Patents
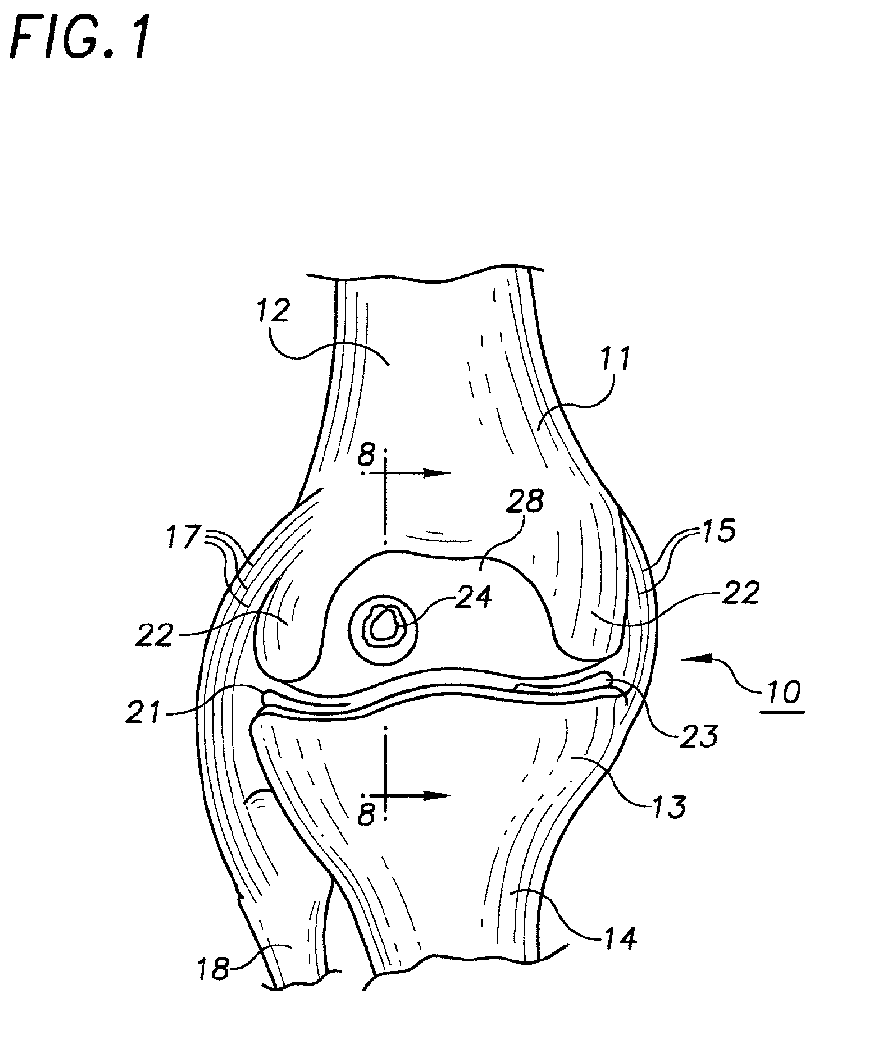
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
56 results about "Recipient site" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Particulate acellular tissue matrix
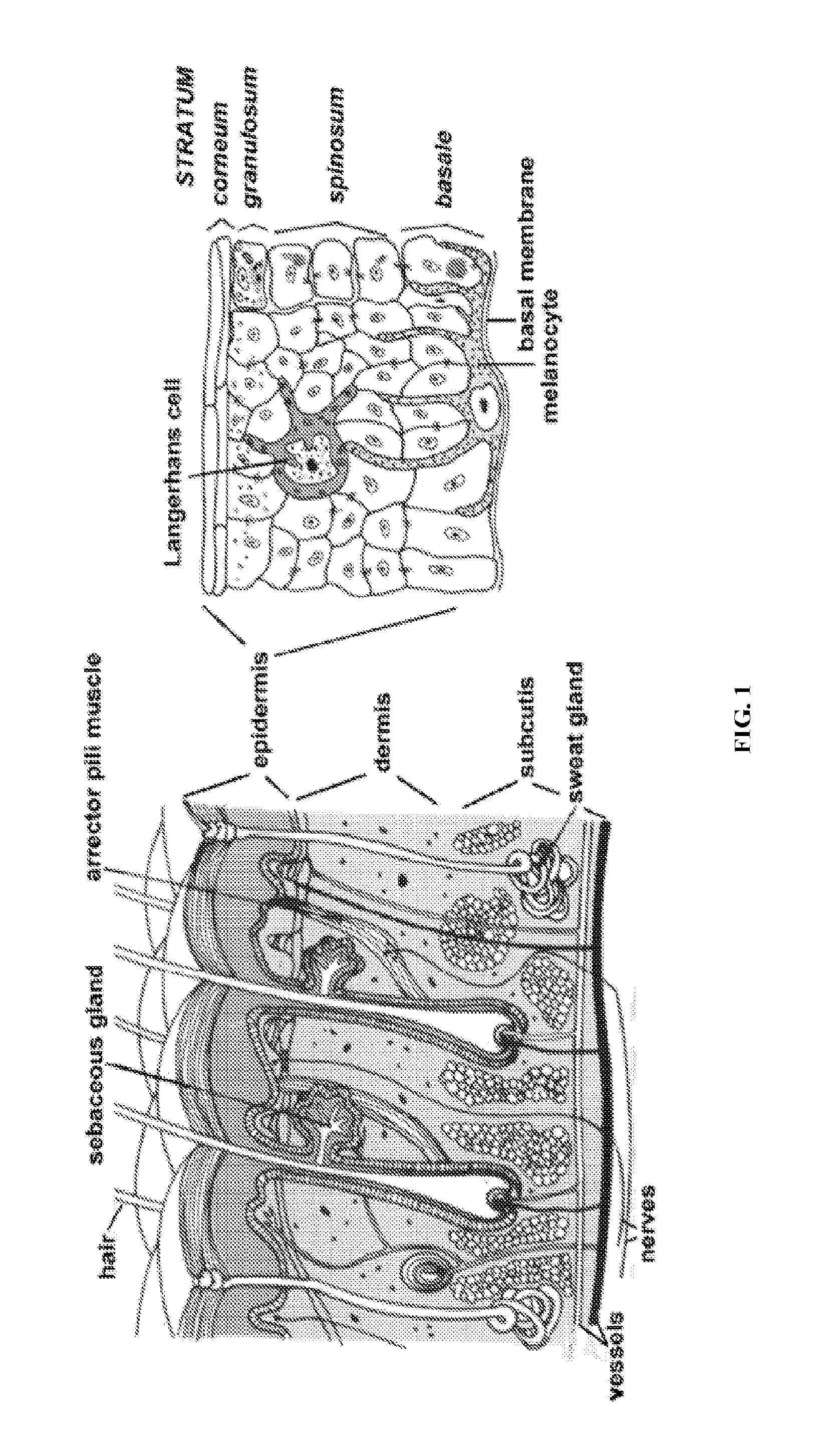
A method of processing an acellular tissue matrix to give a particulate acellular tissue matrix includes: cutting sheets of dry acellular tissue matrix into strips; cryofracturing the dry acellular tissue matrix strips at cryogenic temperatures; separating the resulting particles by size at cryogenic temperatures; and freeze drying the fraction of particles desired size to remove any moisture that may have been absorbed to give a dry particulate acellular tissue matrix. Rehydration of the dry particulate acellular tissue matrix may take place just prior to use. The particulate acellular tissue may be applied to a recipient site, by way of injection, spraying, layering, packing, in-casing or combinations thereof. The particulate acellular tissue may further include growth and stimulating agents selected from epidermal growth factor, fibroblast growth factor, nerve growth factor, keratinocyte growth factor, platelet derived growth factor, vasoactive intestinal peptide, stem cell factor, bone morphogetic proteins, chondrocyte growth factor and combinations thereof. Other pharmaceutically active compounds may be combined with the rehydrated particulate material including: analgesic drugs; hemostatic drugs; antibiotic drugs; local anesthetics and the like to enhance the acceptance of the implanted particulate material. The particulate material product may also be combined with stem cells selected from mesenchymal stem cells, epidermal stem cells, cartilage stem cells, hematopoietic stem cells and combinations thereof.
Owner:LIFECELL
Method and instrumentation for the preparation and transplantation of osteochondral allografts
InactiveUS20070093896A1Reduce the amount requiredLess likely to be rejected by a recipientSuture equipmentsBone implantDonor boneChondral defect
Provided are procedures and instruments for preparing and transplanting osteochondral allograft plugs to a host bone to repair an articular cartilage defect. An allograft bone plug having a cartilage plate and cancellous bone tissue attached thereto is removed from a donor bone. The allograft plug is further shaped by removing or cutting away cancellous bone tissue to form a cancellous stalk extending from the cartilage plate. The formed cancellous stalk can have any suitable shape including cylindrical, conical, and rectilnear. At the recipient site of the host bone, a cutout is formed corresponding in shape to the allograft plug. The allograft plug is inserted into the cutout such that the cancellous stalk is retained in the host bone and the cartilage plate aligns with the condyle surface of the host bone. Aspects of the invention may also be applicable to preparing and transplanting osteochondral autograft plugs.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Skin grafting devices and methods
The present invention provides skin grafting and devices that comprise a systematic approach to the process of skin grafting, i.e., harvesting, post-excision processing and application of donor skin and pre and post-graft treatment of the recipient site.
Owner:KCI LICENSING INC
Method and apparatus for tissue grafting
ActiveUS20120041430A1Heal fastPromote healingIncision instrumentsSurgical needlesTissue GraftingAnatomy
Exemplary embodiments of apparatus and method for harvesting small portions of tissue (“micrografts”) to form grafts can be provided. For example, a hollow tube can be inserted into tissue at a donor site, where a distal end of the hollow tube can have two or more points or extensions to facilitate separation of the micrografts from the surrounding tissue. The exemplary apparatus can be provided that includes a plurality of such tubes for simultaneous harvesting of a plurality of micrografts. The harvested micrografts can have a small dimension, e.g., less than about 1 mm, or less than about 0.3 mm, which can promote healing of the donor site and / or viability of the harvested tissue. The micrografts can be approximately cylindrical or strip-shaped, and can be placed in a biocompatible matrix to form a graft or directly into tissue at the recipient site. Such exemplary micrografts can be obtained from skin or other types of tissue, e.g., various internal organs.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Retrograde cutting instrument
ActiveUS20080306483A1Reduced intraarticular bone fragmentationMinimal incisionSurgeryLigamentsEngineeringMinimal incision
An instrument for retrograde cutting of sockets or tunnels in bone for arthroscopic tenodesis. A retrograde cutter is used to form a recipient site socket from the inside out, i.e., using a retrograde technique, with minimal incisions of distal cortices and reduced intraarticular bone fragmentation of tunnel rims. The retrograde cutter is provided with a cutting blade that is configured to engage the shaft of the instrument and to lock onto the shaft.
Owner:ARTHREX
Retrograde cutting instrument
An instrument for retrograde cutting of sockets or tunnels in bone for arthroscopic tenodesis. A retrograde cutter is used to form a recipient site socket from the inside out, i.e., using a retrograde technique, with minimal incisions of distal cortices and reduced intraarticular bone fragmentation of tunnel rims. The retrograde cutter is provided with a cutting blade that is configured to engage the shaft of the instrument and to lock onto the shaft.
Owner:ARTHREX
Method and apparatus for tissue grafting and copying
ActiveUS9060803B2Heal fastPromote healingSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsTissue GraftingCopying
Exemplary embodiments of apparatus and method for obtaining one or more portions of biological tissue (“micrografts”) to form grafts are provided. For example, a hollow tube can be inserted into tissue at a donor site, and a pin provided within the tube can facilitate controlled removal of the micrograft from the tube. Micrografts can be harvested and directly implanted into an overlying biocompatible matrix through coordinated motion of the tube and pin. A needle can be provided around the tube to facilitate a direct implantation of a micrograft into a remote recipient site or matrix. The exemplary apparatus can include a plurality of such tubes and pins for simultaneous harvesting and / or implanting of a plurality of micrografts. The harvested micrografts can have a small dimension, e.g., less than about 1 mm, which can promote healing of the donor site and / or viability of the harvested tissue.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
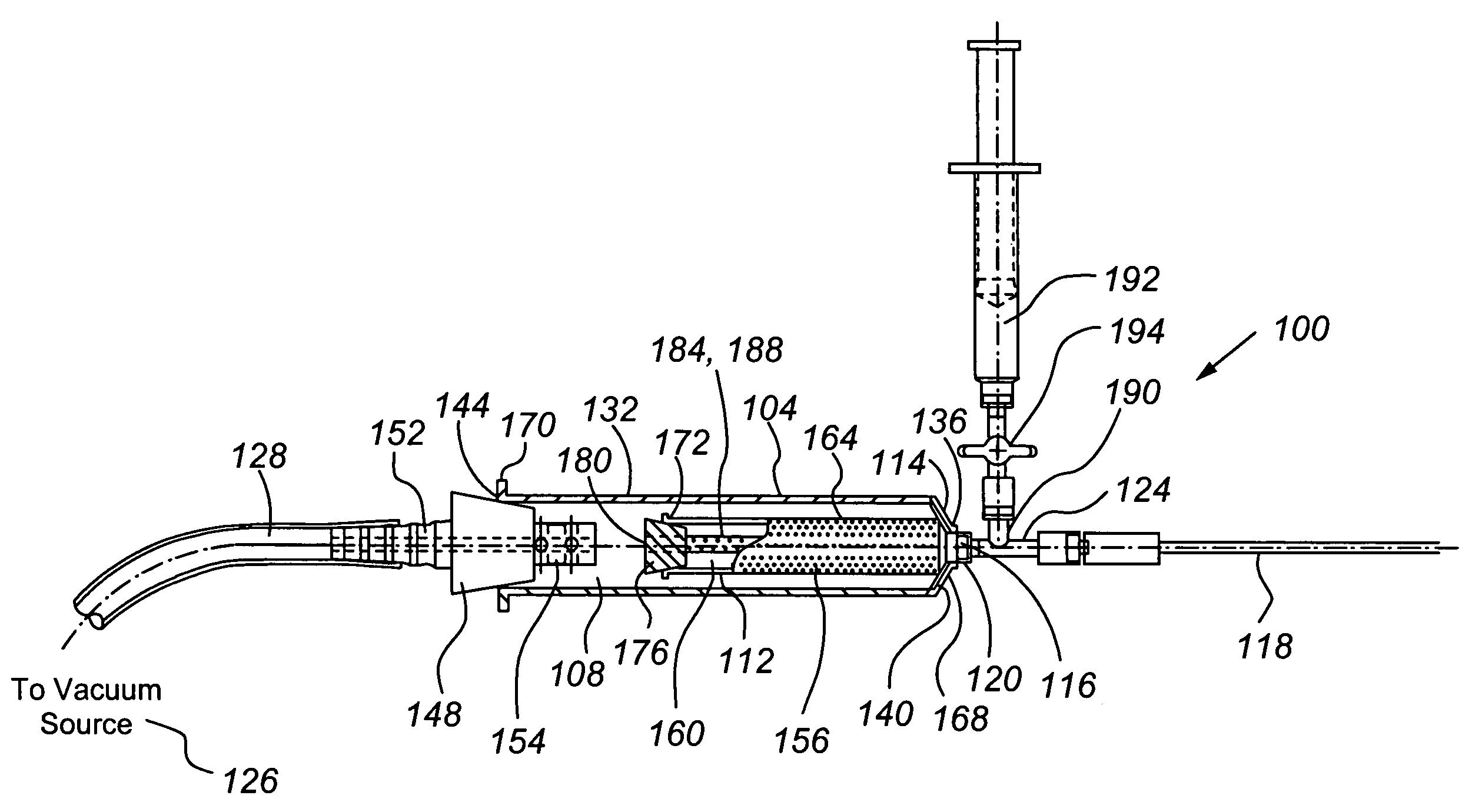
Tissue transplantation method and apparatus
ActiveUS7794449B2Minimize and eliminate needEliminate needInfusion syringesWound drainsTissue GraftMaterial Perforation
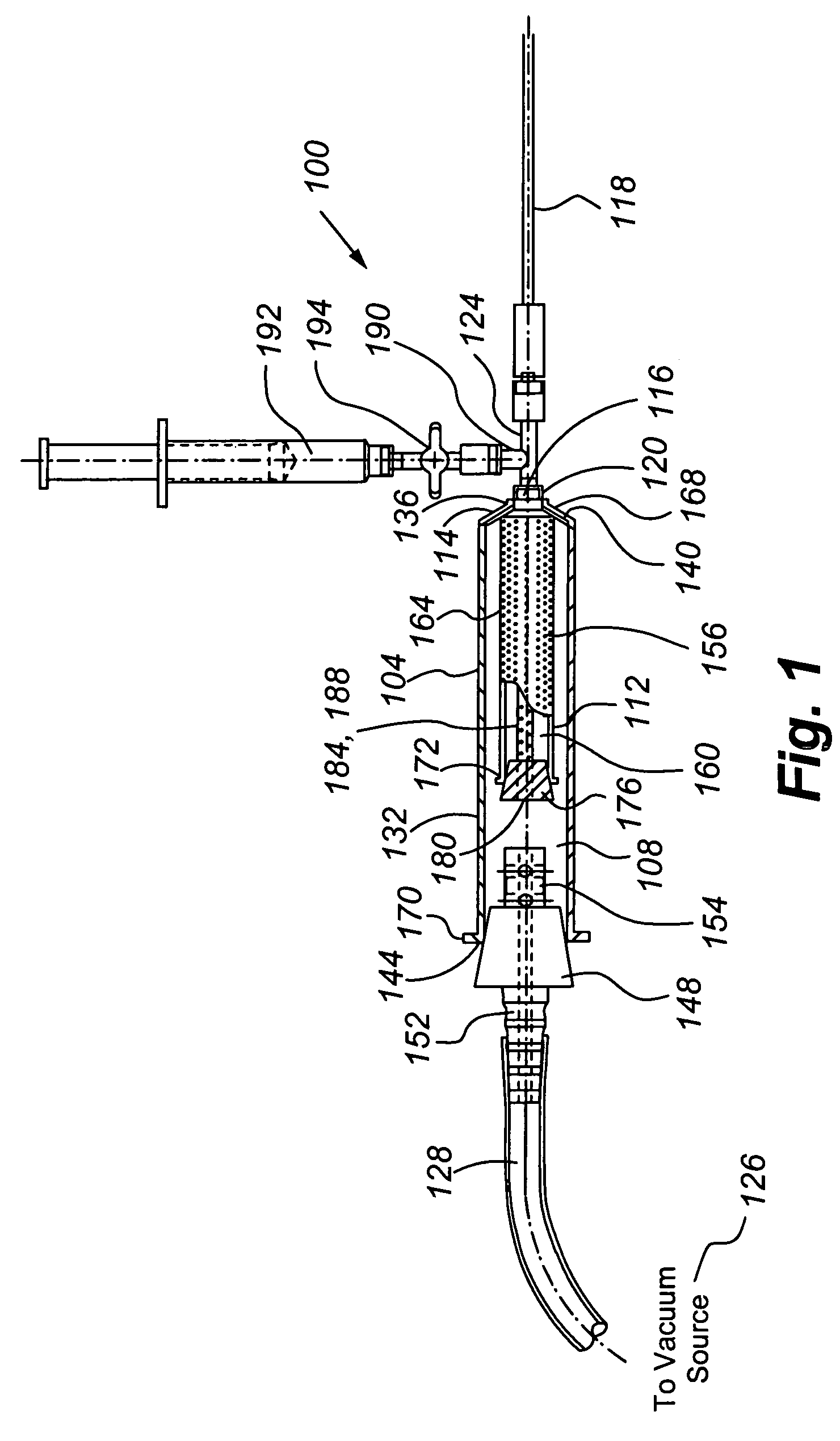
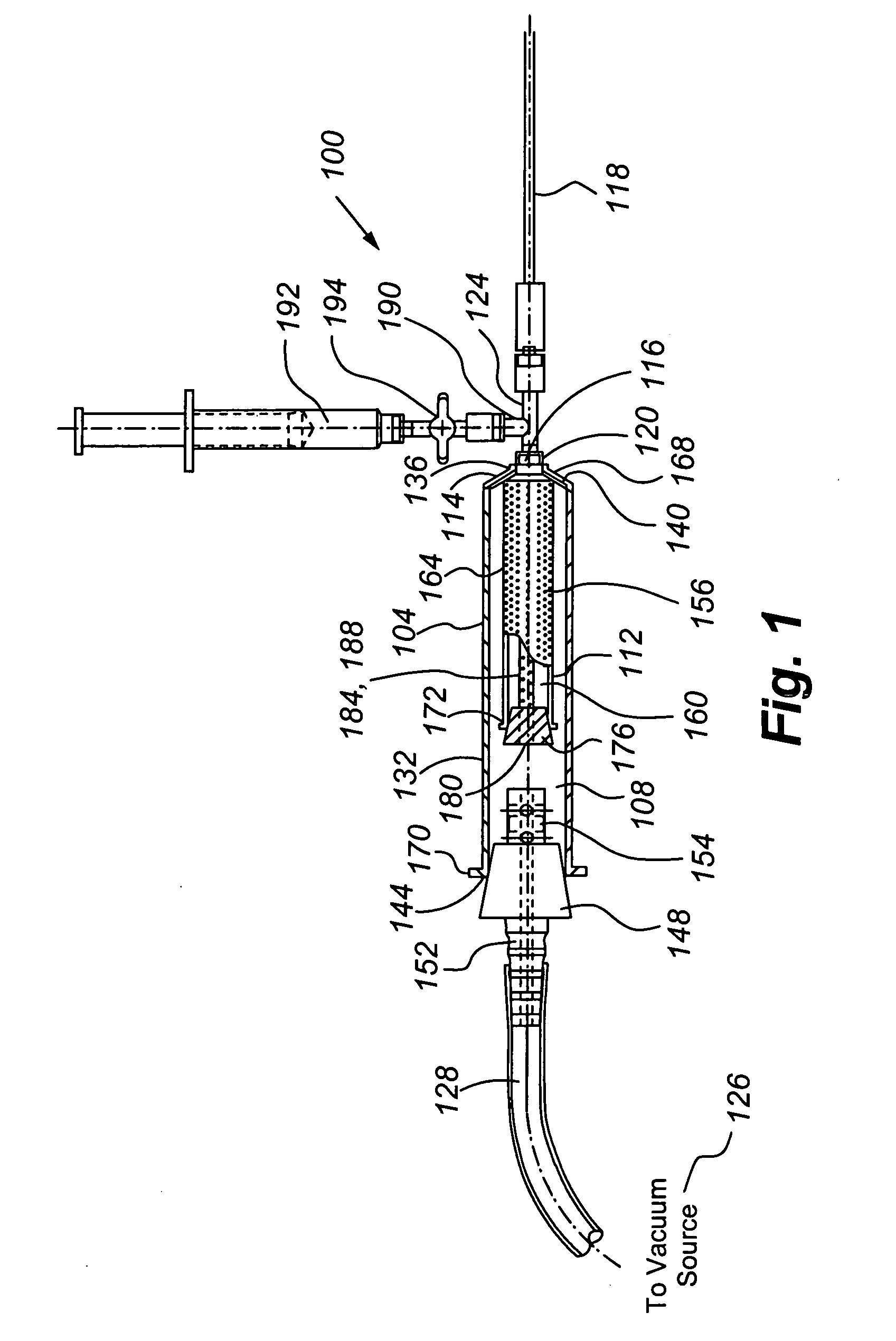
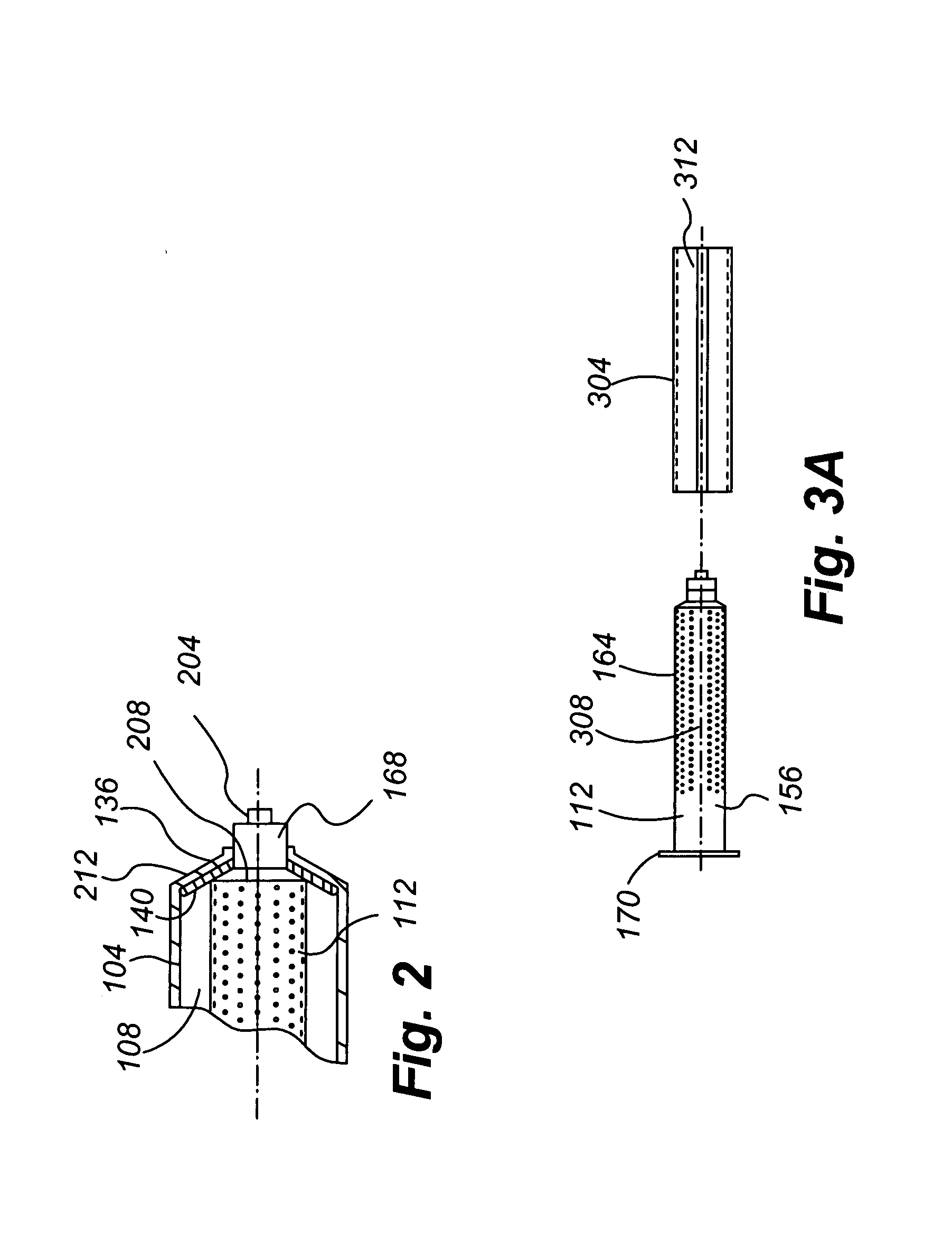
The present invention provides for the transplantation of tissue from a donor site in a body to a recipient site. The device includes an outer chamber having an interior volume in which a perforated inner chamber can be placed. During the aspiration of tissue, a vacuum is formed in the interior volume of the outer chamber, to draw tissue from a cannula into the perforated inner chamber. The perforations are sized such that fat is collected within the inner chamber, while fluids and other materials are drawn through the perforations, away from the collected fat. For reinjection, the inner chamber can be removed from the outer chamber, and a sleeve positioned to cover the perforations and thereby form a syringe body that can be interconnected to a needle and plunger for reinjection of the collected fat.
Owner:SHIPPERT ENTERPRISES
Tissue transplantation method and apparatus
ActiveUS20060213374A1Minimize and eliminate needEliminate needInfusion syringesSurgeryTissue transplantationMaterial Perforation
The present invention provides for the transplantation of tissue from a donor site in a body to a recipient site. The device includes an outer chamber having an interior volume in which a perforated inner chamber can be placed. During the aspiration of tissue, a vacuum is formed in the interior volume of the outer chamber, to draw tissue from a cannula into the perforated inner chamber. The perforations are sized such that fat is collected within the inner chamber, while fluids and other materials are drawn through the perforations, away from the collected fat. For reinjection, the inner chamber can be removed from the outer chamber, and a sleeve positioned to cover the perforations and thereby form a syringe body that can be interconnected to a needle and plunger for reinjection of the collected fat.
Owner:SHIPPERT ENTERPRISES
Instrumentation for the preparation and transplantation of osteochondral allografts
ActiveUS20070135918A1Reduce the amount requiredLess likely to be rejected by a recipientSuture equipmentsBone implantDonor boneChondral defect
Provided are procedures and instruments for preparing and transplanting osteochondral allograft plugs to a host bone to repair an articular cartilage defect. An allograft bone plug having a cartilage plate and cancellous bone tissue attached thereto is removed from a donor bone. The allograft plug is further shaped by removing or cutting away cancellous bone tissue to form a cancellous stalk extending from the cartilage plate. The formed cancellous stalk can have any suitable shape including cylindrical, conical, and rectilinear. At the recipient site of the host bone, a cutout is forined corresponding in shape to the allograft plug. The allograft plug is inserted into the cutout such that the cancellous stalk is retained in the host bone and the cartilage plate aligns with the condyle surface of the host bone. Aspects of the invention may also be applicable to preparing and transplanting osteochondral autograft plugs.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Instrumentation for the preparation and transplantation of osteochondral allografts
ActiveUS20070135917A1Reduce the amount requiredLess likely to be rejected by a recipientSuture equipmentsBone implantDonor boneChondral defect
Provided are procedures and instruments for preparing and transplanting osteochondral allograft plugs to a host bone to repair an articular cartilage defect. An allograft bone plug having a cartilage plate and cancellous bone tissue attached thereto is removed from a donor bone. The allograft plug is further shaped by removing or cutting away cancellous bone tissue to form a cancellous stalk extending from the cartilage plate. The formed cancellous stalk can have any suitable shape including cylindrical, conical, and rectilinear. At the recipient site of the host bone, a cutout is formed corresponding in shape to the allograft plug. The allograft plug is inserted into the cutout such that the cancellous stalk is retained in the host bone and the cartilage plate aligns with the condyle surface of the host bone. Aspects of the invention may also be applicable to preparing and transplanting osteochondral autograft plugs.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
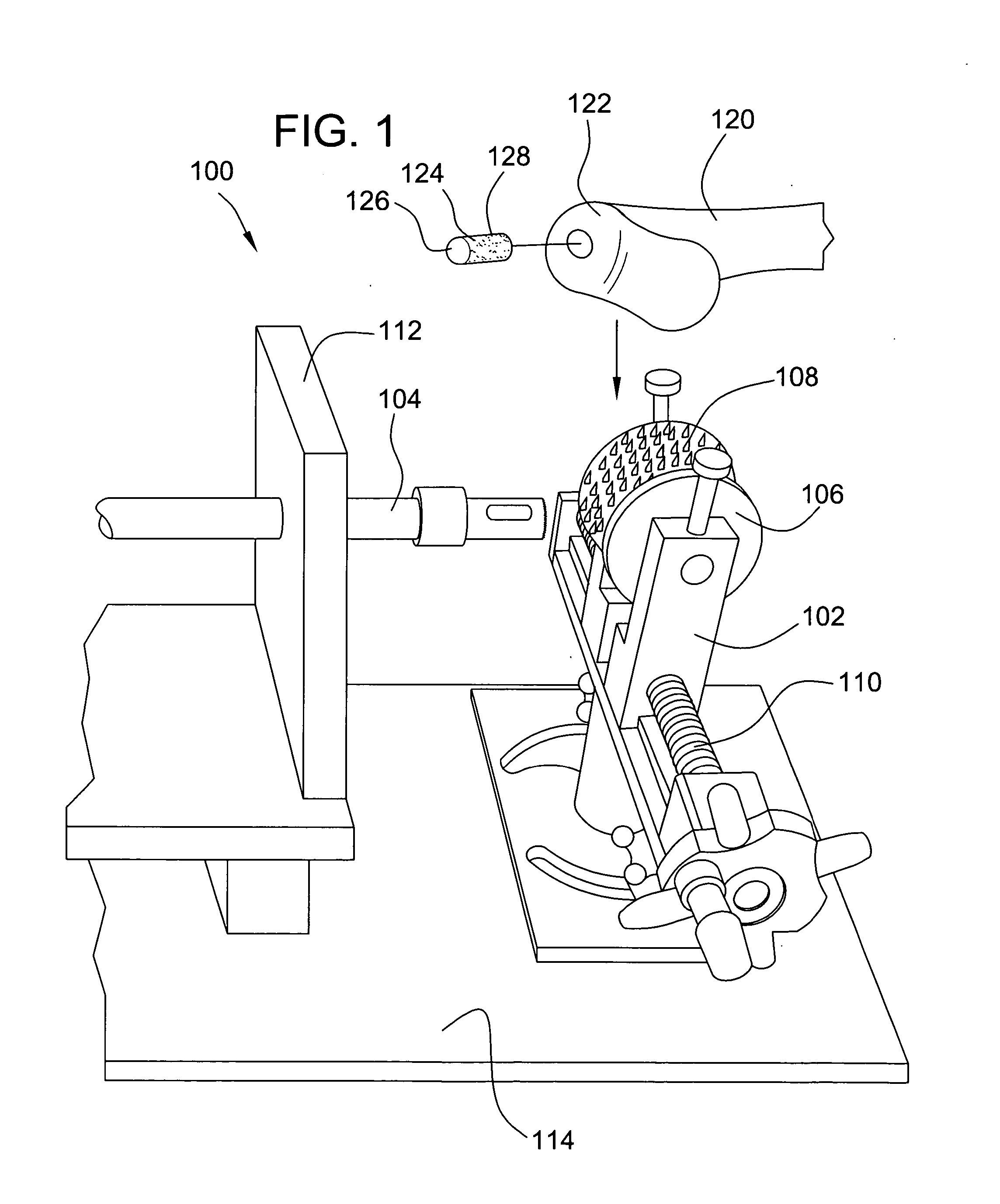
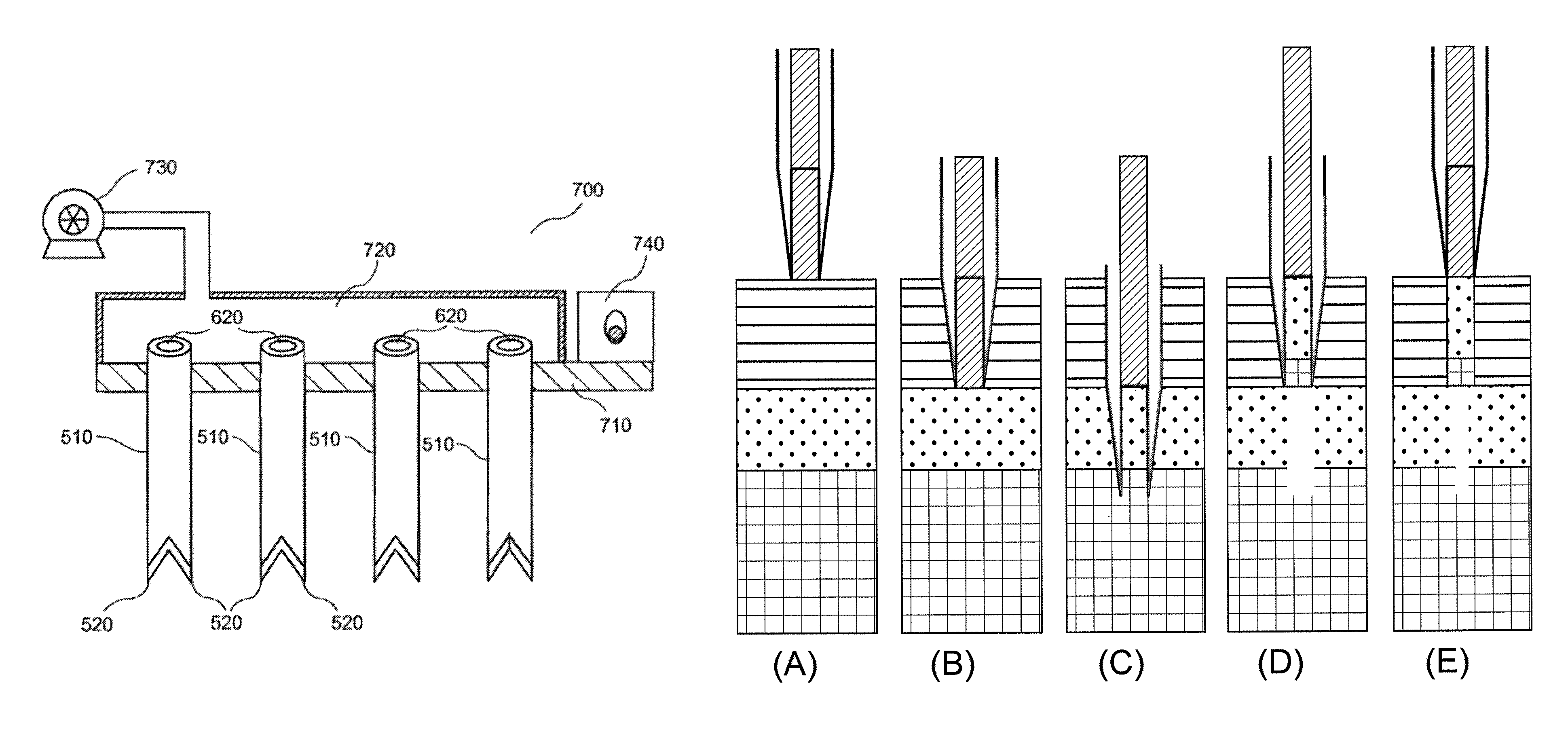
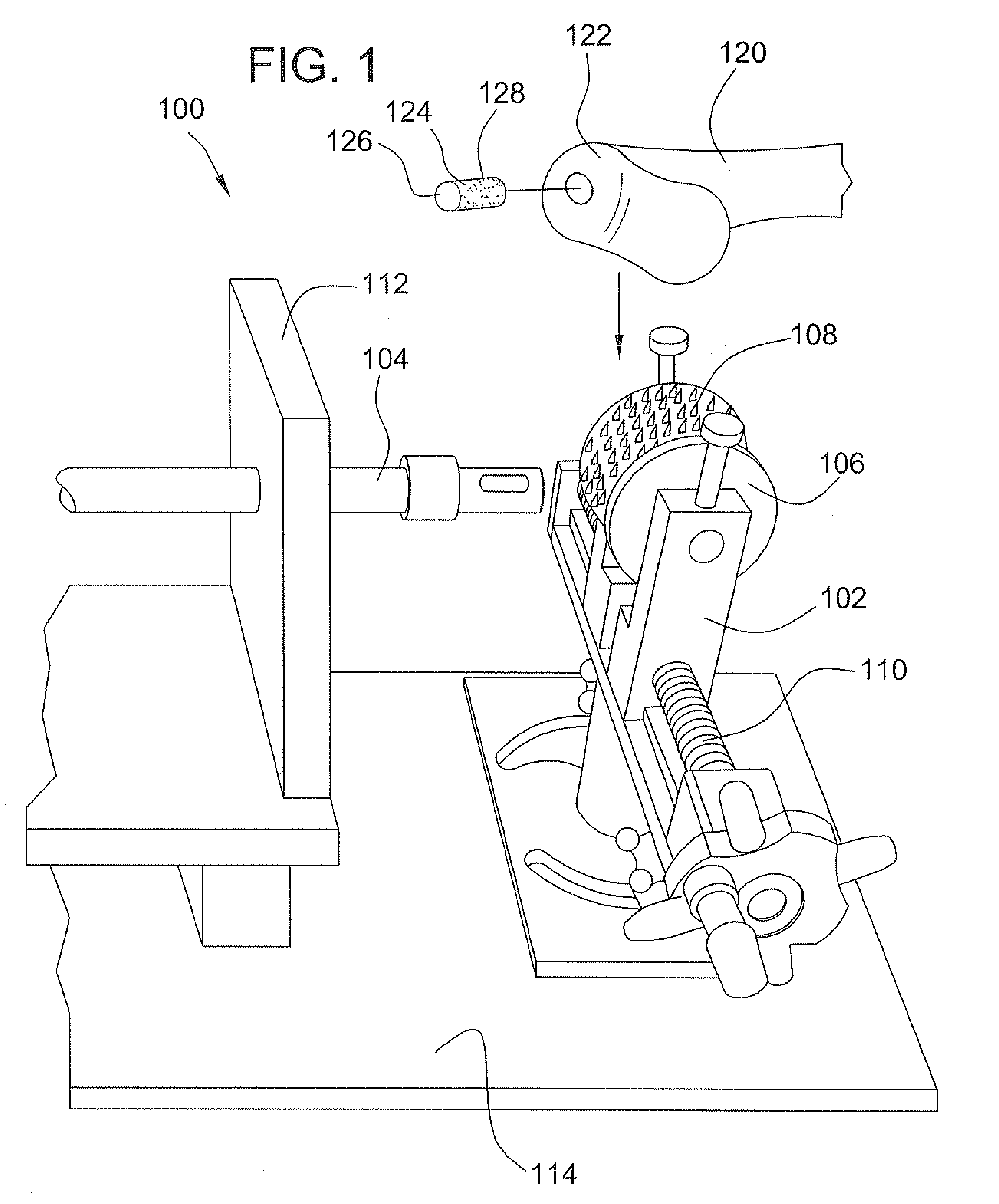
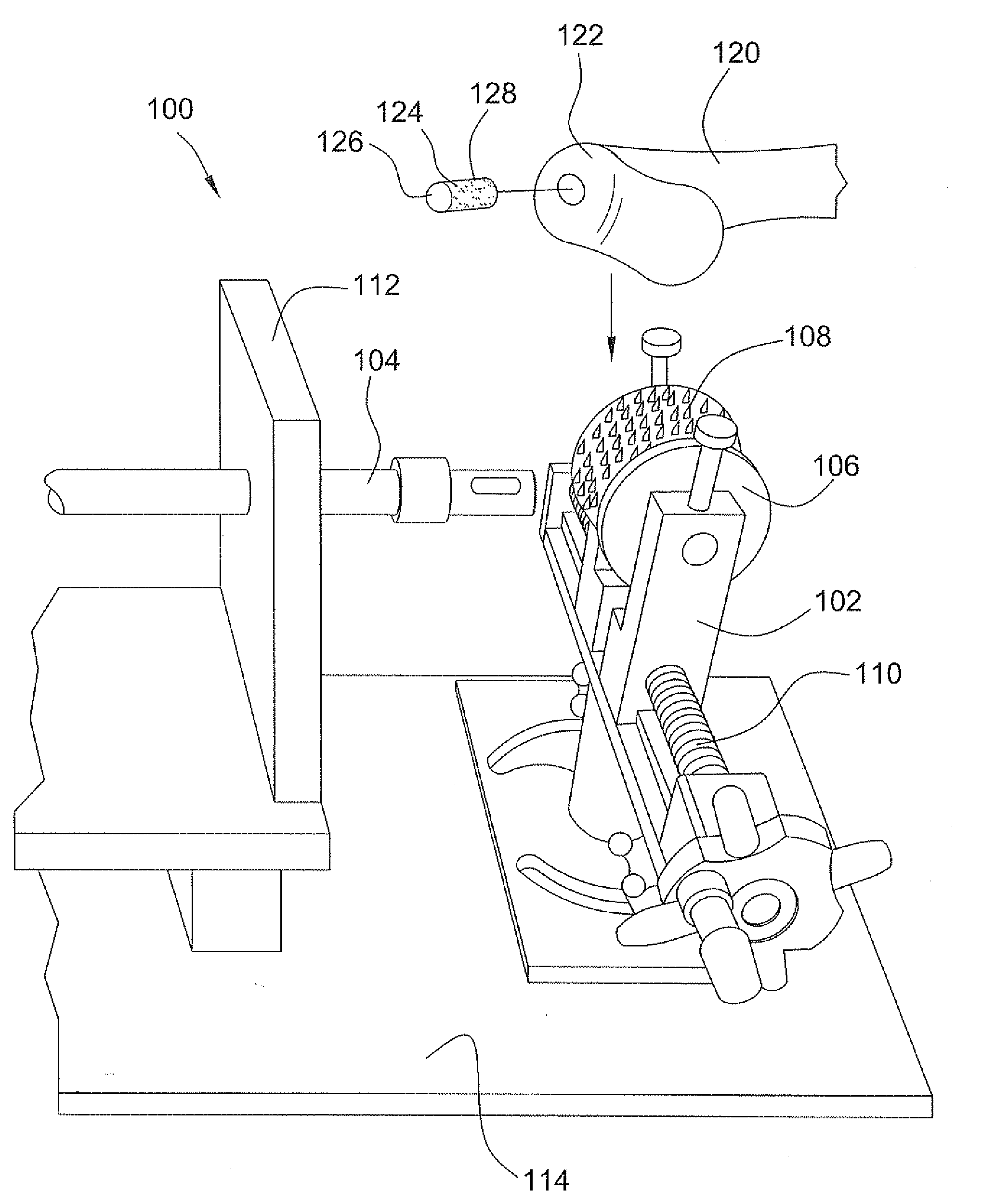
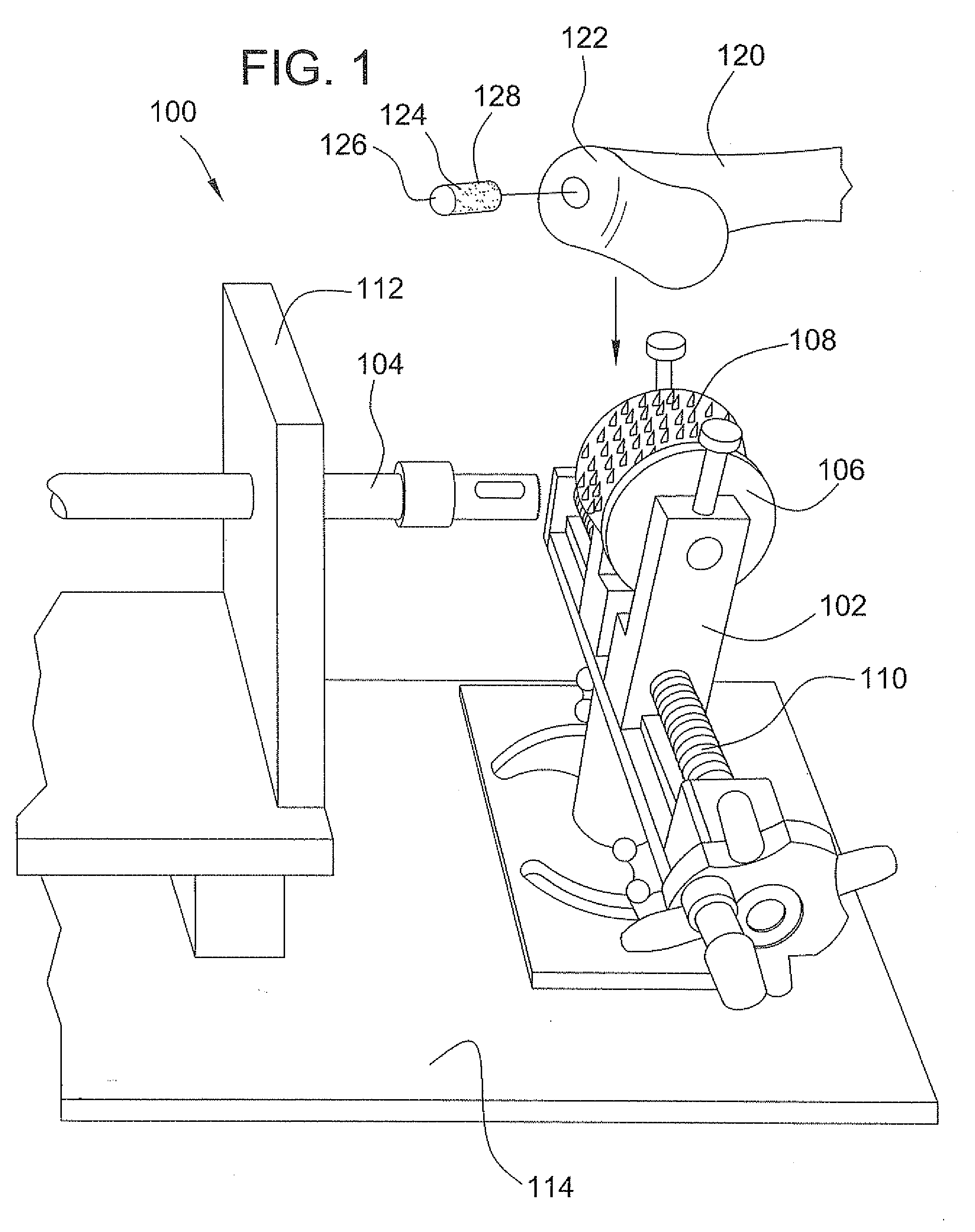
Tissue processing system
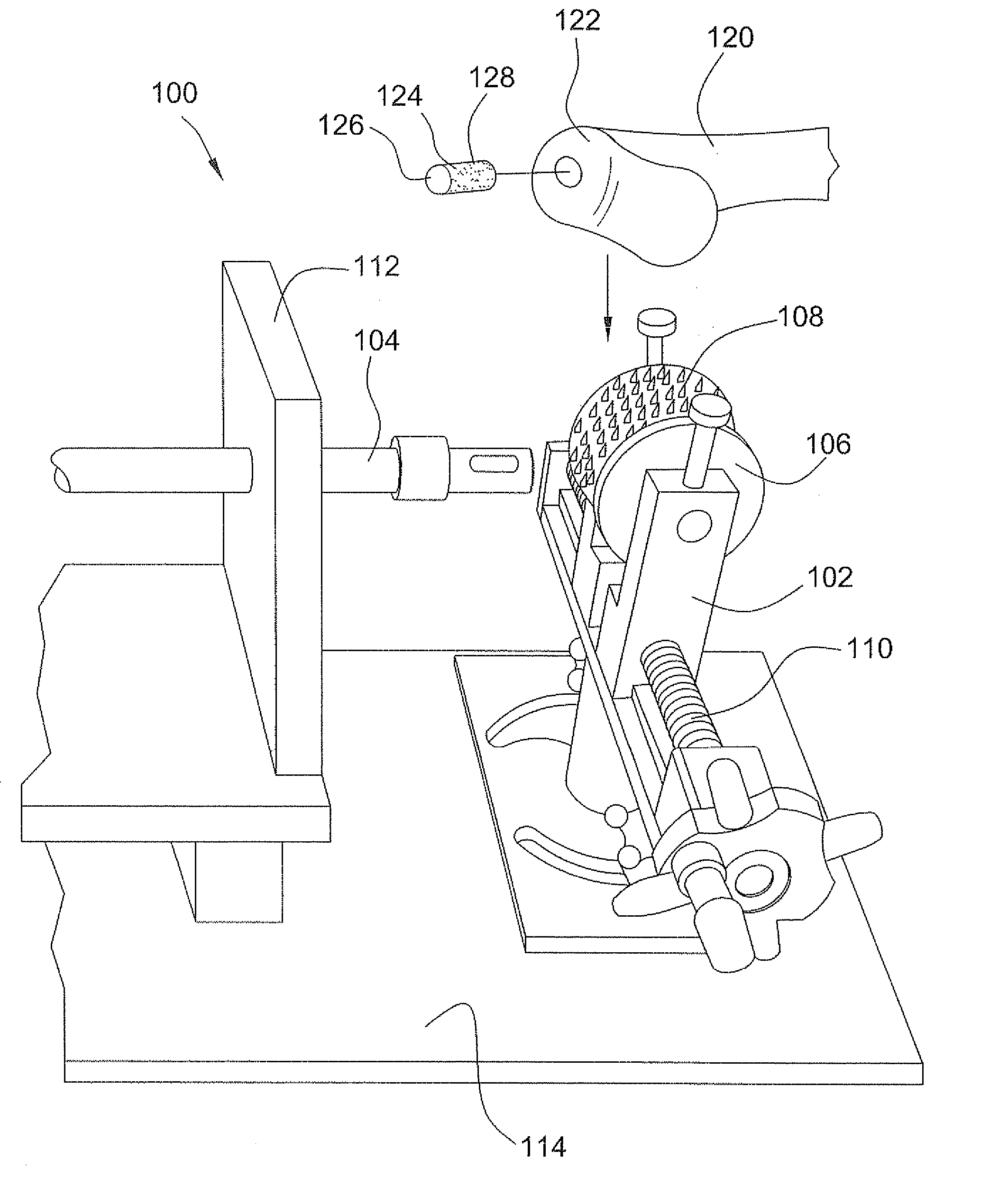
ActiveUS7651507B2Small sizeEasy to disassembleDead animal preservationSurgical sawsTissue ProcessorDonor tissue
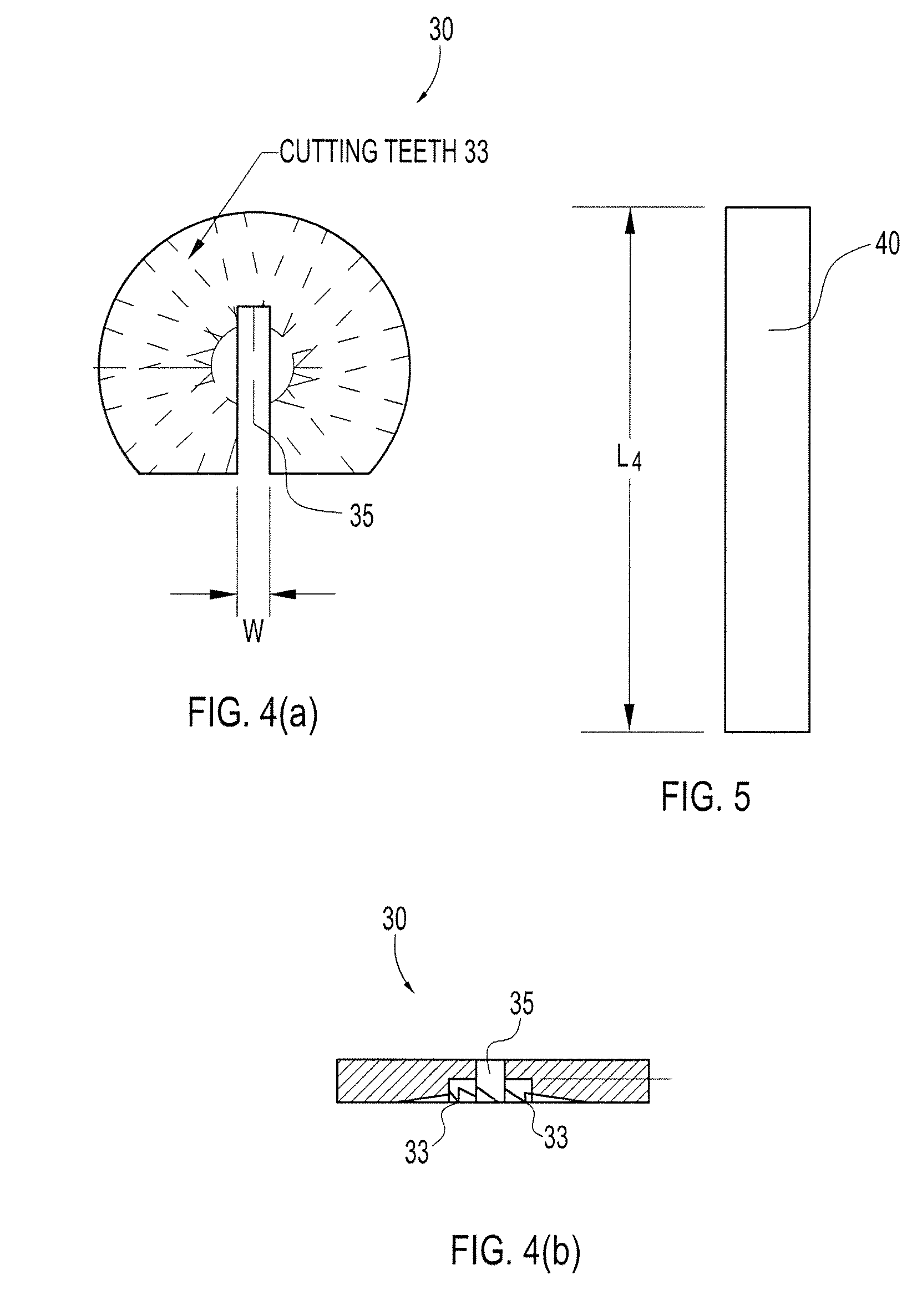
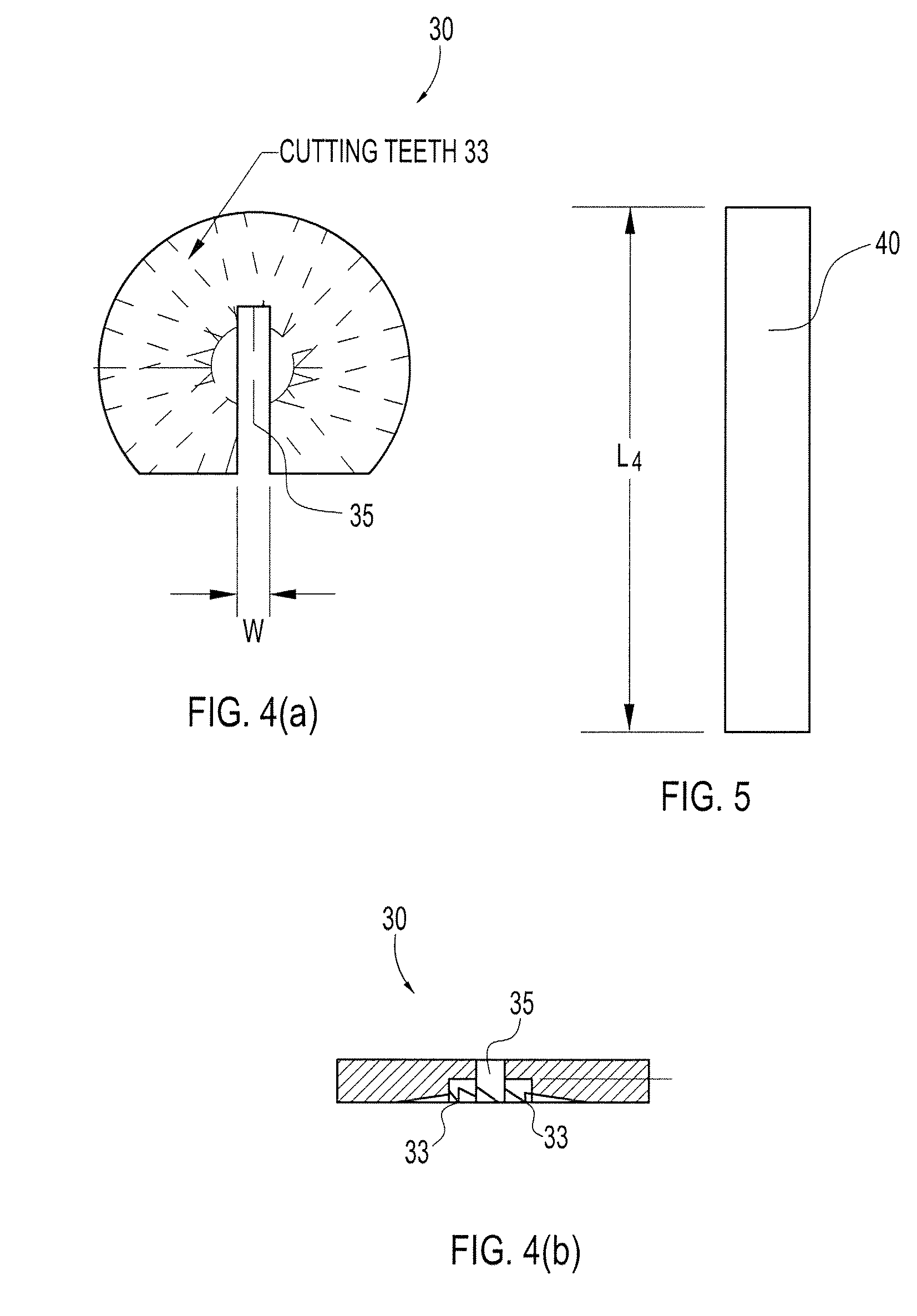
A tissue processing system includes a series of blades arranged in parallel to form a tissue processor. The blades may be adjusted to create a spaced between each blade in the range of 250-1000 microns. A slicer is included to remove a donor tissue to be processed by the processor. The processor is rotatable 90 degrees so as to create uniform micrografts of tissue for transplanting to a recipient site. An extractor is included to remove tissue particles from the processor after they have been cut into an appropriate size. A cutting block may be provided to ensure uniform thickness of cuts of the donor tissue.
Owner:KCI LICENSING INC
Osteochondral allografts
ActiveUS20070135928A1Reduce the amount requiredLess likely to be rejected by a recipientSuture equipmentsBone implantDonor boneChondral defect
Provided are procedures and instruments for preparing and transplanting osteochondral allograft plugs to a host bone to repair an articular cartilage defect. An allograft bone plug having a cartilage plate and cancellous bone tissue attached thereto is removed from a donor bone. The allograft plug is further shaped by removing or cutting away cancellous bone tissue to form a cancellous stalk extending from the cartilage plate. The formed cancellous stalk can have any suitable shape including cylindrical, conical, and rectilinear. At the recipient site of the host bone, a cutout is formed corresponding in shape to the allograft plug. The allograft plug is inserted into the cutout such that the cancellous stalk is retained in the host bone and the cartilage plate aligns with the condyle surface of the host bone. Aspects of the invention may also be applicable to preparing and transplanting osteochondral autograft plugs.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
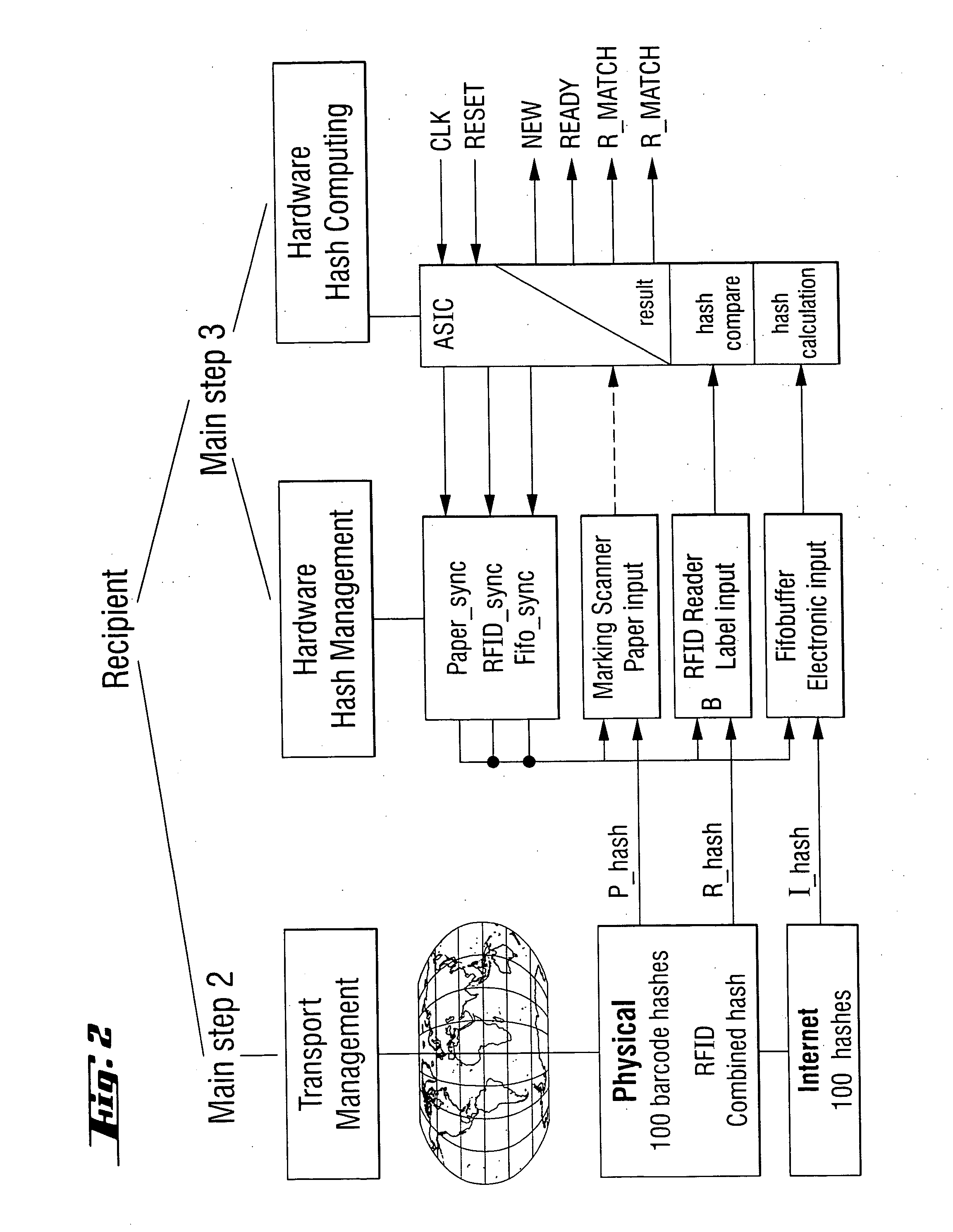
Process for the integrity check of lots of individual package units
InactiveUS20060206714A1Fast and inexpensiveIncrease sampling rateError detection/correctionVolume/mass flow measurementComputer hardwarePaper document
A process for integrity check of lots of individual package units which comprises combining at least one RFID tag and a container which contains a large number of individual package units wherein each of the individual package units is marked with a marking code, the information of these codes of all individual package units is combined, and a hash code is generated based on the combined information of all marking codes of all individual package units, which combined hash code is stored in an RFID tag which is affixed to the container, this combined hash code together with the individual hash codes for the individual package units being stored in the data base of the SENDER site where the container is packed and sealed, the individual hash codes then being transmitted to the RECIPIENT of the said container, the information collected from the RFID tag being compared to the combined hash code which is calculated at the RECIPIENT site from the information received by the SENDER of the said container including all individual hash codes of all package units in the said container, and to the combined hash code calculated from the markings on the individual package units or boxes scanned at the RECIPIENT site, and the application of the said process in the verification of the integrity of pharmaceutical goods, video information such as movies on DVD, audio information such as music on CD, computer files, or paper documents
Owner:ADALBERT GUBO
Skin grafting devices and methods
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
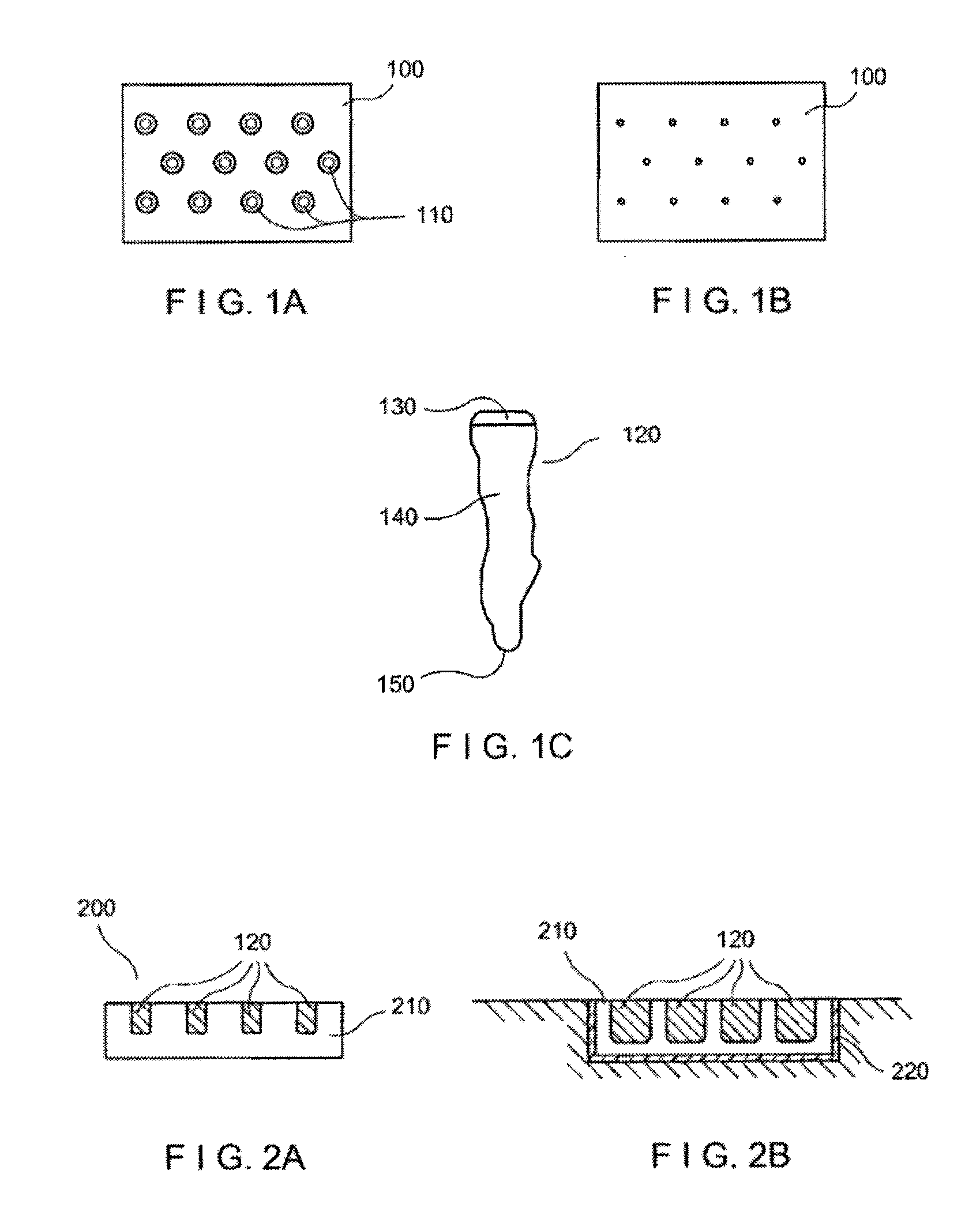
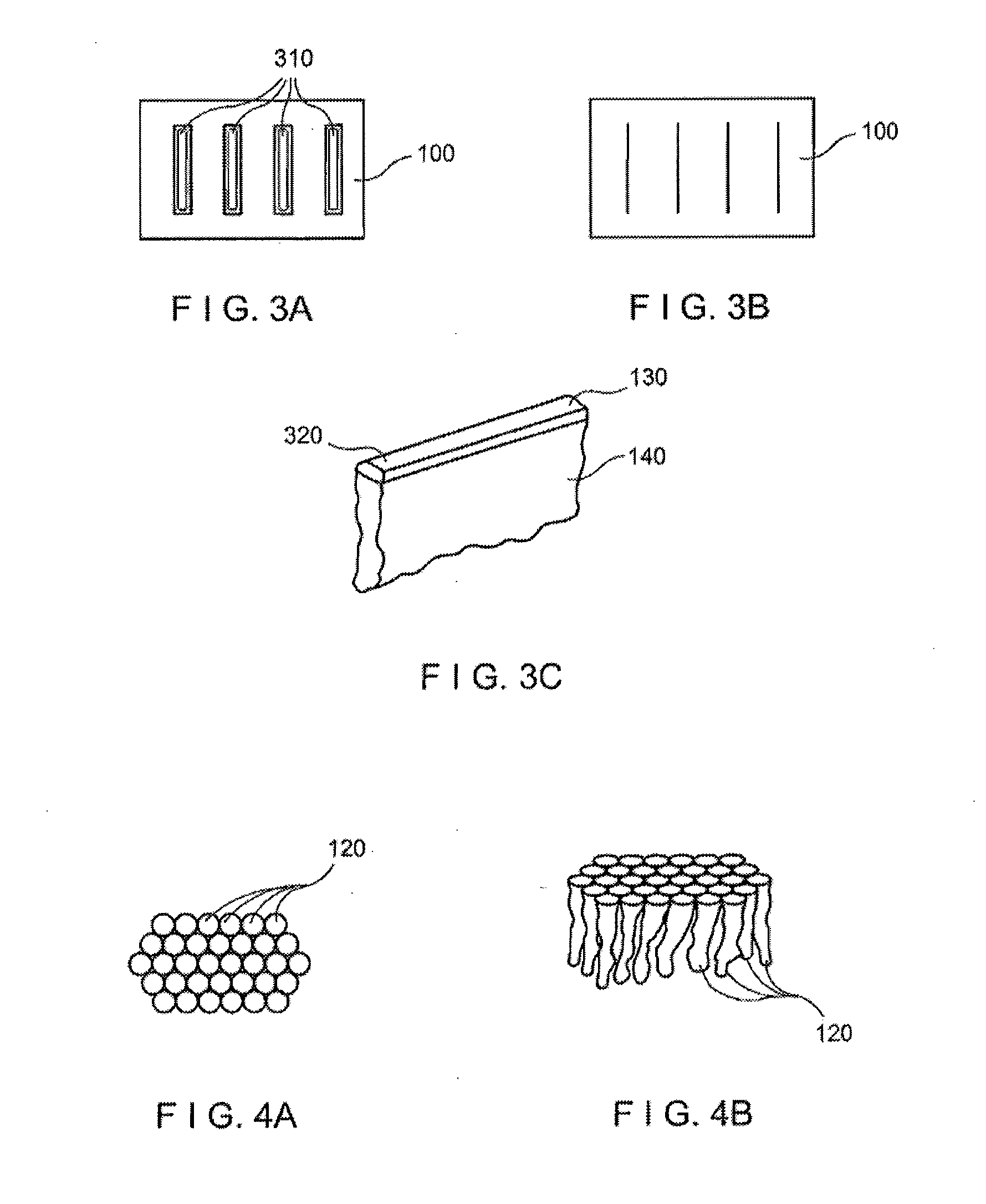
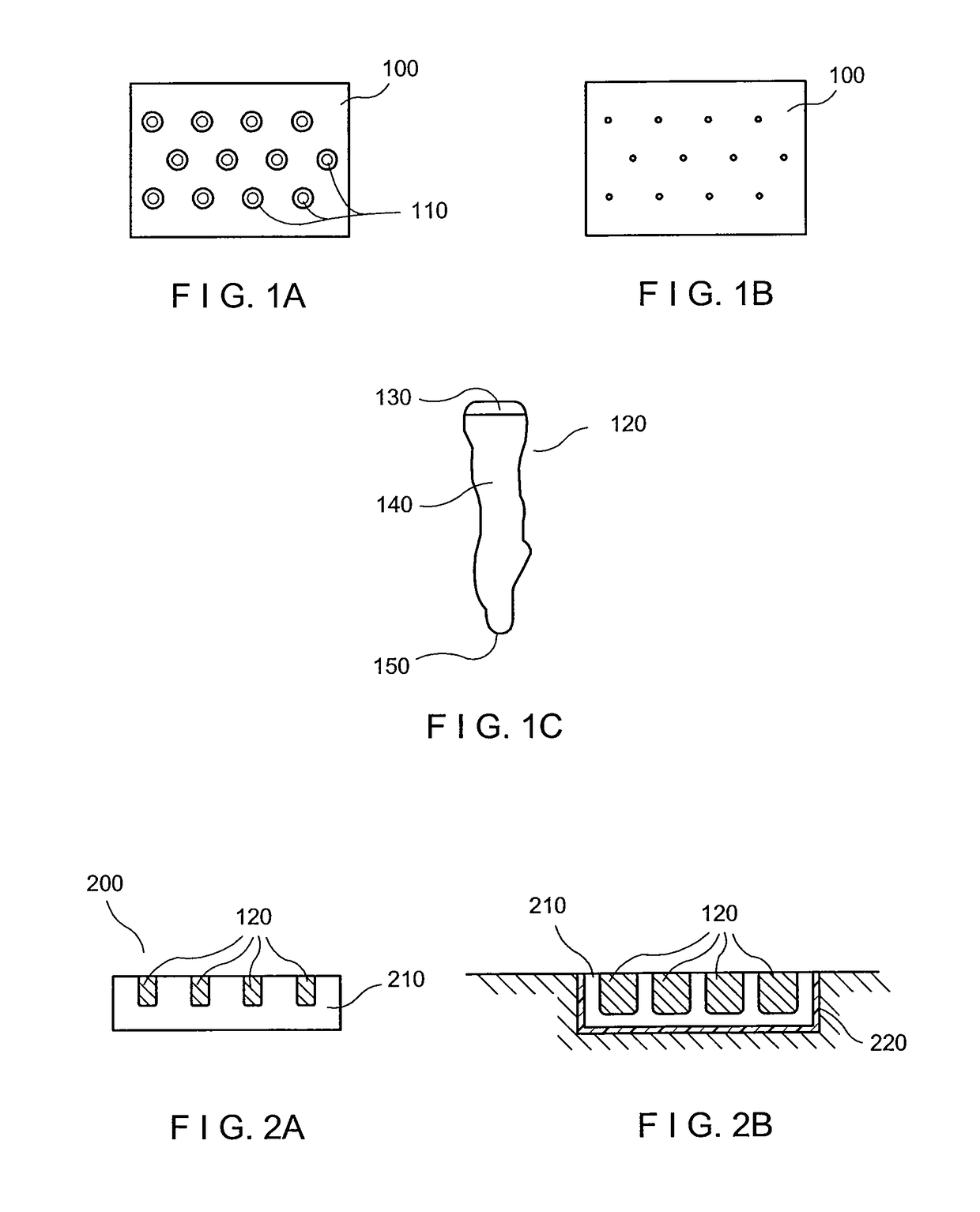
High-density sample support plate for automated sample aliquoting
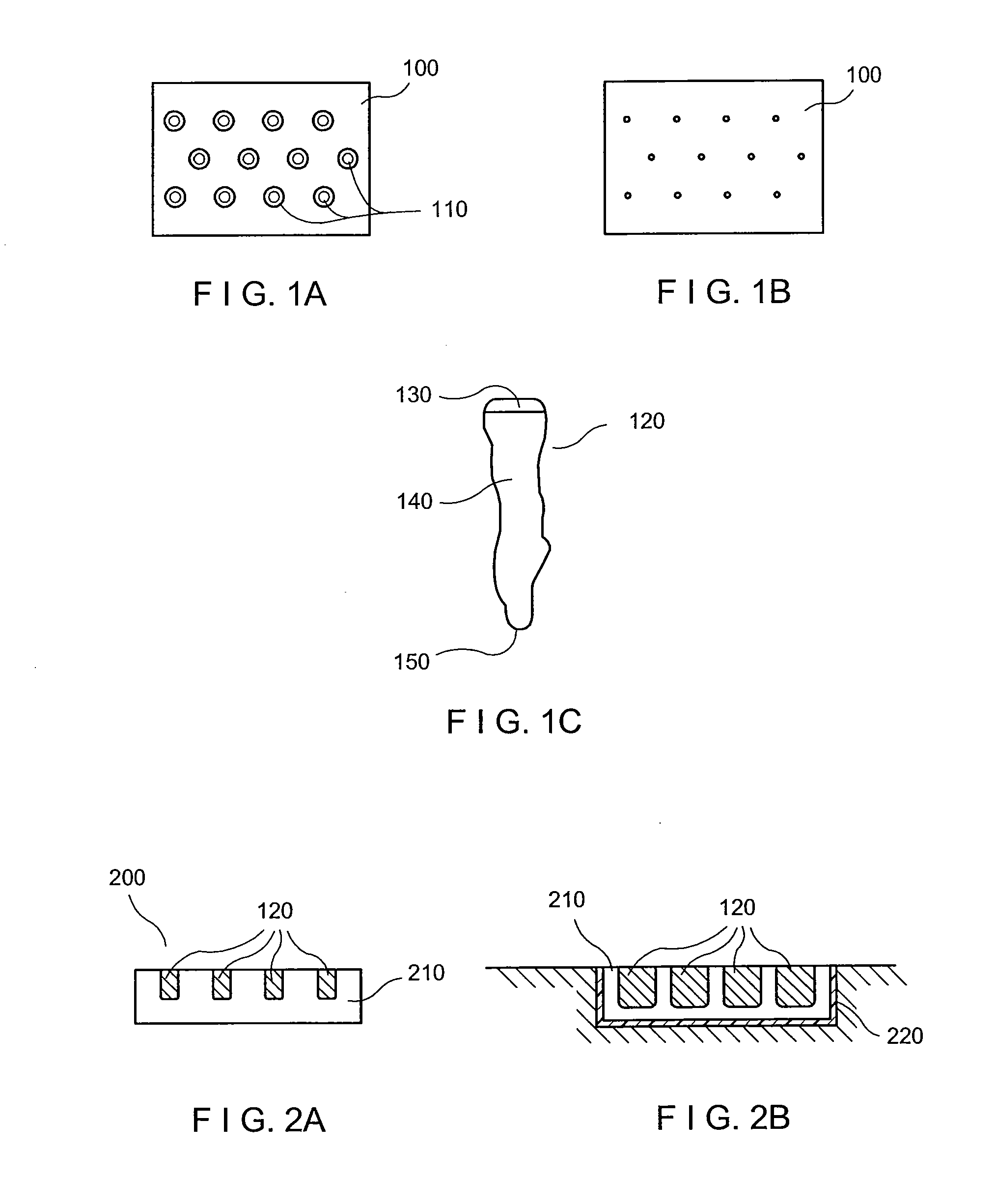
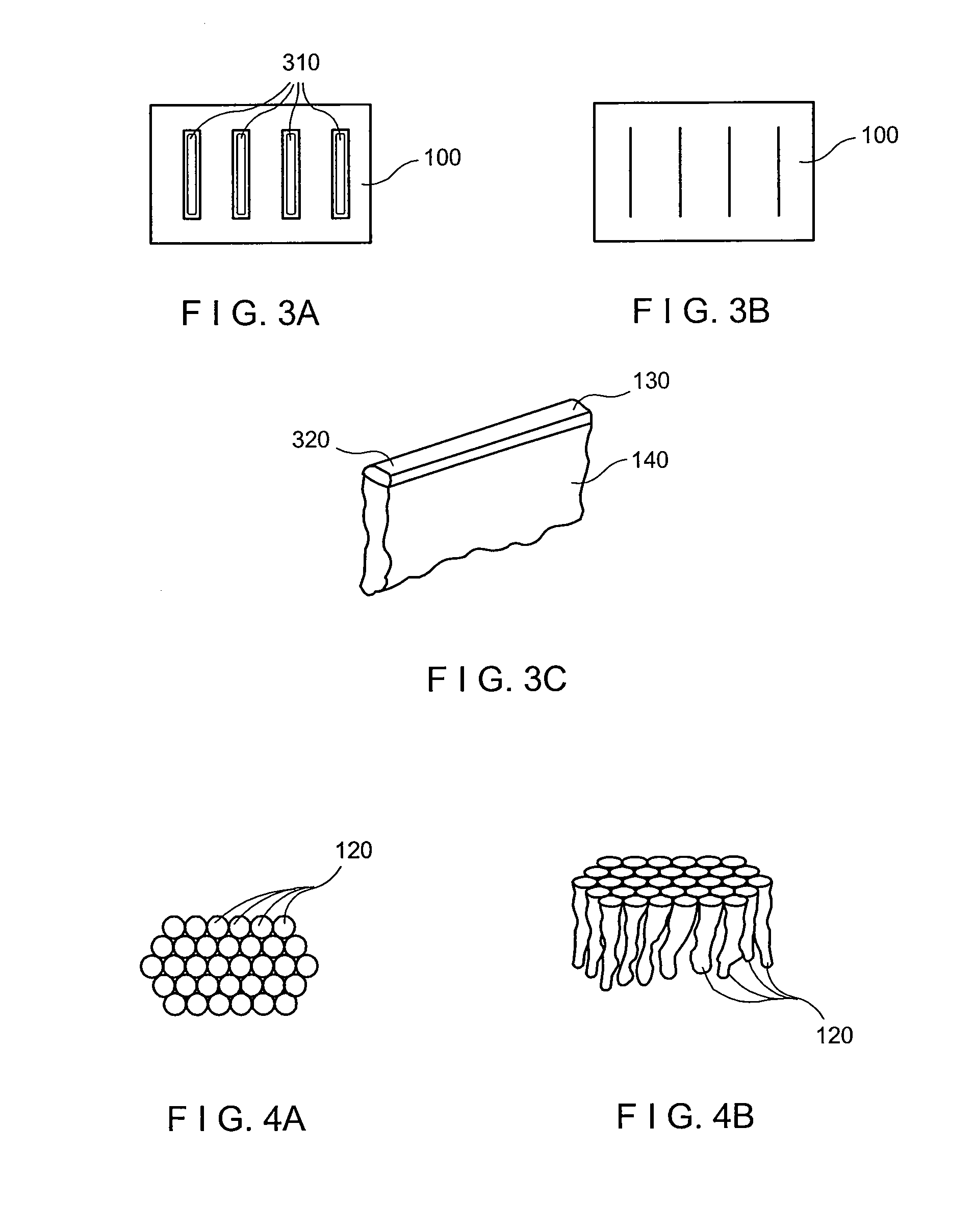
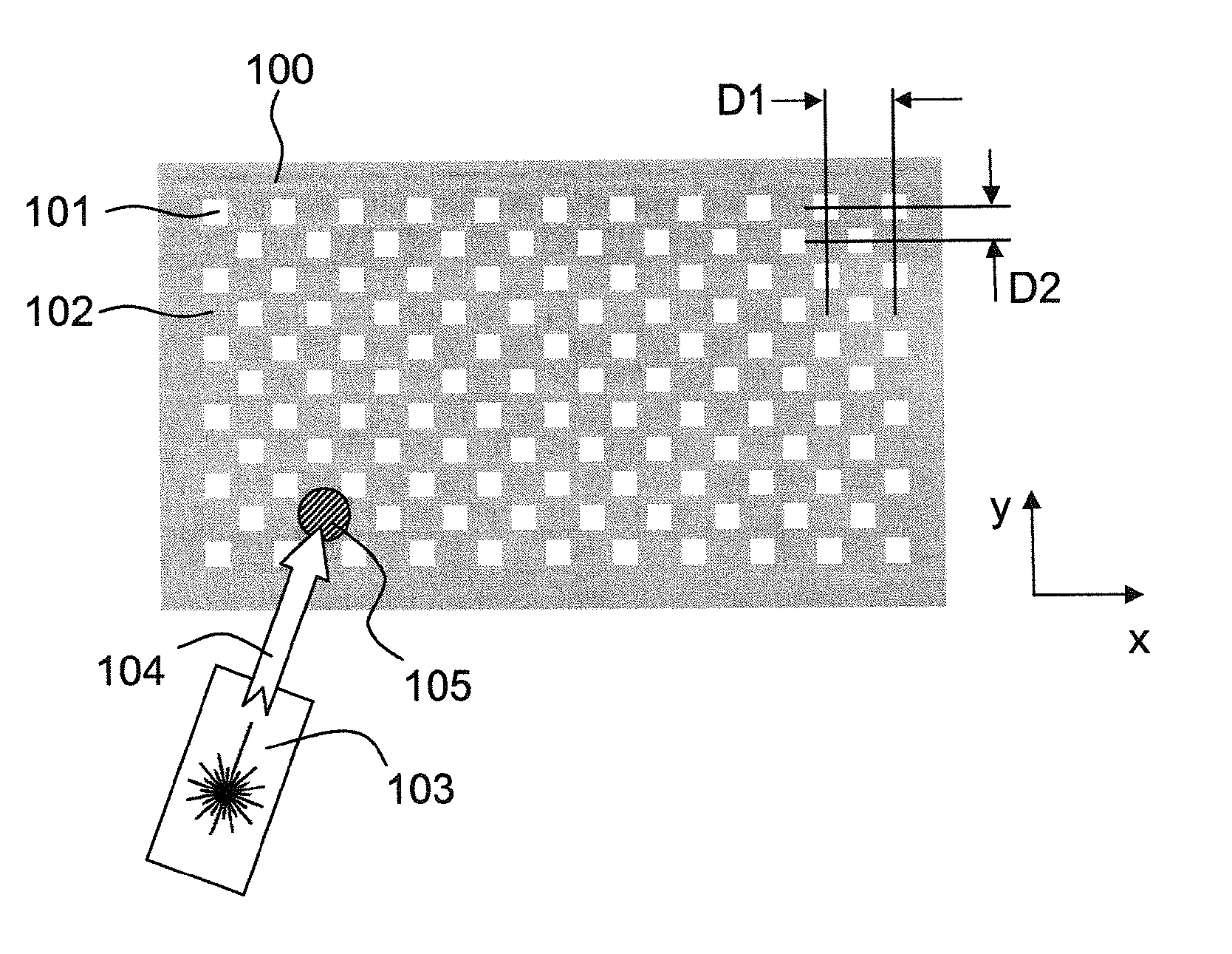
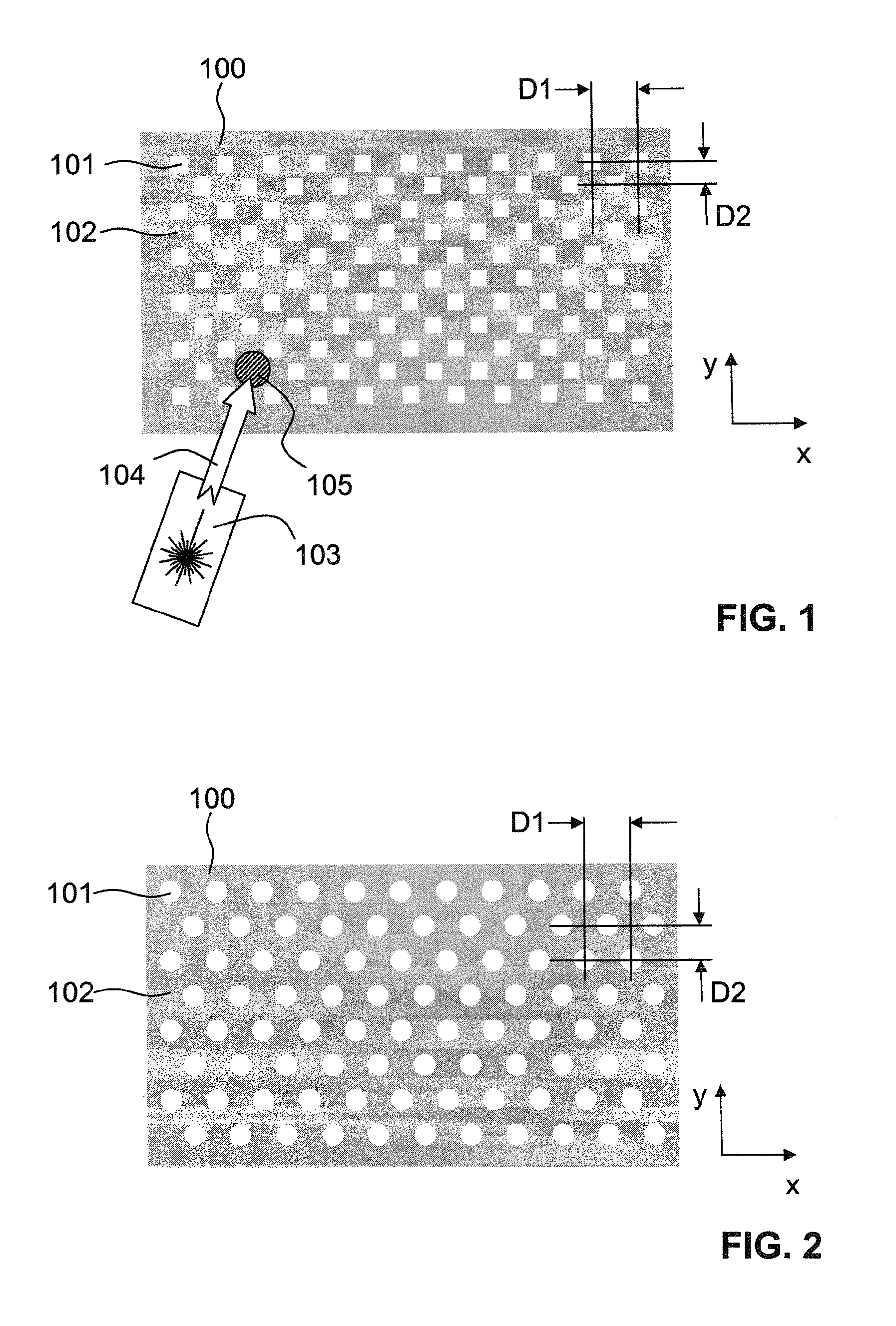
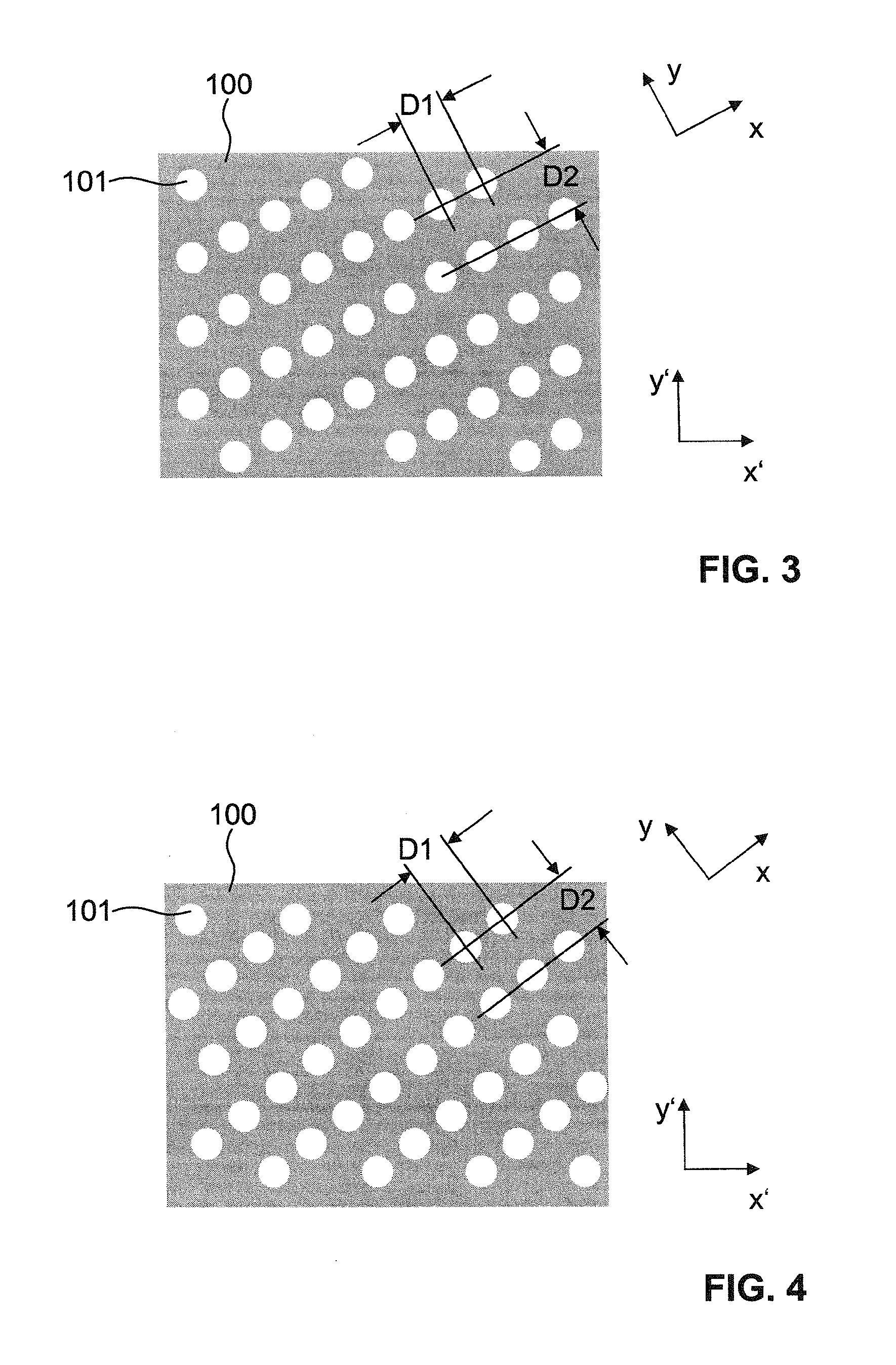
A sample support plate (100) for a variety of possible applications, including MALDI mass spectrometry, is disclosed. A plurality of spatially separated sample recipient sites (101) are arranged on the surface of a substrate. The recipient sites are mutually separated by areas having a different wettability than the recipient sites. They are arranged in a plurality of rows consisting of a plurality of recipient sites whose centers are regularly spaced along a first direction with a predetermined periodicity (D1), the rows being regularly spaced along a second direction perpendicular to the first direction with a predetermined centerline distance (D2). Each recipient site has a maximum lateral dimension that is preferably smaller than the diameter of a beam spot (104) of a desorption laser beam (103). In order to enable unsupervised splitting of bulk liquid samples into droplets at the sample recipient sites, the periodicity along the first direction and the centerline distance along the second direction are chosen such that each recipient sites has a next neighbor at a distance that is less than or equal to three times the minimum lateral dimension of each recipient site. In preferred embodiments, the sample recipient sites are arranged in a checkerboard-type pattern or in rows that are inclined relative to the edges of the sample support plate.
Owner:ETH ZZURICH +1
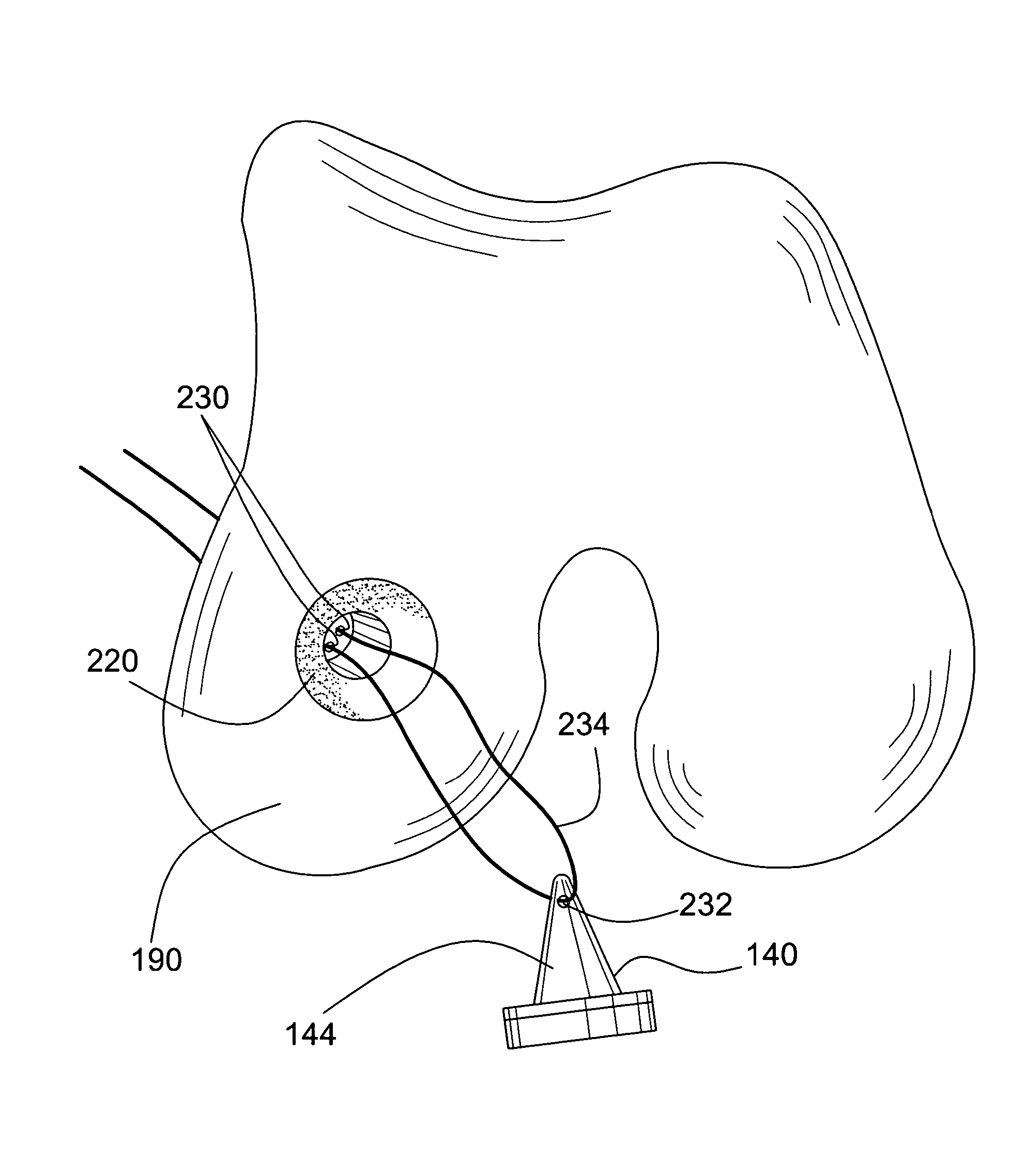
Method and apparatus for harvesting and implanting bone plugs
InactiveUS7819888B2Improve integrityPlacement and alignment and insertionSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsBone plugBiomedical engineering
A system for transplanting a bone plug from a donor site to a recipient site extracts the bone plug from the donor site, and then places a bone plug delivery device having a tip which is at least translucent and, preferably, clear over a tube containing the bone plug. The tip is then placed substantially over a pre-formed hole in the recipient site, whereafter the bone plug is forced from the tube, through the transparent tip, and into the pre-formed hole.
Owner:INNOVASIVE DEVICES
Method for expansion of human corneal endothelial cells
A method for expanding human corneal endothelial cells includes: (a) providing an amniotic membrane with or without amniotic cells, wherein the amniotic membrane has an extracellular matrix; (b) placing onto the amniotic membrane, a sheet of endothelial layer, or a cell suspension including human corneal endothelial stem cells; and (c) culturing the corneal endothelial cells on the amniotic membrane for a duration sufficient for the corneal endothelial stem cells to expand to an appropriate area. The invention also relates to a method for creating a surgical graft for a recipient site of a patient using the method for expanding human corneal endothelial cells, and the surgical graft prepared therefrom.
Owner:TSAI RAY JUI FANG +1
Submerged Substrate Plug Cutter and Related Method
A device for use in cutting plugs of submerged substrate and particularly seagrass plugs for the purpose of transplanting using a corresponding transport receptacle and method. The device utilizes a hollow cutting member with a serrated bottom edge capable of being placed over a targeted area and forced into the submerged substrate, created vacuum pressure in the hollow cutting member, and compressed air injected between the exterior of the hollow cutting member and the submerged substrate to accomplish cutting of a submerged substrate unit. Vacuum pressure in the hollow cutting member is released to transfer the collected unit to the corresponding transport receptacle with a removable bottom. A corresponding method for transplanting a collected seagrass plug is further accomplished by creating a hole at recipient site using the device and removing the transport receptacle's removable bottom to release the plug into the created hole.
Owner:STANTEC CONSULTING SERVICES
Retrograde osteochondral autograft transfer system
Owner:ARTHREX
Preparation method and application of injectable allogeneic adipose acellular matrix particles
ActiveCN108478868ARich sourcesWide variety of sourcesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTissue regenerationAcellular matrixFacial rejuvenation
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of injectable allogeneic adipose acellular matrix particles. The injectable allogeneic adipose acellular matrix particles are obtained in the modes that adipose tissue obtained through liposuction operation is subjected to mechanical chylosis treatment, centrifugal degreasing and a subsequent gentle acellular working procedure, and centrifuged for further degreasing. The adipose tissue comes from human-derived adipose particles discarded by traditional liposuction operation of obese patients. Adipose cell physical crushing and degreasing methods are adopted, a gentle acellular technology is applied, operation is easy and convenient, damage to adipose matrix structure and components is small, an obtained material is closer to thehuman body natural adipose tissue microenvironment, and the three-dimensional structure and active components of the tissue are preserved; and the injectable allogeneic adipose acellular matrix particles can be injected through a 27g of small needle, after injection, proliferation and differentiation of tissue cells in a recipient site are more facilitated, thus tissue repairing and regeneration are promoted, and the long-term filling and rejuvenation effects are achieved. The injectable allogeneic adipose acellular matrix particles are suitable for facial rejuvenation and soft tissue defect repairing.
Owner:易成刚
Cell Suspension and Use Thereof
InactiveUS20150079153A1Avoid cloggingPromotes even distributionBiocideEpidermal cells/skin cellsProgenitorEpithelium
The present invention provides for methods and devices suitable for producing a transplantable cellular suspension of living tissue suitable for promoting tissue regeneration in an epithelium-related procedure, as well as compositions produced therefrom. The cellular suspension can include viable and functioning cells at various stages of differentiation, including undifferentiated / progenitor cells and differentiated cells, as well as those in between. In certain embodiments, the cellular suspension can be subjected to a stress to induce a heat shock response therein, or be exposed to an exogenously supplied agent such as heat shock protein or a fragment thereof, hyaluronic acid, platelet-enriched plasma, and / or growth factors. The cellular suspension can be applied directly to a patient's recipient site for in vivo regeneration, or be cultured or seeded to a matrix for in vitro growth / regeneration.
Owner:AVITA MEDICAL LTD
Systems and methods for hair transplant
PendingUS20210145476A1Increase speedGood curative effectDiagnosticsSurgical needlesHair transplantingHair follicle
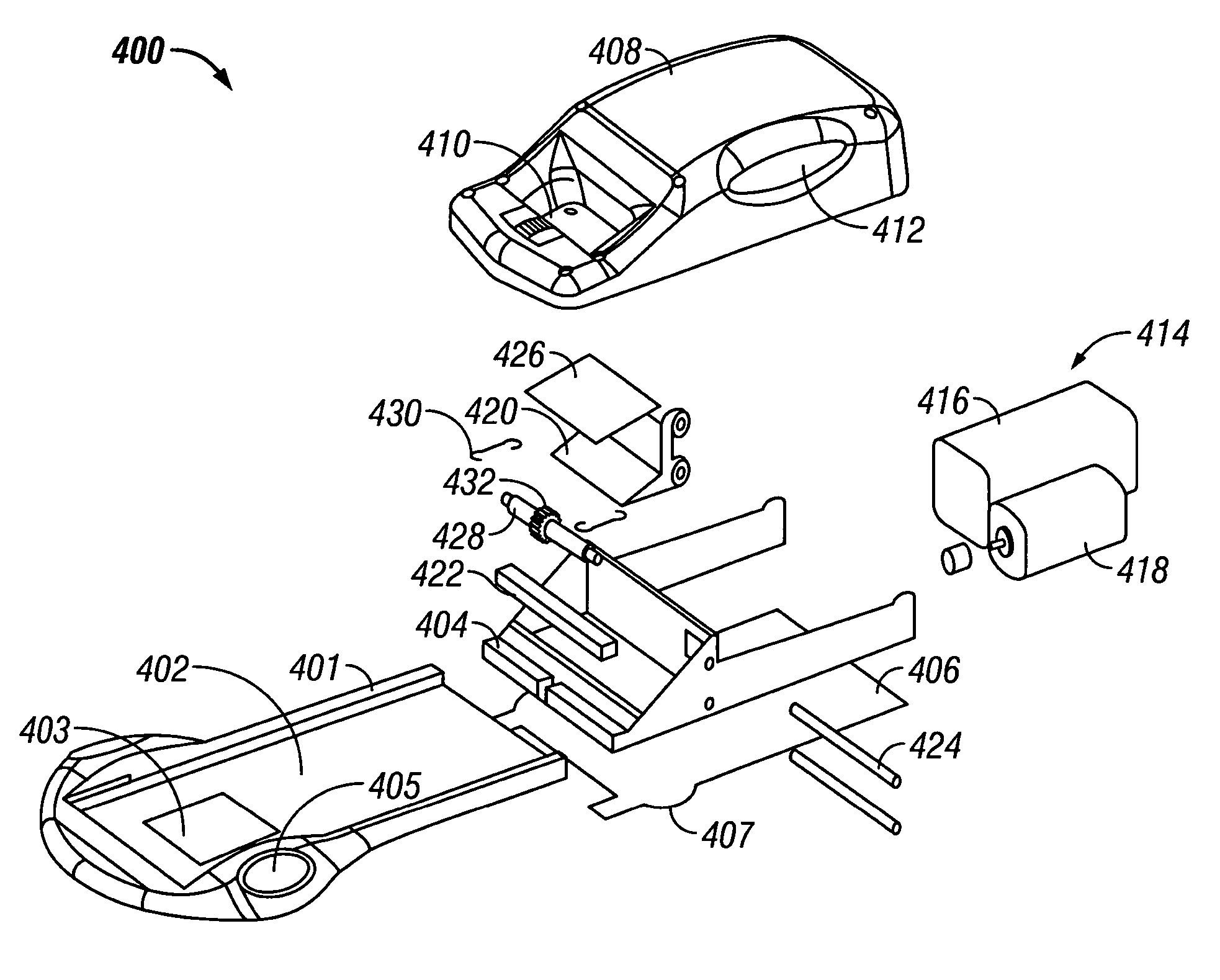
Systems and methods are provided for performing a hair transplant using a hair transplant device. The hair transplant device comprises a coring needle, a splitting needle, a housing, and a user interface. The coring needle forms a coring lumen configured to extract a hair follicle from a donor site. The splitting needle is configured to create an opening in a recipient site. The housing at least partially surrounds one of the coring needle and the splitting needle. The user interface extends from the housing and is movable relative to the coring needle to push the hair follicle from the coring lumen into the opening in the recipient site formed by the splitting needle.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Method and apparatus for tissue grafting
ActiveUS9827006B2Heal fastPromote healingIncision instrumentsSurgical needlesTissue GraftingBiomedical engineering
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
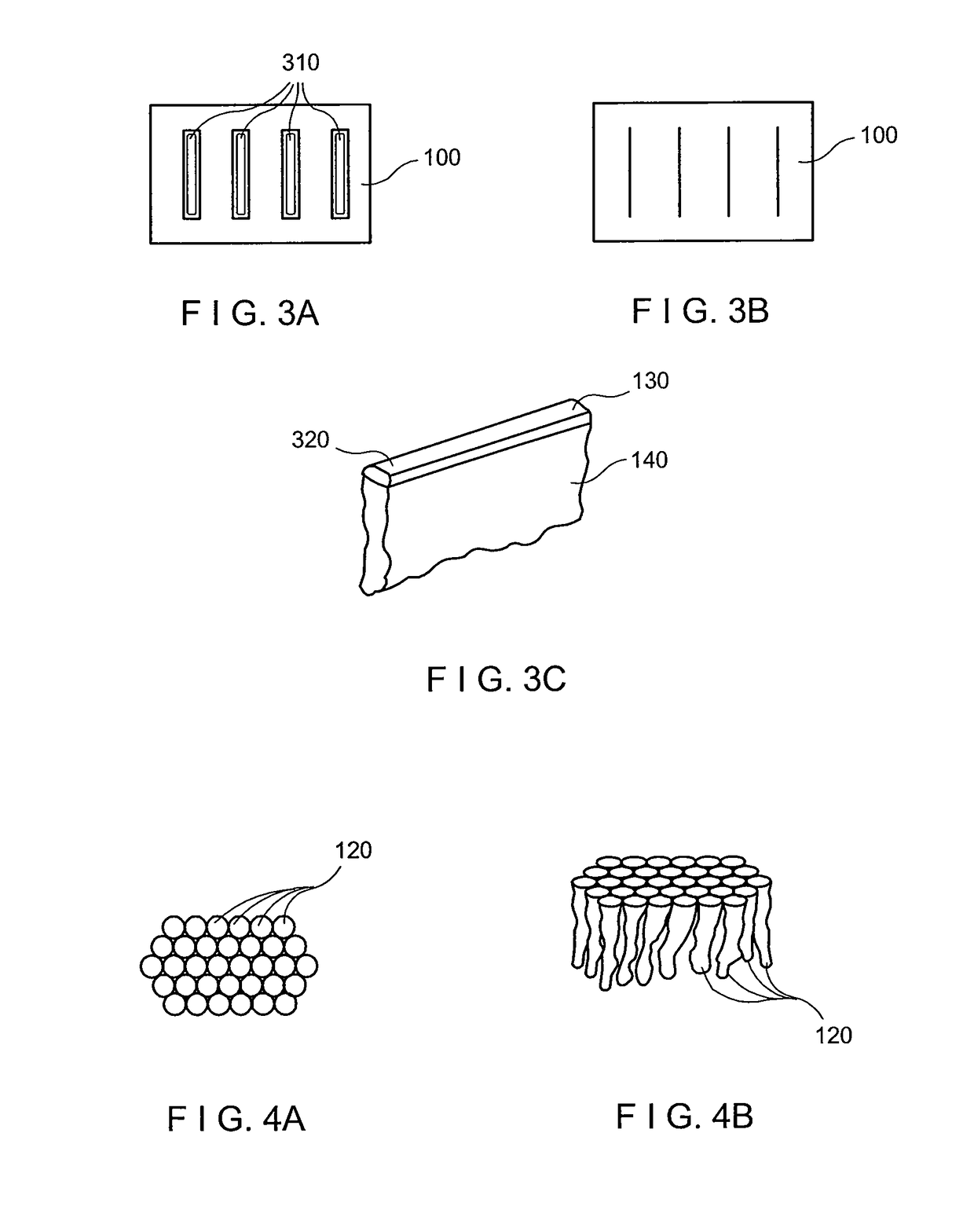
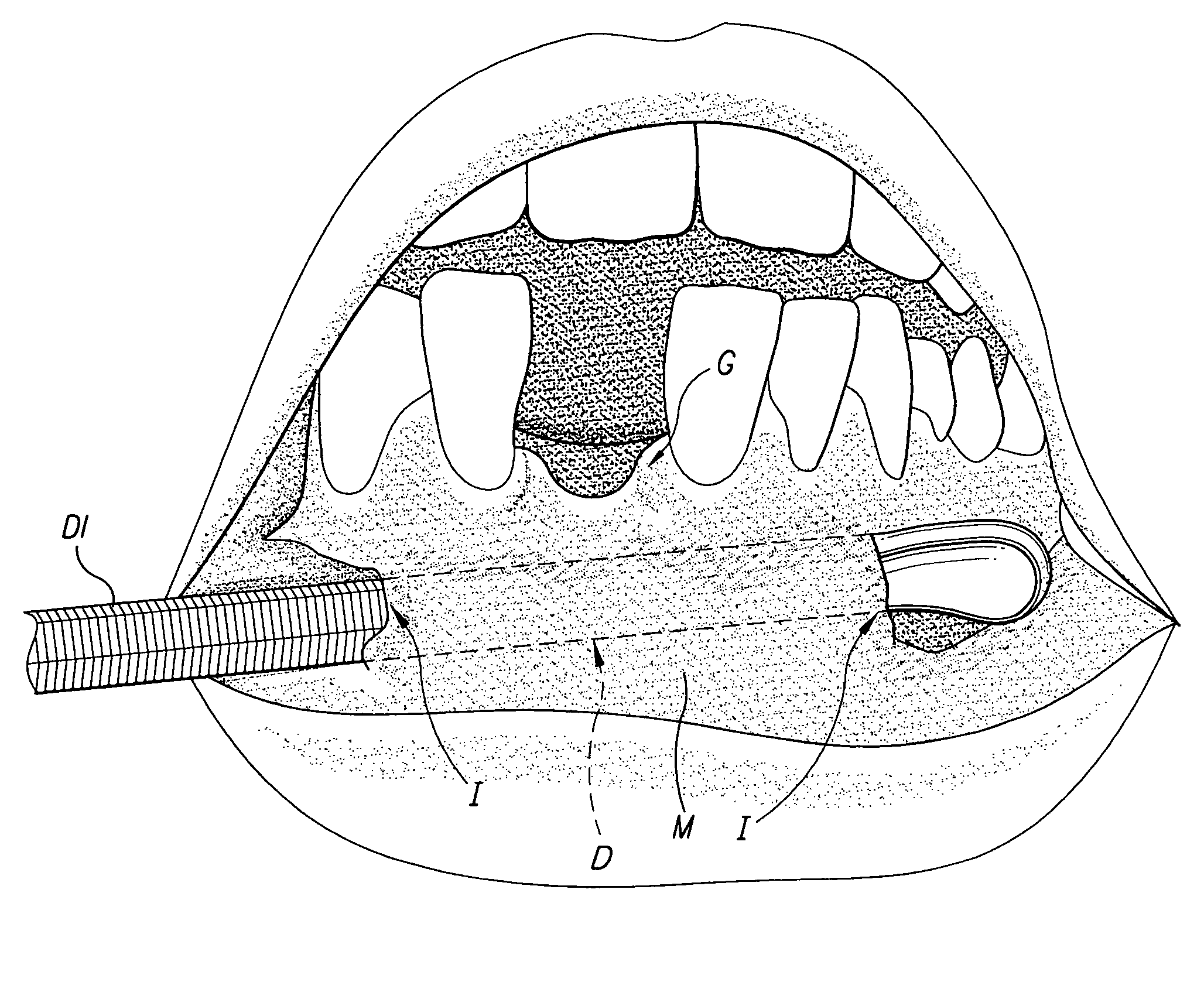
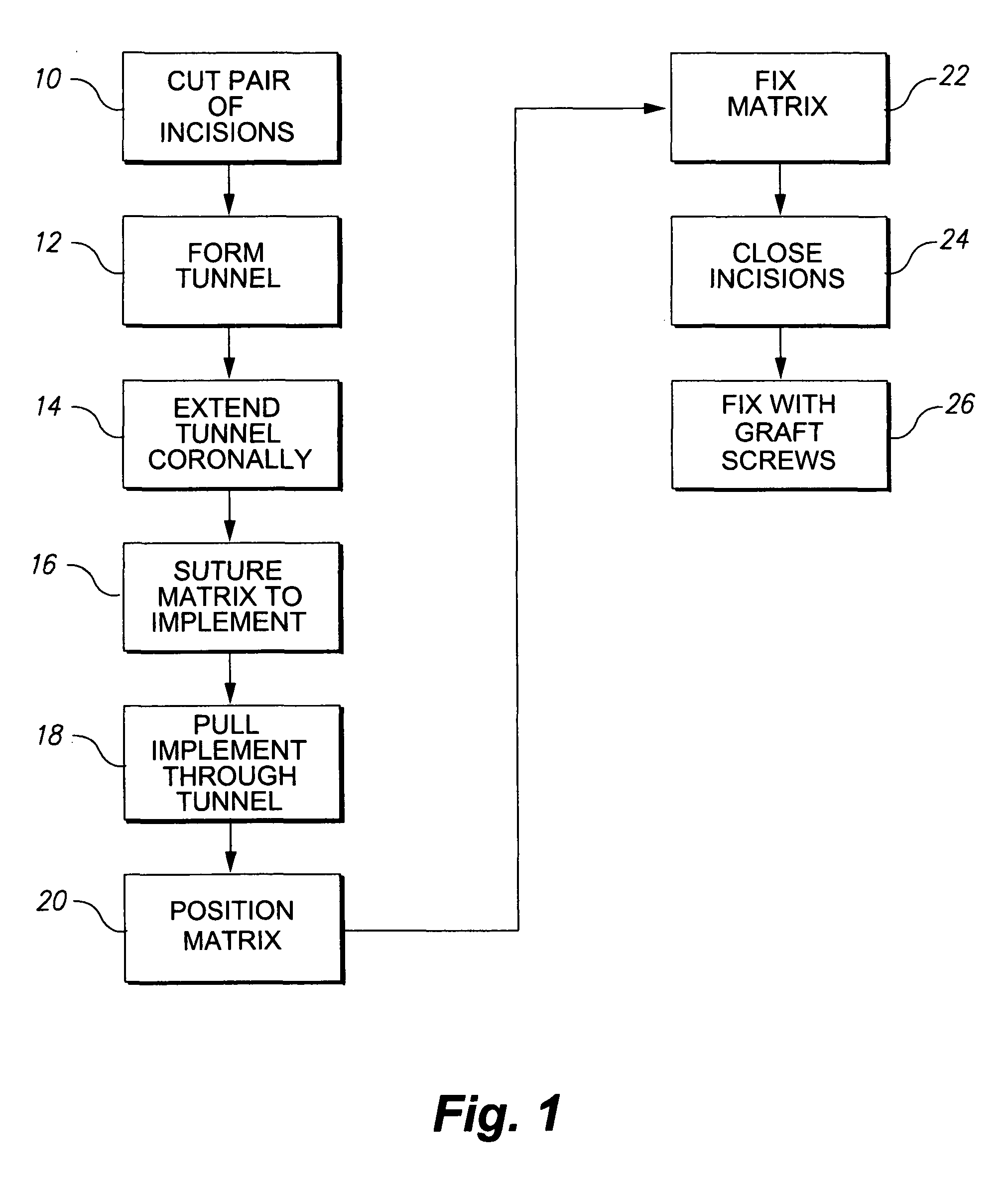
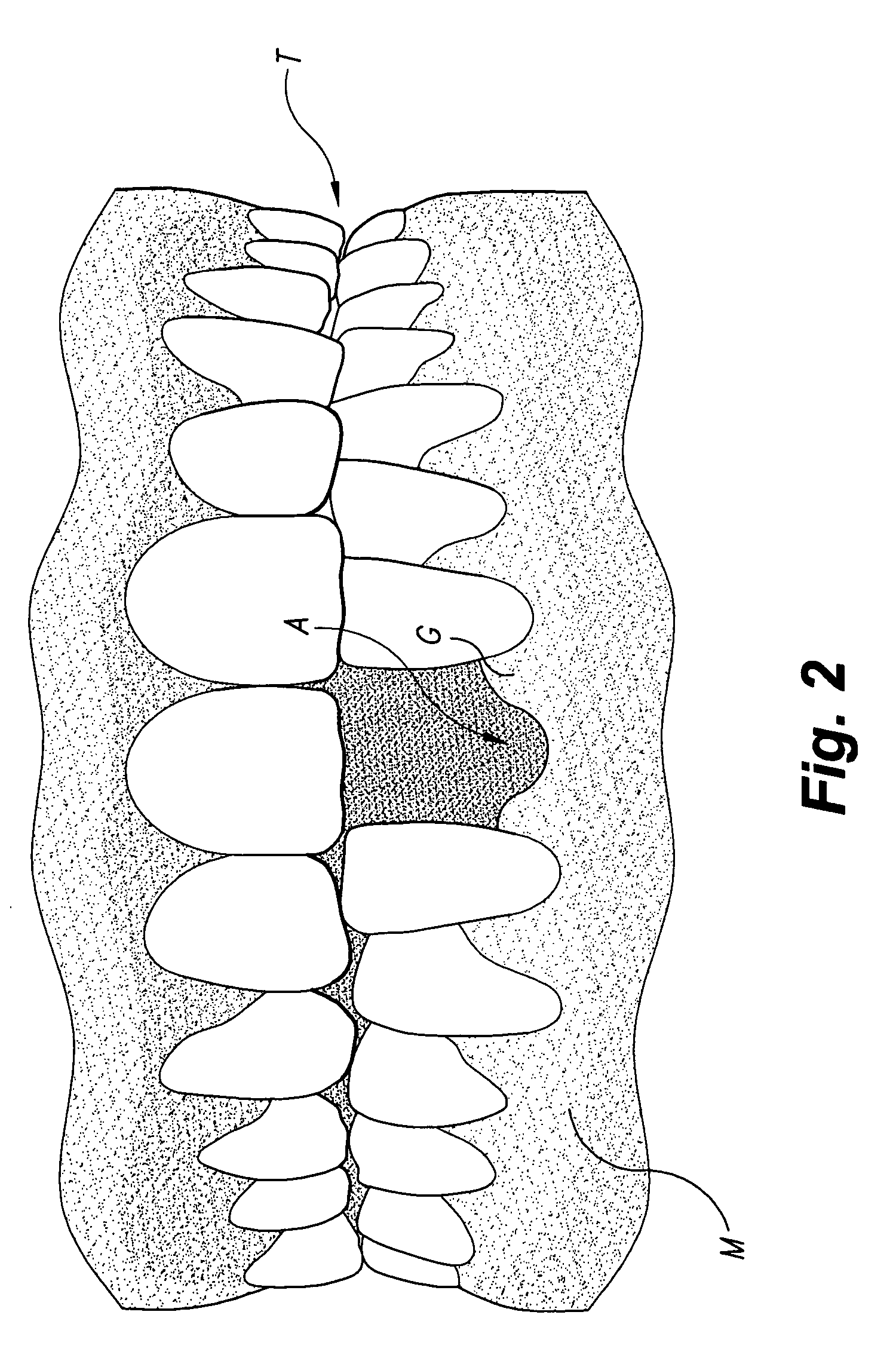
Tunneling method for dental block grafting
The tunneling method for dental block grafting is surgical method for increasing the thickness of the soft tissue of the mouth prior to performing block grafting procedures for dental implants. The method includes cutting a pair of incisions in the mucosa. A tunnel is formed through the mucosa which extends between, and connects, the pair of incisions. The tunnel is then extended coronally to undermine tissue covering the recipient site. An acellular dermal matrix is then sutured to an exposed end of a dental implement pulled through the tunnel to position the acellular dermal matrix within the tunnel. The acellular dermal matrix is then positioned over the recipient site using a periosteal elevator, and the acellular dermal matrix is fixed coronally by suspension sutures. The pair of incisions are closed with interrupted sutures, and a block graft is fixed to the recipient site by a pair of titanium screws.
Owner:KING ABDULAZIZ UNIV
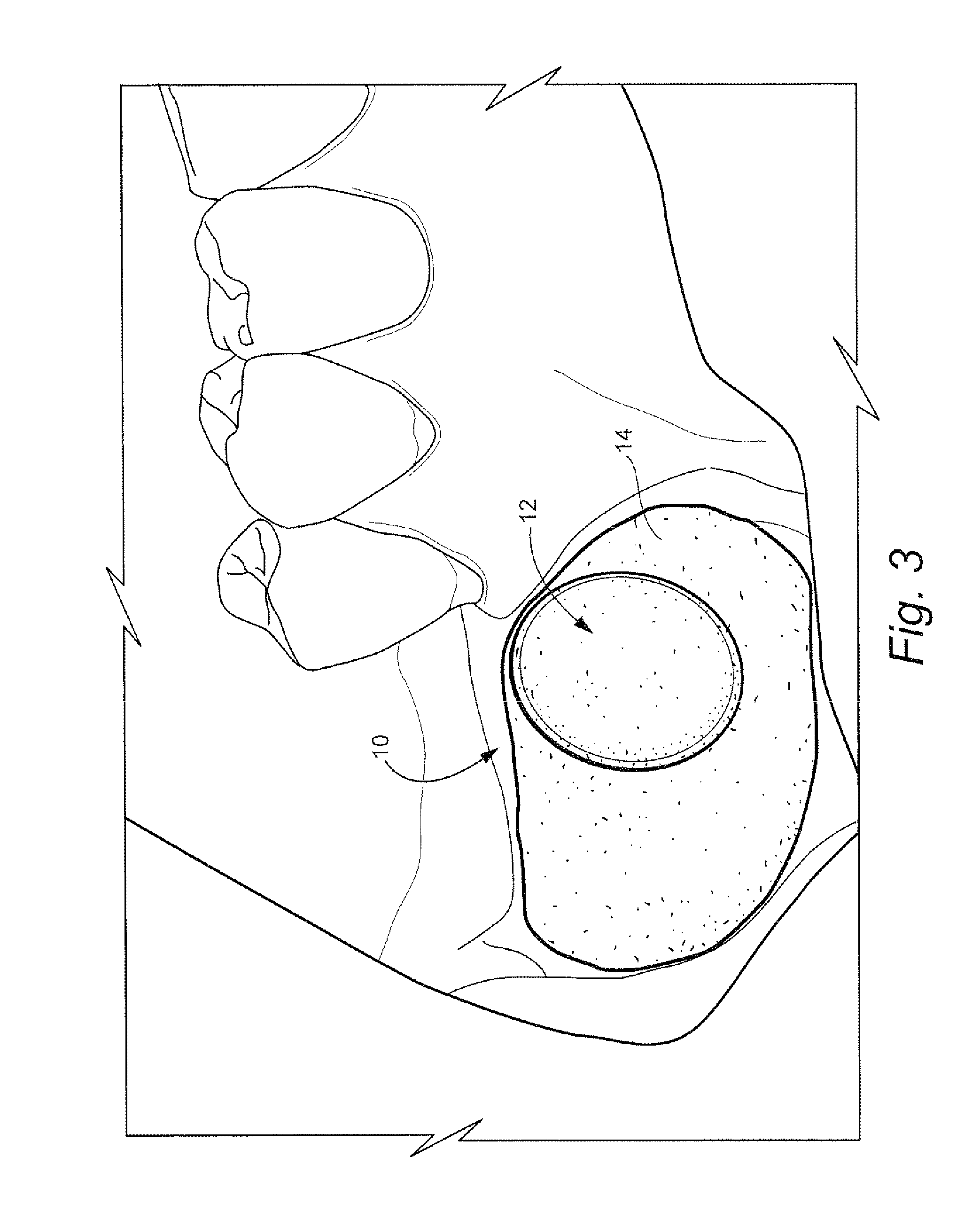
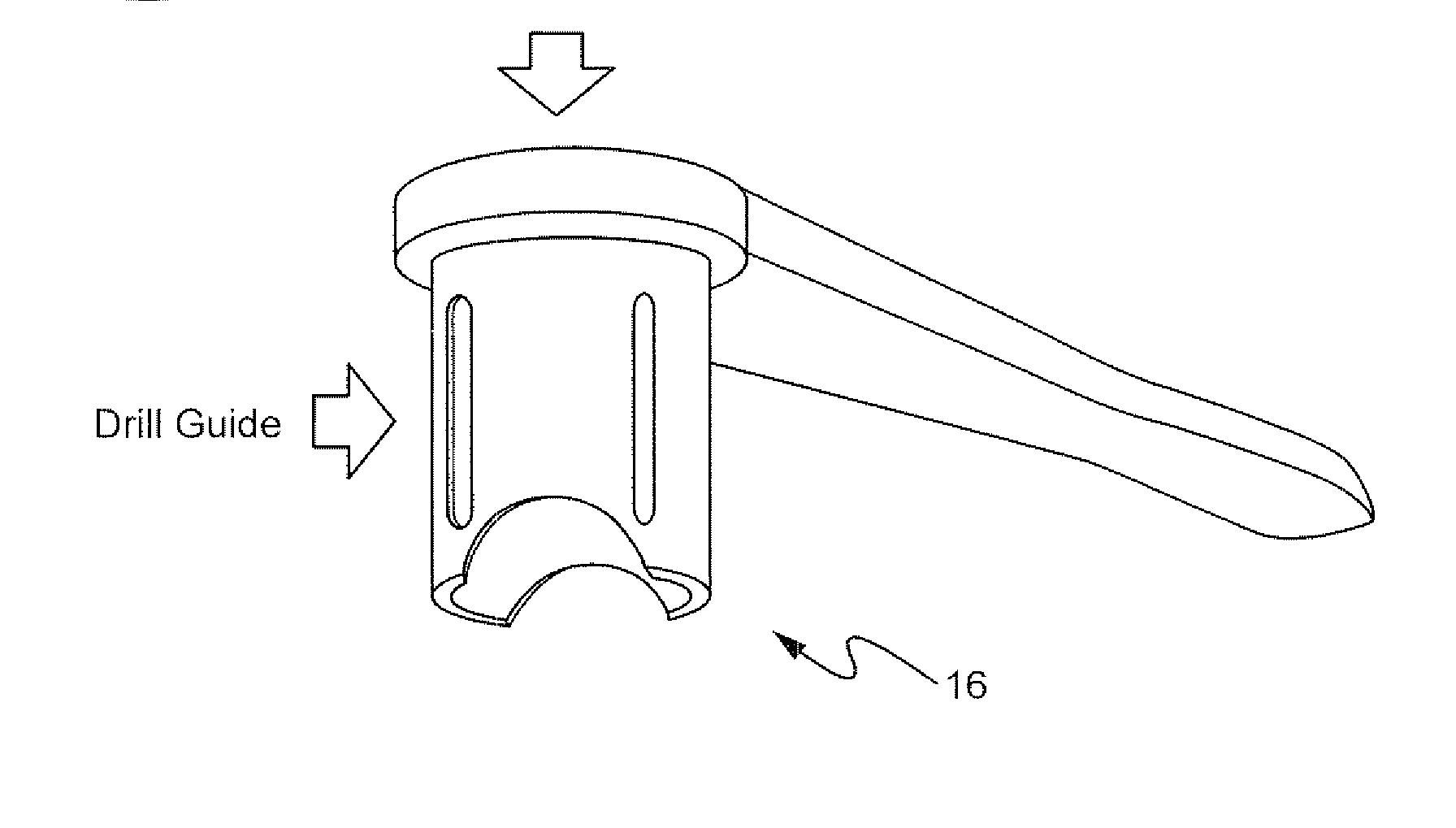
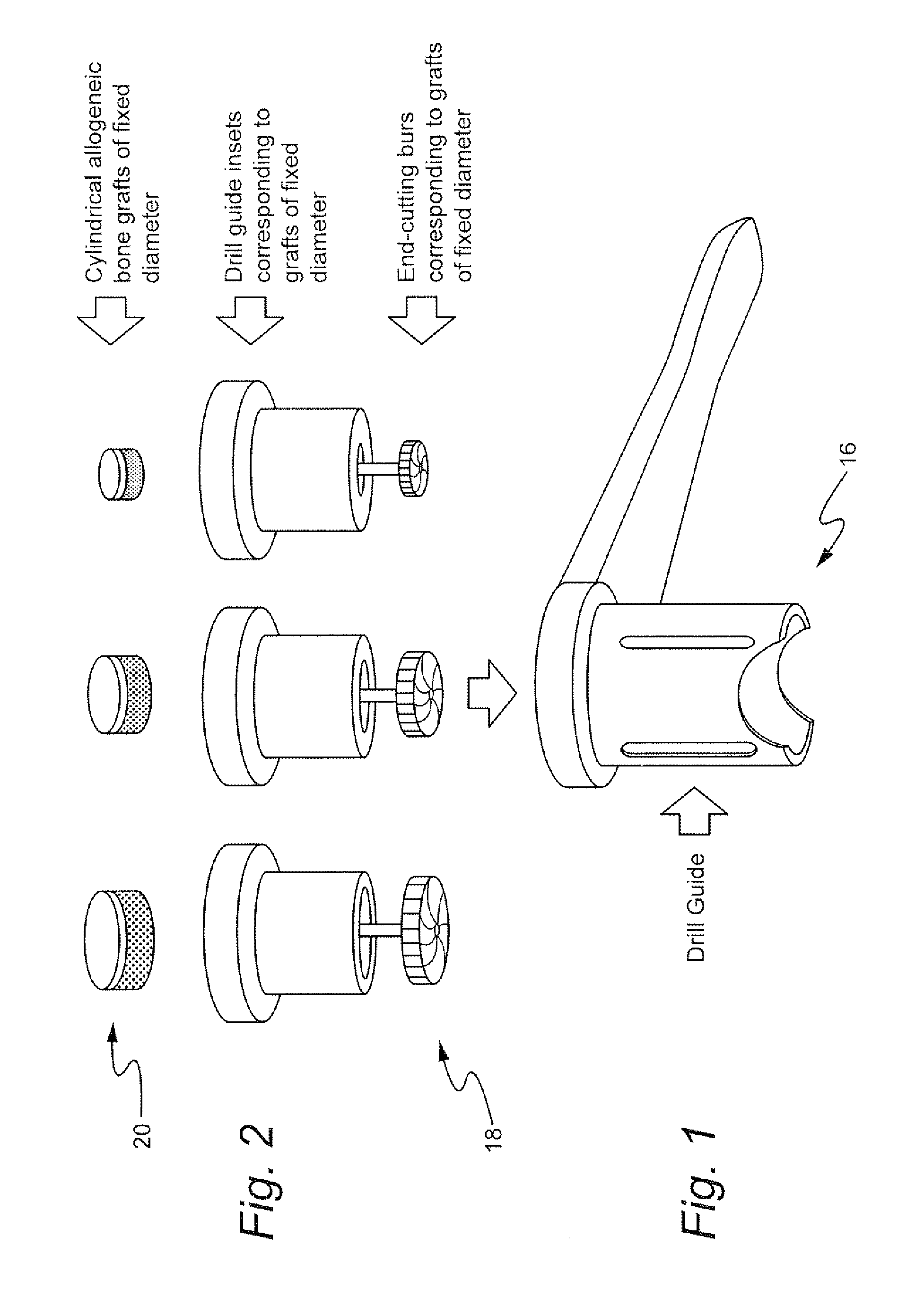
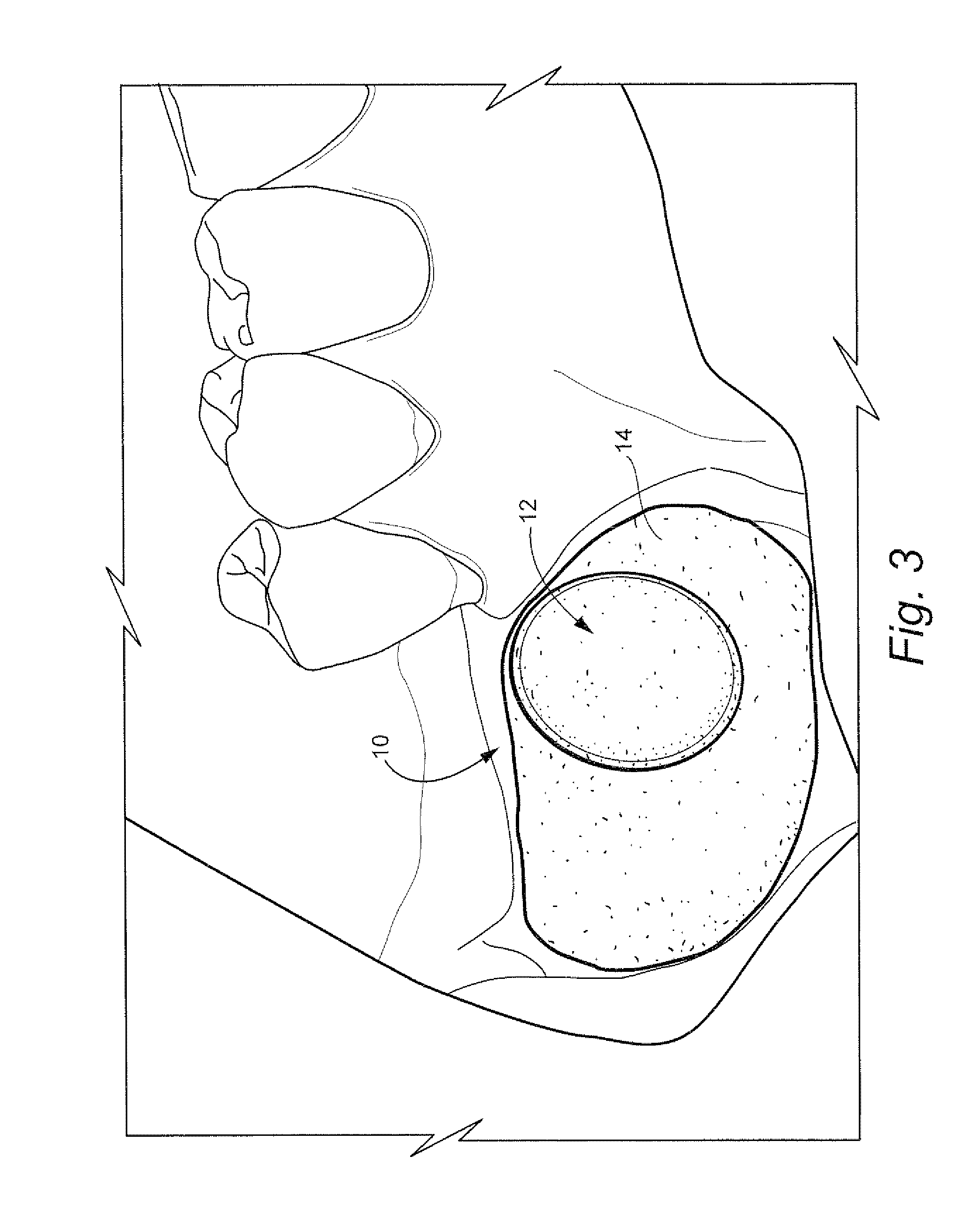
Method for preparing recipient site and implanting allogenic bone graft
A method of fixating allogeneic bone to an area of deficient bone in the jaws comprising: exposing the area of deficient bone by incising and retracting soft tissue; selecting a drill bit having a diameter corresponding to the area of deficient bone to receive donor bone; contacting the selected drill bit with the exposed deficient bone to form a generally cylindrical seat for receiving the donor bone; selecting a section of donor bone having a generally cylindrical shape and circular cross-section corresponding to said formed seat; fixating the donor bone to the formed seat with at least one screw; and closing the soft tissue to cover the previously exposed deficient bone.
Owner:SAWATARI YOH +1
Method for expansion of human corneal endothelial cells
A method for expanding human corneal endothelial cells includes: (a) providing an amniotic membrane with or without amniotic cells, wherein the amniotic membrane has an extracellular matrix; (b) placing onto the amniotic membrane, a sheet of endothelial layer, or a cell suspension including human corneal endothelial stem cells; and (c) culturing the corneal endothelial cells on the amniotic membrane for a duration sufficient for the corneal endothelial stem cells to expand to an appropriate area. The invention also relates to a method for creating a surgical graft for a recipient site of a patient using the method for expanding human corneal endothelial cells, and the surgical graft prepared therefrom.
Owner:TSAI RAY JUI FANG +1
Method of manufacturing block type scaffold
InactiveUS20170157858A1Fast and accurate treatmentTreatment effect be muchAdditive manufacturing apparatusBone implantJaw boneDICOM
Provided is a technique of manufacturing a scaffold for jaw bone or bone reconstruction, by which a scaffold is fast and accurately manufactured to be placed instantly after treatment and simultaneously a scaffold is manufactured to be stably placed in an irregular recipient site or a wide region such as a tumor. A method of manufacturing a block type scaffold include generating a three-dimensional (3D) image of a scaffold to be placed in a recipient site for bone reconstruction by using a medical image file (DICOM file) of CT image data, dividing the 3D image of the scaffold into a plurality of block images, and manufacturing the scaffold by outputting the 3D image of the scaffold by using a 3D printer, wherein a plurality of 3D objects corresponding to the plurality of block images are output to be separable from one another.
Owner:THE CATHOLIC UNIV OF KOREA IND ACADEMIC COOPERATION FOUND
Method for preparing recipient site and implanting allogenic bone graft
A method of fixating allogeneic bone to an area of deficient bone in the jaws comprising: exposing the area of deficient bone by incising and retracting soft tissue; selecting a drill bit having a diameter corresponding to the area of deficient bone to receive donor bone; contacting the selected drill bit with the exposed deficient bone to form a generally cylindrical seat for receiving the donor bone; selecting a section of donor bone having a generally cylindrical shape and circular cross-section corresponding to said formed seat; fixating the donor bone to the formed seat with at least one screw; and closing the soft tissue to cover the previously exposed deficient bone.
Owner:SAWATARI YOH +1
Fine particle tissue filling material for injection and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an injectable filling material of particle tissues, wherein particulate acellular bio-derived materials are mixed with drug-containing release microspheres, after the filling material is evenly mixed with a gel solution before use, the filling material is injected into a recipient site, an operator can arbitrarily model the particle tissue before gel is solidified according to the condition of the recipient site so as to achieve a satisfactory cosmetic effect. The particle tissue material which can be moulded rapidly is implanted in the body to fill defective soft tissues and promote wound healing. Compared with the prior art, the injectable filling material of the particle tissues has high biocompatibility, and is capable of rapid arbitrarily modeling and rapid filling the defect of tissue organs, and can promote fibroblast ingrowth, the formation of new capillary, generation of granulation tissue and wound healing. The injectable filling material of the particle tissues has the following clinical functions that the injectable filling material can be used as a filler of defective soft tissues which is used for repairing body depression deformity; for filling wrinkles or ruga of skins; and for demands of cosmetic surgeries, such as soft tissue arthroplasty and so on.
Owner:SHAANXI RUISHENG BIOTECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com