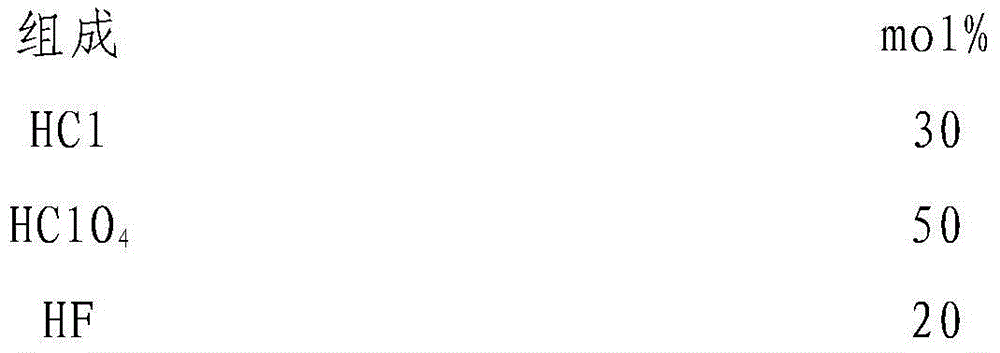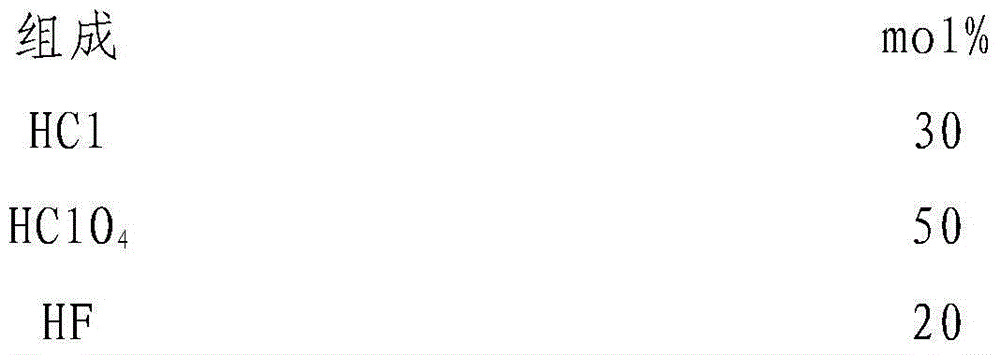Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
134 results about "Fluorophosphate glass" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fluorophosphate glass is a class of optical glasses composed of metaphosphates and fluorides of various metals. It is a variant of phosphate glasses. Fluorophosphate glasses are very unusual in nature. Fluorophosphate glasses have ultra-low theoritical loss of 0.001 dB/km, longer fluorescent lifetime of rare earths, lower coefficient of thermal expansion of ~13×10/°C.
Solid-state luminescent filament lamps
InactiveUS20090212698A1Improve wavelength conversion efficiencyEliminate thermal quenching lossDischarge tube luminescnet screensPoint-like light sourcePhotonicsPhosphate glass
Traditional incandescent and halogen lamps produce a high CRI warm white light with indirect emission patterns at the cost of poor energy efficiency. This new advancement in solid-state lighting enables the production of a new solid-state filament wherein the tungsten filament is replaced with an array of high efficiency LED emitters which combine through an equiangular spiral, or t-spline / TNURCC lightpipe network to produce a single homogeneous blue light source which then pumps a luminescent filament comprised of a phosphor loaded silicone, phosphor loaded polymer, a lanthanide doped fluoro-phosphate glass, glass ceramic tape, quantum dot filled composite, or super-continuum spectrum producing photonic crystalline structure.
Owner:ILLUMINATION MACHINES
Optical glass, optical element and process for the production thereof
InactiveUS20070027017A1Easy to processSuppress chromatic aberrationGlass drawing apparatusGlass forming apparatusAlkaline earth metalRefractive index
Provided are an optical glass having high-refractivity, low-dispersion and anomalous partial dispersion properties, having excellent processability, being excellent as an anomalous partial dispersion glass for suppressing chromatic aberration, containing P5+, Al3+ and alkaline earth metal ions selected from the group consisting of Mg2+, Ca2+, Sr2+ and Ba2+ as essential cationic components and F− and O2− as essential anionic components, wherein the ratio of content of Ba2+ to the total content R2+ of Mg2+, Ca2+, Sr2+ and Ba2+, Ba2+ / R2+, is 0.01 or more but less than 0.5 on the basis of cationic %, and having an Abbe's number (νd) of 68 or more, optical glass having an Abbe's number (νd) of 68 or more, a partial dispersion ratio of 0.535 or more and a frictional abrasion of 500 or less and an optical glass which is to be polished in a polishing step for producing an optical element and which is a fluorophosphate glass having a frictional abrasion of 500 or less.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Nearinfrared-ray absorbing galss, element, light filter and their production method and copper-contained glass
InactiveCN1508087AGood color sensitivity correction characteristicsIncreasing the thicknessOptical filtersSpectral transmittanceThinning
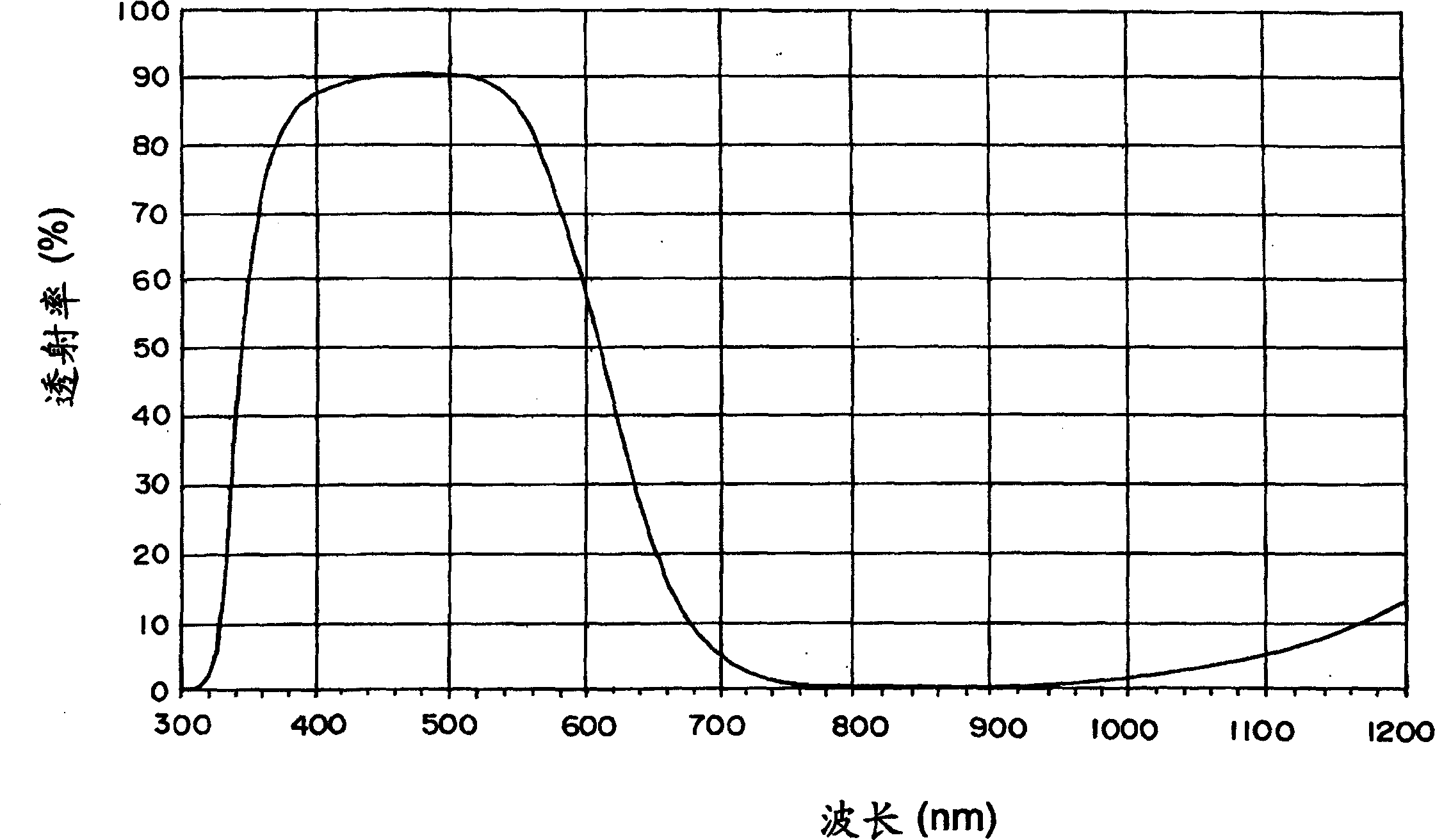
Provided are near-infrared light-absorbing glass in which good color compensating characteristics are maintained even without containing harmful arsenic, permitting the thinning of the glass, and having good weatherability and forming properties; a near-infrared light-absorbing element comprised of such glass; a near-infrared light-absorbing filter employing such glass. Also provided, at low cost, are near-infrared light-absorbing glass permitting good color compensating, a near-infrared light-absorbing element comprised of such glass, and a near-infrared light-absorbing filter comprising such elements. The glass comprises cationic components with a certain composition as well as F<-> and O<2-> as anionic components. Alternatively, the glass is near-infrared light-absorbing glass, wherein the glass exhibits properties, based on a thickness of 0.5 mm, in the spectral transmittance of wavelengths of 400 to 700 nm, that wavelength, at which a 50 percent transmittance is exhibited, is less than 630 nm, transmittance at a wavelength longer than said wavelength is less than 50 percent, transmittance at a wavelength shorter than said wavelength is higher than 50 percent and the viscosity at a liquid phase temperature is 0.5 Pa.s or more. The near-infrared light-absorbing element is comprised of such glass. The near-infrared light-absorbing filter comprises a glass plate comprised of such glass. Alternatively, the glass is comprised of fluorophosphate glass or phosphate glass, and comprises 0.1 weight percent or more of copper based on CuO, 0.005 to 0.5 weight percent of iron based on Fe2O3, 0.01 to 1 weight percent of antimony based on Sb2O3, and no arsenic.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Optical glass, optical element and process for the production thereof
InactiveCN1903765AIncrease refractionImprove machinabilityGlass pressing apparatusAlkaline earth metalRefractive index
Provided are an optical glass having high-refractivity, low-dispersion and anomalous partial dispersion properties, having excellent processability, being excellent as an anomalous partial dispersion glass for suppressing chromatic aberration, containing P5+, Al3+ and alkaline earth metal ions selected from the group consisting of Mg2+, Ca2+, Sr2+ and Ba2+ as essential cationic components and F- and O2- as essential anionic components, wherein the ratio of content of Ba2+ to the total content R2+ of Mg2+, Ca2+, Sr2+ and Ba2+, Ba2+ / R2+, is 0.01 or more but less than 0.5 on the basis of cationic %, and having an Abbe's number (nud) of 68 or more, optical glass having an Abbe's number (nud) of 68 or more, a partial dispersion ratio of 0.535 or more and a frictional abrasion of 500 or less and an optical glass which is to be polished in a polishing step for producing an optical element and which is a fluorophosphate glass having a frictional abrasion of 500 or less.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Near-infrared cut filter and solid-state imaging device
ActiveCN104755969AExcellent near-infrared shielding functionHigh sensitivityTelevision system detailsCoatingsInfraredTransmittance
There are provided a near-infrared cut filter that effectively uses near-infrared absorbing glass and a near-infrared absorbing dye and is excellent in a near-infrared shielding property, and a high-sensitivity solid-state imaging device including the same. A near-infrared cut filter includes: a near-infrared absorbing glass substrate made of CuO-containing fluorophosphate glass or CuO-containing phosphate glass; and a near-infrared absorbing layer containing a near-infrared absorbing dye (A) and a transparent resin (B), on at least one principal surface of the near-infrared absorbing glass substrate, wherein an average value of a transmittance in a 400 nm to 550 nm wavelength range is 80% or more, and an average value of a transmittance in a 650 nm to 720 nm wavelength range is 15% or less.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Fluorophosphate glass, precision press molding preform, optical element blank, optical element and methods of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20090247387A1Quality improvementImprove Optical UniformityOptical articlesOptical elementsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceErosiveness
The present invention provides a fluorophosphate glass containing 30 to 50 cationic % of a phosphorus ingredient in terms of P5+, the glass having, in a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum, a resonance spectrum which is generated near a reference frequency of 31P and has a shape of Gaussian function. The glass of the invention is reduced in volatility and erosiveness.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Phosphate glass, fluorophosphate glass, preform for precision press-molding, optical element and process for the production of thereof
ActiveUS20090325774A1Quality improvementAvoid impuritiesGlass drawing apparatusGlass forming apparatusHalogenBromine
A fluorophosphate glass having a fluorine content of 25% or more by anionic %, which is produced from a glass raw material containing 0.1 to 0.5%, by anionic %, of a halide containing a halogen element selected from chlorine, bromine or iodine, and a phosphate glass having a fluorine content of less than 25% by anionic %, which is produced from a glass raw material containing 0.1 to 5% by anionic %, of a halide containing a halogen element selected from chlorine, bromine or iodine.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Optical glass, preform for press forming, optical element, and processes for producing these
ActiveUS20100113247A1Suppressing of variation of qualitySuppressing volatilizationGlass furnace apparatusGlass drawing apparatusMolten stateRefractive index
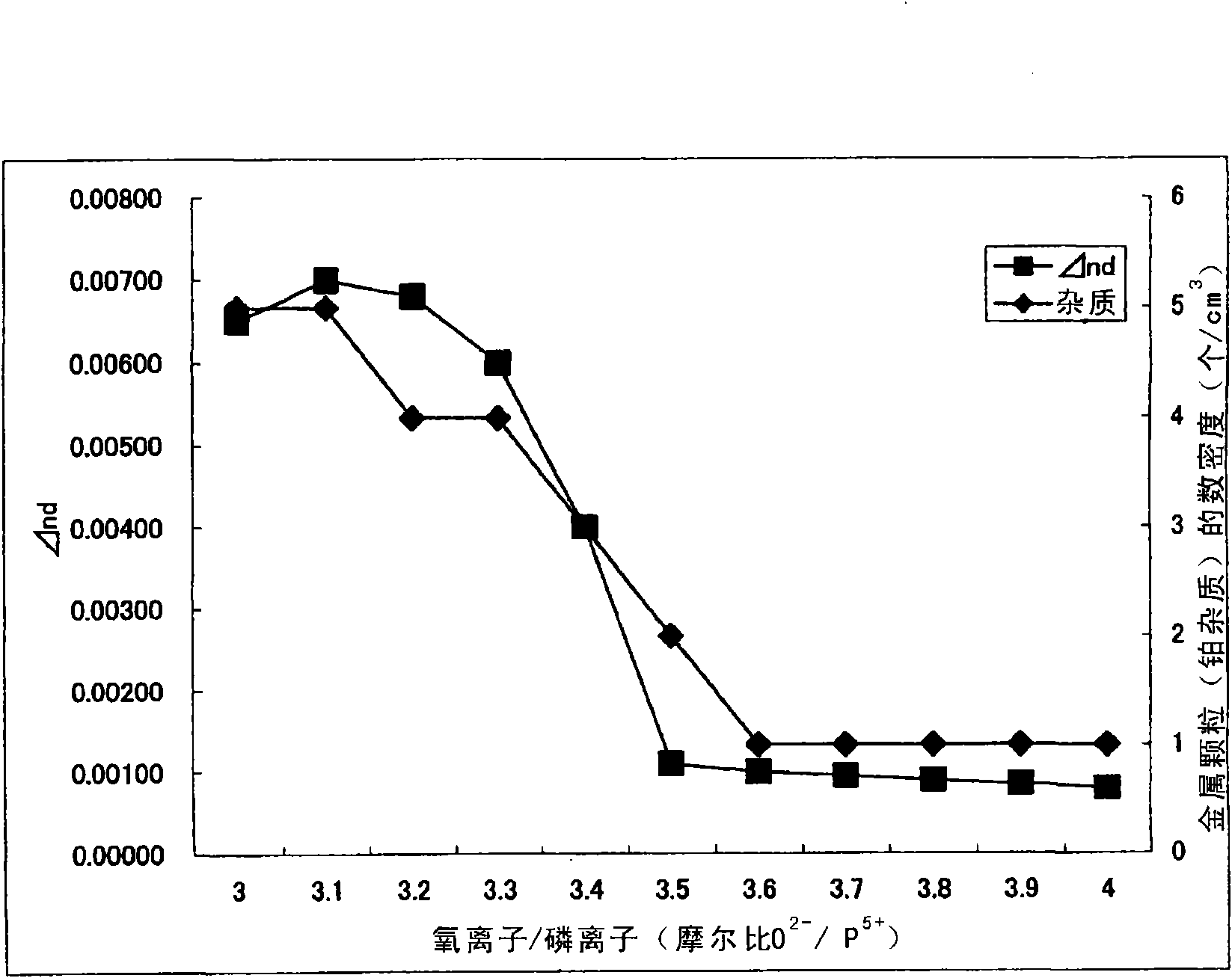
Provided is a low-dispersion optical glass that is formed of a fluorophosphate glass in which the molar ratio of the content of O2− to the content of P5+, O2− / P5+, is 3.5 or more and that has an Abbe's number (νd) of over 70 or has an F− content of 65 anionic % or more, and the optical glass enables the suppression of the volatilization of a glass component when an optical glass formed of a fluorophosphate glass is produced or when an obtained glass in a molten state is caused to flow out to shape it into a glass shaped material, so that the variation of properties such as a refractive index, etc., involved in the fluctuations of a glass composition and the variation of quality such as the occurrence of striae can be suppressed.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Optical glass, glass material for press molding, optical element blank, optical element and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20090298668A1High refractive indexSuppress fluctuationsGlass drawing apparatusGlass forming apparatusRefractive indexOptical glass
A fluorophosphate glass containing: P5+ in an amount of 20 to 45 cationic %; Al3+ in an amount of 15 to 35 cationic %; Ba2+ in an amount of 20 to 50 cationic %; F− in an amount of 20 to 50 anionic %; and O2− in an amount of 50 to 80 anionic %. A molar ratio of O2− / P5+ is larger than or equal to 3.5. In addition, a molar ratio of Al3+ / P5+ is larger than or equal to 0.45. Furthermore, the Abbe number (νd) of the glass is larger than or equal to 66. Finally a refractive index (nd) of the glass satisfies an expression (1): nd≧2.0614−0.0071×νd.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Bismuth containing fluorophosphate glass and method for making thereof
ActiveUS20070010390A1Increased durabilityImprove efficiencyPot furnacesCharging furnaceRare-earth elementRefractive index
New and improved compositions of doped and co-doped bismuth fluorophosphate glasses for lasers is disclosed that have a high refractive index (nD) of approximately 1.6 and higher, high transmission in the near infrared part of the spectrum, and a wide glass forming domain. The disclosed glass systems Al(PO3)3-Ba(PO3)2-Bi(PO3)3-BaF2+RFx+dopands use dopants from the group of oxides and or fluorides of rare earth elements Nd, Er, Yb, Tm, Tb, Ho, Sm, Eu and Pr as well as MnO and mixtures thereof over 100 percent (wt %) of the glass-base composition. These glasses have high chemical durability, radiation resistance, efficiency of laser use in the infrared and blue spectrum, and improved duration of luminescence.
Owner:AFO RES INC
Optical glass, press-molding preform, process for the production thereof, optical element and process for the production thereof
ActiveUS7595272B2Suitable viscosityReduce the temperatureGlass furnace apparatusGlass drawing apparatusRefractive indexOptical glass
A low-dispersion optical glass suitable for producing a quality preform from a molten glass and suitable for precision press-molding, which is a fluorophosphate glass containing, as essential cationic components, P5+, Al3+, at least two members selected from Mg2+, Ca2+, Sr2+ and Ba2+ as divalent cationic components (R2+) and Li+ and containing, by cationic %,10 to 45% of P5+,5 to 30% of Al3+,0 to 20% of Mg2+,0 to 25% of Ca2+,0 to 30% of Sr2+,0 to 33% of Ba2+,1 to 30% of Li+,0 to 10% of Na+,0 to 10% of K+,0 to 5% of Y3+,and0 to 15% of B3+,the molar ratio of the content of F− to the total content of F− and O2−, F− / (F−+O2−), being 0.25 to 0.85,the optical glass having a refractive index (Nd) of 1.40 to 1.58 and an Abbe's number (νd) of 67 to 90.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Fluorophosphate glass, glass material for press molding, optical element blank, optical element and methods of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20090247388A1Improve Optical UniformityReduced volatility and erosivenessGlass shaping apparatusRefractive indexNitrogen atmosphere
The present invention provides a fluorophosphate glass containing phosphorus, oxygen and fluorine as glass ingredients, in which, provided that a refractive index nd of the glass is nd(1) and a refractive index nd after re-melting the glass at 900° C. for 1 hour in a nitrogen atmosphere, cooling the glass to a glass transition temperature and then cooling the glass down to 25° C. at a temperature decrease rate of 30° C. per hour is nd(2), an absolute value of a difference between nd(1) and nd(2) (nd(2)-nd(1)) is equal to or less than 0.00300, and a molar ratio (O2− / P5+) of a content of O2− to a content of P5+ is equal to or more than 3.5. The glass of the invention is reduced in volatility and erosiveness.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Fluorophosphate glass, precision press molding preform, optical element blank, optical element and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20090247386A1Improve Optical UniformityQuality improvementGlass pressing apparatusGlass reforming apparatusNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceResonance
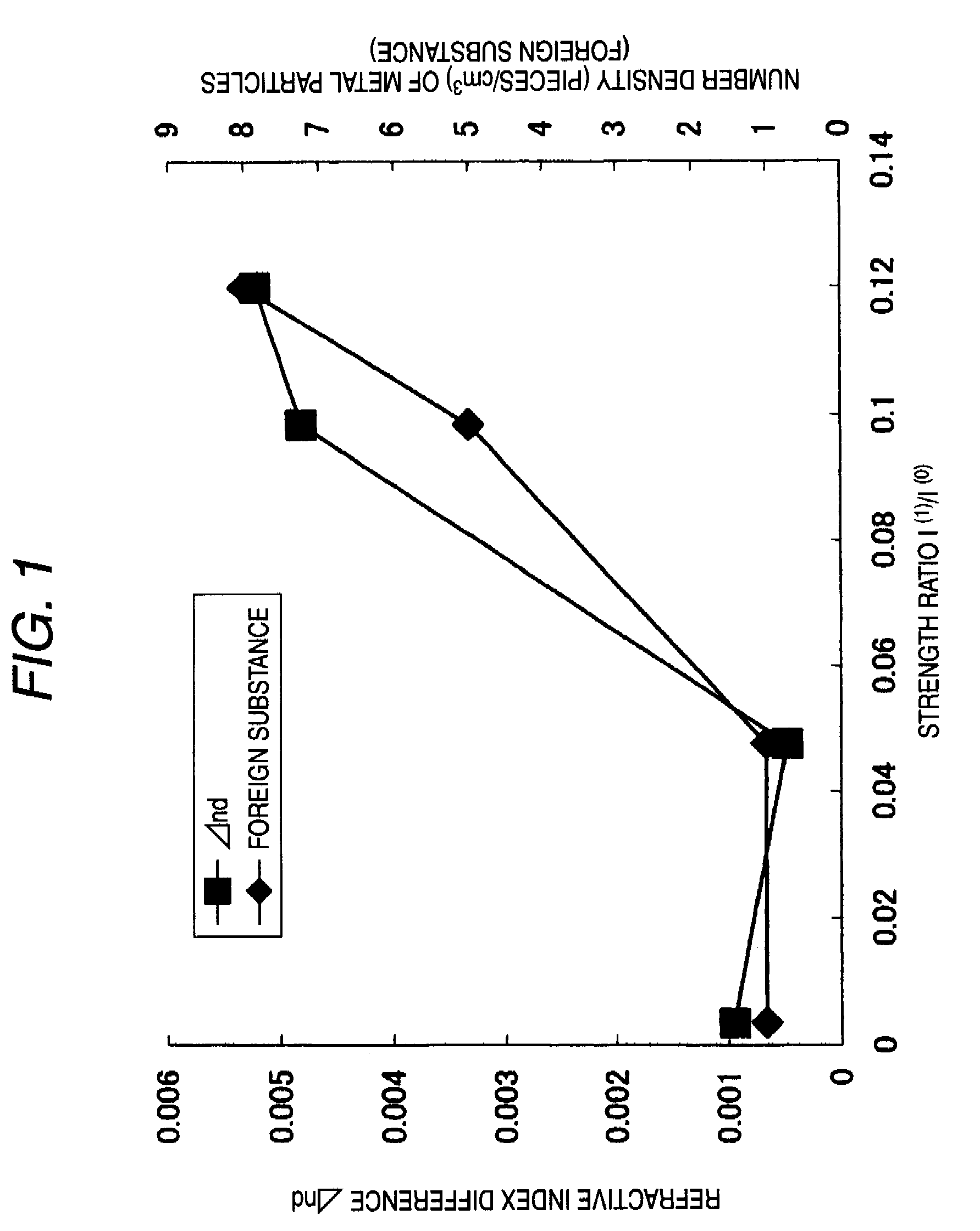
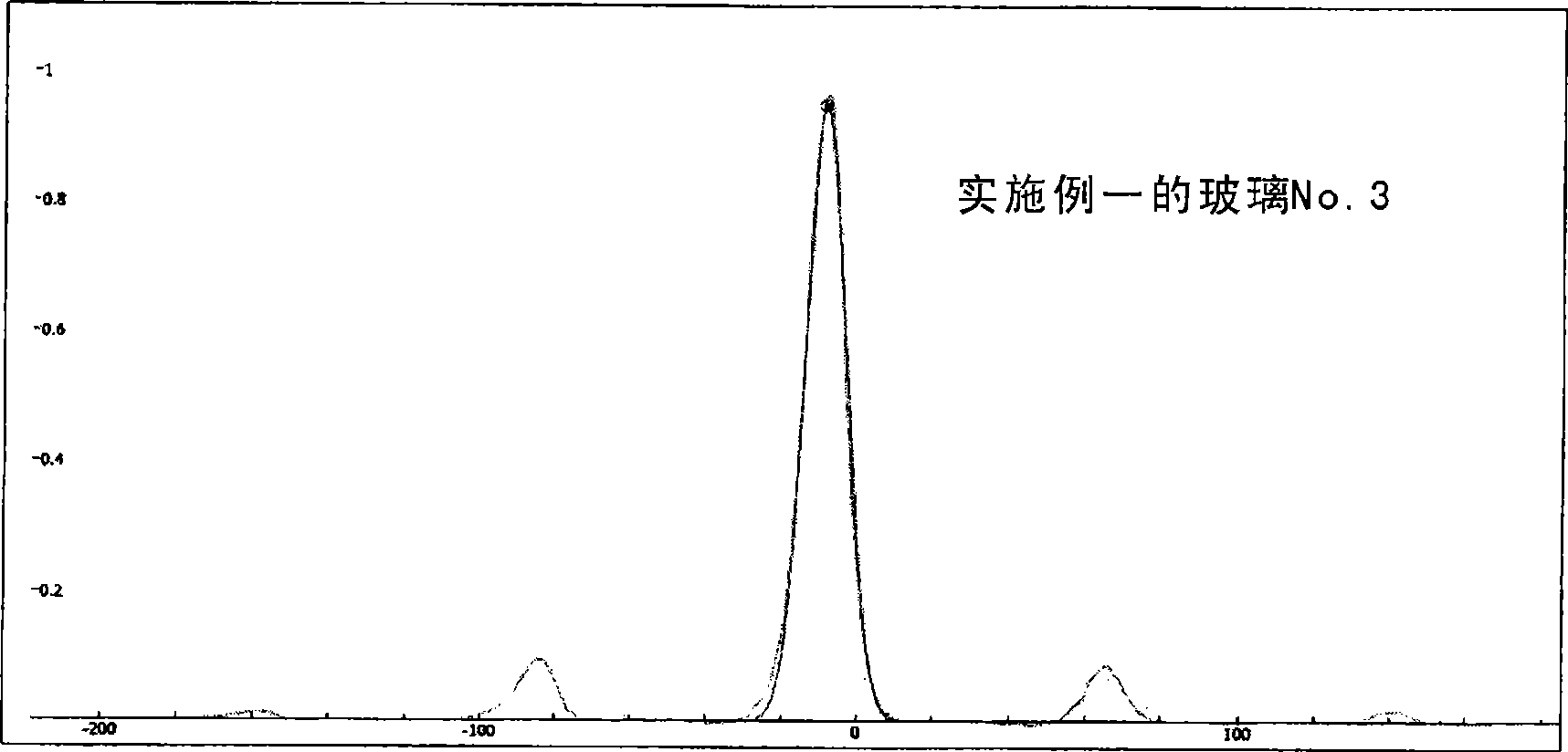
The present invention provides a fluorophosphate glass containing more than 3 cationic % and 30 cationic % or less of a phosphorus ingredient in terms of P5+, the glass having a ratio I(1) / I(0) of equal to or less than 0.08 in which I(0) is a strength of a resonance peak generated near a reference frequency of 31P in a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum and I(1) is a strength of a first-order side band peak of the resonance peak. The glass of the invention is reduced in volatility and erosiveness.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Fluorophosphate glasses
Glass having an optimized degree of cross-linking of the phosphate component in the glass matrix is provided so that excellent weatherability is achieved. These glasses are fluorophosphate glasses that contain copper oxide as colouring component. The glasses can further contain colouring components and are obtainable in a method that includes a bubbling step.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Fluorophosphate glasses
InactiveUS20120165178A1Improve transmittanceReduce transmissionGlass furnace apparatusOptical filtersCopper oxideGlass matrix
Glass having an optimized degree of cross-linking of the phosphate component in the glass matrix is provided so that excellent weatherability is achieved. These glasses are fluorophosphate glasses that contain copper oxide as colouring component. The glasses can further contain colouring components and are obtainable in a method that includes a bubbling step.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Fluorophosphate glass, precision press molding preform, optical element blank, optical element and methods of manufacturing the same
ActiveCN101544469AImprove uniformityGlass pressing apparatusOptical elementsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceErosiveness
The invnetion provides fluoroposphate glass, precision press molding preform, optical element blank, optical element and method of manufacturing the same. A fluorophosphate glass of the invention contains 30 to 50 cationic % of a phosphorus ingredient in terms of P5+, the glass having, in a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum, a resonance spectrum which is generated near a reference frequency of 31P and has a shape of Gaussian function. The glass of the invention is reduced in volatility and erosiveness.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Near infrared cutoff filter
InactiveUS20120199929A1Low costEffectively attenuate α raysMirrorsOptical filtersUltrasound attenuationPhosphate glass
To provide a near infrared cutoff filter at low costs, which is useful as cover glass for a solid state imaging sensor package, by providing a thin film attenuation layer for effectively shielding α rays emitted from substrate glass in a form not to influence the optical characteristics. A near infrared cutoff filter comprising substrate glass made of fluorophosphate glass containing CuO or phosphate glass containing CuO, and a thin film attenuation layer formed on at least one light-permeable surface of the substrate glass to attenuate α rays emitted from the substrate glass.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Bismuth containing fluorophosphate glass and method for making thereof
ActiveUS20090255297A1Increased durabilityImprove efficiencyPot furnacesGlass furnace apparatusRare-earth elementRefractive index
New and improved compositions of doped and co-doped bismuth fluorophosphate glasses for lasers is disclosed that have a high refractive index (nD) of approximately 1.6 and higher, high transmission in the near infrared part of the spectrum, and a wide glass forming domain. The disclosed glass systems Al(PO3)3−BA (PO3)2−Bi(PO3)3−BaF2+RFx+dopands use dopants from the group of oxides and or fluorides of rare earth elements Nd, Er, Yb, Tm, Tb, Ho, Sm, Eu and Pr as well as MnO and mixtures thereof over 100 percent (wt %) of the glass-base composition. These glasses have high chemical durability, radiation resistance, efficiency of laser use in the infrared and blue spectrum, and improved duration of luminescence.
Owner:AFO RES INC
Lens and process for the production thereof
ActiveUS20080084613A1Not to damageGlass pressing apparatusGlass reforming apparatusOptical axisOptoelectronics
A lens formed of a fluorophosphate glass, which has an optical-function surface and has a positioning reference surface for positioning and fixing the lens in the fixing tool (and also for determining the direction in the direction of the optical axis), so that the above optical-function surface is not damaged, both the optical-function surface and the positioning reference surface being transfer surfaces formed by the transfer of form of a molding surface of a mold according to precision press-molding.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Fluorophosphate glass and method for making thereof
New and improved compositions of doped fluorophosphate glasses for lasers have a high refractive index (nD) of approximately 1.6 to 1.7, high transmission in the near infrared part of the spectrum and a wide glass forming domain. These glass systems, Ba(PO3)2—Al(PO3)3—BaF2-Dopants, utilize dopants from the group of: oxides or fluorides of the rare earth elements: Sm, Eu, Nd, Er, Yb, Tm, Tb, Ho and Pr: as well as MnO; and mixtures thereof. The composition of glass includes chemical durability, efficiency of laser use in the infrared spectrum and improved duration of luminescence. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract that will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:AFO RES INC
Fluorophosphate glass, glass preform, optical element, and optical instrument provided with optical element
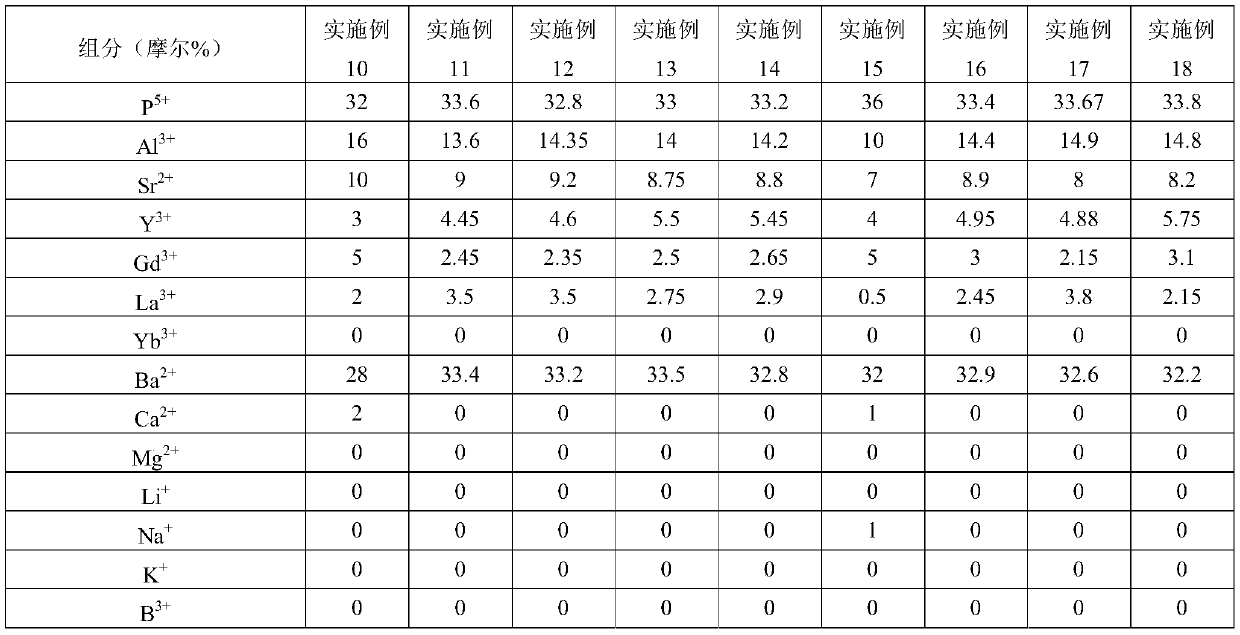
The invention discloses a fluorophosphate glass, a glass preform, an optical element, and an optical instrument provided with the optical element. The fluorophosphate glass comprises cations and anions, and the cations comprise 25-40 mol% of P<5+>, 8-22 mol% of Al<3+>, 0-8 mol% of La<3+>, 1-10 mol% of Y<3+>, 3-15 mol% of Sr<2+>, 25-40 mol% of Ba<2+> and 1-10 mol% of Gd<3+>; and the anions comprise38-50 mol% of F<-> and 50-62 mol% of O<2->, wherein a ratio of n(Y<3+> + La<3+>) / n(P<5+> + Al<3+> + Sr<2+> + Y<3+>) is more than 0.07. The fluorophosphate glass has a refractive index of 1.52-1.60 and an Abbe number of 68 or more, and has excellent optical properties and a low refractive index high temperature coefficient, so the fluorophosphate glass has an excellent thermal stability under strong light, and the stress is not prone to be generated in the glass, thereby the quality of the imaged image is improved, and the needs of the market are met.
Owner:CDGM OPTICAL GLASS
Fluorophosphate glass, precision press molding preform, optical element blank, optical element and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveCN101544468AImprove uniformityGlass pressing apparatusOptical elementsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceErosiveness
The invnetion provides fluoroposphate glass, precision press molding preform, optical element blank, optical element and method of manufacturing the same. A fluorophosphate glass of the invention contains more than 3 cationic % and 30 cationic % or less of a phosphorus ingredient in terms of P<5+>, the glass having a ratio I(1) / I(0) of equal to or less than 0.08 in which I(0) is a strength of a resonance peak generated near a reference frequency of <31>P in a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum and I(1) is a strength of a first-order side band peak of the resonance peak. The glass of the invention is reduced in volatility and erosiveness.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Method for manufacturing optical glass, method for manufacturing precision press molding preform and method for manufacturing optical element
InactiveCN101152970AReduced Manufacturing MethodsPot furnacesGlass furnace apparatusPlatinumForeign matter
PROBLEM TO BE SOLVED: To provide a method for manufacturing optical glass, wherein an amount of a platinum or platinum-alloy foreign matter contained in glass is reduced to reduce the amount of the platinum or platinum-alloy foreign matter deposited in the glass in the case that the optical glass composed of fluorine-containing glass, especially fluorophosphate glass is produced by a melting method.SOLUTION: In the method for manufacturing the optical glass composed of fluorine-containing glass, a glass raw material is dissolved in a vessel made of carbon or a carbide and thereafter, melted in a vessel made of platinum or a platinum-alloy.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Optical glass, preform for press forming, optical element, and processes for producing these
ActiveUS8354352B2Suppressing of variationSuppressing volatilizationGlass furnace apparatusGlass drawing apparatusMolten stateRefractive index
Provided is a low-dispersion optical glass that is formed of a fluorophosphate glass in which the molar ratio of the content of O2− to the content of P5+, O2− / P5+, is 3.5 or more and that has an Abbe's number (νd) of over 70 or has an F− content of 65 anionic % or more, and the optical glass enables the suppression of the volatilization of a glass component when an optical glass formed of a fluorophosphate glass is produced or when an obtained glass in a molten state is caused to flow out to shape it into a glass shaped material, so that the variation of properties such as a refractive index, etc., involved in the fluctuations of a glass composition and the variation of quality such as the occurrence of striae can be suppressed.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Fluorophosphate glass, glass preform, optical element, and optical instrument provided with optical element
The invention discloses a fluorophosphate glass, a glass preform, an optical element, and an optical instrument provided with the optical element. The fluorophosphate glass comprises cations and anions, and the cations comprise 25-40 mol% of P<5+>, 8-22 mol% of Al<3+>, 1-30 mol% of Ln<3+> and 25-55 mol% of R<2+>, wherein the Ln<3+> is at least one La<3+>, Gd<3+>, Y<3+> and Yb<3+>, and the R<2+> isat least one of Ba<2+>, Ca<2+>, Sr<2+> and Mg<2+> and the anions comprise 38-50 mol% of F<-> and 50-62 mol% of O<2->, wherein a ratio of n(Ln<3+>) / n(R<2+>) is more than 0.11. The fluorophosphate glass has a refractive index of 1.52-1.60 and an Abbe number of 68 or more, and has excellent optical properties and a low refractive index high temperature coefficient, so the fluorophosphate glass is suitable for the outdoor high temperature environment, and meets the needs of the market.
Owner:CDGM OPTICAL GLASS
Fluorophoshoric acid glass, die pressing forming glass material, optical element blank, optical element and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN101555099AExcellent optical uniformityGlass pressing apparatusOptical elementsVitrificationErosiveness
The present invention provides a fluorophosphate glass containing phosphorus, oxygen and fluorine as glass ingredients, in which, provided that a refractive index nd of the glass is nd(1) and a refractive index nd after re-melting the glass at 900 DEG C for 1 hour in a nitrogen atmosphere, cooling the glass to a glass transition temperature and then cooling the glass down to 25 DEG C at a temperature decrease rate of 30 DEG C per hour is nd<(2)>, an absolute value of a difference between nd<(1)> and nd<(2)> (nd<(2)>-nd<(1)>) is equal to or less than 0.00300, and a molar ratio (O<2-> / P<5+>) of a content of O<2-> to a content of P<5+> is equal to or more than 3.5. The glass of the invention is reduced in volatility and erosiveness.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Tm-doped fluorophosphate glasses for 14xx amplifiers and lasers
A host material for Tm<3+>-doping is provided. The host material is a fluorophosphate glass having a non-zero concentration of Tm<3+>, cation elements that include at least an alkaline earth, phosphorus, and aluminum, and anion elements that include oxygen (O) and fluorine (F). The fluorine(F) / oxygen (O) ratio (F / (F+O)) for the fluorophosphate glass of the embodiments of the present invention can be in the range of about 0.5 to about 0.85. The fluorophosphate glass further can have an alkali metal concentration of 10 mole % or less to improve durability. The Tm-doped fluorophosphate glass can be incorporated into an amplifier or laser utilized in the 14xx nm wavelength region.
Owner:CORNING INC
Infrared absorbing glass wafer and method for producing same
ActiveUS20130264672A1Reduce curvatureEasy to manufactureOptical filtersSolid-state devicesPhosphateCopper
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Method for treating surface of fluorphosphate glass
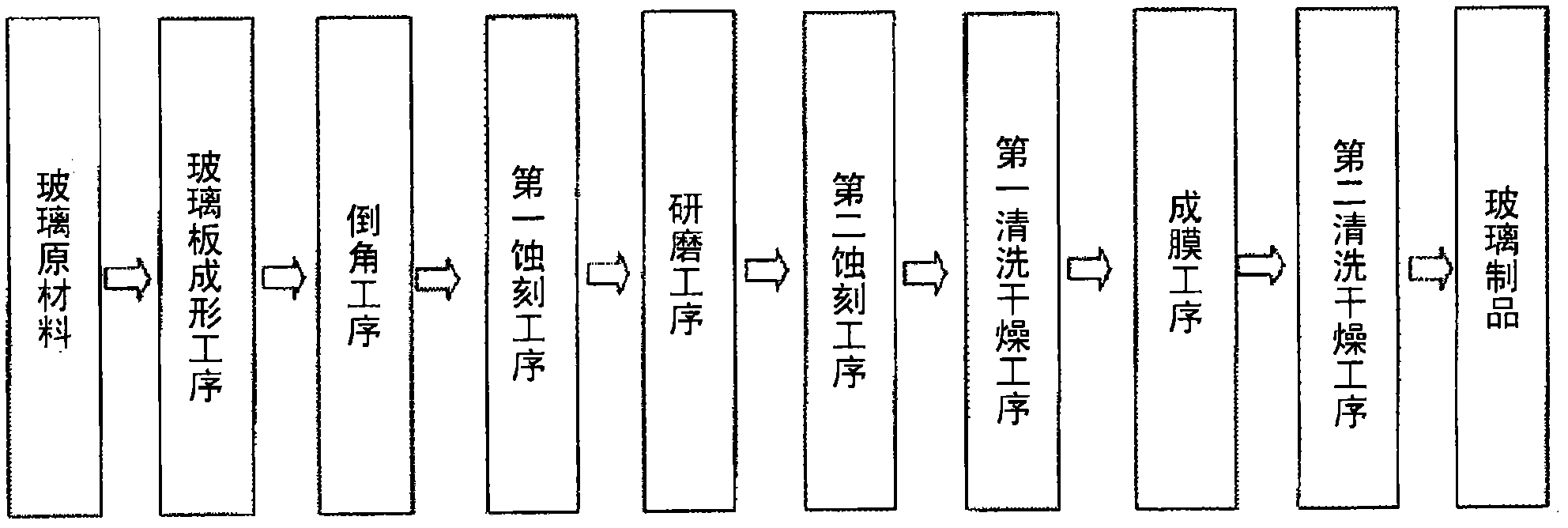
The invention discloses a method for treating the surface of fluorphosphate glass. The method is used for treating the surface of glass by adopting the manner of combination of chemical corrosion and mechanical polishing. According to the method, a crack layer as well as impurities accumulated at scratches, which is caused by machining the fluorphosphate glass, can be effectively eliminated, the surface defects are reduced, and the roughness of the surface of the glass is reduced. The method comprises the following concrete steps: firstly, cleaning impurities, which are accumulated on the surface, with mixed acid to expose the scratches on the surface layer; secondly, corroding the surface of the glass with alkali liquor to remove a microcrack layer and the scratches; finally, performing secondary polishing to enable the surface of the glass to be transparent and smooth. The method has the advantages that the impurities and the crack layer, which are arranged on the surface of the glass, are respectively removed by a mixed acid solution and a mixed base solution, and the roughness of the surface of the glass can be reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Near infrared cut-off filters
Provided is an inexpensive near infrared cut-off filter which, by being provided with a thin-film attenuation layer that effectively blocks a rays emitted from substrate glass and that is in a form so as to not influence optical characteristics, can even be used as cover glass for a solid state imaging sensor package. The thin-film attenuation layer for attenuating a rays emitted from substrate glass is formed on at least one light-permeable surface of substrate glass produced from fluorophosphate glass containing CuO or phosphate glass containing CuO.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com