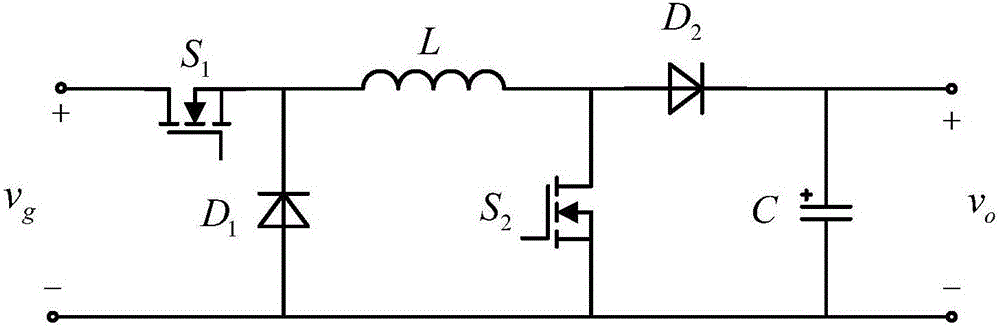
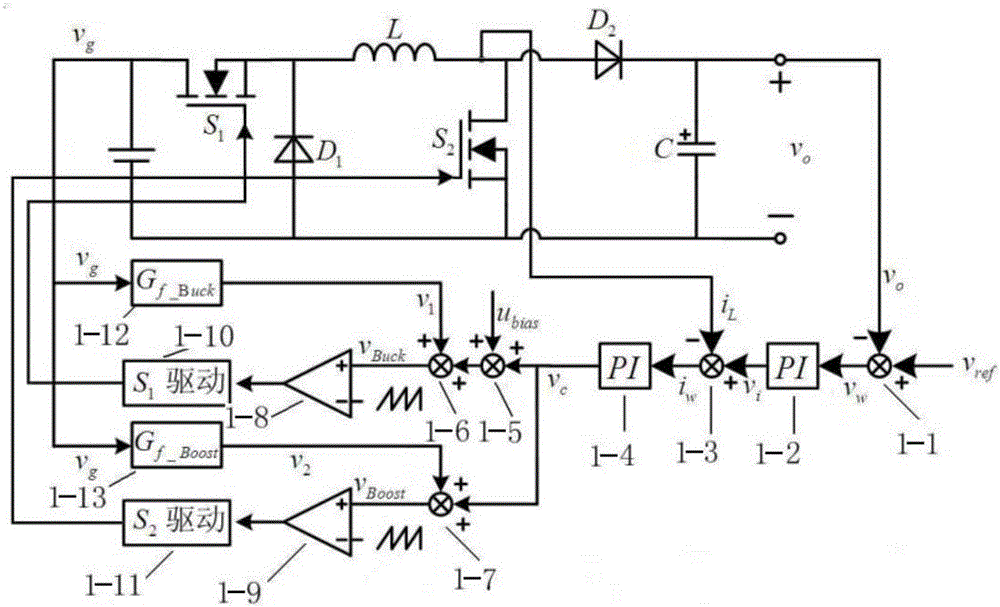
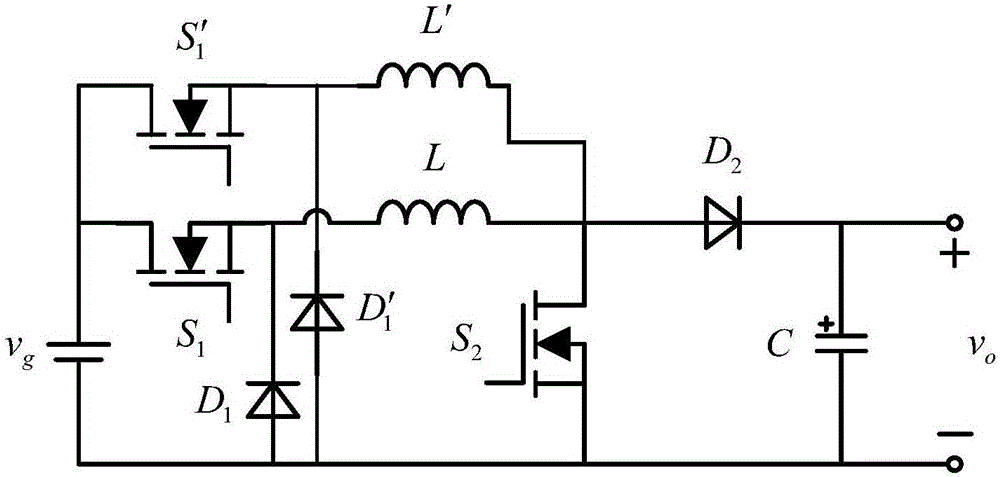
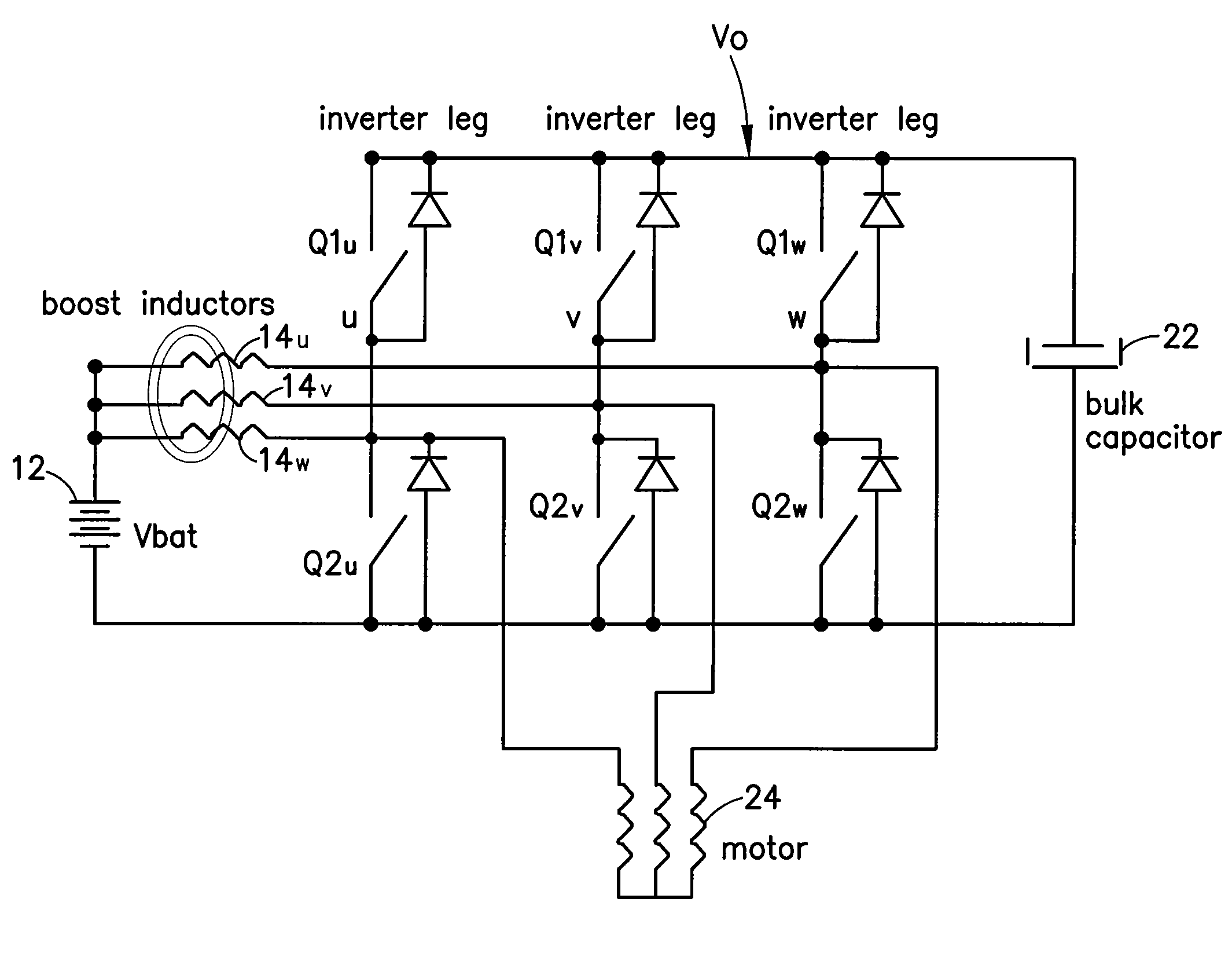
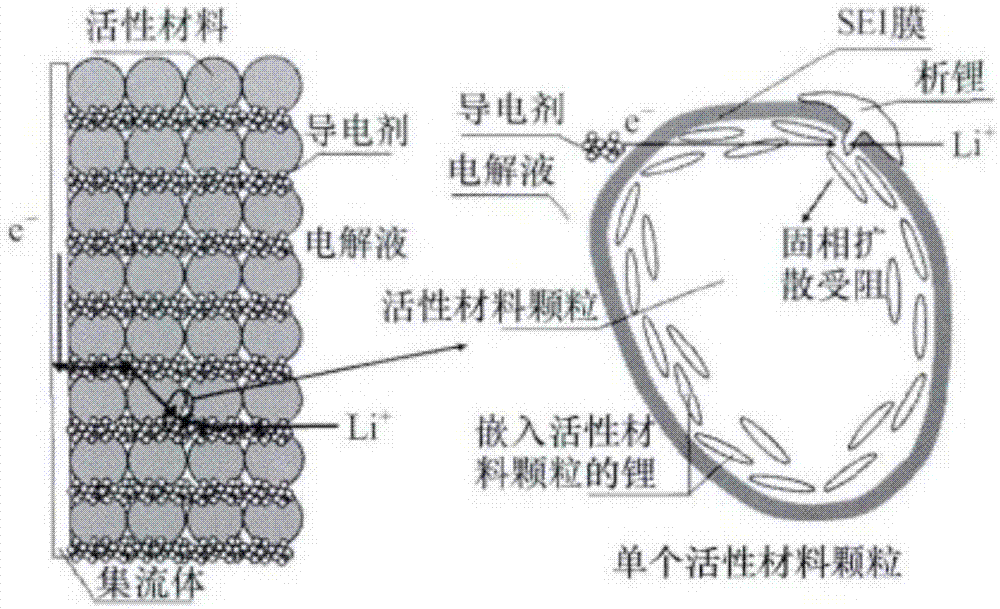
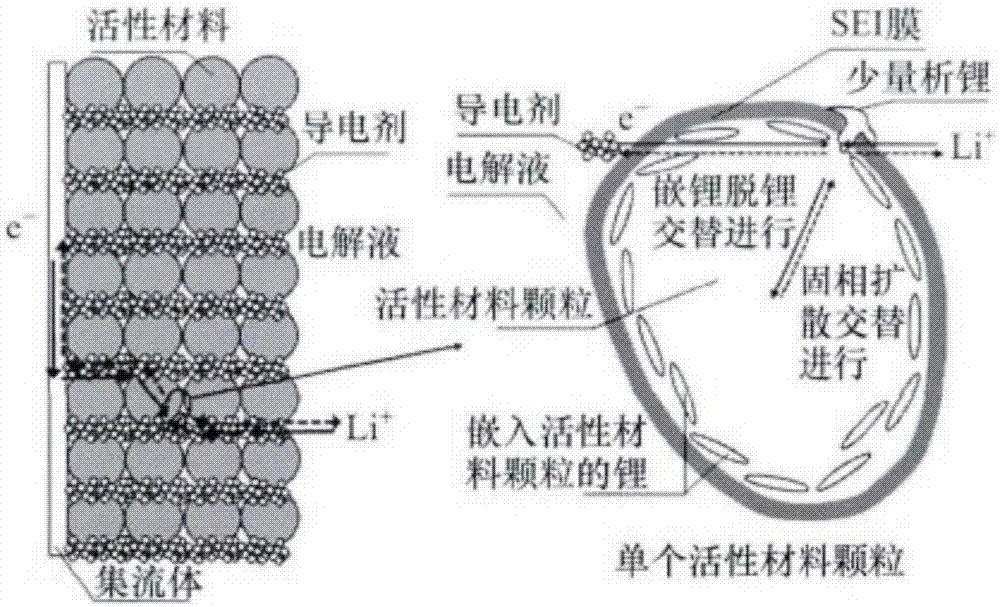
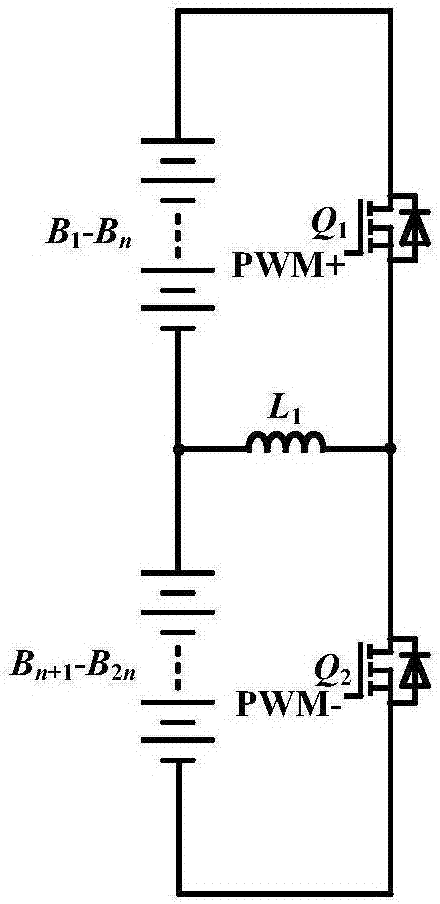
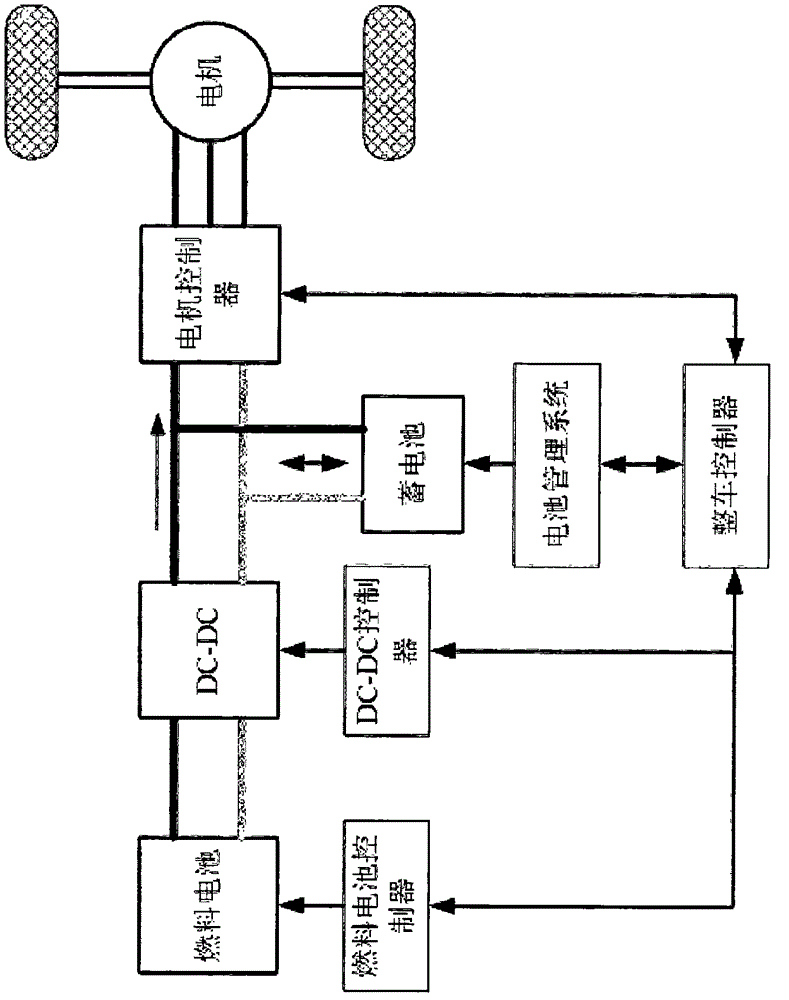
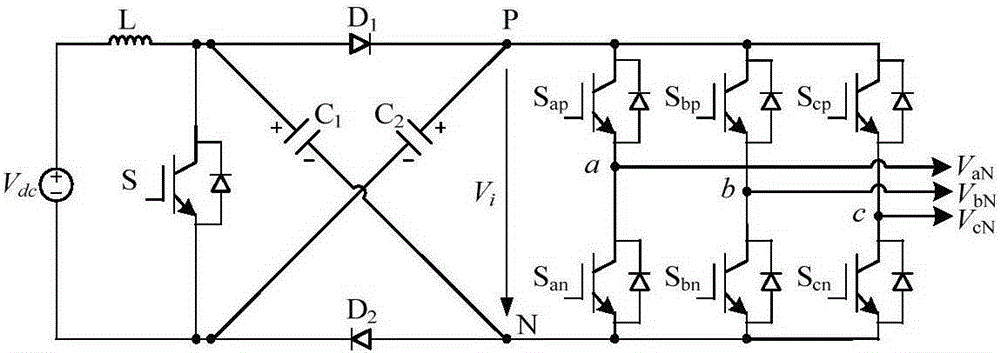
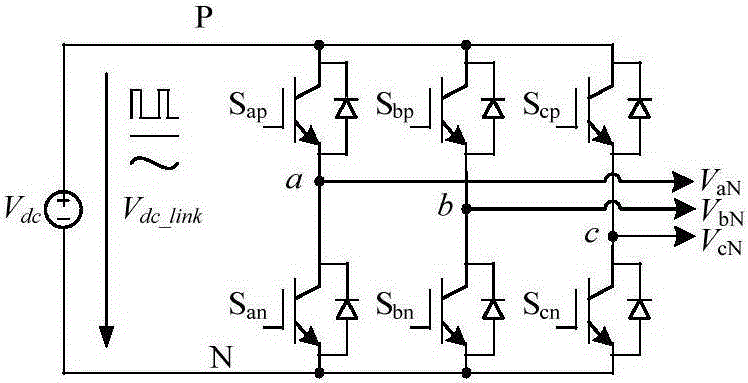
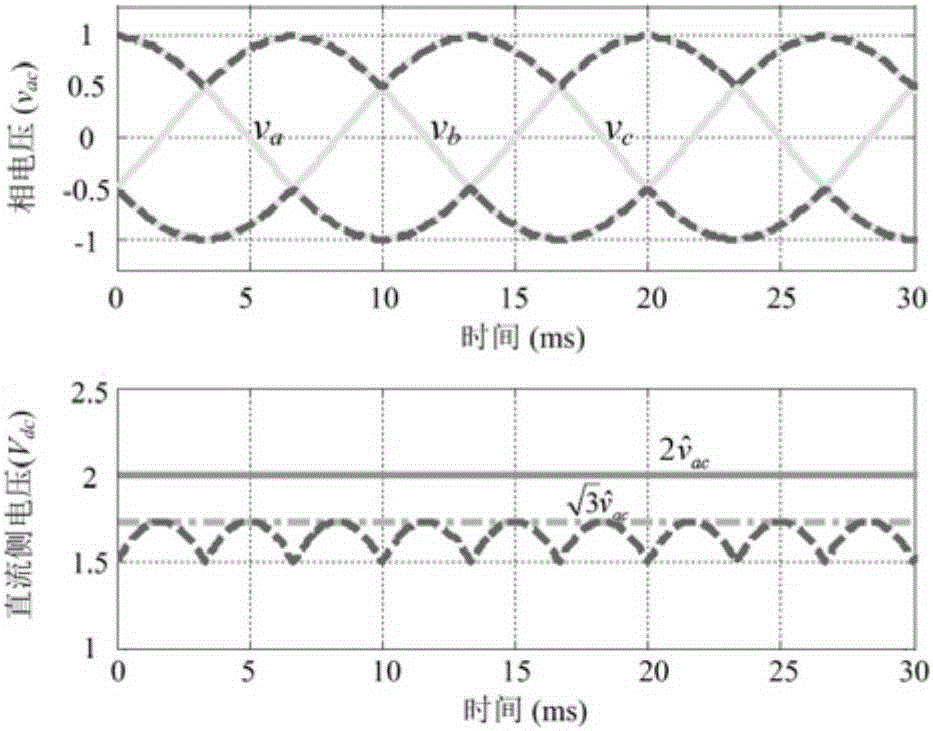
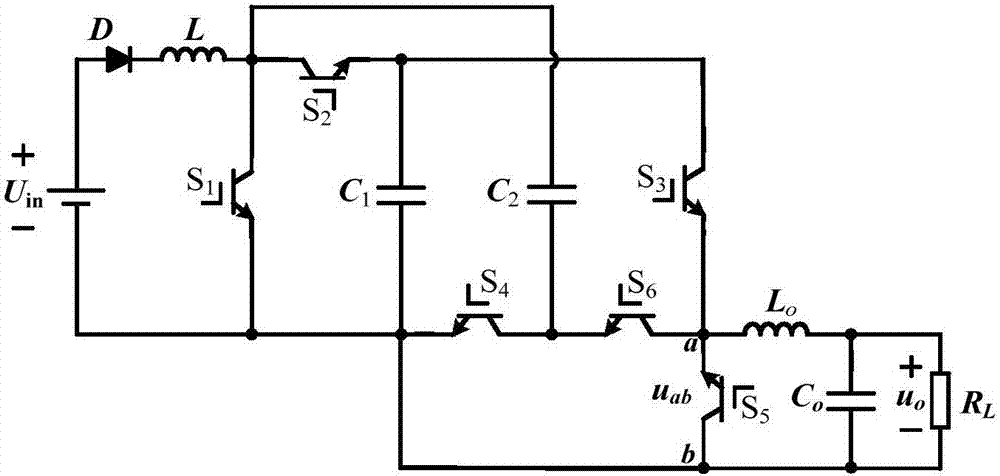
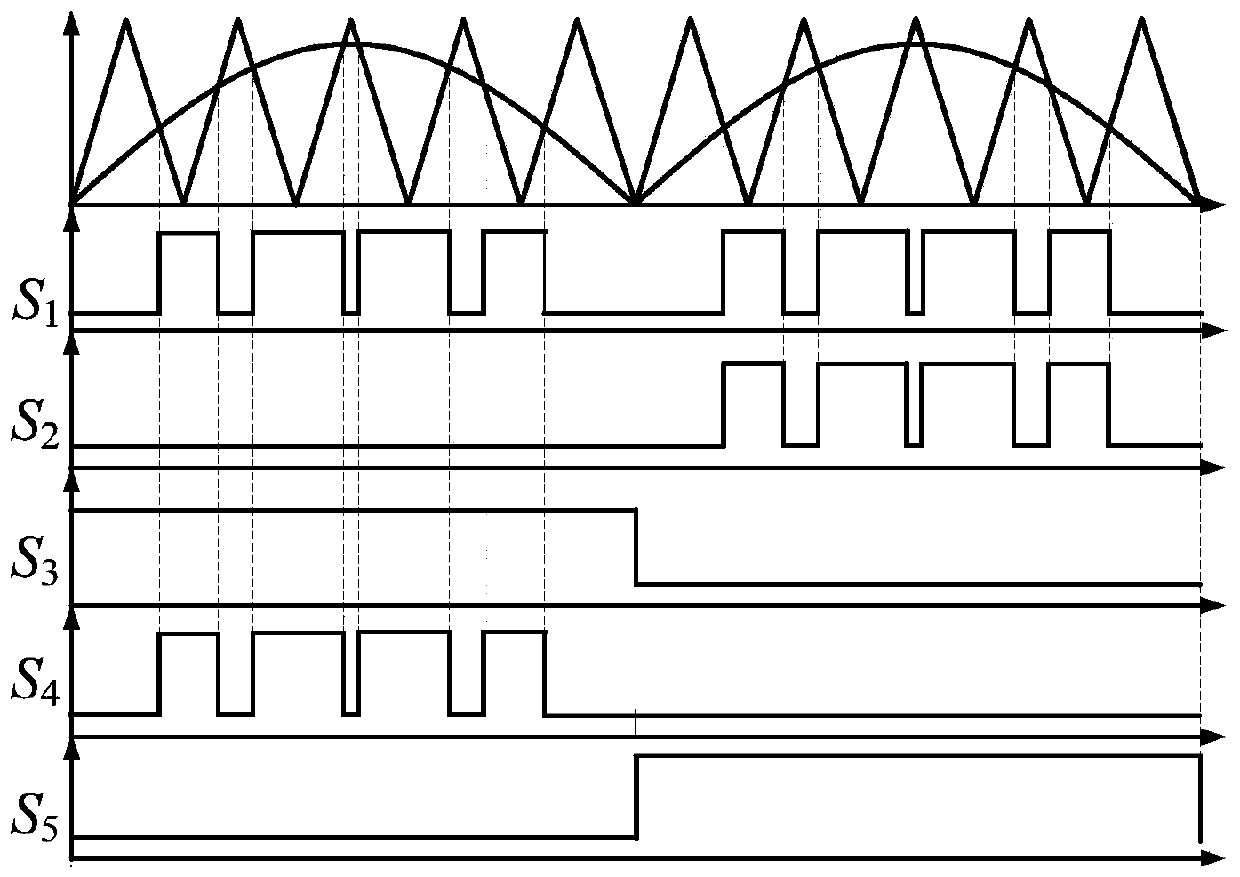
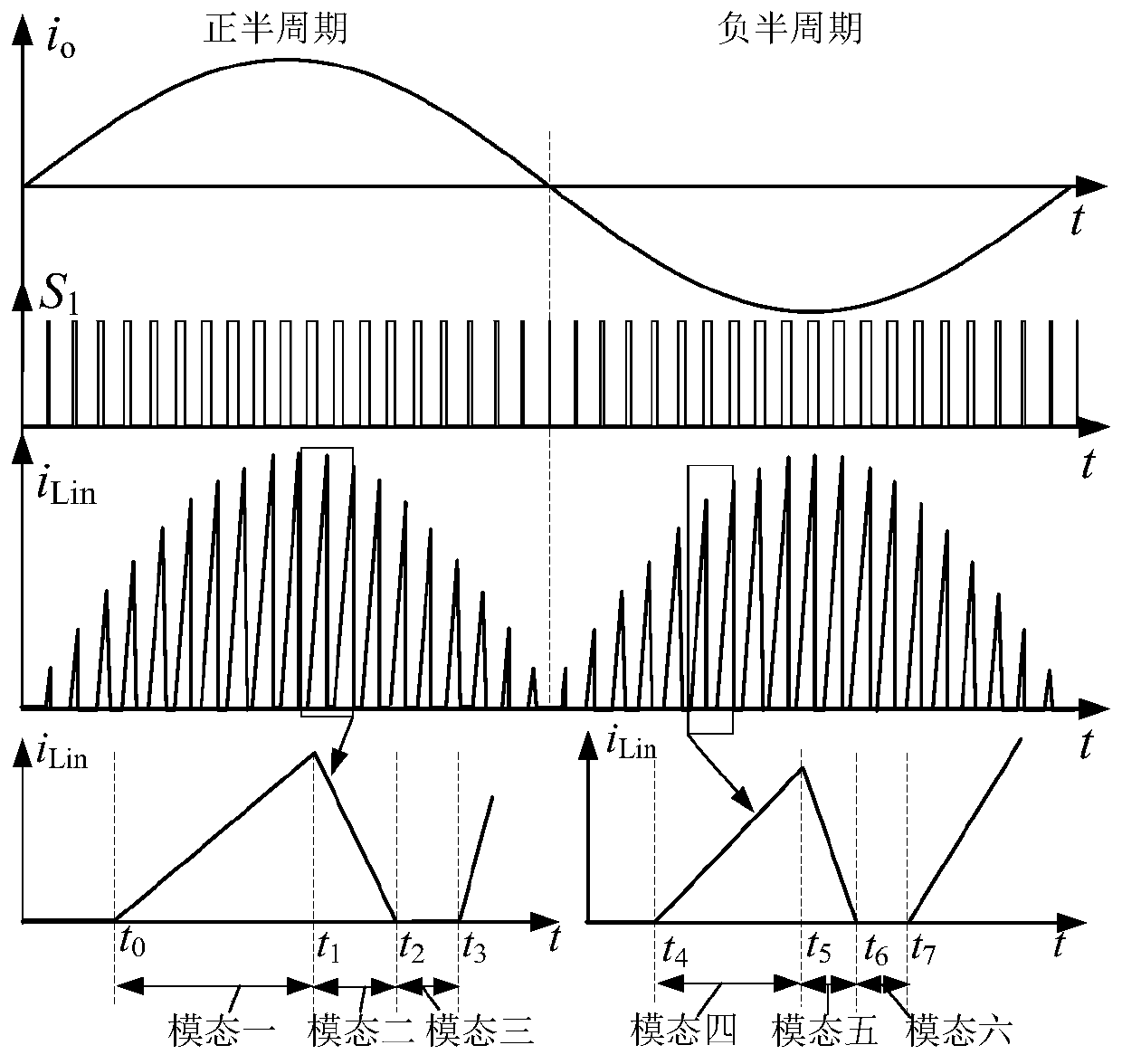
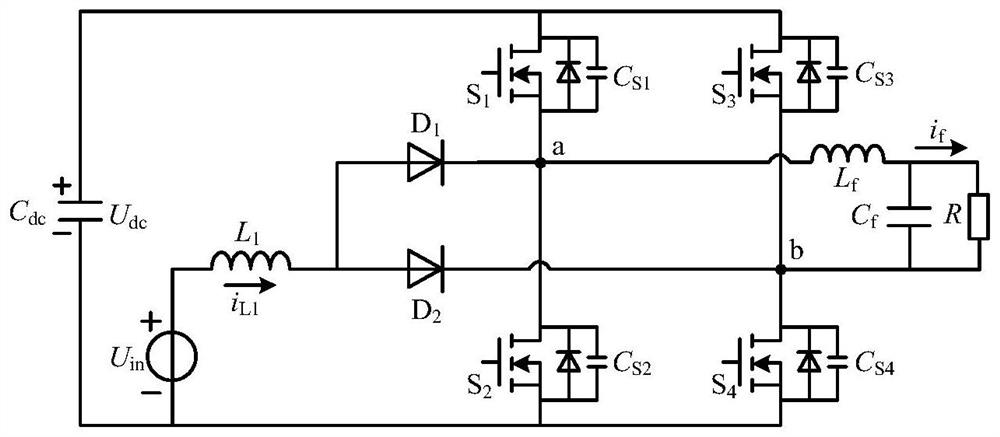
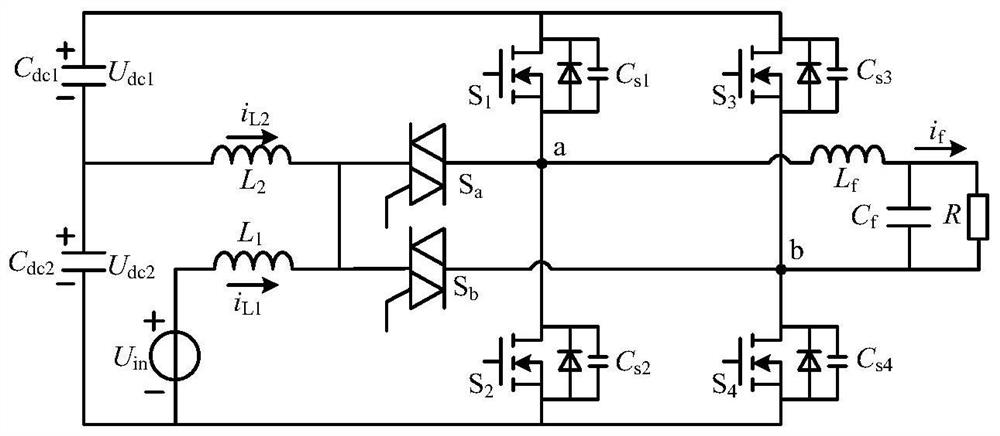
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
151 results about "Boost inverter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
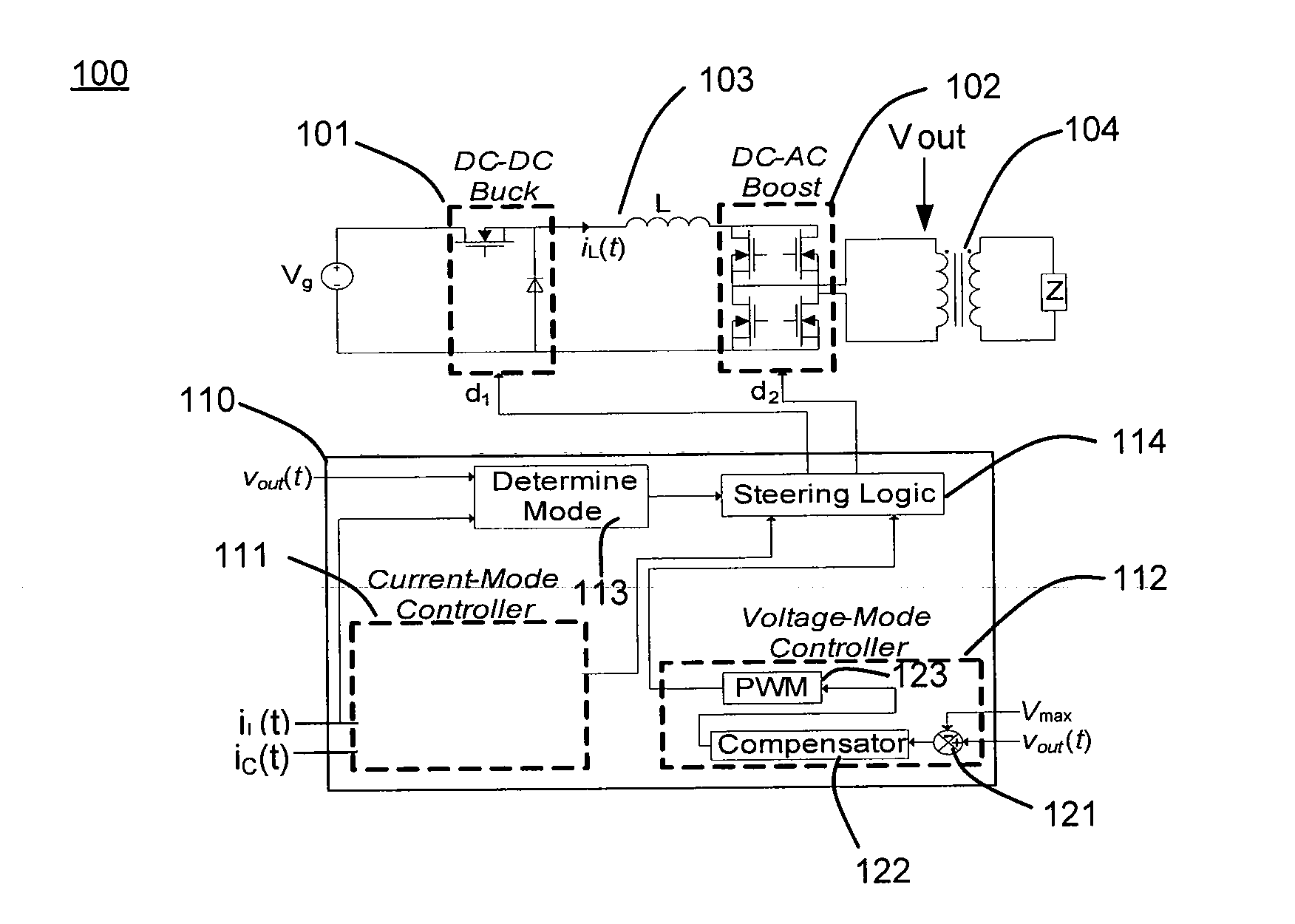
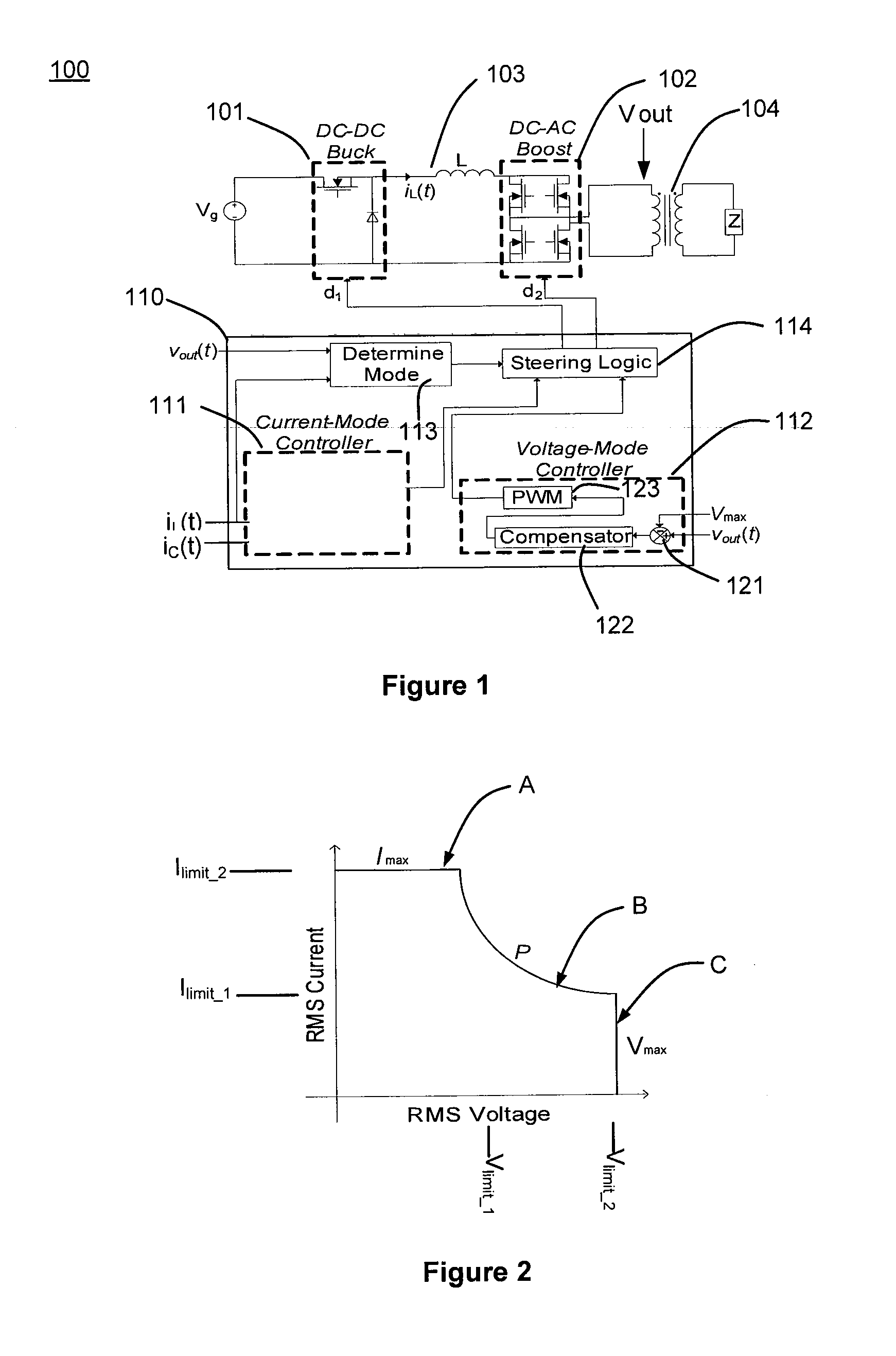
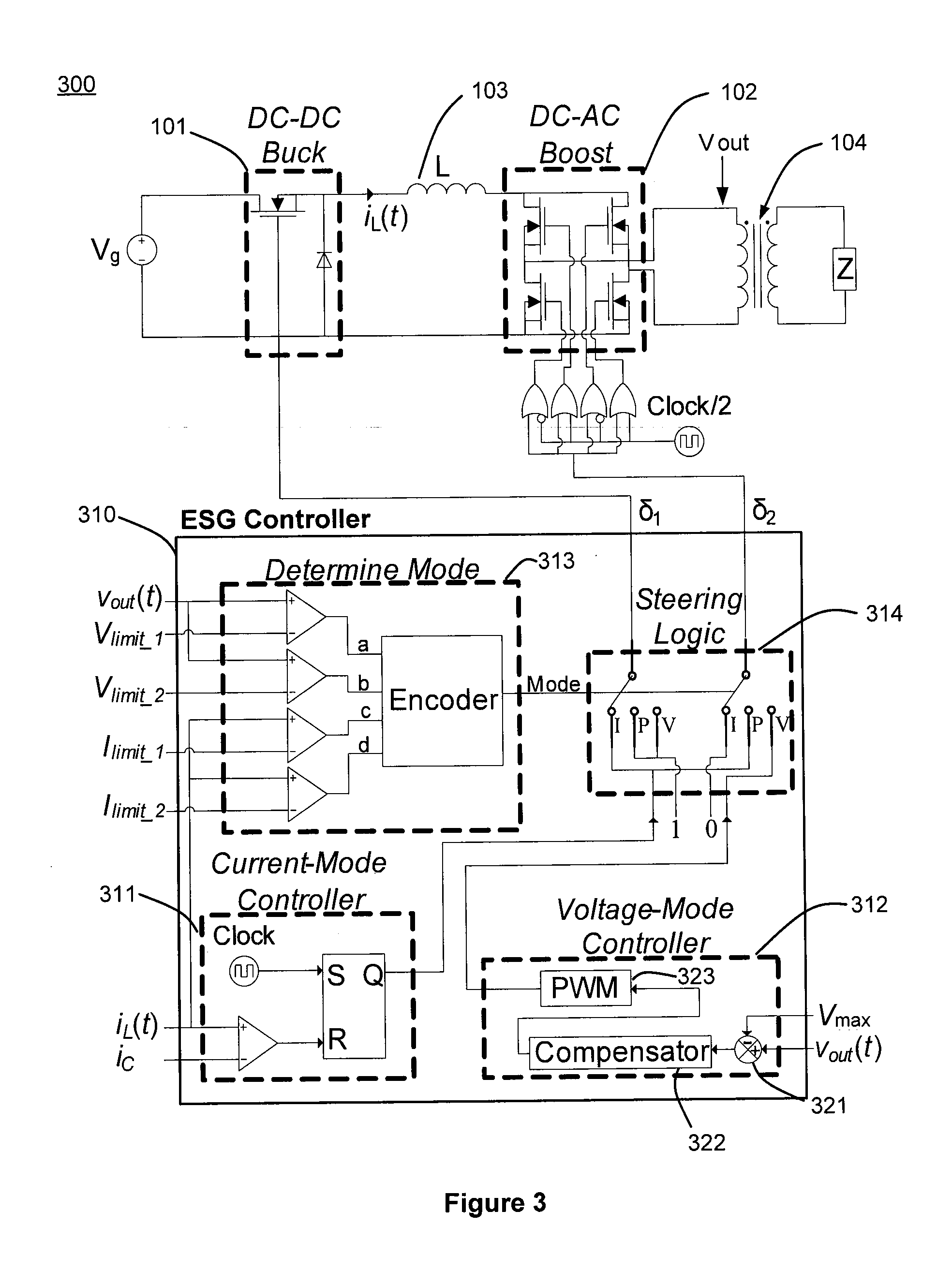
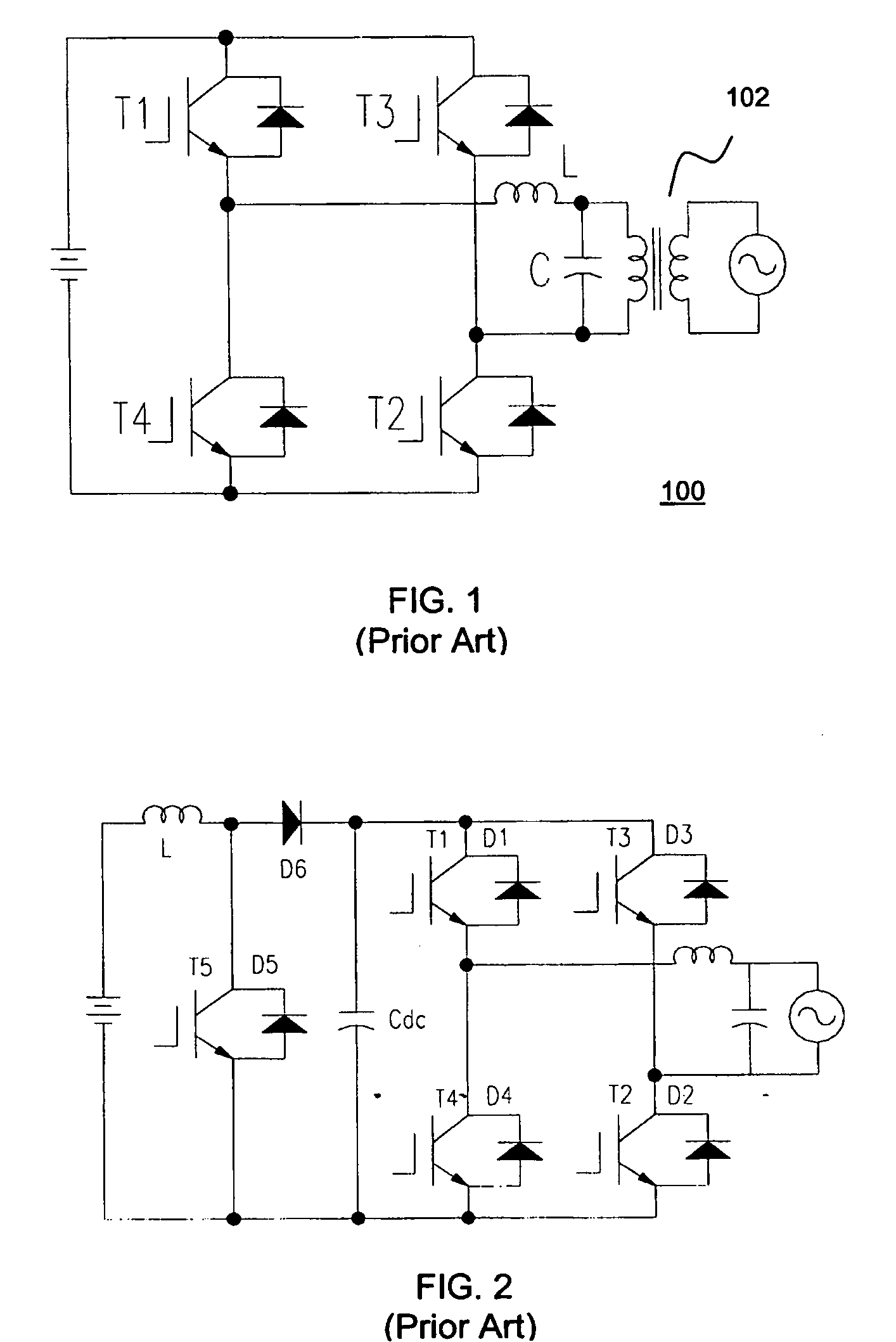
Electrosurgical generator controller for regulation of electrosurgical generator output power
ActiveUS20120215216A1Accurate power source output characteristicProcess safetyControlling energy of instrumentAc-dc conversionElectricityBuck converter
An electrosurgical generator may reduce unintended tissue damage by improving regulation of output power. The electrosurgical generator may control the power during a cycle, and react to a change in power if arcing occurs. Voltage sources, especially, demonstrate the tendency to have large, uncontrolled power excursions during normal electrosurgical use. The magnitude of the power excursions may be dependent on various factors. An exemplary electrosurgical generator control scheme reduces or minimizes the thermal spread by accurately supplying the specified power within a few cycles. Additionally, fast and accurate regulation provided by the constant voltage mode reduces or minimizes unintentional tissue charring. Thus, reduced thermal spread and charring should result in better surgical outcomes by reducing scarring and decreasing healing times. An electrosurgical generator controller may be configured to control both a DC-DC buck converter and a DC-AC boost inverter based in part on electrical parameters of the electrosurgical generator.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
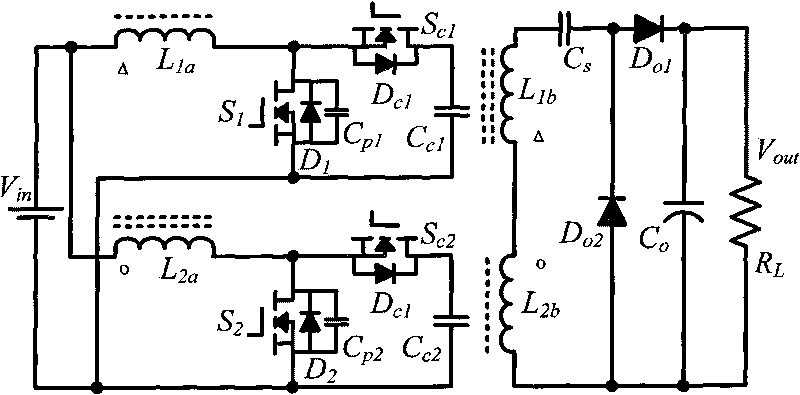
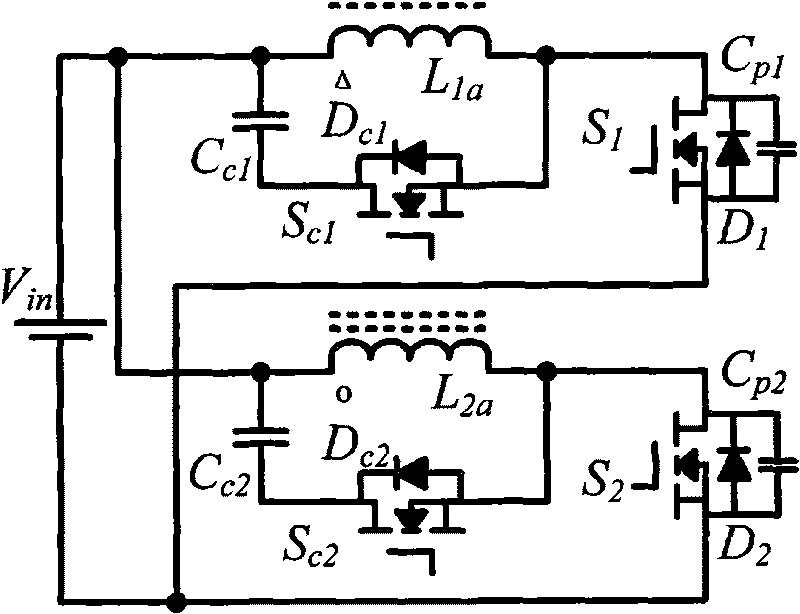
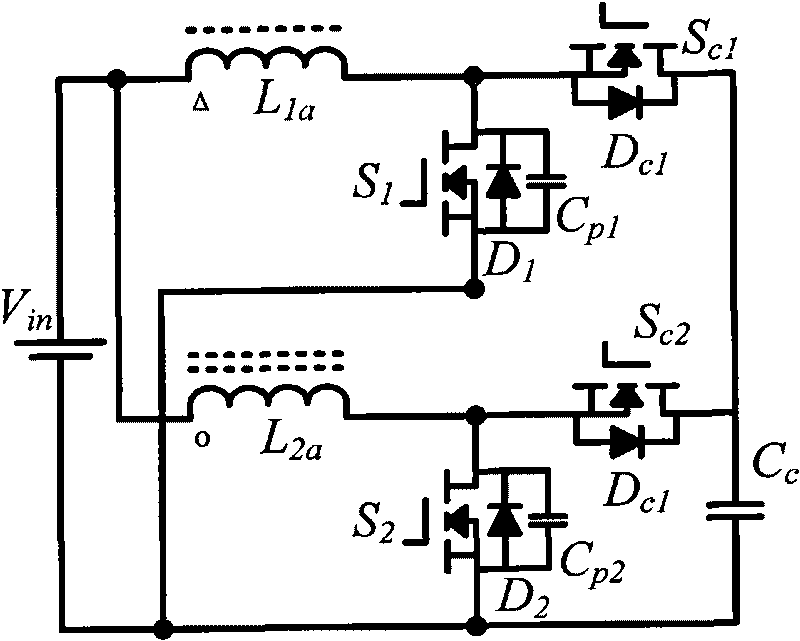
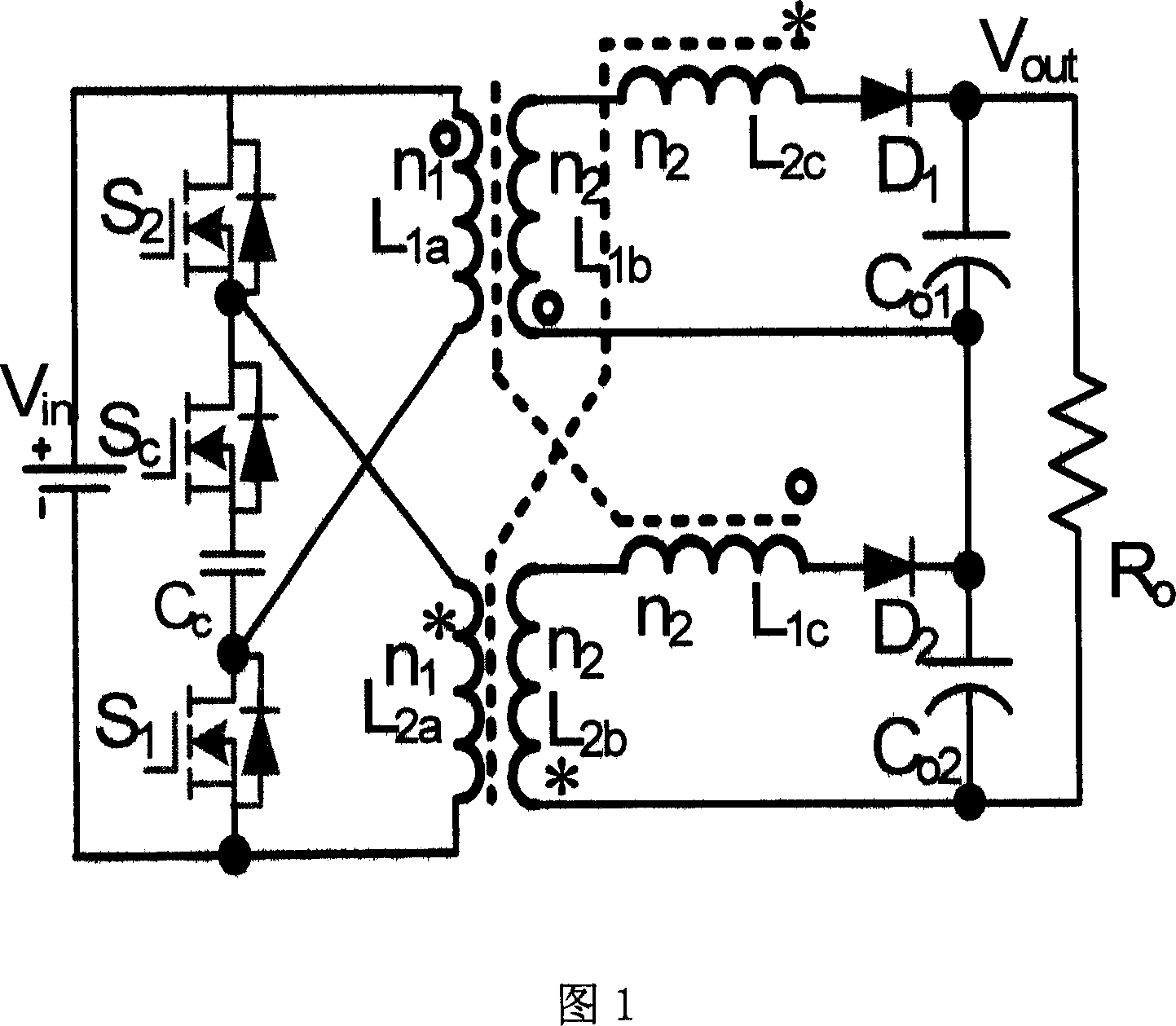
Forward-flyback isolated type boost inverter realized by coupling inductors and application thereof
ActiveCN101702578AIncrease profitReduce volumeApparatus with intermediate ac conversionElectric variable regulationClamp capacitorResonance
The invention discloses a forward-flyback isolated type boost inverter realized by coupling inductors and application thereof, comprising two power switch tubes, two auxiliary switch tubes, four anti-parallel diodes, a switch tube parallel capacitor, two clamp capacitors, two switch capacitors, two output diodes and two coupling inductors respectively provided with two windings. The invention realizes zero-voltage switching on of the power switch tubes through the resonance of the leakage inductance of the two coupling inductors and the switch tube parallel capacitor, absorbs the voltage peak switched off by the switch tubes caused by the leakage inductance and realizes energy lossless transfer by utilizing a clamp circuit comprising the anti-parallel diodes of the switch tubes and the two clamp capacitors, realizes the high gain output of the inverter by utilizing the serial connection of the second windings of the two coupling inductors, further improves the gain of the inverter and lowers the output voltage stress of the diodes by utilizing the switch capacitors and realizes the output zero-current switching off of the diodes by utilizing the leakage inductance of the coupling inductors.
Owner:HOYMILES POWER ELECTRONICS INC
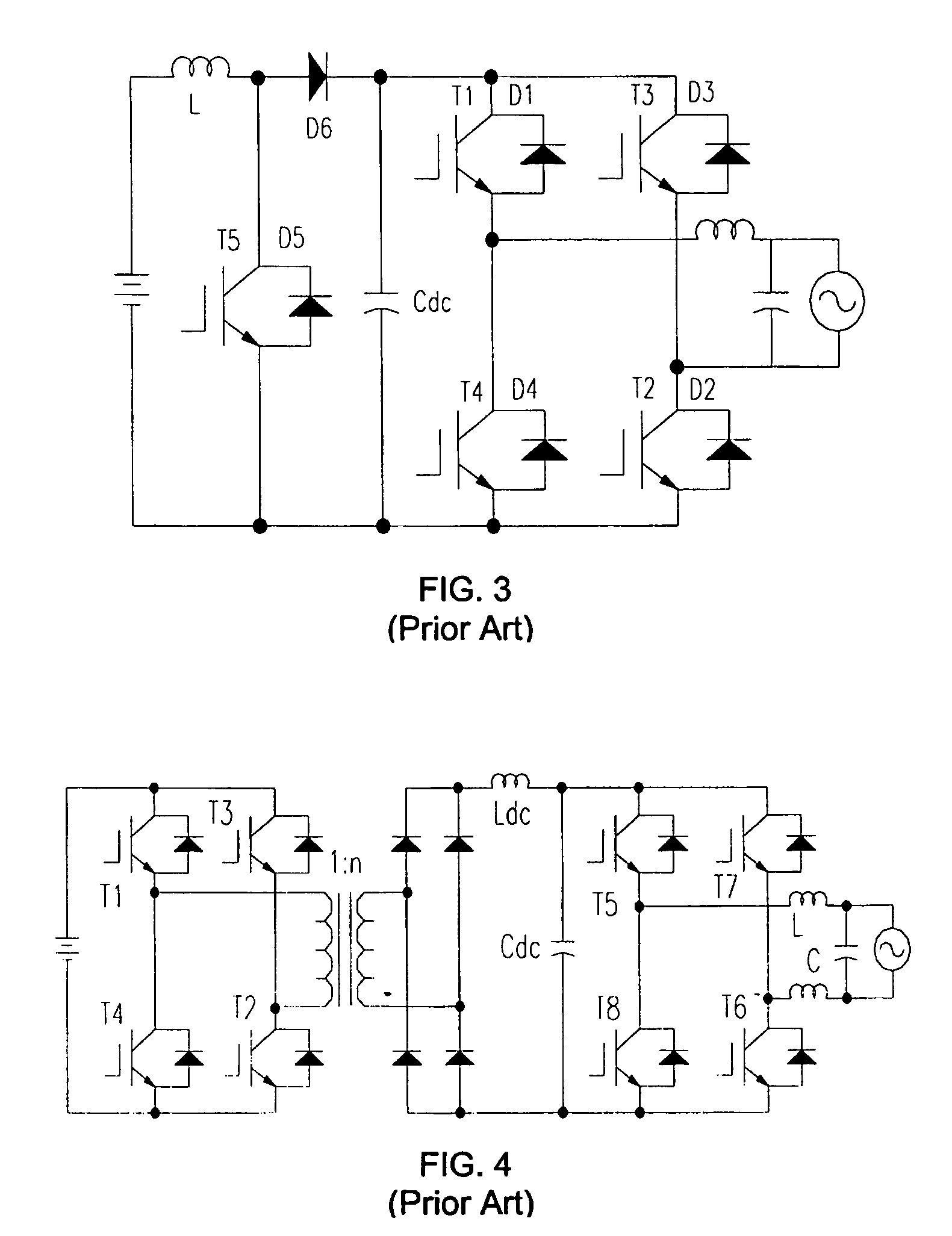
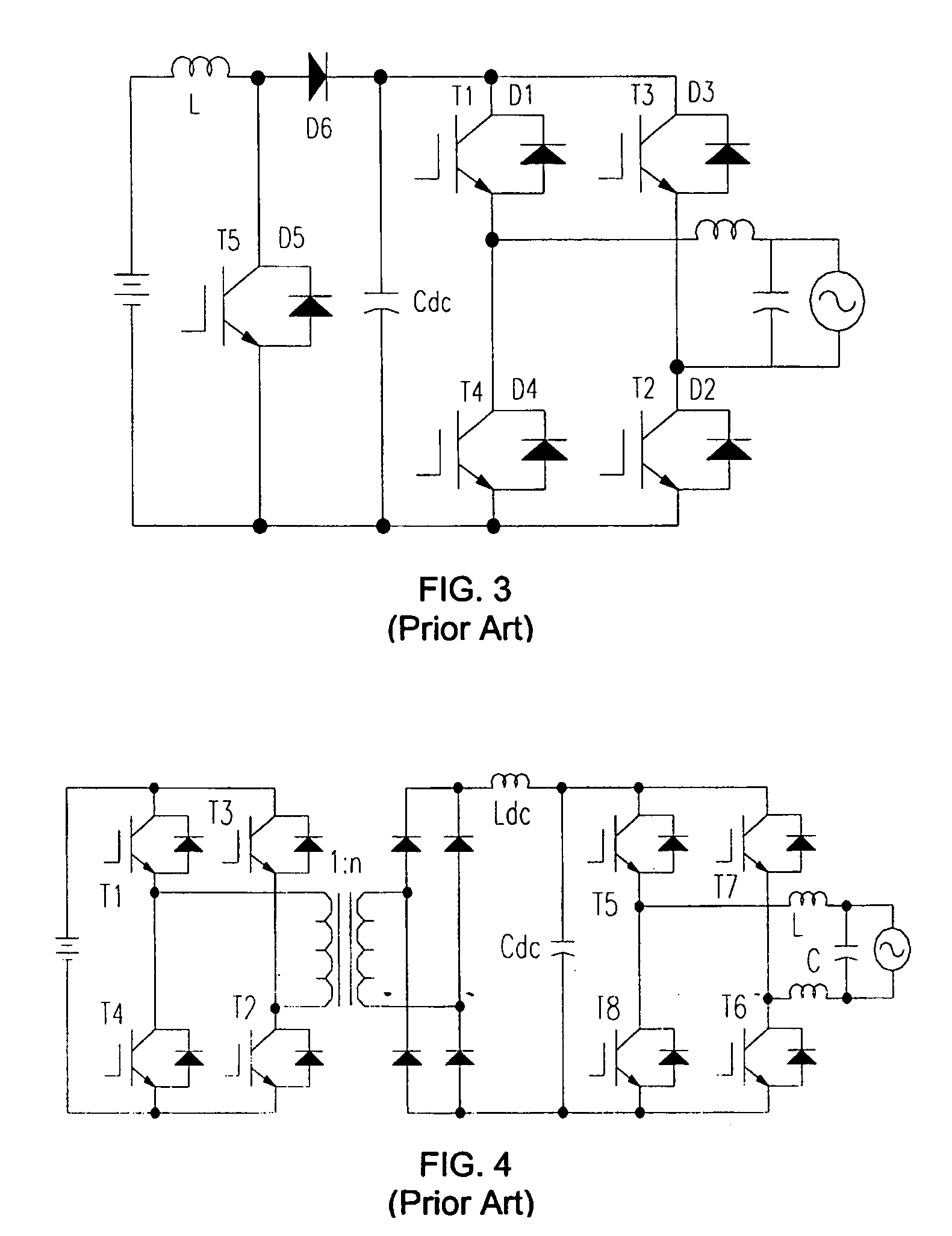
Single-stage buck-boost inverter
InactiveUS7333349B2Low costImprove efficiencyDc network circuit arrangementsDc-dc conversionFuel cellsSingle stage
An improved Single-Stage Buck-Boost inverter (S2B2 Inverter) is provided, using only three or four power semiconductor switches and two coupled inductors in a flyback arrangement. The inverter can handle a wide range of dc input voltages and produce a fixed ac output voltage. The inverter is well suited to distributed power generation systems such as photovoltaic and wind power and fuel cells, for standalone or grid connected applications. The inverter has a single charge loop, a positive discharge loop and a negative discharge loop.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF NEW BRUNSWICK
Single-stage buck-boost inverter
InactiveUS20050270000A1Low costImprove efficiencyDc network circuit arrangementsDc-dc conversionFuel cellsSingle stage
An improved Single-Stage Buck-Boost inverter (S2B2 Inverter) is provided, using only three or four power semiconductor switches and two coupled inductors in a flyback arrangement. The inverter can handle a wide range of dc input voltages and produce a fixed ac output voltage. The inverter is well suited to distributed power generation systems such as photovoltaic and wind power and fuel cells, for standalone or grid connected applications. The inverter has a single charge loop, a positive discharge loop and a negative discharge loop.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF NEW BRUNSWICK
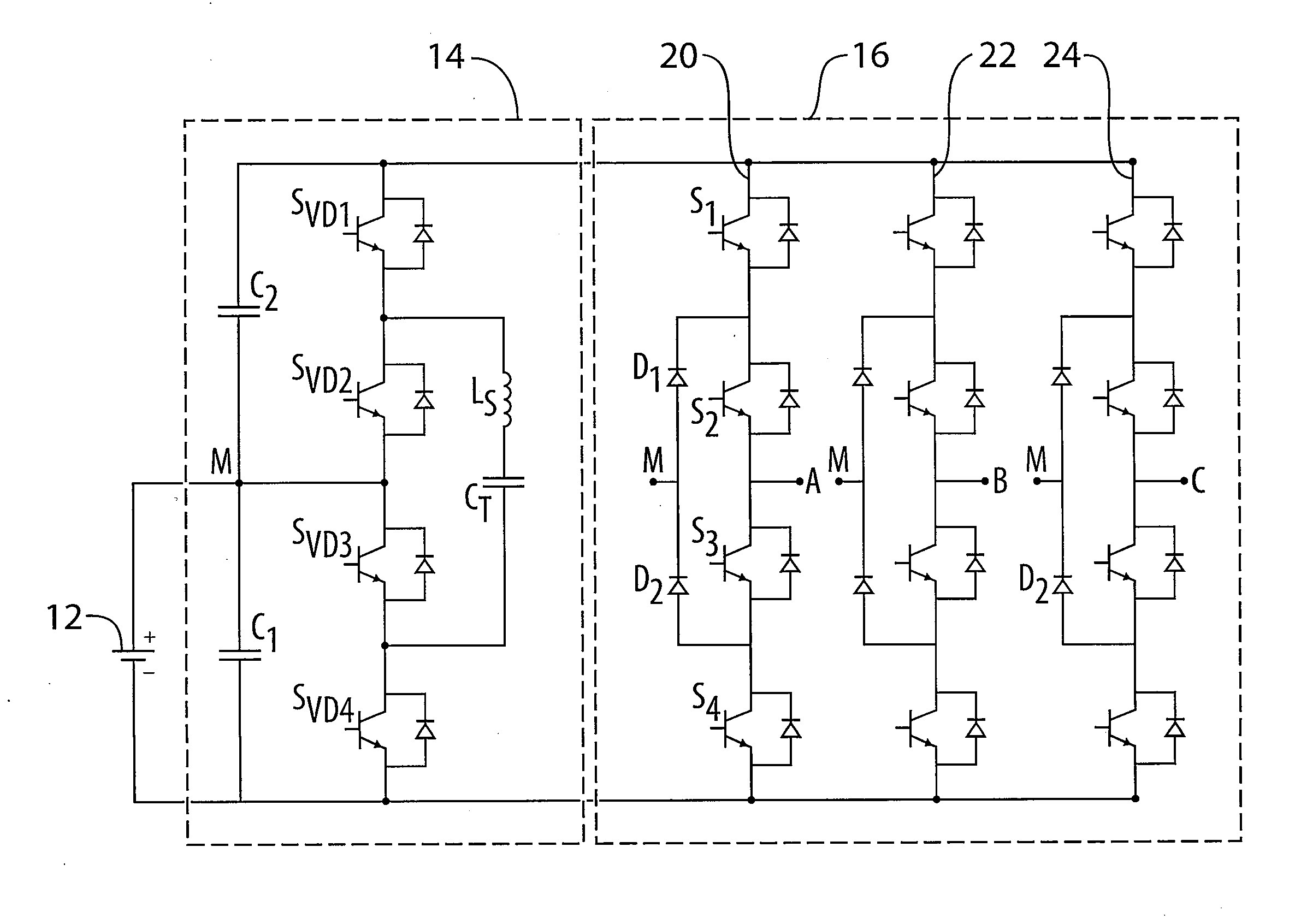
Boost Multilevel Inverter System
InactiveUS20110141779A1Conversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc-dc conversionEnergy transferPeak value
A boost inverter includes a first capacitor for connection in parallel with a dc supply voltage; a second capacitor connected in series with the first capacitor; an energy transfer path including a transfer capacitor and switches connected to the transfer capacitor for cyclically transferring energy from the first capacitor to the transfer capacitor and then from the transfer capacitor to the second capacitor; a multilevel inverter circuit connected in parallel with the series combination of the first and second capacitors, the inverter having at least one phase output for connection to an electric motor; and a PWM controller that activates the energy transfer path when a desired peak-to-peak output voltage exceeds the dc supply voltage and deactivates the energy transfer means when the desired peak-to-peak output voltage is less than the dc supply voltage.
Owner:MAGNA E CAR SYST OF AMERICA
Single-stage boosting inverter with tap inductor
InactiveCN102255542AImprove reliabilityReduce complexityEfficient power electronics conversionDc-ac conversion without reversalCapacitanceSingle stage
The invention discloses a single-stage boosting inverter with a tap inductor, which is shown in a figure described in the specification. The inverter comprises an inversion bridge (B) and a passive network. The passive network comprises an inductor (L), capacitors (C1 and C2), diodes (D1, D2 and D3) and the tap inductor (Lt). A first winding (N1) and a second winding (N2) of the tap inductor (Lt) are connected in series positively. According to the inverter disclosed by the invention, energy is stored in the tap inductor (Lt) by utilizing an ended zero vector state forbidden in the traditional voltage type inverter; the energy is combined with energy supplied by an input power supply in a non-ended zero vector state; and the combined energy is transmitted together to a middle bus so that the voltage of the bus is boosted. Therefore, the inverter can output alternating-current voltage, an amplitude value of which is higher than that of input voltage (Vi); the inverter can satisfy boosting requirements in different application situations by configuring the turn ratio of the tap inductor (Lt); and in the event of being applicable to an alternating-current input situation, the inverter can also realize a power factor correction (PFC) function.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Coupling inductance type double Boost inverter circuits in photovoltaic system
InactiveCN101741273ARealize level one grid-connected power generationTake advantage ofAc-dc conversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsCapacitanceGrid-tie inverter
The invention relates to coupling inductance type double-Boost inverter circuits in a photovoltaic system, which comprises two coupling inductance type Boost circuits sharing a direct current power supply, and alternate current output is taken from two coupling inductance type Boost output capacitors. The invention solves the defects of large power loss of a power switching tube, large power loss of a transformer, low conversion efficiency, low utilization rate of photovoltaic generation and the like in a method in which a single-stage inversion circuit is combined to the grid through an industrial frequency transformer boost mode, a DC-DC boosted circuit is at the front stage and an inverter is at the back stage. The invention comprises two coupling inductance type Boost circuits and uses a full-control type device switching tube, so the inversion circuit can realize four-quadrant operation of energy; and under the conditions that the coupled inductance has lower input voltage and smaller duty ratio, the Boost circuits can also output higher voltage, thus the grid-combined inverter of the invention does not need a booster transformer and can realize primary grid-combined generation.
Owner:SUNHUI NEW ENERGY CO LTD
Wide-input direct current inverter topology and feedforward average current control method thereof
InactiveCN106169868AImprove input dynamic response performanceGood input dynamic response performanceEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionAverage currentInverter topology
The invention belongs to the technical field of power electronic application, and especially relates to a wide-input direct current inverter topology and a feedforward average current control method thereof. The wide-input direct current inverter topology comprises a two-transistor Buck-Boost inverter and an interleaved two-transistor Buck-Boost inverter. The feedforward average current control method applicable to the wide-input direct current inverter topology is composed of an input voltage feedforward module, a mode switching module, a voltage outer ring and a current inner ring. According to the method, input voltage feedforward is introduced into the current inner ring in average current control, a feedforward function from the input voltage feedforward to the current inner ring is computed, simplification is carried out, thereby obtaining feedforward average current control applicable to practical application, and the input dynamic response performance of the inverters in a whole input voltage range is greatly improved; and moreover, by adoption of an interleaving technology, the conversion capacity is increased, the output current ripple is effectively reduced, and the support is provided for the field with wide range input and high power conversion.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING) +1
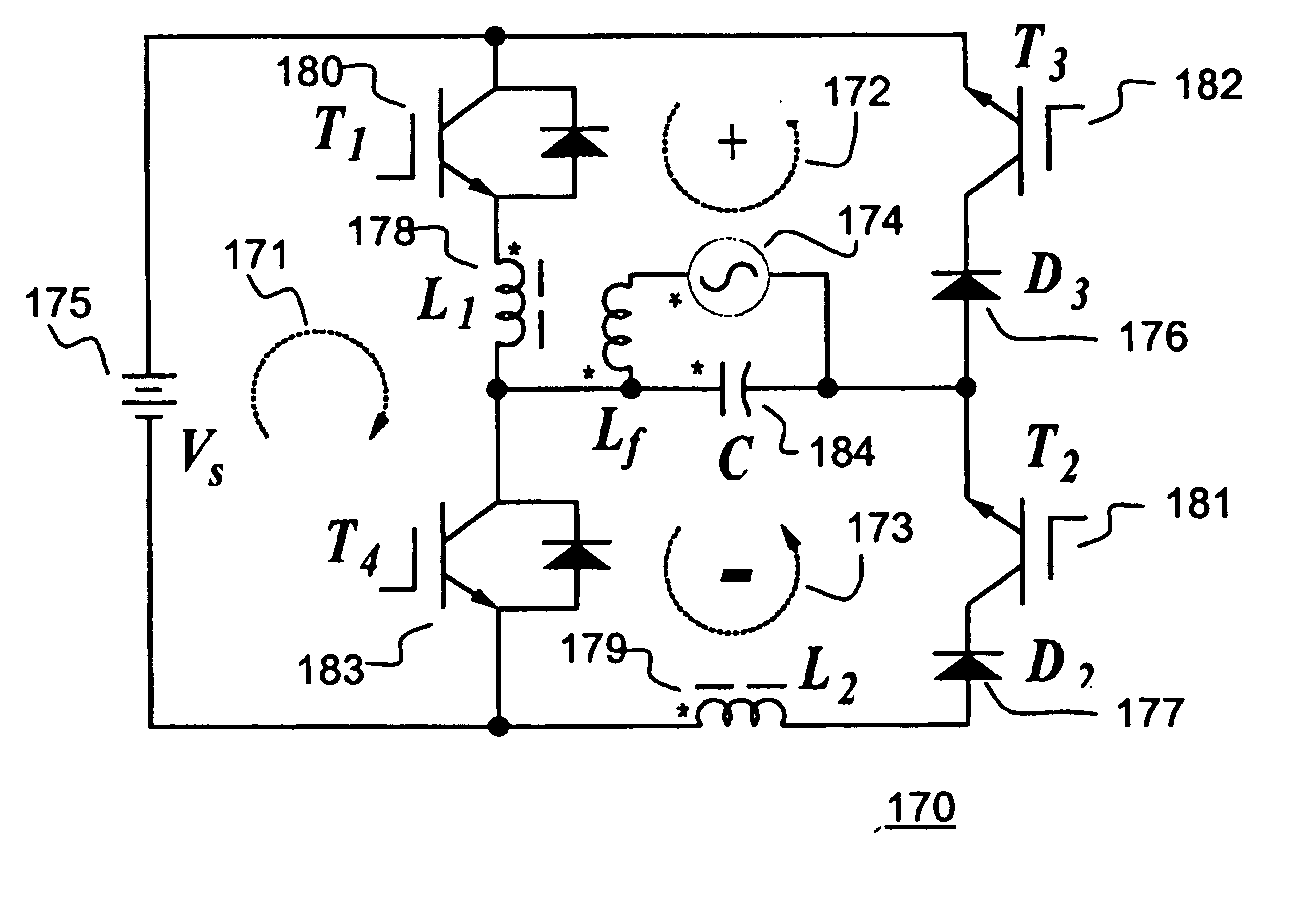
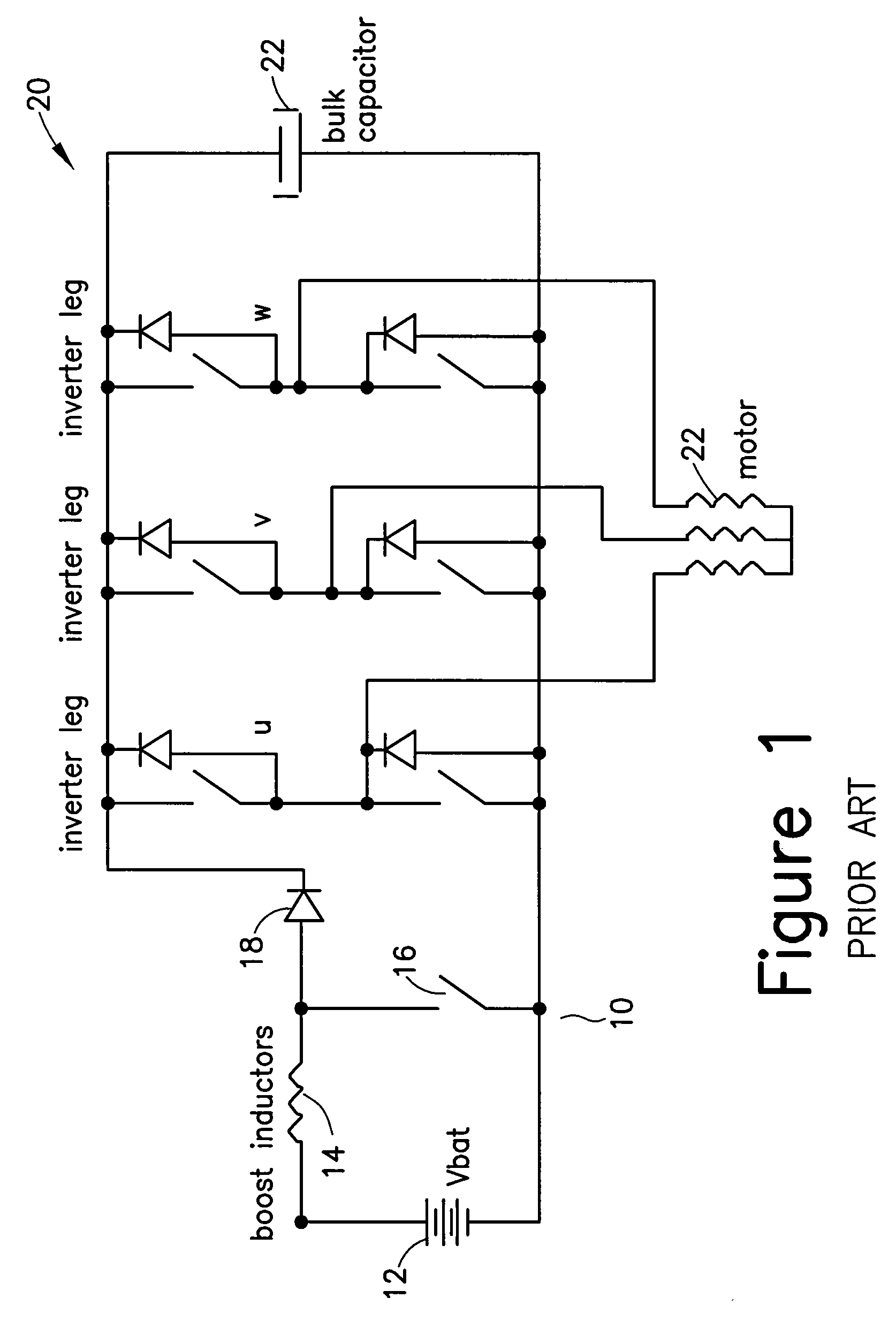
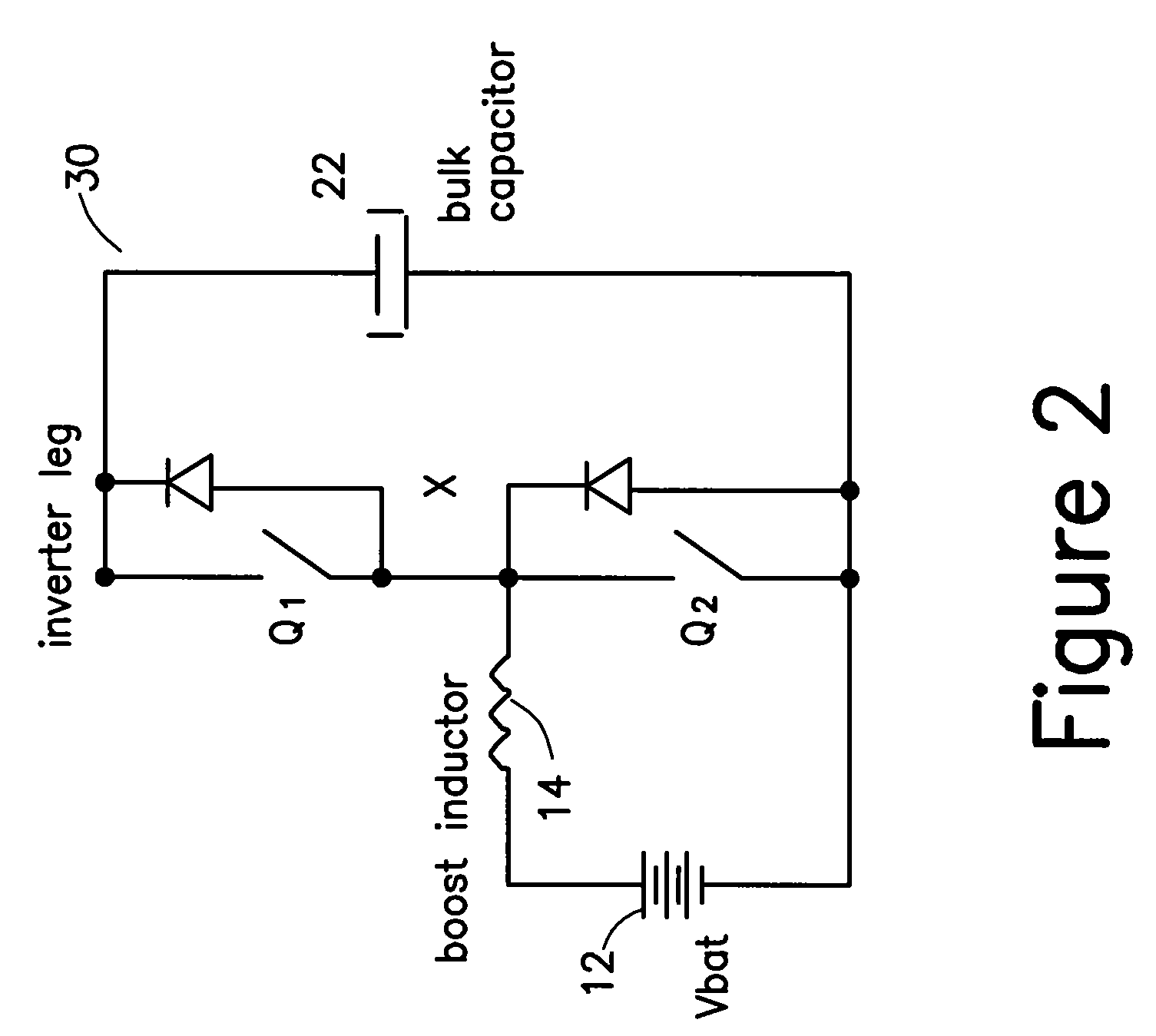
Single stage integrated boost inverter motor drive circuit
InactiveUS20070247123A1Conversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc-dc conversionMotor driveSingle stage
An integrated boost inverter circuit including at least one inverter stage having series connected high- and low-side switches having a common node. Each switch having an anti-parallel connected diode connected across the switch, which diode can be an external diode or an internal body diode of the switch; at least one inductor connectable in series between a voltage source and the node of the at least one inverter stage; a bulk capacitor connected across the at least one inverter stage; and a load being connectable to the node of the at least one inverter stage, wherein at every switching cycle, when the low-side switch of the at least one inverter stage turns-ON the respective at least one inductor is charged and when the low-side switch turns-OFF, the current in the respective at least one inductor re-circulates through the anti-parallel connected diode of the high-side switch into the bulk capacitor.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
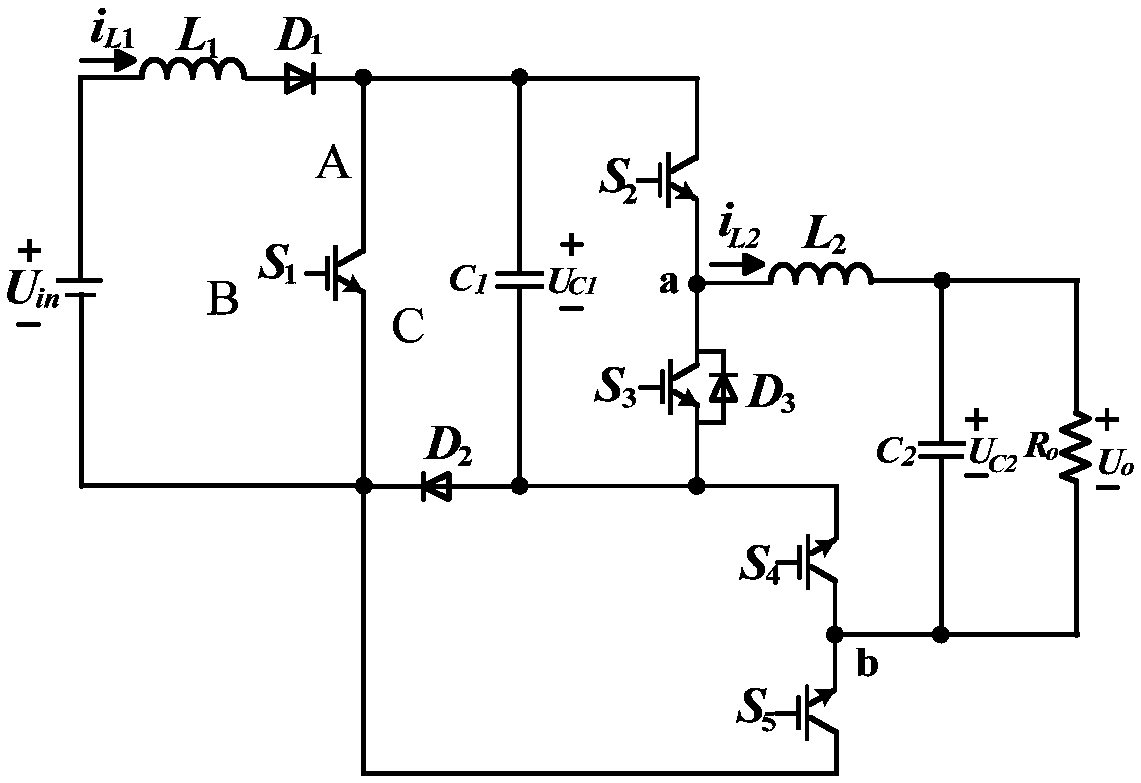
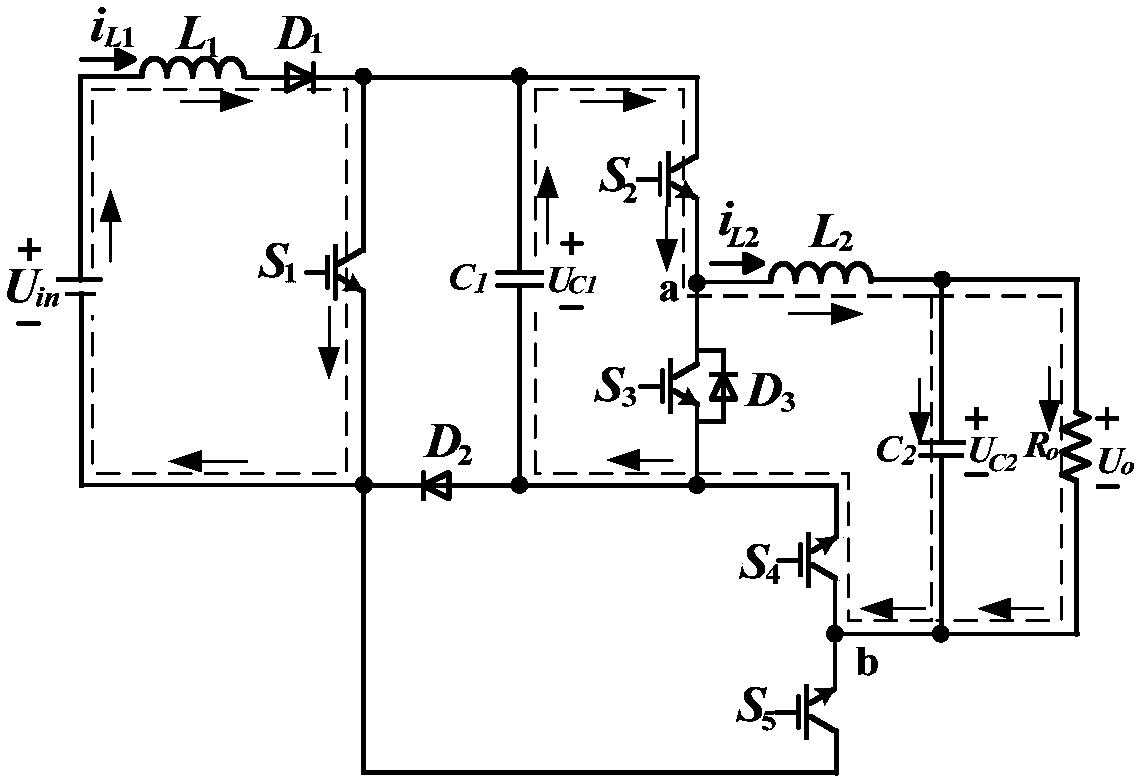
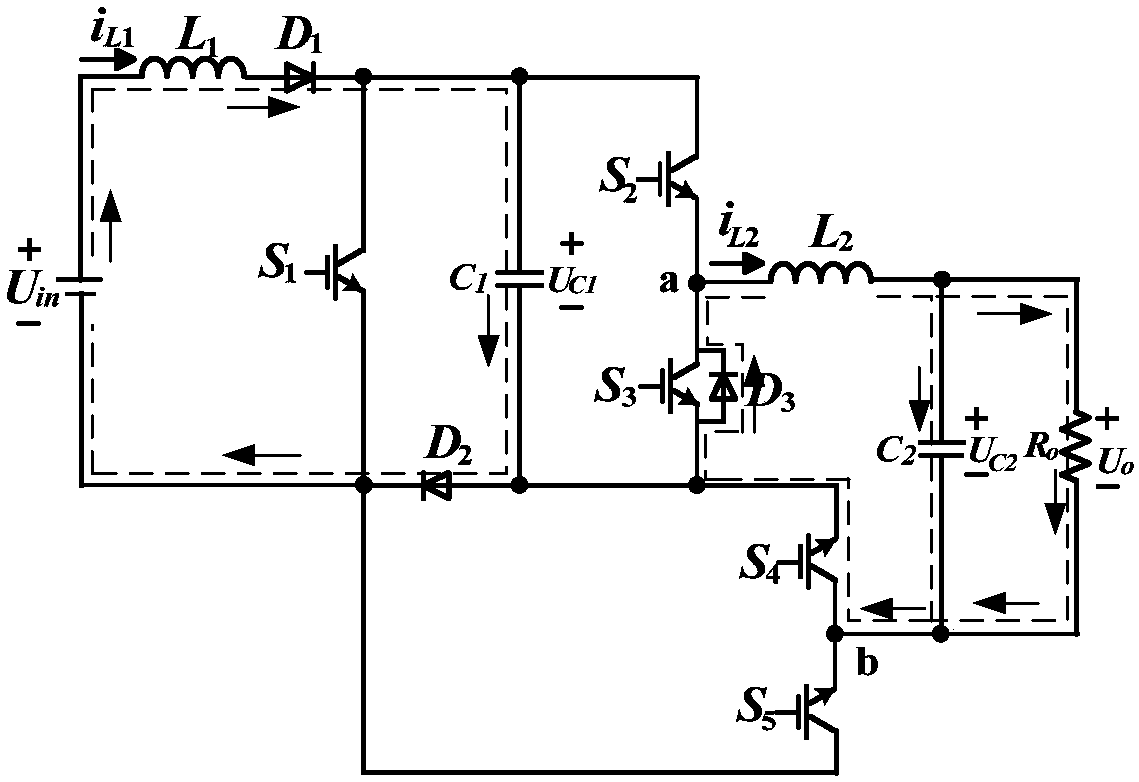
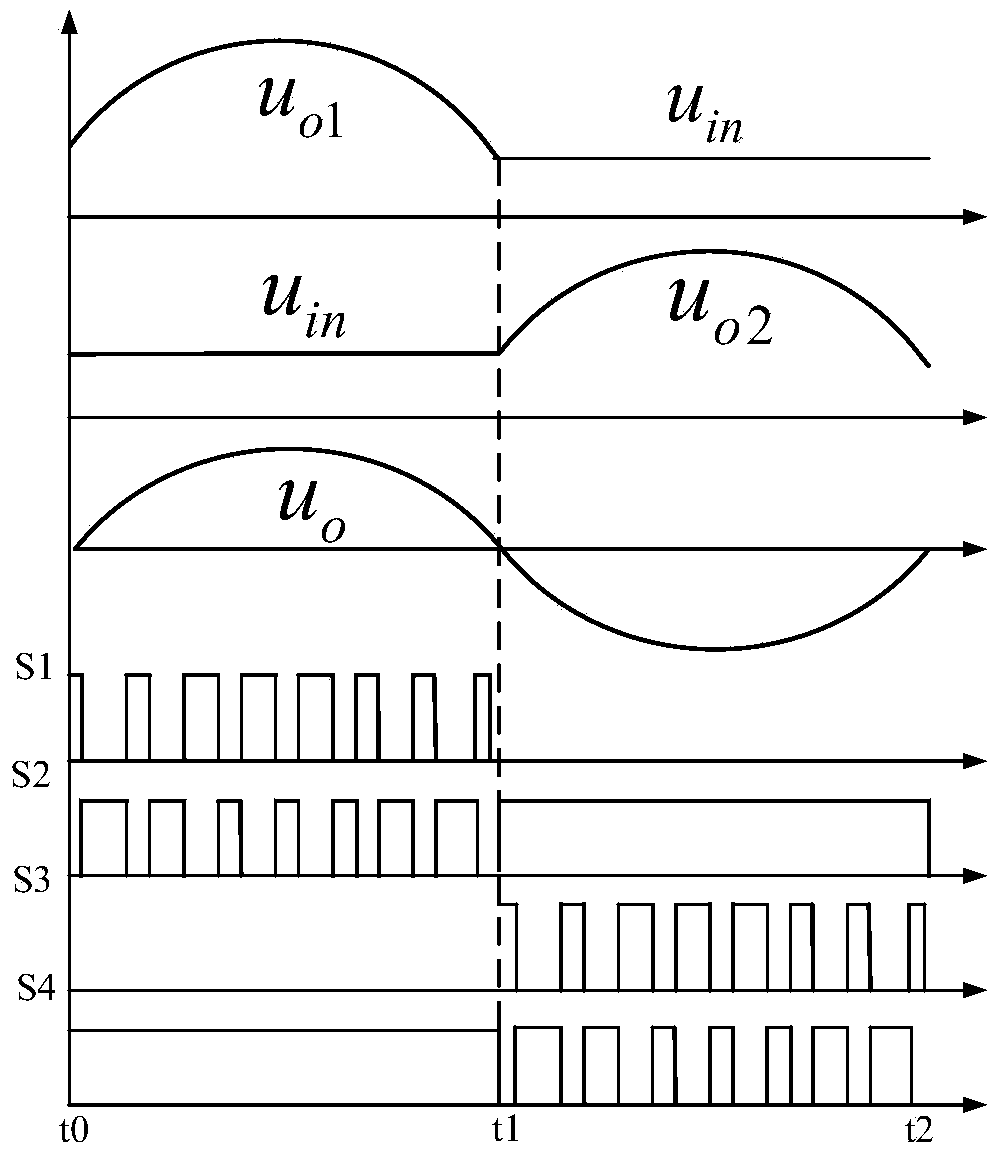
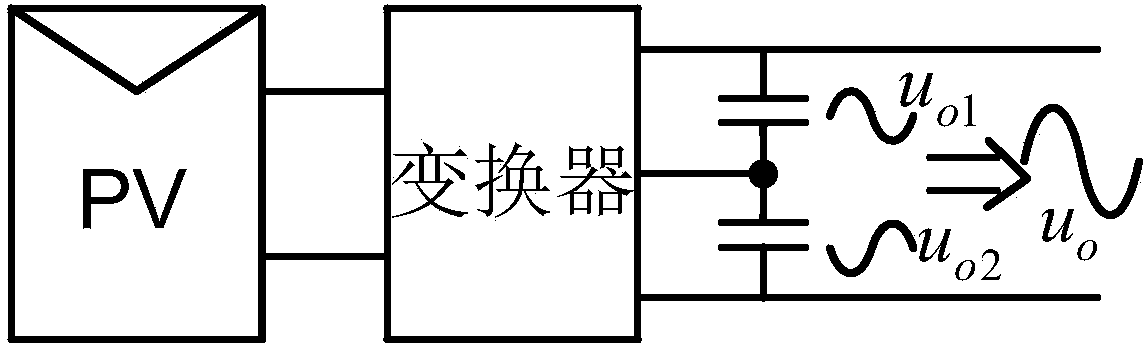
Single-stage boost inverter and control method thereof
ActiveCN107834886AStep-up inverter implementationStable AC outputAc-dc conversionPower inverterSingle stage
The invention discloses a single-stage boost inverter, and belongs to the technical field of power electronic converters. The single-stage boost inverter comprises power switch tubes S1, S2, S3, S4 and S5, diodes D1, D2 and D3, an inductor L1 and a capacitor C1; one end of the inductor L1 is connected with one end of an input power supply Uin; the other end of the inductor L1 is connected with theanode of the diode D1; the cathode of the diode D1 is connected with the A end of the power switch tube S1, the A end of the power switch tube S2 and one end of the capacitor C1, respectively; the anode of the diode D2 is connected with the other end of the capacitor C1, the power switch tube S3, the C end of the power switch tube S4 and the anode of the diode D3, respectively; and the cathode ofthe diode D2 is connected with the C end of the power switch tube S1, the A end of the power switch tube S5 and the other end of the input power supply Uin, respectively. Aiming at the problem of lowstep-up ratio of the boost converter in the prior art, the single-stage boost inverter is high in integration level and relatively high in step-up ratio.
Owner:合肥龙智机电科技有限公司
Boost multilevel inverter system
InactiveUS8498137B2Conversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc-dc conversionEnergy transferPeak value
A boost inverter includes a first capacitor for connection in parallel with a dc supply voltage; a second capacitor connected in series with the first capacitor; an energy transfer path including a transfer capacitor and switches connected to the transfer capacitor for cyclically transferring energy from the first capacitor to the transfer capacitor and then from the transfer capacitor to the second capacitor; a multilevel inverter circuit connected in parallel with the series combination of the first and second capacitors, the inverter having at least one phase output for connection to an electric motor; and a PWM controller that activates the energy transfer path when a desired peak-to-peak output voltage exceeds the dc supply voltage and deactivates the energy transfer means when the desired peak-to-peak output voltage is less than the dc supply voltage.
Owner:MAGNA E CAR SYST OF AMERICA
Vehicle-mounted power battery low-temperature full-time interleaving heating topology circuit and application thereof
The invention discloses a vehicle-mounted power battery low-temperature full-time interleaving heating topology circuit and application thereof. The circuit comprises a first battery pack and a secondbattery pack, wherein two Buck-Boost inverter circuits which are connected in parallel are connected in parallel with a to-be-heated battery pack; the Buck-Boost inverter circuits are respectively controlled by two pairs of PWM (Pulse-Width Modulation) signals of which phase angles are different for a set angle; when a single battery of the first battery pack is heated by a first Buck-Boost inverter circuit, a single battery of the second first battery pack is heated by the second Buck-Boost inverter circuit, and thus full-time battery heating is achieved. By adopting the interleaving heatingtopology circuit disclosed by the invention, under the condition that a battery pack is not further damaged, the heating speed can be remarkably increased, and the heating efficiency can be remarkably improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Fuel battery hybrid power automobile system
ActiveCN105059133AAvoid damageIncrease boost capacityPropulsion by batteries/cellsVehicular energy storageFuel cellsSingle stage
The invention discloses a fuel battery hybrid power automobile system, and belongs to the field of B60W or B60K classification. The system comprises a fuel battery pack, a single-stage boost inverter, a storage battery pack and a motor. The fuel battery pack serves as an input power supply (Vin) of the single-stage boost inverter. The single-stage boost inverter is connected with the storage battery pack (Bat) and finally connected to the motor, and comprises a coupled inductor, wherein a primary side winding and a secondary side winding of the coupled inductor are tightly coupled, and the number of turns of the primary side winding N1 is smaller than the number of turns of the secondary side winding N2. An excitation inductor is in parallel connection with the two ends of the primary side winding of the coupled inductor. The cost of the fuel battery hybrid power automobile system can be lowered, the structure of the fuel battery hybrid power automobile system can be simplified, the reliability of the fuel battery hybrid power automobile system can be improved, and the service life of the fuel battery hybrid power automobile system can be prolonged.
Owner:殷艳波
Single-stage boost inverter
InactiveCN102104341ASimple topologyInsufficient realizationAc-dc conversionCapacitanceCoupling inductor
The invention discloses a single-stage boost inverter, which comprises a coupling inductor of which a primary secondary-side winding is tightly coupled and N1 is smaller than N2; one end of an excitation inductor is connected with the cathode of a first diode, the anode of a second diode, and one end of a first capacitor, and the other end of the first capacitor is connected with the anode of a third diode; the anode of the first diode is connected with the anode of a power supply; the cathode of the second diode is connected to one end of a secondary-side winding of the coupling inductor; the other end of the secondary-side winding is connected with the cathode of the third diode and the direct current (DC) bus positive terminal of an inverter; one end of a second capacitor is connected with the DC bus positive terminal, and the other end of the second capacitor is connected with the cathode of the power supply; the other end of the first capacitor is connected with the DC bus negative terminal of the inverter and one end of the inductor, while the other end of the inductor is connected with the cathode of the power supply. By employing a shoot-through zero vector which is not allowed by a conventional inverter by the invention, the DC bus voltage of the inverter is boosted, the deficiency of a conventional voltage inverter is overcome, and the inverter is free from shoot-through phenomenon caused by electromagnetic interference, and is not needed to be inserted into a dead area.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Single-stage non-isolated non-electrolytic-capacitor double-Zeta inverter
InactiveCN104578856AEasy to chooseRealize the buck-boost inverter functionEfficient power electronics conversionDc-ac conversion without reversalCapacitanceElectrolysis
The invention relates to a single-stage non-isolated non-electrolytic-capacitor double-Zeta inverter. The single-stage non-isolated non-electrolytic-capacitor double-Zeta inverter comprises two Zeta circuits capable of realizing buck-boost output and connected in series through output to realize DC / AC single-phase inversion, and has the basic functions that the buck-boost inversion can be realized, and the double-Zeta buck-boost inverter can still realize the inversion function normally when the input direct voltage is smaller or the variation range is wider; the whole circuit is free of a shoot-through phenomenon in a bridge arm, and the reliability is high; the circuit structure is simple, the control is easy, the cost of the whole circuit is low, and the operating efficiency is high; the design of parameters of the circuit is simple, and the parameters of the circuit can be designed according to a design method of a direct current Zeta circuit; as no electrolytic capacitor is arranged in the circuit, the service life of the circuit is long; as inductor current works in a continuous state, EMI is reduced; only four active devices are arranged in the whole circuit, and are two-way devices, so that the circuit can realize two-way flow of energy.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
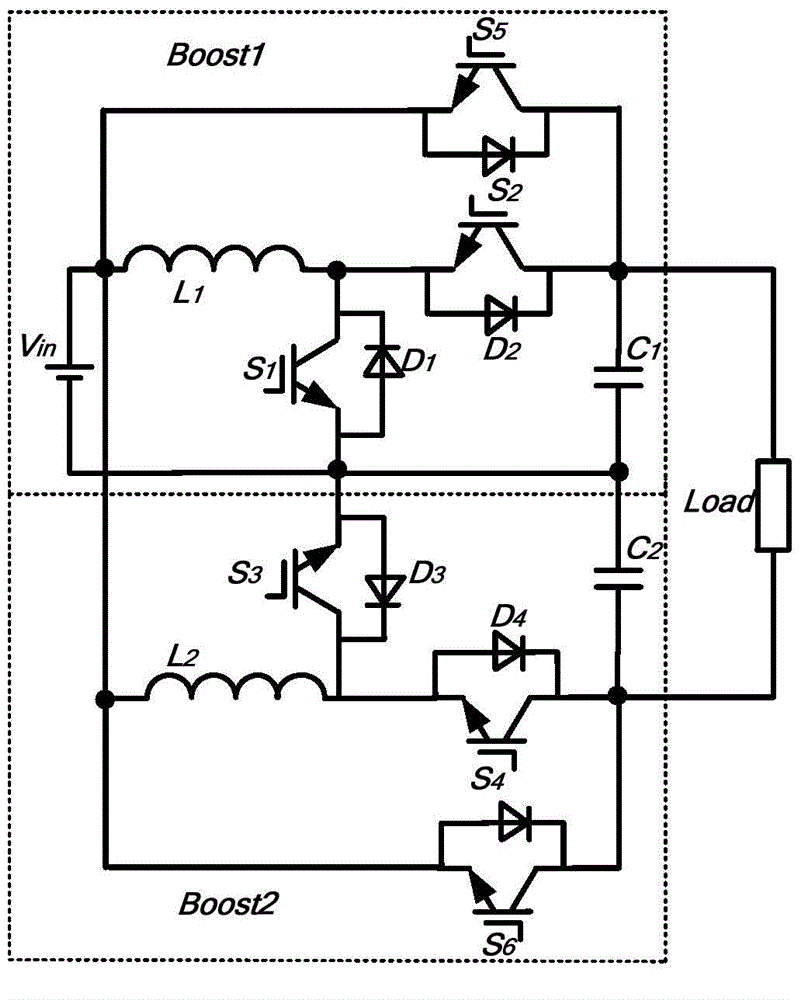
Half-cycle modulation method for double-Boost inverter
InactiveCN103997238ABig rippleHigh copper consumptionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionDc-ac conversion without reversalPower flowPower switching
The invention discloses a half-cycle modulation method for a double-Boost inverter. The modulation method includes modulation of Boost 1 switching tube and modulation of Boost 2 switching tube in the double-boost inverter. The half-cycle modulation method enables the power switching tubes to work in a half-cycle high-frequency modulation state. The method includes: at an output voltage positive half cycle, the Boost 1 switching tube carries out high-frequency modulation boosting, and the Boost 2 switching tube carries out work frequency switching; and at an output voltage negative half cycle, the Boost 2 switching tube carries out high-frequency modulation boosting and the Boost 1 switching tube carries out work frequency switching. Under the same voltage gain, compared with traditional methods, the half-cycle modulation method enables the voltage and current stresses of the switching tubes to become smaller, the total switch-on times of the switching tubes to be reduced and the switch-on loss to be reduced. The inductive current ripples are reduced and inductive copper loss and iron loss are reduced and the efficiency of the double-Boost inverter is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
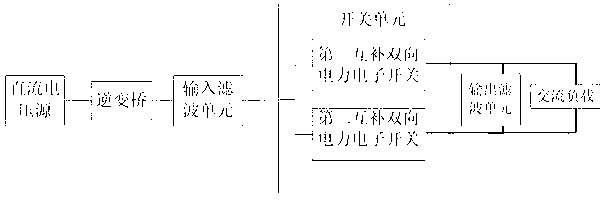
Single-stage bidirectional buck-boost inverter
InactiveCN103078548AAchieving a boost outputTo achieve a buck outputAc-dc conversionPower inverterSingle stage
The invention relates to a single-stage bidirectional buck-boost inverter, which belongs to the technical field of power electronic converters. The input end of the single-stage bidirectional buck-boost inverter is connected with a direct-current voltage source, and the output end of the single-stage bidirectional buck-boost inverter is connected with an alternating-current load. The single-stage bidirectional buck-boost inverter comprises an inverter bridge, an input filter unit, a switching unit and an output filter unit which are sequentially connected. The switching unit comprises a first complementary bidirectional power electronic switch and a second complementary bidirectional power electronic switch. In the buck mode, the second complementary bidirectional power electronic switch is normally switched on, the circuit is equivalent to the conventional buck inverter, and bucked output is carried out; in the boost mode, the first complementary bidirectional power electronic switch and the second complementary bidirectional power electronic switch are complementarily switched on, and boosted output is carried out. The single-stage bidirectional buck-boost inverter disclosed by the invention can carry out boosted output and bucked output without a boost conversion circuit, and also realizes bidirectional energy transmission.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Tri-lever boosting inverter
InactiveCN101442269AEfficient use ofSimple topologyDc-ac conversion without reversalThree levelCapacitance
The invention discloses a three-level boost inverter in power electronic field. In the invention, a branch circuit consisting of a first diode and a first capacitor is connected in parallel with a branch circuit consisting of a second capacitor and a second diode and then is connected in parallel with a second switching tube to form a switched capacitor network, a third switching tube is connected with a fourth switching tube, a fifth switching tube is connected with a sixth switching tube, a branch circuit consisting of the third switching tube and the fourth switching tube and a branch circuit consisting of the fifth switching tube and the sixth switching tube are connected in parallel to form a single-phase inverting bridge network, the switched capacitor network produces a multi-level voltage and transmits the multi-level voltage to the inverting bridge network, a knot is drawn from a connecting part of the third switching tube and the fourth switching tube and is connected with an output filtering inductor, the output filtering inductor is connected with one end of an output capacitor, both ends of the output capacitor are connected in parallel with a load, and the voltage at both ends of the output capacitor is an output voltage. The three-level boost inverter also realizes effective direct-current voltage boost while realizing the conversion from the direct-current voltage to the multi-level voltage, and has remarkable boost capacity and adjustable boost transformation ratio.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
High gain isolating active clamping boost transducer
ActiveCN1976193AIncrease output gainImprove circuit efficiencyDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationTransducerFlyback diode
An active clamping-boosting inverter of high-gain isolation type is prepared as realizing high gain output of said inverter by series-connecting the third winding to output capacity of two coupled inductances, absorbing and transferring leakage energy of two coupled inductances nondestructively by series circuit prepared by the first clamping capacity and the first auxiliary switching tube, utilizing series circuit and parallel capacity to realize zero voltage turn on and turn off of said auxiliary switch.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Single-stage buck-boost dual-Boost inverter and control method thereof
InactiveCN104104252AReduce current stressReduce switching lossesDc-ac conversion without reversalSingle stageConduction loss
The invention discloses a single-stage buck-boost dual-Boost inverter. The inverter comprises a Boost1 boosted circuit, a Boost1 bypass switch tube, a Boost2 boosted circuit, and a Boost2 bypass switch tube. The invention further discloses a control method of the inverter. The method comprises the following steps: controlling the Boost1 boosted circuit and the bypass switch tube thereof to work to be in a boosting state in a positive half period of sine wave; controlling the Boost2 boosted circuit and the bypass switch tube to work to be in a boosting state in the negative half period of the sine wave. Under the same voltage gain, the voltage stress and the current stress of the switch tube are smaller, the total time of conducting the switch tube is reduced, the conduction loss is lowered, the inductive current ripple is lowered, and the copper loss and the iron loss of the inductance are reduced. The power frequency switching of the bypass switch tube provides loop for the current of the positive half-cycle circuit and the negative half-cycle circuit, the conduction loss of loop current in the traditional dual-Boost inverter is reduced, and the efficiency of the dual-Boost inverter is promoted.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Pulse width modulation method for maximum boost and minimum switching frequency of diode-assistant buck-boost inverter
InactiveCN105186910AReduce voltage stressReduce frequencyAc-dc conversionMiddle frequencyFundamental frequency
The invention discloses a pulse width modulation method for maximum boost and minimum switching frequency of a diode-assistant buck-boost inverter. The pulse width modulation method comprises the following steps of: controlling a voltage average value of an intermediate DC side within a switching period (T<s>) to an instantaneous maximum value of an envelope line of three-phase AC output phase voltage, namely line voltage, and thus, the equivalent switching frequency of a power semiconductor device in an inverter bridge can be reduced to 1 / 3f<s> (f<s> is equal to 1 / T<s>). By the method, the voltage gain of the diode-assistant buck-boost inverter is further increased, the voltage stress and the switching loss of a switching device are reduced, and the power conversion efficiency of a converter is improved. Moreover, with the adoption of the modulation method disclosed by the invention, the inductance current and the capacitance voltage of the DC side of the inverter contain low-frequency ripple wave which is six times of fundamental frequency. By the modulation method, the diode-assistant buck-boost inverter is simultaneously applicable for distributed power supply systems such as 400-800Hz middle-frequency airborne and boat.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Boost inverter
ActiveCN107086807ANo leakage currentReduce lossEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionCapacitanceEngineering
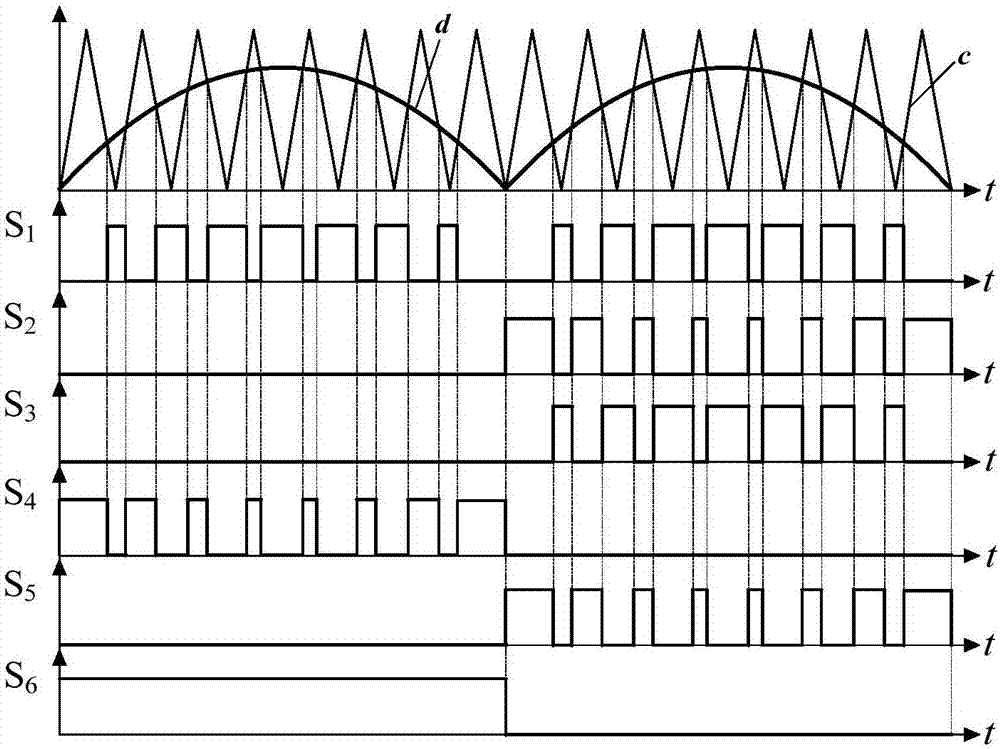
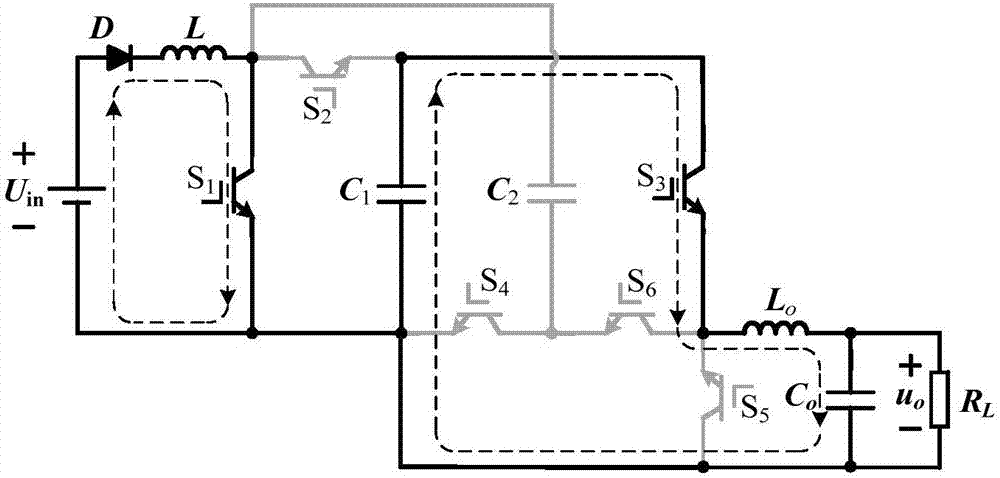
The invention discloses a boost inverter, and belongs to the technical field of power electronic converters. A positive electrode of a power supply Uin is connected with one end of a boost inductor L, a negative electrode of the Uin is grounded, the other end of the boost inductor L is connected with the first end of a switch tube S1, the first end of a switch tube S2 and one end of a capacitor C2, the second end of the switch tube S1 is grounded, the other end of the capacitor C2 is connected with the first end of a switch tube S4 and the second end of a switch tube S6, and the second end of the switch tube S4 is grounded. The second end of the switch tube S2 is connected with one end of a capacitor C1 and the first end of a switch tube S3, the other end of the capacitor C1 is grounded, the second end of the switch tube S3 is connected with the first end of the switch tube S6 and the second end of the switch tube S5, and the first end of the switch tube S5 is grounded. For the problems that a traditional boost inverter has high frequency leakage current, and the conversion efficiency is low, the conversion efficiency of the boost inverter is high, and no high frequency leakage current exists.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
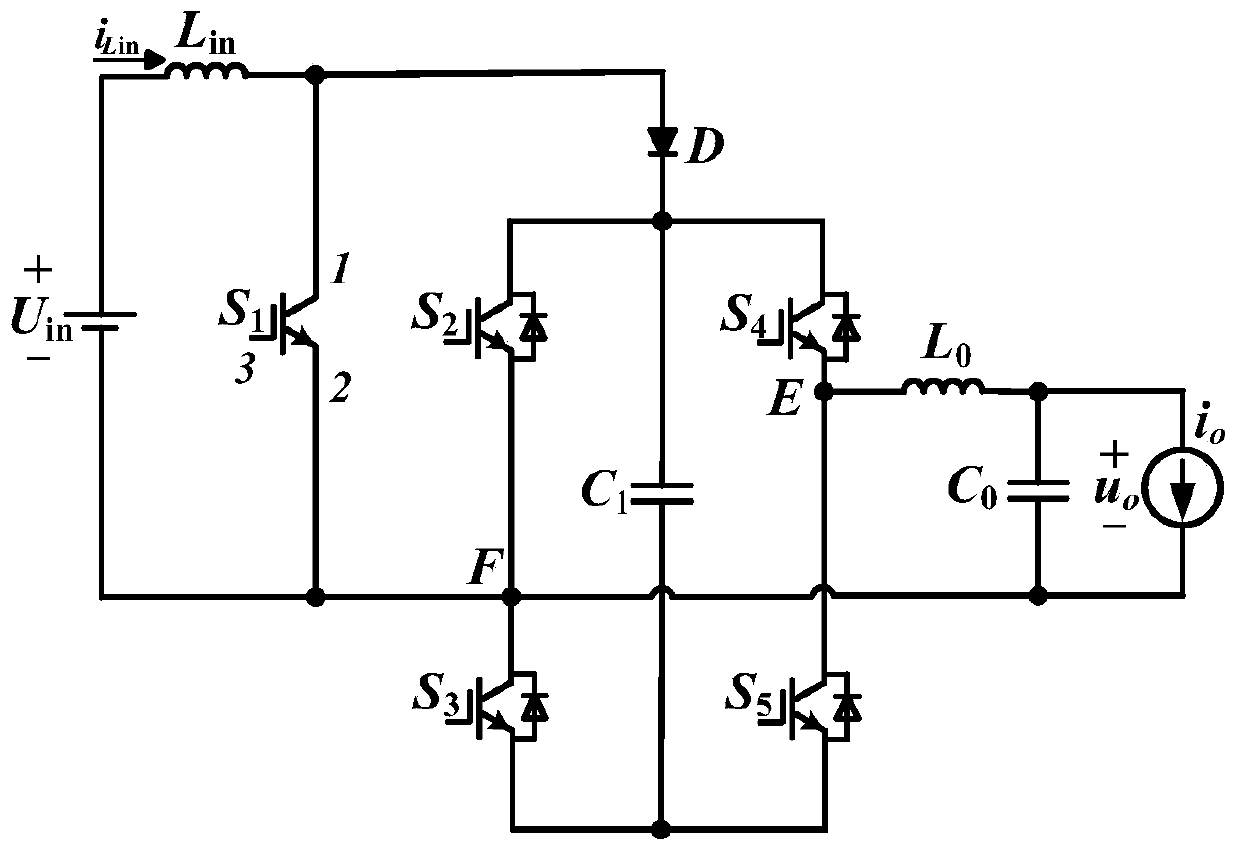
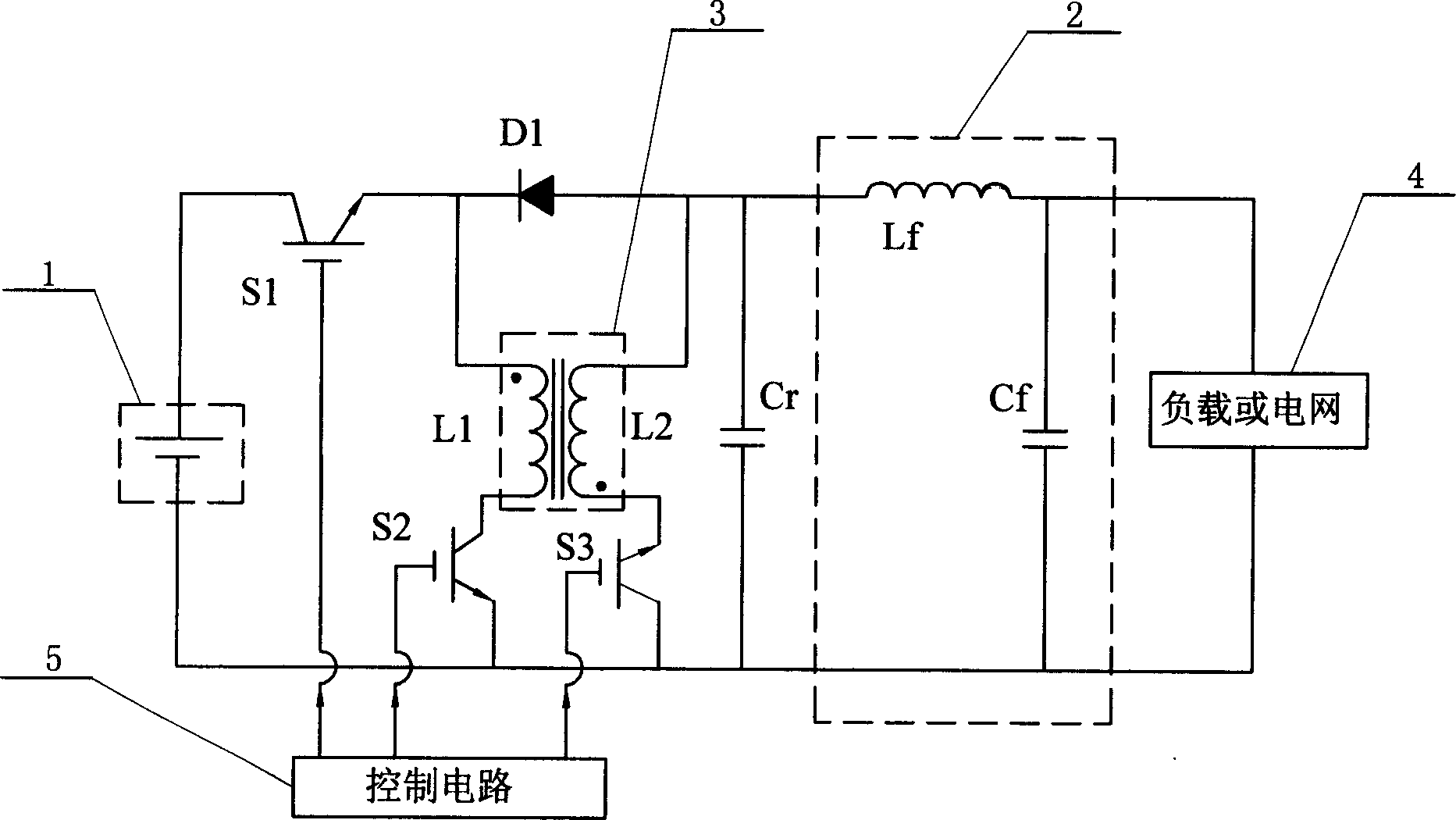
Portable rechargeable microsecond pulse power supply
ActiveCN106899060AOverall small sizeEasy to carryTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsAc-dc conversionEngineeringHigh pressure
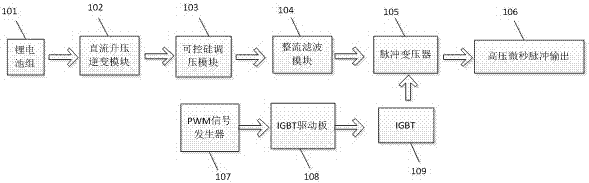
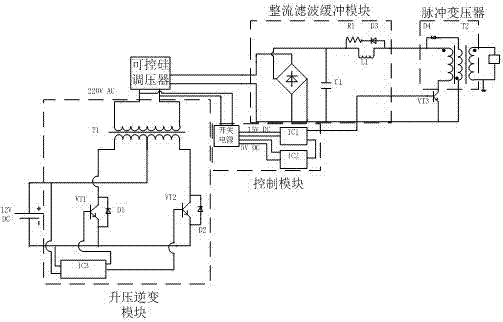
The invention relates to a portable rechargeable microsecond pulse power supply. The structure includes a lithium battery pack, a direct current boosting inverter module, a silicon controlled voltage regulation module, a rectification and filtering module, a pulse transformer, a high voltage microsecond pulse output, a PWM signal generator, an IGBT driver board and an IGBT; the lithium battery is connected with the input end of the direct current boosting inverter module, the output end of the direct current boosting inverter module is connected with the input end of the silicon controlled voltage regulation module, the silicon controlled voltage regulation module is connected with the input end of the rectification and filtering module, the output end of the rectification and filtering module is connected with the first input end of the pulse transformer, and the tail end of the pulse transformer is provided with the high voltage microsecond pulse output; and the output end of the PWM signal generator is connected with the input end of the IGBT driver board, the IGBT driver board is connected with the input end of the IGBT, and the output end of the IGBT is connected with the second input end of the pulse transformer. The advantages are as follows: (1) the portable rechargeable microsecond pulse power supply does not need to be electrified when used, is small in volume and convenient to carry; (2) the power supply can realize long-time no-load operation; and (3) the power supply adopts modular design, is simple in structure and is low in cost.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
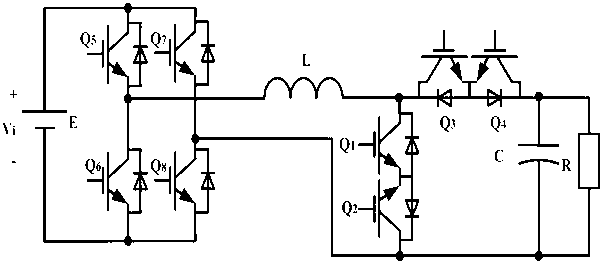
Single-stage boost inverter
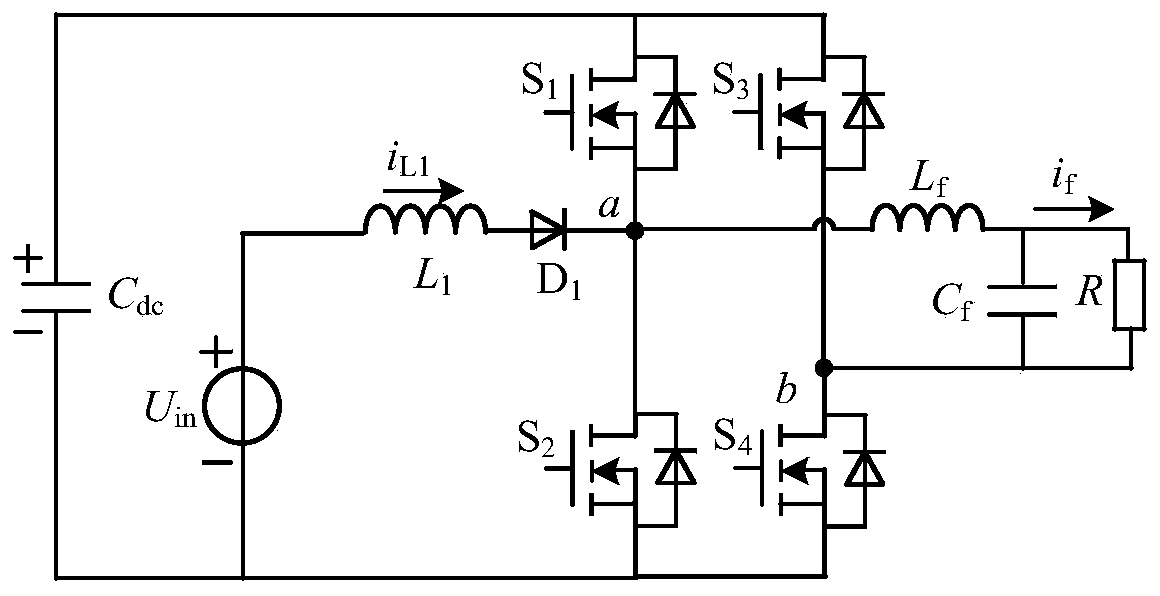
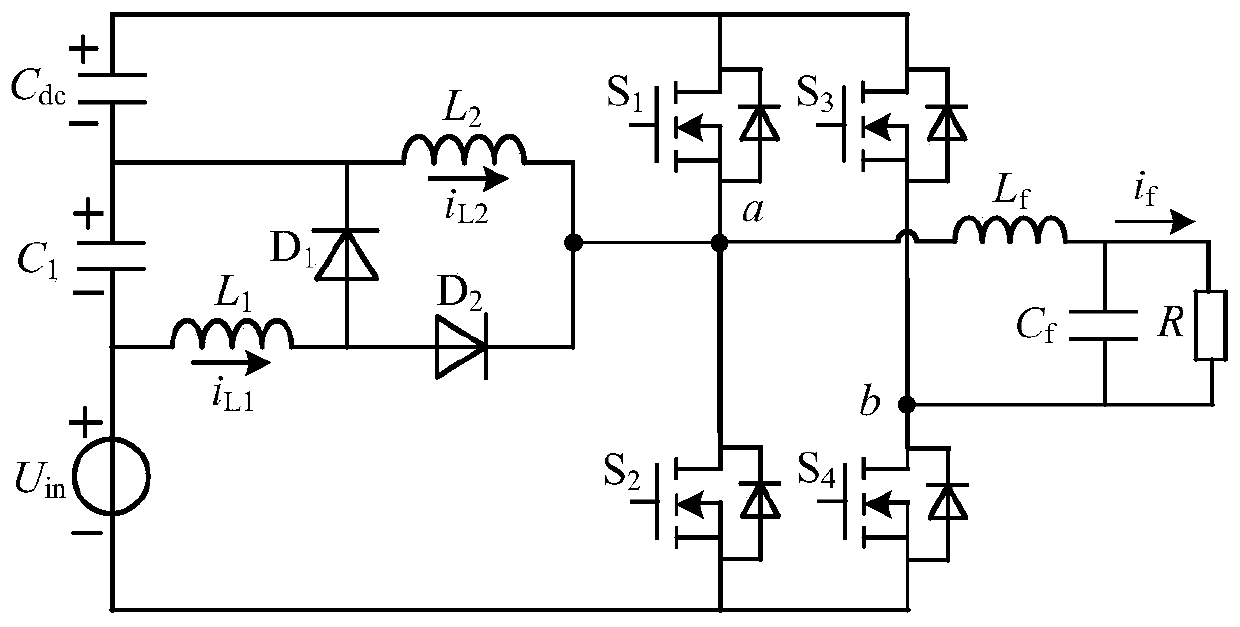
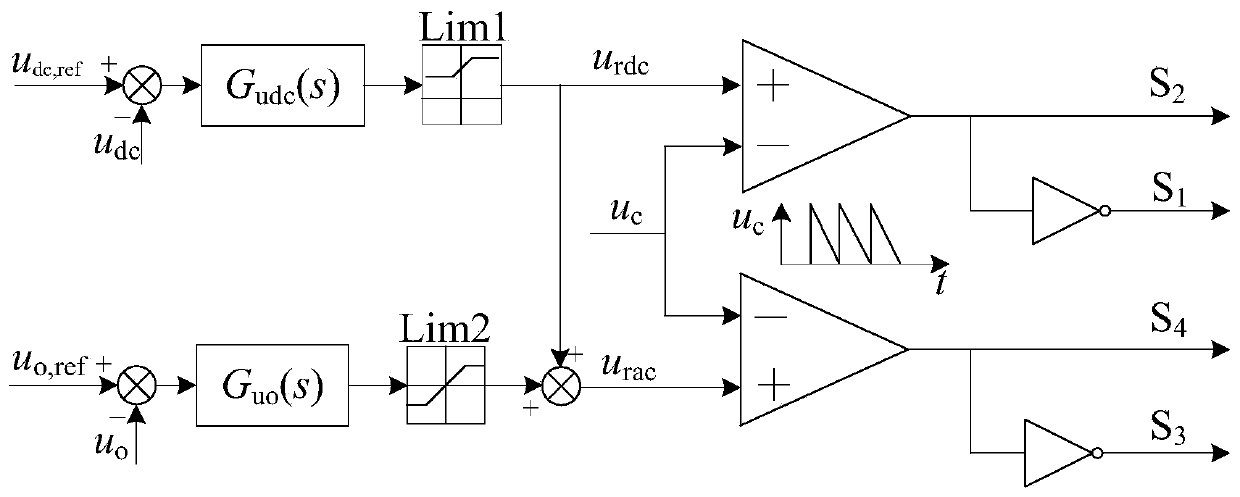
The invention discloses a single-stage boost inverter. By taking full advantages of a distributed inductor and a parasitic inductor, the distributed inductor, the parasitic inductor and an external capacitor form a passive network and are participated in the working condition of the single-stage boost inverter. According to the single-stage boost inverter with medium and high power, when the through vector state of the single-stage boost inverter is converted into a non-through state, distributed inductance and parasitic inductance exist in a direct current bus link, and then extremely high voltage spike can be generated on a direct current bus of the inverter, so that a power tube is easy to burn out. In order to improve the reliability of the inverter, a stage of suppression circuit is needed to be added. A stage of suppression circuit does not need to be specially added to the single-stage boost inverter disclosed by the invention, and the single-stage boost inverter is suitable for lower power levels and also suitable for higher power levels.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
CCM single-bridge-arm integrated single-phase boost inverter and control method
ActiveCN111600502AImprove conversion efficiencyReduce current stressEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionCapacitanceCapacitor voltage
The invention discloses a CCM single-bridge-arm integrated single-phase boost inverter and a control method. Compared with a traditional Boost integrated boost inverter, the inverter provided by the invention has the advantage that high-gain boost inversion in a CCM mode is realized by only additionally arranging one inductor, one capacitor and one diode. Because the input current is continuous, the current stress and the on-state loss of the inductor and the power tube are greatly reduced, the boosting capability does not change sharply along with the load power, and the system reliability isimproved; moreover, the boost bridge arm can adopt PWM control for voltage regulation, so that the inverter is suitable for various boost inversion occasions where the output power cannot be adjustedand the input voltage changes in a wide range such as photovoltaic power generation and independent inversion, and the application range is wider. In addition, the inverter also has the advantages ofstrong boosting capability, high conversion efficiency, low capacitor voltage stress, simple structure, low cost and the like.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
Converter and modulation method thereof
ActiveCN109980978AAvoid interferenceNo high frequency leakage currentAc-dc conversionDc-dc conversionCapacitanceEngineering
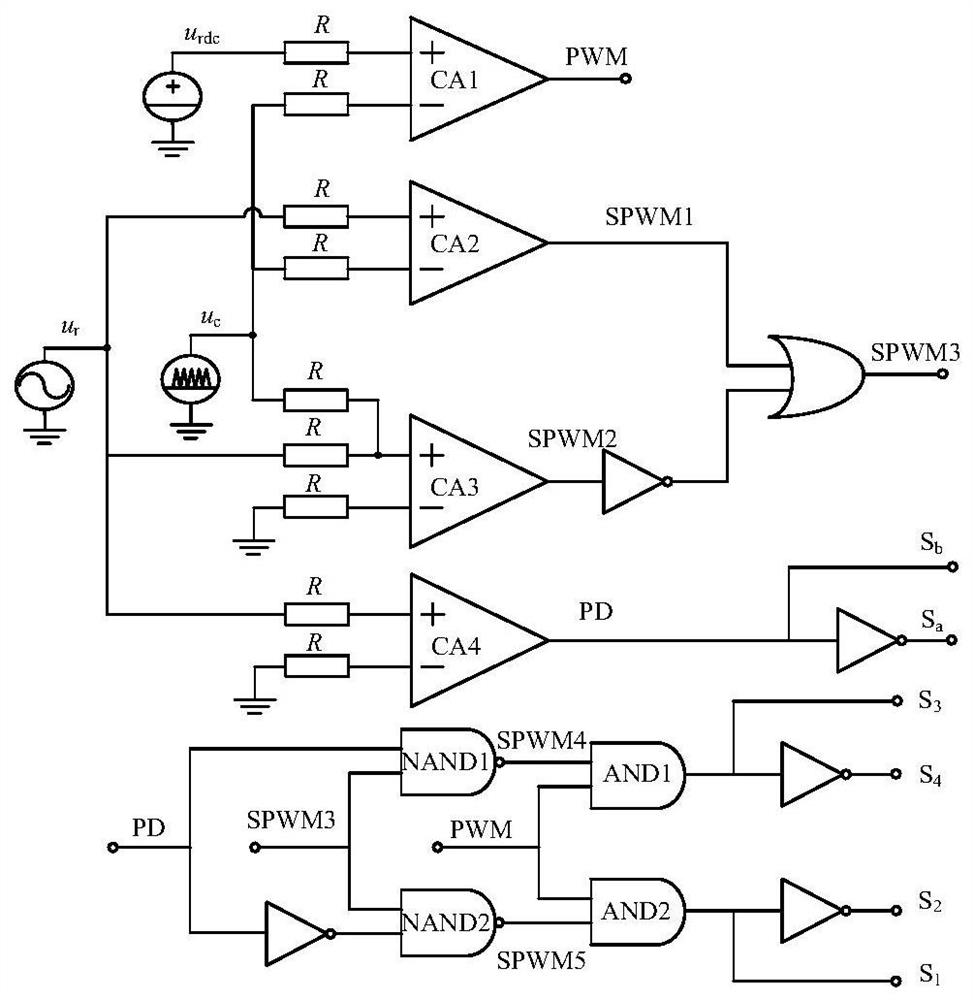
The invention discloses a converter and a modulation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of power electronic converters. One end of the DC side of the converter is connected with one end of an inductor Lin, the other end of the inductor Lin is connected with a terminal 1 of a power switch transistor S1 and a conduction end of a switching device, a cut-off end of the switching deviceis connected with terminals 1 of power switch transistors S2, S4 and one end of a capacitor C1, the other end of the capacitor C1 is connected with terminals 2 of power switch transistors S3, S5, theother end of the DC side of the converter, terminals 2 of the power switch transistors S1, S2, a terminal 1 of the power switch transistor S3 and one end of the AC side are all grounded, a terminal 1of the power switch transistor S5 and a terminal 2 of the power switch transistor S4 are connected at the other end of the AC side. In addition, the invention further provides a corresponding modulation method, a bidirectional converter and a corresponding modulation method thereof. In allusion to a problem of high-frequency leakage current existing in the traditional boost inverter, the converter disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high integration degree and small volume and can effectively solve the problem of high-frequency leakage current.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Zero-voltage soft-switching single-phase boost inverter and control method
ActiveCN112260568ASolve the problem of serious reverse recovery lossImprove conversion efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionCapacitanceSoft switching
The invention belongs to the technical field of inverters, and discloses a zero-voltage soft-switching single-phase boost inverter and a control method. The inverter comprises two auxiliary switch tubes, a first inductor L1, a first bridge arm, a second bridge arm and an auxiliary branch, wherein the two auxiliary switch tubes are conducted in a complementary mode, and the auxiliary branch is composed of a first direct-current bus capacitor Cdc1, a second direct-current bus capacitor Cdc2 and a second inductor L2. In a positive half power frequency period, the first bridge arm works in an SPWMmode, and the second bridge arm works in a PWM mode; and in a negative half power frequency period, the working states of the first bridge arm and the second bridge arm are exchanged. According to the inverter, zero-voltage soft switching of two bridge arm lower tubes and one bridge arm upper tube is realized, the problem of serious reverse recovery loss of an anti-reverse diode in a traditionalintegrated inverter is effectively solved, and the conversion efficiency is improved.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
Tri-switch single-stage voltage boosting/reducing inverter
ActiveCN1808870ASimple structureLow costAc-dc conversionApparatus with intermediate ac conversionSingle stageEngineering
This invention relates to distribution generation system single buck to boost inverter, which adopts High frequency reverse interfere through main self-switch, first assistant switch tube and second assistant switch tube PWM to control its single inverter and uses basic Bick to Boost DC to DC circuit and combines two Buck t oBuck DC to DC circuits together to realize buck and boost to get new type of single inverter.
Owner:TIANJIN WEIHAN ELECTRIC CO LTD
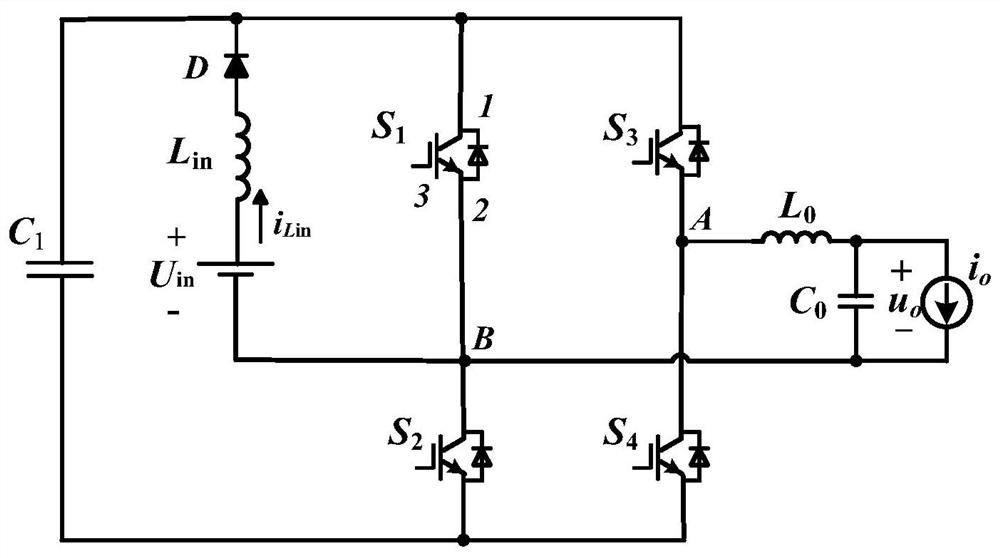
Non-isolated integrated boost DC/AC converter and control method thereof
ActiveCN112737293ANo high frequency leakage currentSmall footprintAc-dc conversionPhotovoltaicsCapacitanceControl theory
The invention discloses a non-isolated integrated boost DC / AC converter and a control method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of power electronic converters. The DC / AC converter comprises power switch tubes S1, S2, S3 and S4, a diode D, an inductor Lin and a capacitor C1. One end of the direct current side of one converter is connected with one end of an inductor Lin, the other end of the inductor Lin is connected with the anode of the diode D, the cathode of the diode D is connected with terminals 1 of a power switch tube S1 and a power switch tube S3 and one end of a capacitor C1, and the other end of the capacitor C1 is connected with terminals 2 of a power switch tube S2 and a power switch tube S4; the other end of the direct current side, the terminal 2 of the power switch tube S1, the terminal 1 of the power switch tube S2 and one end of the alternating current side are all grounded; and the terminal 2 of the power switch tube S3 and the terminal 1 of the power switch tube S4 are connected to the other end of the alternating current side. Aiming at the problem that a traditional boost inverter has leakage current, the boost inverter is high in integration level and small in size, and the problem of leakage current can be effectively solved.
Owner:合肥名龙电子科技有限公司
Three-phase Boost integrated boost inverter and hybrid modulation method thereof
InactiveCN109302092AHigh voltage gainThe output voltage THD is smallAc-dc conversionDc-dc conversionFull bridgeEngineering
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com