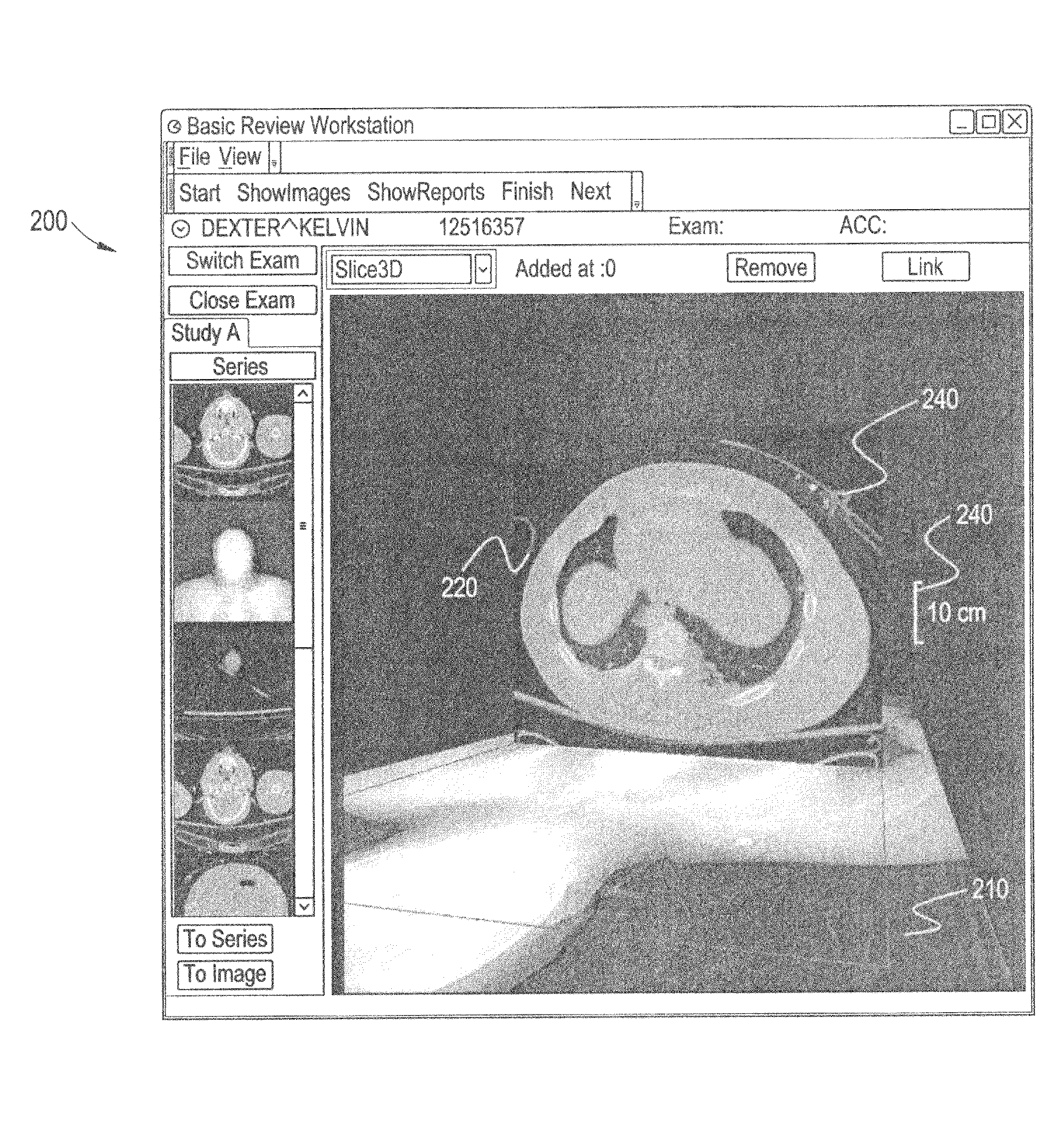
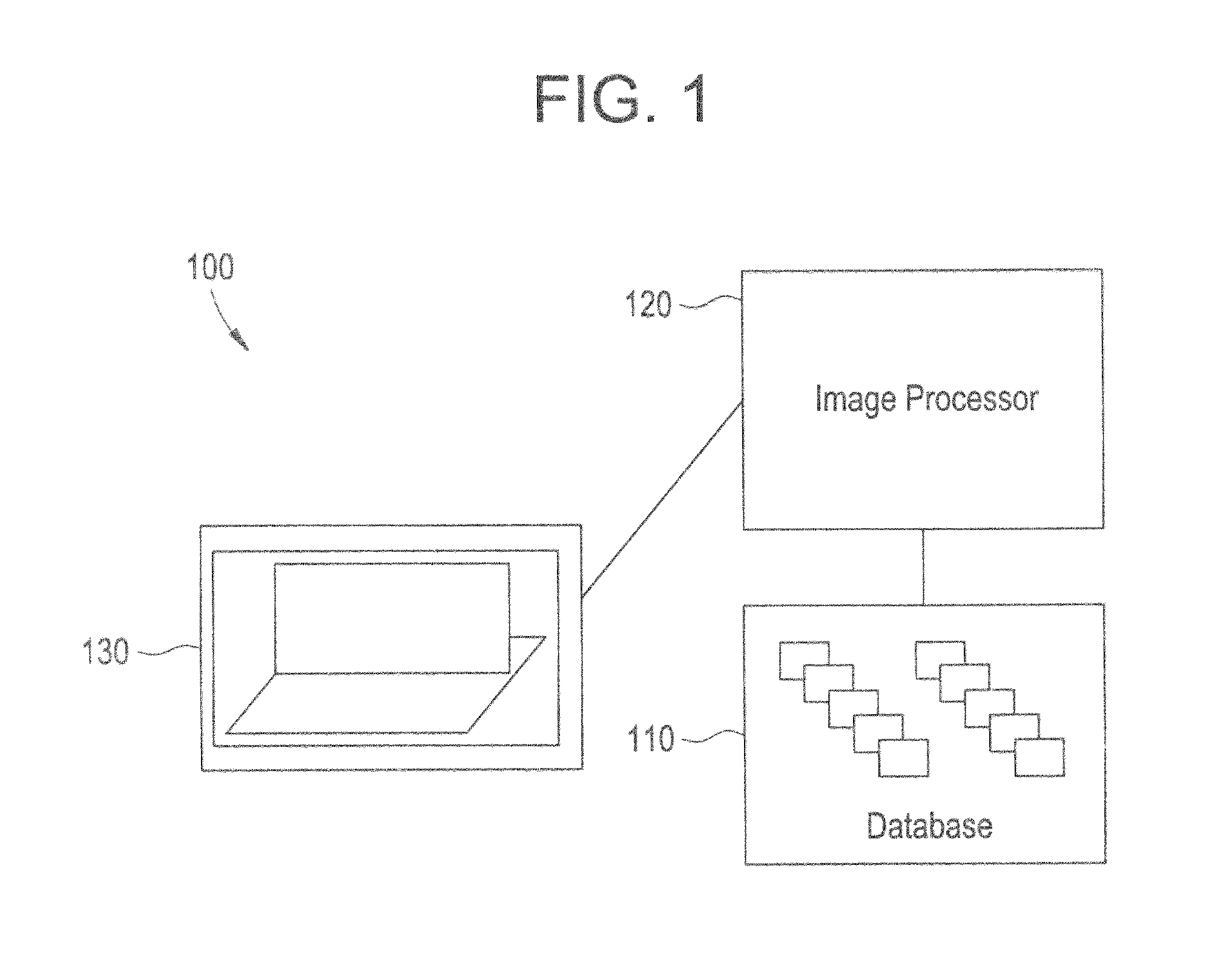
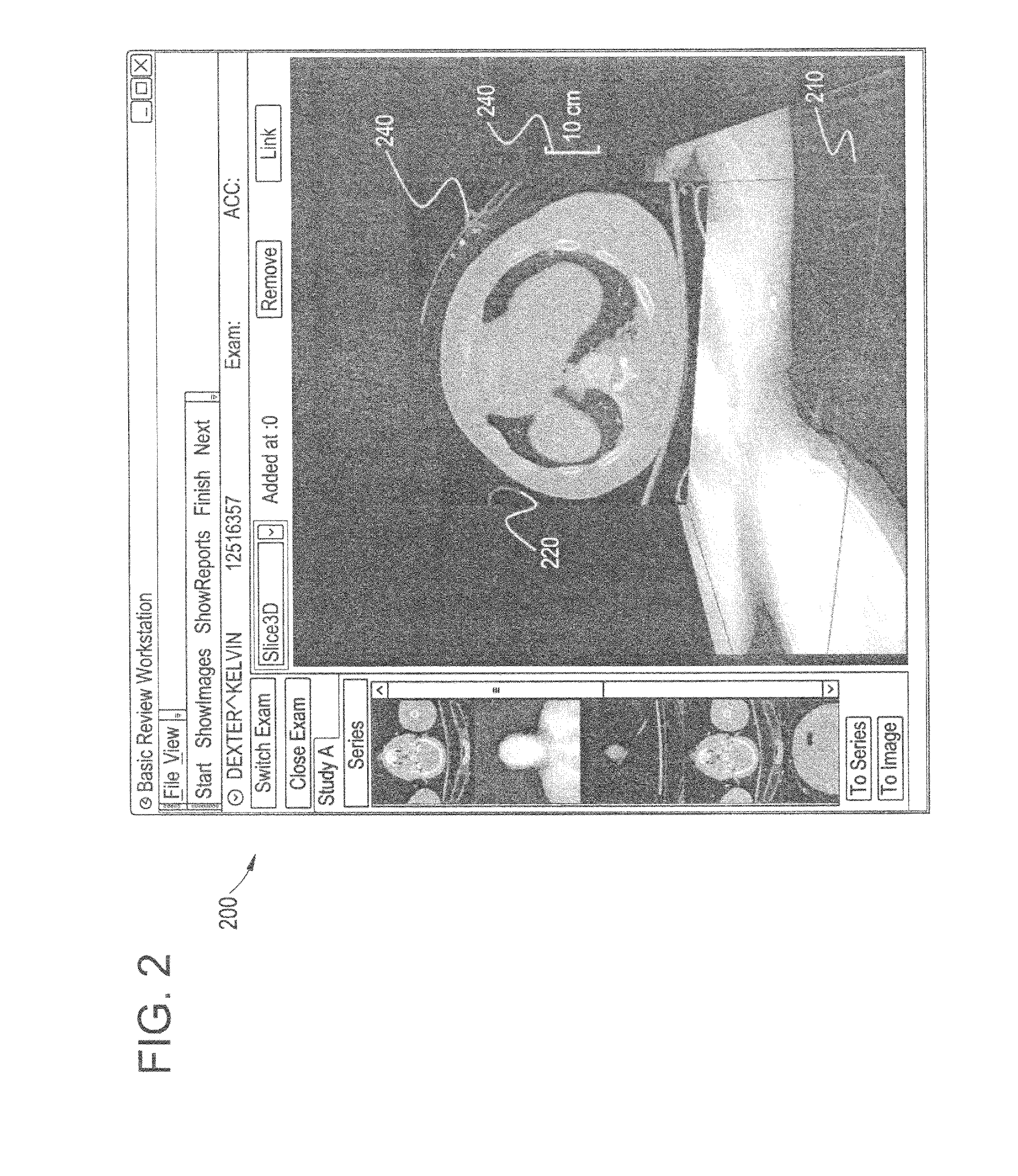
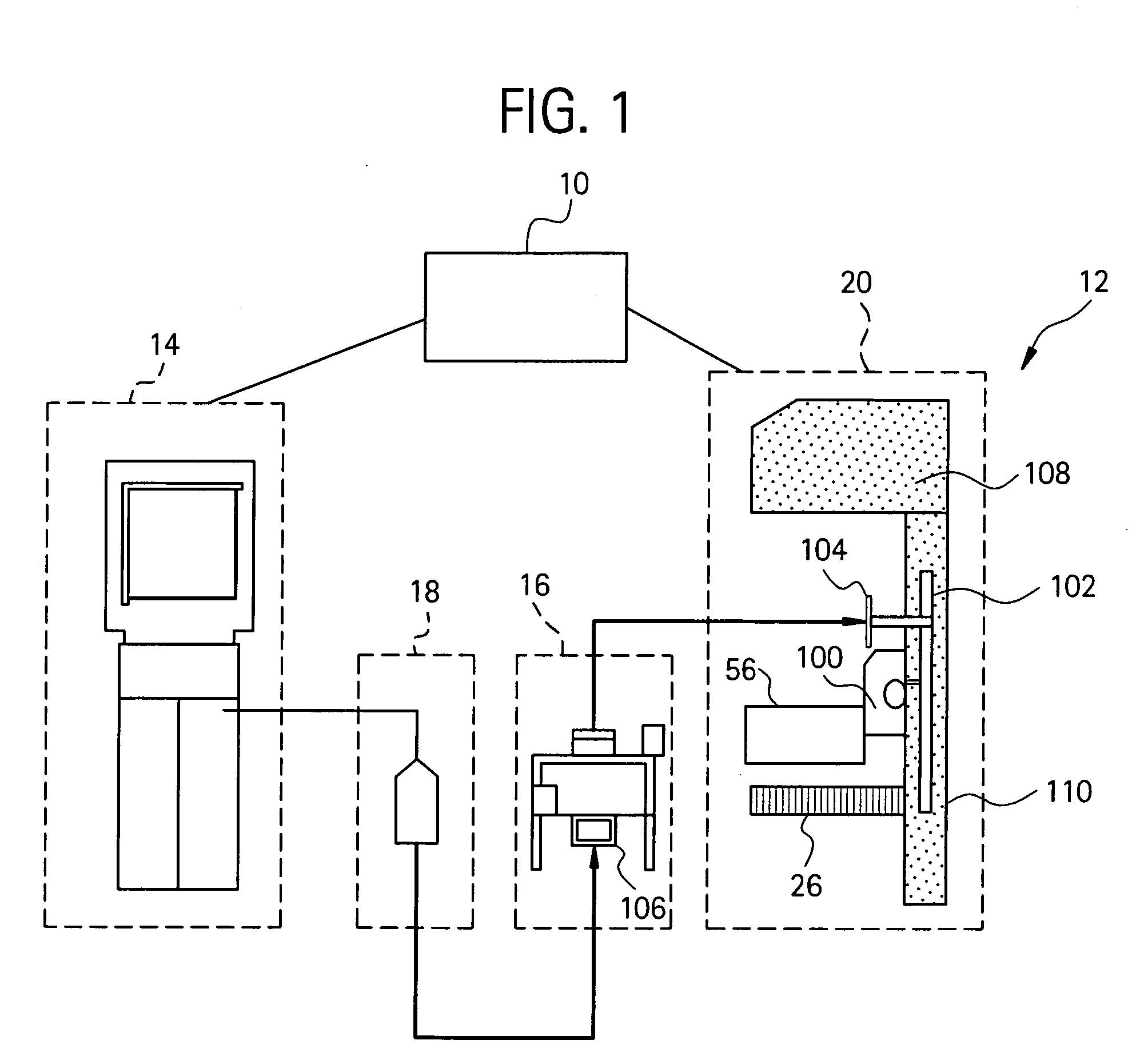
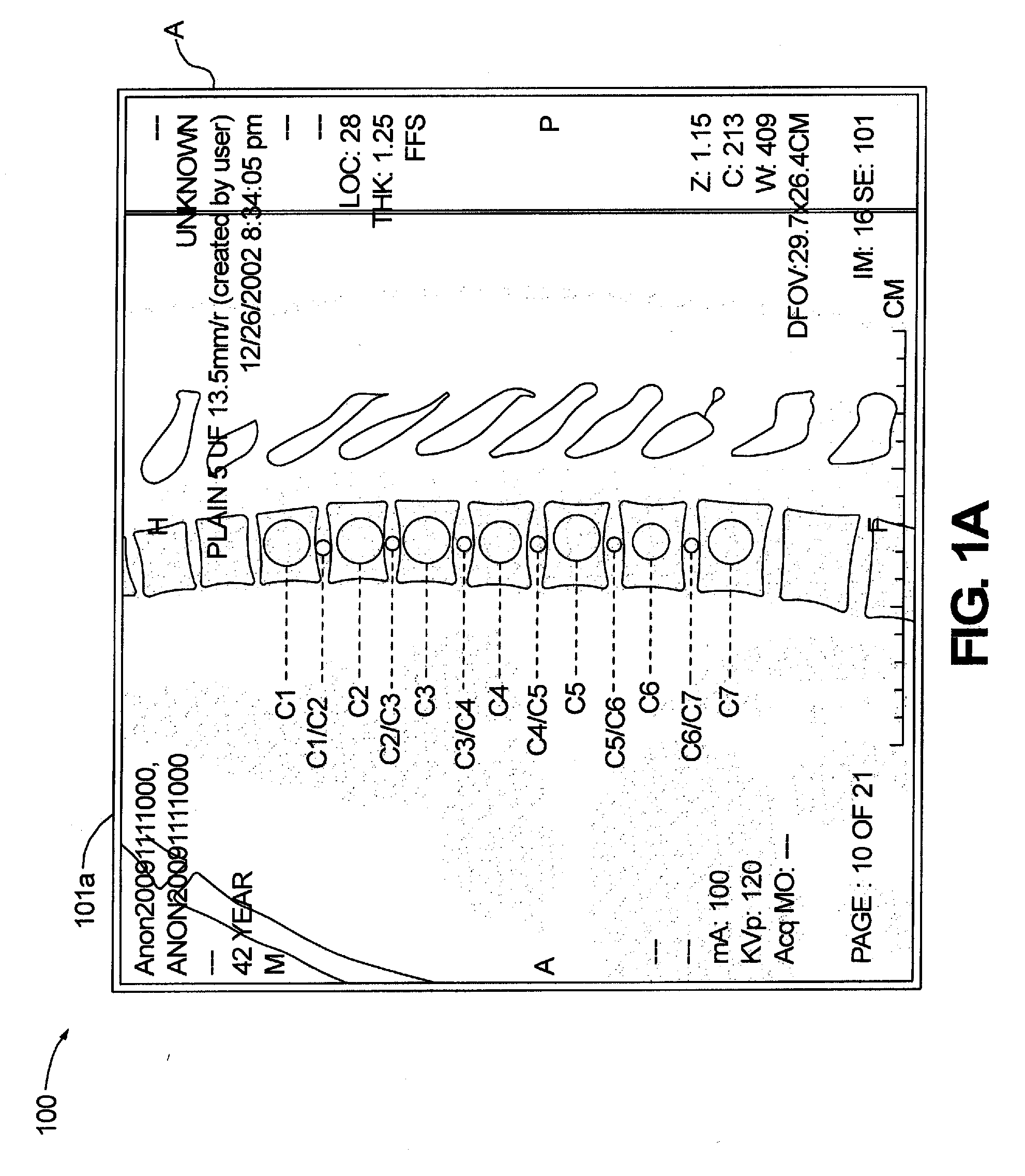
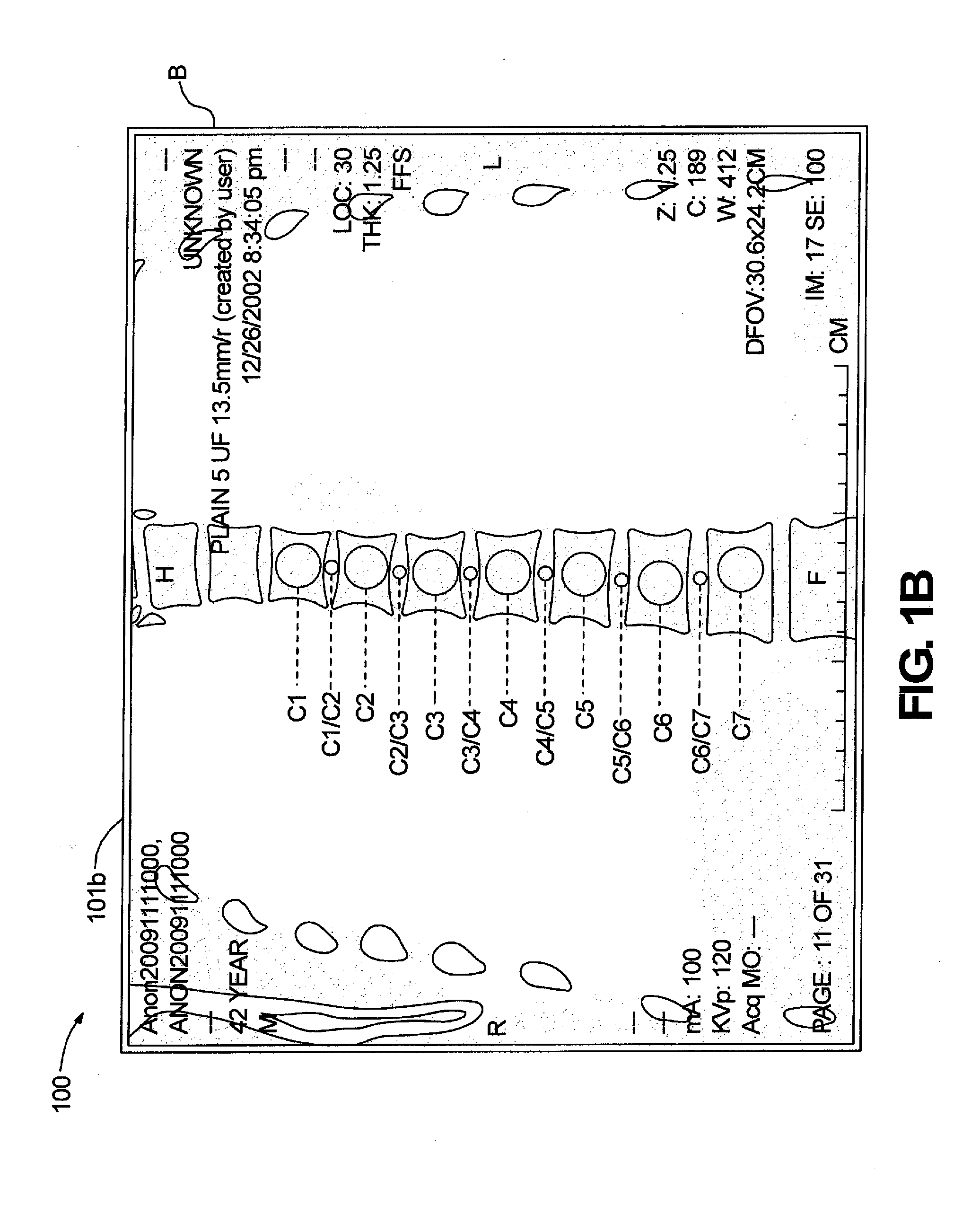
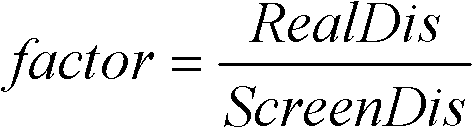Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
115 results about "Image Reslicing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
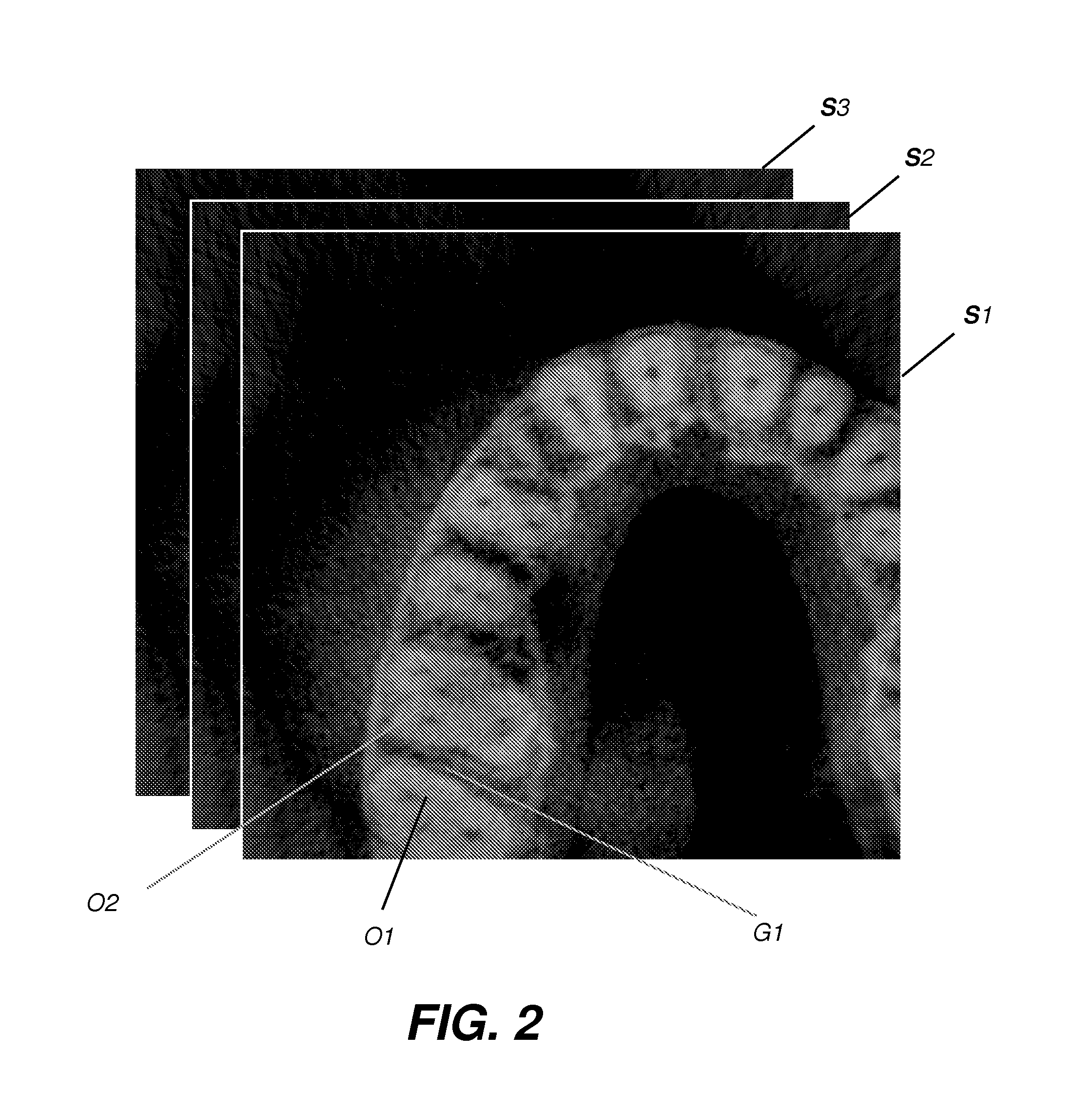
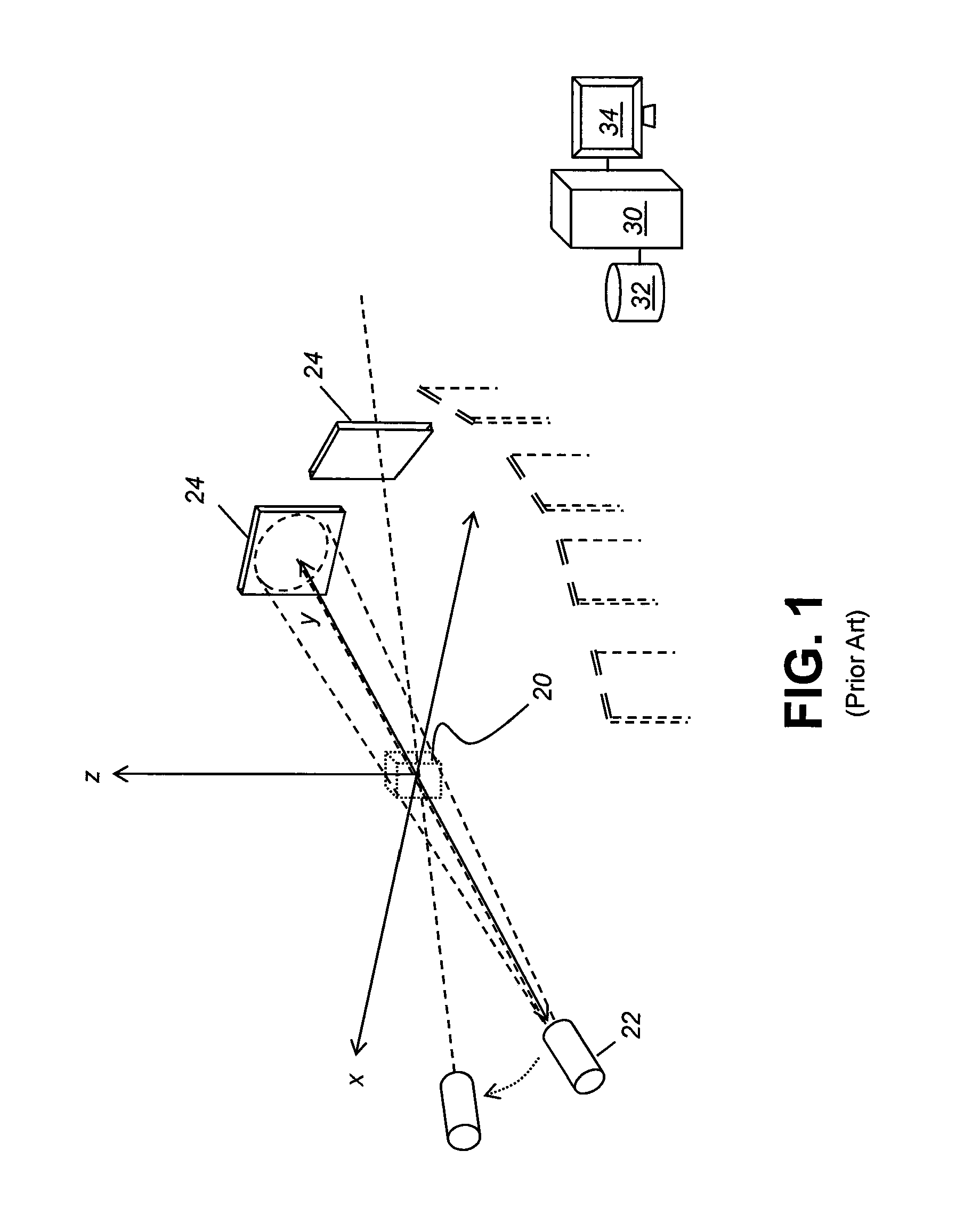
Changing from one set of 2D slices to another set. The latter may have a different thickness and/or cut through the subject at a different angle than the original set.
Method and apparatus for determining symmetry in 2d and 3d images
InactiveUS20040240753A1Accurate and fast determinationMaximizing modified local symmetry indexImage enhancementImage analysisSagittal plane3d image
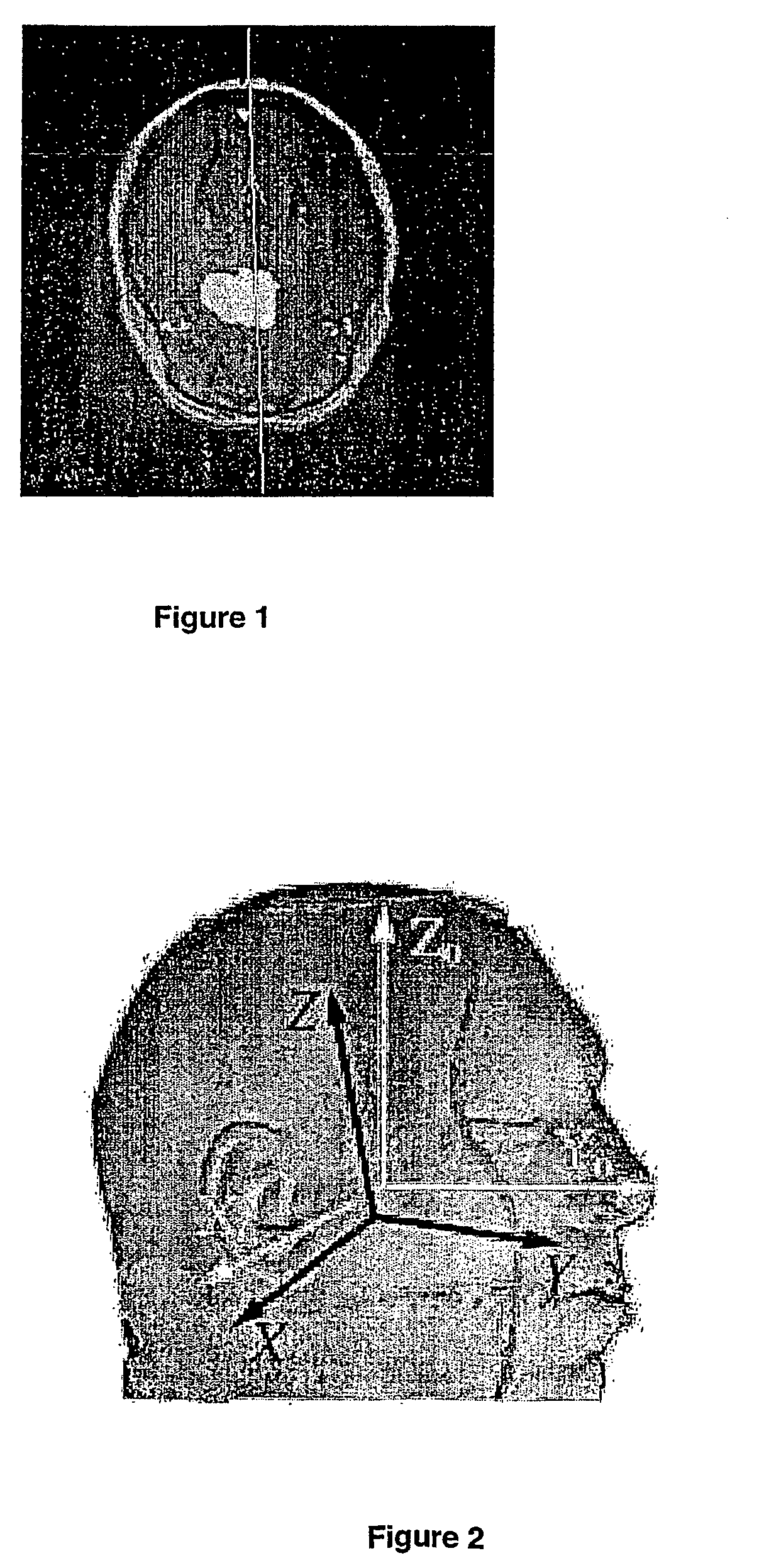
The present invention is suitable for use in determining symmetry in images, namely 2D images or 3D images, which comprise 2D images slices. In a preferred form, a method is disclosed for extracting a midsagittal plane MSP of human brains from radiological images. The method includes the steps of: 1) determining axial slices to be processed from said radiological images; 2) analysing said axial slices to determine fissure line segments; and 3) calculating plane equation of MSP from said fissure line segments.
Owner:KENT RIDGE DIGITAL LABS
System and Method for Segmenting a Region in a Medical Image
ActiveUS20080267468A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementSonificationShape change
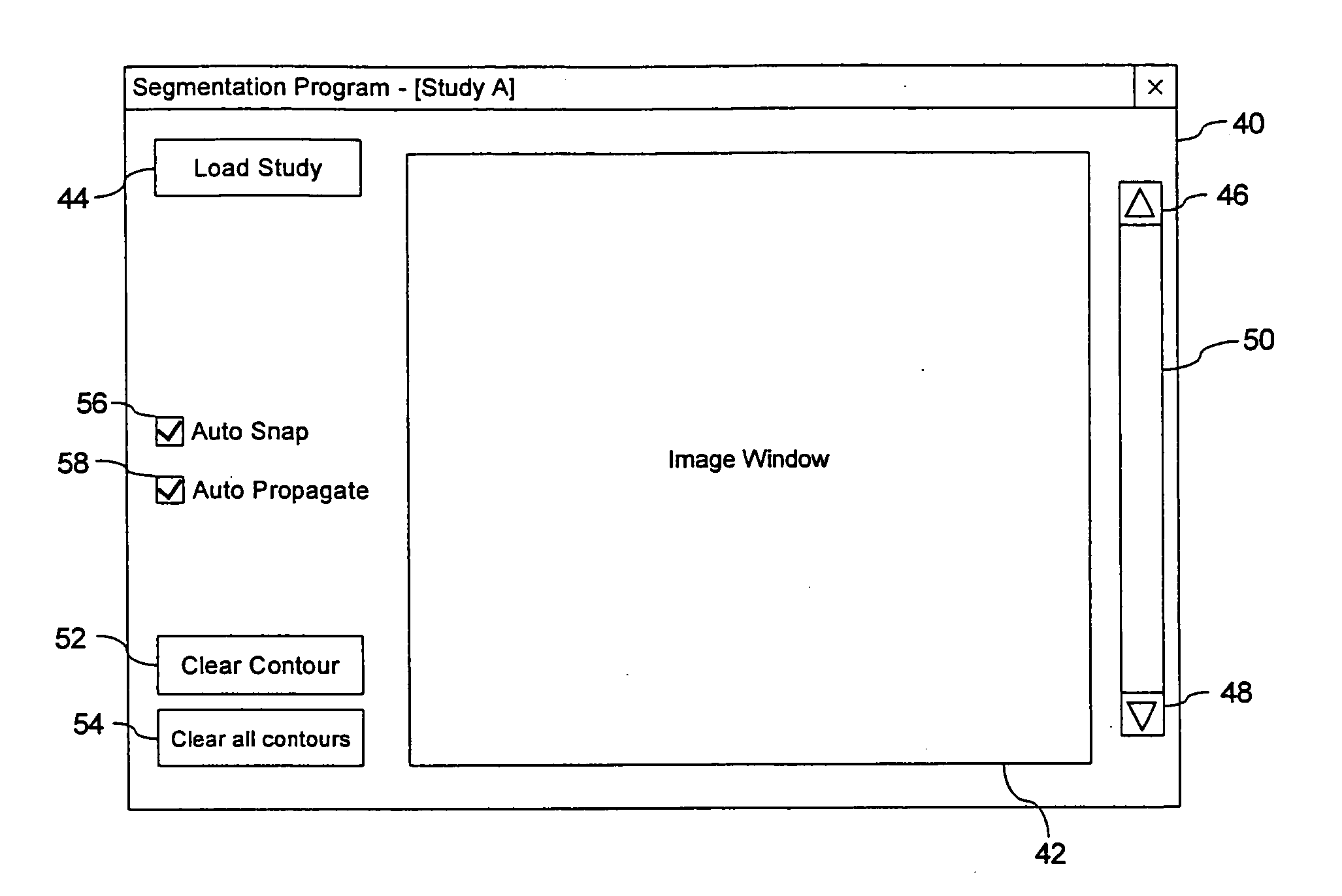
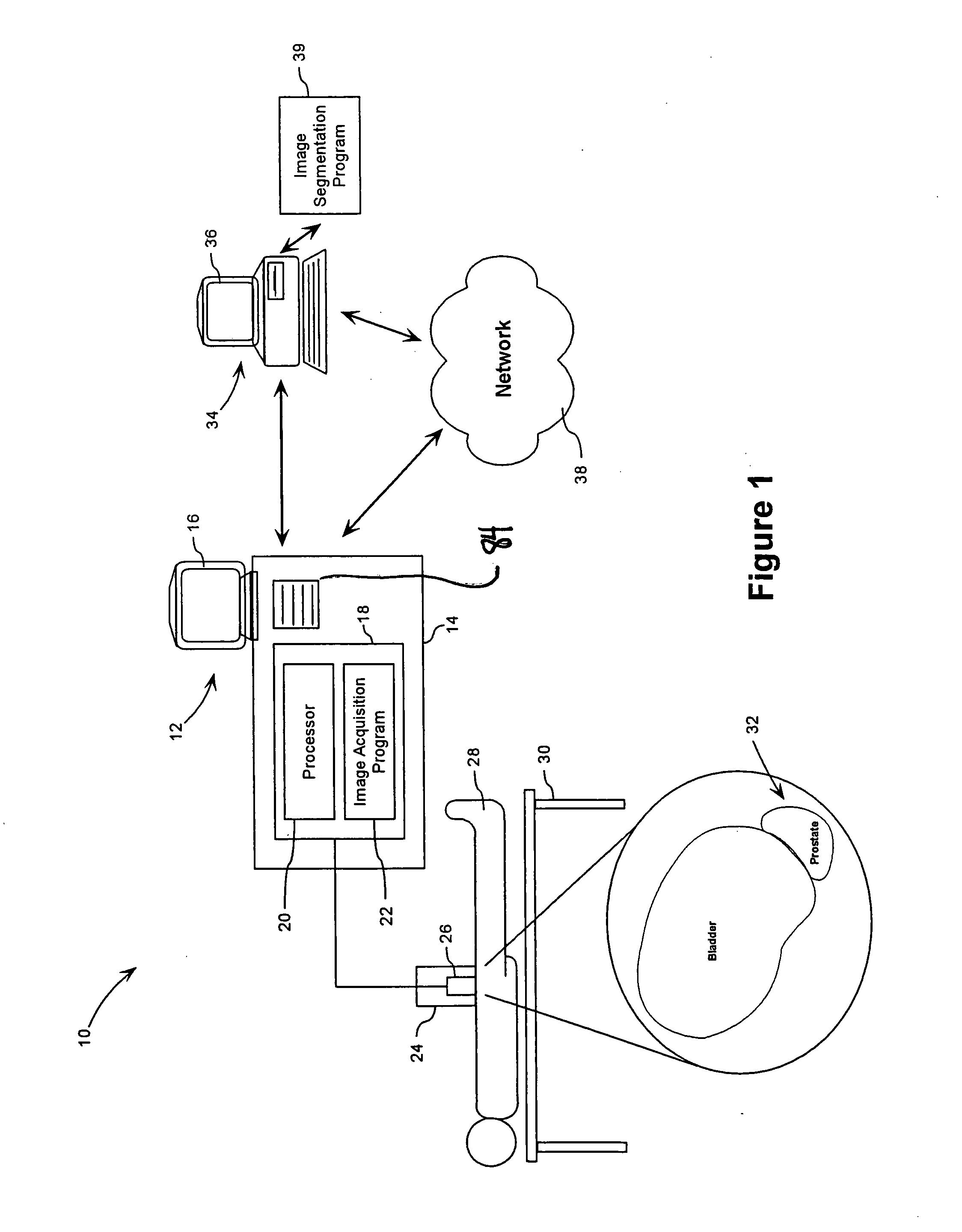
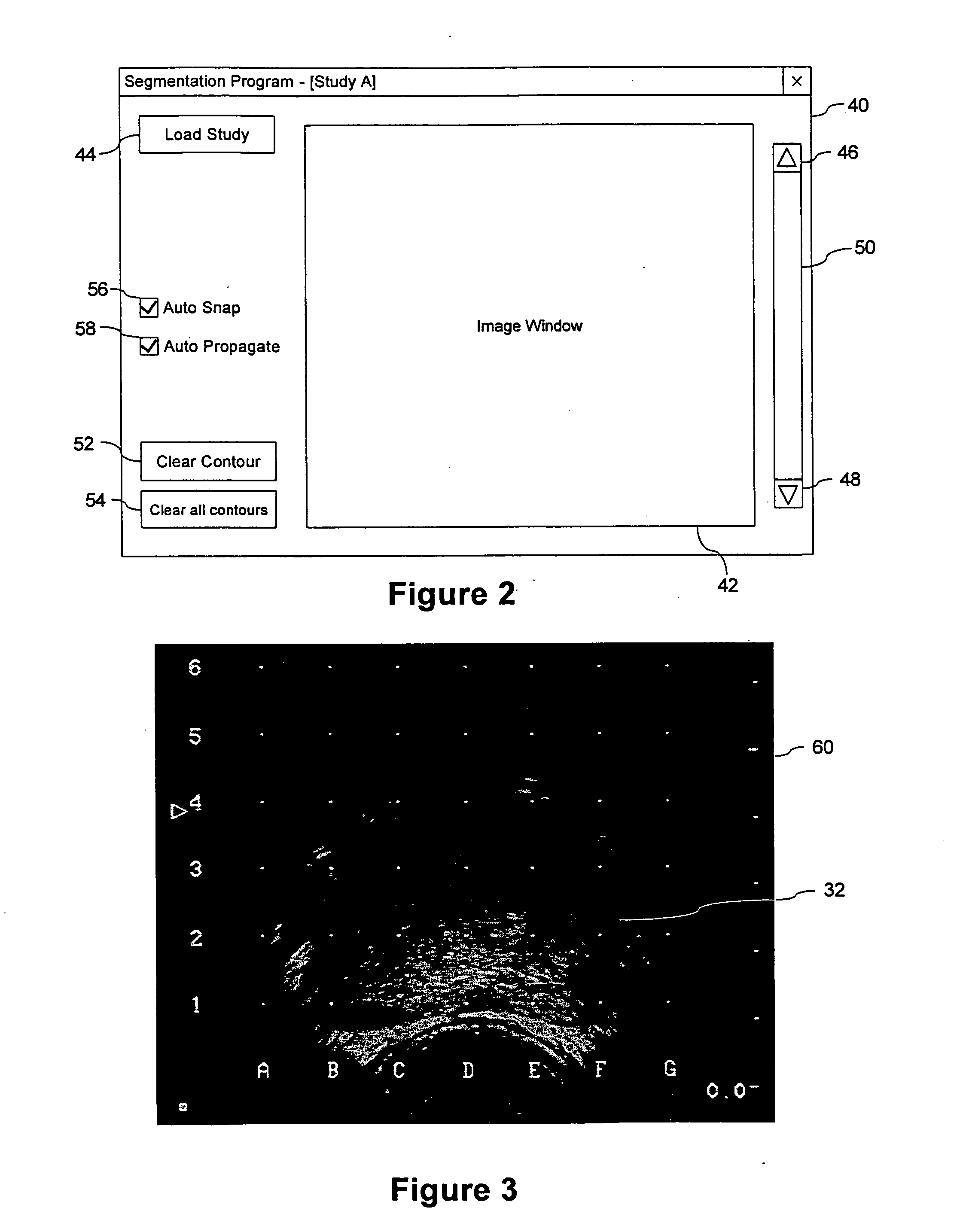
A method and computer program are provided for segmenting a prostate from a medical image such as an ultrasound image. Each slice in a study is analysed and uses a manual initialization to obtain an initial contour, in which a user selects initial points that are automatically rendered on the image. An automatic refinement stage then snaps the contour to the prostate boundary in the image based on a pre-stored anatomical atlas and edge information obtained from the image. A manual adjustment stage may then be performed and if selected, the contour is automatically propagated to the next image slice to avoid the manual initialization. An auxiliary image slice may be referred to, which indicates how the prostate shape changes from slice to slices e.g. by providing a perpendicular profile.
Owner:MERATIVE US LP
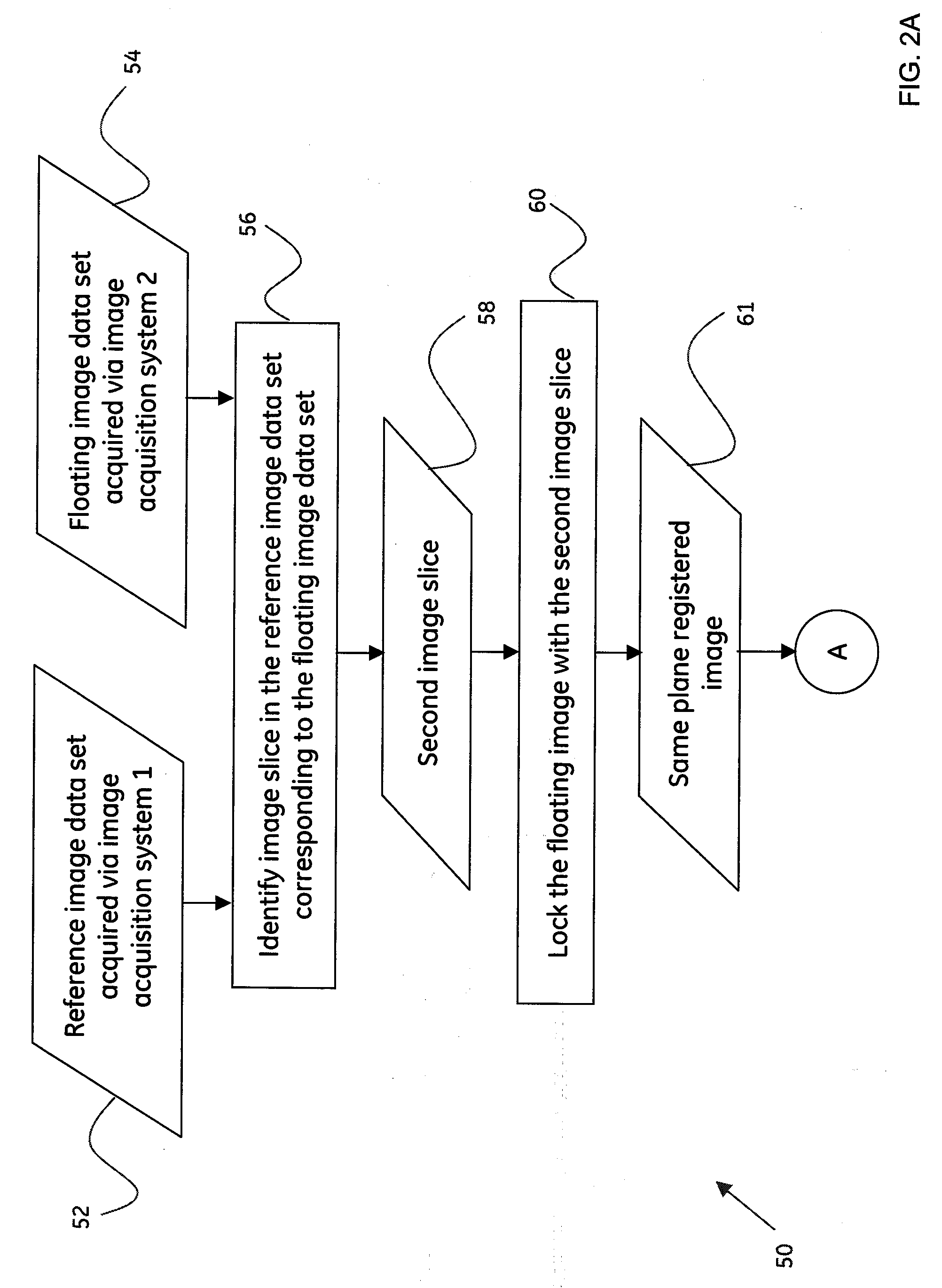
Enhanced system and method for volume based registration
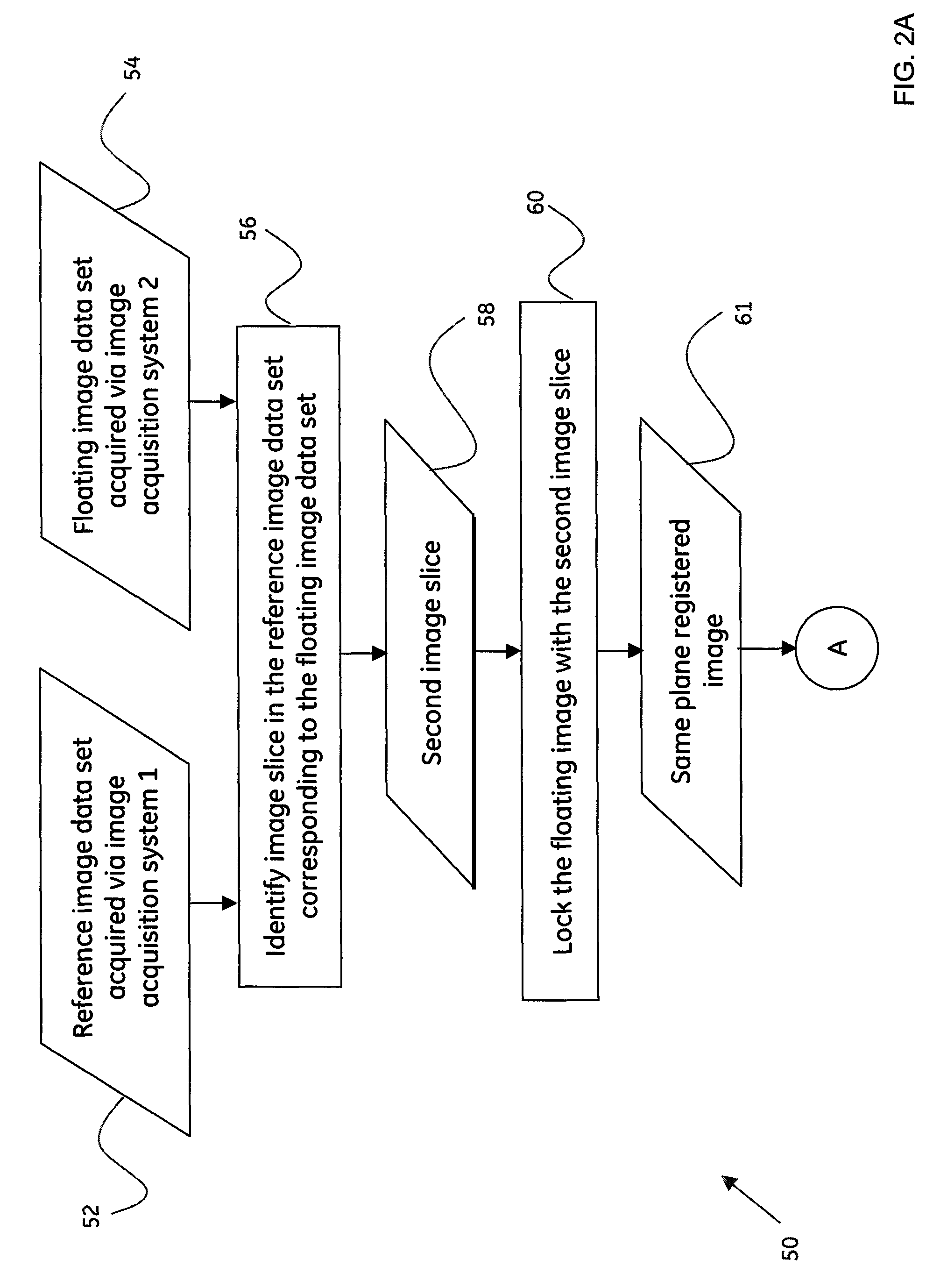
A method for volume based registration of images is presented. The method includes receiving a first image data set and at least one other image data set. Further the method includes identifying a first image slice in the at least one other image data set corresponding to the first image data set. The method also includes selecting a first point of interest on at least one of the first image data set or the first image slice in the at least one other image data set. In addition, the method includes selecting a second point of interest on the other of the first image data set or the first image slice in the at least one other image data set, wherein the second point of interest corresponds to the first point of interest. Moreover, the method includes translating one of the first image data set, the first image slice, or both, in a first direction, a second direction and a third direction to align the first point of interest with the second point of interest. Also, the method includes registering the first image data set and the at least one other image data set. Systems and computer-readable medium that afford functionality of the type defined by this method is also contemplated in conjunction with the present technique.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Considerations when colon segmentation differs between CAD processing and visualization
A system and method for preserving CAD marks falling outside the three-dimensional rendering on a visualization display following segmentation of CT medical image slices for review by a user is disclosed. The CT medical images are processed by both a CAD algorithm and a visualization workstation. The CAD algorithm reports detected suspicious regions to the visualization workstation for display on the three-dimensional rendering of the medical images as well as creates a list of the detections to notify the user. If the detected CAD marks are not located on the three-dimensional rendering of the medical images, the user is notified. The user can the view the detected CAD marks on the two-dimensional CT medical images.
Owner:ICAD INC
Systems and methods for segmentation of volumetric objects by contour definition using a 2D interface integrated within a 3D virtual environment ("integrated contour editor")
Systems and methods for a fully integrated contour editor are presented. In exemplary embodiments of the present invention a 2D interface which allows a user to define and edit contours on one image slice of the data set at a time is provided along with a 3D interface which allows a user to interact with the entire 3D data set. The 2D interface and the 3D interface are fully integrated, and contours defined or edited within the 2D interface are simultaneously displayed in the appropriate location of the 3D data set. The 2D contour can be created and edited with various readily available tools, and a region of interest indicated within the 3D data set causes the relevant 2D slice to be displayed in the 2D interface with an indication of the user selected area of interest. In exemplary embodiments of the present invention, systems can automatically generate contours based on user definition of a top and bottom contour, and can implement contour remapping across multiple data sets.
Owner:BRACCO IMAGINIG SPA
Systems and methods for image processing of 2D medical images
ActiveUS8009891B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementImaging processingDisplay device
Certain embodiments of the present invention provide a system for image processing including a database, an image processor, and a display. The database includes a plurality of image slices. Each image slice in the plurality of image slices is based at least in part on an object. The image processor is adapted to generate a display image. The display image includes a selected image slice rendered about perpendicular to a localizer image. The selected image slice is selected from the plurality of image slices. The display is adapted to display the display image.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method, system and computer program product for multi-modality registration using virtual cursors
A method for multi-modality registration using virtual cursors including receiving a two-dimensional image dataset for an object at a first position and receiving a three-dimensional image dataset for the object at the first position. The three-dimensional image dataset includes a plurality of image slices. The two-dimensional image dataset is registered with the three-dimensional image dataset without taking into account a magnification factor. A user cursor position for a location in the two-dimensional image dataset is received. A slice of interest in the three-dimensional image dataset is received. The slice of interest is selected from the plurality of image slices in the three-dimensional image dataset. A shadow cursor position for a location in the three dimensional dataset is calculated. The shadow cursor position corresponds to the user cursor position and the calculating includes a correction for the magnification factor corresponding to the shadow cursor position for the slice of interest. The shadow cursor position is output.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
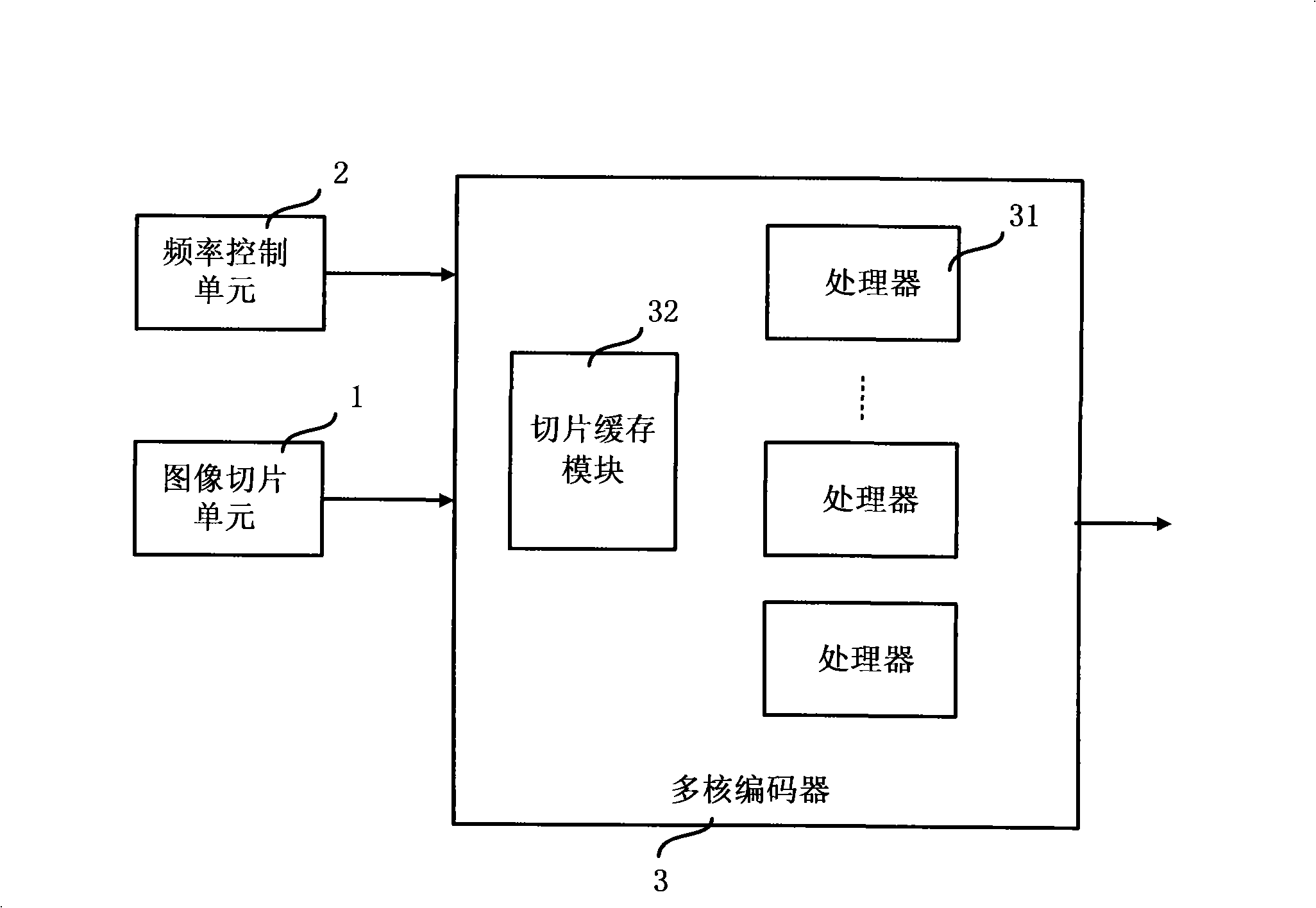
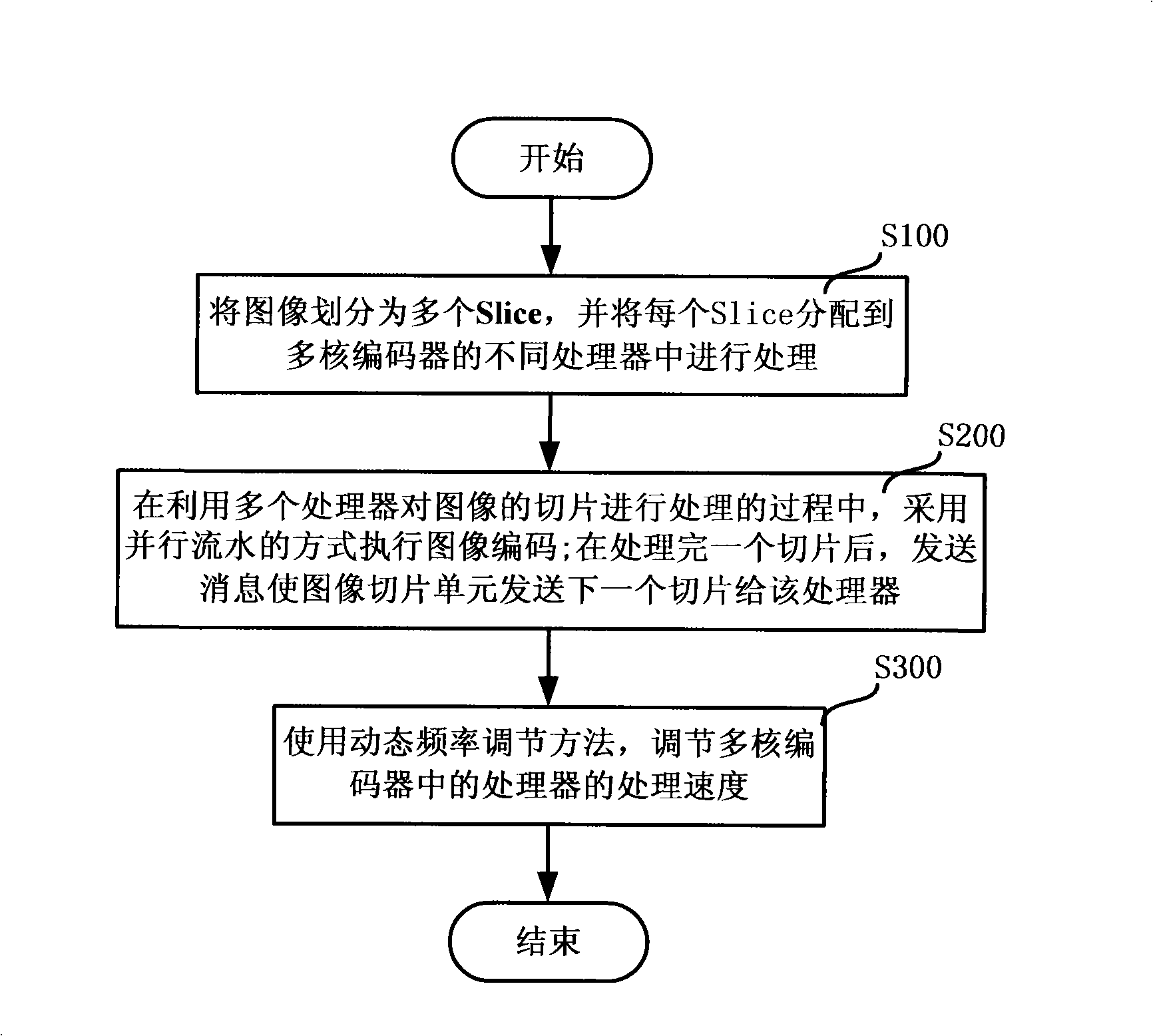
A multi-processor video coding chip device and method
ActiveCN101267564ADoes not affect running speedRun syncTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationComputer architectureMulti processor
The invention discloses a device and a method for a multiprocessor video coding chip. The device comprises a multi-core coder including multiple processors, and an image slice unit. The image slice unit is used for segmenting a video image into multiple slices, and distributing the slices to different processors of the multi-core coder; the multi-core coder is used for imaging coding by means of parallel pipeline when processing the image slices by multiple processors, and sending a massage to the image slice unit after a processor of the multi-core coder finishes processing one slice, such that the image slice unit sends a next slice to the processor. The device also comprises a frequency control unit for adjusting the processing speeds of the processors of the multi-core coder by using dynamic frequency adjusting method. The invention can greatly reduce power consumption without affecting the running speed of a whole task.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Adaptive visualization for direct physician use
ActiveUS20130121548A1Accurate decisionAccurate diagnostic decisionImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical structuresOptical property
A method of modifying a three dimensional (3D) volume visualization image of an anatomical structure in real time to separate desired portions thereof. The method includes providing a two dimensional (2D) image slice of a 3D volume visualization image of an anatomical structure, identifying portions of the anatomical structure of interest, and providing a prototype image of desired portions of the anatomical structure. The method then includes using an evolver to evolve parameters of an algorithm that employs a transfer function to map optical properties to intensity values coinciding with the portions of the anatomical structure of interest to generate an image that sufficiently matches the prototype image. If the parameters match the prototype image, the method then includes applying the transfer function to additional 2D image slices of the 3D volume visualization image to generate a modified 3D volume visualization image of the anatomical structure. The method includes using a pattern recognizer to assist the evolver, to classify whether a view is normal or abnormal, and to extract the characteristic of an abnormality if and when detected.
Owner:AI VISUALIZE INC
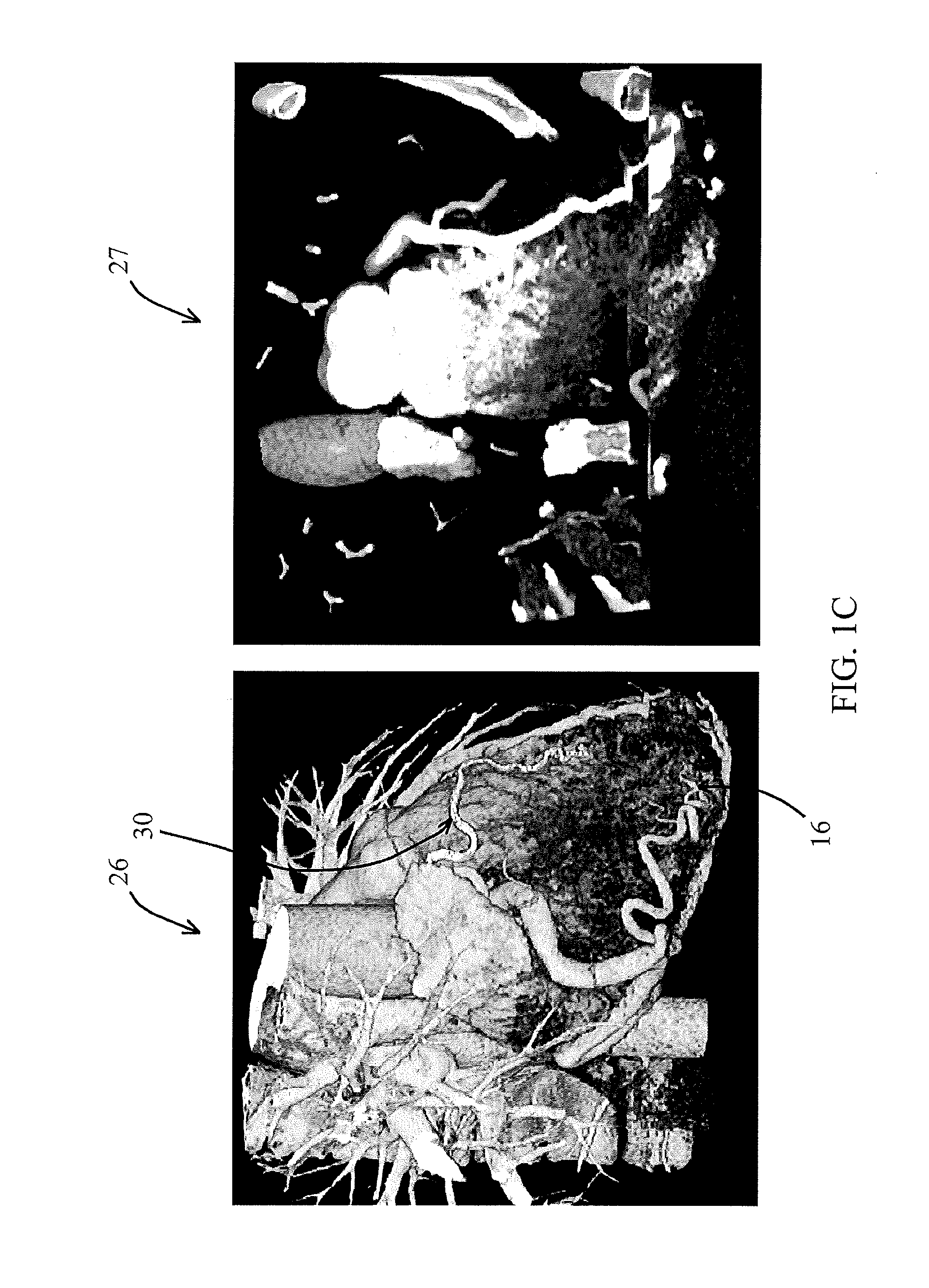
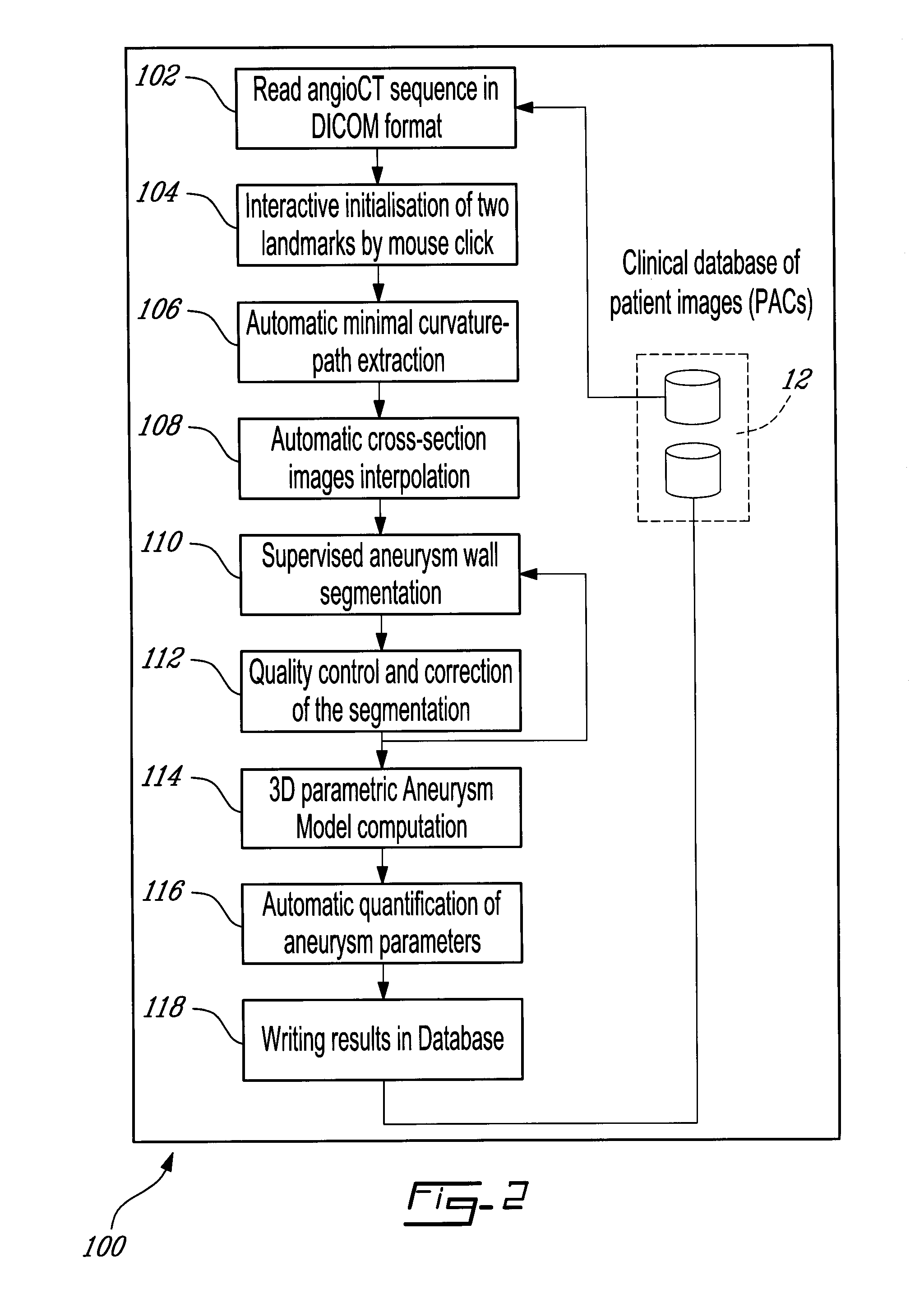
Method for tracking 3D anatomical and pathological changes in tubular-shaped anatomical structures
InactiveUS20100309198A1Image enhancementDetails involving processing stepsAnatomical structures3d image
A method for visualizing the anatomy of a region of interest of a tubular-shaped organ based on acquired three-dimensional image slices of the region of interest. Prior to segmentation, reference markers are positioned interactively in the image slices, a minimum curvature path connecting the reference markers is automatically extracted and cross-sectional images are interpolated along a plane normal to a tangent vector of the minimum curvature path. A segmented area corresponding to the region of interest is then delimited in each cross-sectional image and, using this segmented area, a three-dimensional surface representation of the region of interest is computed to readily quantify attributes, such as a maximal diameter and a volume, of the region of interest. When the image sets are acquired in different imaging geometries, the image sets may further be co-registered prior to segmentation, resulting in image sets superimposed in the same geometrical reference frame.
Owner:VAL CHUM PARTNERSHIP
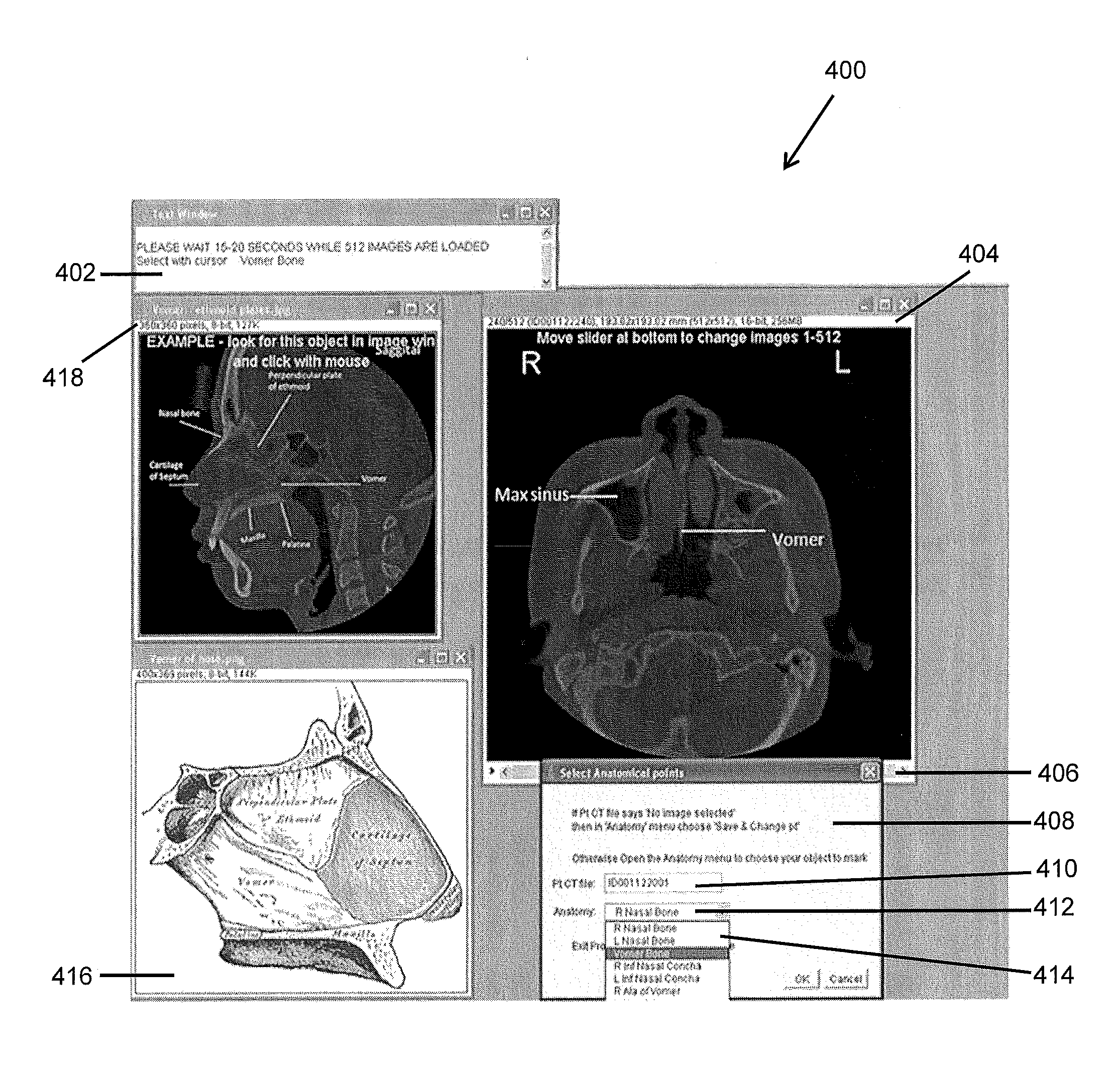
System and Method for Propagation of Spine Labeling
A system and method of labeling orthogonal or otherwise spatially related image views and related images is provided. The present invention provides automated progression for the labeling of vertebral and inter-vertebral regions, propagation of labels between views and images within a series, centering of label regions relative to the spine, circular lists of predefined labels, and label displays for individual slices of an orthogonal or axial view as a user scrolls through the plurality of image slices of the given view. In a further aspect, the present invention provides automated labeling of vertebral and inter-vertebral regions when a user provides labels for the adjacent two inter-vertebral or vertebral regions.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
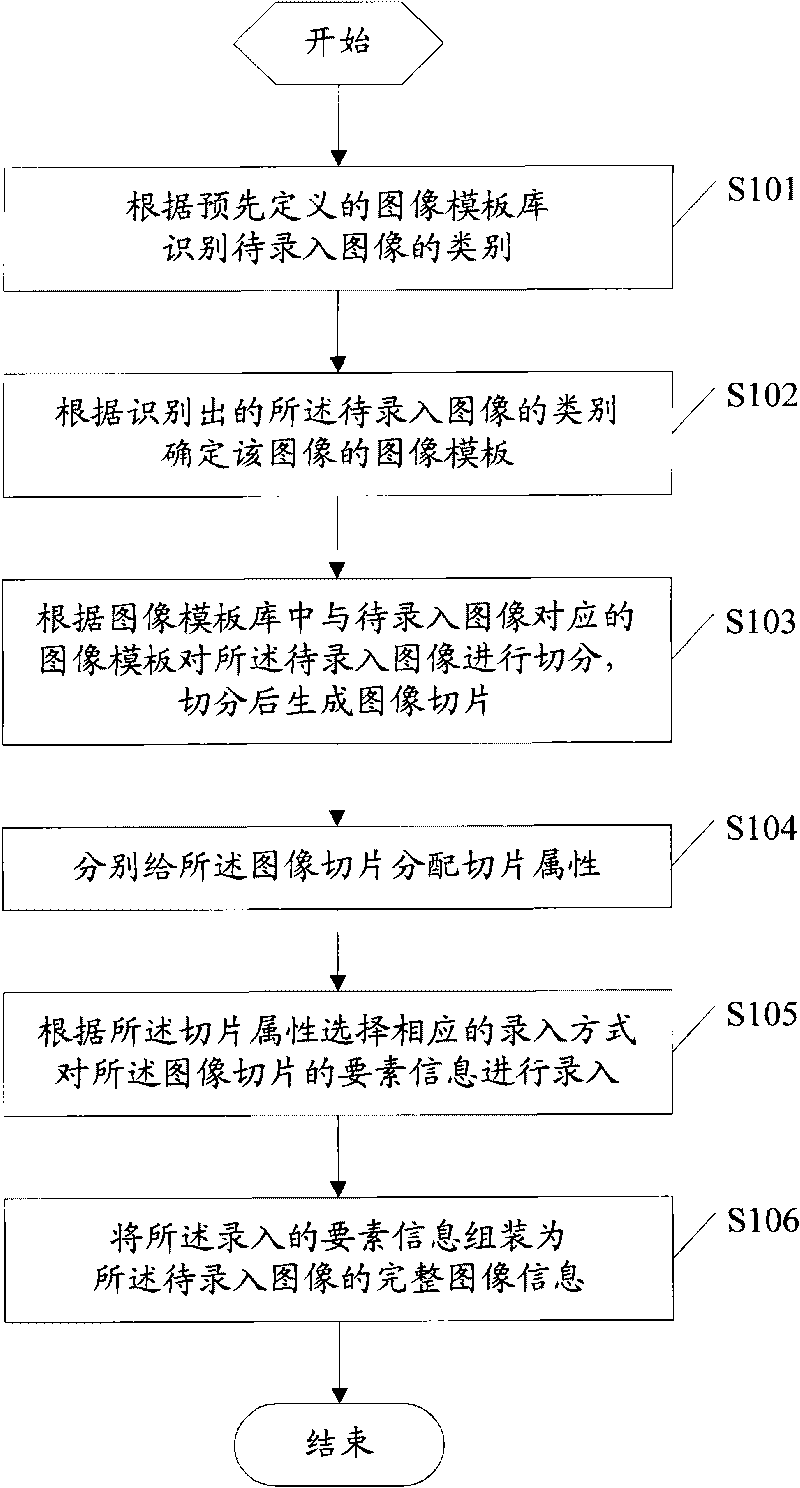
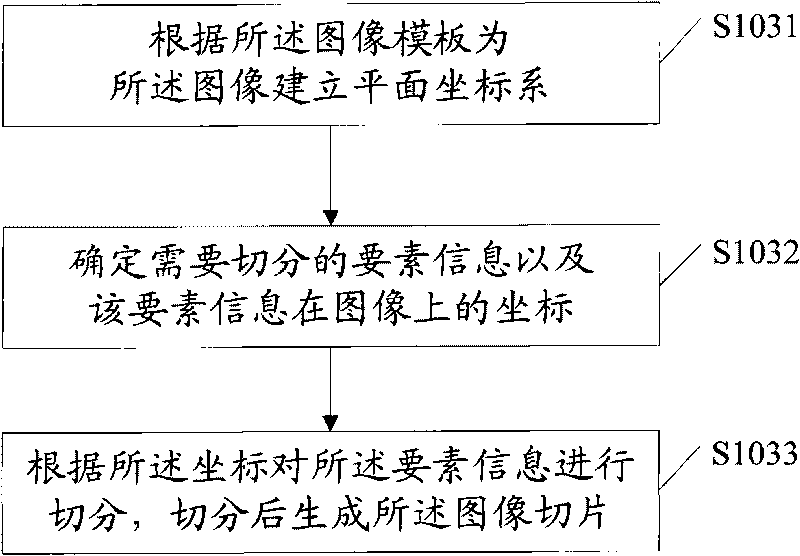
Method of image information input and system thereof
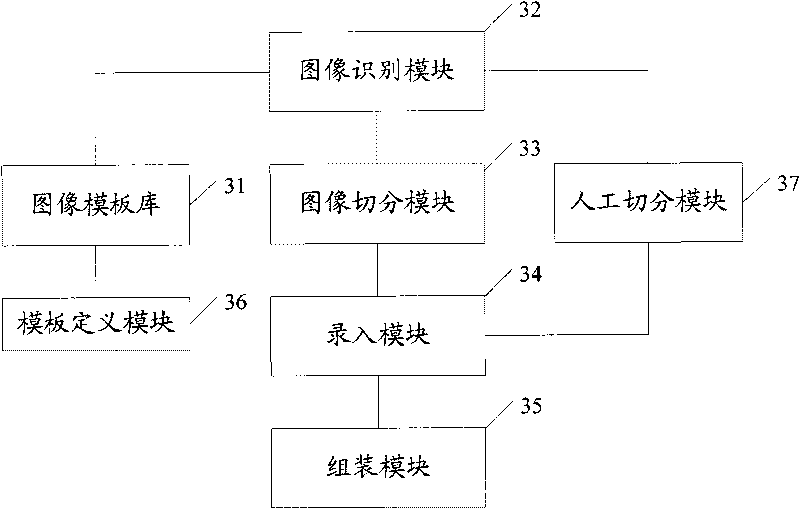
ActiveCN101739441AImprove securityImprove confidentialityCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsPattern recognitionConfidentiality
The invention provides a method of image information input, which comprises the following steps: identifying the category of the images for input according to the pre-defined image template base, determining the image template for the image according to the category identified, segmenting the image for input according to its template and produce image slices, each of which is distributed with slice attribute, choose proper input mode to input the elements of information of the images slices according to their attributes, assembling the input elements of information into a complete image information of the input images. The system carries out slicing the input images according to the pre-defined image templates and effectively prevents the input personnel or check operators from directly obtaining the complete original image, thus protects the private or sensitive information from leaking and enhances the safety and confidentiality of the image data collection.
Owner:CHINA CONSTRUCTION BANK
Feature Dependent Extended Depth of Focusing on Semi-Transparent Biological Specimens
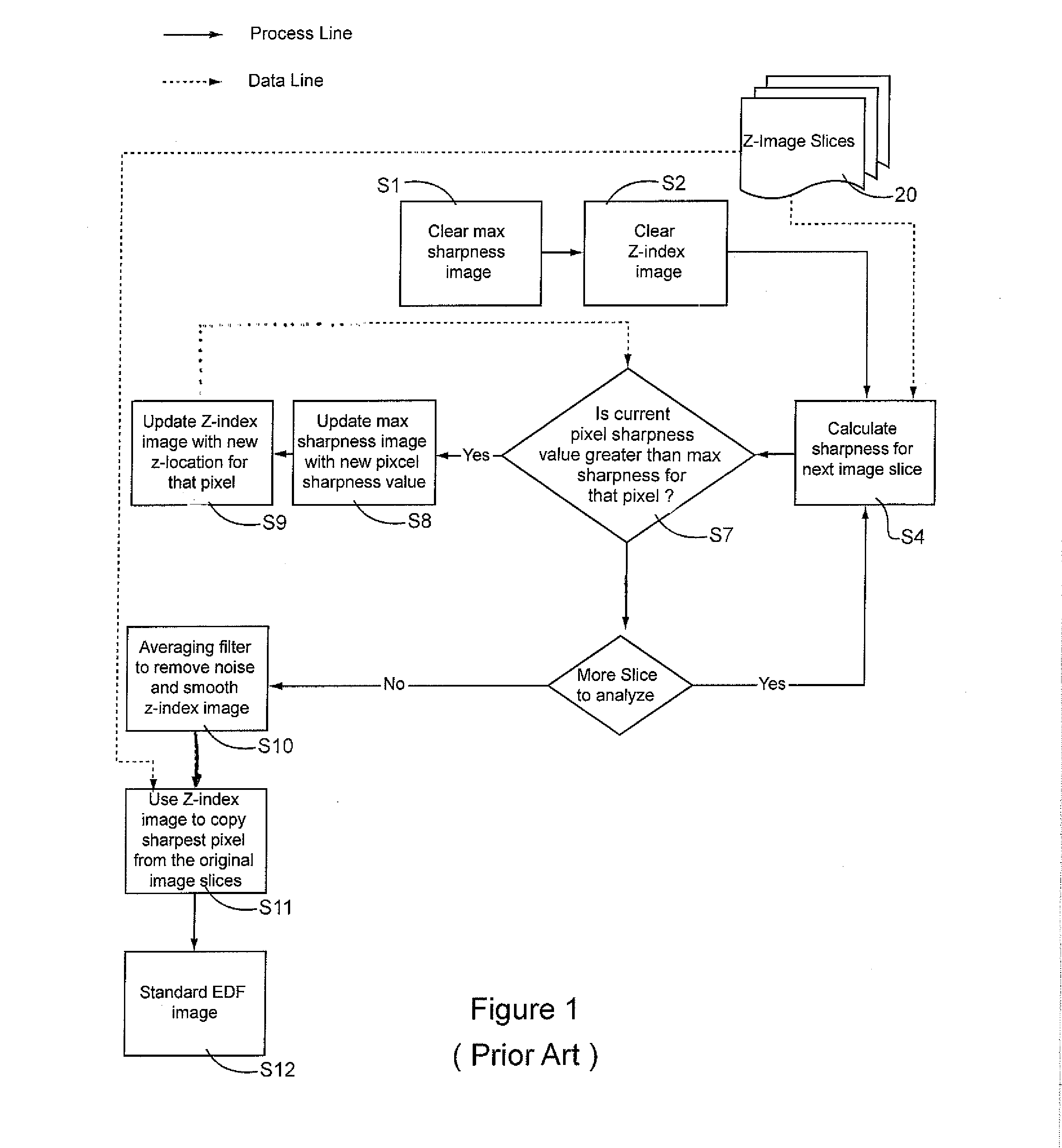
A method and system for constructing a digital image of a three-dimensional biological specimen that displays diagnostically important information—substantially to the exclusion of unimportant information. The system de-enhances features in a cellular specimen which are not diagnostically important and enhances those which are The system selects the sharpest pixel for each pixel location from among a stack of image slices and copies them into a composite image
Owner:CDX MEDICAL IP INC
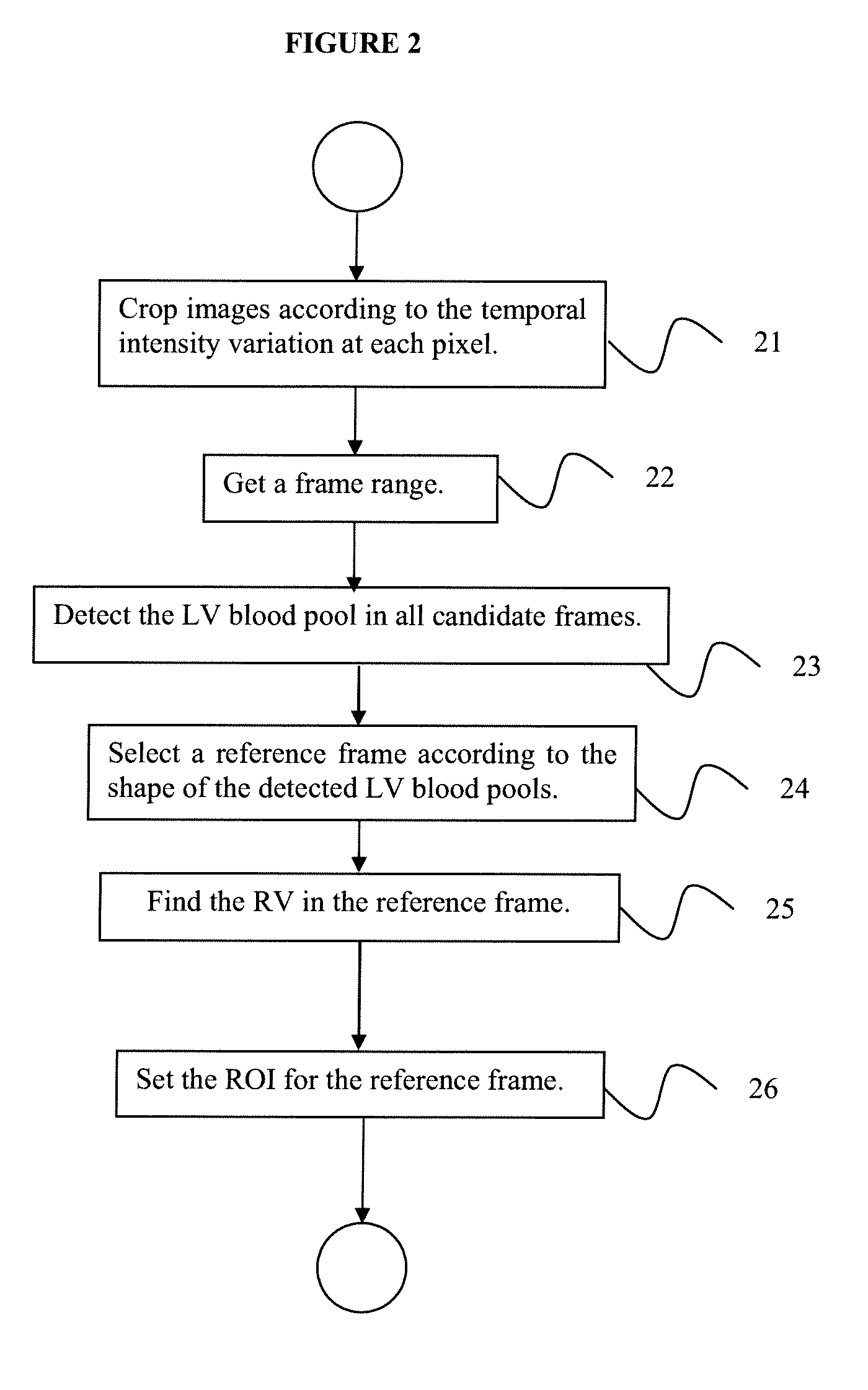
System and method for generating mr myocardial perfusion maps without user interaction
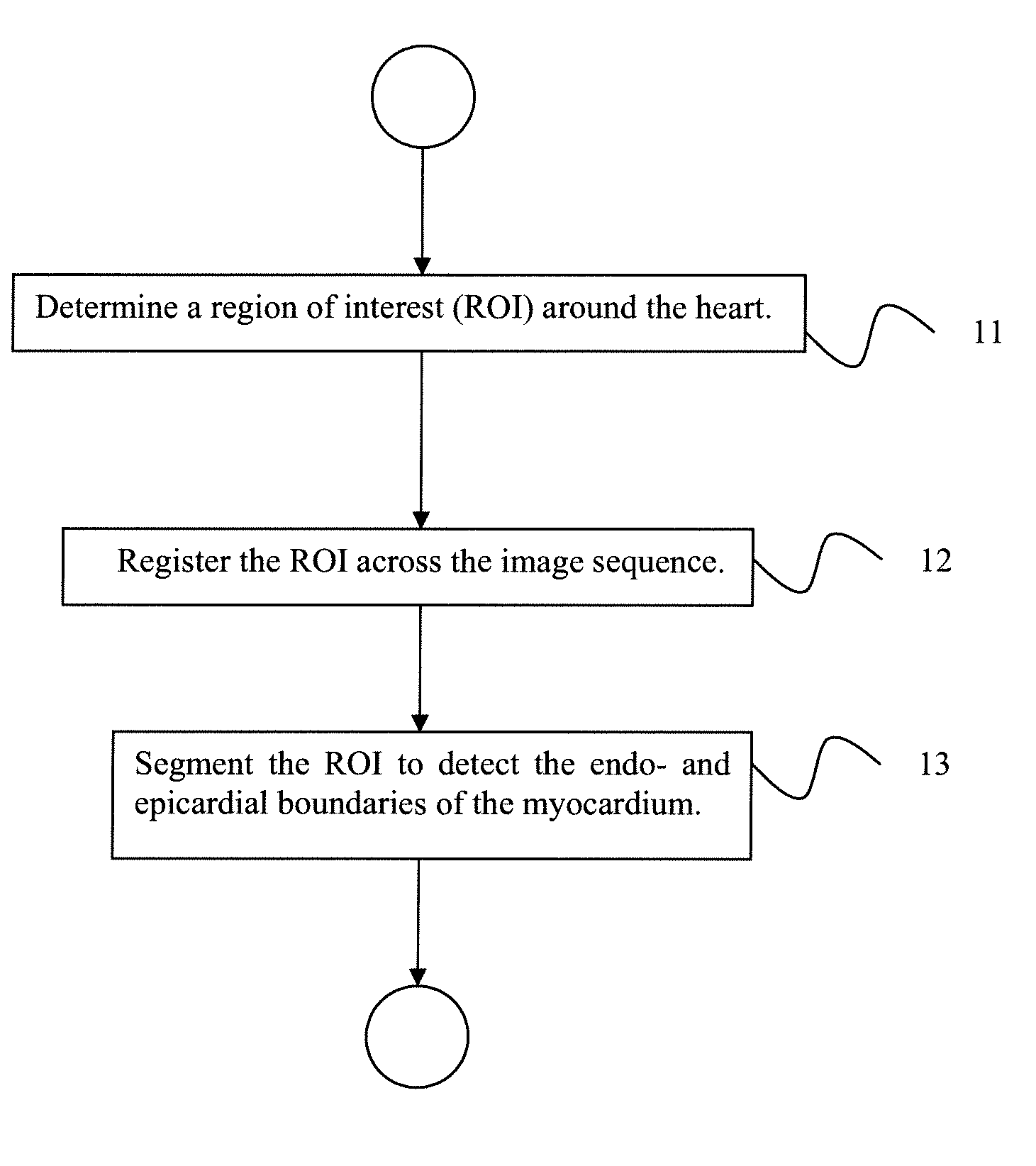
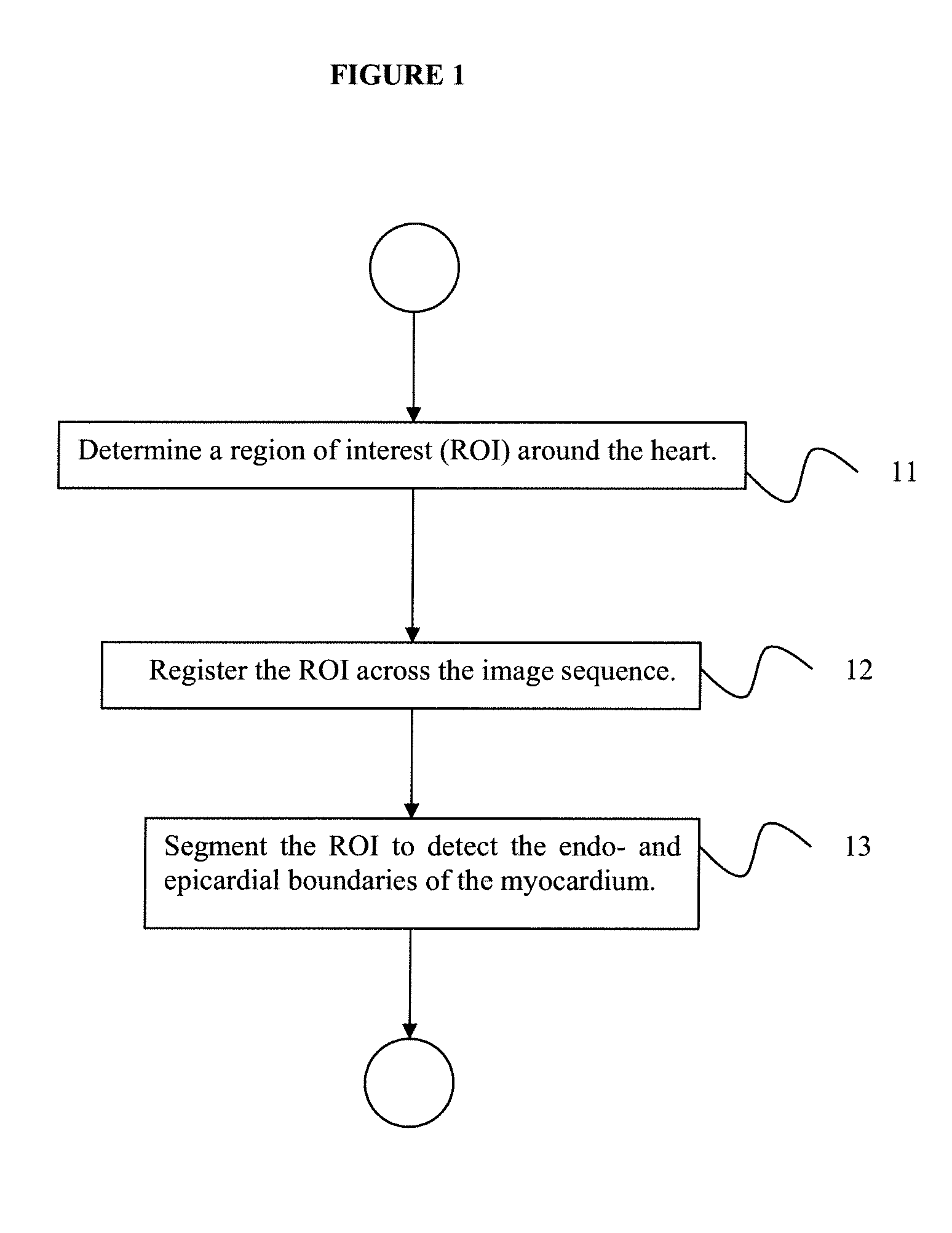
A method for automatically generating a myocardial perfusion map from a sequence of magnetic resonance (MR) images includes determining a region of interest (ROI) in a reference frame selected from a time series of myocardial perfusion MR image slices, registering each image slice in the time series of slices to the reference frame to obtain a series of registered ROIs, and using the series of registered ROIs to segment endo- and epi-cardial boundaries of a myocardium in the ROI.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
System and methods for anatomical structure labeling
InactiveUS20110311116A12D-image generationCharacter and pattern recognitionAnatomical structuresImage Reslicing
An imaging system and methods for processing a two-dimensional image from three-dimensional image information is disclosed. Images are segmented into foreground regions and background regions. An object-centered coordinate system is created and a hierarchical anatomical model is accessed to classify object in order to identify an anatomical object. The anatomical text labels are generated and positioned on the image slices and at least one image slice is displayed.
Owner:CREIGHTON UNIVERSITY
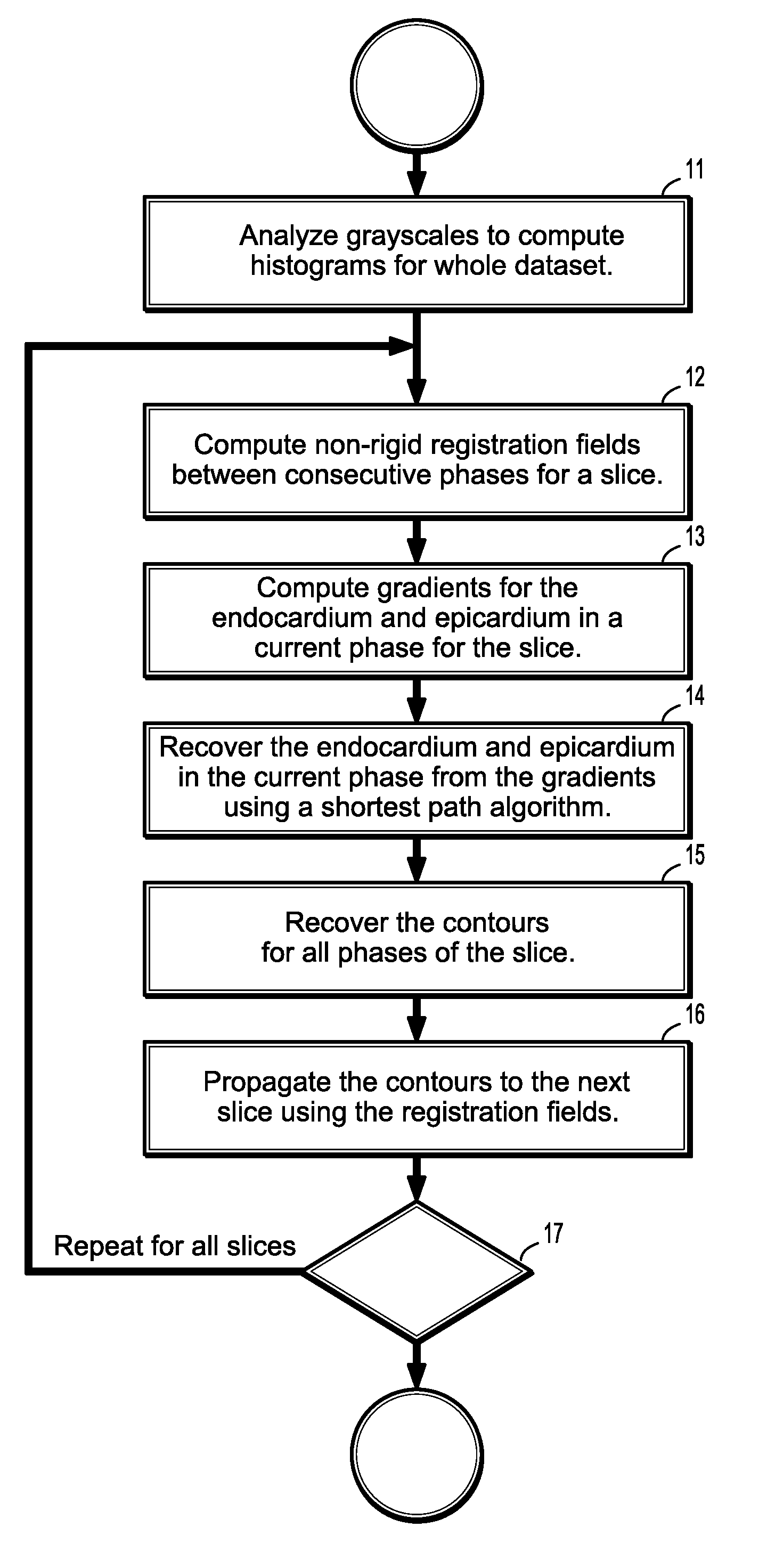
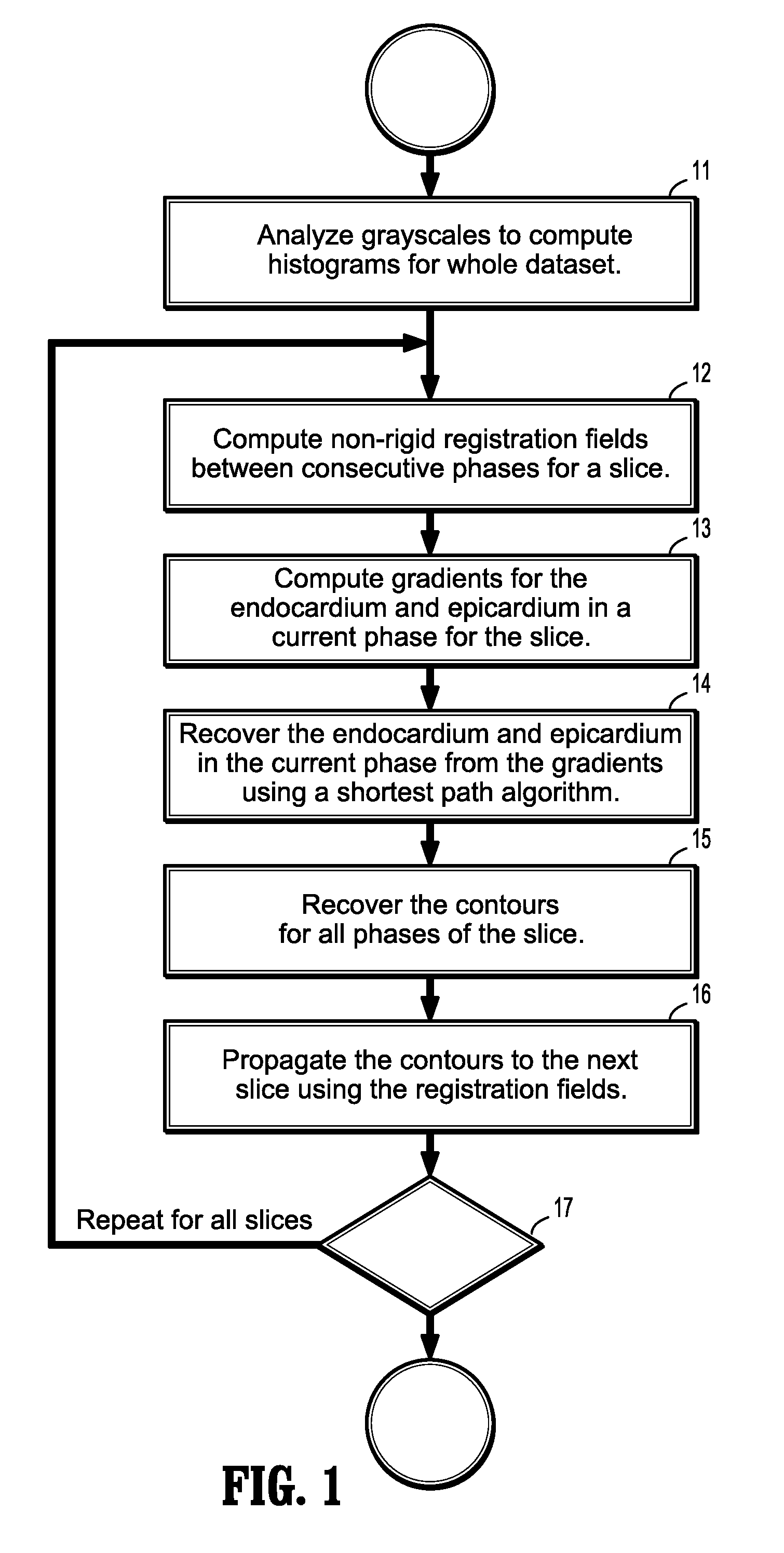
System and method for cardiac segmentation in mr-cine data using inverse consistent non-rigid registration
InactiveUS20110081066A1Guaranteed to be accurate and consistentImage enhancementImage analysis3d imageCardiac cycle
A method for cardiac segmentation in magnetic resonance (MR) cine data, includes providing a time series of 3D cardiac MR images acquired at a plurality of phases over at least one cardiac cycle, in which each 3D image includes a plurality of 2D slices, and a heart and blood pool has been detected in each image. Gray scales of each image are analyzed to compute histograms of the blood pool and myocardium. Non-rigid registration deformation fields are calculated to register a selected image slice with corresponding slices in each phase. Endocardium and epicardium gradients are calculated for one phase of the selected image slice. Contours for the endocardium and epicardium are computed from the gradients in the one phase, and the endocardium and epicardium contours are recovered in all phases of the selected image slice. The recovered endocardium and epicardium contours segment the heart in the selected image slice.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Remotely viewing large tiled image datasets
InactiveUS7872650B2Easy to navigateGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionData setImage resolution
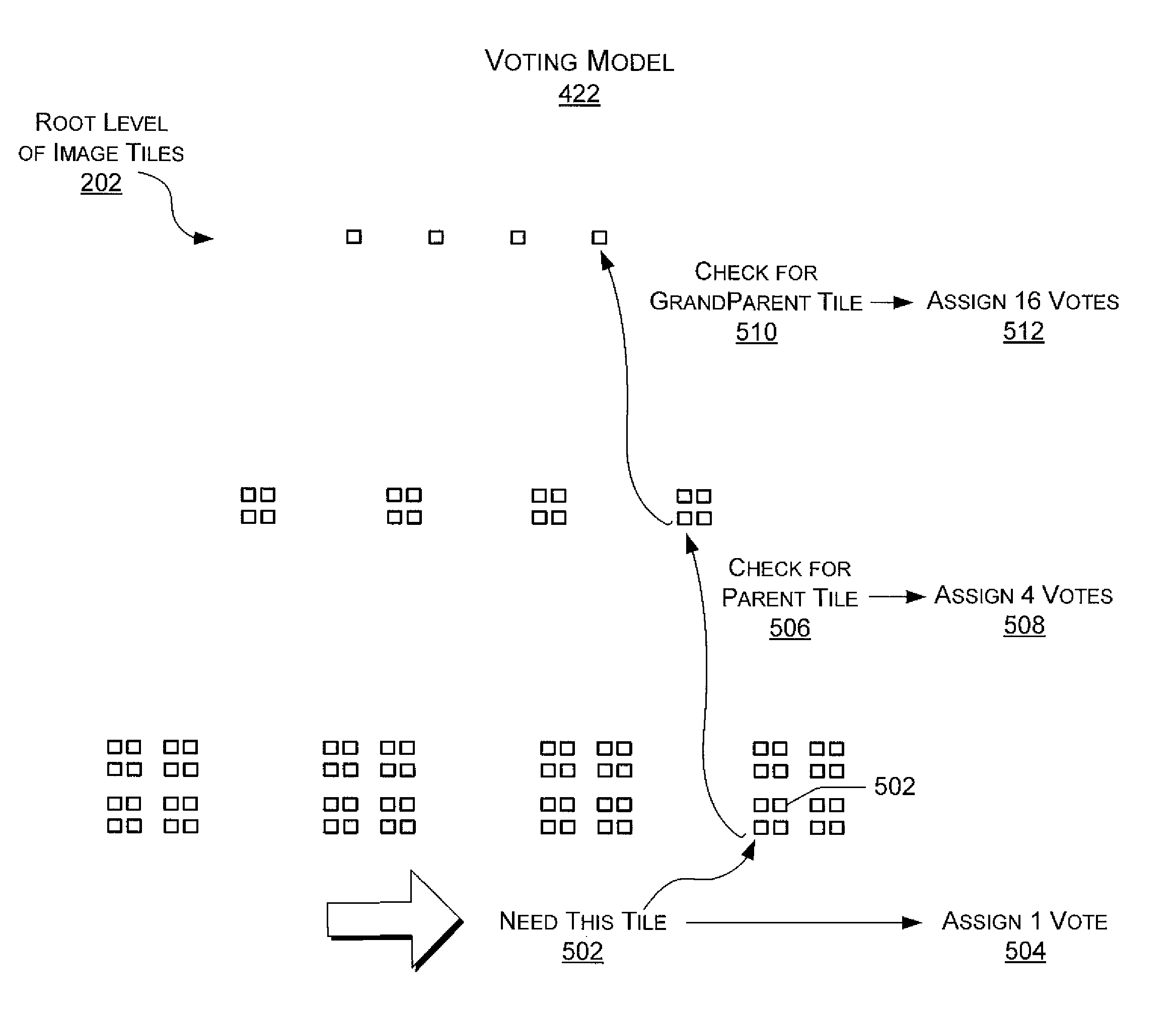
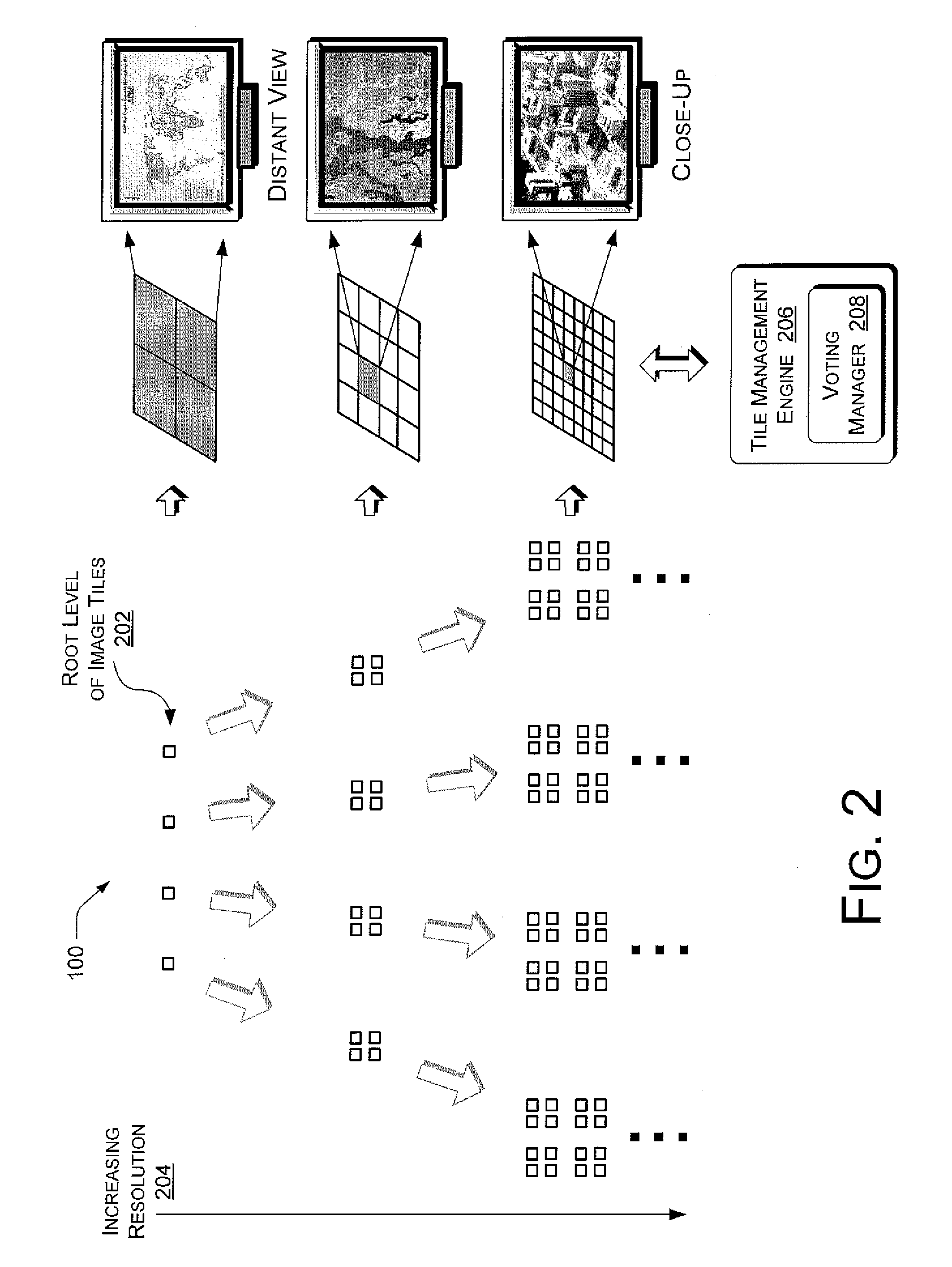
Systems and methods are described for remotely viewing large tiled image datasets, such as global maps at multiple resolution levels. A voting schema immediately retrieves the image tiles in a multi-resolution image dataset that are most likely to provide temporary complete coverage of a given browser view while more numerous optimal image tiles for the current resolution level of the browser view are still downloading. Image tiles that are not locally available are assigned one vote toward immediate download while their parent and higher-order image tiles accumulate increasing multiples of the vote. This provides panning and zooming such that it is difficult for a user to outdrive the update speed of the changing view. The system can also enhance navigation to provide natural and responsive movement of the browser viewport while image tiles are being downloaded.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Image segmentation of organs and anatomical structures
ActiveUS20130044930A1Reduce image noiseFacilitate the further image registration proceduresImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical structuresImage segmentation
A system and method to conduct image segmentation by imaging target morphological shapes evolving from one 2-dimension (2-D) image slice to one or more nearby neighboring 2-D images taken from a 3-dimension (3-D) image. One area defined by a user as a target on an image slice can be found in a corresponding area on a nearby neighboring image slice by using a deformation field generated with deformable image registration procedure between these two image slices. It allows the user to distinguish target and background areas with the same or similar image intensities.
Owner:PATHFINDER THERAPEUTICS +1
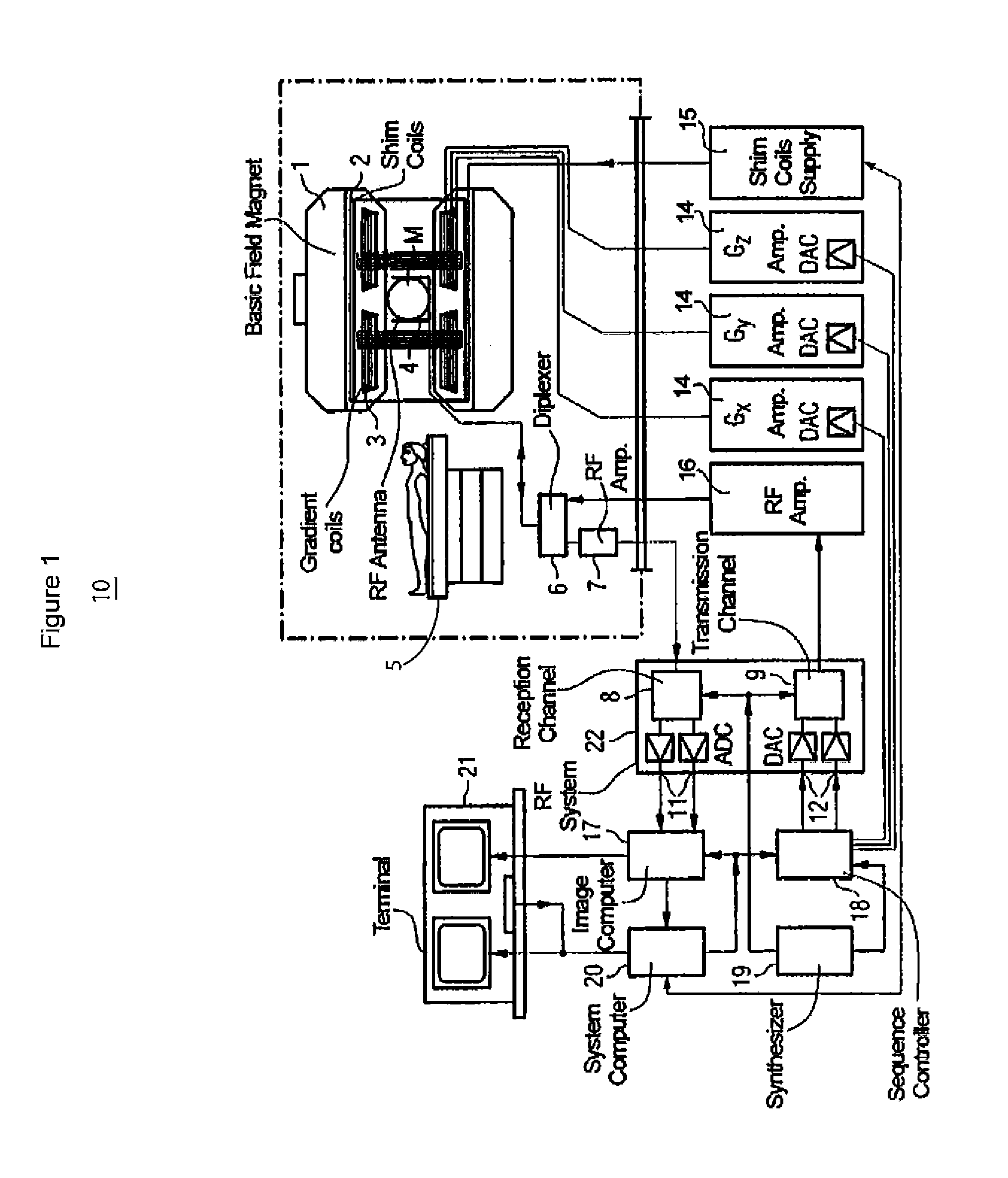
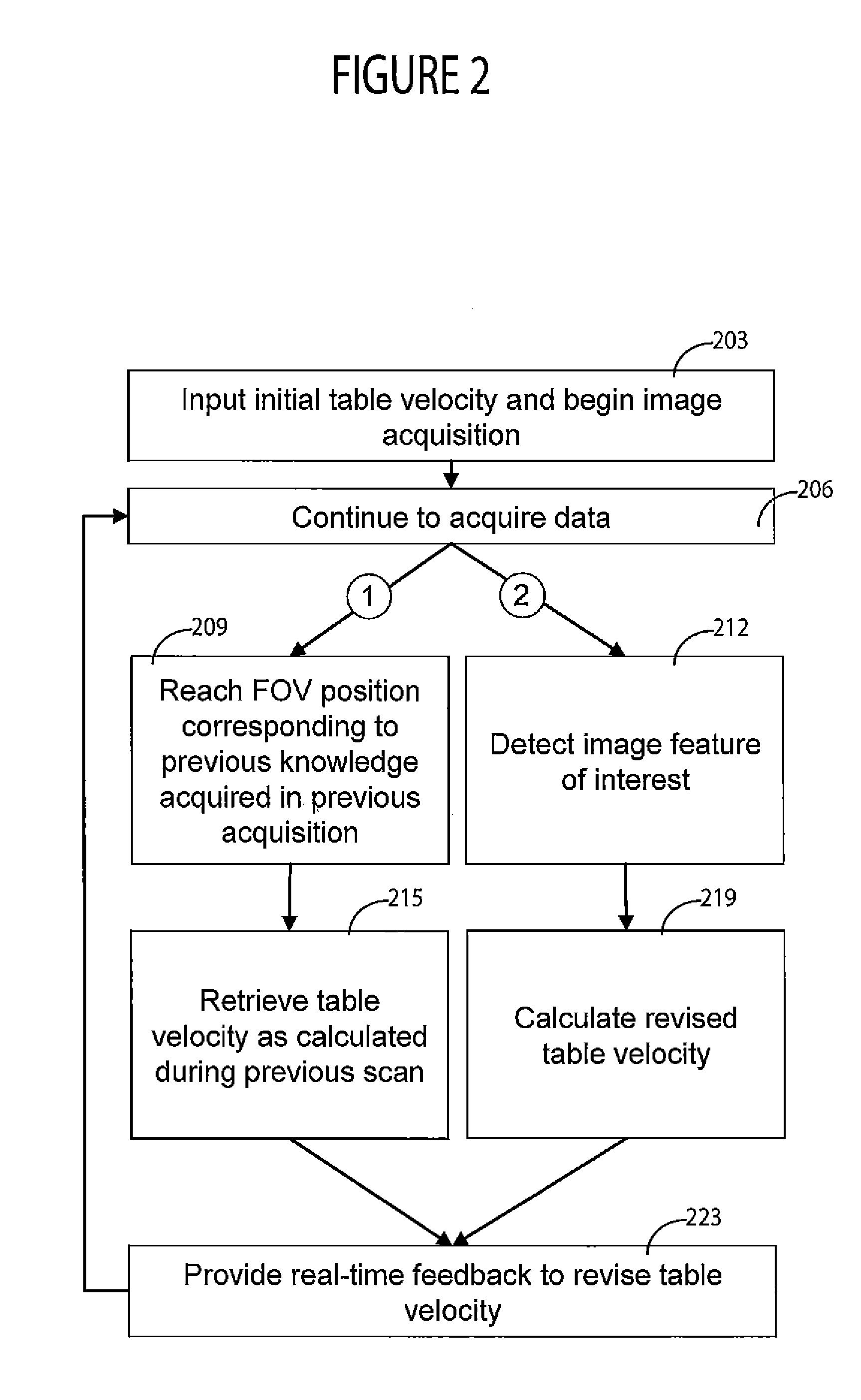
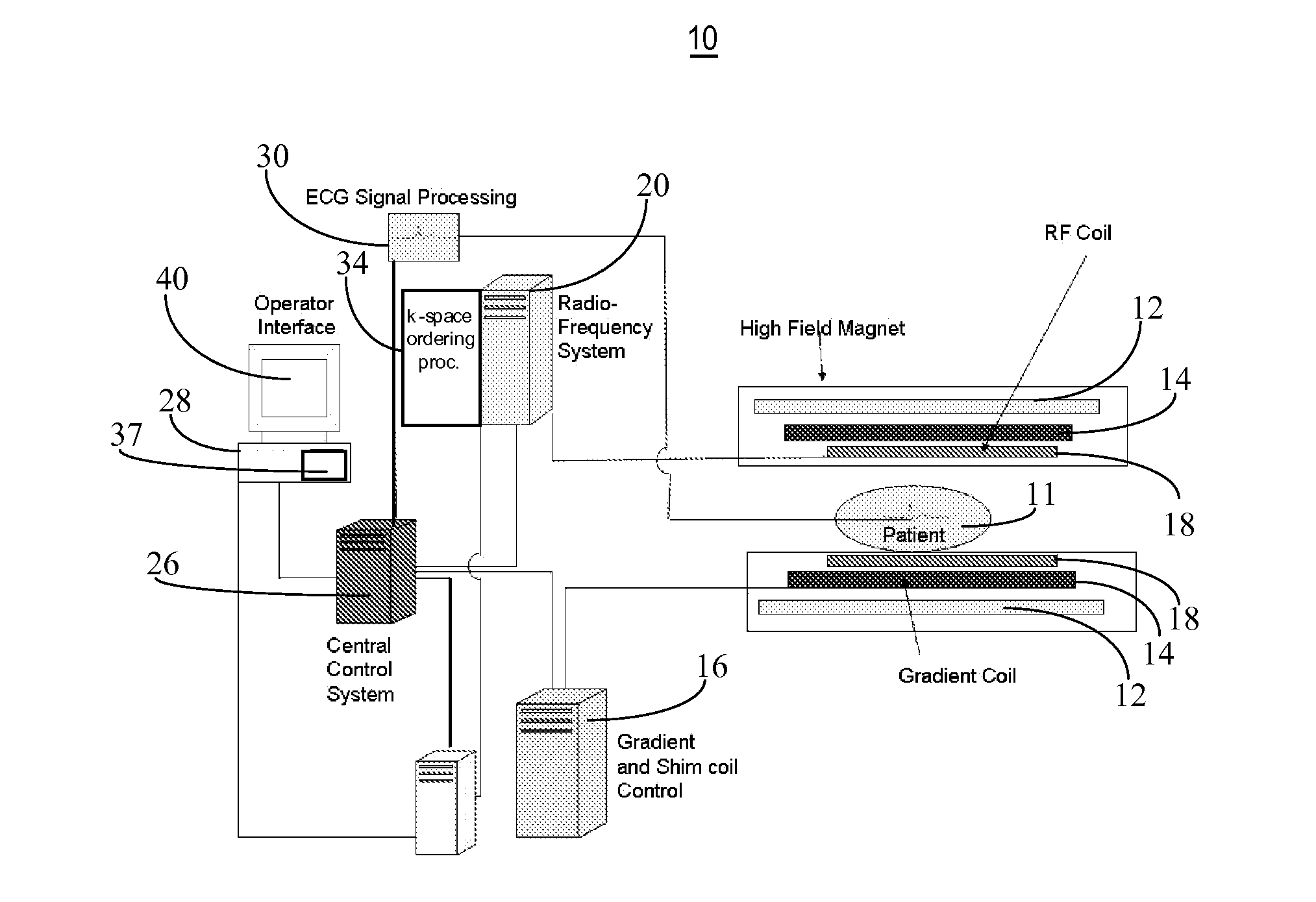
Patient Support Table Control System for Use in MR Imaging
A system for Non-Contrast Agent enhanced MR imaging includes an MR image acquisition device for acquiring imaging datasets comprising one or more image slabs individually comprising multiple image slices. An image data processor processes data representing an acquired image slice to detect a predetermined anatomical feature of a patient by detecting an edge of the anatomical feature in response to detection of pixel luminance transitions. A patient support table controller automatically moves a patient table at a velocity adaptively and dynamically determined by, selecting data modifying table velocity from predetermined information associating an anatomical feature with table velocity modification data in response to detection of the anatomical feature and adaptively determining a table velocity using the modification data.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Measurement system for medical images
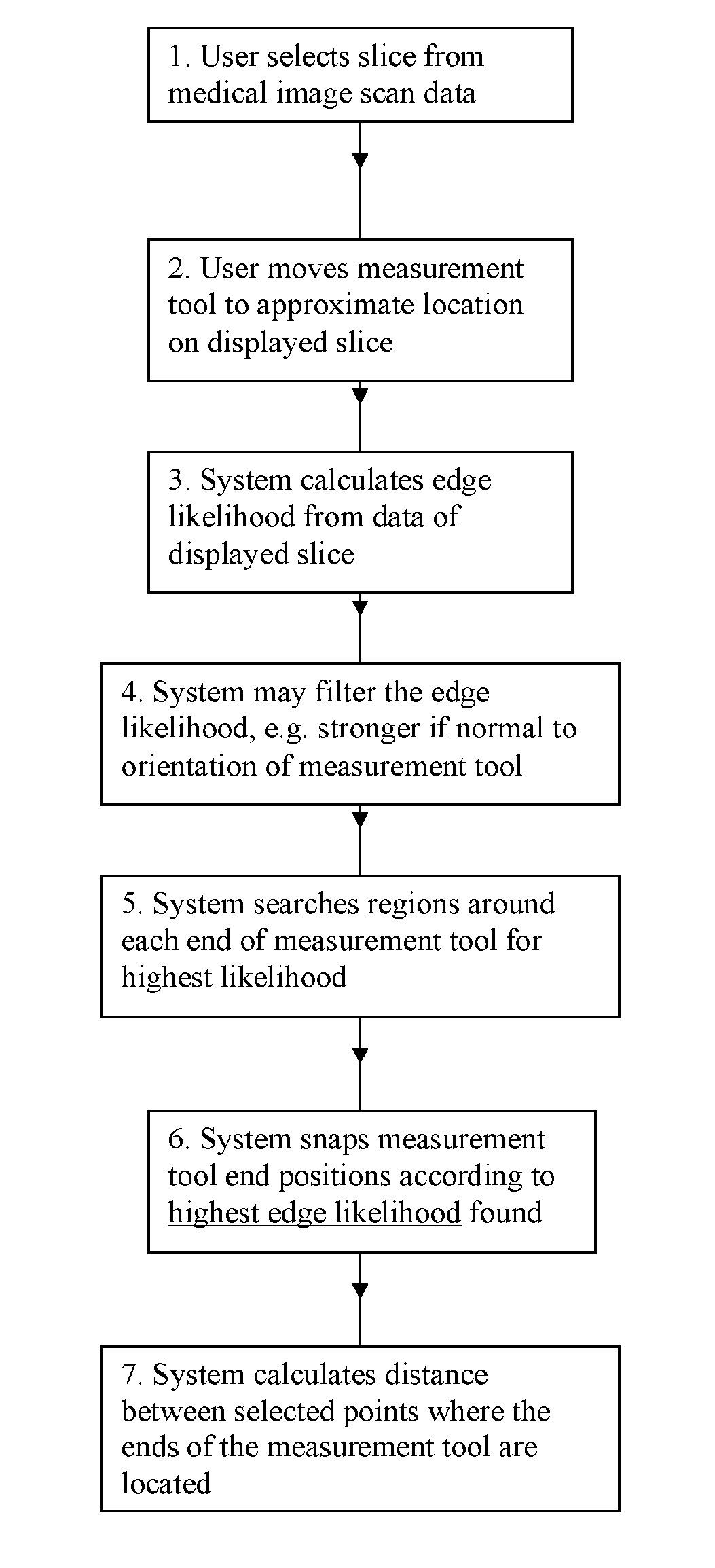
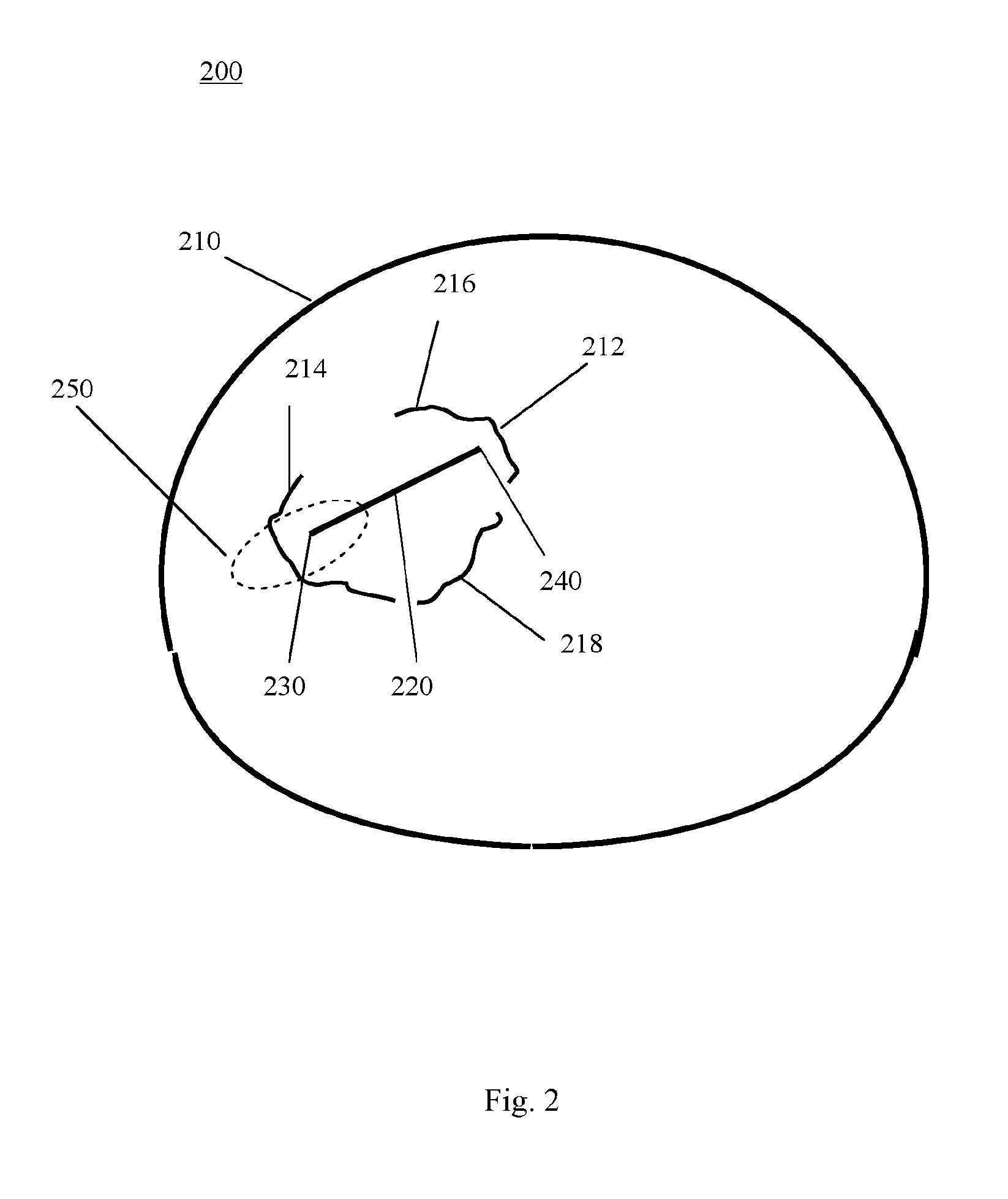
ActiveUS20140029815A1Improve accuracyGood repeatabilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementComputer visionImage Reslicing
A method of measuring a parameter of a structure (212) on a medical image (200) comprises a measurement tool (220) displayed on a slice of the image. An automated point detection function identifies a point within at least one region (250) of the image that optimises the placement of the respective end of the measurement tool (220). The region may be 2-d or 3-d. The identified point(s) are then used to calculate the parameter, which may be distance, angle, area or volume. The measurement tool (320) may move to the identified points (330, 340). A system (2000), computer program and computer-readable medium are also provided. The invention may make the measurement of tumours, and measurements of the spacing within or between various structures on a medical image, more accurate and / or more consistent.
Owner:MIRADA MEDICAL
Three dimensional pixel super-resolution microscopic imaging method
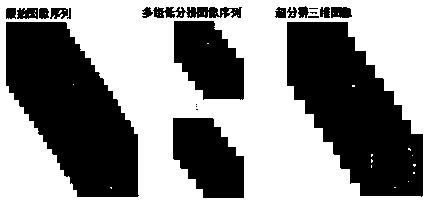
ActiveCN104111242AReduce magnificationLow priceFluorescence/phosphorescenceSensor planeHigh resolution image
A three dimensional pixel super-resolution microscopic imaging method is characterized by comprising the following steps: carrying out space vector scanning on a sample, wherein the scanning vector can form a non-right-angle spacial deflection angle with the plane horizontal direction X and vertical direction Y of an image collection device sensor or a Z axis direction of a microscope, so as to make that two neighbored image slices can be scanned by a step size of a sub pixel displacement along the X, Y, and Z directions; collecting the original three dimensional image sequence A by the image collecting device, cutting the original image sequence A into a plurality of groups of three dimensional image sequences Bi according to the lossless sampling principle, carrying out a super-resolution treatment on Bi to generate a three dimensional high resolution image E, and carrying out a deblurring treatment on E so as to obtain a clear high resolution image F. The spacial reflection angles formed by the scanning vector with the horizontal direction X, the vertical direction Y, and the Z axis of the microscope can be identical or different.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
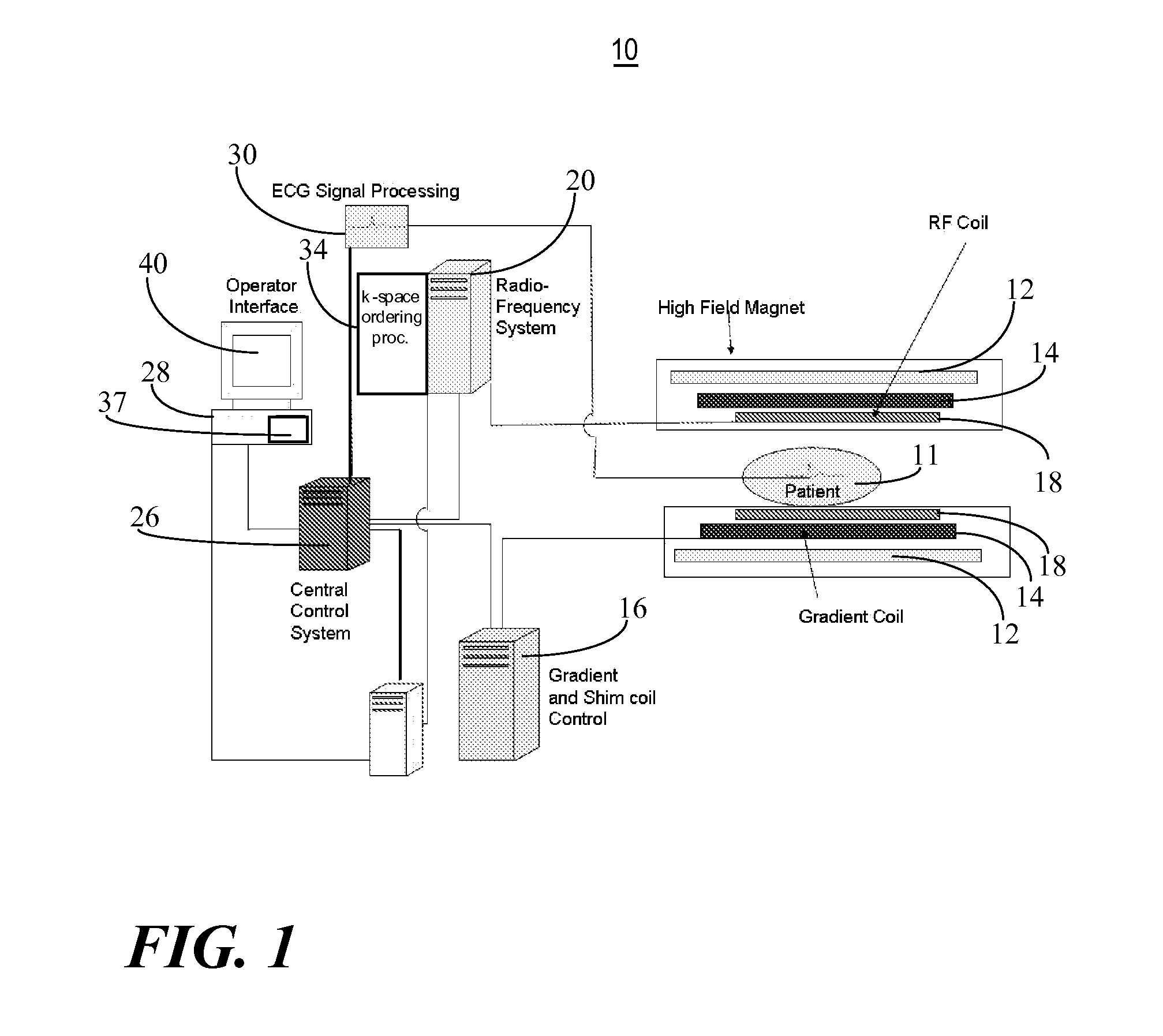
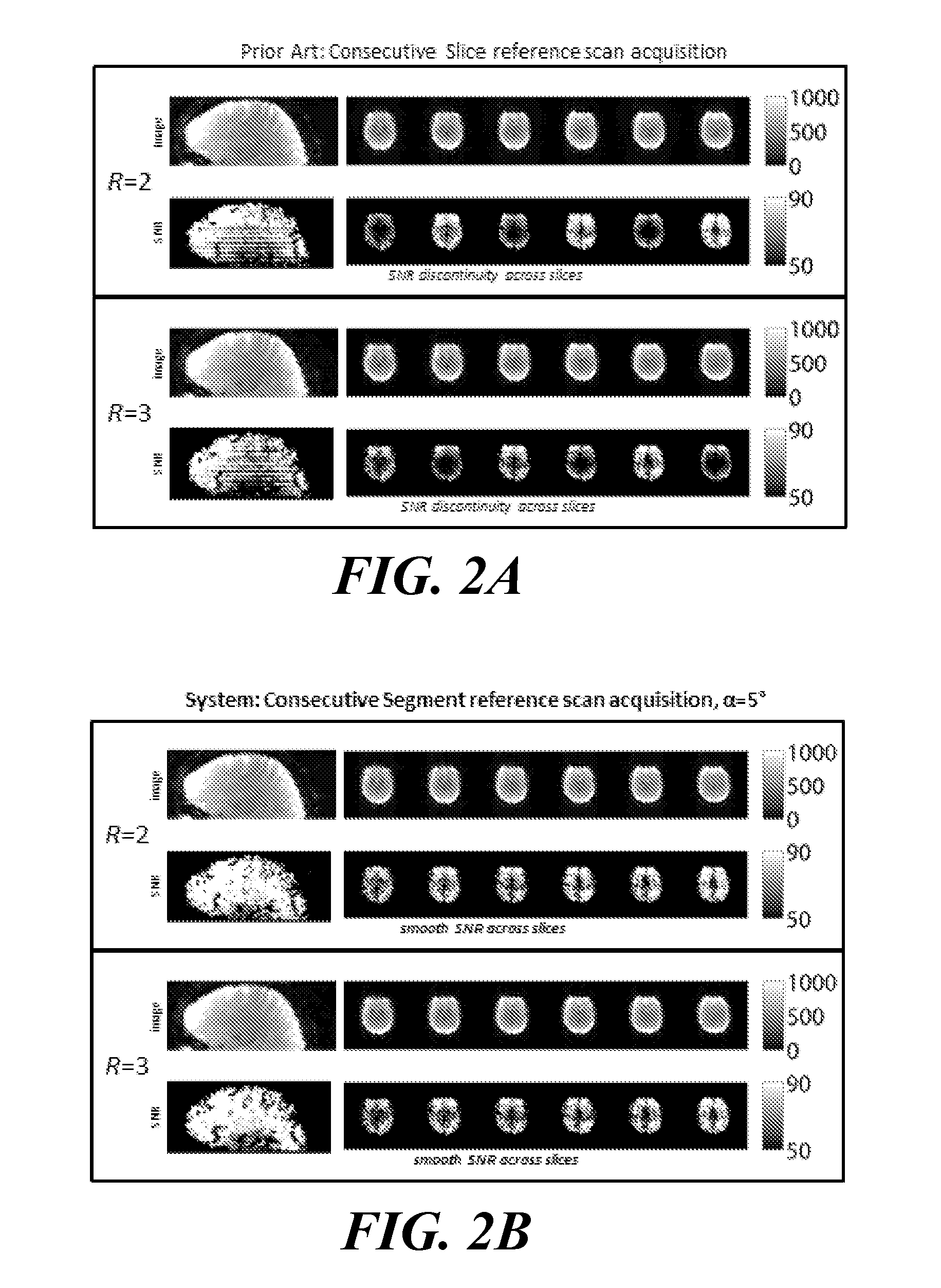
System for Accelerated Segmented MR Image Data Acquisition
ActiveUS20140037171A1Accelerates segmented magnetic resonance (MR) image data acquisitionReconstruction from projectionMagnetic measurementsMagnetic field gradientResonance
A system for accelerated segmented magnetic resonance (MR) image data acquisition includes an RF (Radio Frequency) signal generator and a magnetic field gradient generator. The RF signal generator generates RF excitation pulses in anatomy and enabling subsequent acquisition of associated RF echo data. The magnetic field gradient generator generates magnetic field gradients for anatomical volume selection, phase encoding, and readout RF data acquisition in a three dimensional (3D) anatomical volume. The RF signal generator and the magnetic field gradient generator acquire consecutive segments of k-space line data representative of an individual image slice in a gradient echo method by adaptively varying RF excitation pulse flip angle between acquisition of the consecutive segments.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH +1
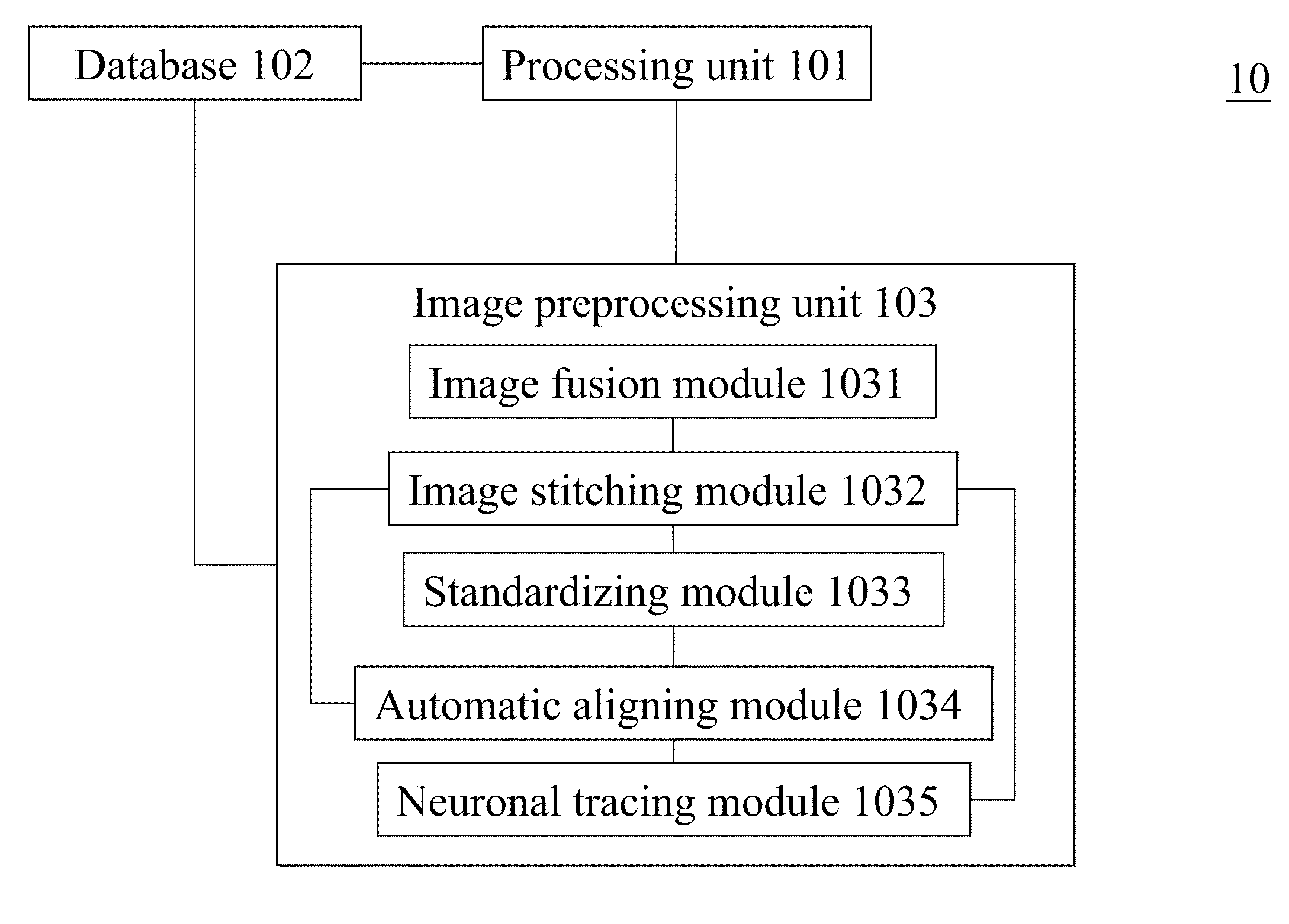
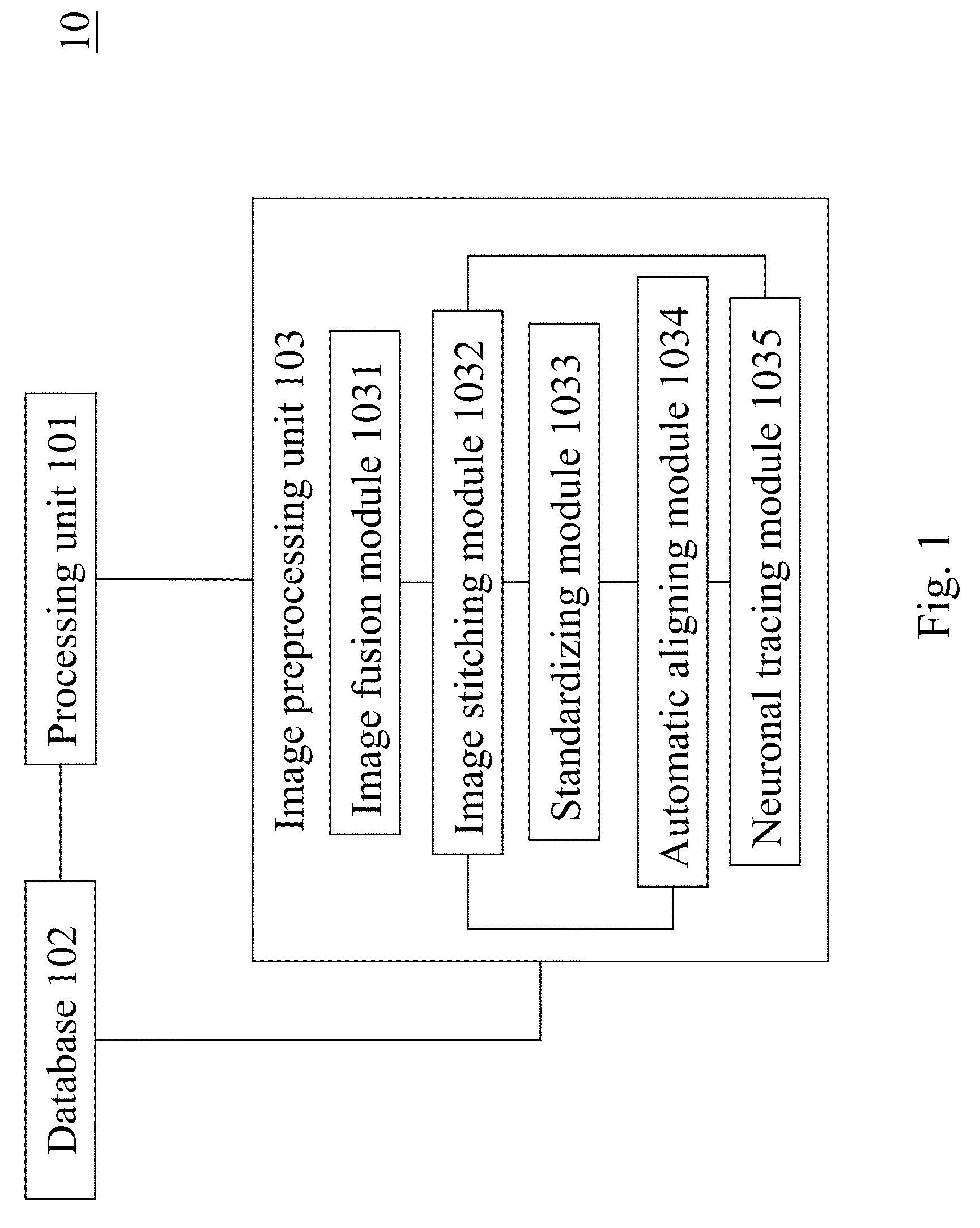
Image preprocessing system for 3D image database construction
The present invention discloses an image preprocessing system, which includes a processing unit; an image preprocessing unit coupled to the processing unit to preprocess image slice data, wherein the image preprocessing unit includes an image fusion module to estimate missing values between different image slice data and an image stitching module to stitch different image slice data into stitched image data; and a database coupled to the processing unit to store the preprocessed image slice data.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
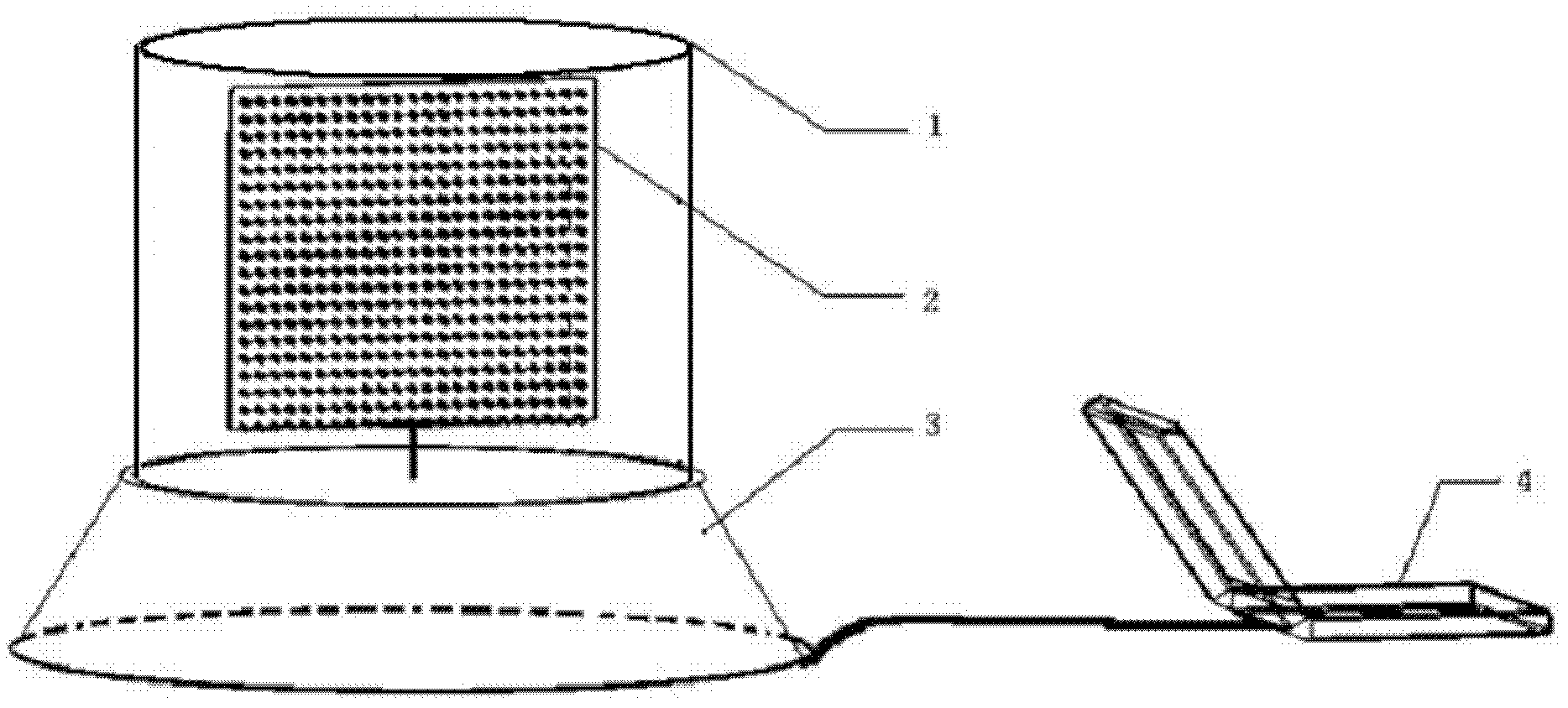
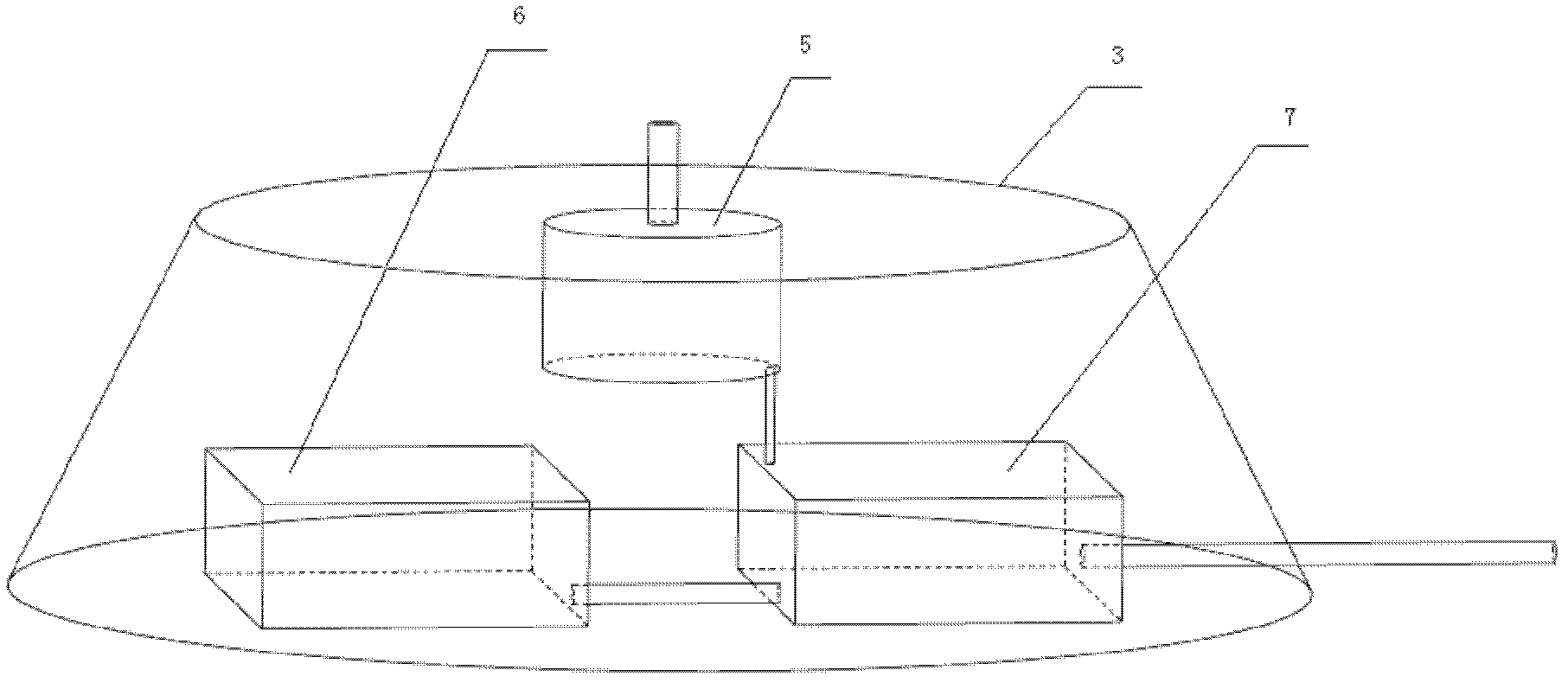
Naked eye 3D (Three-Dimensional) display system
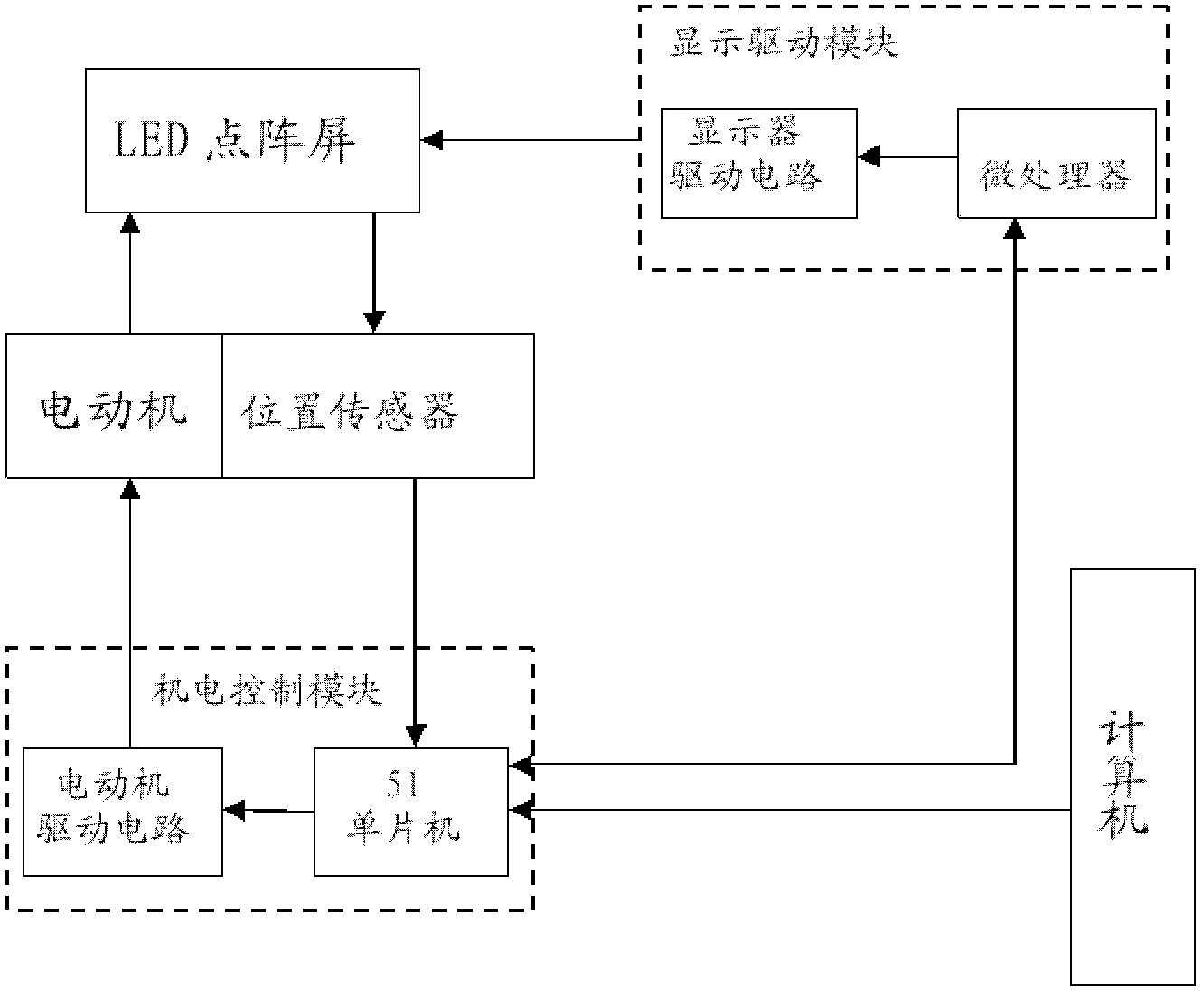
InactiveCN102447935ARealistic 3D spatial relationshipPrevent fallingStatic indicating devicesSteroscopic systemsDot matrixPersistence of vision
The invention relates to a naked eye 3D (Three-Dimensional) display system, which aims to solve the technical problem that at present, a 3D image is observed, an auxiliary equipment or a 2D (Two-Dimensional) computer display screen are needed to display a rotating 2D image for expressing a 3D effect, so that the display has no the real 3D effect, and a 3D object can not be observed from multi angles. The system mainly comprises a display, an electromechanical control module, a display driving module and a computer, wherein the display adopts a rotatable LED (Light-emitting Diode) dot matrix screen, and rotates at a preset speed, the screen rotates to different positions to display different images, the image is actually the 'slices' of the 3D image, due to the persistence of vision, the slices of the image are quickly and continuously displayed in a 3D space to form the 3D image with the 3D effect, the LED dot matrix rotating screen is driven by the electromechanical control module to detect the position of the screen and carry out feedback, the display driving module is used for driving each pixel point on the LED dot matrix screen, and the computer is used for outputting a control and display signal. By utilizing the system, the display content is more intuitive and more real, and the system can be widely applied into lighting products, advertisement display, teaching aid, and the like.
Owner:SHENYANG AEROSPACE UNIVERSITY
Method for processing scalp positioning images of brain tumors
ActiveCN102592283AEasy to implementShorten operation timeImage analysis3D modellingImaging equipmentImage Reslicing
The invention discloses a method for processing scalp positioning images of brain tumors, which comprises the following steps of: (1) preliminarily estimating a scalp projected area of a brain tumor of a patient, adhering two mark points which can be identified by an imaging device in the area, obtaining a two-dimensional medical image slice set from the imaging device, and reconstructing a three-dimensional profile of a scalp layer; (2) manually drawing a profile line of the tumor on a two-dimensional image, and reconstructing the surface of the tumor; (3) determining the positions of the two mark points on the two-dimensional image, and reconstructing the mark points; and (4) rotating a profile image of the reconstructed three-dimensional profile image to an appropriate position, and then printing the image in an equal proportion. Compared with the prior art, the method disclosed by the invention is implemented simply; and when the method is applied to the positioning of a brain tumor, the positioning precision meets the demands of tumor resection through a craniotomy, the shortening of operation time and the reduction of surgical traumas are facilitated, and the incision length can be minimized under the premise of guaranteeing good exposures.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
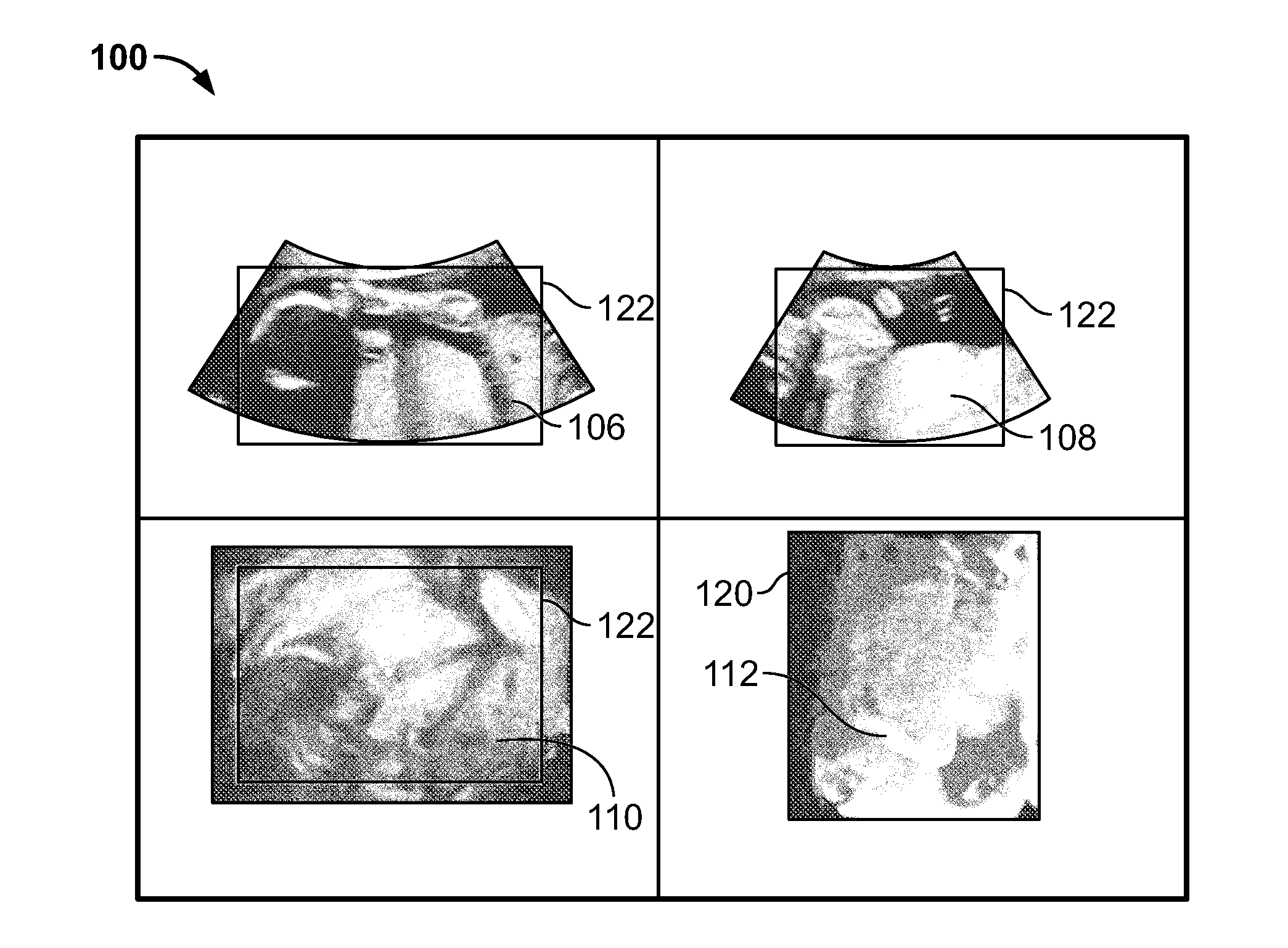
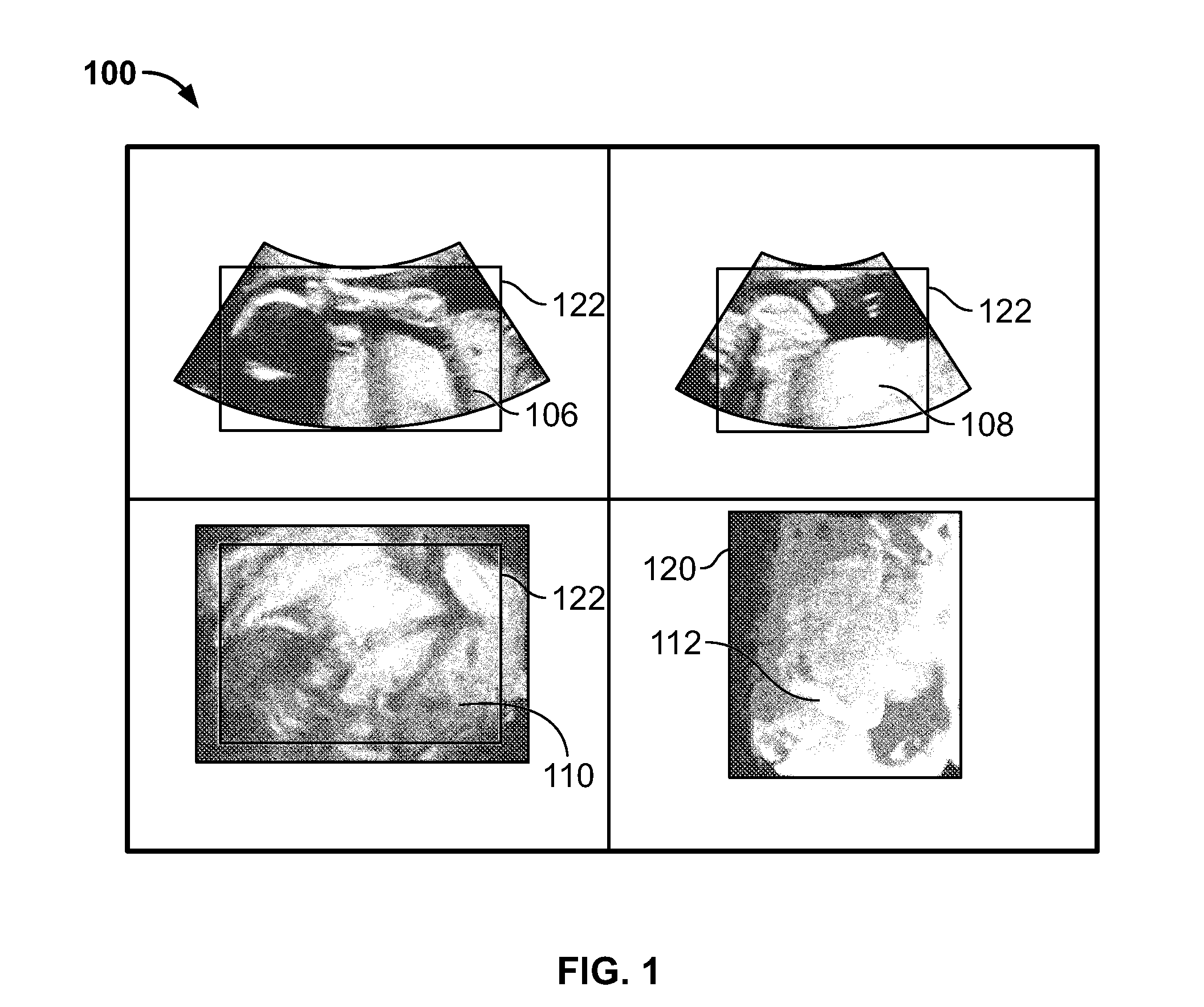
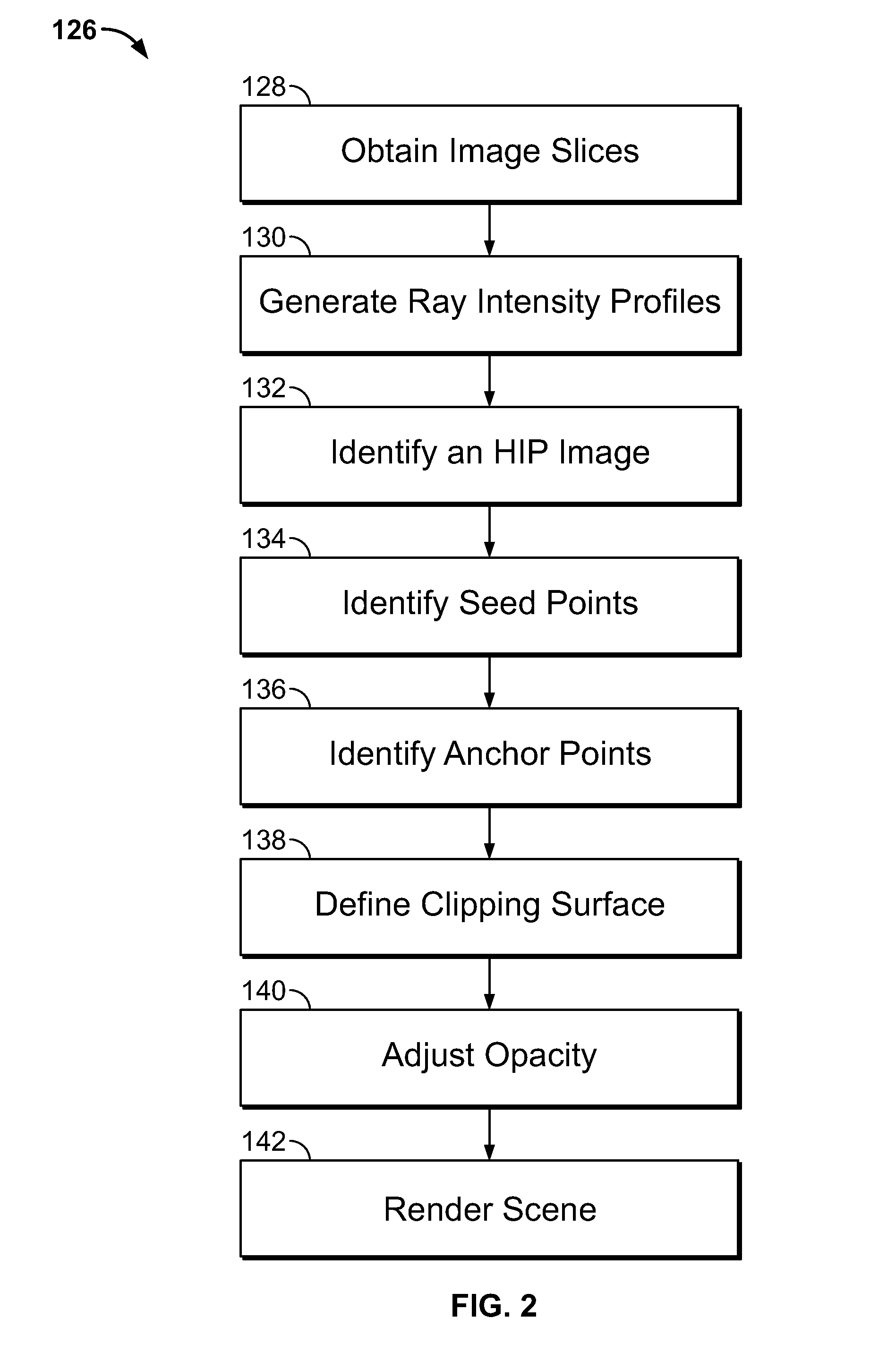
Methods and systems for removing occlusions in 3D ultrasound images
Methods and system for visualizing 3D ultrasound data are provided. One method includes obtaining image slices from a volumetric image data set and generating a ray profile using one or more rays through at least one of the image slices, wherein the one or more rays extend along a depth of the volumetric image data set. The method further includes identifying one or more seed points along the one or more rays and defining a clipping surface using the one or more seed points, wherein the clipping surface defines a rendering region within the volumetric image data set. The method also includes rendering a 3D image of the rendering region within the volumetric image data set.
Enhanced system and method for volume based registration
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for tooth dissection in cbct volume
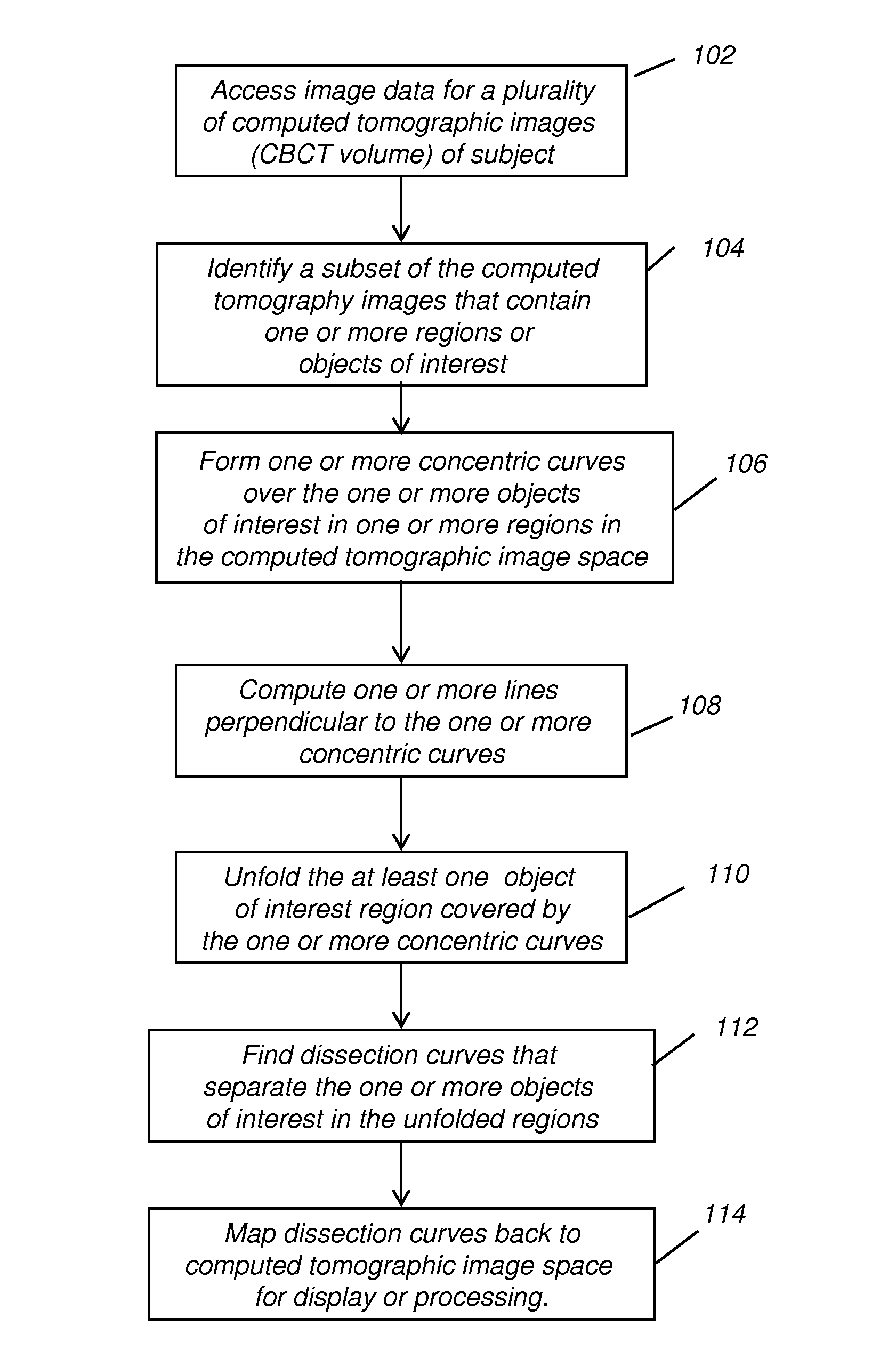
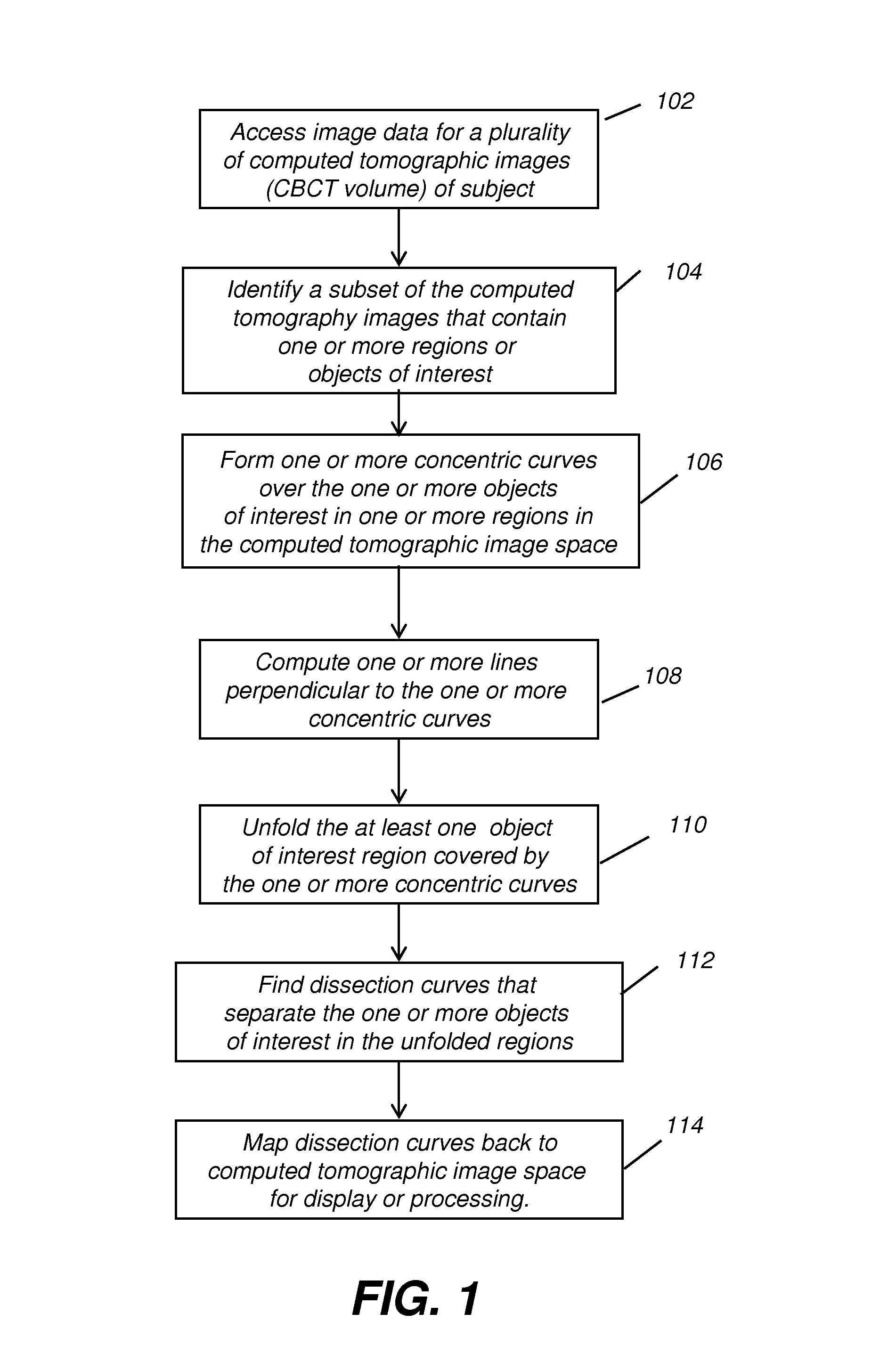
ActiveUS20130022254A1Speed of computationCorrection capabilityImage enhancementImage analysisGeometric primitiveDissection
A method of generating a dissection curve between a first and a second object in a volume image. The method accesses volume image data of a subject as a set of image slices and identifies a region of the volume image data that includes at least the first and second objects. At least one starting point in the volume image data is defined for the dissection curve according to a geometric primitive entered by an operator. Successive dissection curve points are identified according to points of minimum intensity in successive image slices. The dissection curve that connects the identified plurality of successive dissection curve points is displayed.
Owner:CARESTREAM DENTAL TECH TOPCO LTD
Method for sorting ct image slices and method for constructing 3D ct image
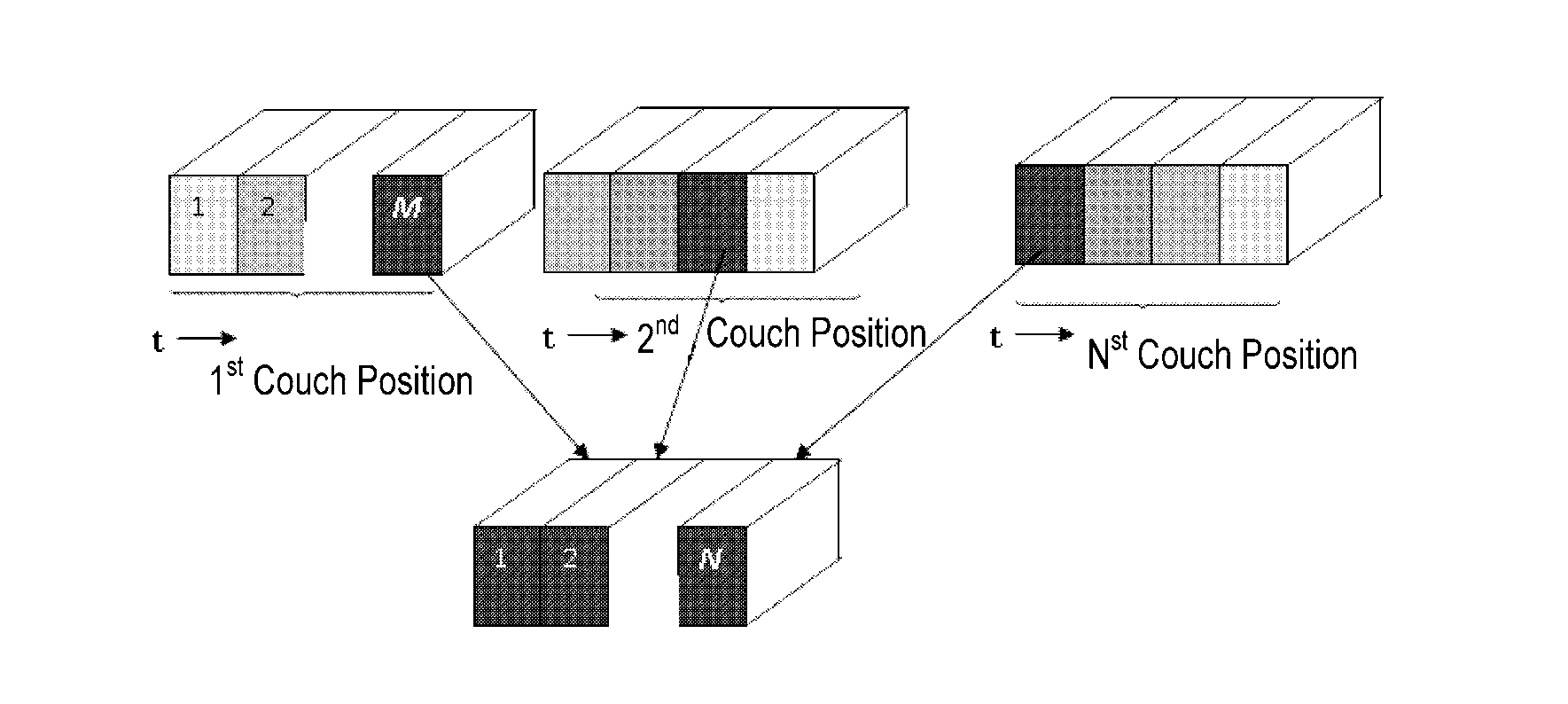
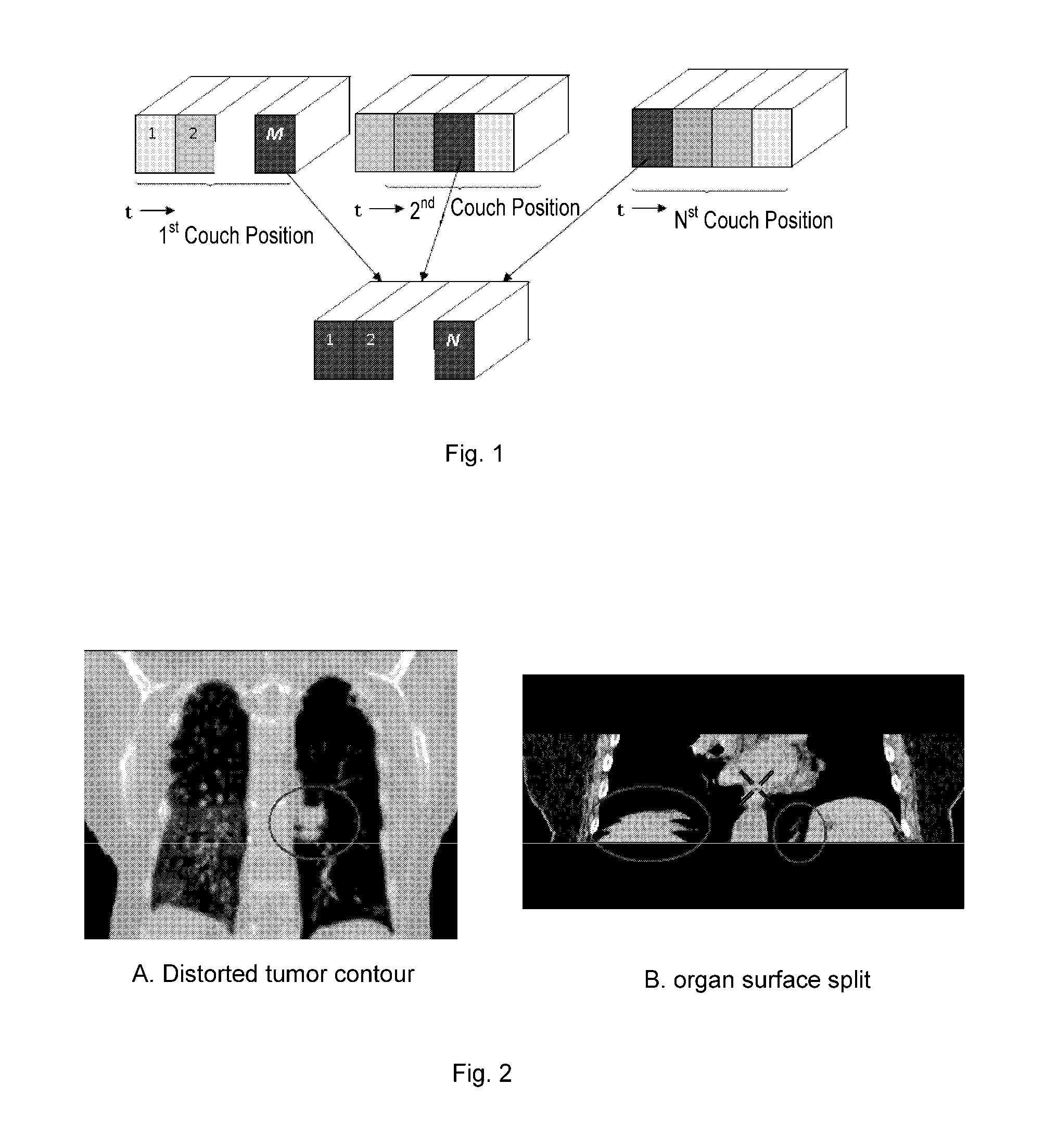
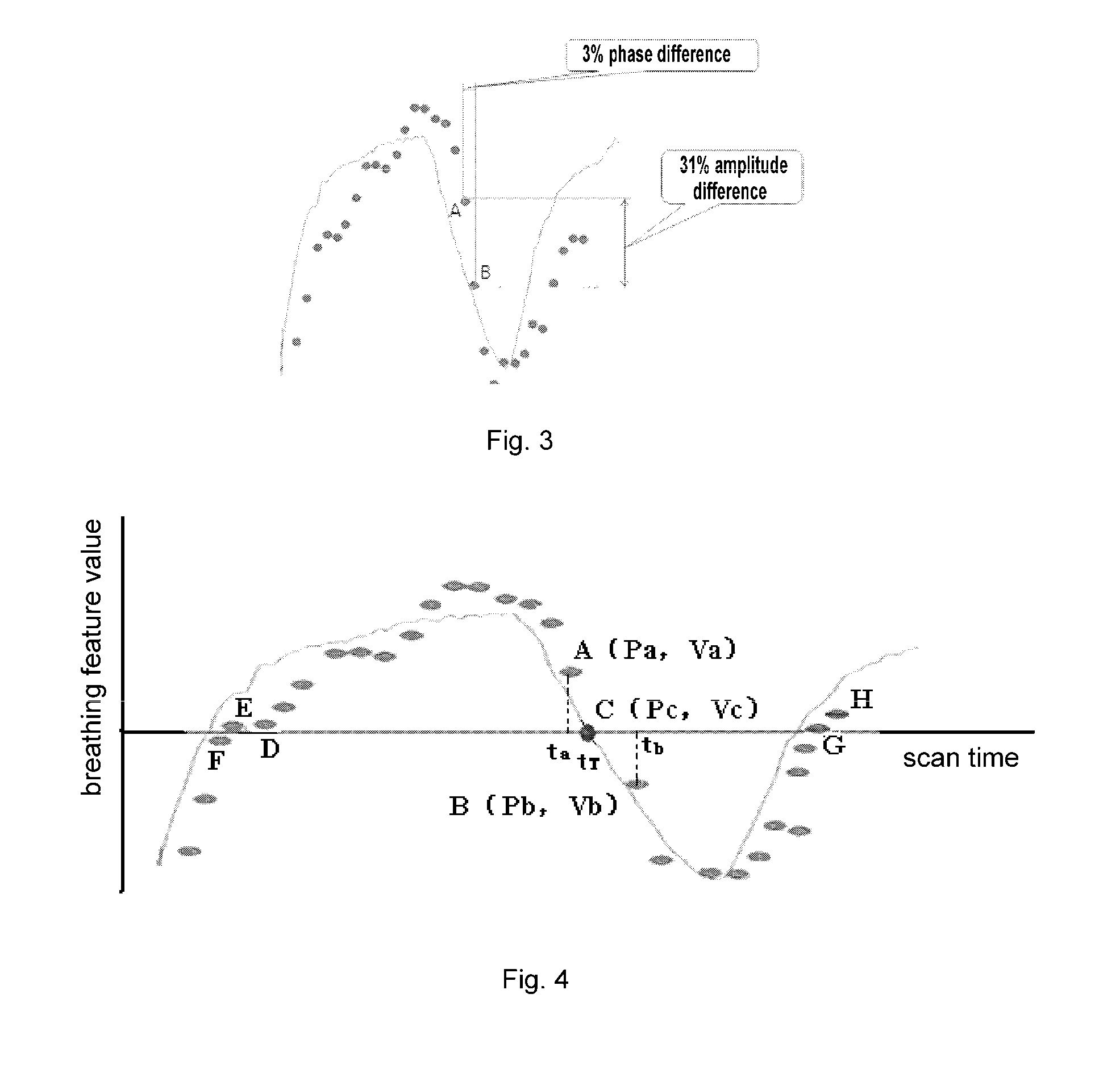
ActiveUS20130195341A1Reduce and eliminate defectReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionRespiratory phase3d image
A method for sorting CT image slices comprising, if no image slice comprises a target respiratory phase at a couch position, determining a target breathing feature value corresponding to the target respiratory phase based on a respiratory motion curve of a scanned patient, searching from a plurality of image slices at the couch position for one or more image slices comprising a breathing feature value close to the target breathing feature value to serve as candidate image slices, and selecting, based on a breathing feature value difference between the breathing feature value of each of the candidate image slices and the target breathing feature value and / or an image difference between each of the candidate image slices and at least one reference image slice, a single image slice from the candidate image slices for constructing the 3D CT image for the target respiratory phase.
Owner:GE HANGWEI MEDICAL SYST
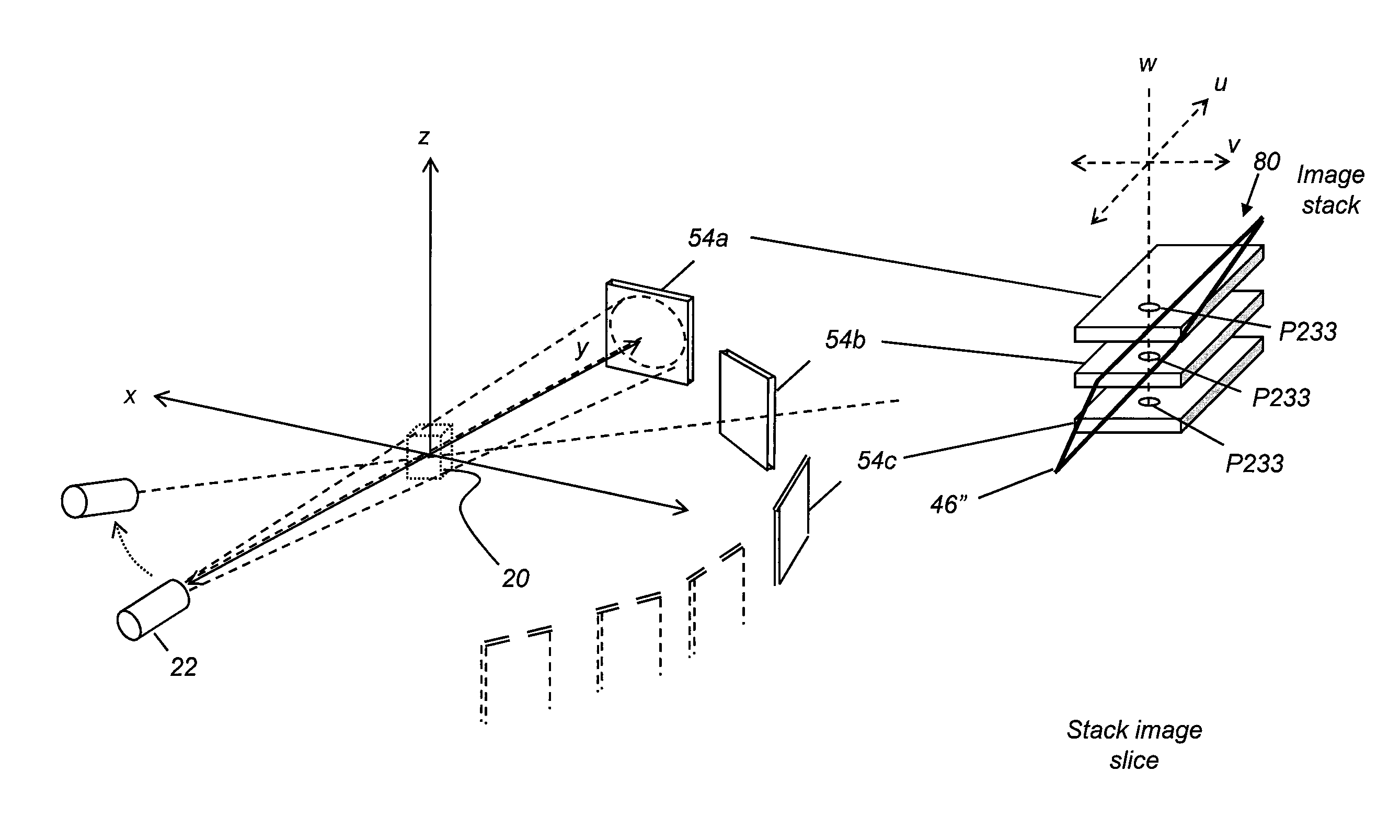
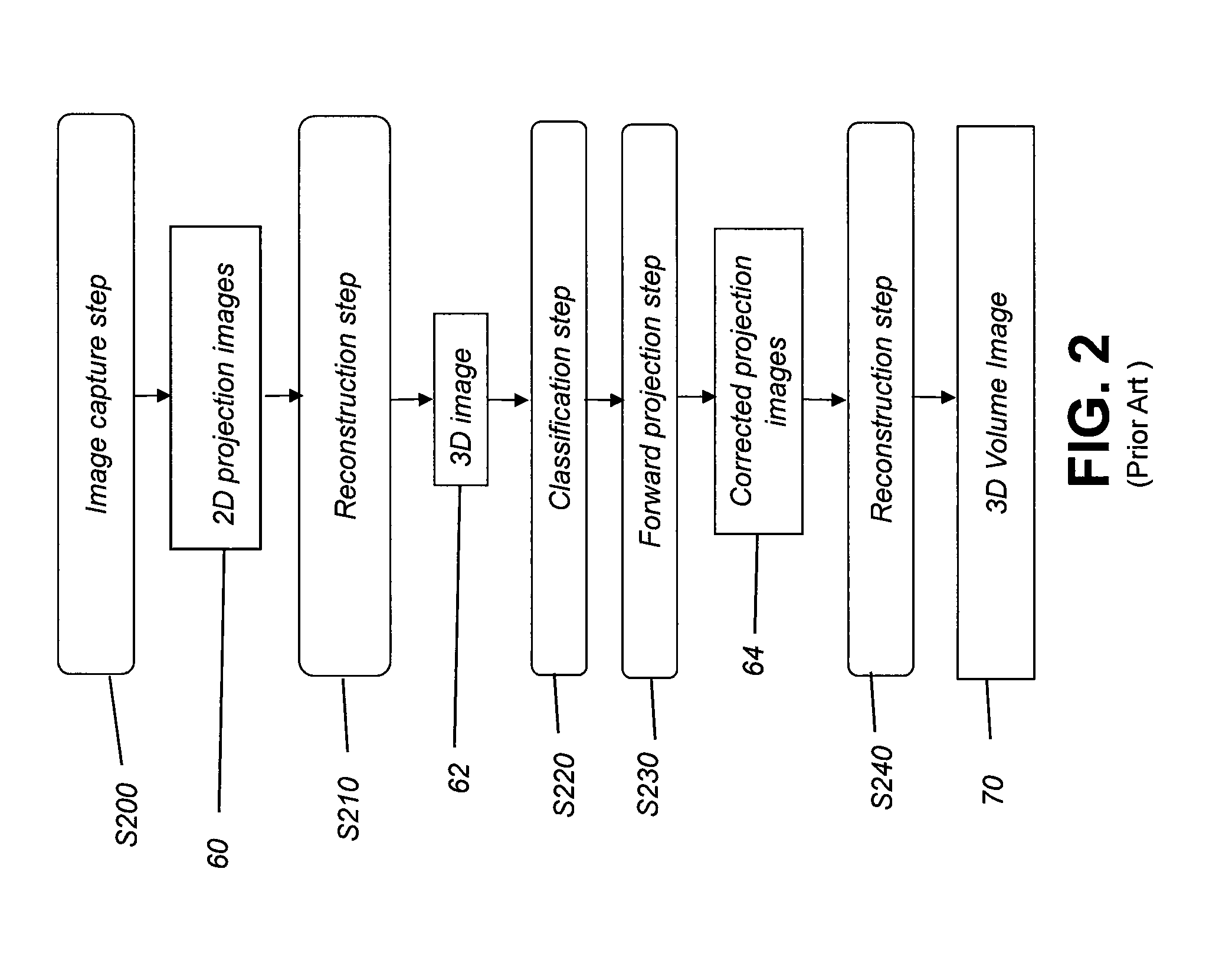
Metal artifacts reduction for cone beam ct using image stacking
InactiveUS20150178917A1Improve efficiencyReduce computing needsImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionMetal ArtifactLight beam
Method and / or apparatus embodiments can process volume image data of a subject. An exemplary method includes obtaining a first group of two-dimensional radiographic images of the subject, wherein each of the images is obtained with a detector and a radiation source at a different scan angle. The method arranges image data from the first group of images in an image stack so that corresponding pixel data from the detector is in register for each of the images in the image stack. Pixels that represent metal objects are segmented from the image stack and data replaced for at least some of the segmented pixels to generate a second group of modified two-dimensional radiographic images. The second group of images is combined with the first group to generate a three-dimensional volume image according to the combined images and an image slice from the three-dimensional volume image is displayed.
Owner:CARESTREAM DENTAL TECH TOPCO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com