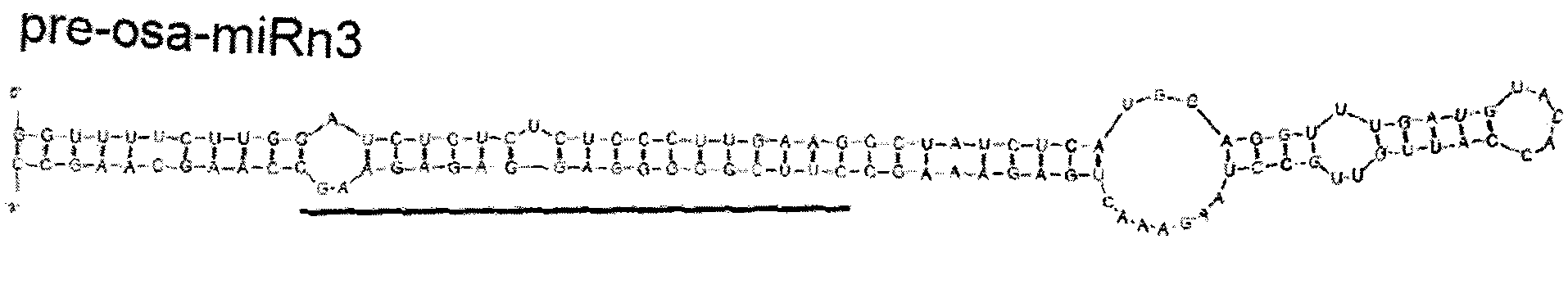Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
69 results about "BHLH Transcription Factors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
BHLH transcription factors are often important in development or cell activity. BMAL1-Clock is a core transcription complex in the molecular circadian clock. Other genes, like c-Myc and HIF-1, have been linked to cancer due to their effects on cell growth and metabolism.
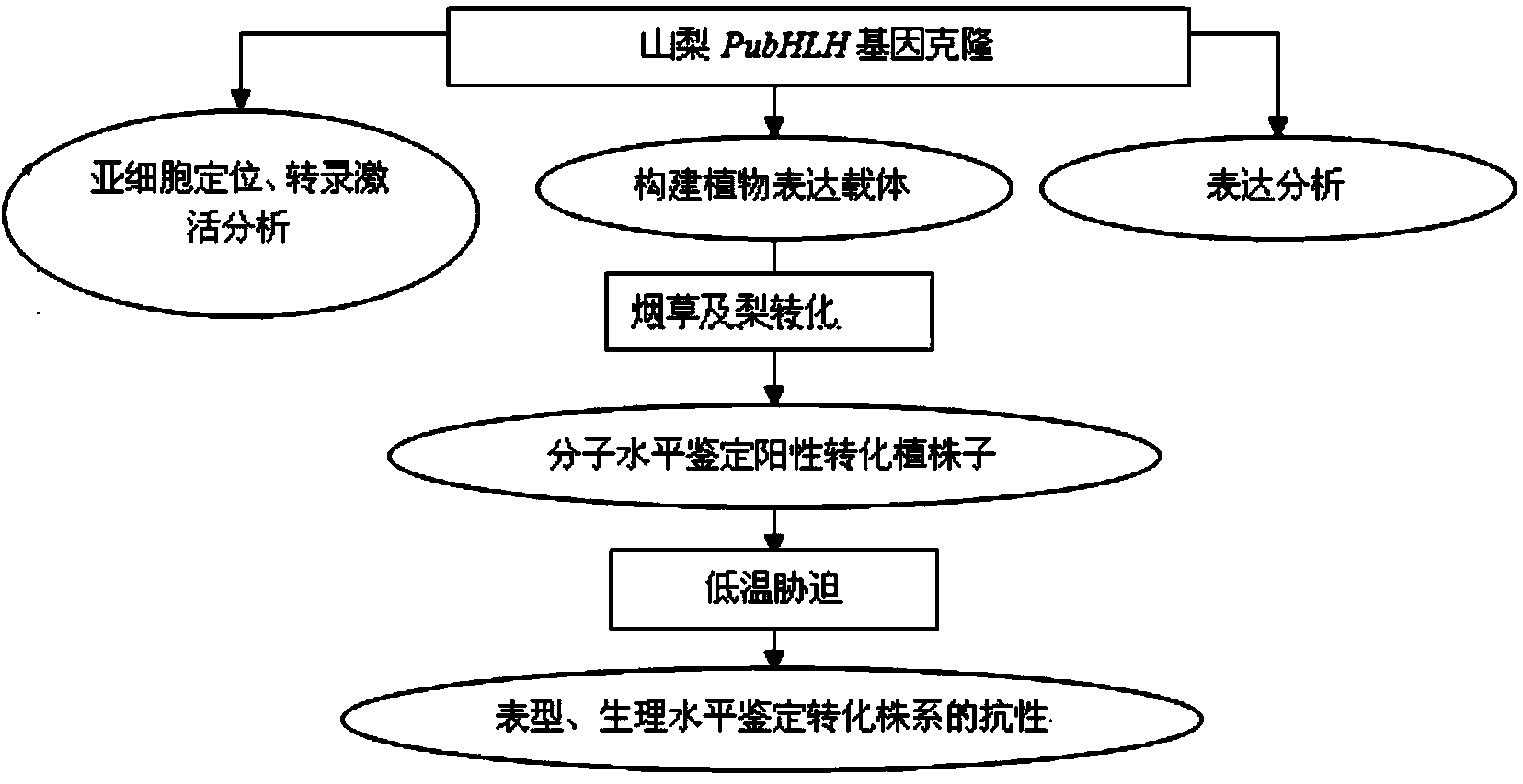
Sorb cold-resistant transcription factor PubHLH and application thereof
ActiveCN104031923AHas the function of regulating cold resistanceImprove cold resistanceBacteriaPlant peptidesBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a sorb cold-resistant transcription factor PubHLH and an application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of sorb bHLH transcription factor gene PubHLH is represented by SEQ ID NO: 1 in a sequence table; 409-2043bp position of the sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1 is a coding area of the gene; an amino acid sequence coded by the coding area is represented by SEQ ID NO: 1. A new bHLH gene PubHLH is cloned in the sorb; an agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation method is used for transforming the gene to tobacco and pear; cold resistance ability of the obtained transgenic plant is obviously improved; biological functional verification shows that the cloned PubHLH gene has cold resistance regulation function. The sorb bHLH transcription factor gene PubHLH provided by the invention can be applied to improvement of plant cold resistance or construction of cold-resistant transgenic plant.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
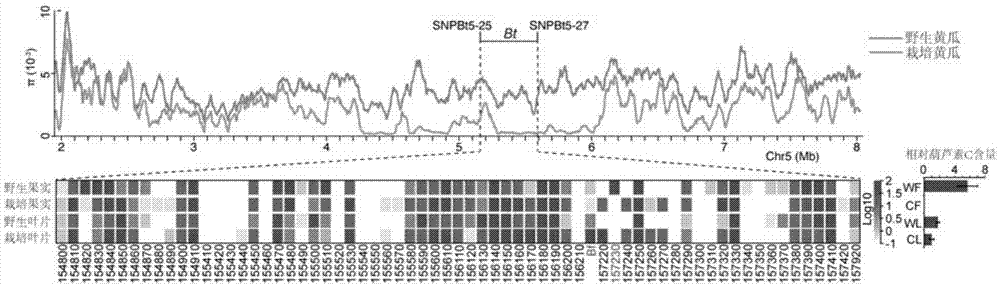
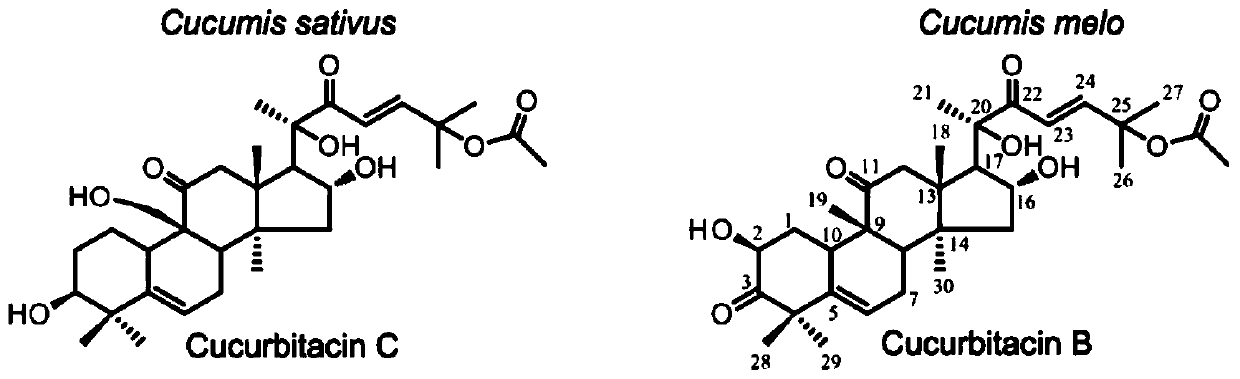
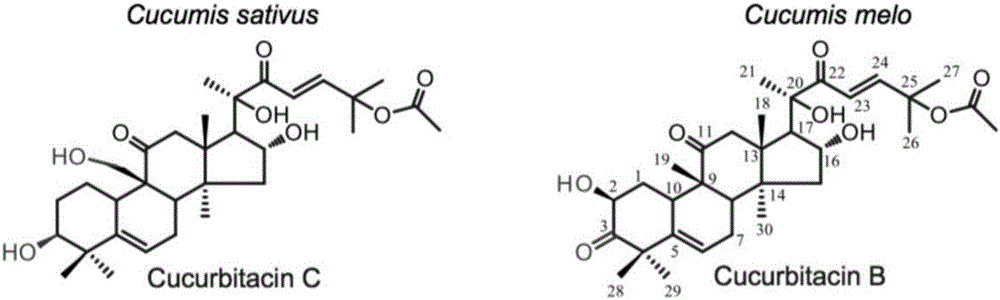
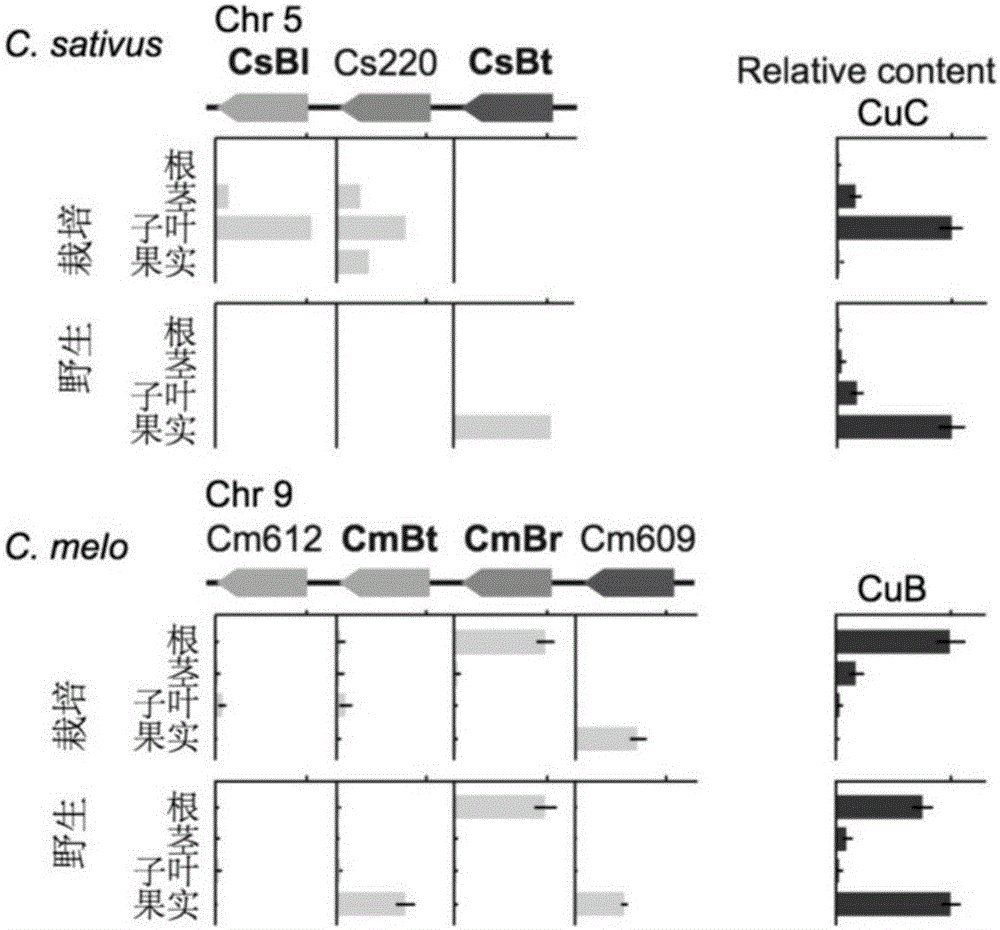
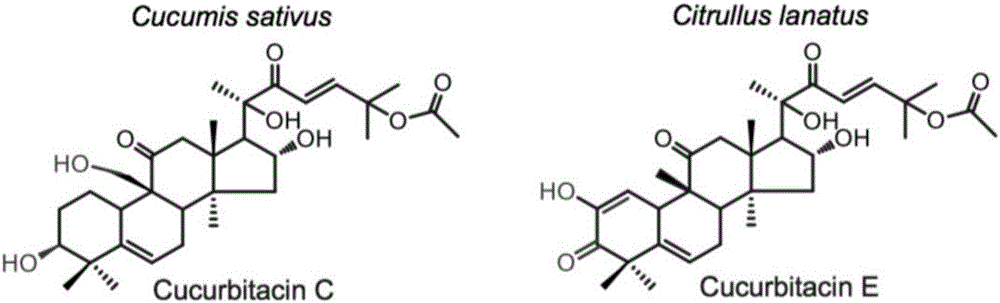
Transcription factor Csa5G157230 participating in regulation of synthesis of cucumber cucurbitacine C and application thereof
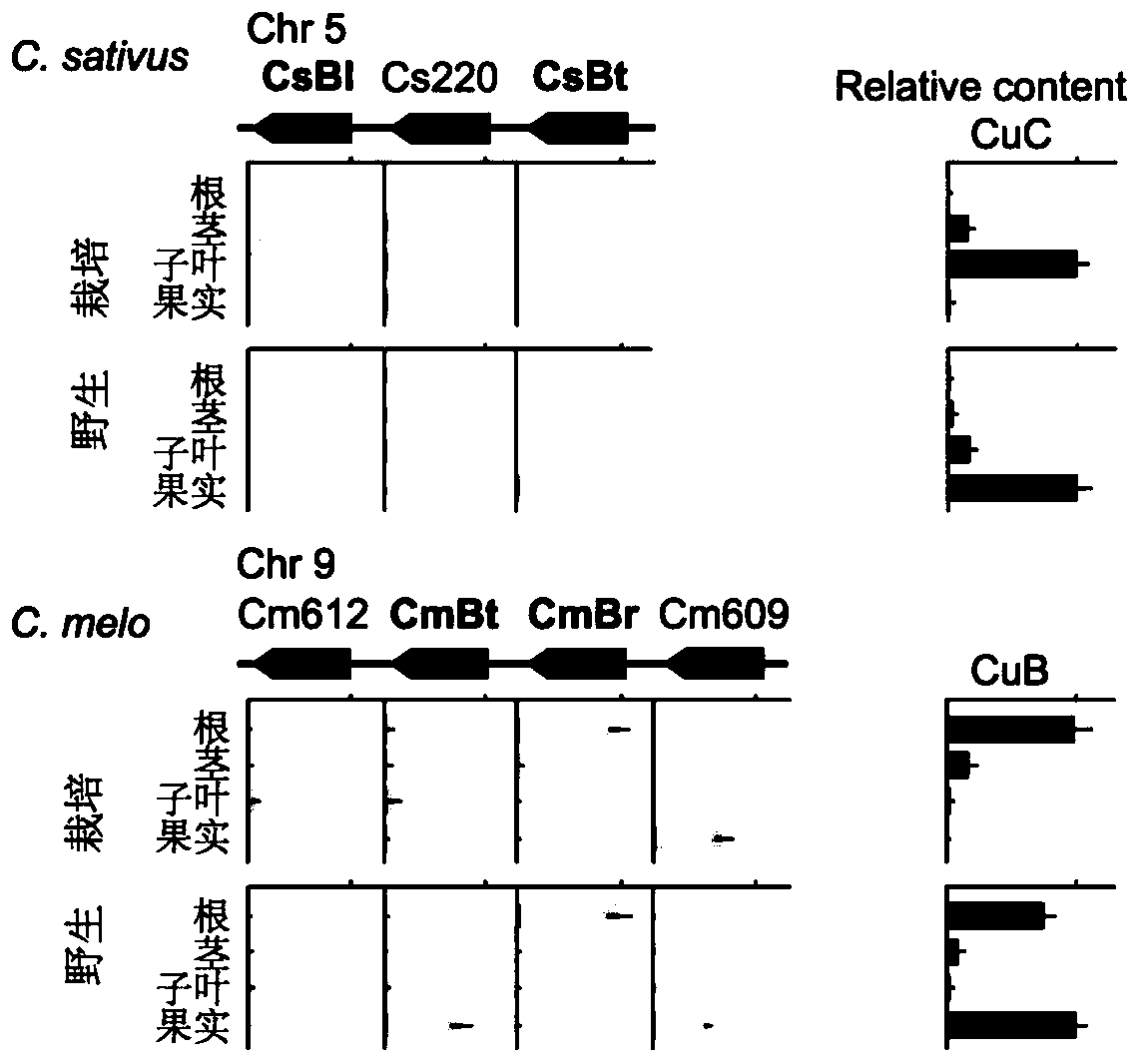
The invention provides a transcription factor Csa5G157230 participating in regulation of synthesis of cucumber cucurbitacine C and application thereof. The transcription factor is one of two bHLH transcription factors (Csa5G157230 and Csa5G156220) which are found in cucumber genome firstly and used for controlling synthesis of bitter taste; the two bHLH transcription factors are used for controlling the forming of the bitter taste in fruits and leaves respectively; simple crossing of yeast, a gel tissue system and instantaneous expression of tobacco prove that the two transcription factors can be combined to a bitter taste synthesis promoter region and used for activating transcription of a synthesis gene; meanwhile, the bitter taste characteristics of cucumber plants can be restored by expressing the corresponding transcription factors in the leaves or fruits of the cucumber free of bitter taste abundantly. The invention further discloses a molecular mechanism for forming bitter taste of cucumber and provides theoretical basis for breeding cucumber free of bitter taste and molecular assisted breeding goals.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Transcription factor Csa5G156220 participating in regulation and control of cucumber cucurbitacin C synthesis and application of transcription factor
The invention provides a transcription factor Csa5G156220 participating in regulation and control of cucumber cucurbitacin C synthesis and an application of the transcription factor. The transcription factor is one of two bHLH (Basic Helix Loop Helix) transcription factors (Csa5G157230 and Csa5G156220) which are used for controlling the bitterness synthesis and found in cucumber genome for the first time, wherein the two bHLH transcription factors are respectively used for controlling the forming of the bitterness in fruits and leaves. Proved by yeast one-hybrid, gel tissue system and tobacco transient expression, the two transcription factors can be combined to a bitterness synthesis promoter region to activate the transcription of synthetic genes; in the meantime, abundant expression of corresponding transcription factors in bitterness-free cucumber leaves and fruits can restore the bitterness character of cucumber plant. The invention further discloses a molecular mechanism forming the cucumber bitterness so as to provide a theoretical basis and a molecular assisted breeding aim for the bitterness-free cucumber breeding.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
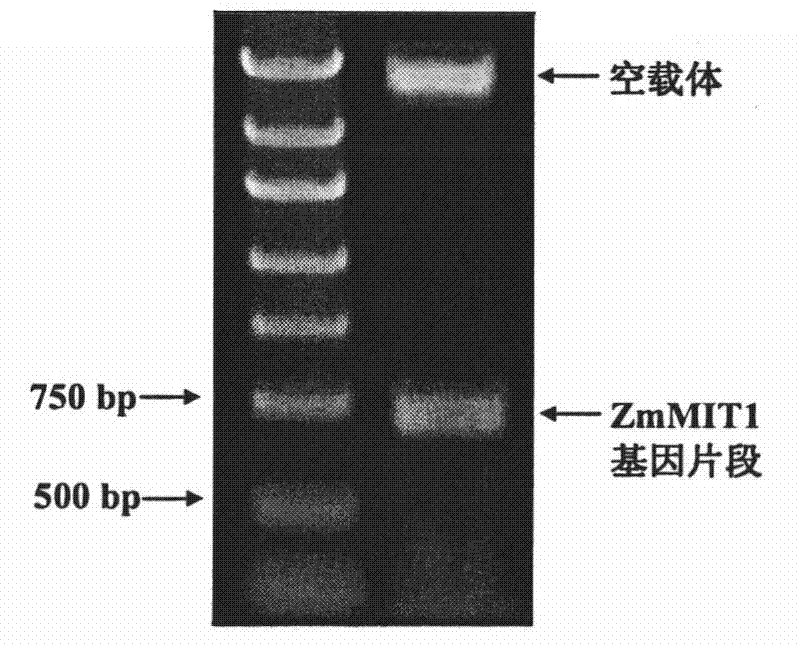
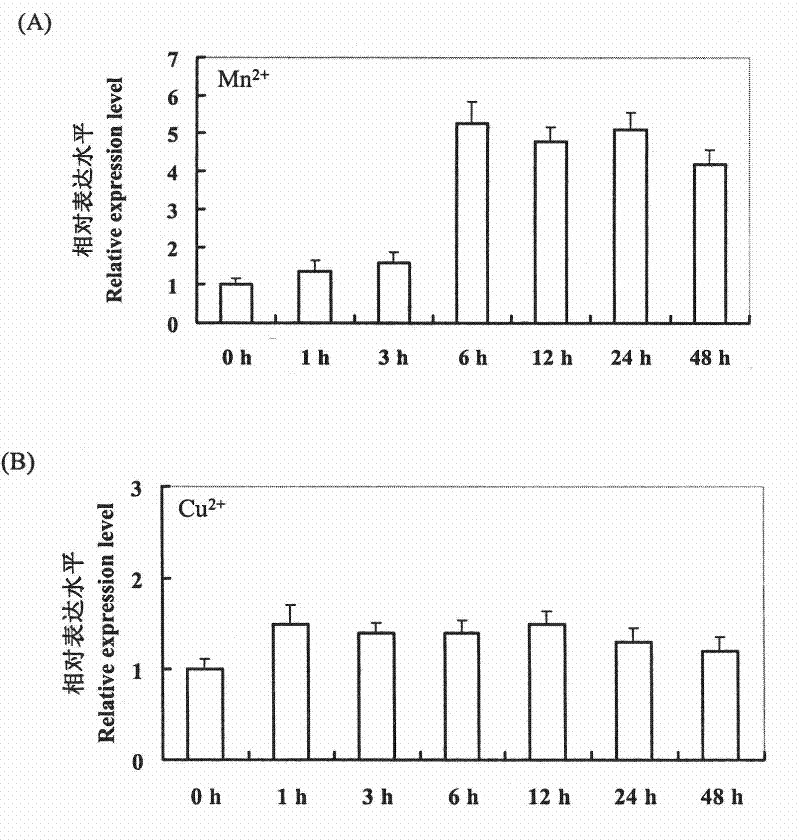
Corn bHLH transcription factor gene ZmMIT1 and use thereof for coding protein
InactiveCN102229937AGreat potential for economic benefitsPlant peptidesFermentationNicotiana tabacumAgricultural science
The invention provides a corn bHLH transcription factor (Manganese-Induced Transcription Factor1) coding gene ZmMIT1 which expresses under induction of heavy metal manganese stress and use thereof for coding a protein. The gene can improve the resistance to heavy metal manganese stress in plants, in particular the manganese poisoning resistance in tobacco. The ZmMIT1 has a bright application prospect in field of heavy metal pollution resistance in corn.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +1
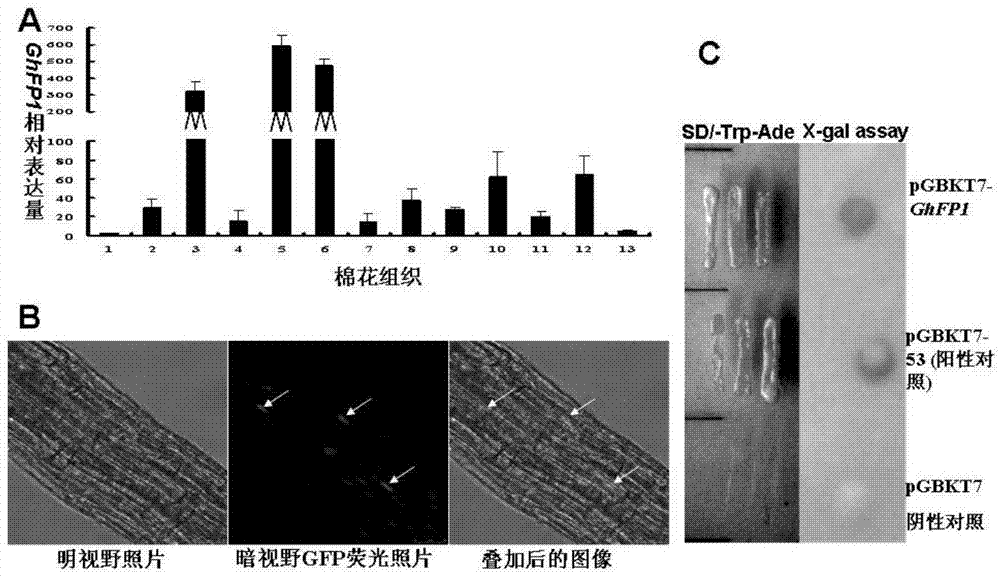
Identification and application of cotton bHLH transcription factor gene GhFP1 and promoter thereof
ActiveCN104711266AHigh specific expression activityHigh elongationMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesAgricultural sciencePromoter activity
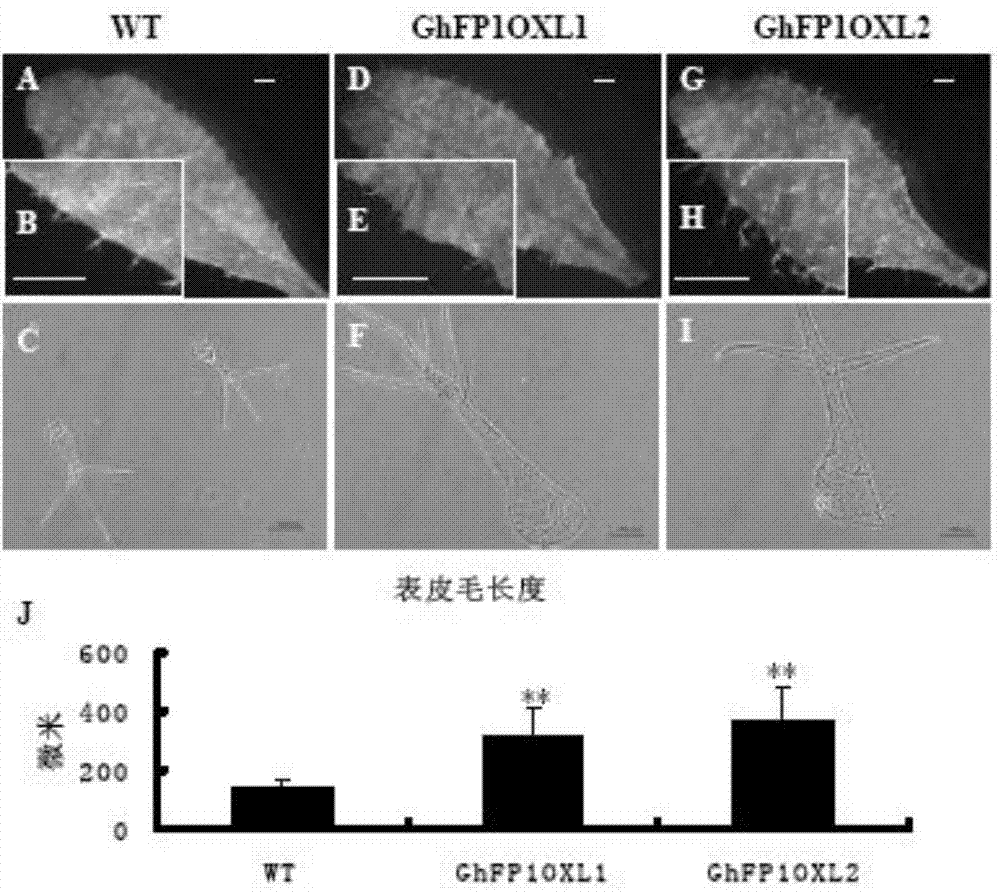
The invention relates to a cotton GhFP1 gene which belongs to a member of a bHLH transcription factor gene family, the cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) full length is 1262bp, and the cotton GhFP1 gene can code a bHLH protein containing 355 amino acids. GhFP1 is respectively expressed in various tissues of cotton, and is highly expressed in the fiber development premetaphase. The GhFP1 promoter segment with the length of 1061bp is separated and cloned. The analysis on the activity of the promoter by using the GUS report gene indicates that the promoter has higher specific expression activity in cotton fibers. The experiment indicates that the overexpression of GhFP1 in Arabidopsis thaliana results in increase of leaf epidermal hair; and the overexpression of GhFP1 in cotton results in enhancement of expression of related genes of cotton fibrocyte brassinolide and increase of ripe cotton fiber length. The result proves that the GhFP1 protein performs positive regulating actions and promotes elongation of fibrocytes in the cotton fiber elongation process, and thus, possibly has important application value in improving the cotton fiber quality and increasing the cotton yield.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
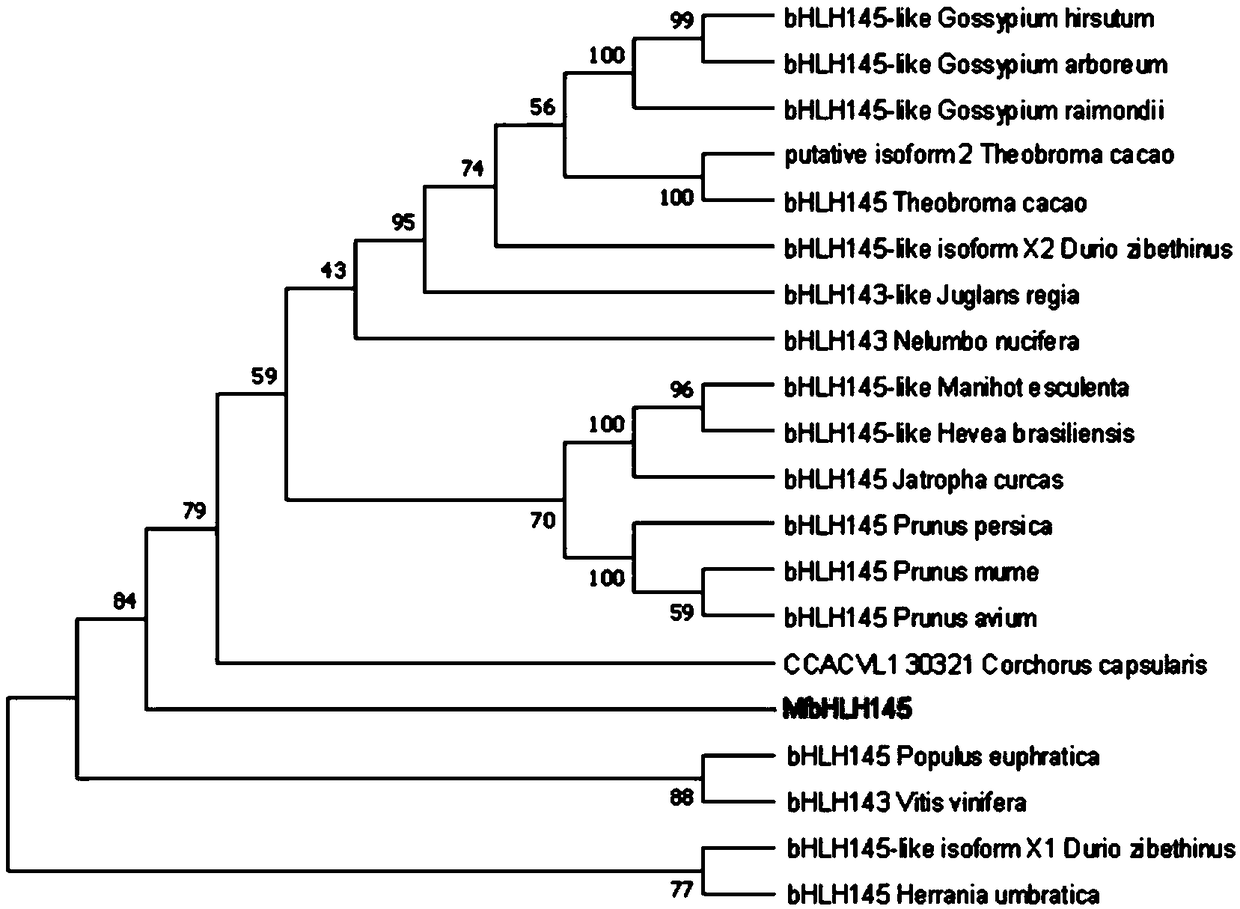
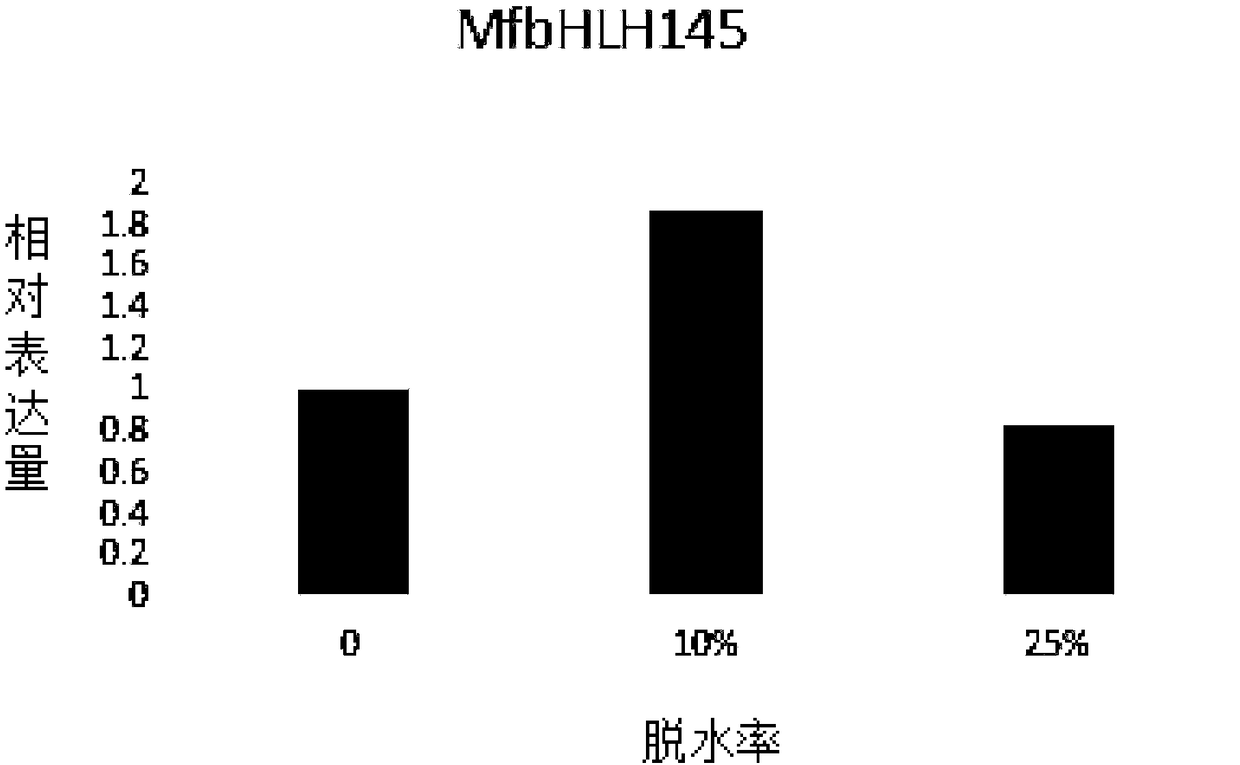
Myrothamnus flabellifolia gene MfbHLH145 and application thereof
InactiveCN109180792AImprove drought toleranceImprove tolerancePlant peptidesFermentationNucleotideBHLH Transcription Factors
The invention discloses a Myrothamnus flabellifolia gene MfbHLH145 and an application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is represented by SEQ. ID. NO.1; and the amino acid sequence of the encoded protein of the gene is represented by SEQ. ID. NO.2. The drought-resistant bHLH transcription factor of Myrothamnus flabellifolia is studied to improve the drought resistance of plants in orderincrease the drought resistance of the plants.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Artemisia apiacea bHLH transcription factor as well as encoding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN102372769AConducive to large-scale industrial productionHigh expressionFungiBacteriaSynthesis methodsRaw material
The invention discloses an artemisia apiacea bHLH transcription factor as well as an encoding gene and an application thereof. The artemisia apiacea bHLH transcription factor provided by the invention is protein shown as a) or b): a) protein which consists of amino acid sequences and is shown in sequences 2 in a sequence table; and b) protein which is derived from a), is formed through substituting and / or deleting and / or adding amino acid sequences shown by the sequences 2 in the sequence table through one or a plurality of amino acid residues and is relevant to the artemisinin synthesis. The bHLH transcription factor is instantaneously translated into artemisia apiacea plants to be overexpressed, the expression quantity of the key enzyme in regulated and controlled artemisinin biosynthetic metabolism is greatly improved, and the artemisia apiacea bHLH transcription factor can be used for producing artemisinin. The regulated and controlled artemisinin synthesis method solves the problem of raw material limitation, has a simple production process and is favorable for the large-scale industrial production of the artemisinin.
Owner:GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI GSCAS
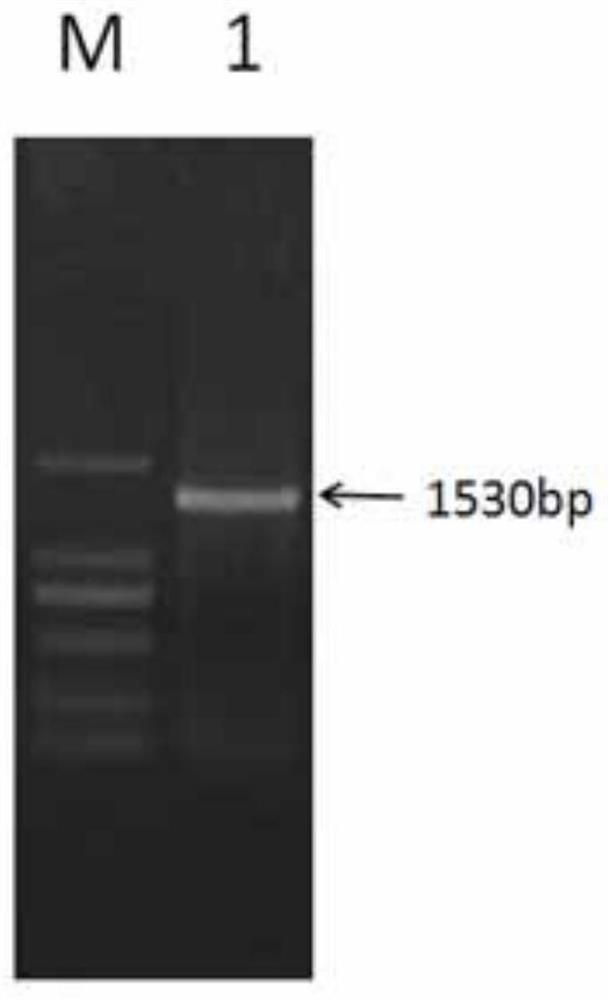
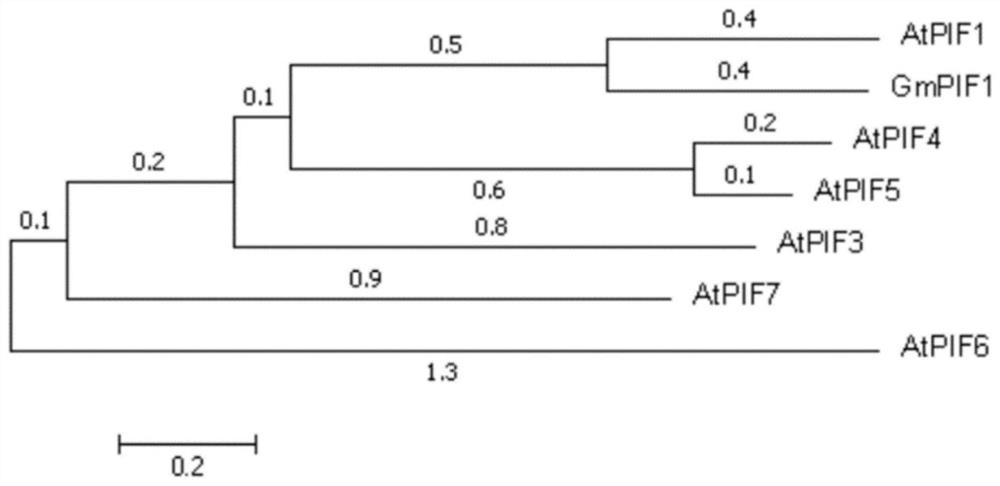
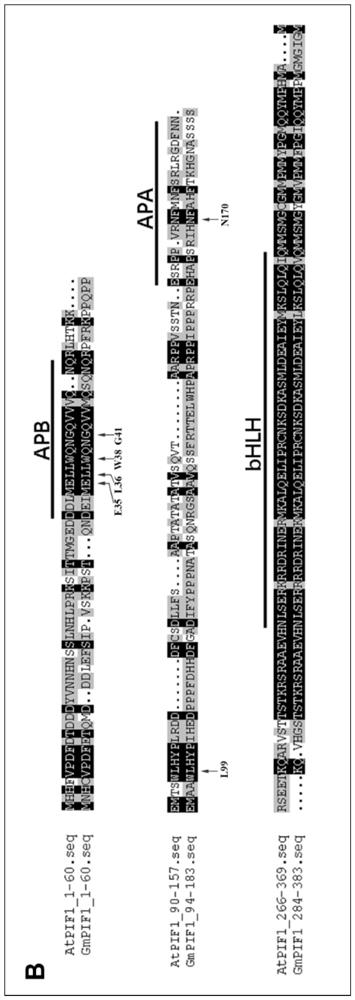
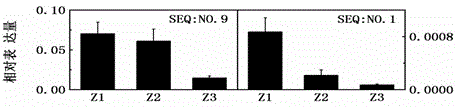
Application of soybean bHLH transcription factor GmPIF1 gene in promoting isoflavone synthesis
ActiveCN111690662AIncrease contentPromote accumulationPlant peptidesFermentationEnzyme GeneNucleotide
The invention relates to application of a soybean bHLH transcription factor GmPIF1 gene in promoting isoflavone synthesis, and belongs to the field of gene engineering and molecular biology. Accordingto the application of the soybean bHLH transcription factor GmPIF1 gene in promoting isoflavone synthesis, the nucleotide sequence of the soybean bHLH transcription factor GmPIF1 gene is shown as SEQID No. 1. The application has the beneficial effects as follows: the GmPIF1 promotes accumulation of isoflavone in soybean hairy roots, a new method is provided for increasing the content of soybeanisoflavone, the soybean isoflavone can be synthesized more efficiently through the bioengineering technology and the gene regulation and control method, and the defects that the artificial cultivationbreeding period is long, hybridization traits are unstable, and screening is difficult are overcome. The transcription factor GmPIF1 gene is transferred into soybean hairy roots, so that the transcription factor GmPIF1 gene is overexpressed in the hairy roots, the content of isoflavone in the hairy roots is increased, and the expression of related enzyme genes in an isoflavone synthetic pathway is regulated.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Chrysanthemum bHLH transcription factor involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis and regulation
The invention provides a chrysanthemum bHLH transcription factor (CmbHLH2) involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis and regulation. A nucleotide sequence of the chrysanthemum bHLH transcription factor is shown as SEQ: NO.1. When the CmbHLH2 and a CmMYB6 coordinate to perform instantaneous over-expression in tobacco leaves, anthocyanin accumulation can be strongly induced to change the original green color of the leaves into a red color. Therefore, by means of transgenosis, over-expression of the CmbHLH2 in a plant is achieved or expression of the CmbHLH2 in the chrysanthemum plant is inhibited so that anthocyanin synthesis enhanced and inhibited transgenic plants can be obtained respectively, and the colors and luster of the transgenic plants can change with anthocyanin synthesis change.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Application of panax japonicus transcription factor gene PjbHLH1
ActiveCN105087600AIncrease contentHigh expressionFermentationGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyEnzyme Gene
The invention discloses application of panax japonicus transcription factor gene PjbHLH1, namely, application in improving the expression quantity of key enzyme genes in the biological synthesis of panax japonicus saponins, and increasing the content of saponins in panax japonicus callus. The nucleotide sequence of the PjbHLH1 gene is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, and bHLH transcription factors are coded. Through the adoption of functional genomics and techniques related to metabolic engineering, a panax japonicus PjbHLH1 transcription factor is proved to have the effect of positively regulating the biological synthesis of panax japonicus saponins; when the panax japonicus PjbHLH1 transcription factor gene disclosed by the invention is established on a plant expression vector and transferred into the panax japonicus callus for over expression, the expression quantity of the key enzyme genes in the synthetic route of panax japonicus saponins is increased, and the yield of panax japonicus saponins is increased.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
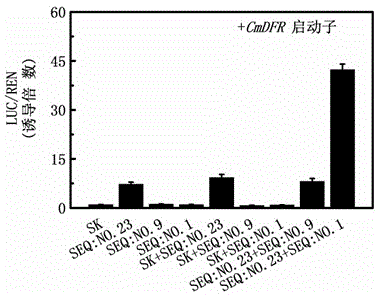
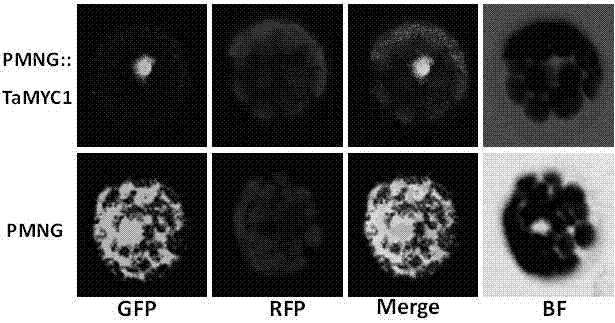
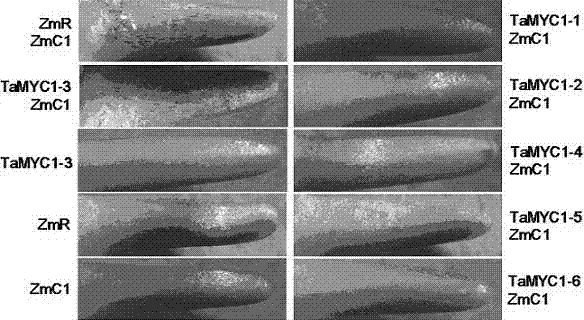
Major gene TaMYC1 for controlling the character of purple seed coat in common wheat and application of the gene
The invention relates to a major gene TaMYC1 for controlling the character of purple seed coat in common wheat, wherein the gene is sourced from a bHLH transcription factor TaMYC1 from the wheat varieties of Highland 115 and Opata. The gene has the nucleotide sequence represented as the 1st-4584th loca in the sequence table represented as the SEQ ID No.1. The gene can be applied to cultivation of a transfection plant.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF SCI NORTHWEST HIGHLAND BIOLOGY INST
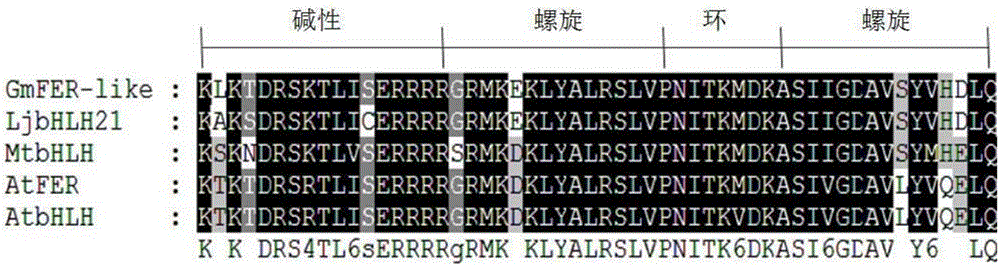
Soybean bHLH transcription factor gene GmFER and encoded protein and application thereof
InactiveCN106399326AImprove toleranceHigh expressionGenetically modified cellsNon-animal cellsYeastBiotechnology
The invention discloses a soybean bHLH transcription factor gene GmFER and encoded protein and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the gene GmFER is as shown in SEQ ID No.1, and the amino acid sequence of the protein encoded by the gene is as shown in SEQ ID No. 2. A semi-quantitative detecting result shows that the gene GmFER is mainly expressed in soybean roots; the expression quantity of the gene GmFER is increased evidently after Cd stress, that is to say, the gene GmFER is induced by Cd; by overexpressing the gene GmFER in yeast and plants, the Cd tolerance of the yeast and plants can be increased, and the gene GmFER is high in application value.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
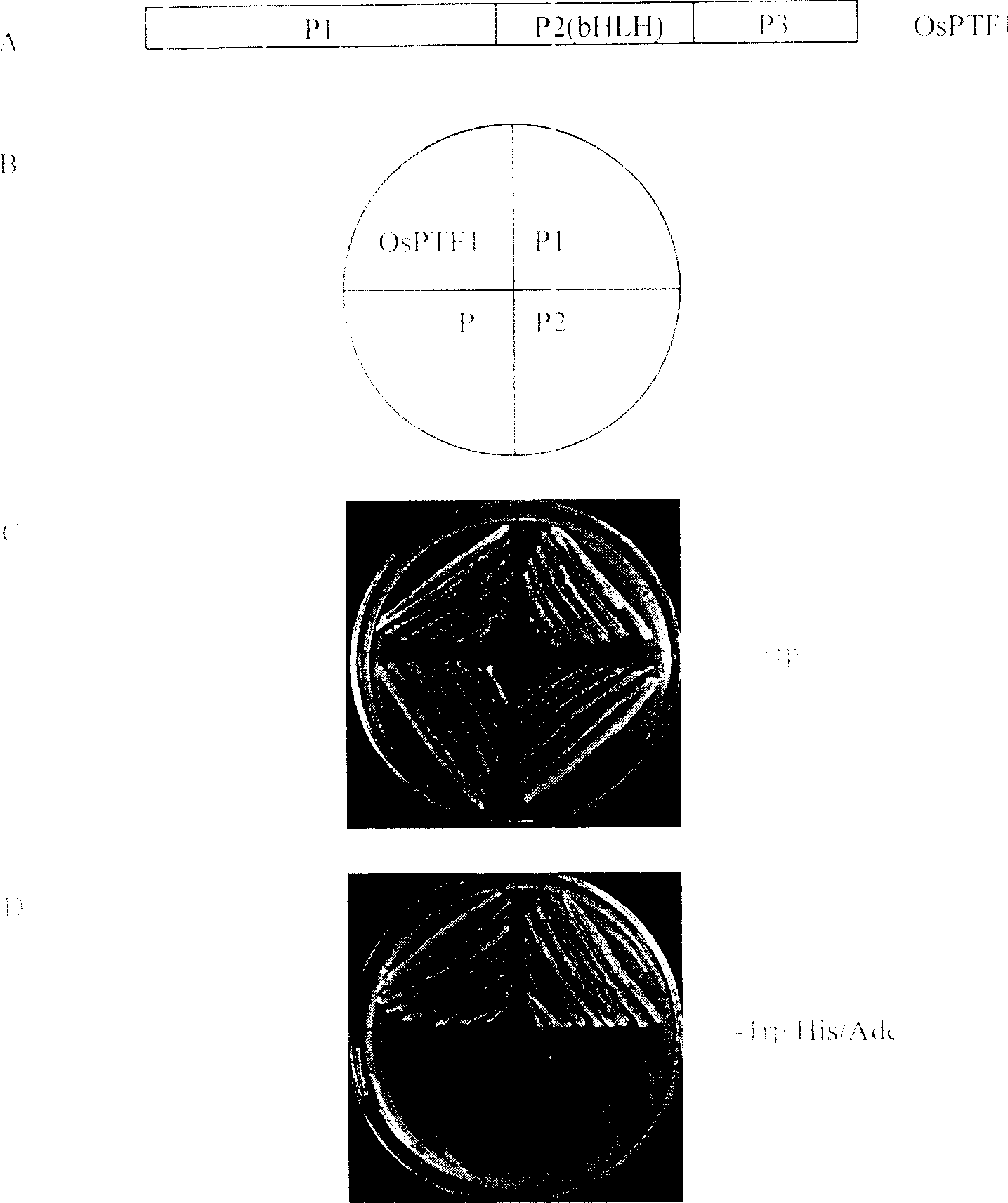
Plant phosphorus hunger inducing transcription factor OsPTF1
InactiveCN1436848AImprove phosphorus starvation toleranceReduce the applicationSugar derivativesGenetic engineeringBHLH Transcription FactorsWild type
The present invention discloses one kind of plant phosphorus hunger inducing transcription factor OsPTF1. OsPTF1 is one new kind of gene separated from rice and comprises 1862 bases, and the nucleic acid encodes one rice root system phosphorus hunger inducing strengthening expressed bHLH transcription factor. Some data shows that the gene has constitutive expression in rice leaf and phosphorus hunger inducing expression in root. OsPTF1 joins the plant phosphorus utilizing process. Transgenic plant after expressing said gene has phosphorus hunger tolerance higher than that of wild plant. Therefore, utilizing the gene and technological process of the present invention can raise the phosphorus hunger tolerance of plant and cell.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
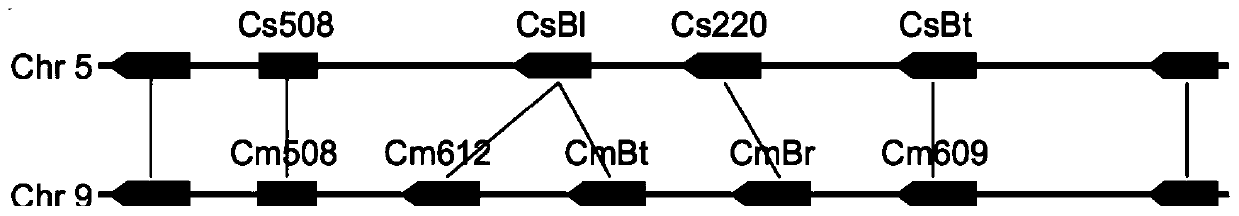
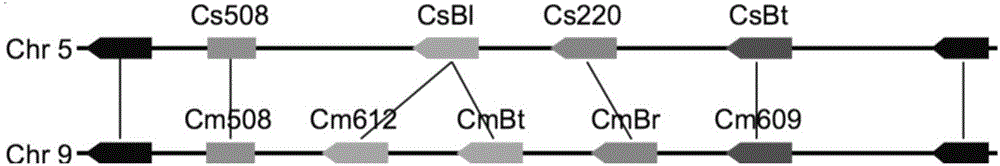
Transcription factors participating in regulating and controlling synthesis of bitter principles of cucumis melo and application of transcription factors
ActiveCN110317829ACo-domesticationPlant peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionNicotiana tabacumCotyledon plant
The invention provides transcription factors participating in regulating and controlling synthesis of bitter principles of cucumis melo and application of the transcription factors. A comparative genomics method is utilized for the first time, and the two bHLH transcription factors CmBr and CmBt for controlling synthesis of bitter taste are discovered in genomes of the cucumis melo, and separatelycontrol formation of the bitter taste in roots and wild fruits. Through a yeast one-hybrid technology, a gel retardation test and a tobacco transient expression system, it is proved that the two transcription factors can be directly combined with a promoter region of a bitter principle synthesis gene, and then the expression of the synthesis gene is activated; meanwhile, through transient expression of cotyledons of the cucumis melo, it is proved genetically that the overexpression of CmBr and CmBt can activate the expression of the bitter taste synthesis gene, so that the cotyledons withoutthe bitter taste obtain the phenotype of the bitter taste. The CmBt gene is located in a domestication region. The invention further discloses a molecular mechanism for formation of the bitter taste of the cucumis melo, and a theoretical basis is provided for breeding of the cucumis melo without the bitter taste.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
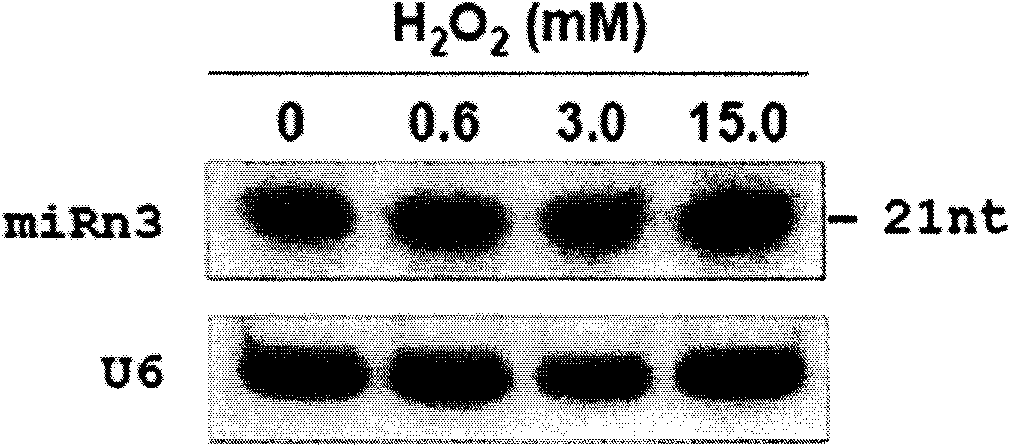
miRNA-n3 derived from rice and application thereof
InactiveCN101892232ALow base error rateHigh sensitivityVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsSocial benefitsAgricultural science
The invention discloses miRNA-n3 derived from rice and application thereof. The miRNA-n3 protected by the invention is RNA shown in a sequence 1 of a sequence table. The pre-miRNA-n3 protected by the invention is the RNA shown in a sequence 2 of the sequence table. The invention also protects the application of the RNA shown in the sequence 1 in inhibiting the gene expression of bHLH transcription factors and / or promoting the degradation of mRNA of the bHLH transcription factors, wherein the bHLH transcription factor is shown in a sequence 3 of the sequence table. By using the miRNA-n3, the plant which has important phenotypes in the aspects of growth and development as well as adverse situation stress tolerance is expected to be obtained, thereby having important biological significancesand potential application value, providing valuable gene resources for the culturing of rice improved varieties (for example culturing of stress-resistant rice), having important research value and potential social benefits and being applied to the production practice finally.
Owner:WUXI RES INST OF APPLIED TECH TSINGHUA UNIV +1
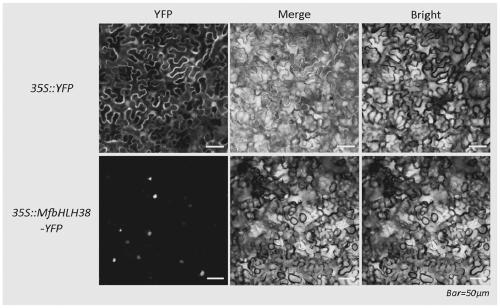
Myrothamnus flabellifolia gene MfbHLH38 and application thereof
The invention discloses a myrothamnus flabellifolia gene MfbHLH38 and application thereof. A nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown in SEQ ID NO.1; and an amino acid sequence of protein encoded by the gene is shown in SEQ ID NO.2. A drought resistance bHLH transcription factor of myrothamnus flabellifolia is studied to improve drought resistance and salt tolerance of plants and enhance the drought resistance and salt tolerance of plants.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Soybean bHLH transcription factor and encoding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN105753955AImprove toleranceReduce accumulationMicroorganism based processesNucleic acid vectorAgricultural scienceBHLH Transcription Factors
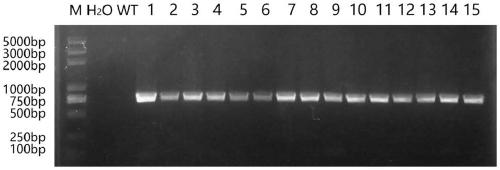
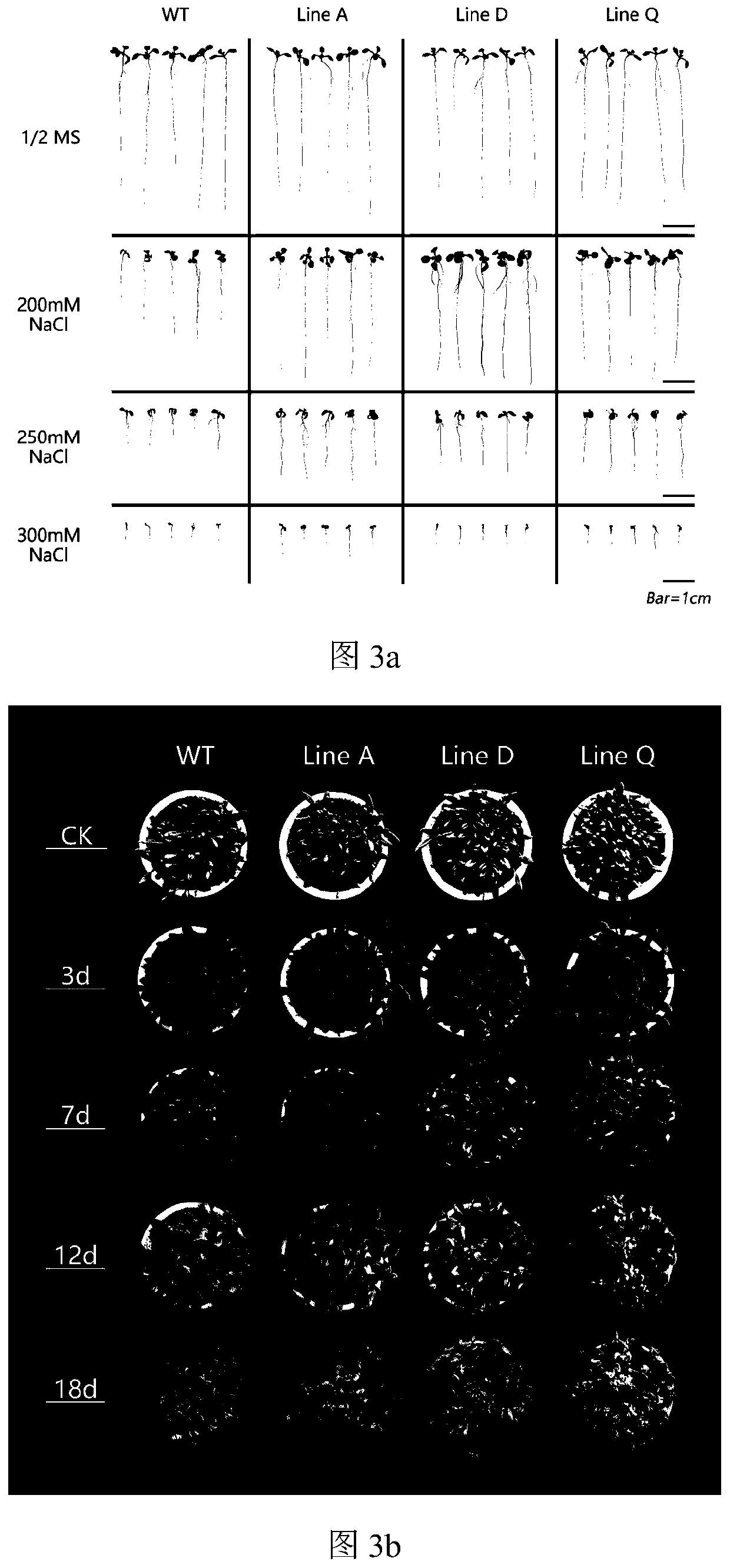
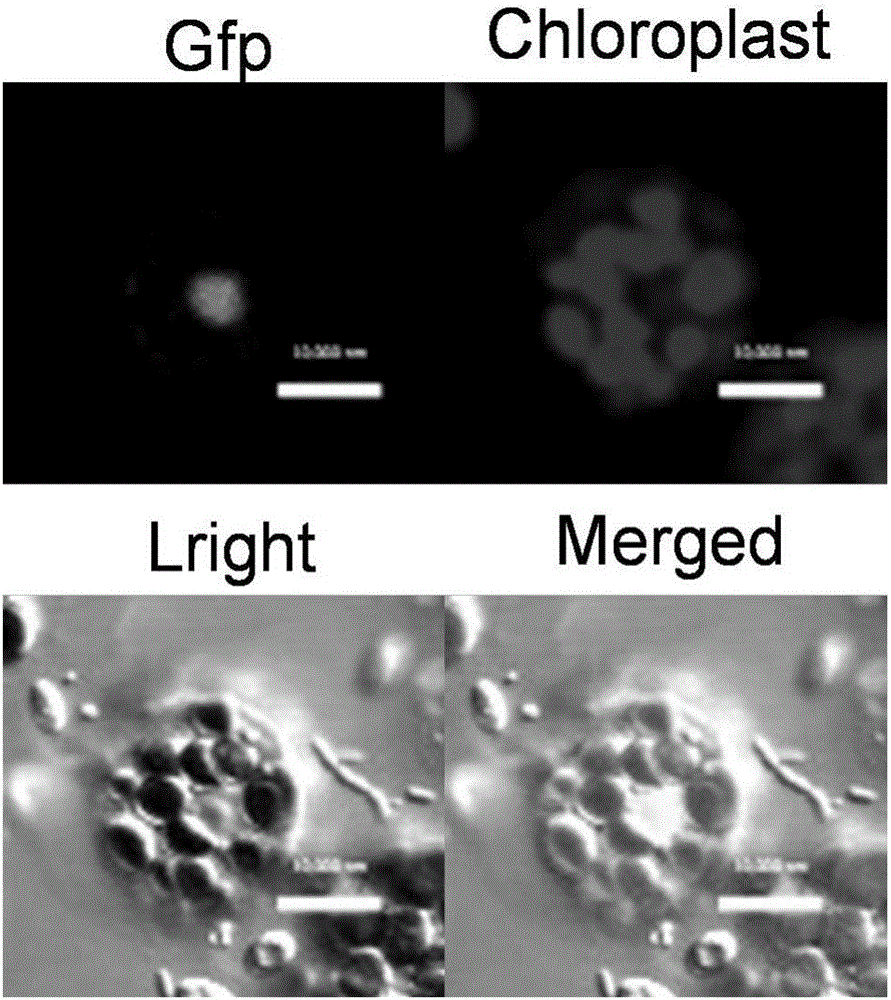
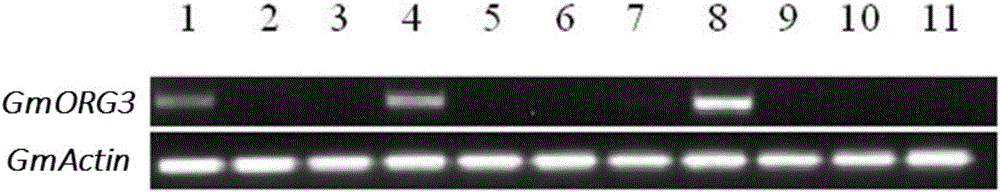
The invention discloses a bHLH transcription factor and an encoding gene and application thereof. The protein has an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2 or the amino acid sequence which is formed by replacing, missing or adding one or more amino acids in the sequence and has the same function. The encoding gene GmORG3 of the bHLH transcription factor shows resistance on Cd stress when in over-expression, so that the GmORG3 gene in the soybean is separated and cloned; the anti-Cd mechanism of the soybean is disclosed; and the anti-Cd molecular breeding of plants can be carried out through gene operation means to improve the Cd resistance of the plants.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
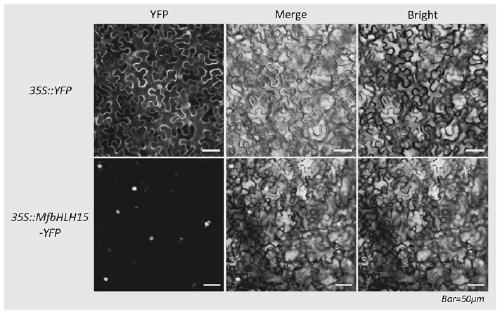
Myrothamnus flabellifolia gene MfbHLH15 and application thereof
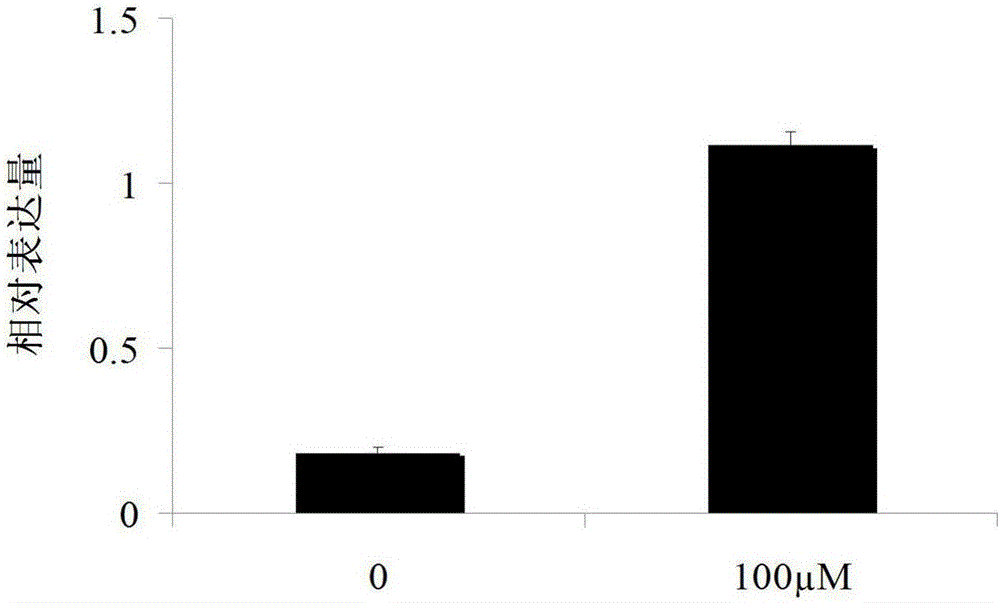
The invention discloses a myrothamnus flabellifolia gene MfbHLH15 and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.1; and the amino acid sequence of a protein encodedby the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. Through the research on drought-resistant bHLH transcription factors of myrothamnus flabellifolia and improvement on the drought-resistant and salt-tolerant performance of plants, the drought-resistant and salt-tolerant performance of the plants is improved.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Transcription factor participating into regulation of muskmelon bitter principle synthesis and application of transcription factor
The invention provides a transcription factor participating into regulation of muskmelon bitter principle synthesis and application of the transcription factor. A comparative genomics method is firstly utilized for finding two bHLH transcription factors CmBr and CmBt which control bitter synthesis in a muskmelon genome, the two bHLH transcription factors are respectively used for controlling the bitter formation at the root part and in the wild fruit. A yeast one-hybrid technology, a gel retardant experiment and a tobacco transient expression system are used for proving that the two transcription factors can be directly combined to a promoter region of a bitter principle synthesis gene, and can activate the expression of the synthesis gene; the muskmelon cotyledon transient expression proves that the overexpression of each of the CmBr and the CmBt can activate the expression of the bitter synthesis gene from the genetics, so that the bitter-free cotyledon can acquire the bitter phenotype. The CmBt gene is located in a domestication region. The invention further discloses a molecule mechanism of the muskmelon bitter formation, and provides the theoretical basis for the breeding of the bitter-free muskmelon.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
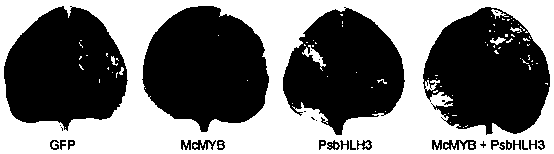
Myrciaria cauliflora myb transcription factor McMYB and plum bHLH transcription factor PsbHLH and application thereof
ActiveCN108588089AIncrease contentBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementNicotiana tabacumNucleotide
The invention relates to a myrciaria cauliflora myb transcription factor McMYB, a protein and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The invention provides themyrciaria cauliflora myb transcription factor McMYB which has a nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID No.1 as shown in the specification. The myrciaria cauliflora myb transcription factor McMYB is capable ofregulating and controlling expression of a myb gene joining in biosynthesis of anthocyanin of myrciaria cauliflora, and study shows that McMYB gene expression is positively correlated with the contentof anthocyanin in peel of myrciaria cauliflora, and is capable of intensively inducing tobacco leaves to accumulate anthocyanin. Results show that McMYB provided by the invention is capable of effectively regulating and controlling biosynthesis of anthocyanin of plants. The myrciaria cauliflora myb transcription factor McMYB has a transcription regulation and control function on biosynthesis of anthocyanin, and can be applied to biosynthesis of anthocyanin of plants.
Owner:POMOLOGY RES INST FUJIAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
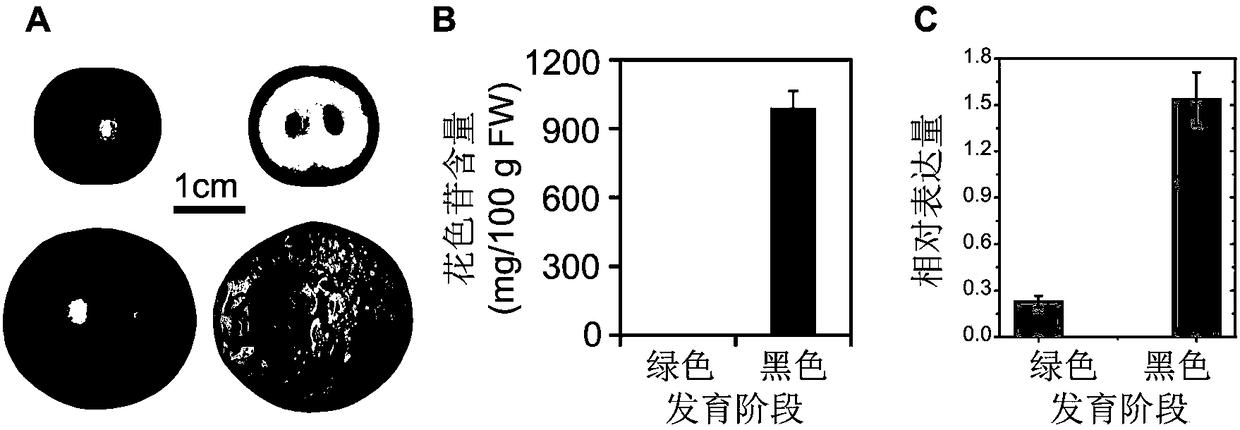
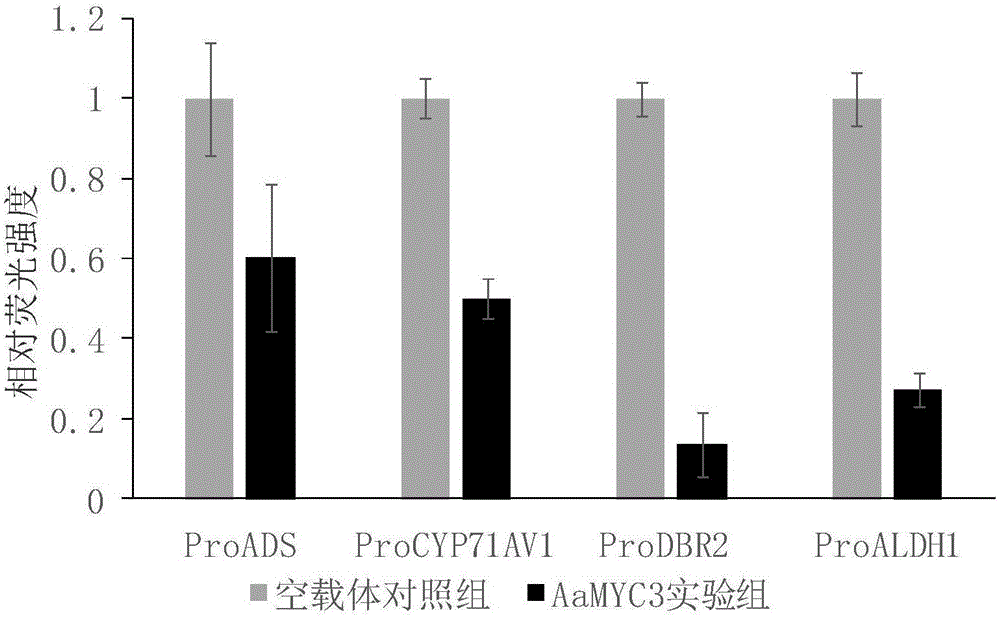
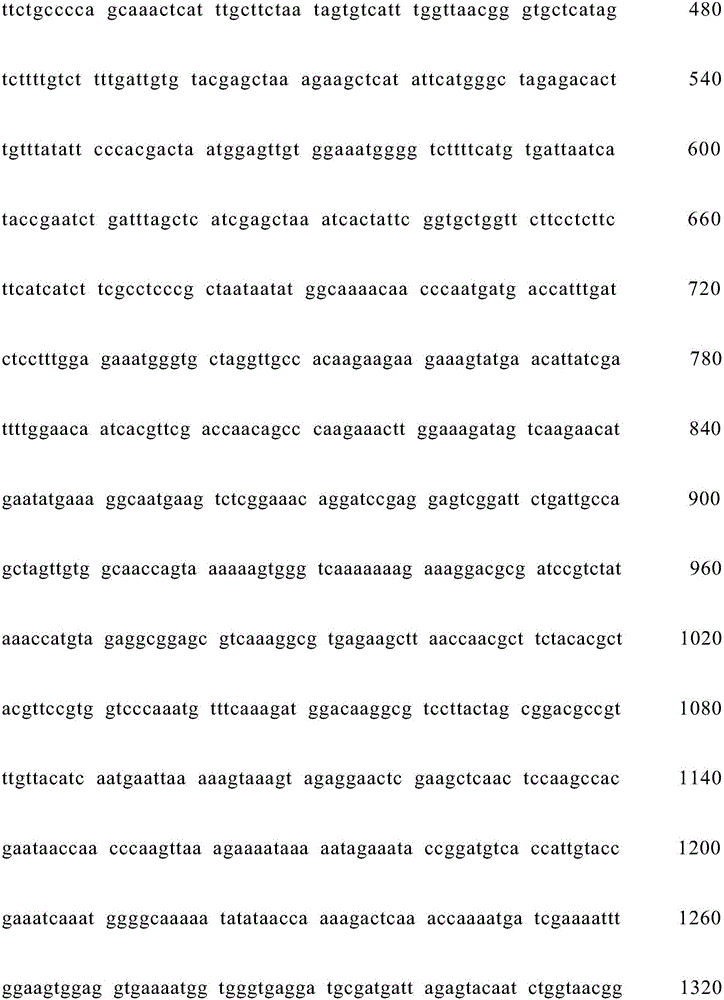
Artemisia-apiacea bHLH transcription factor coded sequence and clone method and application thereof
The invention discloses a cloning method and application of an artemisia-apiacea AaMYC3 gene coded sequence. The cloning method includes the specific steps of cloning of a gene AaMYC3; constructing of a plant expression vector with the gene; the activation effect of the gene on a specific gene promoter of an artemisinin biosynthetic pathway. The nucleotide sequence of the artemisia-apiacea AaMYC3 gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, and the coded amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The invention further discloses the application of the AaMYC3 gene to activating expression of the four specific gene promoters including ADS, CYP71AV1, DBR2 and ALDH1 of the artemisinin biosynthetic pathway. According to the cloning method an application, the AaMYC3 gene can be applied to artemisia apiacea with the RNAi method, the antisense inhibiting method and the like, quality is improved, and the content of artemisinin in artemisia apiacea can be increased.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
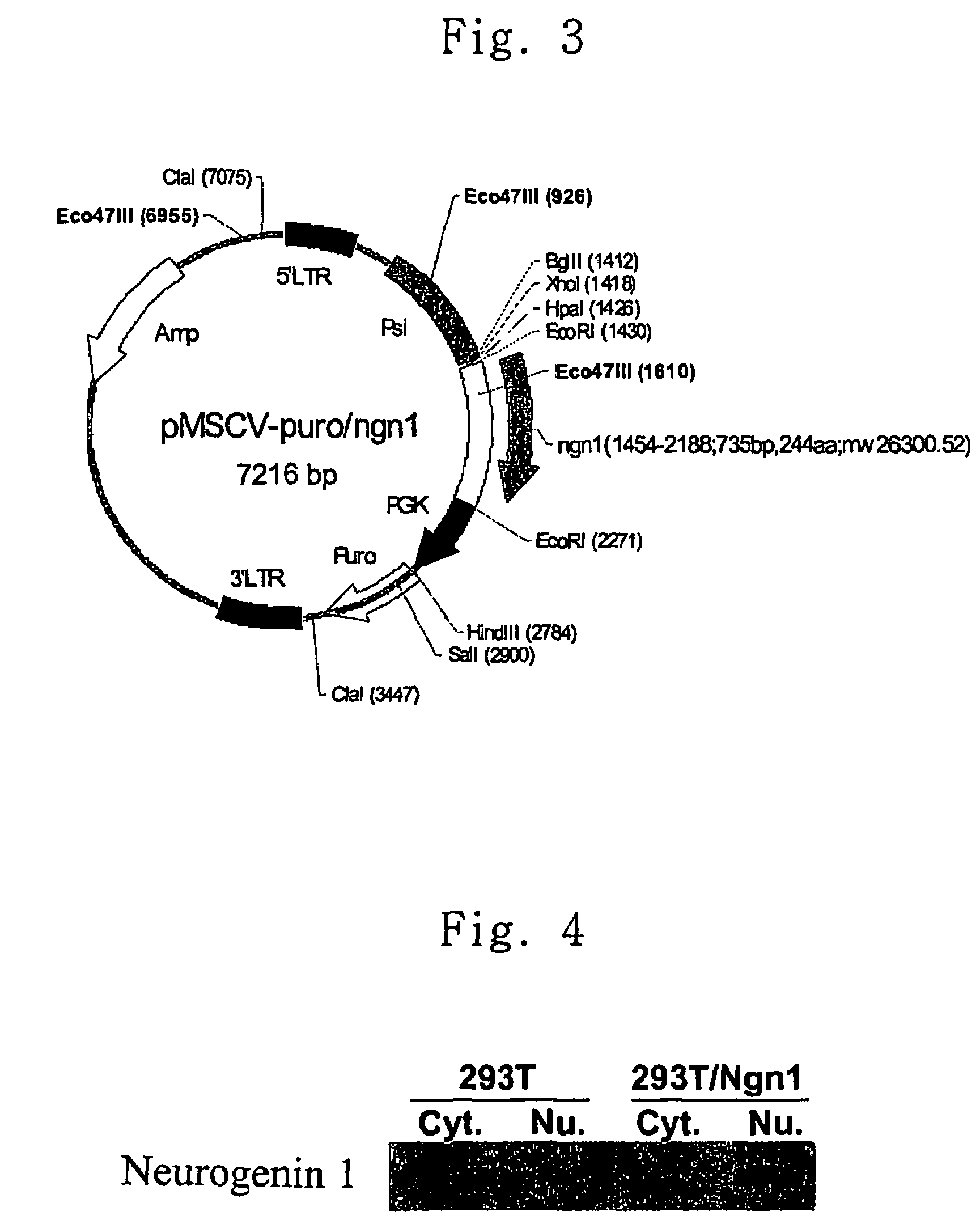
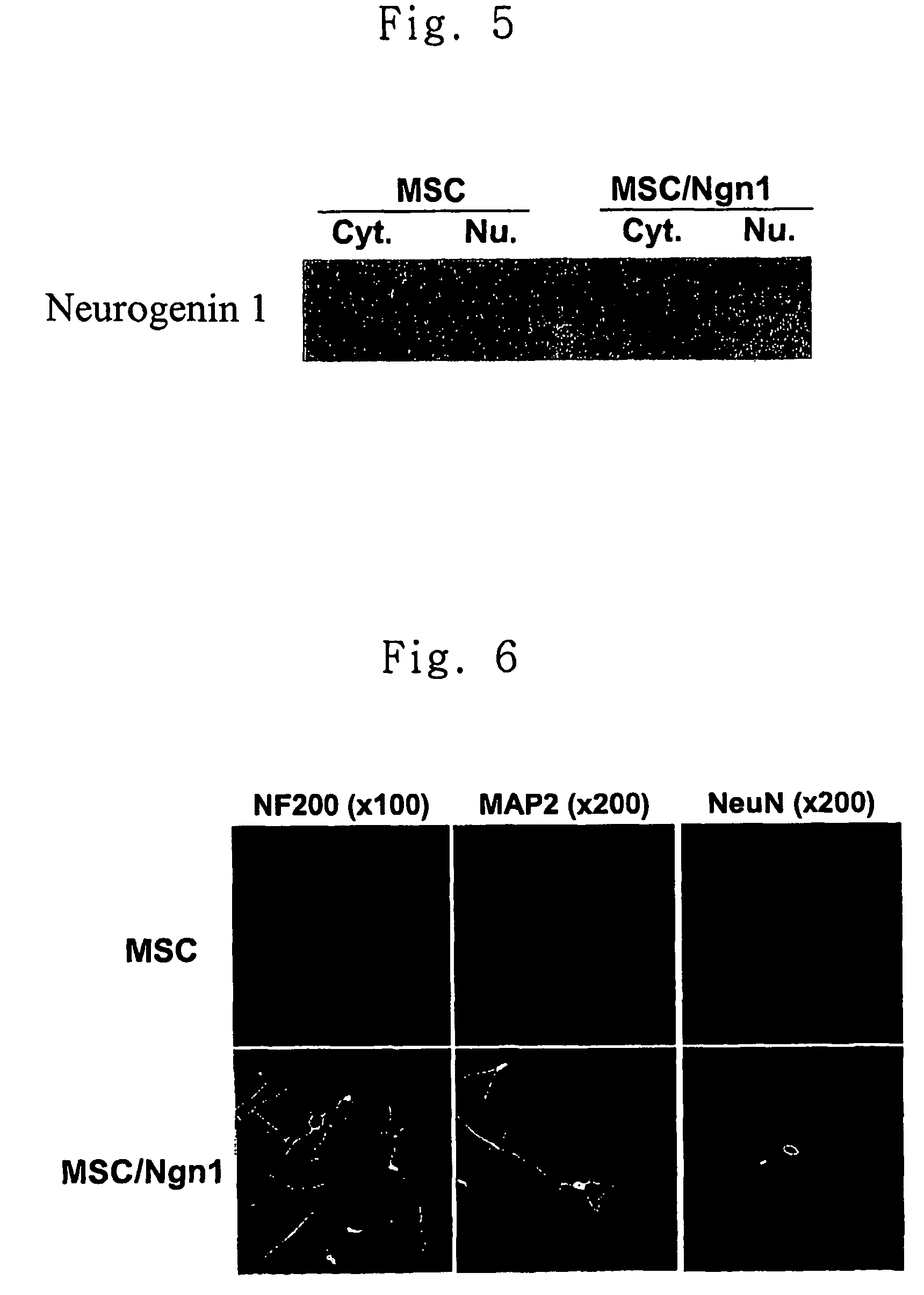
Method for transdifferentiating mesenchymal stem cells into neuronal cells
ActiveUS7732203B2Improve the level ofBiocideGenetic material ingredientsCerebral paralysisInjury cause
Owner:AJOU UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
Transcription factor participating in regulating watermelon bitter principle and application thereof
ActiveCN106518994ATranslation terminated earlyMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesYeastGene Position
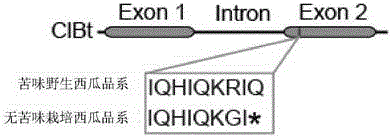
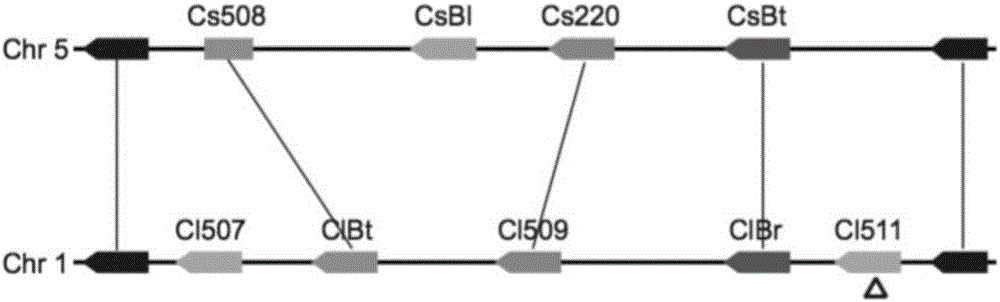
The invention provides a transcription factor participating in regulating watermelon bitter principle and an application thereof. Two bHLH transcription factors ClBr and ClBt controlling bitterness synthesis are discovered in watermelon genome for the first time by use of comparative genomics, wherein the two bHLH transcription factors control the formation of bitterness in the root and wild fruits respectively. The yeast one-hybrid technology, gel retardation experiment and tobacco transient expression system prove that the two transcription factors can be directly combined to the promoter area of the bitter principle synthesis gene and activate the expression of the synthesis gene; and meanwhile, through the transient expression of watermelon cotyledon, the overexpression of ClBr and ClBt is genetically proven to activate the expression of the bitterness synthesis gene so that the bitterless cotyledon obtains a bitterness phenotype. The ClBt gene encodes the mutation of an SNP so that the bitter fruit loses bitterness; and moreover, the gene positioned in an acclimation area is an acclimation gene. The invention further discloses a molecular mechanism forming watermelon bitterness and provides a theoretical basis for bitterless watermelon breeding.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
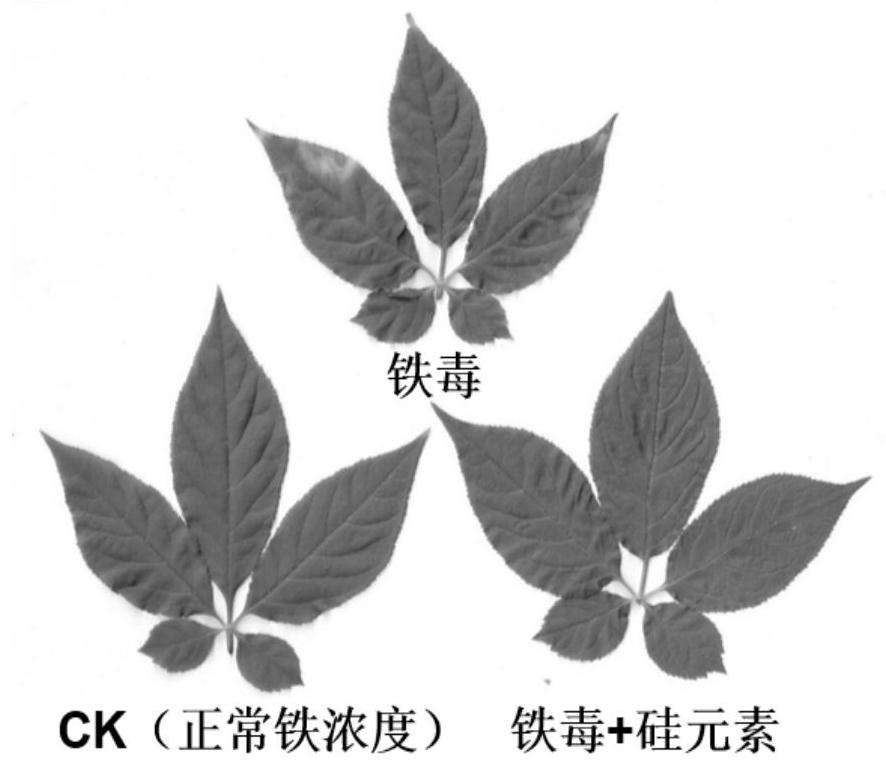
Ginseng PgbHLH149 transcription factor and application thereof
ActiveCN111909252AIncrease resistanceRelieves Iron Toxicity SymptomsPlant peptidesFermentationETS transcription factor familyBHLH Transcription Factors
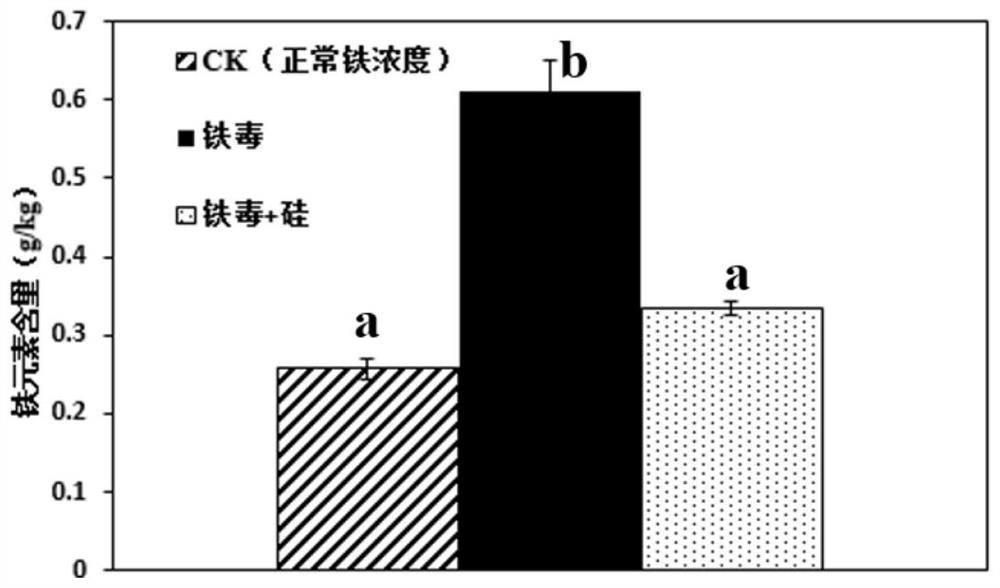
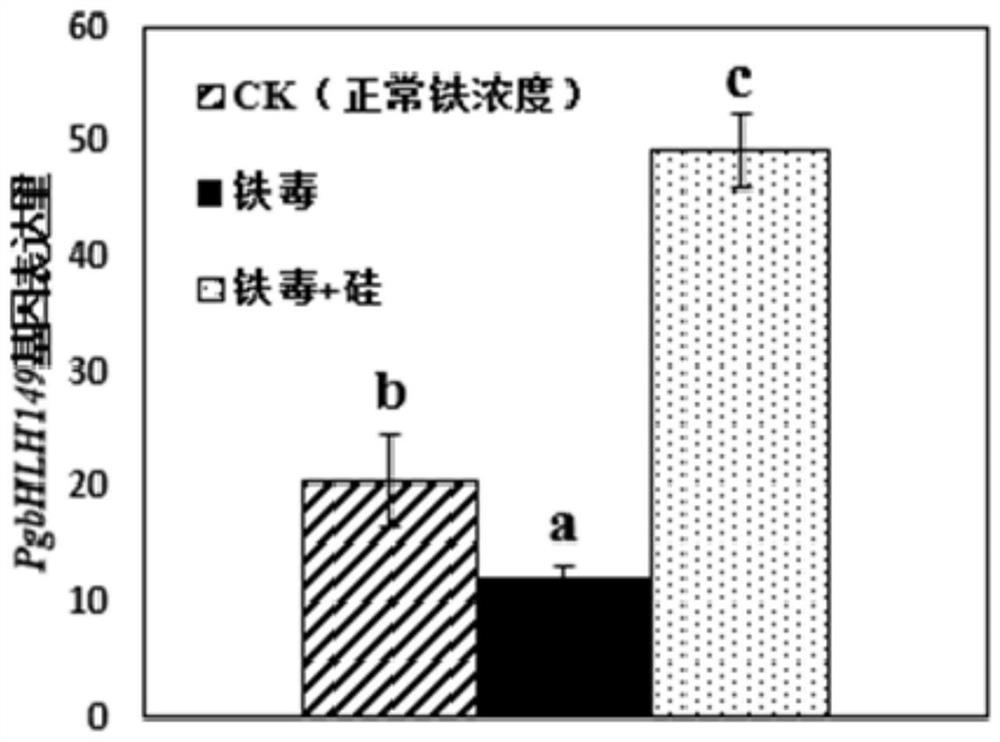
The invention provides a ginseng PgbHLH149 transcription factor and application thereof, and relates to the field of plant transcription factors. According to the ginseng PgbHLH149 transcription factor, through an effective exogenous substance screening test for relieving iron toxicity stress of ginseng, it is found that the symptom of the iron toxicity of the ginseng can be effectively relieved by adding a proper amount of silicon elements under iron toxicity stress, in combination with transcriptome and element analysis results, the new transcription factor-PgbHLH149 transcription factor inthe bHLH transcription factor family is explored, the expression quantity of a PgbHLH149 gene and the iron accumulation quantity in a ginseng body have a remarkable negative correlation trend, namelythe higher the expression quantity of the PgbHLH149 gene is, the lower the iron accumulation quantity in the ginseng body is; and a PgbHLH149 transgenic arabidopsis thaliana experiment shows that theoverexpression of the PgbHLH149 gene in an arabidopsis thaliana can improve the resistance of a transgenic plant to iron toxicity stress.
Owner:INST OF SPECIAL ANIMAL & PLANT SCI OF CAAS
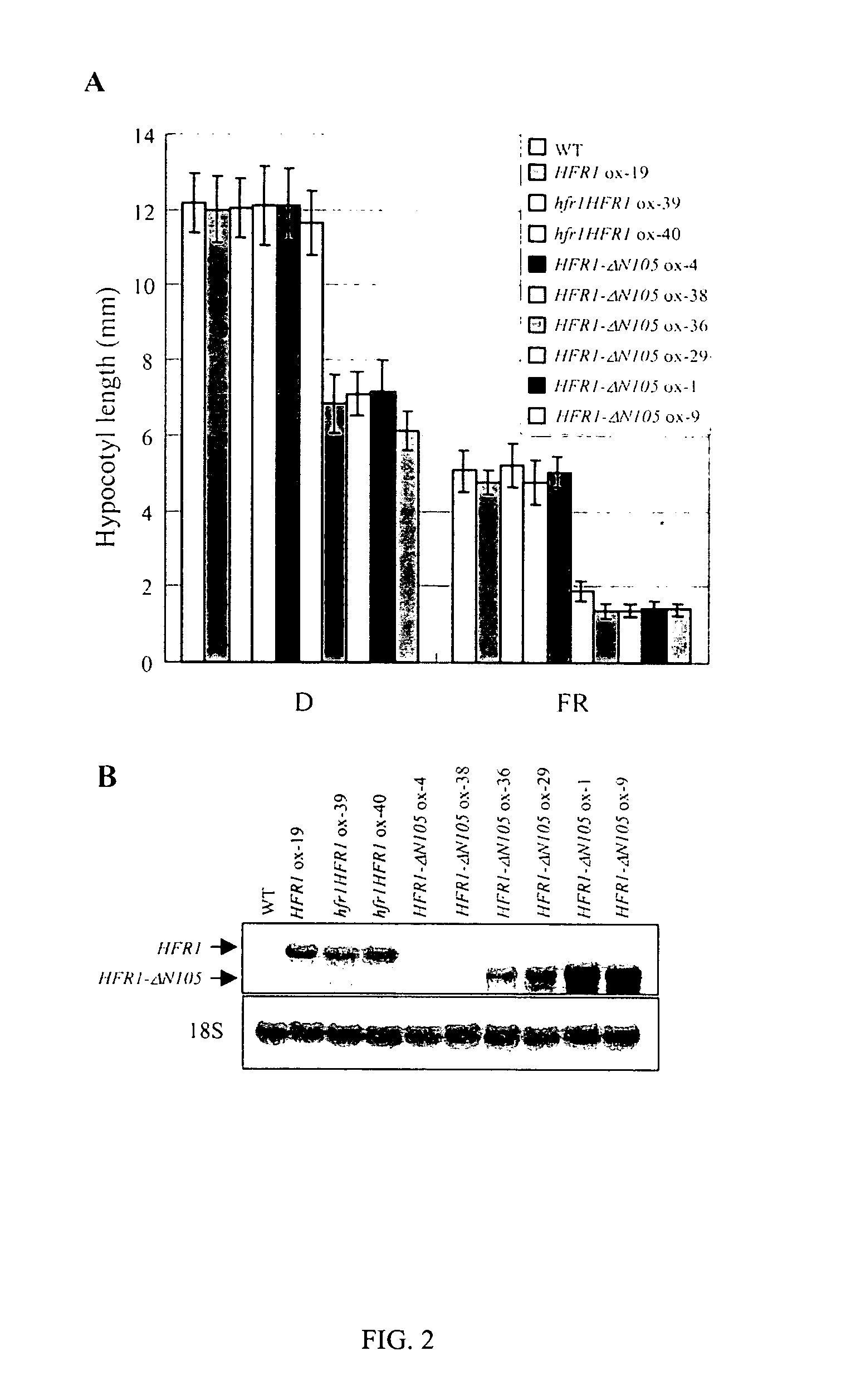
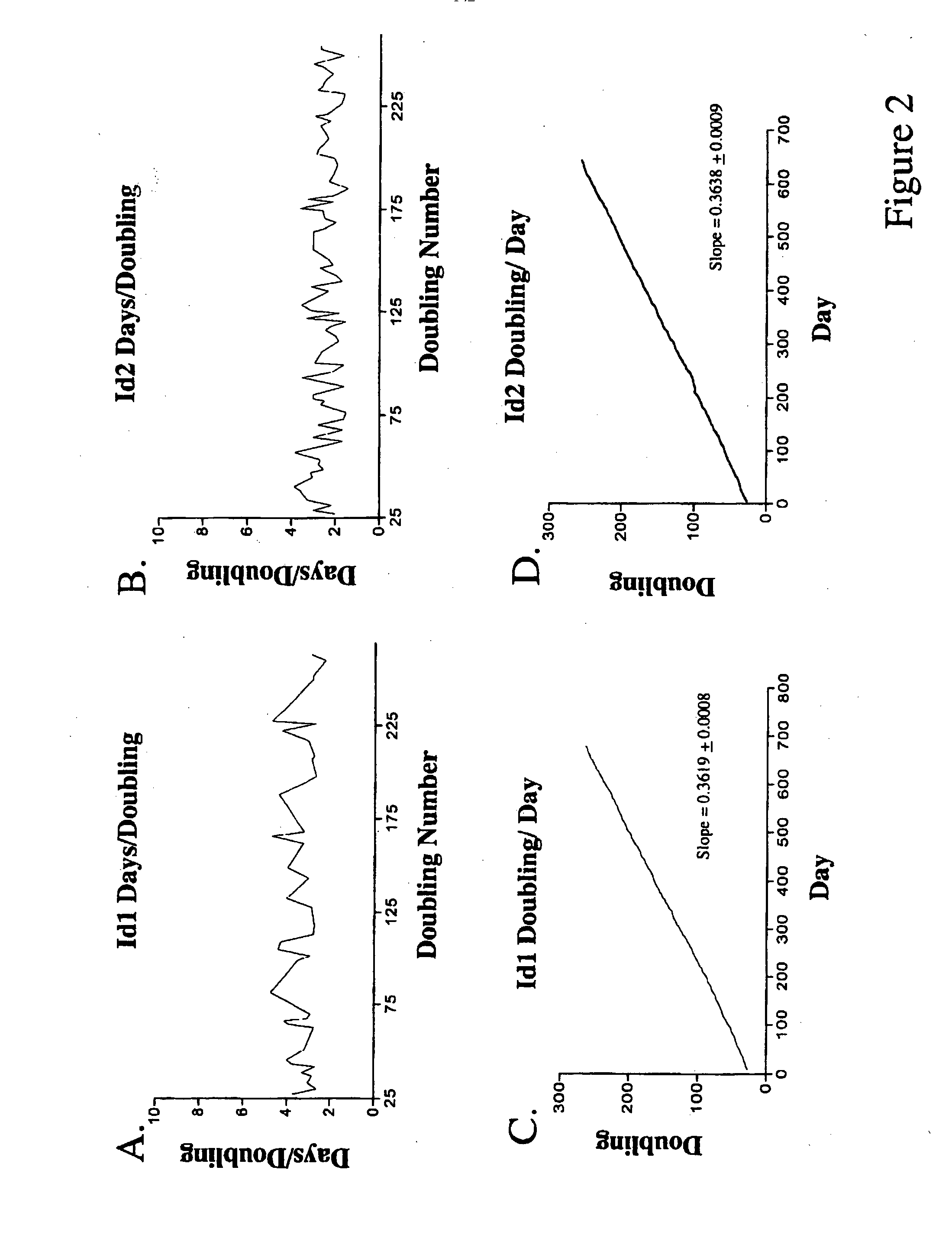
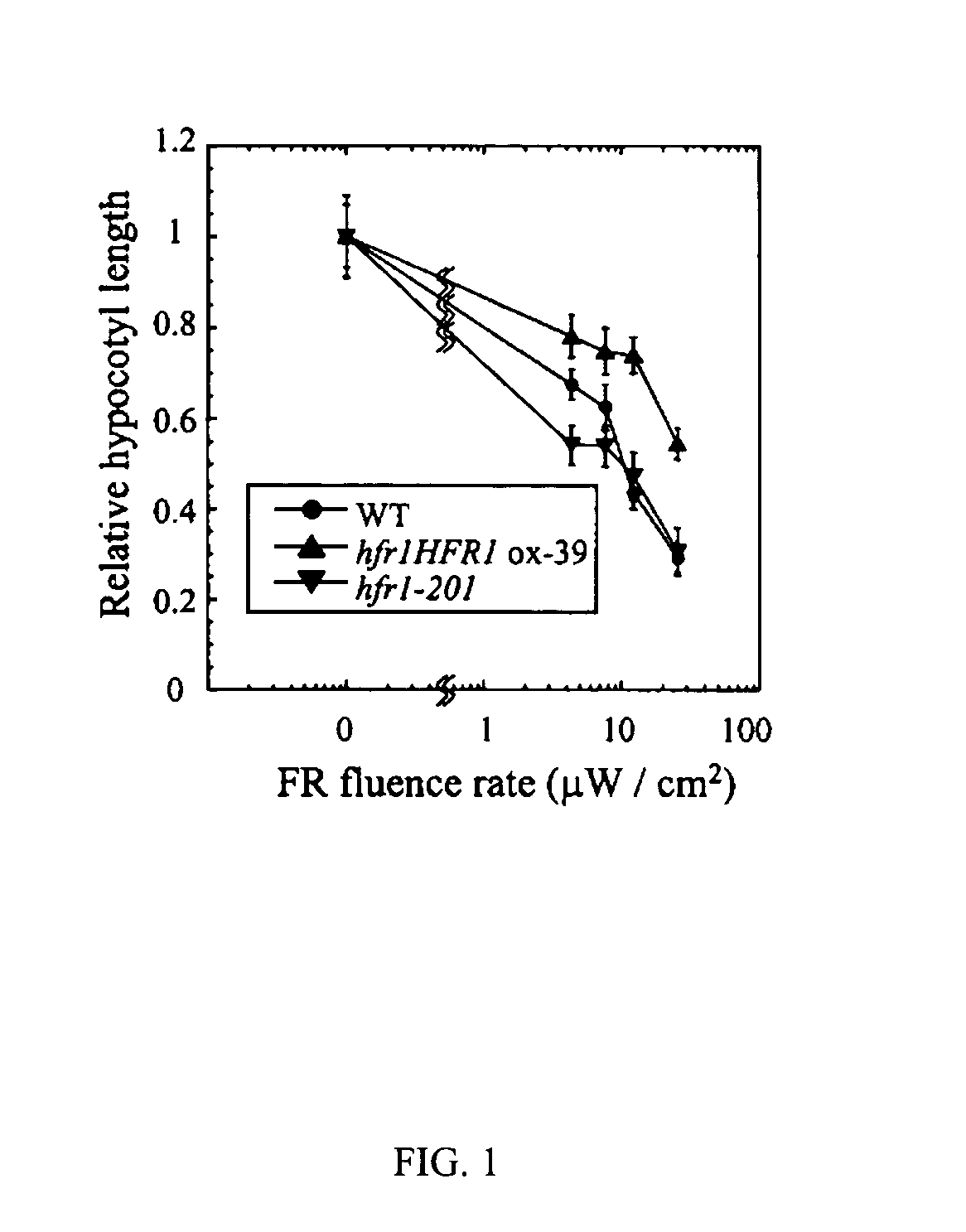
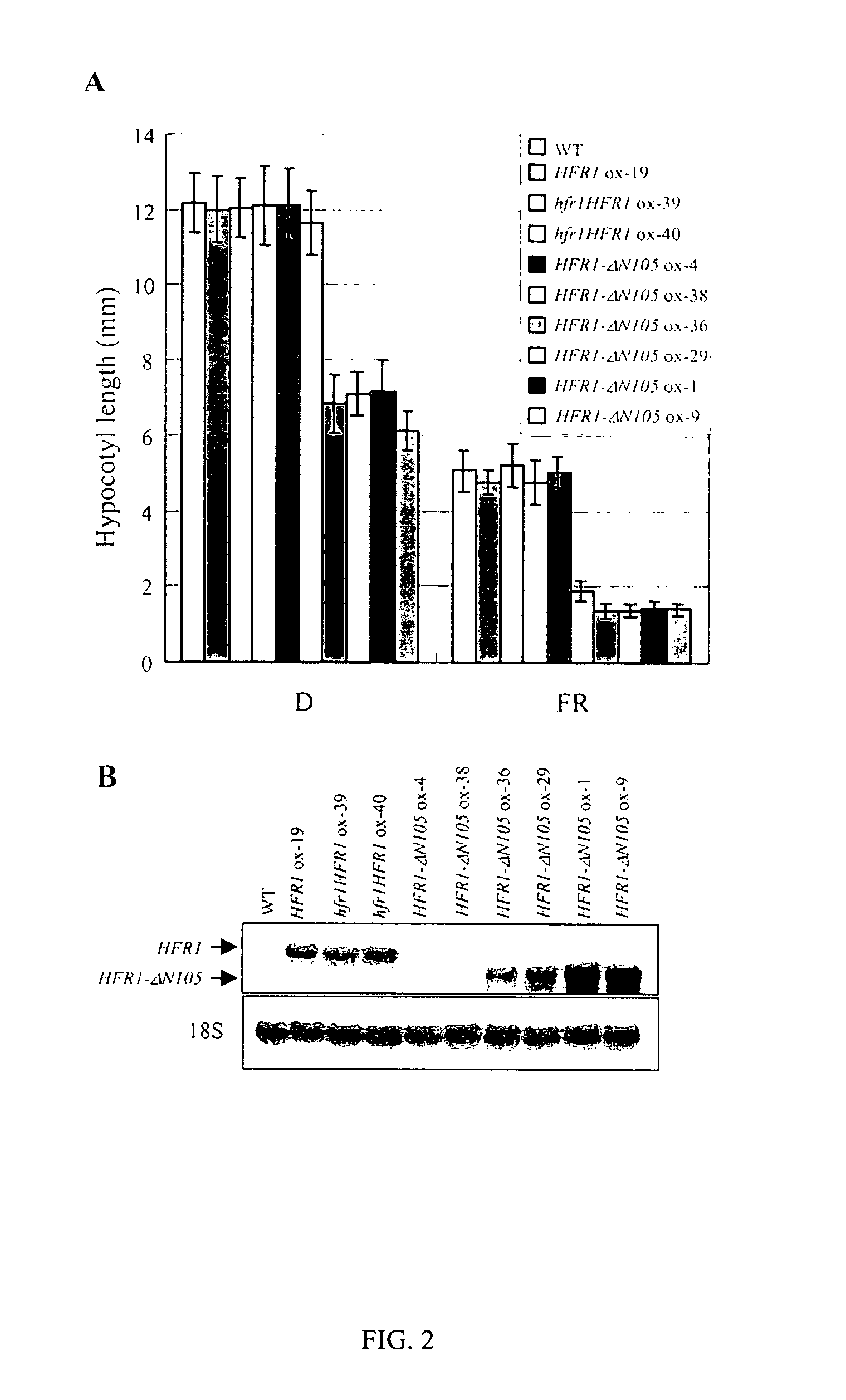
Hyperactive light signal related molecule of HFR1-deltaN105 and transgenic plant thereof
ActiveUS20050039225A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesHypocotylTransgene
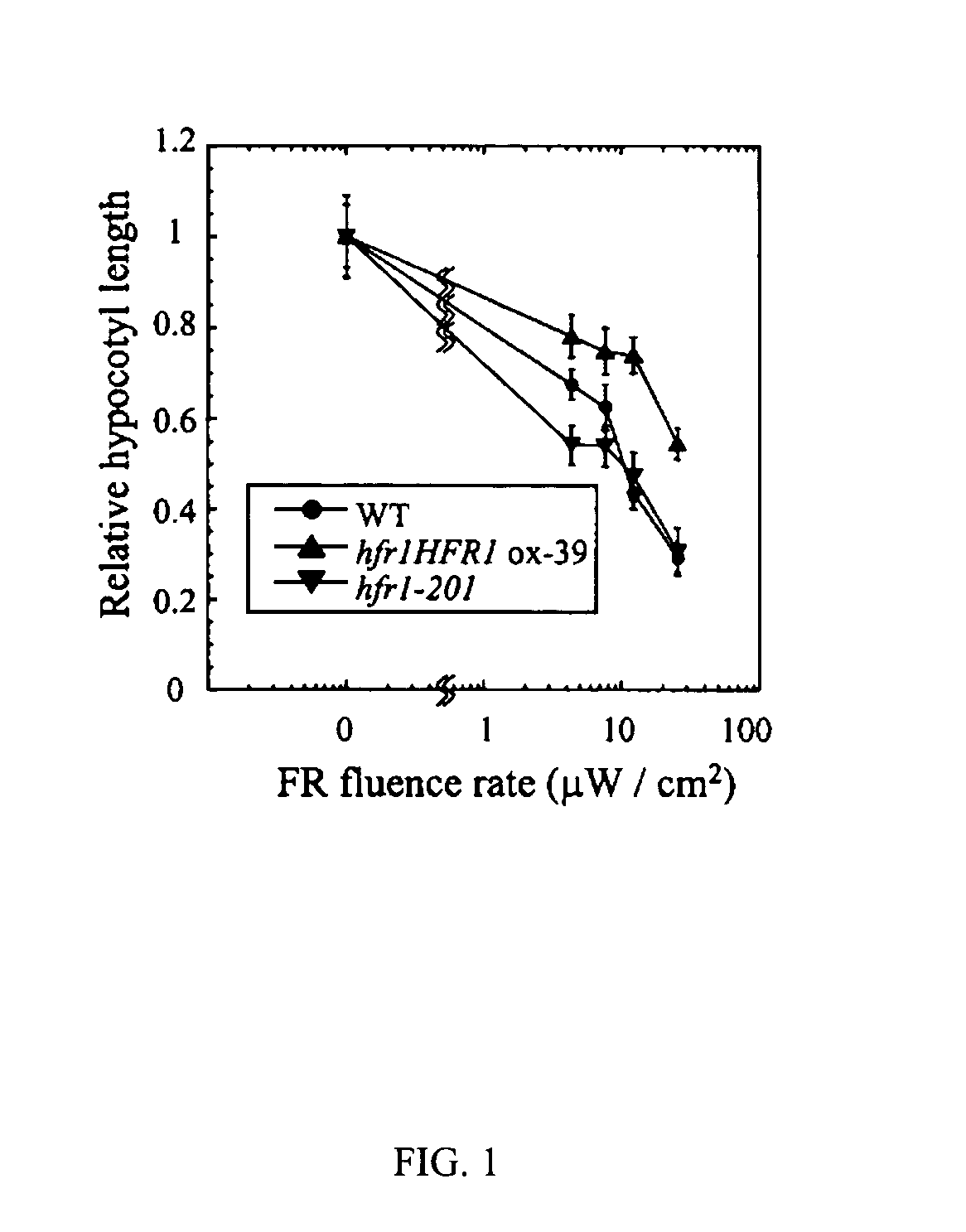
This invention is about the functionally hyperactive light signal related molecule, HFR1-ΔN105, of which the nucleic acids that encode N-terminal 105 amino acid residues were deleted. HFR1 as a bHLH transcription factor functions in a subset of phytochrome A signaling cascade and it was reported to be regulated negatively by COP1. Experiments with a HFR1-ΔN105 overexpressing plant revealed that the deletion of N-terminal amino acids makes the HFR1 more active in photomorphogenic development such as germination and de-etiolation. In addition, the transgenic plants showed hypersensitive photo-responses in the inhibition of hypocotyl elongation, dependently on another positive element of light signaling, a bZIP protein, HY5. The end-of-day far-red light response and petiole elongation were suppressed in the HFR1-ΔN105 overexpressing plants. These results suggest that N-terminal region of HFR1 negatively regulate HFR1 function and that HFR1-ΔN105 is hyperactive.
Owner:KOREA KUMHO PETROCHEMICAL CO LTD
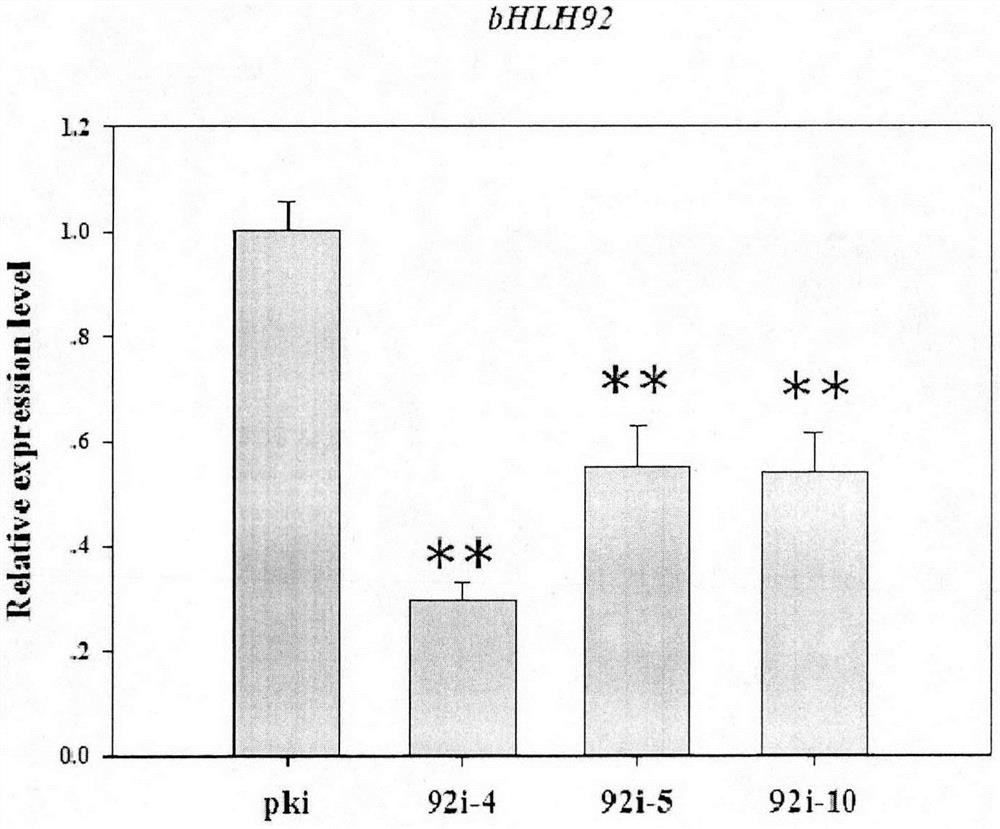
SmbHLH92 gene cloning primer, expression vector, function of regulating salvianolic acid biosynthesis and application
The invention discloses an encoding gene sequence of a Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge bHLH transcription factor SmbHLH92 for regulating and controlling salvianolic acid synthesis. The gene SmbHLH92 provided by the invention has a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.1, and protein encoded by the gene has an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.2. A subcellular localization experiment shows that the SmbHLH92 is localized in a cell nucleus. An SmbHLH92-RNAi vector is constructed, Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge is subjected to genetic transformation, transgenic hairy roots are obtained, and compared with a reference strain (a strain obtained by transforming an RNAi empty vector), the SmbHLH92-RNAi strain has the advantage that the content of four phenolic acid components in the SmbHLH92-RNAistrain is remarkably increased. A real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR result shows that the expression quantity of a key enzyme gene in a salvianolic acid pathway is remarkably increased in the SmbHLH92-RNAi strain. The SmbHLH92 provided by the invention has a function of negatively regulating and controlling the biosynthesis of salvianolic acid compounds, and the compounds show outstanding curative effects in the aspect of treating cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. The invention provides a new research thought for increasing the content of the salvianolic acid compounds by utilizing genetic engineering, and provides a target gene for developing excellent variety breeding of the Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Clam DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) binding inhibitor mmID2 genes as well as encoding proteins and application thereof
InactiveCN103849624APromote proliferationInhibition of DifferentiationVertebrate cellsArtificial cell constructsNucleotideFactor ii
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology and in particular relates to clam DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) binding inhibitor mmID2 genes as well as encoding proteins and application thereof. The cRNA sequence of the clam mmID2 is shown as a nucleotide sequence shown in a sequence table SEQ ID No.1. The clam CDNA is amplified to total cRNA sequence 1017bp of the mmID2 by utilizing the clam EST sequence information, wherein the complete reading frame is 351bp and complete coding proteins contain 116 amino acids and have a typical basic helix-loop-helix (helix-loop-helix, HLH) structure. The mmID2 protein has an obvious effect on proliferation of animal cells. The mmID2 has wide application prospects in aspects of promoting cell proliferation and inhibiting cell differentiation and can serve as a growth addition factor for promoting shellfish cell proliferation to be used for establishing a cell culture system.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
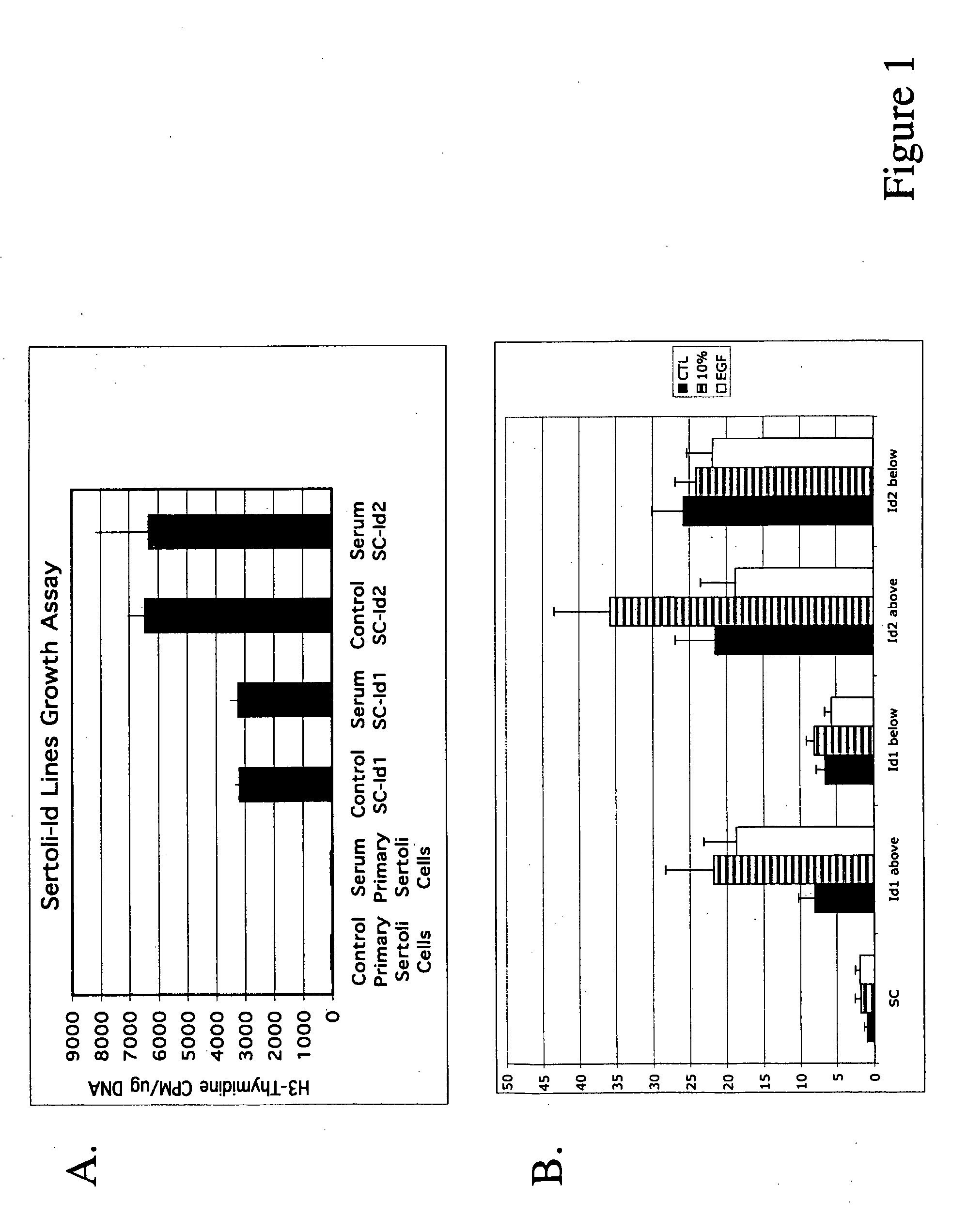
Modified Cells Expressing a Protein That Modulates Activity of Bhlh Proteins, and Uses Thereof
The present invention relates to modified cells carrying a heterologous gene sequence encoding a protein, such as an Inhibitor of differentiation (Id) gene sequence that binds a basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) protein to inhibit cell growth, differentiation and / or tumorigenesis of the modified cells. The modified cells are differentiated, proliferate and do not become tumorigenic when grafted into a recipient subject. Additionally, the modified cells produce a factor or factors that enhance the viability of co-grafted organs, tissues or cells. Thus, the modified cells are useful for testing agents for effects on the cells, for co-grafting with transplant organs, tissues or cells. The modified cells are also useful for enhancing the viability of thawing cells that have been cryo-preserved. In one embodiment, the modified cells are modified Sertoli cells.
Owner:WASHINGTON STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
Hyperactive light signal related molecule of HFR1-DeltaN105 and transgenic plant thereof
Owner:KOREA KUMHO PETROCHEMICAL CO LTD
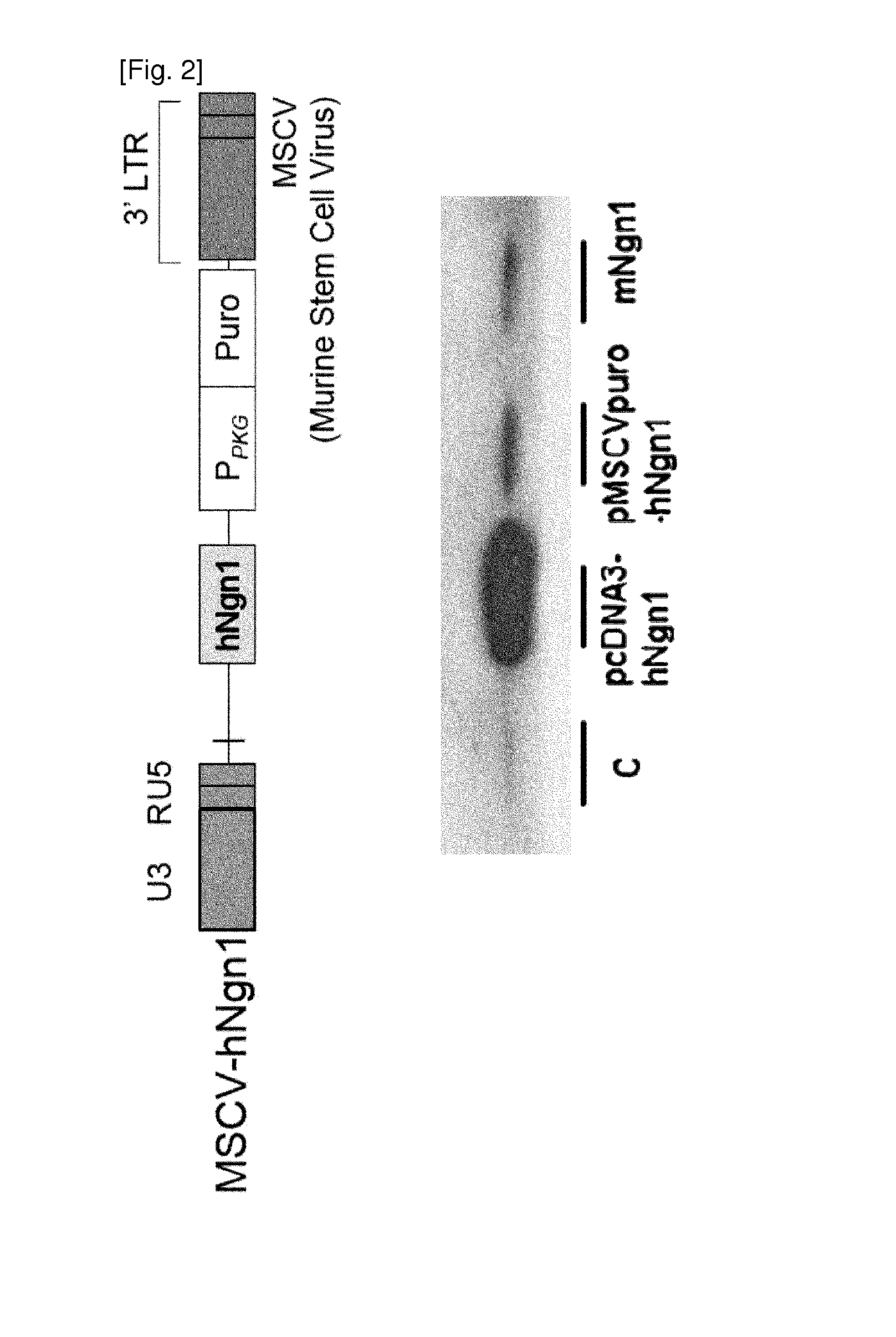
Adult stem cell line introduced with hepatocyte growth factor gene and neurogenic transcription factor gene with basic helix-loop-helix motif and uses thereof
The present invention relates to an adult stem cell line introduced with an HGF gene and a neurogenic transcription factor gene of a bHLH family, a preparation method of the adult stem cell line, a composition for the prevention or treatment of neurological diseases comprising the adult stem cell line, and a method for treating neurological diseases comprising the step of administering the composition to a subject having neurological diseases or suspected of having neurological diseases. The adult stem cells according to the present invention, which are introduced with an HGF gene and a neurogenic transcription factor gene of a bHLH family, can be used to overcome chronic impairment caused by cell death following stroke. Thus, the adult stem cells can be developed as a novel therapeutic agent or widely used in clinical trial and research for cell replacement therapy and gene therapy that are applicable to neurological diseases including Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer disease, and spinal cord injury as well as stroke.
Owner:CELL & BRAIN CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com