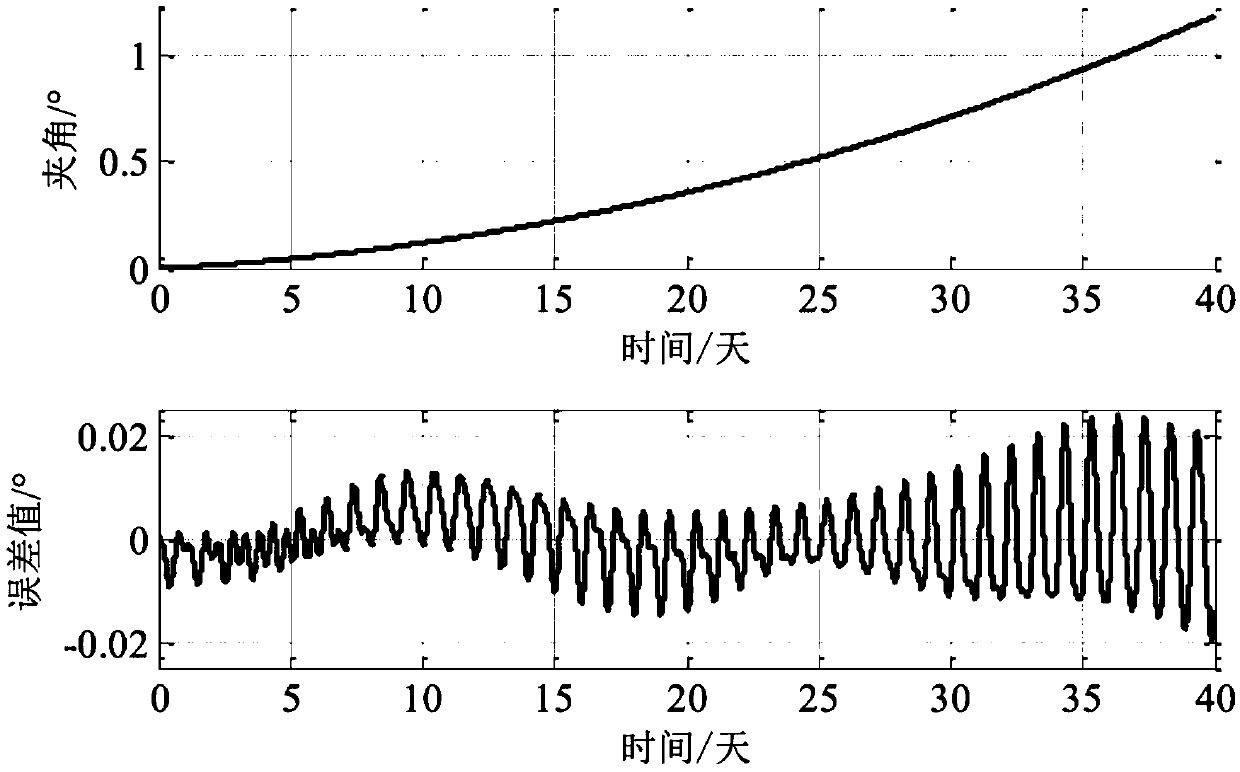
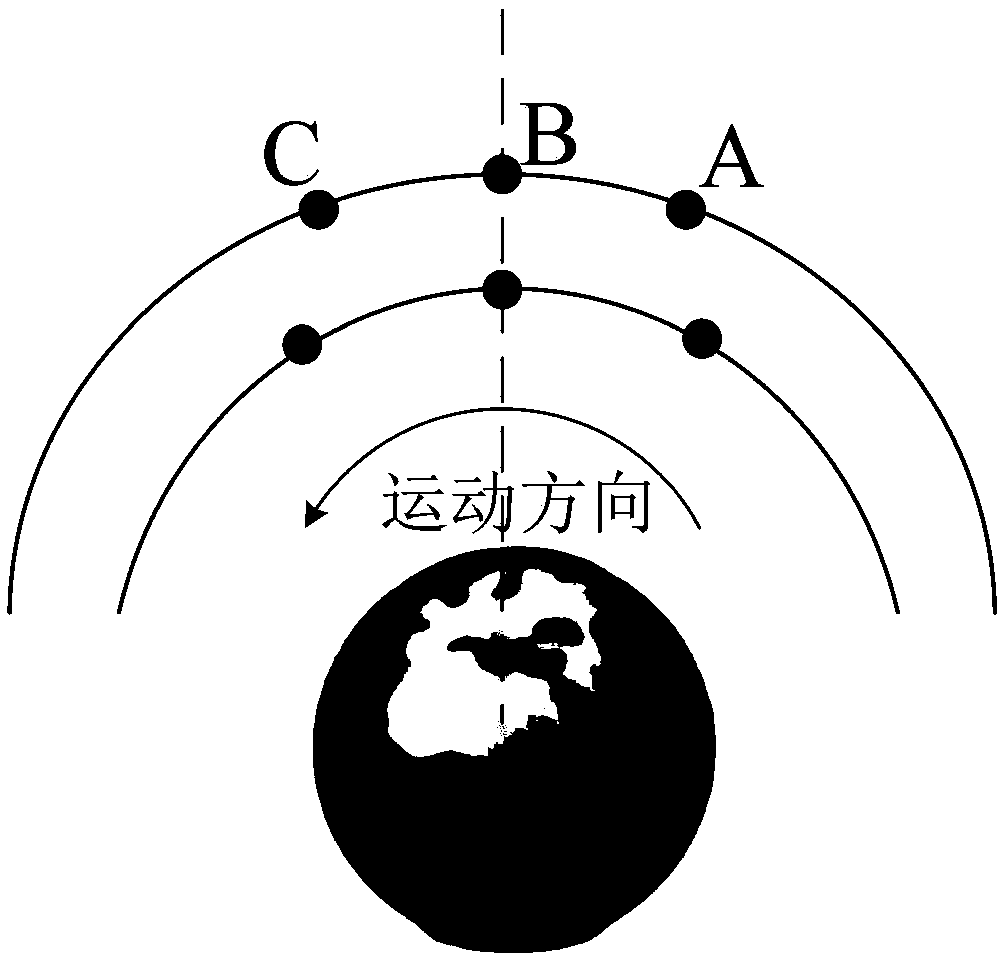
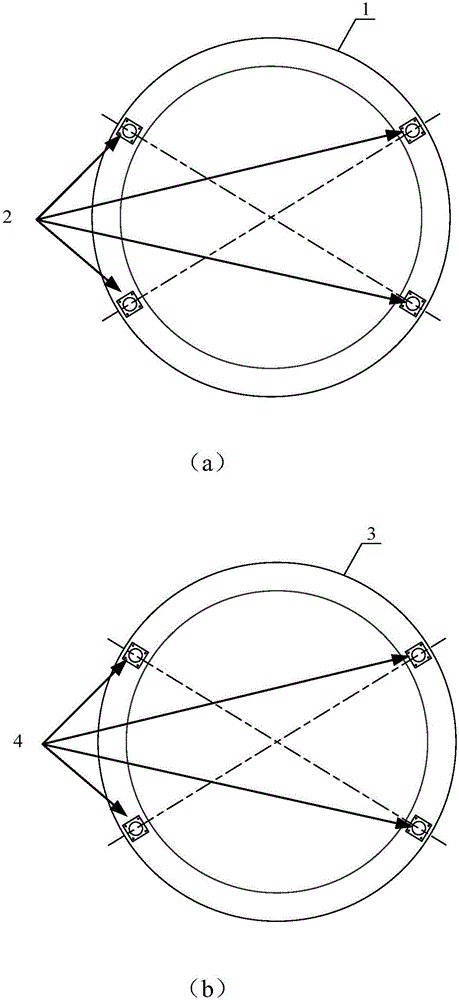
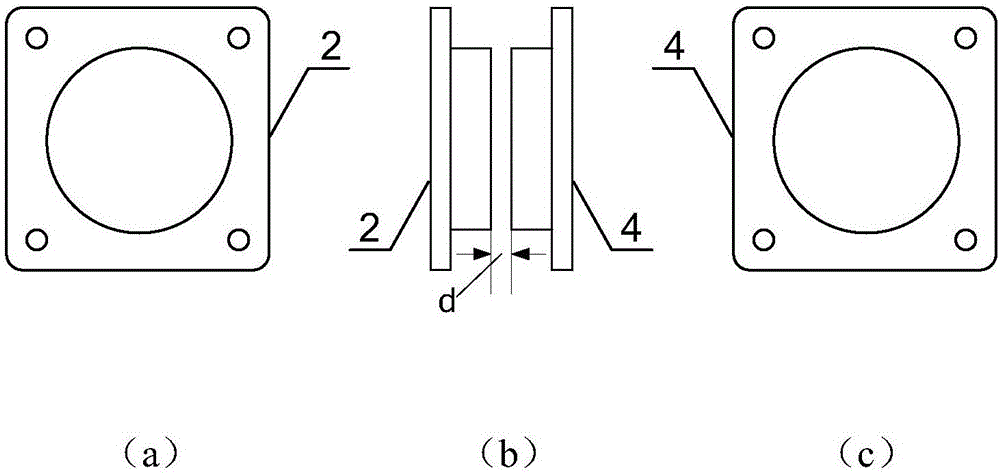
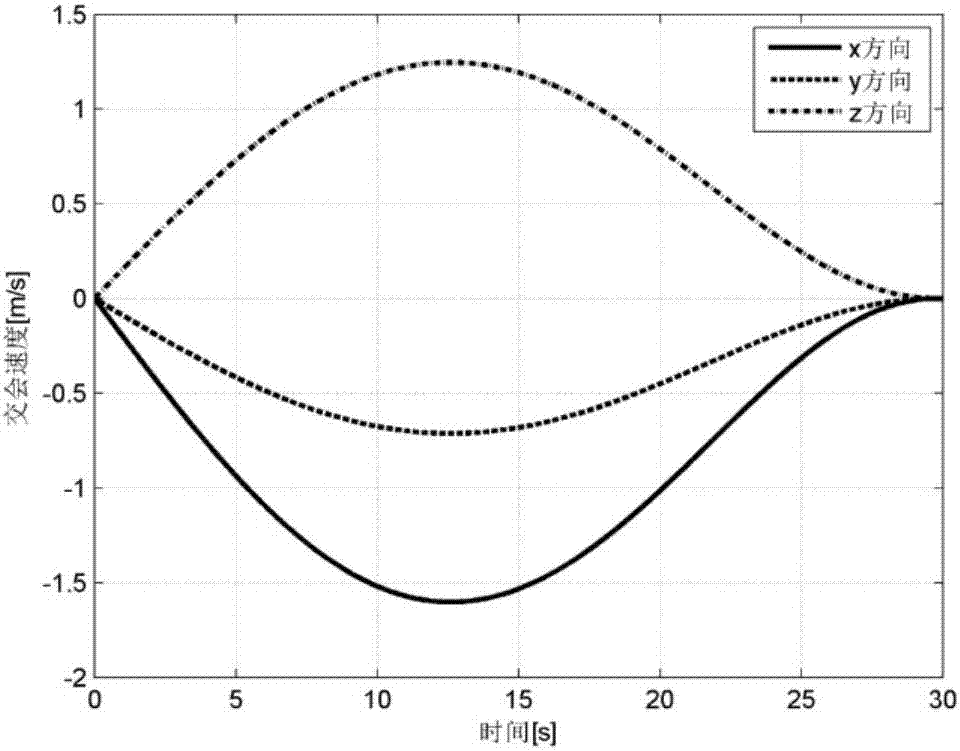
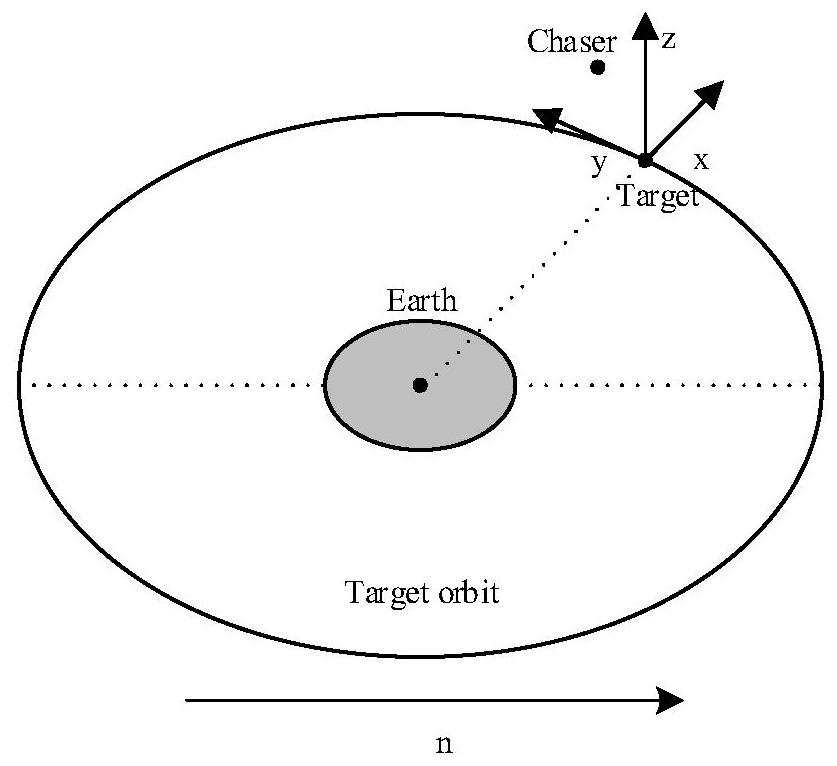
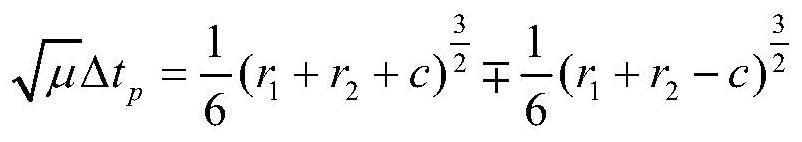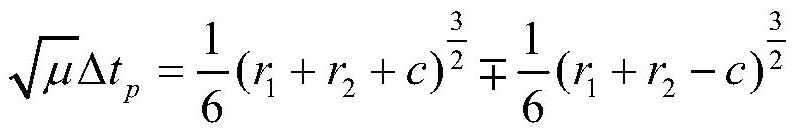Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
62 results about "Spacecraft rendezvous" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
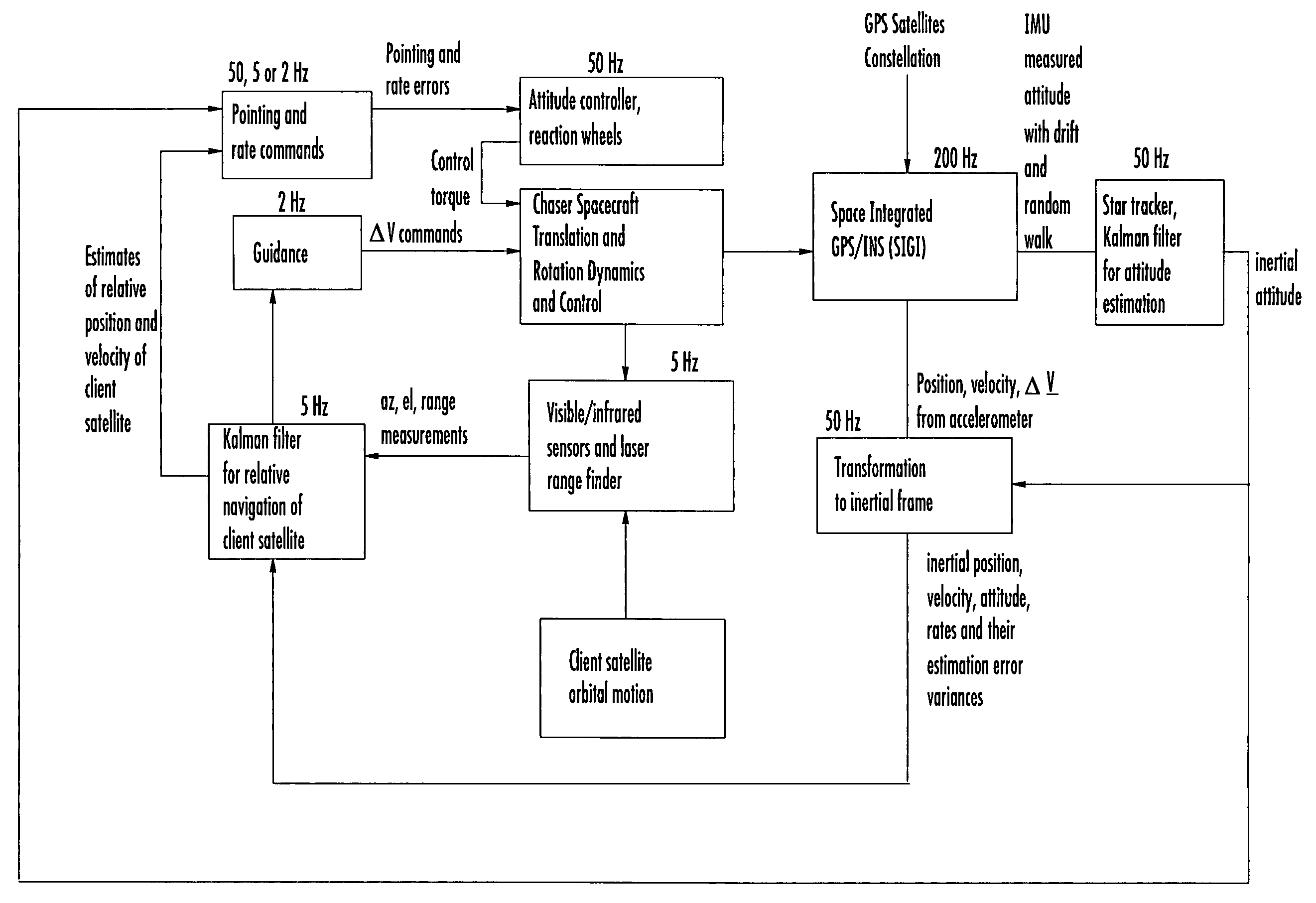
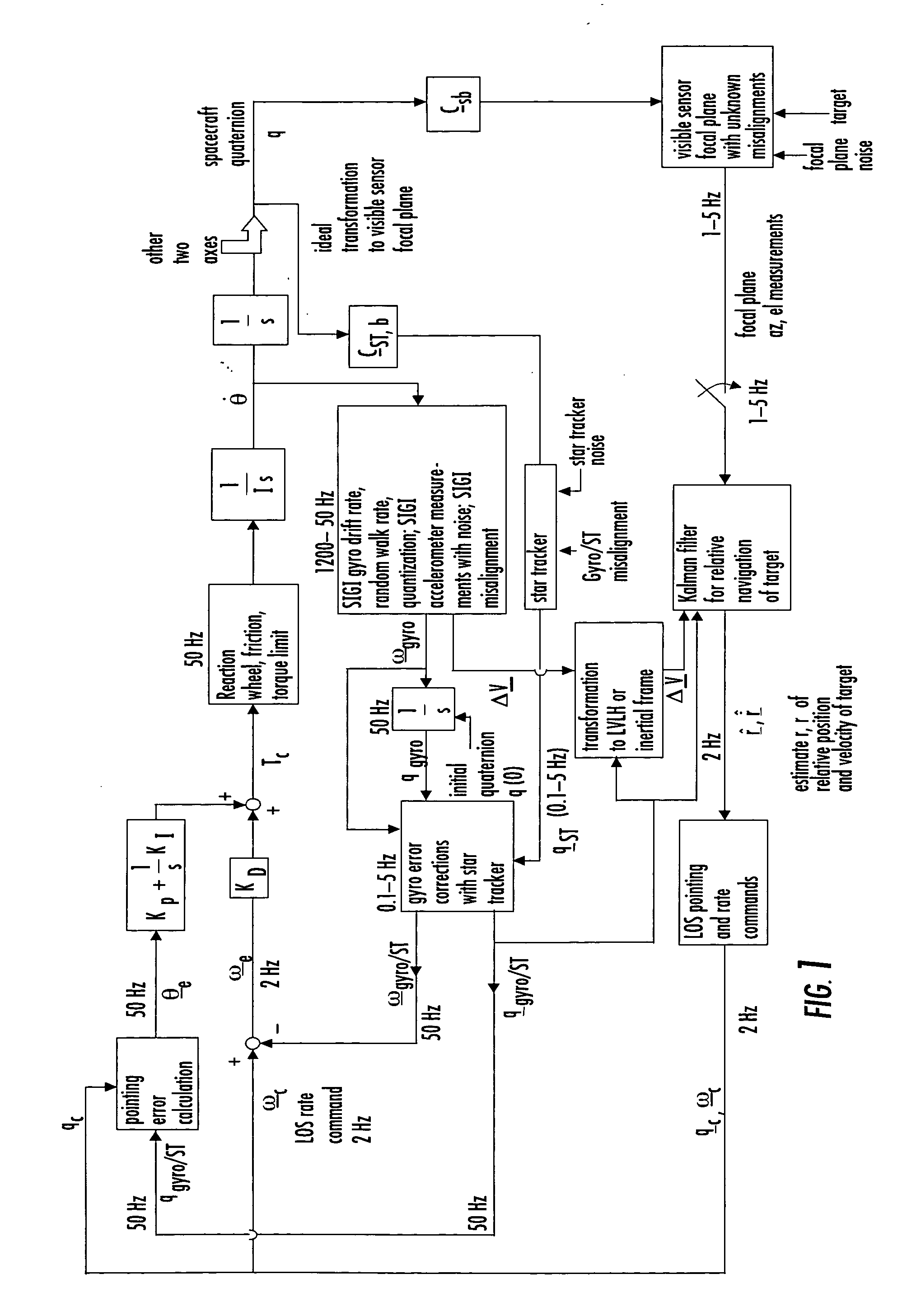
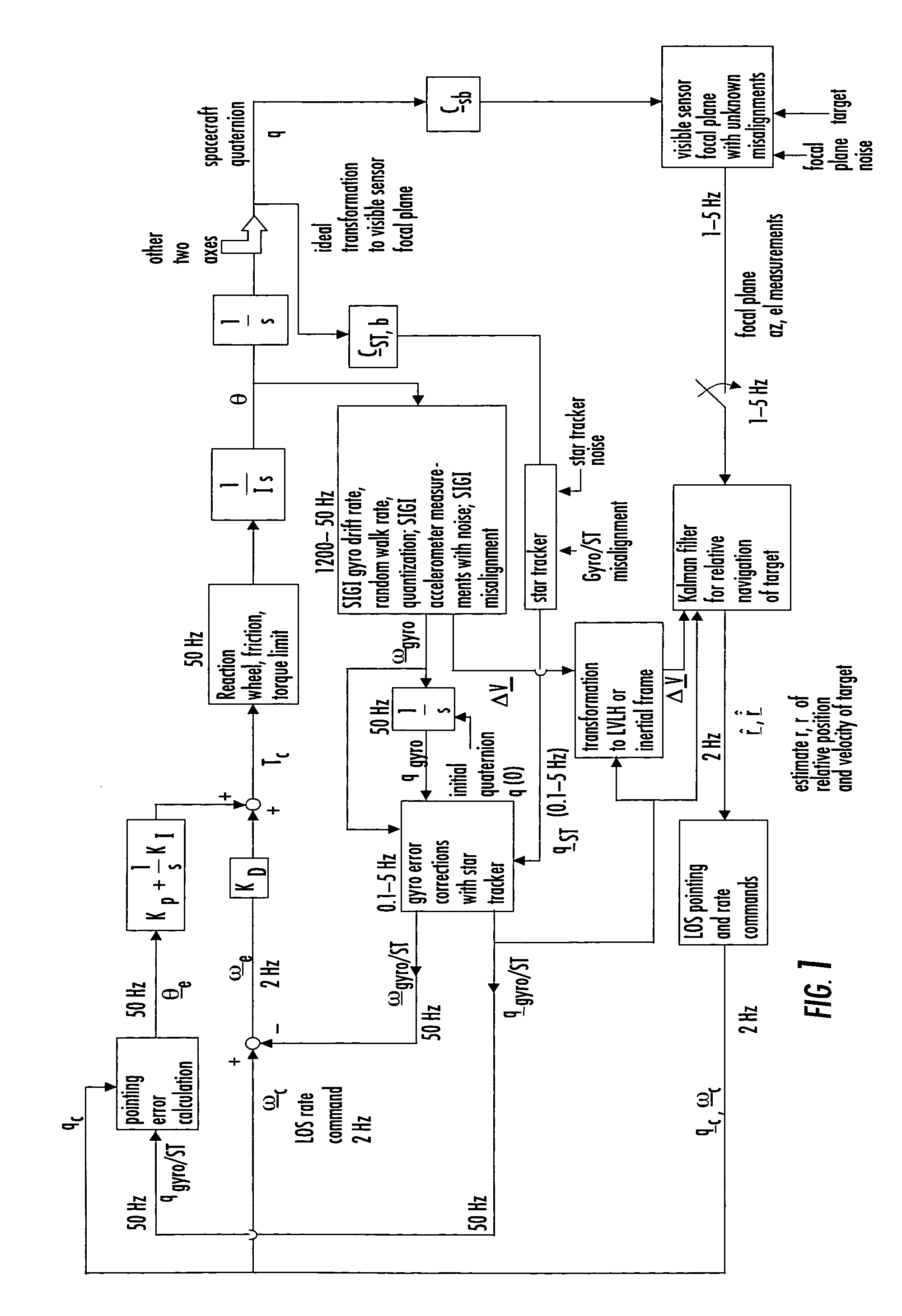
Laser range finder closed-loop pointing technology of relative navigation, attitude determination, pointing and tracking for spacecraft rendezvous
InactiveUS20050060092A1Improved functionality and precisionImprove ObservabilityInstruments for road network navigationCosmonautic vehiclesGyroscopeClosed loop
A closed-loop LRF pointing technology to measure the range of a target satellite from a chaser satellite for rendezvous is provided that includes several component technologies: LOS angle measurements of the target satellite on a visible sensor focal plane and the angles' relationships with the relative position of the target in inertial or LVLH frame, a relative navigation Kalman filter, attitude determination of the visible sensor with gyros, star trackers and a Kalman filter, pointing and rate commands for tracking the target, and an attitude controller. An analytical, steady-state, three-axis, six-state Kalman filter is provided for attitude determination. The system and its component technologies provide improved functionality and precision for relative navigation, attitude determination, pointing, and tracking for rendezvous. Kalman filters are designed specifically for the architecture of the closed-loop system to allow for pointing the laser rangefinder to a target even if a visible sensor, a laser rangefinder, gyros and a star tracker are misaligned and the LOS angle measurements from the visible sensor are interrupted.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
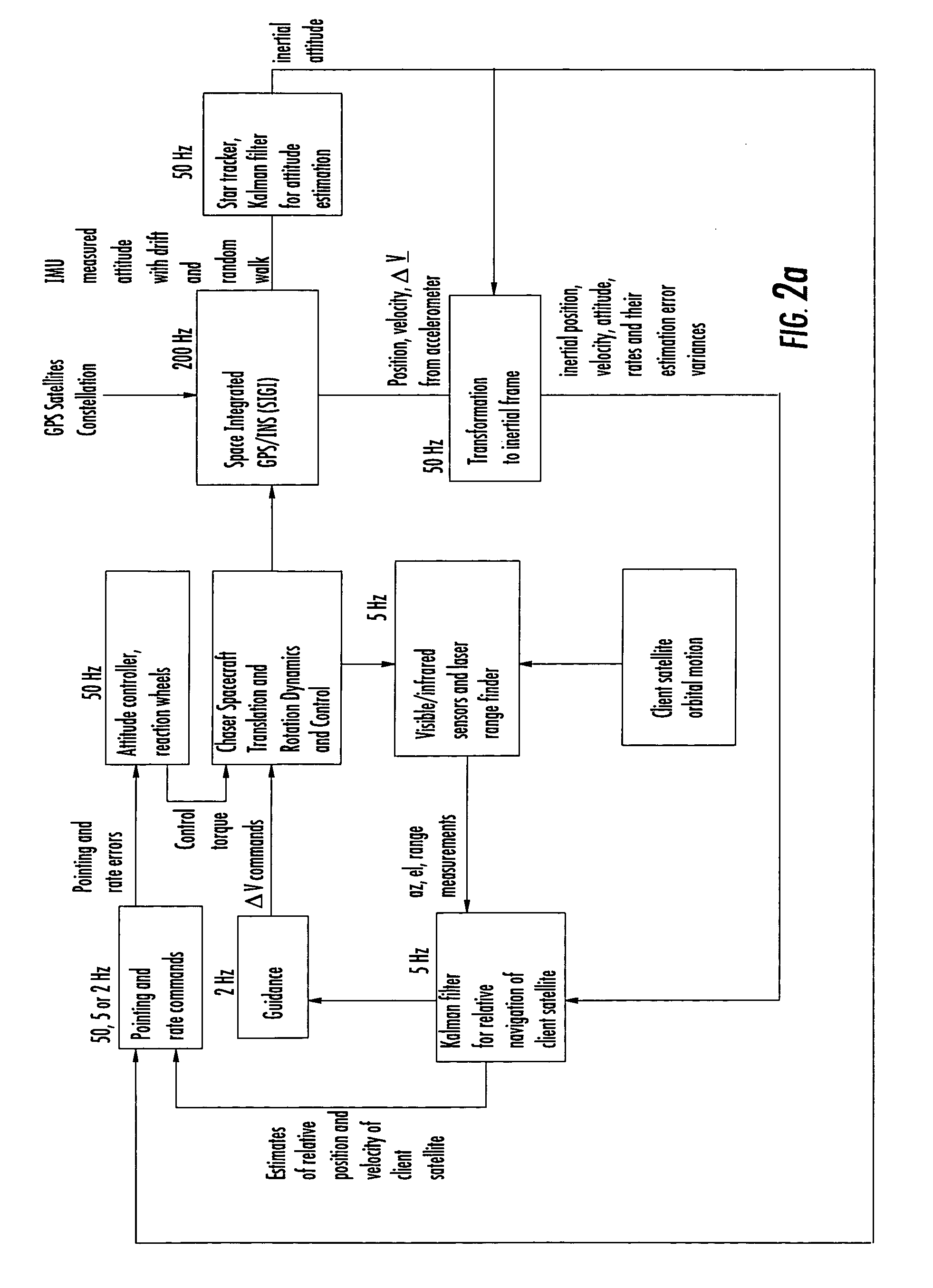
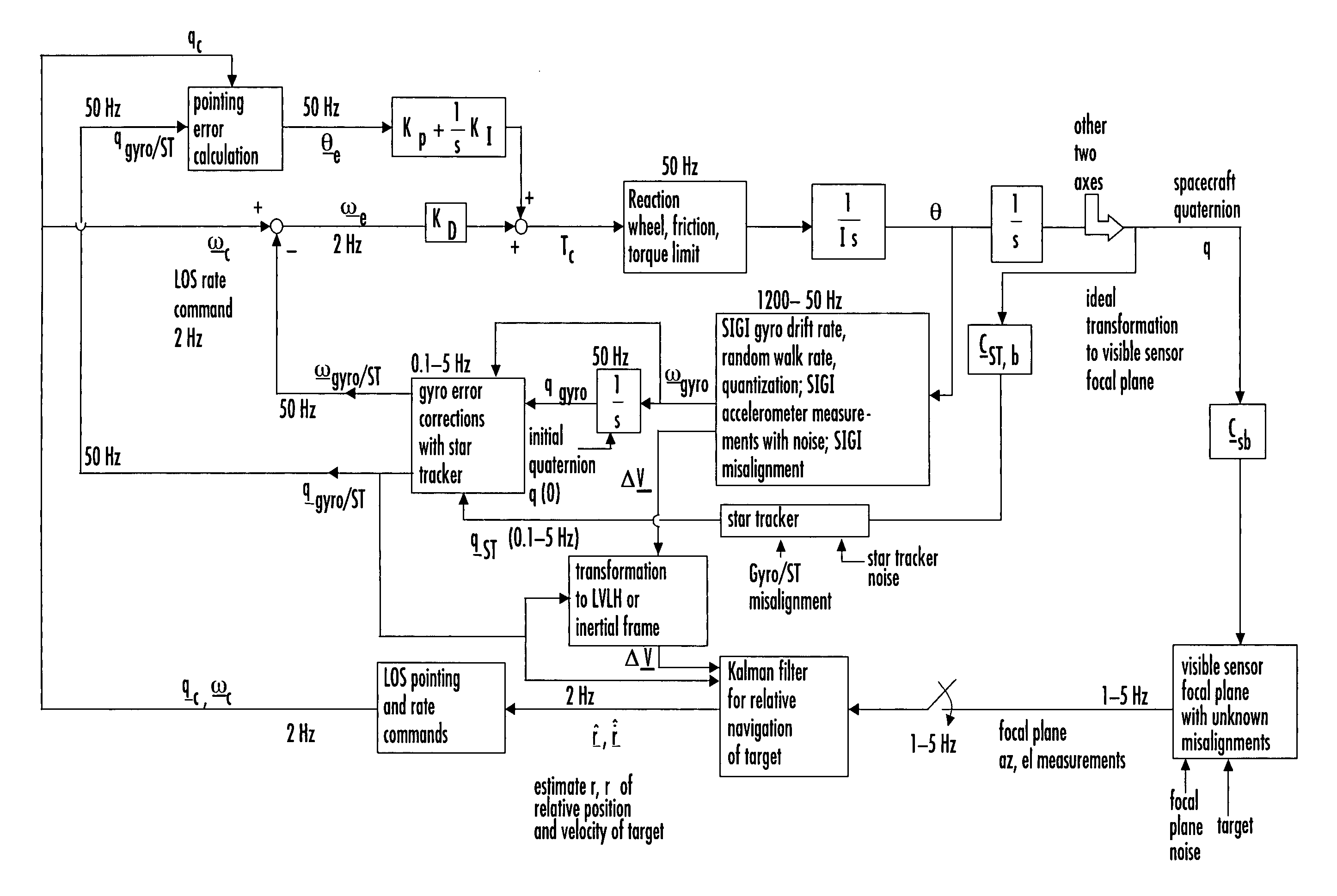
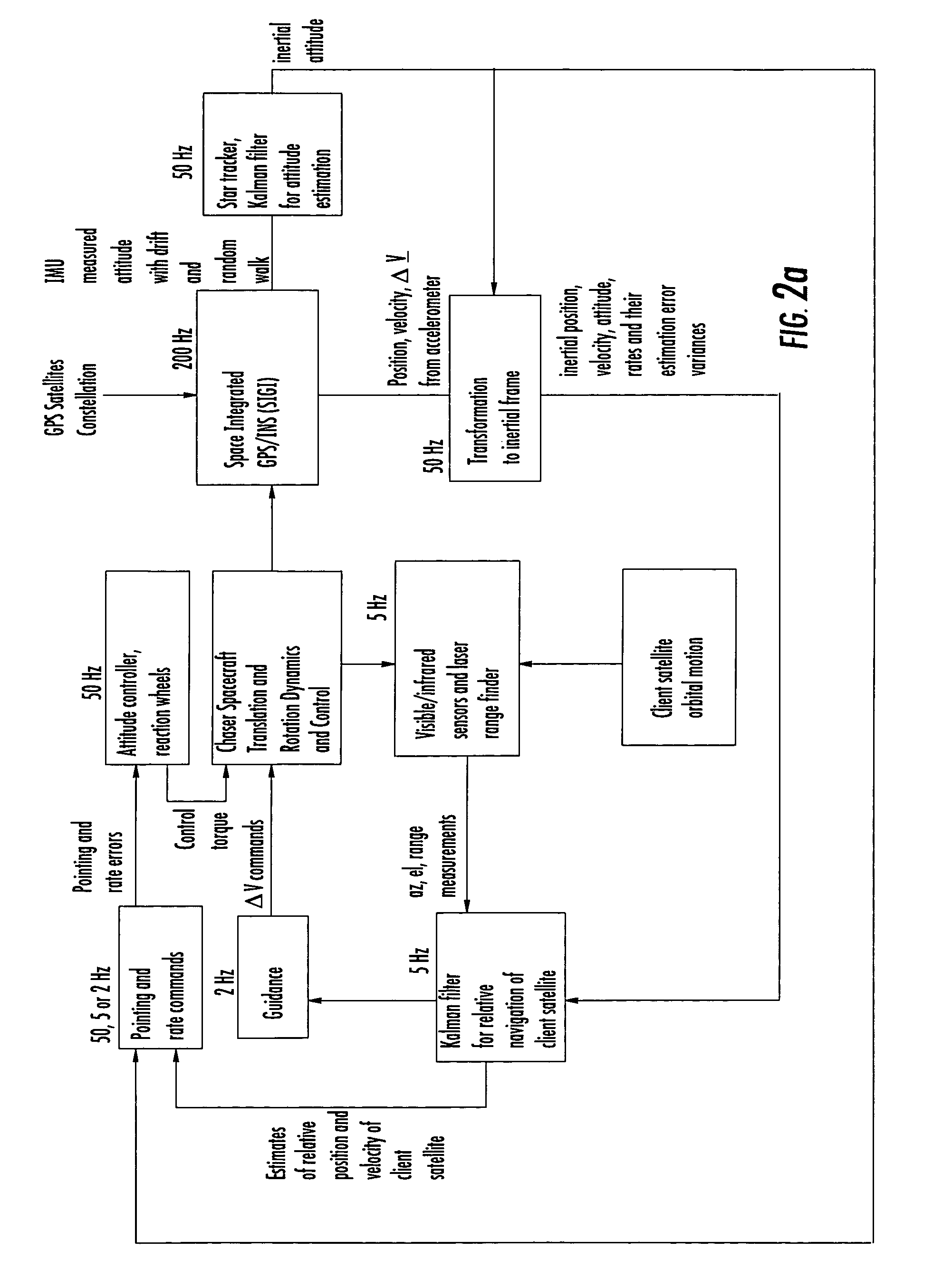
Laser range finder closed-loop pointing technology of relative navigation, attitude determination, pointing and tracking for spacecraft rendezvous
InactiveUS7142981B2Improved functionality and precisionImprove ObservabilityInstruments for road network navigationDigital data processing detailsKaiman filterLaser ranging
A closed-loop LRF pointing technology to measure the range of a target satellite from a chaser satellite for rendezvous is provided that includes: LOS angle measurements of the target, a relative navigation Kalman filter, attitude determination of the visible sensor with gyros, star trackers and a Kalman filter, pointing and rate commands for tracking the target, and an attitude controller. An analytical, steady-state, three-axis, six-state Kalman filter is provided for attitude determination. The system provides improved functionality and precision for relative navigation, attitude determination, pointing, and tracking for rendezvous. Kalman filters are designed for the closed-loop system to allow for pointing the laser rangefinder to a target even if a visible sensor, a laser rangefinder, gyros and a star tracker are misaligned and the LOS angle measurements from the visible sensor are interrupted.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Super-close optimized collision-avoidance proximity method for failure satellite
ActiveCN105549606AMeet space constraintsEnsuring safety and collision-free mission requirementsAttitude controlNatural satelliteClosed loop feedback
The invention relates to a super-close optimized collision-avoidance proximity method for a failure satellite, and belongs to the technical field of spacecraft encounter. An object, namely the failure satellite, is designed into an envelope model in the sphere and ellipsoid combined form to simplify configuration of the object; posture rolling of the object is considered, a relative dynamic model of the object and a tracked star as well as constraints of the path of the tracked star are derived in the dynamic object system; positional nondeterminacy caused by navigation and measurement errors is considered, and the flight forbidden area of the tracked start is further broadened by combining the collision possibility problem; and a safe collision avoidance path is planned on the basis of the Gauss pseudospectral method, and closed-loop feedback control is carried out. According to the invention, spatial limitation in super-close proximity are considered, and requirements for a safe collision free task can be met; and the posture coupling feature of a close proximity spacecraft is emphasized, and whether the distance between the aircrafts satisfies the constraints can be directly determined.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY +1
Method for determining orbit transferring strategy of time-limited spacecraft coplanar rendezvous
InactiveCN109592079AMeet the requirements of light conditionsAccurate serviceCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusLimit timeSpacecraft rendezvous
The invention provides a method for determining an orbit transferring strategy of time-limited spacecraft coplanar rendezvous, and belongs to the field of the time-limited spacecraft coplanar rendezvous. The problem that the accuracy of the rendezvous algorithm calculation is affected caused by the poor observation effect at rendezvous time due to the fact that an existing spacecraft rendezvous technology has relatively low requirements on lighting conditions is solved. The method comprises the steps that the theoretical limiting time of the entire rendezvous process between a target spacecraft and a service spacecraft is calculated; then the two speed increments and the used time of orbit transferring in the service spacecraft orbit transferring process are calculated; initial values of the movement time of an initial orbit and initial values of the movement time of a target orbit for the optimized variable service spacecraft are calculated; integral is carried out on the rendezvous process to obtain position vectors of the service spacecraft and the target spacecraft at the rendezvous time and the angle of the position vectors; when the angle reaches 0 degree, at the moment, themovement time of the initial orbit and the movement time of the target orbit are used as the orbit transferring parameters and the orbit transferring strategy. According to the method, the calculationresults are accurate, and the iterative calculation process is simple.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Simulation system for rendezvous and docking of spacecraft
ActiveCN105109711AOvercoming motion trajectoryOvercoming gestureCosmonautic condition simulationsAir bearingSix degrees of freedom
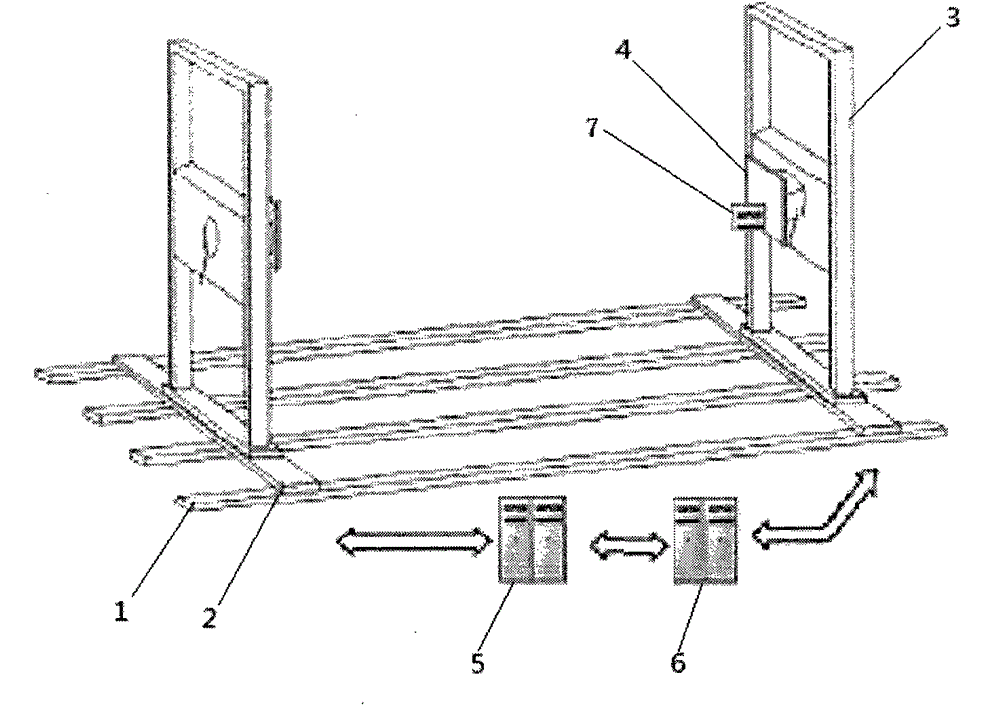
A simulation system for rendezvous and docking of a spacecraft comprises a horizontal support module, a target six-degree-of-freedom air bearing table, a tracking six-degree-of-freedom air bearing table, a master control module, and a monitor and display module. Actual features of weight and quality of a rendezvous and docking spacecraft can be simulated by six-degree-of-freedom air bearing tables, a six-degree-of-freedom test on a last translation closing stage can be carried out depending on actual rendezvous and docking spacecraft-mounted devices such as a docking mechanism. Compared with the prior art, in the simulation system, an indoor GPS unit module can measure positions and attitudes and transmit to the master control module and the monitor and display module in real time, the rendezvous and docking process of a spacecraft can be visually, accurately and real controlled and simulated, and the success rate of a simulation test can be raised. In addition, the simulation system can verify the rationality of a work sequence during the rendezvous and docking process of the spacecraft, the reliability and validity of the rendezvous and docking process of the spacecraft can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
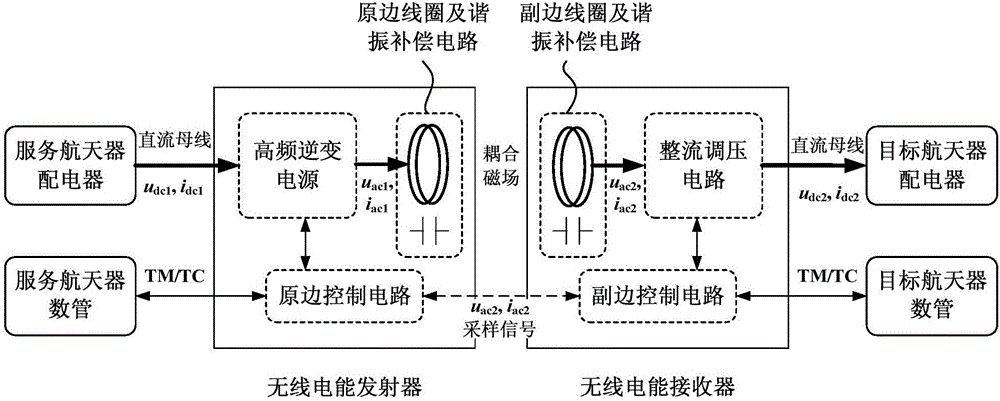
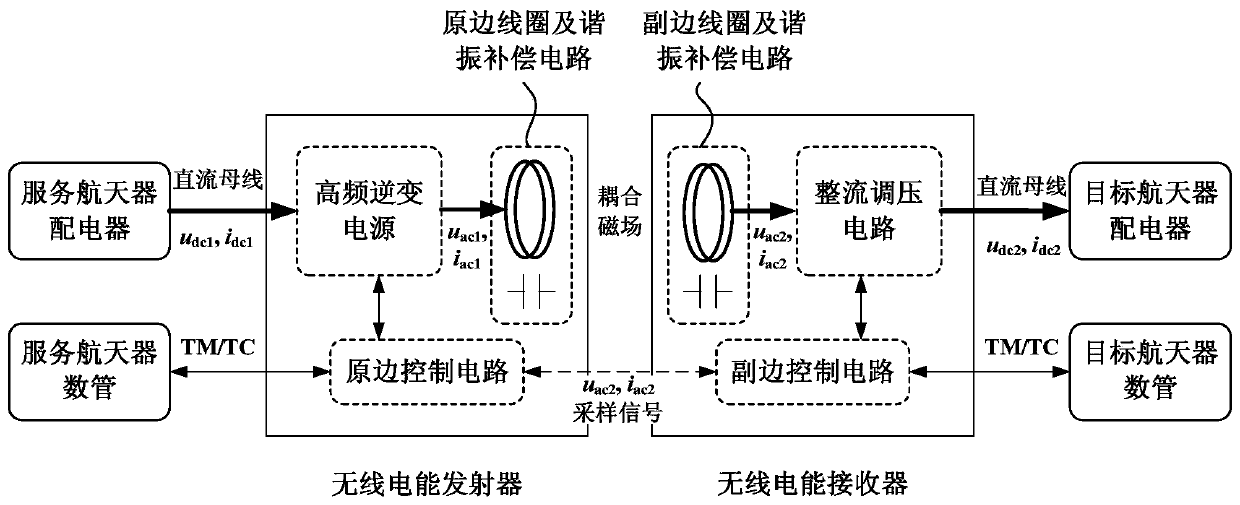
Wireless electric power and signal transmission system for spacecraft rendezvous and docking parallel-operated power supply
ActiveCN106787251AThere will be no safety issues such as sparkingReduce control precision requirementsNear-field transmissionCircuit arrangementsElectric power transmissionElectric power system
The invention discloses a wireless electric power and signal transmission system for spacecraft rendezvous and docking parallel-operated power supply. One or a plurality groups of wireless electric power transmission units are configured on a spacecraft rendezvous and docking mechanism; each group of transmission units consist of electric power transmitting devices and electric power receiving devices. Wireless transmission of electric power and signals can be achieved by using a technique based on electromagnetic induction principles, under same power transmission conditions, the weight and the size of the system are equivalent to those of a wired electric power transmission mode, the electric power transmission efficiency of the system is greater than 85%, that is, the electric power transmission efficiency is higher than that of the wired transmission mode. By adopting the wireless electric power and signal transmission system, the problems that a power supply mode of a conventional electric connector has high abutting precision requirements, abutting interface design is complex, potential hazard of electric sparks can be caused as contact metal is exposed, and the like, can be solved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
Linear-feedback global stabilization method for controlling limited spacecraft rendezvous control system
ActiveCN106407619AGuaranteed global asymptotic stabilityFast convergenceGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsLinear state feedbackStabilization control
The invention provides a linear-feedback global stabilization method for controlling a limited spacecraft rendezvous control system and relates to a controller design method of the spacecraft rendezvous control system. A thruster arranged on a chasing spacecraft can only provide finite thrust, so that the system must face the problem of control limitation. The control quality is reduced or even the system instability is generated if the problem is ignored. Aiming at the defect of the prior art, a linear state feedback-based global stabilization control law is provided and an optimal selection scheme of control law parameters is given, so that the condition that a closed-loop system has a fastest convergence speed is ensured. The linear-feedback global stabilization method has the advantages that: firstly, the provided control law is linear and is convenient to design and implement; secondly, the global asymptotic stability of the closed-loop system is ensured; and finally the optimal parameters are given to ensure that the closed-loop system has the fastest convergence speed. The linear-feedback global stabilization method is used for the field of spacecraft rendezvous control.
Owner:黑龙江省工研院资产经营管理有限公司
Method for extracting pose measurement feature points based on target feature modeling
InactiveCN102915539AReduce energy consumptionShorten the timeImage analysisPattern recognitionRandom noise
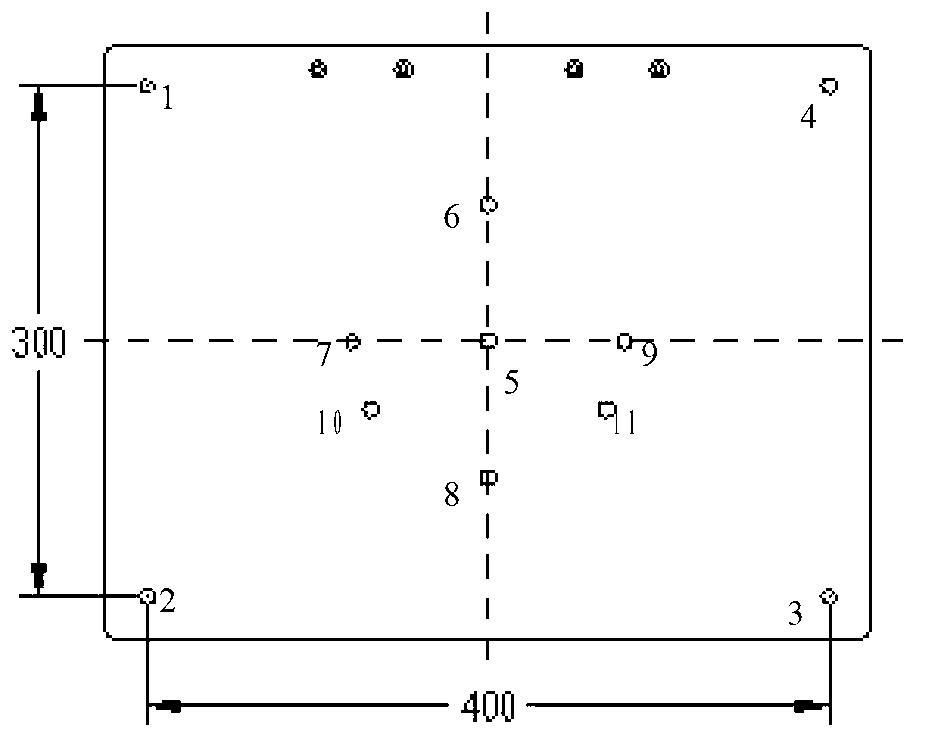
The invention relates to a method for extracting pose measurement feature points based on target feature modeling, in particular to a method for extracting feature points under complex celestial background on the basis of target feature modeling and belongs to the technical field of rendezvous and docking. The method includes: firstly, setting four low-consumption light emitting diodes forming a diamond on a target spacecraft; using a spacecraft trace camera to acquire optical feature point images under the complex celestial background in the approach stage of rendezvous and docking of the spacecraft, and performing adaptive threshold binarization and smooth filtering to obtain a binary image; and searching planar diamond structures in the image to obtain image plane coordinates of the spacecraft optical feature points. Interference of the celestial background can be eliminated effectively, random noise can be eliminated, optical plane coordinates of the optical feature points can be obtained easily, results are stable and reliable, and the method is easy to implement.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Rendezvous and docking method of spacecraft based on virtual reality and multimodal man-machine interface
InactiveCN109062398AEasy to judgeFast learningInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingFeature extractionFlight vehicle
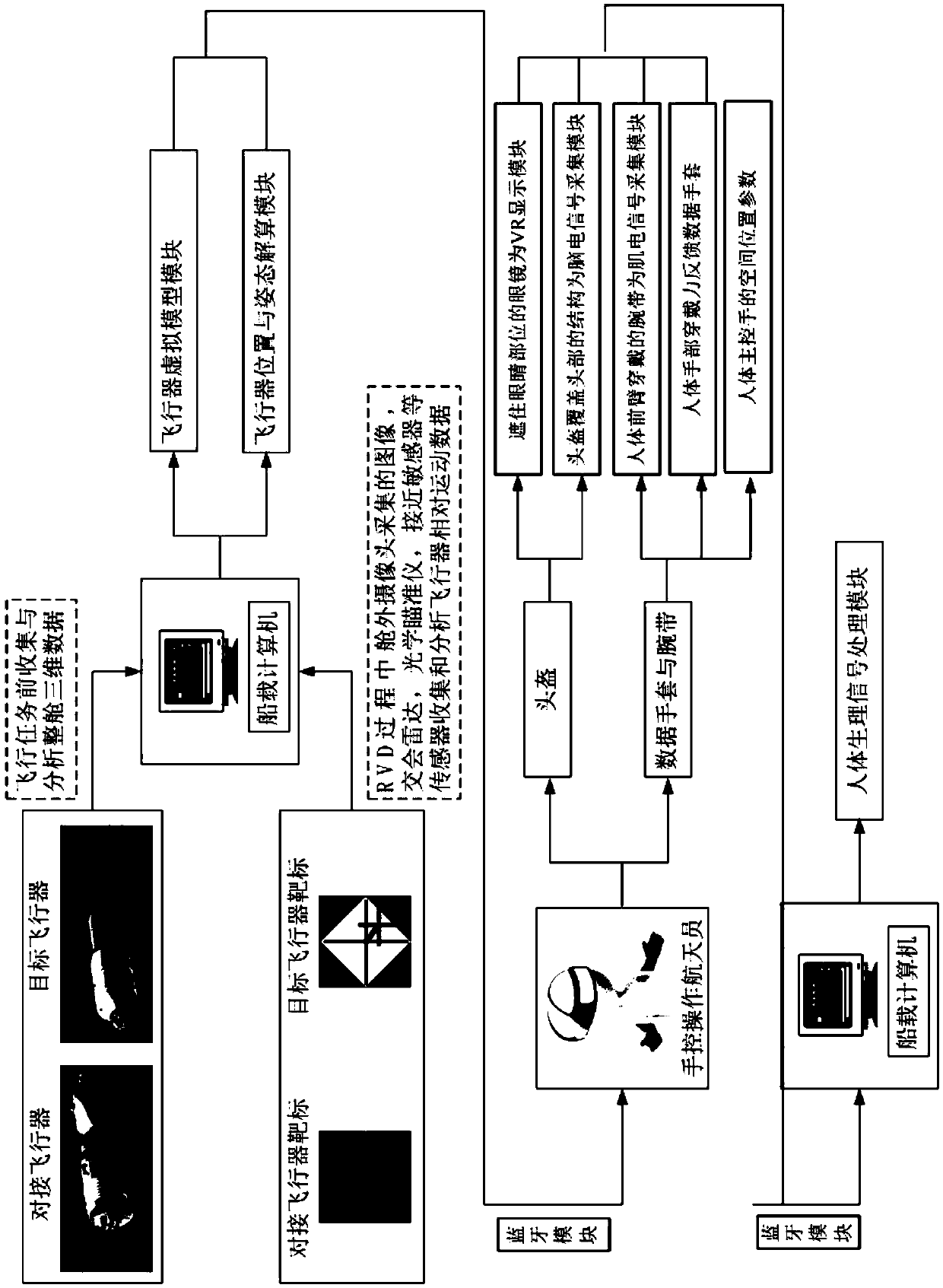
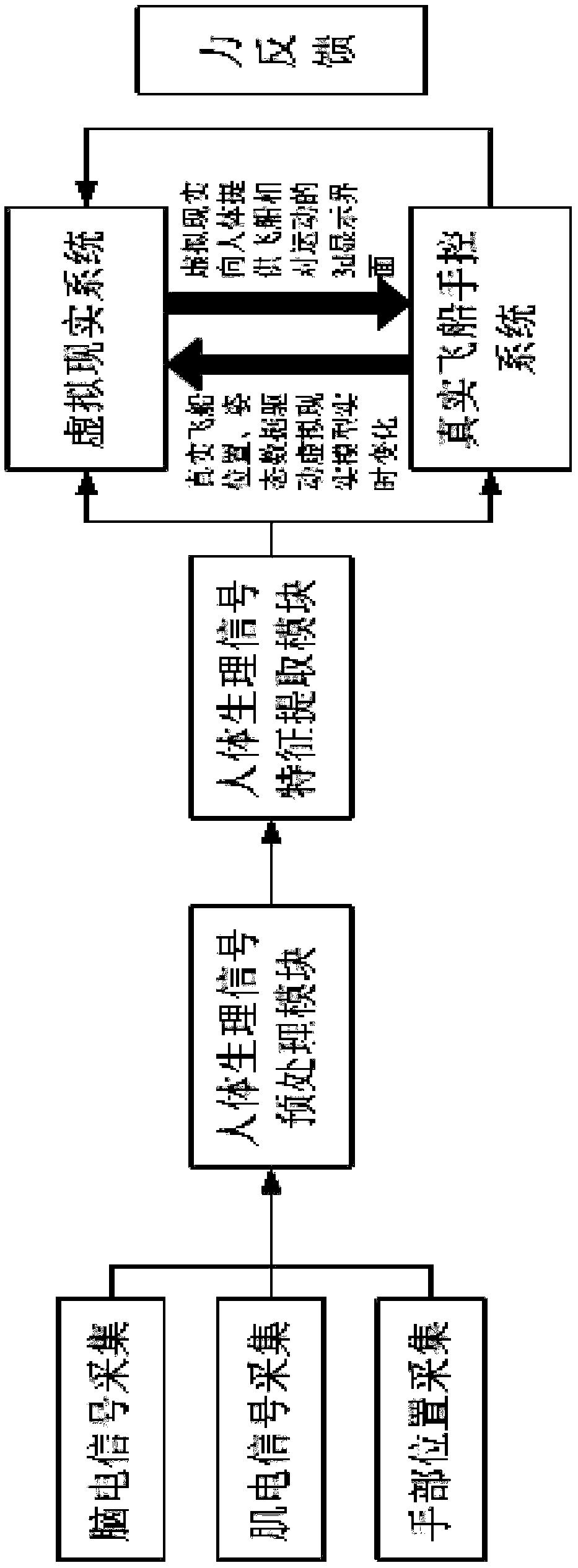
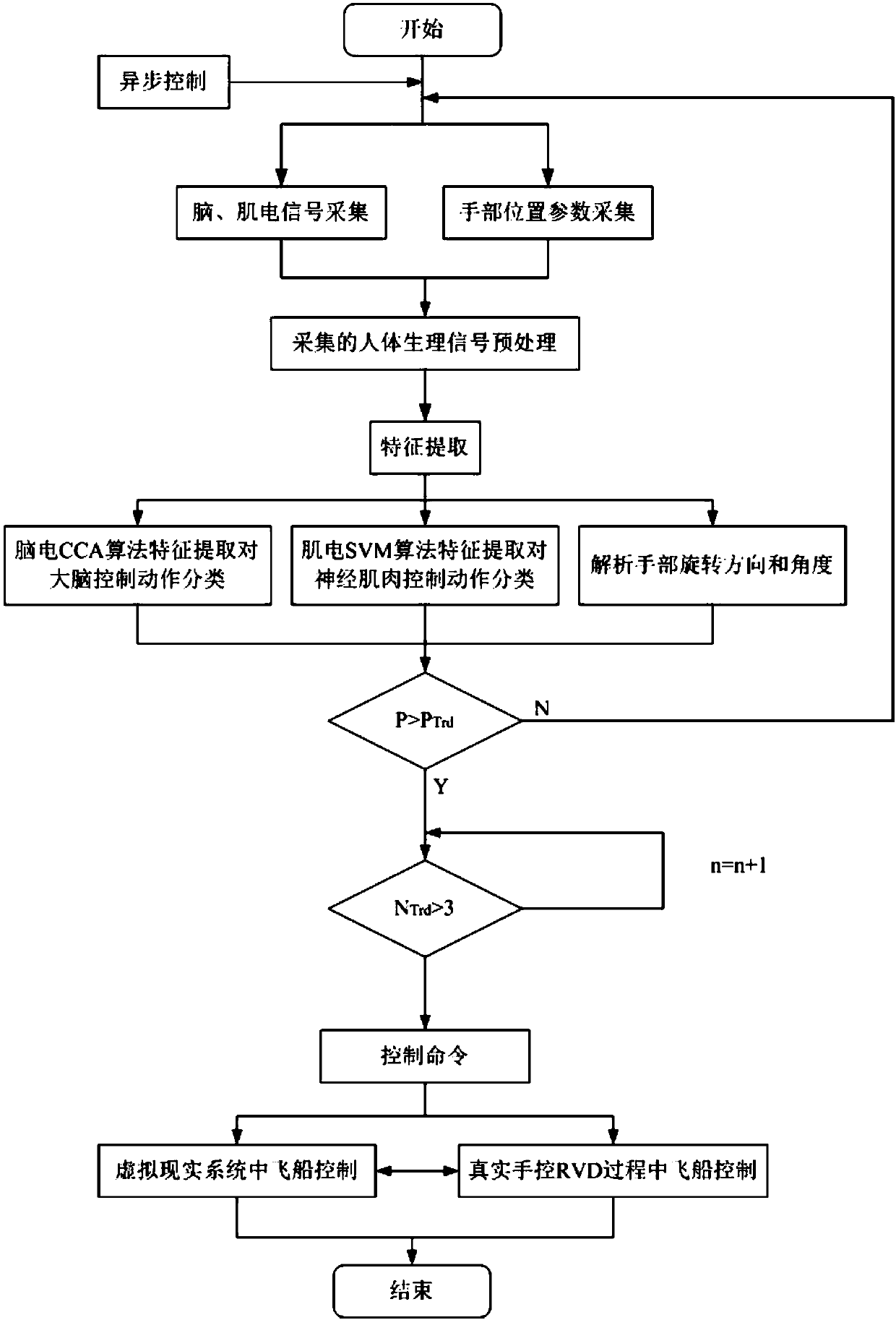
A rendezvous and docking method of spacecraft based on virtual reality and multimodal man-machine interface is provided. The invention discloses an aircraft rendezvous and docking method and system based on virtual reality technology and multi-modal man-machine interface, which is characterized in that: the whole cabin three-dimensional data of the docked aircraft and the target aircraft are inputto a shipboard computer to model the two aircraft three-dimensionally; the whole cabin three-dimensional data of the docked aircraft and the target aircraft are inputted to a ship-borne computer; electroencephalogram, electromyogram and hand position parameters are collected. The EEG signal, EMG signal and hand position parameter information are preprocessed. Feature extraction of EEG, EMG and hand position parameters are performed; based on the parameters extracted from the features, corresponding control commands are generated to adjust the position and attitude of the docking vehicle. Thereal-time attitude and position changes of the docking vehicle are calculated and fed back to the astronauts so that the astronauts can feel the changes of the spacecraft position and attitude. Astronauts can be better assisted to complete the manually controlled RVD mission by directly converting the intention information of the brain and limbs into the control information of the vehicle.
Owner:SCI RES TRAINING CENT FOR CHINESE ASTRONAUTS +1
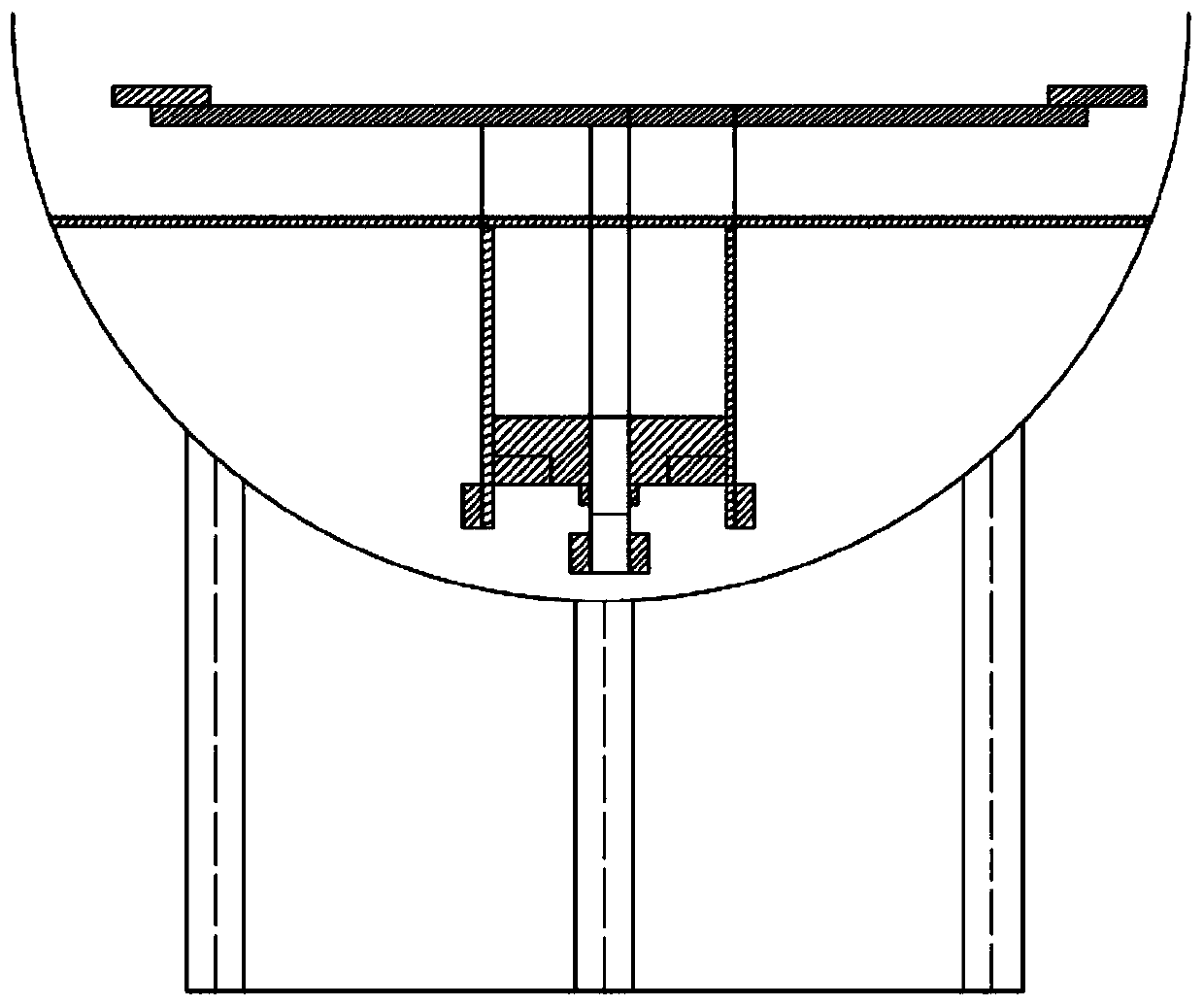
Spacecraft rendezvous and docking multi-degree-of-freedom semi-physical simulation method and device thereof
InactiveCN103606332ASimple structureMany degrees of freedomEducational modelsMulti degree of freedomEngineering
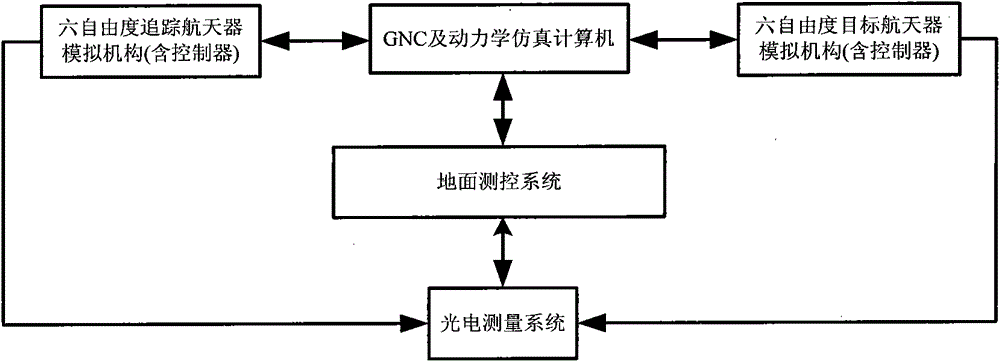
The invention provides a spacecraft rendezvous and docking multi-degree-of-freedom semi-physical simulation method and a device thereof. The device comprises a machine body, a cross beam, a vertical beam, a three-shaft turntable, a motion simulation device controller, a GNC system and a measurement system. The machine body is mounted on a ground base. The cross beam is placed on the guide rail of the machine body. The vertical beam is installed on the guide rail of the cross beam. The three-shaft turntable is installed on a vertical beam guide rail. The motion simulation device controller, the GNC system and the measurement system are placed next to a system. Based on a similarity theorem and a scaling ratio criterion, the effective travel range of a simulation device is determined according to an aircraft actual flight range, and assuming that a scaling parameter is k, according to the actual flight condition of the aircraft, assuming that an aircraft true maximum speed, an acceleration, an angular speed and an angular acceleration are v[max], a[max], omega[max], and alpha[max] respectively, the maximum speed, the acceleration, the angular speed and the angular acceleration of the simulation device are determined as k*v[max], k*a[max], omega[max], and alpha[max]. The method and the device have the advantages of a wide application range, a simple structure, and multi degrees of freedom.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Gain switching method of spacecraft rendezvous system and maximal attraction domain estimation
InactiveCN105843077AImprove dynamic performanceSimple calculationSimulator controlLinear matrixClosed loop
The invention discloses a gain switching method of a spacecraft rendezvous system and maximal attraction domain estimation. The method comprises steps that firstly, a spacecraft rendezvous relative movement model is established, secondly, the gain switching method of the spacecraft rendezvous system is proposed, and lastly, the maximal attraction domain estimation of a closed loop system can be given through the gain switching method. According to the method, a spacecraft asymmetric performer saturation control problem is converted into a performer symmetric saturation control problem, controller calculation only requires solving linear matrix inequalities, calculation is simple and easy to carry out, dynamic performance of the closed loop system is improved, and the maximal attraction domain estimation of the closed loop system is further given.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Time-varying feedback finite-time stabilization method of control limited spacecraft rendezvous control system
ActiveCN110727199AGuaranteed Rendezvous MissionFast convergenceAdaptive controlSolution of equationsFeedback controller
The invention relates to a time-varying feedback finite-time stabilization method of a control limited spacecraft rendezvous control system. The stabilization method comprises the steps of: (1), establishing an orbital dynamics model of the control limited spacecraft rendezvous control system, and obtaining a state-space equation; (2), establishing a parametric Lyapunov equation, analyzing the property thereof, according to the positive definite solution P(gamma) of the parametric Lyapunov equation, designing an explicit linear time-varying feedback control law in a control limited condition,namely, designing a state feedback controller of the control limited spacecraft rendezvous control system; and (3), designing controller parameters by constructing an explicit Lyapunov function and utilizing the property of the parametric Lyapunov equation solution, and ensuring that a tracking spacecraft and a target spacecraft complete a rendezvous task in limited time. By means of the time-varying feedback finite-time stabilization method of the control limited spacecraft rendezvous control system in the invention, limited time stabilization of the spacecraft rendezvous control system in the control limited condition can be realized.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Gradient separate zone optimization design method for spacecraft pulse rendezvous trajectory
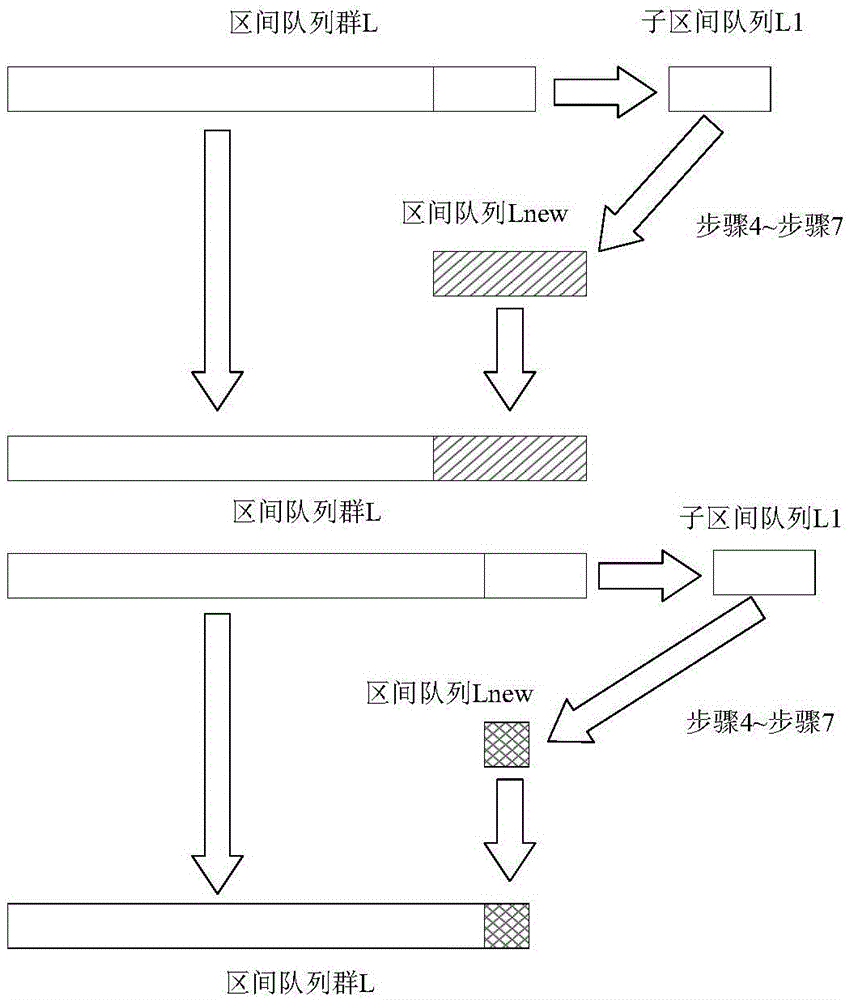
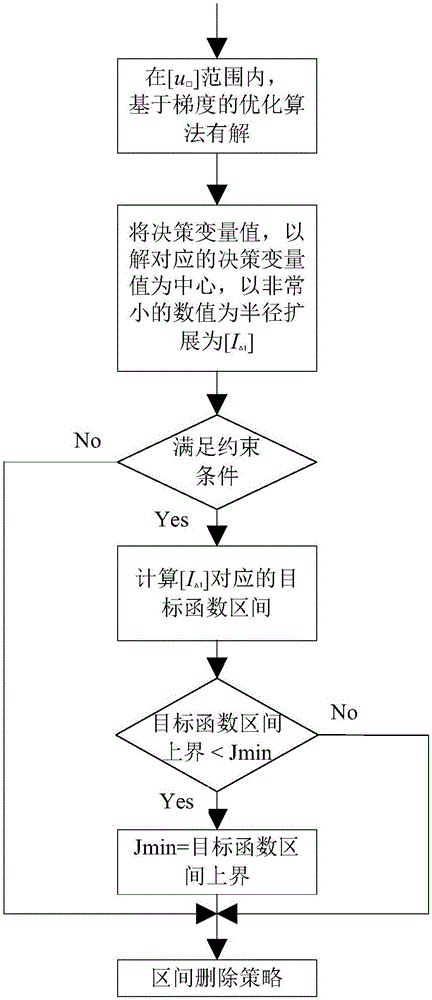
ActiveCN105005651AGuaranteed global optimalityNo overflowSpecial data processing applicationsInterval arithmeticMathematical model
The invention provides a gradient separate zone optimization design method for a spacecraft pulse rendezvous trajectory, belongs to orbit design and optimization technologies in the field of spacecraft orbit dynamics and control, and in particular belongs to a rendezvous trajectory design technology in which a spacecraft rendezvous trajectory global optimization solution is obtained through calculation based on an interval arithmetic mathematical model. For a global issue of the method, a gradient optimization result is only used to determine an interval separation point and update a value of an upper bound of a target function, thereby preserving globalness of an interval optimization algorithm. For a large computation amount in the interval optimization algorithm, a gradient optimization method is introduced, so that the value of the upper bound of the target function can be quickly updated, and a gradient segmentation method can be used; in combination with a symbol segmentation method and an interval optimization strategy, intervals that do not comprise an optimal solution are effectively separated and removed, thereby improving operational efficiency. To solve the problem that the interval optimization algorithm has a high storage requirement, only a limited number of intervals are selected for processing in each iteration, so as to ensure that a storage space overflowing phenomenon does not occur in an operation.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for controlling autonomous rendezvous between spacecrafts under action of impulse thrust
InactiveCN102354217ADisadvantages of Eliminating Disturbance Moment EffectsAvoid calculationPosition/course control in three dimensionsLoop controlLinear matrix
The invention relates to a method for controlling an autonomous rendezvous between spacecrafts under action of impulse thrust, which belongs to the technical field of aerospace, and aims to solve the problem that a traditional method for controlling the rendezvous between the spacecrafts under the action of the impulse thrust is easy to be influenced by a disturbance moment because of adopting anopen-loop control mode. The method for controlling the autonomous rendezvous between the spacecrafts under the action of the impulse thrust comprises the following steps: establishing a kinetic modelof the relative motion between the spacecrafts, and converting a state space model of the relative motion into a discrete motion model; introducing state feedback control rate in the impulse action process; introducing virtual energy functions for a impulse action motion and a free motion; determining three inequalities meeting the requirement that the spacecrafts realize the autonomous rendezvous, satisfying a finite impulse thrust inequality, and converting the inequalities into linear matrix inequalities related with X1,X2 and Y1; and calculating a state feedback gain matrix K according tothe worked-out X1 and Y1 matrixes to obtain a state feedback sampling control law u(k)=Kx(k) of the relative motion between the spacecrafts, which meets the design requirement. The method for controlling the autonomous rendezvous between the spacecrafts under the action of the impulse thrust is suitable for the autonomous rendezvous process of the spacecrafts.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
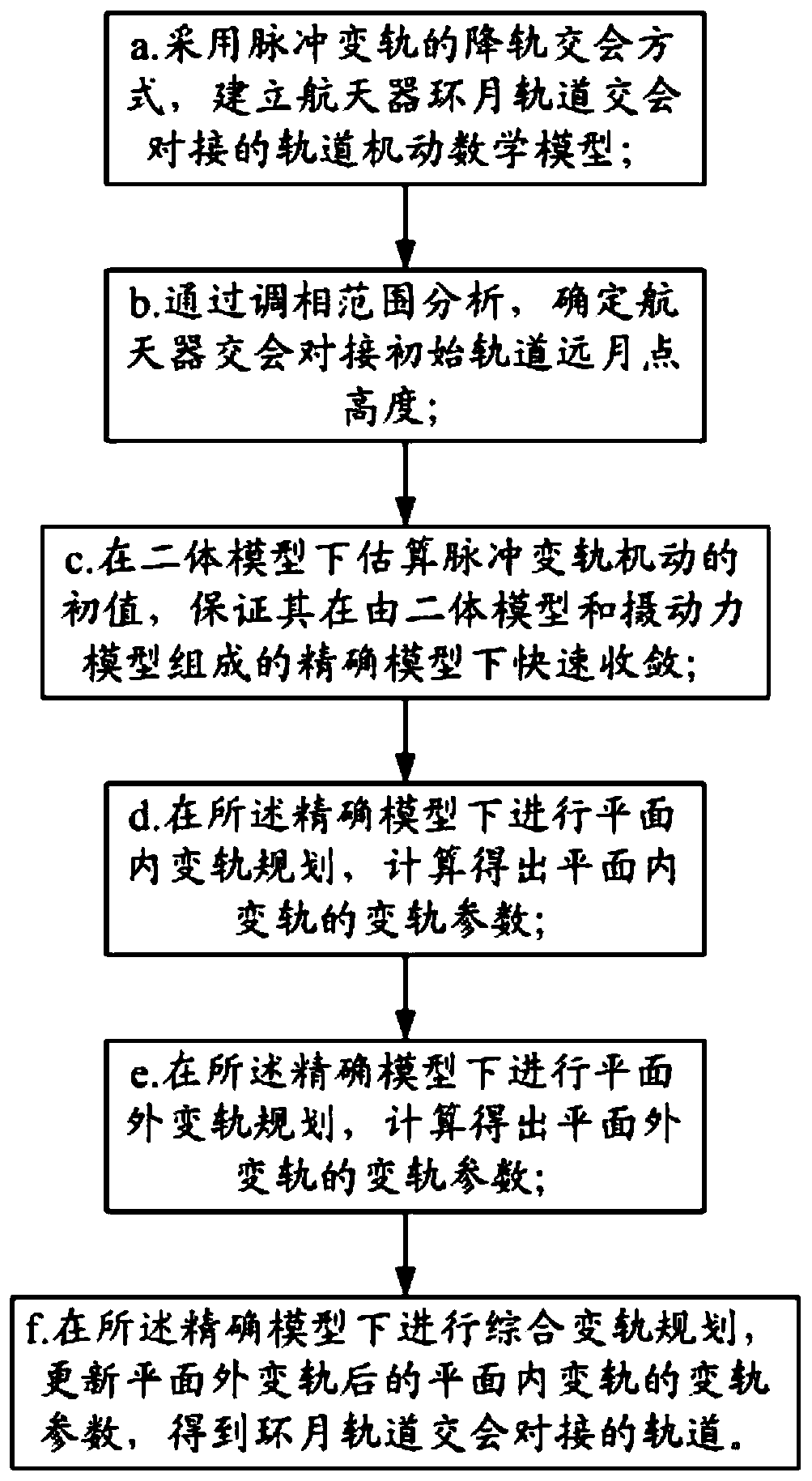
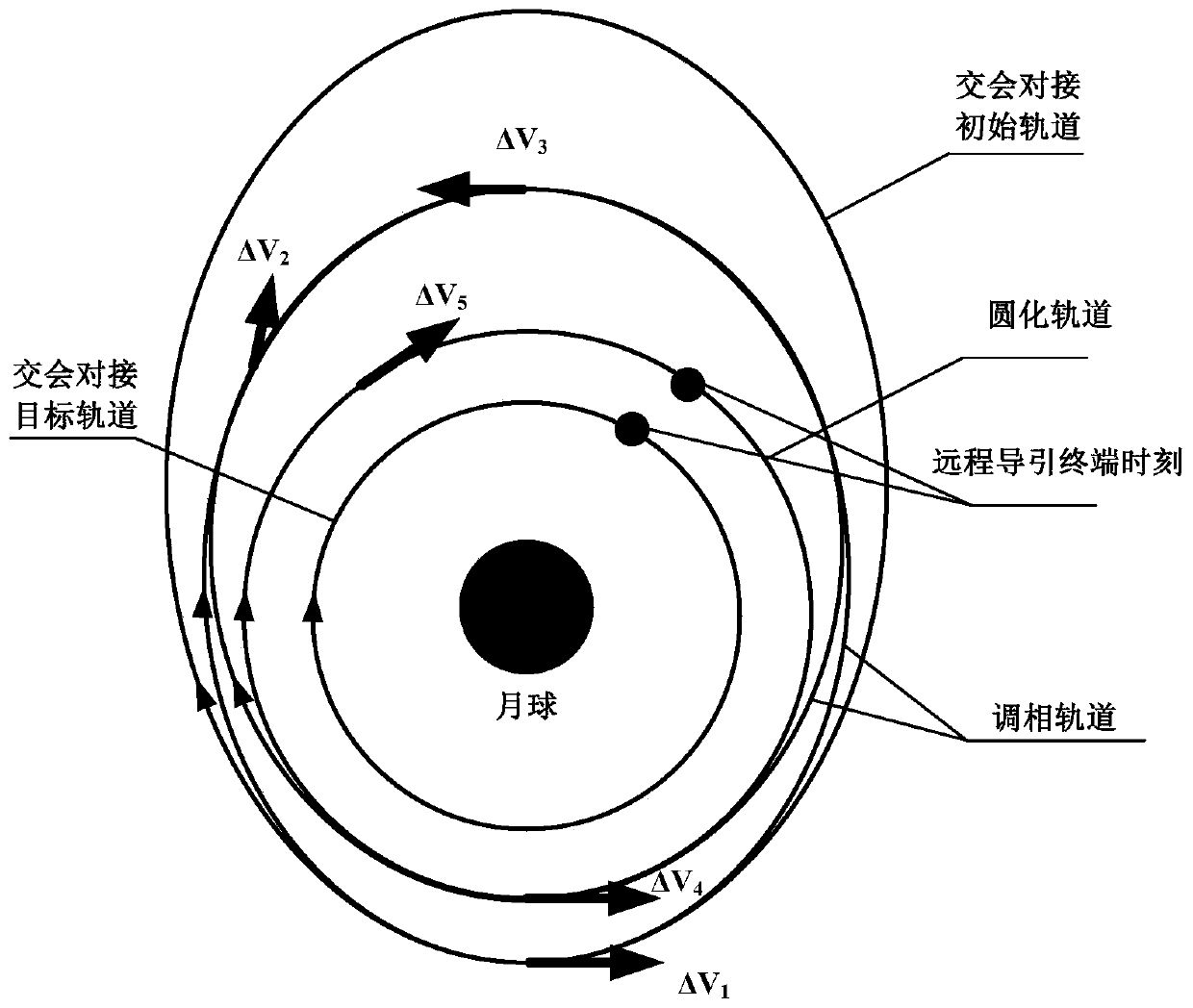
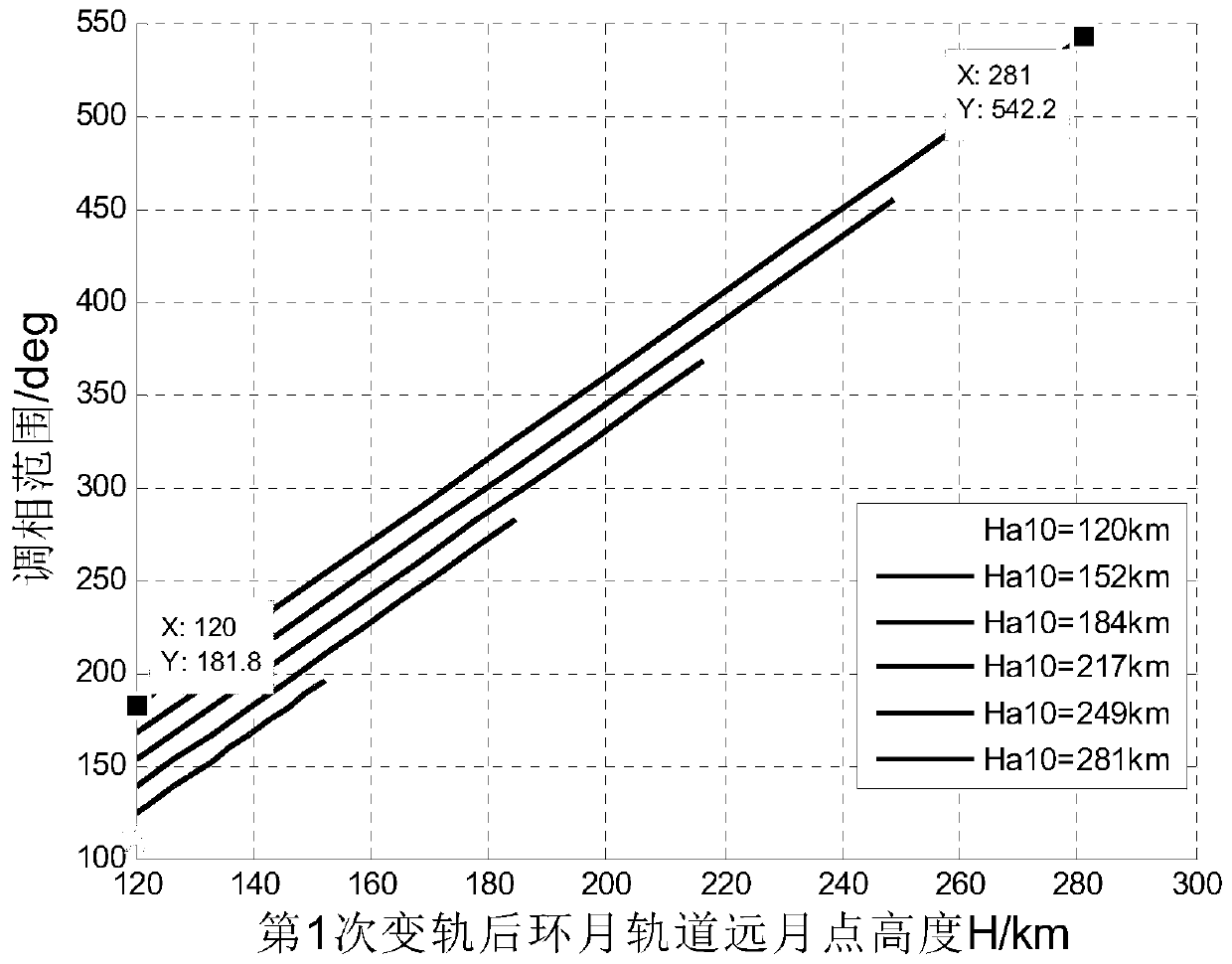
Orbit design method for spacecraft lunar orbit rendezvous and docking
ActiveCN110765504AFast solutionFast convergenceDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsMathematical modelClassical mechanics
The invention relates to an orbit design method for spacecraft lunar orbit rendezvous and docking, which comprises the following steps: a, establishing an orbit maneuvering mathematical model for spacecraft lunar orbit rendezvous and docking by adopting an orbit descending rendezvous mode of pulse orbit transfer; b, determining the height of a spacecraft rendezvous and docking initial orbit lunarpoint through phase modulation range analysis; c, estimating an initial value of the pulse orbital transfer maneuver under the two-body model, and ensuring that the initial value is quickly convergedunder an accurate model consisting of the two-body model and a perturbation force model; d, performing in-plane orbital transfer planning under the accurate model, and obtaining orbital transfer parameters of in-plane orbital transfer through calculation; e, performing out-of-plane orbital transfer planning under the accurate model, and orbital transfer parameters of out-of-plane orbital transferare obtained through calculation; and f, performing comprehensive orbit transfer planning under the accurate model, updating orbit transfer parameters of in-plane orbit transfer after out-of-plane orbit transfer, and obtaining a lunar orbit rendezvous and butt joint orbit.
Owner:BEIJING SPACE TECH RES & TEST CENT
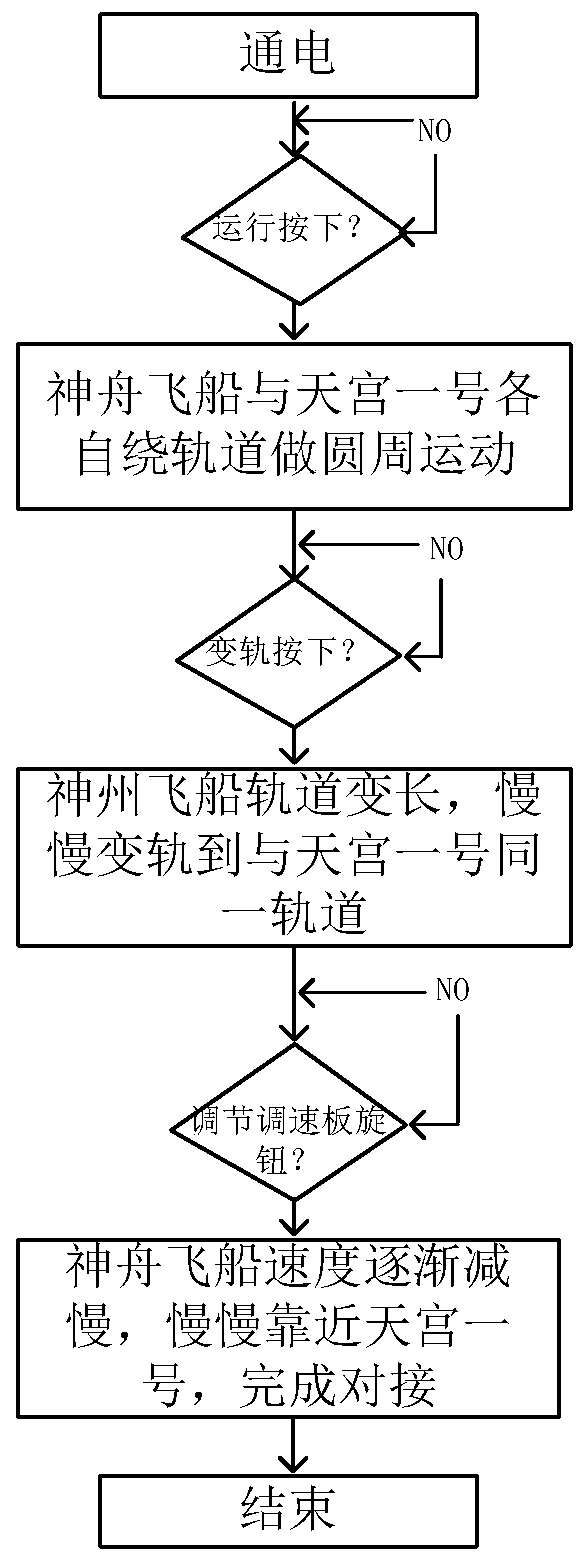
Magnetic levitation science education device for demonstrating rendezvous and docking of spacecrafts
InactiveCN110428715AEasy to learnIncrease interest in scientific explorationEducational modelsDynamic modelsElectric machine
The invention belongs to the technical field of teaching demonstration devices, and discloses a magnetic levitation science education device for demonstrating rendezvous and docking of spacecrafts. The device includes two motors enabling two tracks having different lengths to make circular motions around the center of a circle through transmission gears; electric push rods, installed on the tops of the motors, wherein each electric rod is connected to one of the motors through a transmission gear; and a magnetic levitation device used for adjusting the revolution speed and direction of the motors, wherein the magnetic levitation device is connected to the motors by conductors. Based on a dynamics model, a control mathematical space of relative postures and positions of rendezvousing spacecrafts is constructed and a proportional differential control parameter design method is applied to control of relative positions. The magnetic levitation science education device for demonstrating rendezvous and docking of spacecrafts uses the magnetic levitation technology, the lever principle, the transmission principle and so on, and the theoretical knowledge of spacecraft rendezvous and docking is studied in depth during production. A carefully selected docking presentation mode well reflects the postures and trajectories of rendezvous and docking of spacecrafts.
Owner:钱航
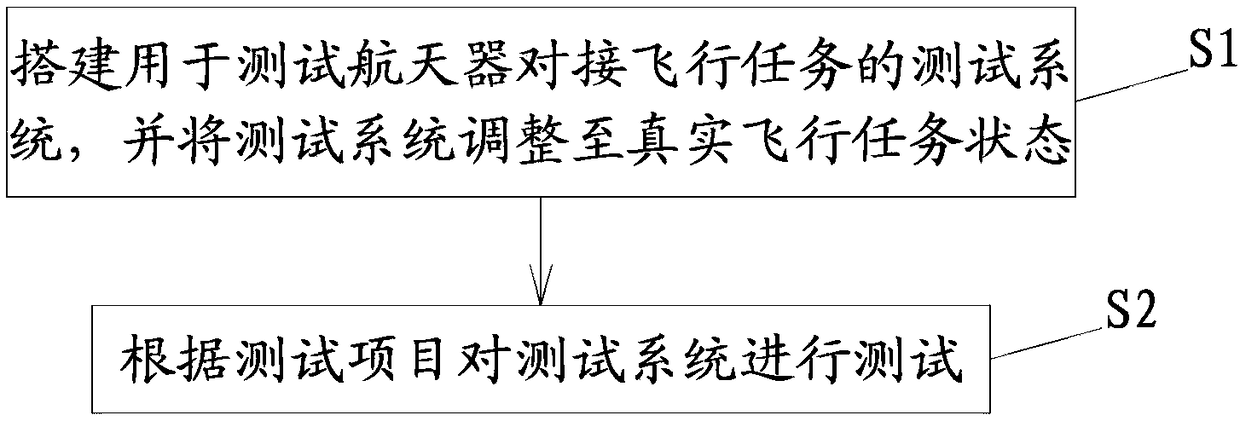
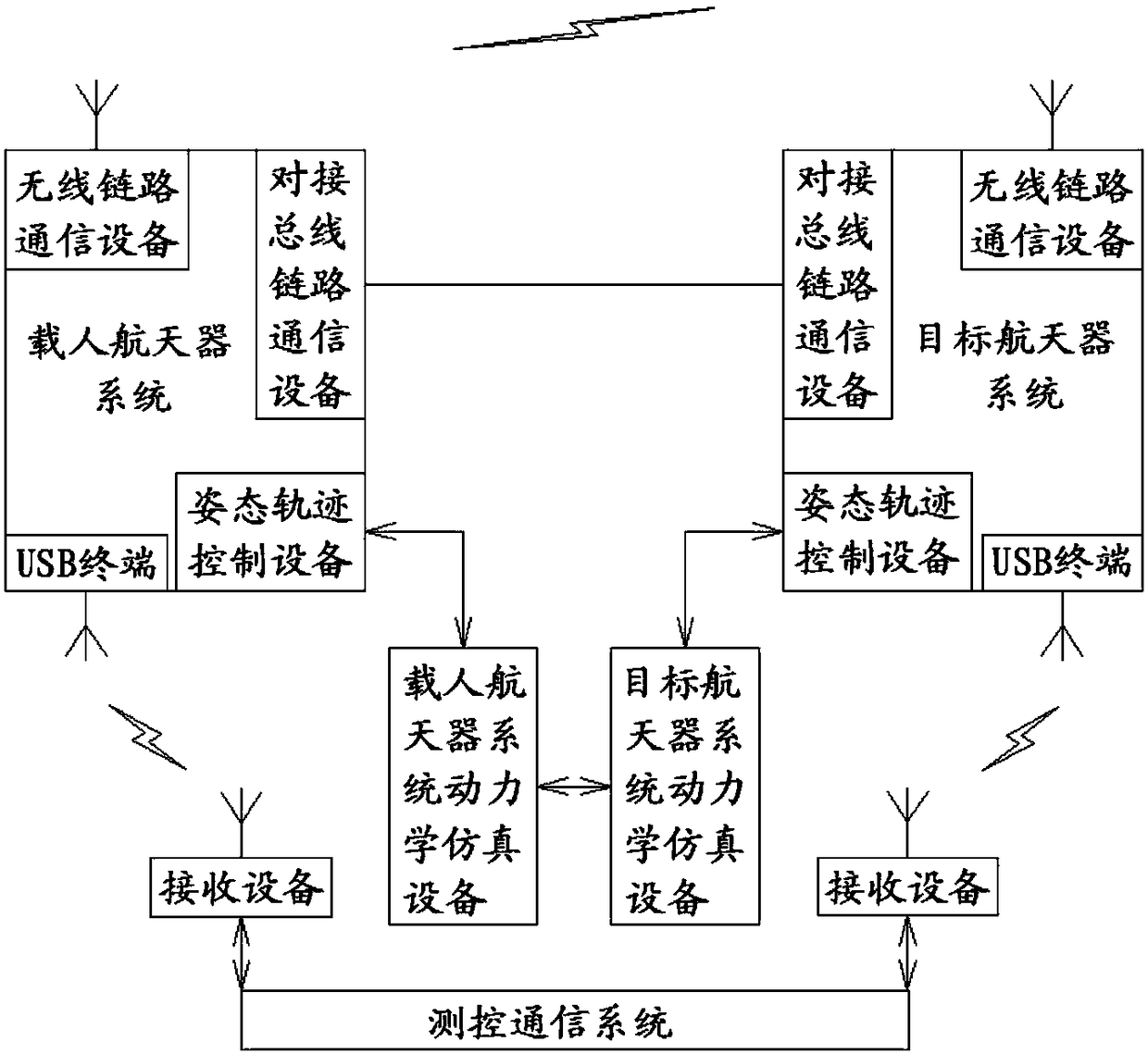
System test method for spacecraft docking flight mission
ActiveCN108418728AImprove effectivenessGuaranteed successful implementationData switching networksCommunications systemSystem testing
The invention relates to a system test method for a spacecraft docking flight mission. The method includes the following steps: S1, constructing a test system for testing a spacecraft docking flight mission, and adjusting the test system to a real flight mission state; and S2, testing the test system according to a test project. By really carrying various equipment in an spacecraft rendezvous anddocking mission through an astronaut system, a manned spacecraft system, a target spacecraft system and a measurement and control communication system, interfaces among the astronaut system, the manned spacecraft system, the target spacecraft system and the measurement and control communication system can be verified according to a real on-orbit flight mission, the effectiveness of various systemtests during the docking flight mission can be improved, and the successful implementation of an actual rendezvous and docking flight mission can be further ensured.
Owner:BEIJING SPACE TECH RES & TEST CENT
Switching controller design method of constrained space spacecraft orbital rendezvous system
ActiveCN110262225AFast convergenceSmall amount of calculationAdaptive controlRiccati equationControl system
The invention discloses a switching controller design method of constrained space spacecraft orbital rendezvous. A switching controller based on residence time is designed by means of mathematical modeling of a space spacecraft rendezvous system, conversion of an asymmetric saturation function, a residence time method of a switching controller, a parametric Riccati equation method and the like. A control system with asymmetric input saturation is equivalently expressed as the control system with a plurality of asymmetric input saturation. In fact, the obtained equivalent symmetric input saturation system is essentially a switching system. The designed controller only needs to solve the parametric Riccati equation in an offline mode, which is simple and easy to operate, and a calculation amount is low. By using the control method provided in the invention, a convergence speed of a control system state can be effectively increased and a requirement of an aerospace field to fast convergence performance of the control system can be satisfied.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
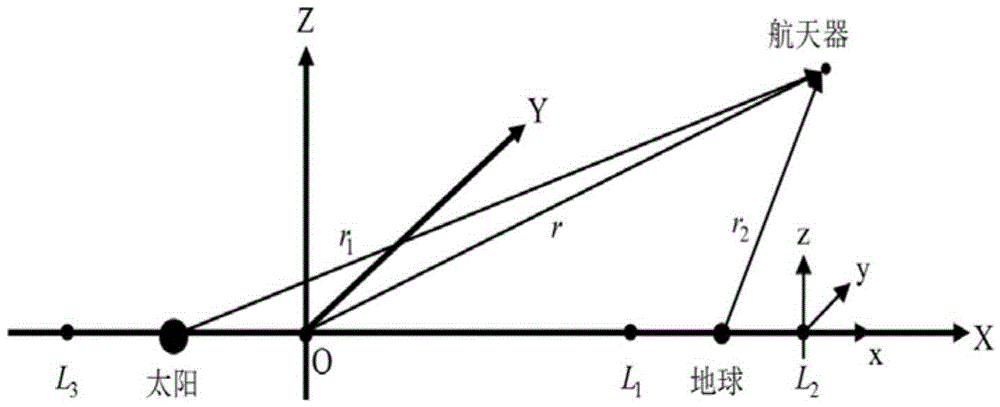
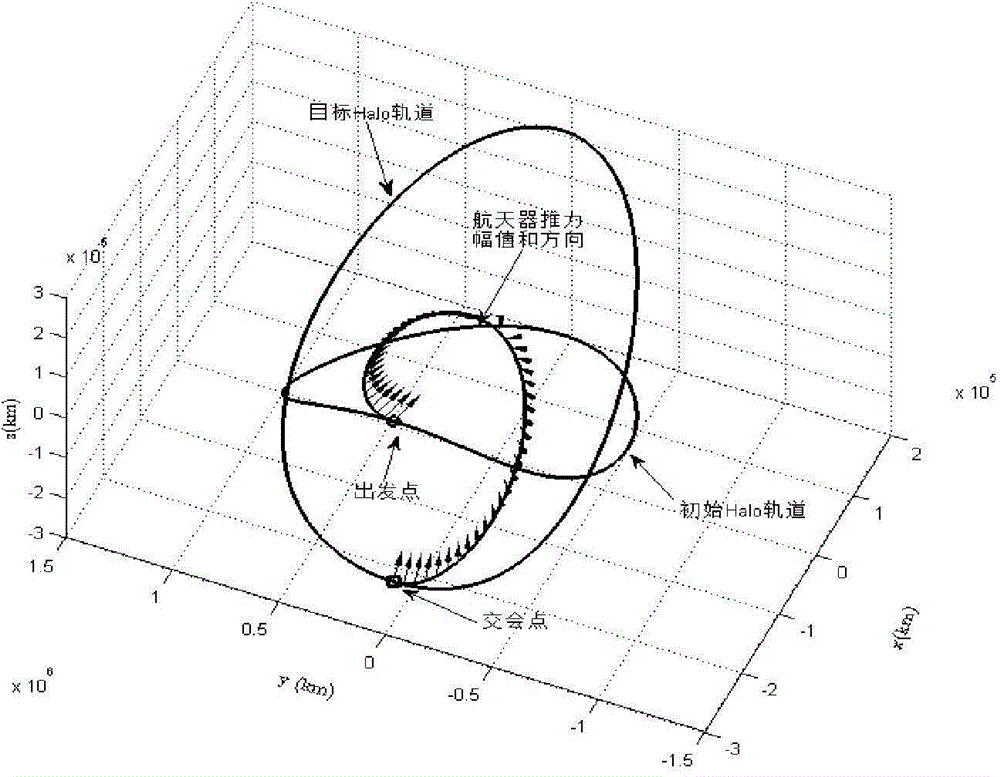
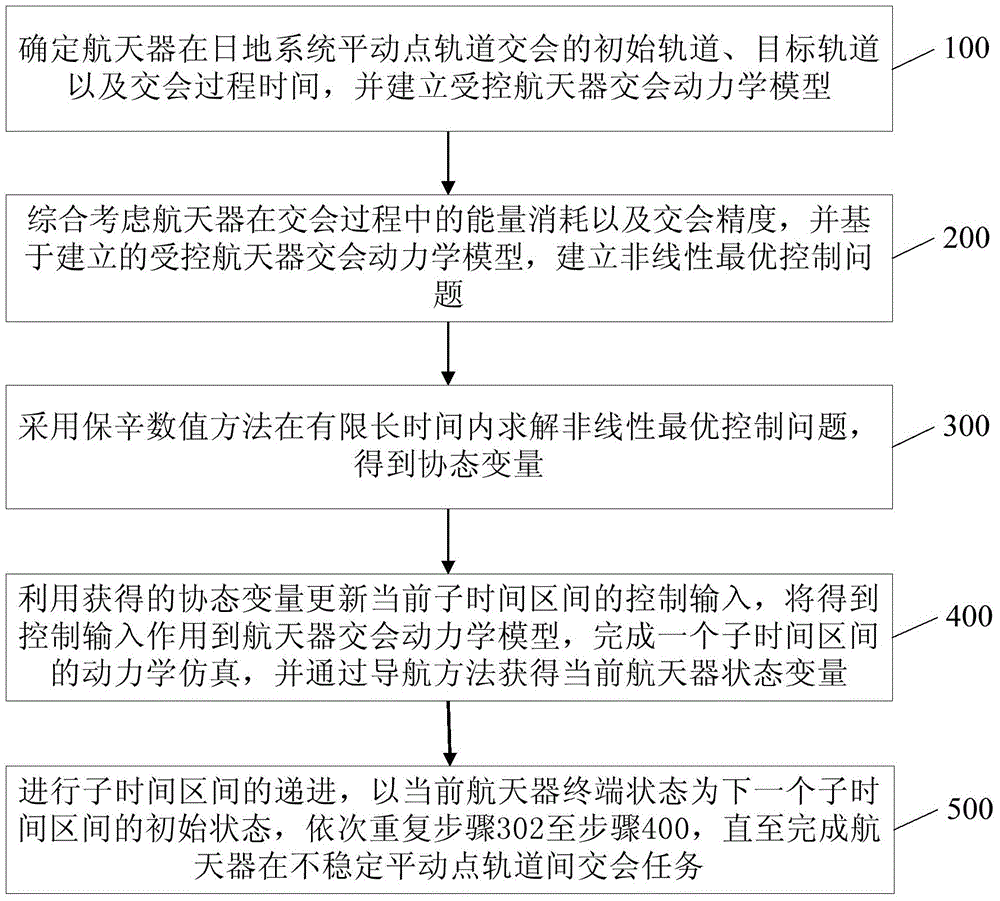
Rendezvous control method for spacecrafts between orbits at instable libration points of solar-terrestrial systems
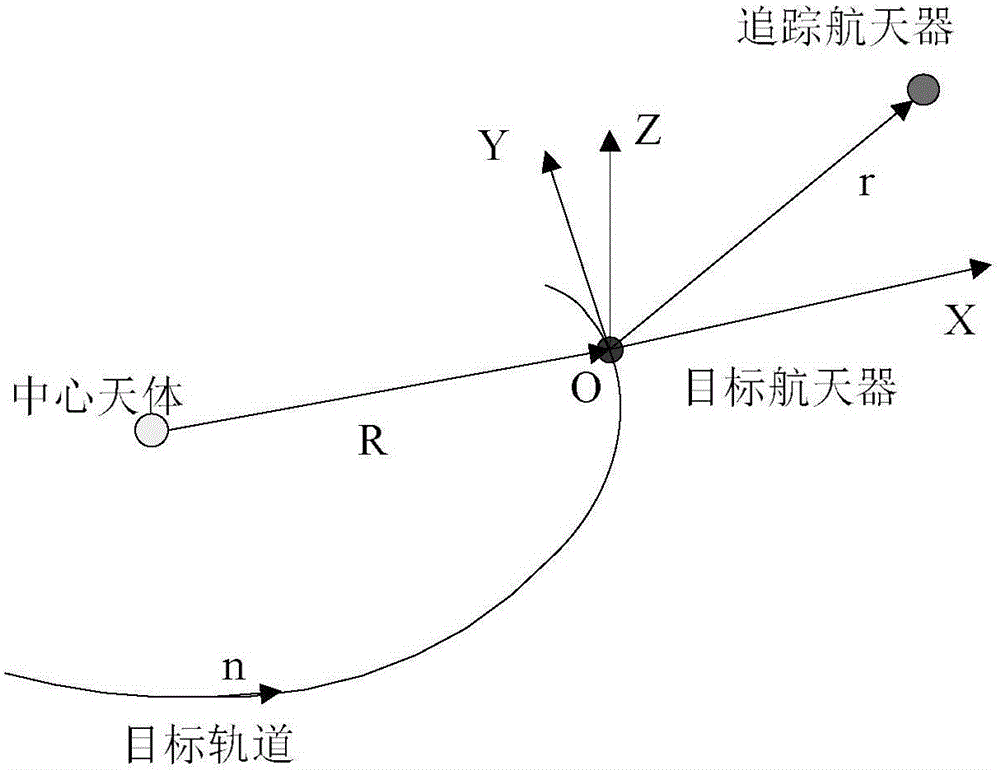
InactiveCN104793613AQuickly solve real-time computing problemsAvoid navigation errorsVehicle position/course/altitude controlAdaptive controlNonlinear optimal controlEngineering
The invention provides a rendezvous control method for spacecrafts between orbits at instable libration points of solar-terrestrial systems. The rendezvous control method includes determining rendezvous initial orbits, target orbits and rendezvous process time of the spacecrafts between the orbits at the libration points of the solar-terrestrial systems and building rendezvous kinetic models of the controlled spacecrafts; creating nonlinear optimal control problems on the basis of the built rendezvous kinetic models of the controlled spacecrafts; solving the nonlinear optimal control problems by the aid of symplectic preservation numerical processes within a long finite time to obtain co-state variables; updating control input in current time subintervals by the aid of the obtained co-state variables, kinetically simulating each time subinterval and acquiring state variables of the current spacecrafts by the aid of navigation processes; carrying out progression on the time subintervals, utilizing terminal states of the current spacecrafts as initial states of a next time subinterval, and sequentially repeatedly carrying out procedures from a step 302 to a step 400 until rendezvous tasks of the spacecrafts between the orbits at the instable libration points are completed. The rendezvous control method has the advantage that the high-precision spacecraft rendezvous objectivity and performance can be guaranteed by the rendezvous control method.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
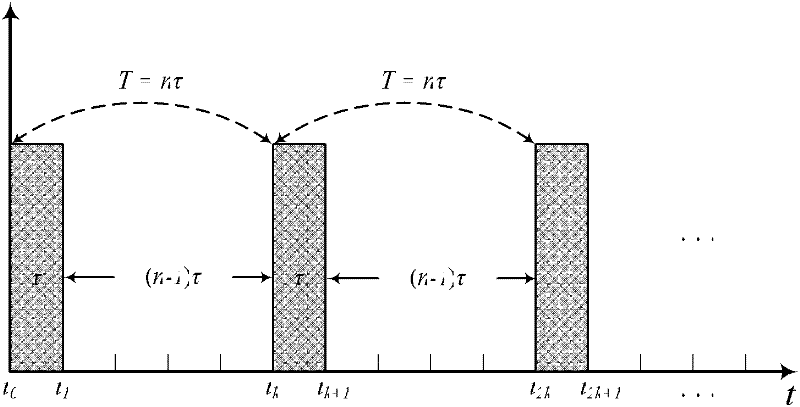
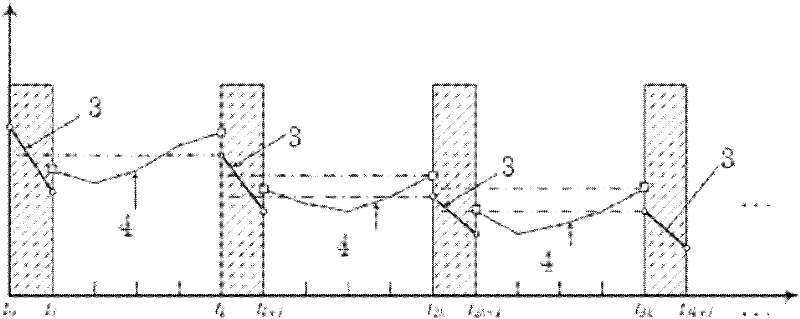
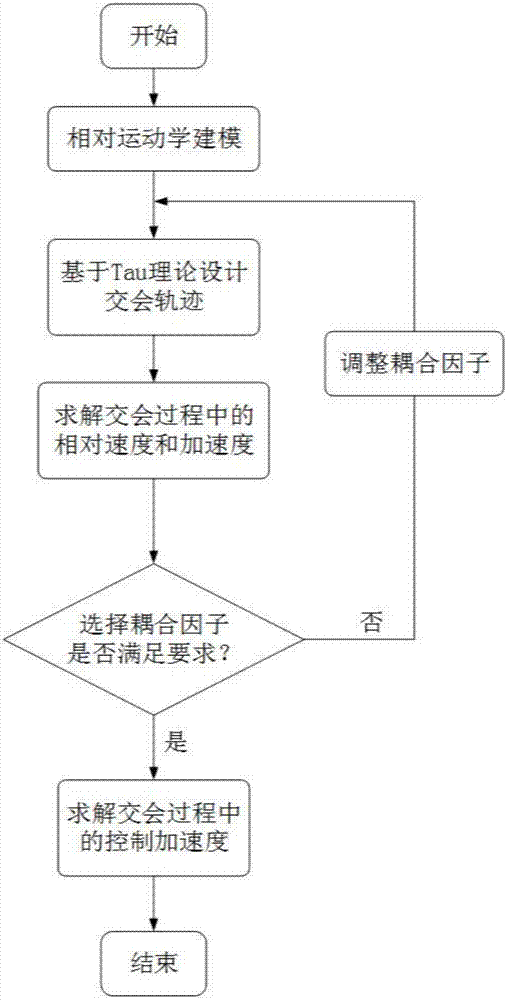
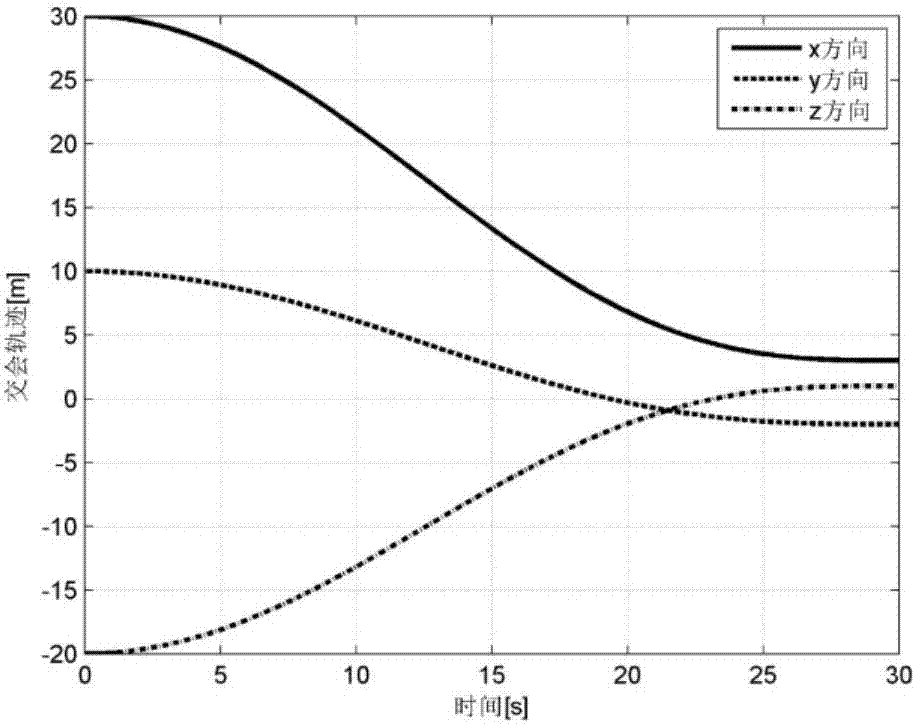
Tau theory-based spacecraft rendezvous guidance method
ActiveCN107168051AImprove environmental adaptabilityReduce computing burdenAdaptive controlEnergy transferInverse dynamics
The present invention discloses a Tau theory-based spacecraft rendezvous guidance method. The Tau theory-based spacecraft rendezvous guidance method is provided according to material and energy transfer tasks between orbit spacecrafts. With the Tau theory-based spacecraft rendezvous guidance method adopted, a suitable rendezvous trajectory can be designed. According to the method of the invention, a relative motion model in a near-distance rendezvous process is analyzed; the expression form of the rendezvous trajectory is given based on the Tau theory; derivation is performed through using the rendezvous trajectory, so that a speed required in the rendezvous process is obtained; and an accelerated speed required in the rendezvous process is solved through using an inverse dynamics method on the basis of the speed required in the rendezvous process. The method provided by the invention is a bionic method; the instinctive movement of animals in the nature, which has been continuously optimized through thousands of years, is concluded and summarized, and therefore, the method has certain optimality; and the rendezvous trajectory designed by using the method can not only satisfy rendezvous requirements, but also has excellent adaptability.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Spacecraft autonomous rendezvous and docking guidance strategy generation method based on reinforcement learning
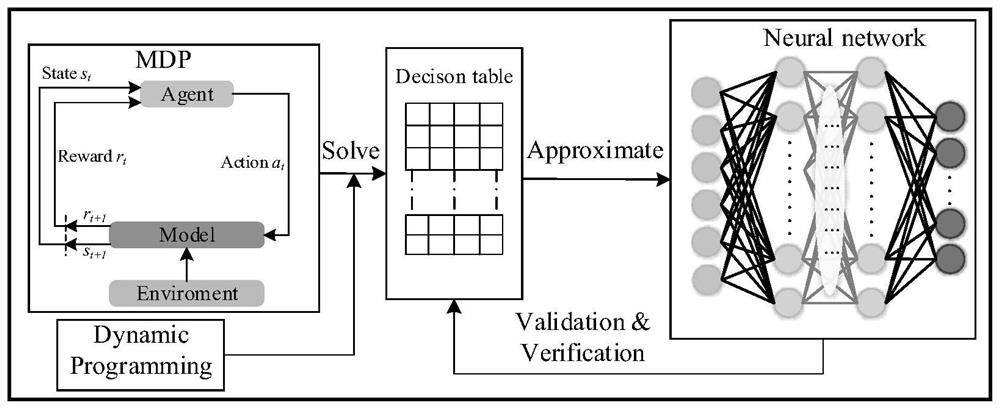
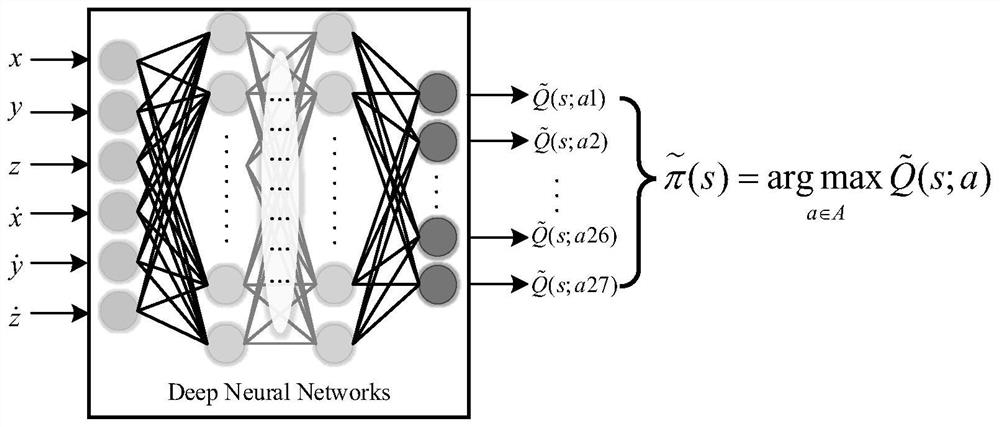
PendingCN114036631AFew samplesFast convergenceGeometric CADCosmonautic vehiclesDecision tableEngineering
The invention discloses a spacecraft autonomous rendezvous and docking guidance strategy generation method based on reinforcement learning. The method comprises the following steps: modeling a spacecraft rendezvous and docking process into a Markov decision process model; solving the Markov decision process model by adopting a dynamic programming algorithm to obtain scores of different actions adopted in all states, and generating a decision table; taking all states in the decision table as training data features, taking scores of all states in the decision table under each action as training data labels, and constructing training data; constructing a neural network model, and training the neural network model by adopting the training data to obtain a neural network model serving as approximate representation of the decision table; for a certain state, calculating scores of all actions in the state through the obtained neural network model, and selecting the action with the maximum score as the optimal guidance strategy; and based on the optimal guidance strategy, enabling the spacecraft to perform autonomous rendezvous and docking.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
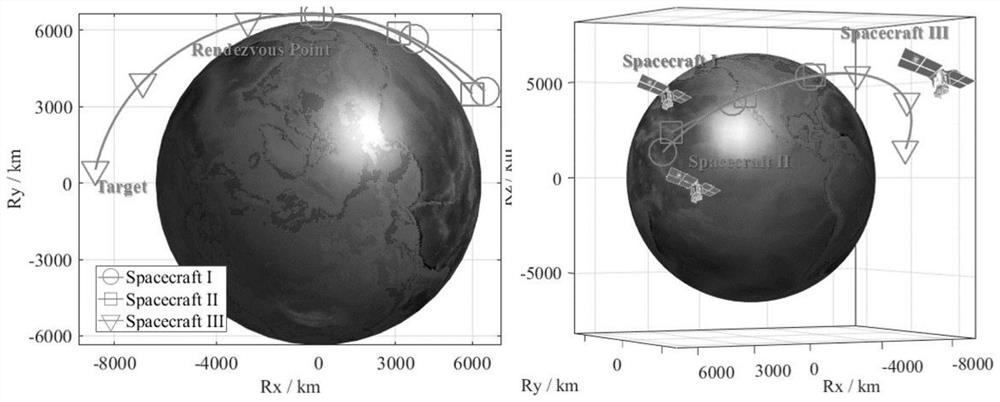
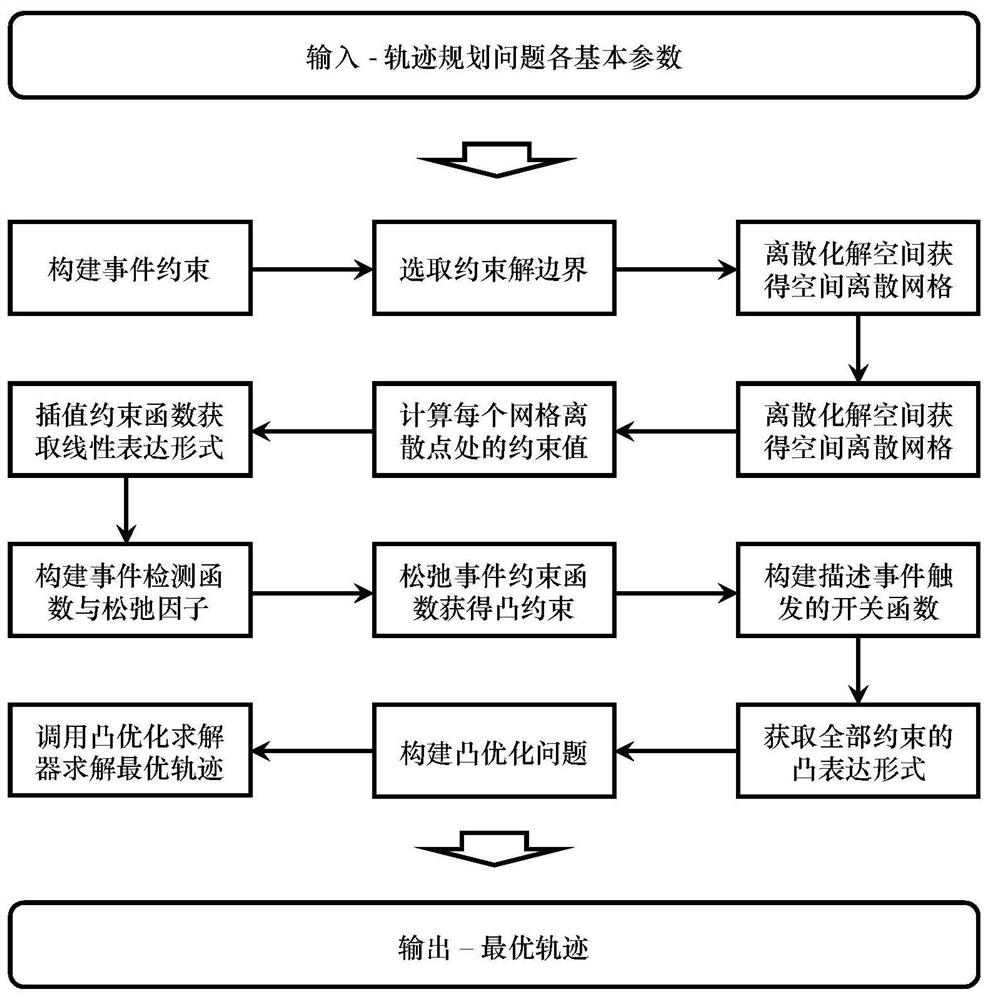
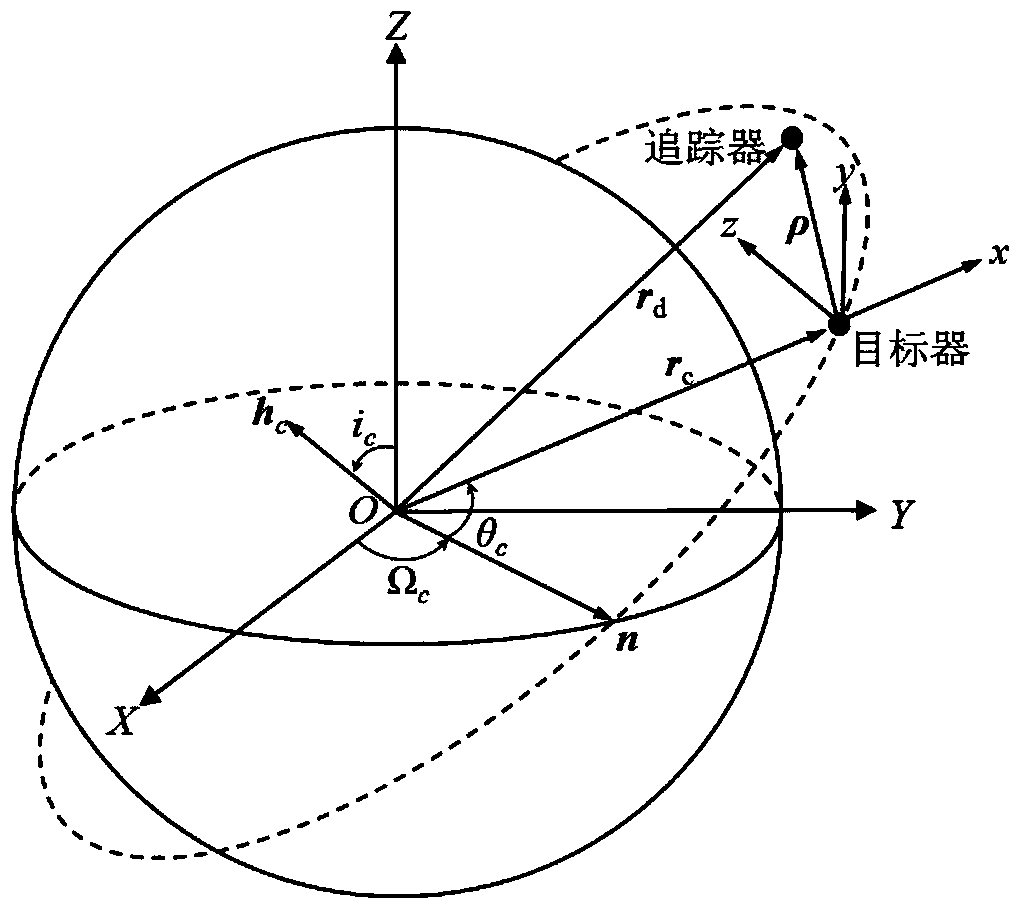
Spacecraft rendezvous and docking trajectory planning event constraint convexity method
PendingCN113722821AFast convergenceImprove computing efficiencyGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationAlgorithmSimulation
The invention discloses a spacecraft rendezvous and docking trajectory planning event constraint convexity method, and belongs to the technical field of aerospace. The implementation method comprises the following steps of: discretizing an event constraint solution space to obtain a series of spatially discrete grids; calculating a constraint function value at each discrete grid boundary point, and performing interpolation on constraint function data to obtain a linear expression form of a constraint function; constructing an event detection function, and performing relaxation and convex grid judgment constraint on an event constraint function to obtain a convex event constraint function form; constructing a switching function, describing an original event trigger function, and obtaining a convex expression form of the event trigger function; and solving the convex expression form to obtain an optimal spacecraft rendezvous and docking trajectory, thereby improving convergence and efficiency of spacecraft rendezvous and docking trajectory planning with event constraints on the premise of not changing an original problem solution space.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method for controlling optimal continuous thrust under J2 perturbation by adopting relative navigation information
InactiveCN109613932ASuitable for autonomous operationCalculation speedPosition/course control in three dimensionsRelative motionEngineering
The invention relates to a method for controlling optimal continuous thrust under J2 perturbation by adopting relative navigation information, and relates to the field of spaceflight orbit control. The method aims at solving the problem of rendezvousing of two spacecrafts operating on an elliptical orbit under J2 perturbation, and the continuous thrust optimal orbit control method which achieves rapid calculation and can be used in orbit is provided under the situation that information of the target aircraft is unknown, and the tracking spacecraft only adopts the relative navigation information. The method does not need an optimized initial predicted value, the influences of earth J2 perturbation on the two-satellite approaching process are considered, and the method is suitable for continuous thrust orbit rendezvousing under the elliptical orbit. The method faces the field of orbit rendezvousing, autonomous orbit rendezvousing of the tracking spacecraft to the target spacecraft can beachieved only through relative motion information of the tracking spacecraft and the target spacecraft without the need of support provided by the ground, and thus quite high on-orbit application value is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
Autonomous spacecraft rendezvous control method based on finite time fast nonsingular terminal sliding mode
ActiveCN112000006AShorten the timeFast convergenceHigh level techniquesAdaptive controlControl cellClassical mechanics
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Spacecraft rendezvous and docking device and method
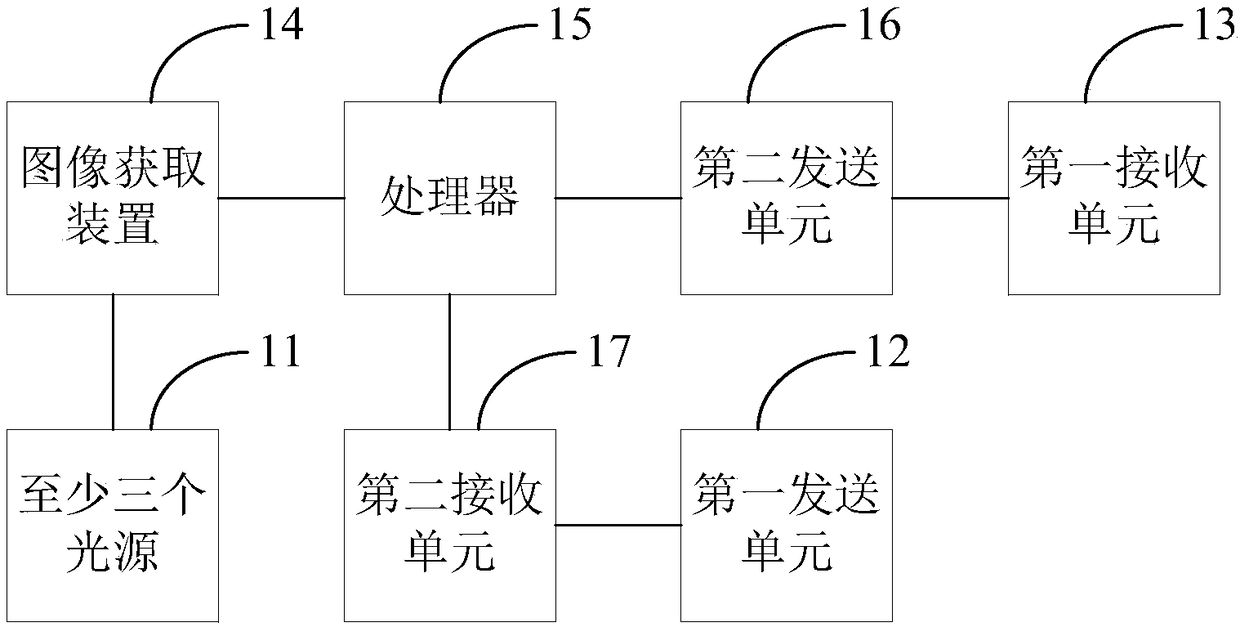
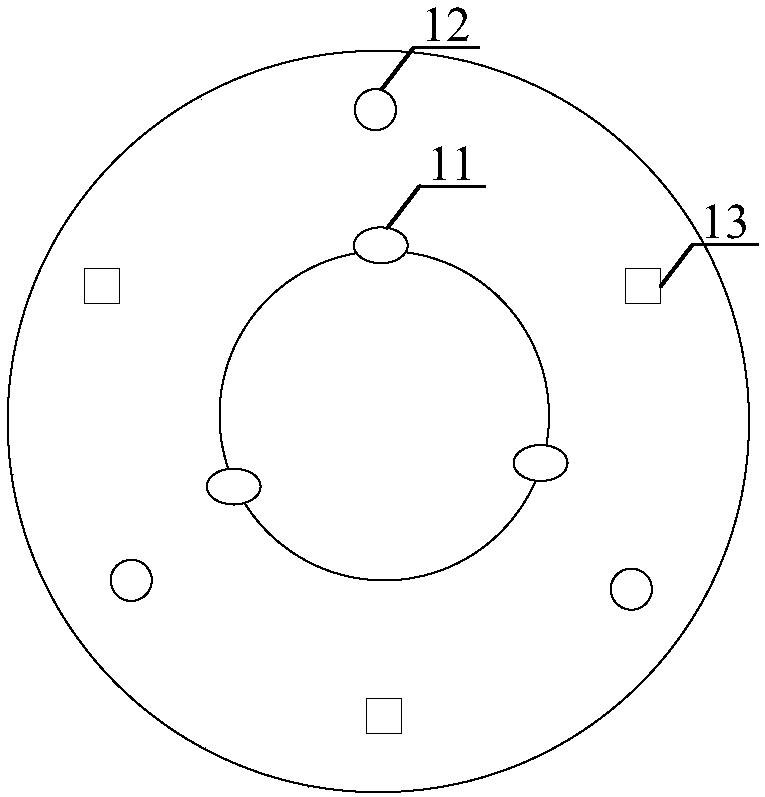
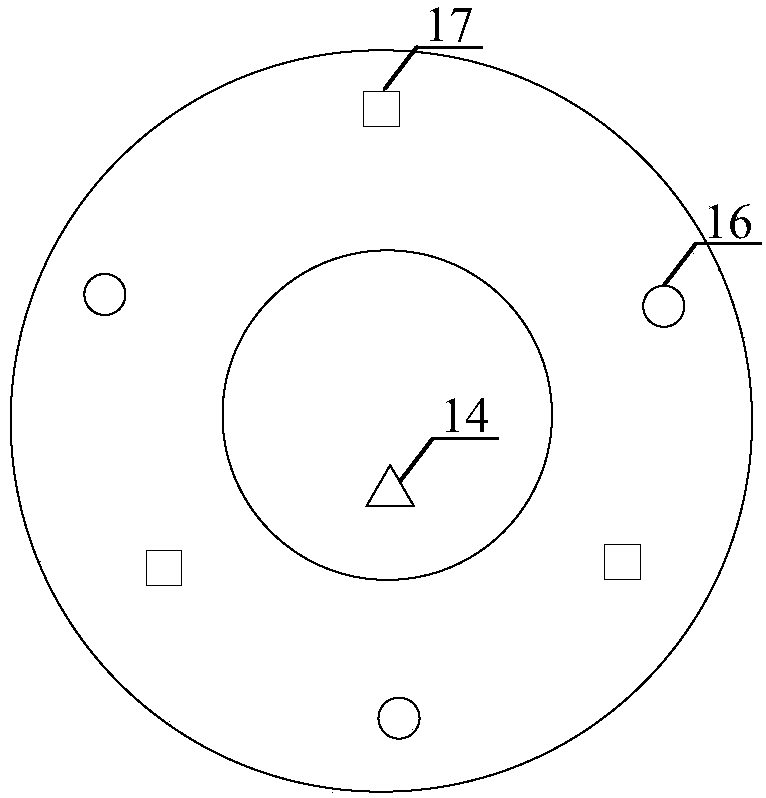
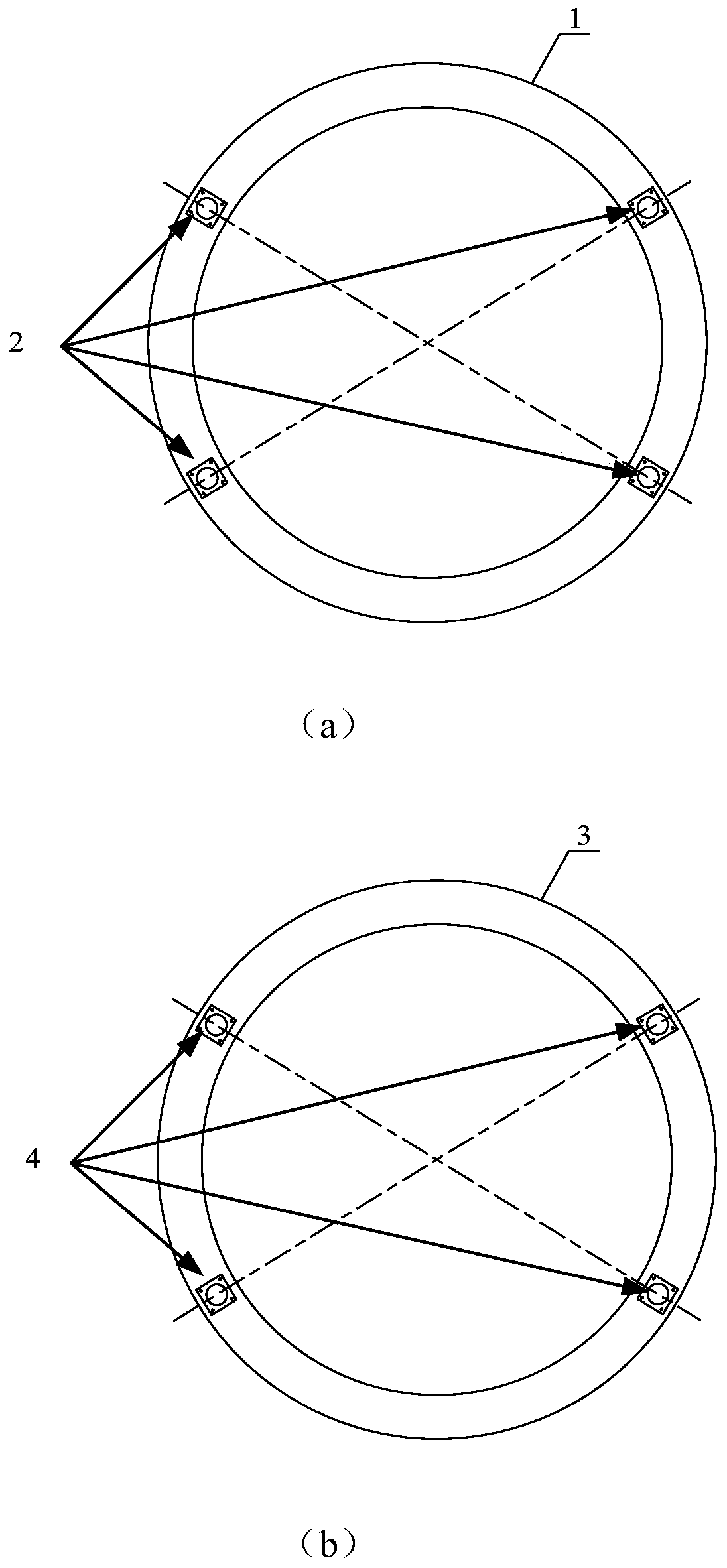
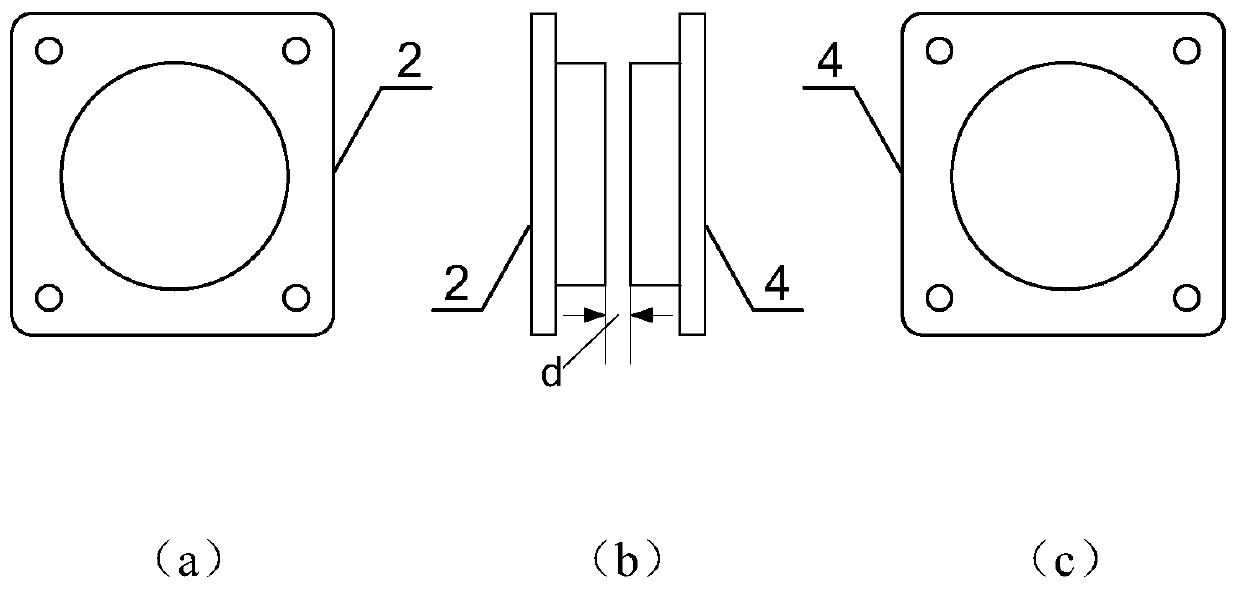
InactiveCN108263644AEliminate manual adjustmentsImprove securityCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic component separationSpace rendezvousComputer science
The invention provides a spacecraft rendezvous and docking device and method. Images of at least three light sources in the spacecraft rendezvous and docking device are obtained by an image obtainingdevice in the spacecraft rendezvous and docking device; according to the obtained images, information of the relative position between the image obtaining device and a target spacecraft is obtained, and therefore a tracking spacecraft can be automatically guided to an initial aiming point of the target spacecraft based on the information of the relative position; and manual adjusting links can beomitted at the final approaching stage and parking and docking stage during mutual docking, the tracking spacecraft can be precisely aligned with the initial aiming point of the target spacecraft through an automatic aligning mode, the success possibility of rendezvous and docking is increased, and thus docking safety is improved.
Owner:PLA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE INFORMATION ENG UNIV PLA SSF IEU
Carrier rocket task planning method for rapid spacecraft rendezvous
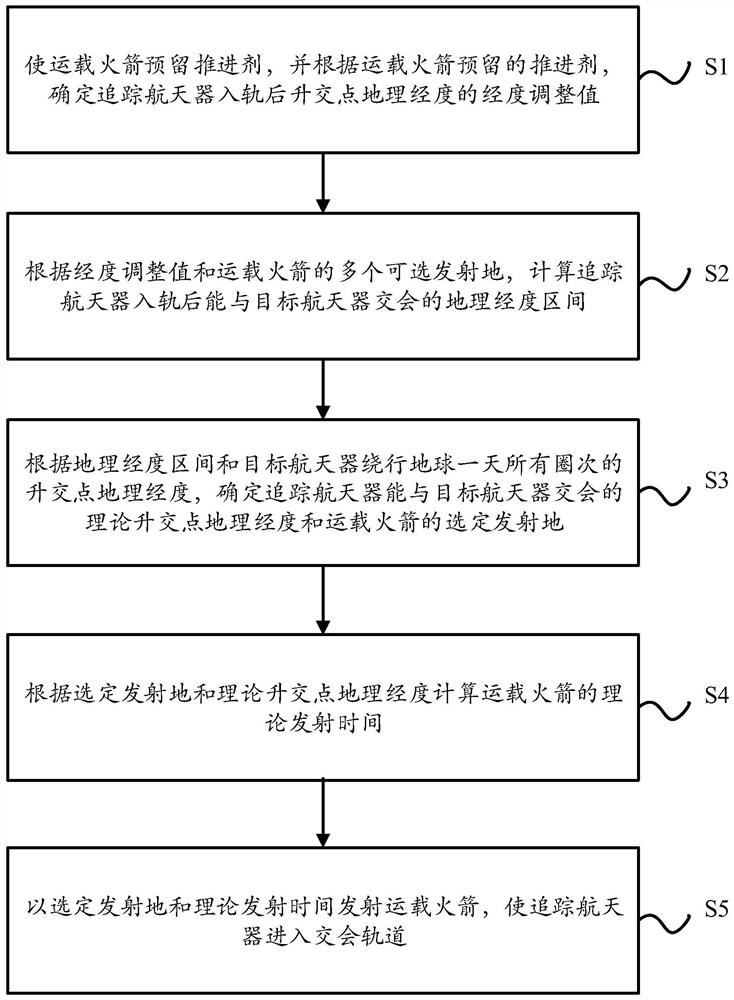
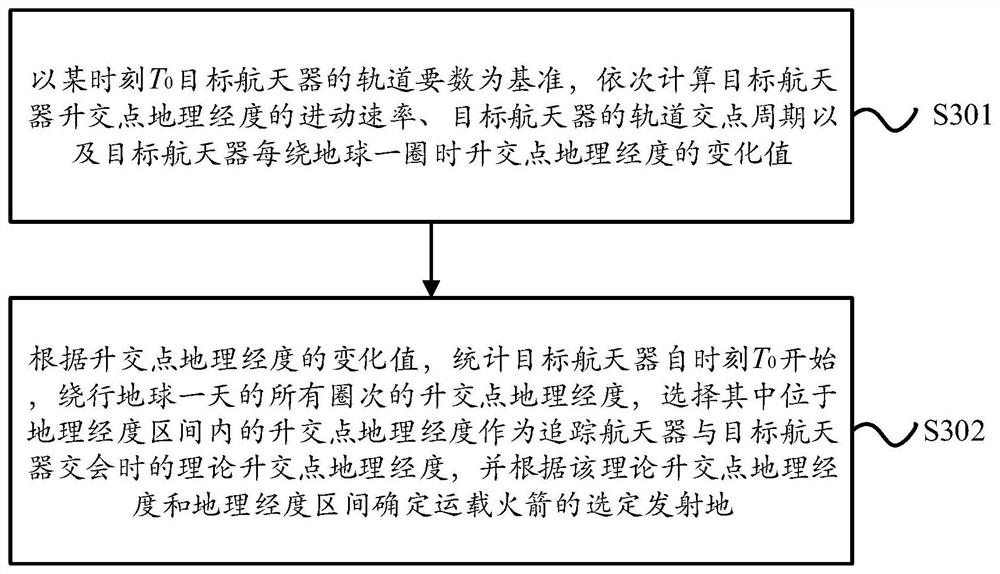
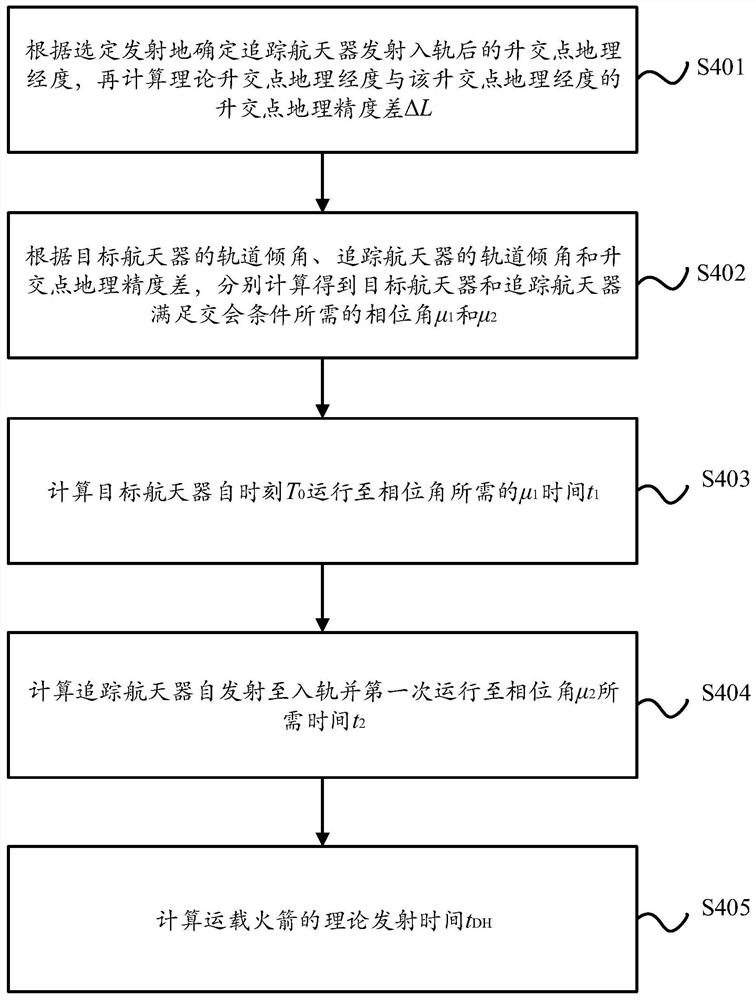
The invention discloses a carrier rocket task planning method for rapid spacecraft rendezvous, and relates to the technical field of aerospace. The method comprises the following steps of S1, determining a longitude adjustment value of geographic longitudes of ascending nodes of a tracking spacecraft according to a propellant reserved by a carrier rocket; S2, calculating a geographic longitude interval in which the tracking spacecraft can rendezvous with a target spacecraft after the tracking spacecraft enters an orbit according to the longitude adjustment value and a plurality of selectable launching sites of the carrier rocket; S3, determining the geographic longitudes of the theoretical ascending nodes and a selected launching site of the carrier rocket according to the geographic longitude interval and the geographic longitudes of the ascending nodes of all circles of the target spacecraft orbiting the earth in one day; S4, calculating theoretical launching time according to the selected launching site and the geographic longitudes of the theoretical ascending nodes; and S5, launching the carrier rocket at the selected launching site and the theoretical launching time to enablethe tracking spacecraft to enter a rendezvous orbit. According to the carrier rocket task planning method, at least one launching moment can be ensured in one day, so that the tracking spacecraft canrendezvous with the target spacecraft rapidly.
Owner:THE GENERAL DESIGNING INST OF HUBEI SPACE TECH ACAD
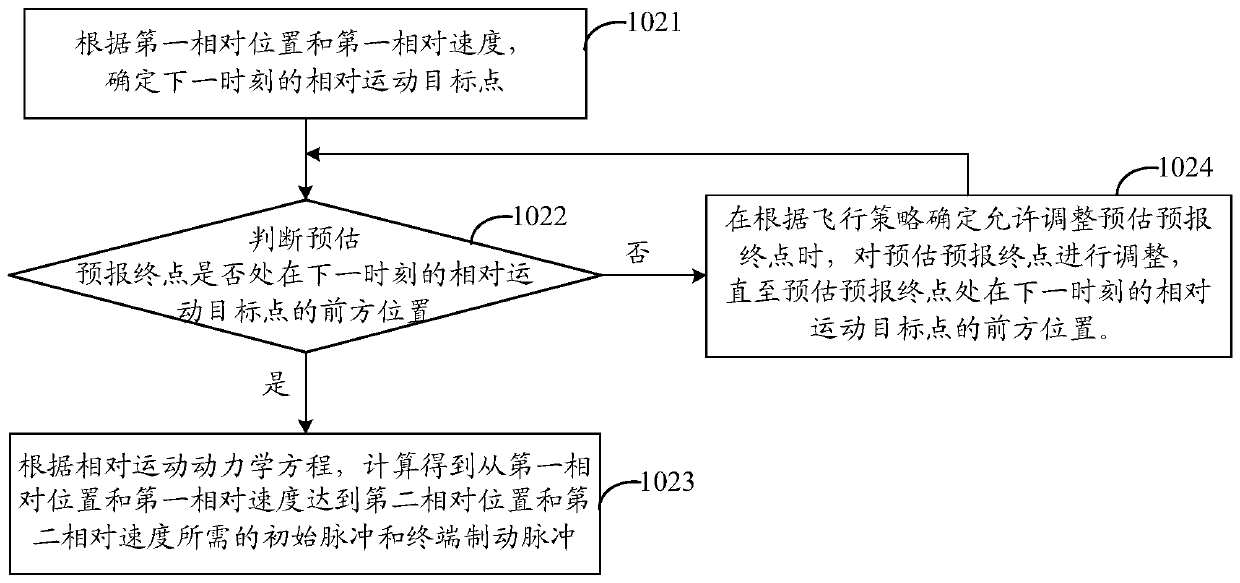
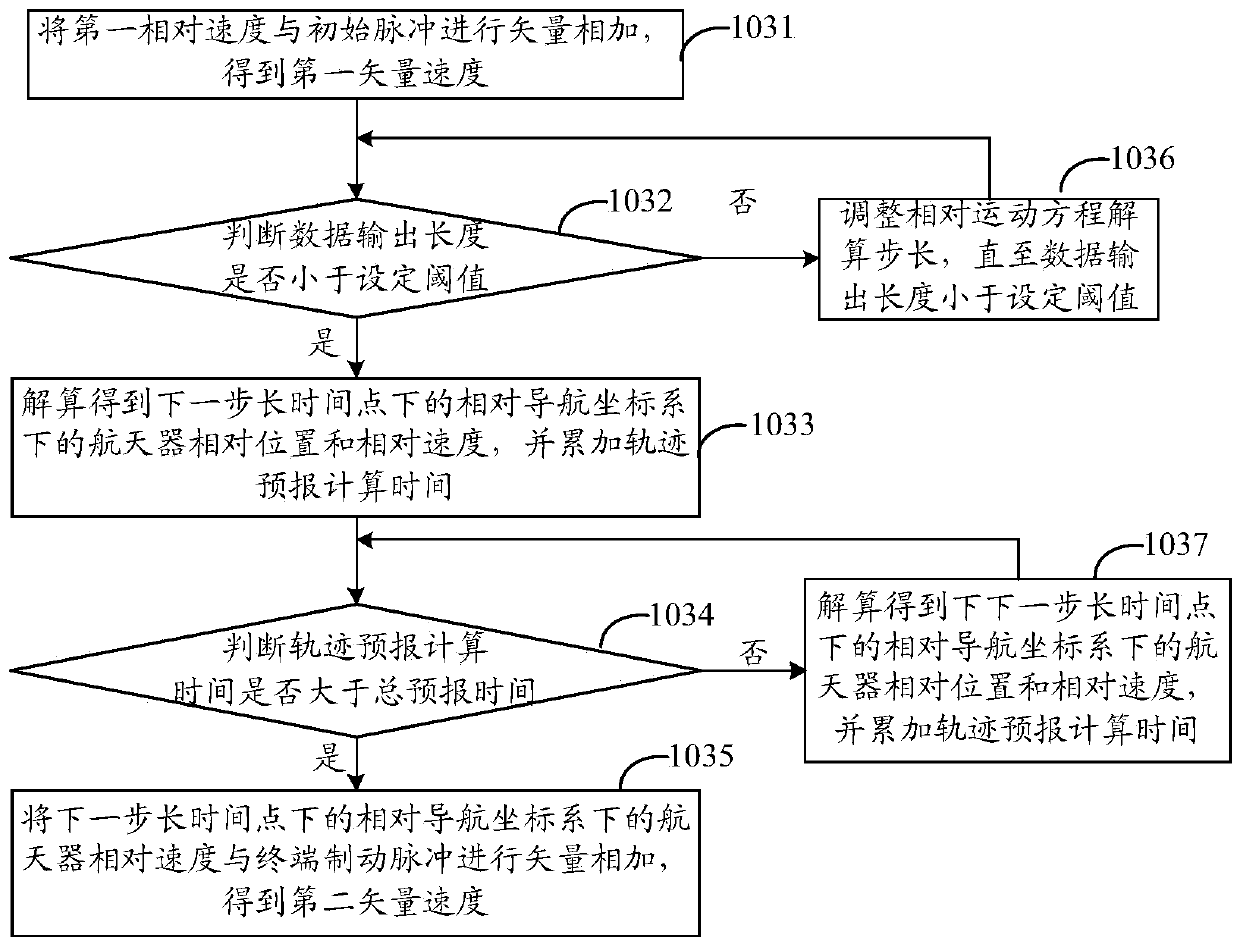
Track prediction processing method based on in-orbit data fusion
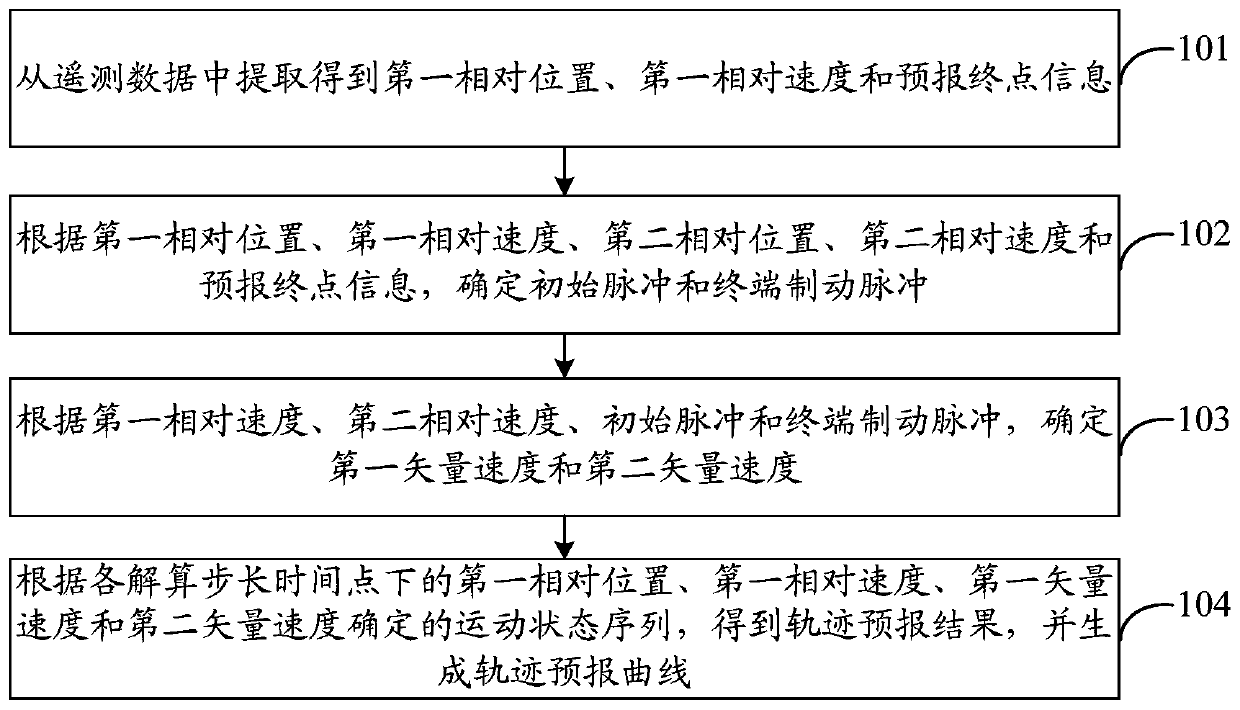
The invention discloses a track prediction processing method based on in-orbit data fusion. The method comprises the following steps of determining an initial pulse and a terminal brake pulse according to a first relative position, a first relative speed, a second relative position, a second relative speed, and a predicted destination information extracted from telemeasuring data; determining a first vector speed and a second vector speed according to the first relative speed, the second relative speed, the initial pulse, and the terminal braking pulse; and acquiring a track prediction resultaccording to a motion state sequence determined by the first relative position, the first relative speed, the first vector speed, and the second vector speed under each resolving step length time point, and generating a track prediction curve. In the invention, the specific requirements of real-time performance, accuracy, customizability and in-orbit state consistency to the track prediction during a spacecraft rendezvous and docking flight control mission process are realized, a track can be accurately predicted and can be clearly and effectively displayed, and a reference is provided for ground flight control monitoring and decision making.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
A radio energy and signal transmission system for spacecraft rendezvous and docking and grid-connected power supply
ActiveCN106787251BThere will be no safety issues such as sparkingReduce control precision requirementsNear-field transmissionCircuit arrangementsElectric power transmissionElectricity
The invention discloses a wireless power and signal transmission system for spacecraft rendezvous and docking and grid-connected power supply. One or more groups of wireless power transmission units are configured on the spacecraft rendezvous and docking mechanism. Each group of transmission units is composed of an electric energy transmitting device and an electric energy receiving device. The device consists of using technology based on the principle of electromagnetic induction to realize wireless transmission of power and signals. Under the condition of transmitting the same power, the weight and size of the system are equivalent to those of wired power transmission, and the efficiency is greater than 85%, which is higher than that of wired transmission. It can solve the problems existing in the traditional electrical connector power supply mode such as high docking accuracy requirements, complex docking interface design, exposed contact metal, and potential spark hazards.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
Method for controlling autonomous rendezvous between spacecrafts under action of impulse thrust
InactiveCN102354217BDisadvantages of Eliminating Disturbance Moment EffectsAvoid calculationPosition/course control in three dimensionsLoop controlLinear matrix
The invention relates to a method for controlling an autonomous rendezvous between spacecrafts under action of impulse thrust, which belongs to the technical field of aerospace, and aims to solve the problem that a traditional method for controlling the rendezvous between the spacecrafts under the action of the impulse thrust is easy to be influenced by a disturbance moment because of adopting anopen-loop control mode. The method for controlling the autonomous rendezvous between the spacecrafts under the action of the impulse thrust comprises the following steps: establishing a kinetic modelof the relative motion between the spacecrafts, and converting a state space model of the relative motion into a discrete motion model; introducing state feedback control rate in the impulse action process; introducing virtual energy functions for a impulse action motion and a free motion; determining three inequalities meeting the requirement that the spacecrafts realize the autonomous rendezvous, satisfying a finite impulse thrust inequality, and converting the inequalities into linear matrix inequalities related with X1,X2 and Y1; and calculating a state feedback gain matrix K according tothe worked-out X1 and Y1 matrixes to obtain a state feedback sampling control law u(k)=Kx(k) of the relative motion between the spacecrafts, which meets the design requirement. The method for controlling the autonomous rendezvous between the spacecrafts under the action of the impulse thrust is suitable for the autonomous rendezvous process of the spacecrafts.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
semi-major axis iteration space transfer orbit calculation method for Lambert orbital transfer problem based on Newton iteration
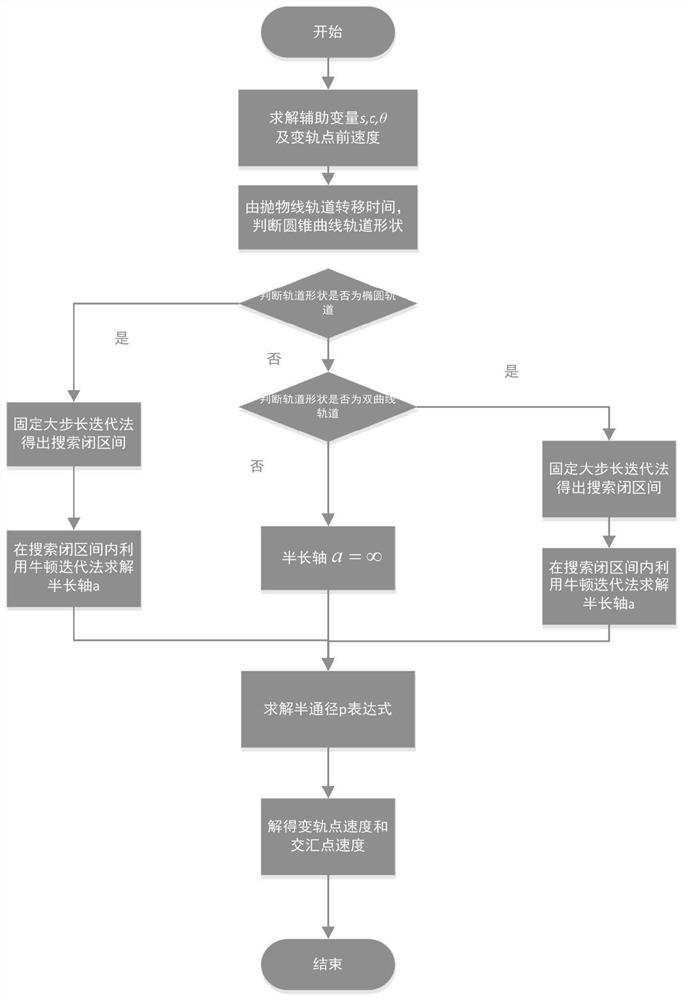
PendingCN111753244AImprove solution efficiencySolve the problem of solving space transfer orbitComplex mathematical operationsAnalytical equationsComputational physics
The invention discloses an improved solving method for a Lambert orbital transfer problem based on a Newton iteration thought. The method comprises the steps of 1, calculating a transfer angle theta,an auxiliary variable c and an auxiliary variable s; 2, determining the shape of the track according to the transfer angle and the auxiliary variable in the step 1; 3, when delta t is larger than delta tp, determining that the transfer orbit is an elliptical orbit, and carrying out solving; 4, when delta t is smaller than delta tp, determining that the transfer orbit is a hyperbolic orbit, and carrying out solving; 5, when delta t is equal to delta tp, determining that the transfer orbit is a parabola orbit, and carrying out solving; 6, expressing the Lambert orbital transfer problem analytical equation in the steps 3-5 as a function of a conic curve semi-major axis, and calculating a conic curve semi-drift diameter; 7, calculating orbital transfer point speed and intersection speed; and 8, proving the high efficiency and accuracy of the improved solving method for the Lambert orbital transfer problem based on the Newton iteration thought. The invention aims to improve the solving speed of the Lambert orbital transfer problem in spacecraft rendezvous.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com