Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
104 results about "Force profile" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
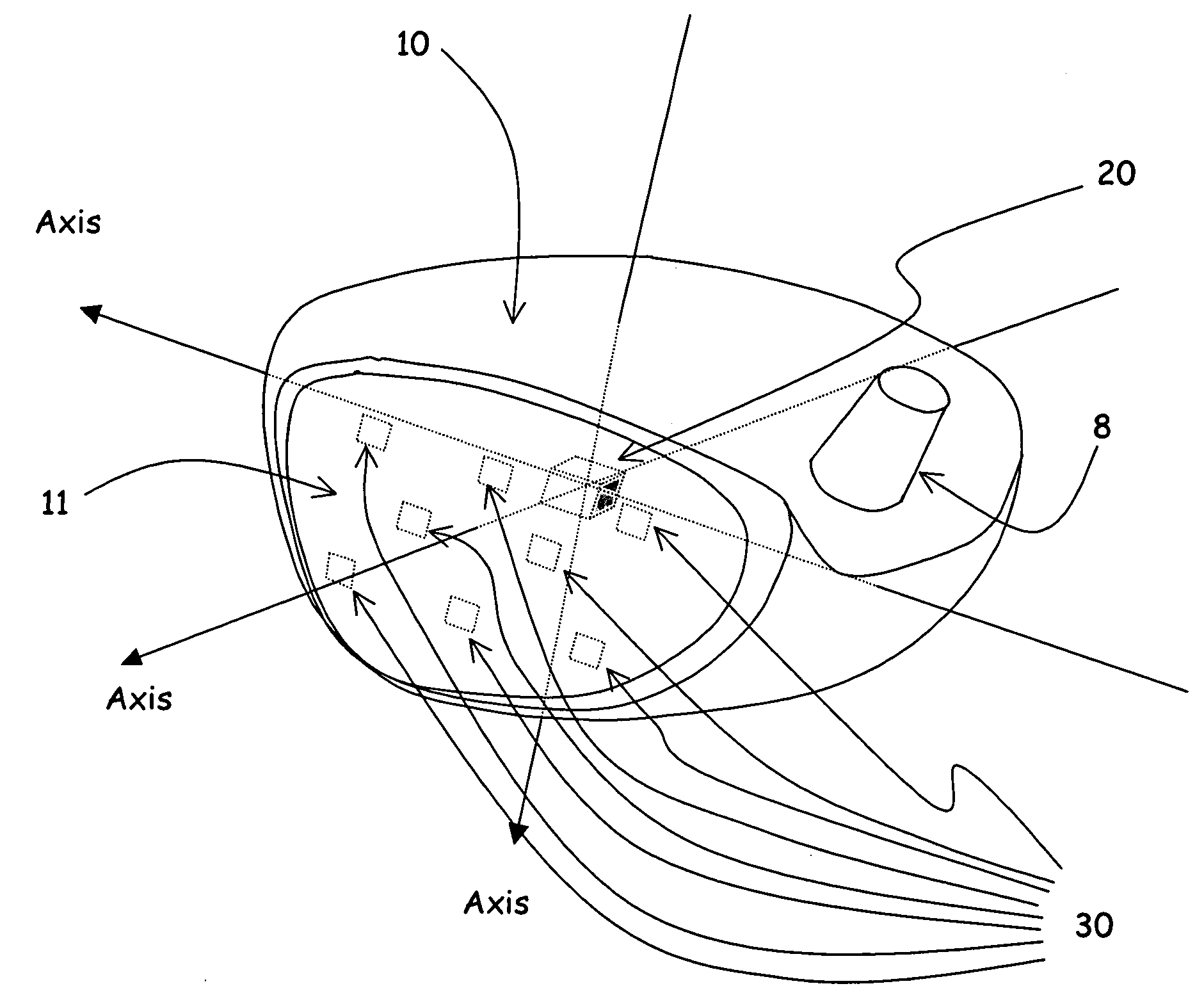
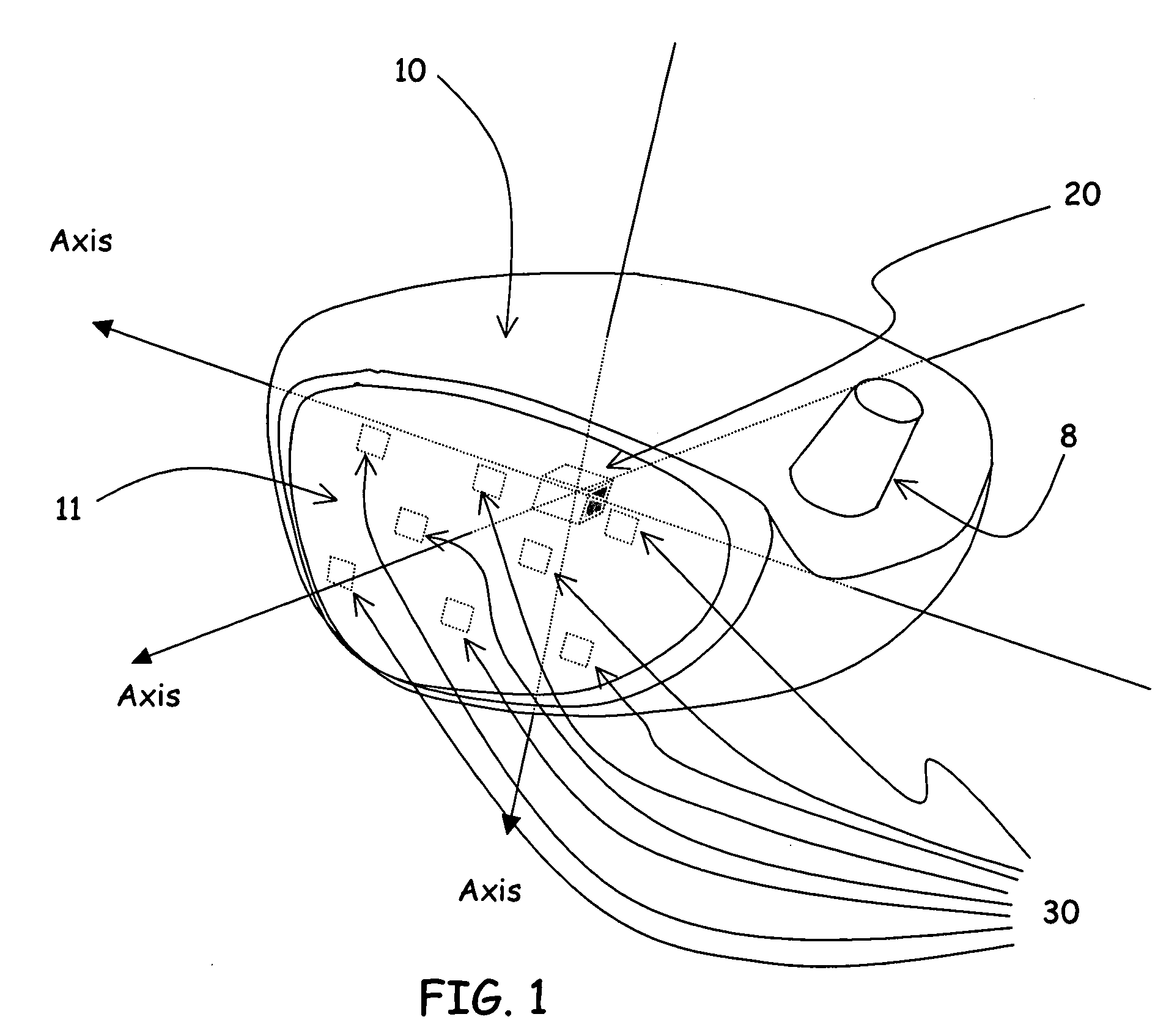
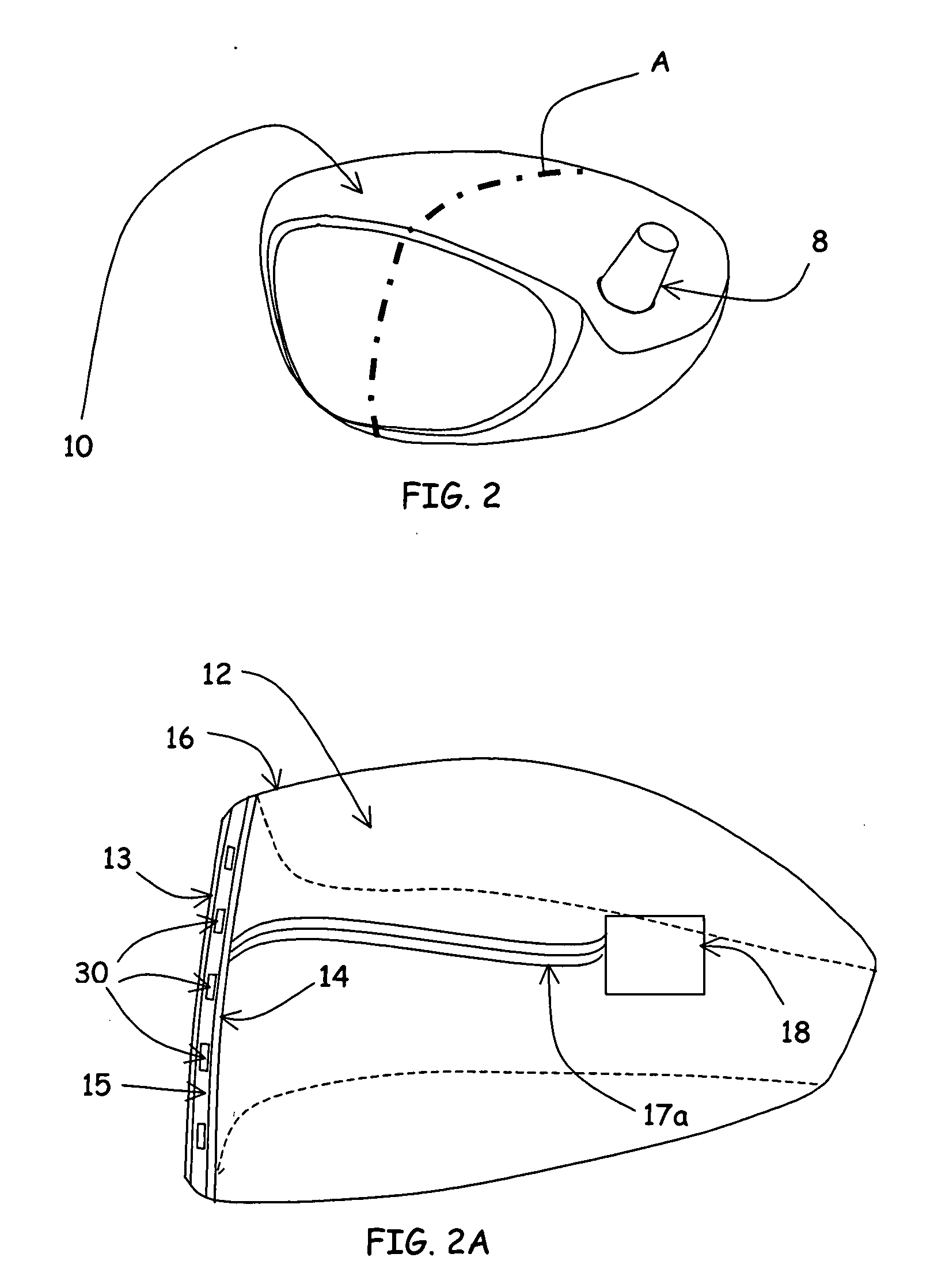
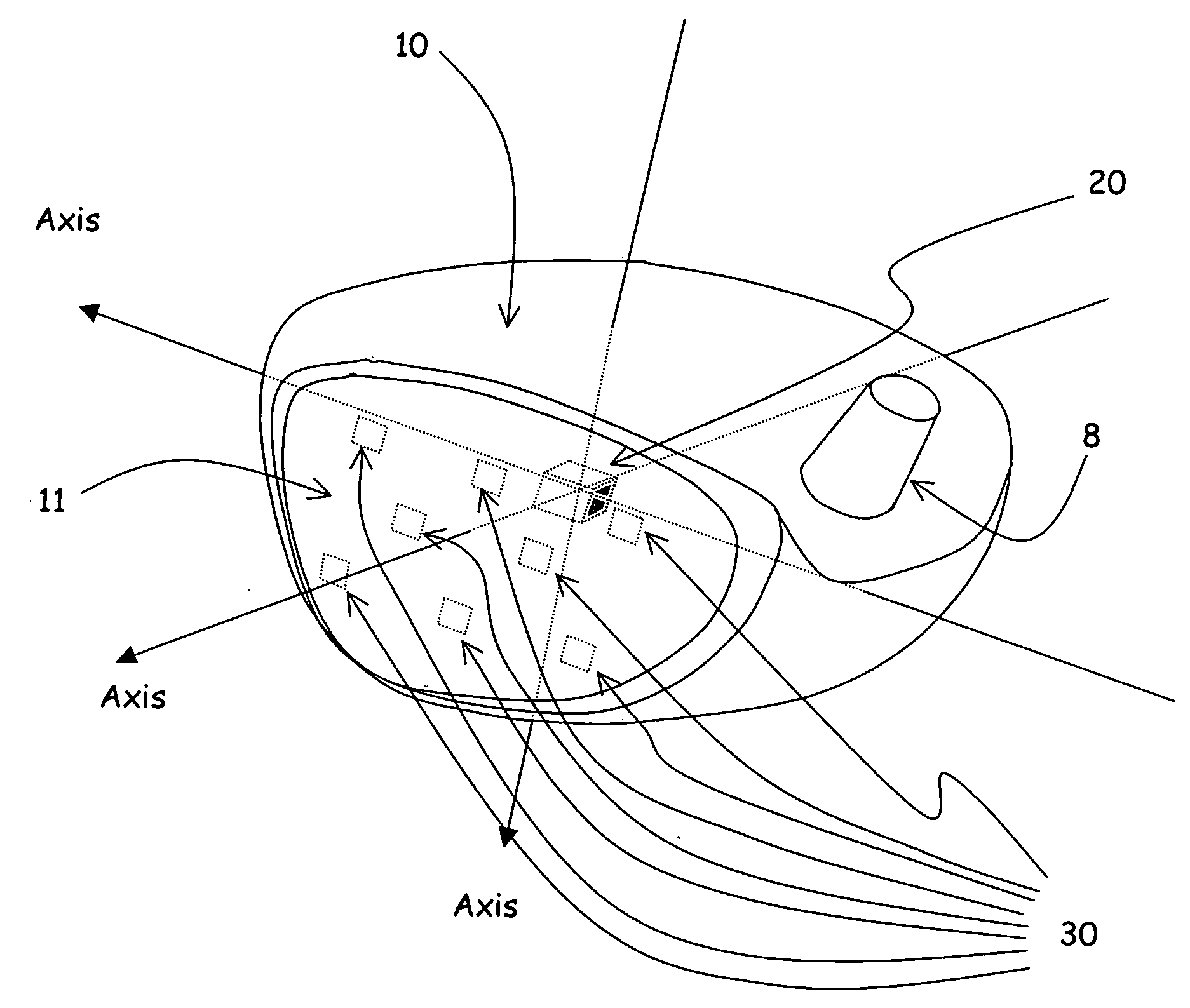
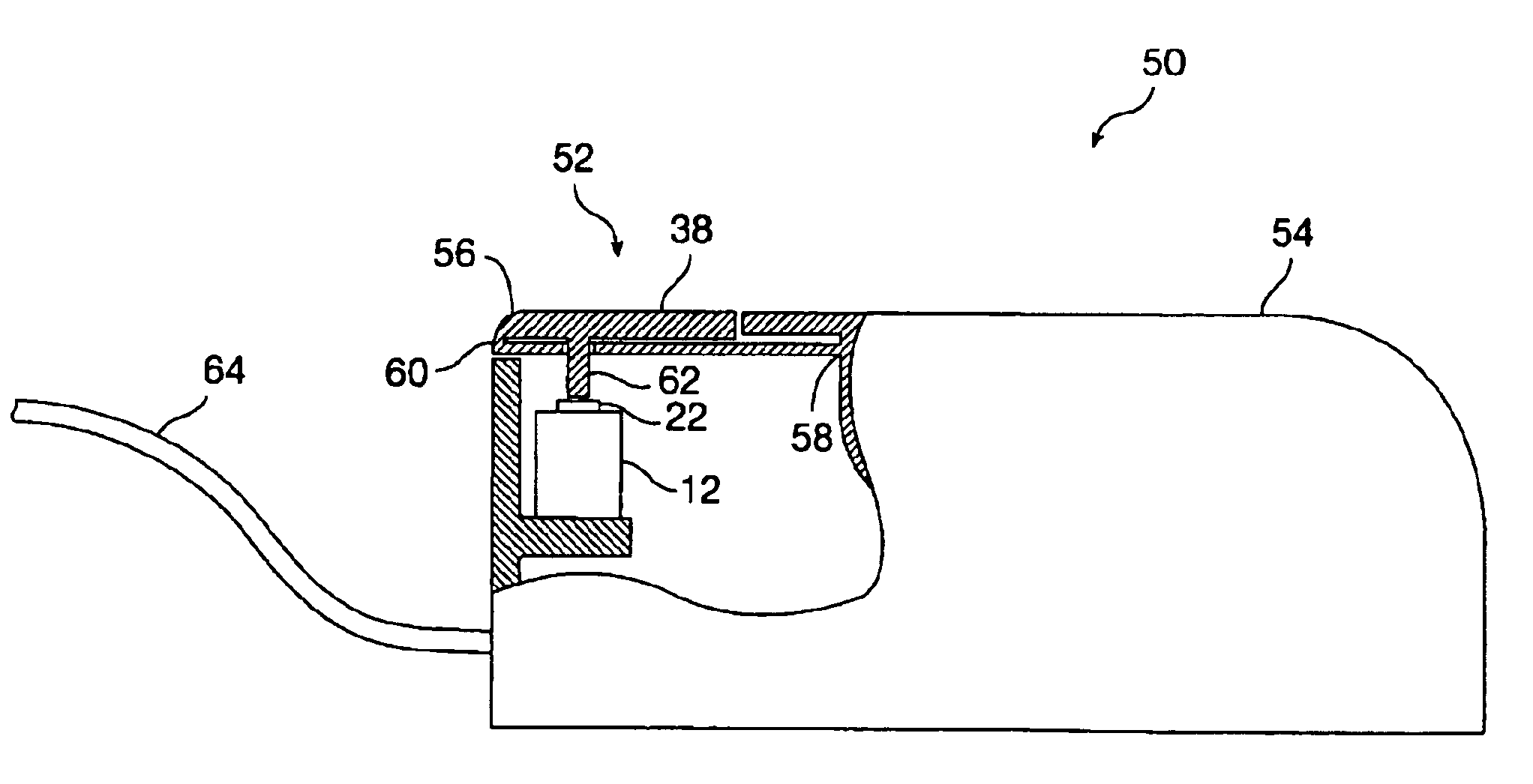
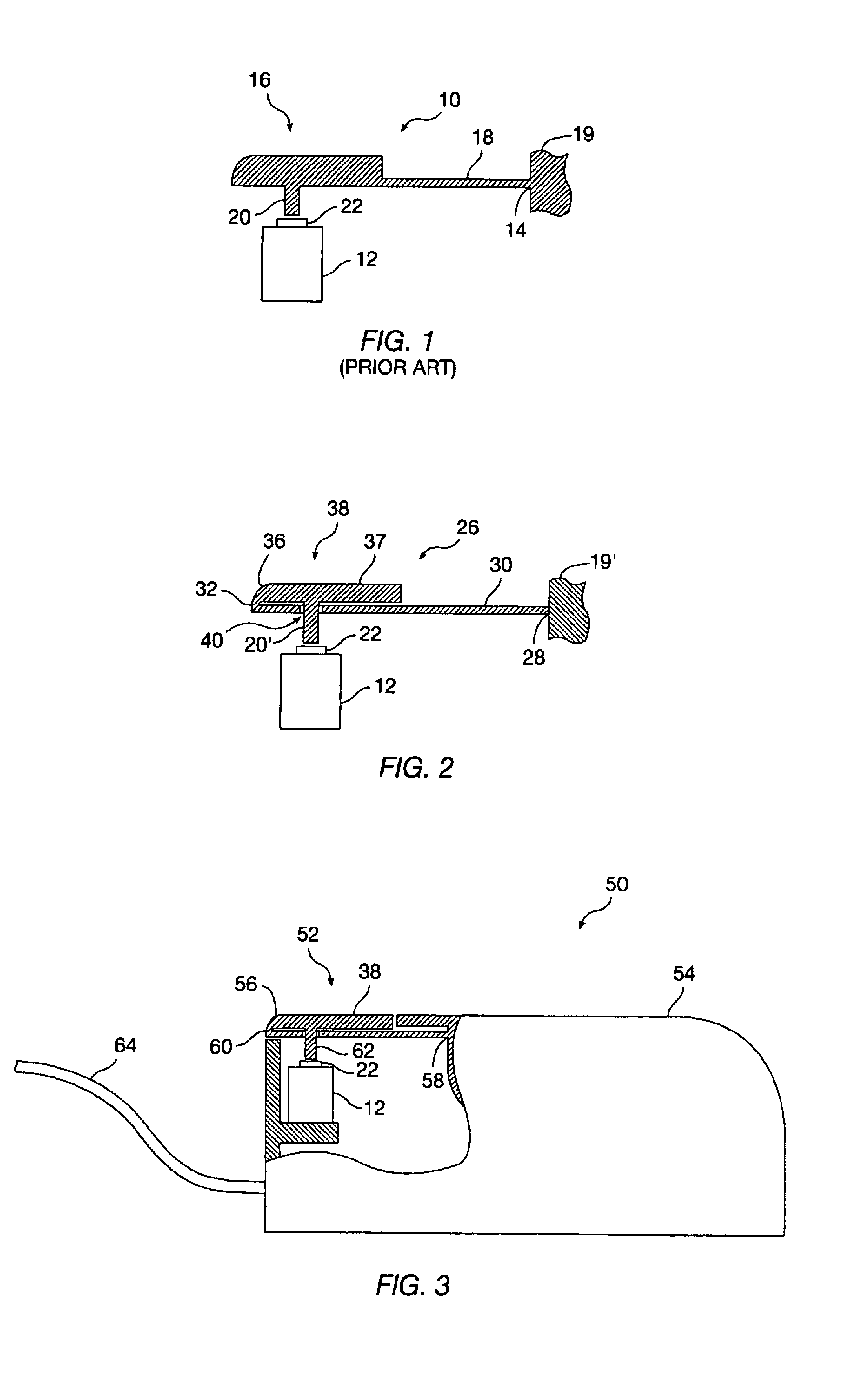
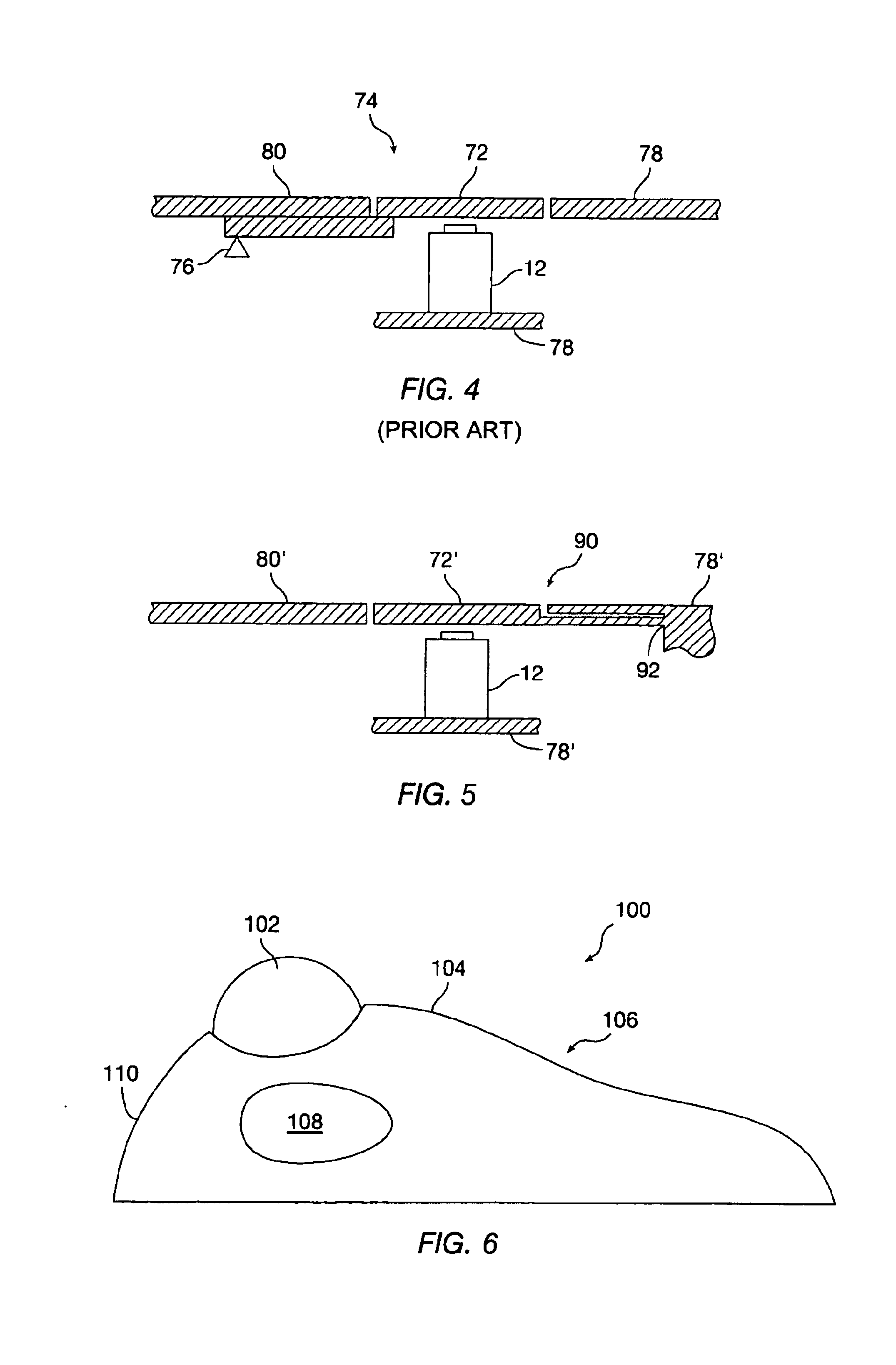
Golf swing analysis apparatus and method
A method and integrated golf club apparatus for directly measuring physical parameters of the golf club head motional acceleration swing forces, golf club head face, golf ball impact forces, and subsequent calculations of other metrics useful to a golfer's understanding of the effectiveness of his or her golf swing and impact result in totality. The physical parameters that are directly measured include three dimensional motion force vectors of club head prior to, during and after impact and full impact pressure force profiles across the golf clubface with respect to time. The sensors are connected to electronics which condition, record and store the time varying sensors information electronically, then process and translate the information into one of several forms for delivery to a human interface function.
Owner:GOLF IMPACT
Golf swing analysis apparatus and method
A method and integrated golf club apparatus for directly measuring physical parameters of the golf club head motional acceleration swing forces, golf club head face, golf ball impact forces, and subsequent calculations of other metrics useful to a golfer's understanding of the effectiveness of his or her golf swing and impact result in totality. The physical parameters that are directly measured include three dimensional motion force vectors of club head prior to, during and after impact and full impact pressure force profiles across the golf clubface with respect to time. The sensors are connected to electronics which condition, record and store the time varying sensors information electronically, then process and translate the information into one of several forms for delivery to a human interface function.
Owner:GOLF IMPACT
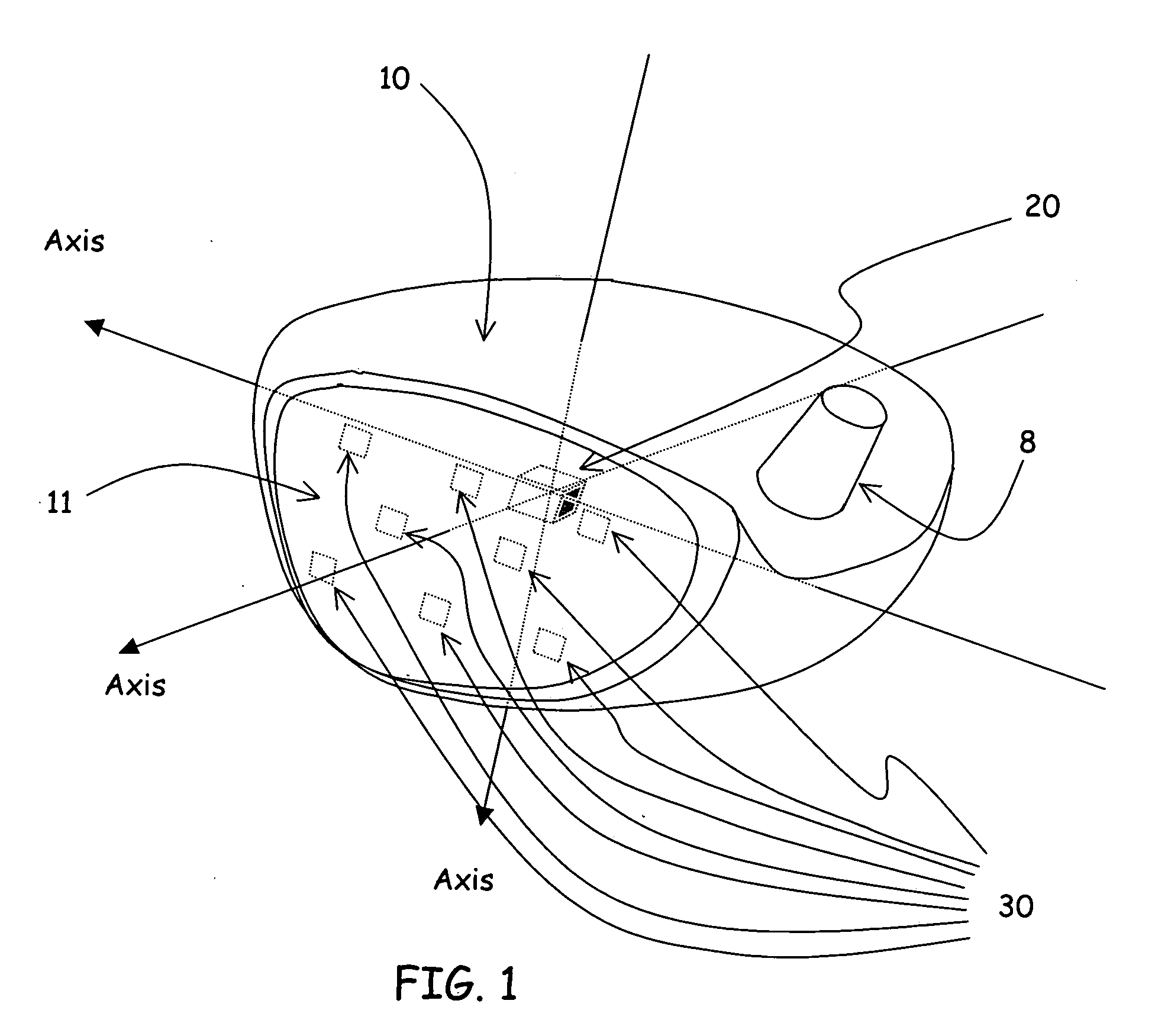
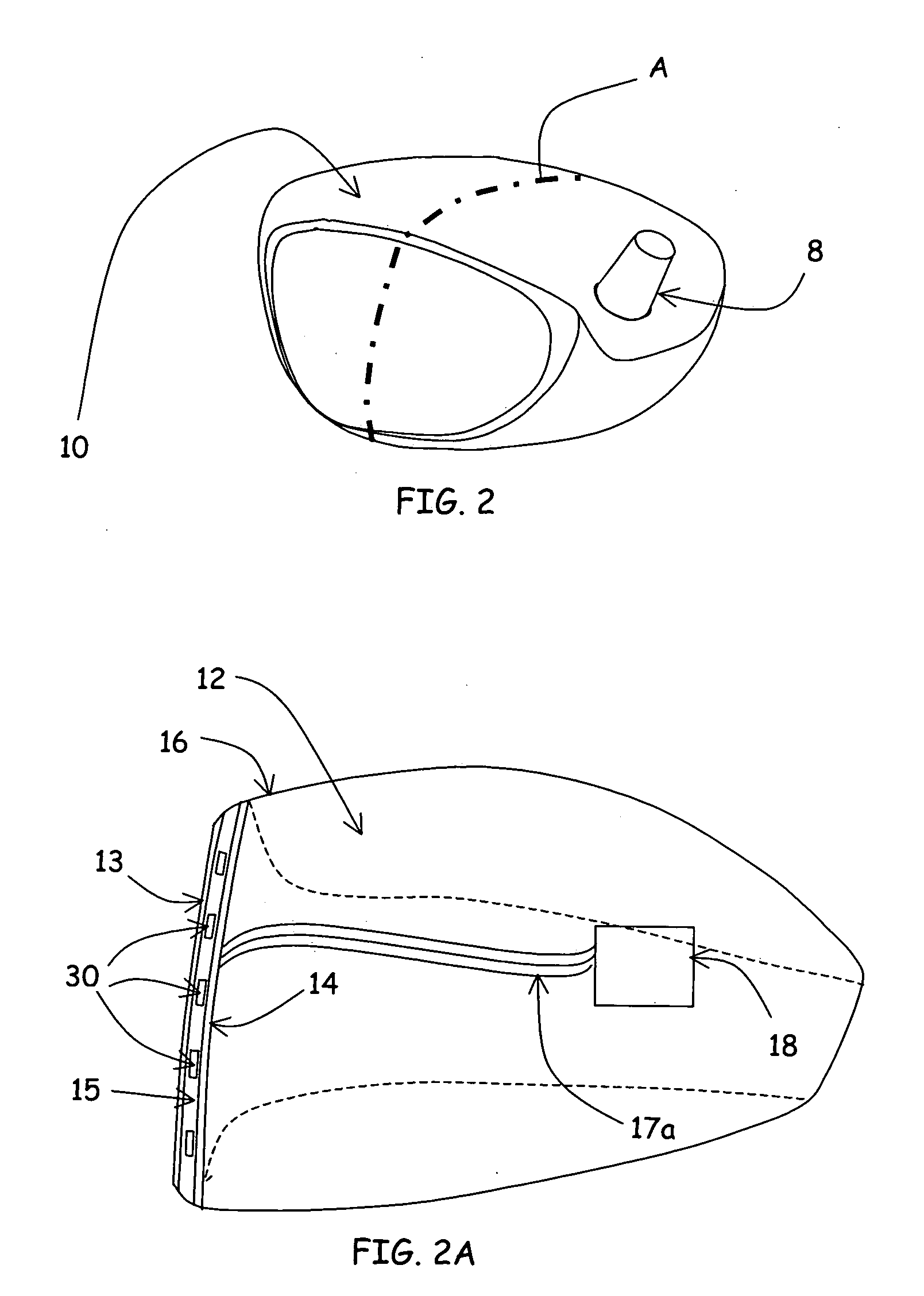
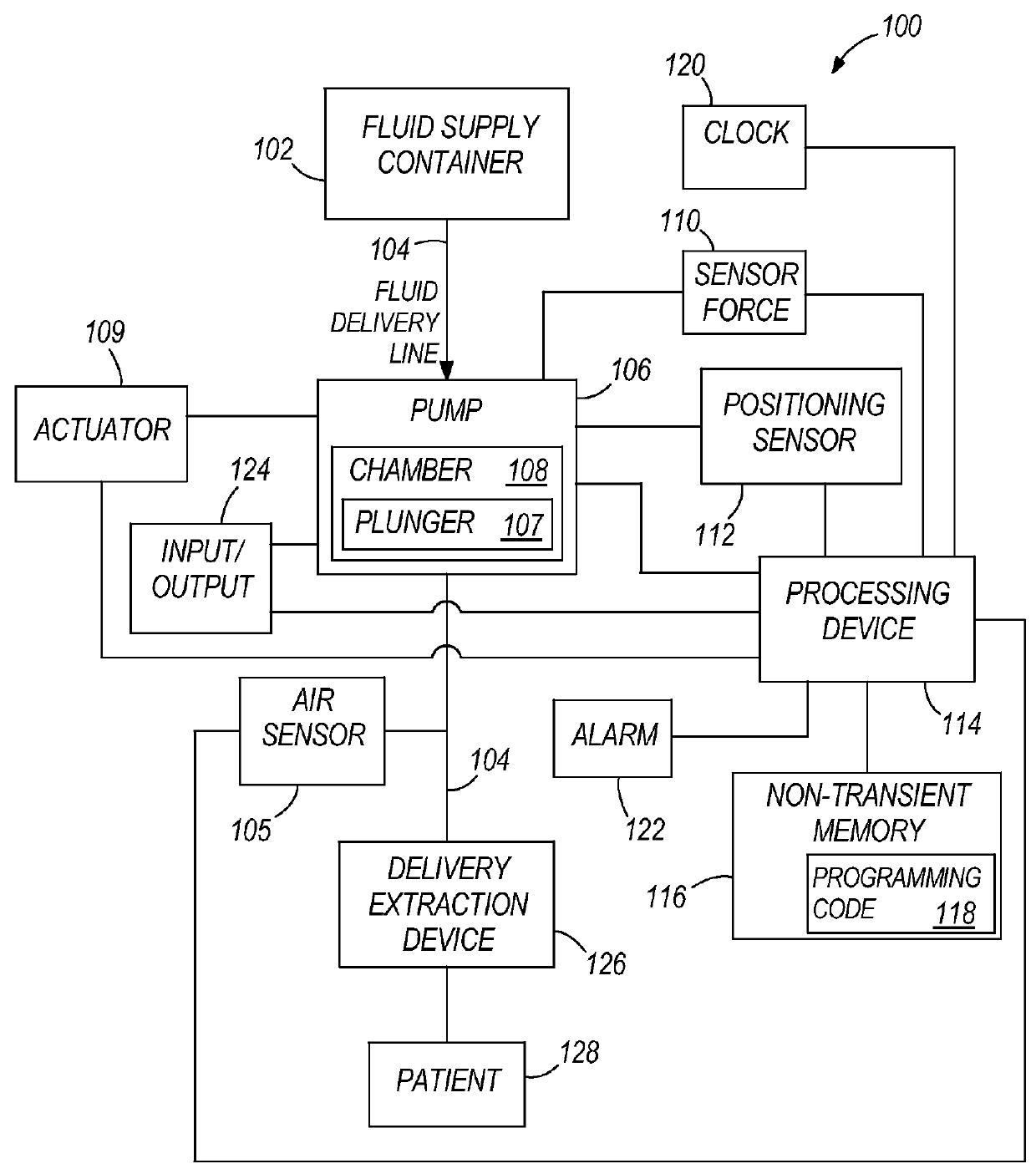
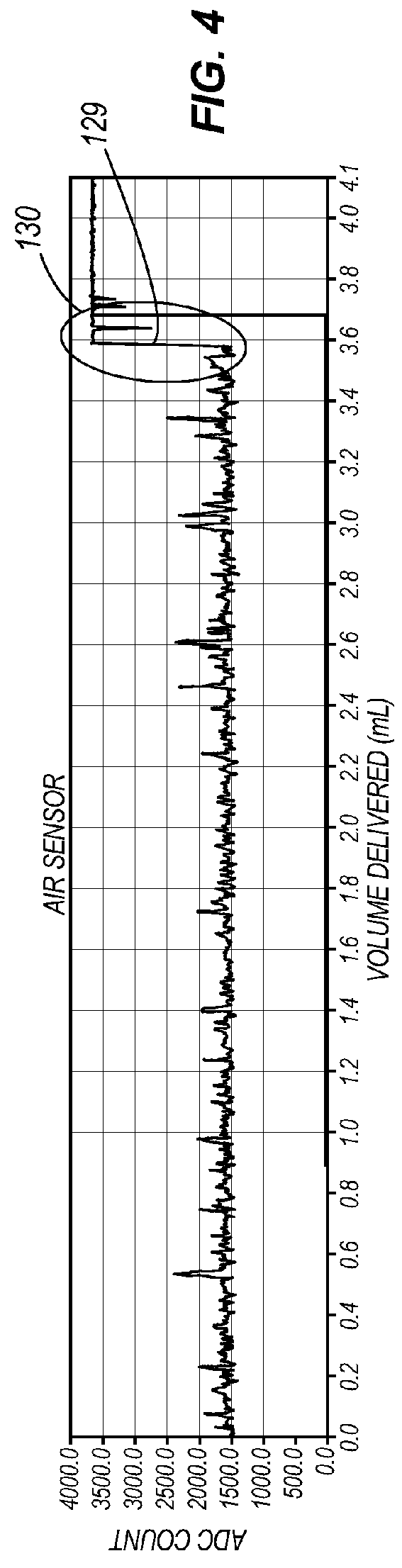
Air detection system and method for detecting air in a pump of an infusion system
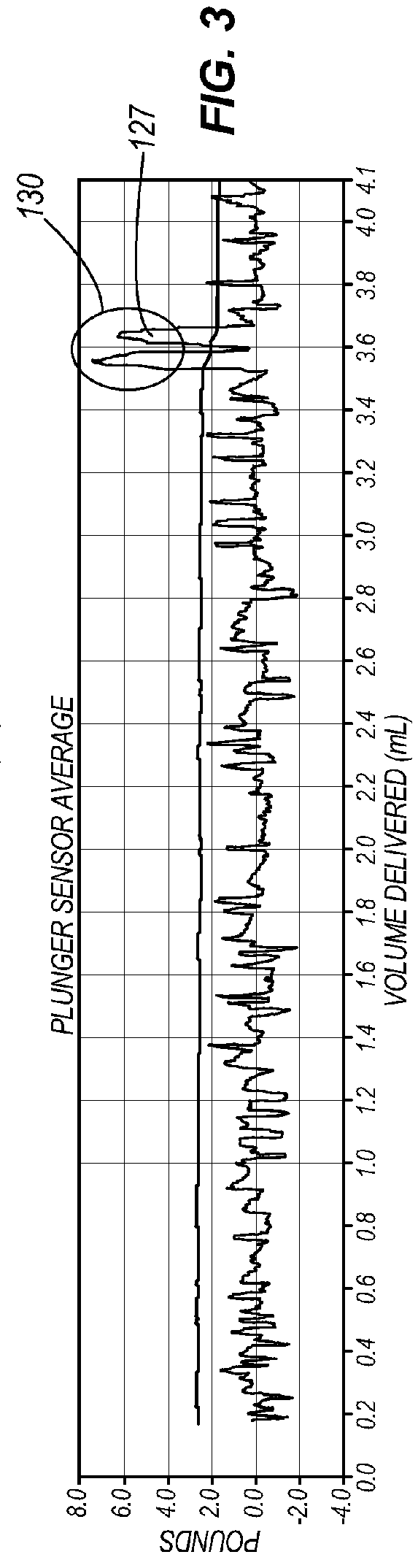
Various systems and methods for detecting air in a chamber of an infusion system are disclosed. In one embodiment, a determination is made that air is contained in the chamber on the basis of a change in the average force exerted against the plunger utilizing a derivative spike for event detection and a systematic reduction in the average force to confirm the nature of the change. In another embodiment, a determination is made that the chamber contains air when a difference between the current force profile and a baseline force profile crosses a threshold. In an additional embodiment, a force profile is classified as being an air force profile or a liquid force profile based on extracted features of the force profile.
Owner:ICU MEDICAL INC
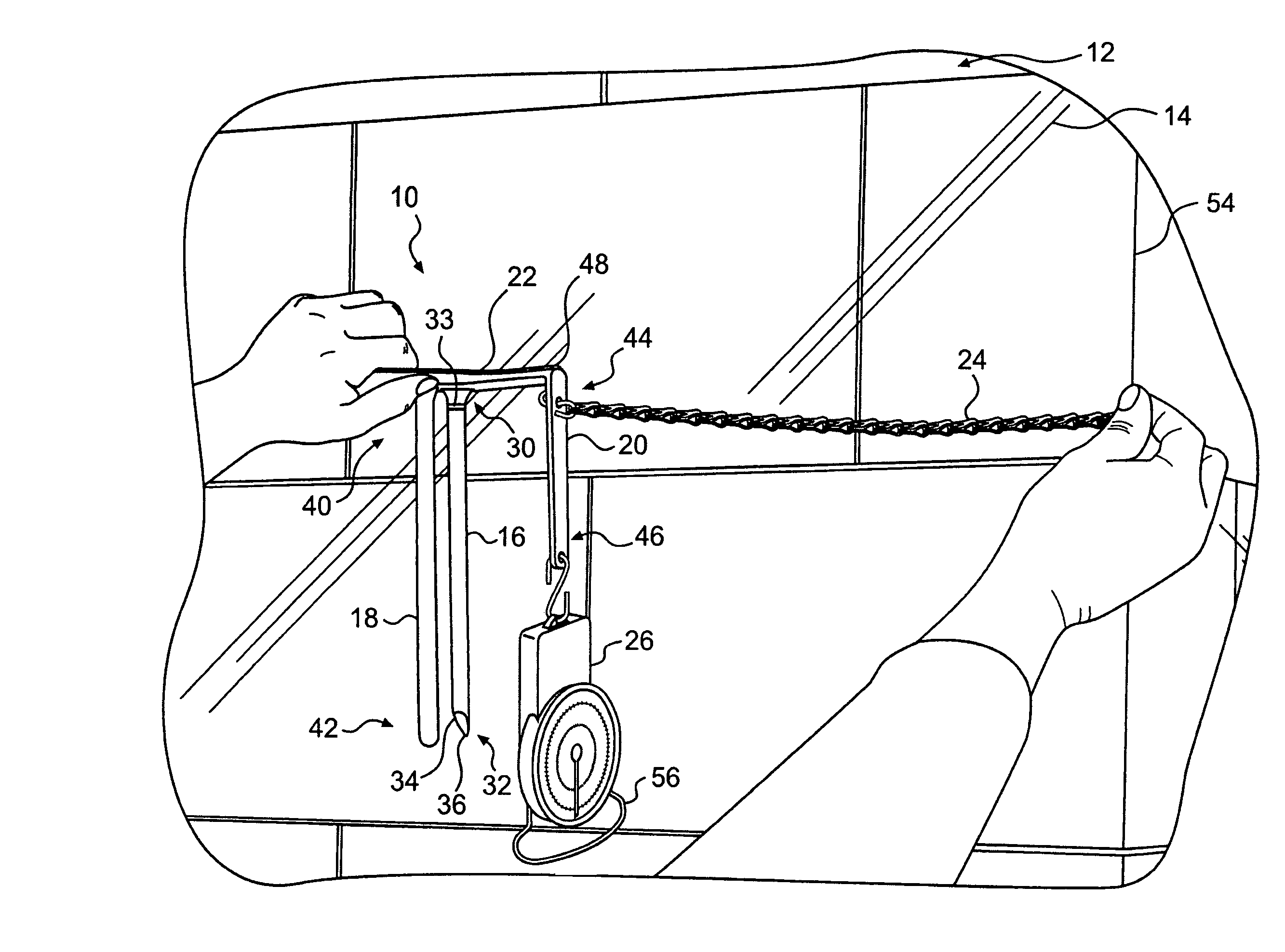
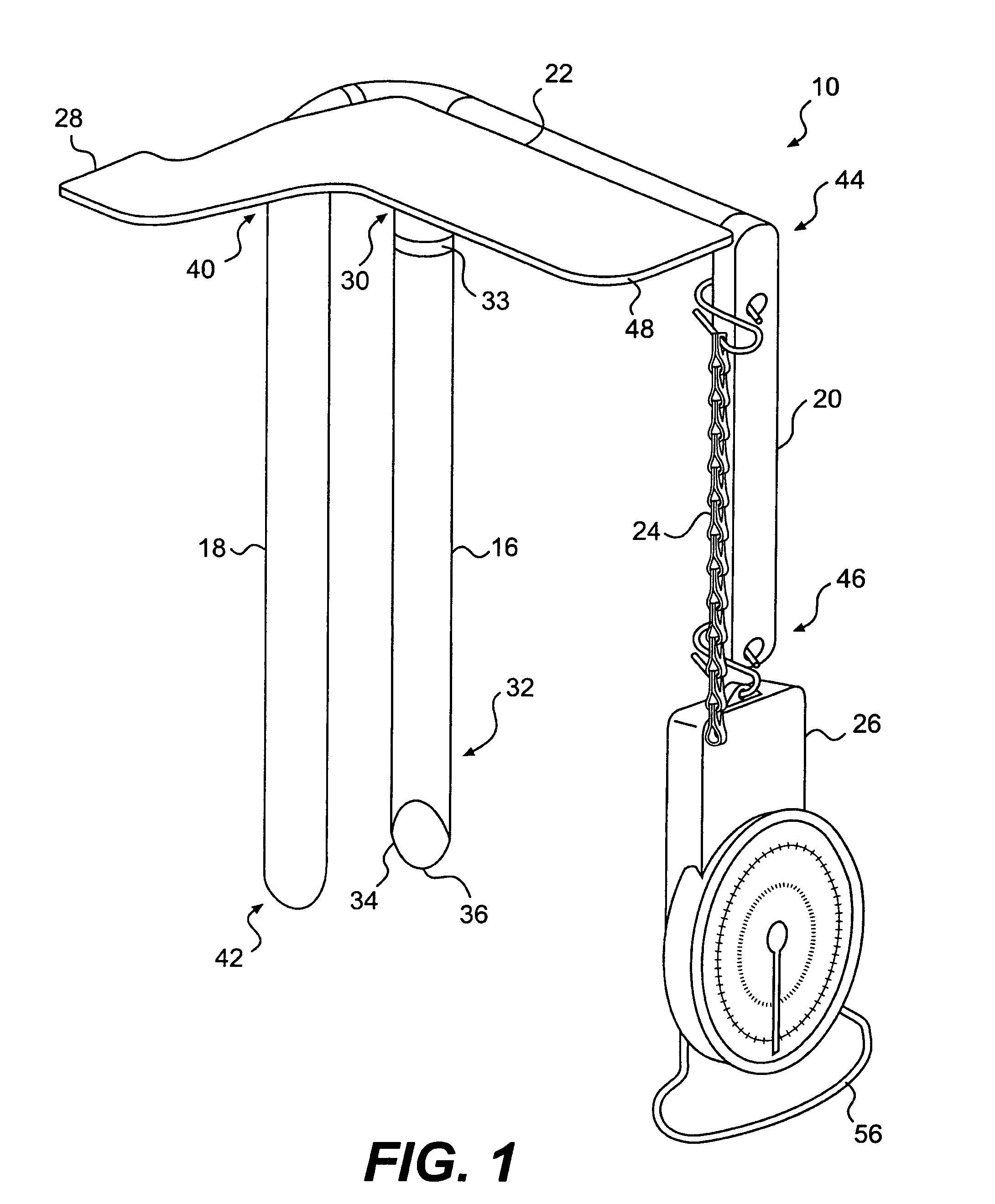
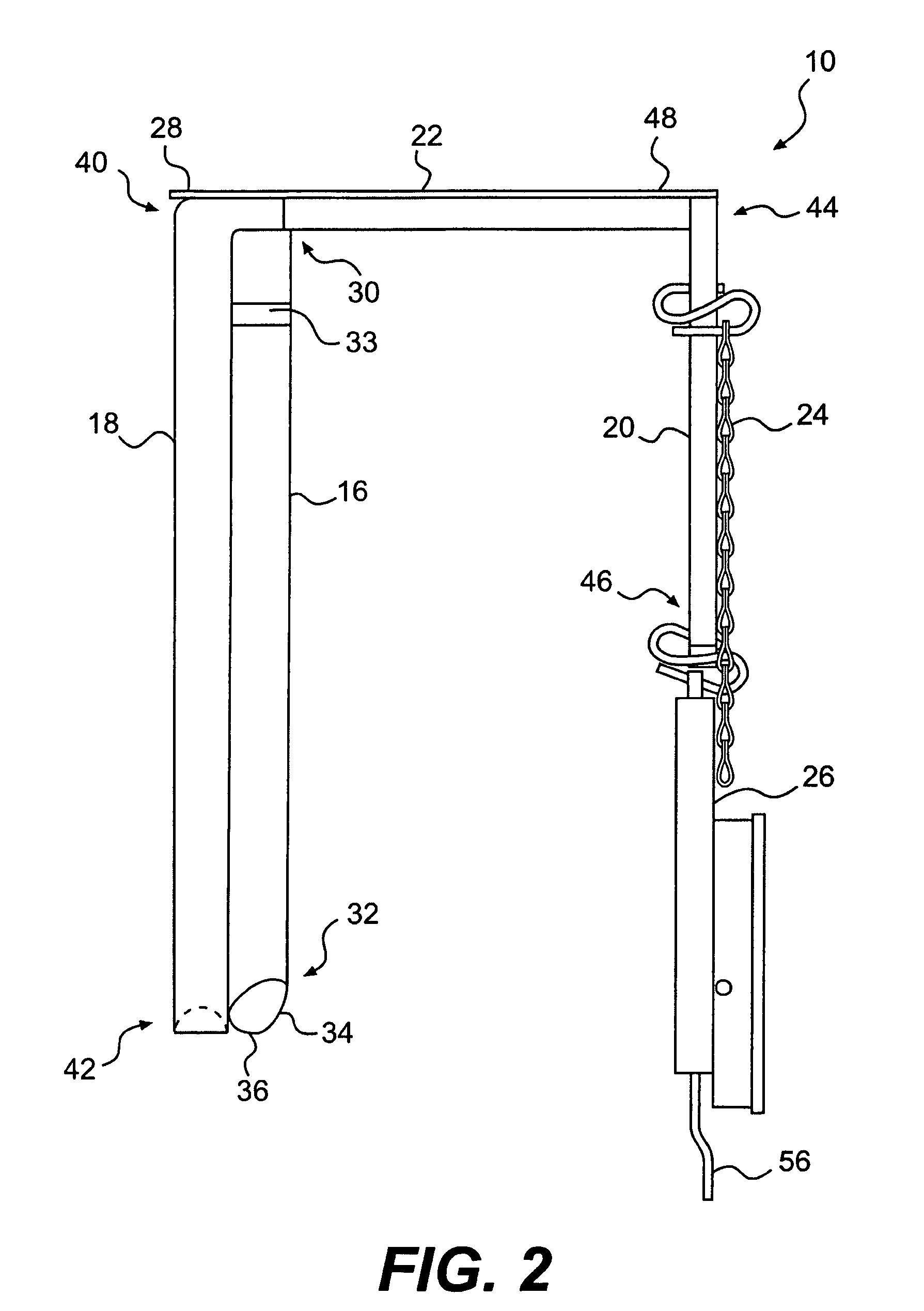
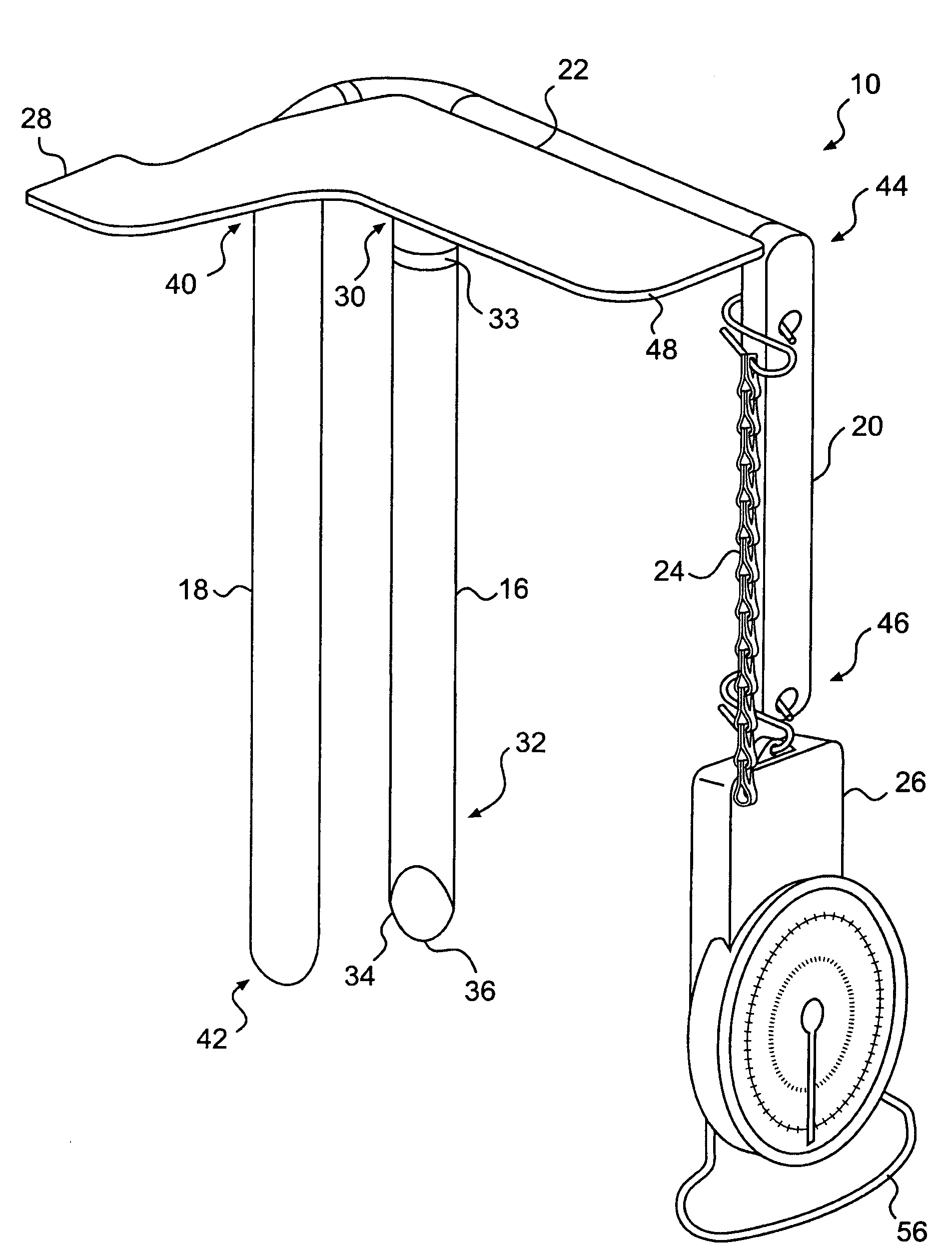
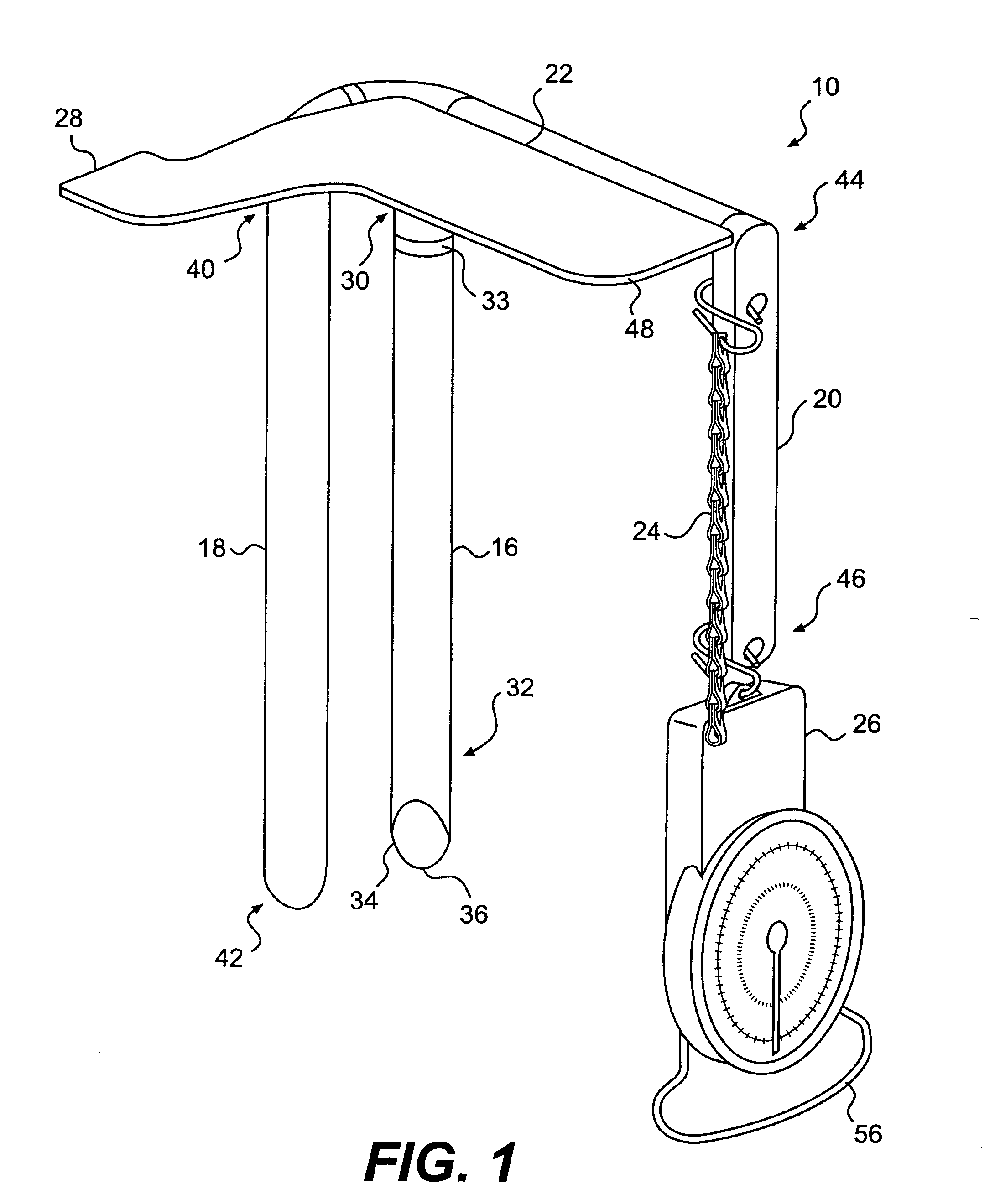
Apparatus and method for measuring containment force in a wrapped load and a control process for establishing and maintaining a predetermined containment force profile
An apparatus and method for measuring containment force on a load is provided. The apparatus may include a first longitudinally extending arm configured to engage a first side of packaging material wrapped around the load. The apparatus may also include a second longitudinally extending arm configured to engage a second side of the packaging material, the second side being opposite the first side. The apparatus may further include an indicator positioned substantially perpendicularly to the first and second arms, a third longitudinally extending arm, and a force gauge configured to measure a force exerted on the third longitudinally extending arm.
Owner:LANTECH COM
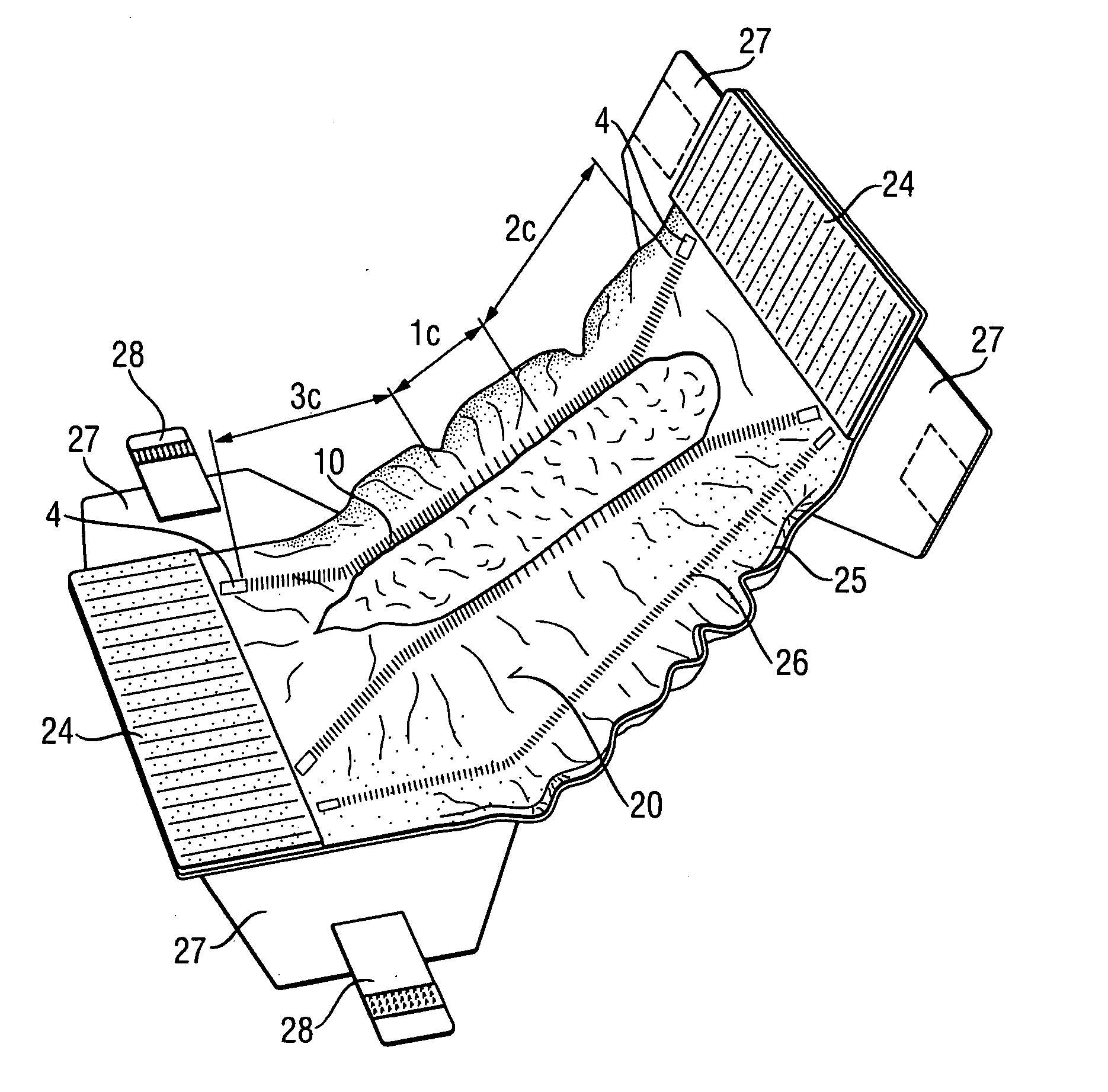
Absorbent articles with comfortable elasticated laminates
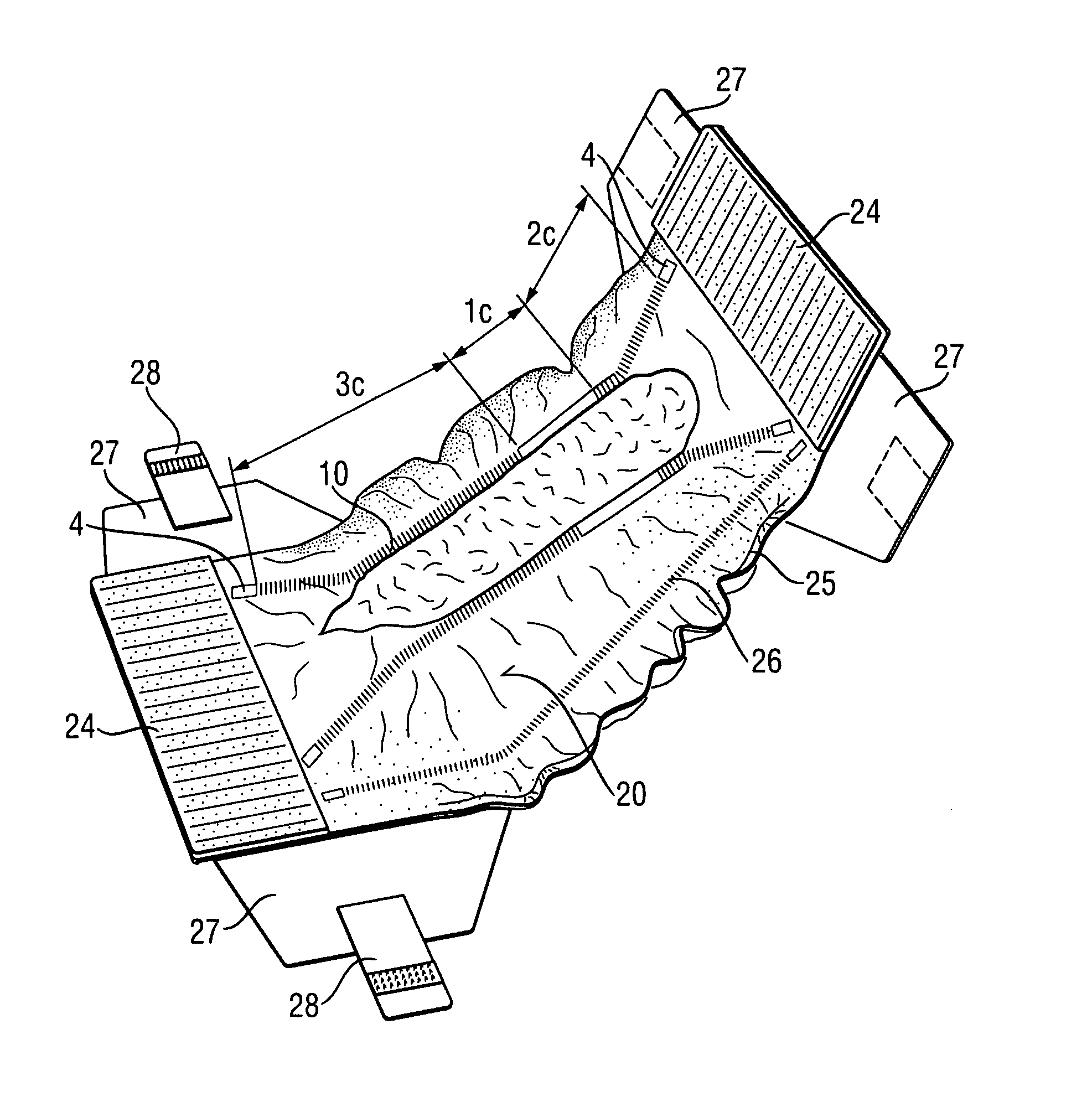
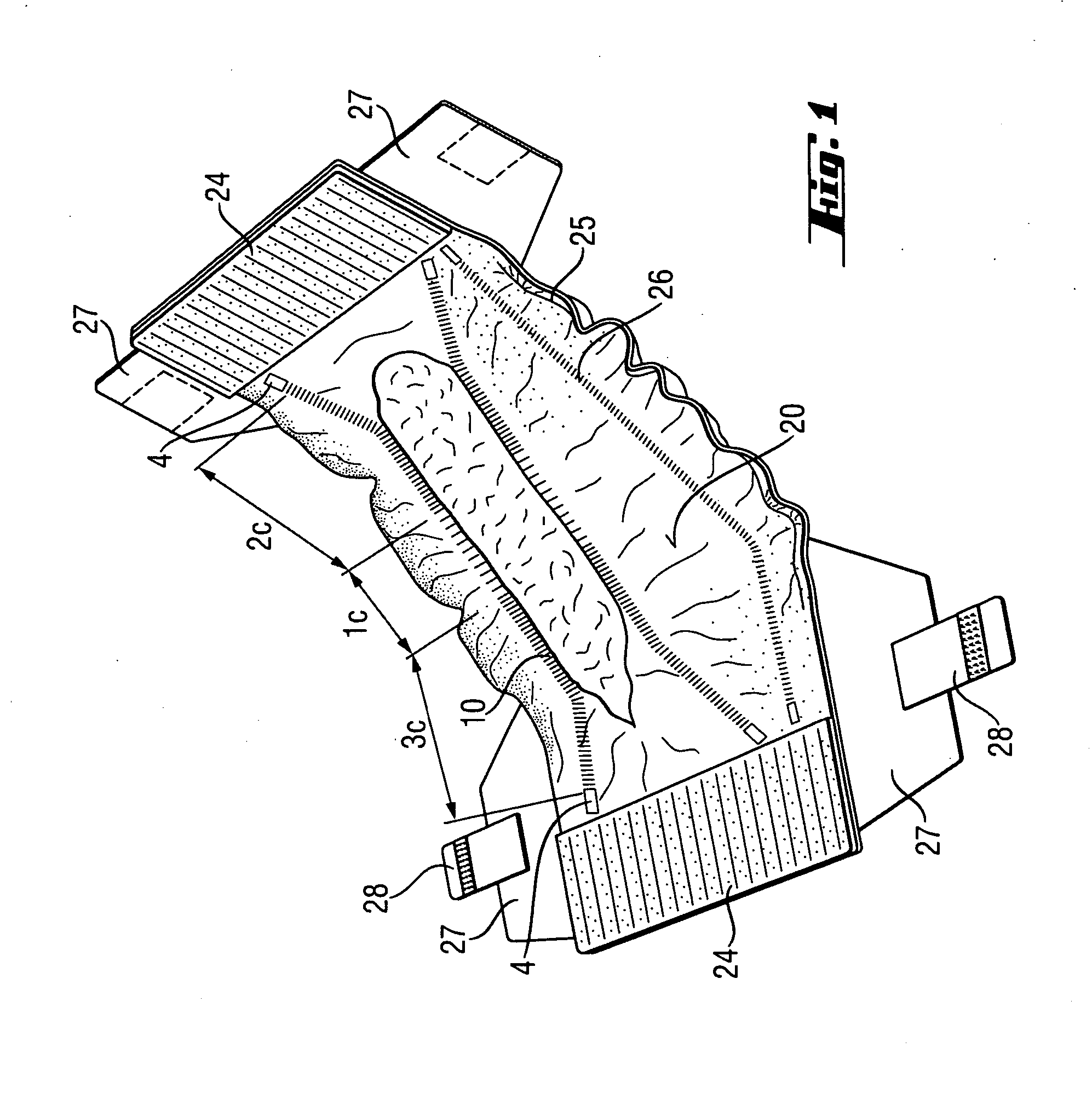
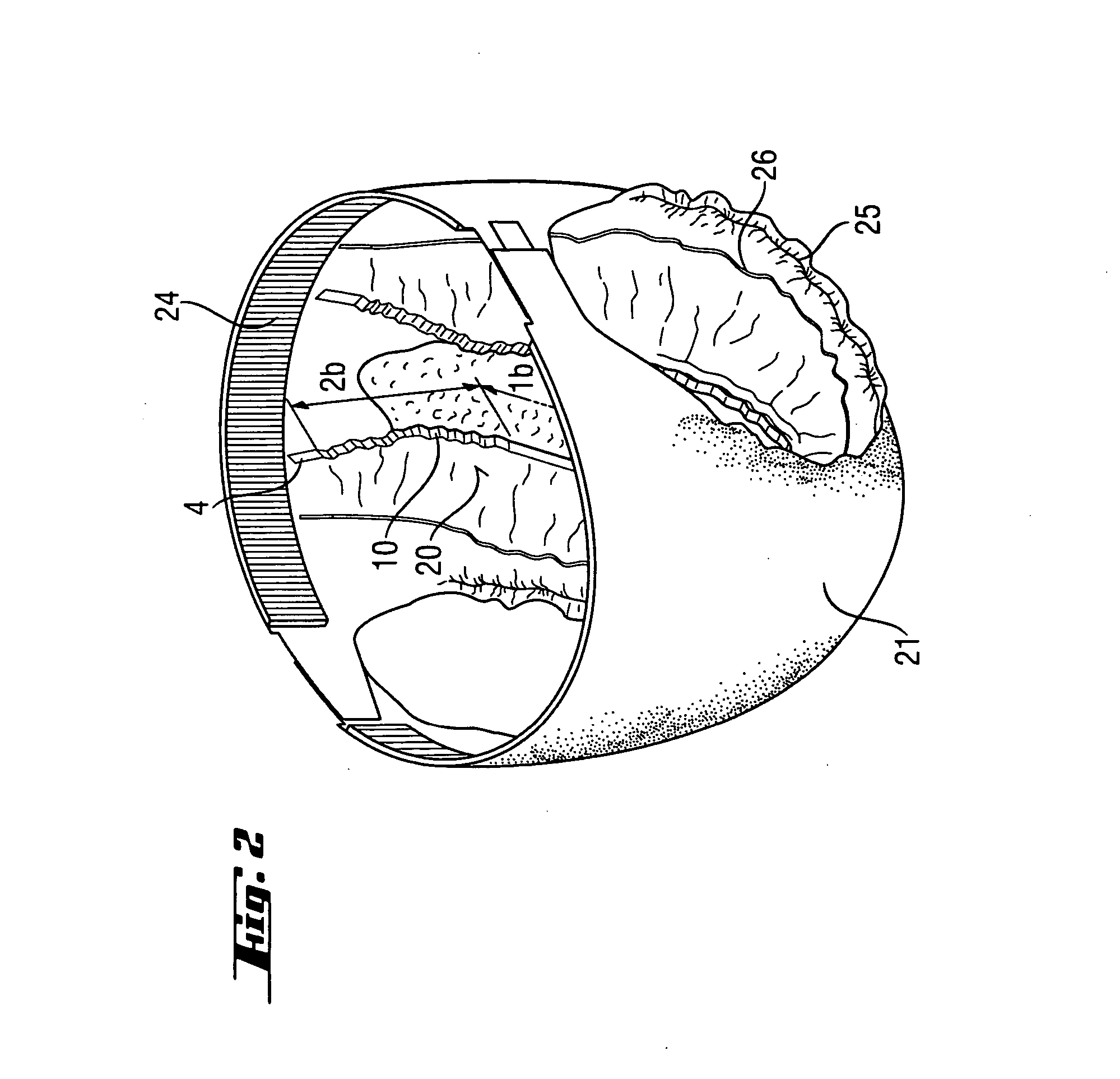
An absorbent article that includes a component with an elastic laminate portion, which provides y-direction elongation. The elastic laminate portion is a support sheet and an elastic material, together forming a laminate portion of the component. The elastic laminate portion has zones, each with a different degree of maximum elongation. The zones also have different wrinkle heights and / or densities, such that one or more zones are created that cause less or no pressure marks, whilst overall an excellent force profile is maintained, resulting in well performing, comfortable to wear absorbent articles.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Electromechanical dynamic force profile articulating mechanism
InactiveUS20070047051A1Eliminate needReduced superadditionFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsSemiconductor devicesElectrical conductorParallel plate
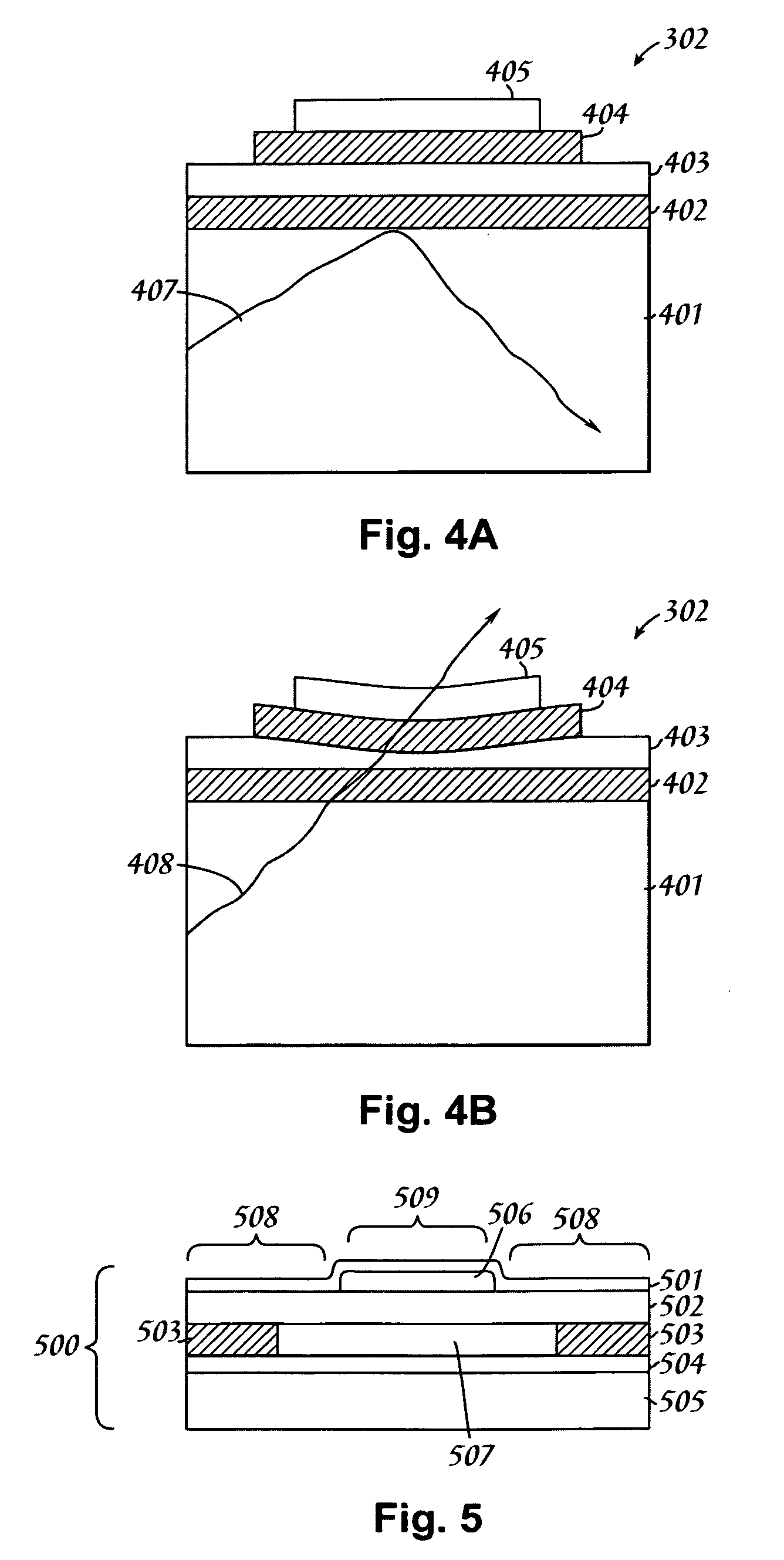
An electromechanical dynamic force profile articulating mechanism for recovering or emulating true parallel plate capacitor actuation behaviors from deformable membranes used in MEMS systems. The curved deformation of flexible membranes causes their MEMS behavior to deviate from known interactions between rigid plates that maintain geometric parallelism during ponderomotive actuation. The present invention teaches three methods for reacquiring parallel plate behavior: superaddition or in situ integration of a rigid region within or upon the deformable MEMS membrane; creation of isodyne regions to secure parallelism by altering the force profile upon the membrane by introducing tuned and shaped voids within the conductive region associated with the membrane; and a hybrid composite approach wherein the conductive region is deposited after deposition of a raised rigid zone, thereby emulating isodyne behavior due to the increased inter-conductor distance in the vicinity of the rigid zone, in conjunction with rigidity benefits stemming directly from said zone.
Owner:RAMBUS DELAWARE
Force-based input device having an elevated contacting surface
InactiveUS20080030482A1Easy to determinePrecise positioningInput/output processes for data processingEngineeringContact element
A projected force-based input device comprising a projected or elevated contacting element configured to receive an applied force, a sensing element located in a different plane with respect to the contacting element, and a sensing portion operably supported to displace in response to the applied force. The sensing element further comprises a plurality of sensors operable to output sensor data corresponding to the applied force, wherein the sensor data facilitates the determination of a location of the applied force occurring about the contacting element, as well as the profile of the applied force over time (e.g., waveform), otherwise known as the force profile. One or more transfer elements may also be present, which function to relate the contacting element to the sensing portion of the sensing element so as to transfer substantially all of the applied force from the contacting element to the sensing element. Adequate rigidity between the elevated contacting element, and transfer elements, and the sensing element is intended to be maintained in order to prevent interference with any mounting or other structures or objects, and to permit the input device to operate properly.
Owner:QSI CORPORATION
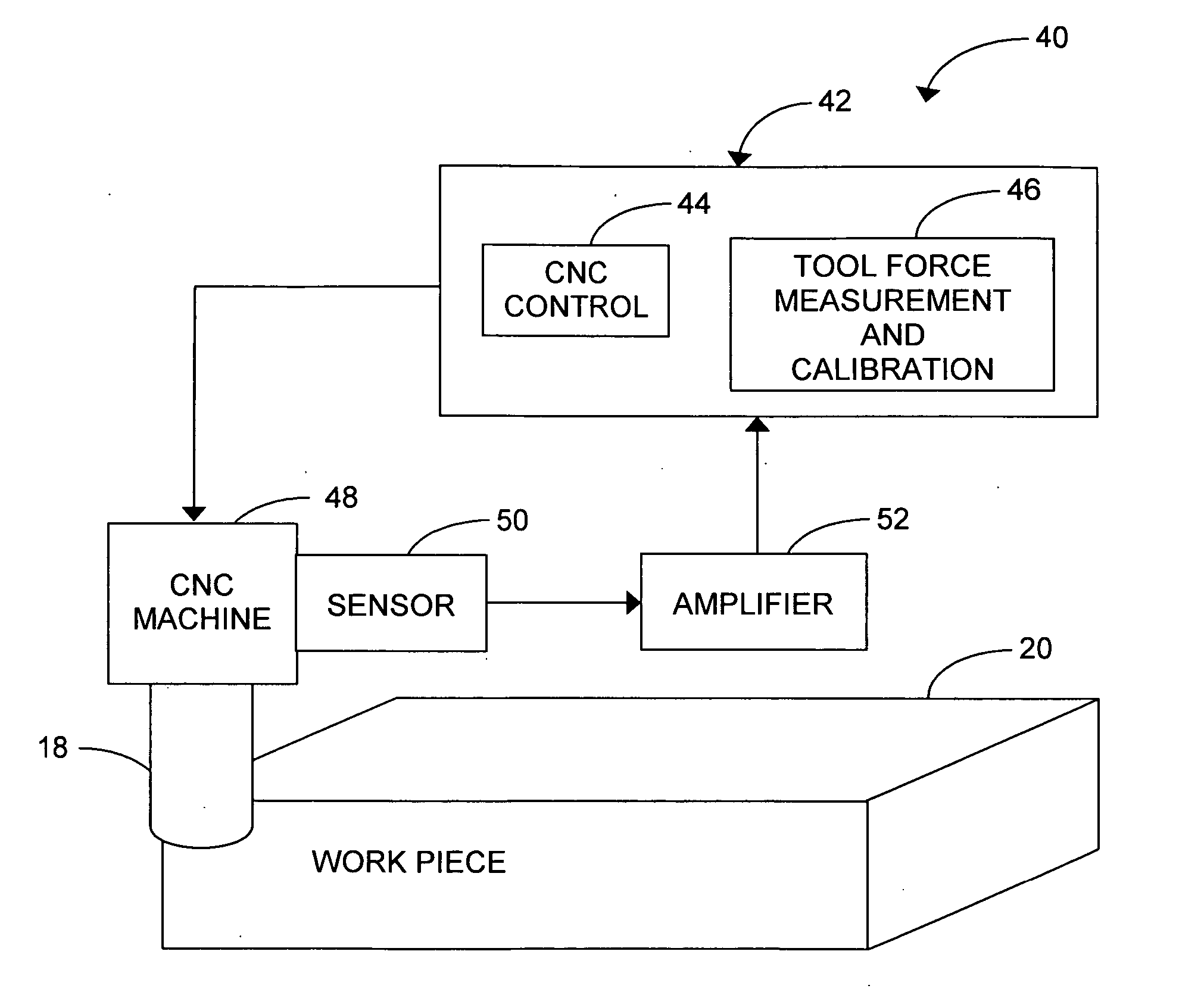
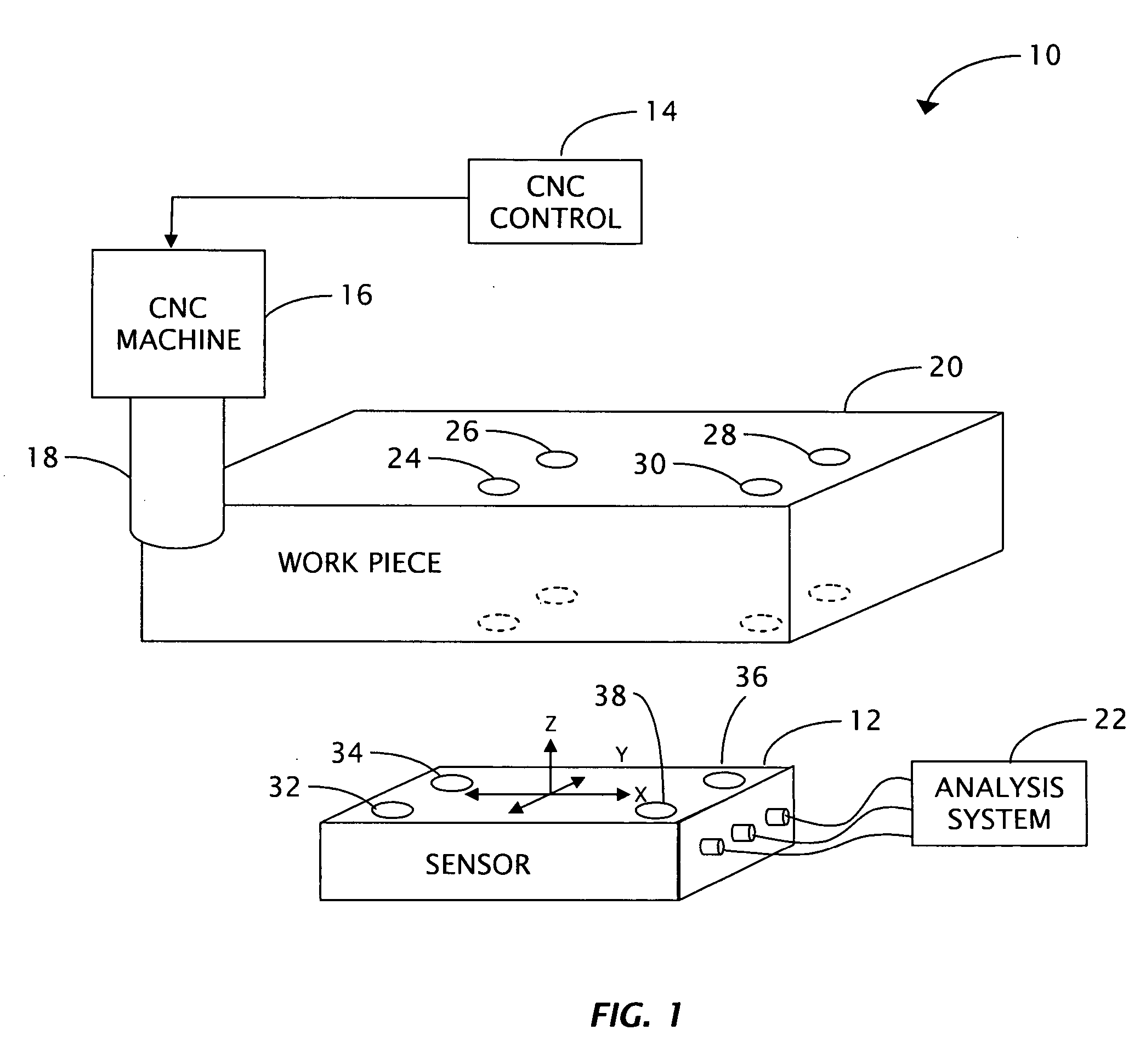
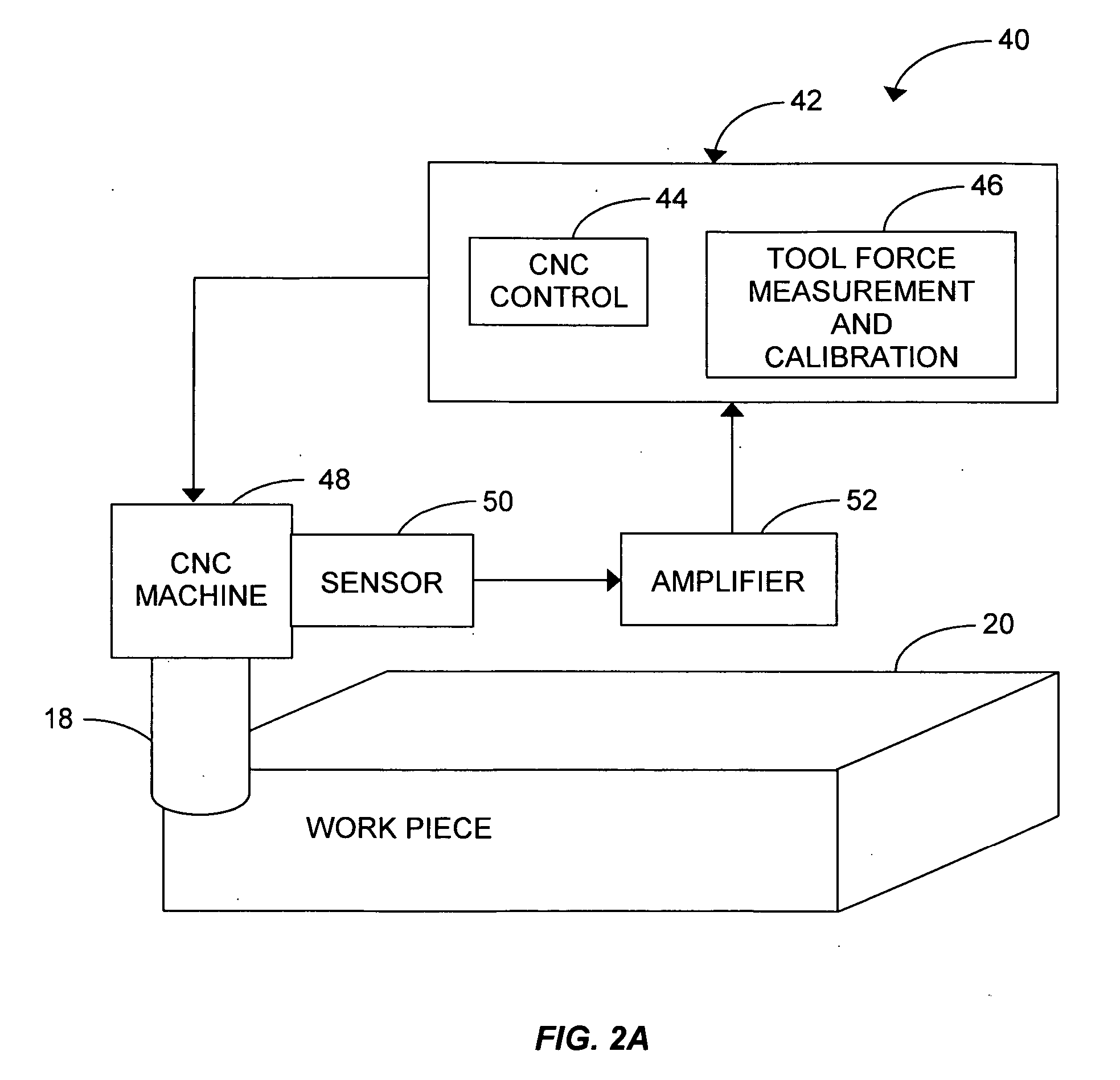
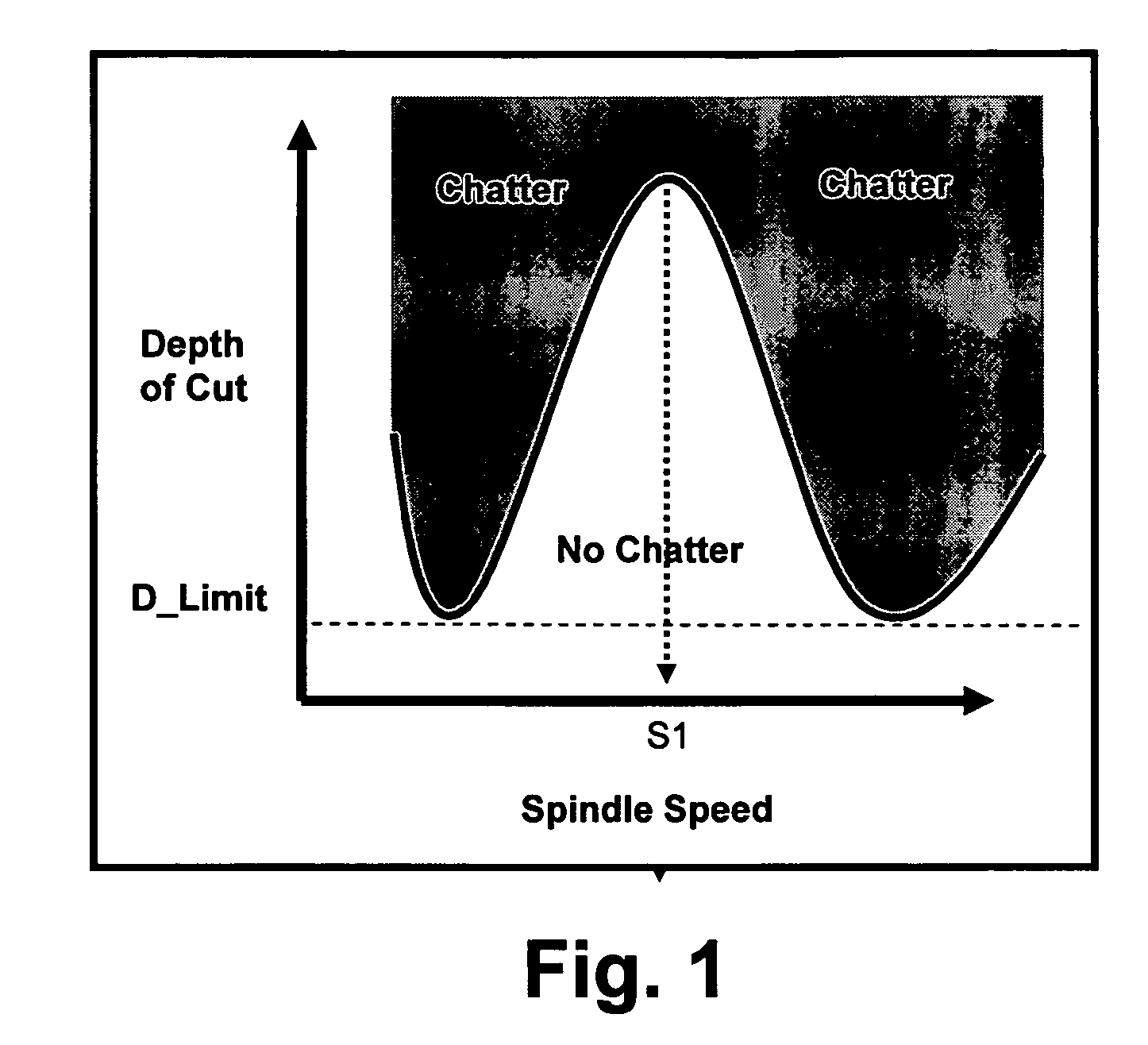
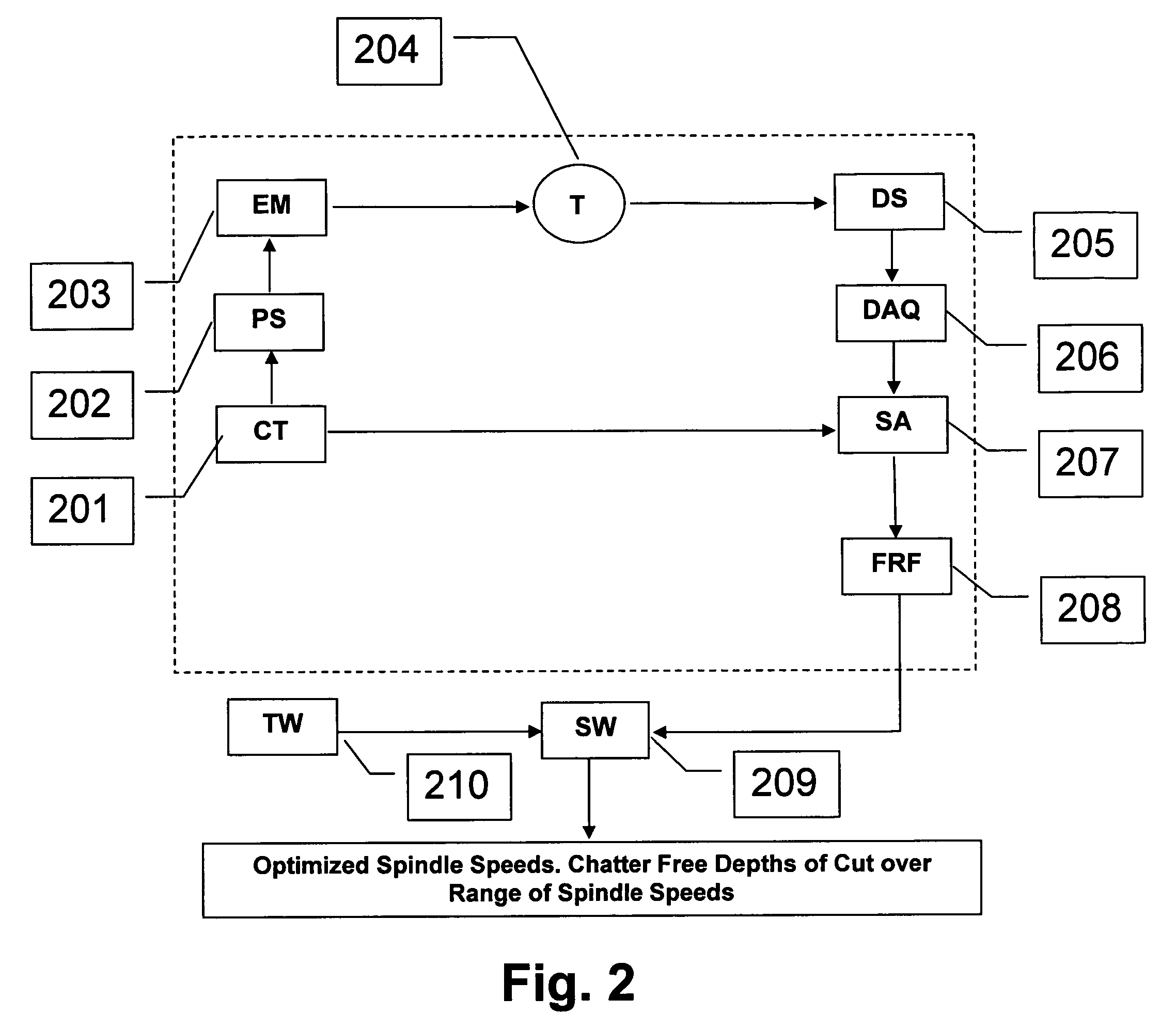
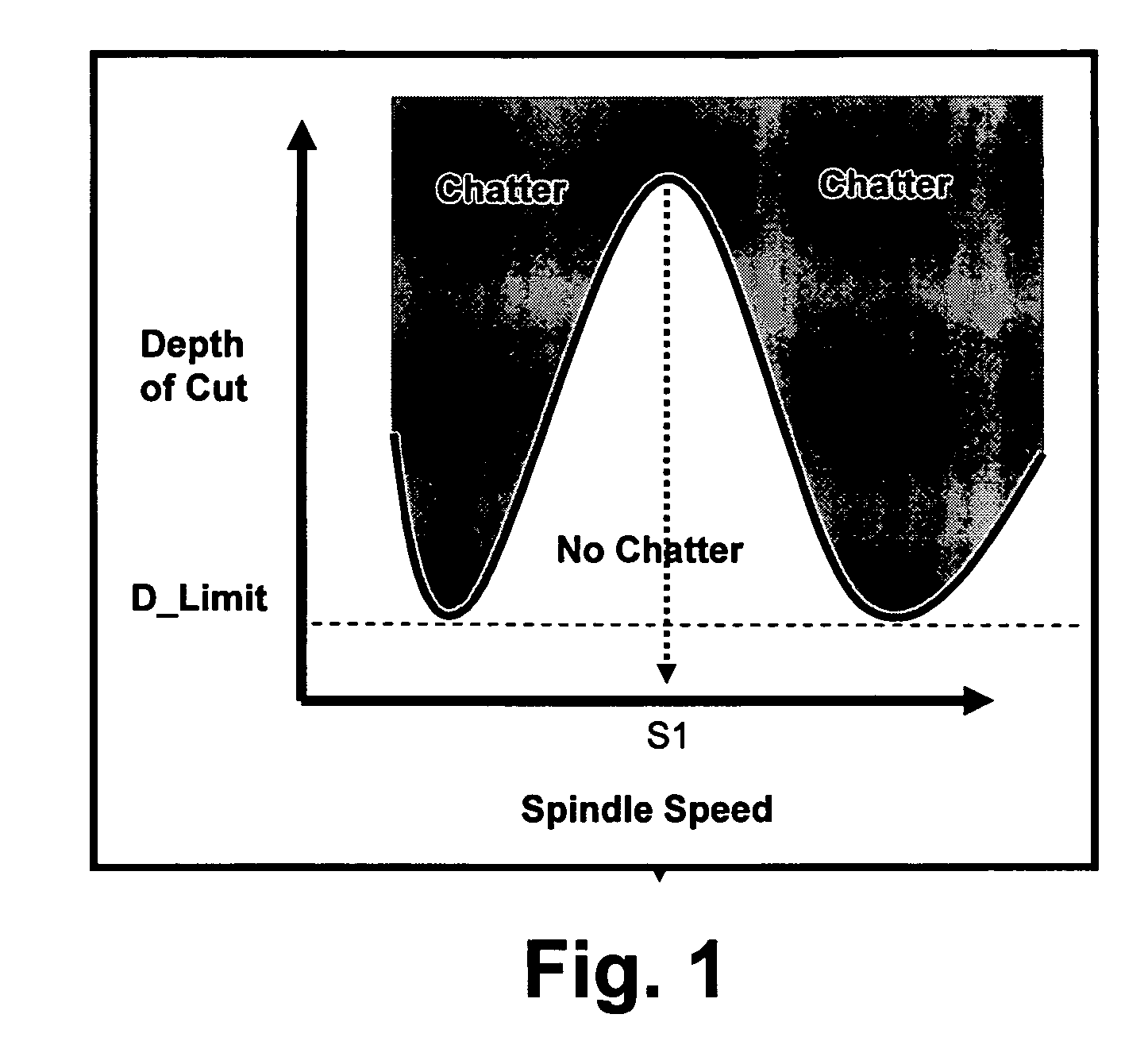
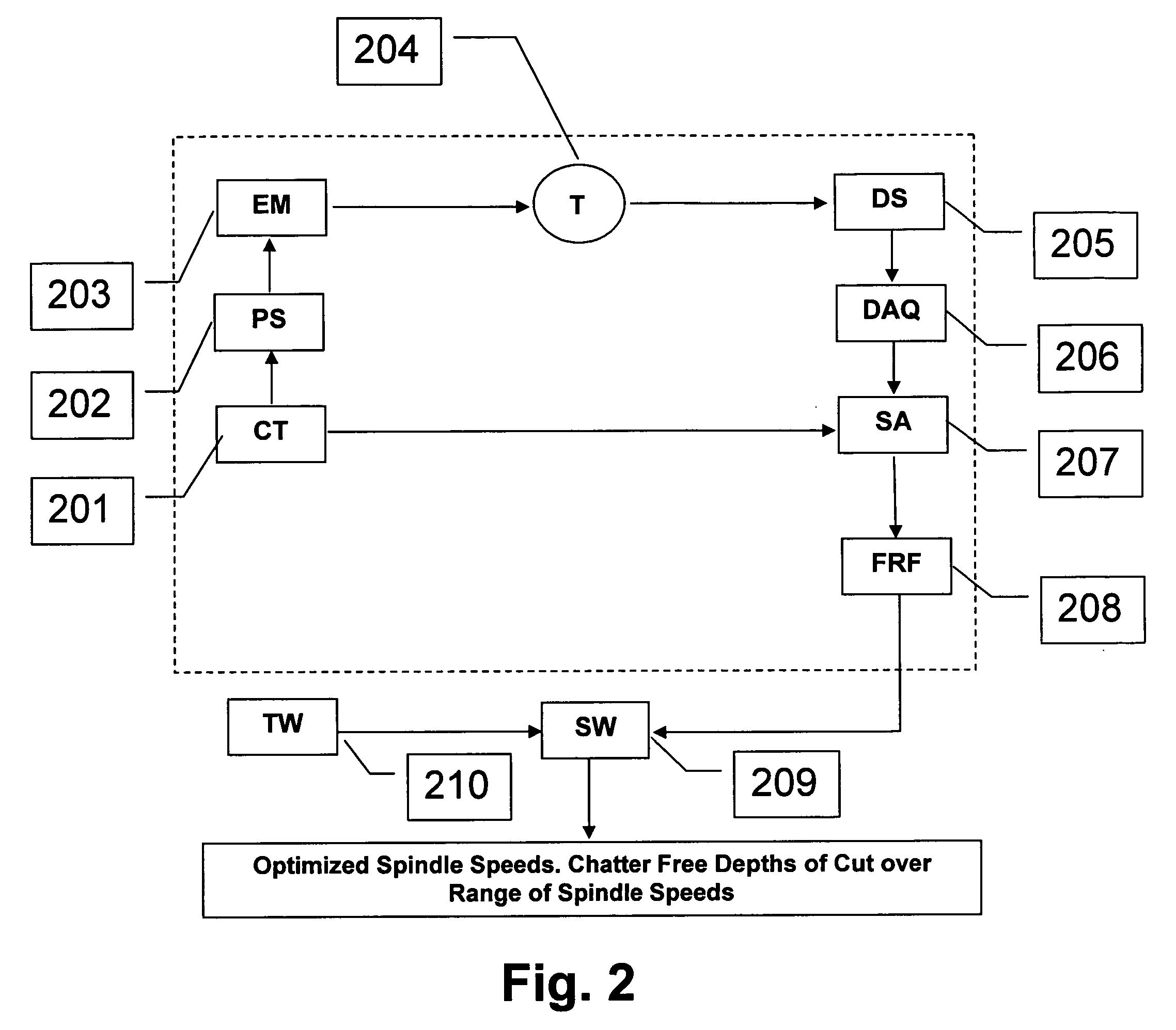
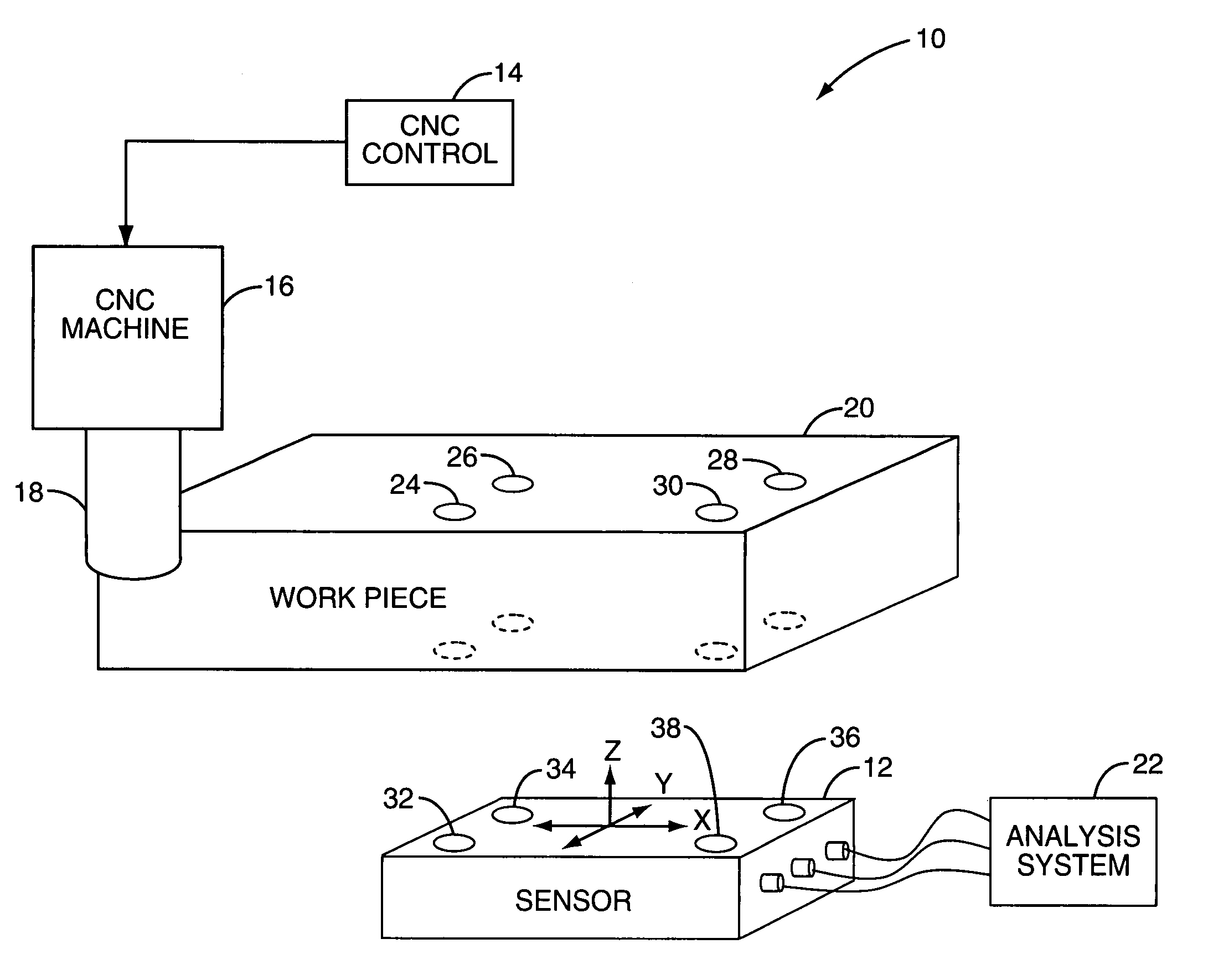
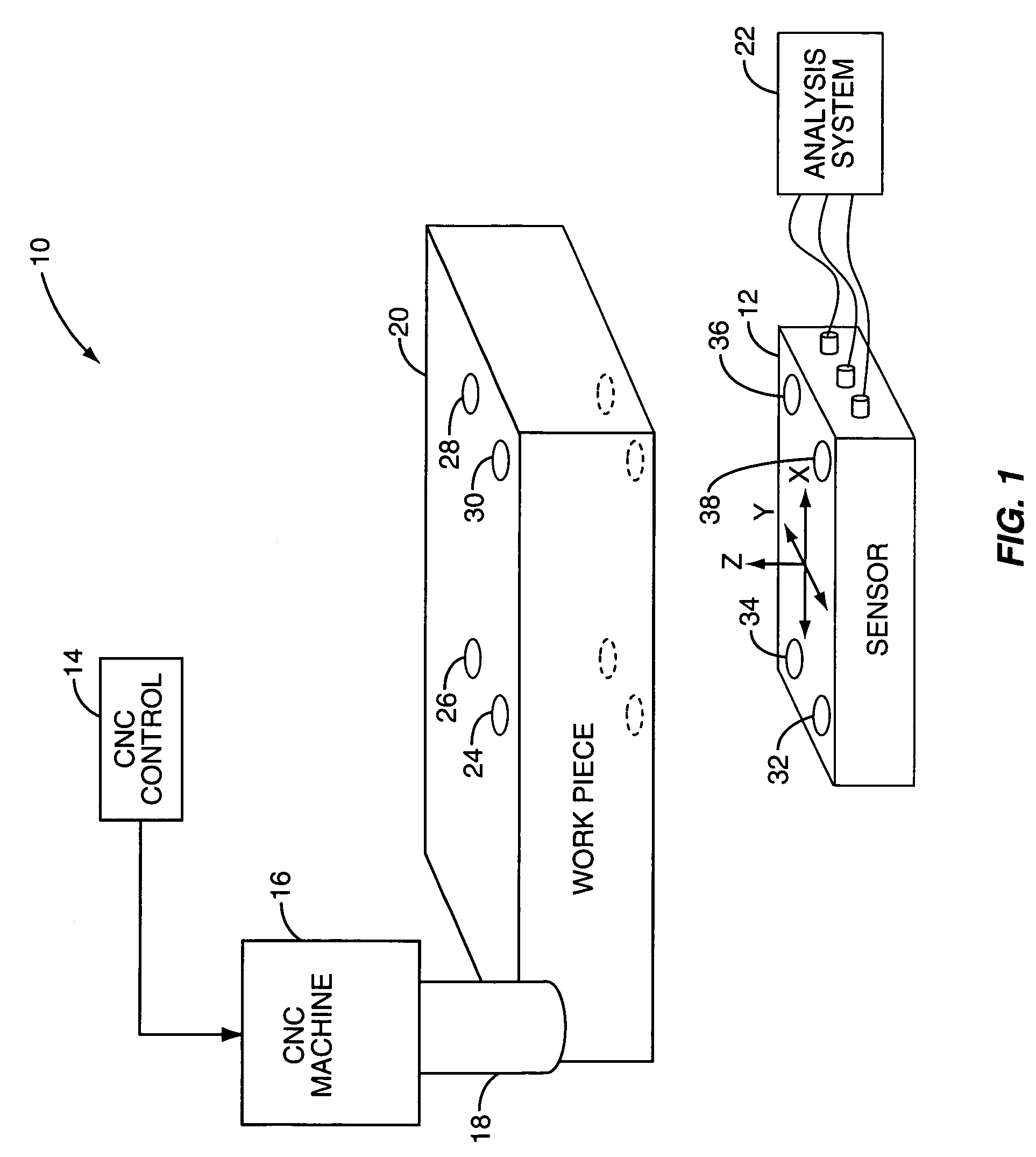
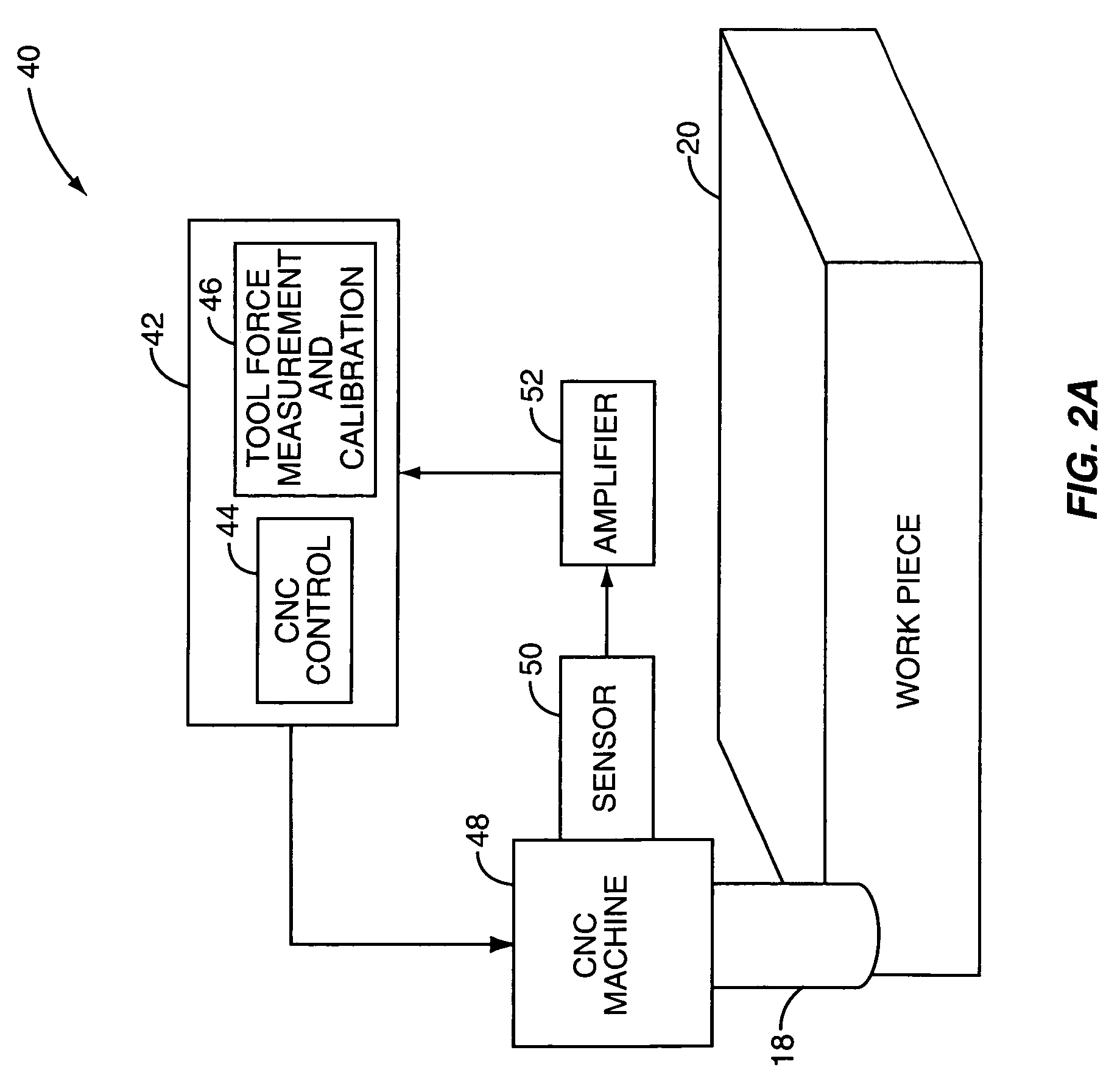
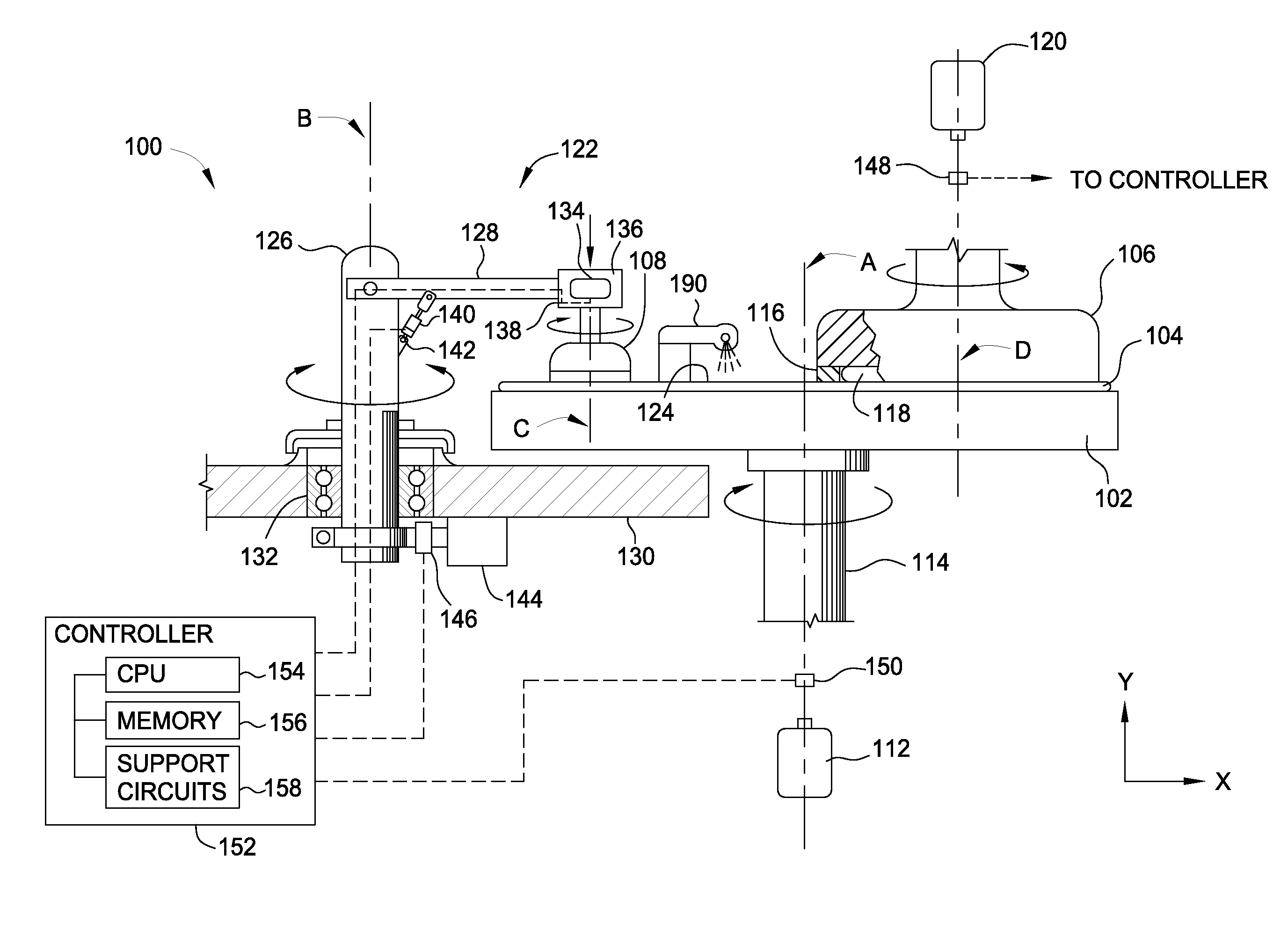
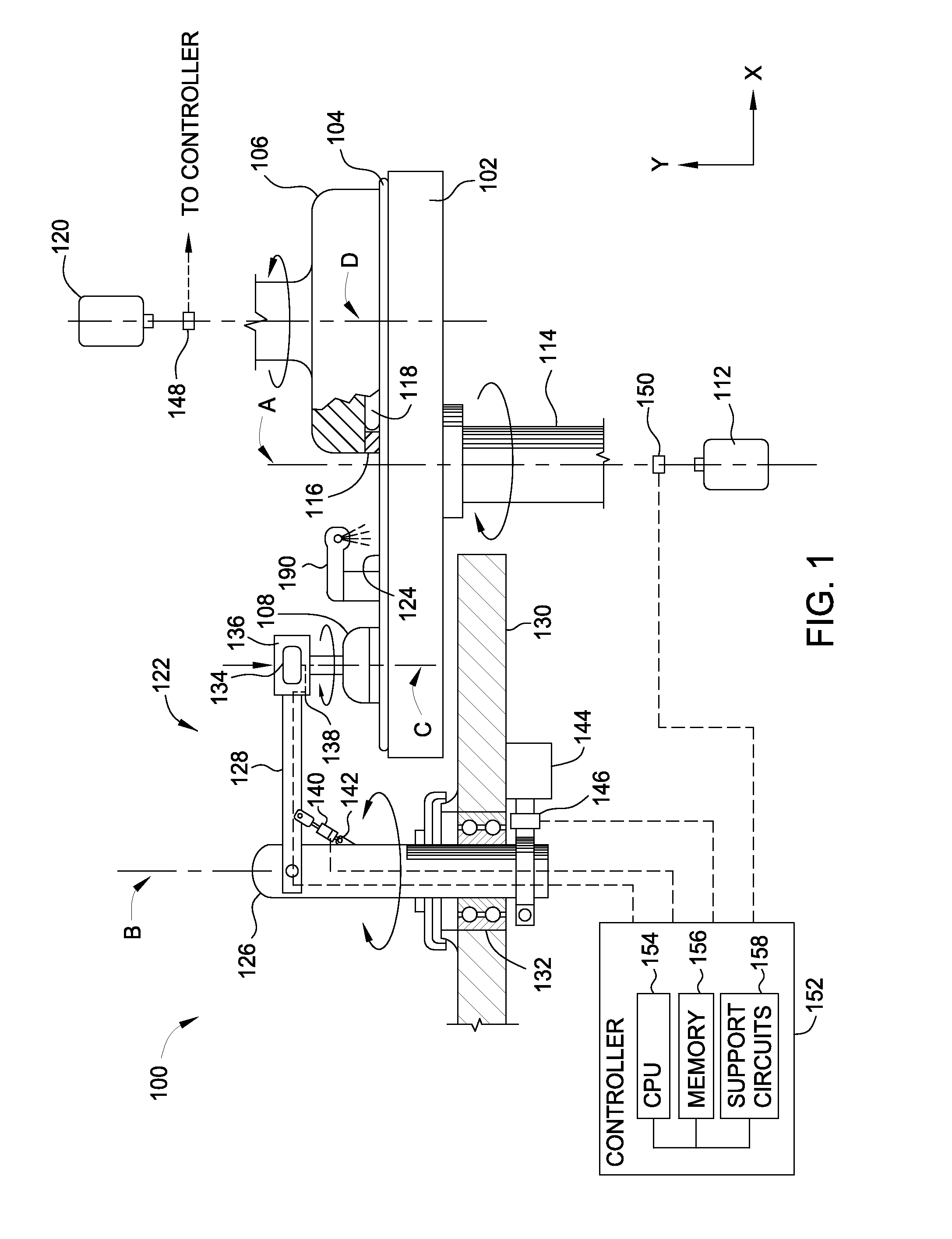
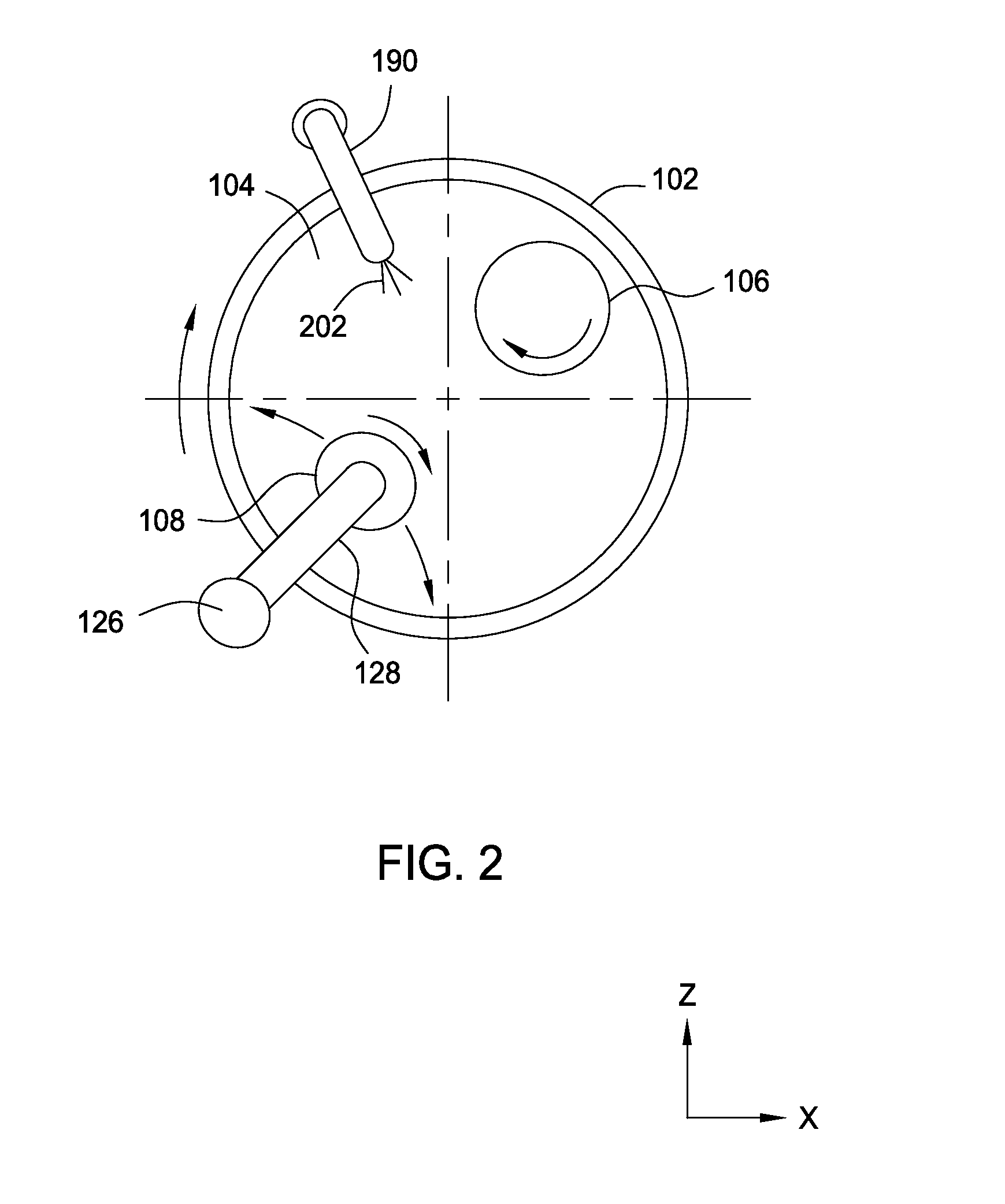
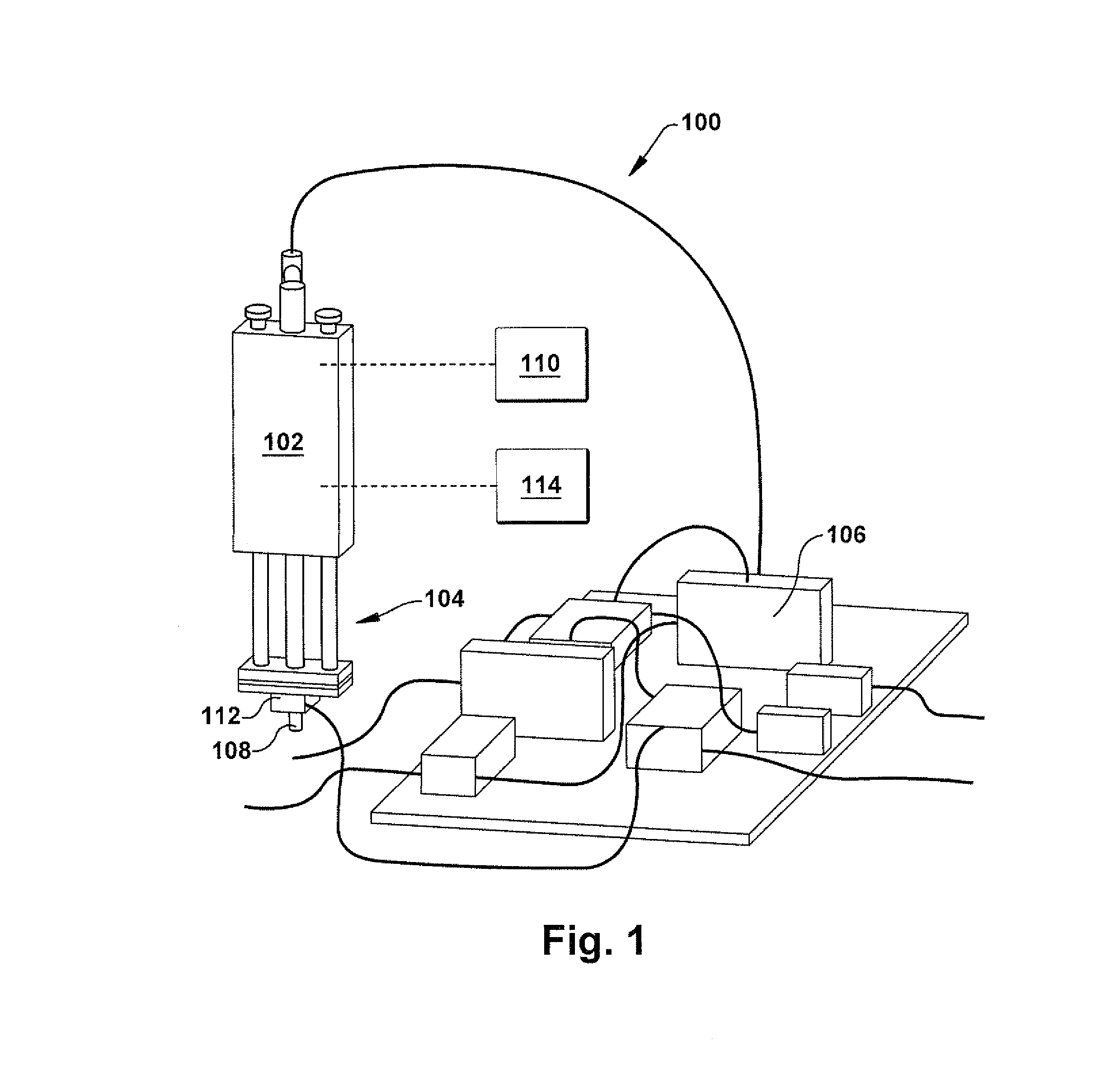
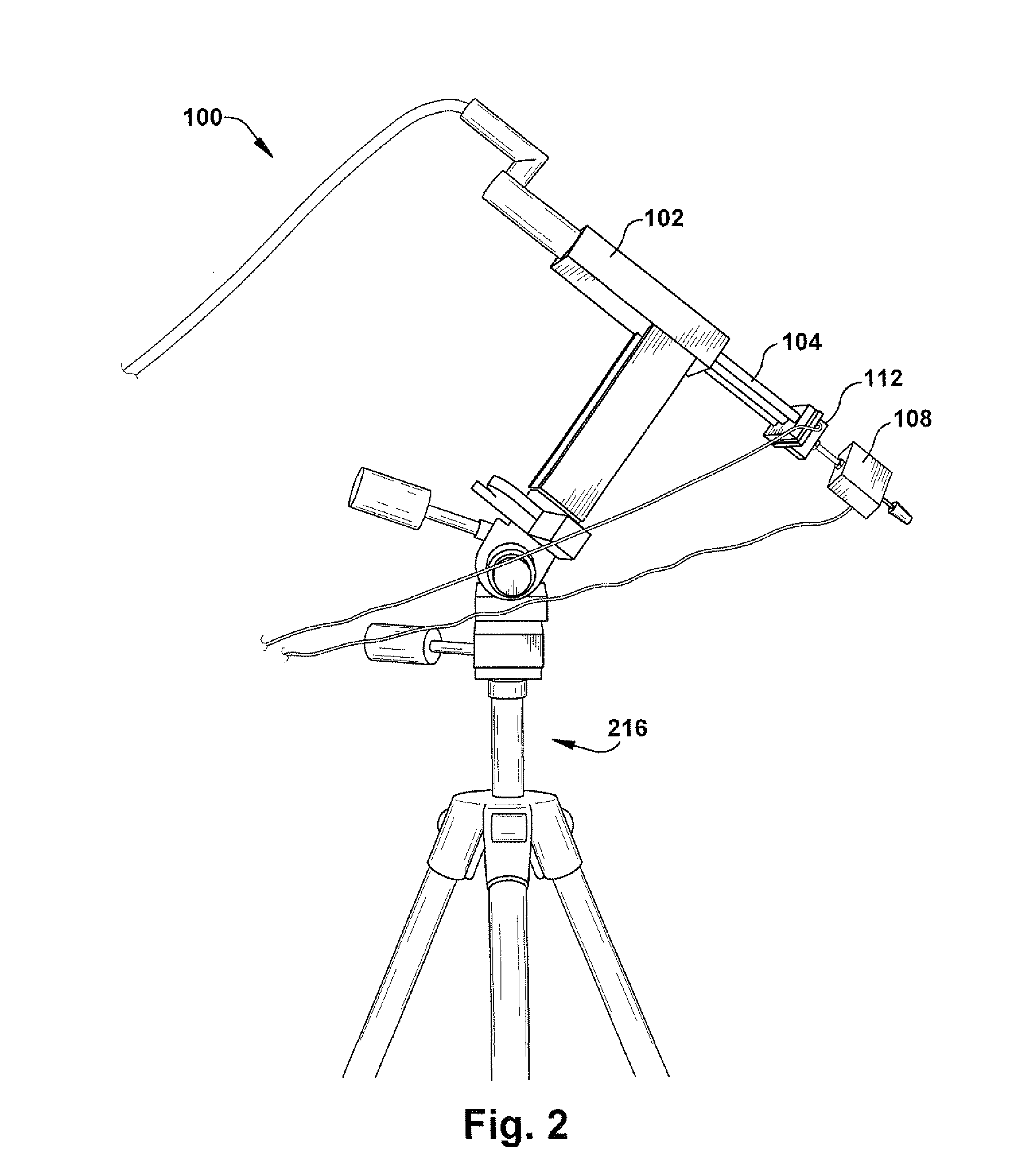
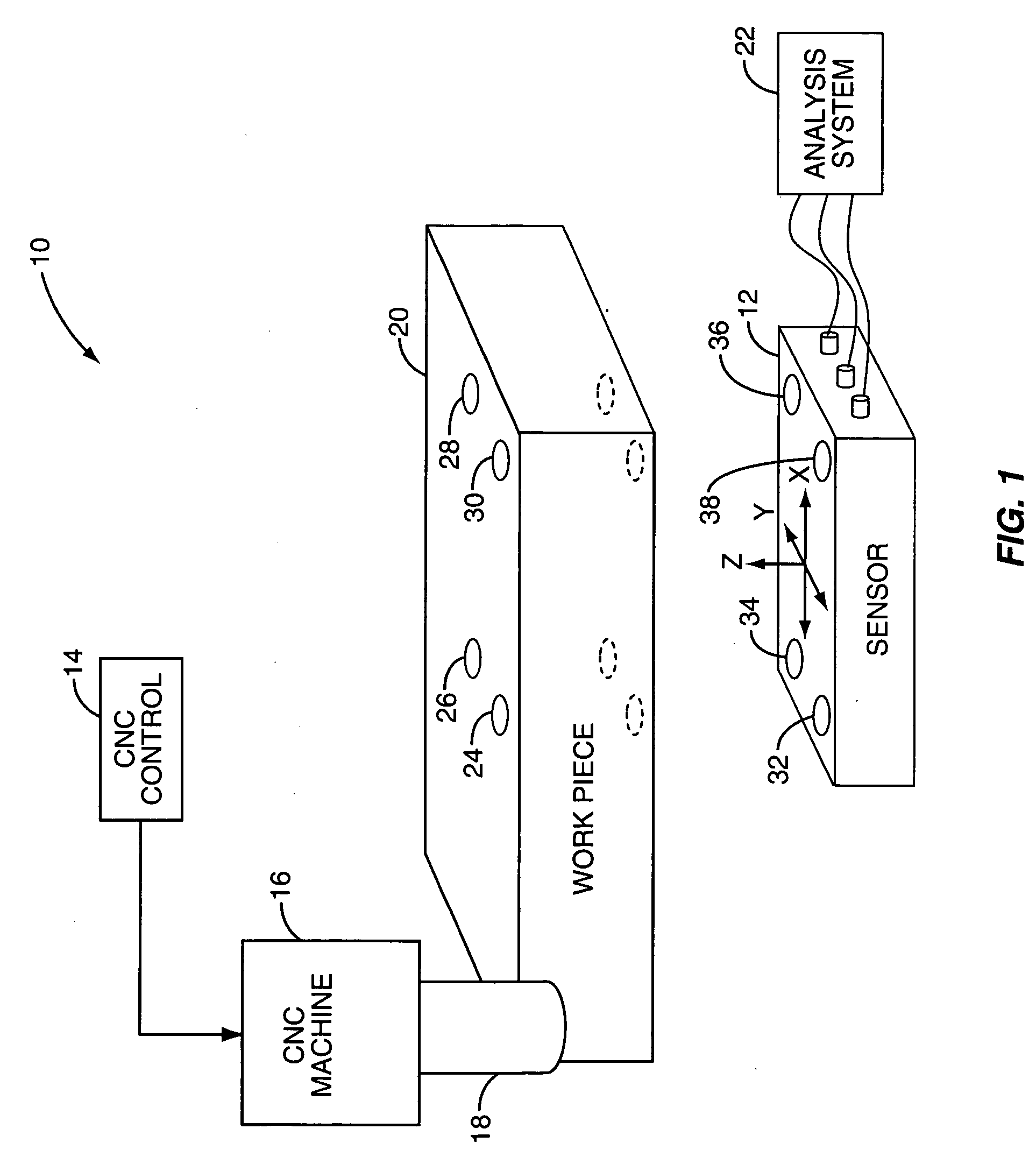
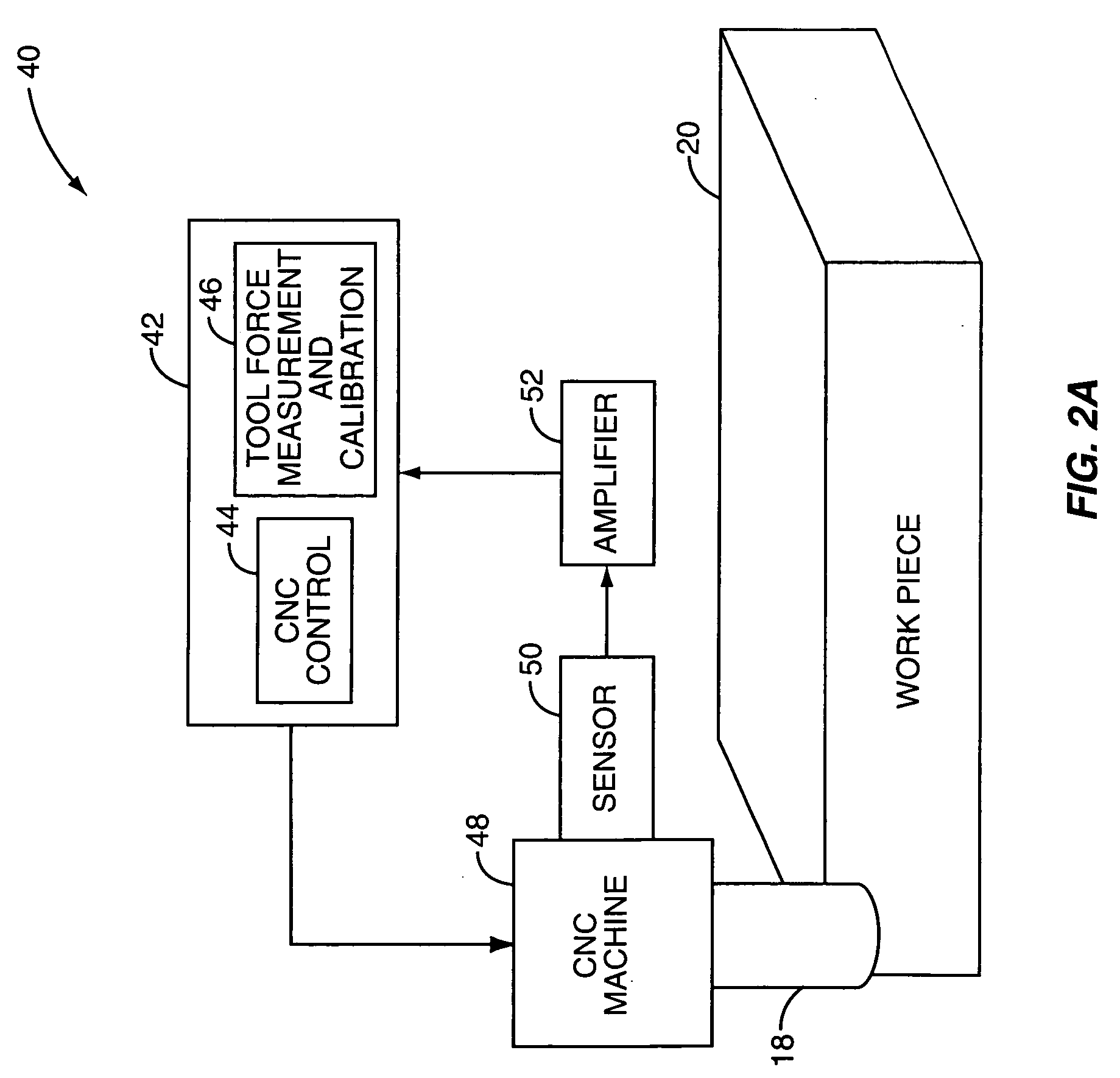
Sensor-based measurement of tool forces and machining process model parameters
InactiveUS20070016325A1Inexpensive but accurate monitoringAddressing Diversity InsufficiencyProgramme controlForce measurementSacrificial partElectric machinery
A system and method are provided for real-time measurement of tool forces. A relationship between a sensor characteristic and tool forces is determined by first directly measuring tool forces for a standard tool, work piece, and part program in a central facility. A force profile indicative of the tool forces and the standard tool, work piece, and part program are provided to a user at a user facility. The sensor characteristic for a CNC machine at the user facility is then measured for the standard tool, work piece, and part program. Based on the force profile determined at the central facility, the relationship between the sensor characteristic and tool forces is determined. Thereafter, the sensor characteristic of the CNC machine is measured for a work piece, part program and desired tool and converted to tool forces using the relationship between the sensor characteristic and tool forces. The resulting tool forces may be combined with a process model to obtain process model parameters or cutting energies for the work piece and the desired tool. In cases where the sensor is not conveniently attached to the work piece or when the part program is not sufficiently robust in cutting conditions to accurately determine the process model parameters, the work piece and part program are replaced by a sacrificial work piece and sacrificial part program. The sacrificial work piece and sacrificial part program are selected to both accommodate the sensors and to provide sufficient robustness in cutting conditions to accurately determine the process model parameters for the sacrificial work piece. The process model parameters for the desired work piece are obtained from the process model parameters by, first, obtaining the averaged tangential tool forces for the desired work piece and for the sacrificial work piece by measuring the spindle motor power and applying the relationship between spindle motor power and tangential tool forces for each work piece, second, obtaining a ratio of the averaged tangential tool forces for the desired work piece and the sacrificial work piece and, third, applying this ratio to the process model parameters for the sacrificial work piece to obtain predicted values for the tool forces and the process model parameters for the desired tool and desired work piece.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF NEW HAMPSHIRE
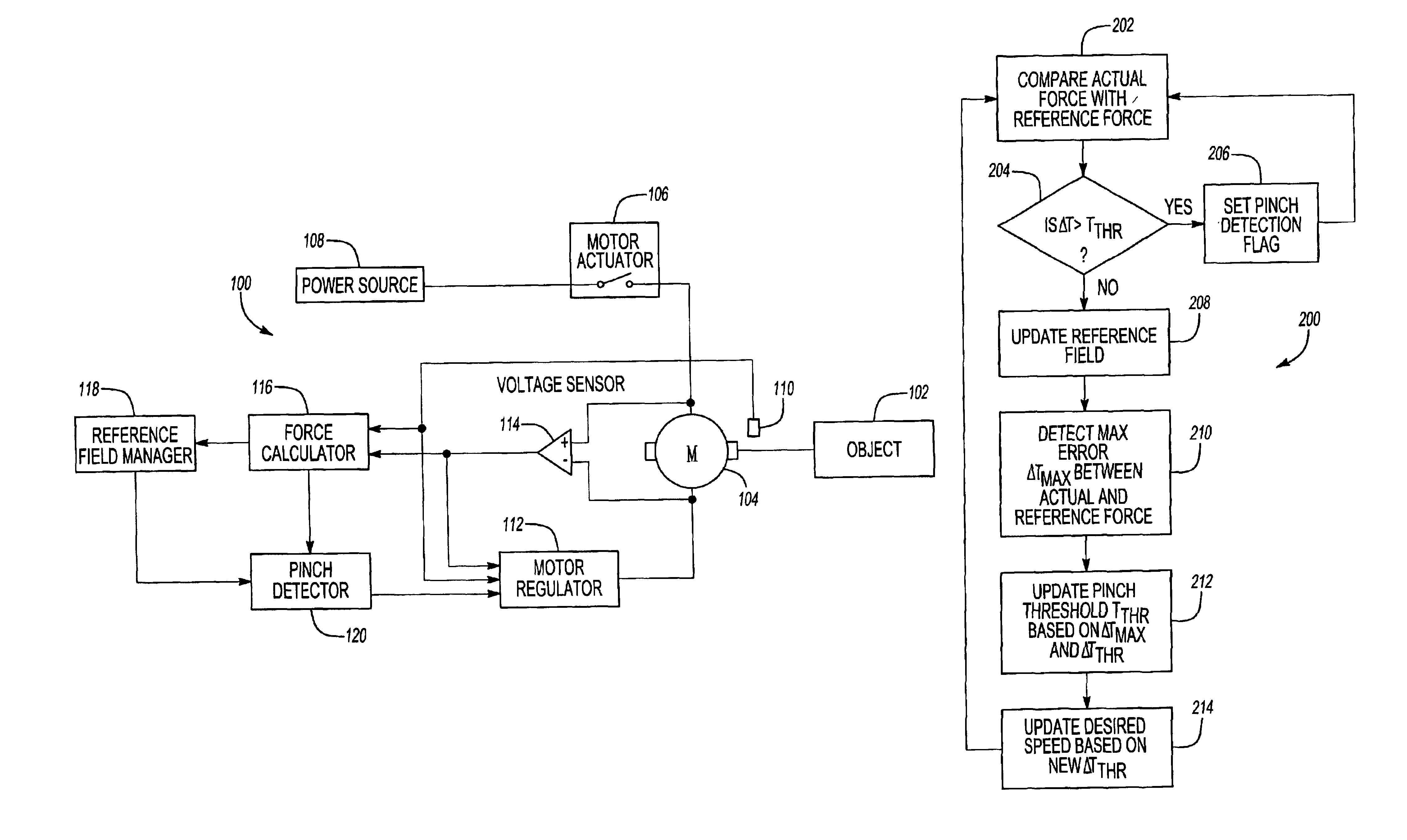
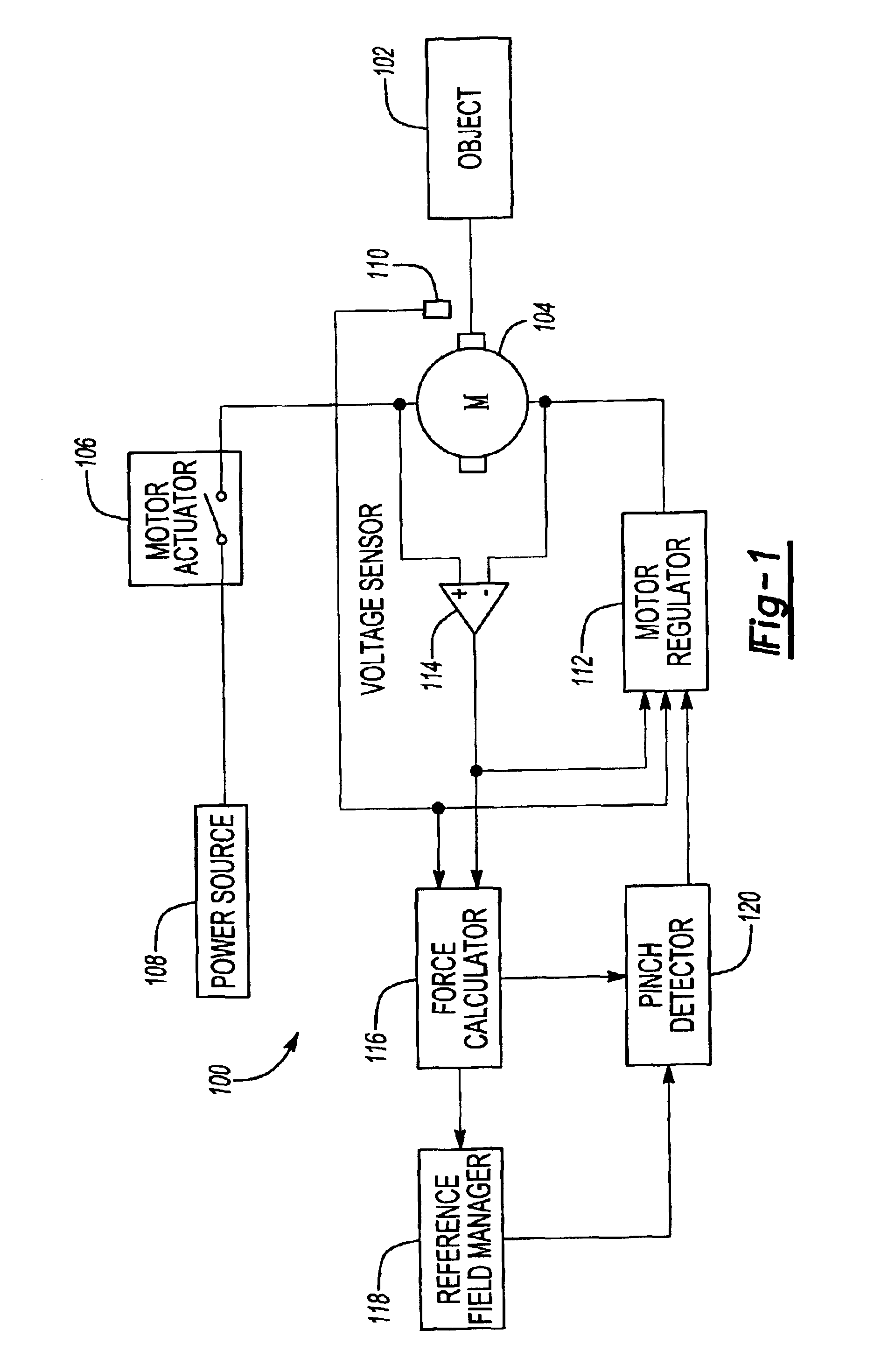
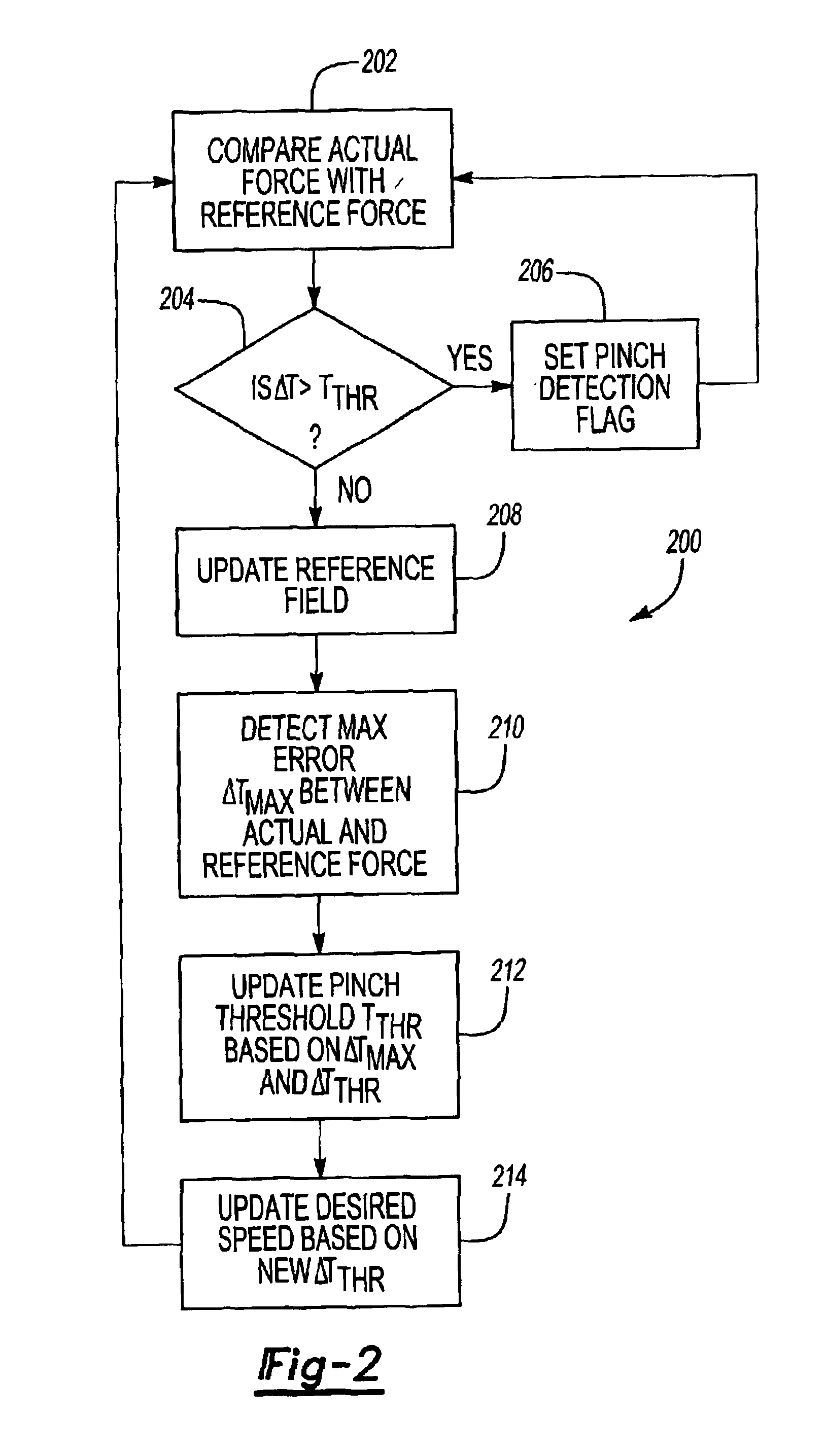
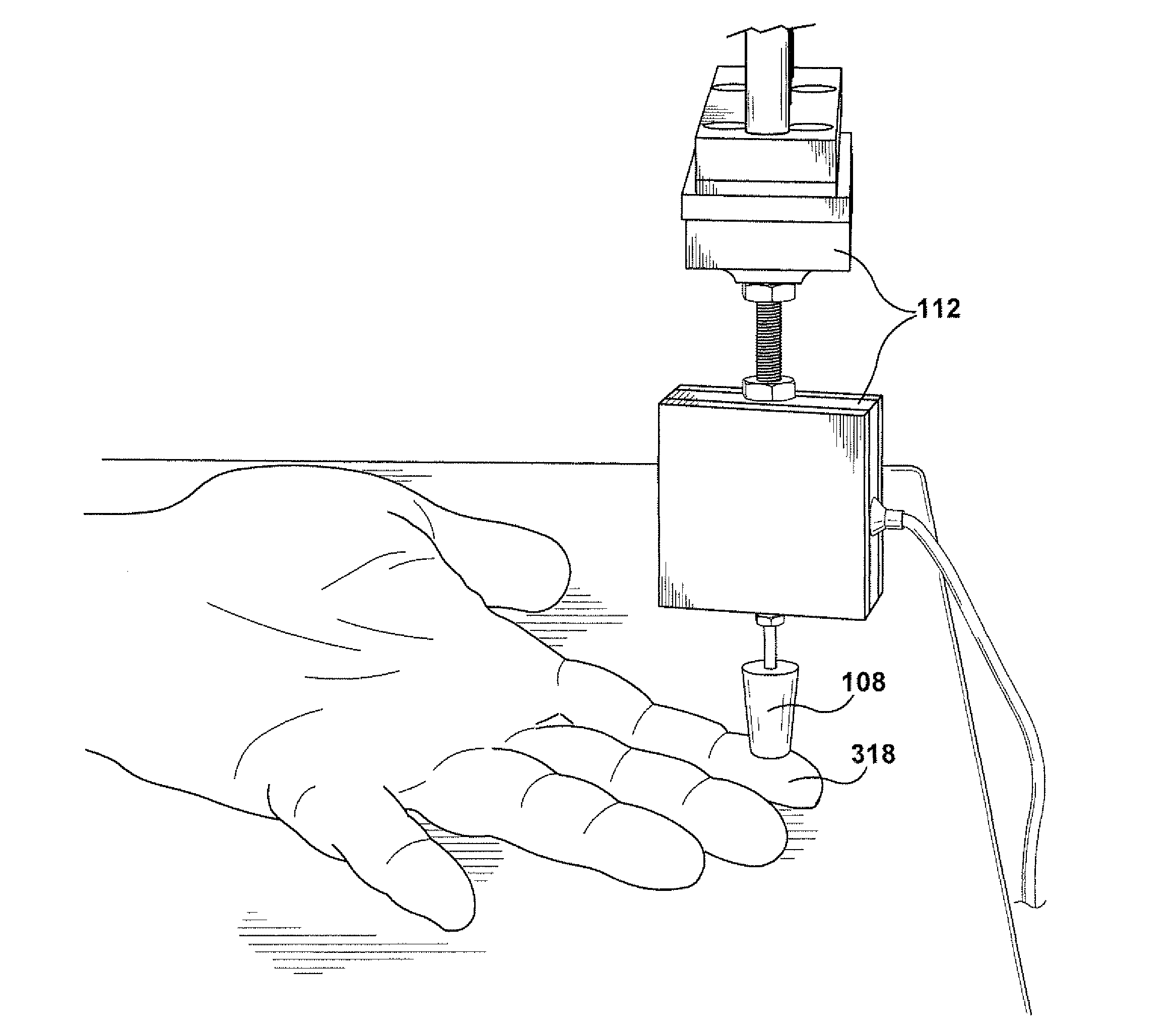
Pinch detection system
InactiveUS6840113B2Accurate pinch detectionAccurate detectionParameter calibration/settingDC motor speed/torque controlForce profileMotor speed
A pinch detection system and method controls the speed of a motor moving an object by first calculating the actual motor force and then comparing the actual motor force with a reference force value in a reference field. A pinch condition is indicated if the difference between the actual force and the reference force exceeds a selected pinch threshold. The difference is also used to update the reference field, the pinch threshold and the desired speed of the motor so that the reference field will eventually reflect the actual force profile of the object. The updated pinch threshold is also used to control the motor speed so that the pinching force remains constant regardless of the pinch threshold value.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE SYST INC
Apparatus and method for measuring containment force in a wrapped load and a control process for establishing and maintaining a predetermined containment force profile
An apparatus and method for measuring containment force on a load is provided. The apparatus may include a first longitudinally extending arm configured to engage a first side of packaging material wrapped around the load. The apparatus may also include a second longitudinally extending arm configured to engage a second side of the packaging material, the second side being opposite the first side. The apparatus may further include an indicator positioned substantially perpendicularly to the first and second arms, a third longitudinally extending arm, and a force gauge configured to measure a force exerted on the third longitudinally extending arm.
Owner:LANTECH COM
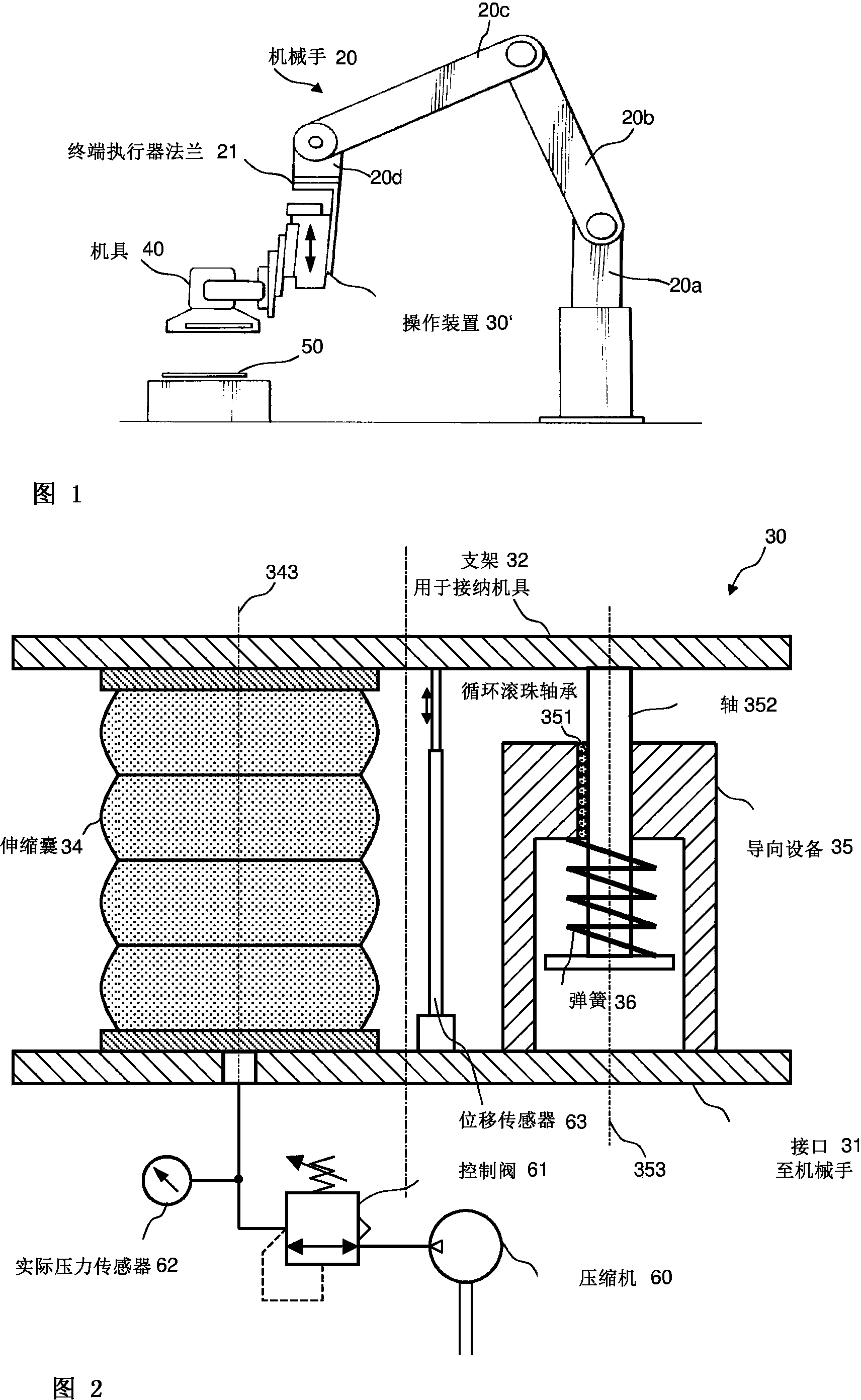
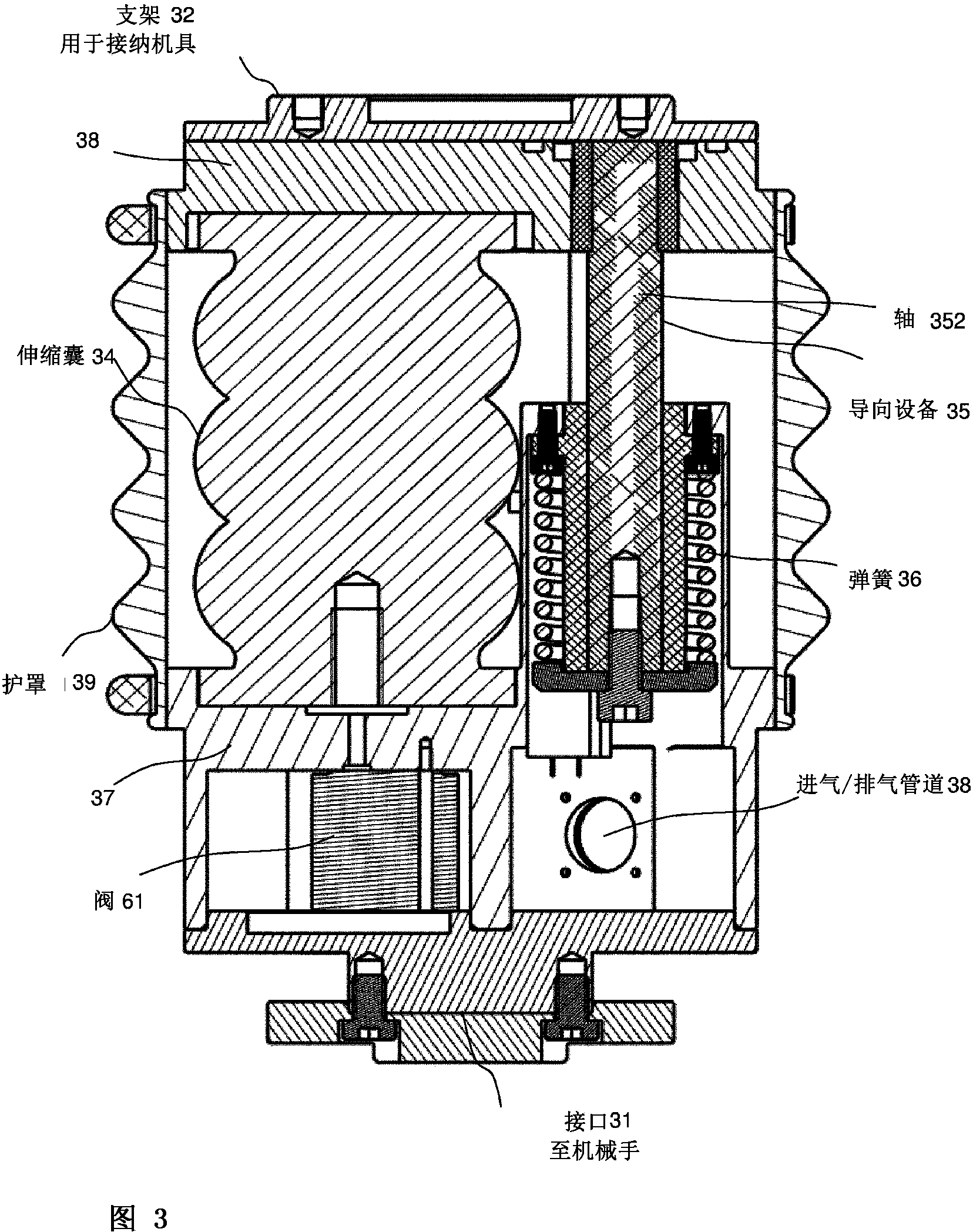
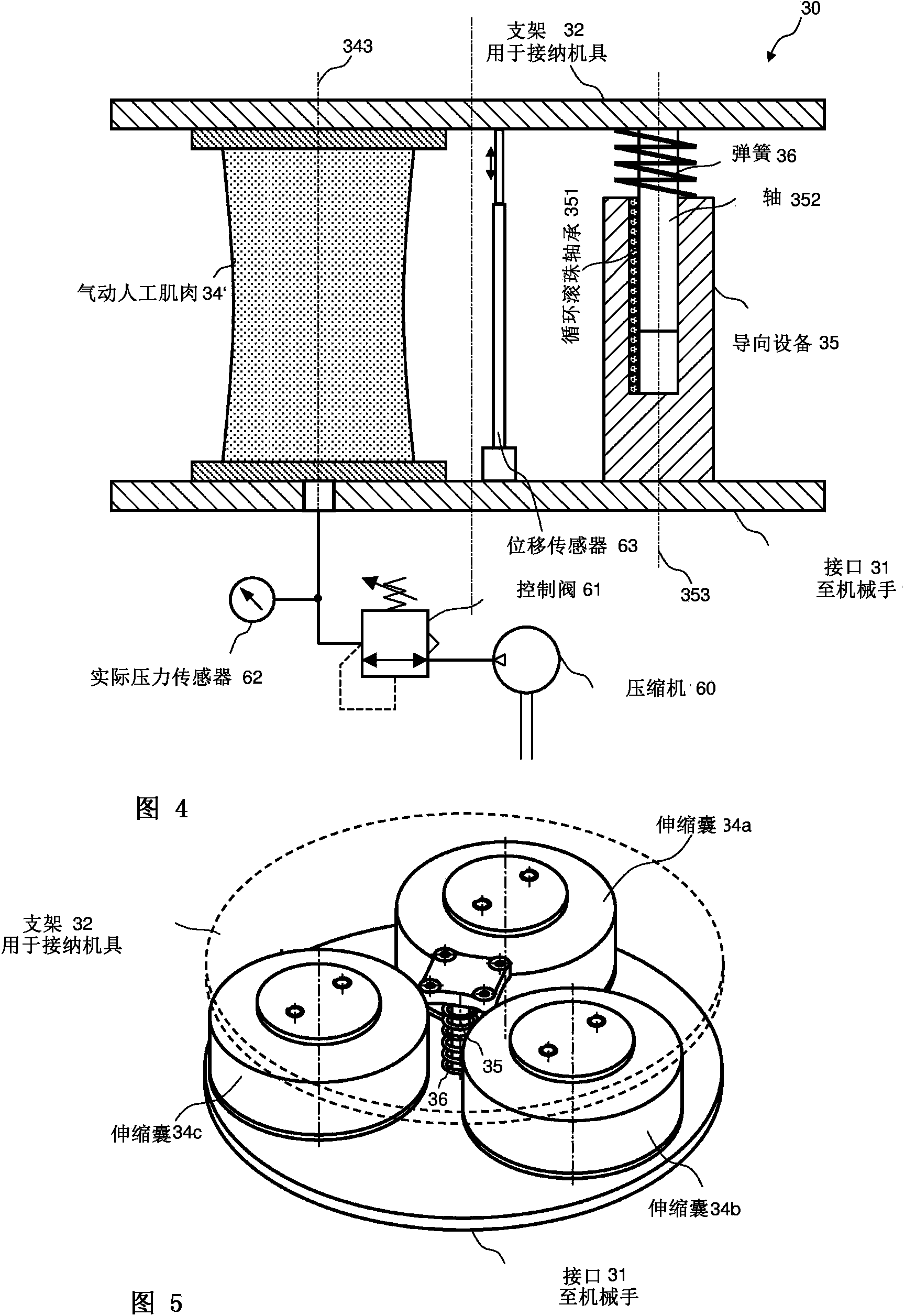
Active handling apparatus and method for contact tasks
ActiveCN103429400AAdjust contact forceProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorEngineeringContact force
A handling apparatus for automated or robot-supported contact tasks is disclosed. The handling apparatus has the following components: a mechanical interface for releasably or fixedly connecting the handling apparatus to a manipulator; a holder, which is movable in relation to the interface, for holding a tool; at least one static-frictionless adjusting element for positioning the holder in relation to the interface to the manipulator; a sensor device for directly or indirectly measuring the force acting on the at least one adjusting element; and a regulating device which is configured to regulate the contact force depending on a predefinable force profile when there is contact between the handling apparatus and a surface.
Owner:FERROBOTICS COMPLIANT ROBOT TECH
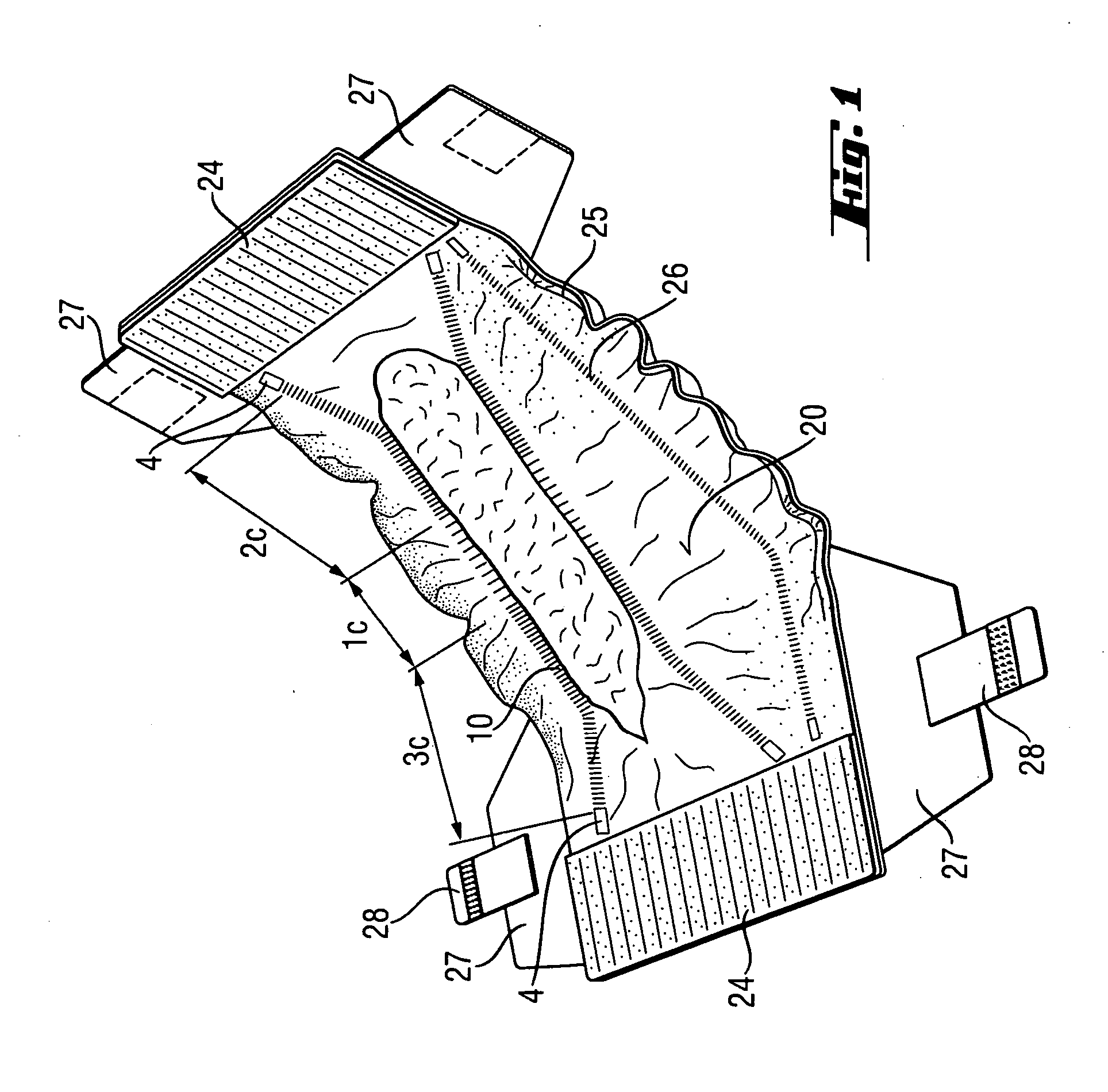
Absorbent articles with comfortable elasticated laminates
An absorbent article comprising a topsheet with a large opening for receiving feces. The topsheet has an elastic laminate portion with y-direction elongation. The laminate portion has a first zone, a second zone and, optionally, a third zone. The zones have different degrees of maximum elongation and / or different wrinkle heights and / or densities. The zones are configured such that one or more zones are created that cause less or no pressure marks. Overall, the topsheet maintains an excellent force profile, resulting in well performing, comfortable to wear absorbent articles that provide isolation of feces away from the skin.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
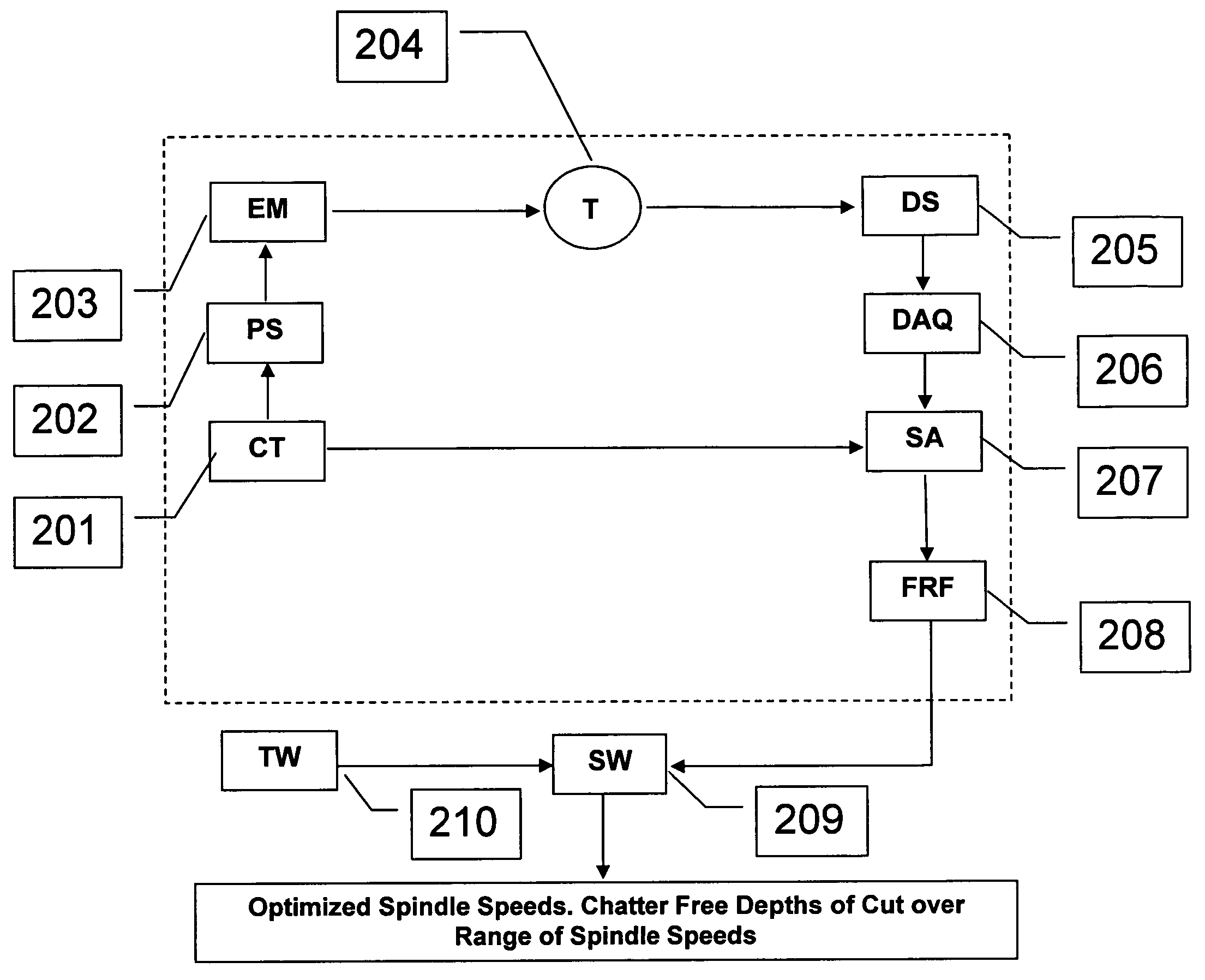
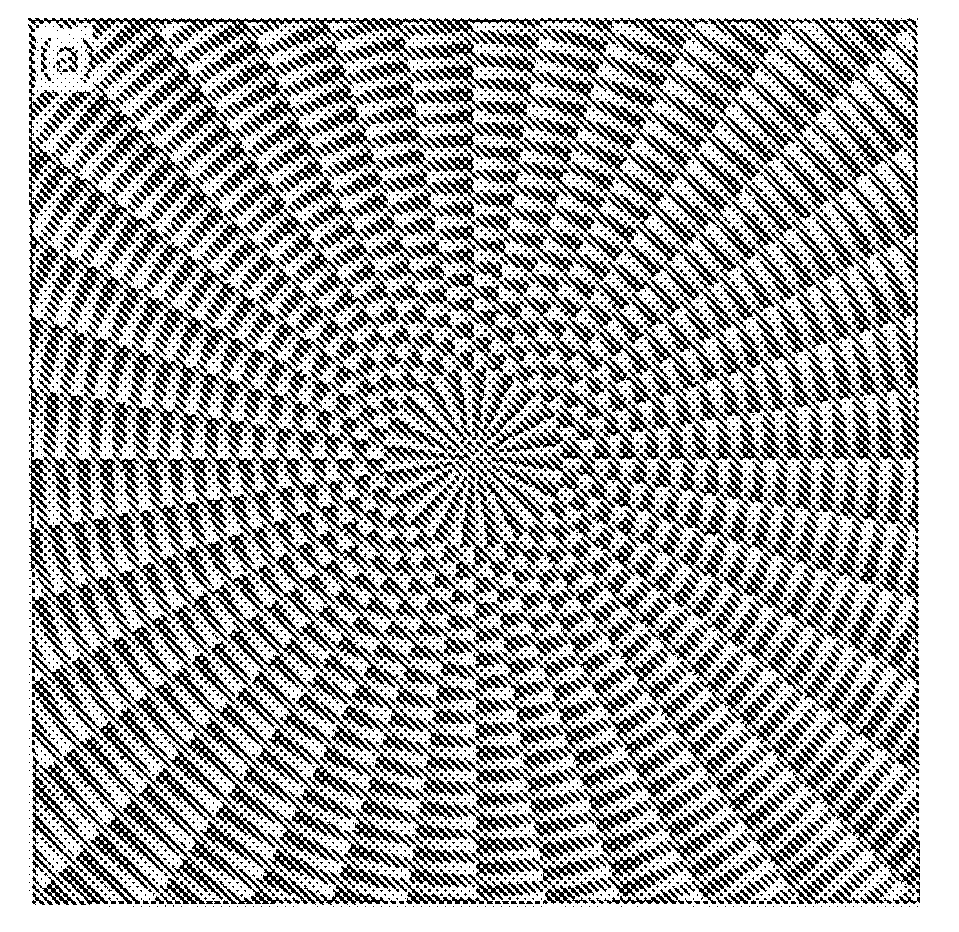
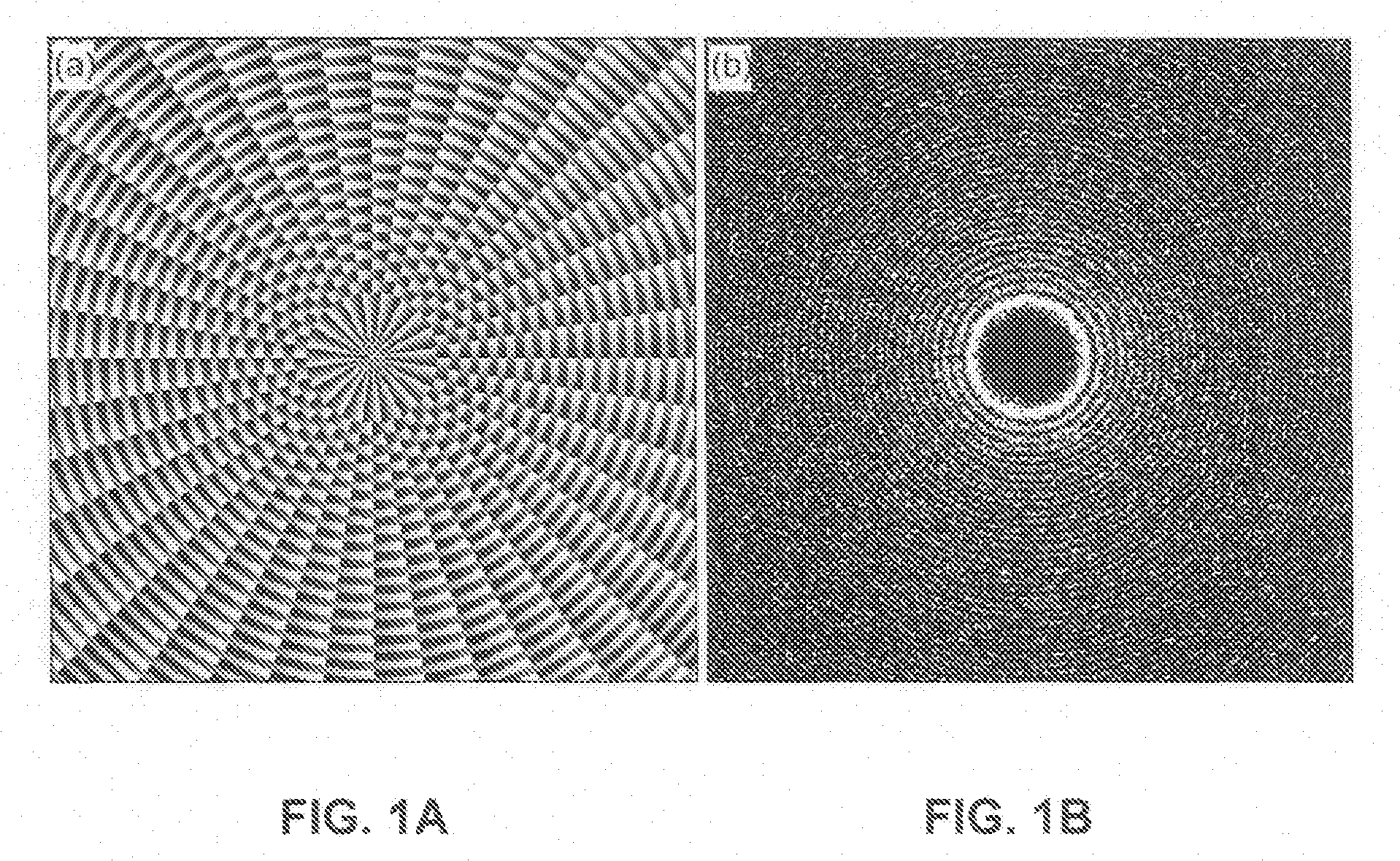
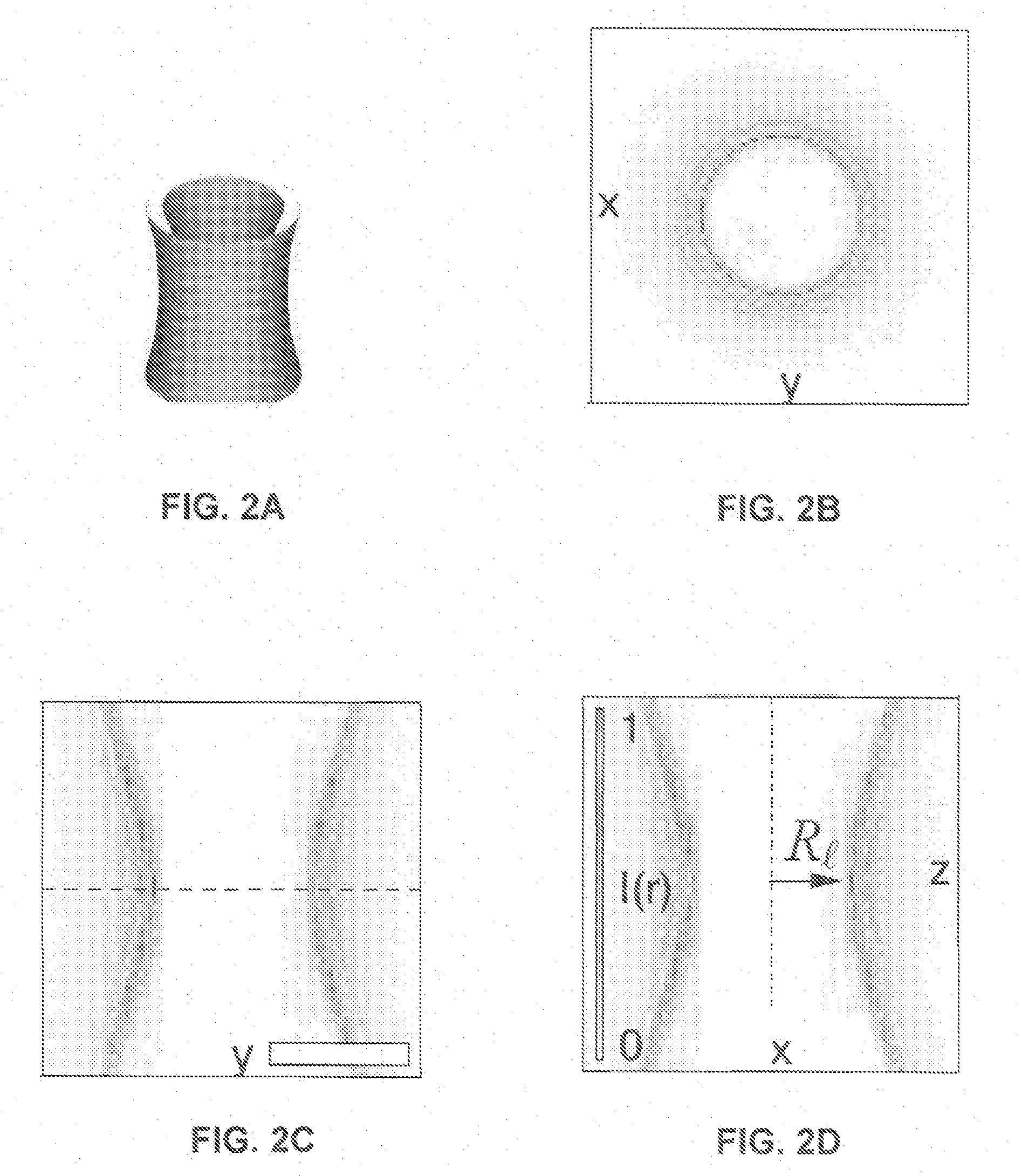
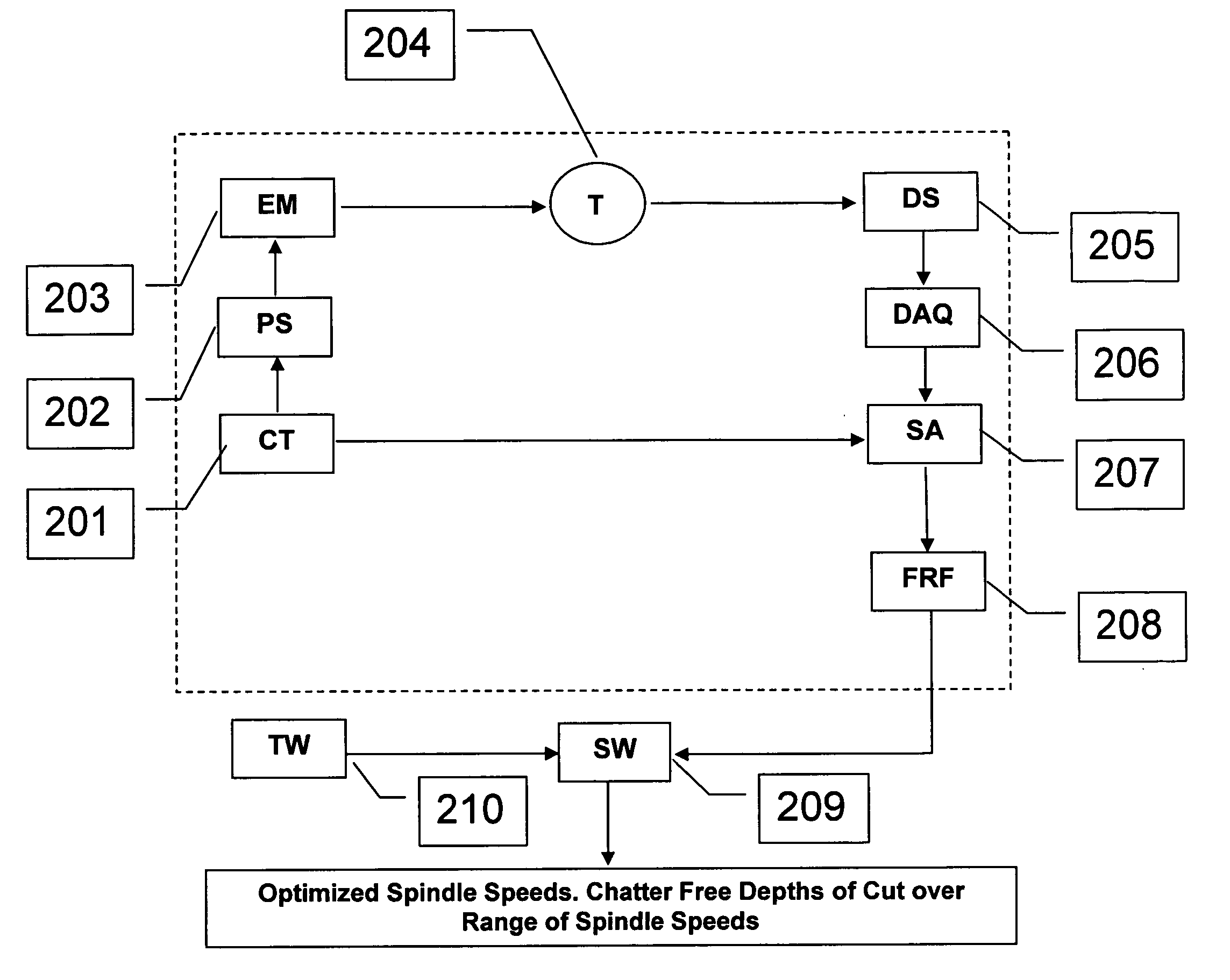
Active electromagnetic device for measuring the dynamic response of a tool in a CNC machine
InactiveUS6993410B2Minimal expertiseVibration measurement in solidsMachine part testingAccelerometerAutomatic control
The present invention provides a device for determining the dynamics of a tool sited in a CNC machine, as encapsulated by the Frequency Response Function. The device uses an actively controlled electromagnet to excite forces on the tool. The force is excited in a non-contact manner, allowing the force to be applied to both a stationary and a rotating tool. The displacement is measured by standard means, such as accelerometers, optical displacement or capacitance sensors. The ratio of the force and the displacement in the frequency domain is the Frequency Response Function. The force may be applied as a pure sine wave, providing the Frequency Response Function at the frequency of the sine wave. Varying the frequency of the sine wave provides the Frequency Response Function over the range of frequencies of interest. The control of the force profile is handled entirely by the automated controls and requires no special skills, training or manual interaction by the user. No separate force sensor is required, since the electromagnetic force on the tool may be accurately determined from the design of the electromagnet and the tool position, geometry and material.
Owner:ESTERLING DONALD M
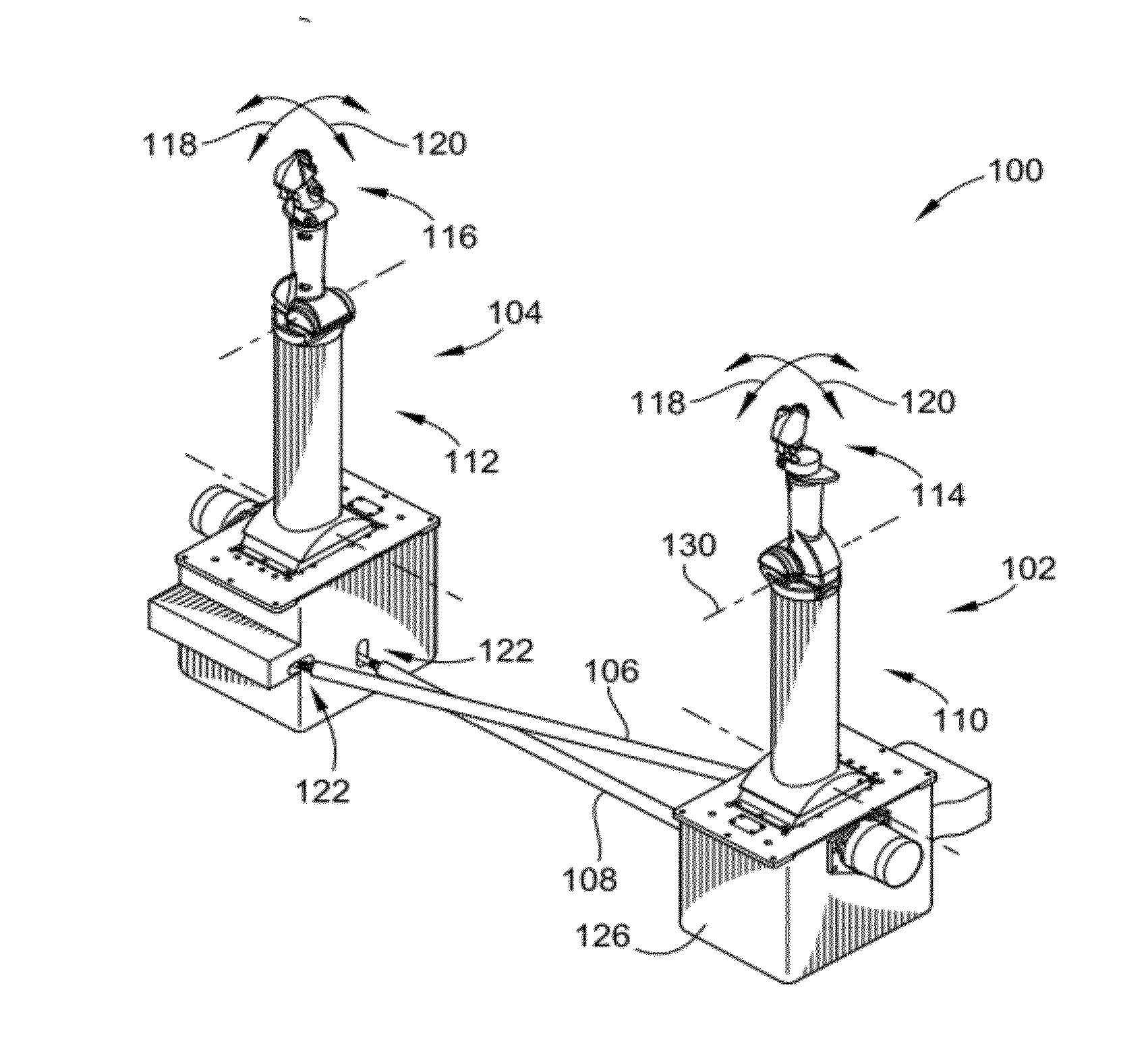
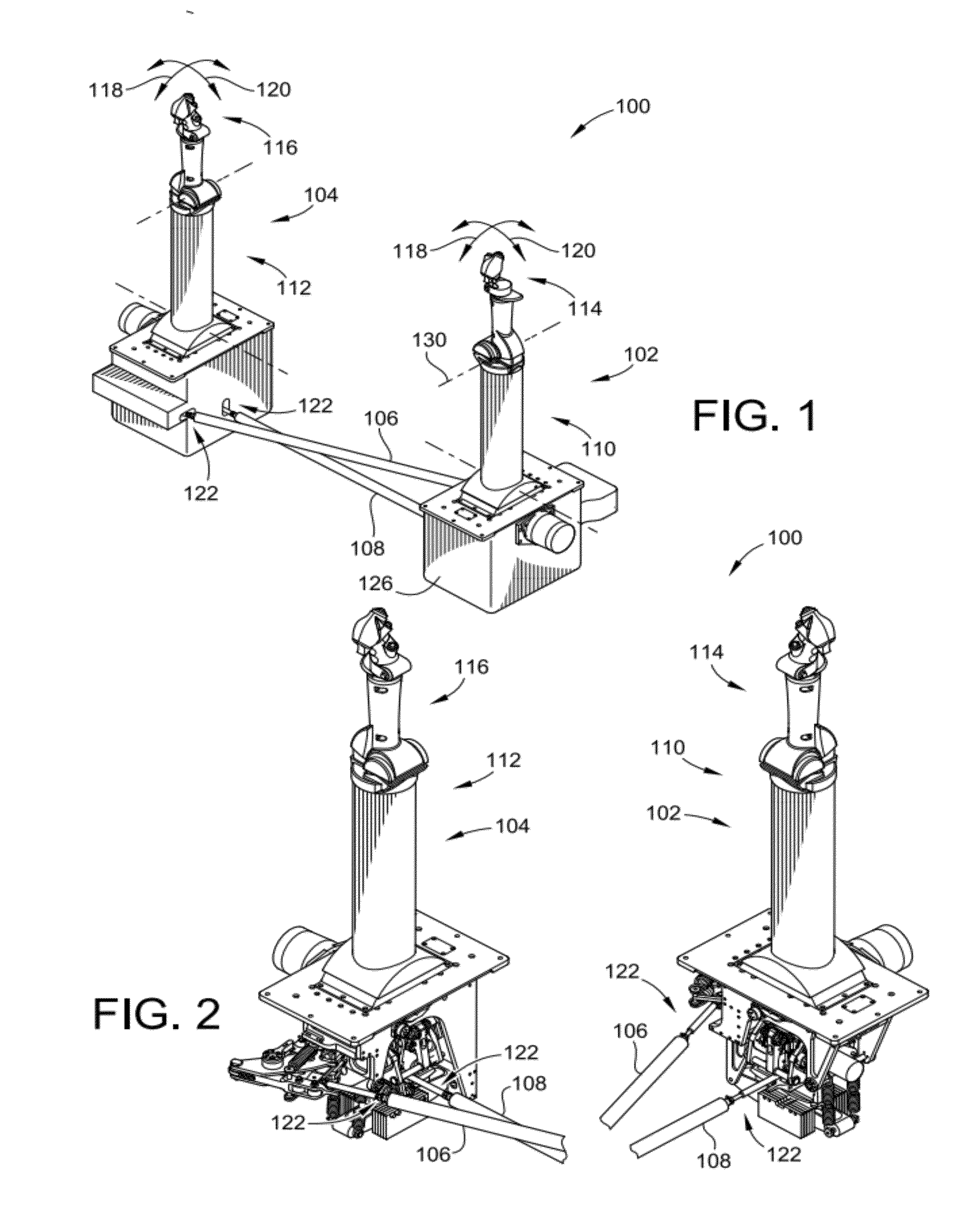
Line replaceable, fly-by-wire control columns with push-pull interconnect rods
ActiveUS20120097800A1Improved profileReduce tensionManual control with multiple controlled membersMechanical apparatusFly-by-wirePush pull
A control input system is provided. The system includes a pair of control columns that are selectively interconnected such that manipulation of one of the control columns is translated to the other one of the control columns. The system includes a disconnect arrangement for each of the degrees of freedom (pitch and roll) of the system that operably disconnects the two control columns such that the two control columns can operate independently such as in the event of failure of one of the control columns. The system may also include a discontinuous force profile for a restoring force mechanism that provides tactile feedback to the pilots simulating resistance provided by control surfaces of the aircraft. The system may also include an autopilot lockout mechanism that increases the force profile experienced by the pilots when autopilot mode is entered.
Owner:WOODWARD MPC
Method of injection molding with constant-velocity flow front control
In order to injection mold parts at a constant flow front velocity in a mold cavity of an injection molding system, particularly where the mold cavity has a varying thickness along its length, mold modeling software is used to calculate the cross-sectional area as a function of the distance from the gate, percentage of fill, or length of the mold cavity. Based on that cross-sectional area, the mold modeling software determines an appropriate recommended ram force profile and / or melt pressure profile that would result in filling the mold cavity at a constant flow rate. An injection molding system is then operated according to the recommended ram force profile and / or melt pressure profile.
Owner:IMFLUX INC
Three-dimensional holographic ring traps
ActiveUS20080137161A1Substantial degree of freedom and precisionImproved manipulation and separation and movementLaser detailsMasersMomentumAngular momentum
A method and system for preparing and using three dimensional optical ring traps. The method and system includes applying a single phase hologram to be able to independently control shape and force profile of an optical trap but without employing orbital angular momentum for the control parameter of an optical ring trap to manipulate an object.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Active electromagnetic device for measuring the dynamic response of a tool in a CNC machine
InactiveUS20040236529A1Minimal expertiseVibration measurement in solidsMachine part testingAccelerometerAutomatic control
The present invention provides a device for determining the dynamics of a tool sited in a CNC machine, as encapsulated by the Frequency Response Function. The device uses an actively controlled electromagnet to excite forces on the tool. The force is excited in a non-contact manner, allowing the force to be applied to both a stationary and a rotating tool. The displacement is measured by standard means, such as accelerometers, optical displacement or capacitance sensors. The ratio of the force and the displacement in the frequency domain is the Frequency Response Function. The force may be applied as a pure sine wave, providing the Frequency Response Function at the frequency of the sine wave. Varying the frequency of the sine wave provides the Frequency Response Function over the range of frequencies of interest. The control of the force profile is handled entirely by the automated controls and requires no special skills, training or manual interaction by the user. No separate force sensor is required, since the electromagnetic force on the tool may be accurately determined from the design of the electromagnet and the tool position, geometry and material.
Owner:ESTERLING DONALD M
Device for delivering a medicament
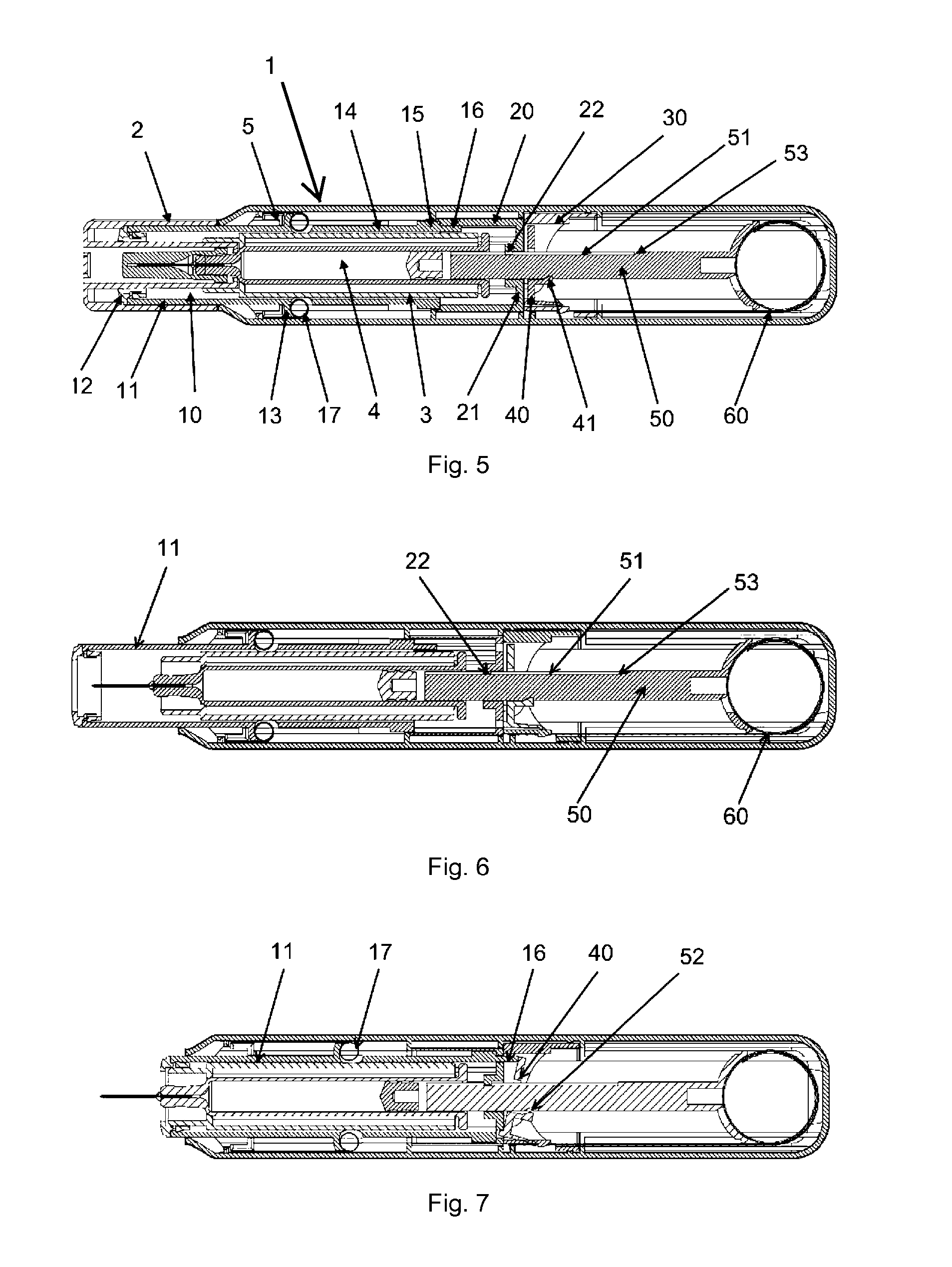
ActiveUS8460245B2Function increaseReduce riskAutomatic syringesIntravenous devicesEngineeringBiomedical engineering
Owner:SHL MEDICAL AG
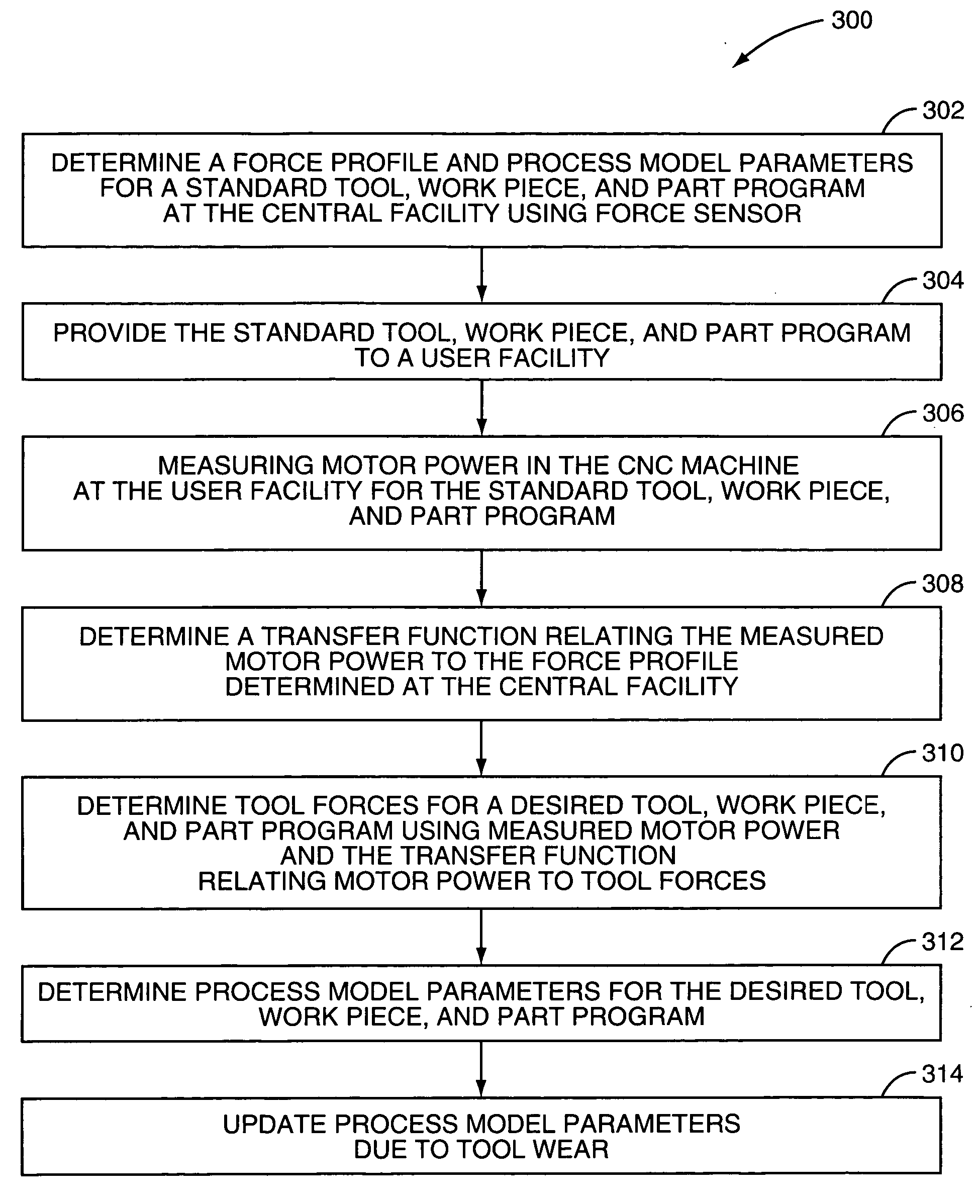
Real-time measurement of tool forces and machining process model parameters
A system and method are provided for real-time measurement of tool forces. A relationship between a motor characteristic and tool forces is determined by first directly measuring tool forces for a standard tool, work piece, and part program in a central facility. A force profile indicative of the tool forces and the standard tool, work piece, and part program are provided to a user at a user facility. The motor characteristic for a CNC machine at the user facility is then measured for the standard tool, work piece, and part program. Based on the force profile determined at the central facility, the relationship between the motor characteristic and tool forces is determined. Thereafter, the motor characteristic of the CNC machine is measured for a desired tool, work piece, and part program and converted to tool forces using the relationship between the motor characteristic and tool forces.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF NEW HAMPSHIRE +1
Pad conditioning force modeling to achieve constant removal rate
InactiveUS20130122783A1Extended service lifeConstant rateGrinding drivesBelt grinding machinesControl theoryForce profile
A method and apparatus for conditioning a polishing pad in a CMP system is provided. In one embodiment, a method for conditioning a polishing pad includes applying a down force to the conditioning disk that urges the conditioning disk against the polishing pad, measuring a torque required to sweep the conditioning disk across the polishing pad, determining a change in down force by comparing the measured torque to a model force profile (MFP), and adjusting the down force that the conditioning disk applies against the polishing pad in response to the determined change.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Apparatus and method for exerting force on a subject tissue
An apparatus for exerting force on a subject tissue includes a linear motor for generating a force according to a predetermined force profile incorporating at least one motion control parameter. The linear motor is directly coupled to a motor output member to drivingly produce linear motion of the motor output member under direction of a motor controller executing the predetermined force profile. A tissue-contacting member is connected to the motor output member for directly proportional linear motion therewith. A load cell provides load cell feedback to the motor controller. The motor controller adjusts the motion of the motor output member responsive to the load cell feedback to substantially conform the motion to the predetermined force profile. The linear motor moves the tissue-contacting member to contact the subject tissue according to the predetermined force profile and responsively initiate a subject reaction to the exerted force.
Owner:CEREBRAL DIAGNOSTICS CANADA
Real-time measurement of tool forces and machining process model parameters
A system and method are provided for real-time measurement of tool forces. A relationship between a motor characteristic and tool forces is determined by first directly measuring tool forces for a standard tool, work piece, and part program in a central facility. A force profile indicative of the tool forces and the standard tool, work piece, and part program are provided to a user at a user facility. The motor characteristic for a CNC machine at the user facility is then measured for the standard tool, work piece, and part program. Based on the force profile determined at the central facility, the relationship between the motor characteristic and tool forces is determined. Thereafter, the motor characteristic of the CNC machine is measured for a desired tool, work piece, and part program and converted to tool forces using the relationship between the motor characteristic and tool forces.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF NEW HAMPSHIRE +1
Electromechanical dynamic force profile articulating mechanism
InactiveUS20080212158A1Eliminate needReduced superadditionOptical elementsElectrical conductorParallel plate
An electromechanical dynamic force profile articulating mechanism for recovering or emulating true parallel plate capacitor actuation behaviors from deformable membranes used in MEMS systems. The curved deformation of flexible membranes causes their MEMS behavior to deviate from known interactions between rigid plates that maintain geometric parallelism during ponderomotive actuation. The present invention teaches three methods for reacquiring parallel plate behavior: superaddition or in situ integration of a rigid region within or upon the deformable MEMS membrane; creation of isodyne regions to secure parallelism by altering the force profile upon the membrane by introducing tuned and shaped voids within the conductive region associated with the membrane; and a hybrid composite approach wherein the conductive region is deposited after deposition of a raised rigid zone, thereby emulating isodyne behavior due to the increased inter-conductor distance in the vicinity of the rigid zone, in conjunction with rigidity benefits stemming directly from said zone.
Owner:RAMBUS DELAWARE
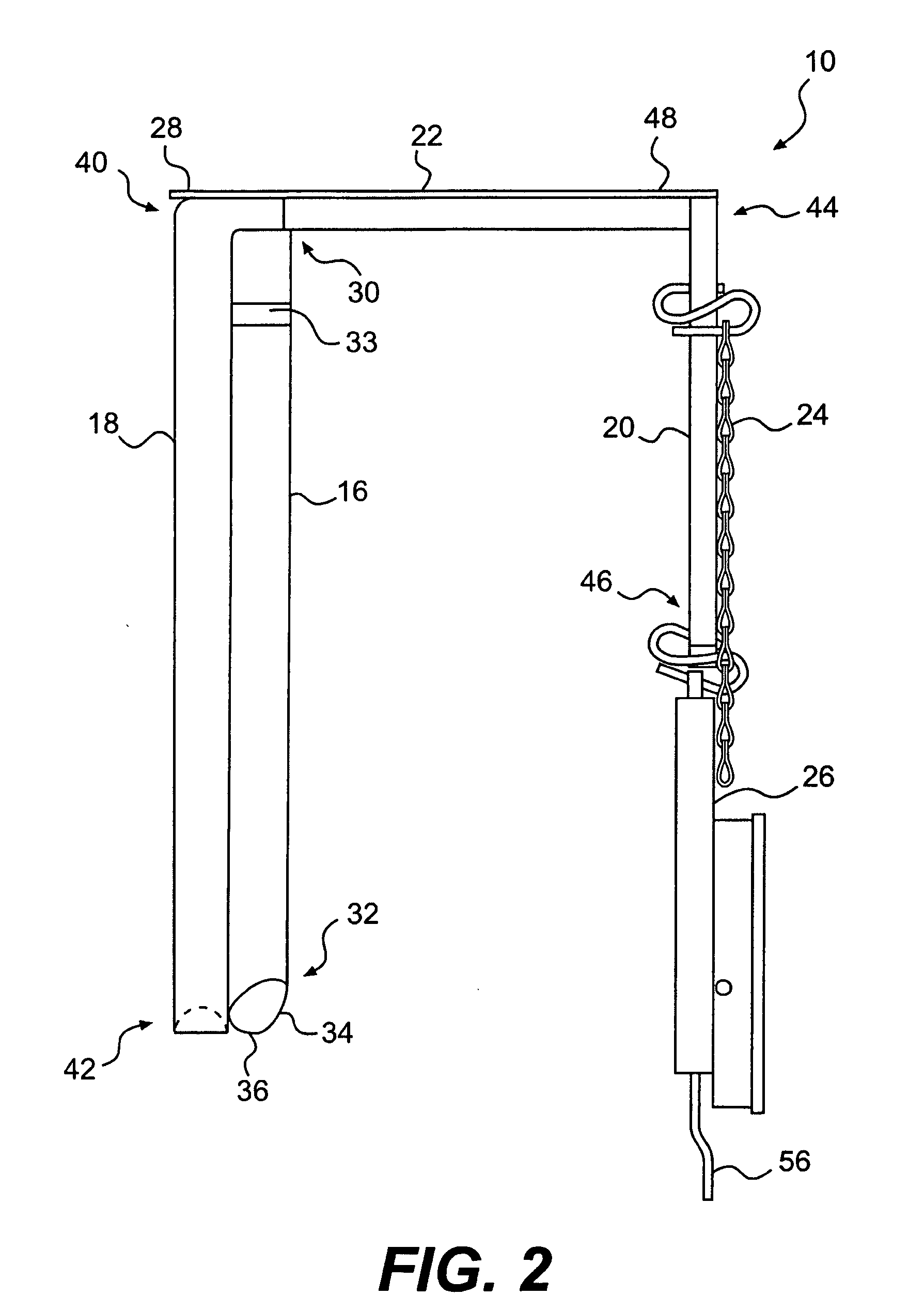
Variable adjustable door latch
ActiveUS20110291848A1Reduce the amount requiredImprove protectionAlarmsWing arrangementsEngineeringMechanical engineering
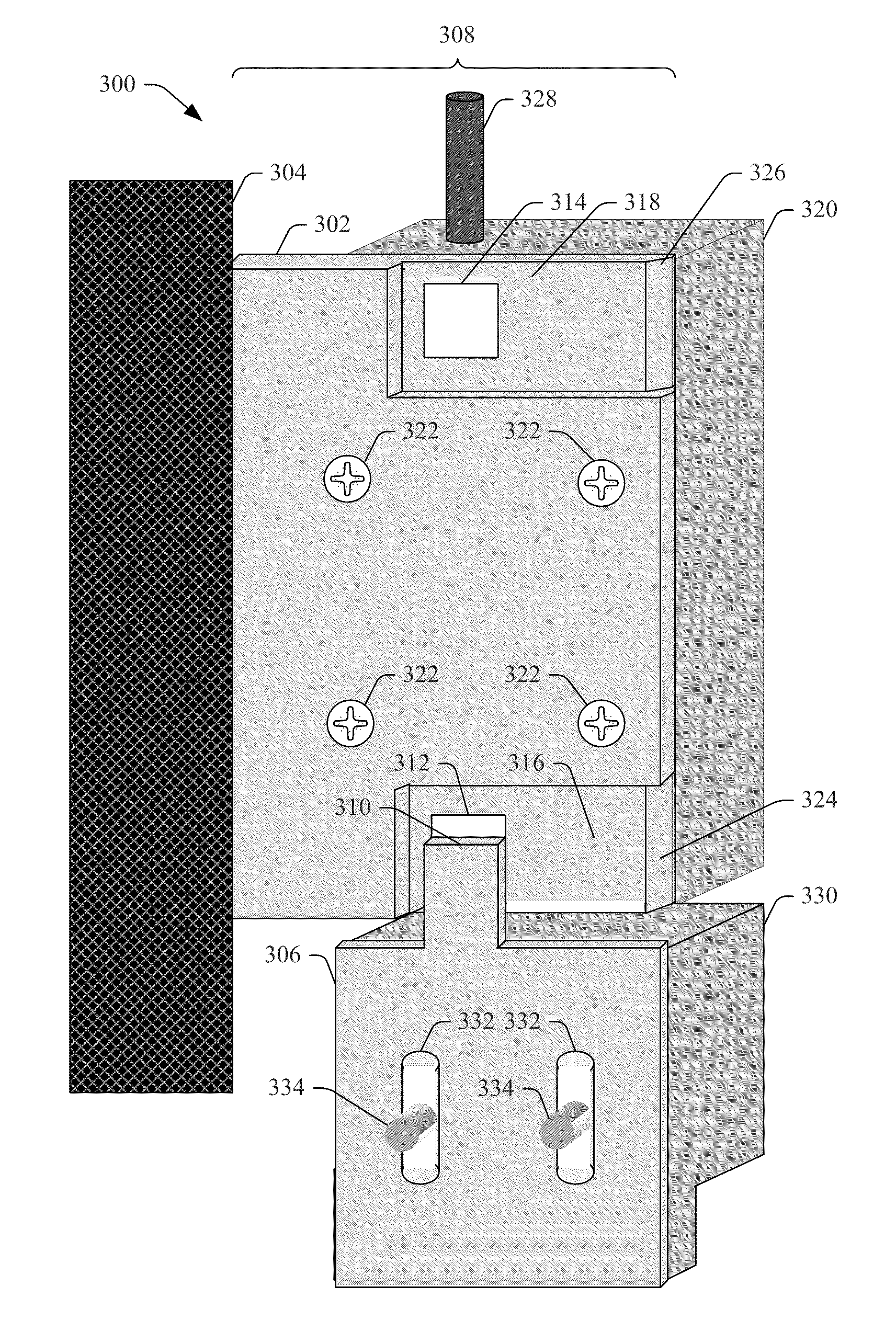
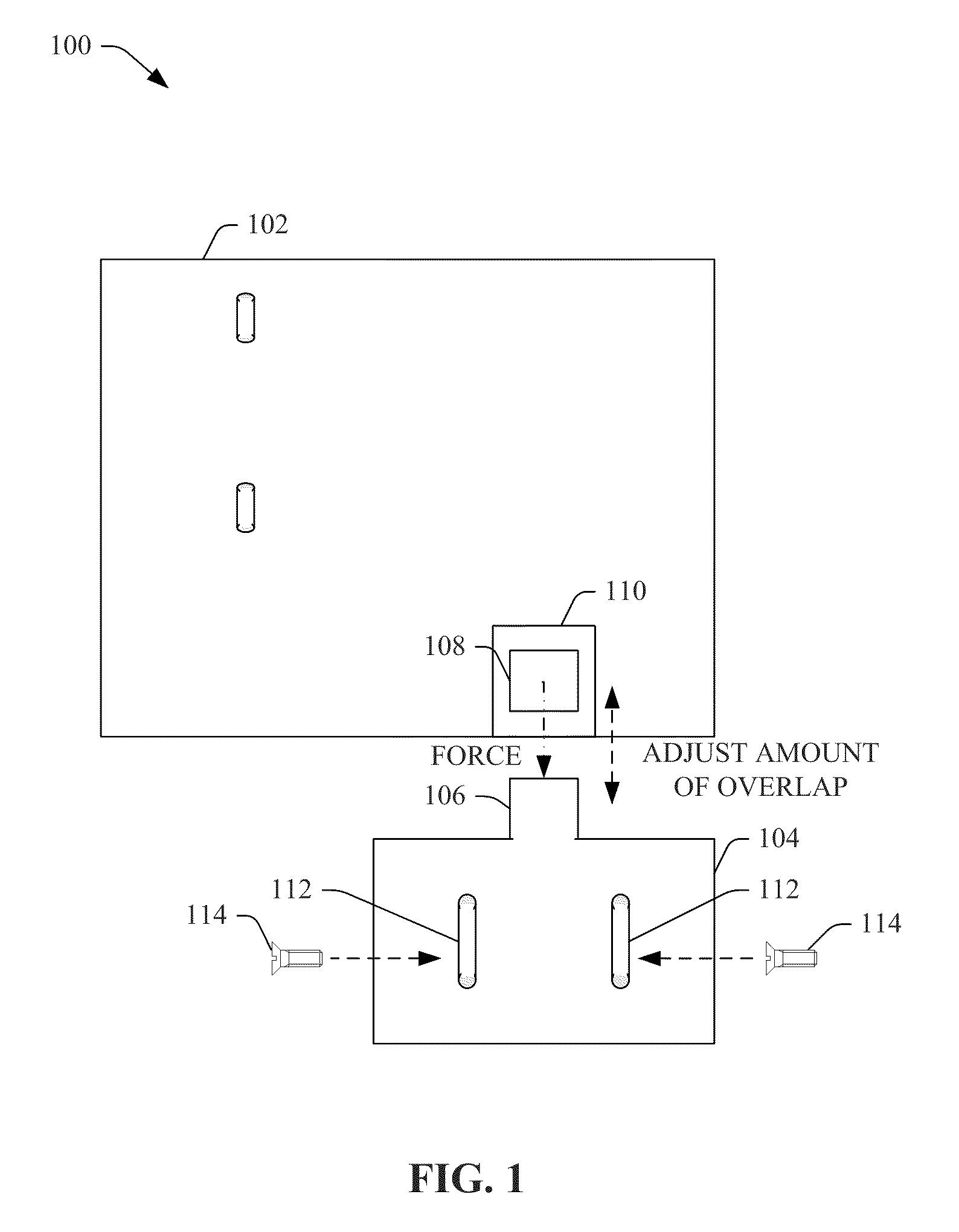
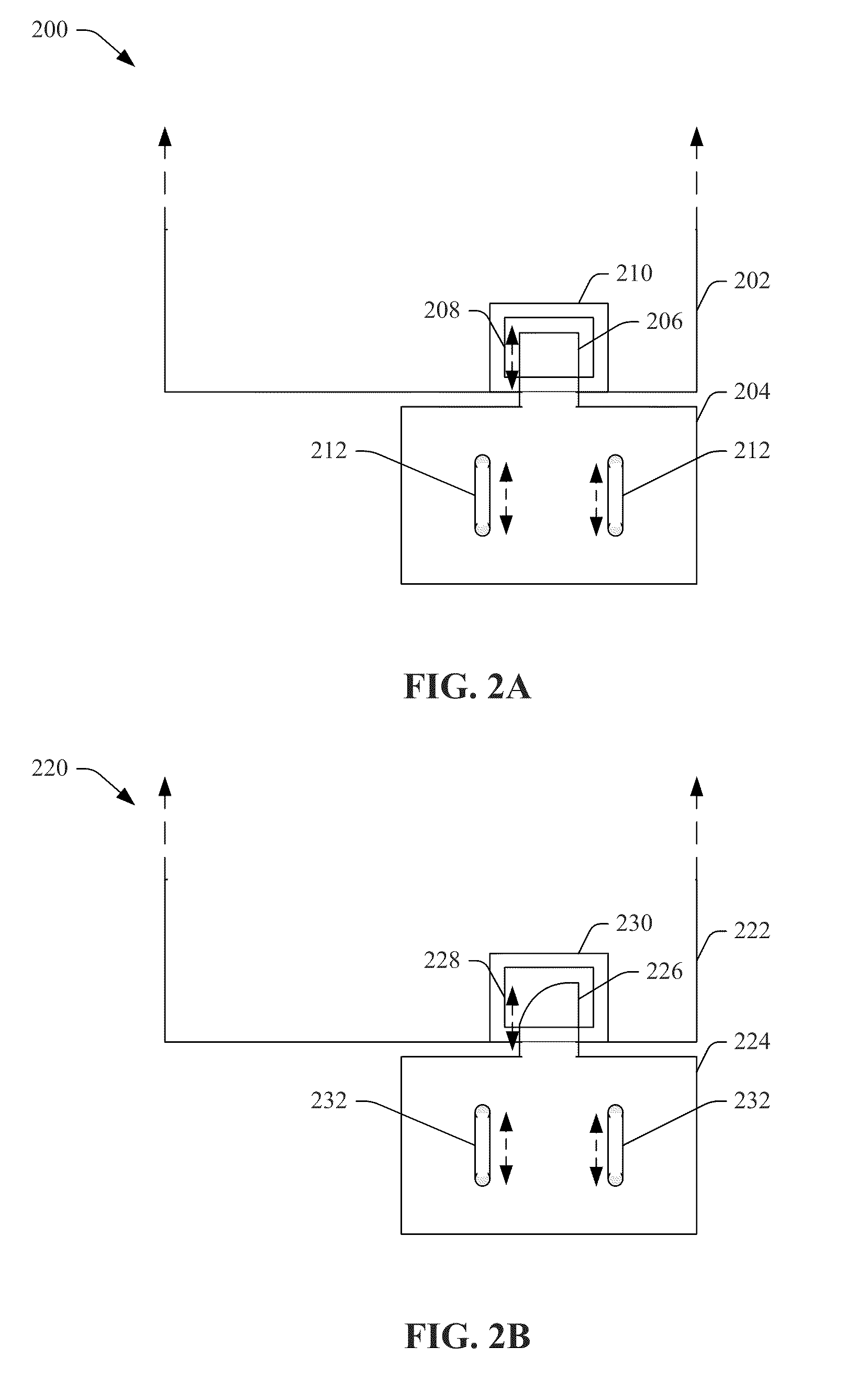
Systems, methods, and devices that efficiently stop and latch a door are presented. A first bracket component is attached to a door frame and has an overhang portion, comprising a holder component, that extends into the doorway to act as a door stop. A second bracket component, comprising an extended portion, is desirably adjusted in position in relation to the holder component and attached to the door such that the extended portion has a desired amount of overlap on the holder component, wherein the amount of overlap corresponds to an amount of latching force in accordance with the force profile associated with the extended portion based at least in part on shape of the extended portion. An operation device is attached to the first bracket component and / or second bracket component and the door latching holds the door in the desired position to facilitate operations of the operation component.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
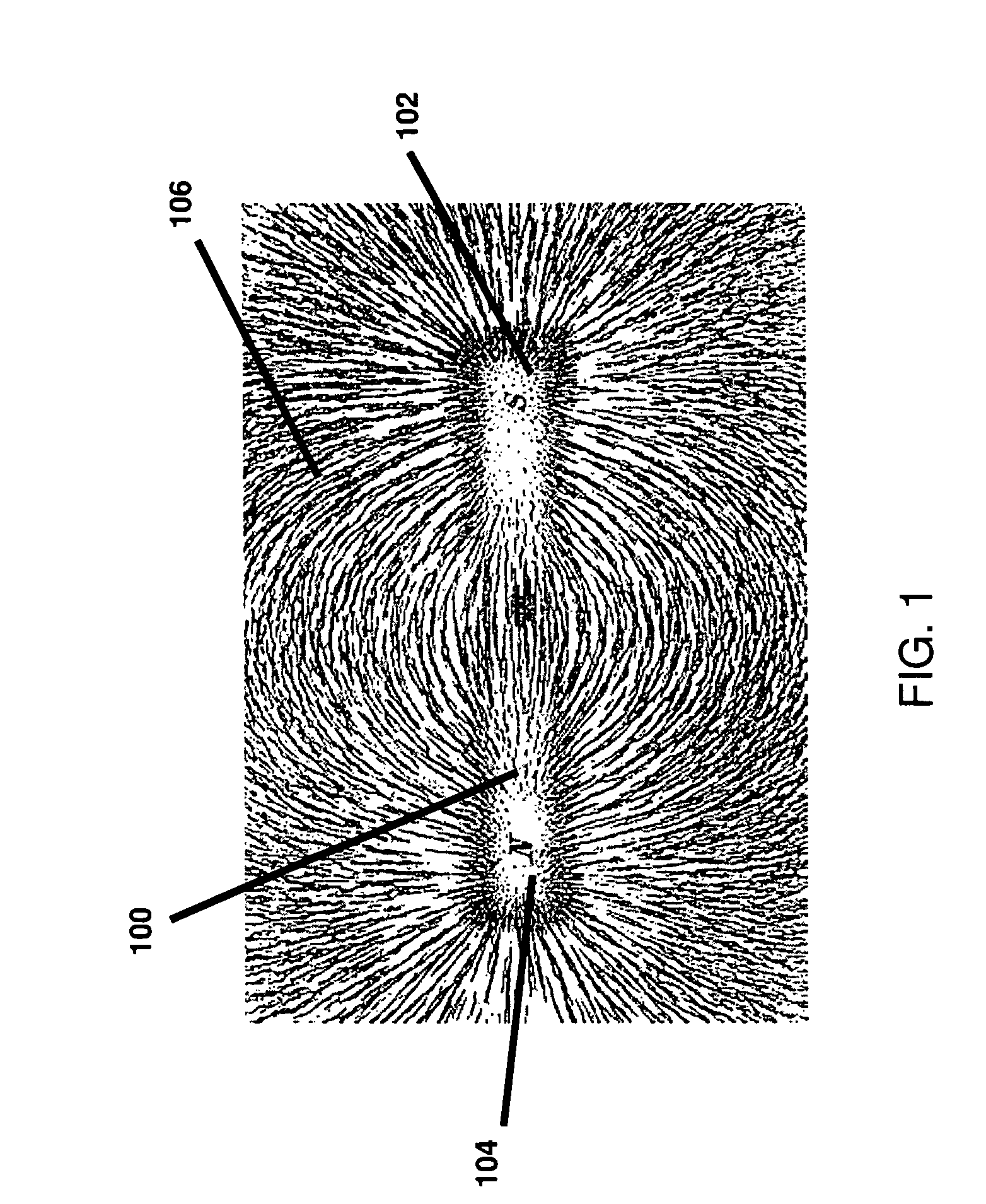
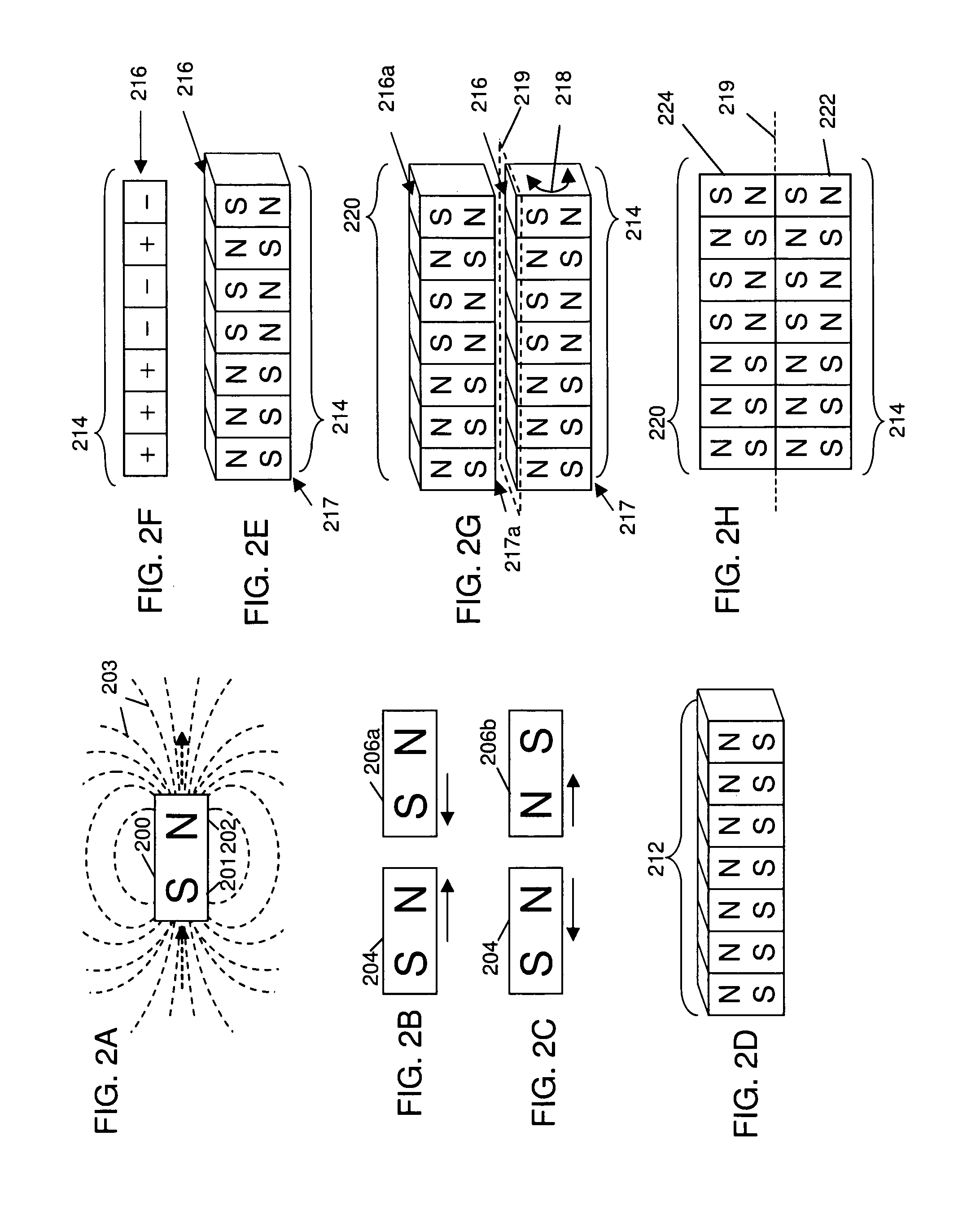
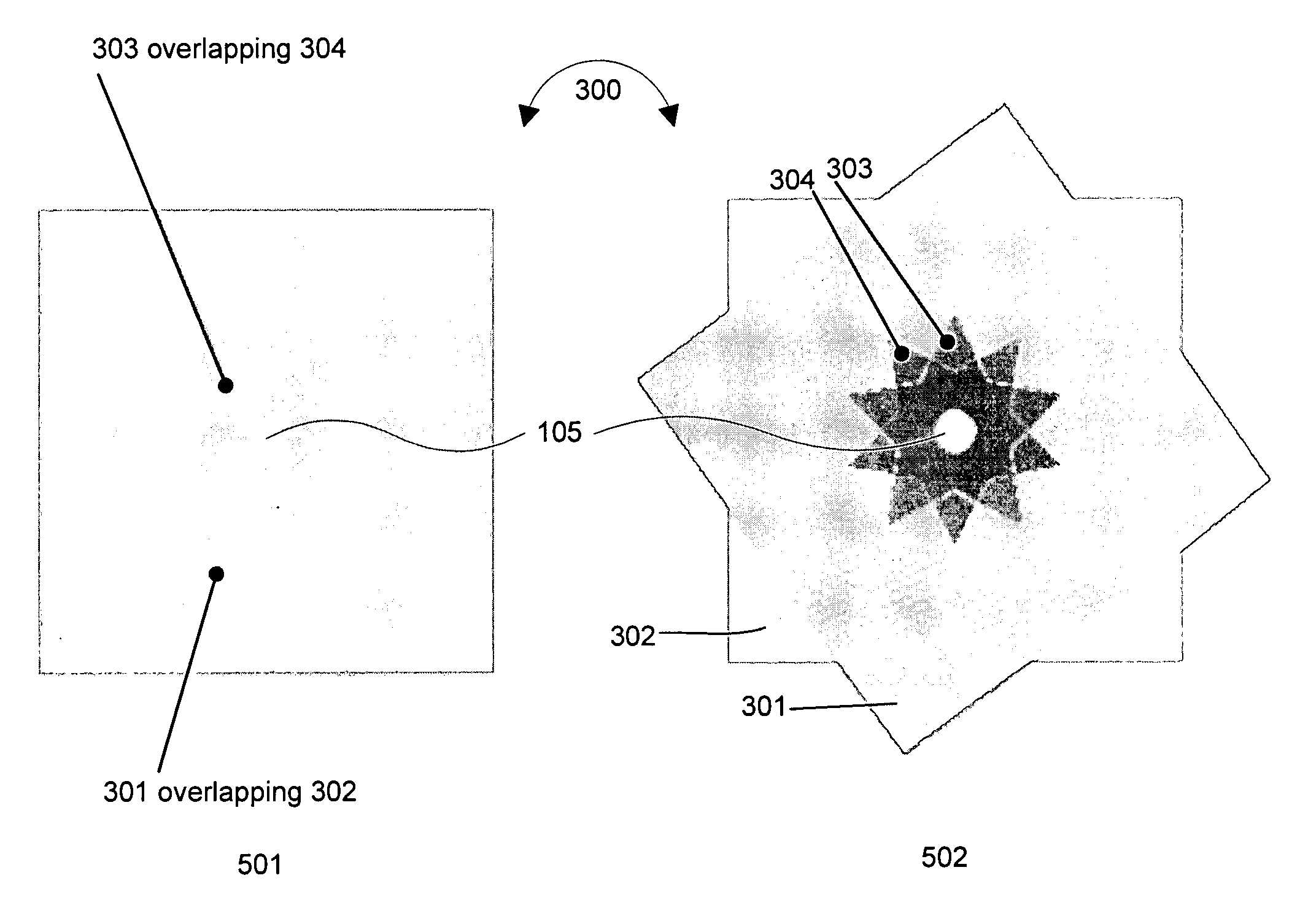
Magnetic force profile system using coded magnet structures
InactiveUS7839247B2Snap fastenersElectromagnets without armaturesMagnetic tension forceCondensed matter physics
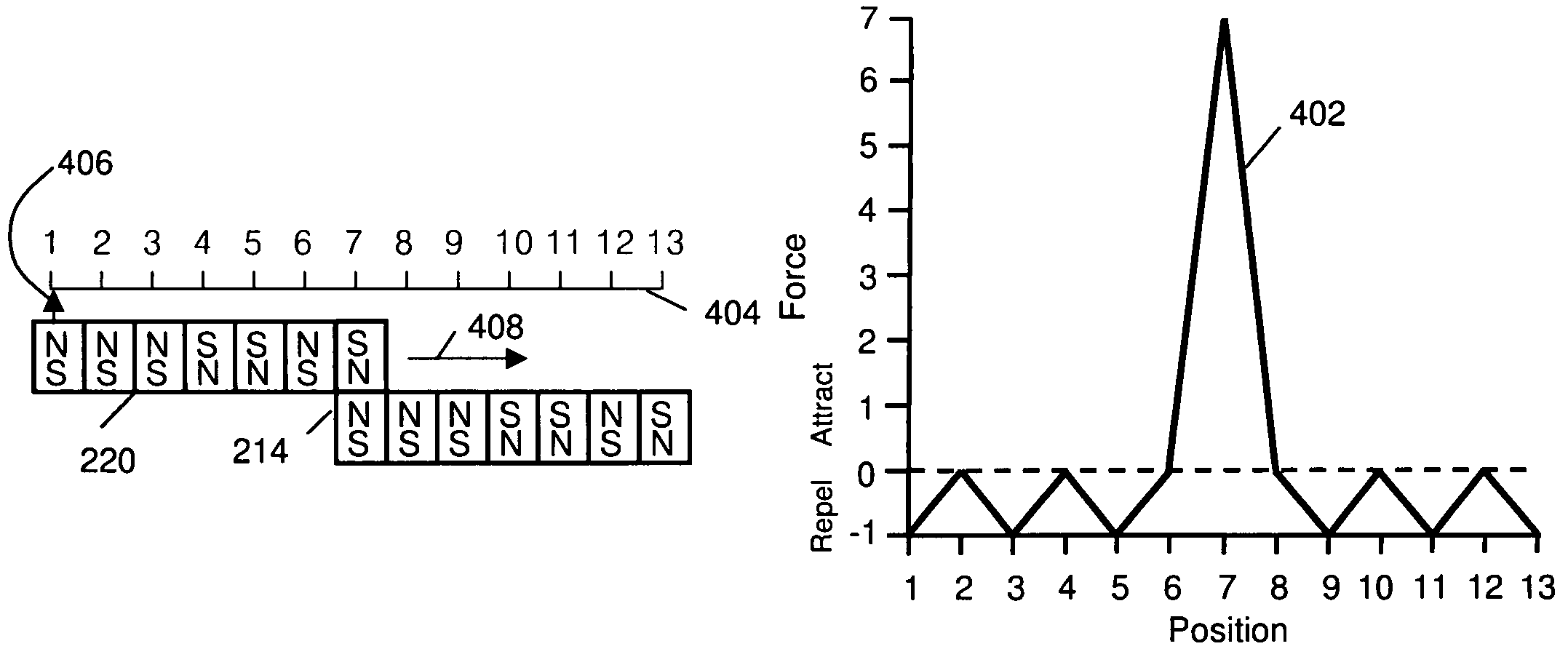
An improved field emission system and method. The invention pertains to field emission structures comprising electric or magnetic field sources having magnitudes, polarities, and positions corresponding to a desired spatial force function where a spatial force is created based upon the relative alignment of the field emission structures and the spatial force function. The invention herein is sometimes referred to as correlated magnetism, correlated field emissions, correlated magnets, coded magnetism, or coded field emissions. The magnetic field sources may be arranged according to a code having a desired autocorrelation function. In particular, a high peak to sidelobe autocorrelation performance may be found desirable. Specific exemplary embodiments are described with magnetic field sources arranged in a ring structure. Exemplary codes are described and applied to magnetic field source arrangements. Specific codes found by the inventors are described.
Owner:CORRELATED MAGNETICS RES LLC
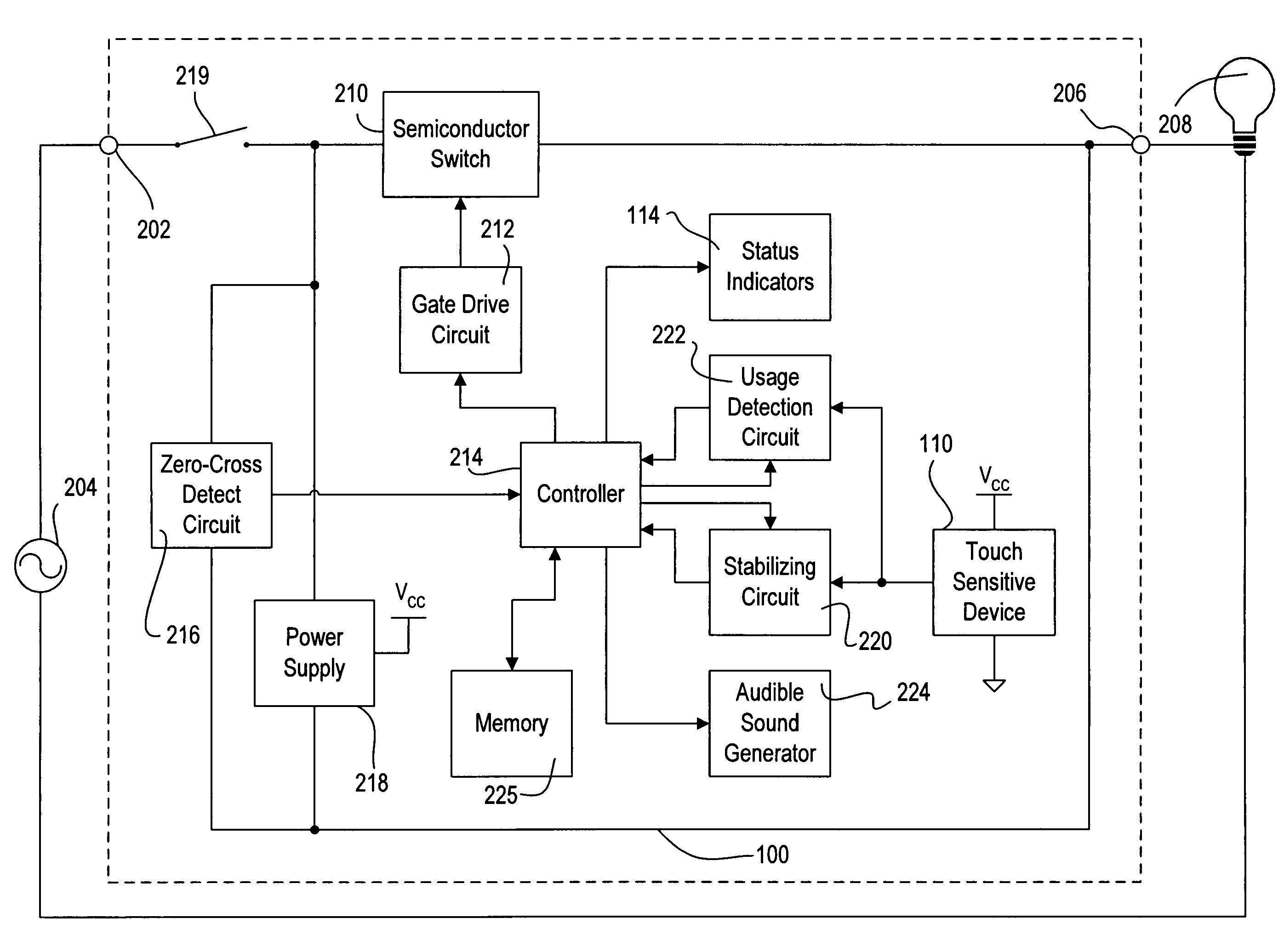
Touch screen having a uniform actuation force and a maximum active area
A load control device for controlling the amount of power delivered to an electrical load from an AC power source comprises a touch sensitive device having a touch sensitive front surface responsive to a point actuation. The front surface is adapted to be provided in an opening of a faceplate such that the front surface of the touch sensitive actuator extends through the opening at a distance equal to or greater than the depth of the faceplate. According to the present invention, the operational area of the front surface is maximized to substantially the entire area of the front surface. Further, a minimum magnitude of a force of each of the point actuations is substantially equal at each of the respective positions on the front surface of the touch sensitive actuator, such that the front surface provides a substantially uniform force profile.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
Device for Delivering a Medicament
ActiveUS20100249721A1Function increaseReduce riskAutomatic syringesIntravenous devicesBiomedical engineeringDrug delivery
Owner:SHL MEDICAL AG
Reverse cantilever assembly for input devices
InactiveUS6844873B2Reduce force requirementsEnhanced Haptic FeedbackSnap-action arrangementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsConstant forceHand size
A computer pointing device, such as a mouse or trackball, includes a reverse cantilever button assembly to match strength-related variations in user hand size. In one embodiment a button assembly is built with two cantilever beams, the fulcrums for each beam being at opposite ends of the button assembly. The stiffness of the two beams can be selected to obtain an increasing, decreasing, or constant force profile necessary to activate the associated electronic switch as one moves along the external surface of the button assembly from the palm end toward the fingertip end. An increasing force profile provides lower actuating force for operators with smaller hands, while providing greater tactile feedback for operators with larger hands.
Owner:JOHNSON PETER W
Multi-Position Magnetic Detents
InactiveUS20080303618A1Easy and cost-effective to manufactureEasy to manufactureElectromagnets without armaturesPermanent magnetsDocking stationDetent
Various embodiments for magnetic detent assemblies provide for detent devices with improved performance and manufacturability. In one embodiment, magnetic detent assemblies provide for custom detent positions and custom force profiles by including a pair of unitary magnetic components each having a special geometry. In an embodiment, the changing area of overlap (and hence magnetic flux) between the magnetic components can give rise to the custom detent positions and custom force profiles. In a specific embodiment, the magnetic components can comprise an N-point star shaped geometry, where the number and distribution of the start wings can be varied to define customized detent positions and the contour of the star wings can be varied to create customized force profiles. In other embodiments, devices such as laptop computers and docking stations for handheld electronic devices can implement multi-position detent hinges with the magnetic detent assemblies.
Owner:APPLE INC
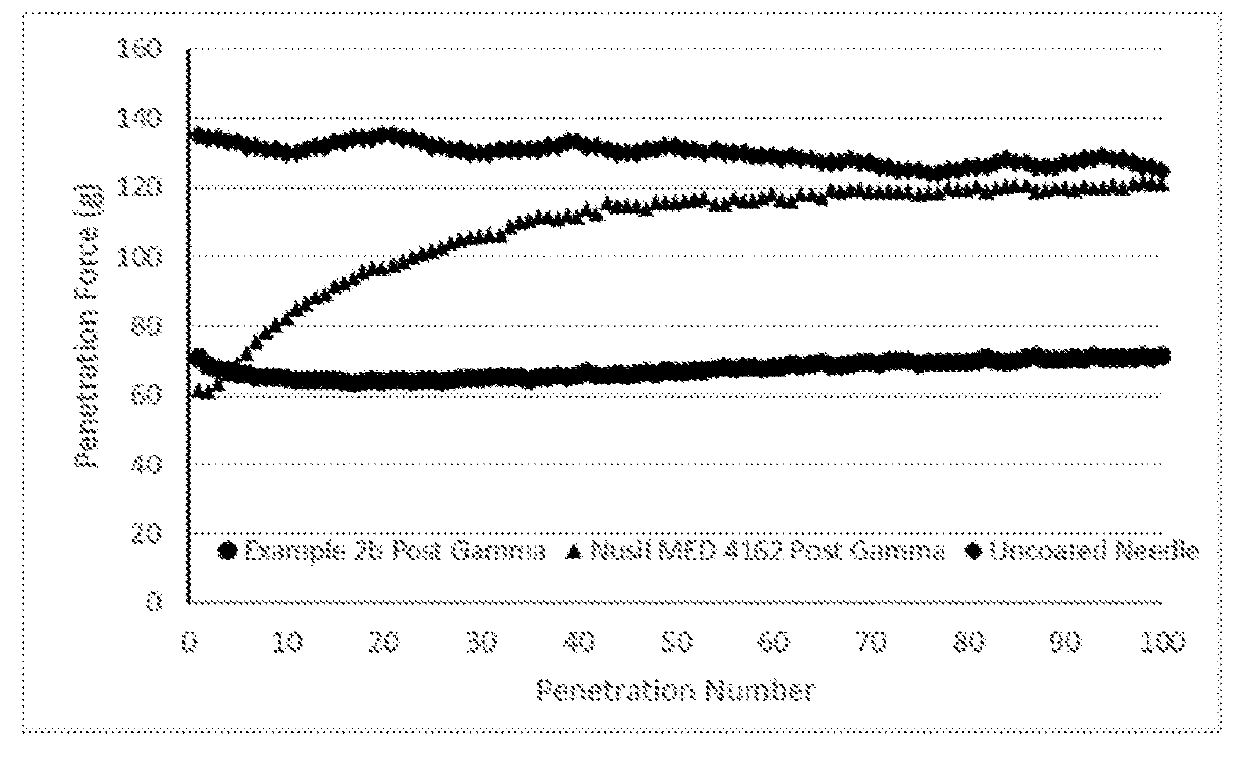
Method of Applying Rapid Cure Silicone Lubricious Coatings
A silicone coating process that improves the durability of silicone coatings on the surfaces of surgical needles and other medical devices. The silicone coated surgical needles or medical devices produced by this process have both superior lubricity and durability for ease of repeated and successive passes through tissue. The coating compositions used in the novel process contain an excess amount of polymethylhydrosiloxane cross-linker. After curing, the process utilizes gamma radiation to treat the lubricious coatings. The coatings have improved durability and performance. The penetration performance of needles coated by this novel method remains constant and flat over at least one hundred repeat passes through tissue or tissue simulation media. This provides a consistent or flat tactile response from the needles to the hand of the surgeon during a lengthy closure process, rather than an unpredictably increasing force profile. The process is also advantageous to coat reusable instruments, robotic instruments, and instruments used in minimally invasive procedures.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com