Transgenic organism
a technology of transgenic cells and organisms, applied in the field of transgenic cells and transgenic organisms, can solve the problems of limited use of these vectors, significant disadvantages of internal promoters, and examples of viruses used in these vectors, and achieve the effect of efficient production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
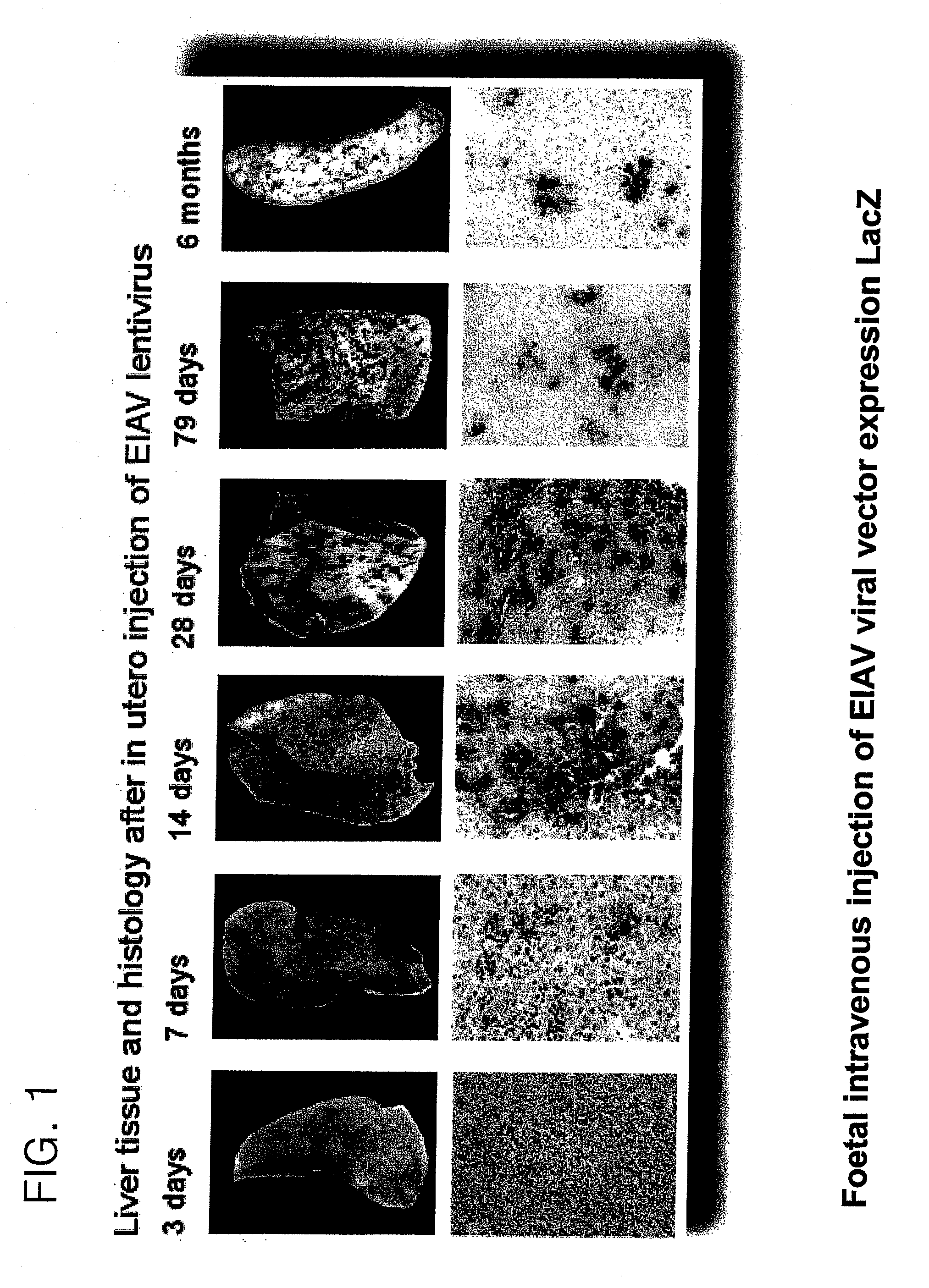
EIAV Transduction of Perinatal Animals
Preparation of VECTOR
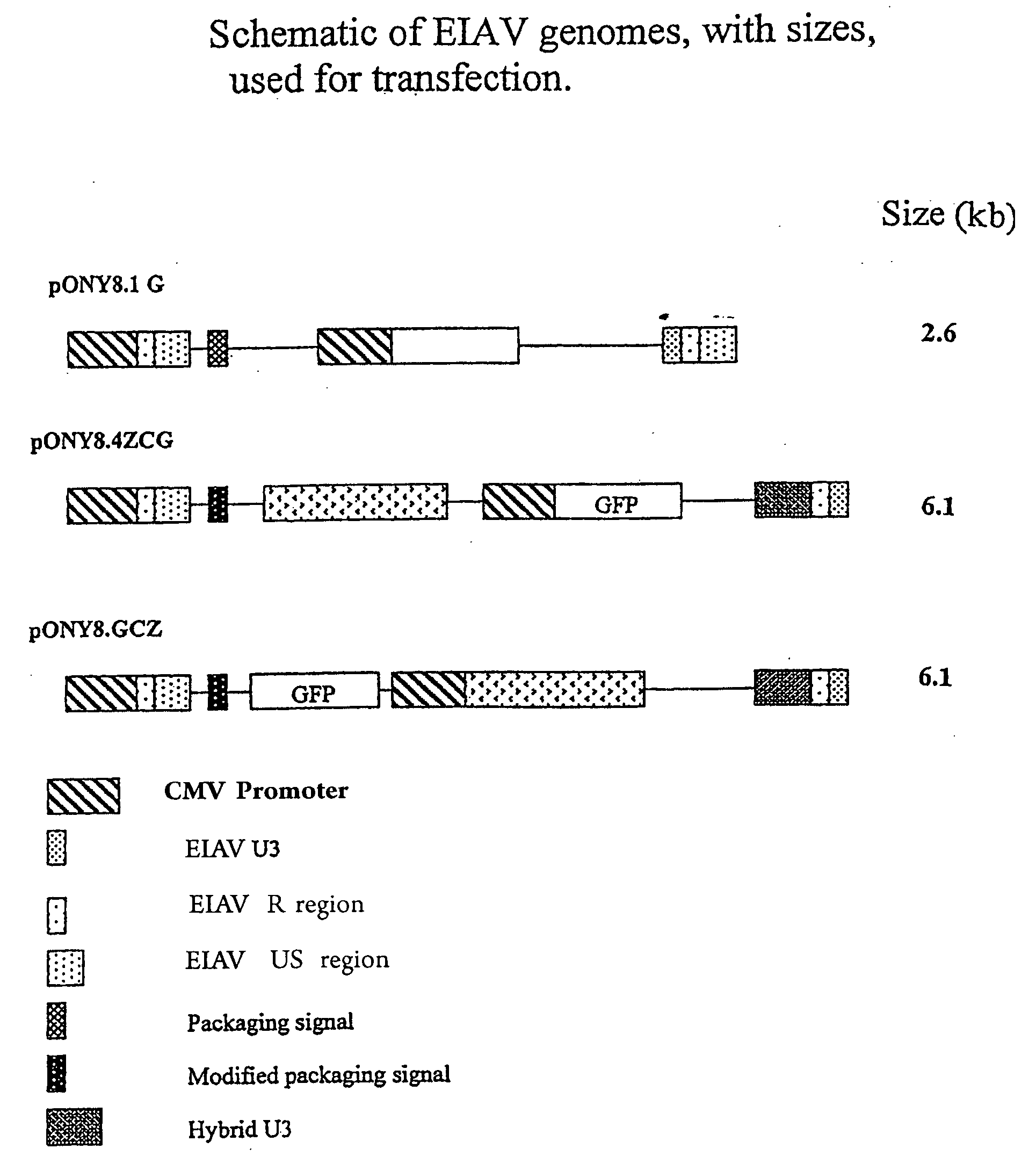
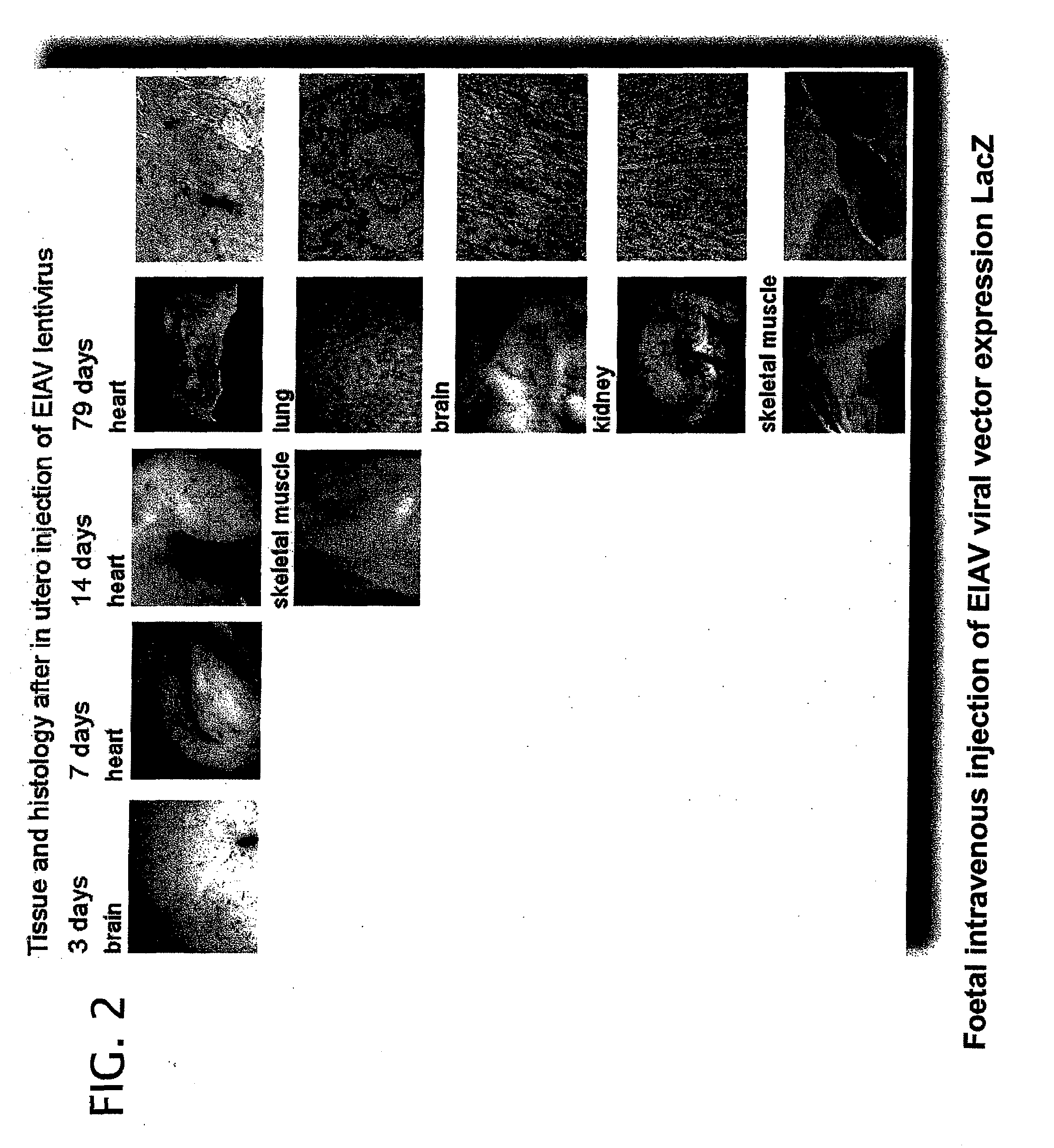
[0280]Vector was prepared by transient co-transfection of 293T human embryonic kidney cells as previously described (Mitrophanous et al 1999). The EIAV vector genome, SMART2Z, expresses the β-galactosidase reporter gene from an internal CMV promoter. It contains the EIAV central polypurine tract (cPPT) (Stetor et al 1999) and the Woodchuck Hepatitis Post-Transcriptional Regulatory Element (WPRE) (Donello et al 1998).
Administration of Vector
[0281]Vector was administered by injecting foetuses intra-vascularly as follows:
[0282]Under isoflurane anaesthesia a full depth midline laporotomy was performed to expose the uteri of pregnant mice at 16 days gestation. For each foetus 2×107 T.U. (transforming units) of vector was administered in a total volume of 20 μl, using a 34-gauge needle (Hamilton), into a peripheral yolk sac vessel. Up to five foetuses were injected per dam. The laporotomy was closed by suturing layer to layer and ...
example 2
[0286]This Example is carried out following the methodology of Example 1. Haemophilia is a blood condition in which an essential clotting factor is either partly or completely missing. It is an X-linked recessive disorder. There are two types of haemophilia, the most common being haemophilia A, in which Factor VIII is lacking. In haemophilia B, Factor IX is lacking. EIAV is used to deliver factor VIII or IX by EIAV to the umbilical vein of haemophiliac foetus or hepatic portal vein of perinates.
Preparation of the Vector
[0287]A vector such as those described in our co-pending GB0202403.1. In more detail:
[0288]pONY 8.4 series of vectors has a number of modifications which enable it to function as part of a transient or stable vector system totally independent of accessory proteins, with no detrimental effect on titre. Conventionally lentiviral vector genomes have required the presence of the viral protein rev in producer cells (transient or stable) in order to obtain adequa...
example 3
[0303]This Example is carried out following the methodology of Example 1. Cystic fibrosis is an hereditary recessive disorder caused by mutation of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR), a protein that is thought to have a role in ion transport, mucus rheology, inflammation and bacterial adherence. EIAV is used to deliver CFTR by to the amniotic fluid for transduction of lung.
[0304]An EIAV viral vector (such as those described above) expressing CFTR (the wild type ORF or a codon optimised ORF) is administered following the methodology in Example 1 and including either intragastrointerstinal delivery intralung or intraamniotic fluid. A suitable promoter such as CMV or human promoter / enhancers such as PGK is used to express the gene. In addition inducible promoters such as the Tet system can be used to regulate the expression. As an alternative tissue specific promoter / enhancers can be used to limit expression to the cell types.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com