Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
50 results about "Instruction window" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
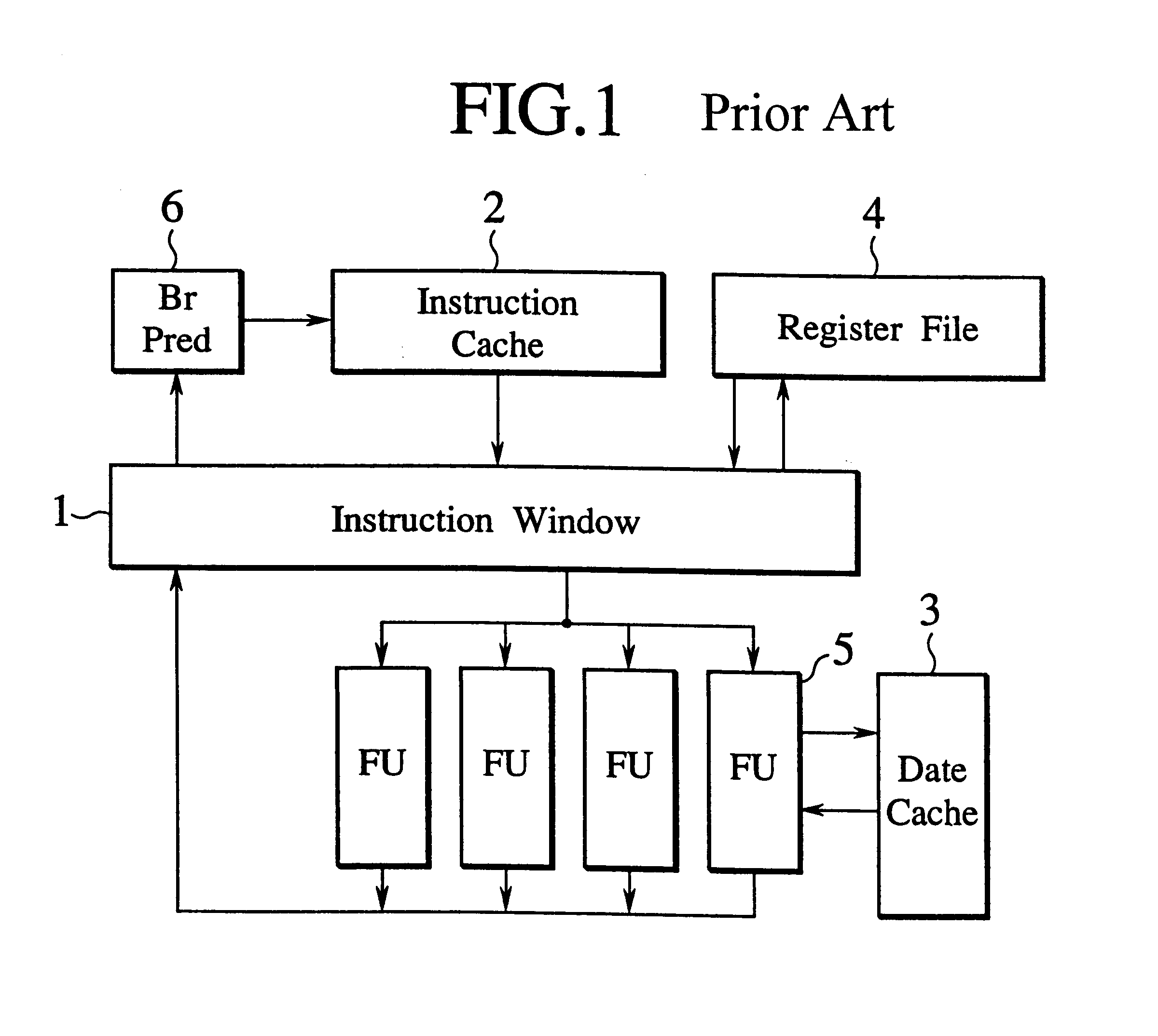
An instruction window in computer architecture refers to the set of instructions which can execute out-of-order in a speculative processor. In particular, in a conventional design, the instruction window consists of all instructions which are in the re-order buffer (ROB). In such a processor, any instruction within the instruction window can be executed when its operands are ready. Out-of-order processors derive their name because this may occur out-of-order (if operands to a younger instruction are ready before those of an older instruction).
Methods for identifying malicious software
ActiveUS7644441B2Memory loss protectionEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesGraphicsEncrypted function
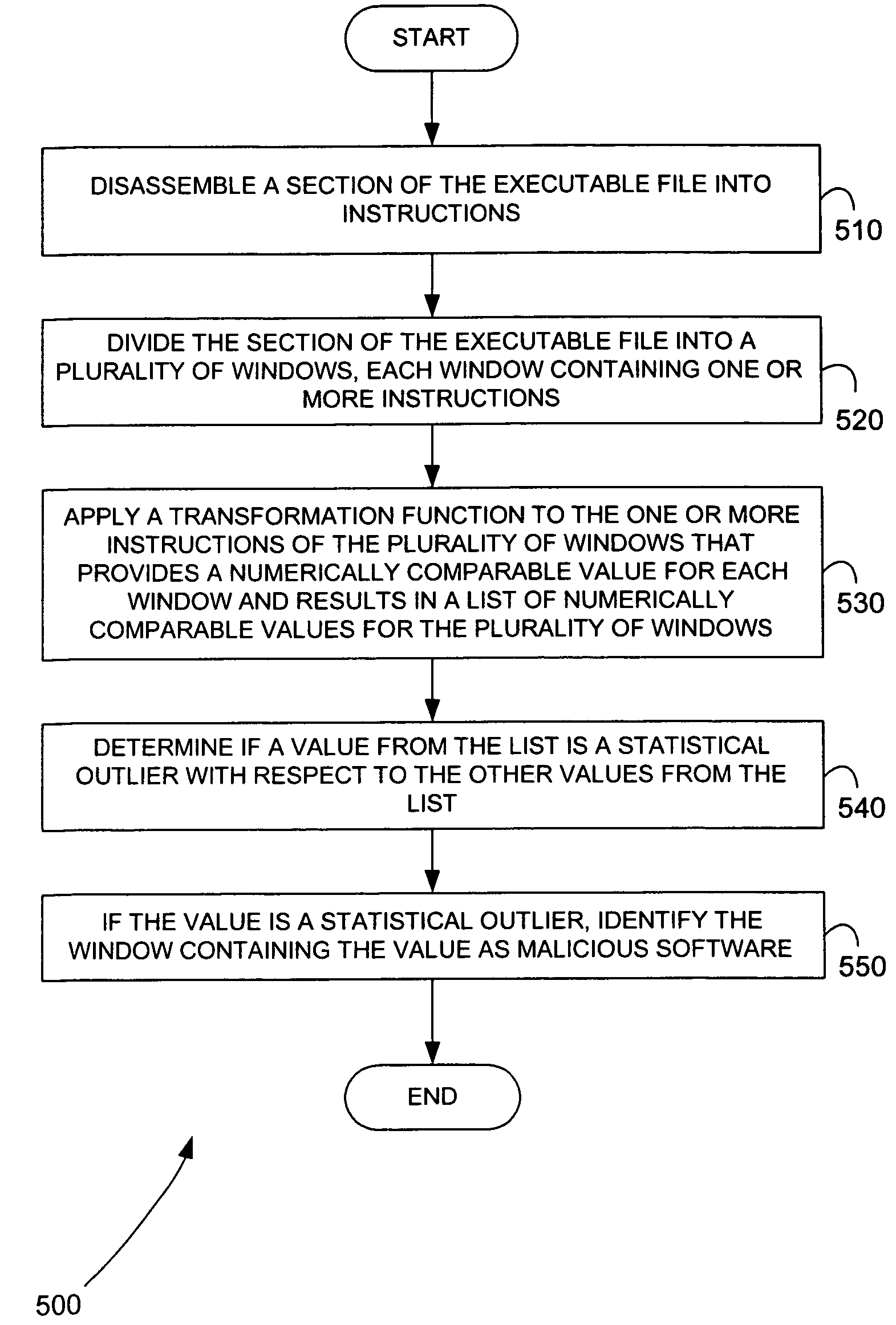
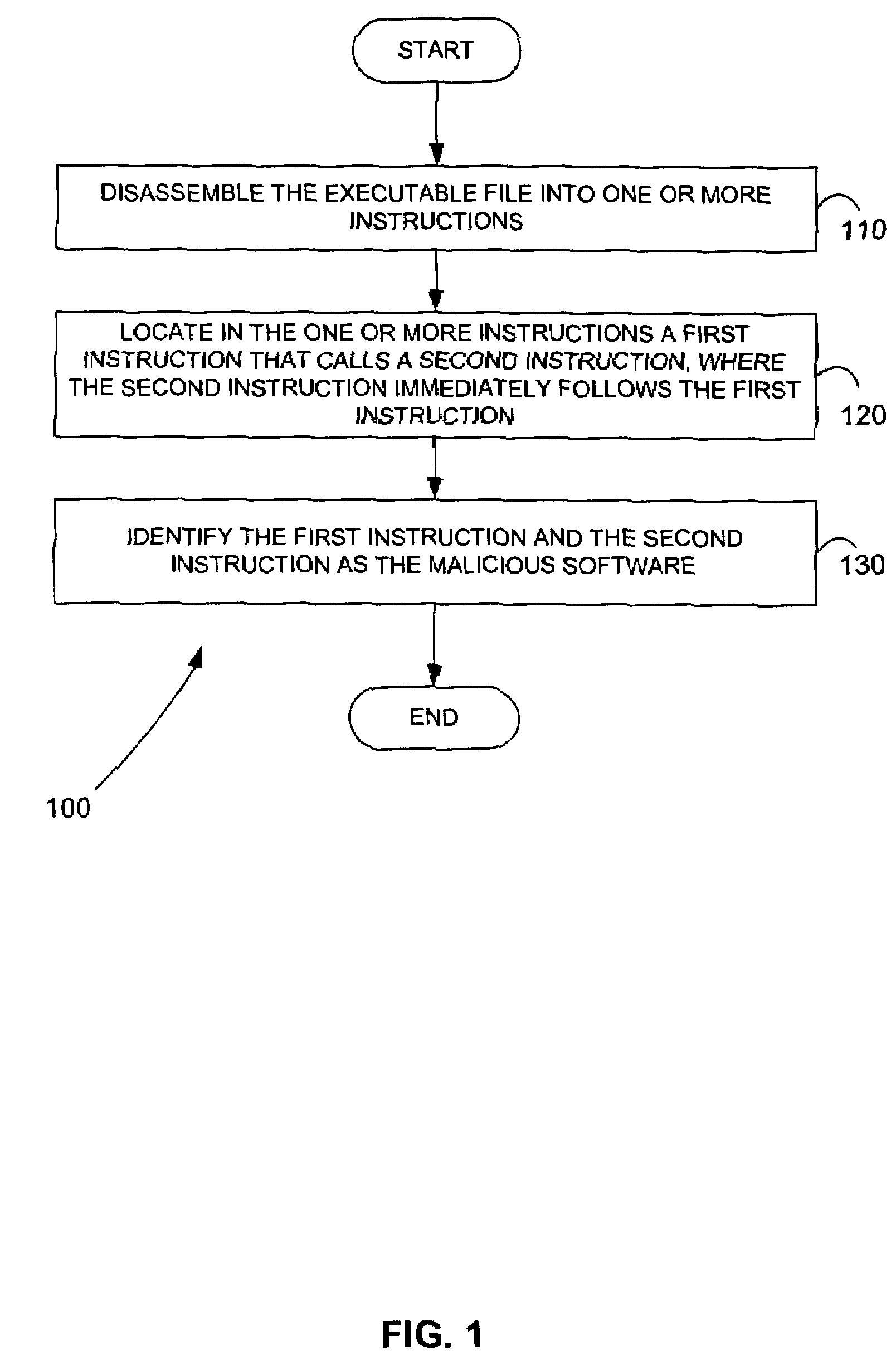
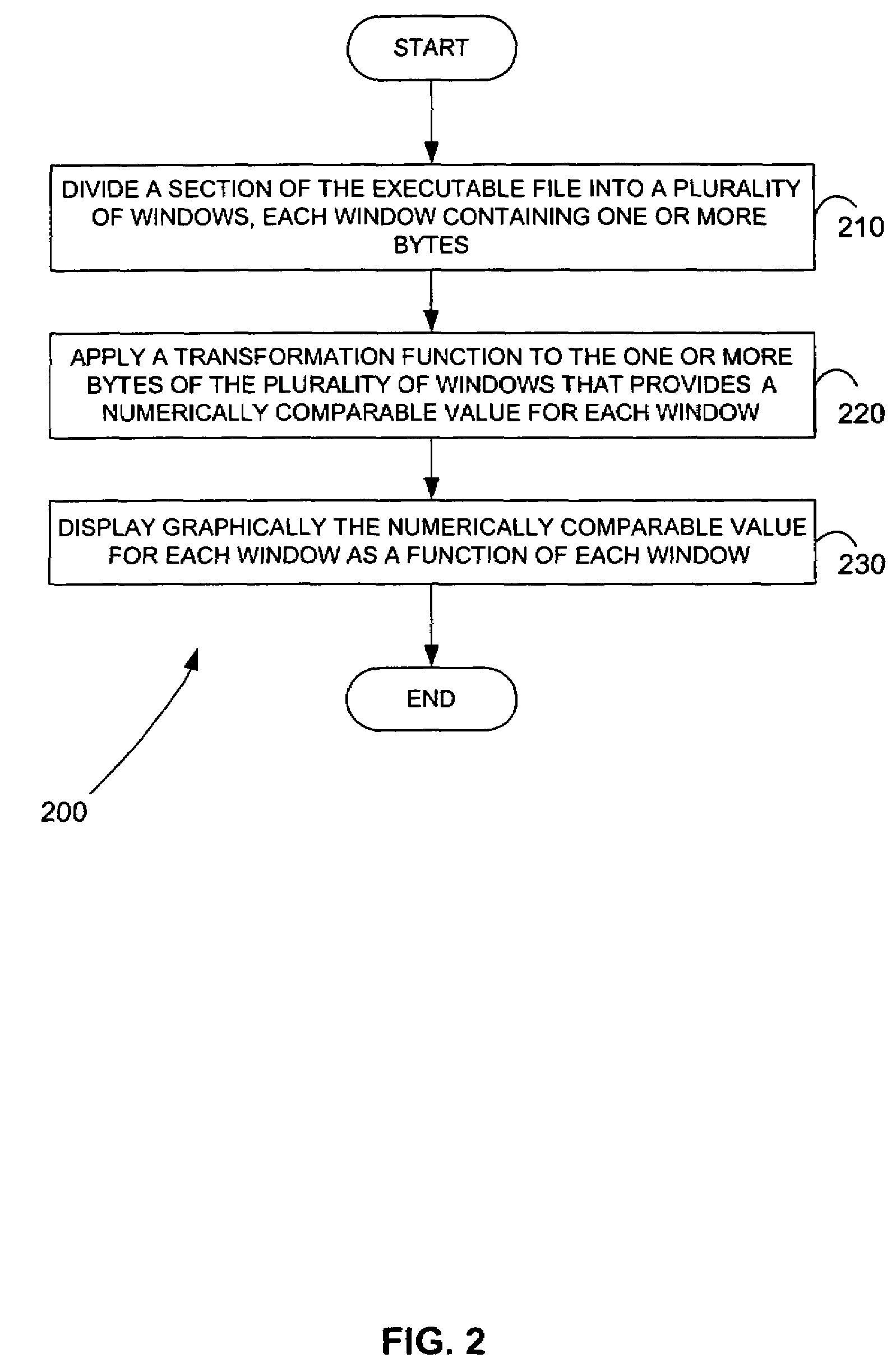
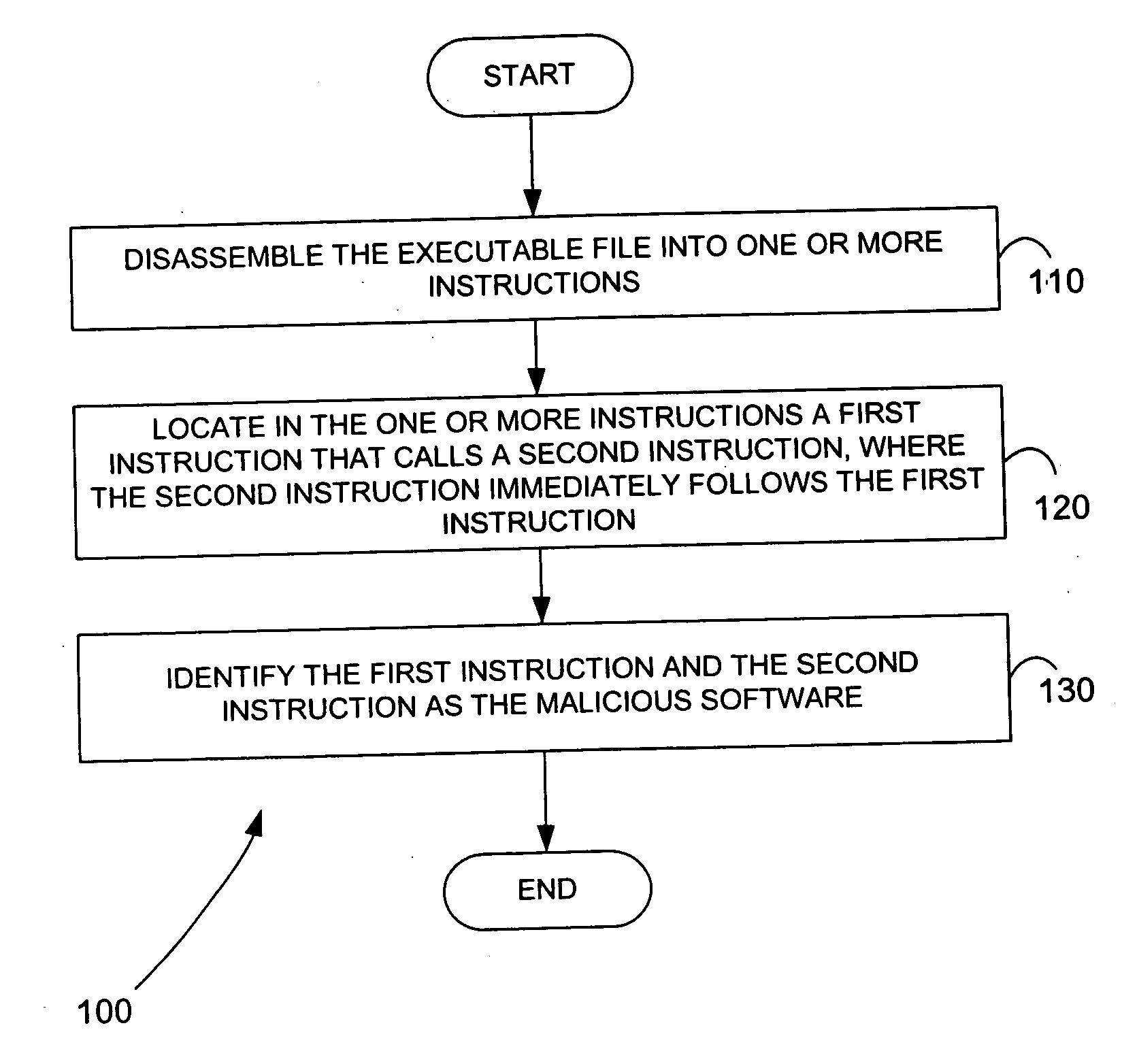
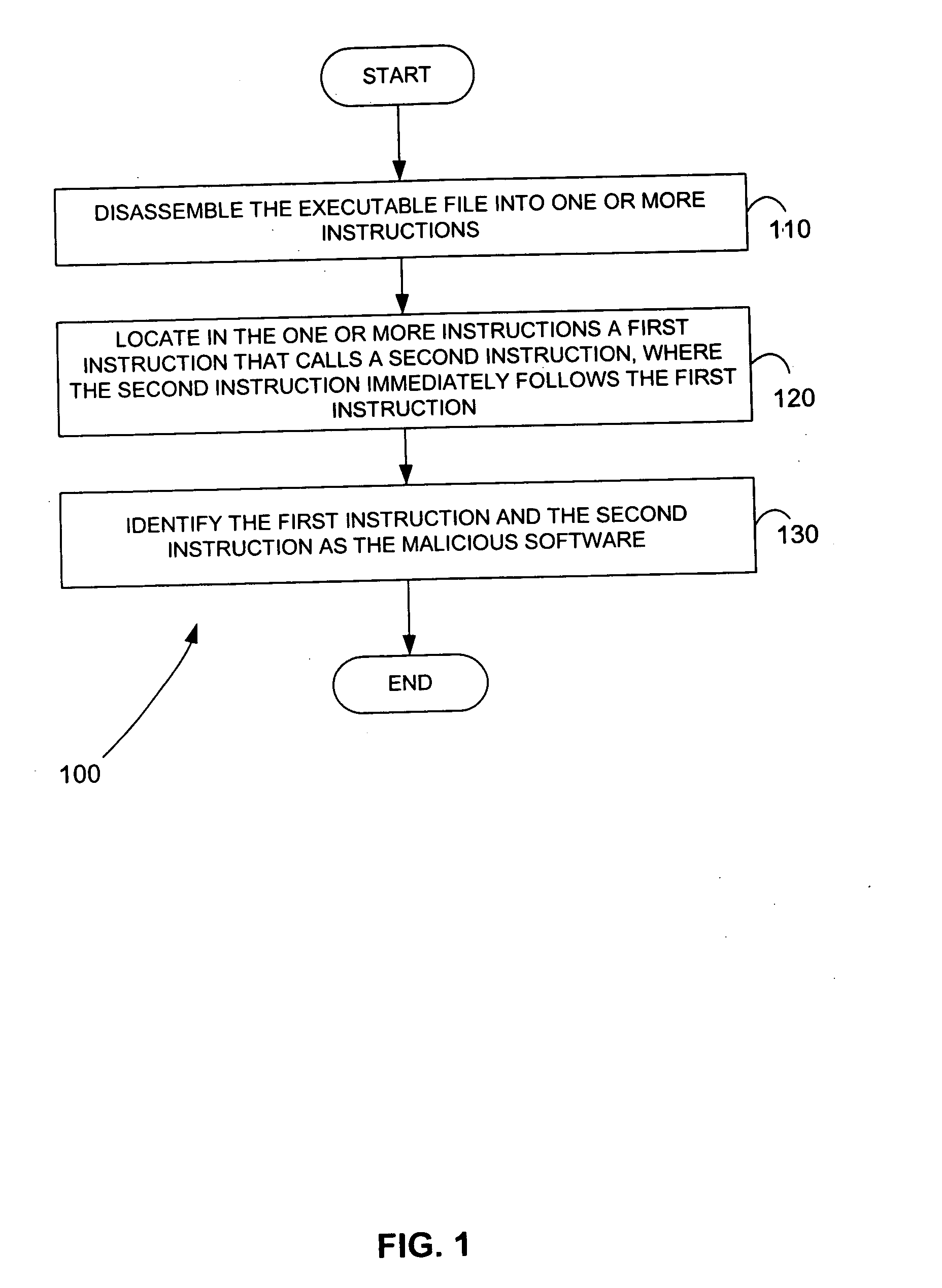
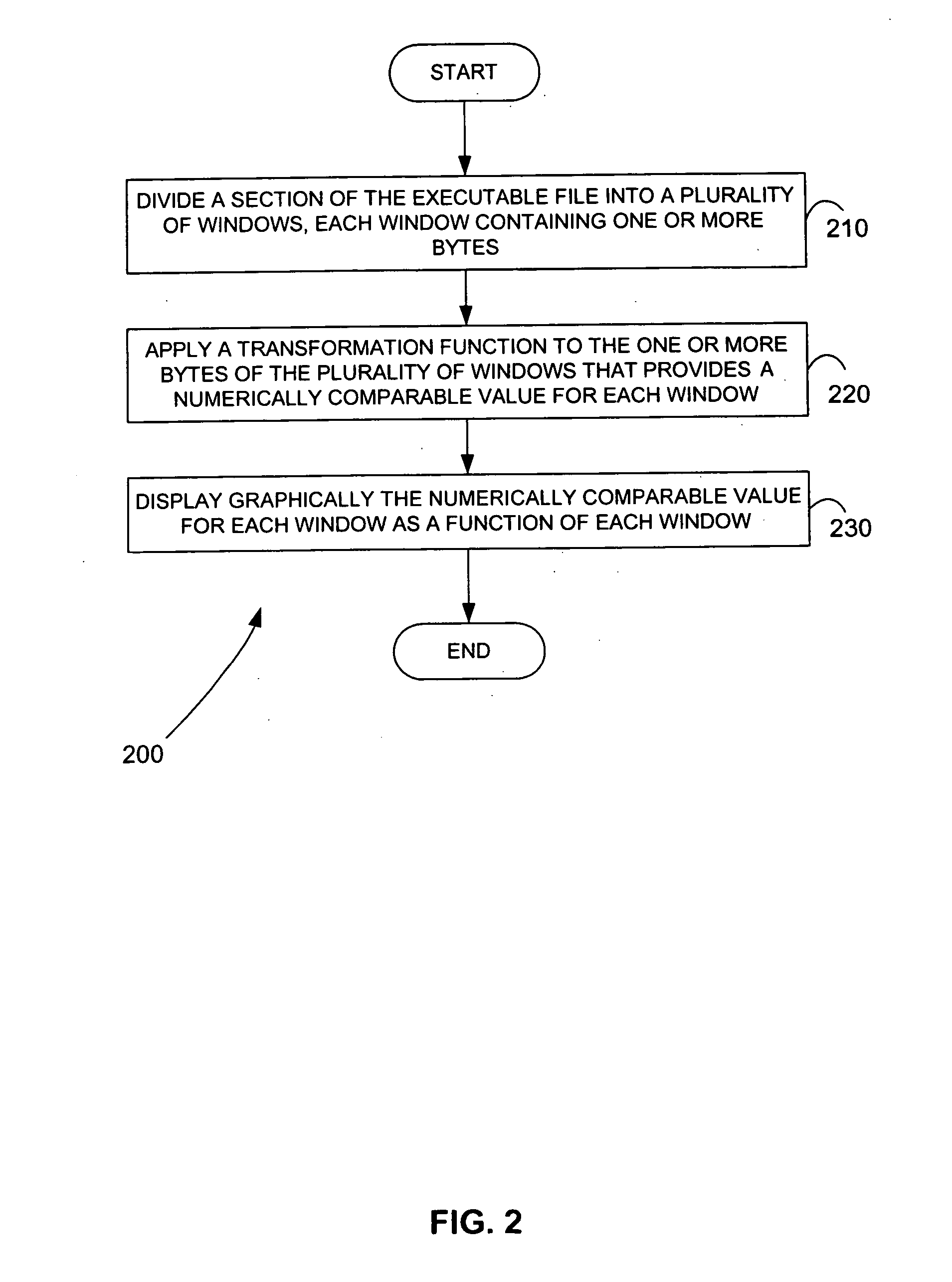
Malicious software is identified in an executable file by identifying malicious structural features, decryption code, and cryptographic functions. A malicious structural feature is identified by comparing a known malicious structural feature to one or more instructions of the executable file. A malicious structural feature is also identified by graphically and statistically comparing windows of bytes or instructions in a section of the executable file. Cryptography is an indicator of malicious software. Decryption code is identified in an executable file by identifying a tight loop around a reversible instruction that writes to random access memory. Cryptographic functions are identified in an executable file be obtaining a known cryptographic function and performing a string comparison of the numeric constants of the known cryptographic function with the executable file.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Methods for identifying malicious software
ActiveUS20050223238A1Design be often employMemory loss protectionEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesGraphicsEncrypted function
Malicious software is identified in an executable file by identifying malicious structural features, decryption code, and cryptographic functions. A malicious structural feature is identified by comparing a known malicious structural feature to one or more instructions of the executable file. A malicious structural feature is also identified by graphically and statistically comparing windows of bytes or instructions in a section of the executable file. Cryptography is an indicator of malicious software. Decryption code is identified in an executable file by identifying a tight loop around a reversible instruction that writes to random access memory. Cryptographic functions are identified in an executable file be obtaining a known cryptographic function and performing a string comparison of the numeric constants of the known cryptographic function with the executable file.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Fast just-in-time (JIT) scheduler
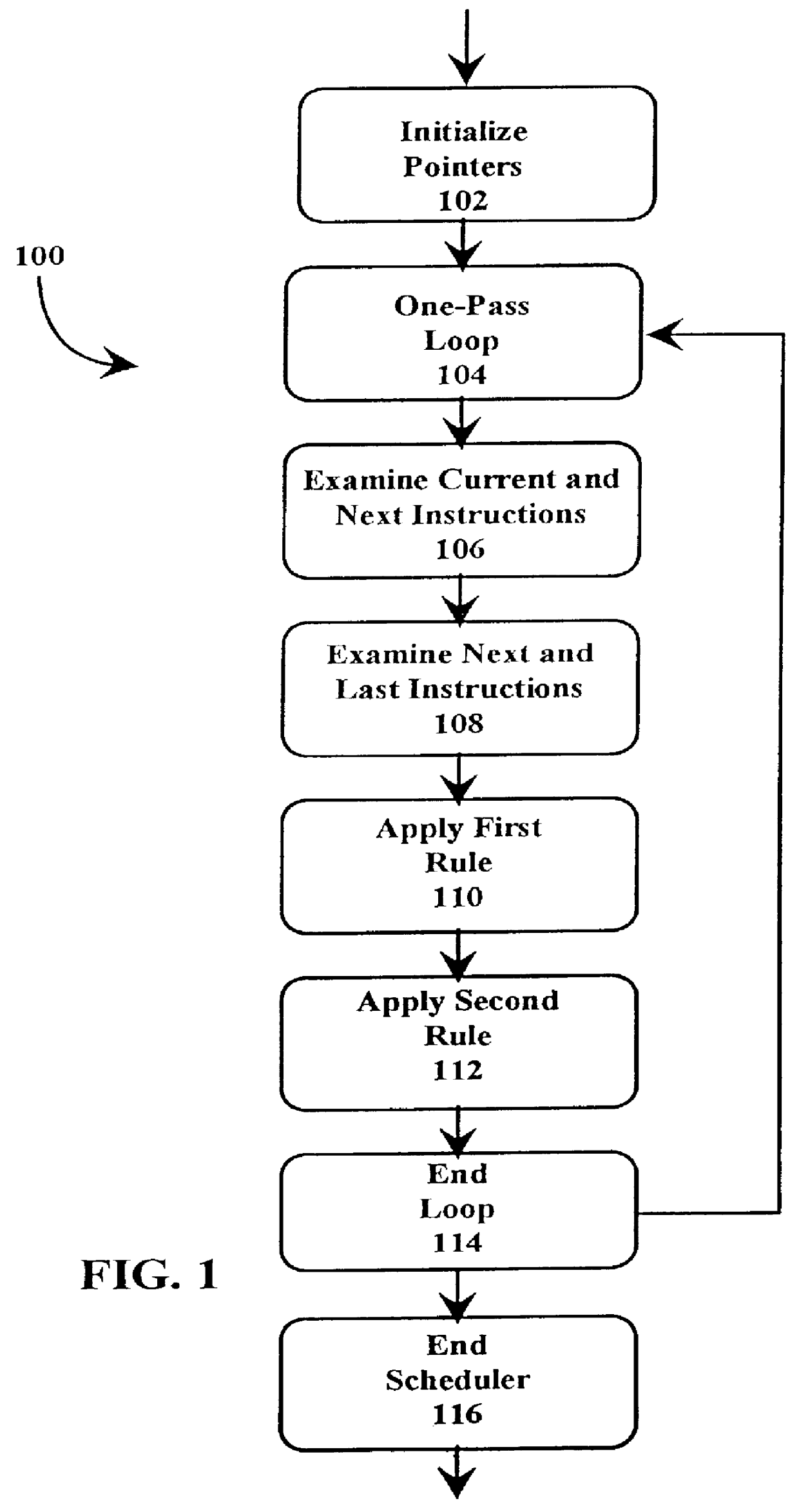
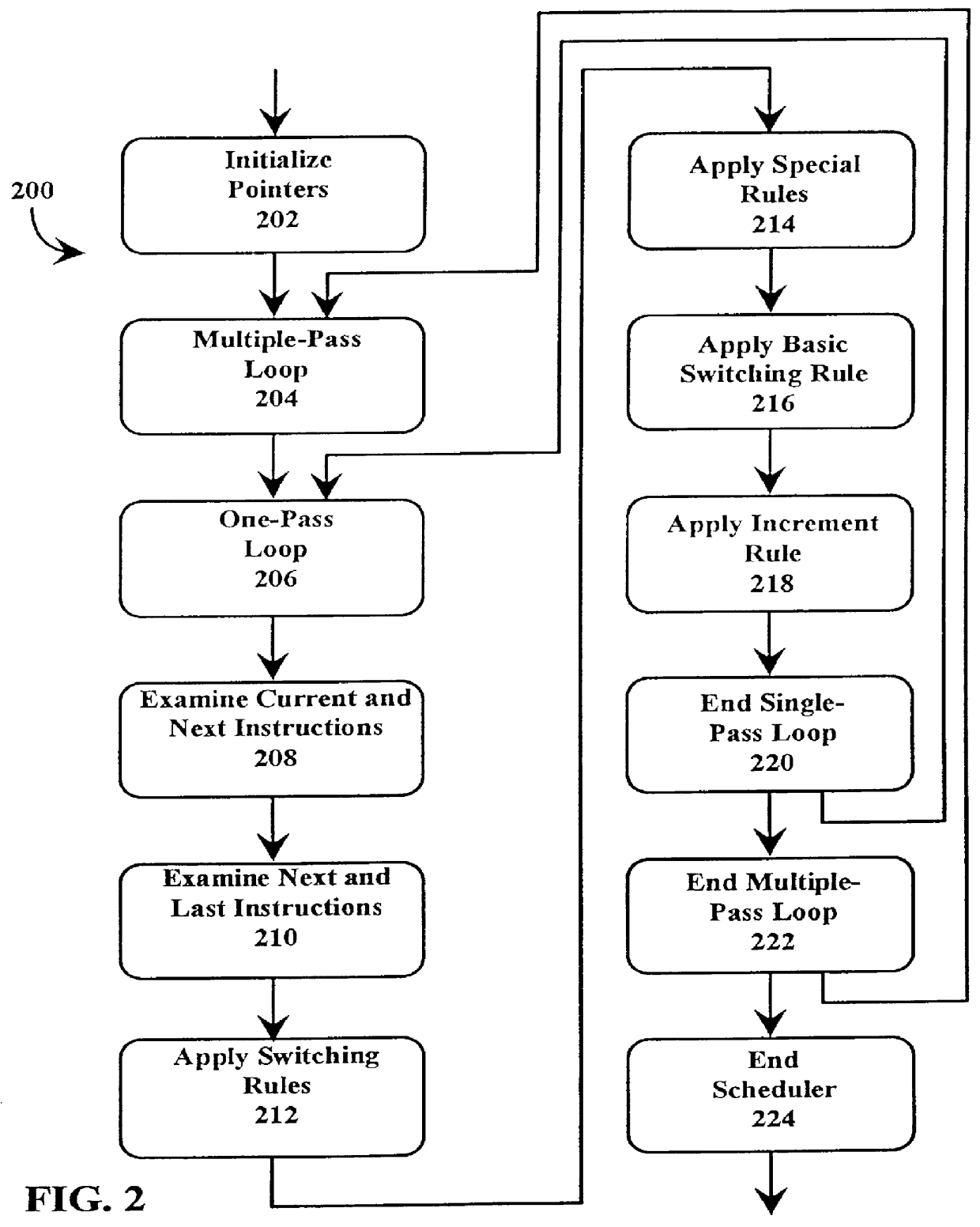
A just-in-time (JIT) compiler typically generates code from bytecodes that have a sequence of assembly instructions forming a "template". It has been discovered that a just-in-time (JIT) compiler generates a small number, approximately 2.3, assembly instructions per bytecode. It has also been discovered that, within a template, the assembly instructions are almost always dependent on the next assembly instruction. The absence of a dependence between instructions of different templates is exploited to increase the size of issue groups using scheduling. A fast method for scheduling program instructions is useful in just-in-time (JIT) compilers. Scheduling of instructions is generally useful for just-in-time (JIT) compilers that are targeted to in-order superscalar processors because the code generated by the JIT compilers is often sequential in nature. The disclosed fast scheduling method has a complexity, and therefore an execution time, that is proportional to the number of instructions in an instruction block (N complexity), a substantial improvement in comparison to the N2 complexity of conventional compiler schedulers. The described fast scheduler advantageously reorders instructions with a single pass, or few passes, through a basic instruction block while a conventional compiler scheduler such as the DAG scheduler must iterate over an instruction basic block many times. A fast scheduler operates using an analysis of a sliding window of three instructions, applying two rules within the three instruction window to determine when to reorder instructions. The analysis includes acquiring the opcodes and operands of each instruction in the three instruction window, and determining register usage and definition of the operands of each instruction with respect to the other instructions within the window. The rules are applied to determine ordering of the instructions within the window.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
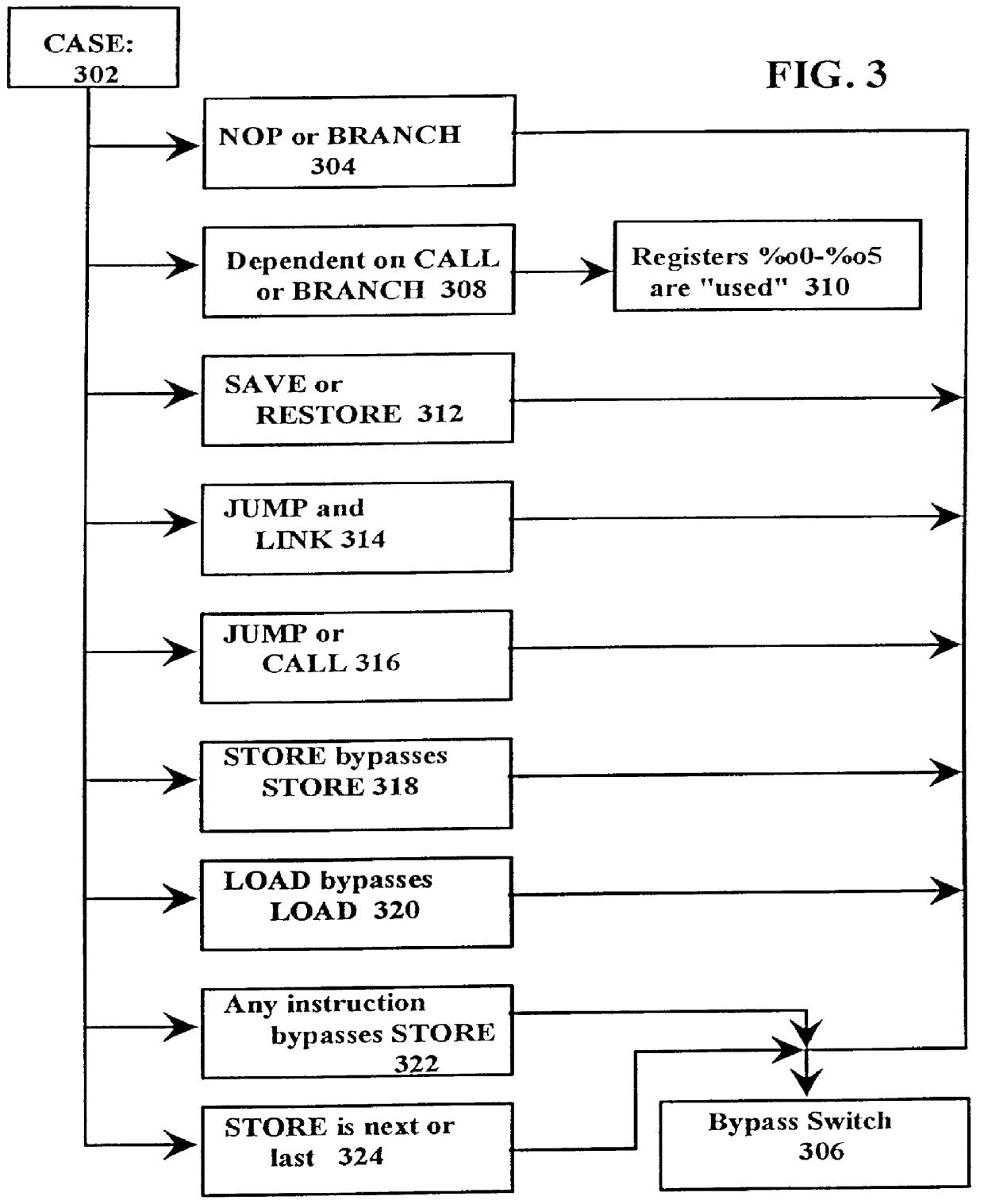
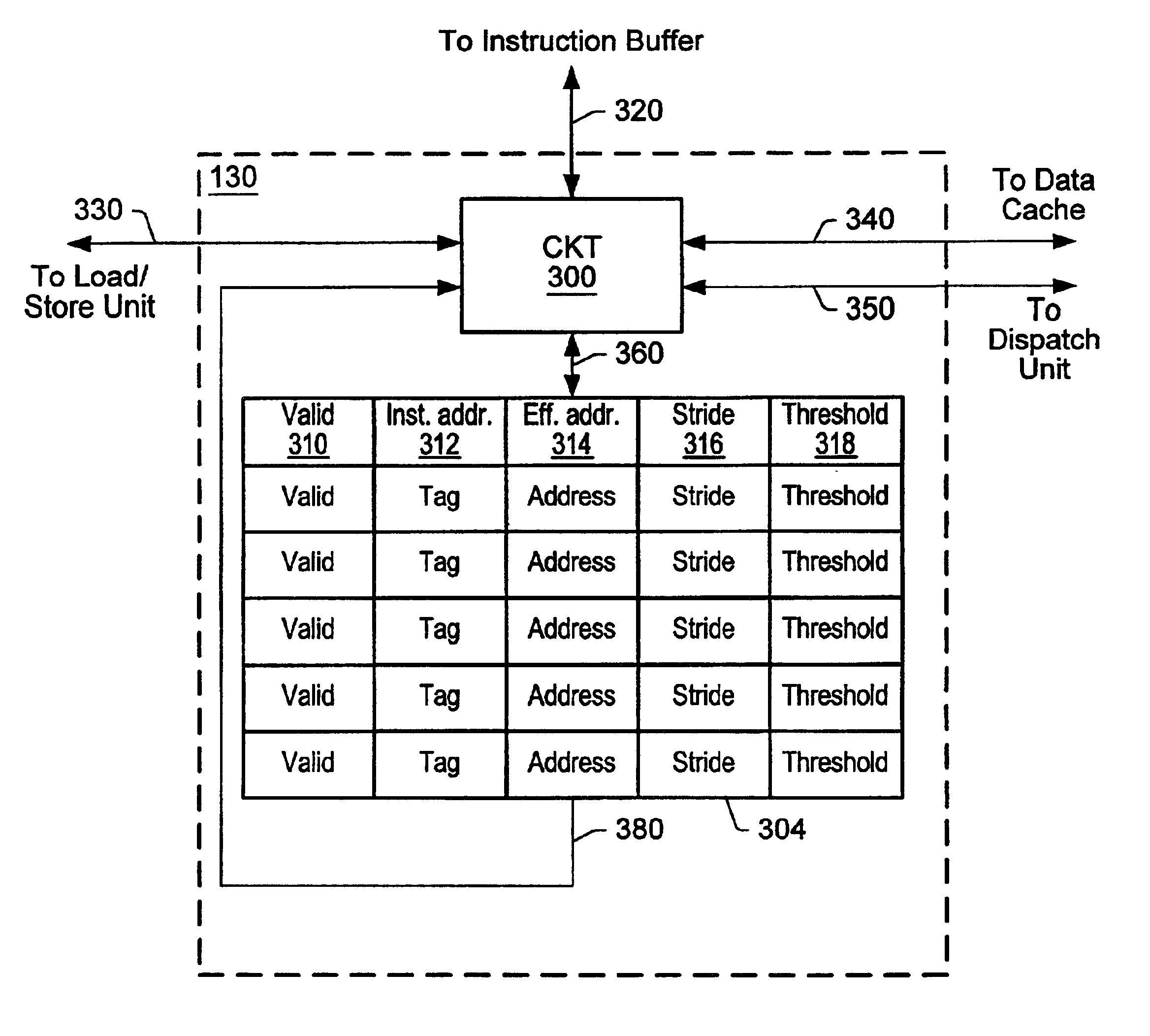
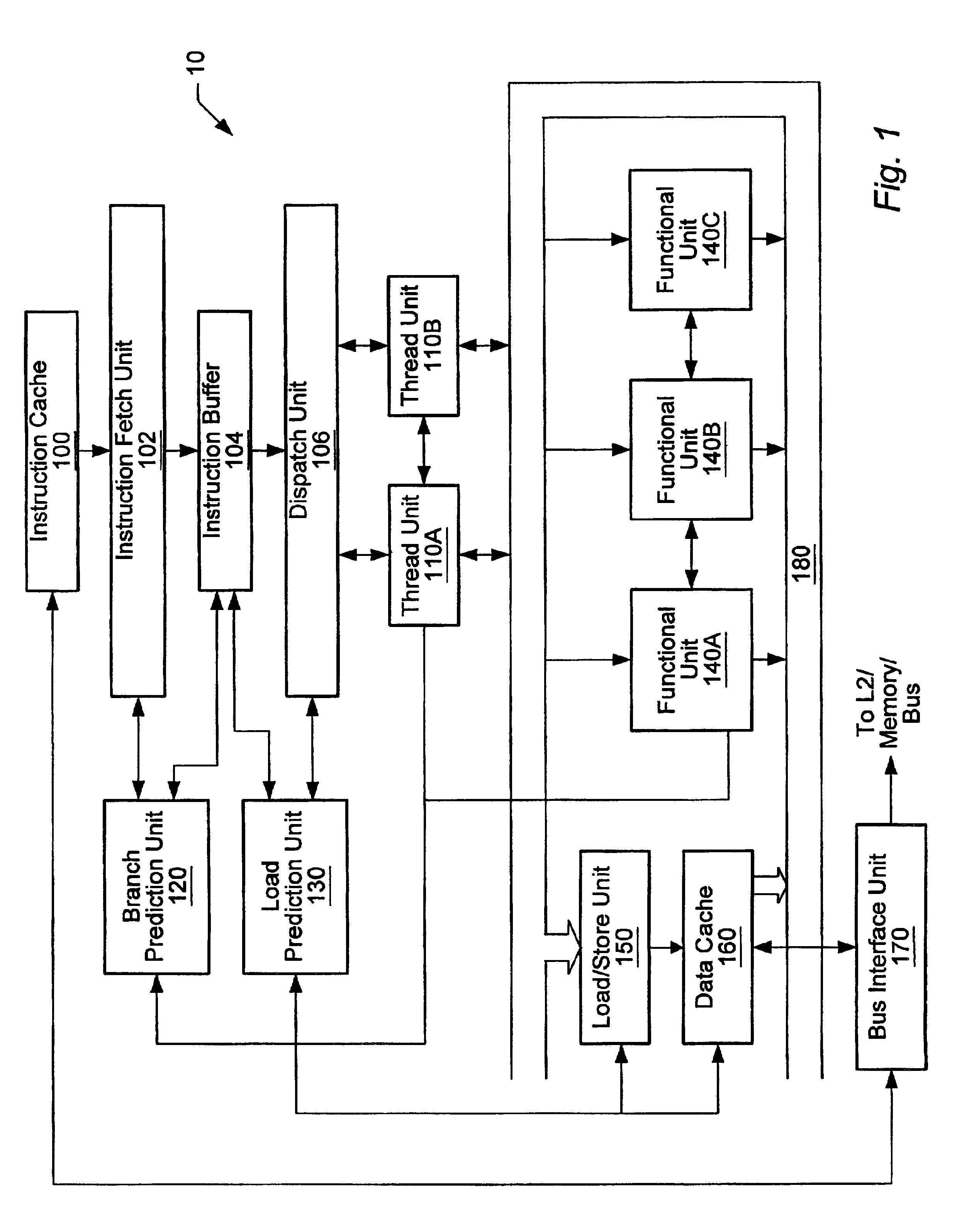
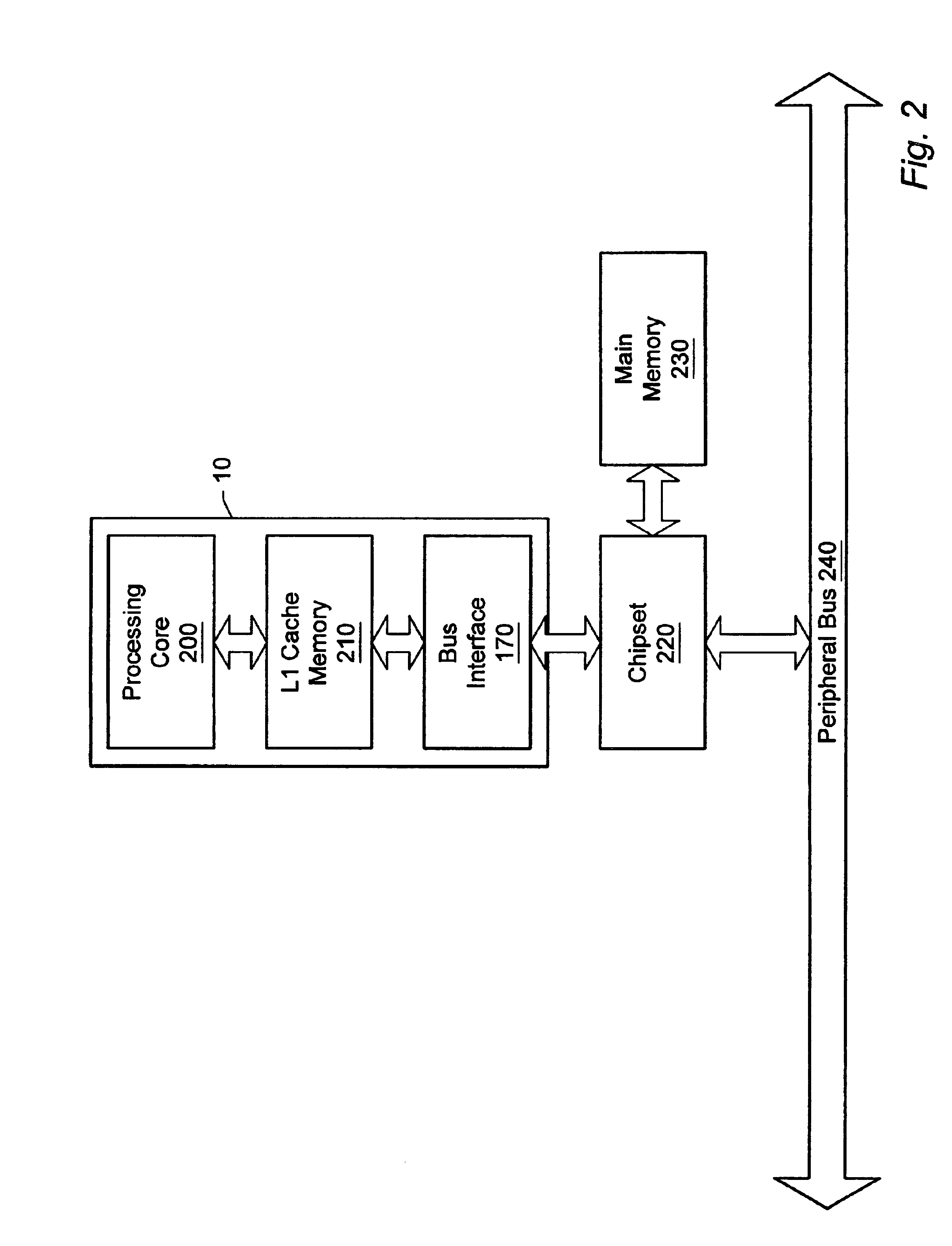
Threshold-based load address prediction and new thread identification in a multithreaded microprocessor
ActiveUS6907520B2Memory access latencyTake advantage ofMemory architecture accessing/allocationDigital computer detailsLoad instructionInstruction window
A method and apparatus for predicting load addresses and identifying new threads of instructions for execution in a multithreaded processor. A load prediction unit scans an instruction window for load instructions. A load prediction table is searched for an entry corresponding to a detected load instruction. If an entry is found in the table, a load address prediction is made for the load instruction and conveyed to the data cache. If the load address misses in the cache, the data is prefetched. Subsequently, if it is determined that the load prediction was incorrect, a miss counter in the corresponding entry in the load prediction table is incremented. If on a subsequent detection of the load instruction, the miss counter has reached a threshold, the load instruction is predicted to miss. In response to the predicted miss, a new thread of instructions is identified for execution.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Processor provided with a data value prediction circuit and a branch prediction circuit
InactiveUS6516409B1Digital computer detailsNext instruction address formationProcessor registerInstruction window
A processor includes at least one functional unit configured to execute an instruction. The processor also includes an instruction window configured to supply the instruction to the functional unit. The processor further includes a register file configured such that data and a result of execution of the instruction are temporarily stored in the register file. The processor still further includes a branch prediction circuit having a branch execution unit and a branch prediction table. The processor also includes a data value prediction circuit configured to predict a first operand value which will be used by the functional unit and a second operand value which will be used by the branch execution unit to predict a direction of a branch and to store the direction of the branch in the branch prediction table. With such a processor, a branch prediction is made by executing a branch instruction rather than by referring to the history of the branch instruction.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Scheduling threads
InactiveUS20120192195A1Easy to implementAvoiding thread starvationEnergy efficient ICTMultiprogramming arrangementsInstruction windowMulti-core processor
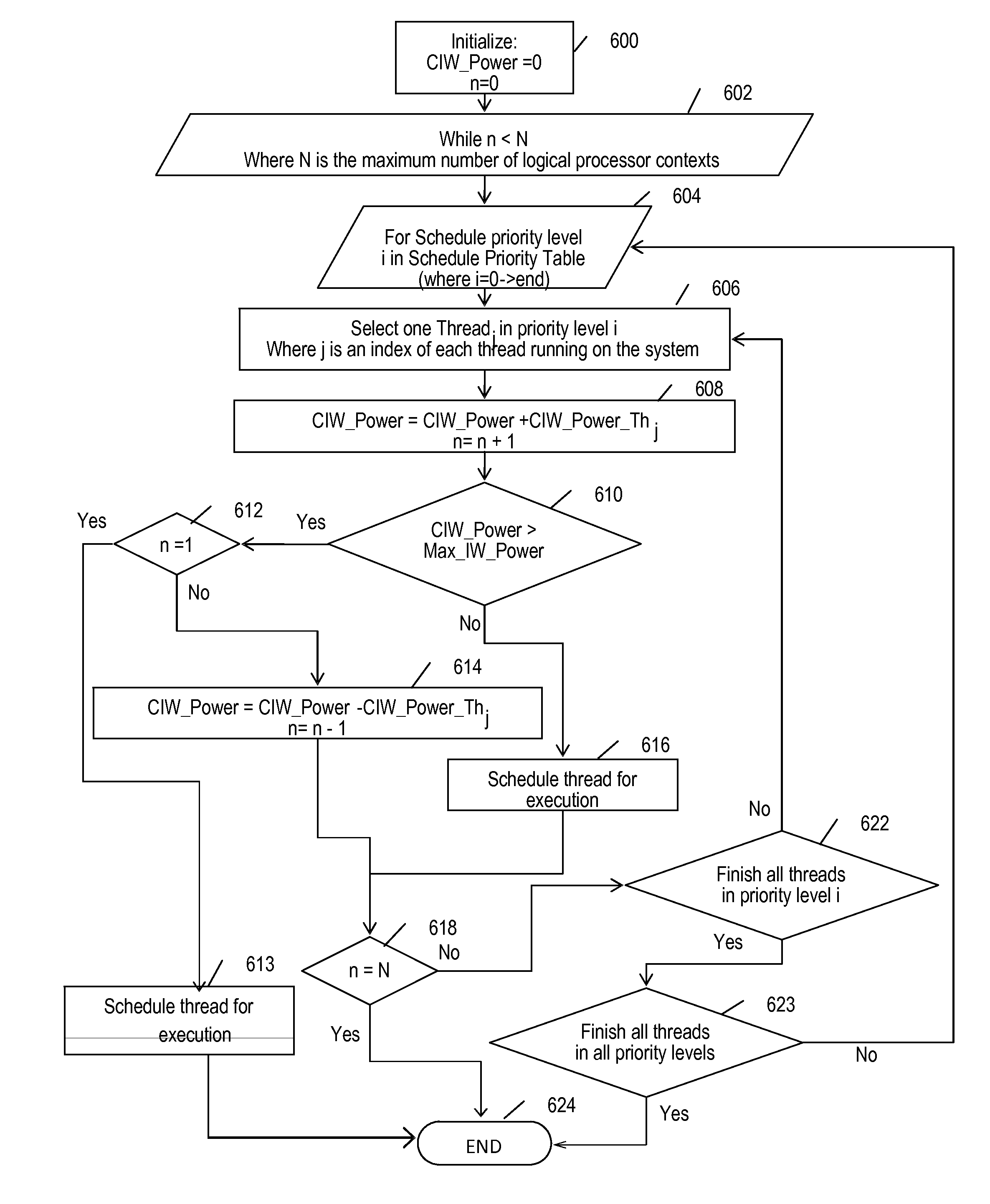
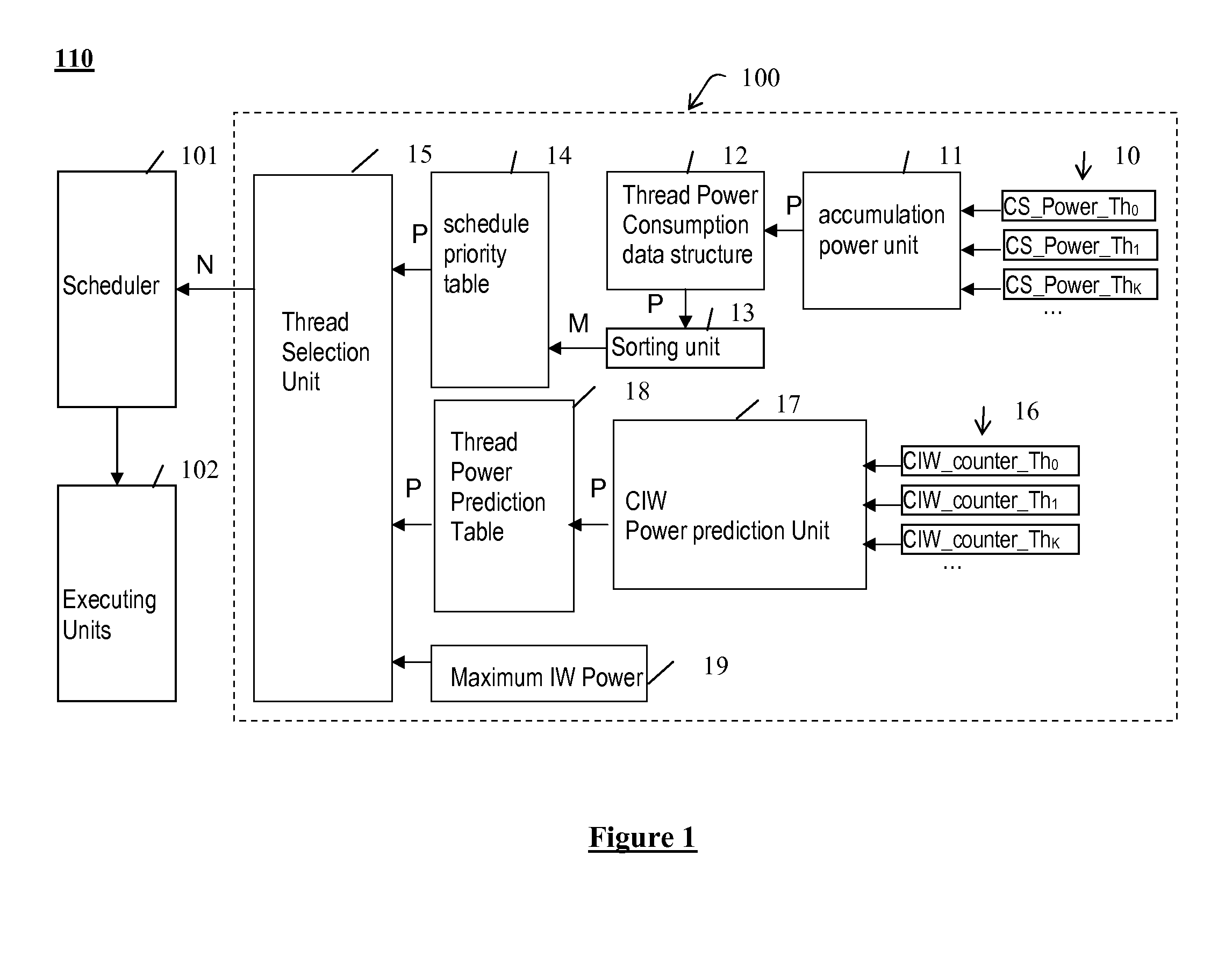
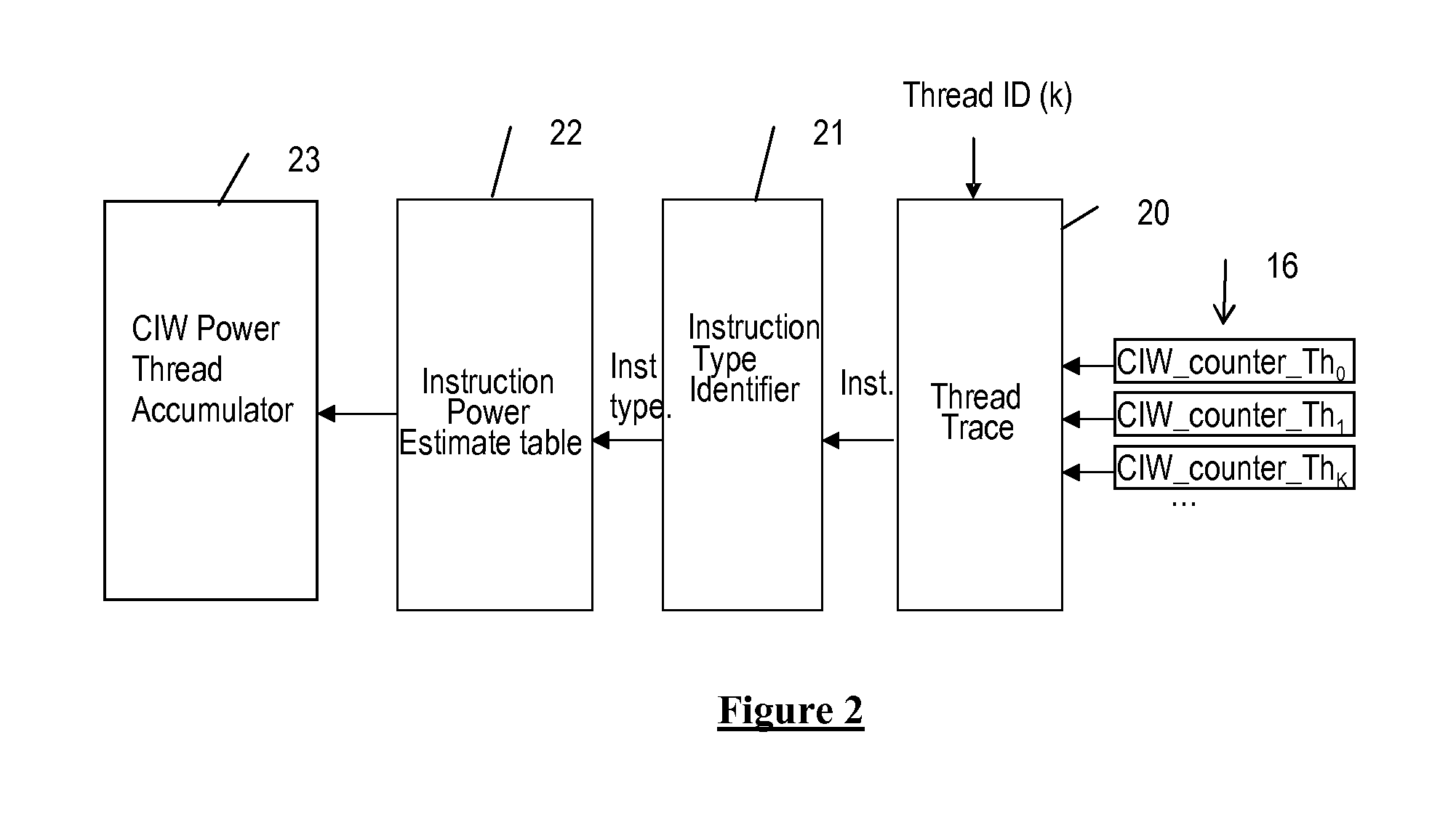
Scheduling threads in a multi-threaded / multi-core processor having a given instruction window, and scheduling a predefined number N of threads among a set of M active threads in each context switch interval are provided. The actual power consumption of each running thread during a given context switch interval is determined, and a predefined priority level is associated with each thread among the active threads based on the actual power consumption determined for the threads. The power consumption expected for each active thread during the next context switch interval in the current instruction window (CIW_Power_Th) is predicted, and a set of threads to be scheduled among the active threads are selected from the priority level associated with each active thread and the power consumption predicted for each active thread in the current instruction window.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and device for realizing reading command execution
ActiveCN102364431AReduce execution latencyImprove performanceMachine execution arrangementsInstruction windowBloom filter
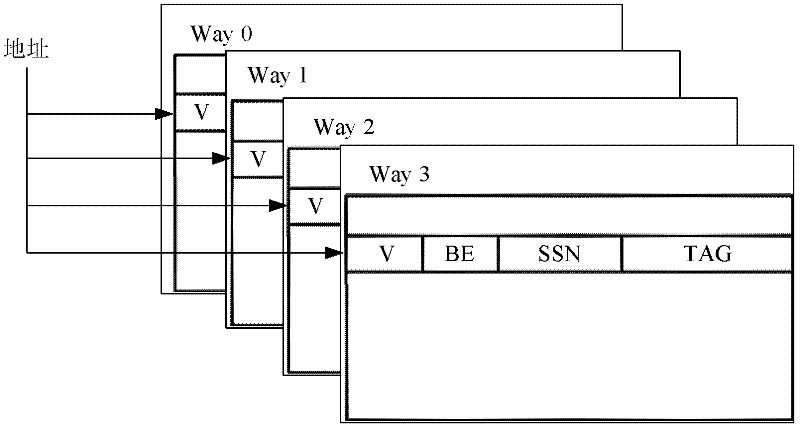
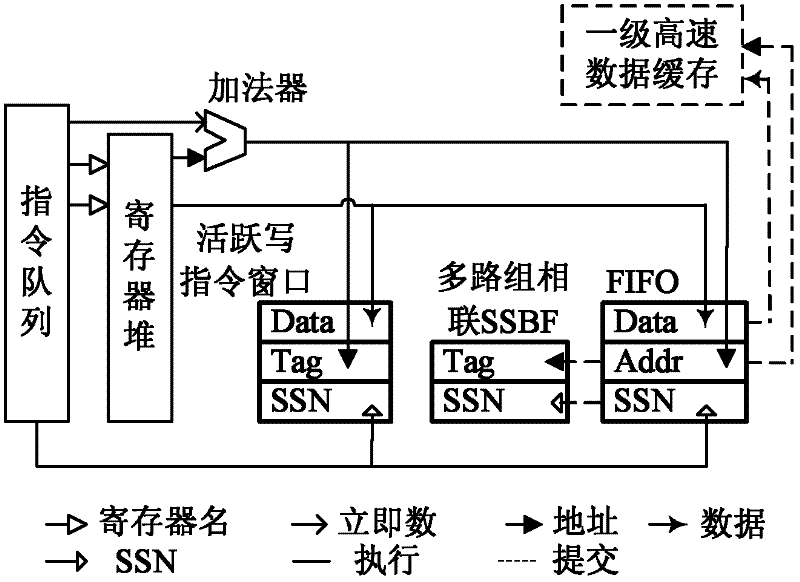
The invention discloses a method and a device for realizing reading command execution. The method comprises the following steps of: in an execution stage of a write command, recording the information of the write command by adopting a corresponding path in groups of an active write command window with a plurality of parallel path groups, and replacing the oldest write command records in all paths of the group; and when the write command enters a filtering pipeline stage, recording the information of the write command by adopting a corresponding path is a corresponding group in a write command sequence Bloom filter with a plurality of parallel path groups, and replacing the oldest write command records in all paths of the group. By the method and the device, the execution delay of a reading command can be shortened by realizing large-area presumptive access data forwarding, thereby effectively improving the read command execution performance of a processor.
Owner:BEIJING PKUNITY MICROSYST TECH
Scheduling threads based on an actual power consumption and a predicted new power consumption
InactiveUS8677361B2Easy to implementAvoid hungerEnergy efficient ICTProgram initiation/switchingInstruction windowMulti-core processor
Owner:IBM CORP
Structure and method for achieving very large lookahead instruction window via non-sequential instruction fetch and issue
ActiveUS7650485B1Improve processor performanceProgram initiation/switchingDigital computer detailsProcessor registerInstruction window
A multithreading processor achieves a very large lookahead instruction window by allowing non-sequential fetch and processing of the dynamic instruction stream. A speculative thread is spawned at a specified point in the dynamic instruction stream and the instructions subsequent to the specified point are speculatively executed so that these instructions are fetched and issued out of sequential order. Very minimal modifications to existing processor design of a multithreading processor are required to achieve the very large lookahead instruction window. The modifications include changes to the control logic of the issue unit, only three additional bits in the register scoreboard.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
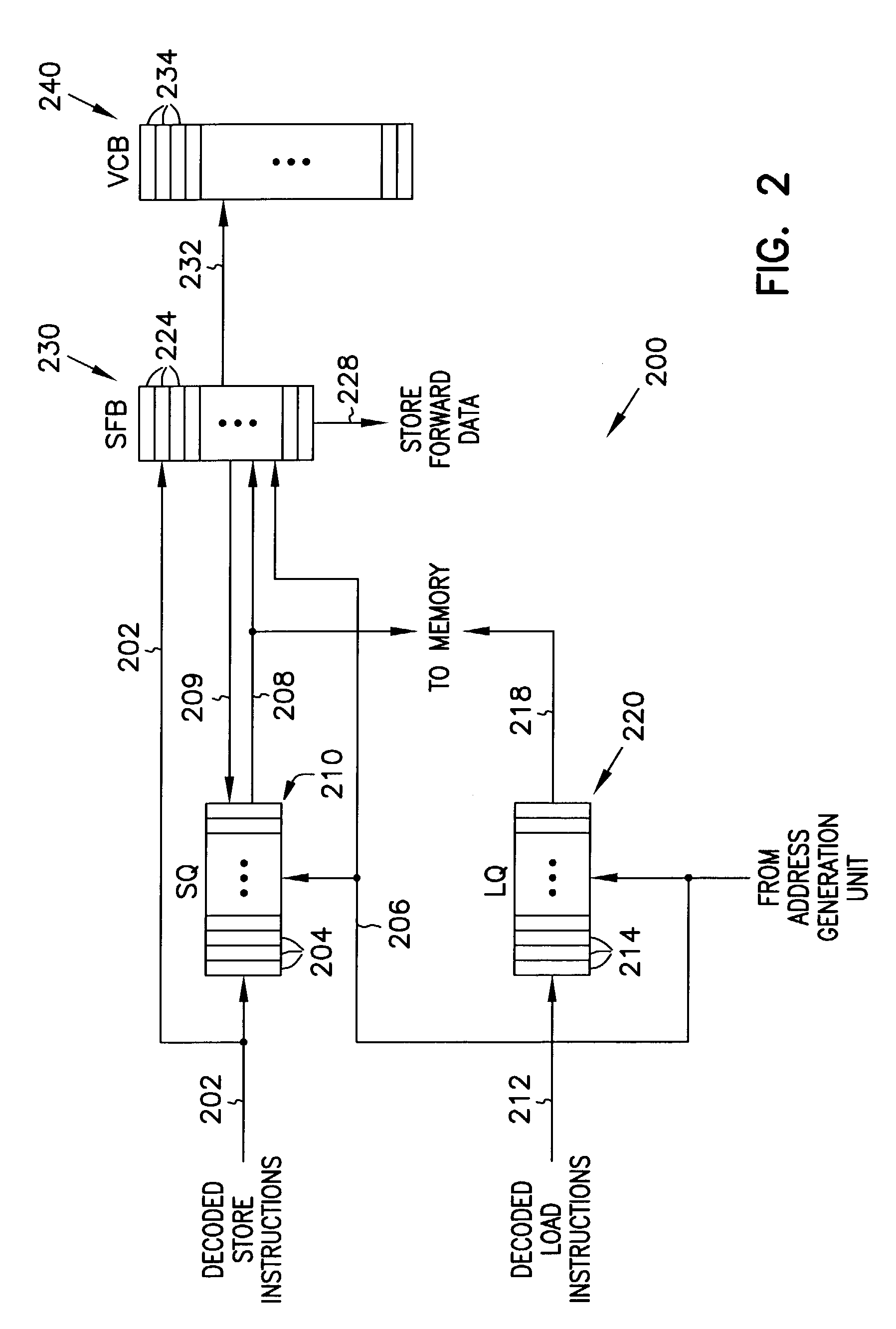
Memory disambiguation for large instruction windows
InactiveUS7418552B2Digital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionLoad instructionInstruction window
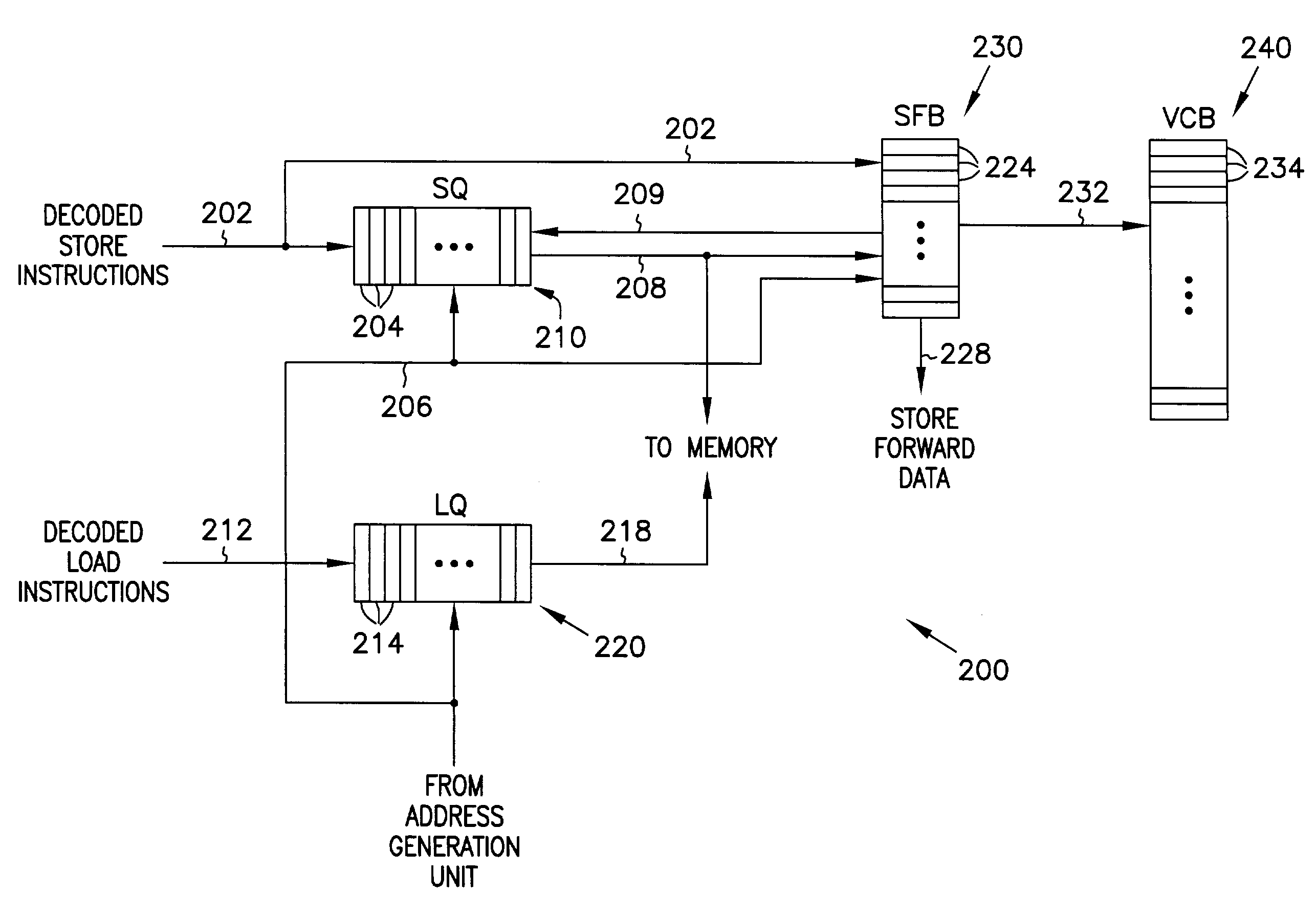
A memory disambiguation apparatus includes a store queue, a store forwarding buffer, and a version count buffer. The store queue includes an entry for each store instruction in the instruction window of a processor. Some store queue entries include resolved store addresses, and some do not. The store forwarding buffer is a set-associative buffer that has entries allocated for store instructions as store addresses are resolved. Each entry in the store forwarding buffer is allocated into a set determined in part by a subset of the store address. When the set in the store forwarding buffer is full, an older entry in the set is discarded in favor of the newly allocated entry. A version count buffer including an array of overflow indicators is maintained to track overflow occurrences. As load addresses are resolved for load instructions in the instruction window, the set-associative store forwarding buffer can be searched to provide memory disambiguation.
Owner:INTEL CORP
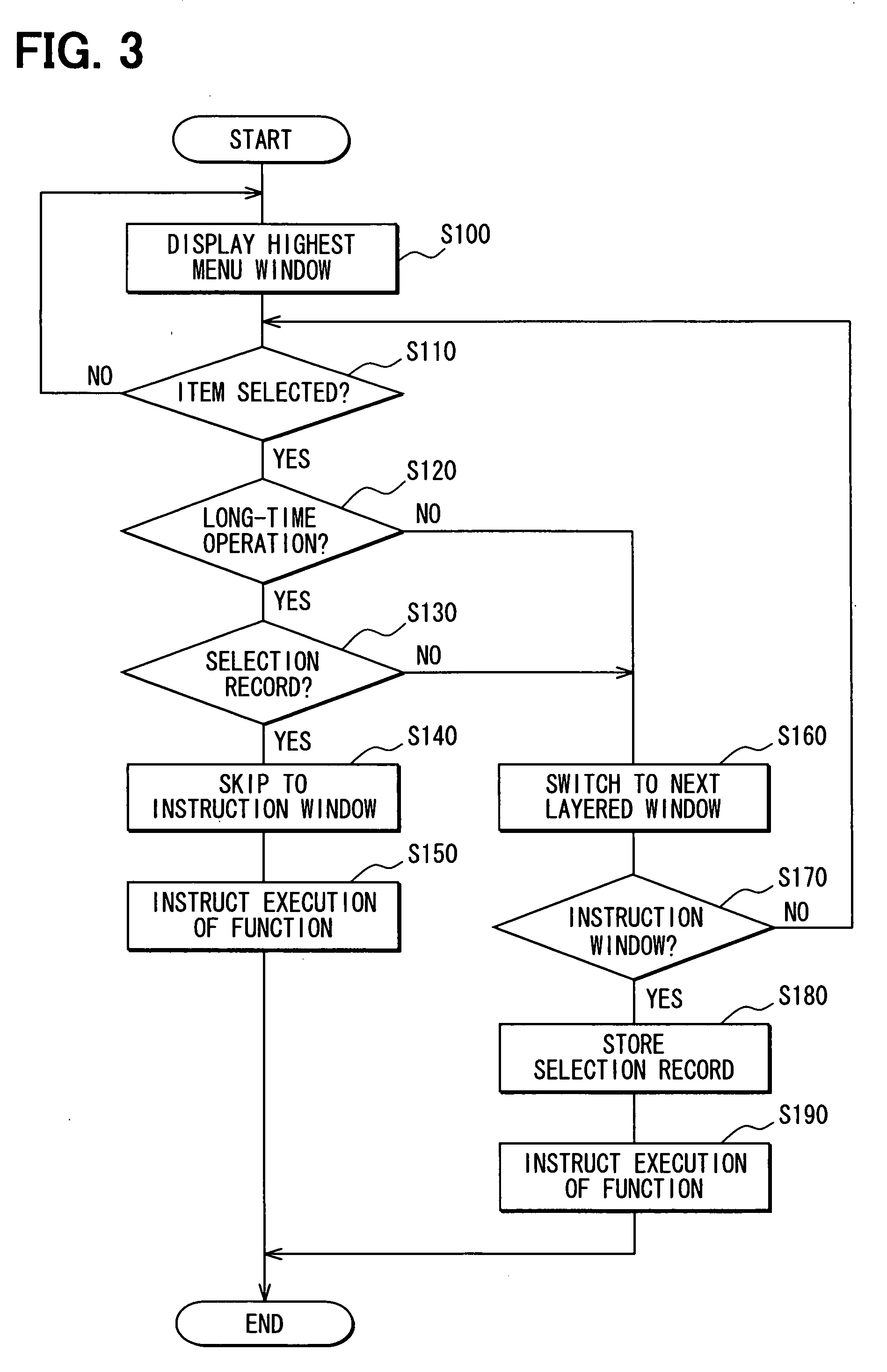
Operation system
InactiveUS20070186190A1Easy transitionEasy to operateNavigation instrumentsInput/output processes for data processingOperational systemComputer graphics (images)
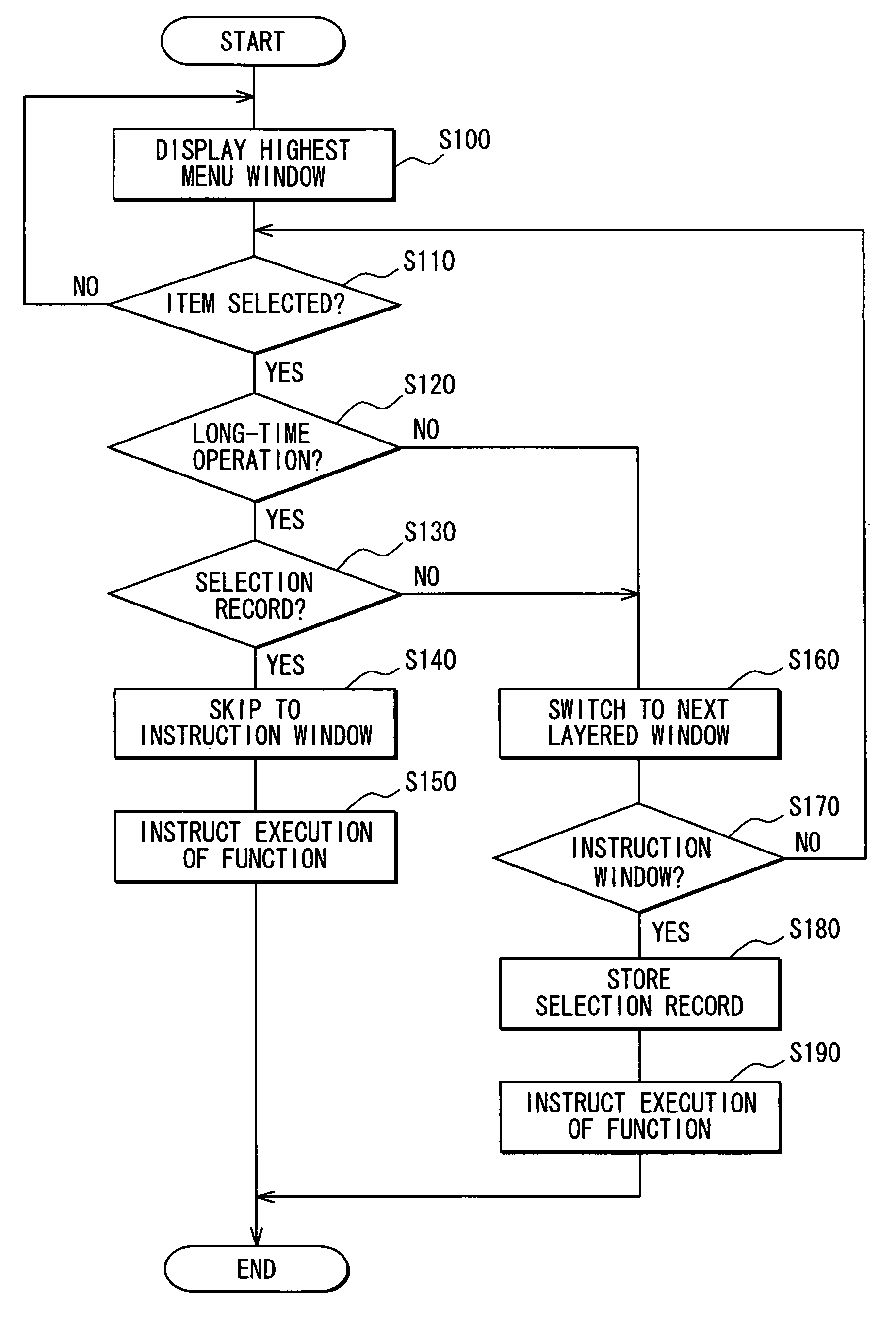
In a navigation device, multi-layered menu windows are sequentially displayed in a display unit and narrowed down by repeatedly selecting an item in each menu window to thereby consequently display a certain instruction window for instructing an execution of a function. This selection procedure is stored such that a selection record, which indicates an association with the certain instruction window, is assigned to each of the selected items in the displayed menu windows. When a certain item assigned the selection record is operated more than a predetermined time period, the currently displayed menu window including the certain item is switched to the certain instruction window without intermediate menu windows displayed. Thus, when intending to display the certain instruction window, which was previously displayed after the selection procedure, a user can significantly simplify the selection procedure and decrease workloads.
Owner:DENSO CORP
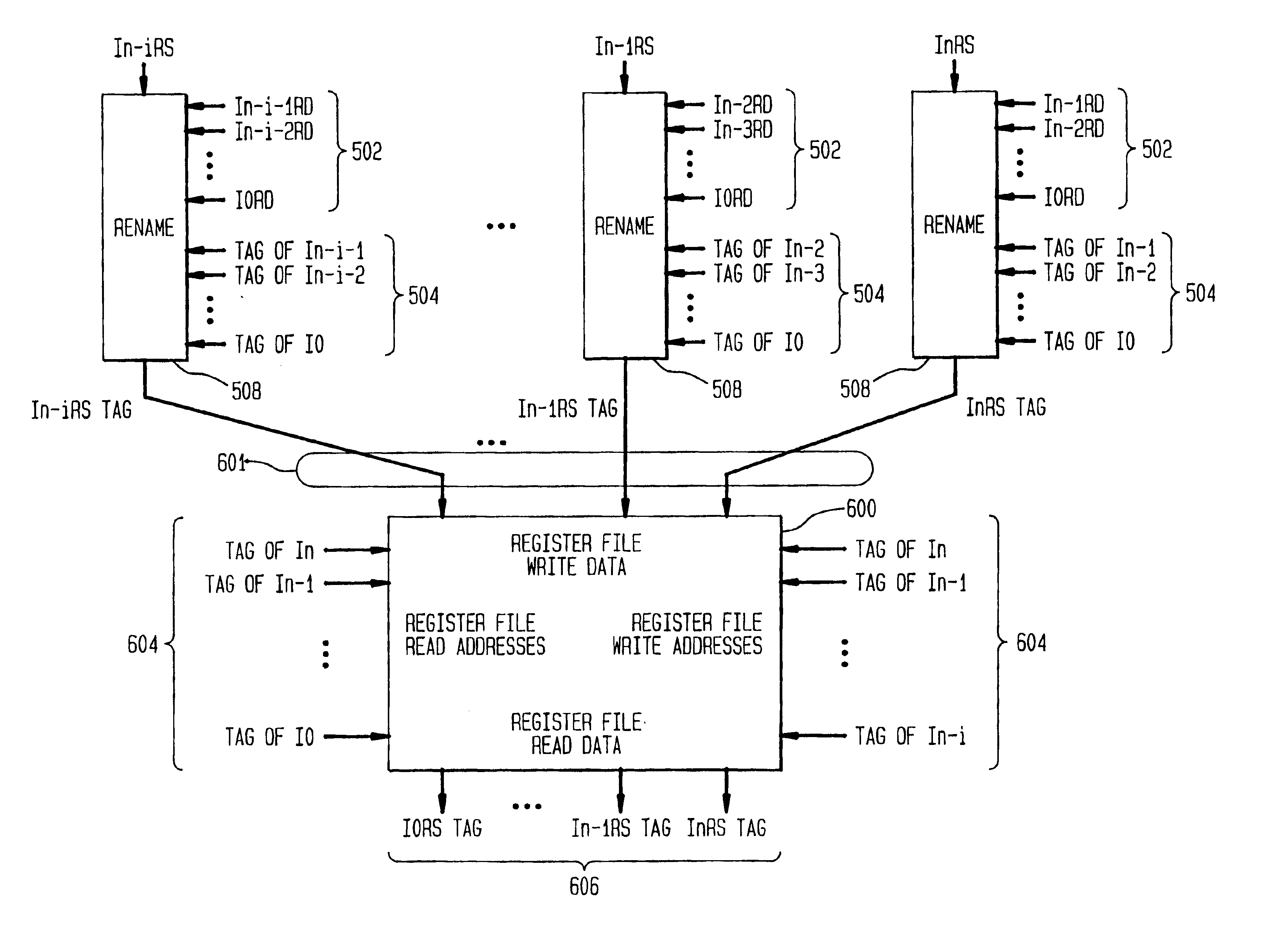
System and method for register renaming
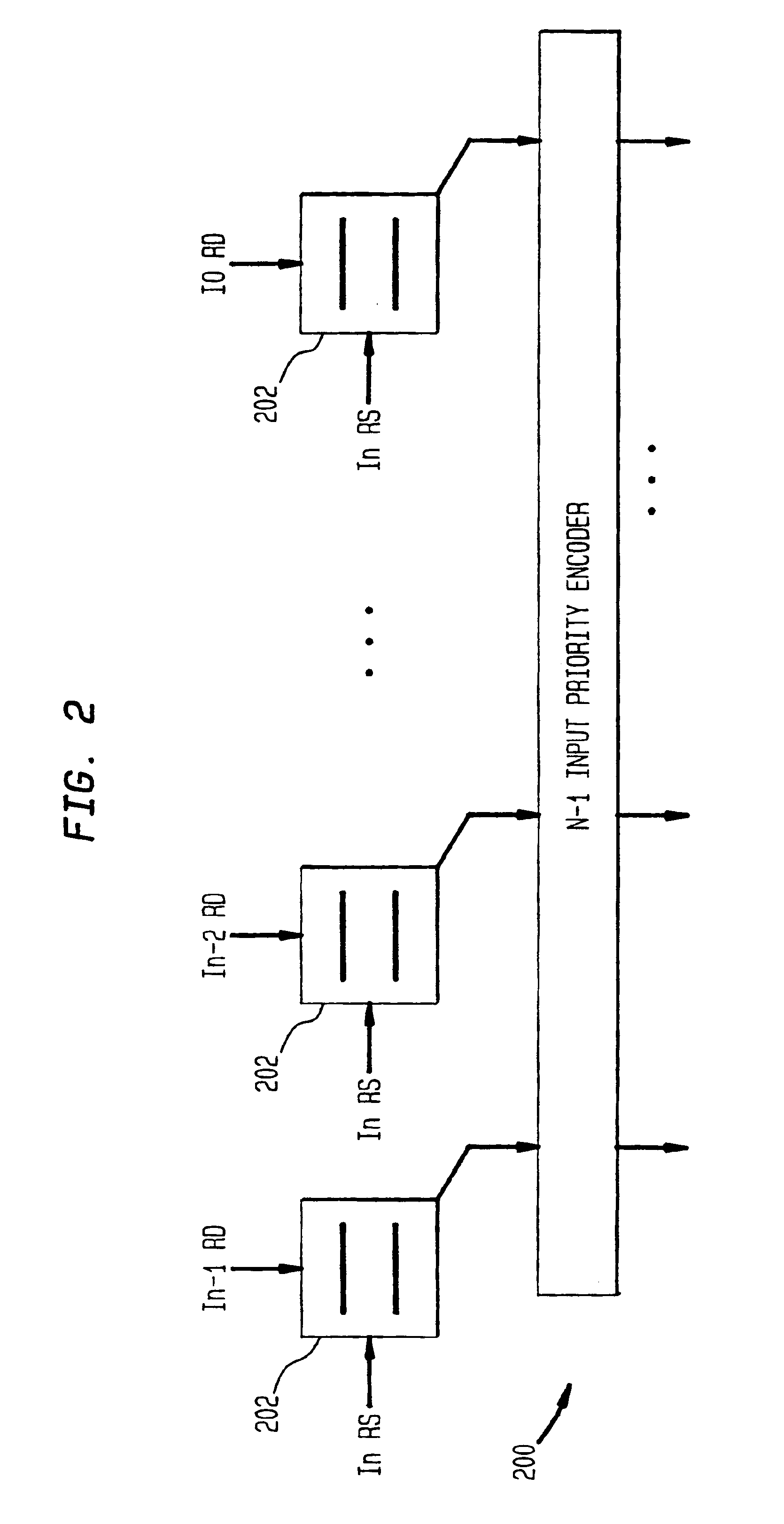
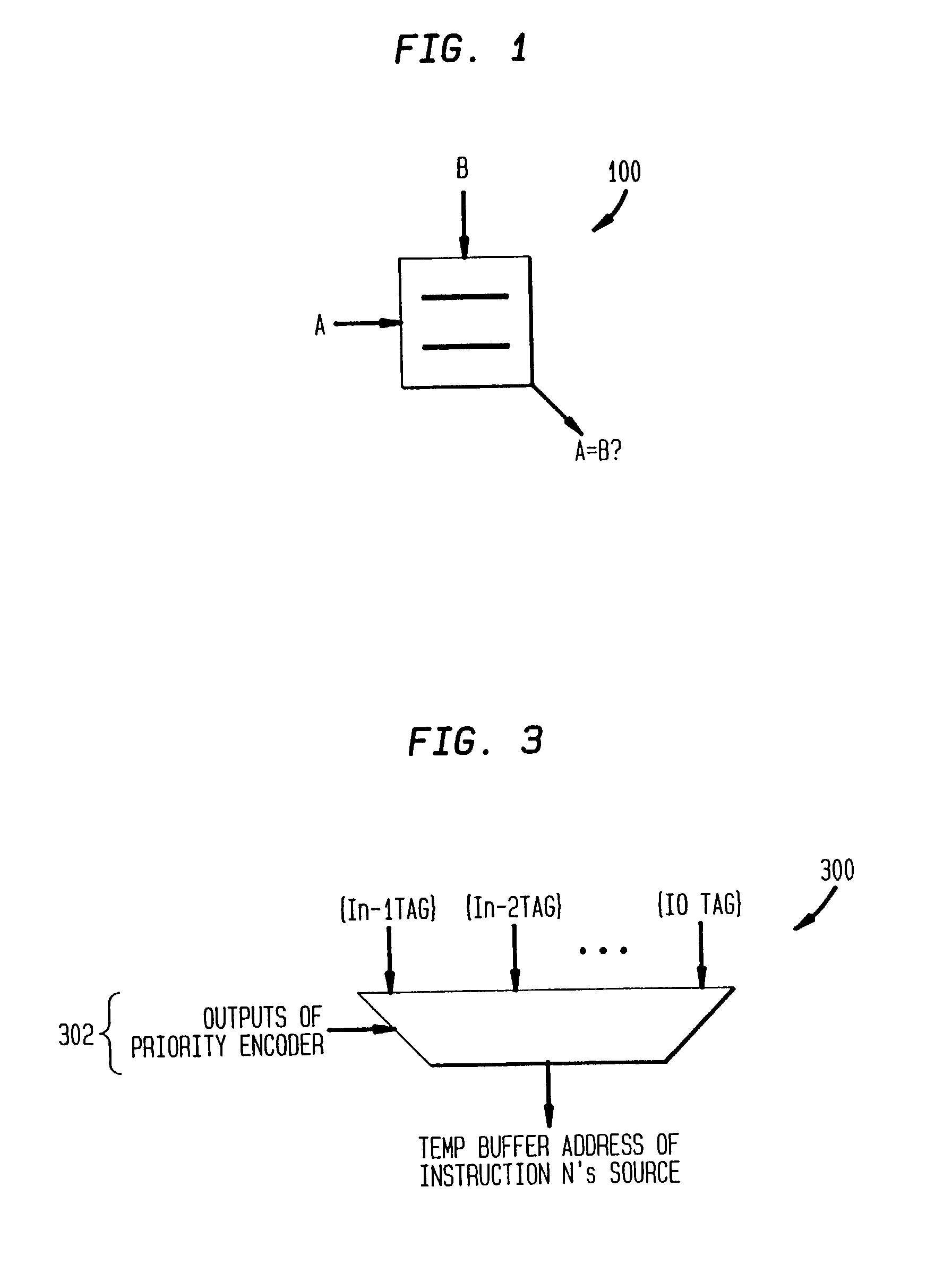
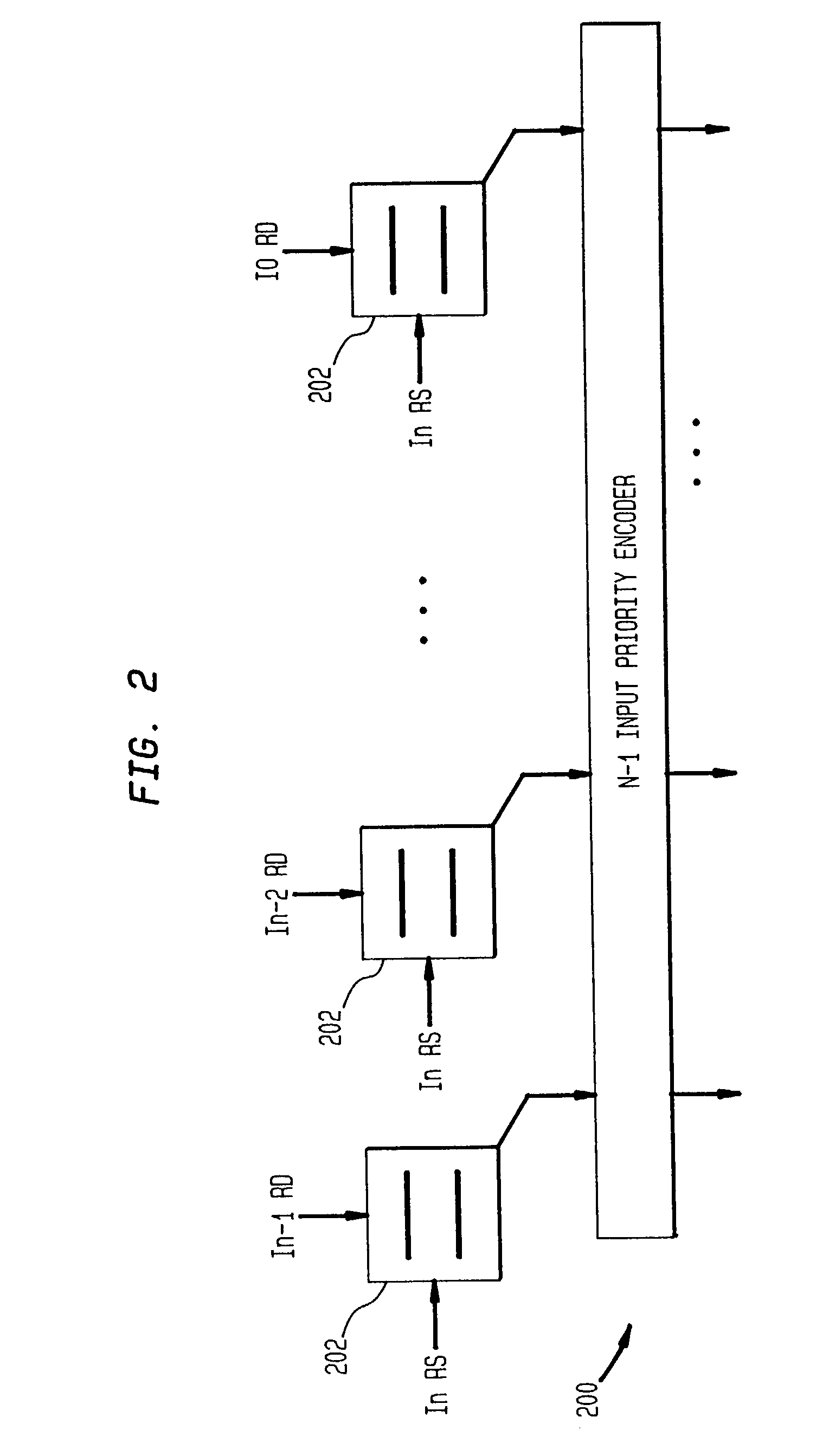
InactiveUS6922772B2Reduce in quantityInhibit outputDigital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionInstruction windowInstruction distribution
A system and method for performing register renaming of source registers in a processor having a variable advance instruction window for storing a group of instructions to be executed by the processor, wherein a new instruction is added to the variable advance instruction window when a location becomes available. A tag is assigned to each instruction in the variable advance instruction window. The tag of each instruction to leave the window is assigned to the next new instruction to be added to it. The results of instructions executed by the processor are stored in a temp buffer according to their corresponding tags to avoid output and anti-dependencies. The temp buffer therefore permits the processor to execute instructions out of order and in parallel. Data dependency checks for input dependencies are performed only for each new instruction added to the variable advance instruction window and register renaming is performed to avoid input dependencies.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
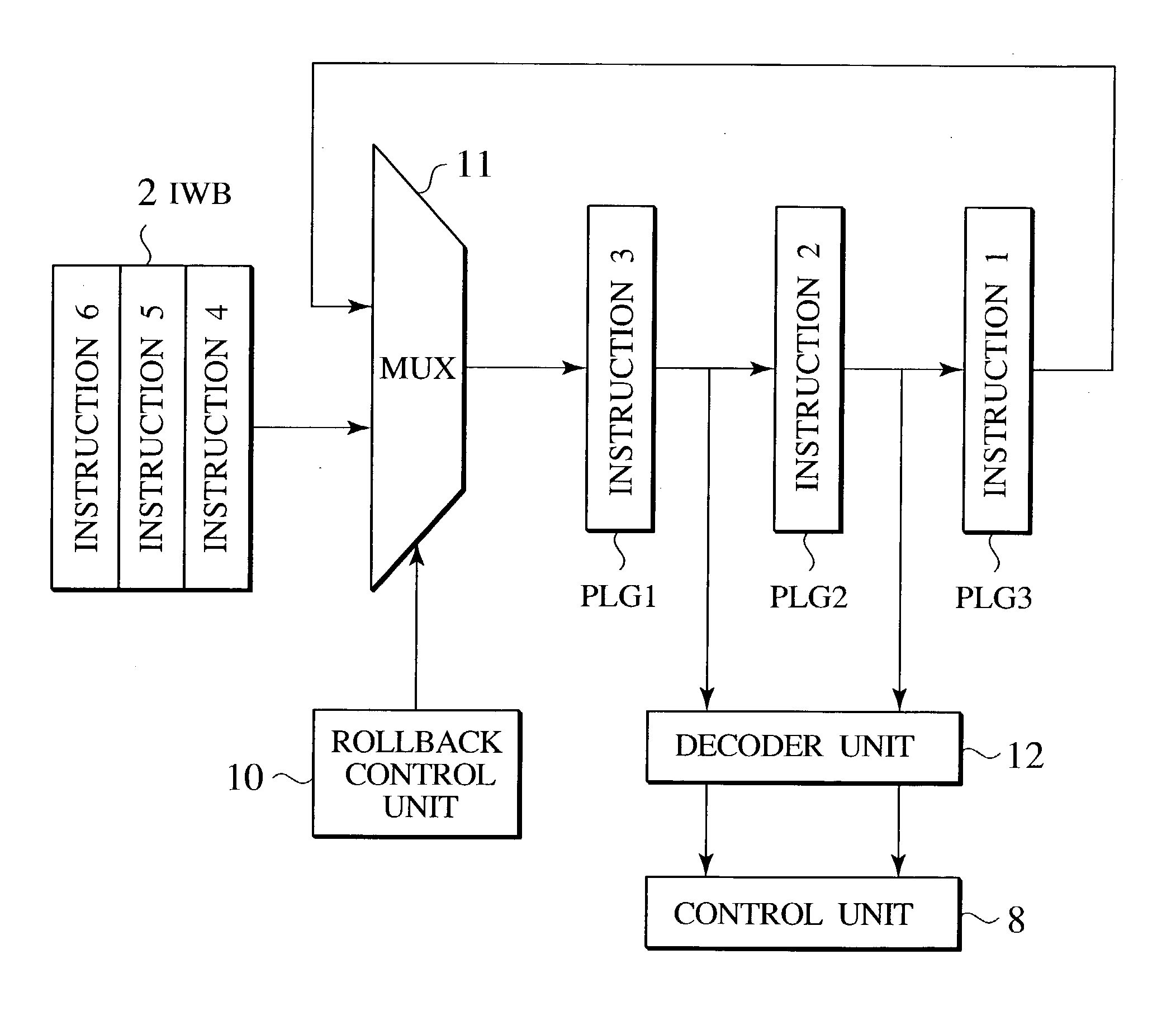
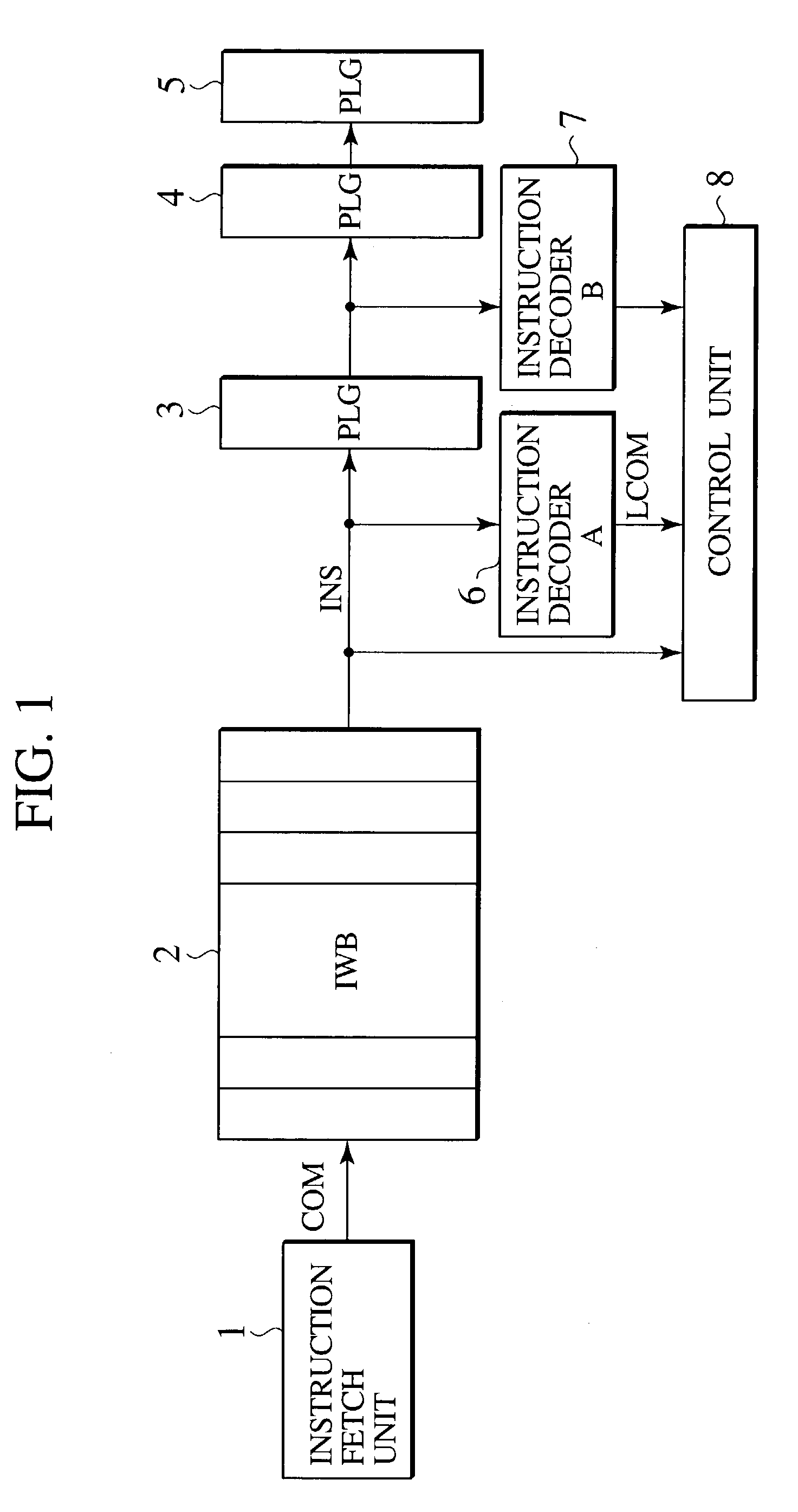
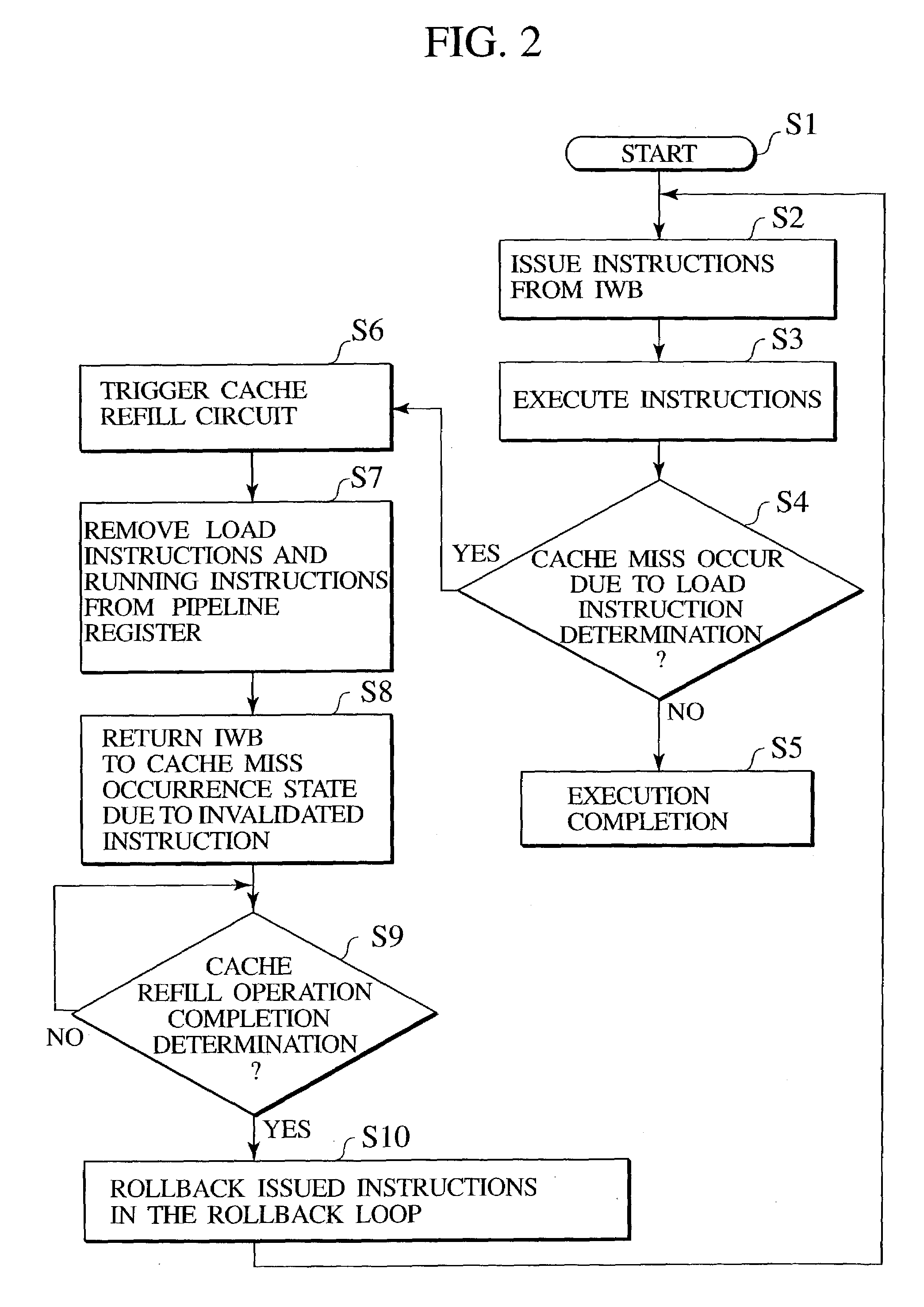
Instruction rollback processor system, an instruction rollback method and an instruction rollback program
InactiveUS20040168046A1Digital computer detailsNext instruction address formationMultiplexerInstruction window
An instruction rollback processor system according to the present invention is provided. The instruction rollback processor system includes: an instruction window buffer storing a plurality of instructions not yet executed and are arranged in a predetermined order; a multiplexer receiving an output of the instruction window buffer; and a rollback unit connected between the output side of the multiplexer and another input of the multiplexer.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
System and method for register renaming
InactiveUS6970995B2Reduce in quantityInhibit outputDigital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionInstruction windowData dependency
A system and method for performing register renaming of source registers in a processor having a variable advance instruction window for storing a group of instructions to be executed by the processor, wherein a new instruction is added to the variable advance instruction window when a location becomes available. A tag is assigned to each instruction in the variable advance instruction window. The tag of each instruction to leave the window is assigned to the next new instruction to be added to it. The results of instructions executed by the processor are stored in a temp buffer according to their corresponding tags to avoid output and anti-dependencies. The temp buffer therefore permits the processor to execute instructions out of order and in parallel. Data dependency checks for input dependencies are performed only for each new instruction added to the variable advance instruction window and register renaming is performed to avoid input dependencies.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
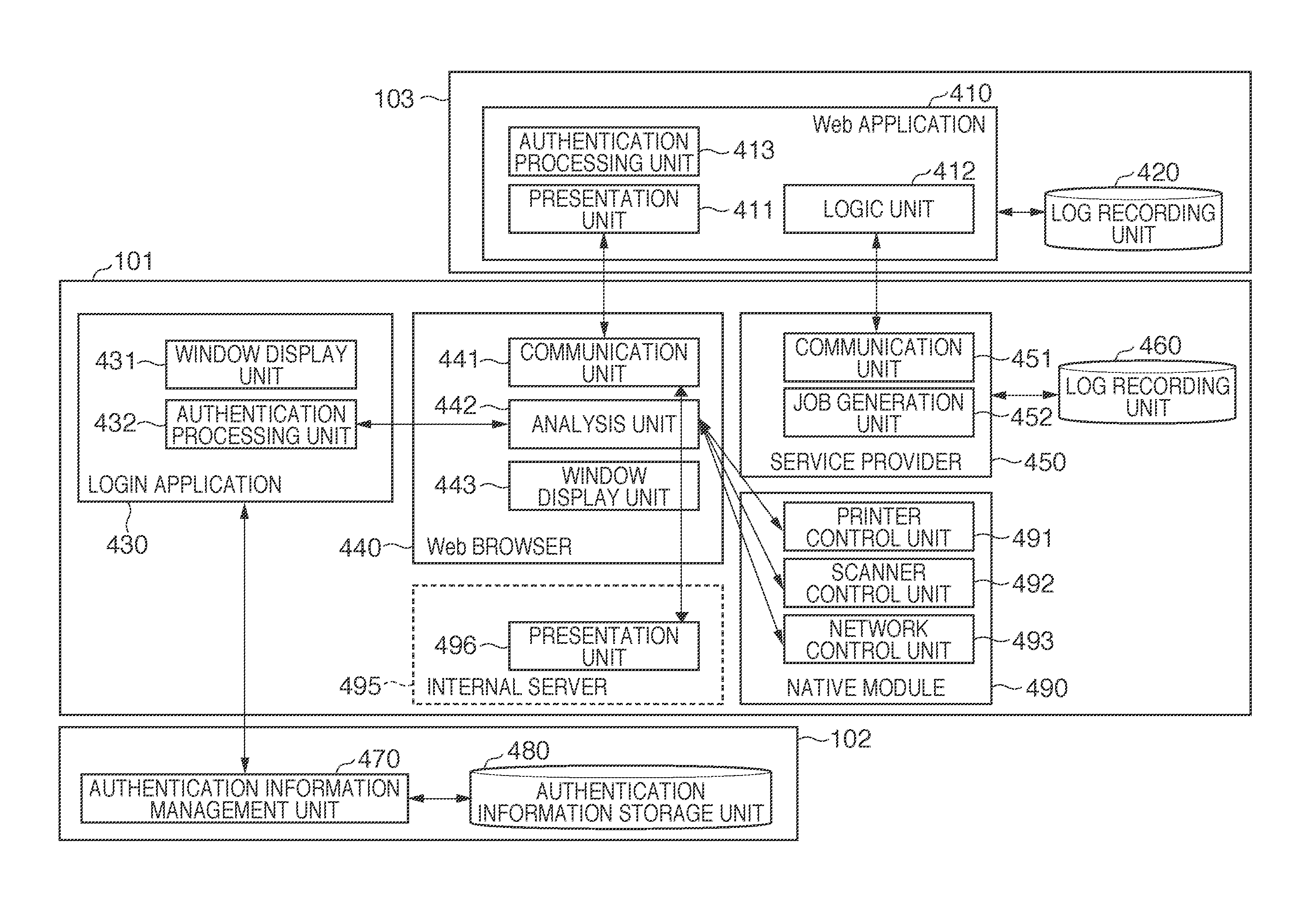
Information processing apparatus, user interface display control method of the same, and storage medium storing program
InactiveUS20110072356A1Eliminate the problemAppropriate displayMultiple digital computer combinationsInput/output processes for data processingComputer hardwareInformation processing
The device information of an information processing apparatus is acquired. It is determined, based on the acquired device information, whether a function of the information processing apparatus is usable. Upon determining that the function of the information processing apparatus is usable, a file to display the execution instruction window of processing using the function of the information processing apparatus is requested of the server. On the other hand, upon determining that the function of the information processing apparatus is not usable, a file to display a warning window is requested from the server.
Owner:CANON KK
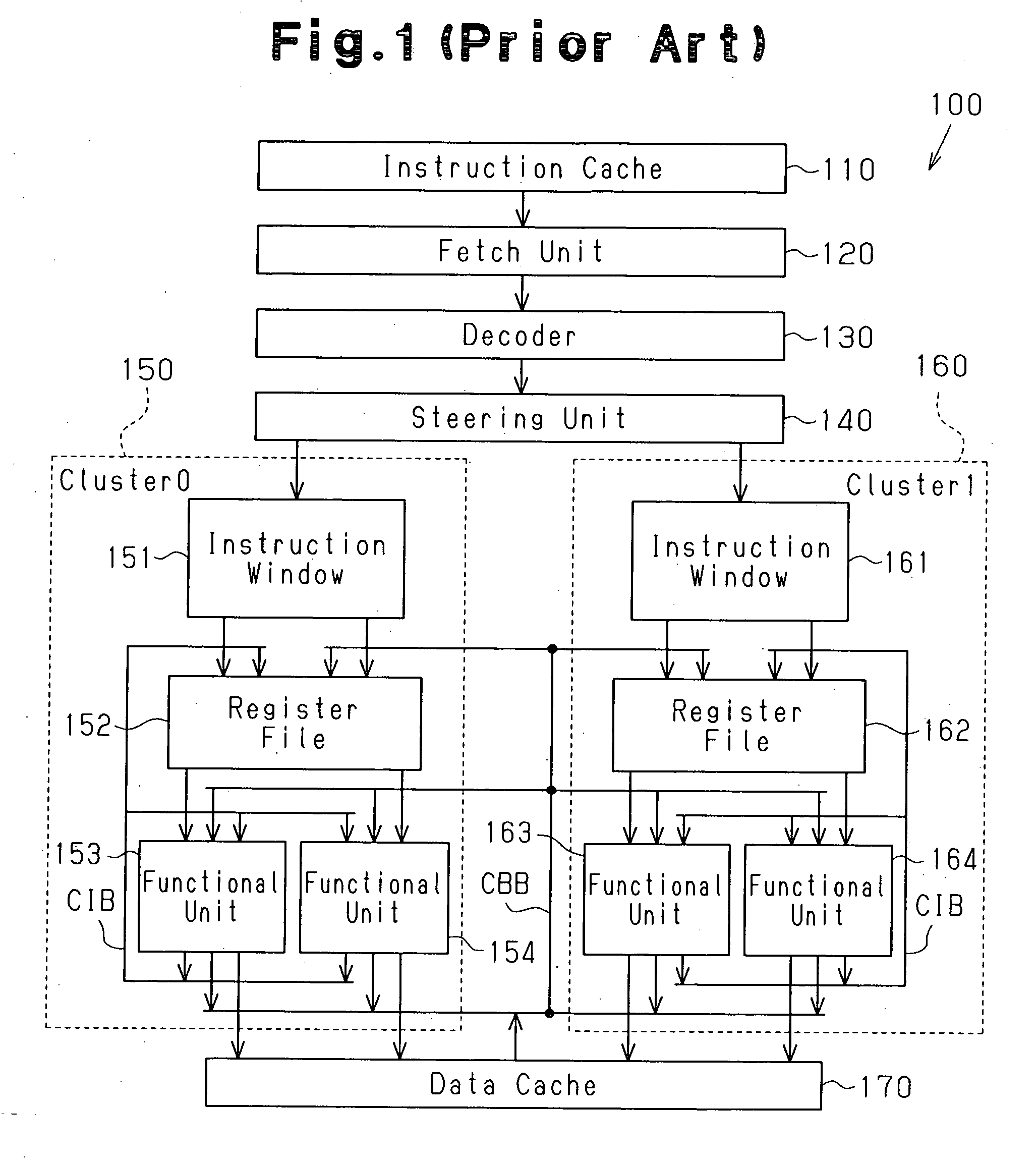
Clustered superscalar processor with communication control between clusters
InactiveUS7373485B2Improve performanceReduce error rateRegister arrangementsGeneral purpose stored program computerScalar processorProcessor register
Owner:NAGOYA UNIVERSITY
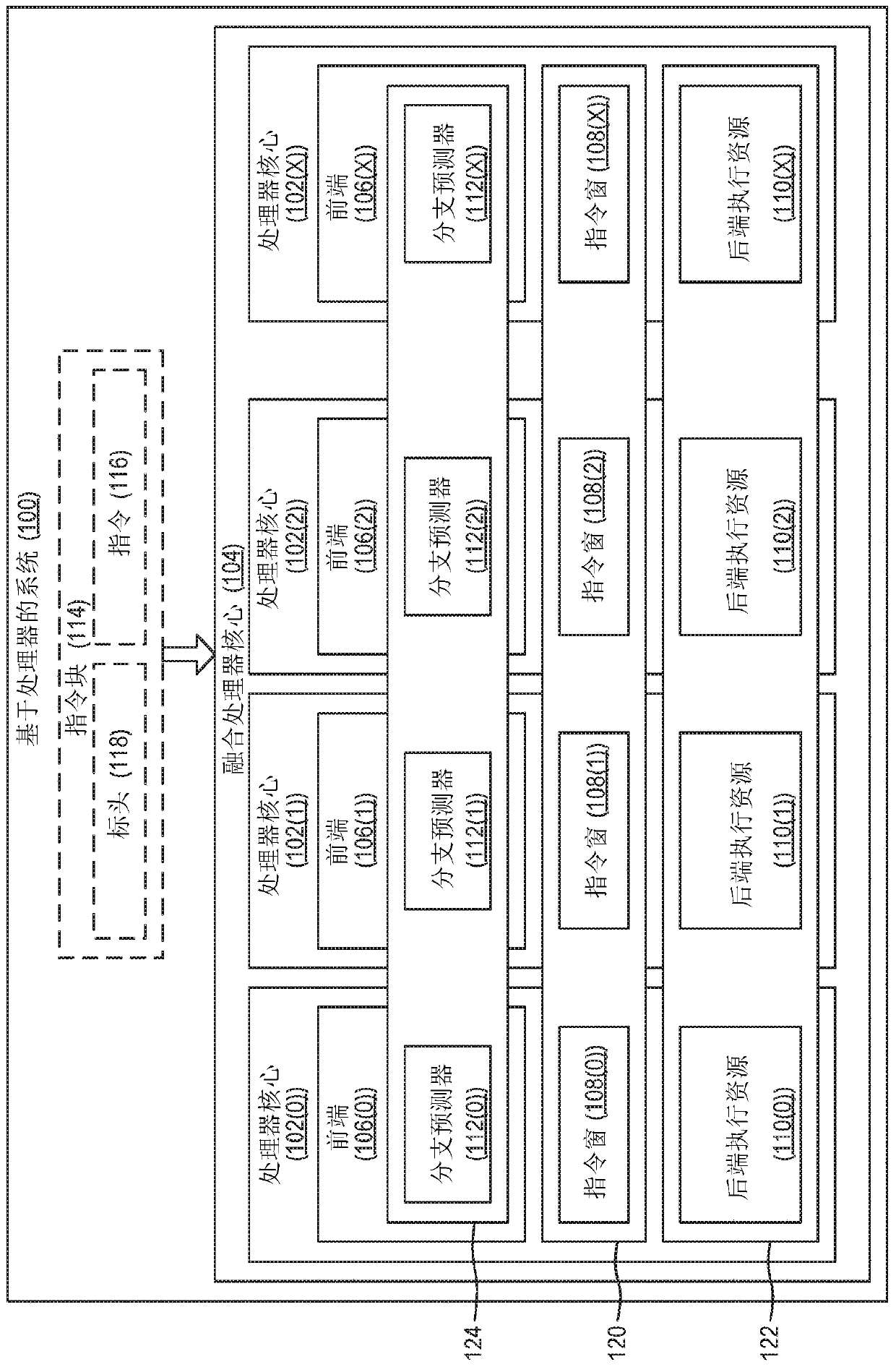
Distinct system registers for logical processors
ActiveCN108027772AEasy to handleMemory architecture accessing/allocationSingle instruction multiple data multiprocessorsProcessor registerInstruction window
Distinct system registers for logical processors are disclosed. In one example of the disclosed technology, a processor includes a plurality of block-based physical processor cores for executing a program comprising a plurality of instruction blocks. The processor also includes a thread scheduler configured to schedule a thread of the program for execution, the thread using the one or more instruction blocks. The processor further includes at least one system register. The at least one system register stores data indicating a number and placement of the plurality of physical processor cores toform a logical processor. The logical processor executes the scheduled thread. The logical processor is configured to execute the thread in a continuous instruction window.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Operation system
InactiveUS7814434B2Easy to operateEliminate operationNavigation instrumentsInput/output processes for data processingOperational systemComputer graphics (images)
In a navigation device, multi-layered menu windows are sequentially displayed in a display unit and narrowed down by repeatedly selecting an item in each menu window to thereby consequently display a certain instruction window for instructing an execution of a function. This selection procedure is stored such that a selection record, which indicates an association with the certain instruction window, is assigned to each of the selected items in the displayed menu windows. When a certain item assigned the selection record is operated more than a predetermined time period, the currently displayed menu window including the certain item is switched to the certain instruction window without intermediate menu windows displayed. Thus, when intending to display the certain instruction window, which was previously displayed after the selection procedure, a user can significantly simplify the selection procedure and decrease workloads.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Clustered superscalar processor and communication control method between clusters in clustered superscalar processor
InactiveUS20060095736A1Reduce error rateImprove performanceRegister arrangementsGeneral purpose stored program computerScalar processorProcessor register
A clustered superscalar processor for reducing the miss rate of a register cache and reducing the possibility of miss penalties. The processor checks before storing an instruction in an instruction window whether there is a data dependency relationship between the instruction that will be stored in the instruction window and a previous instruction stored in the instruction window. When there is a data dependency relationship, the execution result of the previous instruction of one cluster is communicated to a register cache of another cluster that executes the instruction having a data dependency relationship with the previous instruction.
Owner:NAGOYA UNIVERSITY
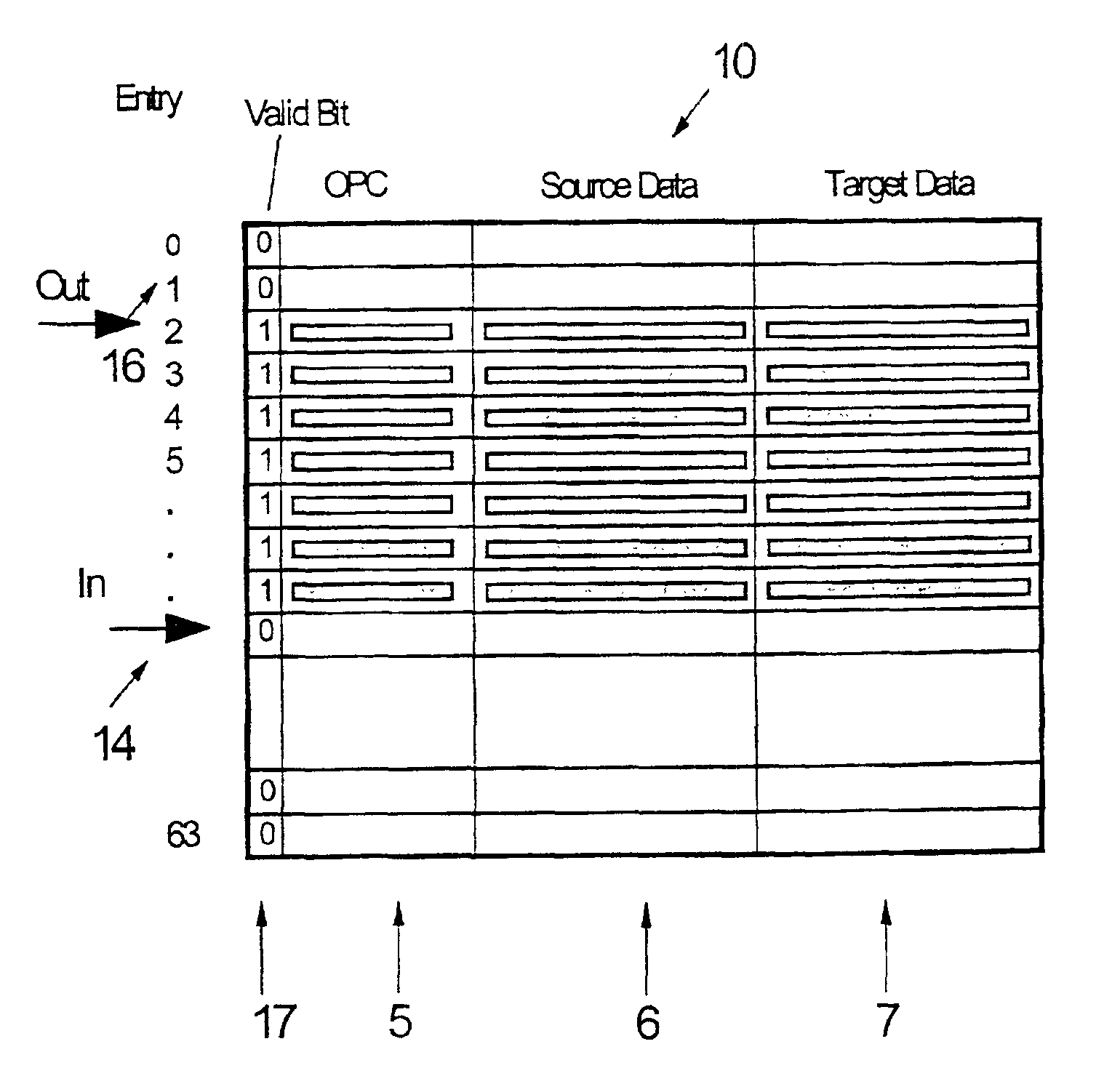
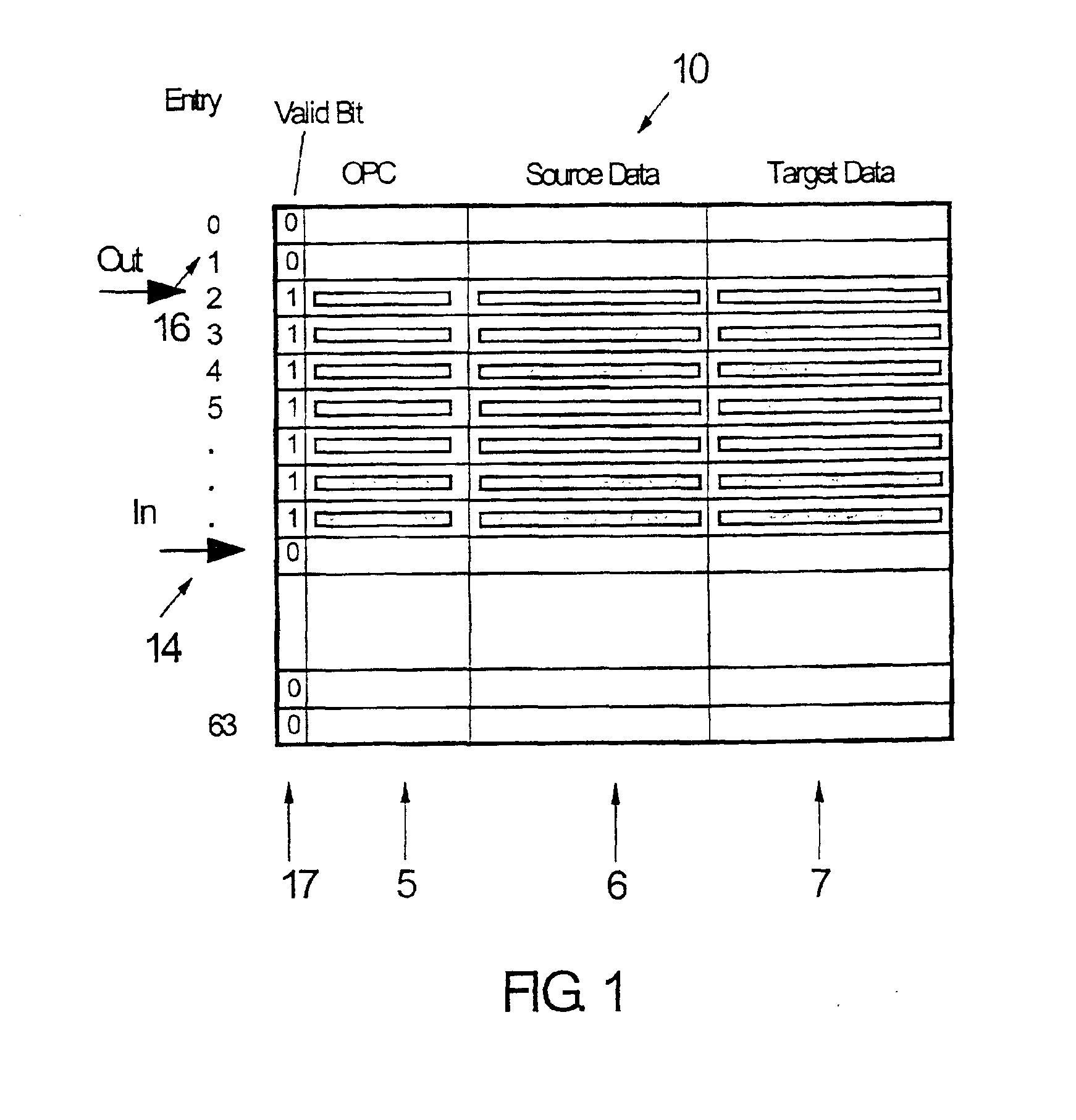
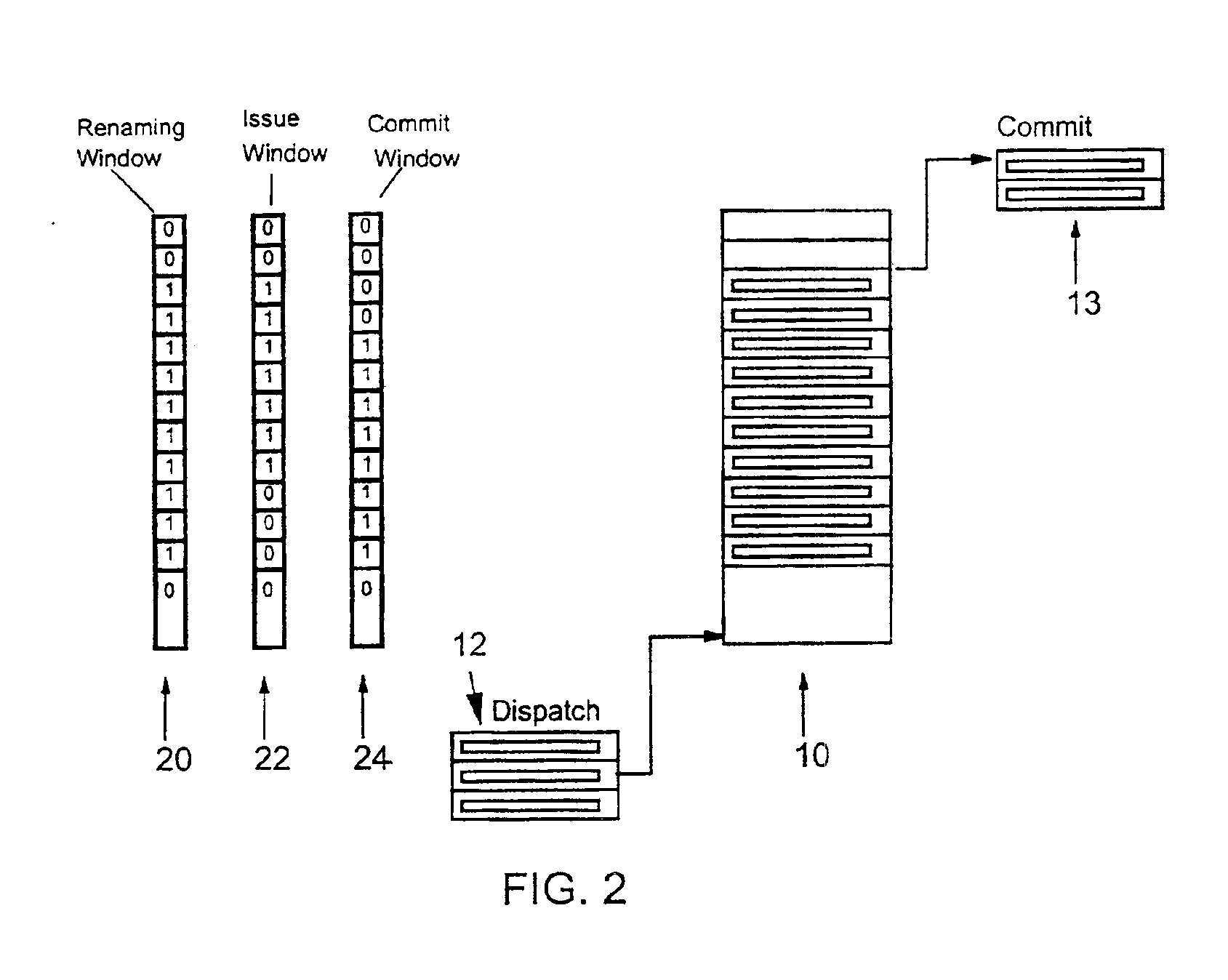
Method and system to improve usage of an instruction window buffer in multi-processor, parallel processing environments
InactiveUS6918119B2Easy to useImprove efficiencyConcurrent instruction executionInput/output processes for data processingMulti processorInstruction window
The present invention relates to a method and system for determining the status of each entry in an instruction window buffer in multi-processor, parallel processing environments. A combinatorial circuit, which automatically generates active instruction window status information, is added to the buffer itself. This status information is used by a plurality of processes like renaming registers and issuing and committing instructions as an output associated with a respective buffer entry.
Owner:IBM CORP
Decoupled processor instruction window and operand buffer
ActiveCN107810476AMemory architecture accessing/allocationInstruction analysisInstruction windowEngineering
A processor core in an instruction block-based microarchitecture is configured so that an instruction window and operand buffers are decoupled for independent operation in which instructions in the block are not tied to resources such as control bits and operands that are maintained in the operand buffers. Instead, pointers are established among instructions in the block and the resources so thatcontrol state can be established for a refreshed instruction block (i.e., an instruction block that is reused without re-fetching it from an instruction cache) by following the pointers. Such decoupling of the instruction window from the operand space can provide greater processor efficiency, particularly in multiple core arrays where refreshing is utilized (for example when executing program codethat uses tight loops), because the operands and control bits are pre-validated.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Economical exercise trainer for workout of the arm, waist and abdomen
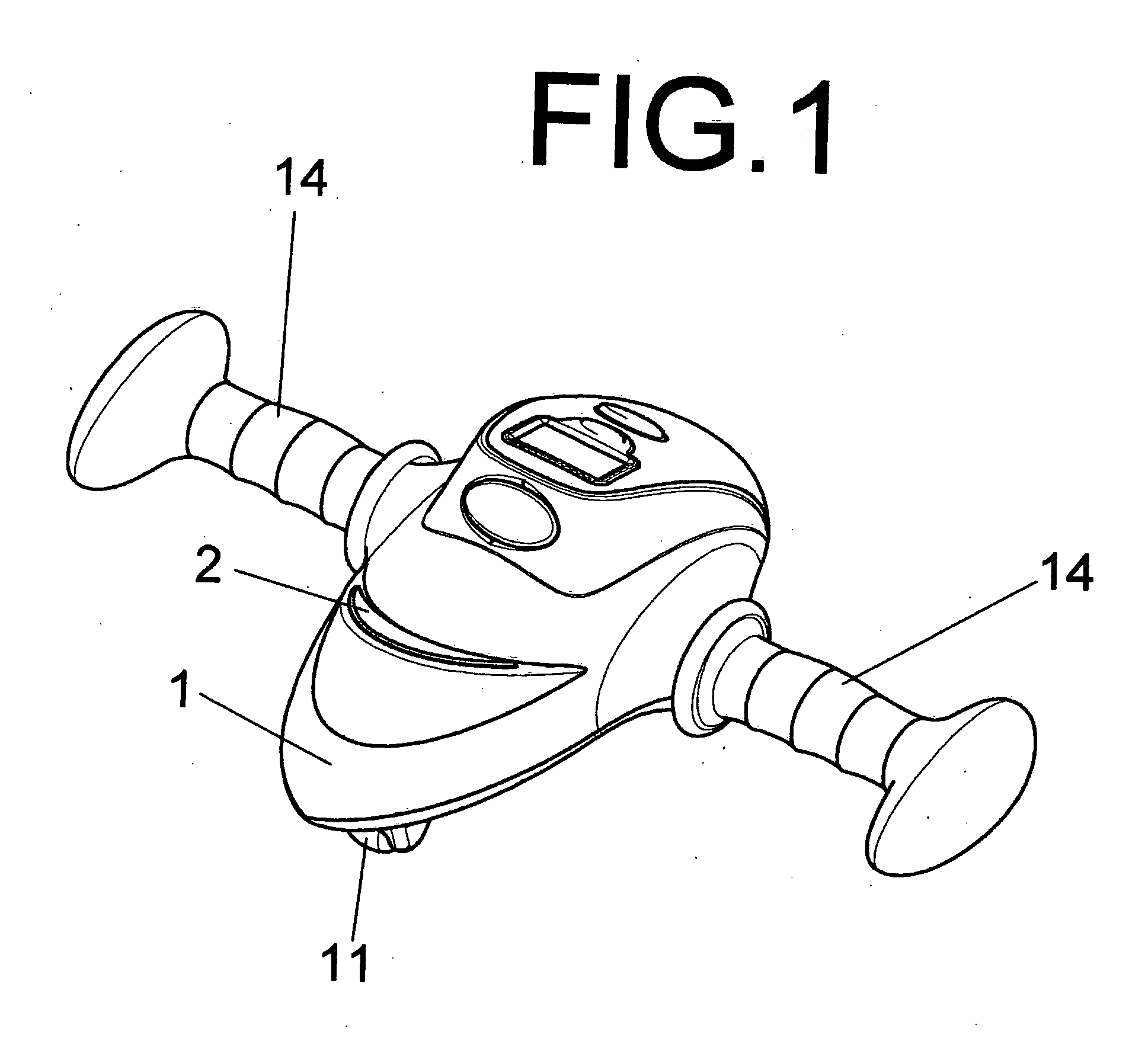
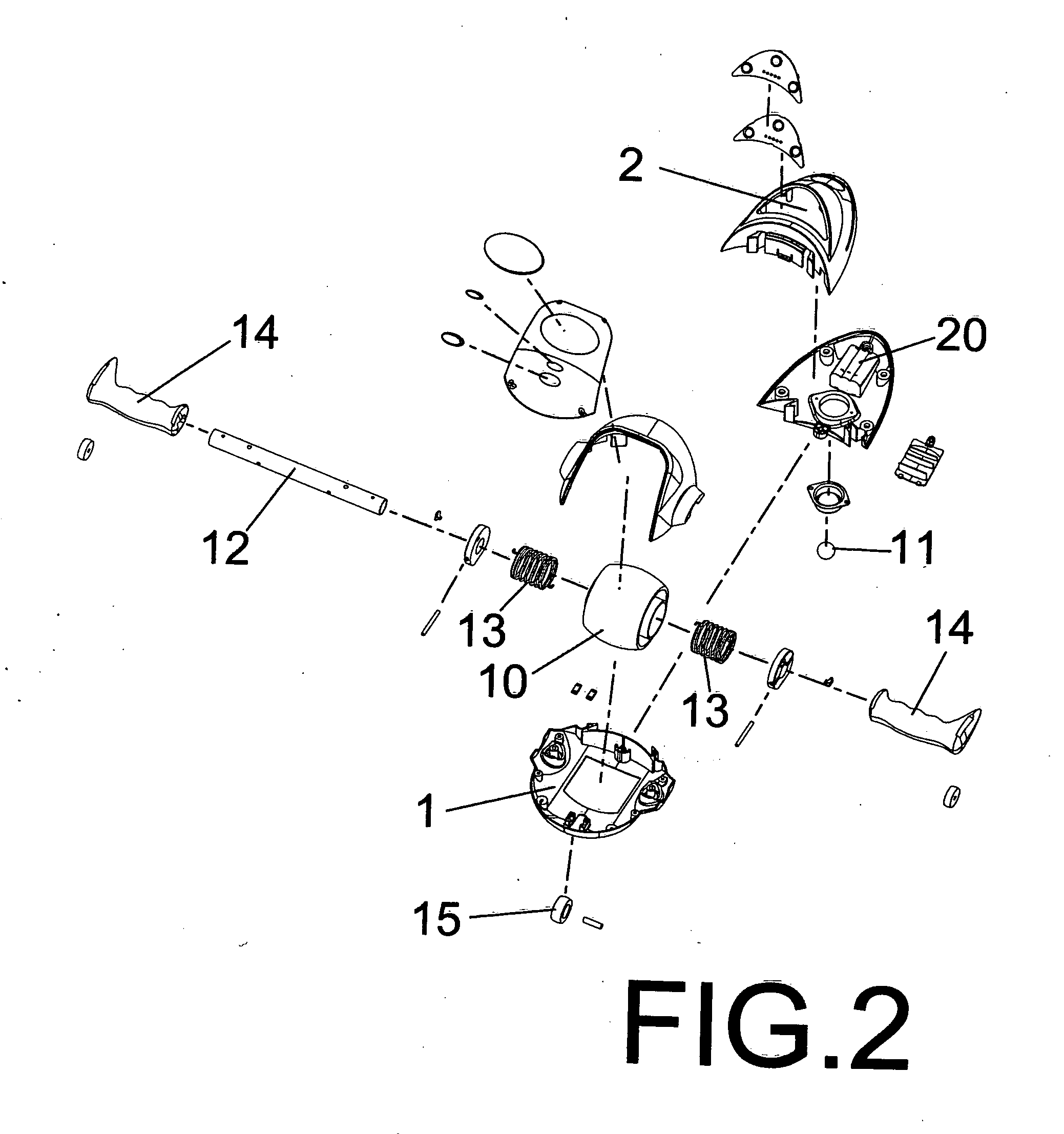
InactiveUS20130065741A1Add funImprove sustainabilityMovement coordination devicesMuscle exercising devicesInstruction windowAbdomen
The present invention is an economical exercise trainer or workout of the arm, waist and abdomen. It is an economically improved design for workout of the arm, waist and abdomen. On the top portion of the unit frame is a video signal instruction window and at the bottom is disposed a slightly protruded driven pulley and swing roller. Inside the unit frame is disposed a circuit controller for controlling the video signal instruction window to generate different lamp shadow direction changes. The driven pulley and the swing roller are slightly protruded beyond the bottom of the stand and between the driven pulley and shaft sleeve rod is disposed a reset spring, and two sides of the shaft rod protrude leftward and rightward to form the grip handles for holding. Such repeated back and forth exercise would be effective for workout of your arm, waist and abdomen.
Owner:HO WEI TEH
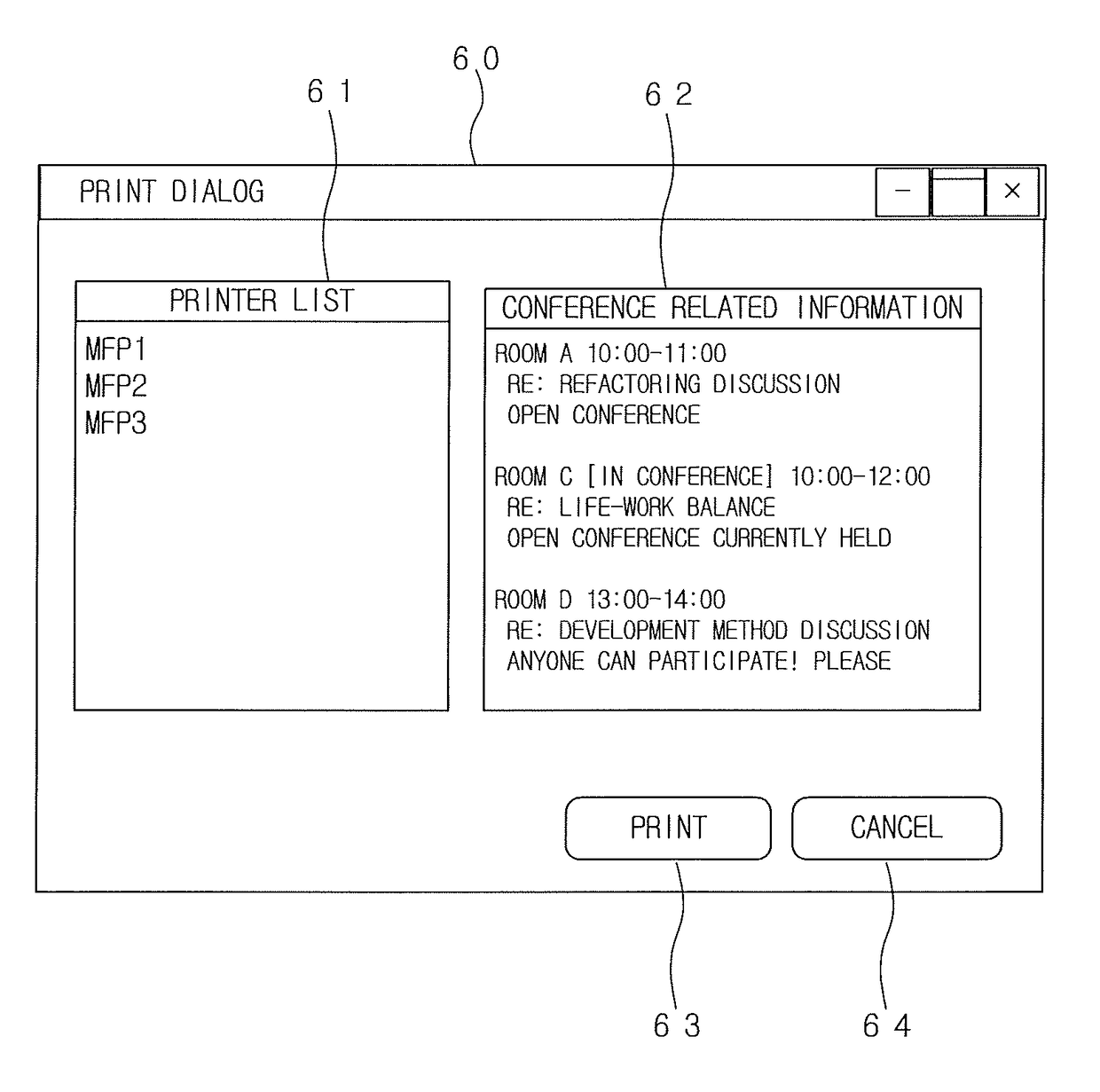
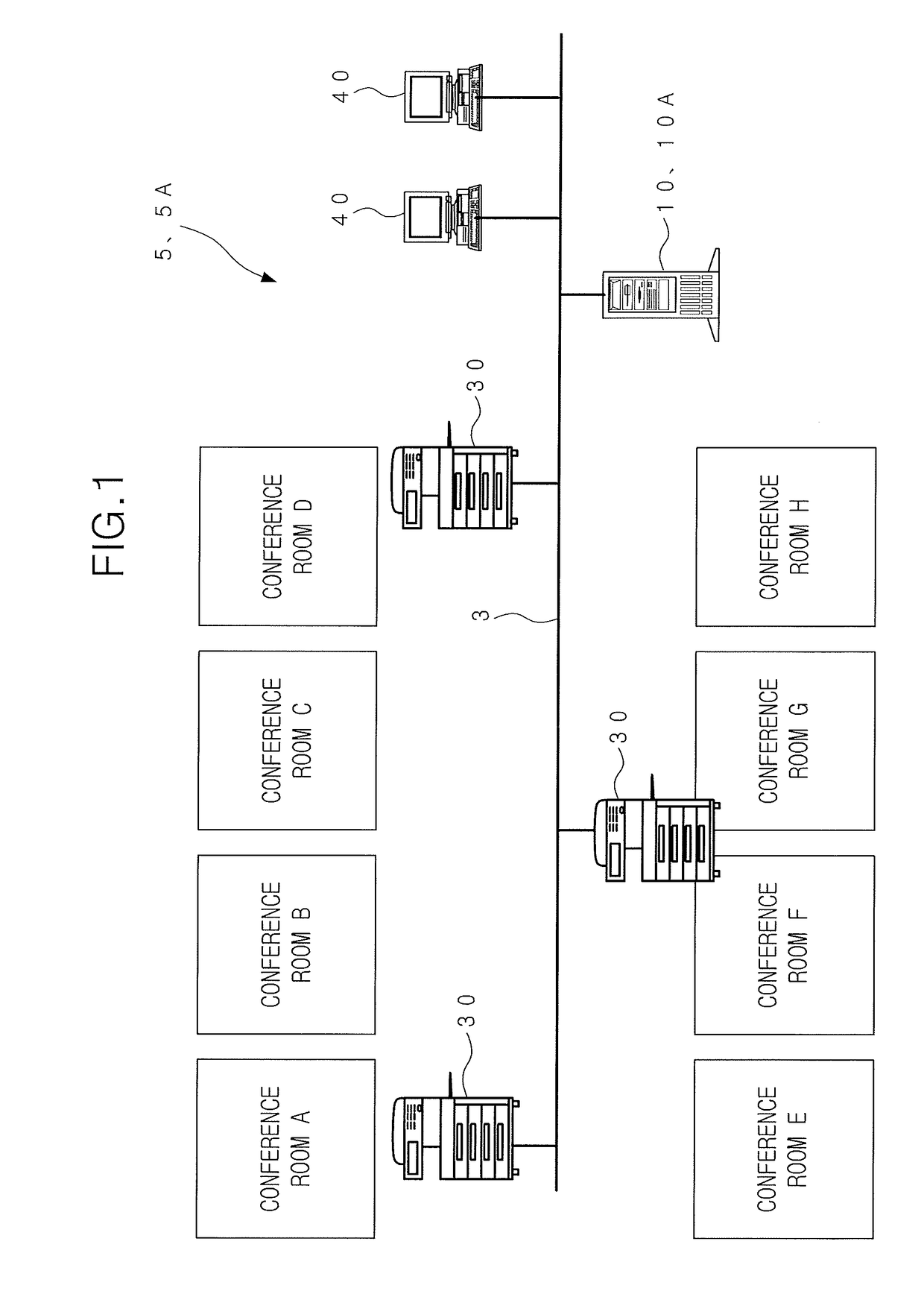
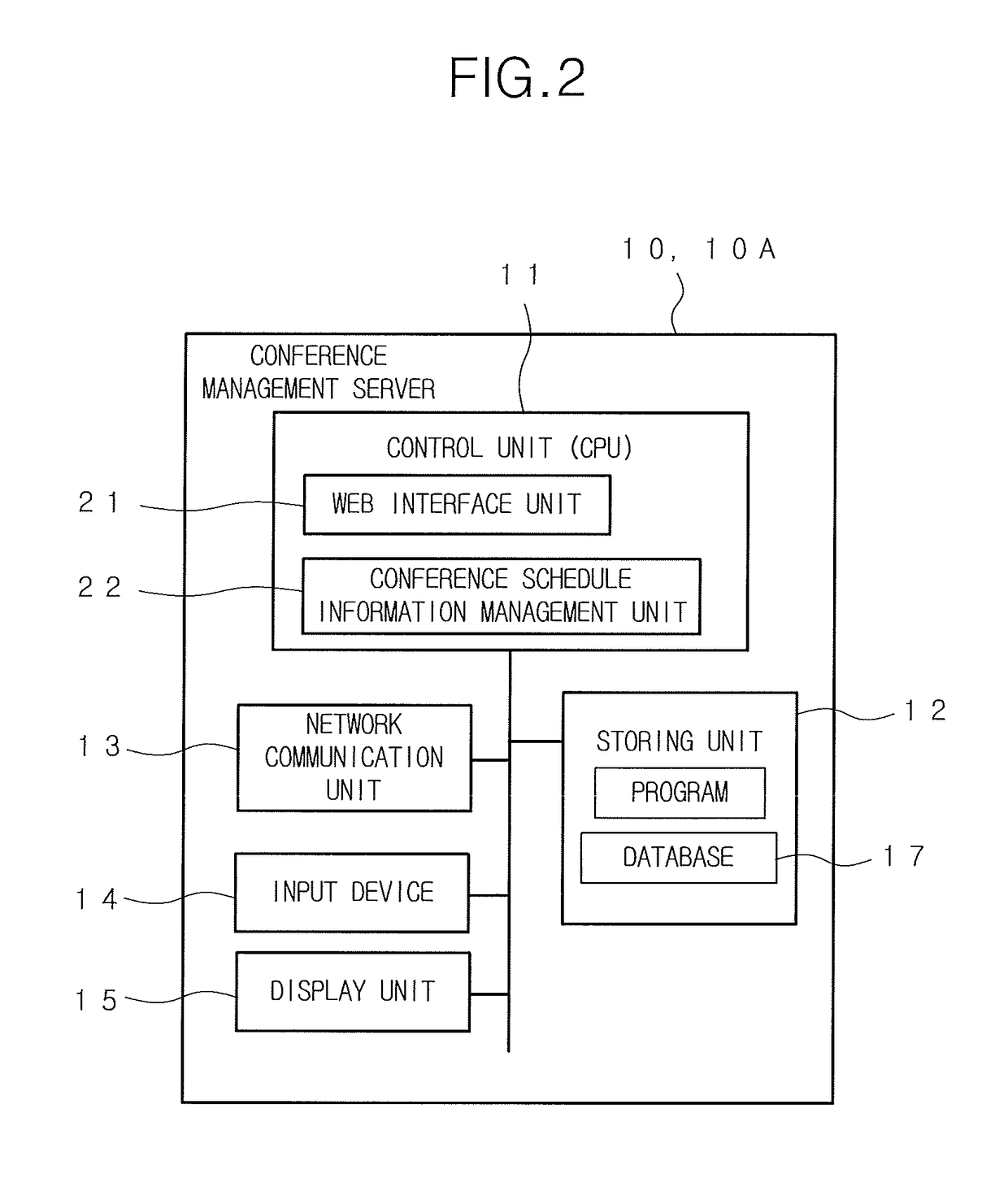
Non-transitory computer-readable recording medium and conference system
ActiveUS20170318167A1Visual presentation using printersPictoral communicationInformation processingInstruction window
Disclosed is a non-transitory computer-readable recording medium in which a program is stored, wherein the program causes an information processing device to: obtain conference information of a conference; and prepare and display a print instruction window having a function for receiving a selection of a print apparatus used for a printing in a list of one or more print apparatuses by displaying the list and having a function for receiving an instruction for starting the printing, the print instruction window indicating the obtained conference information.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Instruction rollback processor system, an instruction rollback method and an instruction rollback program
InactiveUS7213130B2Digital computer detailsNext instruction address formationMultiplexerInstruction window
An instruction rollback processor system according to the present invention is provided. The instruction rollback processor system includes: an instruction window buffer storing a plurality of instructions not yet executed and are arranged in a predetermined order; a multiplexer receiving an output of the instruction window buffer; and a rollback unit connected between the output side of the multiplexer and another input of the multiplexer.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
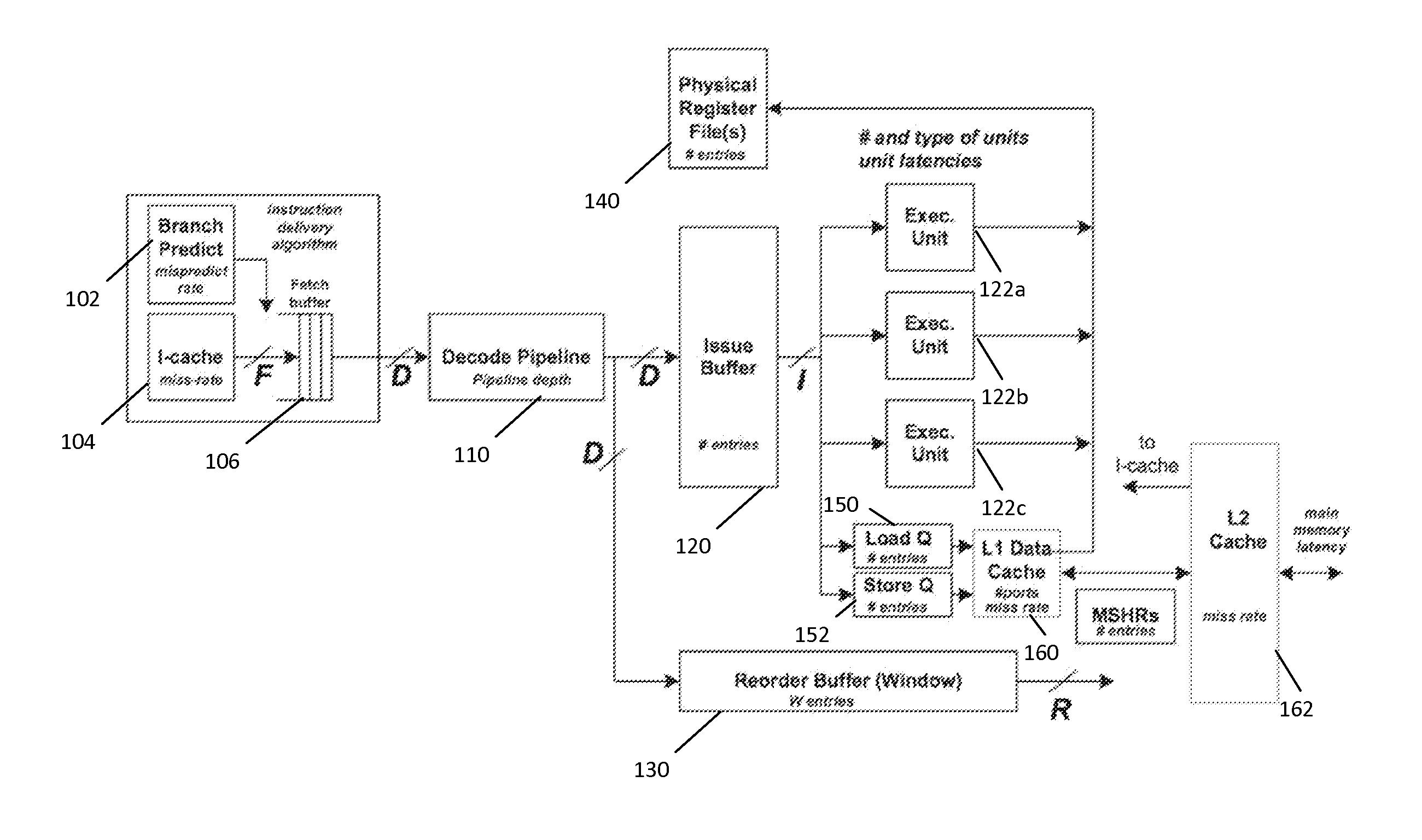
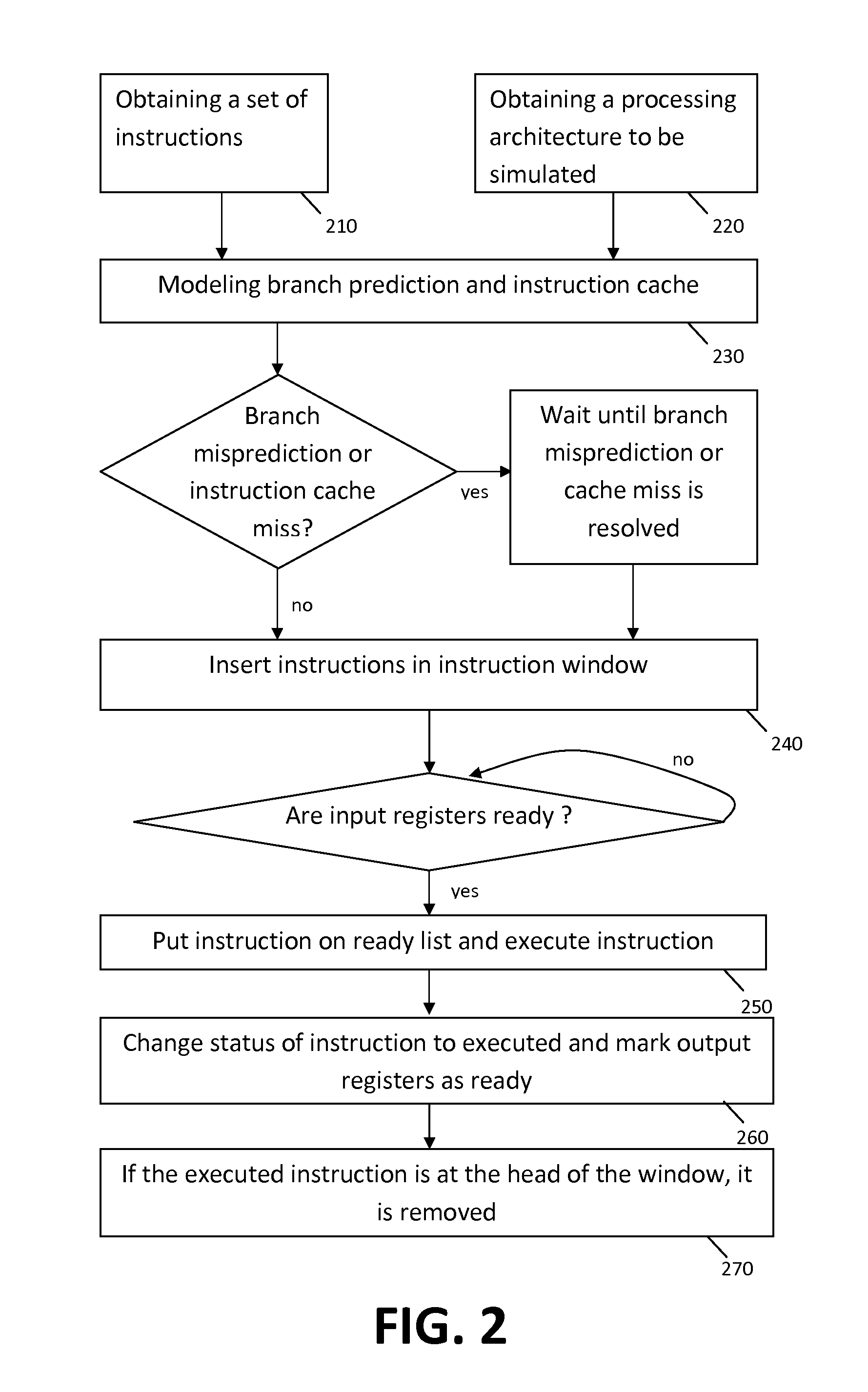
Instruction window centric processor simulation
ActiveUS20150193242A1Accurate modelingThe result is accurateDesign optimisation/simulationSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationInstruction windowRegister renaming
A method and system are described for simulating a set of instructions to be executed on a processor. The method comprises performing a performance simulation of the processor over a number of simulation cycles. Performing the performance simulation of the processor comprises modeling an instruction window for the cycle and deriving a performance parameter of the processor without modeling a reorder buffer, issue queue(s), register renaming, load-store queue(s) and other buffers of the processor.
Owner:UNIV GENT
Performing distributed branch prediction using fused processor cores in processor-based systems
InactiveCN109716293AConcurrent instruction executionMemory systemsComputer architectureInstruction window
Performing distributed branch prediction using fused processor cores in processor-based systems is disclosed. In one aspect, a distributed branch predictor is provided as a plurality of processor cores supporting core fusion. Each processor core is configured to receive a program identifier from another of the processor cores (or from itself), generate a subsequent predicted program identifier, and forward the predicted program identifier (and, optionally, a global history indicator) to the appropriate processor core responsible for handling the next prediction. The processor core also fetchesa header and / or one or more instructions for the received program identifier, and sends the header and / or the one or more instructions to the appropriate processor core for execution. The processor core also determines the processor core that will handle execution of the predicted program identifier, and sends that information to the processor core that received the predicted program identifier as an instruction window tracker.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Instruction obtaining device for processor and processor with same
InactiveCN103631566AShorten the timeConcurrent instruction executionInstruction unitInstruction window
The invention relates to an instruction obtaining device for a processor. The instruction obtaining device comprises an instruction caching unit, an instruction buffer unit, an instruction window and an instruction achieving logical unit, wherein the instruction caching unit is used for storing instructions and transmitting the instructions stored in the instruction caching unit to the instruction buffer unit in order; the instruction buffer unit is used for transmitting instructions needing to be executed at present and obtained by the instruction achieving logical unit at one time to the instruction window to be stored; the instruction achieving logical unit obtains the instructions from the instruction window, processes the instructions and outputs and executes the instructions; the instruction achieving logical unit also returns read pointers and write pointers of current execution instructions back to the instruction buffer unit. The invention further relates to a processor with the instruction obtaining device. The instruction obtaining device for the processor and the processor with the instruction obtaining device have the advantage of shortening instruction output time on the whole.
Owner:SHENZHEN ZHONGWEIDIAN TECH
Automatic early-warning window-lowering device for preventing asphyxia of human bodies in vehicle
PendingCN107650837AImprove intelligenceSolve trappedTransmission systemsPower-operated mechanismStart timeIn vehicle
The invention provides an automatic early-warning window-lowering device for preventing asphyxia of human bodies in a vehicle. The automatic early-warning window-lowering device comprises a start button, wherein a control module controls a timer module for timing when the start button is pressed and the timer module simultaneously starts human body sensing modules while starting timing; during thetiming process of the timer module, the human body sensing modules sense the presence of human vital signs and transmits feedback signals to the control module; the control module controls a motor controller according to the feedback signals of the human body sensing modules; and a stepping motor controls a car window lifting and lowering device according to commands from the motor controller soas to control the opening and closing of car windows. The automatic early-warning window-lowering device for preventing the asphyxia of the human bodies in the vehicle determines the presence of the human vital signs in the vehicle during a preset period of time by virtue of the sensing of sensors when the vehicle stops running, and further controls the opening and closing, the opening size and the opening speed of the car windows by virtue of the stepping motor, so as to solve the problems that the human bodies are trapped in the vehicle or the car windows are mistakenly opened.
Owner:何小霞
Executing multiple programs simultaneously on a processor core
ActiveCN110249302AImprove performanceConcurrent instruction executionEnergy efficient computingMultiple contextComputer architecture
Systems and methods are disclosed for allocating resources to contexts in block-based processor architectures. In one example of the disclosed technology, a processor is configured to spatially allocate resources between multiple contexts being executed by the processor, including caches, functional units, and register files. In a second example of the disclosed technology, a processor is configured to temporally allocate resources between multiple contexts, for example, on a clock cycle basis, including caches, register files, and branch predictors. Each context is guaranteed access to its allocated resources to avoid starvation from contexts competing for resources of the processor. A results buffer can be used for folding larger instruction blocks into portions that can be mapped to smaller-sized instruction windows. The results buffer stores operand results that can be passed to subsequent portions of an instruction block.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Performing distributed branch prediction using fused processor cores in processor-based systems
InactiveUS20180081690A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationConcurrent instruction executionInstruction windowProgramme identification
Performing distributed branch prediction using fused processor cores in processor-based systems is disclosed. In one aspect, a distributed branch predictor is provided as a plurality of processor cores supporting core fusion. Each processor core is configured to receive a program identifier from another of the processor cores (or from itself), generate a subsequent predicted program identifier, and forward the predicted program identifier (and, optionally, a global history indicator) to the appropriate processor core responsible for handling the next prediction. The processor core also fetches a header and / or one or more instructions for the received program identifier, and sends the header and / or the one or more instructions to the appropriate processor core for execution. The processor core also determines the processor core that will handle execution of the predicted program identifier, and sends that information to the processor core that received the predicted program identifier as an instruction window tracker.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com