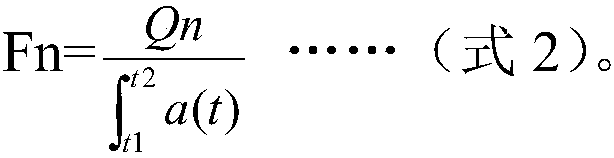Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
44 results about "Arterial input function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
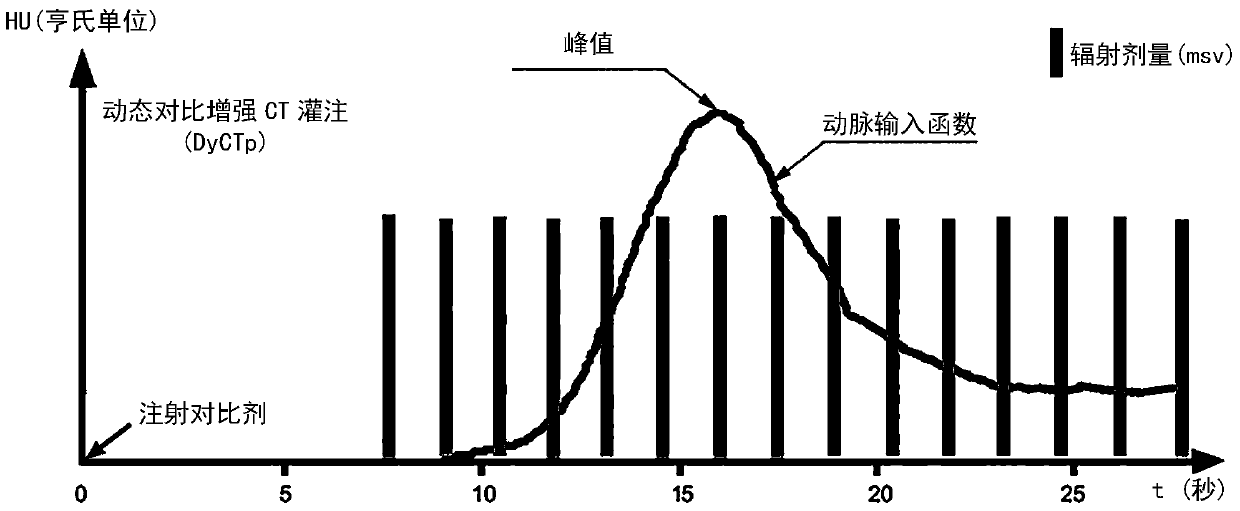
The arterial input function (AIF) is the concentration-time curve of the contrast agent (indicator) measured in an arterial vessel that feeds the organ of interest.
Automated determination of arterial input function areas in perfusion analysis
InactiveUS20140163403A1Well formedMagnetic measurementsCatheterImaging modalitiesArterial input function
Automatic arterial input function (AIF) area determination is provided that can be used to facilitate the generation of parametric maps for perfusion studies based on various imaging modalities and covering a variety of tissues. Automatic AIF determination can be accomplished by extracting characteristic parameters such as maximum slope, maximum enhancement, time to peak, time to wash-out, and wash-out slope. Characteristic parameter maps are generated to show relationships among the extracted characteristic parameters, and the characteristic parameter maps are converted to a plurality of two-dimensional plots. Automated segmentation of non-AIF tissues and determination of AIF areas can be accomplished by automatically finding peaks and valleys of each phase of AIF areas on the plurality of two-dimensional plots.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
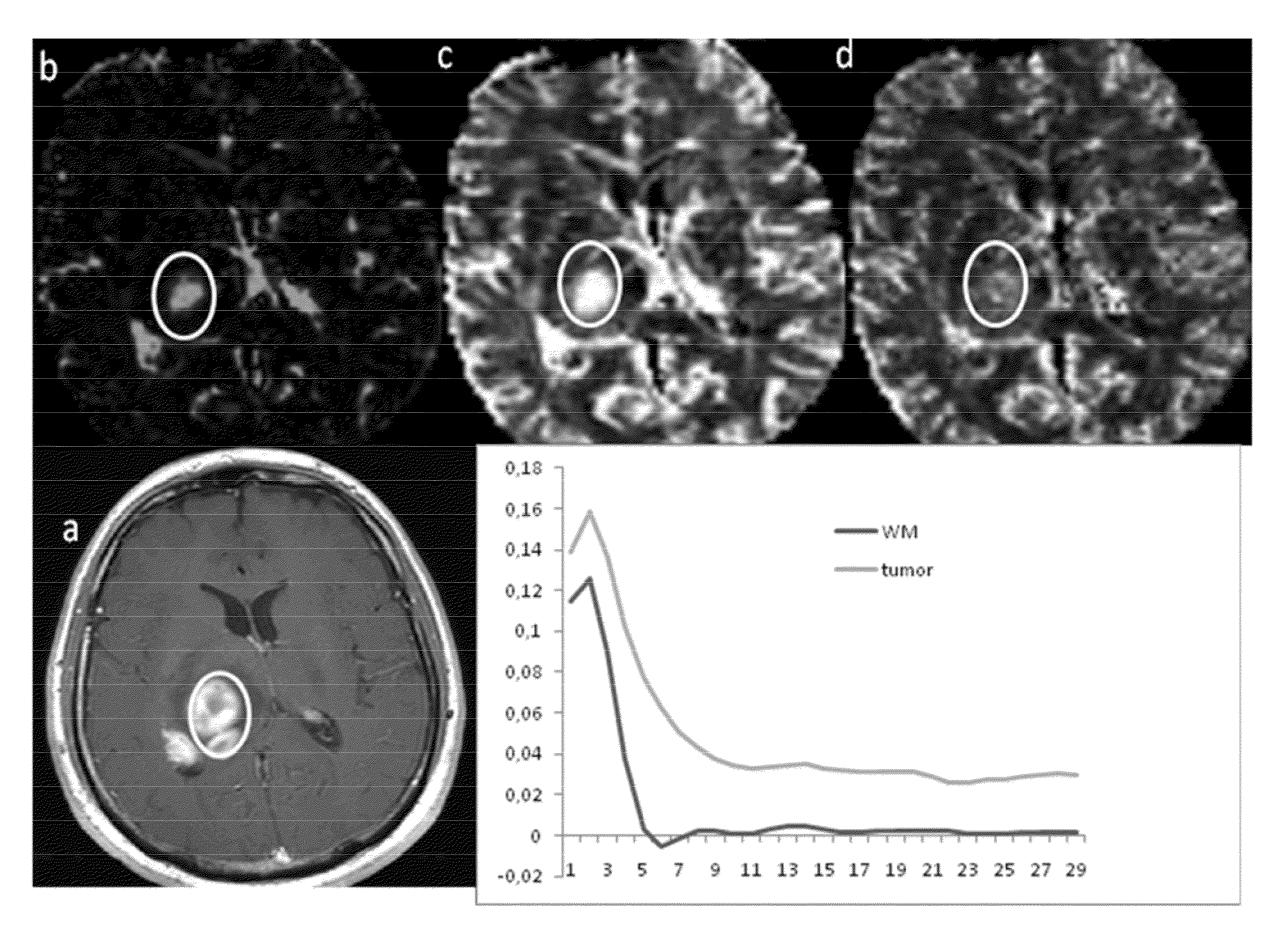
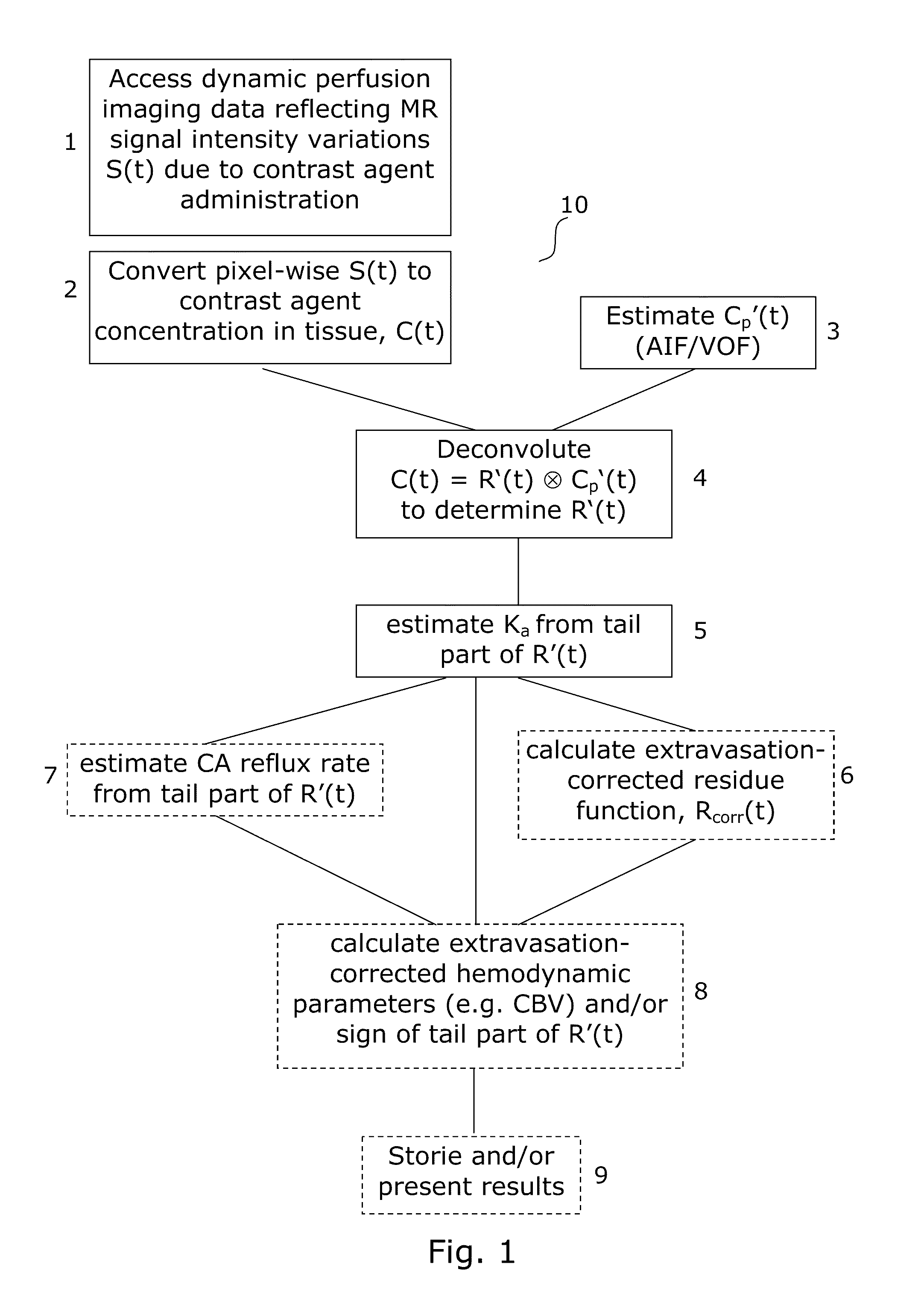
Estimating and correcting for contrast agent extravasation in tissue perfusion imaging
ActiveUS20110257519A1Good estimateRobust estimationImage enhancementImage analysisDynamic contrastArterial input function
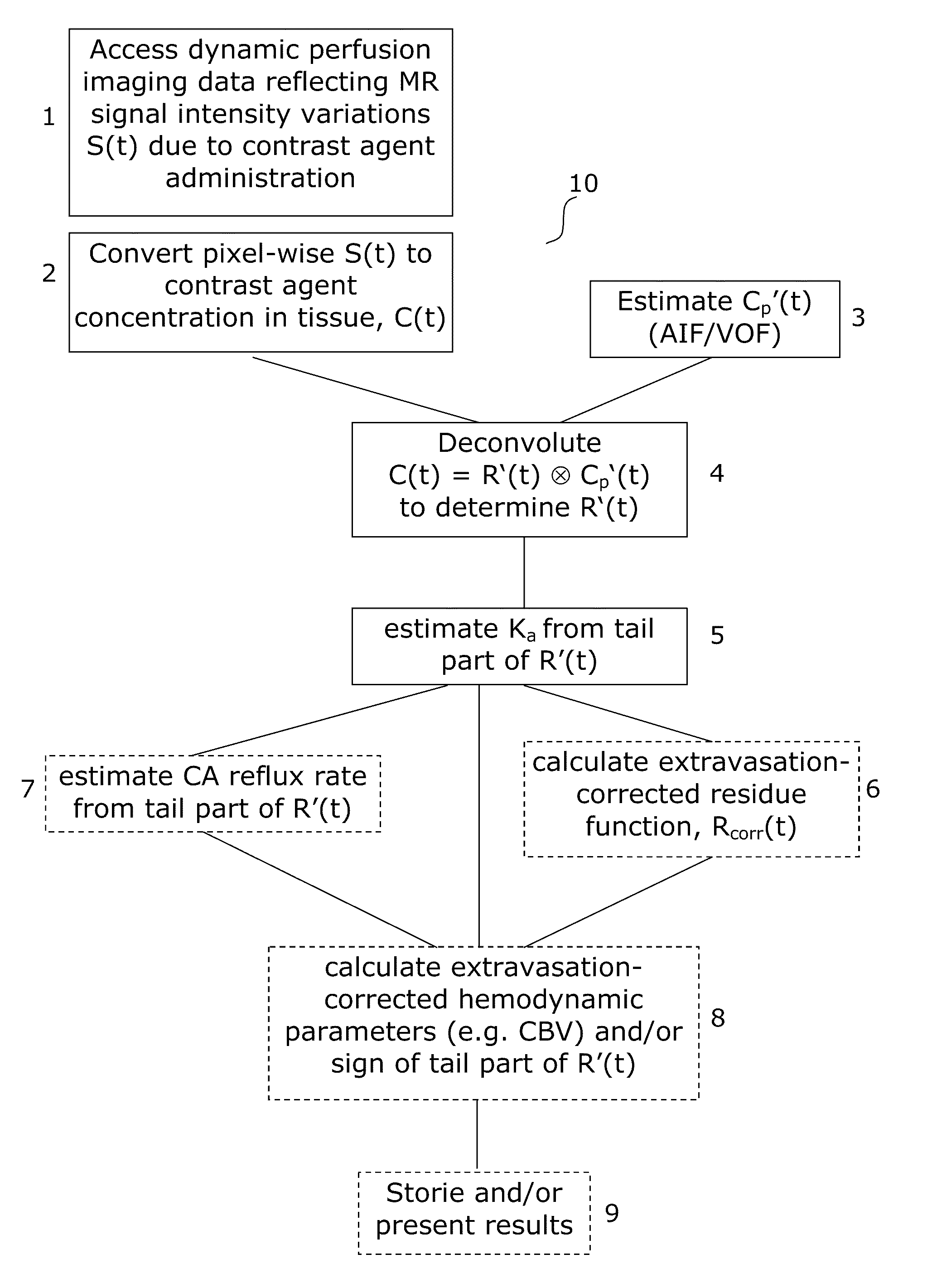
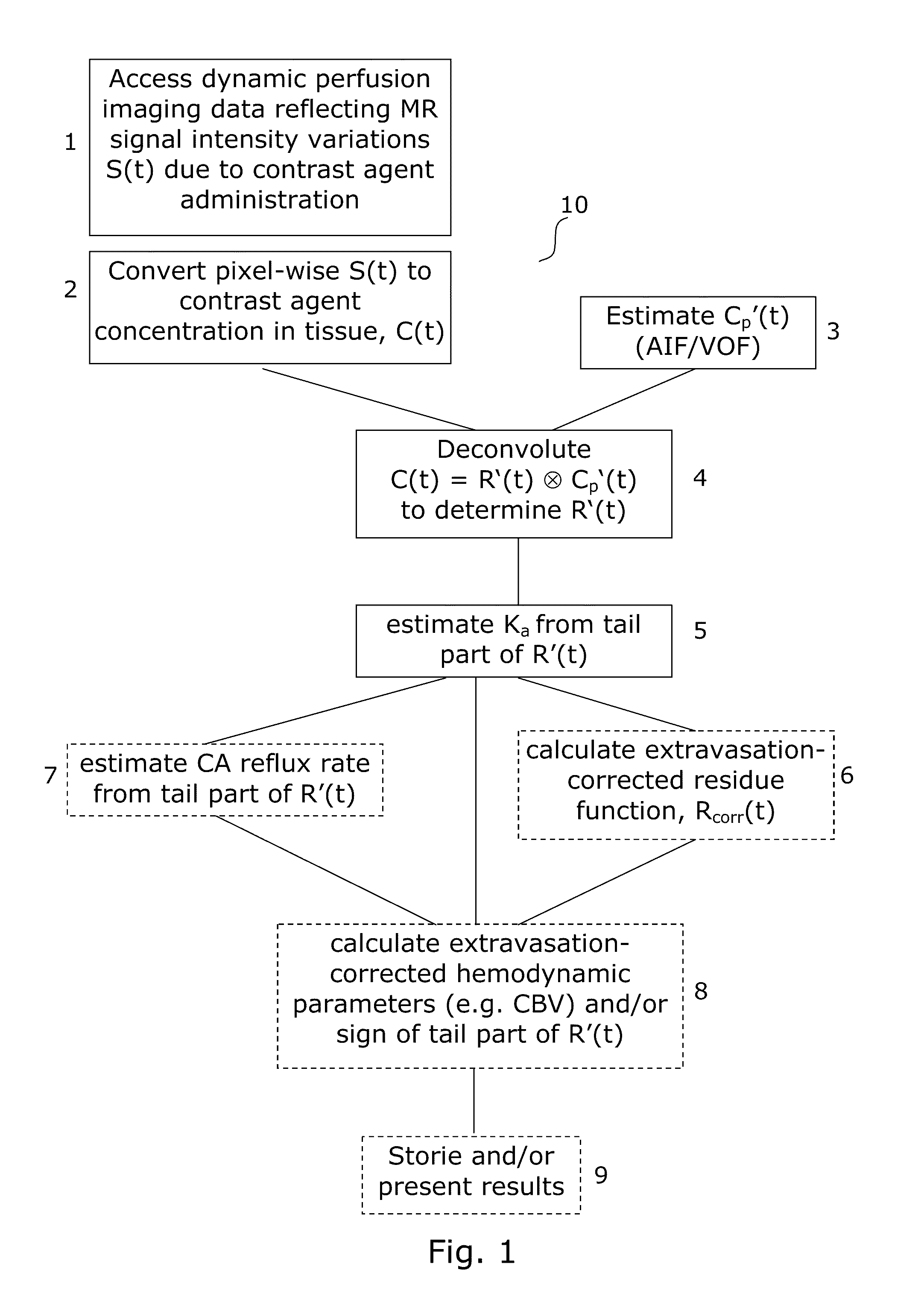
The invention provides a method, an image analysis software product, and a system for medical imaging analysis for estimating contrast agent extravasation in contrast agent based perfusion imaging such as MRI dynamic contrast enhanced (DCE) imaging, and in particular correction, compensation, or visualization of extravascular leakage of contrast agent in tumors. According to the invention, the effect of extravasation is directly manifested in the tail part of an observed, apparent residue function, R′(t), obtained directly by de-convoluting the expression C(t)=R′(t)Cp′(t) with the arterial input function (AIF). A leakage rate or extravasation constant is determined directly from the tail part of the determined apparent residue function. The invention also relates to distinguishing between T1-dominant and T2*-dominant extravasation effects in perfusion imaging to from the sign of the tail part of the determined apparent residue function and to an automated method for DSC-MRI involving correction for contrast agent extravasation and partial volume effects.
Owner:UNIV OSLO HF
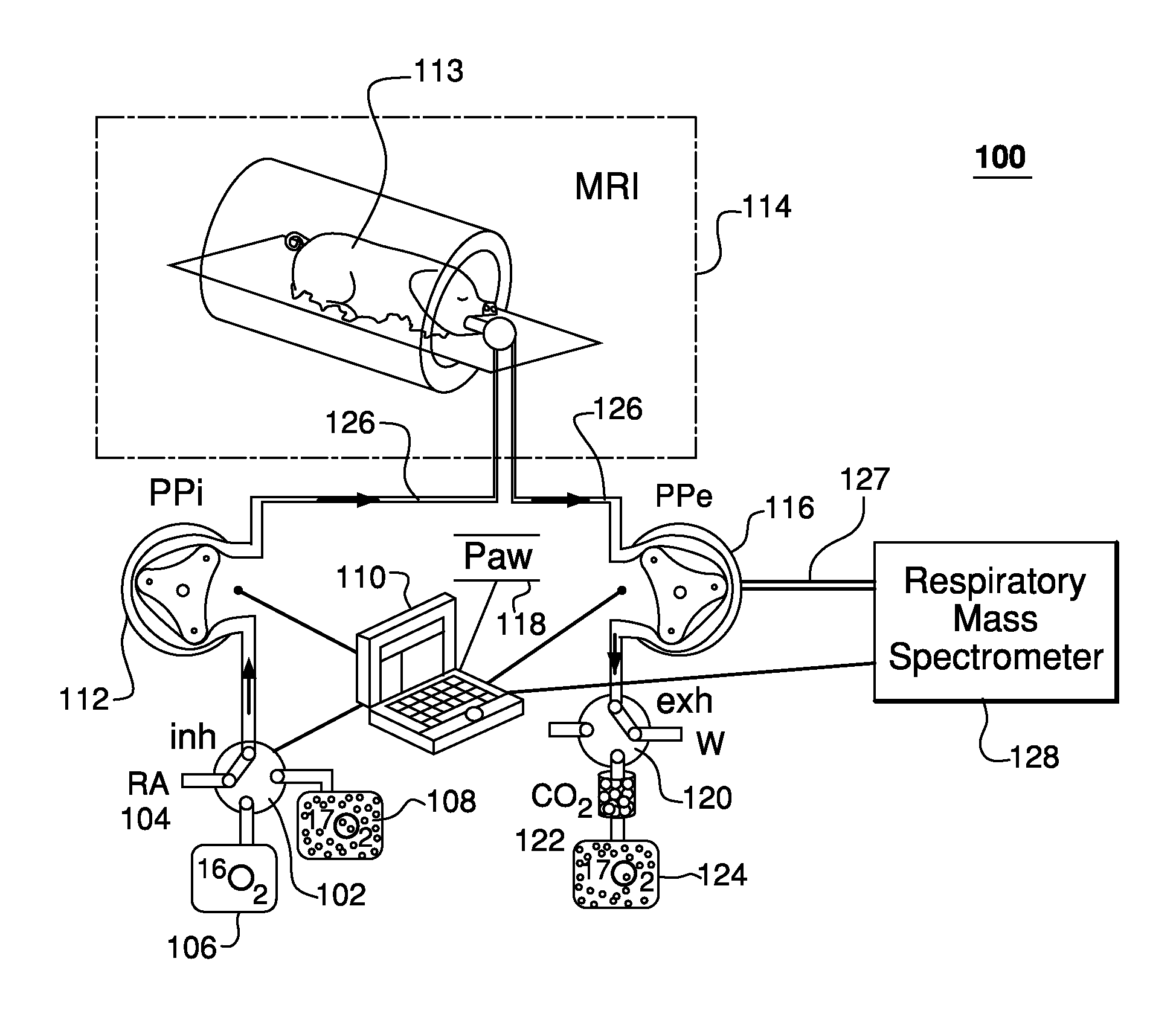
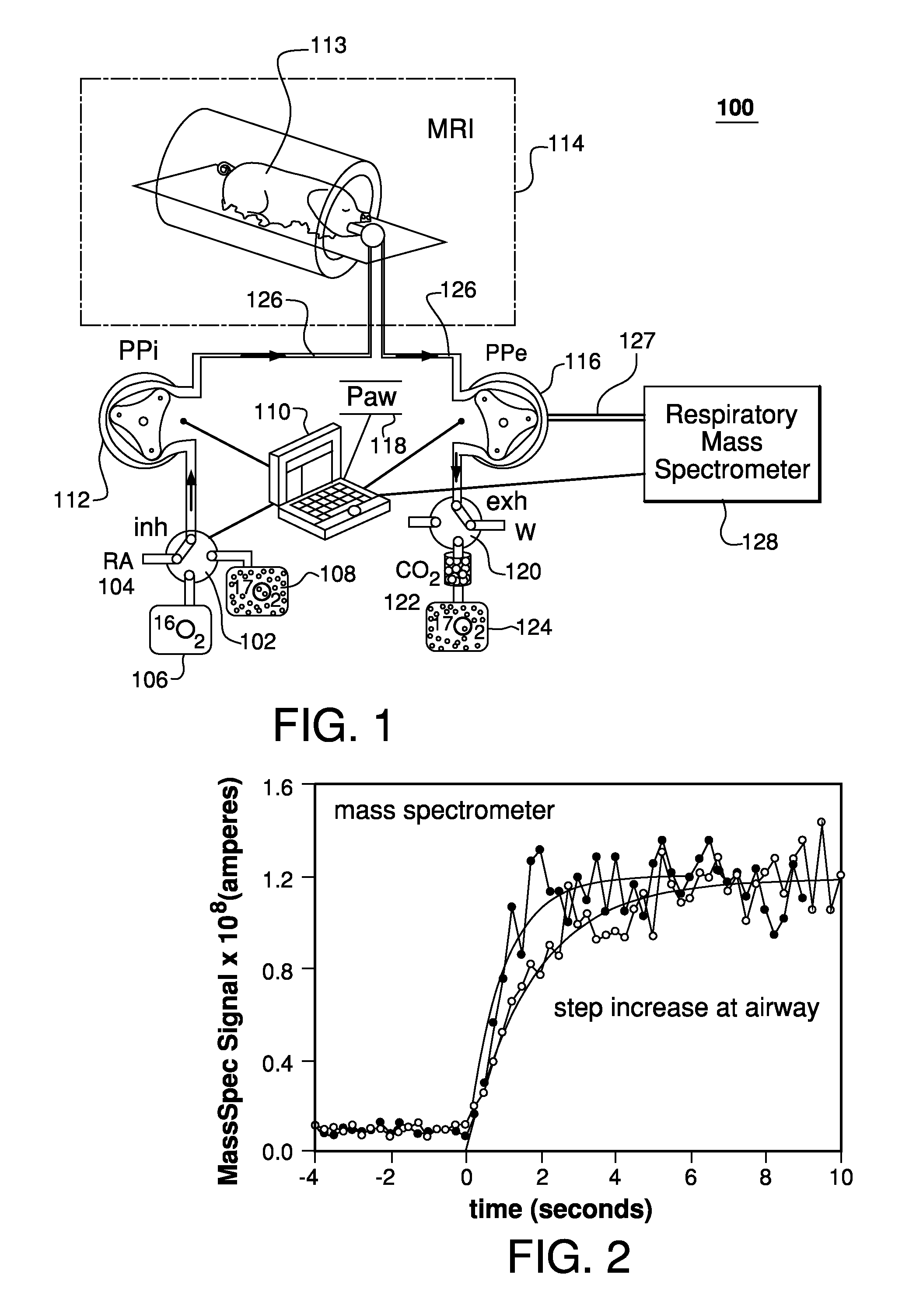
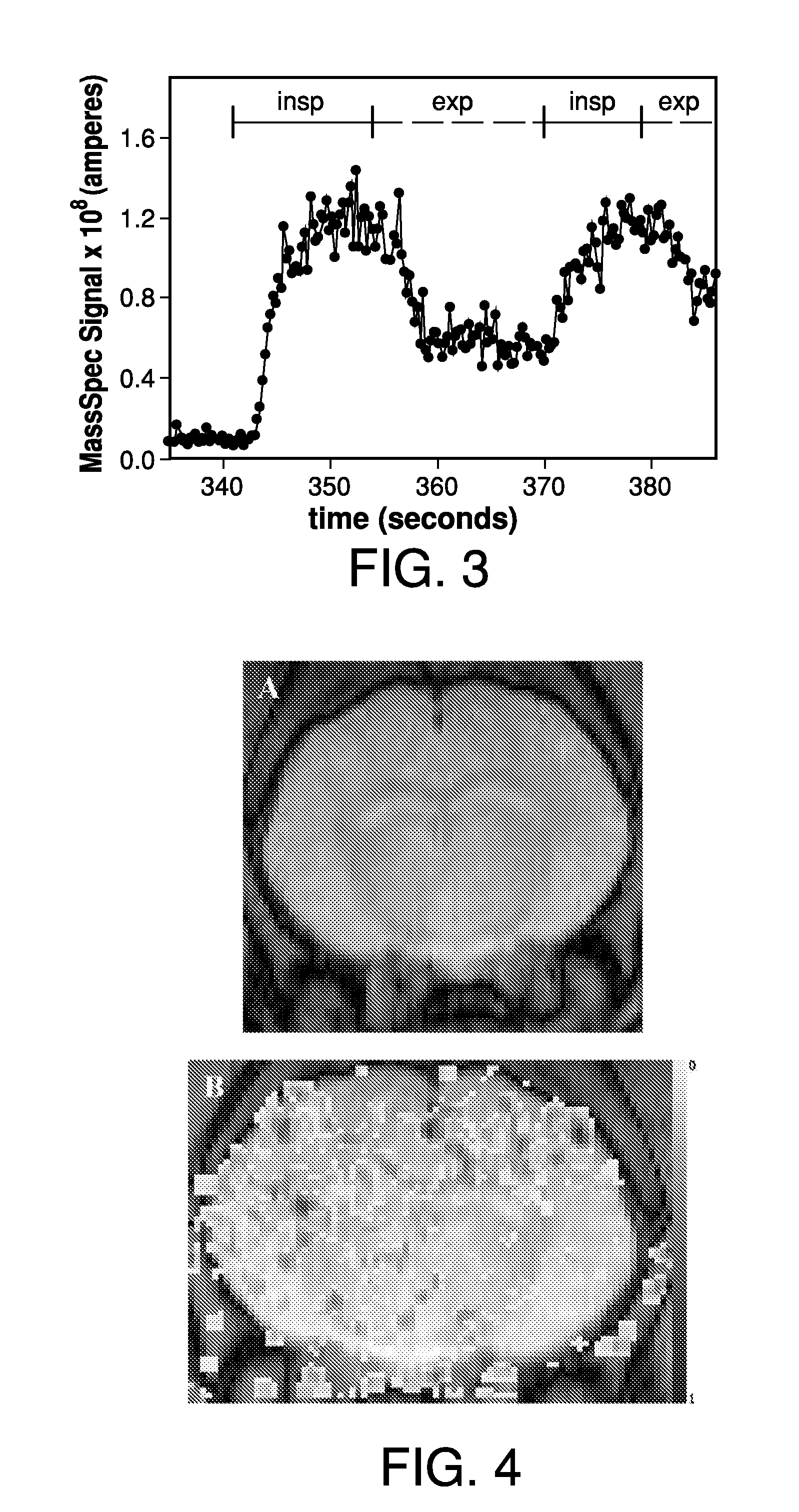
Method and apparatus for providing pulses inhalation of 17o2 for magnetic resonance imaging of cerebral metabolism
ActiveUS20100282258A1Easy to explainEliminate needRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesArterial input functionCerebral ventricle
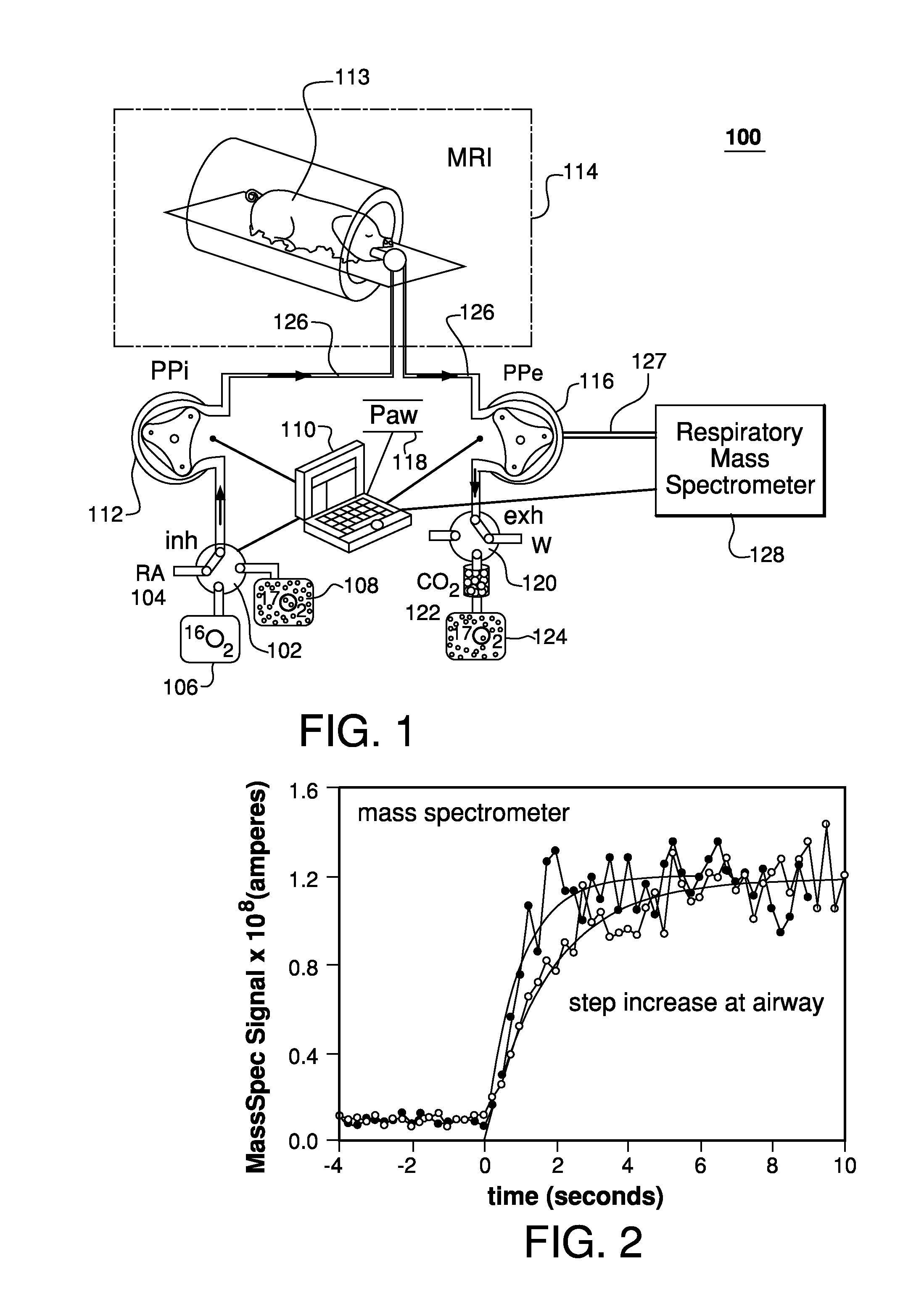
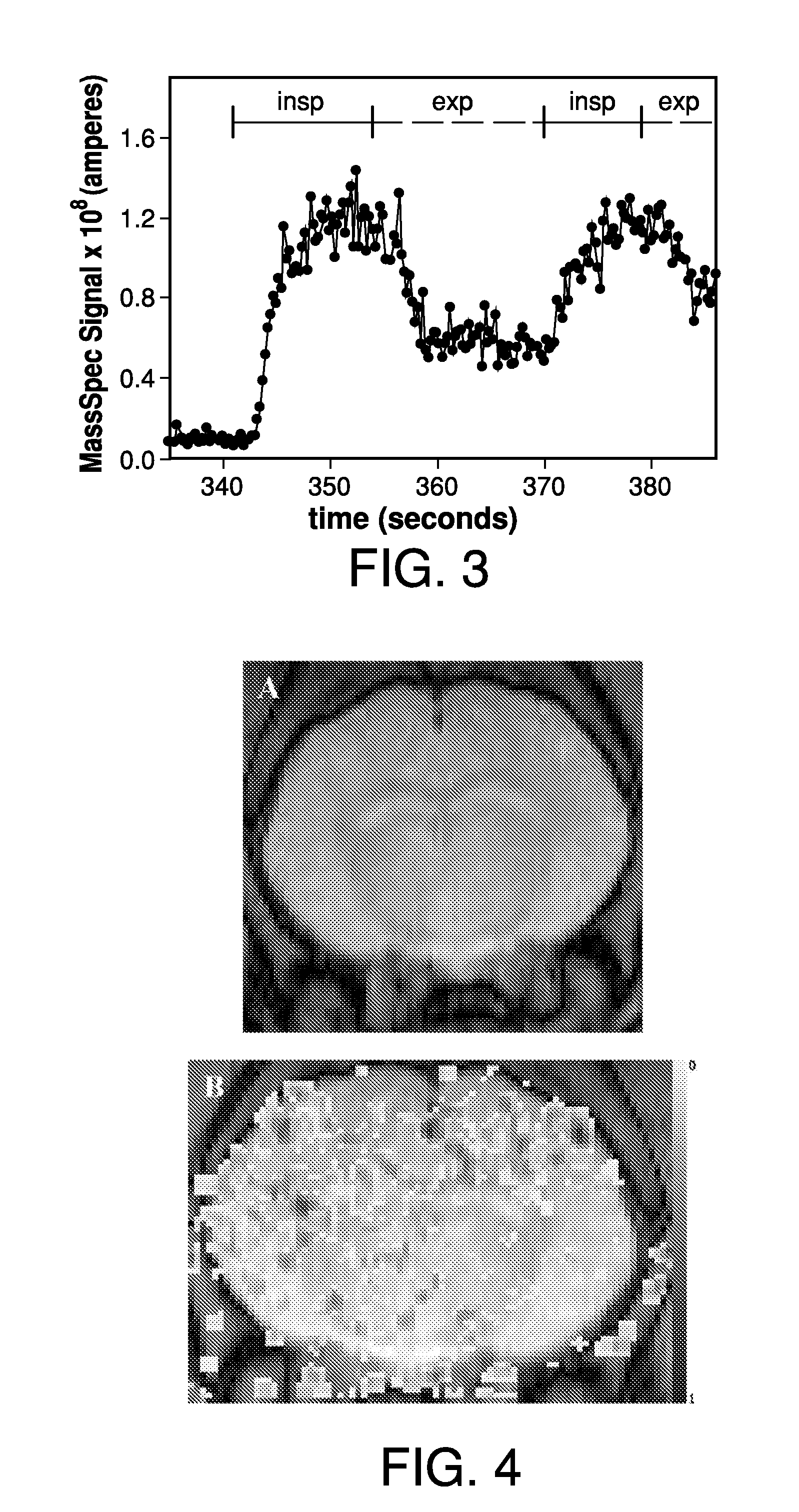
Prior approaches have delivered O2 to a subject by inhalation, but the relationship between local signal changes and metabolism has been complicated by H217O created in non-cerebral tissues. During a brief pulse of 17O2 inhalation, this arterial input function for H217O is negligible due to convective transport delays. Additional delays in the arterial input function due to restricted diffusion of water makes pulsed inhalation of 17O2 even more effective. Accordingly, ventilator system are provided to deliver 17O2 as a brief pulse to a subject. Subsequent MR imaging demonstrates delayed appearance of H217O in the cerebral ventricles, suggesting that the arterial input function of H217O is delayed by restricted water diffusion in addition to convective transit delays. Delivery as a brief pulse therefore offers significant advantages in relating MR signal changes directly to metabolism.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Estimating and correcting for contrast agent extravasation in tissue perfusion imaging
ActiveUS8718747B2Robust estimationAccurately determineImage enhancementImage analysisDynamic contrastArterial input function
The invention provides a method, an image analysis software product, and a system for medical imaging analysis for estimating contrast agent extravasation in contrast agent based perfusion imaging such as MRI dynamic contrast enhanced (DCE) imaging, and in particular correction, compensation, or visualization of extravascular leakage of contrast agent in tumors. According to the invention, the effect of extravasation is directly manifested in the tail part of an observed, apparent residue function, R′(t), obtained directly by de-convoluting the expression C(t)=R′(t)Cp′(t) with the arterial input function (AIF). A leakage rate or extravasation constant is determined directly from the tail part of the determined apparent residue function. The invention also relates to distinguishing between T1-dominant and T2*-dominant extravasation effects in perfusion imaging to from the sign of the tail part of the determined apparent residue function and to an automated method for DSC-MRI involving correction for contrast agent extravasation and partial volume effects.
Owner:UNIV OSLO HF
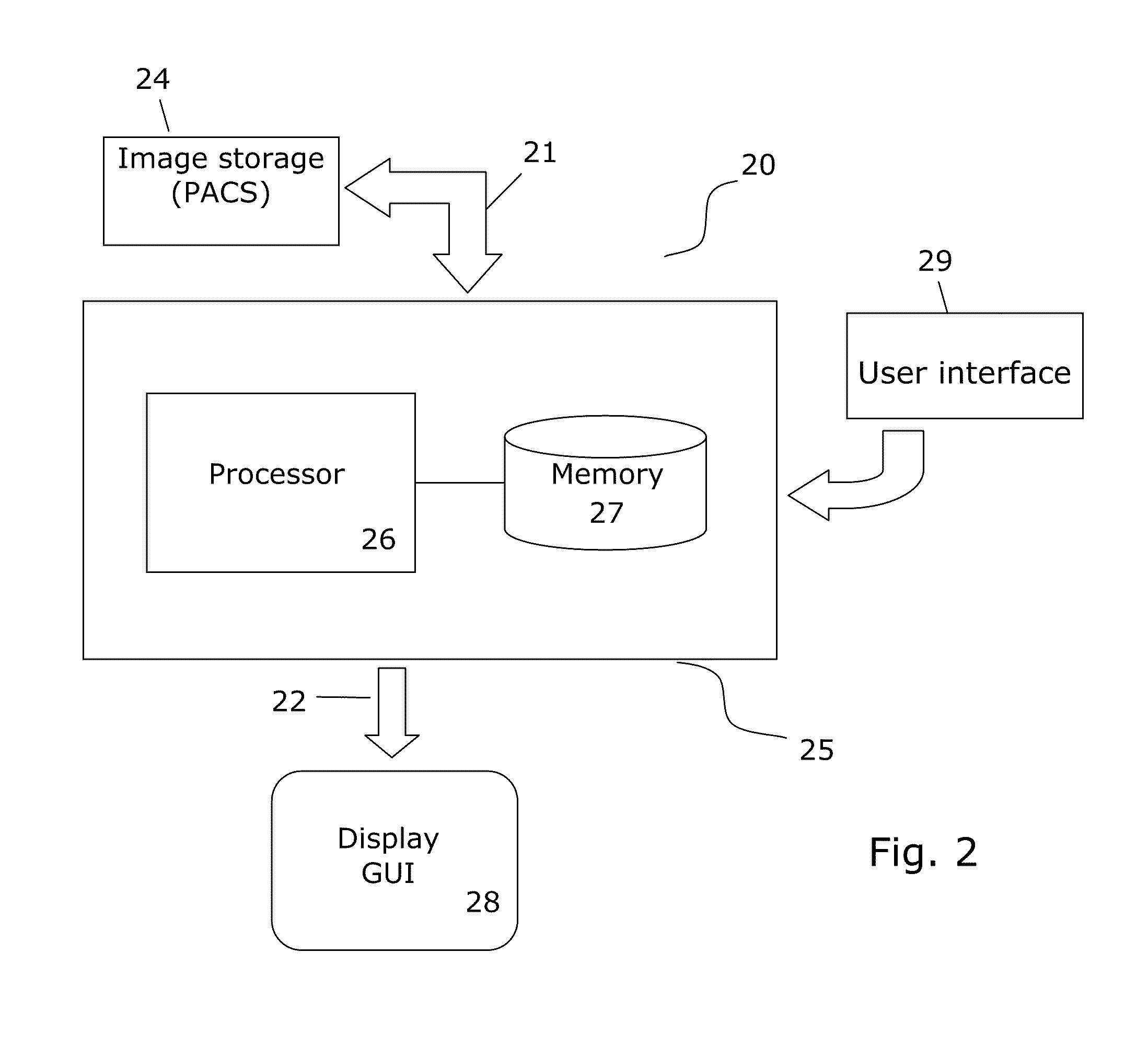
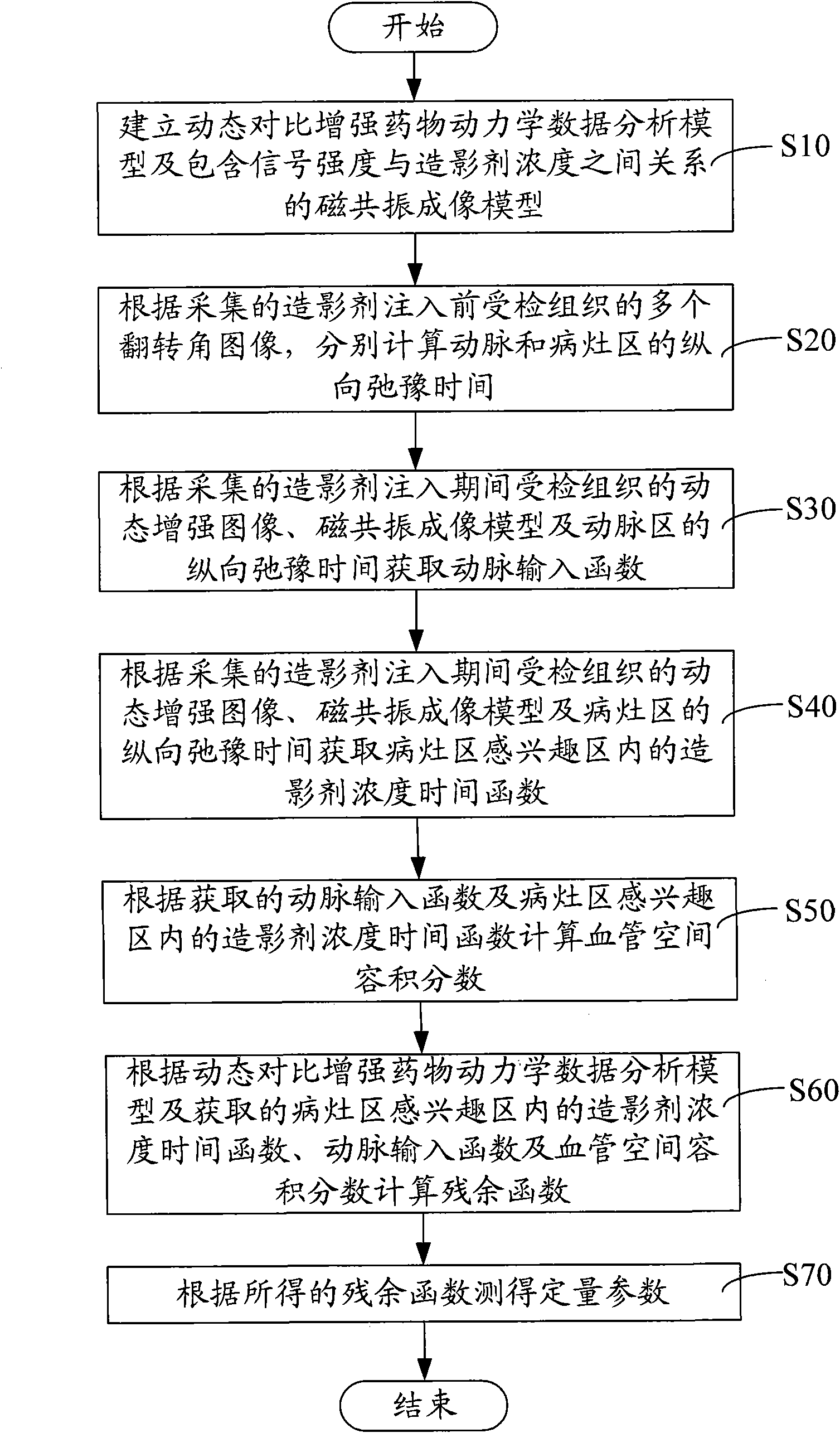
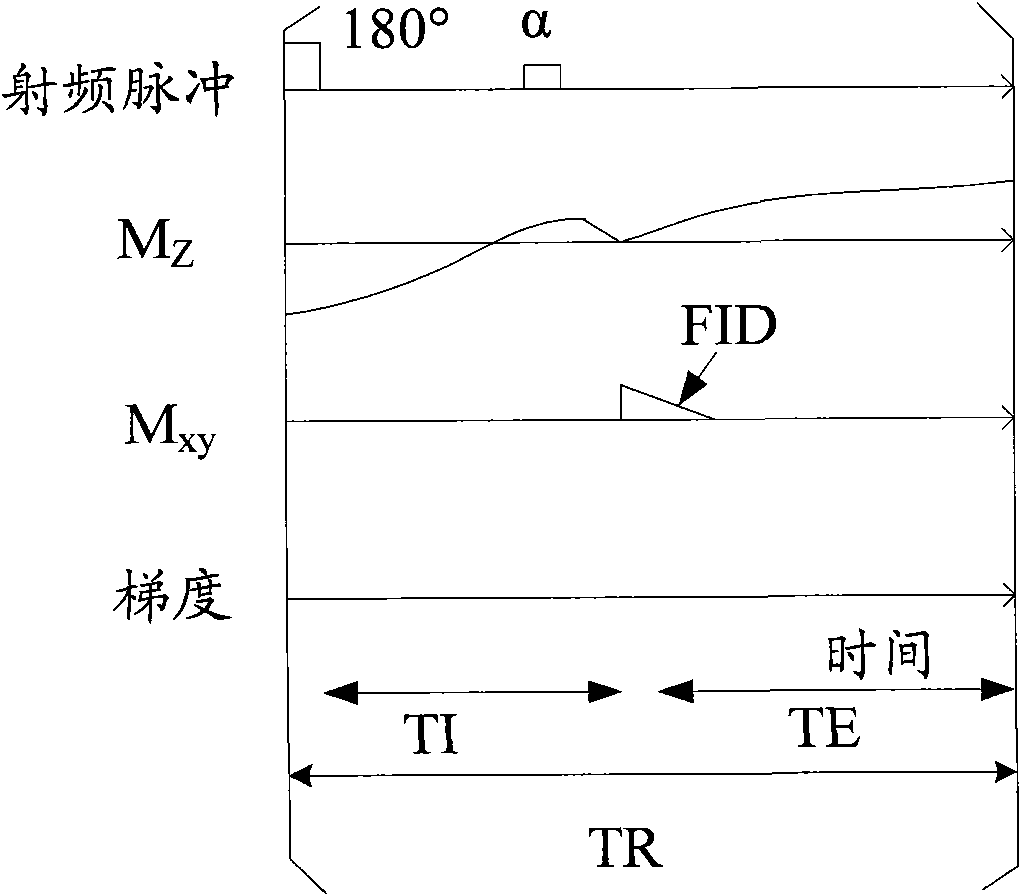
Method and system for calculating quantitative parameter of magnetic resonance imaging
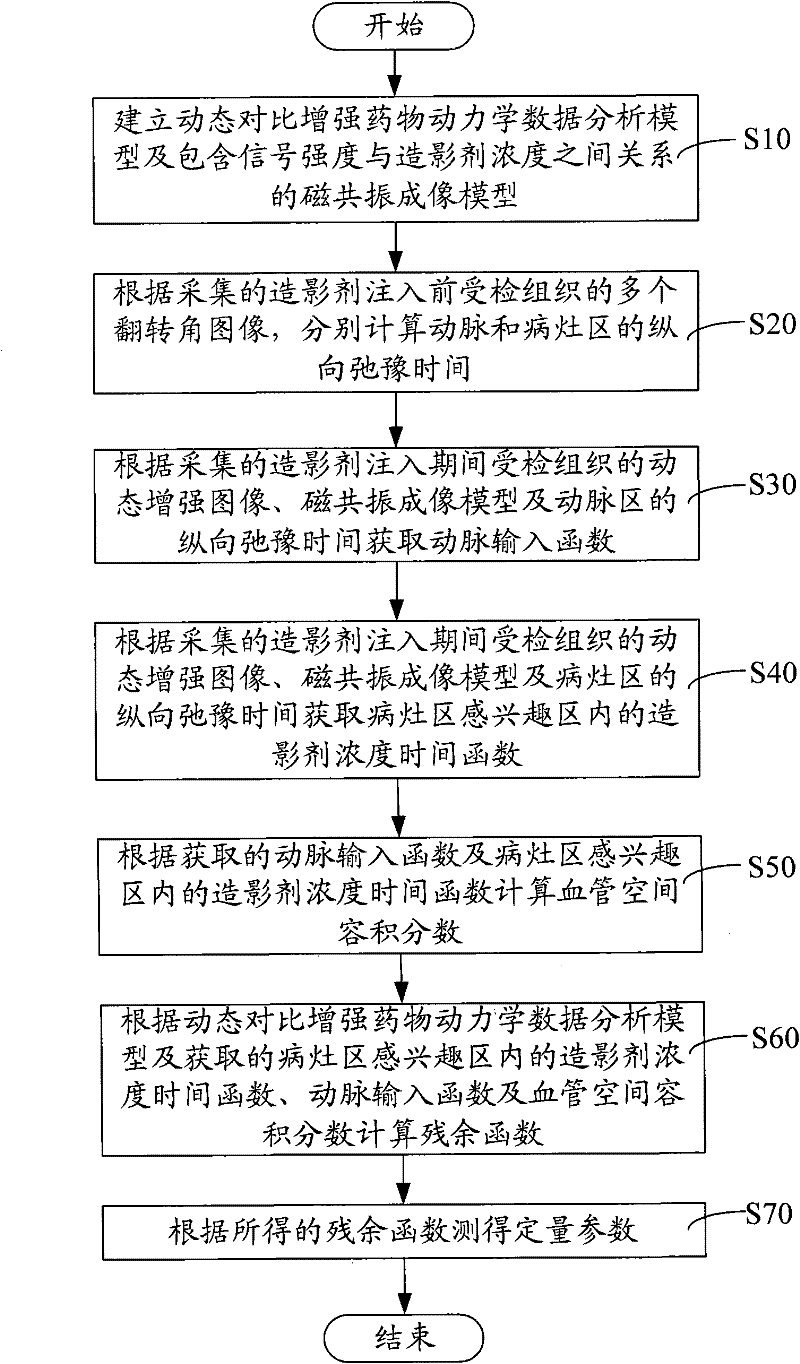
The invention discloses a method and a system for calculating a quantitative parameter of magnetic resonance imaging. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a dynamic comparison enhancement drug dynamics data analysis model and a magnetic resonance imaging model containing the relationship between the signal intensity and the concentration of a contrast mediummagnetic resonance imaging model; calculating a residual function according to the dynamic comparison enhancement drug dynamics data analysis model and the acquired quantitative parameter according to the acquired residual function. In the method and the system for calculating the quantitative parameter of magnetic resonance imaging, the quantitative parameter can be also improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
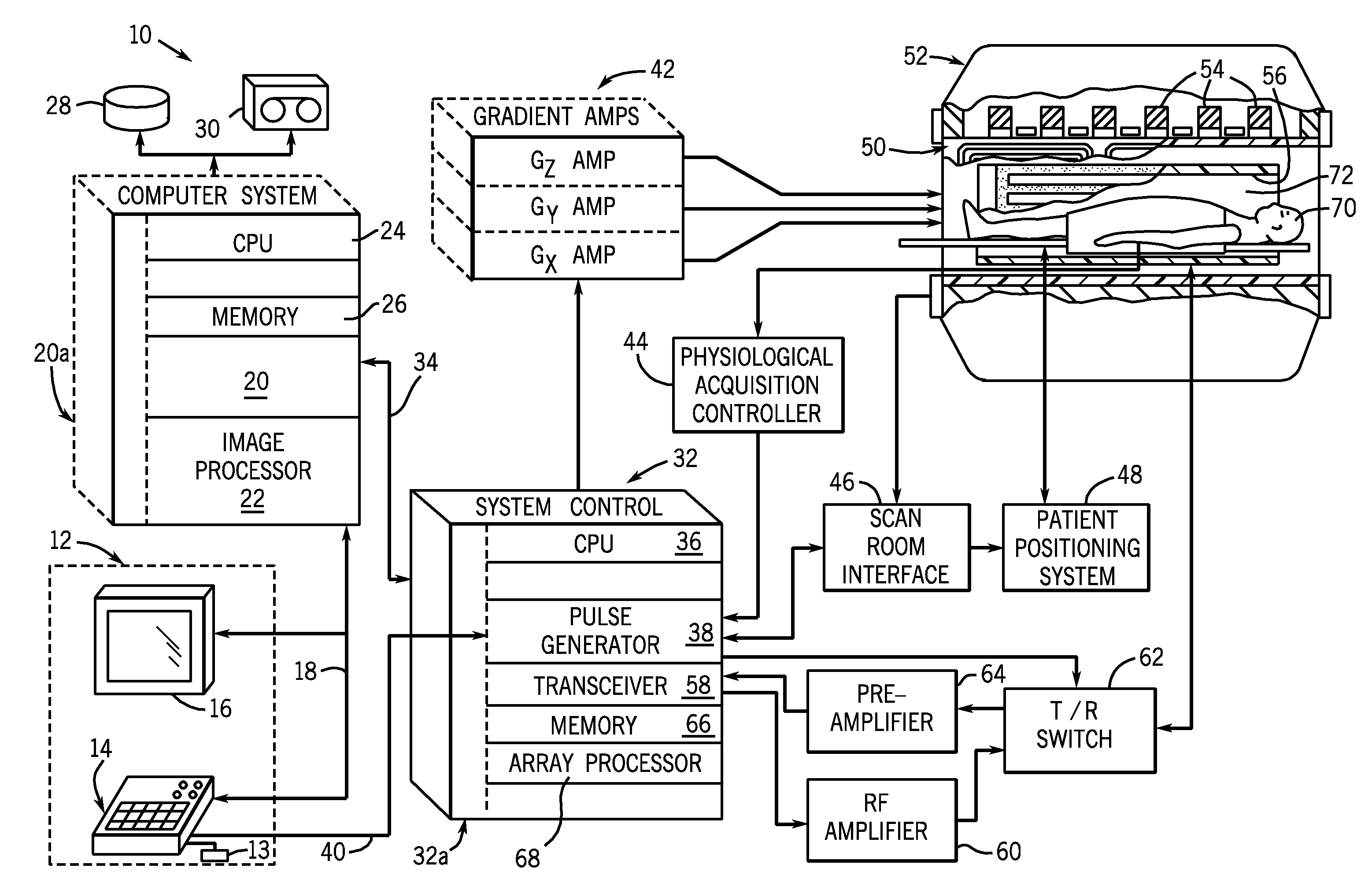
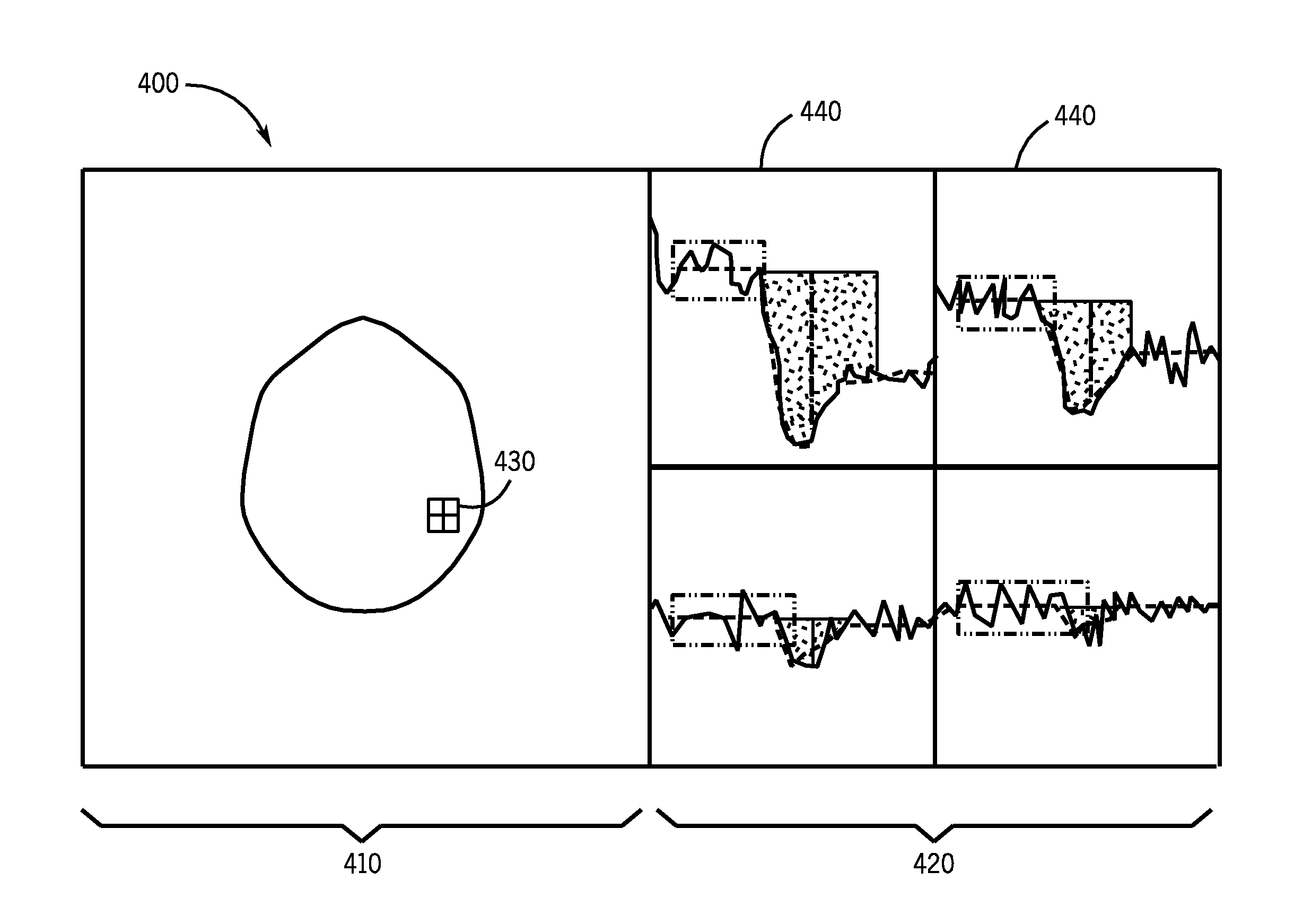
Method, apparatus and user interface for determining an arterial input function used for calculating hemodynamic parameters
A graphical user interface and method allows a user to interactively select an arterial input function. An anatomical image and time-course data corresponding to a selected region of interest are displayed simultaneously. The time-course data is displayed as an array of graphs, annotated with best-fit curves and parameters derived from fitting the time-course data. The region displayed in the graphs may be updated by panning and zooming with a mouse in the image. Time-course data corresponding to a graph is selected for use in deriving an arterial input function. The arterial input function is used to calculate maps of hemodynamic parameters.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
CT scan perfusion method and device
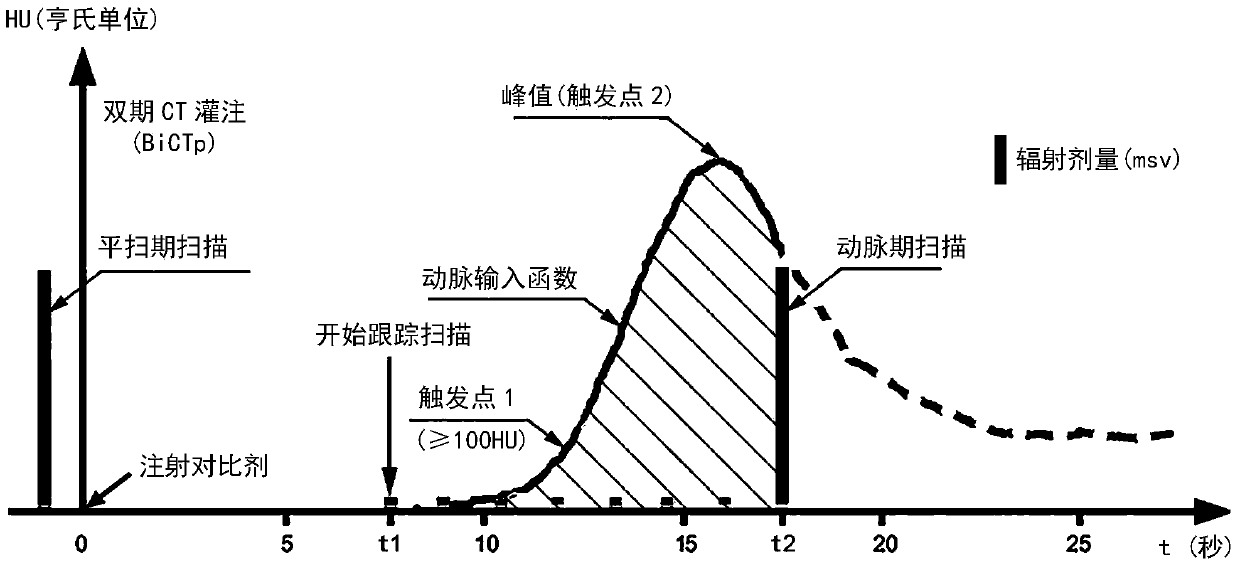
ActiveCN104688259AReduce radiation doseImprove complianceComputerised tomographsTomographyComputed tomographyArterial input function
The invention provides a CT scan perfusion method and device. The method includes the following steps: after a prescribed time t1 has passed since injection of a contrast agent, carrying out a single-slice CT tracking scan of the contrast agent concentration in the artery with a first radiation dosage; during scan tracking, trigging a scan program when a trigger point is reached, and carrying out an arterial phase scan of a visceral organ at a time t2 with a second radiation dosage, which is larger than the first radiation dosage, so as to obtain an arterial phase CT value; obtaining a CT value increment according to the arterial phase CT value; setting a time density curve of the contrast agent in the artery as an arterial input function during the contrast agent scan tracking process, and obtaining the blood flow volume of the visceral organ according to the arterial input function and the CT value increment. The CT scan perfusion method avoids repeated scans of the visceral organ in the traditional method, so as to reduce radiation on a human body, achieve simpler and easier operations and accurate results, and lessen the discomfort of an examinee.
Owner:中国人民解放军总医院第八医学中心
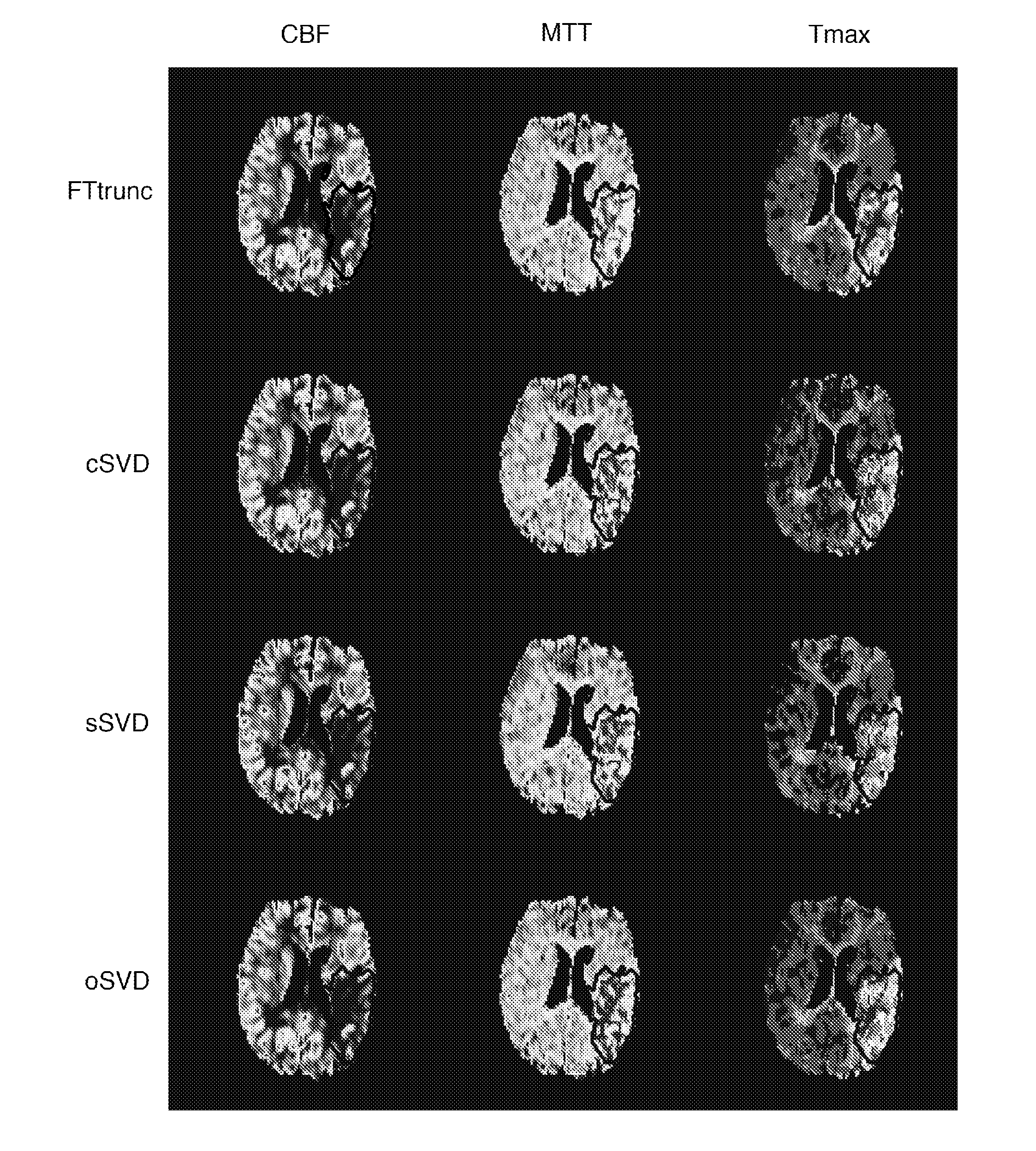
Optimized quantitative method of blood volume in magnetic resonance perfusion imaged image
InactiveCN101718848ASuppress quantization errorImprove signal-to-noise ratioMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsCorrection algorithmArterial input function
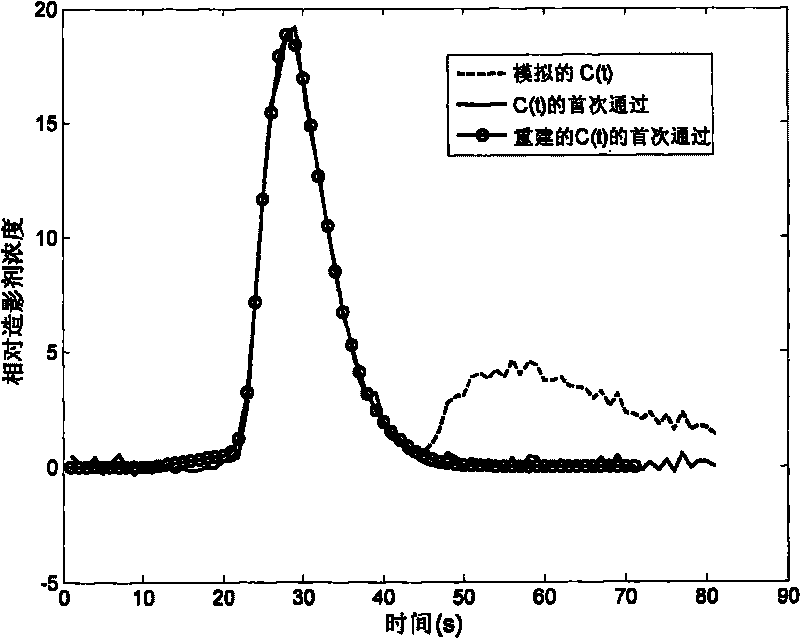
The invention relates to an optimized quantitative method of blood volume in a magnetic resonance perfusion imaged image. The optimized quantitative method is technically characterized by comprising the steps of: selecting an artery input function with a typical double-peak shape from an encephalic main central artery of the magnetic resonance perfusion imaged image; carrying out a convolution operation on a contrast agent concentration time sequence signal and the artery input function to obtain a residual function with similar single-peak shape; using gamma function fitting to select the artery input function to obtain a first pass of the artery input function; carrying out the convolution operation on the first pass of the artery input function which is obtained by fitting and the residual function, thus reestablishing a first pass component in an initial time-contrast agent concentration curve; and quantizing the blood volume by using the reestablished first pass component and inhibiting quantization error. By combining a first pass reestablishing algorithm with a contrast agent percolation effect correction algorithm, the invention furthers to inhibit the blood volume quantization error.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Method, apparatus and user interface for determining an arterial input function used for calculating hemodynamic parameters
A graphical user interface and method allows a user to interactively select an arterial input function. An anatomical image and time-course data corresponding to a selected region of interest are displayed simultaneously. The time-course data is displayed as an array of graphs, annotated with best-fit curves and parameters derived from fitting the time-course data. The region displayed in the graphs may be updated by panning and zooming with a mouse in the image. Time-course data corresponding to a graph is selected for use in deriving an arterial input function. The arterial input function is used to calculate maps of hemodynamic parameters.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
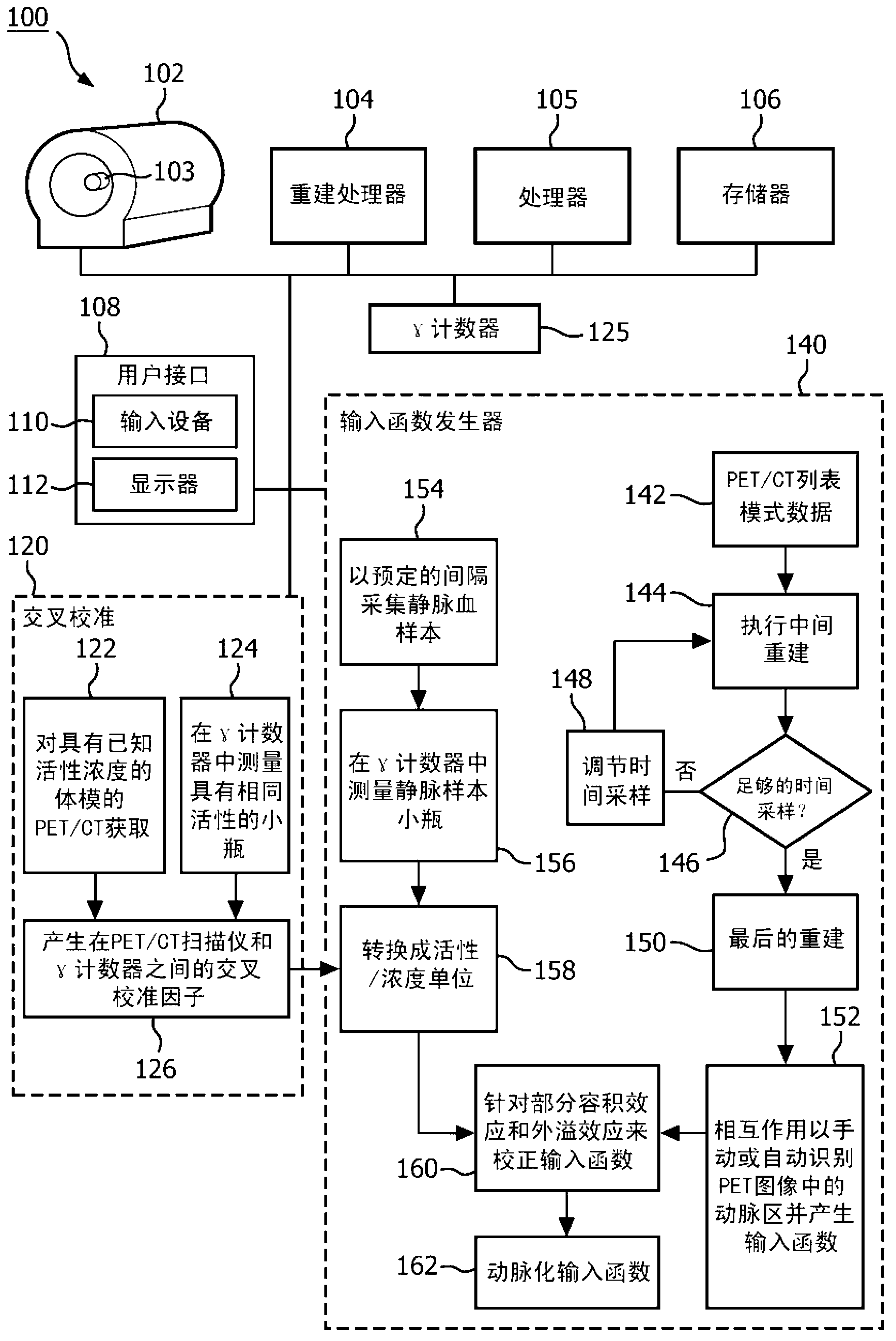
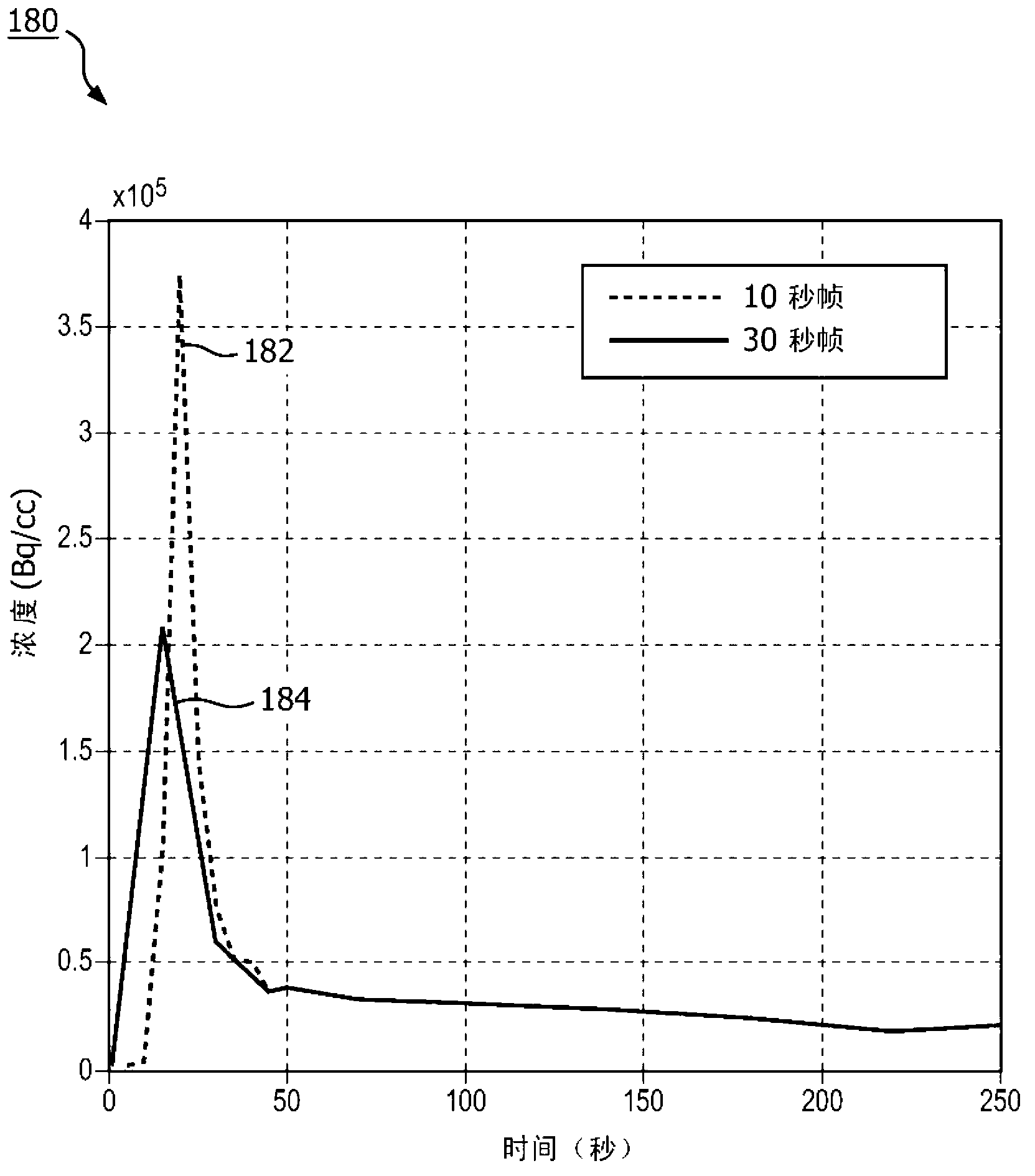
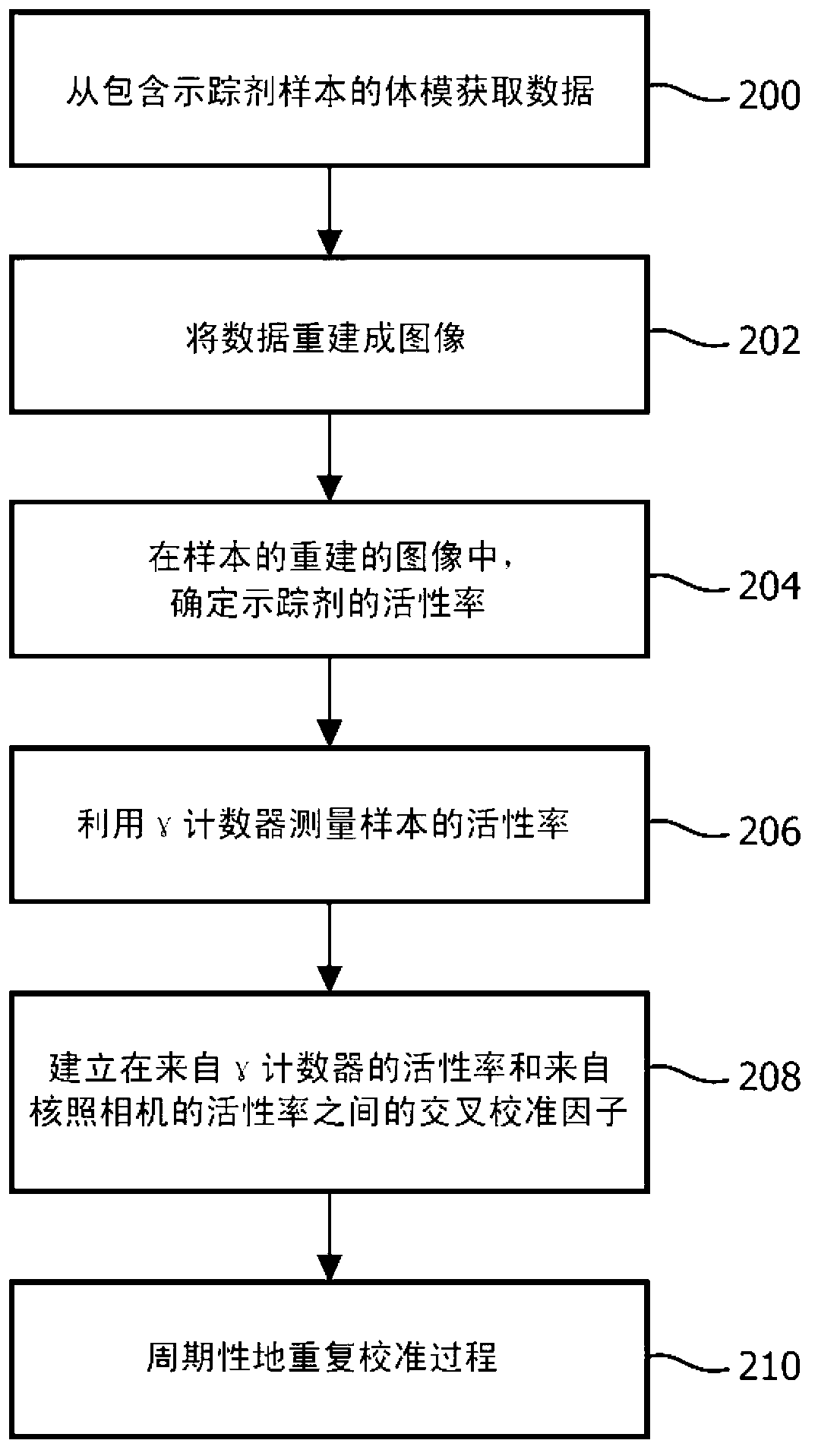
Integrated work-low for accurate input function estimation
When estimating an arterial input function or a patient under study, cross- calibration factors are generated by comparing nuclear scan data of a radioactive material (e.g., F18) and measuring a sample of the radioactive material in a gamma counter. The derived cross-calibration factors are applied to venous samples collected from the patient during a nuclear scan after infusion with a radioactive tracer, to convert gamma values counted by the gamma counter into concentration values. The concentration values are used to optimize an initial estimated input function, thereby generating an arterialized input function.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
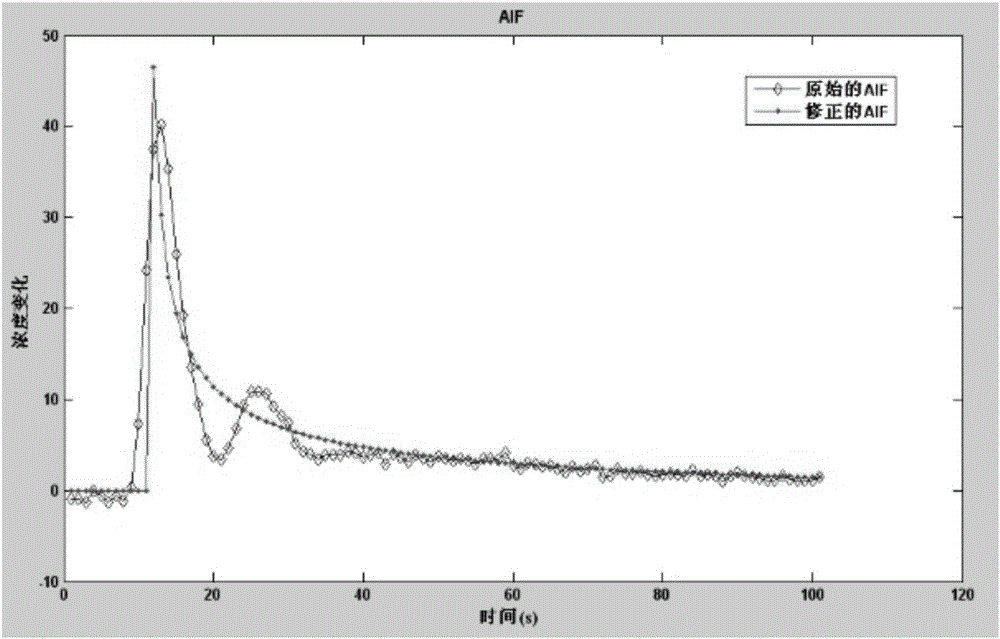
Magnetic resonance perfusion imaging postprocessing method and system thereof
ActiveCN105701815AReduce sensitivityImprove post-processing speedImage enhancementImage analysisRegion selectionArterial input function
The invention provides a magnetic resonance perfusion imaging postprocessing method and a system thereof. The method comprises the following steps of perfusing image filtering to an original brain, removing a brain edge and acquiring a filtered brain perfusion image; receiving an area selection instruction of a user, acquiring a selected area of a middle artery area in the filtered brain perfusion image and outputting a weighted artery input curve assessing an artery input function; according to an improved Gamma function, fitting the weighted artery input curve and a concentration time curve respectively so as to obtain the optimized artery input curve and the concentration time curve; according to an improved singular matrix decomposition method based on a non-parametric model, solving a relative quantification parameter of perfusion. Through carrying out weighted optimization on AIF and a solving matrix, sensitivity to a noise is reduced; a simplified and effective Gamma function is used to carry out fitting, a non-linear problem is converted into linear solution, and a post-treatment speed is accelerated.
Owner:SHENZHEN ANKE HIGH TECH CO LTD
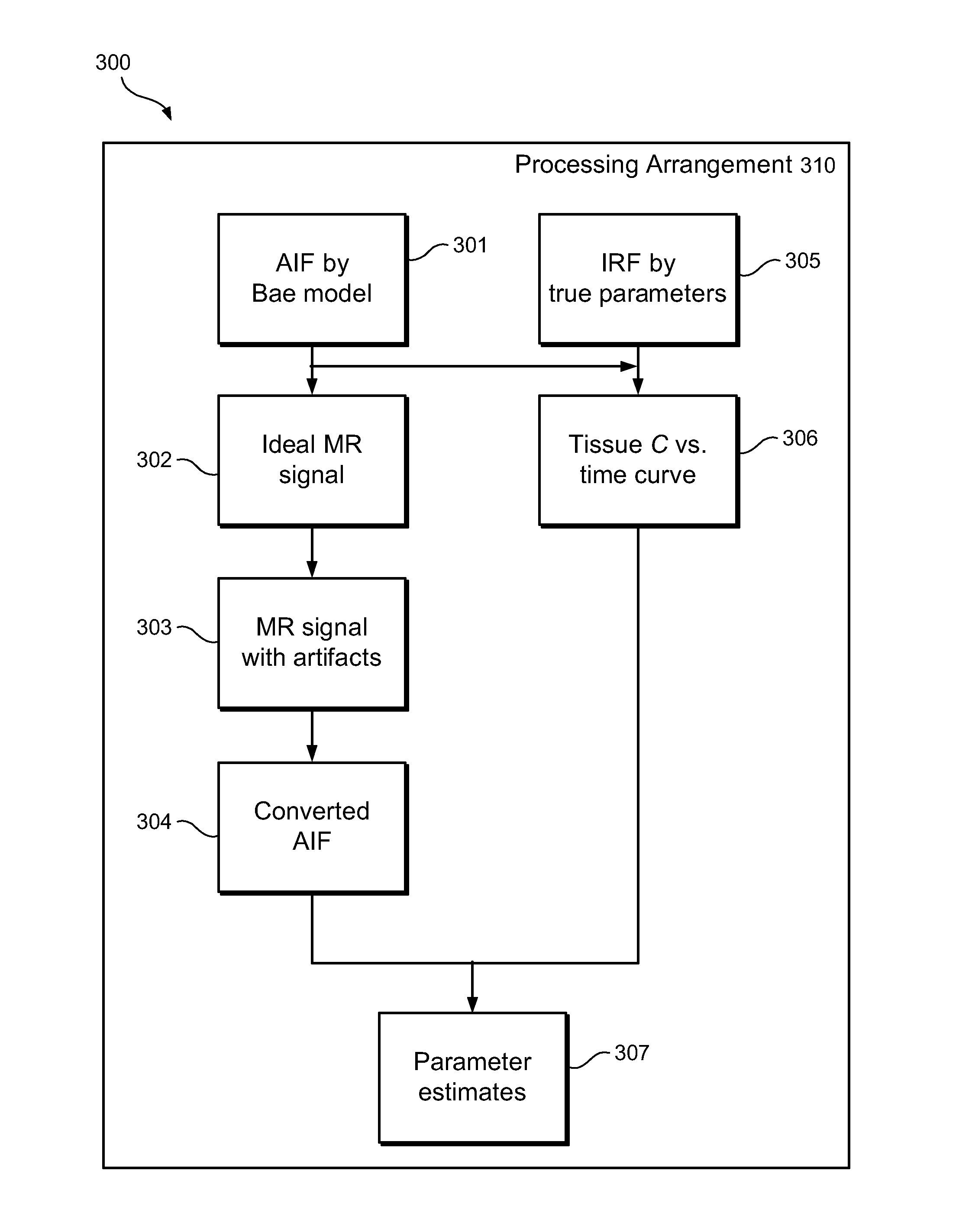
System, method and computer-accessible medium for utilizing cardiac output to improve measurement of tracer input function in dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20120095328A1Image enhancementDiagnostic signal processingIndicator dilutionDynamic contrast
Exemplary embodiments of method, system and computer-accessible medium according to the present disclosure can be provided for converting magnetic resonance (MR) arterial signal intensity versus time curves to arterial input functions (AIF) with less susceptibility to artifacts such as flow-related enhancement. Exemplary methods, systems and computer-accessible medium can be used to constrain AIF to satisfies the indicator dilution principle, according to which the area under an initial pass component of AIF can be equal to the injected dose divided by the cardiac output. For example, Monte Carlo simulations of MR renography and tumor perfusion protocols can be performed for comparison with conventional methods.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV +1
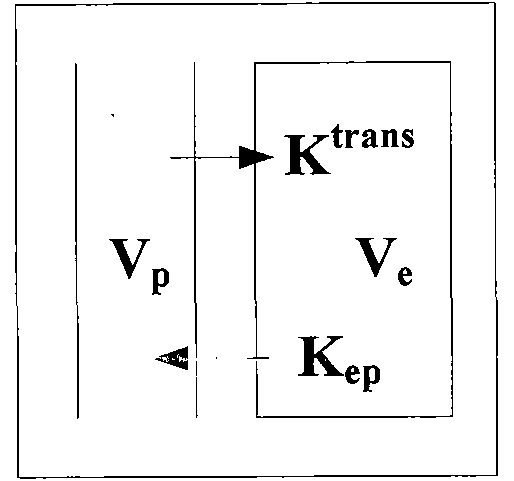
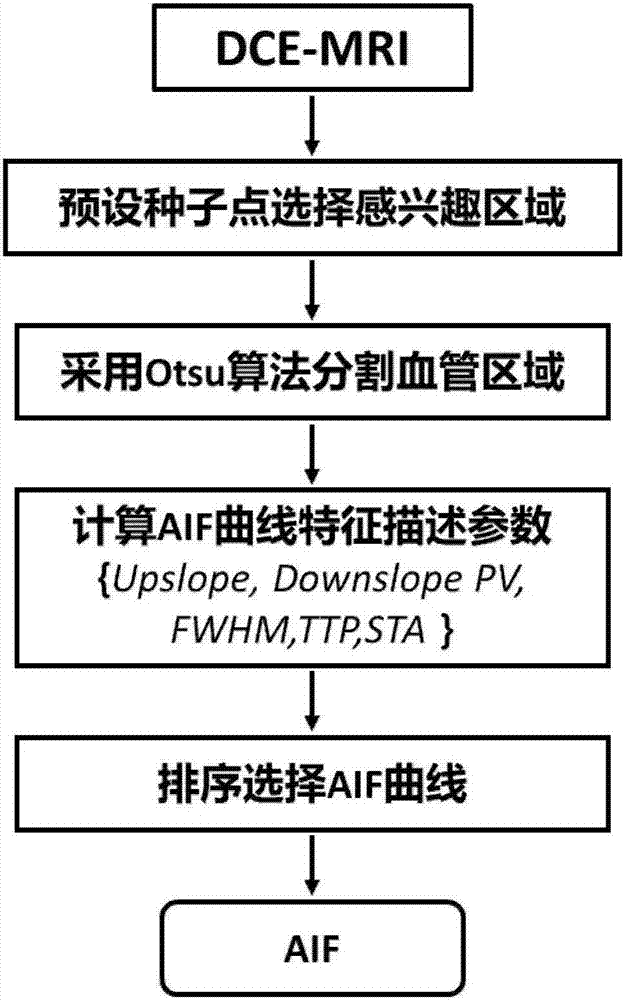
Pharmacokinetic parameter estimation method based on contrast agent enhancement curve
InactiveCN107315896AEfficiently evaluate volume fractionsReduce the impactSpecial data processing applicationsPattern recognitionEstimation methods
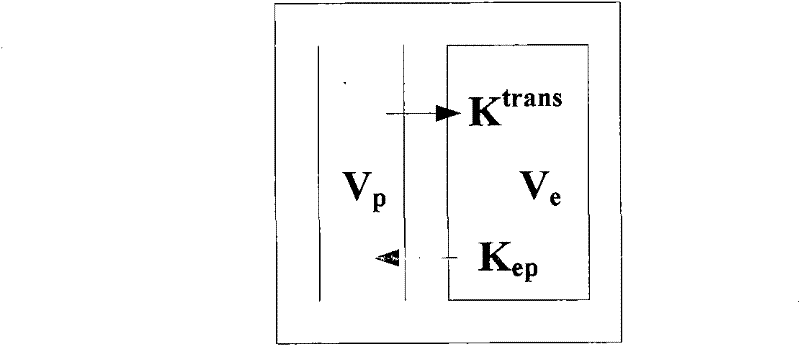
The present invention relates to a pharmacokinetic parameter estimation method based on the contrast agent enhancement curve, relates to the field of physiological parameter estimation, and discloses a regularized multi-blind-channel parameter estimation method. The method comprises the following steps: 1) using an arterial input function curve feature to automatically select the arterial input function curve; 2) using a contrast agent enhancement curve feature to cluster the global contrast agent enhancement curve to obtain three types of typical contrast agent enhancement curves; and 3) designing the regularized multi-blind-channel parameter estimation method according to the three typical contrast agent enhancement curves obtained in step 2), and estimating a pharmacokinetic parameter inverse flow coefficient; and 4) using the two-compartment model to estimate other pharmacokinetic parameters of vascular permeability, space volume fraction, and vascular volume fraction.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
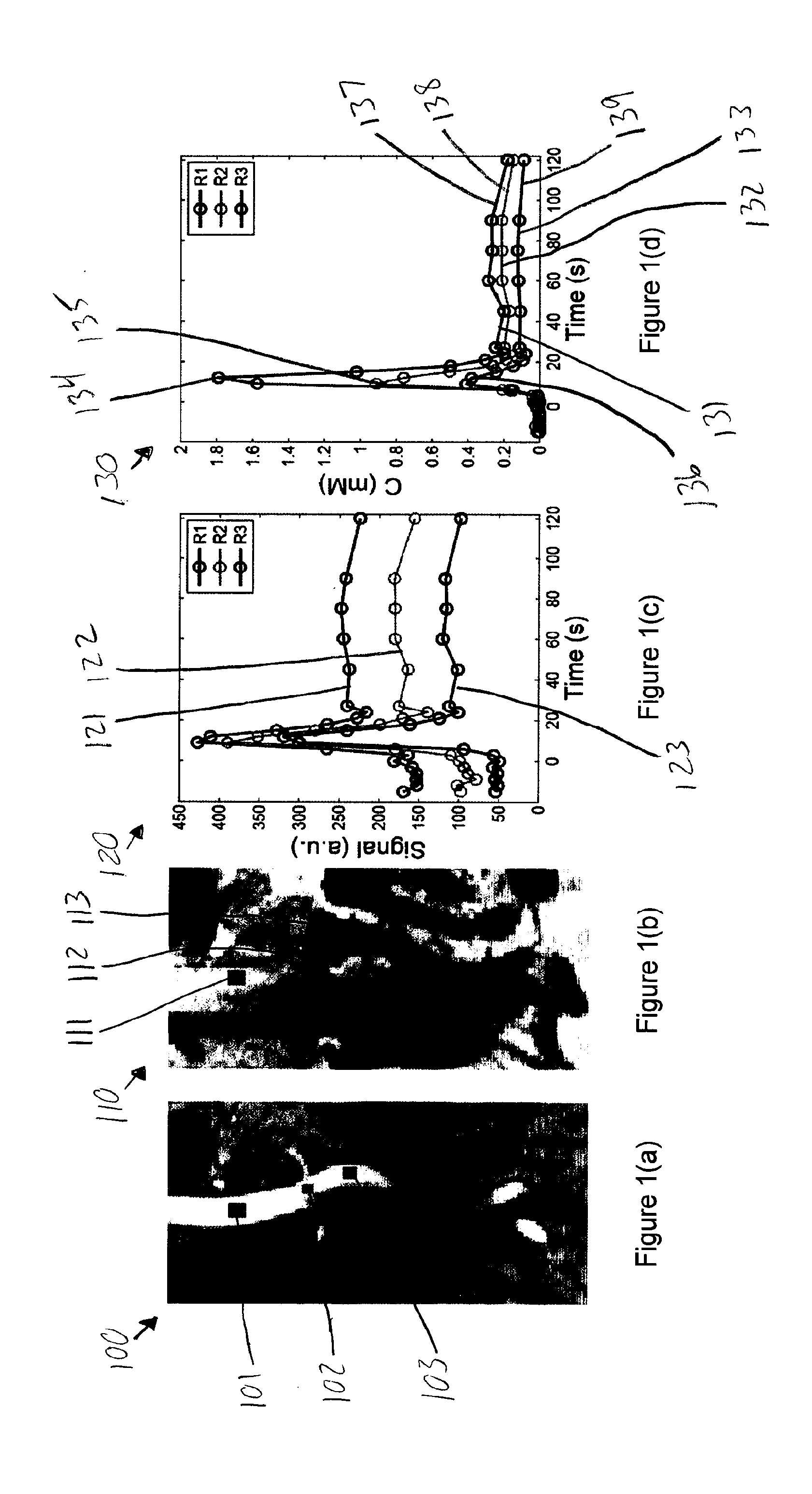
Method for extracting arterial input function and application thereof to dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging
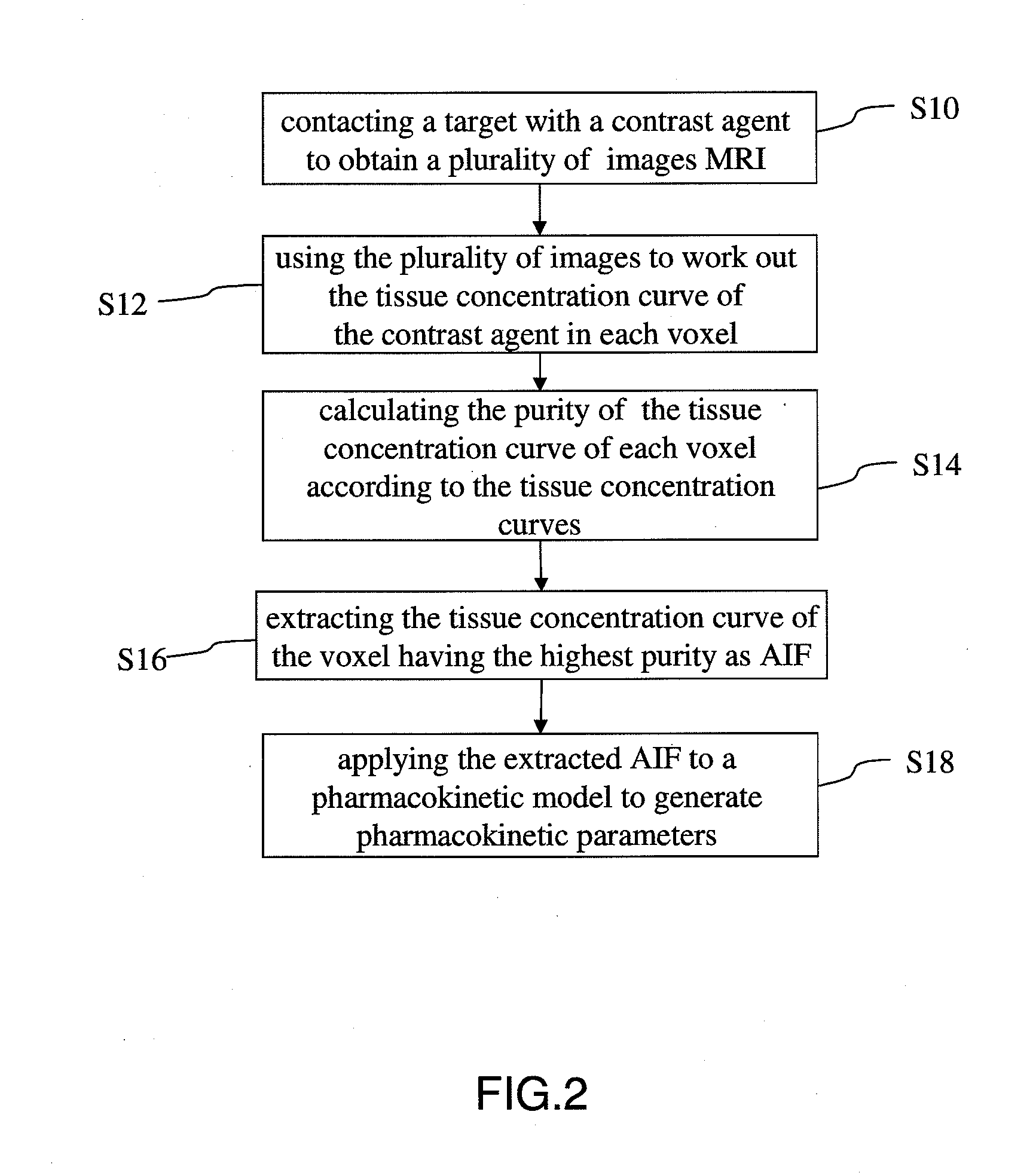
ActiveUS20140241604A1Improve efficiencyImprove reliabilityImage enhancementImage analysisTissue concentrationsVoxel
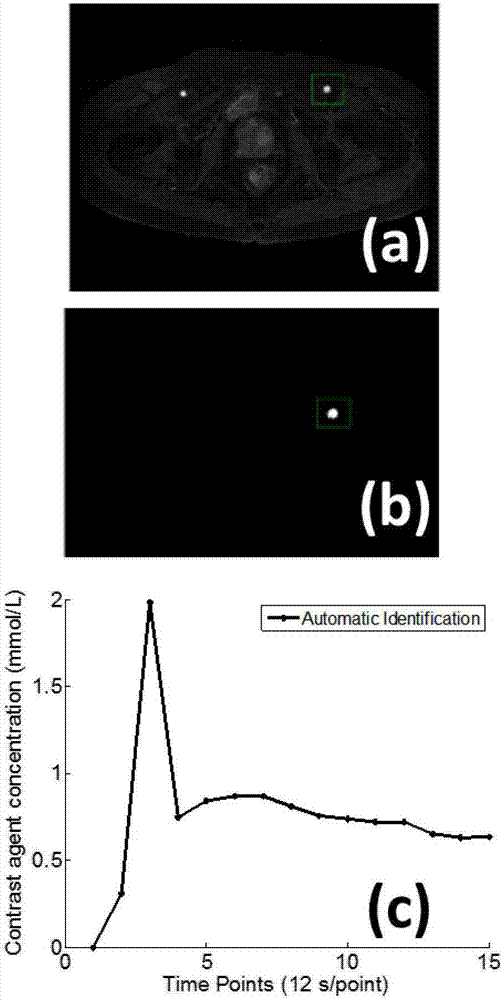
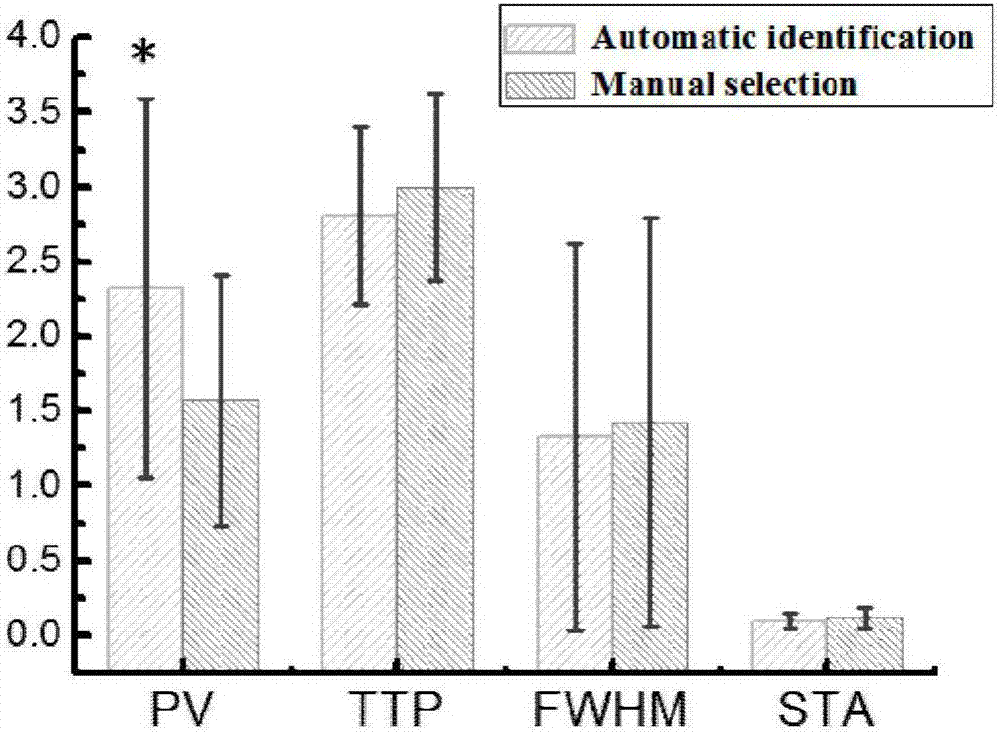
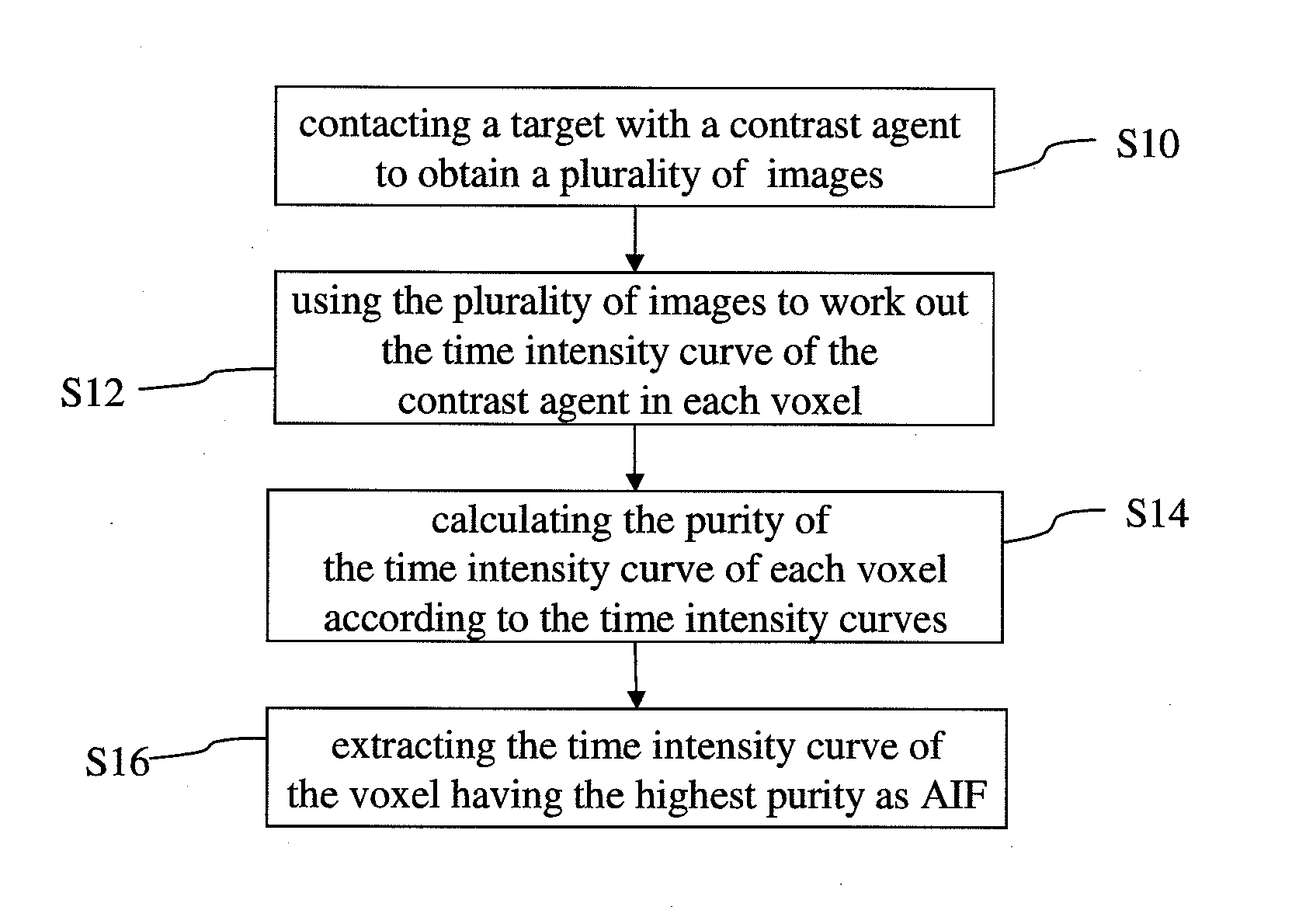
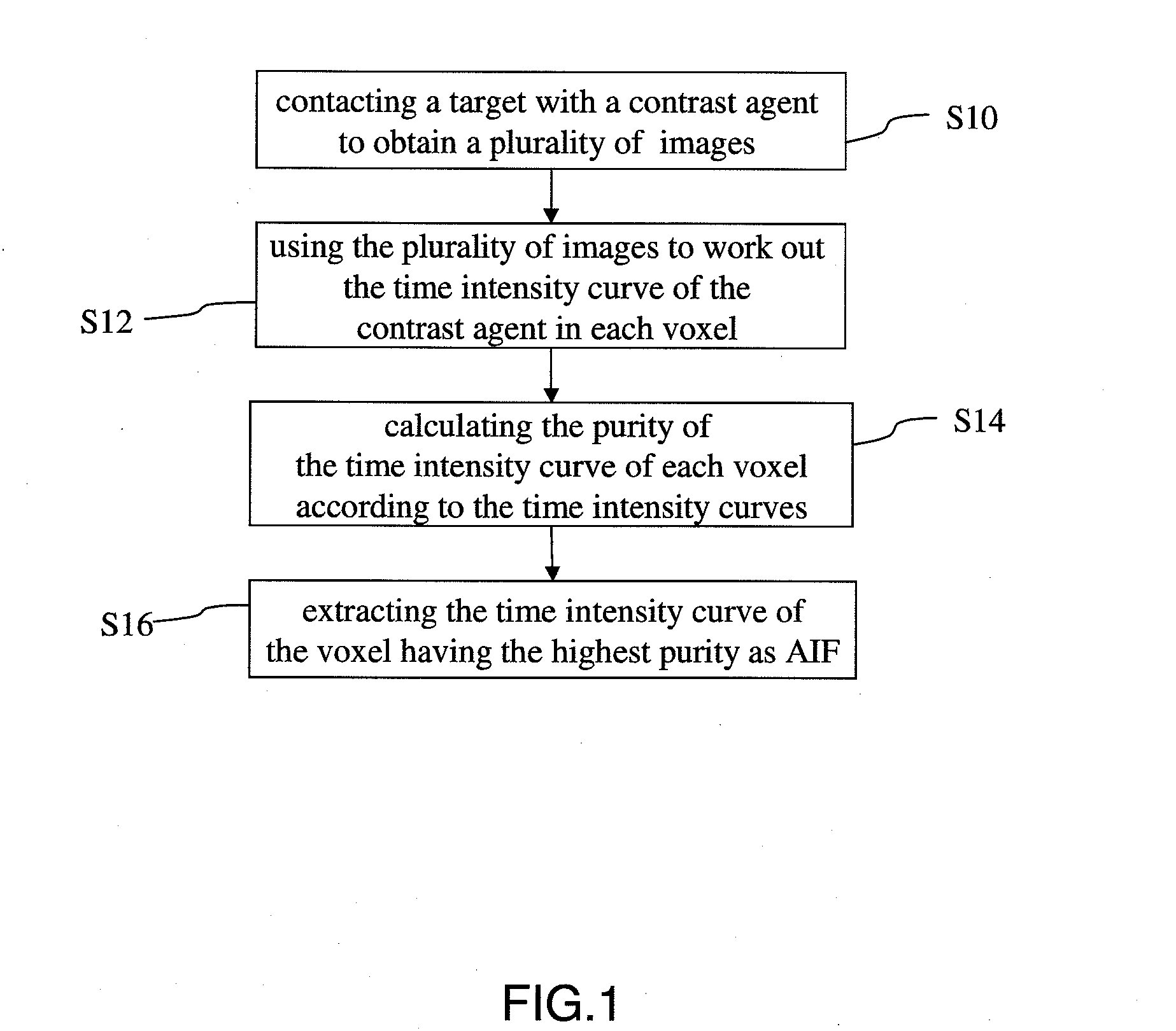
The present invention discloses a method for extracting AIF and an application thereof to DCE-MRI. The method comprises steps: contacting a target tissue with a contrast agent to obtain a plurality of images; using the plurality of images to work out the tissue concentration curve of the contrast agent in each voxel; calculating the purity of the tissue concentration curve of each voxel according to the tissue concentration curves; and extracting the voxel having the highest purity as the optimized arterial location; and extracting the tissue concentration curve of the voxel having the highest purity as the arterial input function. The extracted AIF is applied to a pharmacokinetic model to obtain associated pharmacokinetic parameters. The present invention not only improves the accuracy and reliability of the derived quantitative indexes but also promotes the efficiency of the quantitative analysis.
Owner:CHANG GUNG UNIVERSITY
Calculation of perfusion parameters in medical imaging
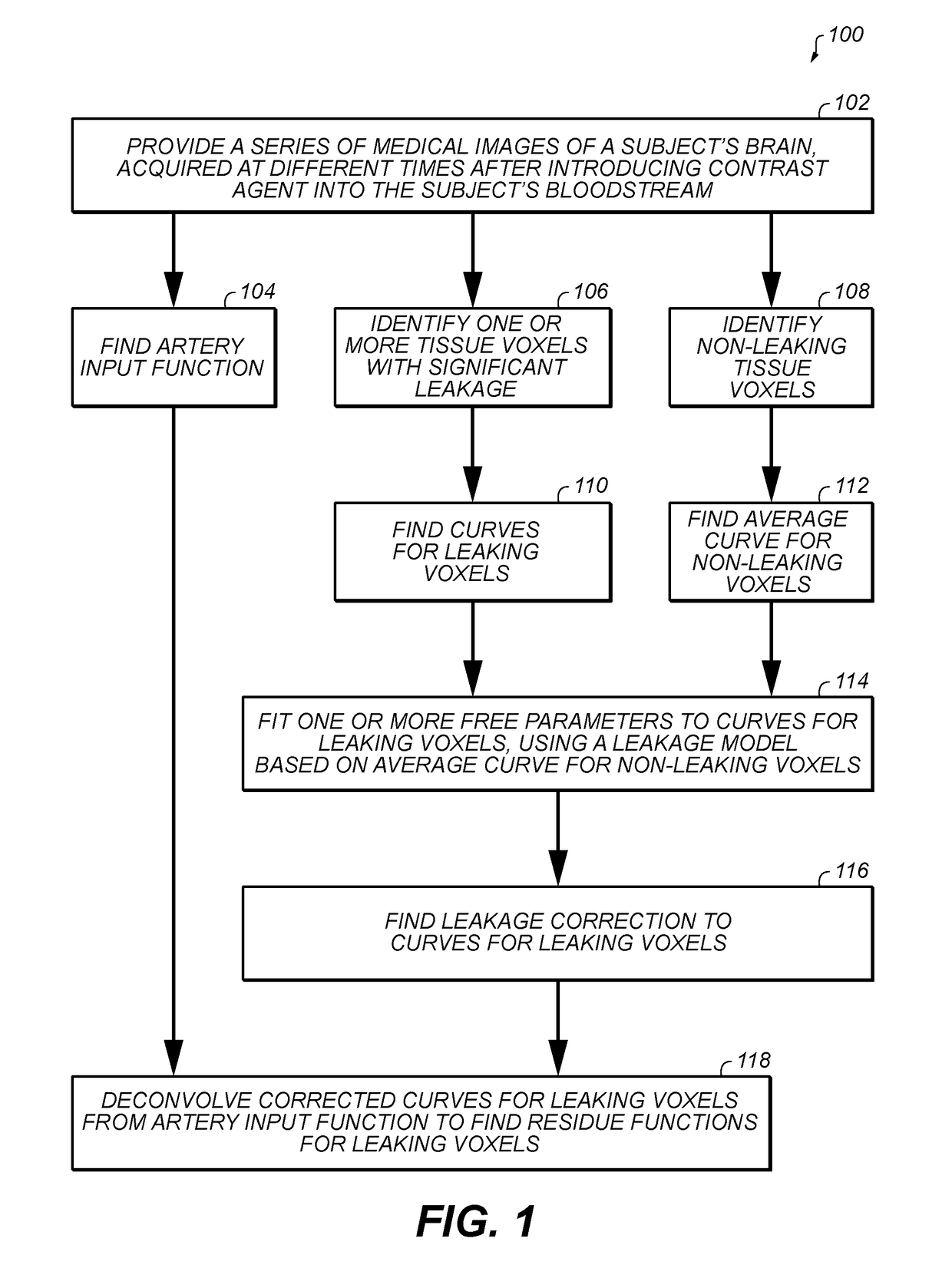
A method of determining a residue function in brain tissue, from medical images acquired after introducing contrast agent into the blood, correcting for contrast agent leakage into the tissue, comprising: a) providing time signals indicating contrast agent concentration for leaking voxels, a time signal indicating average contrast agent concentration for non-leaking voxels, and an artery input function, all derived from the images; b) fitting the leaking voxel signals to a model time signal with a free parameter for leakage rate, the model assuming that the concentration of contrast agent perfusing through a leaking voxel has a same shape as a function of time as the average contrast agent concentration for non-leaking voxels; c) using the best fit leakage rate parameter to make a correction for leakage to the leaking voxel signals; and d) deconvolving the corrected signals from the artery input function, to find the residue function.
Owner:PHILIPS MEDICAL SYST TECH
Expanded Pharmacokinetic Model for Population Studies in Breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
A method for pharmacokinetic analysis, including: receiving time-series medical image data of a patient introduced with a contrast agent; identifying a reference region in the medical image data; identifying a plurality of points of interest in the medical image data; measuring an intensity of voxels in the reference region; and for each point of interest, measure an intensity of voxels therein, use the measured reference region and point of interest intensities to obtain an expression relating the point of interest's voxel concentration to that of the reference region, wherein the expression is a five-parameter nonlinear model with no reference to an arterial input function; and obtain values for each of the five-parameters by solving the expression and use the obtained values to determine whether the point of interest is malignant.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
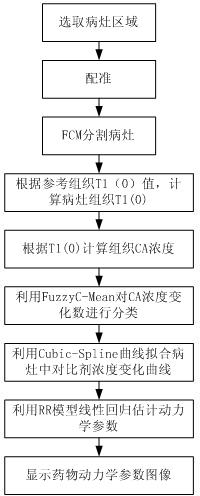
Quantitative analysis method based on lung MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) dynamic enhancement scanning
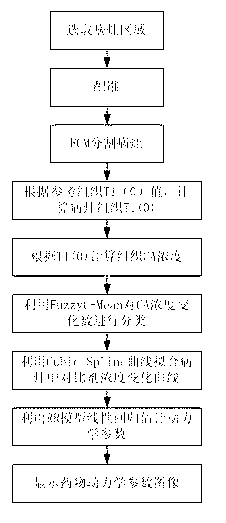
InactiveCN102708291AAvoid measuringReduce work intensitySpecial data processing applicationsVoxelArterial input function
The invention relates to a quantitative analysis method based on lung MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) dynamic enhancement scanning. A reference region model, a FuzzyC-Mean algorithm and a fixed T1 algorithm are combined, and T1(0) of a tissue of interest is calculated through the T1 value of a given reference tissue, so that the shortcoming that scanning needs to be performed twice when a traditional double-flip angle Ti(0) calculation method is adopted can be overcome; a tissue model is taken as reference for avoiding the measurement of signals in an arterial region for getting an arterial input function, so that the working strength of researchers can be reduced; and automatic and precise segmentation is performed according to signal changes and the differences with a normal tissue in a tumor region during the period of injecting a contrast agent in the segmentation of a tumor in the lung, a traditional algorithm of calculating voxel by voxel in parameter estimation is changed, the voxels are classified according to the characteristics of concentration changes of the voxels, the calculation is performed gradually, and the calculation efficiency is greatly improved; and furthermore, the method has a better effect of suppressing the impacts of magnetic resonance signal noise on calculation result.
Owner:伍建林
Method and apparatus for providing pulses inhalation of 17O2 for magnetic resonance imaging of cerebral metabolism
ActiveUS8554305B2Easy to explainEliminate needRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesArterial input functionMedicine
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Method for obtaining a blood flow parameter
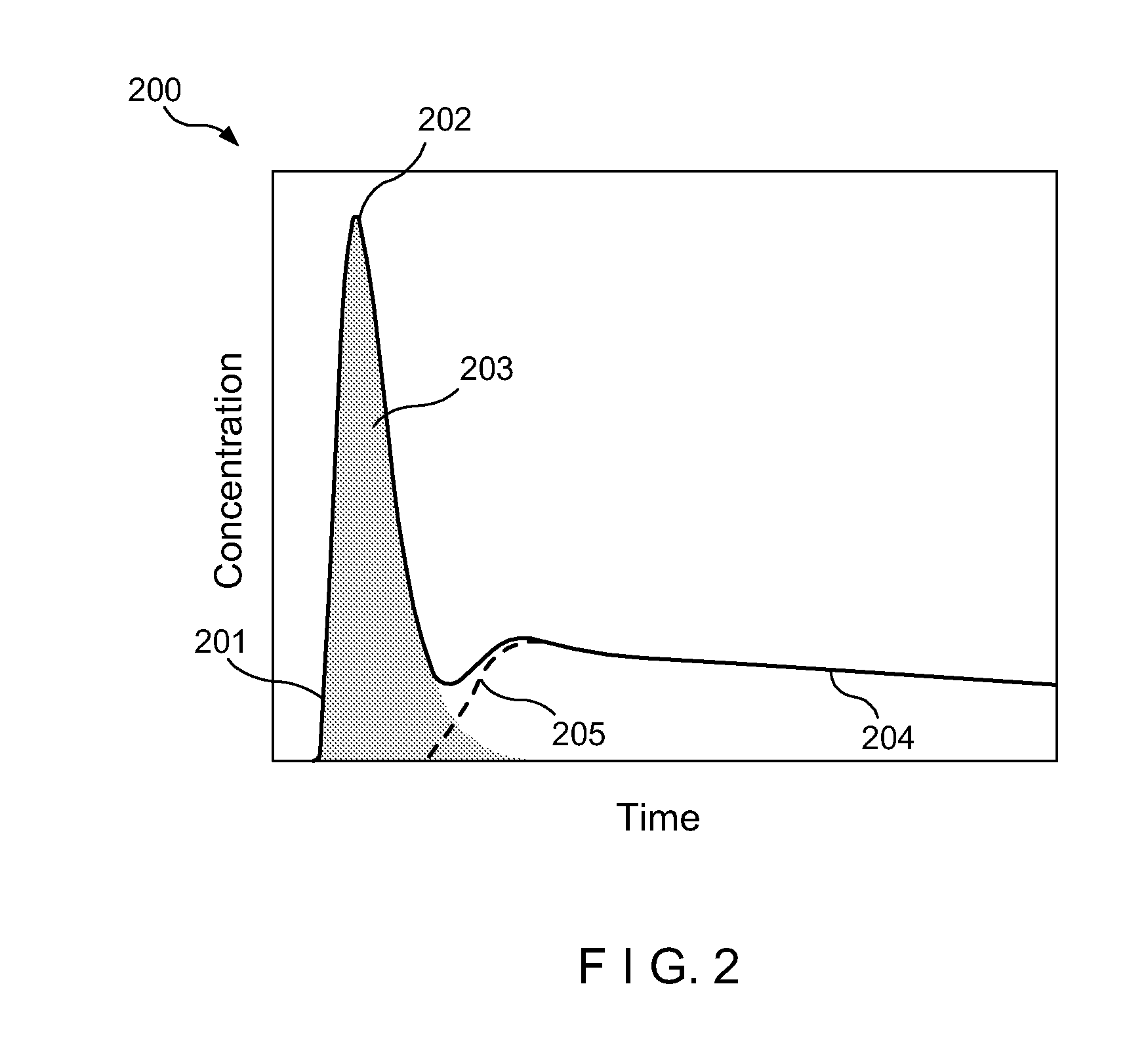
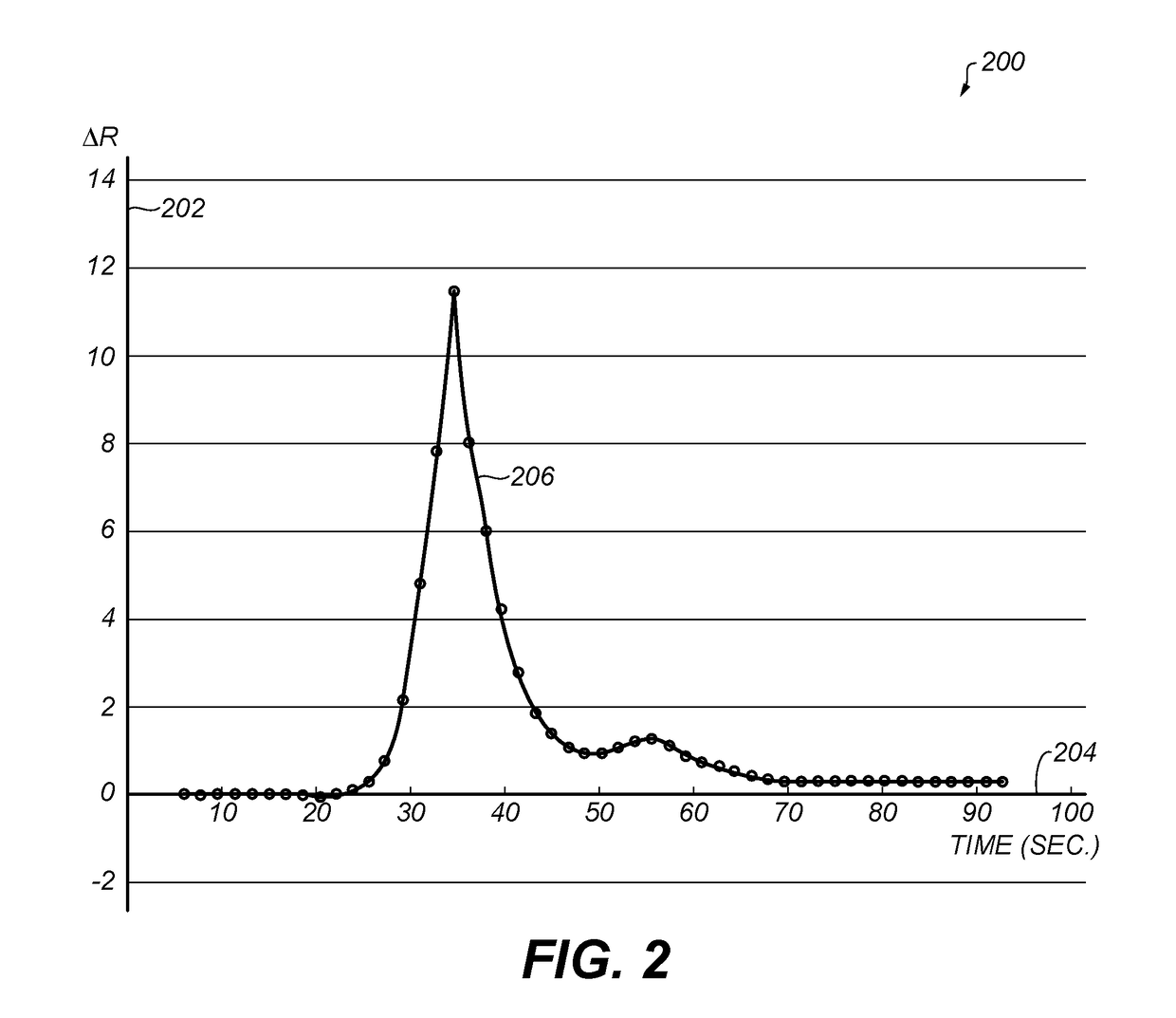
InactiveUS20130039553A1Unnecessary biasOptimized for comparisonMagnetic measurementsBlood flow measurement devicesMedicineConcentration curve
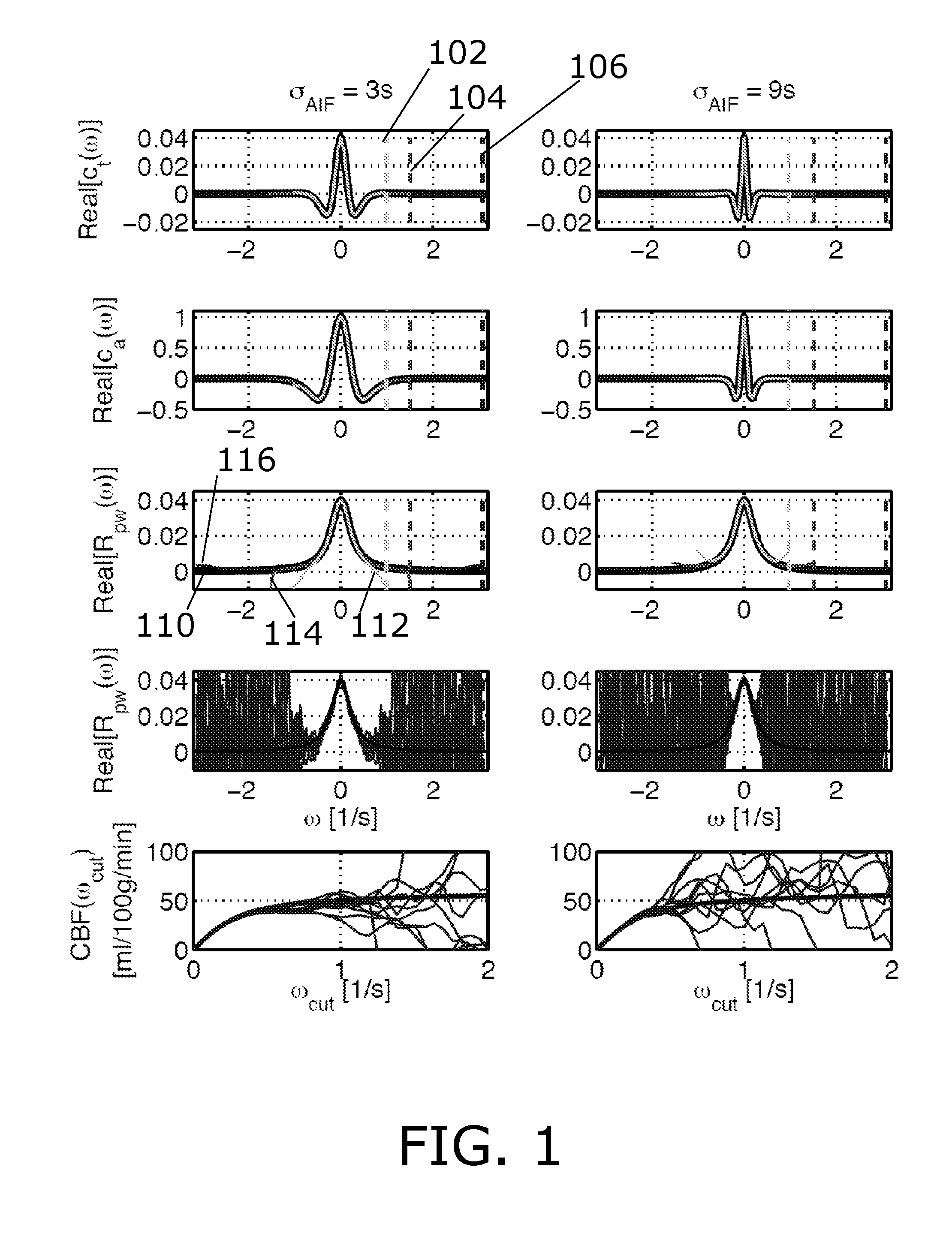
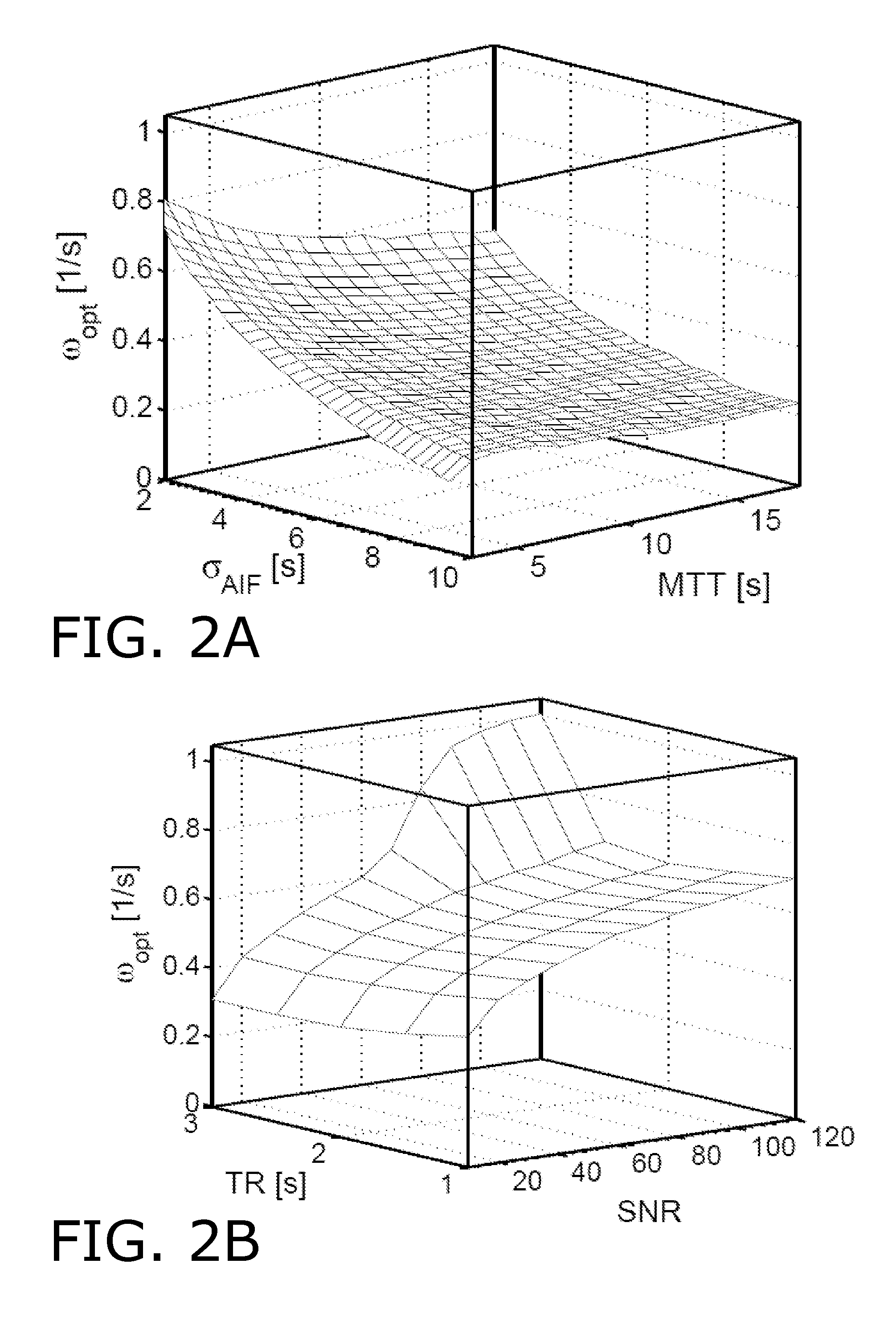
The present invention relates to a method for obtaining a blood flow parameter. More particularly a method is presented wherein a first concentration curve is deconvolved with a second concentration curve and wherein a characteristic frequency is determined by an analysis in the frequency domain, the characteristic frequency being a frequency above which noise dominates the result of said deconvolution. A filter having the characteristic frequency is applied on the result of the deconvolution so as to disregard high frequency components, and the filtered result of the deconvolution is processed into a blood flow parameter. In an advantageous embodiment, the characteristic frequency may be dependent on a shape and / or width of an arterial input function and / or other parameters. The invention furthermore relates to a computer program product and a system for obtaining a blood flow parameter.
Owner:AARHUS UNIV
Method for analyzing blood flow by using medical image
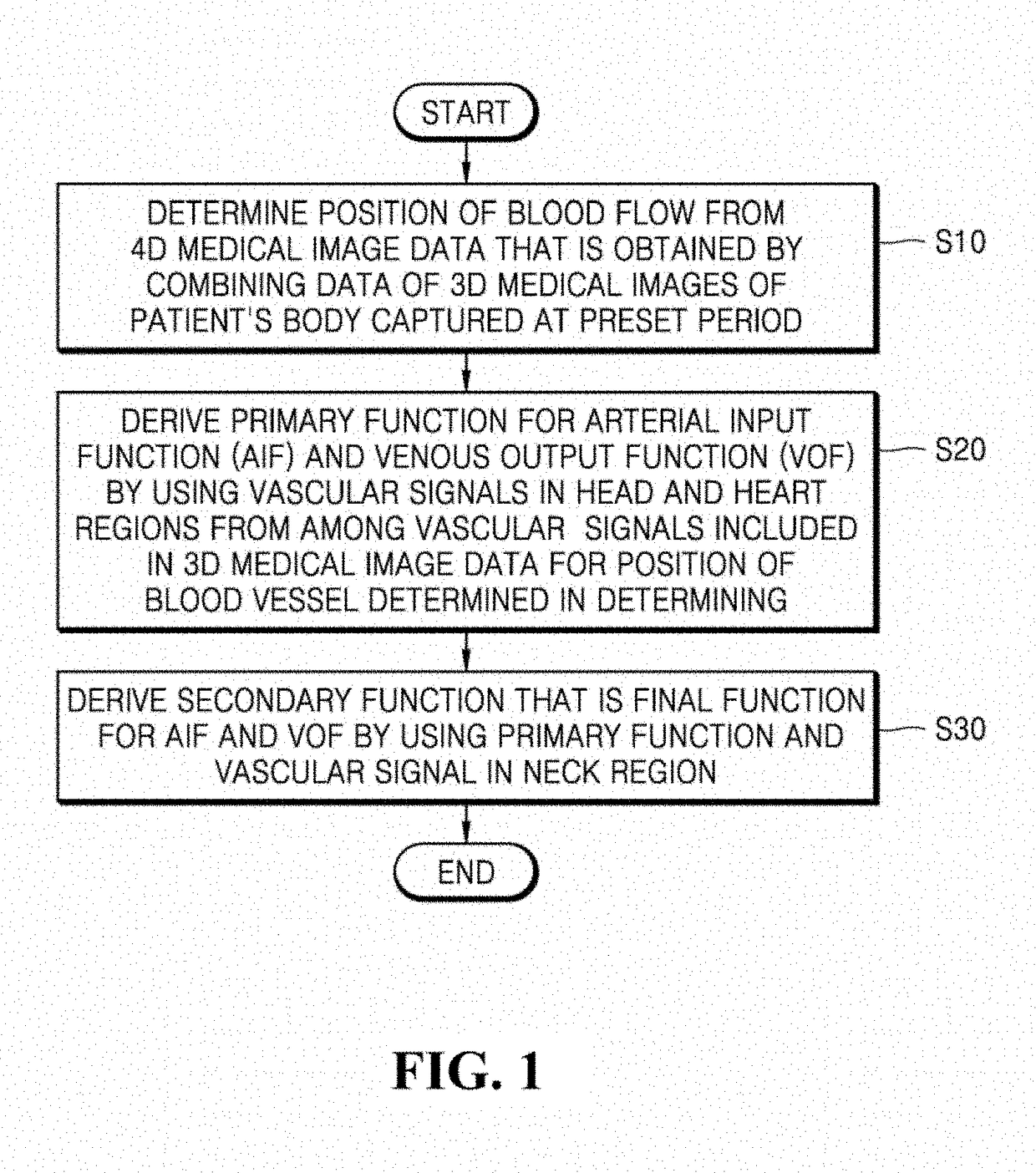
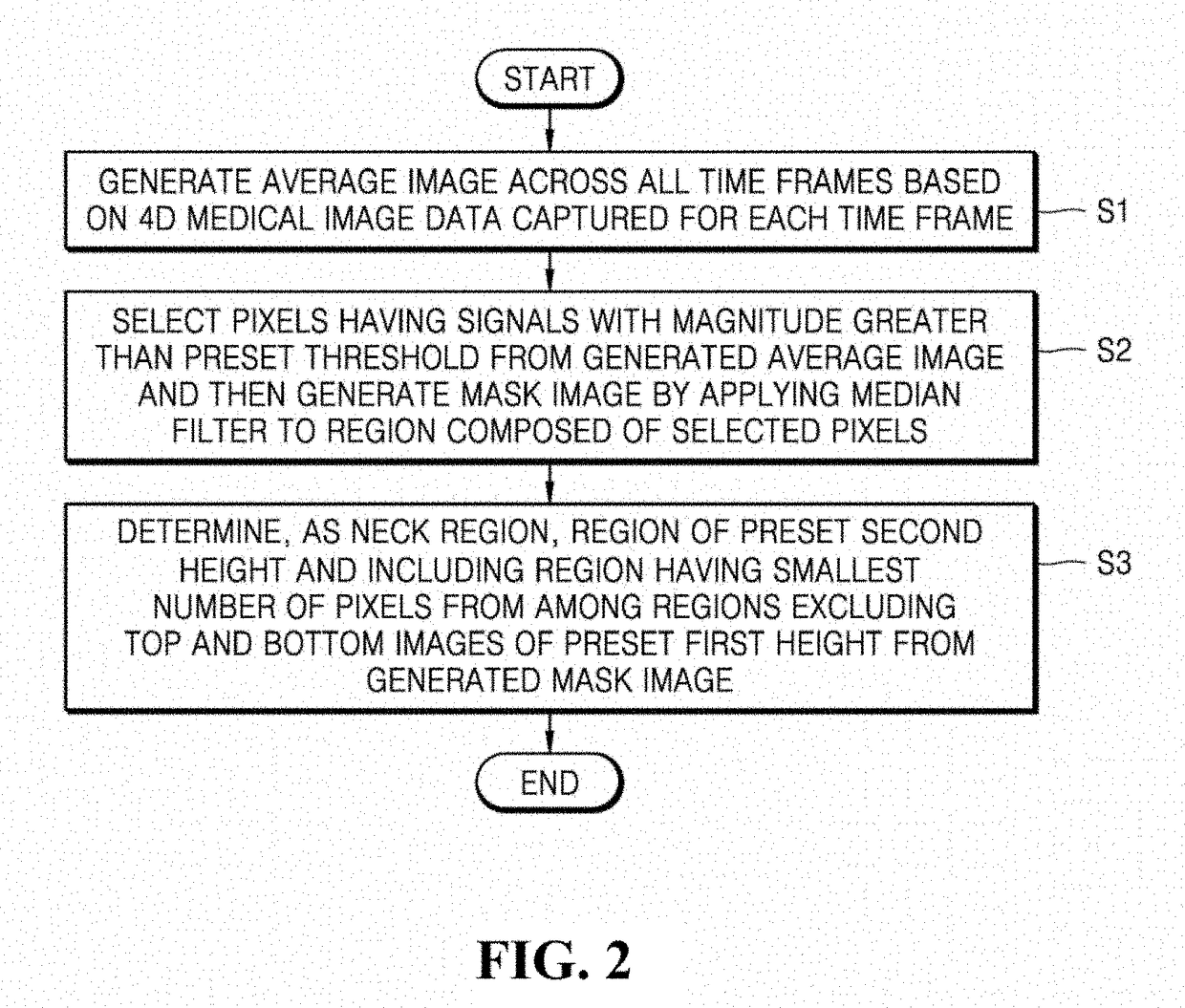
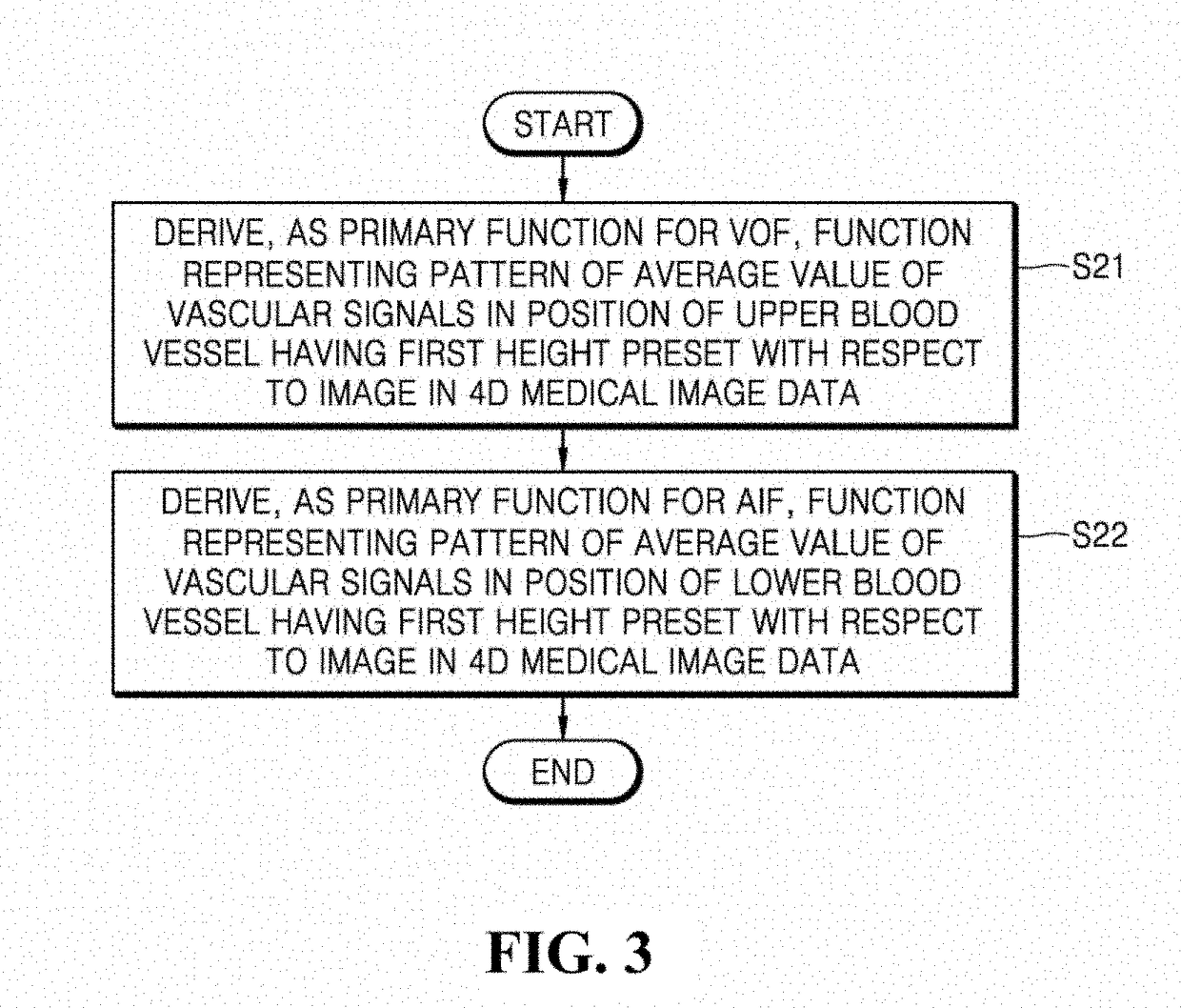
ActiveUS20190038150A1Accurate detectionHighly accurate arterial input function functionImage enhancementImage analysisVenous blood flowArterial input function
Provided is a technique for deriving a mathematical function for defining arterial and venous blood flow in the body by using a four-dimensional medical image. A method of analyzing blood flow by using a medical image according to an embodiment of the present disclosure includes: determining a position of a blood vessel from four-dimensional medical image data that is obtained by combining data of three-dimensional medical images of a patient's body captured at a preset period; deriving a primary function for an arterial input function and a venous output function by using a vascular signal in a head region and a vascular signal in a heart region from among vascular signals included in three-dimensional medical image data for the position of the blood vessel determined in the determining; and deriving a secondary function that is a final function for the arterial input function and the venous output function by using the primary function and a vascular signal in a neck region.
Owner:THE CATHOLIC UNIV OF KOREA IND ACADEMIC COOPERATION FOUND
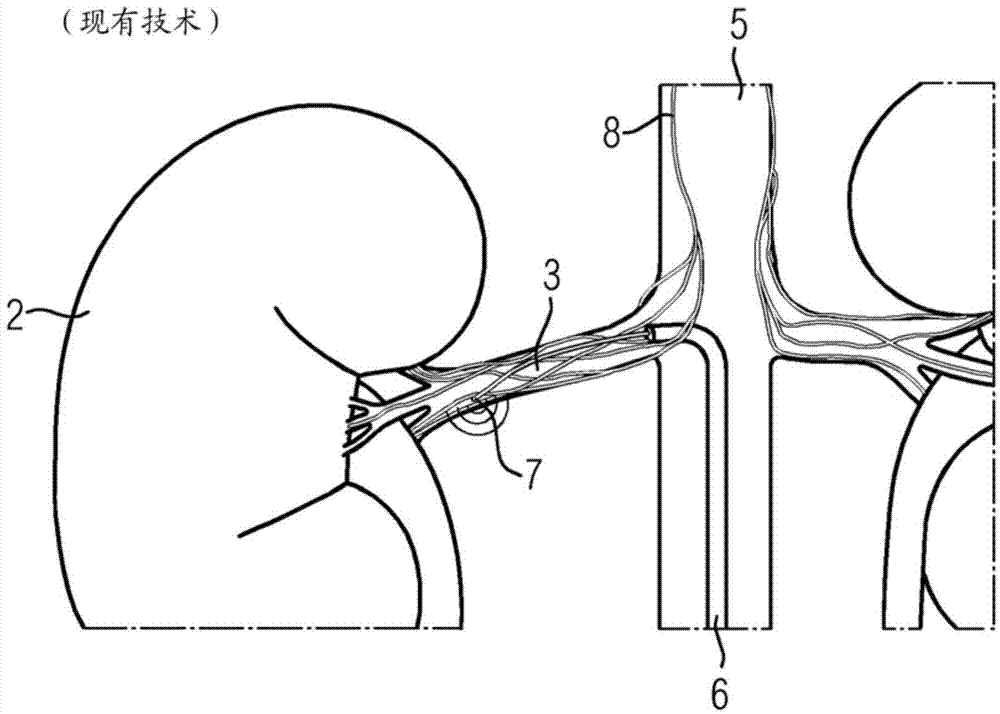
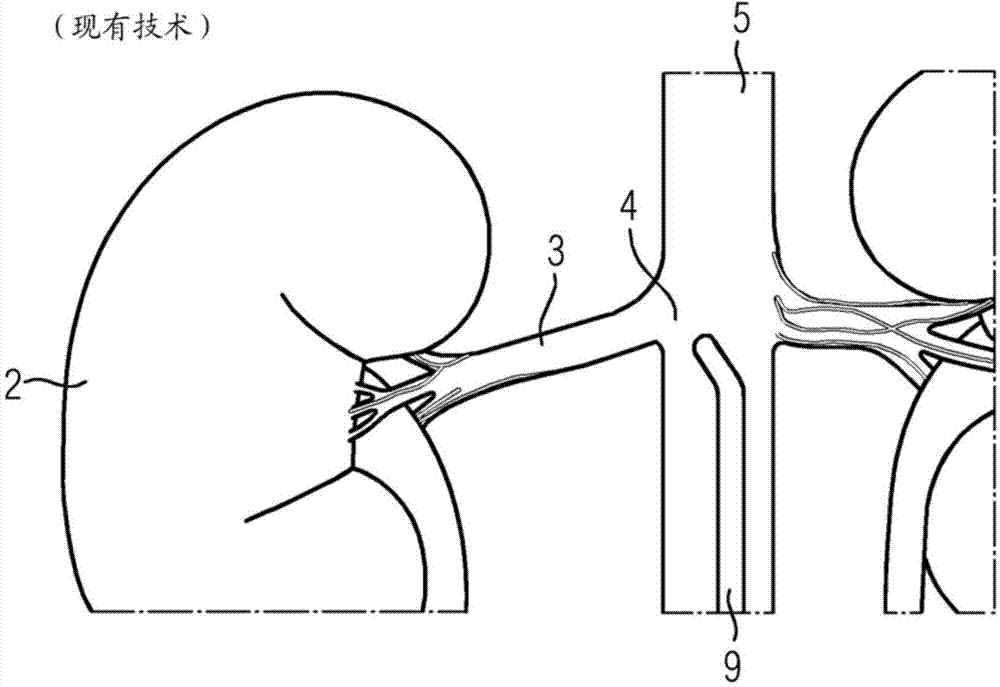
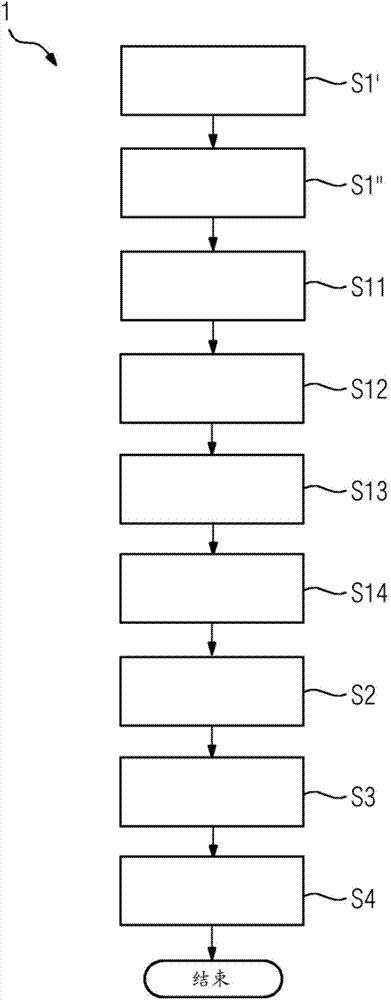
Method and device for determining a damage characteristic value of a kidney
The invention relates to elements of a method (1) for determining a damage characteristic value of a kidney (2). Images comprising the kidney (2) and the kidney artery (3) are entered into the method (1), from a three-dimensional digital subtraction angiography which is carried out by administering a contrast medium at the proximal end of the kidney artery (3) and comprises a fill run and a mask run, said method (1) comprising the following method steps: S1) determining a parenchymal blood volume into which the subtractions from images of the fill run and the mask run of the three-dimensional digital subtraction angiography are entered, additionally determining an arterial input function and normalising the parenchymal blood volume with said arterial input function; S2) segmenting the kidney (2), determining an average normalised parenchymal blood volume value, and determining a total value of the parenchymal blood volume into which the normalised parenchymal blood volume values of the segmentation of the kidney (2) are entered; S3) receiving an average normalised parenchymal blood volume normal value and a total normal value for a parenchymal blood volume, and determining at least one damage characteristic value of the kidney (2) into which the average normalised parenchymal blood volume value and the average normalised parenchymal blood volume normal value and / or the total value of the parenchymal blood volume and the total normal value of a parenchymal blood volume are entered; S4) issuing the at least one damage characteristic value of the kidney (2).
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
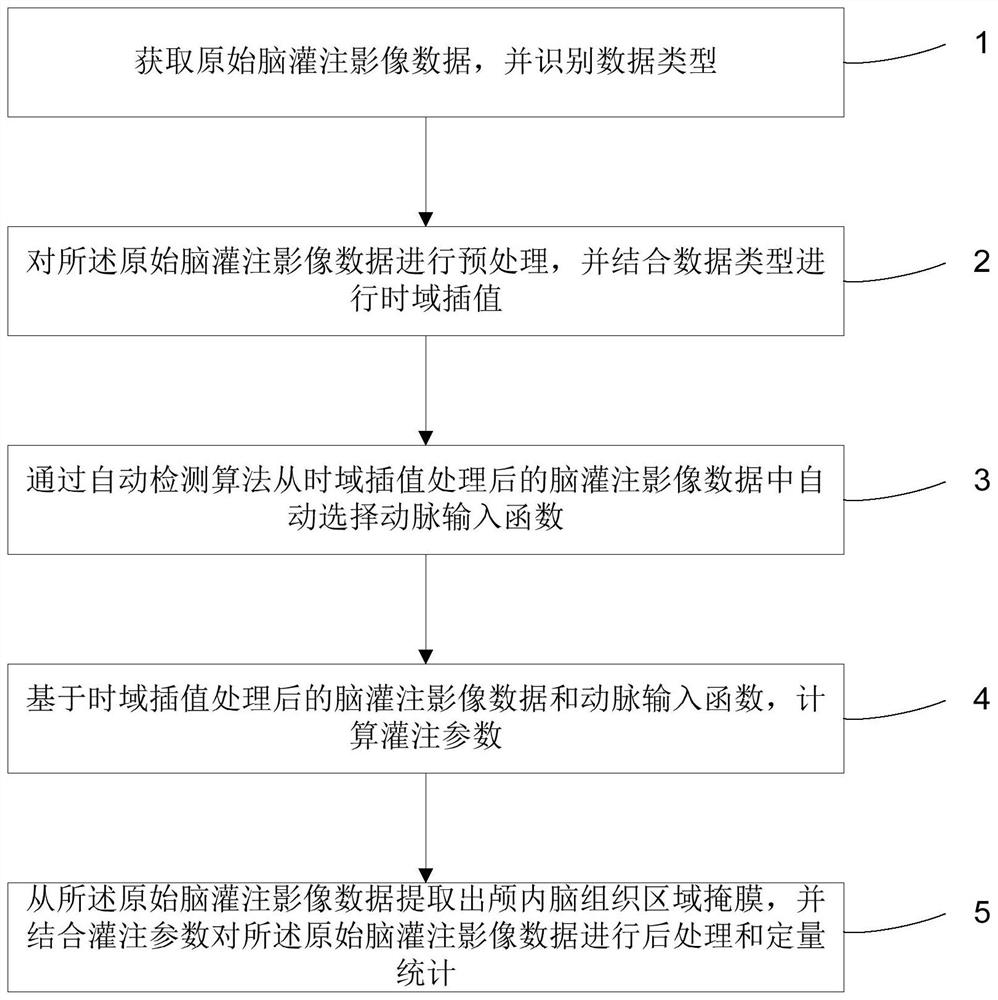
Brain perfusion image processing method, system and device and storage medium
PendingCN114119563AQuality improvementAutomatic removalImage enhancementImage analysisTime domainData ingestion
The invention discloses a brain perfusion image processing method, system and device and a storage medium, and the related method comprises the steps: obtaining original brain perfusion image data, and recognizing the data type; preprocessing the original brain perfusion image data, and performing time domain interpolation in combination with a data type; automatically selecting an artery input function from the cerebral perfusion image data after the time domain interpolation processing through an automatic detection algorithm; calculating perfusion parameters based on the brain perfusion image data after the time domain interpolation processing and an artery input function; and extracting an intracranial brain tissue area mask from the original brain perfusion image data, and performing post-processing and quantitative statistics on the original brain perfusion image data in combination with perfusion parameters. According to the scheme, preprocessing, function selection and parameter calculation can be automatically carried out on the brain perfusion image, and a quantitative analysis result is given.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Device and method for obtaining outflow effect parameter based on perfusion image
ActiveCN114359262AImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionArterial input functionNuclear medicine
The invention discloses a device and method for obtaining outflow effect parameters based on perfusion images, and the method comprises the detection steps: continuously collecting the perfusion images and an artery input function after perfusion, aligning the perfusion images of a subsequent time phase with a first time phase image, and removing artifacts and images which cannot be aligned; the method comprises the following steps of: acquiring a perfusion image, converting the perfusion image into a contrast agent concentration image, acquiring a residual function of each pixel point in the perfusion image based on an Indicator-Dilution principle, and calculating an outflow effect parameter, and measuring the outflow effect of the tissue by fully utilizing a residual function curve in a quantitative post-processing process of the MR or CT perfusion image. The residual function curve reflects the response of the tissue to the pulse blood flow (containing the contrast agent), so that the descending part of the residual function is the direct response of the outflow effect of the contrast agent in perfusion, and the measured outflow effect parameter is more accurate than the direct use of the dynamic perfusion curve.
Owner:XIEHE HOSPITAL ATTACHED TO TONGJI MEDICAL COLLEGE HUAZHONG SCI & TECH UNIV +1
A post-processing method and system for magnetic resonance perfusion imaging
ActiveCN105701815BReduce sensitivityImprove post-processing speedImage enhancementImage analysisRegion selectionArterial input function
The invention provides a magnetic resonance perfusion imaging postprocessing method and a system thereof. The method comprises the following steps of perfusing image filtering to an original brain, removing a brain edge and acquiring a filtered brain perfusion image; receiving an area selection instruction of a user, acquiring a selected area of a middle artery area in the filtered brain perfusion image and outputting a weighted artery input curve assessing an artery input function; according to an improved Gamma function, fitting the weighted artery input curve and a concentration time curve respectively so as to obtain the optimized artery input curve and the concentration time curve; according to an improved singular matrix decomposition method based on a non-parametric model, solving a relative quantification parameter of perfusion. Through carrying out weighted optimization on AIF and a solving matrix, sensitivity to a noise is reduced; a simplified and effective Gamma function is used to carry out fitting, a non-linear problem is converted into linear solution, and a post-treatment speed is accelerated.
Owner:SHENZHEN ANKE HIGH TECH CO LTD
Medical perfusion image processing method and medical imaging equipment
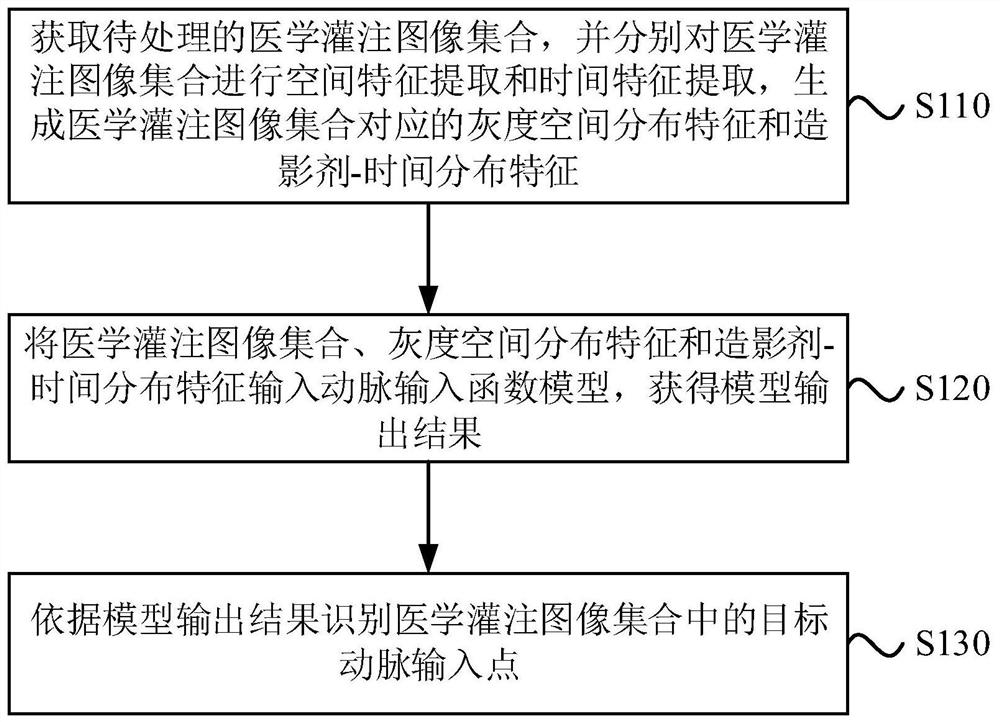
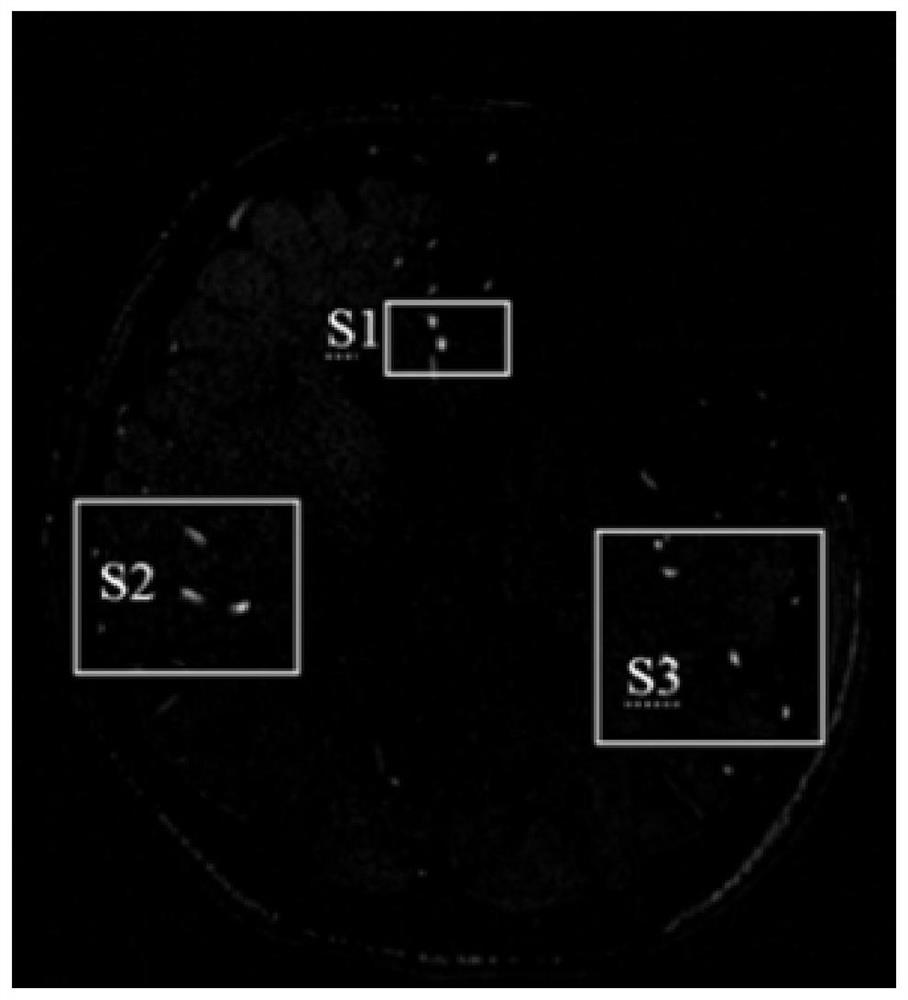
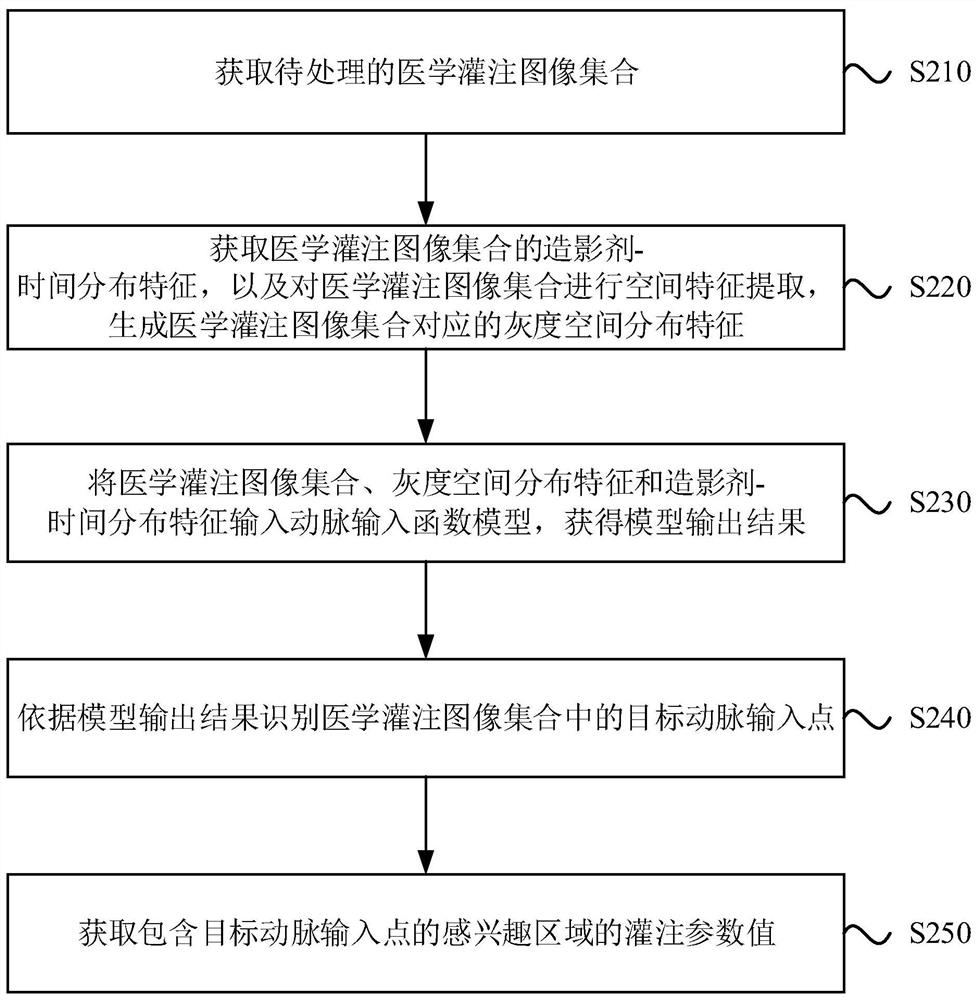
PendingCN111862259AAvoid Positioning MistakesImprove accuracyReconstruction from projectionImage generationImaging processingFeature extraction
The embodiment of the invention discloses a medical perfusion image processing method and medical imaging equipment. The method comprises the steps: acquiring a medical perfusion image set to be processed, performing spatial feature extraction and time feature extraction on the medical perfusion image set, and generating gray scale spatial distribution features and contrast agent-time distributionfeatures corresponding to the medical perfusion image set; inputting the medical perfusion image set, the gray scale space distribution characteristics and the contrast agent-time distribution characteristics into an artery input function model to obtain a model output result; and identifying a target artery input point in the medical perfusion image set according to the model output result. According to the technical scheme, the artery input point can be recognized from the medical perfusion image more quickly and accurately.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
CT scan perfusion method and device
ActiveCN104688259BReduce radiation doseImprove complianceComputerised tomographsTomographyHuman bodyRadiation Dosages
The present invention provides a CT scan perfusion method and its device, comprising: starting from the moment t1 when a predetermined time elapses from the injection of the contrast agent, performing a single-layer CT tracking scan on the concentration of the contrast agent in the aorta with the first radiation dose; In the scan tracking, when the trigger point is reached, the scanning program is triggered, and at time t2, the arterial phase scan is performed on the organ with a second radiation dose greater than the first radiation dose, to obtain the arterial phase CT value; according to the arterial phase CT value Obtain the increase of CT value; set the arterial input function represented by the time density curve of the contrast agent in the artery during the scanning and tracking of the contrast agent, and obtain the blood flow of the organ according to the increase of the arterial input function and the CT value . The CT scanning perfusion method of the present invention avoids multiple repeated scans of the organs in the traditional method, not only can reduce the radiation dose to the human body, but also can make the operation simpler and easier, the result is accurate, and the patient's pain is reduced. discomfort.
Owner:中国人民解放军总医院第八医学中心
System and method for measuring artery input function in dynamic perfusion image post-processing
PendingCN114077863AGet efficient and stableGood reproducibilityImage enhancementImage analysisVoxelAlgorithm
The invention provides a system for measuring an artery input function in dynamic perfusion image post-processing. The system comprises: a preprocessing module, which is used for preprocessing original time density curves, and screening out curves with regular shapes as an initial curve set; a clustering analysis module, which is used for performing clustering analysis on the initial curve set, and selecting one type of curves with a minimum clustering center as candidate curves; a post-processing module, which is used for marking voxel positions corresponding to the candidate curves in a three-dimensional space, calculating connected components of the space and a number of voxels of each component, removing components smaller than a set volume, and calculating an average curve of each remaining spatial component to obtain target curves; a classification module, which is used for extracting characteristic parameters of the target curves, calculating the conformity of the target curves by using a linear weighting model, and screening out a final AIF curve according to the conformity. The system can efficiently and stably obtain an AIF curve.
Owner:深圳市铱硙医疗科技有限公司
Method of generating an enhanced perfusion image
A method of generating an enhanced perfusion image comprising the use of a blind deconvolution algorithm and the adiabatic approximation to the Johnson and Wilson model (aaJW) and generation of an image, wherein the blind deconvolution algorithm and the aaJW model are used in the generation of values of the following parameters: voxel specific arterial input function cp[t] and voxel specific tissue residue function r[t].
Owner:STIFTELSEN UNIVTSFORSKNING BERGEN
Method and system for calculating quantitative parameter of magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveCN101912262BImprove accuracyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsArterial input functionDynamic data
The invention discloses a method and a system for calculating a quantitative parameter of magnetic resonance imaging. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a dynamic comparison enhancement drug dynamics data analysis model and a magnetic resonance imaging model containing the relationship between the signal intensity and the concentration of a contrast mediummagnetic resonanceimaging model; calculating a residual function according to the dynamic comparison enhancement drug dynamics data analysis model and the acquired quantitative parameter according to the acquired residual function. In the method and the system for calculating the quantitative parameter of magnetic resonance imaging, the quantitative parameter can be also improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Expanded pharmacokinetic model for population studies in breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
A method for pharmacokinetic analysis, including: receiving time-series medical image data of a patient introduced with a contrast agent; identifying a reference region in the medical image data; identifying a plurality of points of interest in the medical image data; measuring an intensity of voxels in the reference region; and for each point of interest, measure an intensity of voxels therein, use the measured reference region and point of interest intensities to obtain an expression relating the point of interest's voxel concentration to that of the reference region, wherein the expression is a five-parameter nonlinear model with no reference to an arterial input function; and obtain values for each of the five-parameters by solving the expression and use the obtained values to determine whether the point of interest is malignant.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com