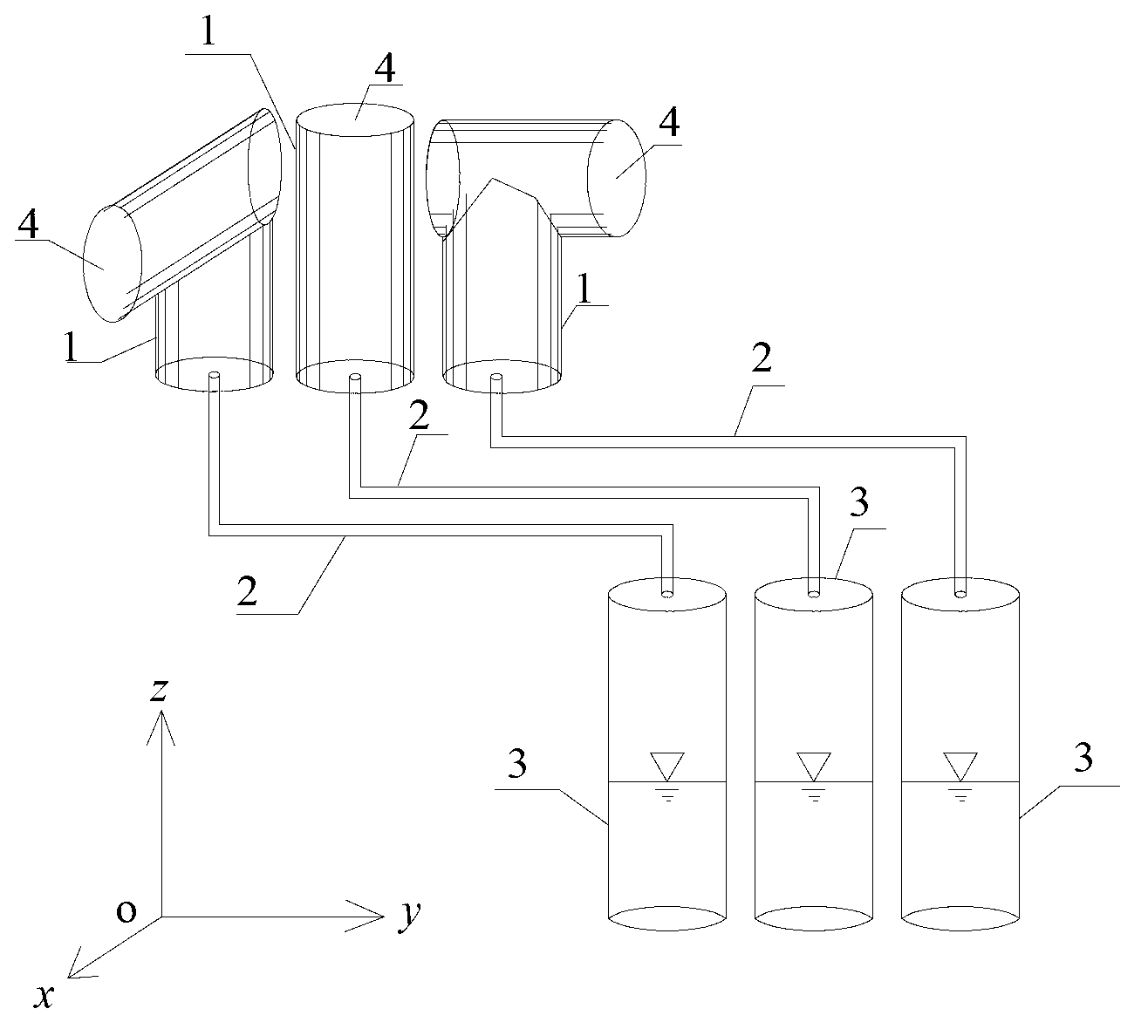
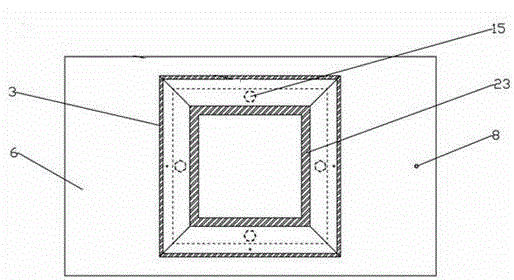
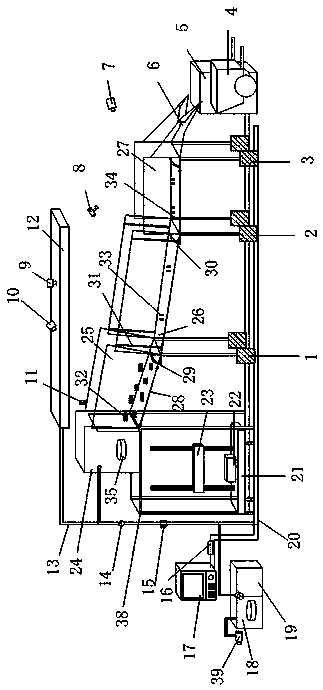
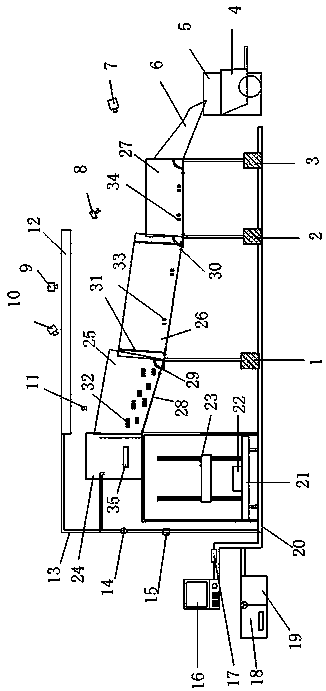
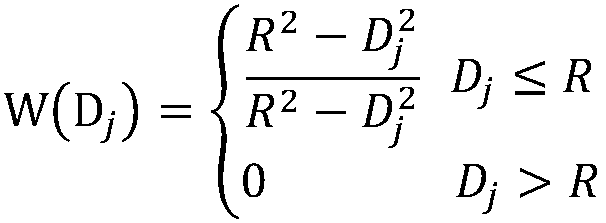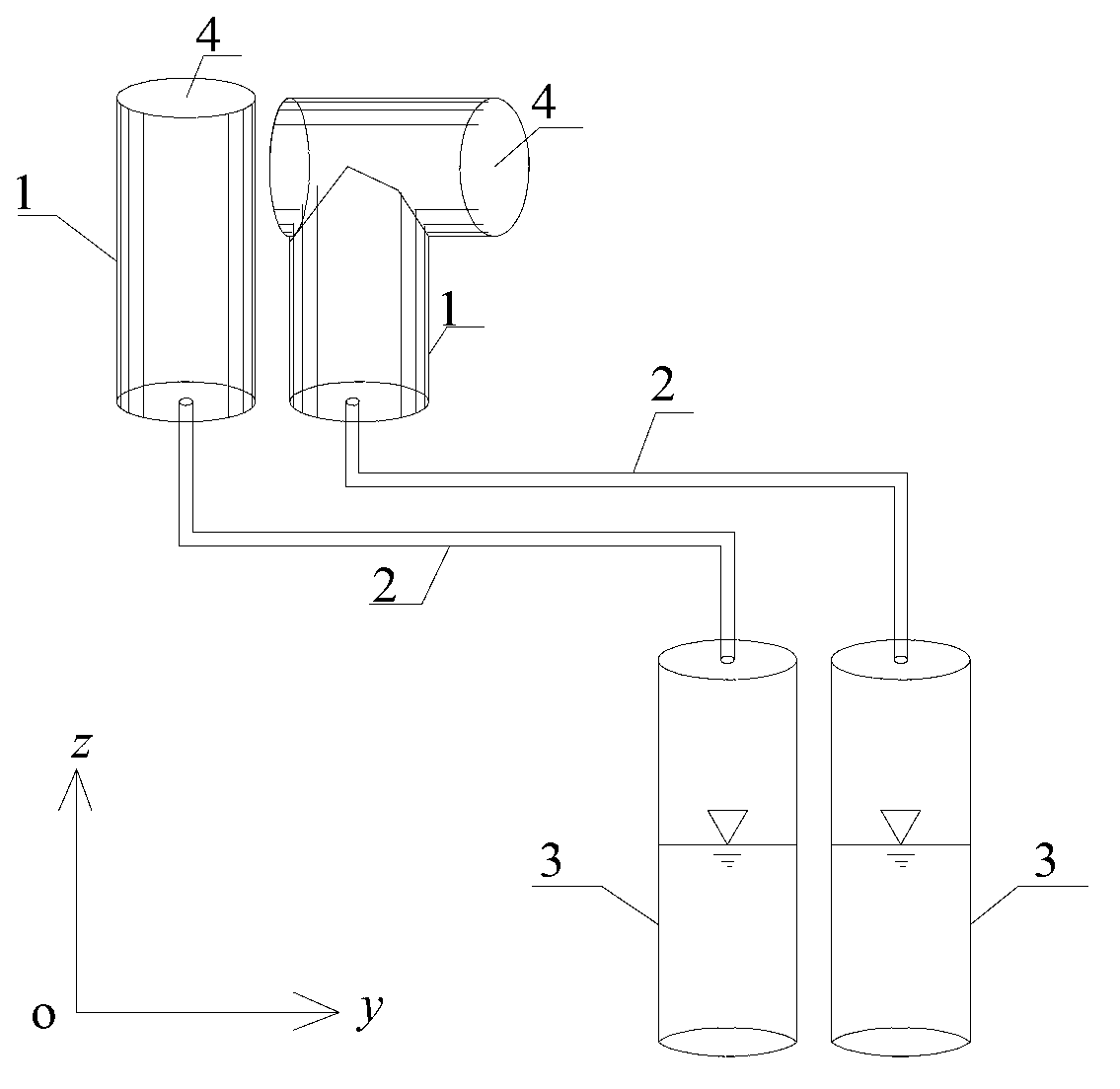Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
149 results about "Rain intensity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The intensity of rainfall is a measure of the amount of rain that falls over time. The intensity of rain is measured in the height of the water layer covering the ground in a period of time.
Regional automatic weather station hourly rainfall data quality control method
ActiveCN106950614AImproving Observational Data QualityRainfall/precipitation gaugesICT adaptationWeather radarRainfall estimation
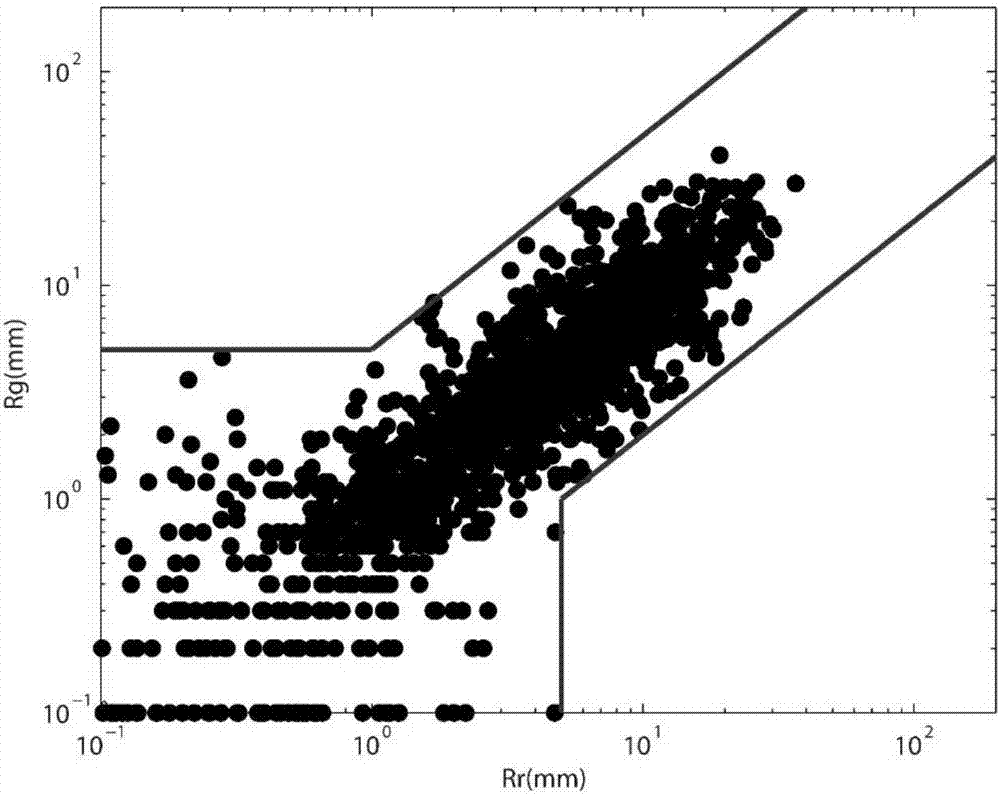
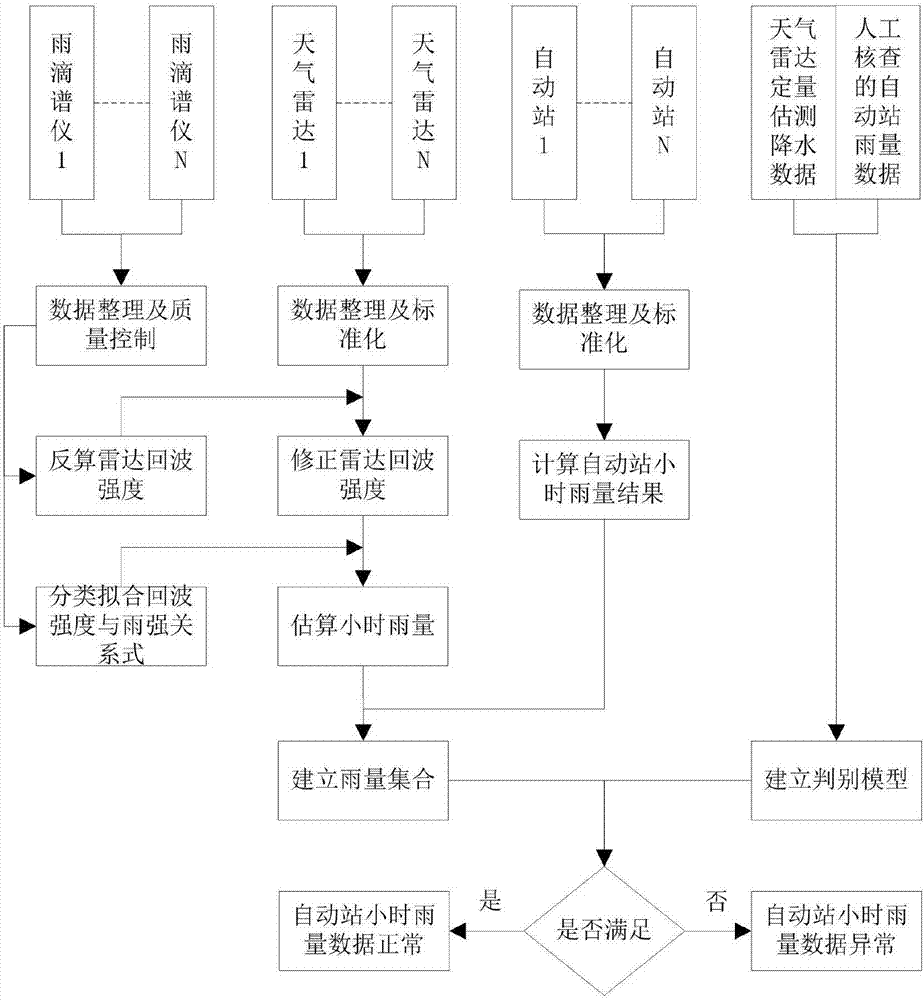
The invention discloses a regional automatic weather station hourly rainfall data quality control method. The method comprises the steps that a discriminant model is established according to historical data; raindrop spectrometer data, weather radar data and automatic weather station rainfall data are collated in real time; the data of a number of raindrop spectrometers are used to evaluate and revise a radar echo intensity result; the relationship between the radar echo intensity and the rain intensity is fitted according to different precipitation types; the fitted relationship is substituted into a radar quantitative estimation precipitation module to realize radar quantitative rainfall estimation to acquire hourly rainfall; the set of weather radar estimated hourly rainfall and regional automatic weather station hourly rainfall is established; and comparing with the pre-established discriminant model is carried out to judge whether the regional automatic weather station hourly rainfall data are abnormal. The automatic weather station rainfall data are accurate and reliable. The observation data quality is improved. The method lays a good foundation for weather monitoring, early warning, forecasting and other businesses.
Owner:中船鹏力(南京)大气海洋信息系统有限公司
NRIET X-band radar cooperative networking analysis method
InactiveCN108693534AImprove spatial resolutionImprove time resolutionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationClassification methodsRain intensity
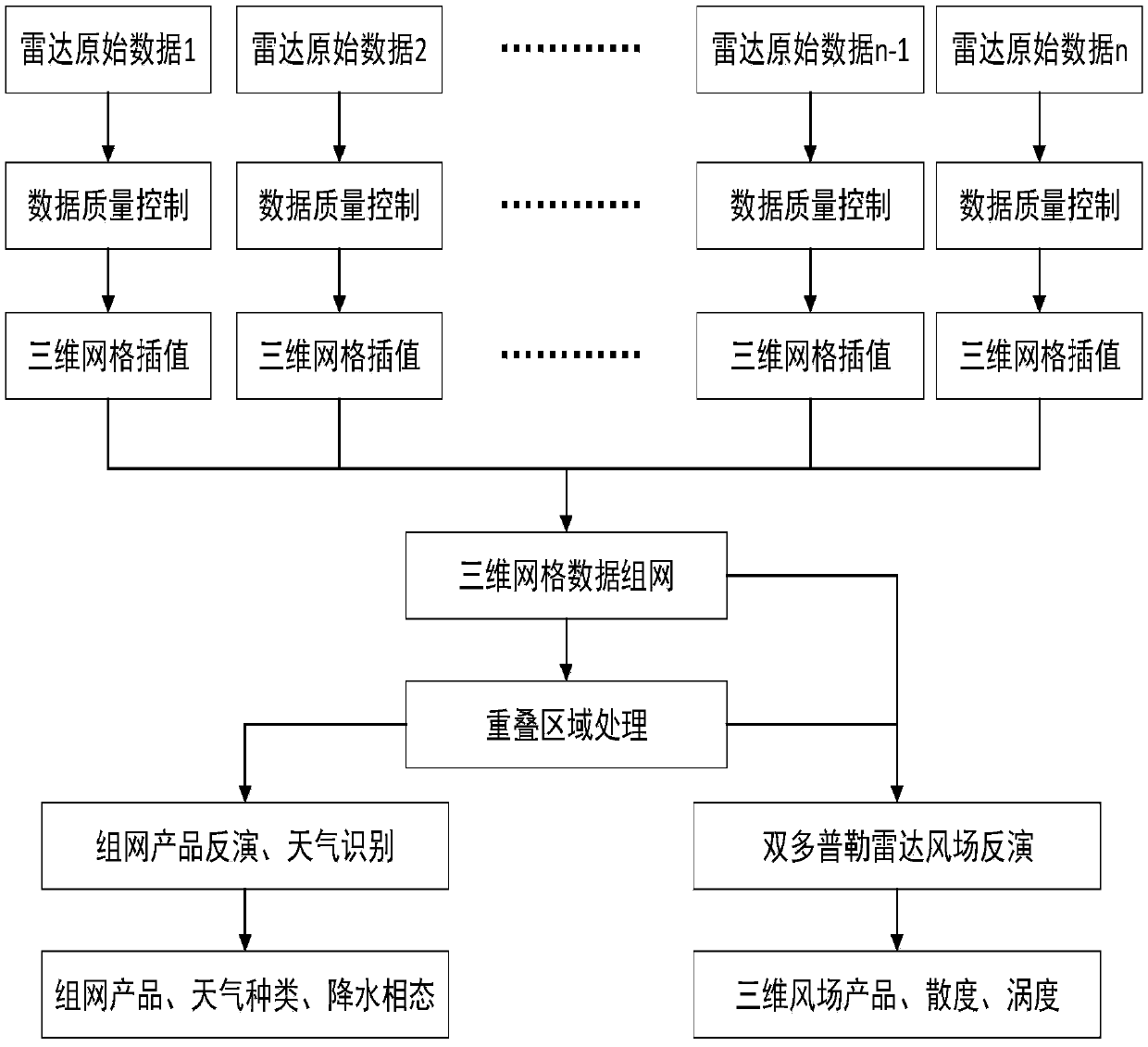
The invention discloses a NRIET X-band radar cooperative networking analysis method. The method comprises the steps that data are collected; the data quality is controlled; a distance weight interpolation technology is used, and a three-dimensional cressman interpolation method is used to perform lattice interpolation on radar echo, radial wind and each polarization; three-dimensional data networking is carried out; for a three-dimensional wind field inversed by a dual Doppler radar, the inversed wind field is constrained by a mass continuous equation, and the three-dimensional wind field is acquired by repeatedly iteratively solving the equation; the vertical velocity w is acquired by the mass continuous equation, and a trace boundary condition is used to adjust a vertical motion field, wherein the upper boundary of the mass continuous equation is set to integrate down; based on a radar product reflectivity algorithm, a combined reflectivity puzzle product and an echo top puzzle product are generated; through Z-R relationship, quantitative precipitation is estimated to acquire a rain intensity product; a texture classification method is used to identify a precipitation stratus convection region; and a fuzzy logic algorithm is used to recognize the phase state of precipitation particles in each region at different stages of a precipitation process.
Owner:NANJING NRIET IND CORP
A rainfall observation method integrating satellite remote sensing and mobile communication base station signals
ActiveCN109697323AHigh precisionOvercoming deficiencies that are difficult to verifyRainfall/precipitation gaugesClimate change adaptationRain intensityDrainage basin
The invention discloses a rainfall observation method integrating satellite remote sensing and mobile communication base station signals, which comprises the following steps of: for each microwave link in a target area, respectively establishing the connection between rain attenuation and rain intensity by adopting different rain attenuation and rain intensity models, and deducing the corresponding link rainfall intensity; dividing grids for the target area, and deducing the regional rainfall capacity under different rain attenuation and rain intensity models in the historical period; optimizing a rain attenuation and rain intensity model through large-scale observation data in a historical period of satellite remote sensing; and observing real-time rain intensity information with high spatial resolution based on real-time dynamic rain attenuation data of the mobile communication base station by adopting the optimized rain attenuation and rain intensity model. The method gives full play to the advantages of a satellite remote sensing rainfall observation technology and a microwave link real-time rainfall intensity observation technology, provides a real-time, dynamic and high-precision rainfall observation mode, and can provide important and highly operable reference basis for flood prevention and disaster reduction and drainage basin planning.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Optical moisture sensor
ActiveUS20110054794A1Rainfall/precipitation gaugesBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsRain intensityMoisture sensor
A moisture sensor is provided that simultaneously achieves ruggedness, sensitivity, wide dynamic range, versatility of application, and low cost. The outer, top service of the sensor is a lens having a predetermined geometric shape which preferably makes the rain sensor resistant to the build up of debris on the outer surface as well as being effectively self-cleaning. Within a housing of the rain sensor, at least one light emitter and at least one light detector are each deployed on a substantially planar circuit board facing such outer lens surface. So arranged, light rays from the at least one emitter strike the outer lens surface and is reflected about 90°, whereupon it strikes the outer lens surface once more and is again reflected therefrom about 90° to focus back onto the at least one detector. Raindrops present on the outside surface of the sensor affect the intensity of the light rays reflected and signals from the at least one light detector are sent to control circuitry within the rain sensor. A microprocessor in the sensor processes the resulting data to detect rain intensity over a wide range so as to be capable of being effectively deployed for applications such as to emulate a tipping bucket style rain detector, providing condensation sensing, and automatically adjusting the strength of the light rays emitted by the at least one light emitter to provide improved consistency of operation of the sensor over time.
Owner:HYDREON CORP
Windshield wiper controller, optical raindrop detector and detection method thereof
ActiveUS20130275007A1Eliminate distractionsImprove recognition accuracyDigital data processing detailsInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsLight guideRain intensity
There is provided an optical raindrop detector including a light source, a light guide, an image sensor and a processing unit. The light source alternatively emits light with different brightness values. The light guide has an incident surface, a detection surface and an ejection surface, wherein the light source emits incident light into the light guide via the incident surface, and a plurality of microstructures are formed on the ejection surface to reflect the incident light to become scattered light toward the detection surface. The image sensor receives reflected light formed by raindrops in front of the detection surface reflecting the scattered light to penetrate the light guide and eject from the ejection surface, and generates image frames corresponding to the different brightness values of the light source. The processing unit calculates differential images of the image frames to accordingly identify rain intensity.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
X-band weather radar and rainfall station data fusion method and system
ActiveCN108761576AImprove estimation accuracyReasonable structure distributionRainfall/precipitation gaugesICT adaptationWeather radarWeight coefficient
The invention discloses an X-band weather radar and rainfall station data fusion method and system. The method comprises a step of acquiring rainfall station rainfall data measured by the rainfall stations covered by a whole detection area of a meteorological radar, a step of acquiring radar echo intensity data generated by the meteorological radar and latticing the radar echo intensity data toobtain lattice point echo intensity data, a step of inverting the lattice point echo intensity data into lattice point rain intensity data and obtaining original lattice point rainfall data in a wholerainfall process through a linear average accumulation method, a step of searching rainfall stations in a certain range with a lattice point as a center and calculating a distance weight coefficientof the grid point based on the distance between the grid point and a searched rainfall station, and a step of fusing the rainfall station rainfall data of measured by the rainfall stations to the original lattice point rainfall data of the lattice point with the combination of the distance weight coefficient to obtain grid rainfall data after the grid fusion. According to the system, a distance weight coefficient fusion method is used to improve the estimation accuracy of the regional rainfall.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST STATE GRID SHANXI ELECTRIC POWER +1
Method for measuring intensity of atomization rainfall formed by flood discharge in hydropower engineering
ActiveCN102841390AImprove regularityHigh precisionRainfall/precipitation gaugesAtmospheric sciencesRain intensity
The invention belongs to the field of hydraulic and hydro-power engineering, and relates to a method for measuring the intensity of atomization rainfall formed by flood discharge in hydropower engineering. The method comprises the following steps of: collecting atomization rain by using two or three rain collecting tanks, wherein the shapes of the inlets of the rain collecting tanks is completely same, and each inlet plane is vertical to each other on space; respectively gathering the collected rainfall in corresponding water measuring tank by independent guide pipes to measure the intensity of the rainfall, and finally, calculating by subjecting the measured intensity of rainfall to a vectorial resultant to obtain the corresponding total atomization rainfall intensity and the rainfall direction. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for the observation of a model and a proto-model of the atomization rainfall in hydropower engineering, and the measured rainfall intensity data is excellent in regularity and high in precision, so that the research on the mechanism of atomization of flood discharge is prompted greatly, the atomization forecast accuracy of hydropower station engineering is enhanced, and the reliable guarantee is provided to the prevention of the disaster of atomization of flood discharge.
Owner:NANJING HYDRAULIC RES INST
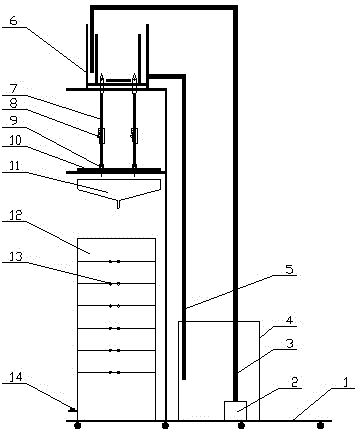
Multifunctional indoor rain water infiltration simulating experiment device for unsaturated soil
InactiveCN104458529APermeation Process MonitoringReal-time determination of permeation parametersPermeability/surface area analysisSuction forcePore water pressure
The invention discloses a multifunctional indoor rain water infiltration simulating experiment device for unsaturated soil. A plurality of water penetrating holes are formed in the middle of an experiment device platform; the upper surface of the experiment device platform corresponding to the water penetrating holes is connected with a cuboid demountable rigid retaining wall; a closed pressure water container of which the water pressure is adjustable is mounted on the lower surface of the experiment device platform; a plurality of prepared holes are formed in the outer wall of the cuboid demountable rigid retaining wall; the pressure water container and a closed water supply tank are connected with a pressure pump through a pneumatic valve. After the adoption of the technical scheme, the rain water infiltration simulating experiment device has the benefits that rain intensity and rainfall duration are controlled by adjusting the pressure pump and a flow control valve to realize simulation of rainfall working conditions; physical mechanical parameters of water content of unsaturated soil, suction force of base material, and the like during a rain water or underground water level lifting process can be monitored in real time through the sensors inserted in the prepared holes in the rigid retaining wall.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Optical moisture sensor
ActiveUS8271198B2Rainfall/precipitation gaugesBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsRain intensityWide dynamic range
A moisture sensor is provided that simultaneously achieves ruggedness, sensitivity, wide dynamic range, versatility of application, and low cost. The outer, top service of the sensor is a lens having a predetermined geometric shape which preferably makes the rain sensor resistant to the build up of debris on the outer surface as well as being effectively self-cleaning. Within a housing of the rain sensor, at least one light emitter and at least one light detector are each deployed on a substantially planar circuit board facing such outer lens surface. So arranged, light rays from the at least one emitter strike the outer lens surface and is reflected about 90°, whereupon it strikes the outer lens surface once more and is again reflected therefrom about 90° to focus back onto the at least one detector. Raindrops present on the outside surface of the sensor affect the intensity of the light rays reflected and signals from the at least one light detector are sent to control circuitry within the rain sensor. A microprocessor in the sensor processes the resulting data to detect rain intensity over a wide range so as to be capable of being effectively deployed for applications such as to emulate a tipping bucket style rain detector, providing condensation sensing, and automatically adjusting the strength of the light rays emitted by the at least one light emitter to provide improved consistency of operation of the sensor over time.
Owner:HYDREON CORP
Laser raindrop spectrograph
InactiveCN101866022ARealize continuous automatic observationRealize continuous acquisitionRainfall/precipitation gaugesICT adaptationArea networkLaser array
The invention discloses a laser raindrop spectrograph capable of continuously and automatically observing, which is characterized in that laser array arranging method is utilized to continuously detect the size, the number and the speed of raindrops, and raindrop spectrum parameters of rainfall, rain intensity and the like are computed according to measured raindrop particle information. A control system comprising DSP (Digital Signal Processor) and a field programmable gate array FPGA is arranged, wherein the FPGA is responsible for completing the data acquisition of each pixel in a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) laser array, and parallel computing ability of the FPGA is shown and an image edge detection arithmetic is utilized to compute the size, the number and the speed of the raindrops; and the DSP analyzes and computes the raindrop spectrum parameters according to the information of the size, the number and the speed of the raindrops and uploads the raindrop spectrum parameters to an upper machine at definite time through a CAN (controller area network) bus.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Calibrating device of field calibration rainfall sensor
The invention relates to a calibrating device of a field calibration rainfall sensor. The calibrating device comprises an outer casing and a combined funnel, a counter and two water outlet pipes arranged inside the outer casing, wherein the top surface of the outer casing is provided with a great / small rain intensity water injection hole capable of simulating rain water flow speed, a reset button inlaid with a counter liquid crystal display screen and the counter as well as a conducting wire plug jack; the upper opening edge of the combined funnel is fixedly connected with the inner side circumference of the top surface of the outer casing; the inside of the combined funnel is provided with a middle clapboard; the upper end of the middle clapboard is propped on the inner side of the top surface of the outer casing, while the lower end is positioned on the bottom of the combined funnel; the middle clapboard and the combined funnel are formed into an integrated structure; and the bottom of the combined funnel is respectively provided with two water outlet pipes simulating great / small rain intensity flow speed, and the two water outlet pipes simulating the rain intensity flow speed and the combined funnel are formed into an integrated structure. The calibrating device has the advantages that the device has scientific design, compact structure and stable and reliable technical performance and can carry out field calibration of an ombrometer. Therefore, the calibrating device can be widely used in nation-wide observatories, hydrological stations, armies and scientific research institutions to carry out the field calibration of the rainfall sensors.
Owner:LIAONING METEOROLOGIC INFORMATION & TECHN SAFEGUARD CENT
Automatic rainstorm runoff sampling and monitoring device and method
ActiveCN109000976ASolve sealing, storage problemsTo achieve most of the collectionRainfall/precipitation gaugesWithdrawing sample devicesWater qualityBottle
The invention discloses an automatic rainstorm runoff sampling and monitoring device and an automatic rainstorm runoff sampling method. The automatic rainstorm runoff sampling and monitoring device comprises a base, a power supply, and a rainfall collector, a flow monitor, a signal transceiving and data storage device and a water sample collecting, sealing and storing integrated device which are mounted on the base and connected with the power supply, and a sampling bottle turnplate system connected to the upper side of the water sample collecting, sealing and storing integrated device. Through use of the automatic rainstorm runoff sampling and monitoring device, automatic collection, monitoring and storage of a runoff water sample in the field can be achieved. Through the automatic watersample collecting, sealing and storing integrated device, the sealing and storage problems of the water sample are solved; through the rainfall monitor and the flow monitor, device opening is achievedon the basis of the rain intensity, and during collection and monitoring, the function of collecting more rainwater at a large flow, collecting less rainwater at a small flow is achieved; through a water quality monitoring probe, the function of monitoring physical indexes of the water quality while the water sample is collected is achieved.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
Method for generating control signals adapted to be sent to actuators in a water drainage network
ActiveUS20180356772A1Maximizing volume of waterVolume maximizationProgramme controlElectric controllersControl signalActuator
The inventions comprises a computer implemented method for generating control signals adapted to be sent to actuators, such as gates and pumps, in a water drainage network DN in an area, said method comprising—receiving DN data comprising one or more of DN topology of the area, rain intensity measures, water level measures, from the sensors or from an external source,—generating or receiving objective functions to optimize,—receiving a selection of a multi-objective optimization method, this multi-objective optimization preferably comprising lexicographic method or weighted sum method,—generating an optimization problem,—solving the optimization problem thereby generating the strategies to be sent to actuators in the water drainage network DN.
Owner:SUEZ INT
Method for measuring rainfall intensity in real time by using tipping-bucket rain gauge
InactiveCN104503001AHigh precisionEasy to maintain laterRainfall/precipitation gaugesICT adaptationUltrasound attenuationRain gauge
The invention discloses a method for measuring rainfall intensity in real time by using a tipping-bucket rain gauge. The method comprises the following steps: placing the tipping-bucket rain gauge into a rainfall measuring area, initializing a system coefficient, and starting a rainfall intensity measuring system; circularly detecting whether a tipping bucket is overturned or not in a time slice T; if the tipping bucket is overturned, calculating instant rain intensity E by using the overturning time interval t of the tipping bucket, and entering next circulation; otherwise, judging whether t exceeds a maximum value tmax or not; if t exceeds the maximum value, judging that rainfall does not occur, E=0, and entering next circulation; otherwise, judging whether attenuation waiting time tdec exceeds an attenuation time limit t'thd or not, executing rain intensity attenuation processing if the attenuation waiting time tdec exceeds the attenuation time limit t'thd, and entering next circulation. By adopting the method, the problems of poor accuracy and poor instantaneity in calculation of the tipping-bucket rain gauge are solved, and batch application of the tipping-bucket rain gauge to the industries or fields of traffic needing real-time rain intensity measurement is facilitated.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
Adjustable debris flow starting simulation experiment system under combined action of rainfall and confluence
PendingCN108335612AUniform surface flowUniform foggy rainfallEducational modelsWater flowEngineering
The invention relates to an adjustable debris flow starting simulation experiment system under combined action of rainfall and confluence. The bottom of a material tank of the experiment system can bereplaced, so that not only can the matching degree of the roughness of the bottom of the tank with an original experiment soil body be ensured, but also the water permeability of the bottom of the tank can be fully considered; the width of the material tank of the experiment system can be adjusted according to the characteristics of debris flow in an area, so that the universal applicability is realized; an artificial rainfall system of the experiment system expands the continuously-varying rainfall intensity range, can fully consider the similarity between an artificial rainfall type and a rainfall process and can achieve the purpose of characterizing the corresponding encounter process by adopting rainfall, rain intensity and rainfall type; water for simulating rear confluence scour inthe debris flow starting test can be proportioned into a certain concentration, so that the similarity of experimental flow concentration is ensured; the experiment simulation device can achieve integrated control, avoid tedious steps during the experiment operation and classify experiment wastes at the end of an experiment.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Rain-intensity-controllable unsaturated soil rainwater infiltration simulation system
ActiveCN103604734AEasy to buryFully contactedPermeability/surface area analysisPoint to point controlSoil infiltration
The invention discloses a rain-intensity-controllable unsaturated soil infiltration simulation system which comprises a test bench with pulleys at the bottom part; a water supply tank, an overflow water tank and a model tank are arranged on the test bench, the model tank is a top-opening round bucket, a plurality of separators respectively with a reserved hole at the center are arranged inside the model tank, a drain valve is arranged at the bottom of the model tank, a water supply pump is arranged in the water supply tank, the water supply pump is connected to the overflow water tank by a water supply pipe, the overflow water tank is connected to the water supply tank with an overflow water pipe, a raindrop generator is connected to the bottom of the water supply tank, the raindrop generator includes a guide pipe, a regulating valve, a syringe needle and a dead plate, a funnel is fixed on the lower surface of the dead plate, and a discharge hole of the funnel is arranged above an opening of the top of the model tank; to the rain-intensity-controllable unsaturated soil infiltration simulation system performs point-to-point control through the raindrop generator, and is accurate in rainfall and high in test precision.
Owner:TAIZHOU UNIV
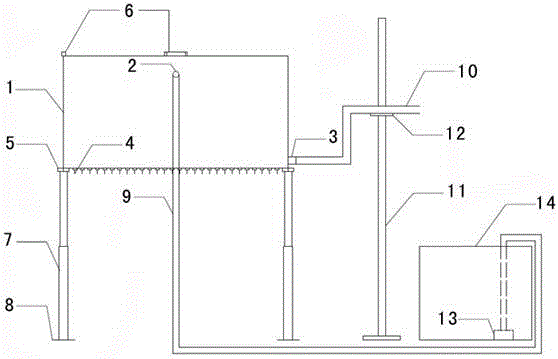
Field artificial rainfall simulator and application method thereof
The invention discloses a field artificial rainfall simulator comprising a water tank. The water tank is fixed to the ground by means of a leveling support. Plate levels are arranged at the top of the water tank. Needles for simulating rainfall are arranged at the bottom of the water tank. The water tank is connected to a magnetic pump arranged in a water storage tank by means of a water inlet pipe. The magnetic pump is used for injecting a solution in the water storage tank into the water tank. The solution in the water tank flows into the water storage tank via an overflow water outlet pipe which is movably mounted on a water level adjusting support. According to the field artificial rainfall simulator and an application method thereof provided in the invention, a water level-rainfall intensity relation curve only needs to be measured once, and one water level corresponds to one rainfall intensity, thereby avoiding the problem of measuring the rainfall intensities before every experiment. The height of the overflow water outlet pipe is adjusted to control the water level in the water tank, thereby control the rain intensity, and then continuously varying rainfall intensities can be obtained without repeatedly changing needles. In addition, local evaporation capacity can be roughly obtained. The field artificial rainfall simulator is applicable to complex terrains in field, and the method is simple, and easy to operate, high in working efficiency, showing a broad application prospect.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Red-bed region rock landslide prewarning method and application thereof
ActiveCN107476275AImprove the accuracy of early warningImprove accuracyIn situ soil foundationTerrainLandslide
The invention discloses a red-bed region rock landslide prewarning method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of landslide prevention engineering. The prewarning method comprises the following steps: (a) a slope alpha of a landslide mass, an area A of the landslide mass, an upper side area Au of the landslide mass and an upper side surface slope beta of the landslide mass are determined through field surveying and mapping; (b) the rainfall is monitored to obtain the rainfall time and the average rainfall intensity; (c) landslide prewarning judging factors P are calculated according to a formula 1 by terrain factors and rainfall factors; and (d) the rock landslide prewarning grades are divided by the landslide prewarning judging factors P; when P is not lower than 1.85, the possibility is high; when P is not lower than 1.45 and lower than 1.85, the possibility is medium; and when P is lower than 1.45, the possibility is low. The prewarning method deeply researches the terrain conditions and the rainfall conditions formed by the rock landslide, builds precise prewarning calculation models of the rock landslide, determines the prewarning grade of the rock landslide, and greatly improves the prewarning accuracy and applicability.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Intelligent multi-frequency microwave rainfall monitoring method
ActiveCN112051576AWide coverageImprove monitoring accuracyWeather condition predictionDesign optimisation/simulationAtmospheric sciencesRain intensity
The invention discloses an intelligent multi-frequency microwave rainfall monitoring method which is wide in coverage, high in monitoring precision of each rainfall grade and low in construction cost,and adopts multi-frequency microwave equipment which can send and receive a plurality of microwave frequency bands; a plurality of frequency bands and independent model training of each rain intensity level are adopted to invert an optimal monitoring frequency band under different rain intensity levels; after rain intensity intelligent pre-identification, the system selects an optimal monitoringfrequency band corresponding to the rain intensity level to perform rainfall data inversion; the multi-frequency microwave system is more flexible to apply under various rain intensities and higher ininversion precision.
Owner:江苏微之润智能技术有限公司
Detecting Rain Intensity With Traffic Radar
ActiveUS20170315230A1Controlling traffic signalsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionProgram instructionTraffic signal
A radar camera of a signalized traffic control system determines rain intensity, compares it to a threshold, then adjusts traffic signal operation. Rain intensity of a level relative to the threshold causes the traffic control system to operate in a rain intensity mode. The rain intensity mode has the system hold a call to a traffic light controller during the time when rain intensity is above the threshold. The traffic control system includes a radar camera, traffic controller, a computer with memory, and program instructions. A manner of operation includes sampling camera radar, counting the number of raindrops and raindrop size within a predetermined range, determining rain intensity using the measured raindrop parameters / characteristics, comparing the determined rain intensity with a rain intensity threshold, and operating the traffic controller accordingly while the rain intensity is above the threshold.
Owner:MS SEDCO
Early warning method for landslide disasters of single pipeline
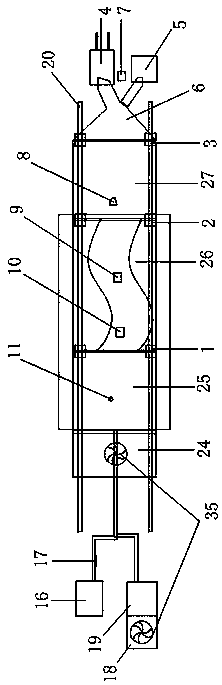
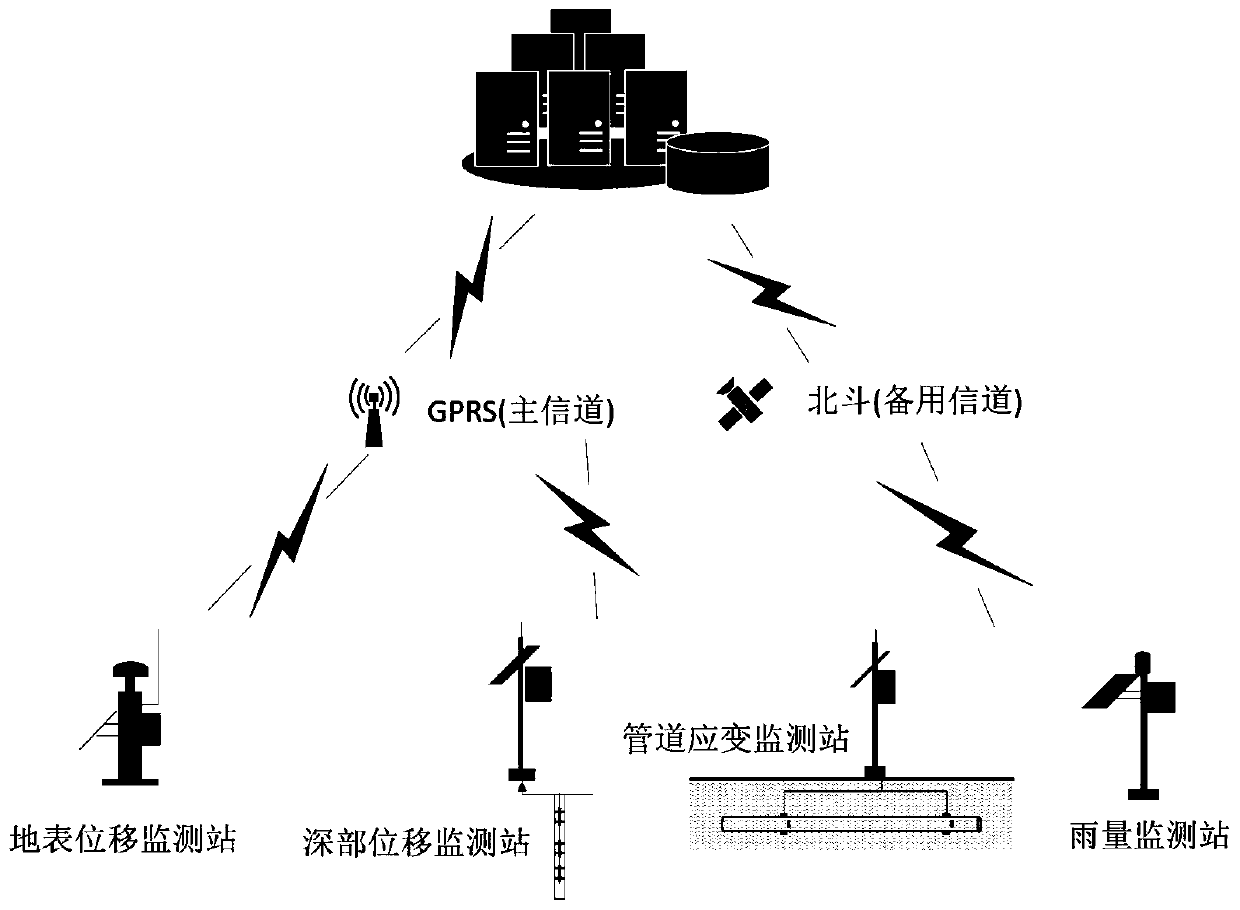
ActiveCN110211338AImprove the accuracy of early warningRealize early warningRainfall/precipitation gaugesTransmission systemsLandslideRain intensity
The invention discloses an early warning method for landslide disasters of a single pipeline, and relates to the technical field of early warning of landslide disasters of pipelines. The method comprises the following steps: monitoring landslide deformation data (landslide surface displacement B and deep displacement S), rainfall data (rain intensity I and duration T) and pipeline strain data (pipeline strain value epsilon) of the single pipeline, and constructing a three-dimensional early warning matrix model based on a ground disaster deformation index X, an external induction index Y and amechanical index Z of the pipeline, so that early warning of landslide disaster risks of the single pipeline is realized. The early warning method for landslide disasters of the single pipeline breaksthrough the traditional early warning technical method of manually setting a single index, comprehensively considers the influences of disaster body deformation (ground disaster deformation), receptors (pipeline stress) and external inducing factors (rainfall), enables early warning results to be more practical, and greatly improves the early warning precision of landslide disasters of pipelines.
Owner:SICHUAN INST OF GEOLOGICAL ENG INVESTIGATION
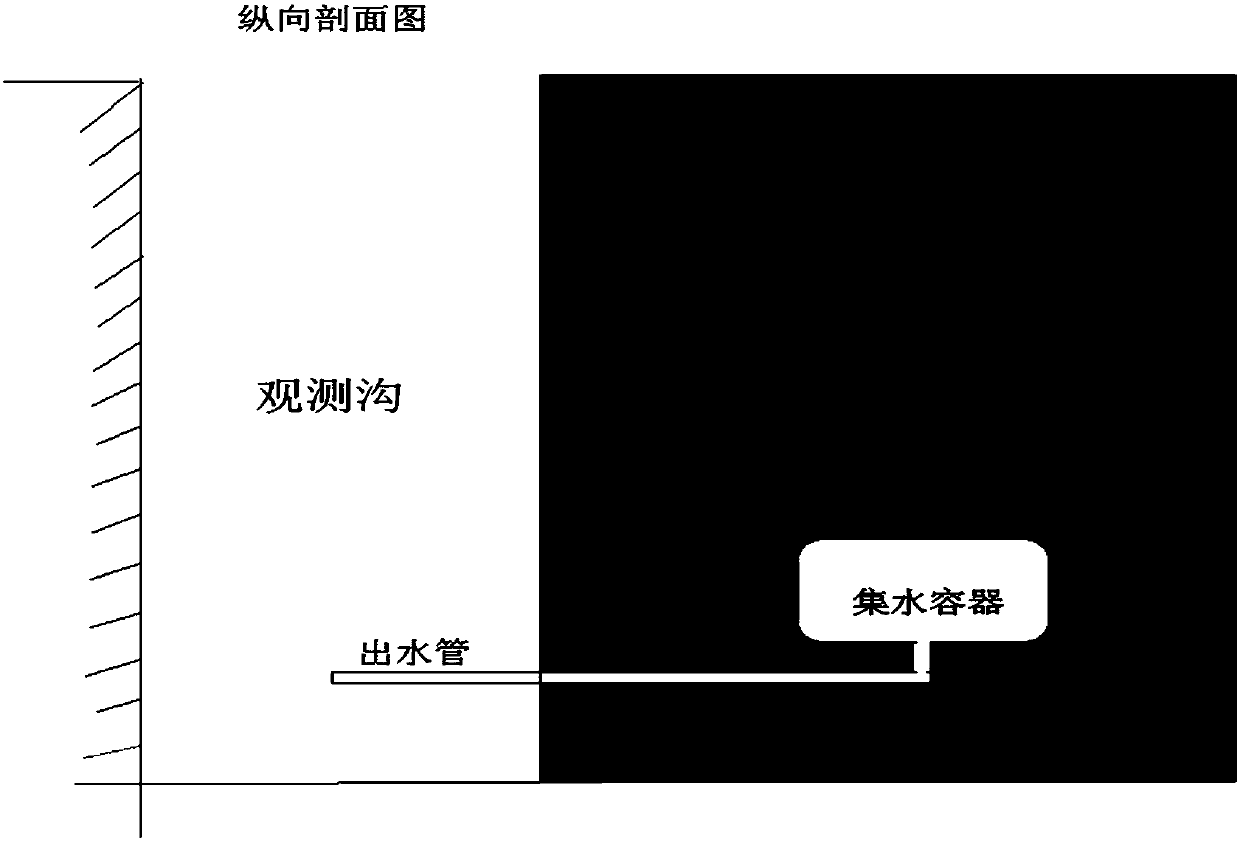
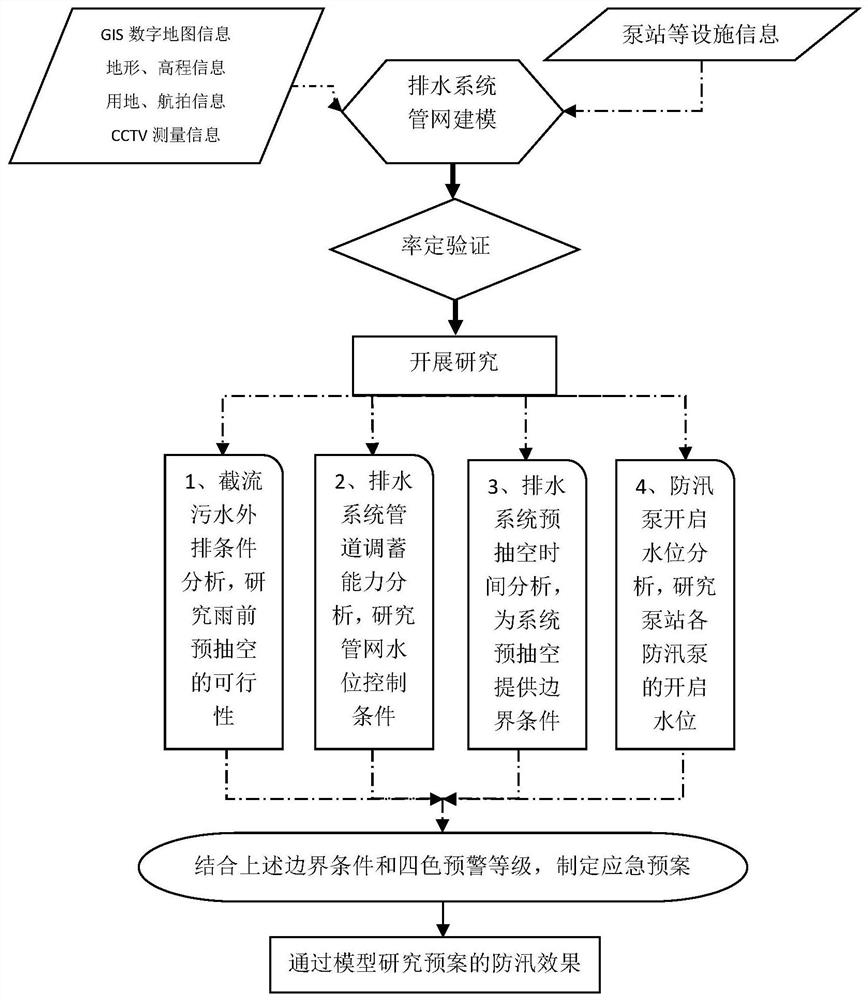
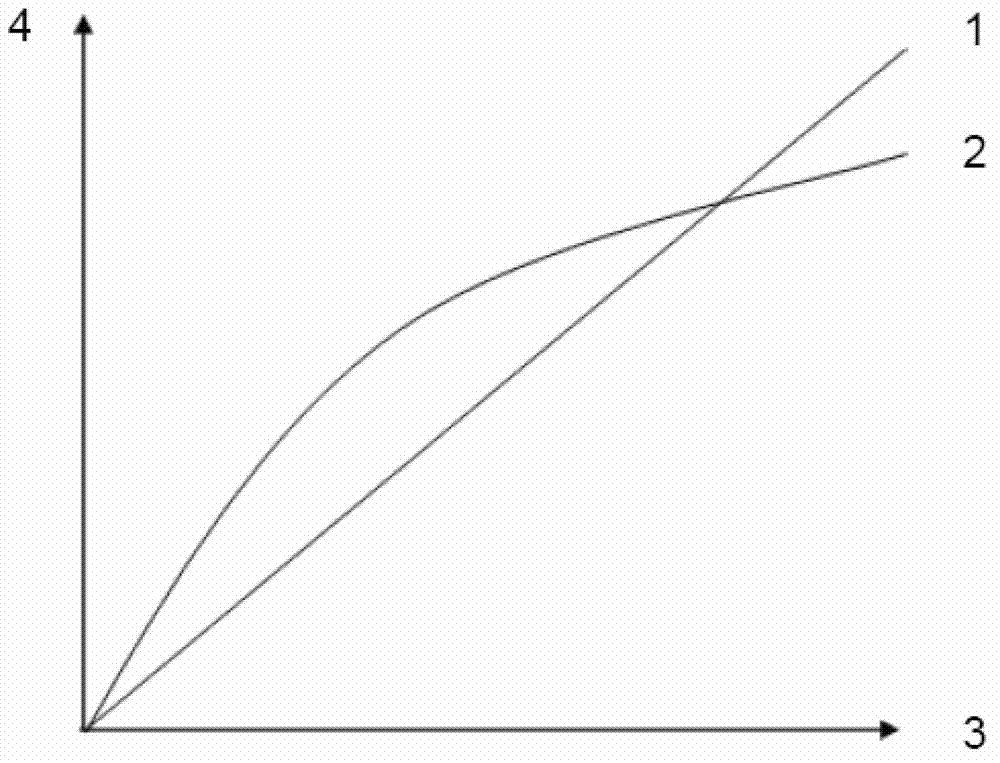
Drainage system waterlogging prevention emergency plan making method
PendingCN112052561AReduce risk of waterloggingImprove scienceClimate change adaptationDesign optimisation/simulationHydrometryEnvironmental resource management
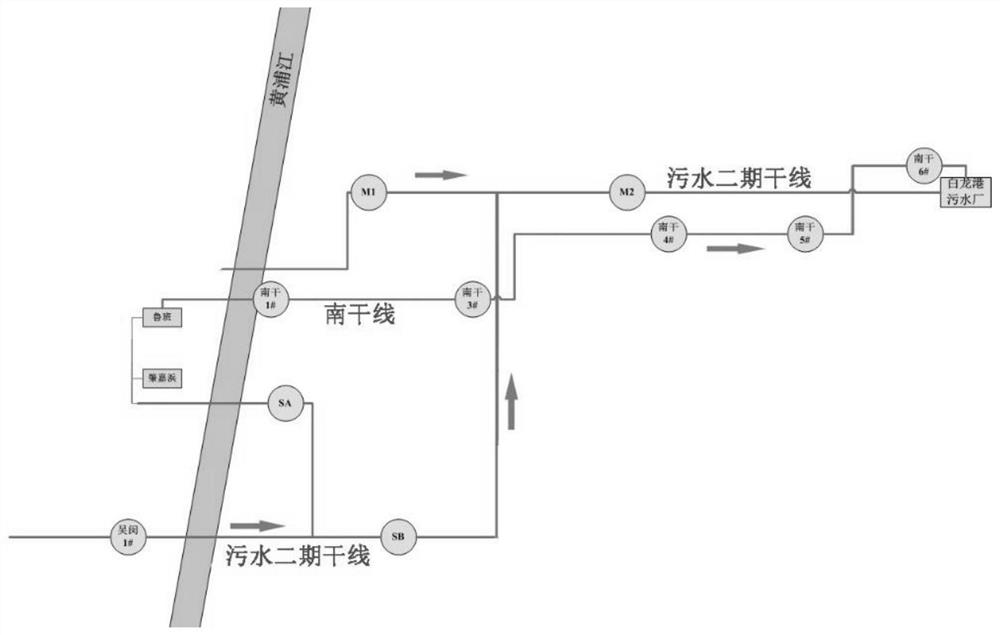
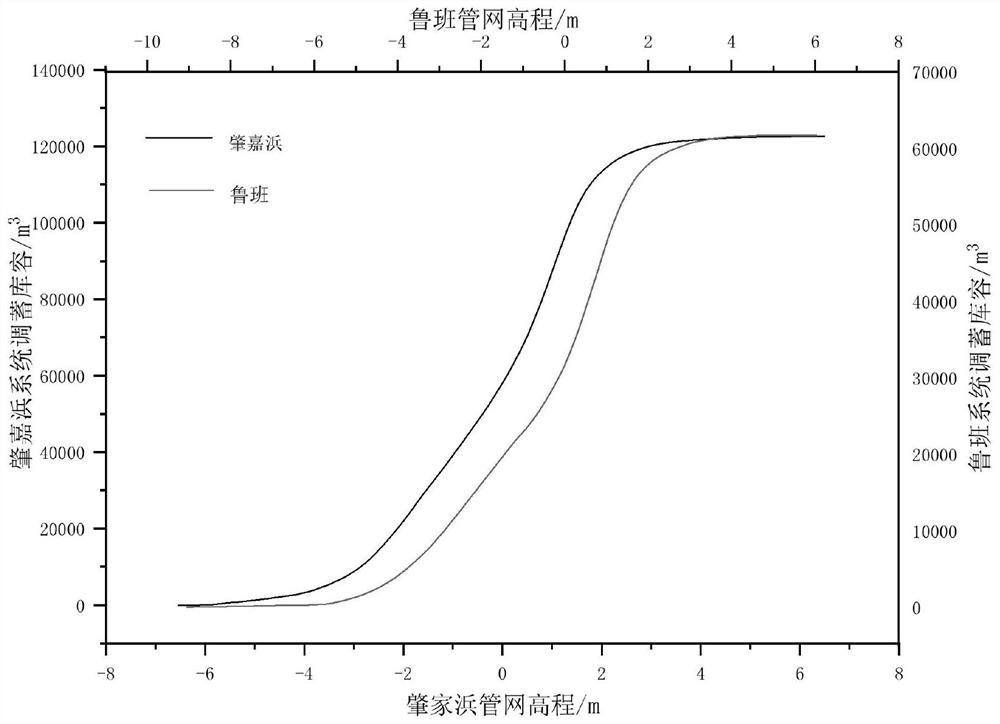
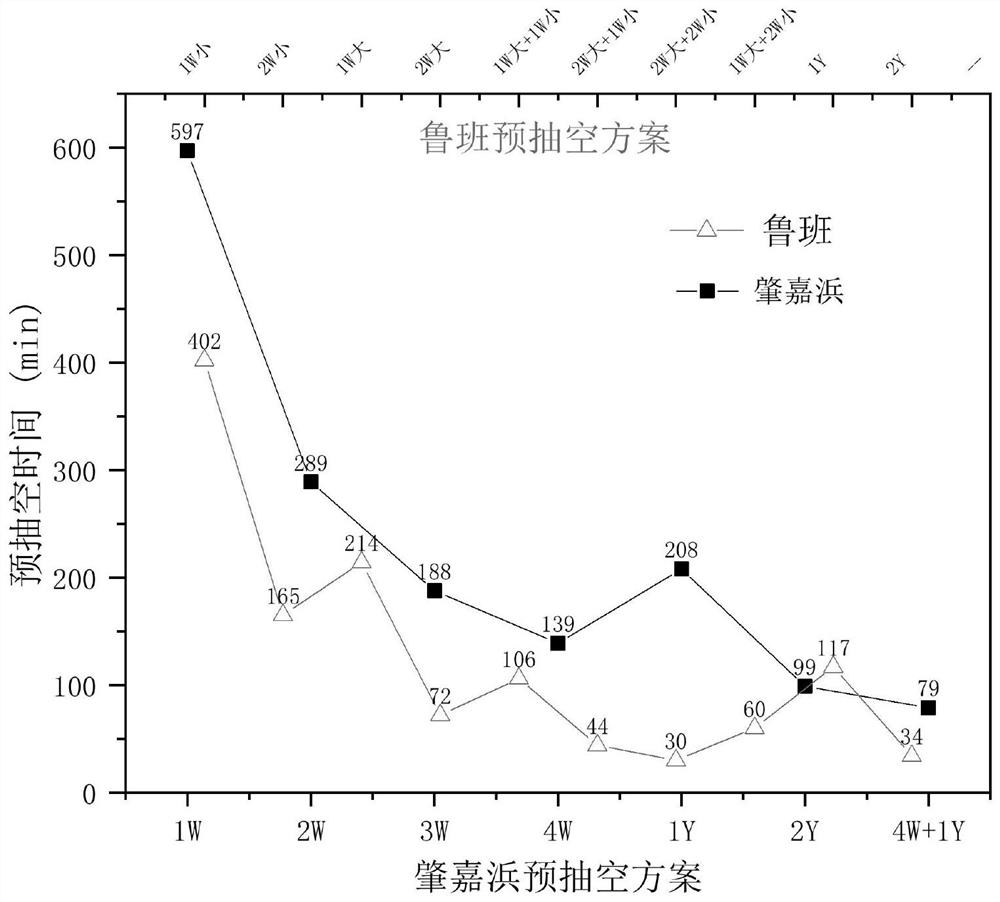
Owner:上海市水务规划设计研究院 +1
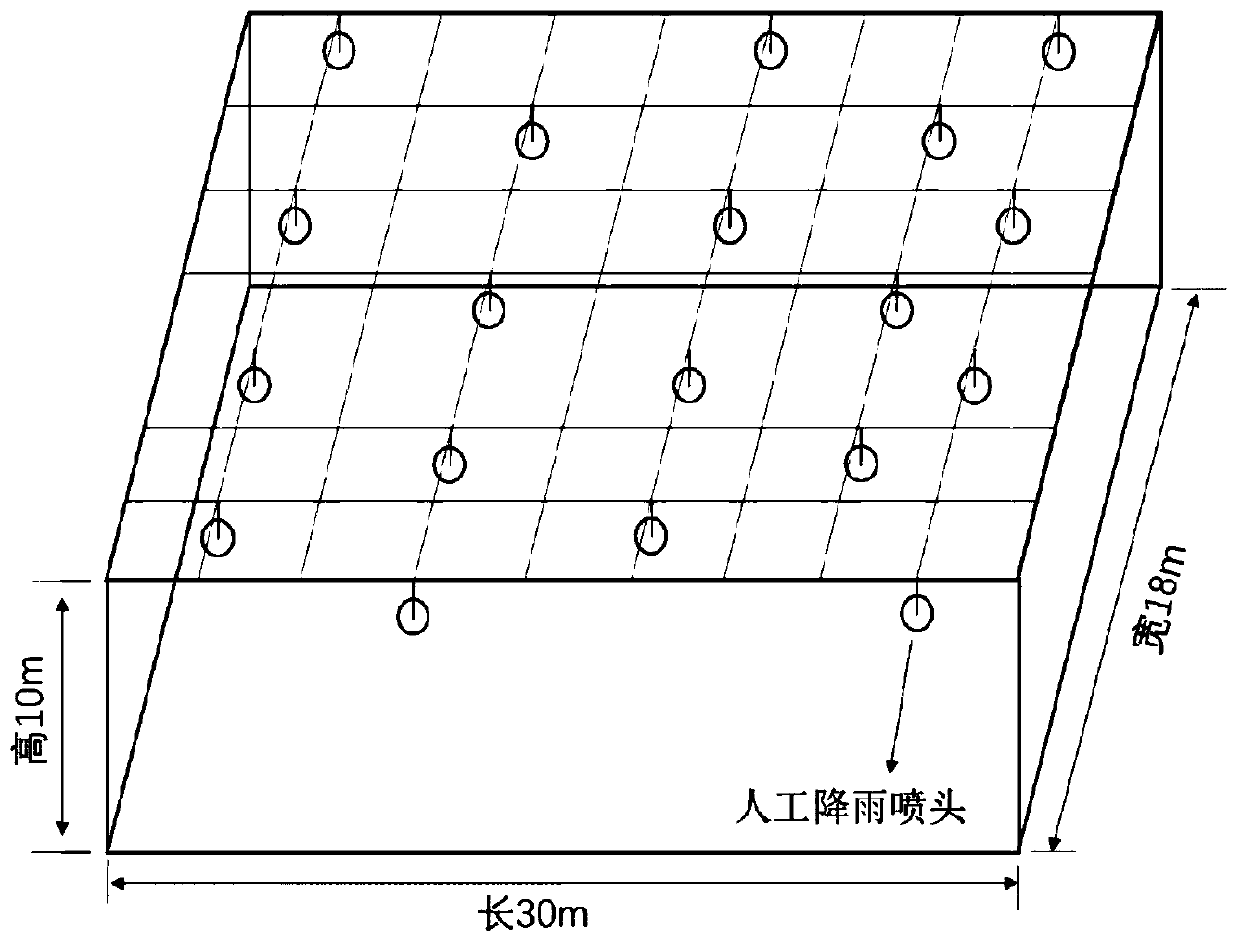
Artificial simulated rainfall device for side slope full-scale model test
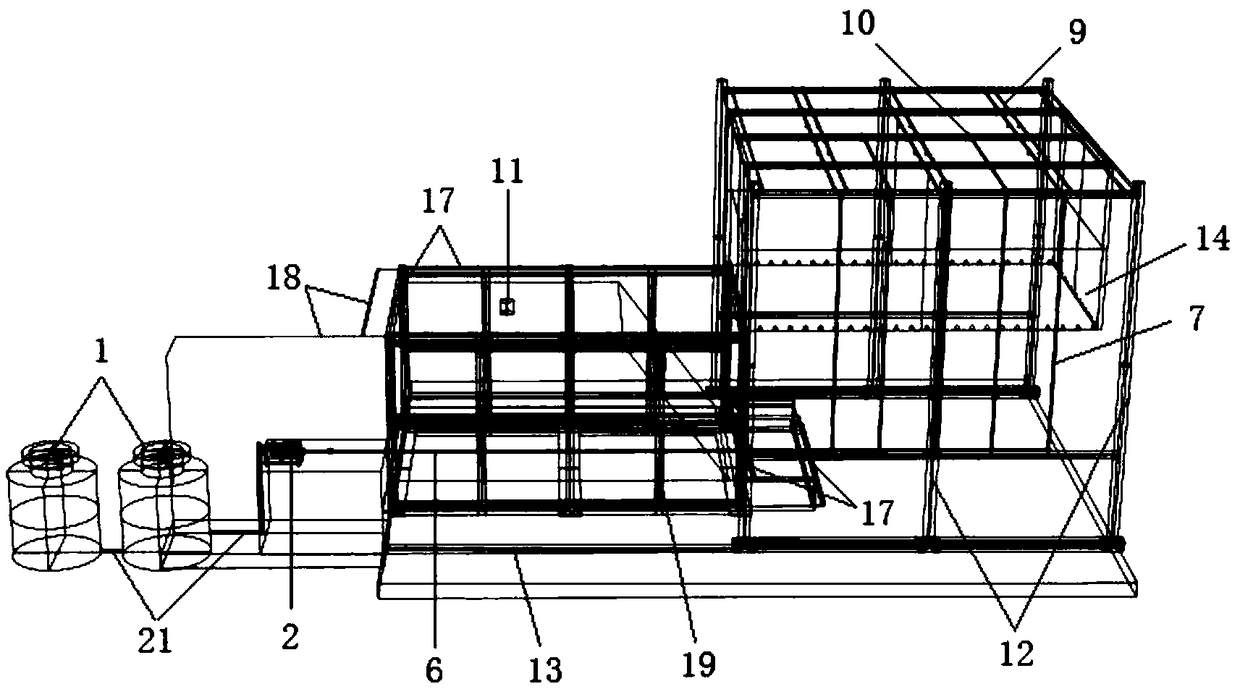
PendingCN109061112AFast stabilizationLarge adjustment rangeEarth material testingEngineeringModel test
The invention discloses an artificial simulated rainfall device for a side slope full-scale model test. The device is mainly composed of a water supply system, a spraying system, a movable bracket anda rainwater backflow system. The water supply system is mainly used for providing power source, and adjusting pipeline pressure through a variable frequency self-priming pump at the same time; the spraying system generates simulated rainfall for the whole system, and simultaneously perform real-time monitoring for rainfall intensity through a rain gauge; the movable bracket is mainly used for keeping out natural rainfall, keeping out wind and collecting rainwater sprayed to the outside of a model box; and the backflow system is used for recycling the rainwater at a slope toe and the rainwatercollected by a rain curtain, thus, water cyclic utilization efficiency of the whole device is improved. The artificial simulated rainfall device for the side slope full-scale model test is convenientto operate, simple in structure, low-cost in manufacturing and environment-friendly can generate the artificial simulated rainfall highly similar to the natural rainfall, has a wide adjustable rain intensity range, and can provide technical assurance for carrying out the side slope full-scale model test and acquiring reliable test data.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN) +1
Simulated observation device and method for deep infiltration characteristics of slope rainfall
PendingCN107843527ALow priceFacilitate a large number of applicationsSurface/boundary effectPermeability/surface area analysisRainfall simulationSoil science
The invention relates to a simulated observation device and method for deep infiltration characteristics of slope rainfall. The device comprises a slope soil body observation unit capable of setting different slopes and soil textures, a deep soil water catchment unit capable of collecting soil water deep infiltration of a specific depth slope, and a rainfall simulation unit capable of simulating different rainfall and rainfall intensity. The method comprises the following steps: establishing the slope soil body observation unit, installing the deep soil water catchment unit in the unit, setting rainfall events of different characteristics by utilizing the rainfall simulation unit, and by measuring the water quantity occurrence characteristics in the catchment unit, including water quantityand time of occurrence, determining the soil water deep infiltration quantity characteristics of the specific depth slopes at different slope angles on different soil textures under different rainfall conditions, and providing an experiment basis for soil water balance analysis for the slope environment.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Drainage waterlogging prevention emergency scheme design system
PendingCN111898911AShorten design timeSimulation is accurateClimate change adaptationDesign optimisation/simulationMathematical modelEnvironmental engineering
The invention belongs to the field of waterlogging prevention engineering, and relates to a drainage waterlogging prevention emergency scheme design system, which comprises an input module, a drainagesystem information module, a rainfall selection module, a intercepted sewage discharge module, a drainage pipe regulation and storage module, a drainage pipe river-releasing critical rain intensity module, a scheme design module and an output module. The invention further discloses application of the system. According to the drainage and waterlogging prevention emergency scheme design system, a mathematical model and waterlogging prevention experience are combined for the first time; drainage conditions under different rainfall conditions are accurately and quickly simulated, corresponding drainage and waterlogging prevention scheme references are provided, the design time of the drainage and waterlogging prevention scheme is greatly shortened, and a powerful basis is provided for reducing the waterlogging prevention cost and the waterlogging prevention loss as much as possible.
Owner:上海市水务规划设计研究院 +1
Method of avoiding brake disc scoring in a vehicle
ActiveCN103010194ALess interferenceEasy to cleanAutomatic initiationsBraking componentsAutomatic brakingEngineering
The invention relates to a method for avoiding reducing scoring of the brake disc or the brake drum of a vehicle driven under humid conditions. According to the method, a detection value is determined, and when the detection value arrives at a pre-determined trigger threshold value, an automatic braking program is executed along with speed reduction of the vehicle which basically cannot be noticed by the driver. According to the invention, the detection value is formed by multiplying at least one of parameters of rain intensity based parameter, brake-activation-free driving time parameter and a speed parameter which relies on the vehicle speed.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Microwave rain attenuation law artificial rainfall experimental method with adjustable link length
ActiveCN111257884AAccurate and reliable first-hand experimental dataRainfall/precipitation gaugesDesign optimisation/simulationAtmospheric sciencesRain gauge
The invention discloses a microwave rain attenuation law artificial rainfall experimental method with adjustable link length. The method comprises the following steps: 1) designing and calculating rainfall intensities in different recurrence periods to form an experimental rainfall process, and simulating artificial rainfall by using an artificial rainfall hall; 2) constructing a corner reflector,and dynamically adjusting the length of a microwave link; 3) installing an experimental microwave device, and selecting a microwave link of a specific microwave frequency band as an experimental link; 4) acquiring measurement data on the experimental link under different rainfall intensity conditions by using a self-metering rain gauge; and 5) according to the measurement data, obtaining the whole process of the experiment rainfall intensity change, and analyzing and calculating the microwave rain attenuation law. The microwave rain attenuation process under the conditions of different rain intensities and different link lengths is simulated in an artificial rainfall device, the microwave rain attenuation law is mined and analyzed, accurate and reliable first-hand experimental data is provided for revealing the real microwave rain attenuation law, and a good foundation is laid for accurate rainfall monitoring.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Wind, light and rain sensor and use method thereof
InactiveCN105242331ASimple structureReasonable designIndication of weather conditions using multiple variablesCombined useEngineering
The invention relates to a wind, light and rain sensor and a use method thereof. The objective of the invention is to solve the technical problems of poor structure design, poor wireless triggering effects and little possibility of combining with a smart phone existing in existing similar products. The sensor comprises a shell, a lithium battery, a circuit board and a solar panel. The wind, light and rain sensor is characterized in that the shell is provided with more than two wind, light and rain intensity indicating lights and buttons; the sensor further comprises an independent controller; the circuit board is provided with a wireless controller triggering circuit; and the controller is provided with a signal receiver and a signal transmitter. According to the sensor, a transmission mechanism is triggered to operate through the controller, and at the same time, the controller transmits closed and open state signals to a network data processor in a house through the signal transmitter; the network data processor wirelessly transmits the closed and open state signals to a smart phone; the smart phone is configured with controller APP monitoring software; and the controller APP monitoring software transmits commands to the controller through the network data processor.
Owner:宁波市富金园艺灌溉设备有限公司
Pin grid type indoor artificial rainfall test system and method
InactiveCN110297073AAvoid Waterlogging ProblemsSimple structureEarth material testingPeristaltic pumpTime function
The invention discloses a pin grid type indoor artificial rainfall test system comprising a soil sample room module, a simulated rainfall module and a control module, wherein the simulated rainfall module is connected to the soil sample room module and the control module, respectively. A method of using the artificial rainfall test system comprises the following steps of calibrating the relationship between the flow rate q at the output end of a peristaltic pump and the PLC output pulse frequency f, carrying out soil sample filling of the artificial rainfall test system, giving a rain intensity-time function R(t) and a rainfall duration D, dividing the rainfall duration D into n segments according to the adjustment precision, and calculating the PLC pulse frequency f corresponding to eachsegment of the rainfall duration. According to the PLC pulse frequency f, the artificial rainfall experiment is carried out by the PLC programmable controller and the stepper motor driver. The pin grid type indoor artificial rainfall test system provided by the invention realizes the artificial rainfall test with high output precision, programmable control, convenient operation and reliable performance.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Windshield wiper controller, optical raindrop detector and detection method thereof
ActiveUS8914197B2Eliminate distractionsImprove recognition accuracyDigital data processing detailsScattering properties measurementsLight guideRain intensity
There is provided an optical raindrop detector including a light source, a light guide, an image sensor and a processing unit. The light source alternatively emits light with different brightness values. The light guide has an incident surface, a detection surface and an ejection surface, wherein the light source emits incident light into the light guide via the incident surface, and a plurality of microstructures are formed on the ejection surface to reflect the incident light to become scattered light toward the detection surface. The image sensor receives reflected light formed by raindrops in front of the detection surface reflecting the scattered light to penetrate the light guide and eject from the ejection surface, and generates image frames corresponding to the different brightness values of the light source. The processing unit calculates differential images of the image frames to accordingly identify rain intensity.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com