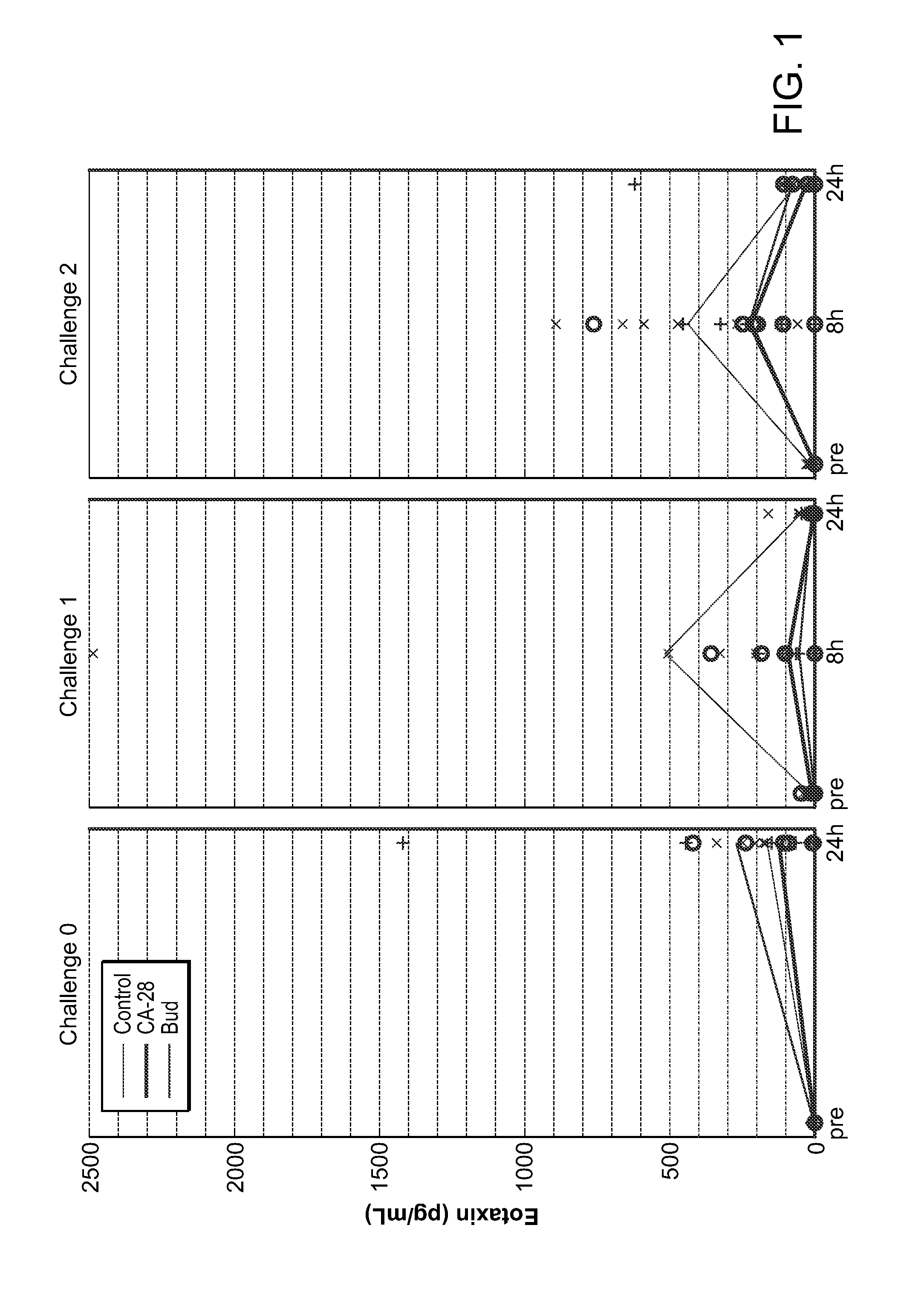
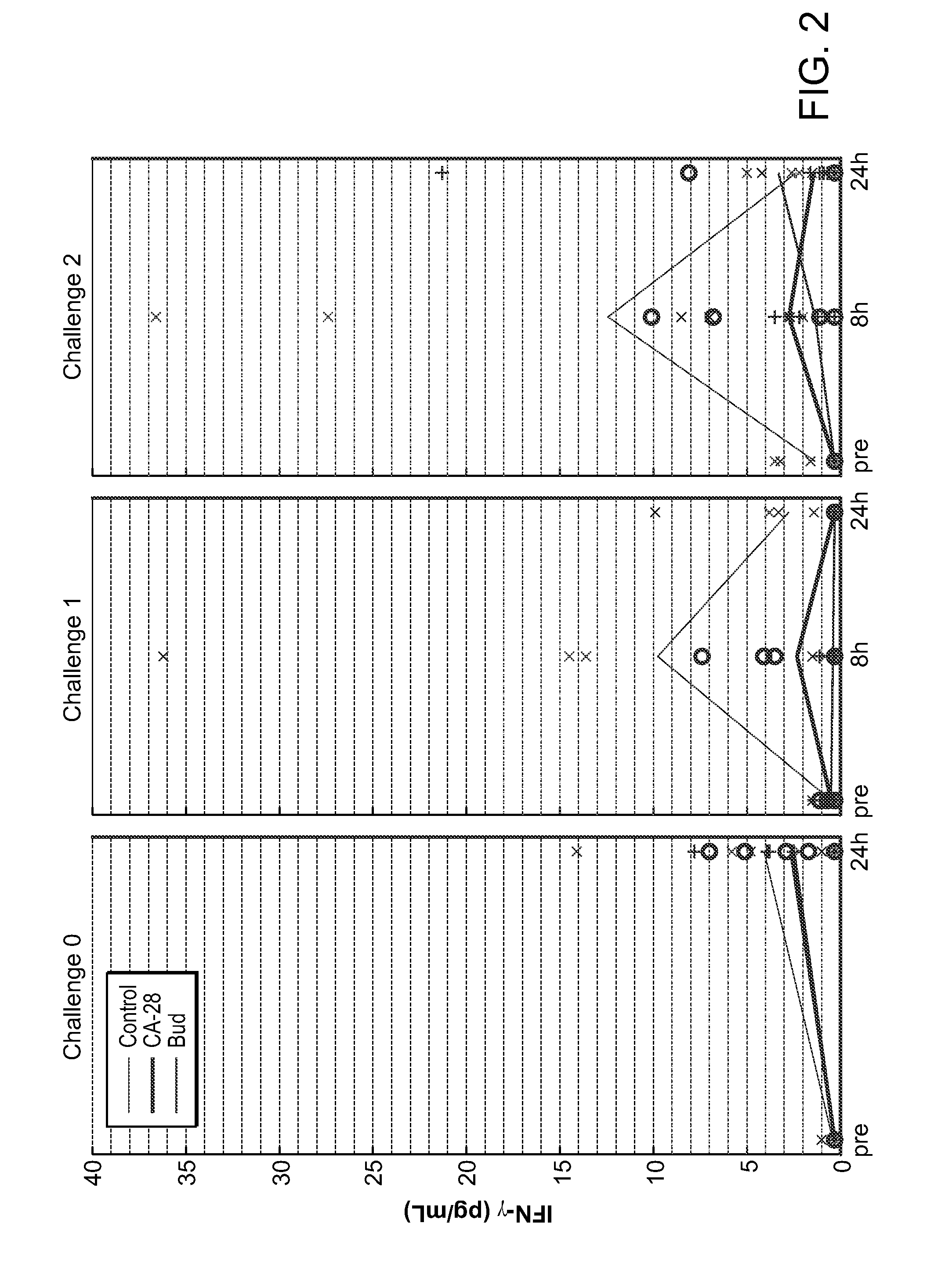
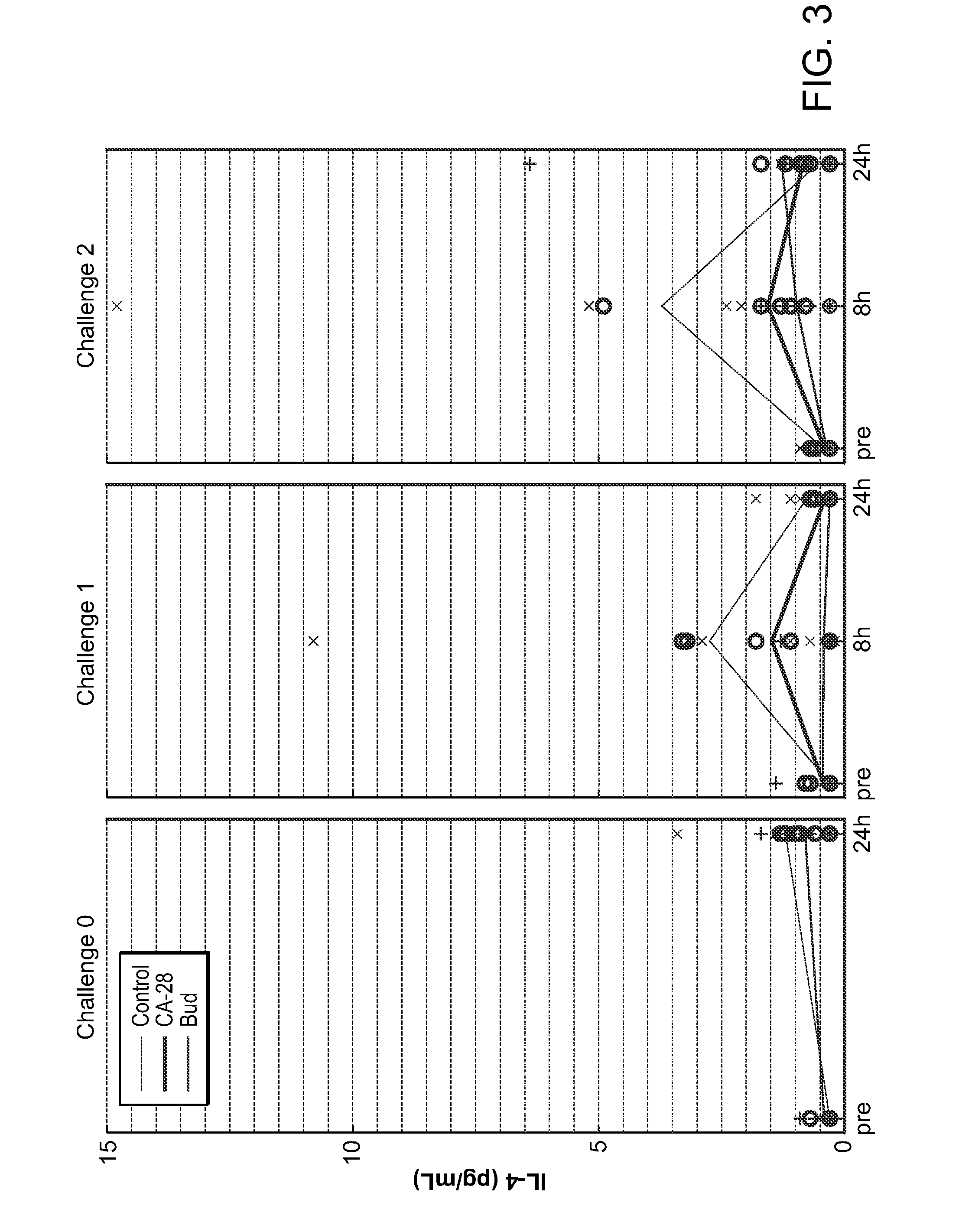
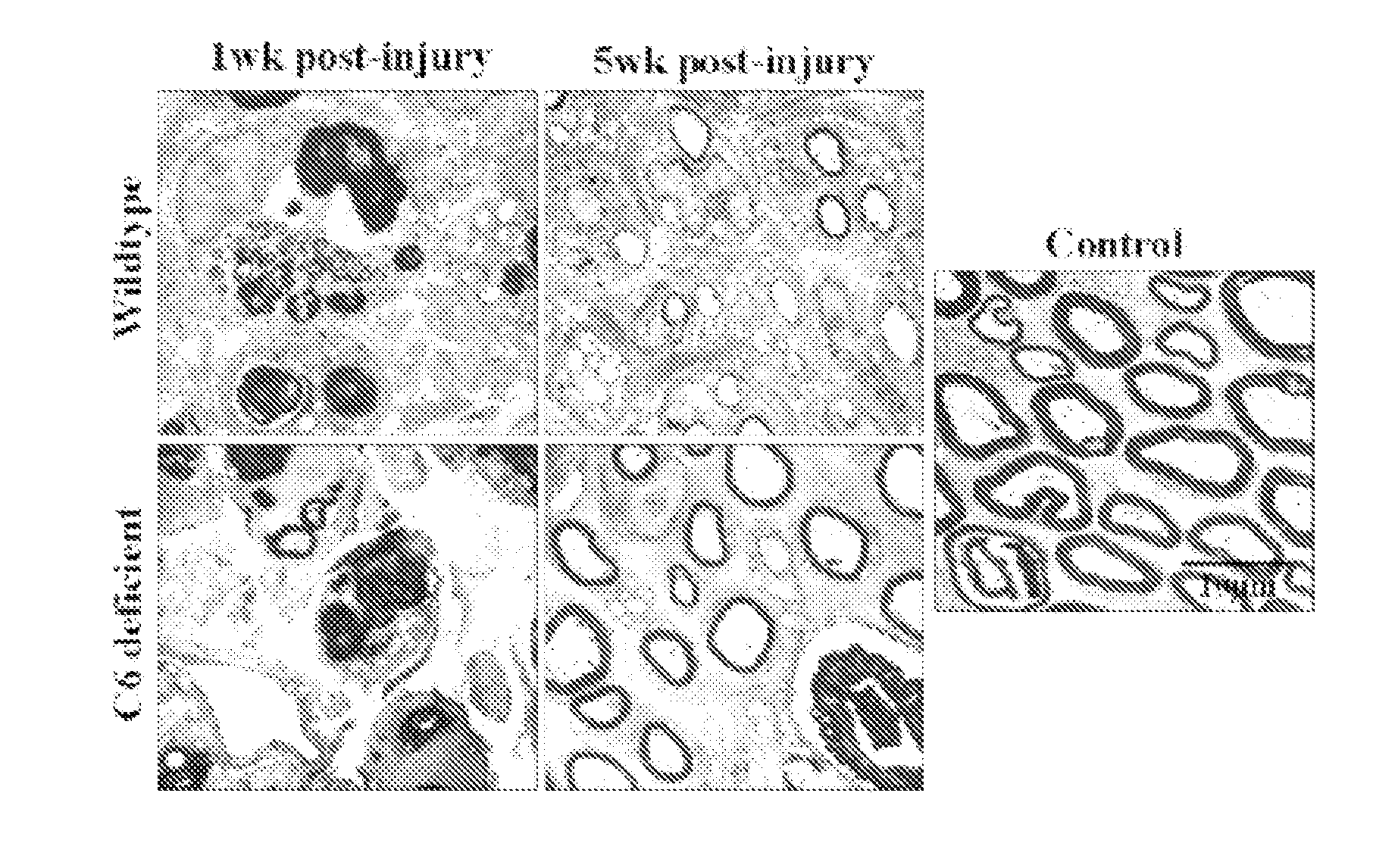
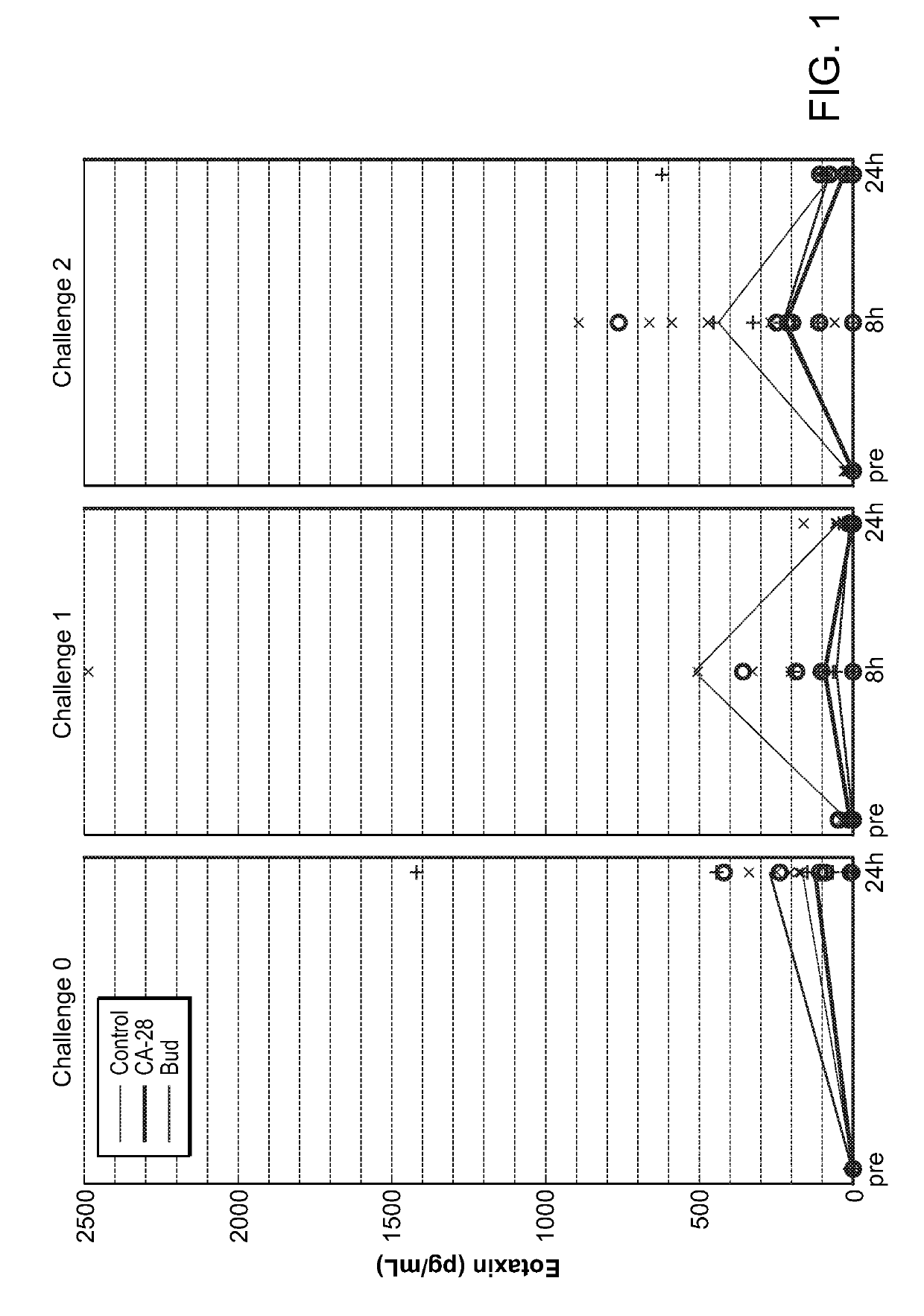
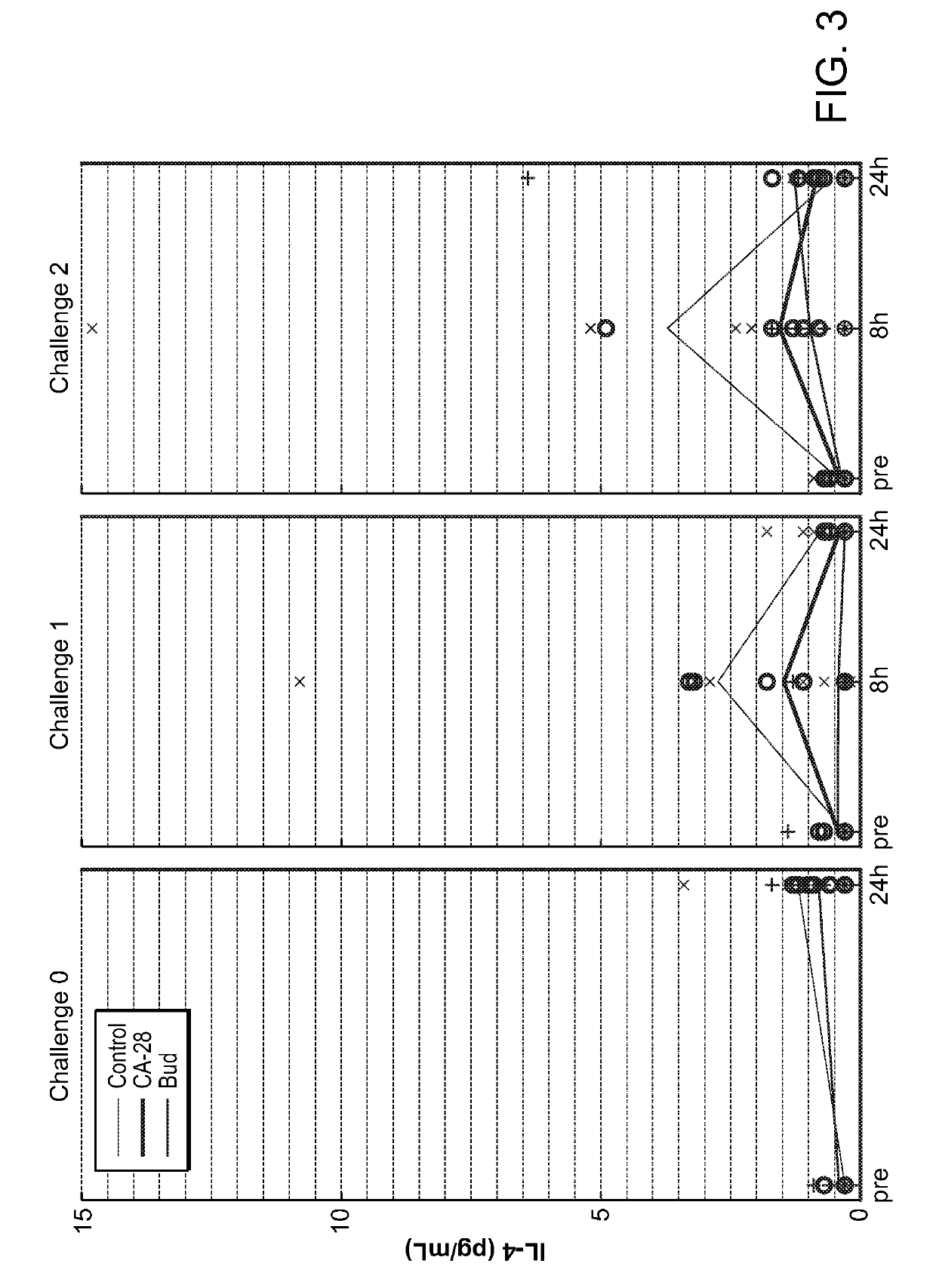
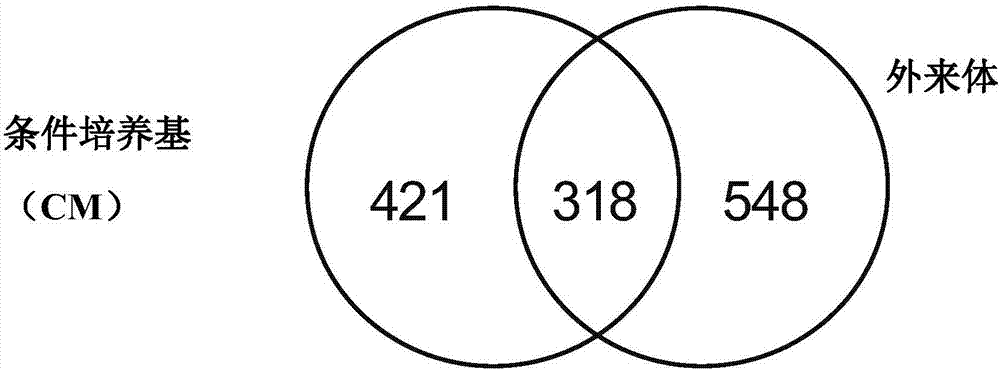
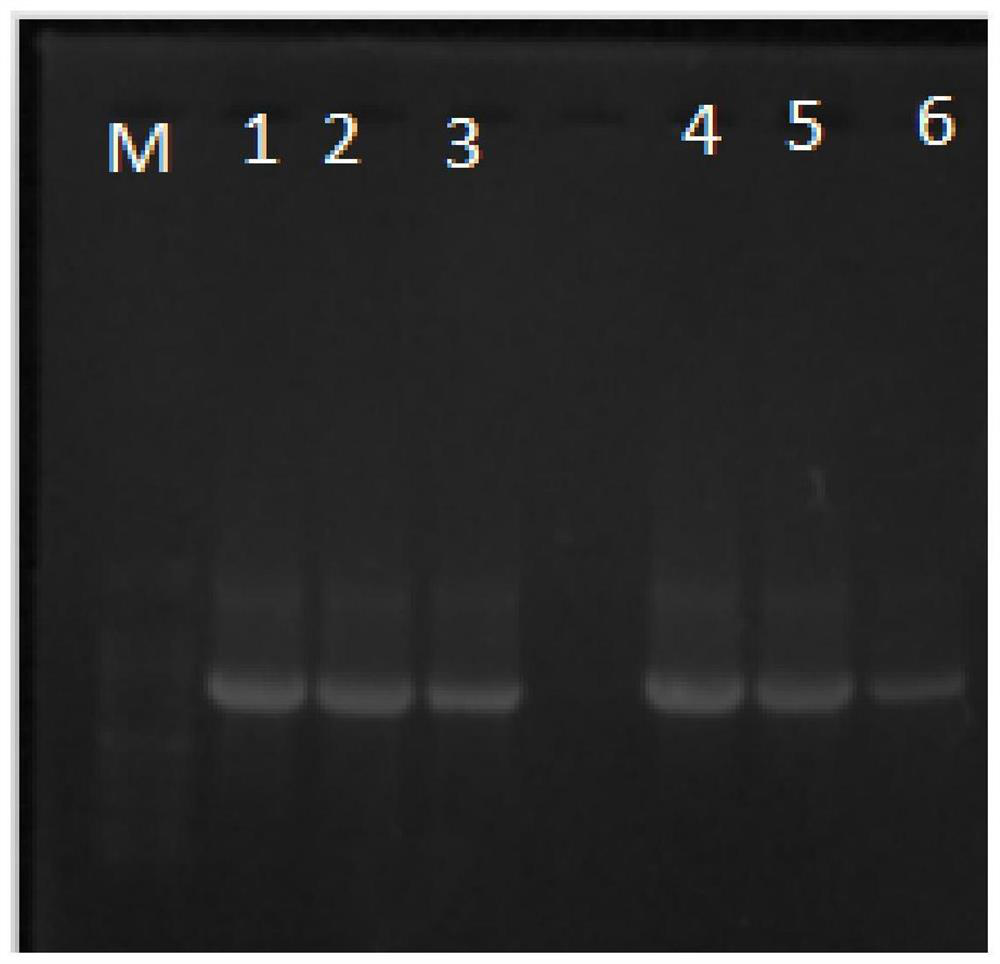
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
37 results about "Complement inhibition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methods of treating chronic disorders with complement inhibitors
ActiveUS20140371133A1Organic active ingredientsSenses disorderObstructive Pulmonary DiseasesDisease cause
In some aspects, the invention provides methods of treating a subject in need of treatment for a chronic complement-mediated disorder. In some aspects, the invention provides methods of treating a subject in need of treatment for a Th17-associated disorder. In some aspects, the invention provides methods of treating a subject in need of treatment for a chronic respiratory system disorder. In some aspects, the invention provides methods of administering a complement inhibitor to a subject. In some embodiments, a method of treating a subject comprises administering multiple doses of a complement inhibitor to the subject according to a dosing schedule that leverages the prolonged effect of complement inhibition in chronic respiratory disorders. In some embodiments, a subject has chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. In some embodiments, a subject has asthma.
Owner:APELLIS PHARMA
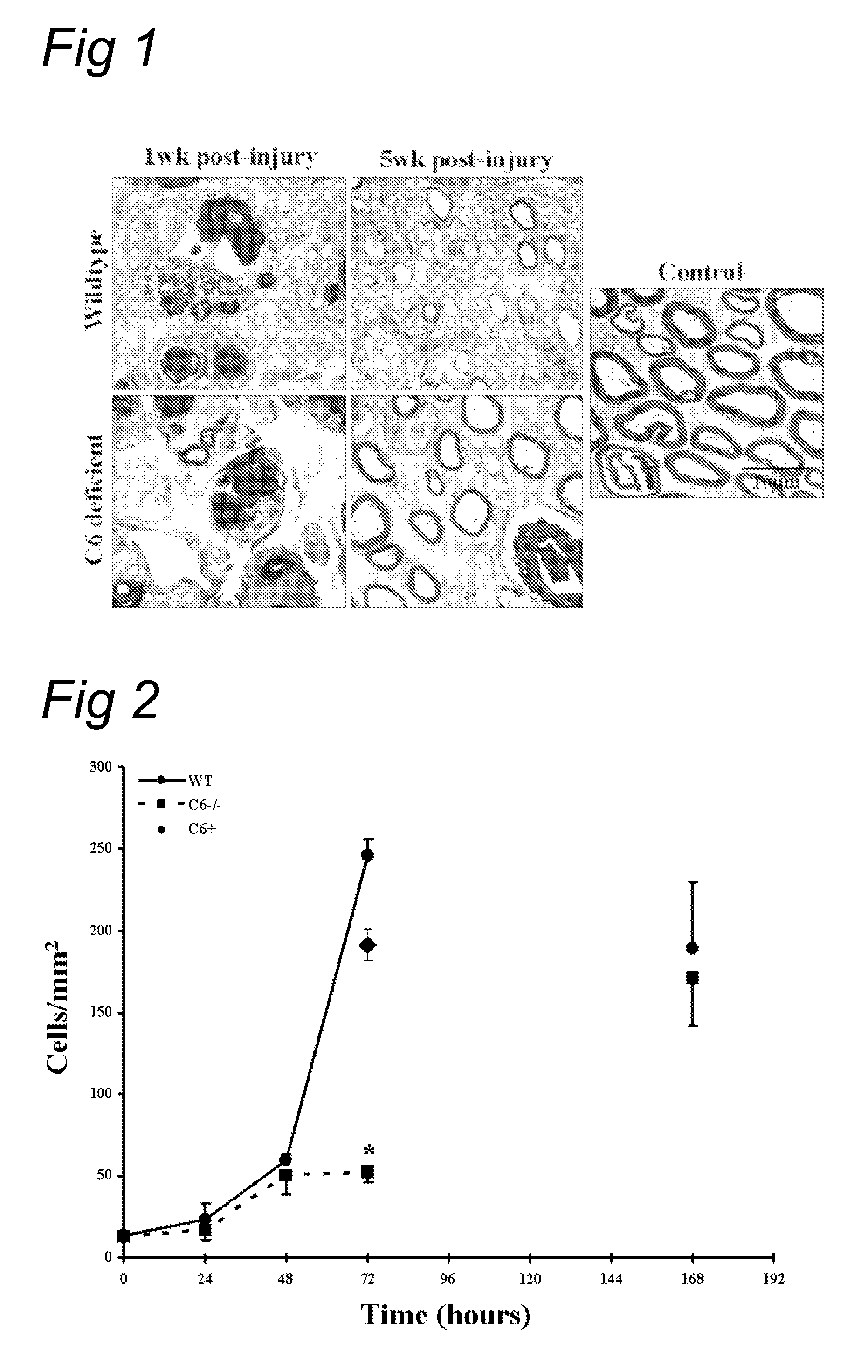
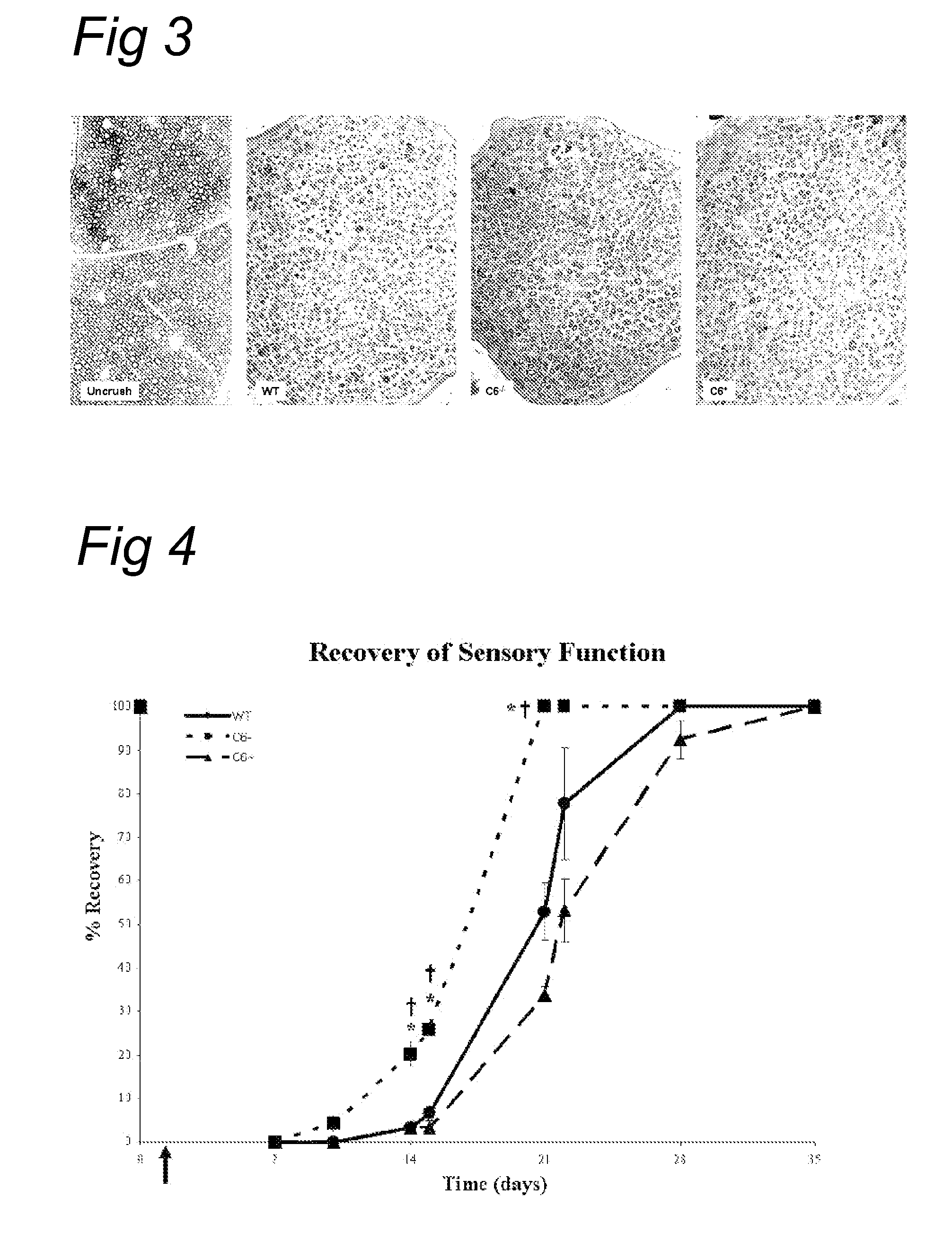
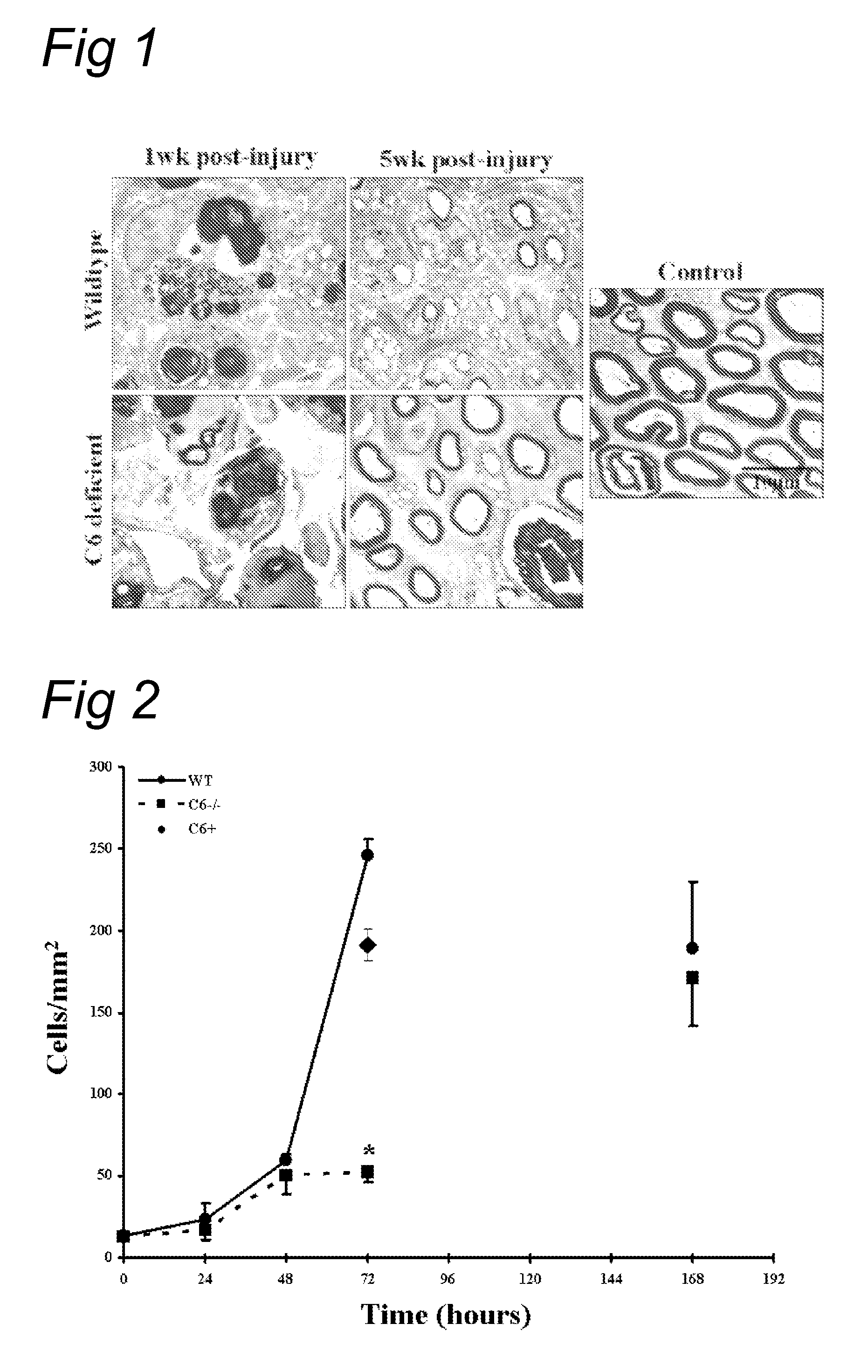
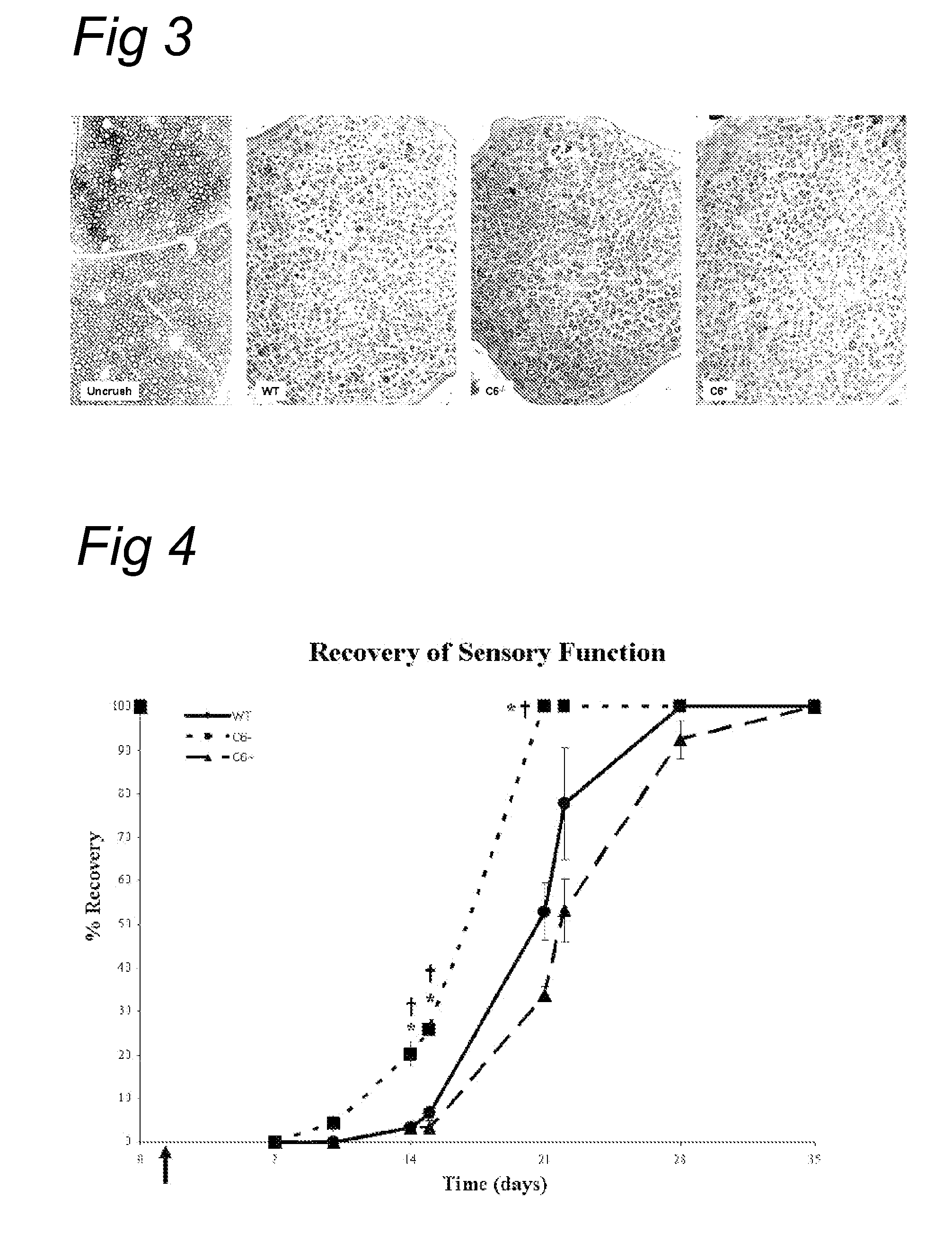
Complement inhibition for improved nerve regeneration
ActiveUS20100143344A1Improve regenerative abilityPromote regenerationBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseNervous system
The present invention relates to methods and medicaments used for treating conditions that require axonal regeneration, e.g. in mammals affected by injury or disease of the central or peripheral nervous system. The medicaments used in these methods facilitate axonal regeneration by inhibition of the complement system. Conditions requiring axonal regeneration that may be treated in accordance with the invention include physical injuries as well as neurodegenerative disorders of the peripheral or central nervous system.
Owner:REGENESANCE
Local Complement Inhibition for Treatment of Complement-Mediated Disorders
ActiveUS20100166862A1Improve in vivo stabilityLow failure rateOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryDiseaseComplement Inhibitors
The present invention features the local administration of complement inhibitors for treatment of complement-mediated disorders. In certain embodiments the invention features inhibiting activation of one or more locally produced complement proteins. The invention provides sustained release formulations and devices comprising a complement inhibitor and methods of use thereof.
Owner:APELLIS PHARMA
Complement inhibition for improved nerve regeneration
ActiveUS8703136B2Improve regenerative abilityPromote regenerationNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseNervous system
The present invention relates to methods and medicaments used for treating conditions that require axonal regeneration, e.g. in mammals affected by injury or disease of the central or peripheral nervous system. The medicaments used in these methods facilitate axonal regeneration by inhibition of the complement system. Conditions requiring axonal regeneration that may be treated in accordance with the invention include physical injuries as well as neurodegenerative disorders of the peripheral or central nervous system.
Owner:REGENESANCE
Methods of treating hemolytic anemia
InactiveUS20070116710A1Requirement be decreaseStabilization of hemoglobin levelGenetic material ingredientsFermentationAntibodyCompound (substance)
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria or other hemolytic diseases are treated using a compound which binds to or otherwise blocks the generation and / or the activity of one or more complement components, such as, for example, a complement-inhibiting antibody.
Owner:ALEXION PHARM INC
Local complement inhibition for treatment of complement-mediated disorders
ActiveUS8580735B2Improve in vivo stabilityLow failure ratePowder deliverySenses disorderDiseaseComplement Inhibitors
The present invention features the local administration of complement inhibitors for treatment of complement-mediated disorders. In certain embodiments the invention features inhibiting activation of one or more locally produced complement proteins. The invention provides sustained release formulations and devices comprising a complement inhibitor and methods of use thereof.
Owner:APELLIS PHARMA
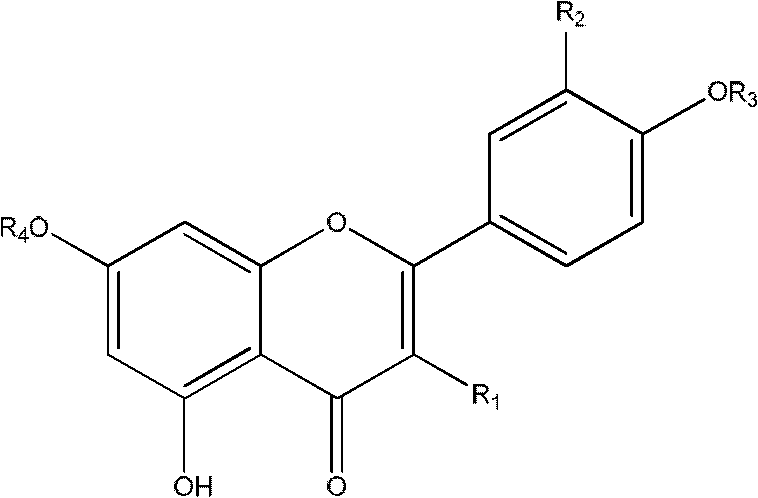
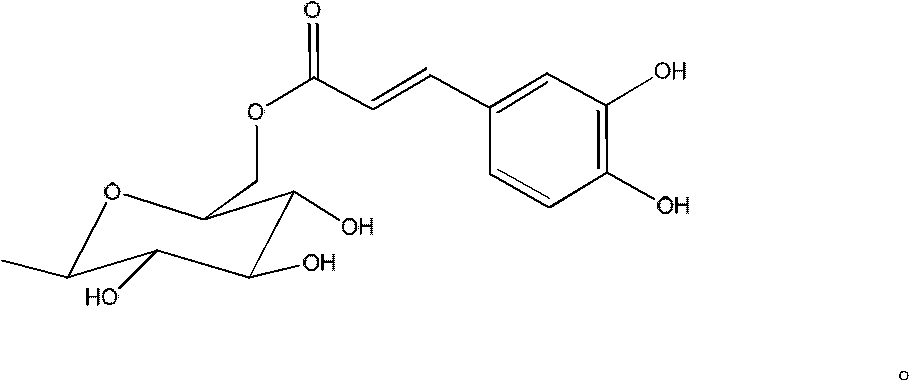
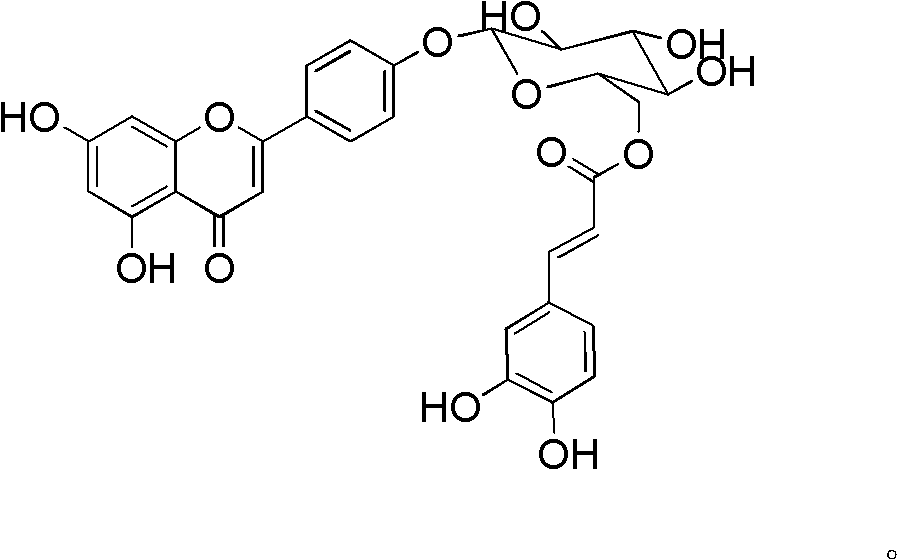
Acylated flavonoid glycoside compounds and application thereof in preparation of complement inhibitor medicines
InactiveCN102304158ASignificant anticomplement activityHigh activityOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesDiseaseHemolysis
The invention discloses acylated flavonoid glycoside compounds shown as a formula I and application thereof in preparation of complement inhibitor medicines. Acylated flavonoid glycosides extracted and separated from cudweed herb are proved to inhibit hemolysis caused by activation of a complement system in a classical pathway through in vitro experiments, and have complement inhibition effect; the activity of each monomericcompound is higher than that of a total extract of cudweed herb; and the acylated flavonoid glycoside compounds are good complement inhibitors and have low effective concentration, can serve as active ingredients to prepare novel complement inhibitor medicines for treating various diseases caused by abnormal activation of complements, are low in toxicity, safe in administration and rich in raw material sources and have great clinical application value. The structure of the formula I is shown as the specifications, wherein R1 and R2 are same or different, and respectively H, OH or OCH3; and R3 and R4 are respectively H or groups shown in the specifications.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Prunella vulgaris polysaccharide, and preparation method and purpose thereof
InactiveCN103626880AStrong anti-complement activityDoes not affect anticoagulant effectOrganic active ingredientsImmunological disordersIn vitro testIn vivo
The invention belongs to the field of Chinese medicine, relates to Prunella vulgaris polysaccharide, and a preparation method and purpose thereof in preparing anticomplement medicines. The Prunella vulgaris polysaccharide including uniform polysaccharide PW-PS1 and PW-PS2 is prepared from a dry fruit aqueous extract of a labiatae plant Prunella vulgaris Linn. Through in vitro tests, the uniform polysaccharide is proved to have strong anticomplement activity and inhibition effects on classical pathway and alternative pathway of a complement system; besides, the polysaccharide does not have the anticoagulant effect influencing in vivo activity and can be used for the preparation of complement inhibition medicaments. The PW-PS1 effects on C1q, C3 and C9 components of the complement system, and the PW-PS2 effects on the C1q, C2, C3, C5 and C9 components of the complement system.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Methods of detecting therapeutic exosomes
We describe a method of detecting a therapeutic exosome, the method comprising detecting an activity of an exosome. The activity may be selected from the group consisting of: (a) immunodulatory activity; (b) complement inhibition activity; (c) proteasome activity; (d) glycolytic enzyme activity; (e) anti-oxidative activity; (f) extracellular matrix (ECM) modifying activity; (g) NT5E (CD73) ecto-5'-ectonucleotidase activity; (h) ion homeostasis activity; and (i) chaperone activity. If the exosome is detected as having one or more such activities, the exosome is likely to comprise a therapeutic exosome having therapeutic activity.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Methods of treating chronic disorders with complement inhibitors
ActiveUS10039802B2Organic active ingredientsSenses disorderObstructive Pulmonary DiseasesDisease cause
In some aspects, the invention provides methods of treating a subject in need of treatment for a chronic complement-mediated disorder. In some aspects, the invention provides methods of treating a subject in need of treatment for a Th17-associated disorder. In some aspects, the invention provides methods of treating a subject in need of treatment for a chronic respiratory system disorder. In some aspects, the invention provides methods of administering a complement inhibitor to a subject. In some embodiments, a method of treating a subject comprises administering multiple doses of a complement inhibitor to the subject according to a dosing schedule that leverages the prolonged effect of complement inhibition in chronic respiratory disorders. In some embodiments, a subject has chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. In some embodiments, a subject has asthma.
Owner:APELLIS PHARMA
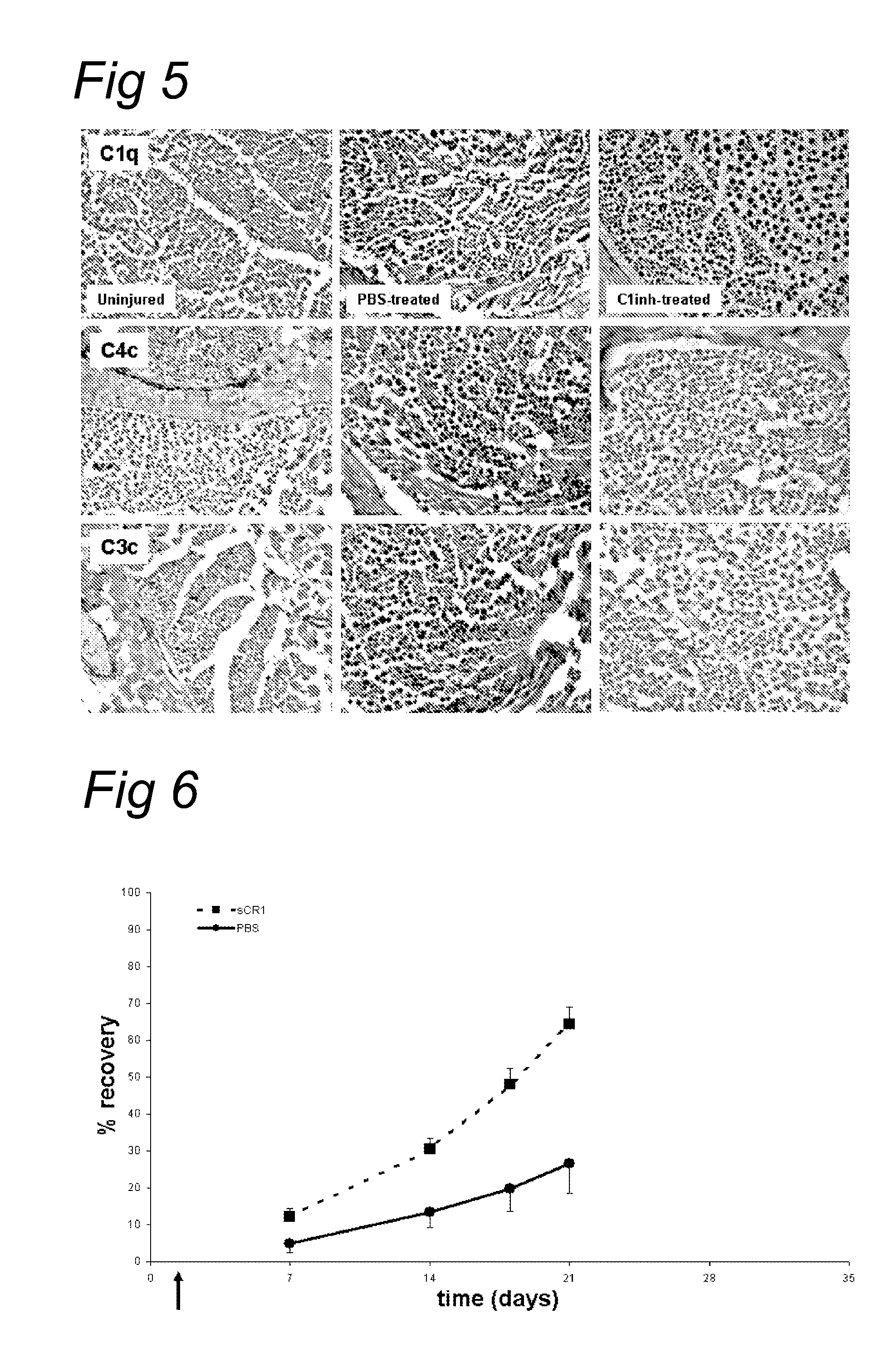
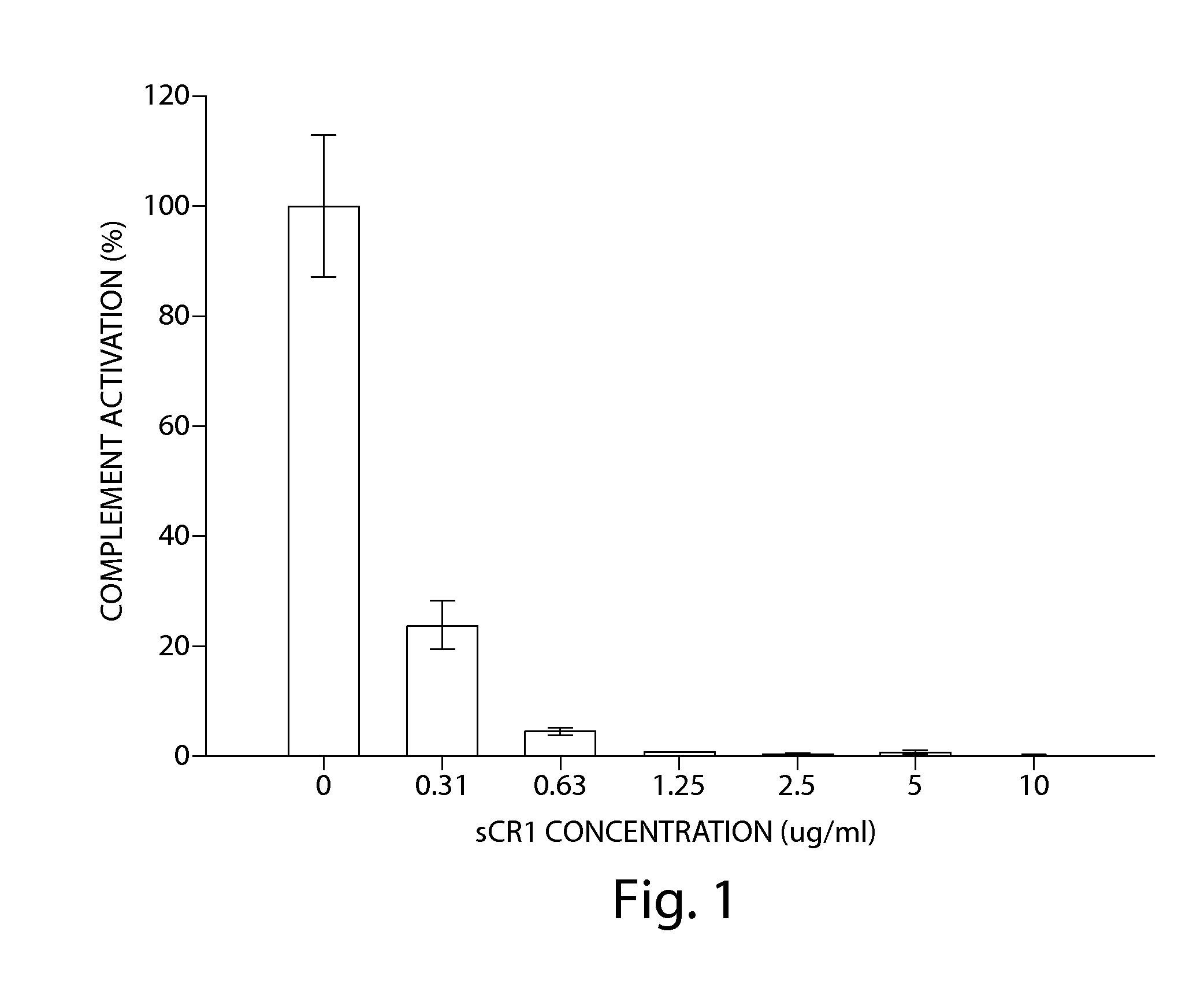
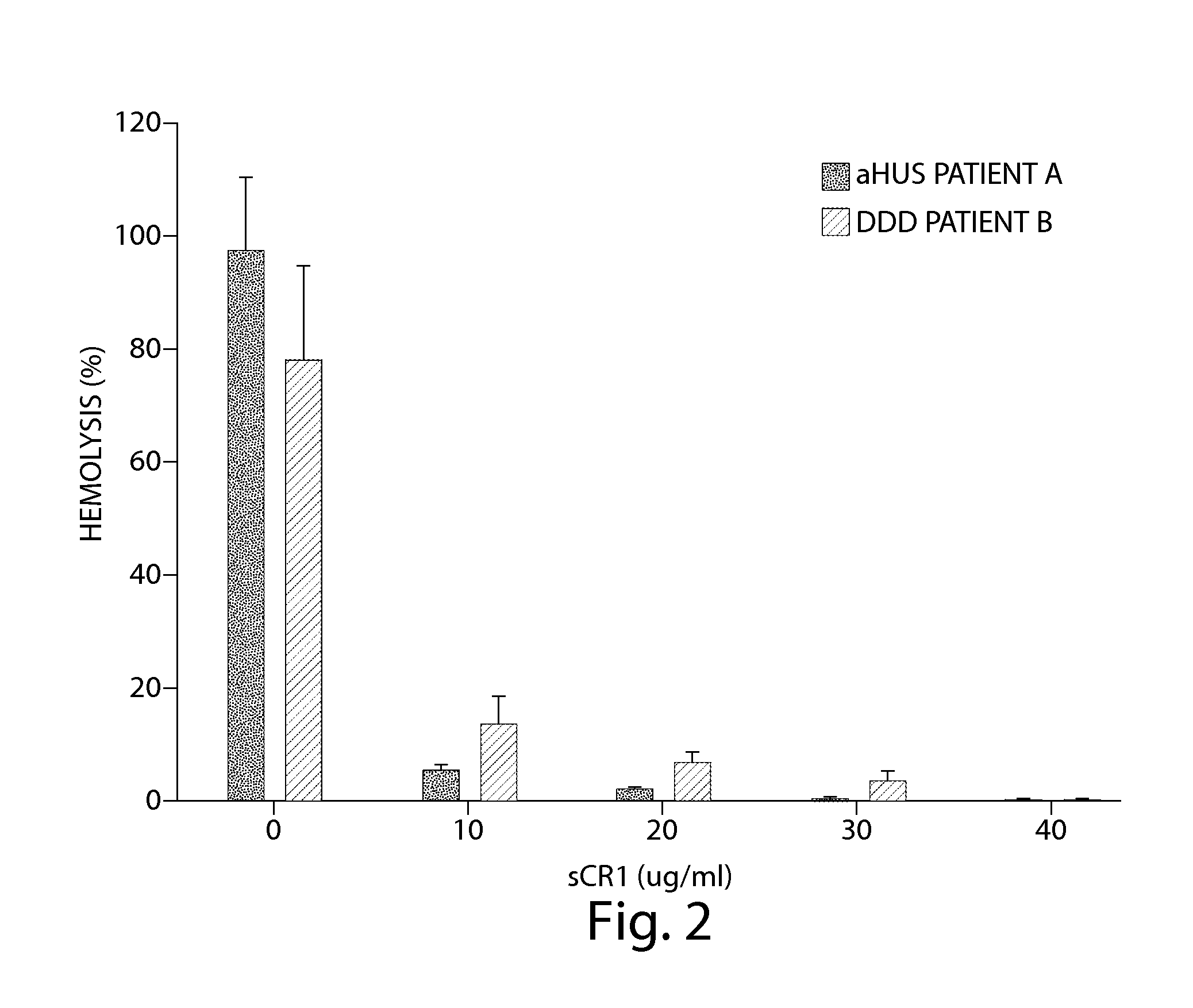
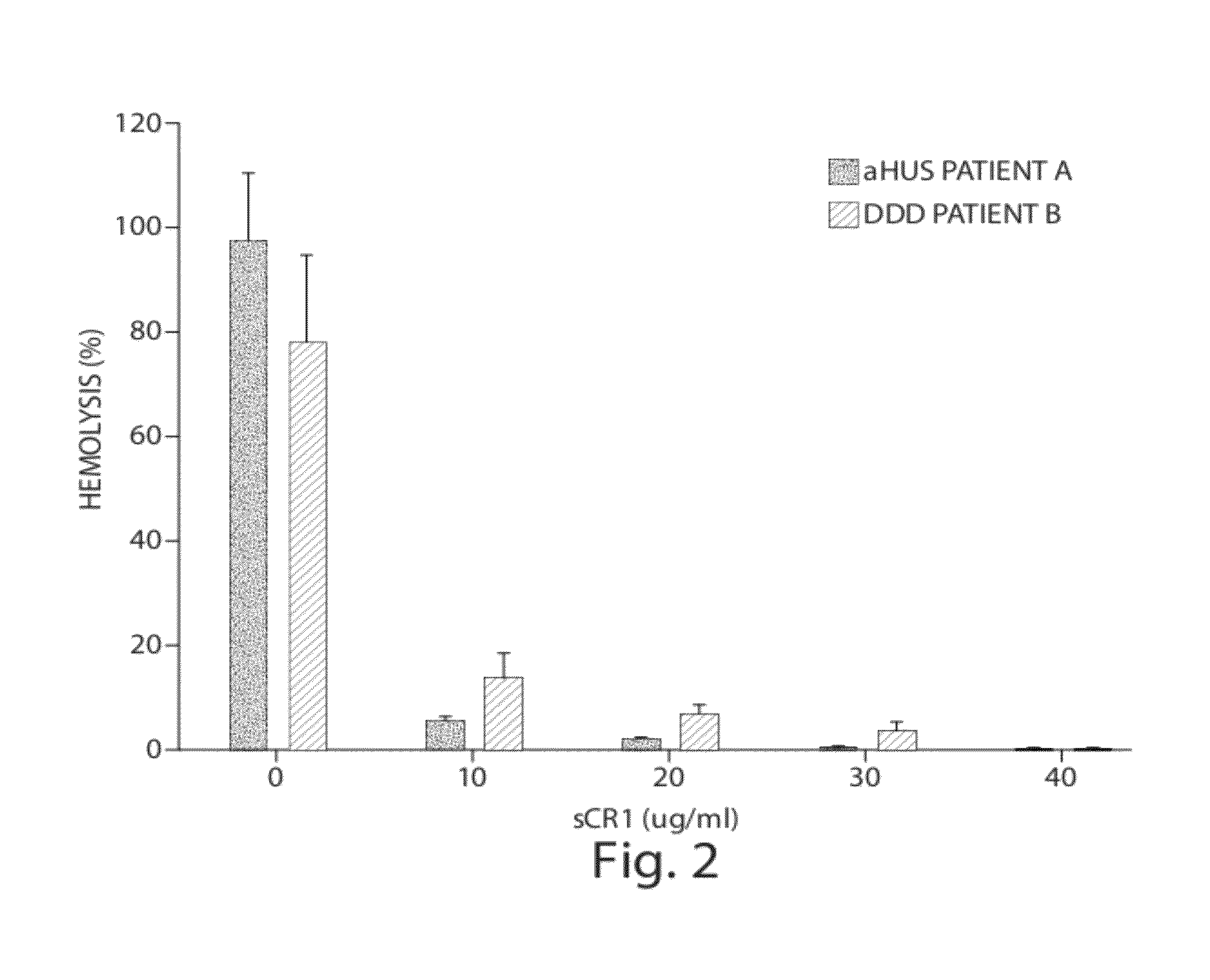
TREATMENT OF CHRONIC NEPHROPATHIES USING SOLUBLE COMPLEMENT RECEPTOR TYPE I (sCR1)
ActiveUS20120071413A1Reduce decreaseReduces C depositionPeptide/protein ingredientsUrinary disorderBiological activationComplement receptor I
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND +1
Novel targeted fusion protein with anti-inflammatory action and use thereof
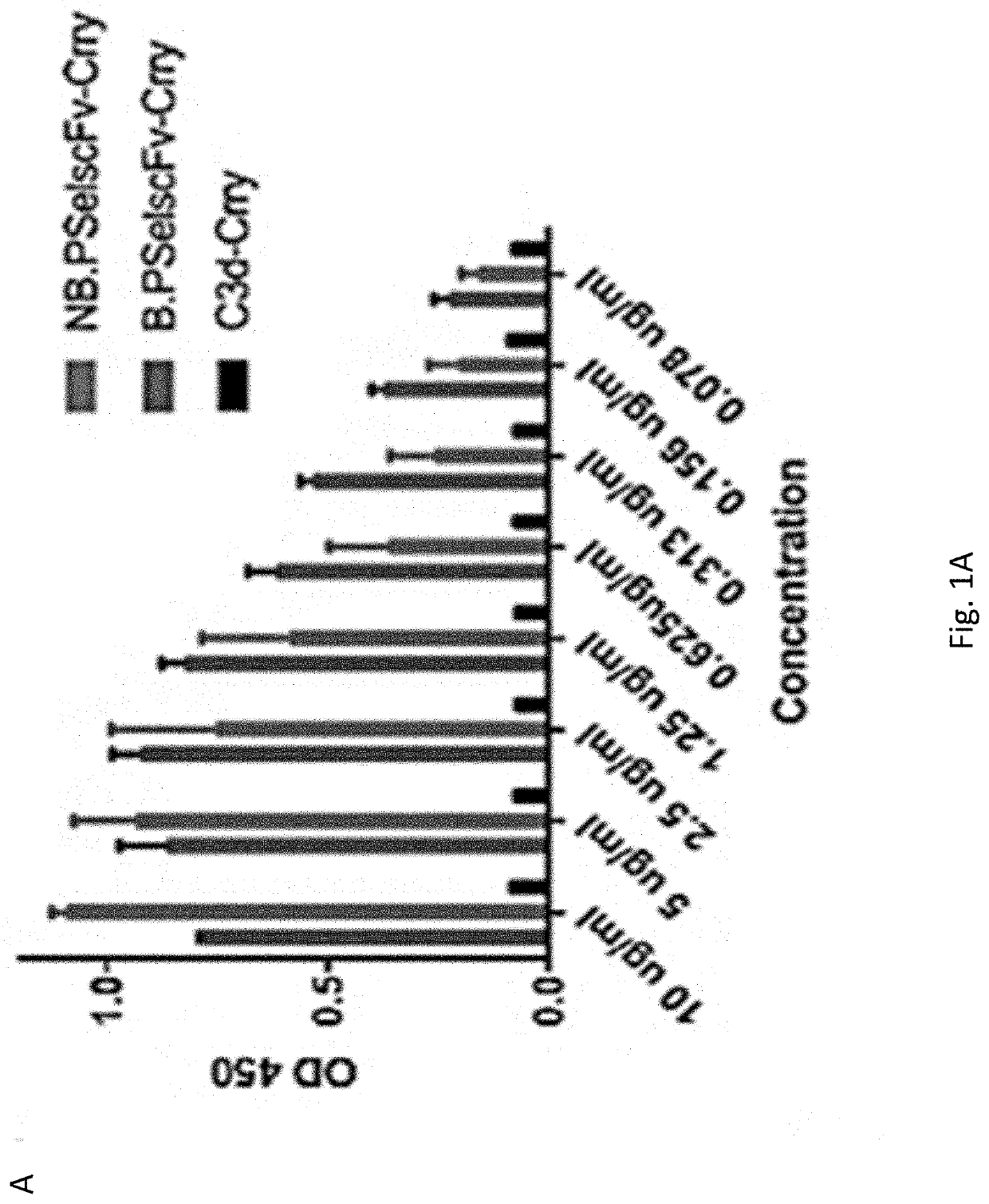
The invention discloses a target fusion protein with the anti-inflammatory action, in particular an anti-P lectin single chain antibody target complement inhibitor ScFv-Crry and application thereof. The invention aims to provide the anti-P lectin single chain antibody target complement inhibitor ScFv-Crry with the specific targeting property and application of the ScFv-Crry to the preparation of medicines for treating organism inflammatory reactions. The anti-P lectin single chain antibody target complement inhibitor ScFv-Crry is the fusion protein which is obtained through the connection between an amino end connected with an anti-P lectin single chain antibody ScFv and a complement inhibitor Crry(1-319aa). Experiments show that the ScFv-Crry can remarkably improve the efficiency of the cell cracking mediated by an inhibiting complement, be highly aggregated at an immunity damaged position, and obviously inhibit the generation and development of inflammation. Therefore, the ScFv-Crry can be prepared into target P lectin complement inhibitor new genetic engineering target protein medicines aiming at treating inflammatory reactions. The ScFv-Crry has important contributions to the field of pharmacy and bright application prospect.
Owner:INST OF PLA FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
Factor H binding peptides and uses thereof
ActiveUS8962795B2Reduce activationPharmaceutical containersMedical packagingBinding peptideBiological activation
Factor H-binding peptides that binds to a region of factor H that does not impede the complement-inhibitory activity of factor H are disclosed. When immobilized onto the surface of a biomaterial, these peptides recruit factor H, resulting in a substantial inhibition of biomaterial-induced complement activation in a biological substance exposed to the biomaterial.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Methods of distributing complement-inhibiting drugs to patients receiving a complement inhibitor
This disclosure relates to methods of authorizing distribution of complement-inhibiting drugs to patients who have a complement-associated disorder in a manner to ensure that the patients are aware of the possible dangers of discontinuing treatment with the drugs. A database is prepared comprising patient information including experiencing adverse clinical events after discontinuing the drug treatment. The information in the database is collected and may be reported. The patients are given a warning as to adverse events that may occur if treatment with the complement inhibiting drugs is discontinued.
Owner:ALEXION PHARMA INC
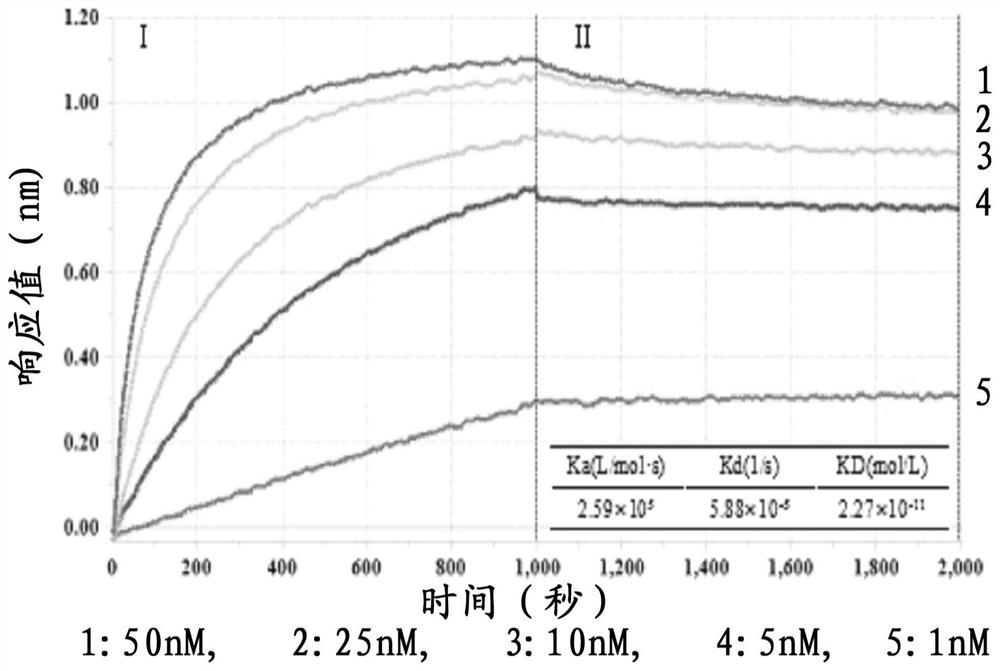
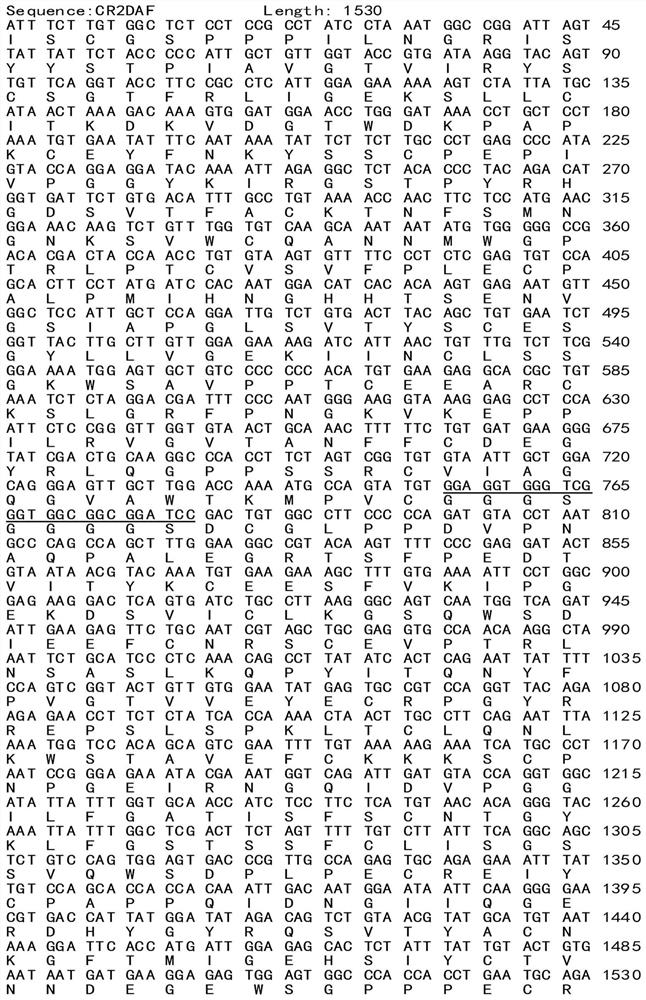
Humanized targeted complement inhibitor protein double-mutant mCR2-mDAF and application thereof
ActiveCN110330561AExcellent anti-adhesion/anti-inflammatory target inhibition effectFast gatheringPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticDiseaseAutoimmune disease
The invention discloses a complement inhibitor DAF mutant, a fusion protein thereof with a complement receptor 2 mutant and use of the fusion protein in preparation of medicines treating autoimmune diseases. The DAF mutant is a molecular modification obtained by computer modeling and amino acid substitution. The fusion protein of the DAF mutant and the complement receptor 2 mutant has higher ligand binding and dissociation rates than wild-sequence fusion protein thereof, and has better ligand binding force. Biological distribution experiments prove that the fusion protein can rapidly aggregatein the arthritis position after entering a rheumatoid arthritis mouse model, and has a significant anti-adhesion / anti-inflammatory targeted inhibitory effect. In treatment for MRL / lpr lupus erythematosus mice, the fusion protein can significantly increase the survival rate of the mice, and symptoms such as proteinuria, glomerular score, interstitial inflammation, vasculitis and crescent / necrosisin the mice in the treatment group are significantly improved.
Owner:BEIJING COMPLEMENT THERAPEUTICS LTD
Recombinant Fusion Proteins Targeting P-selectin, and Methods of Use Thereof for Treating Diseases and Disorders
The present invention describes compositions and methods for targeting complement inhibition to sites of p-selectin expression, and compositions for inhibiting p-selectin and complement.
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV +2
Methods of treating chronic disorders with complement inhibitors
In some aspects, the invention provides methods of treating a subject in need of treatment for a chronic complement-mediated disorder. In some aspects, the invention provides methods of treating a subject in need of treatment for a Th17-associated disorder. In some aspects, the invention provides methods of treating a subject in need of treatment for a chronic respiratory system disorder. In some aspects, the invention provides methods of administering a complement inhibitor to a subject. In some embodiments, a method of treating a subject comprises administering multiple doses of a complement inhibitor to the subject according to a dosing schedule that leverages the prolonged effect of complement inhibition in chronic respiratory disorders. In some embodiments, a subject has chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. In some embodiments, a subject has asthma.
Owner:APELLIS PHARMA
Methods of detecting therapeutic exosomes
We describe a method of detecting a therapeutic exosome, the method comprising detecting an activity of an exosome. The activity may be selected from the group consisting of: (a) immunodulatory activity; (b) complement inhibition activity; (c) proteasome activity; (d) glycolytic enzyme activity; (e) anti-oxidative activity; (f) extracellular matrix (ECM) modifying activity; (g) NT5E (CD73) ecto-5'-ectonucleotidase activity; (h) ion homeostasis activity; and (i) chaperone activity. If the exosome is detected as having one or more such activities, the exosome is likely to comprise a therapeutic exosome having therapeutic activity.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Human source targeted complement inhibitor protein mCR2-DAF and application
ActiveCN109929026ATurn easilyA clear dose-dependent relationshipCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseAutoimmune disease
The invention discloses a complement receptor 2 variant, a fusion protein of the complement receptor 2 variant and a complement inhibitor and application of the fusion protein in preparing a medicament for treating autoimmune diseases. The complement receptor 2 variant is a molecular modified body obtained after computer modeling and amino acid replacement, has higher ligand binding and dissociation rate and better ligand binding force than a wild sequence of the complement receptor 2 variant. The biological distribution experiment proves that the fusion protein provided by the invention can rapidly and highly aggregate at an arthritis part after entering a rheumatoid arthritis mouse model, and has a remarkable anti-adhesion / anti-inflammation targeted inhibition effect. In the treatment ofMRL / lpr lupus erythematosus mice, the fusion protein can obviously improve the survival rate of the mice, and symptoms such as proteinuria, glomerular integral, interstitial inflammation, vasculitis,crescent / necrosis and the like of the mice in the treatment group are obviously improved.
Owner:BEIJING COMPLEMENT THERAPEUTICS LTD
HB-NC4 recombinant protein and preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN113024675AStrong targetingExtended stayConnective tissue peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsComplement inhibitionNucleotide sequenc
The invention provides HB-NC4 recombinant protein and a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biological medicines, the recombinant protein is formed by recombination of an N-terminal non-collagen structural domain 4 and an HB heparin binding structural domain of NC4 human collagen IX. The amino acid residue sequence of the recombinant protein is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1. A nucleotide sequence for coding the recombinant protein is shown as SEQ ID NO.3 or a sequence with genetic code degeneracy. In the nucleotide sequence for coding the recombinant protein, the nucleotide sequence for coding the heparin binding domain is as shown in SEQ ID NO.4, and the nucleotide sequence for coding the N-terminal non-collagen domain 4 of the human collagen IX is as shown in SEQ ID NO.5 or has a sequence with genetic code degeneracy. The invention also discloses the preparation method of the HB-NC4 fusion protein. The HB-NC4 fusion protein retains the complement inhibition activity of the N-terminal domain 4 of collagen IX, can directly target cartilage and retain the complement inhibition activity, and the targeting property and retention time of the fusion protein are greatly improved.
Owner:SHANDONG FIRST MEDICAL UNIV & SHANDONG ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Fusion protein of antibody targeted complement regulatory factor for treating myasthenia gravis
InactiveCN102115499AReduce in quantityDegree of reductionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingSingle-Chain AntibodiesEngineered genetic
The invention discloses a fusion protein scFV-CD55 of an acetylcholine receptor-resistant single-chain antibody targeted complement regulatory factor CD55. The CD55 is targeted to neuromuscular transmission through single-chain antibody to inhibit combination of the antibody of a pathogenic acetylcholine receptor and the pathogenic acetylcholine receptor, block the cascade of a complement, protect the acetylcholine receptor and eliminate immune injury caused by complement system activation, so that myasthenia gravis is treated in a targeted way. The scFv-CD55 is obtained by coupling acetylcholine receptor-resistant single-chain antibody to the amino terminal of the complement regulatory factor CD55(SCR1-4) through (G4S1)3 connecting peptide. By means of genetic engineering, soluble scFV-CD55 can be obtained through prokaryotic expression and purification. Experiments prove that: the fusion protein scFV-CD55 maintains the affinity of the acetylcholine receptor and the complement inhibition function of the CD55, the complement inhibition function of the scFV-CD55 is obviously improved in cellular experiments, and the complement deposition on immune injury parts is reduced. The invention develops a new biological agent for treating the myasthenia gravis, and the biological agent has wide application prospect.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Anti-Inflammatory Antibodies Target Complement Inhibitors
The invention discloses an anti-P-selectin single-chain antibody targeted complement inhibitor ScFv-CD59 and application thereof. The invention aims to provide an anti-P-selectin single-chain antibody targeted complement inhibitor ScFv-CD59 with specific targeting and the application thereof in preparing medicaments for treating systemic inflammations. The anti-P-selectin single-chain antibody targeted complement inhibitor ScFv-CD59 is a fusion protein obtained by connecting the amino terminal of the anti-P-selectin single-chain antibody ScFv with the complement inhibitor CD59 by using a connecting peptide. The experiment proves that the ScFv-CD59 can obviously improve the efficiency of inhibiting the complement-mediated cell cracking, can achieve high-degree accumulation at the immune injury part, can obviously inhibit the occurrence and degeneration of inflammations and can obviously reduce the side effect of infection caused by the complement inhibitor. Therefore, the ScFv-CD59 can be used as an active ingredient to be prepared into a novel gene engineering targeted protein medicament with a targeted P-selectin complement inhibitor for treating inflammations. The invention plays an important role in the pharmaceutical field and has wide application prospects.
Owner:INST OF PLA FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
Compstatin analogues and their medical uses
PendingUS20220306695A1Improve stabilityStability advantageAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderDisulfide bondingSide chain
Compstatin analogues having improved binding and complement-inhibiting activity as compared to the 13 amino acid compstatin peptide (ICWQDWGHHRCT (cyclic C2-C12)) are described, in particular compstatin analogues that additionally possess useful physicochemical properties. The analogues have a thioether bond rather than a disulfide bond between the side chains of the f residues corresponding to cysteines 2 and 12 of compstatin which may increase stability. The analogues may also have an isoleucine residue at position 3 in place of the wild type valine residue, which provides compstatin peptides with improved binding and complement-inhibiting activity and also enables the introduction of other modifications, for example modifications that are capable of increasing solubility, such as the introduction of charged or polar amino acids at position 9 and / or the introduction of N- and / or C-terminal sequences.
Owner:ZP SPV 3 KS
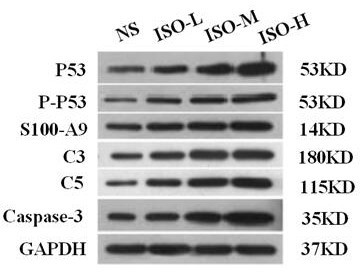
Application of Bupleurum Polysaccharides in Medicines for Treating Myocardial Injury
ActiveCN109453189BReduce myocardial damageIncreased myocardial damageOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderComplement S-ProteinPharmaceutical drug
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Human target complement inhibitor protein mcr2-fh and its application
ActiveCN110128547BTurn easilyExcellent anti-adhesion/anti-inflammatory target inhibition effectPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunologic disordersAutoimmune condition
The invention discloses a fusion protein of a complement receptor 2 variant and a complement inhibitor fH and an application of the fusion protein in the preparation of a drug for treating autoimmune diseases. The complement receptor 2 variant is a molecular modification obtained after computer modeling and amino acid substitution, and has higher ligand binding and dissociation rates and better ligand binding capacity than its wild-type sequence. The biological distribution experiment proves that the fusion protein provided by the present invention can rapidly and highly aggregate in the arthritis site after entering the rheumatoid arthritis mouse model, and has significant anti-adhesion / anti-inflammatory targeting inhibition effect. In the treatment of MRL / lpr lupus erythematosus mice, the fusion protein can significantly improve the survival rate of mice. Symptoms such as necrosis were significantly improved.
Owner:BEIJING COMPLEMENT THERAPEUTICS LTD
Human targeted complement inhibitor protein mCR2-CD59 and application thereof
ActiveCN109970870AImprove survival rateImprove bindingCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsAntipyreticDiseaseAutoimmune disease
The invention discloses a fusion protein of a complement receptor 2 mutant and a complement inhibitor CD 59 and application thereof to preparing autoimmune disease treating drugs. The complement receptor 2 mutant is a molecular modified body obtained through computer modelling and amino acid replacement and is higher in ligand binding and dissociation rate and ligand binding force compared with wild sequences. Biological distribution test shows that the fusion protein can be highly concentrated at arthritic parts after entering mouse models with rheumatoid arthritis and achieve significant anti-adhesion / anti-inflammatory targeted inhibition effects; when applied to treating MRL / lpr (Murphy Roths large / lymphoproliferation) mice with systemic lupus erythematosus, the fusion protein can significantly improve the survival rate of the mice, and symptoms of the mice of a treatment group such as proteinuria, glomerular score, interstitial inflammation, vasculitis and crescent glomerulonephritis / necrosis can be significantly improved.
Owner:BEIJING COMPLEMENT THERAPEUTICS LTD
Targeted immunosuppressant TCABCD59 for preventing and treating infectious inflammation
ActiveCN113801244AInhibition of activationImprove survival rateAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsIMMUNE SUPPRESSANTSSingle-Chain Antibodies
The invention discloses a targeted complement inhibitor fusion protein C3d-ScFv-CD59 of a single-chain antibody of a human anti-complement C3d molecule and a complement inhibitor CD59. The fusion protein has excellent antigen binding activity, and in-vitro inhibition experiments show that C3d-ScFv-CD59 has a more obvious inhibition effect corresponding to a single effector molecule CD59, and the effect is realized by identifying that the C3d component in a complement activation region plays a complement inhibition role. The C3d-ScFv-CD59 is used for treating influenza / bacteria co-infected mice, the survival rate is obviously increased, lung lesions are obviously relieved, the targeted complement inhibition effect is obvious, and the C3d-ScFv-CD59 has an obvious treatment effect compared with the single effector molecule CD59, and it proves that the fusion protein provided by the invention has an excellent application prospect in preparation of drugs for treating influenza virus and bacteria co-infected pneumonia.
Owner:中国人民解放军疾病预防控制中心
Human target complement inhibitor protein mcr2-daf and its application
ActiveCN109929026BTurn easilyA clear dose-dependent relationshipCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunologic disordersAutoimmune condition
The invention discloses a complement receptor 2 variant, a fusion protein of the complement receptor 2 variant and a complement inhibitor and application of the fusion protein in preparing a medicament for treating autoimmune diseases. The complement receptor 2 variant is a molecular modified body obtained after computer modeling and amino acid replacement, has higher ligand binding and dissociation rate and better ligand binding force than a wild sequence of the complement receptor 2 variant. The biological distribution experiment proves that the fusion protein provided by the invention can rapidly and highly aggregate at an arthritis part after entering a rheumatoid arthritis mouse model, and has a remarkable anti-adhesion / anti-inflammation targeted inhibition effect. In the treatment ofMRL / lpr lupus erythematosus mice, the fusion protein can obviously improve the survival rate of the mice, and symptoms such as proteinuria, glomerular integral, interstitial inflammation, vasculitis,crescent / necrosis and the like of the mice in the treatment group are obviously improved.
Owner:BEIJING COMPLEMENT THERAPEUTICS LTD
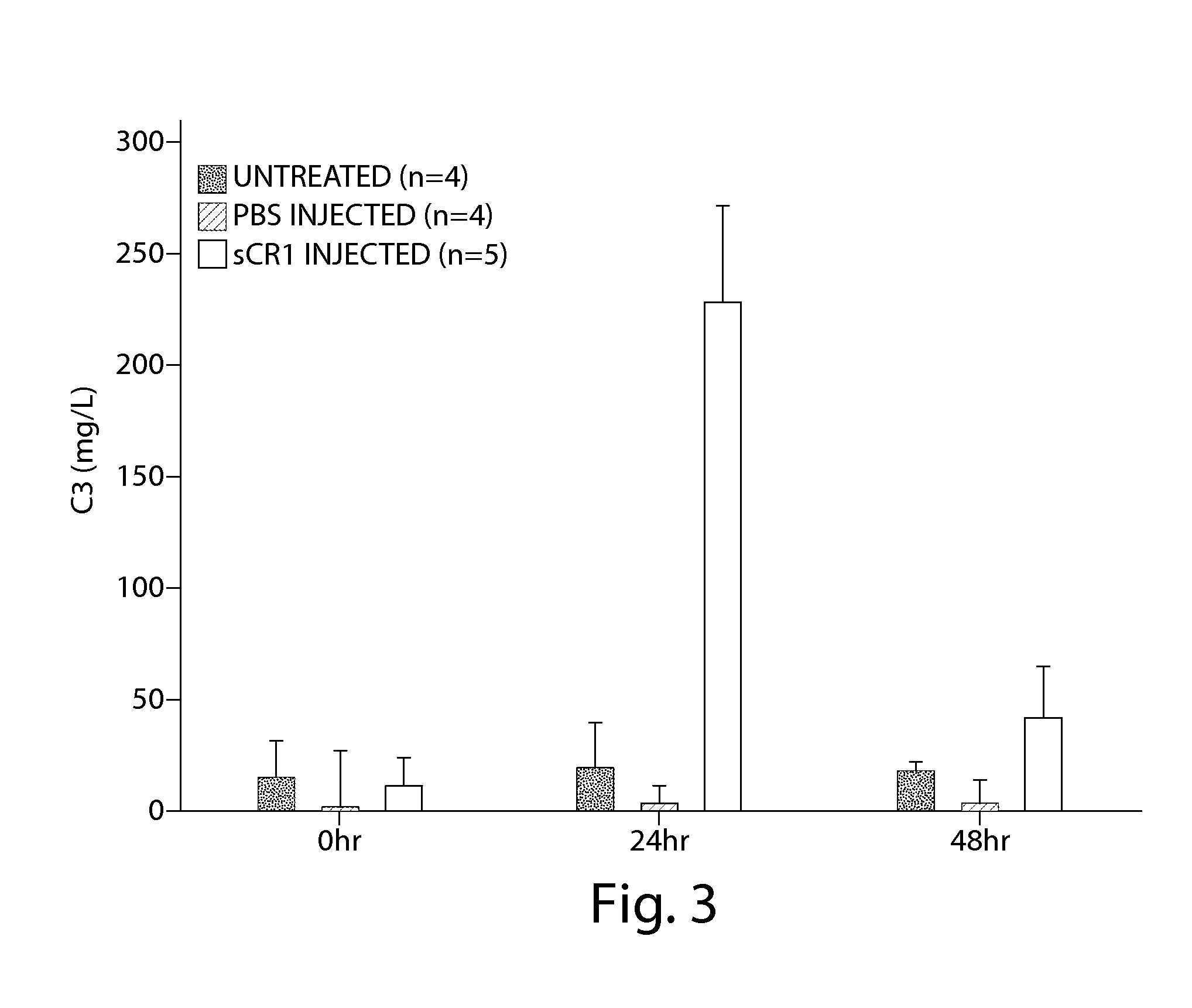
Treatment of chronic nephropathies using soluble complement receptor type I (sCR1)
ActiveUS9295713B2Reduces C depositionReduce depositionPeptide/protein ingredientsUrinary disorderNephrosisBiological activation
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND +1
Prunella vulgaris polysaccharide and its preparation method and use
InactiveCN103626880BStrong anti-complement activityDoes not affect anticoagulant effectOrganic active ingredientsImmunological disordersIn vitro testIn vivo
The invention belongs to the field of Chinese medicine, relates to Prunella vulgaris polysaccharide, and a preparation method and purpose thereof in preparing anticomplement medicines. The Prunella vulgaris polysaccharide including uniform polysaccharide PW-PS1 and PW-PS2 is prepared from a dry fruit aqueous extract of a labiatae plant Prunella vulgaris Linn. Through in vitro tests, the uniform polysaccharide is proved to have strong anticomplement activity and inhibition effects on classical pathway and alternative pathway of a complement system; besides, the polysaccharide does not have the anticoagulant effect influencing in vivo activity and can be used for the preparation of complement inhibition medicaments. The PW-PS1 effects on C1q, C3 and C9 components of the complement system, and the PW-PS2 effects on the C1q, C2, C3, C5 and C9 components of the complement system.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com