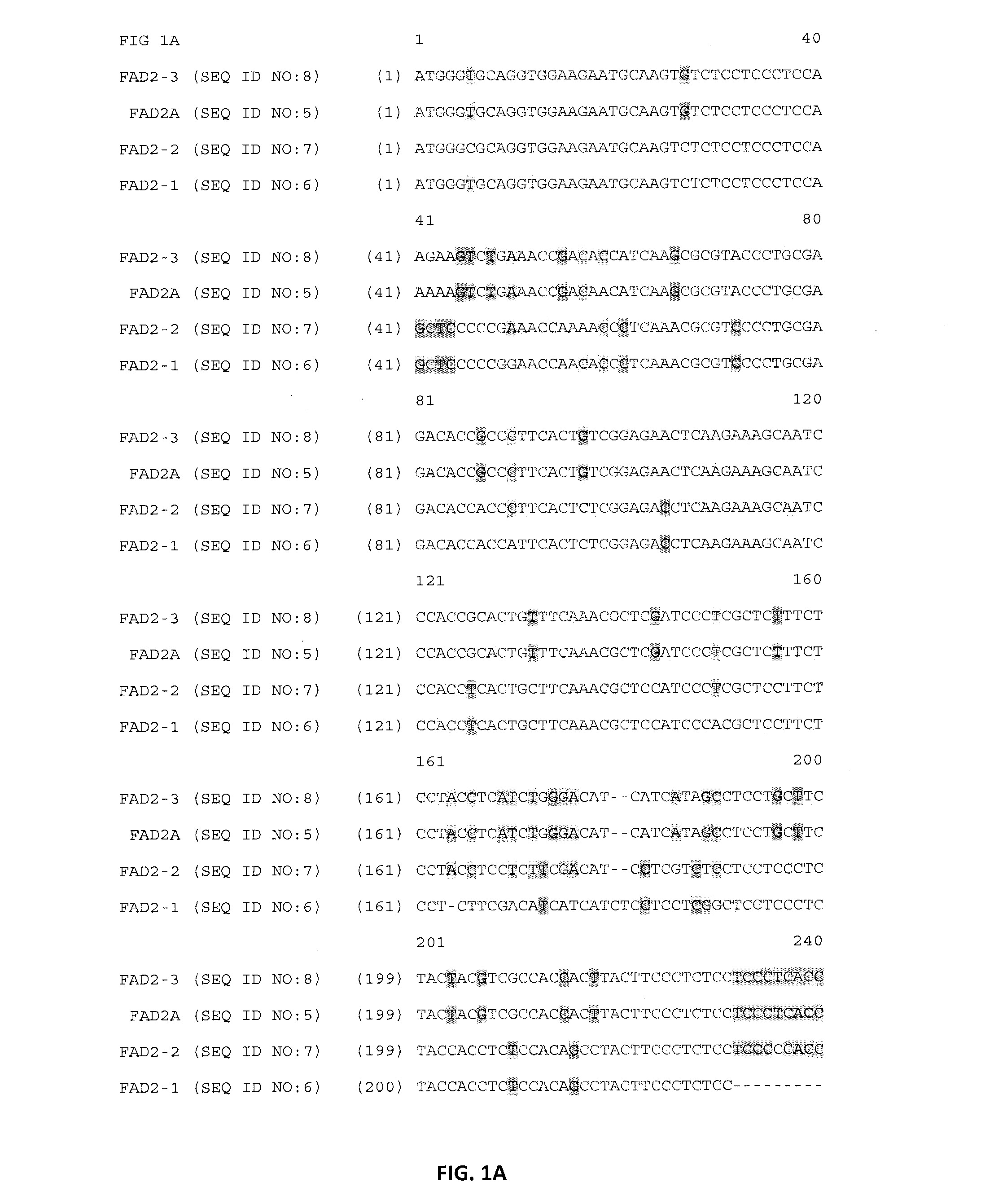
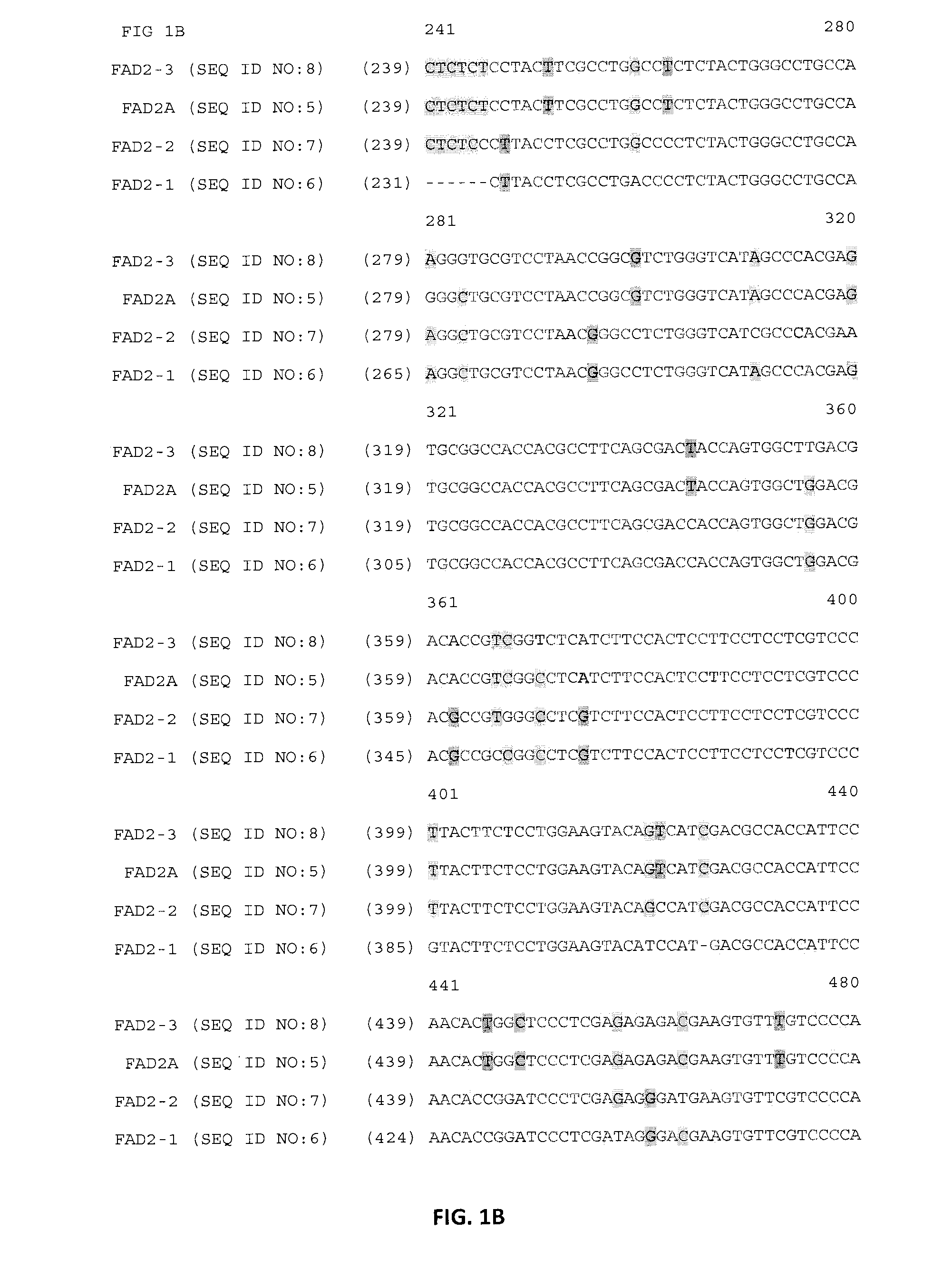
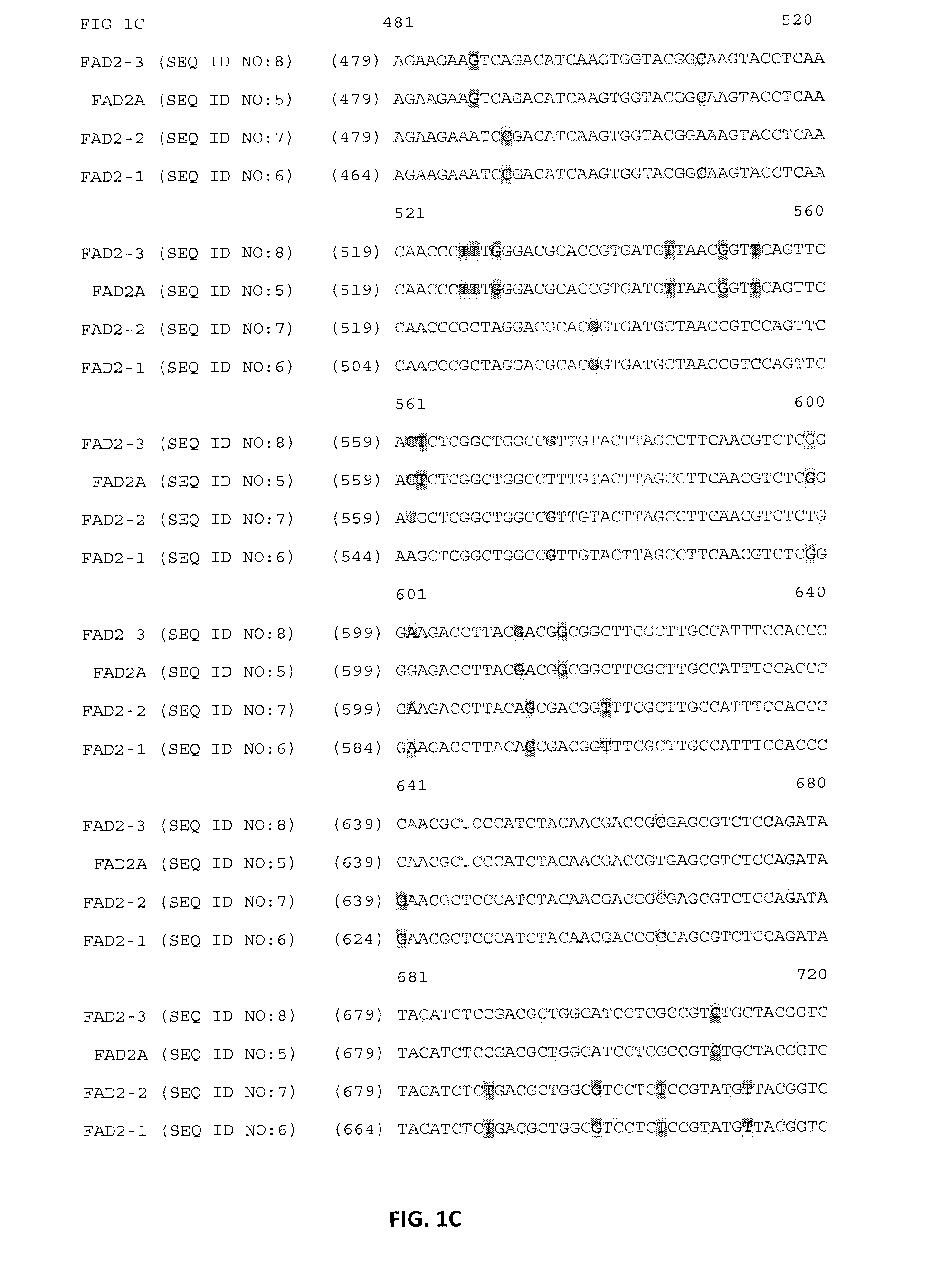
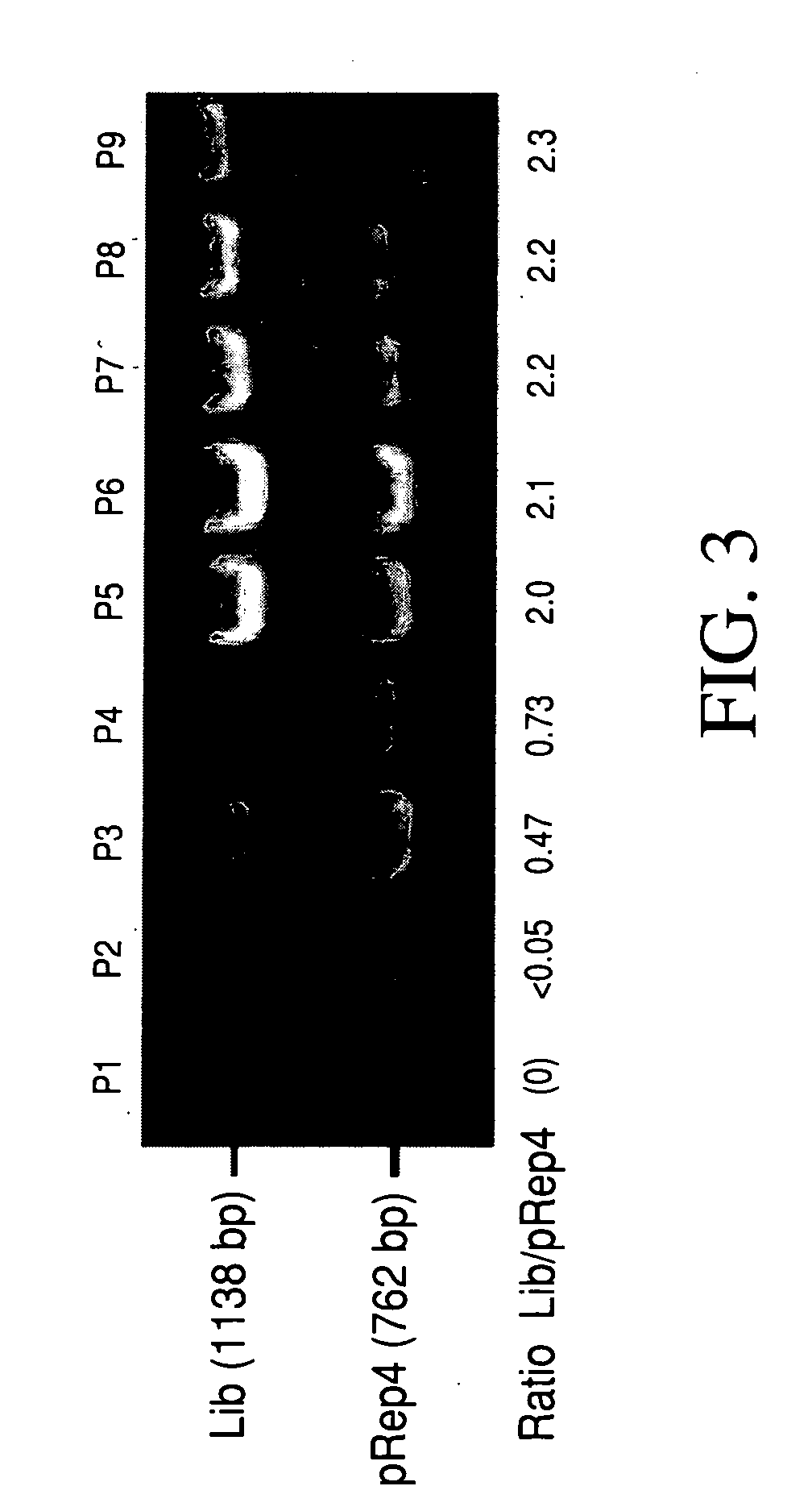
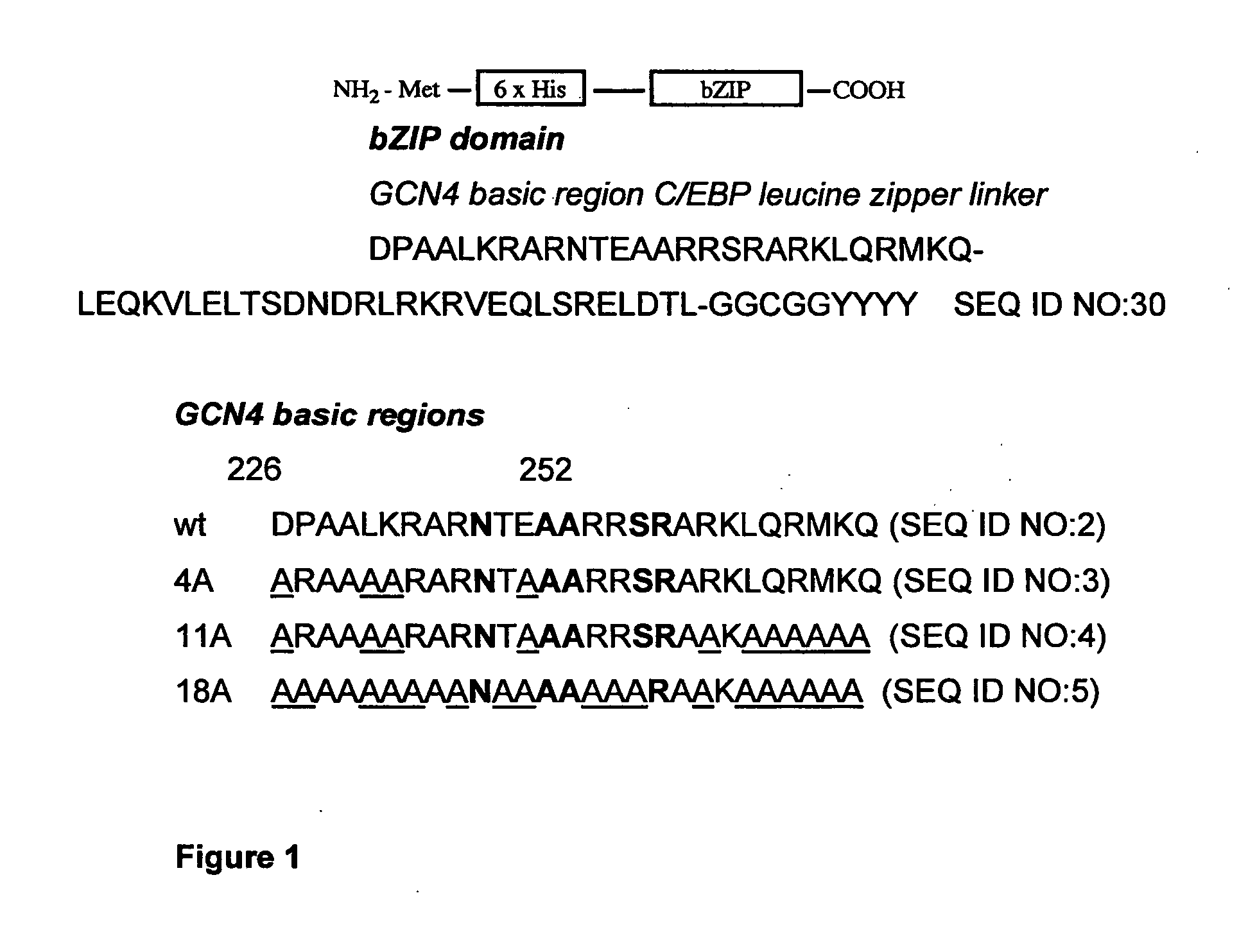
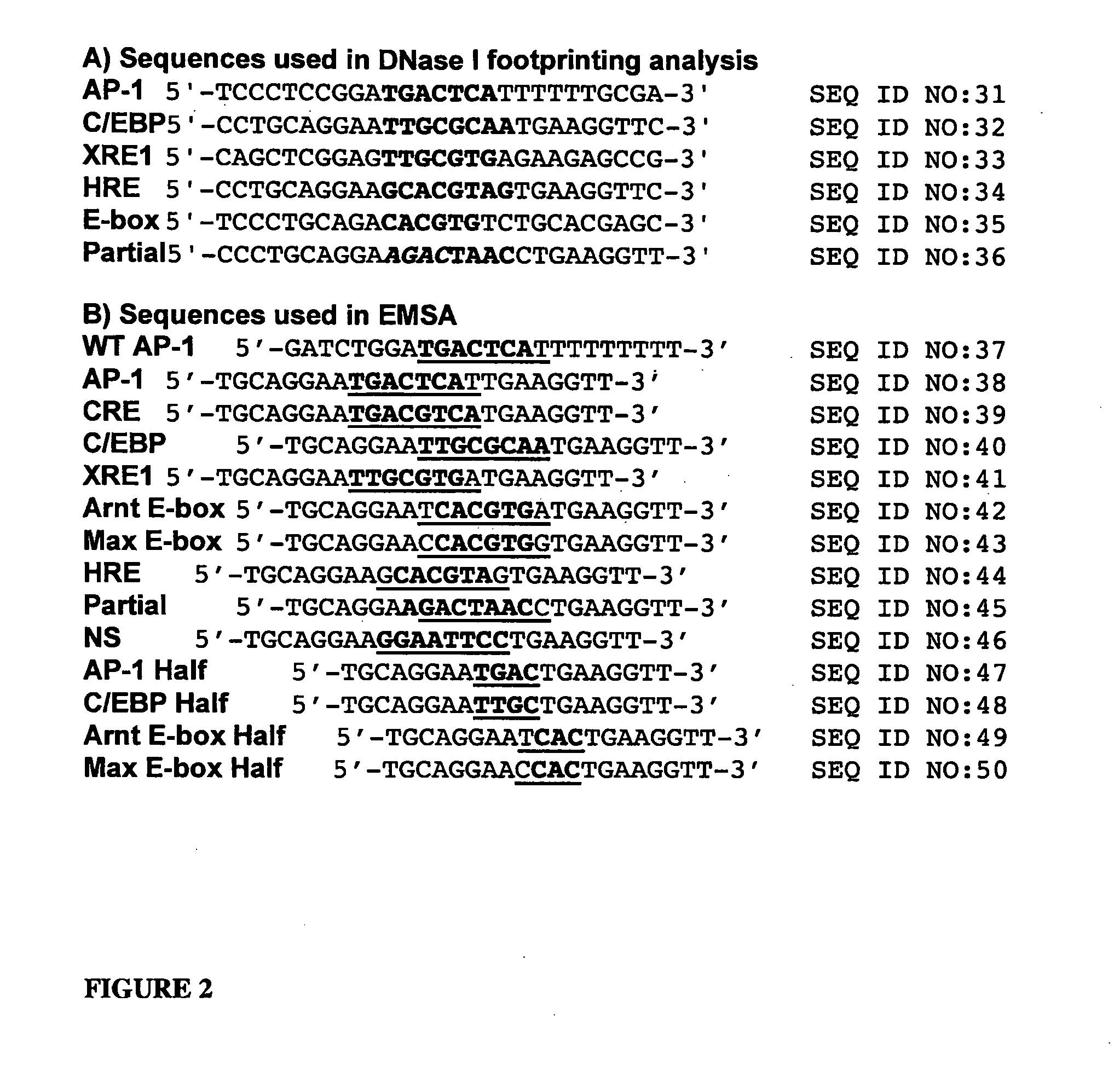
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
74 results about "Leucine zipper" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
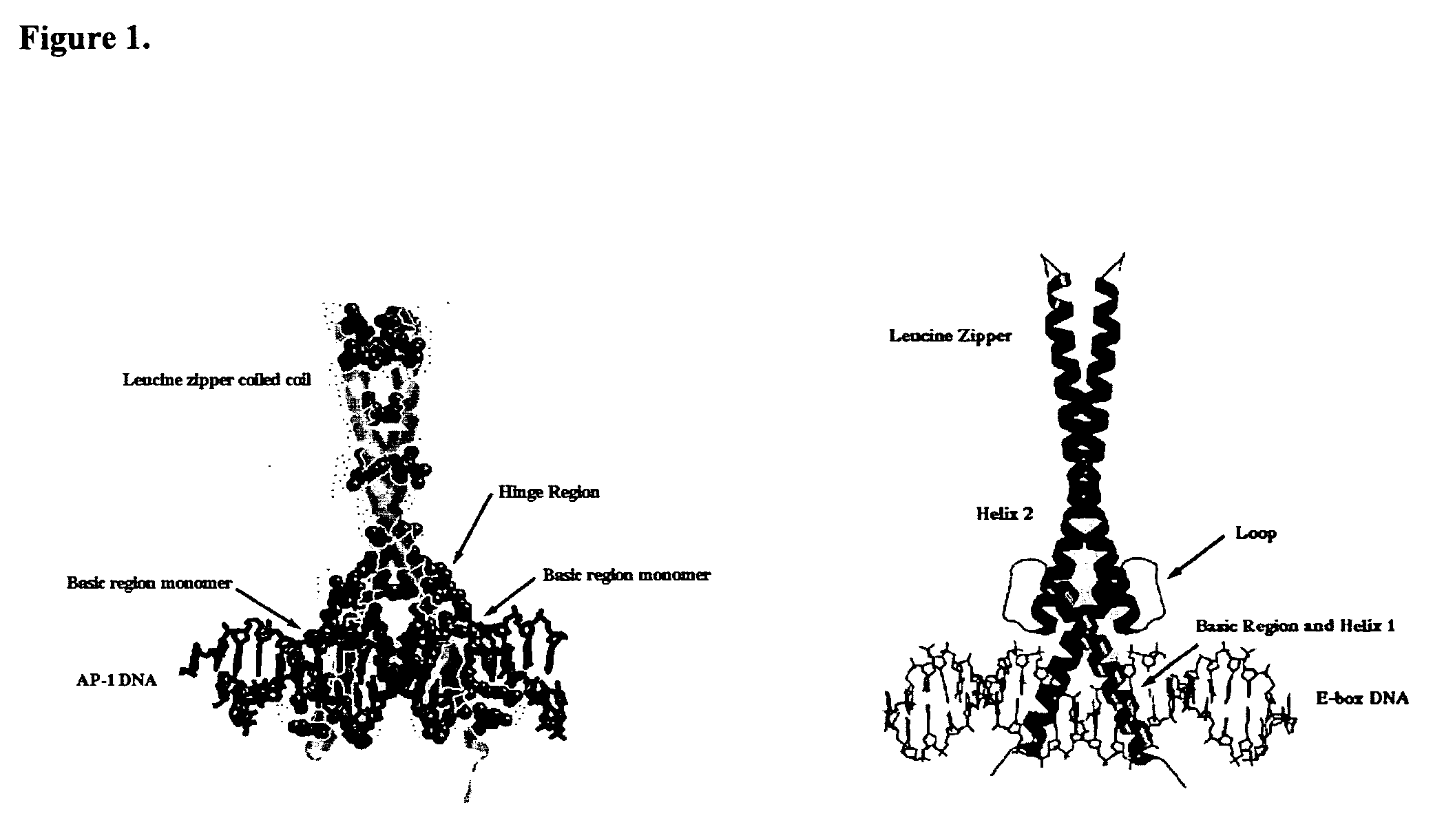
A leucine zipper (or leucine scissors) is a common three-dimensional structural motif in proteins. They were first described by Landschulz and collaborators in 1988 when they found that an enhancer binding protein had a very characteristic 30-amino acid segment and the display of these amino acid sequences on an idealized alpha helix revealed a periodic repetition of leucine residues at every seventh position over a distance covering eight helical turns. The polypeptide segments containing these periodic arrays of leucine residues were proposed to exist in an alpha-helical conformation and the leucine side chains from one alpha helix interdigitate with those from the alpha helix of a second polypeptide, facilitating dimerization.
Engineered transgene integration platform (ETIP) for gene targeting and trait stacking
An Engineered Transgene Integration Platform (ETIP) is described that can be inserted randomly or at targeted locations in plant genomes to facilitate rapid selection and detection of a GOI that is perfectly targeted (both the 5′ and 3′ ends) at the ETIP genomic location. One element in the subject disclosure is the introduction of specific double stranded breaks within the ETIP. In some embodiments, an ETIP is described using zinc finger nuclease binding sites, but may utilize other targeting technologies such as meganucleases, CRISPRs, TALs, or leucine zippers. Also described are compositions of, and methods for producing, transgenic plants wherein the donor or payload DNA expresses one or more products of an exogenous nucleic acid sequence (e.g. protein or RNA) that has been stably-integrated into an ETIP in a plant cell. In embodiments, the ETIP facilitates testing of gene candidates and plant expression vectors from ideation through Development phases.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
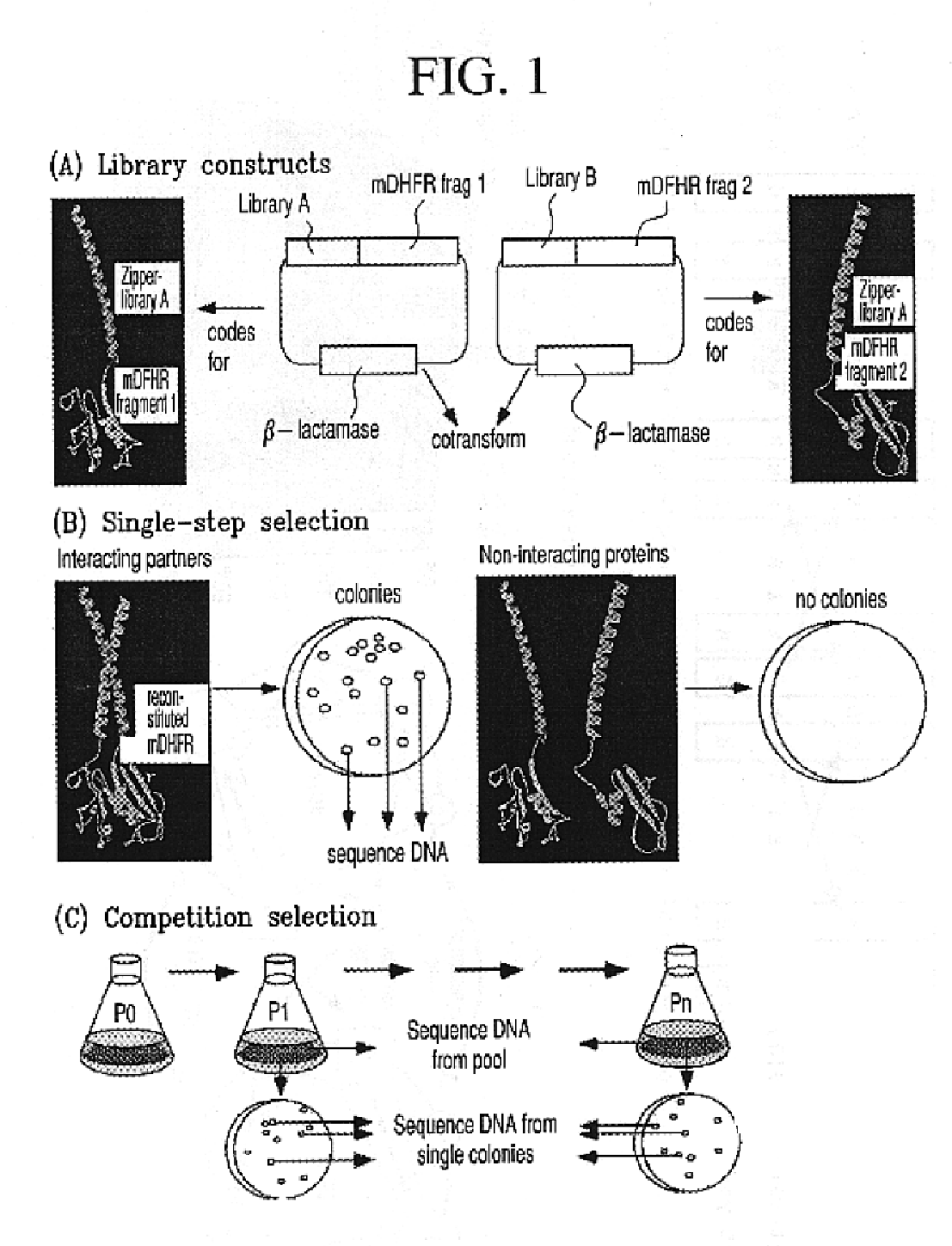
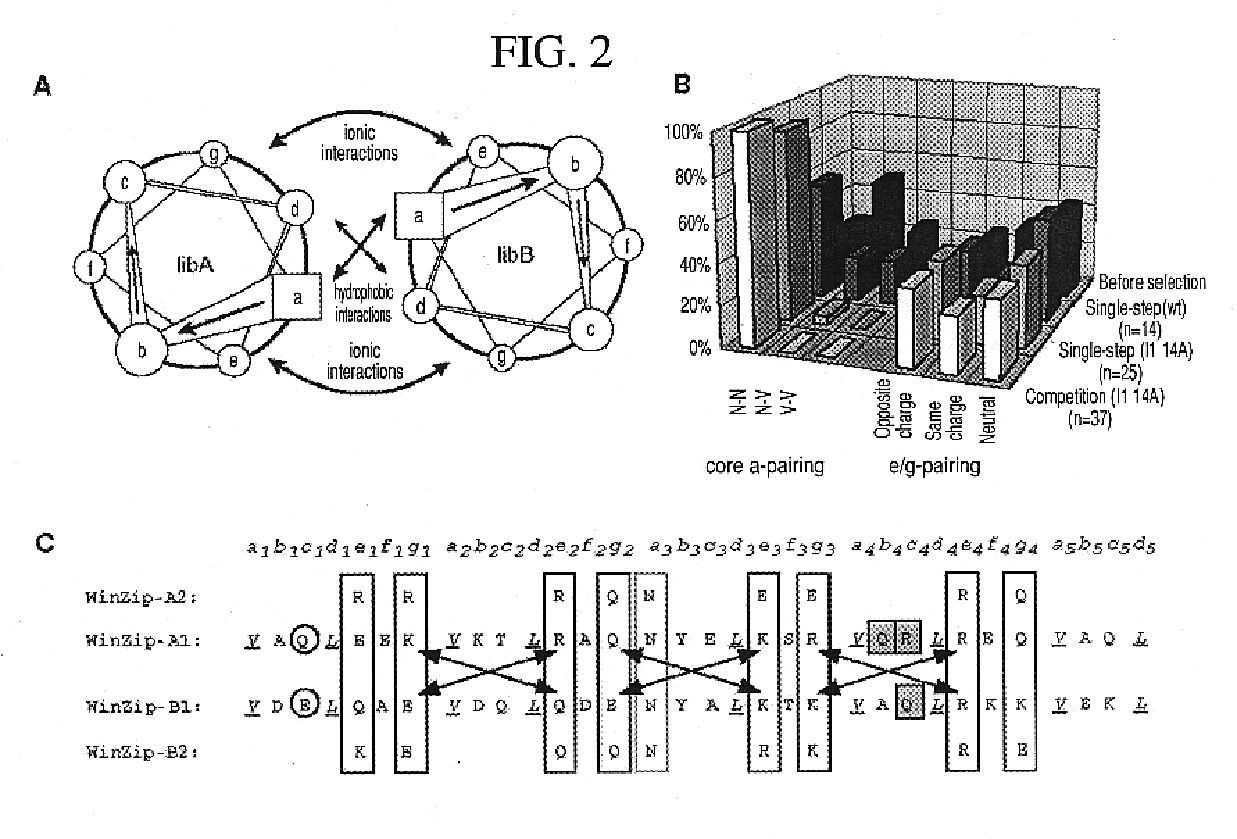
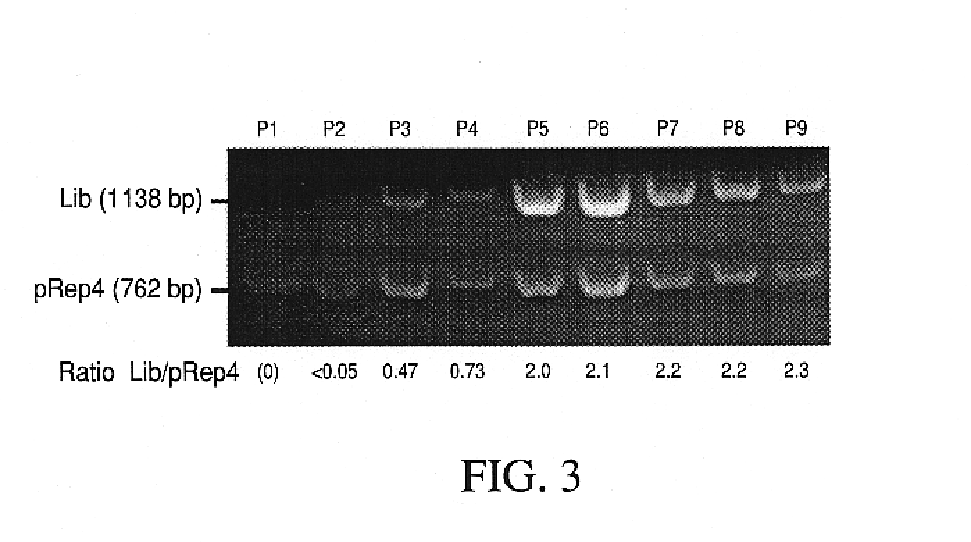
Vivo library-versus-library selection of optimized protein-protein interactions
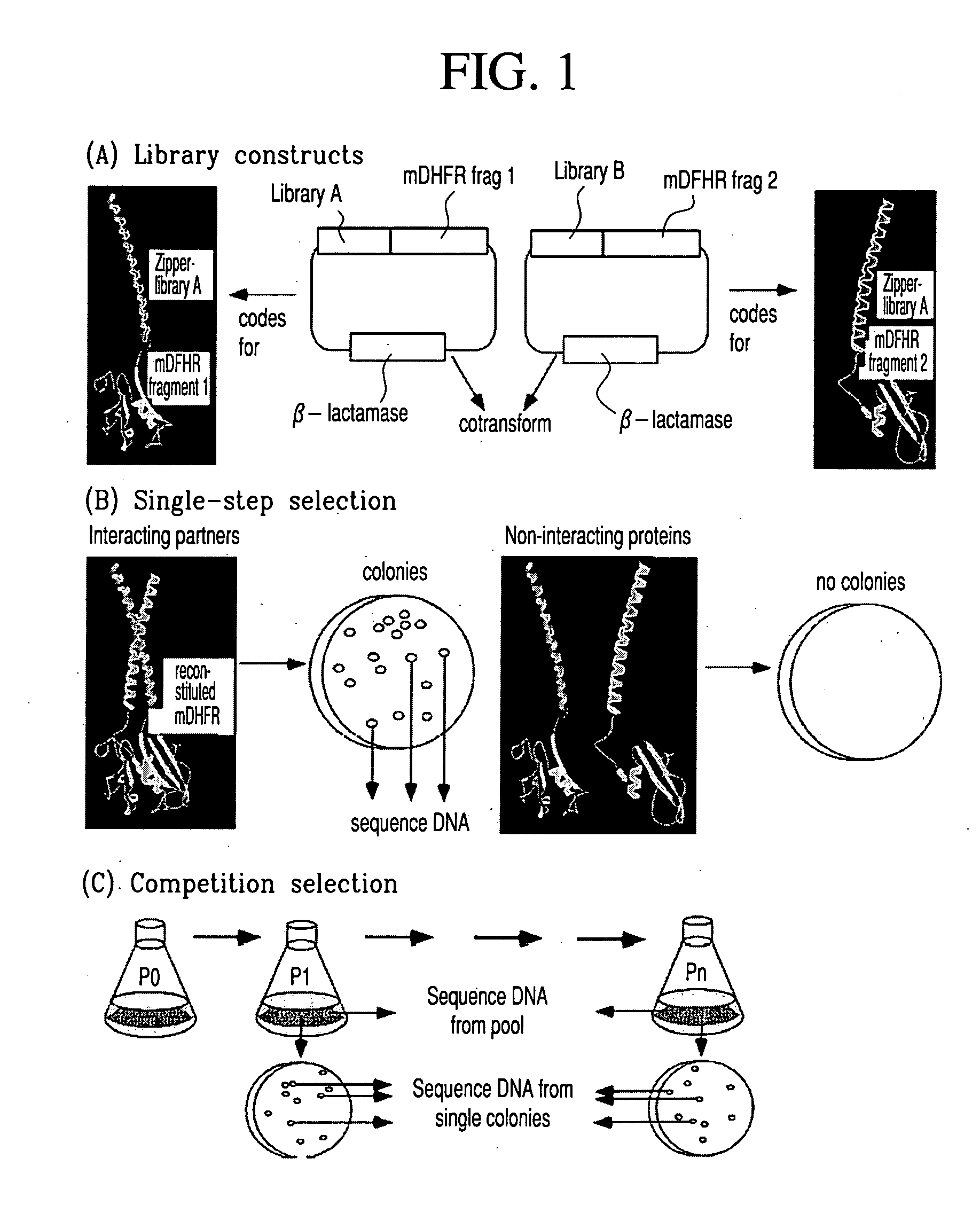
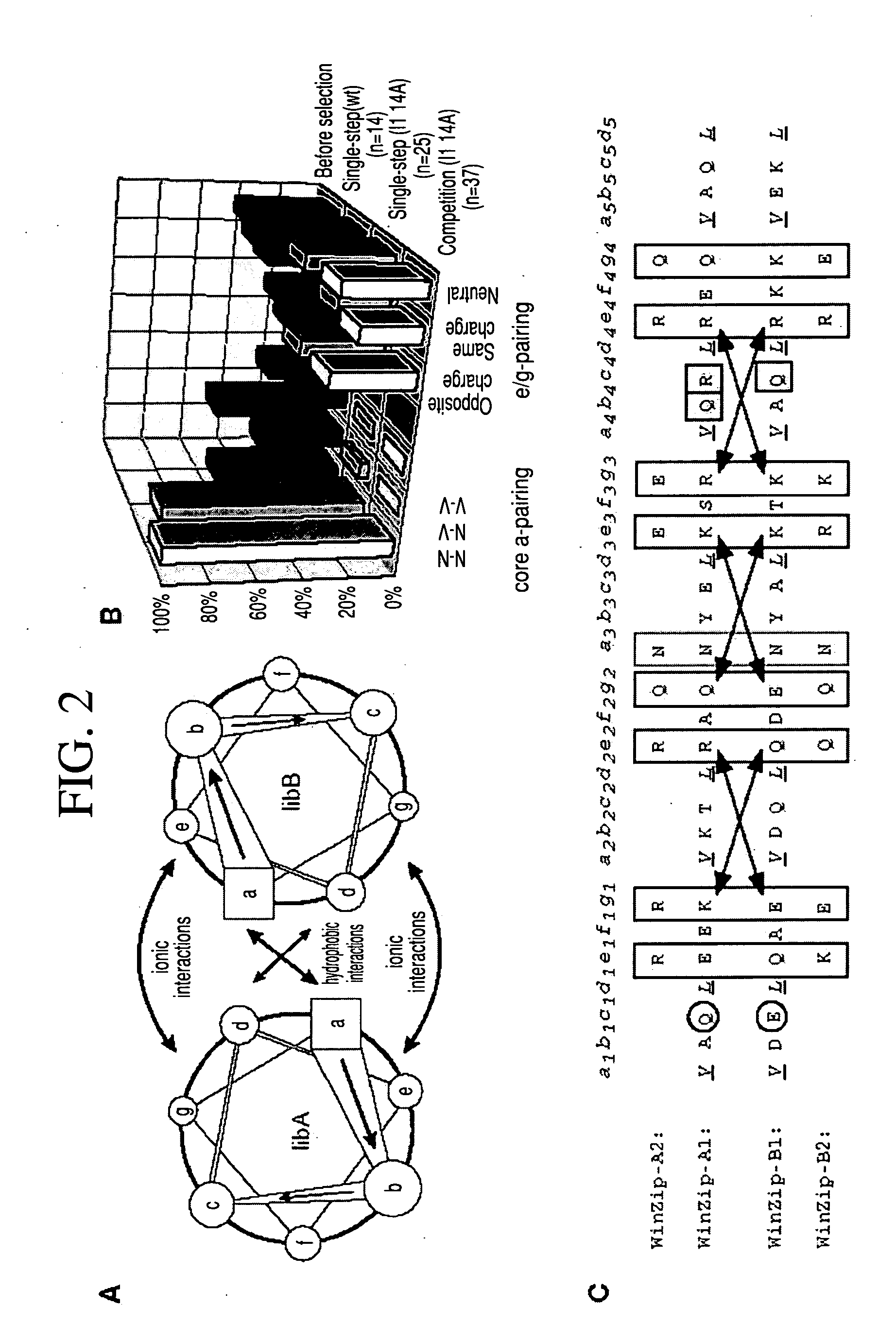
The present invention describes a rapid and efficient in vivo library-versus-library screening strategy for identifying optimally interacting pairs of heterodimerizing polypeptides. It allows for the screening of a protein library against a second protein library, rather than against a single bait protein, and thus has numerous applications in the study of protein-protein interactions. Additionally, it allows for the application of different selection stringencies. Two leucine zipper libraries, semi-randomized at the positions adjacent to the hydrophobic core, were genetically fused to either one of two designed fragments of the enzyme murine dihydrofolate reductase (mDHFR), and cotransformed into E. coli. Interaction between the library polypeptides was required for reconstitution of the enzymatic activity of mDHFR, allowing bacterial growth. Analysis of the resulting colonies revealed important biases in the zipper sequences relative to the original libraries, which are consistent with selection for stable, heterodimerizing pairs. Using more weakly associating mDHFR fragments, we increased the stringency of selection. We enriched the best performing leucine zipper pairs by multiple passaging of the pooled, selected colonies in liquid culture, as the best pairs allowed for better bacterial propagation. This competitive growth allowed small differences among the pairs to be amplified, and different sequence positions were enriched at different rates. We applied these selection processes to a library-versus-library sample of 2.0×106 combinations, and selected a novel leucine zipper pair which may be appropriate for use in further in vivo heterodimerization strategies.
Owner:ODYSSEY THERA INC
Plants having improved growth characteristics and a method for making the same
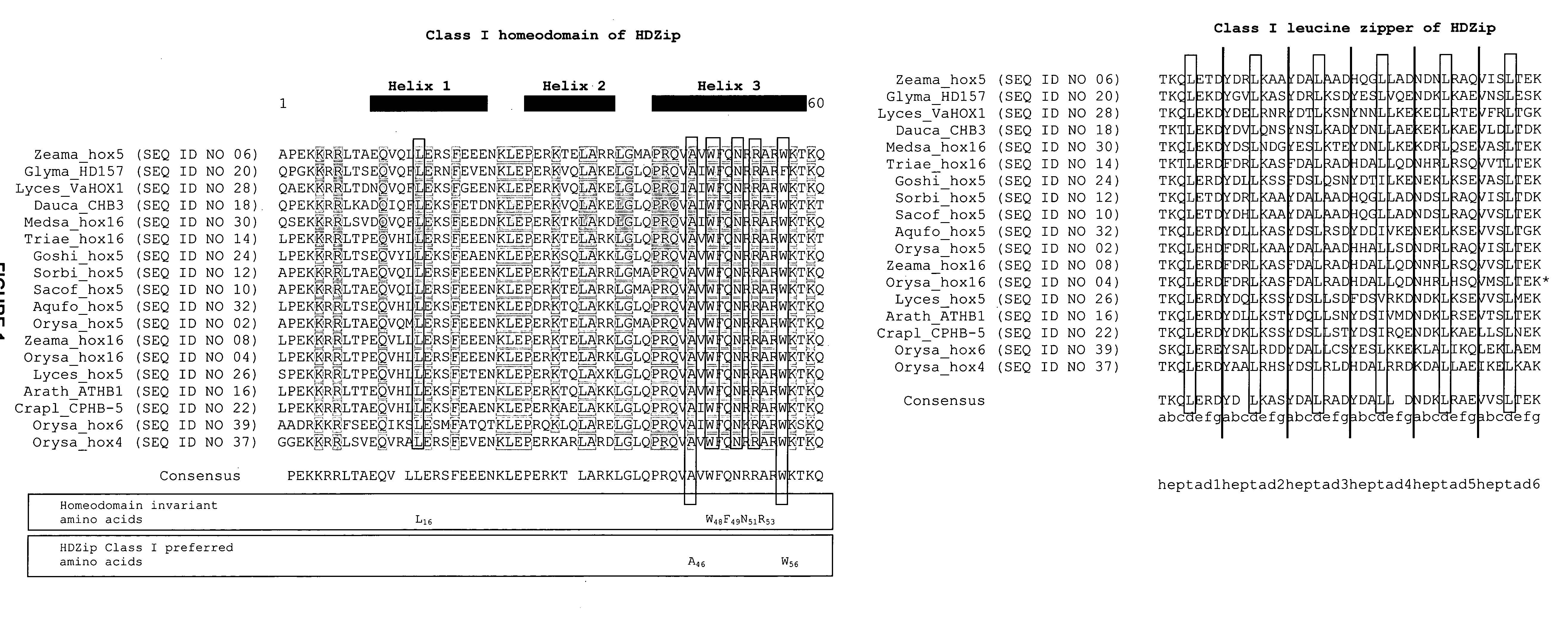
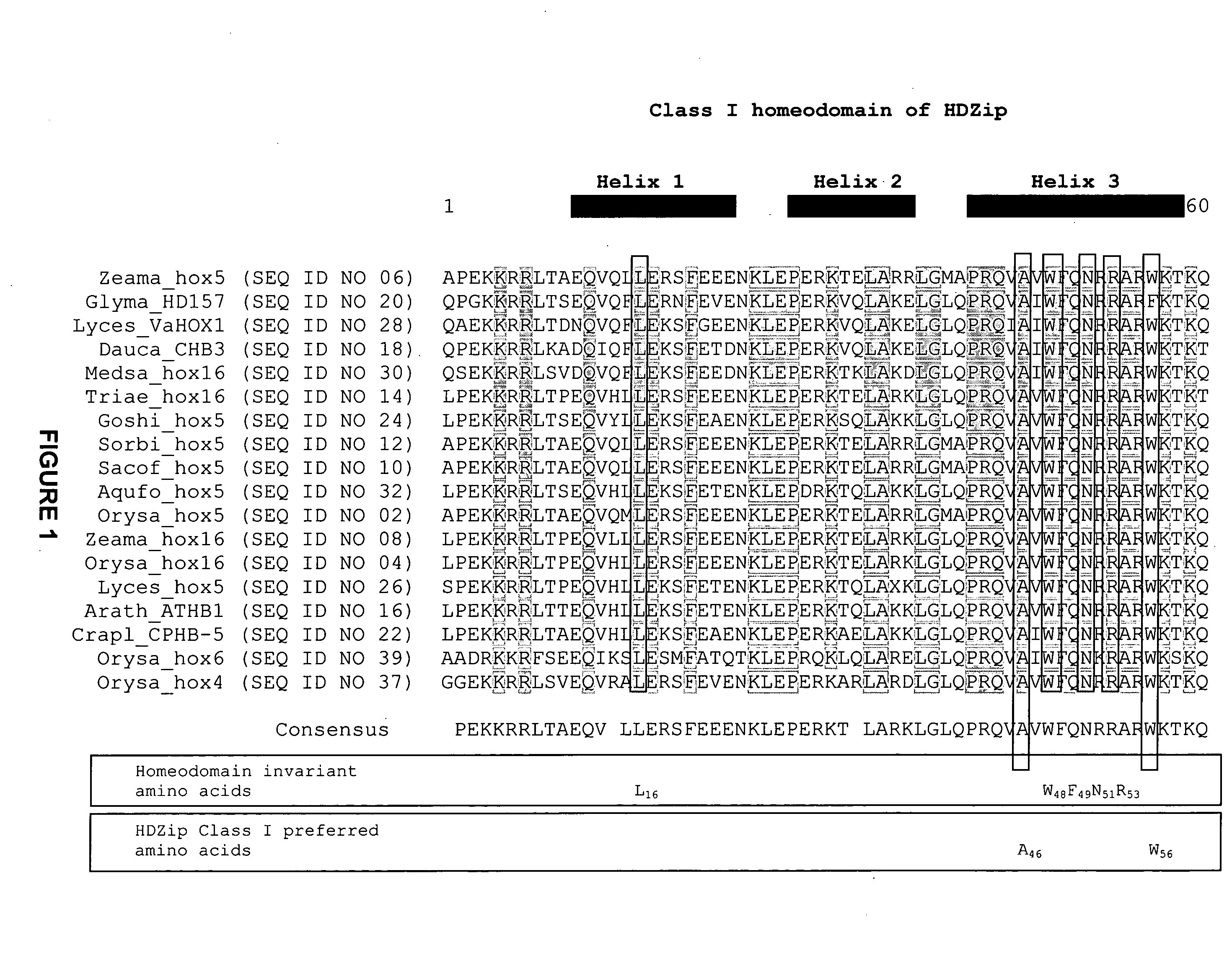
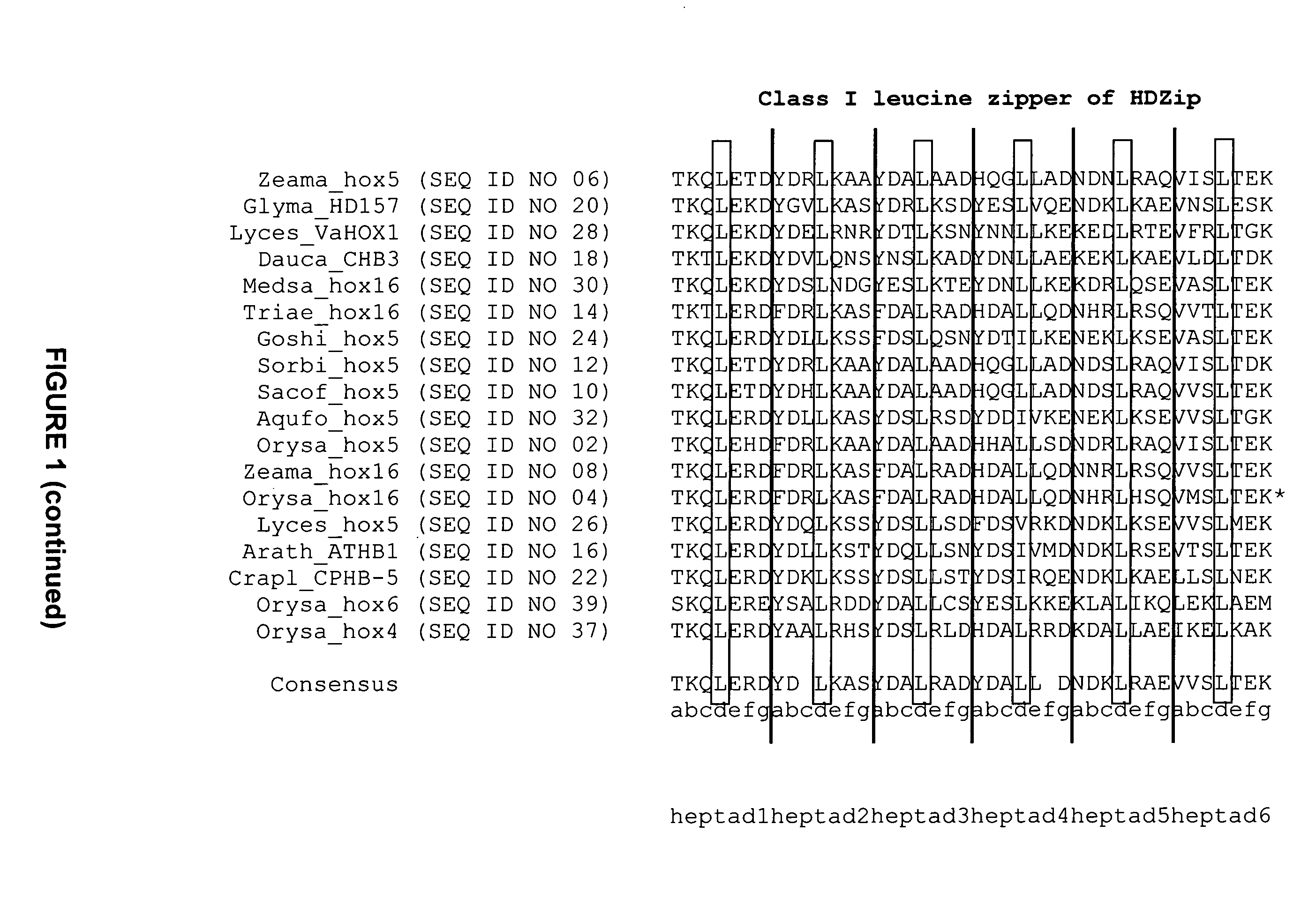
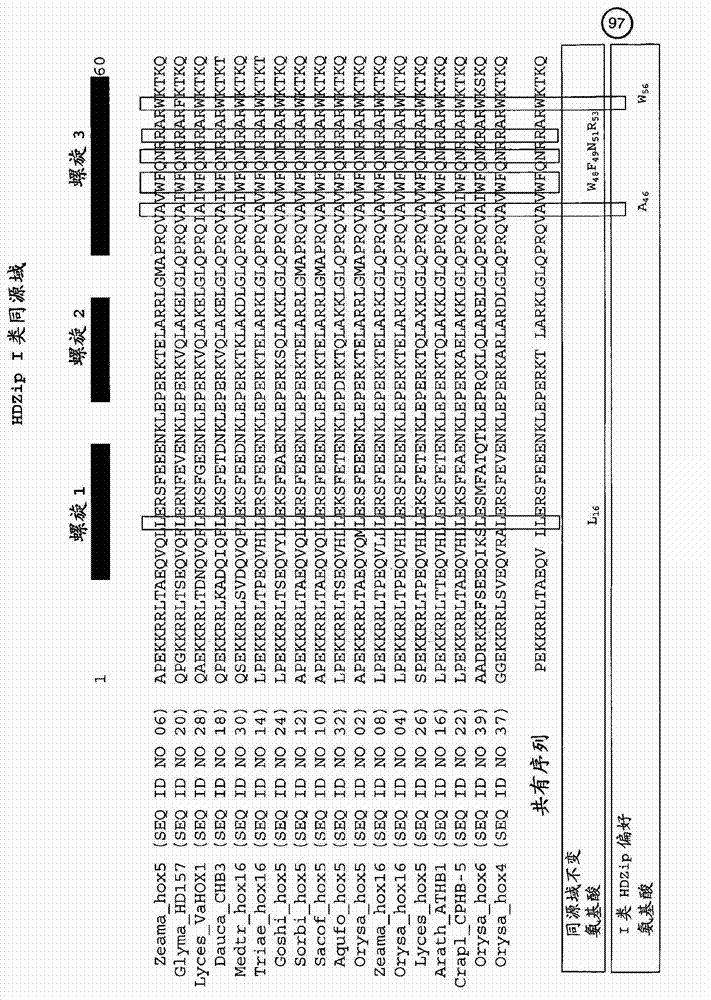
InactiveUS20080127365A1Improve featuresSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyGlycogen synthase I
The present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for improving plant growth characteristics relative to corresponding wild type plants. More specifically, the present invention concerns a method for improving plant growth characteristics comprising modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a class I homeodomain leucine zipper (HDZip) hox5 polypeptide or a homologue thereof; or comprising modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a nitrate transporter protein (NRT) or a homologue thereof; or comprising modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a polypeptide denoted Yield Enhancing Protein 16 (YEP16); or comprising modulating expression in a plant of a Group I glycogen synthase kinase (Group I shaggy-like kinase) or a homologue thereof. The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a class I HDZip hox5 polypeptide or a homologue thereof; or having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a NRT protein or a homologue thereof; or having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a polypeptide denoted YEP16; or having modulated expression of a Group I shaggy-like kinase or a homologue thereof, which plants have improved growth characteristics relative to corresponding wild type plants. The invention also provides constructs useful in the methods of the invention.
Owner:CROPDESIGN NV
Nucleic acid vectors for immunization
InactiveUS20100098718A1Rapid and high antibody responseEfficient transportSsRNA viruses positive-senseBacteriaVaccinationNucleic Acid Vaccines
A dimeric protein comprising a first fusion protein and a second fusion protein, wherein the first fusion protein comprises a targeting domain, a leucine zipper domain, and an antigen; and wherein the second fusion protein comprises a targeting domain, a leucine zipper domain, and optionally an antigen. Nucleic acid vectors encoding proteins of the invention are provided, particularly for use in nucleic acid vaccination.
Owner:CHIRON CORP
Minimalist bZIP Proteins and uses thereof
InactiveUS20070141672A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesBHLH ProteinsCell biology
The present invention provides minimalist bZIP proteins having a basic region derived from bHLH proteins fused to a leucine zipper dimerization domain derived from bZIP proteins and methods and uses thereof in the treatment of cancer. The present invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions for treating cancer.
Owner:SHIN JUMI
Method for stabilization of proteins using non-natural amino acids
InactiveUS7449443B2Peptide/protein ingredientsProtein composition from yeastsCoiled coil proteinTert-leucine
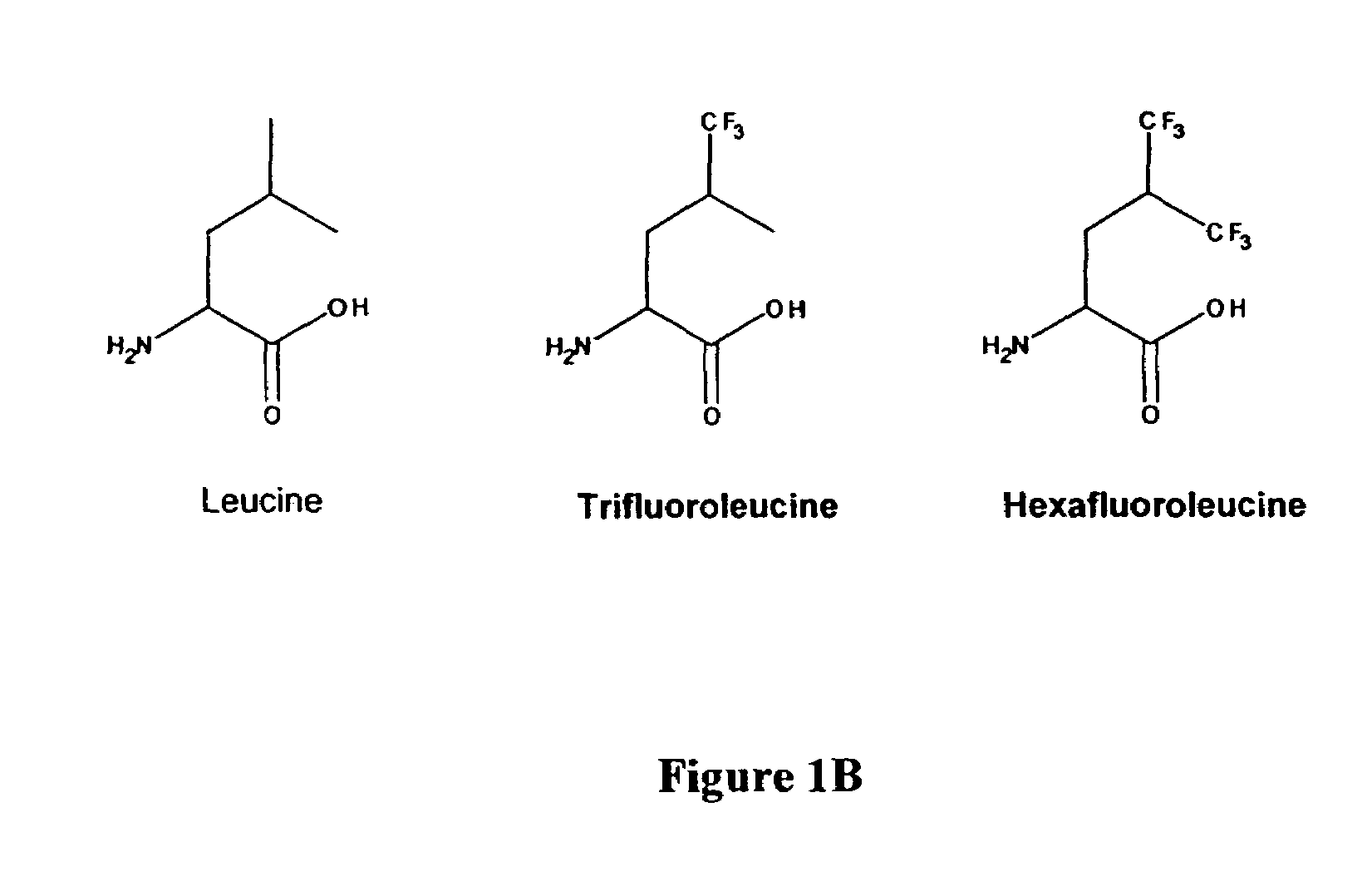
The present invention provides a method for producing modified stable polypeptides introducing at least one non-natural amino acid into the hydrophobic region of the polypeptide. The thermal and chemical stability of such polypeptides is improved compared to those properties of its corresponding wild type proteins.The invention further provides purified leucine zipper and coiled-coil proteins in which the leucine residues have been replaced with 5,5,5-trifluoroleucines, and the modified proteins so produced demonstrate increased thermal and chemical stability compared to their corresponding wild-type natural proteins.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Pharmacologic inhibition of Myc function
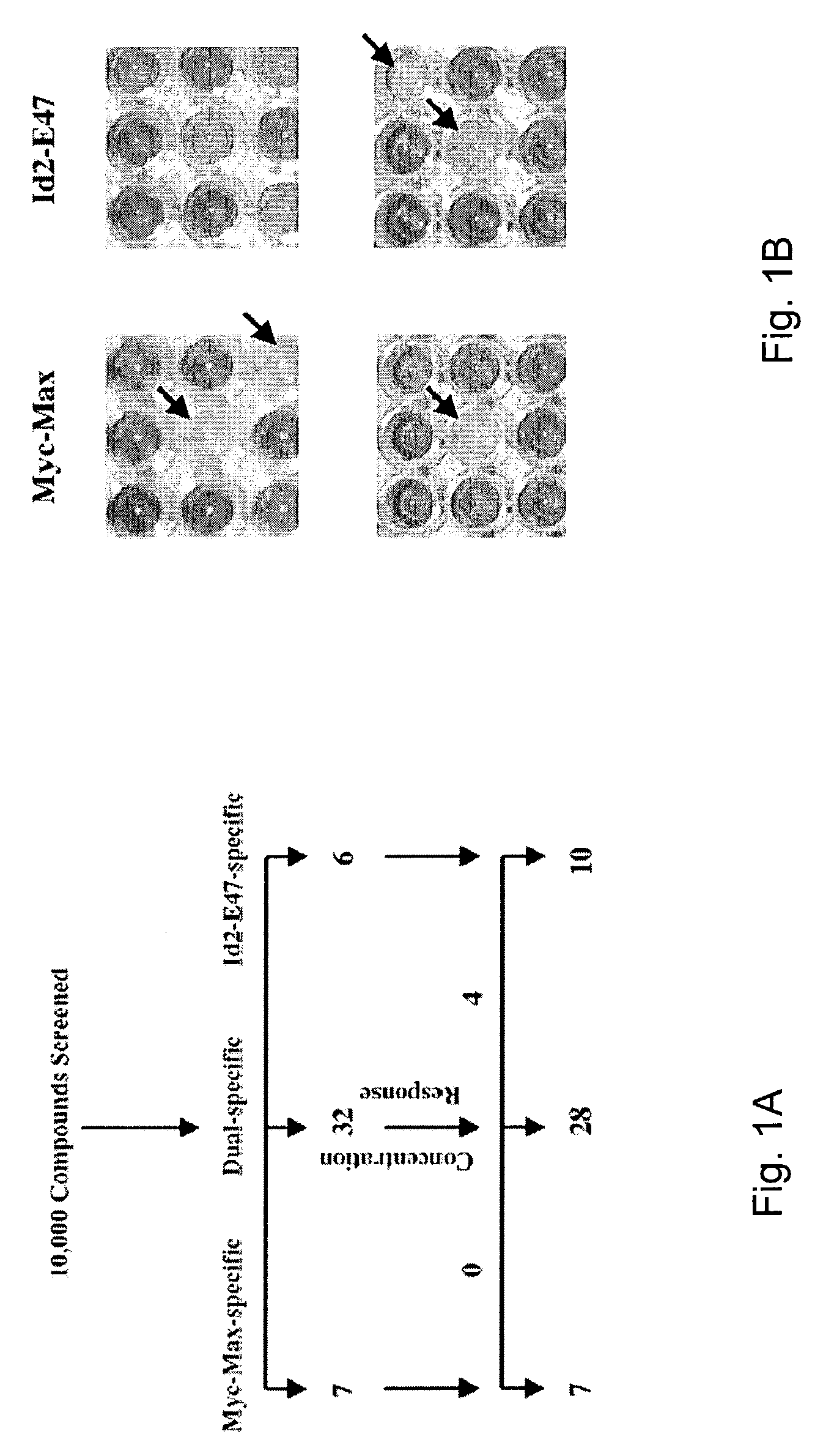
The c-Myc oncoprotein, a helix-loop-helix-leucine zipper (HLH-ZIP) transcription factor, is frequently deregulated in human cancers. All known functions of c-Myc, including those pertaining to transformation, require that it heterodimerize with another HLH-ZIP protein, Max. Using a high throughput yeast-based assay, we identified seven low molecular weight substances that inhibit c-Myc-Max association. Each compound also prevented this interaction in vitro and inhibited the growth of c-Myc-expressing fibroblasts, although not of fibroblasts lacking c-Myc. Finally, short-term exposure of c-Myc over expressing fibroblasts to several of the compounds markedly reduced their in vivo tumorigenicity. These studies suggest that yeast-based assays can be used to identify inhibitors of protein-protein interactions and that these frequently function in mammalian cells. The signature specificities of each of the c-Myc-Max compounds identified here further suggest synergistic in vivo function.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Transcription factor gene induced by water deficit conditions and abscisic acid from Helianthus annuus, promoter and transgenic plants
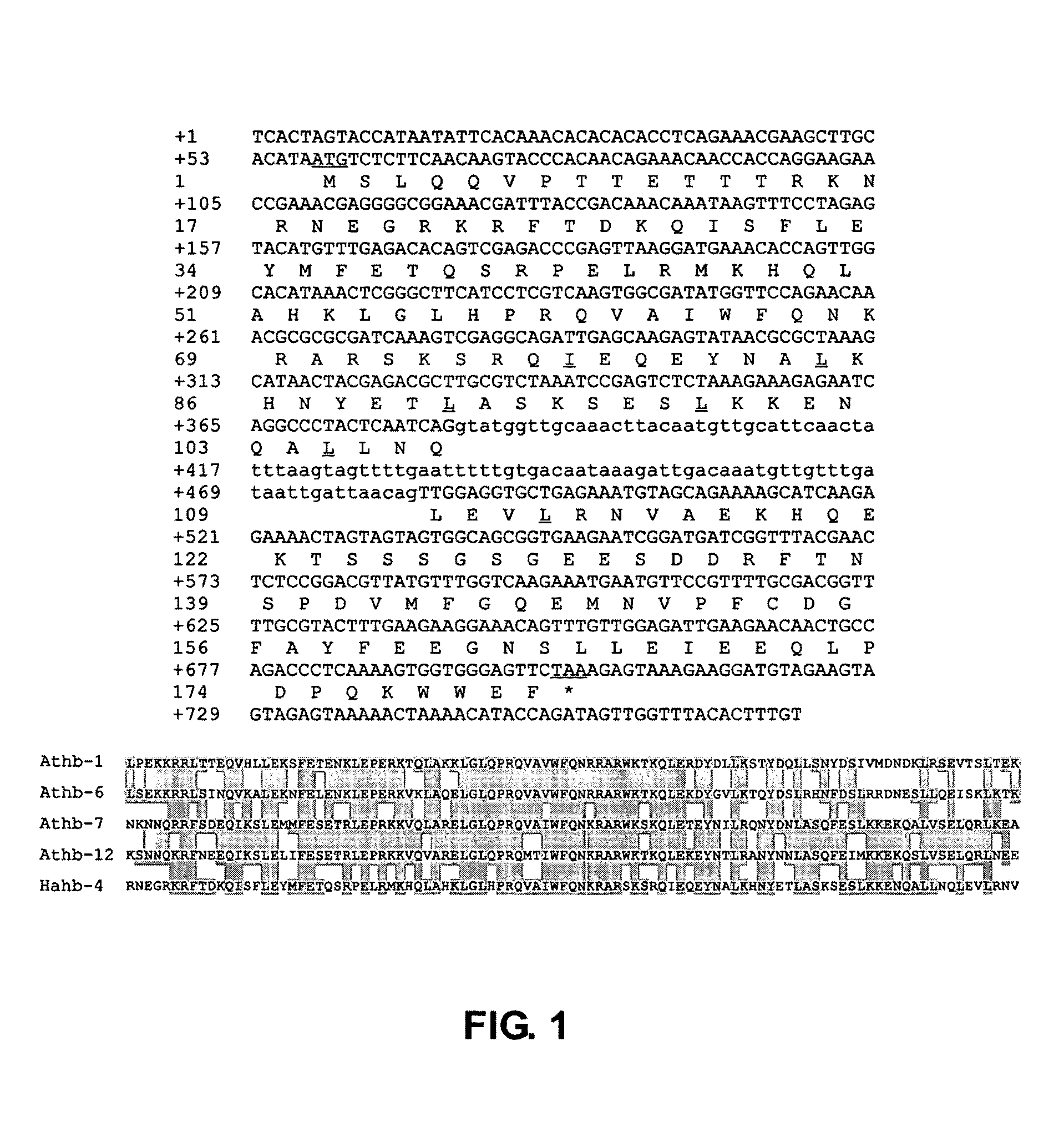
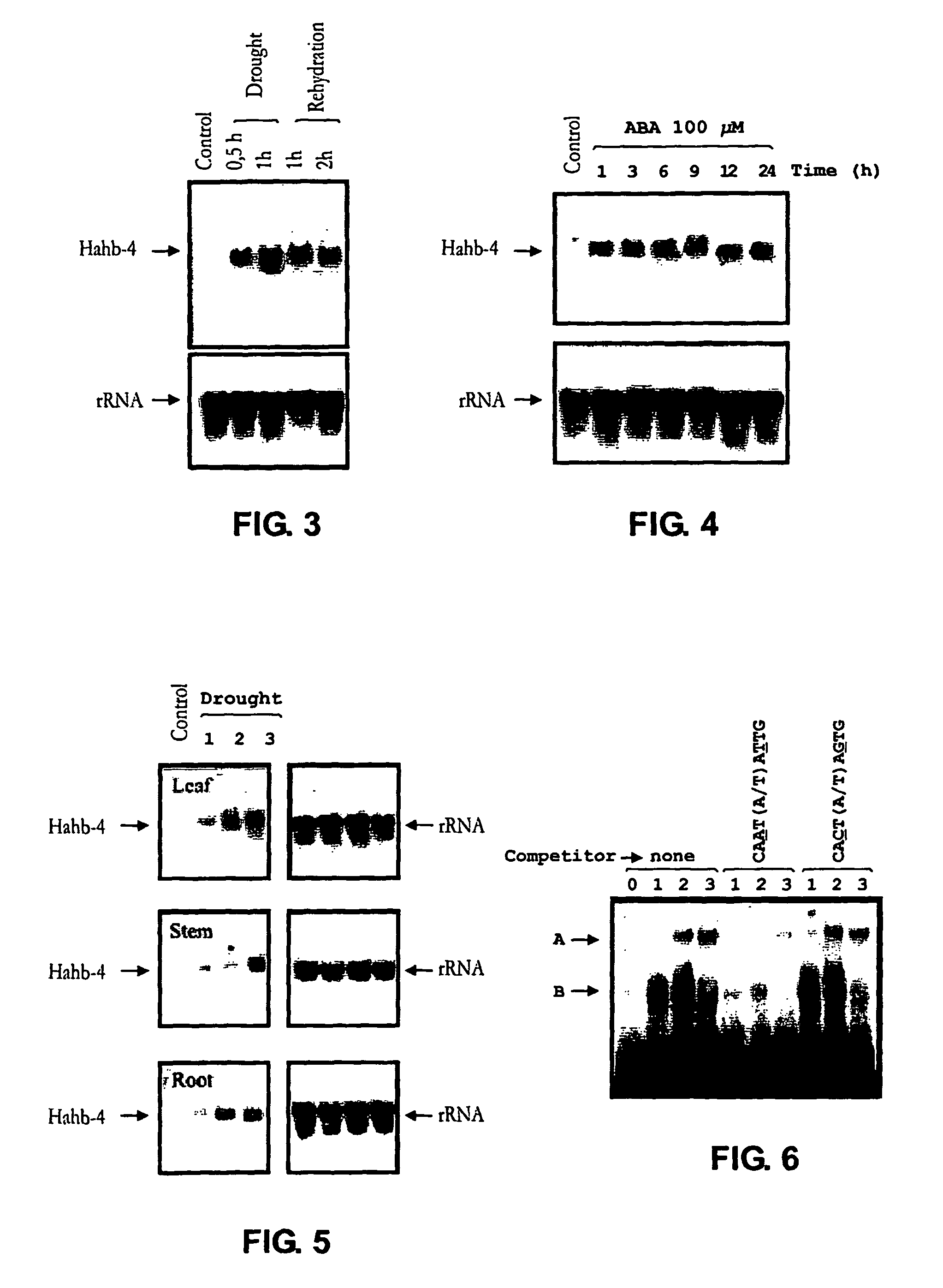
A new transcription factor coding gene induced by water deficit or abscisic acid of Helianthus annuus, having a homeodomain associated to a leucine zipper, was characterized. The transcription factor is useful to be cloned in DNA constructions for transforming host cells and plants. The transgenic plants comprising the transcription factor gene are tolerant and resistant to harmful environmental conditions such as water stress and high salinity. A nucleic acid promoting sequence is also provided wherein the sequence is induced by water deficit or abscisic acid. Constructions, host cells and transgenic plants that comprise the transcription factor gene are provided.
Owner:BIOCERES
Methods and compositions for cellular reprogramming
Disclosed herein are methods and pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment of retinitis pigmentosa, macular degeneration and other retinal conditions by interfering with expression of genes, such as those encoding photoreceptor cell-specific nuclear receptor and neural retina-specific leucine zipper protein, in cells of the eye. These methods and compositions employ nucleic acid based therapies.
Owner:YOUHEALTH BIOTECH LTD +1
Plants having enhanced yield-related traits and a method for making the same
InactiveUS20090241218A1Enhanced yield-related traitsIncrease productionClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesGrowth plantWild type
The present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for improving various plant growth characteristics by modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a GRP (Growth-Related Protein). The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a GRP, which plants have improved growth characteristics relative to corresponding wild type plants or other control plants. The invention also provides constructs useful in the methods of the invention. The GRP may be one of the following: Extensin Receptor-Like Kinase (ERLK), F-Box WD40 (FBXW) polypeptide, RAN-Binding Protein (RANBP), Golden2-like Transcription Factor (GLK), REV delta homeodomain leucine zipper domain polypeptide, CLE protein, and Seed Yield Regulator (SYR) protein.
Owner:CROPDESIGN NV
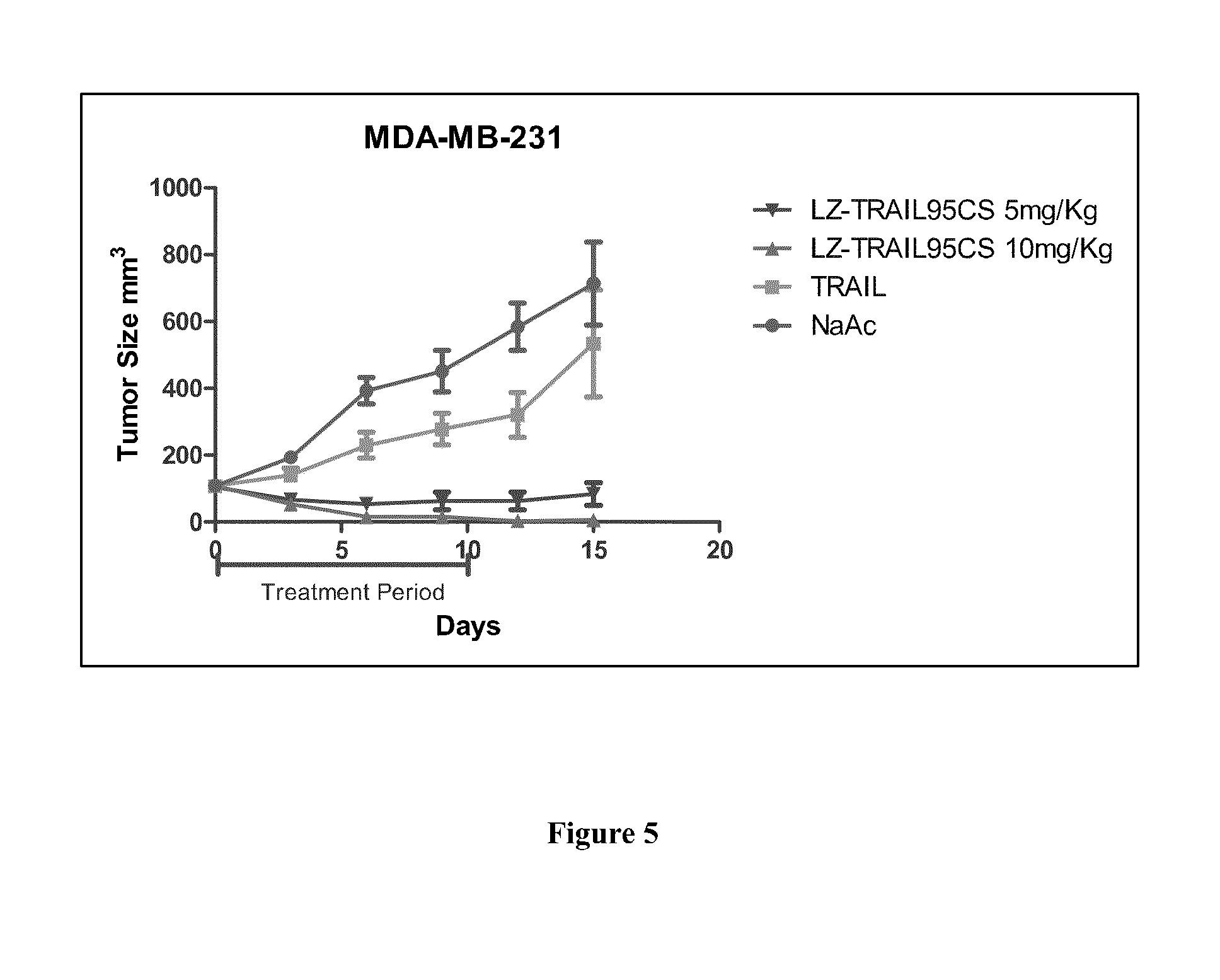
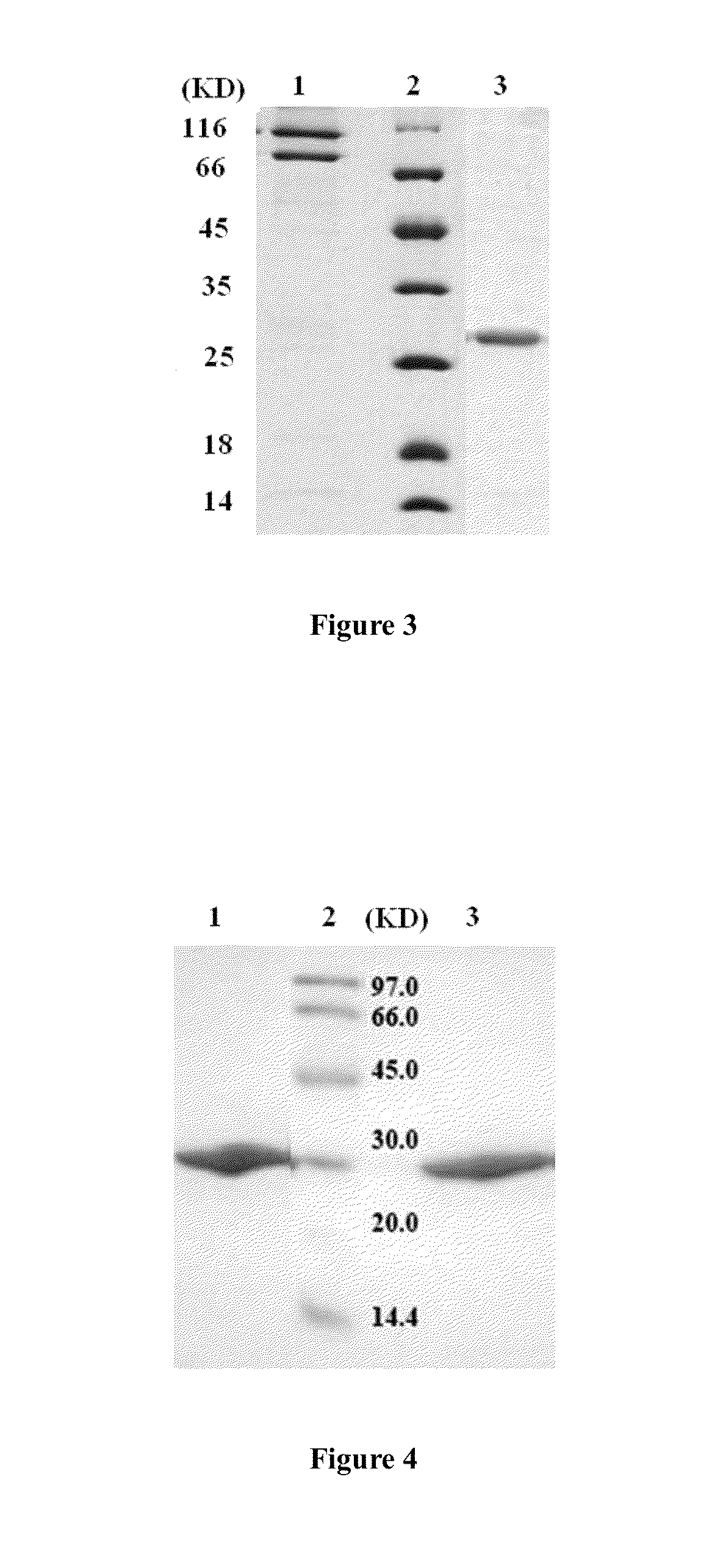
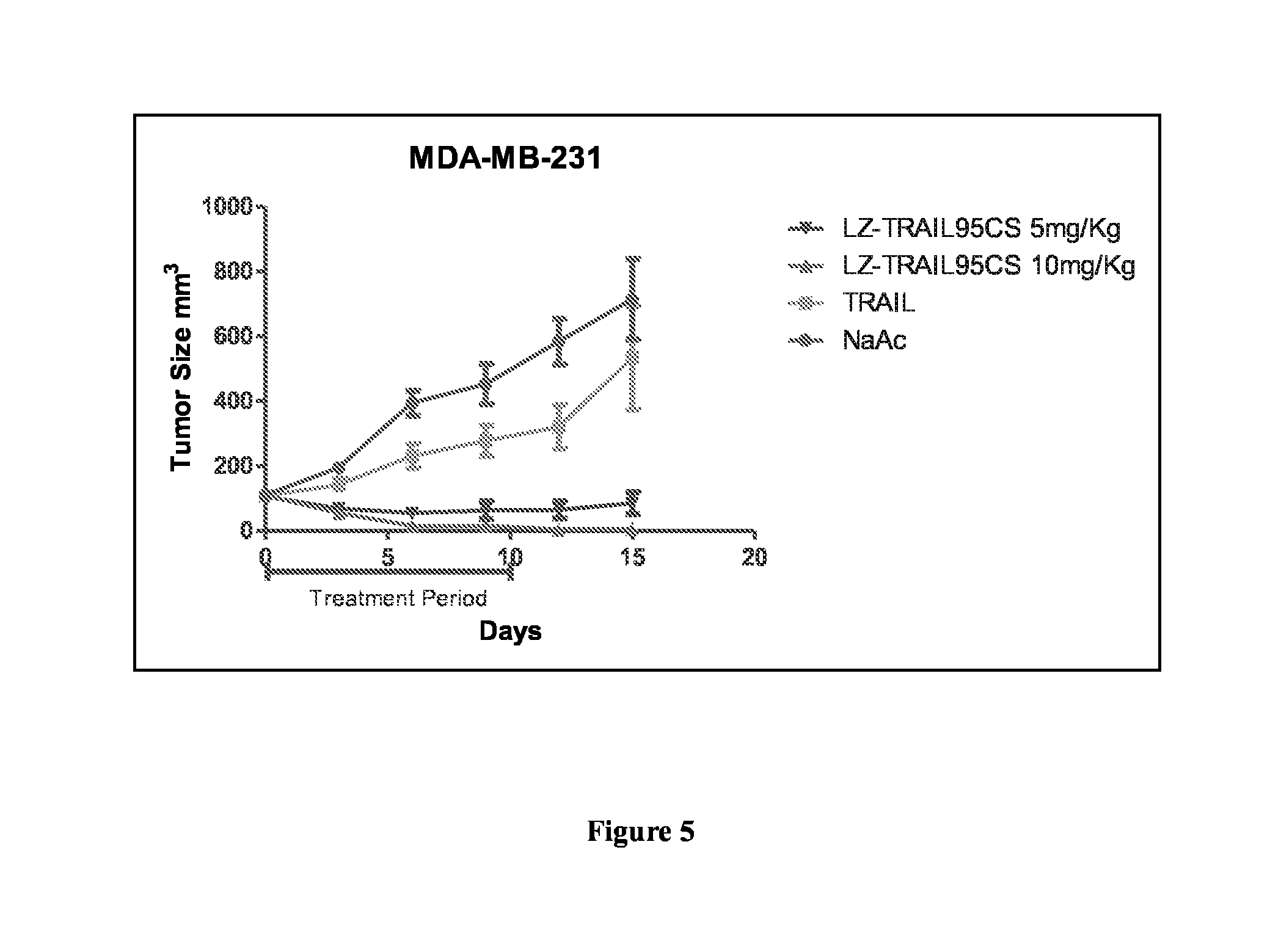
Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) fusion protein, its preparation and applications
The invention, relating to the field of biotechnology, provides TRAIL fusion protein, a DNA sequence encoding the fusion protein, a vector containing the DNA sequence, a host cell or a transgenic animal containing the vector, a preparation method of the fusion protein and applications of the fusion protein. The TRAIL fusion protein from N-terminal to C-terminal comprises crosslinking region, humanized leucine zipper sequence and humanized TRAIL protein, humanized TRAIL extracellular region or fragments of humanized TRAIL extracellular region, can observably increase stability, prolong the half life in animal body and improve treatment effect, and has extensive application prospect.
Owner:JIANGSU SIMCERE PHARMACEUTICAL R & D CO LTD
Plants having enhanced yield-related traits and a method formaking the same
The present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for improving various plant growth characteristics by modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a GRP (Growth-Related Protein). The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a GRP, which plants have improved growth characteristics relative to corresponding wild type plants or other control plants. The invention also provides constructs useful in the methods of the invention. The GRP may be one of the following: Extensin Receptor-Like Kinase (ERLK), F- Box WD40 (FBXW) polypeptide, RAN-Binding Protein (RANBP), Golden2-like Transcription Factor (GLK), REV delta homeodomain leucine zipper domain polypepetide, CLE protein, and Seed Yield Regulator (SYR) protein.
Owner:CROPDESIGN NV
New-type label protein and application thereof
InactiveCN101570756AHybrid peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionProtein targetProtein C
The invention provides a method for expressing a target protein, which comprises the following steps that the fusion protein of a leucine zipper 1, a carboxyl terminal region of a homothetic ubiquitin molecule and the target protein is expressed in a host cell; the fusion protein is mixed with the rebuilding protein of the homothetic ubiquitin molecule containing the amino terminal region of the homothetic ubiquitin molecule and a leucine zipper 2 in order to produce a rebuilding product which is processed by the specific prolease of the homothetic ubiquitin molecule, and thus, the target protein is obtained. The invention also provides a reagent kit for the expression of the target protein, the reagent kit comprises a structuring object for expressing the target protein, an encoding gene containing the encoding gene of the leucine zipper 1 and the carboxyl terminal region of the homothetic ubiquitin molecule and the rebuilding protein or the rebuilding structuring object of the homothetic ubiquitin molecule.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Down-regulation of a homeodomain-leucine zipper i-class homeobox gene for improved plant performance
Methods for modulating plants using optimized ZmME293 down-regulation constructs are disclosed. Also disclosed are nucleotide sequences, constructs, vectors, and modified plant cells, as well as transgenic plants displaying increased seed and / or biomass yield, improved tolerance to abiotic stress such as drought or high plant density, improved nitrogen utilization efficiency, increased ear number and / or reduction in time to scenescence.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Plants having improved growth characteristics and a method for making the same
InactiveCN102925455AMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationGrowth plantWild type
The present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for improving plant growth characteristics relative to corresponding wild type plants. More specifically, the present invention concerns a method for improving plant growth characteristics comprising modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a class I homeodomain leucine zipper (HDZip) hox5 polypeptide or a homologue thereof; or comprising modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a nitrate transporter protein (NRT) or a homologue thereof; or comprising modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a polypeptide denoted Yield Enhancing Protein 16 (referred to as YEP16); or comprising modulating expression in a plant of a Group I glycogen synthase kinase (Group I shaggy-like kinase) or a homologue thereof. The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a class I homeodomain leucine zipper (HDZip) hox5 polypeptide or a homologue thereof; or having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a nitrate transporter protein (NRT) or a homologue thereof; or having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a polypeptide denoted Yield Enhancing Protein 16 (hereinafter referred to as YEP16); or having modulated expression of a Group I glycogen synthase kinase (Group I shaggy-like kinase) or a homologue thereof, which plants have improved growth characteristics relative to corresponding wild type plants. The invention also provides constructs useful in the methods of the invention.
Owner:CROPDESIGN NV
Fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS) enrichment to generate plants
InactiveUS20140075593A1Other foreign material introduction processesTissue cultureFluorescenceBinding site
An Engineered Transgene Integration Platform (ETIP) is described that can be inserted randomly or at targeted locations in plant genomes to facilitate rapid selection and detection of a GOI that is perfectly targeted (both the 3′ and 5′ ends) at the ETIP genomic location. One element in the invention is the introduction of specific double stranded breaks within the ETIP. In some embodiments, an ETIP is described using zinc finger nuclease binding sites, but may utilize other targeting technologies such as meganucleases, TALs, CRISPRs, or leucine zippers. Also described are compositions of, and methods for producing, transgenic plants wherein the donor or payload DNA expresses one or more products of an exogenous nucleic acid sequence (e.g. protein or RNA) that has been stably-integrated into an ETIP in a plant cell. In embodiments, the ETIP facilitates testing of gene candidates and plant expression vectors from ideation through Development phases.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Therapeutic TRAIL Fusion Protein and Preparation and Use Thereof
InactiveUS20140206843A1Good for healthLow toxicityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsChimerin ProteinsHalf-life
This invention relates to the biotechnology area, and provides a kind of TRAIL chimeric protein, DNA sequence encoding this chimeric protein, vectors comprising this DNA, host cells or transgenic animals that contain one of the vectors, and preparation methods for the said chimeric protein and its applications. The said TRAIL fusion protein from the N to C terminal comprises human leucine zipper sequence, human TRAIL protein, human TRAIL extracellular domain or a fragment thereof. The chimeric protein has significantly enhanced stability, prolonged half-life in animals, increased efficacy and thus has broad application future.
Owner:MAGELLAN PHARMA
Alleles for regulating and controlling two types of main stem table fur types of upland cotton, and single stranded conformational polymorphism (SSCP) molecular marker for identification thereof
The invention discloses alleles for regulating and controlling two types of main stem table fur types of upland cotton, and a single stranded conformational polymorphism (SSCP) molecular marker for identification thereof. On the research basis of defining that an HDI gene in a homeobox-homeodomain-leucine zipper protein family IV is a key gene of affecting table fur generation of the upland cotton, the alleles GhHD1a and b for regulating and controlling regeneration of two types of stem table furs of the upland cotton are identified for the first time; a molecular marker for screening the two alleles by using the SSCP technology is invented. The molecular marker can rapidly identify two kinds of table fur types. The alleles prove that two genetypes of the HD1 have close relationship to two table fur types, a foundation is established for researching the molecular mechanism of generating table furs and fibers, the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) molecular marker capable of directly identifying the table fur type of the upland cotton in a laboratory is developed, and a rapid technology is provided for rapidly breeding different fur types of new cotton varieties.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Rna interference mediated inhibition of btb and cnc homology 1, basic leucine zipper transcription factor 1 (bach 1) gene expression using short interfering nucleic acid (sina) sequence listing
The present invention relates to compounds, compositions, and methods for the study, diagnosis, and treatment of traits, diseases and conditions that respond to the modulation of Bach1 gene expression and / or activity, and / or modulate a Bach1 gene expression pathway. Specifically, the invention relates to double-stranded nucleic acid molecules including small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules that are capable of mediating or that mediate RNA interference (RNAi) against Bach1 gene expression.
Owner:SCHERING AG
Novel coronavirus S protein receptor binding domain fusion protein containing oligomerization structural domain and application of novel coronavirus S protein receptor binding domain fusion protein
Owner:THE INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Plants having improved growth characteristics and a method for making the same
InactiveUS8853492B2Improve featuresSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyGlycogen synthase I
The present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for improving plant growth characteristics relative to corresponding wild type plants. More specifically, the present invention concerns a method for improving plant growth characteristics comprising modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a class I homeodomain leucine zipper (HDZip) hox5 polypeptide or a homologue thereof; or comprising modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a nitrate transporter protein (NRT) or a homologue thereof; or comprising modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a polypeptide denoted Yield Enhancing Protein 16 (YEP16); or comprising modulating expression in a plant of a Group I glycogen synthase kinase (Group I shaggy-like kinase) or a homologue thereof. The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a class I HDZip hox5 polypeptide or a homologue thereof; or having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a NRT protein or a homologue thereof; or having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a polypeptide denoted YEP16; or having modulated expression of a Group I shaggy-like kinase or a homologue thereof, which plants have improved growth characteristics relative to corresponding wild type plants. The invention also provides constructs useful in the methods of the invention.
Owner:CROPDESIGN NV
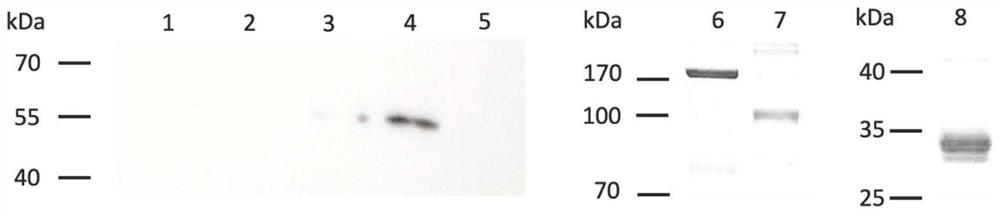
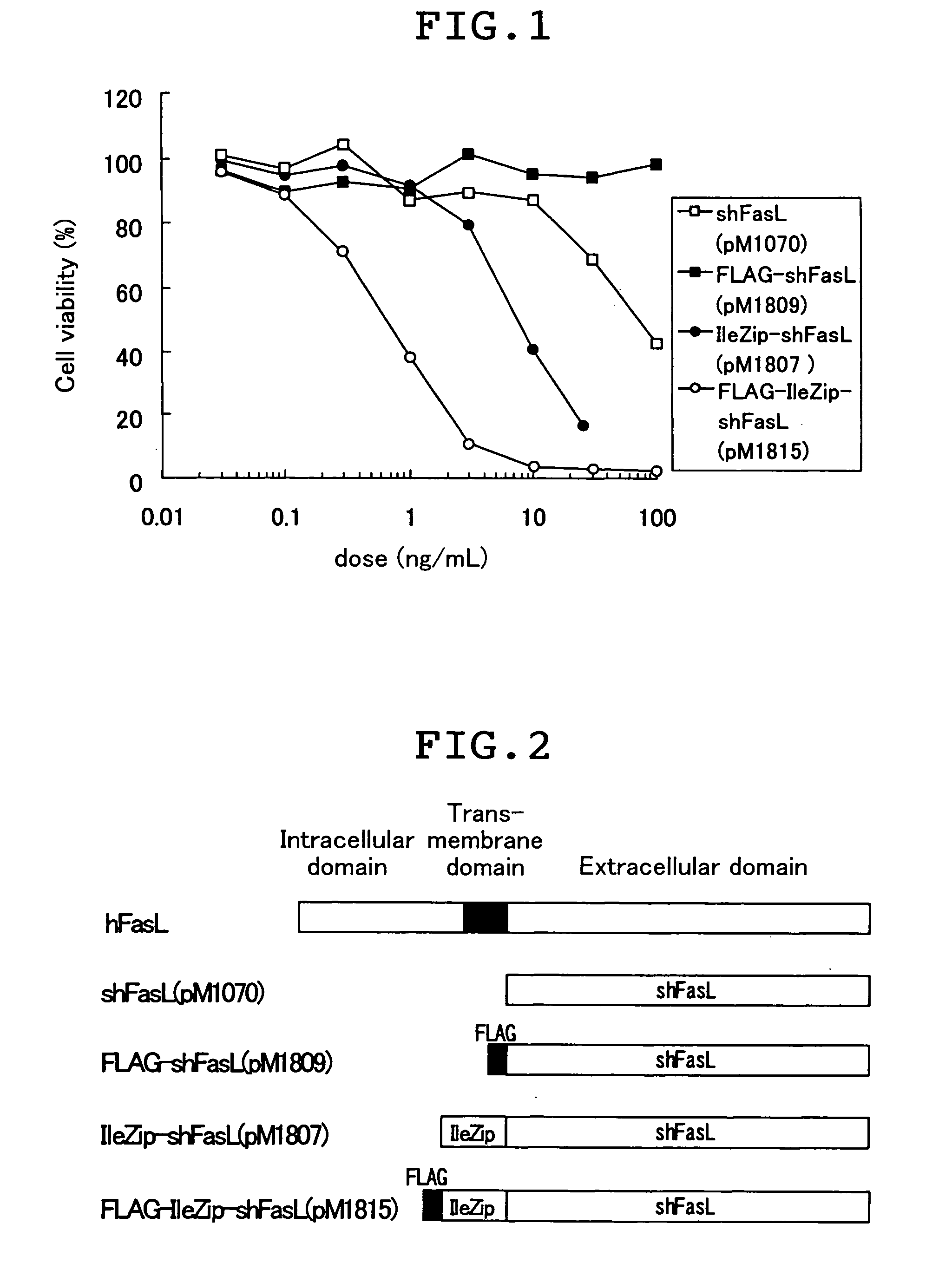
Fas ligand-fused proteins
InactiveUS20040053249A1Improve biological activityIncrease productionAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGenetic material ingredientsTransmembrane proteinBiological organism
Provided by this invention is a fusion protein which is capable of binding to Fas, and which comprises a peptide comprising at least a part of the amino acid sequence of Fas ligand, a peptide having oligomerization ability, and a peptide which increases recombinant protein production. Also provided are a method for using the FLAG-like peptide for the purpose of increasing the production of the recombinant protein, and a method for using the FLAG-like peptide for the purpose of increasing the biological activity of the fusion protein of the leucine zipper and the transmembrane protein.
Owner:MOCHIDA PHARM CO LTD
Marek's Disease Virus Vaccine Compositions and Methods of Using Thereof
InactiveUS20100233206A1Reduce pathogenicityAltering pathogenicityNervous disorderViral antigen ingredientsPhosphorylationMarek's disease
Marek's disease virus (MDV), the etiologic agent of Marek's disease, is a potent oncogenic herpesvirus. MDV is highly contagious and elicits a rapid onset of malignant T-cell lymphomas in chickens within weeks after infection. MDV codes for an oncoprotein, Meq, that shares resemblance with the Jun / Fos family of b-ZIP transcription factors. Earlier studies showed that Meq is responsible for development for T-cell lymphomas in chicken. In order to identify specific regions within the Meq gene, a series of recombinant MDV were generated in which a mutated gene was introduced in place of parental Meq gene. Various mutations were introduced at the phosphorylation sites, basic region, leucine zipper region and transactivation regions of the Meq gene. Several of these mutations have been shown to have an attenuated phenotype in chickens. In one embodiment, the present invention contemplates exploiting these mutations to develop MDV vaccines that are able to protect against challenge with highly virulent MDV strains.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
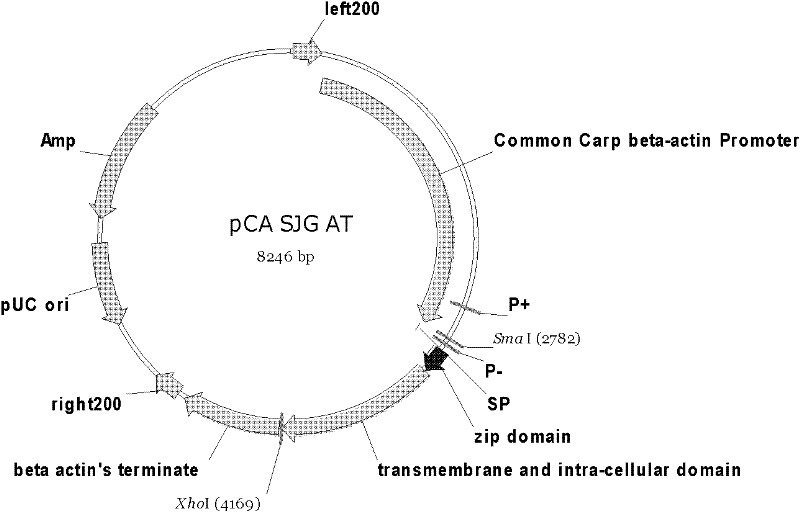
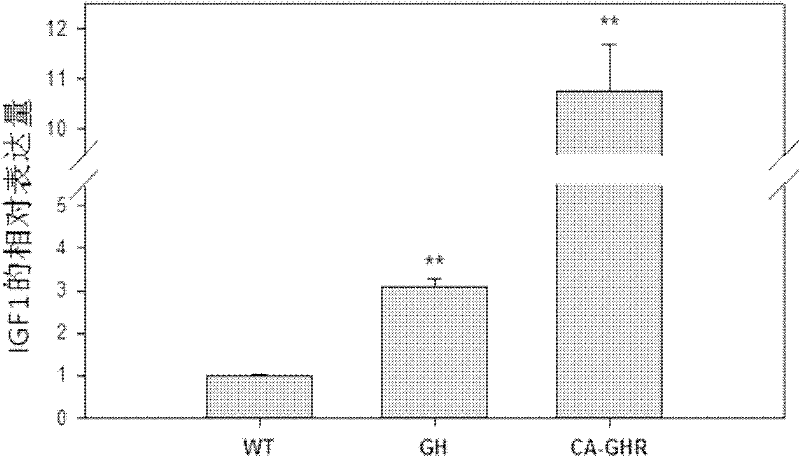
Continuously activated growth hormone receptor gene of fishes, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102241763AHigh activitySignificant growth-promoting effectReceptors for hormonesFermentationSomatotropic hormoneNucleotide
The invention discloses a continuously activated growth hormone receptor gene of fishes, and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: respectively performing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification on growth hormone receptor (GHR) signal peptide, a c-Jun leucine zipper region, a GHR transmembrane region and an intracellular region of carp, and combining another turn of bridge-PCR amplification to obtain a continuously activated GHR recombinant gene segment; and cloning the obtained recombinant gene into an expression vector pCA-AT to obtain a recombinant gene vector pCA-SJG-AT for gene transfer. A protein encoded by the gene has the amino acid sequence shown as SEQIDNO:1; and a separated recombinant gene has the nucleotide sequence shown as SEQIDNO:2. The application of the recombinant gene in quick growth of transgenic fish has the advantages that: (1) the activity of the recombinant GHR protein for promoting a signal channel is high, and the efficiency of the continuously activated GHR effect is more than 3 times higher than that of GH effect; and (2) the transgene of the continuously activated GHR gene has obvious growth promotion effect, and the transgenic fish has a growth speed which is over 50 percent higher than that of contrast fish.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
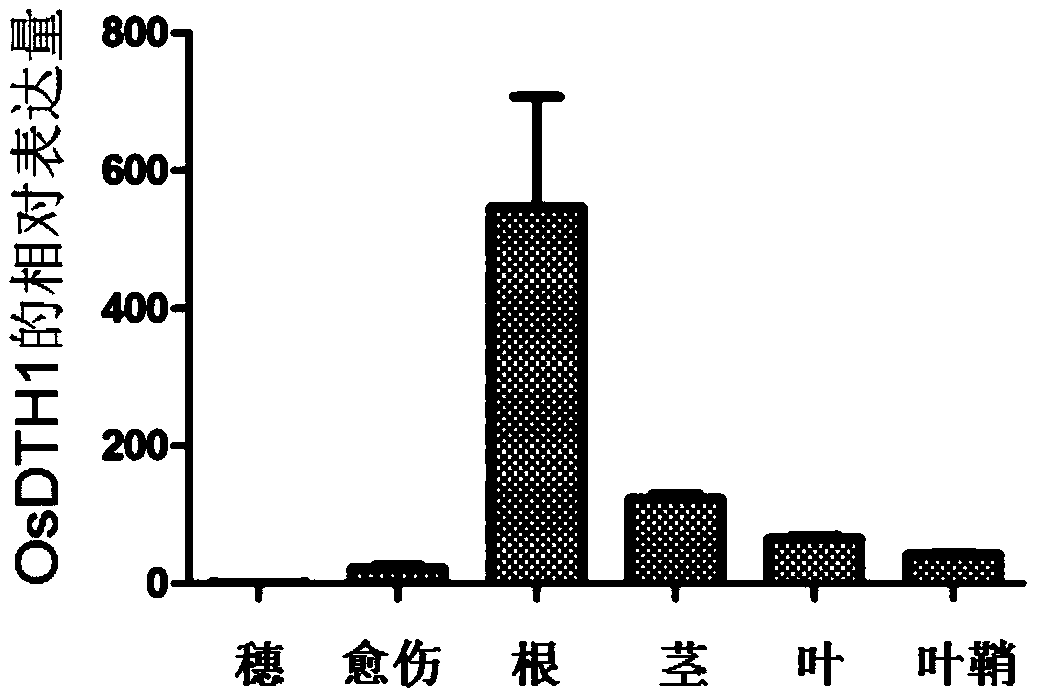
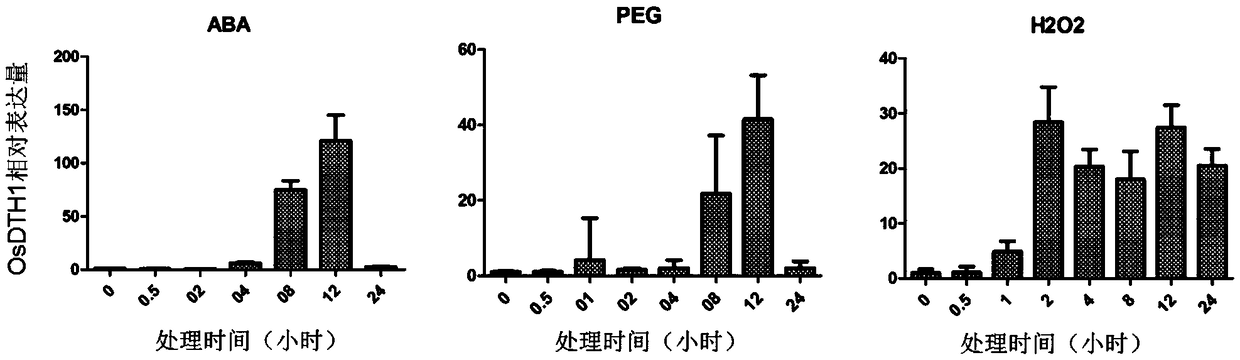
Rice stress resistance related gene OsDTH1 related to and its encoded protein and application thereof
InactiveCN109295070AImprove resistance to peroxidative stressResponsive to stressPlant peptidesFermentationAbscisic acidSalinity
The invention discloses an OsDTH1 gene separated and cloned from paddy rice (DNA) fragments and related to rice stress resistance. The gene encodes a transcription factor, which belongs to the basic region-leucine zipper (bZIP) protein family. The OsDTH1 gene is performed with inducible expression of high salinity, low temperature, high temperature and abscisic acid (ABA), and overexpression of OsDTH1 can improve osmotic stress resistance capability of paddy rice during seedling stage and is related to rice stress resistance. The rice gene has obvious response to adverse situation, can be applied to plant stress resistance breeding, and improves stress resistance of plants.
Owner:SHANGHAI AGROBIOLOGICAL GENE CENT
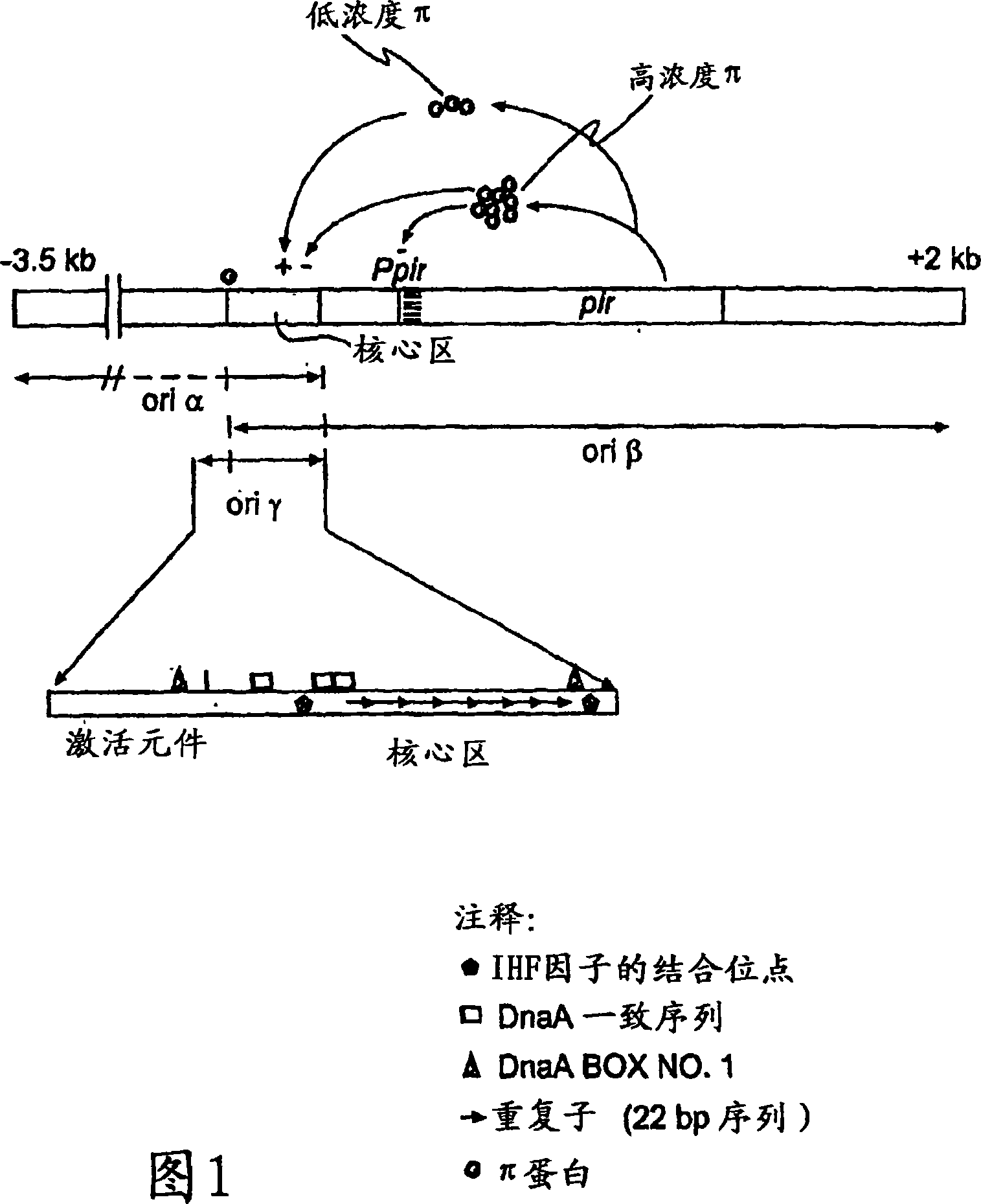
Circular DNA molecule having a conditional origin of replication, process for their preparation and their use in gene therapy
InactiveCN101182534AShorten the lengthImprove bioavailability in vivoNervous disorderBacteriaHeterologousOrigin of replication
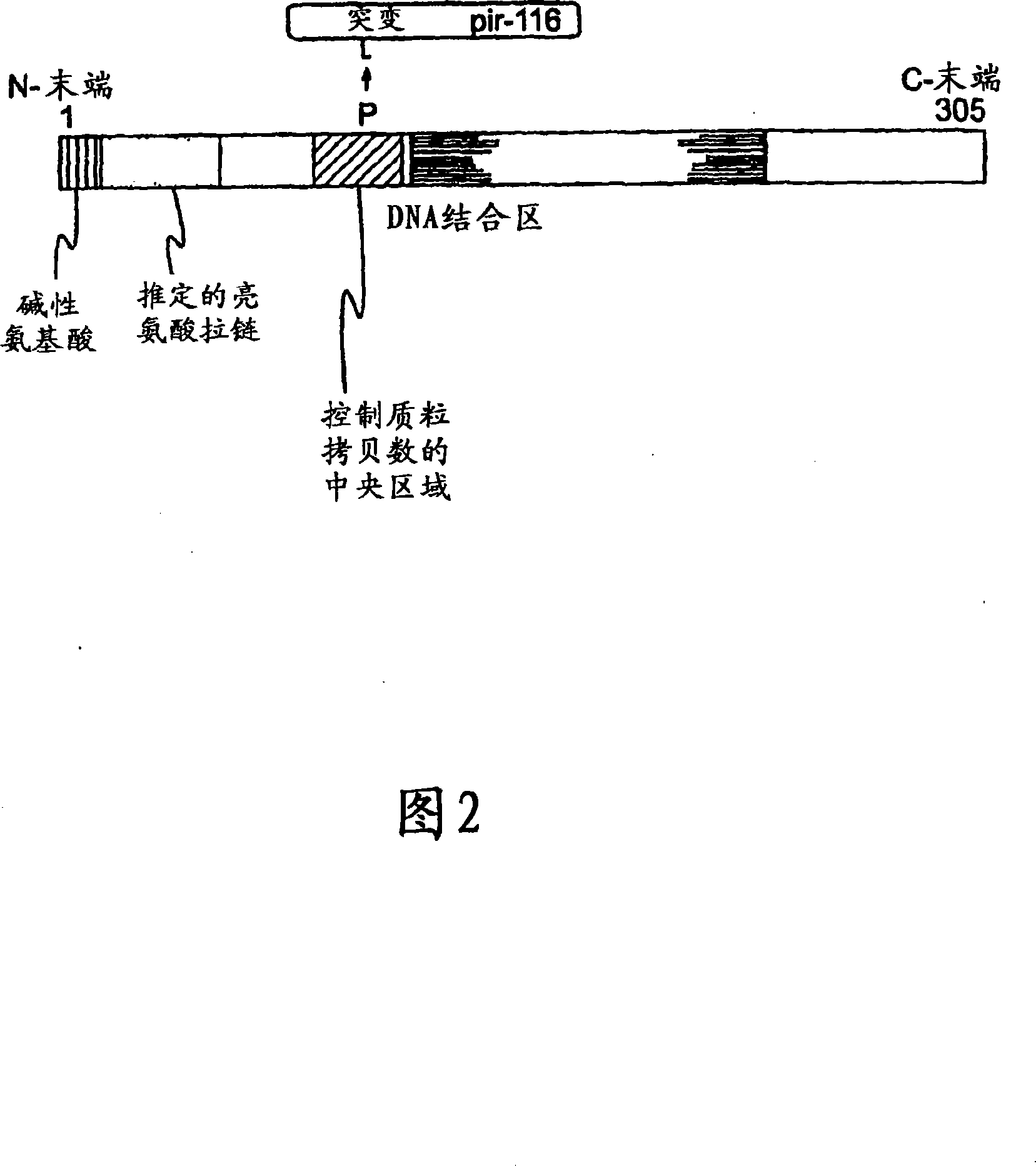
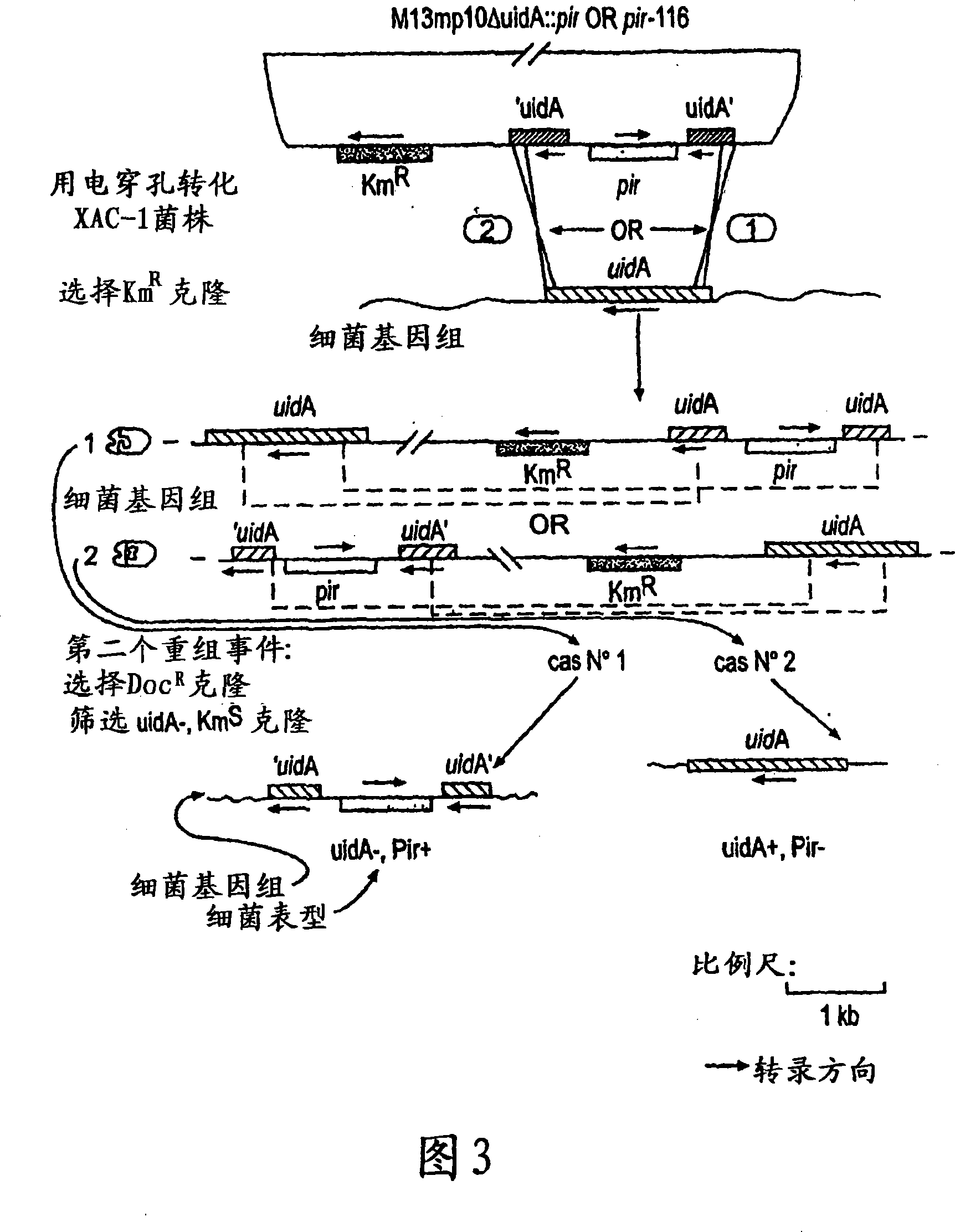
A prokaryotic recombinant host cell comprising a heterologous replication initiation protein that activates a conditional origin of replication and an extrachromosomal DNA molecule comprising a heterologous therapeutic gene and a conditional origin of replication whose functionality in the prokaryotic recombinant host cell requires a replication initiating protein which is foreign to the host cell is described. The host cell may comprise a pir gene having at least one mutation, which may occur in the pir gene copy number control region, the pir gene leucine zipper-like motif, or the pir gene DNA binding region.
Owner:AVENTIS PHARMA INC
Traditional Chinese medicine aqueous solution for treating condyloma acuminata and preventing relapse and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109731079AEffective treatmentEffectively treat both symptoms and root causesAntiviralsBird material medical ingredientsSide effectTreatment effect
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicine aqueous solution for treating condyloma acuminata and preventing relapse. The traditional Chinese medicine is prepared from, by weight, 8-9 partsof honeysuckle flowers, 10-12 parts of dandelions, 5-8 parts of radix sophorae flavescentis, 10-11 parts of herba portulacae, 3-5 parts of milkvetch roots, 5-7 parts of hedyotis diffusa, 5-8 parts ofamur cork tree bark, 7-9 parts of isatis roots, 3-5 parts of radices lithospermi, 4-6 parts of coix seeds, 1-3 parts of bighead atractylodes rhizomes, 10-20 parts of an embedding carrier and 2-3 parts of goose fat. The embedding carrier is prepared by compounding the raw materials of soya bean lecithin, leucine zipper peptide and glycerin trioleate. A preparation method of the traditional Chinesemedicine aqueous solution includes the following steps of 1, extraction of the medicine effective components; S2, preparation of the embedding carrier; S3, medicine carrying, wherein 10-20 parts of the embedding carrier prepared in S2 and mixed liquid medicine extracted in S1 are incubated under the condition of 55 DEG C for 1 h, the traditional Chinese medicine components are embedded into the carrier, and the traditional Chinese medicine aqueous solution for treating condyloma acuminata and preventing relapse is obtained. The traditional Chinese medicine aqueous solution has a more durablemedicine effect for treating condyloma acuminata and a complete treatment effect, and is free of toxic and side effects and low in relapse rate.
Owner:王玺
In vivo library-versus-library selection of optimized protein-protein interactions
The present invention describes a rapid and efficient in vivo library-versus-library screening strategy for identifying optimally interacting pairs of heterodimerizing polypeptides. It allows for the screening of a protein library against a second protein library, rather than against a single bait protein, and thus has numerous applications in the study of protein-protein interactions. Additionally, it allows for the application of different selection stringencies. Two leucine zipper libraries, semi-randomized at the positions adjacent to the hydrophobic core, were genetically fused to either one of two designed fragments of the enzyme murine dihydrofolate reductase (mDHFR), and cotransformed into E. coli. Interaction between the library polypeptides was required for reconstitution of the enzymatic activity of mDHFR, allowing bacterial growth. Analysis of the resulting colonies revealed important biases in the zipper sequences relative to the original libraries, which are consistent with selection for stable, heterodimerizing pairs. Using more weakly associating mDHFR fragments, we increased the stringency of selection. We enriched the best performing leucine zipper pairs by multiple passaging of the pooled, selected colonies in liquid culture, as the best pairs allowed for better bacterial propagation. This competitive growth allowed small differences among the pairs to be amplified, and different sequence positions were enriched at different rates. We applied these selection processes to a library-versus-library sample of 2.0×106 combinations, and selected a novel leucine zipper pair which may be appropriate for use in further in vivo heterodimerization strategies.
Owner:ODYSSEY THERA INC
Minimalist bZIP derivatives that bind to noncanonical gene regulatory sequences
InactiveUS20070009938A1Microbiological testing/measurementGenetic material ingredientsBiological regulationDisease
The invention provides a method of specifically targeting noncanonical gene regulatory sequences using a minimalist basic region-leucine zipper bZIP derivative. Also provided are methods of modulating transcription and treating diseases and cancers using the minimalist basic region-leucine zipper bZIP derivatives.
Owner:SHIN JUMI
Therapeutic TRAIL fusion protein and preparation and use thereof
InactiveUS9403892B2Improve stabilityLong half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHalf-lifeTRAIL Protein
This invention relates to the biotechnology area, and provides a kind of TRAIL chimeric protein, DNA sequence encoding this chimeric protein, vectors comprising this DNA, host cells or transgenic animals that contain one of the vectors, and preparation methods for the said chimeric protein and its applications. The said TRAIL fusion protein from the N to C terminal comprises human leucine zipper sequence, human TRAIL protein, human TRAIL extracellular domain or a fragment thereof. The chimeric protein has significantly enhanced stability, prolonged half-life in animals, increased efficacy and thus has broad application future.
Owner:MAGELLAN PHARMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com