Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33 results about "Model-specific register" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A model-specific register (MSR) is any of various control registers in the x86 instruction set used for debugging, program execution tracing, computer performance monitoring, and toggling certain CPU features.
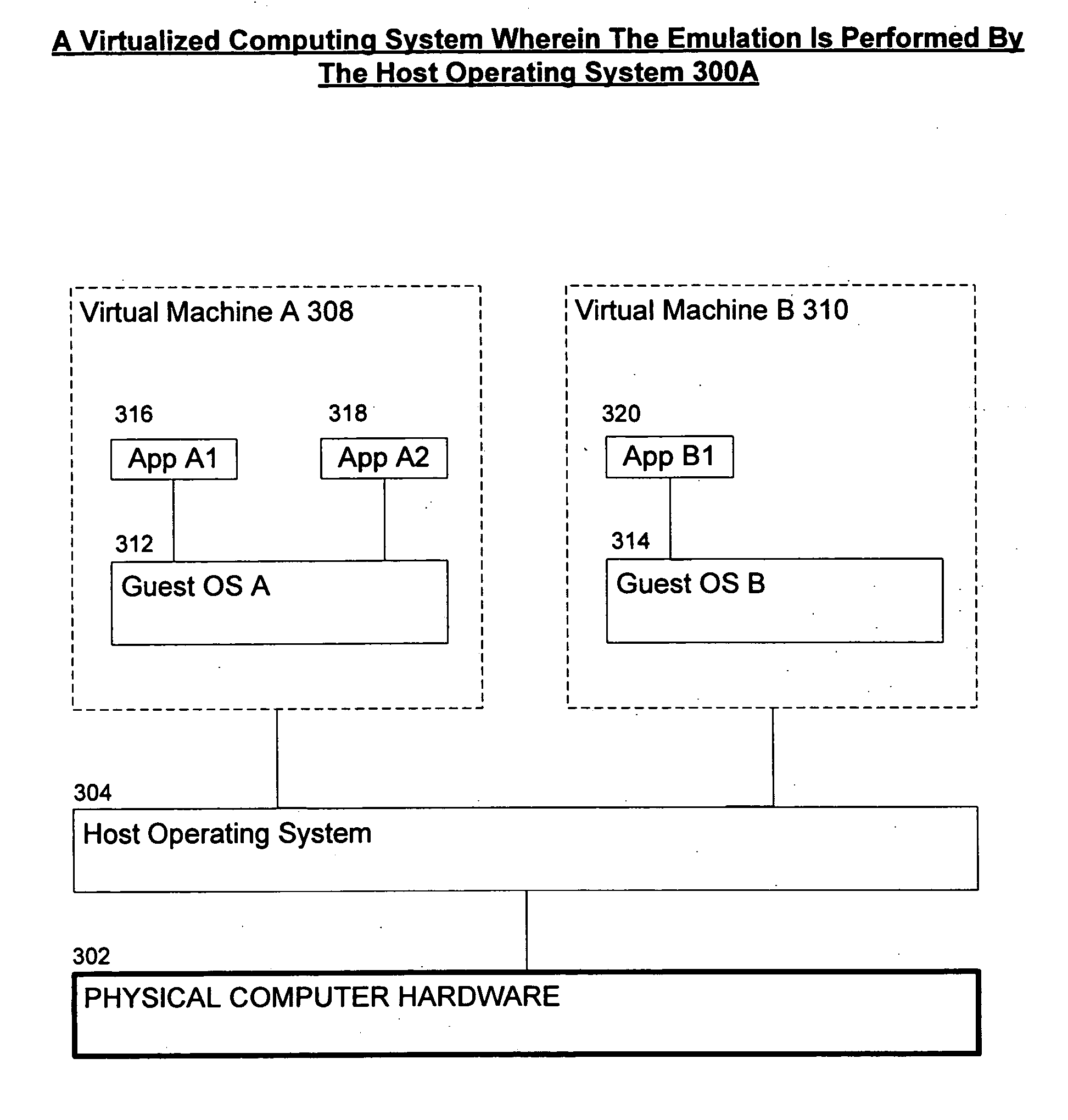
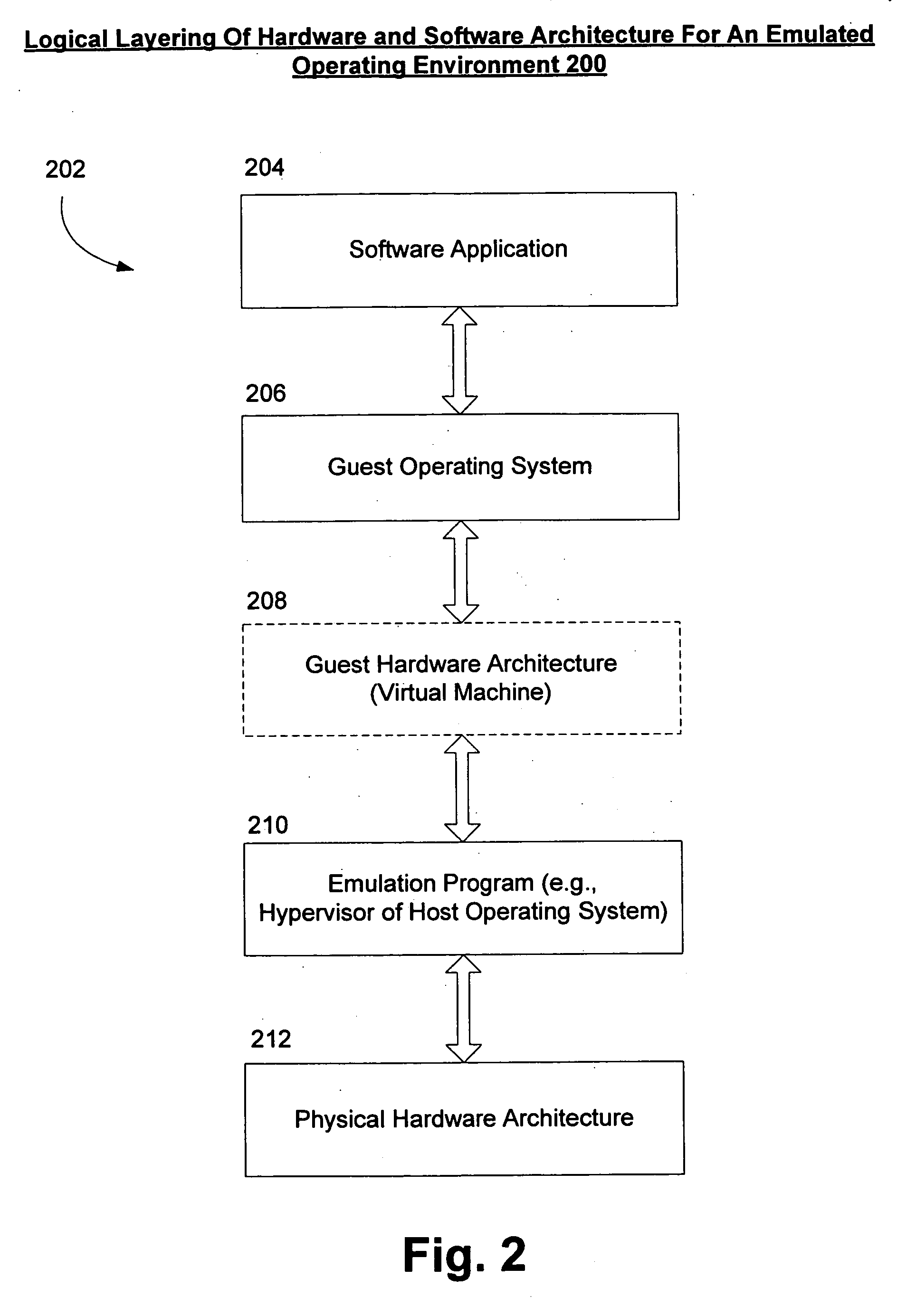
Systems and methods for hypervisor discovery and utilization
ActiveUS20060248528A1Software simulation/interpretation/emulationMemory systemsVirtual deviceComputer science
Systems and methods are provided, whereby partitions may become enlightened and discover the presence of a hypervisor. Several techniques of hypervisor discovery are discussed, such as detecting the presence of virtual processor registers (e.g. model specific registers or special-purpose registers) or the presence of virtual hardware devices. Upon discovery, information (code and / or data) may be injected in a partition by the hypervisor, whereby such injection allows the partition to call the hypervisor. Moreover, the hypervisor may present a versioning mechanism that allows the partition to match up the version of the hypervisor to its virtual devices. Next, once code and / or data is injected, calling conventions are established that allow the partition and the hypervisor to communicate, so that the hypervisor may perform some operations on behalf of the partition. Four exemplary calling conventions are considered: restartable instructions, a looping mechanism, shared memory transport, and synchronous or asynchronous processed packets. Last, cancellation mechanisms are considered, whereby partition requests may be cancelled.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
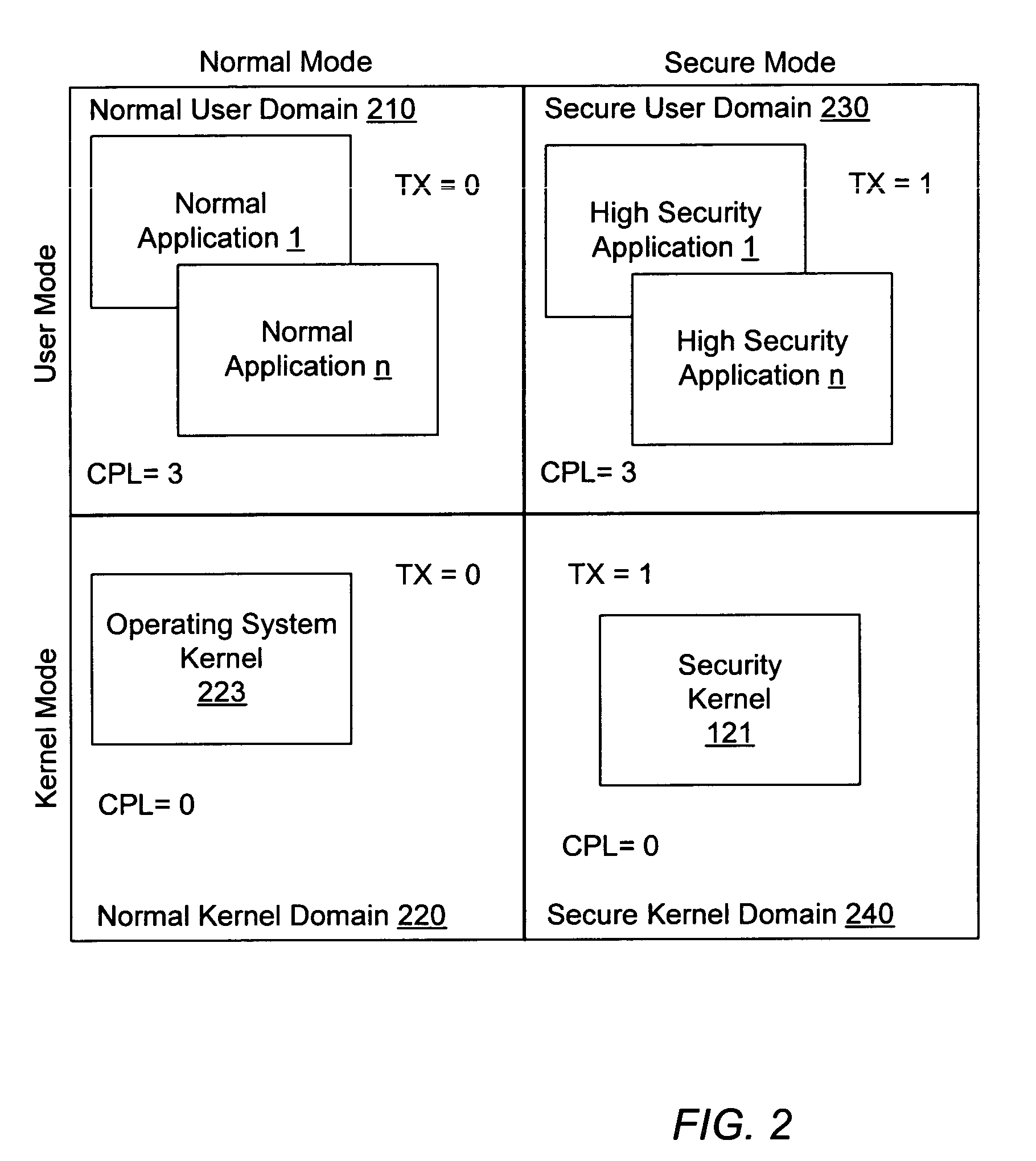
Method of controlling access to model specific registers of a microprocessor
ActiveUS7043616B1Internal/peripheral component protectionProgram controlModel-specific registerMicroprocessor
A method of controlling access to a model specific register of a microprocessor. A method of controlling access to a model specific register of a processor having a normal execution mode and a secure execution mode may include storing processor state and mode information in the model specific register. Further, the method may include protection logic allowing a software invoked write access to modify the information within the model specific register during the normal execution mode. The method may further include security logic selectively inhibiting the software invoked write access during the secure execution mode.
Owner:ADVANCED SILICON TECH
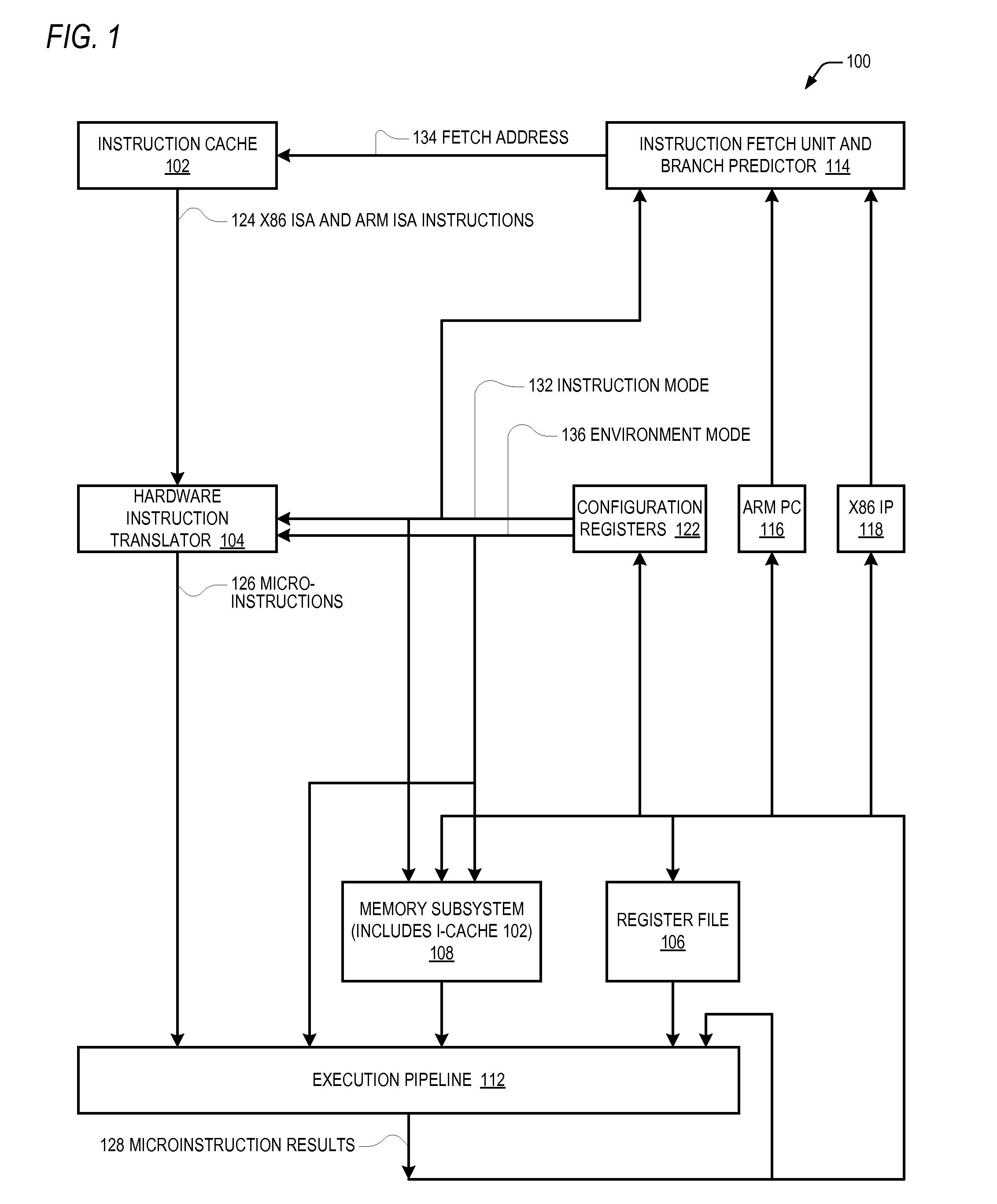
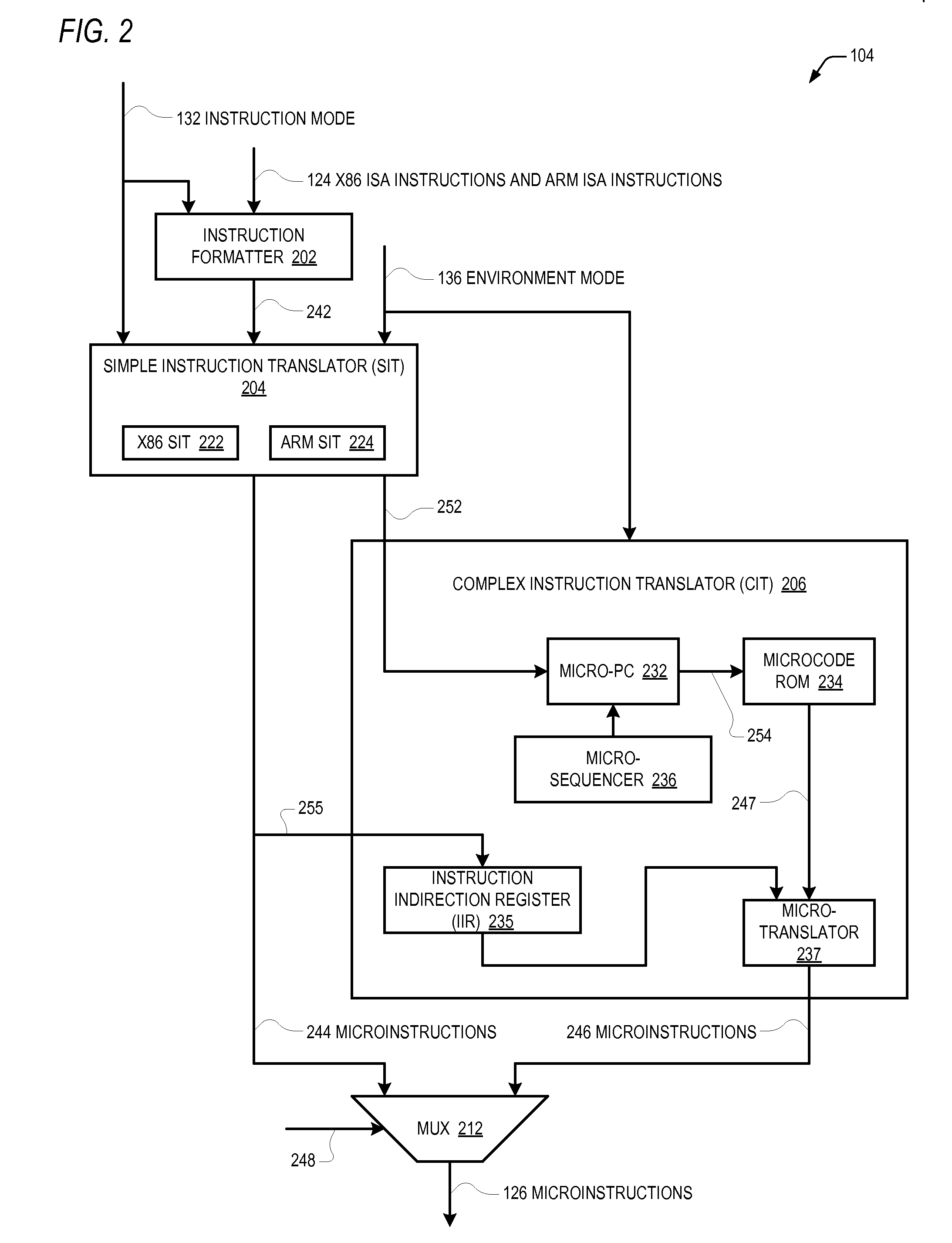
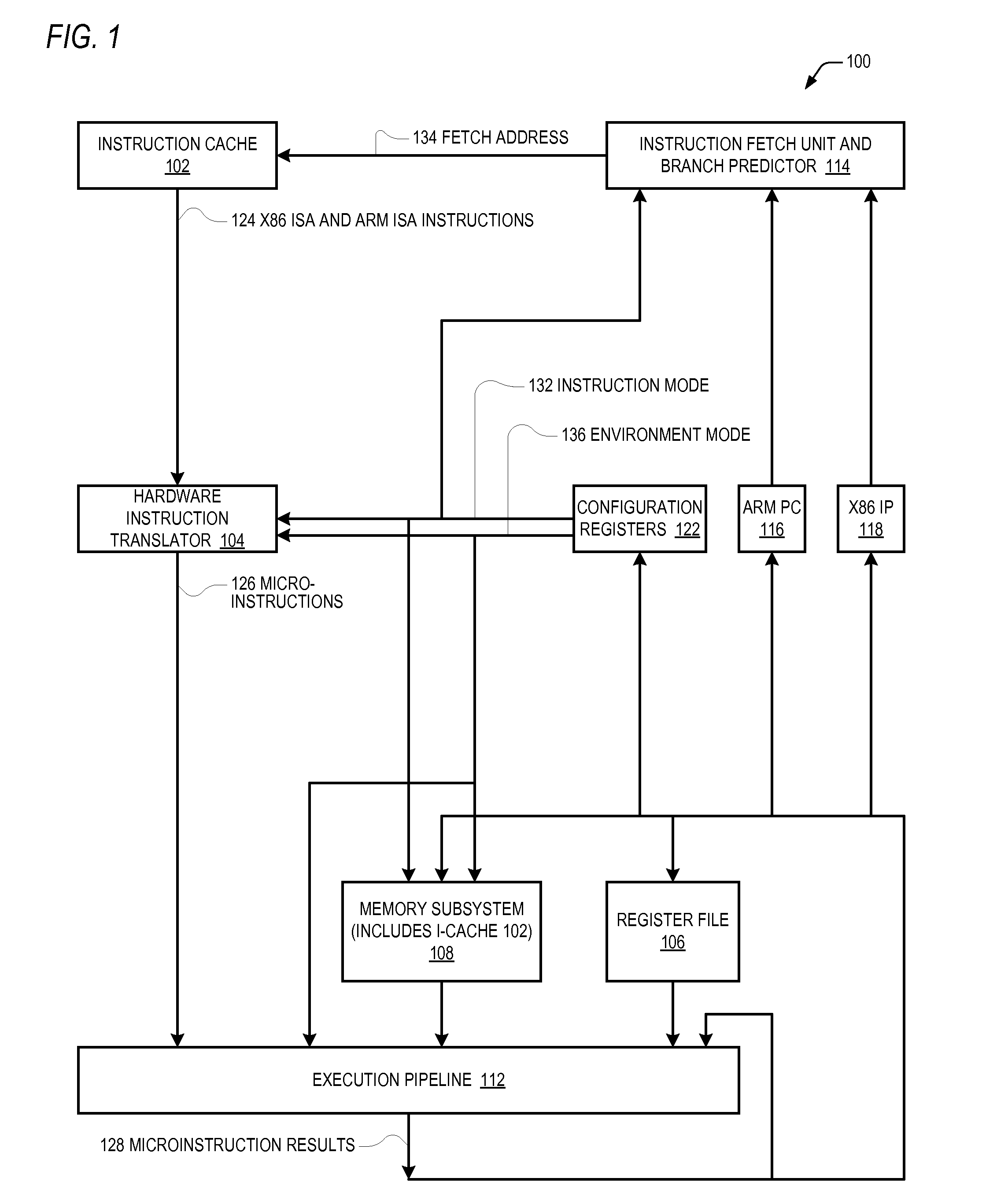
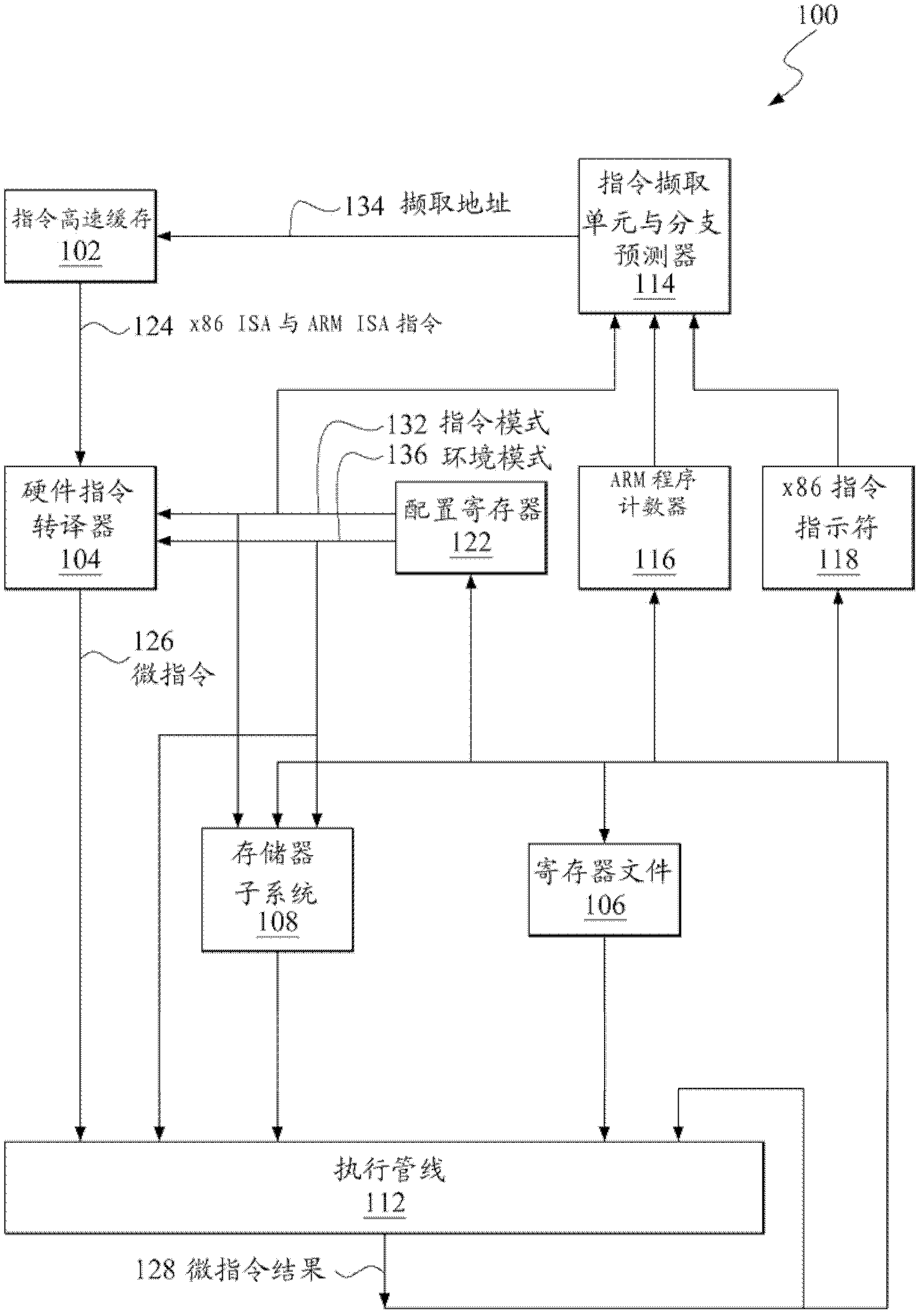
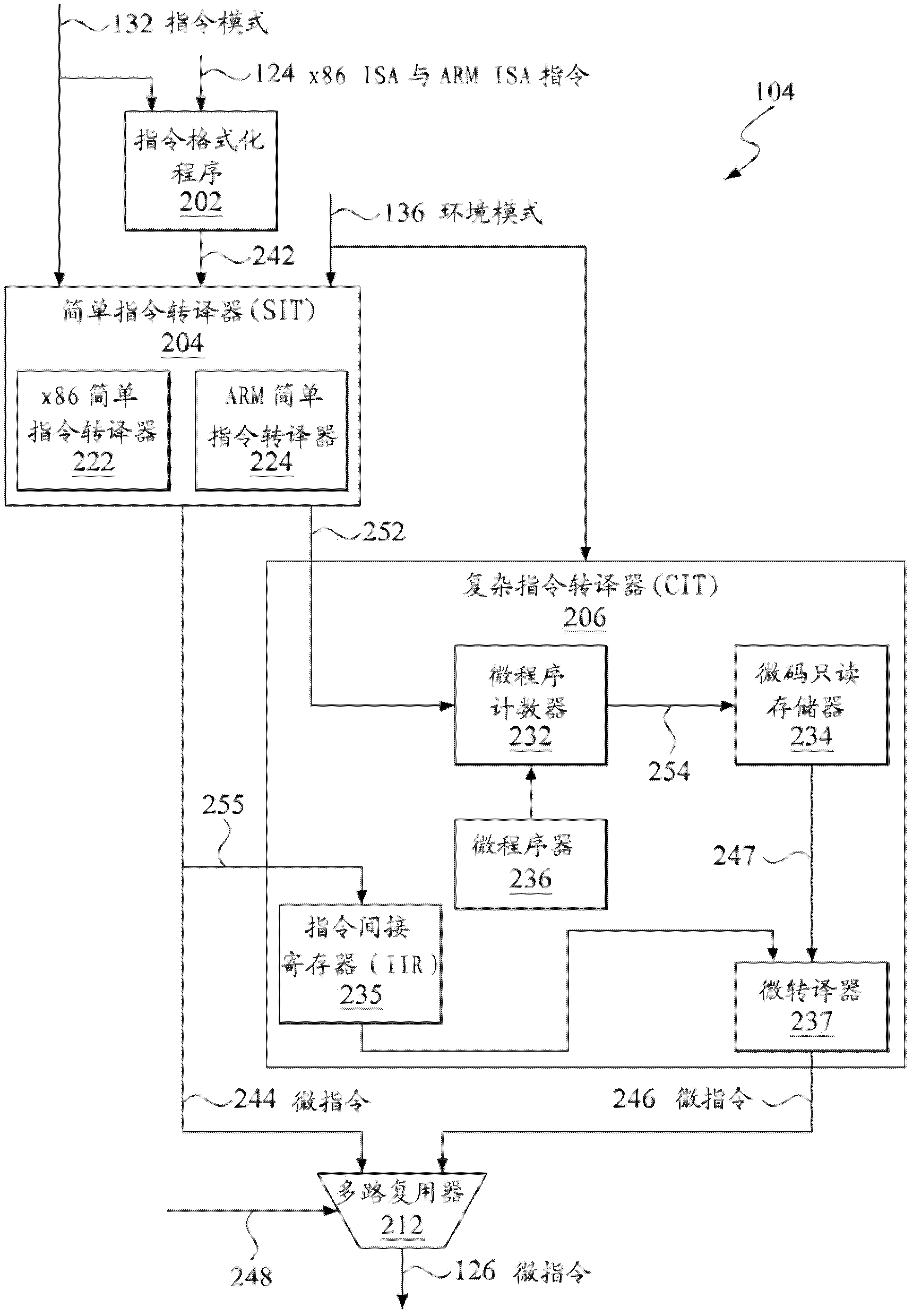
Control register mapping in heterogeneous instruction set architecture processor
ActiveUS20130067199A1Runtime instruction translationDigital computer detailsProgram instructionProcessor register
A microprocessor capable of running both x86 instruction set architecture (ISA) machine language programs and Advanced RISC Machines (ARM) ISA machine language programs. The microprocessor includes a mode indicator that indicates whether the microprocessor is currently fetching instructions of an x86 ISA or ARM ISA machine language program. The microprocessor also includes a plurality of model-specific registers (MSRs) that control aspects of the operation of the microprocessor. When the mode indicator indicates the microprocessor is currently fetching x86 ISA machine language program instructions, each of the plurality of MSRs is accessible via an x86 ISA RDMSR / WRMSR instruction that specifies an address of the MSR. When the mode indicator indicates the microprocessor is currently fetching ARM ISA machine language program instructions, each of the plurality of MSRs is accessible via an ARM ISA MRRC / MCRR instruction that specifies the address of the MSR.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Using a model specific register as a base I/O address register for embedded I/O registers in a processor
InactiveUS6711673B1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital computer detailsPage address registerProcessor register
A processor includes an input / output (I / O) register that is mapped into input / output (I / O) address space. The processor also includes a base address register that is loaded with a base address. The base address register may be a model specific register (MSR). The input / output register is accessed with an input / output instruction at an address determined according to the base address and an offset therefrom. The base address register may be accessible to software operating at a high privilege level and not accessible to software operating at a lower privilege level, while the I / O register is accessible to software operating at the lower privilege level. The processor determines when an I / O access is to the processor I / O register and accesses that I / O register without causing an input / output bus cycle that would otherwise occur.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Accessing model specific registers (MSR) with different sets of distinct microinstructions for instructions of different instruction set architecture (ISA)
ActiveUS9043580B2Runtime instruction translationDigital computer detailsProgram instructionProcessor register
A microprocessor capable of running both x86 instruction set architecture (ISA) machine language programs and Advanced RISC Machines (ARM) ISA machine language programs. The microprocessor includes a mode indicator that indicates whether the microprocessor is currently fetching instructions of an x86 ISA or ARM ISA machine language program. The microprocessor also includes a plurality of model-specific registers (MSRs) that control aspects of the operation of the microprocessor. When the mode indicator indicates the microprocessor is currently fetching x86 ISA machine language program instructions, each of the plurality of MSRs is accessible via an x86 ISA RDMSR / WRMSR instruction that specifies an address of the MSR. When the mode indicator indicates the microprocessor is currently fetching ARM ISA machine language program instructions, each of the plurality of MSRs is accessible via an ARM ISA MRRC / MCRR instruction that specifies the address of the MSR.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Instructions and logic to provide base register swap status verification functionality
InactiveUS20150178078A1Instruction analysisDigital computer detailsRegister exchangeModel-specific register
Instructions and logic provide base register swap status verification functionality. Embodiments include a processor having a first model specific register (MSR) to store a first base address corresponding to a segment for a first execution context and a second MSR to store a second base address corresponding to a segment for a second context. A third register stores a base register swap status field corresponding to the segment of the first and second contexts. A decode unit decodes a swap instruction and execution logic executes an exchange of the first MSR value and the second MSR value responsive to the swap instruction. The execution logic determines if said exchange of the first MSR value and the second MSR value completed successfully, and changes a value of the base register swap status field responsive to a determination that said exchange completed successfully.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Control register mapping in heterogenous instruction set architecture processor
ActiveCN102937889AConditional code generationInstruction analysisProgram instructionProcessor register
A microprocessor capable of running both x86 instruction set architecture (ISA) machine language programs and Advanced RISC Machines (ARM) ISA machine language programs. The microprocessor includes a mode indicator that indicates whether the microprocessor is currently fetching instructions of an x86 ISA or ARM ISA machine language program. The microprocessor also includes a plurality of model-specific registers (MSRs) that control aspects of the operation of the microprocessor. When the mode indicator indicates the microprocessor is currently fetching x86 ISA machine language program instructions, each of the plurality of MSRs is accessible via an x86 ISA RDMSR / WRMSR instruction that specifies an address of the MSR. When the mode indicator indicates the microprocessor is currently fetching ARM ISA machine language program instructions, each of the plurality of MSRs is accessible via an ARM ISA MRRC / MCRR instruction that specifies the address of the MSR.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Method and apparatus for user-level thread synchronization with a monitor and MWAIT architecture
ActiveUS20170185458A1Program synchronisationEnergy efficient computingHardware threadProcessing core
Instructions and logic provide user-level thread synchronization with MONITOR and MWAIT instructions. One or more model specific registers (MSRs) in a processor may be configured in a first execution state to specify support of a user-level thread synchronization architecture. Embodiments include multiple hardware threads or processing cores, corresponding monitored address state storage to store a last monitored address for each of a plurality of execution threads that issues a MONITOR request, cache memory to record MONITOR requests and associated states for addresses of memory storage locations, and responsive to receipt of an MWAIT request for the address, to record an associated wait-to-trigger state of monitored addresses for execution cores associated with an MWAIT request; wherein the execution core is to transition a requesting thread to an optimized sleep state responsive to the receipt of said MWAIT request when said one or more MSRs are configured in the first execution state.
Owner:INTEL CORP
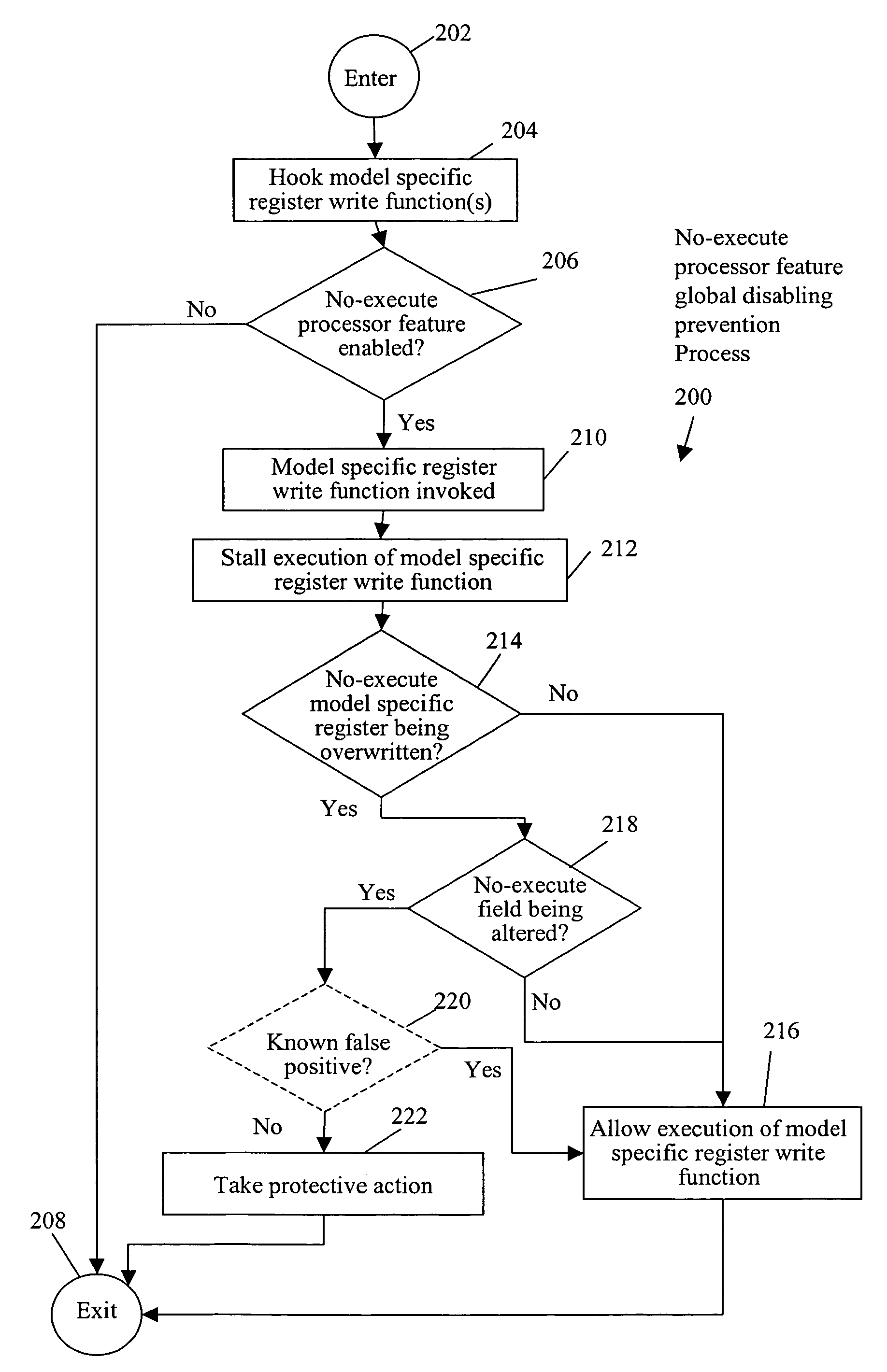
No-execute processor feature global disabling prevention system and method
ActiveUS7540026B1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionModel-specific registerExecution model
A method includes stalling execution of a model specific register write function to write to a model specific register of a processor having a no-execute processor feature enabled, determining that the model specific register is a no-execute model specific register of the processor, and determining whether a no-execute field in the no-execute model specific register is being altered. Upon a determination that the no-execute field is being altered, the method further includes taking protective action to prevent disabling of the no-execute processor feature.
Owner:CA TECH INC
Apparatus and method for updating set of limited access model specific registers in a microprocessor
ActiveUS20100064117A1Save potentially large amount of revenueShorten the timeUser identity/authority verificationUnauthorized memory use protectionLimited accessOperating system
A microprocessor having model specific registers (MSRs) includes, for each of the MSRs, an associated default value that indicates whether the MSR is protected or non-protected and an associated fuse that, if blown, toggles the associated default value from protected to non-protected or non-protected to protected. In one embodiment, microcode that does the following in response to the microprocessor encountering an instruction that accesses a specified MSR: determines whether the fuse associated with the specified MSR is blown or unblown, uses the default value associated with the MSR as an indicator of whether the MSR is protected if the associated fuse is unblown; toggles the associated default value to generate the indicator if the associated fuse is blown; protects access to the MSR if the indicator indicates the MSR is protected; and refrains from protecting access to the MSR if the indicator indicates the MSR is non-protected.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
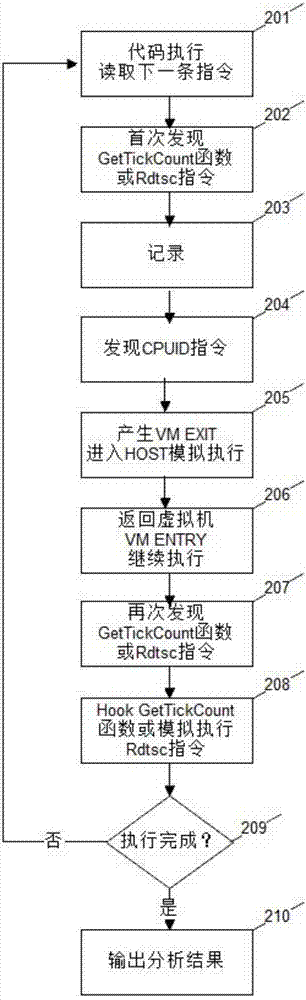
Method for establishing virtual machine countermeasure technology based on hardware virtualization technology
InactiveCN106934281ASolve the practical problems of confrontationDoes not break integrityPlatform integrity maintainanceVirtualizationCountermeasure
The invention discloses a method for establishing a virtual machine countermeasure technology based on a hardware virtualization technology. The method comprises the following steps of 1, enabling CPU hardware virtualization characteristic support in a virtual machine; 2, loading a driver program to enter a Host mode; 3, taking over all input output operations and MSR (Model Specific Register) operations, and intercepting all instructions capable of generating VM Exit; 4, performing environment setting for the instructions; 5, running a monitored program; 6, when a VM Exit generation event occurs, in combination with environment information analysis, judging whether an anti-virtual machine behavior exists or not; 7, continuing to monitor a behavior of a sample until the end; and 8, outputting a final analysis result. Through the steps, monitoring of a privileged instruction is finished, an anti-virtual machine technology countermeasure method for malicious codes, which cannot be realized in a conventional method, is realized, the integrity of the sample is not destroyed, and detection is not bypassed by the malicious codes, so that the actual problem of anti-virtual machine technology countermeasure of the malicious codes is solved.
Owner:XINGHUA YONGHENG BEIJING TECH CO LTD
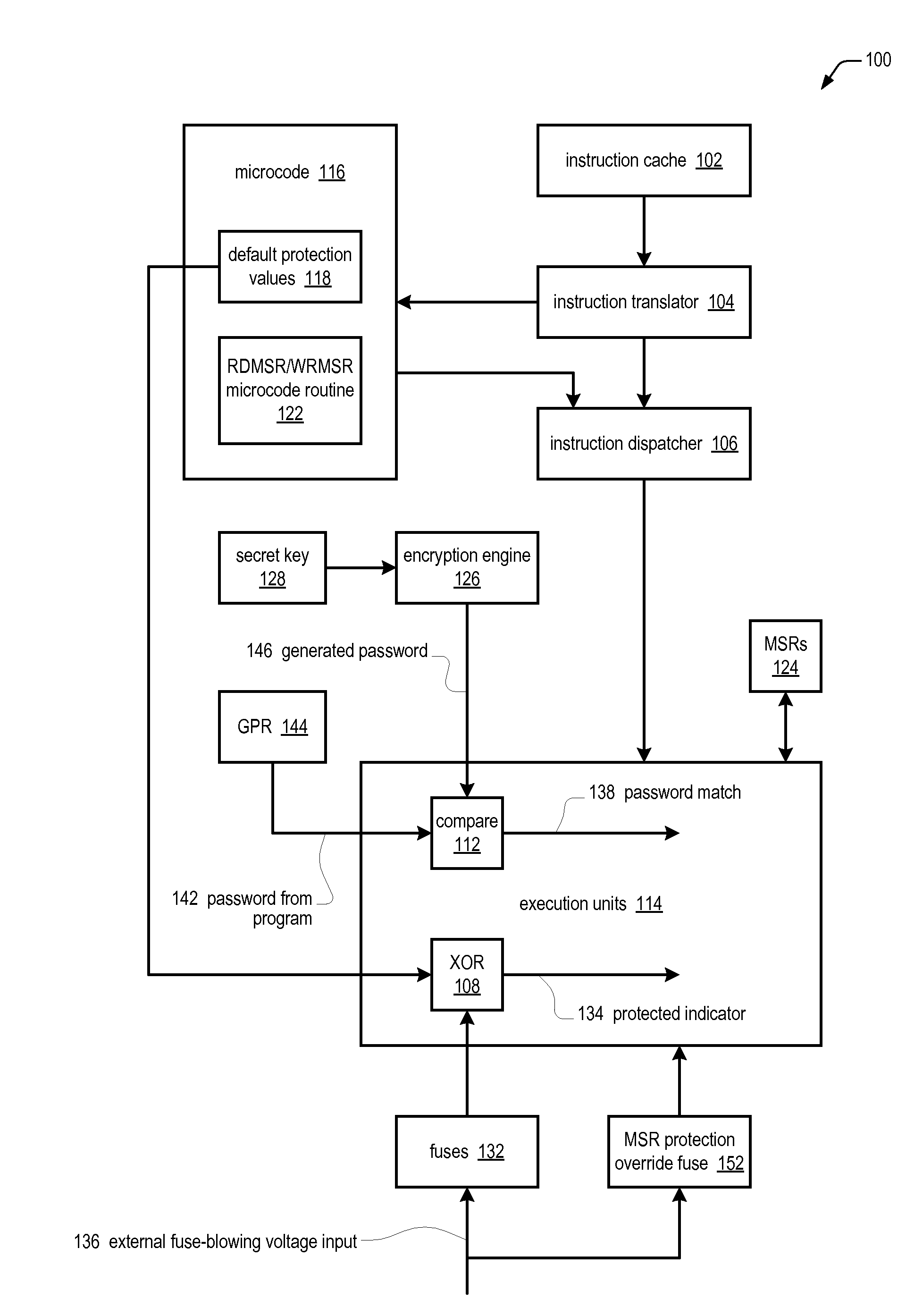
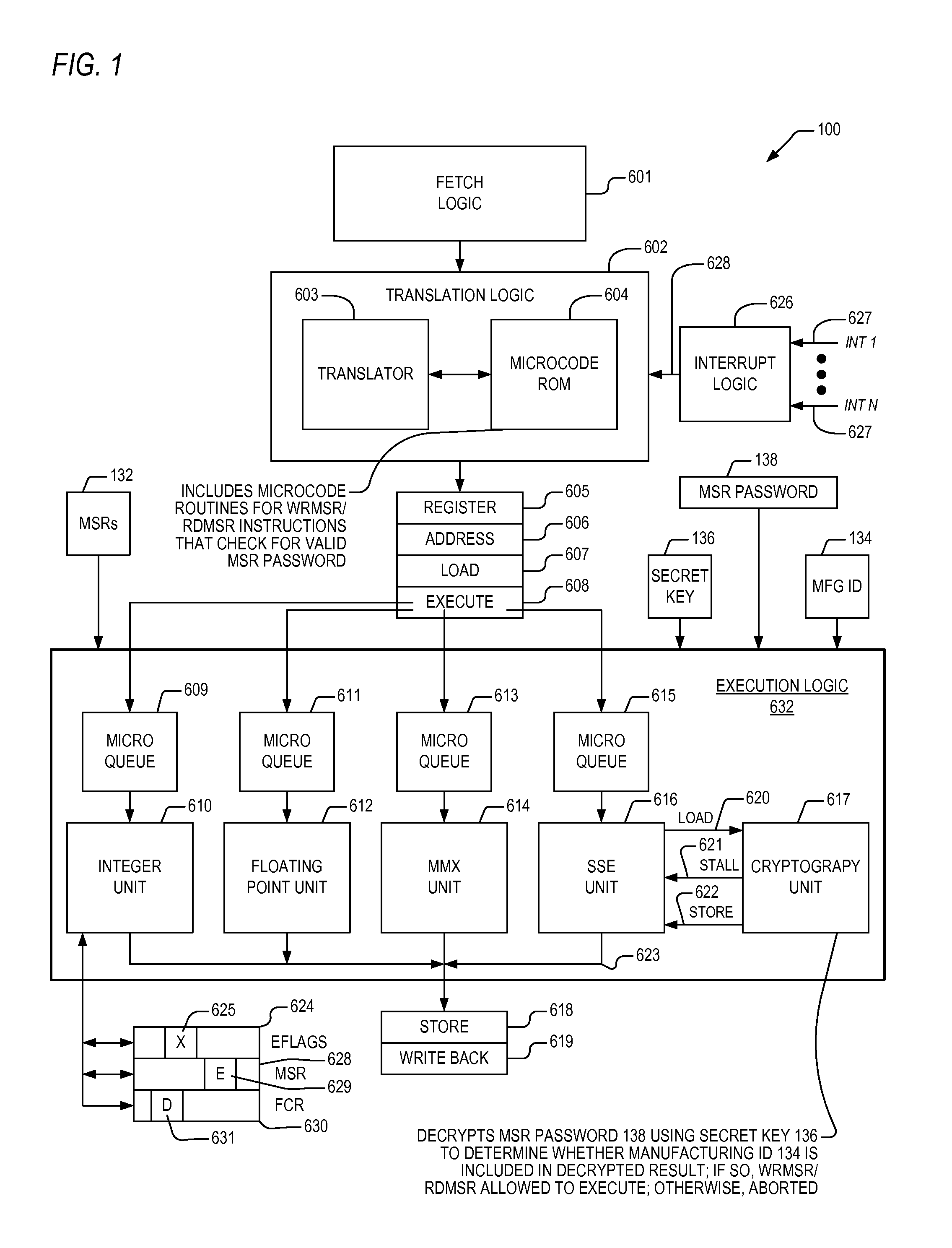
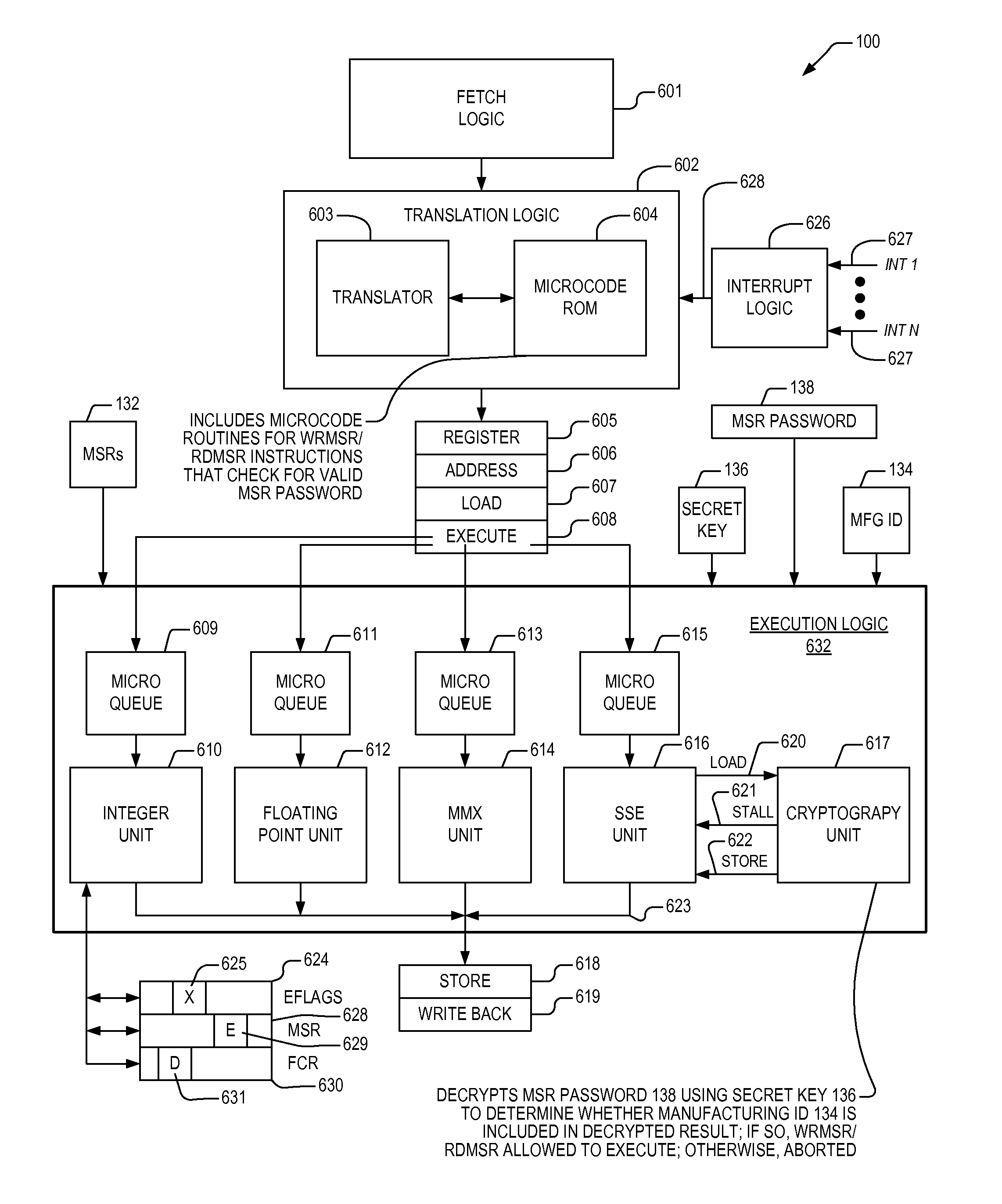
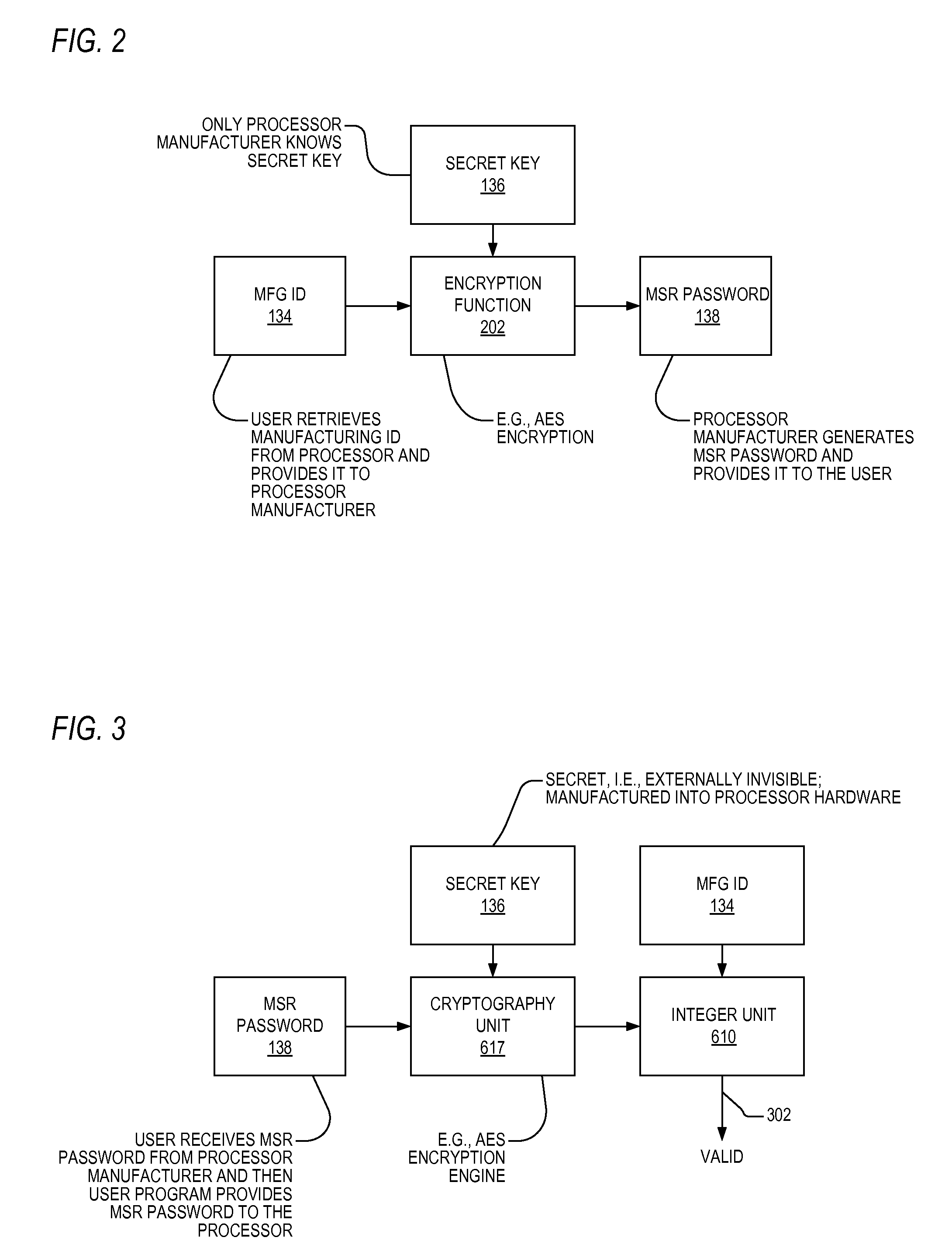
Apparatus and method for limiting access to model specific registers in a microprocessor
A microprocessor having a control register to which the manufacturer of the microprocessor may limit access. The microprocessor includes a manufacturing identifier that uniquely identifies the microprocessor and that is externally readable from the microprocessor by a user. The microprocessor also includes a secret key, manufactured internally within the microprocessor and externally invisible. The microprocessor also includes an encryption engine, coupled to the secret key, configured to decrypt a user-supplied password using the secret key to generate a decrypted result in response to a user instruction instructing the microprocessor to access the control register. The user-supplied password is unique to the microprocessor. The microprocessor also includes an execution unit, coupled to the manufacturing identifier and the encryption engine, configured to allow the instruction access to the control register if the manufacturing identifier is included in the decrypted result, and to otherwise deny the instruction access to the control register.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
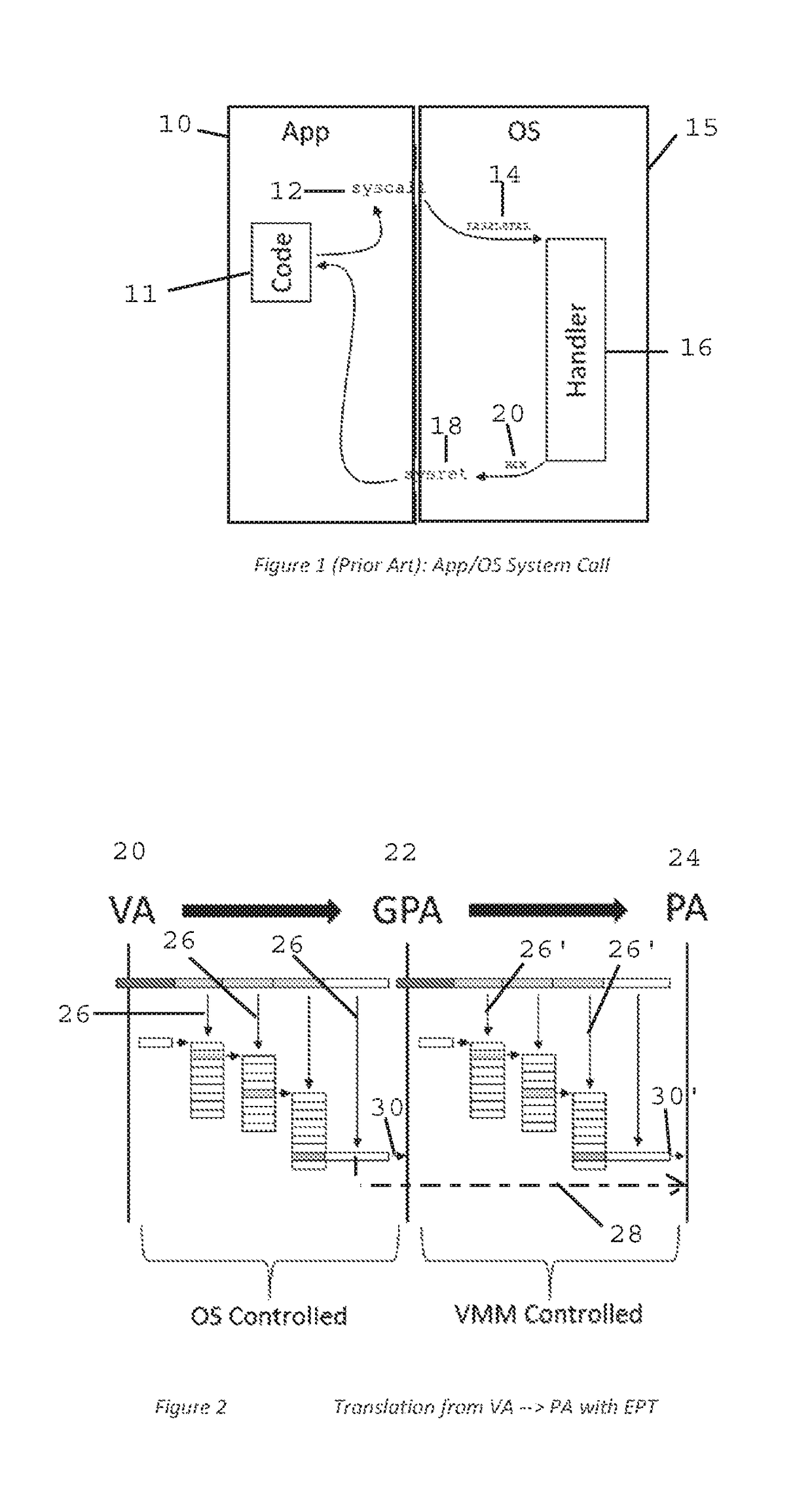
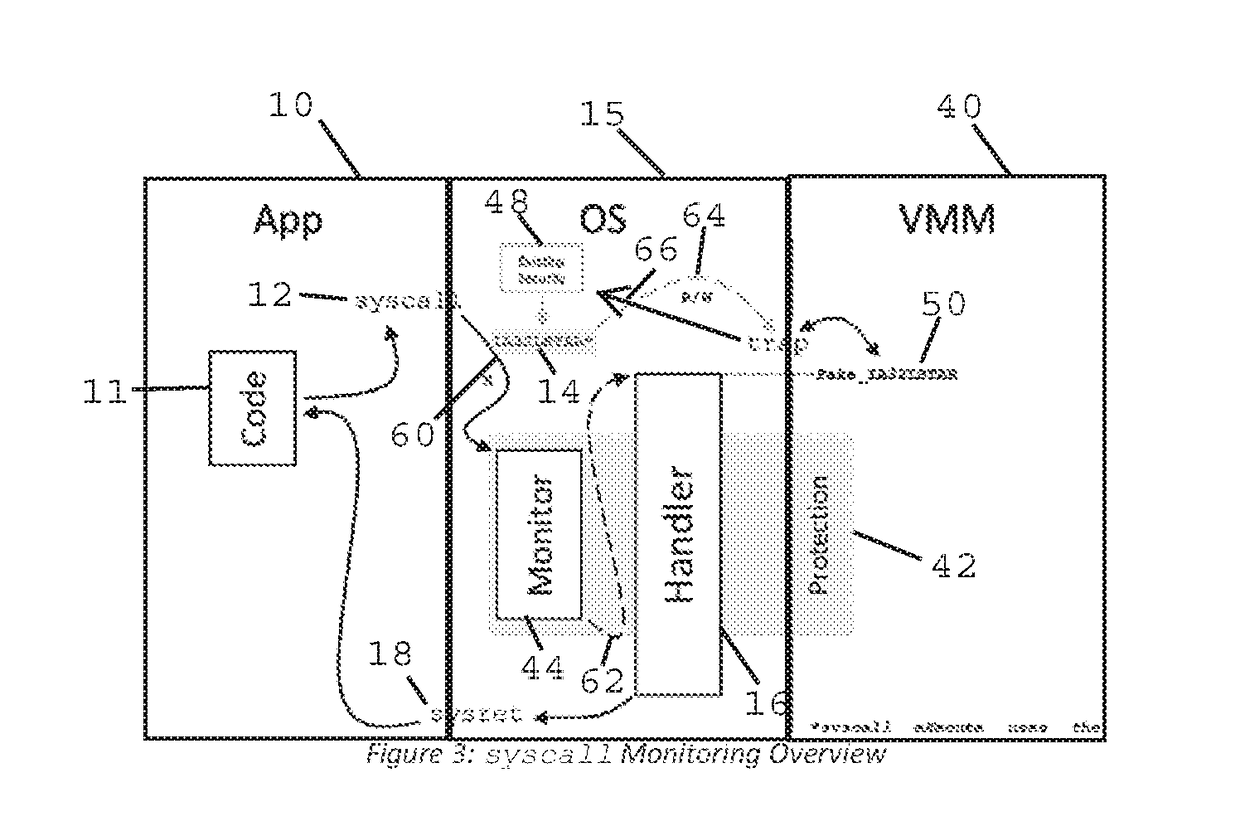
Method and Apparatus for Sysret Monitoring of System Interactions
ActiveUS20170109189A1Effective monitoringEfficiently securingPlatform integrity maintainanceSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationSystem callApplication software
A security system and method efficiently monitors and secures a computer to defend against malicious intrusions, and includes an in-band software monitor disposed within a kernel in communication with an operating system (OS) of the computer. The monitor intercepts system calls made from an MSR (Model Specific Register), to execute monitoring operations, and subsequently returns execution to the OS. An out-of-band hypervisor communicably coupled to the OS, has read shadow means for trapping read requests to the MSR, and write mask means for trapping write requests to the MSR. The hypervisor includes means for responding to the trapped read and write requests so that presence of the monitor is obscured. Sysret monitoring means intercepts calls to a sysret instruction, executes sysret monitoring operations, and subsequently returns execution to an application running on the computer.
Owner:ALERT LOGIC
Method for power optimization in virtualized environments and system implementing the same
InactiveUS20190102233A1Reduce effortNegligible overheadResource allocationEnergy efficient computingWorkloadA domain
A power optimization system and method for virtualized environments at least comprising a domain layer on which a plurality of virtual machines are implemented, a hardware layer and hypervisor layer configured for abstracting between the virtual machines of the domain layer and the hardware layer, wherein the system comprises a hardware interface to set a limit on the power consumption of at least one processing means implemented in a hardware layer and a software structure for performing an optimization of the available resource allocations for the running workload in terms of power consumption, wherein the software structure is an Observe-Decide-Act control loop structure, comprising an observe stage, a decide stage and an act stage, and wherein the observe stage interfaces with means configured for reading performance values inside at least one model specific register of the at least one processing means.
Owner:POLITECNICO DI MILANO
Method and Apparatus for Hypervisor Based Monitoring of System Interactions
ActiveUS20170168865A1Effective monitoringEfficiently securingHardware monitoringComputer security arrangementsOperational systemSystem call
A security system and method efficiently monitors and secures a computer to defend against malicious intrusions, and includes an in-band software monitor disposed within a kernel in communication with an operating system (OS) of the computer. The monitor intercepts system calls made from an MSR (Model Specific Register), to execute monitoring operations, and subsequently returns execution to the OS. An out-of-band hypervisor communicably coupled to the OS, has read shadow means for trapping read requests to the MSR, and write mask means for trapping write requests to the MSR. The hypervisor includes means for responding to the trapped read and write requests so that presence of the monitor is obscured.
Owner:ALERT LOGIC
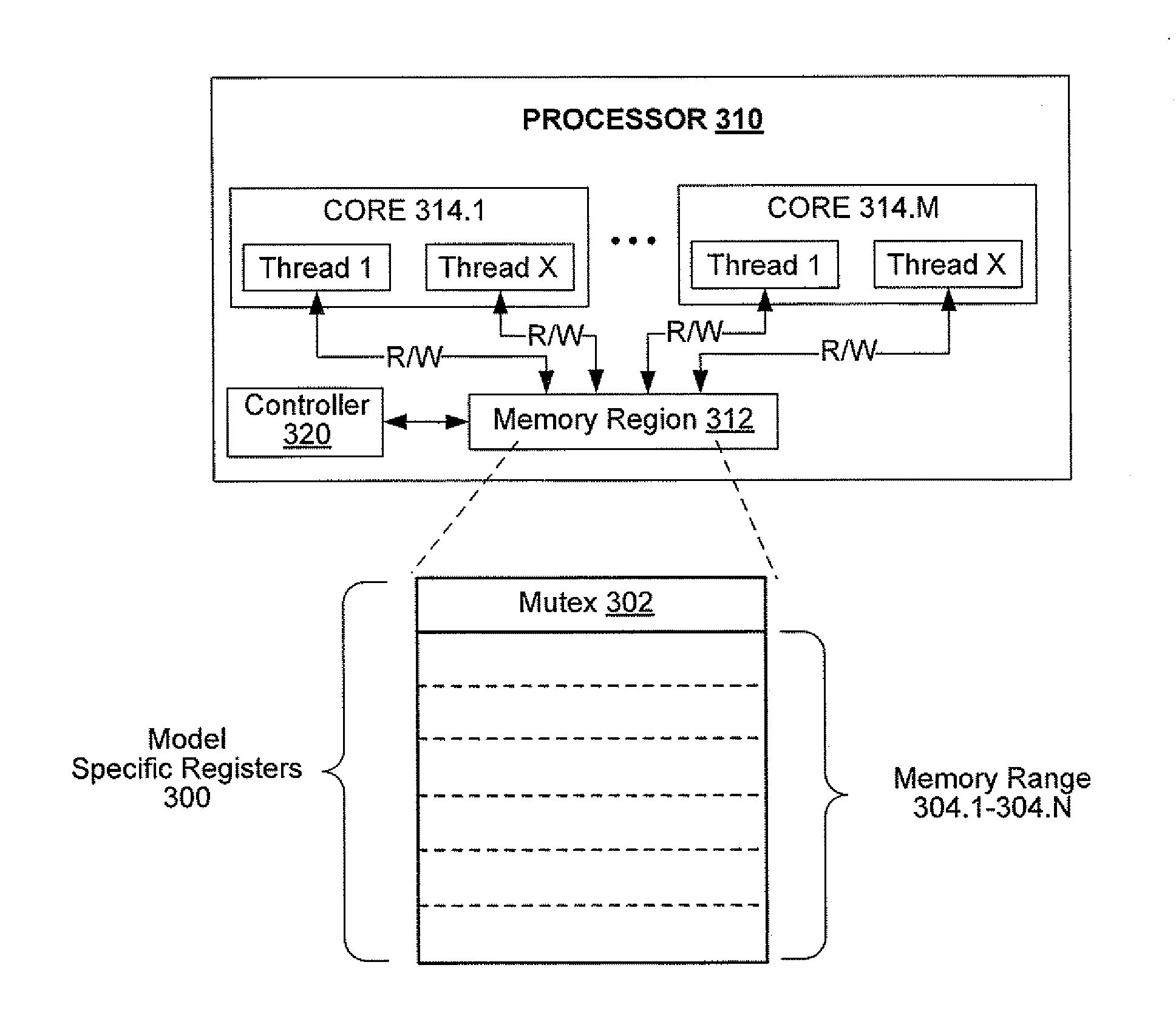
System and method to provide single thread access to a specific memory region
Processing logic and a method to provide single thread access to a specific memory region without suspending processing activity for all other cores and / or threads within or in association with a processor, computer system, or other processing apparatus. Single thread access may be provided through implementation of microcode which may control thread access to model specific registers (“MSRs”) within a processor. One MSR may provide a mutex, which a single thread may claim, and another MSR may provide a range of memory locations, which may be accessed by the thread that has claimed the mutex.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Systems and methods for hypervisor discovery and utilization
ActiveUS8635612B2Software simulation/interpretation/emulationMemory systemsProcessor registerVirtual device
Systems and methods are provided, whereby partitions may become enlightened and discover the presence of a hypervisor. Several techniques of hypervisor discovery are discussed, such as detecting the presence of virtual processor registers (e.g. model specific registers or special-purpose registers) or the presence of virtual hardware devices. Upon discovery, information (code and / or data) may be injected in a partition by the hypervisor, whereby such injection allows the partition to call the hypervisor. Moreover, the hypervisor may present a versioning mechanism that allows the partition to match up the version of the hypervisor to its virtual devices. Next, once code and / or data is injected, calling conventions are established that allow the partition and the hypervisor to communicate, so that the hypervisor may perform some operations on behalf of the partition. Four exemplary calling conventions are considered: restartable instructions, a looping mechanism, shared memory transport, and synchronous or asynchronous processed packets. Last, cancellation mechanisms are considered, whereby partition requests may be cancelled.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method for detecting existence of virtual machine monitor (VMM) under Windows platform
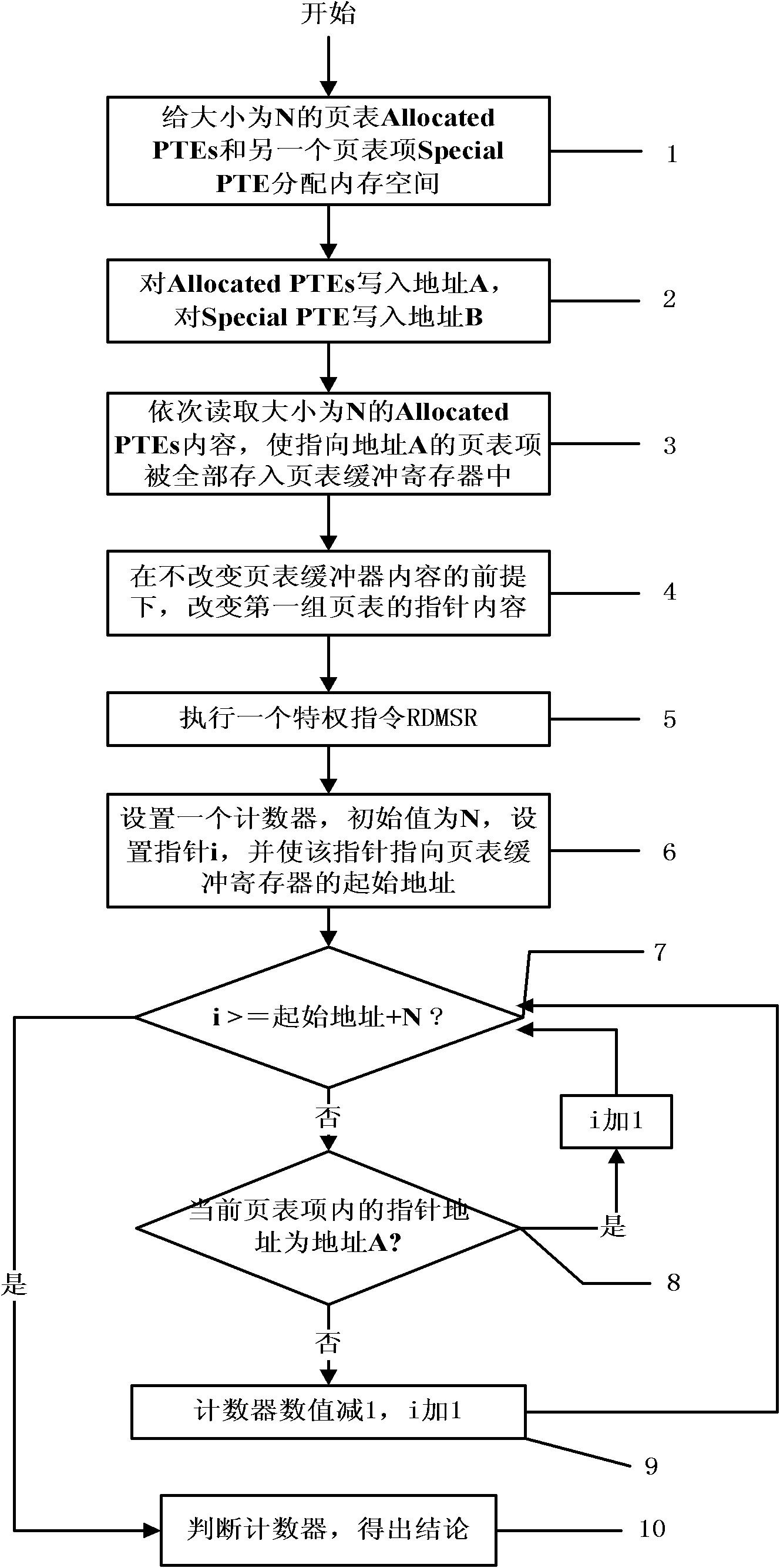
ActiveCN102063594AOvercome limitationsImprove general performancePlatform integrity maintainanceSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationInternal memoryPage table
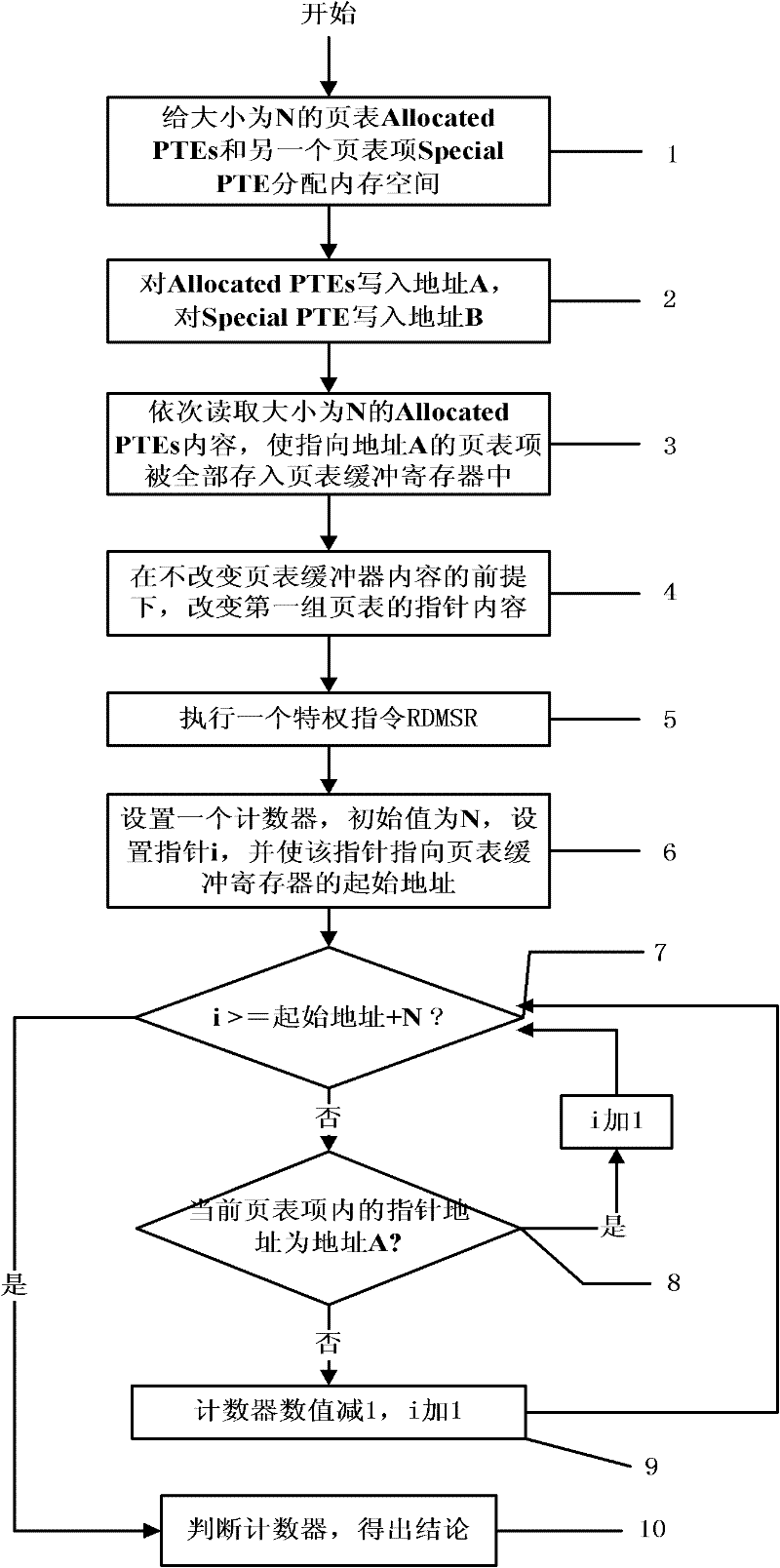
The invention discloses a method for detecting the existence of a virtual machine monitor (VMM) under a Windows platform, aiming at solving the problem that malicious codes use the VMM as a platform for hiding self behaviors and providing malicious services, and providing a method for detecting the existence of the VMM through resource differences. In a technical scheme, the method comprises the steps of: firstly, allocating internal memory spaces for Allocated PTEs (Page Table Entries) and a Special PTE; writing an address A before mapping modification for the Allocated PTEs; writing an address B after mapping modification for the Special PTE; accessing the Allocated PTEs in sequence to ensure that all PTEs pointing to the address A are stored into a page table buffer register; sequentially modifying the pointer contents of the Allocated PTEs into the address B pointed by the Special PTE; executing a privileged instruction RDMSR (Read from Model Specific Register) in a Windows system; and setting a counter, traversing all page table entries in the page table buffer register, and judging whether the VMM exists in the current system by judging whether the numerical value of the counter is consistent with N. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for effectively detecting the VMM so as to improve system security.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Read-write method for special module register
InactiveCN101430656ACause crashShorten the timeError detection/correctionProcessor registerData storing
The invention discloses a reading-writing method of a model-specific register, wherein, the model-specific register is arranged in a central processing unit, and the central processing unit is provided with a plurality of model-specific registers. The method comprises the following steps: first, acquiring an address of a model-specific register and write-in data; reading storage data stored in the model-specific register; and judging whether the write-in data are null data; and then deciding whether to write the storage data back to the model-specific register according to a judgment result of the write-in data.
Owner:邳州世纪益圆家居有限公司
Intracluster and intercluster interprocessor interrupts including a retract interrupt that causes a previous interrupt to be canceled
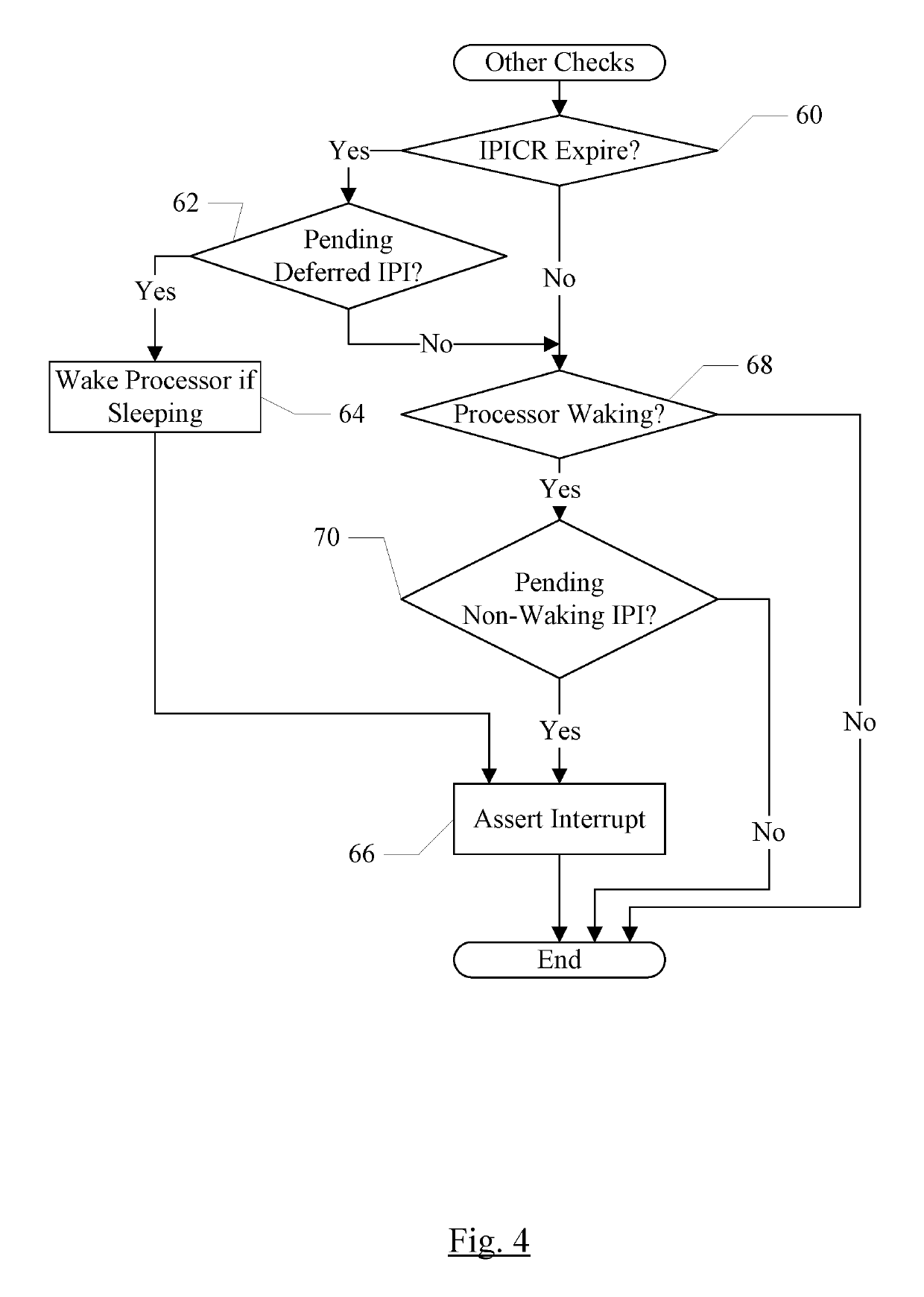
ActiveUS10496572B1Lower latencyReduce transmissionDigital data processing detailsProgram controlTime limitInter-processor interrupt
In an embodiment, processors may have associated special purpose registers (SPRs) such as model specific registers (MSRs), used to communicate IPIs between the processors. In an embodiment, several types of IPIs may be defined, such as one or more of an immediate type, a deferred type, a retract type, and / or a non-waking type. The immediate IPI may be delivered and may cause the target processor to interrupt in response to receipt of the IPI. The deferred IPI may be delivered within a defined time limit, and not necessarily on receipt by the target processor. The retract IPI may cause a previously transmitted IPI to be cancelled (if it has not already caused the target processor to interrupt). A non-waking IPI may not cause the target processor to wake if it is asleep, but may be delivered when the target processor is awakened for another reason.
Owner:APPLE INC
System and method to provide single thread access to a specific memory region
InactiveUS10095557B2Program synchronisationSpecific program execution arrangementsProcess logicParallel computing
Processing logic and a method to provide single thread access to a specific memory region without suspending processing activity for all other cores and / or threads within or in association with a processor, computer system, or other processing apparatus. Single thread access may be provided through implementation of microcode which may control thread access to model specific registers (“MSRs”) within a processor. One MSR may provide a mutex, which a single thread may claim, and another MSR may provide a range of memory locations, which may be accessed by the thread that has claimed the mutex.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and apparatus for SYSRET monitoring of system interactions
ActiveUS9733976B2Multiprogramming arrangementsPlatform integrity maintainanceOperational systemSystem call
A security system and method efficiently monitors and secures a computer to defend against malicious intrusions, and includes an in-band software monitor disposed within a kernel in communication with an operating system (OS) of the computer. The monitor intercepts system calls made from an MSR (Model Specific Register), to execute monitoring operations, and subsequently returns execution to the OS. An out-of-band hypervisor communicably coupled to the OS, has read shadow means for trapping read requests to the MSR, and write mask means for trapping write requests to the MSR. The hypervisor includes means for responding to the trapped read and write requests so that presence of the monitor is obscured. Sysret monitoring means intercepts calls to a sysret instruction, executes sysret monitoring operations, and subsequently returns execution to an application running on the computer.
Owner:ALERT LOGIC
Method and apparatus for user-level thread synchronization with a monitor and MWAIT architecture
Instructions and logic provide user-level thread synchronization with MONITOR and MWAIT instructions. One or more model specific registers (MSRs) in a processor may be configured in a first execution state to specify support of a user-level thread synchronization architecture. Embodiments include multiple hardware threads or processing cores, corresponding monitored address state storage to store a last monitored address for each of a plurality of execution threads that issues a MONITOR request, cache memory to record MONITOR requests and associated states for addresses of memory storage locations, and responsive to receipt of an MWAIT request for the address, to record an associated wait-to-trigger state of monitored addresses for execution cores associated with an MWAIT request; wherein the execution core is to transition a requesting thread to an optimized sleep state responsive to the receipt of said MWAIT request when said one or more MSRs are configured in the first execution state.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method for detecting existence of virtual machine monitor (VMM) under Windows platform
ActiveCN102063594BOvercome limitationsImprove general performancePlatform integrity maintainanceSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationInternal memoryPage table
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Data processing device and data processing method
ActiveUS11398899B2Improve securityImprove security levelKey distribution for secure communicationComputer hardwareComputer architecture
A data processing method includes the following steps: a processor receives a symmetric wrapping key, and when an application needs to use a user private key, the processor executes an encryption and decryption instruction in a hardware-acceleration instruction-set. The encryption and decryption instruction is configured to apply the symmetric wrapping key to decrypt a wrapped private key that corresponds to the application to obtain the user private key. In addition, the symmetric wrapping key is stored in a model specific register of the processor.
Owner:VIA ALLIANCE SEMICON CO LTD
Shell Intel CPU Msr (Intel central processing unit model-specific register) reading tool implementation and application method
InactiveCN107133138AShorten the timeLow costDetecting faulty computer hardwareNetwork packetModel-specific register
The invention discloses a shell Intel CPU Msr reading tool implementation and application method. The implementation method comprises selecting a programming environment and creating a data package; creating files in formats of .dec, .dsc, .sc, .inf and .c to writing code tags; encoding the code tags inside cmd (command) to generate a tool for reading an Intel CPU Msr. Compared with the prior art, the shell Intel CPU Msr reading tool implementation and application method is applicable to testing and debug of Intel CPU Msr reading and saves serial devices and console terminals, thereby saving time and reducing the cost; the entire implementation process of the shell Intel CPU Msr reading tool implementation and application method can be achieved only by running under shell without any other devices, thereby being simple, convenient and high in practicality.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU YUNHAI INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for hypervisor based monitoring of system interactions
A security system and method efficiently monitors and secures a computer to defend against malicious intrusions, and includes an in-band software monitor disposed within a kernel in communication with an operating system (OS) of the computer. The monitor intercepts system calls made from an MSR (Model Specific Register), to execute monitoring operations, and subsequently returns execution to the OS. An out-of-band hypervisor communicably coupled to the OS, has read shadow means for trapping read requests to the MSR, and write mask means for trapping write requests to the MSR. The hypervisor includes means for responding to the trapped read and write requests so that presence of the monitor is obscured.
Owner:ALERT LOGIC
Apparatus and method for limiting access to model specific registers in a microprocessor
A microprocessor having a control register to which the manufacturer of the microprocessor may limit access. The microprocessor includes a manufacturing identifier that uniquely identifies the microprocessor and that is externally readable from the microprocessor by a user. The microprocessor also includes a secret key, manufactured internally within the microprocessor and externally invisible. The microprocessor also includes an encryption engine, coupled to the secret key, configured to decrypt a user-supplied password using the secret key to generate a decrypted result in response to a user instruction instructing the microprocessor to access the control register. The user-supplied password is unique to the microprocessor. The microprocessor also includes an execution unit, coupled to the manufacturing identifier and the encryption engine, configured to allow the instruction access to the control register if the manufacturing identifier is included in the decrypted result, and to otherwise deny the instruction access to the control register.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Apparatus and method for updating set of limited access model specific registers in a microprocessor
ActiveUS8402279B2Save potentially large amount of revenueShorten the timeUnauthorized memory use protectionGeneral purpose stored program computerLimited accessOperating system
Owner:VIA TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com