Method for controlling autonomous rendezvous between spacecrafts under action of impulse thrust
A control method and pulse action technology, which is applied in three-dimensional position/channel control and other directions, and can solve problems such as the influence of disturbance torque
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
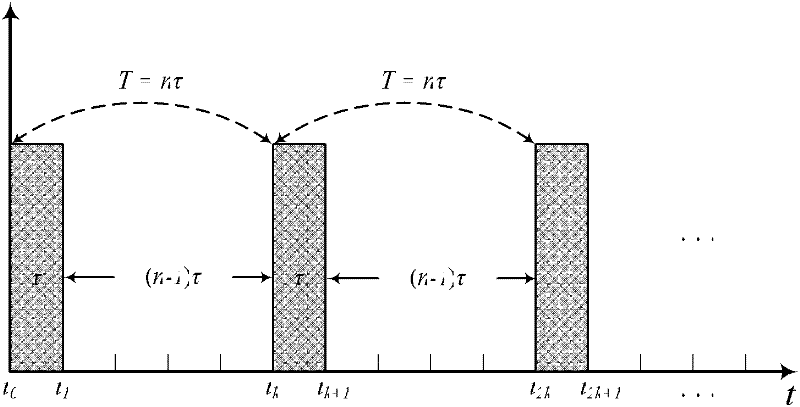
[0068] Specific implementation mode one: combine Figure 1 to Figure 3 Description of this embodiment: a method for autonomous rendezvous control of spacecraft under the action of pulse thrust in this embodiment, the specific process of the control method is:
[0069] Step 1. Establish a relative motion dynamics model of the spacecraft
[0070] For the tracking spacecraft 1 and the target spacecraft 2 that are rendezvous, the orbit of the target spacecraft 2 is a circular orbit, and the relative motion coordinate system is established with the center of mass of the target spacecraft 2 as the origin:
[0071] The center O of the circular orbit is the center of mass of the earth, the x-axis is in the orbital plane of the target spacecraft, and the positive direction is that the center of the earth points to the direction of the spacecraft; the y-axis points to the running direction of the target spacecraft; the z-axis is perpendicular to the orbital plane and is aligned with the...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0122] Specific embodiment two: this embodiment is a further description of step 2 (seven) in the spacecraft autonomous rendezvous control method under the action of a pulse thrust described in specific embodiment one, using the MATLAB linear matrix inequality toolbox to formula Eleven to formula fourteen are solved to obtain its feasible solution (X 1 , X 2 , Y 1 ).
Embodiment
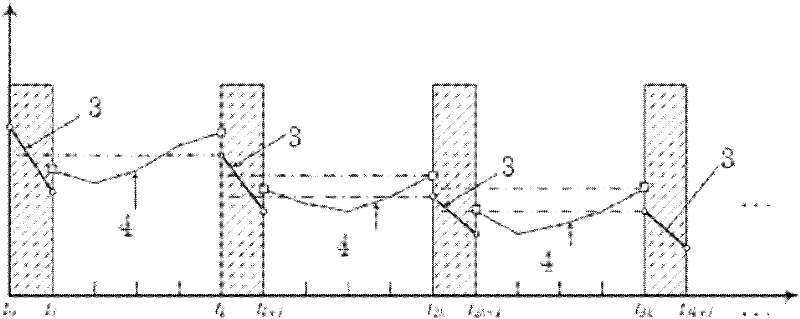
[0123] Example: Combine Figure 4 to Figure 7 Describe this embodiment, set following technical parameters:
[0124] 1) Target spacecraft mass: 200kg;
[0125] 2) The orbital radius of the target spacecraft: 42241km;
[0126] 3) The average angular velocity of the target spacecraft orbit: 0.001117rad / s;
[0127] 4) The relative state of the two spacecraft at the initial moment: [300, 200, 0, 0, 0, 0];
[0128] 5) Set the upper limit of pulse thrust to 100N;
[0129] 6) The sampling period of the discrete state equation is 1s, and the pulse period is 100s;
[0130] Based on the MATLAB simulation software, the rendezvous process of the two spacecraft was simulated. The simulation process and results are as follows:
[0131] Control law solution: Use the linear matrix inequality (LMI) toolbox of MATLAB software to solve formula 11 to formula 14, and obtain the following feasible solutions:
[0132] X 1 = 10 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com