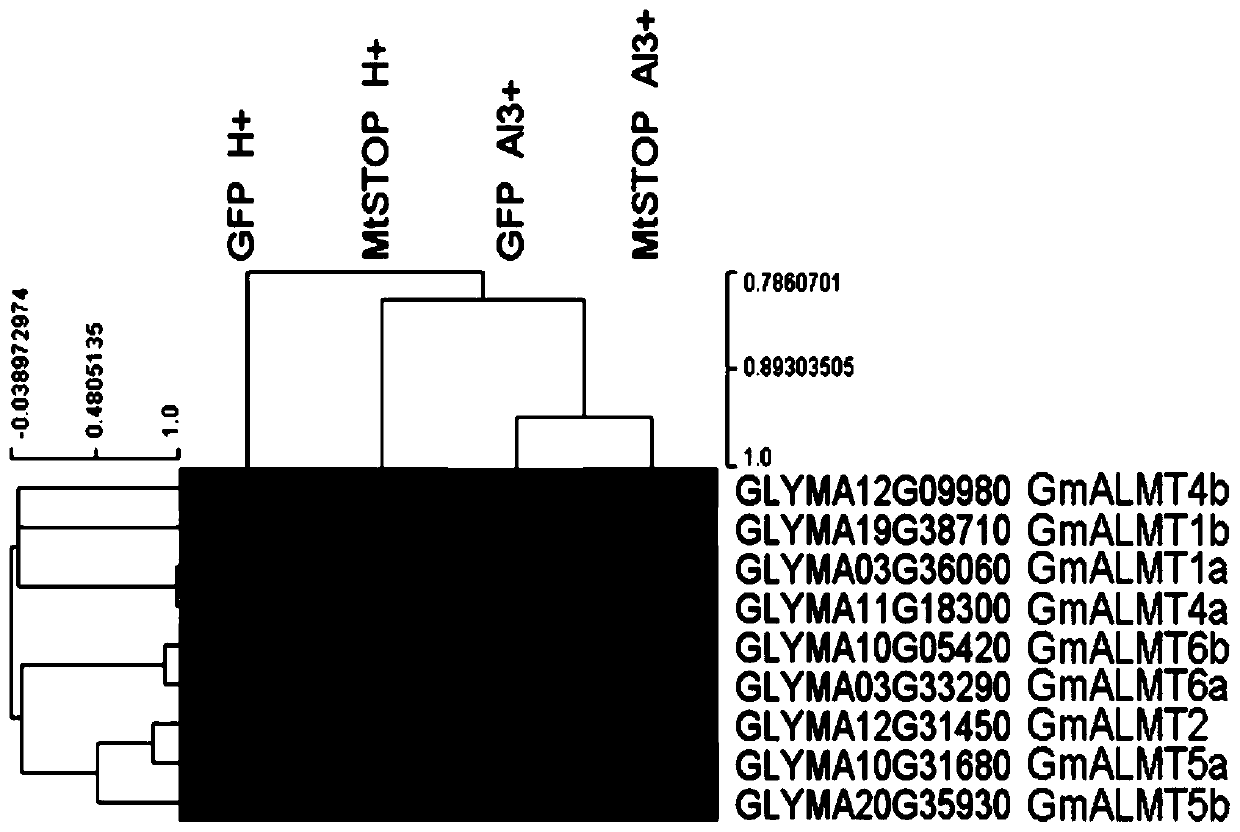
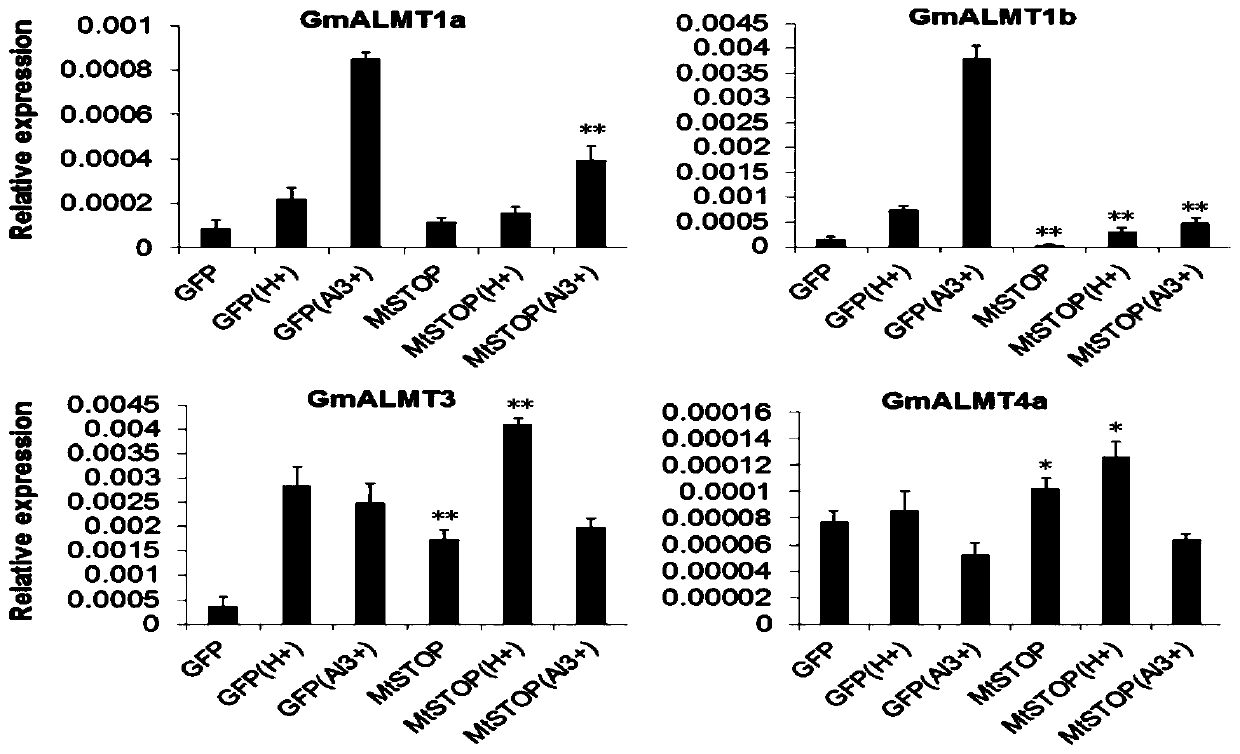
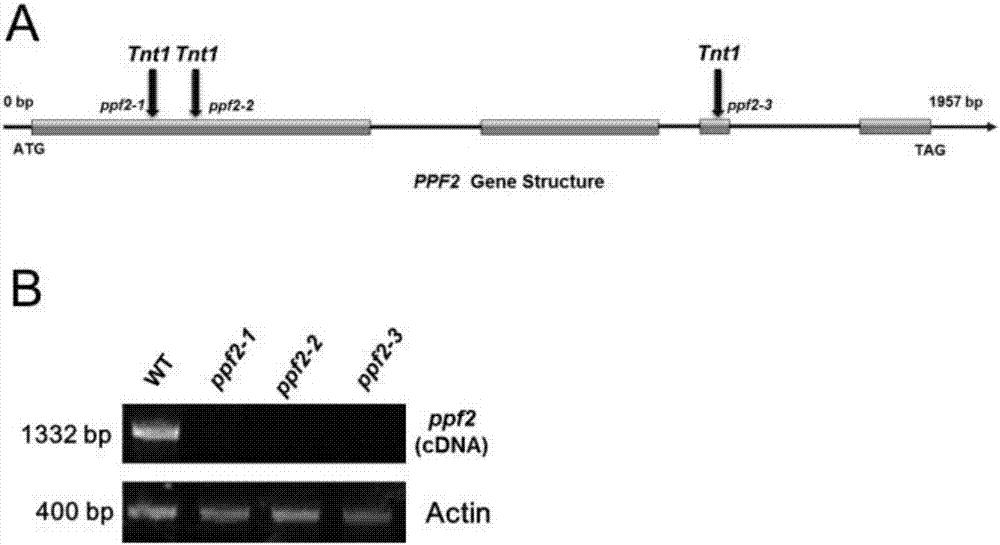
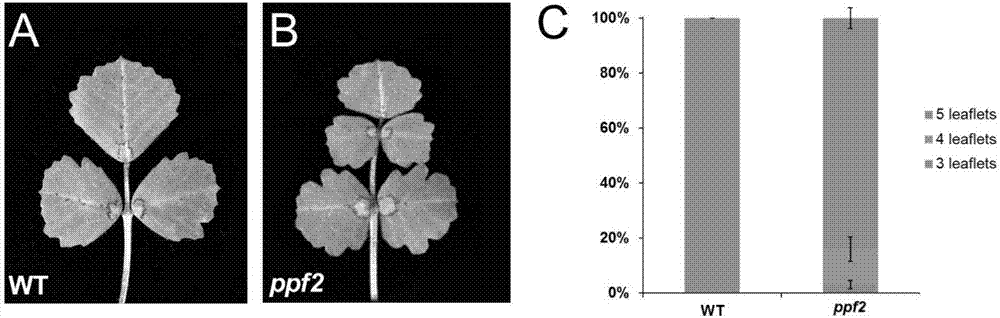
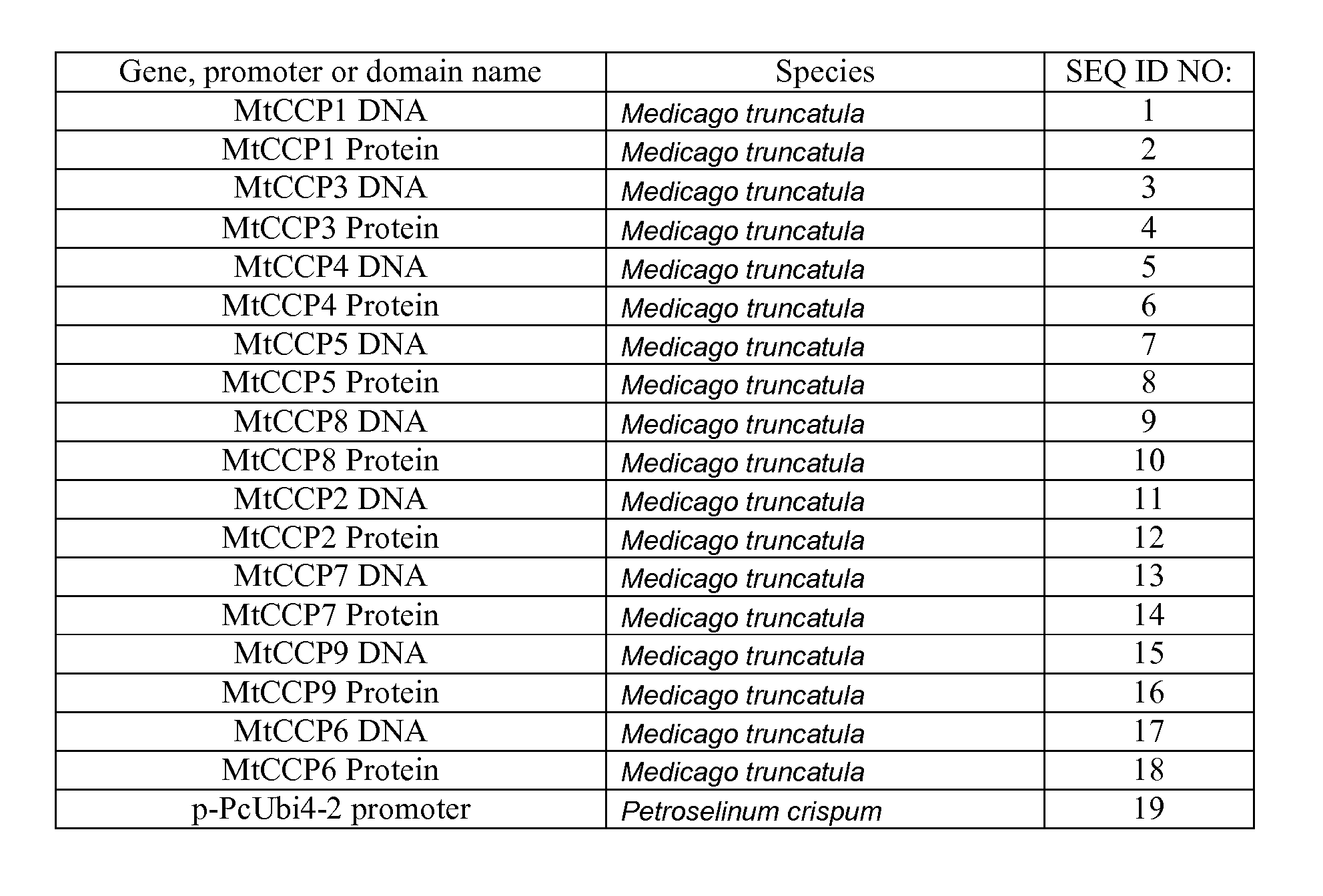
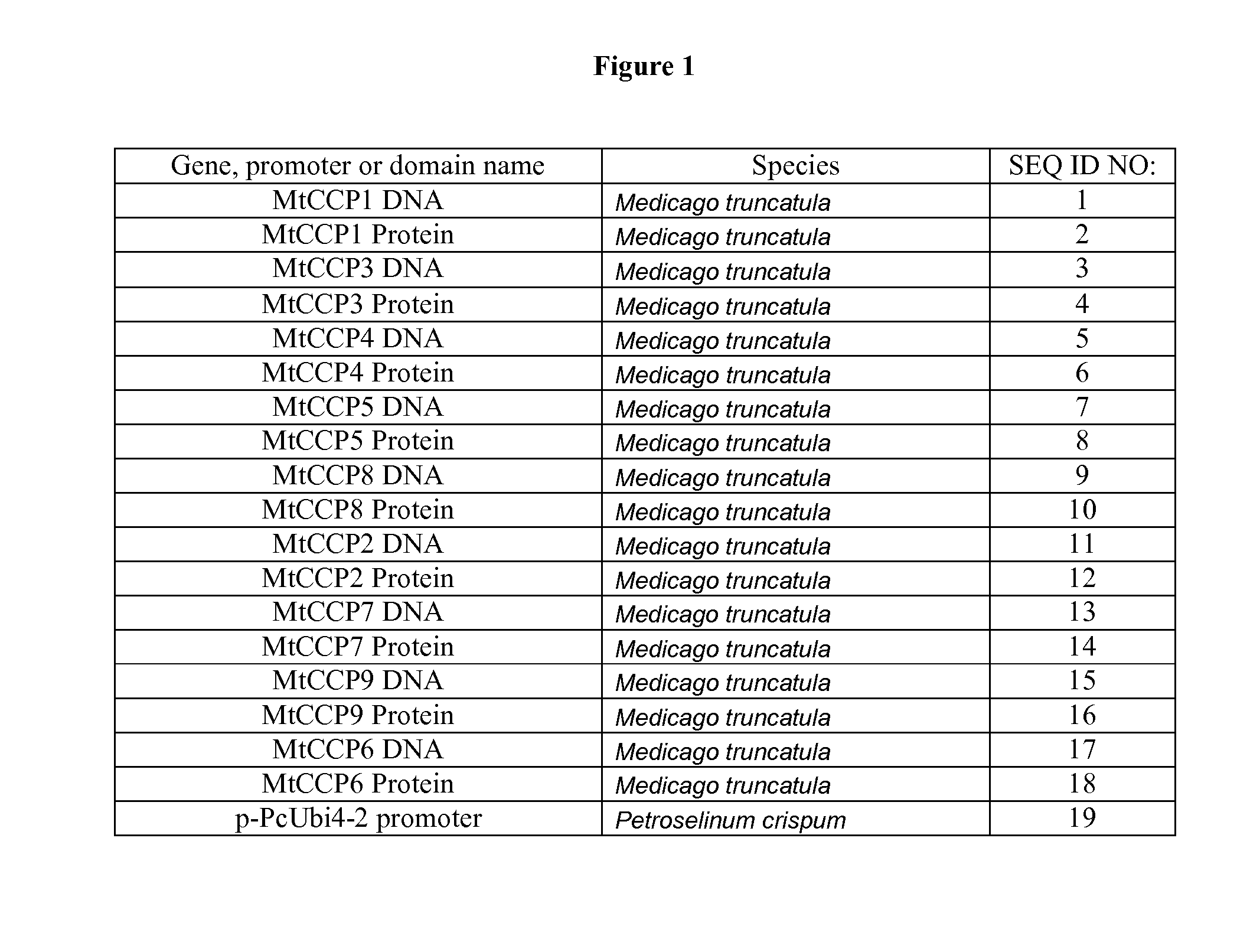
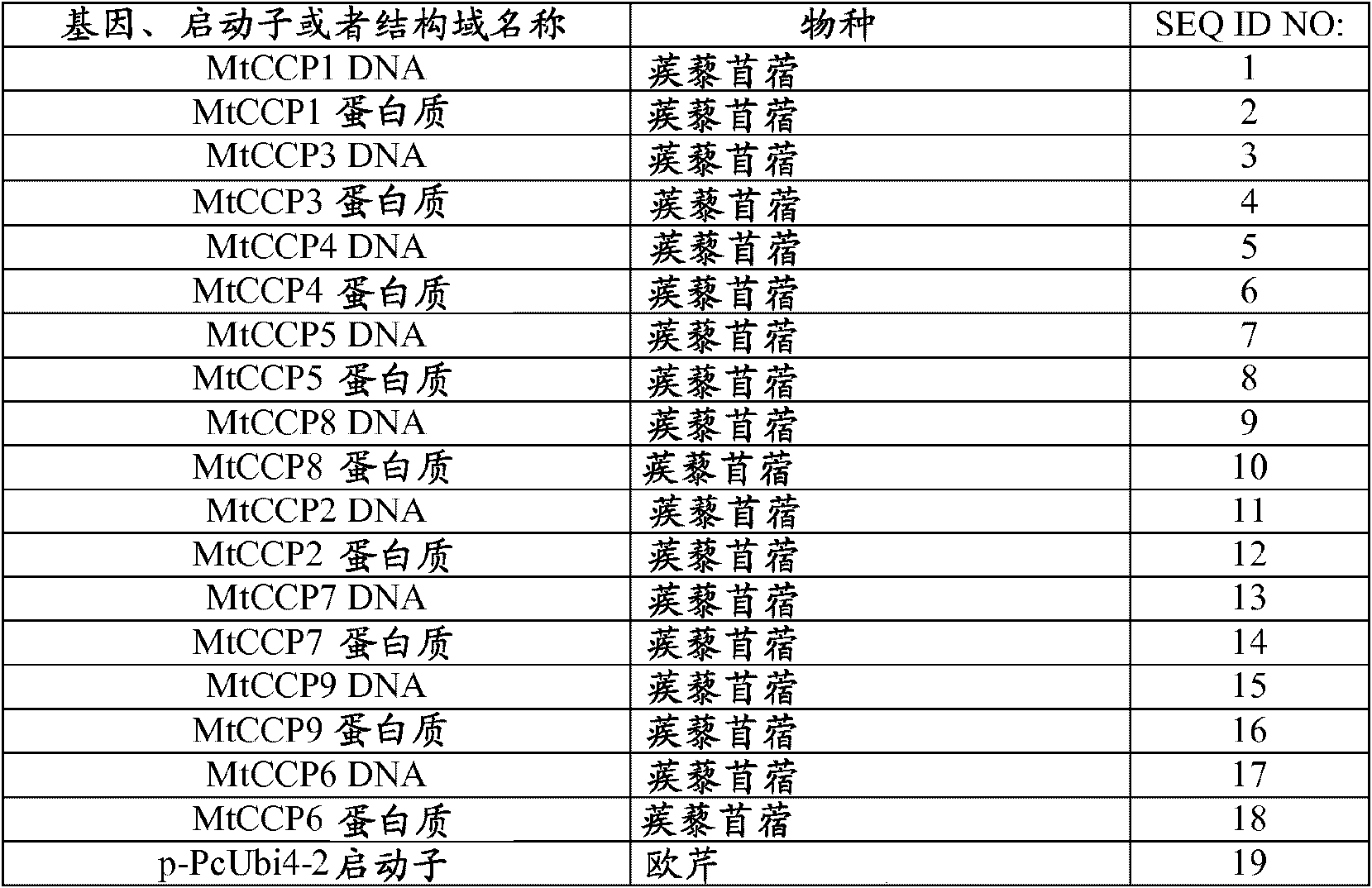
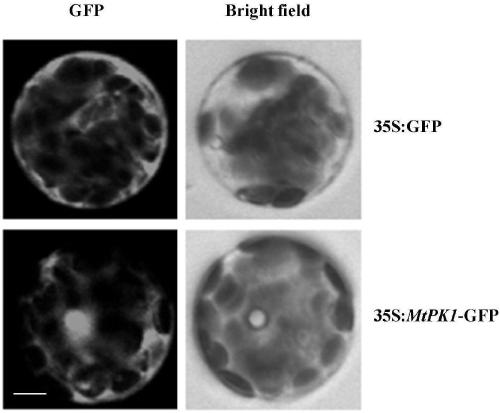
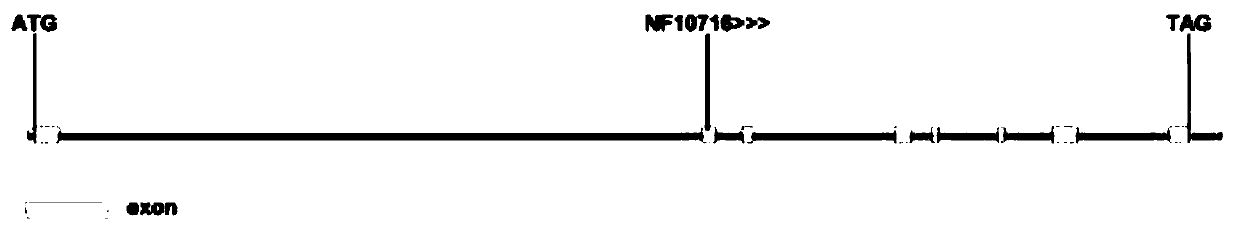
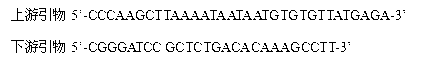Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
56 results about "Medicago truncatula" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Medicago truncatula, the barrelclover, strong-spined medick, barrel medic, or barrel medick, is a small annual legume native to the Mediterranean region that is used in genomic research. It is a low-growing, clover-like plant 10–60 centimetres (3.9–23.6 in) tall with trifoliate leaves. Each leaflet is rounded, 1–2 centimetres (0.39–0.79 in) long, often with a dark spot in the center. The flowers are yellow, produced singly or in a small inflorescence of two to five together; the fruit is a small, spiny pod.
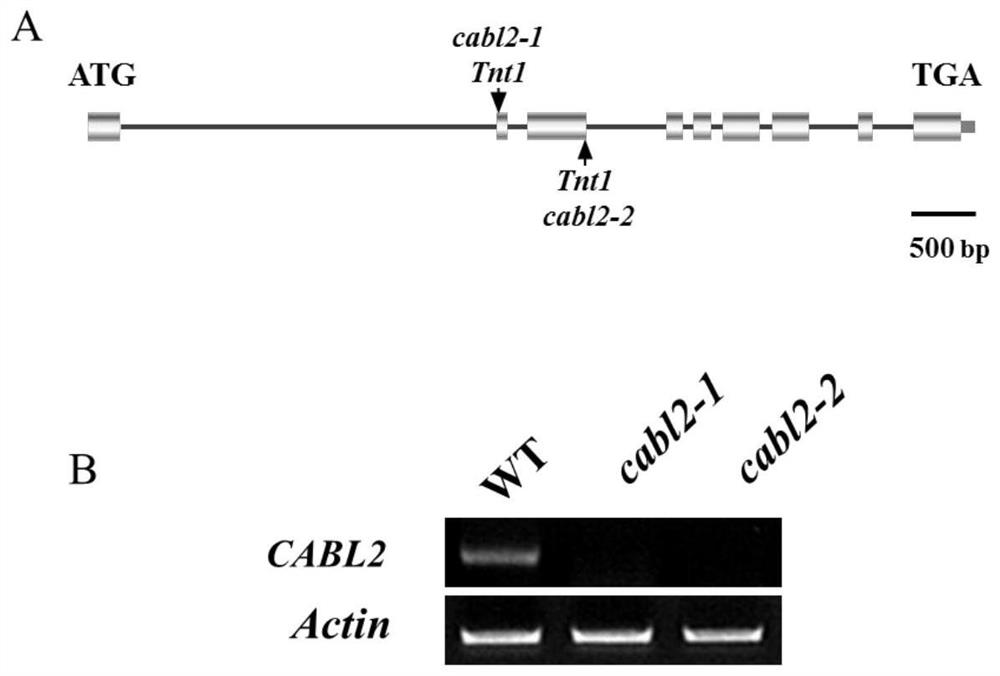
DMI1 gene encodes a protein that is required for the early steps of bacterial and fungal symbioses
InactiveUS7205450B2Enhanced nitrogen and phosphorous acquisitionBryophytesSugar derivativesPlant cellNodulations
The invention relates to isolated DMI11 genes from Medicago truncatula which play a major role both in the early steps of Nod factor signaling that trigger several key developmental responses in the host plant and in the establishment of mycorrhizal symbiosis. The invention also relates to transgenic plants and plant cells expressing the DMI1 protein for increased root nodulation, and methods for transforming plants with a M. truncatula DMI1 gene.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL DE LA RECHERCHE AGRONOMIQUE +1
Methods of identifying genes for the manipulation of triterpene saponins
The invention provides methods for the isolation of plant genes and their regulatory sequences involved in the biosynthesis of triterpene saponins. Also provided by the invention are genes involved in the biosynthesis of triterpenes, including squalene synthase, squalene epoxidase and beta-amyrin synthase from Medicago truncatula. The identification of triterpene biosynthesis genes allows genetic modification of the content and composition of triterpene saponins in plants for crop improvement and the development of drugs, nutriceuticals and functional foods.
Owner:SAMUEL ROBERTS NOBLE FOUND
Plant stress tolerance associated protein, and coded genes and application thereof
ActiveCN101955521AImprove salt toleranceImprove drought resistanceFungiBacteriaDrought resistanceMedicago truncatula
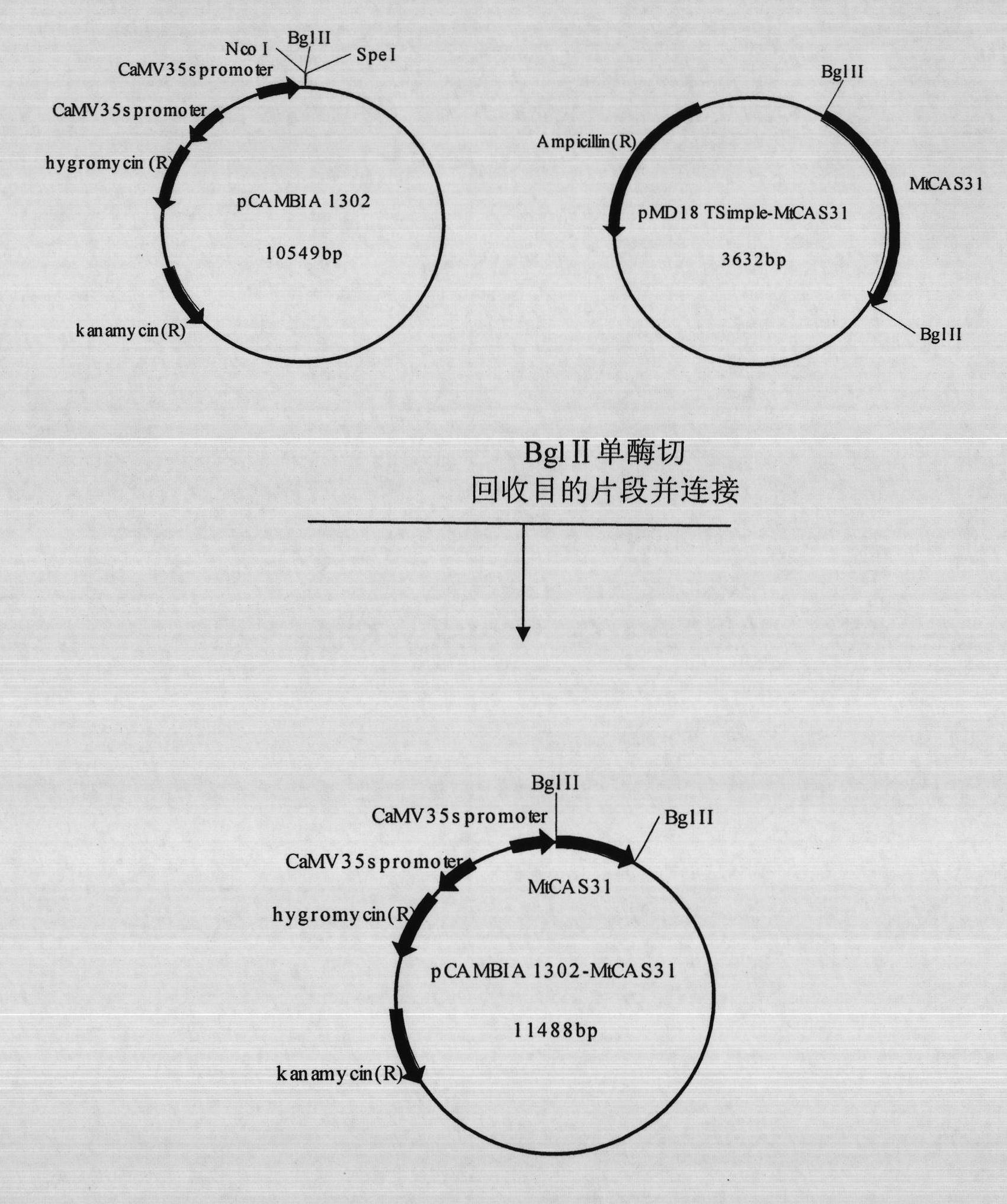
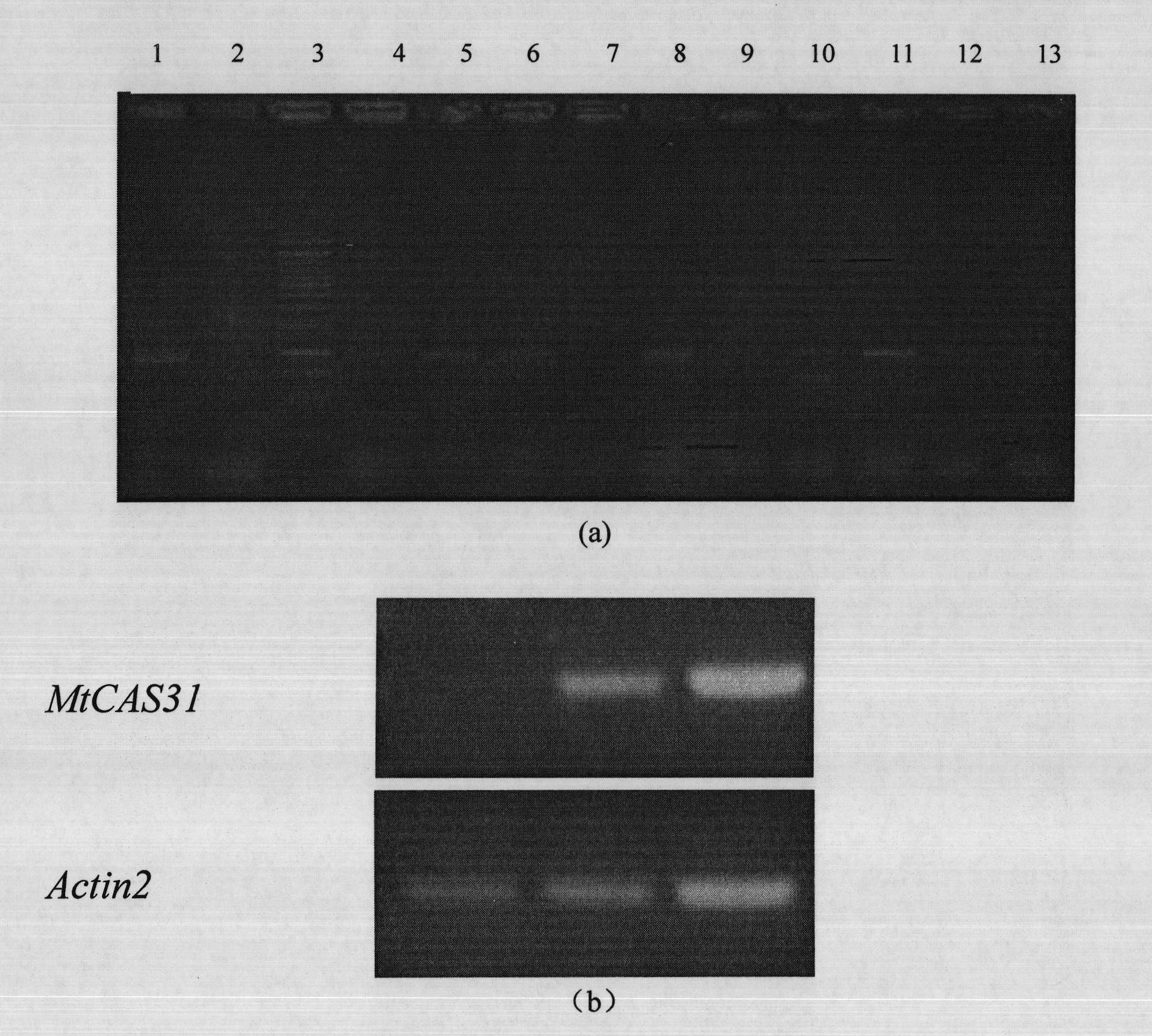
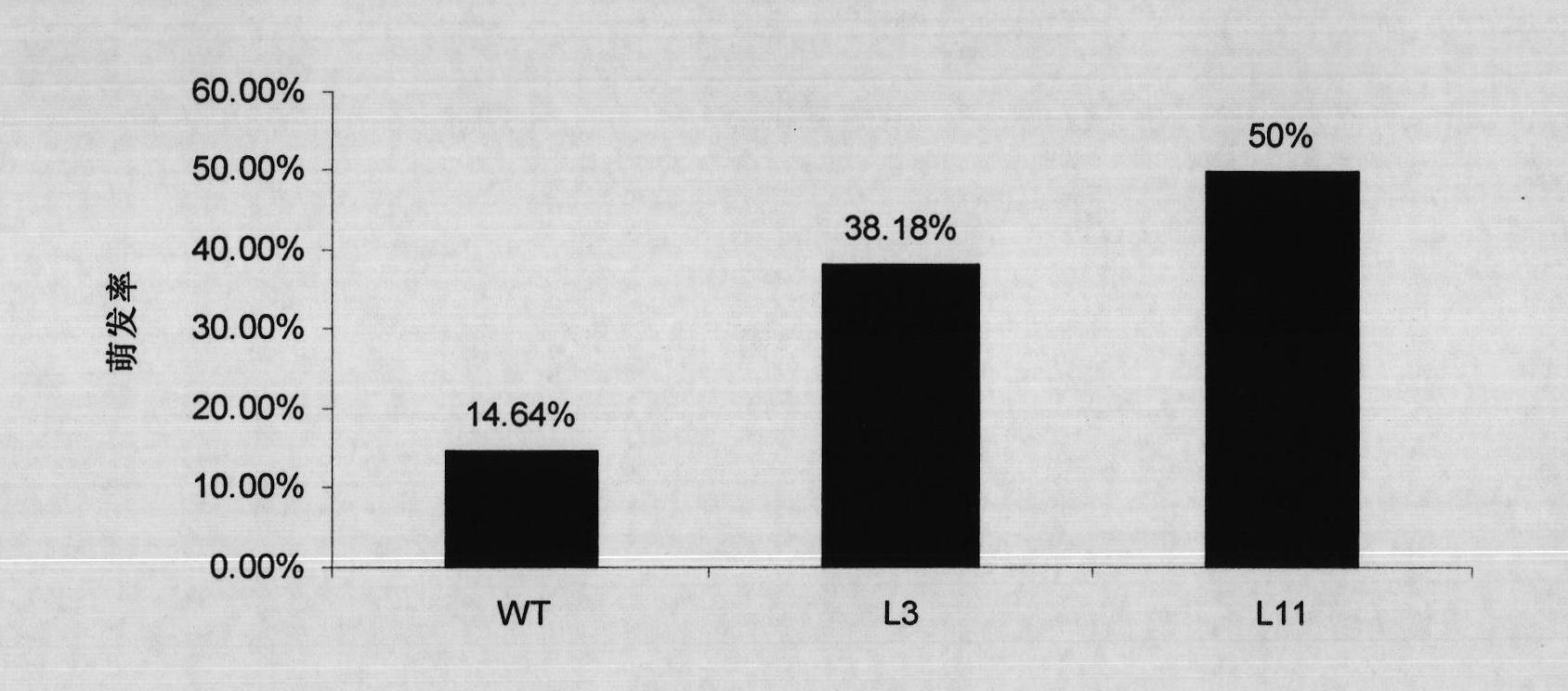
The invention discloses a plant stress tolerance associated protein, and coded genes and application thereof. The protein provided by the invention is named MtCAS31, is from Medicago truncatula A17 and is the protein of 1) or 2): 1) the protein consisting of the amino acid sequence shown as sequence 2 in a sequence list; and 2) the protein derived from 1), associated with plant stress tolerance and formed by substituting and / or deleting and / or adding one or more amino acid residues of the amino acid sequence shown as sequence 2. Experiments show that: a dehydrin gene MtCAS31 selected by the invention has important value in breeding transgenic leguminous crops with salt tolerance and drought resistance.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Genetic manipulation of isoflavonoids
InactiveUS7038113B1Improve the level ofHigh nutritional valueClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesDiseaseCytochrome P450
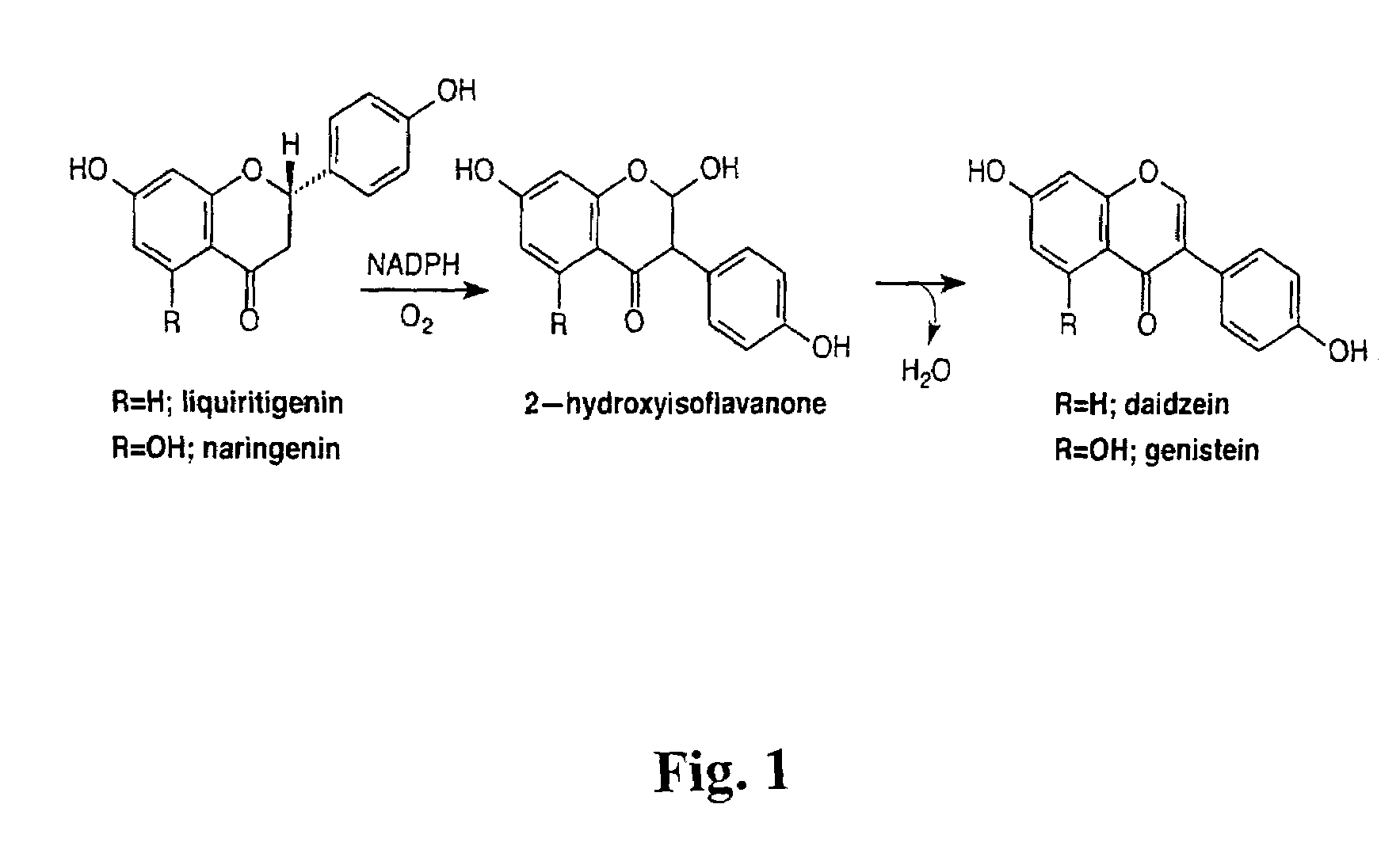
Soybean and Medicago truncatula CYP93C genes have been isolated which encode a cytochrome P450 that can catalyze the aryl migration of a flavanone to yield an isoflavanone intermediate or an isoflavone. Plants can now be genetically engineered to produce isoflavones that provide potential human health benefits and increase disease resistance in plants. Isoflavones can now be produced in transgenic plants species in which isoflavones do not naturally occur, i.e., in species other than legumes. Alternatively, introducing infection-inducible isoflavonoid biosynthesis into non-legumes qualitatively complements these plants phytoalexin defenses against microbial pathogens, whereas over-expression of the isoflavonoid pathway in legumes quantitatively increases this defense response. Finally, modifying the extend of production of isoflavonoids in legume roots positively impacts nodulation efficiency and therefore plant yield.
Owner:SAMUEL ROBERTS NOBLE FOUND
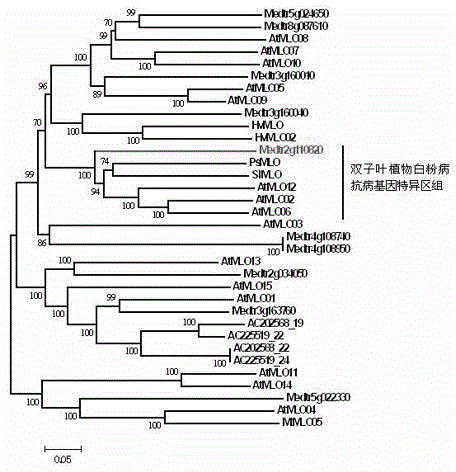
Rapid identification of powdery mildew gene of Medicago truncatula by utilizing comparative genomics
InactiveCN102719445AQuick assist selectionImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyRapid identification
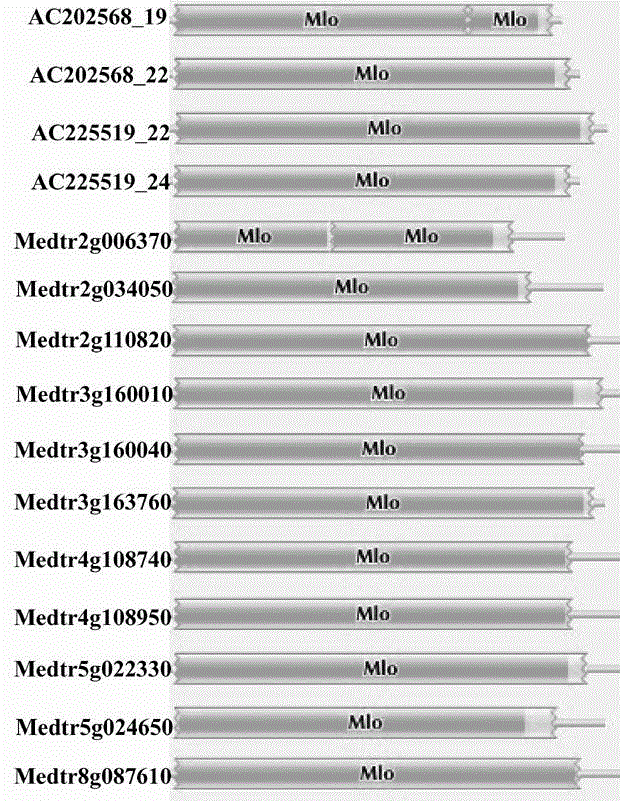
The present invention is rapid identification of a powdery mildew gene of Medicago truncatula, relates to discipline knowledge of plant comparative genomics, genetics and bioinformatics and belongs to the technical field of plant biotechnology. The invention mainly comprises the following steps: 1) download of Medicago truncatula genome sequence and collection of an MLO gene; 2) identification of MLO type gene; 3) MLO gene phylogenetic relationship; and 4) comparison of MLO type powdery mildew gene. The invention effectively shortens a mining cycle of the powdery mildew gene of Medicago truncatula and facilitates the rapid identification of the powdery mildew gene. The identified candidate powdery mildew genes can be used to develop corresponding coseparation functional markers (SNP and SCAR, etc.), and can also be used quickly for molecular marker assisted selection of powdery mildew resistant gene, and has high accuracy. Combined with other disease resistant gene molecular markers, the identified candidate powdery mildew genes can be used in development of multiresistance breeding material, so as to shorten the breeding period and improve breeding efficiency. The invention lays foundation to elaborate molecular mechanism of powdery mildew resistance of Medicago truncatula.
Owner:常熟市支塘镇新盛技术咨询服务有限公司
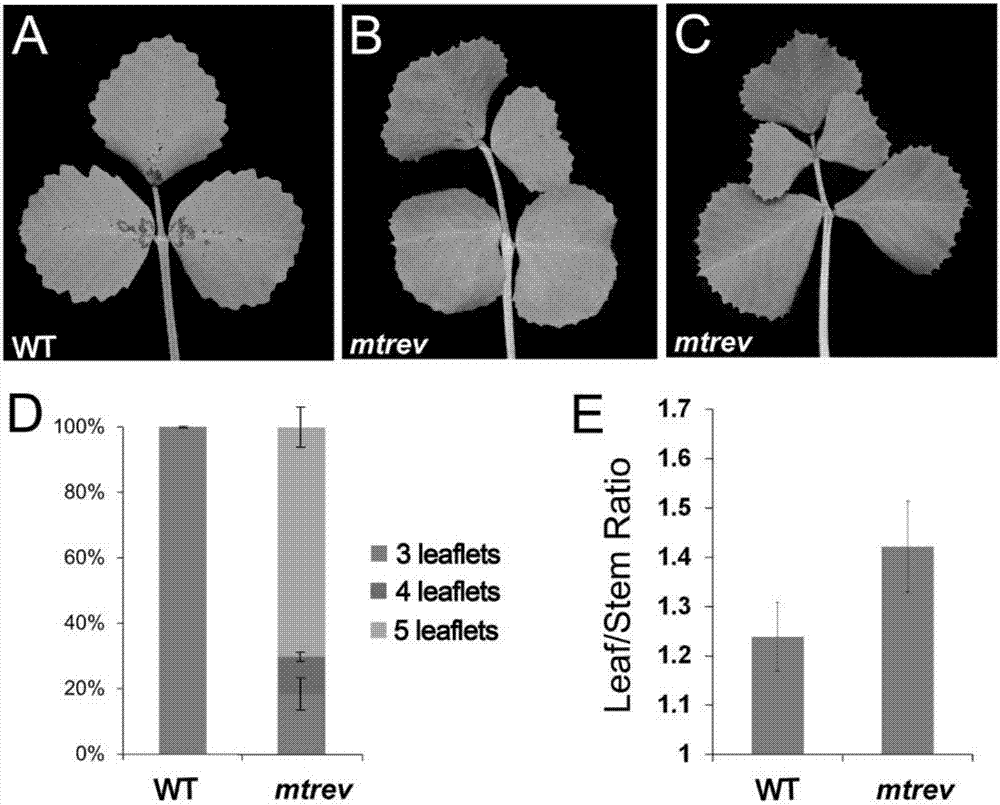
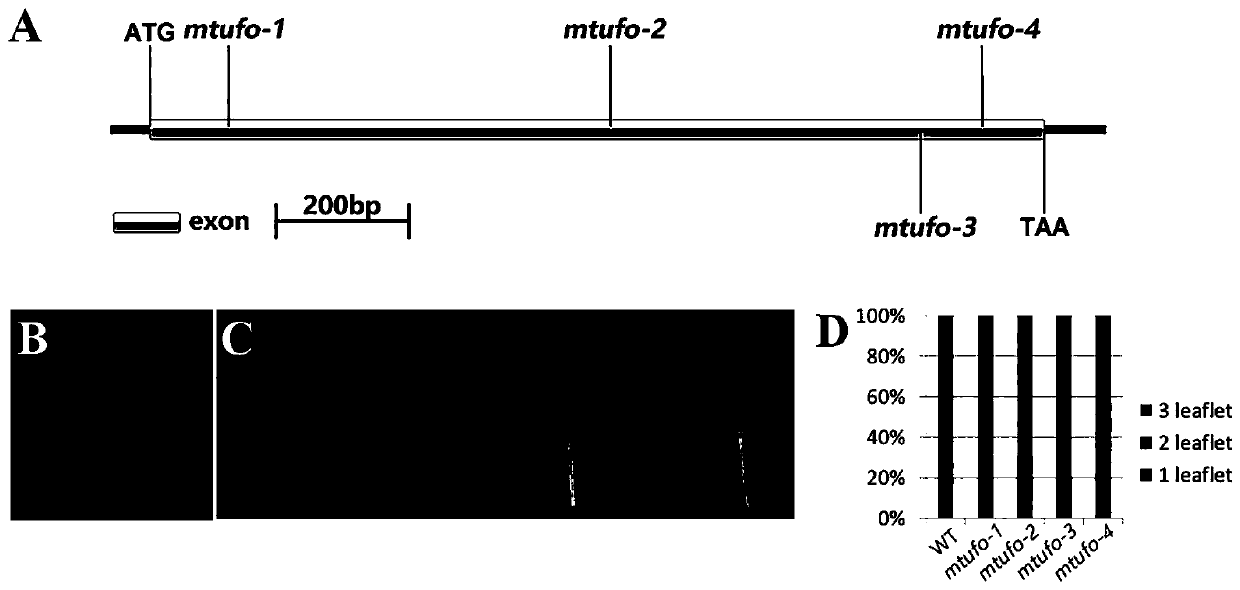
Application of REVOLUTA gene to regulation and control on quantity of leaflets in leguminous plant and leaf-stem ratio
InactiveCN107299104AIncrease the number ofIncrease leaf-to-stem ratioPlant peptidesFermentationAnimal ForagingWild type
The invention discloses application of an REVOLUTA gene (A nucleotide sequence is shown as SEQ ID No.1) to regulation and control on quantity of leaflets in a leguminous plant and leaf-stem ratio. According to the application disclosed by the invention, a knockout mutant strain of the REVOLUTA gene as a medicago truncatula HD-ZIP III gene family member is obtained by first separation, the quantity of the leaflets in the plant is discovered to be changed from three into four or five (the quantity of the leaflets in 81.5 percent of leaves is increased), and meanwhile, the leaf-stem ratio is significantly improved by about 11 percent; an experiment proves that the gene is involved in the regulation and the control on the quantity of the leaflets in the leguminous plant and the leaf-stem ratio; through gene knockout, the transgenic leguminous plant with higher leaflet quantity and leaf-stem ratio than those of a wild type plant can be obtained; after the implementation of the invention, a novel leguminous forage plant can be created and can be used for subsequent forage quality, thereby being of a great significance in the production of the grass industry in China.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Application of medicago truncatula MYB transcription factor MtMYB1
ActiveCN107937413AImprove the efficiency of seed production servicesIncrease productionPlant peptidesFermentationType transformationArabidopsis
The invention discloses application of a medicago truncatula MYB transcription factor MtMYB1. According to the invention, a gene MtMYB1 for regulating and controlling development, flowering phase andgrowth period of floral organs and changing a plant type is colonized from medicago truncatula flower, and the sequence of the gene MtMYB1 is SEQ ID NO.1. The analysis of mRNA (messenger Ribonucleic Acid) expression of the gene shows that the MtMYB1 is expressed in flower tissues with strong advantages; phenotypic change of arabidopsis thaliana for further over-expression of the MtMYB1 shows thatthe MtMYB1 has an important regulation and control effect on the development, the flowering phase and the growth period of the floral organs and the plant type. The invention discloses the applicationof the gene in genetic engineering of morphology, the flowering phase and the growth period of the floral organs as well as plant type transformation.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
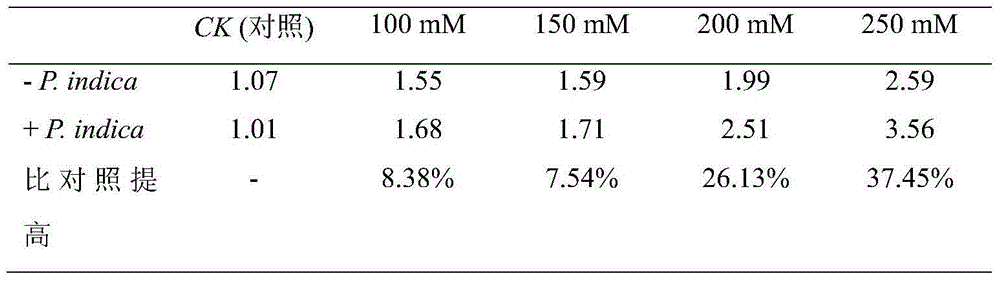
Method for improving salt stress tolerance of medicago truncatula
InactiveCN105850535APromote early germinationImprove germination rateSeed and root treatmentHorticulture methodsSporePiriformospora
The invention relates to a method for improving salt stress tolerance of medicago truncatula. The method comprises the steps: (1) preparing a solid CM complete medium for piriformospora indica; (2) culturing the piriformospora indica and collecting a spore suspension; (3) inoculating the piriformospora indica to the medicago truncatula; and (4) transplanting medicago truncatula seedlings and carrying out later-stage management. According to the method, the piriformospora indica spore suspension is adopted to soak seeds in advance, so that the piriformospora indica can be parasitized to surfaces of the medicago truncatula seeds, the seeds are promoted to germinate ahead of time, and the germination percentage of the seeds is remarkably increased (increased to 95.0% from the original 80.0%); the biological yield of the medicago truncatula can be remarkably increased; and through parasitizing the piriformospora indica to roots of the medicago truncatula, the accumulation of sodium ions in the roots of the medicago truncatula can be lowered, and thus the salt stress tolerance of the medicago truncatula is improved.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Medicago truncatula multi-petal control protein and encoded genes and application thereof
The invention discloses a medicago truncatula multi-petal control protein and encoded genes and application thereof. The medicago truncatula multi-petal control protein is shown as the following (a1)or (a2), wherein (a1) is a protein consisting of the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.2, and (a2) is a protein which is derived from SEQ ID NO.2 through substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or more amino acid residues of the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.2 and has functions the same as the protein of (a1). The genes can control the increase of petals of medicago truncatula, finite growth of plants is achieved, mutation of the leaf morphology is achieved, and the petiole gets shorter.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Treatment method for increasing germination rate of medicago truncatula seeds
InactiveCN103782687ASolve the problem of germplasm with low germination rateSolve the bottleneck problem of growthGerminating apparatusBiological studiesGermplasm
The invention discloses a treatment method for increasing the germination rate of medicago truncatula seeds. The treatment method comprises the steps of after disinfecting the medicago truncatula seeds, soaking the medicago truncatula seeds by using a 0.1 mmol / L sodium nitroprusside solution for 48h, and culturing the medicago truncatula seeds in a dark place for 7 days at the temperature of 25+ / -1 DEG C and 12h illumination (3000LX) / 12h to promote seed germination. The treatment method for increasing the germination rate of the medicago truncatula seeds has the beneficial effects that the 0.1mmol / L sodium nitroprusside (SNP) solution is used for treating the medicago truncatula seeds so that the germination is remarkably promoted, and the germination rate reaches 62.14 percent, and is increased by 54.47 percent in comparison with those of a contrast group. Sodium nitroprusside is nontoxic at a low concentration, few in consumption amount when being used for treating the seeds, economical, short in time and high in effect taking speed; the seeds are not damaged, and the method is simple and is not influenced by factors such as season, weather, and natural hazard. By using the method, the problem of low germination rate of the medicago truncatula seeds can be solved, and germplasm resources with good germplasm are provided for biological study of legumes and production of medicago truncatula.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
Alumite-stress transgenic soybean and application thereof
InactiveCN110358789AIncrease productionFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionGenetically modified soybeanPlant variety
The invention discloses an alumite-stress transgenic soybean and application thereof. The transgenic soybean is infected by agrobacterium, and exogenous zinc finger protein transcription factors are integrated in a transgenic soybean genome; the amino acid sequence encoded by the zinc finger protein transcription factors is shown in SEQIDNO.1. The transgenic soybean is obtained after the zinc finger protein transcription factors separated from medicago truncatula are transformed and expressed in soybean plants. The production and application of the alumite-stress transgenic soybean are provided and of great significance for cultivating acid-aluminum resistant plant varieties and improving the crop yield in southern acid aluminum soil, and lay a foundation for further research on acid-aluminum resistance of crops.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Application of PINNATE PENTAFOLIATA2 gene in regulating and controlling leaflet quantity of leguminous plants
InactiveCN107338255AIncrease the number ofPlant peptidesGenetic engineeringLegeriomycetaceaeAnimal Foraging
The invention discloses an application of a PINNATE PENTAFOLIATA2 gene (a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1) in regulating and controlling leaflet quantity of leguminous plants. According to the invention, a knockout mutant strain of the medicago truncatula PINNATE PENTAFOLIATA2 gene is obtained through separation for the first time; and it is discovered that the quantity of leaflets of plants is turned to 5 from 3, and a few of plants have 4 leaflets. Up to 97% of leaves of the obtained plants have increased leaflet quantity, and the data is much greater than existing multifoliate alfalfa varieties. It is proved that the gene participates in regulating and controlling of the leaflet quantity of leguminous plants. Transgenic leguminous plants, which are higher than wild-type plants in leaflet quantity, can be obtained by knocking out the gene, predicting that novel leguminous forage plants can be created with the implementation of the invention, and subsequent forage quality can be improved; therefore, the invention has great significance for grass industry production in China.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Nematode-Resistant Transgenic Plants
InactiveUS20110145945A1Overcome problemsAlleviate and nematode infestationBryophytesClimate change adaptationNucleotideSoybean cyst nematode
The invention provides nematode-resistant transgenic plants and seed comprising polynucleotides encoding Medicago truncatula cysteine cluster proteins which comprise no more than four cysteine residues in the respective mature peptides. The invention also provides methods of producing transgenic plants with increased resistance to soybean cyst nematode and expression vectors for use in such methods.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Primer pair, kit comprising same, application of primer pair and method for detecting medicago truncatula ecotypic A17 and R108
ActiveCN108411030AAvoid false positivesAvoid false negativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDNA fragmentationRepeatability
The invention provides a primer pair, a kit comprising the same, application of the primer pair and a method for detecting medicago truncatula ecotypic A17 and R108 and relates to the field of biotechnology. The primer pair comprises a primer NST480-F and a primer NST480-R, which have sequences separately shown as SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2 and meanwhile can simultaneously amplify DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) fragments of different lengths of the medicago truncatula ecotypic A17 and R108, so that a user can distinguish whether a sample to be detected contains the medicago truncatula ecotypic A17 and R108 through one amplification. When applied to detecting the medicago truncatula ecotypic A17 and R108, the primer pair has the advantages of being high in sensitivity, accuracy and repeatability, rapid, convenient and the like and solves the problem that the prior art lacks a rapid and accurate method for detecting and identifying the medicago truncatula ecotypic A17 and R108.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Nematode-resistant transgenic plants
InactiveCN102124025AIncrease nematode resistanceClimate change adaptationPlant peptidesNucleotideSoybean cyst nematode
The invention provides nematode-resistant transgenic plants and seed comprising polynucleotides encoding Medicago truncatula cysteine cluster proteins which comprise no more than four cysteine residues in the respective mature peptides. The invention also provides methods of producing transgenic plants with increased resistance to soybean cyst nematode and expression vectors for use in such methods.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
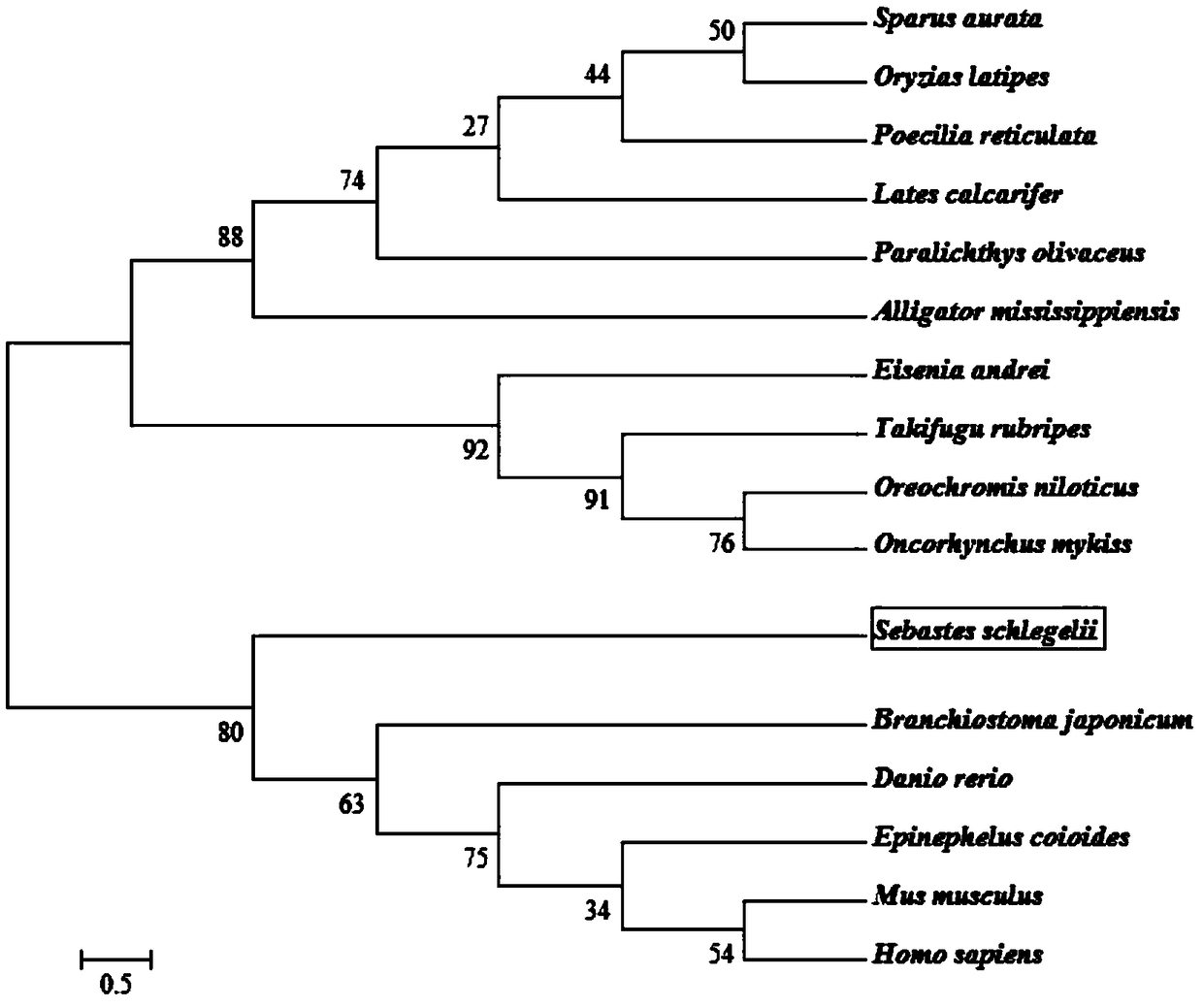
Sebastes schlegeli calreticulin gene and application
PendingCN109182339AAccurate and rapid amplificationStrong specificityPlant peptidesFermentationAgricultural scienceSebastes
The invention discloses a sebastes schlegeli calreticulin gene and an application. The sebastes schlegeli calreticulin gene is an arbitrary one of DNA molecules as shown in (a1) to (a4): a DNA molecule having a coding region as shown in SEQ ID NO.1; (a2) a DNA molecule as shown in SEQ ID NO.3; (a3) a DNA molecule which is hybridized with the DNA sequence defined by (a1) or (a2) under a strict condition and codes the protein in claim 1; and (a4) a DNA molecule which is sourced from medicago truncatula and has more than 90 percent of homology with the DNA sequence defined by (a1) or (a2) or (a3). The sebastes schlegeli calreticulin gene has the advantages of short cycle, simple operation, low price, strong specificity and the like, is economical, and provides technical support to amplification of CRT genes of other species.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
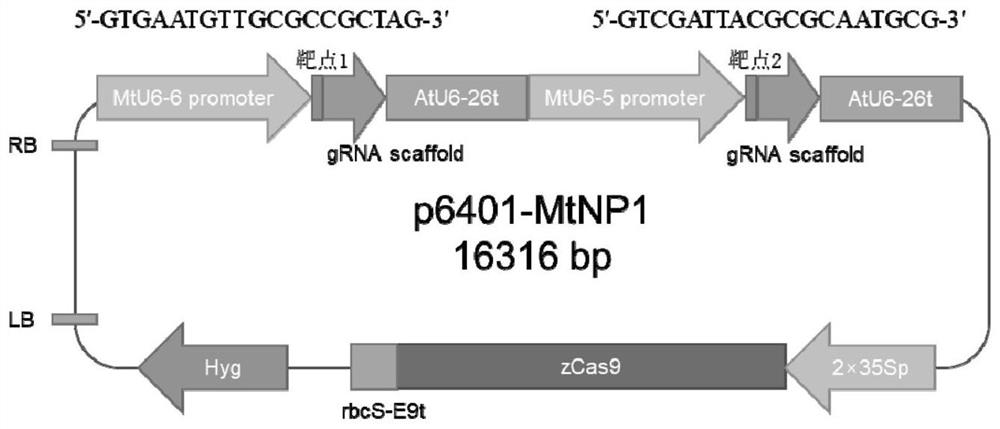
Method for cultivating male sterile line and corresponding maintainer line of alfalfa and related biological material
The invention discloses a method for cultivating a male sterile line and a corresponding maintainer line of alfalfa by using a gene editing technology. An efficient gene editing system is utilized to target medicago truncatula MtNP1 and a homolog MsNP1 of the medicago truncatula MtNP1 in medicago sativa, and agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated genetic transformation is adopted, so that a material in which all alleles of the MtNP1 or the MsNP1 are mutated is obtained, and the phenotype of the material is male sterility; a material retaining a wild-type allele is obtained from the system, and the material is male fertile and can be used as a corresponding maintainer line. The method of cultivating the male sterile line mediated by the gene editing technology and a matched maintainer line is short in period, high in efficiency and good in targeting property, greatly saves the time and economic cost of traditional alfalfa sterile line screening and cultivation, and has important application prospects.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
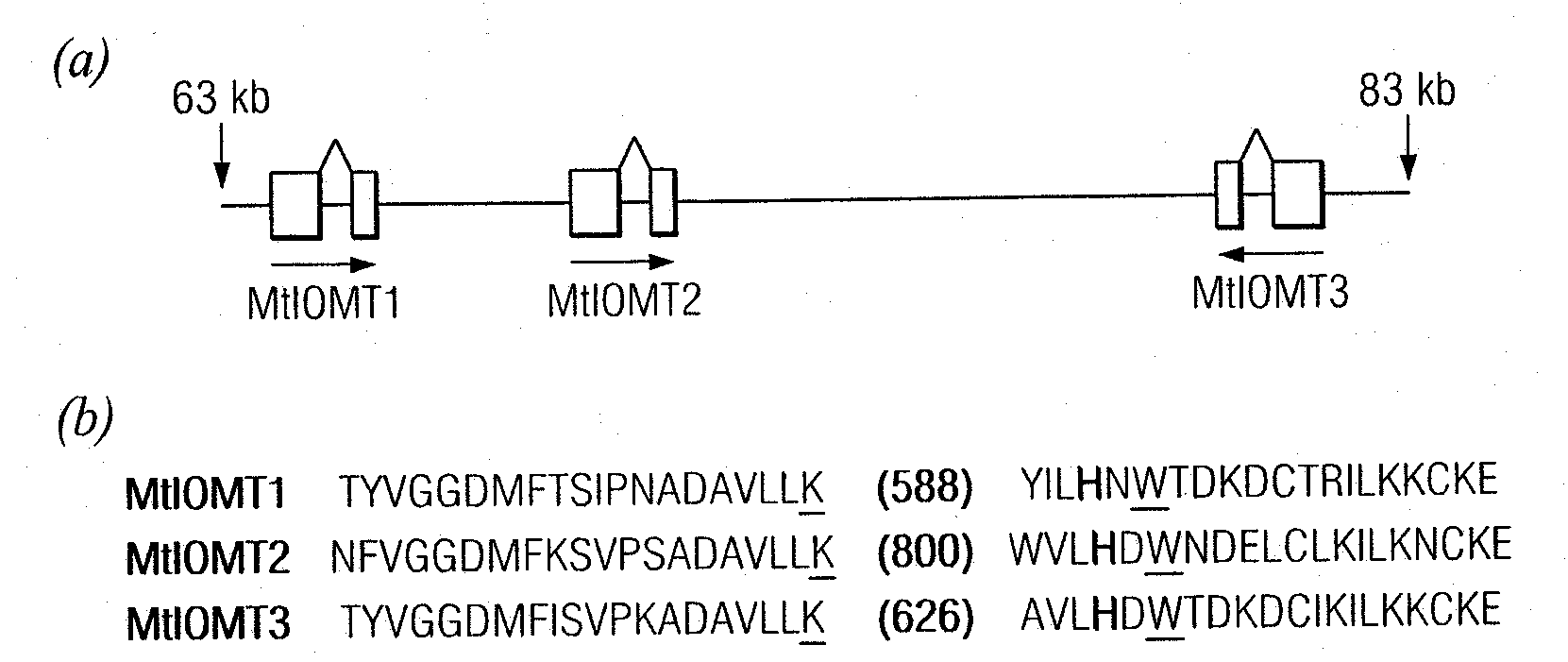
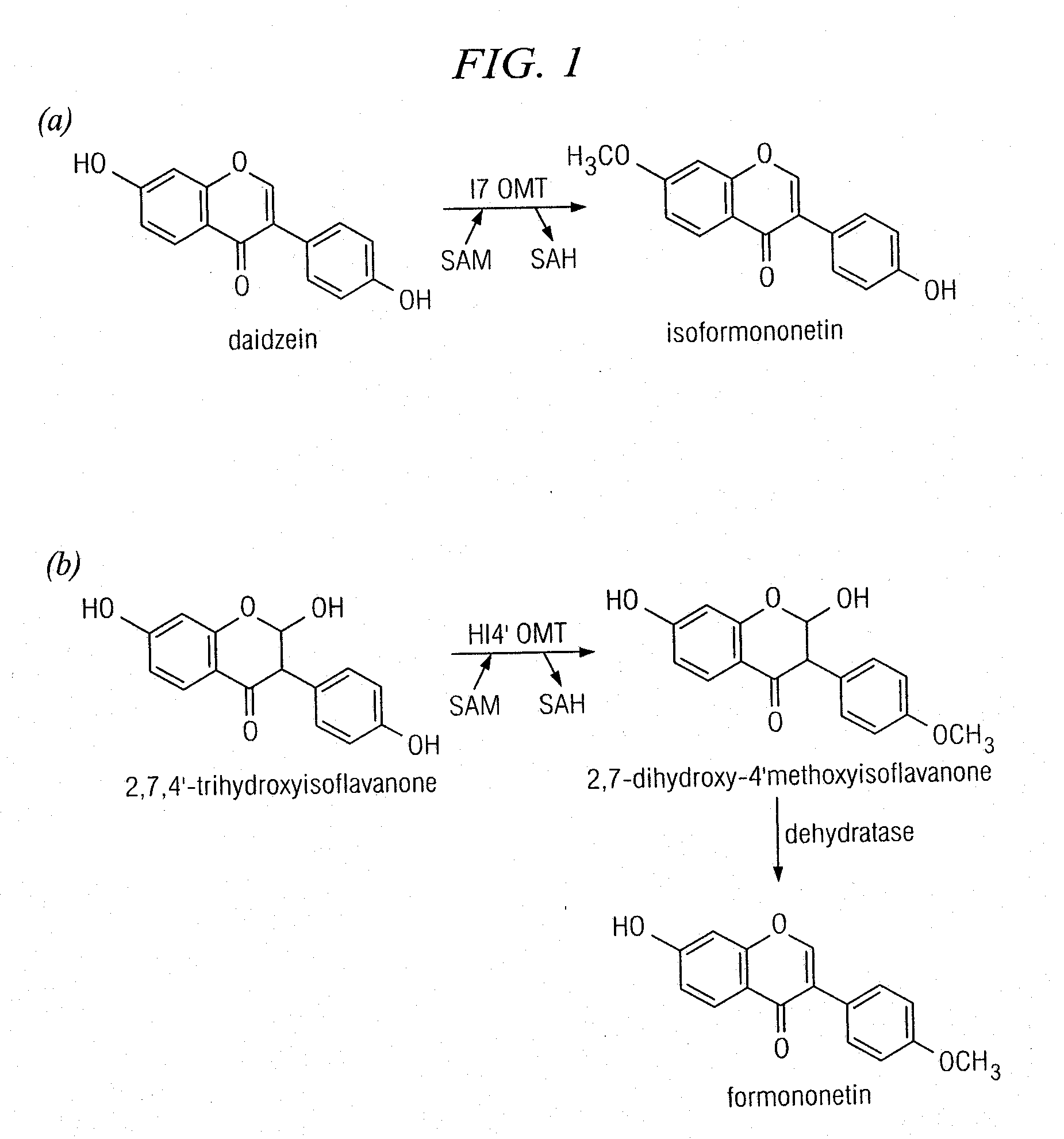
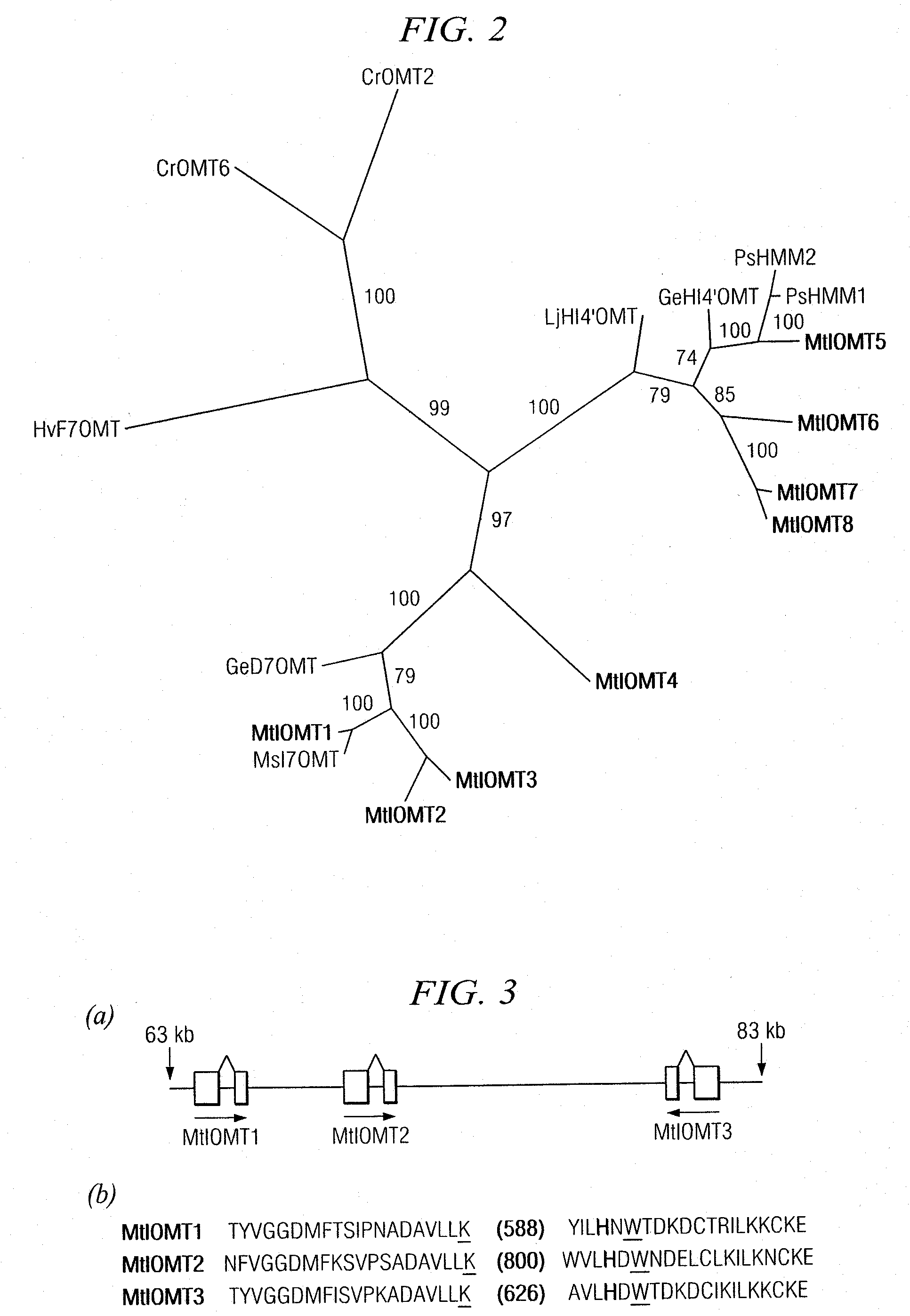
Plant isoflavone and isoflavanone o-methyltransferase genes
The invention provides enzymes that encode O-methyltransferases (OMTs) from Medicago truncatula that allow modification to plant (iso)flavonoid biosynthetic pathways. In certain aspects of the invention, the genes encoding these enzymes are provided. The invention therefore allows the modification of plants for isoflavonoid content. Transgenic plants comprising such enzymes are also provided, as well as methods for improving disease resistance in plants. Methods for producing food and nutraceuticals, and the resulting compositions, are also provided.
Owner:NOBLE RES INST LLC
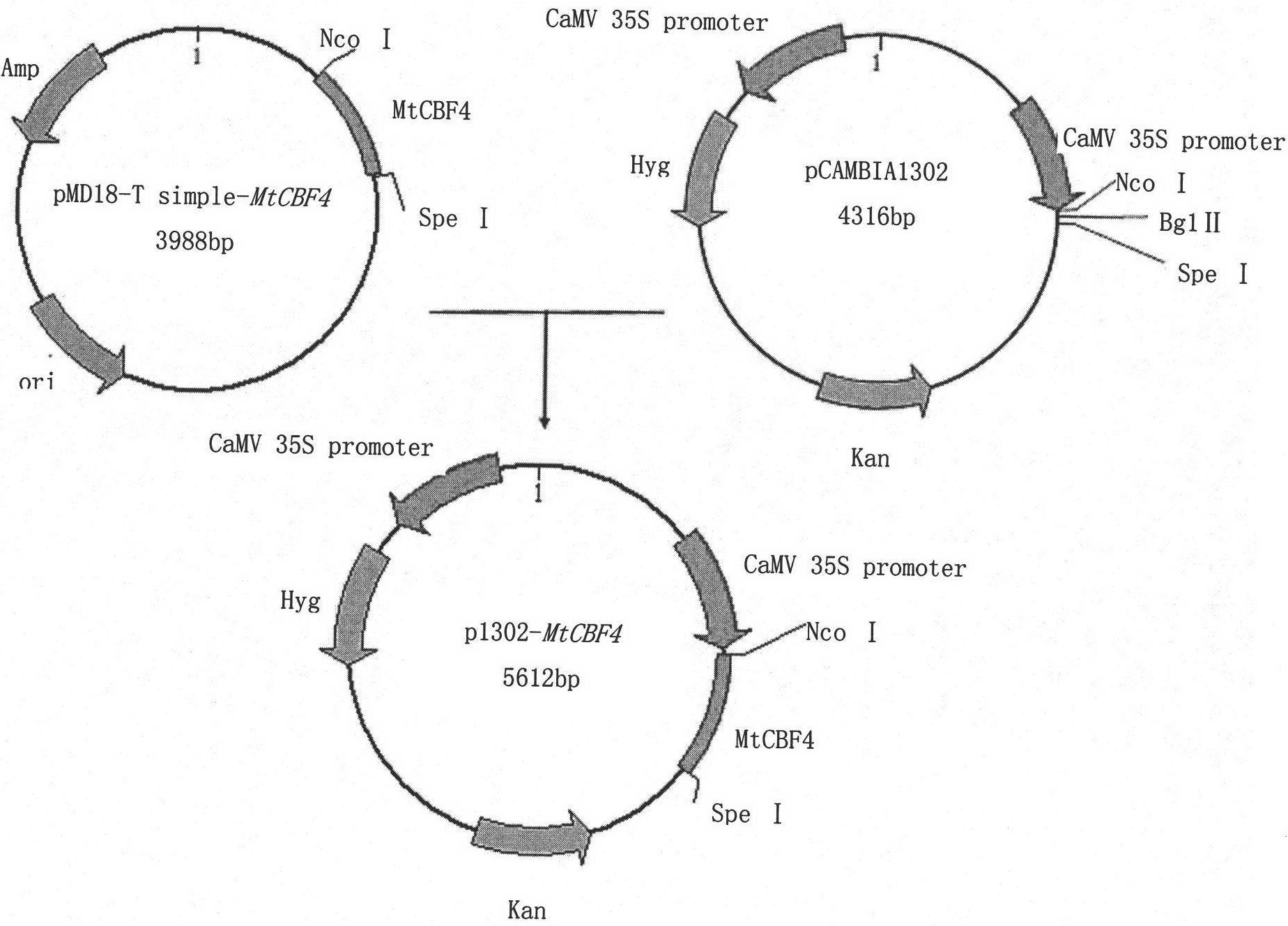
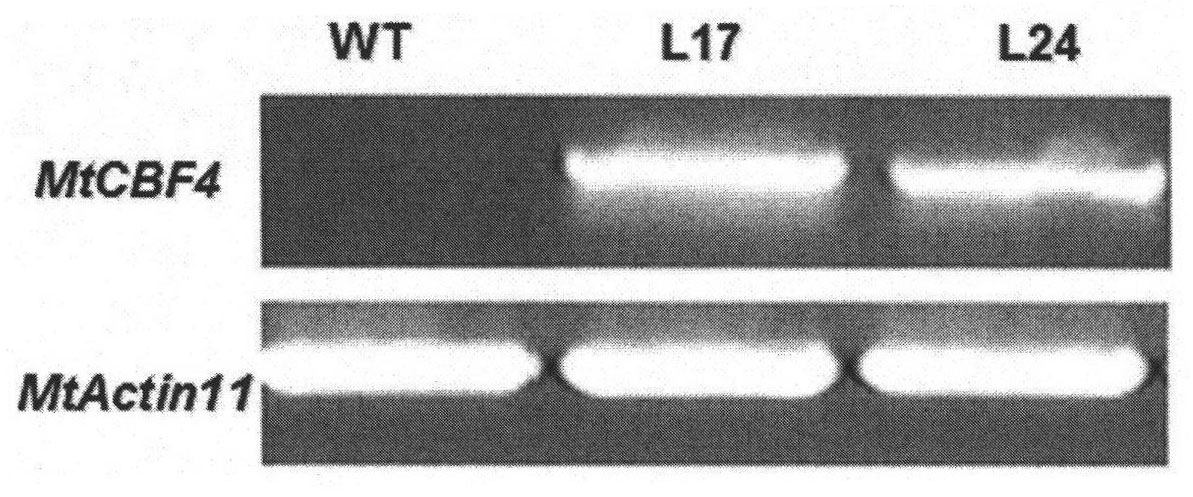
Protein MtCBF4 associated with stress tolerance of plants, encoding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a protein MtCBF4 associated with the stress tolerance of plants, an encoding gene and application thereof. The protein provided by the invention is a protein as the following (a) or (b): (a) the protein consisting of an amino acid sequence shown by a sequence 1 in a sequence table; and (b) the protein which is prepared by carrying out substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or more amino acid residues on the amino acid sequence in the sequence 1, is associated with the stress tolerance of plants and is derived from the sequence 1. The MtCBF4 gene participates in salt stress and drought stress response reactions of medicago truncatula. A transgenic plant, of which the stress tolerance is obviously higher than a starting plant, can be obtained by introducing the MtCBF4 gene into the starting plant. The invention has important value for cultivation of transgenic leguminous crops with salt tolerance and drought tolerance.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
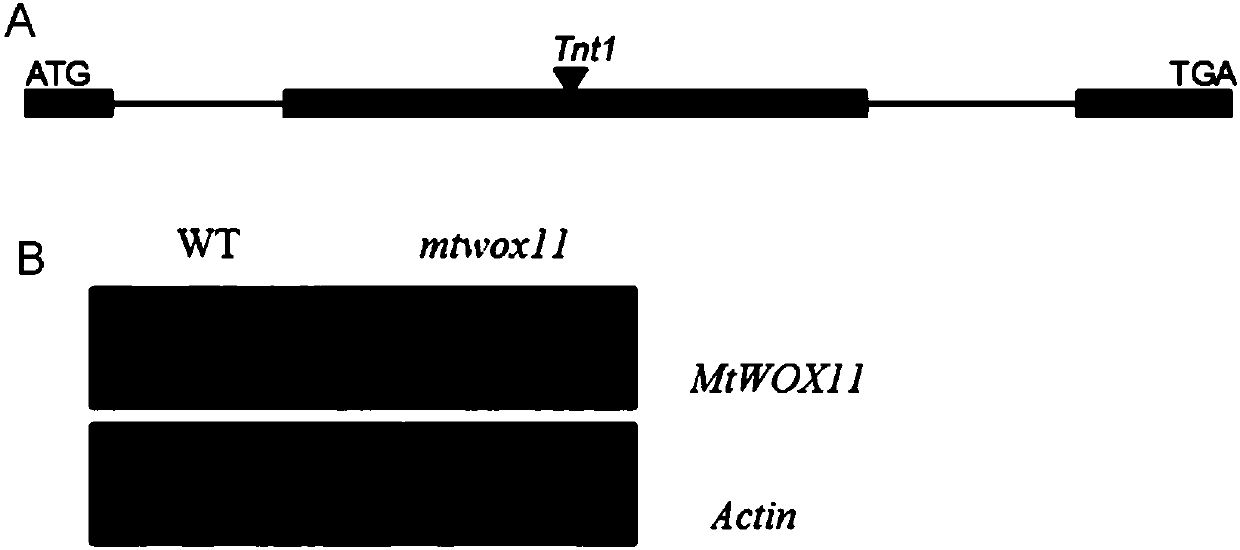
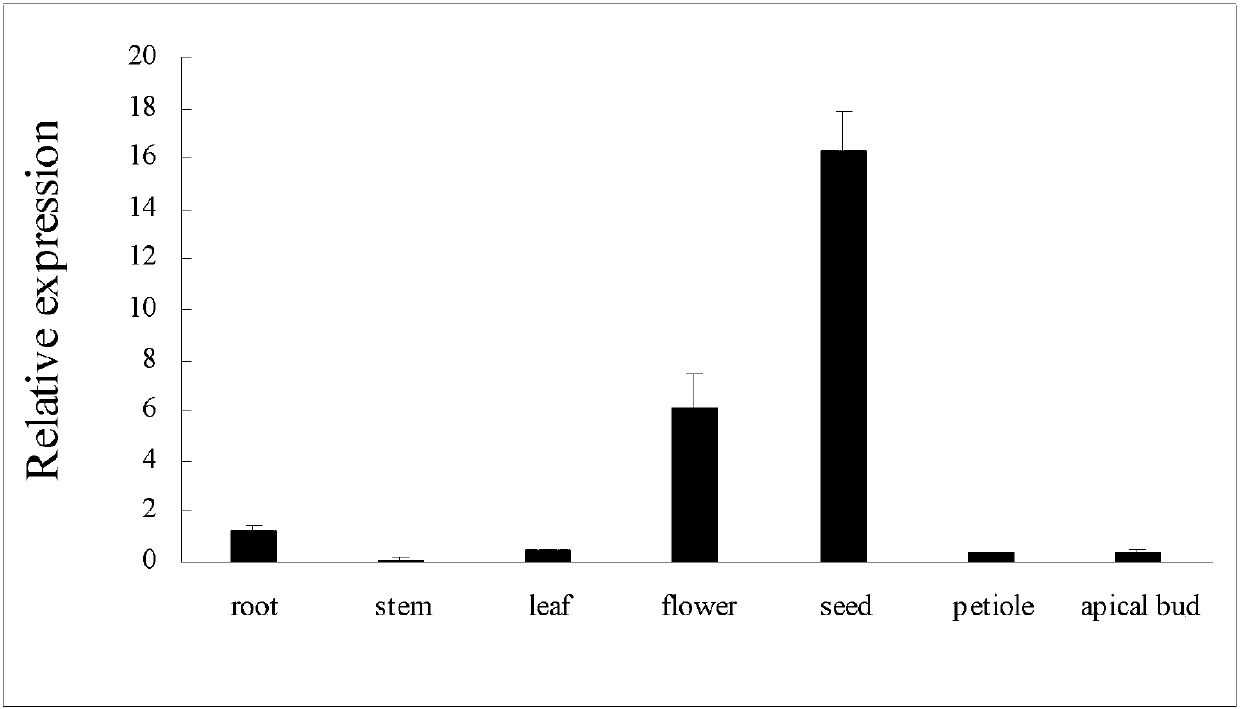
Medicago truncatula Gaertn MtWOX11 gene and application thereof in increasing fatty acid content of seeds
The invention discloses a Medicago truncatula Gaertn WOX family gene Mt WUSCHEL related homeobox11 (MtWOX11). The nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown in SEQ ID No. 1. The invention also disclosesapplication of the gene in increasing the fatty acid content of legume seeds. The analysis of transgenic lines obtained by a genetic transformation method proves that the overexpression of the gene can significantly increase the fatty acid content of seeds of legumes. The gene provided by the invention has wide application prospects, is used for improving the quality of legumes or creating novellegume economic crops, and is of great significance to the production of legume cash crops in China.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
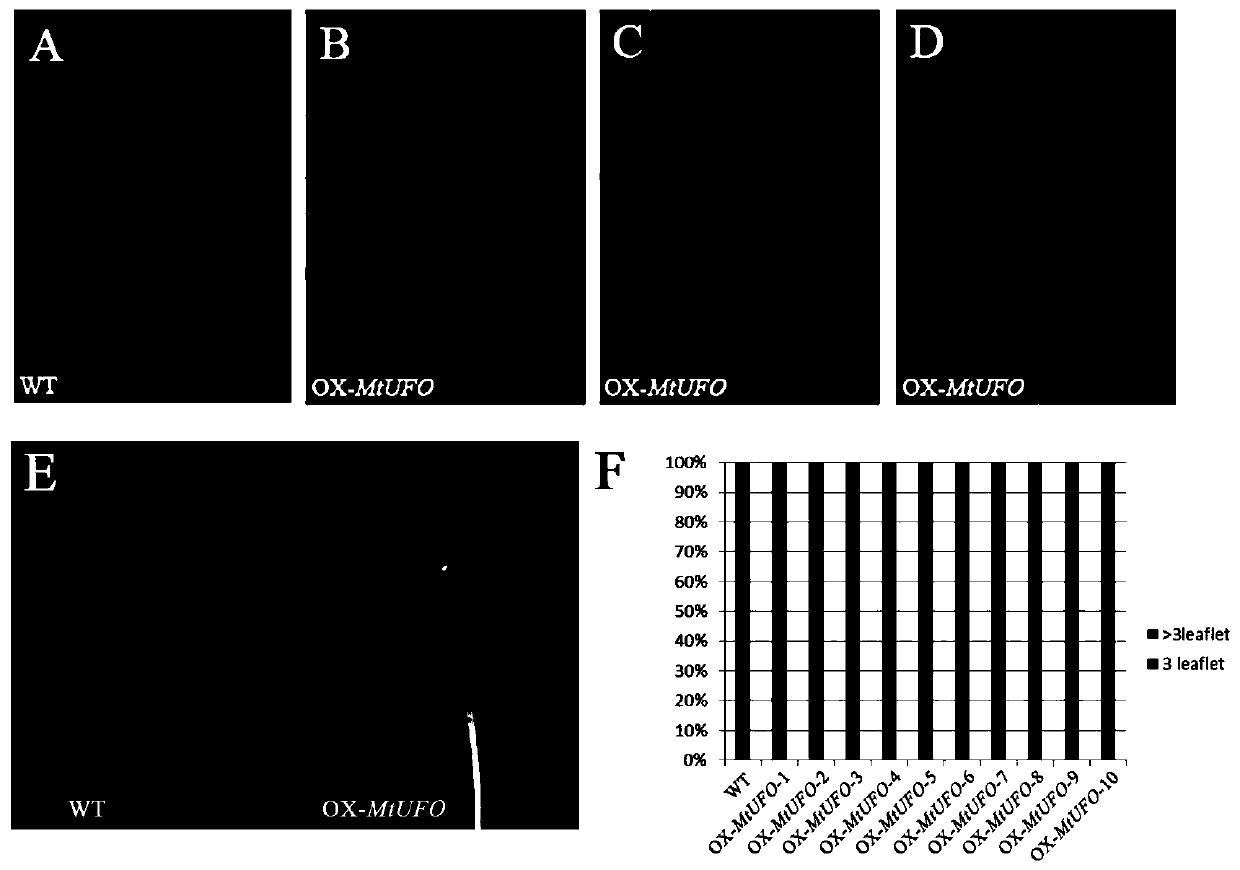
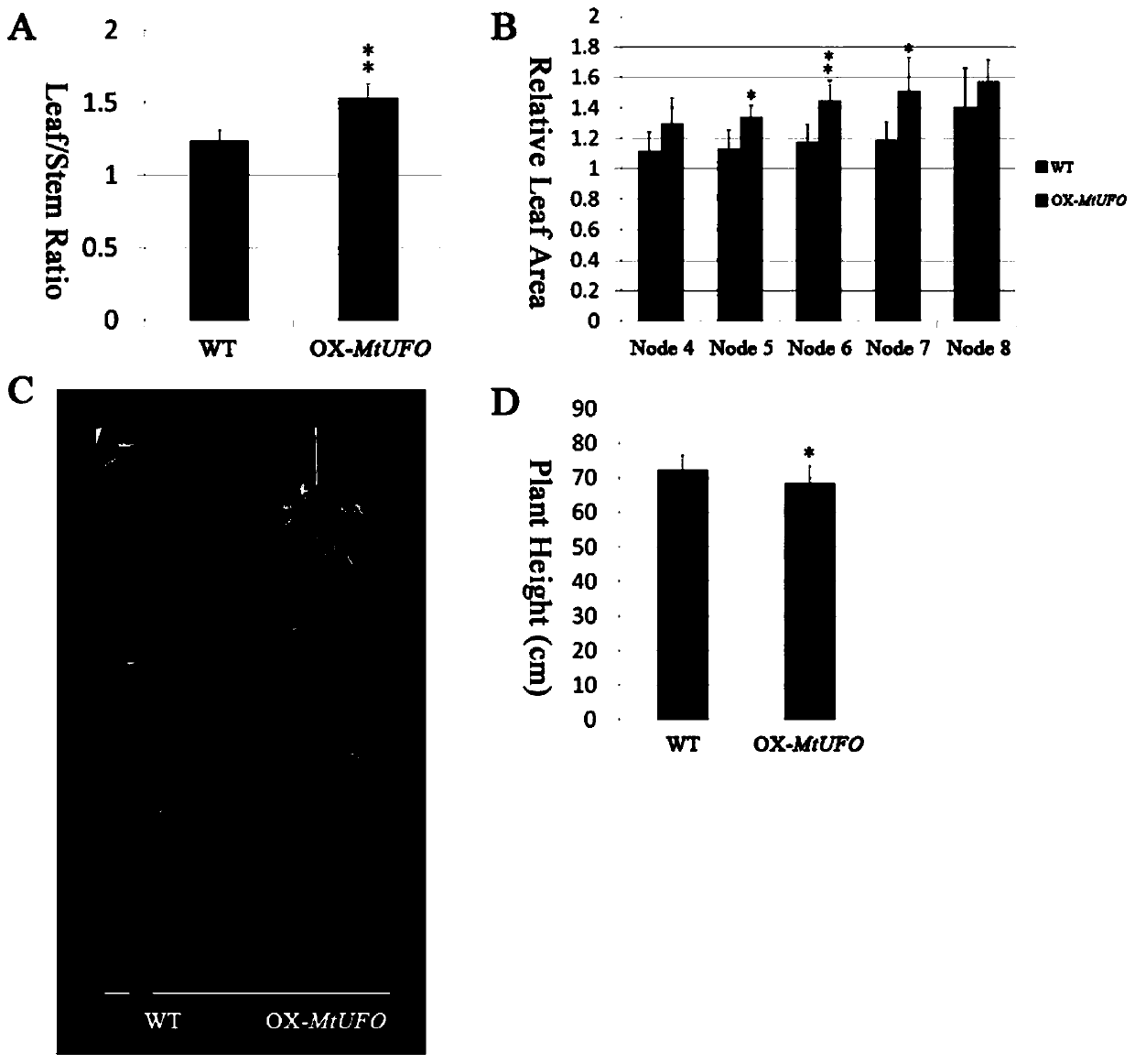
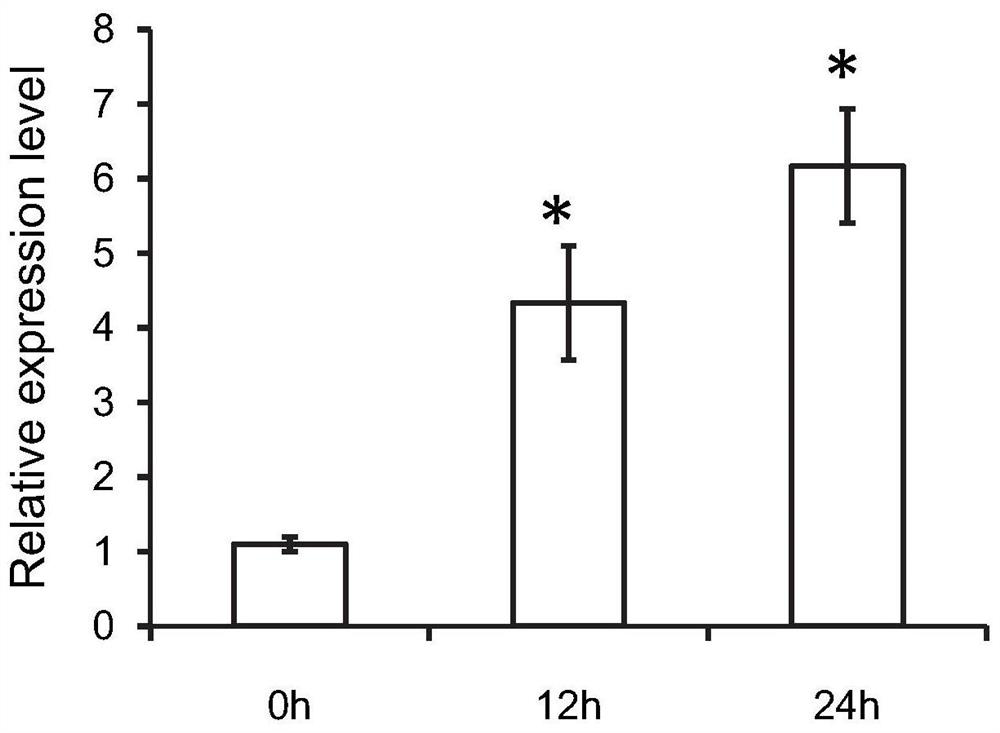
Application of mtunusual FLORAL ORGANS gene in regulation of leaflet number and leaf-to-stem ratio
InactiveCN107384939BQuality improvementIncreased leaf-to-stem ratioPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyGenetics
The invention discloses application of an MtUNUSUAL FLORAL ORGANS gene to the regulation and the control on the leaflet quantity and the leaf-stem ratio of a leguminous plant. According to the application, a knockout mutant strain of the MtUNUSUAL FLORAL ORGANS gene in medicago truncatula is separated and obtained for the first time; proven through an experiment, the gene participates in the regulation and the control on the leaflet number and the leaf-stem ratio of the leguminous plant; a transgenic leguminous plant whose leaflet number and leaf-stem ratio are higher than those of a wild type plant is obtained through the way of over-expressing the gene; the MtUNUSUAL FLORAL ORGANS gene is over-expressed in the medicago truncatula of a compound-leaf species for the first time; the quantity of leaflets of 95 percent of compound leaves can be increased; moreover, the leaf-stem ratio can be increased by approximately 30 percent. The gene is proven to participate in the regulation and the control on the leaflet quantity and the leaf-stem ratio of the leguminous plant; the transgenic leguminous plant whose leaflet number and leaf-stem ratio are higher than those of the wild type plant can be obtained through over-expressing the gene; indicatively, after being implemented, the application is about to be used for creating a novel leguminous forage plant, can be used for subsequent forage quality, and has important significance to Chinese prataculture production.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
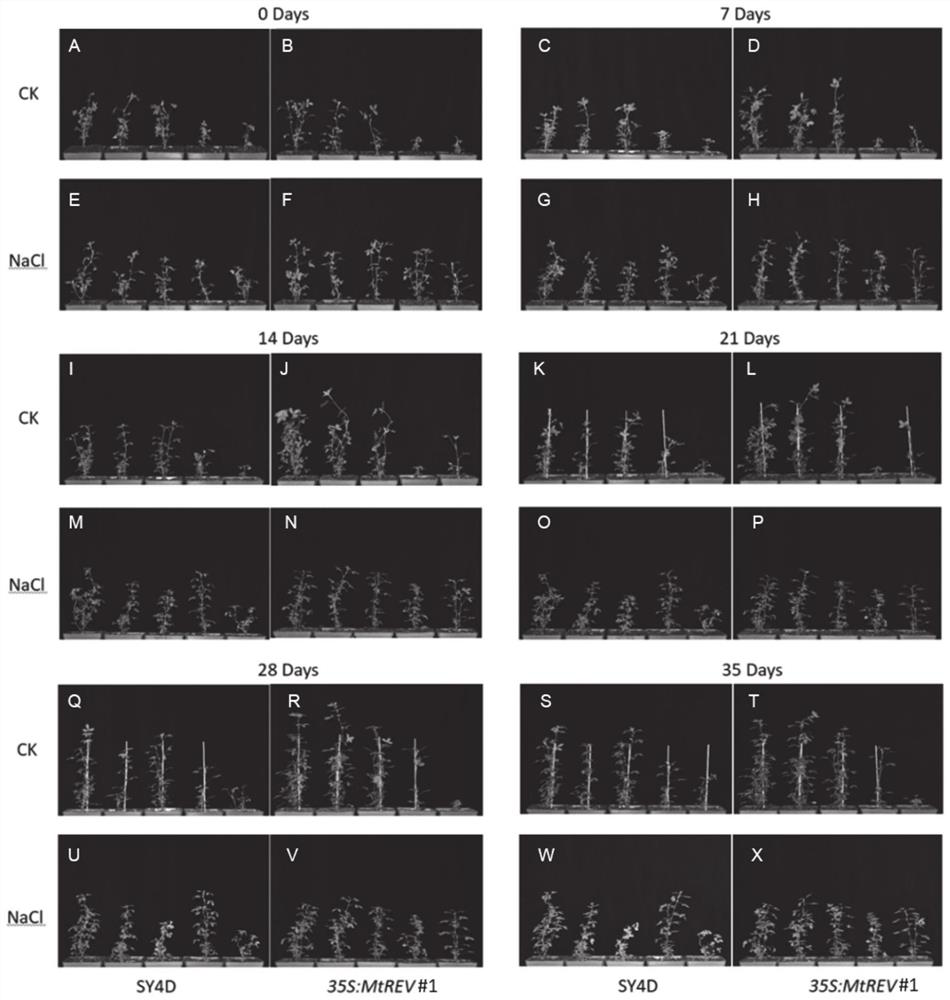
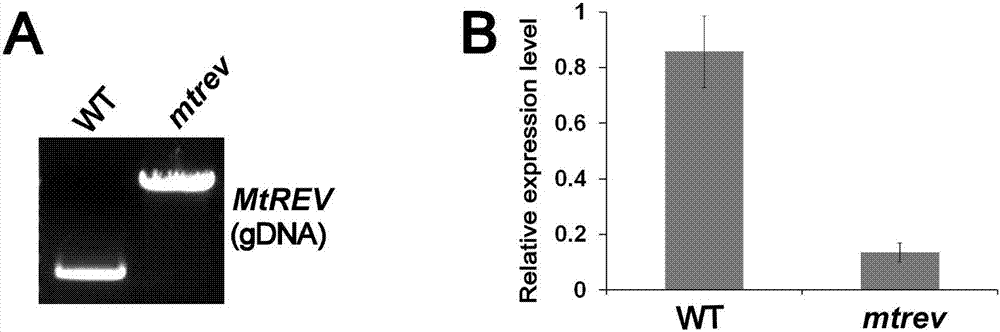
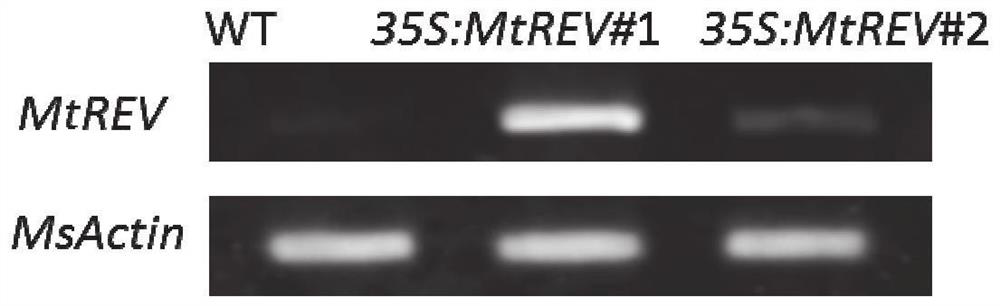
Application of medicagotruncatula gene MtREVOLUTA in improving salt tolerance of leguminous affinis forage Medicago sativa L.
The invention discloses an application of a medicagotruncatula gene MtREVOLUTA and a dicotyledon expression vector pEARLEYGATE100 containing the medicagotruncatula gene MtREVOLUTA in improving salt tolerance of leguminous affinis forage Medicago sativa L. The invention further discloses an application of the medicagotruncatula gene MtREVOLUTA in cultivating salt-tolerant Medicago sativa L. Experiments prove that the gene MtREVOLUTA is a response abiotic stress regulatory gene, and can be massively expressed in affinis leguminous forage Medicago sativa L., and the salt tolerance of transgenic Medicago sativa L. is obviously enhanced. The survival rate of the transgenic plant after high-salt treatment is higher than that of wild Medicago sativa L. SY4D. The application of the medicagotruncatula gene MtREVOLUTA in improving salt tolerance of leguminous affinis forage Medicago sativa L. is indicated to have important significance and economic value.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Photoinduction promoter for promoting specific expression of alfalfa plastocyanin and primers for quickly cloning promoter
The invention discloses a promoter sequence with photoinduction specificity and leaf tissue specificity for promoting expression of alfalfa plastocyanin and a pair of primers for quickly cloning the promoter. The document reports that the plastocyanin is a plastid protein related to plant photosynthesis, and has been proved to be a photoinduction expression protein. The alfalfa plastocyanin promoter has 9 specific elements, including TATAbox, CAATbox and other promoter necessary elements, a specific element G-box(ctttatca) related to photoresponse, and GT-1 basic sequence (aatccaca) and the like related to tissue specificity expression; and the experiment proves that the promoter has certain photoinduction specificity and leaf tissue specificity, and can drive the specific expression of the reported gene GUS in transgenic alfalfa leaf. The primers are specific primers designed in reference to related sequences of Medicago truncatula genome, and are suitable for quickly cloning the alfalfa plastocyanin promoter by a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
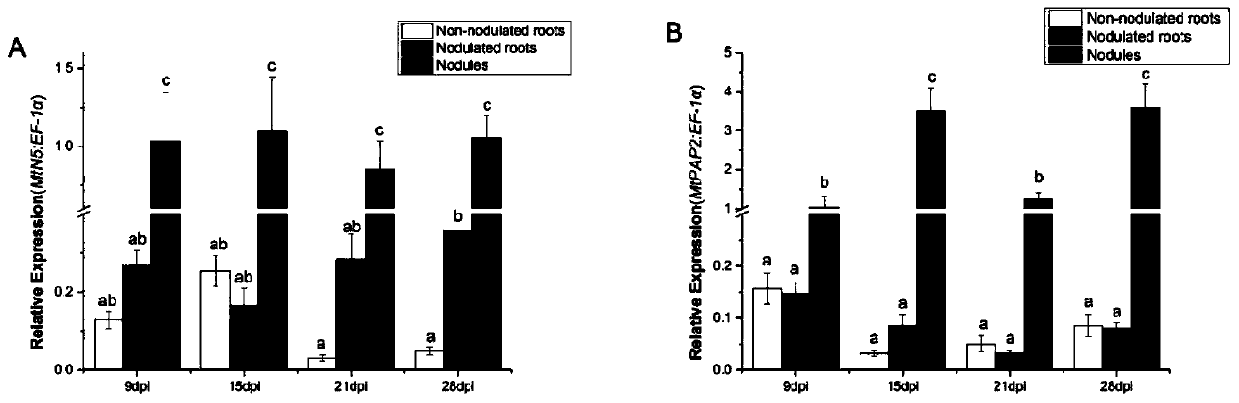
Study method of functions of acid phosphatase in symbiosis of alfalfa root nodules and alfalfa mycorrhiza
ActiveCN111066593AHigh expressionHigh infection ratePlant cultivationCultivating equipmentsBiotechnologyArbuscular mycorrhizal fungi
The invention discloses a study method of functions of acid phosphatase in symbiosis of alfalfa root nodules and alfalfa mycorrhiza, and belongs to the field of studies on legumes. The study method ofthe functions of the acid phosphatase in the symbiosis of the alfalfa root nodules and the alfalfa mycorrhiza comprises the following steps: 1) selecting medicago truncatula seeds, and carrying out surface sterilizing, forced germinating and sprouting; 2) respectively inoculating the sprouted medicago truncatula with sinorhizobium meliloti and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, and carrying out separate pot experiments at different phosphorus concentrations; 3) detecting tissue-specific expression of MtPAP2 in the alfalfa root nodules, tissue-specific expression of MtPAP2 in the alfalfa mycorrhiza, influence of the phosphorus on MtPAP2 gene expression, influence of the phosphorus on the alfalfa root nodules and influence of the phosphorus on the alfalfa mycorrhiza; and 4) studying the roles ofthe sinorhizobium meliloti and the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in the symbiosis with the alfalfa by utilizing spatiotemporal expression, promoter localization, overexpression and silencing means. Thus, direct experimental evidence is obtained to provide new insights on molecular mechanisms of plant response to low phosphorus stress and coordination of phosphorus homeostasis in the plants by themselves.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
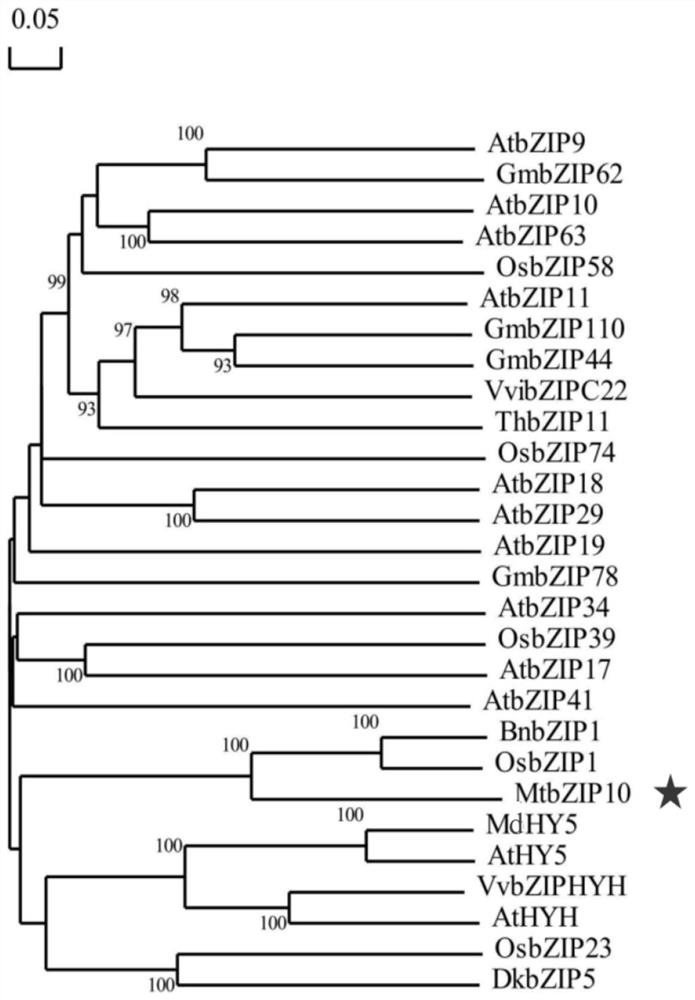
Transcription factor gene for regulating and controlling synthesis of plant flavonoid and use thereof
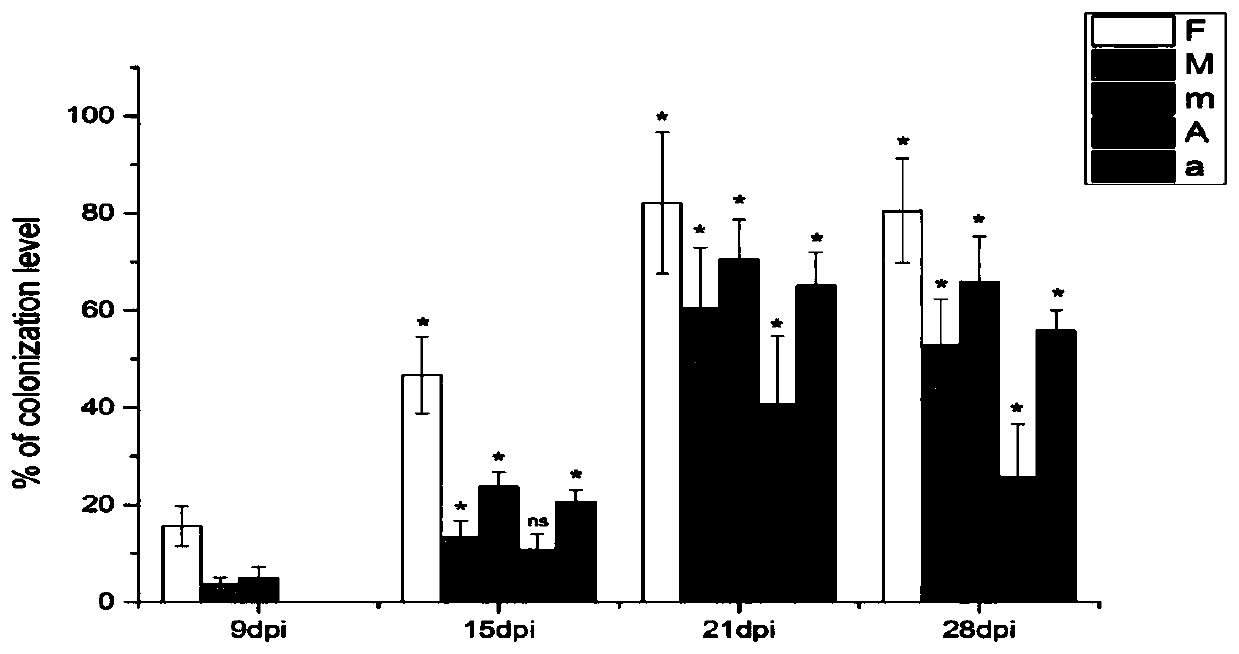
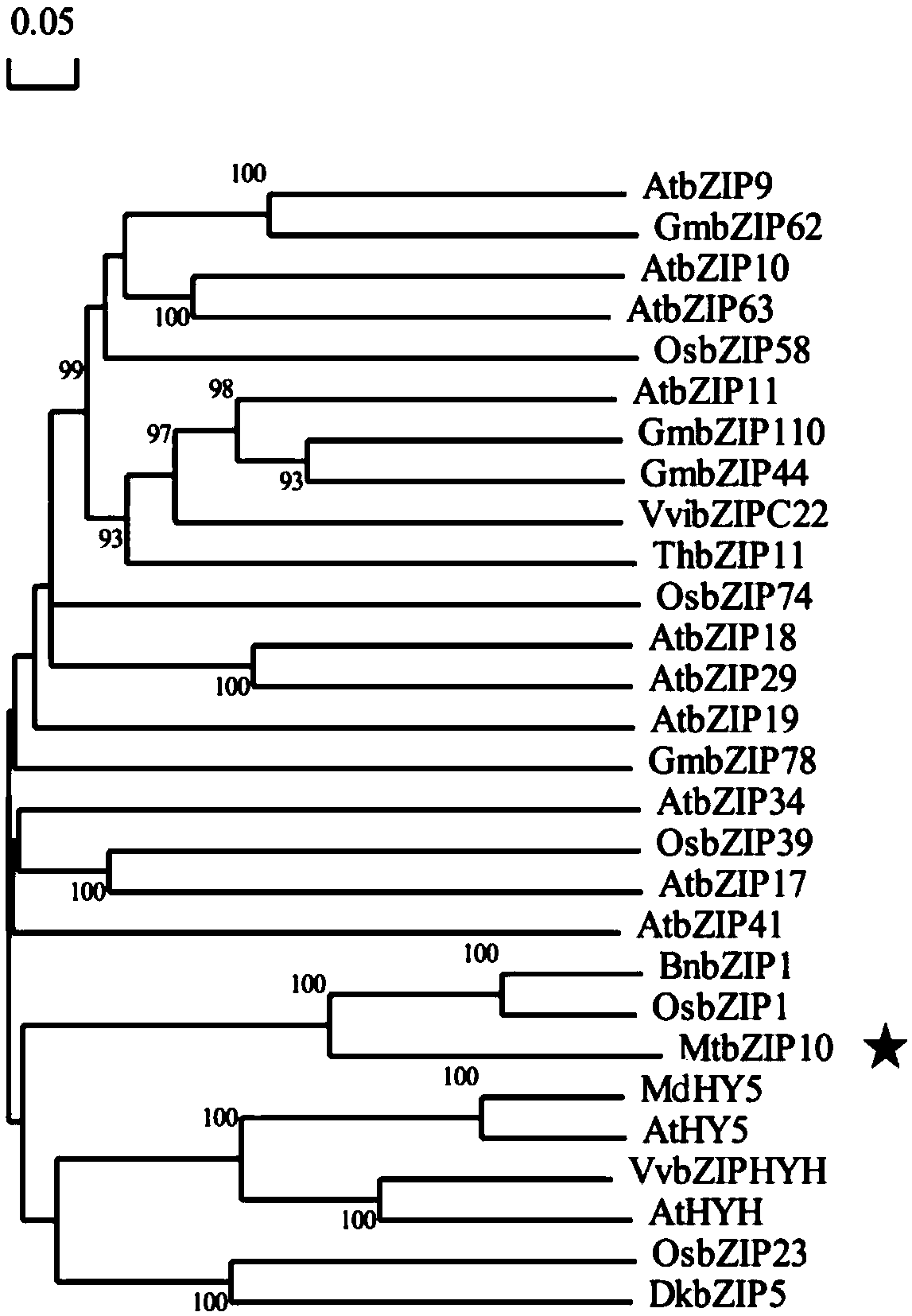
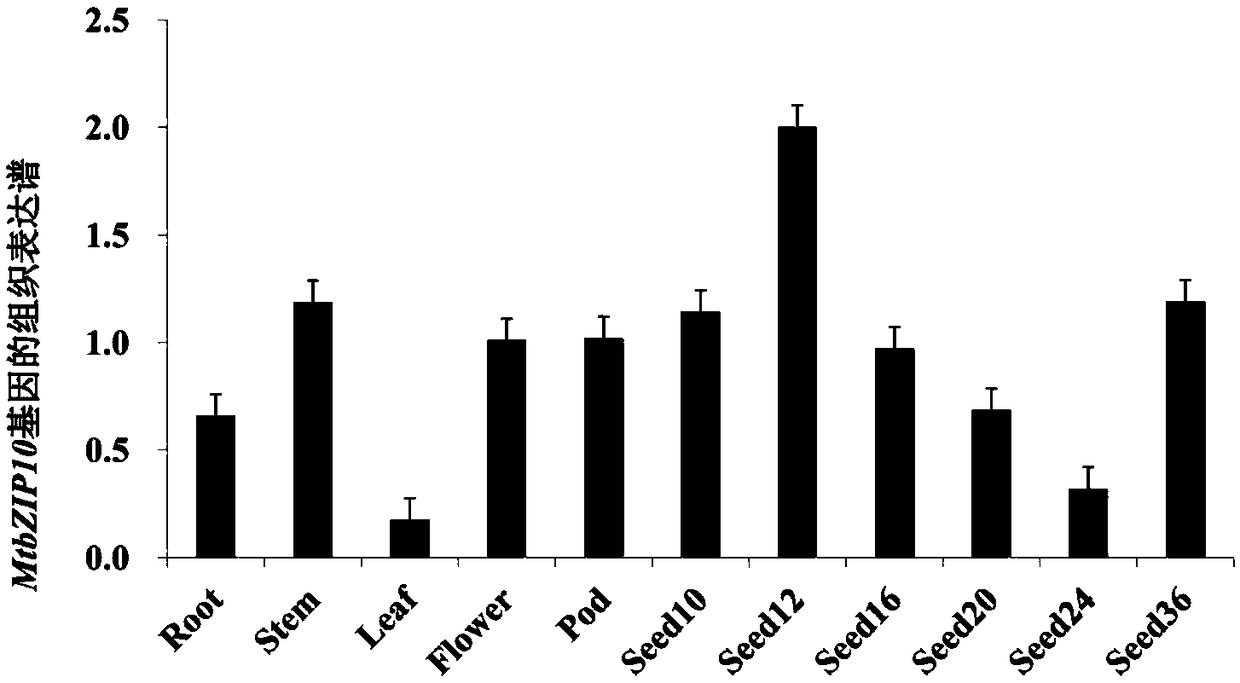
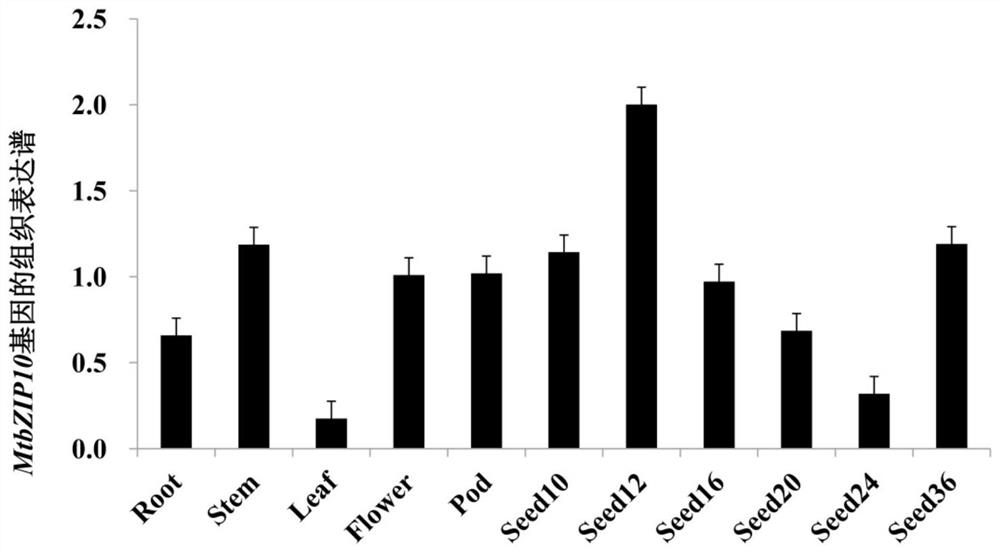
The invention discloses a transcription factor gene for regulating and controlling synthesis of plant flavonoid. The transcription factor gene is an MtbZIP10 gene authenticated from a leguminous plant, namely medicago truncatula, and the gene sequence of the transcription factor gene is represented by SEQ ID NO.1. Furthermore, the invention discloses functions and application of the transcriptionfactor gene. The transcription factor gene has the advantages that the transcription factor gene capable of positively regulating and controlling the synthesis of flavonoid compounds is cloned from the leguminous plant, namely medicago truncatula, the system identification of the functions of the transcription factor gene is carried out, and the system identification result shows that the gene iscapable of activating multiple genes in the biosynthetic pathway of flavonoid and the content of the flavonoid compounds is increased.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
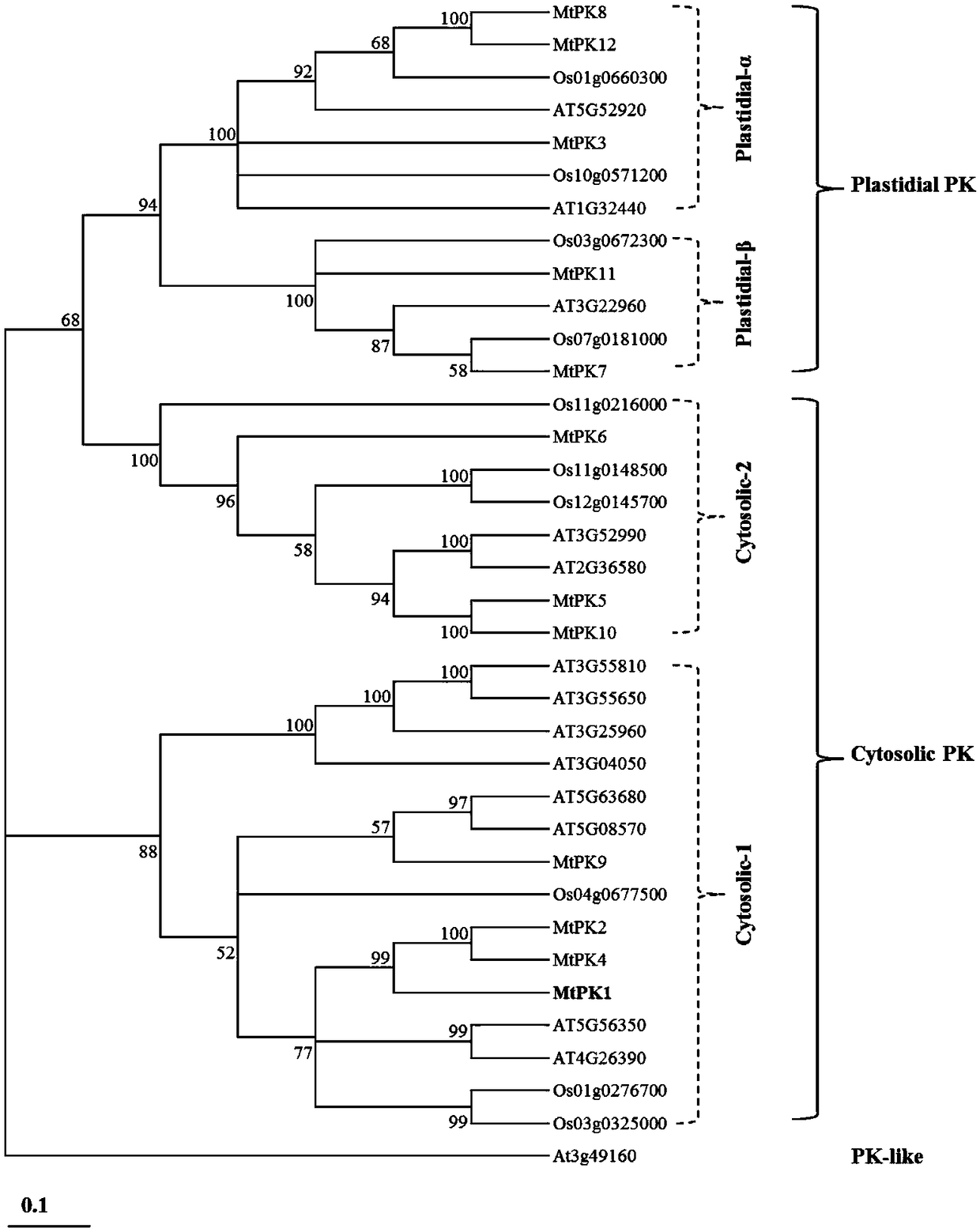
Pyruvate kinase gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a pyruvate kinase gene. The gene sequence of pyruvate kinase is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. The coded amino acid sequence of the pyruvate kinase gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The gene sequence of pyruvate kinase is derived from Medicago truncatula. The pyruvate kinase gene is cloned from the Medicago truncatula and functions of the pyruvate kinase gene are identified systematically, it is discovered that the gene not only can catalyze phosphoenolpyruvate to form pyruvate, but also can participate in biosynthesis of flavonoids.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Primer pair, kit containing same, use and method for detecting ecotypes a17 and r108 of Medicago truncatula
ActiveCN108411030BWide range of usesIncrease productionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDNAVirology
The invention provides a pair of primers, a kit containing the same, a use and a method for detecting ecotypes A17 and R108 of Medicago truncatula, and relates to the field of biotechnology. The primer pair comprises primer NST480‑F and primer NST480‑R, which have the sequences shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2 respectively, and can simultaneously amplify DNA fragments of different fragment lengths of Medicago truncatula ecotypes A17 and R108 , so one amplification can distinguish whether the test sample contains Medicago truncatula ecotypes A17 and R108. Using the above primers to detect Medicago truncatula ecotypes A17 and R108 has the characteristics of strong sensitivity, high accuracy, strong repeatability, fast and convenient, and alleviates the lack of a fast and accurate method for detection and identification in the prior art. Problems with Medicago truncatula ecotypes A17 and R108.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
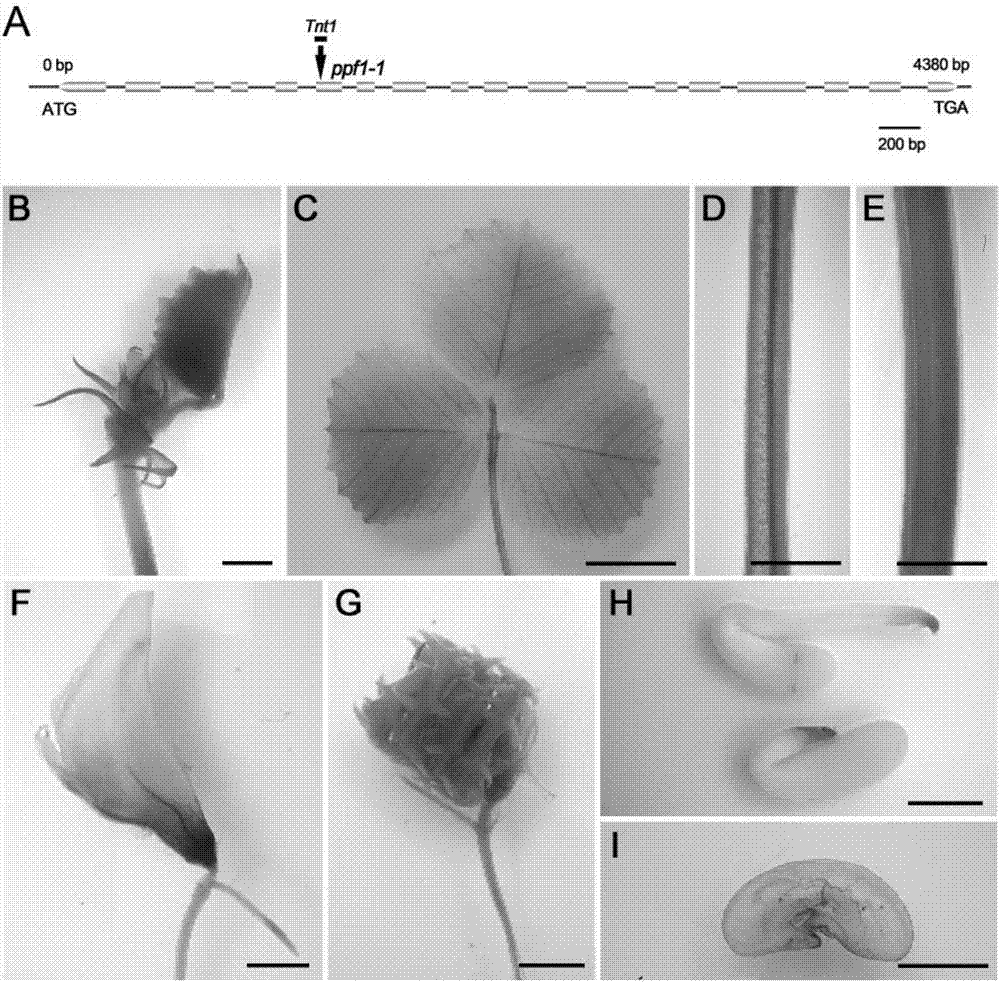
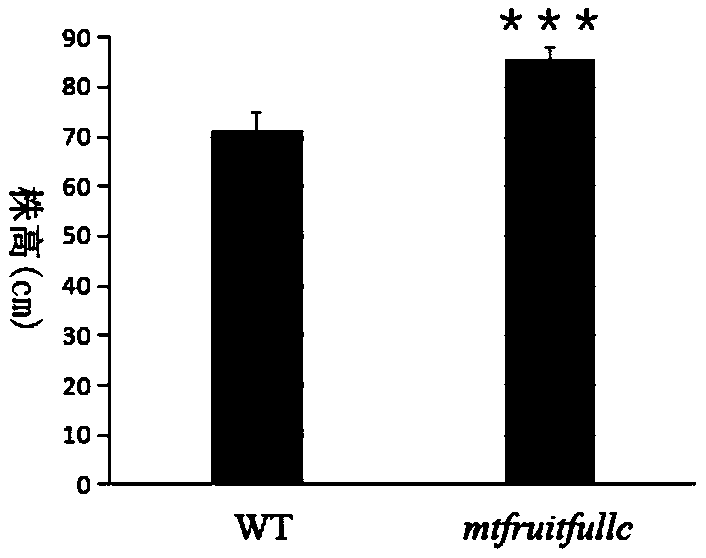
Application of MtFRUITFULLc gene in regulation and control of leaf yield and leaf protein content of leguminous plants
InactiveCN110951746AHigh protein contentThe number of leaves increasesPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses an application of an MtFRUITFULLc gene in regulation and control of leguminous plant leaf yield and / or leaf protein content and / or plant height and / or flowering. The nucleotidesequence of the MtFRUITFULLc gene is as shown in SEQ ID No. 1. According to the invention, by using a mutant library marked by medicago truncatula Tnt1, a mutant with medicago truncatula MtFRUITFULLcgene knocked out is screened. Analysis shows that the MtFRUITFULLc gene is knocked out from medicago truncatula, so that the plant height, the fresh weight of the overground part and the content of leaf protein can be increased in the reproductive period. It is indicated that: after being implemented, the application can create novel leguminous forage plants, can be used for subsequent forage quality research, and has great significance for grassland production in China.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
A plant Medicago truncatula flower organ stigma exposure gene and its encoded protein and application
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A transcription factor gene regulating plant flavonoid synthesis and its application
The invention discloses a transcription factor gene that regulates the synthesis of plant flavonoids. The transcription factor gene is the MtbZIP10 gene identified from the leguminous plant Medicago truncatula, and its gene sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.1. Moreover, the present invention discloses the function of the gene and its application. The advantage of the present invention is that the transcription factor gene that can positively regulate the synthesis of flavonoid compounds is cloned from the leguminous plant Medicago truncatula, and its function is systematically identified, and it is found that the gene can activate the biosynthesis pathway of flavonoids Multiple genes that increase the content of flavonoid compounds.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com