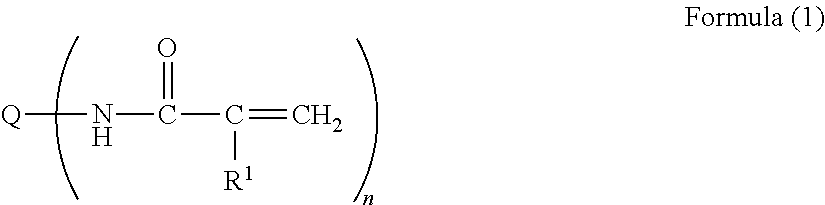Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
75 results about "Dots per inch" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Dots per inch (DPI, or dpi) is a measure of spatial printing, video or image scanner dot density, in particular the number of individual dots that can be placed in a line within the span of 1 inch (2.54 cm). Similarly, the more newly introduced dots per centimeter (d/cm or dpcm) refers to the number of individual dots that can be placed within a line of 1 centimeter (≈ 0.393 in).
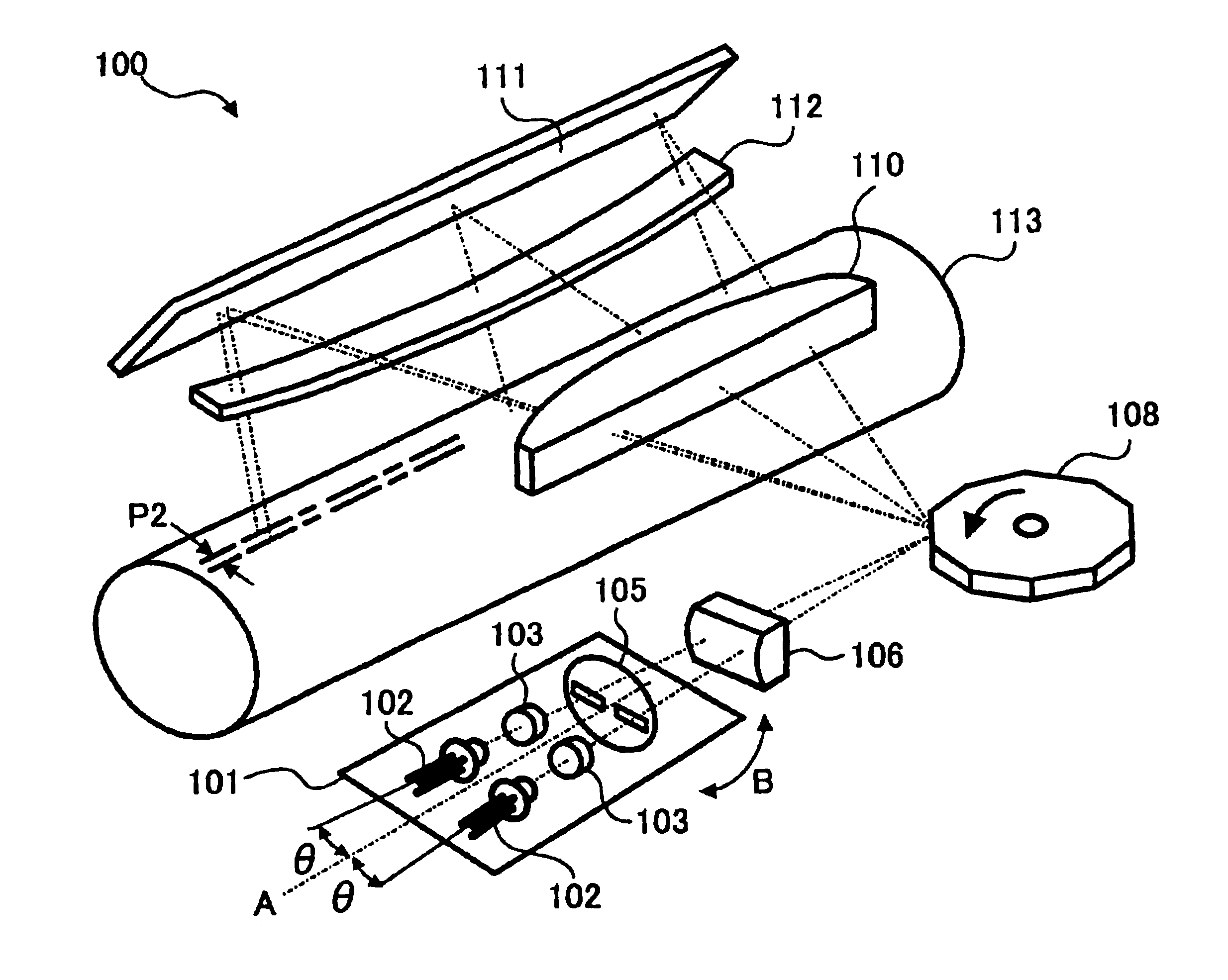
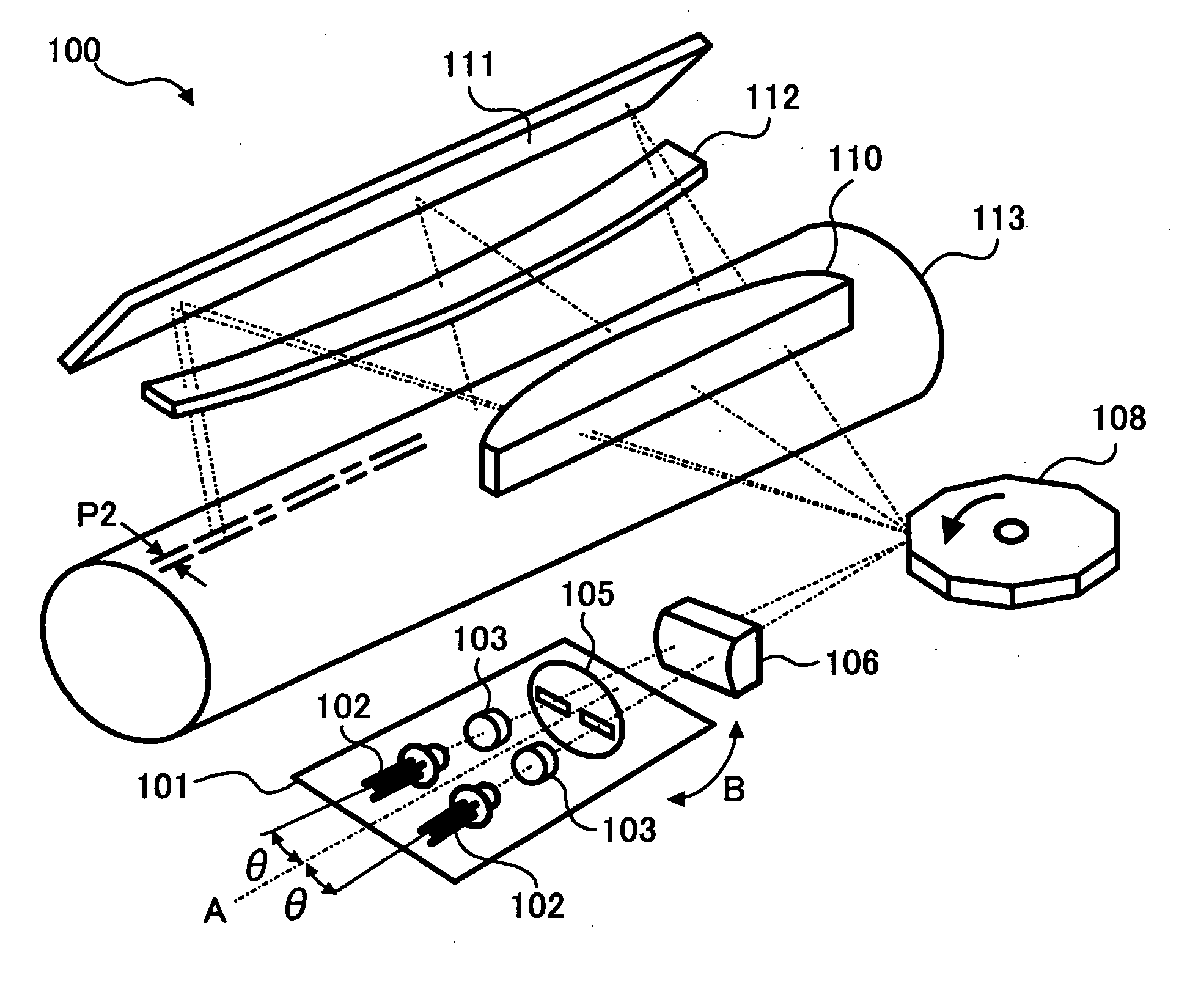
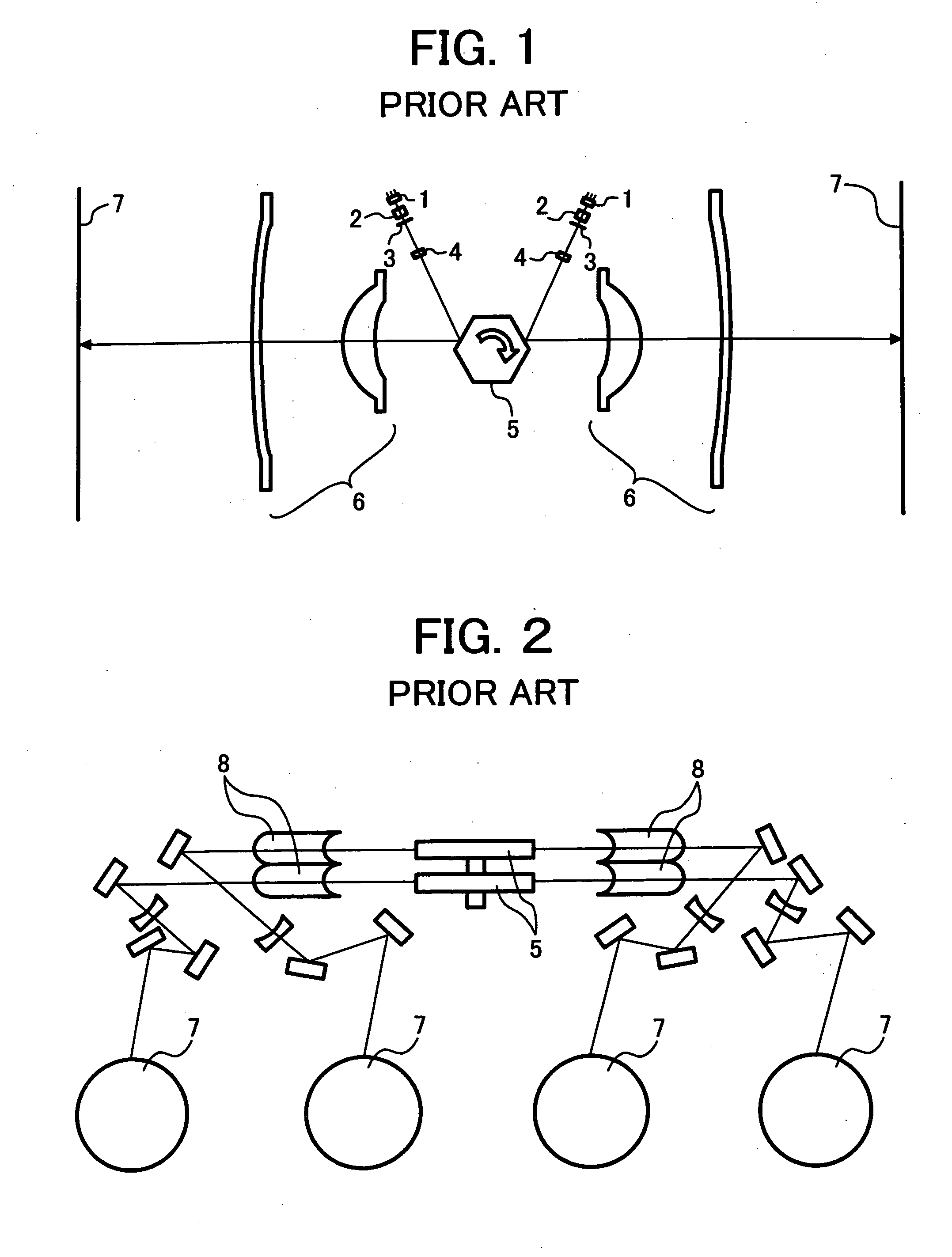
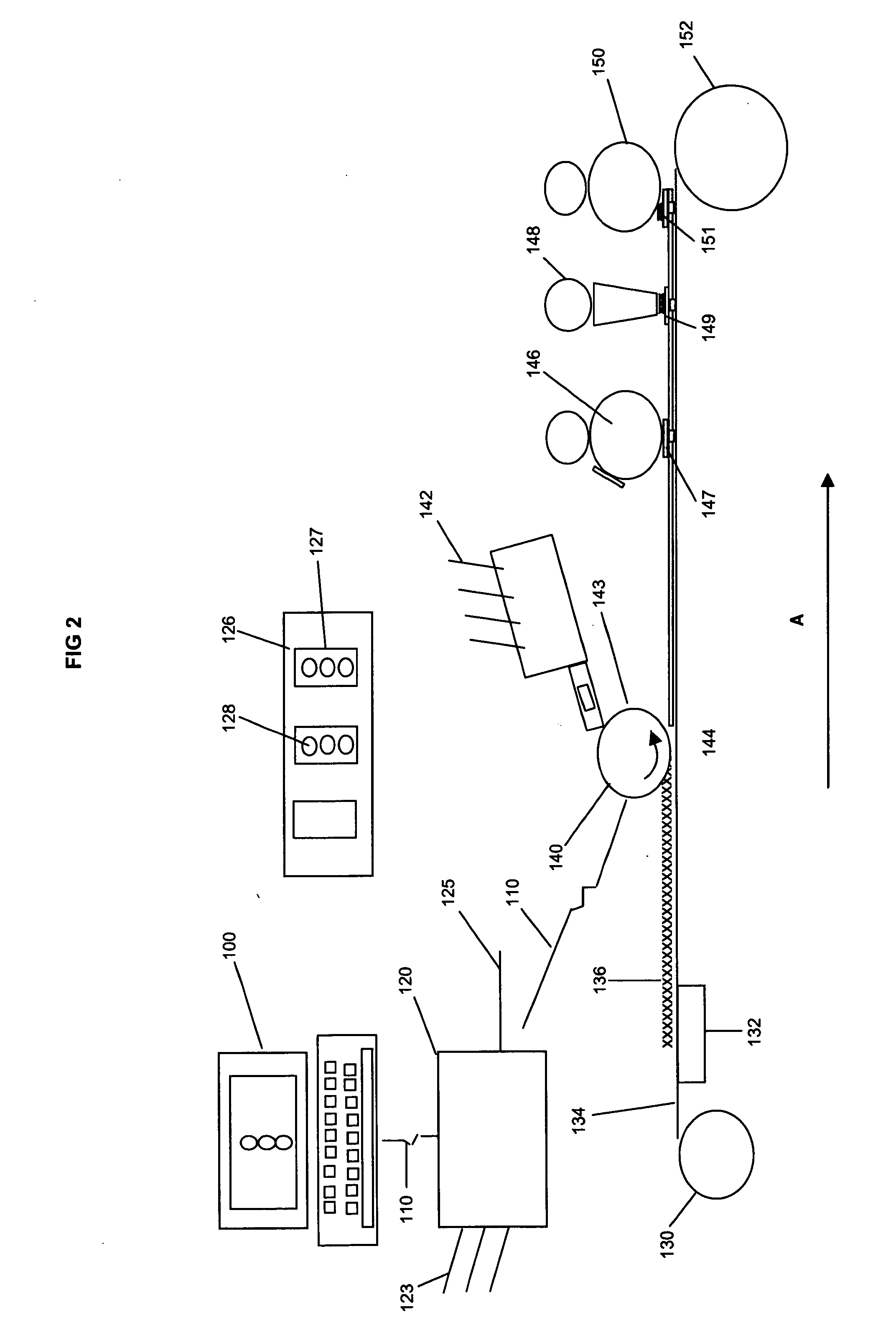
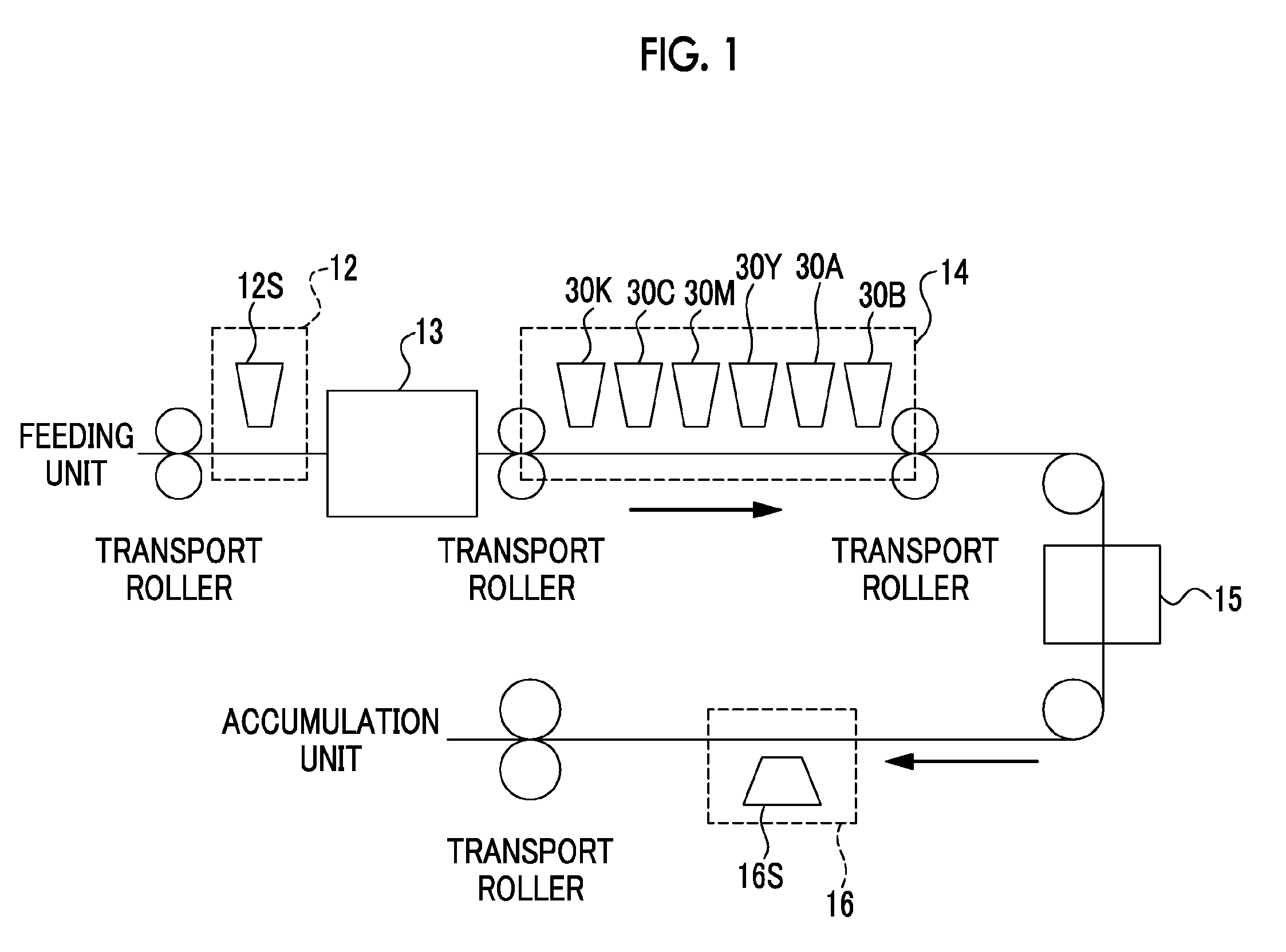
Method and apparatus for multi-beam optical scanning capable of effectively adjusting a scanning line pitch
Owner:RICOH KK
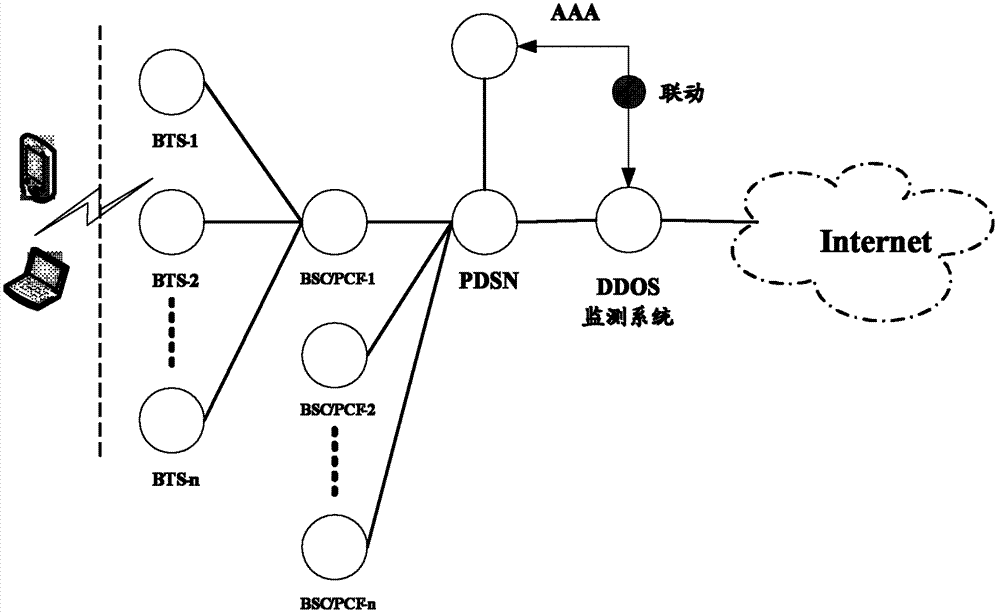
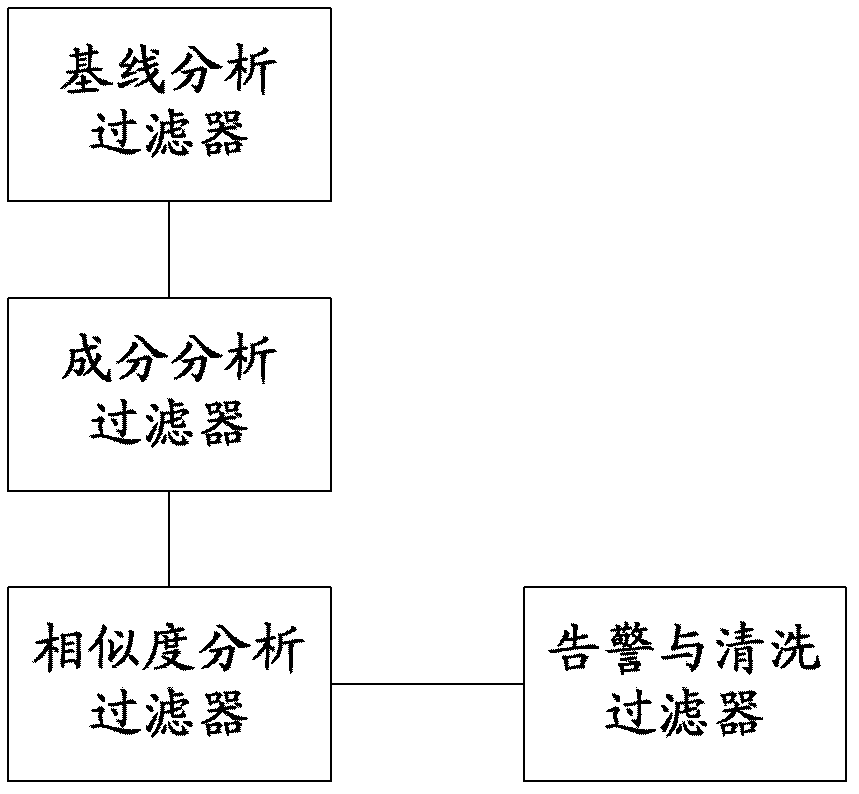
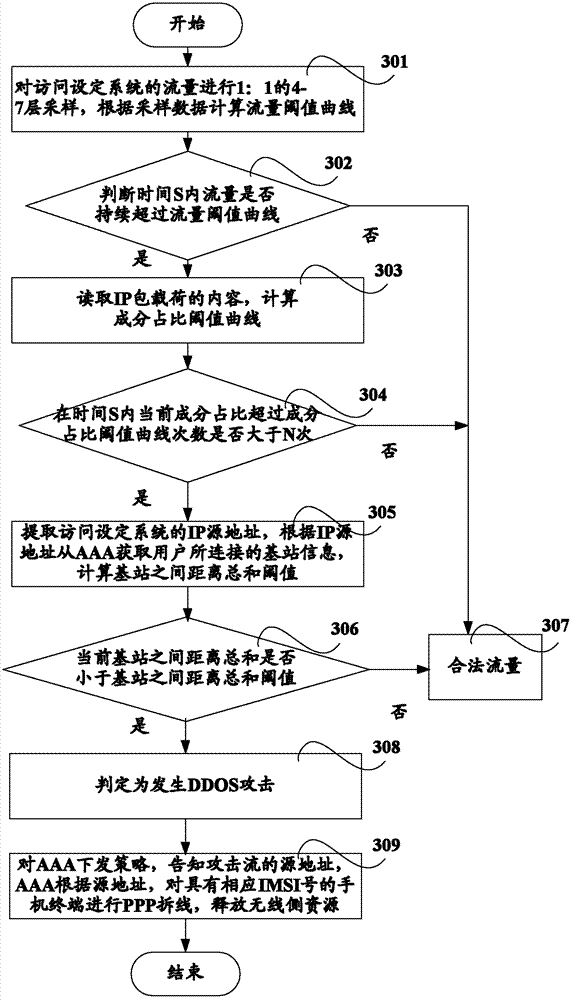
Method and system for monitoring DDOS (distributed denial of service) attacks in small flow
ActiveCN102821081AMake up for the inability to detect low-rate DDoS attacksHigh false positive rateData switching networksSimilarity analysisProtocol Application
The invention discloses a method and a system for monitoring DDOS (distributed denial of service) attacks in small flow, solves the problems that the existing DDOS attack detection technology is high in cost, complex to implement and high in misjudgment rate, cannot respond to DDOS attacks aiming at an application layer and the like, and provides the monitoring scheme of an integrated DPI (dots per inch) technology. A baseline analysis, component analysis and similarity analysis method is used to establish a normal use model, characteristics are accurately matched to detect the attacks in small flow and the application layer attacks, deployment at one point of an operator network and complete coverage of the operator network are achieved, and detection accuracy is increased.
Owner:CHINA TELECOM CORP LTD
Method and apparatus for multi-beam optical scanning capable of effectively adjusting a scanning line pitch
InactiveUS20050105156A1Beam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsElectric discharge tubesCouplingLight beam
An optical scanning apparatus includes light sources, an aperture having, and coupling lenses. Numbers of the light sources and the coupling lenses are equal to each other and the apparatus satisfies an inequality 12.7<(D×β0×m0×dpi) / (2×NA)<38.1 and an equation β0=(β+−β−) / (n−1), wherein D represents a width of the slit of the aperture, β0 represents a beam open angle, mo represents a total lateral magnification ratio, dpi represents a number of dots per inch, NA represents a numerical aperture, β+ represents a positive open angle, β− represents a negative open angle, and n represents the number. Further, an image forming apparatus using this optical scanning apparatus and an image forming method are provided.
Owner:ONO NOBUAKI +4
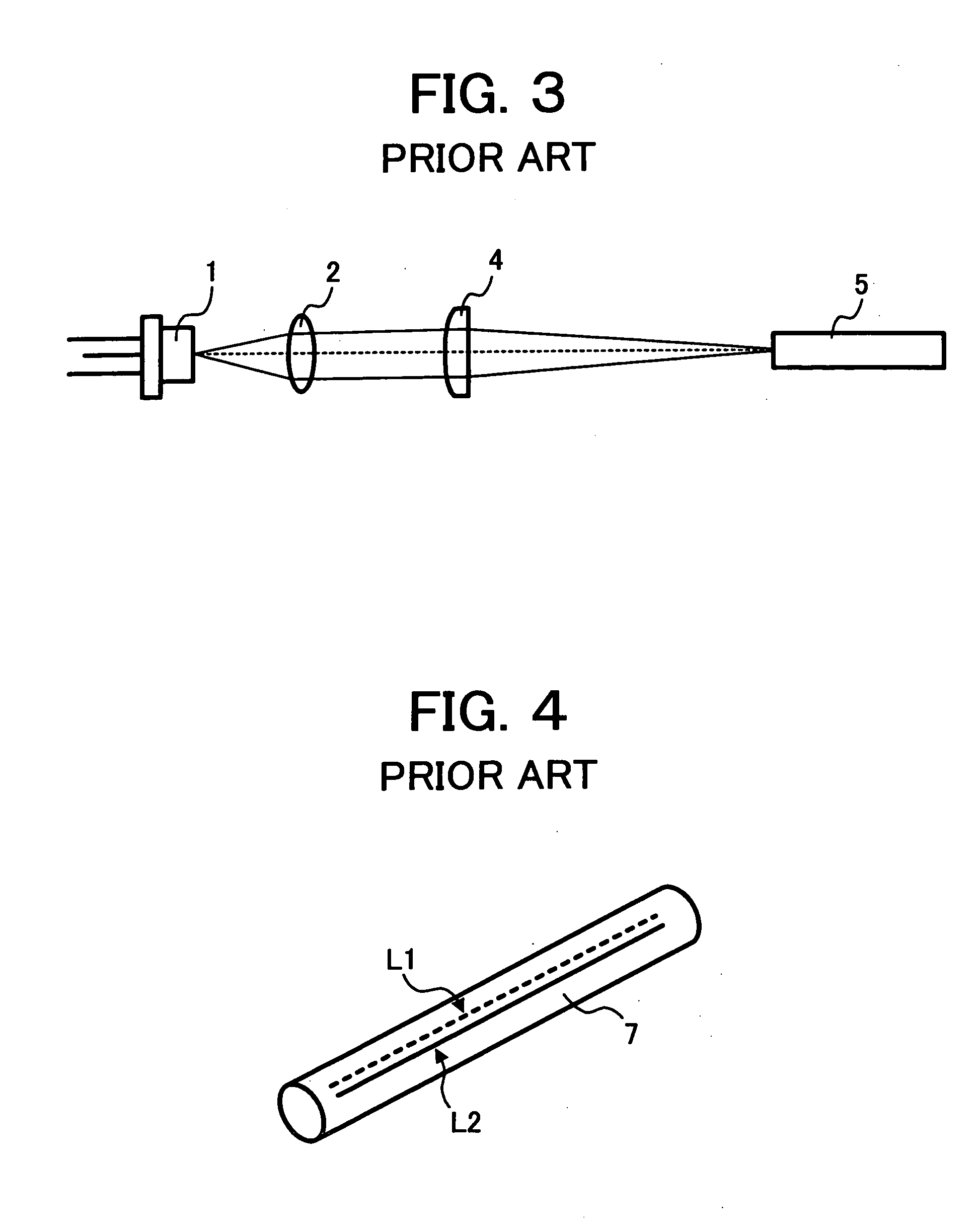
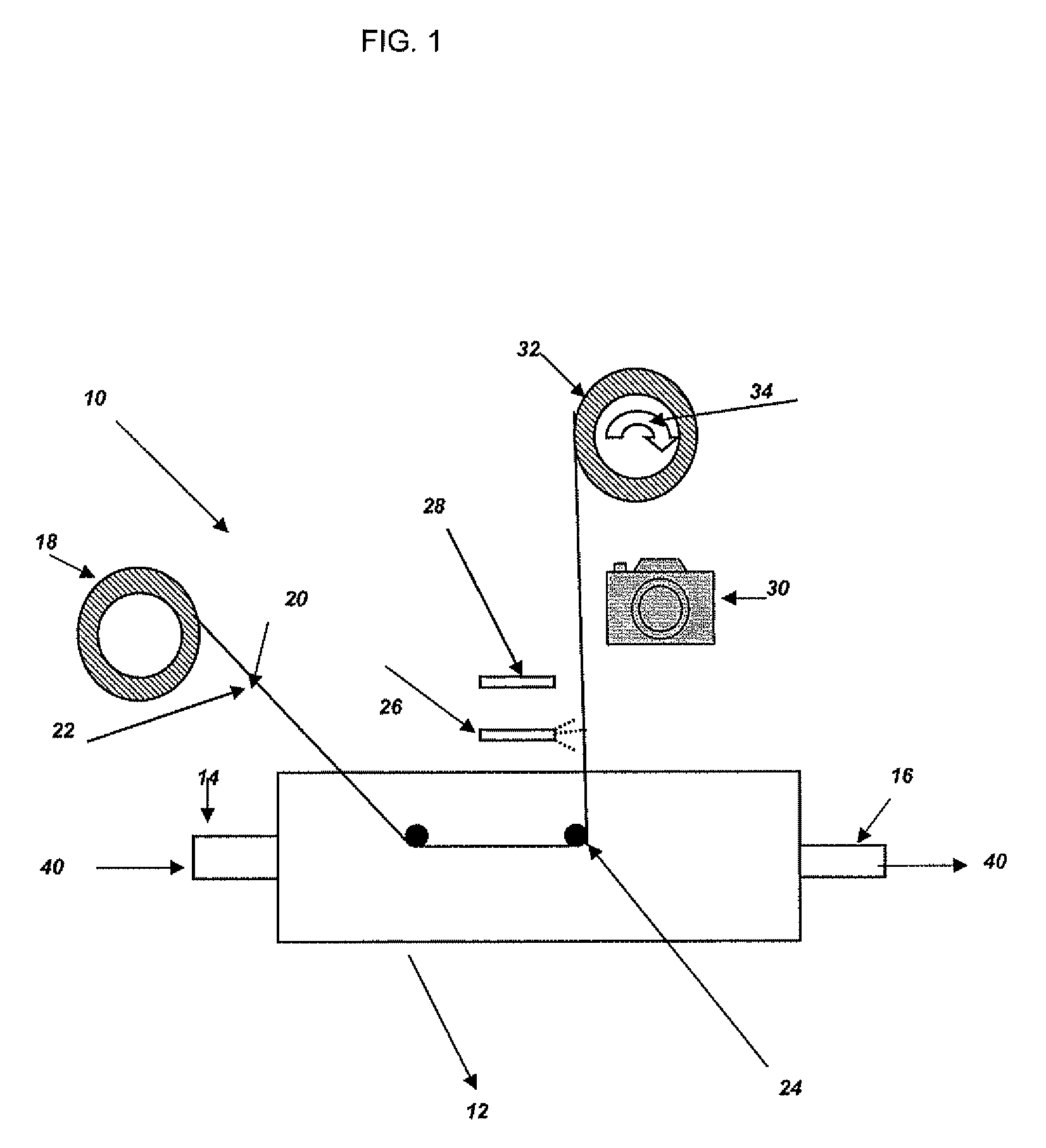
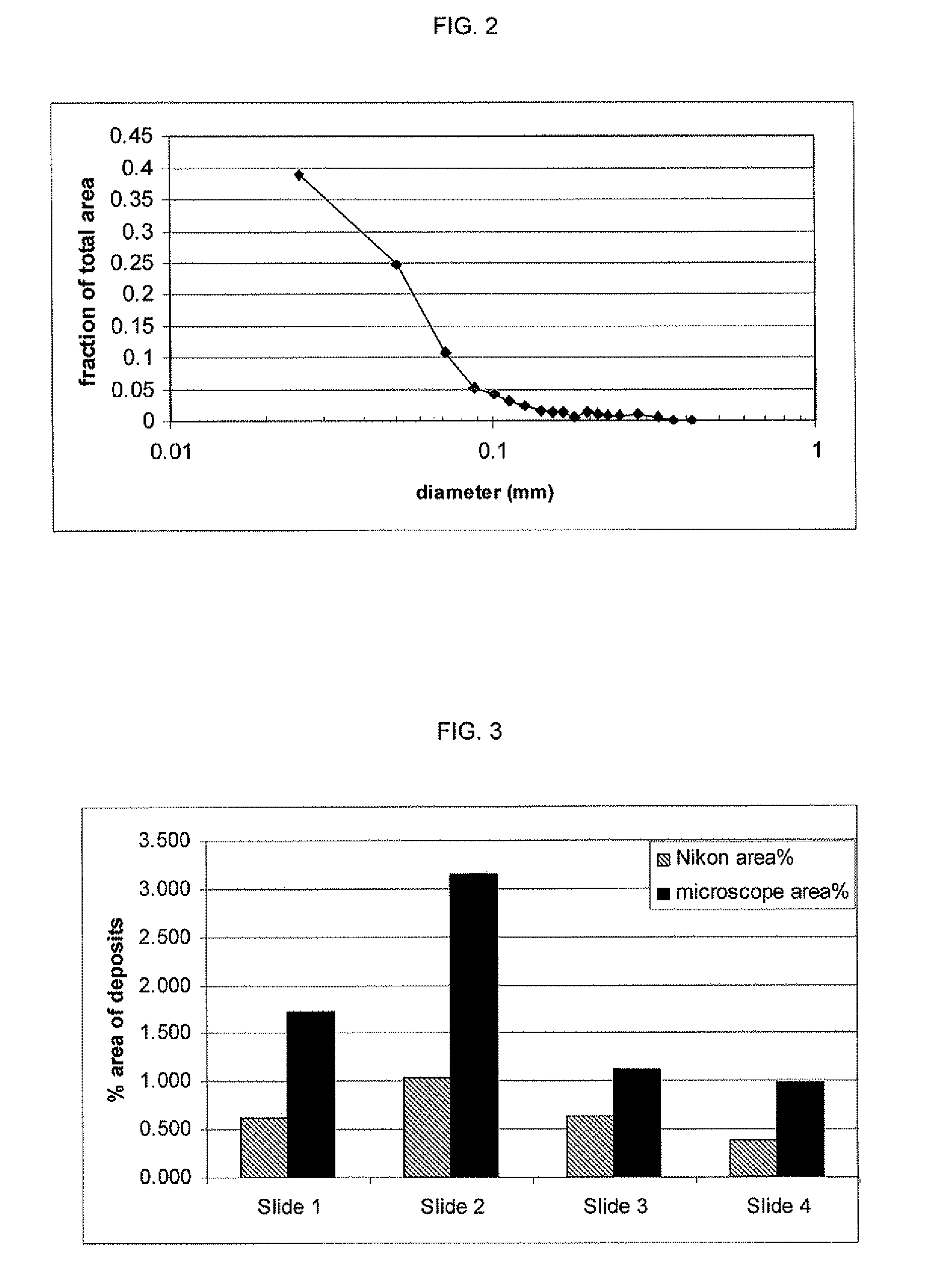
Method and apparatus for measuring deposition of particulate contaminants in pulp and paper slurries
ActiveUS8160305B2Non-fibrous pulp additionFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpParticulatesAdhesive
A method and an apparatus for measuring the depositability of particulate contaminants present in a pulp or paper mill fluid stream and evaluating interactions of such particulate contaminants with other contaminants collects the particulate contaminants on a suitable substrate, such as a plastic film coated with an adhesive or coated with organic contaminate, placed in contact with the pulp or paper mill fluid stream for at least five minutes up to several hours. The amount of contaminants collected on the substrate is quantified and evaluated by taking one or more scanned images of the substrate with a resolution of at least 2,000 dots per inch (DPI) and analyzing the scanned images with image analysis technique.
Owner:SOLENIS TECH CAYMAN
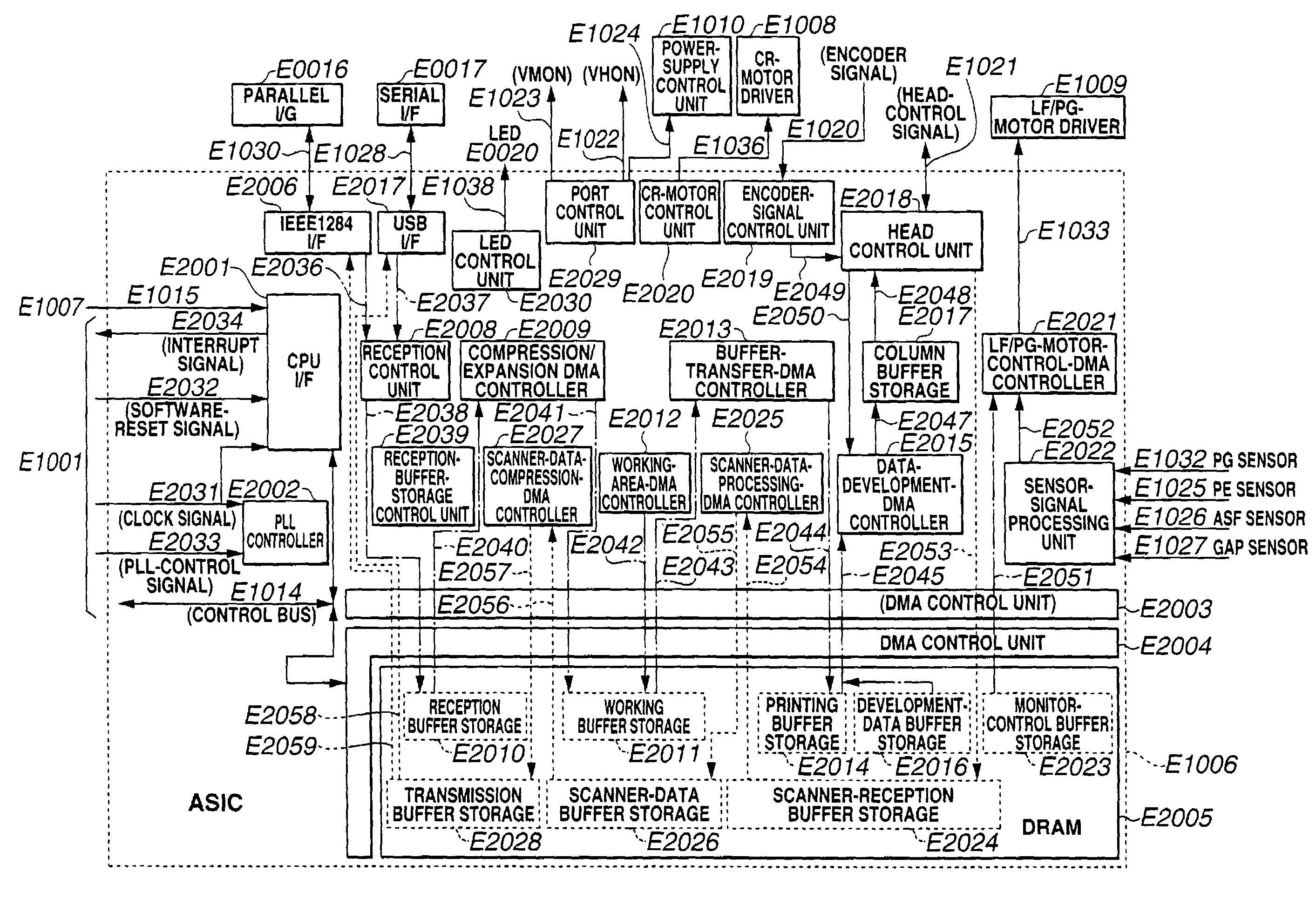
Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and printing apparatus and printing system using the image processing apparatus
InactiveUS7385730B2Reduce memory capacityReduce capacityDigitally marking record carriersVisual representation by matrix printersImaging processingImage resolution
In an apparatus for performing printing using a color ink-jet head having a plurality of ink-discharge-port strings corresponding to ink materials having different color tones, a high-quality image having excellent gradation can be recorded, while reducing the cost of the apparatus and increasing the data processing speed by reducing the capacity of a memory for storing dot arrangement patterns. For that purpose, as a plurality of dot arrangement patterns for determining dot arrangement at output within a M×N-dot region for one input pixel, (1) patterns having a large number of gradation levels that can be represented (for example, nine gradation levels) and a high recording resolution (for example, 1,200 dpi (dots per inch)×2,400 dpi) are used for colors in which uneven stripes tend to be pronouncedly observed (for example, light cyan and light magenta), and (2) patterns having a small number of gradation levels that can be represented (for example, five gradation levels) and a low recording resolution (for example, 1,200 dpi×1,200 dpi) are used for colors in which uneven stripes tend to be less pronouncedly observed (for example, black, cyan, magenta and yellow).
Owner:CANON KK
Display font size adjustment method and apparatus, and terminal device
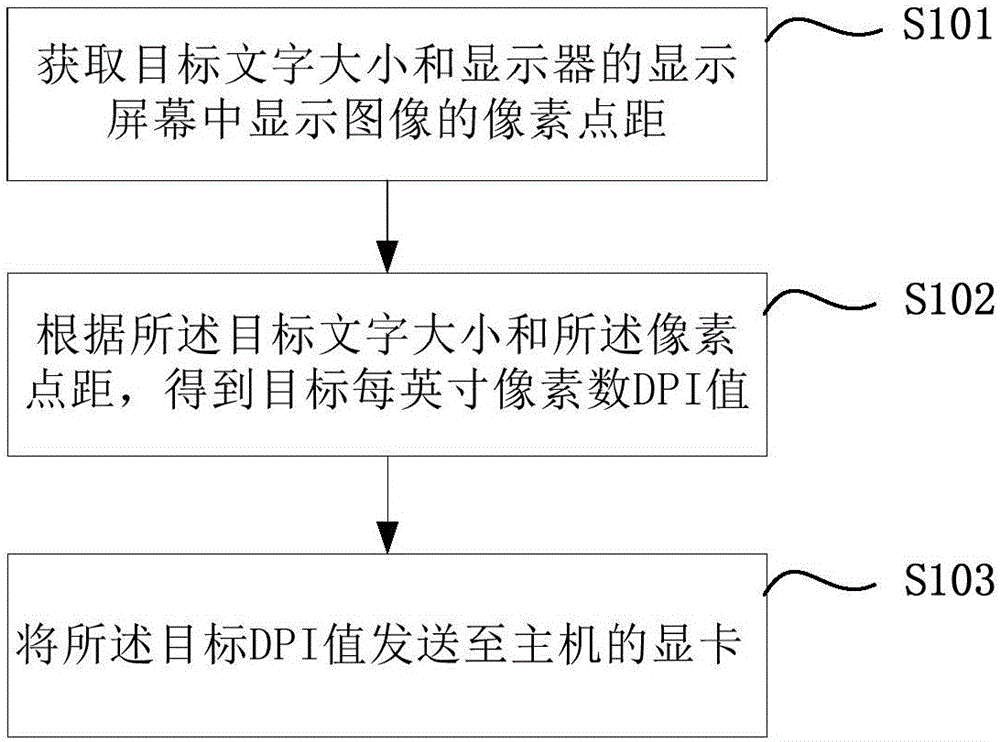
ActiveCN106383689AAvoid visual fatigueSize matchInput/output processes for data processingGraphic cardDisplay device
The invention relates to a display font size adjustment method and apparatus, and a terminal device. The method is applied to a display. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a target text size and a pixel dot spacing of a displayed image in a display screen of a display; obtaining a target dots-per-inch (DPI) value according to the target text size and the pixel dot spacing; and sending the target DPI value to a display card of a host. According to the display font size adjustment method and apparatus, and the terminal device provided by embodiments of the invention, the DPI value of a system text needed to be displayed in the display screen is calculated according to the optimal font size needed to be displayed in the display screen and suitable for a user to watch and the pixel dot spacing of the current display screen through the display, and the DPI value is sent to the display card, so that the display card can update the current DPI value to the target DPI value, the physical font size of the system text is increased and matched with the optimal font size suitable for the user to watch, and visual fatigue of the user is avoided.
Owner:HISENSE VISUAL TECH CO LTD
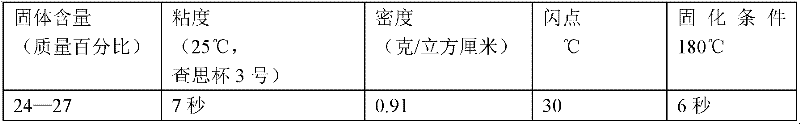
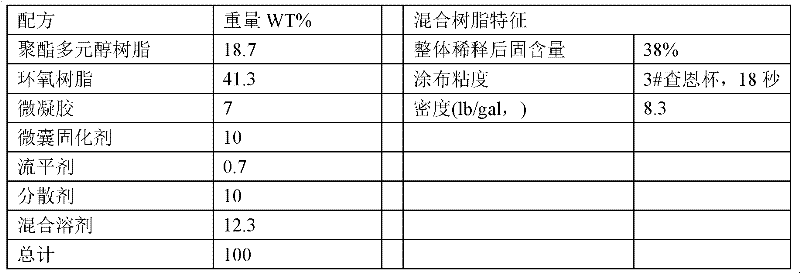
Thermal-transfer coloured crystal glass and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102179984AFine printingRealize large-scale industrial productionDuplicating/marking methodsSynthetic resin layered productsAcrylic resinBoPET
The invention provides thermal-transfer coloured crystal glass which can be used for printing fine texts and images and can realize scale industrial production and a preparation method of the thermal-transfer coloured crystal glass. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: carrying out corona treatment on a surface of a biaxially oriented polyester (BOPET) film; coating organic silicon resins, acrylic resins and a printing oil ink layer in a layered mode and coating a polyester and epoxy mixed resin layer to form a thermal-transfer coating film; hot-pressing a coating on the thermal-transfer coating film by hot-pressing equipment, and transferring the coating to the back of the glass; and carrying out heating and solidification to form thermal-transfer flat or curved coloured crystal glass. The thermal-transfer coloured crystal glass is characterized in that: the oil ink layer is high in high combination firmness, colour consistency is good, temperature resistance and weathering resistance are achieved, a long-term non-discolouring effect is achieved, the colour is uniform, the printing of the texts and the images is fine, and resolution reaches 600 dots per inch (dpi).
Owner:TEC HI PRINTING TECH
Method and apparatus for measuring deposition of particulate contaminants in pulp and paper slurries
ActiveUS20090141963A1Non-fibrous pulp additionFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpParticulatesImaging analysis
A method and an apparatus for measuring the depositability of particulate contaminants present in a pulp or paper mill fluid stream and evaluating interactions of such particulate contaminants with other contaminants collects the particulate contaminants on a suitable substrate, such as a plastic film coated with an adhesive or coated with organic contaminate, placed in contact with the pulp or paper mill fluid stream for at least five minutes up to several hours. The amount of contaminants collected on the substrate is quantified and evaluated by taking one or more scanned images of the substrate with a resolution of at least 2,000 dots per inch (DPI) and analyzing the scanned images with image analysis technique.
Owner:SOLENIS TECH CAYMAN
Digital multi-dimensional image photon platform system and methods of use
ActiveUS20160227184A1Quality improvementOvercome problemsAdditive manufacturing apparatusPattern printingParallaxOutput device
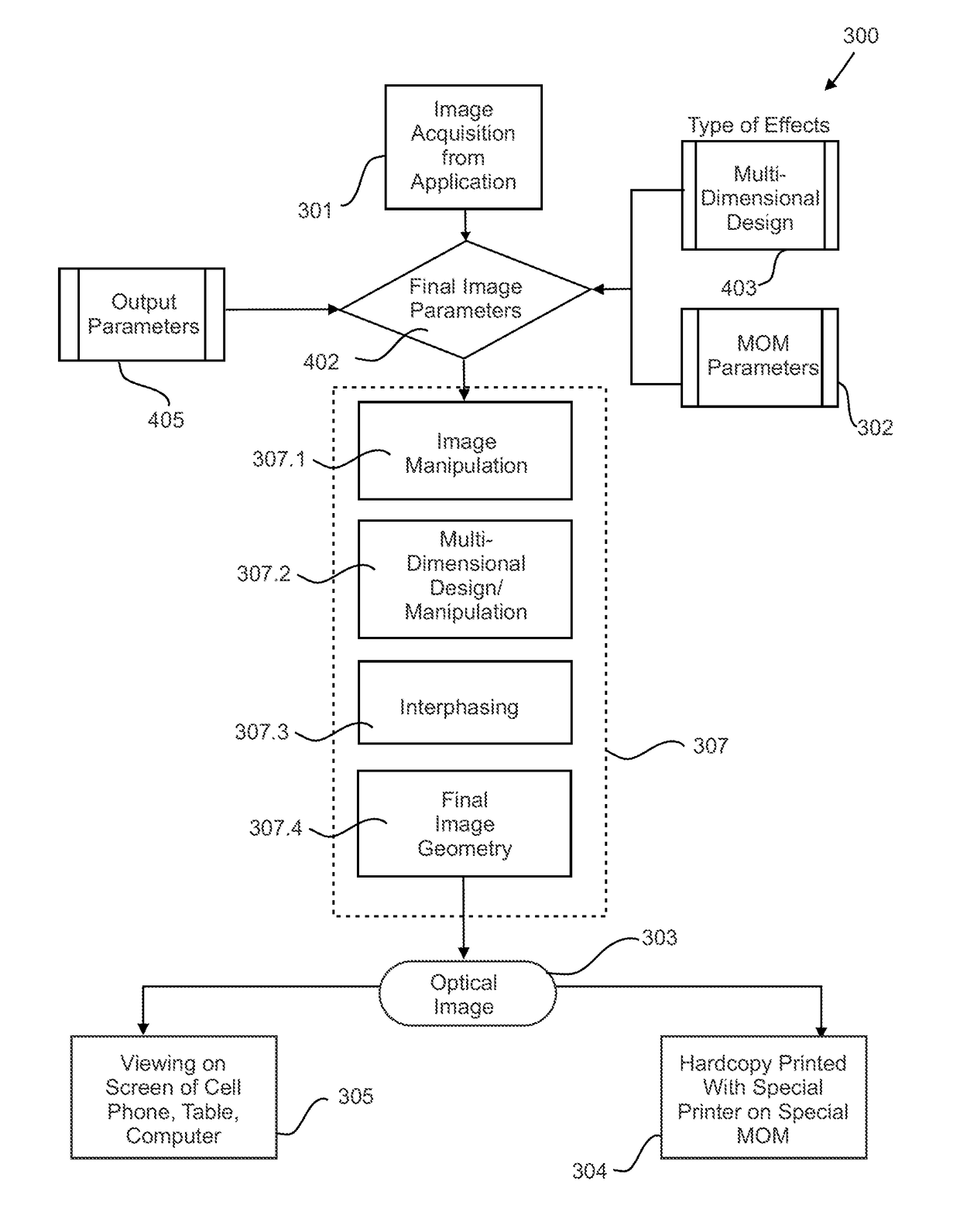
A systematic approach to producing multi-dimensional photon images on a computer platform having applications to input image(s) from various sources, and applications to coordinate and adjust numerous variables which determine the quality of the image, such as the size of the imported images, the output image size, the resolving power of the viewing screen and the width of the resolving elements, the dots per inch of the output device (or pixels per inch), the desired nearest object, the desired furthest object and the determination of the central or the “key subject”, rules of interphasing, the number of frames or layers, the minimum parallax, and the maximum parallax, and, thus, provide a digital multi-dimensional image without jumping images or fuzzy features or other visual distortions by creating high quality output images both in the form of a printed hardcopy or as a viewed image on an appropriate viewing device.
Owner:NIMS JERRY +2
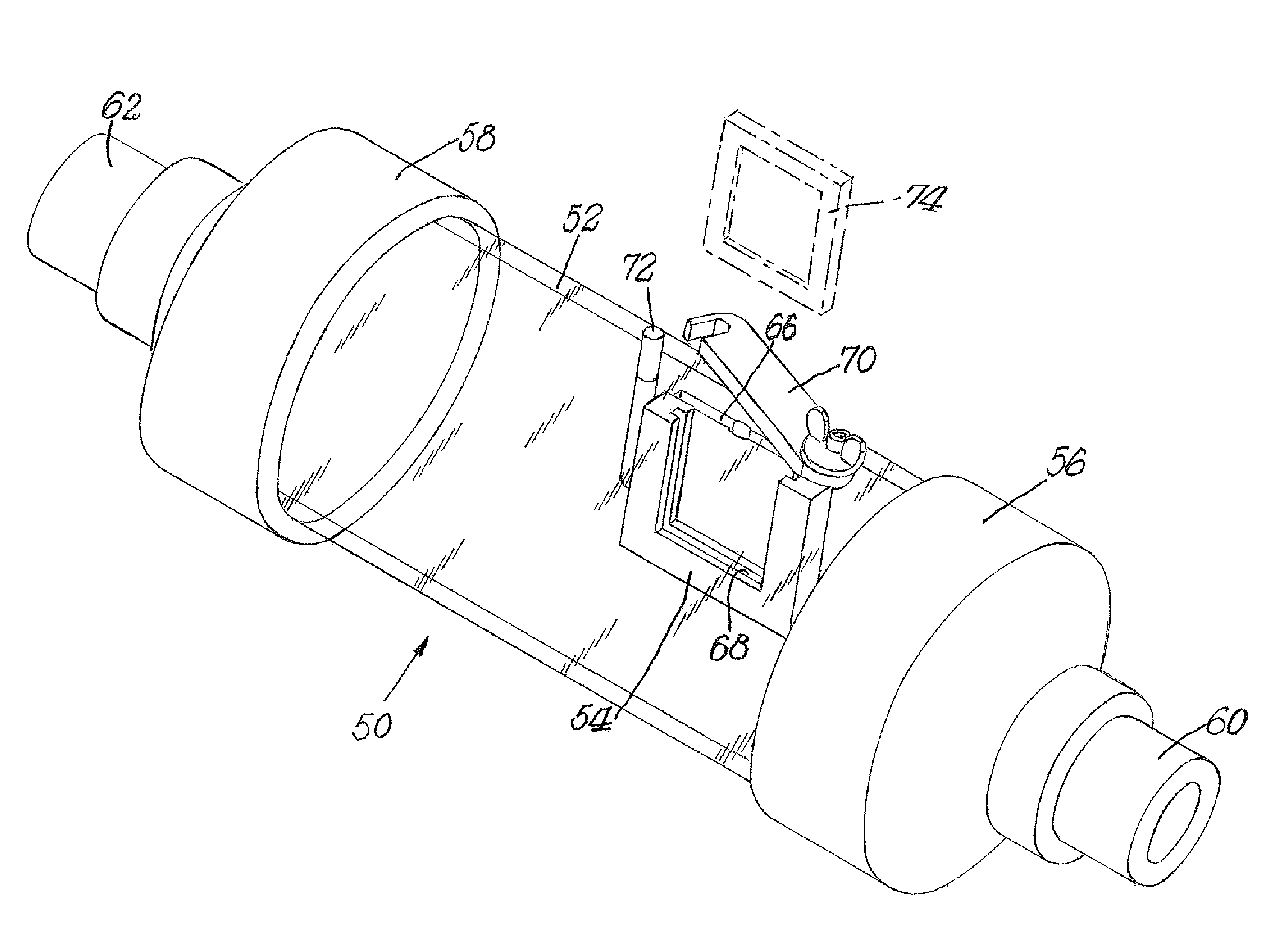
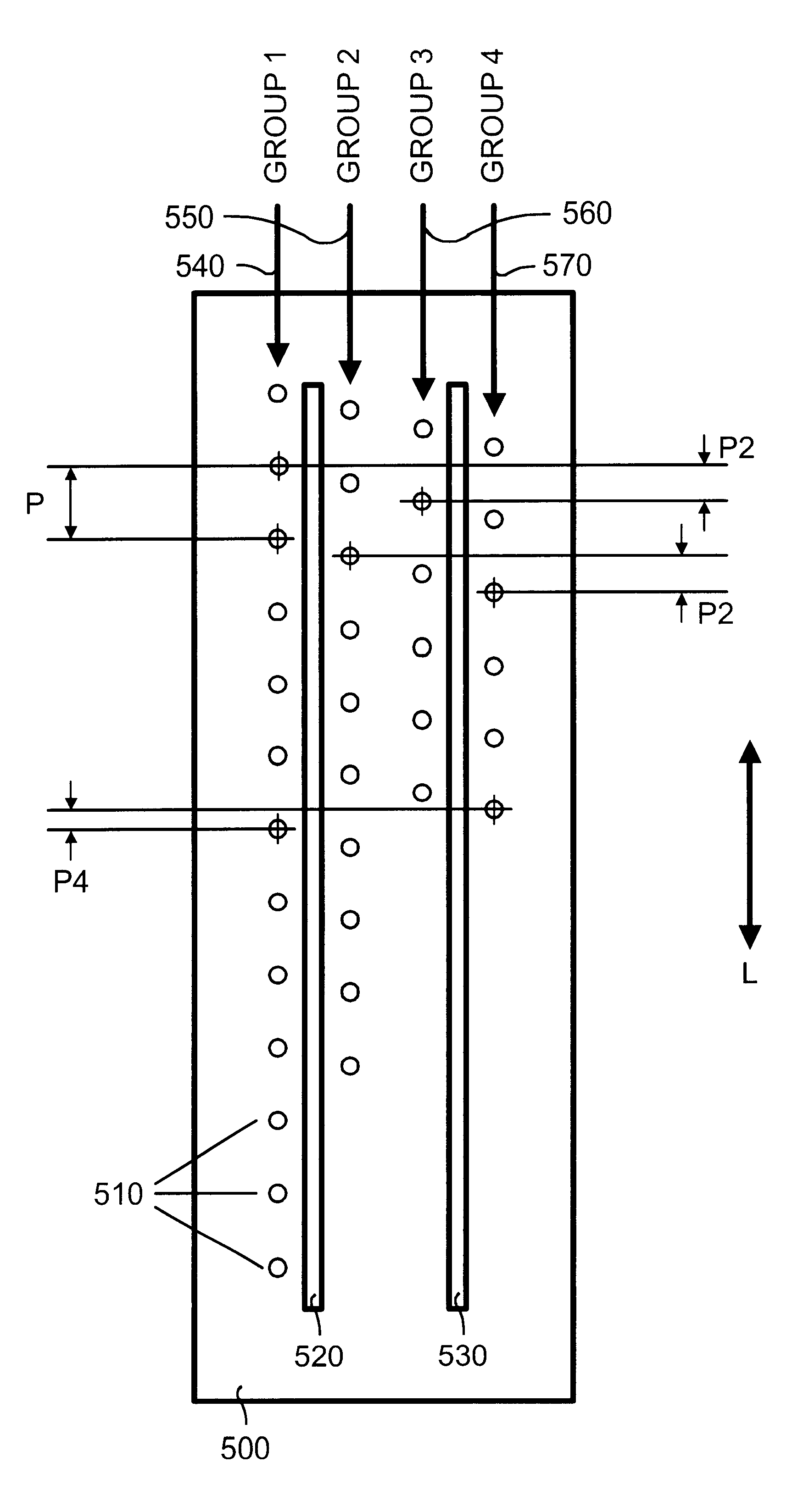
Fluid ejection device with staggered ink drop generators
The present invention includes as one embodiment a fluid ejection device coupled to an ink supply and having multiple printing modes, including a sufficient number of ink drop generators fluidically coupled to the ink supply device and formed in the fluid ejection device and arranged along at least three axes that are substantially parallel and spaced apart from each other to provided printing resolution of at least 600 dots per inch with each printing mode. The plurality of ink drop generators is arranged along four axes that are substantially parallel and spaced transverse to each other and wherein the plurality of ink drop generators arranged along the four axes are staggered with respect to each of the axes to decrease an effective pitch of the fluid ejection device to approximately one-fourth that of a plurality of ink drop generators arranged along a single axis.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
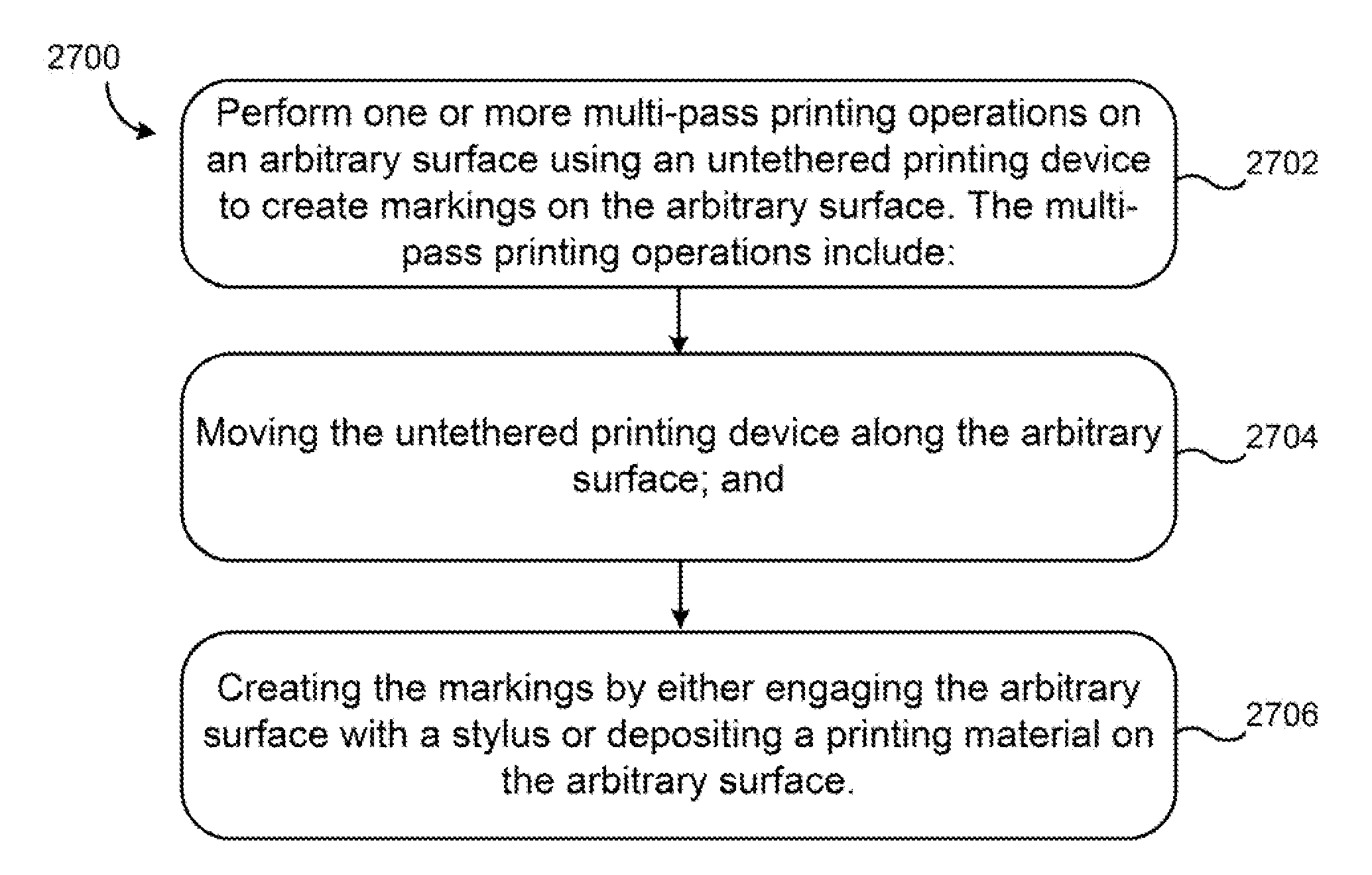
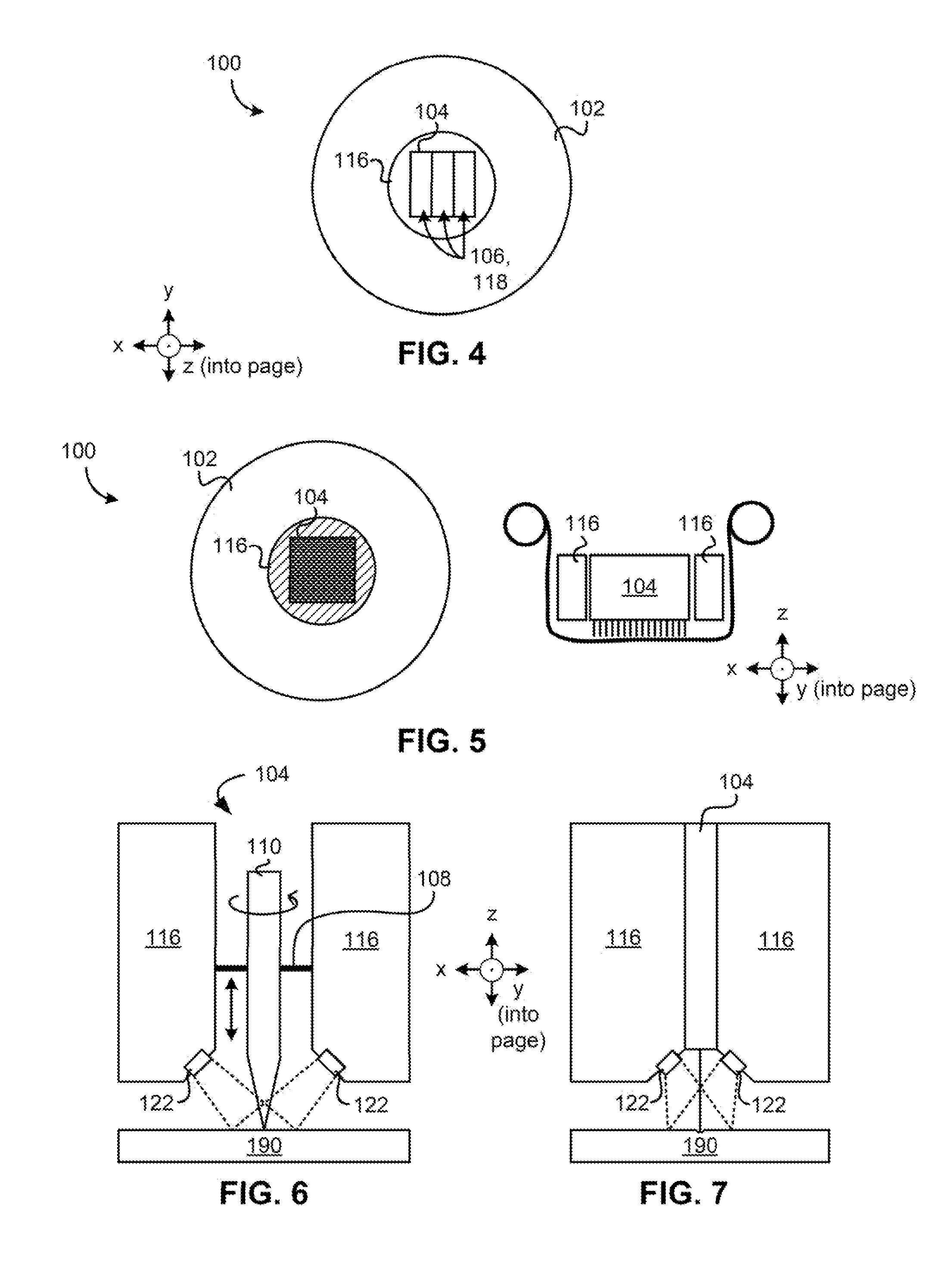
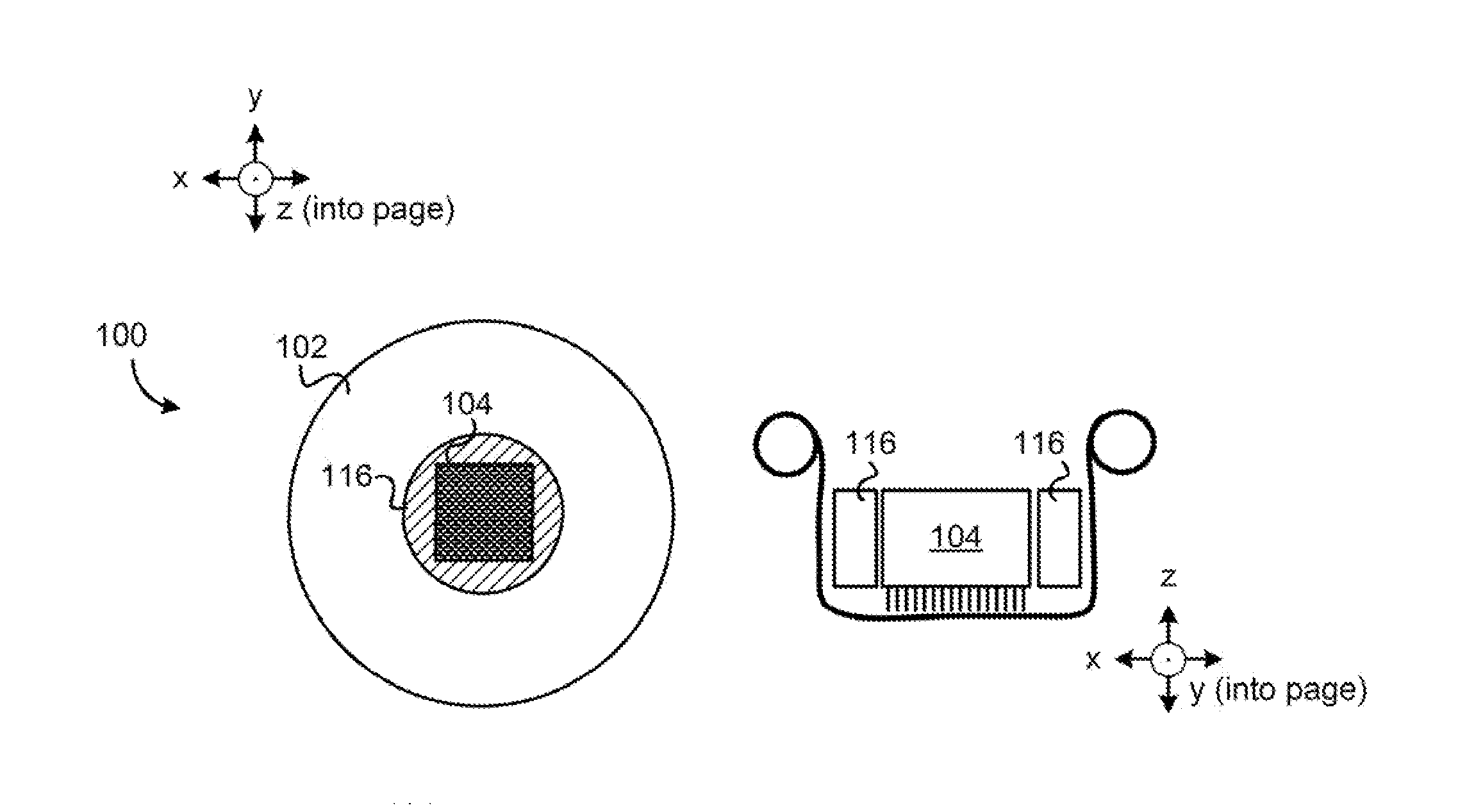
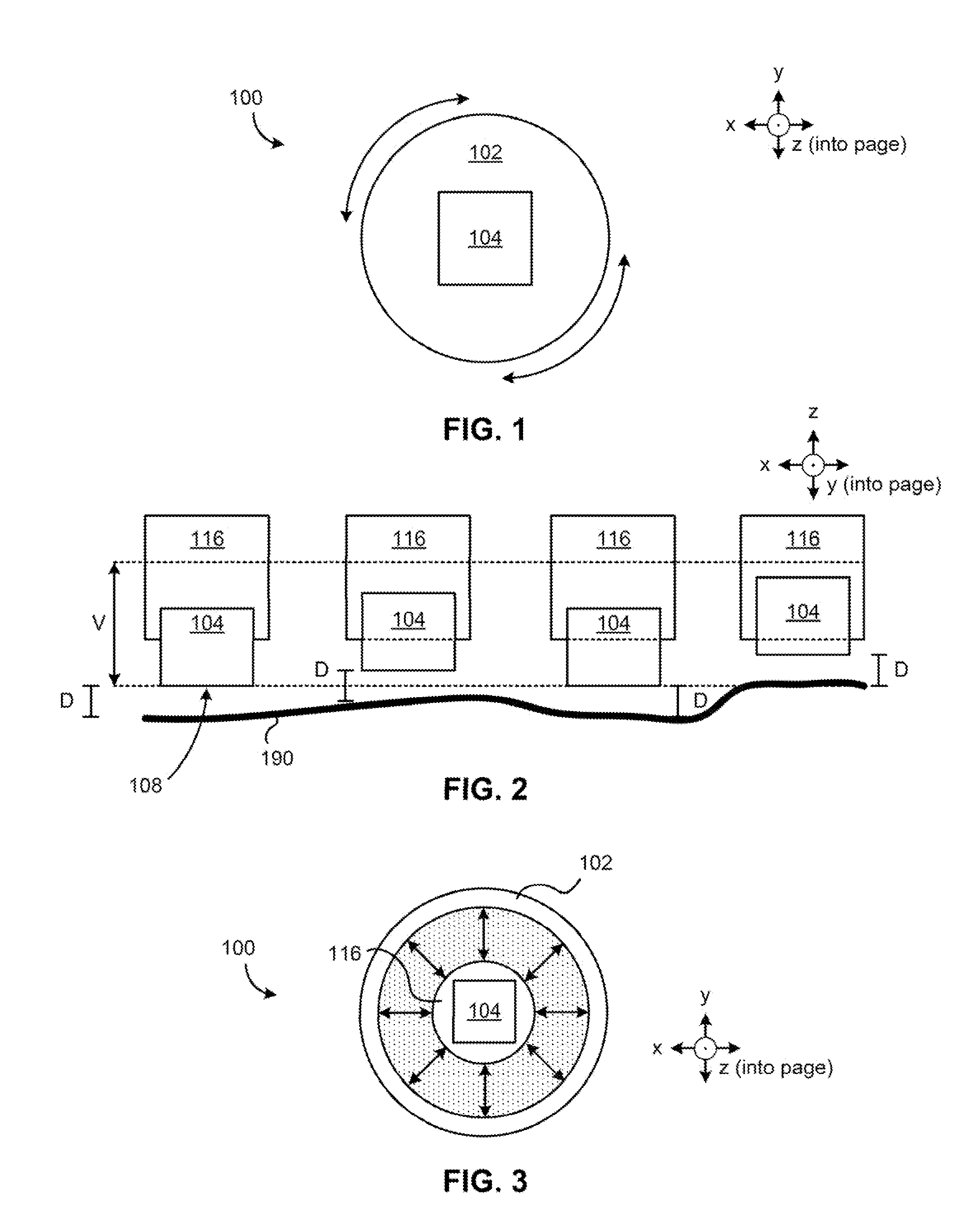
Arbitrary Surface Printing Device for Untethered Multi-Pass Printing
An untethered, arbitrary-surface printing device includes a housing, a print head, positioning means, locomotive means, and sensors configured to perform multi-pass high-precision printing (i.e. at least 300 dots per inch) on nearly any surface texture.
Owner:PRIYADARSHI ROHIT
Arbitrary Surface Printing Device for Untethered Multi-Pass Printing
InactiveUS20150186757A1Digitally marking record carriersVisual representation by matrix printersElectrical and Electronics engineeringDots per inch
An untethered, arbitrary-surface printing device includes a housing, a print head, positioning means, locomotive means, and sensors configured to perform multi-pass high-precision printing i.e. at least 300 dots per inch) on nearly an surface texture.
Owner:PRIYADARSHI ROHIT
Multipixel dots in monochrome drop-on-demand printing
Large, overlapping "mega-dots", placed on small, high resolution pixel locations, are used in high quality monochrome imaging to preserve information to the micro, or pixel, level, thus avoiding the need to use micro-sized droplets. By using multiple passes and multiple pens with different levels of gray ink, one may build a single monochrome 600 dpi (dots per inch) pixel with the composite gray of those droplets at that pixel location as well as the neighboring locations. With careful print modes and multiple passes, one can produce several levels of gray at a particular pixel location. The biggest advantage of using multipixel dots is that the sensitivity to trajectory errors is significantly reduced. For example, a dot that is +E,fra 1 / 150+EE th inch diameter is almost indifferent to a +E,fra 1 / 1200+EE th trajectory error. Even a relatively large +E,fra 1 / 600+EE th inch error has little impact on the large +E,fra 1 / 150+EE th dot (25% error). In reducing the sensitivity to trajectory errors, overall imaging errors, such as banding, can be reduced, and overall image quality enhanced. Optimally, the large dots have a diameter that is about three to five times the pixel size, providing an overlap of three to five dots, respectively.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
System for preparing prime label pressure sensitive intermediate laminates
InactiveUS20060260753A1Reduce preparation timeHigh image resolution productLamination ancillary operationsPaper/cardboard articlesGraphicsImage resolution
The present invention is in the field of composite manufacturing systems that are used in the preparation of articles, namely pressure sensitive laminates such as prime labels and tags. The system of the instant specification includes a computer for creating a file, an image generation means for rendering typically a graphical depiction on one or more surfaces of a substrate, an inserter for placing ribbon or label segments and a web processing apparatus. The labels of the present invention are produced in part, initially from a pre-imaged or printed sheet that are then converted or merged to a roll type of format. The sheets are printed with high quality graphics or images which are then slit or cut to size to form ribbons or label segments for the prime label application and then are converted to or merged with a continuously advancing web to create a continuous roll format. Then the label segments that have been affixed to the web are provided in one or more intermediate configurations to an end user typically for application to consumer packaged goods. More particularly, the pressure sensitive laminates of the instant application can be used to create individual, prime labels having a high or photo quality resolution level such as those about 300 lines per inch or approximately 2500 to 3500 dots per inch.
Owner:WARDKRAFT
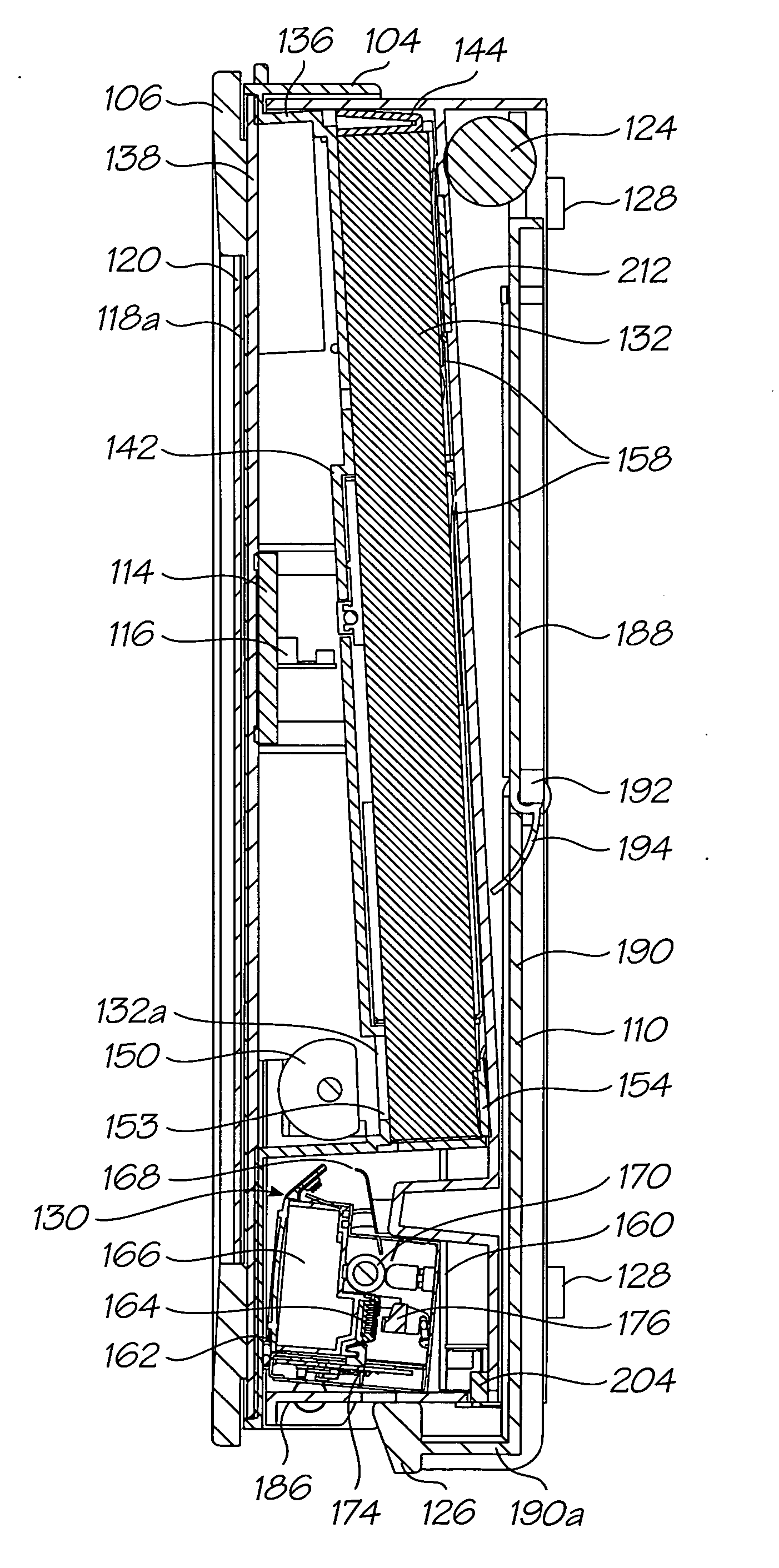
Wall mountable printer with removable cartridge
A printer unit is provided comprising a print engine incorporating a removable pagewidth printhead for printing on print media and a body arranged to house the print engine and to be mountable to a substantially vertical surface so as to suspend the printer unit. Such a wall mountable printer is capable of blending into the design of a home or a work space within office environment whilst providing high-speed, e.g., more than 30 pages per minute, and high-quality, e.g., images of about 1200 dots per inch or more, printing capabilities and ease of use.
Owner:MEMJET TECH LTD
Image amplification method and computer system
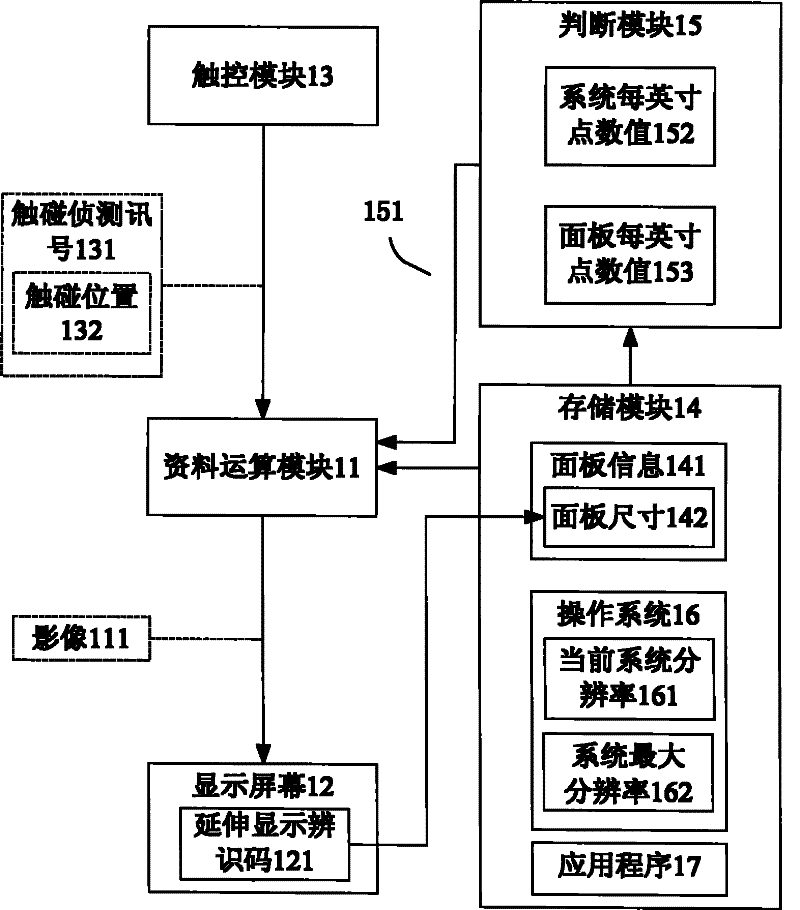
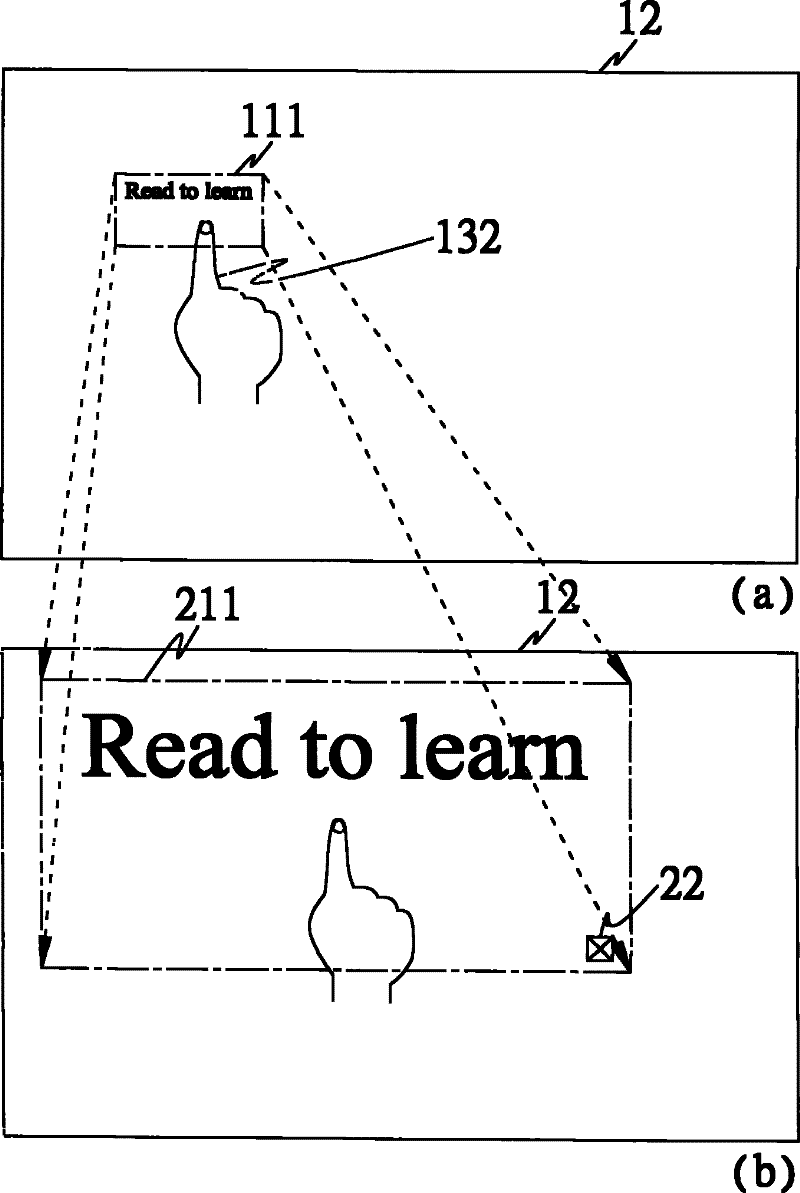
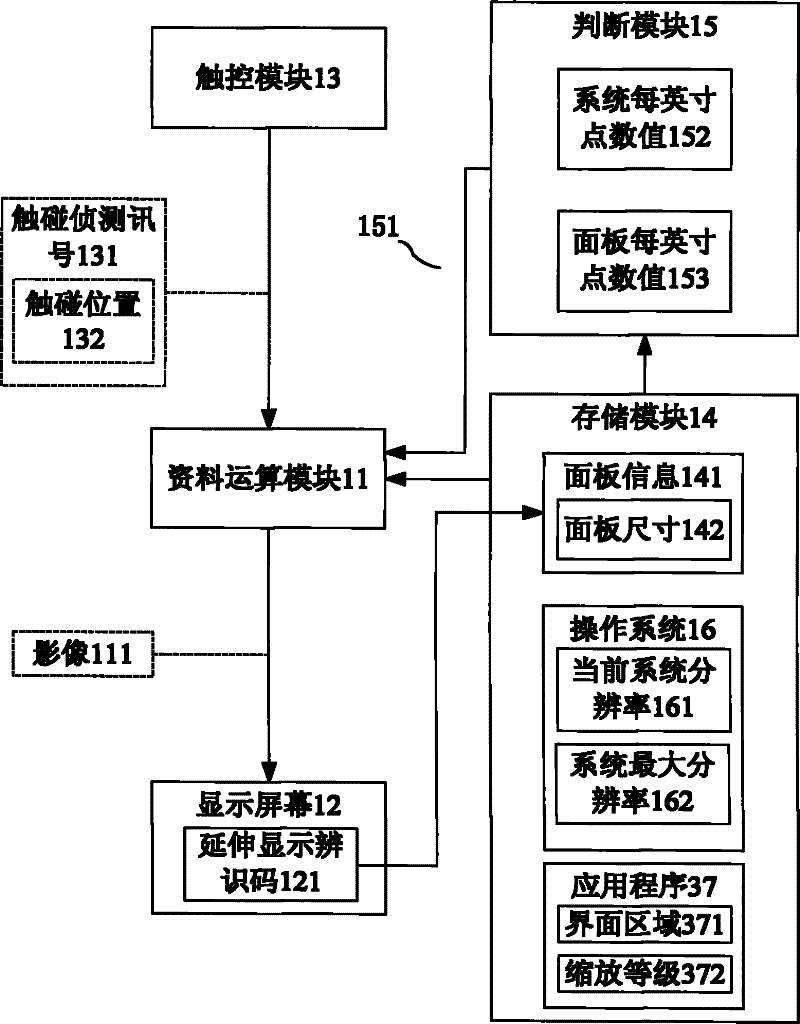
InactiveCN102129338AImprove convenienceImprove readabilityInput/output processes for data processingImage resolutionTouch Senses
The invention discloses an image amplification method and a computer system. The method comprises the following steps of: receiving a touch sensing signal comprising a touched position, and acquiring current system resolution and the panel information such as a panel size of a display screen; and judging whether an image displayed on the display screen is to be amplified or not according to the current system resolution and the panel information, and selectively amplifying the image according to a judgment result. In the embodiment, the image at the touched position of the display screen can be judged whether to be amplified or not by comparing the number of dots per inch (DPI) of the system with the number of DPI of a panel; or, when the touched position is a preset application program, the image can be judged whether to be amplified or not by comparing an interface zoom level of the preset application program with the number of DPI of the system.
Owner:ACER INC
Image forming method
InactiveUS20130229291A1High color reproductionSmall amount of streak defectDuplicating/marking methodsInksColor imageMeth-
The image forming method includes: applying two or more kinds of ink compositions having different hues onto a recording medium to form a multi-color image, each ink composition containing a pigment, water, and 5% by mass to 15% by mass of polyvalent (meth)acrylamide represented by the following formula (1) with respect to the total amount of the ink composition; and applying a treatment solution, containing an aggregation component onto the recording medium. In the image forming method, an average diameter φ1 (μm) of droplets of the ink compositions on the recording medium satisfies the following relational expression (1), and an application density of droplets having a minimum volume of ink composition on the recording medium is 80% or more (Q: n-valent linking group, R1: H, methyl group, n≧2).(2.54×10000 / R)×1.5≦φ1≦(2.54×10000 / R)×1.7 Relational Expression (1)wherein, R represents a resolution (dot per inch) of an image.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
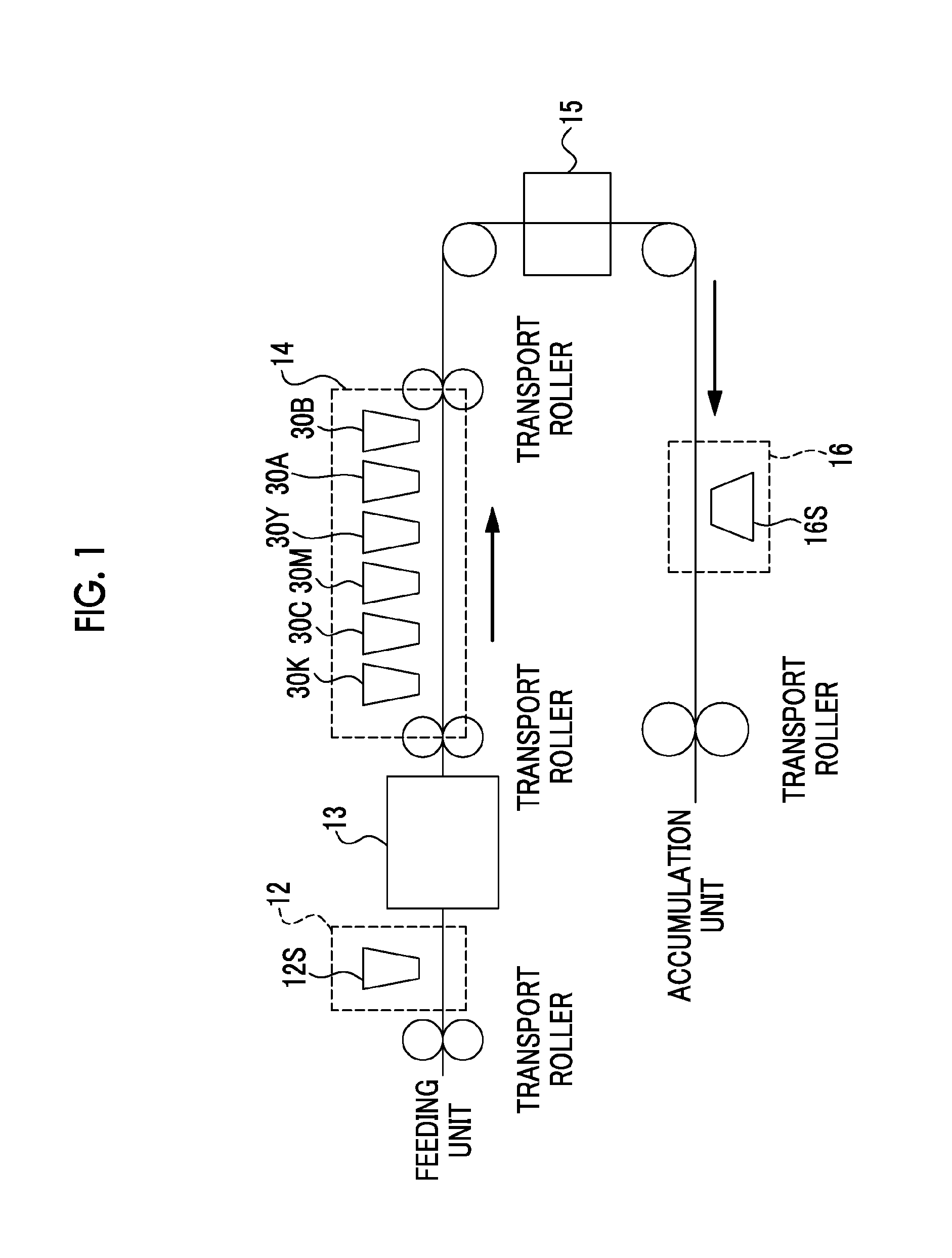
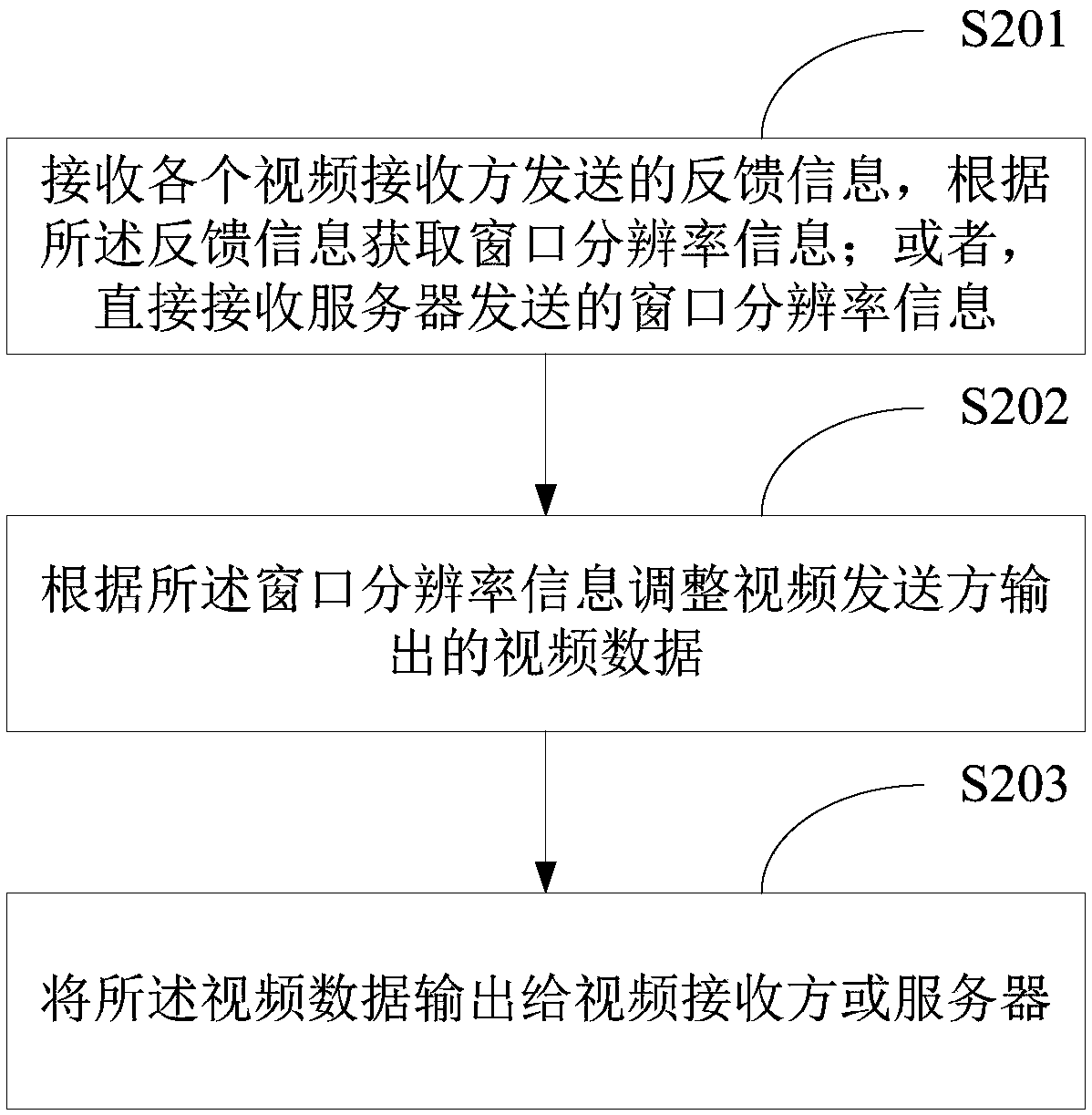
Video transmission system and receiving/sending/transmission methods and devices
ActiveCN108600834ADoes not affect playback qualitySave transmission bandwidthTelevision conference systemsTwo-way working systemsImage resolutionVideo transmission
The invention is applicable to the technical field of communication, and provides a video transmission system and receiving / sending / transmission methods and devices. The video receiving method comprises the steps of: acquiring display window information of each video receiver in real time, wherein the display window information comprises a DPI (Dots Per Inch) parameter of the receiver and the sizeof a display window of the receiver; when the display window information is changed, calculating feedback information of each video receiver according to the display window information of each videoreceiver; sending the feedback information of each video receiver to a video sender or a server, wherein the feedback information is used for regulating video data output by the video sender; and receiving the video data output by the video sender or the server and playing the video data in the display window of each video receiver. In the method, the video sender can display environment information according to a video of the receiver, and a resolution of the video sent out by the video sender is regulated, so that a transmission bandwidth is saved when playing quality is not influenced.
Owner:SHENZHEN INPOR CLOUD COMPUTING CO LTD
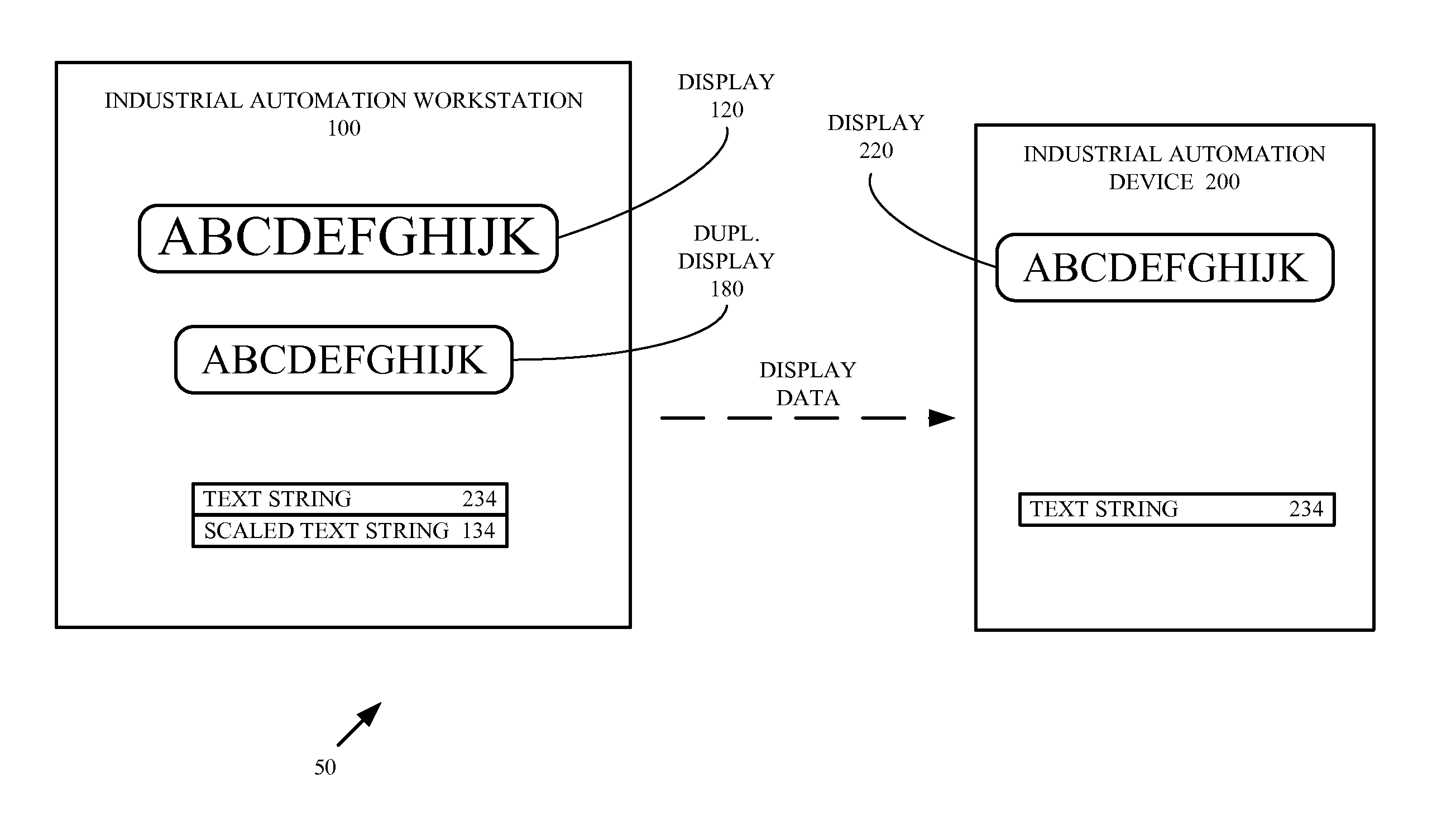
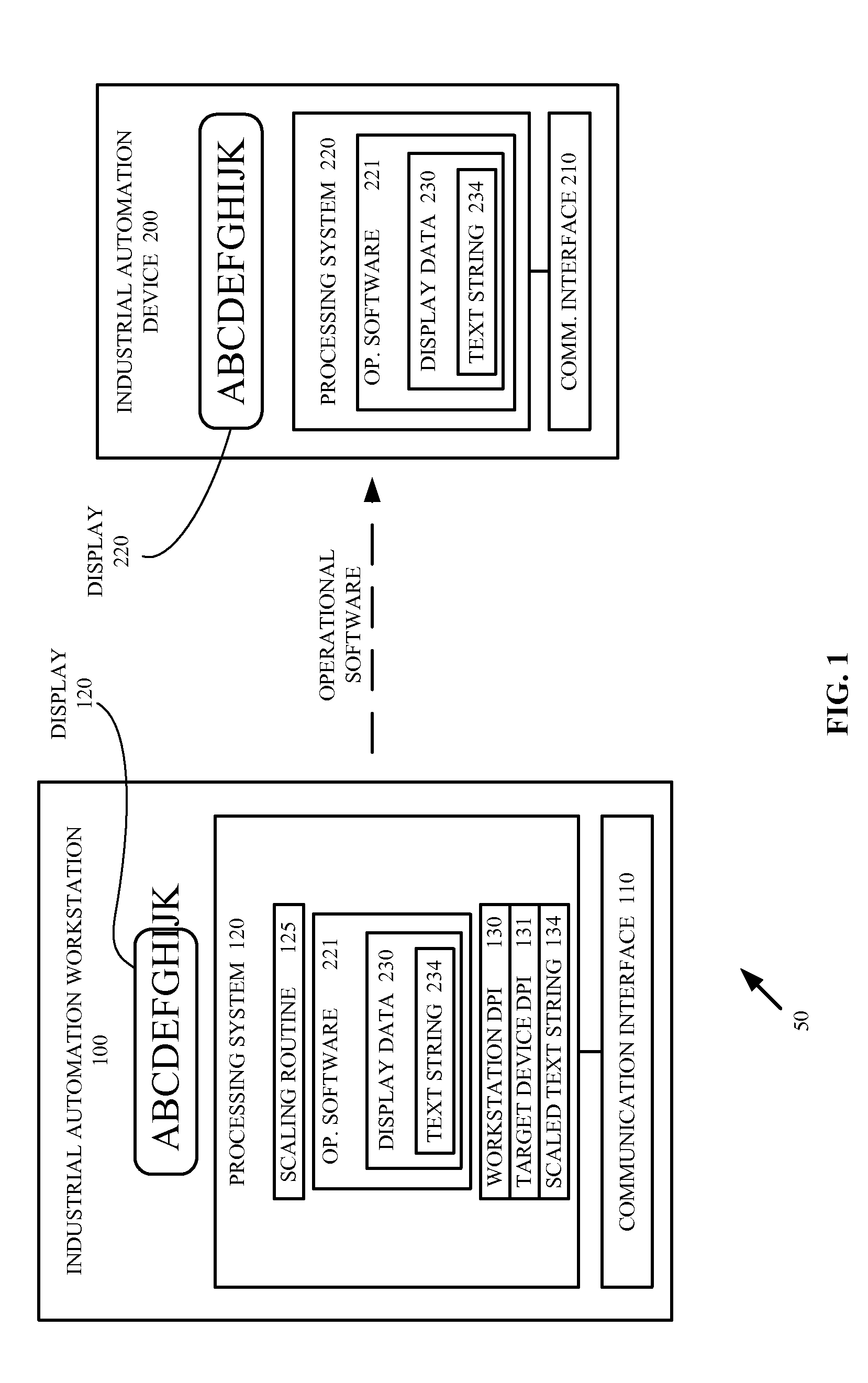
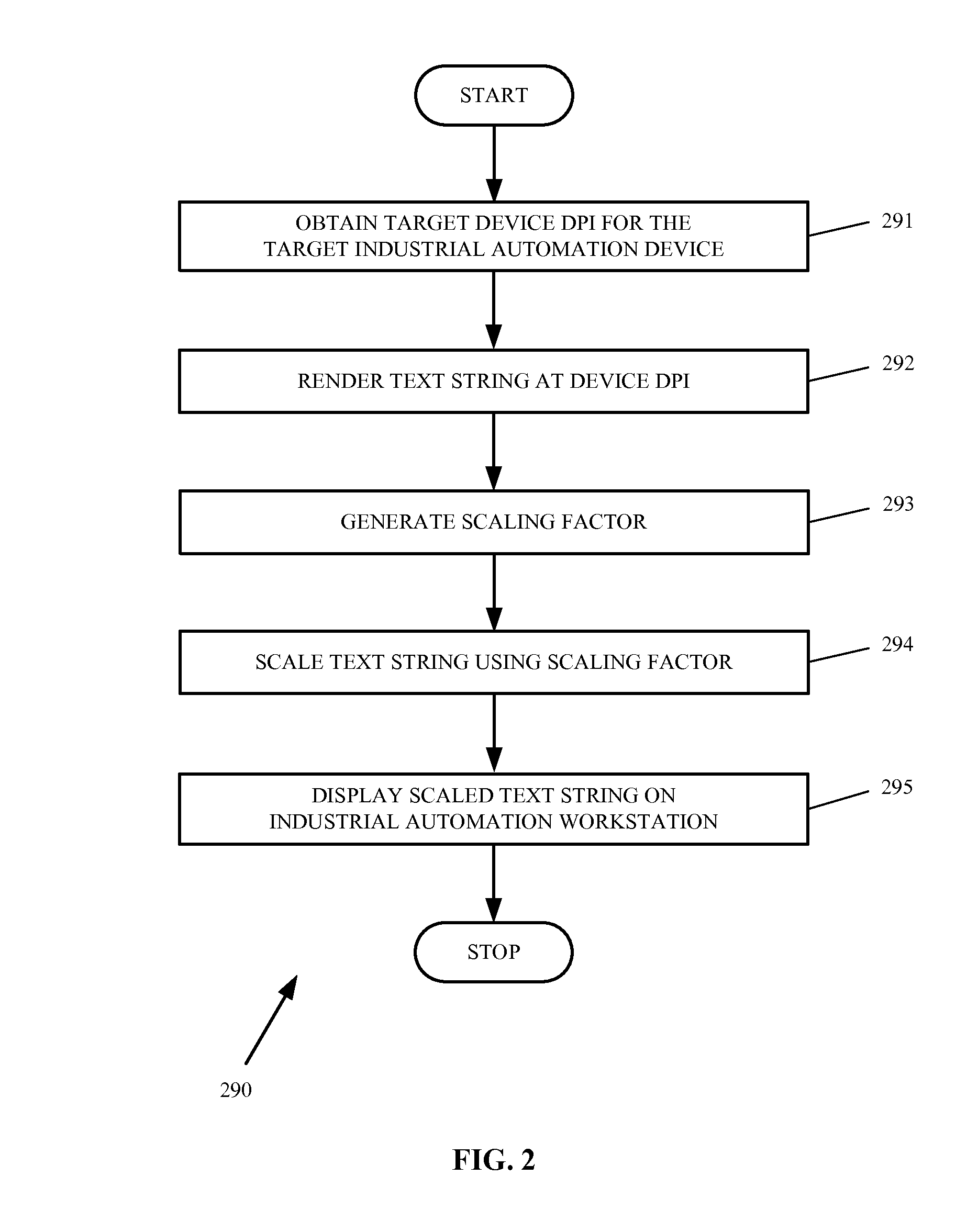
Industrial automation workstation and display method for scaling and displaying text destined for a target industrial automation device
ActiveUS20150121207A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsNatural language data processingCommunication interfaceDisplay device
An industrial automation workstation and display method for scaling and displaying text destined for a target industrial automation device are provided. The industrial automation workstation in one example embodiment includes a communication interface configured to transfer a display data including at least one text string to the industrial automation device and a processing system configured to obtain a target device dots-per-inch (DPI) for a display device of the industrial automation device, render the at least one text string at the device DPI, generate a scaling factor comprising a ratio of a workstation DPI divided by the target device DPI, scale the at least one text string using the scaling factor and generate a scaled text string, and display the scaled text string on a display device of the industrial automation workstation.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
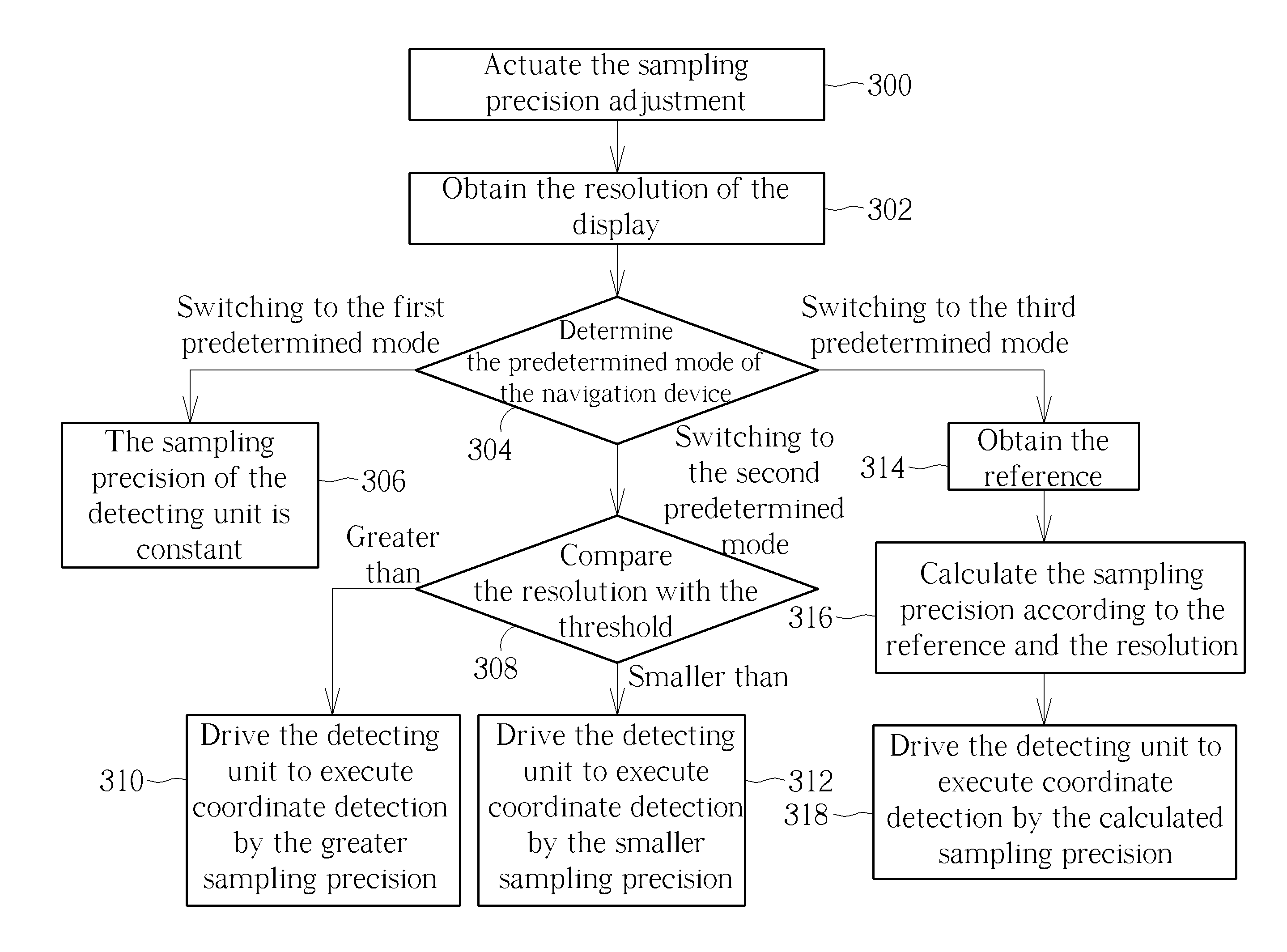
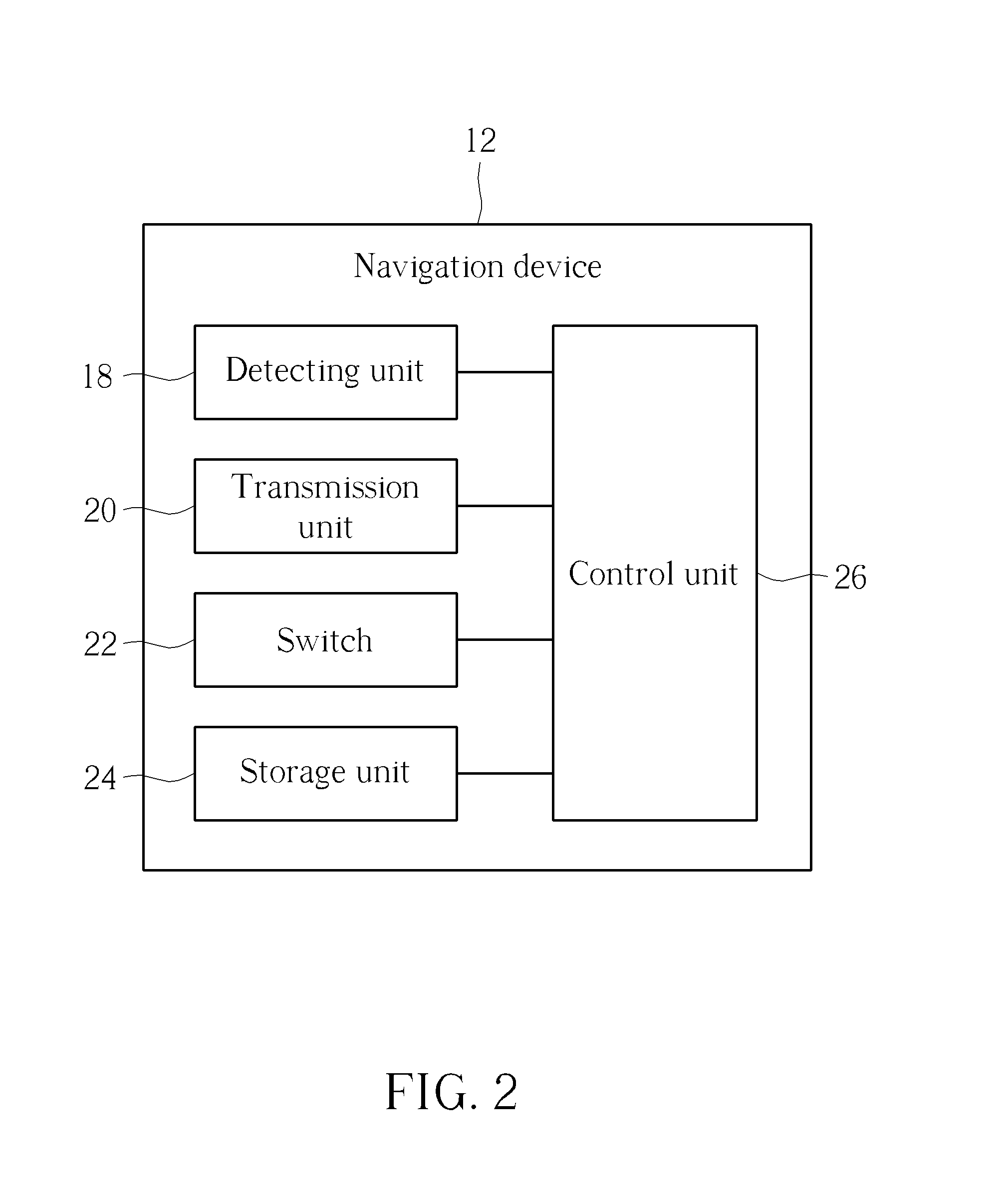
Method of adjusting sampling precision of a navigation device, related navigation device and related terminal device
ActiveUS20150097779A1Improve operational convenienceImprove market competitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingImage resolutionTerminal equipment
A method of adjusting sampling precision of a navigation device is disclosed in the present invention. The sampling precision represents counts per inch (CPI) or dots per inch (DPI) of the navigation device. The method includes determining a predetermined mode of the navigation device, obtaining resolution of a display, and adjusting the sampling precision according to the resolution and the predetermined mode, so that the sampling precision of the navigation device can be accordingly increased and decreased due to variation of the resolution.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
Digital multi-dimensional image photon platform system and methods of use
ActiveUS10178247B2Quality improvementOvercome problemsOptical articlesStereoscopic photographyOutput deviceMulti dimensional
Owner:NIMS JERRY +2
Manufacturing process of multi-point touch single-layer film touch sensor
InactiveCN103914199AReduce configurationSave configuration spaceInput/output processes for data processingChemical solutionAdhesive
The invention relates to a manufacturing process of a multi-point touch single-layer film touch sensor. The process is based on a three-dimensional (3D) printing process to perform layering printing on functional images of the sensor by starting from the bottom layer and overlaying the images layer by layer; after the functional images are formed, the functional images are glued to optical adhesive to be subjected to de-foaming, cutting and forming, and the manufacturing process of the multi-point touch single-layer film touch sensor can be achieved. The manufacturing process of the multi-point touch single-layer film touch sensor has the advantages that the process is single, configuration space of a factory is small, a single 3D printer device is merely required, personnel allocation is small, and producing costs are sharply reduced; the utilization ratio of raw materials is high, and consumables are used for solid printing of functional zone patterns by nearly 100%; proofing can be rapidly achieved, and the production cycle is shortened; the production line is quite short, deficient manufacturing procedure factors are few, and the product yield of the manufacturing process is higher than that of traditional processes; chemical solution treatment is absent, and producing costs are further lowered compared with those of the traditional processes; different dots per inch (dpi), each layer film thickness and the number of layers are set on a 3D printer to manufacture electrode patterns with different impedances.
Owner:FUJIAN BAOFA PHOTOELECTRIC TECH
Digital multi-dimensional image photon platform system and methods of use
ActiveUS10033990B2Quality improvementOvercome problemsSteroscopic systems3D modellingOutput deviceVisual perception
A systematic approach to producing multi-dimensional photon images on a computer platform having applications to a plurality of input image(s) from various sources, and applications to coordinate and adjust numerous variables which determine the quality of the image, such as the size of the imported images, the output image size, the resolving power of the viewing screen and the width of the resolving elements, the dots per inch of the output device (or pixels per inch), the desired nearest object, the desired furthest object and the determination of the central or the “key subject”, rules of interphasing, the number of frames or layers, the minimum parallax, and the maximum parallax, and, thus, provide a digital multi-dimensional image without jumping images or fuzzy features or other visual distortions by creating high quality output images both in the form of a printed hardcopy or as a viewed image on an appropriate viewing device. The digital multi-dimensional image platform based system controls the position and path of light from the original object to the human visual system.
Owner:NIMS JERRY +2
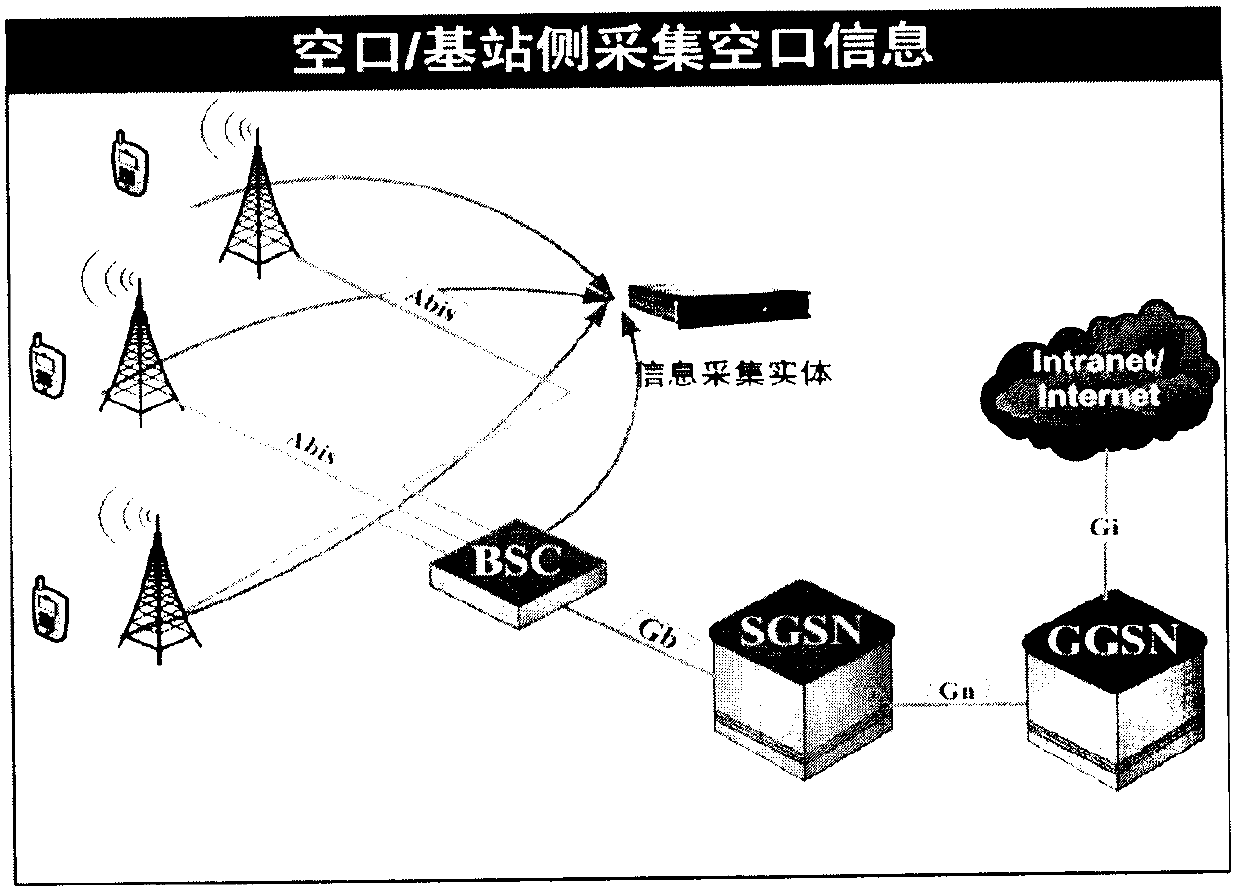
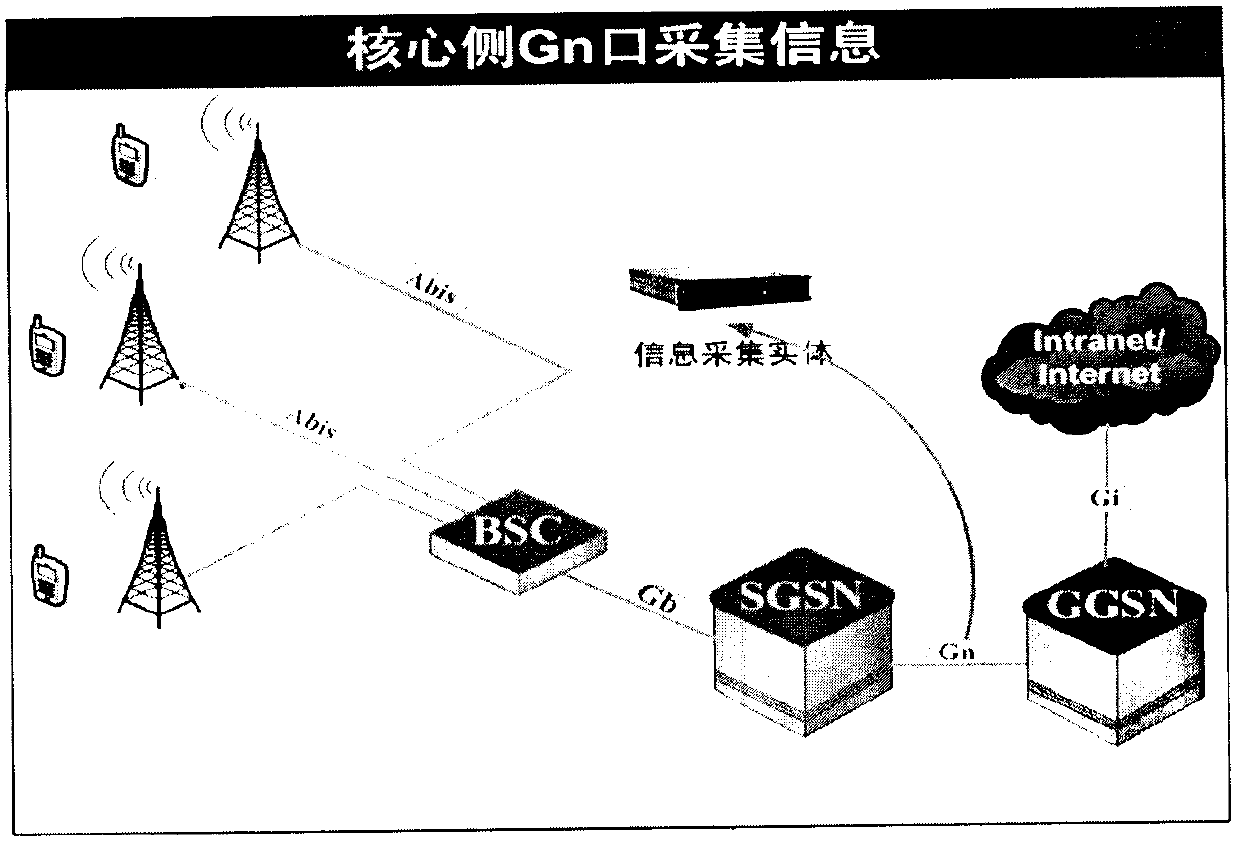
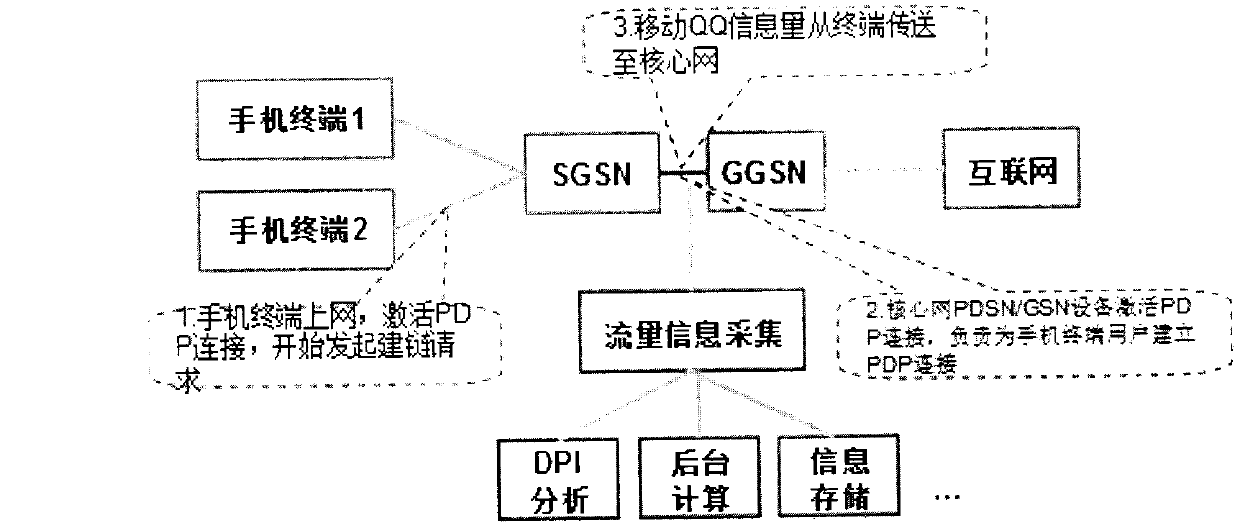
Mobile QQ air interface occupying period calculation method based on dot per inch (DPI) and through conservation of amount of information in general packet radio service (GPRS) environment
InactiveCN102984212AData switching networksWireless communicationGeneral Packet Radio ServiceAir interface
A mobile QQ air interface occupying period calculation method based on dot per inch (DPI) and through conservation of the amount of information in a general packet radio service (GPRS) environment is realized by adding a novel entity between a gateway GPRS support node (GGSN) and a service GPRS supporting node (SGSN) on existing network architecture. Two traditional methods, namely carrying out a drive test (DT) in an air interface and querying base station equipment (both the methods have drawbacks), can be used for acquiring information about air interface resources occupied by a mobile internet user. Currently, most operators build mobile core network DPI systems already; under the premise that no DT instrument is used or a base station resource query function is opened, with the aid of the core network DPI systems built by the operators already, by utilizing acquired application information amount of all core networks, through the DPI technology, with the aid of conservation law of the amount of information, a system can calculate the amount of information carried by the air interface; and then based on a standard rate of GPRS timeslots, the system can calculate air interface resources needed for transmitting the amount of information. Through the calculation method, GPRS air interface resource occupying conditions can be simply, conveniently and quickly calculated so that building cost of an air interface resource monitoring system can be significantly reduced.
Owner:苏州创讯信息科技有限公司
Digital multi-dimensional image photon platform system and methods of use
ActiveUS20160227185A1Quality improvementOvercome problemsSteroscopic systemsOutput deviceMulti dimensional
A systematic approach to producing multi-dimensional photon images on a computer platform having applications to a plurality of input image(s) from various sources, and applications to coordinate and adjust numerous variables which determine the quality of the image, such as the size of the imported images, the output image size, the resolving power of the viewing screen and the width of the resolving elements, the dots per inch of the output device (or pixels per inch), the desired nearest object, the desired furthest object and the determination of the central or the “key subject”, rules of interphasing, the number of frames or layers, the minimum parallax, and the maximum parallax, and, thus, provide a digital multi-dimensional image without jumping images or fuzzy features or other visual distortions by creating high quality output images both in the form of a printed hardcopy or as a viewed image on an appropriate viewing device. The digital multi-dimensional image platform based system controls the position and path of light from the original object to the human visual system.
Owner:NIMS JERRY +2
Digital multi-dimensional image photon platform system and methods of use
ActiveUS20180288241A1Quality improvementOvercome problemsOptical articlesStereoscopic photographyOutput deviceMulti dimensional
A systematic approach to producing multi-dimensional photon images on a computer platform having applications to a plurality of input image(s) from various sources, and applications to coordinate and adjust numerous variables which determine the quality of the image, such as the size of the imported images, the output image size, the resolving power of the viewing screen and the width of the resolving elements, the dots per inch of the output device (or pixels per inch), the desired nearest object, the desired furthest object and the determination of the central or the “key subject”, rules of interphasing, the number of frames or layers, the minimum parallax, and the maximum parallax, and, thus, provide a digital multi-dimensional image without jumping images or fuzzy features or other visual distortions by creating high quality output images both in the form of a printed hardcopy or as a viewed image on an appropriate viewing device. The digital multi-dimensional image platform based system controls the position and path of light from the original object to the human visual system.
Owner:NIMS JERRY +2
Method and device of displaying icon
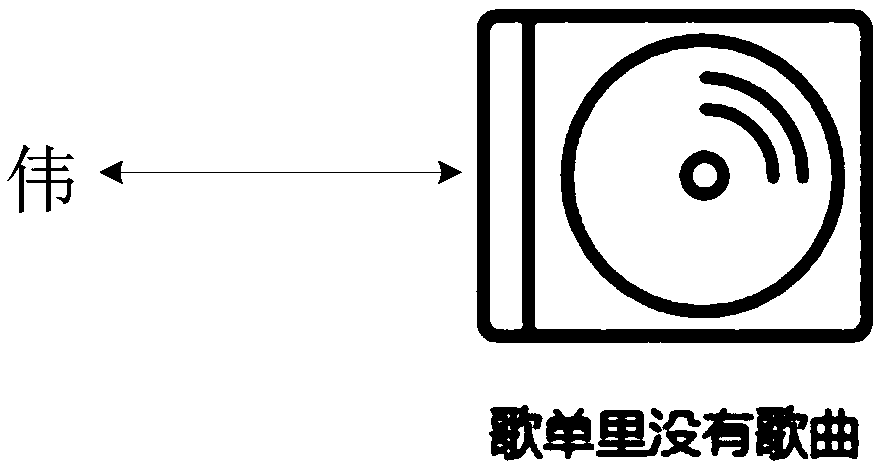
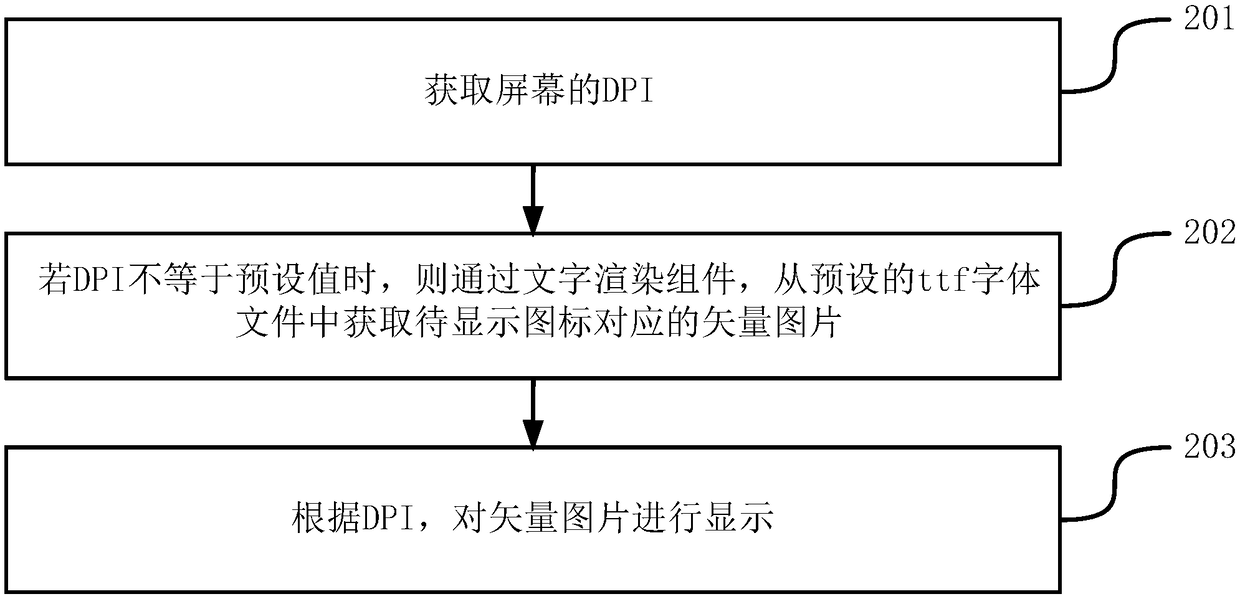
ActiveCN108734662ANot blurredImprove efficiencyTexturing/coloringGeometric image transformationDots per inchComputer technology
The invention provides a method and a device of displaying an icon, and belongs to the field of computer technology. The method includes: acquiring DPI (dots per inch) of a screen; and if the DPI is not equal to a preset value, acquiring a vector picture, which corresponds to the to-be-displayed icon, from a preset ttf font file through a text rendering component, and displaying the vector pictureaccording to the DPI. By adopting the method, occupied storage resources can be enabled to be fewer.
Owner:TENCENT MUSIC ENTERTAINMENT TECH SHENZHEN CO LTD
Digital multi-dimensional image photon platform system and methods of use
ActiveUS9992473B2Quality improvementOvercome problemsAdditive manufacturing apparatusPattern printingParallaxOutput device
A systematic approach to producing multi-dimensional photon images on a computer platform having applications to input image(s) from various sources, and applications to coordinate and adjust numerous variables which determine the quality of the image, such as the size of the imported images, the output image size, the resolving power of the viewing screen and the width of the resolving elements, the dots per inch of the output device (or pixels per inch), the desired nearest object, the desired furthest object and the determination of the central or the “key subject”, rules of interphasing, the number of frames or layers, the minimum parallax, and the maximum parallax, and, thus, provide a digital multi-dimensional image without jumping images or fuzzy features or other visual distortions by creating high quality output images both in the form of a printed hardcopy or as a viewed image on an appropriate viewing device.
Owner:NIMS JERRY +2
Method and apparatus for high-speed inkjet printing
InactiveUS20100085595A1Visual presentation using printersOther printing apparatus8-bit colorUV curing
Image data for printing an image on a printable medium at high speed with an inkjet printer is received in memory in the form of 512 pixels, or a multiple thereof, wide with a resolution of 360 dots per inch, and saved as an 8 bit color TIFF file with no compression and thereafter stripped into multiple printing columns, one for each color, the columns being positioned in a printing flow order with a spacing between columns of 512 pixels, or a multiple thereof, and then this stripped image data is saved as a four bit bitmap file. The printing medium objects are sequentially conveyed under the printheads whereby the stripped image data is printed onto the printing medium by the inkjet nozzle columns to generate the image. UV ink is employed, together with a UV curing light source to provide high-speed curing.
Owner:DEETS II ROBERT M
VoIP (voice over internet protocol) control system and VoIP control method
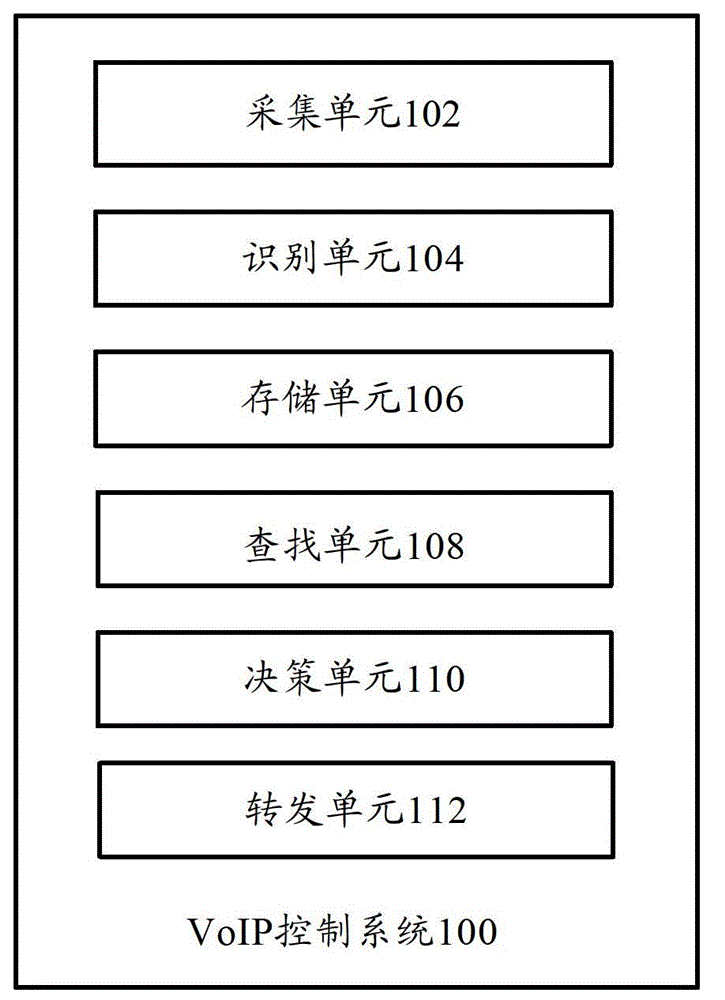
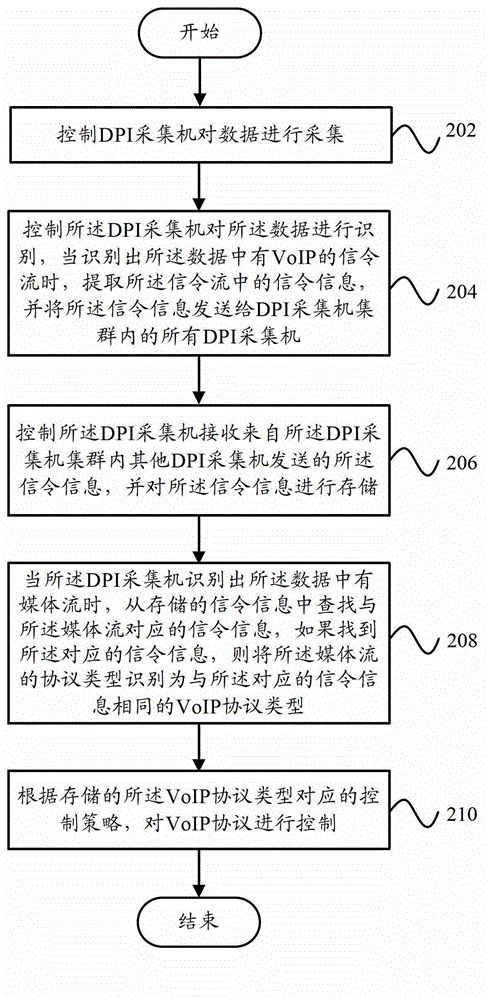
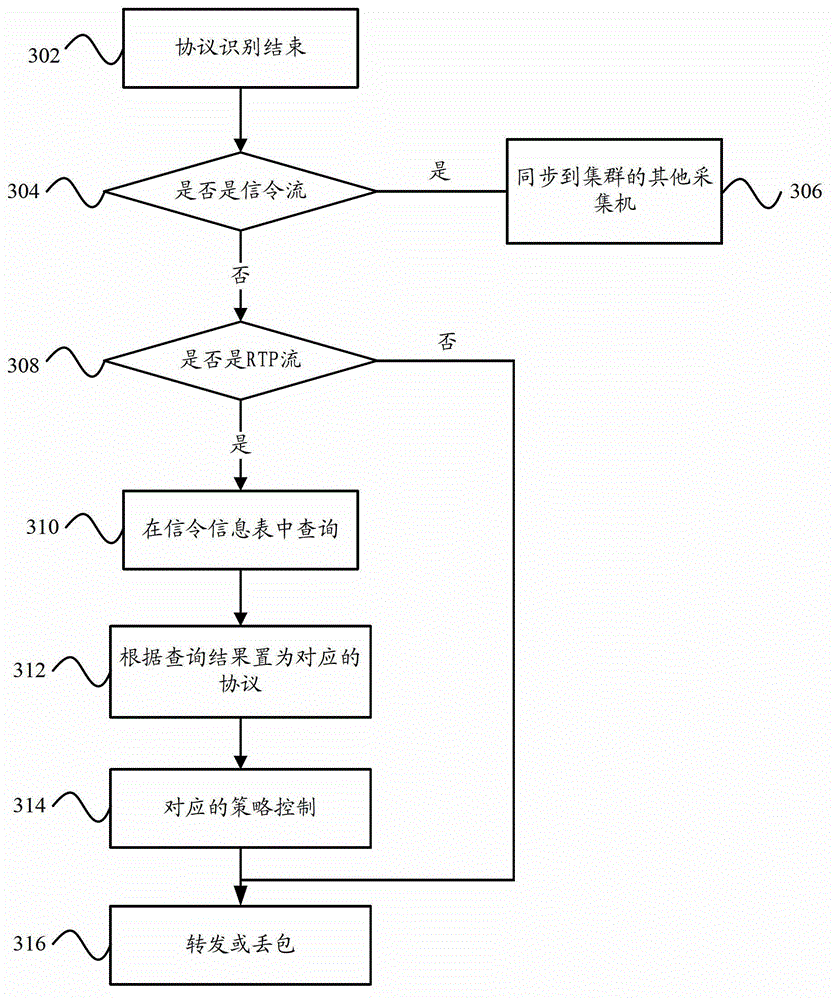
The invention provides a VoIP (voice over internet protocol) control system which comprises an acquisition unit, an identification unit, a storage unit, a search unit and a decision-making unit, wherein the acquisition unit is used for carrying out acquisition on data; the identification unit is used for carrying out identification on data, and when a situation that a VoIP signaling stream exists in the data is identified, extracting signaling information in the signaling stream, and sending the signaling information to other DPI (dots per inch) acquisitors in a DPI acquisitor cluster; the storage unit is used for receiving signaling information sent by the other DPI acquisitors in the DPI acquisitor cluster, and storing the signaling information; the search unit is used for searching signaling information corresponding to a media stream from the stored signaling information when a situation that the media stream exists in the data is identified, if the signaling information is searched, identifying the protocol type of the media stream into a VoIP protocol type the same as that of the information; and the decision-making unit is used for controlling the VoIP protocol according to a control strategy corresponding to the stored VoIP protocol type. Accordingly, the invention also provides a VoIP control method. Through the technical scheme of the invention, under the condition that the signaling stream is separated from the media stream, the VoIP protocol type can be correctly identified, and a corresponding control strategy can be taken for the VoIP protocol type.
Owner:ZICT TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com