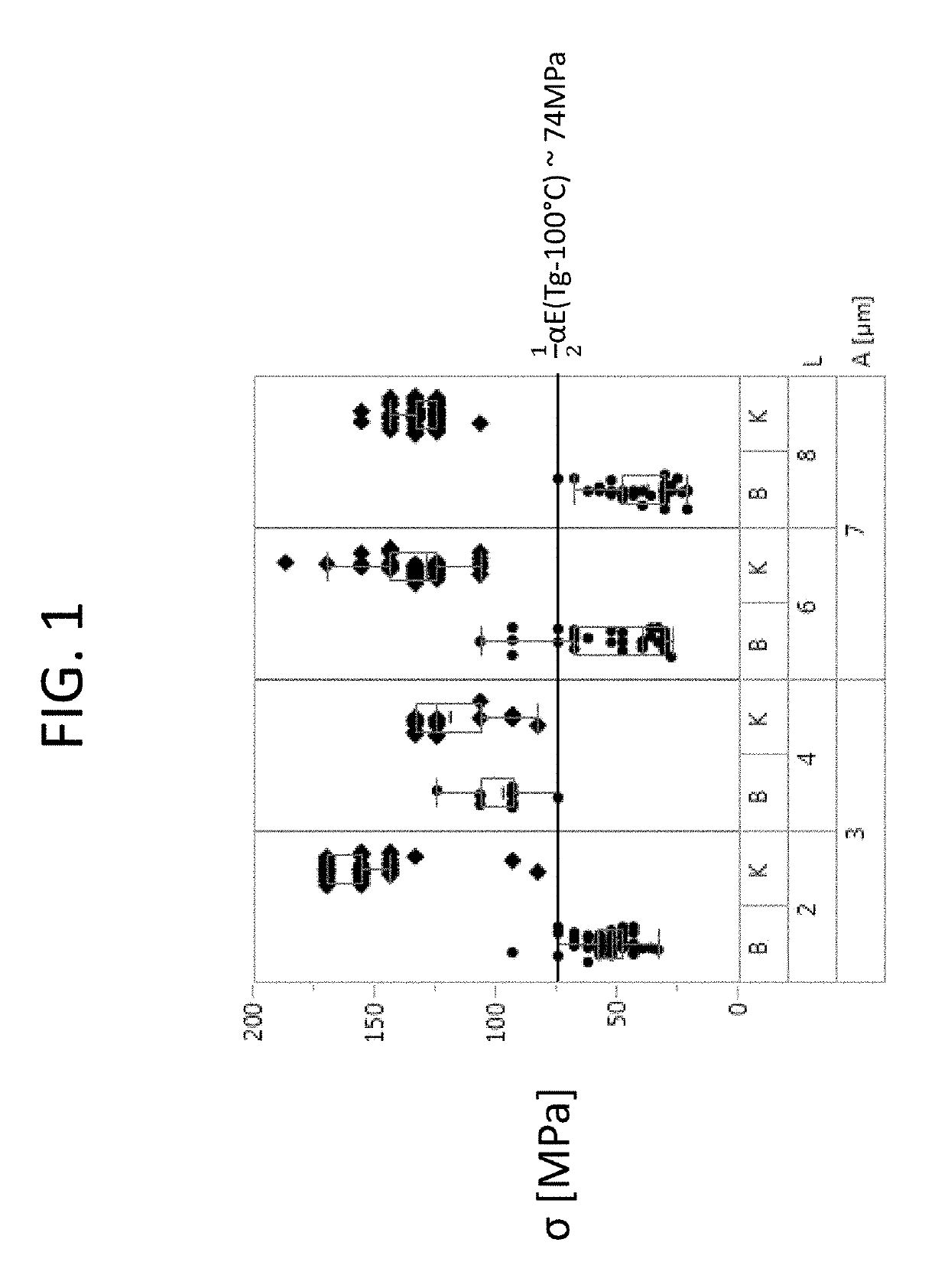
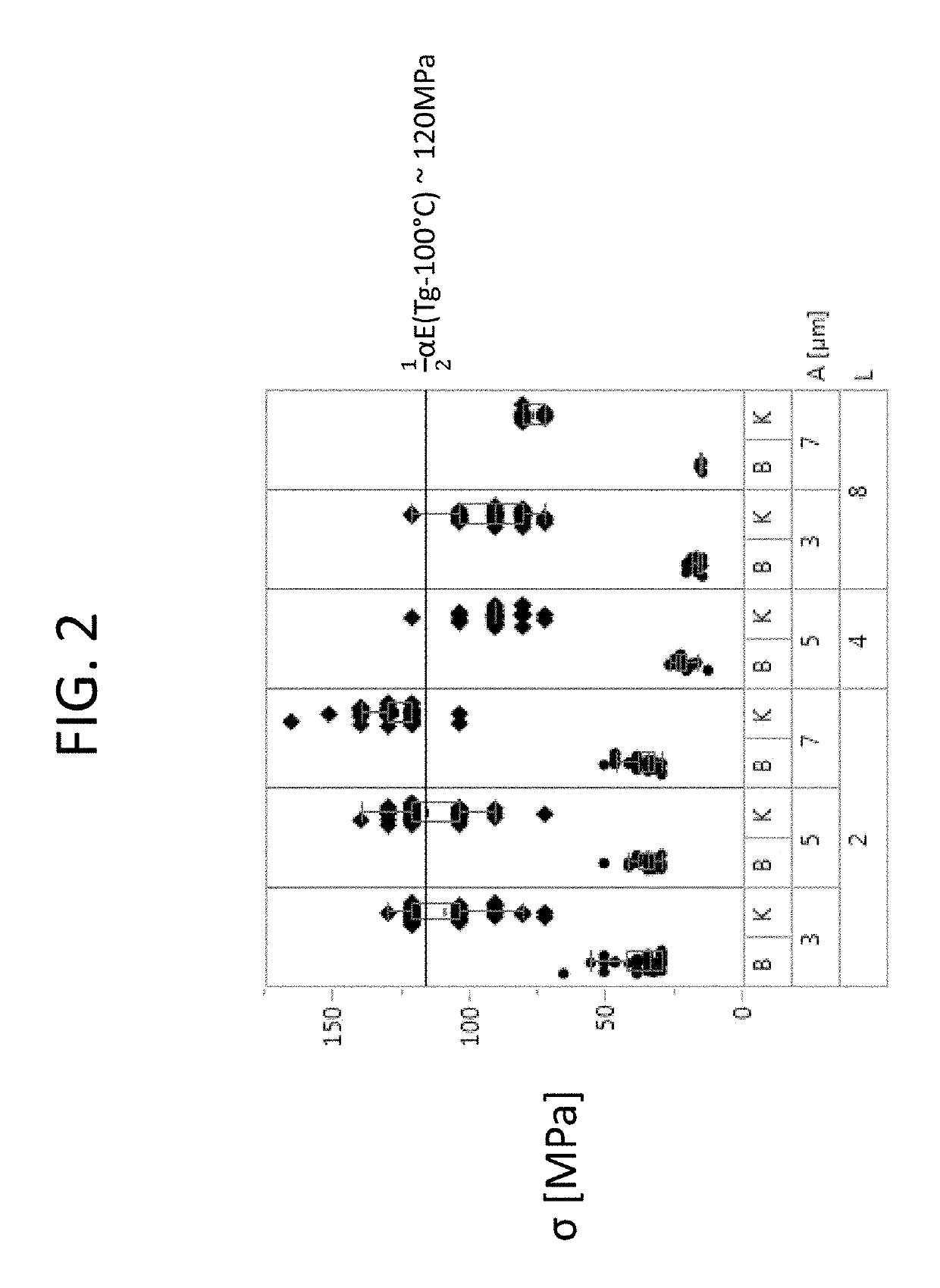
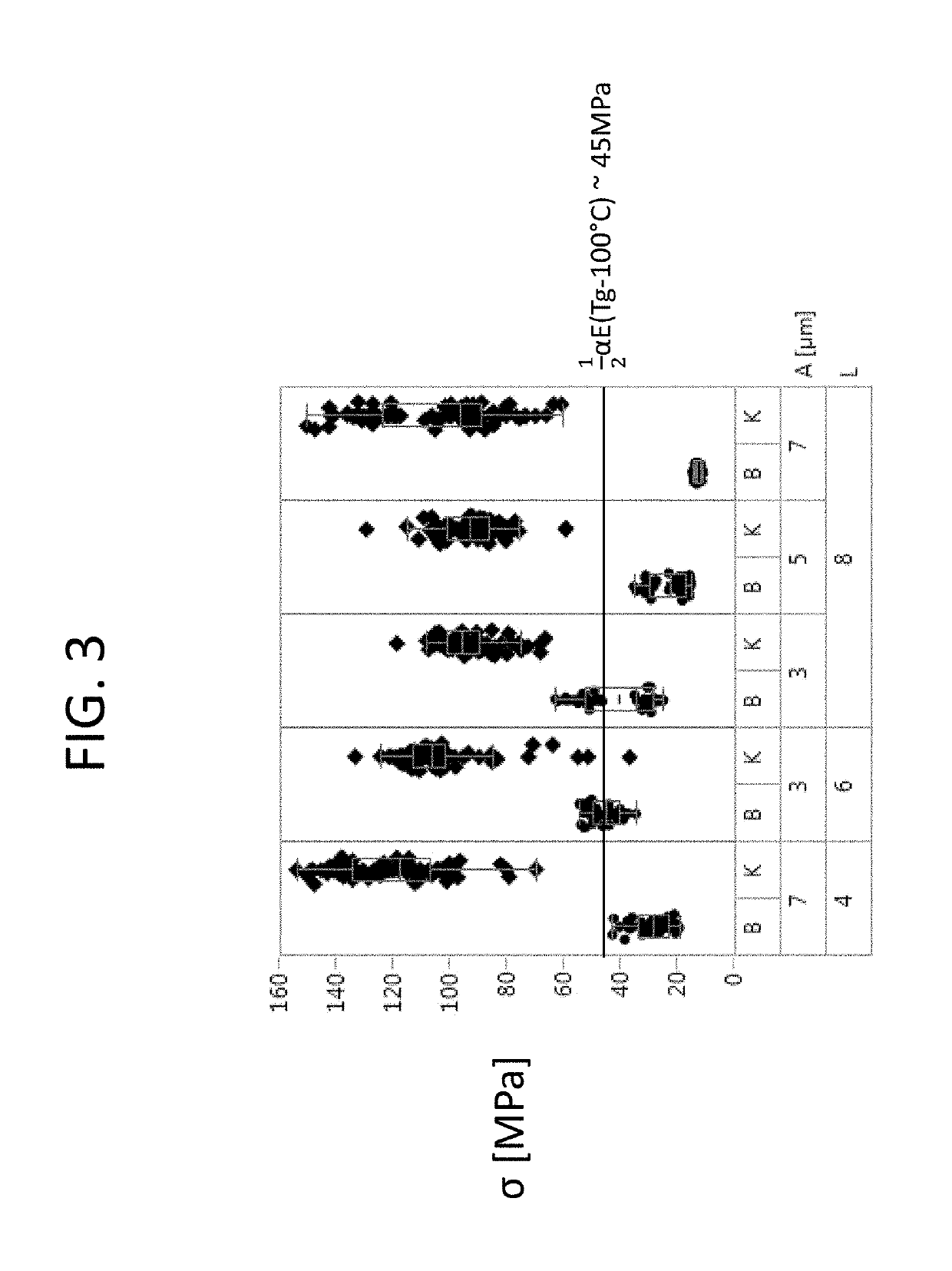
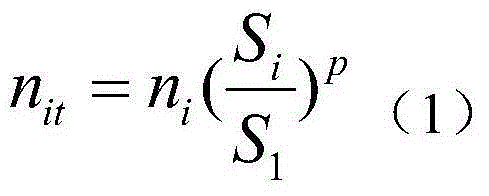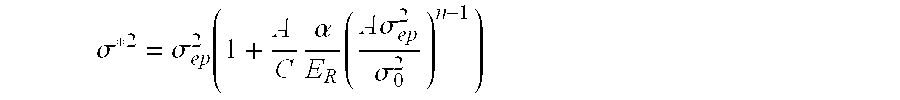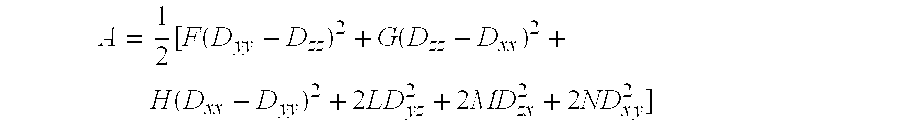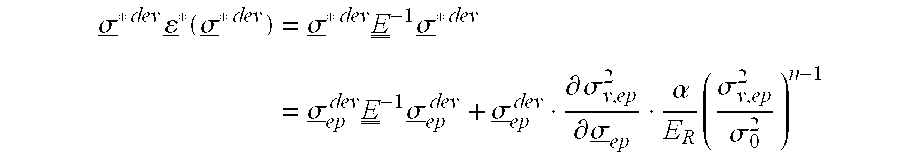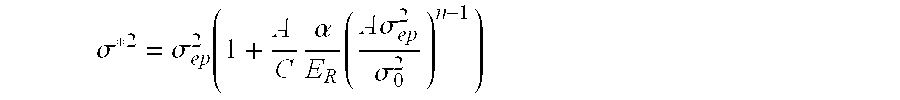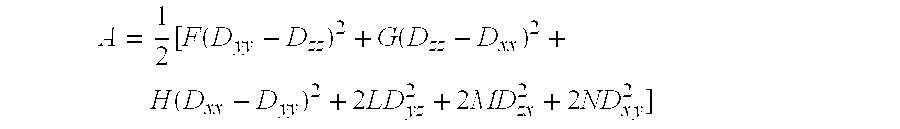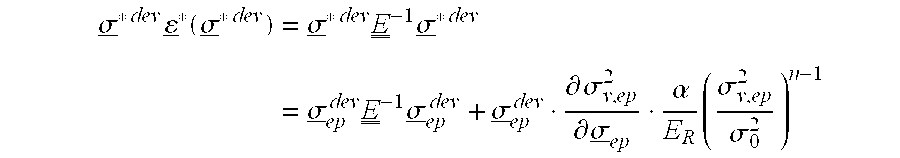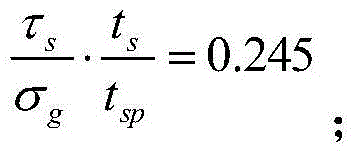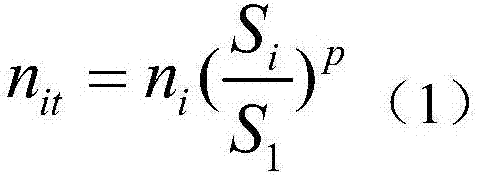Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35 results about "Reference stress" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Stress References. STRESS REFERENCES (return to Stress and Nutrition) “The stress response gives us the strength and speed to ward off or flee from an impending threat. But when it [stress] persists, stress can put us at risk for obesity, heart disease, cancer, and a variety of other illnesses.”.
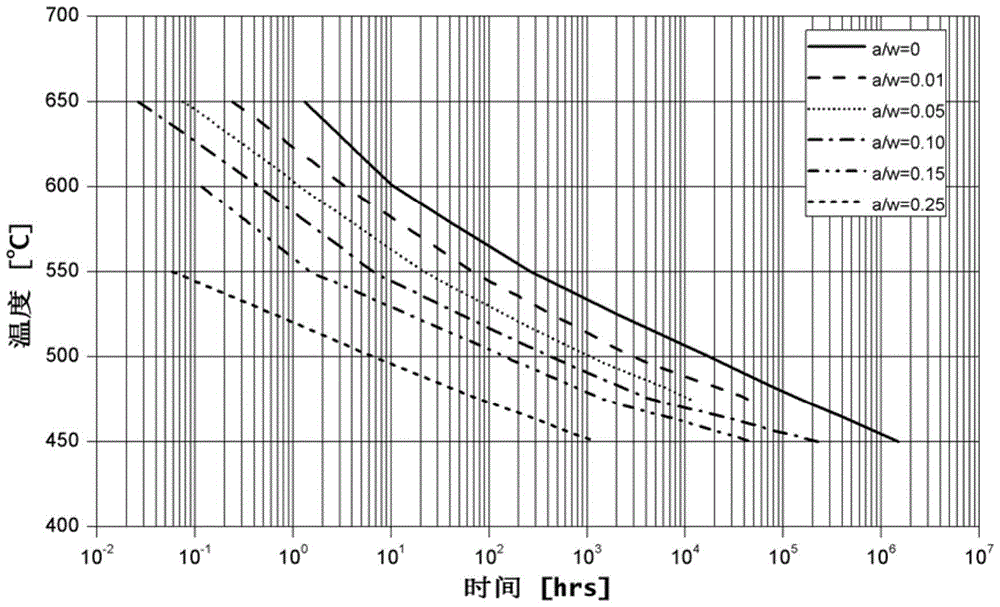
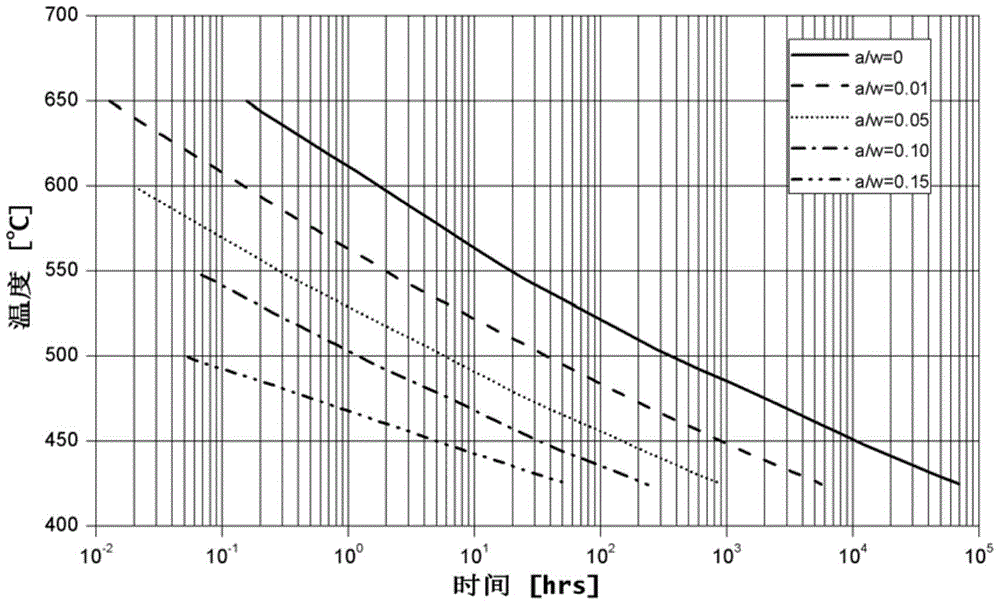
Service life based high-temperature container creep fatigue strength design method
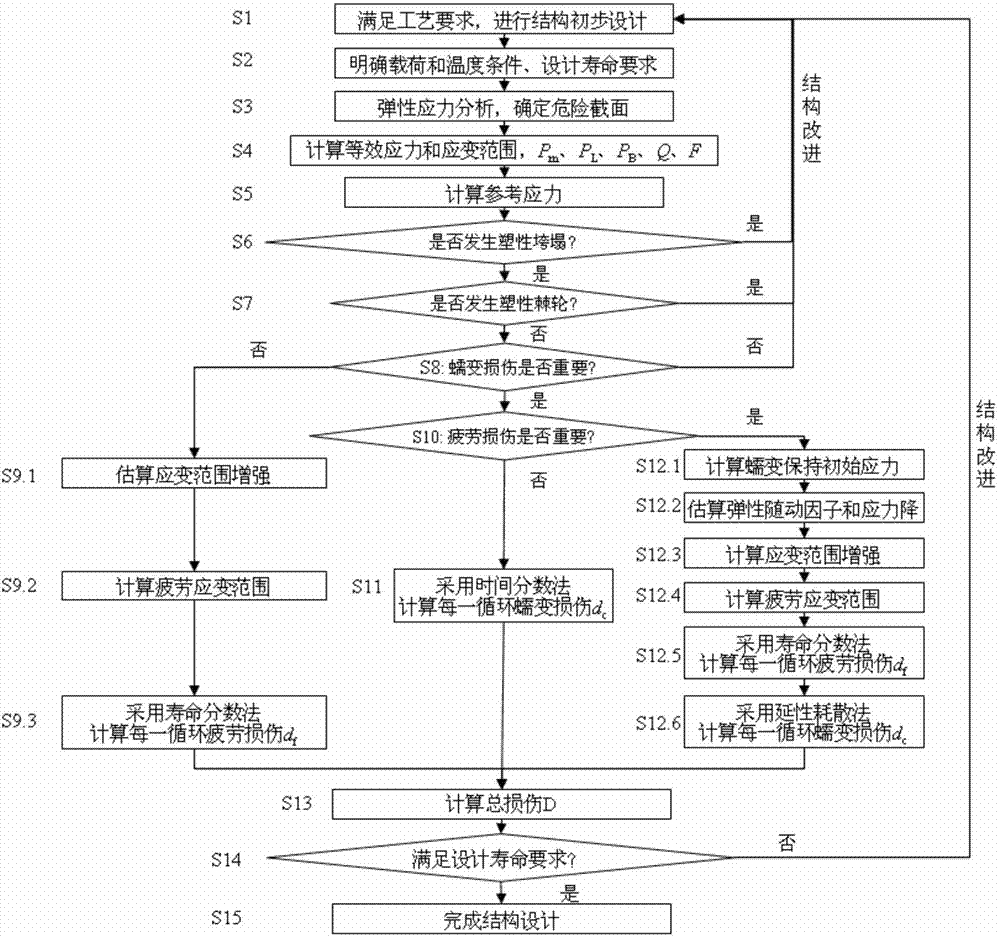
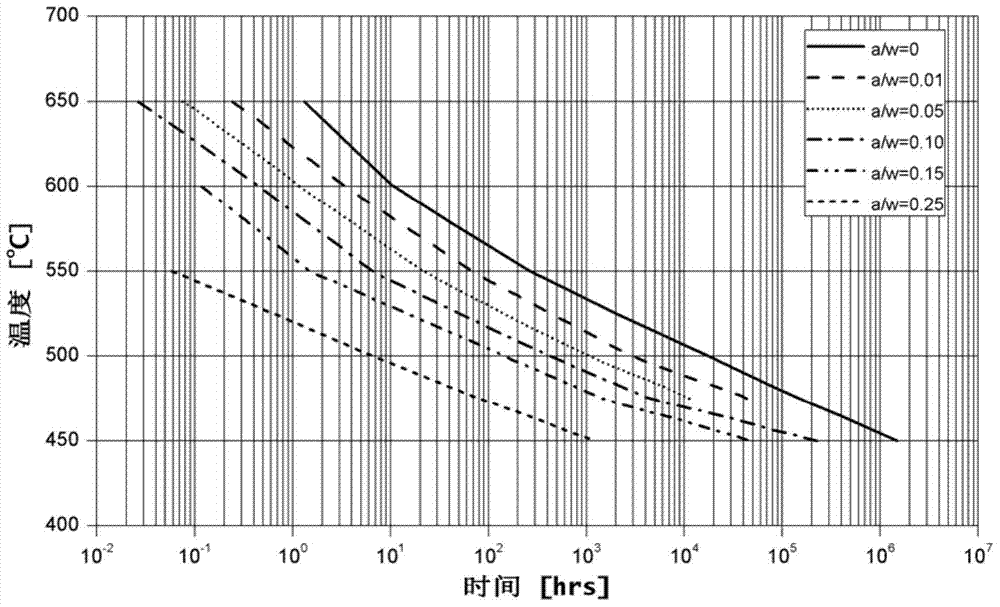
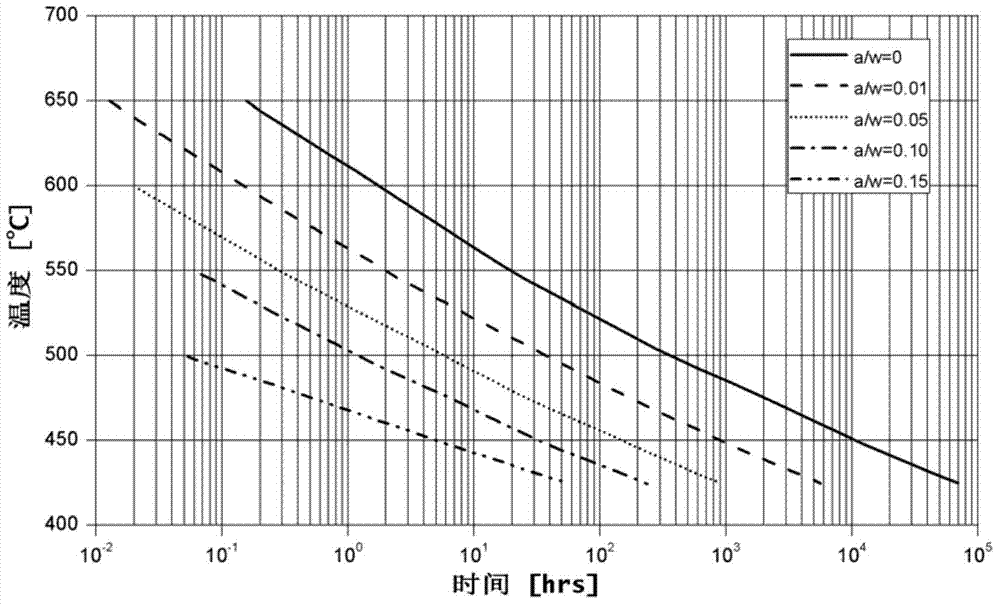
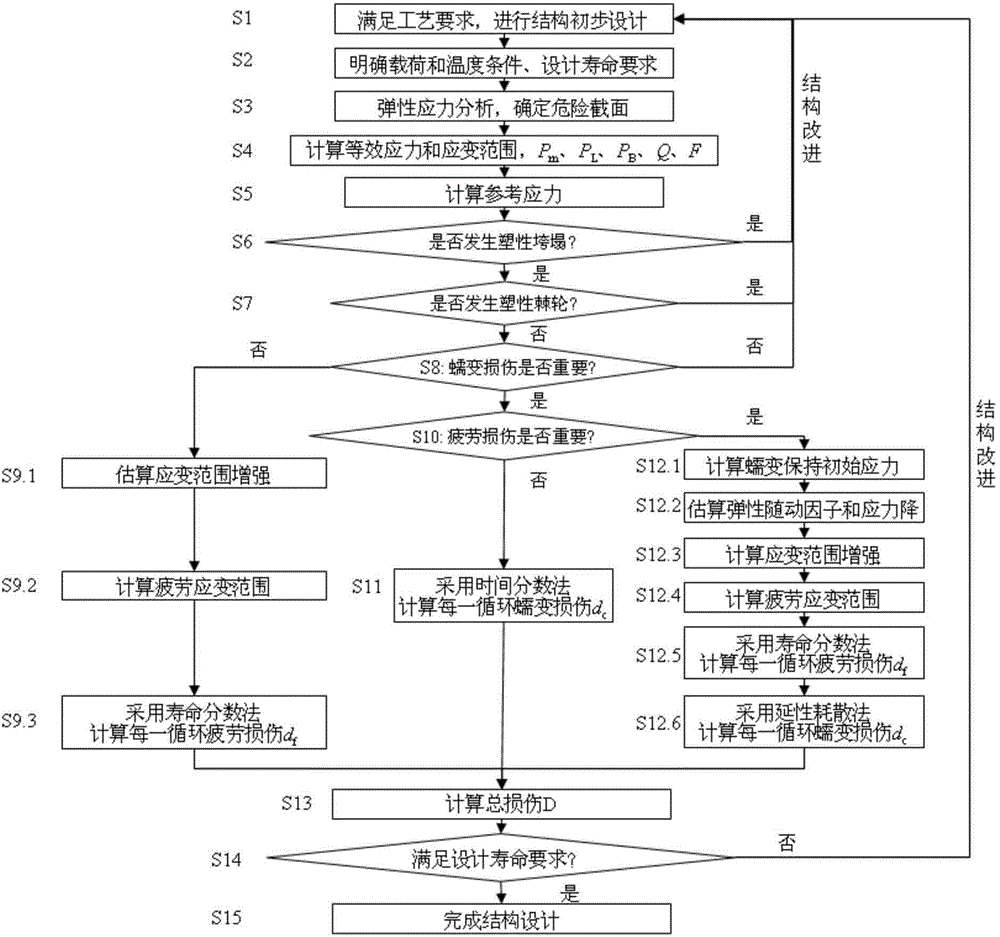
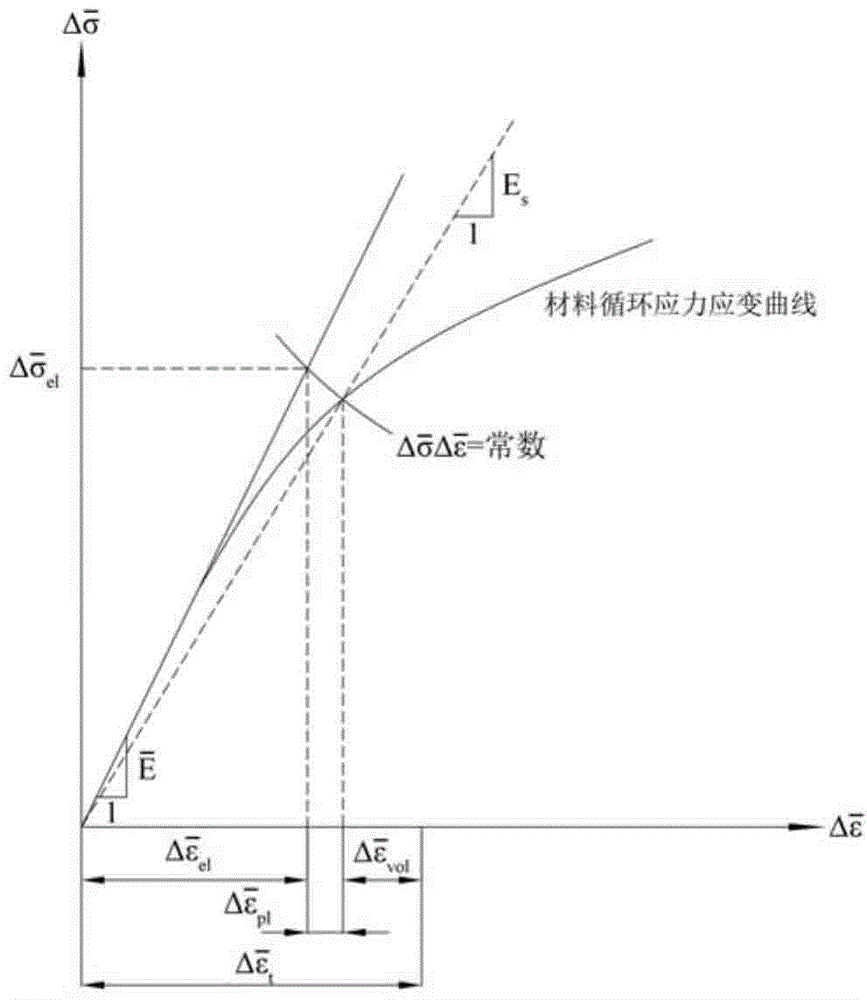
The invention discloses a service life based high-temperature container creep fatigue strength design method. The method comprises the steps of 1, performing structure preliminary design; 2 determining load and temperature conditions and the design service life requirement; 3, determining dangerous sections; 4, calculating the equivalent stress and strain range; 5, calculating reference stress; 6, determining whether plastic collapse occurs; 7 determining whether the plastic ratchet occur; 8, determining whether creep damage is important; 9, estimating fatigue damage of each cycle when the creep damage is not important; 10, determining whether the fatigue damage is important; 11, estimating the creep damage when the fatigue damage is not important; 12, estimating damage of each cycle when the creep damage and the fatigue damage are non-ignorable; 13, estimating creep-fatigue total damage; 14, performing result analysis and structural design improvement; 15, completing structural design. According to the method, the foundation is laid for national establishing of creep and fatigue failure mode based high-temperature pressure container design standards and achieving design and manufacture of high-temperature pressure containers according to the service life.
Owner:HEFEI GENERAL MACHINERY RES INST
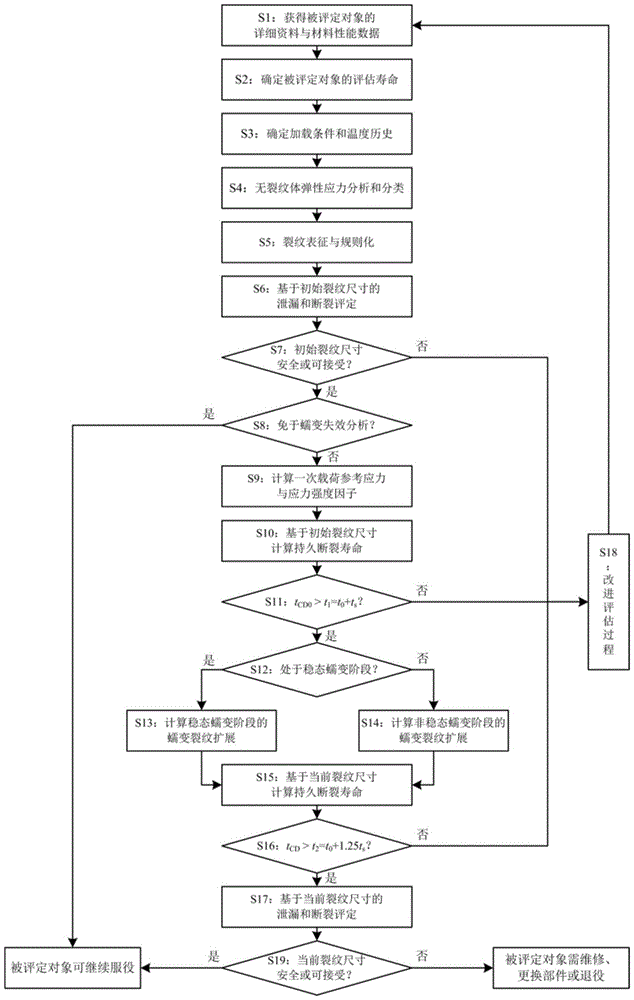
Safety assessment method for high-temperature pressure pipeline with crack type defects
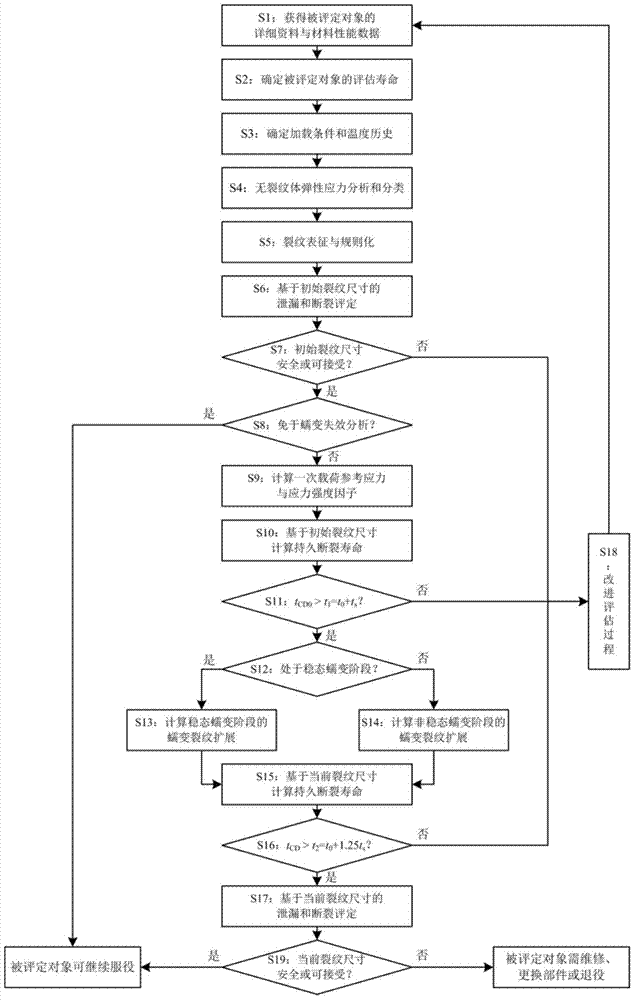
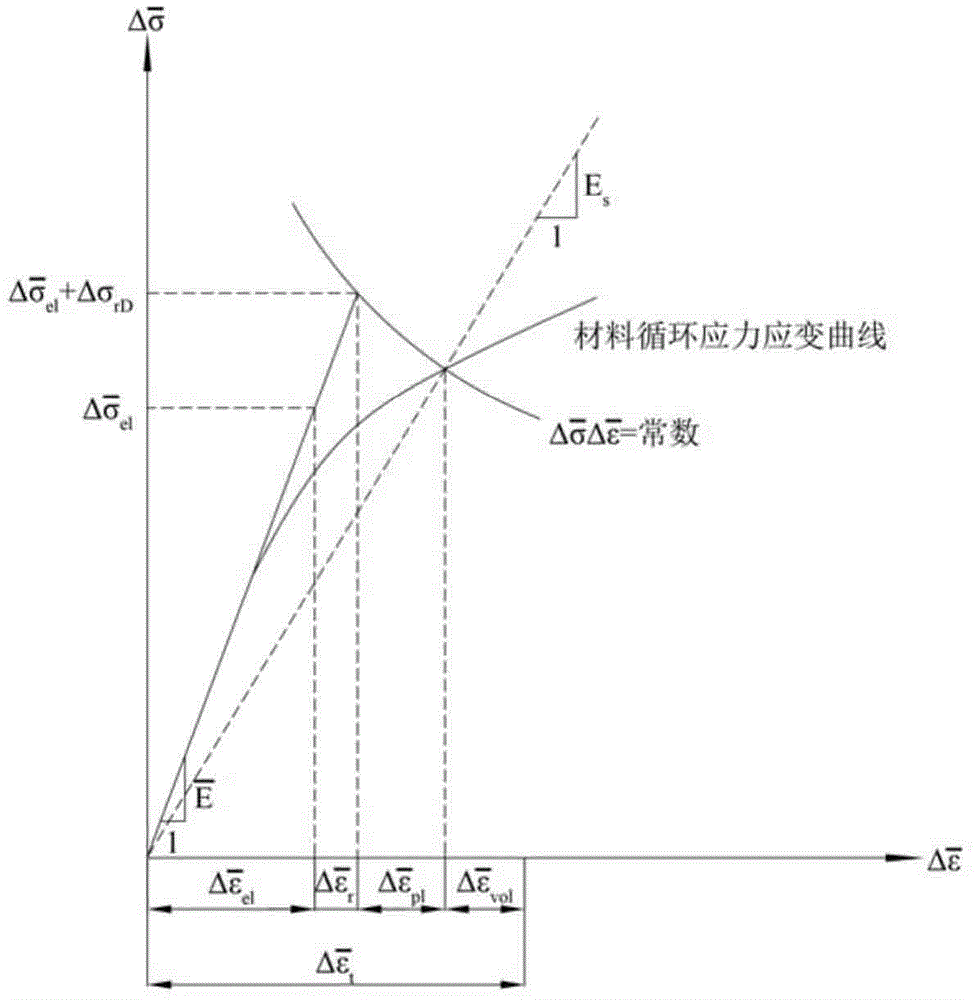
The invention discloses a safety assessment method for a high-temperature pressure pipeline with crack type defects. The safety assessment method for the high-temperature pressure pipeline with crack type defects includes steps that 1, gathering data; 2, definitely evaluating the life span; 3, determining load and temperature; 4, analyzing elastic stress; 5, characterizing crack; 6, assessing initial crack leakage and rupture; 7, judging whether the initial crack is safe; 8, judging whether the initial crack is free of creep analysis; 9, calculating reference stress and stress intensity factors; 10, calculating creep rupture life based on the initial crack size; 11, judging whether the creep rupture life is long enough; 12, judging whether the creep is steady creep; 13, calculating steady state creep crack growth; 14, calculating unsteady state creep crack growth; 15, calculating the creep rupture life based on the current crack size; 16, judging whether the current creep rupture life is long enough; 17, assessing the current crack leakage and rupture; 18, refining and evaluating; 19, judging whether the assessed object is safe. The safety assessment method for the high-temperature pressure pipeline with crack type defects can be used for assessing the safety of the high-temperature pressure pipeline with crack type defects under creep load effect.
Owner:HEFEI GENERAL MACHINERY RES INST
Model for predicting residual fatigue life of concrete member
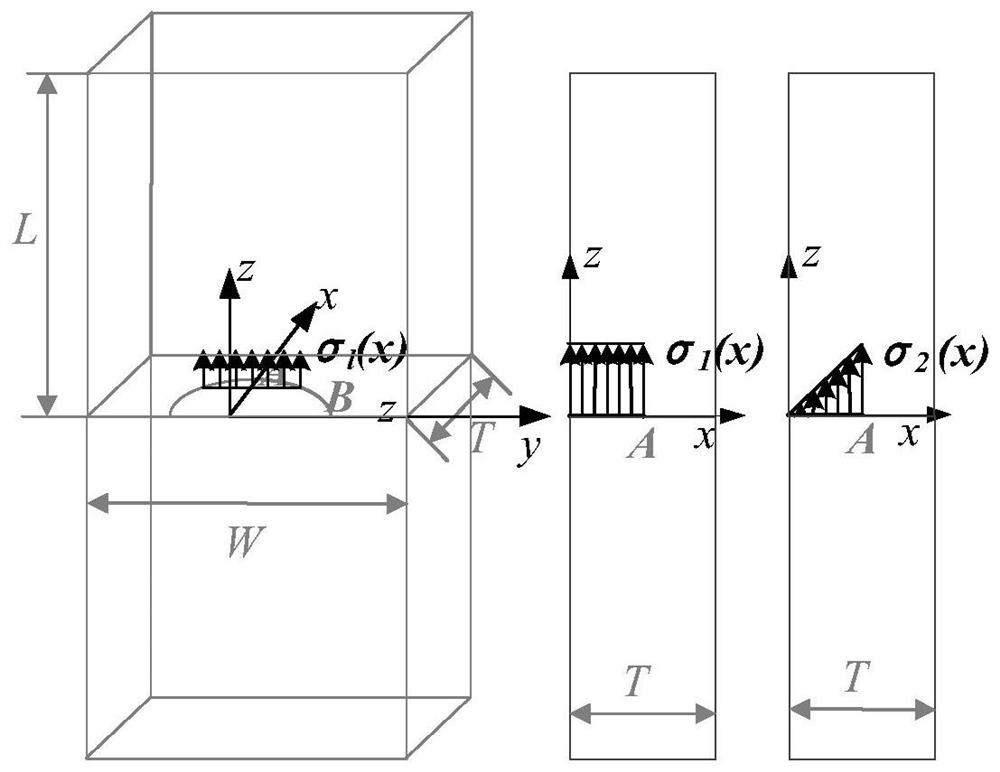
The invention discloses a model for predicting residual fatigue life of a concrete member. The fatigue life of concrete under a random-amplitude fatigue load is effectively predicted more simply and conveniently. A basic conception that the damage situation of the concrete loaded for cycle times ni under a stress level Si is equivalent to that of the concrete loaded for cycle times n1 under a reference stress level S1 is utilized. For random i, the cycle times nit for loading the concrete under the reference stress level S1 when the damage situation of the concrete loaded for cycle times ni under the stress level Si is equivalent to that of the concrete loaded for cycle times nit under the reference stress level S1 can be obtained.
Owner:科利尔环保科技有限责任公司
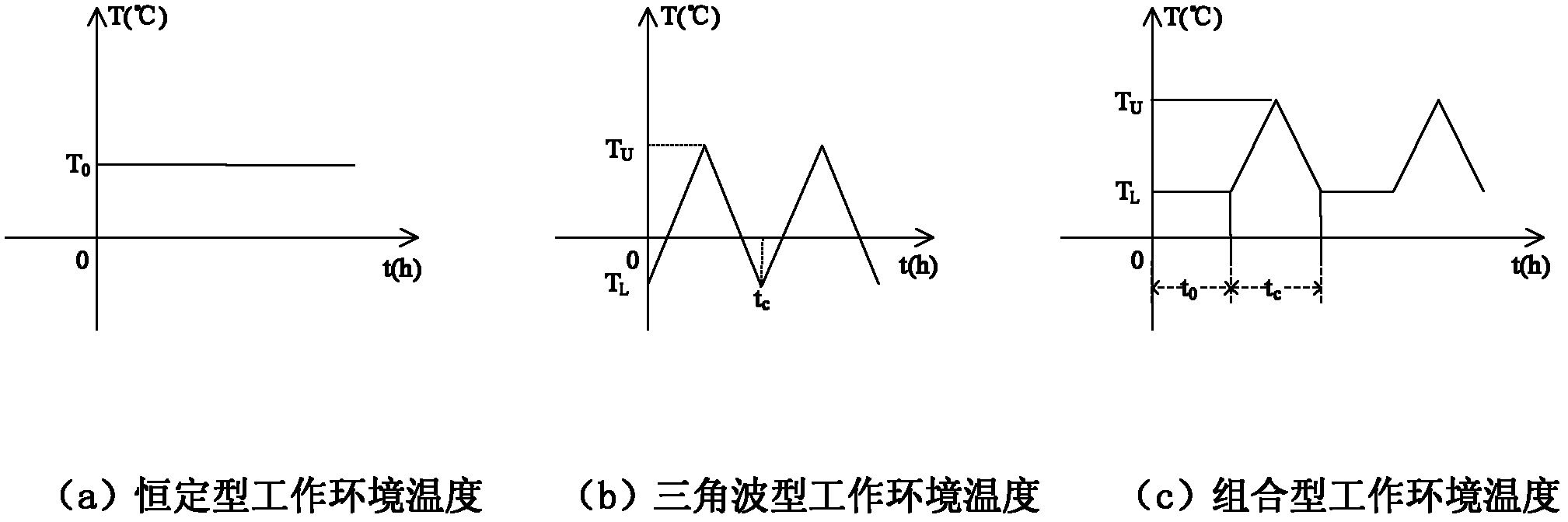
Temperature acceleration reference stress determination method in acceleration life test of spatial electronic equipment
ActiveCN102520279AThe reliability results are accurateThe reliability assessment results are accurateElectrical testingWorking environmentDependability
The invention, which belongs to the electronic product technology filed, relates to a temperature acceleration reference stress determination method in an acceleration life test of spatial electronic equipment. For periodic variation of a working environmental temperature, equal step segmentation is carried out on the environmental temperature and then reliability of a corresponding time slot under each step temperature is respectively calculated; reliability of one period and a whole life telophase is calculated and an improved reliability index computational formula is given; and when the working environmental temperature is selected as an accelerated stress, that is, an acceleration life test of spatial electronic equipment is carried out by improving the working environmental temperature, the improved reliability index computational formula should be employed; and on the premise that the reliability is invariant, the working environmental temperature with periodic variation is converted equivalently into a constant type working environment temperature, so that a reference stress is determined. According to the invention, a technical problem that how to accurately determine a temperature acceleration reference stress when an acceleration life test of spatial electronic equipment is carried out by improving a working environmental temperature can be solved.
Owner:NO 510 INST THE FIFTH RES INST OFCHINA AEROSPAE SCI & TECH
Method of determining the elastoplastic behavior of components consisting of anisotropic material and use of the method
InactiveUS20050065749A1Thermometer detailsThermometers using material expansion/contactionElastic anisotropyCrystalline materials
A method of determining the elastoplastic behavior of components, in particular of gas turbine plants, at high temperatures. First of all, the linear-elastic behavior is determined and the inelastic behavior is taken into account on the basis of the linear-elastic results by using the Neuber rule, the anisotropic characteristics of the components, as occur in particular through the use of single-crystalline materials, are taken into account in a simple manner by using a modified anistropic Neuber rule in the form σ*2=σep2(1+A CαER(A σep2σ02)n-1)where A=inelastic anisotropic correction term, A=12[F(Dyy-Dzz)2+G(Dzz-Dxx)2+H(Dxx-Dyy)2+2L Dyz2+2 MDz x2+2 NDx y2] where F, G, H, L, M and N are the Hill constants, C=elastic anisotropic correction term, C=D•E−1•Dσ*=determined linear stress, σep=estimated inelastic stress, D=direction vector of the elastic and inelastic stresses E−1=inverse stiffness matrix, ER=reference stiffness, σ0=reference stress, and σα, n=material constants.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
Stress measurement method
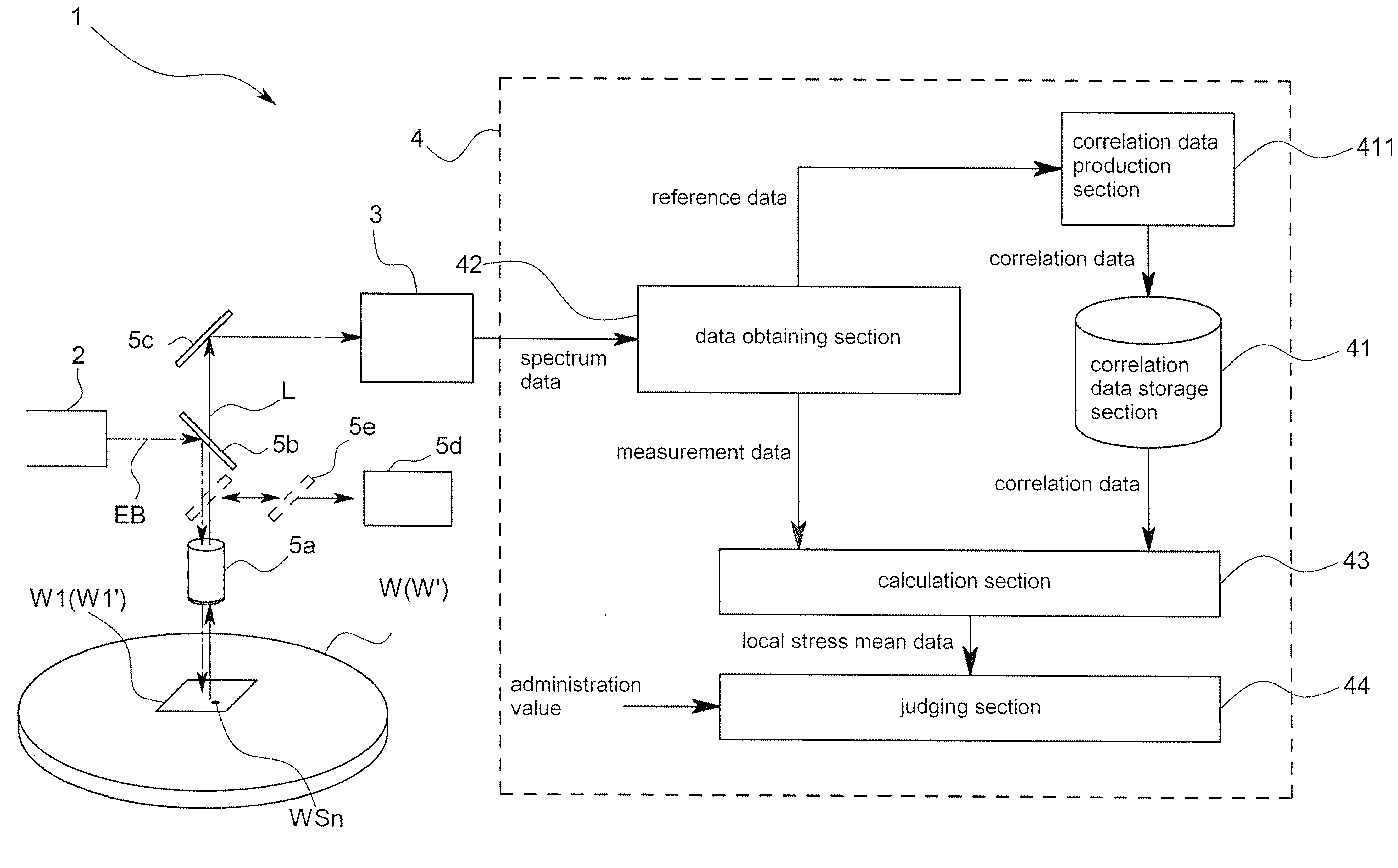
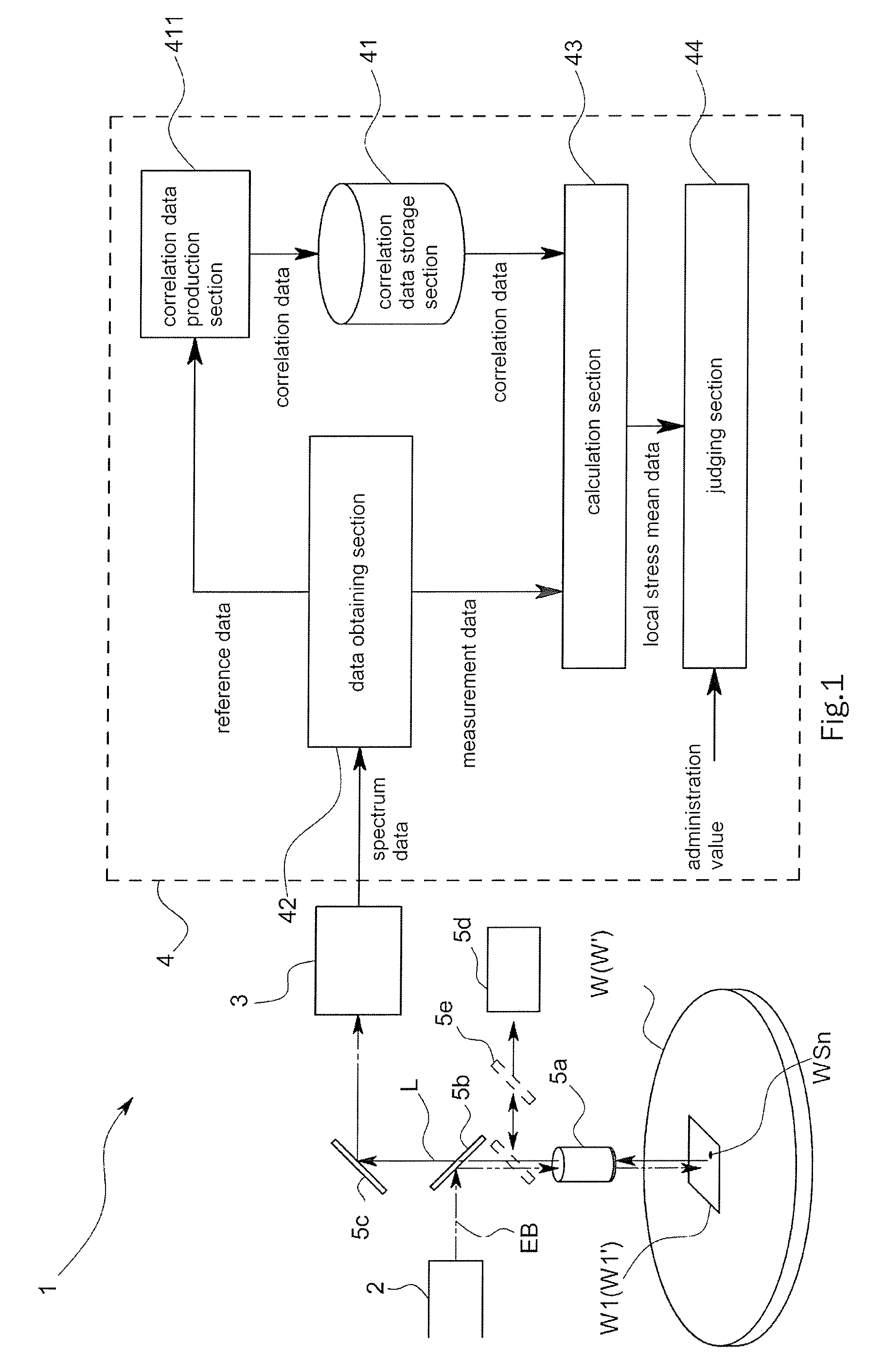
InactiveUS20080084552A1High measurement accuracyImprove accuracyForce measurement by measuring optical property variationWork measurementNon destructiveComputer science
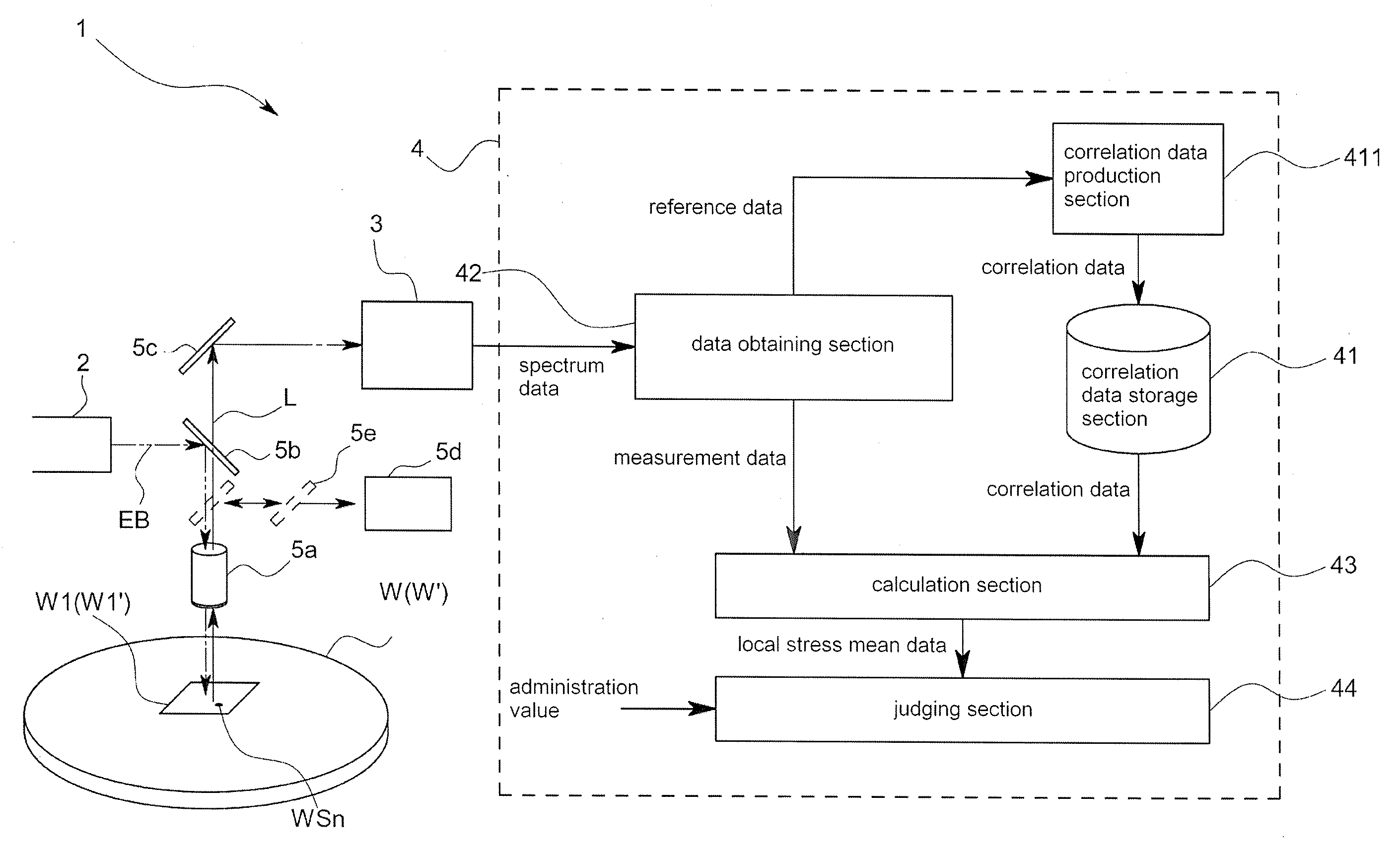
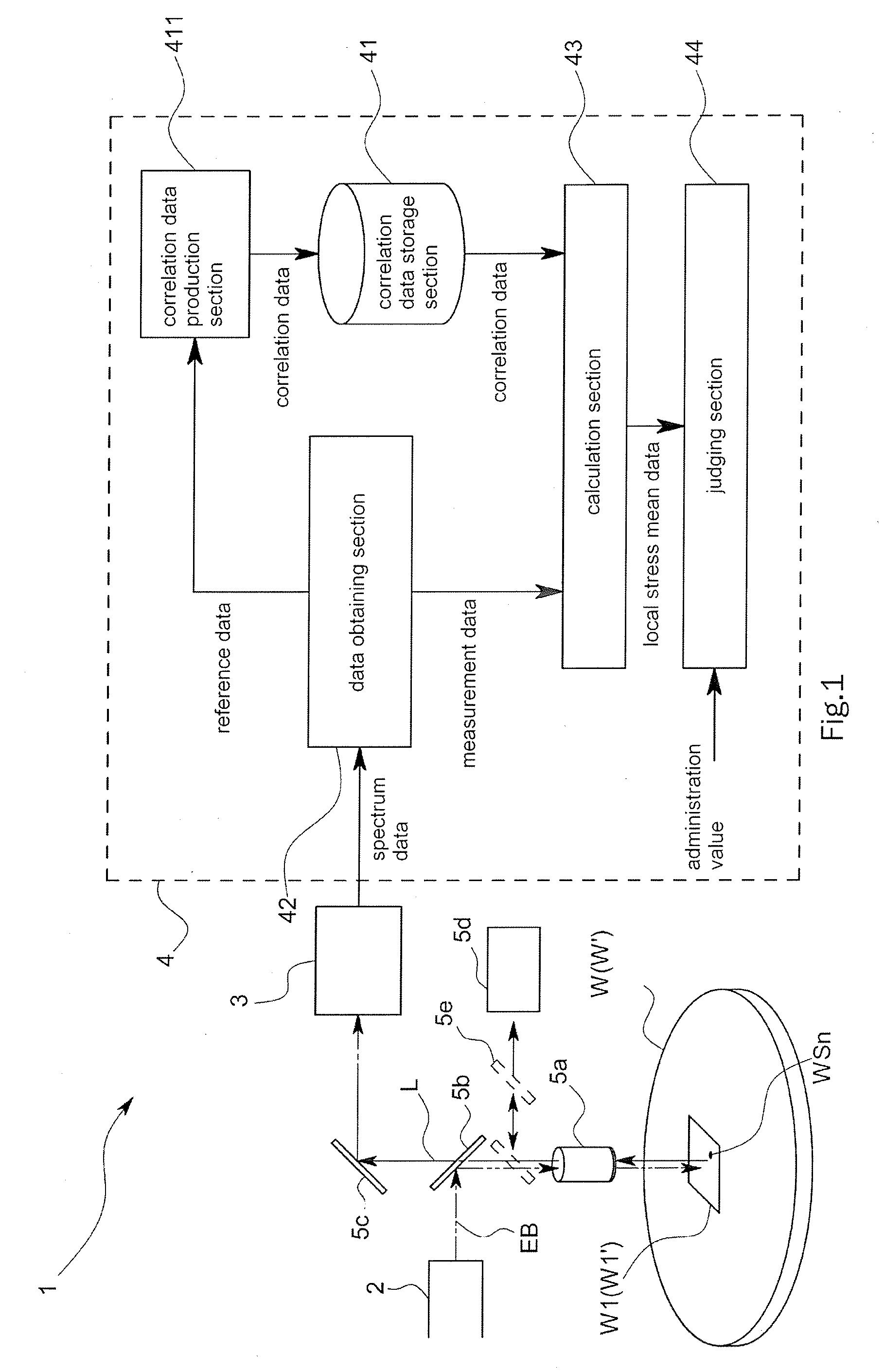
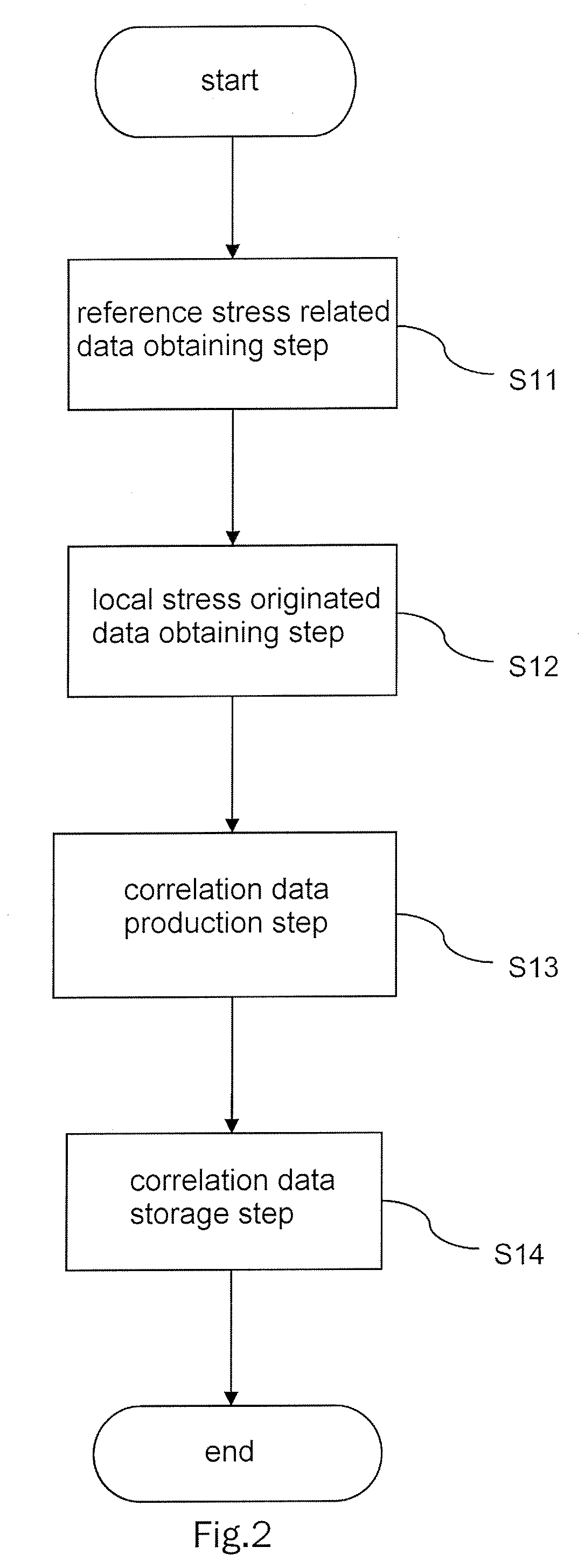
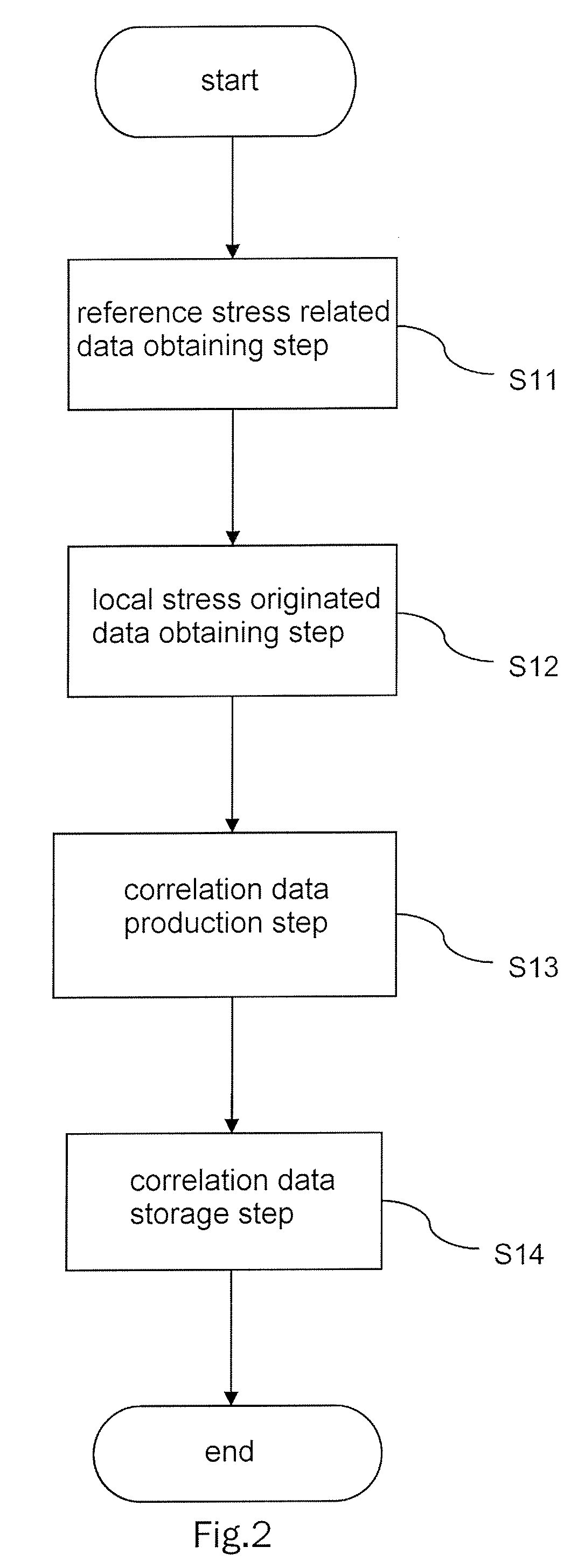
An object of this invention is to provide stress measurement method that is stress of the measuring object nondestructively in a short period of time.In order to attain this object, the stress measurement apparatus 1 comprises a correlation data storage section 41 that analyzes a correlation between reference stress related data obtained from a Raman spectrum L of an entire predetermined area W1 of a reference specimen W and local stress originated data as being data obtained based on a local stress each of which applies to multiple positions WS1˜WSn respectively in the predetermined area W1 and stores correlation data indicating the correlation, a data obtaining section 42 that obtains measurement stress related data from a Raman spectrum L on an entire measurement area W1′, corresponding to the predetermined area W1, of a measurement specimen WS′, and a calculation section 43 that calculates local stress originated data in the measurement area W1′ based on the correlation data and the measurement stress related data.
Owner:HORIBA LTD
Cable tension uncertainty-based method for determining thin film shapes of planar thin film antennas
ActiveCN106886628AAchieve shape optimizationWide range of researchDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsStress distributionEngineering
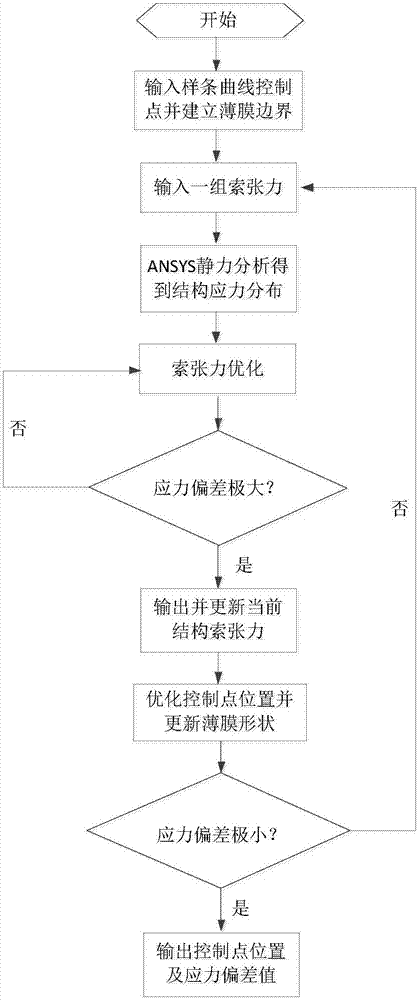
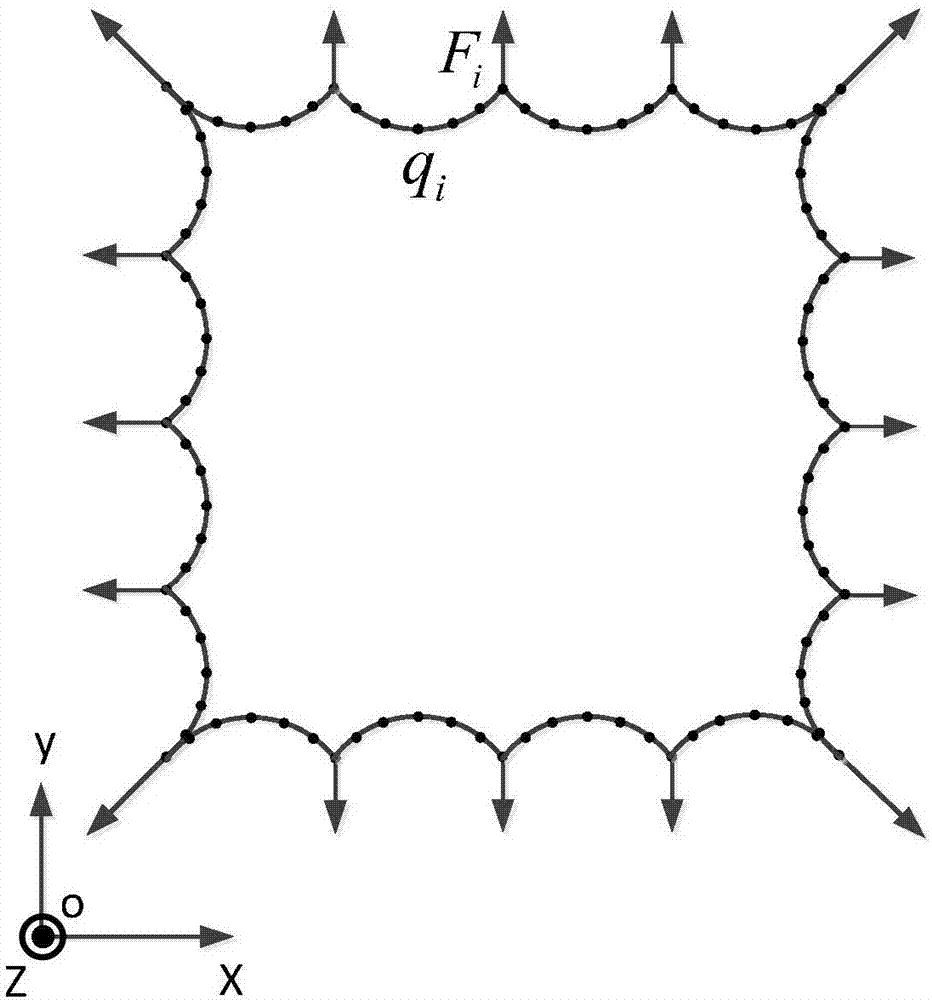
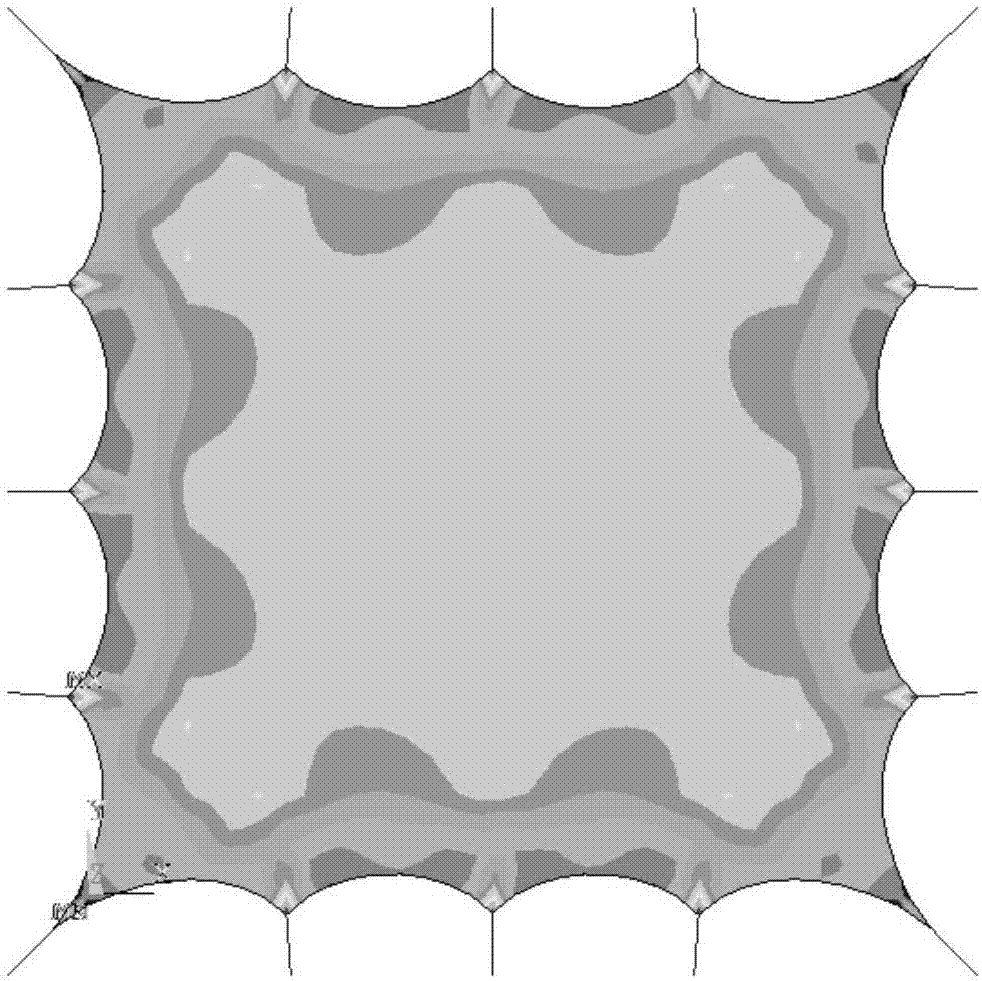
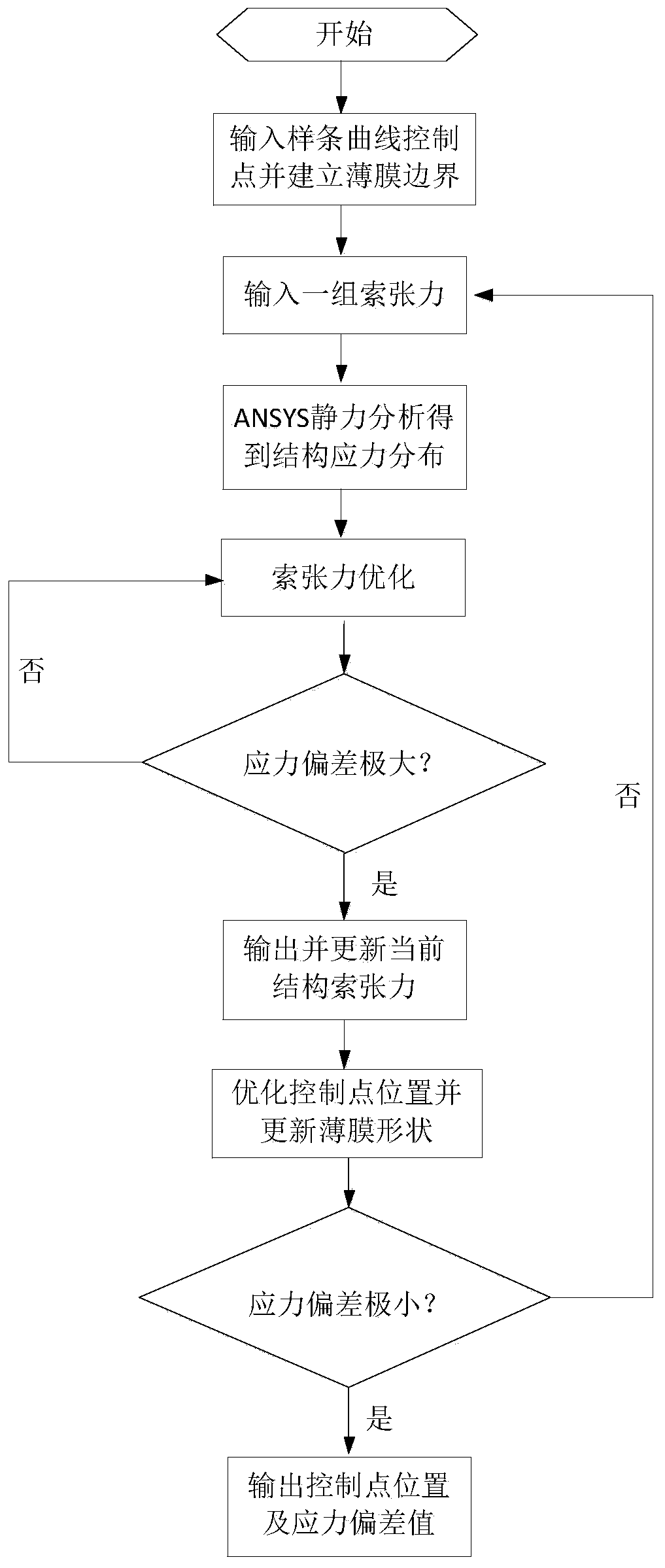
The invention discloses a cable tension uncertainty-based method for determining thin film shapes of planar thin film antennas. The method comprises the following steps of: considering a thin film boundary of a planar thin film antenna as a spline, and establishing a preliminary model of a planar tensioning cable film which takes the spline as a boundary by applying ANSYS; applying a certain tensioning force on a suspension cable, and carrying out static analysis to obtain stress distribution of the cable and the film; defining a deviation range of cable tension, and finding a group of corresponding cable tension when the deviation between a practical stress of a cable-film structure and a reference stress is maximum; searching a next optimal curve control point position through minimizing a stress deviation value output in the step 3); and updating the thin film shape through the optimized curve control point until the relative change amount of the cable-film structure satisfies the accuracy requirement of a convergence criterion, so as to obtain an optimal thin film shape. According to the method, the limits of specific boundary shapes are broken through, and robustness optimization is carried out on the structure, so that the thin film shape is determined more correctly and the service life of materials is prolonged at the same time.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
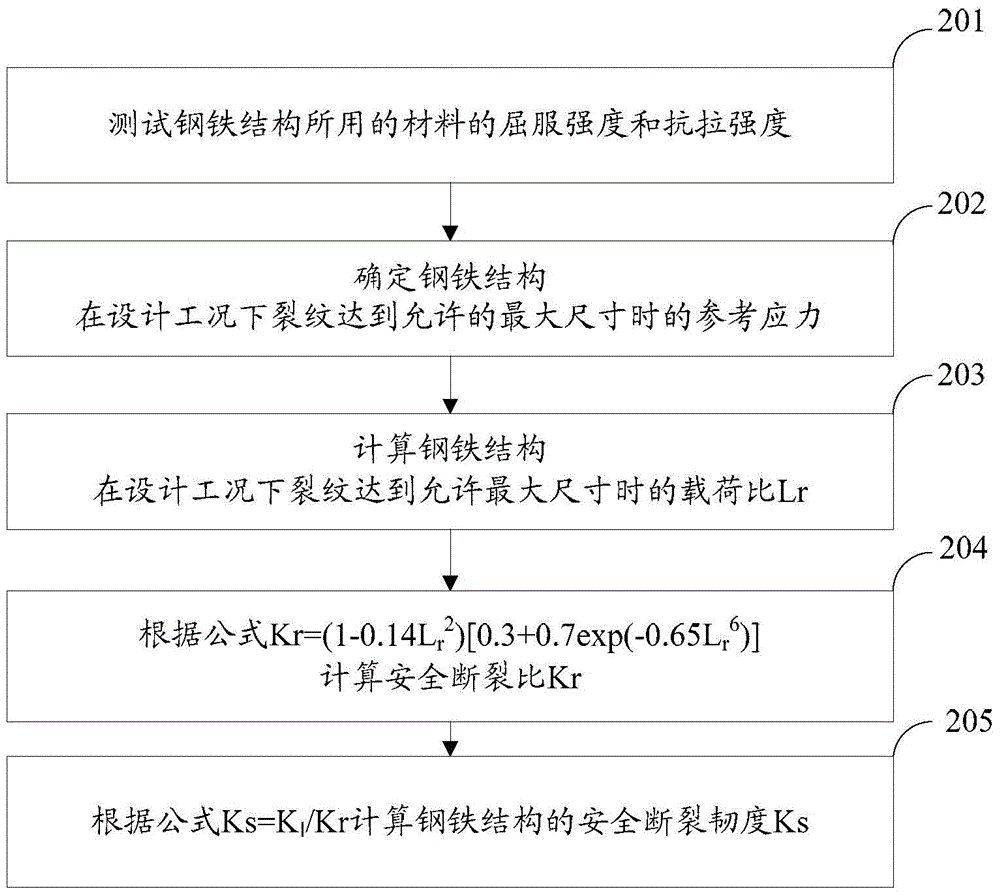
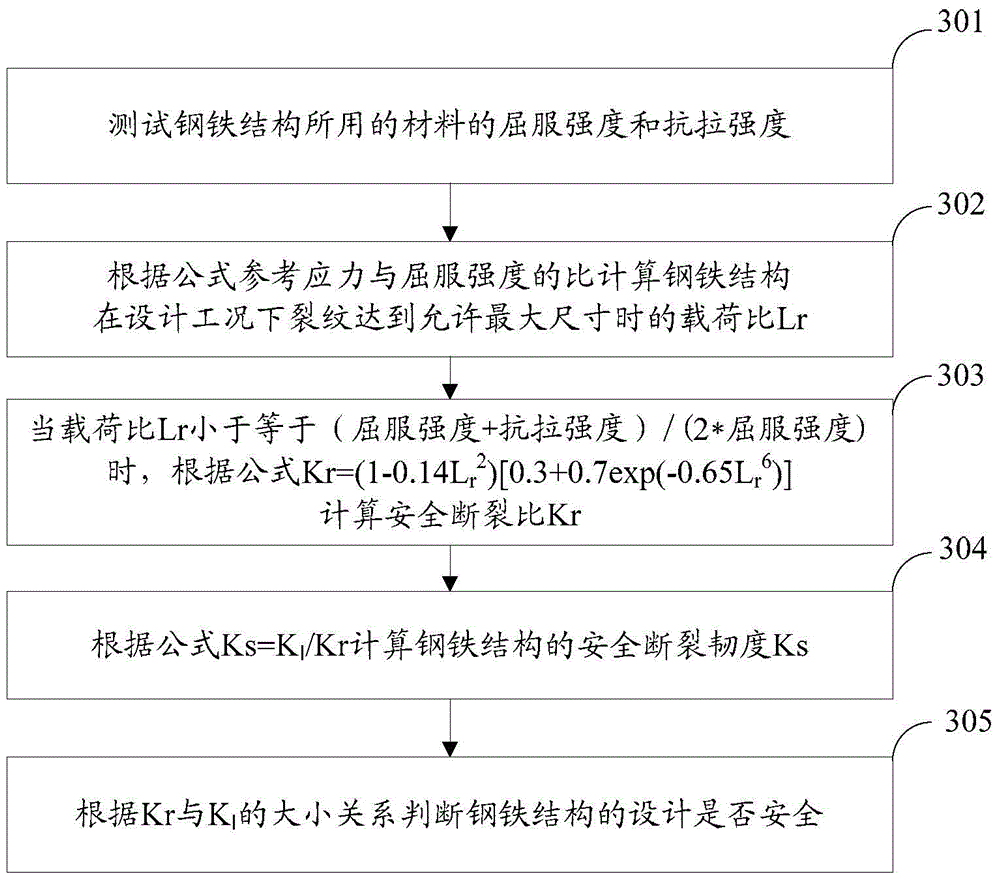
Steel structure safe fracture toughness determination method and steel structure design safety checking method
InactiveCN104807697AReduce failure rateEasy to manufactureMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesStress intensity factorLoad ratio
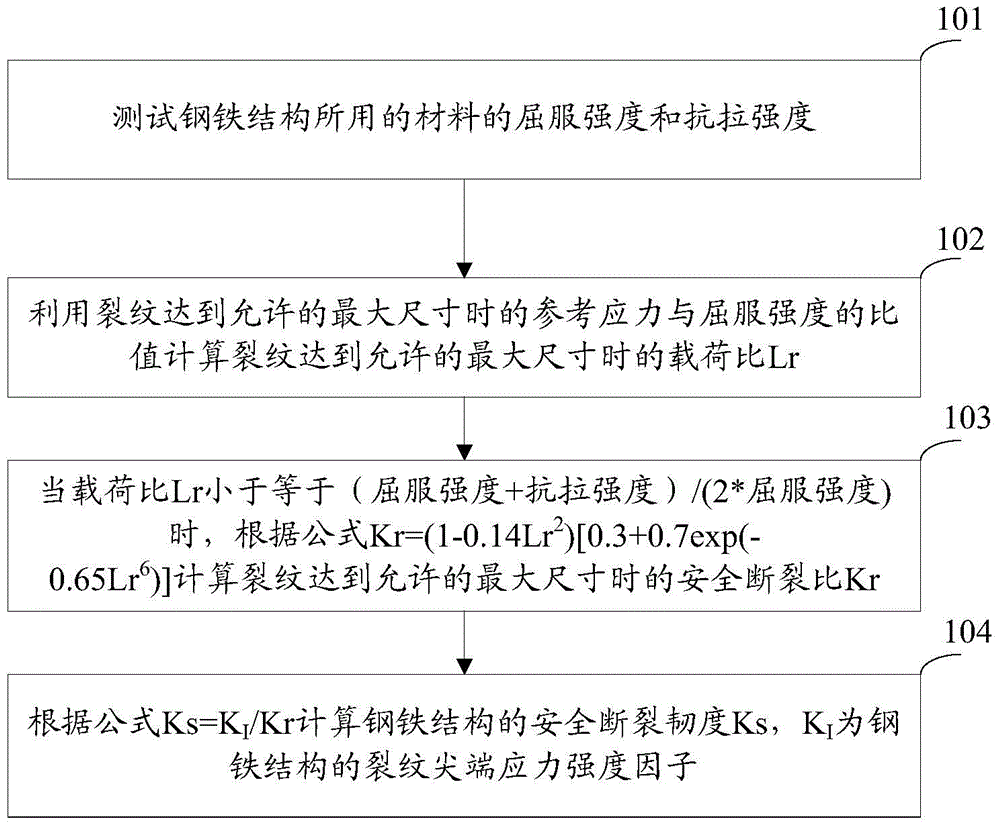
The invention discloses a steel structure safe fracture toughness determination method and a steel structure design safety checking method, and belongs to the technical field of test of mechanical performances of a material. The steel structure safe fracture toughness determination method comprises the following steps: testing the yield strength sigma y and the tensile strength sigma u of the material of a steel structure; calculating the load ratio Lr of the steel structure with the crack reaching an allowed maximum size under design conditions according to a formula of Lr=sigma ref / sigma y, wherein the sigma ref is the reference stress when the crack reaches the allowed maximum size; calculating the safe fracture ratio Kr of the steel structure according to a formula of Kr=(1-0.14Lr<2>)[0.3+0.7exp(-0.65Lr<6>)] when the load ratio is not greater than (sigma y + sigma u) / (2.sigma y); and calculating the safe fracture toughness Ks according to a formula of Ks=KI / Kr, wherein KI is the crack tip stress strength factor of the crack reaching the allowed maximum size. The steel structure safe fracture toughness determination method avoids the problems of high cost and long time brought by special condition requirements for determining the plane strain fracture toughness of the material, is simple and fast to realize by determining the safe fracture toughness through testing the yield strength and the tensile strength of the material, and is in favor of realizing engineering application.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP
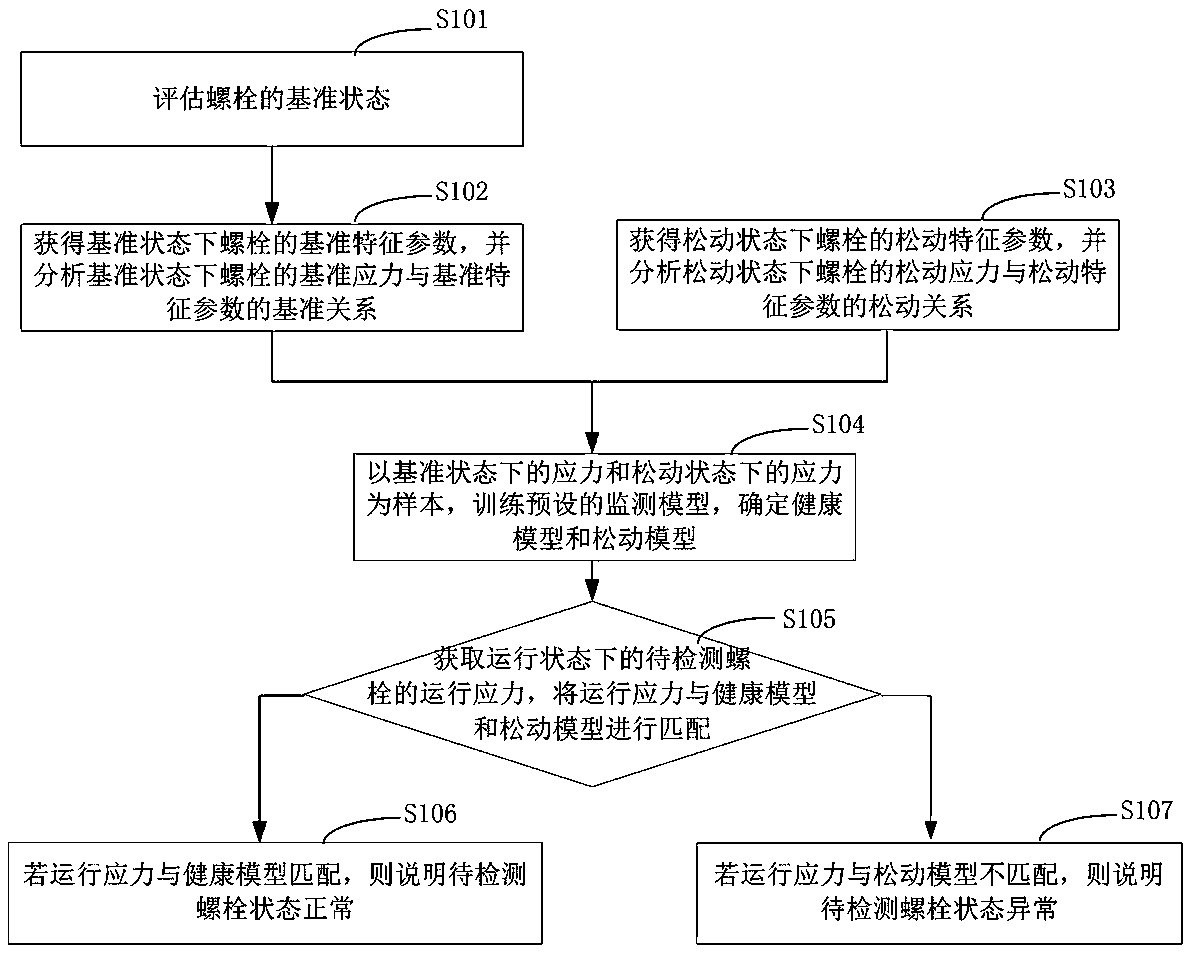
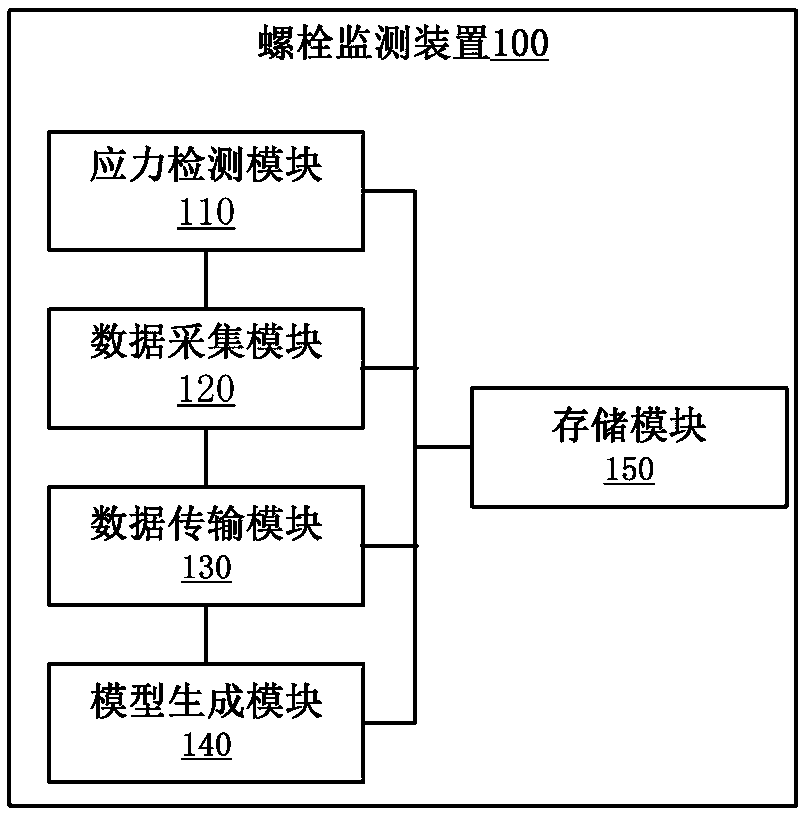
Bolt state monitoring method and device
ActiveCN110990978AEasy to buildReduce security risksGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationStructural engineeringMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a bolt state monitoring method and device. The bolt state monitoring method comprises the steps: the reference state of a bolt is evaluated; reference characteristic parametersof the bolt in the reference state are obtained, and the reference relation between the reference stress of the bolt in the reference state and the reference characteristic parameters is analyzed; loosening characteristic parameters of the bolt in the loosening state are obtained, and the loosening relation between the loosening stress of the bolt in the loosening state and the loosening characteristic parameters is analyzed; taking the stress in the reference state and the stress in the loosening state as samples, a preset monitoring model is trained, and a health model and a loosening modelare determined; and the operation stress of the to-be-detected bolt in an operation state is obtained, and the operation stress is matched with the health model and the loosening model. According tothe bolt state monitoring method and device, measurement of the bolt length and the longitudinal and transverse wave propagation characteristics in the original zero-stress state is avoided, online monitoring is achieved to a large extent, and the defect of manual inspection is overcome.
Owner:HENAN EPRI GAOKE GRP +2
Full-stress structure topological optimization design method based on continuous phase step reference stress
InactiveCN102222150AOptimal stress distribution stateAvoid precocitySpecial data processing applicationsStress distributionTopological optimization
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Method and device for operating a steam power plant, in particular in the part-load range
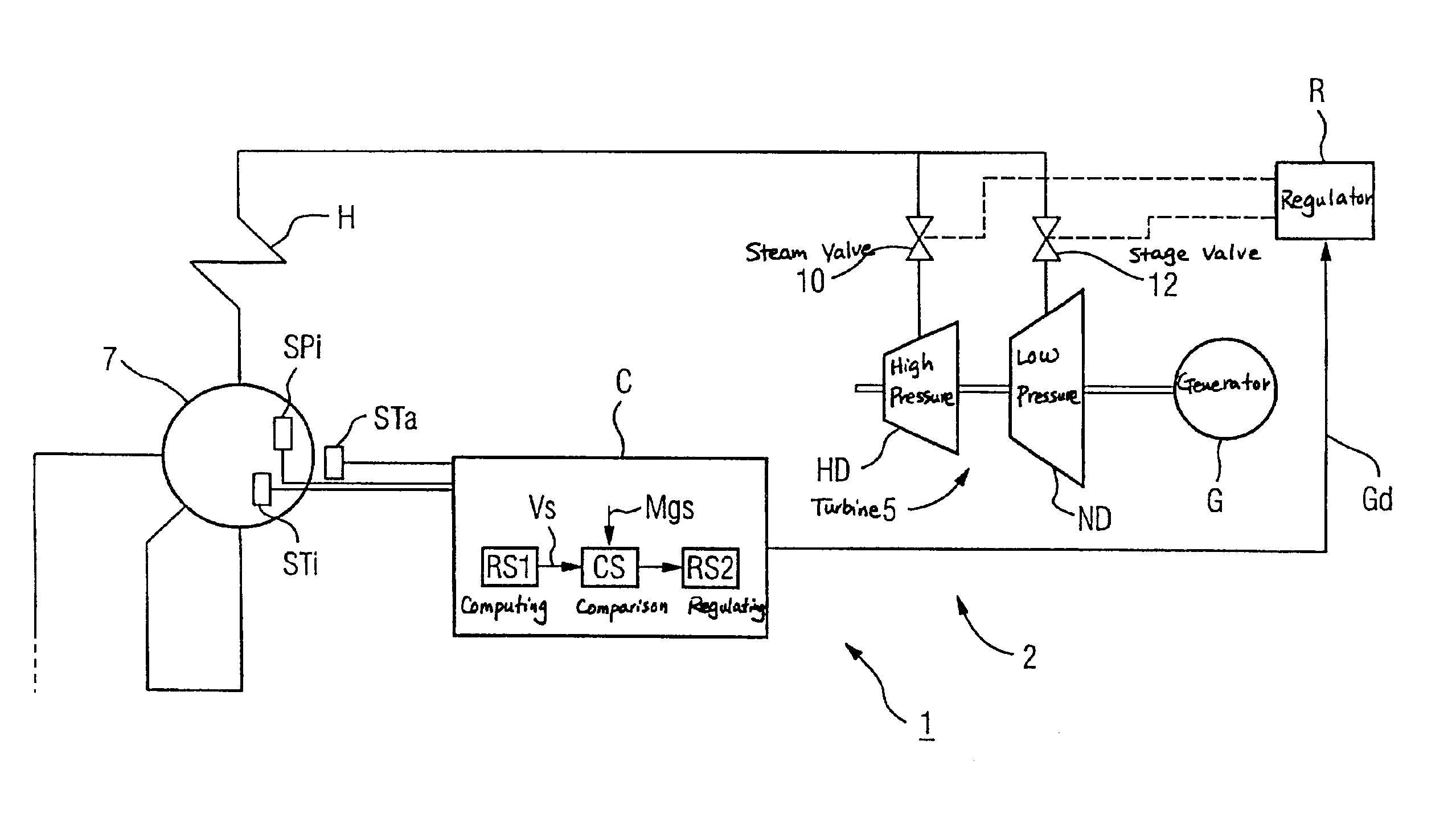
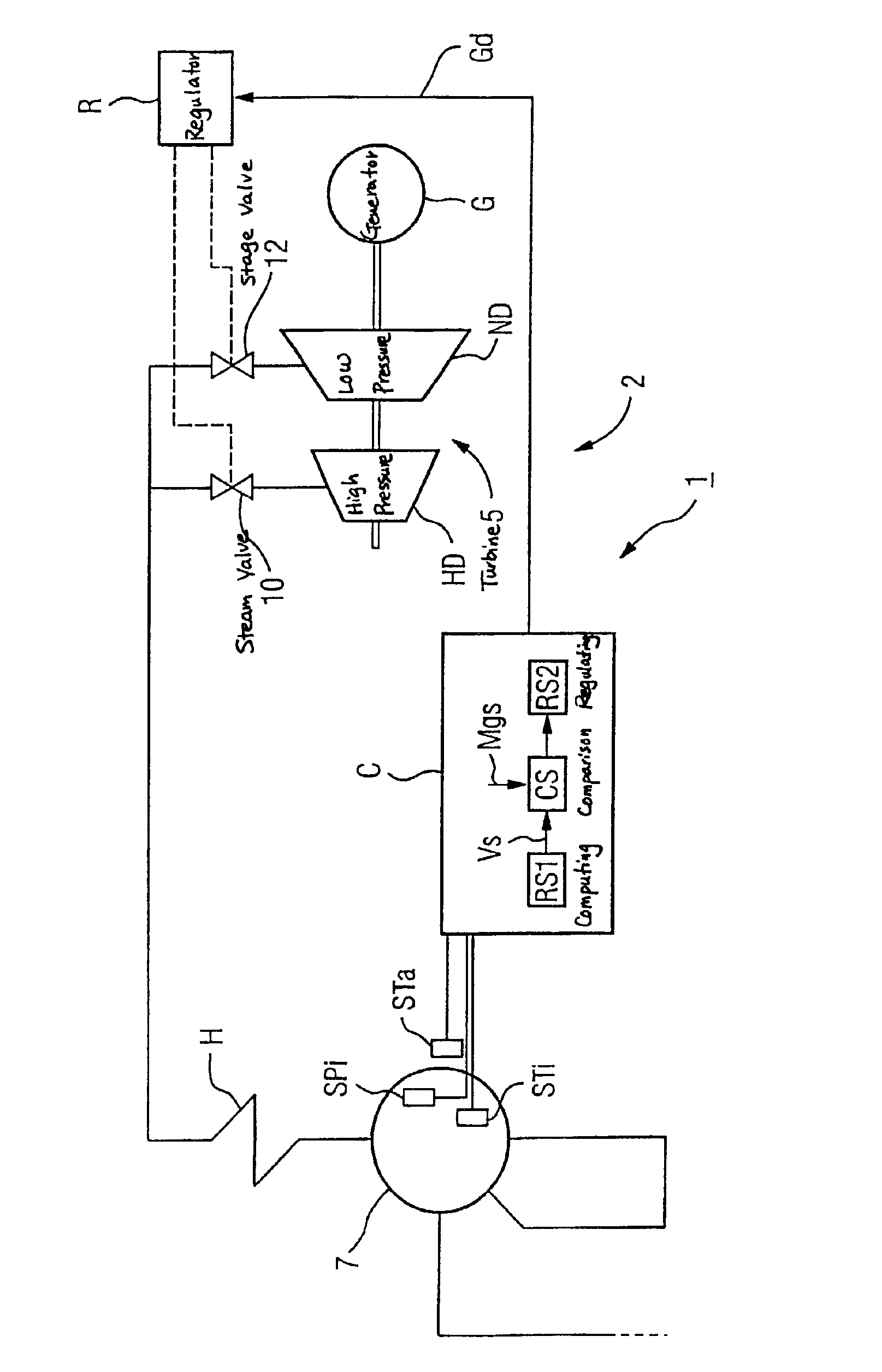
InactiveUS6915635B2Loss in efficiencyImprove efficiencyLiquid degasificationSteam regenerationInternal pressureSteam pressure
It is proposed that, during the operation of a steam turbine of a steam power plant, the internal pressure and also the internal temperature and, in the region outside it, the external temperature be determined in at least one steam-carrying component. As a result of a change in the operating state, in particular in the event of a load change, then, the abovementioned values vary, so that, under some circumstances, the mechanical stresses which in this case act on the steam-carrying component become unacceptably high. Consequently, a spatial temperature distribution and a reference stress of the steam-carrying component are determined from the abovementioned values and compared with a material limit stress. If the reference stress is greater than the material limit stress, a limit steam pressure desired value is determined, and at least one steam valve is set in such a way that the steam pressure on the steam-carrying component corresponds approximately to this limit steam pressure desired value. By the method according to the invention, an automatic reduction in the throttling is obtained, so that the efficiency of the steam power plant, in particular in the part-load range, is increased. A device according to the invention serves for carrying out the method according to the invention.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Stress measurement method
InactiveUS7623223B2Accurately stressHigh measurement accuracyForce measurement by measuring optical property variationWork measurementNon destructiveStress measurement
An object of this invention is to provide stress measurement method that is stress of the measuring object nondestructively in a short period of time.In order to attain this object, the stress measurement apparatus 1 comprises a correlation data storage section 41 that analyzes a correlation between reference stress related data obtained from a Raman spectrum L of an entire predetermined area W1 of a reference specimen W and local stress originated data as being data obtained based on a local stress each of which applies to multiple positions WS1˜WSn respectively in the predetermined area W1 and stores correlation data indicating the correlation, a data obtaining section 42 that obtains measurement stress related data from a Raman spectrum L on an entire measurement area W1′, corresponding to the predetermined area W1, of a measurement specimen WS′, and a calculation section 43 that calculates local stress originated data in the measurement area W1′ based on the correlation data and the measurement stress related data.
Owner:HORIBA LTD
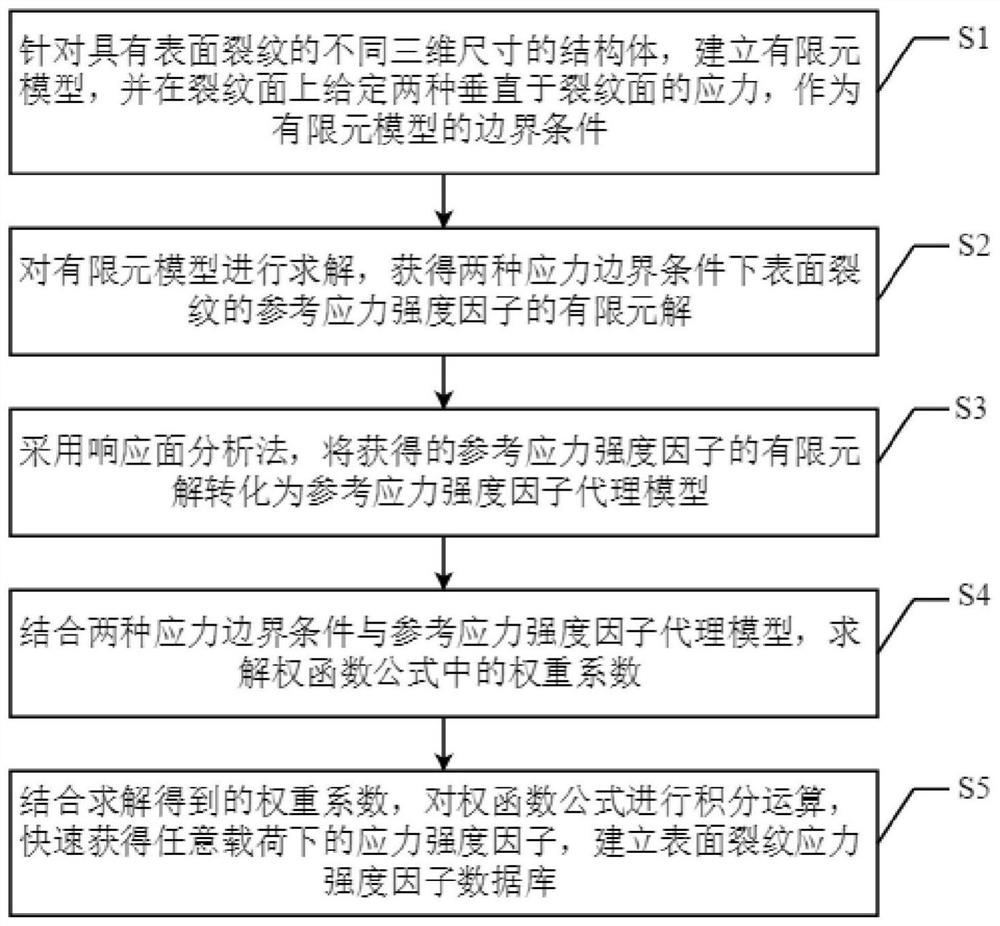
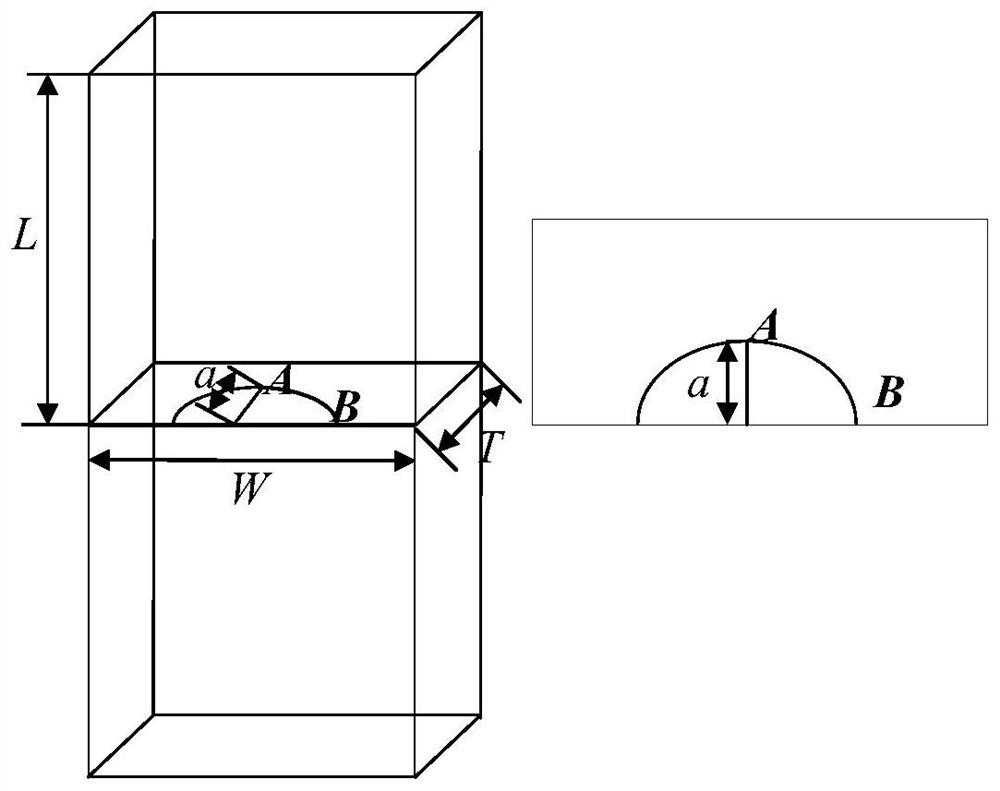
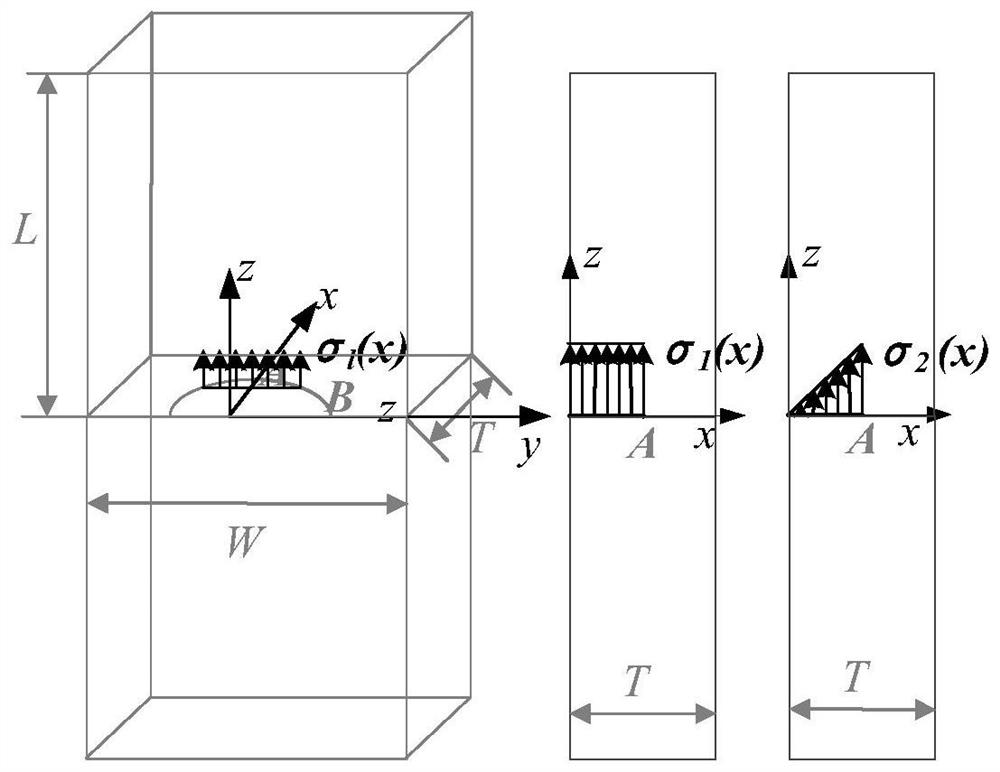
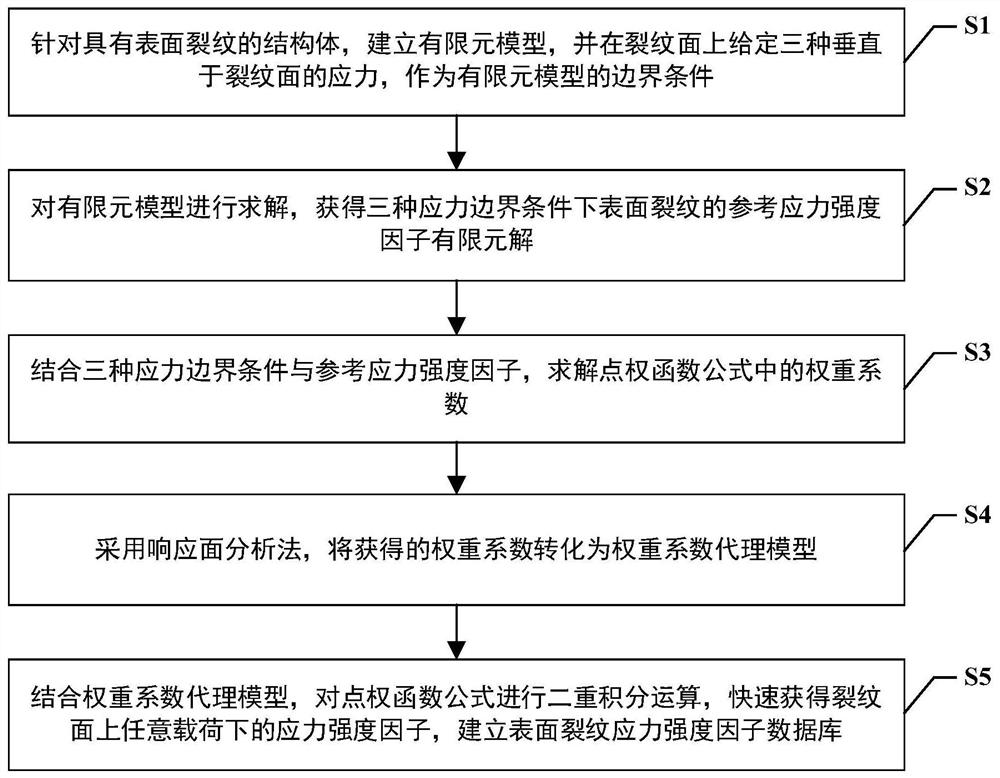
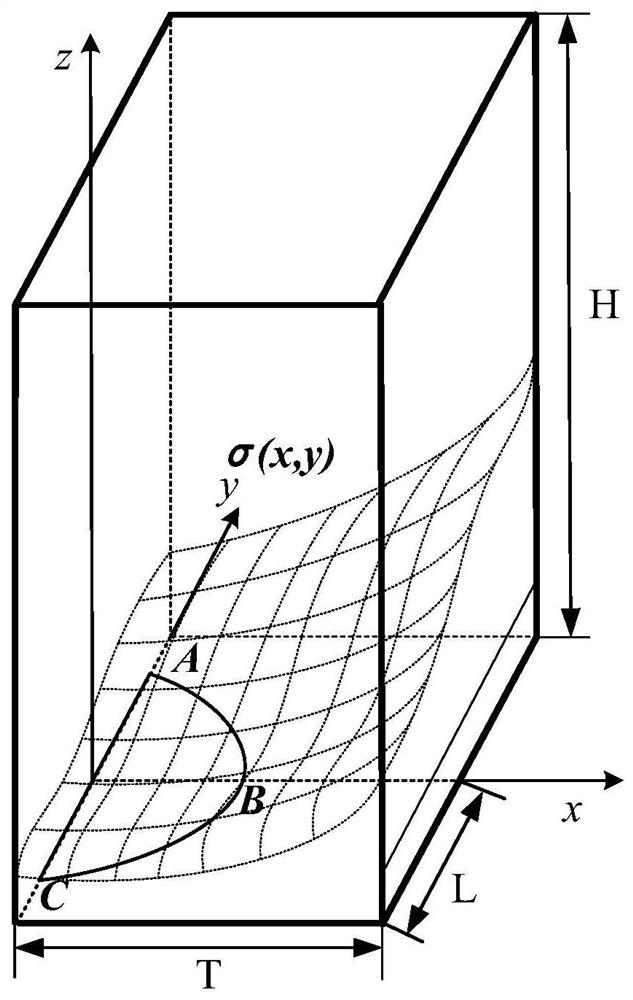
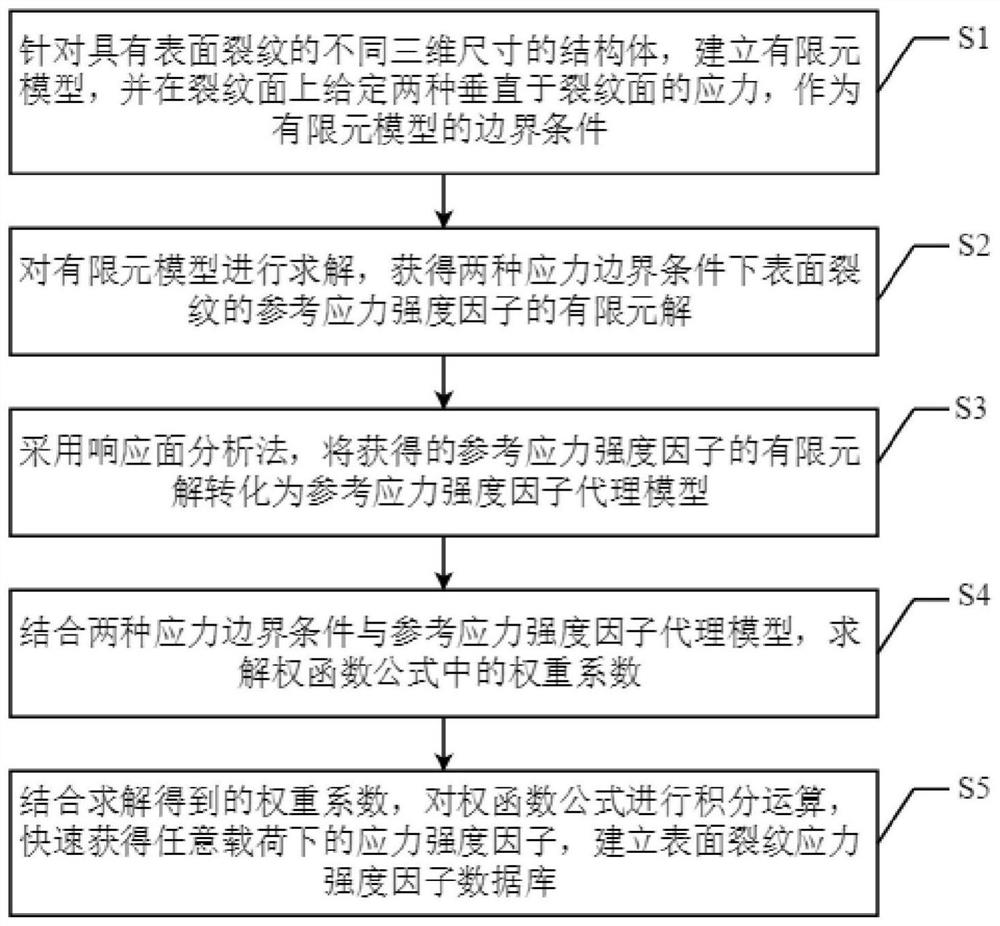
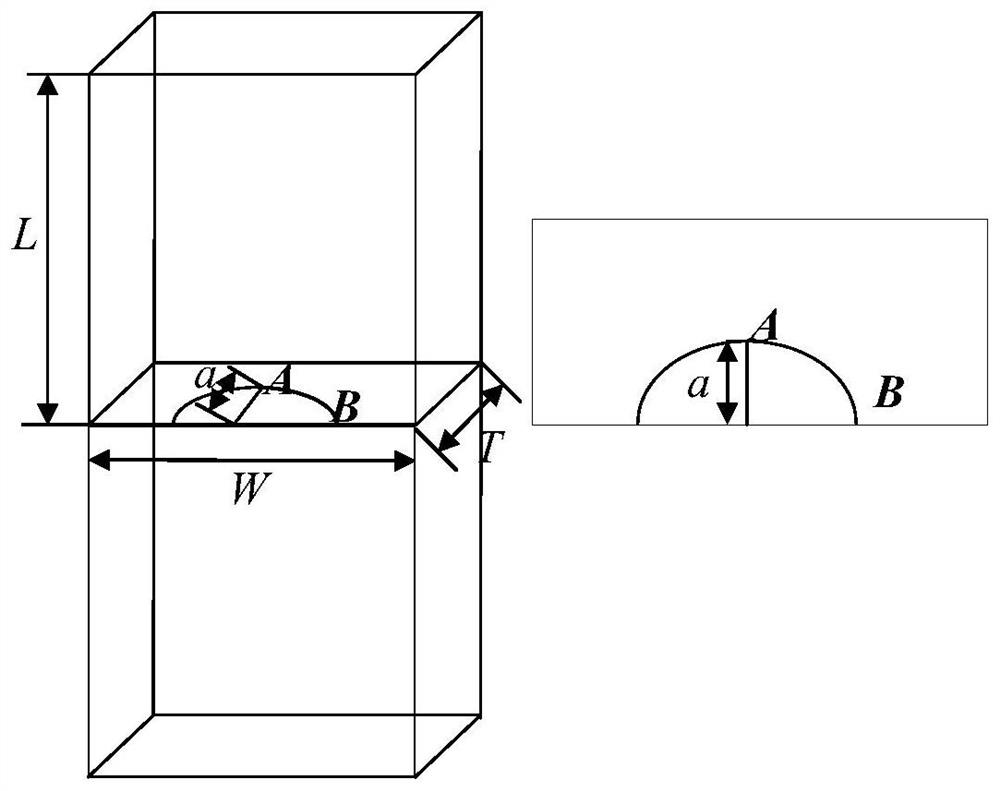
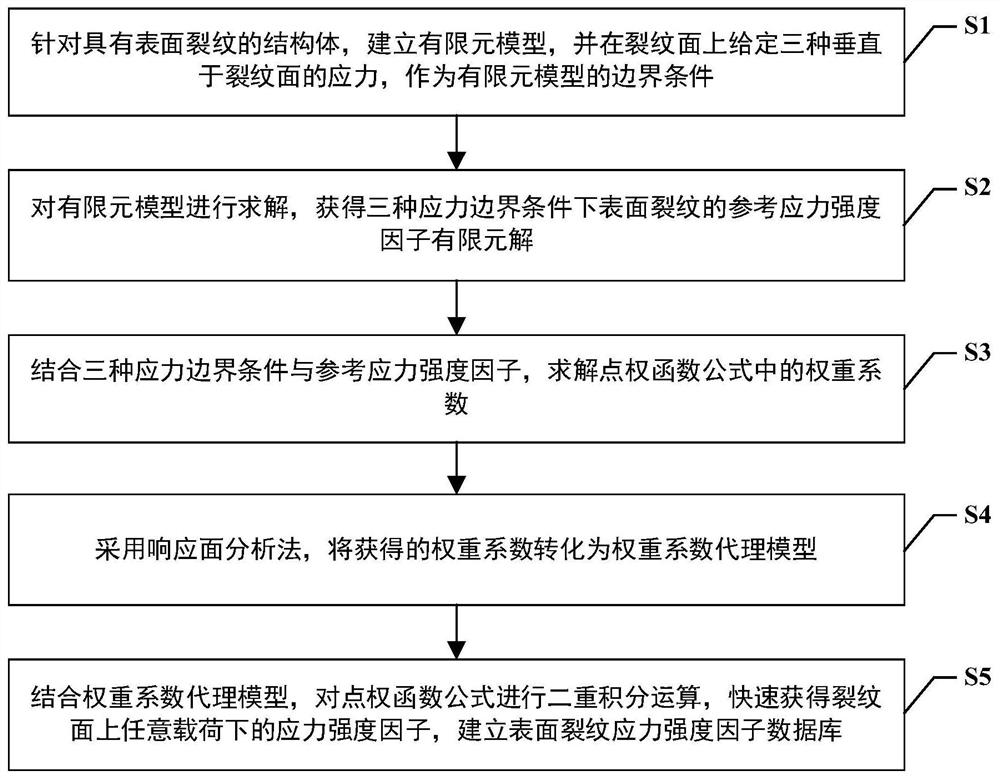
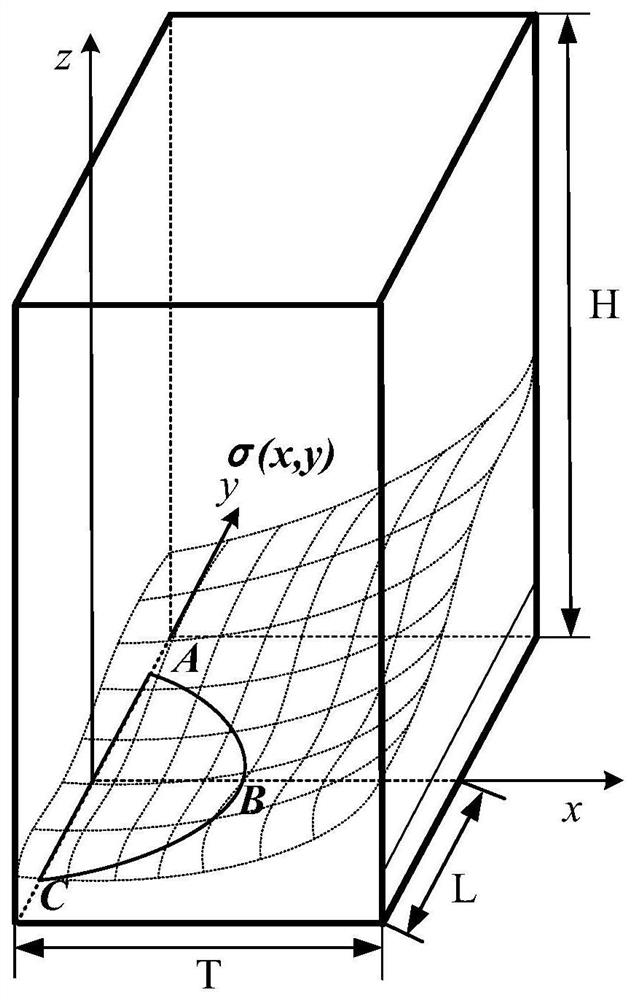
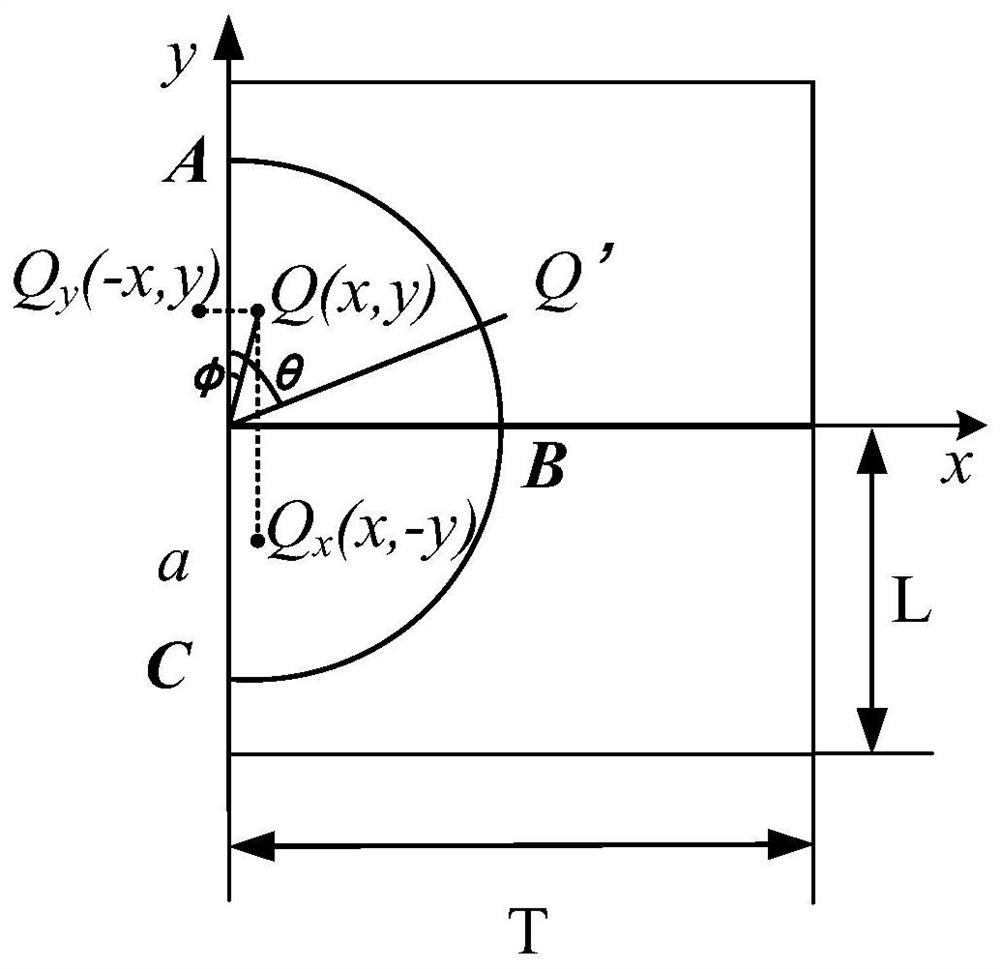
Weight function-based surface crack stress intensity factor database establishment method
ActiveCN111651924AImprove computing efficiencyMake up for limitationsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDamage toleranceEngineering
The invention discloses a weight function-based surface crack stress intensity factor database establishment method, which is used for improving the defect crack propagation calculation efficiency soas to provide a basis for linear elastic fracture mechanical analysis in surface probability damage tolerance evaluation. Specifically, finite element parametric modeling is adopted, a reference stress intensity factor under a given stress gradient is calculated on the basis of a J integral stress intensity factor theory, the calculation precision is not affected by the number of crack tip grids,and the calculation result is accurate; based on a weight function theory, structural bodies with different geometric configurations are established, and the limitation of a stress intensity factor manual is made up by a stress intensity factor efficient calculation method under any stress gradient; compared with a traditional stress intensity factor database, the structure configuration of the surface crack stress intensity factor database based on the weight function method is increased, and the stress intensity factor calculation error of an applicable structure is within 5%.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for separating substrates
ActiveUS20190322564A1Reduce laser powerImprove edge qualityGlass severing apparatusWelding/soldering/cutting articlesEdge strengthEngineering
A method for separating a substrate of a brittle-hard material is provided. The method includes the steps of introducing defects into the substrate at a spacing from one another along a separation line using at least one pulsed laser beam; selecting an average spacing between neighboring defects and a number of laser pulses for generating a respective defect such that a breaking stress (σB) for separating the substrate along the separation line is smaller than a first reference stress (σR1) of the substrate and such that an edge strength σK of the separation edge obtained after separation is greater than a second reference stress (σR2) of the substrate; and separating the substrate after introducing the defects by applying a stress along the separation line.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Method of determining the elastoplastic behavior of components consisting of anisotropic material and use of the method
InactiveUS7050912B2Thermometer detailsThermometers using material expansion/contactionElastic anisotropyCrystalline materials
A method of determining the elastoplastic behavior of components, in particular of gas turbine plants, at high temperatures. First of all, the linear-elastic behavior is determined and the inelastic behavior is taken into account on the basis of the linear-elastic results by using the Neuber rule, the anisotropic characteristics of the components, as occur in particular through the use of single-crystalline materials, are taken into account in a simple manner by using a modified anistropic Neuber rule in the formσ*2=σep2(1+ACαER(Aσep2σ02)n-1)whereA=inelastic anisotropic correction term,A=12[F(Dyy-Dzz)2+G(Dzz-Dxx)2+H(Dxx-Dyy)2+2LDyz2+2MDzx2+2NDxy2] where F, G, H, L, M and N are the Hill constants,C=elastic anisotropic correction term, C=D•E−1•Dσ*=determined linear stress,σep=estimated inelastic stress,D=direction vector of the elastic and inelastic stressesE−1=inverse stiffness matrix,ER=reference stiffness,σ0=reference stress, and σα, n=material constants.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
Judgment method of dual adaptation critical point of expansion direction connection structure DFR (Detail Fatigue Rating)
ActiveCN105574307ASolve the problem of two-way correction critical pointComputationally efficientStructural/machines measurementSpecial data processing applicationsShear stressComputer science
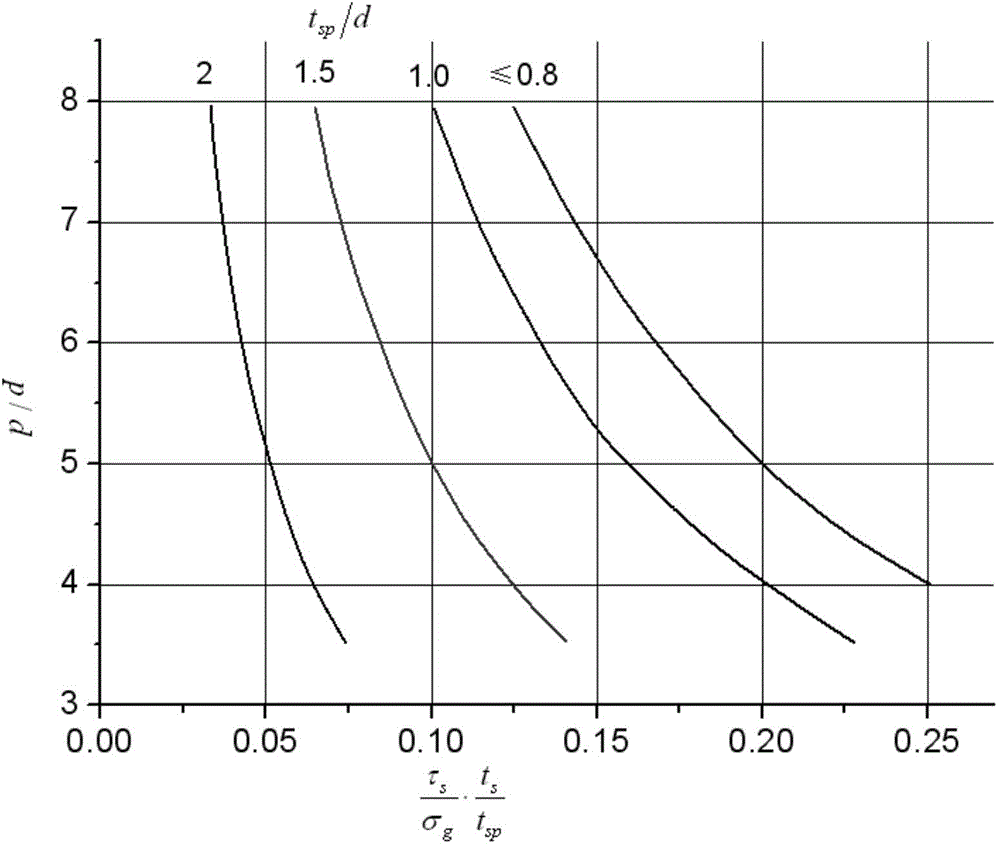
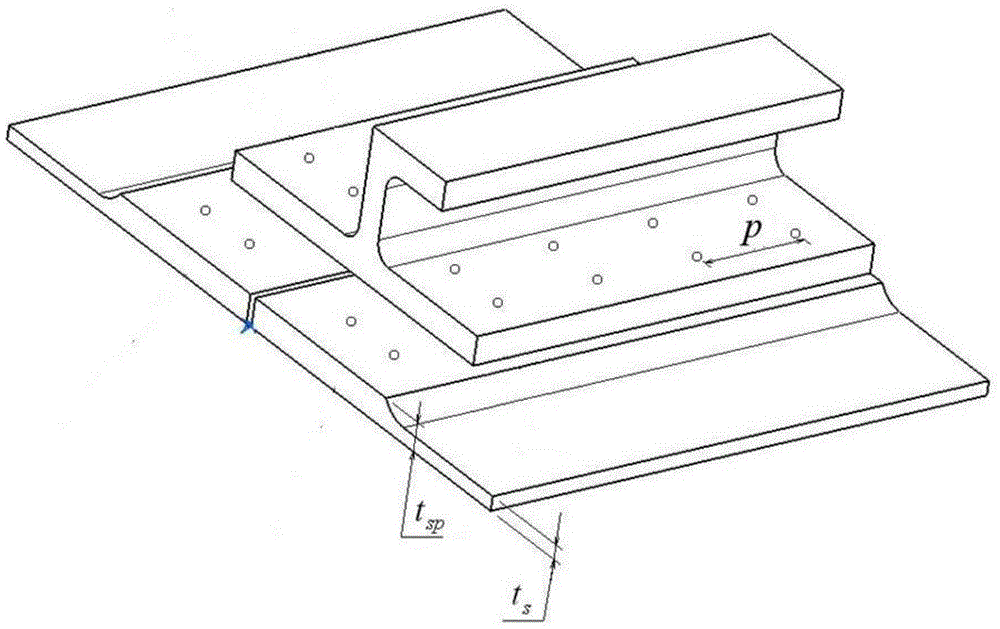
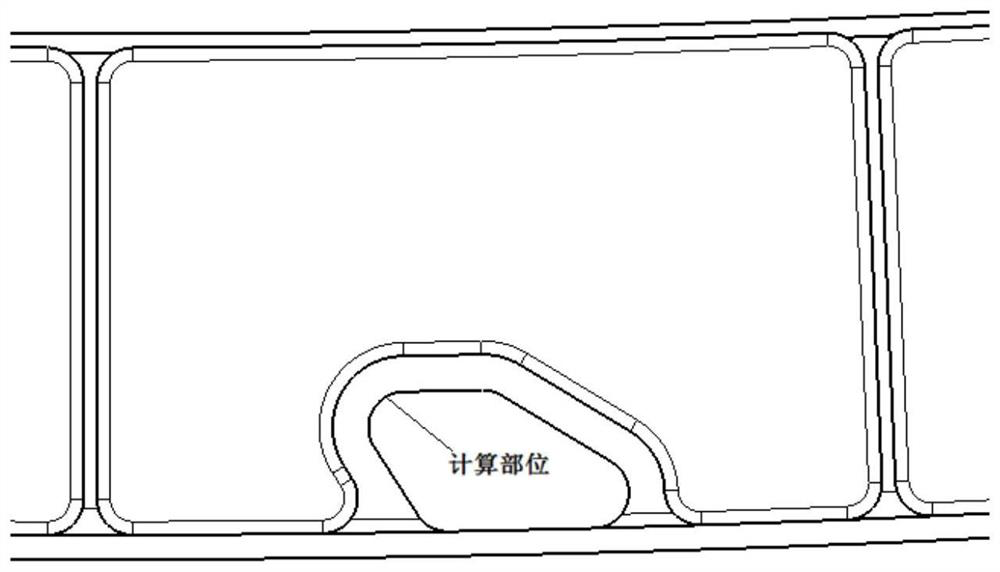
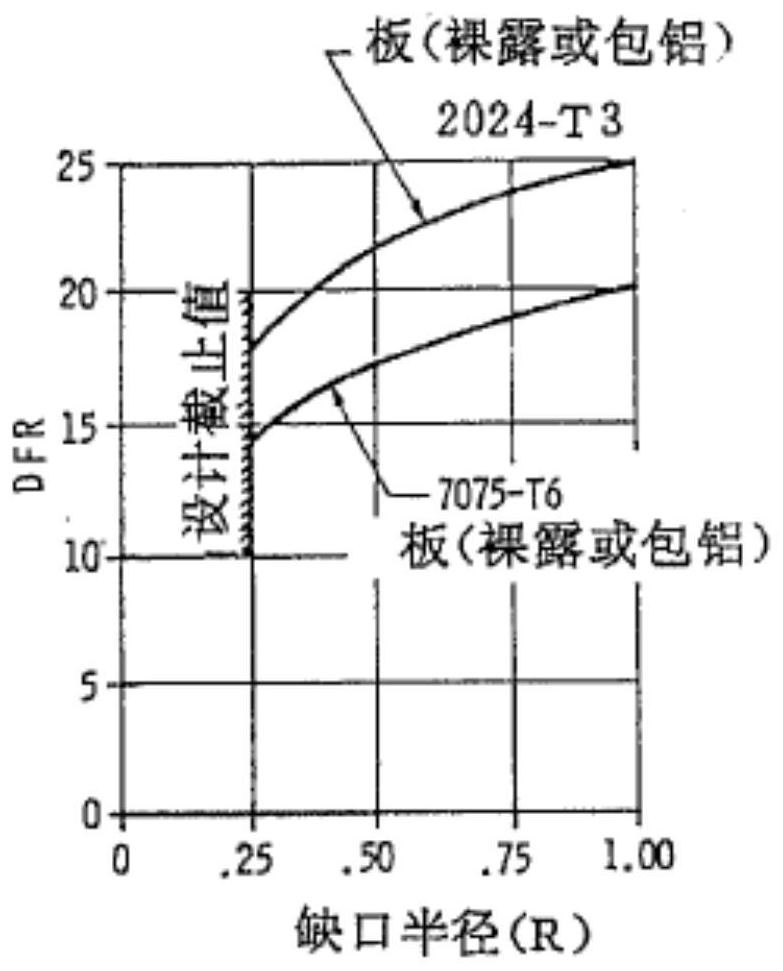
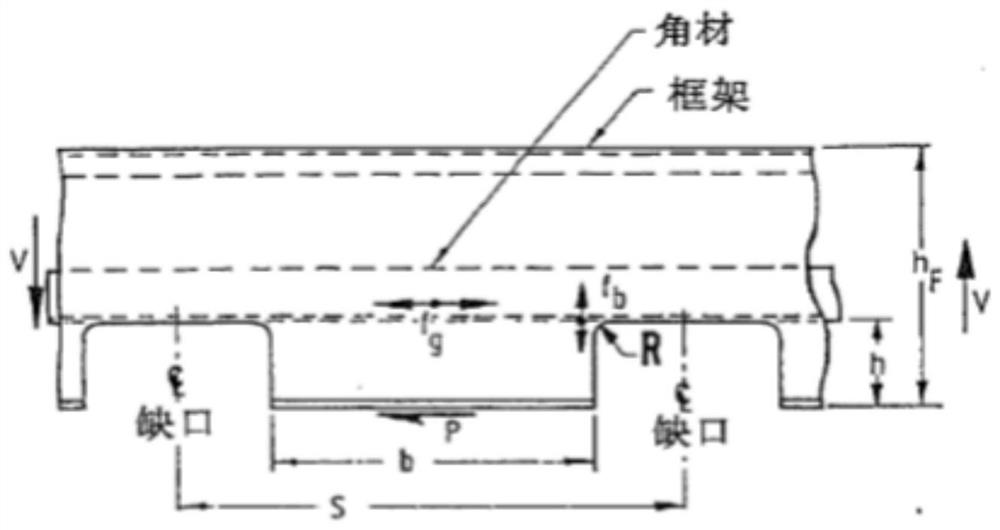
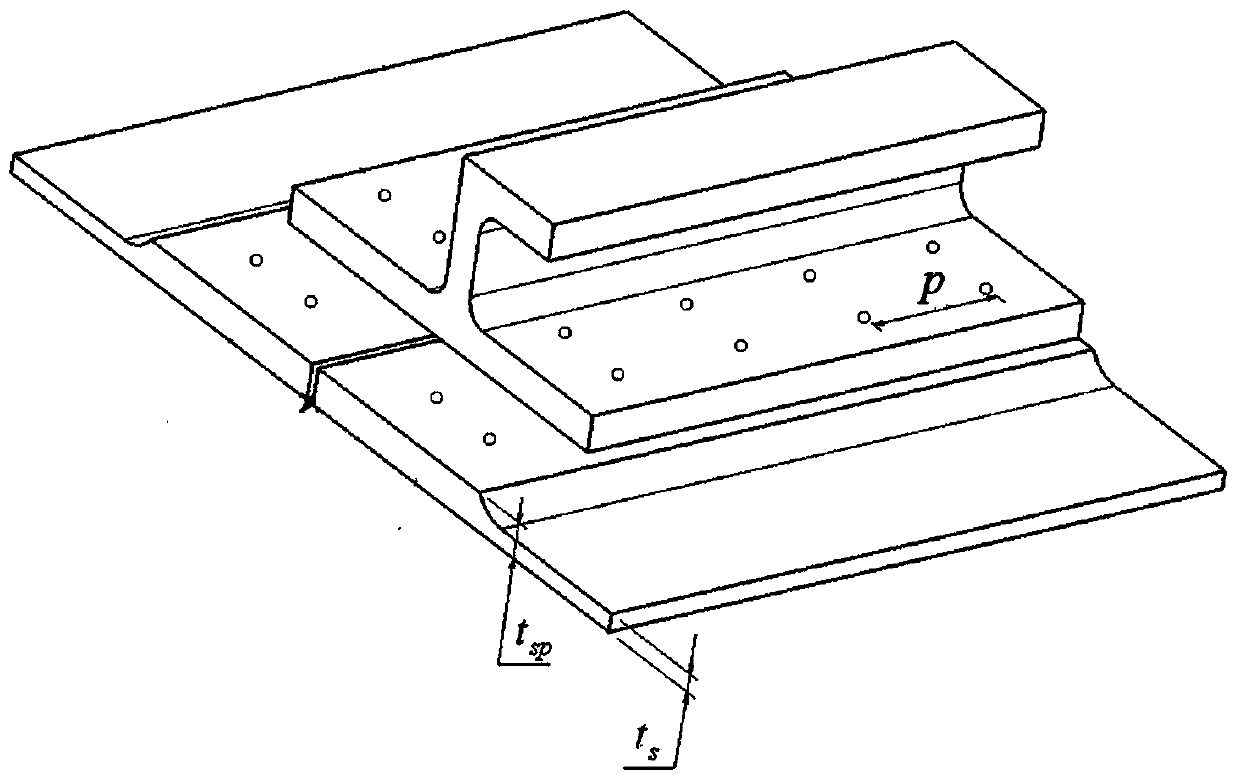
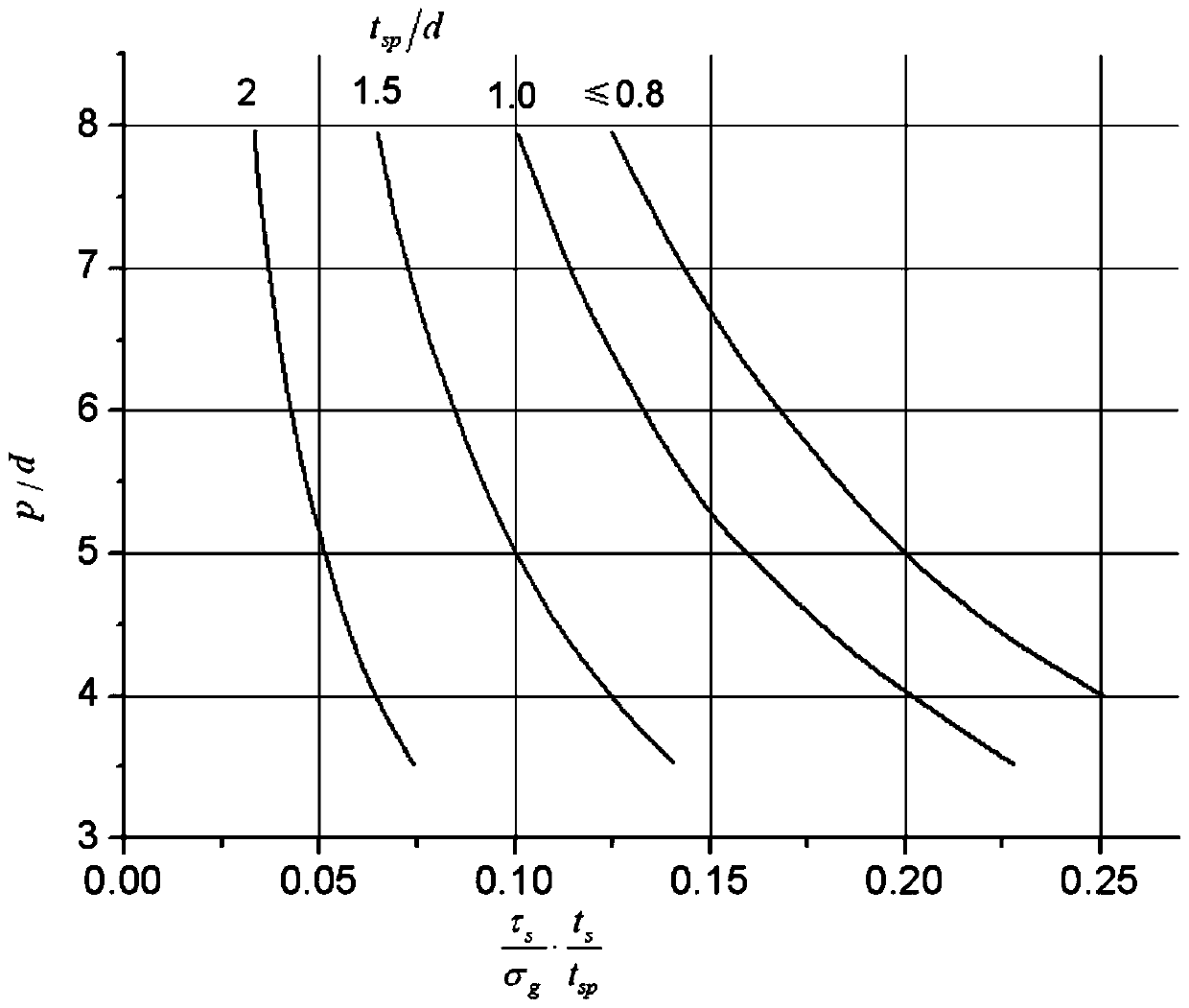
The invention provides a judgment method of a dual adaptation critical point of expansion direction connection structure DFR (Detail Fatigue Rating). The judgment method comprises the following steps: (1) determining an expansion direction connection structure DFR value: obtaining the DFR value according to a formula DFR=DFRbase*A*B*C*C*D*E*Rc; and (2) calculating ([Tau]s / [Delta]g)*(ts / tp): aiming at the specific position of the calculated expansion direction connection structure in an airplane, calculating to obtain the fatigue stress spectra of the position, extracting DFR reference stress [Delta]g, shearing stress [Tau]s in the spectra corresponding to the DFR reference stress [Delta]g, the basic thickness ts of a wallboard and the thickness tsp of the wallboard boss of a connection position, and calculating to obtain the numerical value of the ([Tau]s / [Delta]g)*(ts / tp).
Owner:XIAN AIRCRAFT DESIGN INST OF AVIATION IND OF CHINA
Surface crack strength factor database establishment method based on point weight function method
ActiveCN112989659AThe calculation result is accurateMake up for limitationsDesign optimisation/simulationProbabilistic CADAviationDamage tolerance
The invention discloses a surface crack strength factor database establishment method based on point weight function method, which comprises the following steps of: carrying out integration on stress and weight functions of all points on a surface crack surface, and calculating stress strength factors of the surface crack under a complex stress gradient at a high speed; therefore, providing a basis for linear elastic fracture mechanical analysis in surface probability damage tolerance evaluation. Specifically, finite element parametric modeling is adopted, a cubic structure configuration is established, a reference stress intensity factor under a given stress gradient is calculated based on a J integral stress intensity factor theory, the calculation precision is not influenced by the number of grids at the tip of the crack, and the calculation result is accurate; compared with a general weight function method, the method overcomes the limitation that only one-way change of stress in the crack depth is considered, is suitable for more complex stress conditions, makes up for the limitation of a stress intensity factor manual, provides technical support for probability damage tolerance evaluation of the aero-engine service life limiting piece, and has important engineering significance and actual value.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Accelerated characterization method for long-term creep property of rigid foam
PendingCN113138123AReduce in quantityReduce the impactMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesComputational materials scienceClassical mechanicsStructural engineering
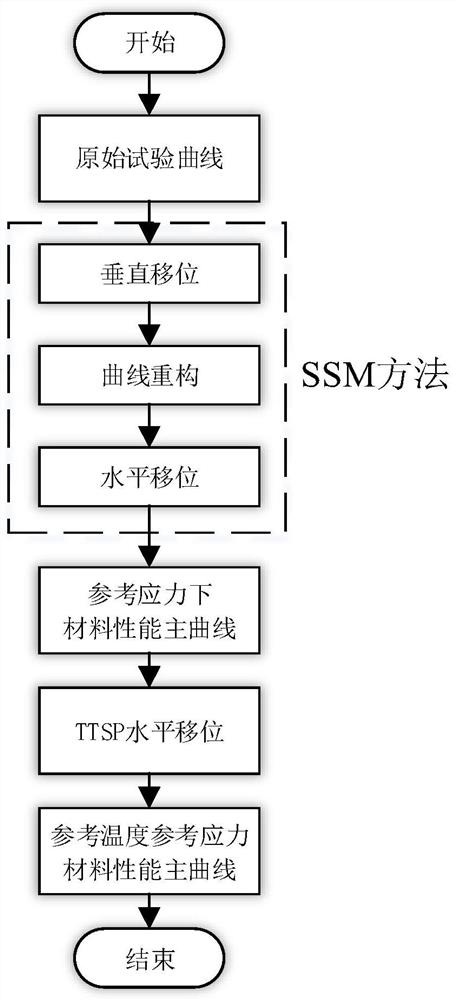
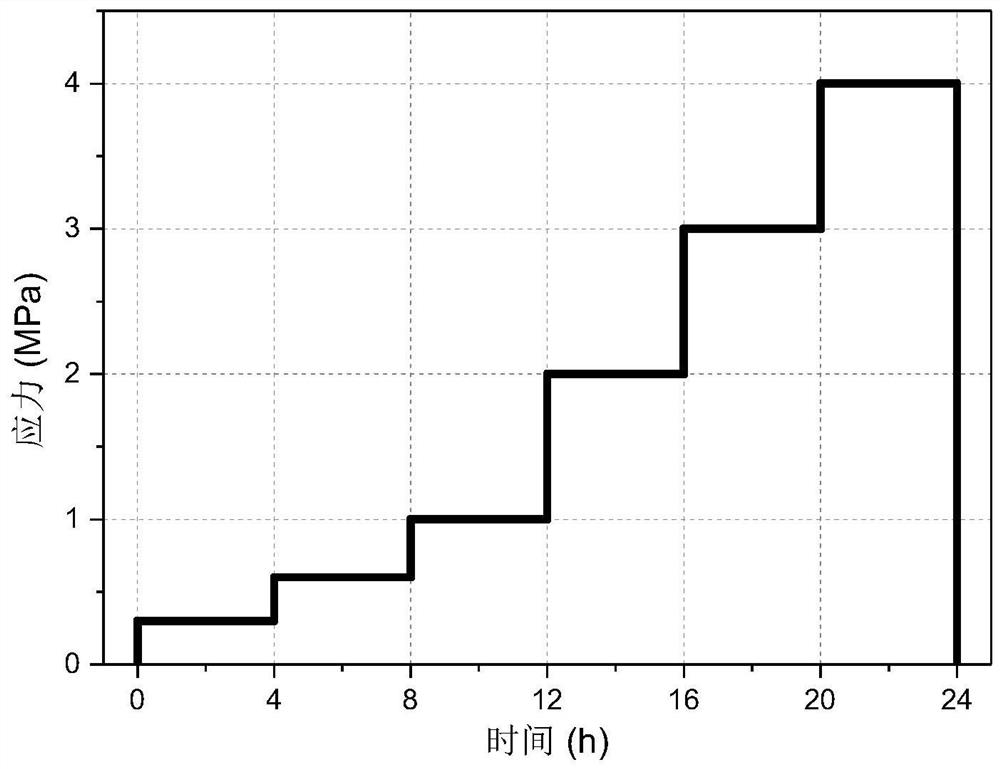
The invention provides an accelerated characterization method for the long-term creep property of rigid foam, which is characterized in that a creep curve of a PMI (polymethacrylimide) material under different temperatures and load conditions is obtained on the basis of step-by-step loading creep tests carried out on the PMI material at four temperatures. A grading equal stress method is combined with a time-temperature equivalence principle to form a grading equal stress-time temperature equivalence method; the creep property main curve of the PMI material is constructed, and the accelerated characterization of the long-term creep property of the PMI material is realized. According to the method, a main curve under reference stress and temperature is constructed in a manner of raising temperature and load and shifting along a logarithmic time axis by applying an equivalence principle in a creep property mechanical test which is originally time-consuming. The time span represented by the main curve can be extended to several or even dozens of orders of magnitude of the test duration, so that the test time is greatly shortened.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Service life based high-temperature container creep fatigue strength design method
The invention discloses a service life based high-temperature container creep fatigue strength design method. The method comprises the steps of 1, performing structure preliminary design; 2 determining load and temperature conditions and the design service life requirement; 3, determining dangerous sections; 4, calculating the equivalent stress and strain range; 5, calculating reference stress; 6, determining whether plastic collapse occurs; 7 determining whether the plastic ratchet occur; 8, determining whether creep damage is important; 9, estimating fatigue damage of each cycle when the creep damage is not important; 10, determining whether the fatigue damage is important; 11, estimating the creep damage when the fatigue damage is not important; 12, estimating damage of each cycle when the creep damage and the fatigue damage are non-ignorable; 13, estimating creep-fatigue total damage; 14, performing result analysis and structural design improvement; 15, completing structural design. According to the method, the foundation is laid for national establishing of creep and fatigue failure mode based high-temperature pressure container design standards and achieving design and manufacture of high-temperature pressure containers according to the service life.
Owner:HEFEI GENERAL MACHINERY RES INST
DFR fatigue calculation method for stringer through hole of transportation aircraft fuselage
ActiveCN112733260AEasy programmingImprove the safety of useGeometric CADSustainable transportationStress ratioShear flow
The invention belongs to the transportation aircraft structure fatigue calculation technology, and relates to DFR fatigue analysis of a transportation aircraft fuselage stringer through hole, which comprises the following steps: step 1, determining the DFR value of the part according to the R angle radius of the fuselage stringer through hole; 2, the system collects the shear flow difference between the front skin and the rear skin of the frame, and determines the reference stress sigma ref of a calculation part by combining the height of stringer passing holes, the distance between stringers, the width of angle parts, the thickness of a frame web and the height of the frame on the basis of a full-aircraft finite element stress calculation result; 3, determining the maximum stress, the minimum stress and the stress ratio in the load spectrum; 4, calculating a ground-air-ground damage ratio lambda; step 5, calculating an equivalent ground-air-ground cycle number nd; 6, calculating the allowable stress [sigma max] of the ground-air-ground cycle; and 7, calculating the fatigue margin f.
Owner:XIAN AIRCRAFT DESIGN INST OF AVIATION IND OF CHINA
Manipulation methods for magnetic liquids
ActiveCN104914889BPitfalls of the method of avoiding cohesive progressFluid pressure control using electric meansDynamic balanceElectronic switch
The invention discloses a magnetic liquid manipulating method. Due to pressure latency, offset exists between pressure data which are used for reference and are processed by an FPGA chip and real pressure derived data. An ARM chip compares the reference pressure data with the real pressure derived data to acquire response data. The reference pressure data are corrected. Pressure data given by a pressure piston are changed. The drive performance of a magnetic liquid micro-displacement drive is improved. The ARM chip applies a manipulating command on a dynamic balance valve of a second processing unit according to reference stress derived data to change the opening of an electronic switch. The gas incoming speed of a pressure piston is changed. Pressure applied by the pressure piston on the magnetic liquid micro-displacement drive is changed. According to the invention, the defect that a method used for manipulating the cohesion progress of magnetic liquid cementing is unavailable in the prior art is avoided.
Owner:SUZHOU JUHUIBANG NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
A Judgment Method for the Critical Point of Dfr Two-way Modification of Spanning Connection Structure
ActiveCN105574307BSolve the problem of two-way correction critical pointComputationally efficientStructural/machines measurementSpecial data processing applicationsShear stressComputer science
The invention provides a judgment method of a dual adaptation critical point of expansion direction connection structure DFR (Detail Fatigue Rating). The judgment method comprises the following steps: (1) determining an expansion direction connection structure DFR value: obtaining the DFR value according to a formula DFR=DFRbase*A*B*C*C*D*E*Rc; and (2) calculating ([Tau]s / [Delta]g)*(ts / tp): aiming at the specific position of the calculated expansion direction connection structure in an airplane, calculating to obtain the fatigue stress spectra of the position, extracting DFR reference stress [Delta]g, shearing stress [Tau]s in the spectra corresponding to the DFR reference stress [Delta]g, the basic thickness ts of a wallboard and the thickness tsp of the wallboard boss of a connection position, and calculating to obtain the numerical value of the ([Tau]s / [Delta]g)*(ts / tp).
Owner:XIAN AIRCRAFT DESIGN INST OF AVIATION IND OF CHINA
A film shape determination method for planar film antennas based on cable tension uncertainty
ActiveCN106886628BAchieve shape optimizationWide range of researchDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsStress distributionEngineering
The invention discloses a cable tension uncertainty-based method for determining thin film shapes of planar thin film antennas. The method comprises the following steps of: considering a thin film boundary of a planar thin film antenna as a spline, and establishing a preliminary model of a planar tensioning cable film which takes the spline as a boundary by applying ANSYS; applying a certain tensioning force on a suspension cable, and carrying out static analysis to obtain stress distribution of the cable and the film; defining a deviation range of cable tension, and finding a group of corresponding cable tension when the deviation between a practical stress of a cable-film structure and a reference stress is maximum; searching a next optimal curve control point position through minimizing a stress deviation value output in the step 3); and updating the thin film shape through the optimized curve control point until the relative change amount of the cable-film structure satisfies the accuracy requirement of a convergence criterion, so as to obtain an optimal thin film shape. According to the method, the limits of specific boundary shapes are broken through, and robustness optimization is carried out on the structure, so that the thin film shape is determined more correctly and the service life of materials is prolonged at the same time.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
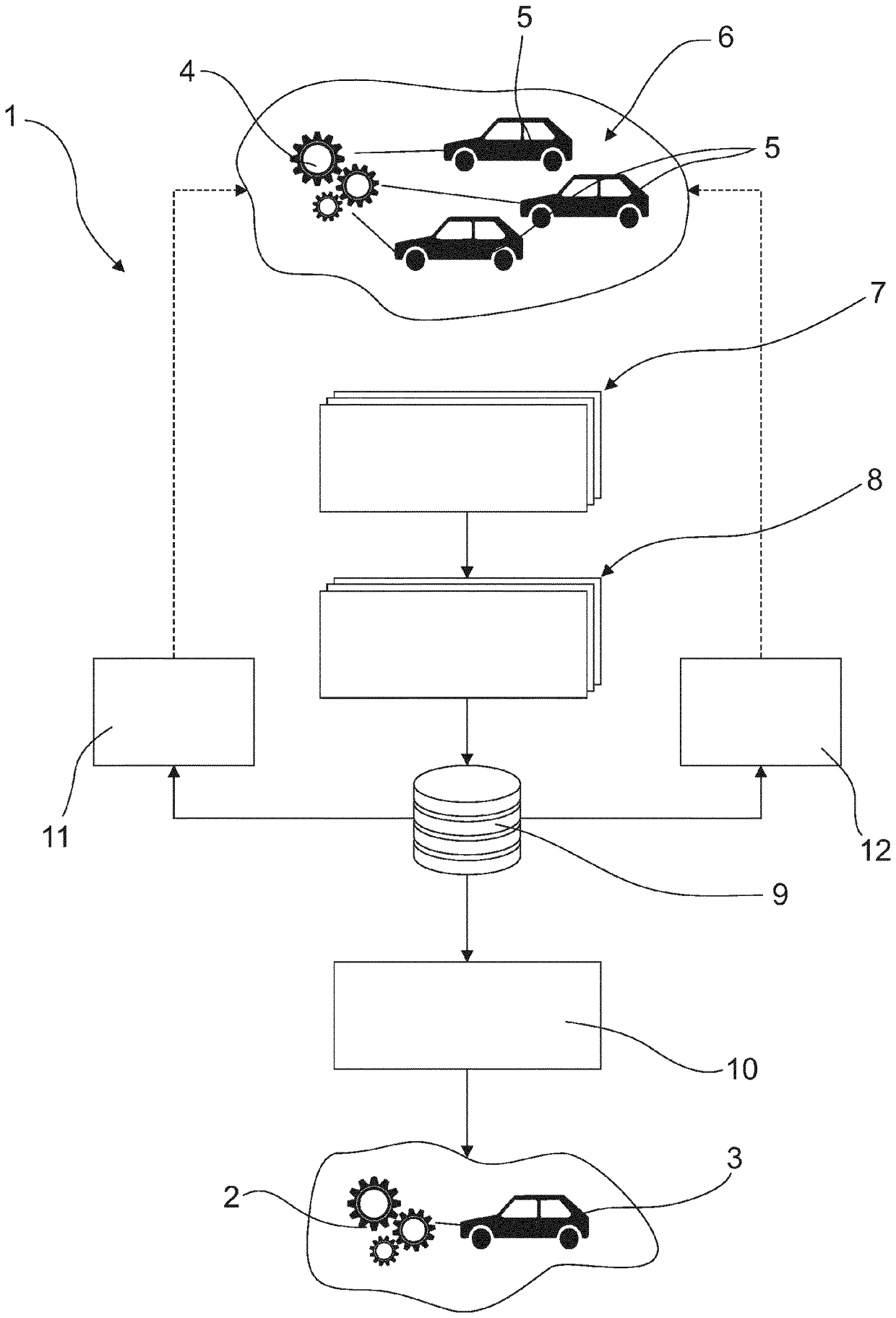
Method for designing and dimensioning a new part of a motor vehicle
PendingCN108604255ALow costSave resourcesGeometric CADTotal factory controlAutomotive engineeringReference stress
The invention relates to a method (1) for designing and dimensioning a new part (2) of a motor vehicle (3). All of the motor vehicles (5) of a motor vehicle fleet (6) have a reference part (4) with anidentical structure, and the reference parts (4) and the new part (2) are of the same component type. Load spectra and damage levels of the reference parts of all the motor vehicles (5) of the motorvehicle fleet (6) are continuously ascertained on the basis of sensor and vehicle state information available in each motor vehicle (5) using specified algorithms. The load spectra and damage levels are stored in a central database (9). A reference stress on a component of the component type is ascertained regularly on the basis of the load spectra and damage levels provided in the central database (9) at a specific point in time for the reference parts (4) of all of the motor vehicles (5) of the vehicle fleet (6). The new part (2) is designed and dimensioned while taking into consideration the reference stress. The reference stress is less than the maximally occurring stress on all of the reference parts (4).
Owner:康佩迪有限责任公司
Detect edge cracks
A method and system for detecting edge cracks of a unit of a sheet metal product is provided. The method includes: calculating a first stress associated with a forming process using a first die; calculating a second stress associated with a finishing process using a second die; combining the first stress and the second stress to formulate the total stresses; simulate sheet metal products to generate baseline stresses; and compare total stresses to baseline stresses to determine whether elements predictively contain edge cracks.
Owner:MAGNA INTERNATIONAL INC
A method for establishing the database of surface crack stress intensity factors based on weight function
ActiveCN111651924BImprove computing efficiencyMake up for limitationsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDamage toleranceEngineering
The invention discloses a method for establishing a database of surface crack stress intensity factors based on a weight function, which is used to improve the calculation efficiency of defect crack expansion, thereby providing a basis for linear elastic fracture mechanics analysis in surface probability damage tolerance evaluation. Specifically, finite element parametric modeling is used to calculate the reference stress intensity factor under a given stress gradient based on the J-integral stress intensity factor theory. The calculation accuracy is not affected by the number of crack tip grids, and the calculation results are accurate; based on the weight function theory, the establishment The efficient calculation method of stress intensity factors under arbitrary stress gradients for structures with different geometric configurations makes up for the limitations of the stress intensity factor manual; compared with the traditional stress intensity factor database, the weight function method based on the present invention The structure configuration of the surface crack stress intensity factor database has increased, and the calculation error of the stress intensity factor of the applicable structure is within 5%.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
A Method for Predicting the Remaining Fatigue Life of Concrete Members
The invention discloses a method for predicting the remaining fatigue life of concrete components, which is a simpler and more convenient way to effectively predict the fatigue life of concrete under variable amplitude fatigue loads. The basic concept is that the damage condition of concrete when loaded for ni cycles under the stress level Si is equivalent to that when loaded for n1 cycles under the reference stress level S1. For any i, the number of cycles nit of concrete loading under the reference stress level S1 can be obtained when it is equivalent to loading the concrete damage of ni cycles under the stress level Si.
Owner:科利尔环保科技有限责任公司
A Method of Establishing Surface Crack Intensity Factor Database Based on Point Weight Function Method
ActiveCN112989659BThe calculation result is accurateMake up for limitationsDesign optimisation/simulationProbabilistic CADDamage toleranceEngineering
The invention discloses a method for establishing a database of surface crack intensity factors based on point weight functions. By integrating the stress and weight functions of all points on the surface crack surface, the stress intensity factors of surface cracks under complex stress gradients are calculated at high speed, thereby Provides the basis for linear elastic fracture mechanics analysis in surface probabilistic damage tolerance assessment. Specifically, finite element parametric modeling is used to establish a cubic structure configuration. Based on the J-integral stress intensity factor theory, the reference stress intensity factor under a given stress gradient is calculated. The calculation accuracy is not affected by the number of crack tip grids. The calculation results Accurate; compared with the general weight function method, the point weight function method overcomes the limitation of only considering the unidirectional change of stress at the crack depth, is suitable for more complex stress situations, and makes up for the limitations of the stress intensity factor manual. The probabilistic damage tolerance assessment of life parts provides technical support, which has important engineering significance and practical value.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
A safety assessment method for high-temperature pressure pipelines with crack-like defects
The invention discloses a safety assessment method for a high-temperature pressure pipeline with crack type defects. The safety assessment method for the high-temperature pressure pipeline with crack type defects includes steps that 1, gathering data; 2, definitely evaluating the life span; 3, determining load and temperature; 4, analyzing elastic stress; 5, characterizing crack; 6, assessing initial crack leakage and rupture; 7, judging whether the initial crack is safe; 8, judging whether the initial crack is free of creep analysis; 9, calculating reference stress and stress intensity factors; 10, calculating creep rupture life based on the initial crack size; 11, judging whether the creep rupture life is long enough; 12, judging whether the creep is steady creep; 13, calculating steady state creep crack growth; 14, calculating unsteady state creep crack growth; 15, calculating the creep rupture life based on the current crack size; 16, judging whether the current creep rupture life is long enough; 17, assessing the current crack leakage and rupture; 18, refining and evaluating; 19, judging whether the assessed object is safe. The safety assessment method for the high-temperature pressure pipeline with crack type defects can be used for assessing the safety of the high-temperature pressure pipeline with crack type defects under creep load effect.
Owner:HEFEI GENERAL MACHINERY RES INST
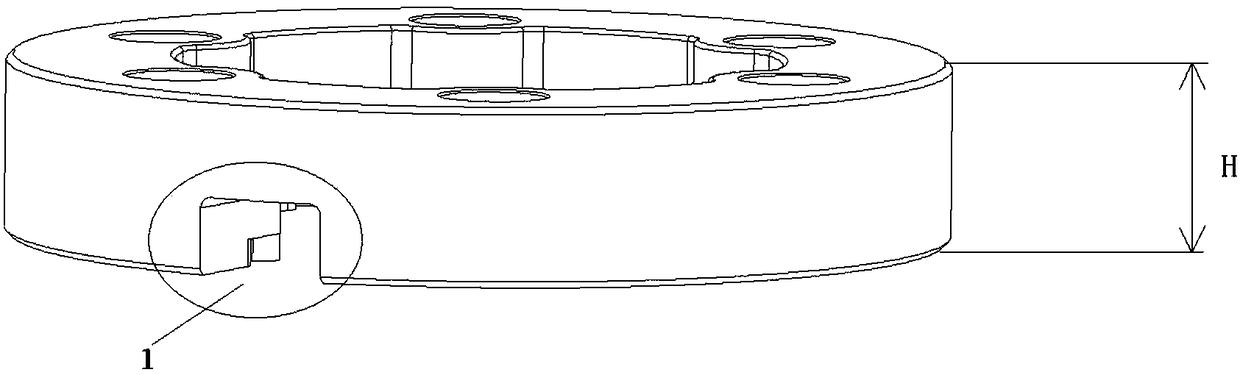
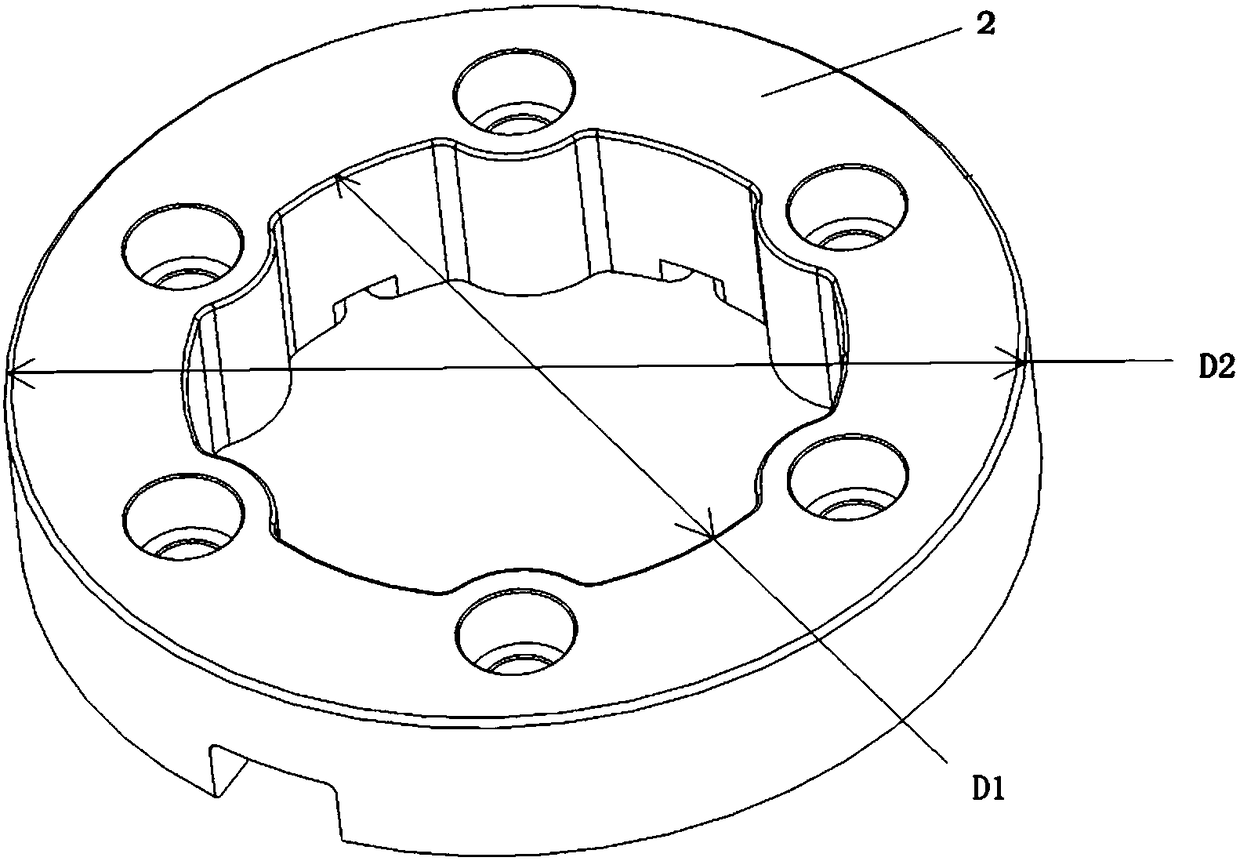
Protective flange plate structure parameter extraction method
InactiveCN108460201ASatisfy the protectionReduce weightGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringDesign methods
The invention discloses a protective flange plate structure parameter extraction method, and belongs to the technical field of flange plate structure design. The method comprises the specific implementation steps of firstly determining influence factors, influencing a stress value, of a flange plate in a pressure-bearing process and a mutual relation among the influence factors; secondly determining a reference bearing weight and a corresponding reference stress function; thirdly determining a reference stress range meeting a condition; and finally according to the reference stress range, determining flange plate inner diameter and thickness meeting the requirements. Through a mutual relation of a flange plate bearing weight, material yield strength and the flange plate inner diameter andthickness, a scientific design method is provided for determining the flange plate inner diameter and thickness; the conformal protective flange plate meets protective performance required for protecting a wellhead radio-frequency identification electronic tag reader; the weight can be reduced; and field application and popularization are facilitated.
Owner:NO 719 RES INST CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com