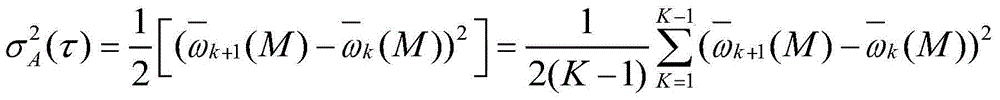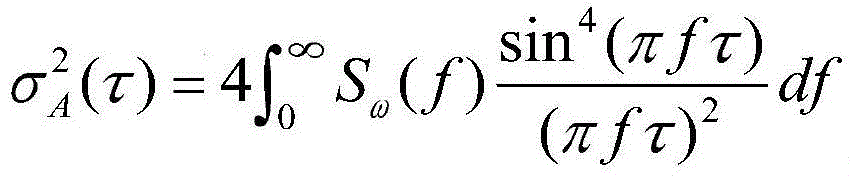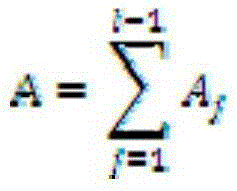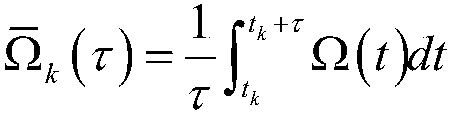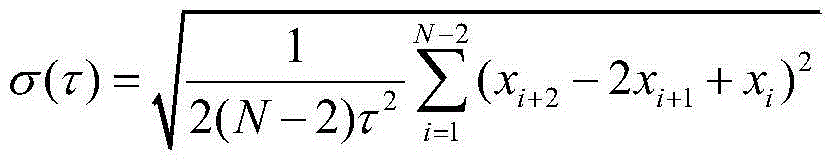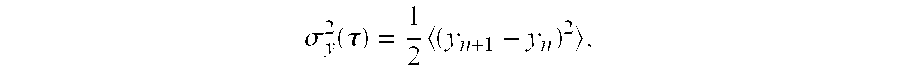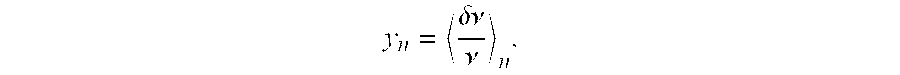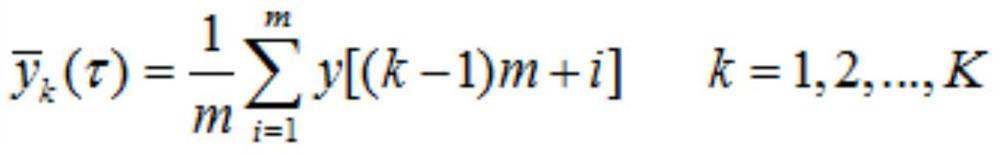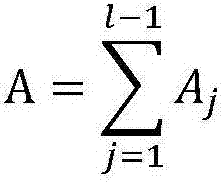Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
46 results about "Allan variance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
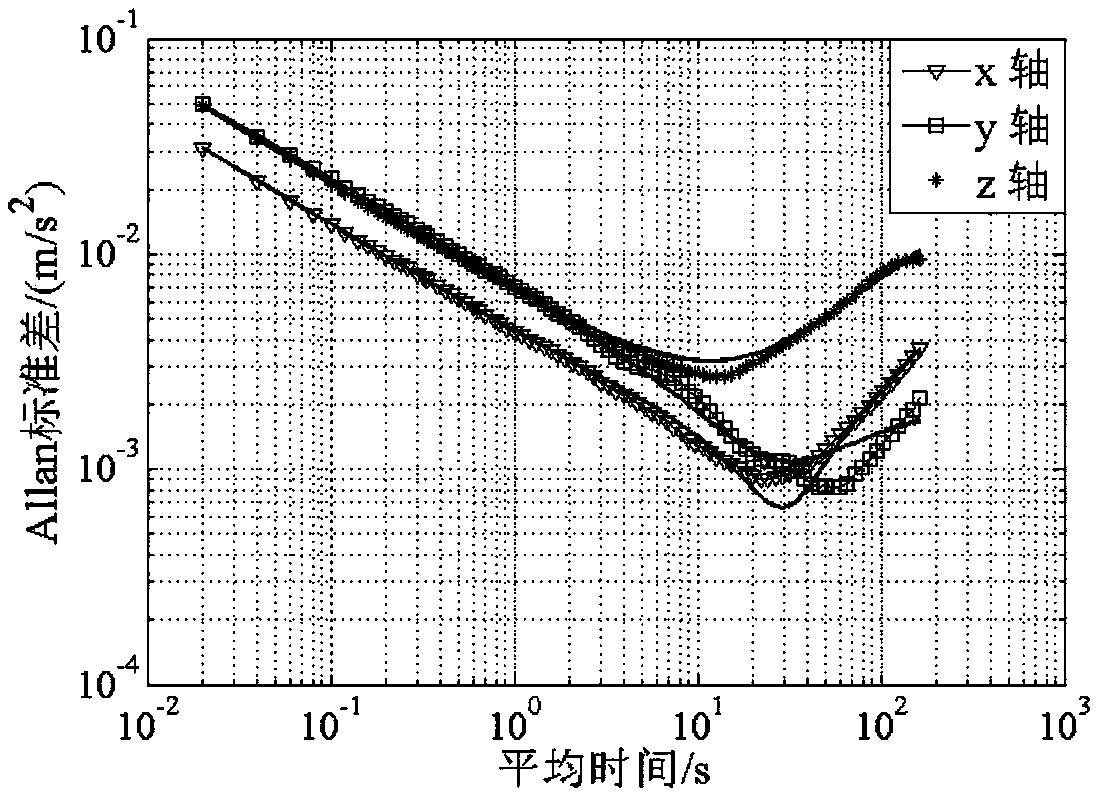
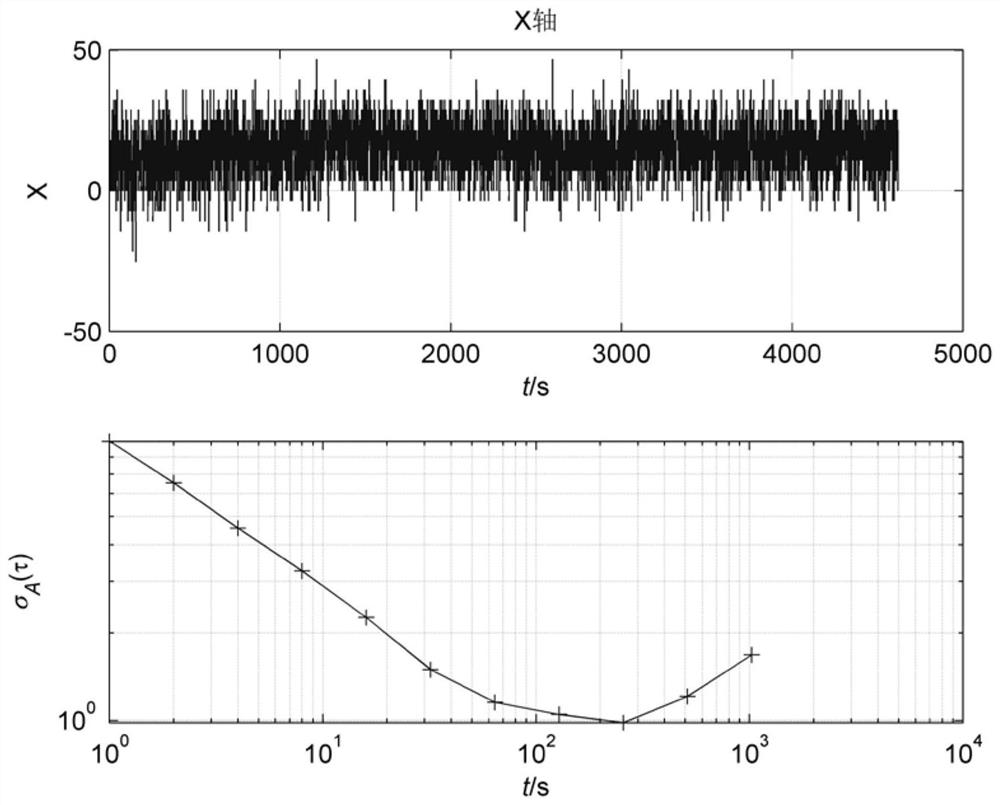
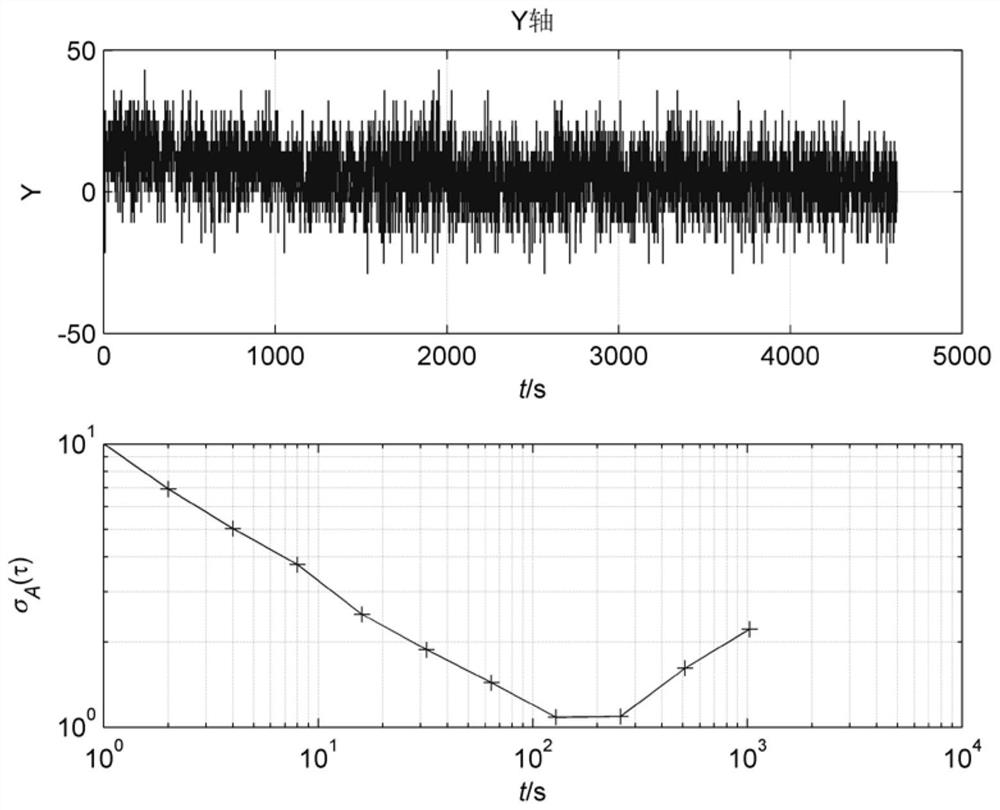
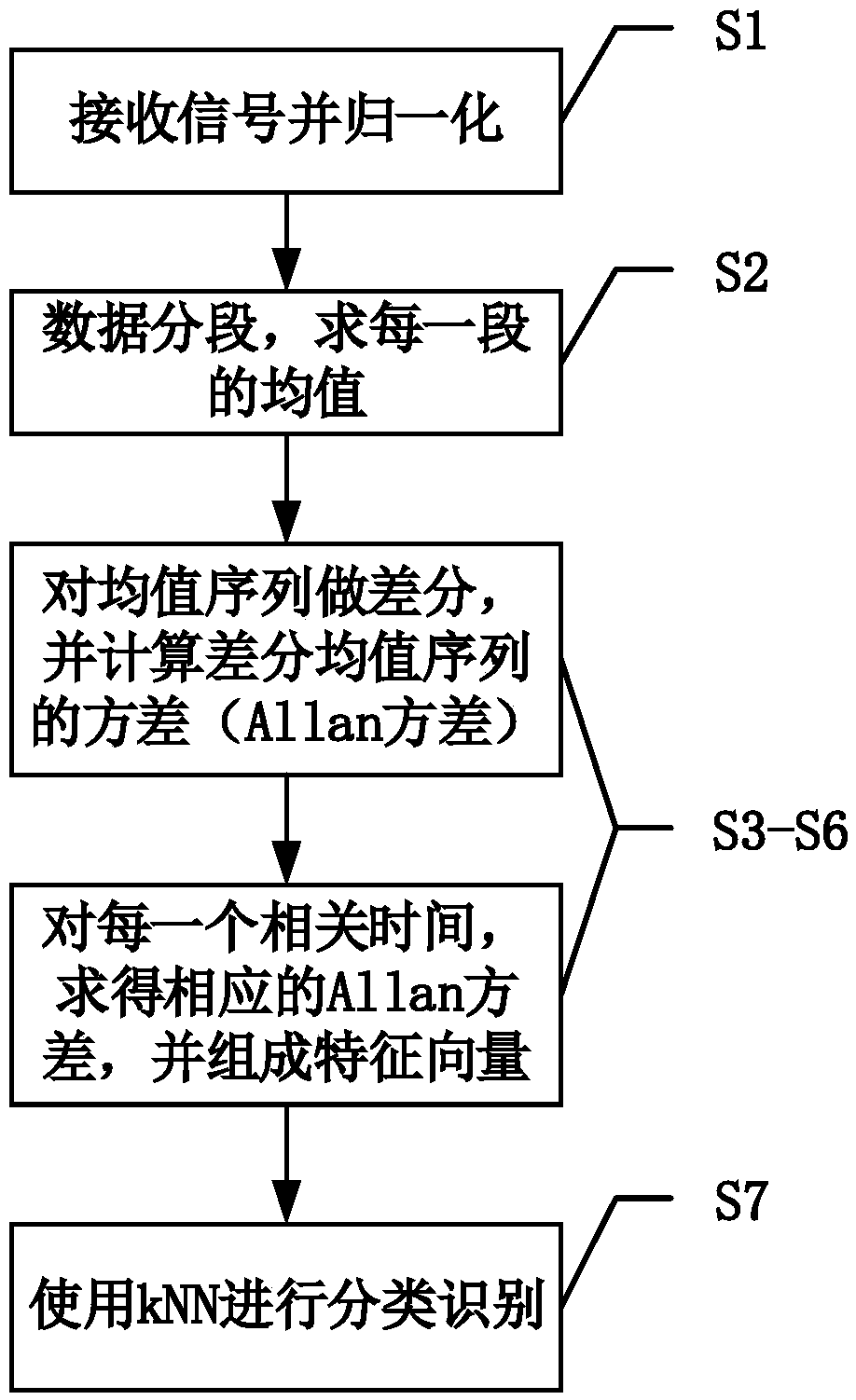
The Allan variance (AVAR), also known as two-sample variance, is a measure of frequency stability in clocks, oscillators and amplifiers, named after David W. Allan and expressed mathematically as σy²(τ). The Allan deviation (ADEV), also known as sigma-tau, is the square root of the Allan variance, σy(τ). The M-sample variance is a measure of frequency stability using M samples, time T between measures and observation time τ.
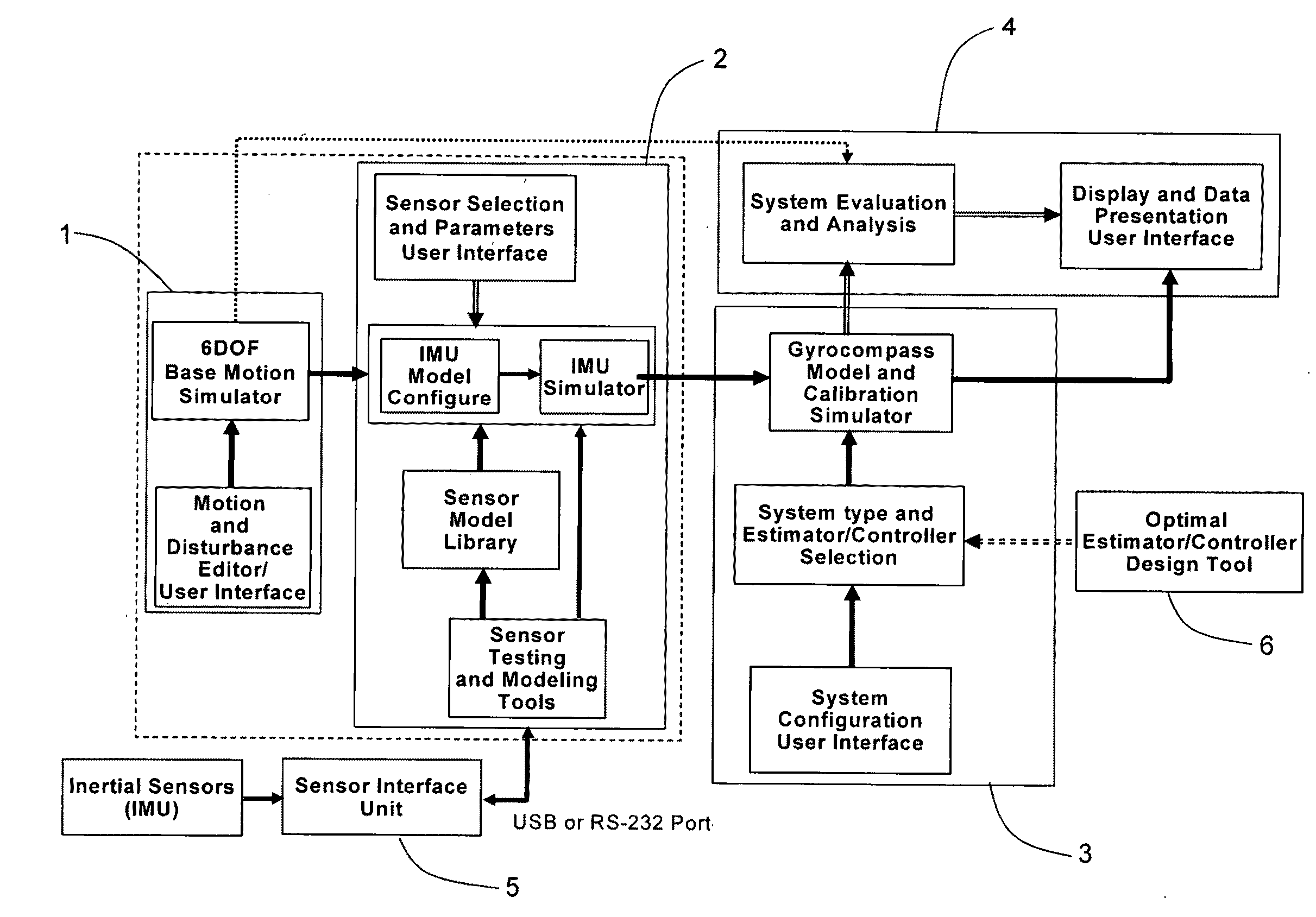
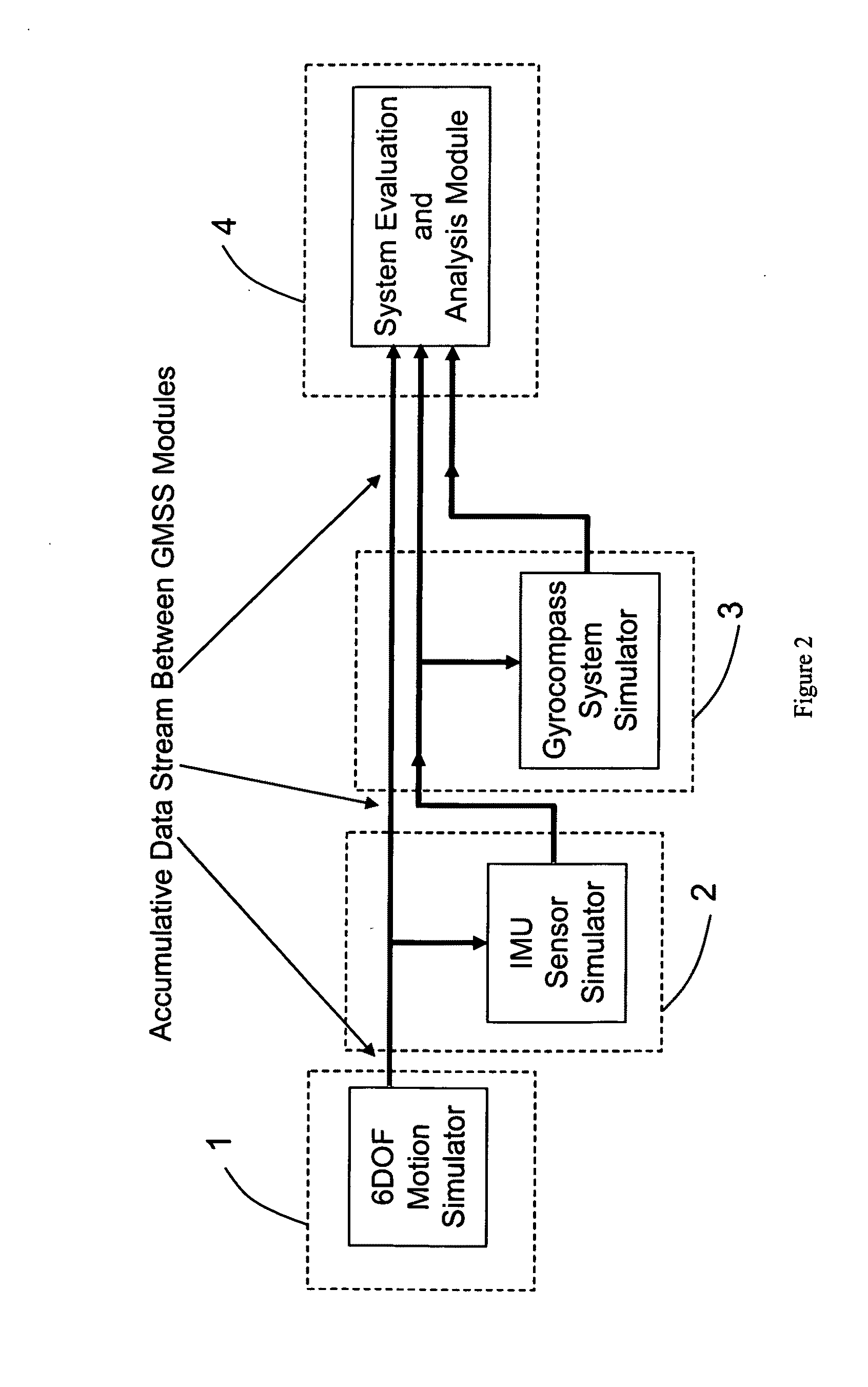
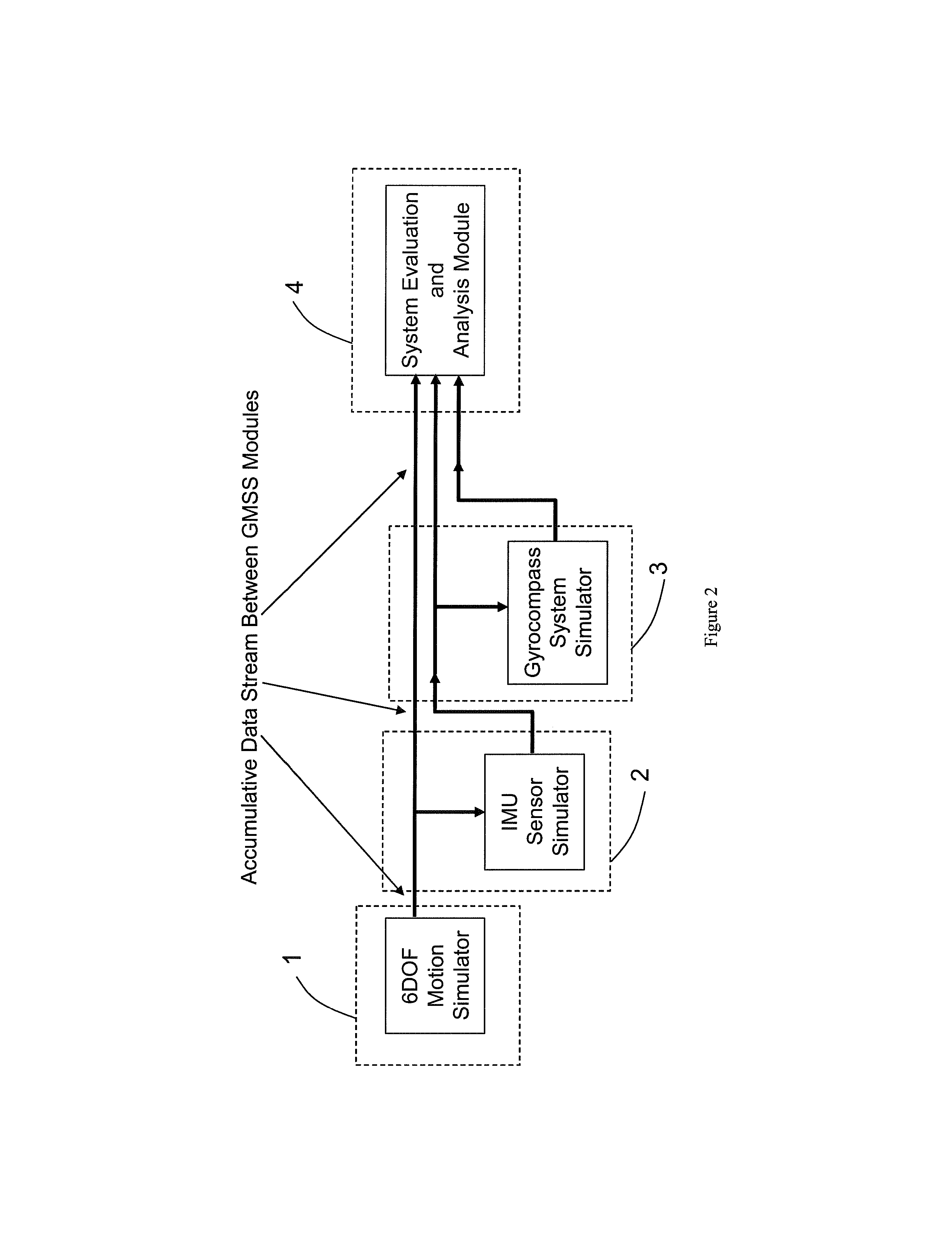
Gyrocompass modeling and simulation system (GMSS) and method thereof
ActiveUS20110093250A1Flexible for programming and testingAvoid spendingGeometric CADRotary gyroscopesStatistical analysisSoftware system
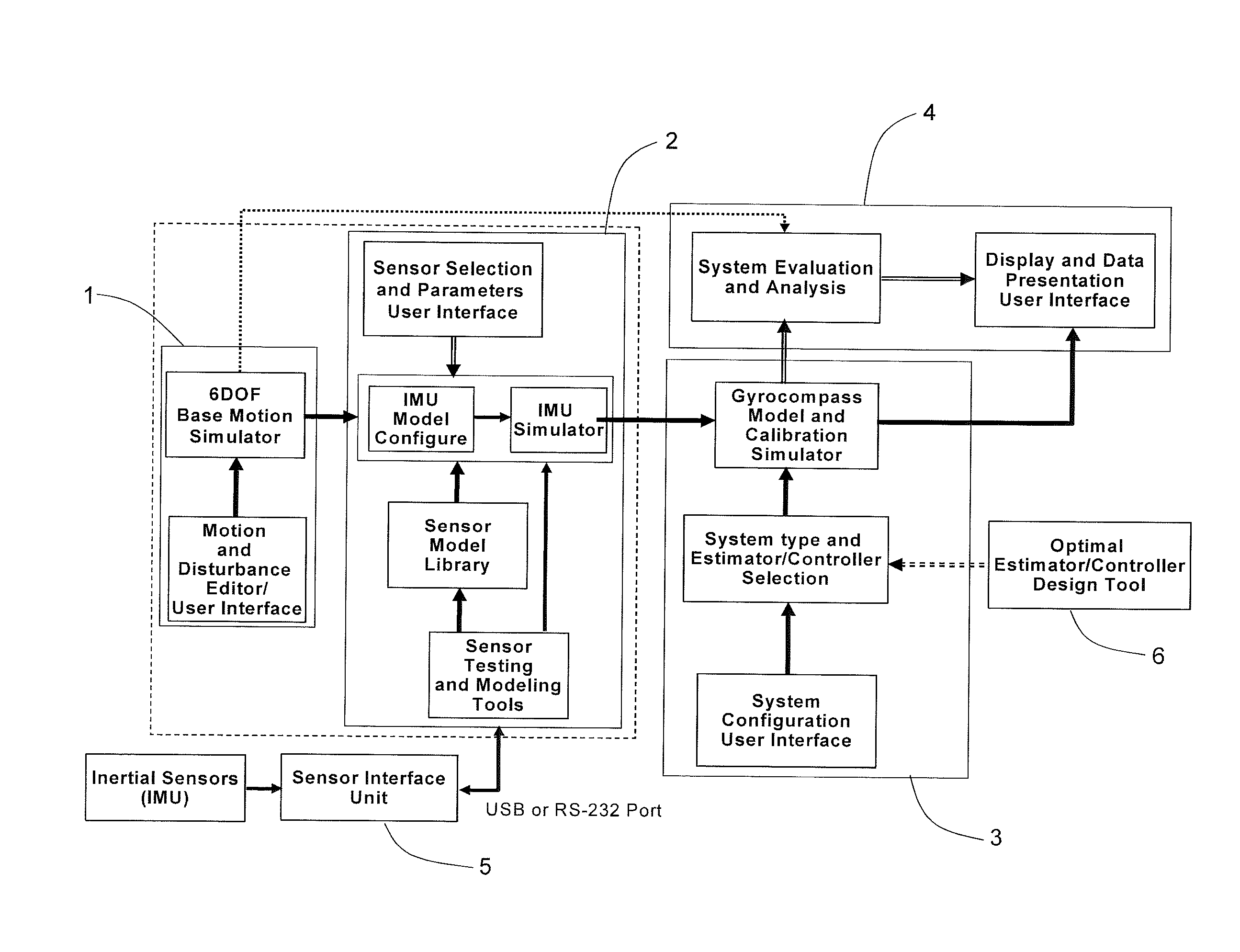
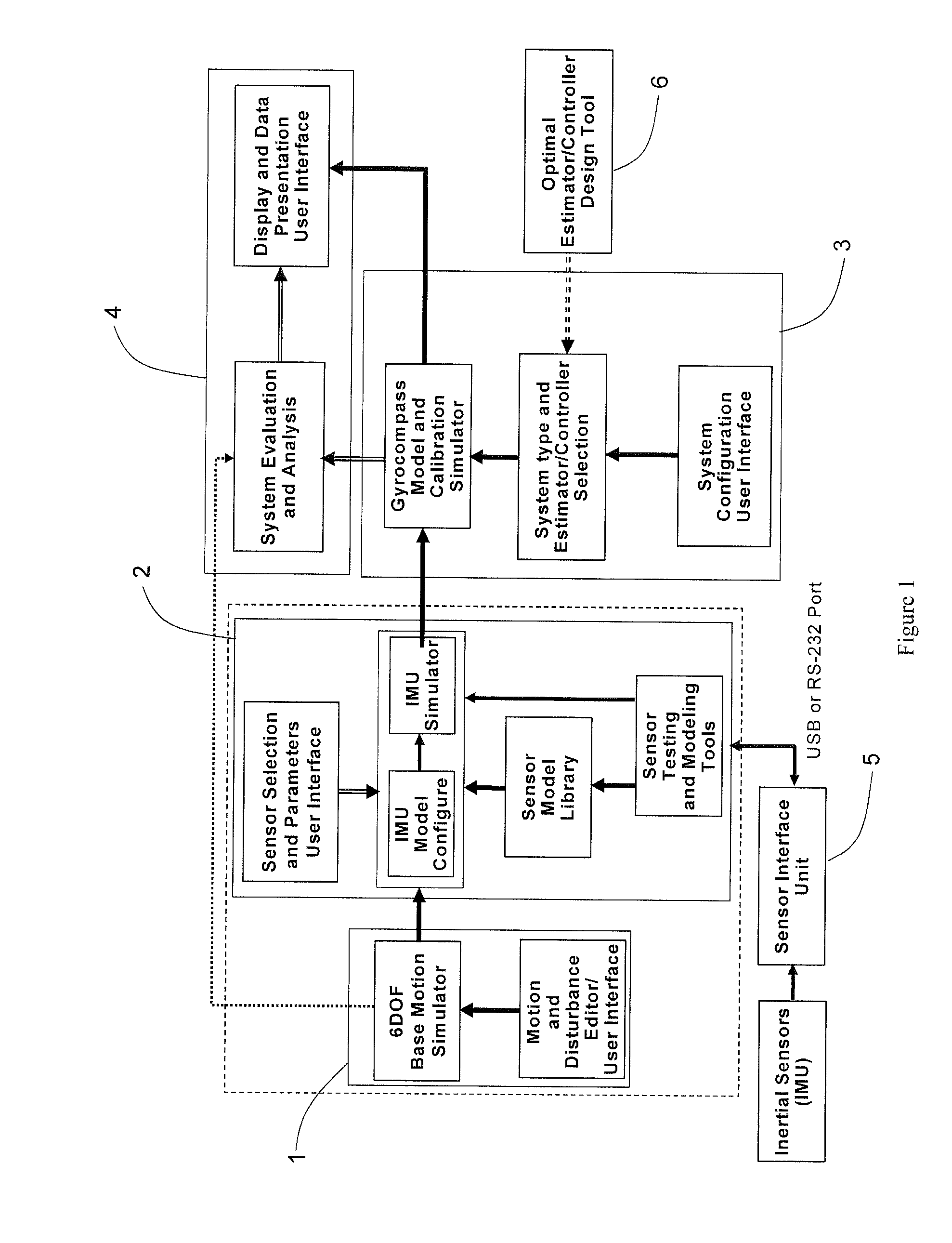
A Modeling, Design, Analysis, Simulation, and Evaluation (MDASE) aspects of gyrocompassing in relation to Far-Target Location (FTL) systems include a Gyrocompass Modeling and Simulation System (GMSS). The GMSS is a modularized software system which has four major components: the 6DOF Motion Simulator, the IMU Sensor Simulator, the Gyrocompass System and Calibration Process Simulator, the Gyrocompass System Evaluation and Analysis Module. Each module has one or two graphic user interfaces (GUIs) as user interfaces for simulation components selection and parameter setting. The modular architecture of GMSS makes it very flexible for programming and testing. And, the component-based software development technology greatly eases system extension and maintenance. The simulators can be used as either an off-line tool or as a real-time simulation tool. The realization of the GMSS can be based on any computer platforms, for it is written in high level language and tools and is portable. The stochastic signal analysis and sensor testing and modeling tools comprise a suite of generic statistical analysis software, including Allan Variance and PSD analysis tools, which are available to every GMSS module and greatly enhanced the system functionality.
Owner:AMERICAN GNC
High-resolution transient frequency stability measuring method
ActiveCN103472299AShort response timeHigh resolutionFrequency measurement arrangementFrequency stabilizationPhase difference
The invention provides a high-resolution transient frequency stability measuring method. The method comprises: first of all, the phase difference value between a reference signal and a detected signal is measured and adjusted so as to enable the value to be stabilized at the edge of a superposed detection resolution, if there are no effects of noise, the continuous detection of superposed information can be maintained, however, if there is signal noise, the phase difference change between the signals is between the inside of an edge and the outside of the edge, and the presence of phase superposed information remains variable, therefore, the phase instability degrees of the signals can be determined according to the continuity and interruption situations of the superposed information, and by detecting the change amount of the phase difference between the signals before and after a sampling time, the transient stabilization degree of a frequency source can be calculated through a formula derived from the Allan variance calculation formula.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Measurement Device and Method for Measuring
ActiveUS20140005975A1Accurate estimateAcceleration measurement using interia forcesDigital computer detailsMeasurement deviceEngineering
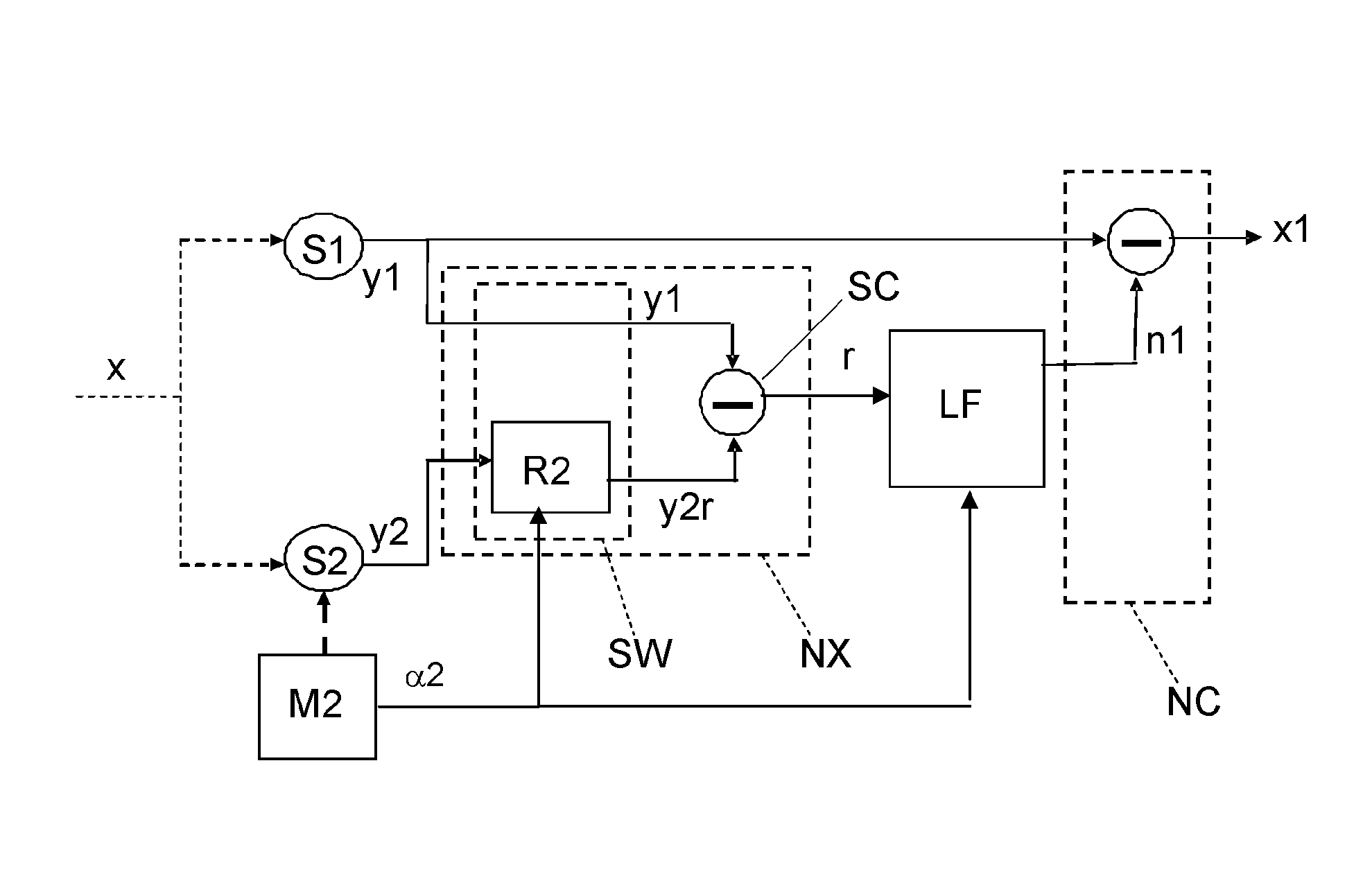
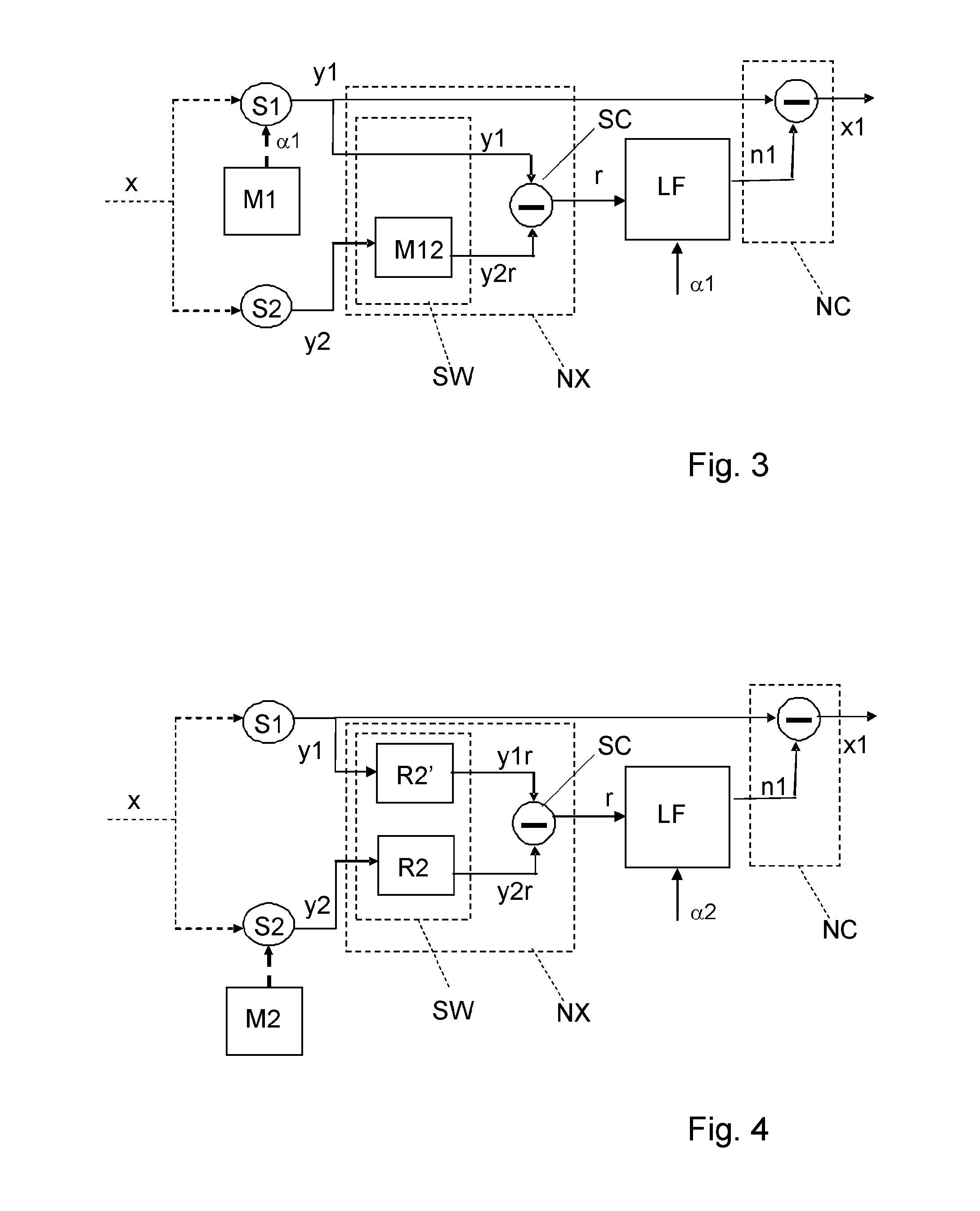
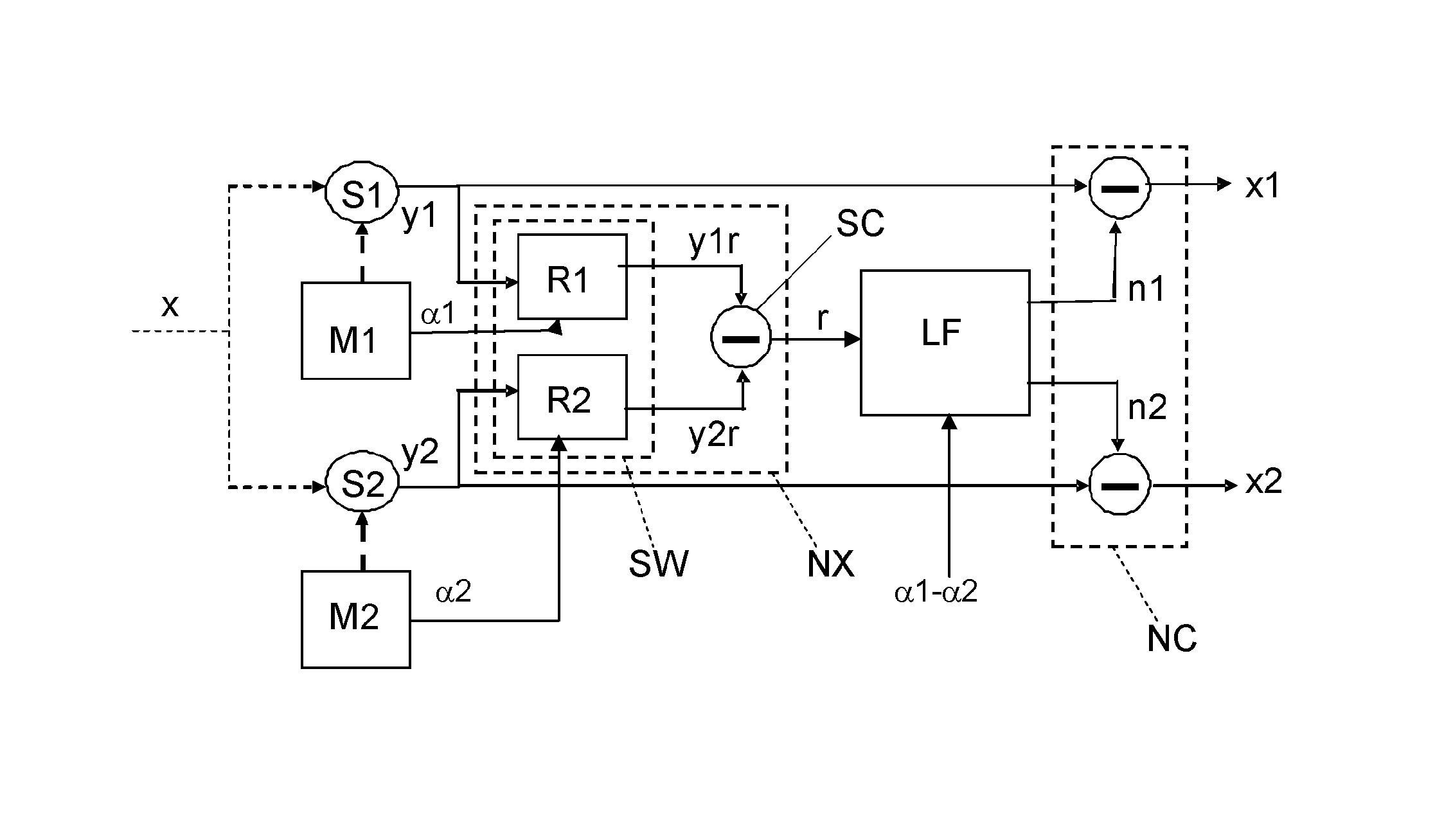
A measuring device is disclosed for measuring a vectorial physical quantity (x), comprising a first and a second sensor (S1, S2), an actuator (M2), a noise extraction unit (NX) and a low frequency noise estimator (LF). The first and a second sensor (S1, S2) are arranged for measuring a component of the vectorial physical quantity (x), and for generating a respective sense signal (y1, y2). The sensors have an Allan variance curve with a minimum value for a particular integration time Tmin, said Allan variance curve having a first tangent line to a portion of the curve for which the integration time approaches 0, and having a second, horizontal, tangent line of constant standard deviation corresponding to said Allan minimum value, said first and said second tangent line having an intersection point for a second particular integration time. The low frequency noise estimator (LF) estimates a low frequency noise component from the difference signal (r) and from information about the relative rotation (a) between the sensors and generates an estimated noise signal (n1) indicative for the estimated value of said noise component. The low frequency noise estimator has an effective integration time that is at least two times a sample time with which the sense signals are obtained, which effective integration time is less than the smallest particular integration time of the sensors comprised in the measuring device and which effective integration time is at most two times said second integration time.
Owner:NEDERLANDSE ORG VOOR TOEGEPAST-NATUURWETENSCHAPPELIJK ONDERZOEK (TNO)
Method for setting random error parameter of fiber gyroscope simulated signal
InactiveCN103033198AImprove reliabilityIncrease authenticityMeasurement devicesGyroscopeSingle fiber
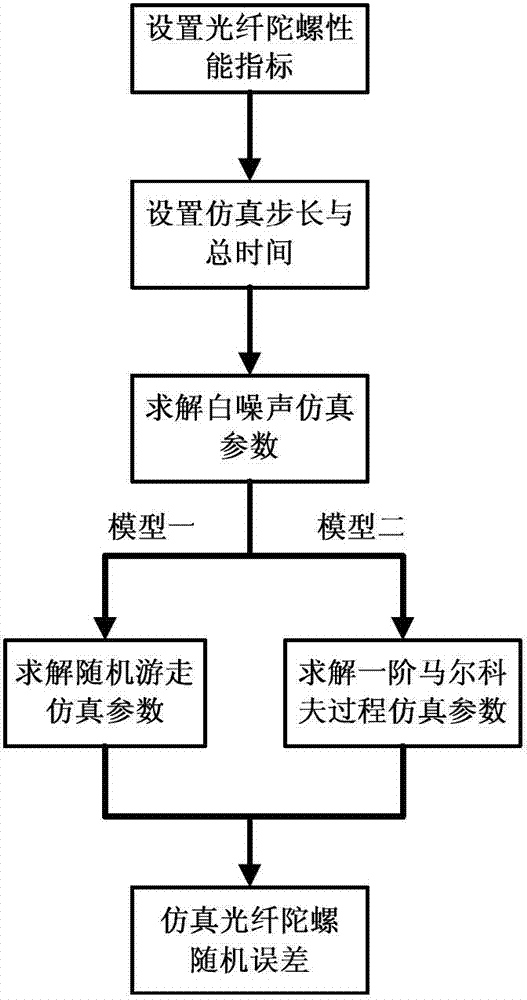
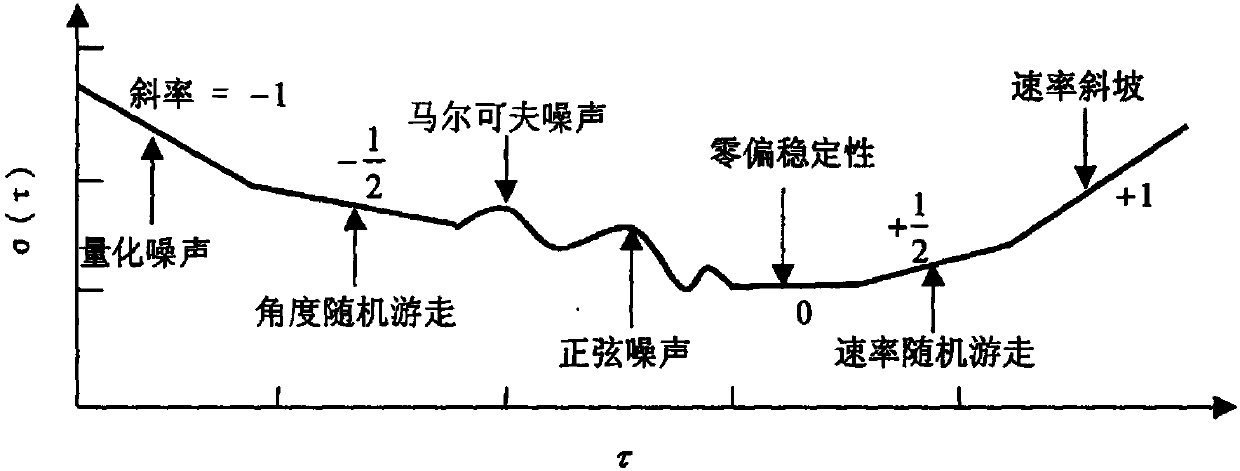
The invention discloses a method for setting a random error parameter in the signal simulation process of a fiber gyroscope. The method is used for solving and setting a random error model parameter in signal simulation by utilizing the performance index of the fiber gyroscope. In the method, the performance index of the fiber gyroscope adopts angle random walk and zero bias stability. The random error model of the simulated signal adopts two schemes comprising a white noise and random walk superposed mode and a white noise and first-order Markoff process superposed mode. The fiber gyroscope signal simulated by the method can reflect the characteristics of the fiber gyroscope with certain precision grade well, and has high reliability and authenticity. The method is used for deducing and setting the random error model parameter in the simulation by utilizing the performance index of the fiber gyroscope, so that the performance of the simulated fiber gyroscope signal is fit with the preset index. The random error model parameter obtained according to ALLAN variance analysis or ARMA modeling analysis only can reflect the random error characteristic of single fiber gyroscope, but the parameter obtained by the method can reflect the random error characteristic of fiber gyroscopes with the same kind, thus having universality.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Measurement device and method for measuring
ActiveUS9441966B2Accurate estimateAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSurveying instrumentsMeasurement deviceEngineering
Owner:NEDERLANDSE ORG VOOR TOEGEPAST NATUURWETENSCHAPPELIJK ONDERZOEK TNO
Data optimization processing method for star sensor
ActiveCN106289238AImprove signal-to-noise ratioEliminate noise errorsNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Filtration
The invention provides a data optimization processing method for a star sensor, and belongs to the technical field of a data optimization processing method. The method can be used for treating data measured by a star sensor and improving the stability and precision of the output attitude of the star sensor. The method mainly used for improved transition, extraction, interpolation and filtration of data measured by the star sensor, optimization processing of data output by the star sensor through a wavelet analysis method using Allan variance fusion, and improvement of the stability and precision of the output attitude of the star sensor. The method has main advantages that: 1) outliers can be accurately removed, and the error redundancy is improved; 2) the low-frequency tendency is smoothed and eliminated and the anti-interference performance is improved; 3) data is kept continuous and evenly spaced, and the stability of the output attitude is improved; 4) noise of internal work and observation environment is inhibited, and the signal-to-noise ratio is effectively increased; and 5) the precision of the output attitude information of the star sensor is improved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Allan variance analysis method of blending genetic algorithm
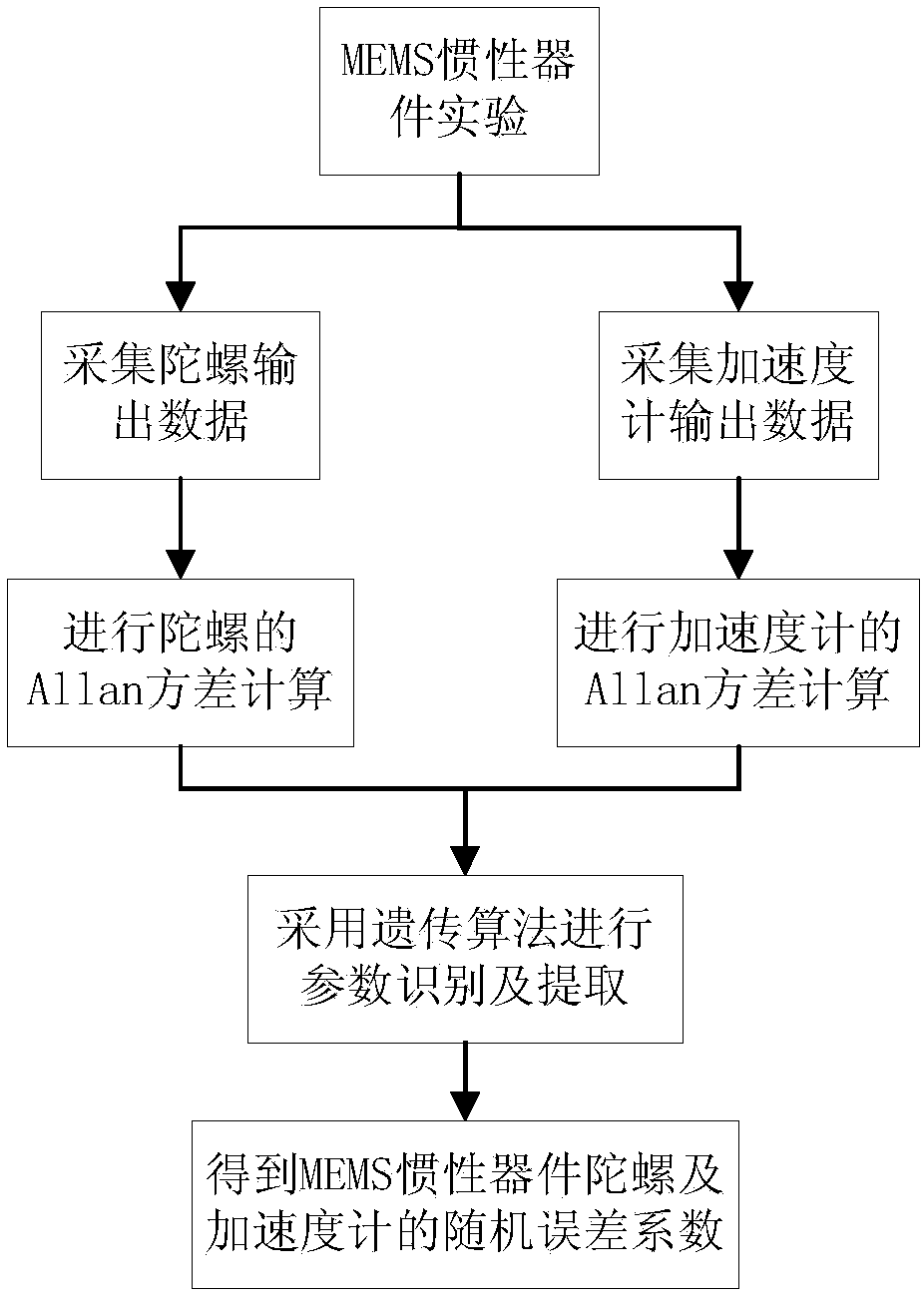
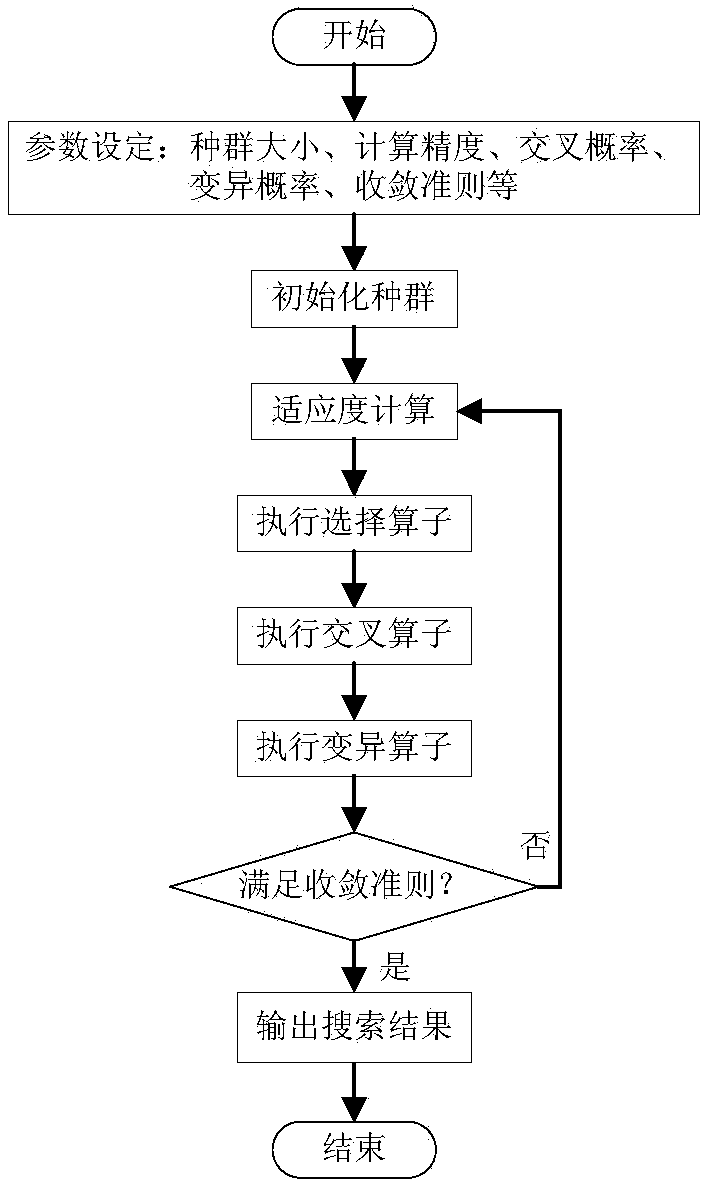
The invention discloses an Allan variance analysis method of a blending genetic algorithm. The method comprises the following steps: establishing an equivalent model between each random error term andthe Allan variance, respectively collecting three-axis angular rates and three-axis acceleration information output by a MEMS gyroscope and an accelerometer under the horizontal and static condition;orderly performing Allan variance computation on the MEMS gyroscope and the accelerometer according to the collected angular rates and the acceleration information, thereby obtaining a numerical value corresponding relation between the Allan variance and the related time T; performing data fitting by using a genetic algorithm to determine various coefficient values in a model, thereby realizing the identification and extraction of the random error term.
Owner:NAVAL UNIV OF ENG PLA
MEMS accelerometer error compensation method based on LMS adaptive filtering and gradient descent
ActiveCN109631889AHandling random noiseTake advantage ofNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAdaptive filtering algorithmAccelerometer
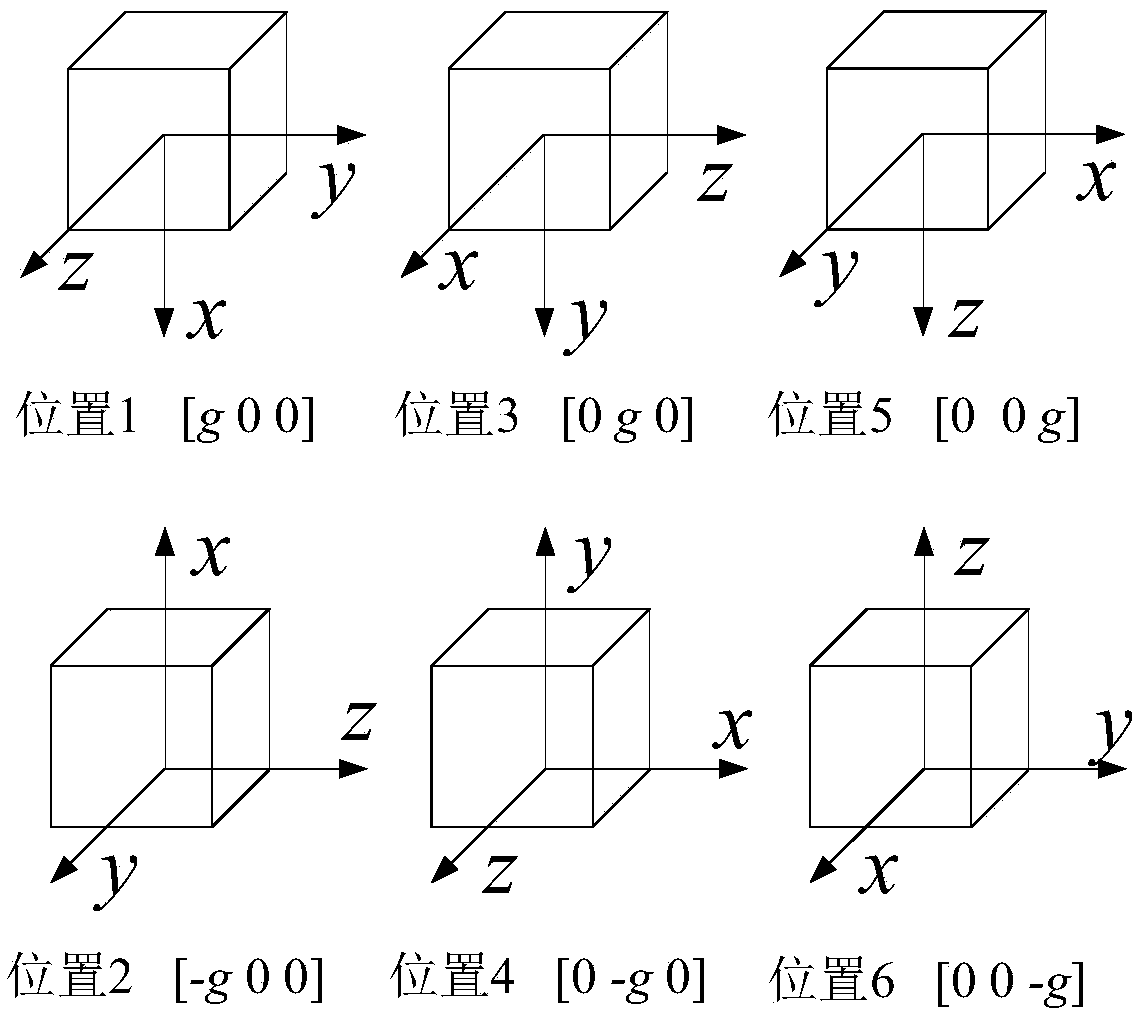
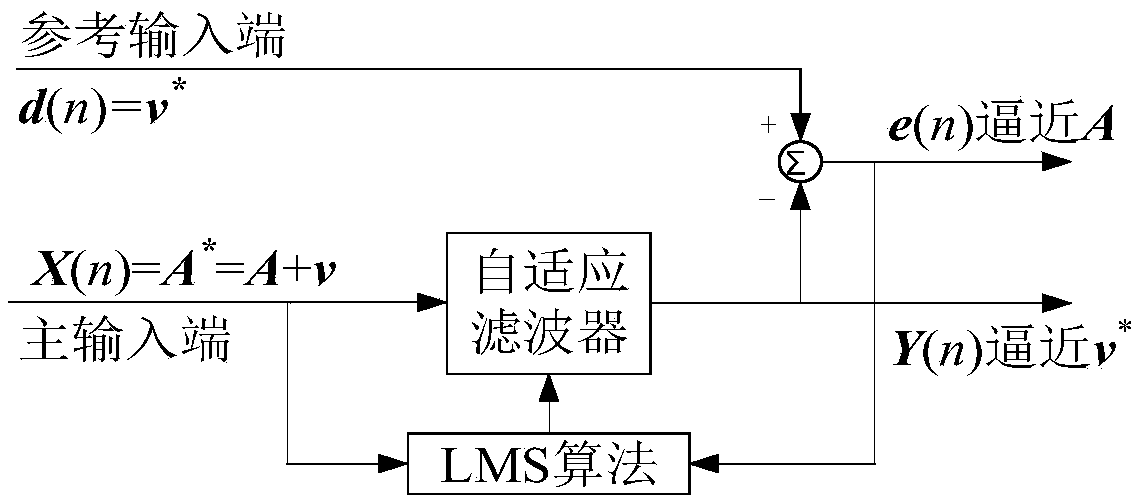
The invention claims for protection of an MEMS accelerometer error compensation method based on LMS adaptive filtering and gradient descent. An MEMS accelerometer error compensation model with a measured value as an input and a true value as an output is established; random noises in actually measured data of the MEMS accelerometer at six positions are analyzed and processed by using an Allan variance and an LMS adaptive filtering algorithm; model parameters are trained by using all processed measurement data as samples; parameter prior values are calculated by using least squares to obtain aninitial value of batch gradient descent; training is carried out to obtain optimal fitting of samples to true model parameters; and error compensation is carried out on the MEMS accelerometer by using the model. The experiments show that the mean value error of output values of the accelerometer is reduced by two magnitude orders after error compensation and the standard deviation is reduced by one order of magnitude. The MEMS accelerometer error compensation method can be applied to high-precision calibration of MEMS accelerometers in the micro inertial measurement unit (MIMU), so that the measurement accuracy and output stability of the accelerometer are improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
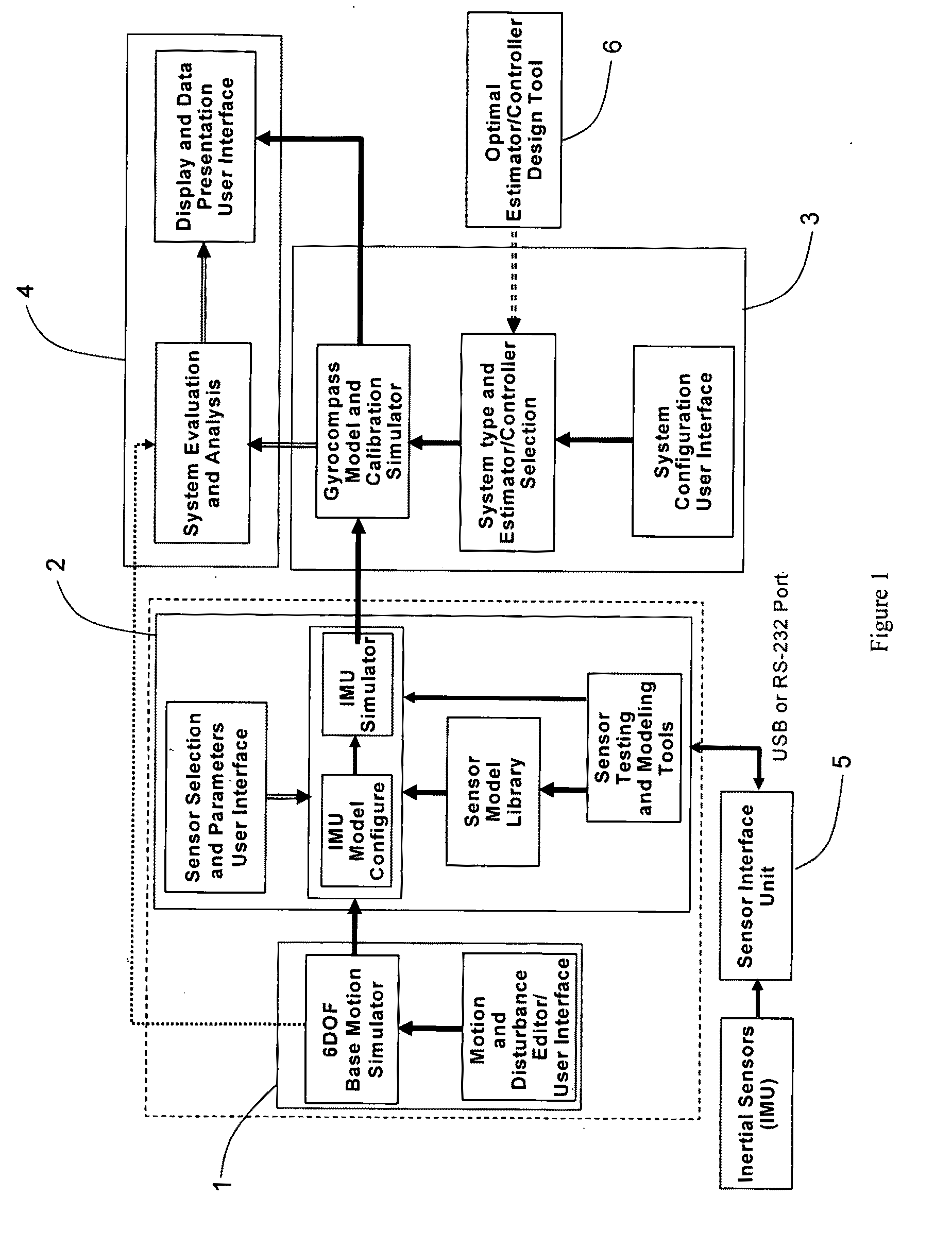
Gyrocompass Modeling and Simulation System (GMSS) and Method Thereof
ActiveUS20130179134A1Flexible for programming and testingAvoid spendingGeometric CADRotary gyroscopesStatistical analysisSystem maintenance
A Modeling, Design, Analysis, Simulation, and Evaluation (MDASE) aspects of gyrocompassing in relation to Far-Target Location (FTL) systems include a Gyrocompass Modeling and Simulation System (GMSS). The GMSS has four major components: the 6 degree-of-freedom (6DOF) Motion Simulator, the IMU Sensor Simulator, the Gyrocompass System and Calibration Process Simulator, and the Gyrocompass System Evaluation and Analysis Module. The modular architecture of GMSS makes it very flexible for programming, testing, and system maintenance. The realization of the GMSS can be based on any computer platforms for the GMSS software is written in high level language and is portable. The stochastic signal analysis and sensor testing and modeling tools comprise a suite of generic statistical analysis software, including Allan Variance and power spectral density (PSD) analysis tools, which are available to every GMSS module and greatly enhanced the system functionality.
Owner:AMERICAN GNC
MEMS gyro random drift error processing method
InactiveCN105021210AHigh precisionEfficient separationMeasurement devicesSpecial data processing applicationsGyroscopeError processing
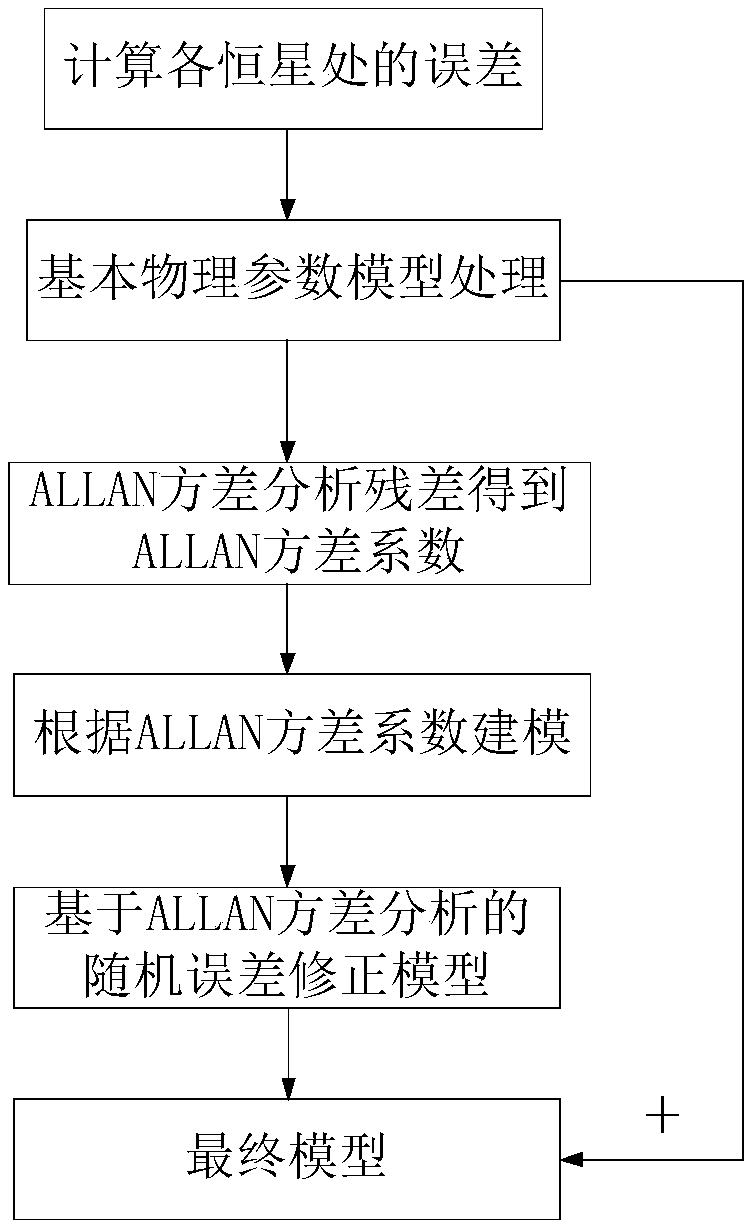
The invention discloses an MEMS gyro random drift error processing method which is characterized in that based on an existing MEMS gyro and at a signal processing back-end, measured data is analyzed by an Allan variance method, various main random error sources are effectively separated and magnitude of each error coefficient is determined; time-series modeling is conducted on the basis of checking and preprocessing the data; and finally, interference noise is effectively inhibited by multiple times of Kalman filtering processing so as to raise precision of the gyro.
Owner:苏州圣赛诺尔传感器技术有限公司
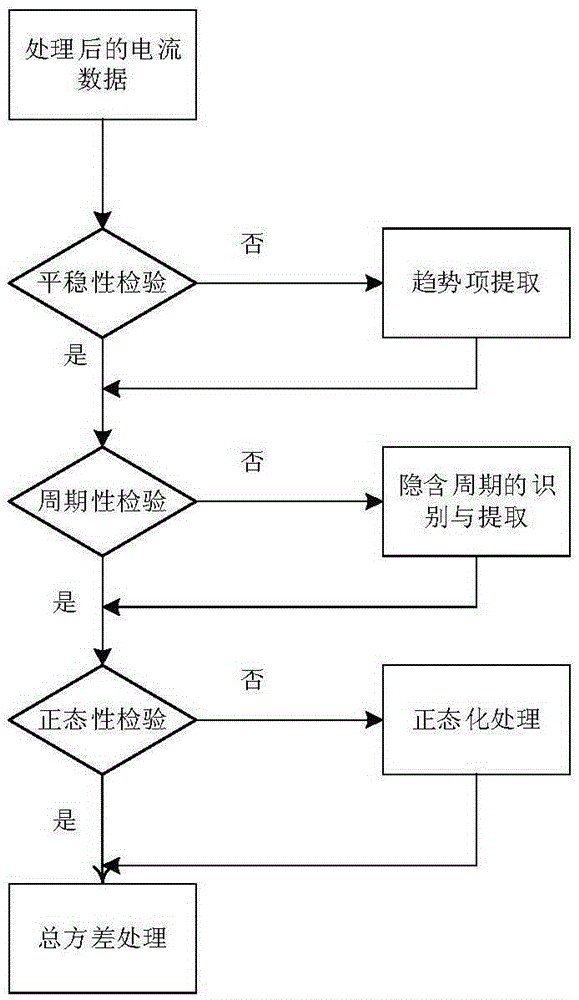
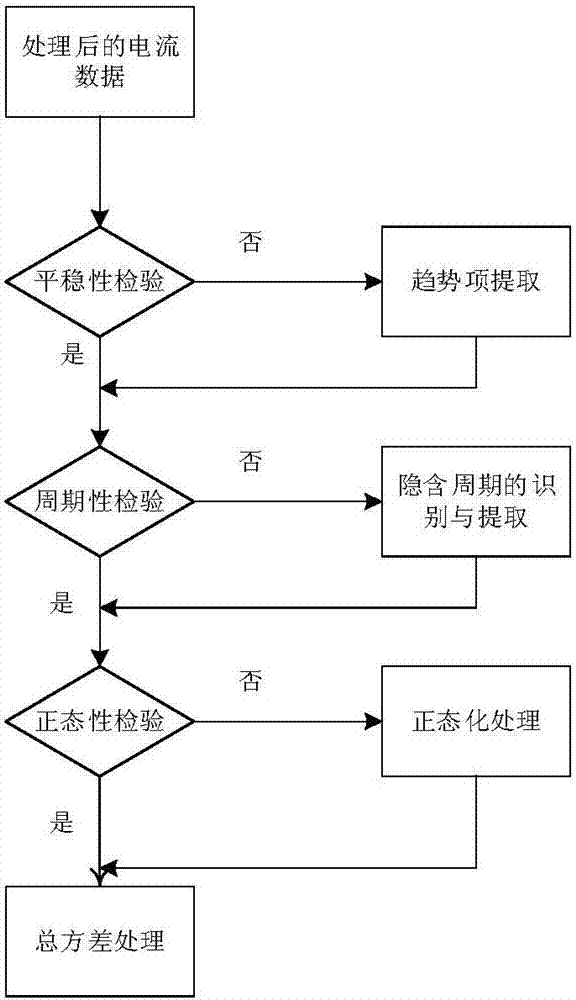
Method for analyzing random error characteristic of optical fiber current transformer based on total variance
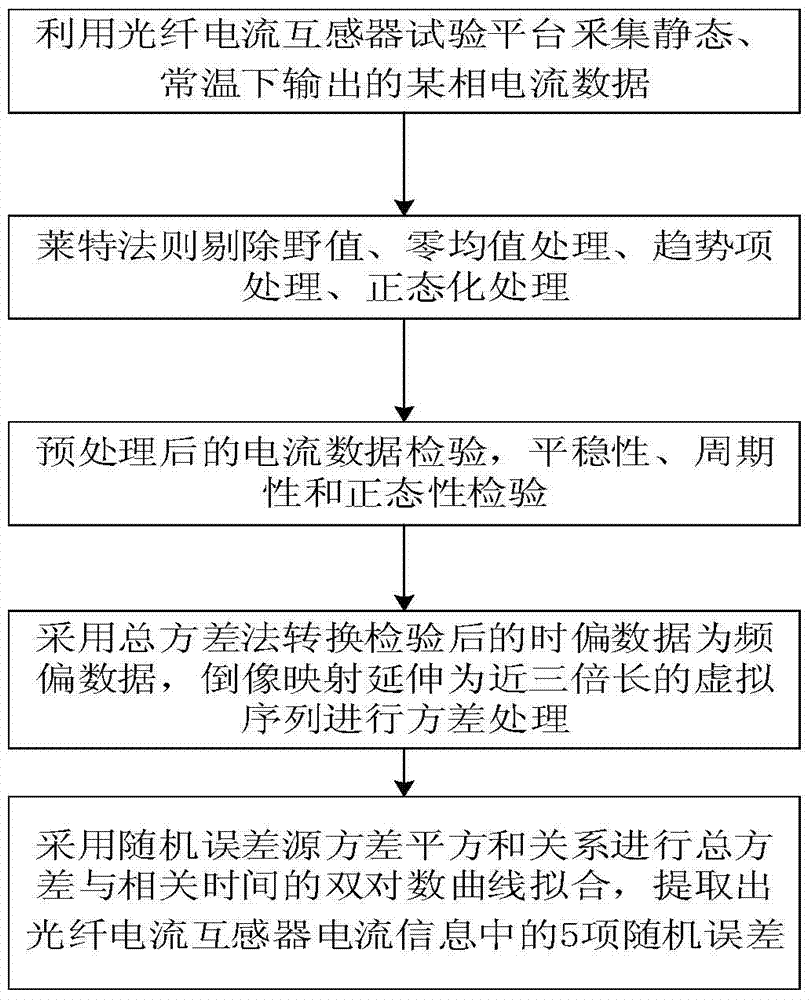
ActiveCN105259398AImprove performance designIncrease freedomVoltage/current isolationCurve fittingZero mean
Provided is a method for analyzing the random error characteristic of an optical fiber current transformer based on total variance. The method comprises the steps as follows: collecting a current signal of an optical fiber current transformer through serial output to get observation data; eliminating outliers from the observation data based on the Letts criterion, carrying out zero-mean, trend term and standardization processing on the data; testing the stability, periodicity and normality of the data after processing to get a stable, normal and zero-mean data sequence; working out the variance of the data sequence through a total variance approach; and finally, carrying out double logarithm curve fitting of the total variance (Sigma<Atol><2>) and the related time (Tau) based on the random error source variance sum-of-squares relation, namely, Sigma<Atol><2>=(R<2>*Tau<2>) / 2+(K<2>*Tau) / 3+B<2>*(2 / Pi)*In2+N<2> / Tau+3*Q<2> / Tao<2>, to extract five random error coefficients in the current information of the optical fiber current transformer. By using the method, the random error characteristic of an optical fiber current transformer can be analyzed more accurately, the defect of the traditional Allan variance method that the estimated value fluctuates greatly is solved effectively, and a guide can be provided for performance design and random error compensation of optical fiber current transformers.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
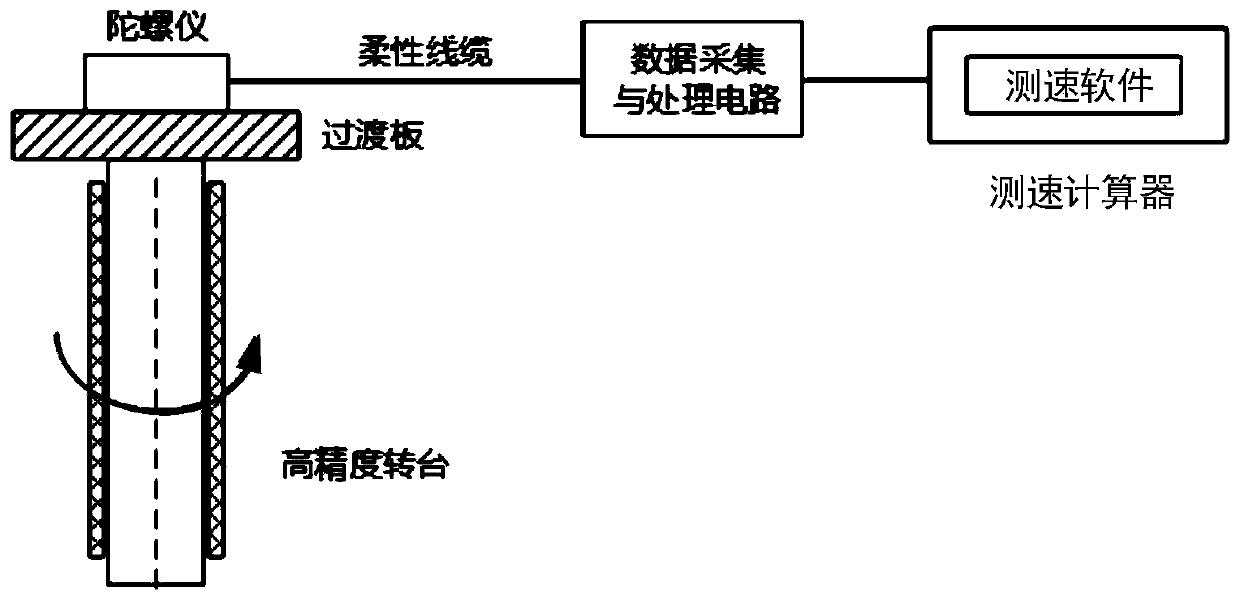
Micro-gyroscope measurement system and method for measuring zero-bias stability by using system
InactiveCN104197957ASimple structureThe result is accurateMeasurement devicesGyroscopePerformance index
The invention discloses a micro-gyroscope measurement system and a method for measuring zero-bias stability by using the system, relates to the performance testing technology of a micro-gyroscope chip and aims at solving the problem that the micro-gyroscope is only selected based on the performance indexes of a data manual due to the lack of a system for testing and comparing mass data on account of the performance of the micro-gyroscope chip in the prior art. The method takes an STM32F103C8 chip as a core processor for communicating with the micro-gyroscope, and comprises the following steps: firstly configuring the micro-gyroscope, then sending information such as angle speed measured by the micro-gyroscope to an upper computer by virtue of a wireless manner, processing the data by virtue of the upper computer and calculating by virtue of Allan variance to obtain the zero-bias stability of the micro-gyroscope. The micro-gyroscope measurement system is simple in structure, is capable of acquiring a large amount of data measured by the micro-gyroscope, processing the data by virtue of software to obtain the zero-bias stability of the micro-gyroscope and providing reliable basis for the selection of the micro-gyroscope, and is suitable for application of a micromachined gyroscope.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Gravity gradient sensor speed selection method based on inertial technology
ActiveCN108287372AImprove measurement resolutionReduce intensityGravitational wave measurementLow noiseAccelerometer
The invention relates to a gravity gradient sensor speed selection method based on the inertial technology, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: S1, determining a frequency interval with low noise energy at a low frequency; S2, analyzing the Allan variance of a combined signal of static accelerometers, and finding out the relevant time period of white noise under a double-logarithmic coordinate system; and converting the relevant time period of white noise into a frequency interval dominated by white noise; and S3, taking the intersection of the frequency interval with lownoise energy at a low frequency determined through a power spectral density analysis method in S1 and the frequency interval dominated by white noise judged through an Allan variance analysis methodin S2 to obtain the final frequency interval of the rotation frequency of a gravity gradient sensor. By using the method, the influence of the noise of accelerometers on the gravity gradient observation signal can be reduced, and the resolution of measurement can be improved.
Owner:TIANJIN NAVIGATION INSTR RES INST
Error range analysis method for gyroscope measuring instrument
ActiveCN109059961AAccurate outputMeasurement devicesMultivariate normal distributionContinuous measurement
The invention discloses an error range analysis method for a gyroscope measuring instrument. The method comprises the following steps of carrying out random noise analysis on a gyroscope by utilizingan Allan variance method to obtain a random noise term and a random noise coefficient; building an azimuth angle error analysis model by utilizing the random noise term and the random noise coefficient; and forming an error model in a gyroscope instrument continuous measurement mode by the azimuth angle error analysis model, an initial point position error range model and a hole drift angle errormodel, and after the error models are superposed according to an error superposition principle, performing multivariate normal distribution to obtain an error range of a wellbore trajectory. Accordingto the method, the Allan variance method is used for analyzing the random noise term of the gyroscope, random noise is selected according to a result of Allan variance analysis to carry out error modeling, and the error range of the wellbore trajectory position is calculated, so that more reliable information is provided for the fields of wellbore anti-collision and the like.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Signal source stability measuring system and method
InactiveCN106908659AStability measurements improvedSpectral/fourier analysisFrequency measurement arrangementTime domainFrequency stabilization
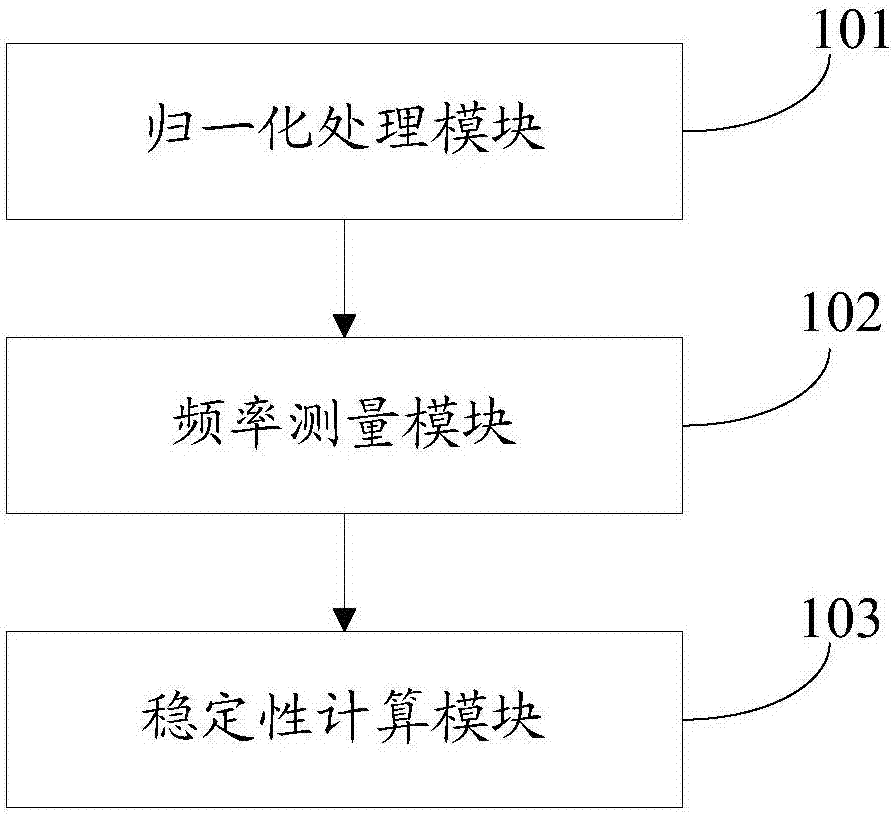
The invention discloses a signal source stability measuring system characterized by comprising a normalization processing module, a frequency measurement module and a stability calculating module, wherein the normalization processing module is used for obtaining frequency division value according to reference frequency and preset signal frequency which needs frequency division, sampling time signals are obtained according to the frequency division value, detected signals are subjected to normalization processing operation, standard 1MHz signal frequency is obtained, the frequency measurement module is used for conducting time domain frequency measurement operation on the detected signals according to the sampling time signals, frequency value of the detected signals can be obtained, the stability calculating module is used for subjecting the frequency value to Allan variance processing operation, frequency stability value of the detected signals is obtained and subjected to linear fitting operation, a measurement result can be obtained, and stability measurement operation can be performed on the detected signals. The signal source stability measuring system and method can help solve a technical problem that a conventional method for measuring stability of a signal source based on standard variance which fluctuates relative to frequency offset is low in accuracy.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
DMTD measuring method and measuring system
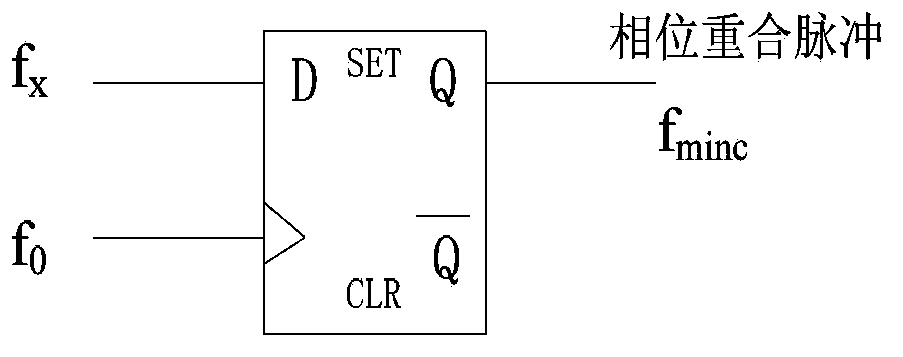
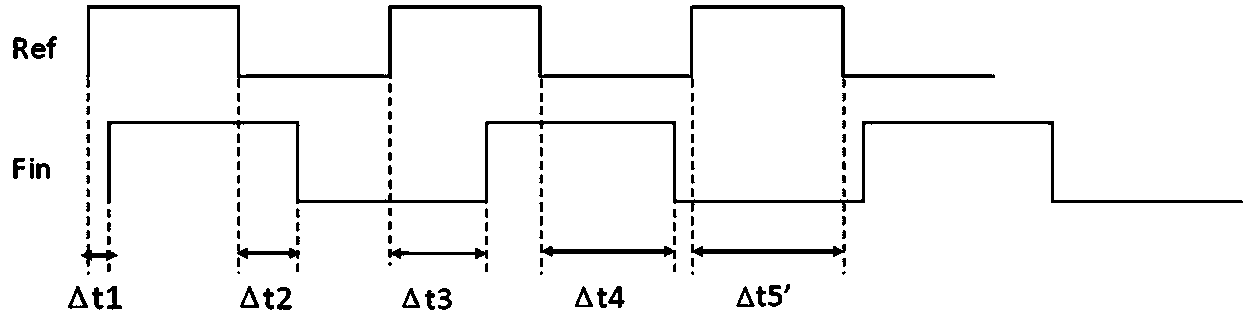
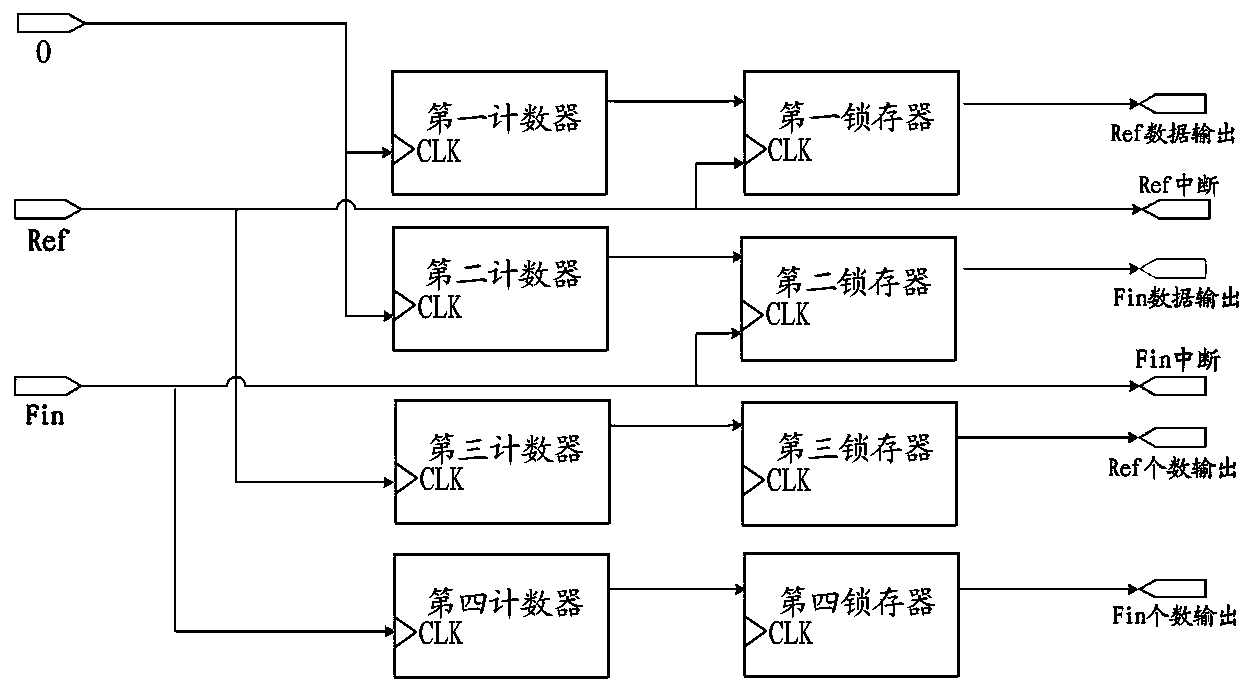
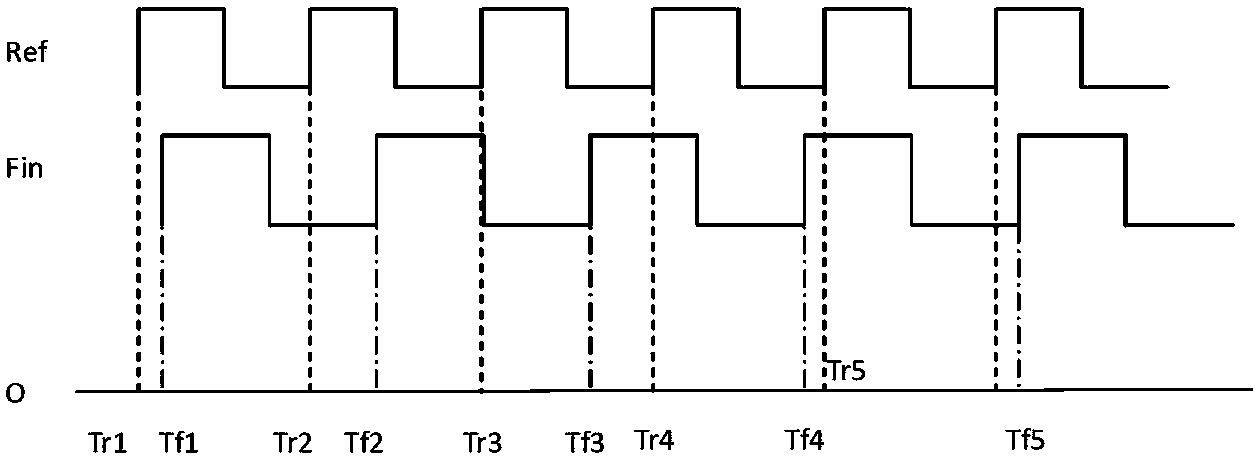
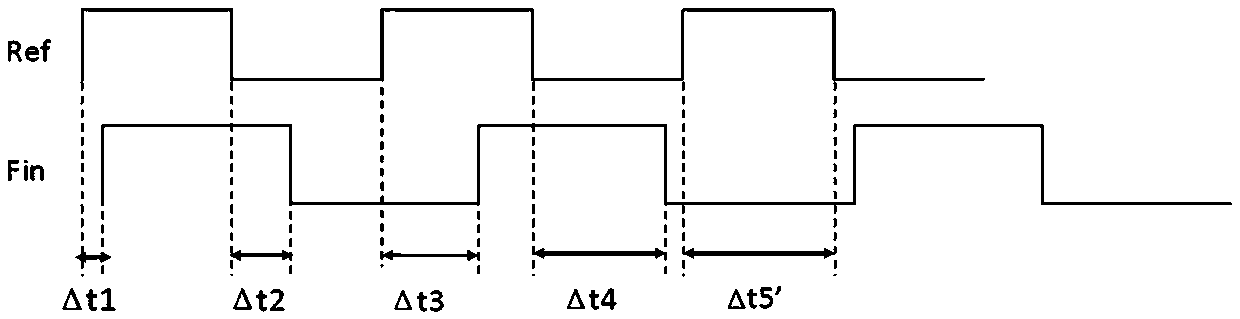
ActiveCN103869156AAvoid inaccurate measurementsResolving period ambiguityHeterodyning/beat-frequency comparisonPhase differenceExclusive or
The invention provides a DMTD measuring method and measuring system. According to the DMTD measuring method and measuring system, an uninterrupted common source signal is selected, two counters are used for acquiring the time counting values of the common source signal respectively in real time, when the rising edges of reference signals and the rising edges of detected signals come respectively, the time counting values of the current two counters are acquired respectively, the number of the rising edges of the reference signals and the number of the rising edges of the detected signals align at each other, the two time counting values corresponding to the aligning numbers are subtracted to obtain an accurate time difference value, and other frequency differences, phase differences, Allan variances and the like can be calculated according to the accurate time difference value. The common source signal mode is used, the problem that a traditional exclusive-OR gate mode can not conduct accurate measurement in times of edge overlapping or when two edge time differences are smaller than hardware response time is solved, and the cycle fuzzy phenomenon which commonly exists in the DMTD measuring process is avoided. In brief, the DMTD measuring method and measuring system can achieve quick, accurate, real-time and unlimited measuring with low cost.
Owner:石家庄数英仪器有限公司
Automatic telescope pointing correction method based on ALLAN variance analysis under motion platform
ActiveCN107608065ACorrect drift errorFix installation errorTelescopesOptical apparatus testingStructural deformationSimulation
The invention discloses an automatic telescope pointing correction method based on ALLAN variance analysis under a motion platform. The positioning precision of a telescope is relevant to the motion precision of a mechanical system and is affected by mechanical and electrical equipment and software control algorithms. With the development of electronic techniques, mechanical errors in processing and assembling are main factors affecting the positioning precision. The mechanical errors mainly include part machining errors, bearing errors, telescope assembly errors, structural deformation and the like. A photoelectric tracking system installed on the motion platform is affected by carrier motions, vibrations and the like. In addition, due to the use of inertial devices, alignment errors, drift errors of inertial sensitive devices and the like are introduced. Base on the basic principle of telescope pointing and pointing error source analysis, an automatic pointing correction model basedon ALLAN variance analysis under the motion platform is established, the correction precision and model stability are improved, and automatic pointing correction is also achieved.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Noise coefficient computing method used for Allan variance analysis technology
ActiveCN103345569ANo negative valuesPlausible physical explanationSpecial data processing applicationsObservational errorRandom noise
The invention discloses a noise coefficient computing method used for the Allan variance analysis technology. The noise coefficient computing method used for the Allan variance analysis technology solves the problems that matrix inversion is singular, noise coefficients have negative values, and the noise coefficients are not optimal, wherein the problems exist in five types of typical random noise coefficient processes in the prior art. The noise coefficient computing method used for the Allan variance analysis technology mainly comprises the following steps that 1) an Allan variance sequence and a corresponding relevant time sequence are preset; 2) a relevant time matrix is computed; 3) a halt condition is set, and linearization is conducted on a target function; 4) initial values of loop iteration related parameters are set; 5) matrix transformation is conducted; 6) sphere transformation is conducted, and an unconstrained optimal increment is computed; 7) a hyperplane nonnegative restriction optimal increment is computed; 8) the noise coefficients are updated; 9) a halt index is computed; 10) whether a halt criterion is met is judged. Random noise coefficients estimated by the noise coefficient computing method can be used for inertial device performance evaluation or accurate modeling of random measurement errors, and has significance for improving navigation accuracy of an inertia matrix integrated navigation system.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Photoelectric module reverse testing method and photoelectric module fault diagnosis and discrimination method
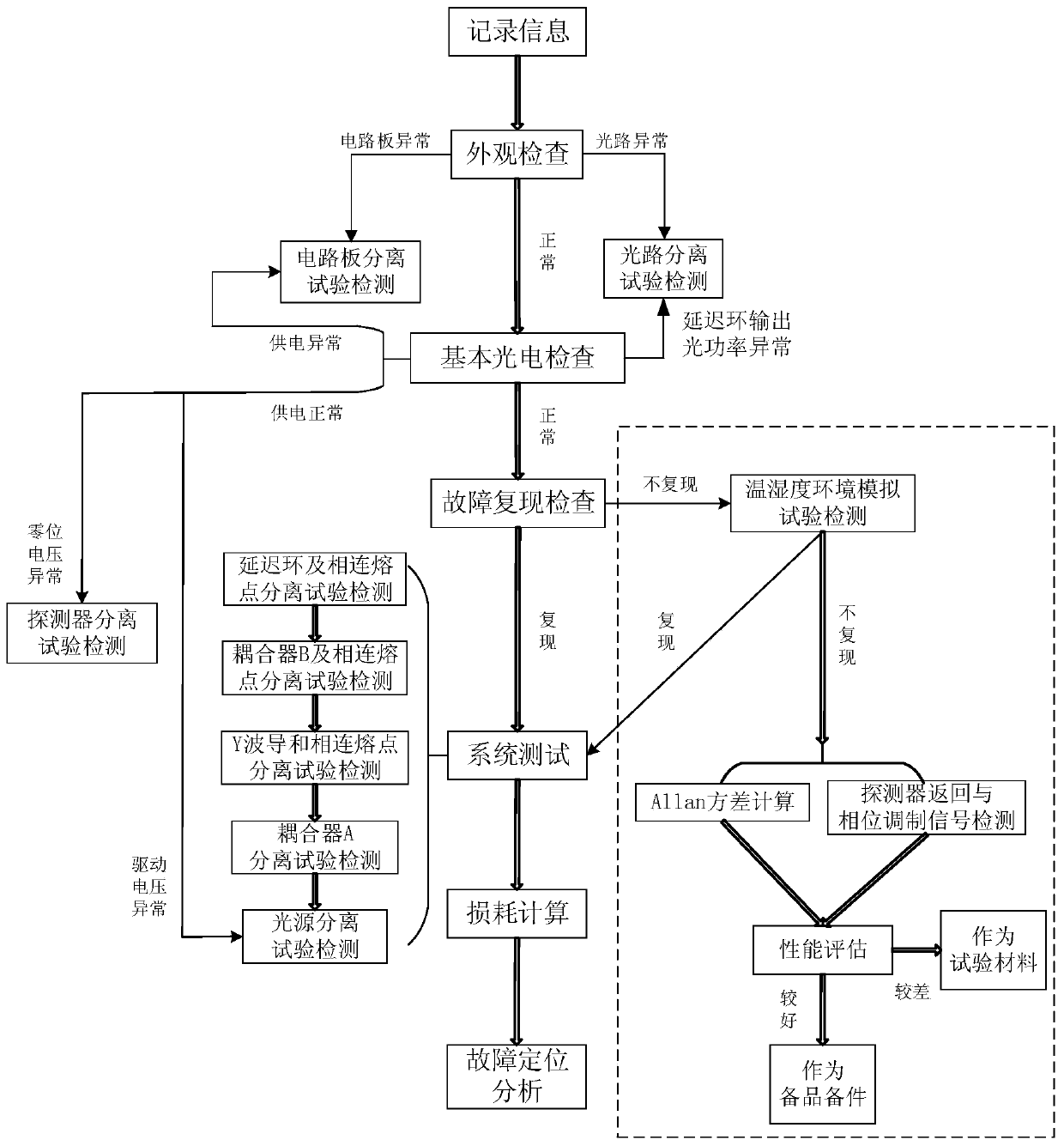
ActiveCN109752684AImprove fault diagnosis efficiencyDiscriminant fast discriminantElectrical measurementsSystem testingTest material
The invention discloses a photoelectric module reverse testing method and a photoelectric module fault diagnosis and discrimination method. The photoelectric module fault diagnosis and discriminationmethod comprises the steps of appearance inspection, basic photoelectric inspection and fault recurrence inspection, and as for a fault recurrence module, system testing, loss calculation and fault positioning analysis continue to be conducted; and as for fault non-recurrence module, temperature and humidity environment simulation test detecting is adopted, if a fault recurs, the system testing step is conducted, if the fault fails to recur, Allan variance calculation, detector return and phase modulation signal detection continue to be conducted, set threshold conditions are compared throughthe calculation results for performance evaluation, the module with poor performance serves as a test material, and the module with the good performance serves as a spare part. The photoelectric module fault diagnosis and discrimination method has the characteristic that fault diagnosis and discrimination are comprehensive, accurate and reliable.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE TIMES OPTICAL ELECTRONICS TECH
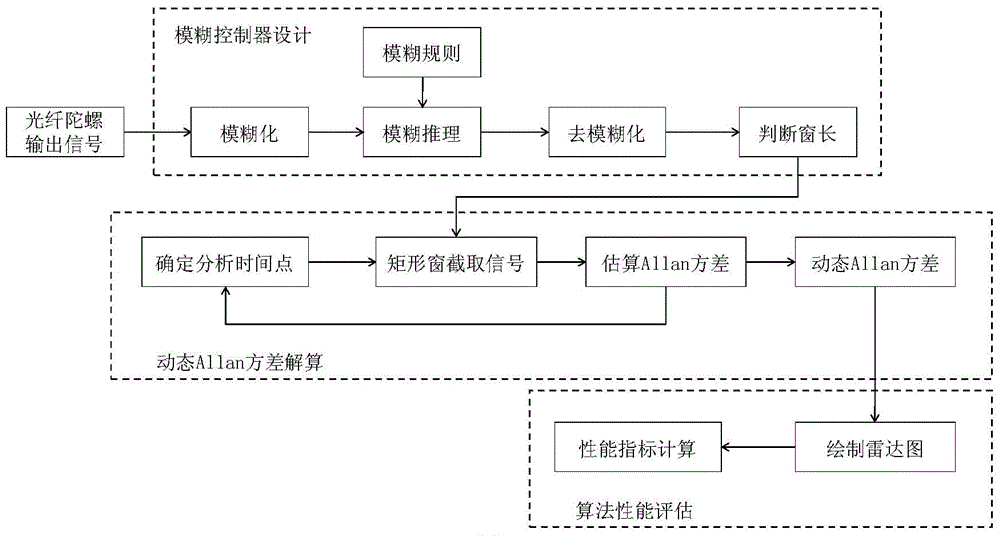
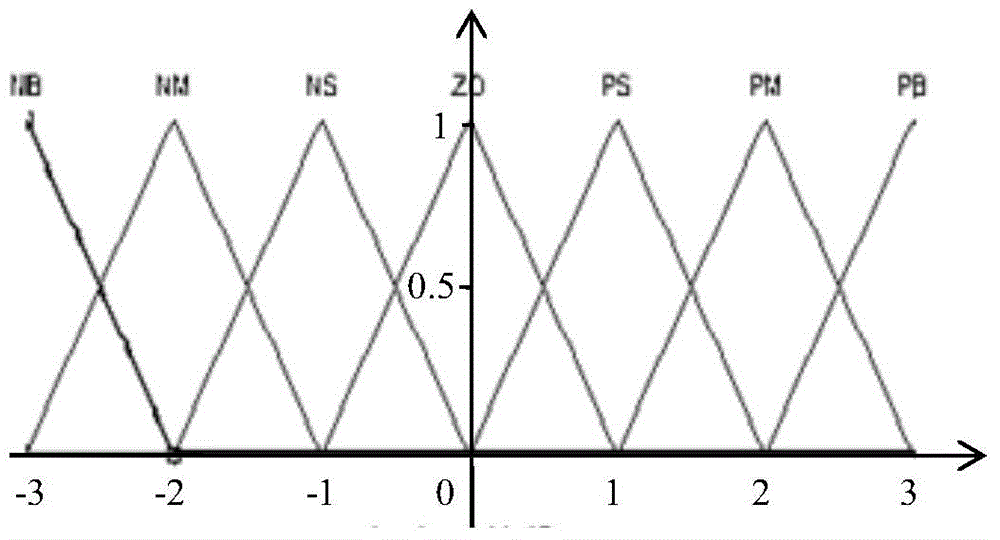
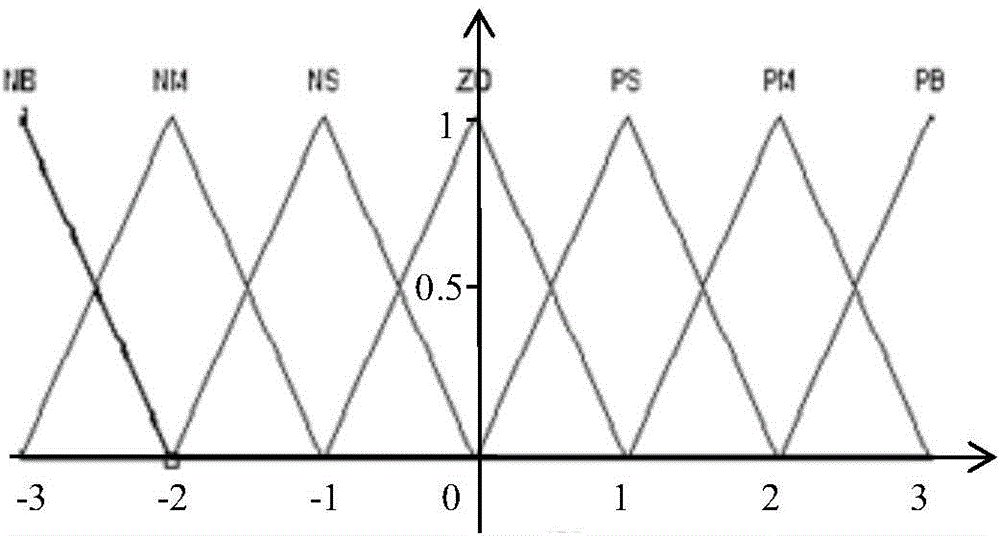
Time-varying window length dynamic Allan variance analysis method on the basis of fuzzy control
ActiveCN104406606AReflect dynamic featuresEase of evaluationMeasurement devicesInformaticsFiberGyroscope
The invention discloses a time-varying window length dynamic Allan variance analysis method on the basis of fuzzy control, and belongs to the technical field of inertial navigation. In the provided method, according to the characteristics of the signals that are output by a fiber-optic gyroscope, a fuzzy controller is designed according to the primary change rate and secondary change rate of the output signals of the fiber-optic gyroscope so as to choose the window length of dynamic Allan variance, the dynamic Allan variance of the signals is calculated, and thus the effective analysis on the dynamic characteristics of the output signals of the fiber-optic gyroscope is achieved. On the basis of the technical scheme mentioned above, an algorithm performance evaluation index on the basis of a radar map is provided, and the effective evaluation on algorithm performance is achieved. The analysis method is suitable for the noise analysis of a fiber-optic gyroscope.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Analysis method for random errors of MEMS gyroscope
PendingCN112729266AGuaranteed accuracyEasy to useSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsGyroscopes/turn-sensitive devicesGyroscopeEngineering
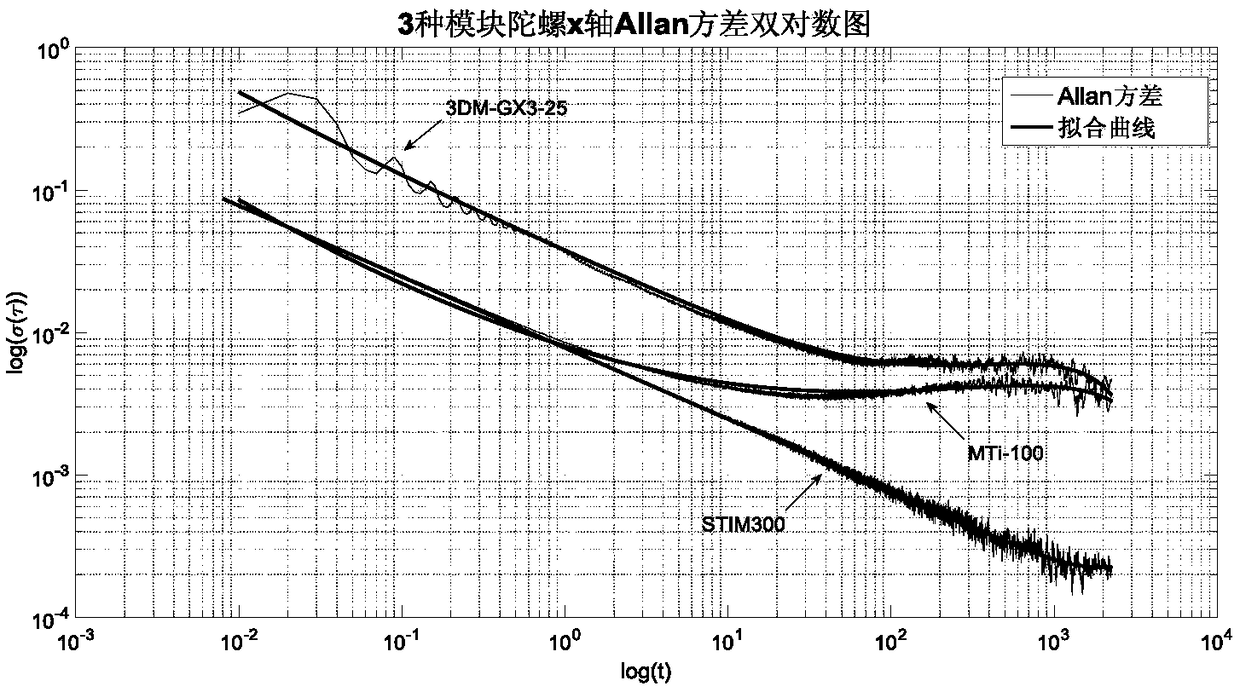
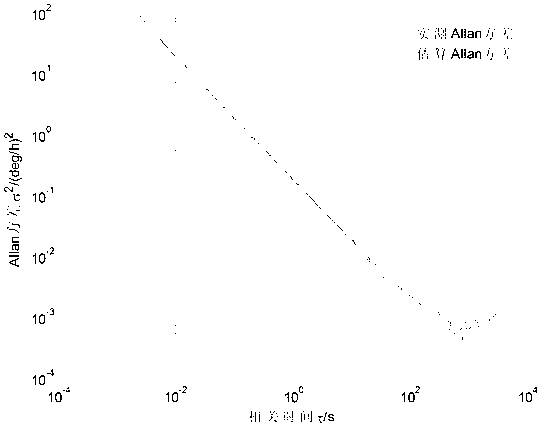
The invention provides an analysis method for random errors of an MEMS gyroscope. The method comprises the following specific steps of: acquiring original output data of the MEMS gyroscope, analyzing the original output data of the MEMS gyroscope according to Allan variance, drawing a double logarithmic curve of Allan, analyzing an error type according to the double logarithmic curve of Allan, calculating and determining a main random error coefficient of the MEMS gyroscope by utilizing the Allan variance, and establishing a filtering model of gyroscope errors according to the main random error coefficient of the MEMS gyroscope. The filtering model of the main random errors of the gyroscope is compensated, and the use precision and performance of the MEMS gyroscope are ensured.
Owner:SHAANXI AEROSPACE TIMES NAVIGATION EQUIP CO LTD
Random error modeling and compensation method for ring laser device based on adaptive Kalman filtering
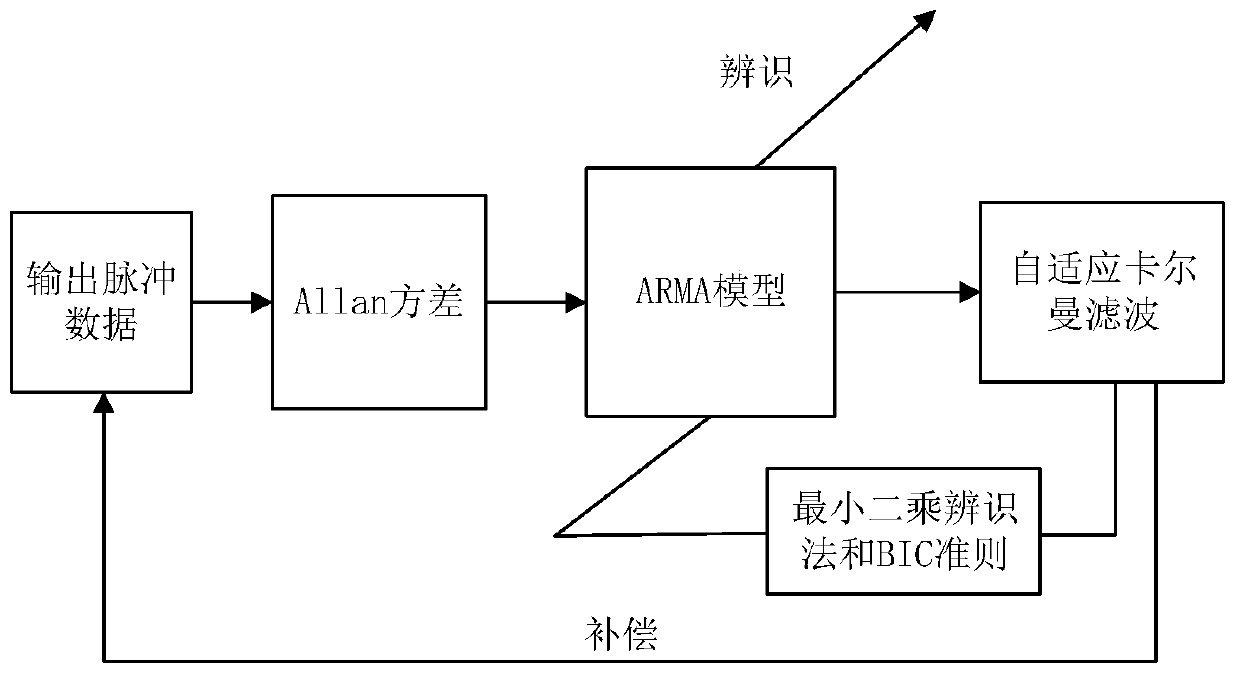
ActiveCN110375772AImprove calibration accuracyReduce random errorMeasurement devicesSimulationRing laser
The invention relates to a turntable on-site rapid calibration device based on a ring laser device, and proposes a random error modeling and compensation method for a ring laser device based on adaptive Kalman filtering. The random error modeling and compensation method belongs to the technical field of inertia calibration, and comprises the steps of: conducting an experimental test to obtain output pulse data of the ring laser device; processing the data and calculating Allan variance; establishing an auto-regressive moving average model (ARMA model) according to the Allan variance; and identifying an order and parameters of the model by utilizing a BIC criterion and the least square method; and designing a compensation method based on adaptive Kalman filtering for the ARMA model, reducing the influence of random errors on model precision, and effectively improving the calibration precision of the ring laser device. The random error modeling and compensation method utilize the annular laser calibration method to realize calibration of an on-site turntable, is simple in operation and has high environmental adaptability, can be used in a wide temperature range, and has the advantages of high precision, good reliability, large dynamic range, no mechanical noise influence and the like.
Owner:BEIJING CHANGCHENG INST OF METROLOGY & MEASUREMENT AVIATION IND CORP OF CHINA
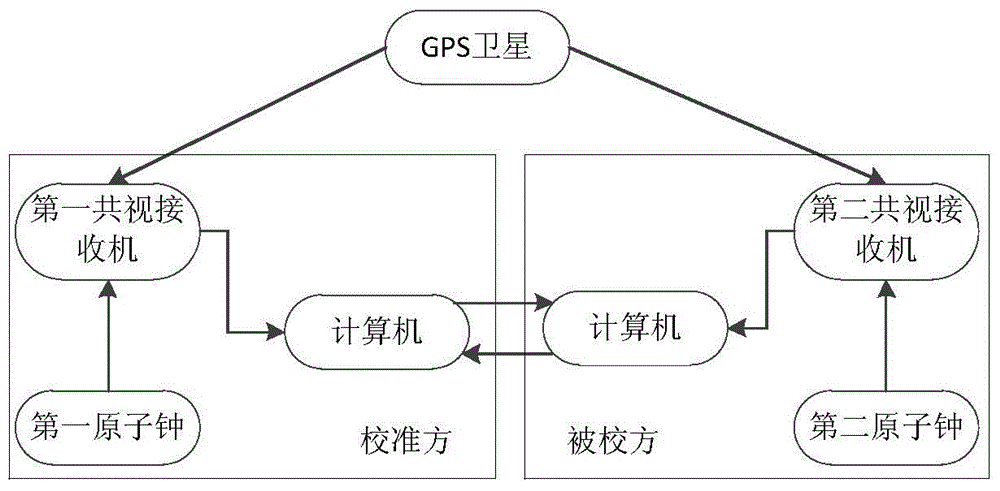
Method for acquiring day frequency stability of atomic clock remote calibration system
ActiveCN104614981ADoes not affect normal workThe method is simple and reliableRadio-controlled time-piecesSatellite dataComputer science
The invention provides a method for acquiring day frequency stability of an atomic clock remote calibration system. The method comprises the following steps: respectively setting an antenna, a common-view time receiver, a computer and an atomic clock on a calibrating party and a calibrated party to form the atomic clock remote calibration system; starting the common-view time receiver and the atomic clock of the calibrating party and the calibrated party; operating for at least three days and storing a CGGTTS standard formatted file; selecting sampling time point in the day according to a principle that absolute value calculation is main and flexible adjustment is complementary; selecting satellite data of the sampling time point of the same satellite which appears in the CGGTTS standard formatted file in all N days; subtracting REFGPS values in the satellite data of the calibrating party from the REFGPS values in the satellite data of the calibrated party in any day from the first day to the nth day to acquire time difference data on that day; acquiring the day frequency stability by using allan variance. The method is simple and reliable, and can replace a traditional carrying clock measuring method.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MEASUREMENT & TESTING TECH
Characterization of logging tool performance
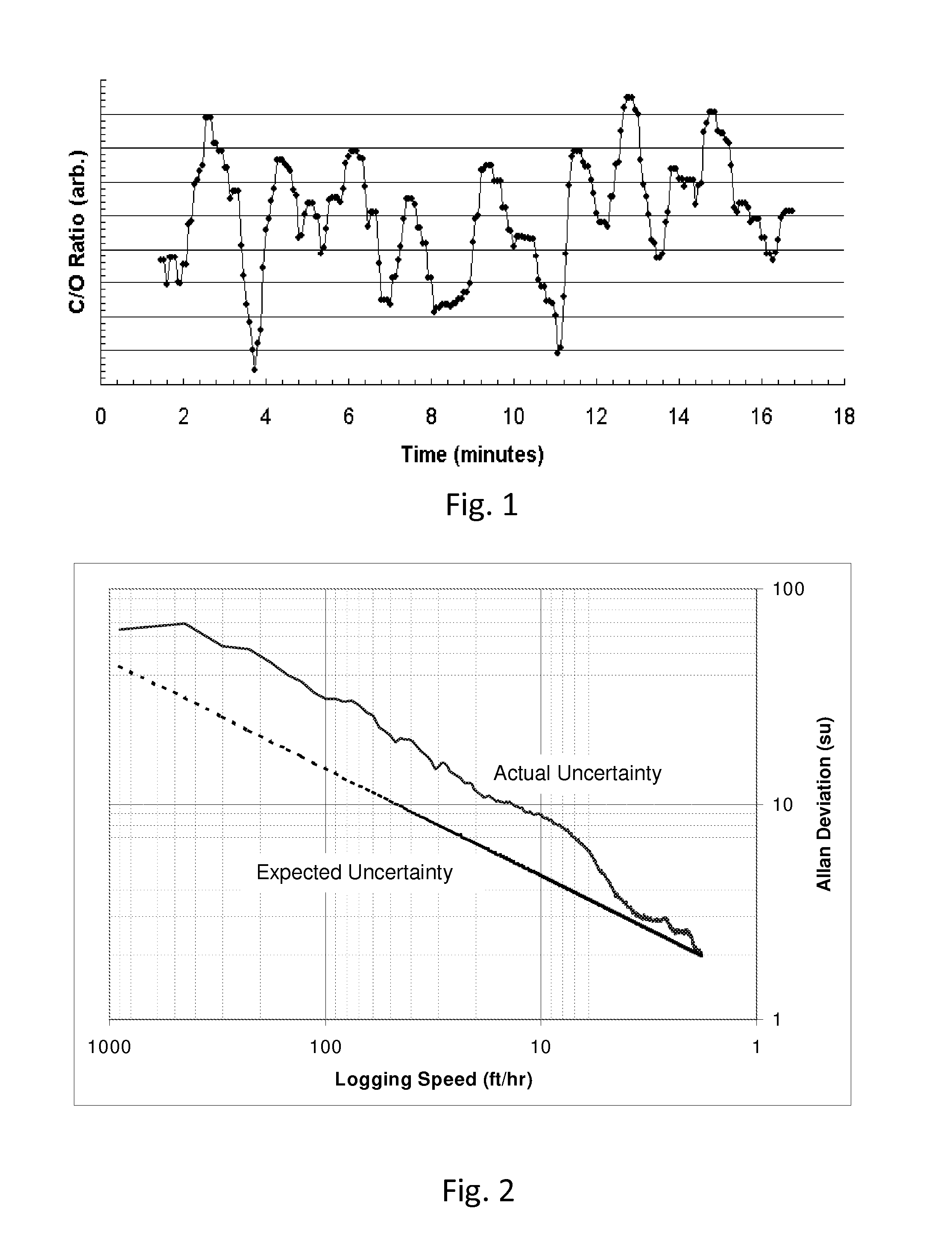
InactiveUS20110093199A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingDigital computer detailsFormation evaluationMeasurement precision
A method for determining the measurement precision of a formation evaluation tool in a borehole comprises: a) conveying the formation evaluation tool into the borehole, b) using the formation evaluation tool to make measurements, and c) analyzing the measurements using mean squared difference stability statistics to generate an output indicative of measurement precision. Step c) may comprise using an Allan variance to assess the measurements taken in step b). The method may further include deriving an optimum logging speed from the analysis performed in step c), which may occur at the lowest value of the Allan variance.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Specific emitter identification method based on Allan variance
ActiveCN108234033AImprove effectivenessCharacter and pattern recognitionTransmission monitoringPattern recognitionNonlinear system
The invention belongs to the technical field of communication, and particularly relates to a specific emitter identification method based on an Allan variance. According to the specific emitter identification method based on the Allan variance, different nonlinear characteristics brought by a nonlinear device in an actual radiation source are utilized. In fact, different radiation sources are taken as different nonlinear systems in the method, and the Allan variance is used for extracting characteristics of the nonlinear systems based on the principle, so that different systems are identified.An Allan standard deviation obtained by calculation under different correlation time has different meanings, a characteristic vector is formed by using the Allan standard deviation under three correlation time, and the identification effectiveness is enhanced.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for improving precision of gyroscope based on Allan variance and random polynomial
ActiveCN112747773AHigh precisionReduce the amount of calculationMeasurement devicesGyroscopeControl theory
The invention discloses a method for improving precision of a gyroscope based on an Allan variance and a random polynomial, and relates to the technical field of instrument precision improvement. The method comprises the following steps of processing angular rate data through an Allan variance method, identifying a noise source which is contained in the data and affects a gyroscope random error, establishing a gyroscope random error model, approaching the gyroscope random error model by utilizing a random polynomial, converting the gyroscope random error model into a differential equation of a determined random polynomial coefficient, solving the differential equation to obtain a coefficient of the random polynomial at each moment, calculating statistical information of an output signal of the gyroscope, further analyzing to obtain error precision of a random error of the gyroscope, and compensating the random error of the gyroscope according to the error precision. According to the invention, a random problem is converted into a deterministic problem; and the precision of the gyroscope is rapidly and effectively improved, the calculation amount is reduced, the calculation time is shortened, meanwhile, the universality is good, and a wide application value is achieved.
Owner:CHINA CONSTR EIGHTH ENG DIV
A kind of double mixing time difference measurement method and measurement system
ActiveCN103869156BAvoid inaccurate measurementsResolving period ambiguityHeterodyning/beat-frequency comparisonPhase differenceExclusive or
The invention provides a DMTD measuring method and measuring system. According to the DMTD measuring method and measuring system, an uninterrupted common source signal is selected, two counters are used for acquiring the time counting values of the common source signal respectively in real time, when the rising edges of reference signals and the rising edges of detected signals come respectively, the time counting values of the current two counters are acquired respectively, the number of the rising edges of the reference signals and the number of the rising edges of the detected signals align at each other, the two time counting values corresponding to the aligning numbers are subtracted to obtain an accurate time difference value, and other frequency differences, phase differences, Allan variances and the like can be calculated according to the accurate time difference value. The common source signal mode is used, the problem that a traditional exclusive-OR gate mode can not conduct accurate measurement in times of edge overlapping or when two edge time differences are smaller than hardware response time is solved, and the cycle fuzzy phenomenon which commonly exists in the DMTD measuring process is avoided. In brief, the DMTD measuring method and measuring system can achieve quick, accurate, real-time and unlimited measuring with low cost.
Owner:石家庄数英仪器有限公司
Unmanned aerial vehicle PM2.5 detecting device based on complementary filtering attitude fusion algorithm
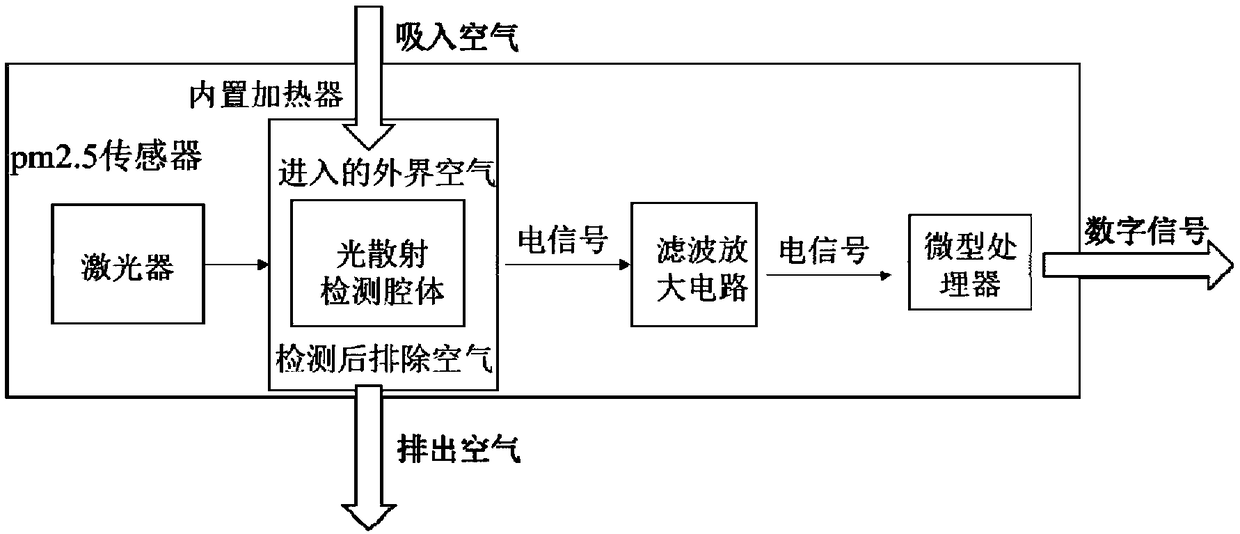
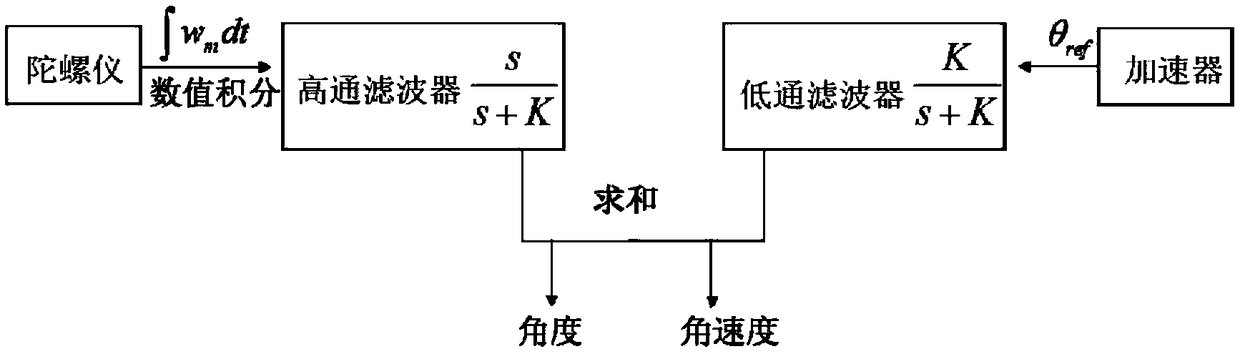
InactiveCN109470613ASolve the problem of low accuracy of height dropImprove stabilityParticle suspension analysisAttitude controlComplementary filterUncrewed vehicle
The invention discloses an unmanned aerial vehicle PM2.5 detecting device based on a complementary filtering attitude fusion algorithm, and belongs to the field of haze environment detection. The unmanned aerial vehicle PM2.5 detecting device comprises a four-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle and a PM2.5 detecting device, wherein the PM2.5 detecting device adopts an AGS-V8PM2.5 dust sensor; an attitude reference system comprises an aircraft stability control module based on the complementary filtering attitude fusion algorithm; the stability control module comprises a complementary filter combining Allan variance analysis with indirect Kalman filtering and combining first-order low-pass filtering with first-order high-pass filtering; the stability of an aircraft is successively controlled twice by two different complementary filtering algorithms, so that the four-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle stays at a certain fixed position more stably. The unmanned aerial vehicle PM2.5 detecting devicecan not only detect the concentration of PM2.5 in air, but also solves the problem that the height drop accuracy of the unmanned aerial vehicle is not high due to too low data refreshing rate of low-cost GPS as well as data lag during high-speed motion, and has the characteristics of strong anti-interference capability and high stability.
Owner:HUNAN ELECTRICAL COLLEGE OF TECH
A Random Error Characteristic Analysis Method of Optical Fiber Current Transformer Based on Total Variance
ActiveCN105259398BImprove performance designIncrease freedomVoltage/current isolationFiberCurve fitting
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
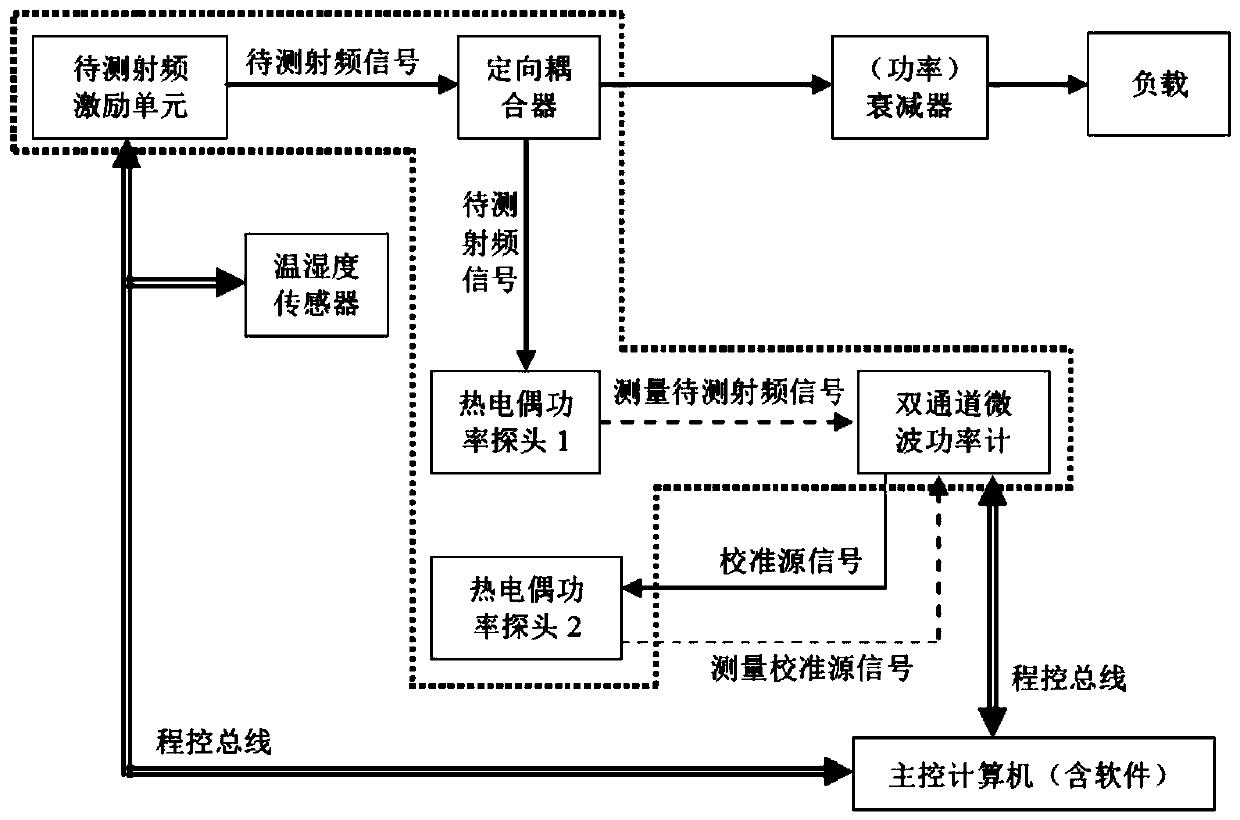
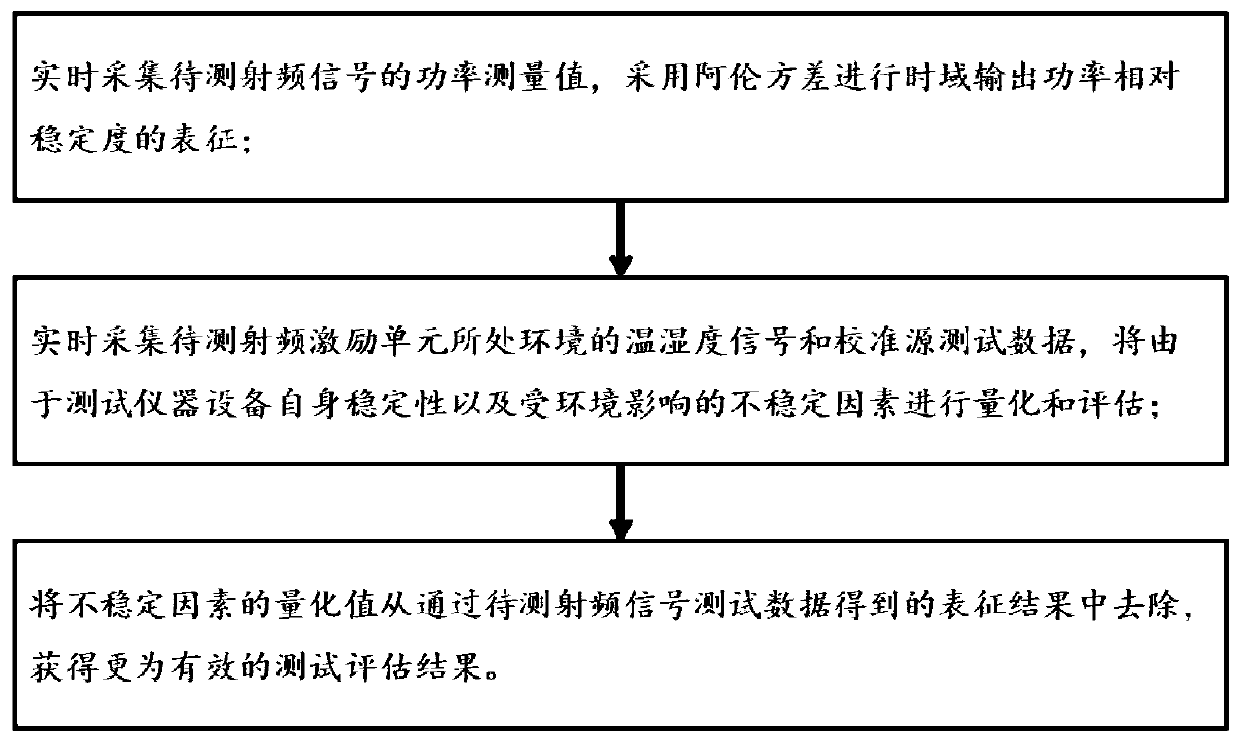
Radio-frequency power relative stability testing circuit and method for quantum precision magnetic detection
ActiveCN110275060AReduce uncertaintyMeet actual needsPower measurement by galvanomagnetic effect devicesInstrumentationPower measure
The invention provides a radio-frequency power relative stability testing circuit and method for quantum precision magnetic detection. According to the radio-frequency power relative stability testing circuit and method for quantum precision magnetic detection, the power measurement values of radio-frequency signals to be tested are collected in real time, and time-domain output power relative stability is characterized by Allan variance; and temperature and humidity signals and calibration source test data of an environment where a to-be-tested radio-frequency excitation unit is located are collected in real time, the stability of test instrument equipment and the unstable factors of environmental influence exerted on the test instrument equipment are quantified and evaluated; and the quantization values of the unstable factors are removed from characterization results obtained through the test data of the radio-frequency signals to be tested, so that a more effective test evaluation result is obtained. With the radio-frequency power relative stability testing circuit and method for quantum precision magnetic detection of the invention adopted, the test problem of the random continuity change tendency of radio frequency power in specific sampling time is solved; the effective characterization and evaluation of a radio-frequency power relative stability index which is lower than 0. 1% or even has a higher order are realized; and the practical requirements of technical application are met.
Owner:THE 41ST INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com