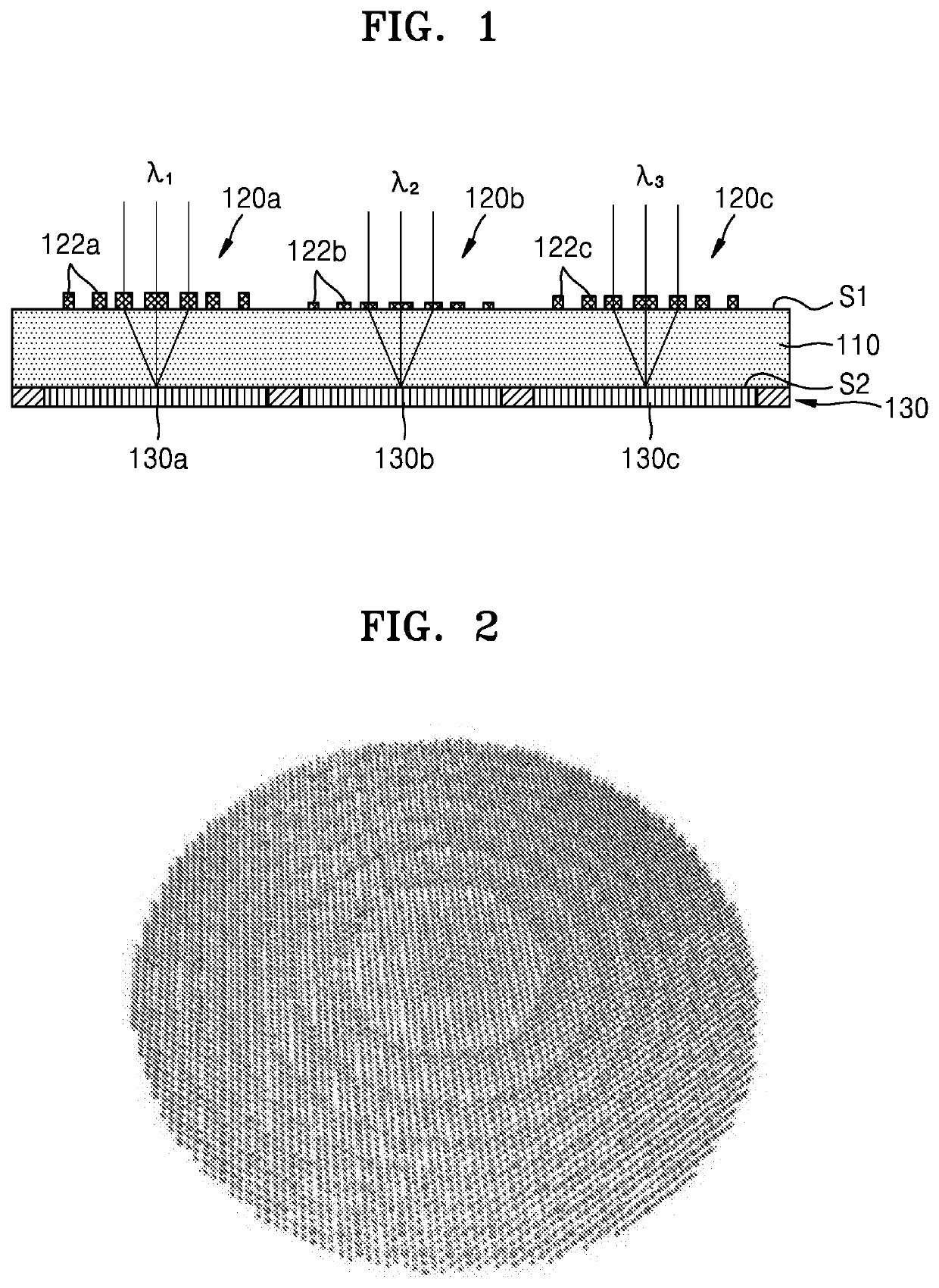
An image sensor includes a substrate, thin lenses disposed on a first surface of the substrate and configured to concentrate lights incident on the first surface, and light-sensing cells disposed on a second surface of the substrate, the second surface facing the first surface, and the light-sensing cells being configured to sense lights passing through the thin lenses, and generate electrical signals based on the sensed lights. A first thin lens and second thin lens of the thin lenses are configured to concentrate a first light and a second light, respectively, of the incident lights onto the light-sensing cells, the first light having a different wavelength than the second light.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
LED focusing optical system
InactiveCN101893205AIncrease brightnessLittle changePoint-like light sourceLighting device detailsLight spotLight beam
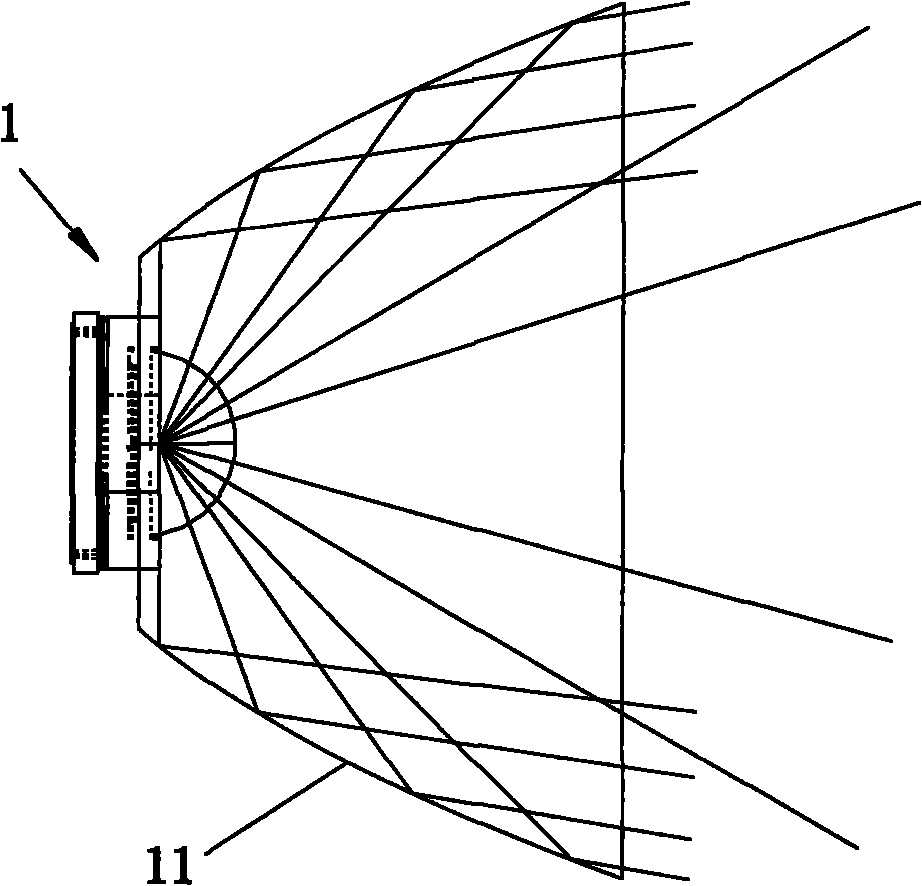
The invention relates to an LED focusing optical system which comprises a reflector, an LED light source arranged at the focal point of the bottom of the reflector and also a thin lens arranged at the opening of the reflector, wherein the surface of the thin lens opposite to the LED light source is a convex surface. The LED focusing optical system realizes high collection of light beams of the LED light source through combination of the thin lens and the reflector to enable the brightness of central light spots to be strong, the influence on an luminescence angle of the system by adding the thin lens is small i.e. the variation of light spots at the outer ring of a lamp is not large, the height of the optical system is only 2-4 times of the size of the light source, and the optical system has the advantages of simple structure, small volume, strong light intensity and large radiation range, therefore, the LED focusing optical system can be widely applied to the field of focusing lamps such as flashlights, miner lamps, headband lamps and the like and fully satisfy the illumination requirement of people to the focusing lamps.
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD +1
Compact folded thin lens
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Endoscope with at least one reversal system with a non-homogeneous refraction index
InactiveUS6301043B1Longitudinal chromatic aberrationHinder advantageSurgeryEndoscopesRefractive indexInhomogeneous material
An endoscope having a distally disposed lens and an optical transmission system which transmits the image of the lens to the proximal end of the endoscope is provided. The transmission system includes at least one reversing system, which includes two elements in mutual mirror-inverted arrangement. Each element includes a rod lens with planar faces and at least one optically thin lens having a planar surface. The rod lenses consist of an inhomogeneous material having a positive dispersion and an inhomogeneous refractive index in the radial direction, while the thin lenses are plano-convex lenses.
Owner:KARL STORZ GMBH & CO KG
Imaging apparatus and image sensor including the same
ActiveUS9946051B2Long focal lengthShort focal lengthTelevision system detailsColor television detailsNanostructureImaging equipment
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
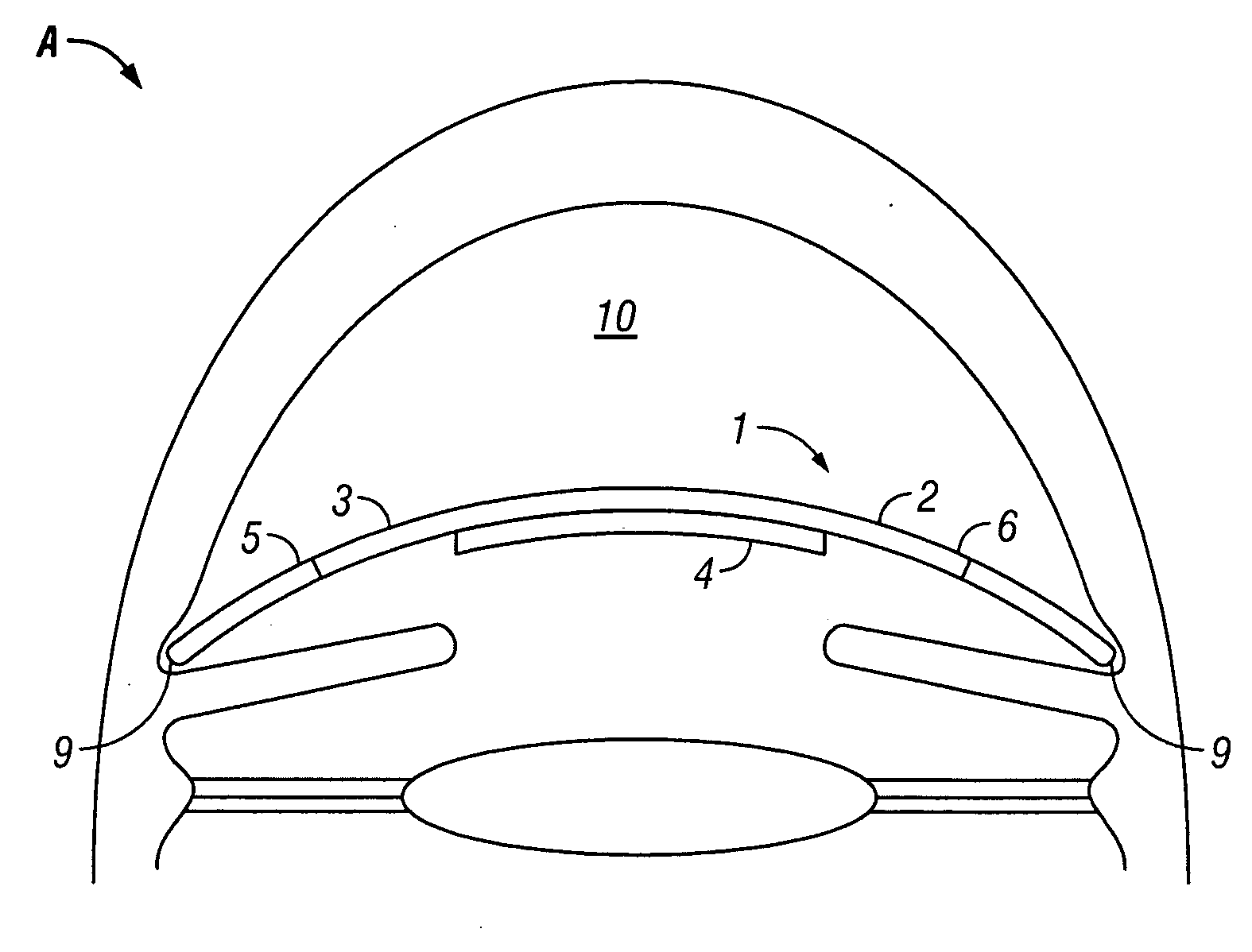
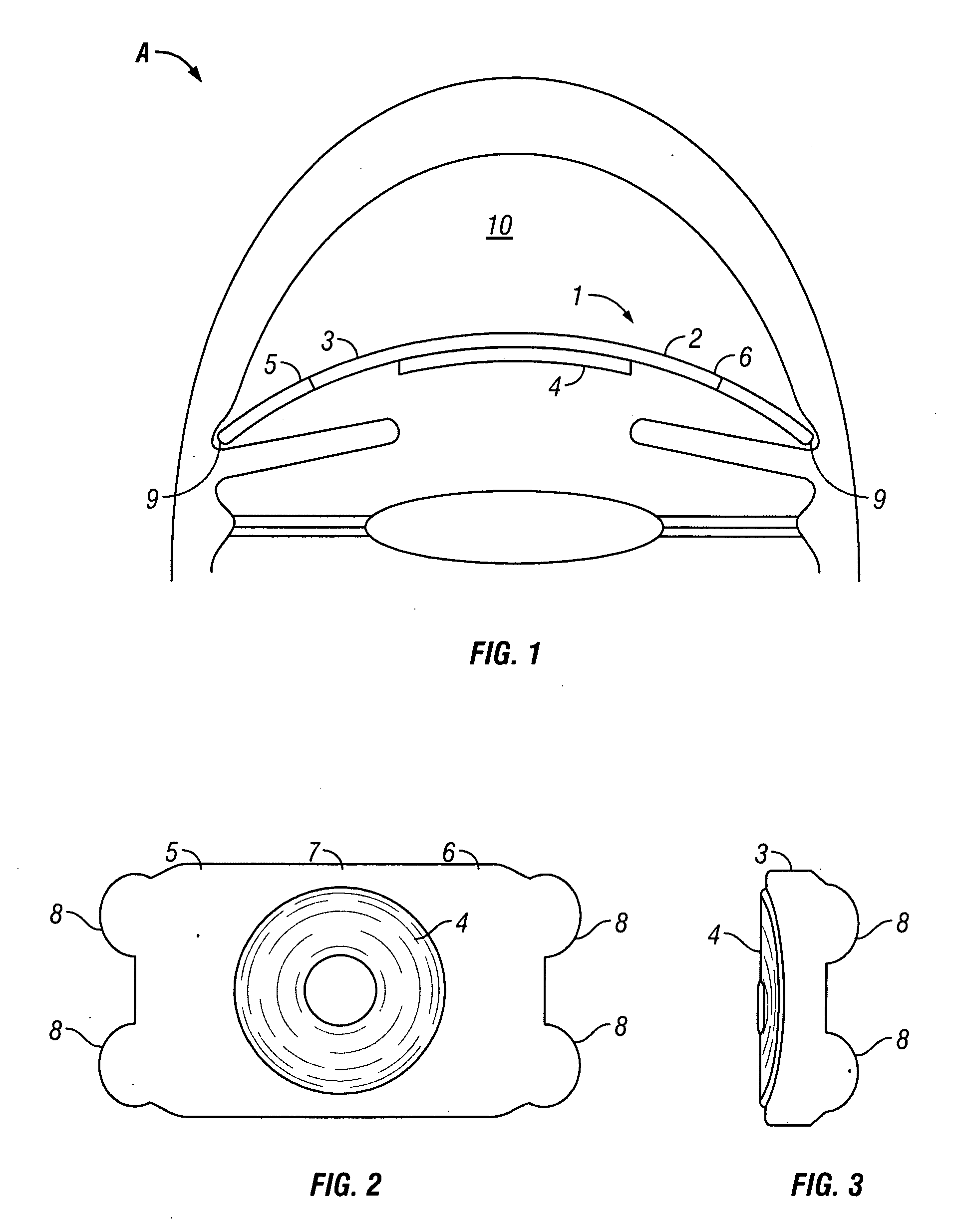
Intraocular thin lens for anterior chamber installation
InactiveUS20090182422A1Impaired night visionRealize automatic adjustmentIntraocular lensIntraocular implantPseudophakia
Owner:NORDAN LEE T +1
Method of distribution of absorption of laser crystal radial-direction non-uniform doping control pump light
InactiveCN103490278AAvoid the risk of falling off or even end face burstingImprove conversion efficiencyLaser output parameters controlActive medium materialPlane mirrorThin lens
The invention relates to a method of distribution of absorption of laser crystal radial-direction non-uniform doping control pump light. The method is characterized in that after the pump light output by an optical fiber coupling laser diode optical fiber output end is gathered by a coupling system, the light field of the pump light is distributed in a Gaussian mode or flat Gaussian mode; a pump light anti-reflection film and an oscillating high-reflection film are plated on the pump end face of a radial-direction non-uniform doping crystal, an output mirror is a plane mirror, and the output mirror and the oscillating light high-reflection film on the pump end face of the crystal form a flat resonant cavity; in the working process, a thermal lens formed in the crystal can be simply equivalent to a thin lens on the pump end face of the radial-direction non-uniform doping crystal, and the resonant cavity becomes a stable cavity through the gather effect of the thermal lens; under the condition that a pump light distribution area and an oscillating light distribution area are determined, the spatial overlapping of the pump light distribution area and the oscillating light distribution area are achieved through the radial-direction non-uniform doping optimization design of the laser crystal. According to the method, ideal space coupling efficiency and ideal beam quality can be achieved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Gaussian Shell model (GSM) shaping method and system
ActiveCN106444048ARich varietyModulate light intensityOptical elementsUltrasound attenuationLight spot
The invention discloses a Gaussian Shell model (GSM) shaping method. After a GSM beam is expanded through a beam expanding mirror and the size of a light spot is changed, the GSM beam vertically enters a first thin lens, and is focused on an amplitude attenuation piece. The light beam from the amplitude attenuation piece is outputted through a second film lens in a collimation manner, thereby obtaining a special part coherent beam. The method can achieve the simultaneous or independent modulation of the light intensity and coherence of the GSM beam, can obtain a result that the distribution of the light intensity and coherence is non-Gaussian distribution, and greatly increases the types of light beams. The invention also discloses a GSM shaping system.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Bionic optical compound eye of integrated structure
InactiveCN103293570AAvoid defectsConvenient high-precision couplingLensPhotovoltaic detectorsCoupling
A bionic optical compound eye of an integrated structure belongs to a microstructural optical component and an application field of the microstructural optical component. The bionic optical compound eye is arranged in an ommatidium array according to certain geometric rules of hexagons, squares and the like. Ommatidiums include a micro lens, a crystal cone and a cylindrical waveguide which are coaxial and arranged along the optical axis or the Z axis from the left to the right. No physical distance is arranged between the plano-convex lens and the crystal cone and between the crystal cone and the cylindrical waveguide along the Z axis so as to form a whole. The micro lens can be seen as a plano-convex thin lens. The length from the top end of the micro lens to the tail end of the crystal cone is the focal length of a spherical refraction surface having the same curvature radius and refraction rate as the micro lens sphere. An image space principal point and a focal point of the ommatidiums of the integrated bionic optical compound eye are closely relevant to the length of the cylindrical waveguide. By applying the bionic optical compound eye of the integrated structure to a photoelectric detection system, a photoelectronic imaging system and the like, the system size can be reduced, the system weight is reduced, and complexity of coupling of the bionic optical compound eye with an image sensor or a photoelectric detector can be reduced.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Ultra-wide-field lens
ActiveCN107121757AShorten the lengthGuaranteed color reproductionOptical elementsOphthalmologyOptical axis
The invention provides an ultra-wide-field lens. The ultra-wide-field lens comprises a first lens, a second lens, a third lens, a fourth lens, a fifth lens, a sixth lens and a seventh lens which are successively configured from an object side to an image side along an optic axis ; the first lens, the second lens and the third lens are respectively of a meniscus lens with negative power, and a concave surface of the first lens, the second lens and the third lens faces the image side; both the fourth lens and the fifth lens are respectively of a thick lens with positive power; the third lens and the fourth lens are cemented together; the sixth lens is a biconcave thin lens with negative power; and the seventh lens is a meniscus lens with positive power, and a concave surface of the seventh lens faces the image side. By adopting a reasonable optical structure, when the ultra-wide-field lens is applied to different types of mobile phones for shooting, a focal length equivalent silent frame is 11mm, an imaging angle range is 120 to 126 degrees, a greater range can be photographed in a same distance, and a higher picture quality can be achieved; and moreover, the overall size is relatively small, the structure is simple, and the cost is lower.
Owner:中山市思创光电科技有限公司
Imaging apparatus and image sensor including the same
An image sensor includes a substrate, thin lenses disposed on a first surface of the substrate and configured to concentrate lights incident on the first surface, and light-sensing cells disposed on a second surface of the substrate, the second surface facing the first surface, and the light-sensing cells being configured to sense lights passing through the thin lenses, and generate electrical signals based on the sensed lights. A first thin lens and second thin lens of the thin lenses are configured to concentrate a first light and a second light, respectively, of the incident lights onto the light-sensing cells, the first light having a different wavelength than the second light.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Optical lens assembly for capturing images and image capture device therewith
ActiveUS20130308033A1Increased costThinning tendencyTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptical axisPrism
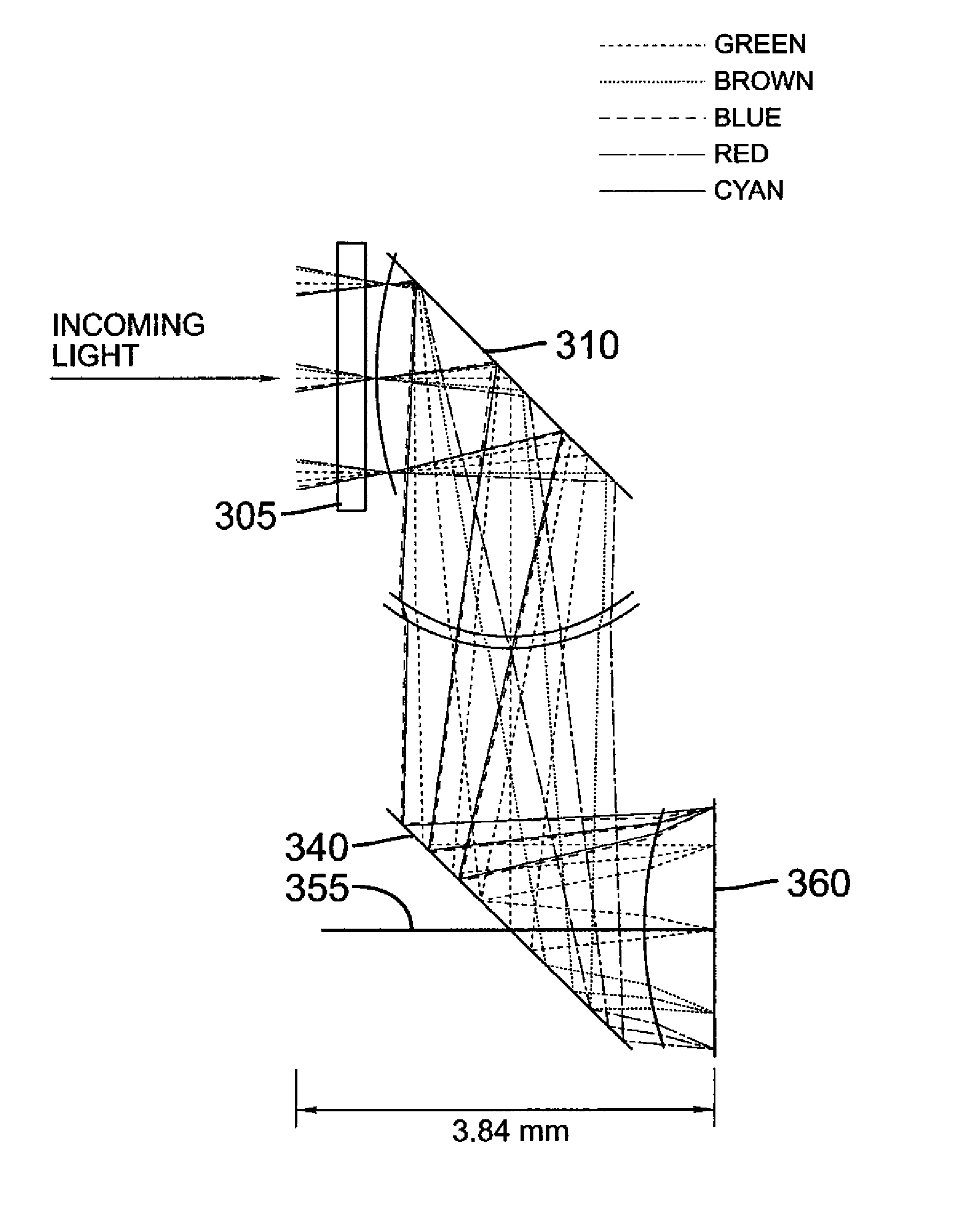
The invention is an optical lens assembly for capturing images and an image capture device therewith. The optical lens assembly for capturing images includes, along an optical axis, a total reflection prism, a first lens group having negative focal power, wherein the first lens group comprises a lens having negative focal power, a second lens group having positive focal power, wherein the second lens group comprises at least one lens having an aspherical optical surface, a third lens group having positive focal power, wherein the third lens group comprises at least one lens having positive focal power and at least one lens having negative focal power, and a fourth lens group having positive focal power, wherein the fourth lens group comprises at least one lens having an aspherical optical surface. Thereby, the aberration can be improved and a thin lens module for capturing images can be achieved.
Owner:ALTEK CORP
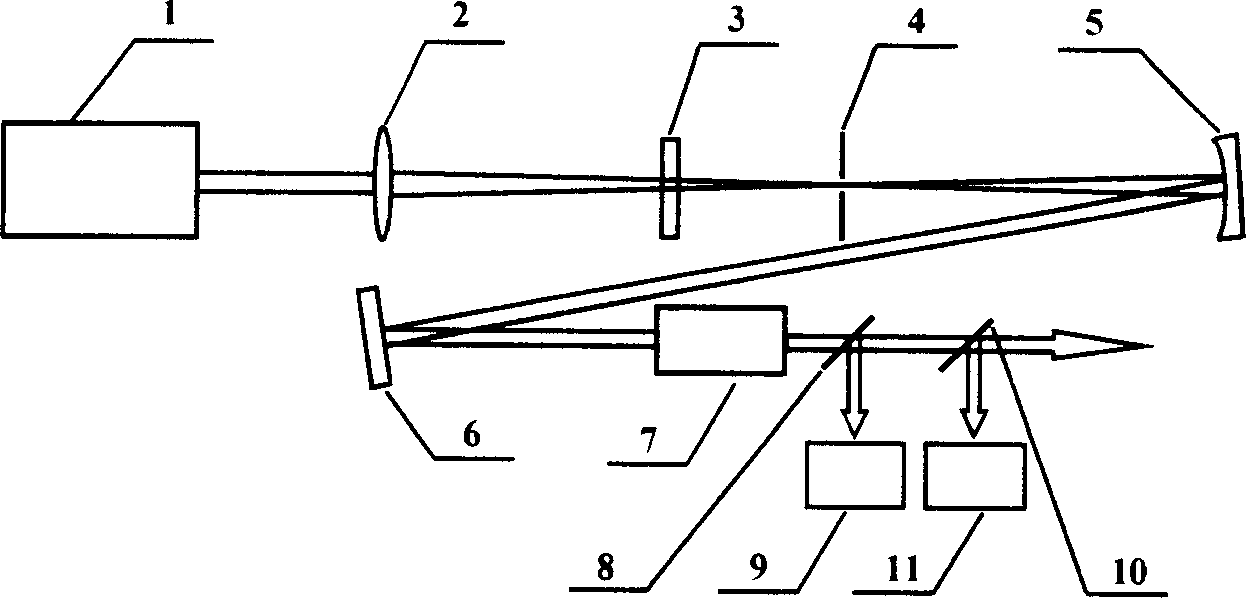
High-energy fly secondary laser pulse outside cavity compressor
InactiveCN1889311AReduce lossesWith transient non-linear characteristicsOptical resonator shape and constructionNon-linear opticsBeam splittingHigh energy
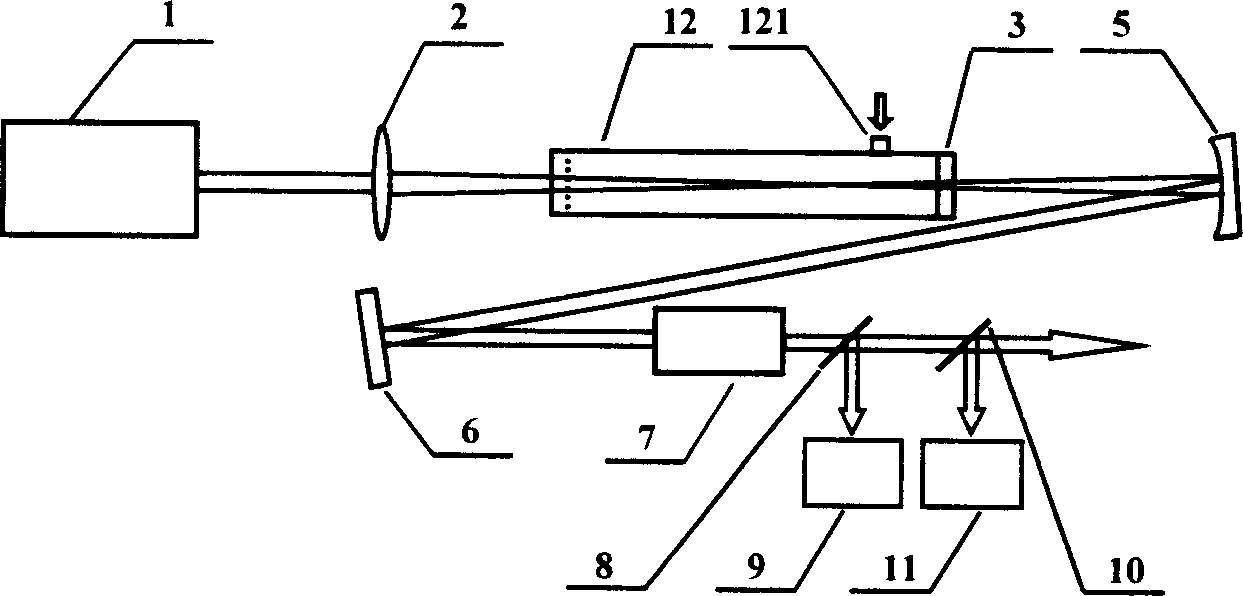
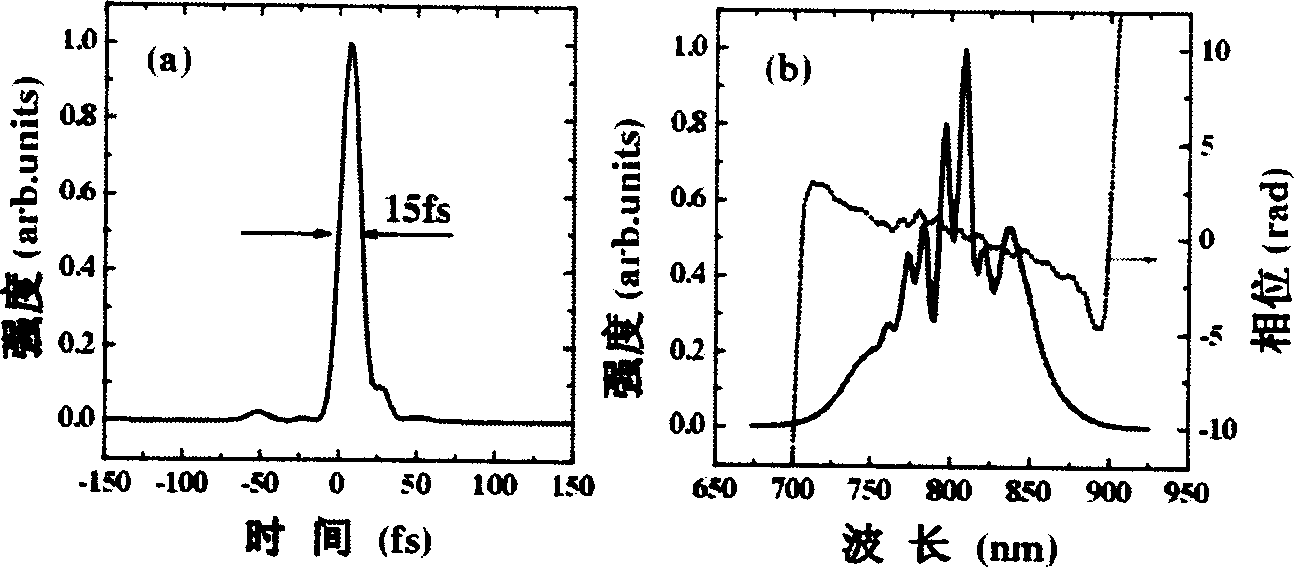
A high energy femtosecond laser pulse outer cavity compression arrangement includes one laser amplifier system, thin lens, pulse compression unit, silvering concave mirror, silvering plane reflection mirror, dispersion compensating element, first broadband beam splitting piece, second broadband beam splitting piece, spectrograph, and pulse measurement instrument. It features said pulse compression unit consisting of solid material and vacuum tube, said solid material being used as vacuum tube back light piece and integrated forming, said vacuum tube side wall having inflation port. Said invented device can avoid damage to filter in high-energy pulse incidence state, suitable for large range energy femtosecond laser pulse compression, different wave band incident pulse, and linear polarization and circular polarization incident pulse.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Particle Detection Using Thin Lenses
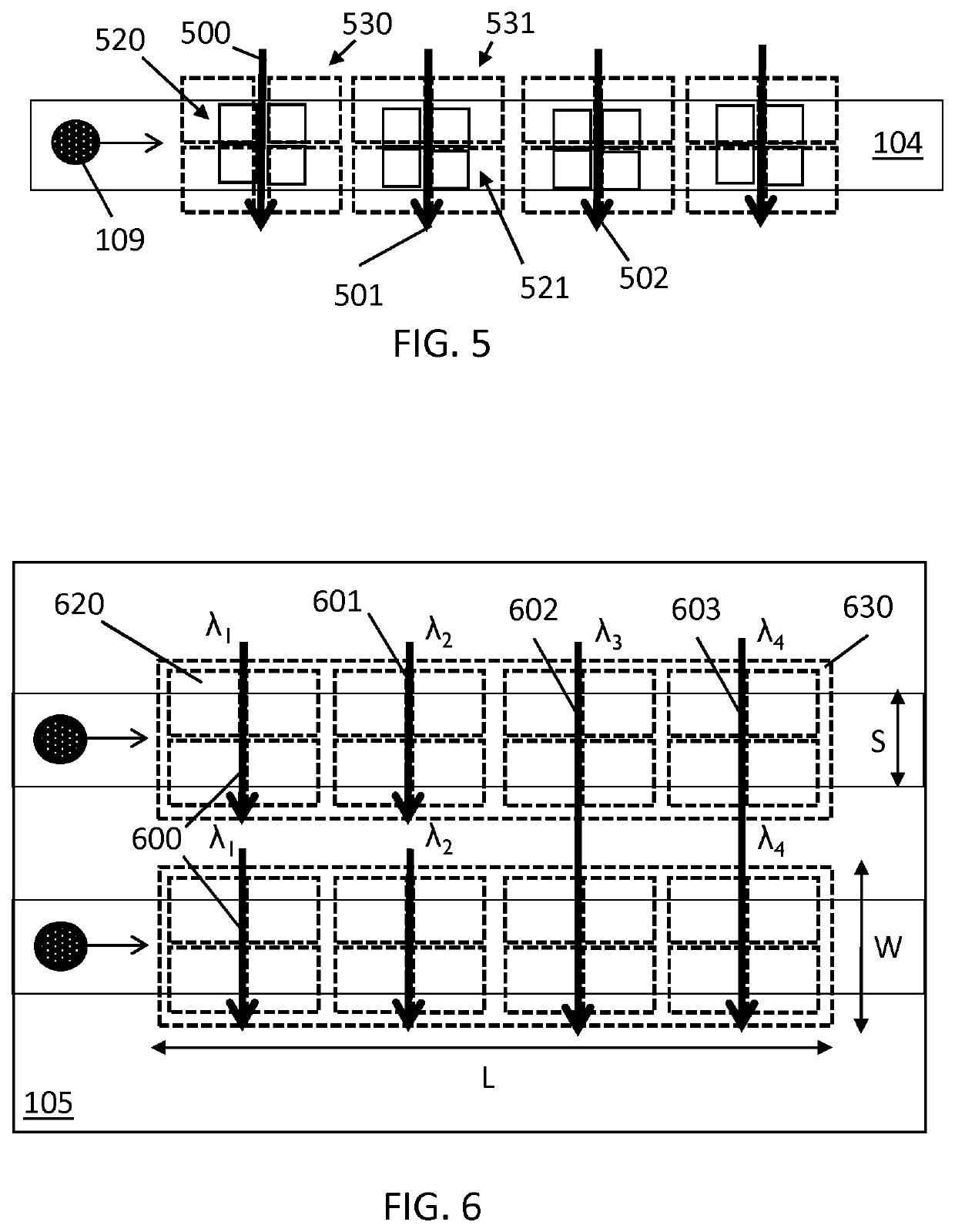
ActiveUS20200018684A1Fast and reliable and compactEfficient analysisScattering properties measurementsIndividual particle analysisEngineeringThin lens
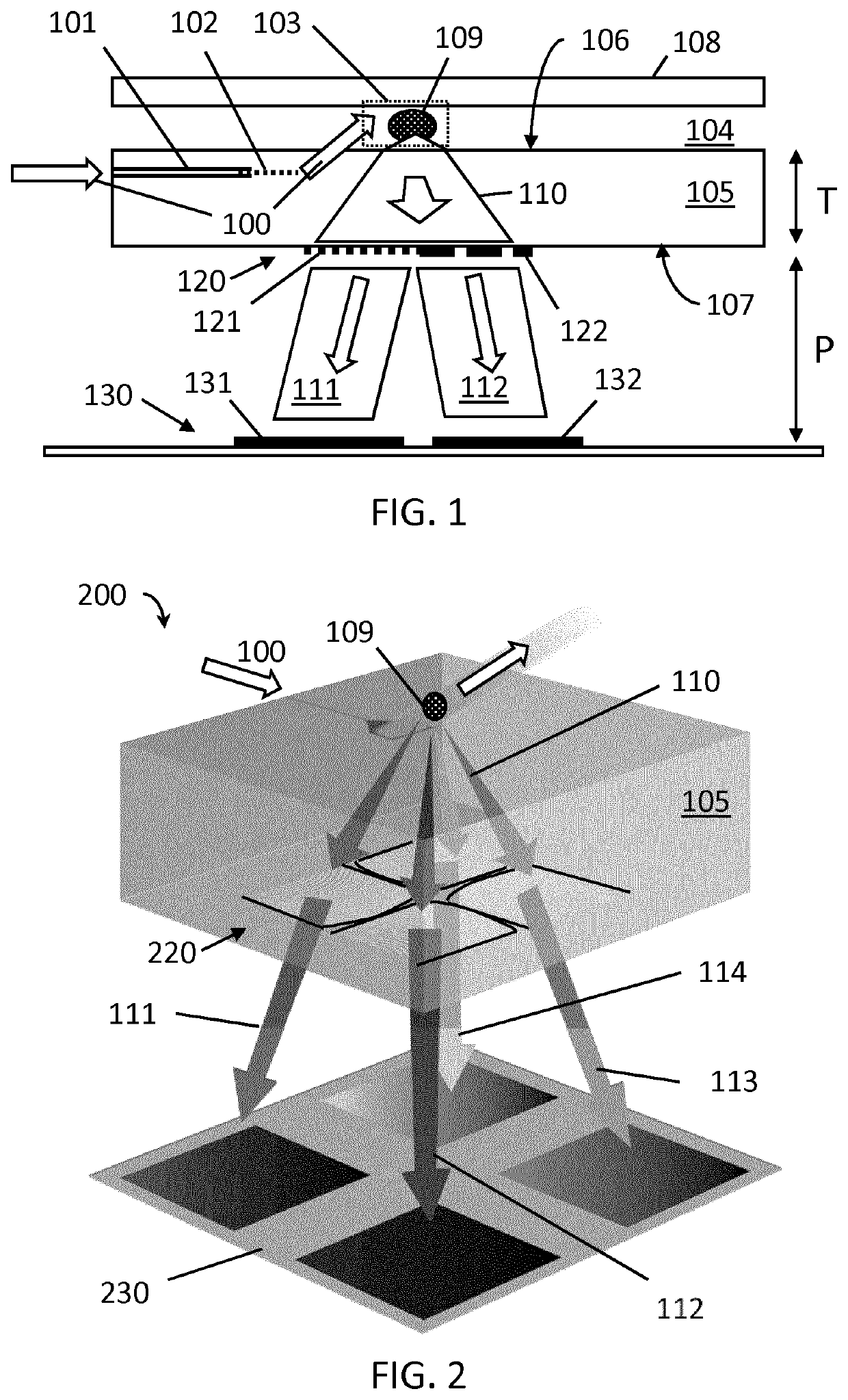
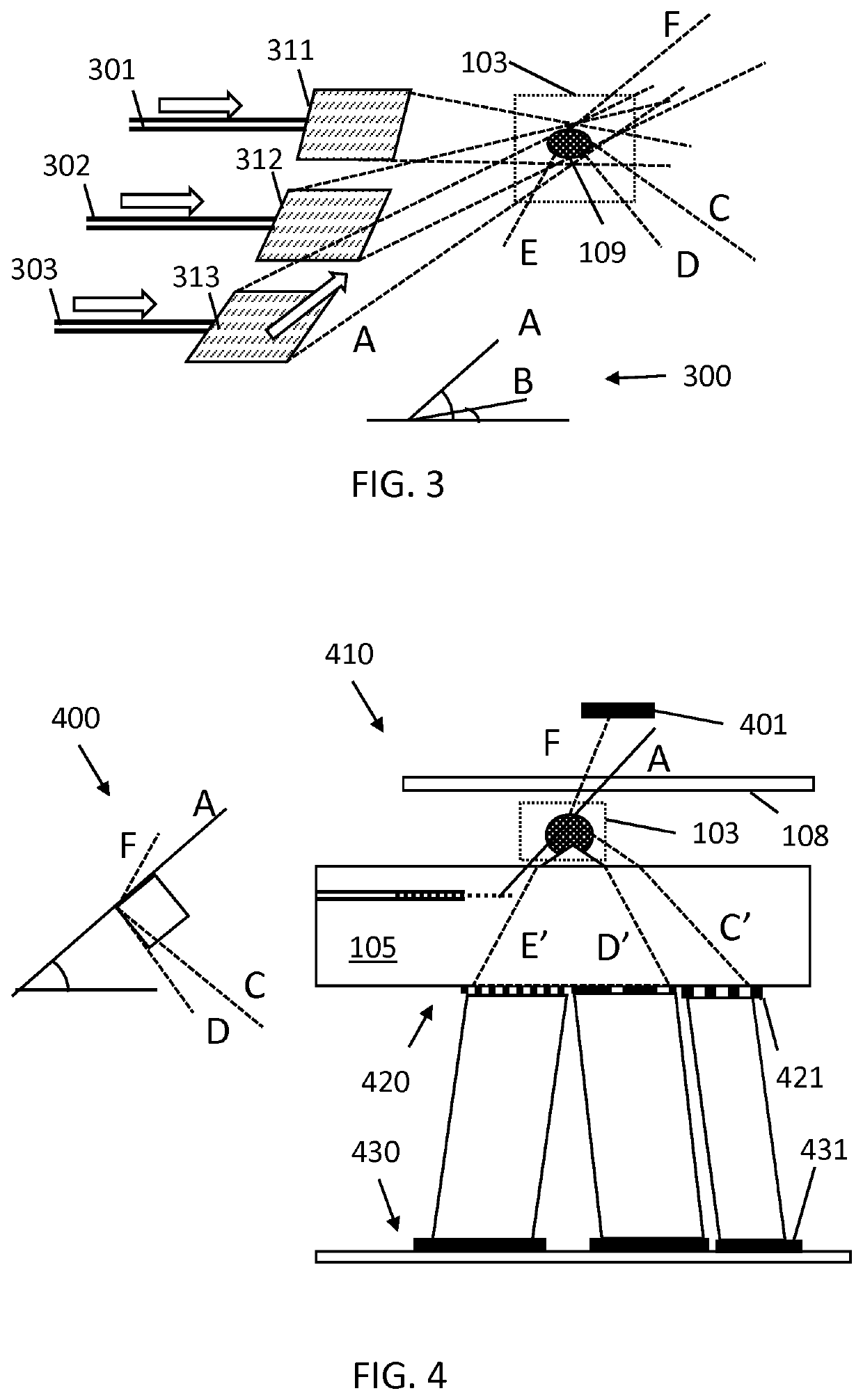
An optical excitation system comprises a substrate (105) comprising at least one delivery means (104), for delivering analytes (109) into at least one region of interest (103), at least one radiation carrier (101) for directing at least one radiation beam from the at least one radiation carrier (101) into the at least one region of interest (103). The substrate (105) includes a thin lens system (120) comprising at least a first thin lens (121), for collimating radiation from the at least one region of interest (103) to a remote detection system (130). A particle sensor and sensing system comprising the excitation system are also provided, for example a modular particle sensor and modular sensing system, wherein the optical excitation system may be single use and disposable.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
Analysis method, verification system and verification method of laser echo transmission characteristic
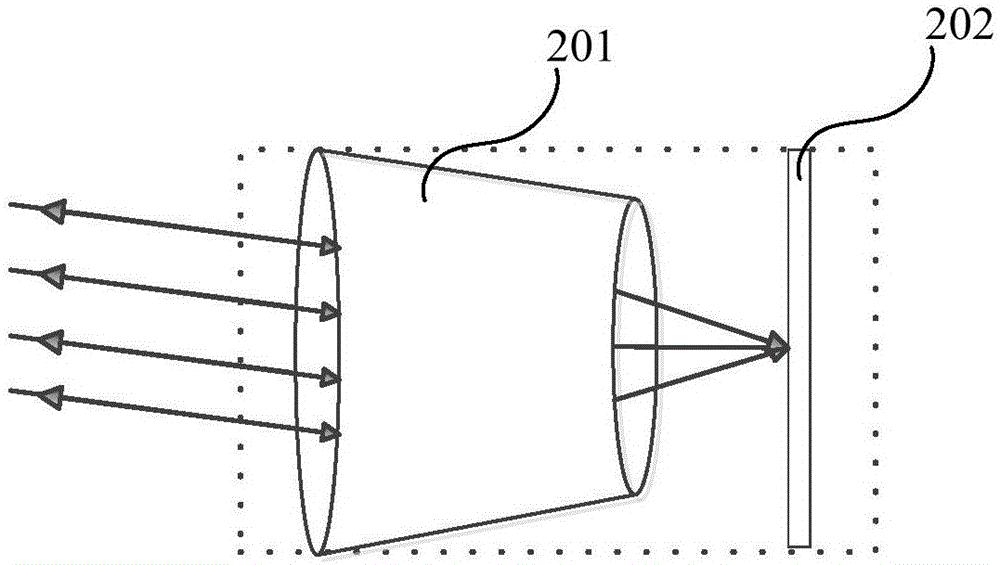
InactiveCN106443638AHigh application valueHigh research valueWave based measurement systemsVerification systemMatrix optics
The embodiment of the invention discloses an analysis method, verification system and verification method of a laser echo transmission characteristic. The analysis method includes the steps: enabling a cat-eye system to be equivalent to a thin lens and a reflector, and enabling the transmission process of a gauss beam irradiation cat-eye system to be equivalent to a 4f system with defocusing amount; utilizing matrix optics to analyze the 4f system to obtain a transmission matrix of the gauss beam irradiation cat-eye system; according to the transmission matrix, an ABCD law of the gauss beam, the transformation rule of a q parameter, and an input parameter of the gauss beam, obtaining a light spot radius of a reflected light beam; and according to the relationship between the divergence angle of the reflected light beam and the light spot radius of the reflected light beam, obtaining the relationship between the divergence angle of the reflected light beam and the defocusing amount. The analysis method of a laser echo transmission characteristic can reveal the rule about influence of the defocusing amount on the cat-eye echo divergence angle, can get a more accurate analysis result compared with the analysis result based on geometrical optics, and has very high application value and research value.
Owner:RUN TECH CO LTD BEIJING
Imaging apparatus and image sensor including the same
An image sensor includes a substrate, thin lenses disposed on a first surface of the substrate and configured to concentrate lights incident on the first surface, and light-sensing cells disposed on a second surface of the substrate, the second surface facing the first surface, and the light-sensing cells being configured to sense lights passing through the thin lenses, and generate electrical signals based on the sensed lights. A first thin lens and second thin lens of the thin lenses are configured to concentrate a first light and a second light, respectively, of the incident lights onto the light-sensing cells, the first light having a different wavelength than the second light.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Imaging apparatus and image sensor including the same
An image sensor includes a substrate, thin lenses disposed on a first surface of the substrate and configured to concentrate lights incident on the first surface, and light-sensing cells disposed on a second surface of the substrate, the second surface facing the first surface, and the light-sensing cells being configured to sense lights passing through the thin lenses, and generate electrical signals based on the sensed lights. A first thin lens and second thin lens of the thin lenses are configured to concentrate a first light and a second light, respectively, of the incident lights onto the light-sensing cells, the first light having a different wavelength than the second light.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Power prism for folded lenses
ActiveUS20200073028A1Lower Z heightReduce the Z-height of a cameraPrismsOptical articlesWaferingDialyte lens
An optical power prism that may be used in folded lens systems that consists of a glass prism and a glass lens attached to a surface of the prism using a thin layer of optical glue or by optical contact. The glass lens does not have a flange and thus the prism can be smaller than prisms used in conventional power prisms with the same lens effective area, thus reducing the Z-height of the power prism when compared to conventional power prisms. An optical glass may be used for the lens that has a higher refractive index than can be provided by optical plastic which allows the lens to be thinner than plastic lenses. The lenses may be formed by molding a glass wafer to form lens shapes on a first surface of the wafer; the molded wafer is then ground from a second surface to singulate the lenses.
Owner:APPLE INC
Thin lens
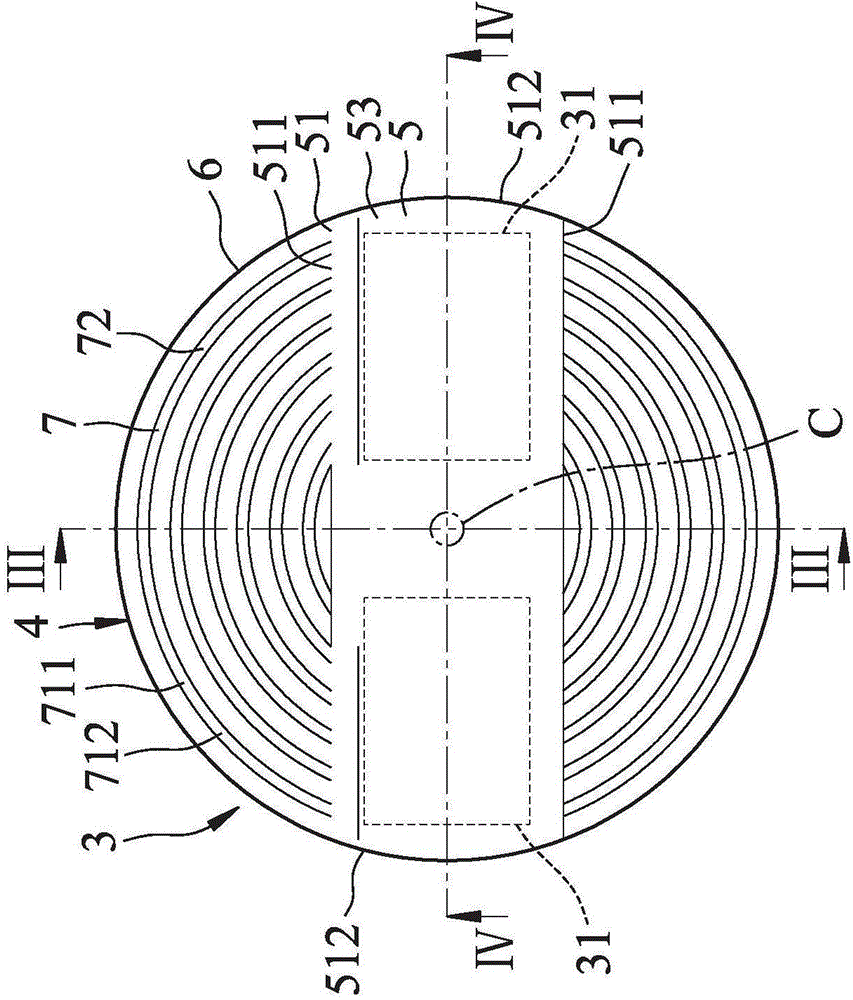
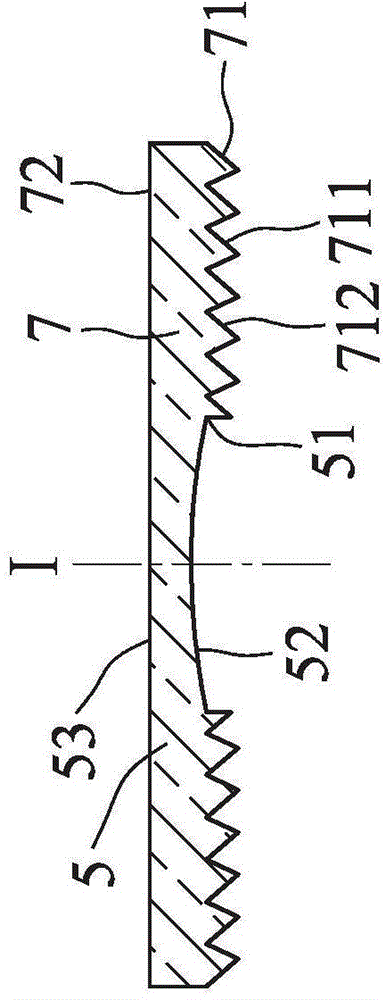
InactiveCN105676323AImprove light extraction efficiencyReduce lossesPoint-like light sourceLensEngineeringRoad surface
The invention relates to a lens, and especially relates to a lens for lighting. The lens comprises a curved surface part, an outer periphery and a toothed grain part. The curved part in the center region includes at least one curved surface, and the outer contour of the curved surface part is non-circular. The outer periphery surrounds the curved surface part. The toothed grain part between the curved surface part and the outer periphery includes a concave-convex grain area. The concave-convex grain area is provided with a concave-convex grain surface which extends outward around a center, and the center of the concave-convex grain area is in the center region. The beneficial effect is that through combination of the curved surface part and the toothed grain part, a uniform light mixing effect is achieved, and wide-angle light can be converged to improve the intensity of illumination in the center. The curved surface part can improve the light output efficiency and reduce light loss.
Owner:GENIUS ELECTRONICS OPTICAL CO LTD
Zooming apparatus of long-distance large-range semiconductor laser lighting device
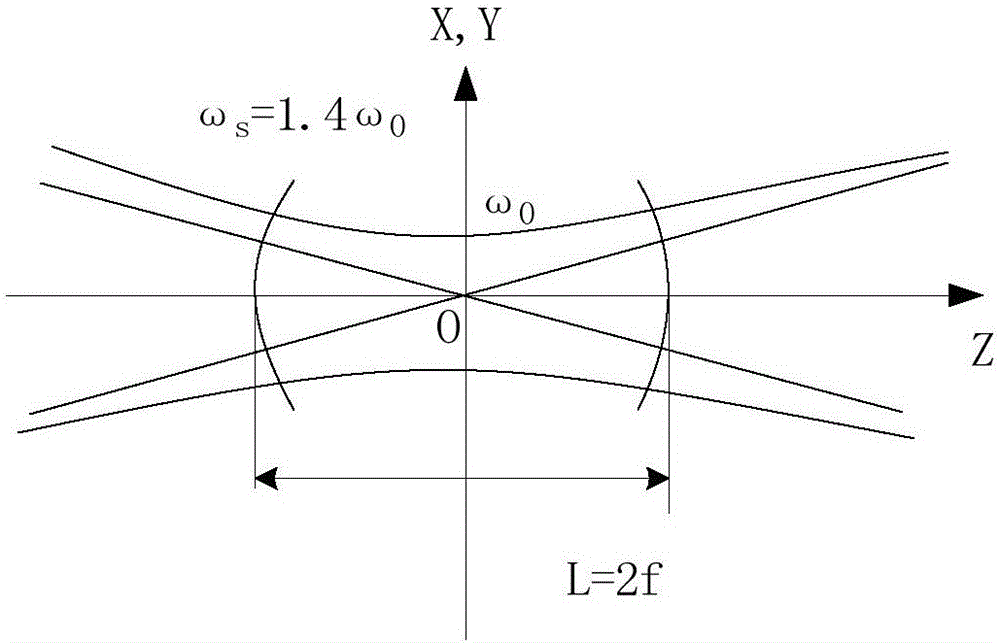
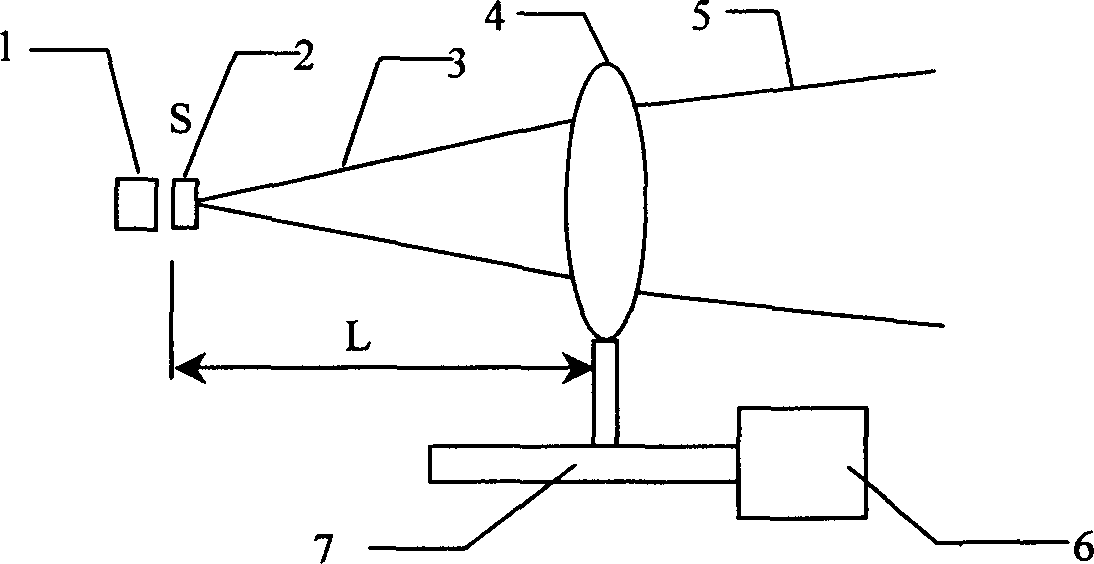
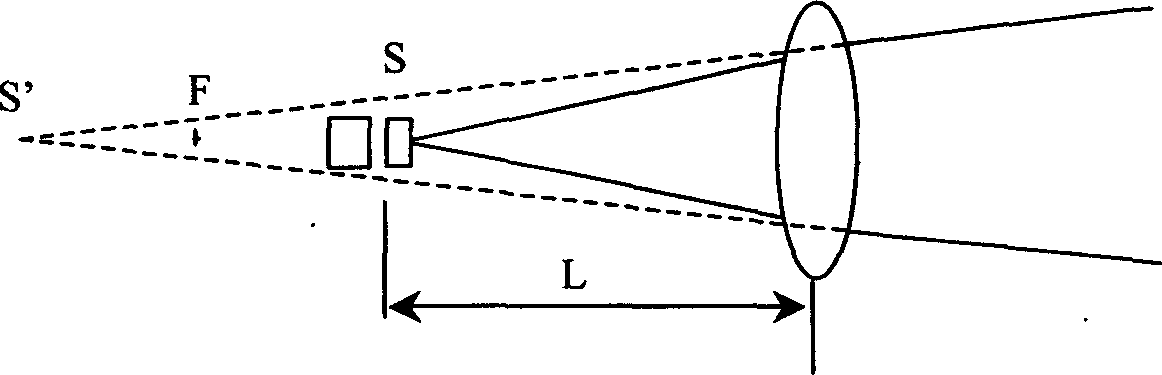
The invention relates to an application technique of semi-conductor laser, especially providing a semi-conductor laser lighting variable-focus device used in remote distance and wide range, wherein the invention comprises a semi-conductor laser; it is characterized in that: the front of laser is arranged with rectify light device, the thin lens group with positive refraction, the rectified light source S at the light axis of thin lens group, and the distance L between thin lens groups between 0 and f, while f is the focus of thin lens group; the lower end of thin lens group is arranged with mechanical transmission device connected to motor. The invention can electrically control the lighting angle and realize wide variation, with small volume and low cost.
Owner:山东神戎电子股份有限公司
Imaging apparatus and image sensor including the same
An image sensor includes a substrate, thin lenses disposed on a first surface of the substrate and configured to concentrate lights incident on the first surface, and light-sensing cells disposed on a second surface of the substrate, the second surface facing the first surface, and the light-sensing cells being configured to sense lights passing through the thin lenses, and generate electrical signals based on the sensed lights. A first thin lens and second thin lens of the thin lenses are configured to concentrate a first light and a second light, respectively, of the incident lights onto the light-sensing cells, the first light having a different wavelength than the second light.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com