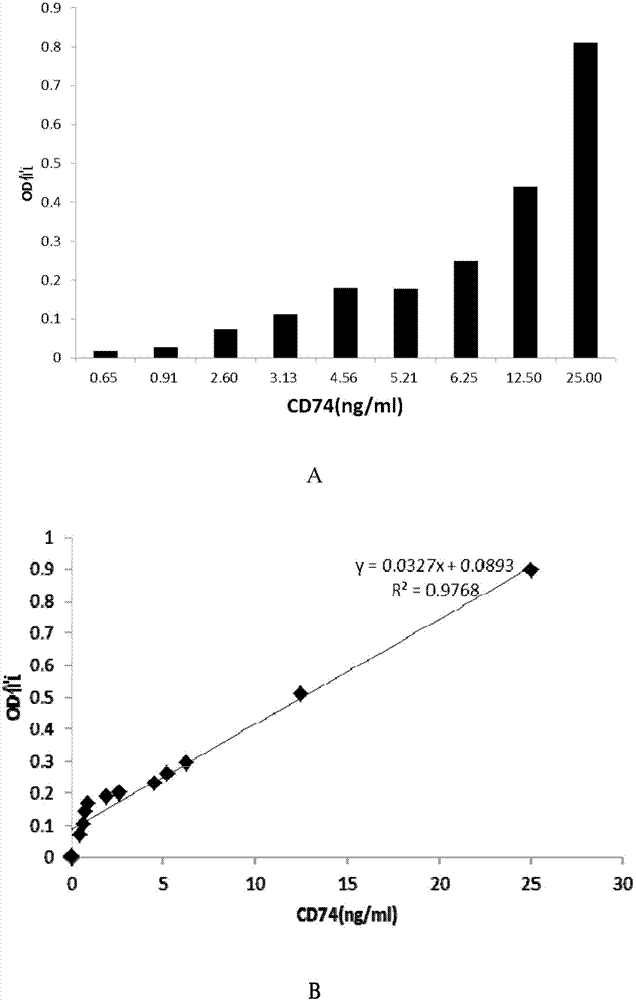
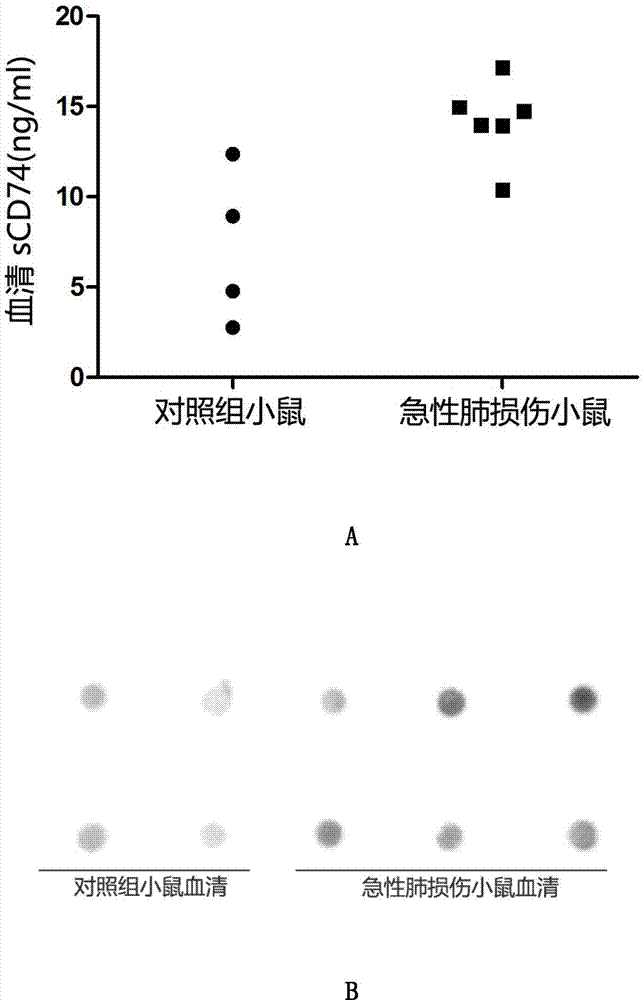
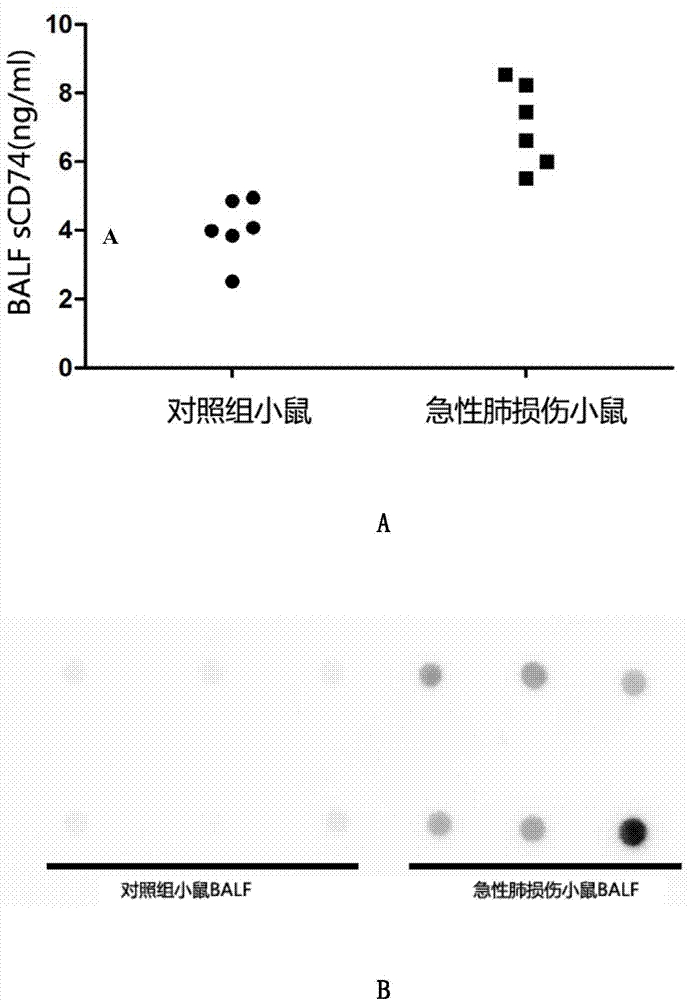
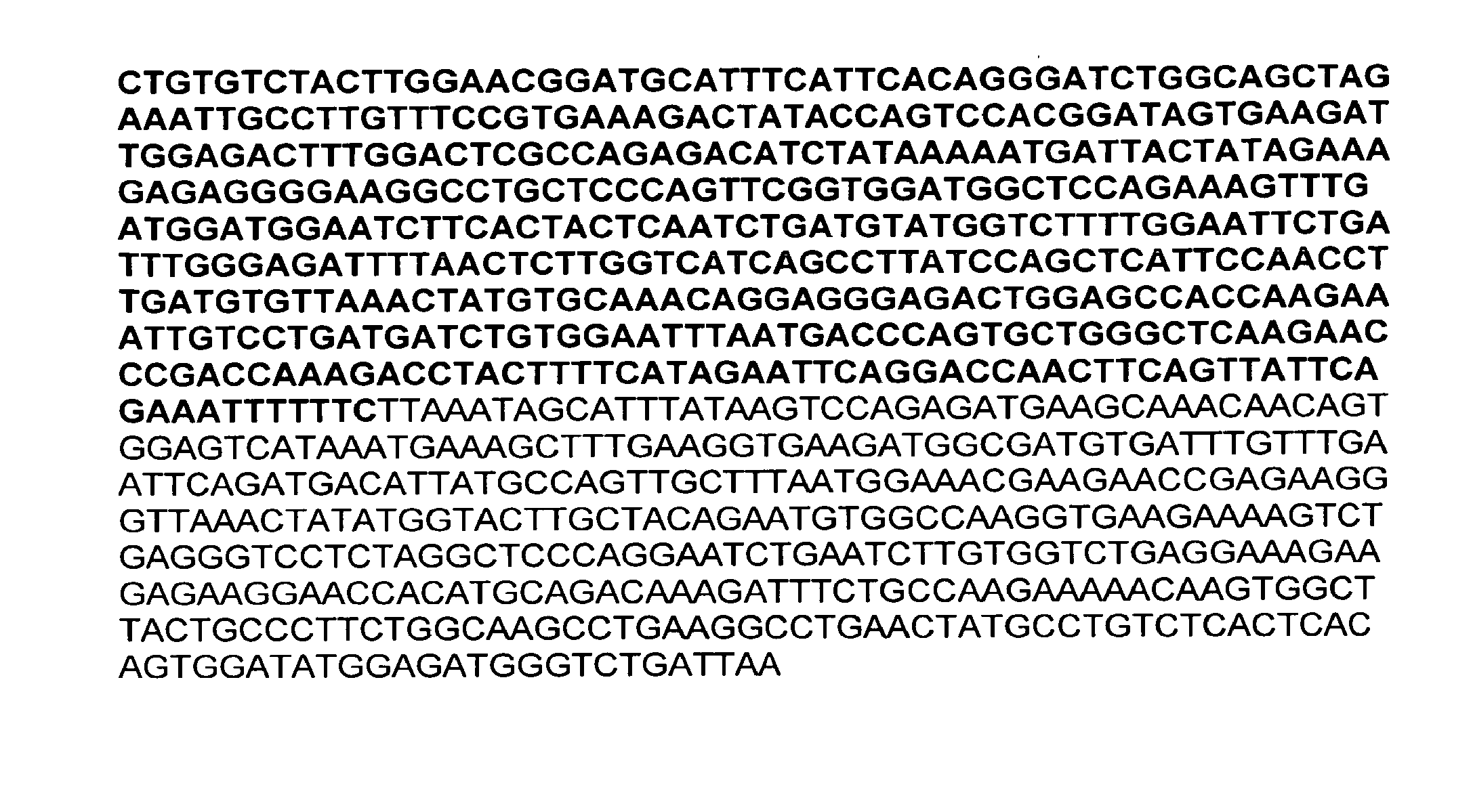Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38 results about "CD74" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
HLA class II histocompatibility antigen gamma chain also known as HLA-DR antigens-associated invariant chain or CD74 (Cluster of Differentiation 74), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD74 gene. The invariant chain (Abbreviated Ii) is a polypeptide involved in the formation and transport of MHC class II protein. The cell surface form of the invariant chain is known as CD74.
Disease therapy with chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) constructs and t cells (car-t) or nk cells (car-nk) expressing car constructs
InactiveUS20160361360A1Maintain self-toleranceModulate durationAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsAutoimmune conditionDebulking Procedure
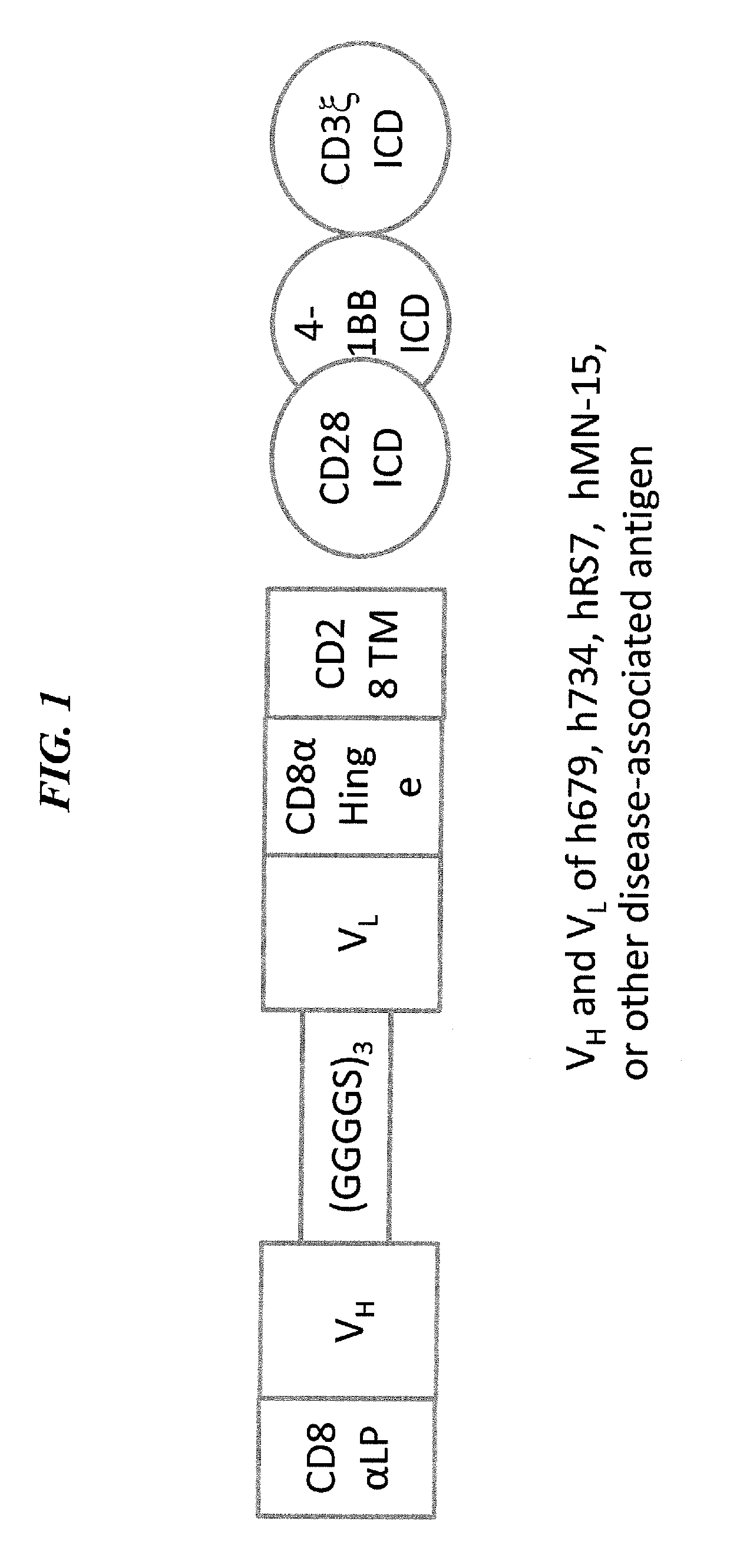
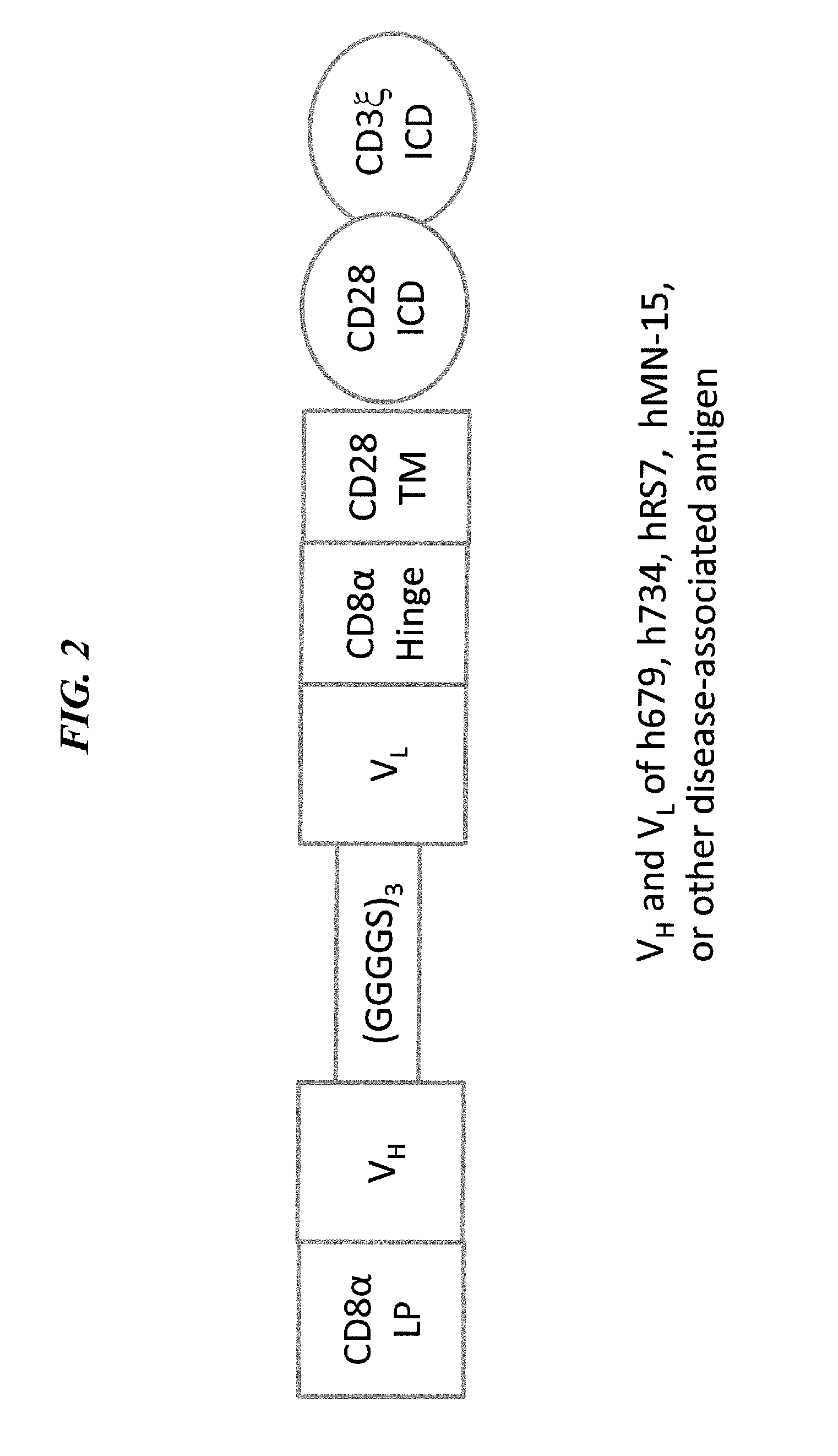
The present invention concerns CAR, CAR-T and CAR-NK constructs, preferably comprising a scFv antibody fragment against a disease-associated antigen or a hapten. More preferably, the antigen is a TAA, such as Trop-2. The constructs may be administered to a subject with a disease, such as cancer, autoimmune disease, or immune dysfunction disease, to induce an immune response against disease-associated cells. Where the constructs bind to a hapten, the subject is first treated with a hapten-conjugated antibody that binds to a disease associated antigen. Therapy may be supplemented by other treatments, such as debulking procedures (e.g., surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy) or coadministration of other agents. More preferably, administration of the construct is preceded by predosing with an unconjugated antibody that binds to the same disease-associated antigen. Most preferably, an antibody against CD74 or HLA-DR is administered to reduce systemic immunotoxicity induced by the constructs.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
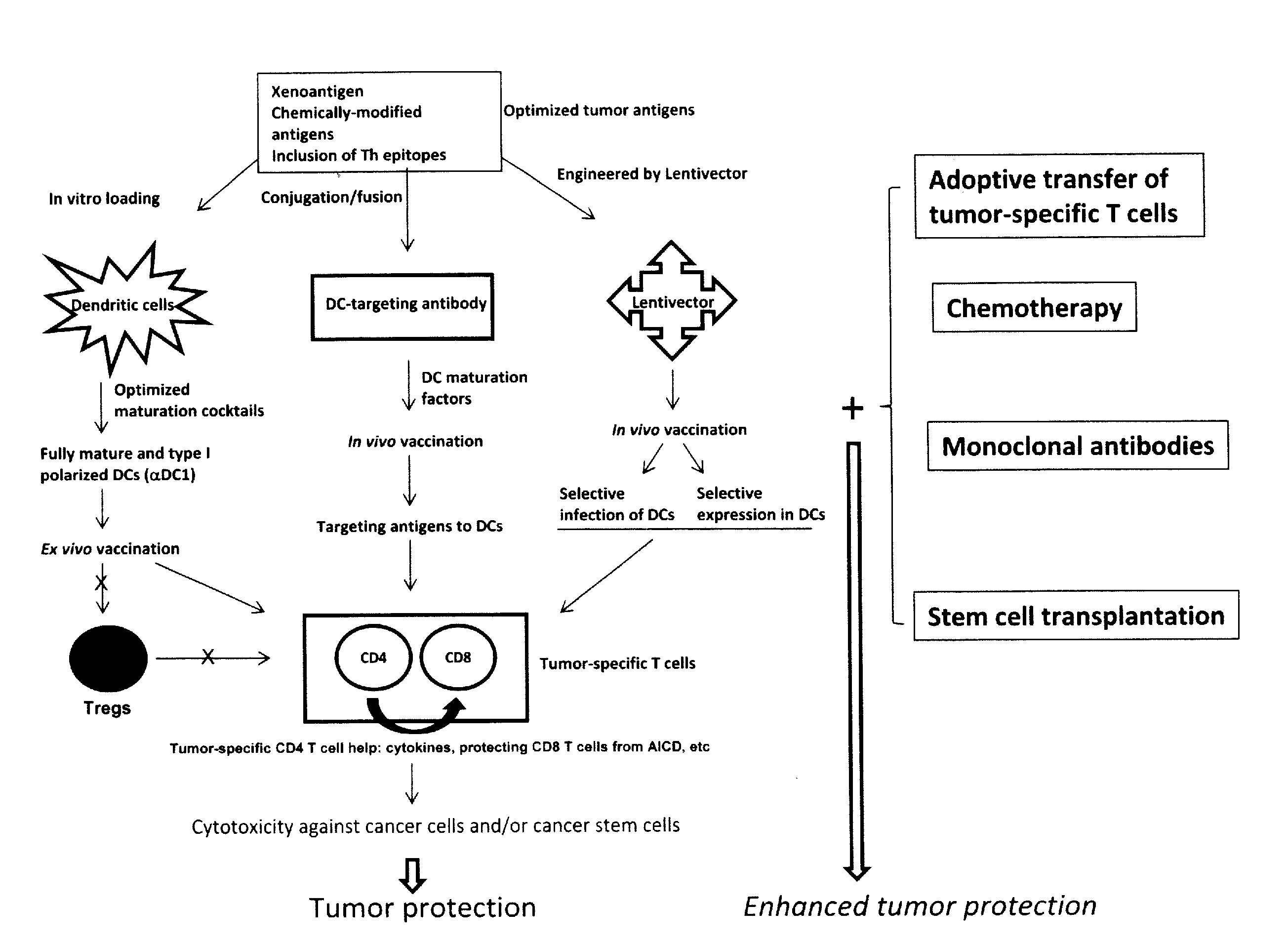
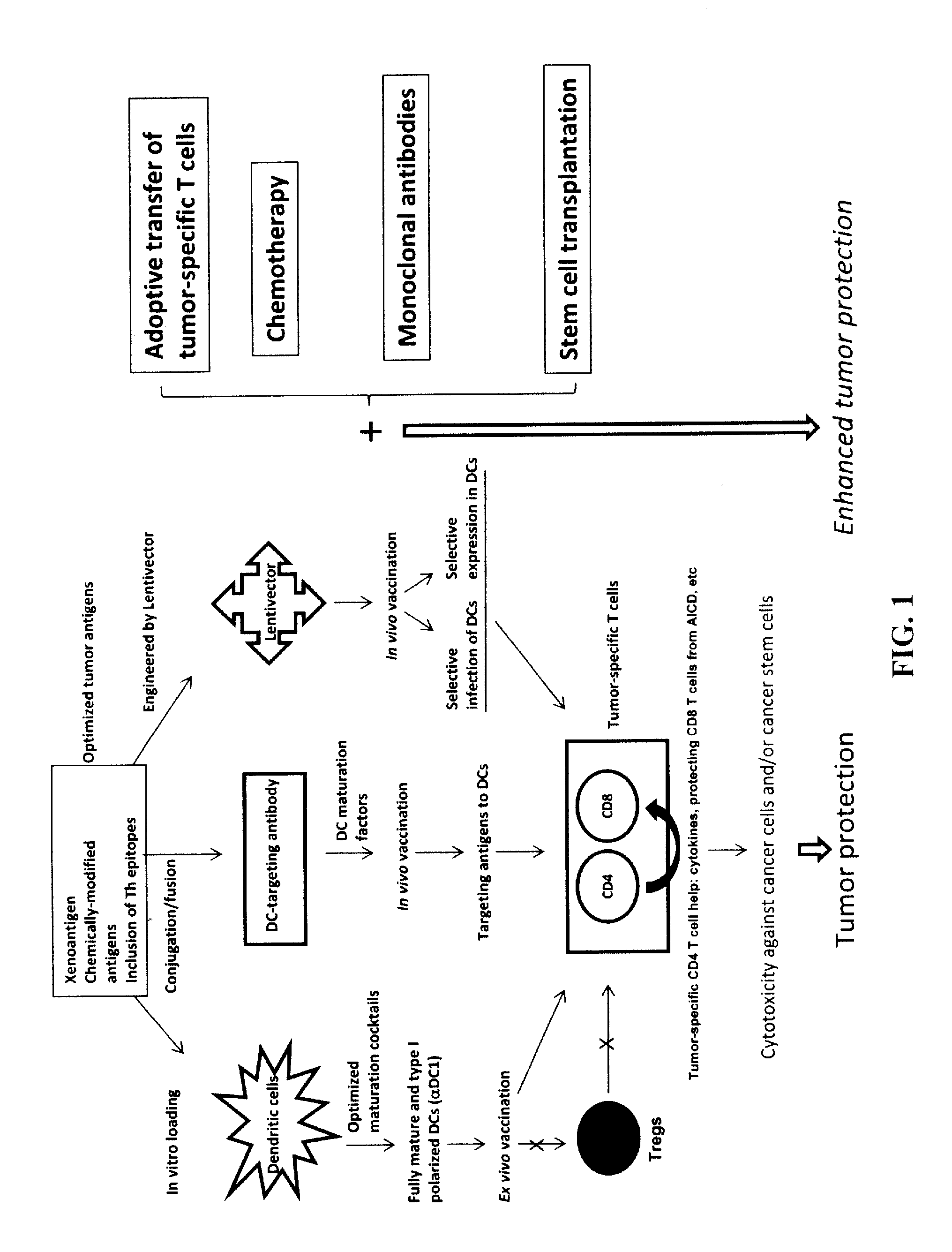
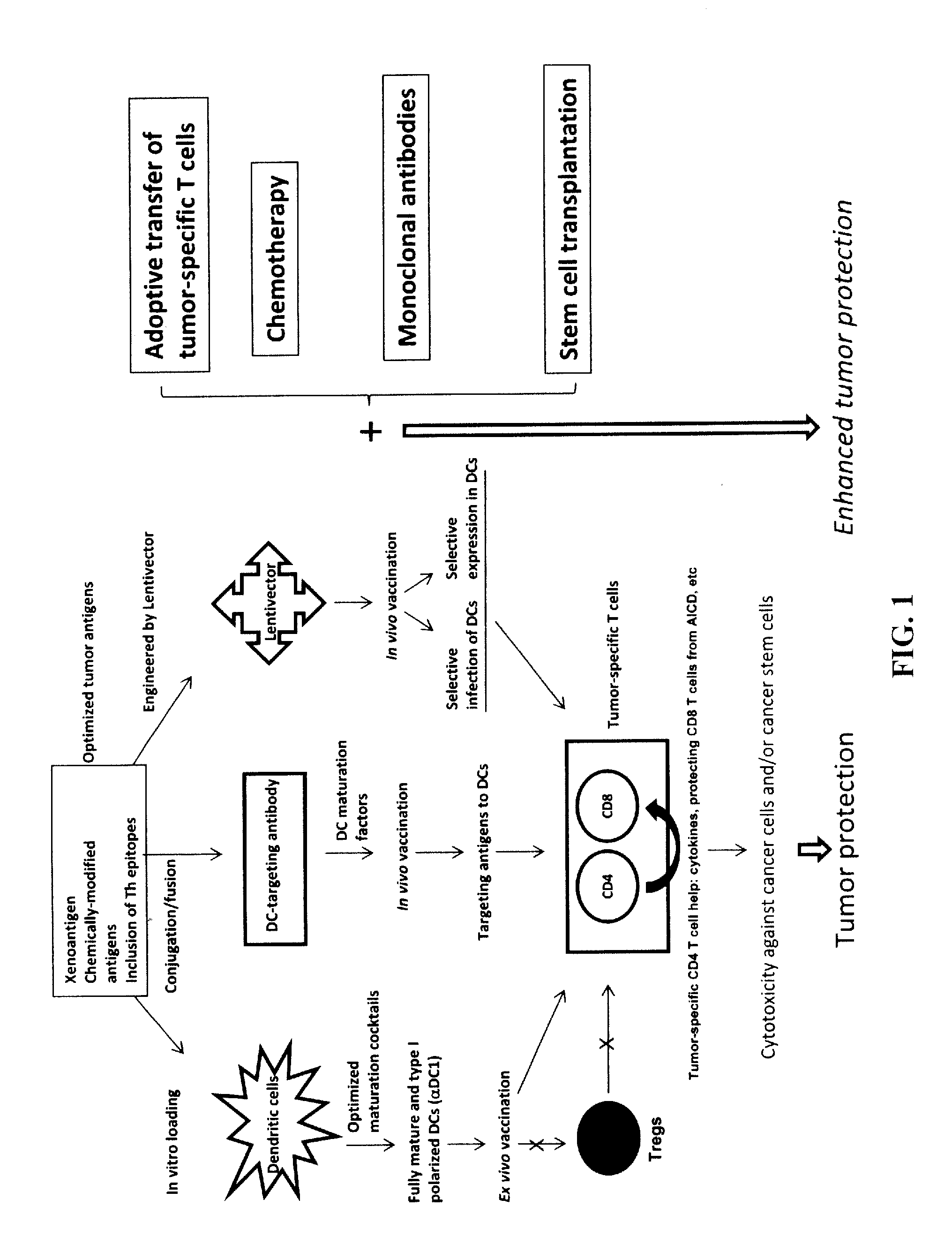
Novel Strategies for Improved Cancer Vaccines
The present invention concerns methods and compositions for forming anti-cancer vaccine complexes. In preferred embodiments, the anti-cancer vaccine complex comprises an antibody moiety that binds to dendritic cells, such as an anti-CD74 antibody or antigen-binding fragment thereof, attached to an AD (anchoring domain) moiety and a xenoantigen, such as CD20, attached to a DDD (dimerization and docking domain) moiety, wherein two copies of the DDD moiety form a dimer that binds to the AD moiety, resulting in the formation of the vaccine complex. The anti-cancer vaccine complex is capable of inducing an immune response against xenoantigen expressing cancer cells, such as CD138negCD20+ MM stem cells, and inducing apoptosis of and inhibiting the growth of or eliminating the cancer cells.
Owner:IBC PHARMACEUTICALS INC
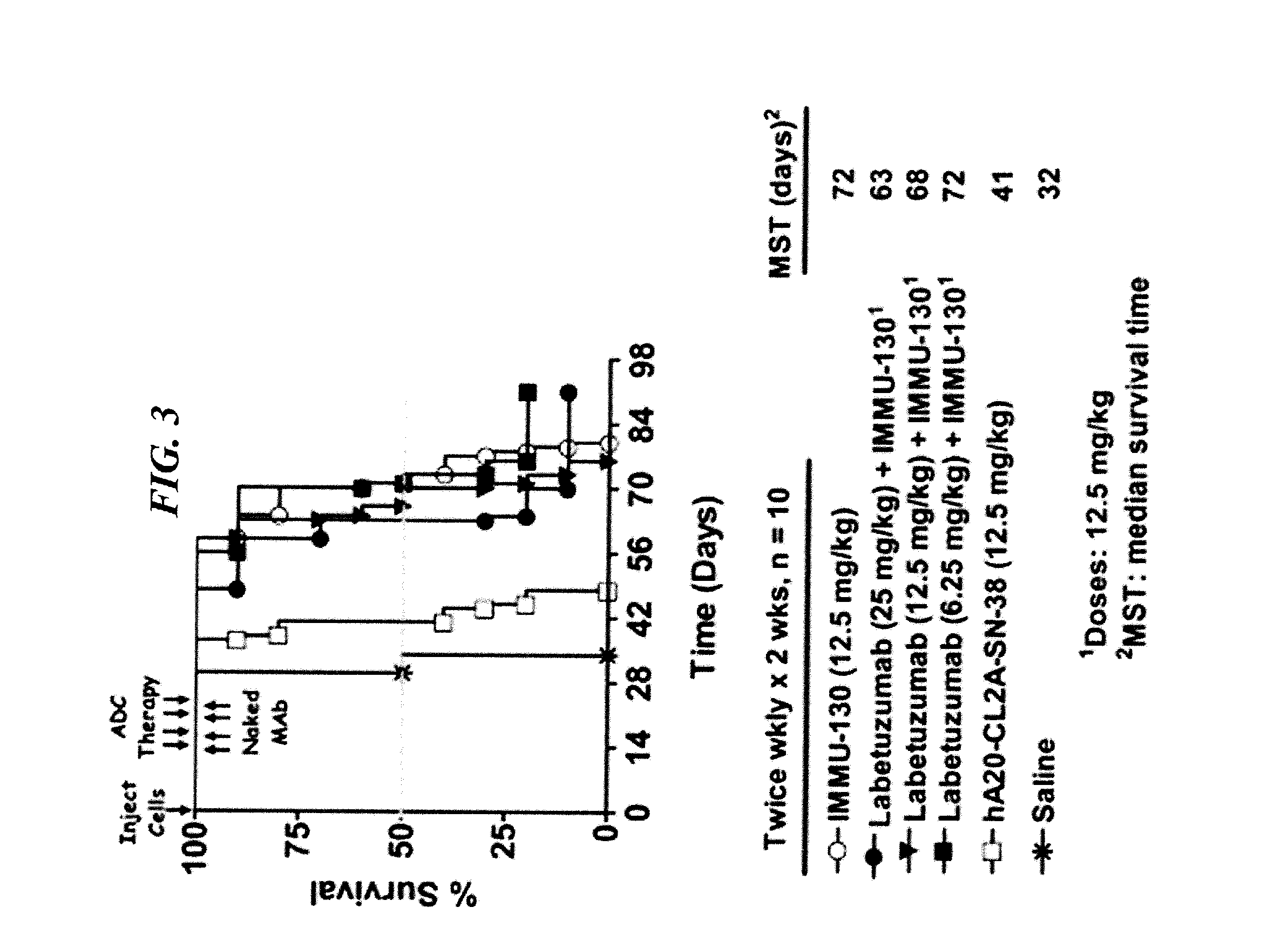
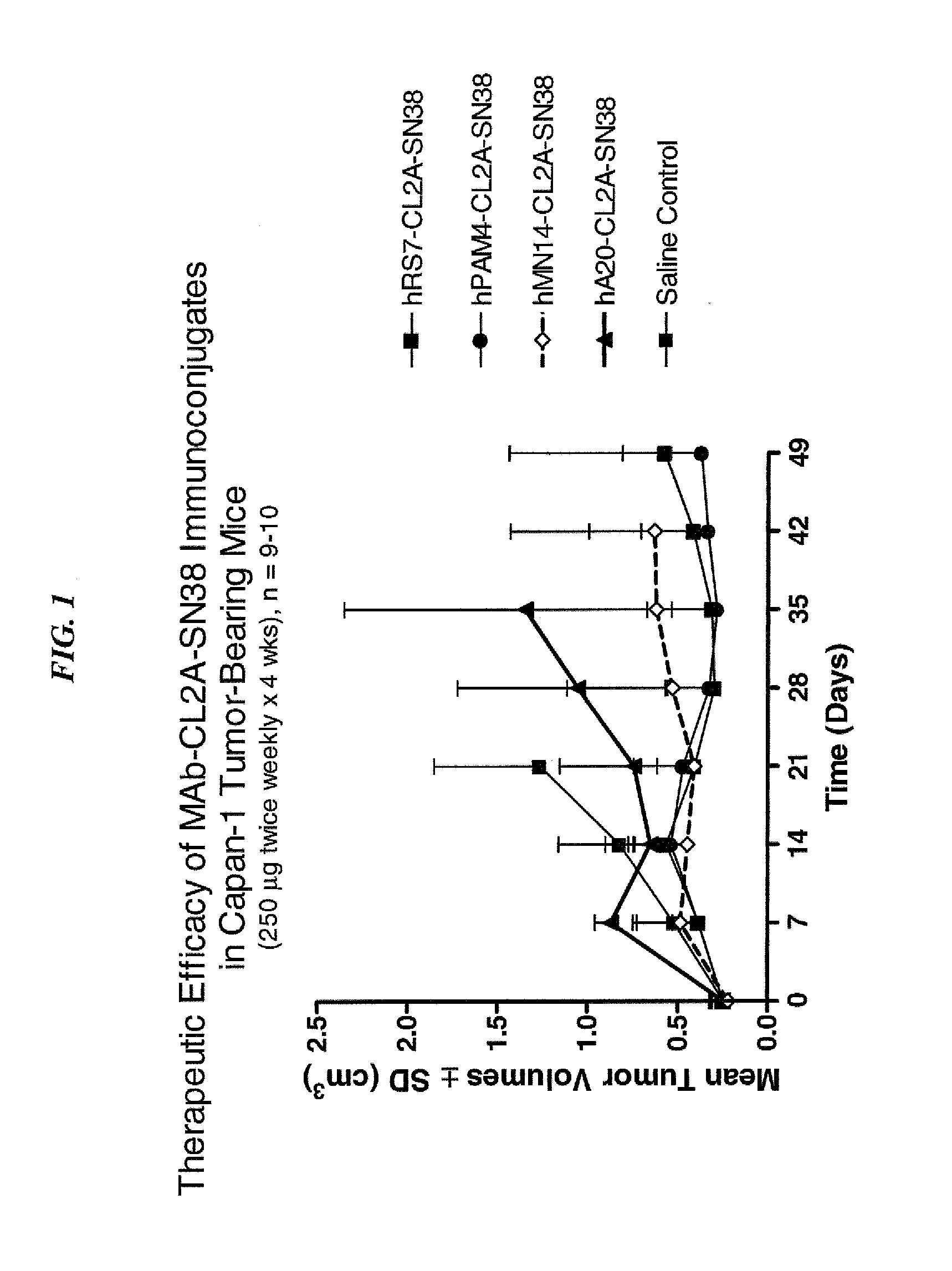
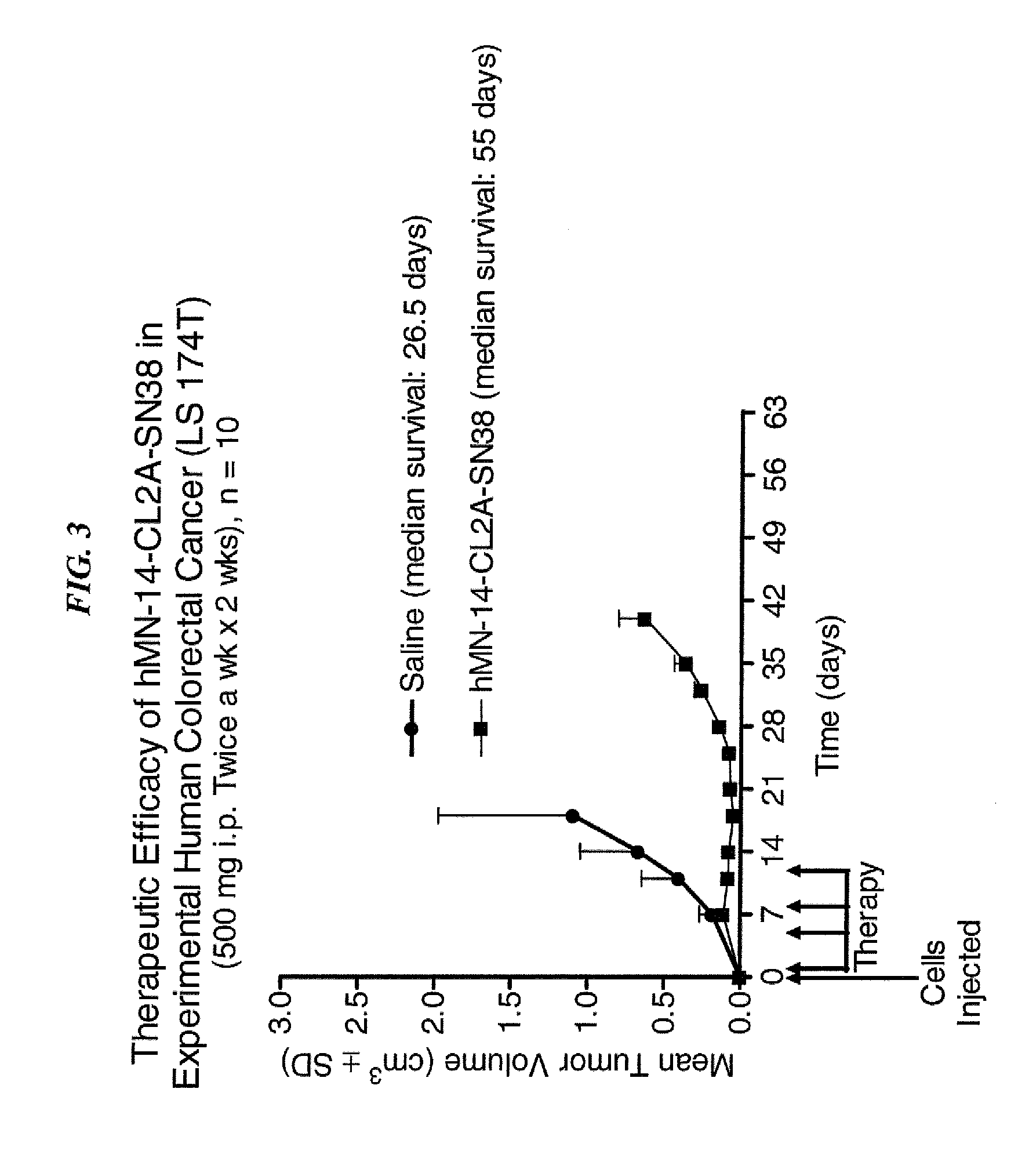
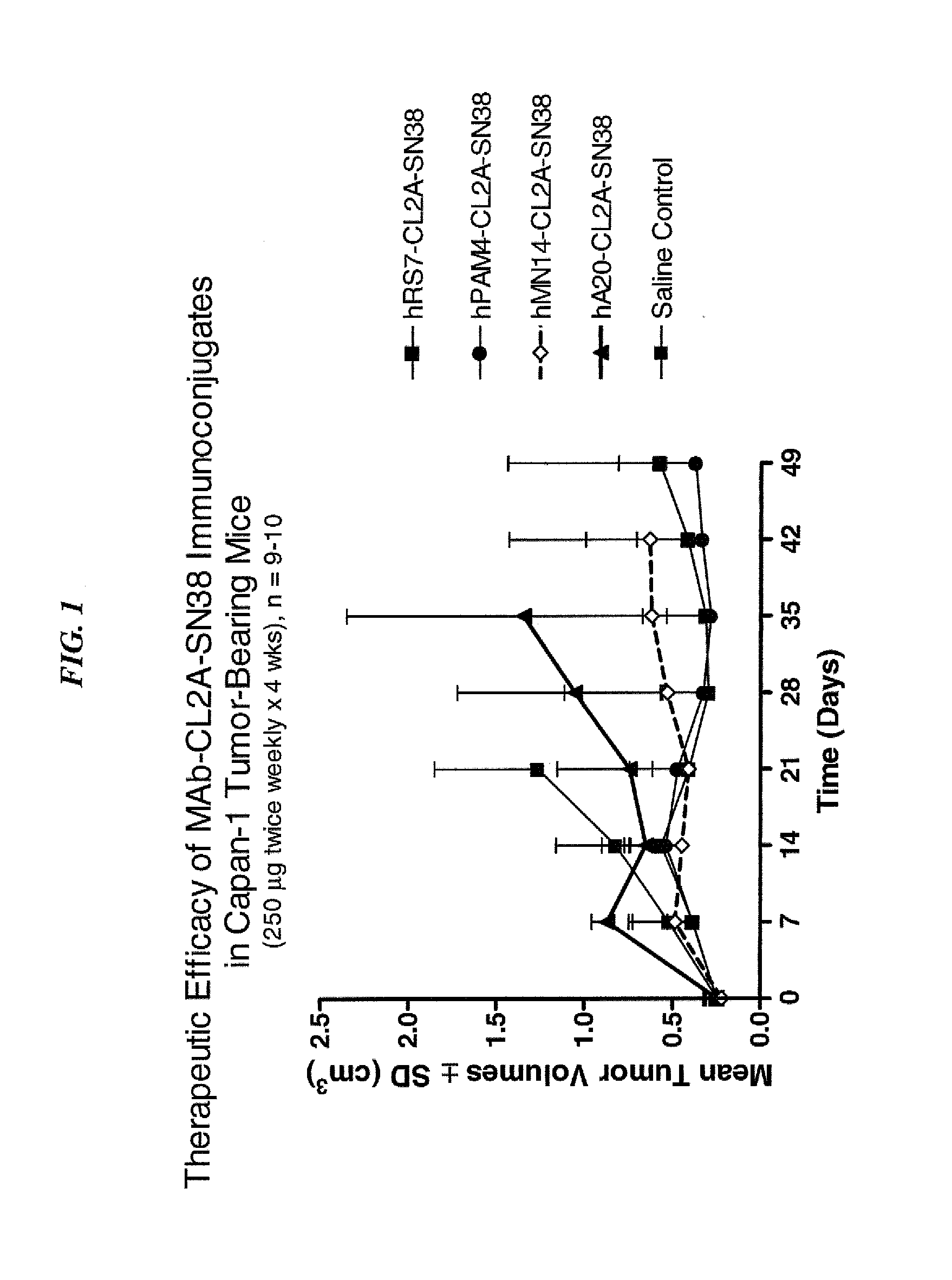
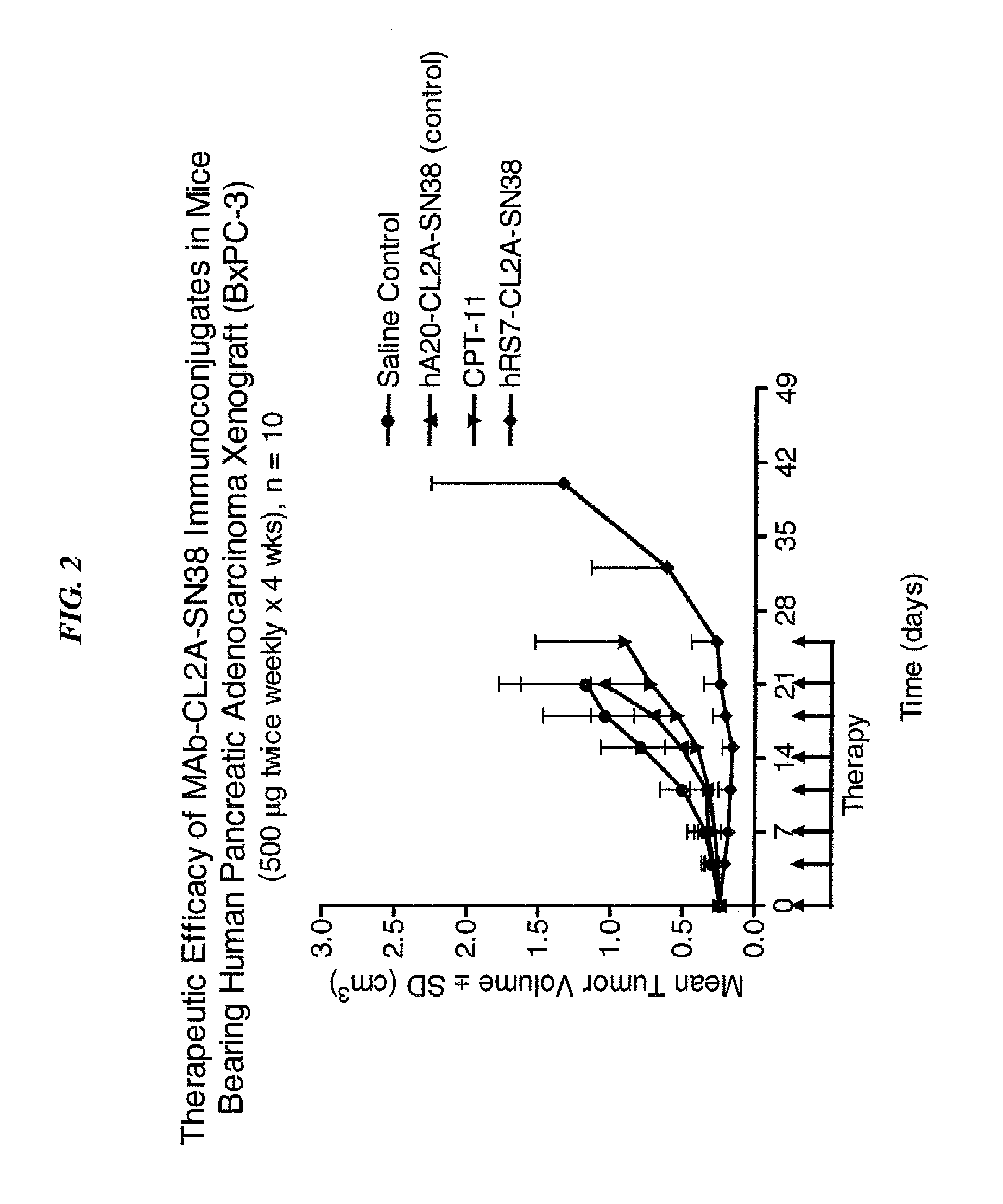
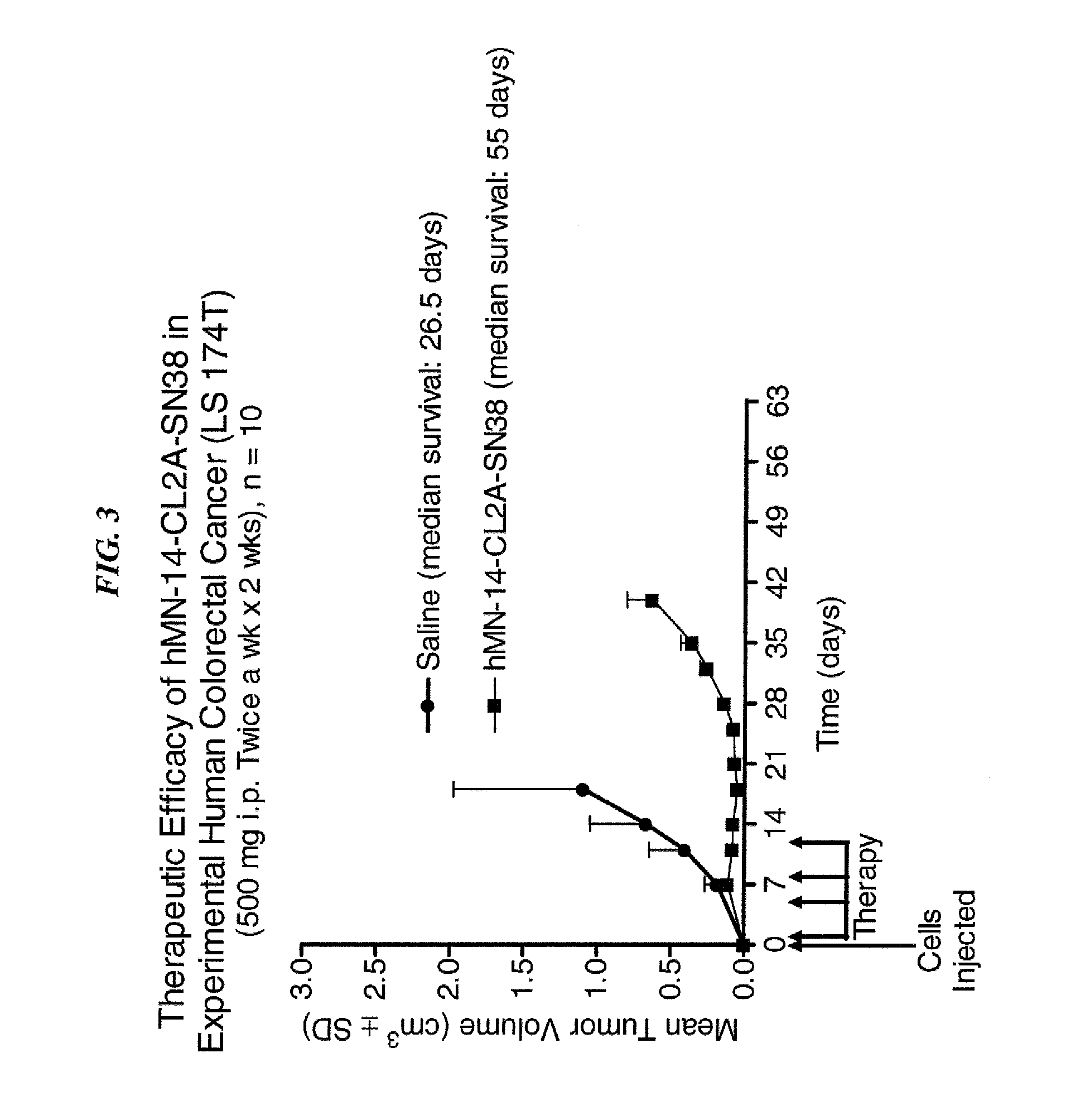
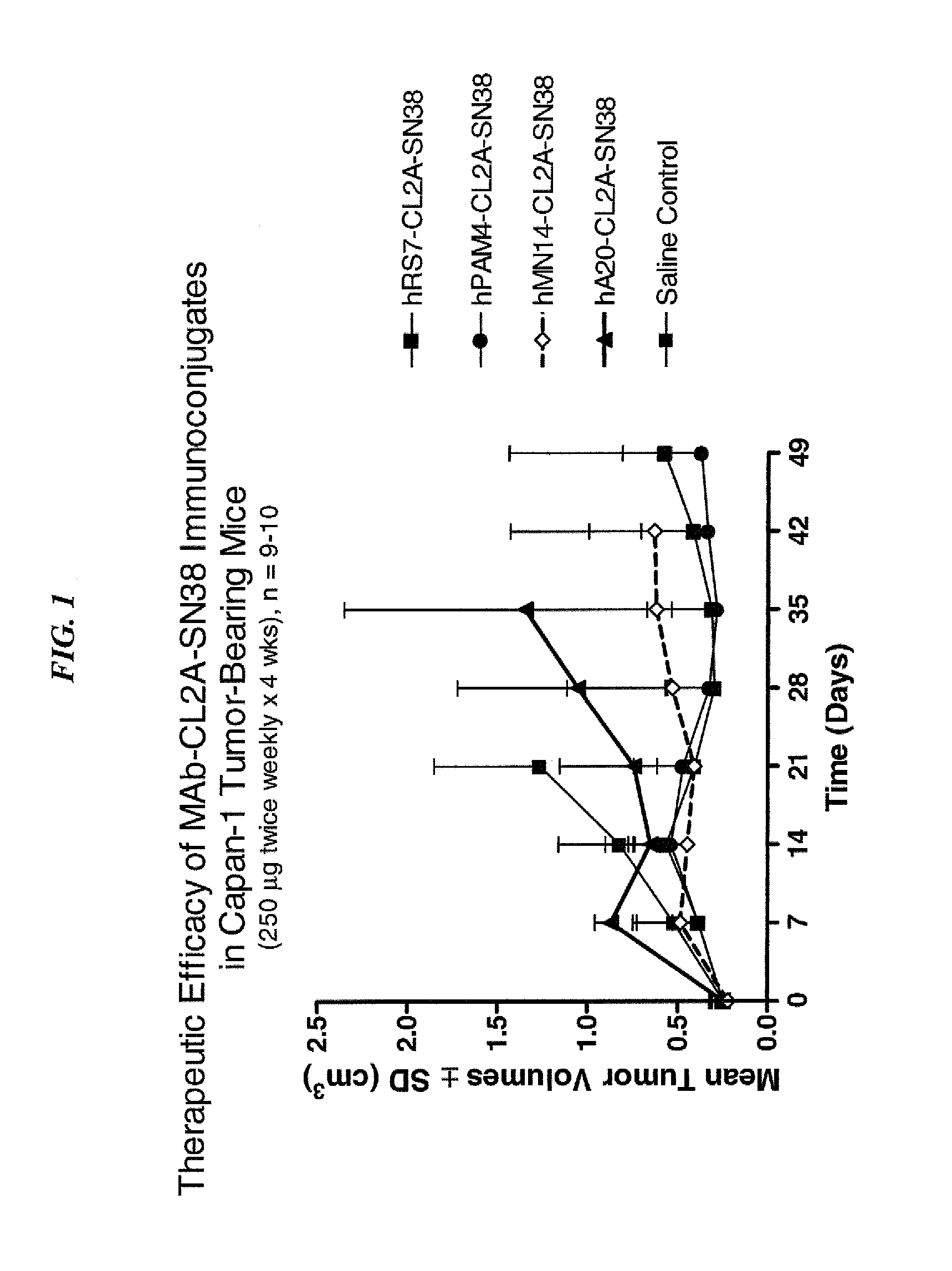
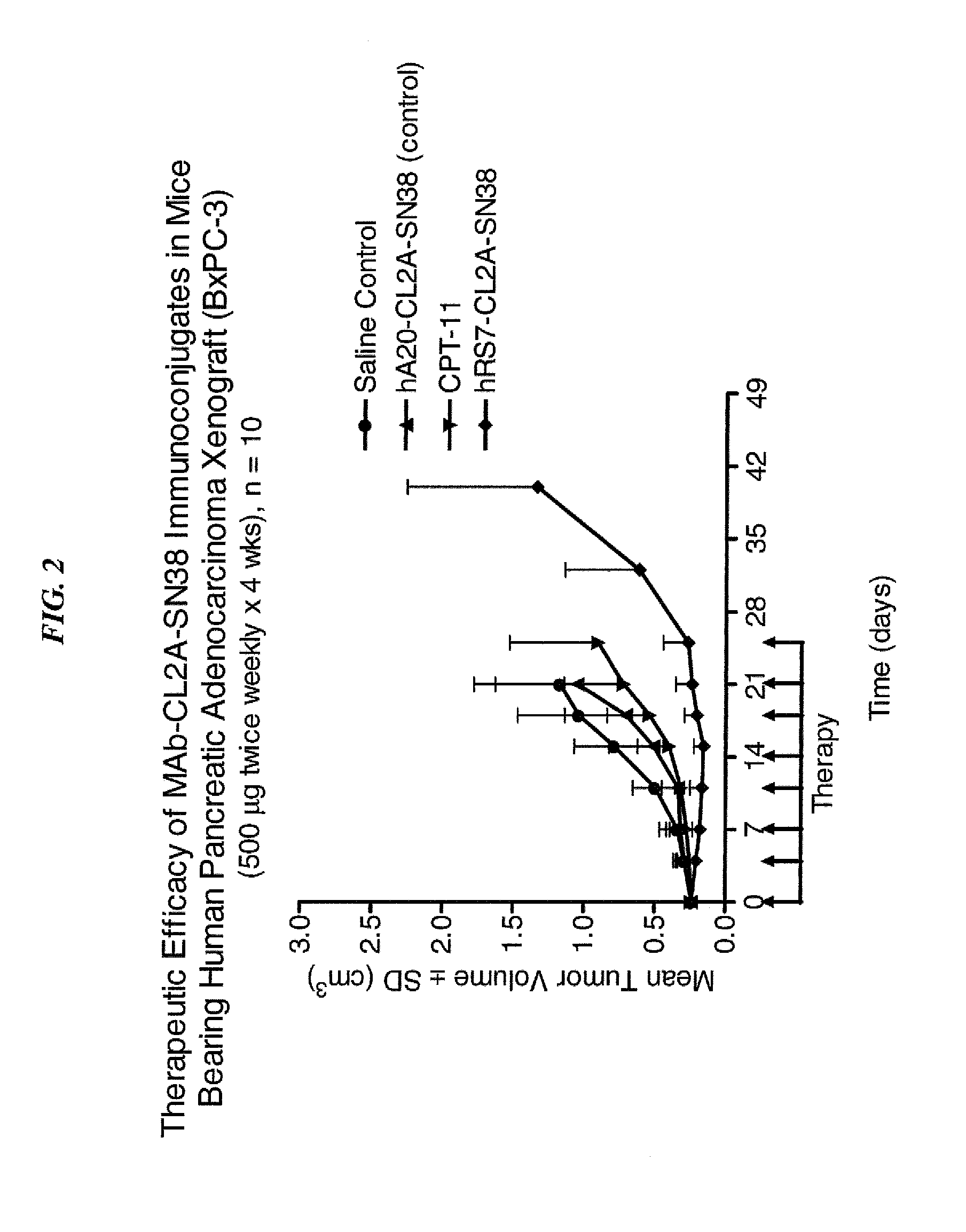
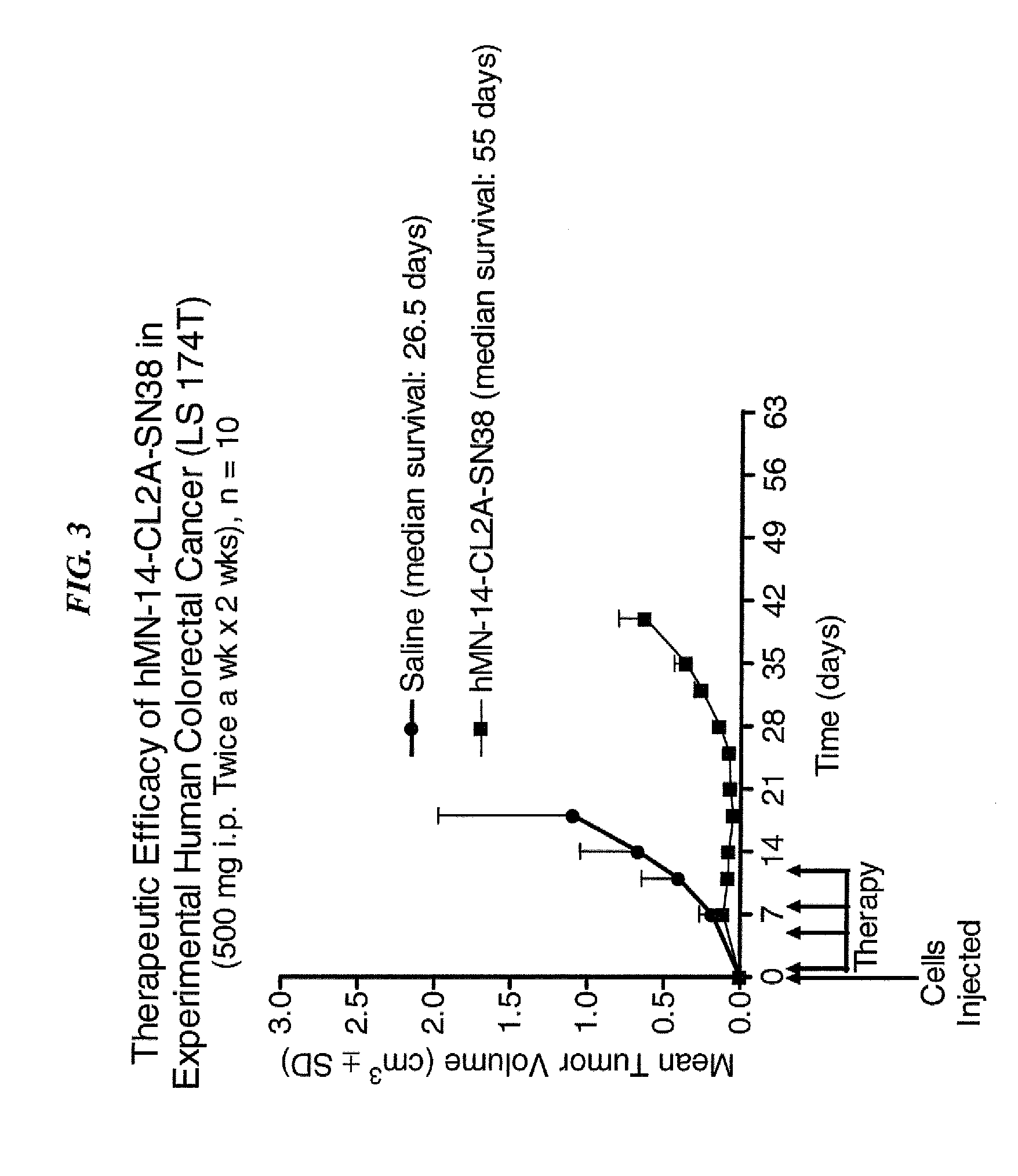
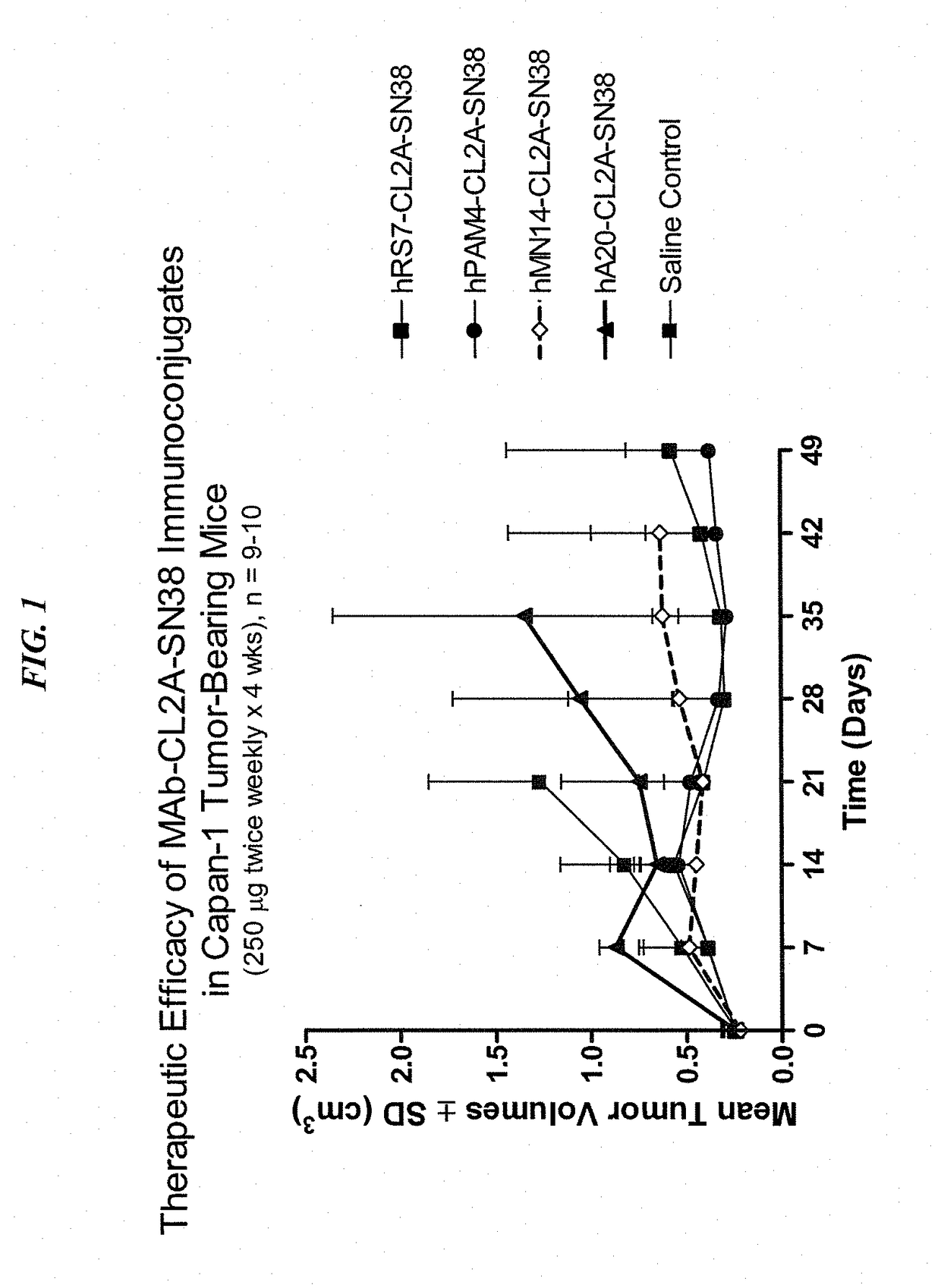
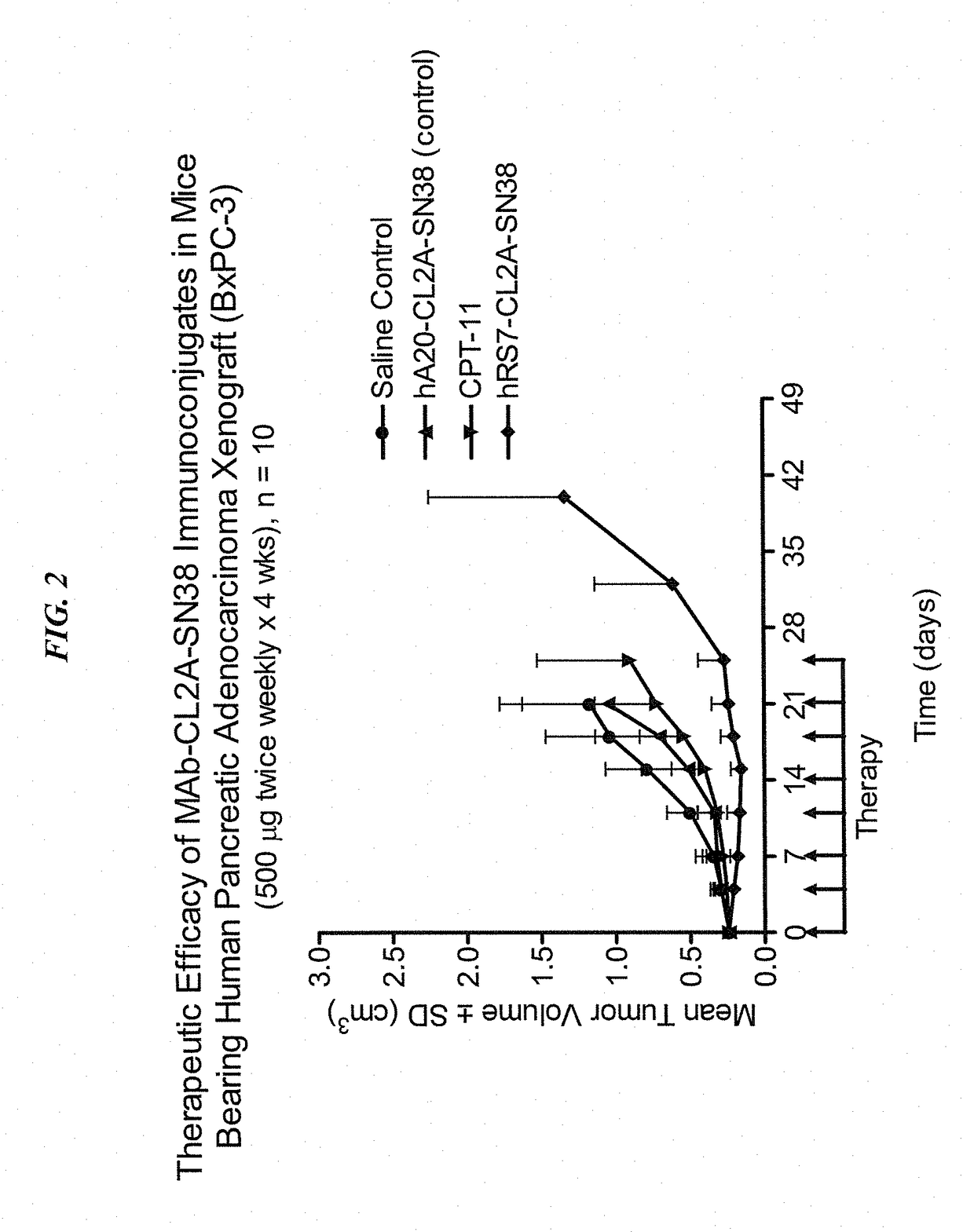
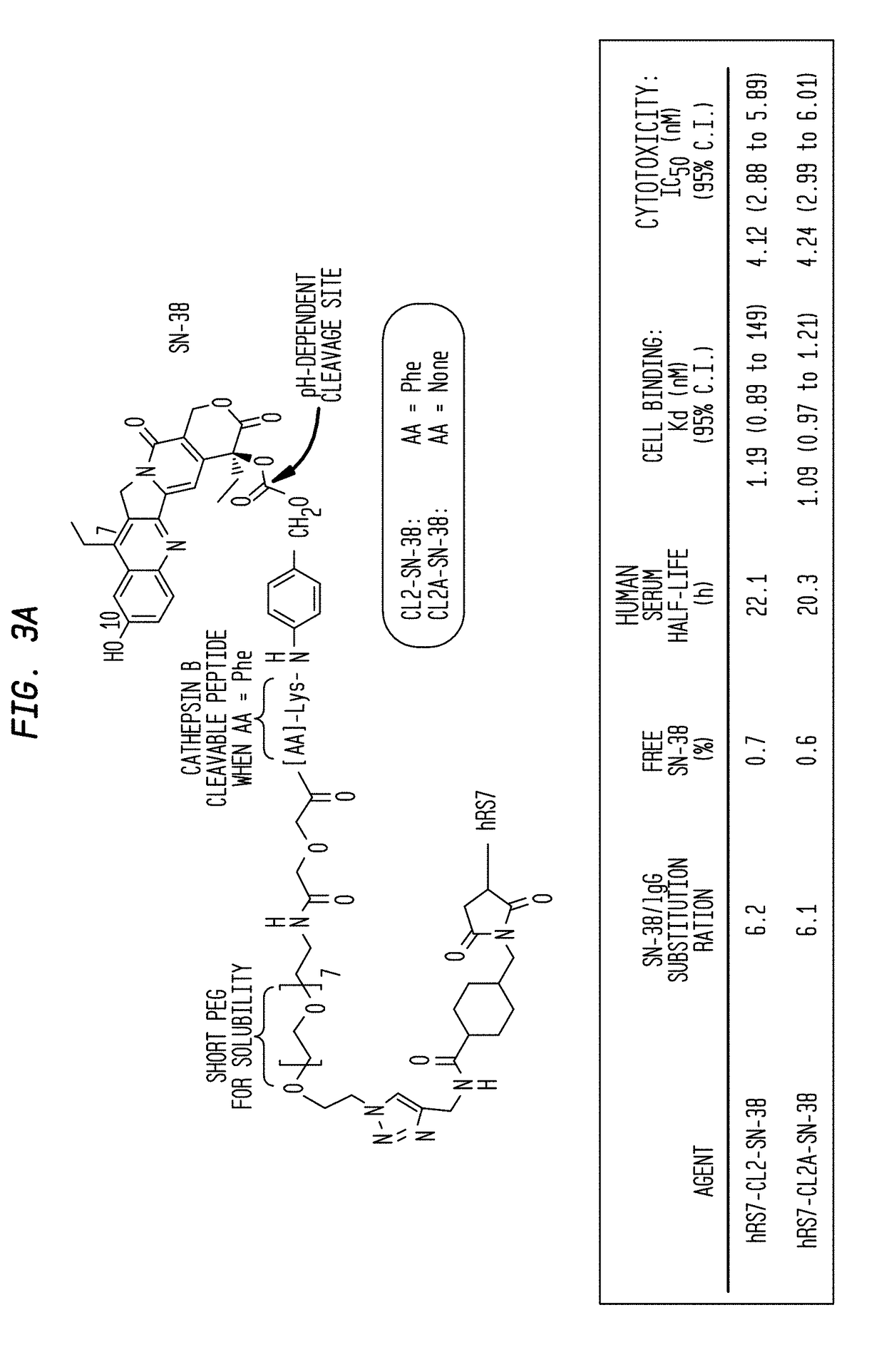
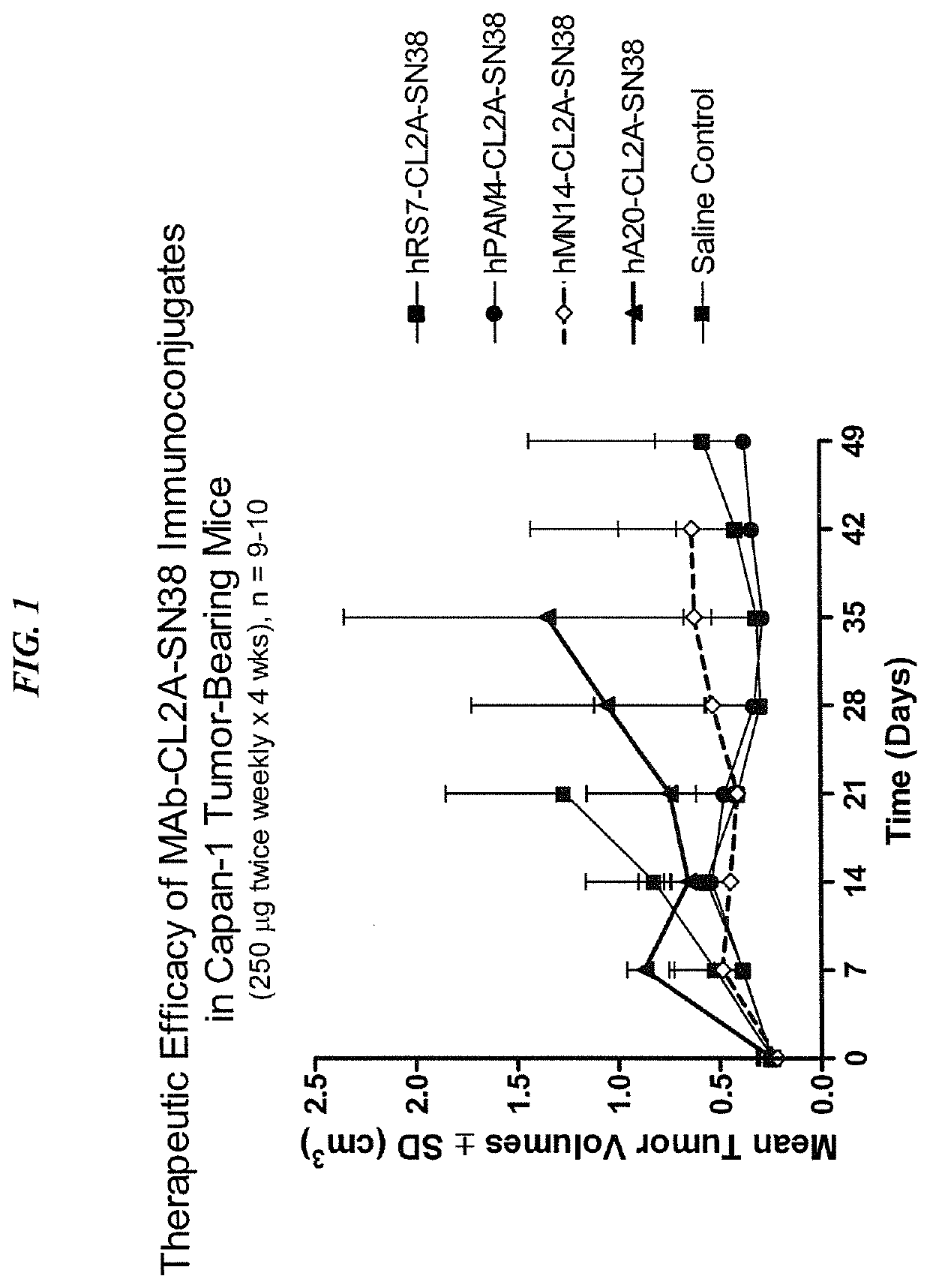
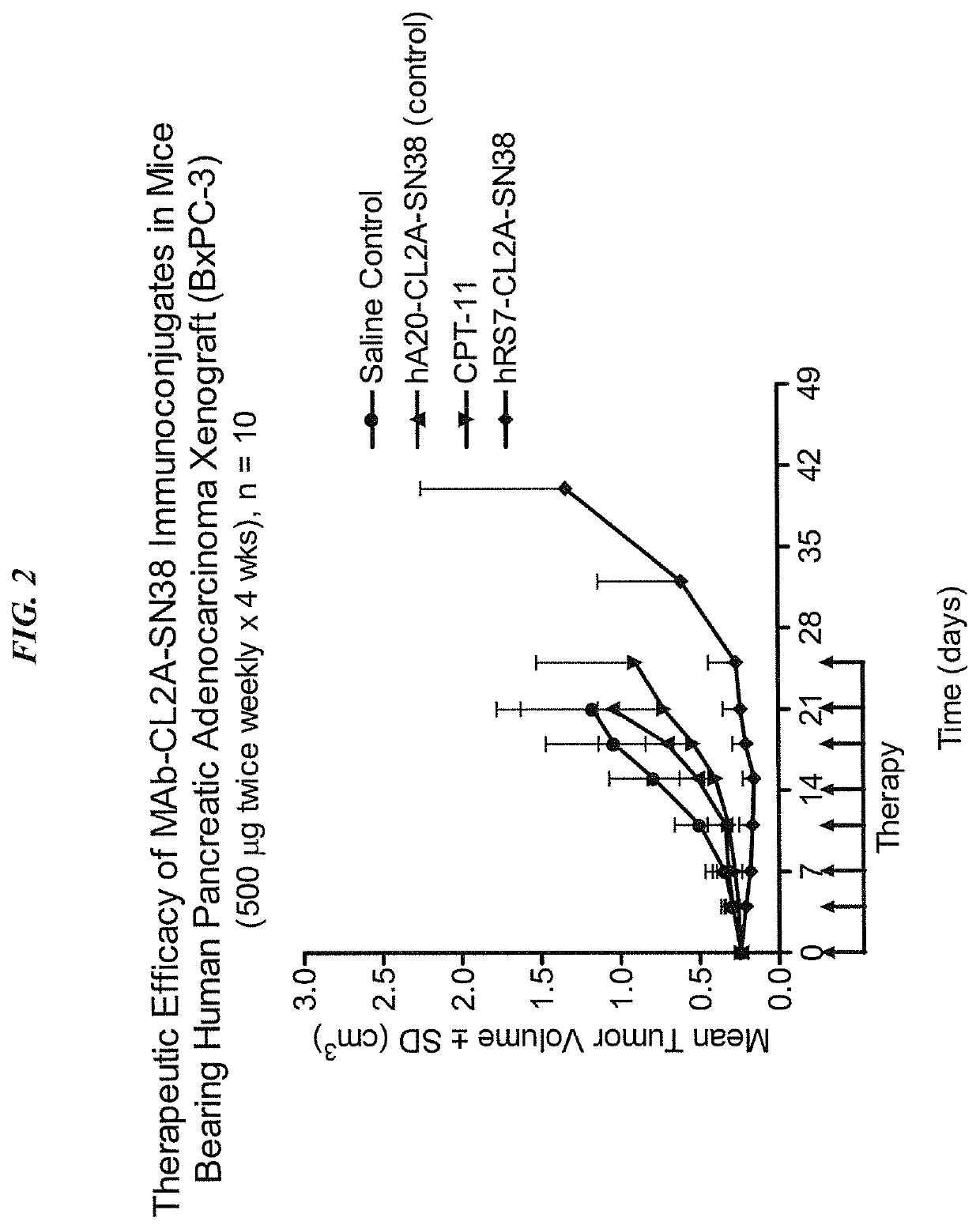
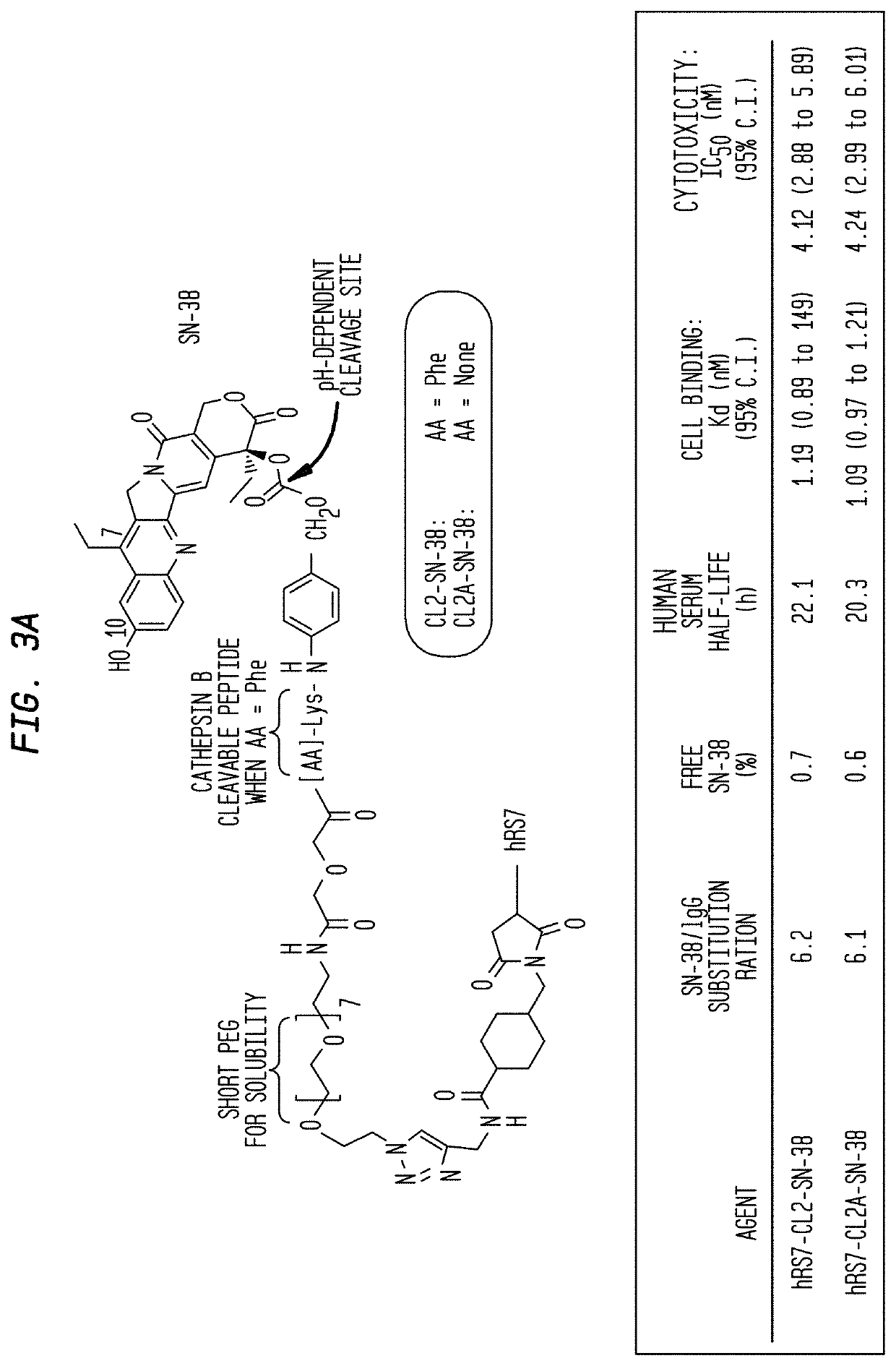
Dosages of Immunoconjugates of Antibodies and SN-38 for Improved Efficacy and Decreased Toxicity
ActiveUS20140170063A1Overcome tumorImprove targetingHeavy metal active ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsCD20Lymphatic Spread
The present invention relates to therapeutic immunoconjugates comprising SN-38 attached to an antibody or antigen-binding antibody fragment. The antibody may bind to EGP-1 ROP-2), CEACAM5, CEACAM6, CD74, CD19, CD20, CD22, CSAp, HLA-DR, AFP or MUC5ac and the immunoconjugate may be administered at a dosage of between 4 mg / kg and 24 mg / kg, preferably 4, 6, 8, 9, 10, 12, 16 or 18 mg / kg. When administered at specified dosages and schedules, the immunoconjugate can reduce solid tumors in size, reduce or eliminate metastases and is effective to treat cancers resistant to standard therapies, such as radiation therapy, chemotherapy or immunotherapy.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Dosages of Immunoconjugates of Antibodies and SN-38 for Improved Efficacy and Decreased Toxicity
ActiveUS20140219914A1Reducing certain severe side effectsReceive treatment wellOrganic active ingredientsRadioactive preparation carriersCD20Lymphatic Spread
The present invention relates to therapeutic immunoconjugates comprising SN-38 attached to an antibody or antigen-binding antibody fragment. The antibody may bind to EGP-1 (TROP-2), CEACAM5, CEACAM6, CD74, CD19, CD20, CD22, CSAp, HLA-DR, AFP or MUC5ac and the immunoconjugate may be administered at a dosage of between 4 mg / kg and 24 mg / kg, preferably 4, 6, 8, 9, 10, 12, 16 or 18 mg / kg. When administered at specified dosages and schedules, the immunoconjugate can reduce solid tumors in size, reduce or eliminate metastases and is effective to treat cancers resistant to standard therapies, such as radiation therapy, chemotherapy or immunotherapy.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Dosages of immunoconjugates of antibodies and SN-38 for improved efficacy and decreased toxicity
ActiveUS9028833B2Reducing certain severe side effectsReceive treatment wellOrganic active ingredientsHeavy metal active ingredientsCD20Lymphatic Spread
The present invention relates to therapeutic immunoconjugates comprising SN-38 attached to an antibody or antigen-binding antibody fragment. The antibody may bind to EGP-1 (TROP-2), CEACAM5, CEACAM6, CD74, CD19, CD20, CD22, CSAp, HLA-DR, AFP or MUC5ac and the immunoconjugate may be administered at a dosage of between 4 mg / kg and 24 mg / kg, preferably 4, 6, 8, 9, 10, 12, 16 or 18 mg / kg. When administered at specified dosages and schedules, the immunoconjugate can reduce solid tumors in size, reduce or eliminate metastases and is effective to treat cancers resistant to standard therapies, such as radiation therapy, chemotherapy or immunotherapy.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Strategies for improved cancer vaccines
The present invention concerns methods and compositions for forming anti-cancer vaccine complexes. In preferred embodiments, the anti-cancer vaccine complex comprises an antibody moiety that binds to dendritic cells, such as an anti-CD74 antibody or antigen-binding fragment thereof, attached to an AD (anchoring domain) moiety and a xenoantigen, such as CD20, attached to a DDD (dimerization and docking domain) moiety, wherein two copies of the DDD moiety form a dimer that binds to the AD moiety, resulting in the formation of the vaccine complex. The anti-cancer vaccine complex is capable of inducing an immune response against xenoantigen expressing cancer cells, such as CD138negCD20+ MM stem cells, and inducing apoptosis of and inhibiting the growth of or eliminating the cancer cells.
Owner:IBC PHARMACEUTICALS INC
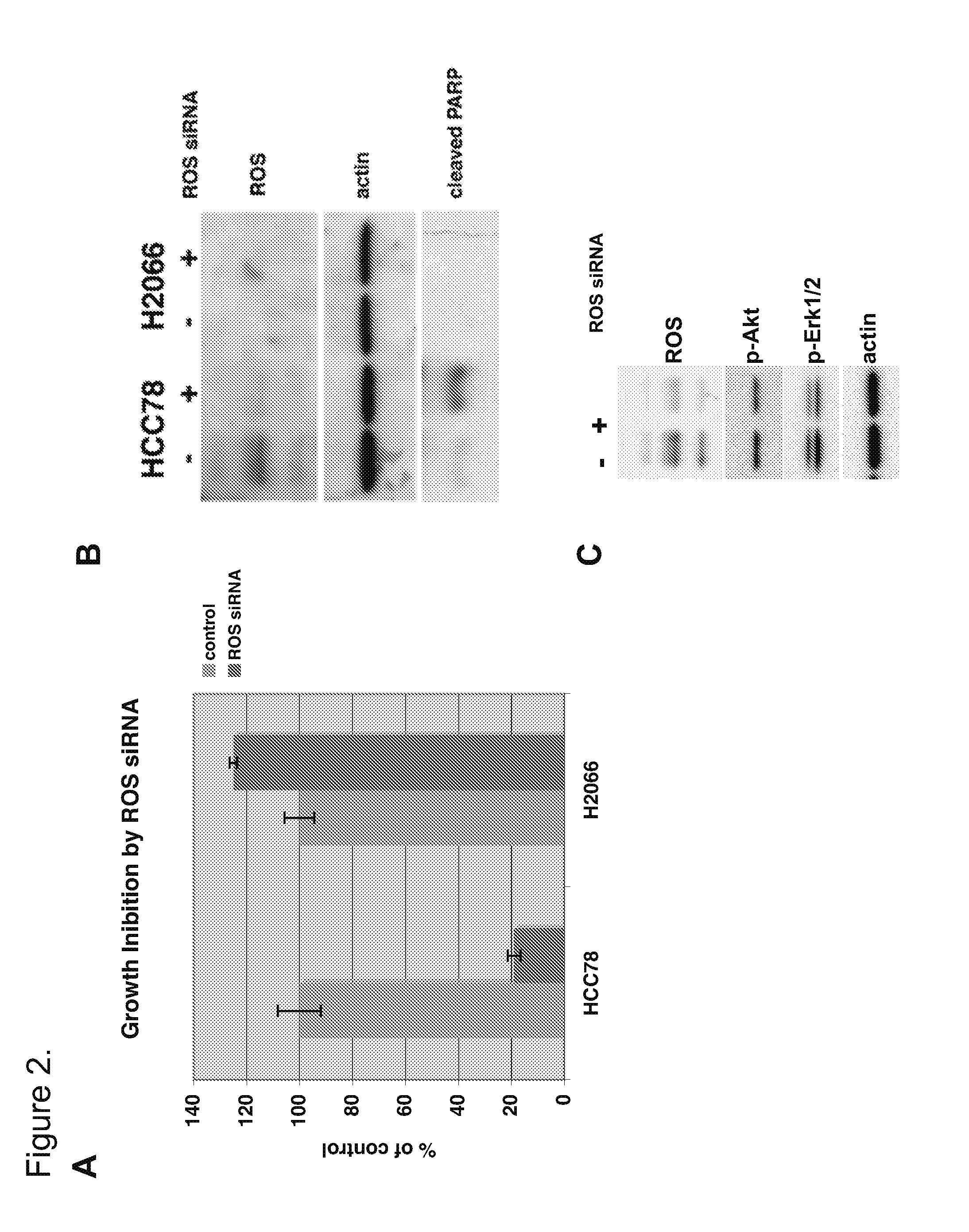
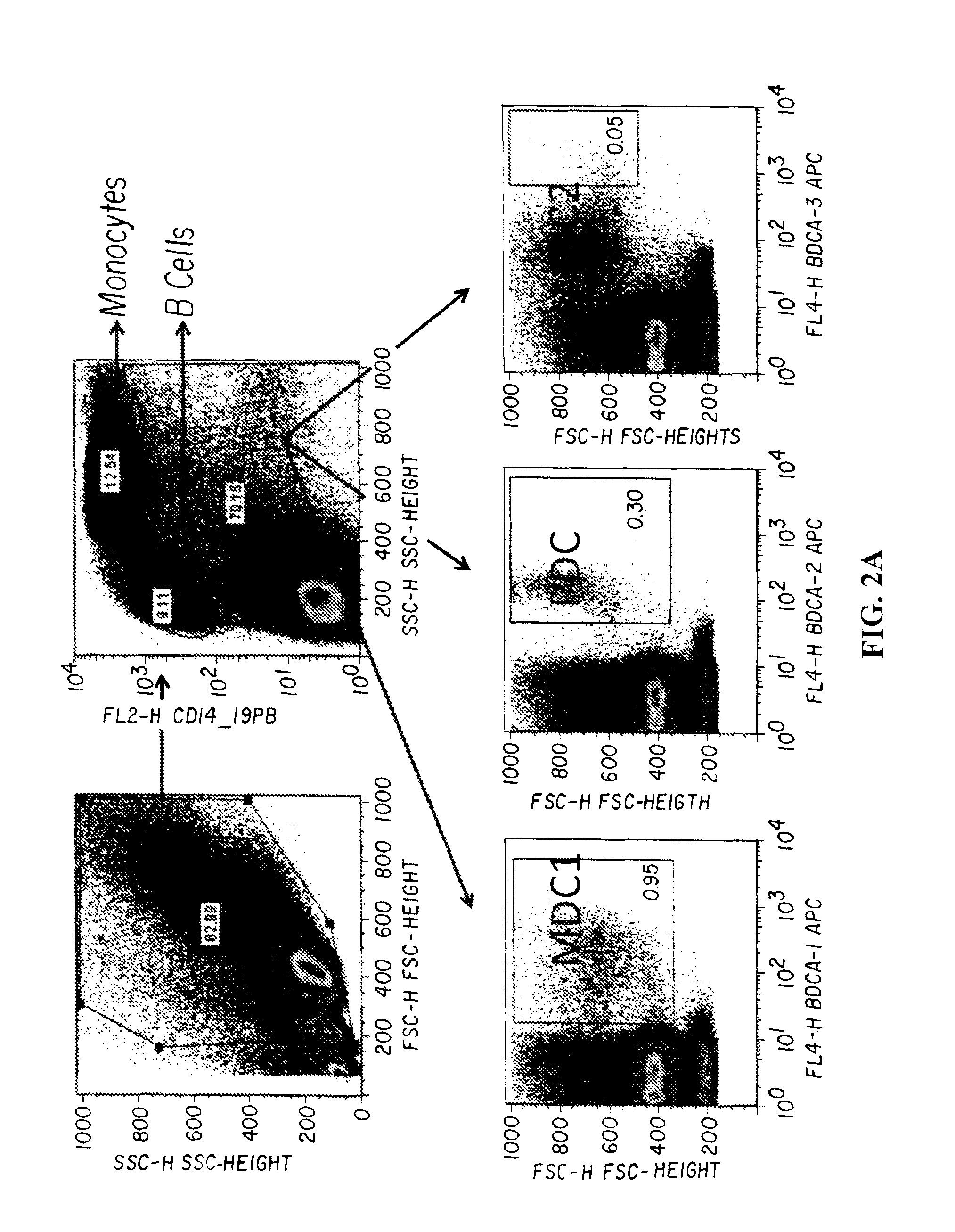
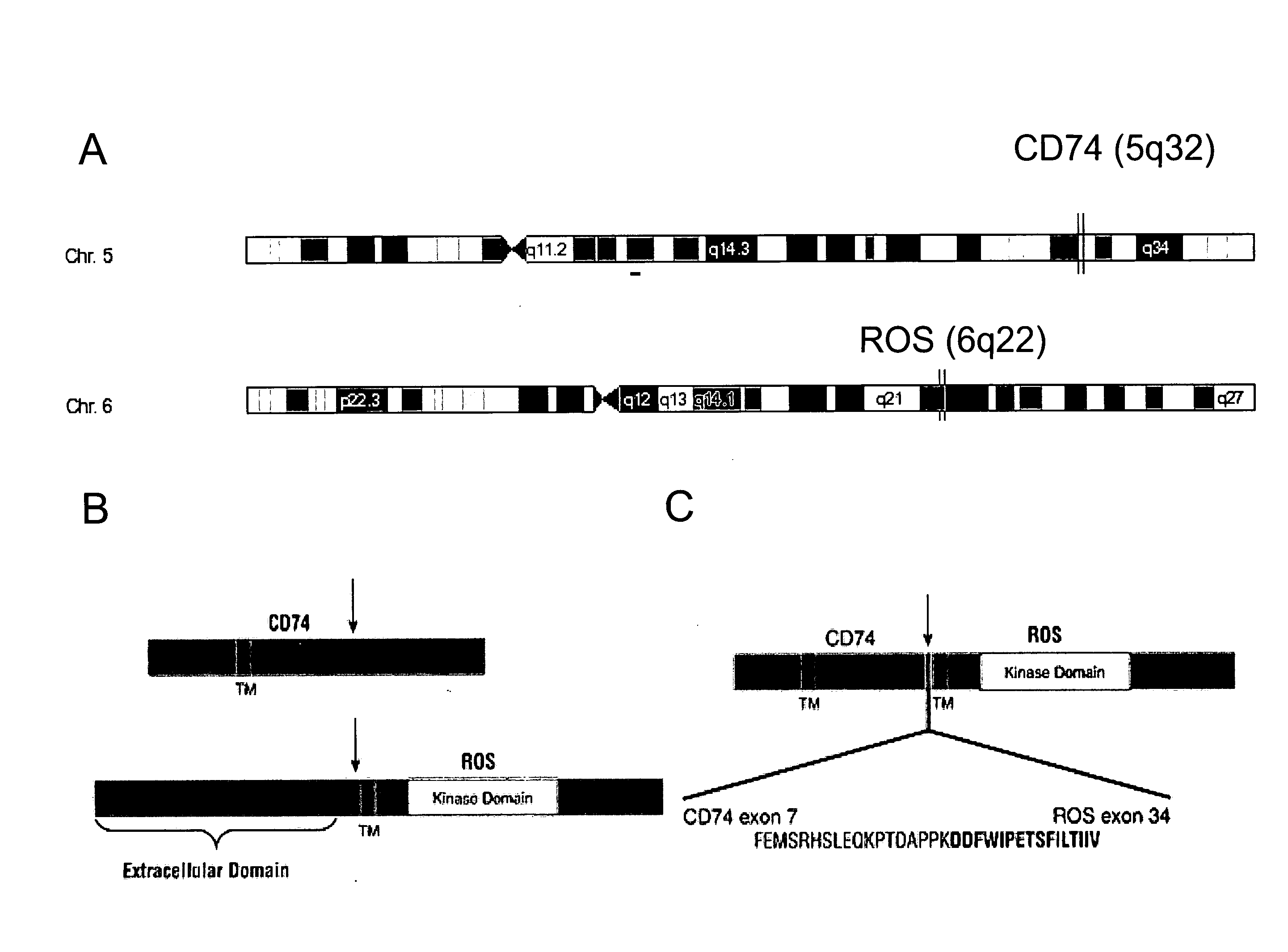
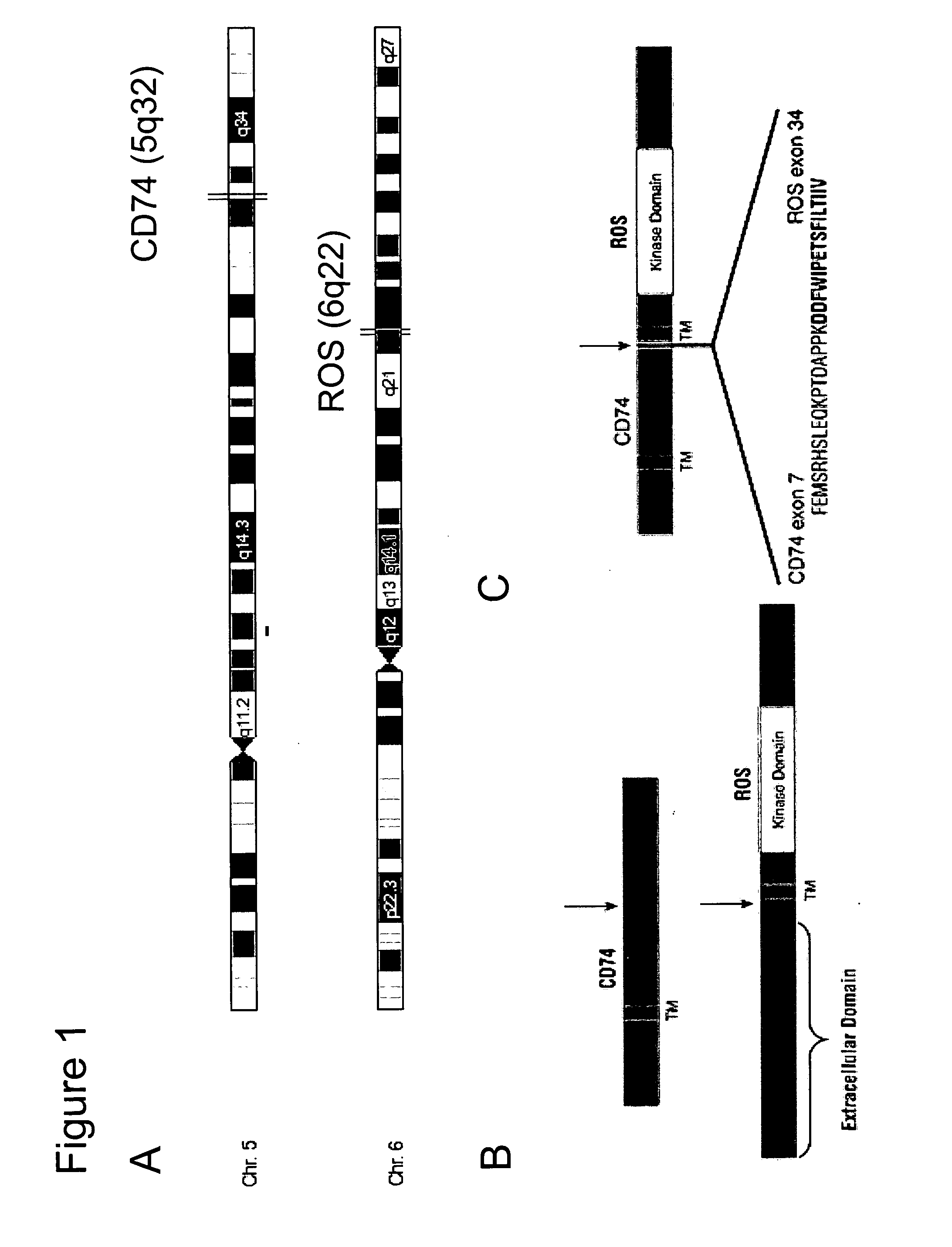
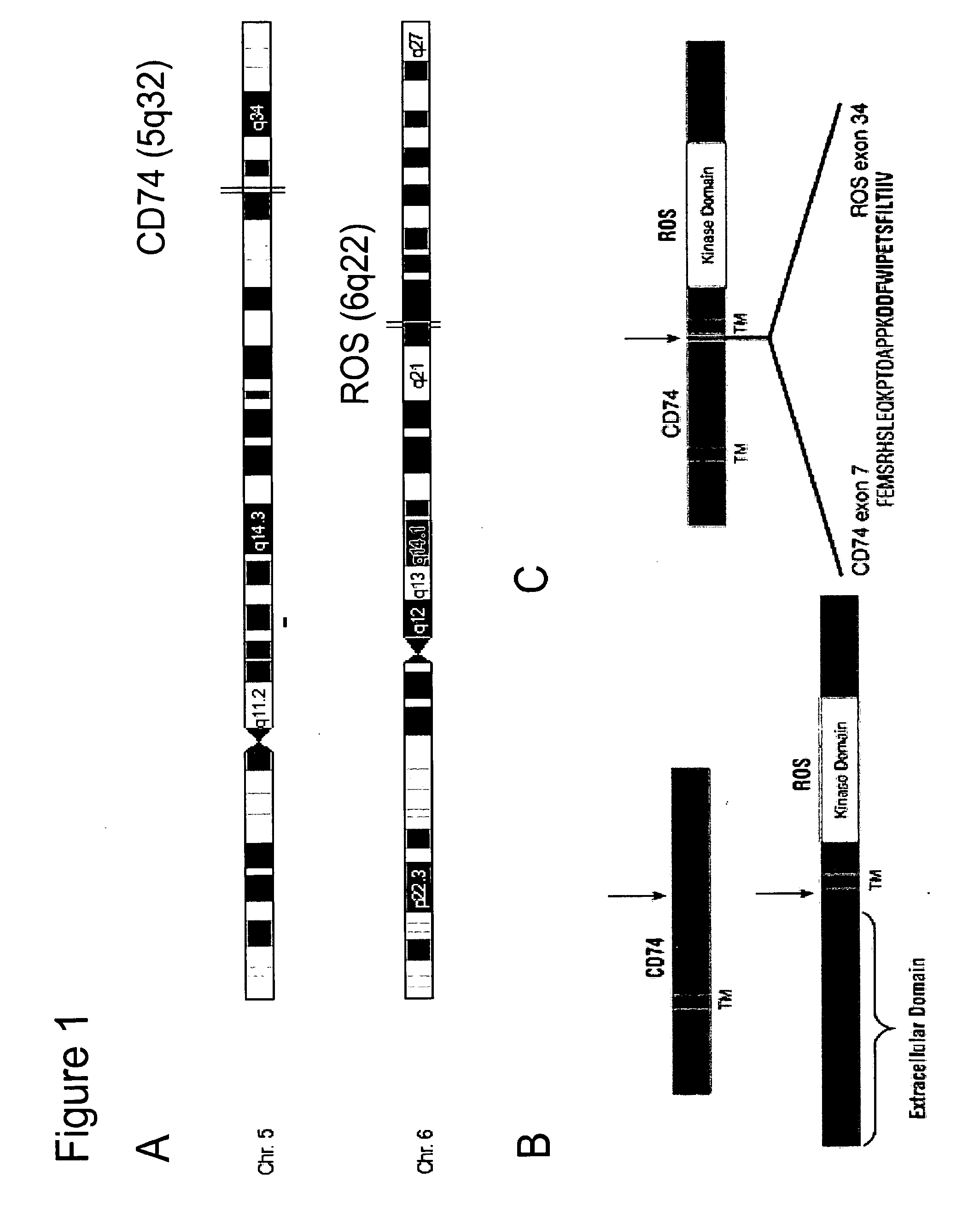
Translocation and Mutant ROS Kinase in Human Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma
ActiveUS20100221737A1Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsTransferasesProto-Oncogene Tyrosine-Protein Kinase ROSNucleotide
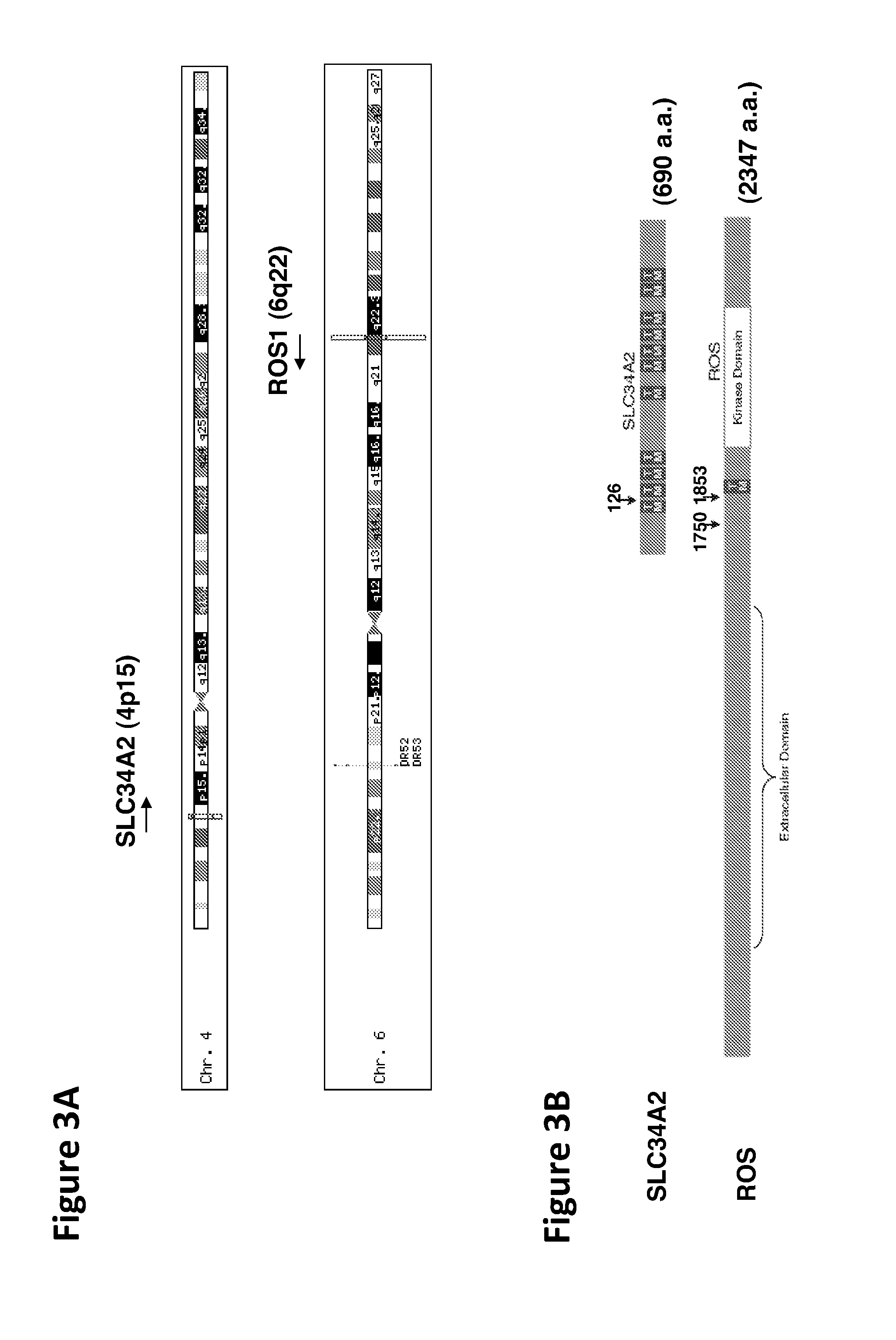
In accordance with the invention, a novel gene translocation, (5q32, 6q22), in human non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) that results in a fusion proteins combining part of CD74 with Proto-oncogene Tyrosine Protein Kinase ROS Precursor (ROS) kinase has now been identified. The CD74-ROS fusion protein is anticipated to drive the proliferation and survival of a subgroup of NSCLC tumors. The invention therefore provides, in part, isolated polynucleotides and vectors encoding the disclosed mutant ROS kinase polypeptides, probes for detecting it, isolated mutant polypeptides, recombinant polypeptides, and reagents for detecting the fusion and truncated polypeptides. The disclosed identification of the new fusion protein enables new methods for determining the presence of these mutant ROS kinase polypeptides in a biological sample, methods for screening for compounds that inhibit the proteins, and methods for inhibiting the progression of a cancer characterized by the mutant polynucleotides or polypeptides, which are also provided by the invention.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
ROS Kinase in Lung Cancer
InactiveUS20120208824A1Inhibit expressionBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementKinase activityNucleotide
The invention provides the identification of the presence of polypeptides with ROS kinase activity in mammalian lung cancer. In some embodiments, the polypeptide with ROS kinase activity is the result of a fusion between a ROS-encoding polynucleotide and a polynucleotide encoding a second (non-ROS) polypeptide. Three different fusion partners of ROS are described, namely proteins encoded by the FIG gene, the SLC34A2 gene, and the CD74 gene. The invention enables new methods for determining the presence of a polypeptide with ROS kinase activity in a biological sample, methods for screening for compounds that inhibit the proteins, and methods for inhibiting the progression of a cancer (e.g., an lung cancer).
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Internalizing Anti-CD74 Antibodies and Methods of Use
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Genes from Chromosome 3, 5 and 11 involved in premature canities
InactiveUS20050208010A1Recovery functionPrecise positioningCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsCUL5Polynucleotide
The invention provides a cosmetic or therapeutic method for combating canities and / or stimulating natural pigmentation and / or treating a pigmentation disorder comprising administering at least one polynucleotide fragment comprising 18 consecutive nucleotides, the sequence of which corresponds to all or part of a gene on human chromosome 3 selected from KIAA 042, CCK, CACNA1D, ARHGEF3 and AL133097 genes, or the sequence of which corresponds to all or part of a gene on human chromosome 5 selected from the KLHL3, HNRPA0, CDC25C, EGR1, C5orf6, C5orf7, LOC51308, ETF1, HSPA9B, PCDHA1 to PCDHA13, CSF1R, RPL7, PDGFRB, TCOF1, AL133039, CD74, RPS14, NDST1, G3BP, GLRA1, C5orf3, MFAP3, GALNT10 and FLJ 117151 genes, or the sequence of which corresponds to all or part of a gene on human chromosome 11 selected from the GUCY1A2, CUL5, ACAT1, NPAT, ATM, AF035326, AF035327, AF035328, BC029536, FLJ20535, DRD2, ENS303941, IGSF4, LOC51092, BC010946, TAGLN, PCSK7 and ENS300650 genes, and diagnostic methods employing same.
Owner:LOREAL SA
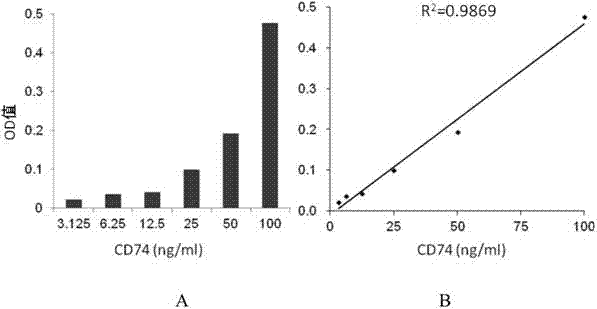
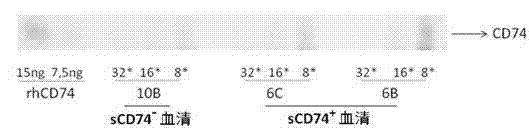
ELISA test kit of human-derived soluble CD74 protein and detection method thereof
ActiveCN103207277AReduce subjectivityHigh sensitivityBiological testingWestern blotSemiquantitative Method
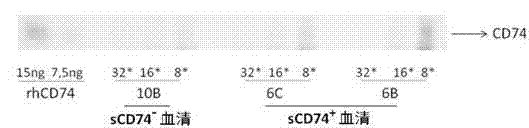
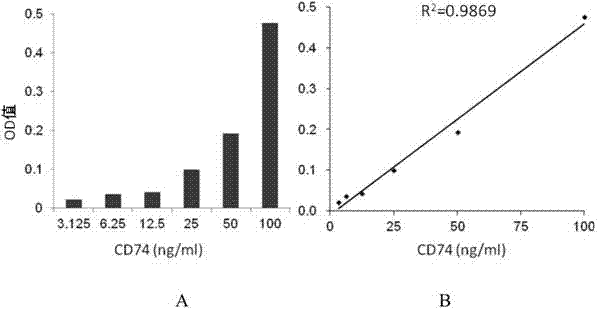
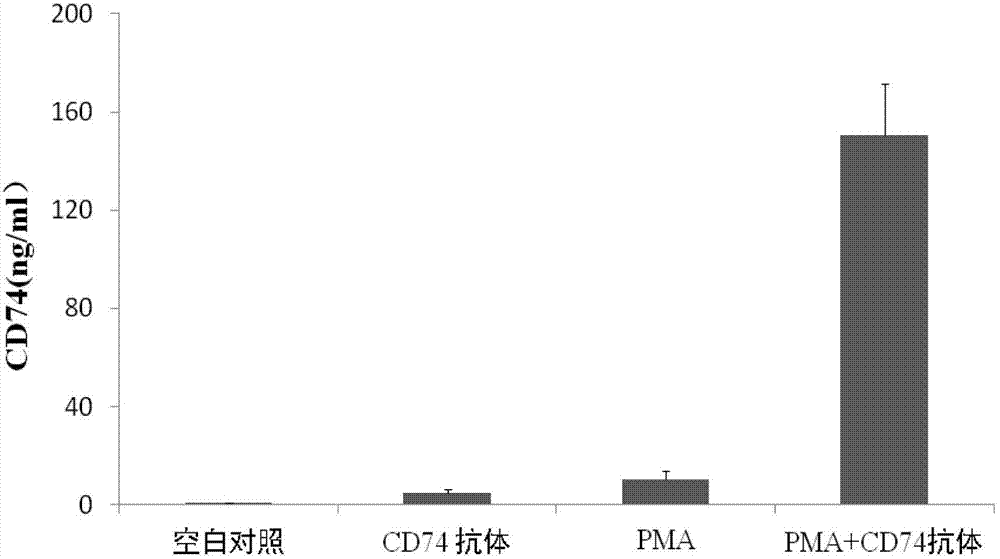
The present invention belongs to the field of immunology and biotechnology, and provides an ELISA test kit of human-derived soluble CD74 protein and a detection method thereof. The kit of the present invention can accurately detect the content of human-derived soluble CD74 protein in body fluid or cell supernatant, and results are quantitatively analyzed by an enzyme-labeling instrument to exclude subjectivity of semi-quantitative methods such as immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence, Western blot and the like; the kit has high sensitivity, the detected content of CD74 protein is as low as 800 pg / ml; according to the invention, no complicated instrument is necessary in detection; the kit is suitable for popularization and application in scientific research institutions and medical institutions, is suitable for large-scale detection of clinical samples, and can rapidly obtain massive data and information related to human-derived CD74 protein.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
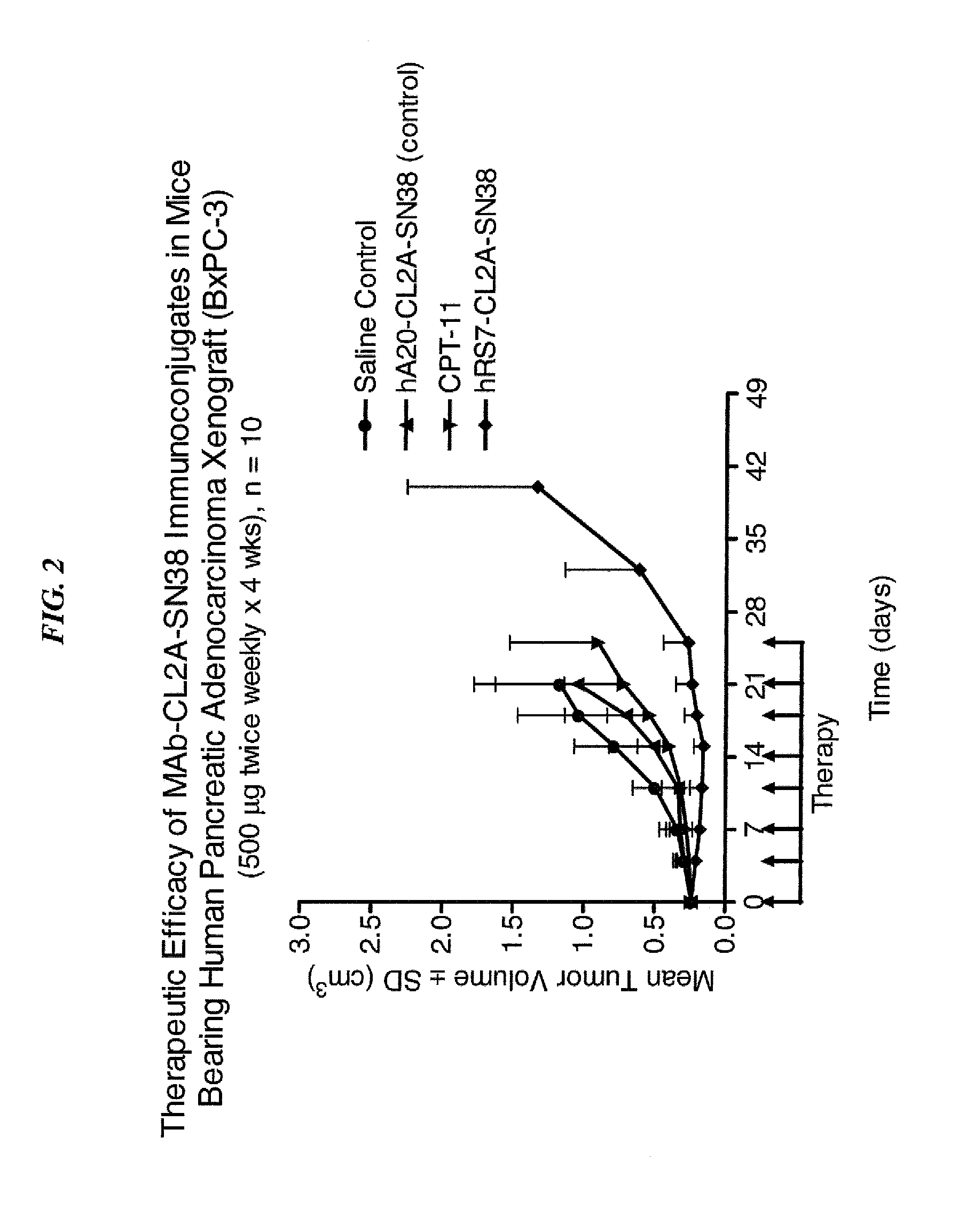
Subcutaneous administration of antibody-drug conjugates for cancer therapy
ActiveUS20180280532A1Good effectLow toxicityInorganic non-active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCD20Lymphatic Spread
The present invention relates to methods of cancer therapy using subcutaneous administration of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). Preferably, the ADC comprises an antibody that binds to Trop-2, CEACAM5, CEACAM6, CD20, CD22, CD30, CD46, CD74, Her-2, folate receptor, or HLA-DR. More preferably, the drug is SN-38. Subcutaneous administration is at least as effective as intravenous administration of the same ADC. Surprisingly, subcutaneous administration can be used without inducing unmanageable adverse local toxicity at the injection site. Subcutaneous administration is advantageous in requiring less frequent administration, substantially reducing the amount of time required for intravenous administration, and reducing the levels of systemic toxicities observed with intravenous administration. When administered at specified dosages and schedules, the ADCs can reduce solid tumors in size, reduce or eliminate metastases and are effective to treat cancers resistant to standard therapies, such as radiation therapy, chemotherapy or immunotherapy.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Subcutaneous administration of antibody-drug conjugates for cancer therapy
ActiveUS10799597B2Increase and decrease frequencyGood effectInorganic non-active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCD20Antiendomysial antibodies
The present invention relates to methods of cancer therapy using subcutaneous administration of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). Preferably, the ADC comprises an antibody that binds to Trop-2, CEACAM5, CEACAM6, CD20, CD22, CD30, CD46, CD74, Her-2, folate receptor, or HLA-DR. More preferably, the drug is SN-38. Subcutaneous administration is at least as effective as intravenous administration of the same ADC. Surprisingly, subcutaneous administration can be used without inducing unmanageable adverse local toxicity at the injection site. Subcutaneous administration is advantageous in requiring less frequent administration, substantially reducing the amount of time required for intravenous administration, and reducing the levels of systemic toxicities observed with intravenous administration. When administered at specified dosages and schedules, the ADCs can reduce solid tumors in size, reduce or eliminate metastases and are effective to treat cancers resistant to standard therapies, such as radiation therapy, chemotherapy or immunotherapy.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
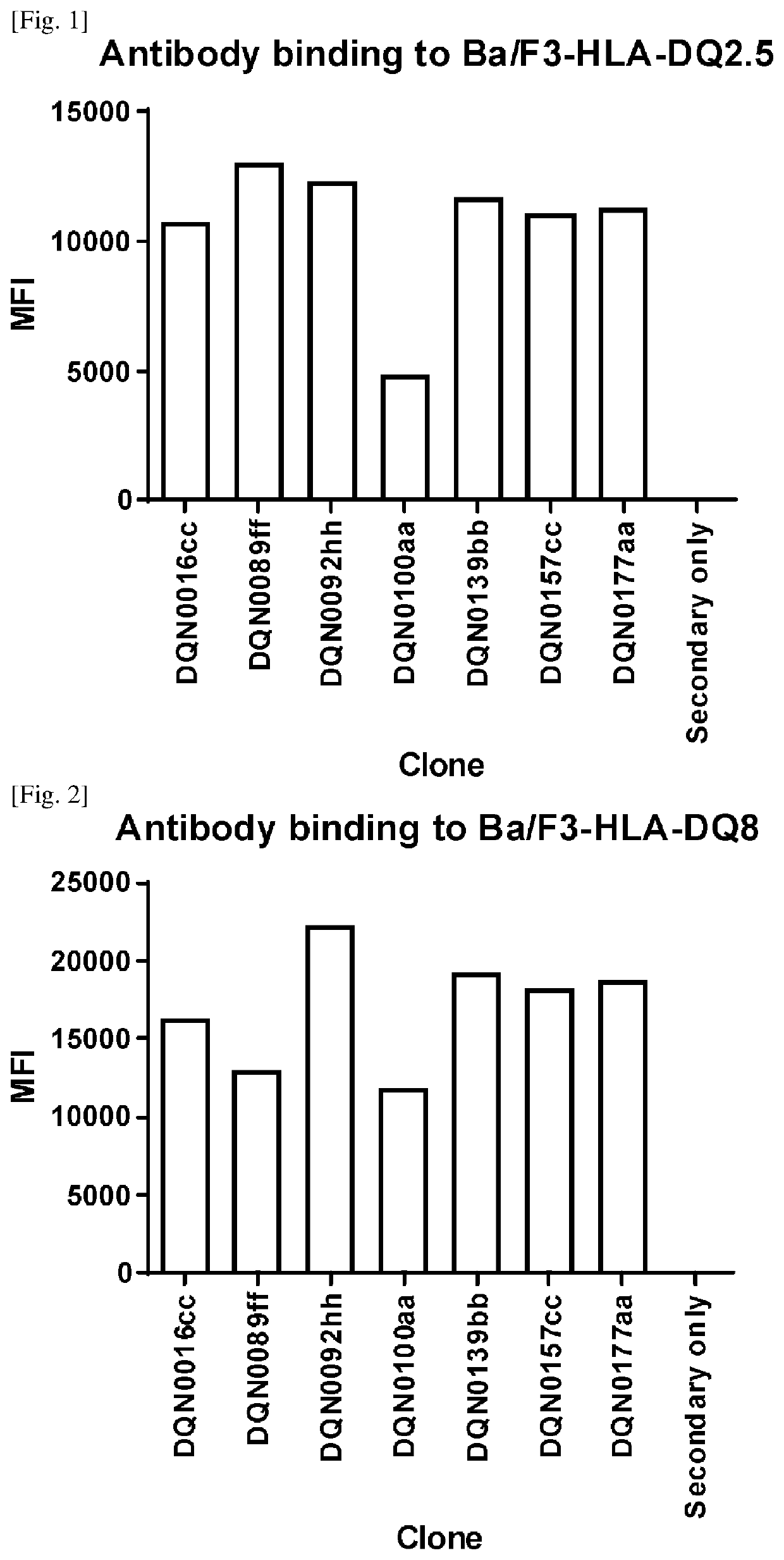
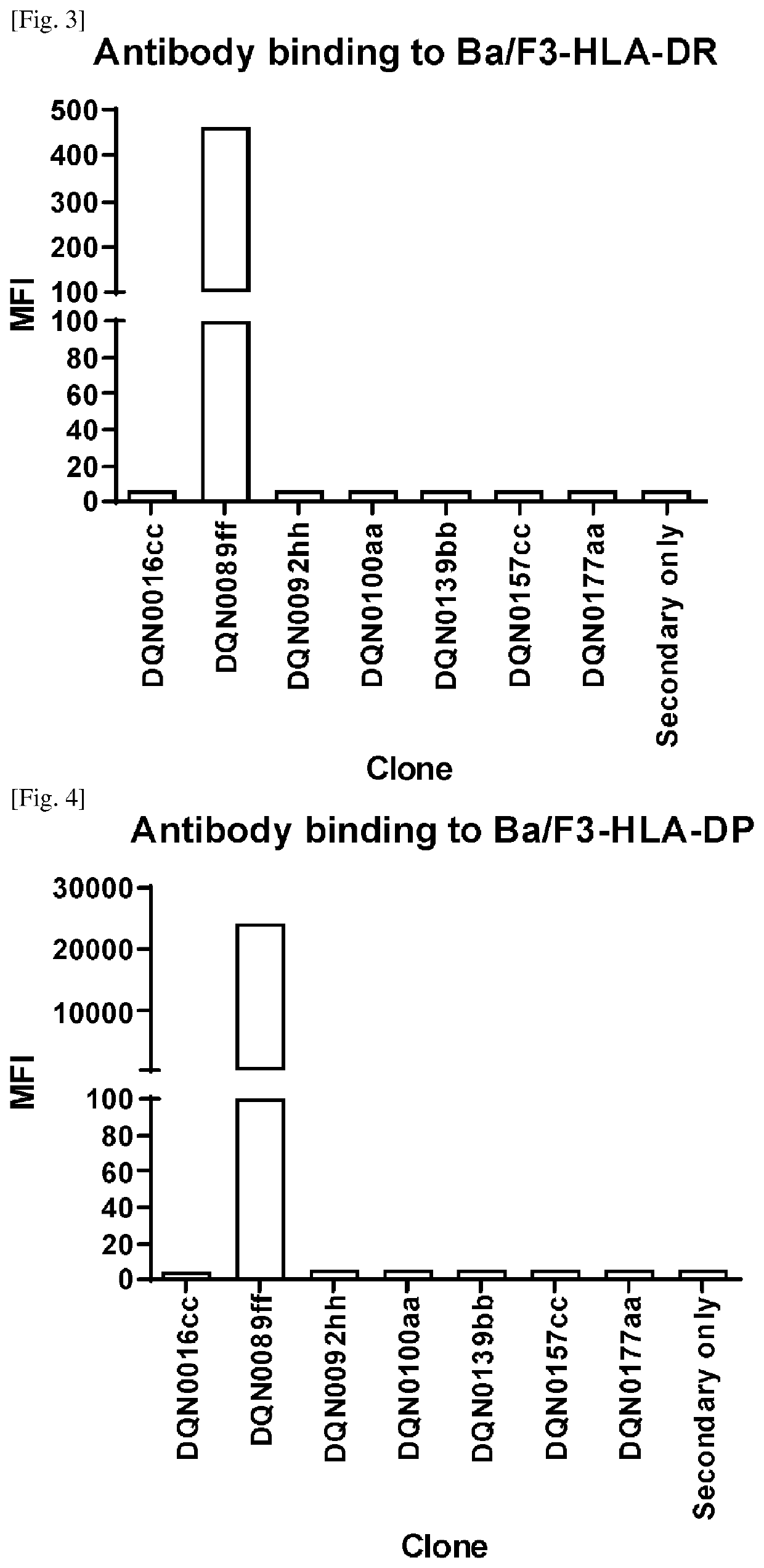
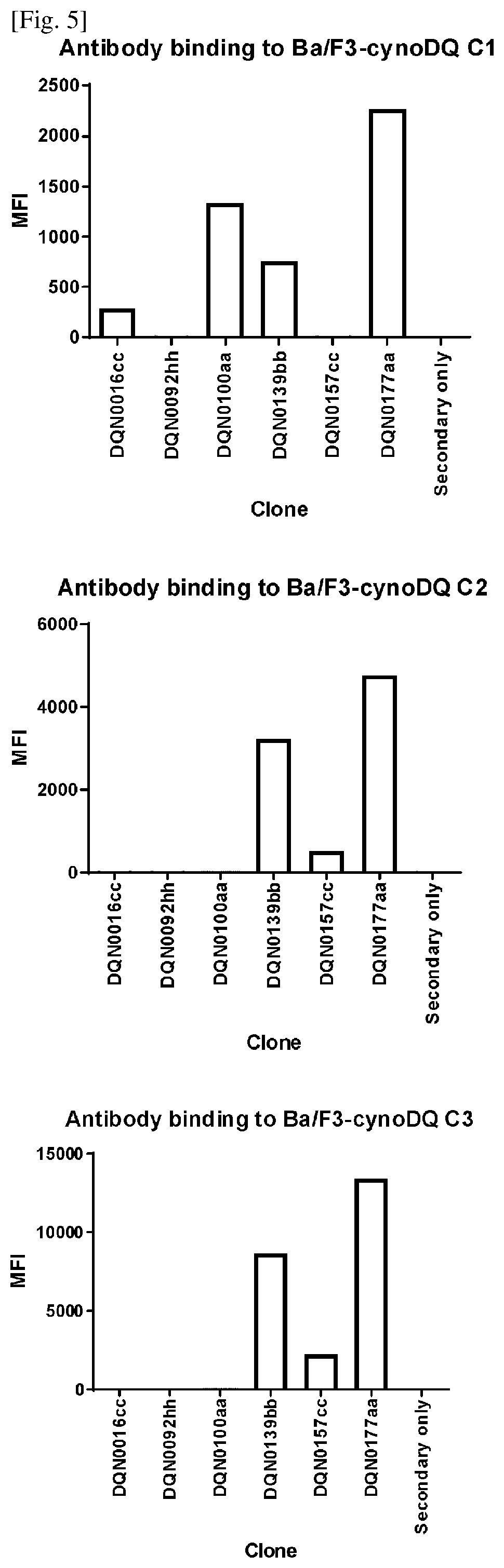
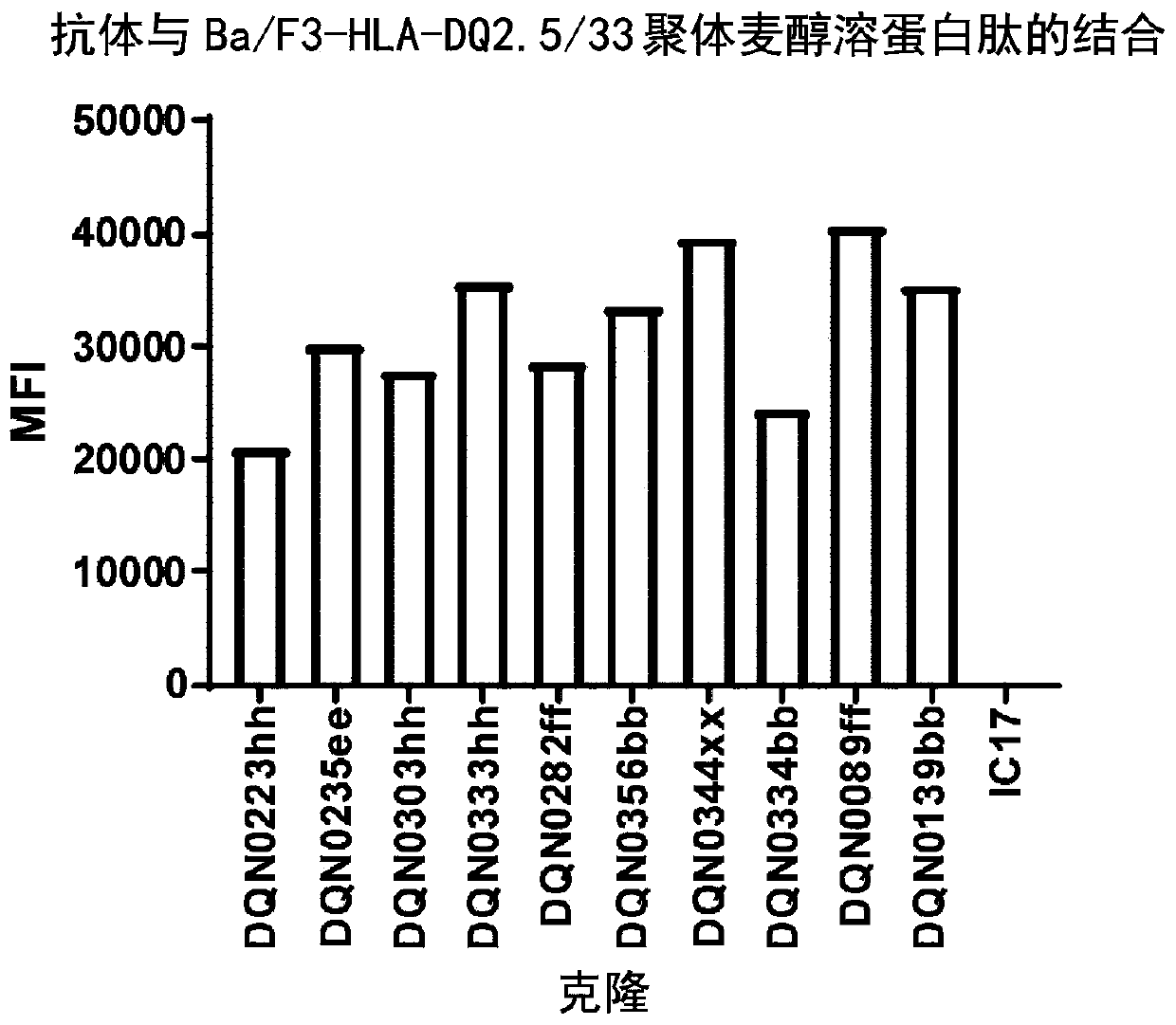
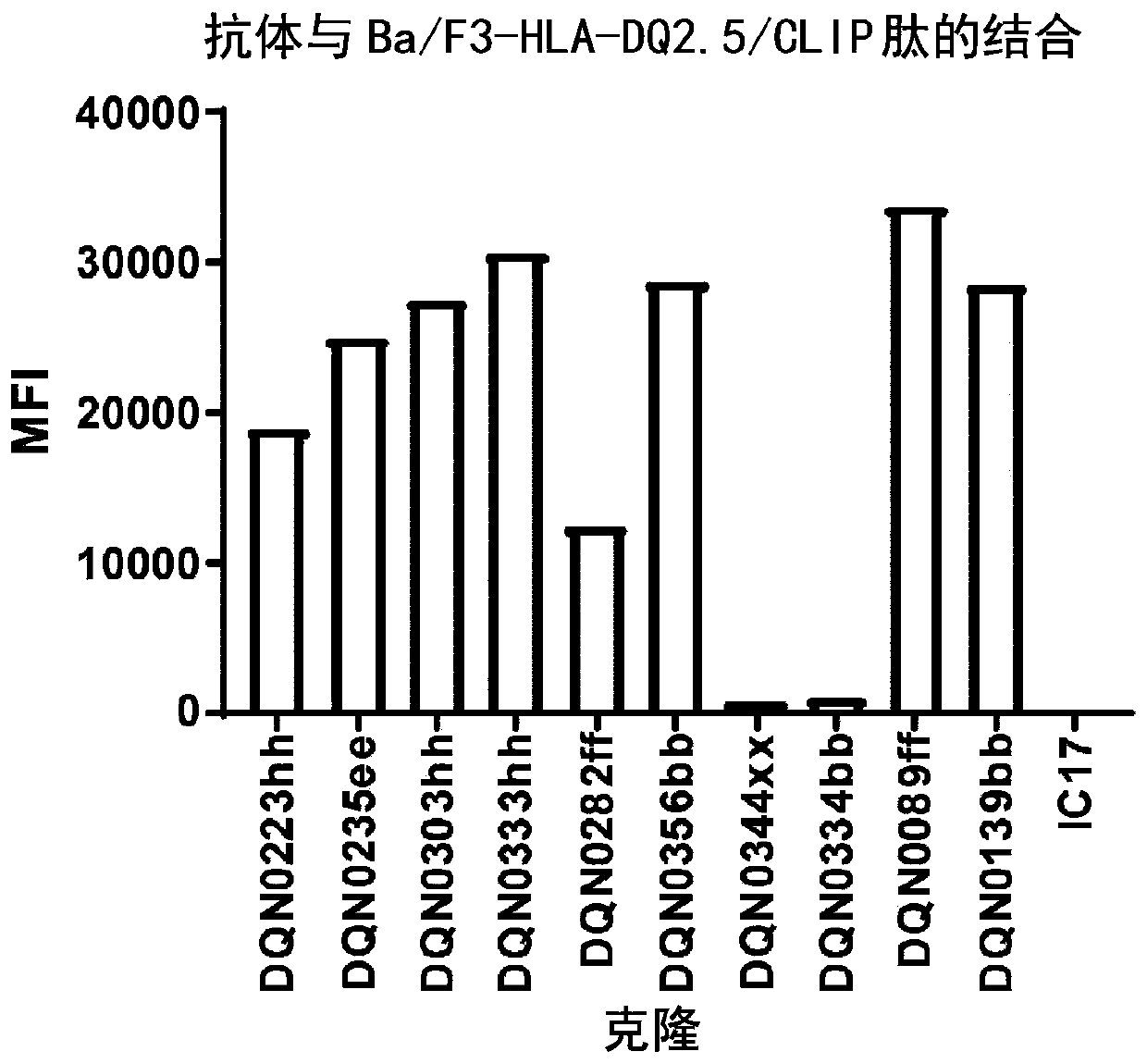
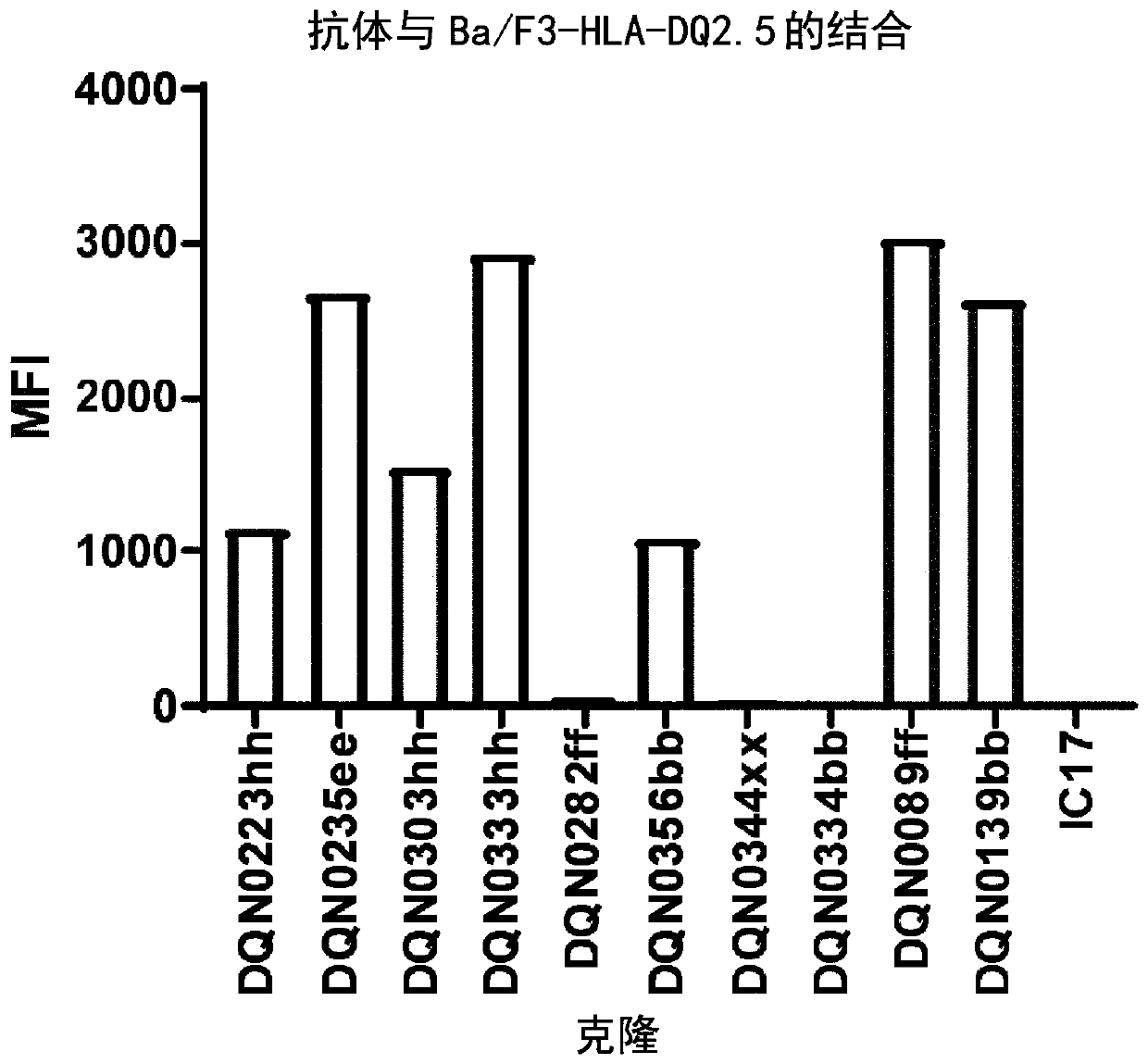
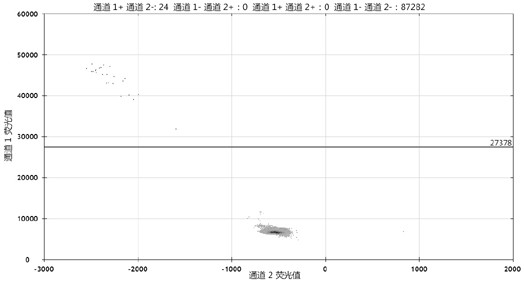
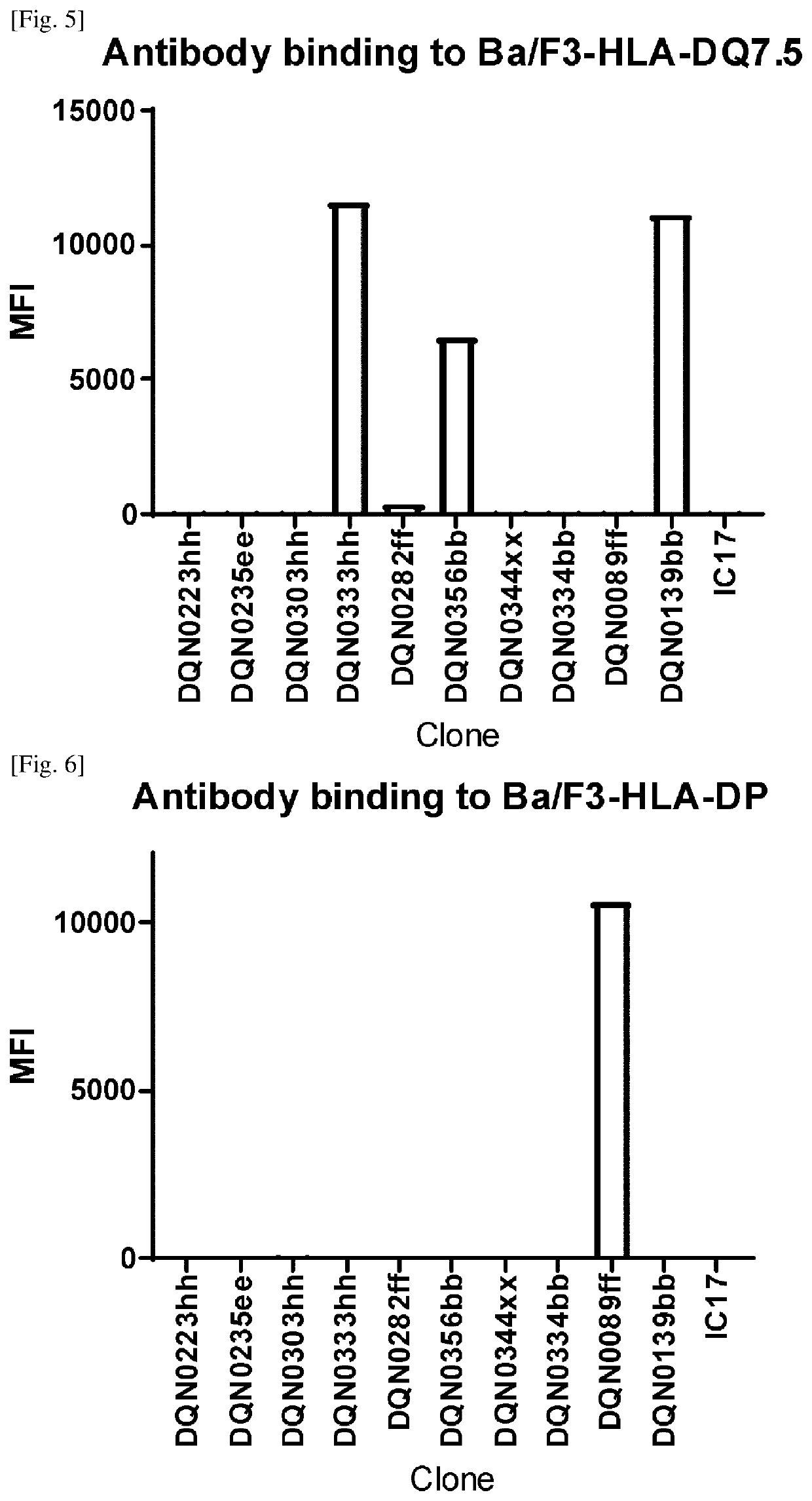
Anti-hla-dq2.5/8 antibody and its use for the treatment of celiac disease
PendingUS20200040085A1Digestive systemImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntiendomysial antibodiesT cell
The invention provides anti-HLA-DQ2.5 / 8 antibodies and methods of using the same. The antibodies of the present invention have binding activity to human HLA-DQ2.5 / 8 and monkey MHC-DQ, but substantially no binding activity to HLA-DR, HLA-DP, or a complex of the invariant chain (CD74) and HLA-DQ2.5 / 8. The antibodies bind to HLA-DQ2.5 / 8 in the presence of a gluten peptide such as gliadin, i.e., bind to HLA-DQ2.5 / 8 forming a complex with the gluten peptide. The antibodies have neutralizing activity against the binding between HLA-DQ2.5 / 8 and TCR, and thus block the interaction between HLA-DQ2.5 / 8 and an HLA-DQ2.5 / 8-restricted CD4+ T cell. The antibodies do not undergo rapid internalization mediated by the invariant chain. These characteristics are particularly useful for treating celiac disease. Thus, the present invention also provides a method of treating celiac disease using the antibodies of the present invention.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
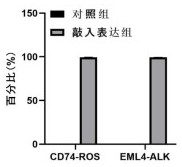
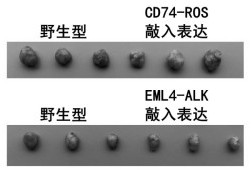
Kit for quantitatively detecting ALK, RET and ROS1 fusion genes based on ddPCR
InactiveCN112852967AHigh sensitivityImprove applicabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementForward primerDisease
The invention discloses a kit for quantitatively detecting ALK, RET and ROS1 fusion genes based on ddPCR. The kit comprises a negative reference substance, a positive reference substance, a PCR reaction solution I and a PCR reaction solution II. The invention provides an RT-PCR quantitative detection system based on ddPCR. The RT-PCR quantitative detection system comprises a forward primer, a reverse primer and a fluorescent probe, wherein the forward primer and the reverse primer aim at fusion genes EML4-ALK, CCDC6-RET and CD74-ROS1 and an internal control gene TBP. According to the kit, a forward primer is designed on a 5'partner gene, a probe and a reverse primer are designed on a 3'driver gene to detect ALK, RET and ROS1 fusion genes, and a detection result is expressed by a copy number in unit volume. Through adoption of a ddPCR detection method, whether EML4-ALK, CCDC6-RET and CD74-ROS1 fusion occurs in a clinical sample can be simply and rapidly detected, an important basis is provided for diagnosis, typing, clinical treatment and prognosis of ALK, RET and ROS1 related tumor diseases, and a new thought is provided for clinical treatment.
Owner:PILLAR BIOSCI INC
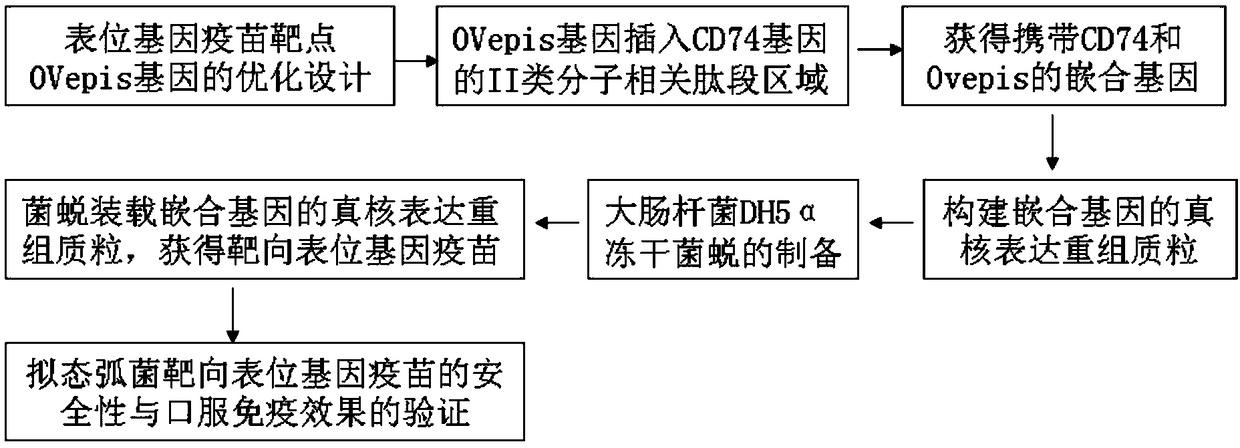
Vibrio mimicus oral target epitope gene vaccine and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108273052ALarge loading capacityEffective phagocytosisAntibacterial agentsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEscherichia coliNucleotide
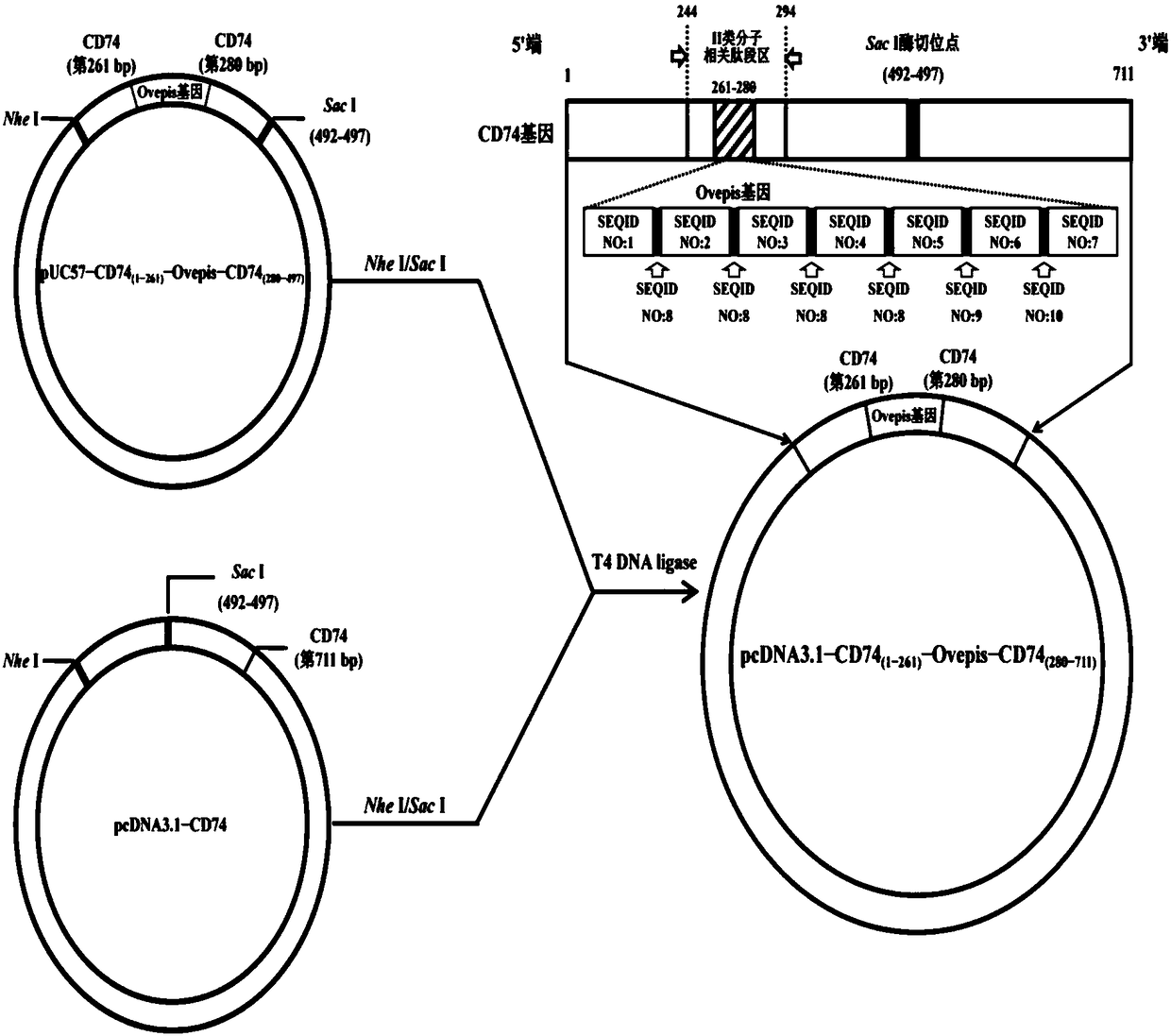
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene vaccines and particularly relates to a vibrio mimicus oral target epitope gene vaccine. The vibrio mimicus oral target epitope gene vaccine comprises the following steps: S1, designing a vaccine target gene OVepis; S2, inserting the vaccine target gene OVepis designed in the S1 into 261-280bp of a related peptide fragment area of a II-type molecule in a protein coding gene CD74 of an immune carrier grass carp, wherein the direction is from 5'end to 3'end of a sequence; forming a CD74(1-261bp)-Ovepis-CD74(280-711bp) mosaic gene of 1020 bp, loading the mosaic gene by using a freeze-drying bacterial ghost of escherichia coli DH5a of a targeted delivery vector, and obtaining the target epitope gene vaccine. The nucleotide sequence of the mosaic gene is shown in SEQ ID NO:20. The vibrio mimicus oral target epitope gene vaccine has the beneficial effects that: the oral target epitope gene vaccine not only prevents the degradation of nuclease in vivo and increases the expression of a DNA encoding gene of the vaccine in a local antigen presenting cell of a mucous membrane, but also efficiently transfers an expressed and processed antigenpeptide to cells T and B, so that the immune effect of the vaccine is greatly improved.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Anti-hla-dq2.5 antibody
PendingCN111225925AImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsImmunological disordersAntiendomysial antibodiesGlutelin
The antibodies of the present invention have specific binding activity to HLA-DQ2.5 and may have binding activity to HLA-DQ2.2 and / or HLA-DQ7.5, but substantially no binding activity to HLA-DQ8, HLA-DQ5.1, HLA-DQ6.3, HLA-DQ7.3, HLA-DR, HLA-DP, or a complex of the invariant chain (CD74) and HLA-DQ2.5. The antibodies bind to HLA-DQ2.5 in the presence of a gluten peptide such as gliadin, i.e., bind to HLA-DQ2.5 forming a complex with the gluten peptide. The antibodies have neutralizing activity against the binding between HLA-DQ2.5 and TCR, and thus block the interaction between HLA-DQ2.5 and anHLA-DQ2.5-restricted CD4+ T cell. The antibodies do not undergo rapid internalization mediated by the invariant chain.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Translocation and mutant ros kinase in human non-small cell lung carcinoma
ActiveUS20150010577A1Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsTransferasesProto-Oncogene Tyrosine-Protein Kinase ROSNucleotide
In accordance with the invention, a novel gene translocation, (5q32, 6q22), in human non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) that results in a fusion proteins combining part of CD74 with Proto-oncogene Tyrosine Protein Kinase ROS Precursor (ROS) kinase has now been identified. The CD74-ROS fusion protein is anticipated to drive the proliferation and survival of a subgroup of NSCLC tumors. The invention therefore provides, in part, isolated polynucleotides and vectors encoding the disclosed mutant ROS kinase polypeptides, probes for detecting it, isolated mutant polypeptides, recombinant polypeptides, and reagents for detecting the fusion and truncated polypeptides; The disclosed identification of the new fusion protein enables new methods for determining the presence of these mutant ROS kinase polypeptides in a biological sample, methods for screening for compounds that inhibit the proteins, and methods for inhibiting the progression of a cancer characterized by the mutant polynucleotides or polypeptides, which are also provided by the invention.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
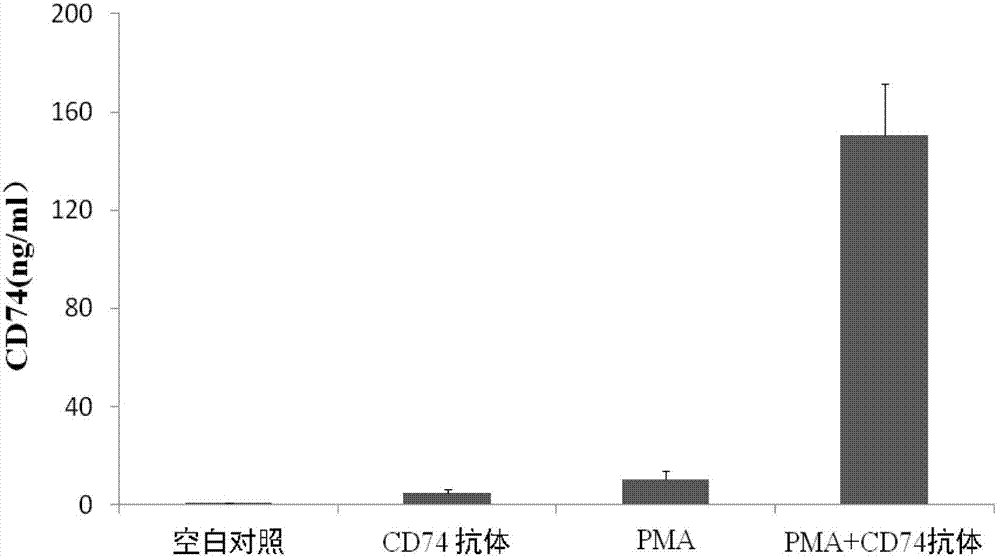
Application of CD74 protein in preparation of kit for identifying macrophage subsets in brains after ischemic injury
The invention discloses an application of a CD74 protein in preparation of a kit for identifying macrophage subsets in brains after ischemic injury. An inventor of the invention finds for the first time that the CD74 protein can distinguish macrophages into two subsets: CD74hi and CD74medium. The application is beneficial to further research on the functions of macrophages in ischemic brain tissues.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
ELISA detection kit for mice-derived soluble CD74 proteins and detection method of ELISA detection kit
InactiveCN104280553AReduce subjectivityHigh sensitivityBiological testingImmunofluorescenceBasic research
The invention provides an ELISA detection kit for mice-derived soluble CD74 proteins and a detection method of the ELISA detection kit, belonging to the technical field of immunology and biology. The kit can accurately detect the content of soluble CD74 proteins in mice body fluid, and a detection result is qualitatively analyzed by ELISA, so that the subjectivity of semiquantitative methods such as immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence and western blot can be eliminated; moreover, the sensitivity is high, and the detected minimum content of the CD74 proteins can reach 781.25 pg / ml. No complicated instrument is needed in the detection, the ELISA detection kit and the detection method are easy to popularize and use in scientific research institutions and universities and medical institutions, basic research biological specimens can be detected on large scale, and a great amount of data and information related to the mice CD74 proteins can be rapidly acquired.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
New fusion gene detected in lung cancer
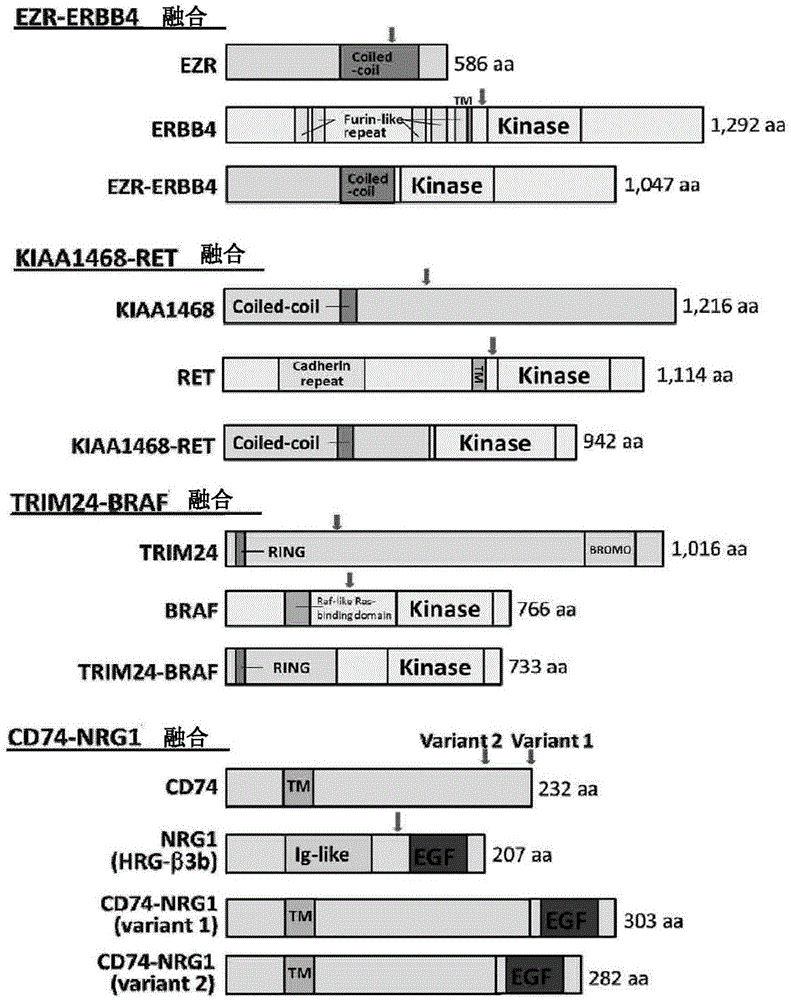
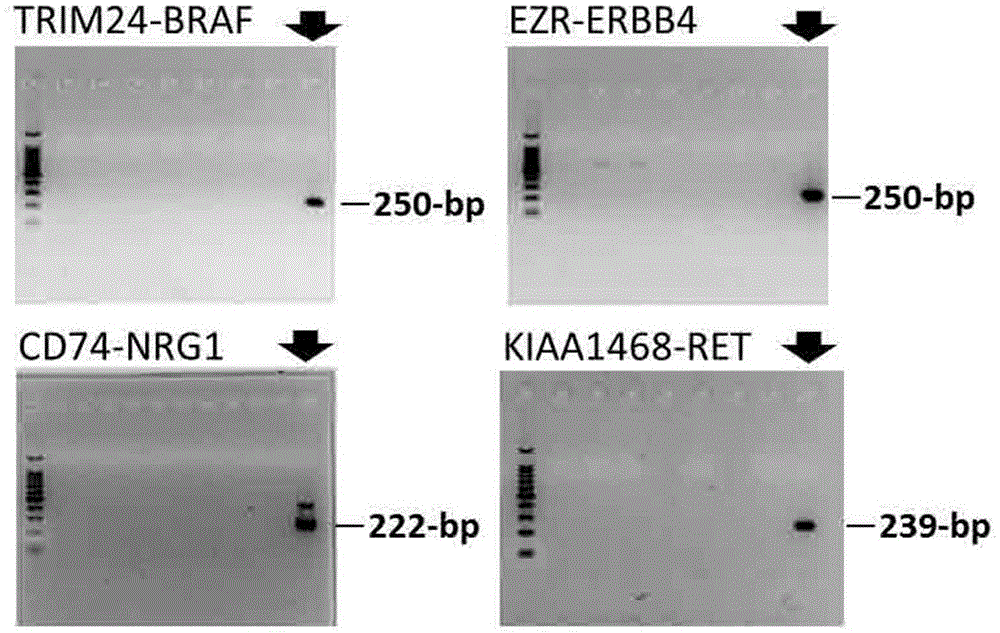
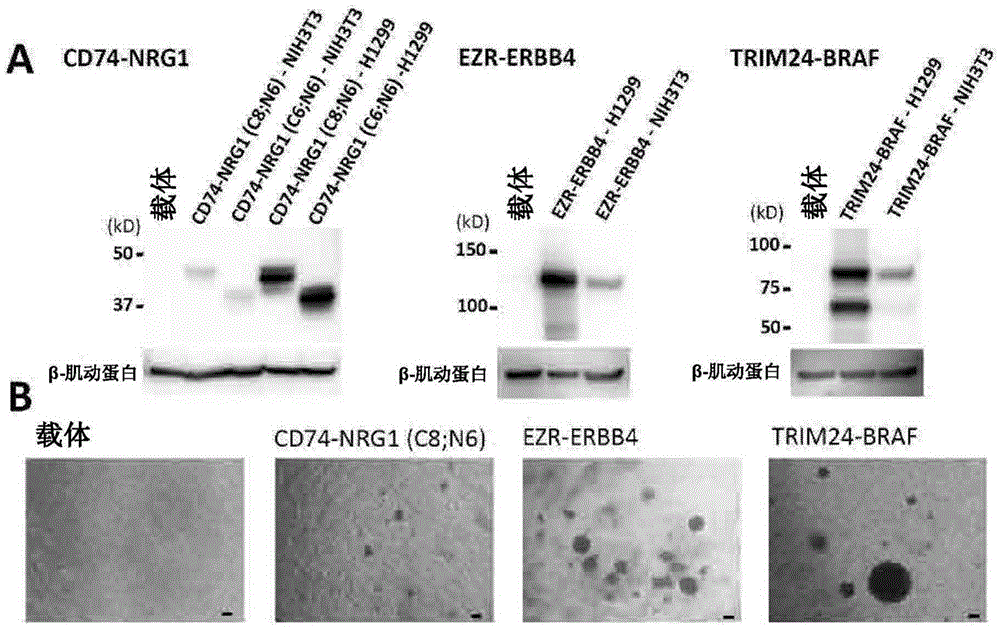
A method for detecting gene fusion that is a mutation responsible for cancer (driver mutation), wherein the method includes a step for detecting, in an isolated sample derived from a subject having cancer, any fusion polynucleotide among an EZR-ERBB4 fusion polynucleotide, KIAA1468-RET fusion polynucleotide, TRIM24-BRAF fusion polynucleotide, CD74-NRG1 fusion polynucleotide, or SLC3A2-NRG1 fusion polynucleotide, or a polypeptide encoded thereby.
Owner:NAT CANCER CENT +2
CD74-ROS1 rearrangement DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) standard substance for molecular diagnosis, RNA (ribonucleic acid) standard substance for molecular diagnosis and application of CD74-ROS1 rearrangement DNA standard substance and RNA standard substance
PendingCN113897438AProvide stableBreakpoints are complete and accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementForeign genetic material cellsROS1A-DNA
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene rearrangement standard substances, and provides a CD74-ROS1 rearrangement DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) standard substance for molecular diagnosis, an RNA (ribonucleic acid) standard substance for molecular diagnosis and application of the CD74-ROS1 rearrangement DNA standard substance and the RNA standard substance. The scheme provided by the invention comprises the following steps: constructing sgRNA of a No.6 intron aiming at a CD74 gene onto a vector pX330 to obtain a plasmid C4, constructing sgRNA of a No.33 intron aiming at an ROS1 gene onto the vector pX330 to obtain a plasmid R3, jointly transfecting a host cell with the plasmid C4 and the plasmid R3 to obtain a recombinant cell, and carrying out monoclonal treatment on the recombinant cell to obtain a cell for preparing a DNA standard substance or an RNA standard substance so as to obtain the DNA standard substance and the RNA standard substance. According to the CD74-ROS1 rearrangement standard substance sequence and cell provided by the invention, a sample can be stably provided for a long time, and the CD74-ROS1 rearrangement standard substance sequence and cell are very suitable for performance evaluation and long-term quality control requirements of LDT or IVD development.
Owner:南京科佰生物科技有限公司
Anti-hla-dq2.5 antibody
InactiveUS20200317790A1High binding activityHigh activityImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsImmunological disordersAntiendomysial antibodiesGlutelin
The antibodies of the present invention have specific binding activity to HLA-DQ2.5 and may have binding activity to HLA-DQ2.2 and / or HLA-DQ7.5, but substantially no binding activity to HLA-DQ8, HLA-DQ5.1, HLA-DQ6.3, HLA-DQ7.3, HLA-DR, HLA-DP, or a complex of the invariant chain (CD74) and HLA-DQ2.5. The antibodies bind to HLA-DQ2.5 in the presence of a gluten peptide such as gliadin, i.e., bind to HLA-DQ2.5 forming a complex with the gluten peptide. The antibodies have neutralizing activity against the binding between HLA-DQ2.5 and TCR, and thus block the interaction between HLA-DQ2.5 and an HLA-DQ2.5-restricted CD4+ T cell. The antibodies do not undergo rapid internalization mediated by the invariant chain.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Lung cancer fusion gene nucleic acid detection quality control product based on CRSIPR-Cas9 technology and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN111607649ARealize all-round monitoringImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetically modified cellsROS1 FusionParaffin embedding
The invention provides a lung cancer fusion gene nucleic acid detection quality control product based on a CRSIPR-Cas9 technology. The lung cancer fusion gene nucleic acid detection quality control product is used for comprehensively monitoring a fusion gene detection process. A preparation method comprises the following steps of: (1) constructing a monoclonal HBE cell strain with specific fusionsites of EML4-ALK and CD74-ROS1 fusion genes by utilizing a CRISPR-Cas9 knock-in technology; (2) constructing a mouse subcutaneous transplantation tumor model by combining the monoclonal HBE cell strain successfully edited in the step (1) with a control wild cell strain; killing the model mouse after the tumor grows to 1cm<3>, collecting tumor tissues, pretreating, fixing, and embedding with paraffin; and (3) constructing a case tissue slice microarray according to a certain mutation / wild ratio by using the tumor tissues collected in the step (2) to obtain lung cancer fusion gene nucleic aciddetection quality control products with different fusion frequencies. The quality control product prepared by the invention has high similarity with non-small cell lung cancer, can truly realize the whole process of lung cancer sample tissue from sampling to detection, and realizes comprehensive monitoring of fusion gene detection.
Owner:苏州艾可瑞斯生物科技有限公司
Proteins binding nkg2d, cd16 and a tumor-associated antigen
PendingCN113164570AImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsCD16Nkg2d receptor
Multi-specific binding proteins that bind NKG2D receptor, CD 16, and a tumor- associated antigen selected from c-MET, KIT, F3, IGF1R, Lewis Y, MUC13, MUC4, MCAM, LRRC32, sialyl-Tn, gpA33, GD3, GM2, EPHA3, TNFRSF10A, TNFSF11, CD74, and PMEL are described, as well as pharmaceutical compositions and therapeutic methods useful for the treatment of cancer.
Owner:DRAGONFLY THERAPEUTICS INC
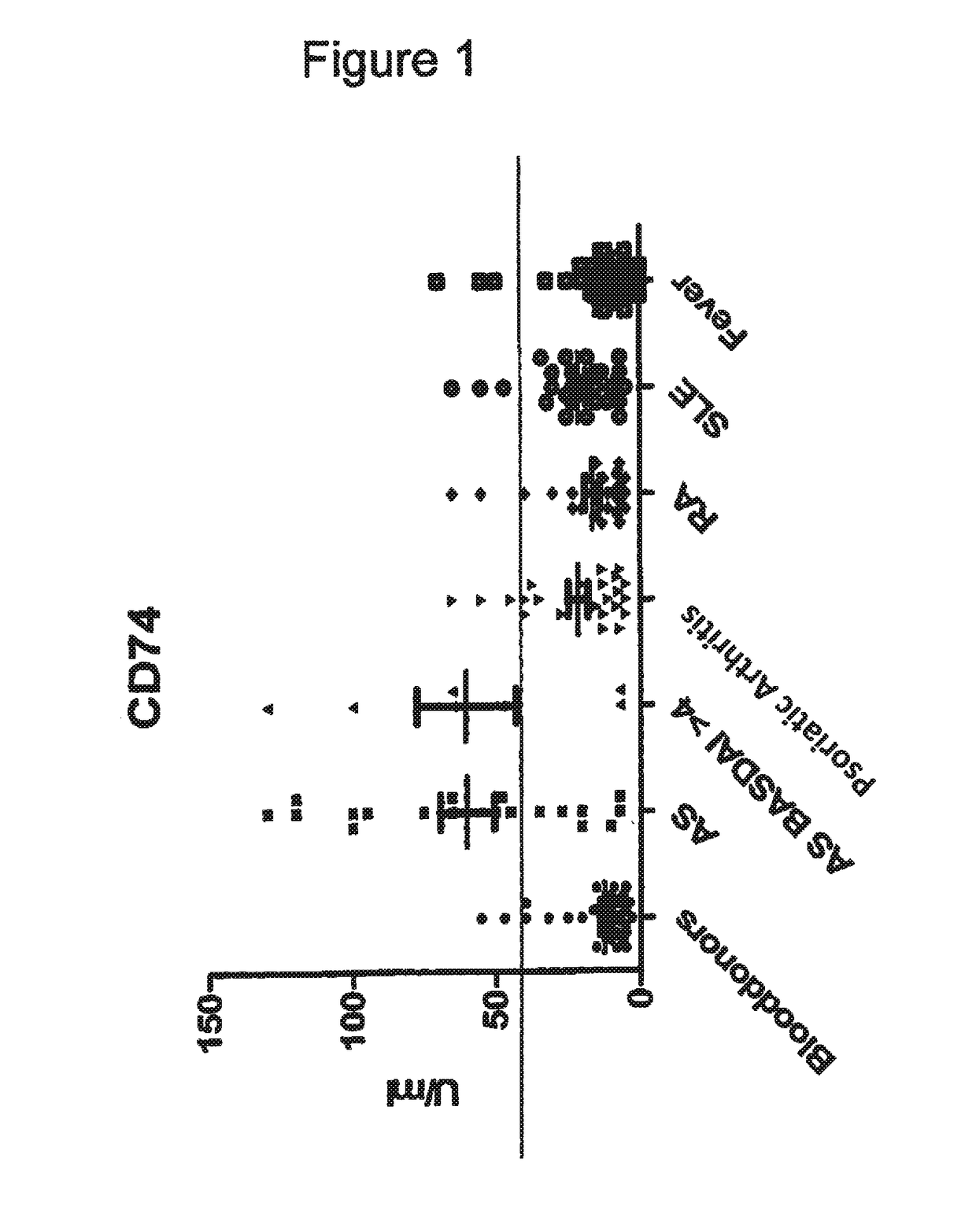
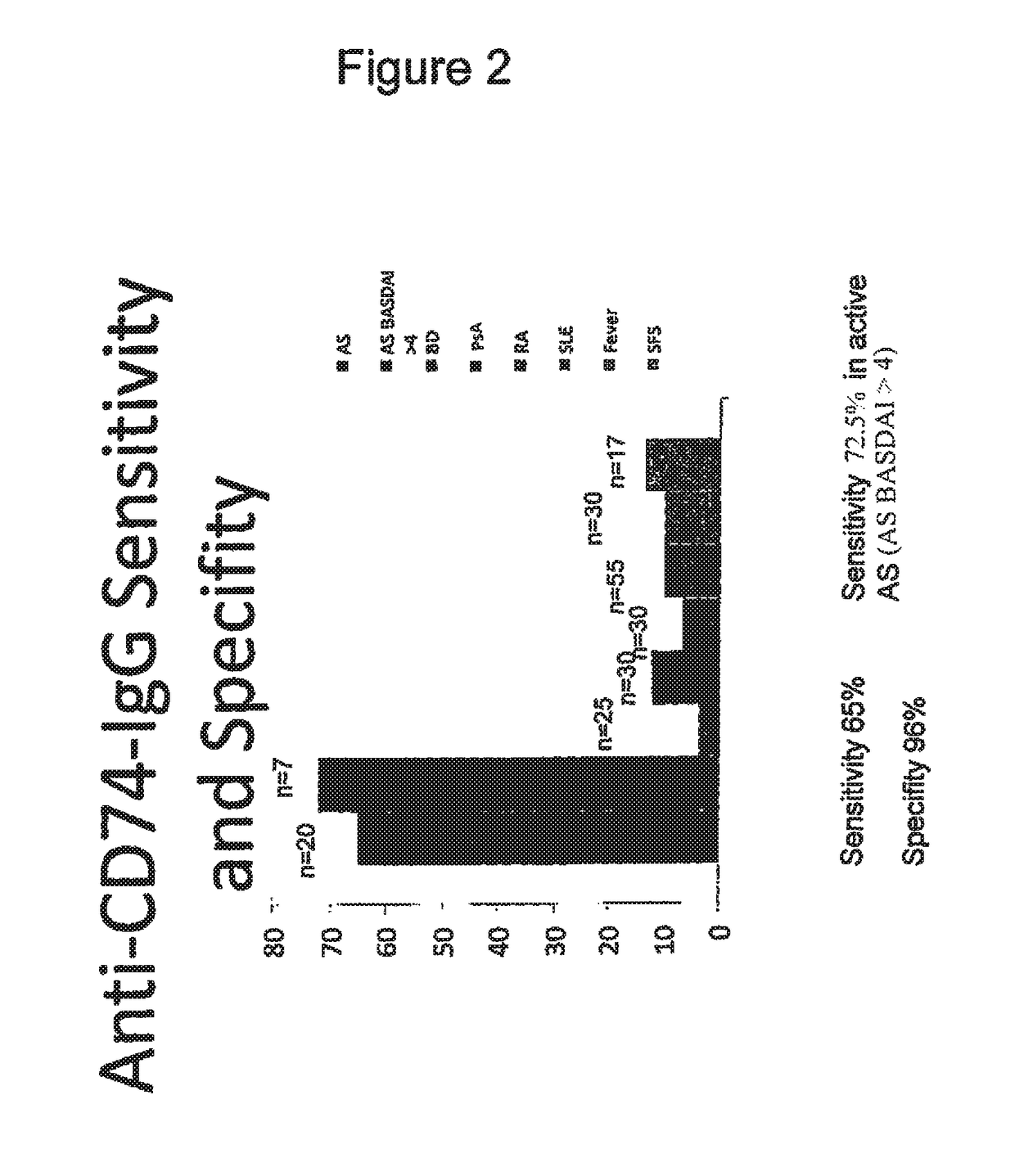
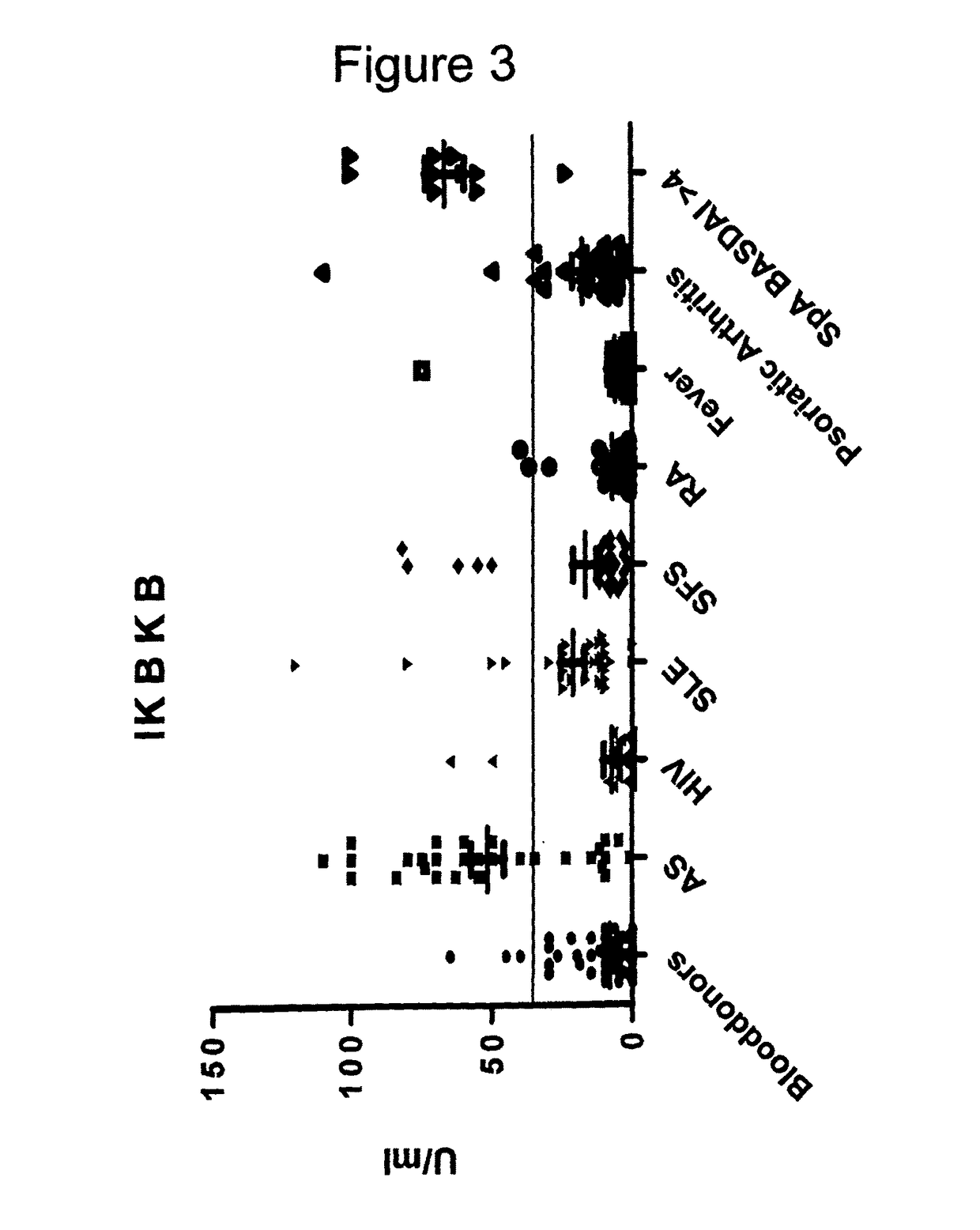
Methods and means for diagnosing spondylarthritis using autoantibody markers
The present invention relates generally to methods for diagnosing the presence or the risk of development or the therapy control of spondyloarthritis (Spa), in particular, of ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and undifferentiated spondyloarthritis in a subject, in particular in mammals. In addition, the present invention relates to test kits for use in the diagnosis of the presence or the risk of development, or for the therapy control of Spa, like AS and undifferentiated spondyloarthritis, in a subject. In particular, the present invention relates to a method for diagnosing the presence or the risk of development, or for the therapy control of Spa, like AS and undifferentiated spondyloarthritis, in a subject analysing for the presence of autoantibodies against CD74 and / or IKBKB in a subject. The presence of autoantibodies against CD74 and / or IKBKB is indicative for the presence or the risk of development, or for the therapy control of Spa, like AS and undifferentiated spondyloarthritis. In particular, detection of the presence of autoantibodies against CD74 and / or IKBKB allows early diagnosis of Spa, in particular, AS and undifferentiated spondyloarthritis.
Owner:MEDIZINISCHE HOCHSCHULE HANNOVER
Compositions and methods of modulating an immune response
InactiveUS20150283226A1Stimulating primary immune responseStimulate immune responseSsRNA viruses negative-senseHydrolysed protein ingredientsDendritic cellLysosomal targeting
Compositions for and methods of stimulating a MHC I mediated immune response comprising stimulating MHC I endolysosomal cross presentation in dendritic cells. Stimulation MHC I endolysosomal cross presentation may comprise over-expression CD74 in dendritic cells and / or targeting antigens to the MHC I endolysosomal cross presentation pathway. Fusion proteins comprising an antigen or fragment thereof and a CD74 endolysosomal targeting sequence are also provided.
Owner:BIOMMUNE TECH
ELISA test kit of human-derived soluble CD74 protein and detection method thereof
ActiveCN103207277BReduce subjectivityHigh sensitivityBiological testingWestern blotSemiquantitative Method
The present invention belongs to the field of immunology and biotechnology, and provides an ELISA test kit of human-derived soluble CD74 protein and a detection method thereof. The kit of the present invention can accurately detect the content of human-derived soluble CD74 protein in body fluid or cell supernatant, and results are quantitatively analyzed by an enzyme-labeling instrument to exclude subjectivity of semi-quantitative methods such as immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence, Western blot and the like; the kit has high sensitivity, the detected content of CD74 protein is as low as 800 pg / ml; according to the invention, no complicated instrument is necessary in detection; the kit is suitable for popularization and application in scientific research institutions and medical institutions, is suitable for large-scale detection of clinical samples, and can rapidly obtain massive data and information related to human-derived CD74 protein.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Fusion peptides with antigens linked to short fragments of invariant chain(CD74)
ActiveUS20190338014A1Improving immunogenicitySame effectCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigenProtein C
The present application provides inter alia a fusion protein comprising a polypeptide wherein the polypeptide consists of a fragment of invariant chain which is operably linked to an antigenic sequence and wherein the fragment of invariant chain consists of a portion of residues 17-97 of SEQ ID NO: 1, wherein the portion comprises at least 5 contiguous residues from residues 77-92 of SEQ ID NO: 1.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA +1
Signature for predicting clinical outcome in human HER2+ breast cancer
ActiveUS9803245B2Reduced survivalConducive to survivalBiocideOrganic active ingredientsOncologyCD79B
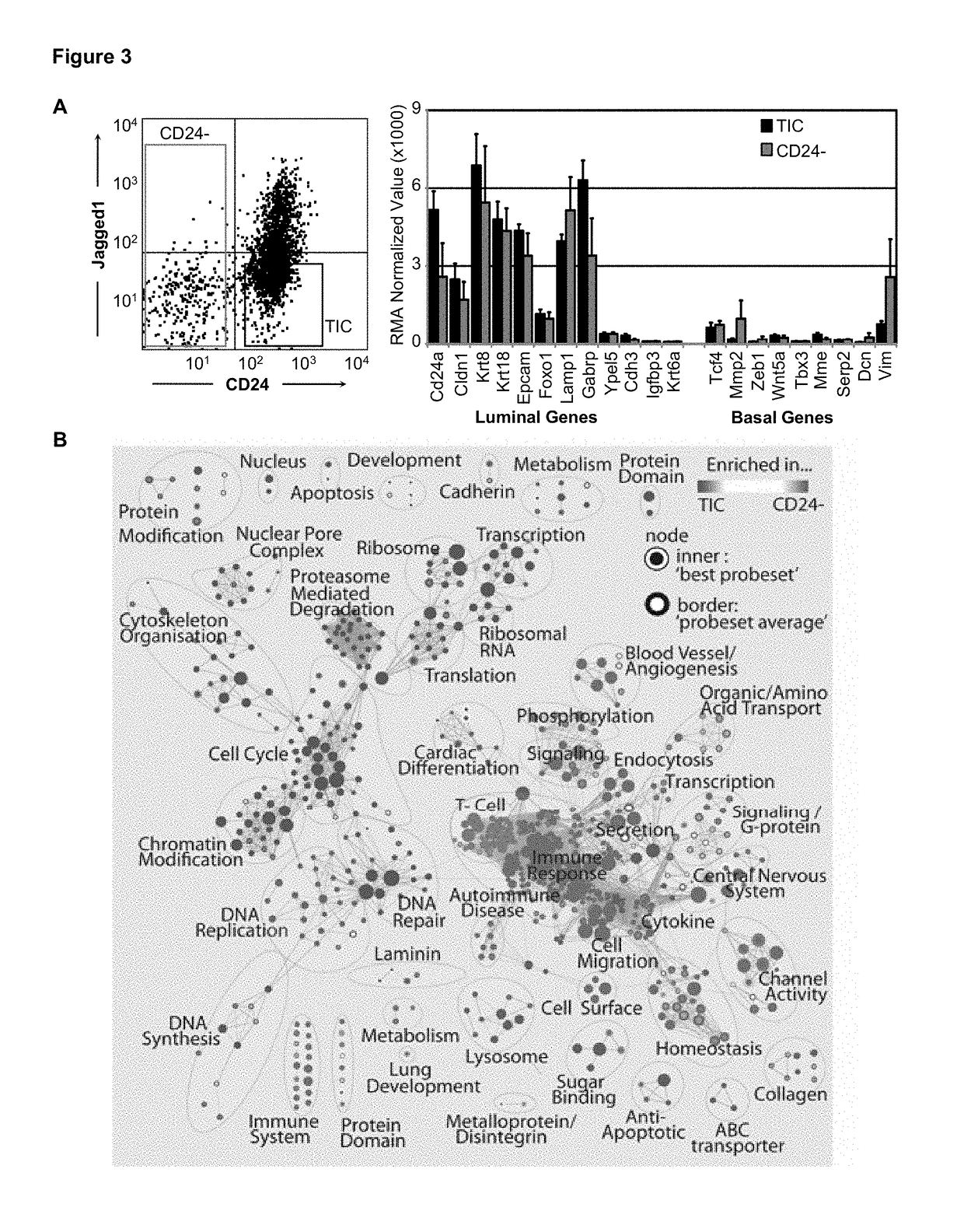
A method of predicting outcome in a subject with for example Her2+ (ERα−) breast cancer comprising: (a) determining a HTICs expression signature comprising determining an expression level of 2 or more HTICS biomarkers selected from Aurkb, Ccna2, Scrn1, Npy, Atp7b, Chaf1b, Ccnb1, Cldn8, Nrp1, Ccr2, C1qb, Cd74, Vcam1, Cd180, Itgb2, Cd72, St8sia4, Kif11, Plk1, Chek1, Mphosph6, Cora1a, Ccl5, Cd3e, Hcls1, Vav1, Plek, Arhgdib, Il2rg, Sash3, Lck, Il2rb, Cybb, Cd79b, Sell, Ccnd2, Tnfrsf1b, Rftn1, Rac2 and Ly86; and (b) calculating a signature score, the signature score comprising a sum of HTICs biomarker expression parameters; wherein a signature score greater than a selected cut-off or control signature score is indicative of a poor outcome (HTICS+) and a signature score less than a selected cut-off is indicative of a good outcome (HTICS−). The methods can be used to prognose outcome and / or select suitable treatment. Arrays and kits for use with the methods are also provided.
Owner:UNIV HEALTH NETWORK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com