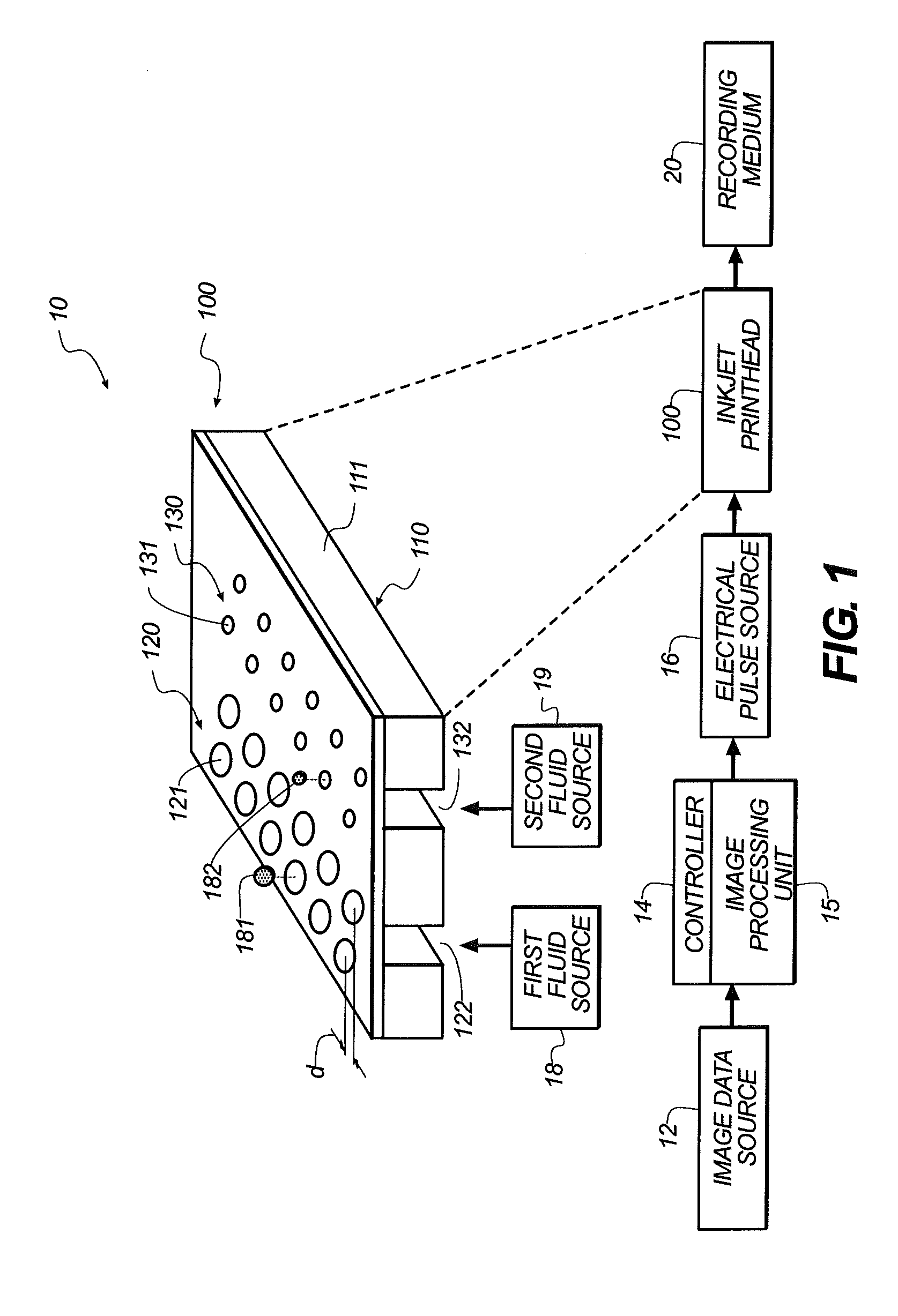
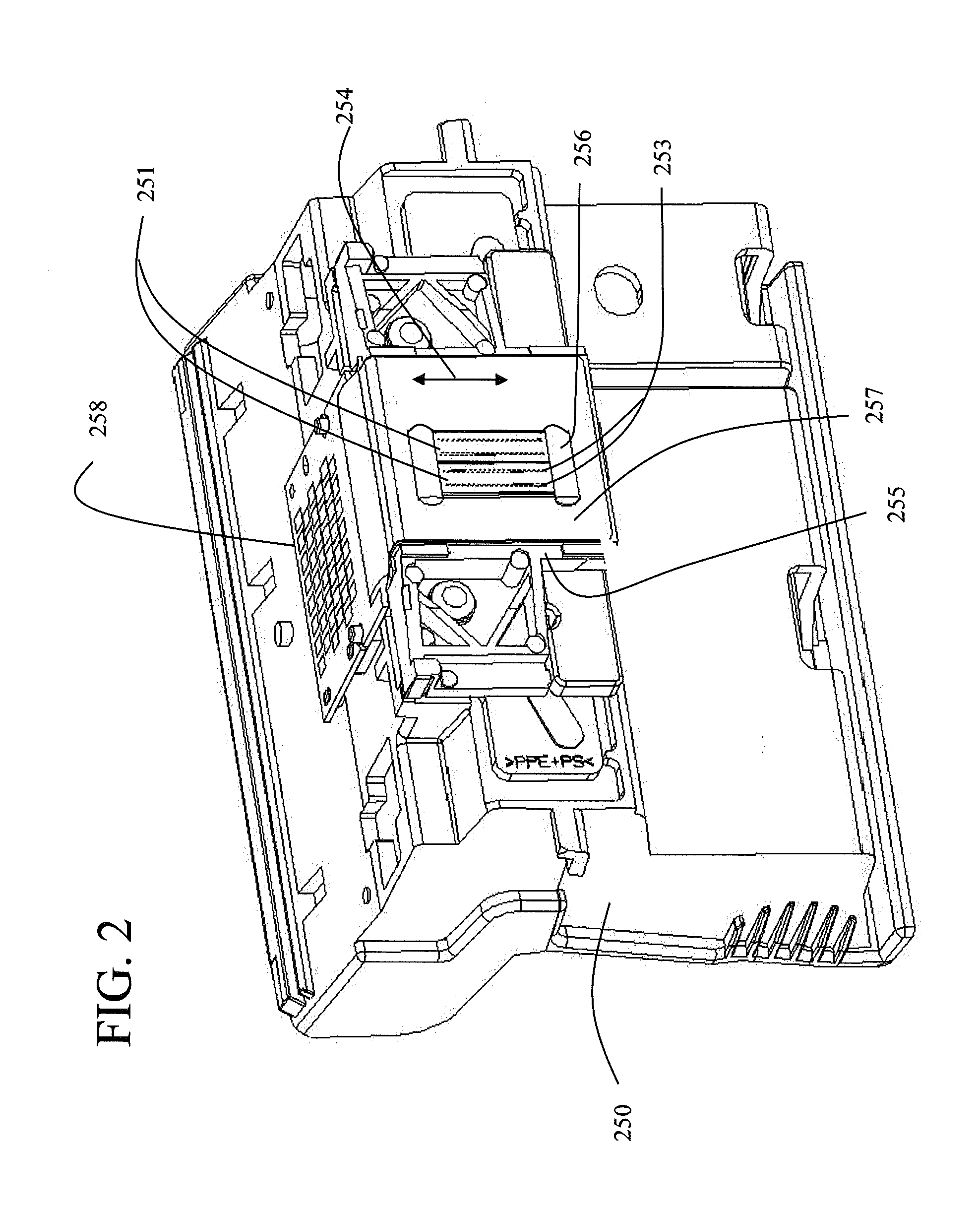
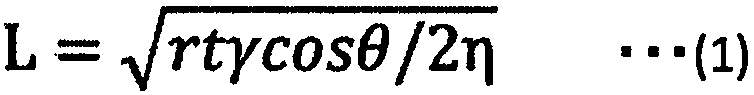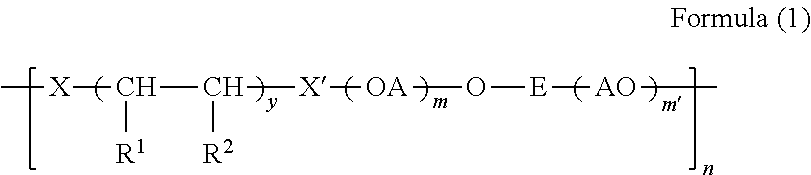Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "Kinetic coefficient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
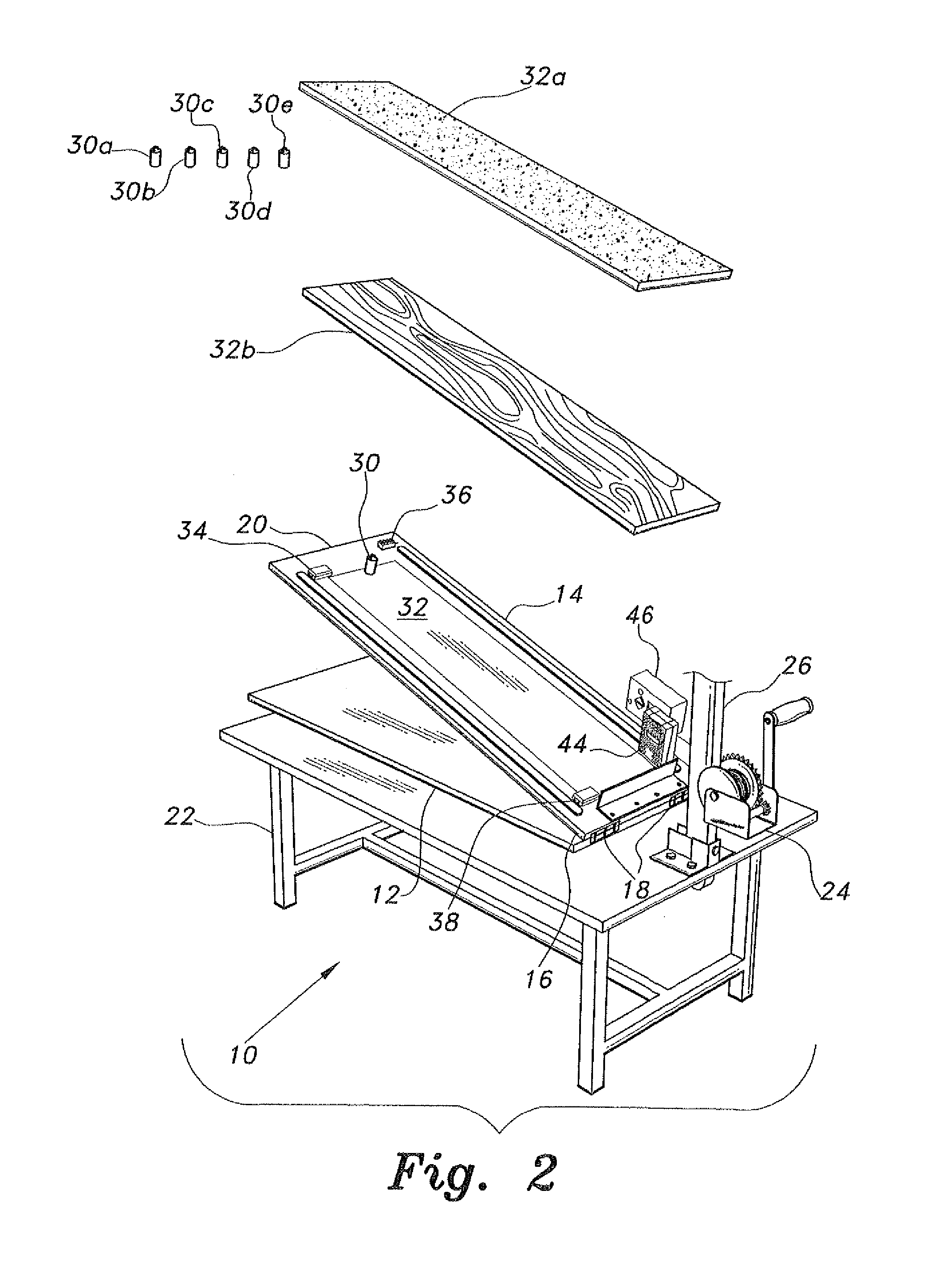
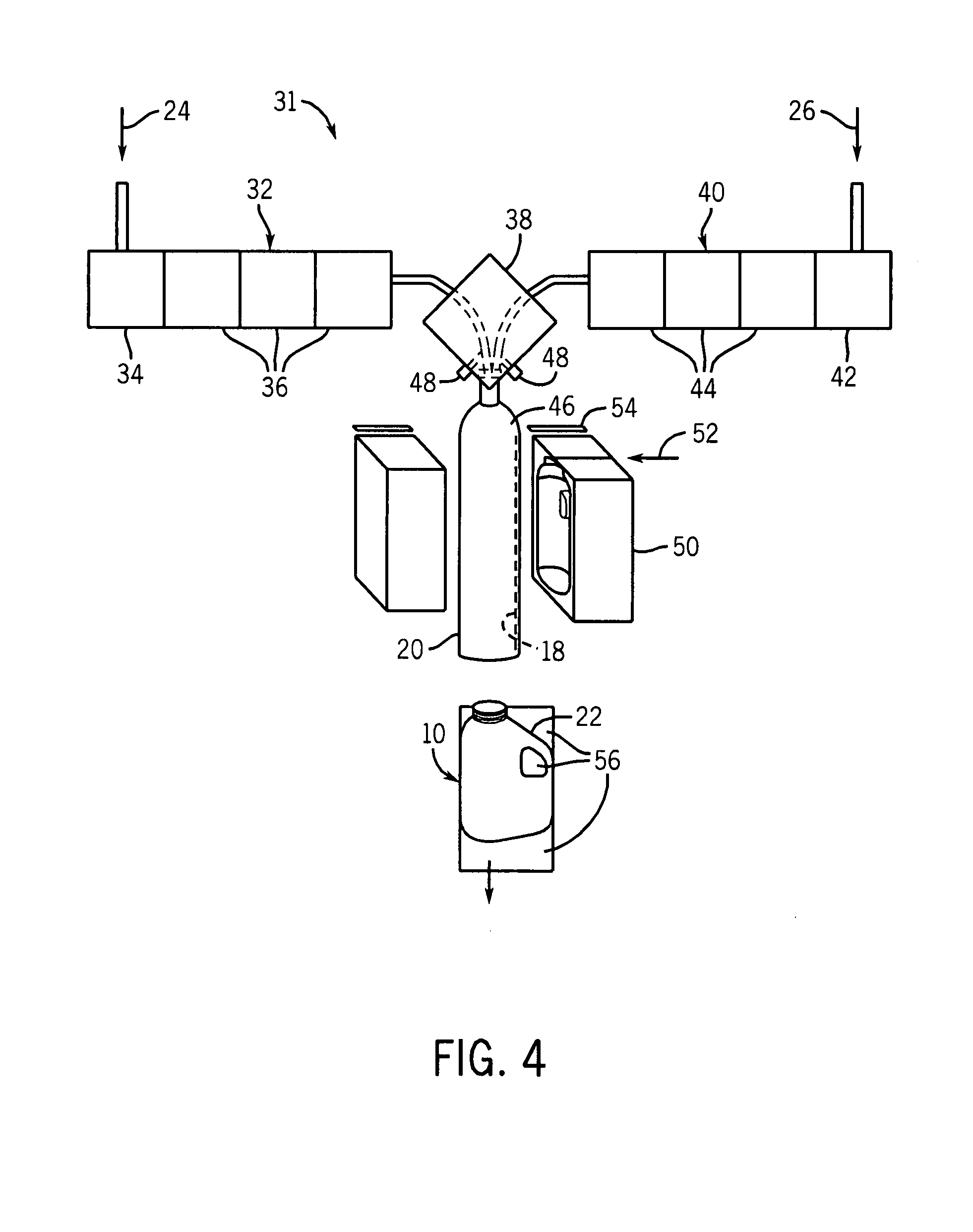
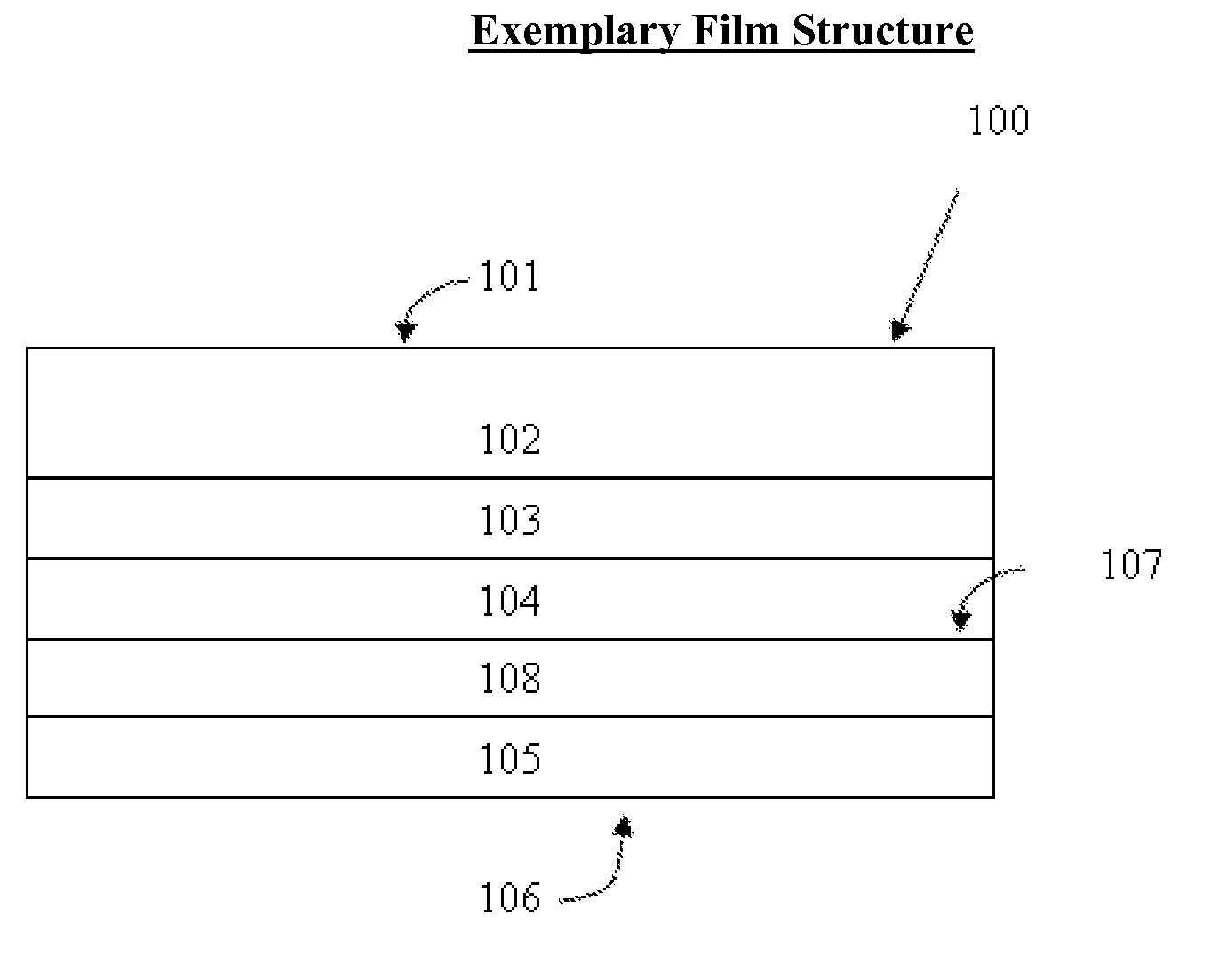
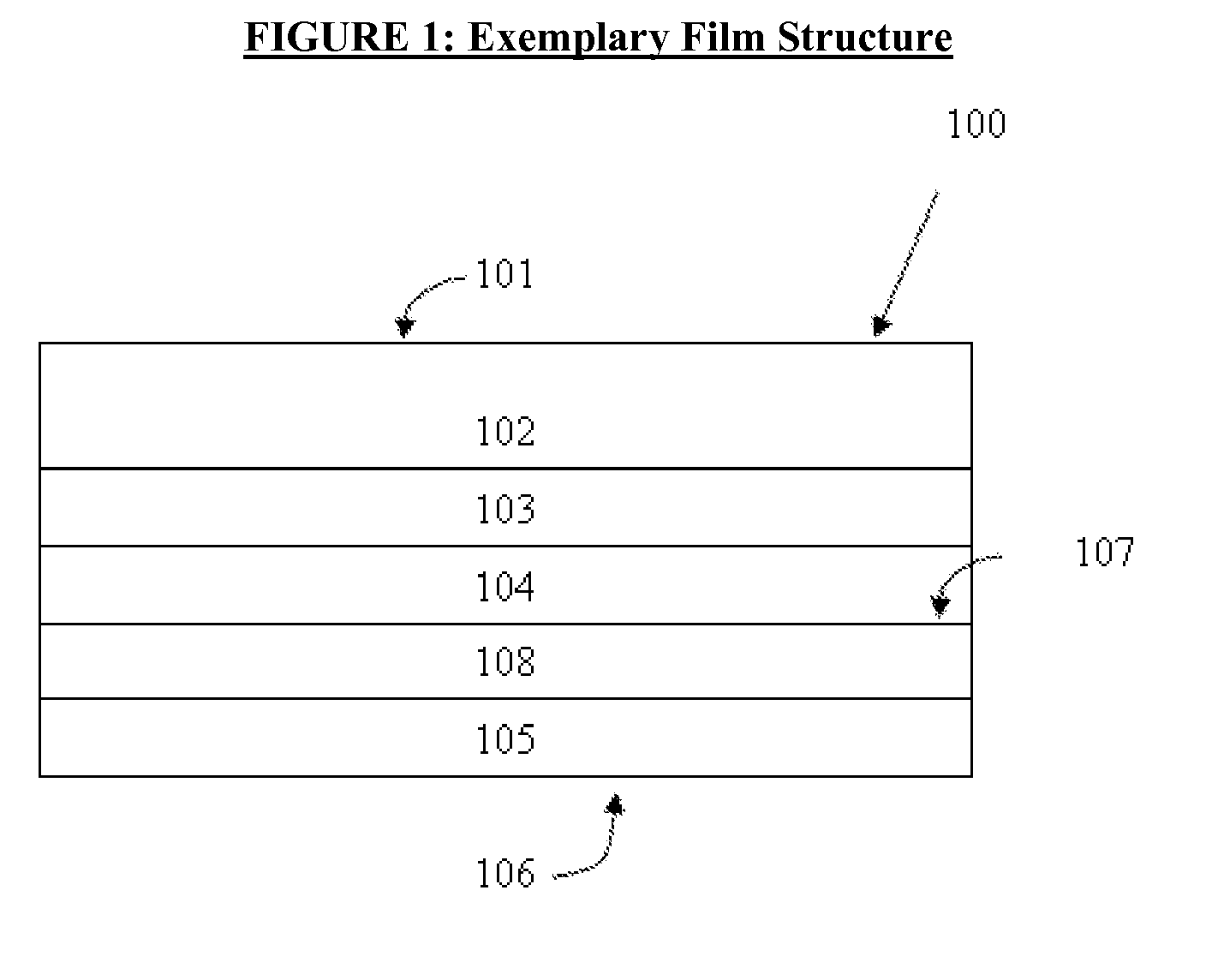
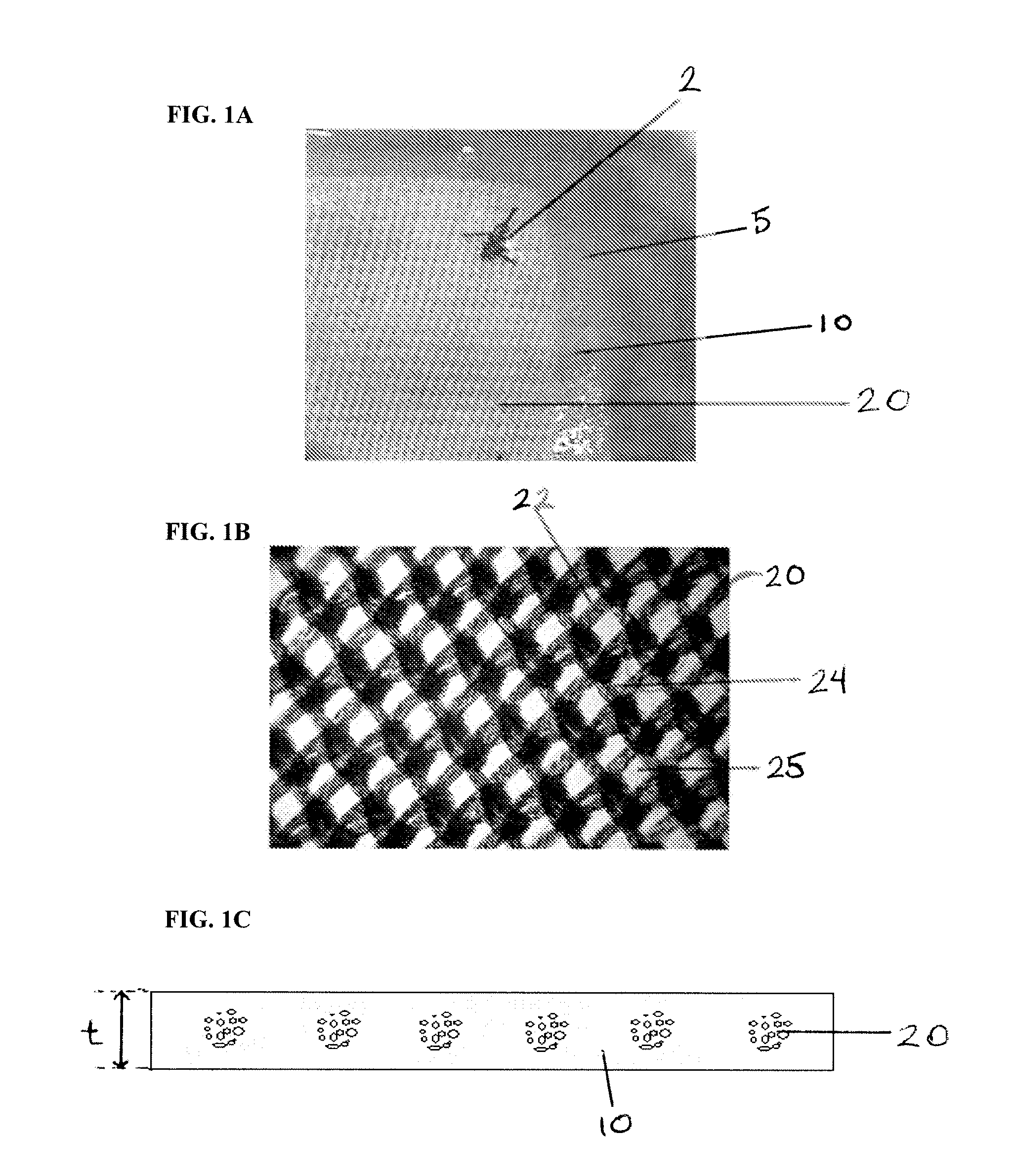
Coated paperboards and paperboard containers having improved tactile and bulk insulation properties
InactiveUS20050112305A1Improve insulation performanceIncrease stiffnessNon-fibrous pulp additionWrappersStatic friction coefficientPaperboard
A method of making a texture-coated and / or insulation coated container from a flat paperboard blank in which a heat-hardenable liquid polymeric binder texturizing and / or insulating agent coating mixture is applied to one surface of the blank in a pattern of covered and open areas. This coating mixture is subjected to heat to cure the polymeric binder and expand the texturizing and / or insulating agent, optionally treated with moisture, and optionally heated to form the blank into the shape of a container, and the container produced by this method. The containers such as cups, plates, etc., are useful in food service. These containers have a coefficient of static friction which is about 0.2 to 2.0 and over and a kinetic coefficient of friction which is about 0.22 to 1.5.
Owner:DIXIE CONSUMER PROD
Apparatus for determining coefficients of friction
InactiveUS20140060149A1Readily apparentUsing mechanical meansInvestigating abrasion/wear resistanceStatic friction coefficientDisplay device
The apparatus for determining coefficients of friction collects data required for determining static and dynamic coefficients of friction between various materials. The apparatus includes a ramp with adjustable slope and a plurality of test masses for placement on the ramp. Upslope lights and sensors, downslope lights and sensors, and a digital angle meter are installed on the ramp. The apparatus has a timing device having a display to show the elapsed time between a test mass passing the upslope sensor and the downslope sensor. The operator can determine the static coefficient of fraction from the tangent of the angle displayed on the digital angle meter when a test mass first begins to slide, and can compute the kinetic coefficient of friction from the angle displayed on the digital angle meter and the elapsed time shown on the timing device.
Owner:KUWAIT UNIV
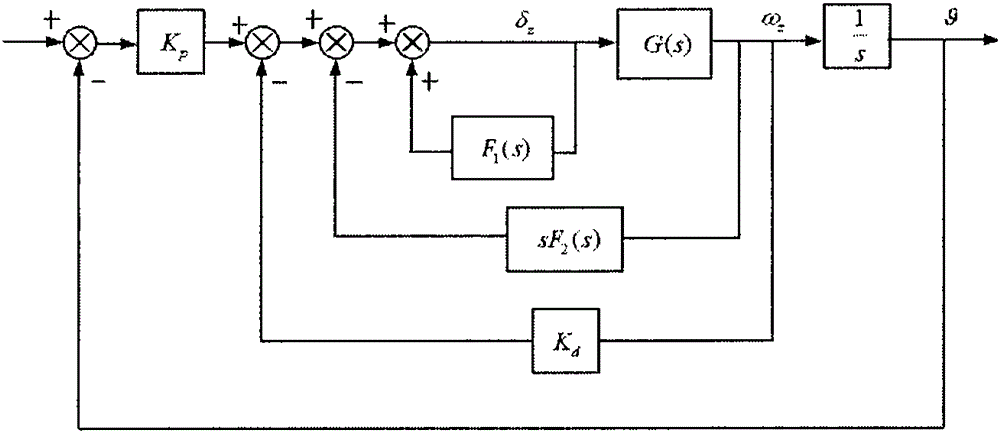
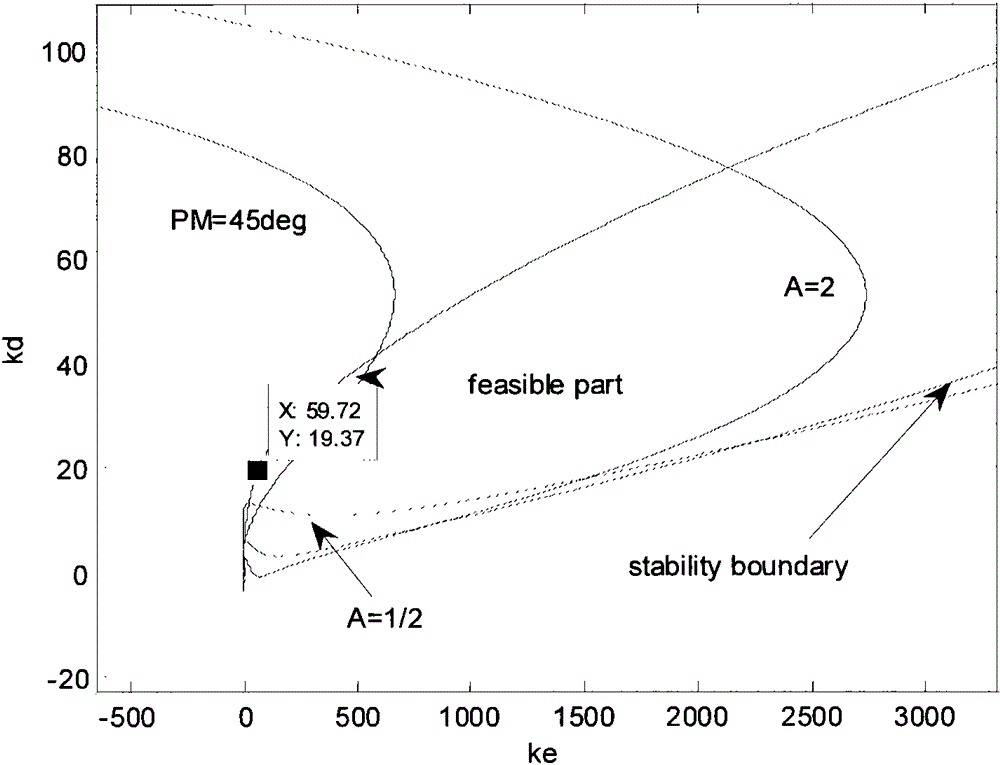
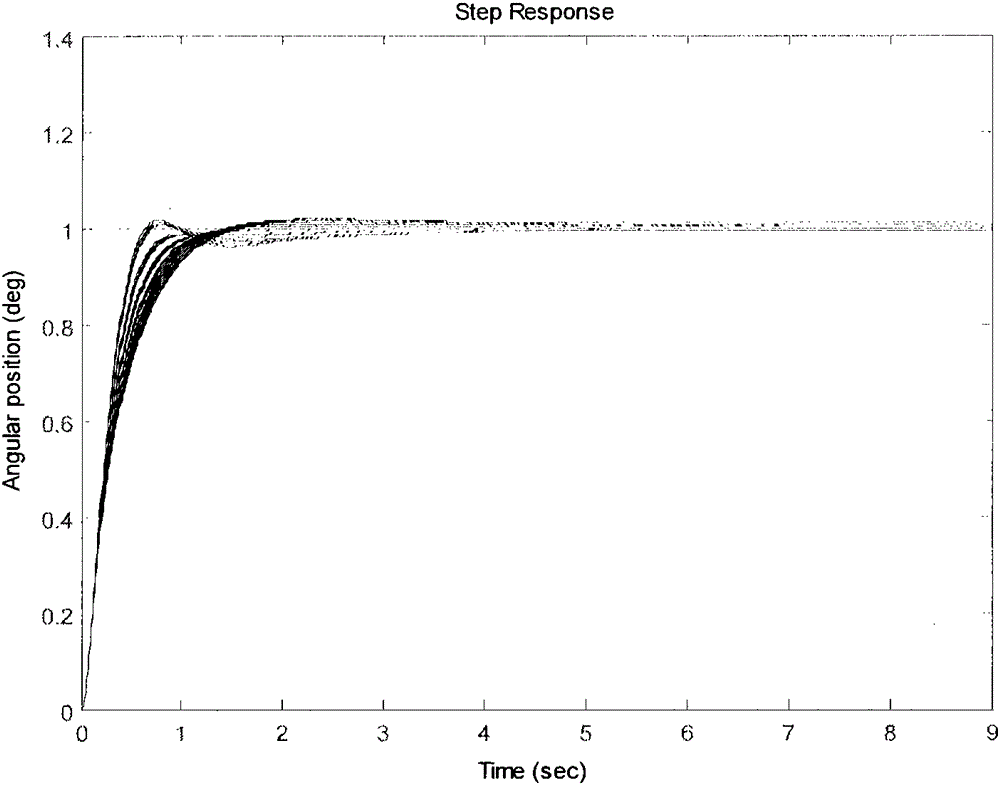
Linear active disturbance rejection control (ADRC) design and parameter tuning of aircraft pitch attitude
The present invention provides a linear active disturbance rejection control (ADRC) design and parameter tuning of aircraft pitch attitude. The linear active disturbance rejection control (ADRC) design and parameter comprises the steps of (1) establishing direct and indirect influence relations which describe an elevator influence pitch angle directly for a pitch nonlinear kinetic equation, (2) for the pitch channel kinetic equation obtained in the step (1), taking all indirect influence items as disturbance, designing a linear expansion state observer, estimating and compensating a linear expansion state observer, and using a simple PD control strategy for a compensated system, (3) using a small perturbation hypothesis principle to carry out linearization to obtain a kinetic coefficient for the nonlinear equation obtained in the step (1), (4) carrying out graphical tuning of a control parameter according to a robust stability index and a dynamic performance index. According to the method, on the basis of ensuring the stable robustness and good dynamic quality of a controller, the form is very simple, at the same time, the pattern parameter tuning method based on a stable margin test factor has a visual characteristic, and the blindness of parameter debugging is avoided.
Owner:孙明玮 +1
Optical fiber and method of measuring coefficient of kinetic friction of optical fiber
InactiveUS7085465B2Low rate of occurrenceVariationGlass optical fibreOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingUltrasound attenuationFrictional coefficient
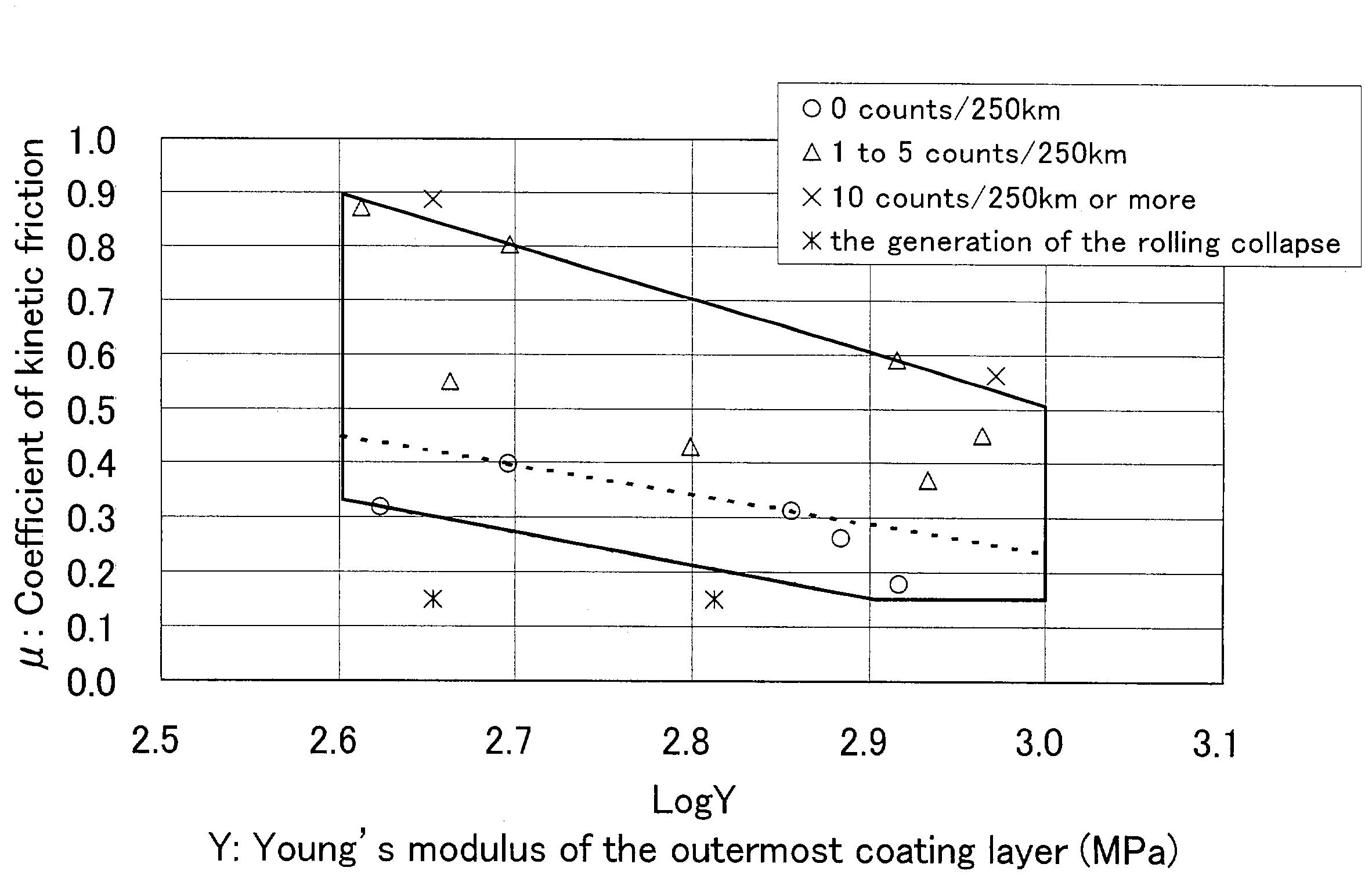
An optical fiber of the present invention comprising a bare optical fiber and one or plural coating layers on the bare optical fiber, wherein Y, the Young's modulus of the outermost coating layer is in the range of 400 to 1000 and μ, a coefficient of kinetic friction which occurs between the outermost coating layers is equal to or larger than 0.15, and further satisfying the following formulas (a) and (b);μ≦−0.9822 Log Y+3.45156 (a)μ≧−0.5418 Log Y+1.74128, (b)wherein the unit of Y is MPa.By the present invention, optical fibers with a low rate of occurrences of the attenuation discontinuity in a measurement result by OTDR and the method of measuring the coefficient of kinetic friction of optical fiber with high reliability are offered.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Sluice assembly for separating heavy particles from slurry
InactiveUS20090078615A1Efficient collectionReduce manufacturing costGas current separationSortingStatic friction coefficientHeavy particle
A sluice assembly for separating heavy particles from slurry is provided. The sluice assembly includes one or more sluice boxes having decks made of plastic having a Shore D hardness between 50-75, a static coefficient of friction less than 0.3 and a kinetic coefficient of friction less than 0.2. In a preferred embodiment, the sluice assembly includes a pair of sluice boxes in which a top sluice box is positioned above the bottom sluice box so that slurry flowing from the downstream end of the first sluice box is received by the upstream end of the bottom sluice box. The bottom deck includes tapered riffles which are arranged to provide “V” shaped diverters for diverting heavier particles for collection. The sluice box upper deck may include laterally extending riffles for collection of heavier particles.
Owner:RAINWATER CHUCK +1
Disposable mat, a container comprising a disposable mat, and a method of promoting the sale of a disposable mat
InactiveUS20070020433A1Synthetic resin layered productsFloor coveringsEngineeringKinetic coefficient
The present invention relates to a disposable mat comprising at least two removable sheets arranged in a stacked configuration. The removable sheets comprise an upper surface and a lower surface, and the kinetic coefficient of friction between the lower surface of a first removable sheet, and the upper surface of a second removable sheet positioned directly underneath said first removable sheet is from about 0.4 to 4. The present invention also relates to a container comprising at least one disposable mat, rolled-up in a cylindrical configuration, and to a method of promoting the sale of a disposable mat.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Image receiving layer for use in non-impact printing
InactiveUS6025100ALow background fogLittle inkDecorative surface effectsDuplicating/marking methodsEngineeringHardness
An image receiving layer for use in non-impact printing, especially in an electrostatographic printing method, is provided with an image receiving surface having a specified ratio between average and maximum roughness and a specified kinetic coefficient of friction against rubber with shore hardness 70. The receiving layer is especially well suited for producing lithographic printing plates with non-impact printing, especially with electrostatographic means.
Owner:AGFA NV
System and method for creating high gloss plastic items via the use of styrenic copolymers as a coextruded layer
ActiveUS8263198B2Synthetic resin layered productsDomestic articlesStatic friction coefficientPolyolefin
The present techniques provide multi-layer plastic structures and methods for making such. The multi-layer plastic structures include an inner surface made from a polyolefin resin, and resistant to environmental stress cracking, and an outer surface that includes a styrenic copolymer. The outer surface has a kinetic coefficient of friction with itself of 0.42 and a static coefficient of friction with itself of 0.44.
Owner:CHEVRON PHILLIPS CHEMICAL CO LP +1
SiC-C/C composite material, uses thereof, and method for producing the same
Provided are SiC-C / C composite materials which have such characteristics as a suitable kinetic coefficient of friction a corrosion resistance in strongly oxidizing and corrosive environment, a creep resistance, and a spalling resistance, a high hardness, and are hardly oxidized or abraded even when exposed to high temperatures with keeping the excellent impact resistance and light weight of the C / C composites. Furthermore, molten metal pumps are provided from which components do not dissolve into the molten metal even when used in molten metal and have sufficient thermal impact resistance and oxidation resistance. The SiC-C / C composite materials can be produced by a method comprising a step of heating a C / C composite and metallic silicon at high temperatures under reduced pressure with flowing an inert gas to grow silicon carbide and simultaneously filling metallic silicon into the remaining pores, a step of increasing the furnace inner pressure to about 1 atm. with or without cooling the furnace and further raising the furnace inner temperature to diffuse the produced silicon carbide or metallic silicon used for filling the pores into the C / C composite comprising carbon fibers and carbon component other than the carbon fibers from the matrix to react with these carbons, and at least the portions of the molten metal pumps contacting with molten metal are made of the SiC-C / C composite materials.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Multilayer Polymeric Film
InactiveUS20130209756A1Suitable for useStampsDecorative surface effectsStatic friction coefficientAntistatic agent
Provided is a film including: (a) an intermediate layer comprising a polymer and an antistatic agent, said intermediate layer having a first side and a second side; (b) a first layer including a polymer, said first layer being on the first side and is printed or printable; and (c) a second layer including a polymer and a non-migratory slip agent, said second layer being on the second side, wherein the film has at least one of (i) a thickness of at least about 30 μm, (ii) a static coefficient of friction of about 0.15 to less than 0.30, and (iii) a kinetic coefficient of friction of about 0.15 to less than 0.30. Also provided are a method for producing such a film, and labels such as cut and stack labels comprising the film.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC +1
Design devices for applying a design to a surface
InactiveUS20090282993A1Prevent lateral movementLiquid surface applicatorsSpraying apparatusStatic friction coefficientCombined use
Compositions, methods, apparatuses, kits, and combinations are described for permanently or temporarily re-designing, decorating, and / or re-coloring a surface. In one embodiment, a stencil is provided that has an embossed top layer and a low-slip bottom layer that has a static coefficient of friction between about 0.2 to about 1.2 and / or a kinetic coefficient of friction that is between about 0.1 to about 1.1 as measured against another surface having the same bottom surface as the stencil. Compositions useful in the present disclosure include a décor product that is formulated to be applied and affixed to a surface. If desired, the décor product may be substantially removed from the surface before being affixed thereto. If a user desires to remove the décor product, the décor product is formulated to be removed by a number of methods including, for example, vacuuming, wet extraction, chemical application, and the like. If the user desires to affix the décor product to the surface in a permanent or semi-permanent manner, the décor product may be affixed to the surface by applying energy thereto in the form of, for example, heat, pressure, emitted waves, an emitted electrical field, a magnetic field, and / or a chemical. The décor product may also be utilized in the form of a kit or in conjunction with a design device, such as a stencil, to control the application of the décor product to create, for example, a pattern on the surface.
Owner:SC JOHNSON & SON INC
Multilayer stencils for applying a design to a surface
InactiveUS8061269B2Liquid surface applicatorsSpraying apparatusStatic friction coefficientCombined use
Compositions, methods, apparatuses, kits, and combinations are described for permanently or temporarily re-designing, decorating, and / or re-coloring a surface. In one embodiment, a stencil is provided that has an embossed top layer and a low-slip bottom layer that has a static coefficient of friction between about 0.2 to about 1.2 and / or a kinetic coefficient of friction that is between about 0.1 to about 1.1 as measured against another surface having the same bottom surface as the stencil. Compositions useful in the present disclosure include a décor product that is formulated to be applied and affixed to a surface. If desired, the décor product may be substantially removed from the surface before being affixed thereto. If a user desires to remove the décor product, the décor product is formulated to be removed by a number of methods including, for example, vacuuming, wet extraction, chemical application, and the like. If the user desires to affix the décor product to the surface in a permanent or semi-permanent manner, the décor product may be affixed to the surface by applying energy thereto in the form of, for example, heat, pressure, emitted waves, an emitted electrical field, a magnetic field, and / or a chemical. The décor product may also be utilized in the form of a kit or in conjunction with a design device, such as a stencil, to control the application of the décor product to create, for example, a pattern on the surface.
Owner:SC JOHNSON & SON INC
Detector, sheet conveying device incorporating the detector, sheet feeding device incorporating the detector, image forming apparatus incorporating the detector, and image reading device incorporating the detector
InactiveUS20180297802A1Function indicatorsElectrographic process apparatusStatic friction coefficientCoefficient of friction
A detector, which is included in a sheet feeding device, a sheet conveying device, an image forming apparatus and an image reading device, contacts and detects a sheet, and includes a base, a sheet contact face to which the sheet contacts, and a coat layer formed on the sheet contact face. A difference Δμ of a static coefficient of friction μs of the coat layer and a kinetic coefficient of friction μd of the coat layer is smaller than and equal to 0.12.
Owner:RICOH KK
Duplexing unit with low friction media guide
A duplexing unit for reversing an orientation of a sheet in an imaging apparatus, the duplexing unit includes: an outer member including an inner surface; an inner member that is housed within the outer member, the inner member including an outer surface, wherein a duplexing path is provided between the inner surface of the outer member and the outer surface of the inner member, and wherein the inner surface of the outer member has a kinetic coefficient of friction that is between 0.05 and 0.30.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
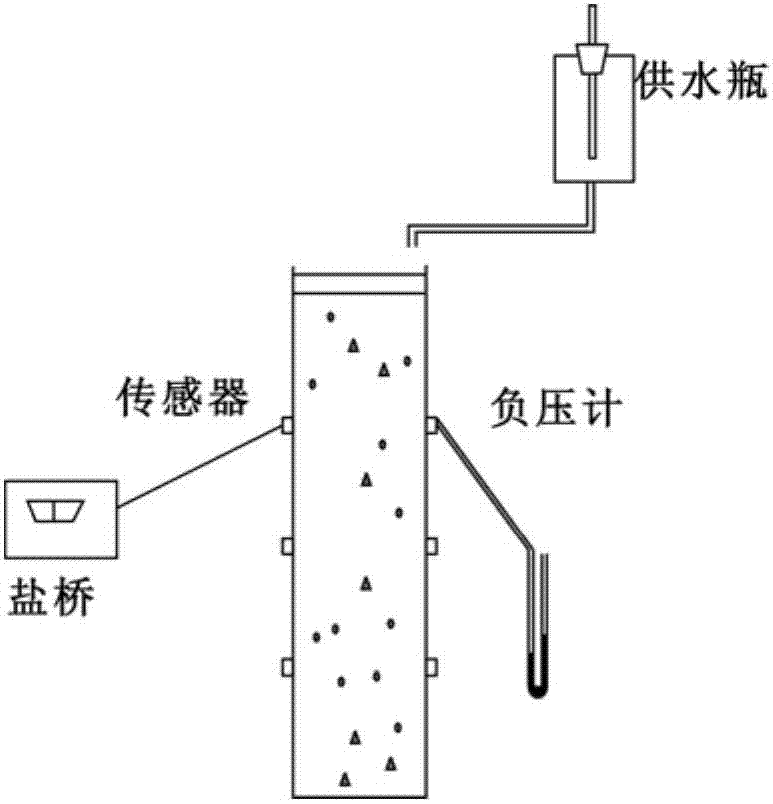
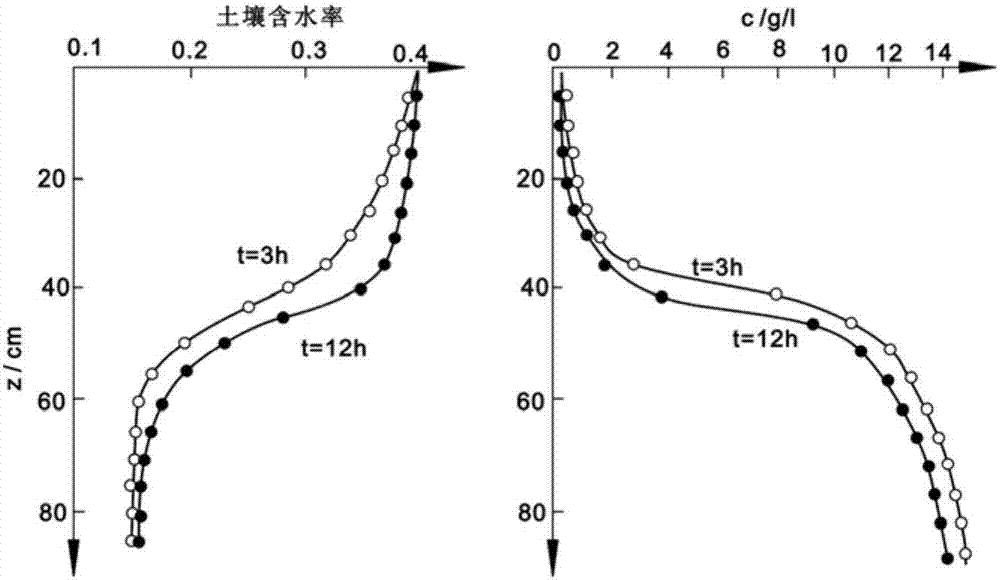
Method and device for determining turbulent kinetic coefficients of unsaturated soil
InactiveCN107167576AImplement parsingTurbulent hydrodynamic parameters are accurateEarth material testingMonitoring siteSoil science
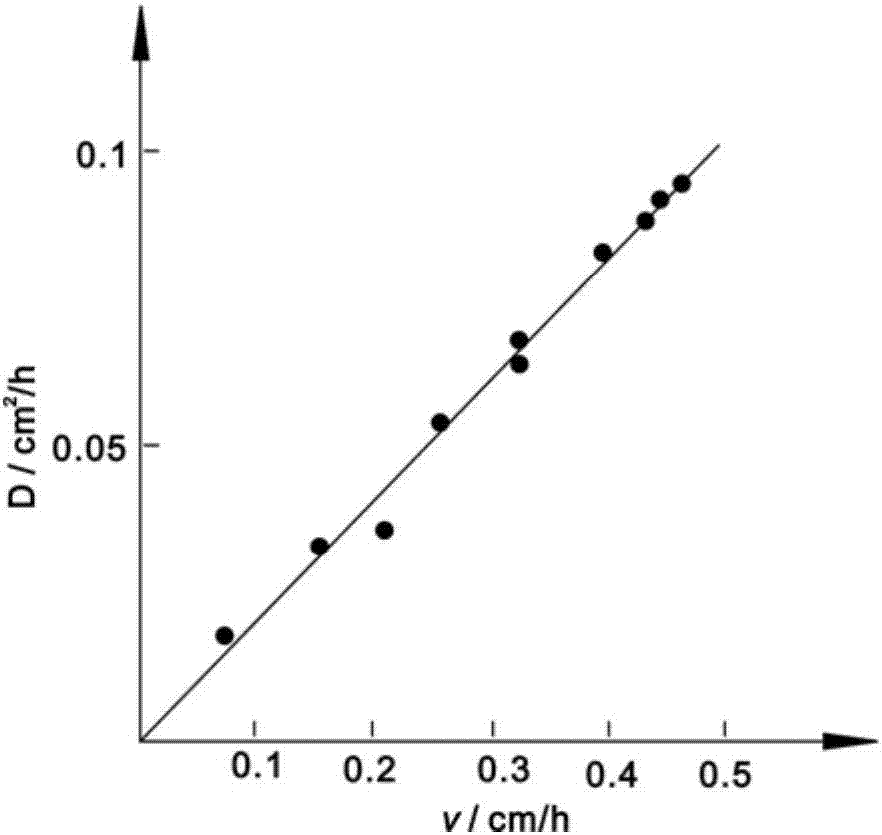
The invention provides a method and a device for determining turbulent kinetic coefficients of unsaturated soil. The method comprises the following steps: conducting filling of soil samples; arranging monitoring sites at regular intervals, arranging a soil matric potential monitoring system and a soil tracing solute concentration monitoring system at each monitoring site for continuous monitoring of changes in soil water content and changes in tracing solute concentration in soil at each monitoring site; dividing sections, and determining soil matric potential of upper and lower boundaries of each section for determination of the water potential difference and water movement flux of each section; calculating average section water flux at any time t based on the water movement flux of each section; converting soil negative pressure into the soil water content, further coupling the determined average section water flux, and calculating the turbulent kinetic coefficient of solute migration by a formula finally. The method has the advantages that a mathematical model is built, operation is facilitated, measurement precision is high, an experimental model is easy to build, conditions are easy to realize, the samples are rich and varied, and results are visual.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
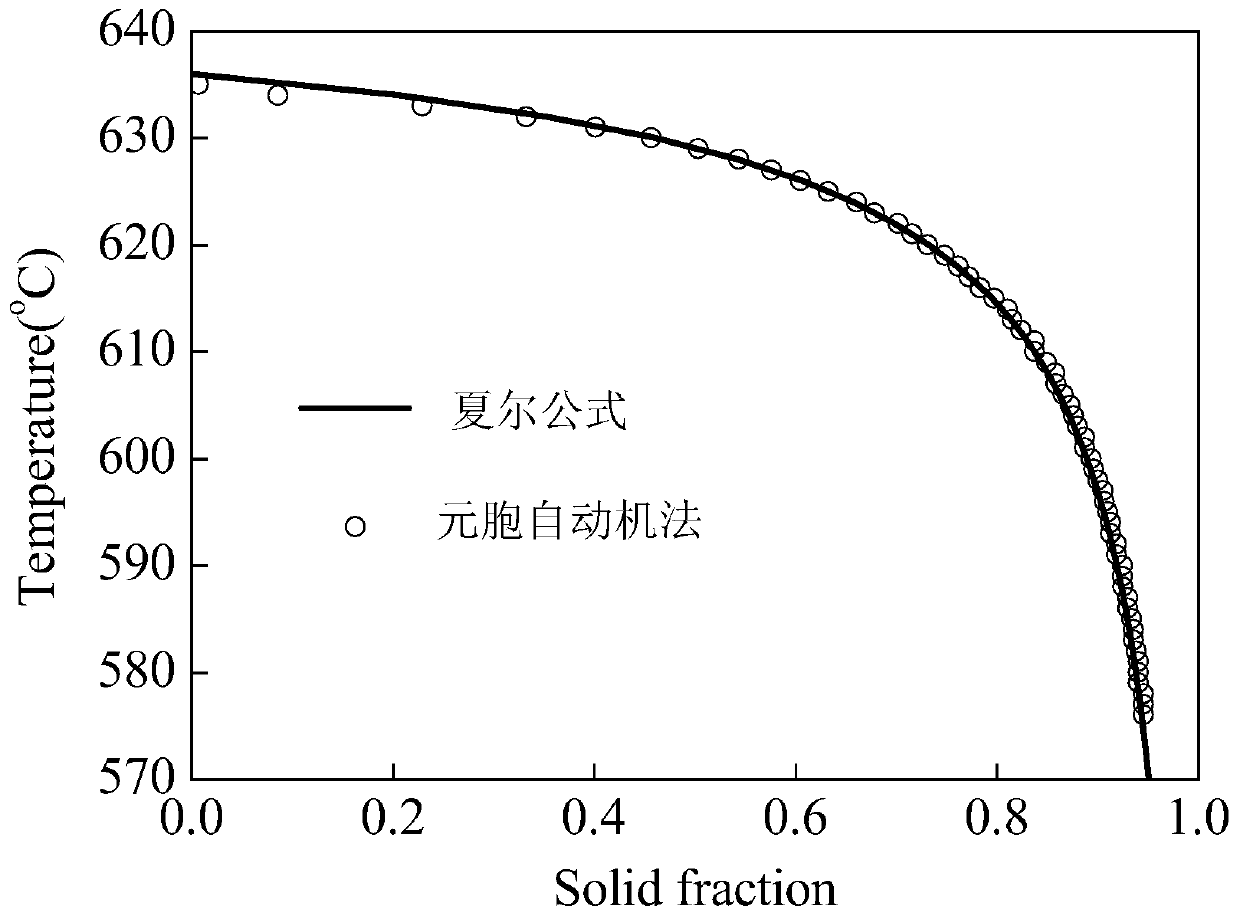
Body-centered cubic alloy microscopic segregation numerical prediction method
ActiveCN110263418AEliminate the effects ofImprove computing efficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsData fileAlloy
The invention discloses a body-centered cubic alloy microscopic segregation numerical prediction method, and relates to a body-centered cubic alloy microscopic segregation numerical prediction method. The objective of the invention is to solve the problem that the microcosmic segregation formation of the body-centered cubic alloy cannot be accurately predicted by the existing method. The method comprises the following steps: 1, carrying out micro-scale mesh generation; 2, the square grids and the three surrounding grids forming a group; 3, completing dendritic crystal growth; 4, determining the state of the grid; 5, determining a dynamic coefficient; 6, further dividing into four local computational domains; 7, calculating nucleation in a local calculation domain; 8, randomly selecting a certain group of pairing grids in the local calculation domain, and judging whether the group has a nucleation phenomenon or not; 9, capturing four groups of surrounding neighbor pairing grids by the mother core grid; 10, calculating parameters; 11, calculating a solute diffusion equation; 12, repeating step 7-11, and outputting a solute component distribution data file; estimating heat treatment time. The method is used for the field of body-centered cubic alloy microscopic segregation numerical prediction.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
System and method for creating high gloss plastic items via the use of styrenic copolymers as a coextruded layer
ActiveUS20090081397A1Synthetic resin layered productsDomestic articlesStatic friction coefficientPolyolefin
The present techniques provide multi-layer plastic structures and methods for making such. The multi-layer plastic structures include an inner surface made from a polyolefin resin, and resistant to environmental stress cracking, and an outer surface that includes a styrenic copolymer. The outer surface has a kinetic coefficient of friction with itself of 0.42 and a static coefficient of friction with itself of 0.44.
Owner:CHEVRON PHILLIPS CHEMICAL CO LP +1
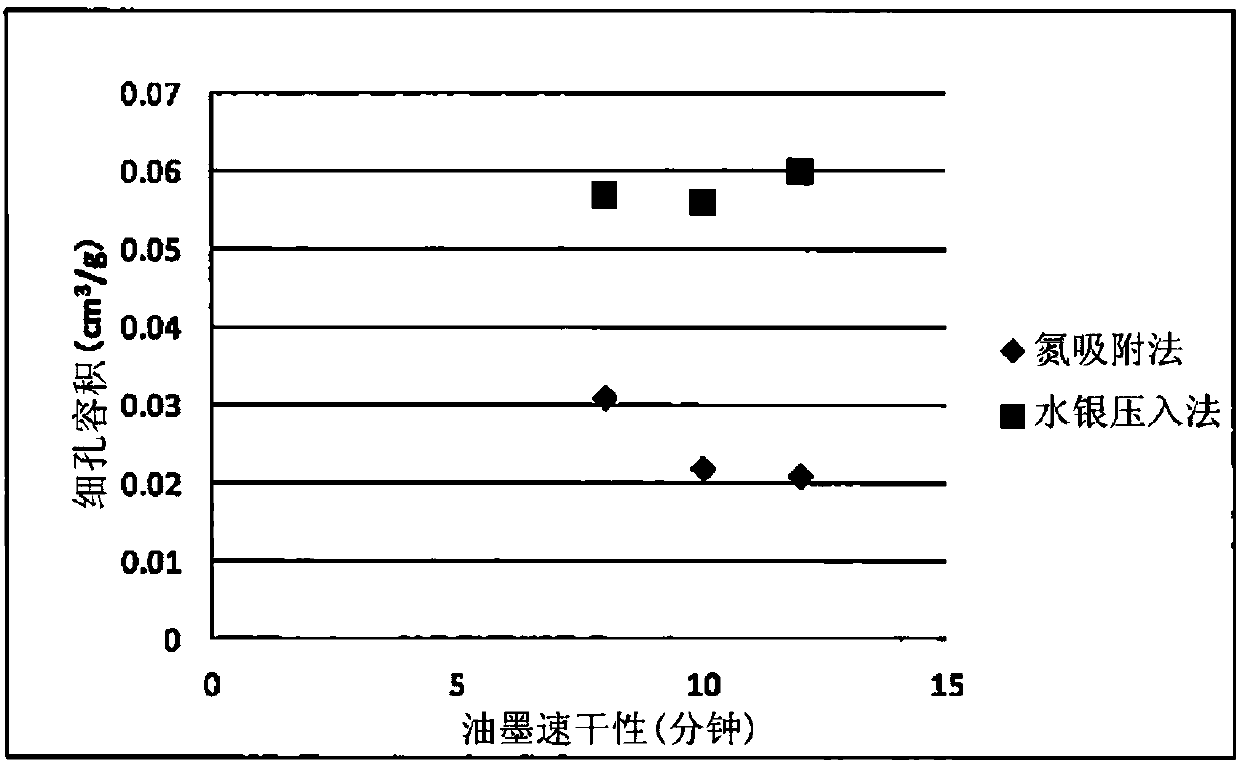
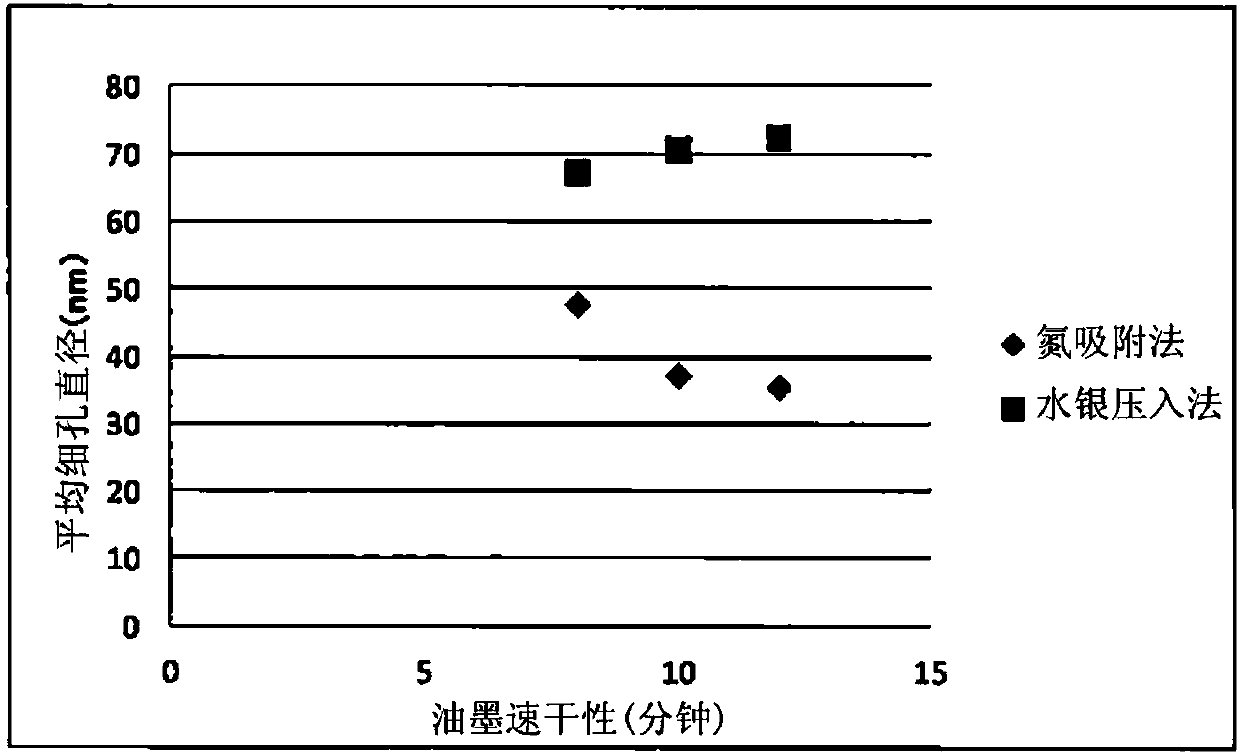
Coated paper, coated base material, and method of evaluating property of ink drying
InactiveCN107923129AEasy alignmentCoatings with pigmentsPaper testingStatic friction coefficientNitrogen
The invention addresses the problems of providing a coated paper having an excellent property of paper alignment, providing a coated base material having an excellent property of ink drying, and providing a method of accurately evaluating the property of ink drying. The first problem is solved by a coated paper for printing that has a white-paper glossiness of less than 30% according to JIS-P8142,and a kinetic coefficient of friction greater than the static coefficient of friction, in terms of the static coefficient of friction and kinetic coefficient of friction measured according to ISO 15359. The second problem is solved by a coated base material having a sheet base material and a pigment coating layer provided thereon, the pore volume V of the pigment coating layer according to nitrogen adsorption being 0.04 cm3 / g or greater. The third problem is solved by a method that includes a step of measuring the pore volume V or the average pore diameter m of the pigment coating layer by nitrogen adsorption.
Owner:NIPPON PAPER IND CO LTD
Antistatic Films and Methods To Manufacture The Same
In embodiments herein, the invention relates to a multilayer printable polymeric film including: (a) at least one layer A including one or more polyolefins and having a first side and a second side; (b) a layer B including one or more polyolefins and having a first side and a second side, where the first side of layer B is located on the second side of layer A; and (c) a printable coating located on the first side of layer A; wherein at least one of layer A or B comprises 0.01 to 50.0 wt. % of at least one polyether-polyolefin block copolymer, based on the weight of the polymers comprising the layer; and wherein the multilayer printable polymeric film has a kinetic coefficient of friction less than 0.65; and a surface tension of greater than about 35 mN / m; on one or both sides of the film.
Owner:JINDAL FILMS AMERICAS LLC
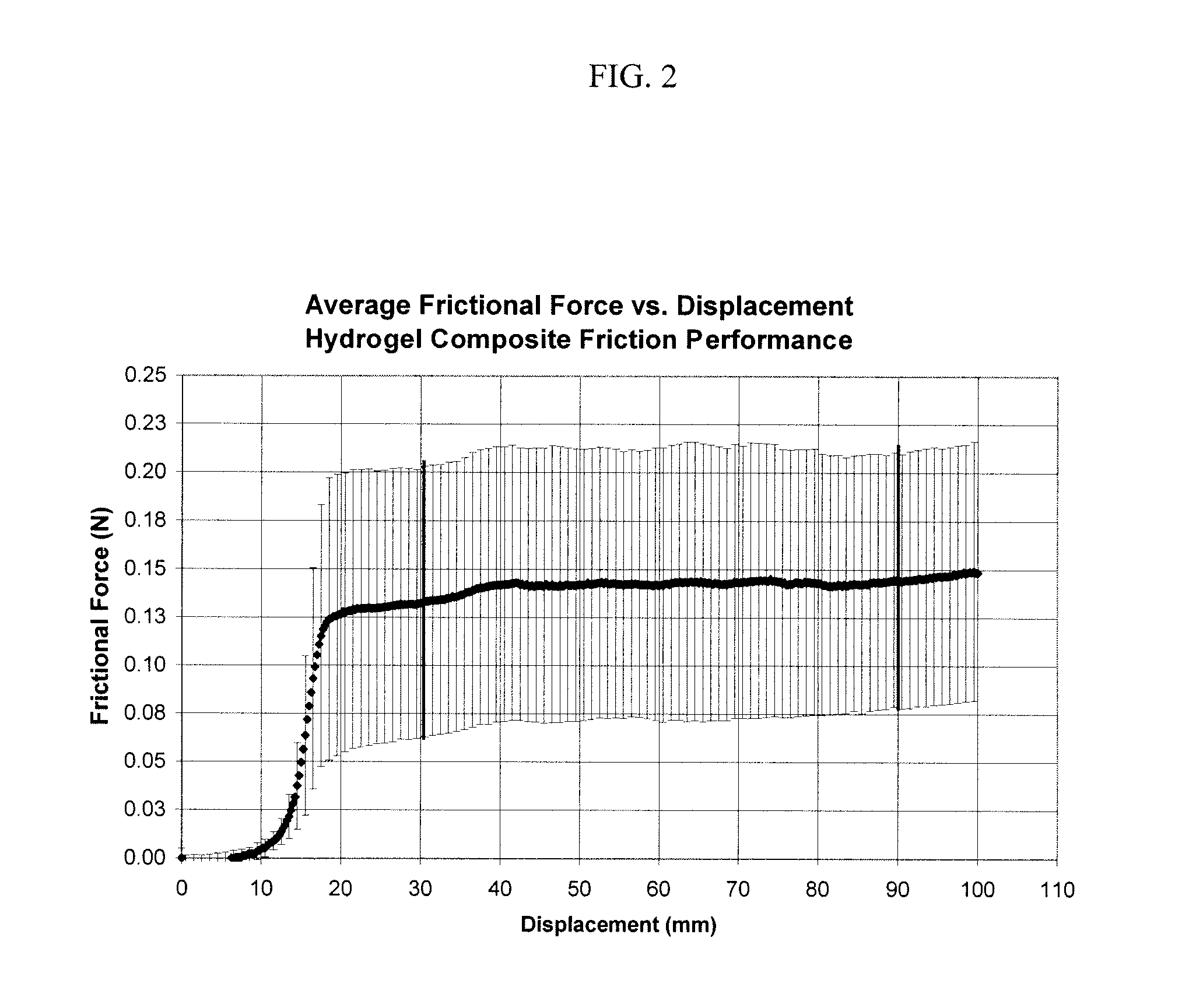
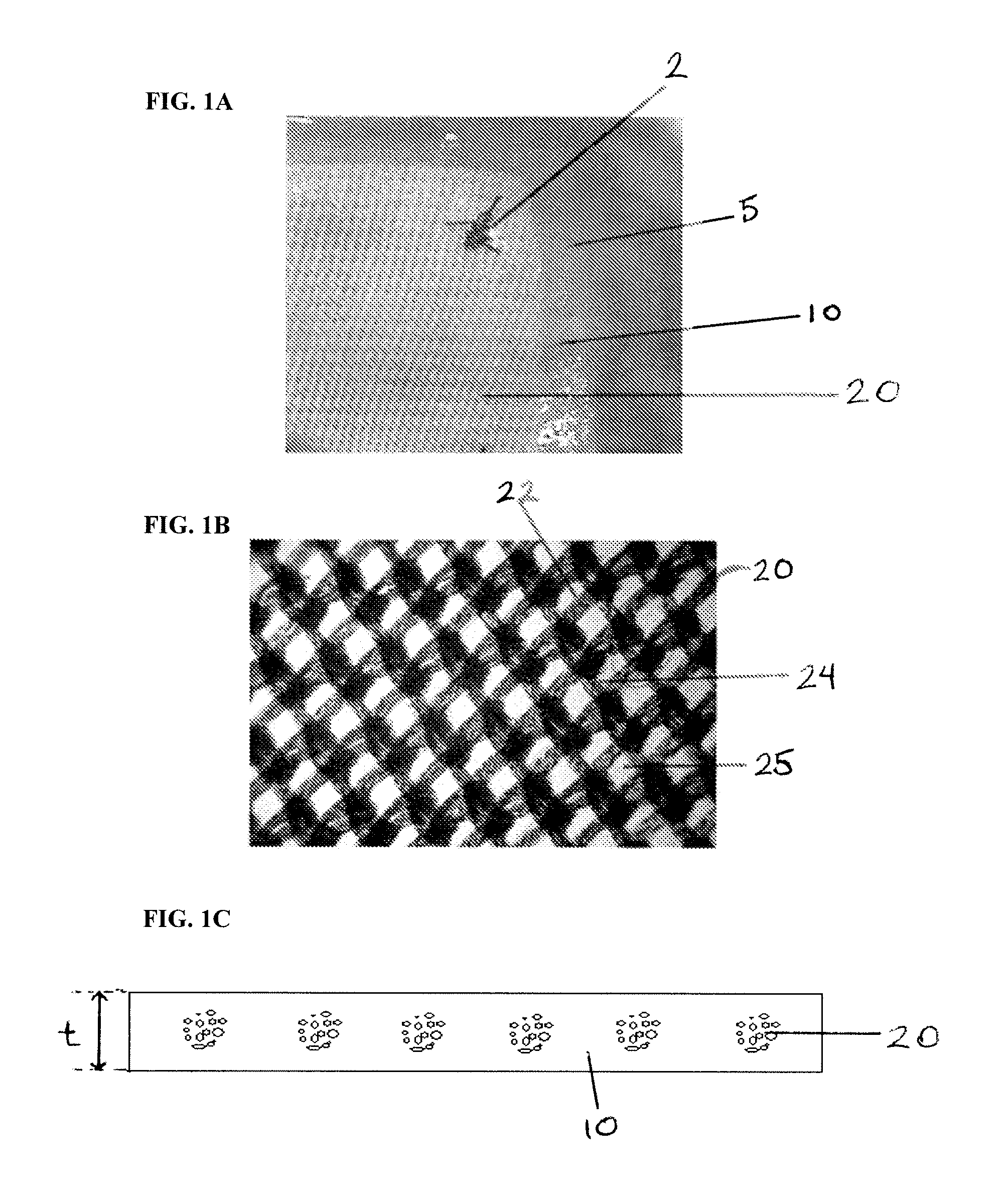
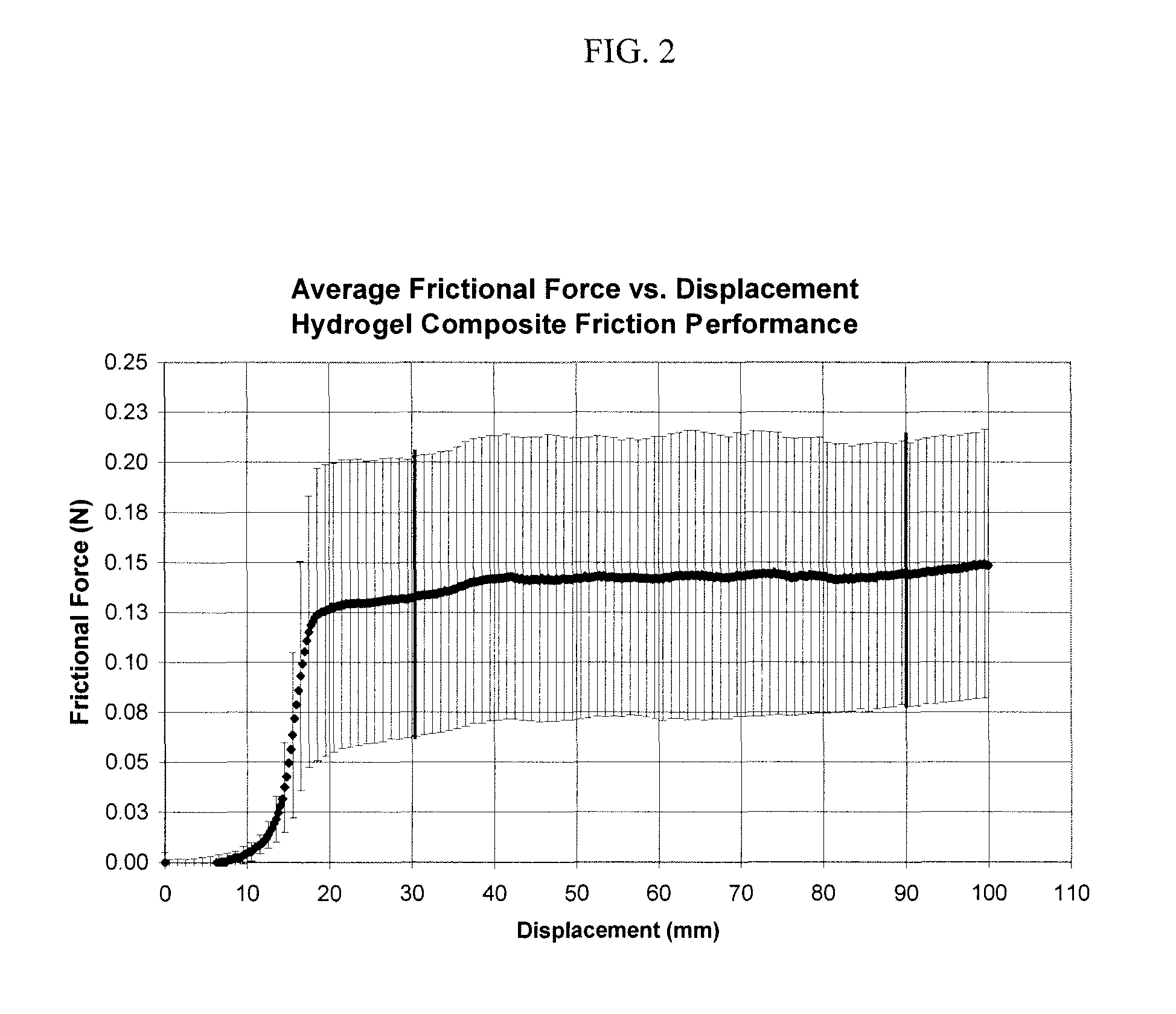
Method of forming and the resulting membrane composition for surgical site preservation
ActiveUS20110270286A1Reduce generationReduce formationWound clampsStatic friction coefficientMedicine
A method of forming and the resulting membrane composition for securement to a patient's bone or tissue to reduce the formation of tissue adhesions following a surgical procedure comprises a first component and a second component. The first component comprises a hydrogel including at least one crosslinked polymer. The second component comprises a textile component. The composition has a thickness between about two tenths of a millimeter (0.2 mm) to about six tenths of a millimeter (0.6 mm), a suture retention strength between about one Newton (1 N) to about thirteen Newtons (13 N), a static coefficient of friction between about one hundredth (0.01) and about one-half (0.5), a kinetic coefficient of friction between about one hundredth (0.01) and about one-half (0.5) and a flexibility of less than thirty millimeters (30 mm) bend length. A method of reducing the occurrence of tissue adhesions following surgery comprises applying the membrane composition to a surgical site.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
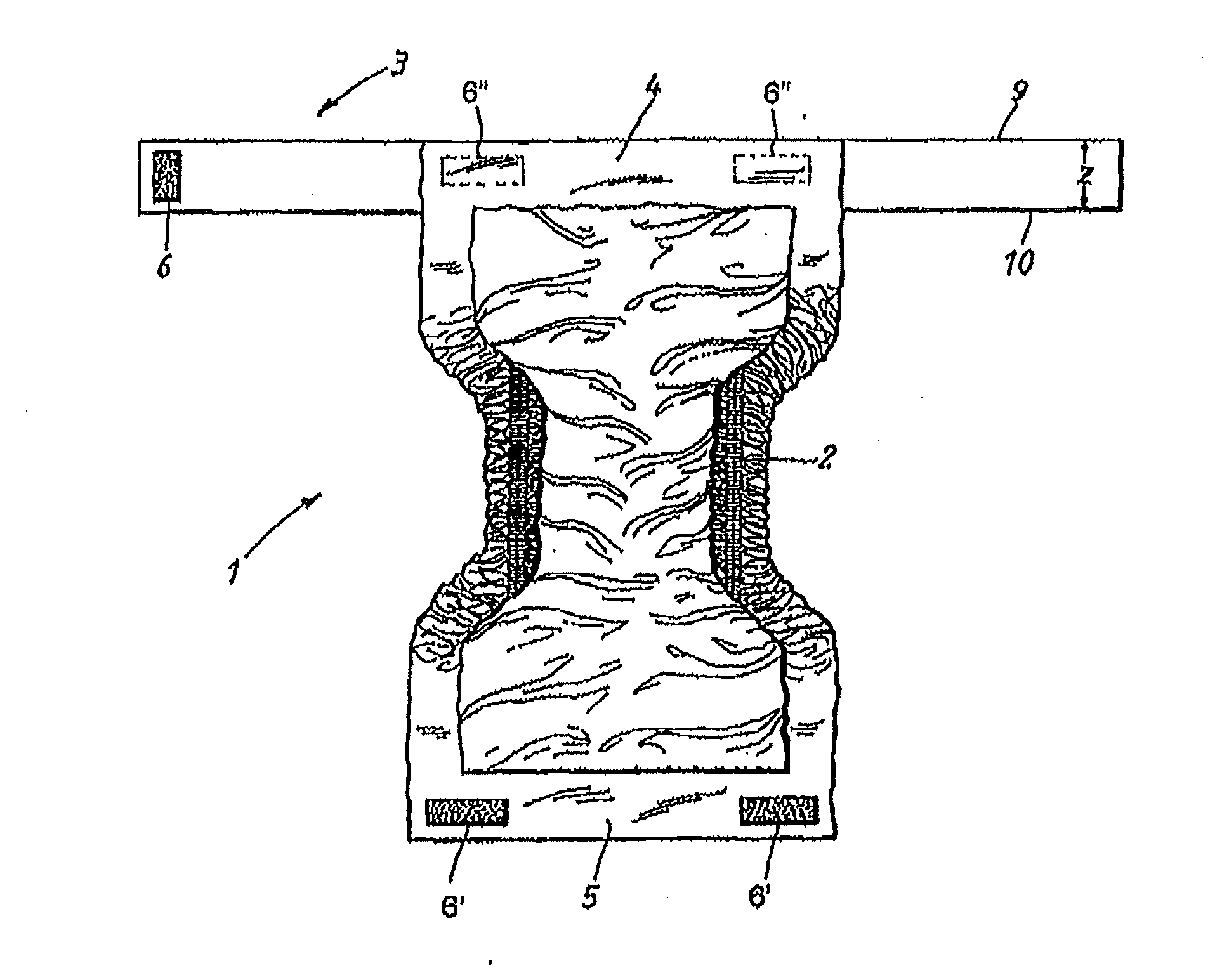
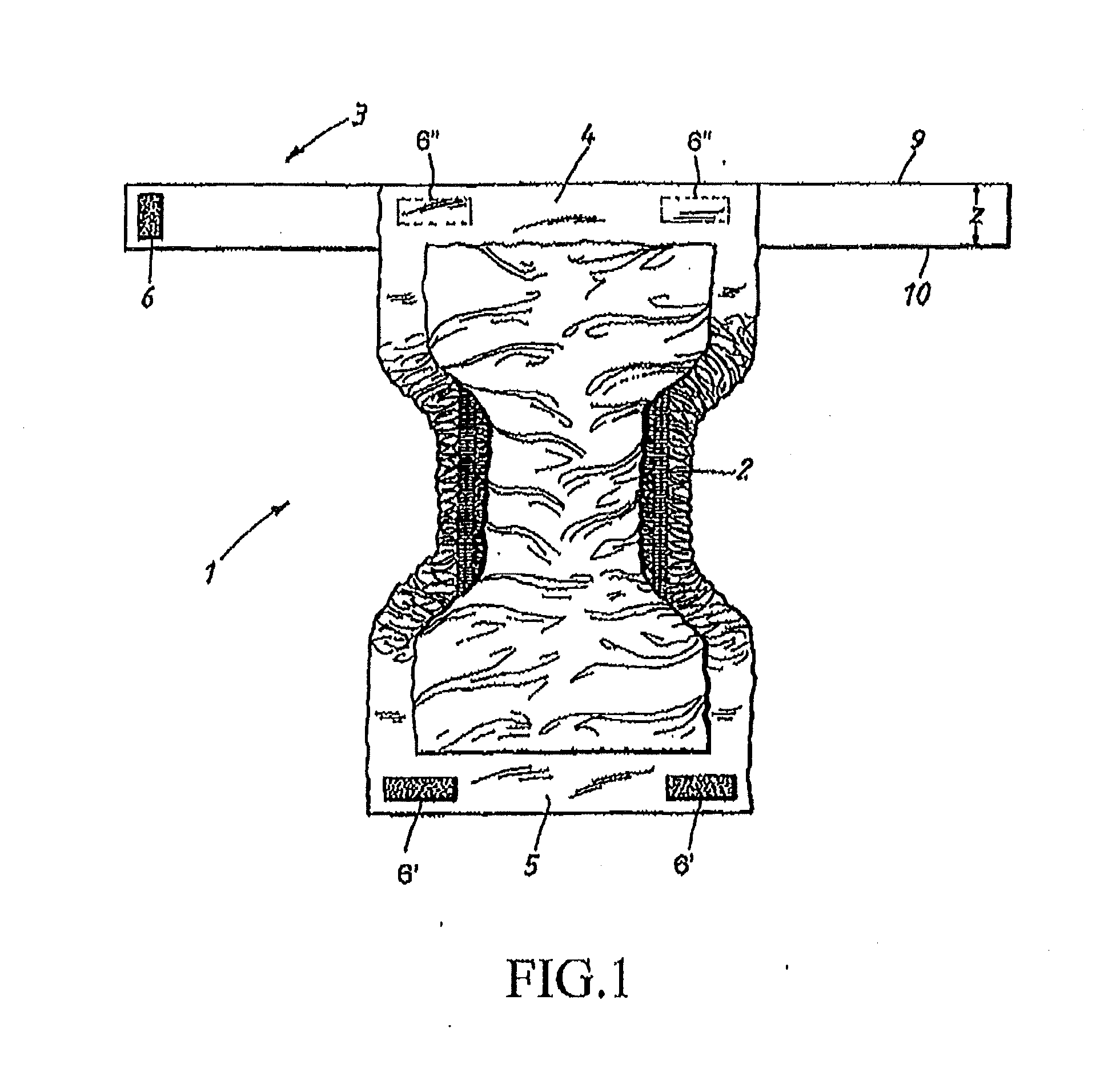
Absorbent belted-article with improved friction between the absorbent pad and the belt
ActiveUS20140142534A1Reduce the differenceAvoid separationAbsorbent padsBaby linensBand shapeAbsorbent Pads
An absorbent article includes an absorbent pad and a belt to which the pad is detachably attached and which is intended to be attached to a separate belt that is placed around the waist of the wearer to hold the pad when the article is being worn, wherein the absorbent pad exhibits a chassis including a liquid-permeable top sheet and a liquid-impermeable back sheet oriented away from the wearer and an absorbent core between the top sheet and the back sheet. The difference in kinetic coefficients of friction measured with ASTM D 1894-08 standard between the back sheet of the pad and the outwardly oriented surface of the belt is at maximum 0.5. The attachment between the belt and the pad will then not cease due to the movement of the article relative to the surroundings when the belted-article is being used, thereby preventing contamination and leakage caused by detachment.
Owner:ESSITY HYGIENE & HEALTH AB
Apparatus for determining coefficients of friction
InactiveUS8997551B2Using mechanical meansInvestigating abrasion/wear resistanceStatic friction coefficientDisplay device
The apparatus for determining coefficients of friction collects data required for determining static and dynamic coefficients of friction between various materials. The apparatus includes a ramp with adjustable slope and a plurality of test masses for placement on the ramp. Upslope lights and sensors, downslope lights and sensors, and a digital angle meter are installed on the ramp. The apparatus has a timing device having a display to show the elapsed time between a test mass passing the upslope sensor and the downslope sensor. The operator can determine the static coefficient of fraction from the tangent of the angle displayed on the digital angle meter when a test mass first begins to slide, and can compute the kinetic coefficient of friction from the angle displayed on the digital angle meter and the elapsed time shown on the timing device.
Owner:KUWAIT UNIV
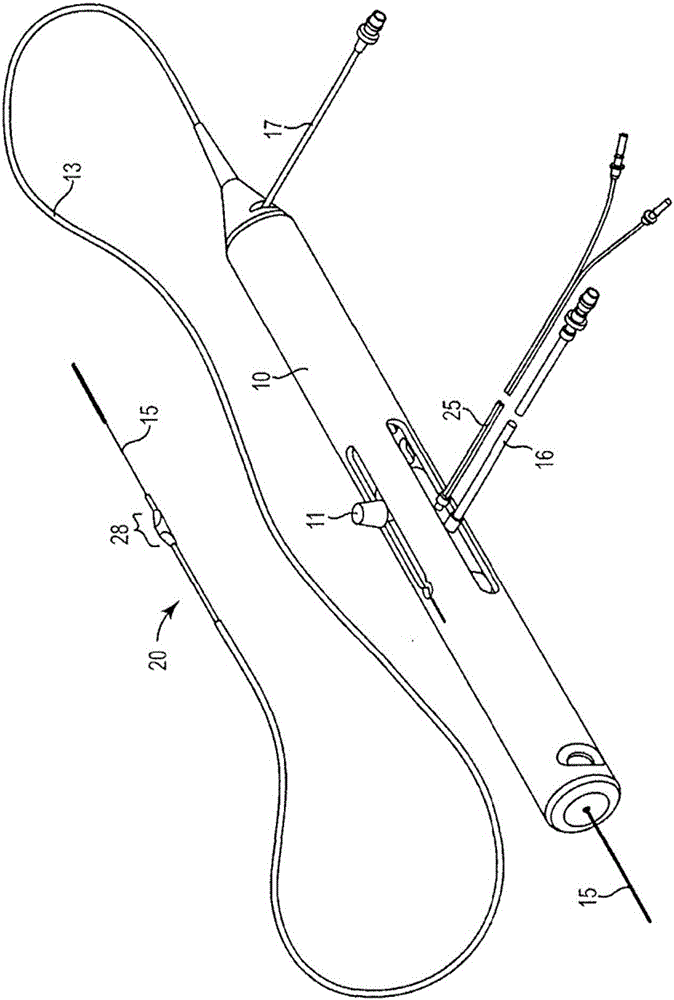
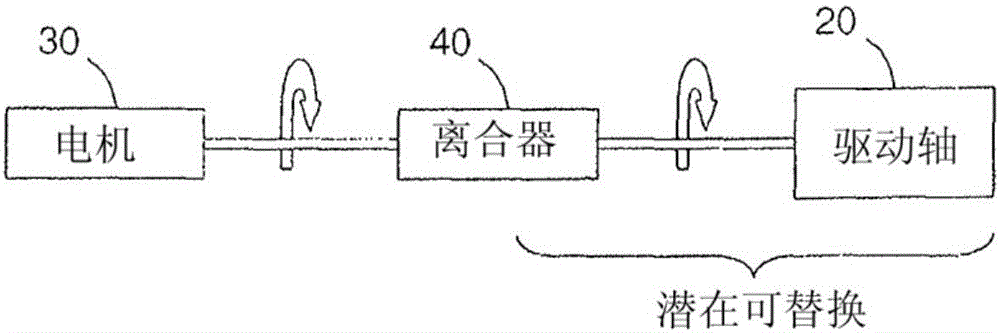
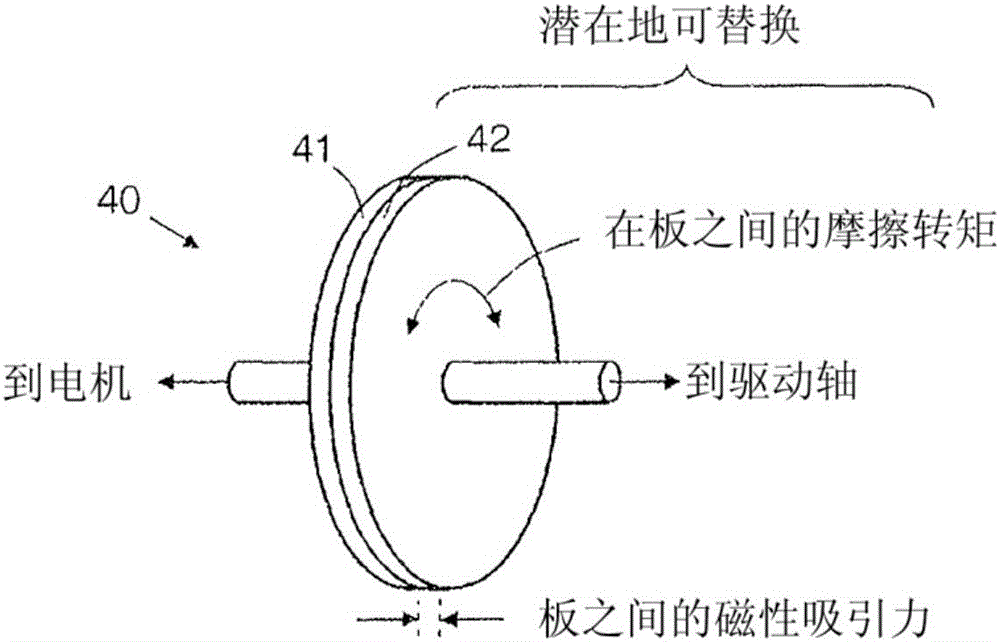
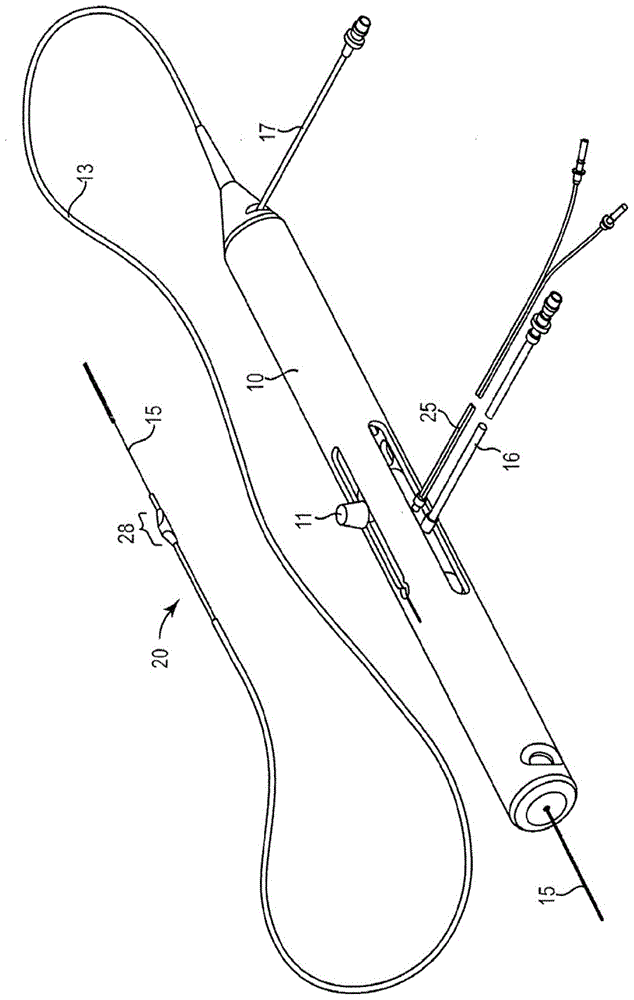
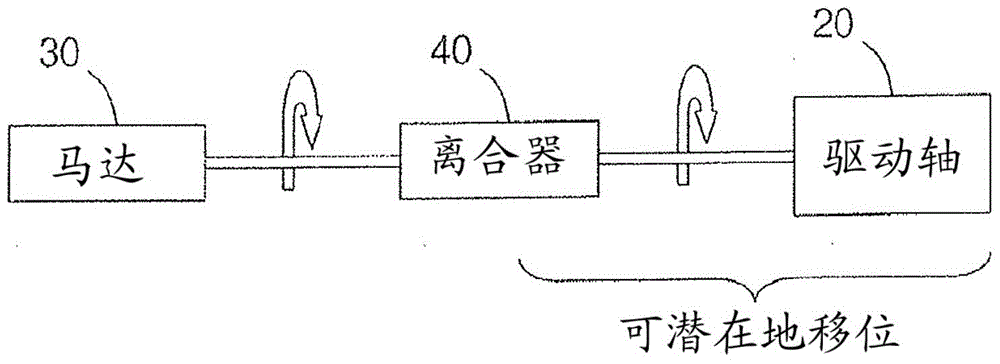
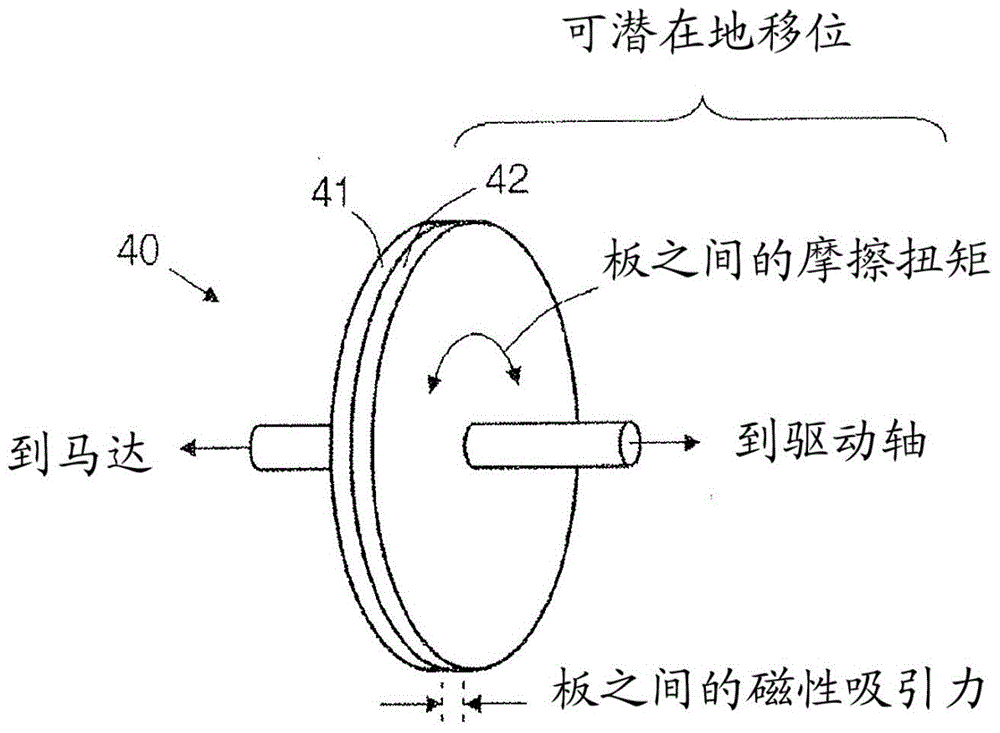
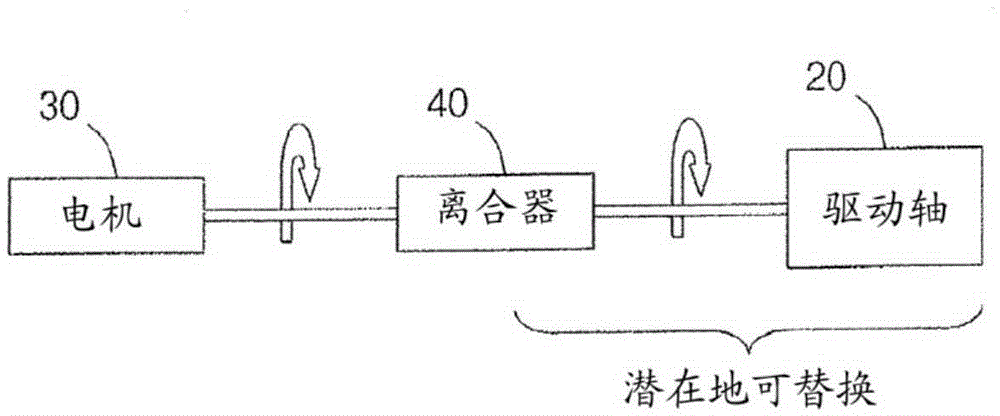
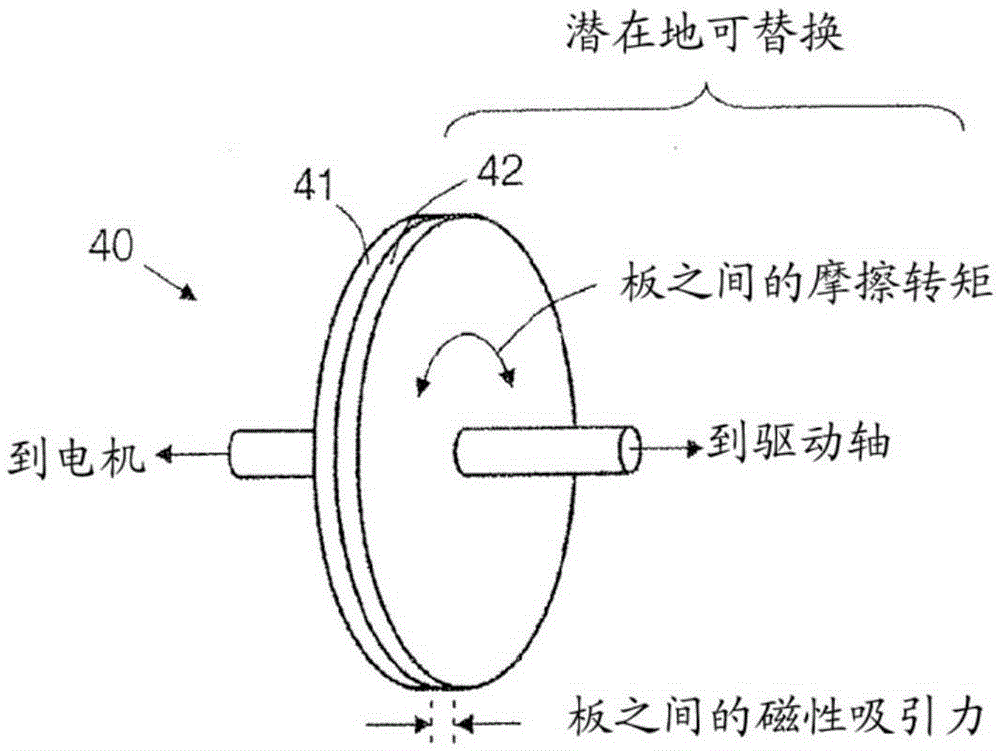
Rotational atherectomy systems and methods with shock absorbing element
A rotational atherectomy system may include a drive shaft, a motor, and a clutch with a threshold torque where the clutch may include a motor plate rotationally connected to the motor, a drive shaft plate rotationally connected to the drive shaft, and a biasing clutch configured to rotationally engage the motor plate and the drive shaft plate, wherein torques less than the threshold torque are transmitted completely between the motor plate and the drive shaft plate, which remain rotationally coupled by static friction, and wherein torques greater than the threshold torque cause the motor plate and the drive shaft plate to rotate relative to one another and cause a residual torque to be transmitted between the motor and the drive shaft, the residual torque being less than the threshold torque and being determined by a kinetic coefficient of friction.
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
Toner for developing electrostatic images
Owner:ZEON CORP
Method of forming and the resulting membrane composition for surgical site preservation
ActiveUS8748508B2Reduce formationSufficient coefficientImpression capsSurgical adhesivesStatic friction coefficientSurgical site
A method of forming and the resulting membrane composition for securement to a patient's bone or tissue to reduce the formation of tissue adhesions following a surgical procedure comprises a first component and a second component. The first component comprises a hydrogel including at least one crosslinked polymer. The second component comprises a textile component. The composition has a thickness between about two tenths of a millimeter (0.2 mm) to about six tenths of a millimeter (0.6 mm), a suture retention strength between about one Newton (1 N) to about thirteen Newtons (13 N), a static coefficient of friction between about one hundredth (0.01) and about one-half (0.5), a kinetic coefficient of friction between about one hundredth (0.01) and about one-half (0.5) and a flexibility of less than thirty millimeters (30 mm) bend length. A method of reducing the occurrence of tissue adhesions following surgery comprises applying the membrane composition to a surgical site.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Rotational atherectomy device with biasing clutch
A rotational atherectomy system may include a drive shaft, a motor, and a clutch with a threshold torque where the clutch may include a motor plate rotationally connected to the motor, a drive shaft plate rotationally connected to the drive shaft, and a biasing clutch configured to rotationally engage the motor plate and the drive shaft plate, wherein torques less than the threshold torque are transmitted completely between the motor plate and the drive shaft plate, which remain rotationally coupled by static friction, and wherein torques greater than the threshold torque cause the motor plate and the drive shaft plate to rotate relative to one another and cause a residual torque to be transmitted between the motor and the drive shaft, the residual torque being less than the threshold torque and being determined by a kinetic coefficient of friction.
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
Rotational atherectomy device with biasing clutch
A rotational atherectomy system may include a drive shaft, a motor, and a clutch with a threshold torque where the clutch may include a motor plate rotationally connected to the motor, a drive shaft plate rotationally connected to the drive shaft, and a biasing clutch configured to rotationally engage the motor plate and the drive shaft plate, wherein torques less than the threshold torque are transmitted completely between the motor plate and the drive shaft plate, which remain rotationally coupled by static friction, and wherein torques greater than the threshold torque cause the motor plate and the drive shaft plate to rotate relative to one another and cause a residual torque to be transmitted between the motor and the drive shaft, the residual torque being less than the threshold torque and being determined by a kinetic coefficient of friction.
Owner:CARDIOVASCULAR SYST INC
Novel device for measuring dynamic coefficient of squeeze film damper
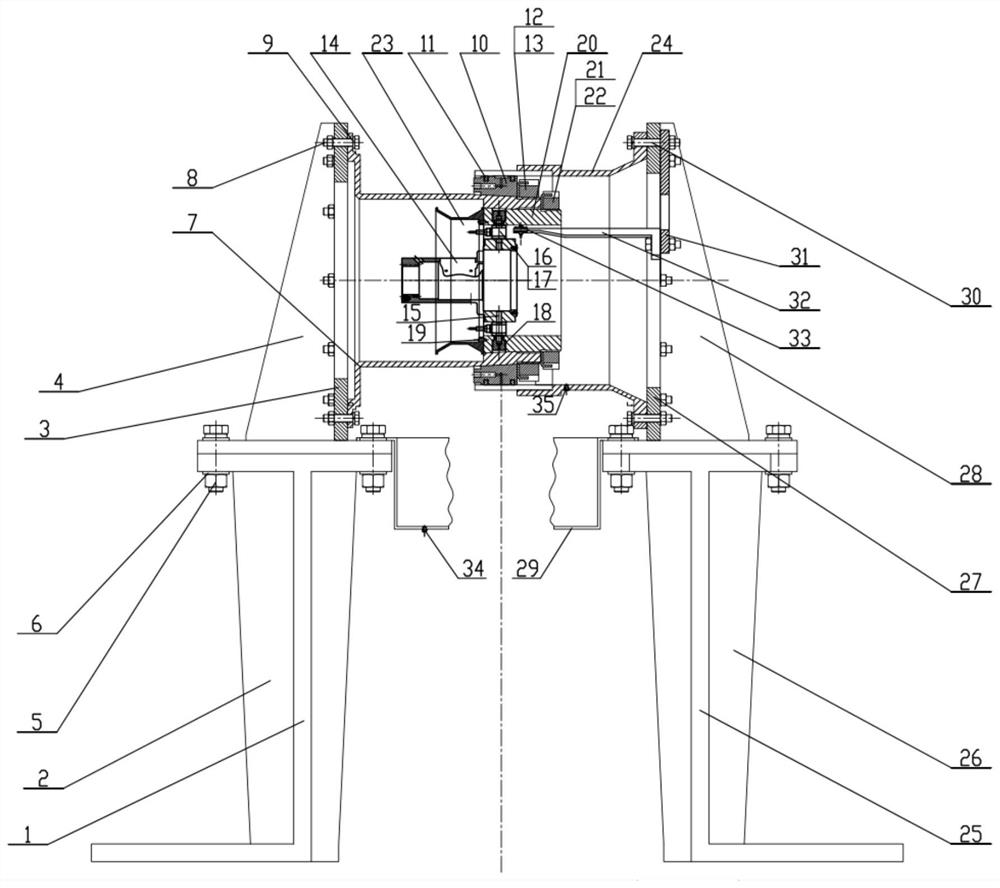
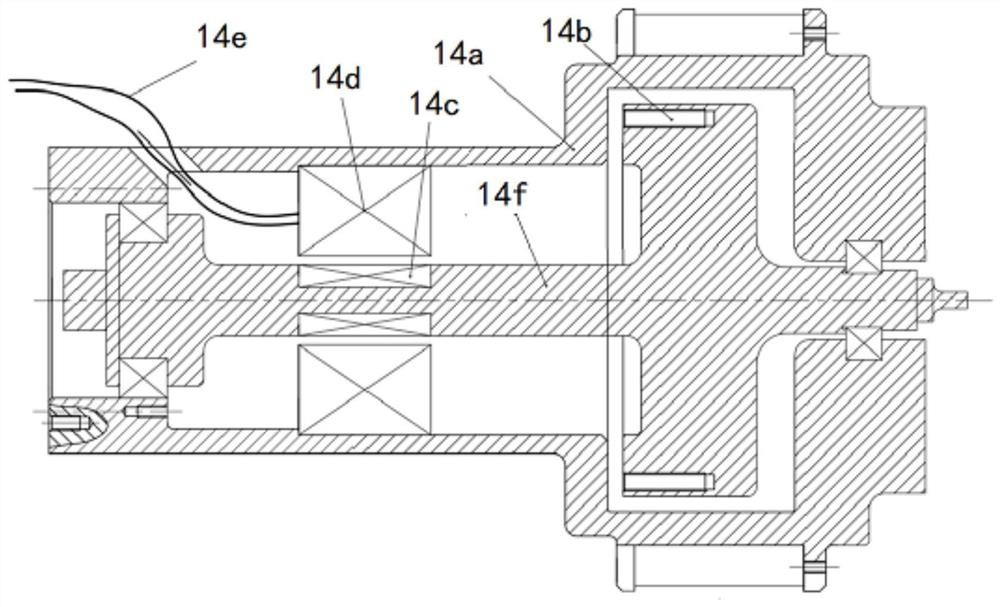
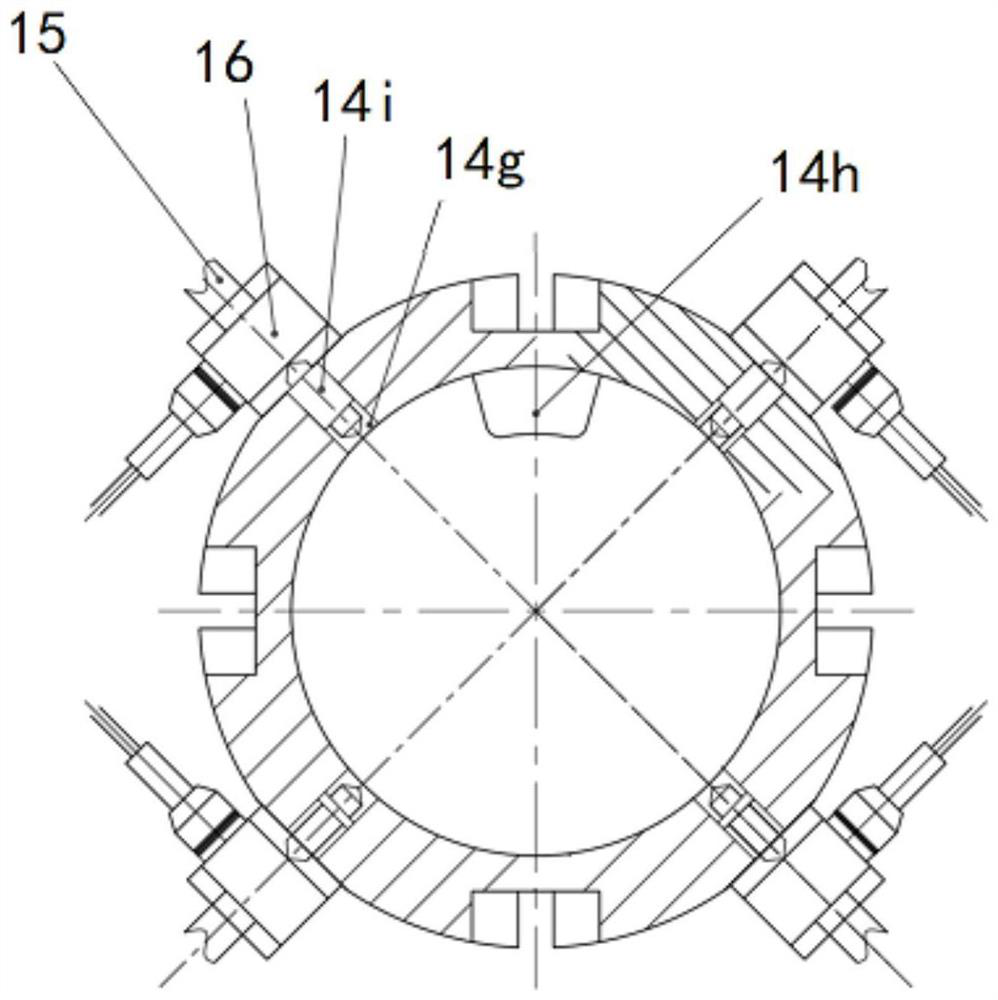
PendingCN113984365AEasy to assess vibration dampingSimplify the actual incentive stateMachine part testingDrive motorSqueeze film
The invention relates to the field of squeeze film dampers, in particular to a novel device for measuring a dynamic coefficient of a squeeze film damper, and aims to solve the problems that an existing squeeze film damper dynamic coefficient measuring device only applies exciting force through power elements such as a driving motor, and the applying mode is poor in reasonability,and the accuracy of damping characteristic evaluation is low. According to the novel device for measuring a dynamic coefficient of a squeeze film damper provided by the invention, a rotary vibration exciter is adopted to excite a weak-rigidity elastic squirrel cage supporting seat, and the excitation state is very close to the working condition of the squeeze film damper in an actual aero-engine and a gas turbine, the identified dynamic coefficient is closer to the actual situation, the vibration reduction performance is easier to evaluate, the rotary vibration exciter is adopted to excite the weak-rigidity elastic squirrel cage supporting seat, the actual excitation state of the rotor is simulated, the problems that the testing device is complex and large in size during actual rotor excitation are solved, and the testing device is small and flexible.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Sealing Sheet for Solar Cells
ActiveCN104106147BImprove qualityEfficient preparationDomestic sealsSynthetic resin layered productsStatic friction coefficientPolyolefin
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Method for identifying dynamic coefficient of squeeze film damper
PendingCN113758697ALow costSimple calculationMachine part testingMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesSqueeze filmControl theory
The invention discloses a method for identifying the dynamic coefficient of a squeeze film damper, belongs to the field of rotor dynamics, and aims to solve the problem that the dynamic coefficient of the squeeze film damper in the rotor rotation process is difficult to test on site by the conventional experimental device. The method depends on a traditional squeeze film damper test device, static loading testing is carried out on an elastic squirrel cage supporting seat and a damper outer ring supporting seat, strain-force transfer coefficients of corresponding structures are measured and calibrated, and when a rotor works normally, strain of cage bar structures on the elastic squirrel cage supporting seat and the damper outer ring supporting seat is monitored; and according to the calibration of the relationship between the strain and the force of the cage strips in the elastic squirrel cage supporting seat and the damper outer ring supporting seat, the external transmission force of the dynamic exciting force of the rotor passing through the elastic squirrel cage supporting seat and the damper outer ring supporting seat is obtained, and the identification of the dynamic coefficient of the squeeze film damper is realized. According to the method, the dynamic coefficients of the squeeze film damper under different rotating speeds of the rotor can be easily identified.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com