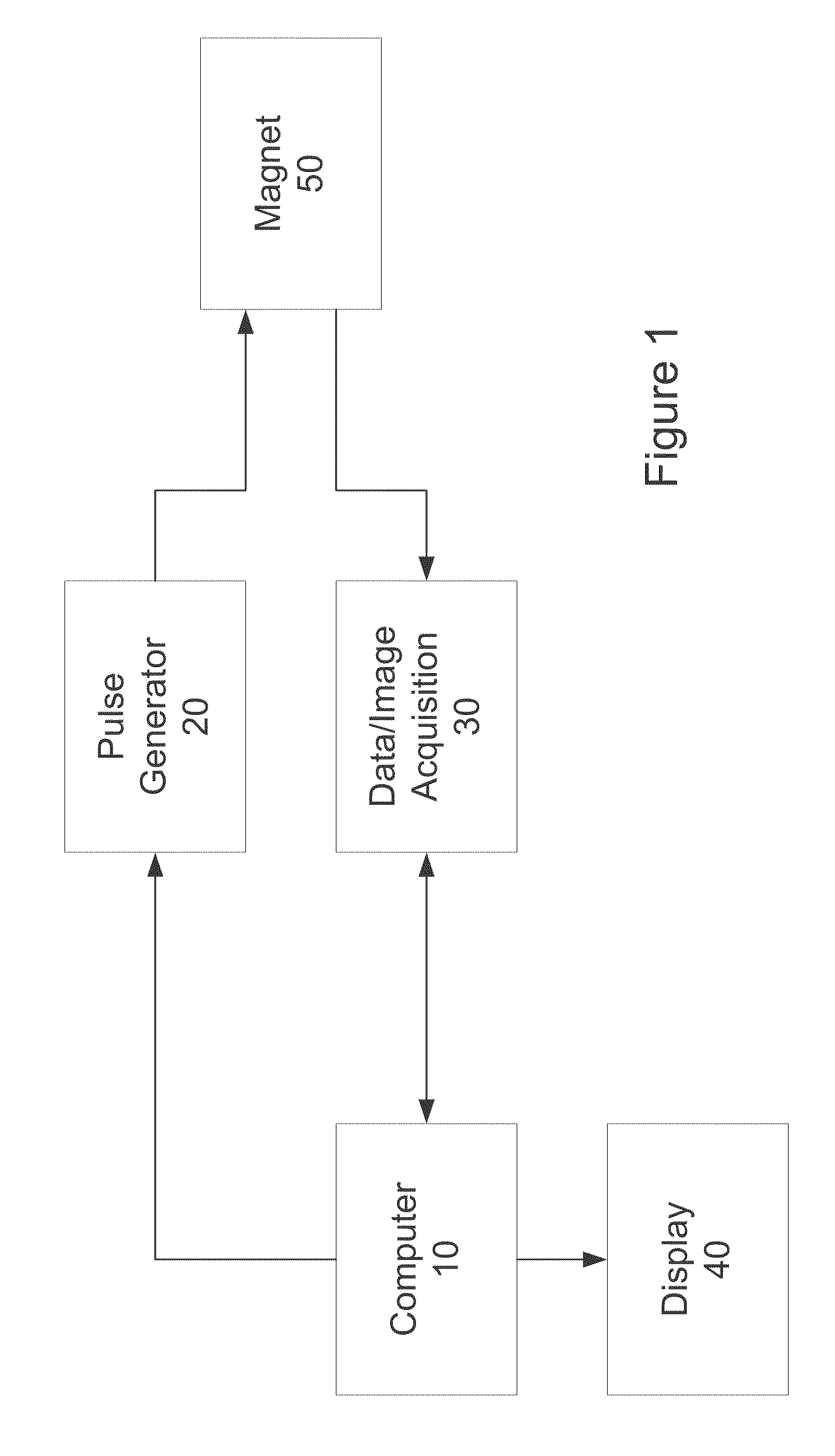
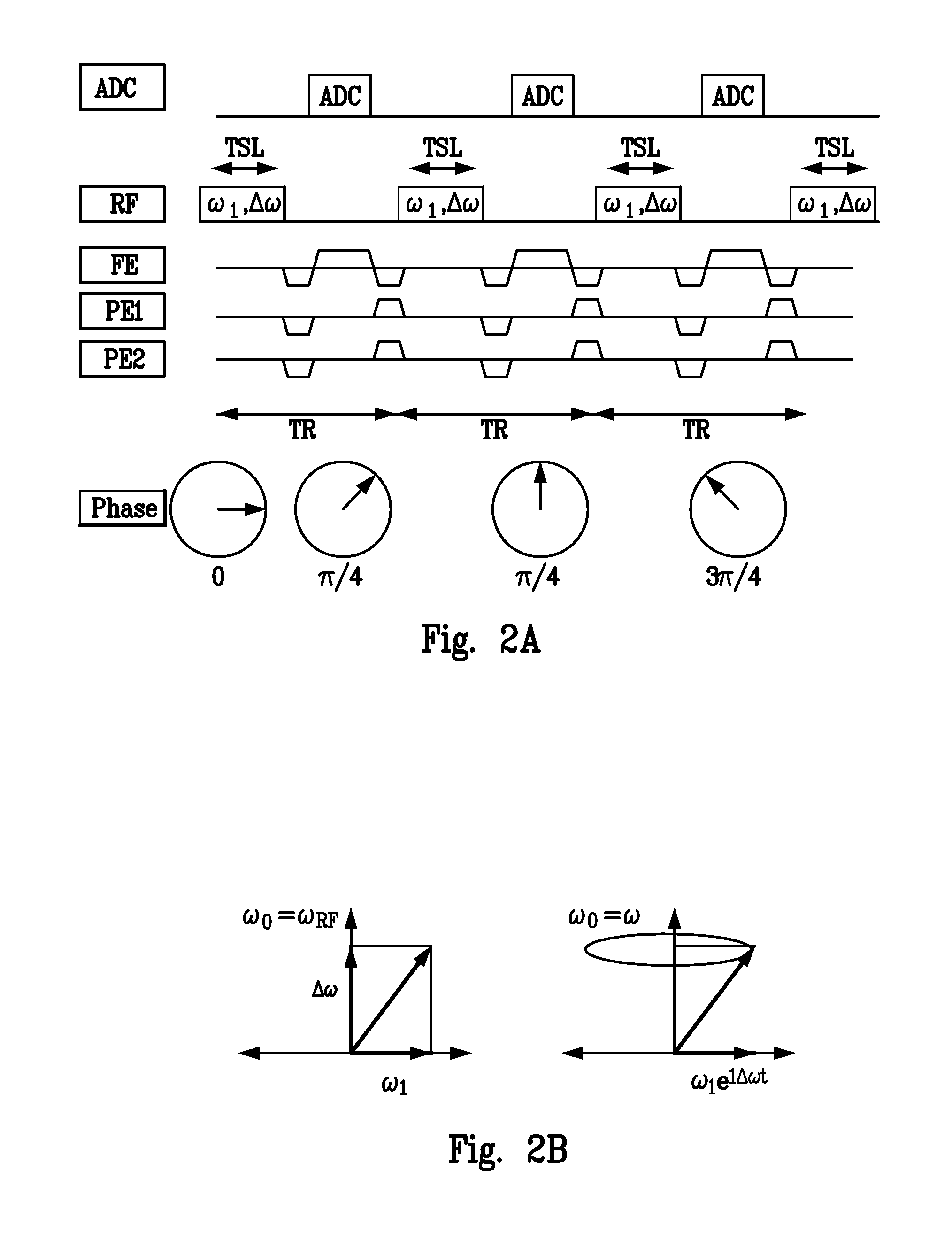
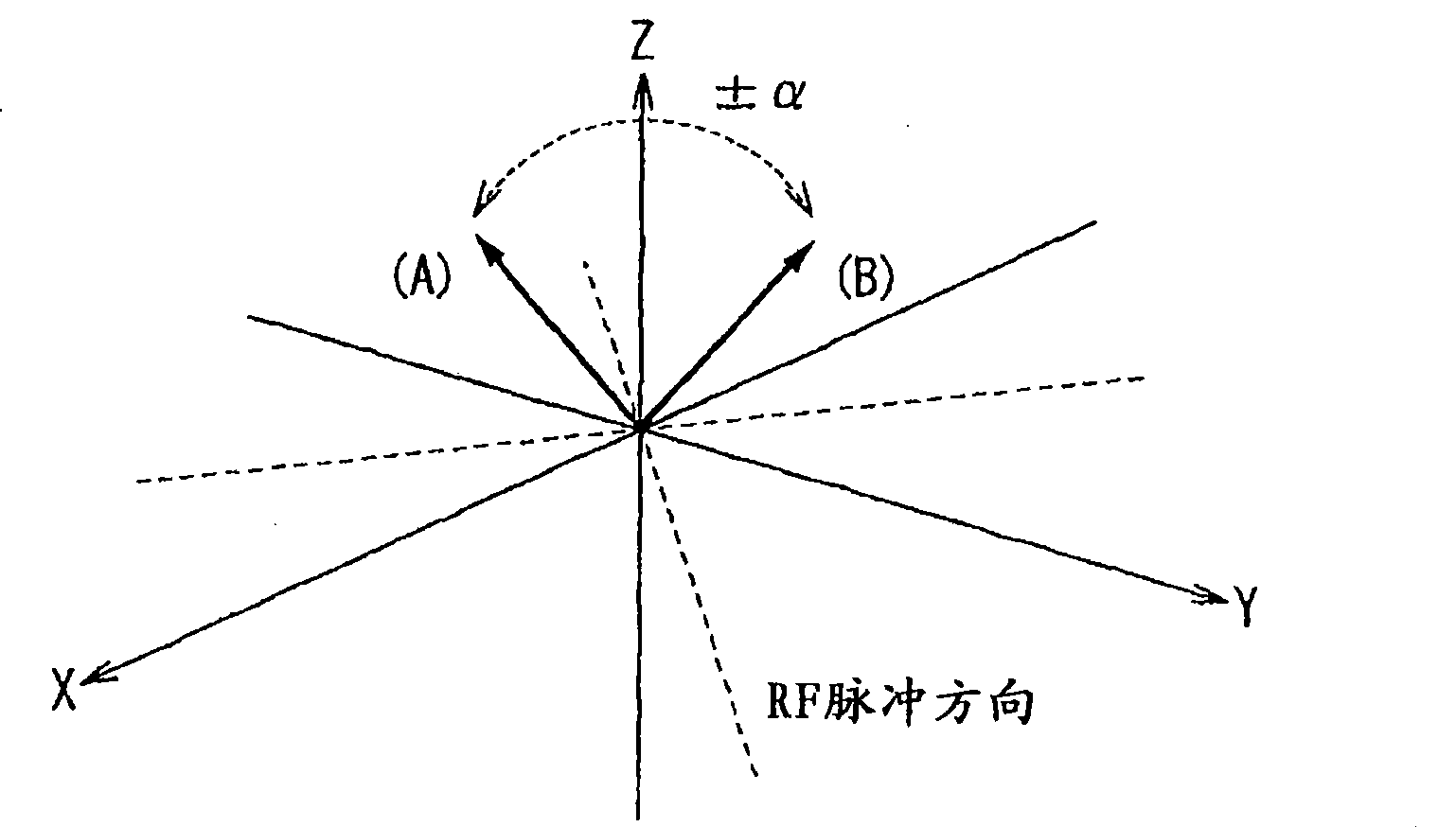
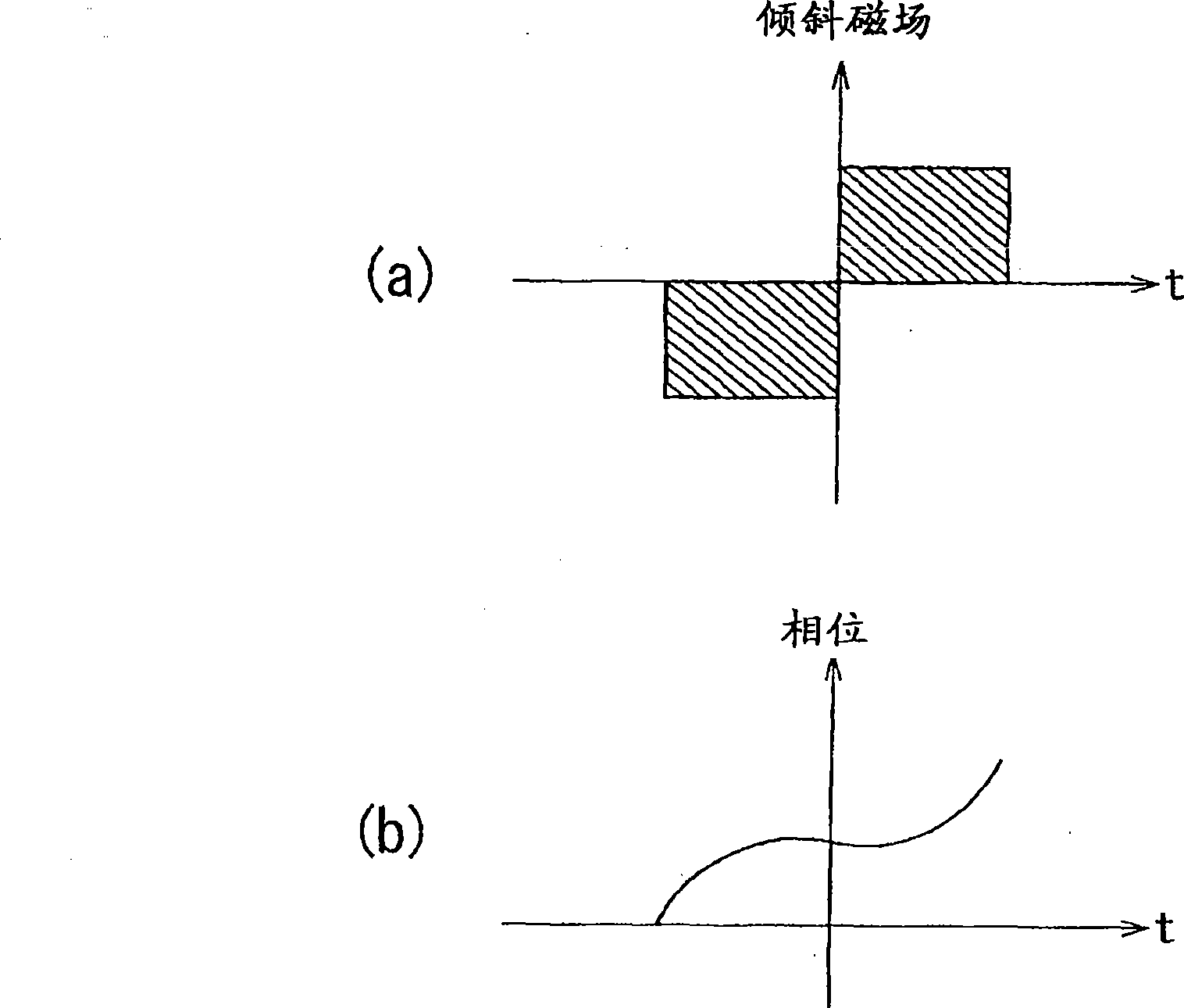
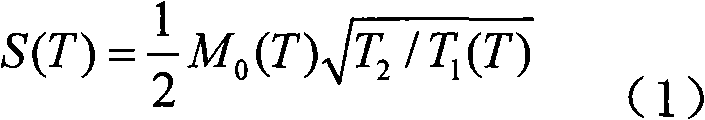Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
89 results about "Steady state free precession" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
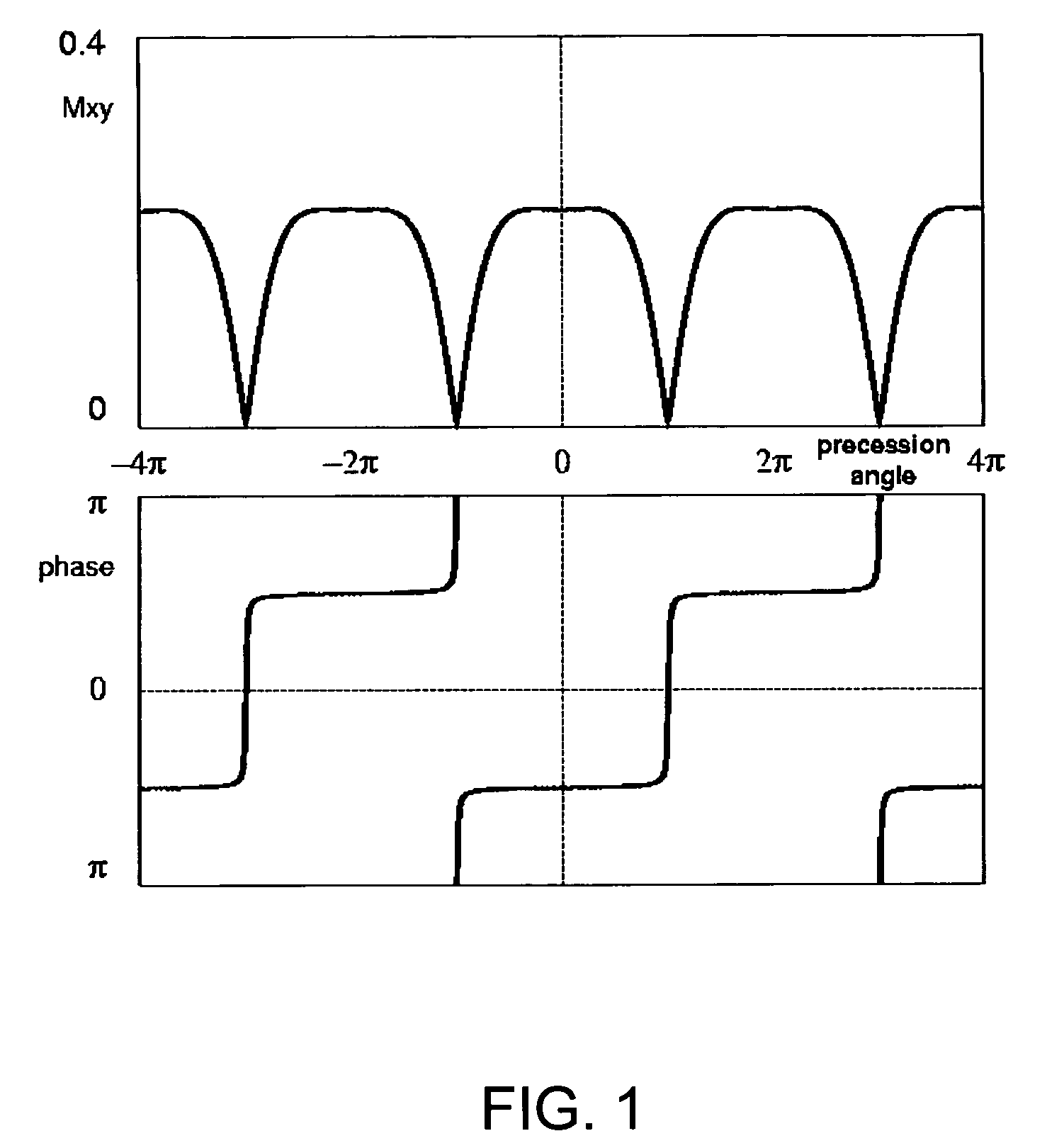
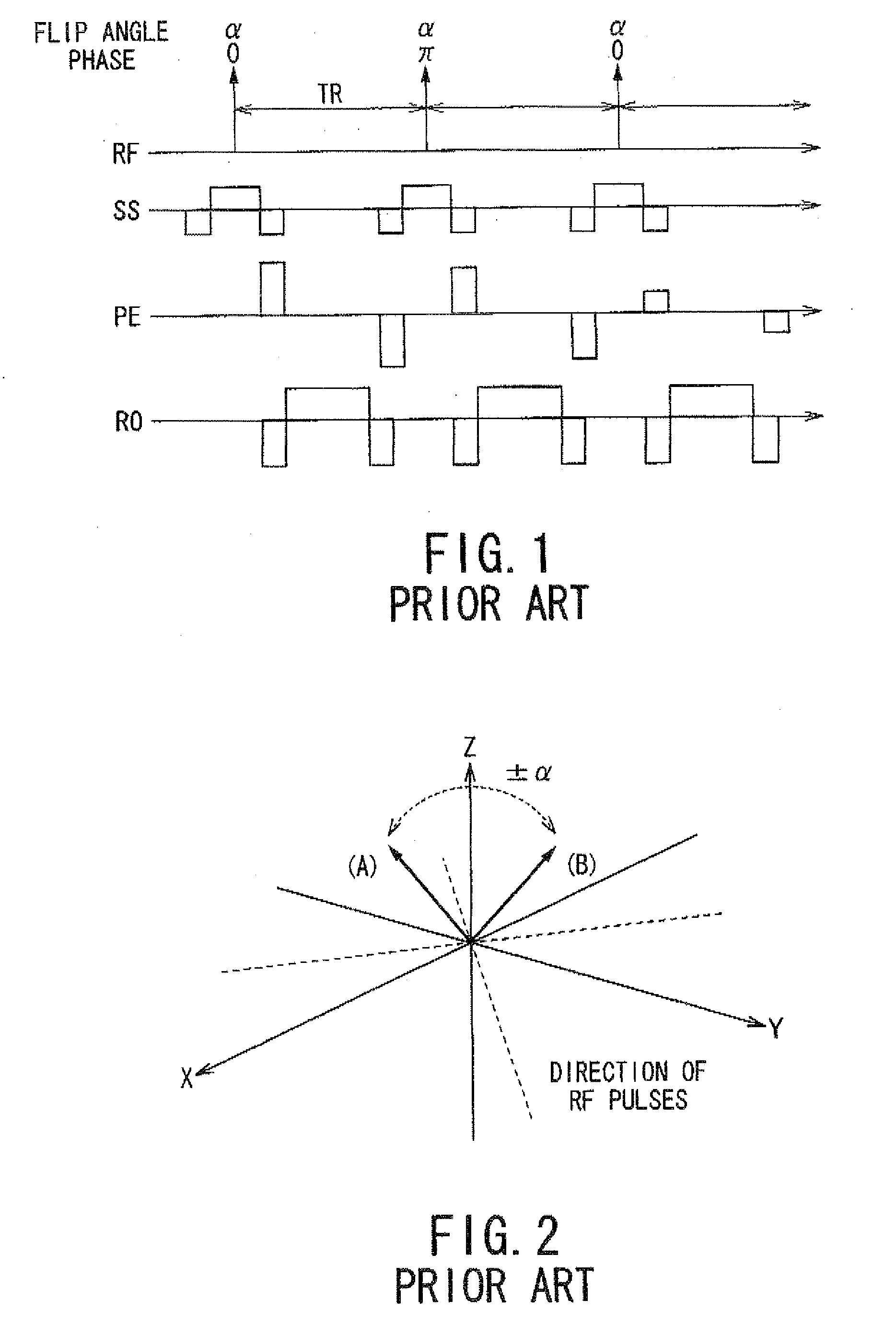
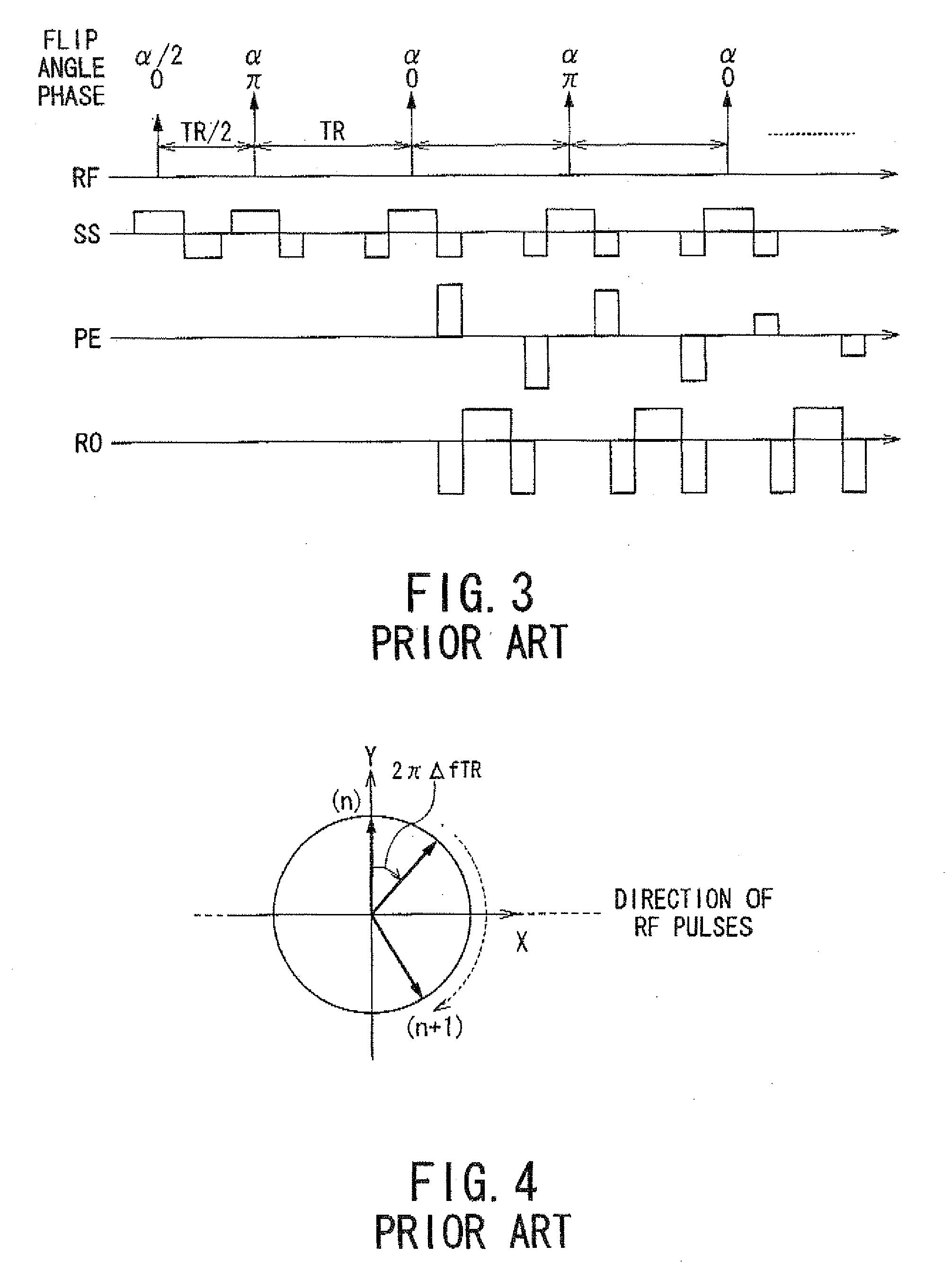
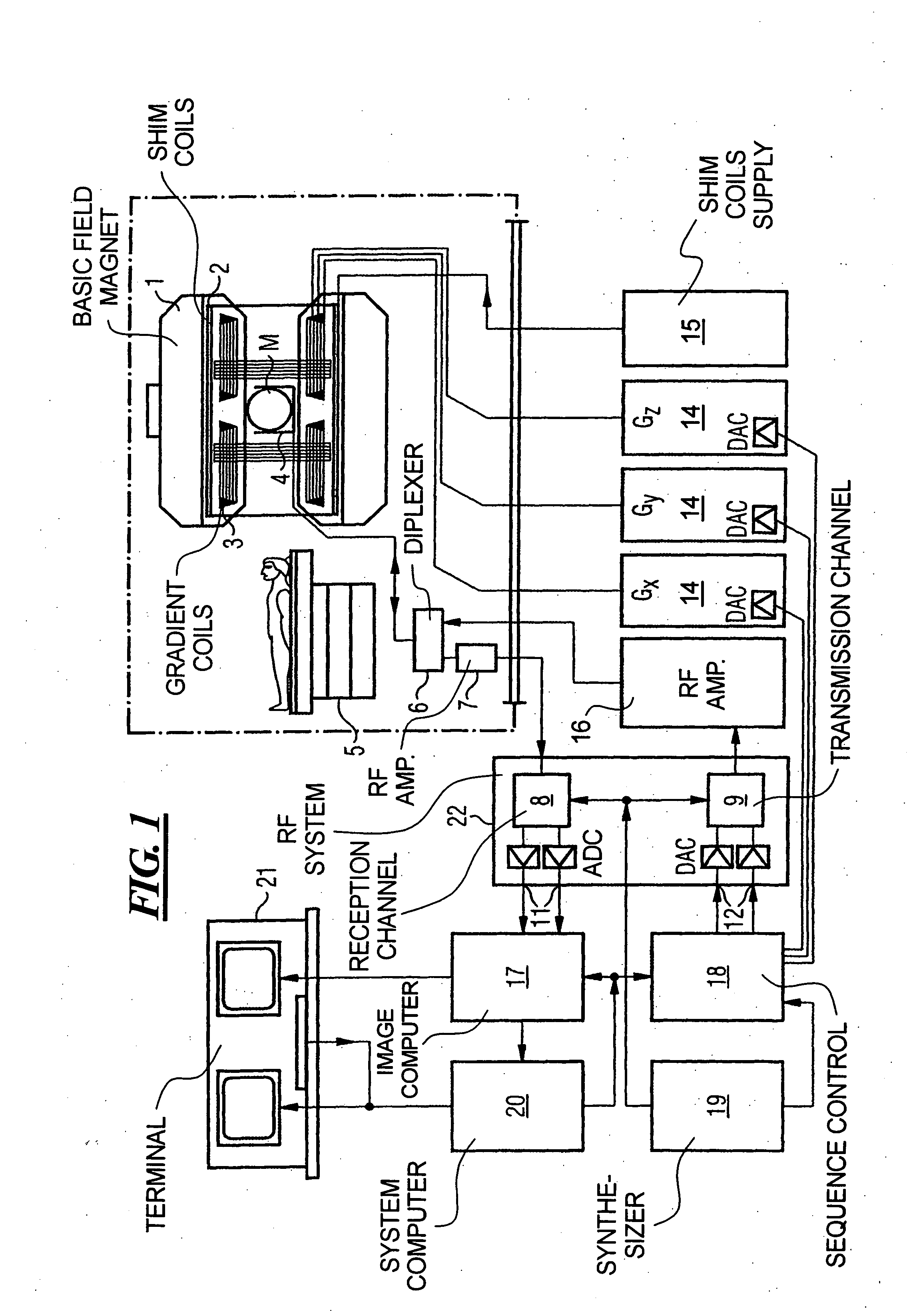
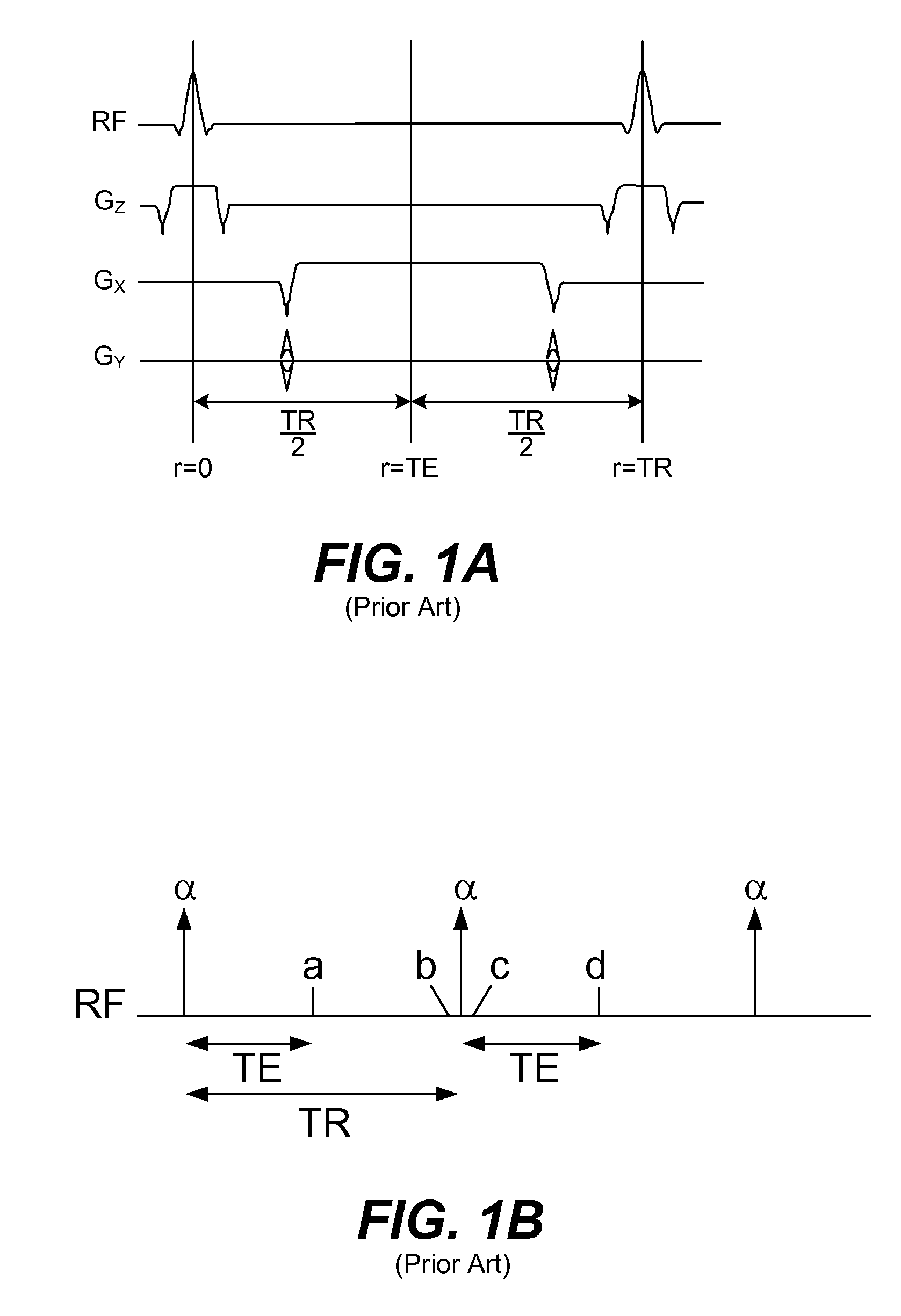
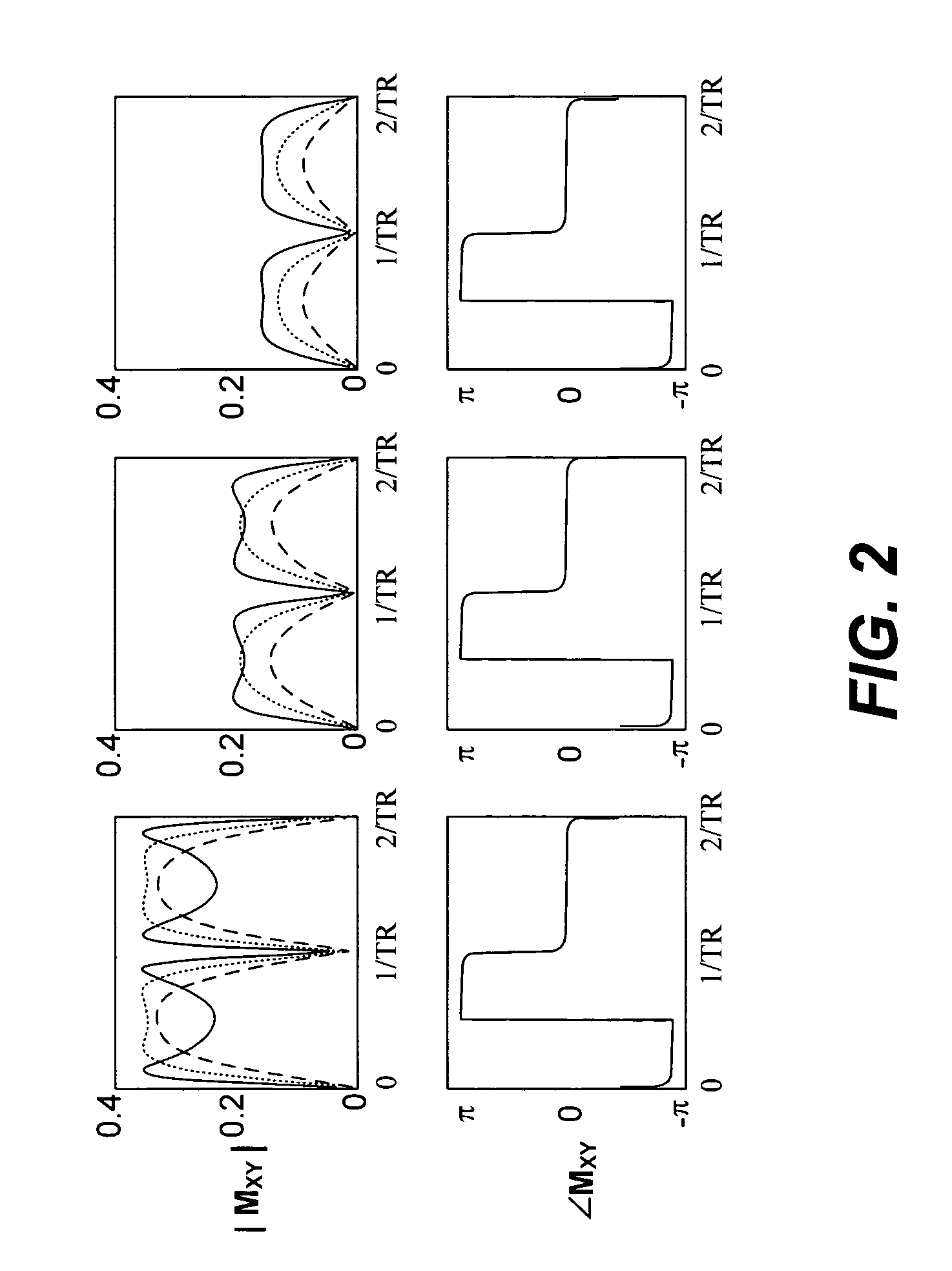
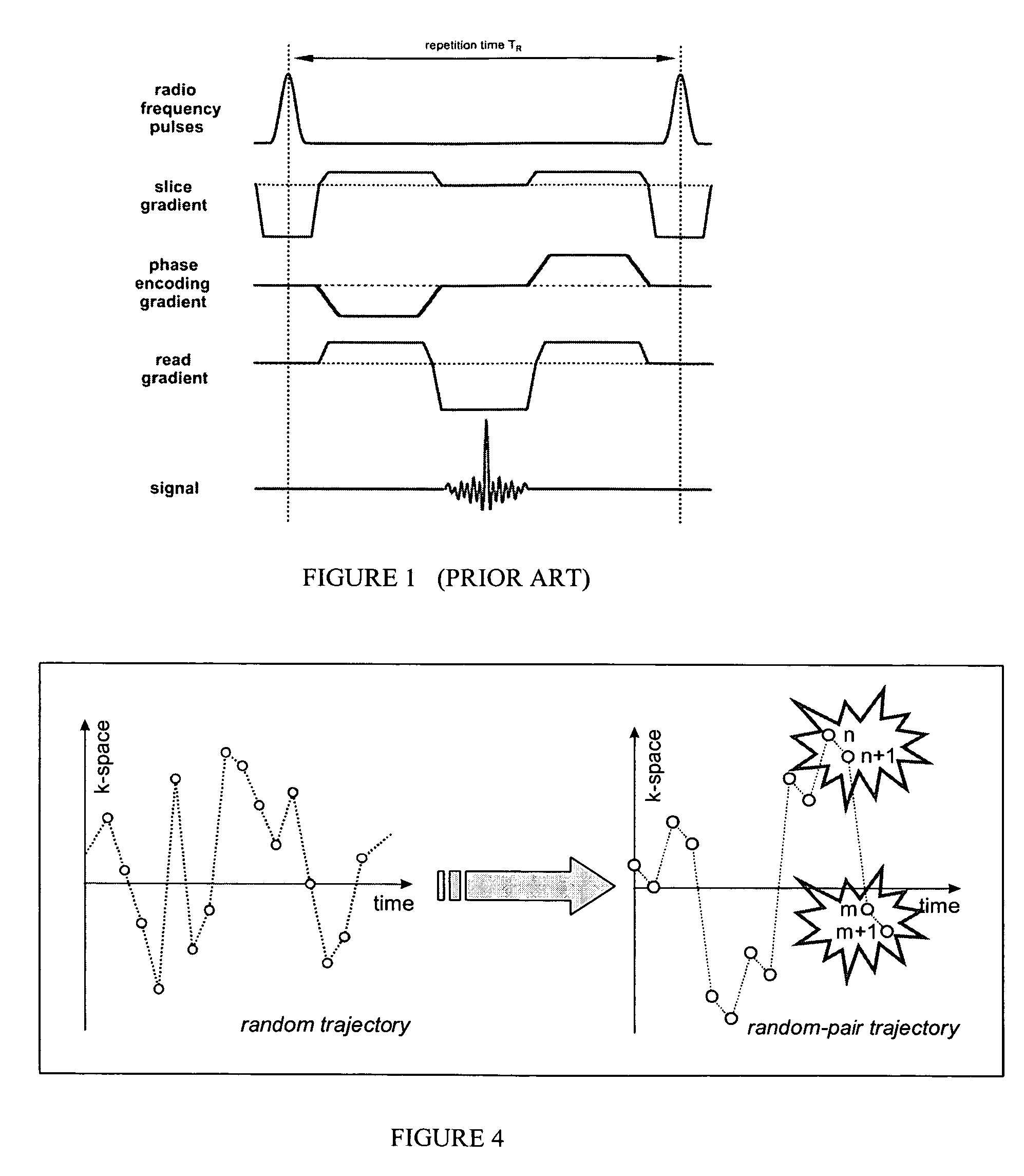
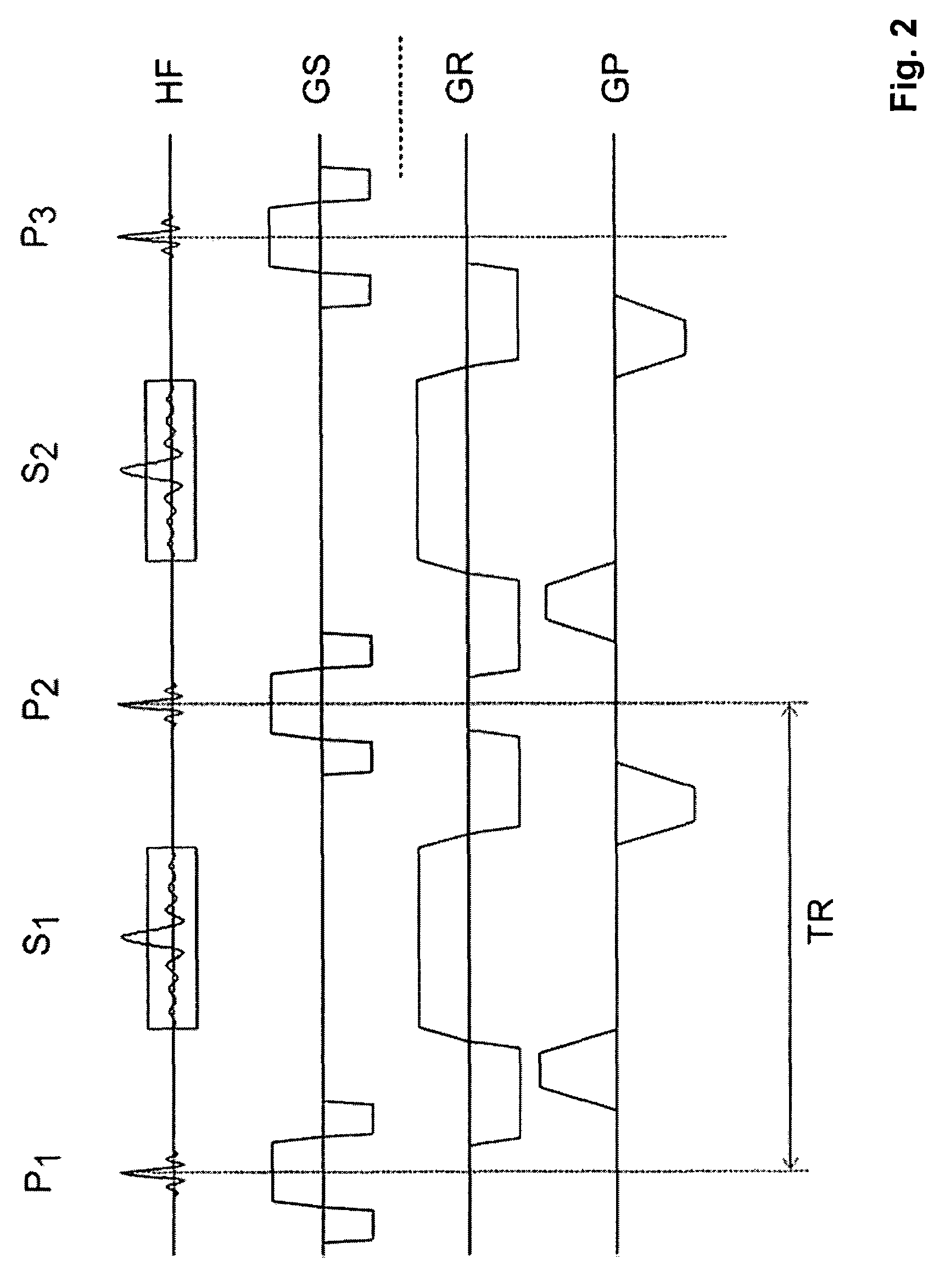
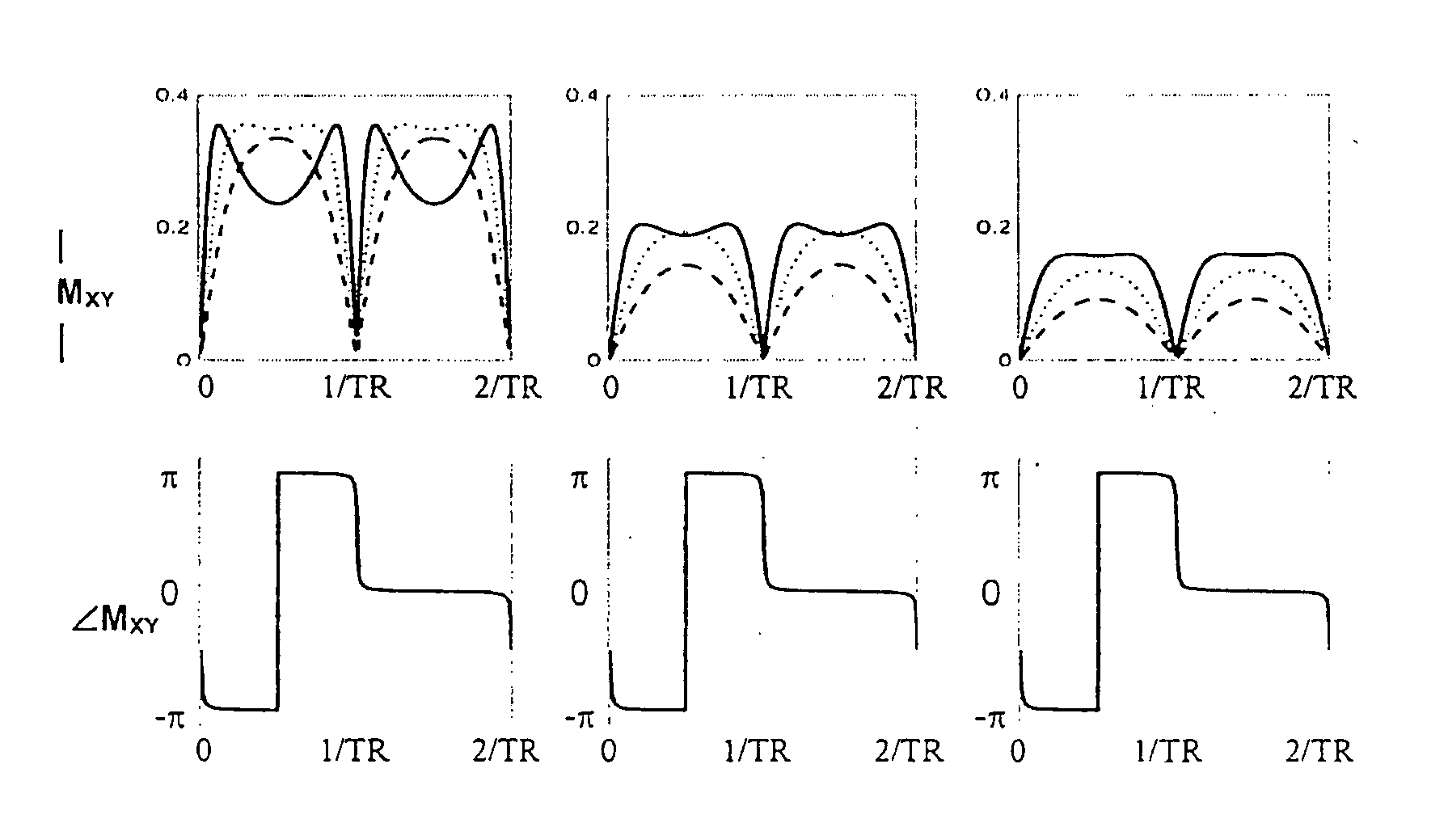
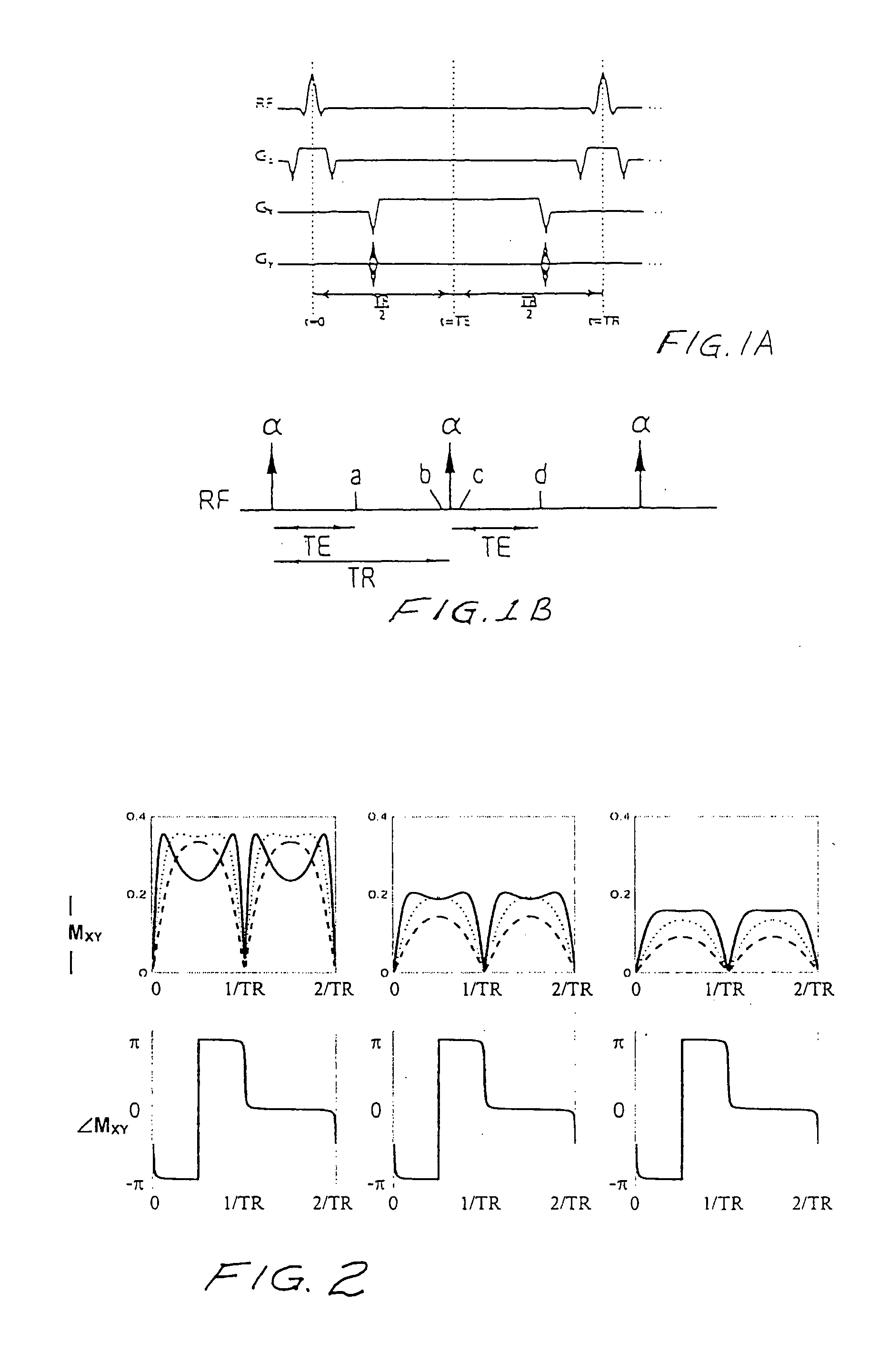
Steady State Free Precession (SFP or SSFP) Steady state free precession is any field or gradient echo sequence in which a non-zero steady state develops for both components of magnetization (transverse and longitudinal) and also a condition where the TR is shorter than the T1 and T2 times of the tissue.
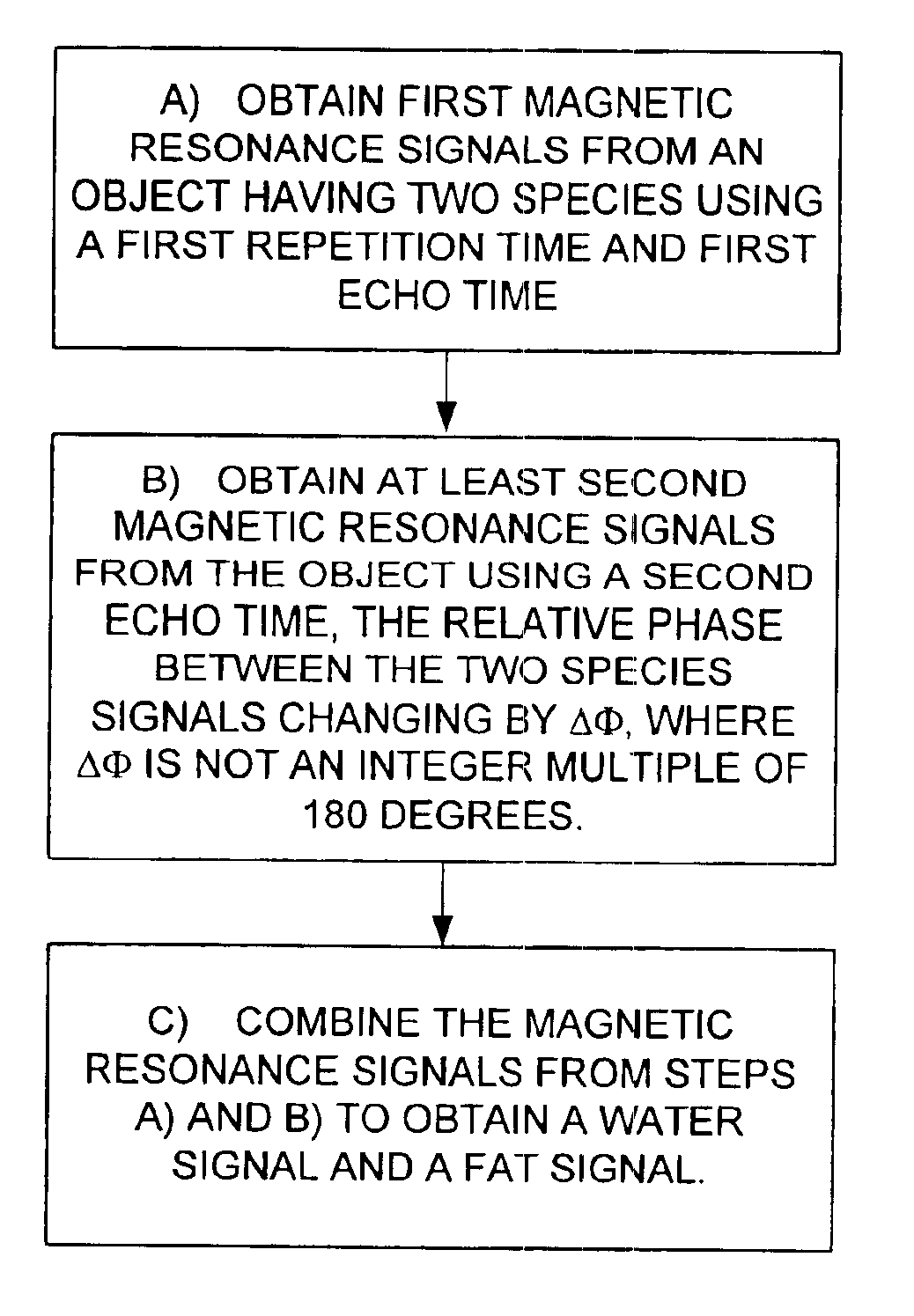
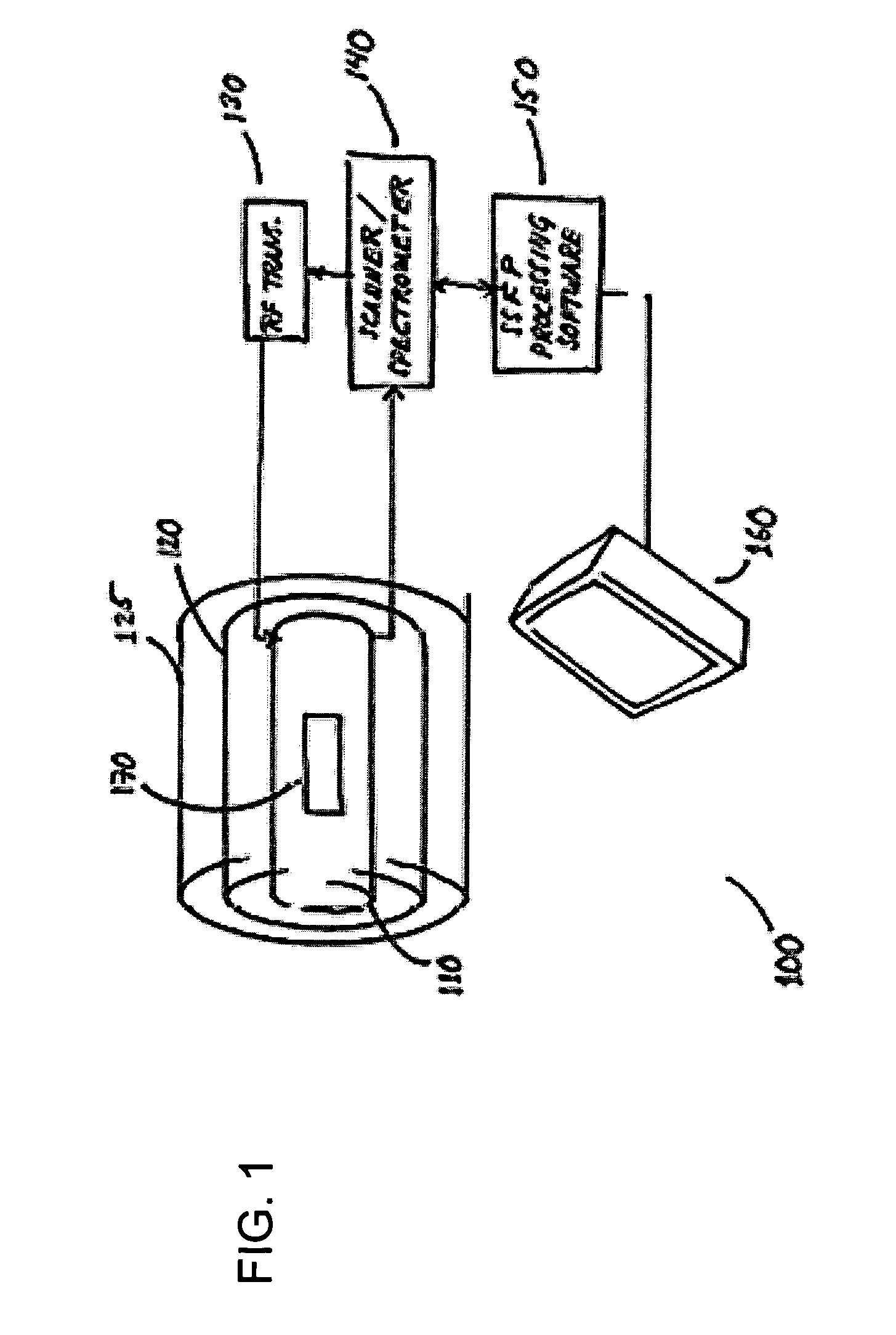
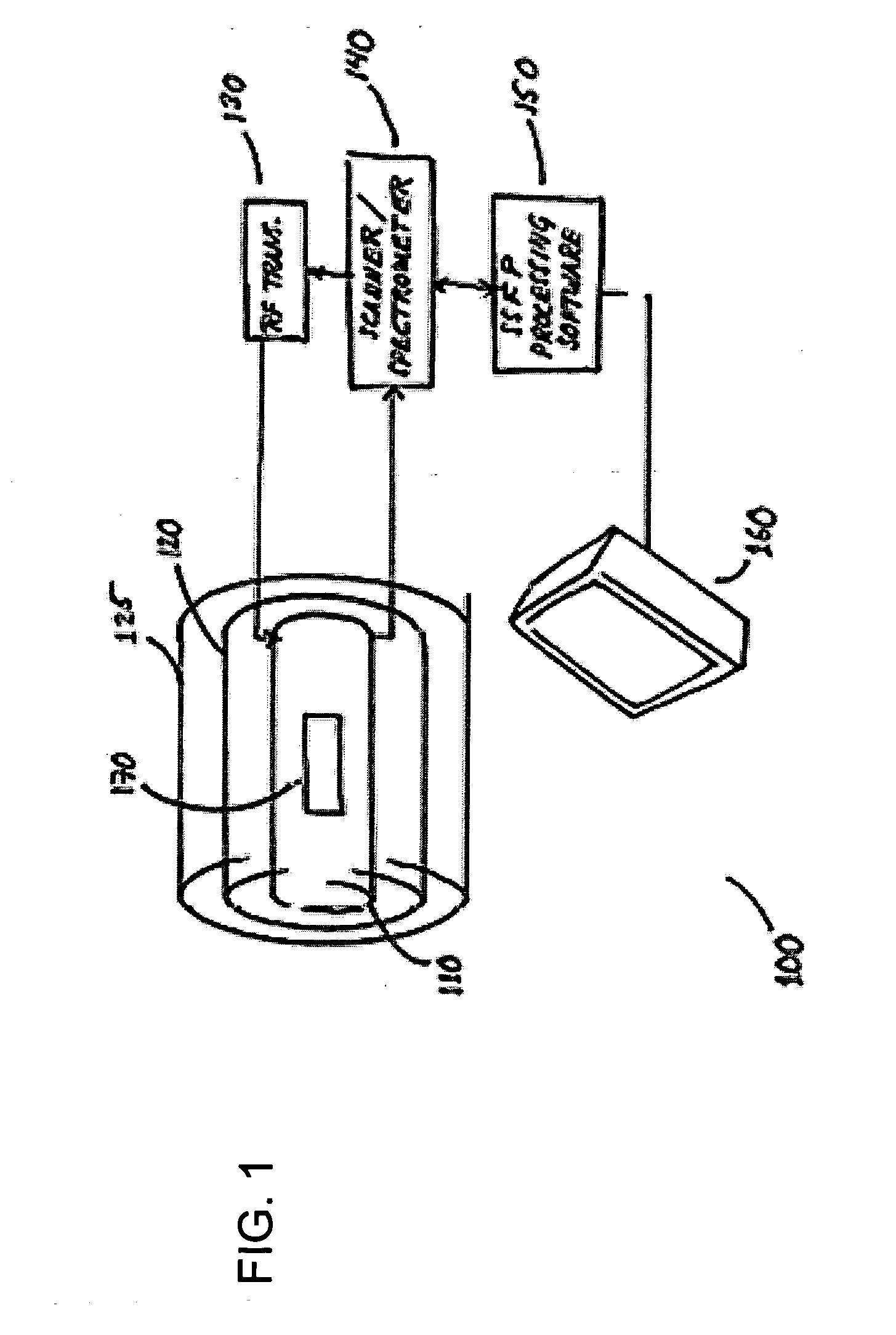
Magnetic resonance imaging with fat-water signal separation
InactiveUS6856134B1Fast imagingMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionArticular cartilageMR - Magnetic resonance
A generalized multi-point fat-water separation process is combined with steady-state free precession (SSFP) to obtain high quality images of articular cartilage with reduced imaging time.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Spectrally selective suppression with steady-state free precession
ActiveUS7253620B1Little disturbanceEnhanced inhibitory effectMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionTransverse magnetizationCine imaging
A method that exploits the intrinsic selectivity of steady-state free precession (SSFP) to perform spectral suppression is disclosed. Such a method avoids the need to incorporate additional spectrally selective pulse sequence elements. The scheme is based on breaking the FISP imaging sequence into short trains having, for example, 8–64 RF pulses. At the moment of echo formation (i.e., TE=TR / 2) after the last full RF pulse of the train, water signal is z-stored. Residual transverse magnetization, which include isochromats phase-opposed to the on-resonance water, is gradient crushed and RF spoiled. The stored magnetization is subsequently re-excited with little disturbance to the on-resonance steady-state water signal. The additional time required to perform the steady-state interruption is typically as little as a single TR, minimally affecting the efficiency of the imaging process. The sequence can be employed repetitively, greatly reducing the amplitude of fat signals throughout a real-time or cine imaging process.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
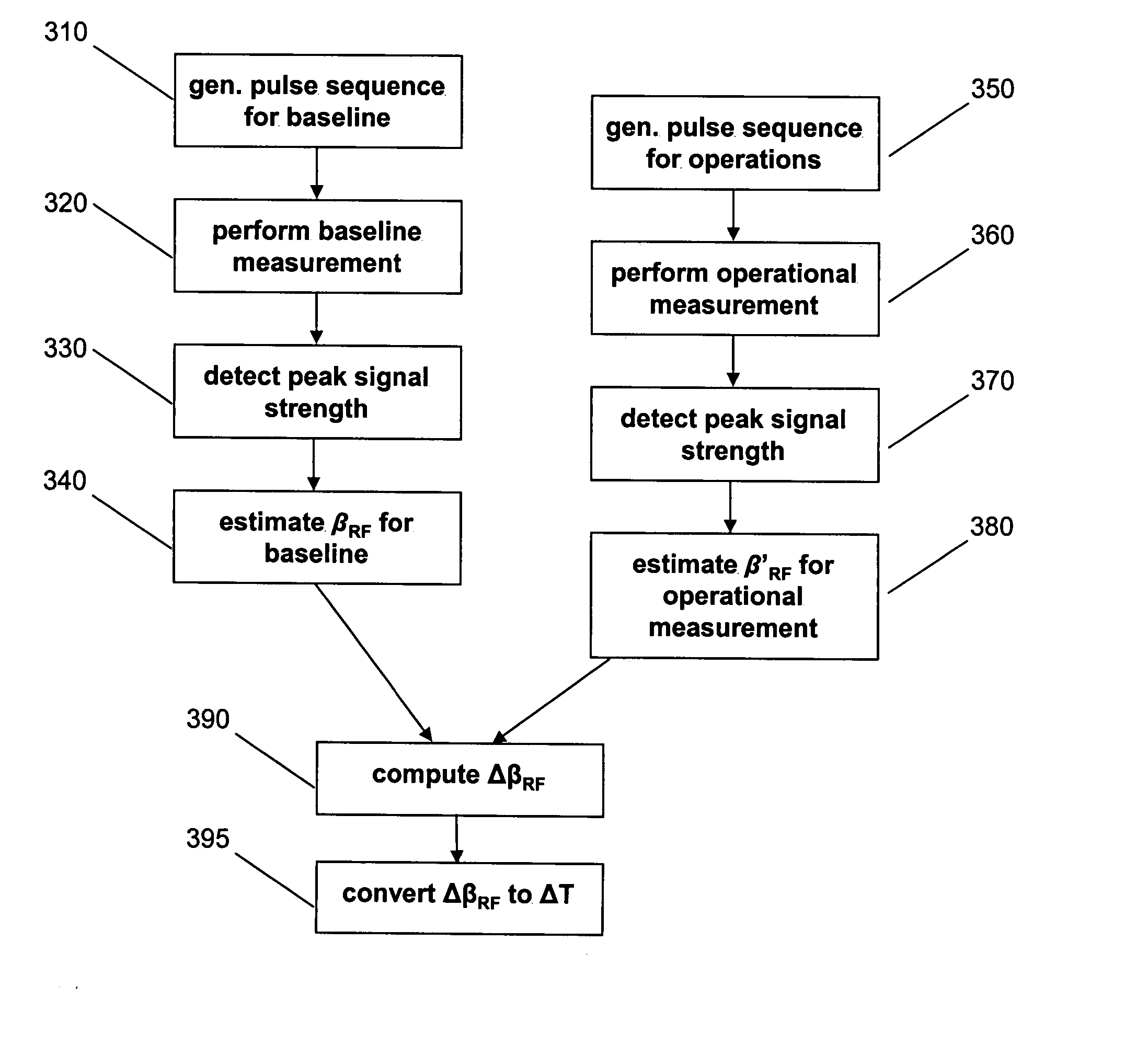
Steady state free precession based magnetic resonance thermometry
ActiveUS7078903B2High resolutionImprove efficiencyMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionProton resonance frequencyProton
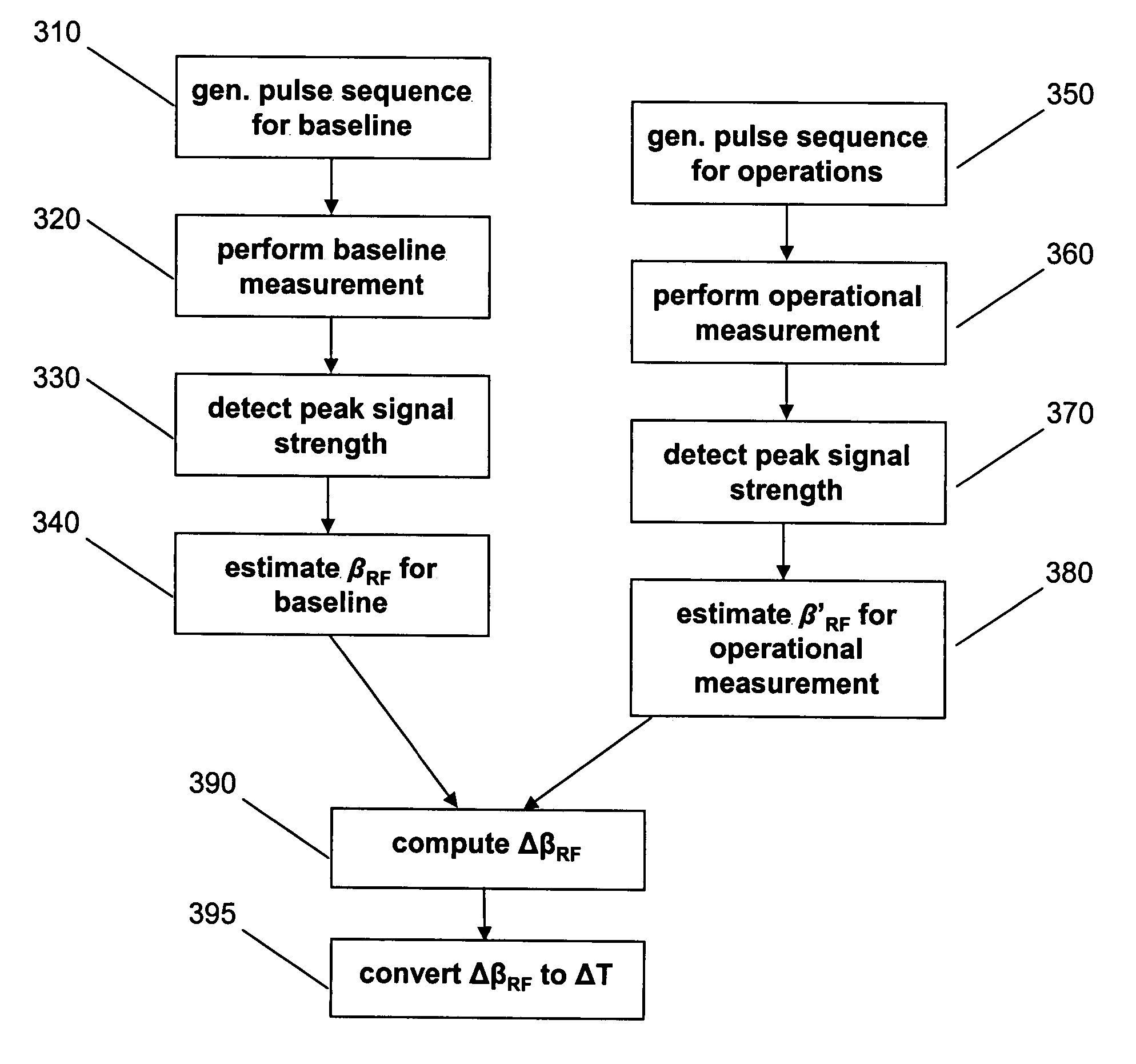
Disclosed is a method and system for steady state free precession based magnetic resonance thermometry that measures changes in temperature on a pixel by pixel basis. The method comprises generating an RF pulse sequence used to find the proton resonance frequency shift, which is proportional to temperature change, processing the resultant MRI data to measure the proton frequency shift, and converting the measured proton frequency shift into change in temperature data. Further disclosed is a method for identifying and compensating for temperature drifts due to core heating of the gradient magnet.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Generic eddy-current compensation in magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS20050258829A1Easy to implementMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionEddy currentCompensation strategy
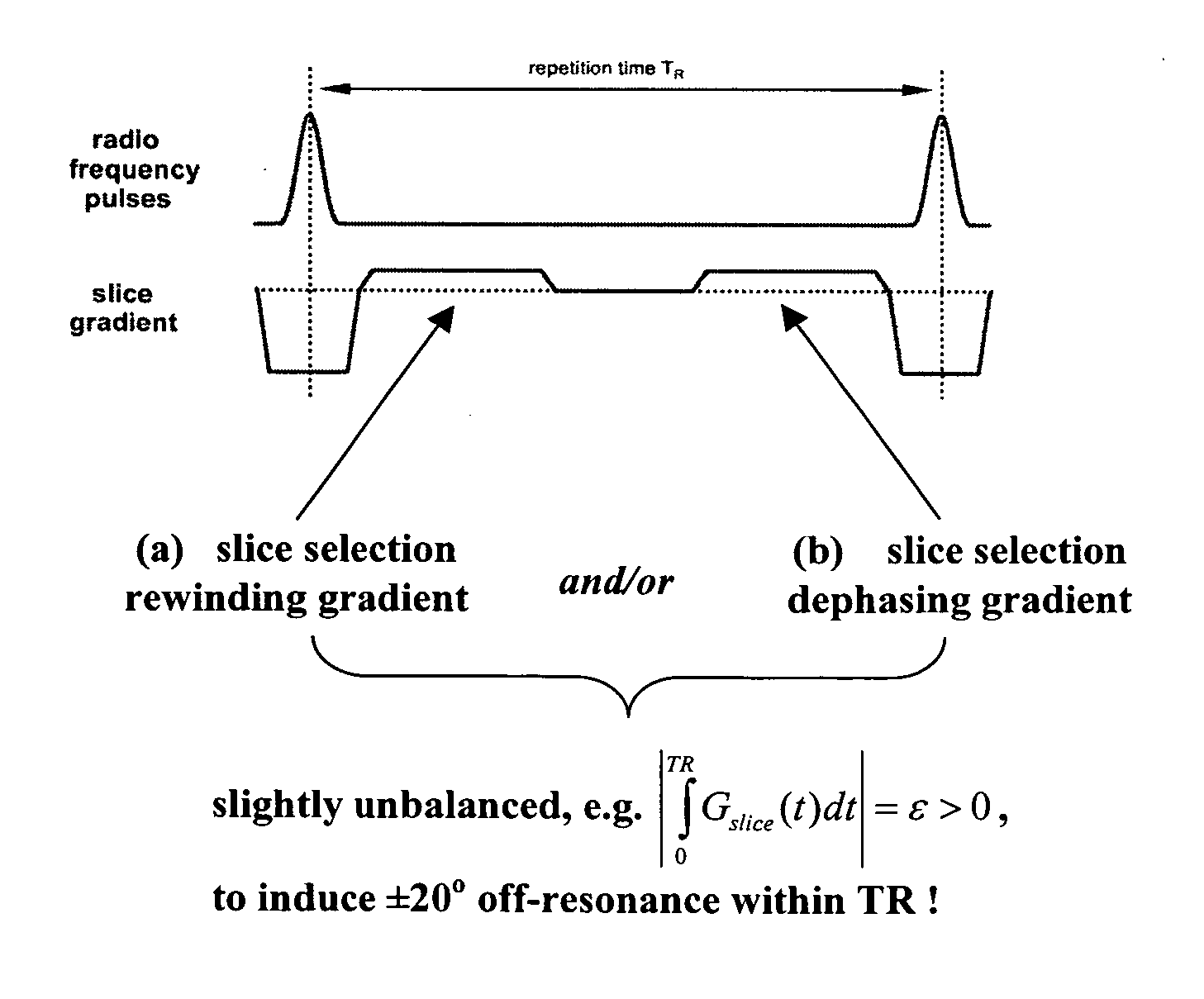
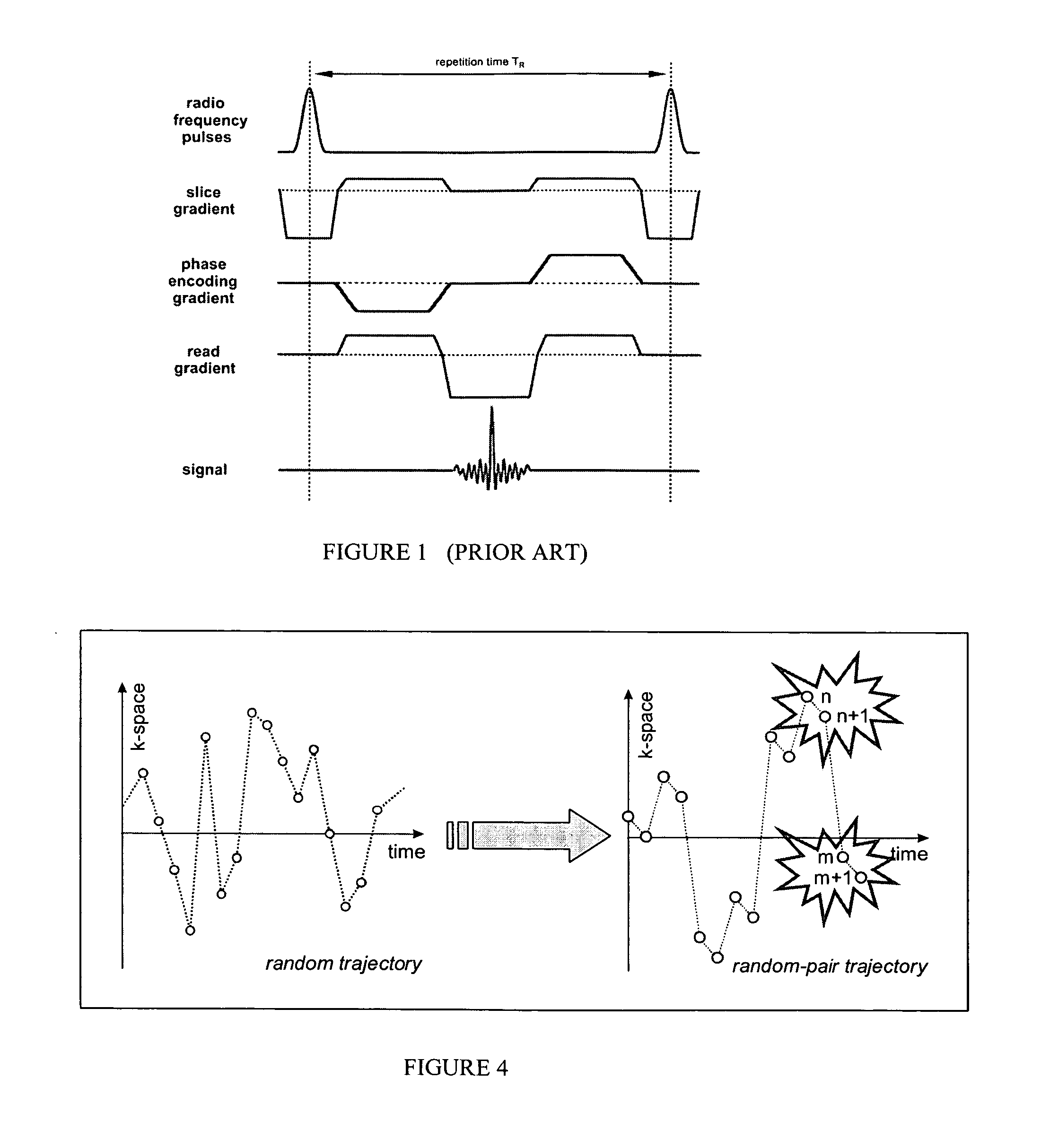
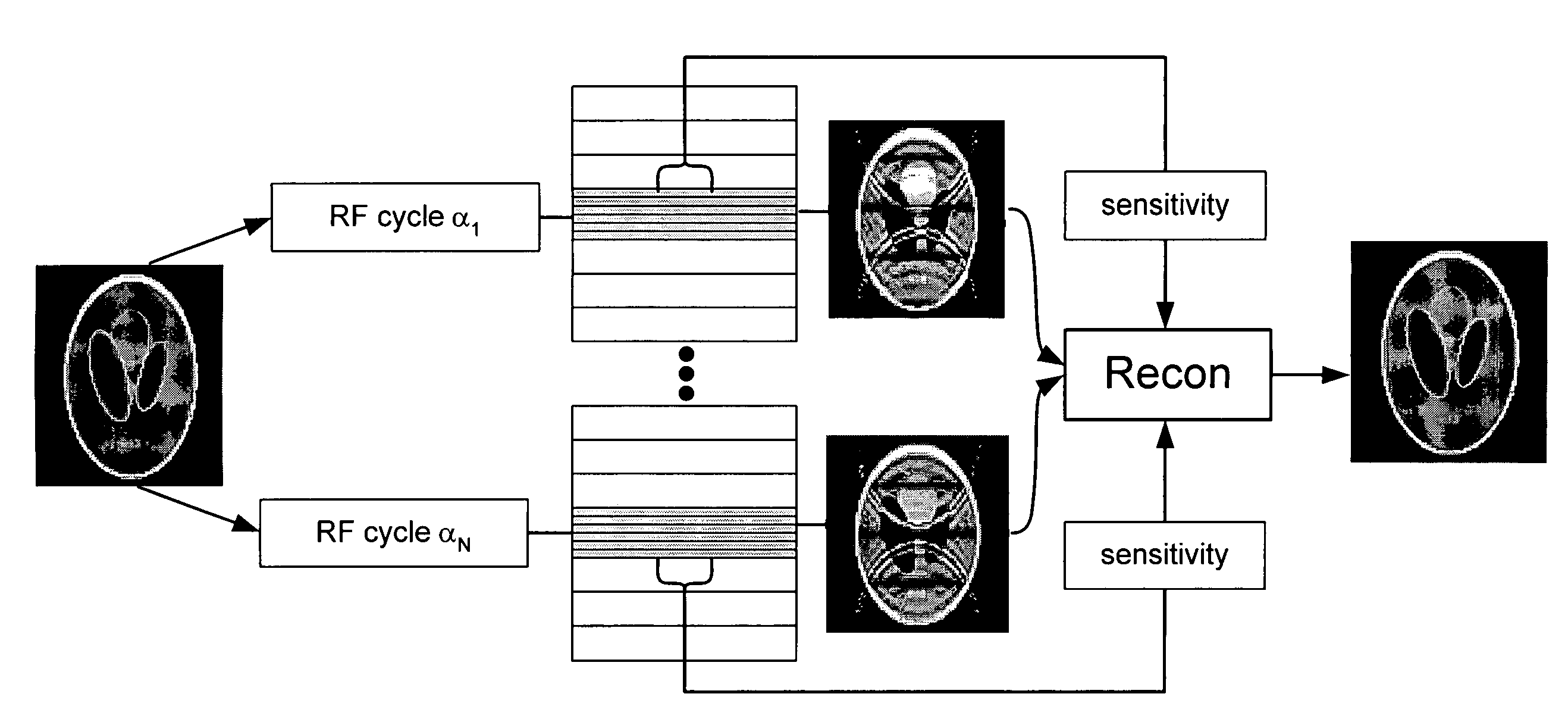
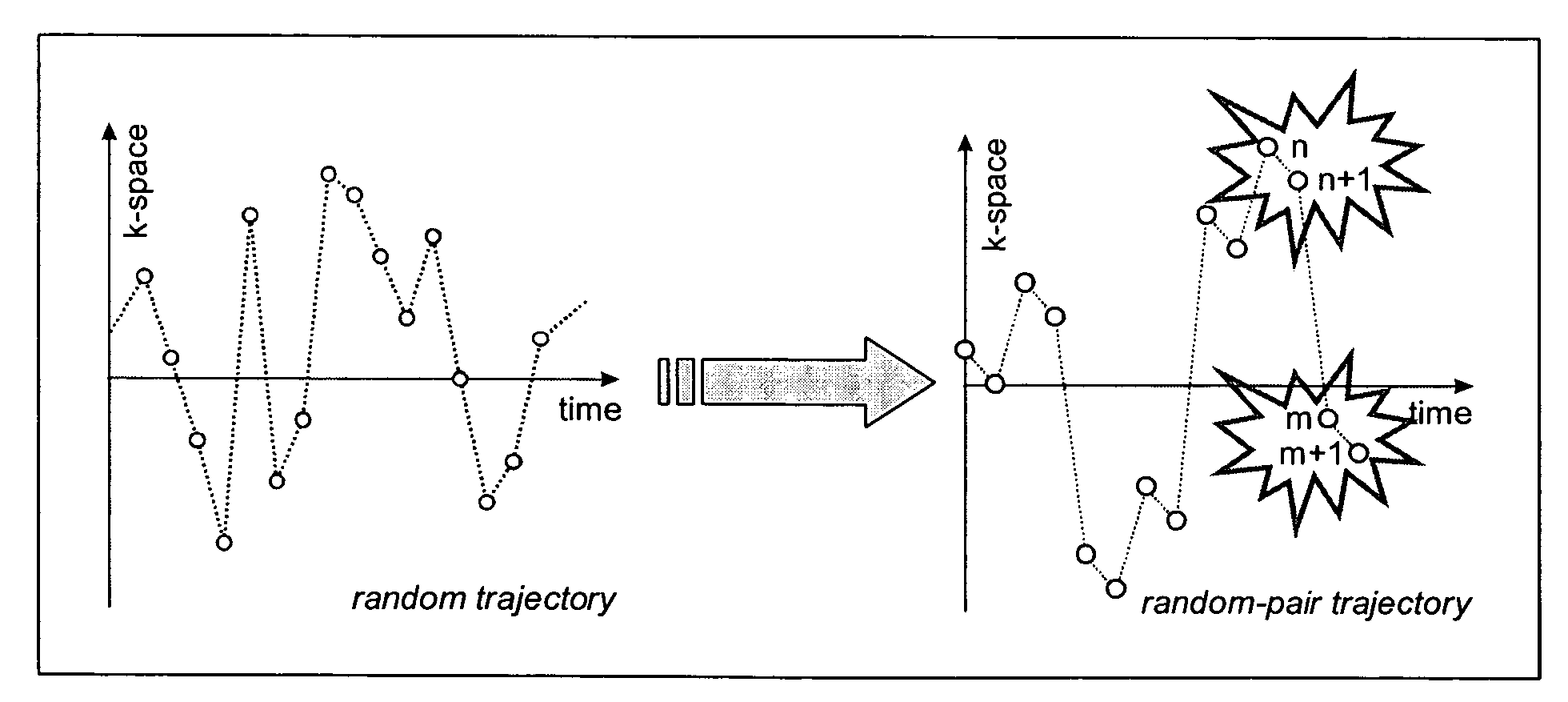
A method of steady-state free precession MR imaging is provided that includes the steps of: (a) providing a balanced steady-state free precession imaging sequence that includes a plurality of phase encoding steps, wherein each phase encoding step comprises a phase encoding gradient and a slice selection gradient; and (b) acquiring imaging data by performing the plurality of phase encoding steps in sequence, wherein the imaging data is acquired is compensated for one or more effects due to eddy-currents, flow, or motion related artefacts due to the implementation of one or more artefact compensation strategies that consist of (i) “pairing” of consecutive phase encoding steps and of (ii) “through slice equilibration” of eddy-current and motion or flow related signal oscillations.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF BASEL
Magnetic resonance imager using cylindrical offset region of excitation, and method
InactiveUS20100104157A1Add featureMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionCoronary arteriesData set
A magnetic resonance imager performing images of a patient imager includes imaging coils. The imager includes receiver coils The imager includes a computer that causes the imaging coils to produce a first steady-state free precession excitation slab with respect to a first position regarding a target of the patient during a first repetition time, and a second steady-state free precession excitation slab with respect to a second position different from the first position regarding the target during a second repetition time; and forming a first 3-D dataset of the target associated with the first excitation slab and a second 3-D image dataset of the target associated with the second excitation slab from information received from the receiver coils. The first 3-D image dataset and the second 3-D image dataset, together defining a series of 3-D image datasets for each repetition time; and producing an image of the target from the series of 3-D image datasets. A method for analyzing a patient. A method to evaluate coronary arteries to assess their degree of stenosis. A computer program which, when executed by a computer of a Magnetic Resonance Imager, forms an image of a patient.
Owner:ALLEGHENY SINGER RES INST
Noninvasive 4-d time-resolved dynamic magnetic resonance angiography
ActiveUS20150327783A1High degree of efficiencyIncrease flexibilityMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSensorsSystoleCardiac cycle
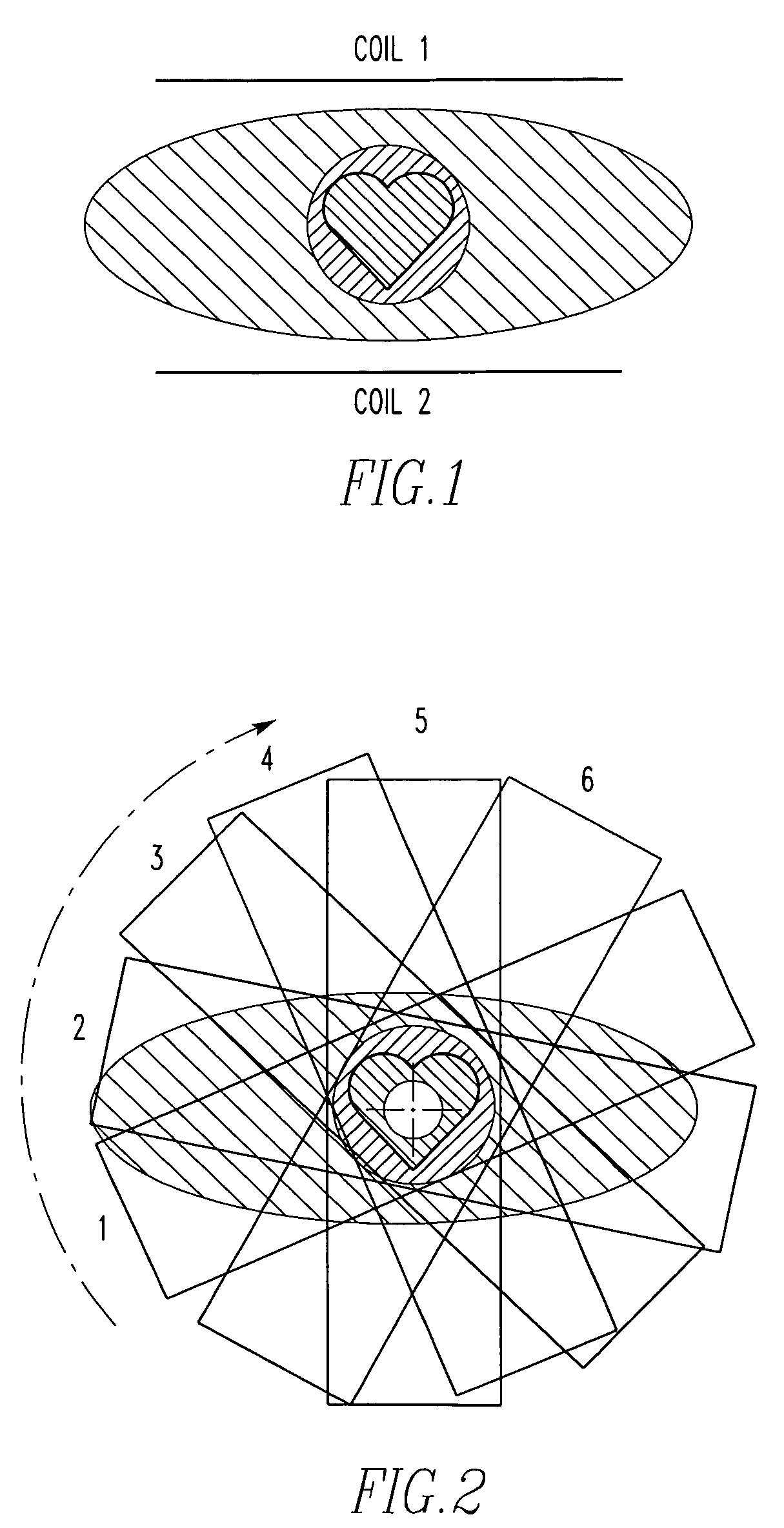
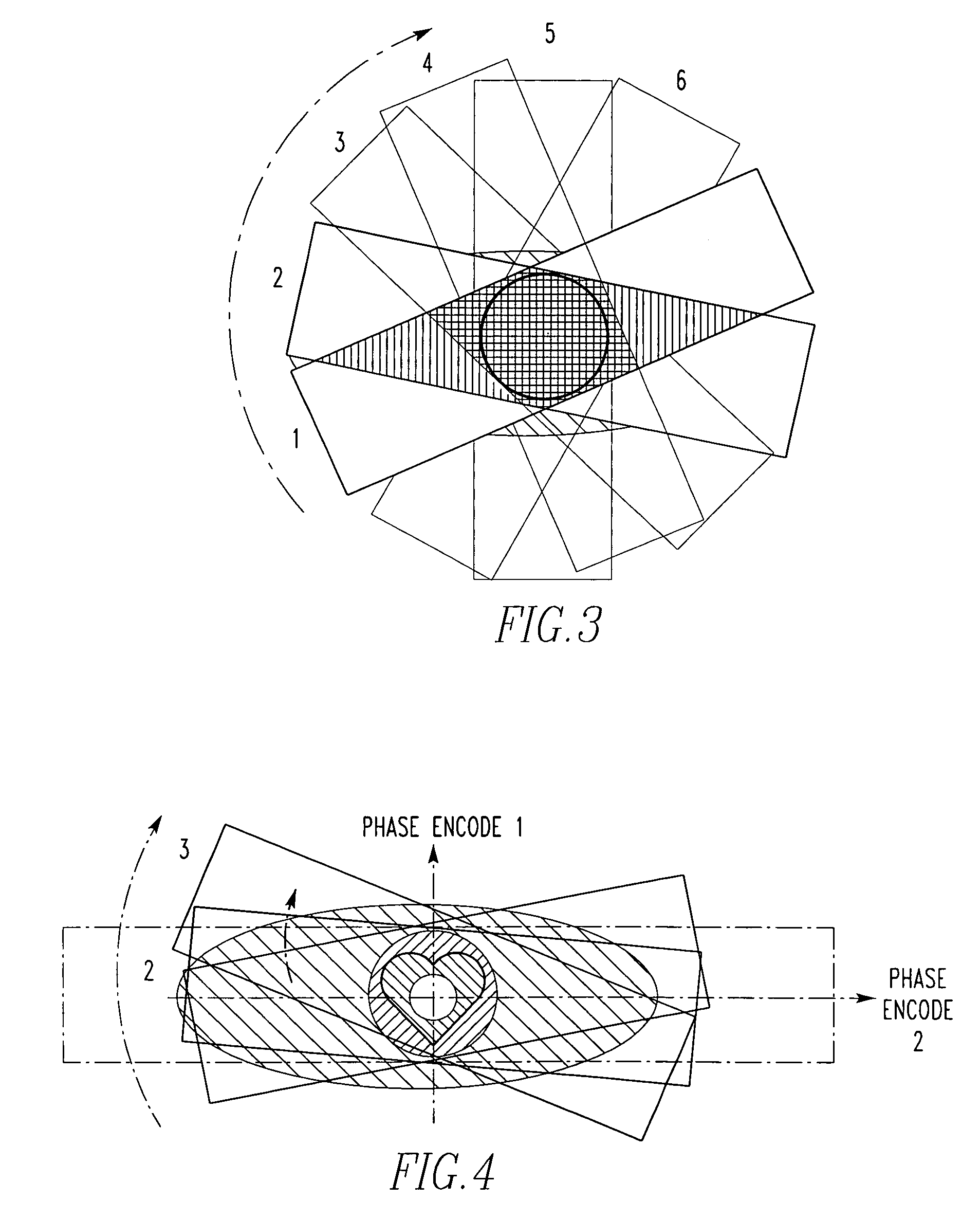
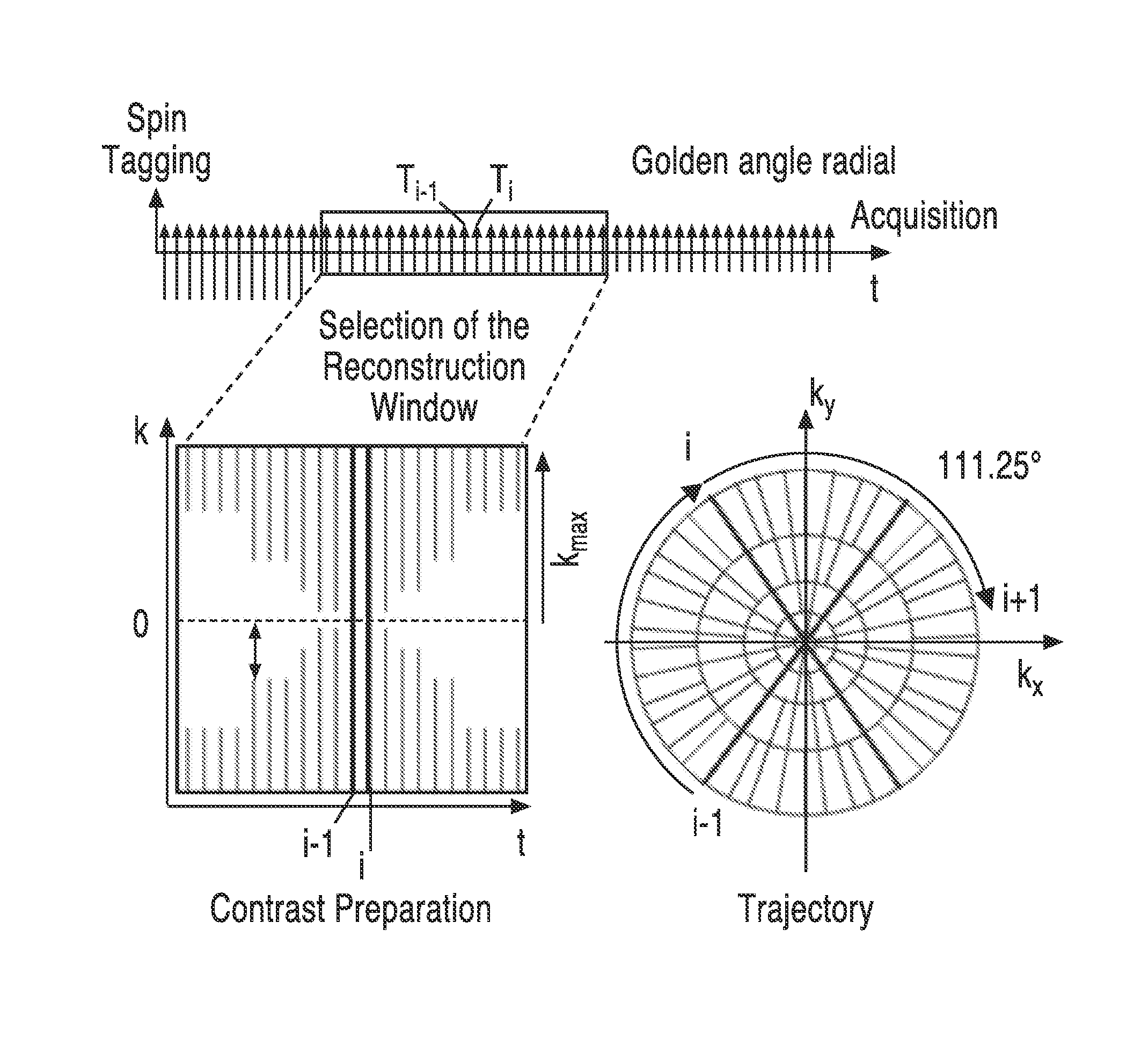
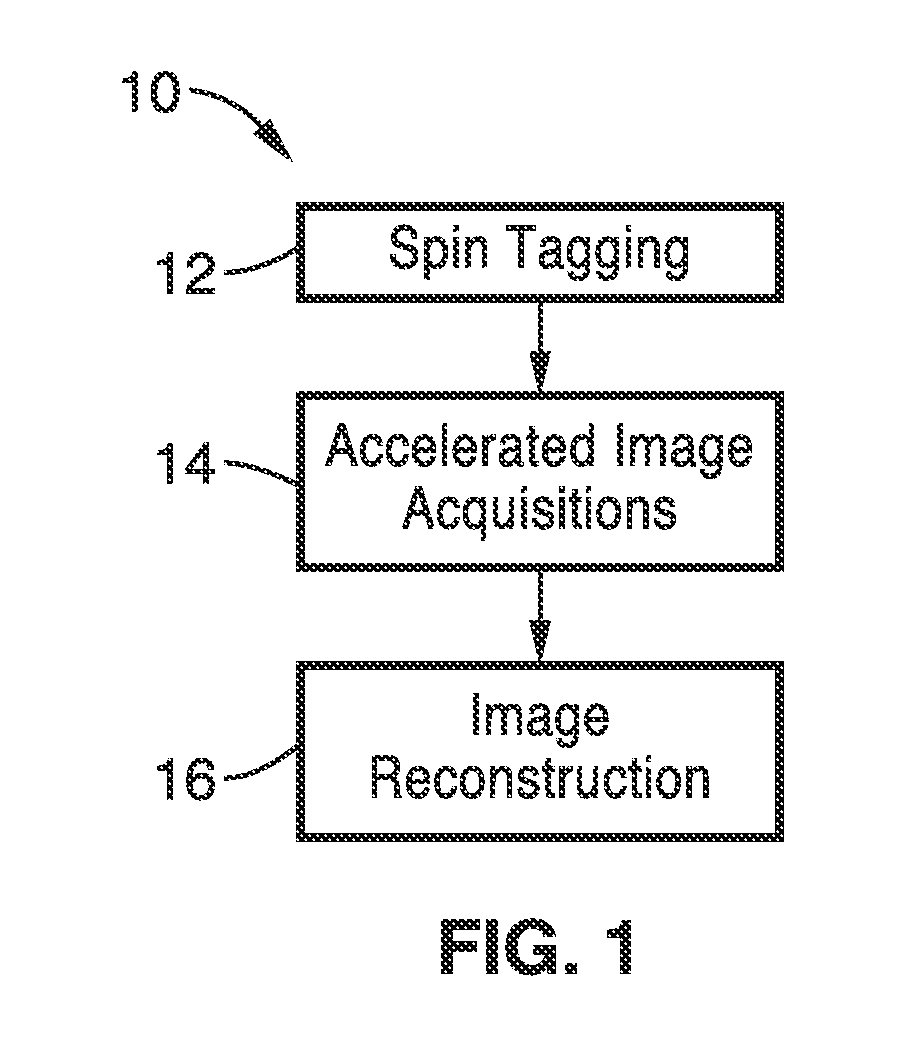
A method for non-contrast enhanced 4D time resolved dynamic magnetic resonance angiography using arterial spin labeling of blood water as an endogenous tracer and a multiphase balanced steady state free precession readout is presented. Imaging can be accelerated with dynamic golden angle radial acquisitions and k-space weighted imaging contrast (KWIC) image reconstruction and it can be used with parallel imaging techniques. Quantitative tracer kinetic models can be formed allowing cerebral blood volume, cerebral blood flow and mean transit time to be estimated. Vascular compliance can also be assessed using 4D dMRA by synchronizing dMRA acquisitions with the systolic and diastolic phases of the cardiac cycle.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +1
Magnetic resonance imaging method for the quantification of the t1 and/or t2 relaxation times in a sample
ActiveUS20140292325A1Fast and accurate quantificationReduce signalingElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using NMRBalanced ssfpEcho signal
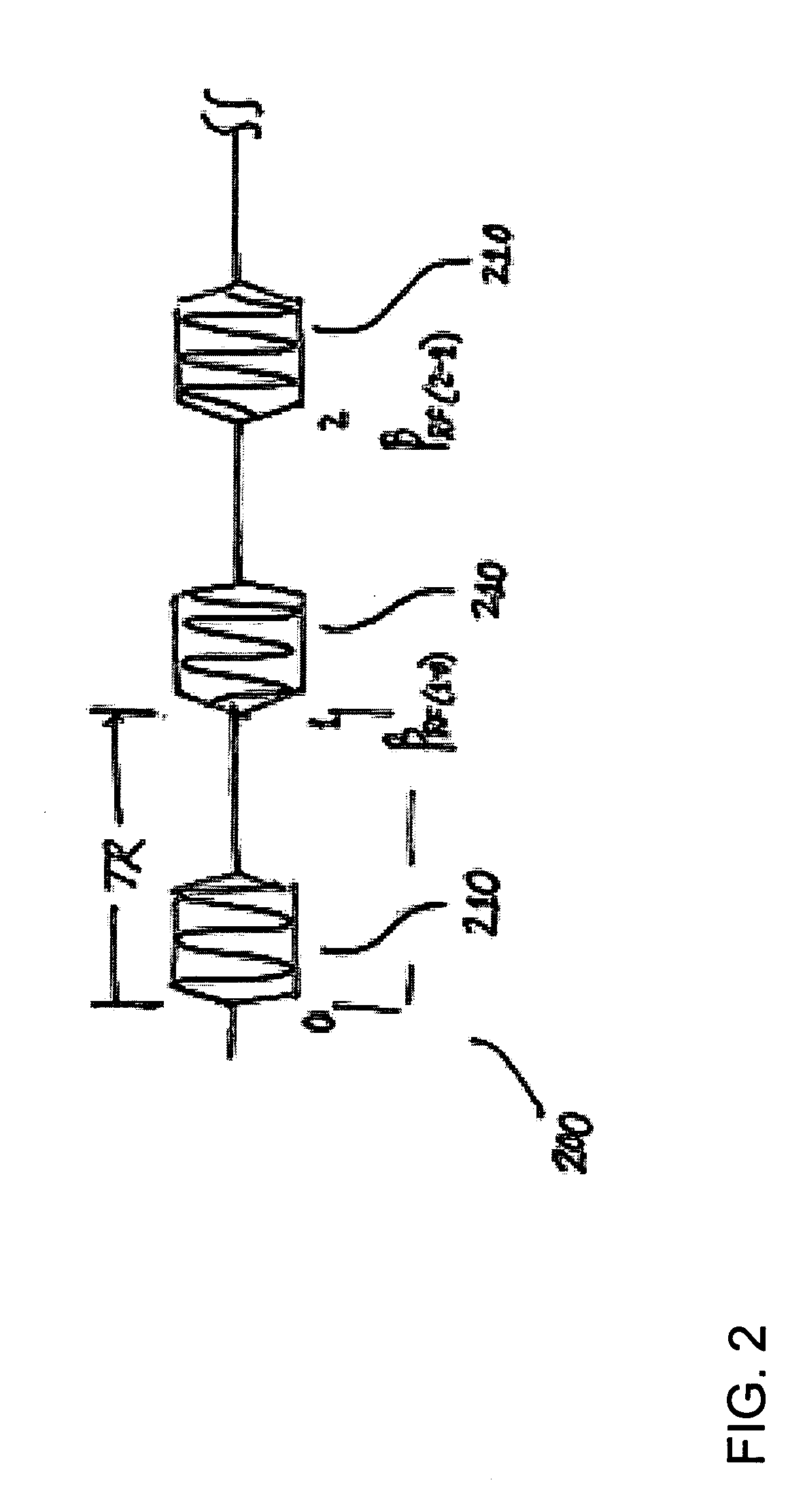
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) method for the quantification of the longitudinal (T1) and / or transverse (T2) relaxation times in a sample is provided. According to this MRI method a sample is subjected to an unbalanced steady state free precession (SSFP) sequence comprising a series of consecutive radiofrequency (RF) pulses. By means of this unbalanced SSFP sequence, the first order SSFP FID signal (F1), the lowest order SSFP FID signal (F0), and the lowest order SSFP Echo signal (F−1) are acquired. Based on the F0-signal, the F1-signal and the F−1-signal the longitudinal (T1) and / or transverse (T2) relaxation times of the sample are determined.
Owner:UNIVSSPITAL BASEL
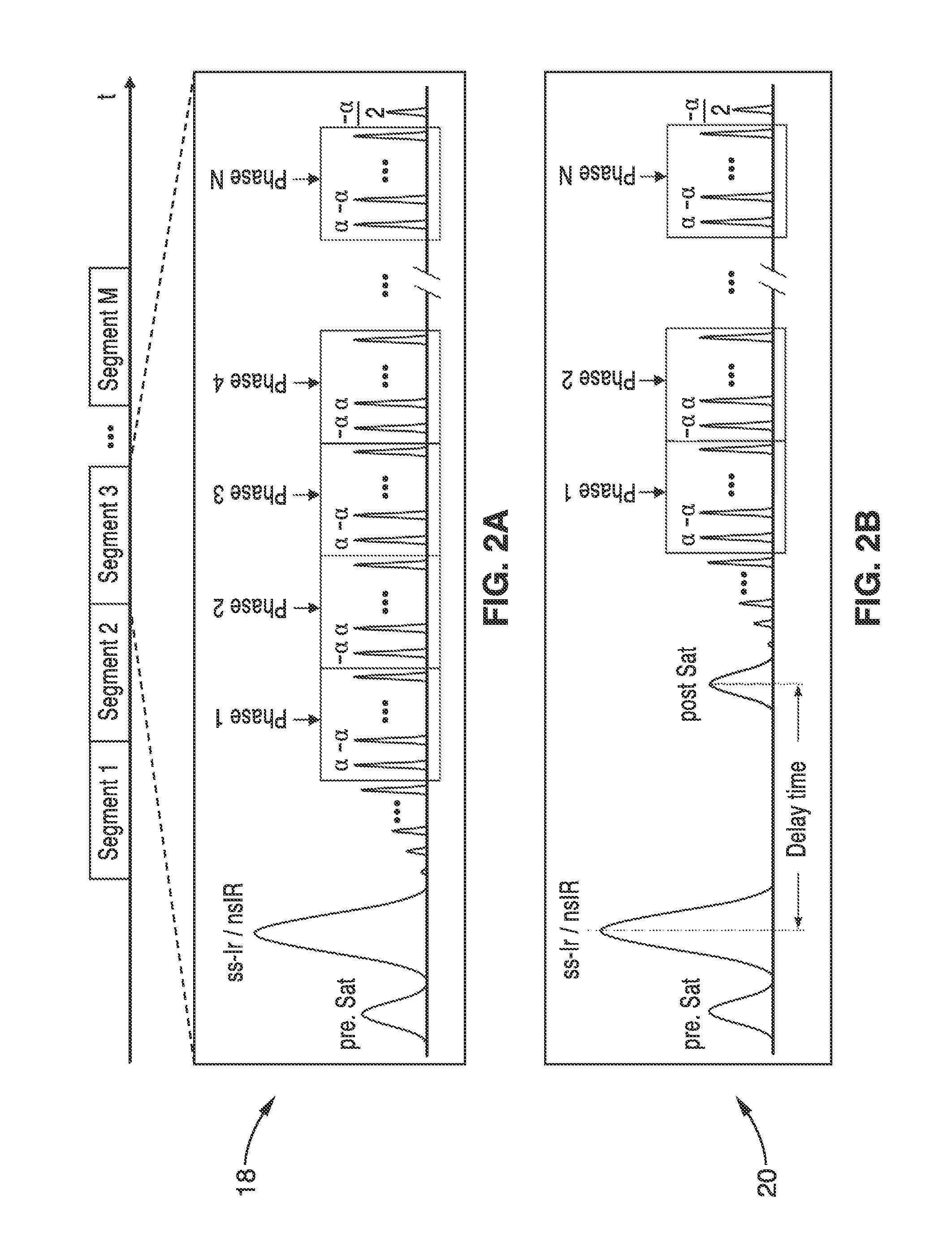
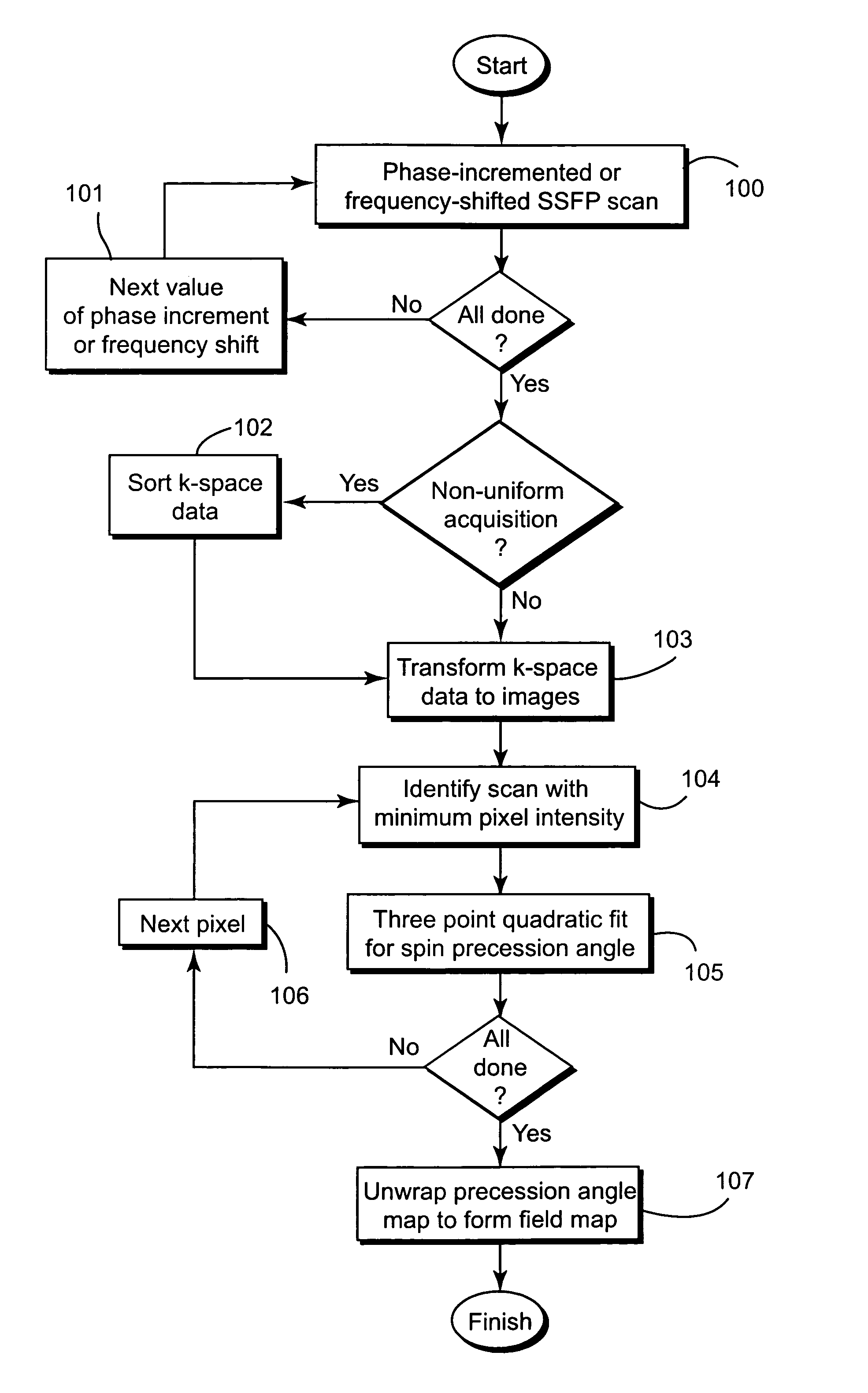
Magnetic field mapping during SSFP using phase-incremented or frequency-shifted magnitude images
InactiveUS7116105B1Magnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionFrequency shiftCondensed matter physics
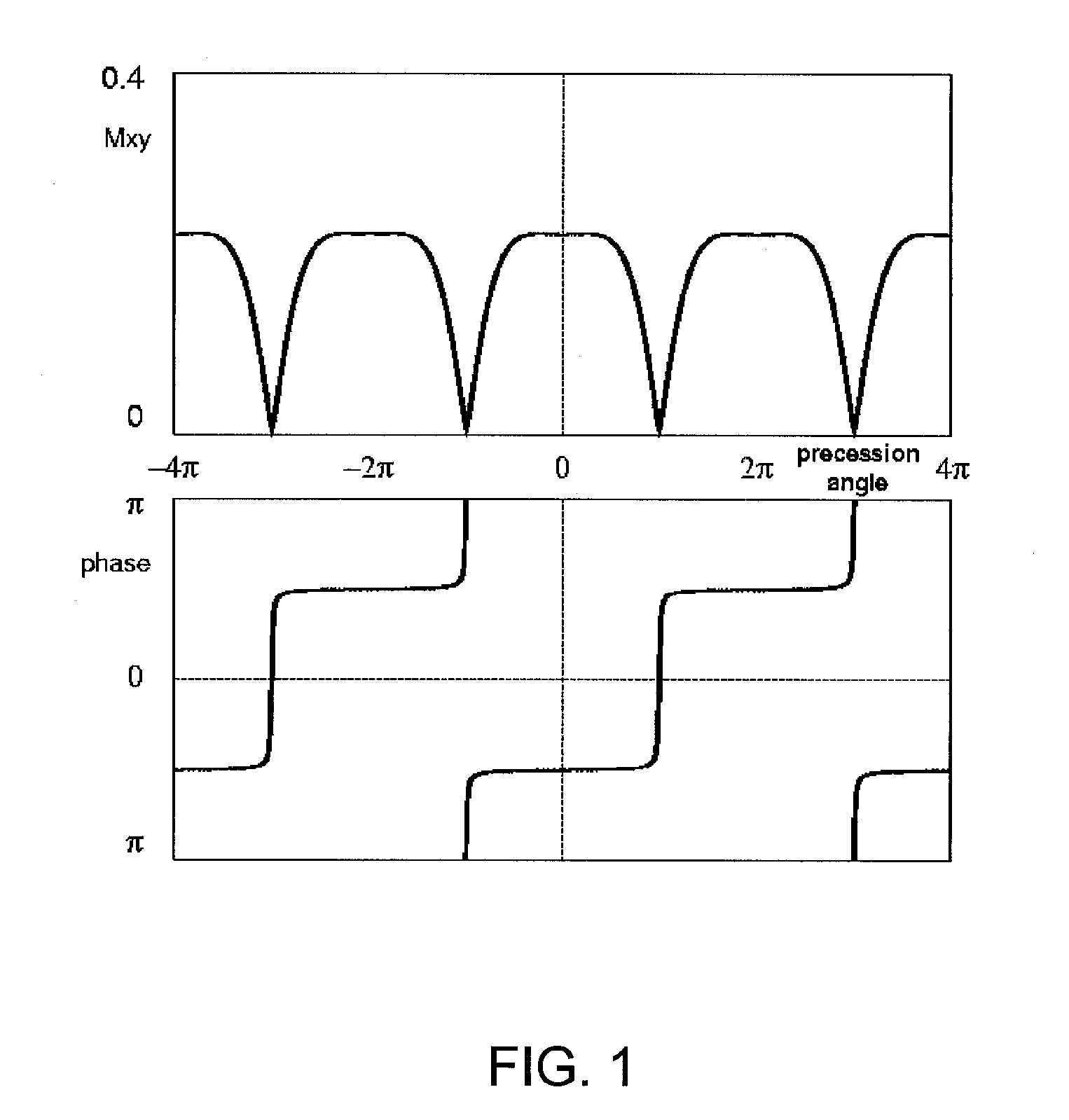
A system has been developed for mapping the magnetic field during a balanced steady-state free precession (SSFP) sequence. Field maps are generated by analyzing the magnitude of images acquired using the SSFP imaging sequences with phase increment or frequency shift. The system maps the magnetic field relevant to the imaging sequence and need not rely on phase information. The field maps may be applied to adjust the hardware for correcting the field anomalies contained in the maps. The field maps may also be used for separation of water and fat signals in SSFP imaging.
Owner:TOSHIBA AMERICA MRI
Water-fat separation magnetic resonance imaging method
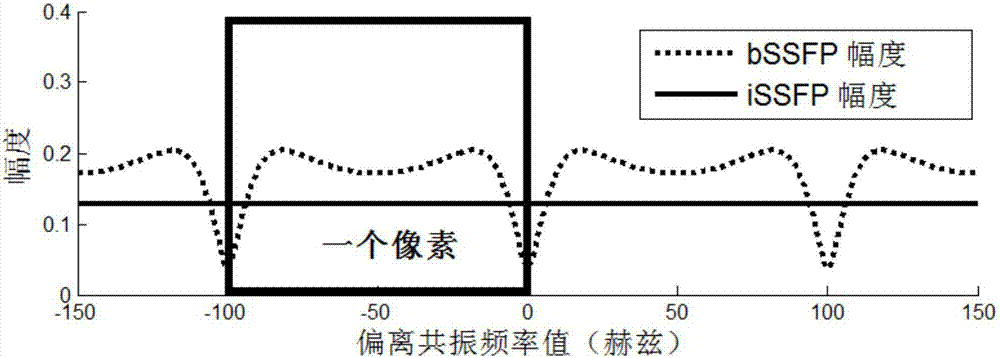
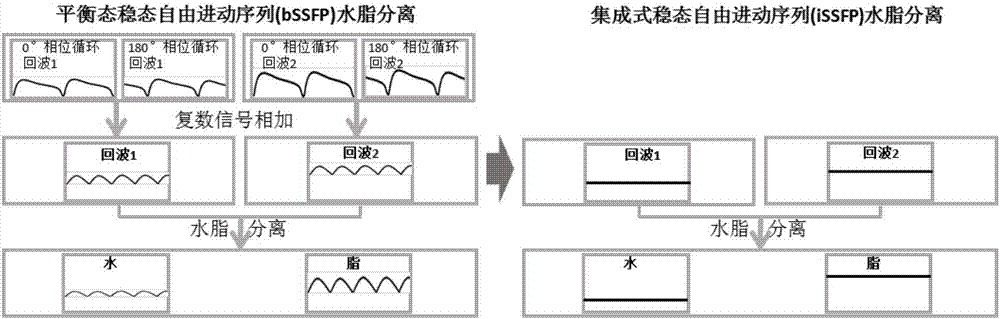
ActiveCN107997763ARemove periodic fluctuationsShorten Separation Scan TimeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsStable statePrecession
The invention relates to a water-fat separation magnetic resonance imaging method. The method is particularly applicable to a high field and super high field magnetic resonance system. The method comprises the following steps of 1, setting an integrated stable-state free precession imaging sequence capable of adjusting multiple echo times; 2, imaging the same imaging area and acquiring a magneticresonance signal corresponding to each echo time; 3, conducting Fourier image rebuilding on the acquired magnetic resonance signal to obtain a magnetic resonance complex number image corresponding toeach echo time; 4, integrating magnetic resonance complex number image information corresponding to the multiple echo times, wherein the magnetic resonance plural number image information comprises anamplitude and a phase; adopting a water-fat separation algorithm to solve images of separated water and fat. The water-fat separation magnetic resonance imaging method can be widely applied to various magnetic resonance high field imaging systems, particularly a super high field imaging system.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and magnetic resonance imaging method
ActiveUS20090160440A1Steady state of magnetization more satisfactorilyMaintained satisfactorilyMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceCenter frequency
A magnetic resonance imaging apparatus includes an input unit, a data acquisition unit and an image generating unit. The input unit inputs information indicating a matter of which resonance frequency is a center frequency of an excitation pulse. The data acquisition unit acquires magnetic resonance data with obtaining a steady state free precession. Each of the plural excitation pulses has a transmission phase varying by a variation amount determined based on a difference between a resonance frequency and the center frequency. The image generating unit generates an image of the desired matter based on the magnetic resonance data.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Steady state free precession magnetic resonance imaging using phase detection of material separation
InactiveUS6922054B2Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionLipid formationMaterial Separation
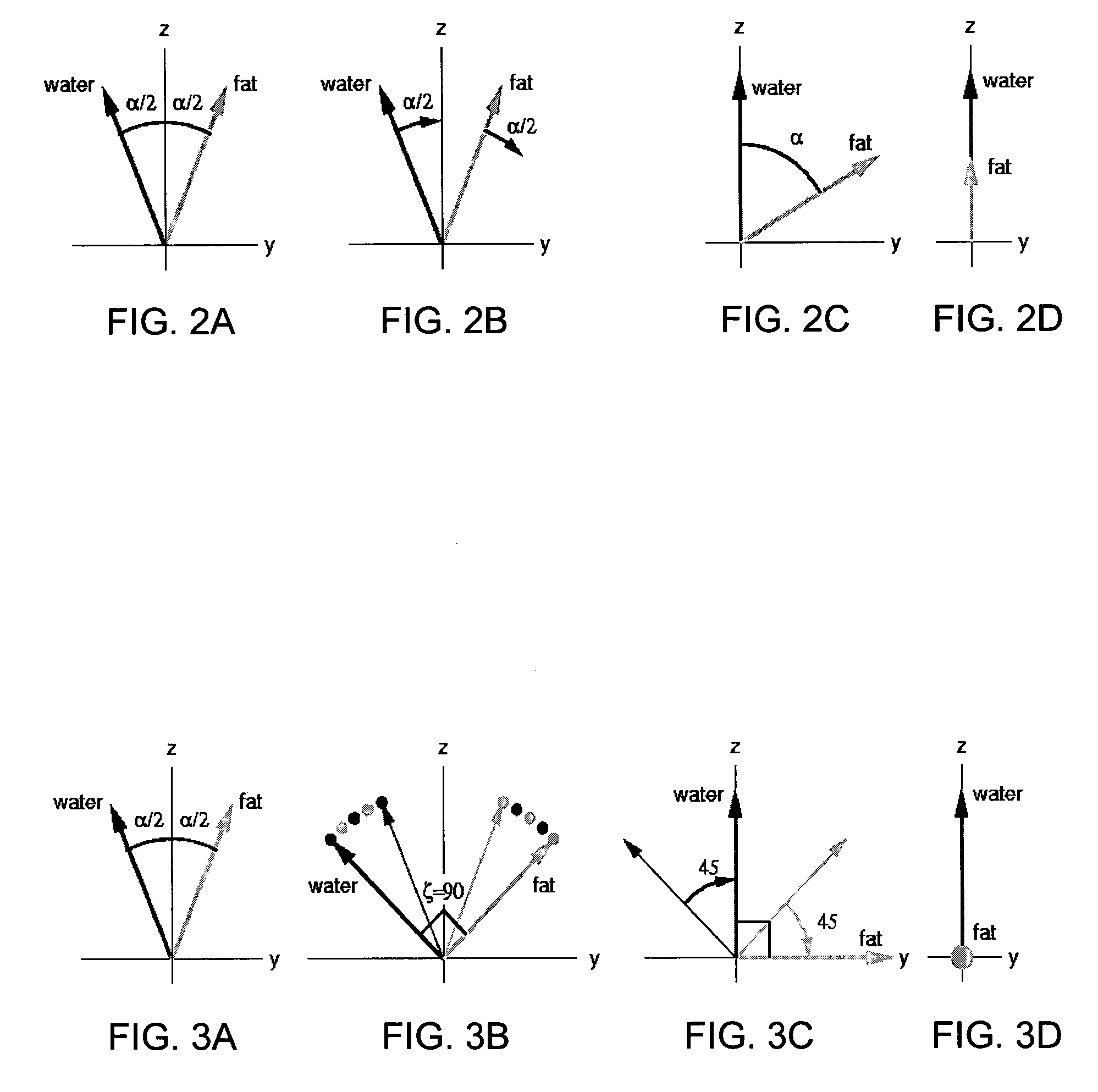
Magnetic resonance imaging of a body uses steady state free precession with material separation for the selective imaging of two species, such as blood or fat. The refocusing property of SSFP is used with signal phase detection to suppress either water or lipid. Phase and / or frequency of the RF excitation pulse and repetition time are selected so that resonant frequencies of water, fw, and lipid, fl, are on opposite sides of the signal null frequency.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
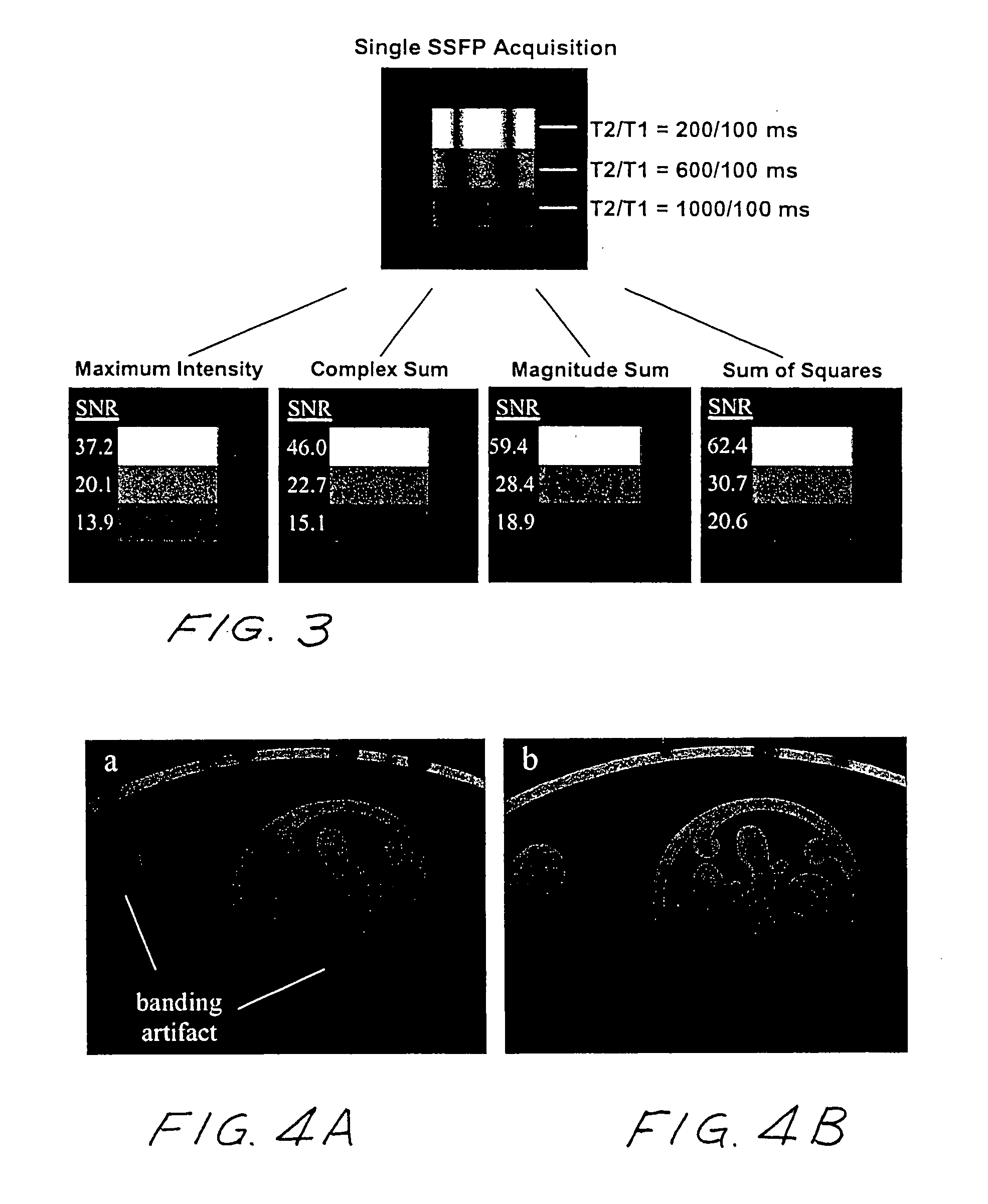
Artifact reduction in SSFP MRI using weighted sum of combined signals
InactiveUS6906516B2Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionPattern recognitionImage signal
Artifact reduction in steady state free precession magnetic resonance imaging uses weighting of acquired image data to emphasize higher signals and then establishing an image signal based on the combined weighted signals. In one embodiment, a SSFP imaging sequence uses phase cycling and acquired image data is squared with the squared data then combined. The final image signal is based on the square root of the squared data.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Magnetic resonance tomography apparatus and method for representation of tissue with very short T2 relaxation time
InactiveUS20060036154A1Short T relaxation timeIncrease contrastMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringResonanceT2 weighted
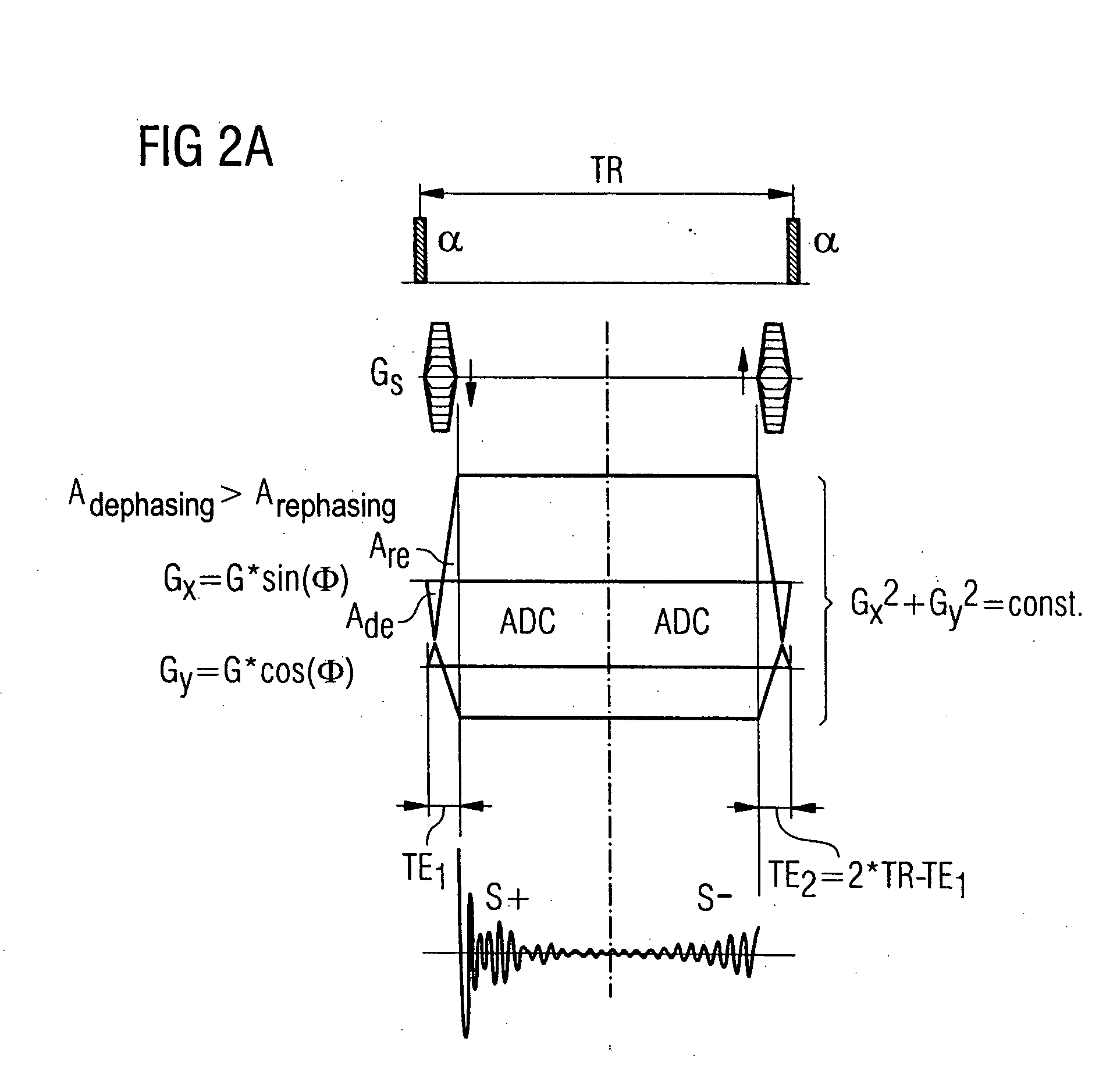
In a magnetic resonance tomography apparatus and method for determination of T2-weighted images of tissue with short T2 time, in the framework of a steady-state free precession sequence with non-slice-selective RF excitation pulses and projection-reconstruction methods, in each sequence repetition a first steady-state is read out in the form of a half echo and a second steady-state signal is read out in the form of a further half echo with very short echo times TE1 and TE2=2TR−TE1, and are combined by weighted addition such that an MRT image of tissue with very short T2 time is obtained with the sequence.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Artifact reduction in SSFP MRI using super field view reconstruction
ActiveUS7132828B2Reduce artifactsReduce scan timeMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionAugmented matrixDistortion
Banding artifacts in steady state free precession (SSFP) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are reduced by acquiring and combining multiple SSFP images in an augmented matrix where an acquisition vector in k-space is equal to a Fourier matrix of the trajectory on a known distortion operator for each trajectory in k-space.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Generic eddy-current compensation in magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS7046004B2Easy to implementMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionEddy currentComputer science
A method of steady-state free precession MR imaging is provided that includes the steps of: (a) providing a balanced steady-state free precession imaging sequence that includes a plurality of phase encoding steps, wherein each phase encoding step comprises a phase encoding gradient and a slice selection gradient; and (b) acquiring imaging data by performing the plurality of phase encoding steps in sequence, wherein the imaging data is acquired is compensated for one or more effects due to eddy-currents, flow, or motion related artefacts due to the implementation of one or more artefact compensation strategies that consist of (i) “pairing” of consecutive phase encoding steps and of (ii) “through slice equilibration” of eddy-current and motion or flow related signal oscillations.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF BASEL
MR imaging method and MRI system
InactiveUS20050168221A1Short timeShort scan timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhase differenceSpins
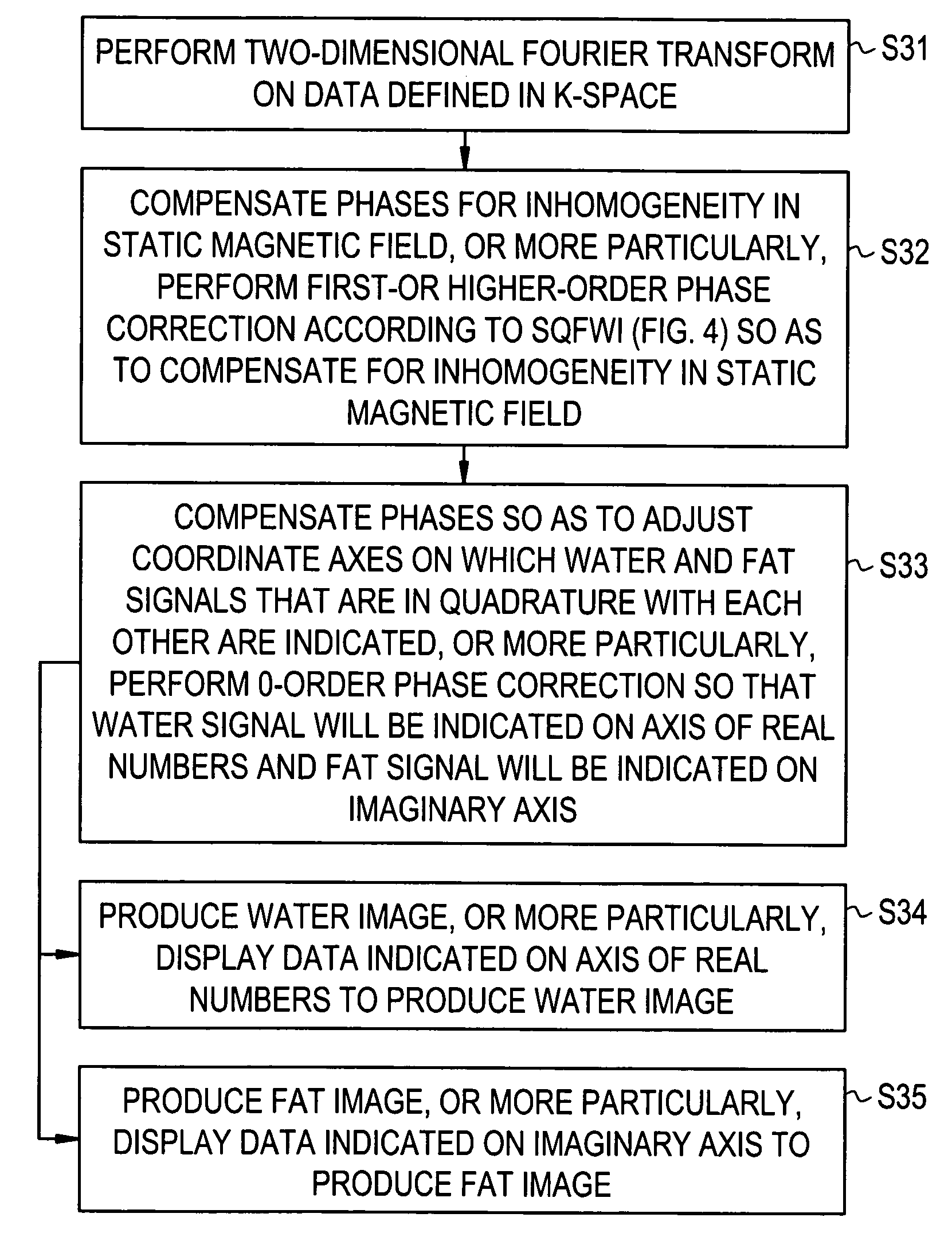
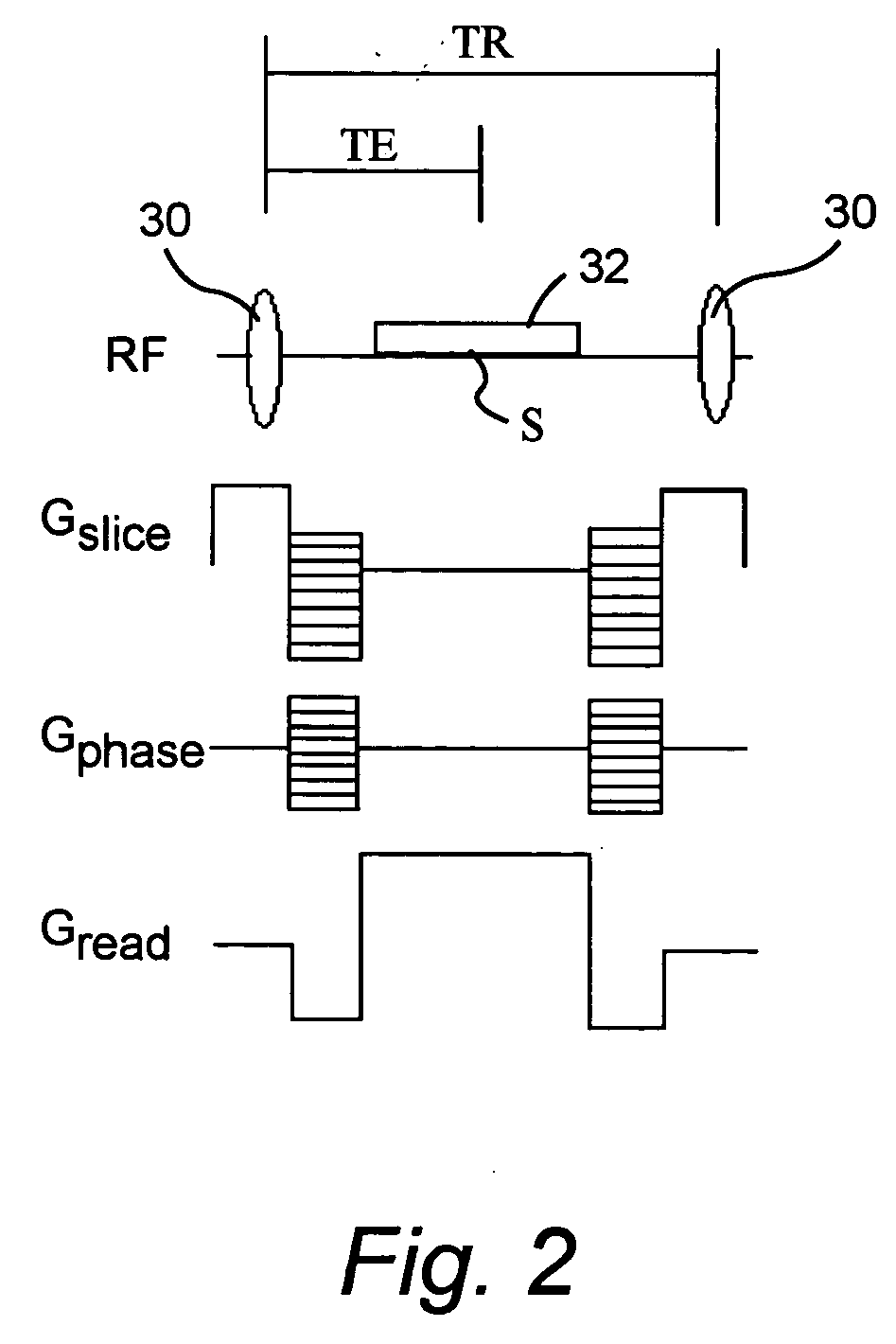
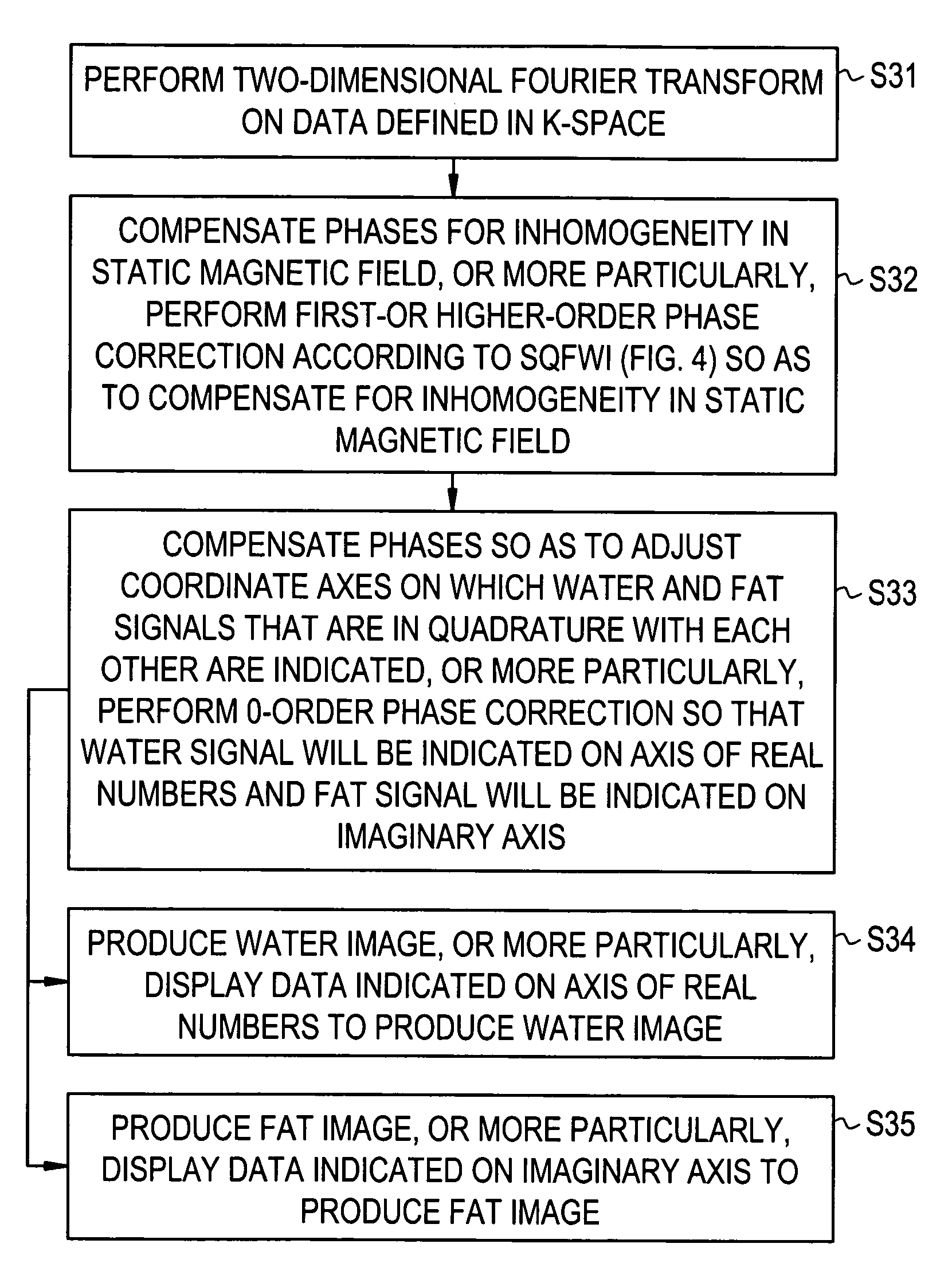
An MR imaging includes acquiring echoes from the object by implementing a pulse sequence which specifies the conditions which should be established with spins excited in the steady-state free precession (SSFP) method, so that the object can be scanned with an echo induced by water contained in the object and an echo induced by fat contained therein in single quadrature with each other or with a phase difference of 90° between the echoes induced by water and fat, constructing a tomographic image by performing frequency transformation on the acquired echoes, compensating the transformed data for the inhomogeneity in a static magnetic field and reconstructing an image, of which water and fat components are separated from each other, according to the result of the compensation.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
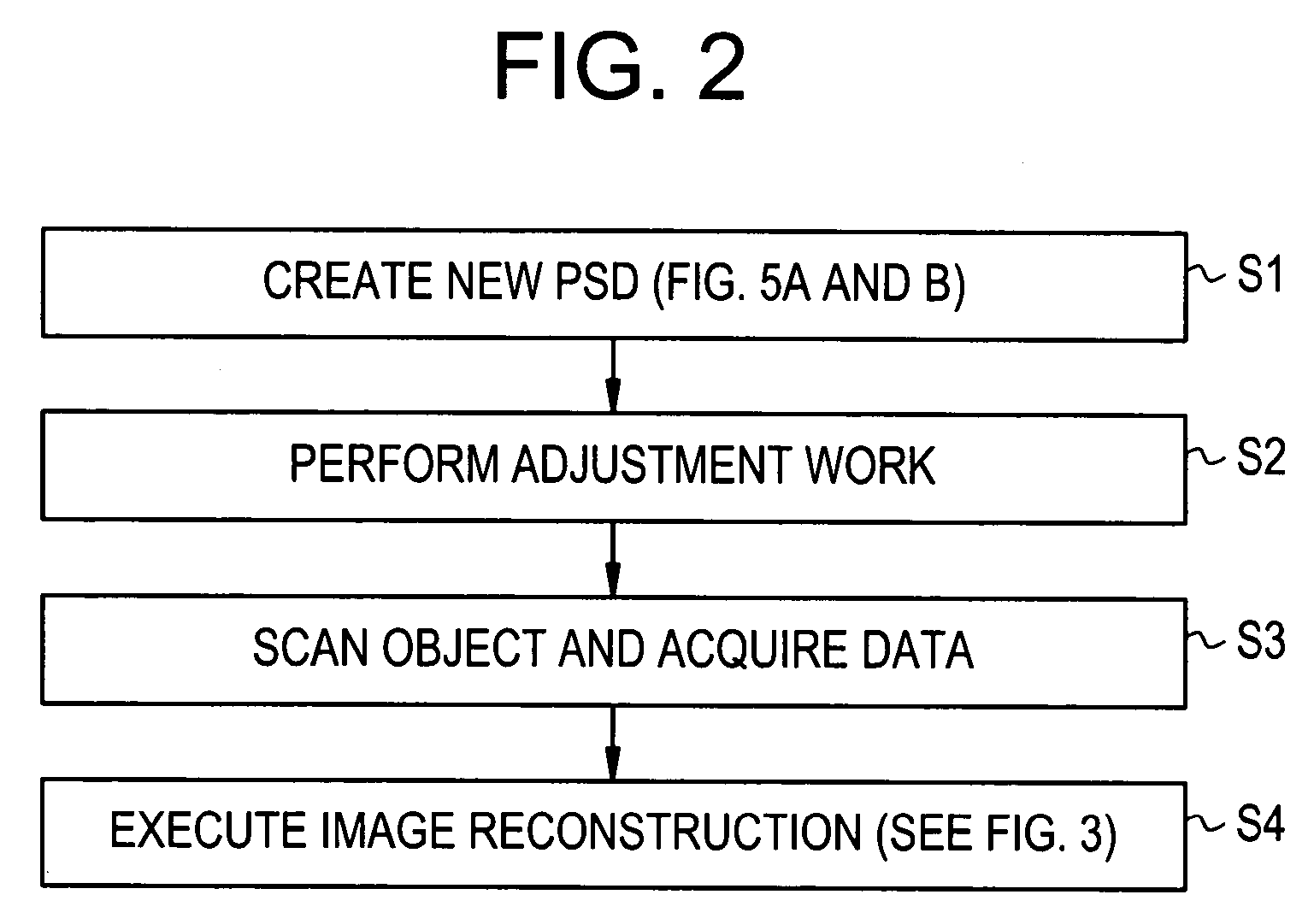
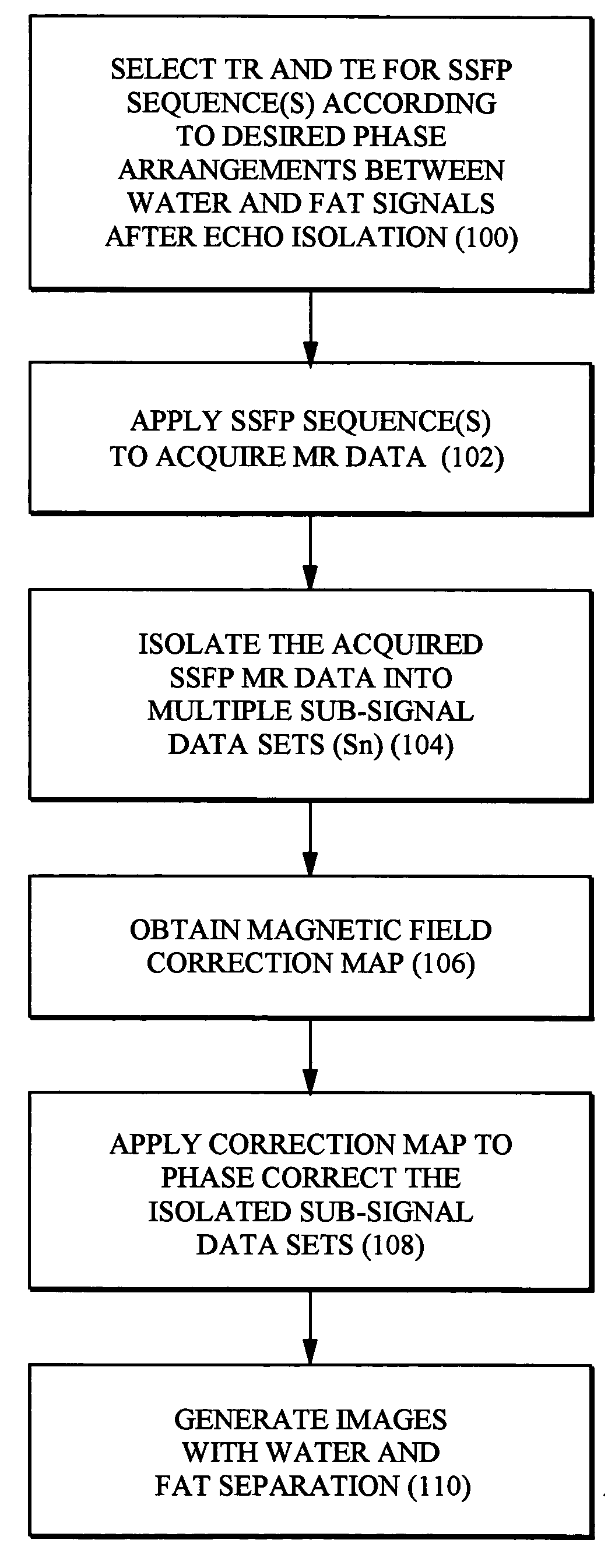
Water fat separated magnetic resonance imaging method and system using steady-state free-precession
InactiveUS20050171422A1Reduce scan timeGood water-fat separationDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsResonanceMultiple echo
Water-fat separated magnetic resonance (MR) images with balanced steady-state free precession (SSFP) are produced. The acquired SSFP signals are isolated into multiple echo components in which the phase arrangements between the water and fat signals are controlled by appropriately selecting the TR and TE values of the SSFP imaging sequence. From the isolated echo components, the effects of the field inhomogeneities are corrected and water and fat images are separated.
Owner:TOSHIBA AMERICA MRI
Magnetic resonance image-forming temperature measurement method based on three-dimensional steady state free precession
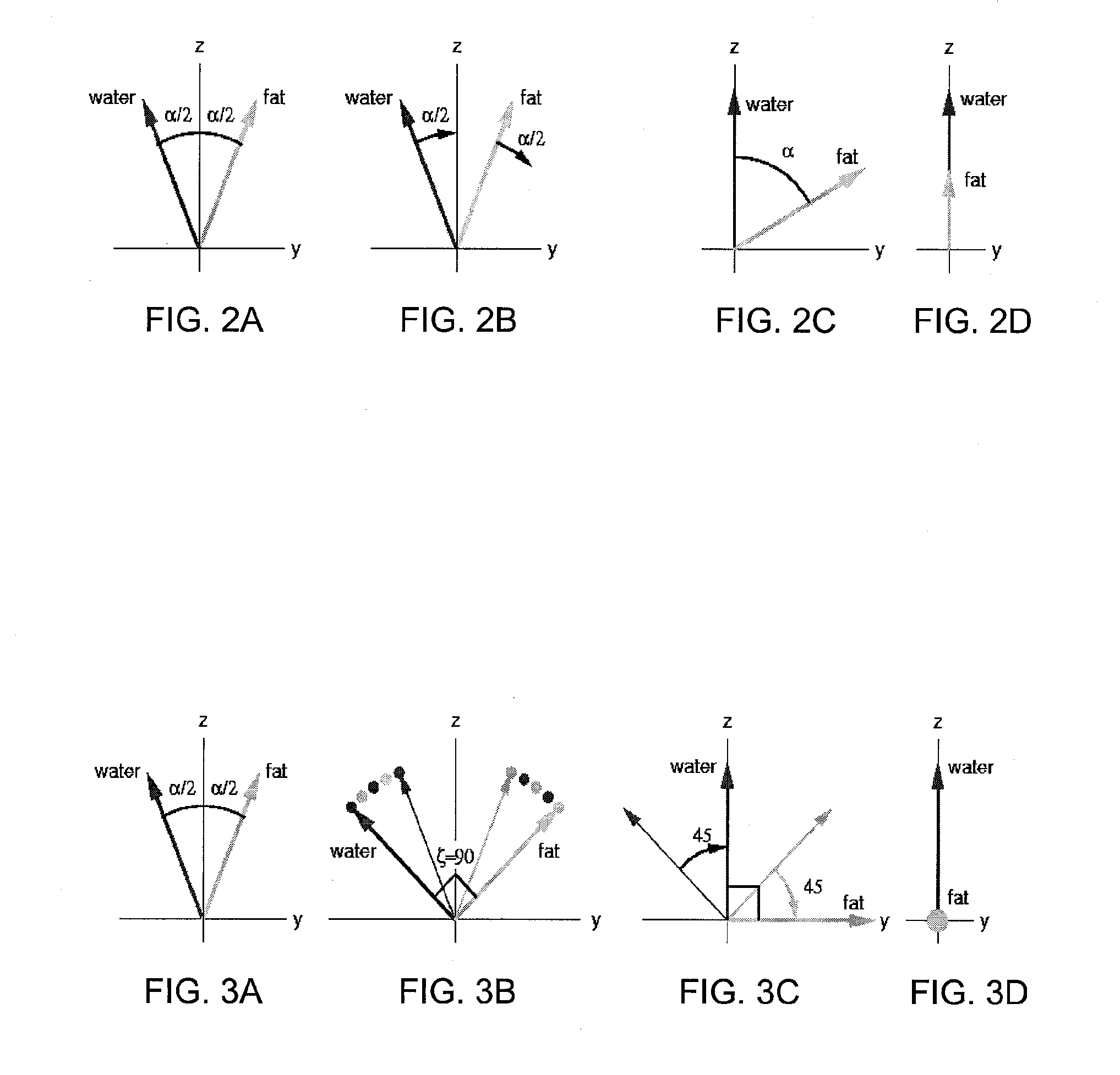
ActiveCN101352342AReduce the impactImprove stabilityMagnetic property measurementsThermometers using physical/chemical changesResonanceAngle alpha
The invention relates to a magnetic resonance imaging temperature measuring method on the basis of three-dimensional free motion, comprising the steps as follows: 1) at initial temperature Tb, the repeating time TR, the temperature coefficients a and b, large turnover angle Alpha1 and small turnover angle Alpha 2 of the three-dimensional stable free motion sequence are determined; 2) images I and I of tissue to be measured are collected so as to gain the superposition images Ib=I+I of the tissue to be measured at the initial temperature Tb; 3) at the to-be-measured temperature Th, under the conditions of temperature coefficient Alpha1 and repeating time T determined in the step 1), the image I of the tissue to be measured is collected; subsequently, under the conditions of temperature coefficient Alpha2 and repeating time T, the image I of the tissue to be measured is collected so as to gain the image I=I+I at the to-be-measured temperature Th of the tissue to be measured; 4) standard image I=Ih / Ib is superposed; 5) the temperature image I of the tissue to be measured is calculated; the value of each point on the temperature image I is the Delta T of the tissue to be measured at the point; 6) the to-be-measured temperature Th equal to Tb+Delta T of the tissue to be measured is worked out.
Owner:SYMBOW MEDICAL TECH
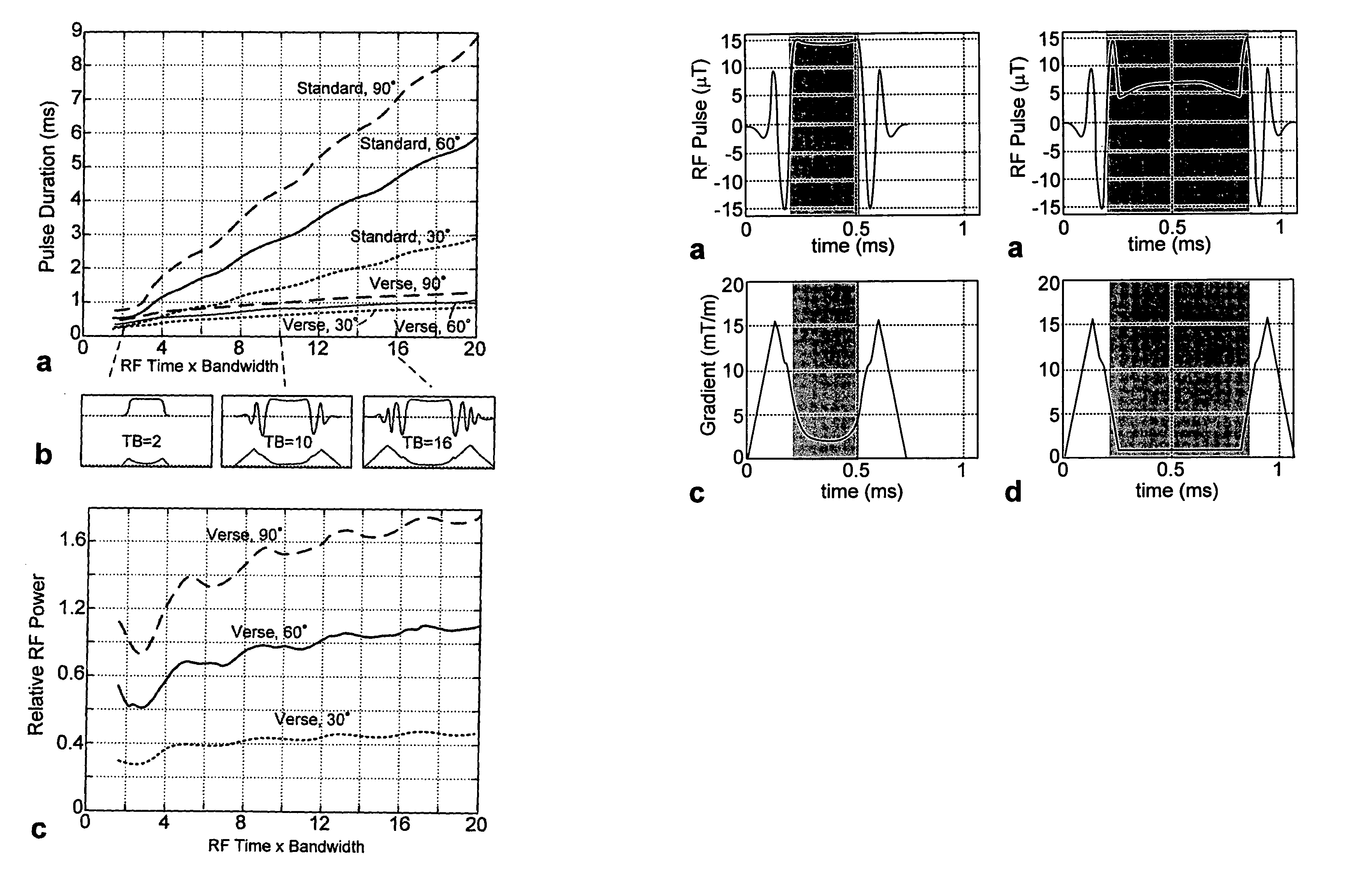
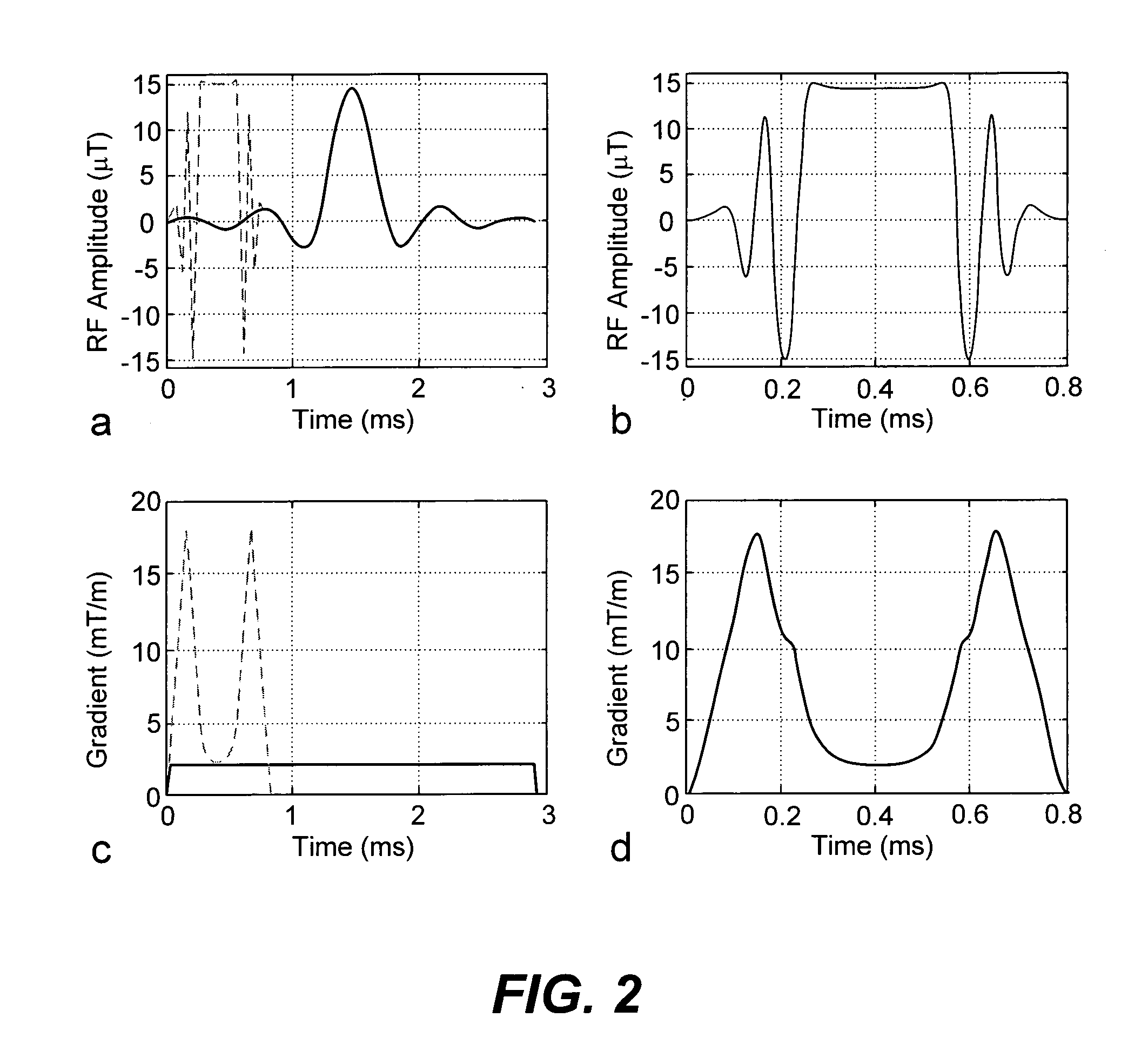
Reduced-time variable rate excitation pulses for rapid MRI
ActiveUS7046003B2Enhance the imageFast imagingMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionPulse sequenceFast mri
A pulse sequence for use in steady state free precession (SSFP) imaging sequences includes a RF pulse and a time-varying gradient pulse based on a conventional design algorithm such as the Shinnar-LeRoux (SLR) pulse design algorithm and in which amplitude of the RF pulse and gradient pulse are increased while pulse time is decreased thereby reducing imaging time and improving slab profiles.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Magnetic resonance imager, method and program which continuously applies steady-state free precession to k-space
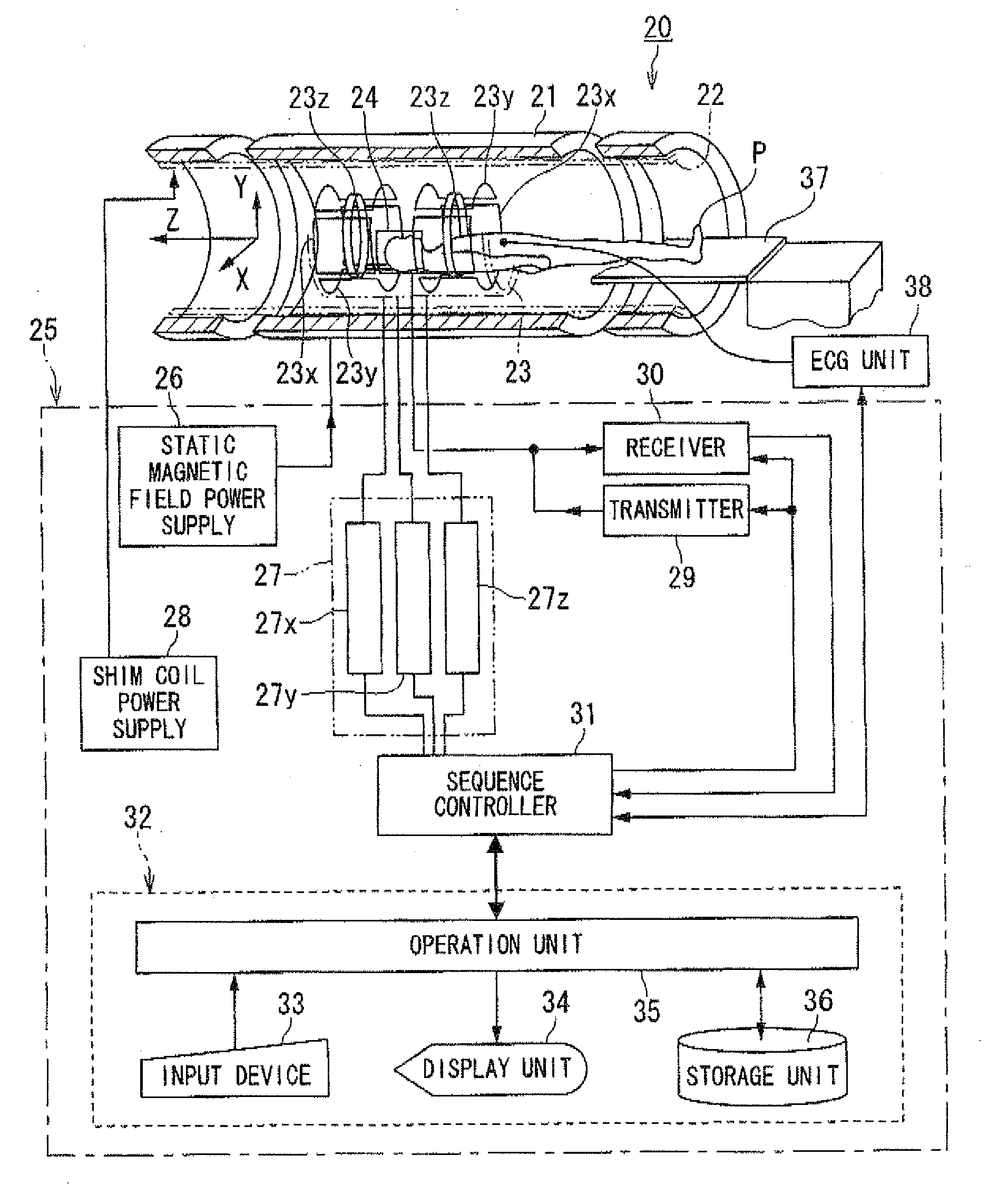
A magnetic resonance imager for forming images of a moving portion of a patient includes imaging coils. The imager includes a computer that causes the imaging coils to apply continuously steady-state free precession to k-space of a magnetic resonance image series of the patient and acquire the image series, and generates images from the image series. A method for forming images of a moving portion of a patient includes the steps of applying continuously steady-state free precession to k-space of a magnetic resonance image series of a patient. There is the step of acquiring the image series. There is the step of generating images from the image series. A method for forming images of a patient includes the steps of triggering a steady-state free precision imaging sequence to an ECG r wave of cardiac cycles of the patient. There is the step of performing the steady-state free precision imaging sequence with imaging coils of a magnetic resonance imaging scanner such that data for a series of k-space data sets associated with the imaging sequence are acquired in a manner that is time resolved through the cardiac cycle, with data acquired over a number of consecutive cardiac cycles. A computer program embodied on a computer readable medium to form an image of a patient with an MRI.
Owner:ALLEGHENY SINGER RES INST
Magnetic resonance imaging method based on steady-state free procession sequence
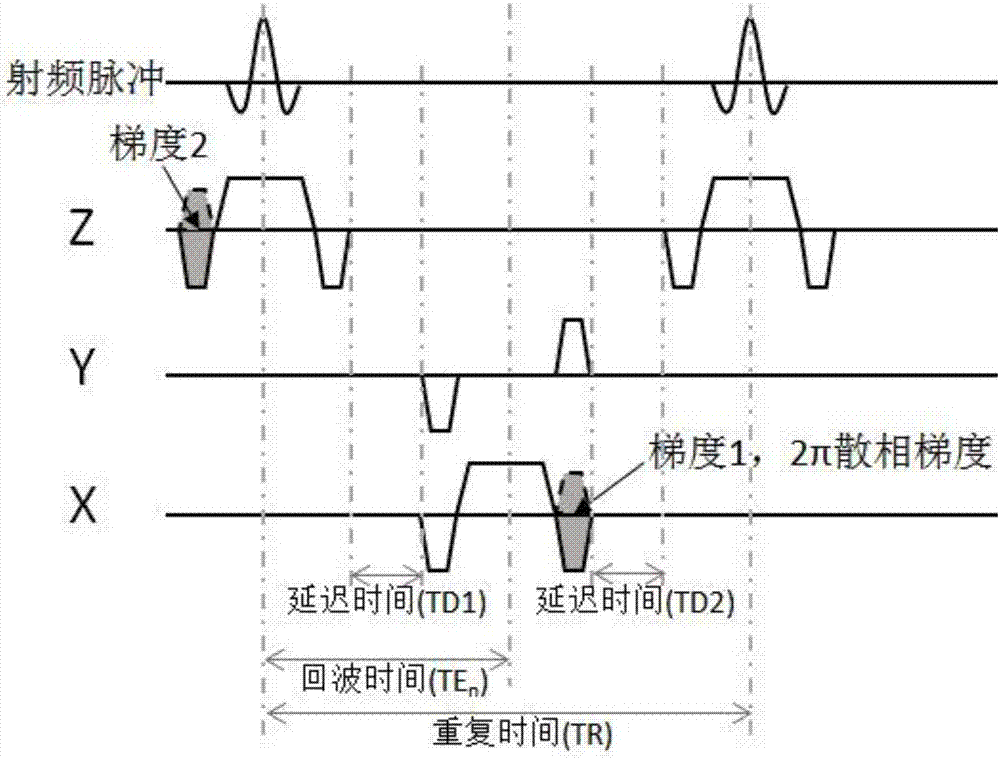
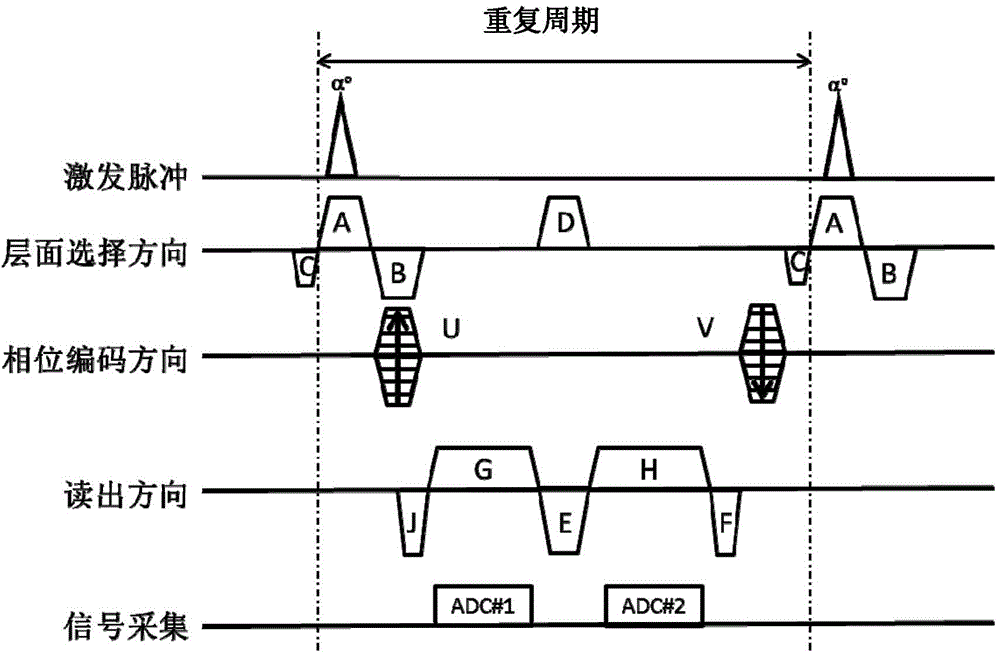
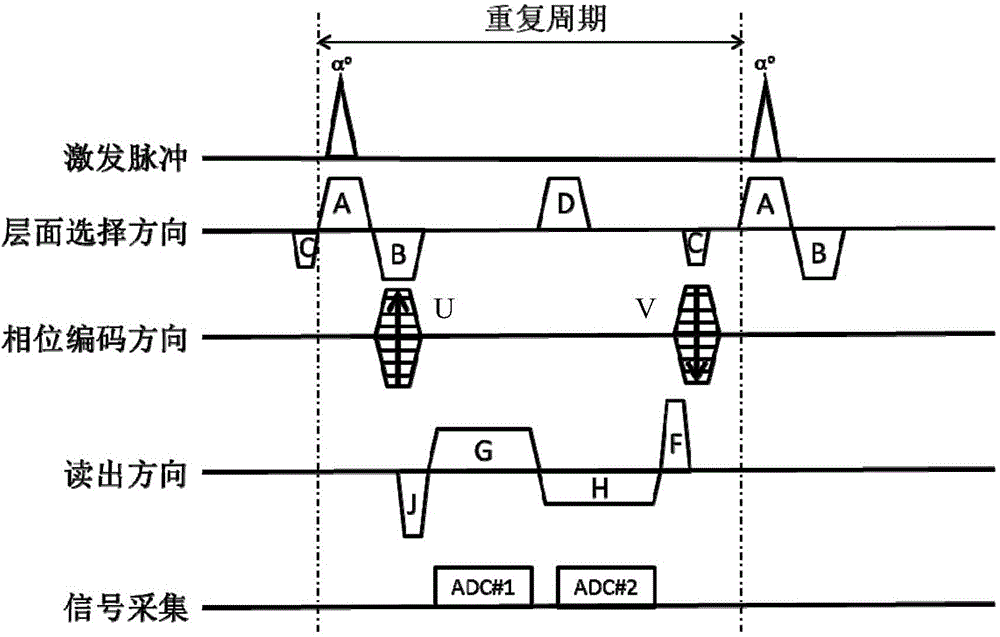
The invention provides a magnetic resonance imaging method based on a steady-state free procession sequence and belongs to the technical field of magnetic resonance imaging. The magnetic resonance imaging method based on the steady-state free procession sequence comprises the steps that excitation pulses and a first-level selection gradient A are applied at the same time; a second-level selection gradient B and a first phase encoding gradient U are applied, and a phase pre-dispersing gradient J is read; a first reading gradient G is applied, and an echo horizontal-movement signal is acquired at the same time; a third-level selection gradient D is applied; a second reading gradient H is applied, and a time reversed steady-state procession signal is acquired at the same time; a reading back-gathering gradient F, a second phase encoding gradient V and a fourth-level selection gradient C are applied, wherein the moment of the gradient A, the moment of the gradient B, the moment of the gradient C and the moment of the gradient D meet the relation: MC=-MA / 2 and 2MB-MD=MA; a k space is filled with obtained signals, and Fourier transformation is conducted, so that a magnetic resonance image is obtained. According to the magnetic resonance imaging method based on the steady-state free procession sequence, the time reversed steady-state procession signal and the time reversed steady-state procession signal can be acquired at the same time, and imaging time is shortened.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
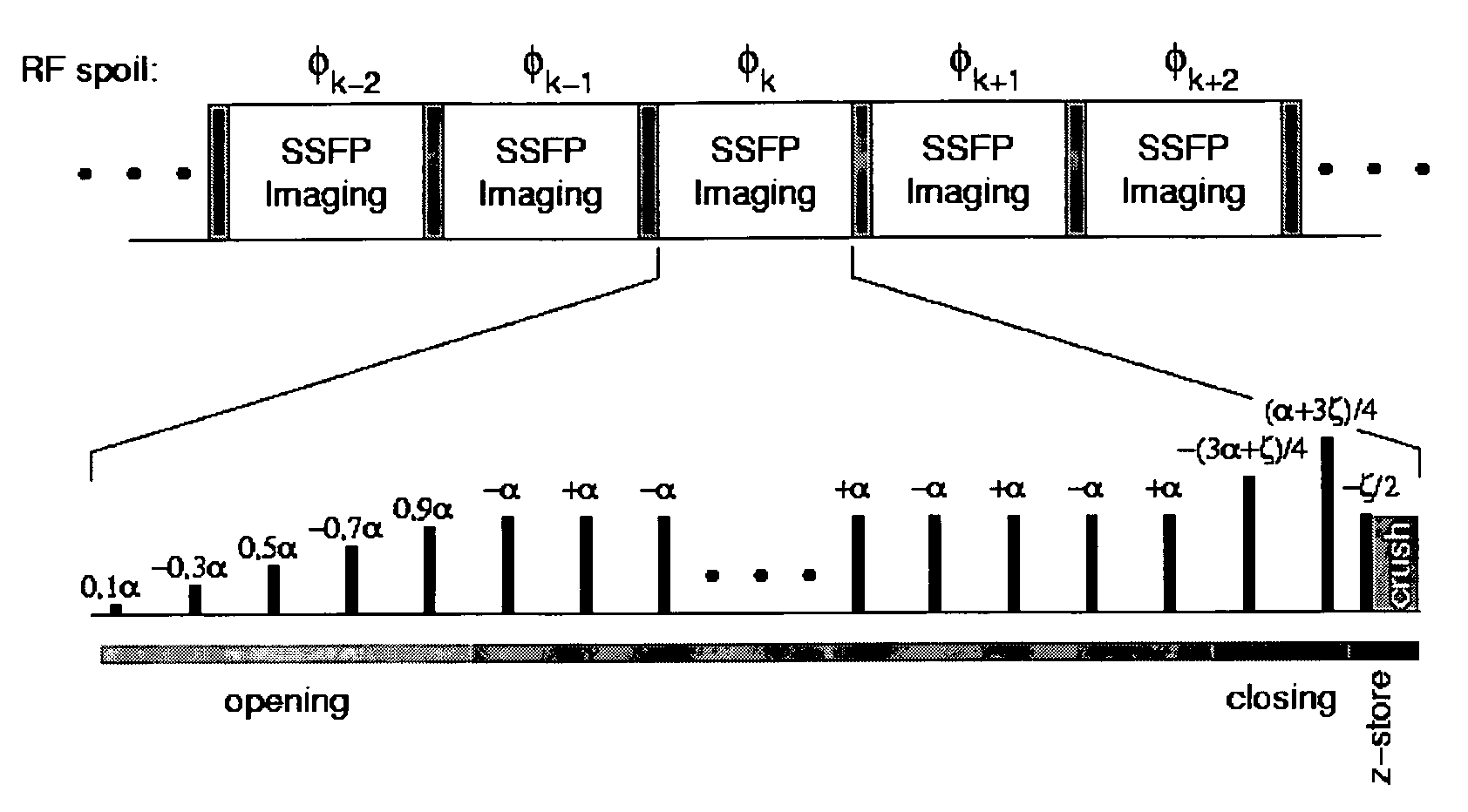
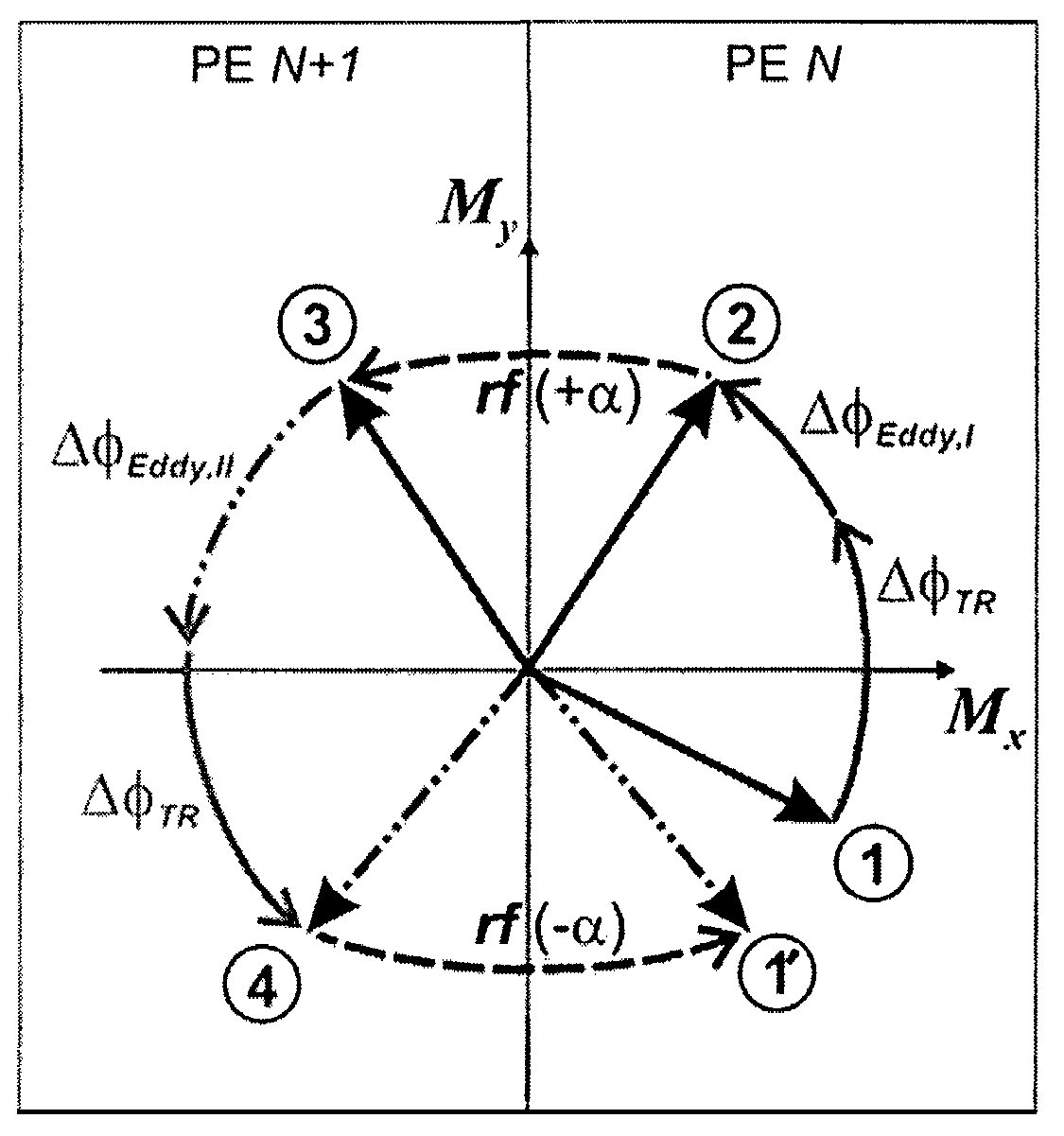
Eddy current compensation with N-average SSFP imaging
ActiveUS7372266B2Ideal eddy current compensationMeasurement time to doubleMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionContinuous measurementNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
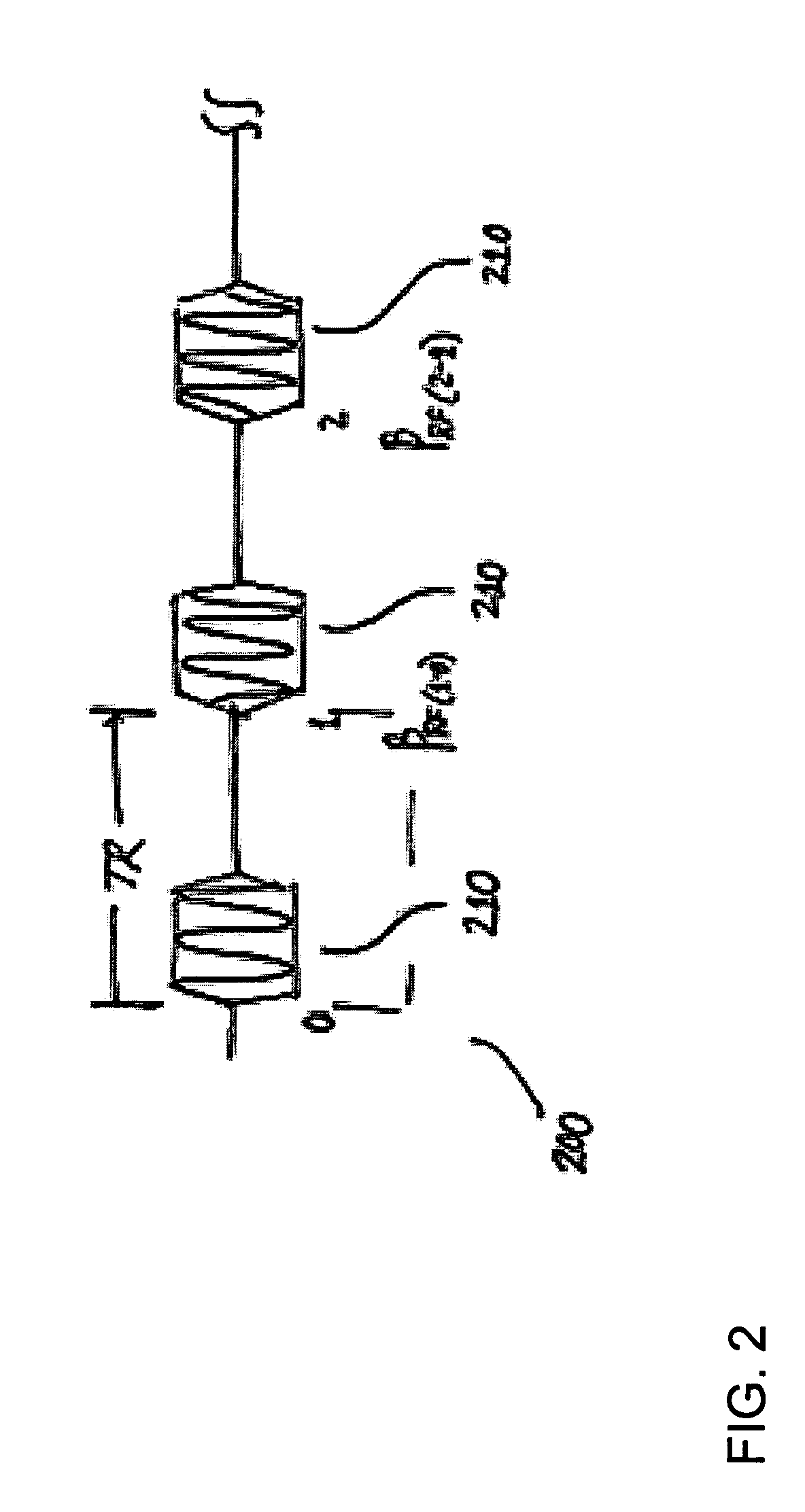
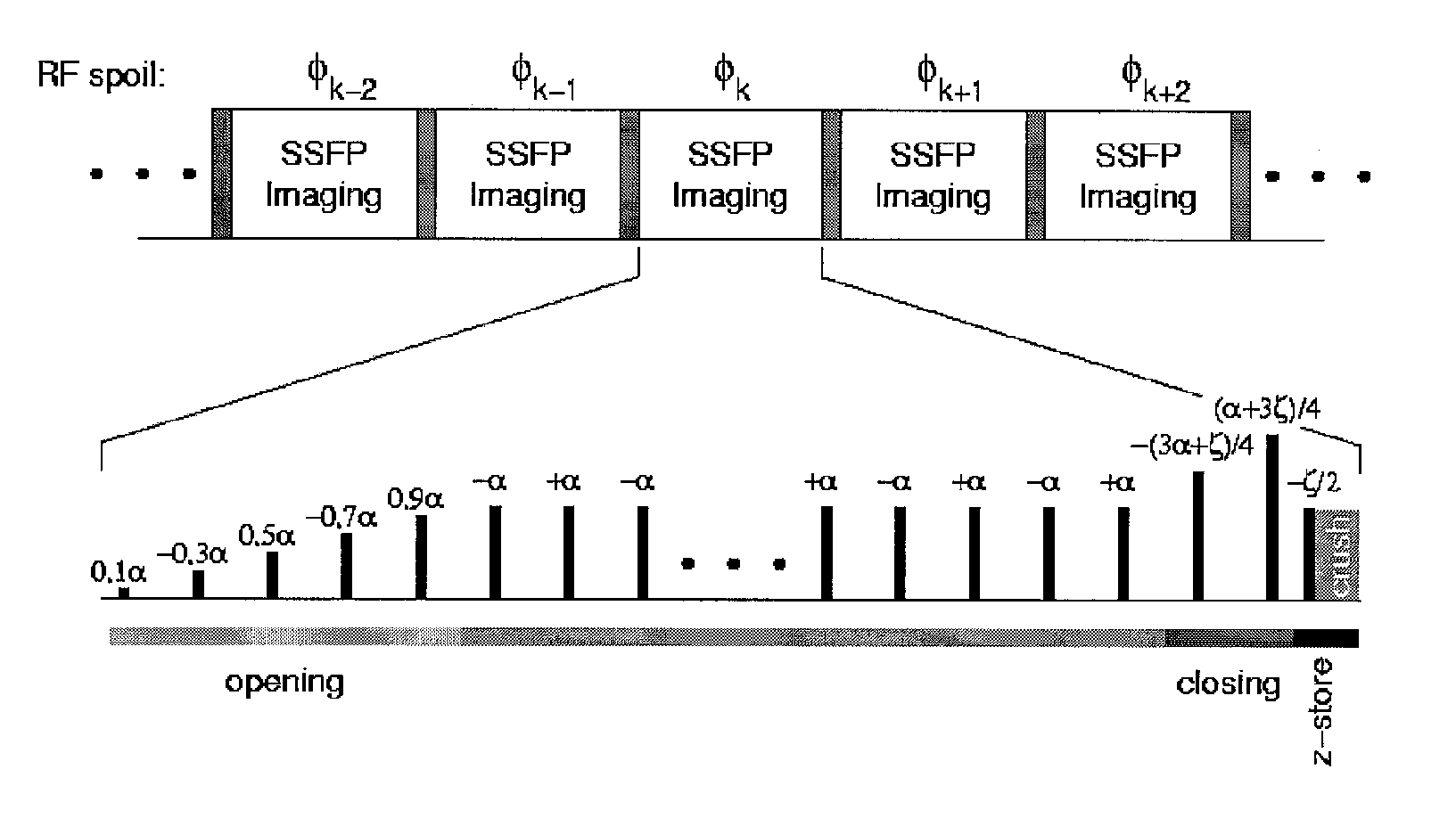
A method according to the technique of a steady state free precession (SSFP) gradient echo method, in particular, of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) tomography, wherein a regular sequence of radio frequency pulses with flip angle α is applied at temporally constant intervals TR, wherein the phase of these pulses is increased in subsequent steps by a constant phase increment, is characterized in that a predetermined phase encoding scheme is performed in such a manner that each individual phase encoding step is identically repeated N times under the following conditions:N is an even number and N≧2;successive measured NMR signals are averaged,which minimizes the artefacts produced due to incrementation of the phase encoding gradients.
Owner:UNIVERSITATSKLINIKUM FREIBURG
Artifact reduction in SSFP MRI using weighted sum of combined signals
InactiveUS20050030023A1Reduce artifactsEnhanced signalMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionPattern recognitionImage signal
Artifact reduction in steady state free precession magnetic resonance imaging uses weighting of acquired image data to emphasize higher signals and then establishing an image signal based on the combined weighted signals. In one embodiment, a SSFP imaging sequence uses phase cycling and acquired image data is squared with the squared data then combined. The final image signal is based on the square root of the squared data.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Spin locked balanced steady-state free precession (slSSFP) with off-resonance spin locked pulses interleaved with imaging gradients
ActiveUS8148982B2Increase contrastEnhanced signalMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetizationBloch equations
A spin locked balanced steady-state free precession (slSSFP) pulse sequence combines a balanced gradient echo acquisition with an off-resonance spin lock pulse for fast MRI. The transient and steady-state magnetization trajectory is solved numerically using the Bloch equations and is shown to be similar to balanced steady-state free precession (bSSFP) for a range of T2 / T1 and flip angles, although the slSSFP steady-state could be maintained with considerably lower RF power. In both simulations and brain scans performed at 7T, slSSFP is shown to exhibit similar contrast and SNR efficiency to bSSFP, but with significantly lower power.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and magnetic resonance imaging method
InactiveCN101441255AMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringImaging conditionMR - Magnetic resonance
The present invention provides a magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and method. The magnetic resonance imaging apparatus comprises a data acquisition unit and an image generating unit. The data acquisition unit configured to acquire magnetic resonance data according to an imaging condition for obtaining a steady state free precession of nuclear magnetic spins in flowing matter in an object by applying plural excitation pulses having a same flip angle with a constant repetition time (TR) and gradient magnetic fields to the object; wherein respective zero order moments of gradient magnetic field within the repetition time (TR), gradient magnetic field for slice selection from each application time of the plural excitation pulses till a center time of a corresponding echo, gradient magnetic field for readout from each application time of the plural excitation pulses till a center time of a corresponding echo, gradient magnetic field for slice selection from a center time of each echo till an application time of a following excitation pulse, gradient magnetic field for readout from a center time of each echo till an application time of a following excitation pulse are zero while a first order moment of at least one of gradient magnetic field for slice selection and gradient magnetic field for readout within the repetition time is nonzero. The image generating unit is configured to generate an image of the flowing matter based on the magnetic resonance data.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
MR imaging method and MRI system
InactiveUS7068031B2Shorten time elapsesEasy to separateDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsPhase differenceSpins
An MR imaging includes acquiring echoes from the object by implementing a pulse sequence which specifies the conditions which should be established with spins excited in the steady-state free precession (SSFP) method, so that the object can be scanned with an echo induced by water contained in the object and an echo induced by fat contained therein in single quadrature with each other or with a phase difference of 90° between the echoes induced by water and fat, constructing a tomographic image by performing frequency transformation on the acquired echoes, compensating the transformed data for the inhomogeneity in a static magnetic field and reconstructing an image, of which water and fat components are separated from each other, according to the result of the compensation.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Spectrally selective suppression with steady-state free precession
ActiveUS20070225591A1Effective imagingEnhanced inhibitory effectMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringFrequency spectrumFat suppression
A method for fat-suppressed imaging is disclosed. Such a method may include storing a first spectral component of an echo signal formed at TR / 2 from a sample, suppressing a second spectral component of the echo signal at TR / 2, re-exciting the stored spectral component after suppressing the second spectral component, and producing an image of the sample based on the re-excited stored spectral component.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Steady state free precession based magnetic resonance thermometry
ActiveUS20050052183A1High resolution real time imageryImprove efficiencyMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionProton resonance frequencyProton
Disclosed is a method and system for steady state free precession based magnetic resonance thermometry that measures changes in temperature on a pixel by pixel basis. The method comprises generating an RF pulse sequence used to find the proton resonance frequency shift, which is proportional to temperature change, processing the resultant MRI data to measure the proton frequency shift, and converting the measured proton frequency shift into change in temperature data. Further disclosed is a method for identifying and compensating for temperature drifts due to core heating of the gradient magnet.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Reduced-time variable rate excitation pulses for rapid MRI
ActiveUS20060061358A1Enhanced imaging slab profileFast imagingMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionPulse sequenceFast mri
A pulse sequence for use in steady state free precession (SSFP) imaging sequences includes a RF pulse and a time-varying gradient pulse based on a conventional design algorithm such as the Shinnar-LeRoux (SLR) pulse design algorithm and in which amplitude of the RF pulse and gradient pulse are increased while pulse time is decreased thereby reducing imaging time and improving slab profiles.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Magnetic resonance method for quantification of transverse relaxation times
ActiveUS8314618B2Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionRapid imagingTransverse relaxation
Apparatus and methods for quantification of transverse relaxation times (T2) using steady-state free precession sequences (generally known as fast imaging sequences) and their sensitivity to a quadratic increase of the RF pulse phase, also known as RF spoiling. Using at least two image acquisitions with different partial RF spoiling increments, T2 can be assessed with high precision and with short acquisition times in the limit of large excitation angles being independent on the longitudinal relaxation time (T1) and magnetization transfer effects as compared to other SSFP based quantitative T2 methods. This invention is not restricted to any kind of target and may be applied in 3D as well as in 2D.
Owner:UNIV HOSPITAL OF BASEL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com