Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
39 results about "Thermal effusivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
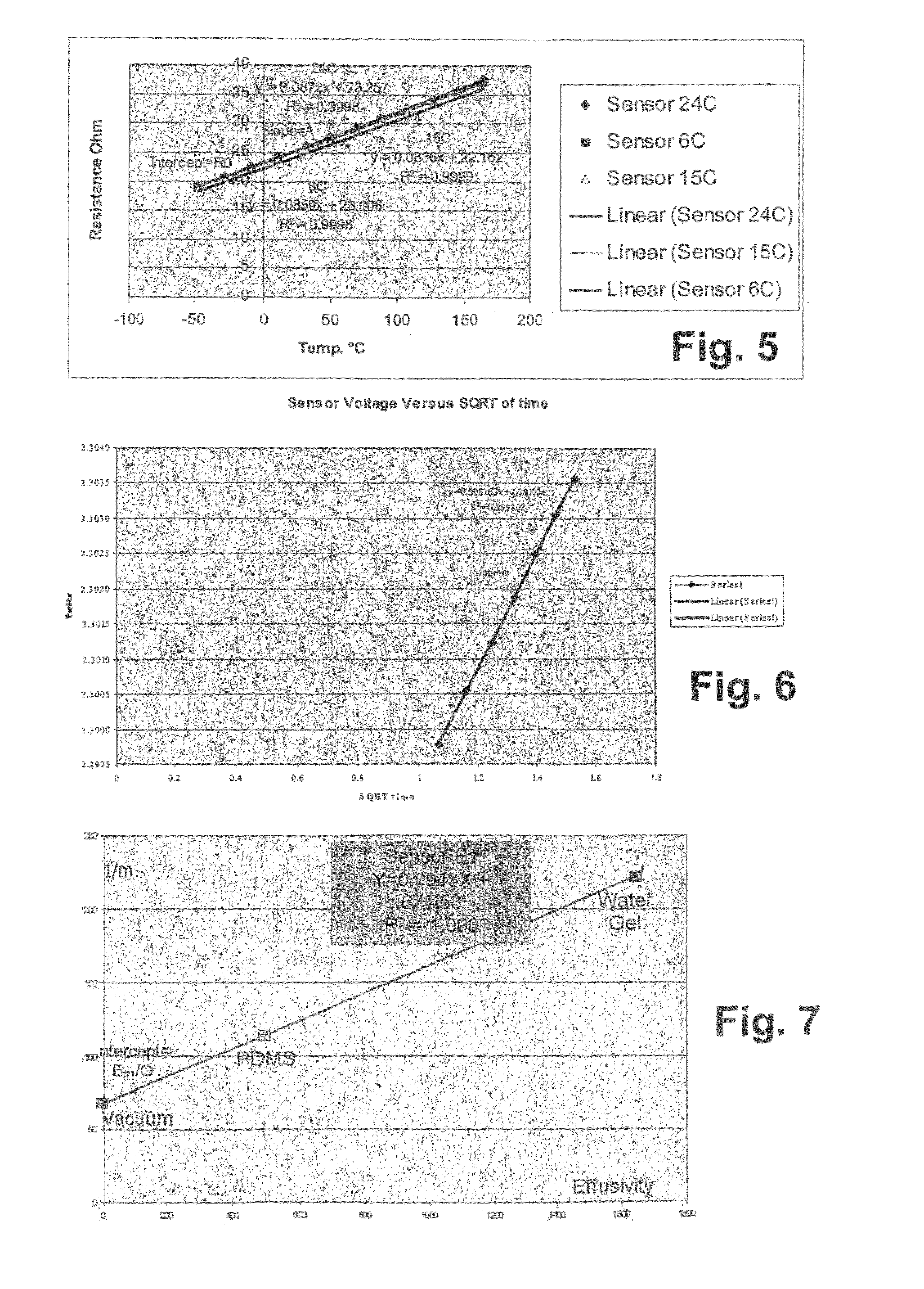
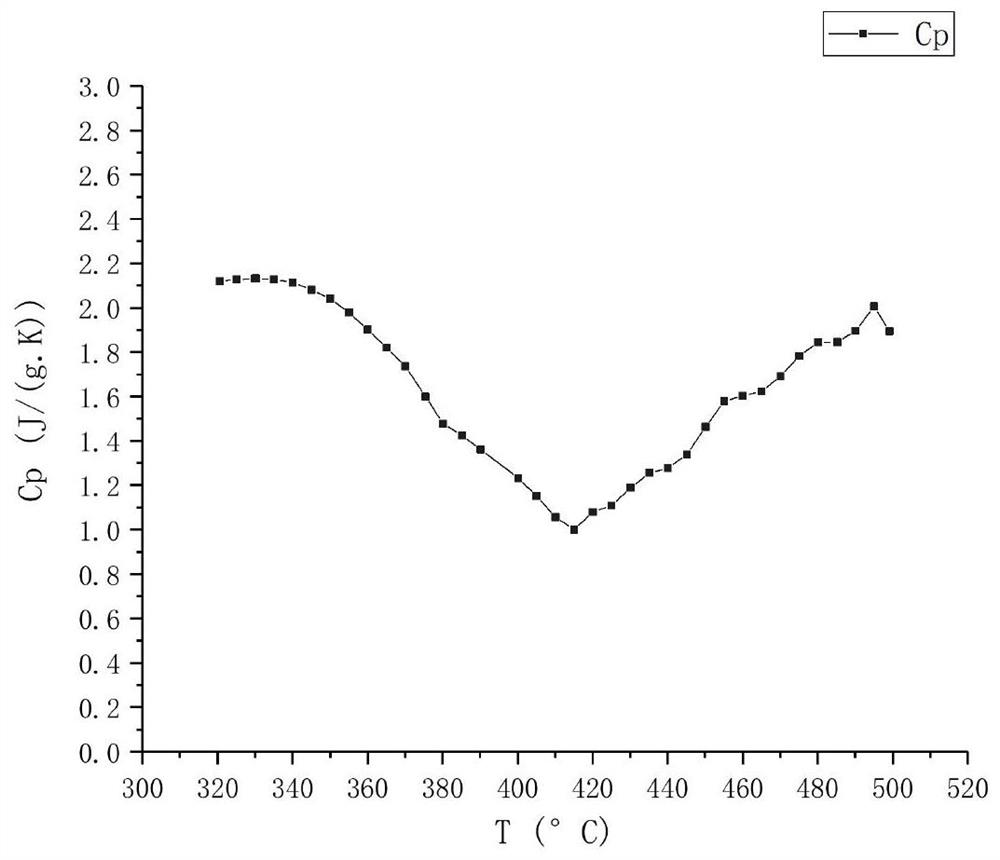
In thermodynamics, the thermal effusivity or thermal responsivity of a material is defined as the square root of the product of the material's thermal conductivity and its volumetric heat capacity. e=(λρcₚ)¹/² Here, λ is the thermal conductivity, ρ is the density and cₚ is the specific heat capacity. The product of ρ and cₚ is known as the volumetric heat capacity. A material's thermal effusivity is a measure of its ability to exchange thermal energy with its surroundings.
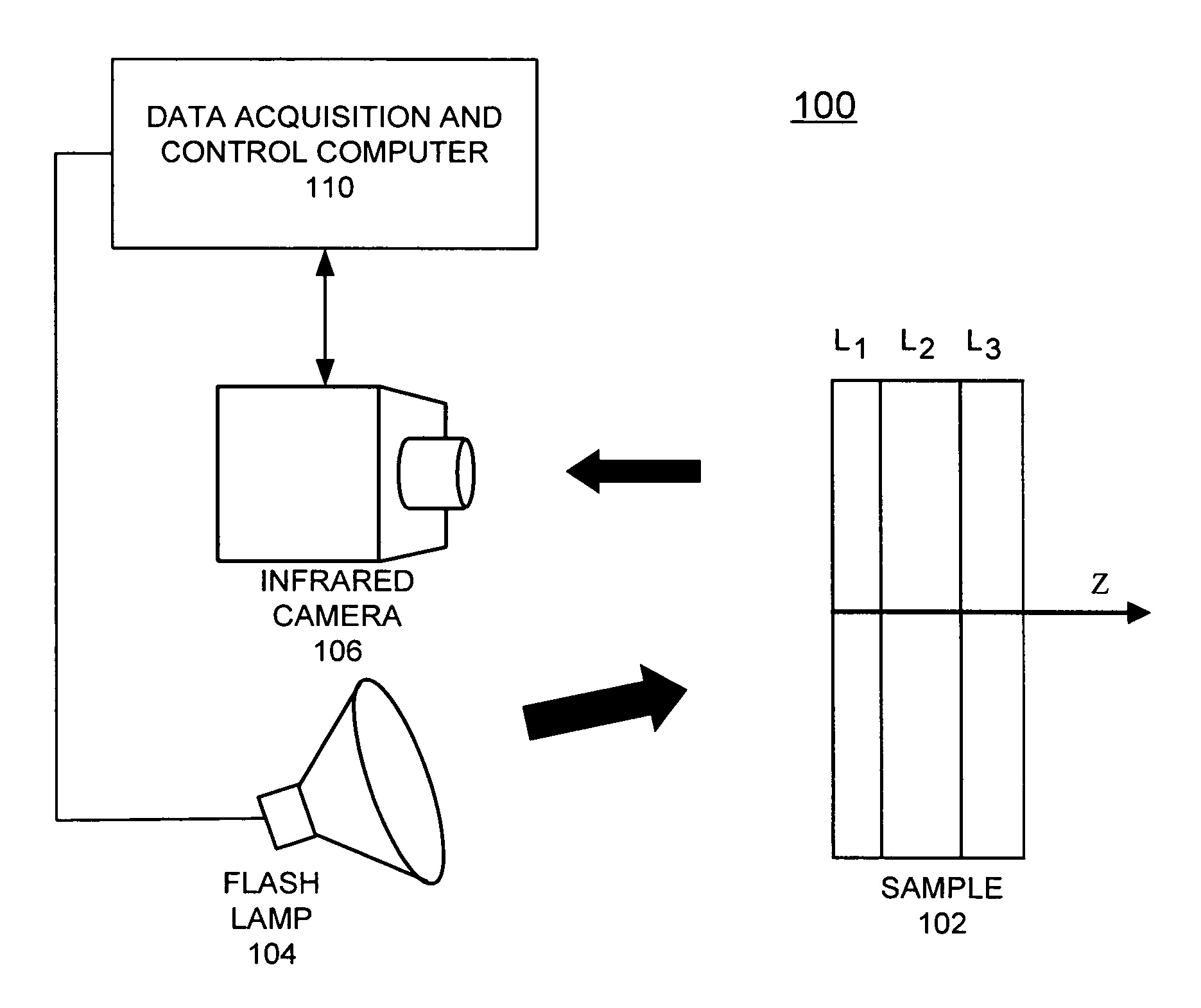
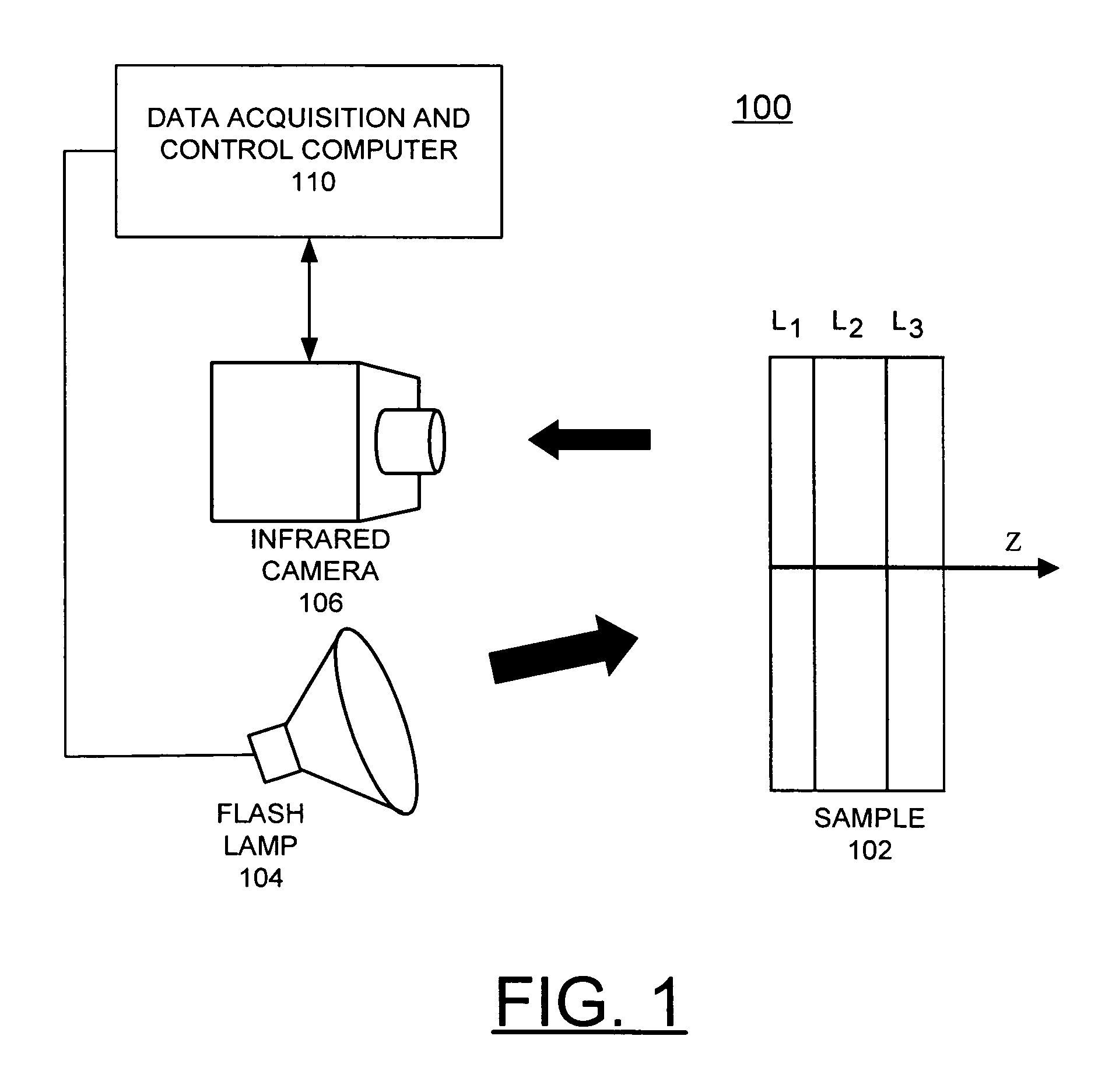
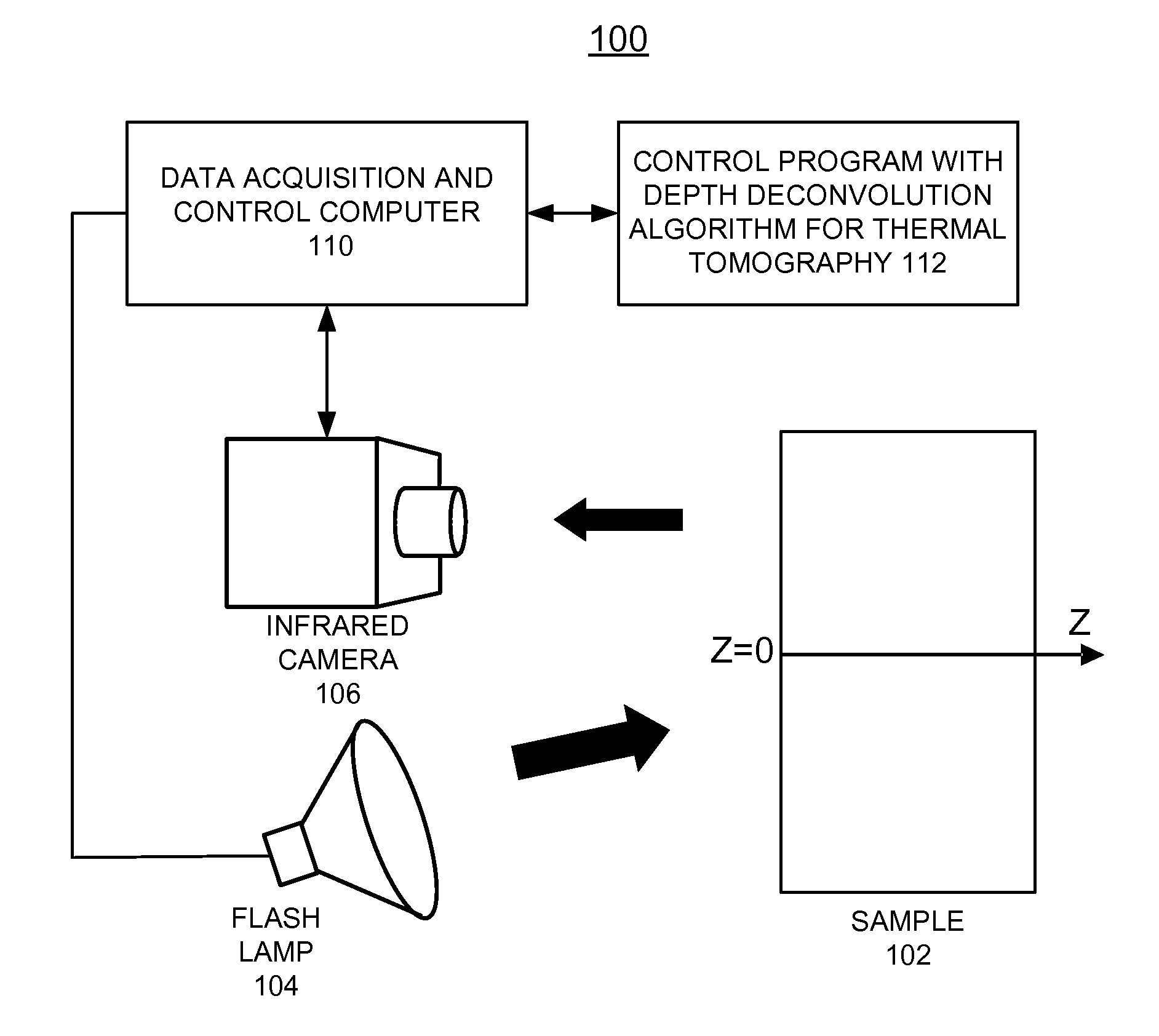
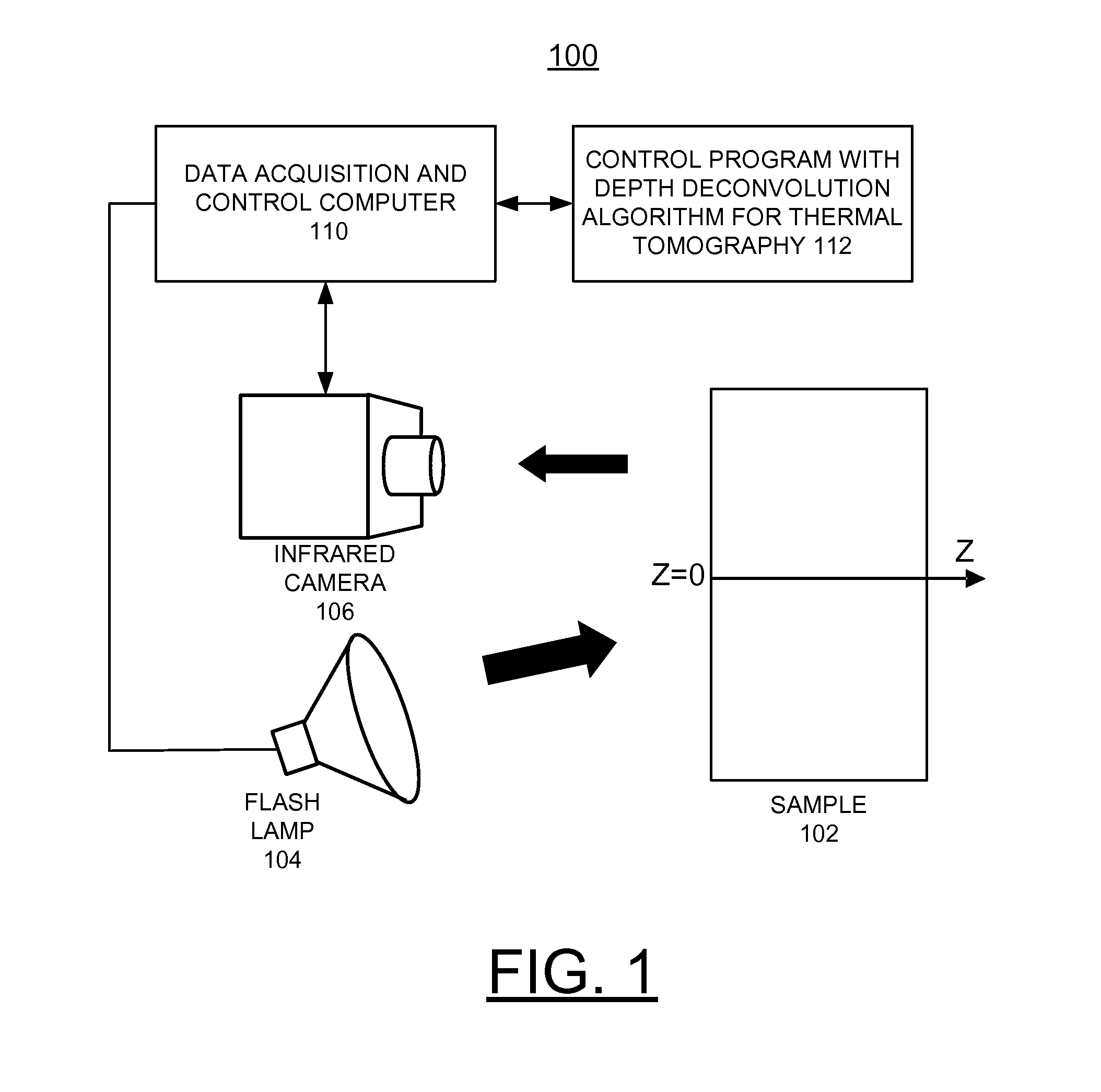
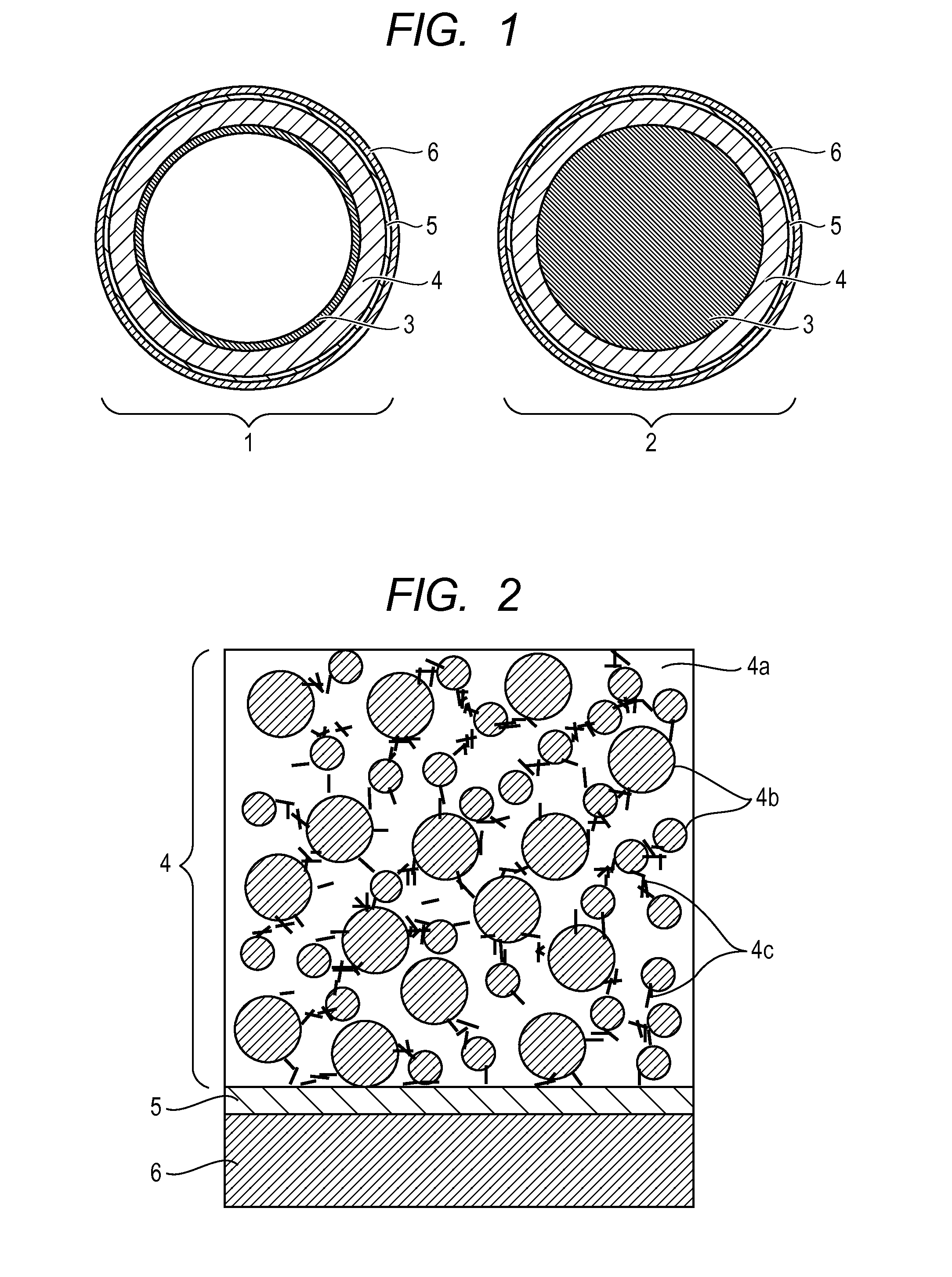
Method for thermal tomography of thermal effusivity from pulsed thermal imaging
ActiveUS7365330B1Improve imaging resolutionShort timeRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansPulse thermographyThermal energy
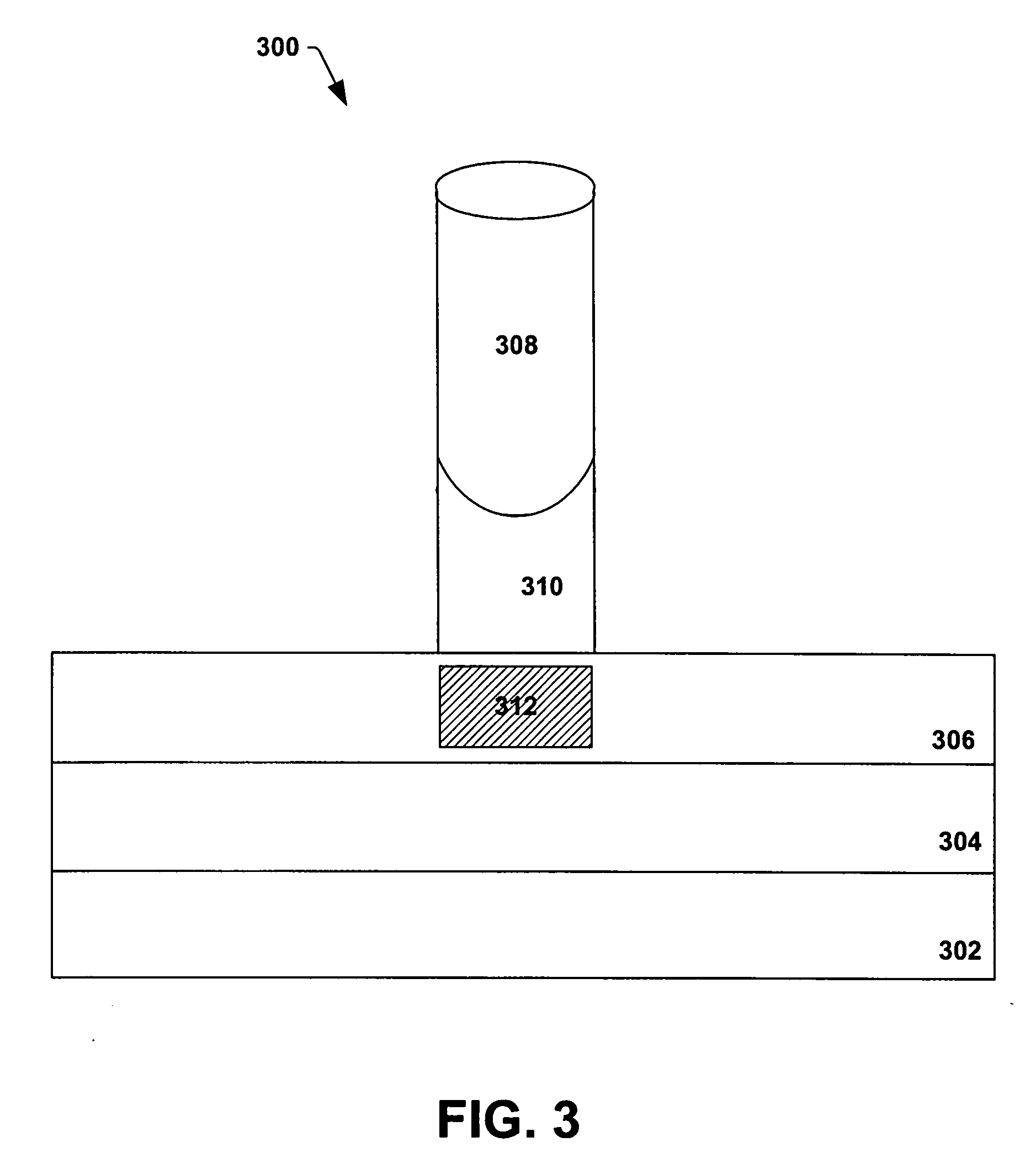
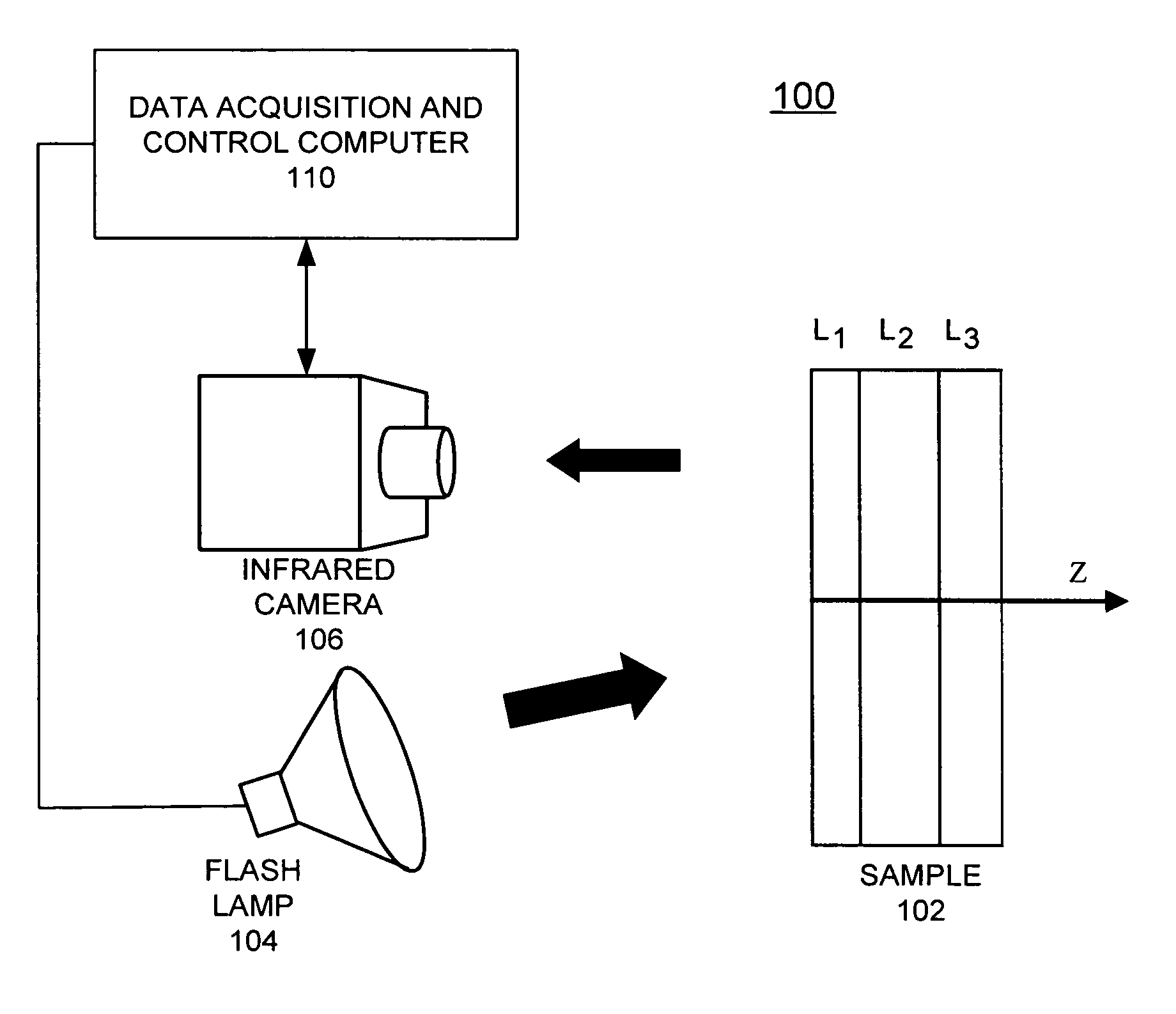
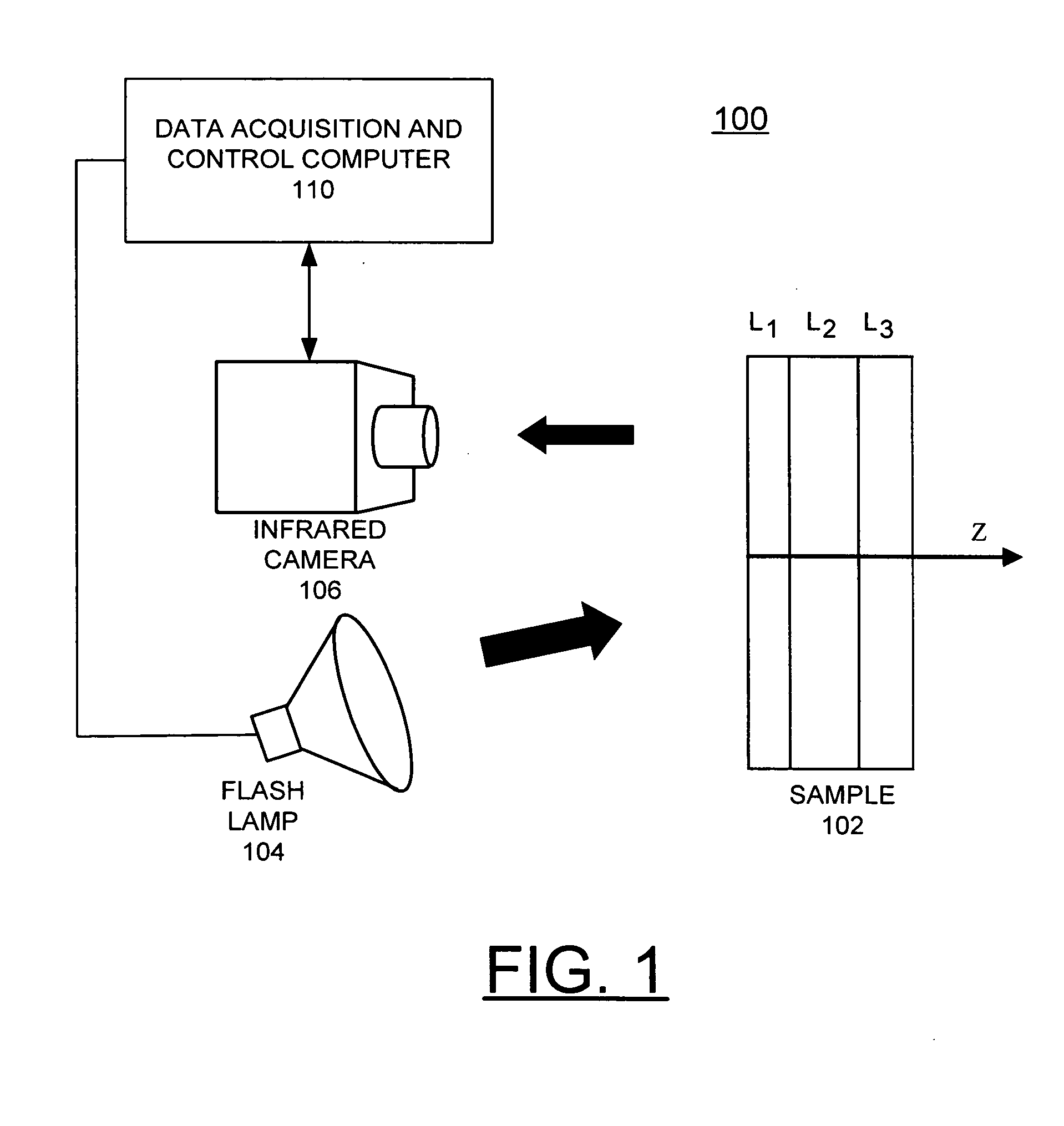
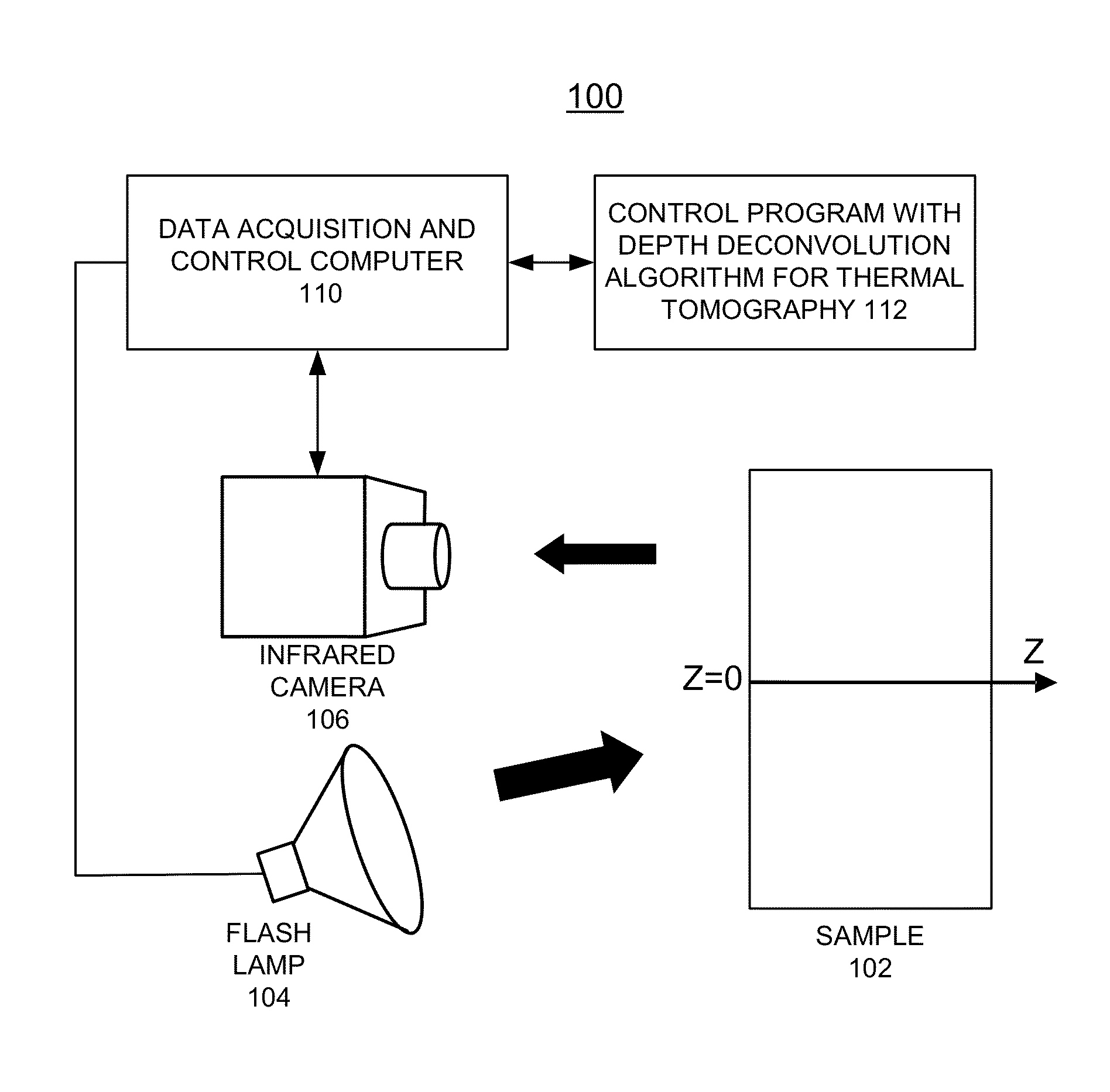
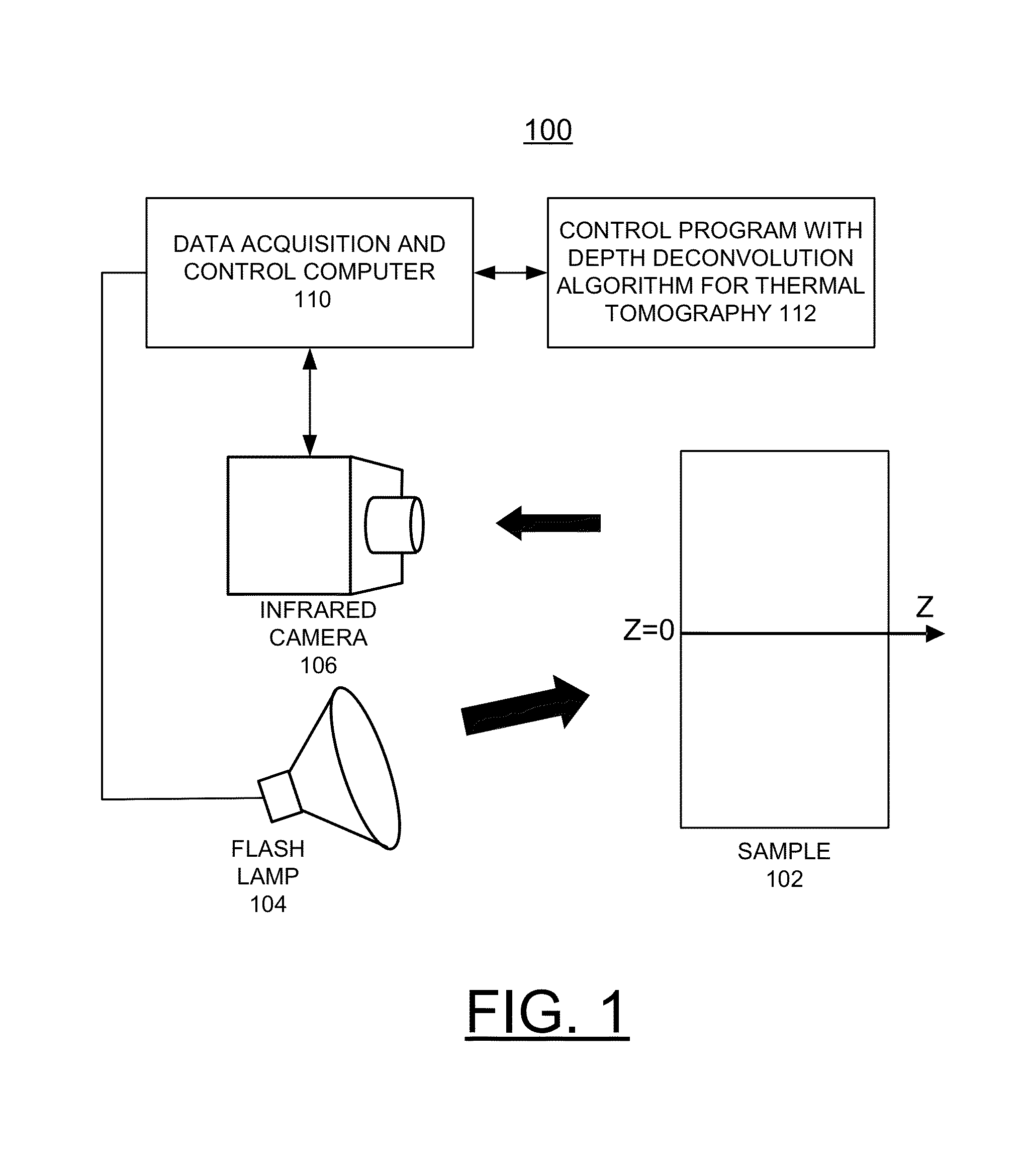
A computer-implemented method for automated thermal computed tomography includes providing an input of heat, for example, with a flash lamp, onto the surface of a sample. The amount of heat and the temperature rise necessary are dependent on the thermal conductivity and the thickness of the sample being inspected. An infrared camera takes a rapid series of thermal images of the surface of the article, at a selected rate, which can vary from 100 to 2000 frames per second. Each infrared frame tracks the thermal energy as it passes from the surface through the material. Once the infrared data is collected, a data acquisition and control computer processes the collected infrared data to form a three-dimensional (3D) thermal effusivity image.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
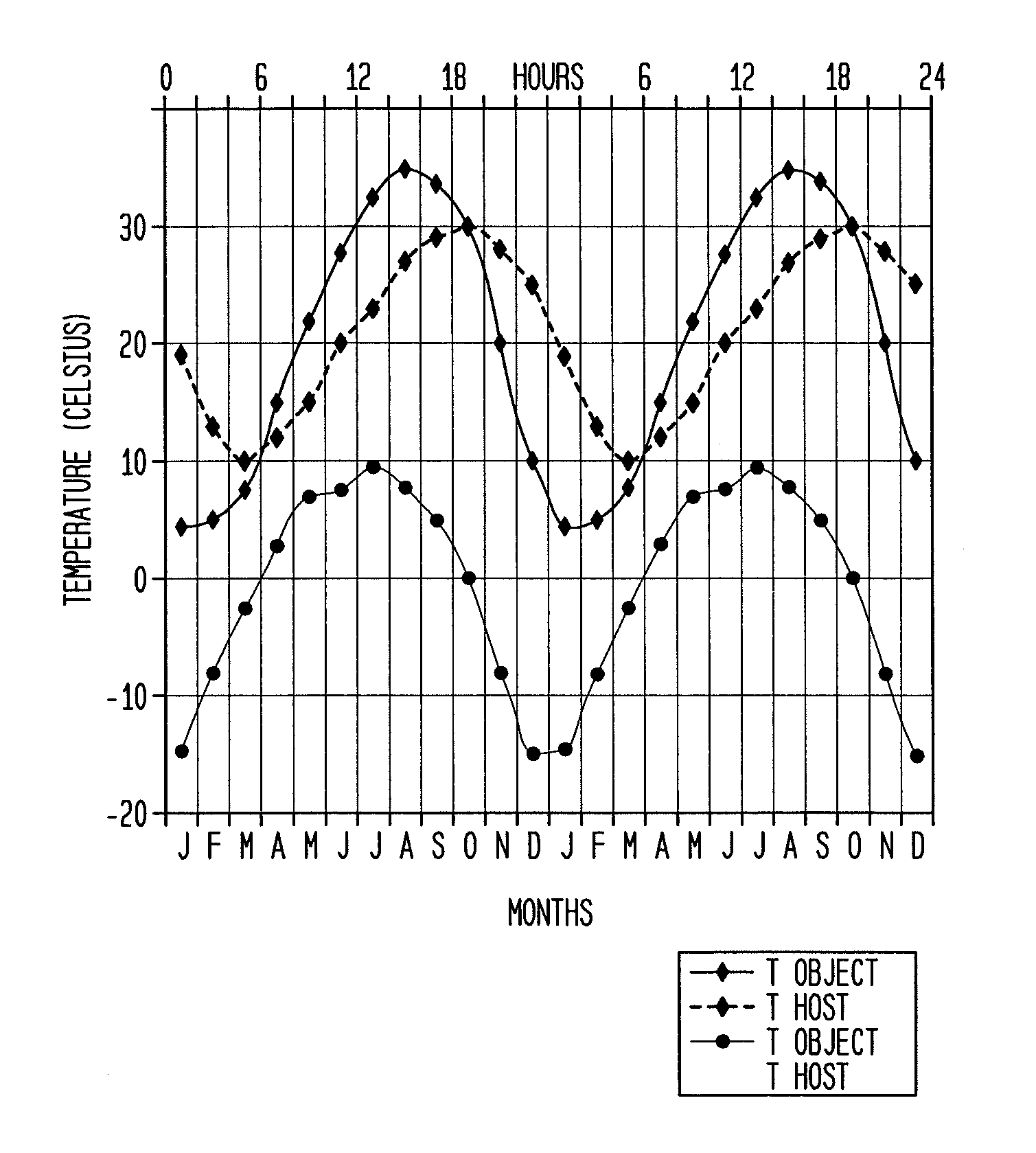
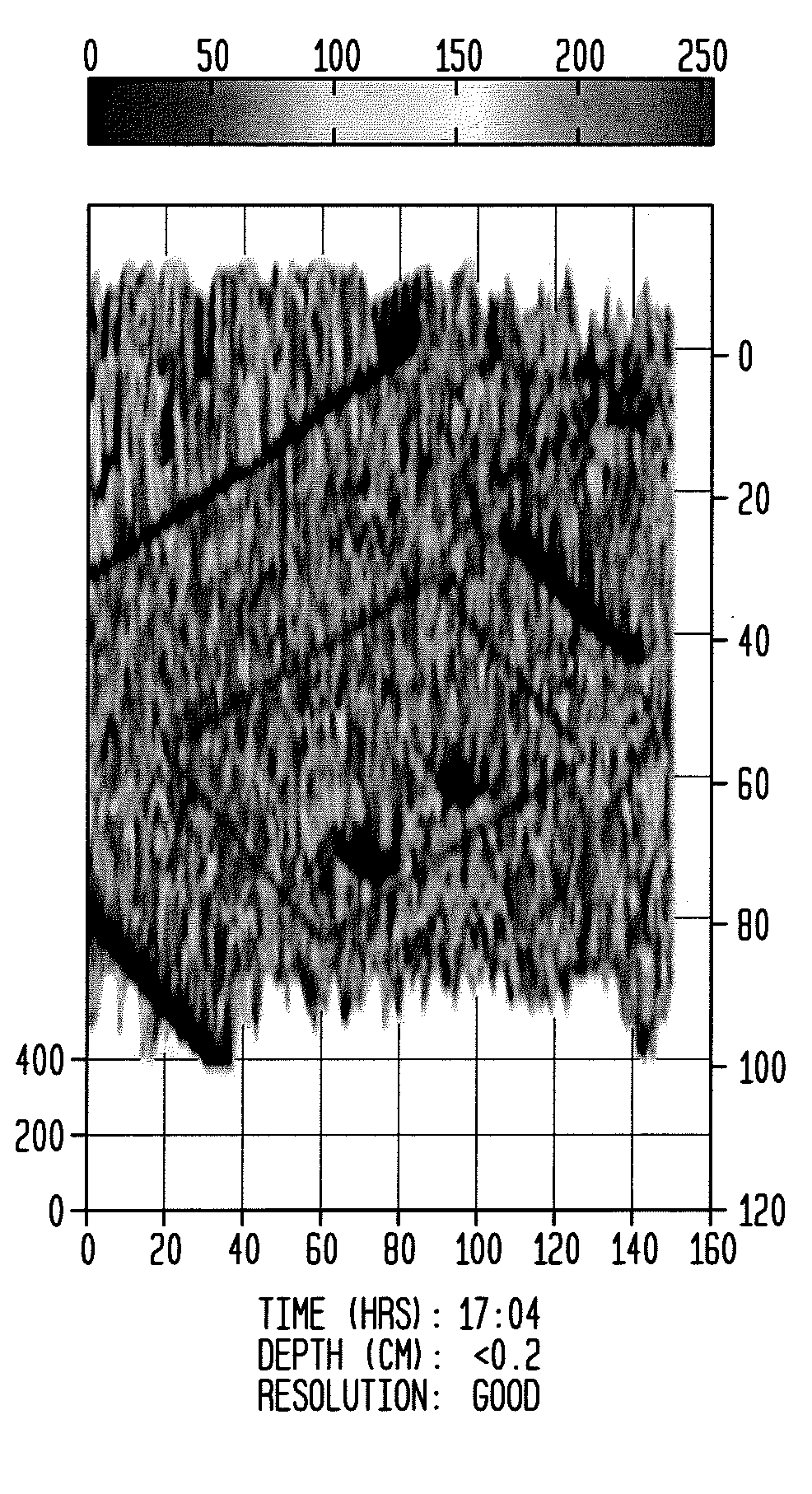
Temporal thermal imaging method for detecting subsurface objects and voids
ActiveUS8494220B2Easy to detectTime differenceThermometers using physical/chemical changesScene recognitionInfraredInfra-red color
A temporal thermal survey method to locate at a given area whether or not there is a subsurface object or void site. The method uses thermal inertia change detection. It locates temporal heat flows from naturally heated subsurface objects or faulty structures such as corrosion damage. The added value over earlier methods is the use of empirical methods to specify the optimum times for locating subsurface objects or voids amidst clutter and undisturbed host materials. Thermal inertia, or thermal effusivity, is the bulk material resistance to temperature change. Surface temperature highs and lows are shifted in time at the subsurface object or void site relative to the undisturbed host material sites. The Dual-band Infra-Red Effusivity Computed Tomography (DIRECT) method verifies the optimum two times to detect thermal inertia outliers at the subsurface object or void border with undisturbed host materials.
Owner:DEL GRANDE NANCY KERR
Thermal paper
ActiveUS20060122059A1Enhance layeringReduce heat transferAblative recordingThermographyPorosityThermal effusivity
The present invention provides a thermal paper composite precursor comprising (a) a substrate layer; and (b) a base layer positioned on the substrate layer, the base layer comprising a binder and at least one porosity improver wherein the thermal paper composite precursor has a thermal effusivity that is at least about 2% less than the thermal effusivity of porosity improver-less thermal paper composite precursor. The thermal paper composite precursor is useful in making thermal paper composite.
Owner:BASF CORP
Method for thermal tomography of thermal effusivity from pulsed thermal imaging
ActiveUS20080111078A1Improve imaging resolutionNo longer providedRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansPulse thermographyThermal tomography
A computer-implemented method for automated thermal computed tomography includes providing an input of heat, for example, with a flash lamp, onto the surface of a sample. The amount of heat and the temperature rise necessary are dependent on the thermal conductivity and the thickness of the sample being inspected. An infrared camera takes a rapid series of thermal images of the surface of the article, at a selected rate, which can vary from 100 to 2000 frames per second. Each infrared frame tracks the thermal energy as it passes from the surface through the material. Once the infrared data is collected, a data acquisition and control computer processes the collected infrared data to form a three-dimensional (3D) thermal effusivity image.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
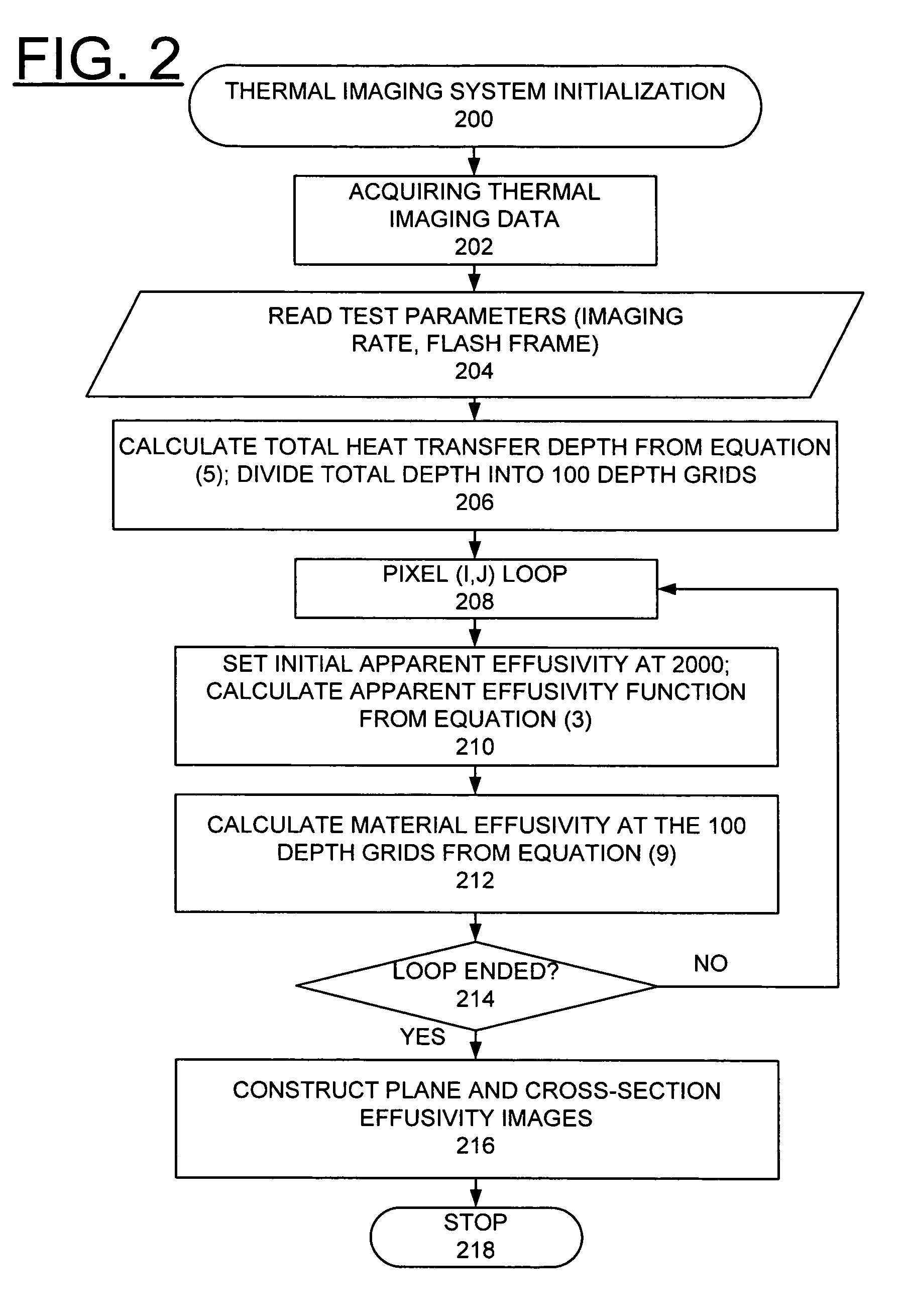
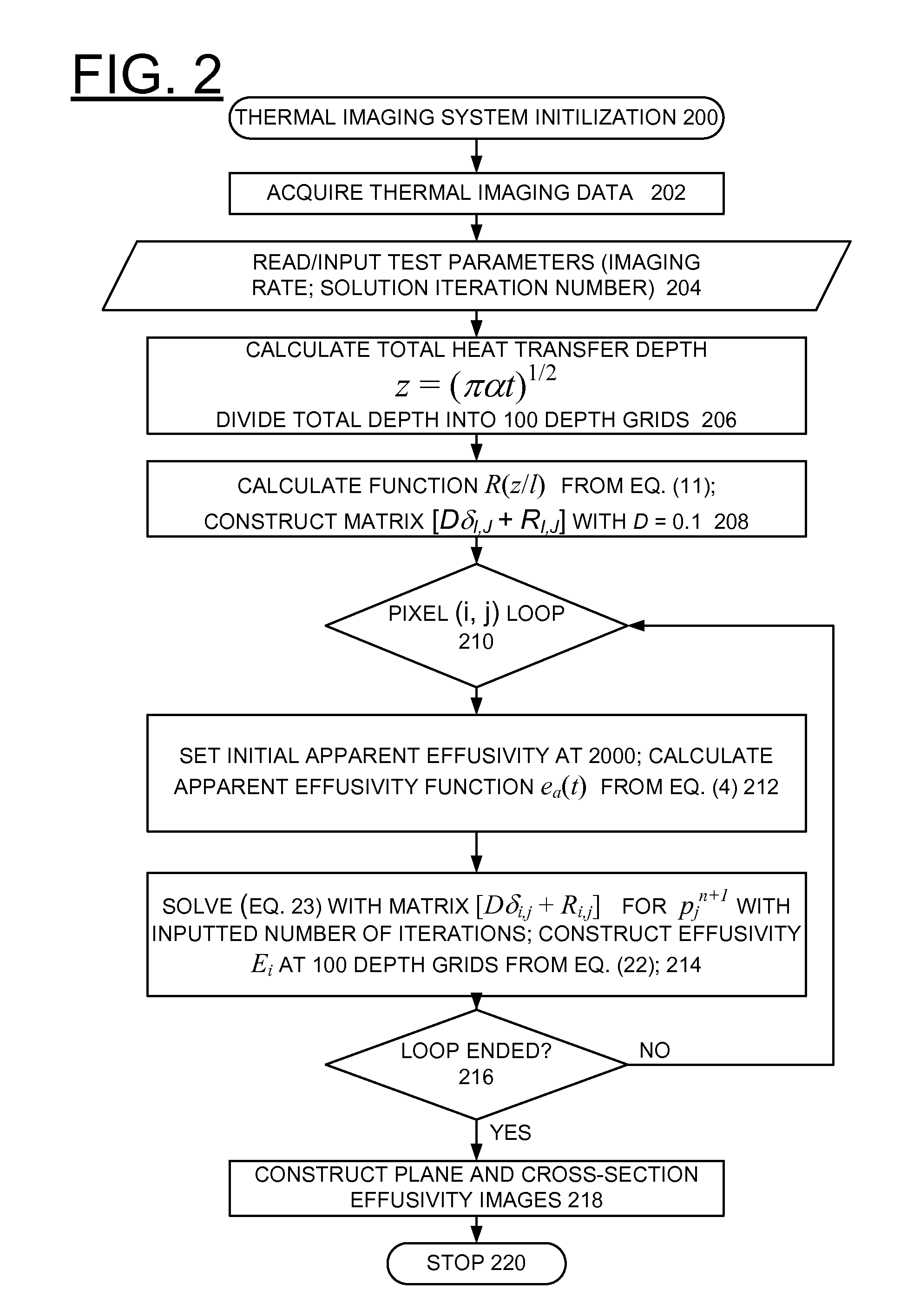
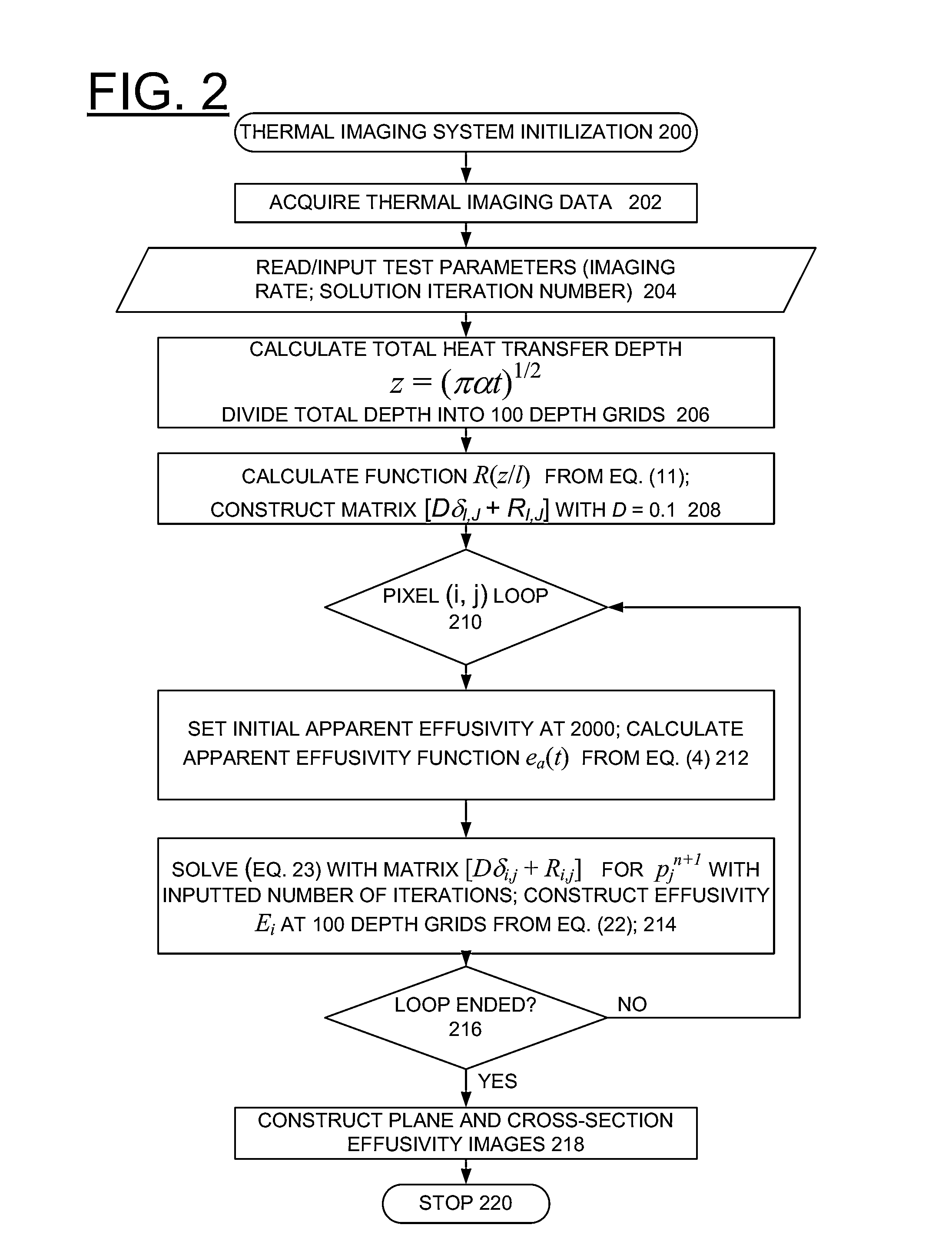
Method for implementing depth deconvolution algorithm for enhanced thermal tomography 3D imaging
InactiveUS20110299752A1High sensitivityEliminate degradationSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansThermal tomographyMatrix solution
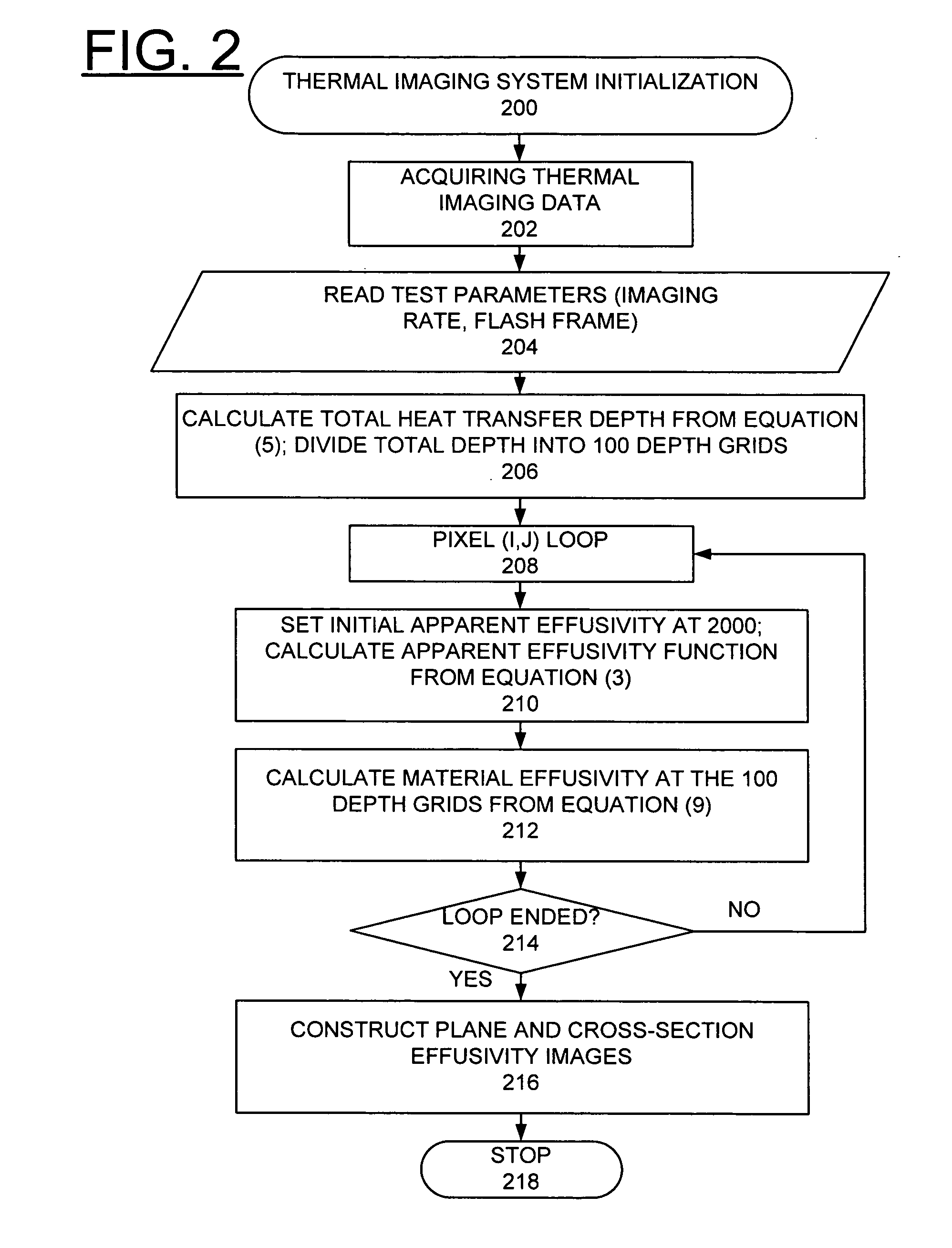
A computer-implemented method, apparatus, and computer program product implement enhanced thermal tomography three-dimensional (3D) thermal effusivity imaging. Experimental thermal imaging data is acquired. A response function is derived and a convolution formulation is constructed from the experimental thermal imaging data. A deconvolution solution procedure is implemented that includes constructing a matrix solution equation with a damping parameter, and solving the matrix solution equation with a selected number of iterations to construct a plurality of effusivity images. Using the novel depth deconvolution algorithm with experimental data acquired from a one-sided pulsed thermal-imaging system provides greater sensitivity for internal sample features substantially eliminating degradation in depth resolution.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Temporal thermal imaging method for detecting subsurface objects and voids
ActiveUS20120134533A1Easy to detectEffectively removing background clutterThermometers using physical/chemical changesScene recognitionInfraredInfra-red color
A temporal thermal survey method to locate at a given area whether or not there is a subsurface object or void site. The method uses thermal inertia change detection. It locates temporal heat flows from naturally heated subsurface objects or faulty structures such as corrosion damage. The added value over earlier methods is the use of empirical methods to specify the optimum times for locating subsurface objects or voids amidst clutter and undisturbed host materials. Thermal inertia, or thermal effusivity, is the bulk material resistance to temperature change. Surface temperature highs and lows are shifted in time at the subsurface object or void site relative to the undisturbed host material sites. The Dual-band Infra-Red Effusivity Computed Tomography (DIRECT) method verifies the optimum two times to detect thermal inertia outliers at the subsurface object or void border with undisturbed host materials.
Owner:DEL GRANDE NANCY KERR
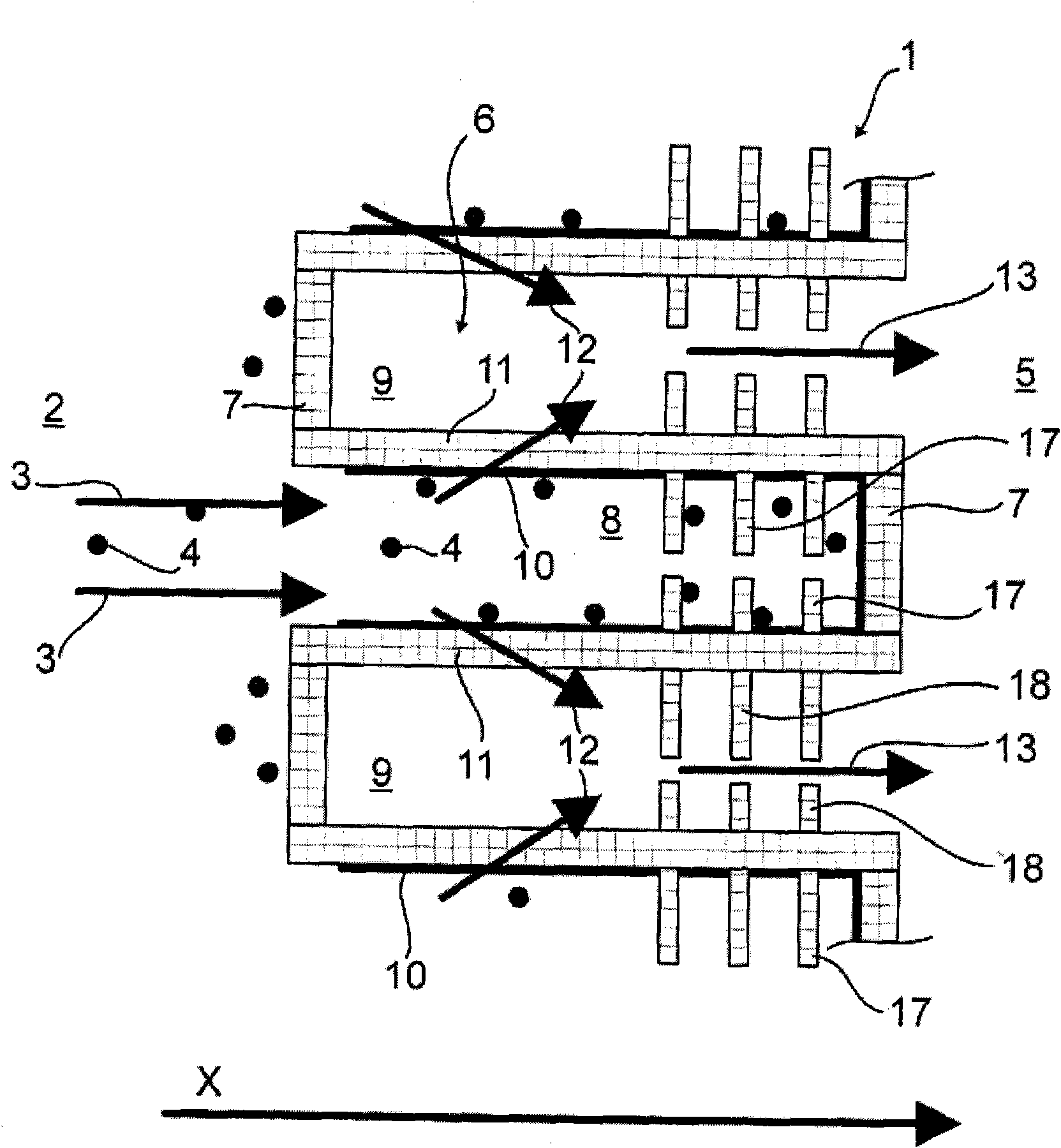
Particulate separator, in particular particulate filter for separating particulates from an exhaust gas flow of a combustion engine
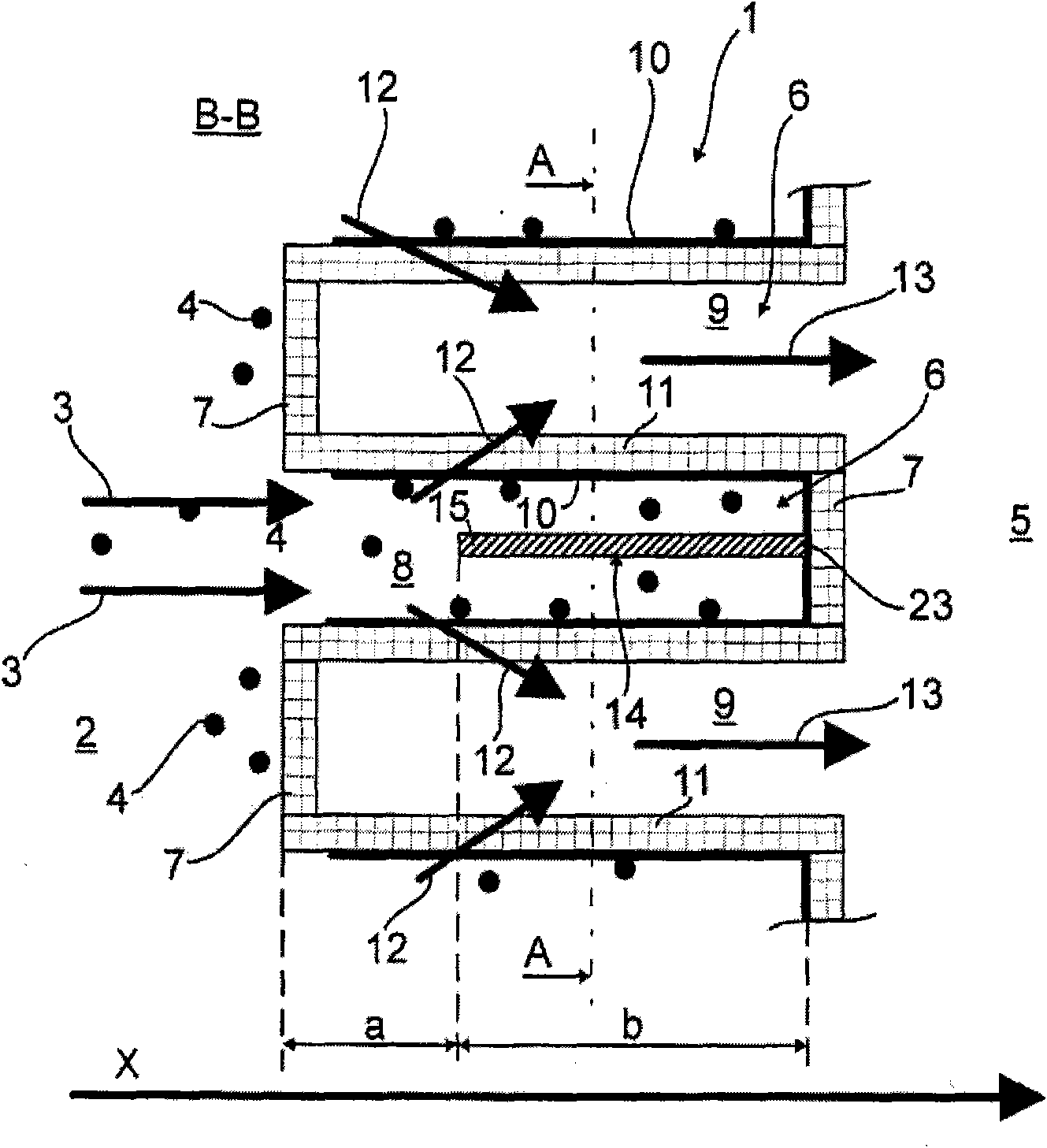
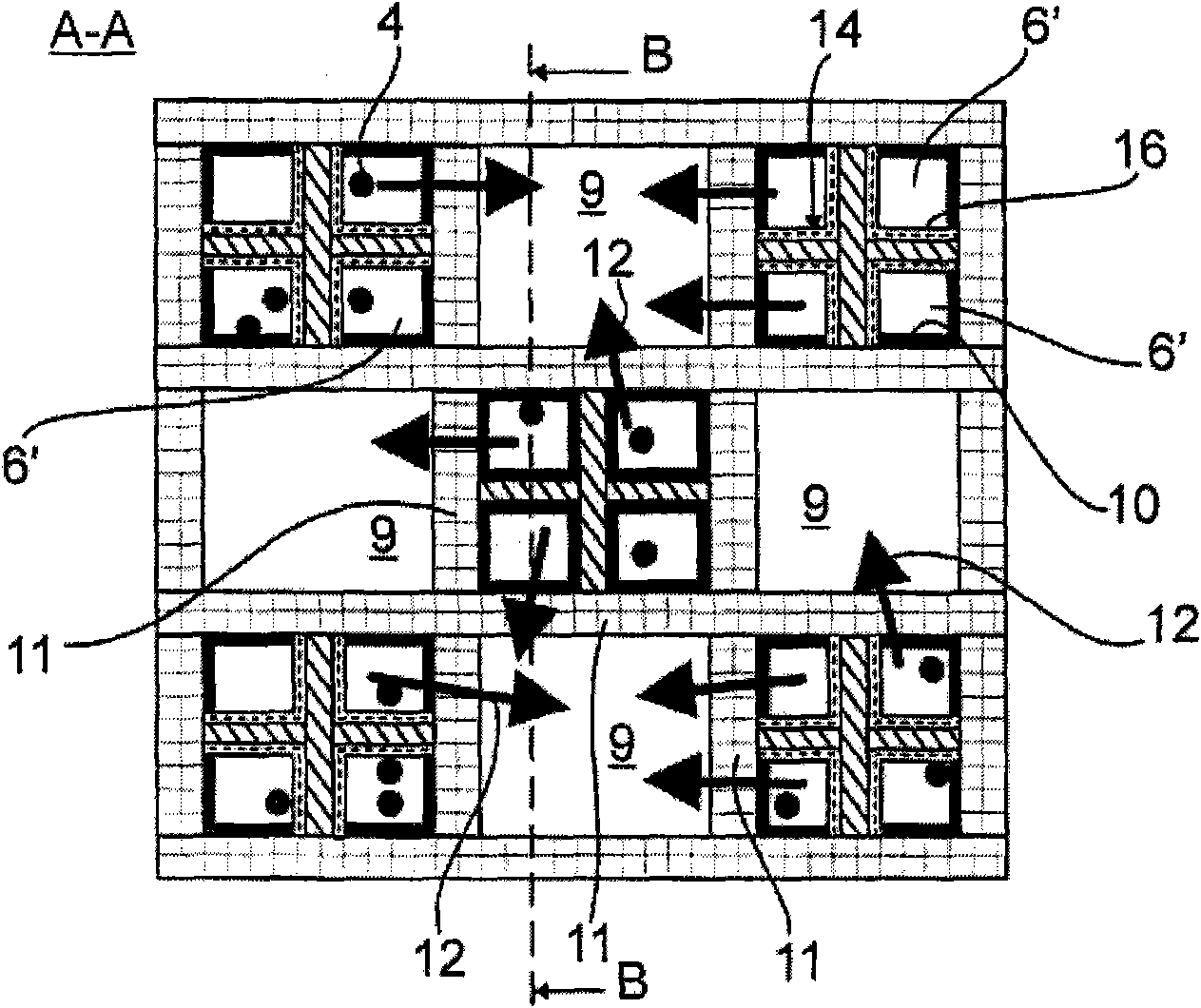
ActiveCN101676527AInternal combustion piston enginesSilencing apparatusParticulatesInternal combustion engine
The particle separator (1) has different heat transfer areas (a,b) in terms of heat storage capacity or heat conductivity or heat transfer characteristics of exhaust gas flows (3,12,13) along the mainflow direction (x) of the exhaust gas flow through the particle separator. A defined heat quantity is transferred from the exhaust gas flows (3,12,13) over the respective assigned particle separatorsection.
Owner:MAN TRUCK & BUS AG
Electrophotographic fixing member, fixing apparatus and electrophotographic image forming apparatus
ActiveUS9063491B2Enhancement in ability supplyReduction in micro rubber hardnessElectrographic process apparatusHardnessEngineering
The present invention is directed to providing a fixing member that has a flexible surface and that can supply a larger amount of heat to a material to be recorded and a toner in a shorter period of time. The fixing member comprises a substrate, an elastic layer and a releasing layer, wherein thermal effusivity in a depth region from a surface of the releasing layer is 1.5 [kJ / (m2·K·sec0.5)] or more, the depth region corresponding to a thermal diffusion length when an alternating-current temperature wave having a frequency of 10 Hz is applied to the surface of the releasing layer, and a surface micro rubber hardness is 85 degrees or less.
Owner:CANON KK
Thermal paper
Owner:BASF CORP
Electrophotographic fixing member, fixing apparatus and electrophotographic image forming apparatus
ActiveUS20140255068A1Enhancement in ability supplyReduction in micro rubber hardnessElectrographic process apparatusAC - Alternating currentHardness
The present invention is directed to providing a fixing member that has a flexible surface and that can supply a larger amount of heat to a material to be recorded and a toner in a shorter period of time. The fixing member comprises a substrate, an elastic layer and a releasing layer, wherein thermal effusivity in a depth region from a surface of the releasing layer is 1.5 [kJ / (m2·K·sec0.5)] or more, the depth region corresponding to a thermal diffusion length when an alternating-current temperature wave having a frequency of 10 Hz is applied to the surface of the releasing layer, and a surface micro rubber hardness is 85 degrees or less.
Owner:CANON KK
Method for implementing depth deconvolution algorithm for enhanced thermal tomography 3D imaging
InactiveUS8465200B2High sensitivityEliminate degradationMaterial thermal conductivityThree-dimensional object recognitionThermal tomographyMatrix solution
A computer-implemented method, apparatus, and computer program product implement enhanced thermal tomography three-dimensional (3D) thermal effusivity imaging. Experimental thermal imaging data is acquired. A response function is derived and a convolution formulation is constructed from the experimental thermal imaging data. A deconvolution solution procedure is implemented that includes constructing a matrix solution equation with a damping parameter, and solving the matrix solution equation with a selected number of iterations to construct a plurality of effusivity images. Using the novel depth deconvolution algorithm with experimental data acquired from a one-sided pulsed thermal-imaging system provides greater sensitivity for internal sample features substantially eliminating degradation in depth resolution.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Device for providing thermoreceptive haptic feedback
ActiveUS10437340B1Reduce the temperatureInput/output for user-computer interactionThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermodynamicsThermal effusivity
A device for providing thermoreceptive haptic feedback includes a first array of low mass elements, arranged in a geometric pattern, the array having a first temperature and a first collective thermal effusivity, and configured for selectively contacting a user, a second array of low mass elements, interspersed among the low mass elements of the first array, and thermally isolated from the low mass elements the first array, the array having a second temperature and a second collective thermal effusivity, and configured for selectively contacting a user, and a means for mechanical switching coupled to the low mass elements of the first and the second arrays and configured to place selected low mass elements of the first and the second arrays in contact with a user, to realize a thermal effusivity between the first collective thermal effusivity and the second collective thermal effusivity.
Owner:SULLIVAN SEAN
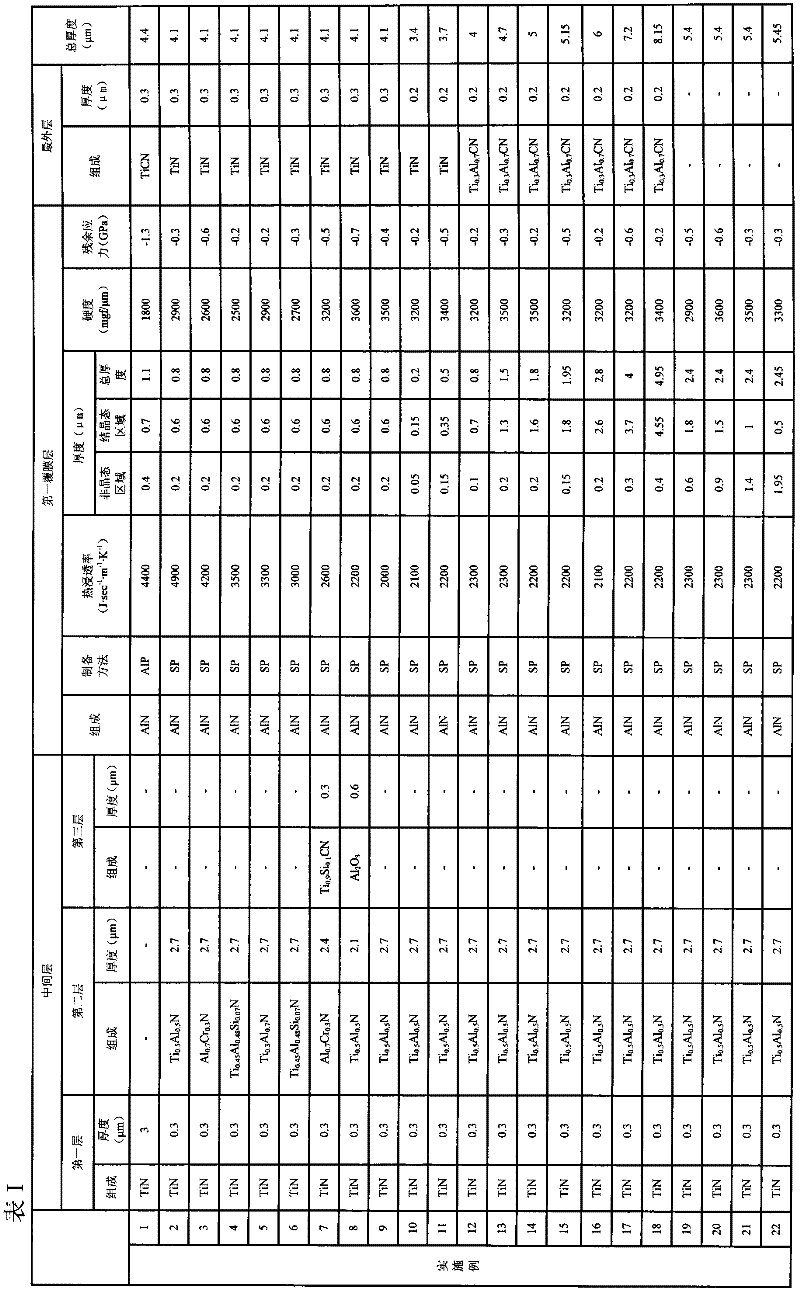
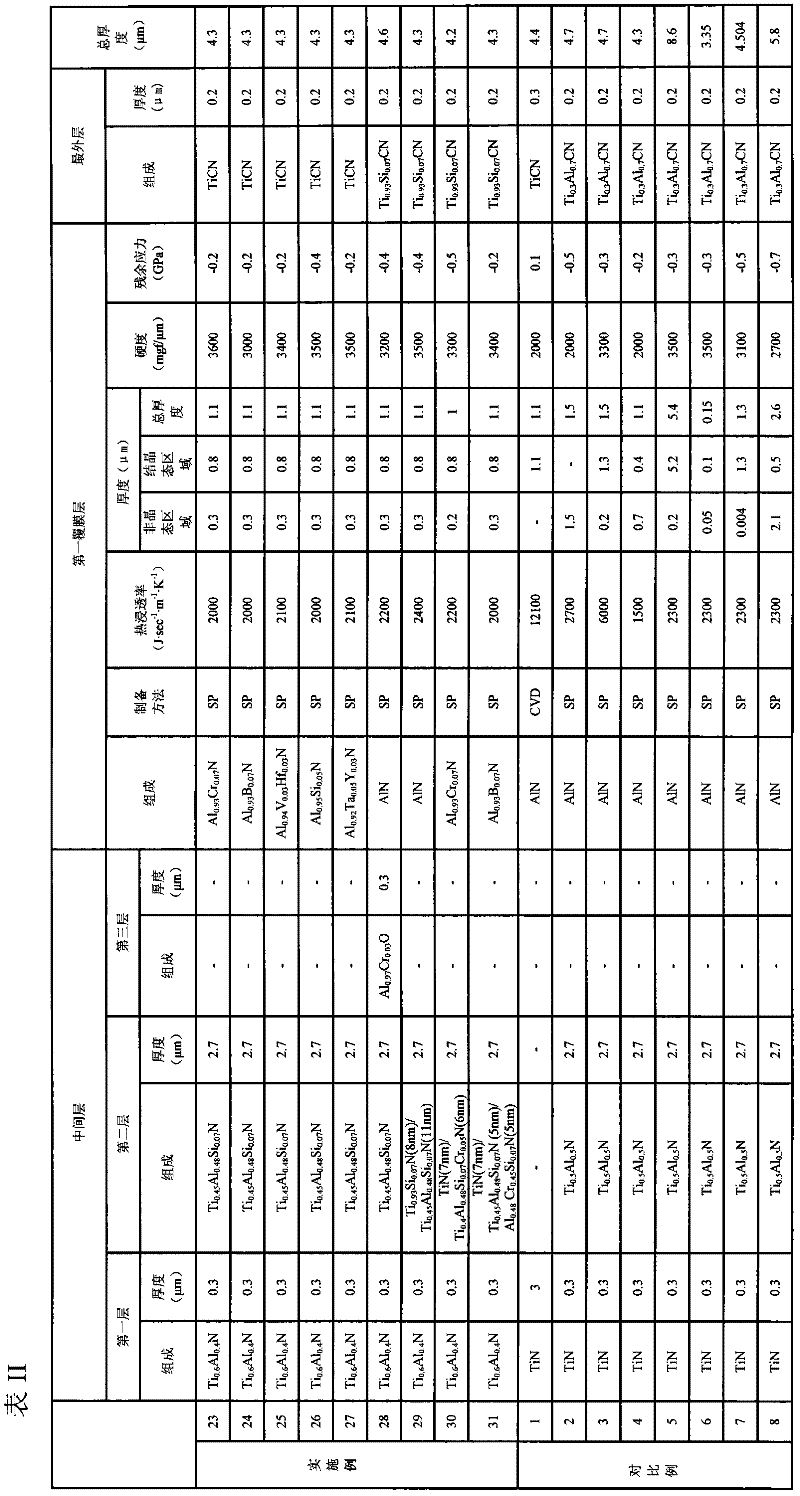
Surface-coated cutting tool
ActiveUS20120009403A1Improve adhesionImprove heat resistanceLayered productsMilling cuttersGas phaseCutting oil
Provided is a surface-coated cutting tool combining superior heat resistance, superior wear resistance, and superior lubricity with high adhesion between a substrate and a coating. A surface-coated cutting tool of the present invention includes a substrate and a coating formed on the substrate, and the coating is characterized in that the coating is formed by physical vapor deposition and includes one or more layers, that at least one of the one or more layers is a first coating layer, that the first coating layer contains aluminum and nitrogen, has a thermal effusivity of 2,000 to 5,000 J·sec−1·m−1·K−1, and has a thickness of 0.2 to 5 μm, that the first coating layer includes an amorphous region and a crystalline region in order from the substrate side, that the amorphous region is amorphous and has a thickness of 0.01 to 2 μm, and that the crystalline region has a crystal structure including a hexagonal structure.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC HARDMETAL CORP
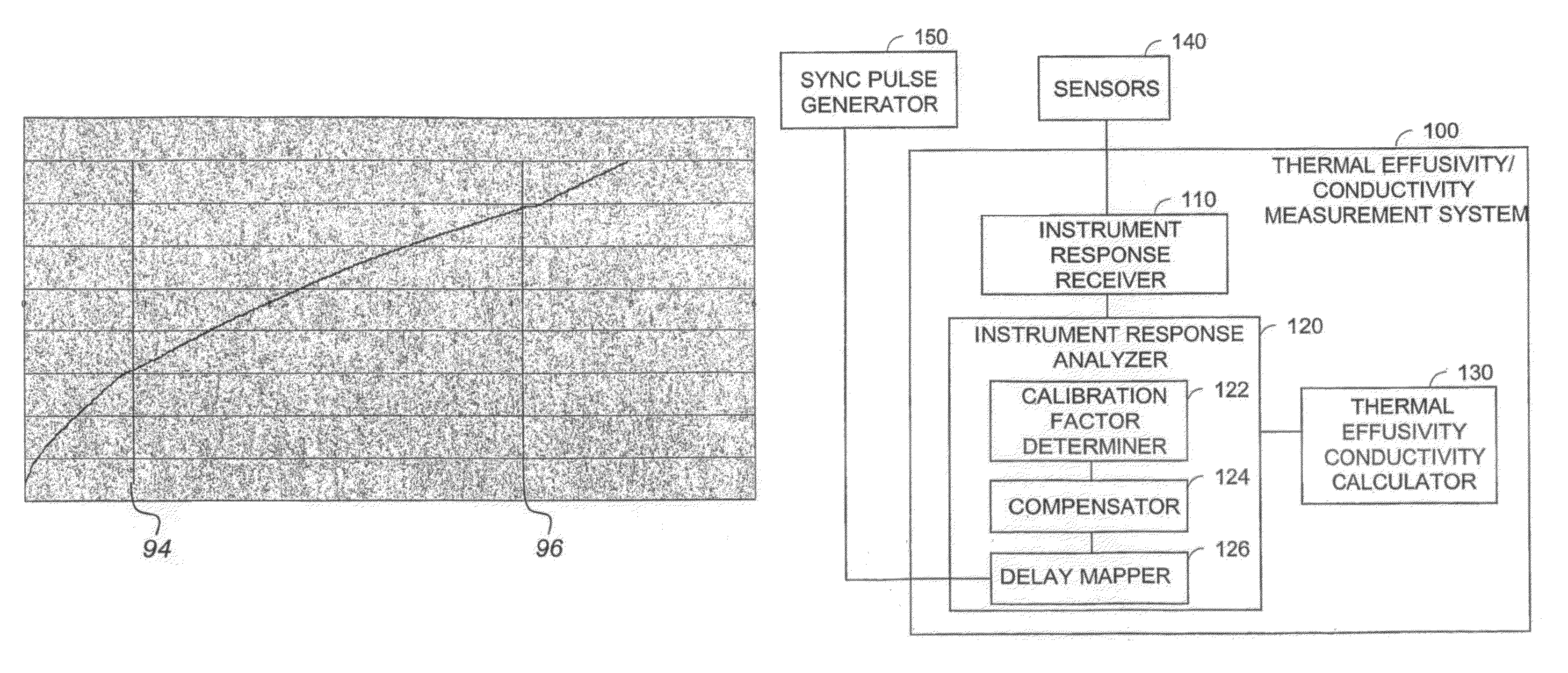
Method and Apparatus for Monitoring Materials
ActiveUS20110002356A1Material thermal conductivityMaterial heat developmentEngineeringMeasure duration
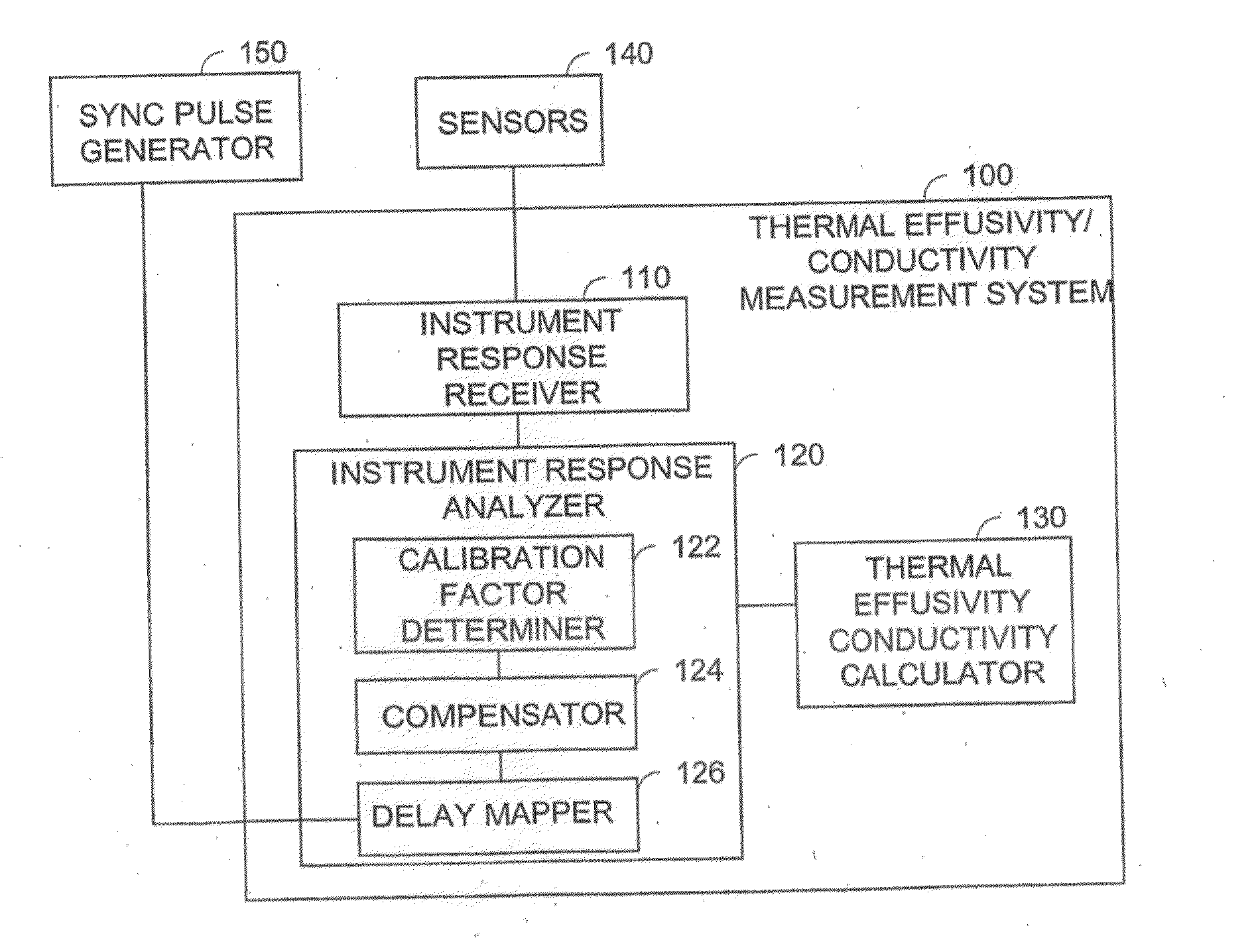
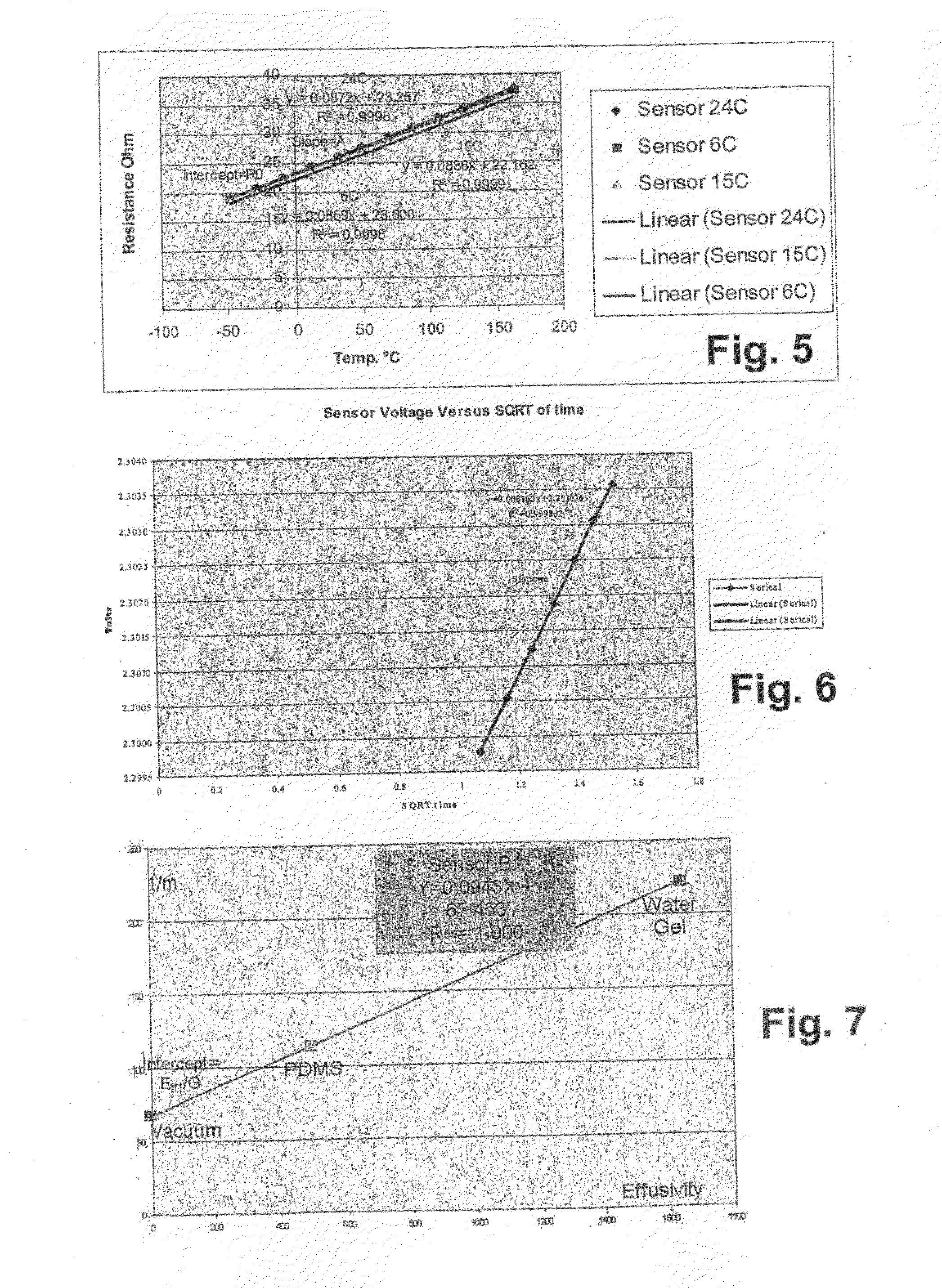
A method and apparatus for monitoring during dynamic processes that determines when effective measurements of thermal effusivity and / or thermal conductivity can be made during a portion of a cycle during a calibration phase, then measures thermal effusivity and / or thermal conductivity during a subsequent dynamic process in dependence upon the time delay value and the measurement duration value until a desired value is obtained. A sensor having a measurement period of between one of two seconds allows monitoring of materials during dynamic processes such as tumbling, blending, mixing, and rocking. For example, measurements can be made until a value indicative of a desired mixture condition is obtained.
Owner:C THERM TECH
Surface-coated cutting tool
ActiveUS20120021199A1Improve heat resistanceImprove wear resistanceLayered productsMilling cuttersHeat resistanceGas phase
Provided is a surface-coated cutting tool combining superior heat resistance, superior wear resistance, and superior lubricity. A surface-coated cutting tool of the present invention includes a substrate and a coating formed on the substrate, and the coating is characterized in that the coating is formed by physical vapor deposition and includes one or more layers, that at least one of the one or more layers is a first coating layer, and that the first coating layer contains aluminum and nitrogen, has a thermal effusivity of 2,000 to 5,000 J·sec−1 / 2·m−2·K−1, has a thickness of 0.2 to 5 μm, and has a crystal structure including a hexagonal structure.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC HARDMETAL CORP
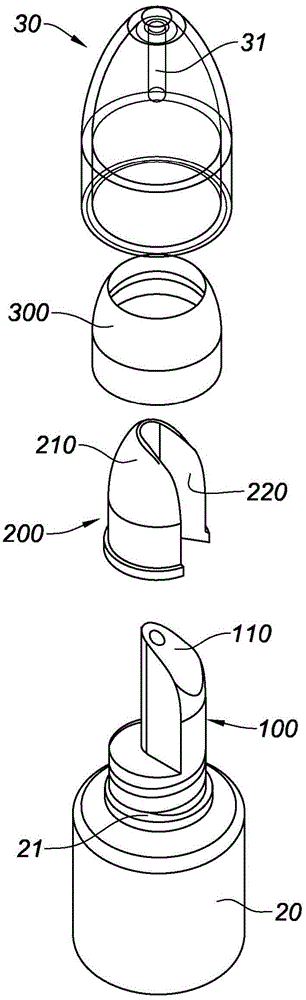
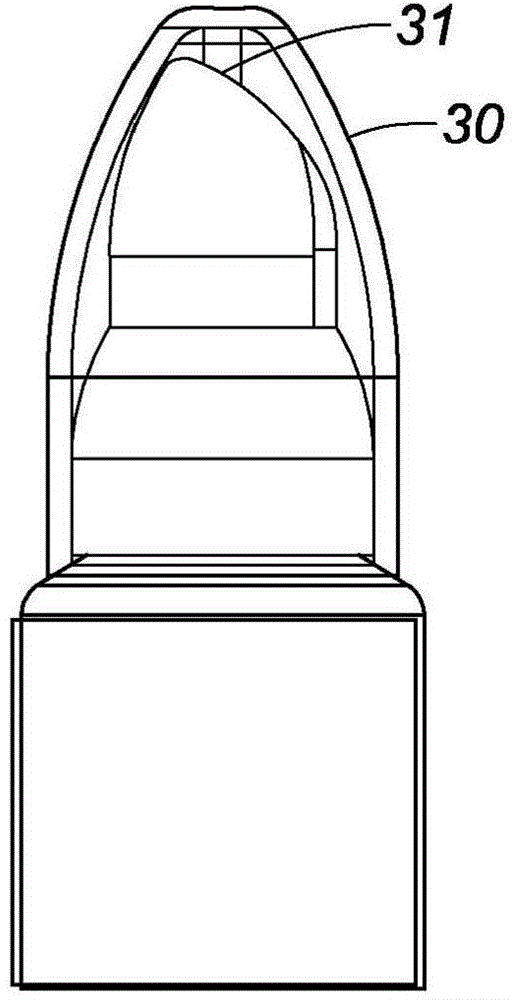
Applicator for a fluid product such as a cosmetic product
An applicator for a fluid product is provided that offers a thermal effect by creating a cold sensation upon application to a surface. The applicator comprises a reservoir containing a fluid product; an end-piece with a dispensing face having an orifice for dispensing the fluid product onto the surface to be treated; and a thermal storage end-piece that includes an application face. The thermal storage end-piece is made from a material having a thermal effusivity that is higher than that of the product dispensing end-piece so as to provide thermal sensations upon contact with the surface to be treated. The application head is shaped so that, by orienting the applicator selectively relative to the surface to be treated, one can place the latter in contact with the dispensing face of the dispensing end-piece while avoiding contact with the application face of the thermal storage end-piece.
Owner:COSMOGEN
Surface-coated cutting tool
ActiveCN102317016AImprove heat resistanceImprove wear resistanceMilling cuttersVacuum evaporation coatingHeat resistanceNitrogen
Disclosed is a surface-coated cutting tool in which the adhesion of a coating upon a base is high and which combines excellent heat resistance, excellent abrasion resistance, and excellent lubricity. The surface-coated cutting tool is provided with a substrate and a coating that has been formed upon said substrate, and is characterized in that: said coating is formed by means of the physical vapor deposition method and comprises one or more layers; at least one layer from among said one or more layers is a first coating layer; said first coating layer comprises Al and N, and has a thermal effusivity in the range of 2000 J / sec-1 m-1 K-1 to 5000 J / sec-1 m-1 K-1 and a coating thickness in the range of 0.2 [mu]m to 5 [mu]m; the first coating layer has an amorphous region and a crystalline region from the substrate side in this order; the amorphous region comprises an amorphous material and has a thickness in the range of 0.01 [mu]m to 2 [mu]m; and the crystalline region comprises a crystal structure that includes a hexagonal structure.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC HARDMETAL CORP
Surface-coated cutting tool
ActiveUS8685530B2Improve heat resistanceImprove wear resistancePigmenting treatmentMilling cuttersHeat resistanceGas phase
Provided is a surface-coated cutting tool combining superior heat resistance, superior wear resistance, and superior lubricity. A surface-coated cutting tool of the present invention includes a substrate and a coating formed on the substrate, and the coating is characterized in that the coating is formed by physical vapor deposition and includes one or more layers, that at least one of the one or more layers is a first coating layer, and that the first coating layer contains aluminum and nitrogen, has a thermal effusivity of 2,000 to 5,000 J·sec−1 / 2·m−2·K−1, has a thickness of 0.2 to 5 μm, and has a crystal structure including a hexagonal structure.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC HARDMETAL CORP
Phase change heat storage heating device capable of improving utilization rate of phase change material
InactiveCN113203114AIncrease profitImprove heat storage effectElectric heating systemHeat storage plantsThermodynamicsWater flow
The invention discloses a phase change heat storage heating device capable of improving the utilization rate of a phase change material. The device comprises an external box body (1) and an internal heat exchange tube structure. Hot water flows in, firstly exchanges heat with the phase change material at the bottom, then flows upwards to exchange heat with the surrounding phase change material, and finally flows out. As the water temperature of the lower part of the device is generally high, the heat exchange temperature difference with the phase change material is large and the heat exchange effect is obvious; and the heat exchange area of the upper part of the device is increased, so that most phase change materials in the device are uniformly and fully heated. Compared with the prior art, the phase change material has good heat storage performance and heat release performance, can store and release more heat, and has higher phase change material utilization rate and heat storage ratio; and manufacturing cost is low, and popularization is easy.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Rotatable heating member and image heating apparatus
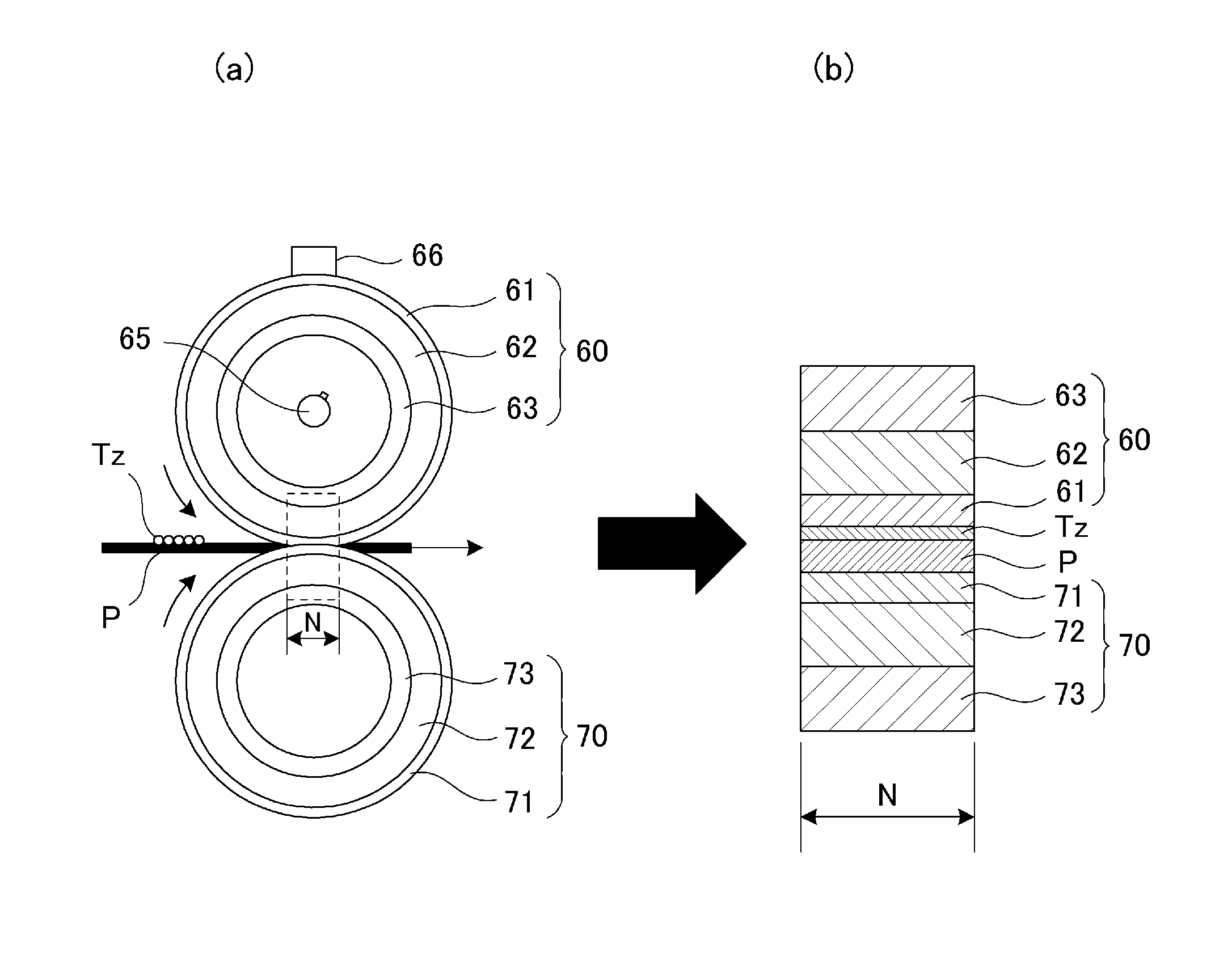
A rotatable heating member incorporating a heat source configured to heat a toner image on a sheet includes an elastic layer and a surface layer provided on the elastic layer. When thermal effusivity of the surface layer is Bs and thermal effusivity of the elastic layer is Be, the following relationship is satisfied:−0.04<(Be−Bs) / Be<0.04.
Owner:CANON KK
Heat regenerating element and heat regenerating material using same
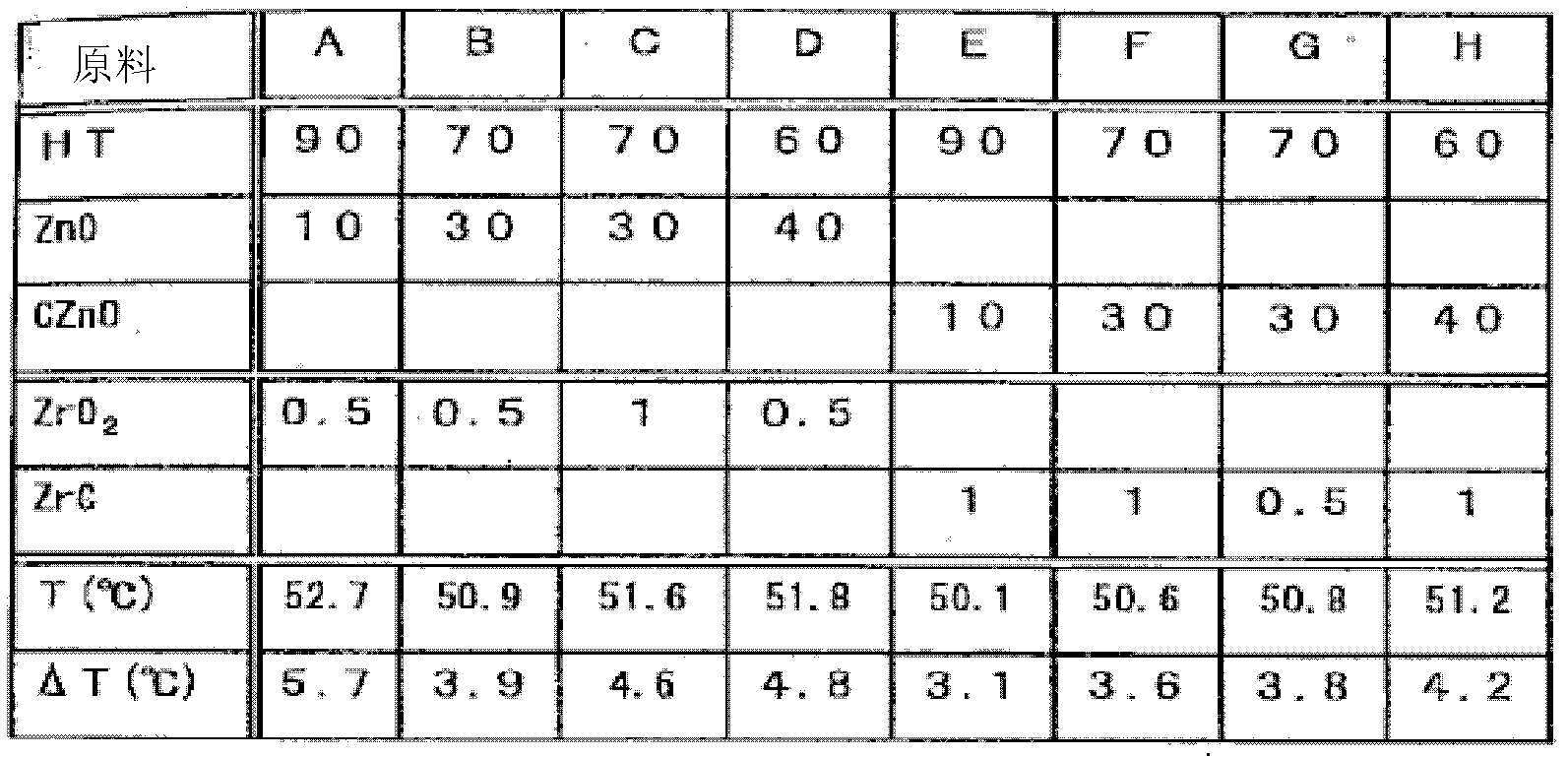
InactiveCN102585780ALow costEfficient accumulationHeat-exchange elementsThin material handlingHydrotalciteEngineering
There is provided a novel heat regenerating element having an excellent heat regenerating property which can accumulate thermal energy and effectively radiate the accumulated thermal energy to various objects. The present invention further provides a heat regenerating material including the heat regenerating element. The heat regenerating element of the present invention includes: 100 parts by weight of a base component composed of 60 to 90 parts by weight of a hydrotalcite compound and a remnant including at least one of zinc oxide and electrically-conductive zinc oxide; and 0.5 to 1 parts by weight of at least one heat regeneration enhancing component selected from a group of zirconium oxide components and zirconium carbide components.
Owner:FIRBEST
Method and apparatus for monitoring materials
ActiveUS8858071B2Material thermal conductivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansTime delaysEngineering
A method and apparatus for monitoring during dynamic processes that determines when effective measurements of thermal effusivity and / or thermal conductivity can be made during a portion of a cycle during a calibration phase, then measures thermal effusivity and / or thermal conductivity during a subsequent dynamic process in dependence upon the time delay value and the measurement duration value until a desired value is obtained. A sensor having a measurement period of between one to two seconds allows monitoring of materials during dynamic processes such as tumbling, blending, mixing, and rocking. For example, measurements can be made until a value indicative of a desired mixture condition is obtained.
Owner:C THERM TECH
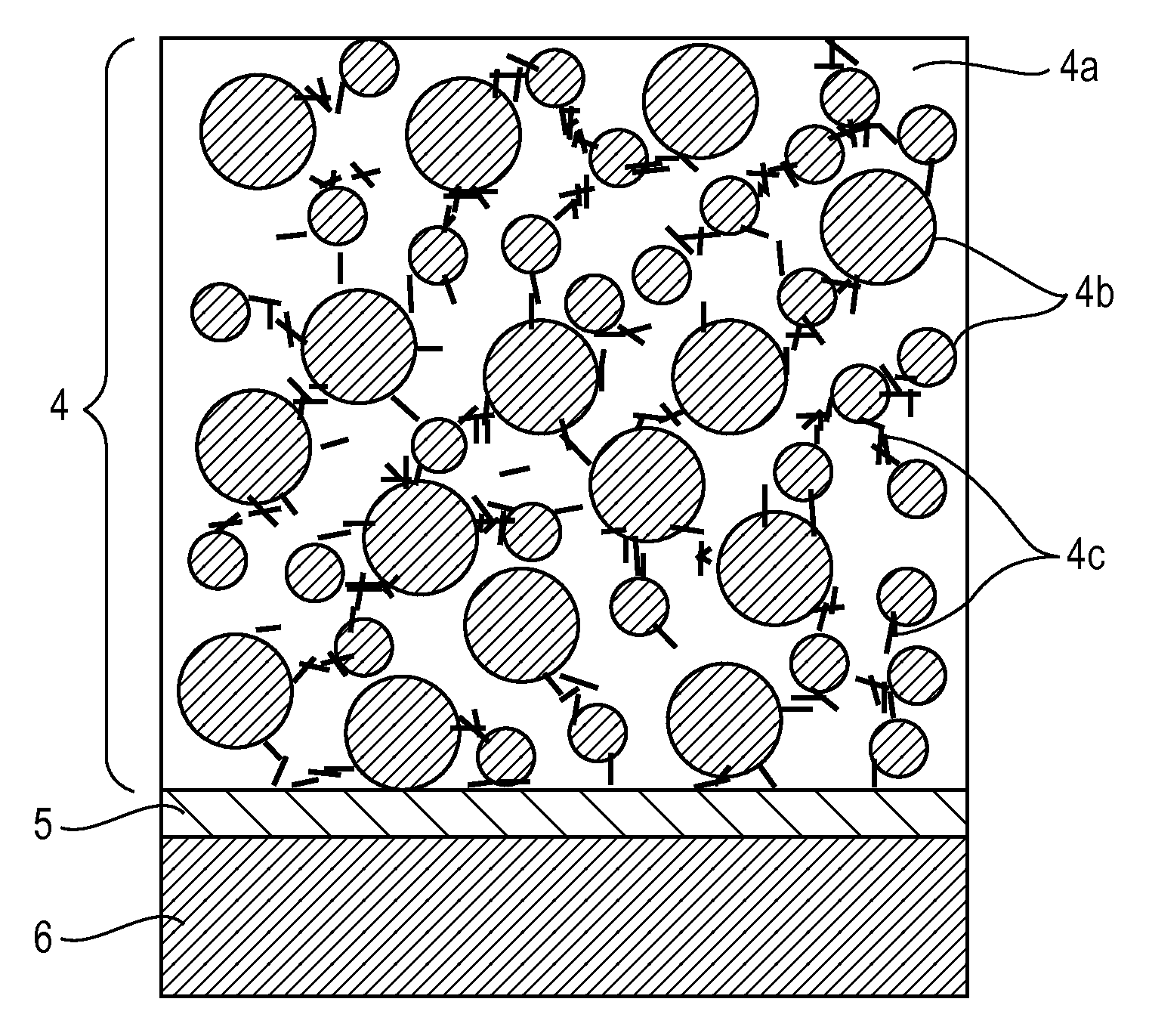
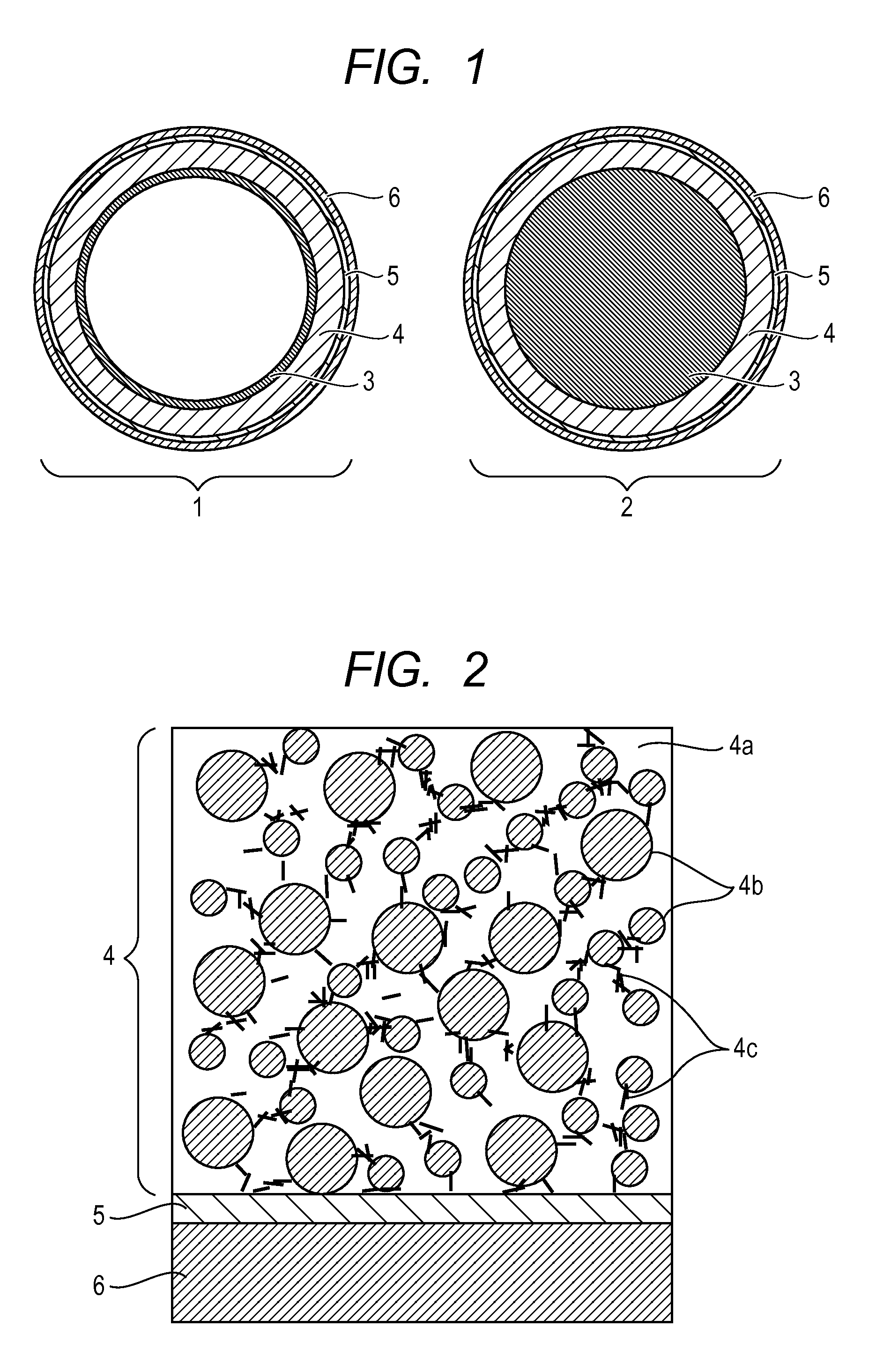
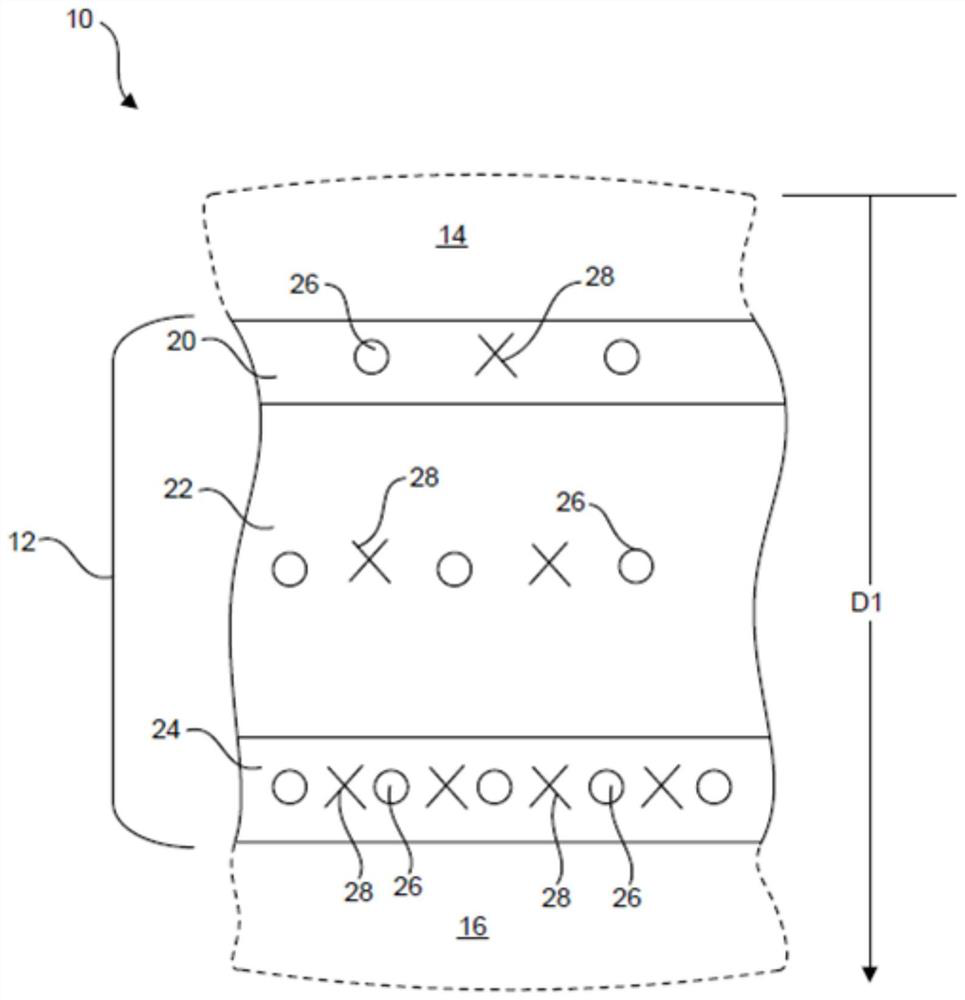
Cooling body support cushion and pillow
Cushions comprise a plurality of separate and distinct consecutive layers (12) overlying over each other in a depth direction. Each layer (12) includes thermal effusivity enhancing material with a thermal effusivity greater than or equal to 2,500 WsO,5 / (m2K), and the total thermal effusivity of increases from layer to layer in the depth direction (D1). The plurality of layers (12) include a plurality of phase change layers (20,22,24) that each comprise a solid-to-liquid phase change material PCM (26) with a phase change temperature within the range of about 6 to about 45 degrees Celsius. The total mass of the PCM (26) increases from layer to layer in the depth direction (D1). At least one layer (20,22,24) of the plurality of phase change layers (12) includes a gradient distribution of the mass of the PCM (26) and the amount of the thermal effusivity enhancing material TEEM (28) thereof that increases in the depth direction (D1).
Owner:SOFT TEX GRP INC
Preparation method of high-heat-conductivity composite heat storage material
InactiveCN106047303AImprove thermal efficiencyNo pollution in the processHeat-exchange elementsFiberCarbon fibers
The invention relates to a preparation method of a high-heat-conductivity composite heat storage material, belonging to the technical field of preparation of heat storage materials. According to the preparation method, the defects of long temperature control time and relatively low heat storage efficiency easily caused in an application process because the heat conduction coefficients of heat storage materials prepared at present are relatively low are solved. The preparation method comprises the steps of removing organic matters from loofah sponge, loading a peach gum concentrated solution, and carrying out carbonizing treatment so as to prepare a carbon fiber material; by taking carbon fiber with excellent heat conducting capacity as a skeleton of the heat storage material, immersing the skeleton into melted glycerin monostearate by virtue of superposition of capillarity and gravity, so as to prevent the formation of gaps in the dense inner part of the skeleton. The heat conduction coefficient of the prepared composite heat storage material can be 18W / mk-20W / mk, the latent heat of phase change can reach 60J / g-90J / g, and the heat conducting efficiency is increased by 10%-15%. Furthermore, the preparation process is simple and environmentally friendly, and the environmental pollution is avoided.
Owner:郭舒洋
Heat storage device, heat storage system and heat storage method
ActiveCN111051804BRestrain the increase in operating costsReduce the situation of becoming insufficient energyCentral heating with accumulated heatHeat storage plantsProcess engineeringHeat storage material
The present invention provides a heat storage device, a heat storage system, and a heat storage method capable of suppressing an increase in running cost, preventing energy shortage even when heat extraction is progressing, and reducing heat radiation loss. The heat storage device includes: a heat storage tank containing a heat storage material having heat storage performance and heat release performance; a heat source unit that generates heat supplied to the heat storage material; A first heat medium flow path, the first heat medium flow path is used for the flow of the first heat medium, and is thermally connected with the heat storage material and the heat source machine; and a plurality of temperature sensors, the plurality of temperature sensors are arranged in the heat storage tank , and measure the temperature of the heat storage material. The plurality of temperature sensors are arranged at positions at different distances from the heat transfer surface of the first heat medium flow path where the first heat medium flow path and the heat storage material come into contact. The heat source machine generates heat based on the detection results of the plurality of temperature sensors.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
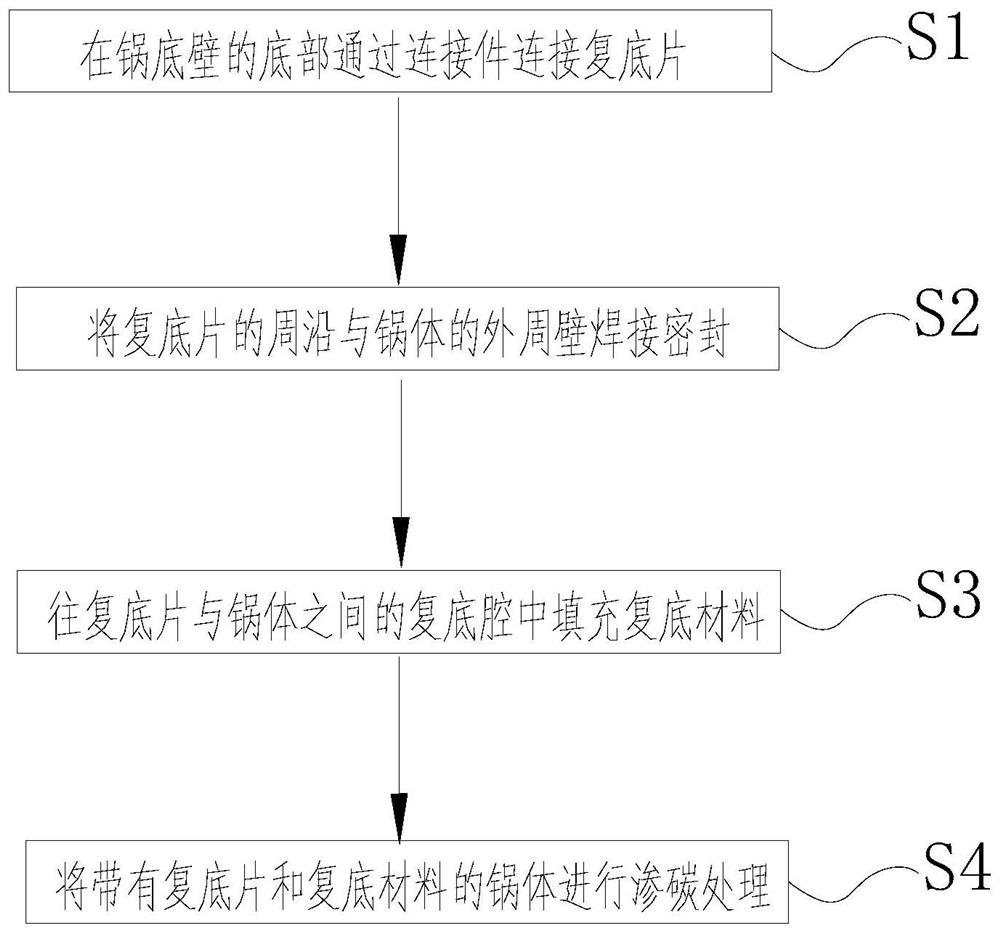
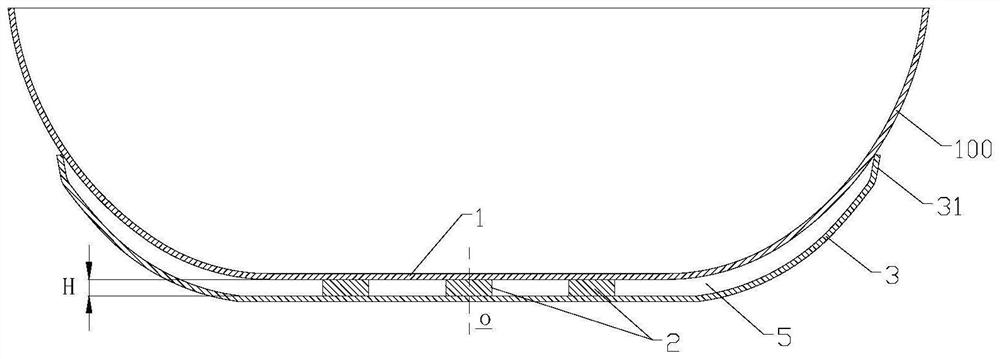
Composite bottom pot body and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN111772461BImprove heat storage effectIncrease heat storageCooking-vessel materialsSoldering apparatusThermal treatmentMechanical engineering
Owner:FOSHAN SHUNDE MIDEA ELECTRICAL HEATING APPLIANCES MFG CO LTD
A medium and high temperature mixed molten salt heat storage system with high latent heat and preparation method
The invention discloses a preparation method of a medium-high temperature mixed molten salt heat storage system with high latent heat. The medium-high temperature mixed molten salt heat transfer heat storage medium with high latent heat adopts a substance comprising the following mass fraction: NaNO 3 The mass percentage is 20%~80%, Na 2 CO 3 The mass percentage is 0% to 30% and the NaOH mass percentage is 10% to 80%, wherein, Na 2 CO 3 The mass percentage is not 0. The low-melting point molten salt heat transfer and heat storage medium provided by the present invention has large phase change latent heat, high upper limit temperature and wide working temperature range, and has good heat transfer and heat storage performance, and is very suitable for medium Heat transfer and heat storage for high temperature solar thermal power generation.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Overlap-type solid heat accumulation device
PendingCN111043887AExtended service lifeSolve temperature problemsHeat storage plantsOhmic-resistance heating detailsBrickEngineering
The invention relates to an overlap-type solid heat accumulation device which comprises at least three groups of heat accumulation components for storing heat energy and an accommodating shell for accommodating the heat accumulation components, the three groups of heat accumulation components are sequentially and adjacently arranged in the accommodating shell from top to bottom; each of the heat accumulation components comprises a heat accumulation body for storing heat energy and a heating wire for releasing heat energy; the heat accumulation bodies are first magnesite bricks and at least twofirst magnesite bricks are adjacently arranged; the surfaces of the first magnesite bricks are of loose porous structures; a through hole is correspondingly formed between every two adjacent first magnesite bricks; the heating wires penetrate through the inner sides of the through holes; a heat exchanger is arranged at the bottom end of the interior of the accommodating shell; and a water inlet pipe and a water outlet pipe are adjacently arranged on one side of the heat exchanger in a communicating manner. In short, according to the technical scheme, compared with the traditional solid heat accumulation device, the overlap-type solid heat accumulation device effectively solves the technical problems that the heat accumulation performance is poor, the energy consumption is high and the heat accumulation device is likely to be damaged through a coherent and compact structure.
Owner:上海中如智慧能源集团有限公司
Surface-coated cutting tool
ActiveUS8685531B2Improve adhesionImprove heat resistancePigmenting treatmentMilling cuttersGas phaseHeat resistance
Provided is a surface-coated cutting tool combining superior heat resistance, superior wear resistance, and superior lubricity with high adhesion between a substrate and a coating. A surface-coated cutting tool of the present invention includes a substrate and a coating formed on the substrate, and the coating is characterized in that the coating is formed by physical vapor deposition and includes one or more layers, that at least one of the one or more layers is a first coating layer, that the first coating layer contains aluminum and nitrogen, has a thermal effusivity of 2,000 to 5,000J·sec−1 / 2·m−2·K−1, and has a thickness of 0.2 to 5μm, that the first coating layer includes an amorphous region and a crystalline region in order from the substrate side, that the amorphous region is amorphous and has a thickness of 0.01 to 2μm, and that the crystalline region has a crystal structure including a hexagonal structure.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC HARDMETAL CORP
Heating element, and preparation method thereof and electric heater
PendingCN113079597ASimple stepsEasy to operateOhmic-resistance heating detailsEngineeringThermal effusivity
The invention provides a heating element, and a preparation method thereof and an electric heater. The heating element comprises: a base material; a first insulating heat storage layer which is arranged on one surface of the base material; a heating layer which is arranged on the surface, far away from the base material, of the first insulating heat storage layer; an infrared heat storage layer which is arranged on the side, away from the base material, of the first insulation heat storage layer and covers the heating layer. The heating element has the high heating speed and the good heat storage performance at the same time, safety is high, and miniaturization and convenience of the electric heater can be achieved easily.
Owner:FOSHAN SHUNDE MIDEA ELECTRICAL HEATING APPLIANCES MFG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com