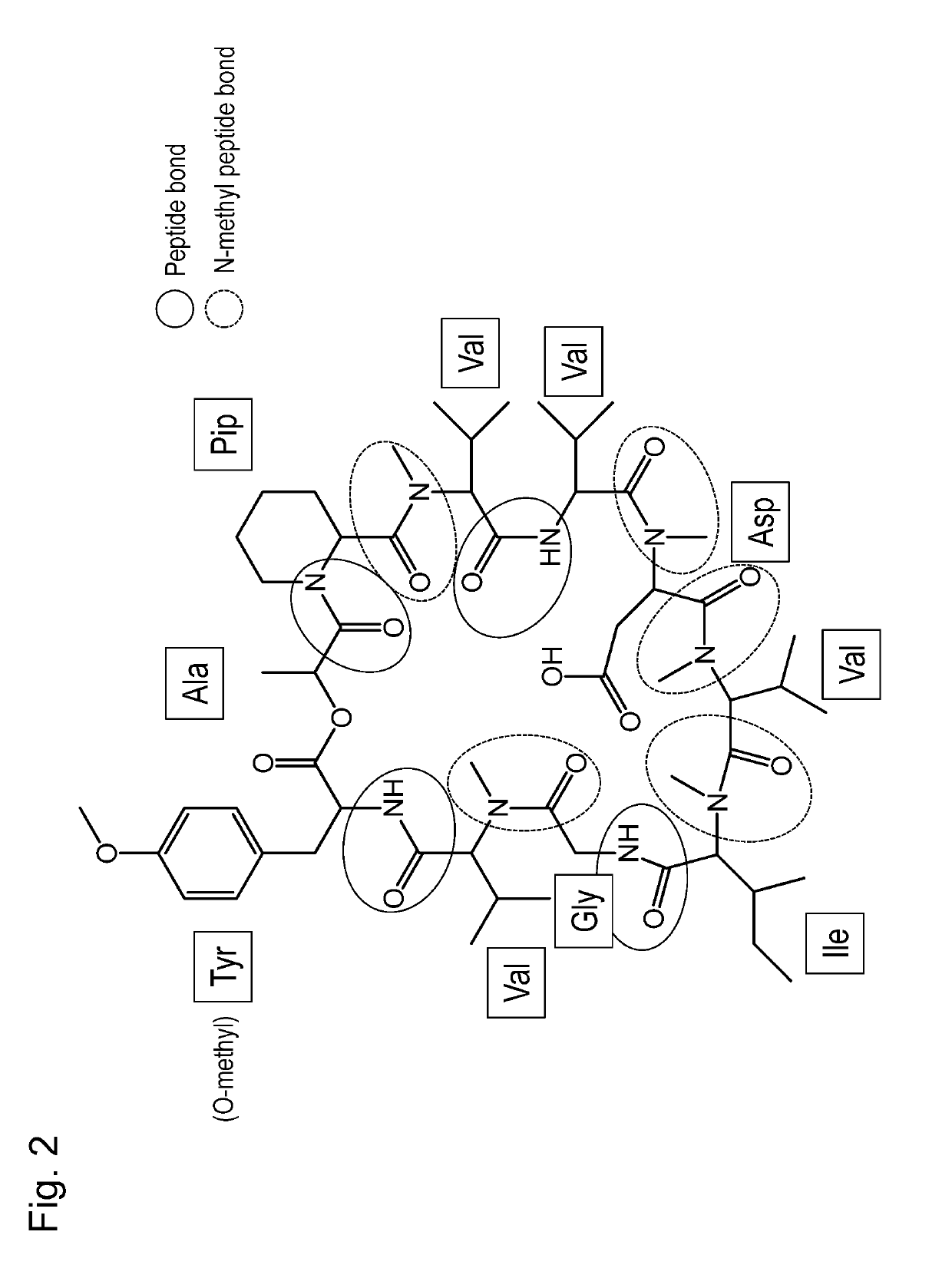
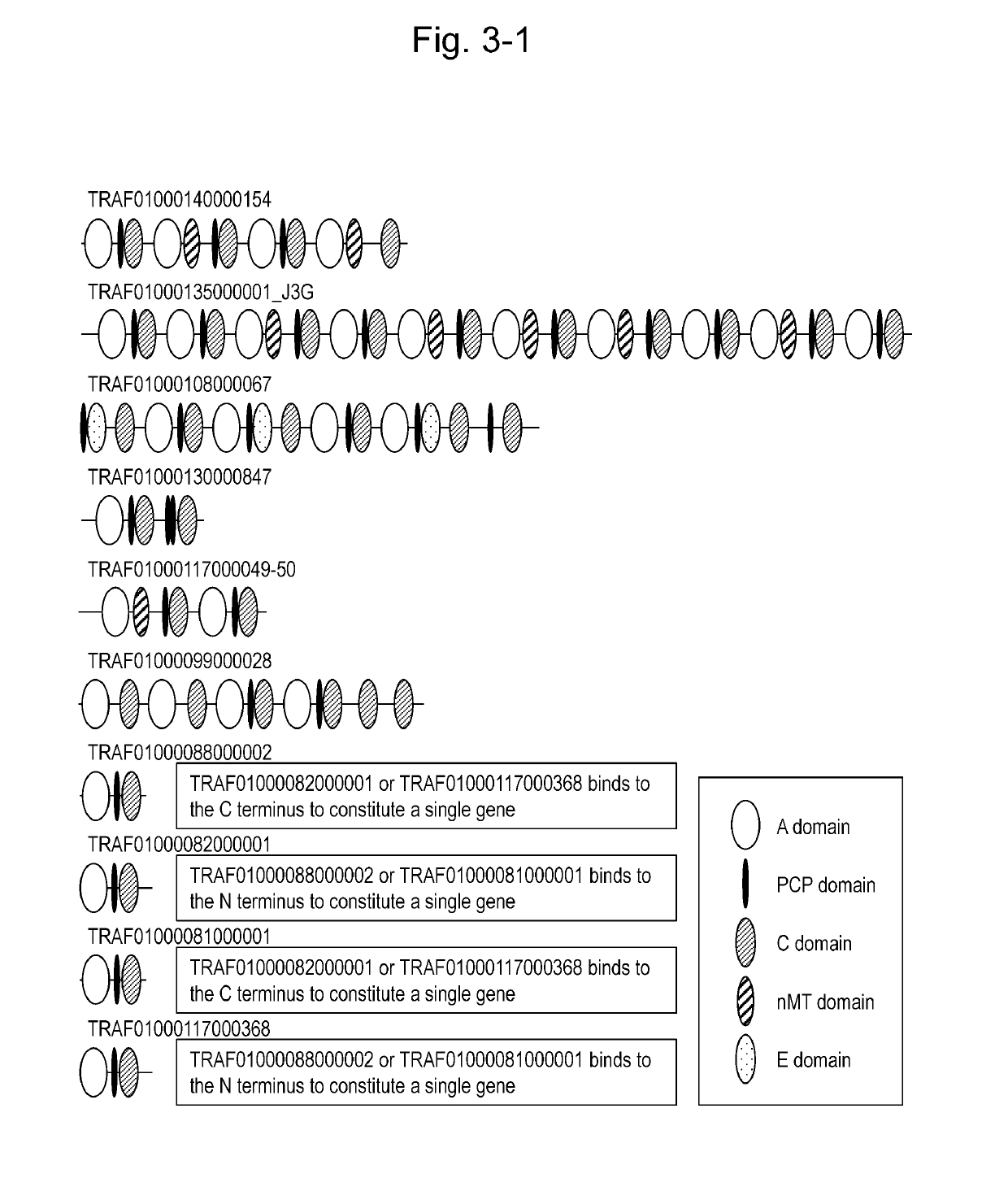
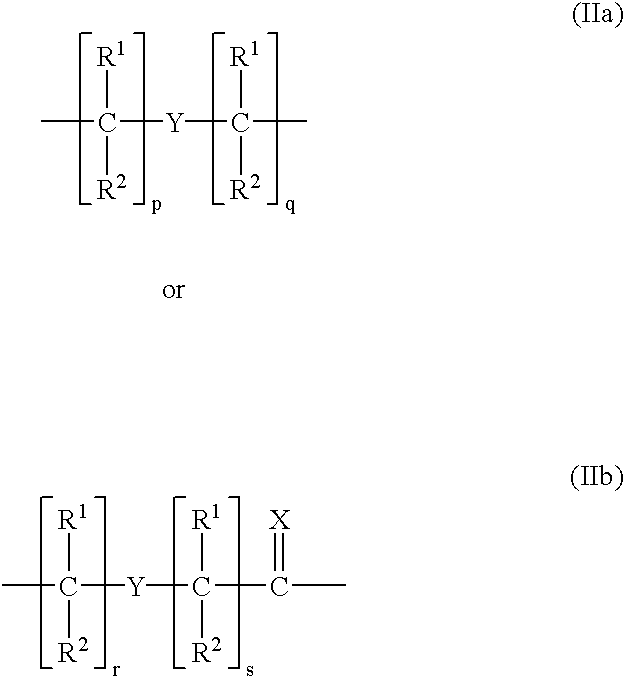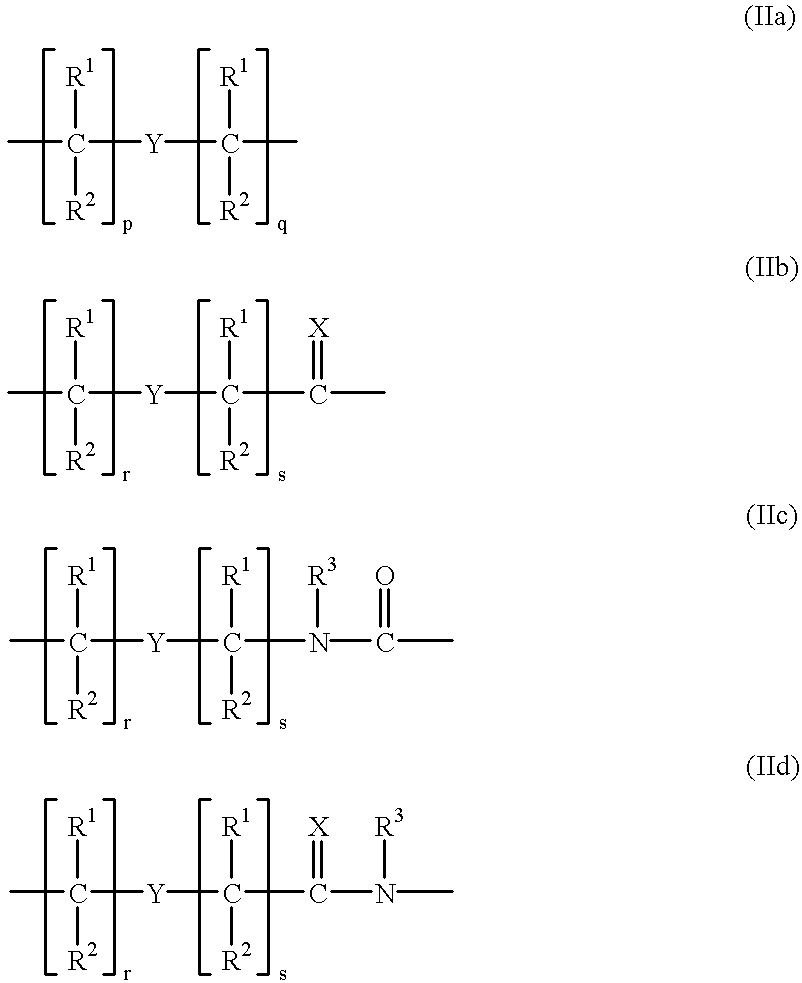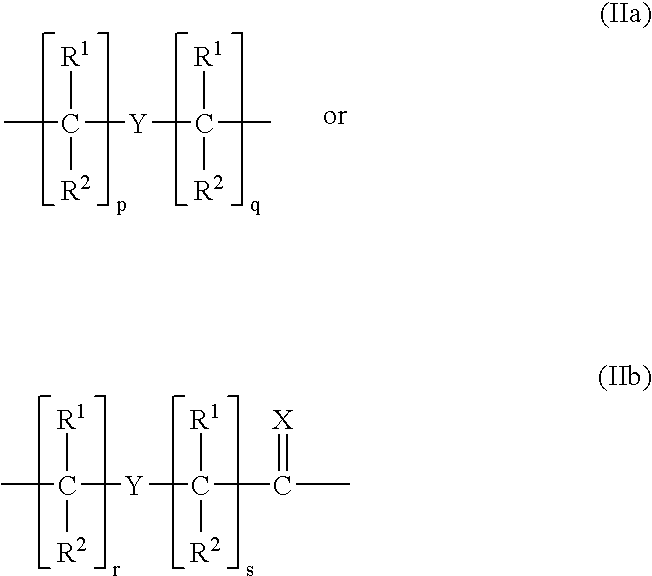Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
48 results about "Peptide backbone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
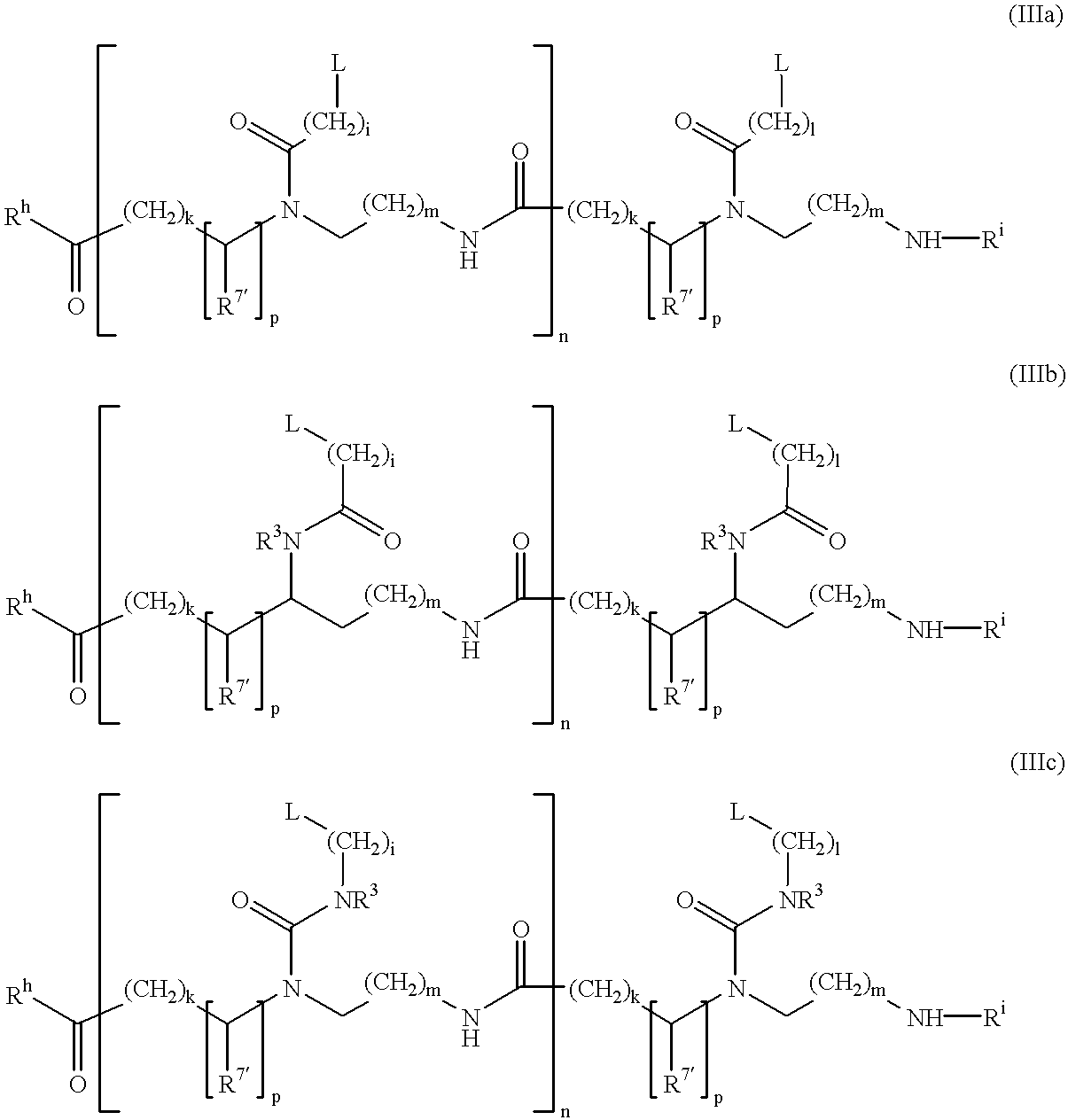
Peptides and peptide backbone Any number of amino acids can chain together by successive peptide bonds. ... The alpha carbons from each amino acid alternate with the peptide bonds to form the “ backbone ” of the peptide. A similar linkage between a large number of amino acids forms polypeptides, which are called proteins when they are large enough and have a defined three-dimensional structure.
Peptide nucleic acids
InactiveUS6395474B1Remove complicationsAvoid less flexibilityPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsPeptide backboneRNA
Owner:BUCHARDT OLE +3
Double-stranded peptide nucleic acids
InactiveUS6228982B1Inhibit bindingPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsDouble strandOrganic chemistry
Owner:NIELSEN PETER E
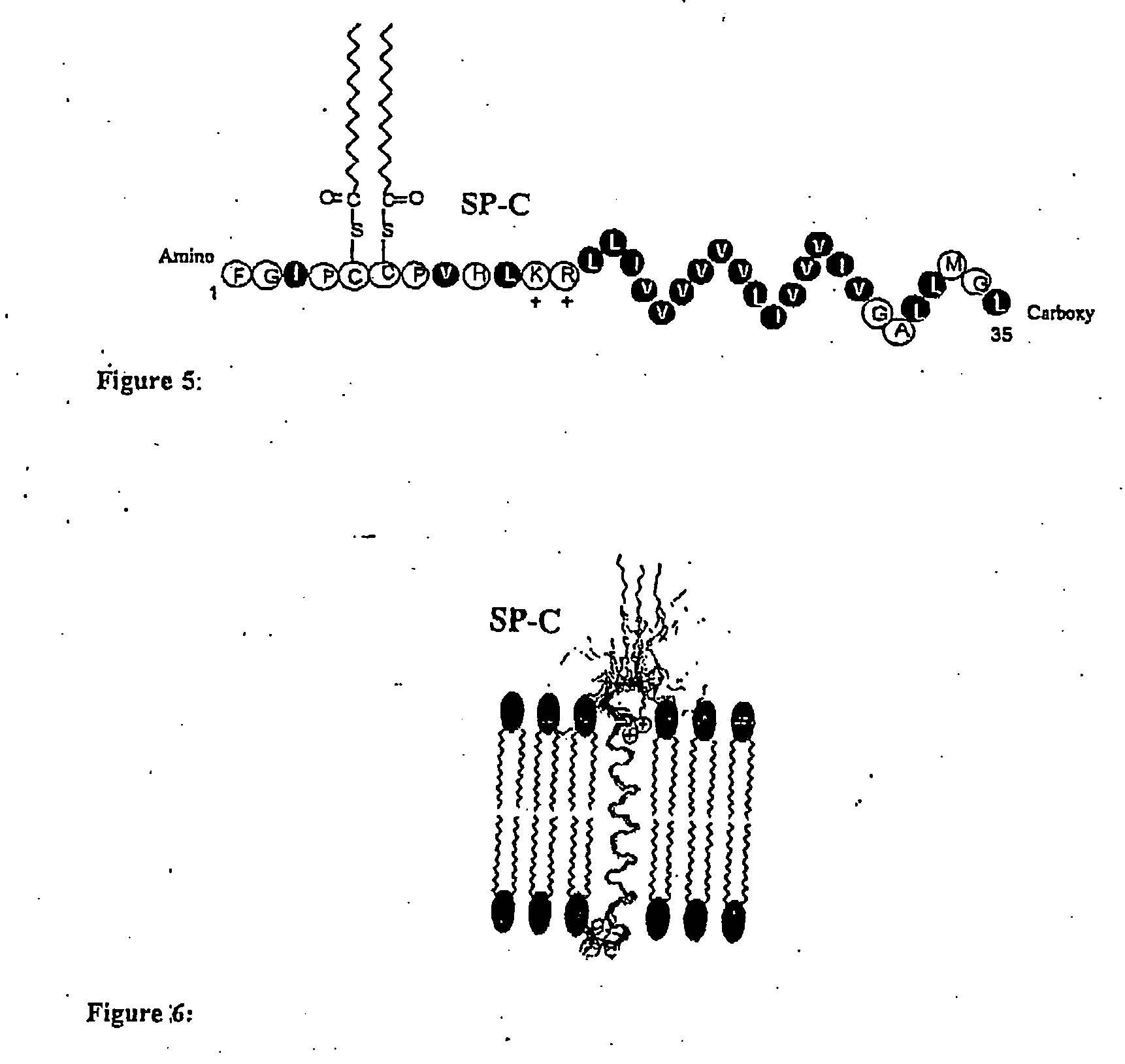
Polypeptoid pulmonary surfactants
InactiveUS6887845B2Low immunogenicityImprove bioavailabilityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsOligomerReverse transcriptase
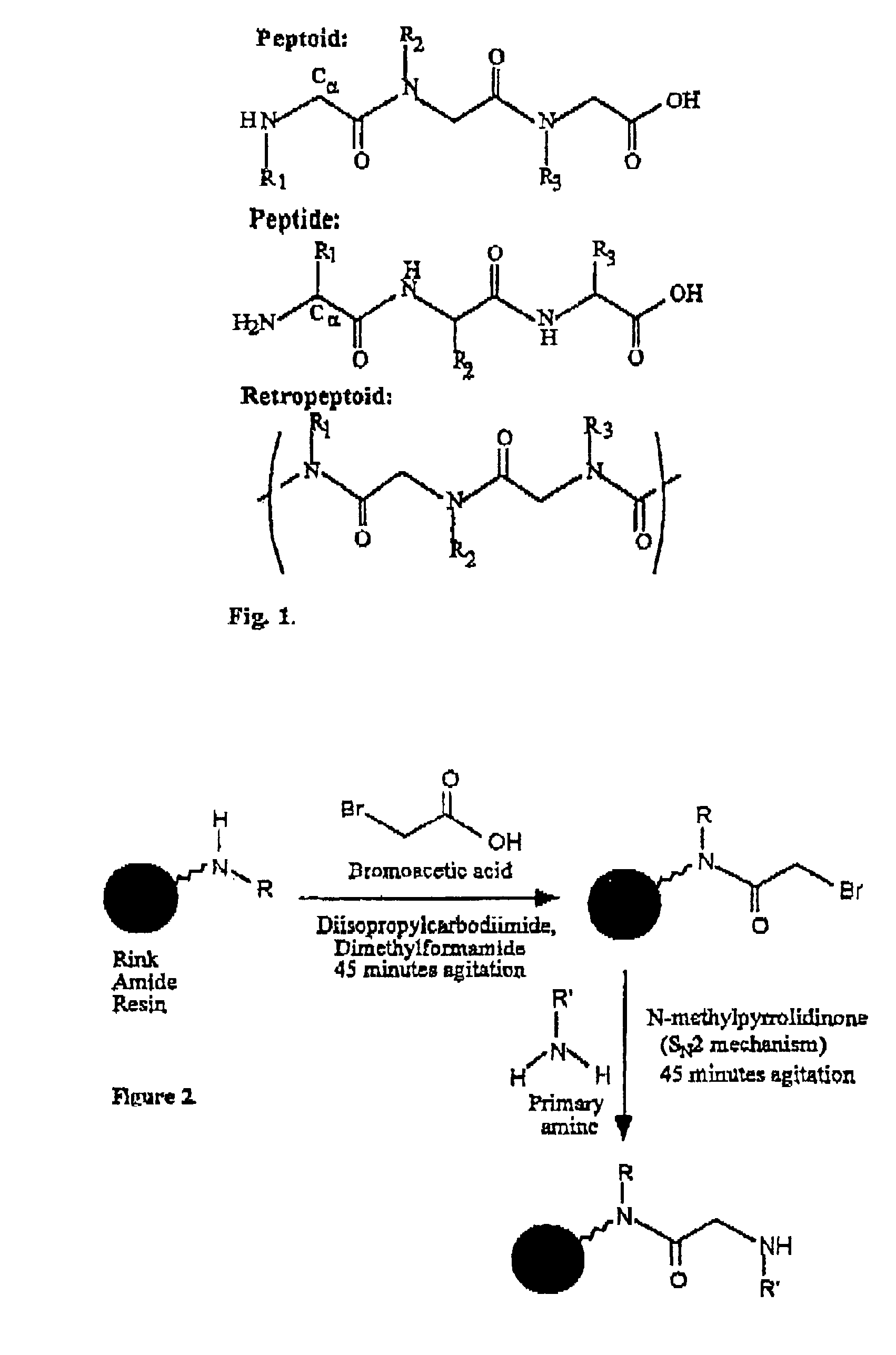
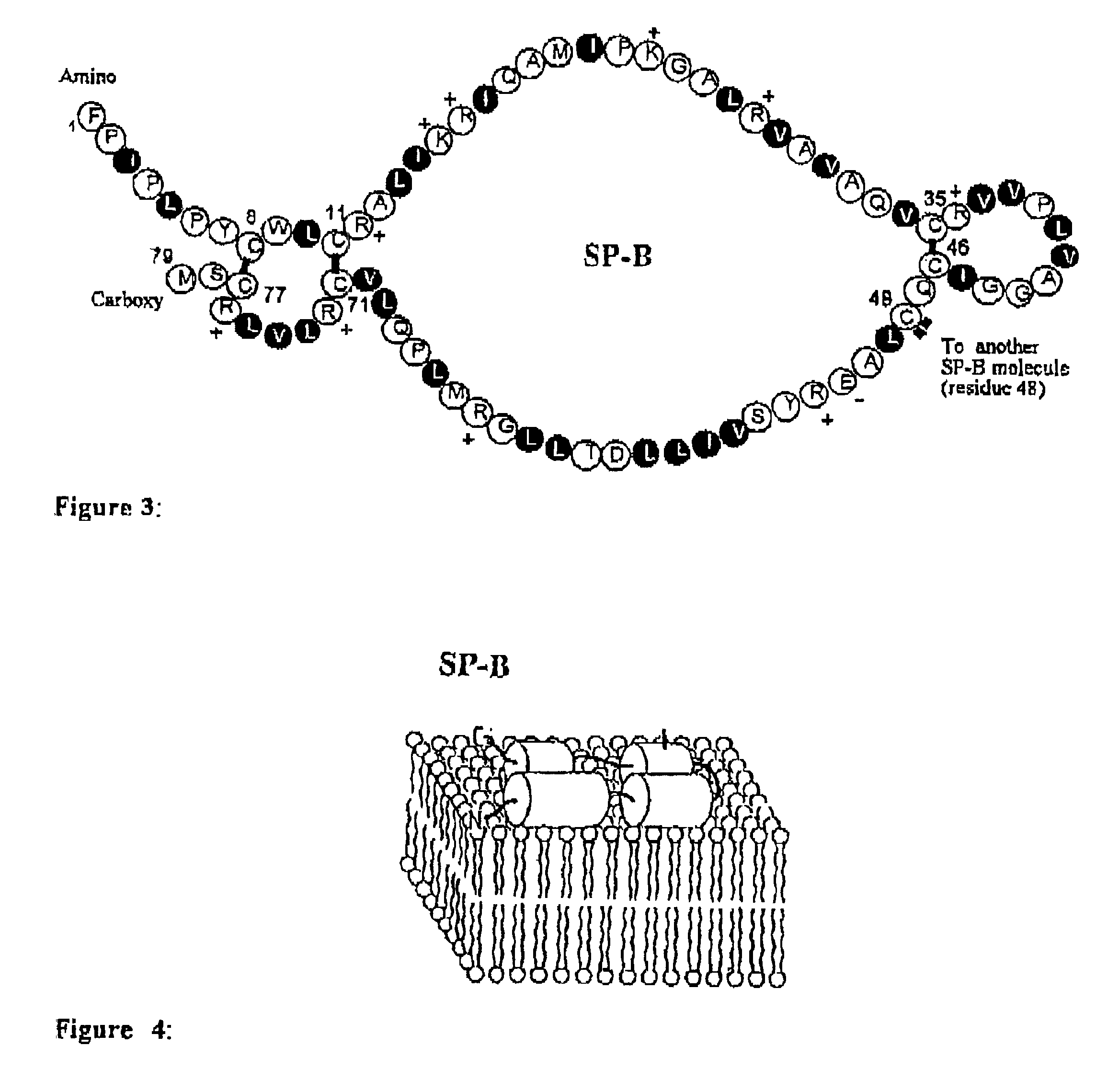
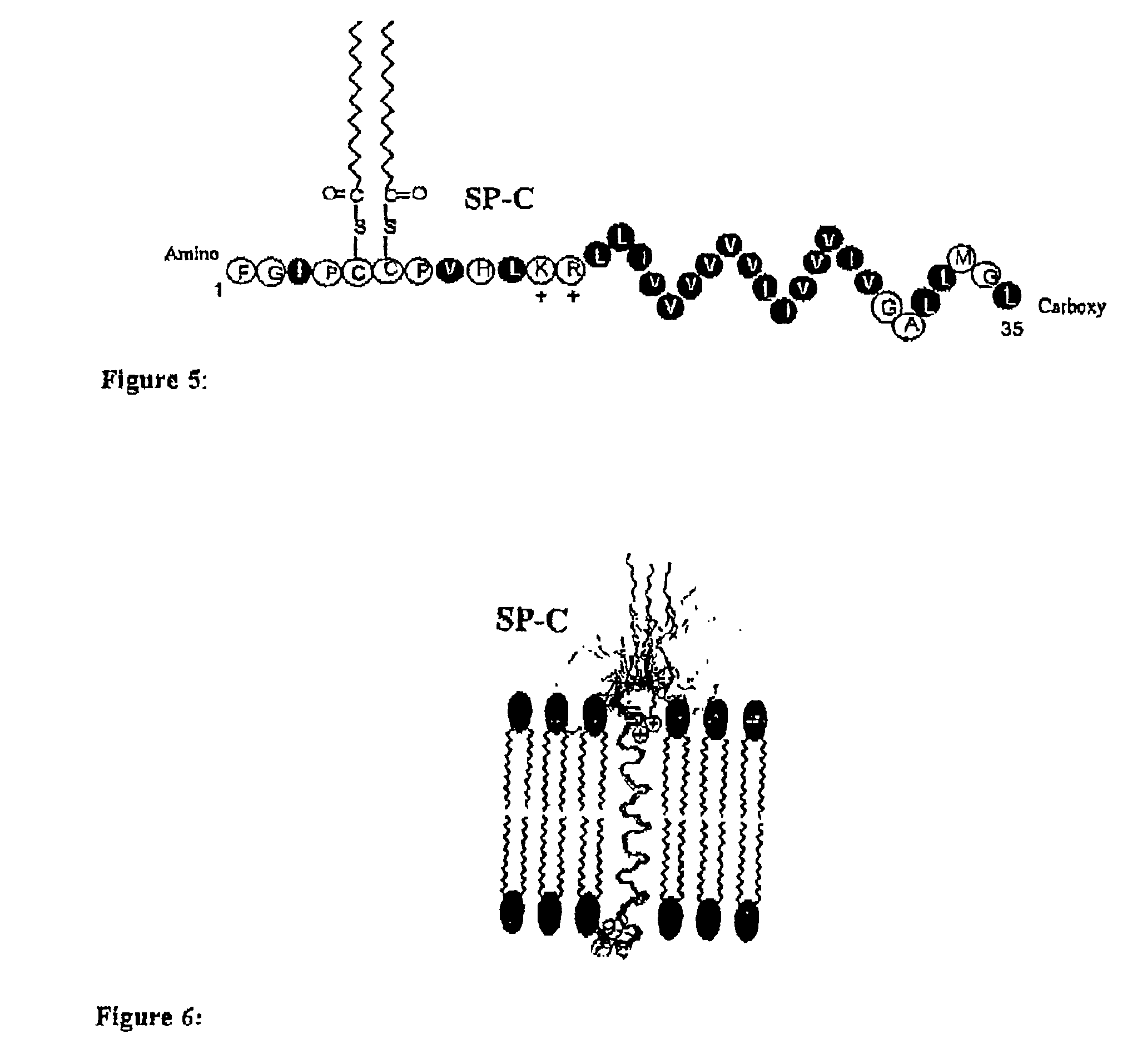
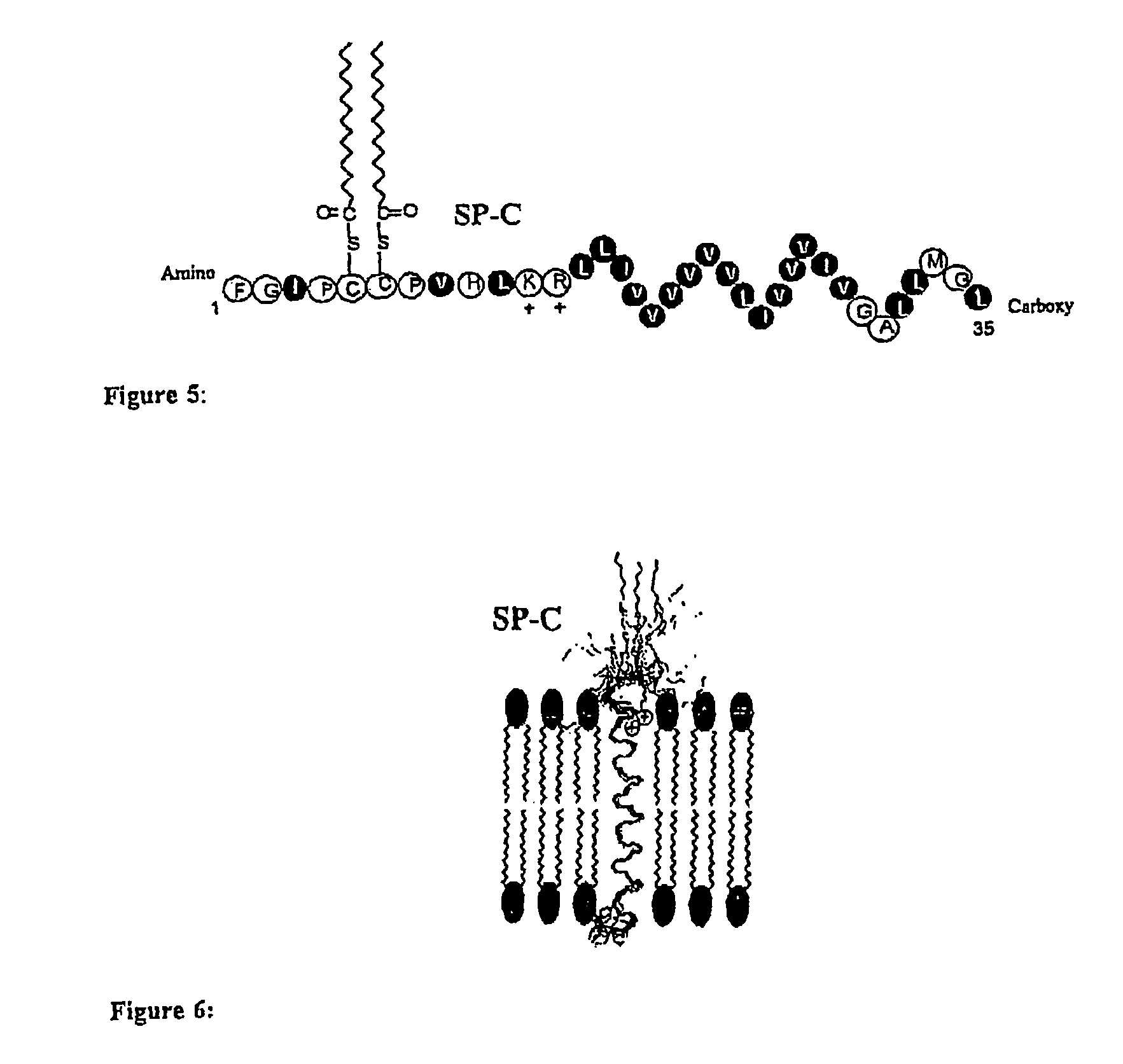
The present invention provides spreading agents based on sequence-specific oligomers comprising a peptoid, a peptide-peptoid chimera, a retropeptoid or a retro(peptoid-peptide) chimera, and methods for using the same, including for the treatment of respiratory distress of the lungs. The spreading agents are sequence-specific oligomers, including retrosequence-specific oligomers, based on a peptide backbone, that are designed as analogs of surfactant protein-B or surfactant protein-C.
Owner:BARRON PH D ANNELISE E +1
Beta -polypeptide foldamers of well-defined secondary structure
InactiveUS6060585AHigh conformational stabilityImprove stabilityOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsProtein secondary structurePeptide backbone
Disclosed are beta -peptides containing cylcoalkyl, cycloalkenyl, and heterocylic substituents which encompass the alpha and beta carbons of the peptide backbone. The beta -peptides adopt stable helical and sheet structures in both the solid state and in solution. Method of generating combinatorial libraries of peptides containing beta -peptide residues and the libraries formed thereby are disclosed.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Compositions for the detection of enzyme activity in biological samples and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS6936687B1Fluorescence enhancementFluorescent signal enhancementPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementProteinase activityFluorophore
The present invention provides for novel reagents whose fluorescence increases in the presence of particular proteases. The reagents comprise a characteristically folded peptide backbone each end of which is conjugated to a fluorophore. When the folded peptide is cleaved, as by digestion with a protease, the fluorophores provide a high intensity fluorescent signal at a visible wavelength. Because of their high fluorescence signal in the visible wavelengths, these protease indicators are particularly well suited for detection of protease activity in biological samples, in particular in frozen tissue sections. Thus this invention also provides for methods of detecting protease activity in situ in frozen sections.
Owner:ONCOIMMUNIN
New compound and application thereof
ActiveCN101928331AStrong antibacterial activityHigh antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaAntibacterial activityBenzyl group
The invention provides a new compound and a preparation method and application thereof. The structure of the compound provided by the invention is shown as a formula (1). Four-potential hydroxyl of glycosyl on benzyl hydroxyl of peptide framework six-potential amino acid of the compound serves as an axial bond and the compound is obtained by fermentation and has the collection number of China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) No.3053. The compound provided by the invention has high antibiotic activity, so that the compound plays a very important role in developing a new antibacterial medicament.
Owner:SHANGHAI LAIYI BIOMEDICAL RES & DEV CENT +2
Peptide nucleic acids and synthetic procedures therefor
InactiveUS20050009041A1Avoid less flexibilityRemove complicationsSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsOrganic chemistryPeptide backbone
Owner:BUCHARDT OLE +3
Beta-polypeptide foldamers of well-defined secondary structure
InactiveUS6613876B1Improve stabilityPeptide librariesOrganic compound preparationProtein secondary structureCombinatorial chemistry
Disclosed are beta-peptides containing cylcoalkyl, cycloalkenyl, and heterocylic substituents which encompass the alpha and beta carbons of the peptide backbone. The beta-peptides adopt stable helical and sheet structures in both the solid state and in solution. Method of generating combinatorial libraries of peptides containing beta-peptide residues and the libraries formed thereby are disclosed.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
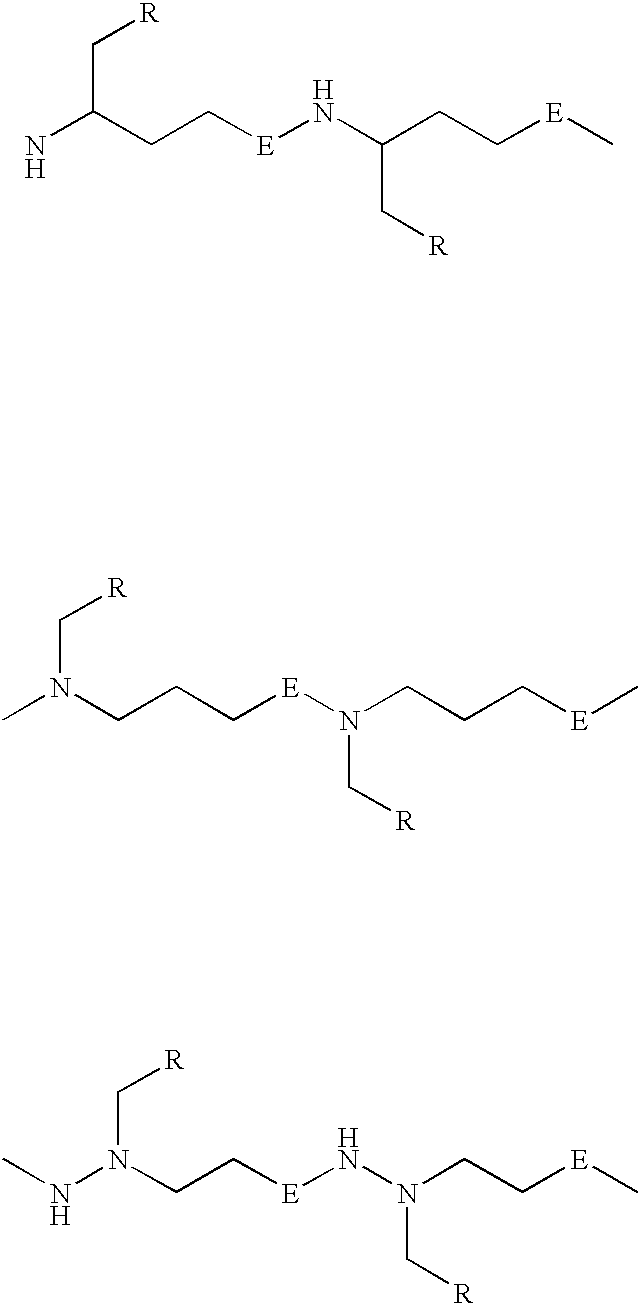
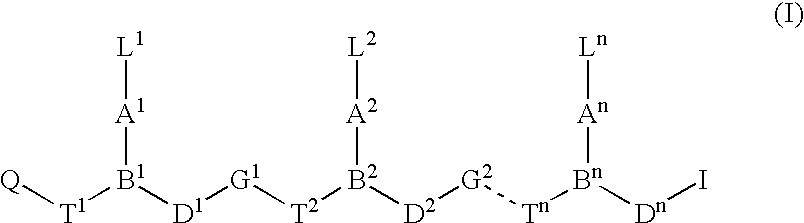
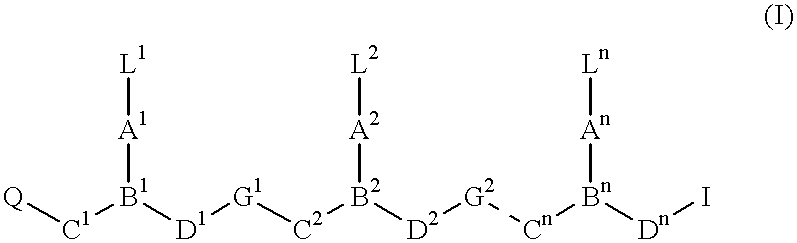
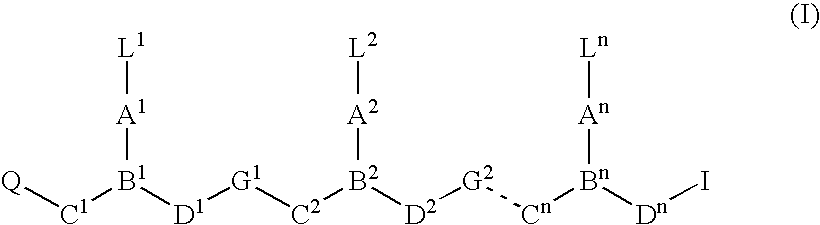
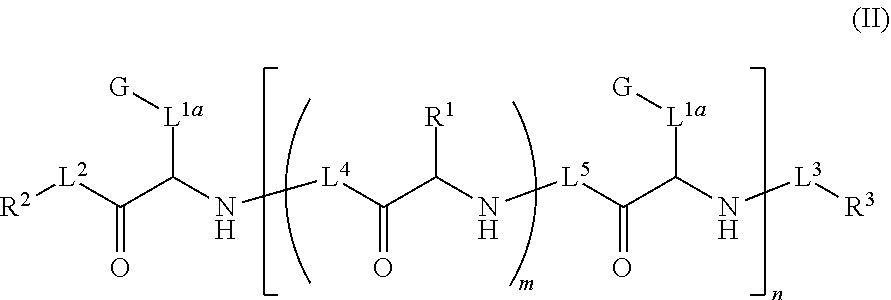
Ultra bright polymeric dyes with peptide backbones
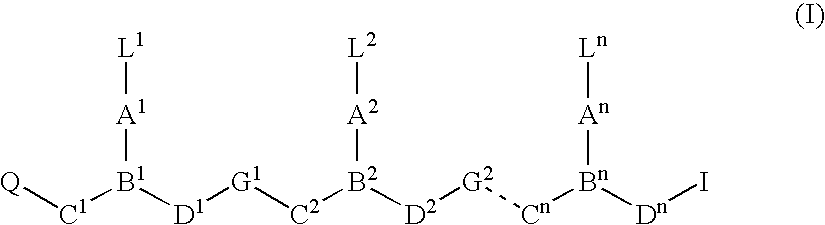
ActiveUS20190153232A1Ensure sufficient separationEasy to mergeOrganic dyesCarrier-bound/immobilised peptidesFluorescenceStereoisomerism
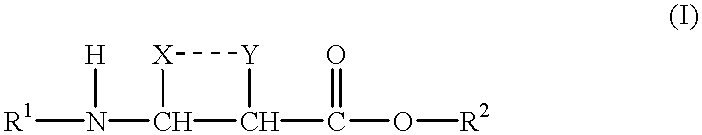
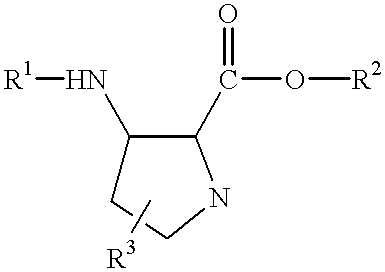
Compounds useful as fluorescent or colored dyes are disclosed. The compounds have the following structure (I), including stereoisomers, salts and tautomers thereof, wherein R1, R2, R3, L1, L2, L3, L4, L5, M, m and n are as defined herein. Methods associated with preparation and use of such compounds are also provided.
Owner:SONY CORP
Biological synthesis gene cluster for Azintamide
InactiveCN101275141AUnderstanding Biosynthetic MechanismsFermentationPlant genotype modificationHeterologousEnzyme Gene
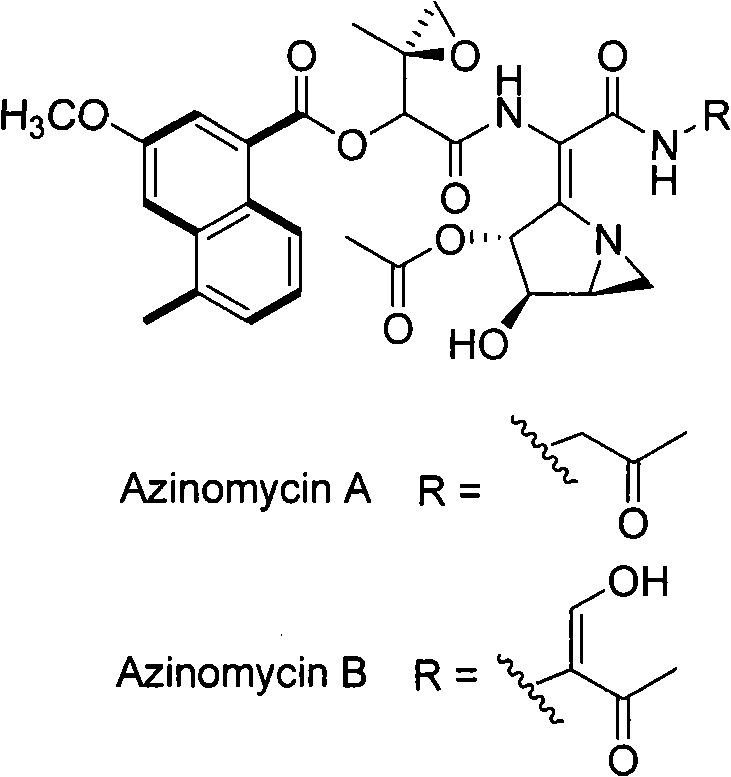
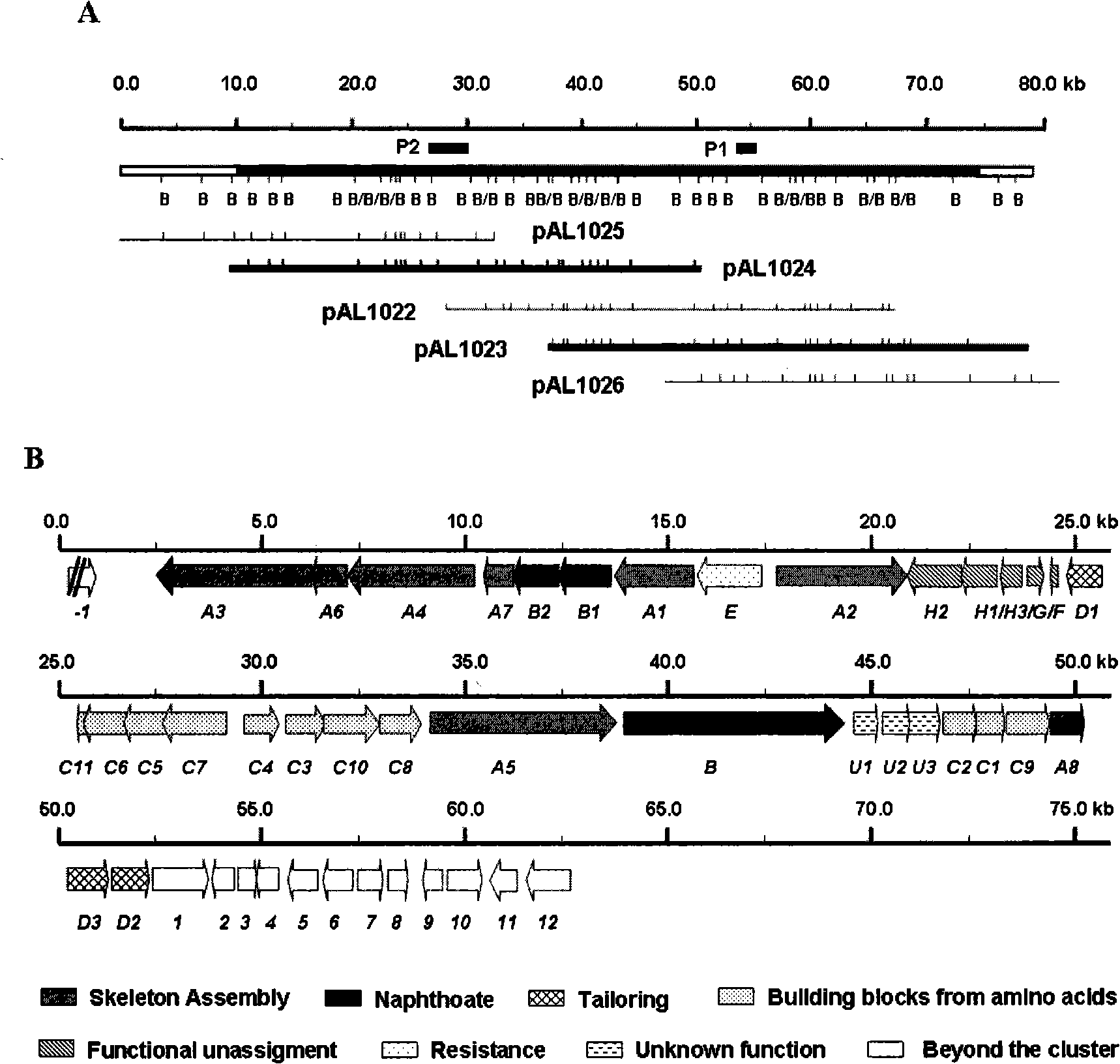
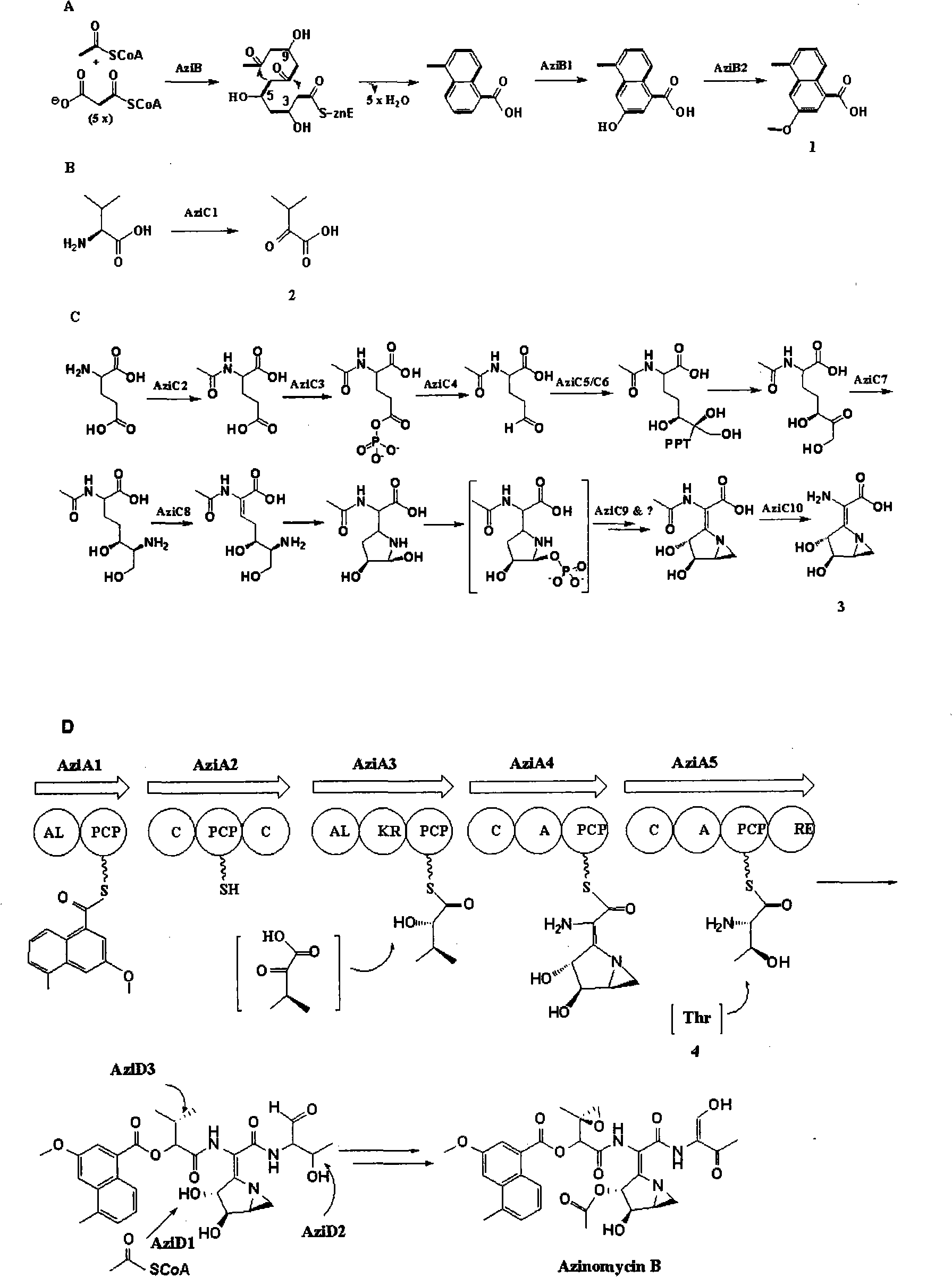
The present invention provides cloning sequencing, analyzing, function research of a biosynthesis gene cluster of an antibiotic-Azinomycin B having antitumor activity produced by streptomyces, and its application. The whole gene cluster includes 34 genes: one repeatedly using I type polyketide synthase gene; two naphthalene ring modification enzyme genes; 8 non-ribosomal polypeptide skeleton synthesis and modification enzyme genes; 11 non-natural amino acid structure unit synthase genes; 1 resistance gene; 3 post modification enzyme genes and 8 genes which functions are not determined. The genetic operation of the biosynthesis gene breaks the synthesis of Azinomycin B; the precursor compound is produced by the heterologous expression of synthesis gene and modification gene of naphthalene ring. The gene of the invention and the protein can be used for searching and finding compound or gene, protein applied in medical, industry or agriculture.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Double-stranded peptide nucleic acids
InactiveUS20030232355A1Inhibit bindingSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsDouble strandPeptide backbone
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
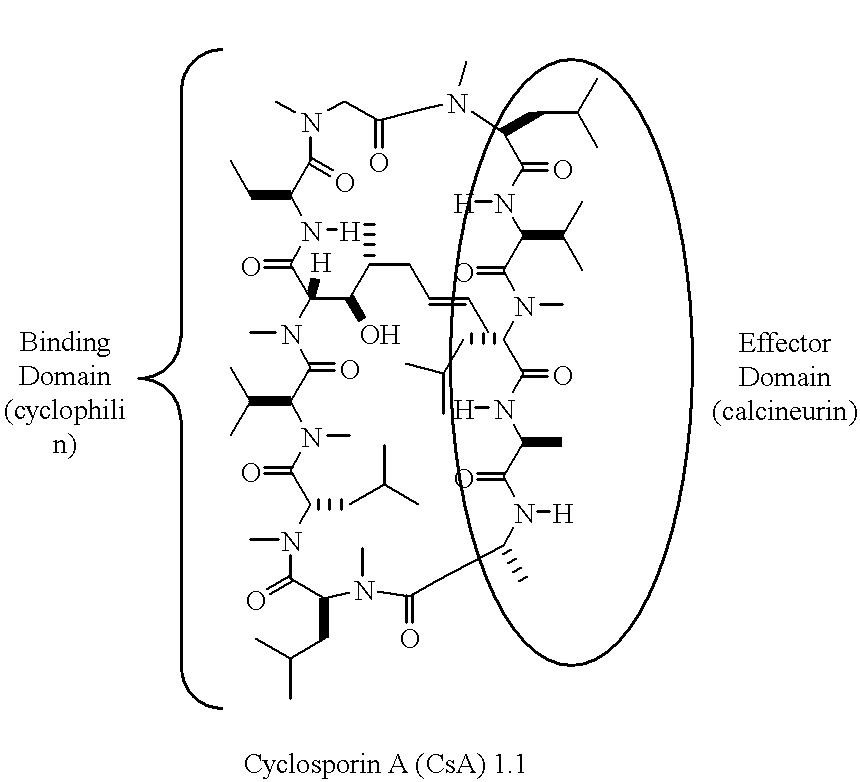
Non-Imuunosuppressive cyclosporins and their use in the prevention and treatment of HIV infection
InactiveUS6270957B1Potent inhibitorHighly effective inhibitor of HIV replicationPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseProteinase activity
Disclosed are cyclosporin analogs having amino acid residue substitutions at positions 1, 3, or 7 of the cyclosporin peptide backbone. Also disclosed are conjugates of these cyclosporin analogs in which an HIV protease inhibitor moiety is conjugated to the position-7 amino acid residue of the cyclosporin. These compounds simultaneously bind to and inhibit cyclophilin and HIV protease. The compounds have good bioavailability and potent HIV inhibitory activity. They are useful in the treatment and prevention of HIV-mediated disorders, including AIDS.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Compositions for the detection of enzyme activity in biological samples and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20080199898A1Fluorescent signal enhancementFluorescence enhancementMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisProteinase activityFluorophore
The present invention provides for novel reagents whose fluorescence increases in the presence of particular proteases. The reagents comprise a characteristically folded peptide backbone conjugated to two fluorophores such that the fluorophores are located opposite sides of a cleavage site. When the folded peptide is cleaved, as by digestion with a protease, the fluorophores provide a high intensity fluorescent signal at a visible wavelength. Because of their high specificity and their high fluorescence signal in the visible wavelengths, these protease indicators are particularly well suited for detection of protease activity in biological samples, in particular in frozen tissue sections. Thus this invention also provides for methods of detecting protease activity in situ in frozen sections.
Owner:ONCOIMMUNIN
Penta-or tetrapeptide binding to somatostatin receptors and the use of the same
InactiveUS20030114362A1Reduce inflammationReduce decompositionIn-vivo radioactive preparationsSomatostatinsApoptosisCarboxylic acid
The subject matter of the present invention is a cyclic or linear tetra- or pentapeptide binding to somatostatin receptors. The compounds of the invention are characterised in that they contain the radical of an amino carboxylic acid bearing a five-membered ring in the peptide backbone which may optionally contain O, S, Se, N, or P. These compounds are easy to prepare and display increased stability against peptidases. The compounds of the present invention induce apoptosis of tumour cells and the use of said compounds for cancer therapy is described. In particular, the compounds are characterised in that they are active even against tumour cells displaying resistance against other somatostatin derivatives such as octreotide. In addition, the use of the compounds of the invention for tumour diagnosis by means of positron-emission tomography is described, as well as their use as agents against neurogenic inflammation.
Owner:NOVASPIN BIOTECH
Compositions for the detection of enzyme activity in biological samples and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS7312302B2Fluorescent signal enhancementFluorescence enhancementPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementProteinase activityFluorophore
The present invention provides for novel reagents whose fluorescence increases in the presence of particular proteases. The reagents comprise a characteristically folded peptide backbone conjugated to two fluorophores such that the fluorophores are located opposite sides of a cleavage site. When the folded peptide is cleaved, as by digestion with a protease, the fluorophores provide a high intensity fluorescent signal at a visible wavelength. Because of their high specificity and their high fluorescence signal in the visible wavelengths, these protease indicators are particularly well suited for detection of protease activity in biological samples, in particular in frozen tissue sections. Thus this invention also provides for methods of detecting protease activity in situ in frozen sections.
Owner:ONCOIMMUNIN
Degradable thiol-ene polymers and methods of making thereof
ActiveUS20180043030A1High activityImprove responseConnective tissue peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsThiol-ene reactionAlkyne
Provided are methods for linking polypeptides (including peptides and proteins) to other moieties using radical imitated thiol-ene chemistries, for example, modifying a polypeptide by introducing reactive thiol groups and reacting the thiol groups with olefin-containing reagents or alkyne-containing reagents under conditions that support radical thiol-ene or thiol-yne reactions. The reactive thiol groups have greater activity for radical thiol-ene reactions that a cysteine thiol group, including thiol groups that are separated from the peptide backbone by at least two carbon atoms, for example, the thiol group of a homocysteine residue. Also provided are compositions and biomaterials containing the linked polypeptides, for example, peptide and protein conjugates, and thiol-ene based biocompatible hydrogel polymers, and their uses in the medical field.
Owner:MOSAIC BIOSCI
Beta-amino acids
InactiveUS20020037997A1High conformational stabilityImprove stabilityPeptide librariesOrganic compound preparationCombinatorial chemistryPeptide backbone
Disclosed are beta-amino acid monomers containing cylcoalkyl, cycloalkenyl, and heterocylic substituents which encompass the alpha and beta carbons of the peptide backbone and beta-polypeptides made from such monomers. Method of generating combinatorial libraries of polypeptides containing the beta-peptide residues and libraries formed thereby are disclosed.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Peptides containing N-substituted D-amino acids for preventing β-strand association
InactiveUS7060671B1Inhibit aggregationInhibition formationNervous disorderIn-vivo radioactive preparationsEnantiomerComputational chemistry
Peptide is disclosed which comprises D-enantiomers of amino acids and is capable of interacting with other β-strand structure to form β-sheet, wherein said peptide is selectively Nα-substituted in one edge (first) of the β-strand-forming section of said peptide while the other edge (second) in the opposite orientation to the first edge in view of peptide backbone plane remains Nα-unsubstituted. Such the Nα-substituted peptide is capable of preventing association of said peptide with other β-strand (target) but permits interaction of said peptide with target β-strand in separate peptide-containing molecules through the Nα-unsubstituted edge. The peptide is useful for preventing β-strand association or aggregation.
Owner:SENEXIS LTD
Modulation of cellular transcription factor activity
InactiveUS6610650B1Inhibit bindingAntibacterial agentsBiocideTranscription factor activityDouble strand
Owner:NEILSEN PETER E
Polypeptoid pulmonary surfactants
InactiveUS8114830B2Resulting resistanceLow immunogenicityPeptide/protein ingredientsAlveolar/pulmonary surfactant peptidesOligomerReverse transcriptase
Owner:MAXWELL BIOSCI INC
Gene involved in synthesis of cyclic peptide compound, method for producing cyclic peptide compound using the same, and transformant comprising the same
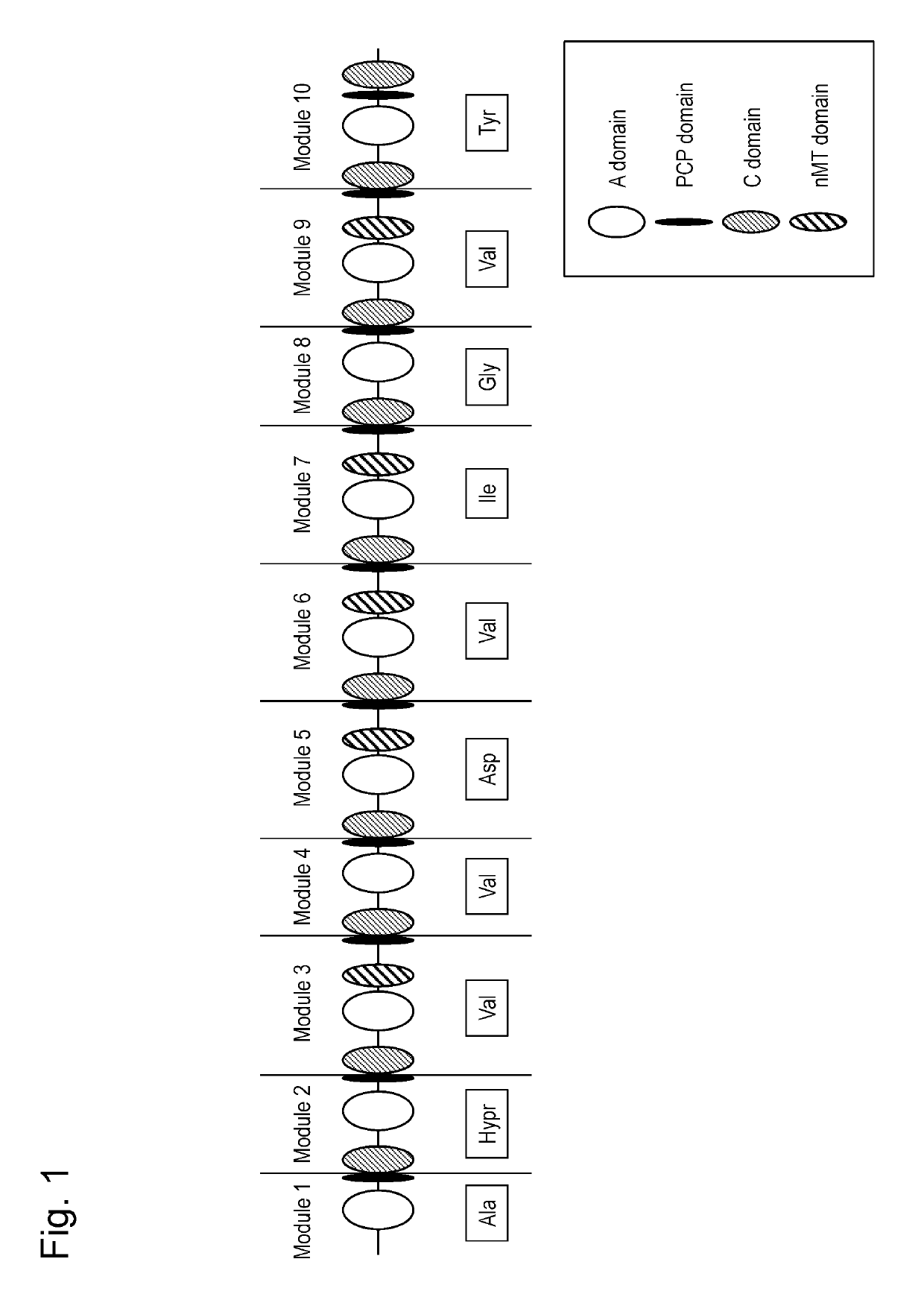
This invention is intended to identify a gene cluster involved in biosynthesis of a cyclic peptide compound produced by a filamentous fungus of the Curvularia species and to establish a system for synthesizing such cyclic peptide compound. The gene is composed of a first module to a tenth module and encodes a protein having activity of synthesizing a nonribosomal peptide constituting a basic peptide backbone of a cyclic peptide compound produced by a filamentous fungus of the Curvularia species.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +2
Degradable thiol-ene polymers and methods of making thereof
Provided are methods for linking polypeptides (including peptides and proteins) to other moieties using radical imitated thiol-ene chemistries, for example, modifying a polypeptide by introducing reactive thiol groups and reacting the thiol groups with olefin-containing reagents or alkyne-containing reagents under conditions that support radical thiol-ene or thiol-yne reactions. The reactive thiol groups have greater activity for radical thiol-ene reactions that a cysteine thiol group, including thiol groups that are separated from the peptide backbone by at least two carbon atoms, for example, the thiol group of a homocysteine residue. Also provided are compositions and biomaterials containing the linked polypeptides, for example, peptide and protein conjugates, and thiol-ene based biocompatible hydrogel polymers, and their uses in the medical field.
Owner:MOSAIC BIOSCI
Peptidic structures incorporating an amino acid metal complex and applications in magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS20150297761A1Improve slackHigh relaxation ratePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsAmino acid side chainDodecane
A method for increasing the relaxivity of a contrast agent having a metal ion complexed to a chelator is disclosed. The metal ion complex is tethered to the remainder of the molecule by at least two points of attachment such that local motion is limited and higher relaxivity can be achieved. In one non-limiting example version of the invention, the alanine analogue of Gd(DOTA), Gd(DOTAla) wherein Gd is gadolinium and DOTA is 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid was integrated into polypeptide structures. This resulted in very rigid attachment of the metal ion complex to the peptide backbone. Rigid molecular structures provide fewer degrees of rotational freedom, resulting in greater control over the rotational dynamics and resultant relaxivity. In the case of Gd(DOTAla), the metal complex is tethered to the peptide via the amino acid side chain to the DOTA moiety and via a dative bond from an amide oxygen to the Gd(III) ion.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Ultra bright polymeric dyes with peptide backbones
ActiveUS11370922B2Fluorescence quenching is reduced and/or eliminatedEasy to separateOrganic dyesCarrier-bound/immobilised peptidesPeptide backboneStereoisomerism
Compounds useful as fluorescent or colored dyes are disclosed. The compounds have the following structure (I), including stereoisomers, salts and tautomers thereof, wherein R1, R2, R3, L1, L2, L3, L4, L5, M, m and n are as defined herein. Methods associated with preparation and use of such compounds are also provided.
Owner:SONY CORP
Polypeptoid pulmonary surfactants
InactiveUS20050209152A1Resulting resistanceLow immunogenicityPeptide/protein ingredientsAlveolar/pulmonary surfactant peptidesOligomerDecreased surfactant
The present invention provides spreading agents based on sequence-specific oligomers comprising a peptoid, a peptide-peptoid chimera, a retropeptoid or a retro(peptoid-peptide) chimera, and methods for using the same, including for the treatment of respiratory distress of the lungs. The spreading agents are sequence-specific oligomers, including retrosequence-specific oligomers, based on a peptide backbone, that are designed as analogs of surfactant protein-B or surfactant protein-C.
Owner:MAXWELL BIOSCI INC
Protein Hydrogels For Treatment Of Neovascular Disease
InactiveUS20190380957A1Improve responseReduce vascular leakageAerosol deliveryTetrapeptide ingredientsDiabetic retinopathyDisease
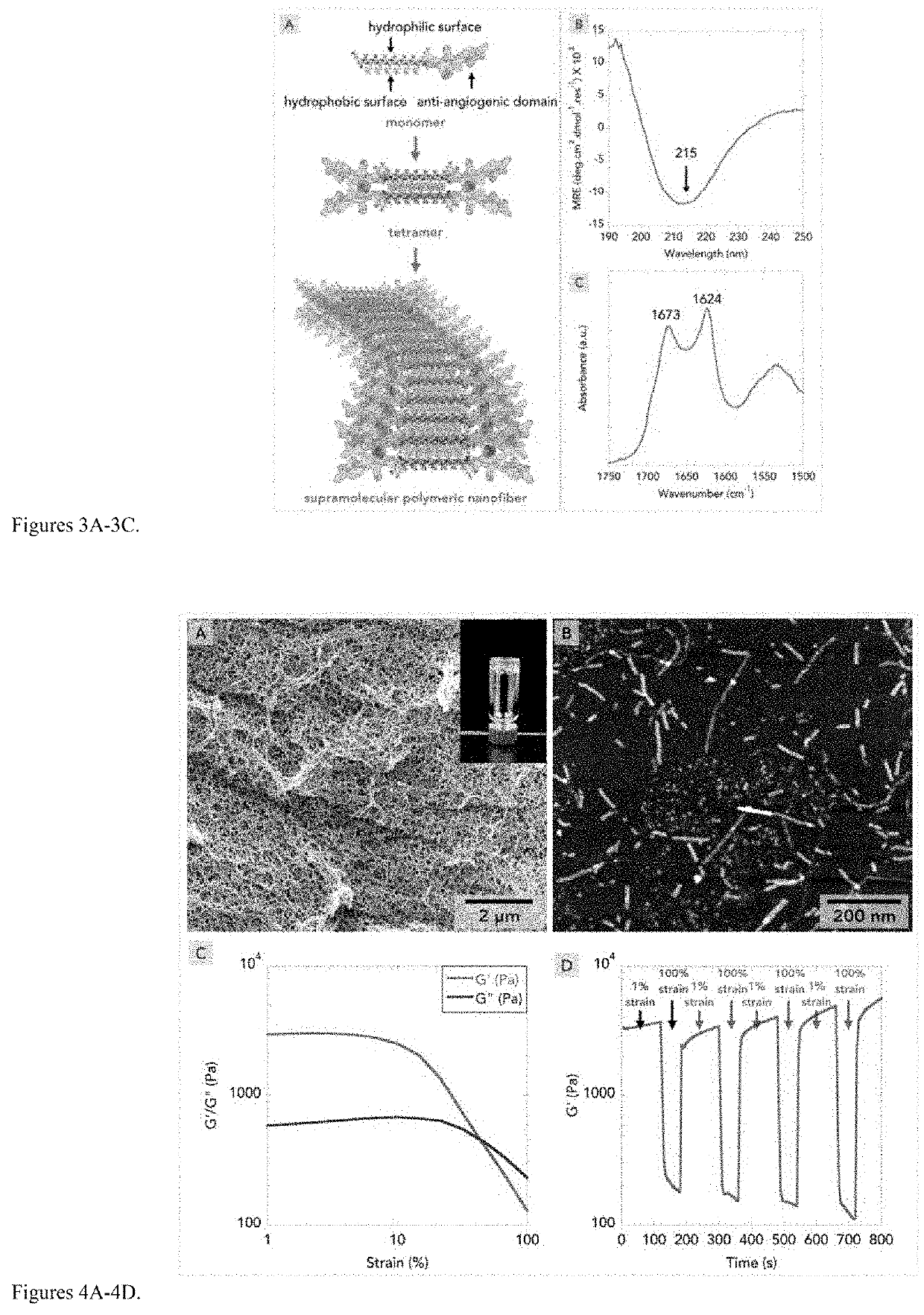
A mimic of an anti-angiogenic peptide is combined with a self-assembling peptide hydrogel to provide improved treatment for pathological neovascularization management. Pathological neovascularization may cause or worsen intraocular posterior segment diseases, such as diabetic retinopathy (DR) and wet age-related macular degeneration (wet AMD). The attachment of a therapeutic anti-angiogenic motif to a fibrillizing peptide backbone that undergoes nanofibrous self-assembly into an injectable hydrogel was found beneficial for the treatment of aberrant neovascularization. The peptide persists for extended periods in a target site for prolonging the therapeutic timeframe. This injectable hydrogel therapy may unlock potential clinical routes for treating many neovascular diseases.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
METHOD FOR SPECIFIC CLEAVAGE OF C Alpha-C BOND AND SIDE CHAIN OF PROTEIN AND PEPTIDE, AND METHOD FOR DETERMINING AMINO ACID SEQUENCE
ActiveUS20170327533A1Improve responseHigh sensitivityParticle separator tubesPeptide preparation methodsSide chainMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
The present invention provides a method for specifically cleaving a Cα-C bond of a peptide backbone and / or a side chain of a protein and a peptide, and a method for determining amino acid sequences of protein and peptide. A method for specifically cleaving a Cα-C bond of a peptide backbone and / or a side chain bond of a protein or a peptide, comprising irradiating a protein or a peptide with laser light in the presence of at least one hydroxynitrobenzoic acid selected from the group consisting of 3-hydroxy-2-nitrobenzoic acid, 4-hydroxy-3-nitrobenzoic acid, 5-hydroxy-2-nitrobenzoic acid, 3-hydroxy-5-nitrobenzoic acid, and 4-hydroxy-2-nitrobenzoic acid. A method for determining an amino acid sequence of a protein or a peptide, comprising irradiating a protein or a peptide with laser light in the presence of the above specific hydroxynitrobenzoic acid to specifically cleave a Cα-C bond of a peptide backbone and / or a side chain bond, and analyzing generated fragment ions by mass spectrometry.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP +1
A kind of method for preparing Nesiritide
ActiveCN104447979BRealize large-scale productionAvoid it happening againHormone peptidesPeptide preparation methodsSide chainPeptide sequence
The invention relates to a method for preparing nesiritide. The specific steps of the invention are: A) synthesizing the tripeptide fragment H-Arg(Boc)2-Arg(Boc)2-His(Trt)-OtBu by a liquid phase method; B) ) using solid-phase synthesis method, starting with 2-CTC-resin, and sequentially coupling amino acids with N-terminal Fmoc protection and side chain protection according to the peptide sequence of nesiritide main chain 1-29; C) in organic base Under certain conditions, iodine was used to fix the ring; D) cleavage to obtain the fully protected nesiritide main chain 1-29 peptide fragment; E) tripeptide fragment H-Arg(Boc)2-Arg(Boc)2-His(Trt) Coupling of ‑OtBu and fully protected nesiritide main chain 1‑29 peptide fragment; F) cleavage, purification, and lyophilization to obtain nesiritide. The invention provides a high-purity, low-cost nesiritide preparation process suitable for large-scale production. This process can not only effectively control the racemic peptide impurity D‑His32‑nesiritide and the missing peptide impurity Des‑Arg31‑nesiritide Peptide or Des‑Arg30‑nesiritide, the yield of nesiritide was also improved by optimizing the ring fixation conditions.
Owner:ADLAI NORTYE BIOPHARMA CO LTD
A ph-responsive non-helix-helix transition antimicrobial polypeptide and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111548388BEasy to preparePeptides are easyAntibacterial agentsPeptide preparation methodsSide chainClick chemistry
The invention discloses a pH-responsive non-helix-helix transition antibacterial polypeptide and a preparation method thereof. The method uses glutamic acid, an essential amino acid with biocompatibility, as a raw material, combined with the click chemistry method, to obtain a cationic polypeptide with a helical structure, which is prepared by modifying half of the maleic anhydride derivative through the side chain of the cationic polypeptide with a helical structure. The pH-responsive non-helical-helical transition antibacterial polypeptide has simple process, convenient operation and low cost, and can efficiently realize the secondary structure transformation under specific pH conditions, effectively reduce the biotoxicity of cationic polypeptides, and improve the bioavailability of cationic polypeptides Spend. In the present invention, through the modification of acid anhydrides with different pH responses, non-helical-helical transition antibacterial polypeptides with different pH conditions can be obtained, and the transformation from a low-activity non-helical structure to a high-activity helical structure can be realized under different physiological conditions. The conversion of cationic peptides can kill bacteria at the site of infection, which has broad application prospects.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com