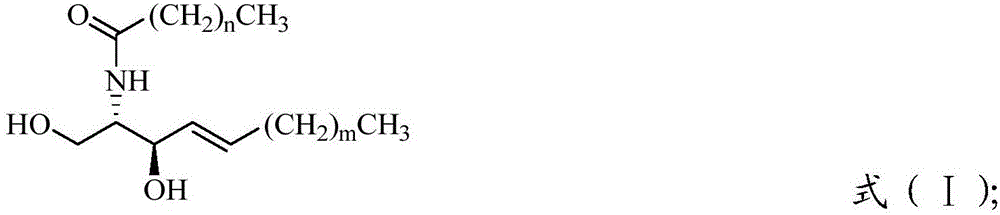Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Neural Growth" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
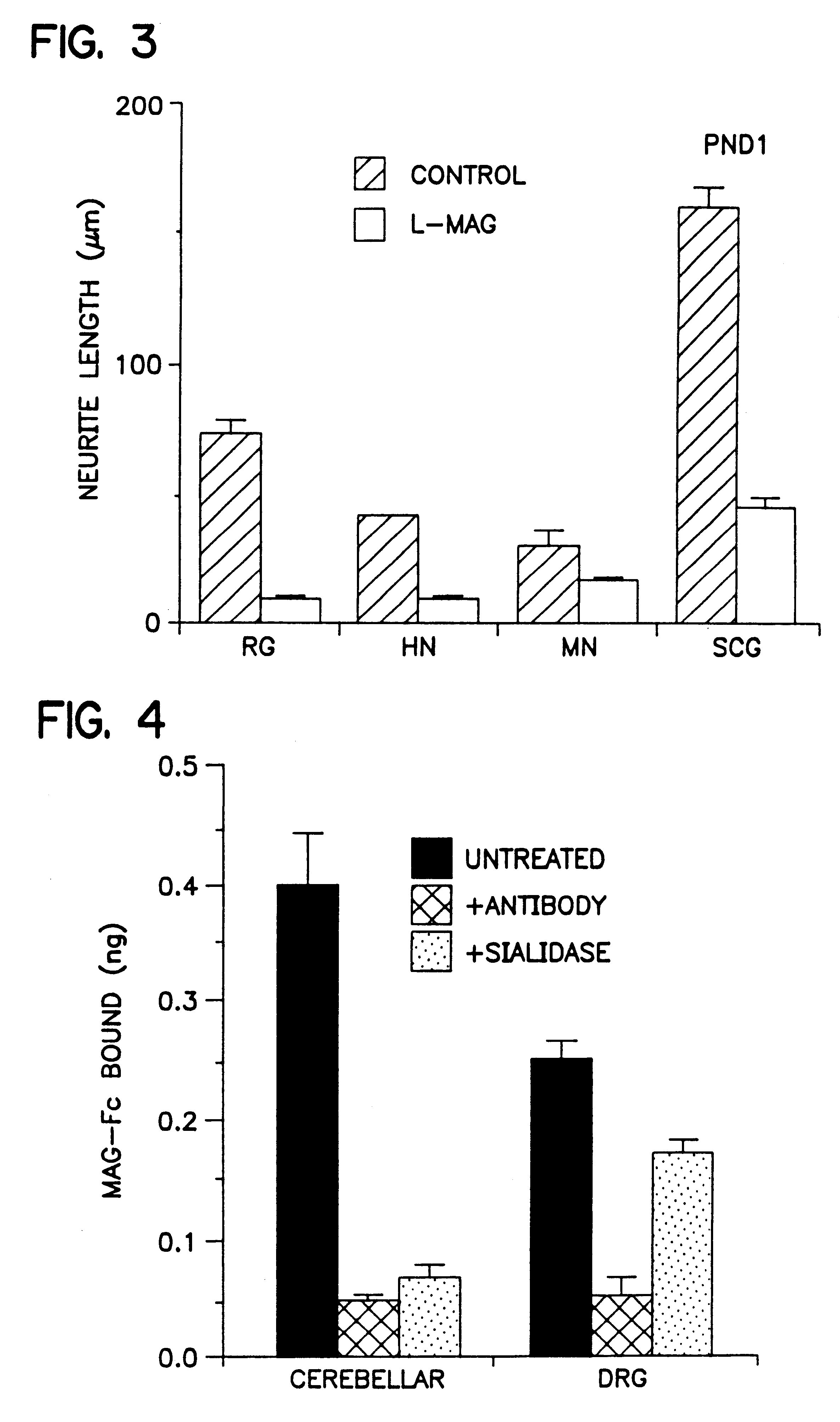
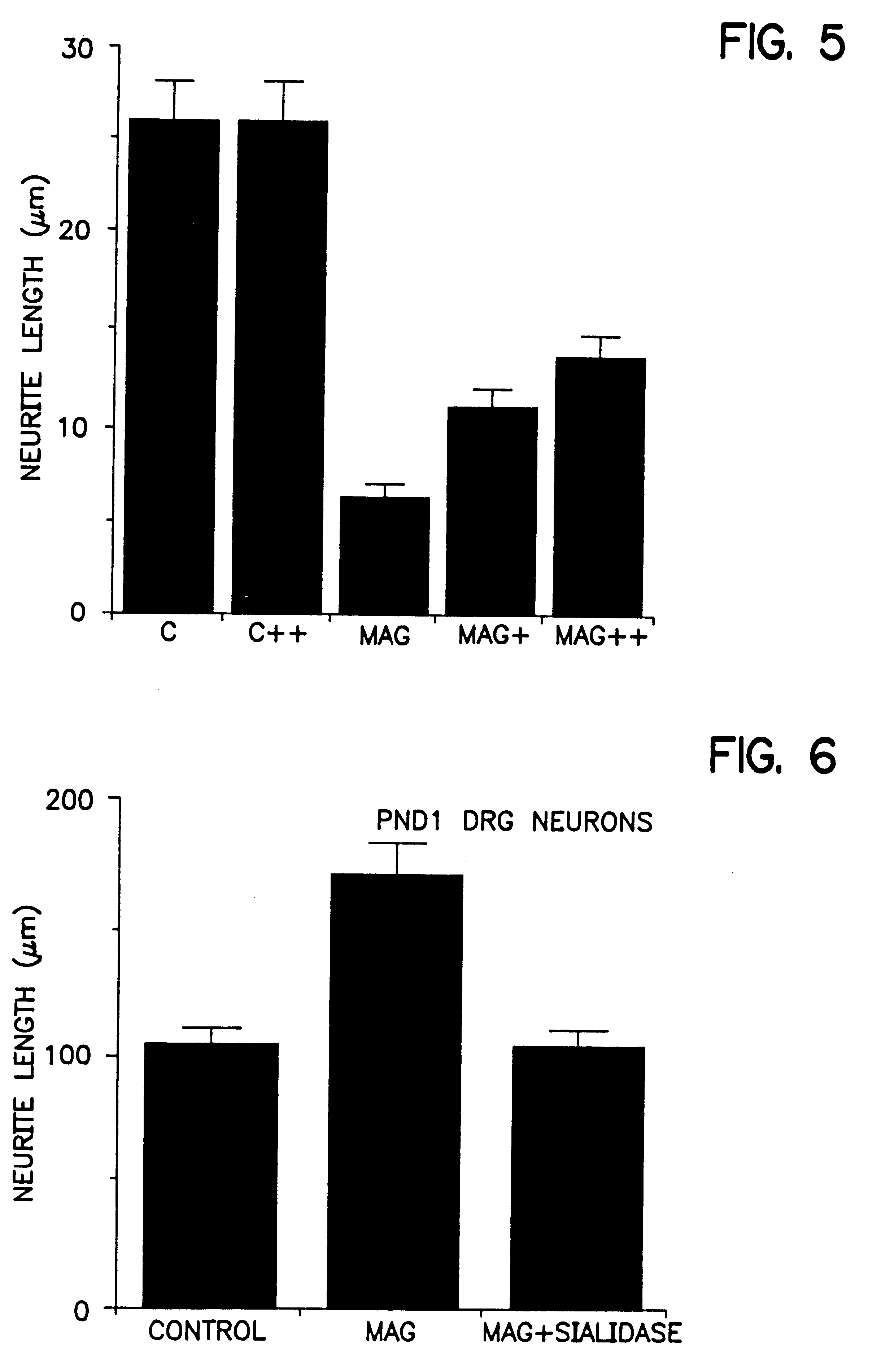
Compositions and methods using myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) and inhibitors thereof
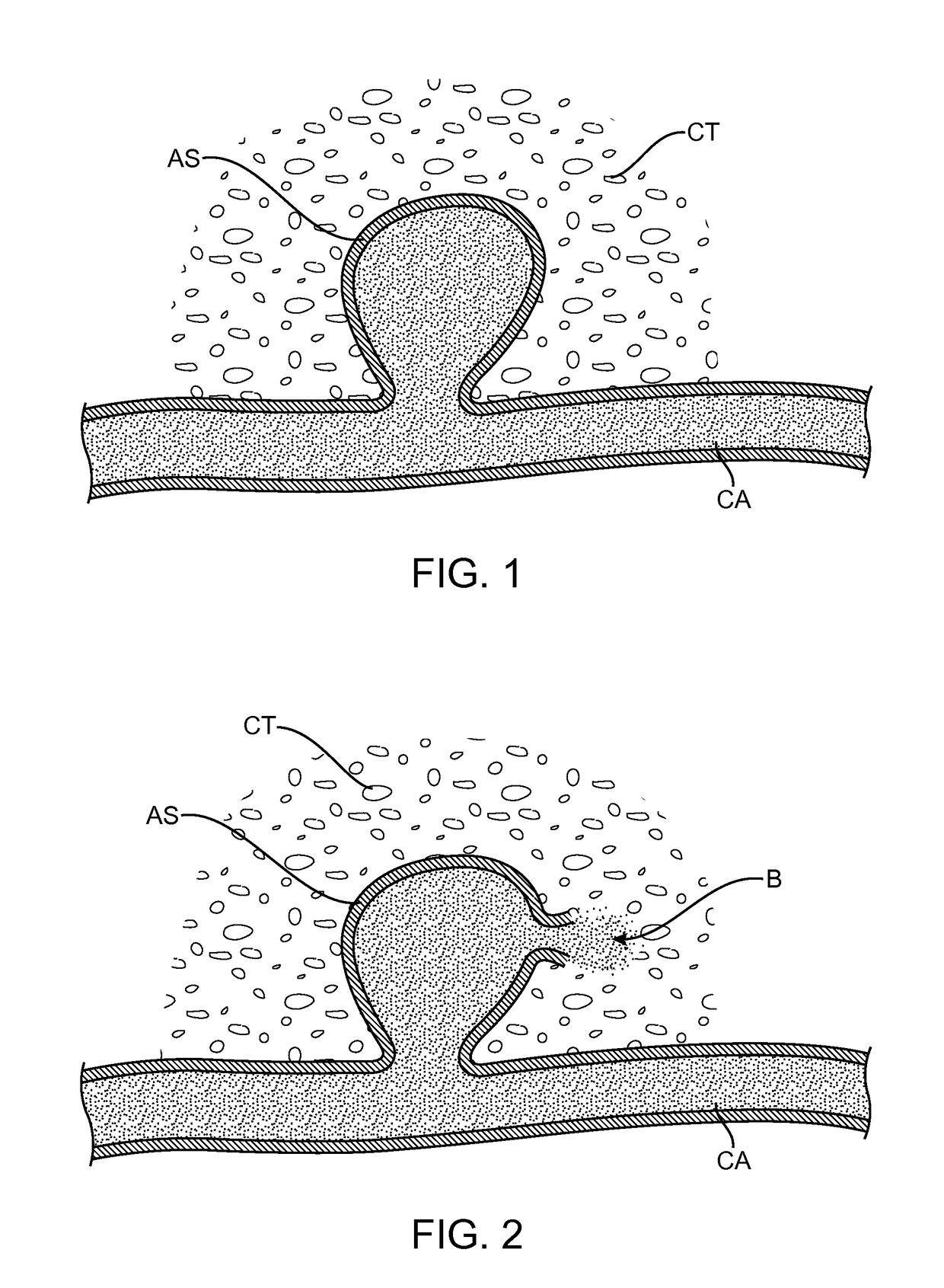
This invention relates to the novel identification of myelin-associated glycoprotein ("MAG") as a potent inhibitor of neural regeneration. More particularly, this invention relates to compositions and methods useful for reversing inhibition of neural regeneration in the central and peripheral nervous system. Assays to monitor the effects of MAG on neural regeneration and to identify agents which will block or promote the inhibitory effects of MAG on neural outgrowth are provided. Screening methods for identifying such agents are also provided. This invention also relates to compositions and methods using agents that can reverse the inhibitory effects of MAG on neural regeneration. Methods for regulating and for promoting neural growth or regeneration in the nervous system, methods for treating injuries or damage to nervous tissue or neurons, and methods for treating neural degeneration associated with disorders or diseases, comprising the step of administering at least one of the compositions according to this invention are provided.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising cyclic glycerophosphates and analogs thereof for promoting neural cell differentiation
InactiveUS6914056B1Reduce and prevent appearanceBiocideNervous disorderNerve degenerationBrain section
Cyclic glycerophosphates and analogs thereof (CGs) are shown to exert neutral promoting activities in target cells. Such activities include promotion of neuronal outgrowth, promotion of nerve growth, provision of dopaminotrophic supporting envrionment in a diseased portion of the brain, prevention of nerve degeneration and nerve rescue. These activities of the CGs render them useful for treatment of various disorders including but not limited to mental disorders such as, for example, schizophrenia, dementia or disorders resulting in learning disablities. In addition, these CGs may be used for the treatment of neurodegenerative conditions such as Altzheimer's diesease, Parkinson's disease, conditions resulting from exposure to harmful environmental factors or resulting from a mechanical injury. The CGs may also be used to treat an individual suffering from a primary neurodengenerative condition in order to prevent or reduce the appearance of secondary degeneration in additional nerves (“nerve rescue”).
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
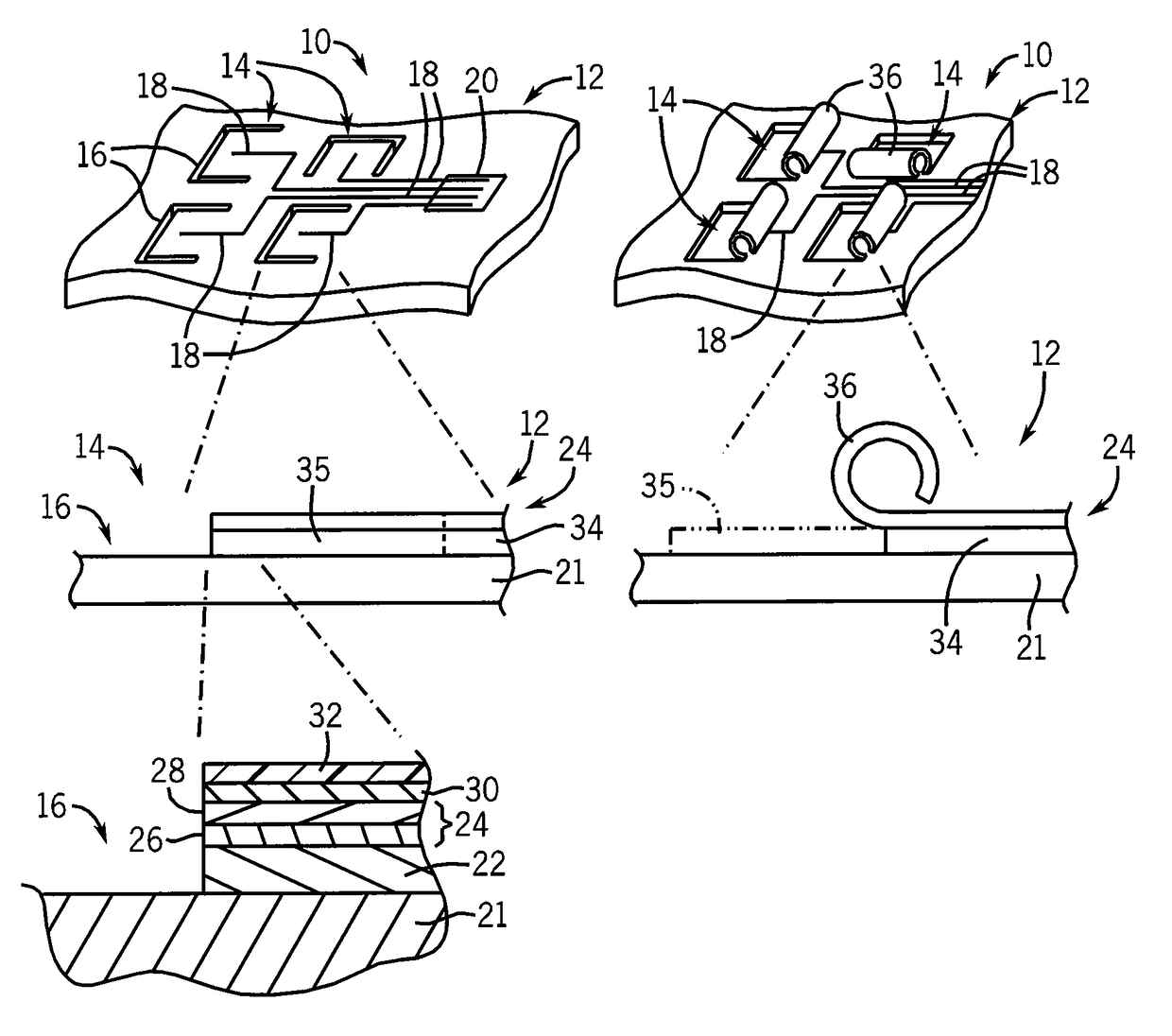
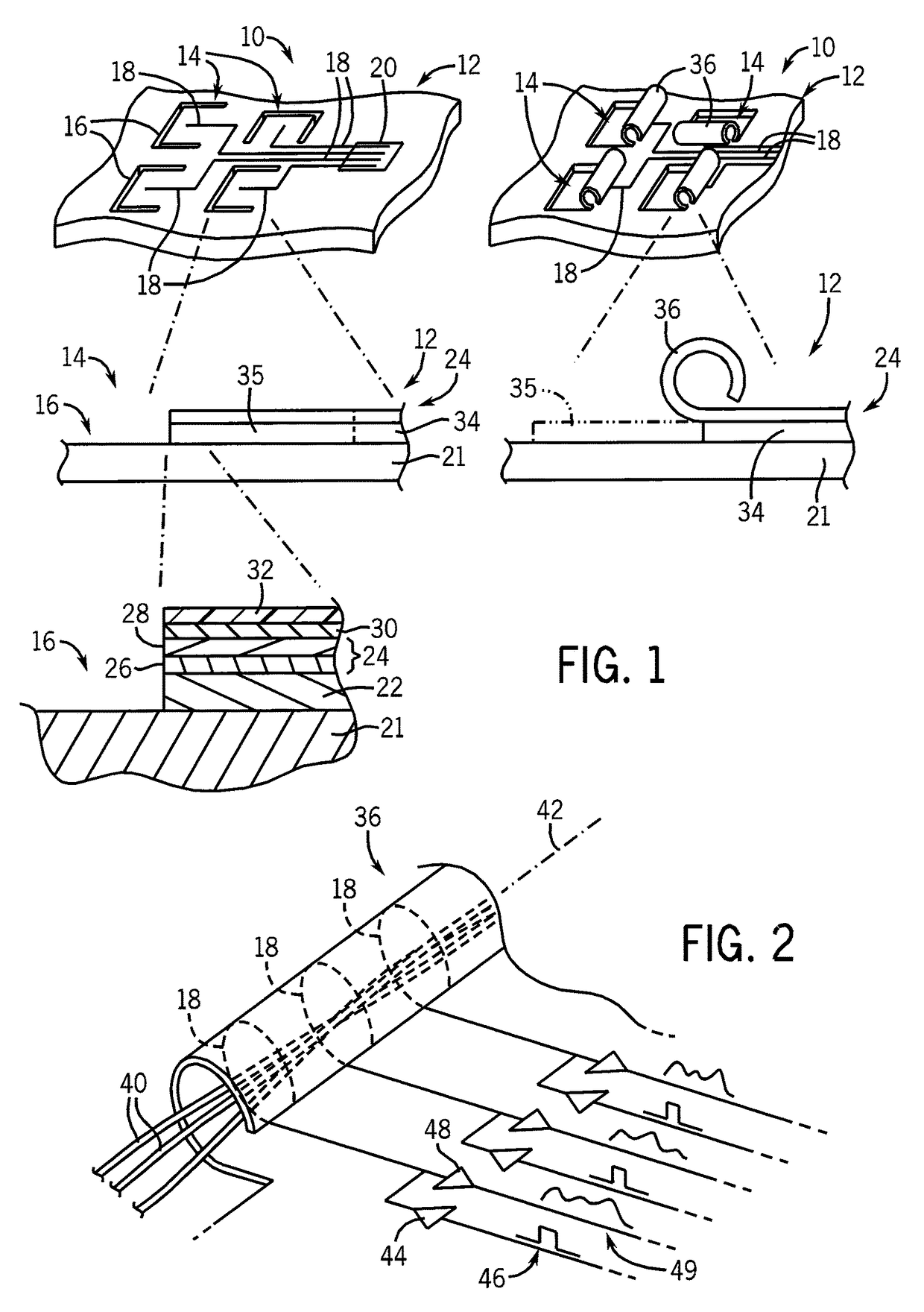
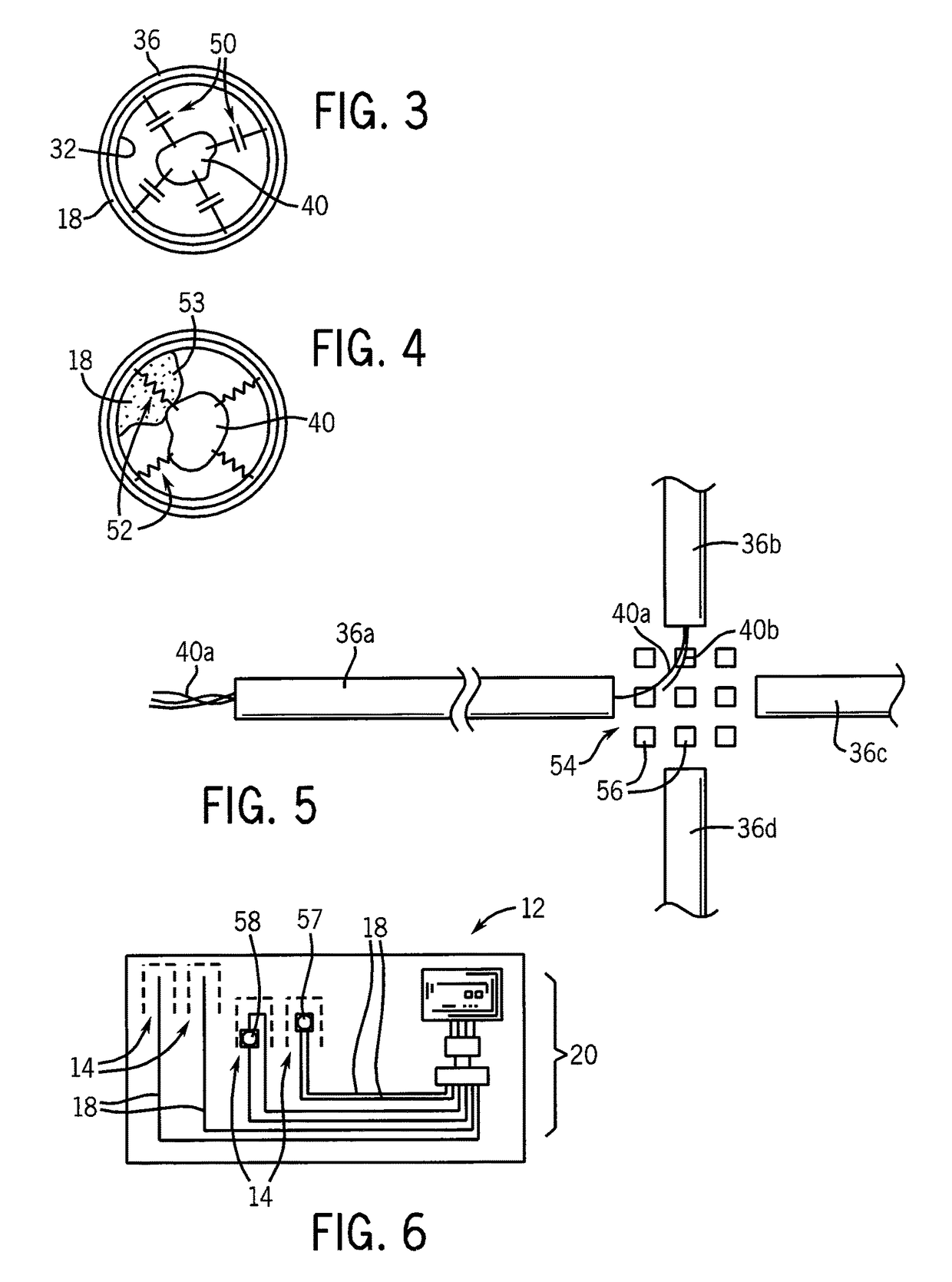
Tubular scaffold for neural growth
ActiveUS20120064628A1Promote neural growthSimple methodSolid-state devicesNervous system cellsEngineeringInterconnection
A scaffold for neurons consists of tubes sized to promote neural growth through the tubes. The tubes may be fixed to a substrate providing electrical or optical paths out from the interior of the tubes from sensors or stimulating probes at one or more locations along the length of the coaxial axons. Steering electrodes at spaces between tubes may be used to selectively promote the growth of interconnections of different axons in a one, two, or three-dimensional fashion.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Methods and use of motoneuronotrophic factor
InactiveUS20040224894A1Peptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against growth factorsMedicineSpinal cord
The invention is directed to a method of administering motoneuronotrophic factors for promoting the survival, growth, proliferation, or maintenance of neurons in an injured but not severed spinal cord. The method is useful for promoting axonal regeneration and for minimizing or inhibiting the effects of scar tissue formation or other elements that prevent nerve growth.
Owner:CHAU RAYMOND MING WAH
Methods for stimulating nervous system regeneration and repair by inhibiting phosphodiesterase type iv
InactiveUS20100056604A1Relieving myelinPromote neuronal survivalBiocideNervous disorderDiseasePhosphodiesterase Type 4
The invention relates to the novel identification of inhibitors of phosphodiesterase type 4 (“PDE4”) as agents which can reverse inhibition of neural regeneration in the mammalian central and peripheral nervous system. The invention provides compositions and methods using agents that can reverse the inhibitory effects on neural regeneration by regulating PDE4 expression. A composition comprising at least one PDE4 inhibitor in an amount effective to inhibit PDE4 activity in a neuron when administered to an animal is provided. Methods for regulating (e.g., promoting) neural growth or regeneration in the nervous system, methods for treating injuries or damage to nervous tissue or neurons, and methods for treating neural degeneration associated with disorders or diseases, comprising the step of administering to an animal a composition comprising a therapeutically effective amount of an agent which inhibits phosphodiesterase IV activity in a neuron are provided.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK
Neurite growth regulatory factors
InactiveUS6103232AAvoid environmentIncrease the areaNervous disorderHydrolasesNerve fiber bundleMyelin
The present invention relates to methods of inducing neurite outgrowth in the central nervous system by antagonizing neural growth inhibitory factors. More particularly, the present invention is directed to use of antibodies to the central nervous system (CNS) myelin associated proteins; such antibodies can be used in the diagnosis and therapies of nerve damage resulting from trauma, infarction, and degenerative disorders of the CNS. In a specific embodiment of the invention, the monoclonal antibody IN-1 may be used to promote neurite outgrowth of nerve fibers over long distances in spinal cord lesions.
Owner:ZURICH UNIV OF
Culture medium for promoting differentiation of rat neural stem cells and use method of culture medium
ActiveCN104017771AHigh differentiation efficiencyNervous system cellsBrain-derived neurotrophic factorNeural Growth
The invention discloses a culture medium for promoting differentiation of rat neural stem cells and a use method of the culture medium. The culture medium contains B-27 Supplement without retinoic acid, L-Glutamine, FBS (fetal bovine serum), beta-NGF (neural growth factor), BDNF (brain derived neurotrophic factor), RA and vitamin E in Neurobasal-A medium. The culture medium is low in cost, the problem of low neural stem cell differentiation efficiency in the prior art is solved, and the efficiency of differentiating neural stem cells into nerve cells is remarkably improved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Neuroprotective effect of growth hormone
InactiveUS7304029B1Increase the effective concentrationEasy to produceNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNeural GrowthHormones regulation
The invention relates to neuroprotection and to medicaments for use therein. Neuroprotection is induced by activation of neural growth hormone receptors, primarily using medicaments comprising growth hormone, growth hormone analogs or ligands which are functionally equivalent. Such medicaments may also include one or more secondary neuroprotective agents.
Owner:NEUREN PHARMA LTD +1
Medical device
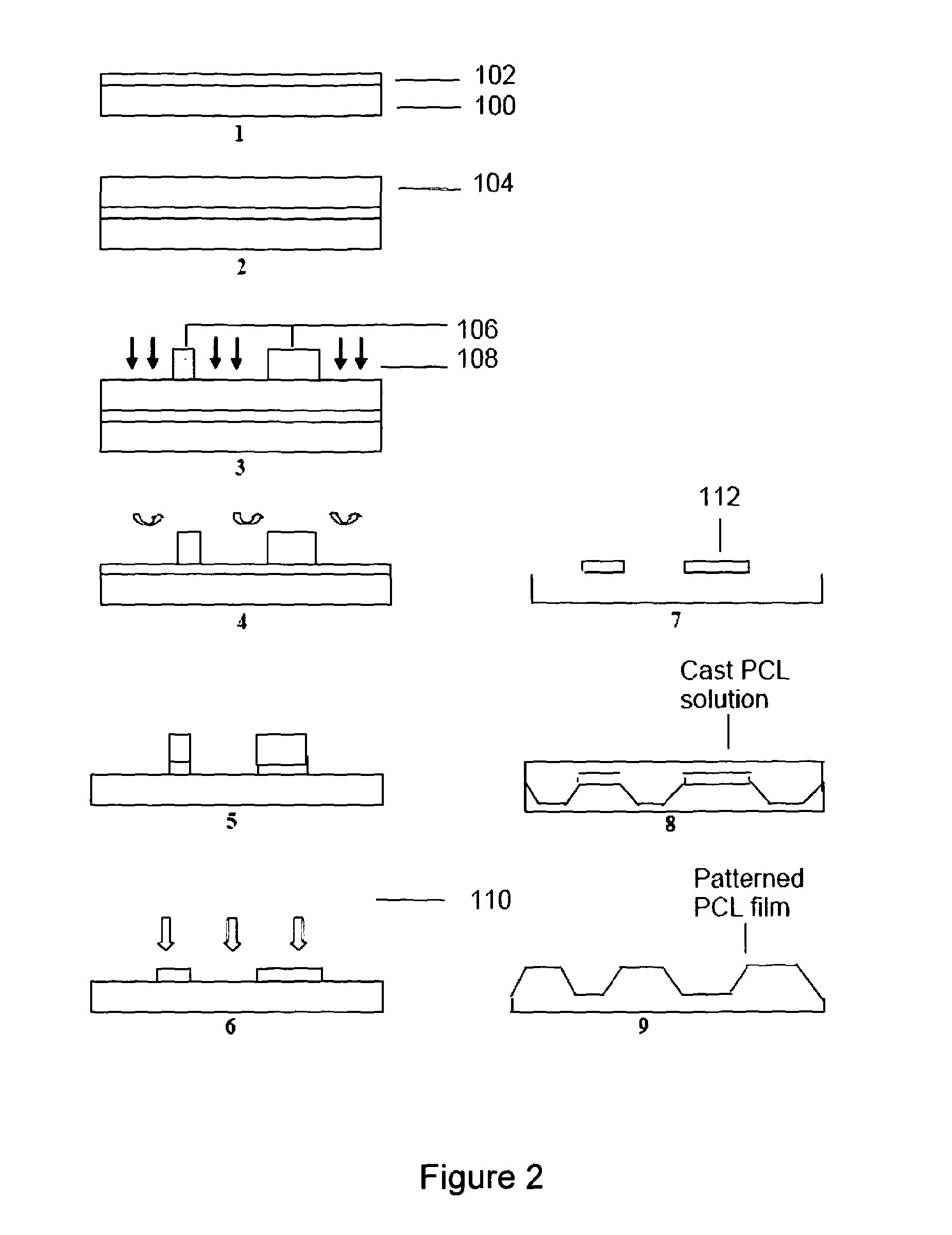
InactiveUS20130184724A1Reduces and avoids irritationIncrease flexibilityNervous system cellsUnknown materialsPeripheral neuronPeripheral nerve
The present invention provides a peripheral nerve growth scaffold including poly ε-caprolactone (PCL) and microgrooves on an inner surface of the scaffold, the scaffold being adapted for use in treatment of damaged peripheral nerves. The microgrooves are suitably arranged as a pattern or array and preferably comprise sloping side walls, which arrangement has been found to provide a favourably environment for nerve and Schwann cell growth and proliferation. Experimental results demonstrate directed and aligned growth, which suitably reduces the rate of formation of neuromas. Embodiments comprising a PCL-PLA blend of the sloping side wall and a groove width greater than the spacing between adjacent grooves has been found to be particularly effective for directed cell growth and proliferation.
Owner:UNIV OF MANCHESTER
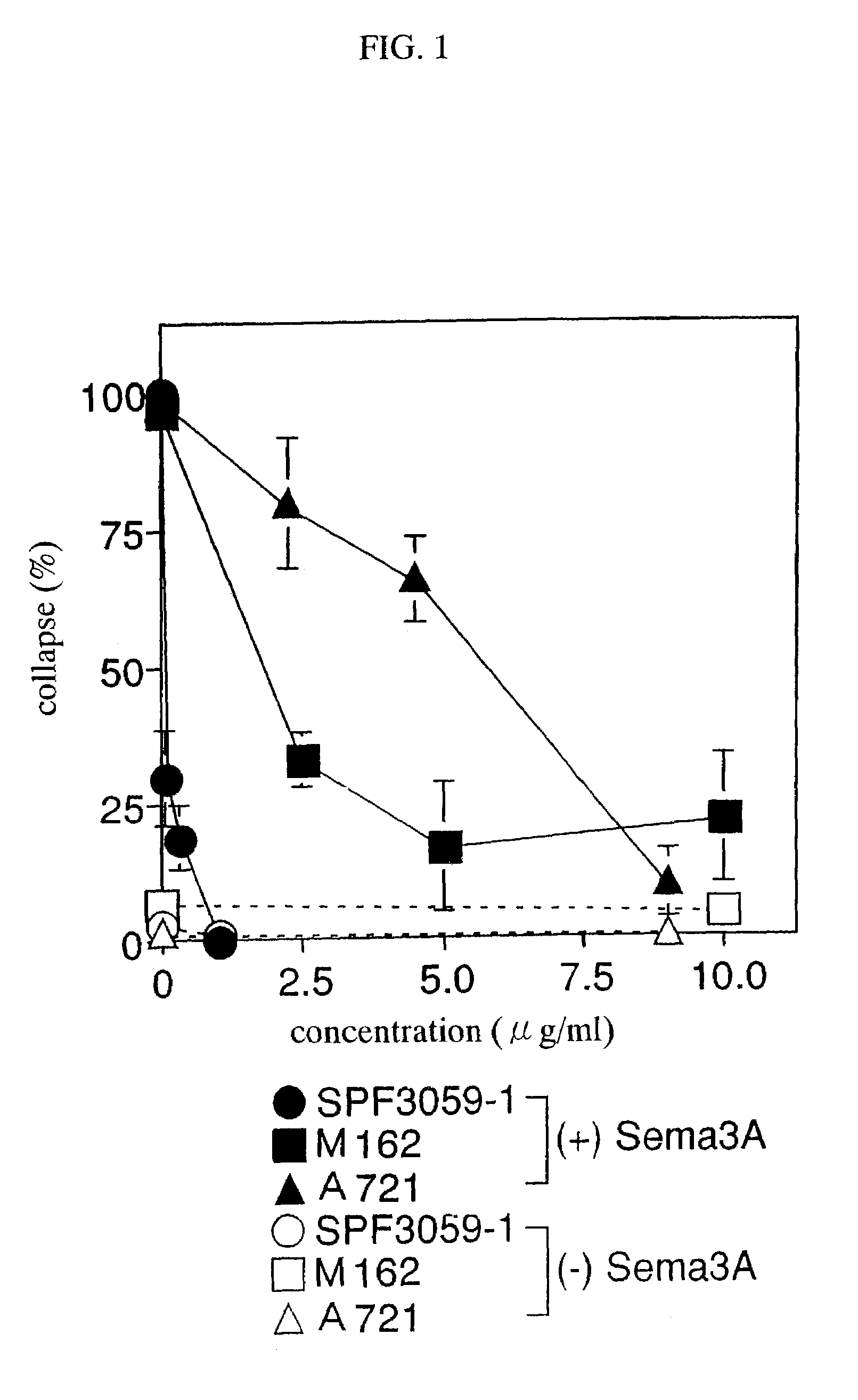
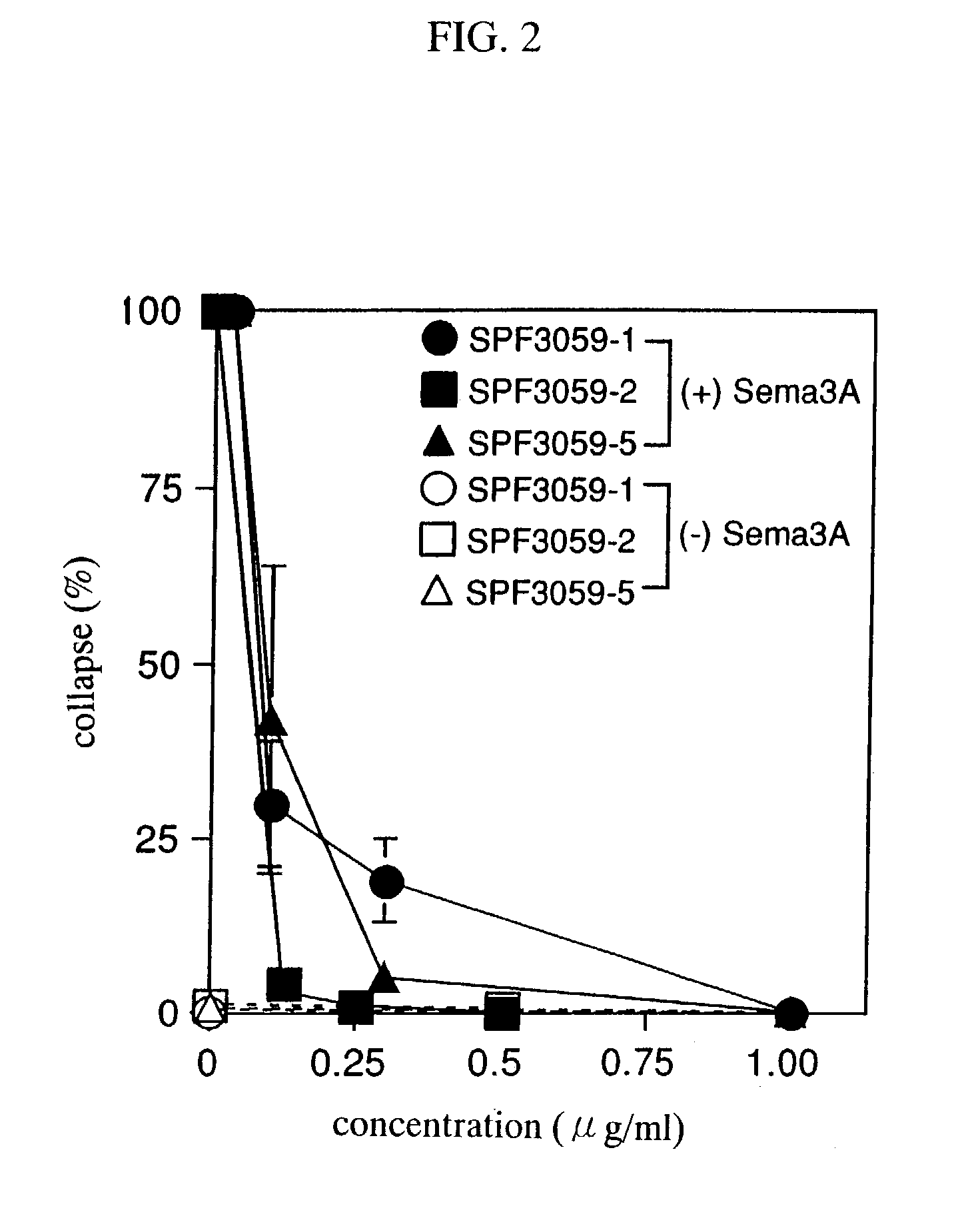
Nerve regeneration promoters containing semaphorin inhibitor as the active ingredient
Owner:SUMITOMO DAINIPPON PHARMA CO LTD
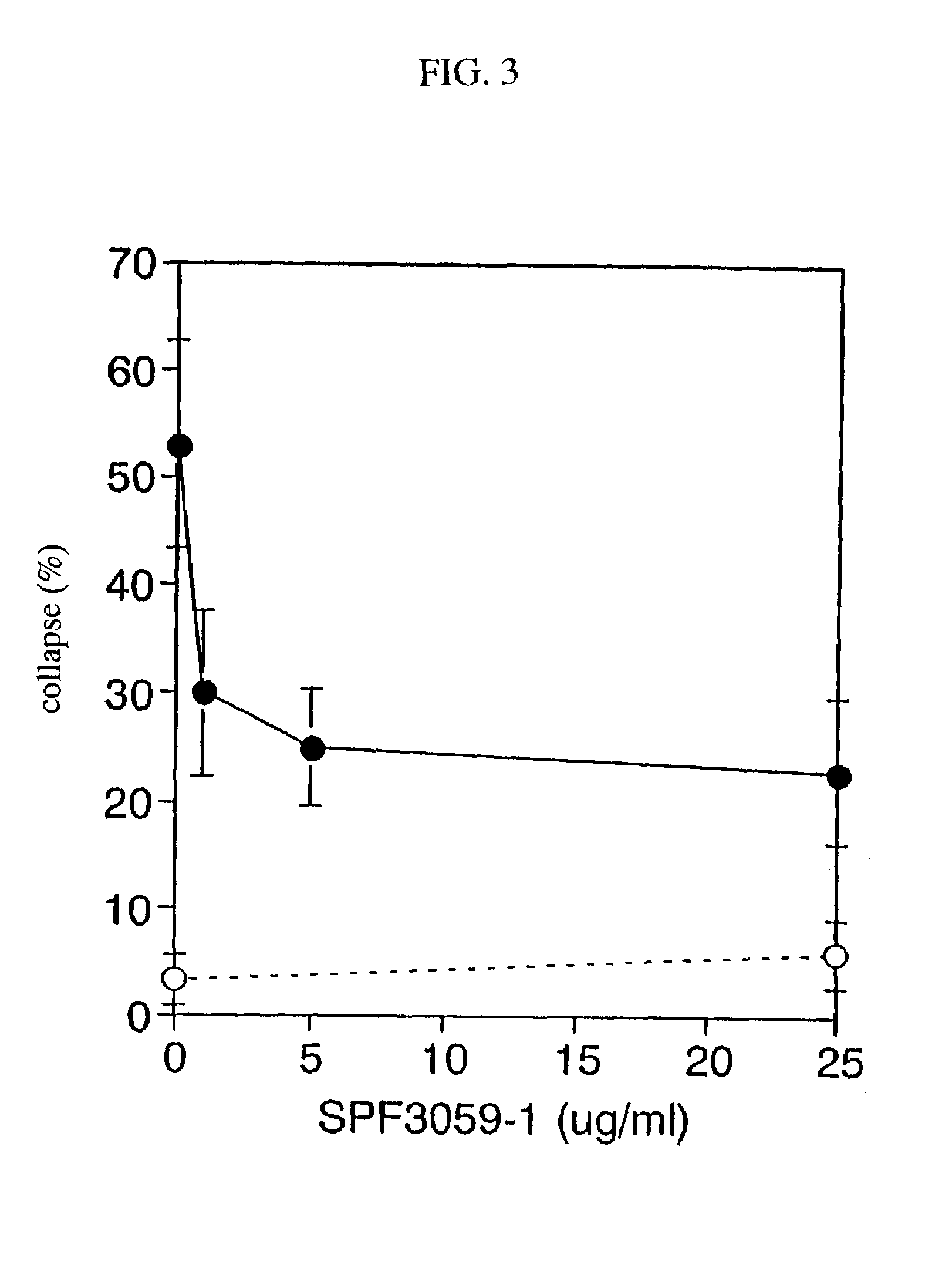
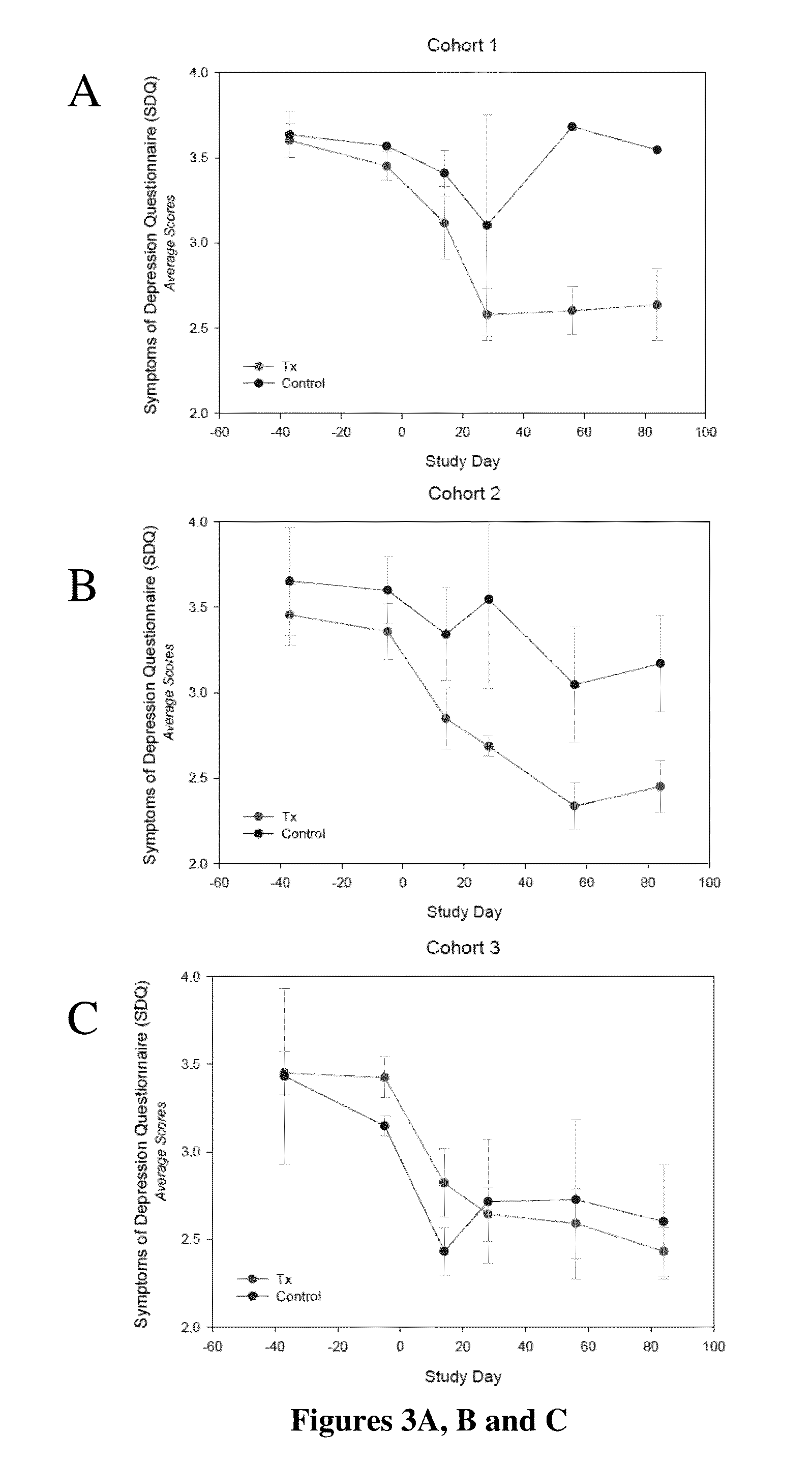
Protocols for treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD)
Although it is known that certain benzylpiperazine-aminopyridines or open chain forms thereof are effective in stimulating neural growth in in vitro tests, it has now been surprisingly found that administering these compounds in a dosage range of 10 mg / day-130 mg / day over 25-35 days is effective in treating Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) such that statistically significant results can be obtained with samples of only six subjects.
Owner:ALTO NEUROSCIENCE INC +1
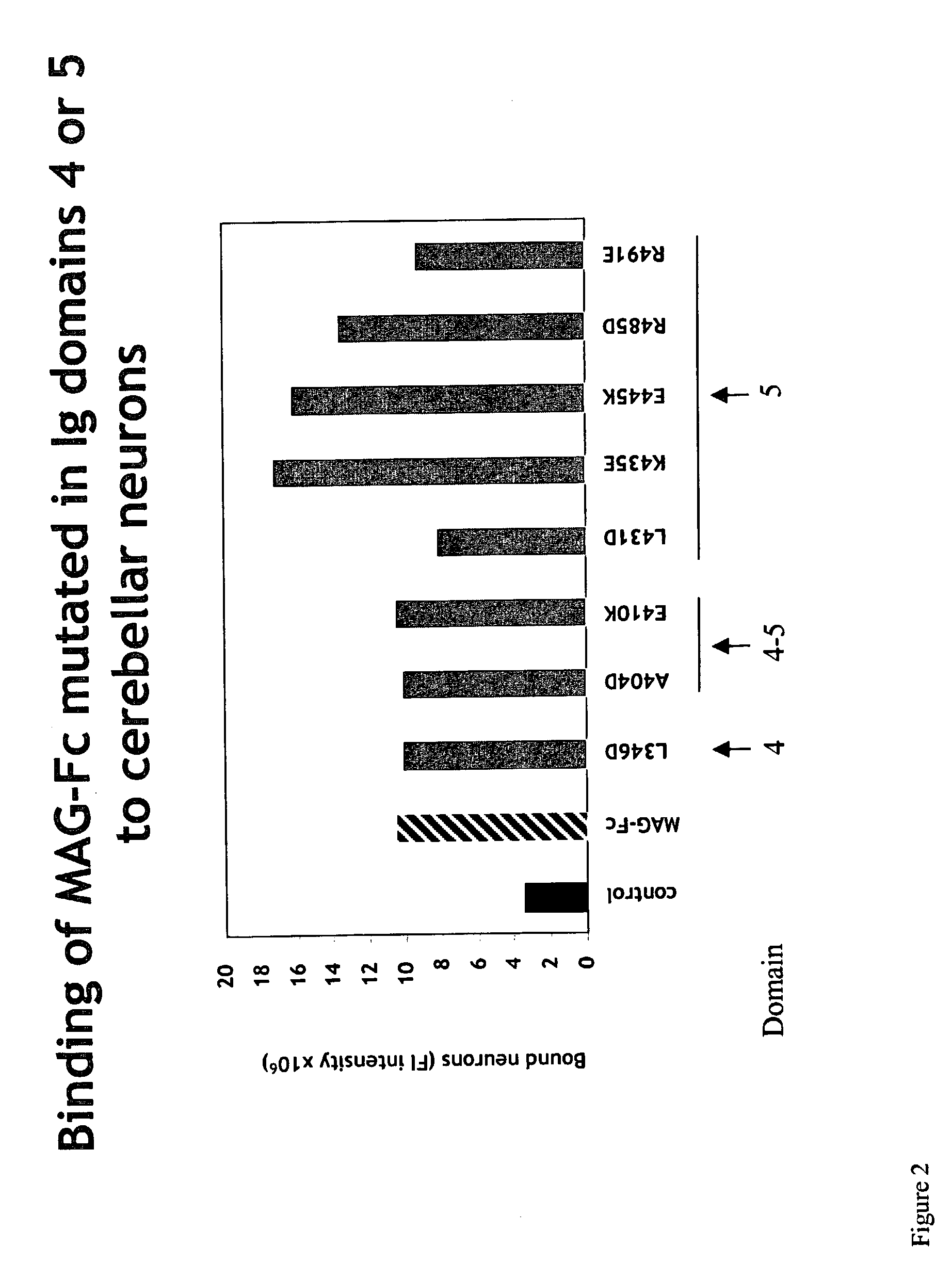
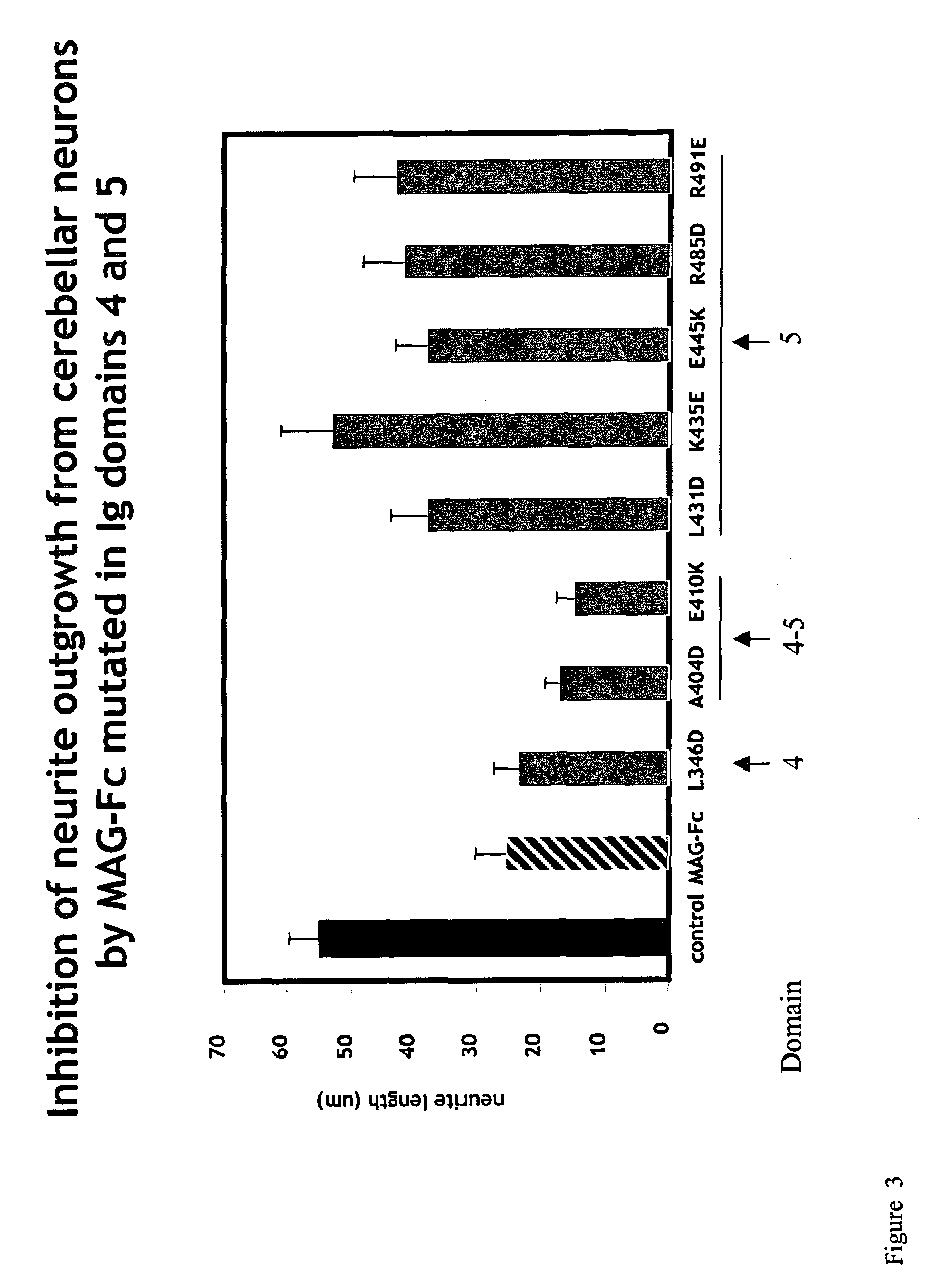
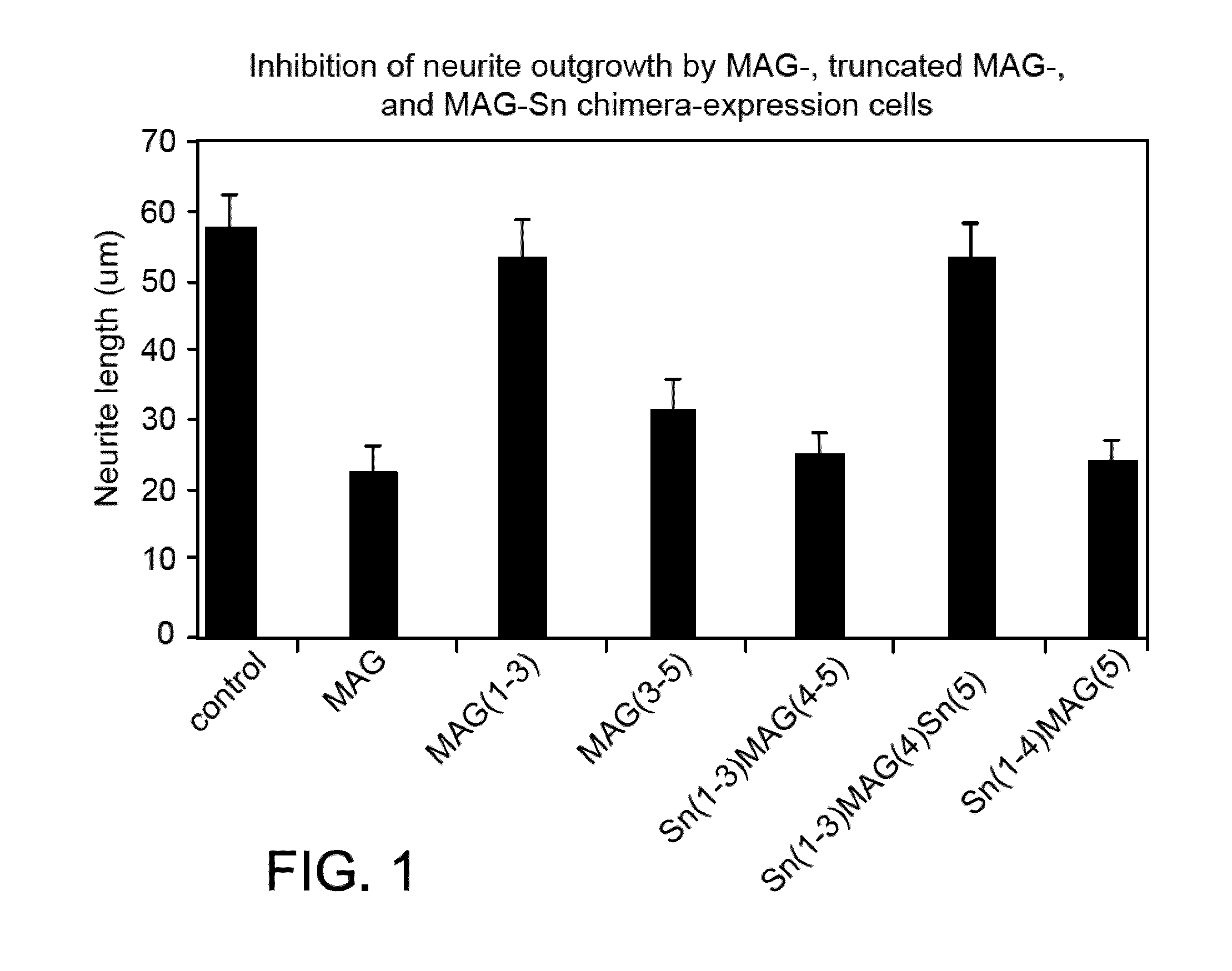
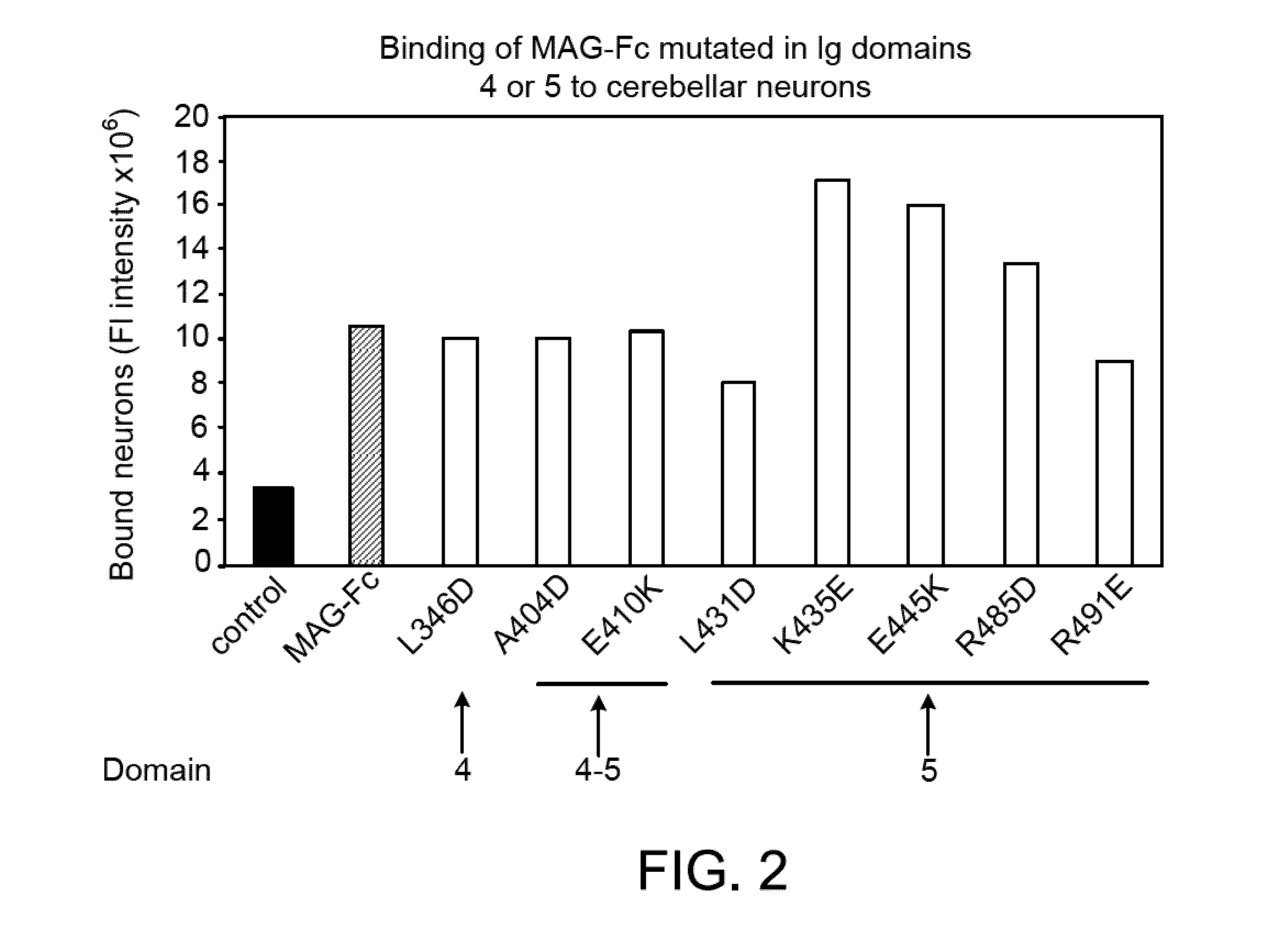
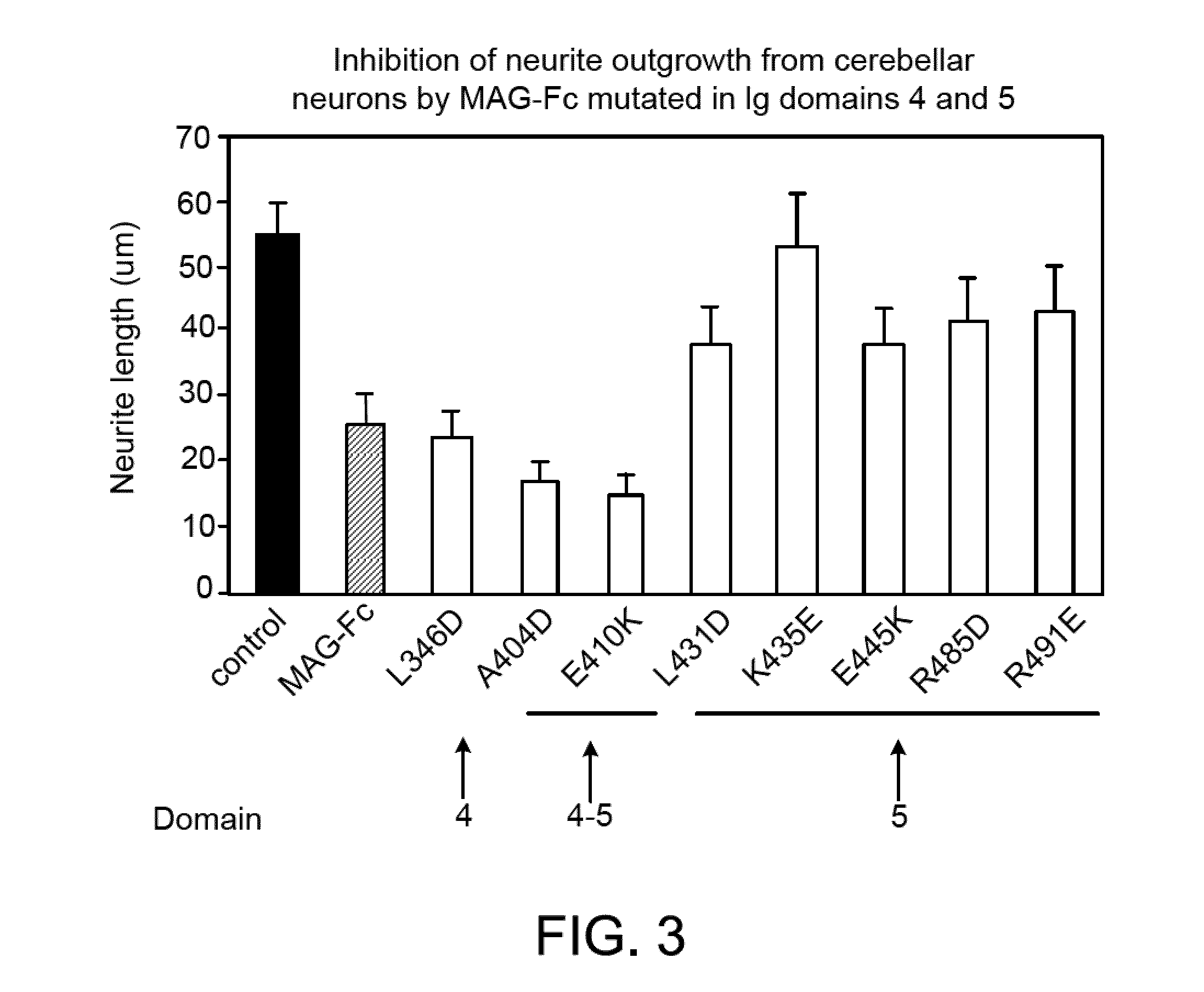
Inhibitors of myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) activity for regulating neural growth and regeneration
InactiveUS7842666B2Reduce and eliminate abilityPromote or inhibit)Nervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseNervous system
The present invention relates generally to products, compositions and methods useful for promoting neural repair and regeneration. The products and compositions of this invention include myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) derivatives that are inhibitors of endogenous MAG (e.g., mutant MAG proteins) and Nogo Receptor (NgR) binding inhibitors that are peptides derived from MAG, Nogo and OMgp that can bind to NgR and block NgR signaling. Peptides that can bind and activate NgR signaling are also provided. Inhibitory MAG derivatives and NgR binding inhibitors are useful for blocking the inhibition of neural regeneration mediated by proteins such as MAG, Nogo and / or OMgp in the nervous system. These inhibitors are also useful for treating neural degeneration associated with injuries, disorders or diseases.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK
Ceramide compound and application
InactiveCN106631871AHigh activityHas the prospect of practical clinical applicationNervous disorderOrganic chemistryChemical compoundNeural Growth
The invention relates to a ceramide compound; in the structural general formula, m=2-12; n=0-20. The ceramide compound has significant pseudo neural growth factor activity, and is the small molecule compound capable of passing through blood-brain barrier. The structural general formula is shown as Figure.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Tubular scaffold for neural growth
ActiveUS9976120B2Promote neural growthSimple methodApparatus sterilizationSolid-state devicesElectricityEngineering
A scaffold for neurons consists of tubes sized to promote neural growth through the tubes. The tubes may be fixed to a substrate providing electrical or optical paths out from the interior of the tubes from sensors or stimulating probes at one or more locations along the length of the coaxial axons. Steering electrodes at spaces between tubes may be used to selectively promote the growth of interconnections of different axons in a one, two, or three-dimensional fashion.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
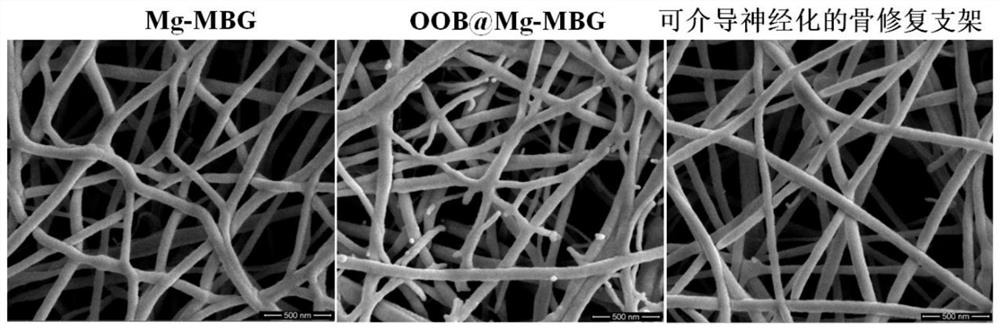
Bone repair scaffold material capable of mediating nervalization and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN113975460APromote repairFast tempoPharmaceutical delivery mechanismElectro-spinningHeterologousBiophysics
The invention discloses a bone repair scaffold material capable of mediating nervalization and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps that heterologous expression bone matrix fusion protein is adsorbed into calcium and magnesium doped mesoporous bioactive glass prepared through a sol-gel and template self-assembly method to serve as an inner core; nerve growth factors capable of promoting nerve growth are loaded into silk protein to serve as a shell, and then the bone repair scaffold material which is of a core-shell structure and can be used for mediating nervalization is prepared through a coaxial electrostatic spinning technology. The bone repair scaffold material capable of mediating the nervalization has good cell compatibility, osteogenic activity, neurogenic activity and calcium deposition promotion effects, can promote proliferation, differentiation and mineralization processes of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in the osteogenic direction, can also promote the survival process of neurons, as a bone repair material, the material has a wide prospect in clinical application of repairing bone defects and restoring consciousness of injured parts.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising cyclic glycerophosphates and analogs thereof for promoting neural cell differentiation
InactiveCN1348375AImprove or reduce unwanted symptomsPreventing or Treating Nerve SalvageNervous disorderMetabolism disorderNerve degenerationSecondary degeneration
Cyclic glycerophosphates and analogs thereof (CGs) are shown to exert neutral promoting activities in target cells. Such activities include promotion of neuronal outgrowth, promotion of nerve growth, provision of dopaminotrophic supporting envrionment in a diseased portion of the brain, prevention of nerve degeneration and nerve rescue. These activities of the CGs render them useful for treatment of various disorders including but not limited to mental disorders such as, for example, schizophrenia, dementia or disorders resulting in learning disablities. In addition, these CGs may be used for the treatment of neurodegenerative conditions such as Altzheimer's diesease, Parkinson's disease, conditions resulting from exposure to harmful environmental factors or resulting from a mechanical injury. The CGs may also be used to treat an individual suffering from a primary neurodengenerative condition in order to prevent or reduce the appearance of secondary degeneration in additional nerves ("nerve rescue").
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Protocols for treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD)
Although it is known that certain benzylpiperazine-aminopyridines or open chain forms thereof are effective in stimulating neural growth in in vitro tests, it has now been surprisingly found that administering these compounds in a dosage range of 10 mg / day-130 mg / day over 25-35 days is effective in treating Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) such that statistically significant results can be obtained with samples of only six subjects.
Owner:ALTO NEUROSCIENCE INC +1
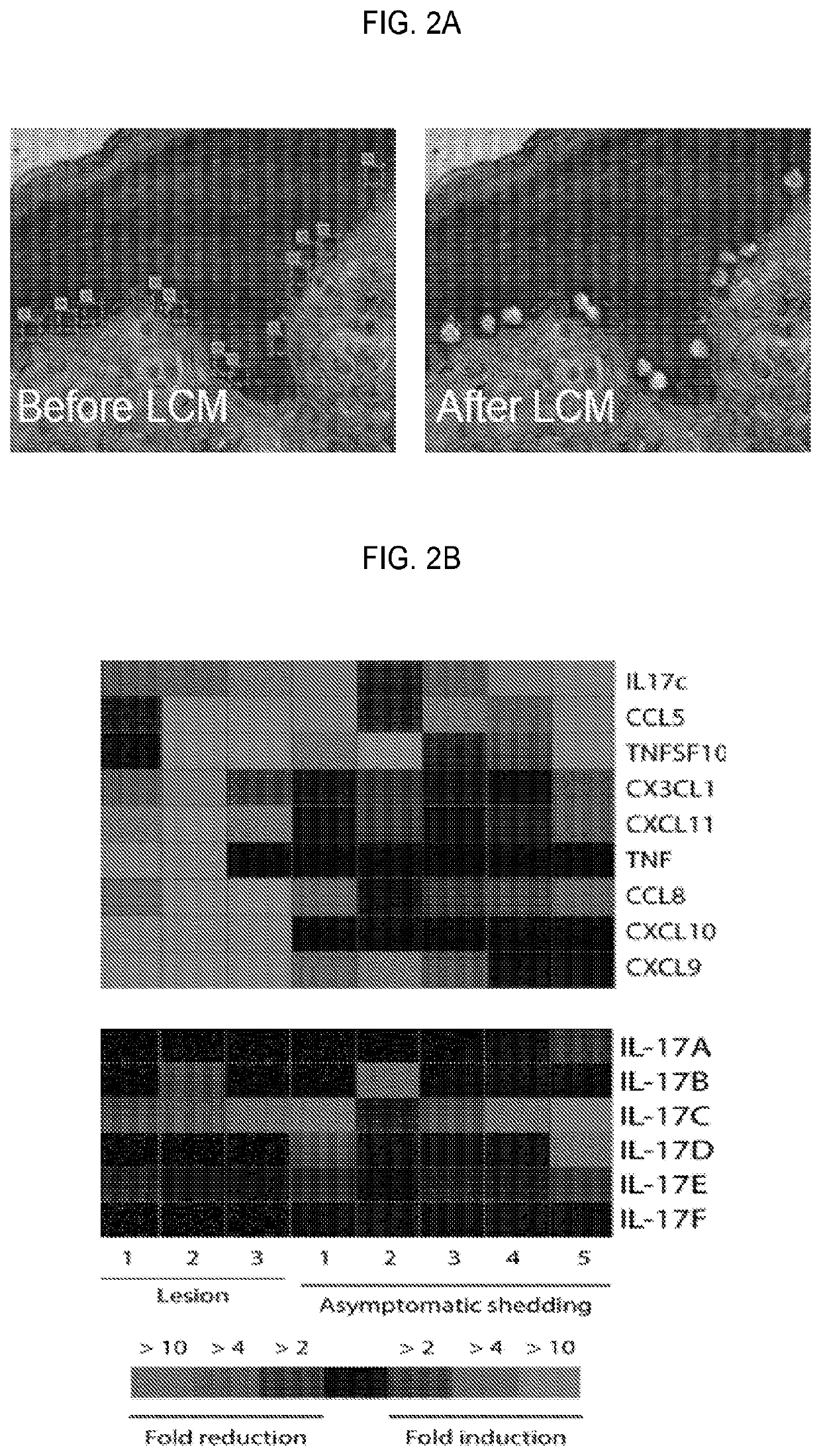
Compositions, kits, and methods using interleukin-17C to promote neural growth and/or neural survival
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
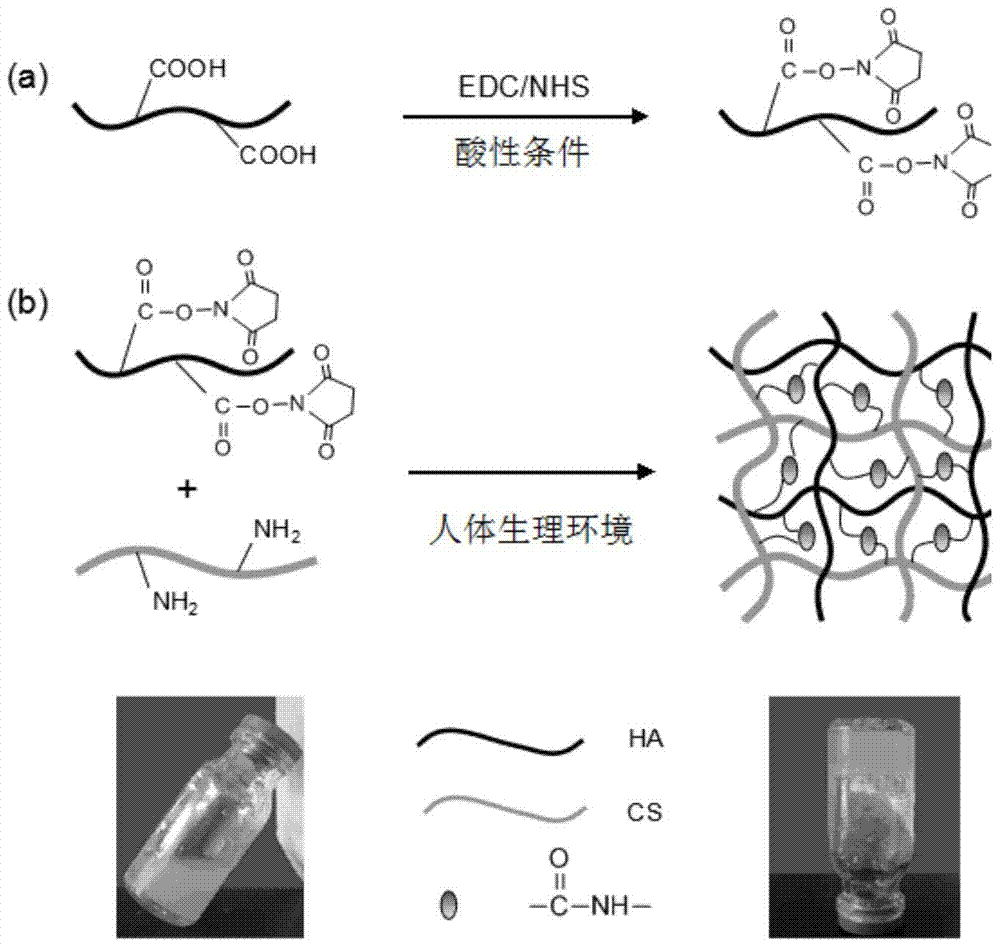
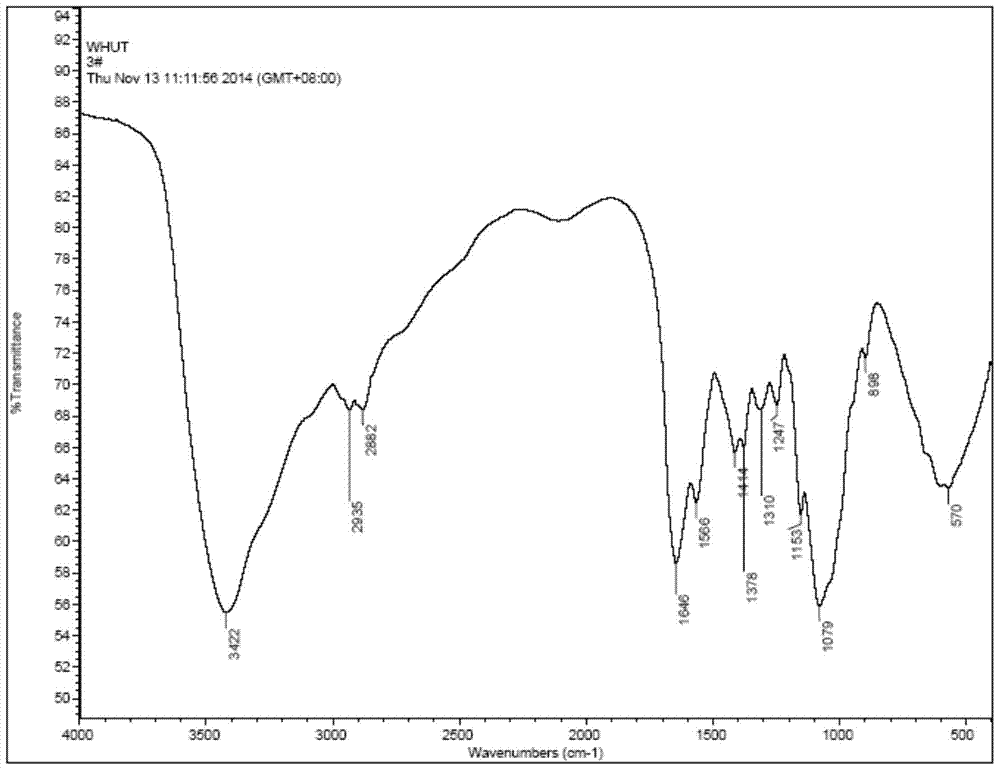
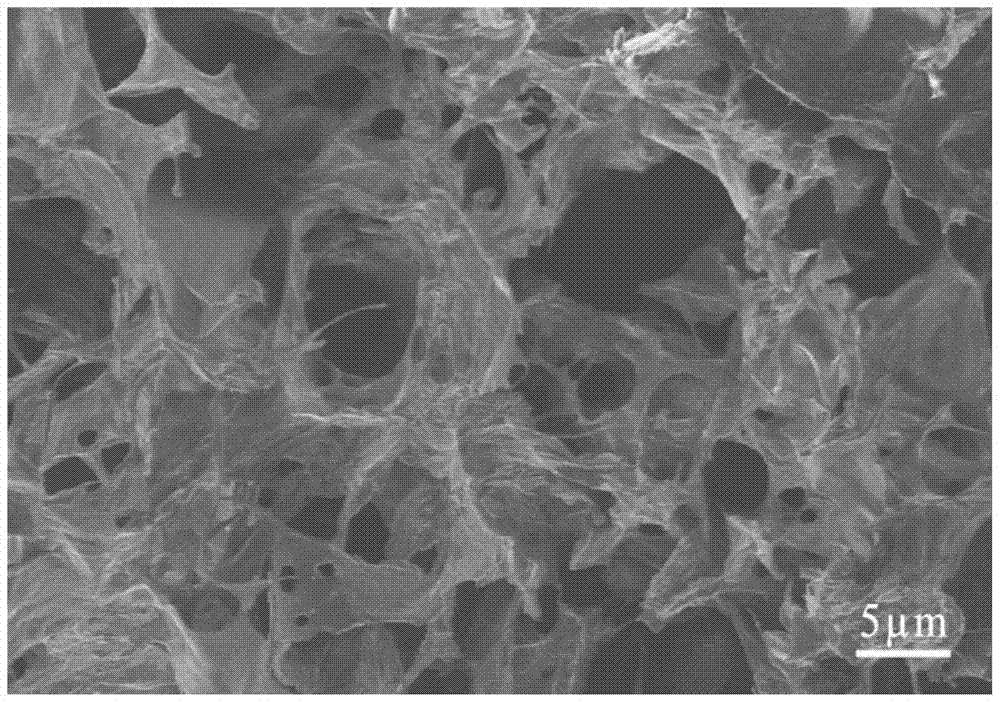
A kind of nerve growth factor injectable in situ hydrogel, preparation and application
The invention relates to NGF (Nerve Growth Factor) injectable in-situ hydrogel as well as preparation and application thereof. The NGF injectable in-situ hydrogel is obtained by adding EDC(1-ethyl amide crosslinking agent-3-(3-dimethyl amino propyl) carbide imine) and NHS (N-hydroxysuccinimide) into an aqueous solution system of hyaluronic acid and chitosan hydrochloride, and adding an NGF after HA-NHS-active ester intermediate by the hyaluronic acid under the action of the EDC / NHS under an acidic condition. The hydrogel has a pH sensitive feature; the conversion process of solution-gel can be completed under physiological conditions of a human body; the NGF injectable in-situ hydrogel can be subjected to in-situ curing under the action of pH in an acceptor at a nerve damage part after the NGF injectable in-situ hydrogel is injected into nerve tissue; the traumatic property of a surgery is avoided. The NGF can be released slowly in vitro by utilizing the environmentally sensitive feature of the hydrogel; the problems of low activity, burst release and the like caused by the facts that a half-life period is short and the diffusion and the degradation are too quick of the NGF are effectively solved; high bioactivity of the NGF is kept; the extension and the myelination of a nerve axon are promoted; therefore, the purpose of repairing nerves is achieved.
Owner:武汉渝联生物科技有限公司
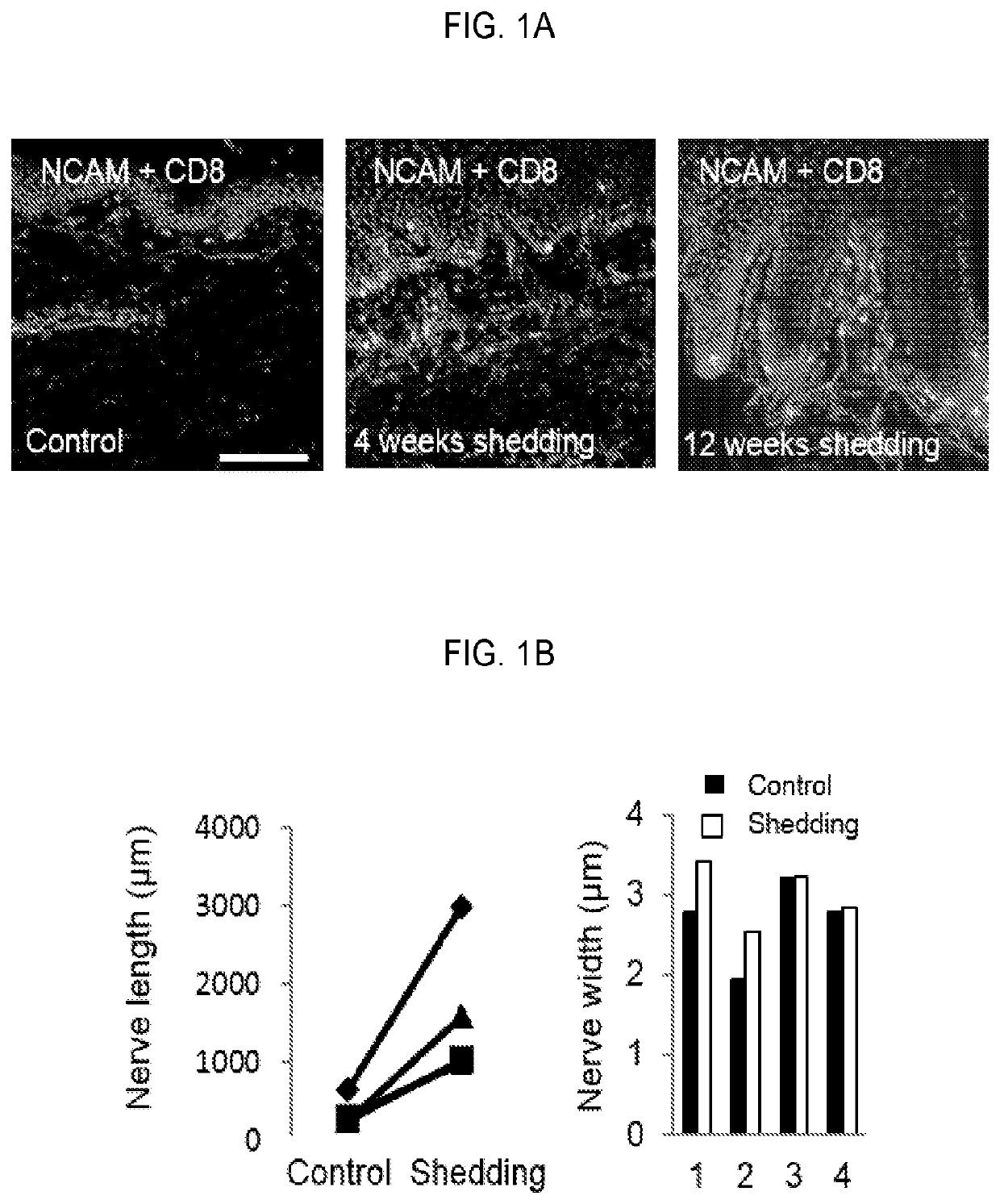
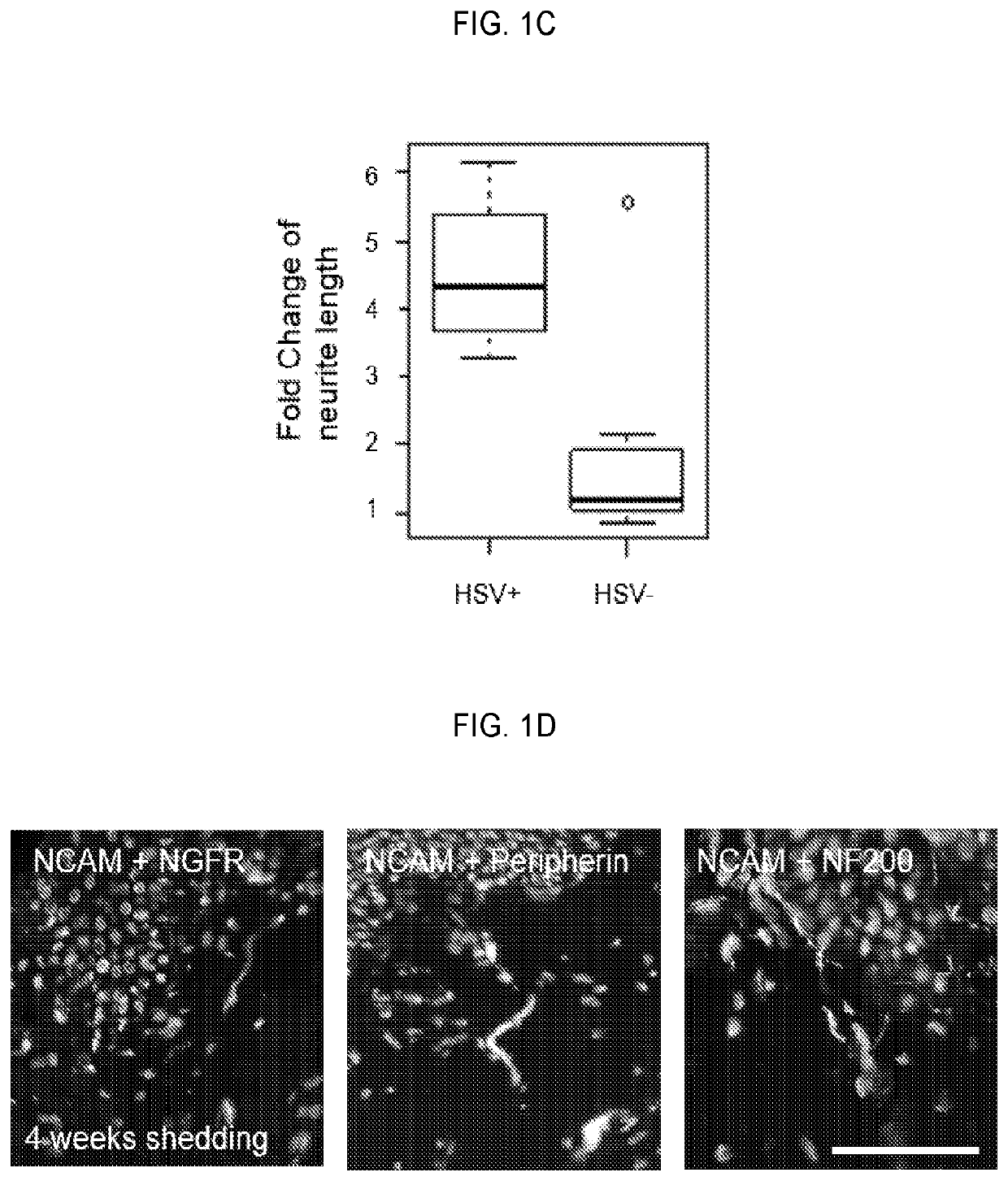
Methods using agonist antibodies to CNS neurite outgrowth modulators
InactiveUS7951373B2Modulate productionEnhances neurite outgrowthImmunoglobulin superfamilyNervous disorderParkinsonismNeural Growth
The invention features a method for promoting neural growth in vivo in the mammalian central nervous system by administering a neural cell adhesion molecule which can overcome inhibitory molecular cues found on glial cells and myelin to promote neural growth. Also featured active fragments, cognates, congeners, mimics, analogs, secreting cells and soluble molecules thereof, as well as antibodies thereto, and DNA molecules, vectors and transformed cells capable of expressing them. The neuroprotective of the agents as well as their ability to promote and effect myelination and remyelination are also disclosed, as are the concomitant benefits that these capabilities confer, in the former instance, with regard to reduction of apoptosis and necrosis, and in the latter instance, the treatment of Parkinsonism, Alzheimer's disease and multiple sclerosis. The invention also includes transgenic mouse lines expressing a neural adhesion molecule in differentiated astrocytes, and cells and tissues derived therefrom. The expression of the neural adhesion molecule enhances neurite outgrowth on central nervous system tissue derived from these transgenic mice. The invention also features methods for enhancing neuronal outgrowth of CNS neurons, for enhancing memory and for increasing synaptic efficacy. Also featured are methods of testing drugs which modulate the effects of the neural adhesion molecule, and assay systems suitable for such methods.
Owner:SCHACHNER MELITTA
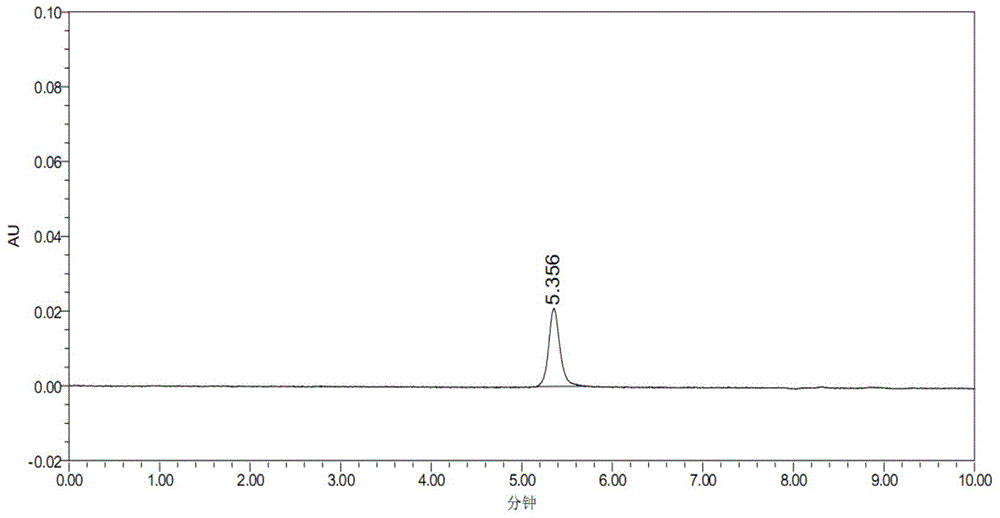
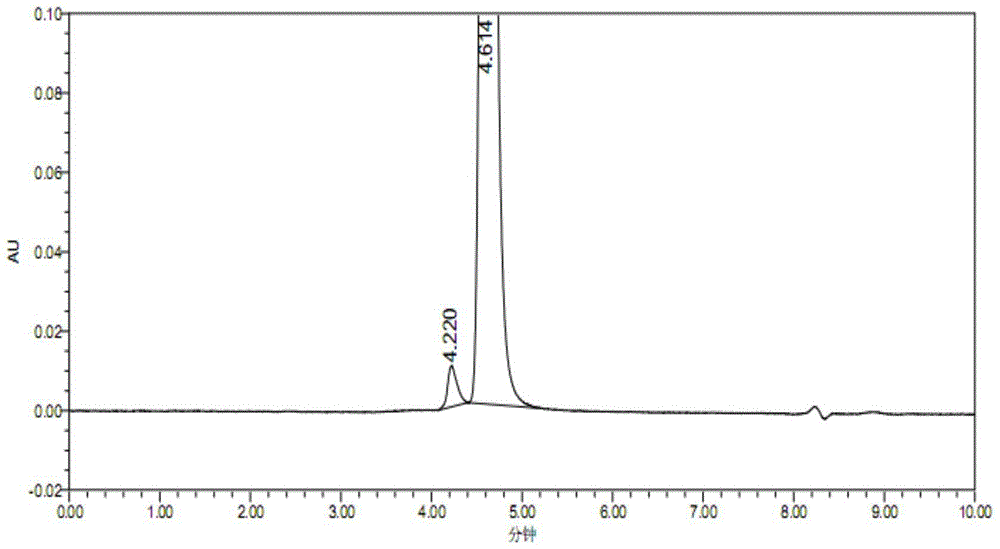
A kind of assay method of nerve growth factor content in nerve growth factor preparation
ActiveCN104931598BEffectively eliminate interferenceEliminate distractionsComponent separationMolecular sievePhosphate
The invention discloses a method for determining content of a nerve growth factor in a nerve growth factor preparation. According to the method, the content of the nerve growth factor is determined by using gel chromatography in ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC); gel chromatography conditions are presented as follows: a gel chromatography column is a UPLC molecular sieve chromatography column of which the molecular weight detection range is 1000 to 80000 Daltons and the pore diameter is 125 to 200 angstroms; the mobile phase is phosphate buffer of which the pH value is 6.5 to 7.2 and the concentration is 0.1 to 0.5M, and contains an organic phase of 5 to 20 percent by volume; the column temperature is 30 to 50 DEG C; the flow rate of the mobile phase is 0.1 to 0.5ml / min; a titanium flow cell is adopted by a detector, and the detection wavelength is 205 to 280nm. According to the method for determining the content of the nerve growth factor in the nerve growth factor preparation, disclosed by the invention, the NGF in the preparation can be accurately quantified.
Owner:STAIDSON (BEIJING) BIOPHARMACEUTICALS CO LTD +1
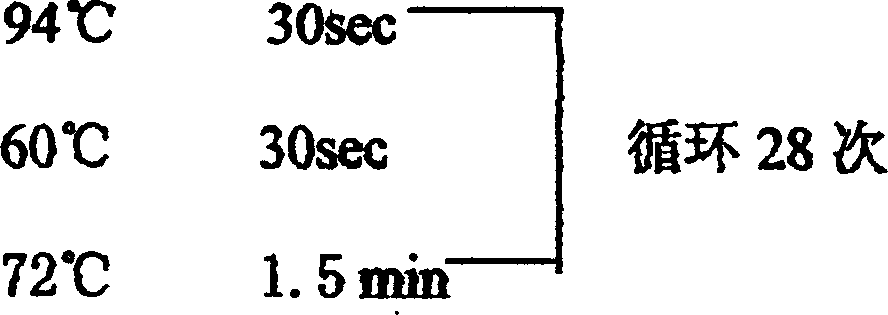
Nerve growth factor cDNA, clone and expresion of Chinese cobra
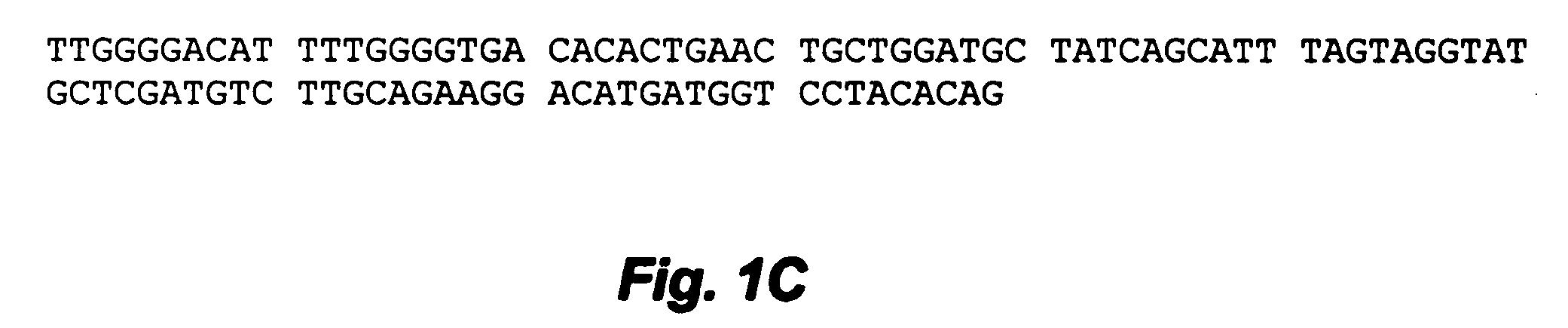
InactiveCN1316021CImproved histological changesFunction increasePeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderPichia pastorisNucleotide
The invention is cDNA, cloning and expression of Chinese cobra neural growth factor (NGF), relating to cDNA and cloning of recombinant Chinese cobra neural growth factor, expression of neural growth factor, a method of using its expression carrier to prepare it and pharmacological use of the mentioned protein, separate-extracting total RNA from the poison gland of Chinese cobra, using RT-PCR method to make reverse transcription to get total cDNA, using the primer designed by us to provide a specific Cdna sequence at a length of 348 bp polynucleotide sequence and also providing a small-molecular weight protein, the molecular weight about 13000, successfully expressed in pichia pastoris. The recombinant neutral growth factor has pharmaceutical use in the aspects of reducing blood sugar and improving pancreas islet as well as curing peripheral polyneuritis caused by diabetes.
Owner:郝文学 +3
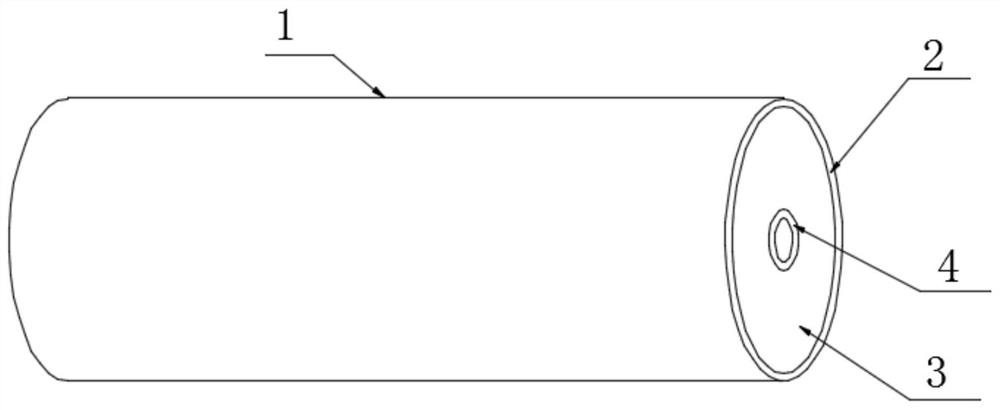
Pump for slowly promoting nerve growth
PendingCN111956869AHigh tensile strengthStretch smoothlyTissue regenerationCoatingsMedicineEngineering
The invention discloses a pump for slowly promoting nerve growth, and particularly relates to the field of biomedical application. The pump comprises a tube body, the tube body comprises a semi-permeable membrane layer, a slow release layer and an impermeable membrane layer, the slow release layer is arranged at the periphery of the impermeable membrane layer, and the semi-permeable membrane layeris arranged at the periphery of the slow release layer; the semi-permeable membrane layer comprises a semi-permeable membrane and a protective layer, the protective layer is located on the peripheryof the semi-permeable membrane, the protective layer comprises an annular support and a cylindrical support, and the annular support is fixedly arranged on the periphery of the cylindrical support; and a plurality of groups of isolating membranes penetrate through the interior of the slow release layer, are arranged around the periphery of the impermeable membrane layer, and comprise elastic fibers and reinforcing fibers. By arranging the semi-permeable membrane layer, the slow release layer and the impermeable membrane layer, the stretching effect on damaged neurons is more uniform, the growth of damaged neurons can be prolonged through repeated micro-damage repairing, irritation to the damaged neurons is low, and growth and recovery of the neurons can be better promoted.
Owner:XIANGYA HOSPITAL CENT SOUTH UNIV
A culture medium for promoting the differentiation of rat neural stem cells and its application method
ActiveCN104017771BHigh differentiation efficiencyNervous system cellsBrain-derived neurotrophic factorNeural Growth
The invention discloses a culture medium for promoting differentiation of rat neural stem cells and a use method of the culture medium. The culture medium contains B-27 Supplement without retinoic acid, L-Glutamine, FBS (fetal bovine serum), beta-NGF (neural growth factor), BDNF (brain derived neurotrophic factor), RA and vitamin E in Neurobasal-A medium. The culture medium is low in cost, the problem of low neural stem cell differentiation efficiency in the prior art is solved, and the efficiency of differentiating neural stem cells into nerve cells is remarkably improved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
System and method for treatment of hemorrhagic stroke
InactiveUS20190054279A1Conducive to survivalReduce deliveryBalloon catheterPeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineNeural Growth
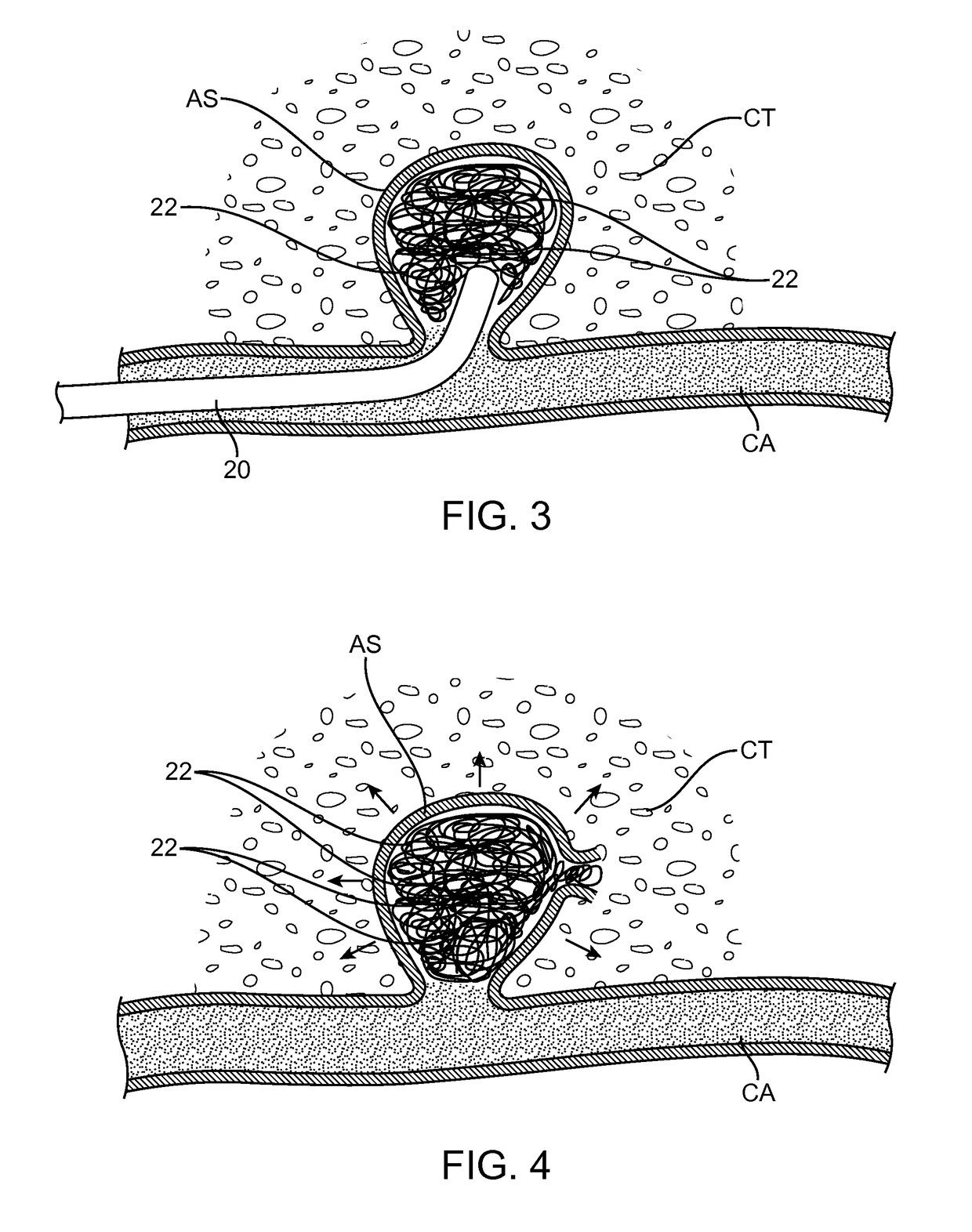
Embodiments of the invention provide apparatus, methods and systems for delivering treatments and for medications to the site of an aneurysm (SOA). One embodiment of a method comprises delivering a neural growth stimulating factor (NGSF) to the site of the aneurysm to grow new nerve cells and / or stimulate the regeneration of damaged nerve cells. The NGSF may be delivered in a carrier such as a gel which can be selected to allow for long term delivery of the NGSF to the SOA. In many embodiments, the NGSF may be delivered to the SOA using a microcatheter based system which includes a microcatheter that can be advanced in the cerebral vasculature. The microcatheter may also be used to delivery occlusive element to the SOA such as occlusive coils or balloon which promote clotting and reduce bleeding at the SOA and together with the carrier allow for long term release of NGSF.
Owner:INCUBE LABS
Preparation method of a drug-carrying system for nerve repair with electrical stimulation and angiogenesis-promoting effects
ActiveCN110975008BMeet the mechanical performance requirementsPrevent collapseElectro-spinningTissue regenerationHuman bodyCell-Extracellular Matrix
Owner:深圳南泥湾科技有限公司
Cell systems using spheroids and methods of making and using the same
The present disclosure generally relates to a cell culturing system, and specifically to a three-dimensional cell culturing system for neuronal cells that promotes both structural and functional characteristics that mimic those of in vivo peripheral fibers, including cell myelination. Using a dual hydrogel construct and spheroids comprising neuronal cells, the present disclosure provides methods,devices, and systems for in vitro spatially-controlled, three-dimensional models that permit intra- and extra-cellular electrophysiological measurements and recordings. The three-dimensional hydrogelconstructs allow for flexibility in incorporated cell types, geometric fabrication, and electrical manipulation, providing viable systems for culture, perturbation, and testing of biomimetic neural growth with physiologically-relevant results.
Owner:TULANE EDUCATIONAL FUND +1
System and method for treatment of hemorrhagic stroke
ActiveUS10137280B2Conducive to survivalReduce deliveryBalloon catheterPeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineNeural Growth
Owner:INCUBE LABS
Inhibitors of myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) activity for regulating neural growth and regeneration
InactiveUS20110306061A1Promote growthPromote regenerationImmunoglobulin superfamilyNervous disorderDiseaseNervous system
The present invention relates generally to products, compositions and methods useful for promoting neural repair and regeneration. The products and compositions of this invention include myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) derivatives that are inhibitors of endogenous MAG (e.g., mutant MAG proteins) and Nogo Receptor (NgR) binding inhibitors that are peptides derived from MAG, Nogo and OMgp that can bind to NgR and block NgR signaling. Peptides that can bind and activate NgR signaling are also provided. Inhibitory MAG derivatives and NgR binding inhibitors are useful for blocking the inhibition of neural regeneration mediated by proteins such as MAG, Nogo and / or OMgp in the nervous system. These inhibitors are also useful for treating neural degeneration associated with injuries, disorders or diseases.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK
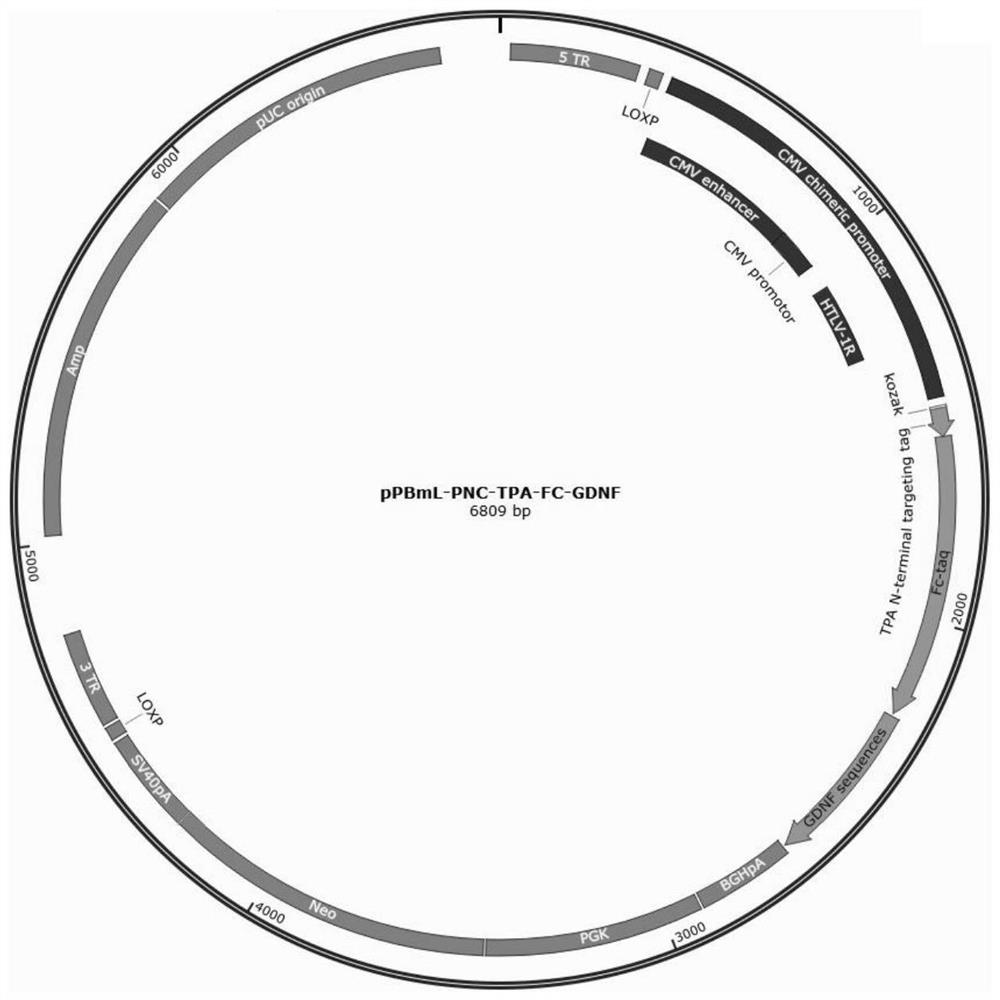
Method for expressing recombinant neurotrophic factor fusion protein, recombinant neurotrophic factor fusion protein and application of recombinant neurotrophic factor fusion protein
PendingCN114075569AHigh purityImprove biological activityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDimerNeural Growth
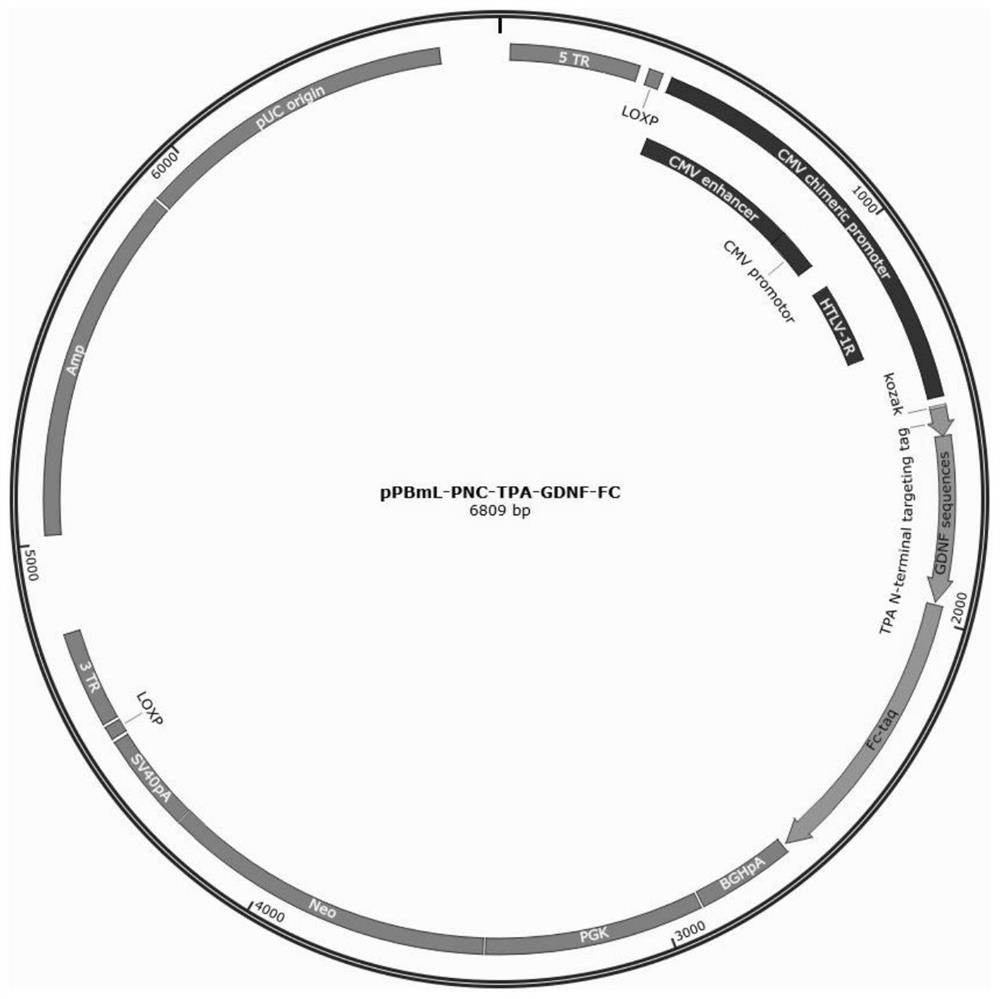
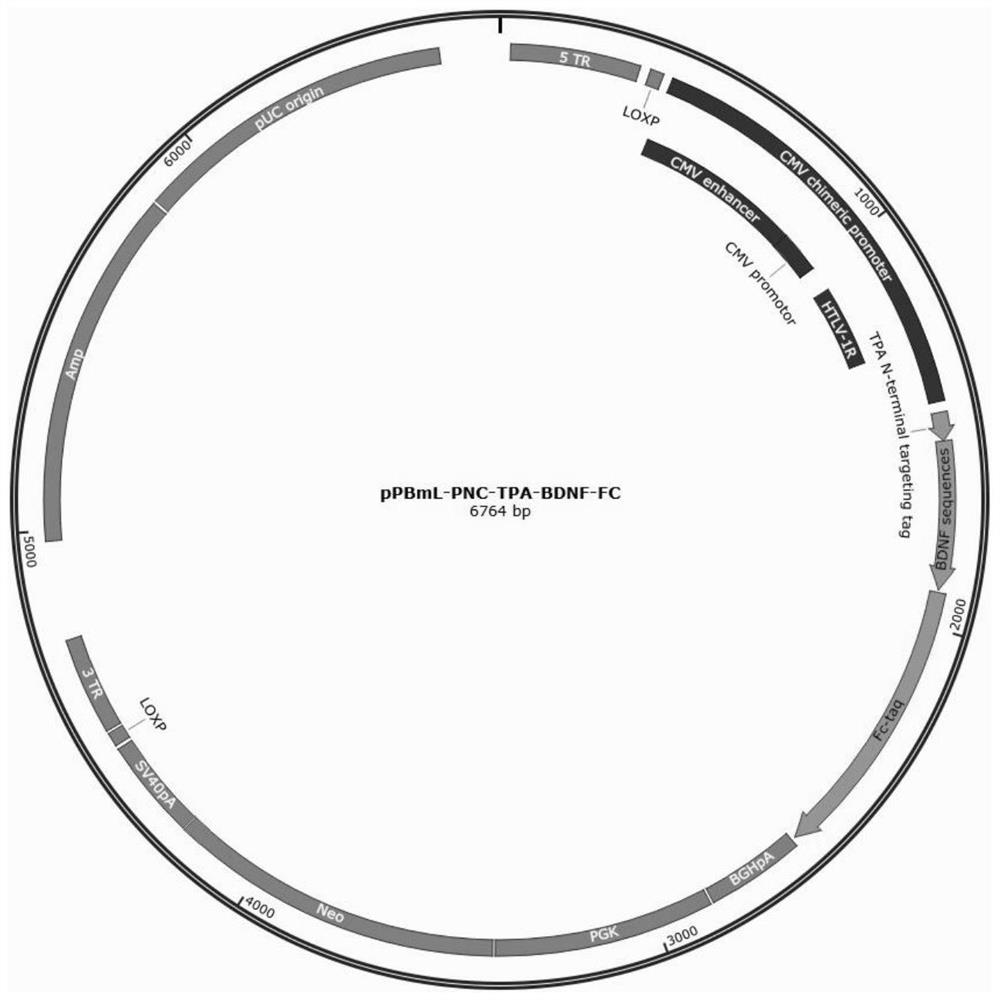
The invention provides a method for expressing recombinant neurotrophic factor fusion protein, the recombinant neurotrophic factor fusion protein and application of the recombinant neurotrophic factor fusion protein, and belongs to the technical field of functional protein. The dimer GDNF / BDNF recombinant protein with high biological activity is obtained by constructing a high-expression vector, using a cell expression system and screening a high-expression cell strain, and the defects that recombinant GDNF / BDNF on the market is low in expression quantity, high in price, low in biological activity and the like are overcome. The obtained GDNF / BDNF has very important significance for basic research and clinical-grade cell culture in the aspects of subsequent nerve growth and development and the like.
Owner:安徽中盛溯源生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com