Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
43 results about "Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The combination of multiple magnetic resonance techniques, including diffusion weighted imaging, dynamic contrast-enhanced imaging, and spectroscopy, to achieve an image that will allow for better identification of tumor size and location, as well as possibly identifying cancer spread and aggressiveness.
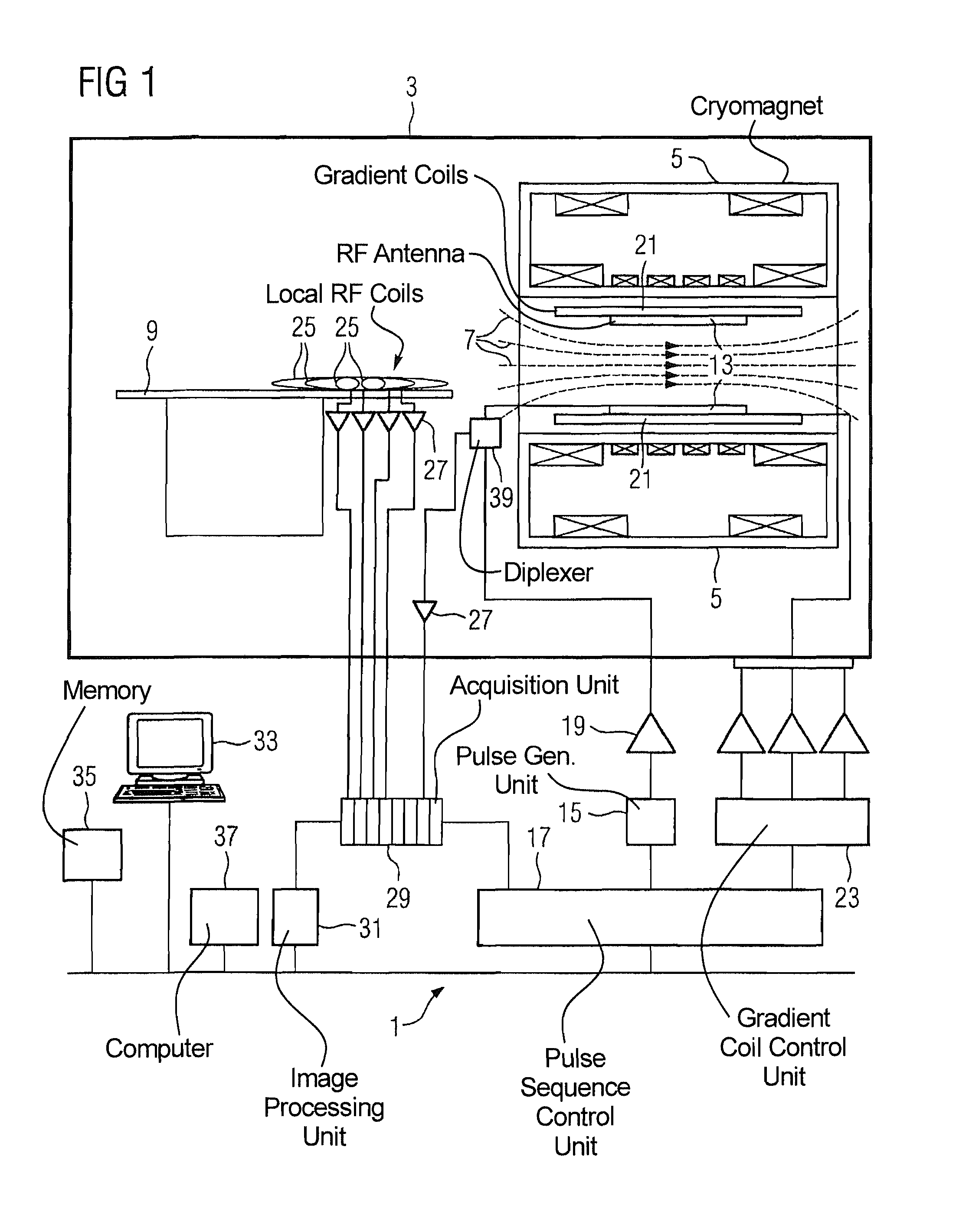
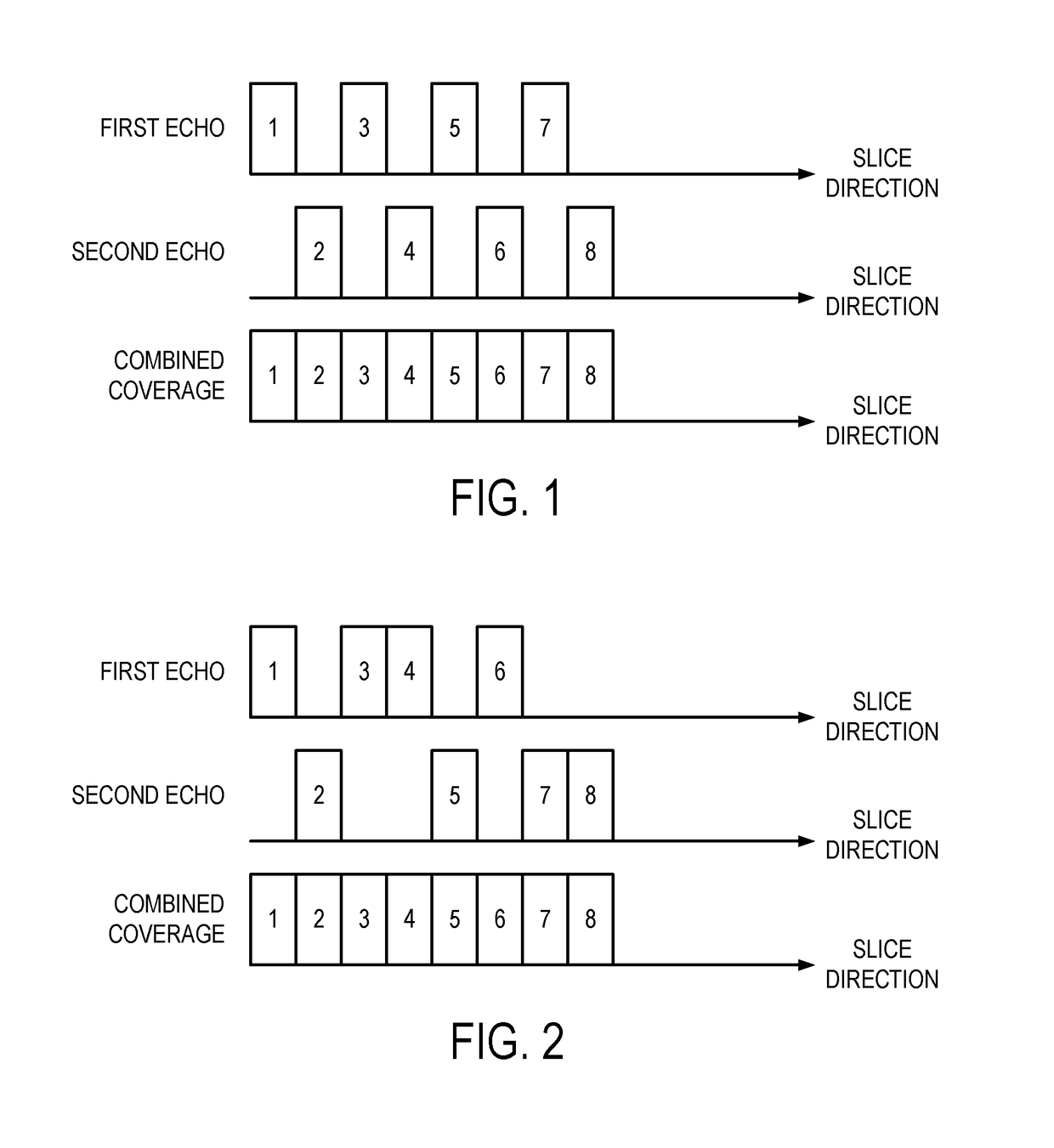
Method for simultaneous multi-slice magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20110254548A1Reliable separationLarge possible separationMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic gradientMulti slice
A method for multi-slice magnetic resonance imaging, in which image data is acquired simultaneously from multiple slice locations using a radio frequency coil array, is provided. By way of example, a modified EPI pulse sequence is provided, and includes a series of magnetic gradient field “blips” that are applied along a slice-encoding direction contemporaneously with phase-encoding blips common to EPI sequences. The slice-encoding blips are designed such that phase accruals along the phase-encoding direction are substantially mitigated, while providing that signal information for each sequentially adjacent slice location is cumulatively shifted by a percentage of the imaging FOV. This percentage FOV shift in the image domain provides for more reliable separation of the aliased signal information using parallel image reconstruction methods such as SENSE. In addition, the mitigation of phase accruals in the phase-encoding direction provides for the substantial suppression of pixel tilt and blurring in the reconstructed images.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
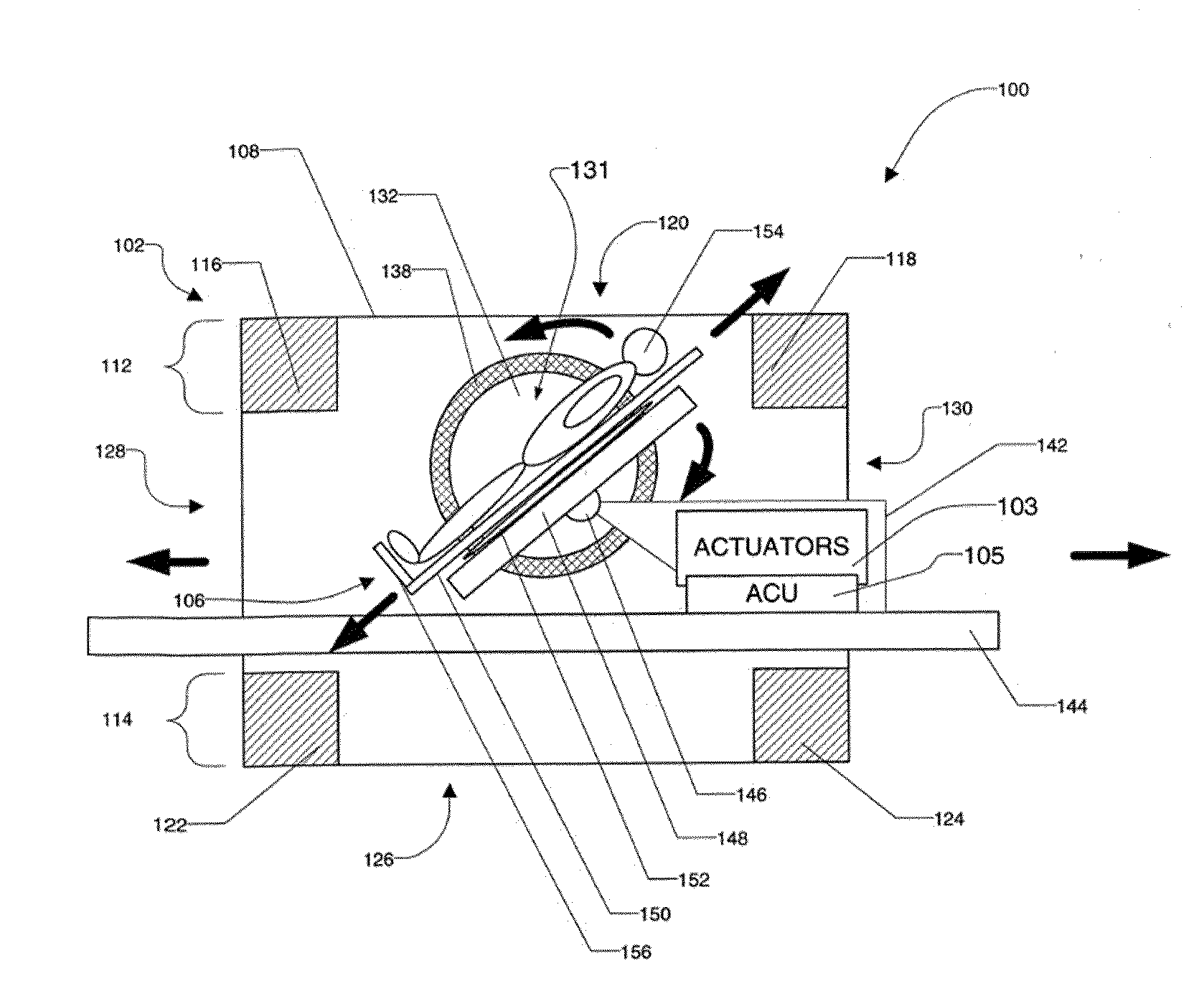
Method for lateral motion magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS7680525B1Speedy and accurate diagnosisEasy accessDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsInterventional magnetic resonance imagingPatient positioning
The method includes positioning a patient within a receiving space of a stand-up MRI apparatus and imaging the region of interest of the patient while the patient moves the region of interest. Further in accordance with the method the patient may be positioned such that the patient faces a pole face of a magnet of the MRI apparatus. The apparatus comprises a patient support which allows imaging of a patient's spine with a gravitational load on the spinal system.
Owner:FONAR
Deep Convolutional Encoder-Decoder for Prostate Cancer Detection and Classification
ActiveUS20180240233A1Image enhancementImage analysisEncoder decoderMultiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging
A method and apparatus for automated prostate tumor detection and classification in multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is disclosed. A multi-parametric MRI image set of a patient, including a plurality of different types of MRI images, is received. Simultaneous detection and classification of prostate tumors in the multi-parametric MRI image set of the patient are performed using a trained multi-channel image-to-image convolutional encoder-decoder that inputs multiple MRI images of the multi-parametric MRI image set of the patient and includes a plurality of output channels corresponding to a plurality of different tumor classes. For each output channel, the trained image-to image convolutional encoder-decoder generates a respective response map that provides detected locations of prostate tumors of the corresponding tumor class in the multi-parametric MRI image set of the patient.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
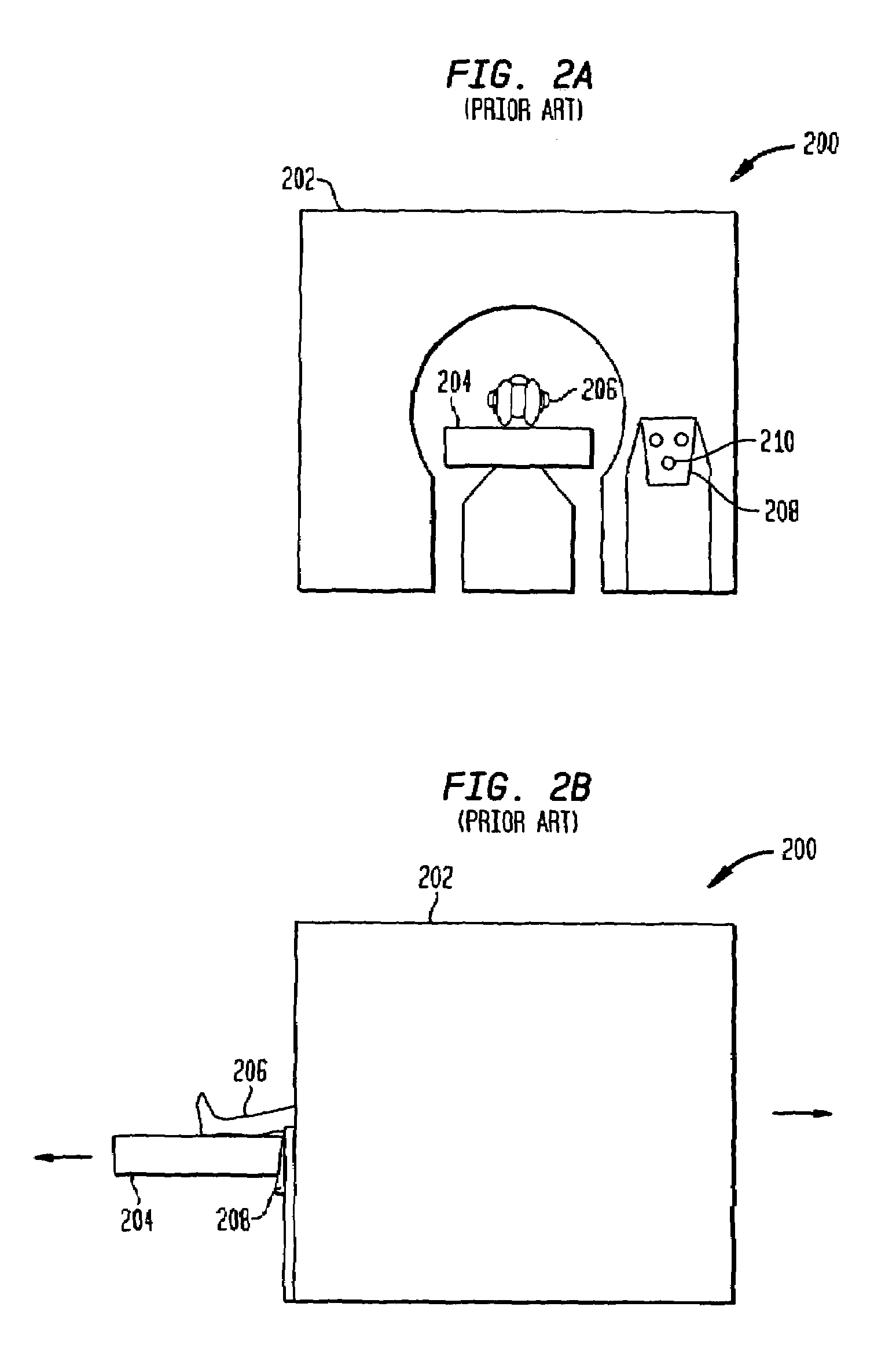
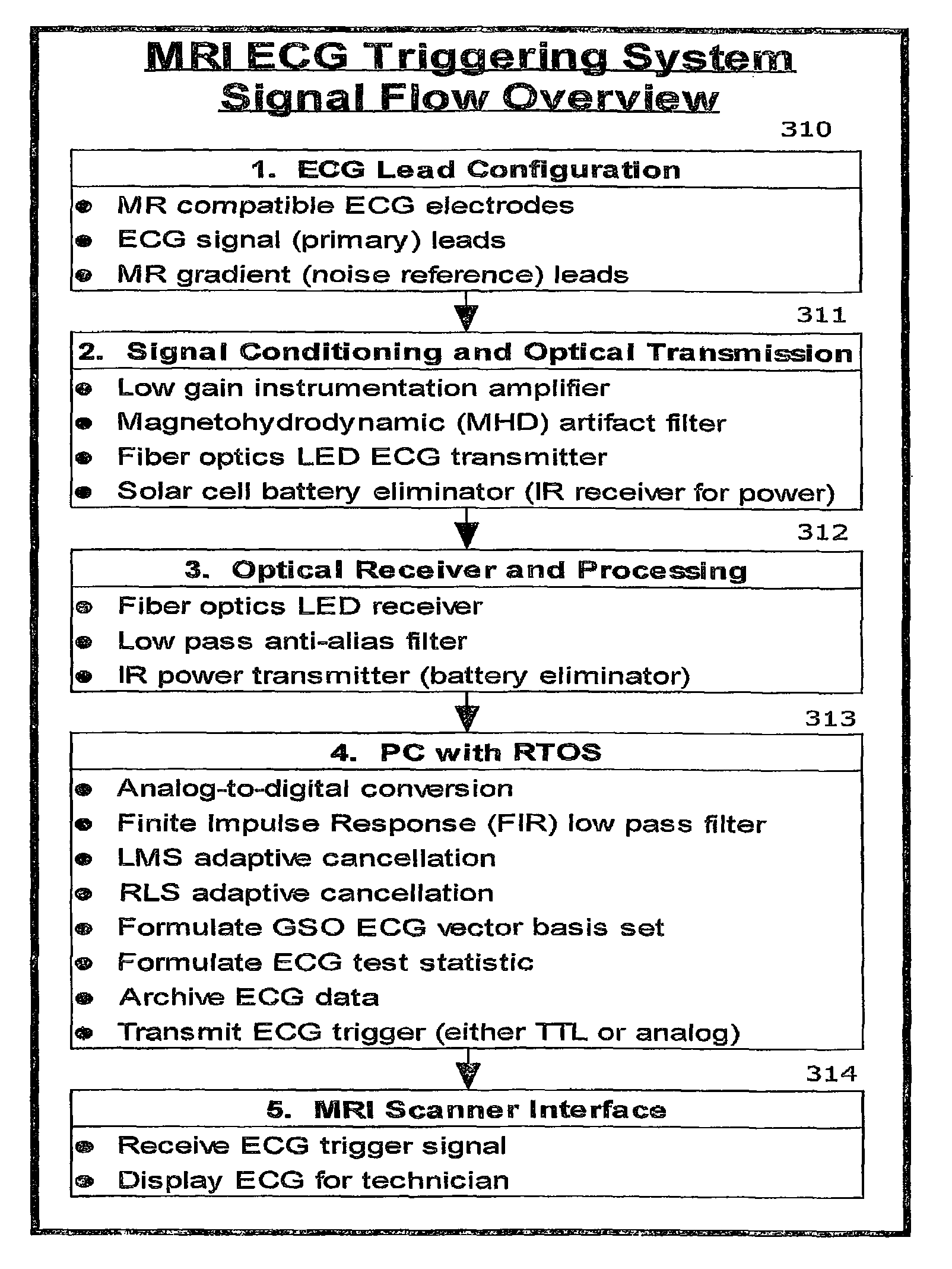
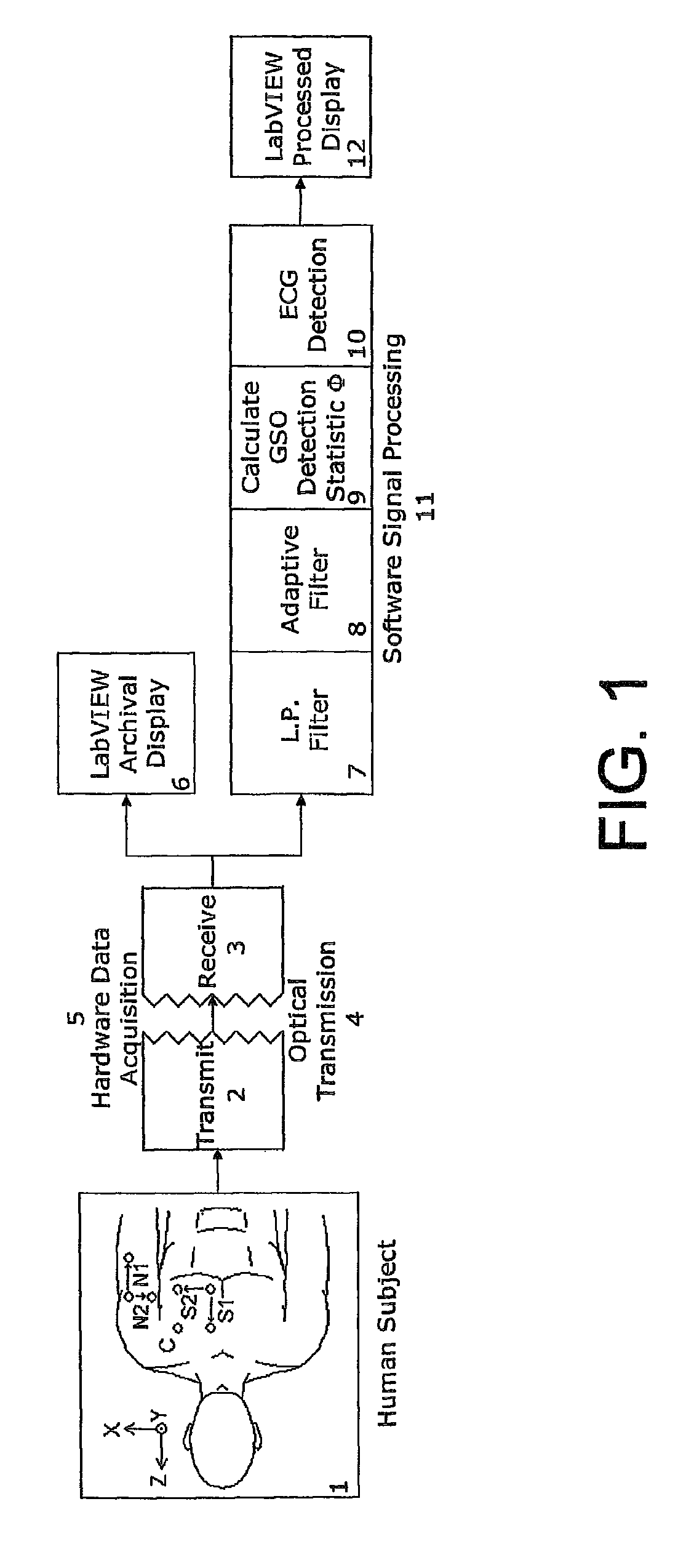
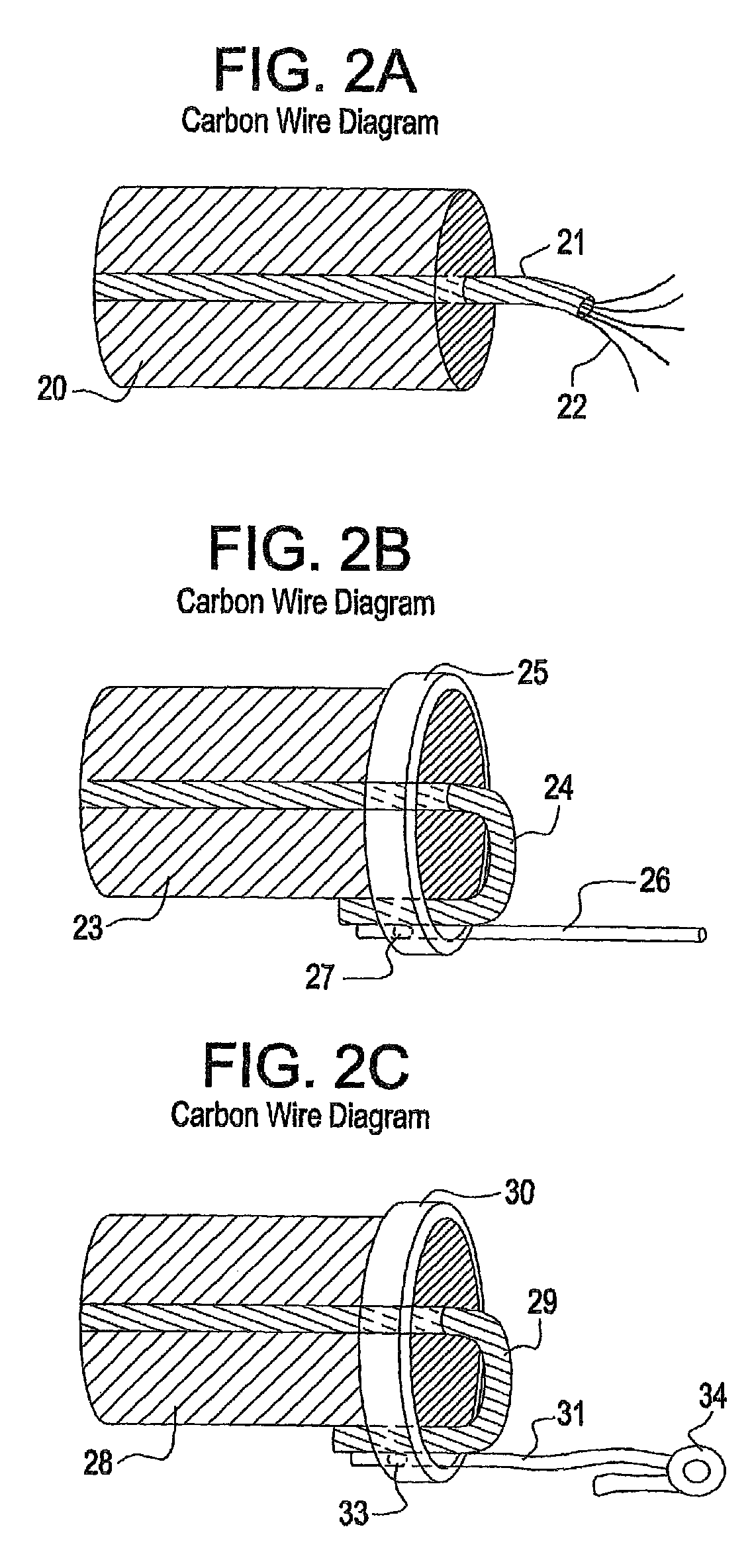
ECG triggered heart and arterial magnetic resonance imaging
High resistance non-metallic ECG leads are used to capture biologically generated electrical signals, and include at least one magnetic resonance noise lead to capture a noise reference signal indicative of electromagnetic noise ambient to the leads generated by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The noise reference signal is canceled from the captured electrical signal using an adaptive canceling noise filter to obtain a processed electrical signal indicative of the biologically generated electrical signal that causes movement in a patient's moving body part, such as the heart. A characteristic of the processing electrical signal indicative of the biologically generated electrical signal that causes the movement is detected to obtain a trigger signal, which is then transmitted to cause the MRI system to capture at least one imagine including the moving body part.
Owner:PERINATRONICS MEDICAL SYST
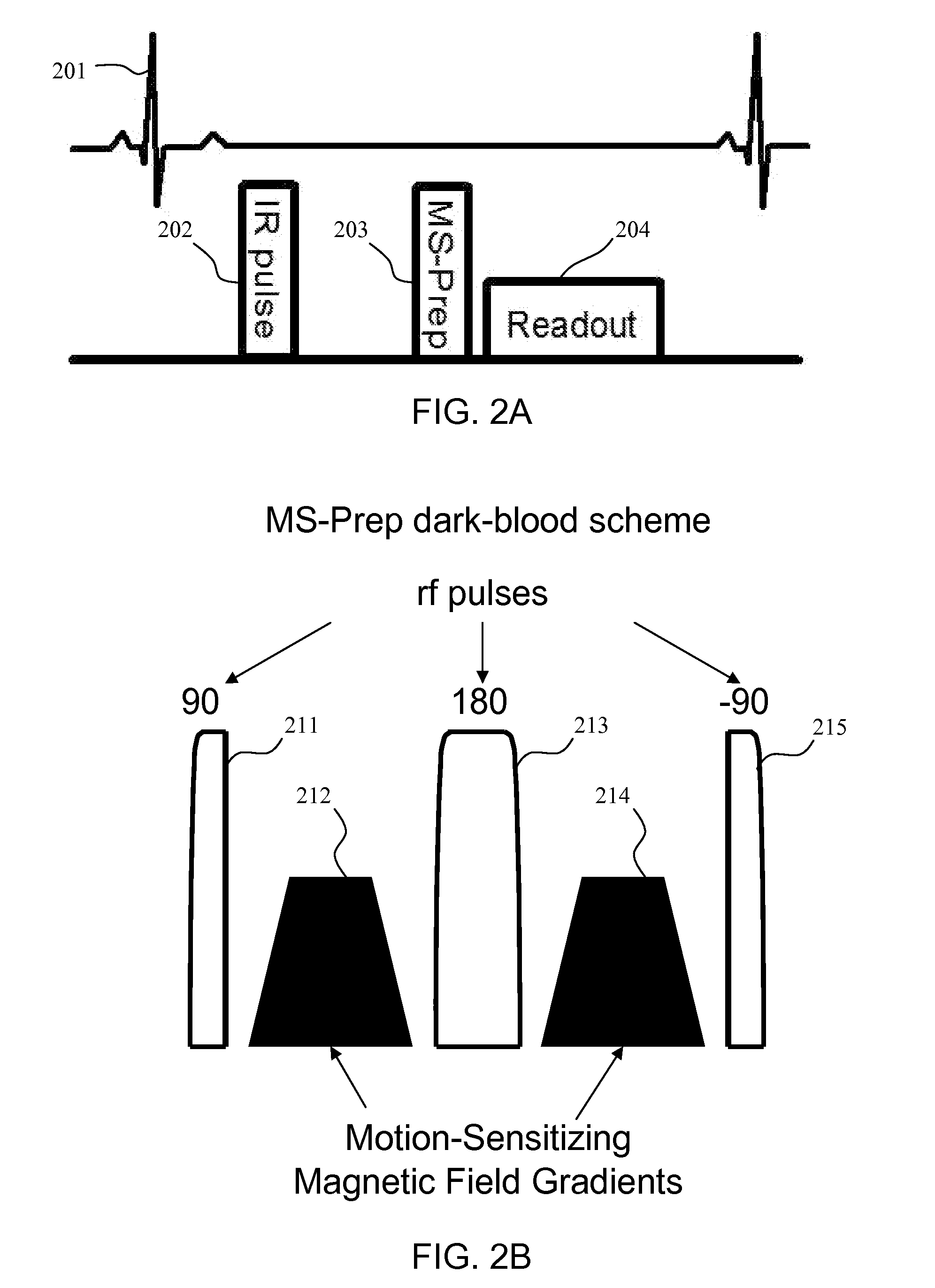
Motion-attenuated contrast-enhanced cardiac magnetic resonance imaging and related method thereof
ActiveUS20100191099A1Improve visualizationReduce signalingElectrocardiographyMagnetic measurementsContrast levelVentricular cavity
A system and method for providing a dark-blood technique for contrast-enhanced cardiac magnetic resonance, improving visualization of subendocardial infarcts or perfusion abnormalities that may otherwise be difficult to distinguish from the bright blood pool. In one technique the dark-blood preparation is performed using a driven-equilibrium fourier transform (DEFT) preparation with motion sensitizing gradients which attenuate the signal in the ventricular cavities related to incoherent phase losses resulting from non-steady flow within the heart. This dark-blood preparation preserves the underlying contrast characteristics of the pulse sequence causing a myocardial infarction to be bright while rendering the blood pool dark. When applied to perfusion imaging, this dark-blood preparation will help eliminate artifacts resulting from the juxtaposition of a bright ventricular cavity and relatively dark myocardium.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Heart magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) image deblurring method based on sparse low rank and dictionary learning
ActiveCN103093430AMotion Blur Kernel AccurateAvoid distortionImage enhancementDictionary learningPattern recognition
The invention discloses a heart magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) image deblurring method based on sparse low rank and dictionary learning. The heart MRI image deblurring method mainly solves the problem that beating of a heart causes the quality reduction of a heart MRI image. The realization process of the heart MRI image deblurring method includes the steps: inputting a heart MRI image; carrying out sparse low rank matrix decomposition on the heart MRI image, and obtaining a sparse part and a low rank part of the image; selecting a sub window from the sparse part of the image; estimating motion blur kernel in the sub window through a method of self-adaption dictionary learning; carrying out deconvolution operation on the heart MRI image through utilization of the estimated motion blur kernel, and obtaining a clear heart MRI image. The heart MRI image deblurring method has the advantages of accurately estimating the motion blur kernel, and the distortion of image deblurring results due to inaccuracy of estimation of the motion blur kernel is avoided.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method for extracting microwave detection breast model based on medical magnetic resonance imaging
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomedical detection, and relates to a method for extracting a microwave detection breast model based on medical magnetic resonance imaging. The method includes the steps: acquiring a T1 weighted magnetic resonance image of a breast portion; enhancing a boundary; performing gray discrete processing; calculating the water content of a tissue corresponding to each pixel for a thoracic gland portion in the magnetic resonance image by the aid of an image gray value; comparing the water content of the tissue corresponding to each pixel with typical water content data of each tissue of a normal human body, determining tissue information of each pixel and defining the pixel as an islet if the tissue information of the pixel cannot be determined; giving the same gray value to the pixels with the determined tissue information and belonging to the same tissue, and normalizing the gray of the magnetic resonance image according to the tissue information; corroding small discrete islets; building the breast model. A breast structure can be really simulated by the method.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
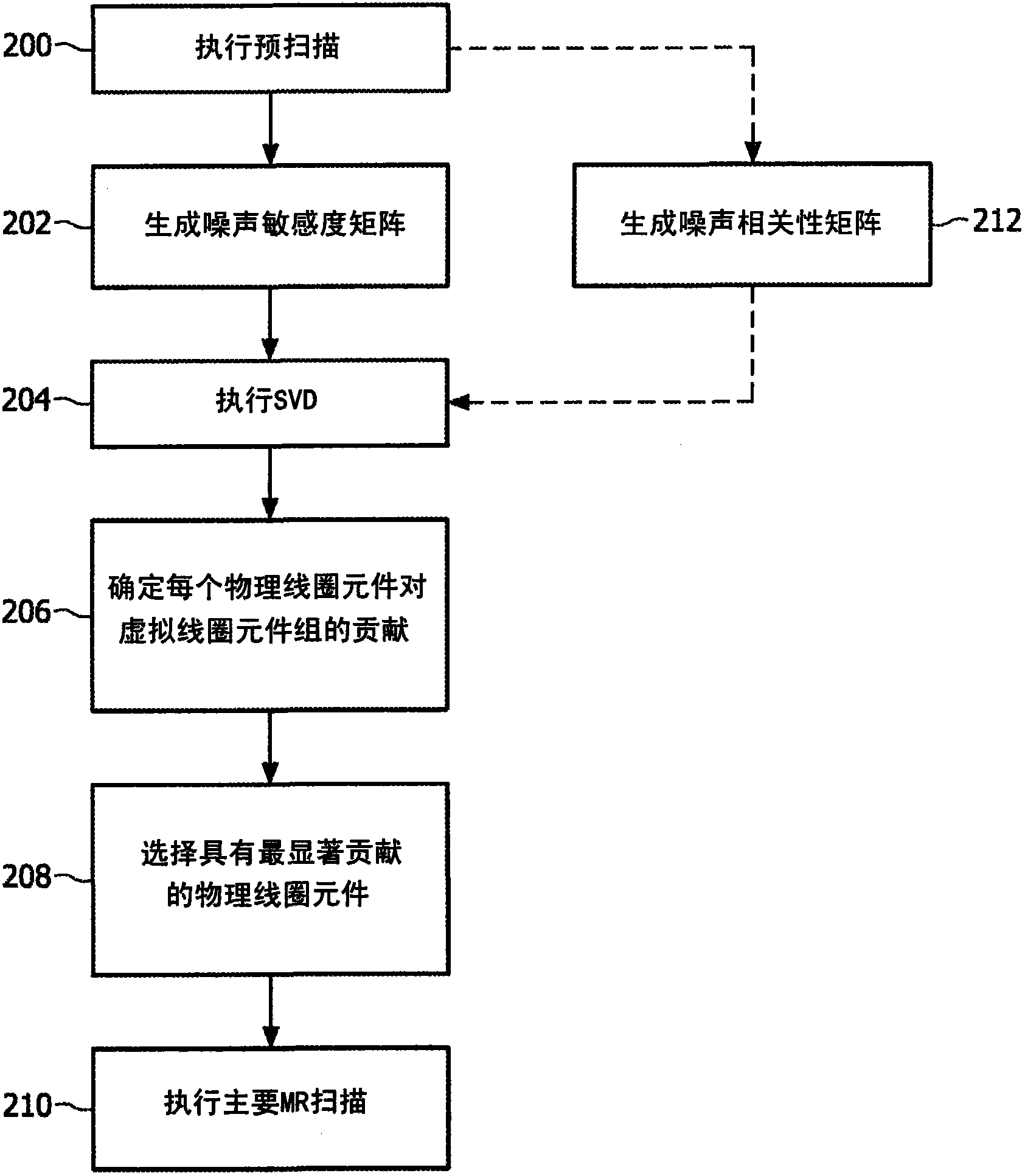
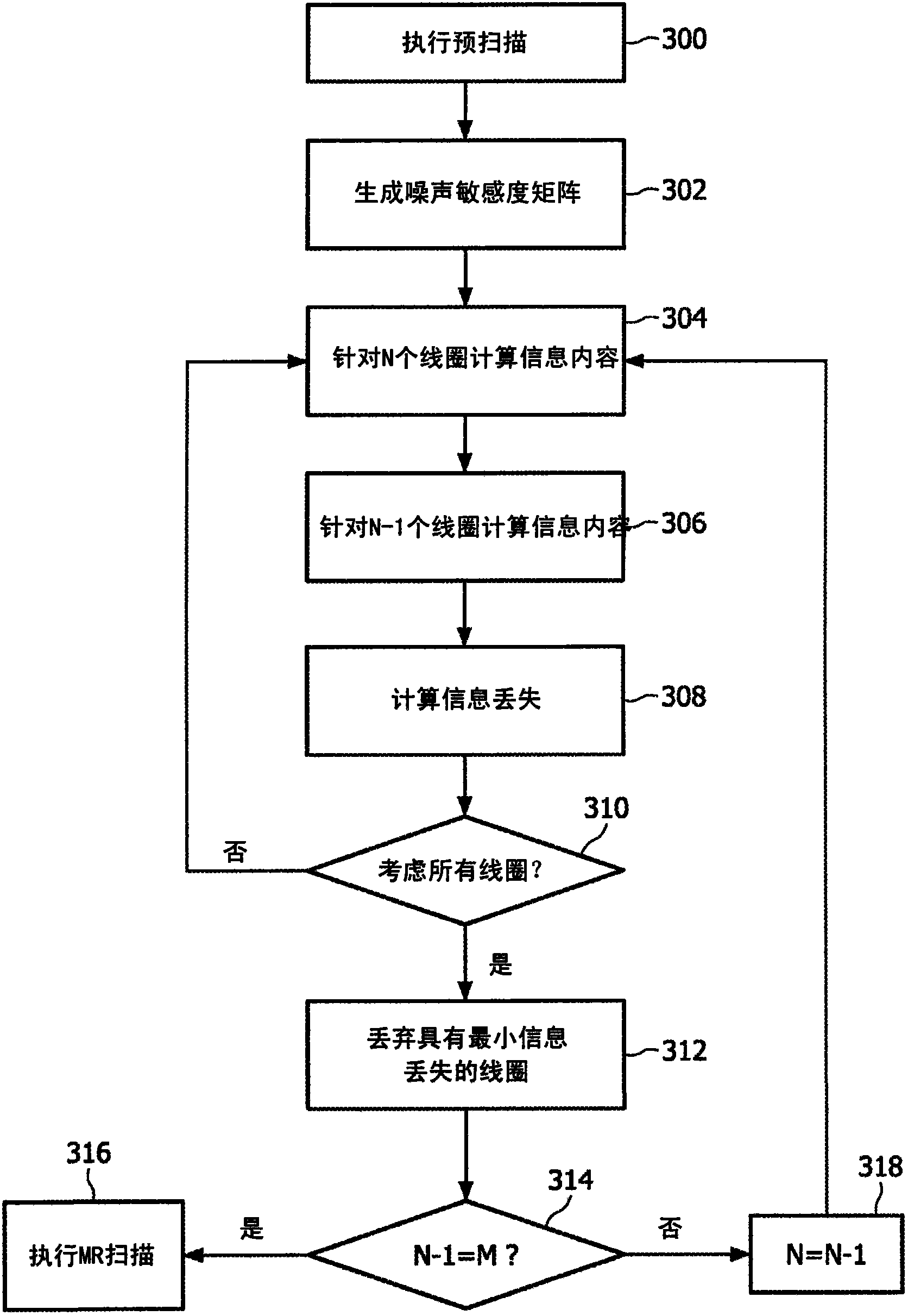
Coil selection for parallel magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveCN101971045AAccurately reflectExact physicsMagnetic gradient measurementsParallel magnetic resonance imagingMagnetic Resonance Imaging Scan
The invention relates to a method of selecting a set of coil elements from a multitude of physical coil elements comprised in a coil array for performing a magnetic resonance imaging scan of a region of interest.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
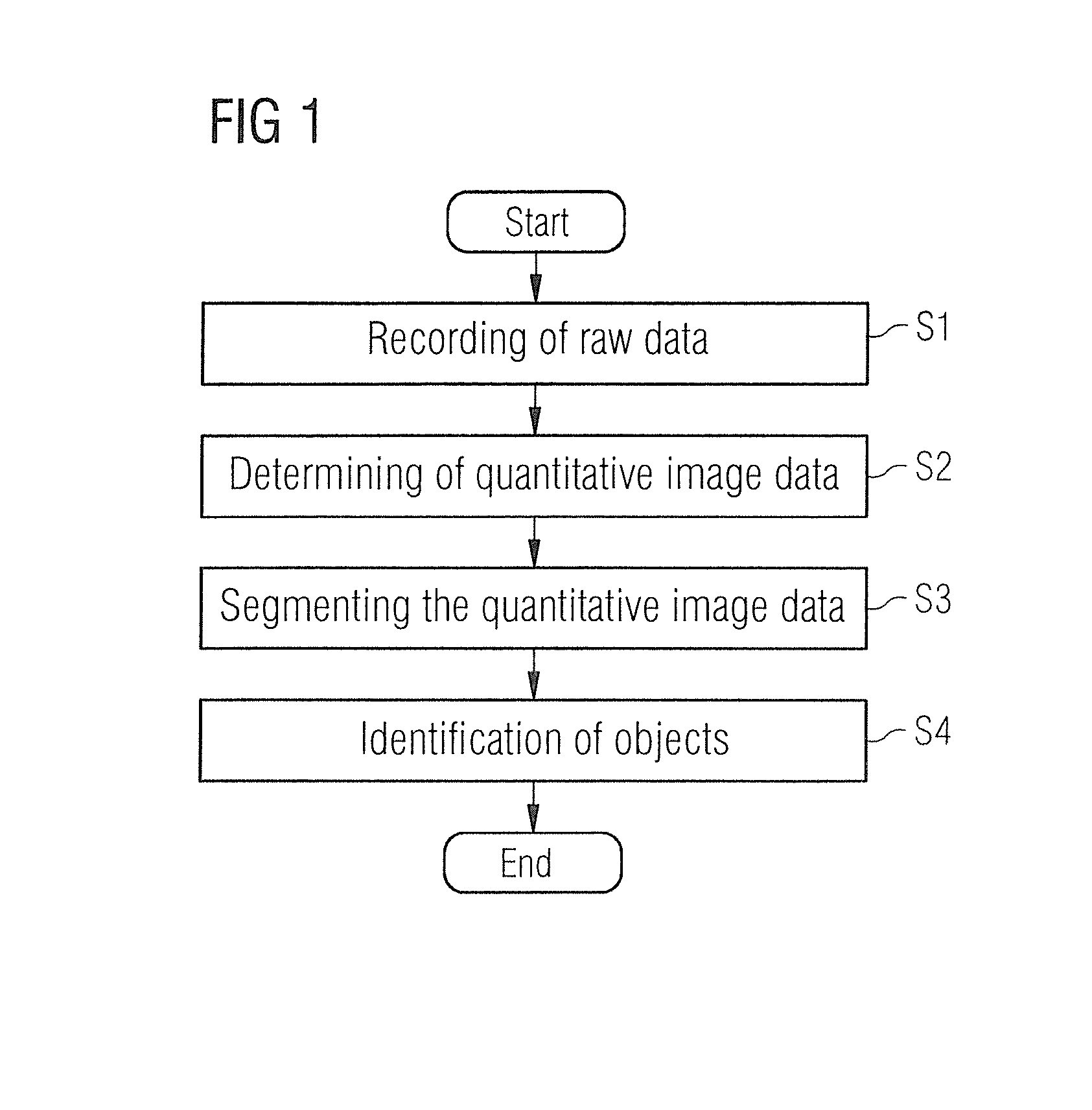
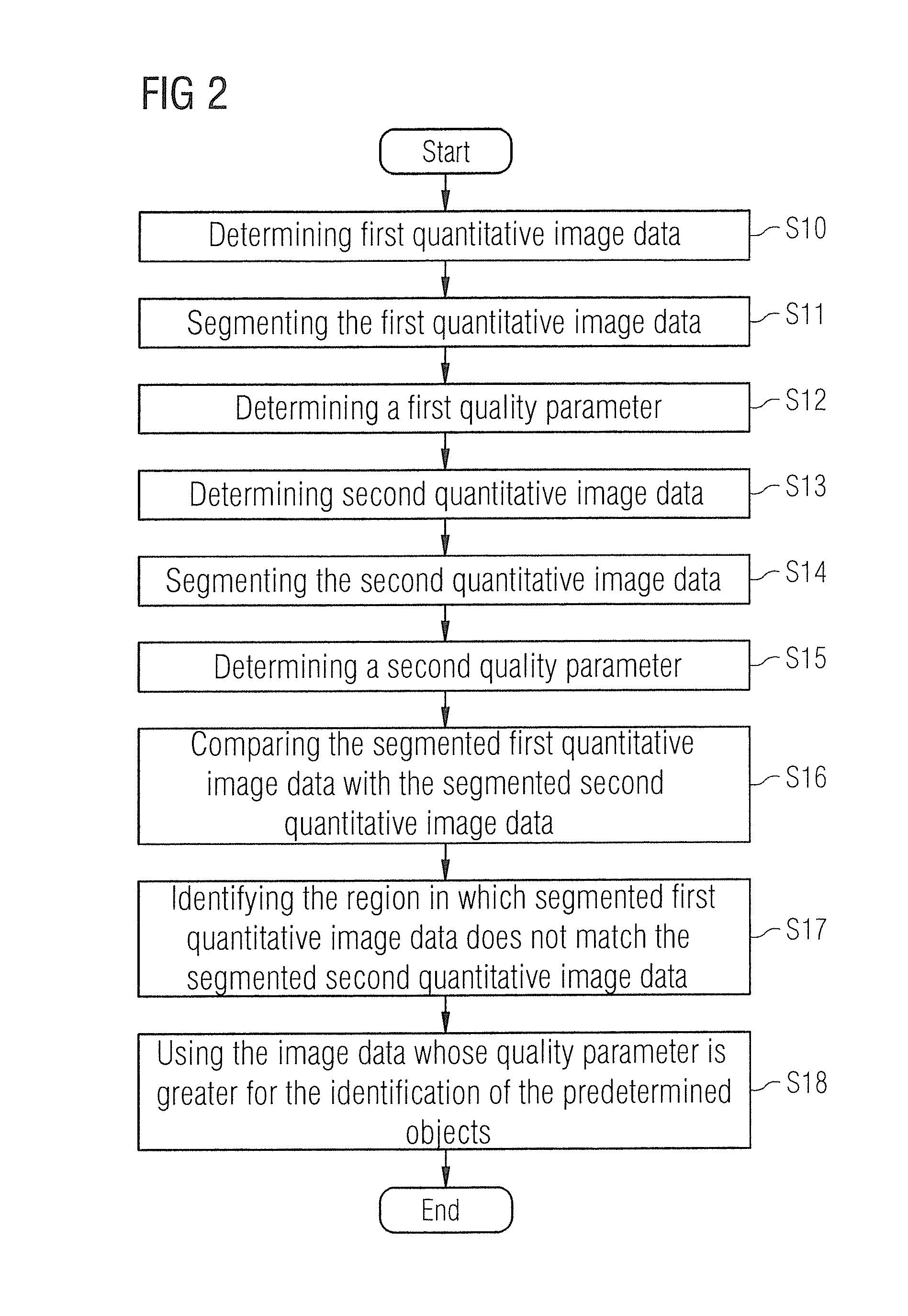
Method and device for segmenting a medical examination object with quantitative magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20160155238A1Avoid disadvantagesPromote reproductionImage enhancementMedical imagingResonanceQuantitative magnetic resonance imaging
In a method and magnetic resonance apparatus for segmenting image data of an examination object, raw data of the examination object are achieved with the operation of a magnetic resonance scanner. Quantitative image data of the examination object are then calculated in a processor from the raw data. At least one physical variable of the examination object is quantitatively ascertained pixelwise and is displayed. The quantitative image data are segmented for identification of predetermined objects in the quantitative image data, and displayed in a display unit.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
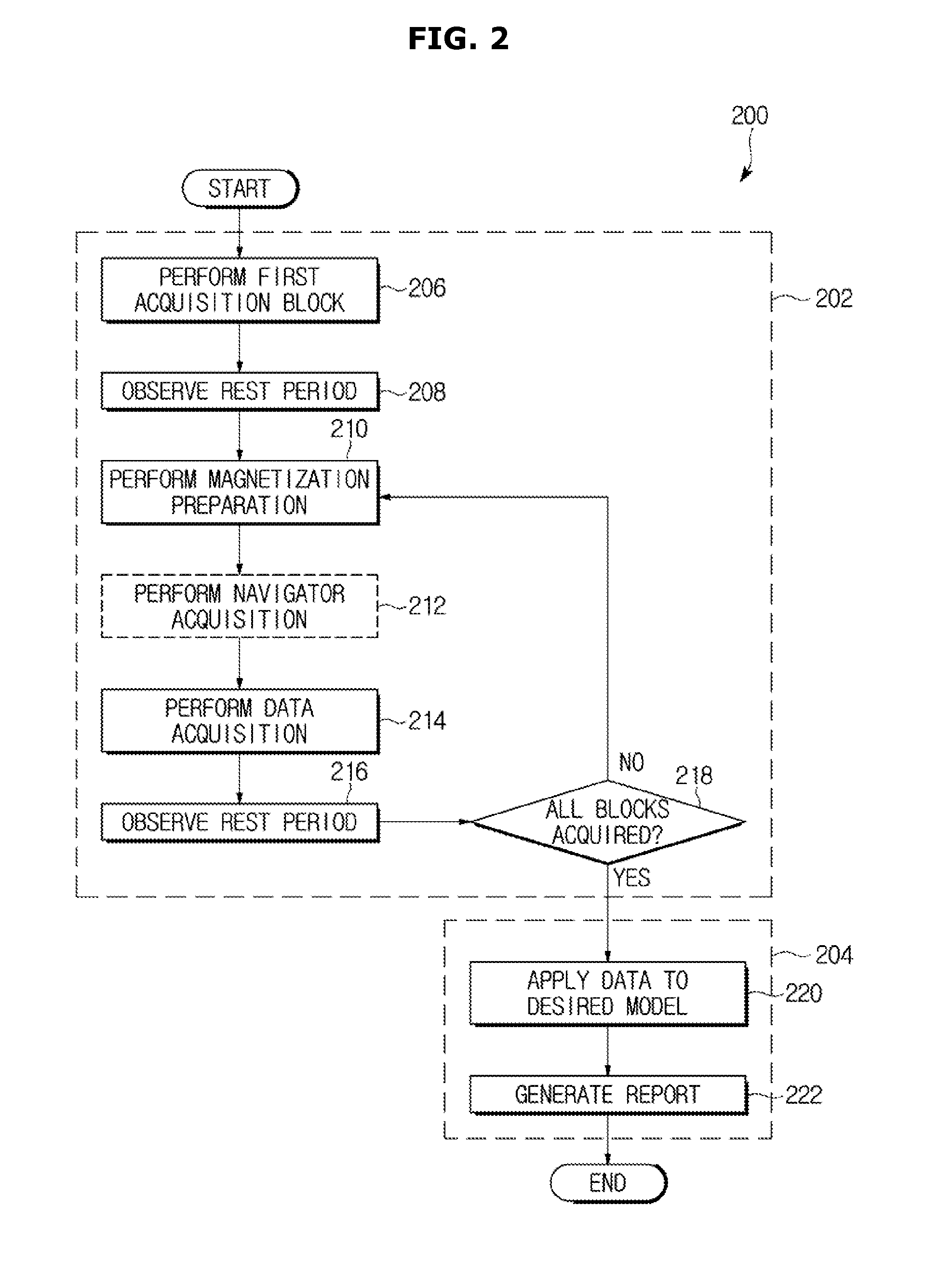
System and method for tissue characterization using multislice magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20150323630A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionRecovery periodMagnetization
An MRI method includes: performing a first data acquisition block of a pulse sequence to acquire a first MR data from a plurality of slices of a subject during a period of fully recovered longitudinal magnetization within the plurality of slices disposed at different locations in the subject; performing a second data acquisition block of the pulse sequence including a magnetization preparation module followed by a recovery period and an imaging sequence executed during the recovery period, to acquire a second MR data from the plurality of slices during the recovery period; and generating a T1 map of the subject based on the first MR data and the second MR data, of the plurality of slices.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
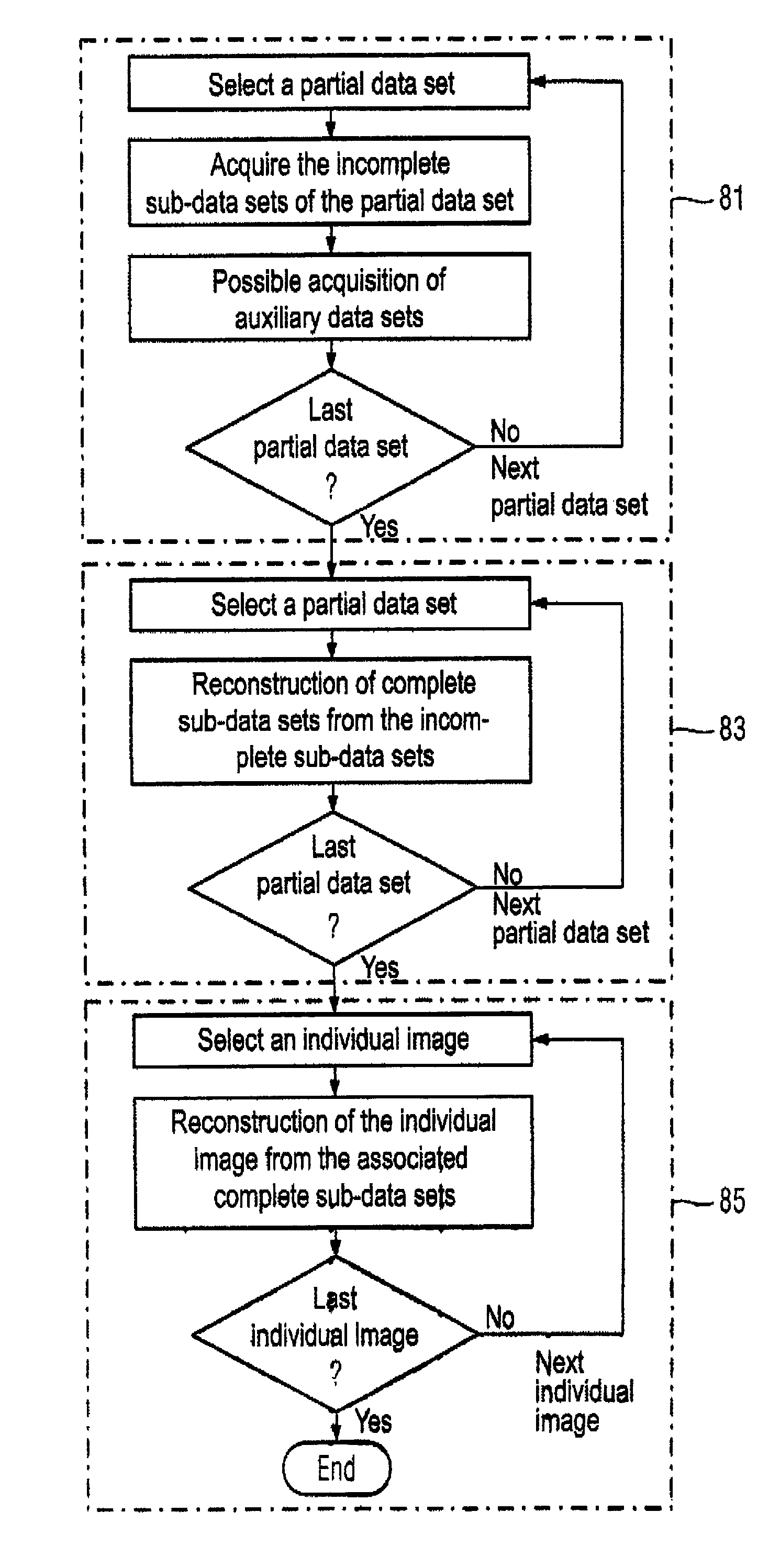
Method and magnetic resonance apparatus for dynamic magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS8073522B2High temporal and spatial resolutionSmall reconstruction timeMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringData setResonance
The invention concerns a method and magnetic resonance apparatus for acquisition and generation of a time-resolved image series of an anatomical organ with a quasi-periodical movement in a subject, k-space is sampled in segments with a number of partial data sets, with the sampling points of each partial data set corresponding to grid points of a Cartesian sampling grid of a k-space segment, and the Cartesian sampling grids of the k-space segments being rotated relative to one another. A series of sub-data sets is incompletely acquired for each partial data set using alternating sampling schemes. Each incomplete sub-data set is associated with one of the individual images. For at least some of the partial data sets, complete sub-data sets are reconstructed from the incomplete sub-data sets. For the reconstruction of the individual images, in each of the individual images, at least some of the complete sub-data sets that are associated with this individual image are used.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
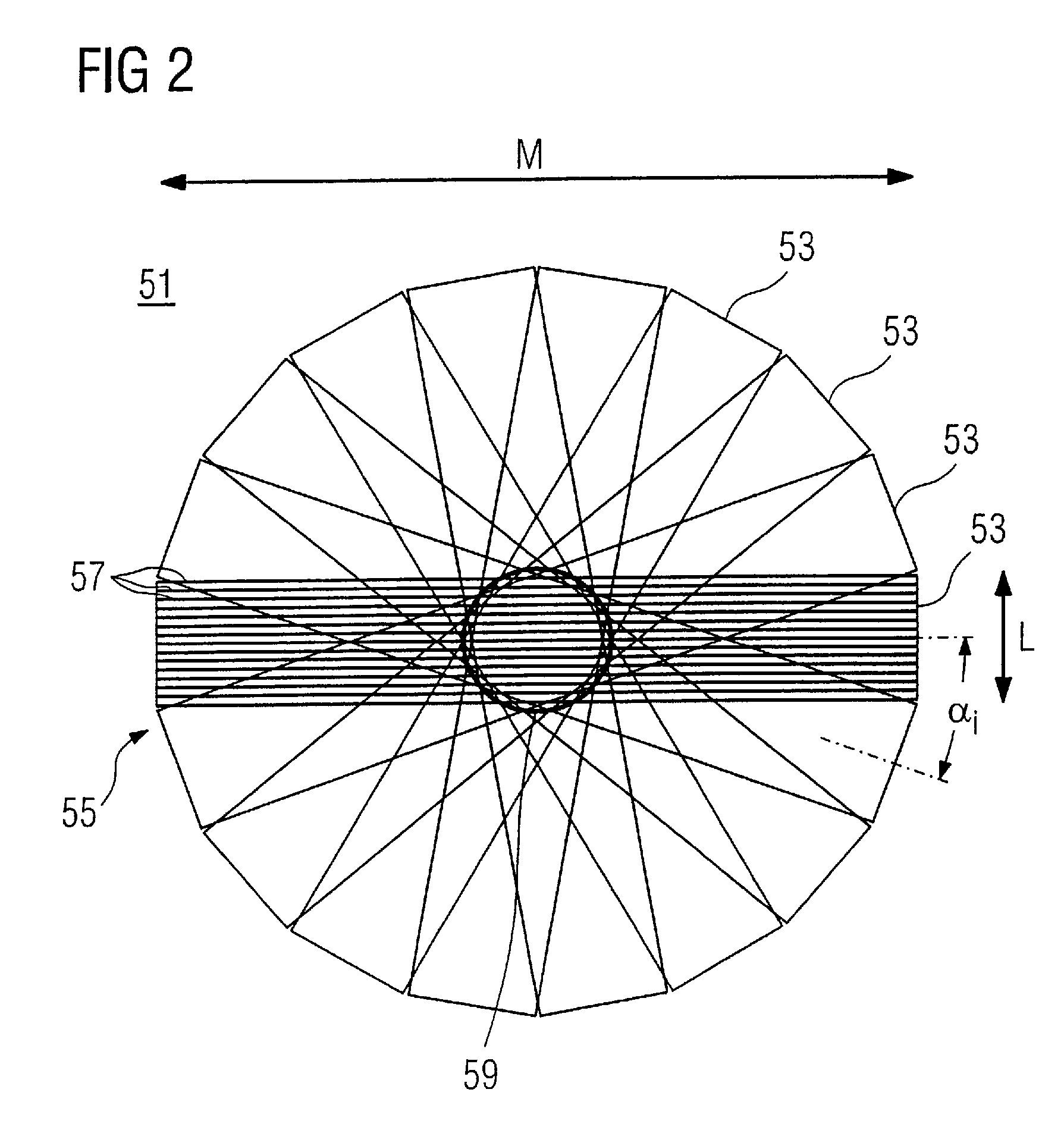
Design method of biplane magnetic resonance imaging system gradient coil
InactiveCN108872896ASolve the problem of large inductanceMagnetic measurementsPower flowCoil inductance
The present invention discloses a design method of a biplane magnetic resonance imaging system gradient coil. The method comprises the steps of: performing three-dimensional continuous triangular meshdivision for a gradient coil area, according to a boundary element method, calculating a coil inductance matrix generated by the gradient coil area mesh node for a target field point, calculating thecurrent and the direction of the gradient coil plane through a coil target gradient value, an inductance constraint condition and a Tikhonov Regularization, and finally employing a stream function method to obtain actual winding distribution of the gradient coil. The design method of a biplane magnetic resonance imaging system gradient coil solves the problem that the coil inductance is large inthe gradient coil.
Owner:河北惠仁医疗设备科技有限公司
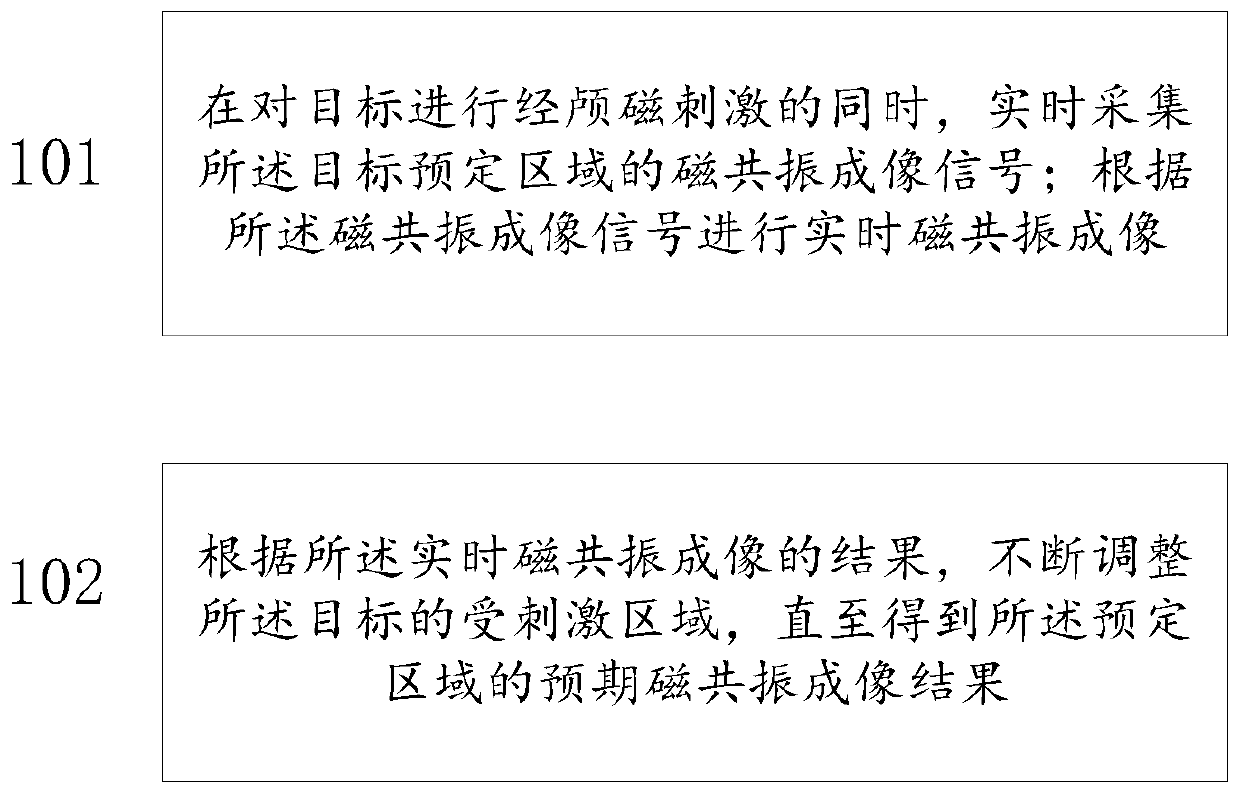
System for transcranial magnetic stimulation
ActiveCN109731227AReal-time magnetic resonanceLive viewElectrotherapyMagnetotherapyPower flowMedicine
The invention discloses a system for transcranial magnetic stimulation. The system comprises a stimulation unit, a magnetic resonance unit and a synchronization unit, wherein the synchronization unitis used for controlling the synchronization of the stimulation unit and magnetic resonance unit. The system can carry out real-time and accurate evaluation on the therapeutic effect of a TMS and can acquire magnetic resonance imaging signals of a preset area of a target in real time while carrying out transcranial magnetic stimulation on the target; real-time magnetic resonance imaging is carriedout according to the magnetic resonance imaging signals. According to a real-time magnetic resonance imaging result, current waveform parameters of a stimulated area of the target or a coil of the stimulation unit are continuously adjusted until an expected magnetic resonance imaging result of the preset area is obtained.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Method and system for dynamic magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveCN104248437AImprove reconstruction qualityAvoid Noisy ReconstructionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSample ModeImaging quality
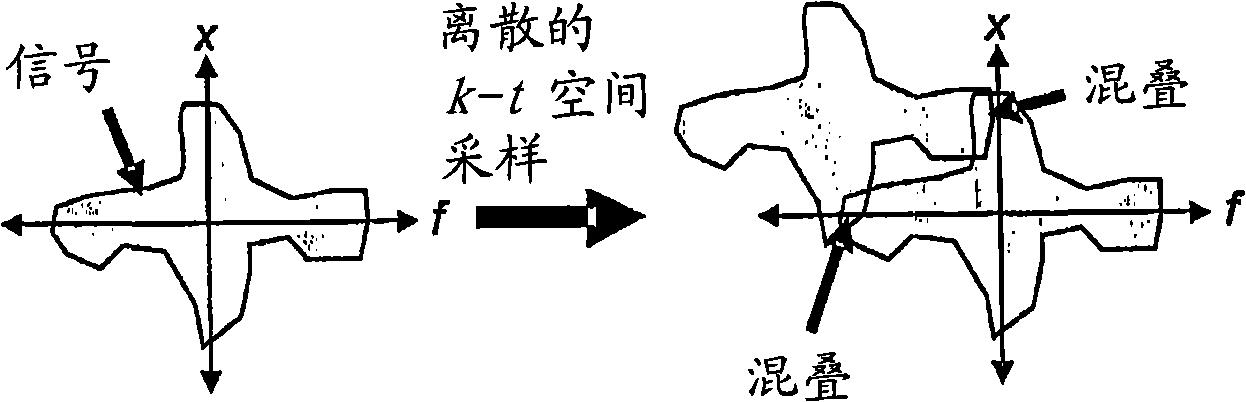
The invention discloses a method and system for dynamic magnetic resonance imaging. A norm sparsity constraint is carried out on a spatial basis on the basis of a conventional PS (Partial Separability) method, so that image artifact and reconstruction noise are more effectively reduced, the image quality is greatly improved, and the reconstruction of a high temporal-spatial resolution dynamic magnetic resonance image is effectively realized. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring K-t spatial navigation data and dynamic image data, which are collected in a sampling mode based on a partial separability method; constructing a dynamic imaging reconstruction model containing a spatial basis function and a temporal basis function based on the partial separability method; acquiring the temporal basis function according to the navigation data; based on the dynamic imaging reconstruction model, estimating the spatial basis function by a least square method according to the temporal basis function and the dynamic image data; utilizing the temporal basis function and the dynamic image data to carry out interpolation recovery on the k spatial dynamic image data, and then carrying out Fourier transformation so as to acquire a reconstructed dynamic magnetic resonance image.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
System and method for z-shim compensated echo-planar magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20160209487A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic susceptibilityPulse sequence
A system and method for imaging a subject includes a first imaging pulse sequence having gradient blips along an x-direction and a y-direction to acquire calibration image data from multiple slices. The imaging pulse sequence also includes a plurality of Z-shimming gradient blips coincident in time with the gradient blips along the x- and y-directions and varied within each slice. A plurality of calibration images are reconstructed from the calibration image data and a comparison image is formed by selecting an image from the calibration images corresponding to at least one of the varied Z-shimming gradient blips for each slice to determine a desired value of the Z-shimming gradient blips. The desired values are used to perform a second pulse sequence to acquire clinical image data from the subject. The second pulse sequence is used to acquire clinical images having been compensated for magnetic susceptibility variations within the subject.
Owner:WEILL CORNELL MEDICINE +1
Coil selection for parallel magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS8502535B2Minimal information lossMagnetic gradient measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionParallel magnetic resonance imagingMagnetic Resonance Imaging Scan
The invention relates to a method of selecting a set of coil elements from a multitude of physical coil elements comprised in a coil array for performing a magnetic resonance imaging scan of a region of interest.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Navigator-based magnetic resonance method and apparatus to detect non-rigid motion in large joint magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20170139026A1Easy accessShort durationDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsResonanceRigid motion
In a magnetic resonance (MR) navigator-based method and apparatus, MR data are acquired from a large joint of a patient, which is not modelable as a whole based on a single rigid body model. The field of view which the MR data are acquired is divided in a processor into multiple sub-sections, with each sub-section being modelable based on a rigid body model. MR navigator signals are acquired from each of the sub-sections, and these navigator signals are used in a motion tracking algorithm that is based on a rigid body model in order to generate a modeling result that tracks the movement of the overall joint within the field of view. The modeling result can be used for prospective or retrospective motion correction of the MR data.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method for simultaneous time-interleaved multislice magnetic resonance imaging
Methods for reducing scan time in magnetic resonance imaging (“MRI”), particularly when imaging three-dimensional image volumes, using a simultaneous time-interleaved multislice (“STIMS”) acquisition are described. The unused time in each repetition time (“TR”) period is exploited to provide an additional reduction in encoding time for a three-dimensional acquisition (e.g., a 3D whole brain coverage). Groups of spatially interleaved slices are excited in a single TR, with the excitation and acquisition of the groups of slices being interleaved in time.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Deep convolutional encoder-decoder for prostate cancer detection and classification
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and system for performing upright magnetic resonance imaging of various anatomical and physiological conditions
Vasculature or parenchyma is imaged using upright MRI techniques, on patients who may have conditions such as congestive heart failure, or otherwise be healthy. When an individual is horizontal, venous drainage is minimized, causing the vessels to remain engorged, also referred to herein as vascular congestion. Vascular congestion results in an enlarging of the vessels and surrounding tissue causing the vessels to be more visible on MRIs. The decrease in vascular visibility in upright subjects is in part, due to an increase in venous drainage. Patients suffering from coronary and / or pulmonary deficiencies (e.g. CHF) experience decreased rates and degrees of venous drainage. In one embodiment, the present invention uses upright imaging to visualize these enlarged vessels.
Owner:FONAR
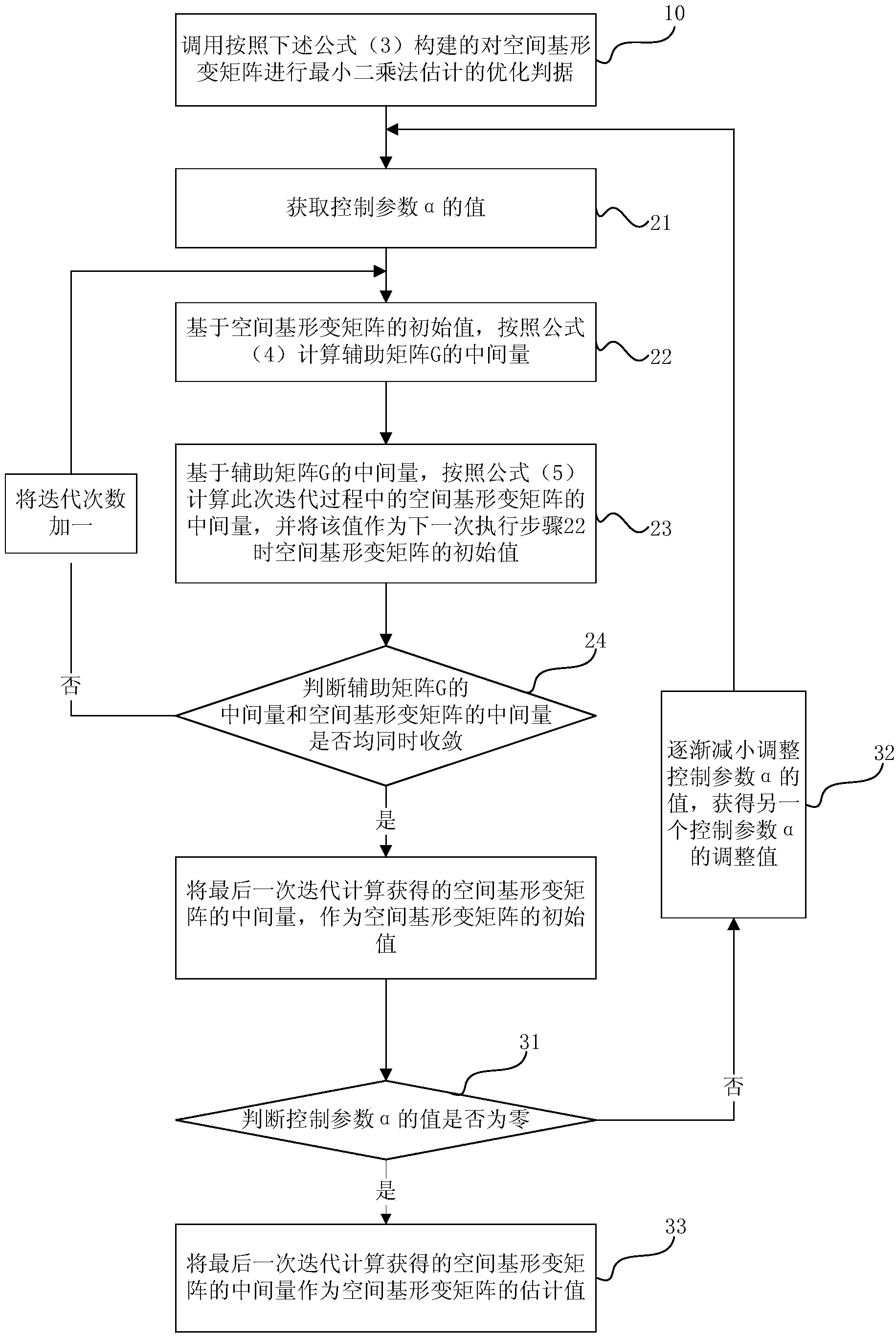
Method for rapidly reconstructing magnetic resonance imaging based on tensor product complex wavelet tight frame
ActiveCN109188327AHigh precisionImprove refactoring qualityMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringContraction methodTight frame
The invention discloses a method for rapidly reconstructing a magnetic resonance imaging based on a tensor product complex wavelet tight frame, and provides a new research method for rapid magnetic resonance imaging. According to the method for rapidly reconstructing the magnetic resonance imaging based on the tensor product complex wavelet tight frame, the K-space data is undersampled by using the Cartesian sampling trajectory mode, so that the scanning speed of a device is greatly improved; the imaging is decomposed from multiple directions based on the sparse transformation of the tensor product complex wavelet tight frame, so that the accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging is improved; the convex optimization problem in imaging reconstruction is solved by using the projection fast iterative soft threshold algorithm, so that the speed of magnetic resonance imaging reconstruction is accelerated; and a regularization parameter is adaptively calculated based on the bivariate contraction method in the projection fast iterative soft threshold algorithm, thus not only the process for blindly selecting parameters is omitted, but also the quality of imaging reconstruction is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Dynamic magnetic resonance imaging method and system
ActiveCN102599910AFast imagingReduce dataDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsTemporal resolutionImaging data
A dynamic magnetic resonance imaging method is characterized by including following steps: sampling to obtain navigation data and dynamic image data; analyzing the navigation data to obtain a temporal basis function; predicting according to the temporal basis function and the dynamic image data so as to obtain a spatial basis function; obtaining signal data according to the temporal basis function and the spatial basis function; and rebuilding the signal data to obtain a magnetic resonance image. Complex image data for a dynamic image are separated into the temporal basis function and the spatial basis function, only the navigation data with high temporal resolution and low spatial resolution and the dynamic image data with high spatial resolution and low temporal resolution are acquired to realize complementation, the data required to be acquired are reduced, and dynamic magnetic resonance imaging speed is increased to a great extent. Besides, the invention further provides a dynamic magnetic resonance imaging system.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
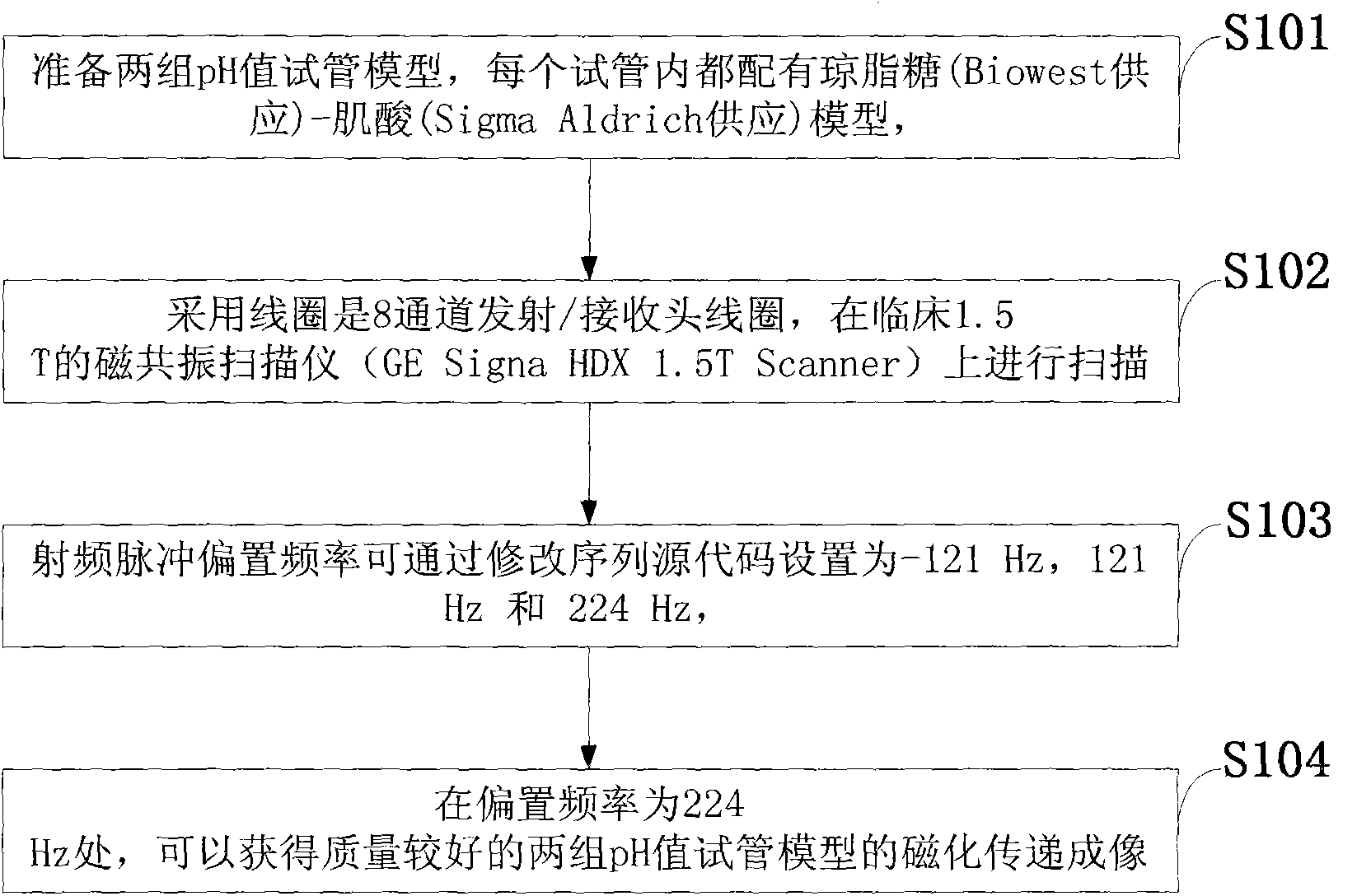
Experiment method based on pH value-sensitive magnetization transfer on 1.5T magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveCN103529412ASimple methodEasy to operateMeasurements using NMRReceiver coilClinical research
The invention discloses an experiment method based on pH value-sensitive magnetization transfer on 1.5T magnetic resonance imaging. The method includes the following steps that two groups of pH value test tube models are prepared, and an agarose-creatine model is arranged in each test tube; scanning is carried out on a clinical 1.5T magnetic resonance scanner, the coil adopted by scanning is an eight-channel transmitter / receiver coil, and the offset frequency of a radio-frequency pulse can be set as negative 121Hz, 121Hz and 224Hz by modifying sequential source codes; and at the offset frequency of 224Hz, the high-quality magnetization transfer imaging of the two groups of pH value test tube models can be obtained. By utilizing the magnetization transfer technology, optimizing sequential parameters and choosing offset frequency, the experiment method can obtain pH value-sensitive magnetization transfer imaging on the clinical 1.5T magnetic resonance scanner, provides an experimental basis for the clinical research of pH value-sensitive magnetization transfer imaging, and is significant in characterizing ischemic tissue-damaged regions and directing the treatment of strokes and the diagnosis of tumors.
Owner:吴仁华
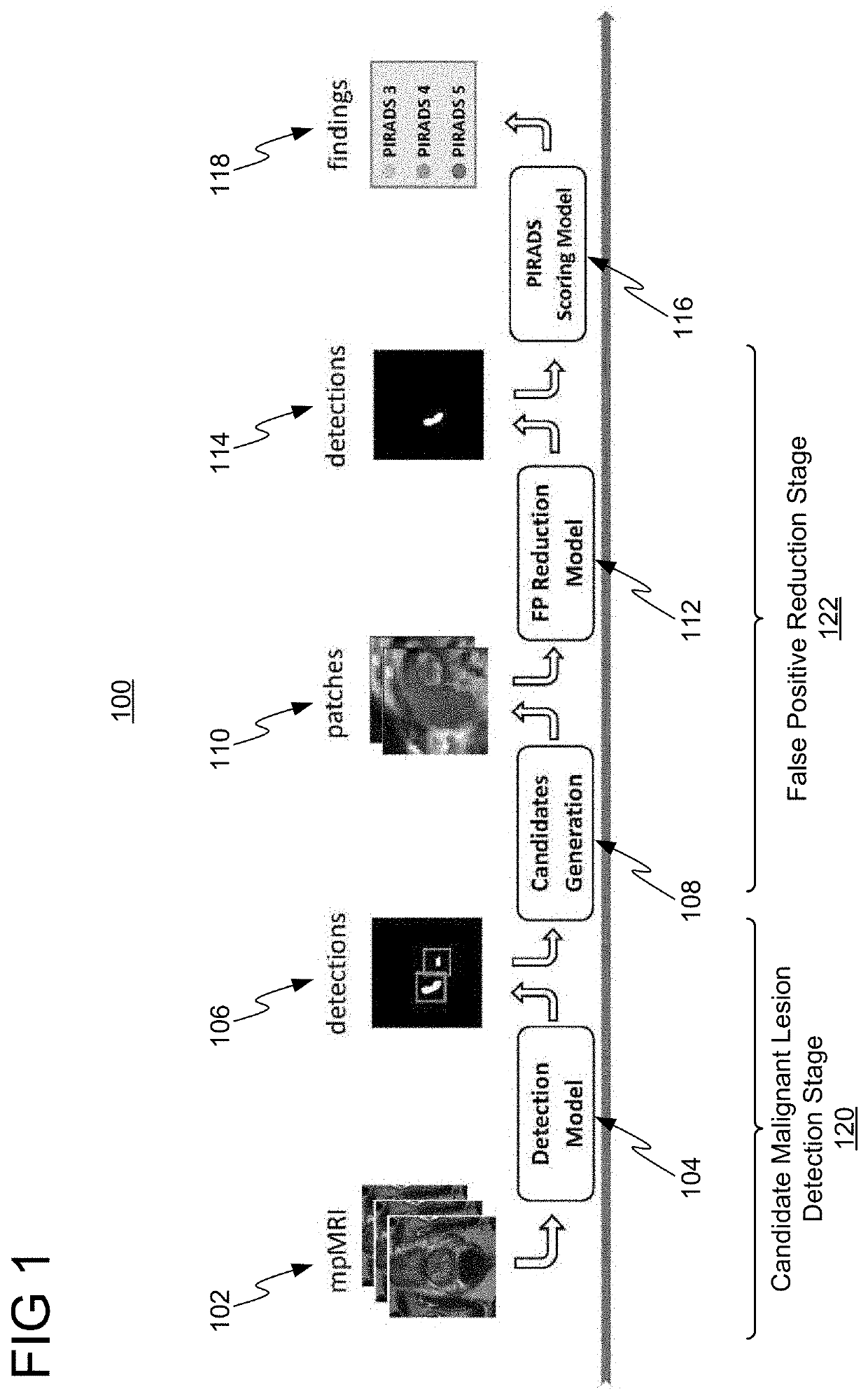
Reducing false positive detections of malignant lesions using multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20210110534A1Reducing false positive detectionImage enhancementImage analysisComputer visionMalignancy
Systems and methods for reducing false positive detections of malignant lesions are provided. A candidate malignant lesion is detected in one or more medical images, such as, e.g., multi-parametric magnetic resonance images. One or more patches associated with the candidate malignant lesion are extracted from the one or more medical images. The candidate malignant lesion is classified as being a true positive detection of a malignant lesion or a false positive detection of the malignant lesion based on the one or more extract patches using a trained machine learning network. The results of the classification are output.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
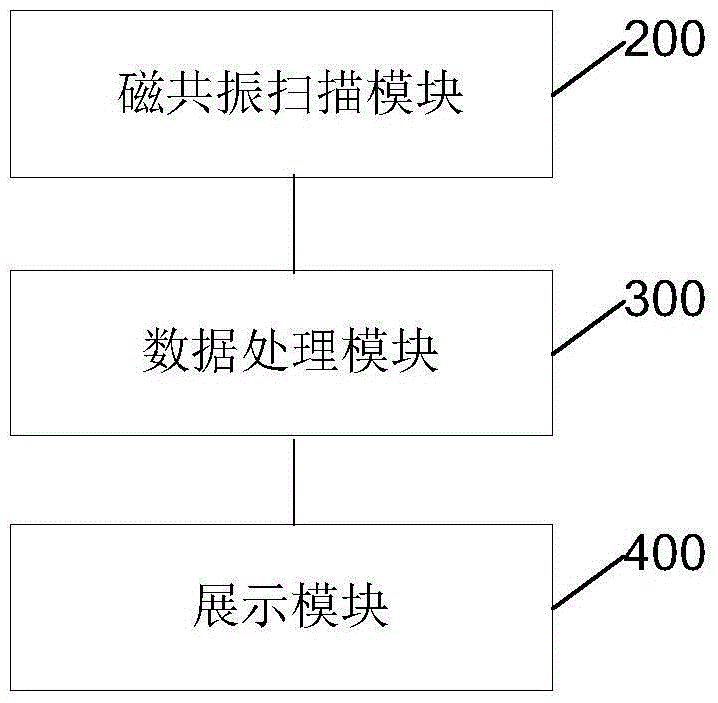
Real-time magnetic resonance imaging data collecting and analyzing method and system
InactiveCN105476636AReal-time acquisitionReal-time analysisDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsImaging dataTime processing
The invention provides a real-time magnetic resonance imaging data collecting and analyzing method and system. The method comprises the steps that scanning is conducted on a testee, and a magnetic resonance scan image sequence is generated in real time; real-time processing is conducted on the magnetic resonance scan image sequence to obtain scan image data subjected to real-time treatment. The system comprises a magnetic resonance scanning module and a data processing module. According to the real-time magnetic resonance imaging data collecting and analyzing method and system, the magnetic resonance scan image sequence is generated through the magnetic resonance scanning module in real time, the magnetic resonance scan image sequence is transmitted to the data processing module in time so as to enable the data processing module to conduct image processing, and therefore real-time collecting and analyzing of magnetic resonance imaging data are achieved. The real-time magnetic resonance imaging data collecting and analyzing system is stable in framework performance, safe, reliable and strong in expandability. In brain science research, compared with offline function magnetic resonance imaging, the real-time function magnetic resonance imaging is more accurate in feedback regulation mode and better in real-time performance.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHENGLAN ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Dynamic magnetic resonance imaging method and system
ActiveCN104248437BImprove reconstruction qualityAvoid Noisy ReconstructionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSample ModeImaging quality
The invention discloses a method and system for dynamic magnetic resonance imaging. A norm sparsity constraint is carried out on a spatial basis on the basis of a conventional PS (Partial Separability) method, so that image artifact and reconstruction noise are more effectively reduced, the image quality is greatly improved, and the reconstruction of a high temporal-spatial resolution dynamic magnetic resonance image is effectively realized. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring K-t spatial navigation data and dynamic image data, which are collected in a sampling mode based on a partial separability method; constructing a dynamic imaging reconstruction model containing a spatial basis function and a temporal basis function based on the partial separability method; acquiring the temporal basis function according to the navigation data; based on the dynamic imaging reconstruction model, estimating the spatial basis function by a least square method according to the temporal basis function and the dynamic image data; utilizing the temporal basis function and the dynamic image data to carry out interpolation recovery on the k spatial dynamic image data, and then carrying out Fourier transformation so as to acquire a reconstructed dynamic magnetic resonance image.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
System and Method for Free-Breathing Quantitative Multiparametric MRI
PendingUS20220179023A1Medical imagingDiagnostic recording/measuringProton density fat fractionData set
A method for proton resonance frequency shift (PRF) and T1-based temperature mapping using a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system includes acquiring, using the MRI system, a set of magnetic resonance (MR) data from a region of interest of a subject by performing a variable-flip-angle multi-echo gradient-echo 3D stack-of-radial pulse sequence. The pulse sequence is configured to acquire radial k-space data in a plurality of segments, each segment acquired with each of a plurality of flip angles. The method further includes generating at least one T1 map based on the set of MR data, generating at least one PRF temperature map based on the set of MR data, generating at least one T1-based temperature map based on the set of MR data and displaying the PRF temperature map and the T1-based temperature map. In another embodiment, the MR data may be used to generate a plurality of quantitative parameter maps for each of the plurality of MR parameters such as T1, proton-density fat fraction (PDFF), and R2*.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Prior-information-enhanced dynamic magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveCN101943747AMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringPrior informationReference image
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Expanded pharmacokinetic model for population studies in breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
A method for pharmacokinetic analysis, including: receiving time-series medical image data of a patient introduced with a contrast agent; identifying a reference region in the medical image data; identifying a plurality of points of interest in the medical image data; measuring an intensity of voxels in the reference region; and for each point of interest, measure an intensity of voxels therein, use the measured reference region and point of interest intensities to obtain an expression relating the point of interest's voxel concentration to that of the reference region, wherein the expression is a five-parameter nonlinear model with no reference to an arterial input function; and obtain values for each of the five-parameters by solving the expression and use the obtained values to determine whether the point of interest is malignant.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
A Nonconvex Low-Rank Reconstruction Method for Fast Magnetic Resonance Imaging
ActiveCN104933683BAccurate reconstructionRecover image detailsImage enhancementSingular value decompositionPattern recognition
The invention relates to a non-convex low-rank reconstruction method for rapid MR imaging. An MR image data reconstruction mathematic model based on low-rank prior information of non-local similar image blocks is established, and iterative solution is carried out on the model in a direction alternative iteration method; a non-convex p norm of the low-rank matrix of the non-local image model with the low-rank prior information is solved by deposition and iteration of Taylor first-order approximation and the singular value, a similar image block is obtained, and a reconstruction image is solved via iteration by increasing the auxiliary variable and separating the variable. The image prior information is used to combine the non-local similarity with the low-rank characteristic of the image block, the Fourier transform and the characteristic of the low-rank matrix are used to simplify the calculation process, the complexity of algorithm is reduced, the performance of the reconstructed MRI images by part of K space data is improved, the image can be reconstructed more accurately with less scanning and measurement, pseudo shadows of the images are reduced, and rapid MRI is realized.
Owner:南昌市云影医疗科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com