Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
146results about How to "Suppresses degradation of display quality" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
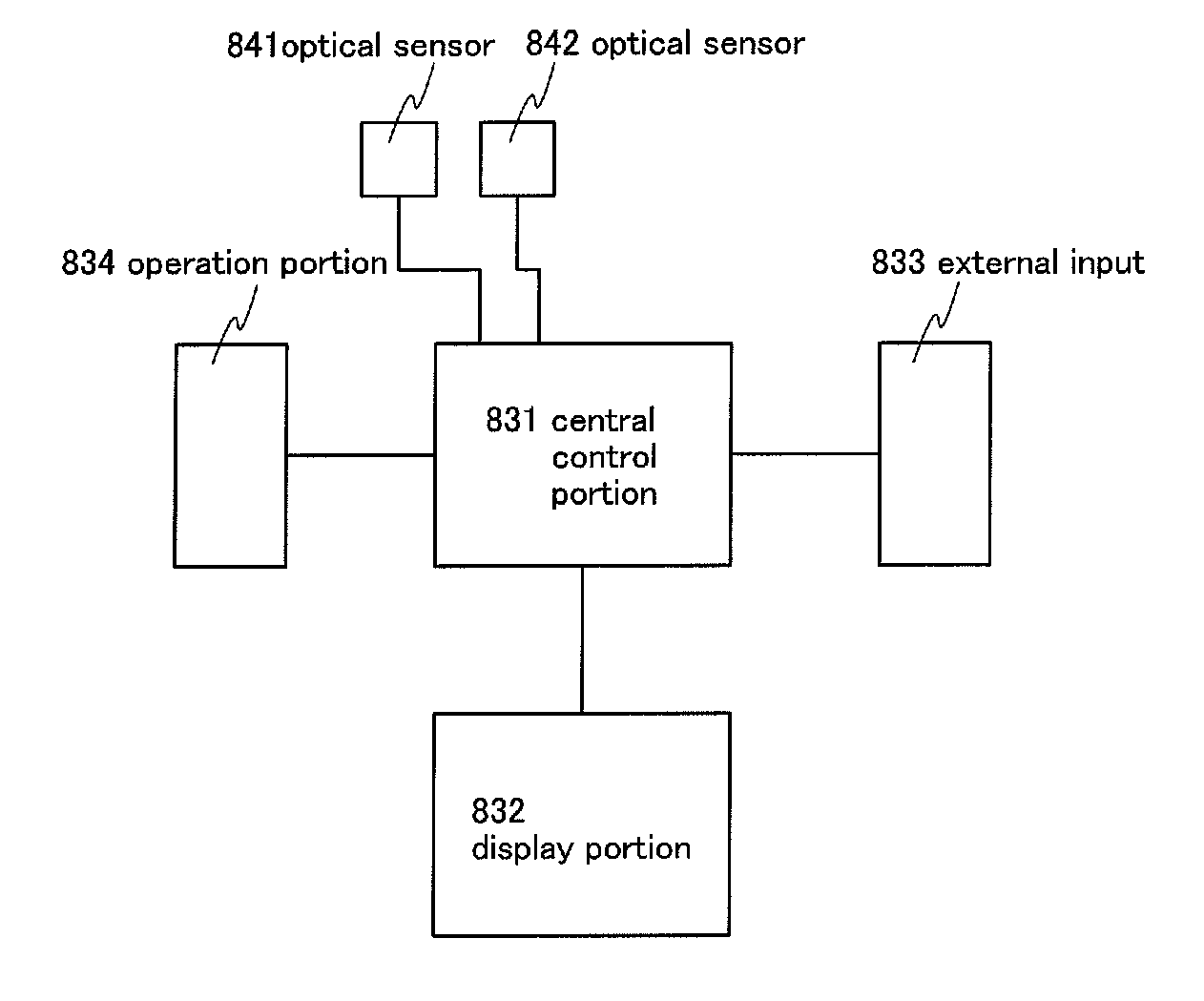
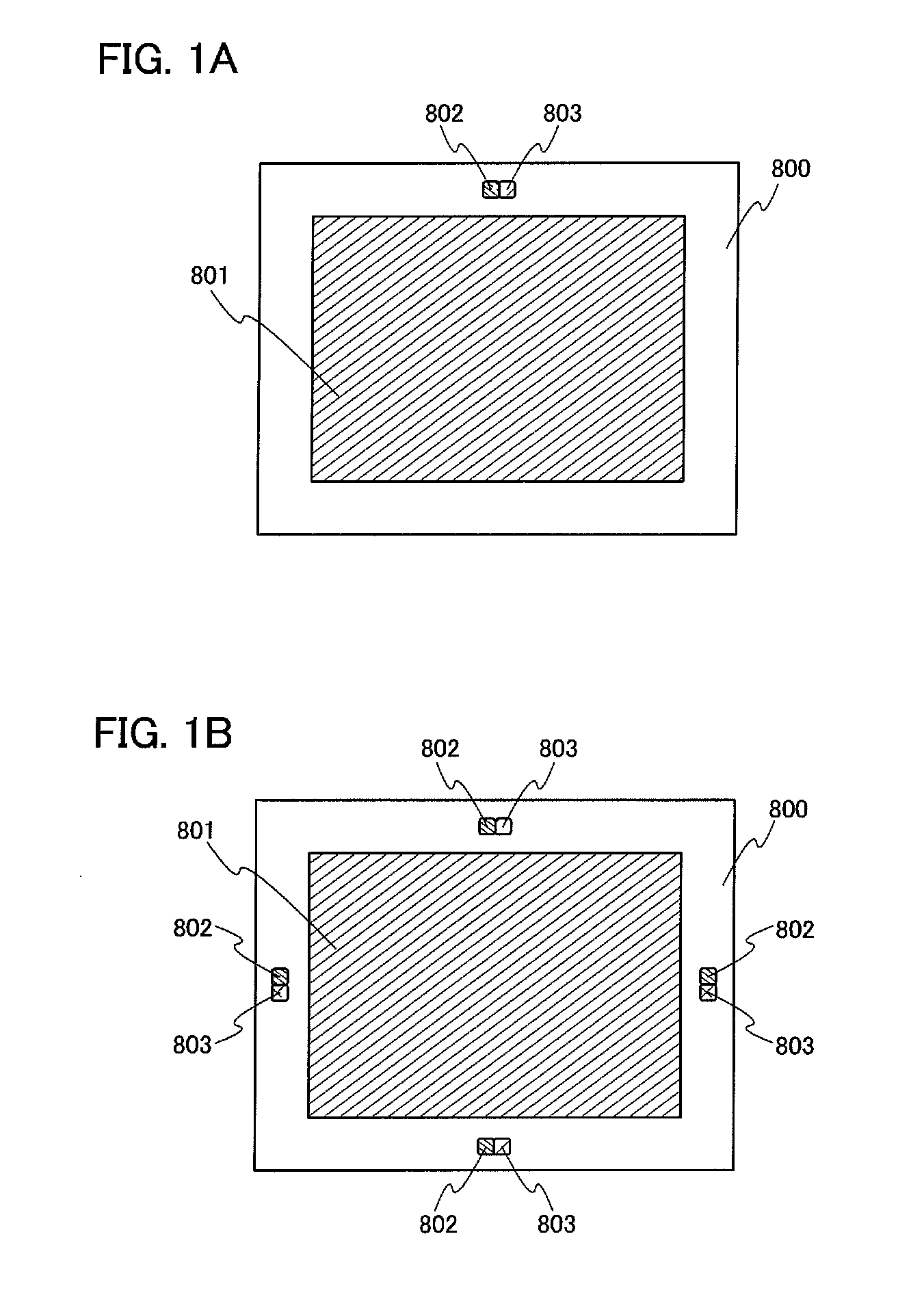
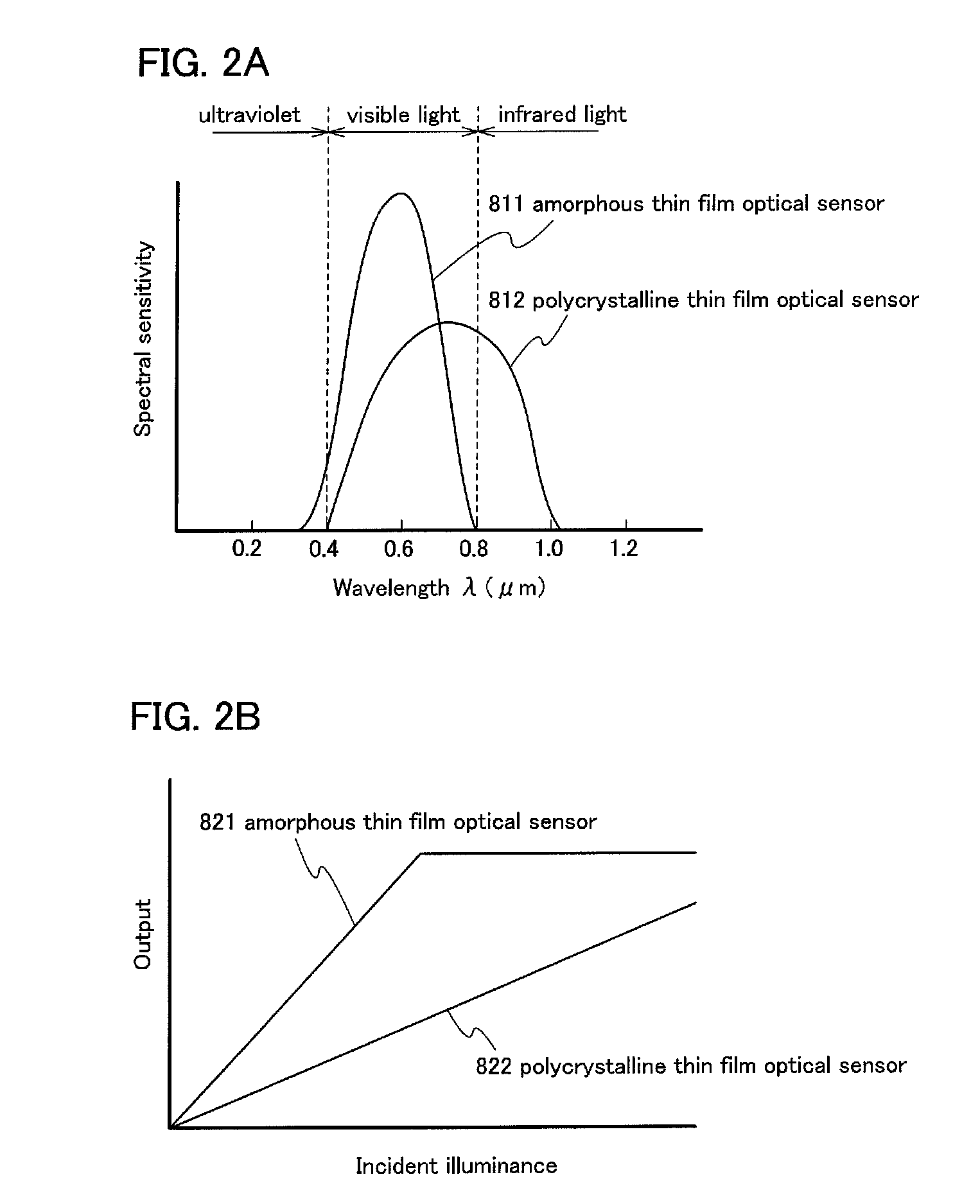
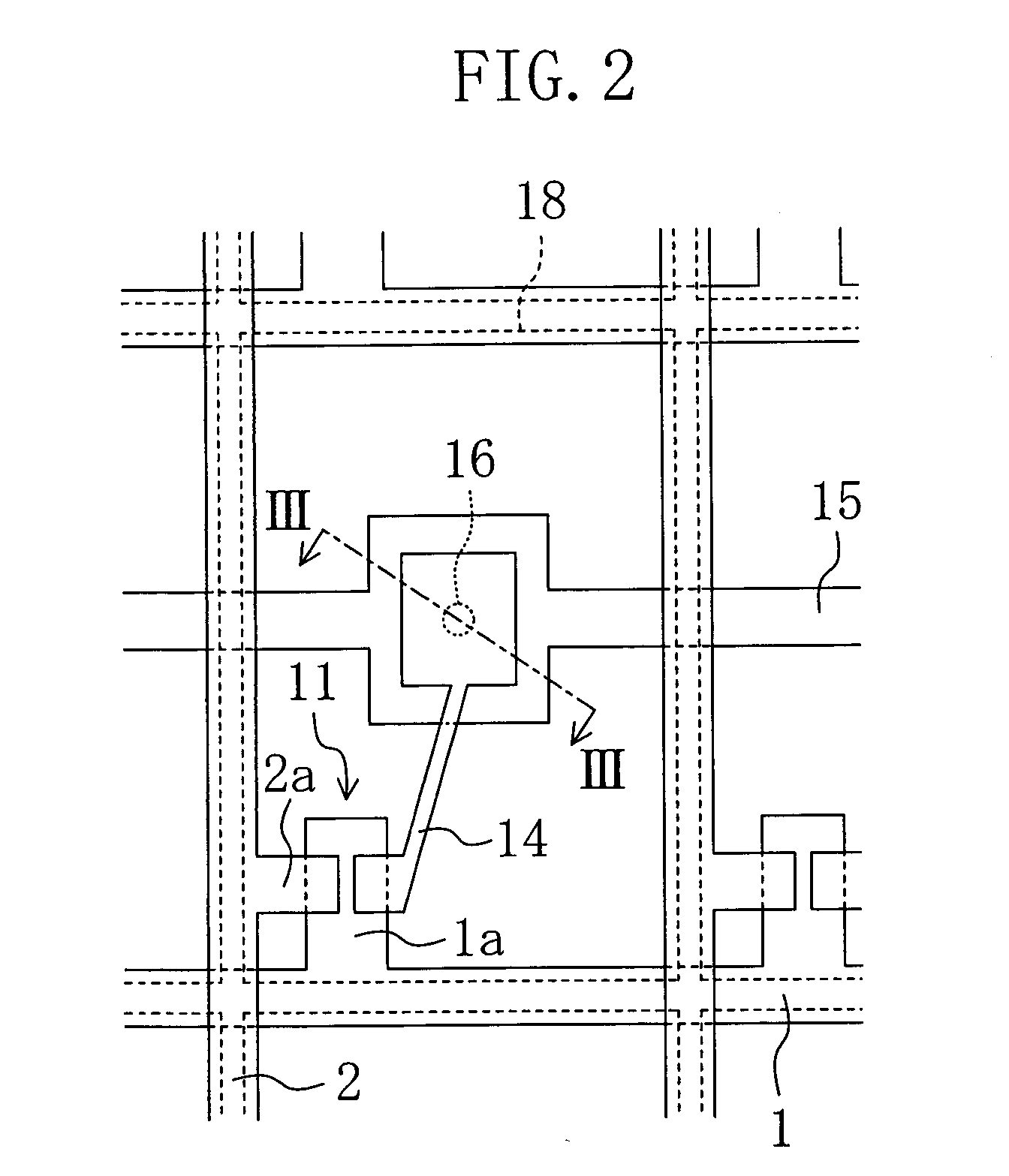
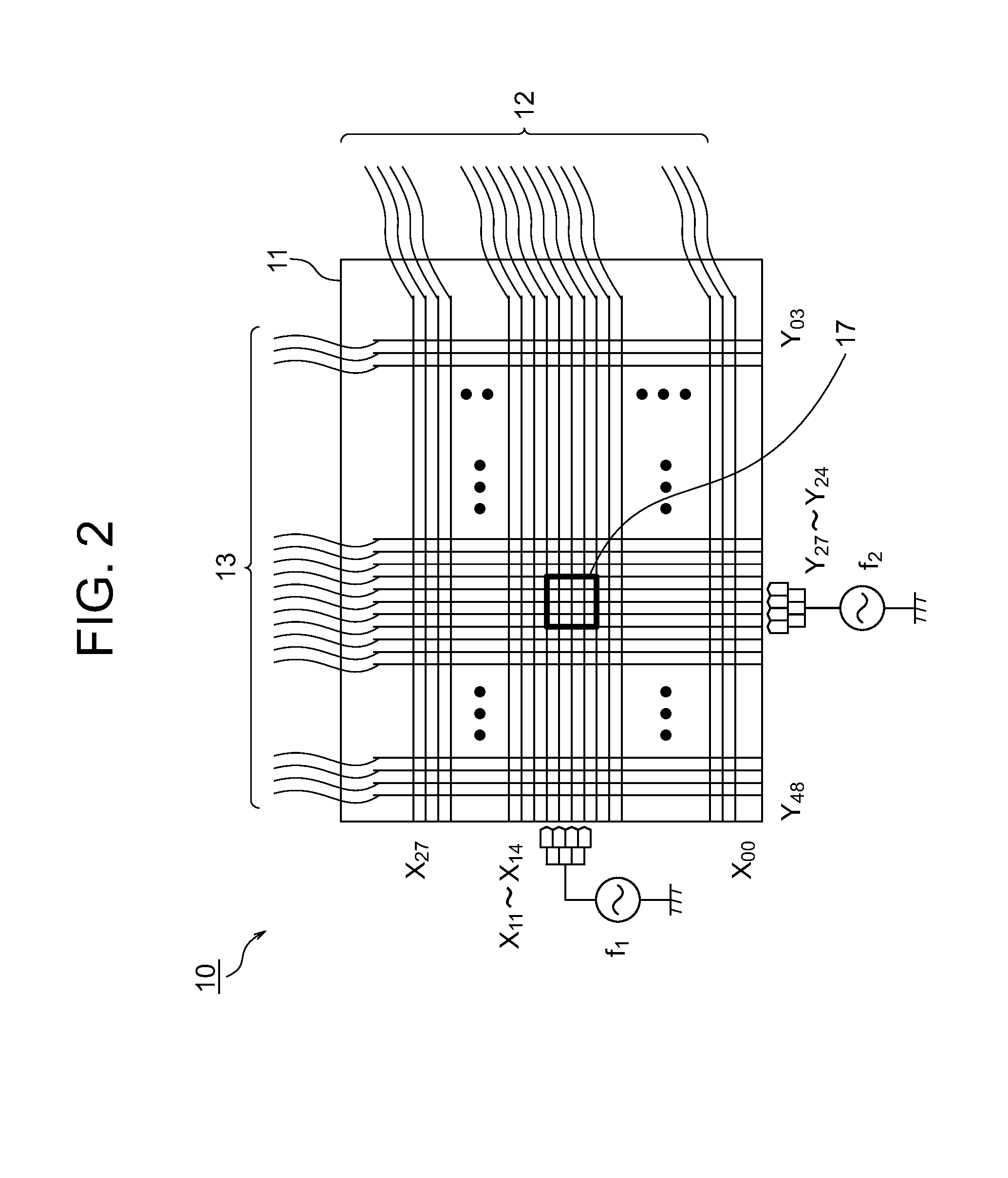
Display device including optical sensor and driving method thereof
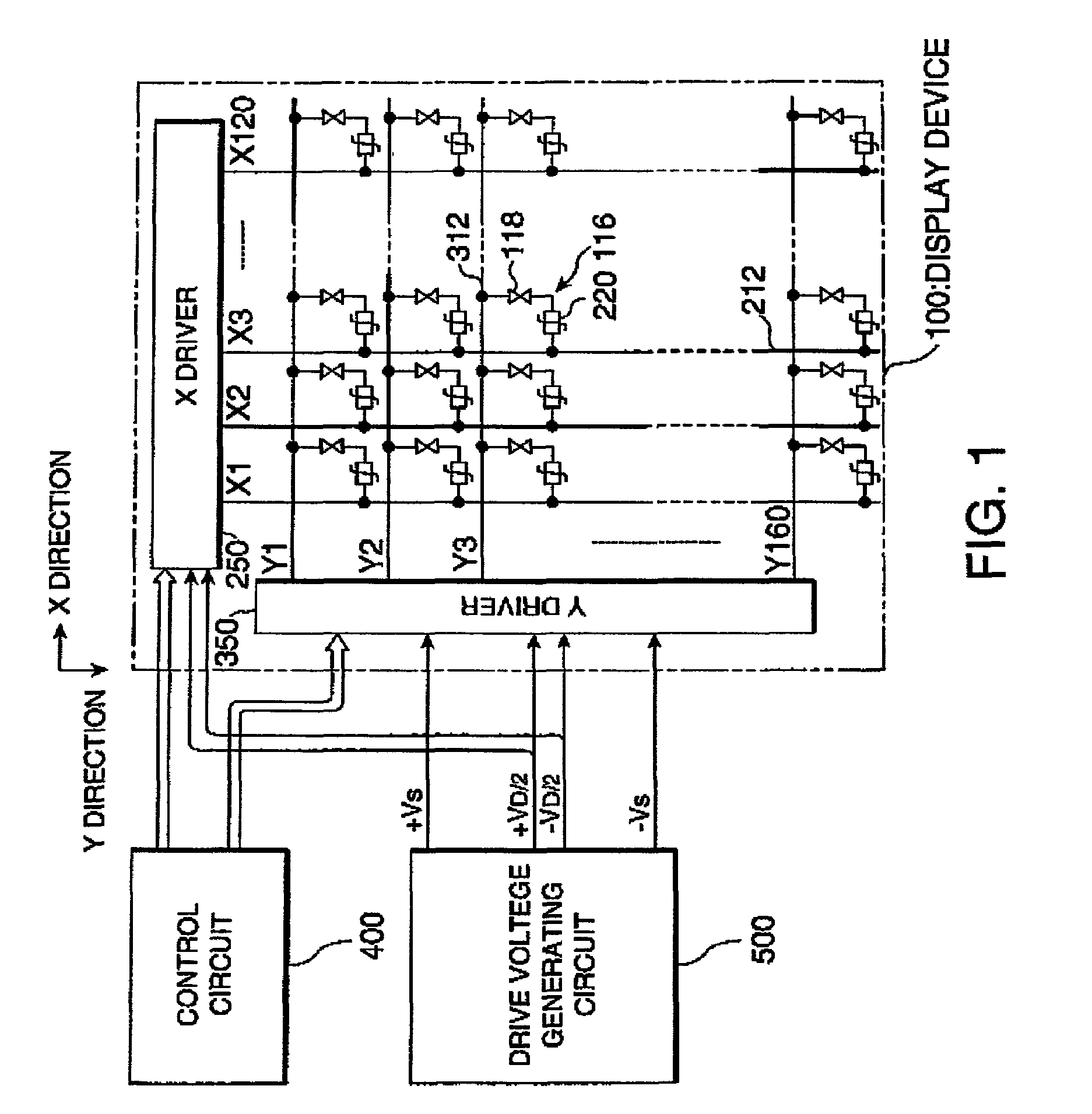
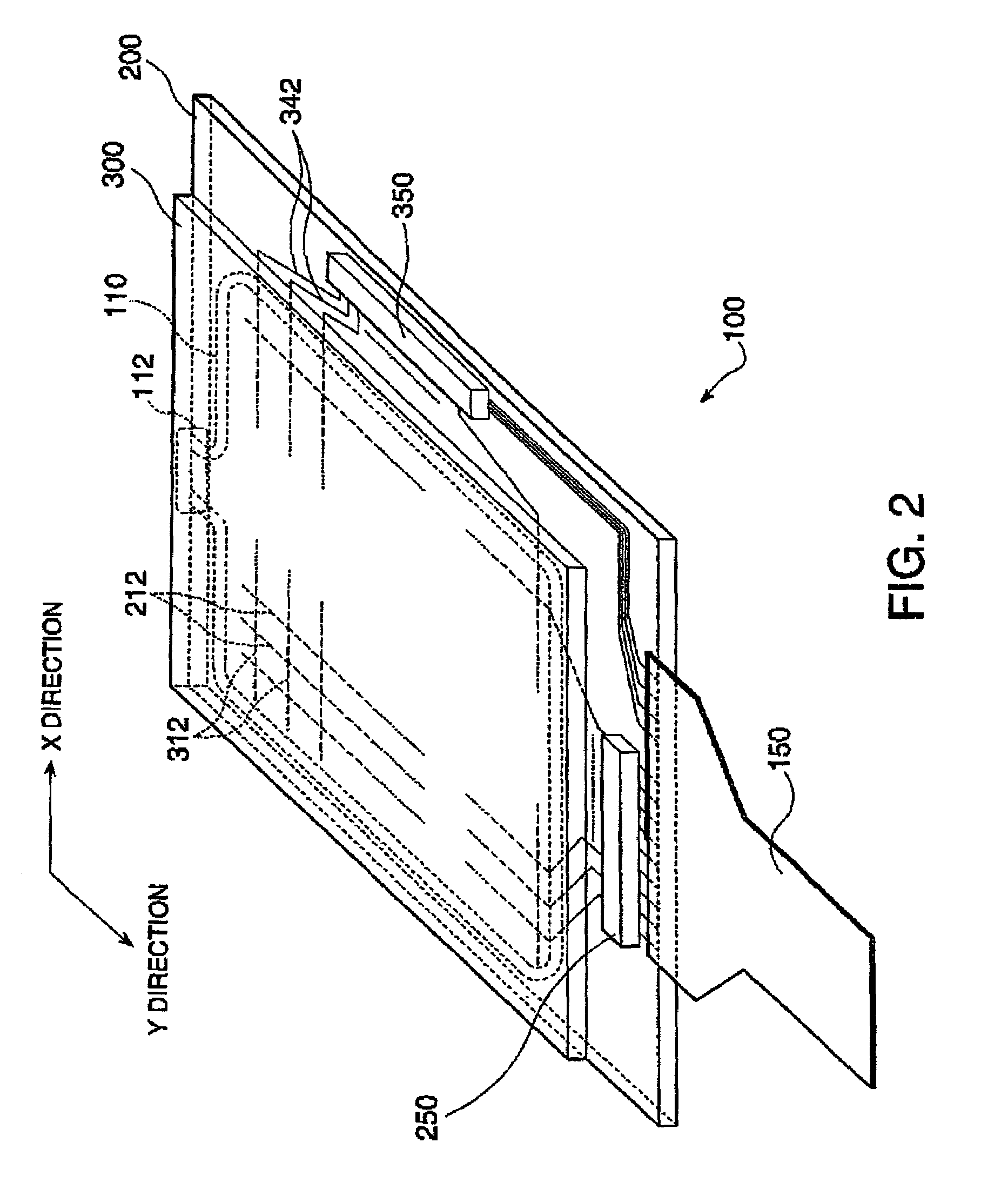
ActiveUS20110148835A1Low power consumptionGood display qualityAdvertisingCathode-ray tube indicatorsOxide semiconductorColor tone
An object is to provide a display device with low power consumption and good display quality. A first substrate is provided with a terminal portion, a pixel electrode, a switching transistor including an oxide semiconductor, a first optical sensor having high optical sensitivity to visible light, and a second optical sensor having optical sensitivity to infrared light and having lower optical sensitivity to visible light than the first optical sensor. The illuminance or color temperature around a display device is detected using the first and second optical sensors, and the luminance or color tone of a display image is adjusted. A second substrate is provided so as to face the first substrate, and is provided with a counter electrode. In a period for displaying a still image, the switching transistor is turned off so that the counter electrode is brought into a floating state.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
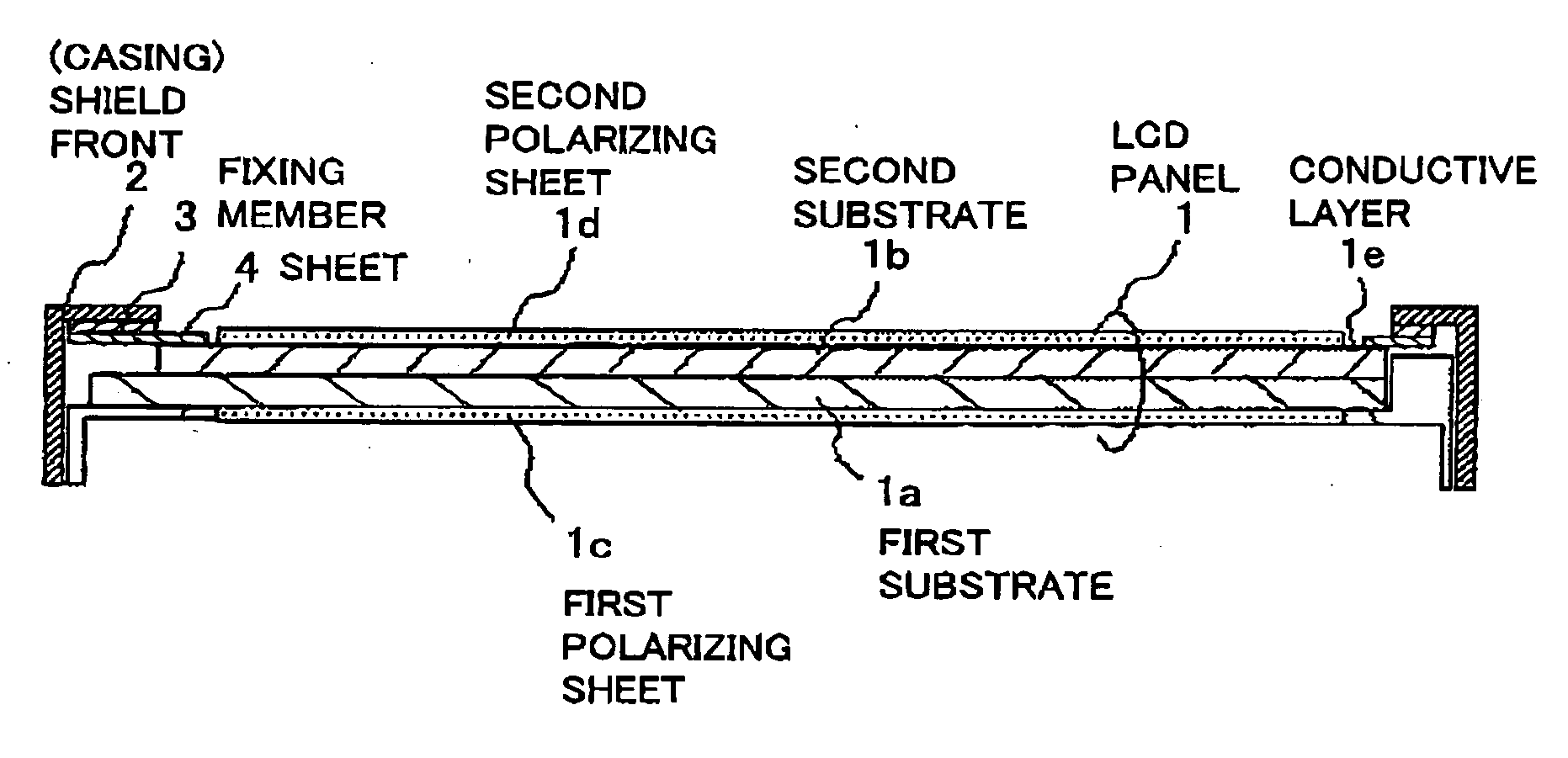
Liquid-crystal display device
InactiveUS20060158579A1Reduce processStrain is causedElectrographic process apparatusNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayElectrical and Electronics engineering
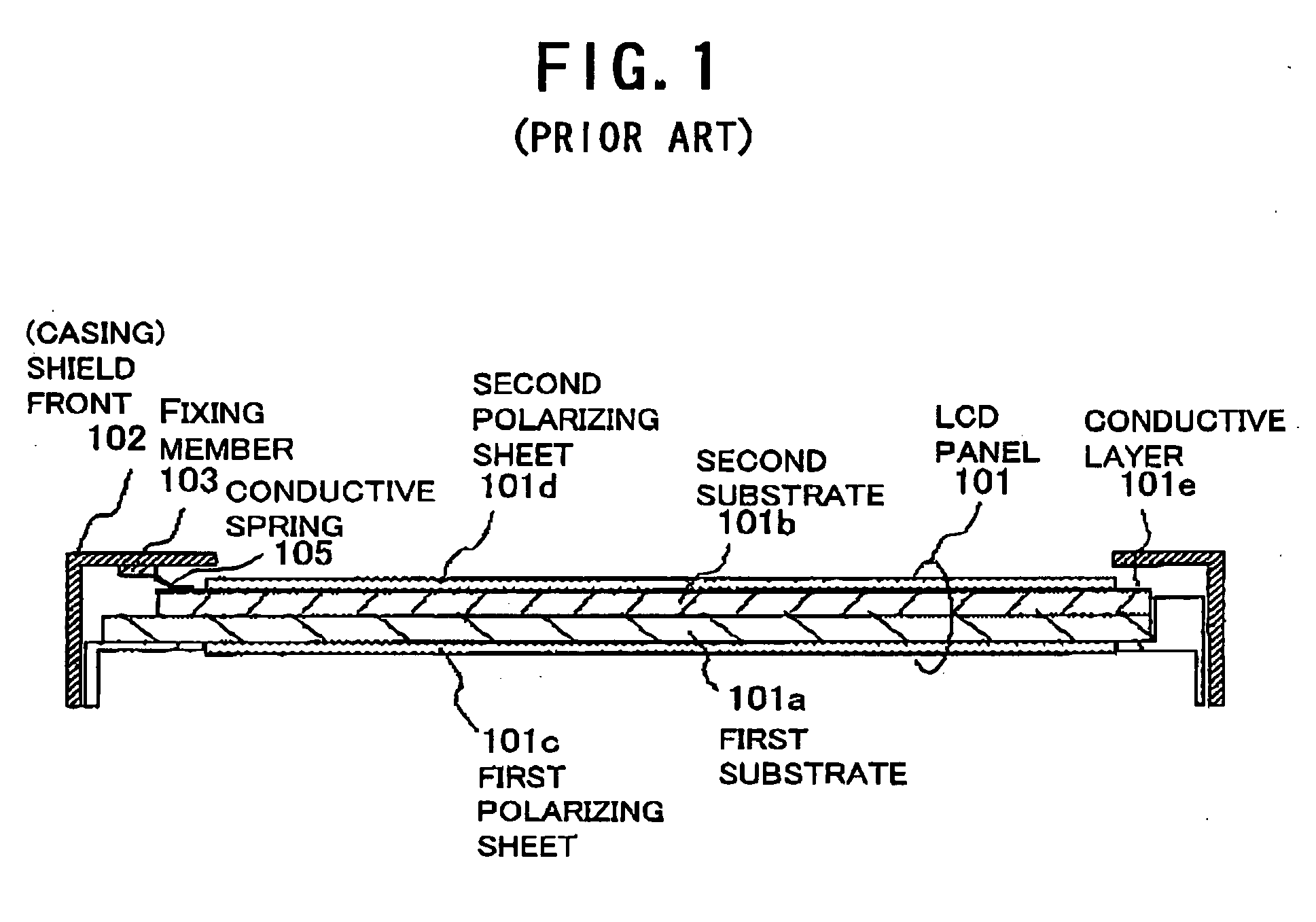
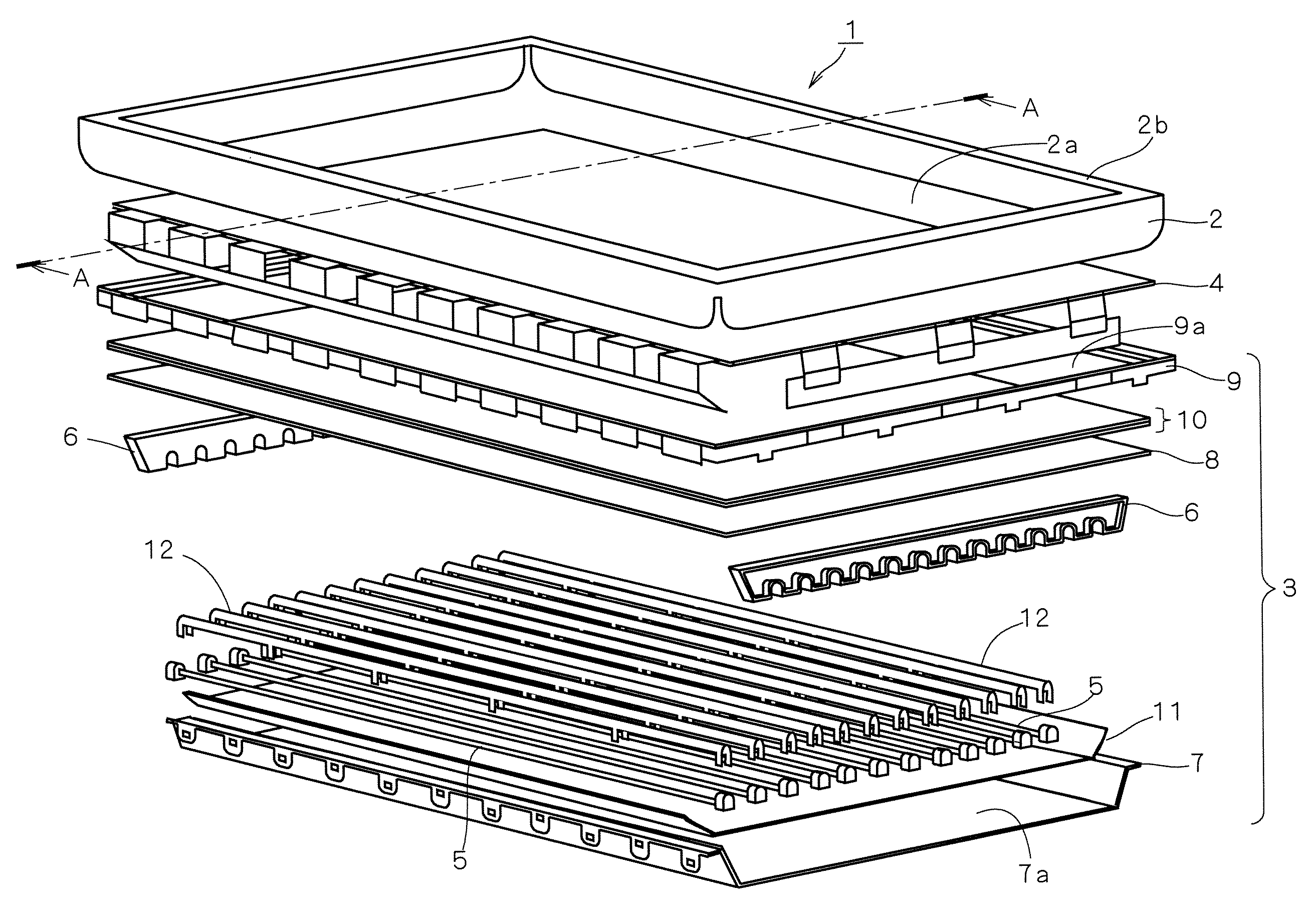
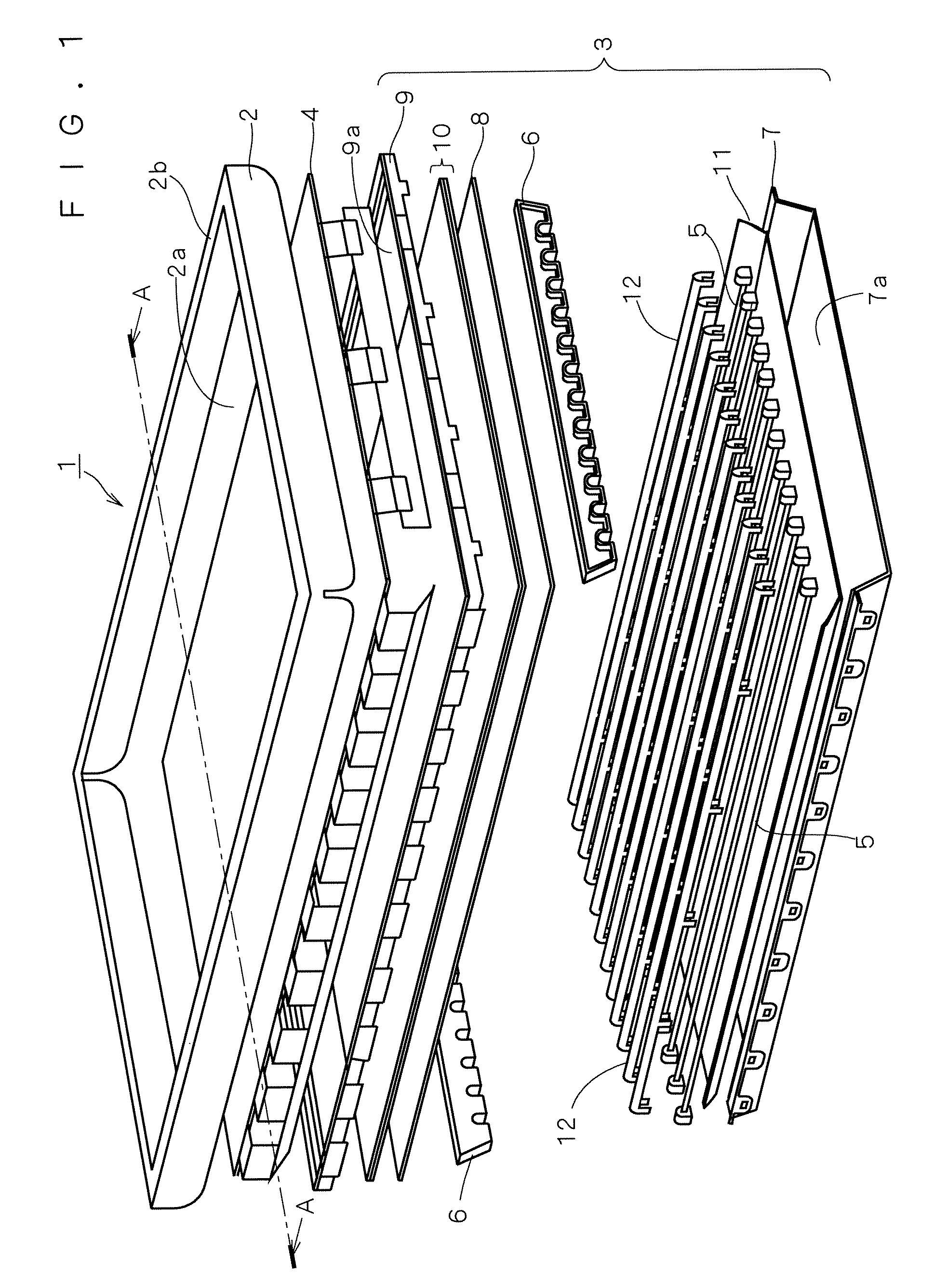
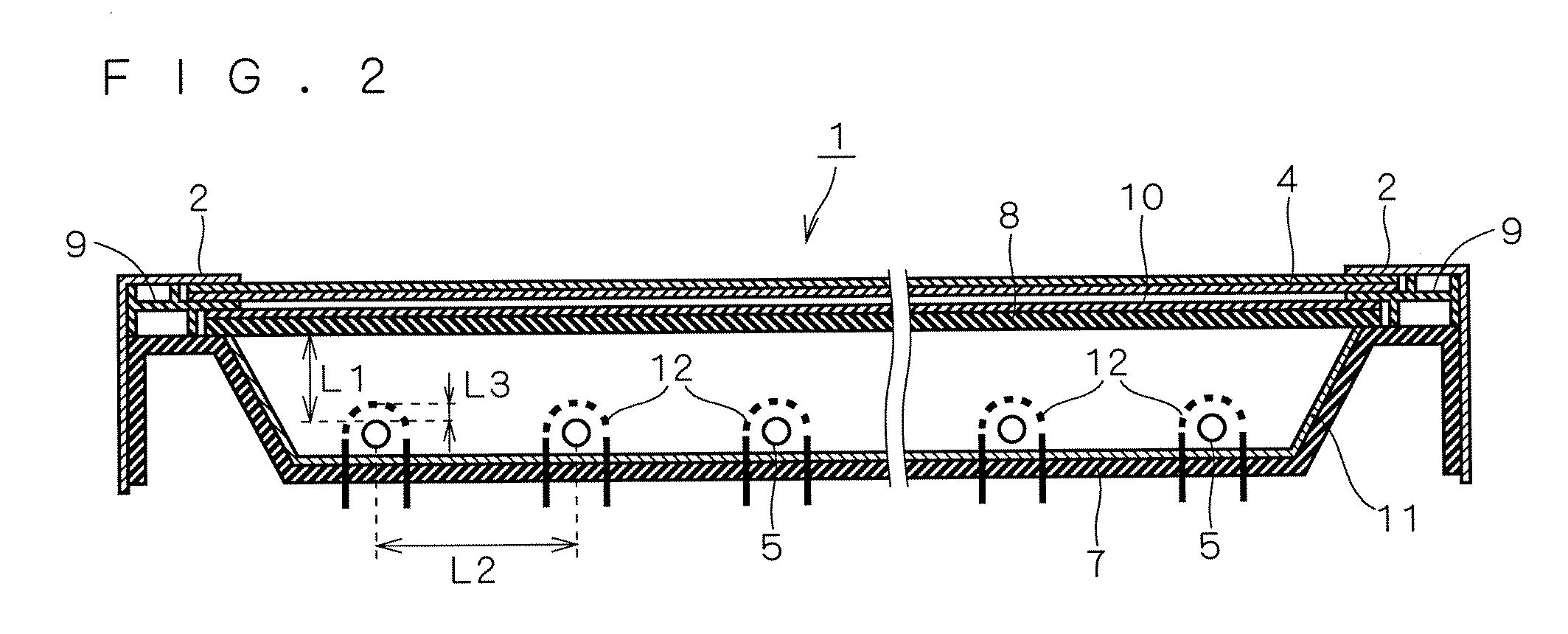
An LCD device suppresses the display quality degradation due to the mechanical strain of an LCD panel, the optical leakage through the gap between the frame-like portion of the casing (the shield front) and the panel, and the dust penetrated through the gap. The window of the casing or shield front is formed to be larger than an outer dimension of the second substrate. A sheet having electrical conductivity and a light-blocking property is placed in an approximately entire region sandwiched by an outer portion of the second substrate and a frame-like portion of the casing that surrounds the window. An electrically conductive layer is formed directly on or indirectly by way of an optical member on a surface of the second substrate, the surface being located on a side of the window. The sheet is connected to an inner surface of the frame-like portion of the casing and to the layer at the outer portion of the second substrate or on the member.
Owner:NEC LCD TECH CORP
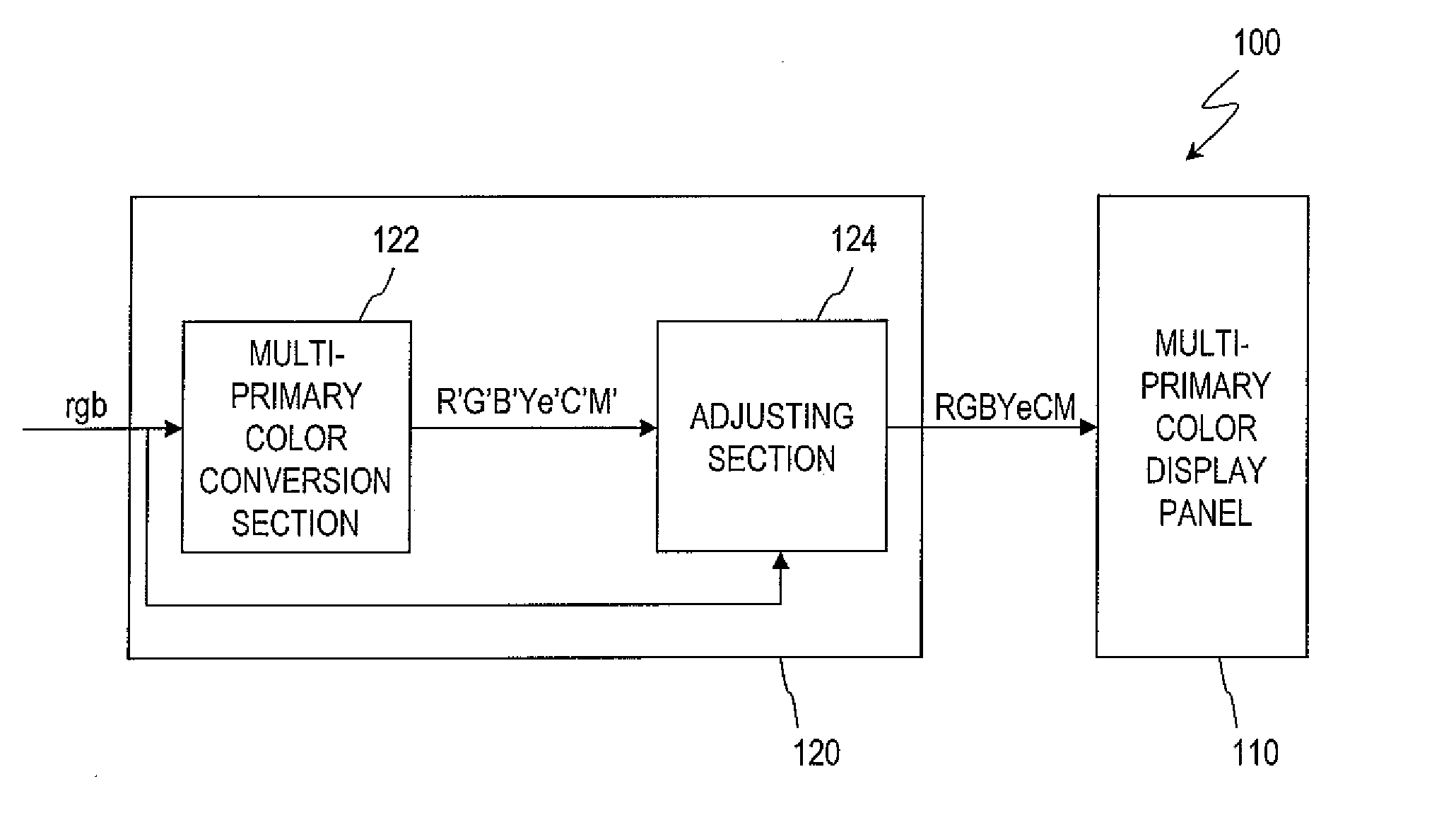
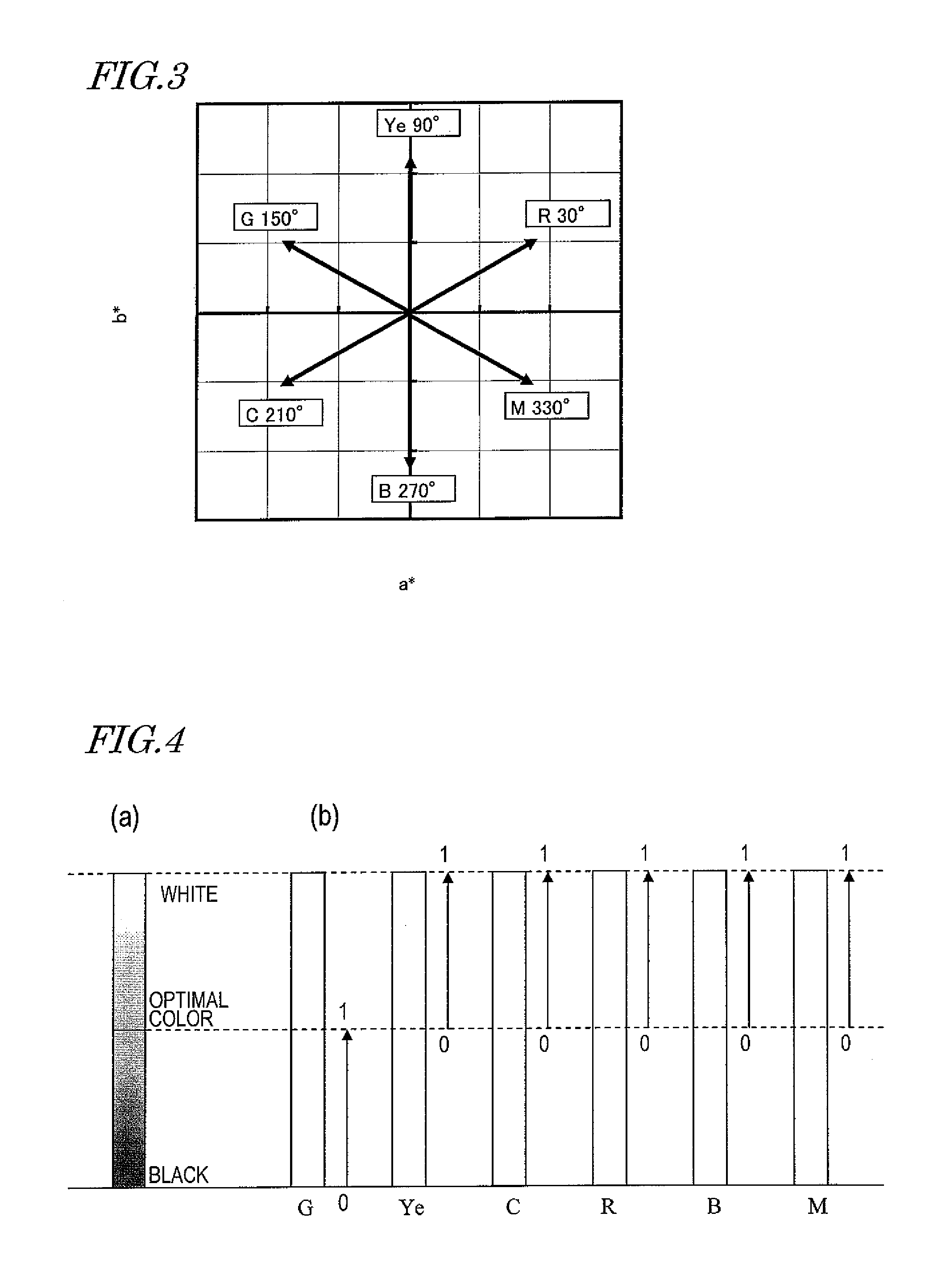
Multi-primary color display device
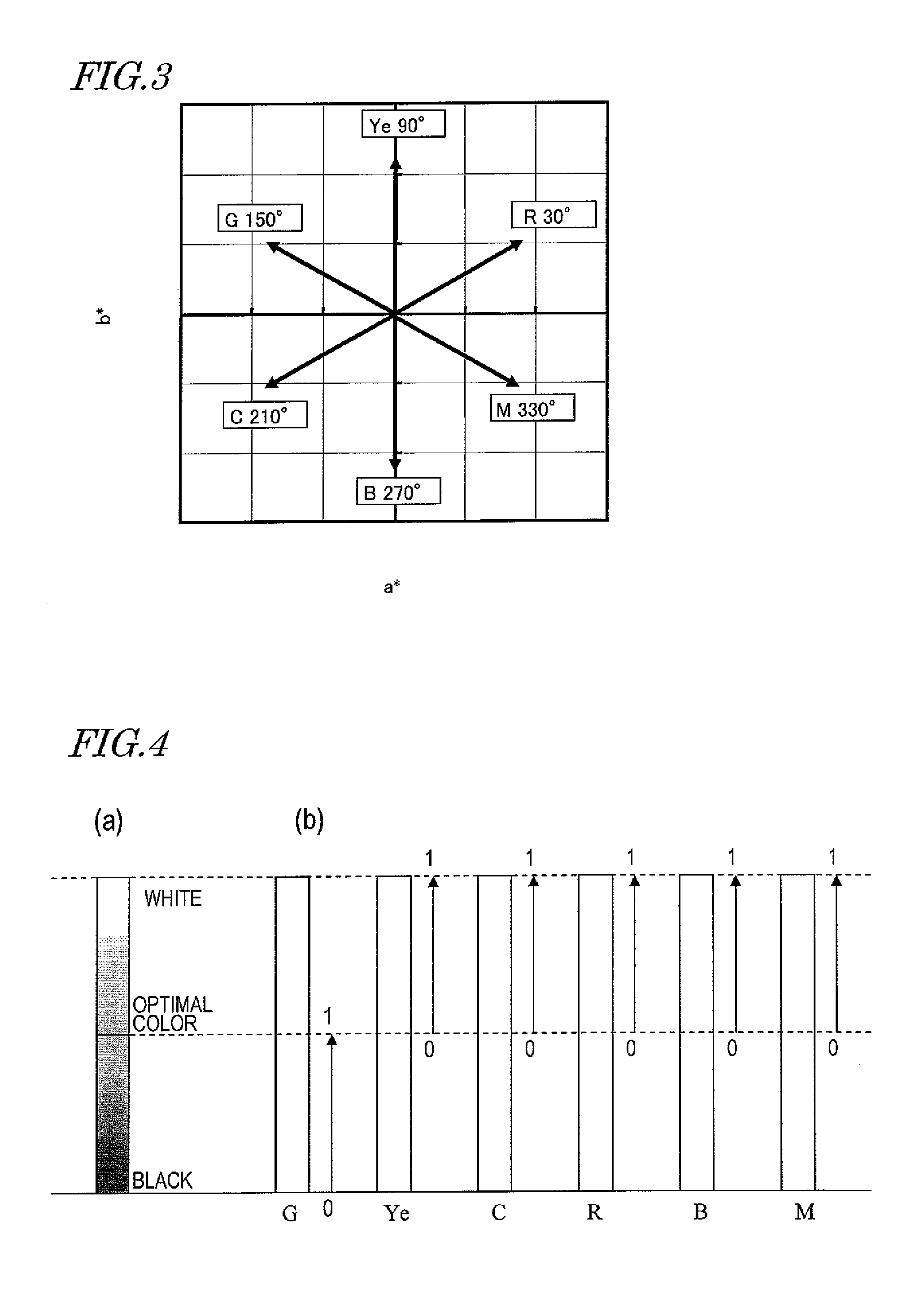
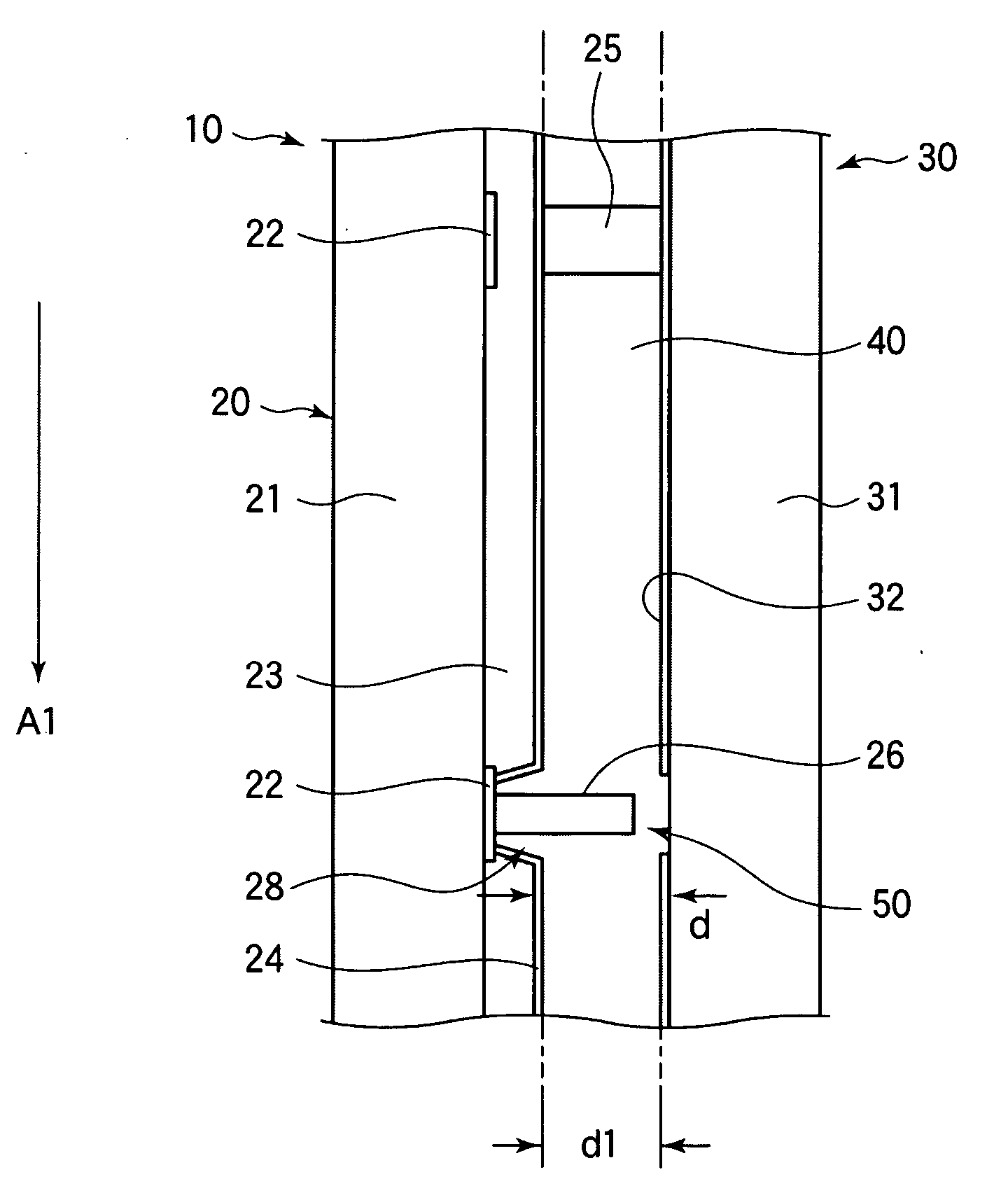
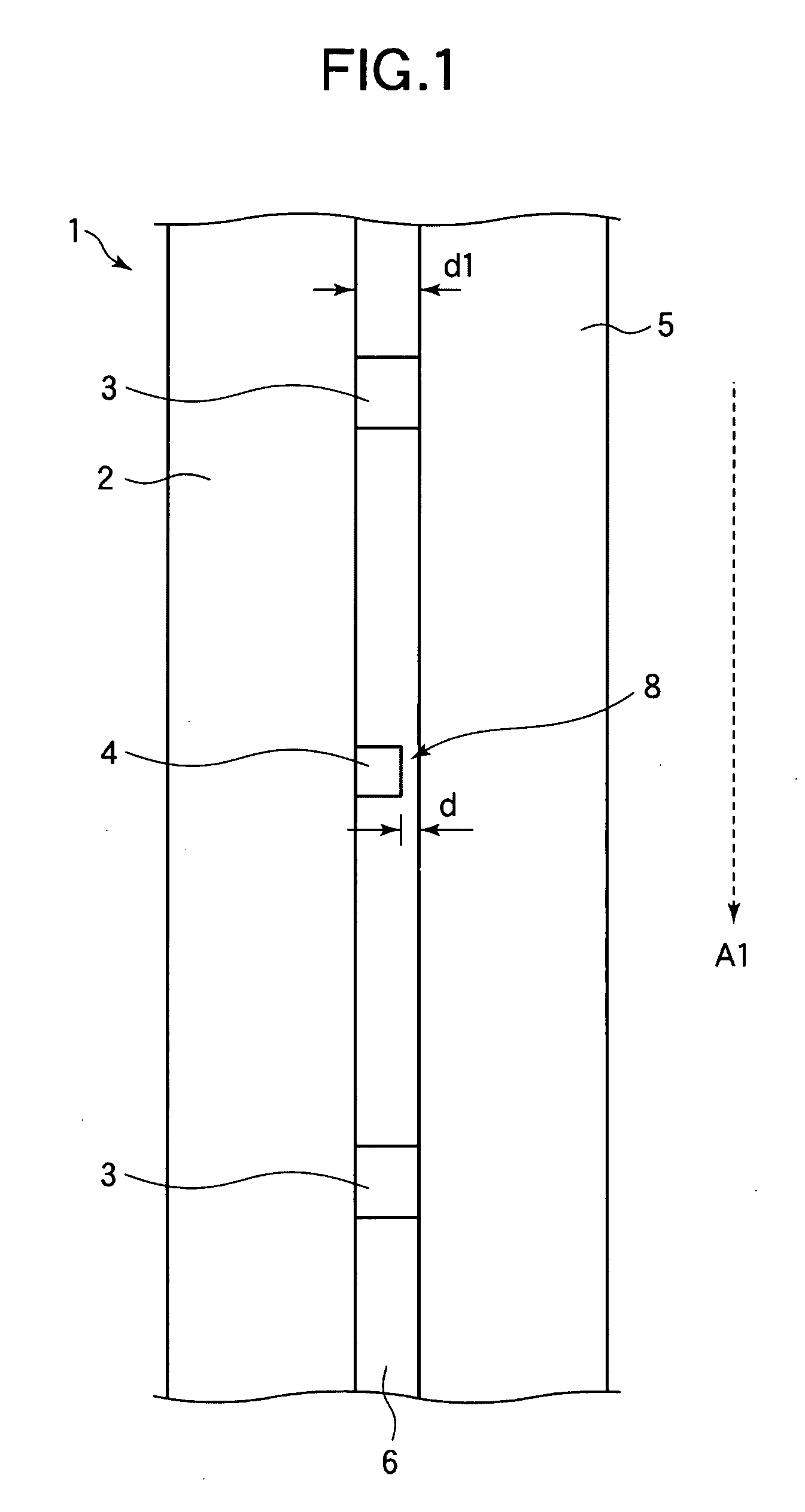
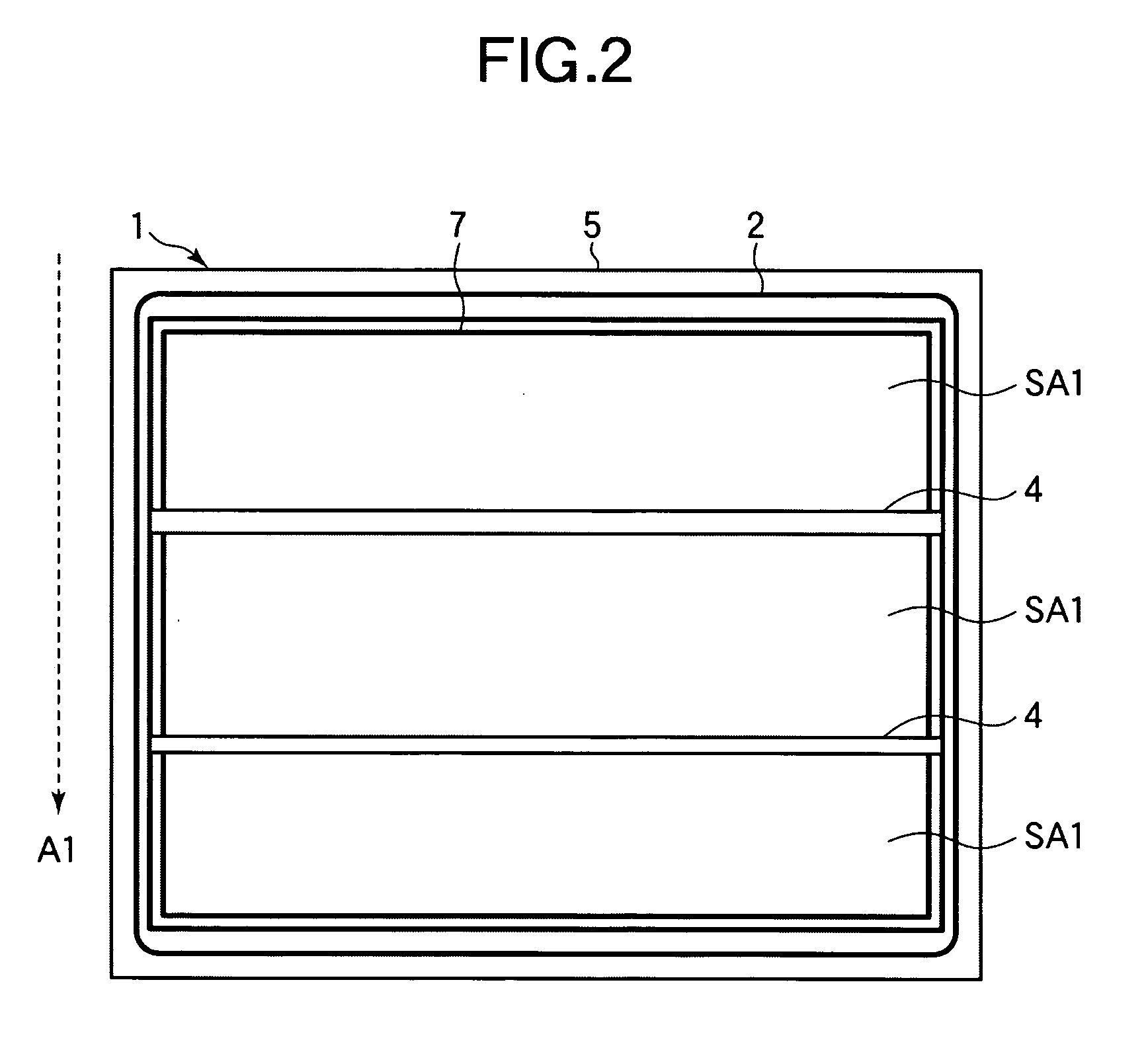
ActiveUS8405687B2Suppresses degradation of display qualityEasy to useColor signal processing circuitsCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer graphics (images)Hue
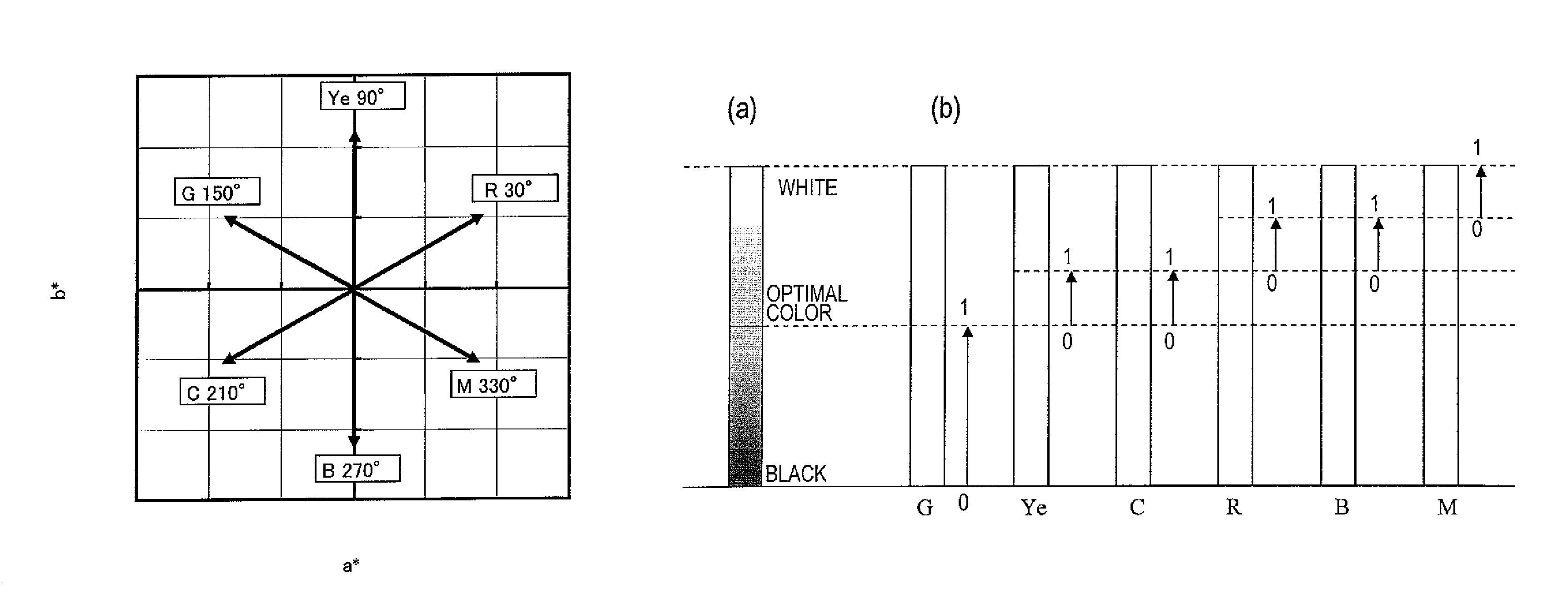
A multi-primary color display device according to the present invention includes pixels, each having a plurality of sub-pixels. The plurality of sub-pixels include first, second, third and fourth sub-pixels for displaying first, second, third and fourth colors having first, second, third and fourth hues. The second and third hues are adjacent to the first hue on both sides thereof on an a*b* plane of an L*a*b* colorimetric system. When a color displayed by each pixel changes from black to an optimal color of the first hue, luminance values of the plurality of sub-pixels are set such that the luminance value of the first sub-pixel starts to be increased and also the luminance values of the second and third sub-pixels start to be increased at a rate of increase lower than the rate of increase of the first sub-pixel.
Owner:SHARP KK
Display device
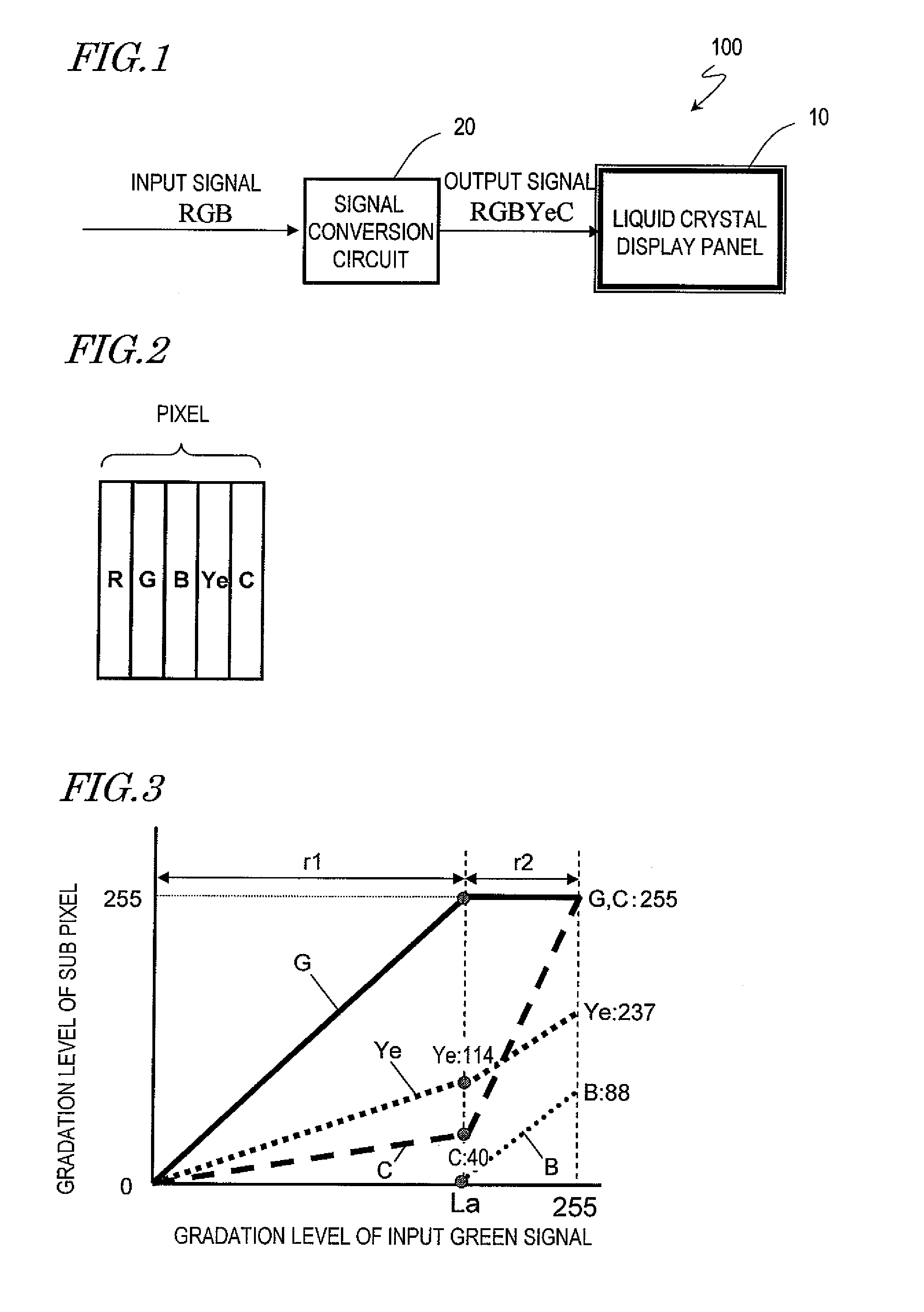
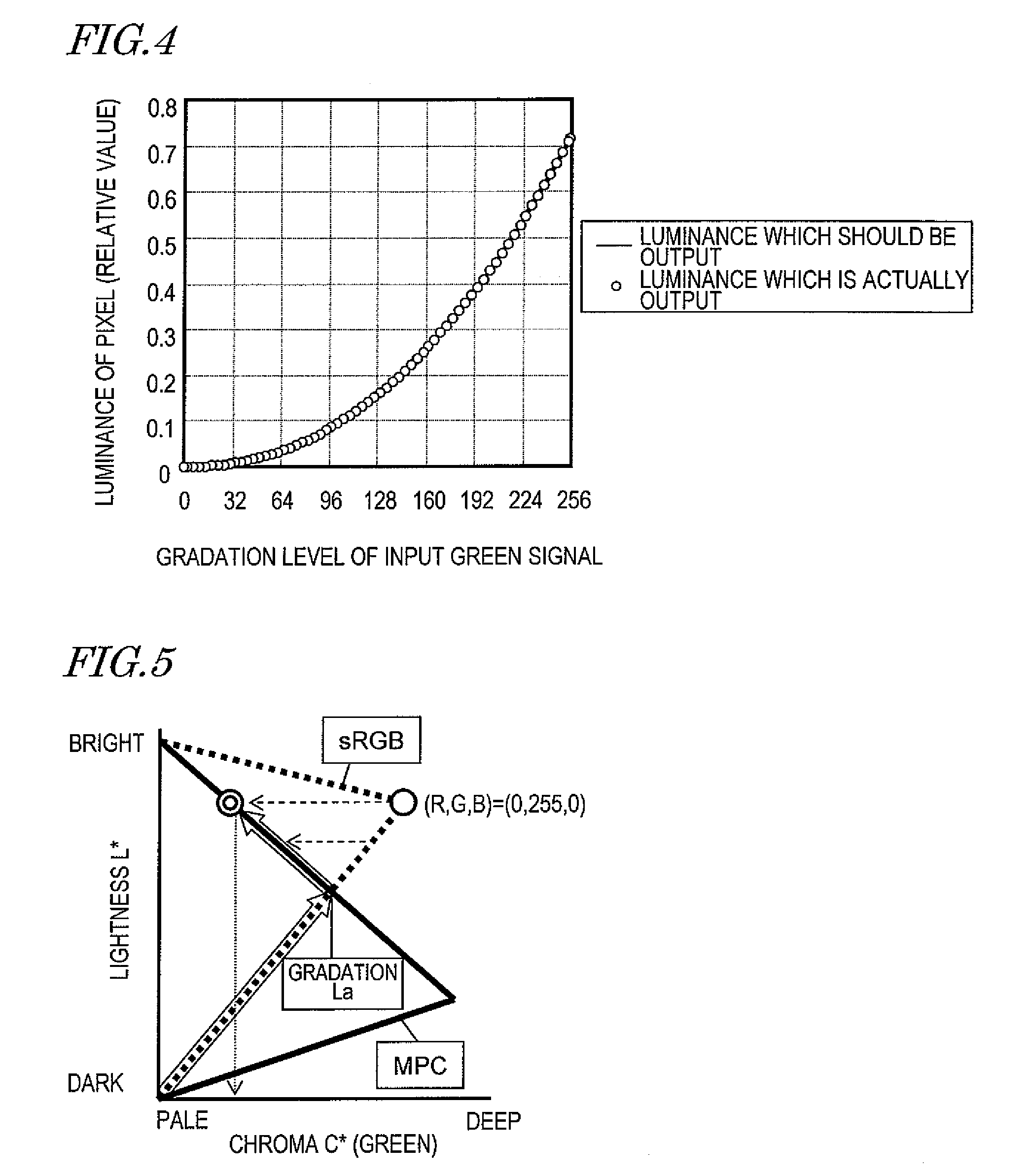
InactiveUS8436875B2Suppresses degradation of display qualityColor signal processing circuitsCathode-ray tube indicatorsSRGBComputer graphics (images)
Owner:SHARP KK
Display device
InactiveUS20050168423A1Deterioration of display qualityNo increase in costCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsDisplay devicePattern recognition
A display device includes a plurality of pixels arranged in a matrix. At least one of the pixels includes two sub-pixel groups. Each of the sub-pixel groups includes sub-pixels of three or more colors. Sub-pixels of the same color in each pixel are driven by the same signal.
Owner:SHARP KK
Display device, electronic apparatus and lighting device
ActiveUS8801260B2Suppresses degradation of display qualityEasy to assemblePlanar/plate-like light guidesNon-linear opticsEffect lightDisplay device
In a lighting device of a display device, a plurality of light emitting elements are mounted on a surface of a light source substrate, and the light source substrate is supported by a light source support member by means of a positioning (fixing) structure such as a metal screw. The plurality of light emitting elements are divided into a plurality of blocks, and the emission light amount can be controlled with respect to each of the blocks. Although the head of the screw is exposed on the surface of the light source substrate, the screw is located between adjacent ones of the blocks. Therefore, even though the illuminating light intensity becomes partially discontinuous owing to the presence of the screw, degradation of display quality originating from such discontinuity can be suppressed.
Owner:138 EAST LCD ADVANCEMENTS LTD
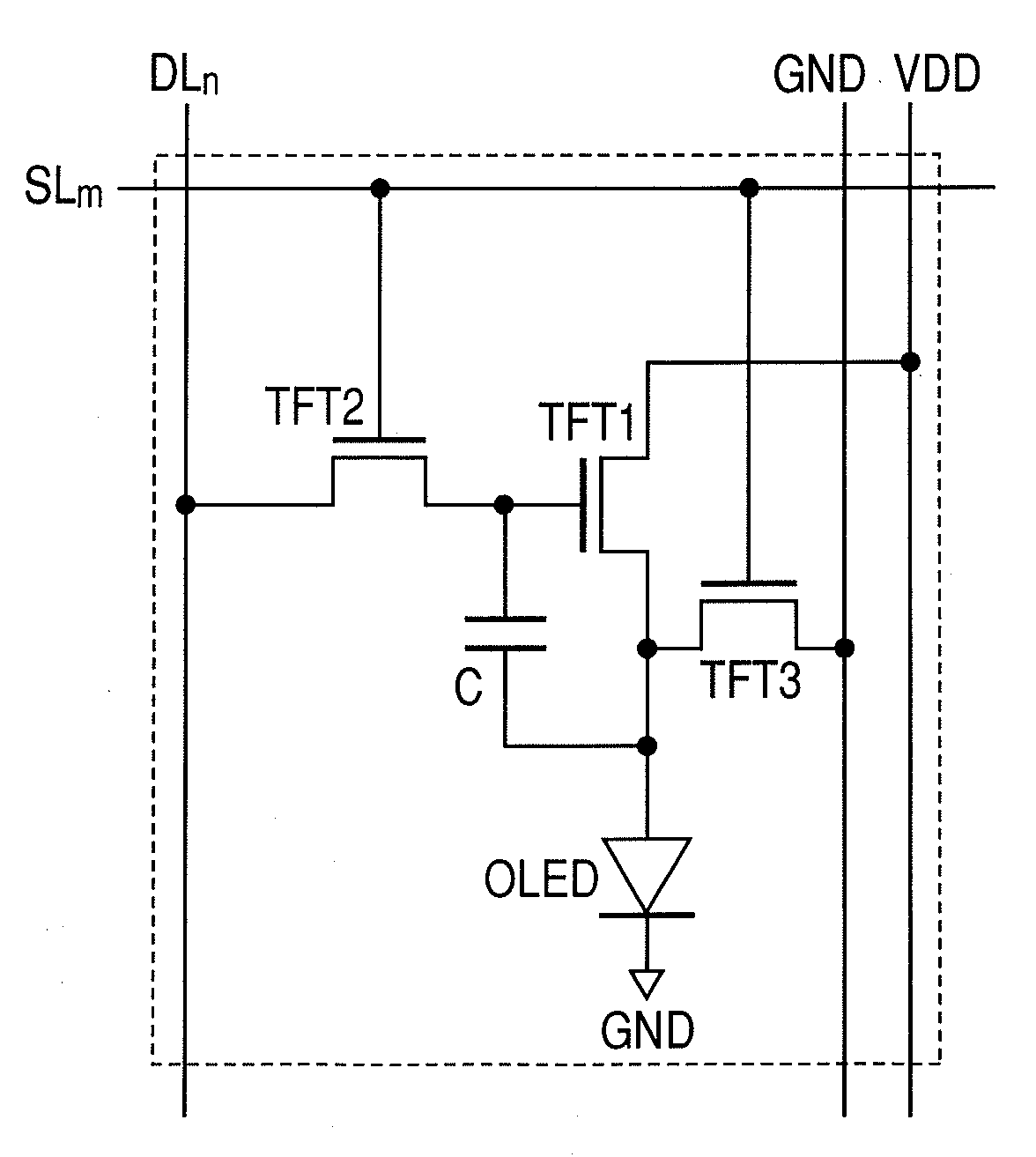
Thin film transistor circuit, light emitting display apparatus, and driving method thereof
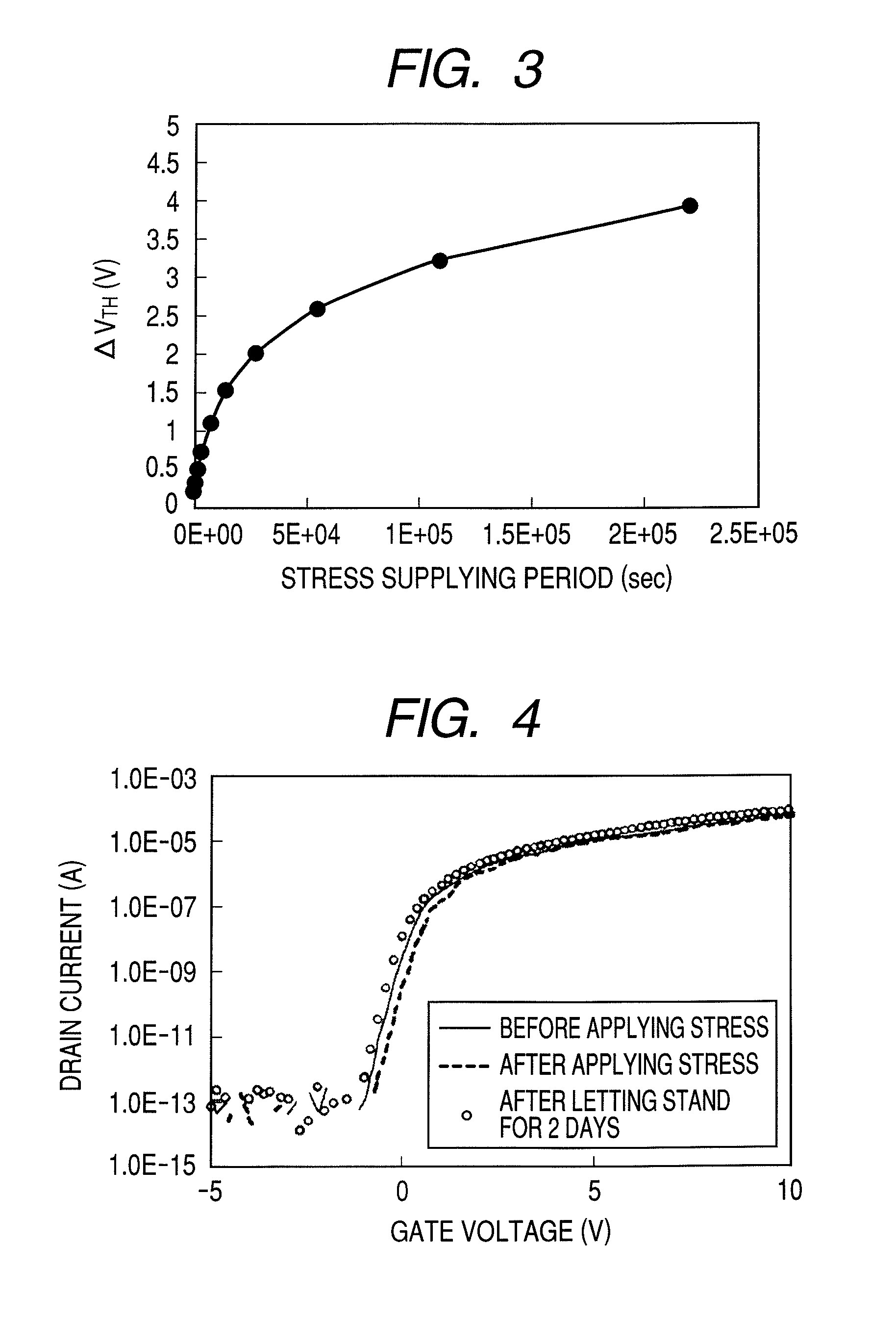
InactiveUS8654114B2Suppresses degradation of display qualityInhibition effectCathode-ray tube indicatorsElectric pulse generatorHemt circuitsElectric stress
In order to suppress an influence of an electrical stress on a TFT characteristic in use of a TFT, a light emitting display apparatus according to the present invention comprises organic EL devices and driving circuits for driving the organic EL devices. The driving circuit includes plural pixels each having a thin film transistor of which a threshold voltage reversibly changes due to the electrical stress applied between a gate terminal and a source terminal, and a voltage applying unit which sets gate potential of the thin film transistor higher than source potential. The voltage applying unit applies the electrical stress between the gate terminal and the source terminal at a time when the thin film transistor is not driven, so as to drive the thin film transistor in a region that the threshold voltage is saturated to the electrical stress.
Owner:CANON KK
Display device having pixels including a plurality of sub-pixels
InactiveUS7710388B2Suppresses degradation of display qualityQuality improvementCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsDisplay deviceComputer vision
A display device includes a plurality of pixels arranged in a matrix. At least one of the pixels includes two sub-pixel groups. Each of the sub-pixel groups includes sub-pixels of three or more colors. Sub-pixels of the same color in each pixel are driven by the same signal.
Owner:SHARP KK
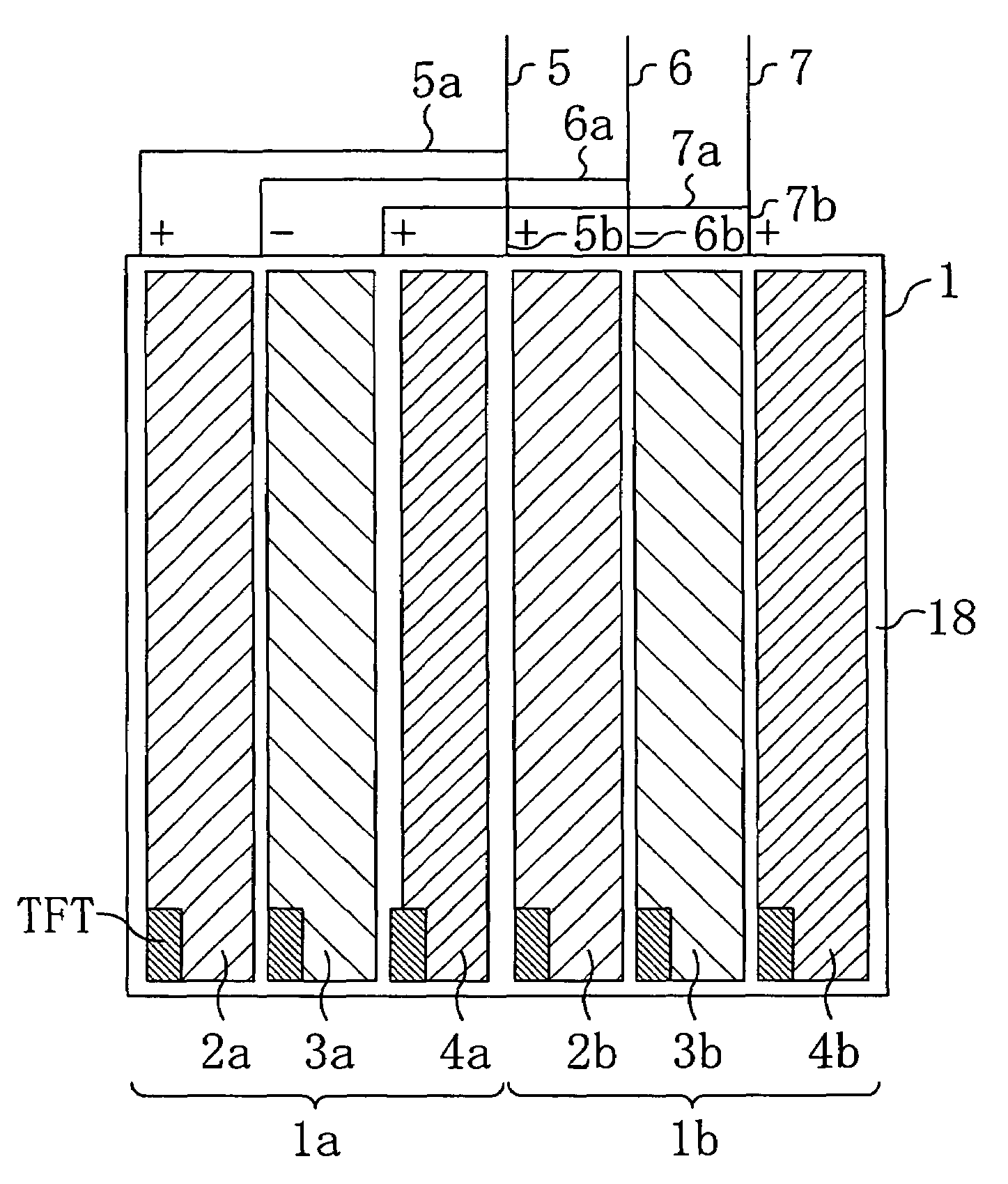
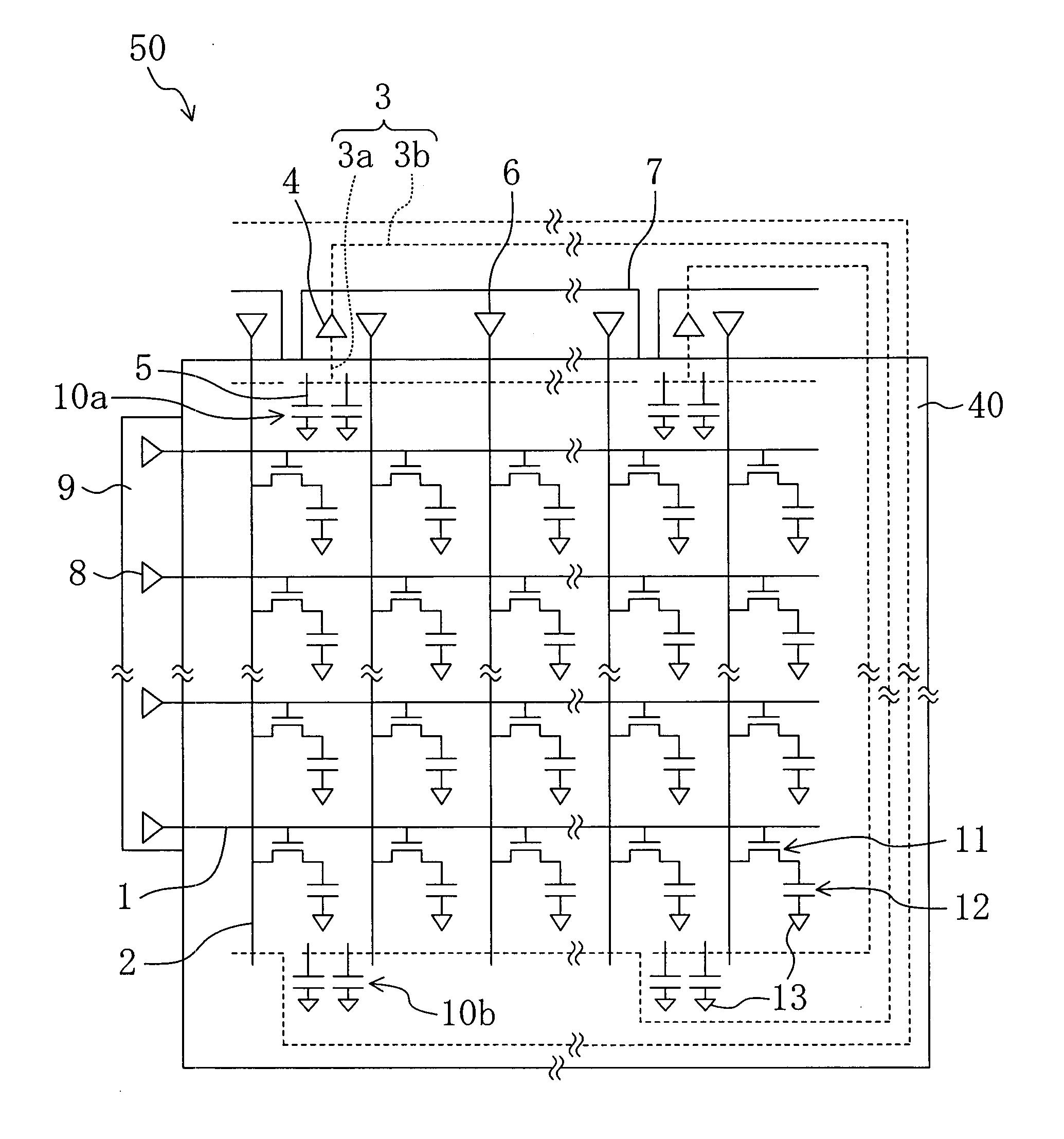
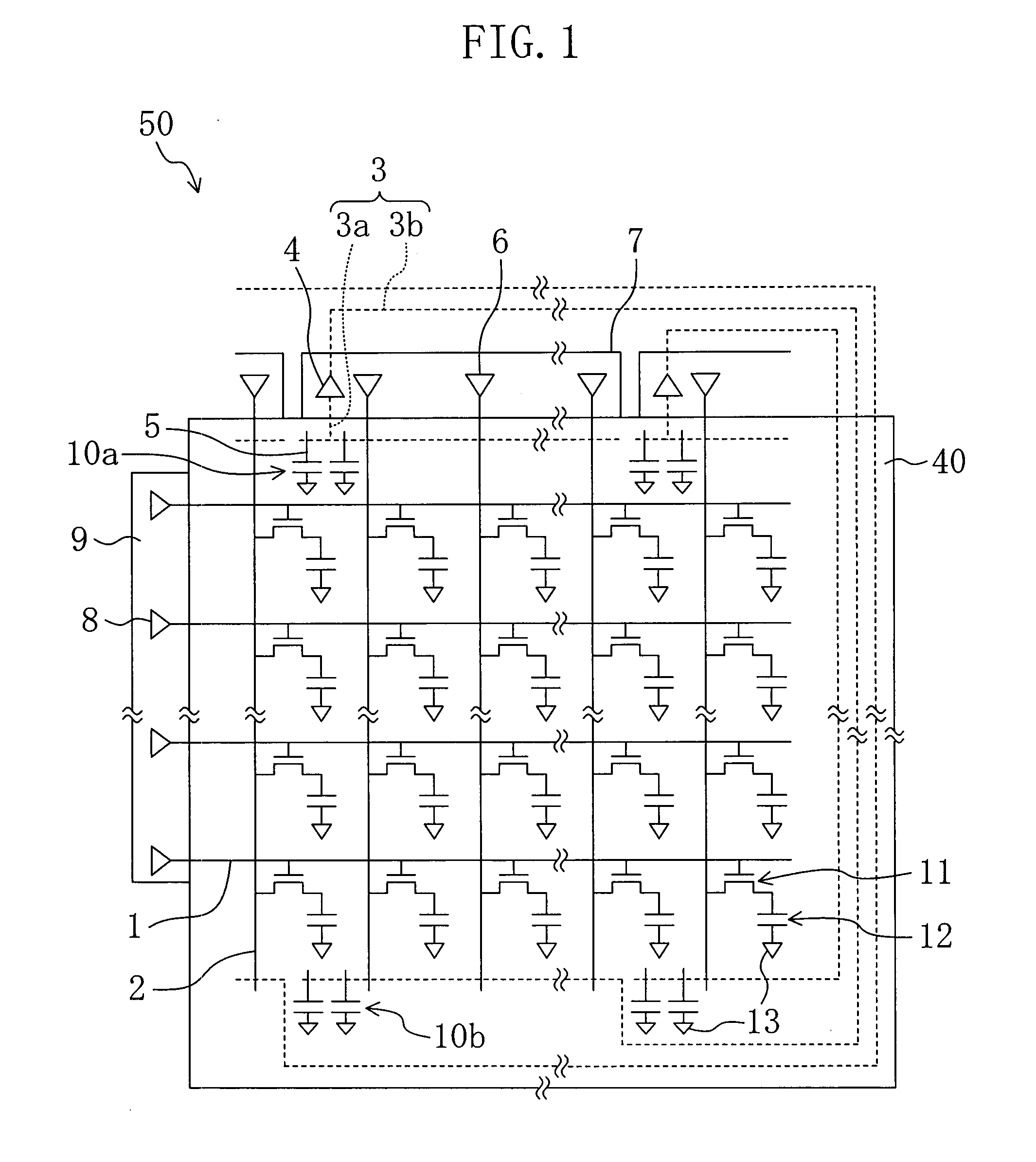
Display Device, Liquid Crystal Display Device, And Method For Producing A Display Device
InactiveUS20070285595A1Suppresses degradation of display qualityCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayDisplay device
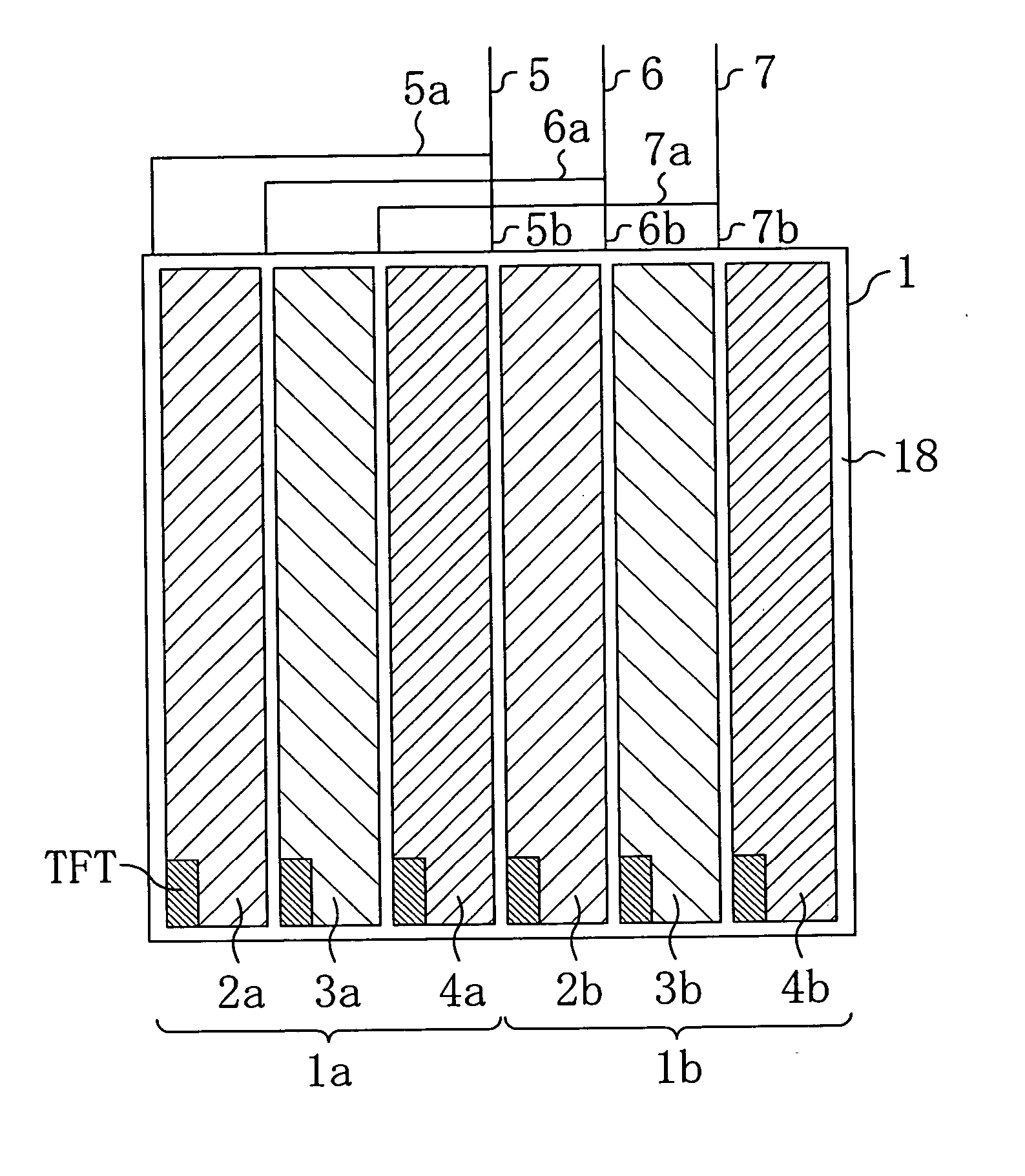
A liquid crystal display device includes: a plurality of source lines (2) to which a signal voltage according to a source signal is applied; a first wire (3a) and a second wire (3b) for fixing a wire breakage that are configured so that they can be connected to opposite ends of at least one of the plurality of source lines (2); and a buffer section (4) provided between the first wire (3a) and the second wire (3b) for impedance conversion along the first wire (3a) and the second wire (3b), wherein the liquid crystal display device includes spare capacitors (10a) and (10b) for adjusting a signal waveform according to the source signal applied to the source lines (2a) and (2b) with the first wire (3a) and the second wire (3b) being connected to the source lines (2a) and (2b).
Owner:SHARP KK
Liquid crystal panel and liquid crystal projector
InactiveUS7002659B1Improve finenessImprove picture qualityColor television detailsNon-linear opticsLCD projectorEngineering
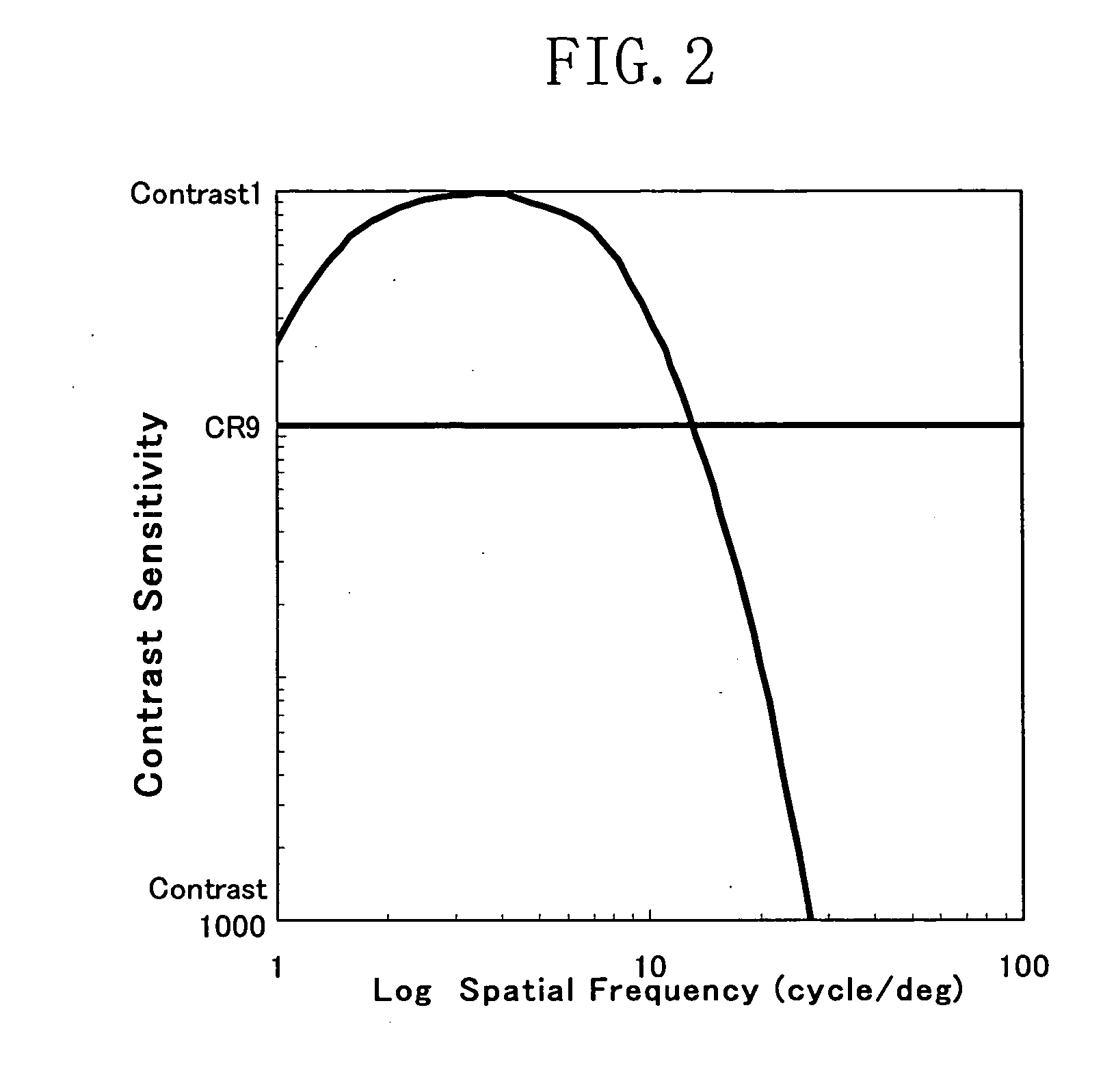
There is provided a liquid crystal panel in which the brightness of an image is high, and deterioration in display quality due to defects such as uneven display or uneven brightness is suppressed. The liquid crystal panel includes a pixel portion including a plurality of thin film transistors and pixel electrodes formed on a first substrate, a second substrate, a liquid crystal and gap holding members provided between the first substrate and the second substrate, and a microlens array including a plurality of microlenses and provided on a surface of the second substrate, the surface being opposite to the first substrate.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD +1
Display device
ActiveUS20140022480A1Improve reliabilitySuppresses degradation of display qualityNon-linear opticsDisplay deviceEngineering
To suppress a variation in characteristics of a transistor due to a released gas from an organic insulating film so that reliability of a display device is increased. The display device includes a transistor, an organic insulating film which is provided over the transistor in order to reduce unevenness due to the transistor, and a capacitor over the organic insulating film. An entire surface of the organic insulating film is not covered with components (a transparent conductive layer and an inorganic insulating film) of the capacitor, and a released gas from the organic insulating film can be released to the outside from exposed part of an upper surface of the organic insulating film.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Liquid crystal display
InactiveUS20060044502A1Display quality is deterioratedLittle irregularityNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
The invention relates to a liquid crystal display filled with a liquid crystal by dispensing the liquid crystal onto a substrate, combining the substrate with an opposite substrate in vacuum with the surface of the substrate having the liquid crystal thereon facing the opposite substrate, and restoring the atmospheric pressure. The invention provides a liquid crystal display in which degradation of display quality due to an irregularity attributable to gravity can be suppressed. The liquid crystal display has a pair of substrates opposite to each other, a liquid crystal sealed between the substrates, a convex portion protruding into the liquid crystal from a surface of at least either of the pair of substrates and extending in a substantially horizontal direction when the pair of substrates is erected in the vertical direction, and a gap formed between the protruding end of the convex portion and a surface of the other substrate.
Owner:SHARP KK
Display device
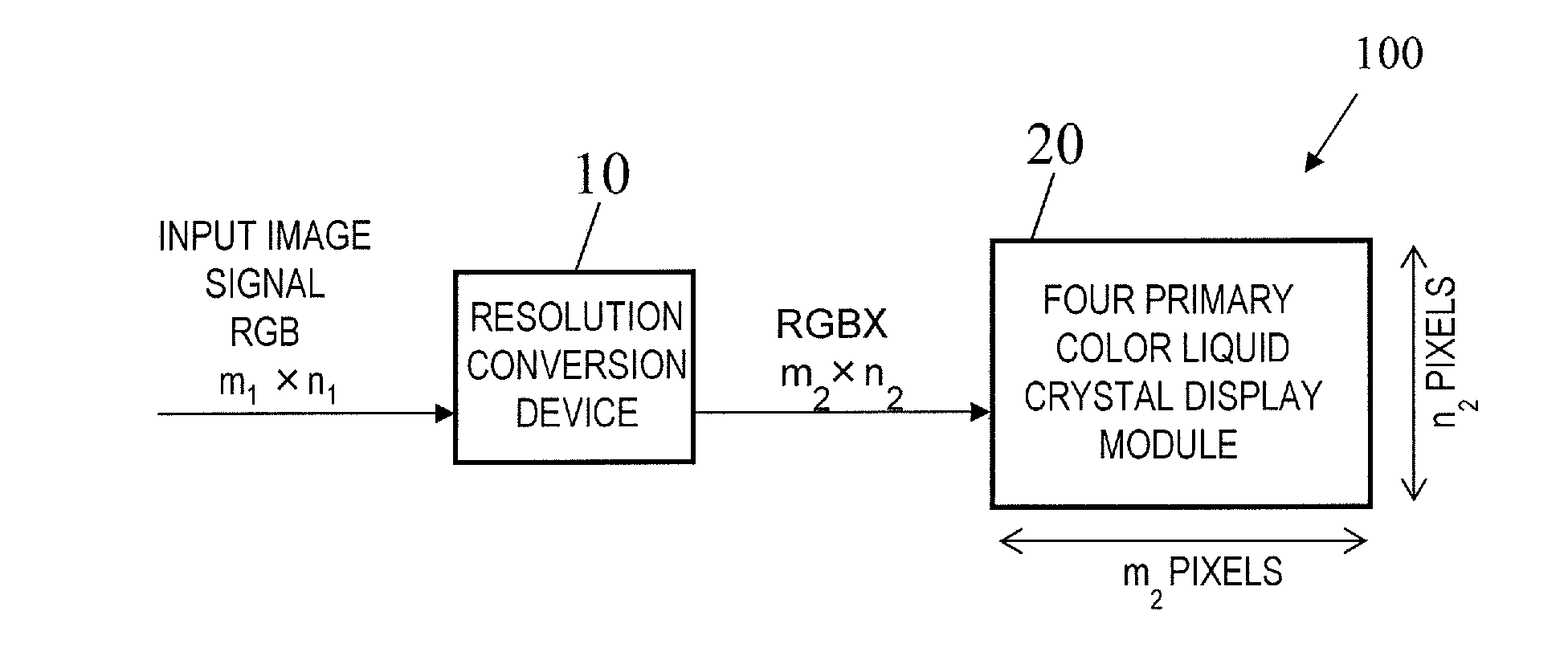
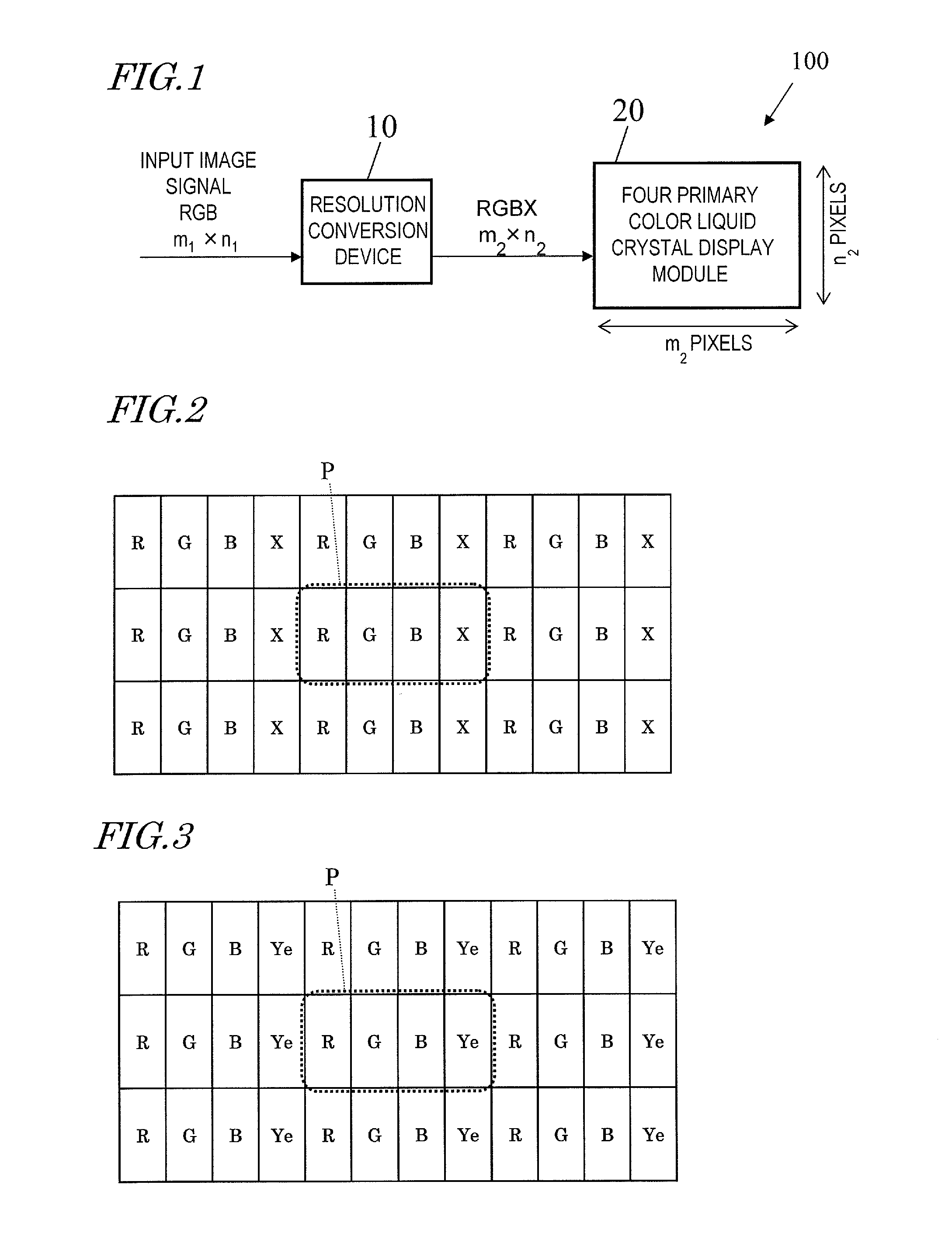
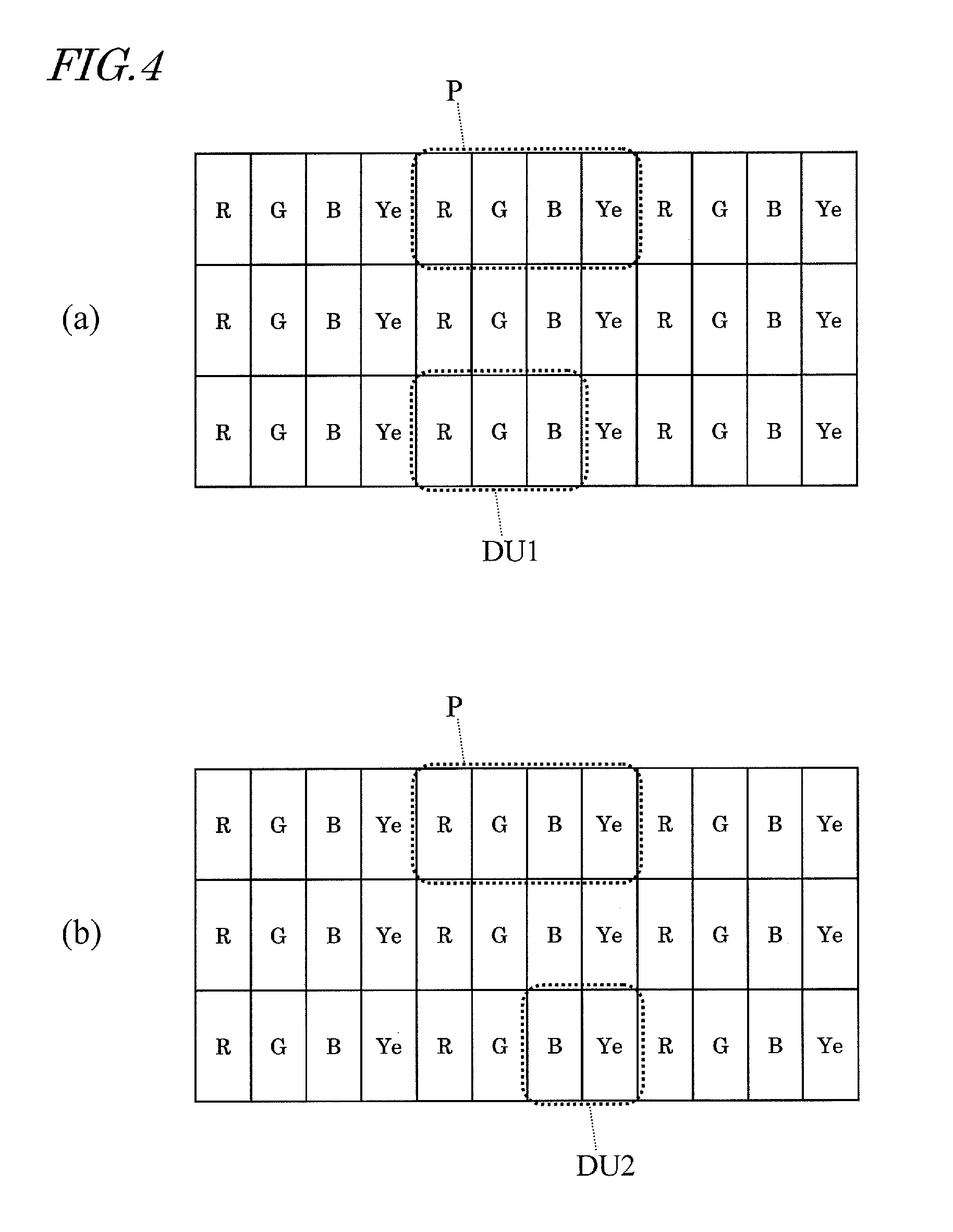
InactiveUS20120313843A1Suppressing decline of display qualitySuppresses degradation of display qualityCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer graphics (images)Image resolution
A display device according to the present invention includes a plurality of pixels arranged in a matrix. Each of the plurality of pixels is formed of four or five types of sub pixels that display different colors from each other. In each pixel, a first sub pixel that displays a color having the highest luminance and a second sub pixel that displays a color having the second highest luminance are located so as not to be adjacent to each other. The four or five types of sub pixels include a plurality of display units, each of which is capable of displaying a specific color and is formed of one sub pixel or two or more continuous sub pixels. In the display device according to the present invention, when an input image has a resolution higher than a display resolution defined by a total number of the plurality of pixels, each of the plurality of display units is usable as a virtual pixel for providing display. According to the present invention, a multiple primary color display device which suppresses the decline of display quality even when the resolution of an input image is higher than the resolution of the display device is provided.
Owner:SHARP KK
Display device, drive circuit thereof, driving method therefor, and electronic equipment
InactiveUS20030011583A1Suppresses degradation of display qualityReduce power consumptionCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsElectrical polarityDisplay device
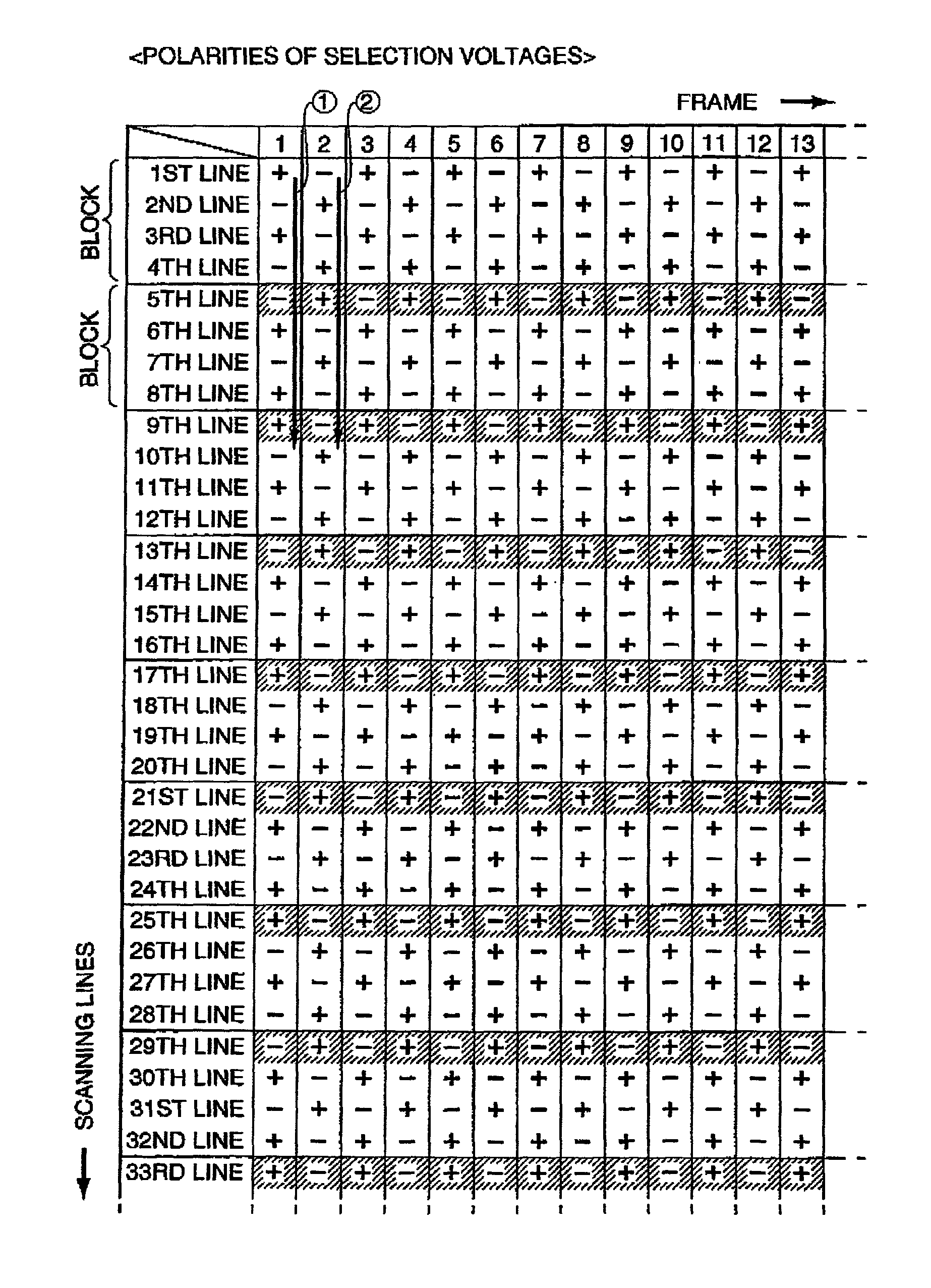
To reduce power consumption while restraining the occurrence of cross talk at the same time. A plurality of scanning lines are bundled into a block, and the polarities of the selection voltages of scanning signals Yi, Yi+1, Yi+2, and Yi+3 supplied to the scanning lines that belong to the same block are alternately inverted. Furthermore, the polarity of the selection voltage of the scanning signal Yi+3 supplied to the scanning line selected last in the block is the same as the polarity of the selection voltage of the scanning signal Yi+4 supplied to the scanning line selected first in a block following the aforesaid block.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Display device and method for driving display device
InactiveUS20100238156A1Increase in circuit areaIncrease in costCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingShift registerData signal
A display device, in at least one embodiment, includes: a gate driver including a plurality of shift register stages each provided so as to correspond to each row, the gate driver outputting a gate signal for turning on switching elements in the each row; and a source driver outputting a data signal in accordance with an image to be displayed. For a row (first row) located at an outermost position from which scanning by use of the gate signal starts, a dummy line is provided. The dummy line is driven by a gate start pulse inputted into a shift register in the first row.
Owner:SHARP KK
Process for producing electrophoretic display device
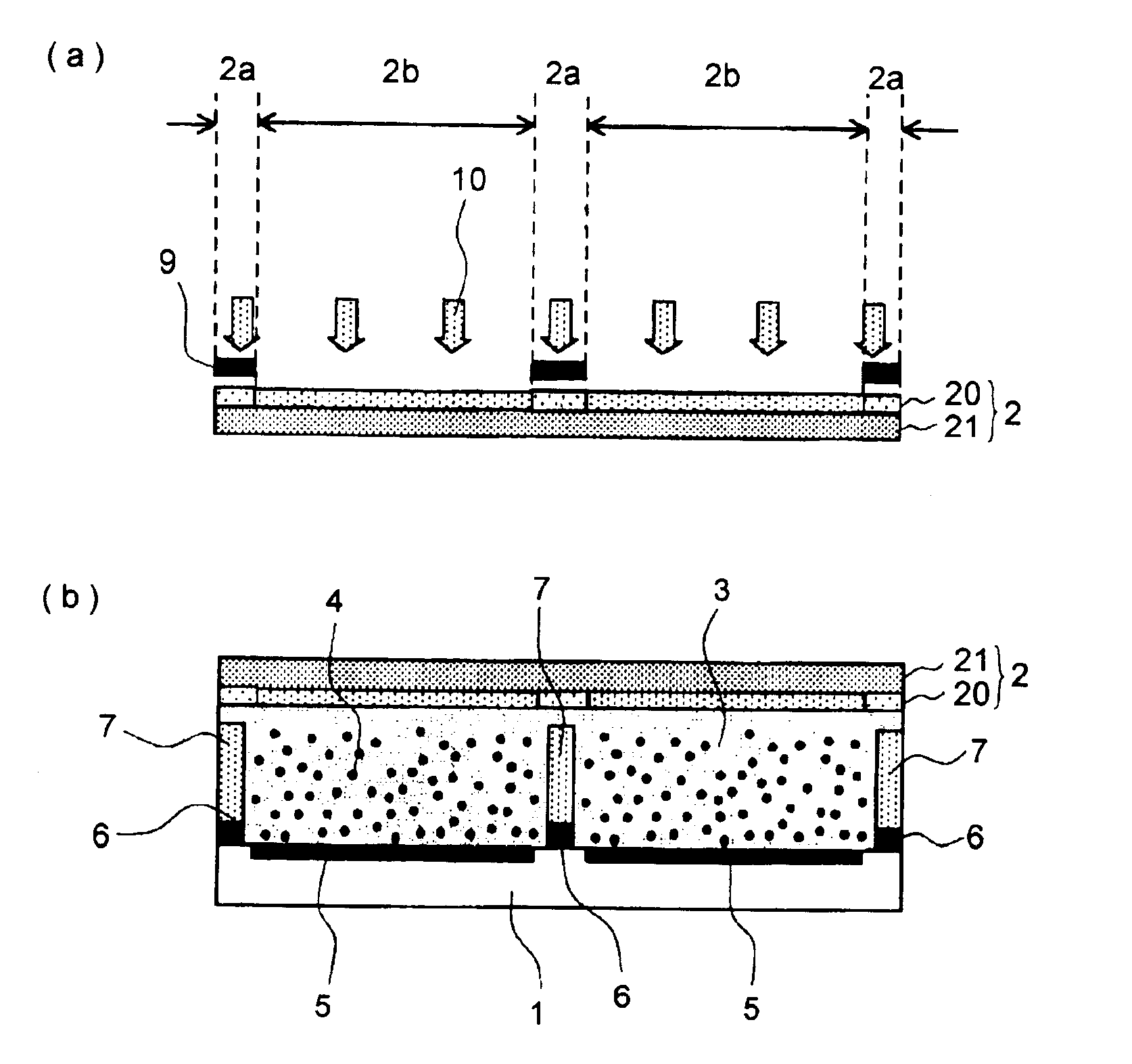
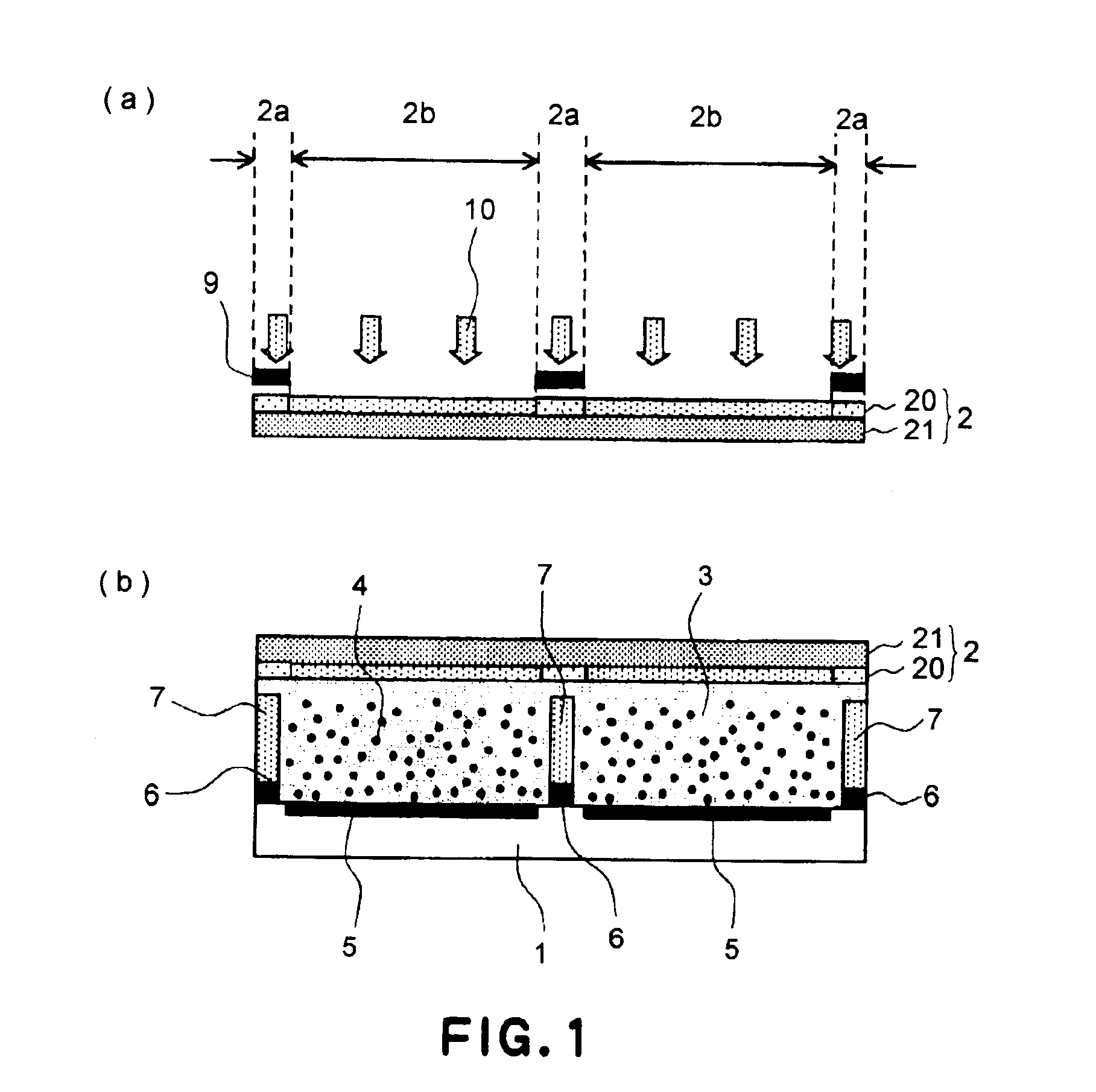
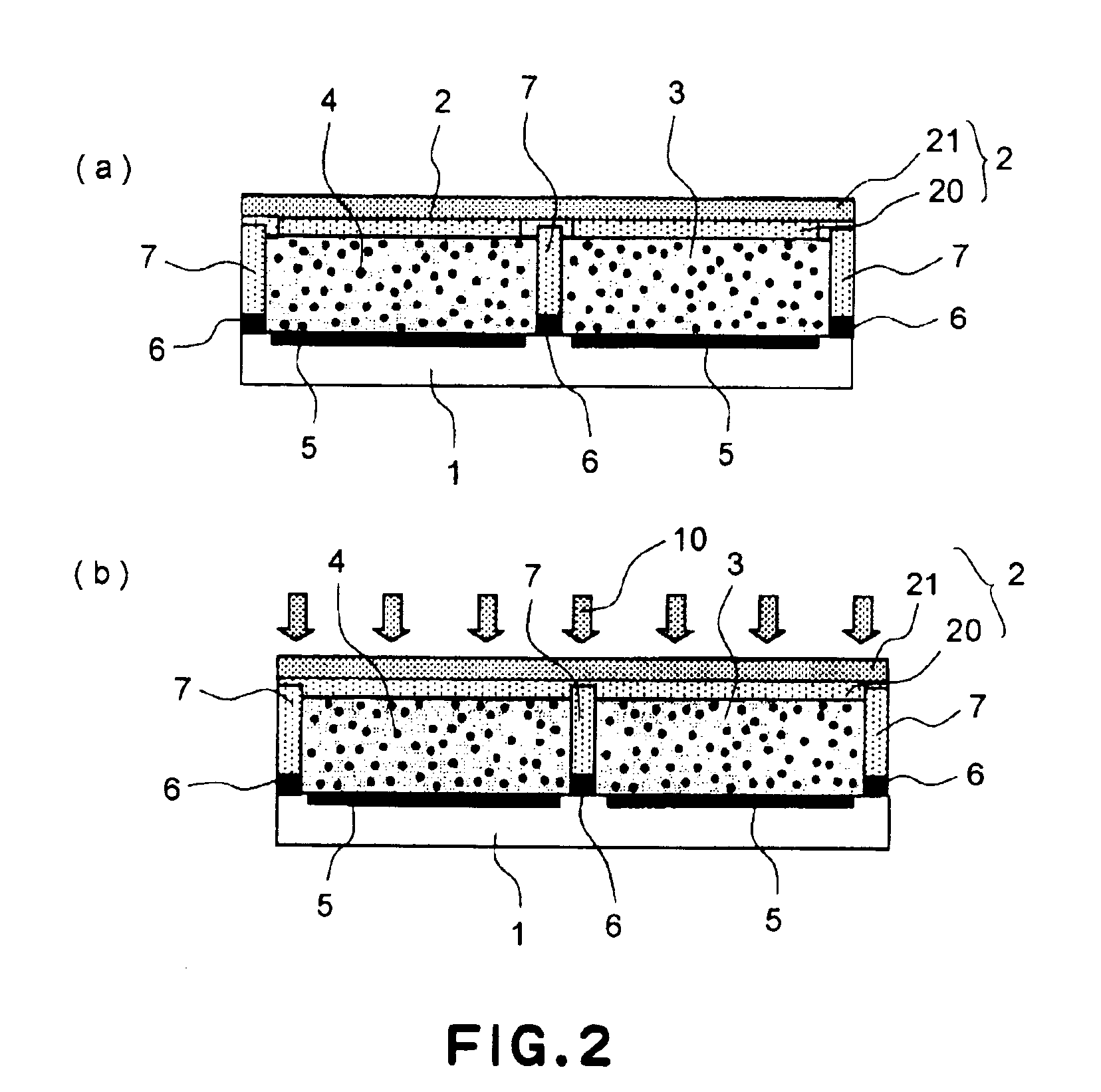
InactiveUS6950226B2Prevent display quality degradationSuppresses degradation of display qualityElectrographic process apparatusElectrographic processes using charge patternElectrophoresesDisplay device
An electrophoretic display device including first and second substrates disposed with a predetermined spacing, a partition member disposed between the first and second substrates, a plurality of electrophoretic particles and an insulating liquid which are sealed up by the substrates and the partition member, and first and second electrodes disposed close to the insulating liquid, is produced through a production process comprising the following steps (A), (B), (C) and (D): (A) a step of filling the insulating liquid and the electrophoretic particles in a recess defined by the first substrate and the partition member, (B) a step of placing a first area of the second substrate to be in contact with the partition member in an uncured state and a second area of the second substrate to be in contact with the insulating liquid in a cured state, (C) a step of causing the first area of the second substrate to contact the partition member and the second area of the second substrate to contact the insulating liquid, and (D) a step of curing the first area of the second substrate contacting the partition member.
Owner:CANON KK
Liquid crystal display device and driving method therefor
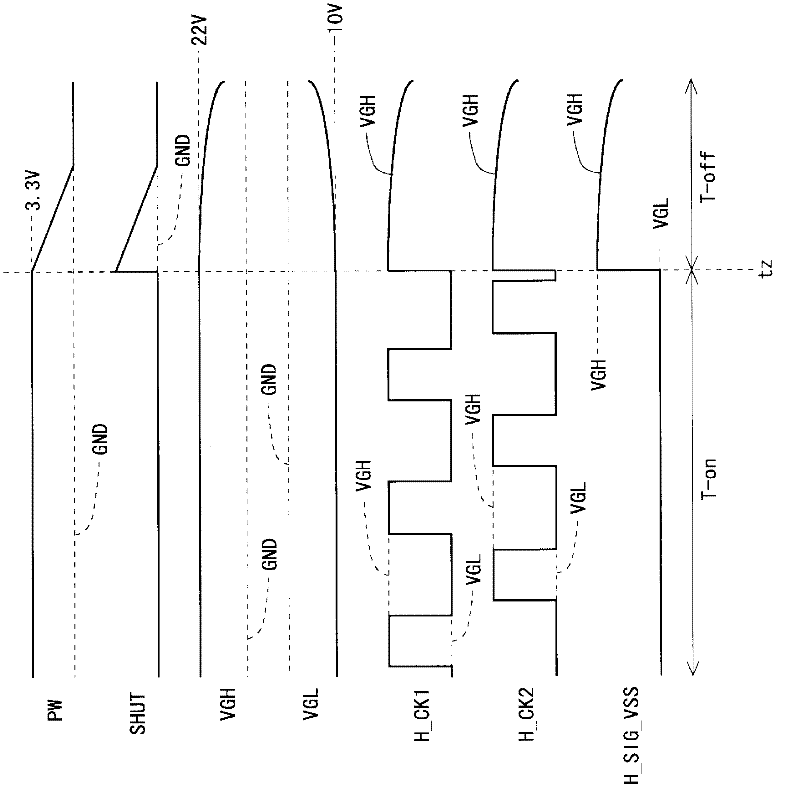
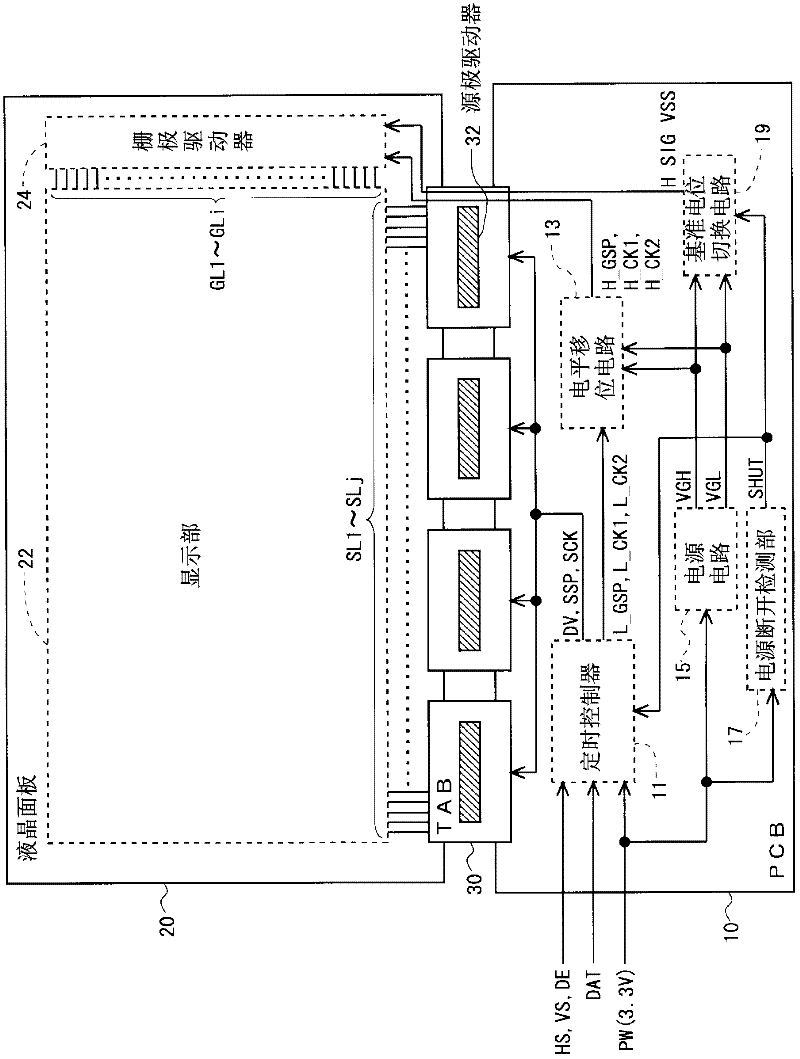
InactiveCN102598105AEasy dischargeSuppresses degradation of display qualityStatic indicating devicesShift registerBistable circuits
Disclosed is a liquid crystal display device provided with a monolithic gate driver, wherein residual charge in a pixel formation portion can be rapidly eliminated when the power is turned off. In a bistable circuit which constitutes a shift register in a gate driver (24), a thin-film transistor having a drain terminal connected to a gate bus line, a source terminal connected to a reference potential line for transmitting a reference potential (H_SIG_VSS), and a gate terminal to which a clock signal (HCK_1, HCK_2) for operating the shift register is given is provided. When a power OFF detection unit (17) detects the cutoff of the supply of power-supply voltage (PW) from the outside, the clock signal (HCK_1, HCK_2) is driven high to turn the thin-film transistor on, and a reference potential switching circuit (19) switches the reference potential (H_SIG_VSS) from a gate off potential (VGL) to a gate on potential (VGH).
Owner:SHARP KK
Tactile sense presentation device, electronic apparatus, and tactile sense presentation method
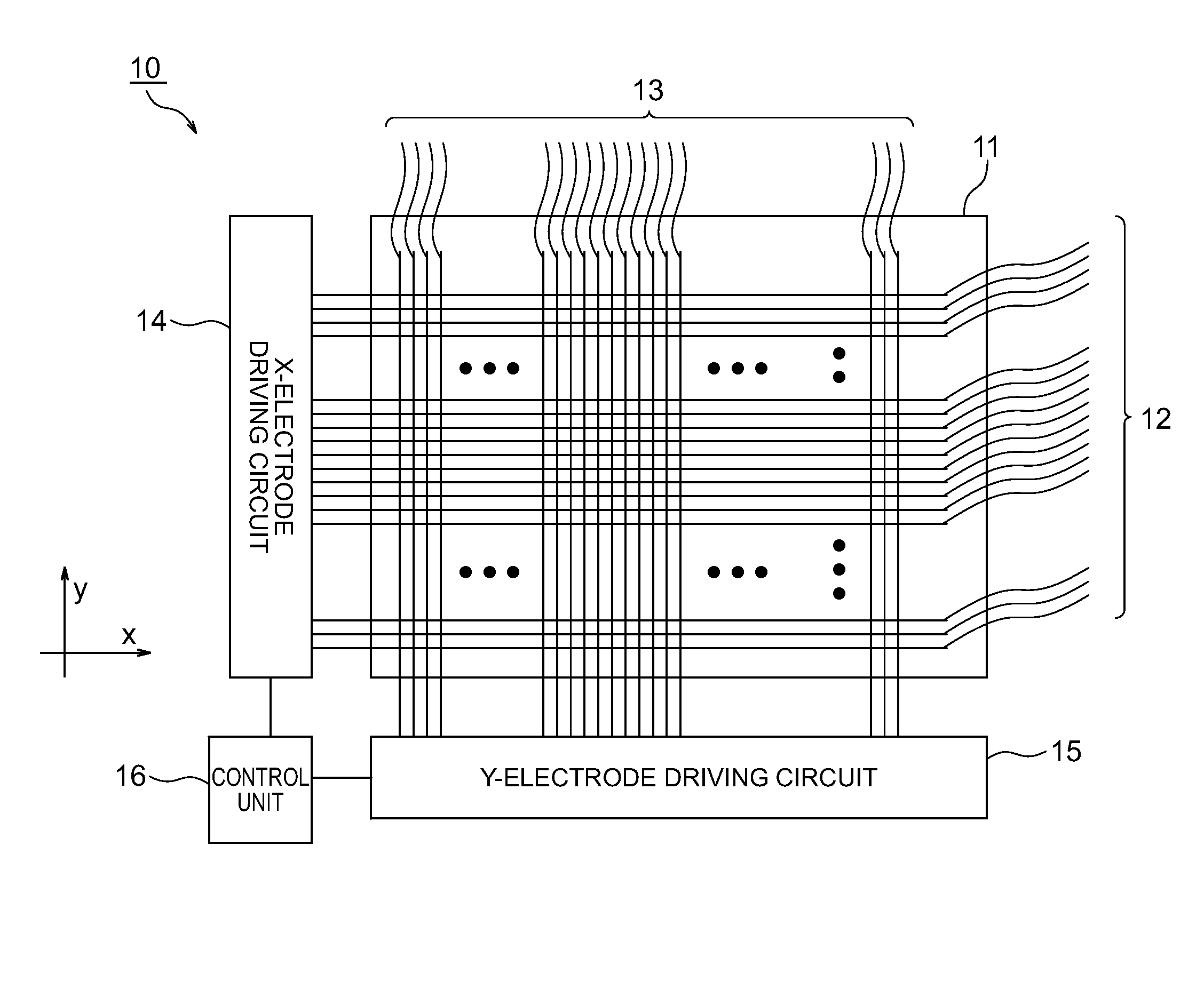
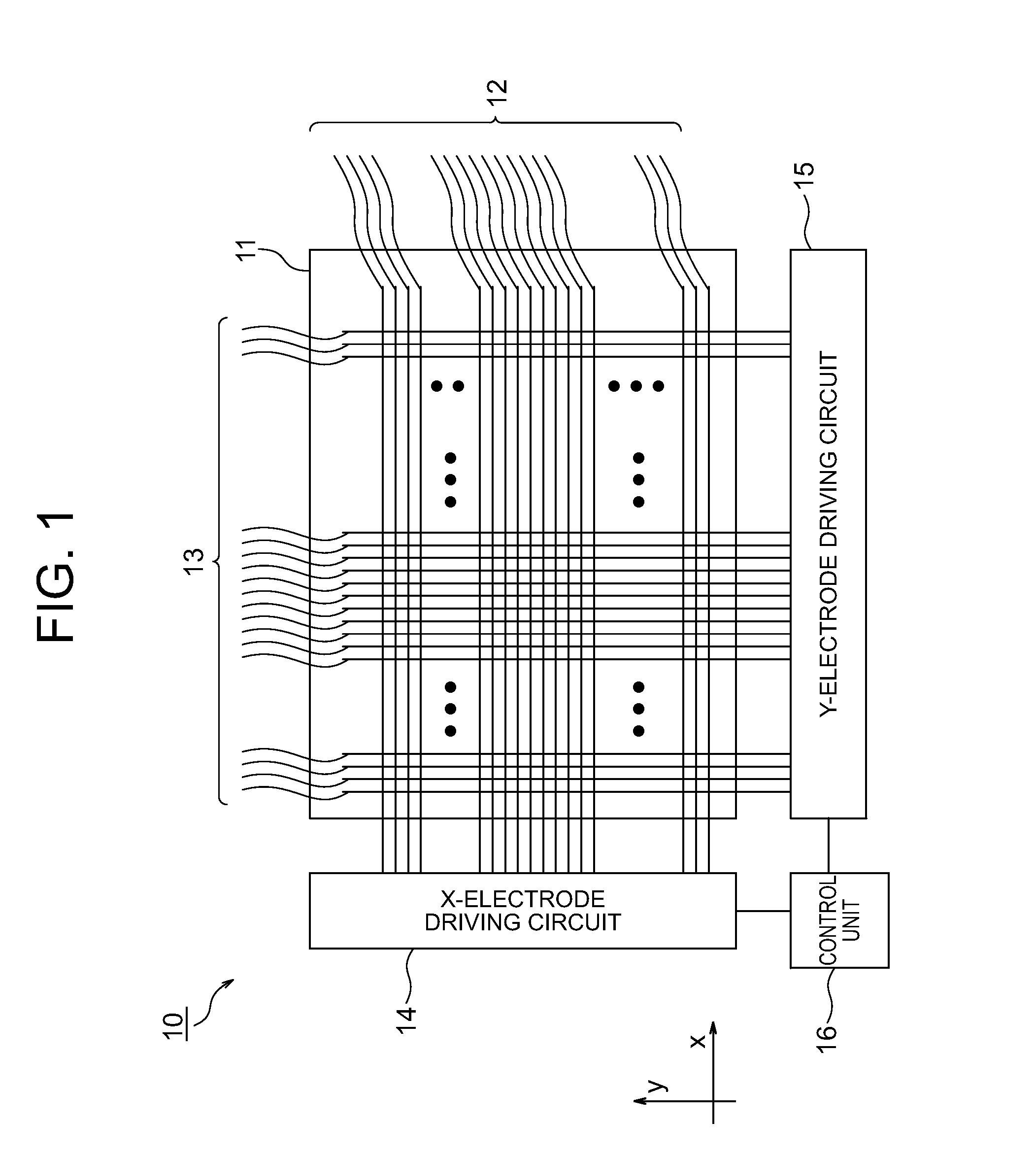
ActiveUS20150103024A1Suppresses degradation of display qualityCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingEngineeringTouch panel
The tactile sense presentation device, capable of effectively presenting a tactile sense (a sense of texture) on a touch panel, includes: a supporting substrate; a plurality of X-electrodes and Y-electrodes extended in parallel to each other on the supporting substrate; and driving circuits (X-electrode driving circuit, Y-electrode driving circuit) which apply a first-frequency voltage signal to the X-electrode corresponding to information regarding a target region inputted from outside among the plurality of X-electrodes, and applies a second-frequency voltage signal to the Y-electrode corresponding to information regarding the target region inputted from outside among the plurality of Y-electrodes to generate electric beat oscillation in the target region by an absolute value of a difference between the first and second frequencies.
Owner:NEC LCD TECH CORP +1
Multi-primary color display device
ActiveUS20110128309A1Suppressing decline of display qualityEasy to useColor signal processing circuitsCathode-ray tube indicatorsComputer graphics (images)Hue
A multi-primary color display device according to the present invention includes pixels, each having a plurality of sub-pixels. The plurality of sub-pixels include first, second, third and fourth sub-pixels for displaying first, second, third and fourth colors having first, second, third and fourth hues. The second and third hues are adjacent to the first hue on both sides thereof on an a*b* plane of an L*a*b* colorimetric system. When a color displayed by each pixel changes from black to an optimal color of the first hue, luminance values of the plurality of sub-pixels are set such that the luminance value of the first sub-pixel starts to be increased and also the luminance values of the second and third sub-pixels start to be increased at a rate of increase lower than the rate of increase of the first sub-pixel.
Owner:SHARP KK
Plane light-source device
InactiveUS20080094831A1Suppress influence of heat and electromagnetic waveAvoid breakingNon-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceLiquid-crystal displayDrop impact
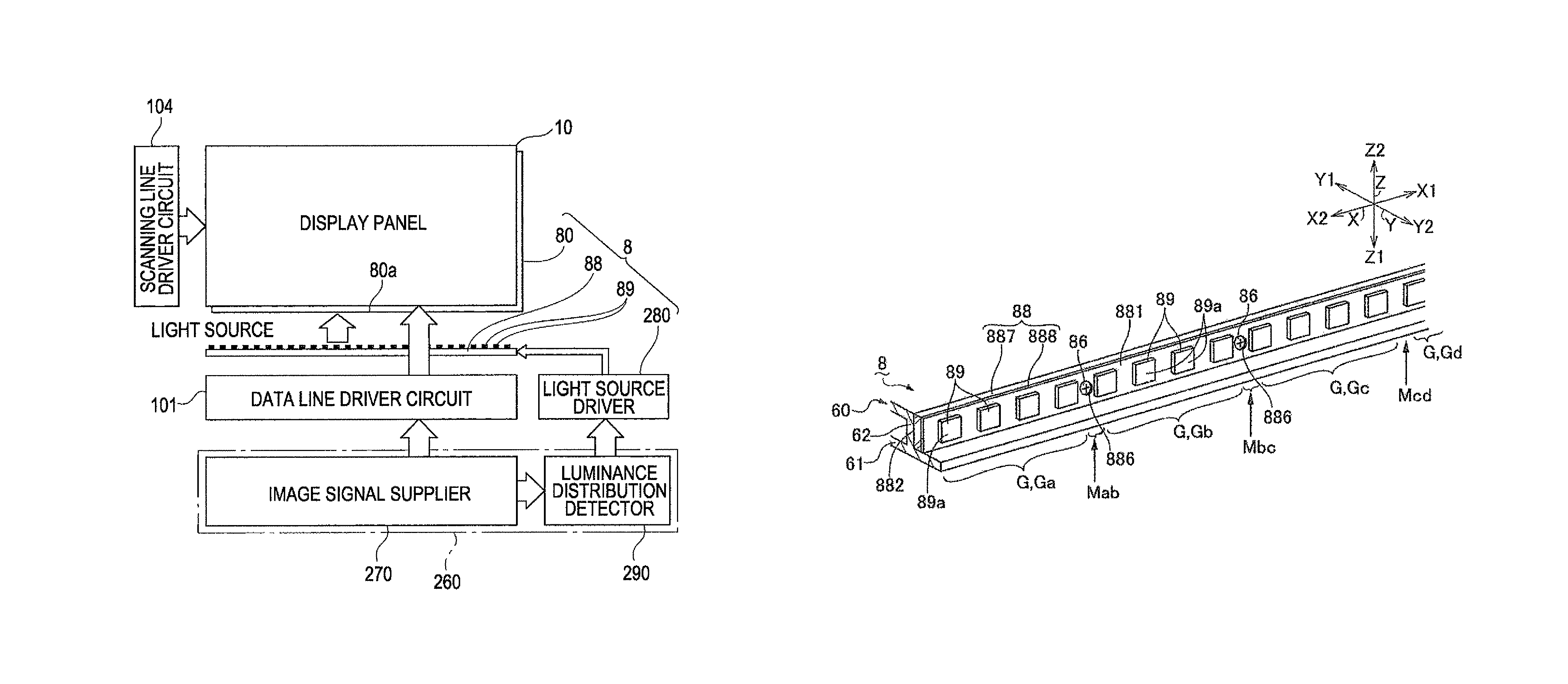
A plane light-source device having lamps disposed behind a diffuser is provided in which influences of heat and electromagnetic waves generated by the lamps are suppressed and the lamps are prevented from being broken on drop impact. A plane light-source device (a direct-type backlight) of a liquid-crystal display apparatus includes a plurality of lamps disposed side by side with a given pitch, a diffuser for diffusing light from the lamps, and metal covers disposed between the diffuser and the lamps. The metal covers each have a plurality of through holes, and they reflect light from the lamps at their respective surfaces that face the lamps.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Shift register circuit, display device provided with same, and shift register circuit driving method
InactiveCN102460587ADisplay quality degradedSuppress crosstalkStatic indicating devicesDigital storageBistable circuitsShift register
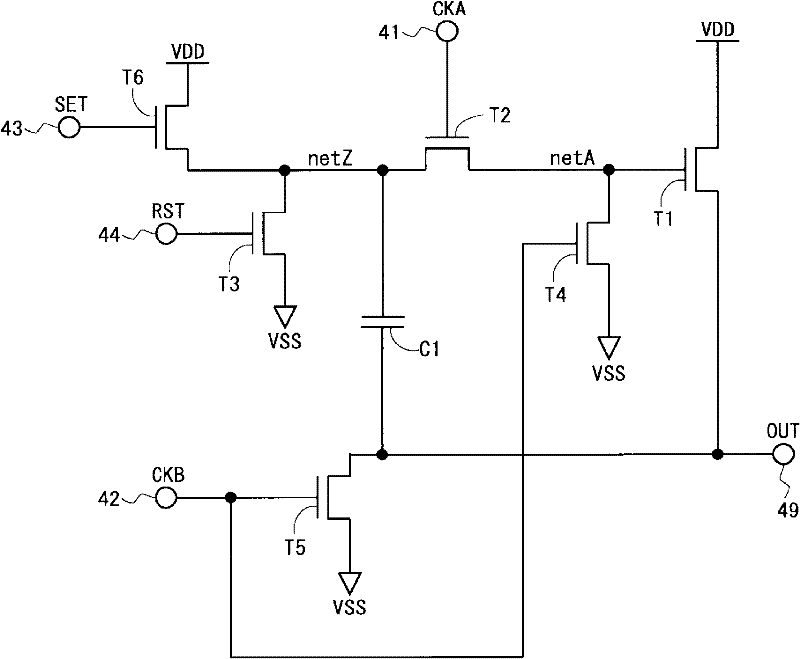
Disclosed is a display device capable of inhibiting degradation of visual quality that has been caused by crosstalk, without causing an increase in frame size or an increase in power consumption. Each bistable circuit is provided with an output terminal (49) that outputs a state signal; a thin-film transistor (T1), the drain terminal of which is given a high-level potential (VDD), and the source terminal of which is connected to the output terminal (49); a thin-film transistor (T2), the source terminal of which is connected to an area netA that is connected to the gate terminal of the thin-film transistor (T1), and the gate terminal of which is given a clock (CKA); a thin-film transistor (T6) for increasing a potential of an area netZ that is connected to the drain terminal of the thin-film transistor (T2); and thin-film transistors (T4, T5, T3) for lowering each of the potentials of netA, netC, and the output terminal (49). A channel area of the thin-film transistor (T1) is made to be larger than a channel area of the thin-film transistor (T2).
Owner:SHARP KK
Display device, electronic device comprising same, and drive method for display device
ActiveUS20150054863A1Improve display qualityReduce power consumptionCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingComputer hardwareLiquid-crystal display
Provided is a display device capable of suppressing reduction in display quality even when pause drive is performed, while allowing the intensity of a light source to be changed in accordance with images to be displayed.In a liquid crystal display device with the CABC function, 7.5-Hz pause drive is performed. A transition period is provided in which images to be displayed are changed gradually from bright image X to dark image Y. In the transition period, the duration of a sub-transition period is five frames. Once the transition period starts, the duration of a vertical display period changes from eight frames to one frame. That is, 7.5-Hz pause drive switches to 60-Hz normal drive. In this manner, the duration of the vertical display period is set to be less than or equal to the duration of the sub-transition period, so that screen refresh is always performed in each sub-transition period of the transition period.
Owner:SHARP KK
Organic electroluminescent element and electronic device
ActiveUS20150287949A1Suppressing lowering of display qualitySuppresses degradation of display qualitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsOrganic electroluminescence
An organic electroluminescent element includes a layer having a shallower LUMO and a higher T1 than those of the first light-emitting layer on the anode side of the first light-emitting layer, and a layer which satisfies at least one of a deeper LUMO and includes a lower T1 than those of the second light-emitting layer on the anode side of the second light-emitting layer, and provides the organic electroluminescent element capable of suppressing the lowering of display quality.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
TFT array substrate, and liquid crystal display panel
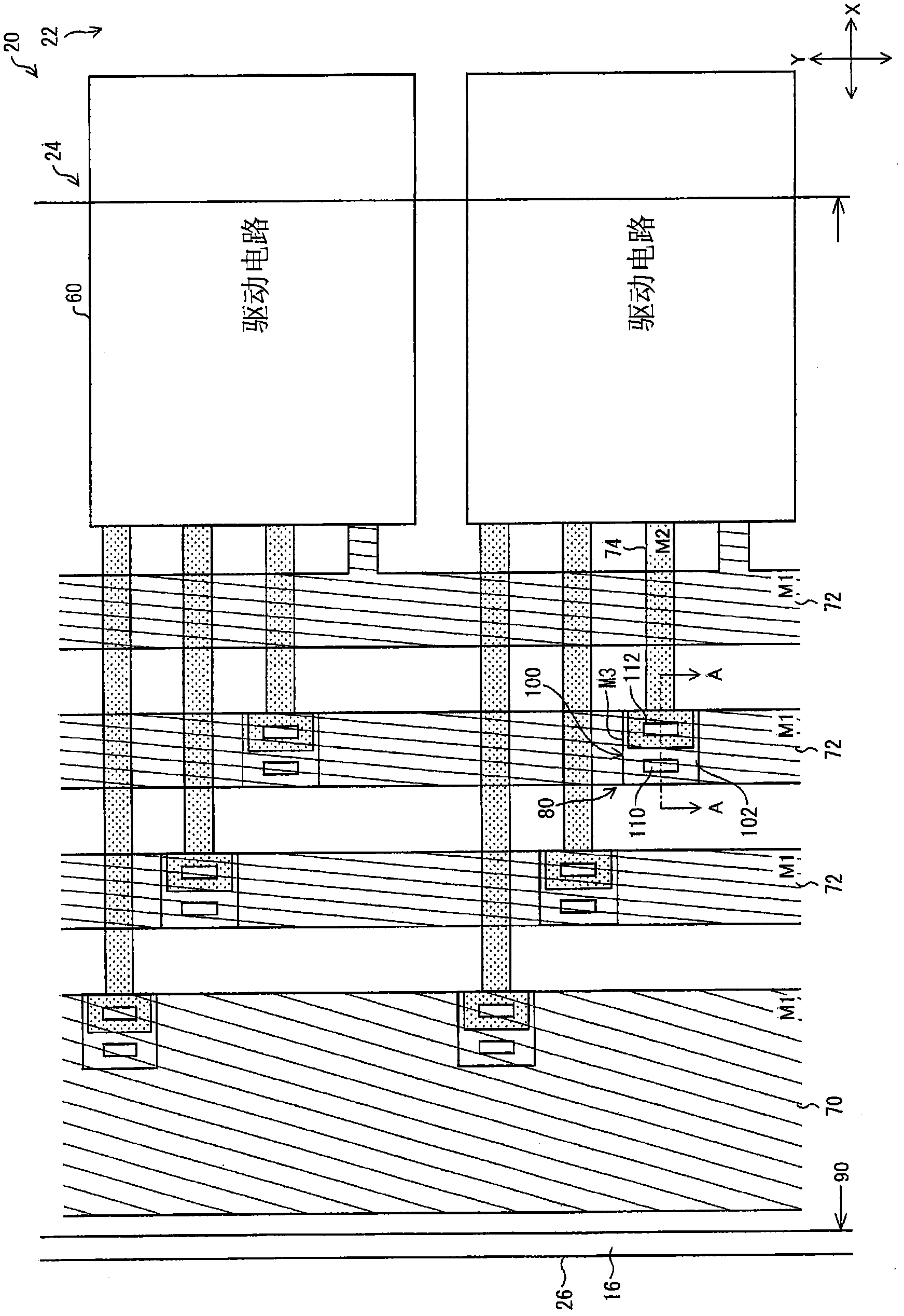
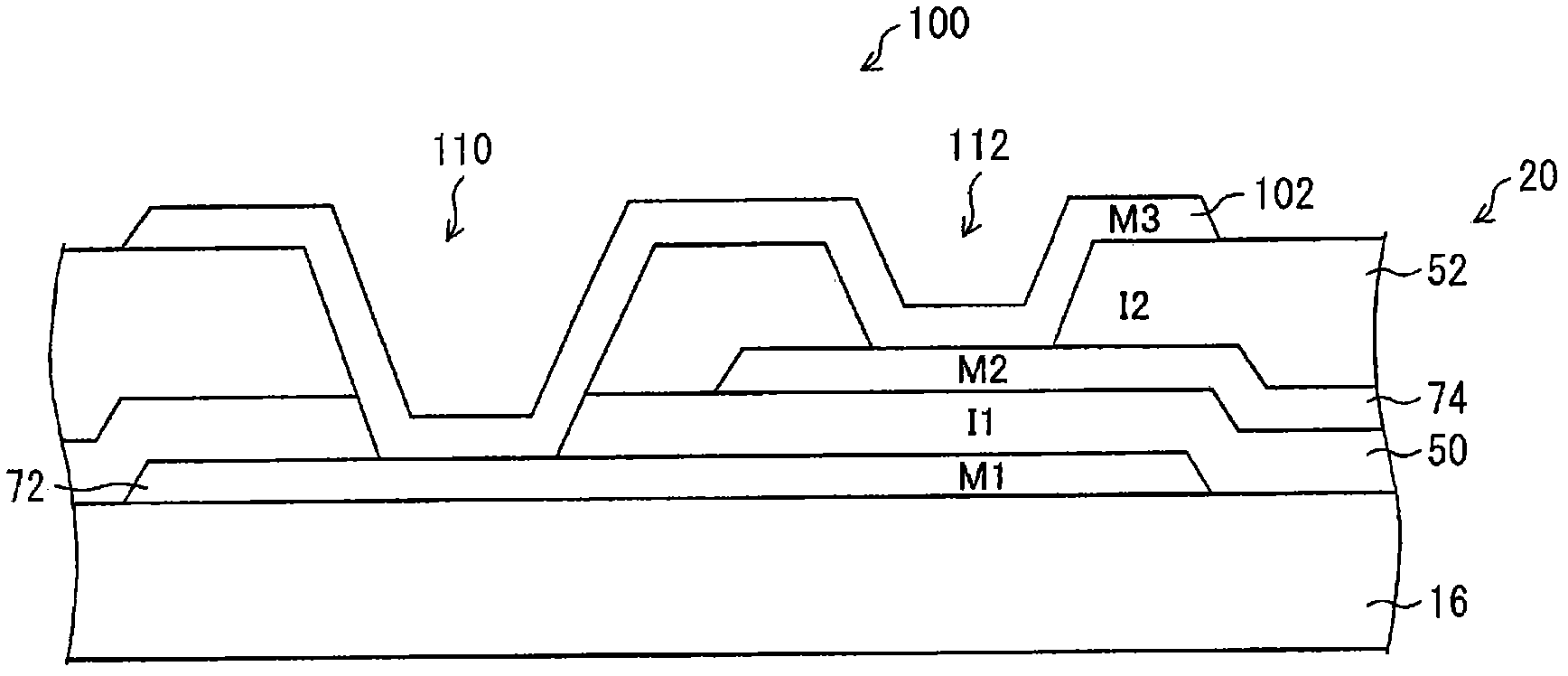
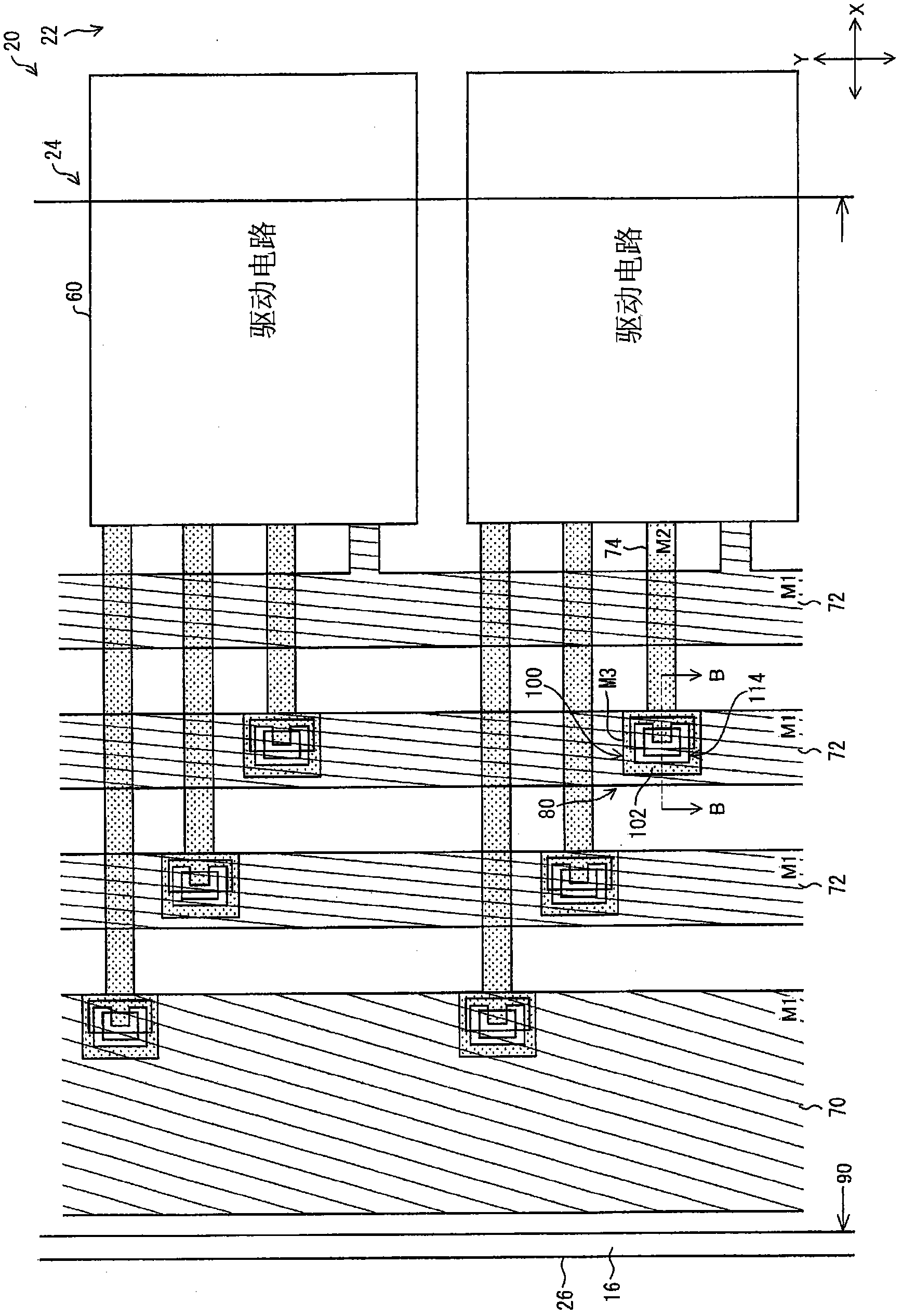
ActiveCN102308253ASuppresses degradation of display qualitySolid-state devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayElectrical conductor
Disclosed is a TFT array substrate (20) wherein TFT elements and pixel electrodes are arranged as a matrix. A gate bus line is formed from a first metal material (M1), a source bus line is formed from a second metal material (M2), and a pixel electrode is formed from a third metal material (M3). In a peripheral region (24), a clock wiring line (72) that is formed from the first metal material (M1), and a branch wiring line (74) that is formed from the second metal material (M2) are connected with each other at a connection part (80) via a connection conductor (102) that is formed from the third metal material (M3). The connection part (80) is provided with a branch wiring via (112) which expose the branch wiring line (74) through the connection conductor (102). At least a part of the branch wiring via (112) overlaps the clock wiring line (72) when viewed in plan.
Owner:SHARP KK
Active matrix substrate, liquid crystal panel, liquid crystal display device, liquid crystal display unit, and television receiver
InactiveUS20120086687A1Suppress decline in display qualitySuppress occurrence of image sticking of a sub-pixelCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsCapacitanceLiquid-crystal display
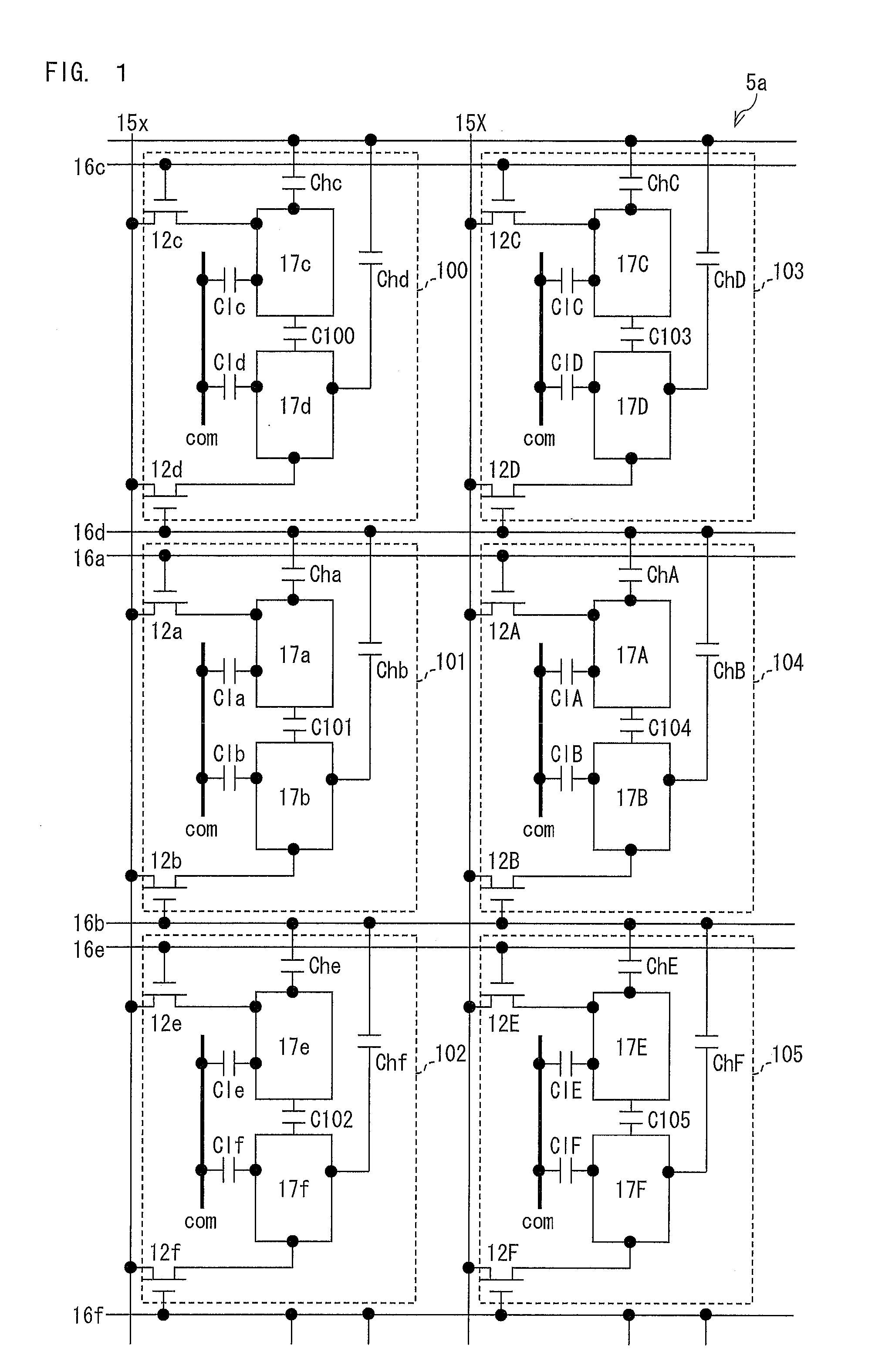
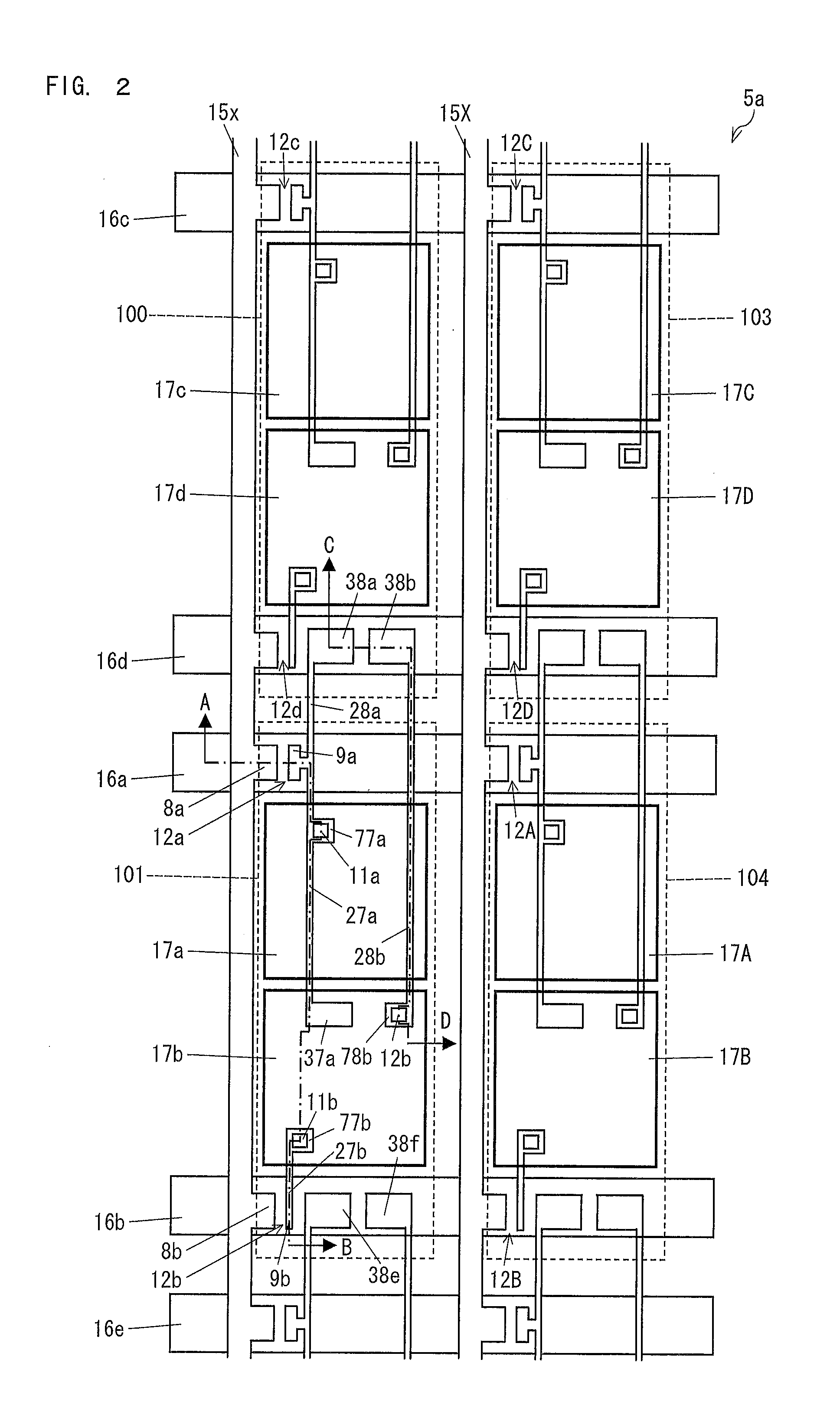
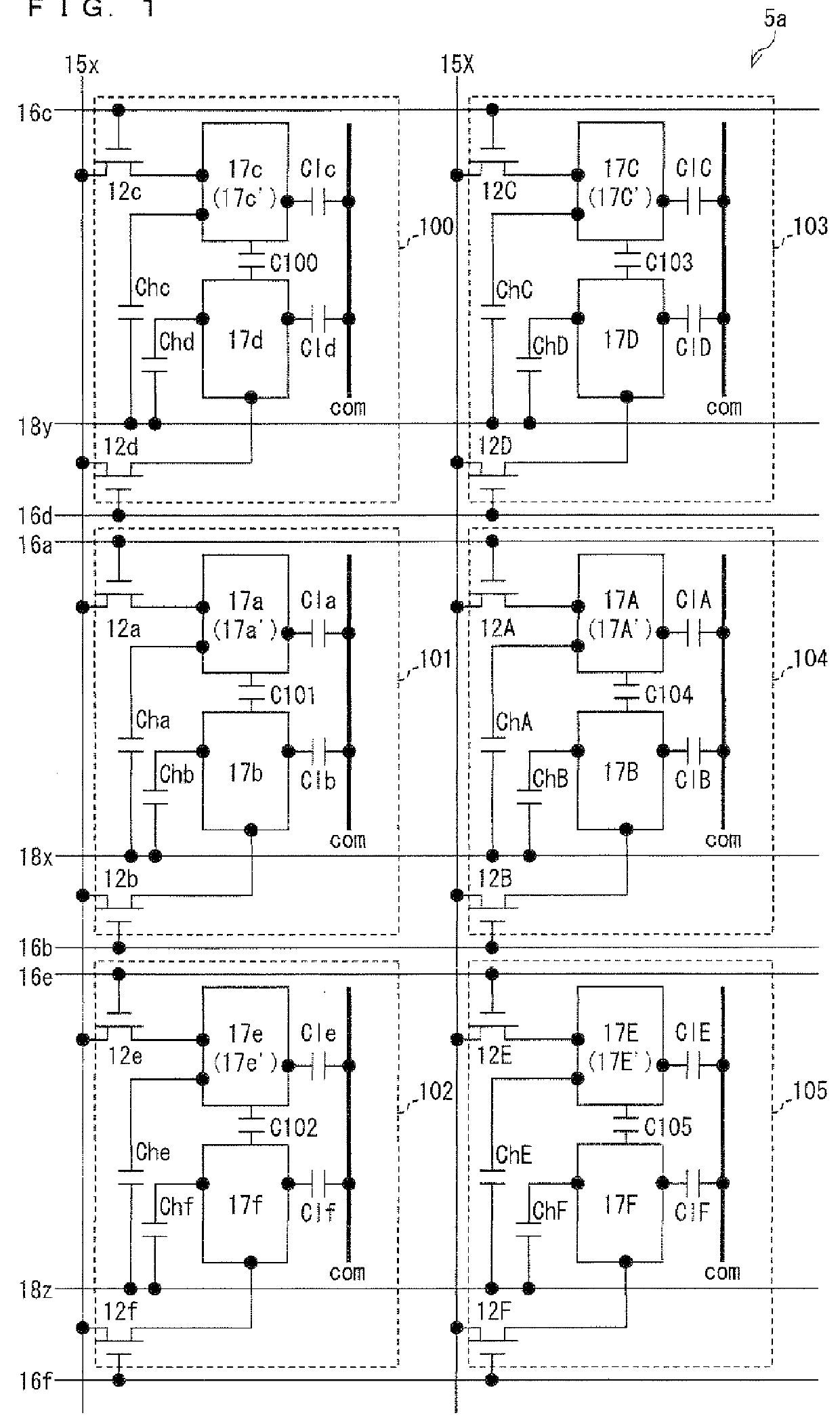
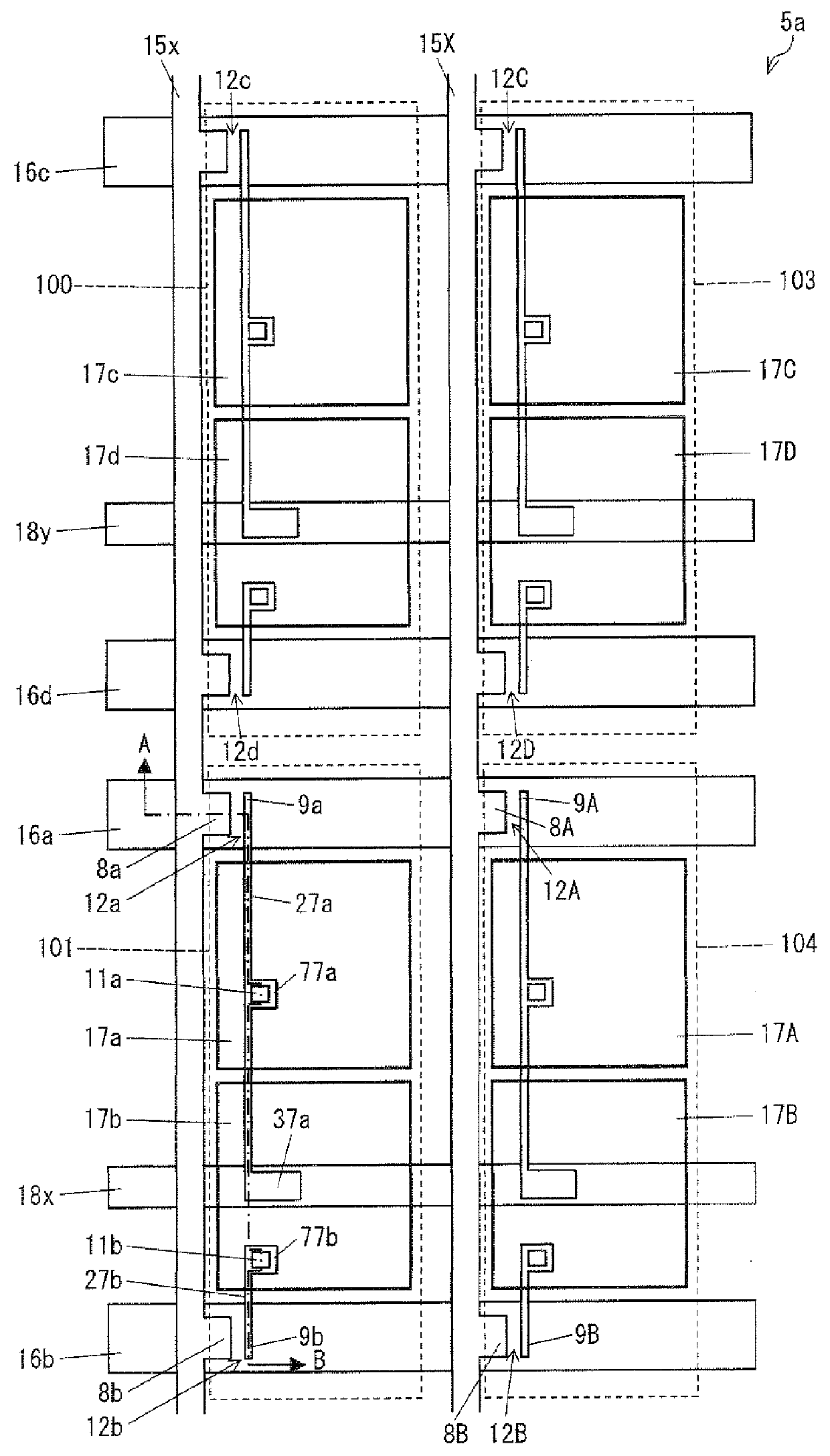
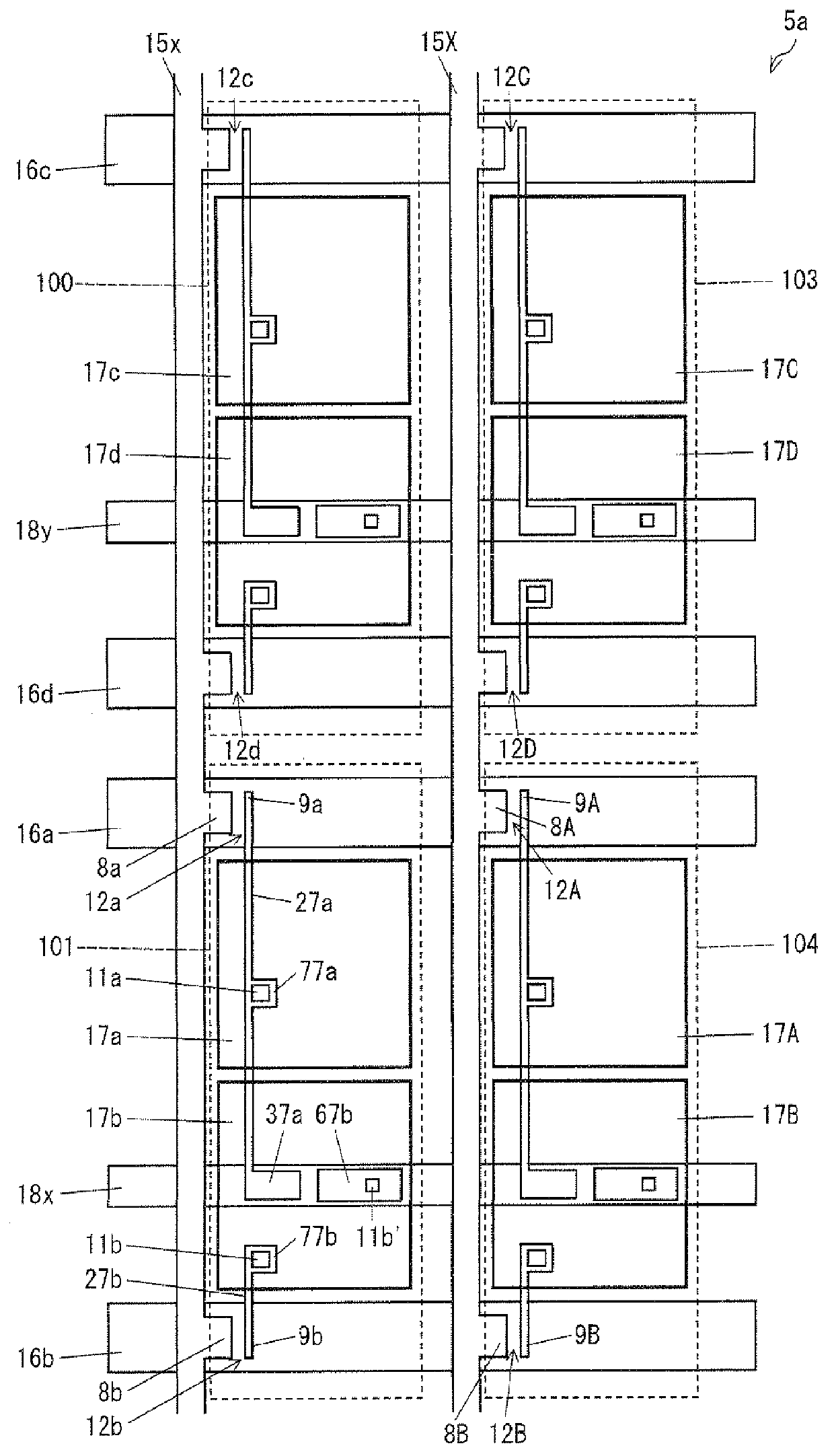
Pixel electrodes (17a and 17b) are provided in a pixel (101), and the pixel (101) is associated with a data signal line (15x), scanning signal lines (16a and 16b), and transistors (12a and 12b). One pixel electrode (17a) is connected to the data signal line (15x) via the transistor (12a). The other pixel electrode (17b) is connected to the pixel electrode (17a) via a capacitor (C101) and is connected to the data signal line (15x) via the transistor (12b). Storage capacitance (Cha and Chb) is formed between the pixel electrodes (17a and 17b) of the pixel (101) and a scanning signal line (16d) associated with a pixel (100). Thus, a configuration of a liquid crystal display device of a capacitively coupled pixel division mode is proposed in which a decline in display quality caused by image sticking of a sub-pixel is less likely to occur.
Owner:SHARP KK
Active matrix substrate, liquid crystal panel, liquid crystal display device, liquid crystal display unit, and television receiver
InactiveUS20110019114A1Improve display qualityPrevent image retentionSolid-state devicesCathode-ray tube indicatorsCapacitanceTelevision receivers
Provided are an active matrix substrate including plural pixel electrodes in a pixel region and a liquid crystal display device (pixel division mode) using the same. Proposed is a configuration of the liquid crystal display device of the capacitor-coupled pixel division mode which hardly causes reduction in display quality due to image-sticking of sub-pixels. The active matrix substrate includes: a data signal line (15x); scanning signal lines (16a and 16b); a transistor (12a) connected to the data signal line (15x) and scanning signal line (16a); a transistor (12b) connected to the data signal line (15x) and scanning signal line (16b); and pixel electrodes (17a and 17b) provided in a pixel region (101), the pixel electrode (17a) being connected to the data signal line (15x) via the transistor (12a), the pixel electrode (17b) being connected to the pixel electrode (17a) via a capacitor and the data signal line (15x) via the transistor (12b), and the transistors (12a and (12b) have identical W / L ratios of channels (each ratio of width W to length L of channel). The present invention can be configured with identical channel sizes without adjusting W / L ratios of channels of the transistors unlike a conventional configuration. Accordingly, deterioration of display quality due to variation in characteristics of transistors can be suppressed.
Owner:SHARP KK
Display device, drive circuit thereof, driving method therefor, and electronic equipment
InactiveUS7196697B2Suppresses degradation of display qualityReduce power consumptionCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsElectrical polarityDisplay device
The present invention provides a drive circuit of a display device that reduces power consumption while restraining the occurrence of cross talk at the same time. The drive circuit can include a plurality of scanning lines that are bundled into a block, and the polarities of the selection voltages of scanning signals Yi, Yi+1, Yi+2, and Yi+3 supplied to the scanning lines that belong to the same block are alternately inverted. Furthermore, the polarity of the selection voltage of the scanning signal Yi+3 supplied to the scanning line selected last in the block is the same as the polarity of the selection voltage of the scanning signal Yi+4 supplied to the scanning line selected first in a block following the aforesaid block. Accordingly, it is possible to reduce power consumption while restraining the degradation in display quality at the same time.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Electro-optical device, driving method, and electronic apparatus
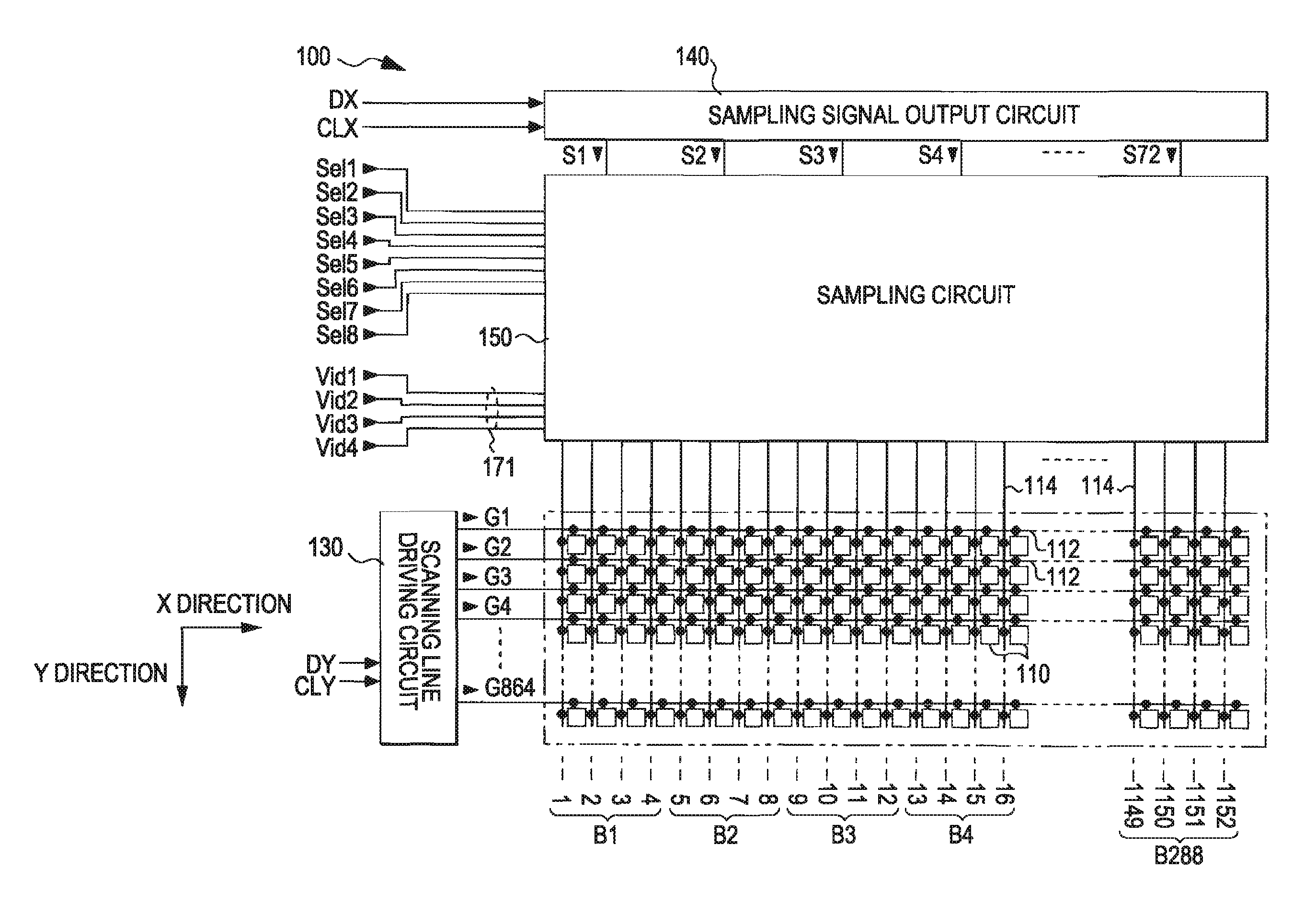
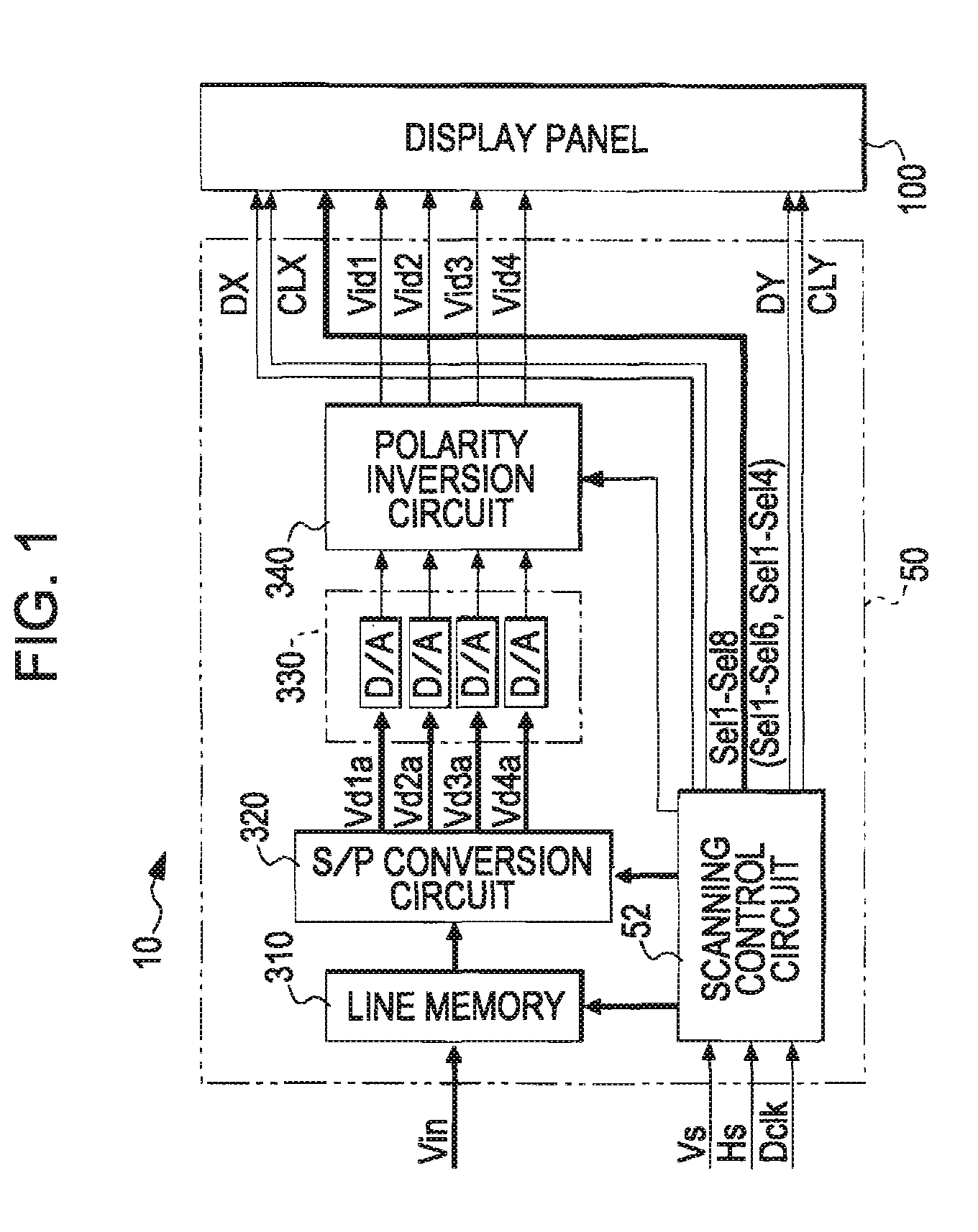
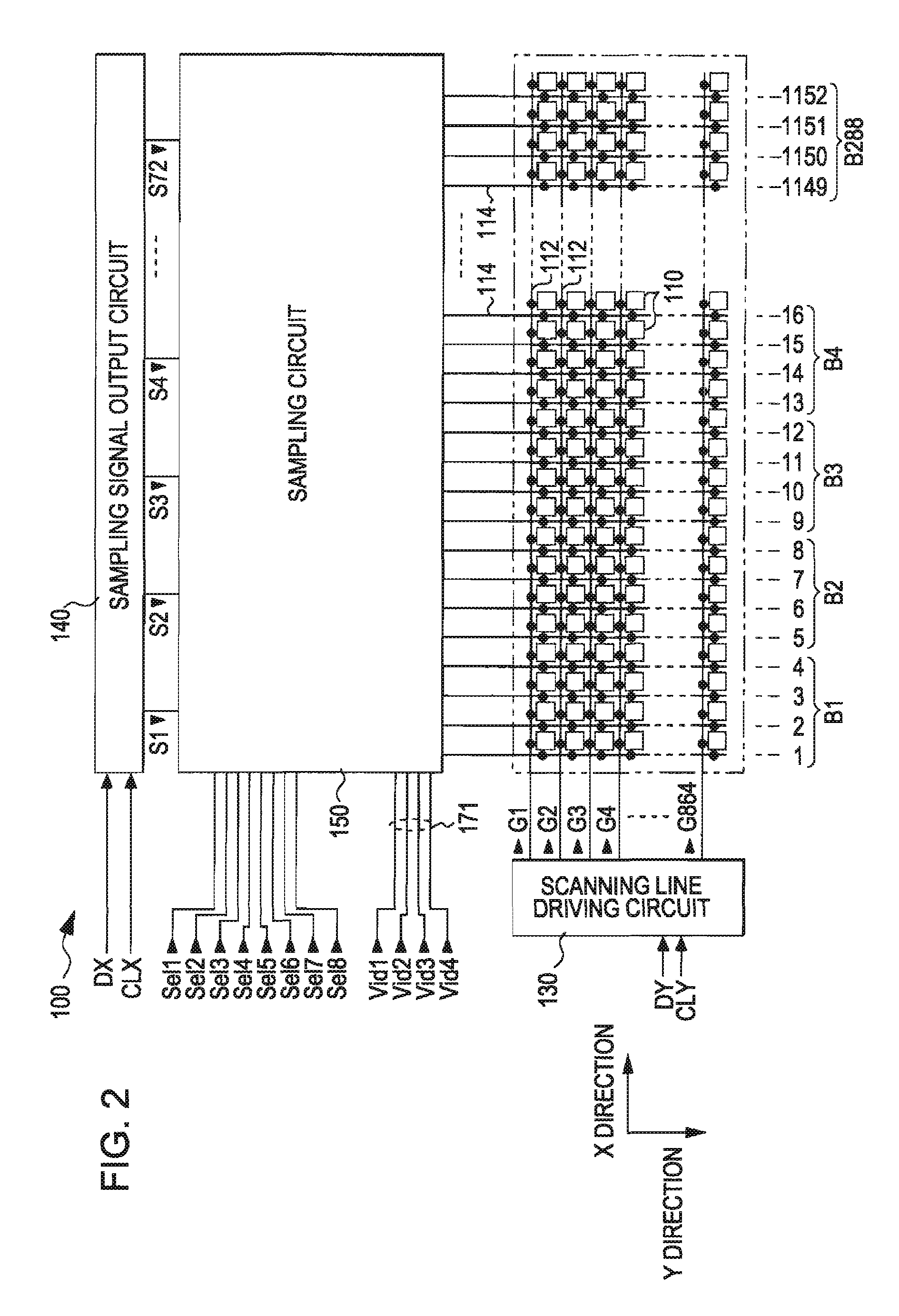
ActiveUS20060284683A1Suppress deterioration of display qualitySuppresses degradation of display qualityTelevision system scanning detailsAmplifier combinationsSampling circuitsEngineering
An electro-optical device includes: a plurality of scanning lines; a plurality of data lines blocked for every “m” (m is an integer of 2 or greater) columns; pixels provided corresponding to the scanning lines and the data lines and showing grayscale specified by data signals sampled to data lines when a scanning line is selected; a scanning line driving circuit which selects the plurality of scanning lines in a predetermined order; a sampling signal output circuit which sequentially outputs a plurality of sampling signals; and a sampling circuit which has sampling switches provided in the data lines, respectively, and having their one ends connected to the data lines, and which turns on the sampling switches to sample data signals supplied to “n” (n is an integer of 2 or greater) image signal lines, to the data lines. The sampling circuit groups the blocks for every “n” blocks, makes individual blocks in the same group correspond to different image signal lines, respectively, to connect the other ends of the sampling switches in the individual blocks to corresponding image signal lines, supplies one sampling signal to two adjacent groups, and when any one sampling signal is supplied, simultaneously turns on sampling switches in the same columns in “n” blocks belonging to one group of two groups corresponding to the sampling signal.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Electroluminescent display
ActiveCN105719597AReduce power consumptionSuppresses degradation of display qualityStatic indicating devicesSemiconductor lamp usageConvertersDigital feedback
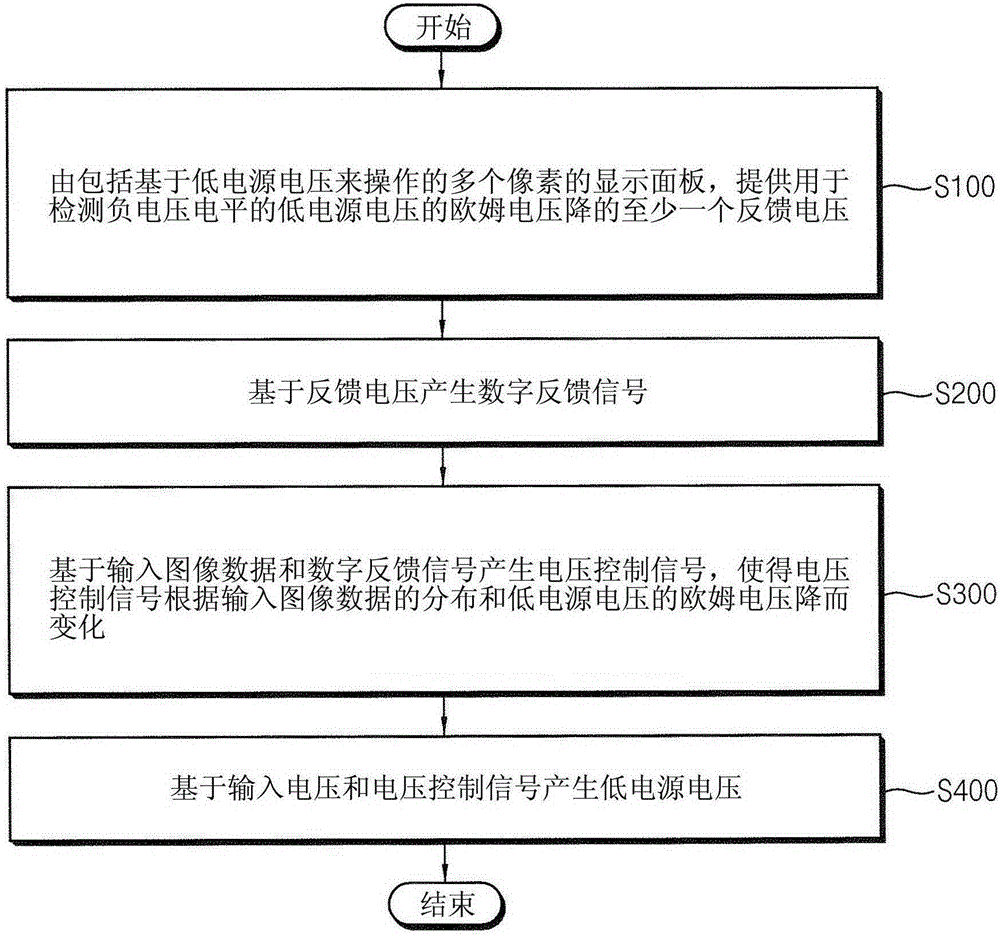
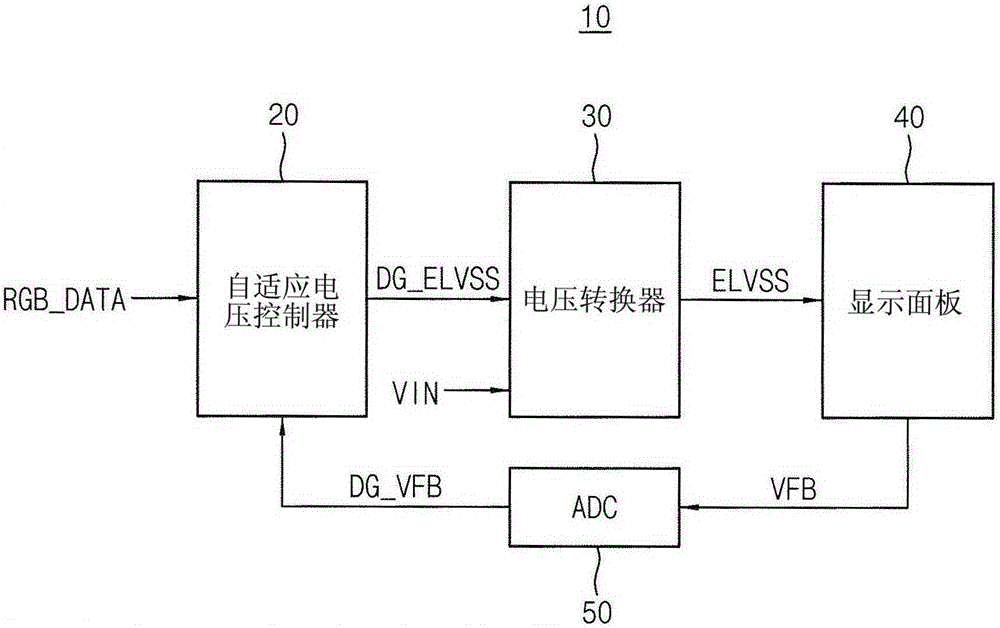
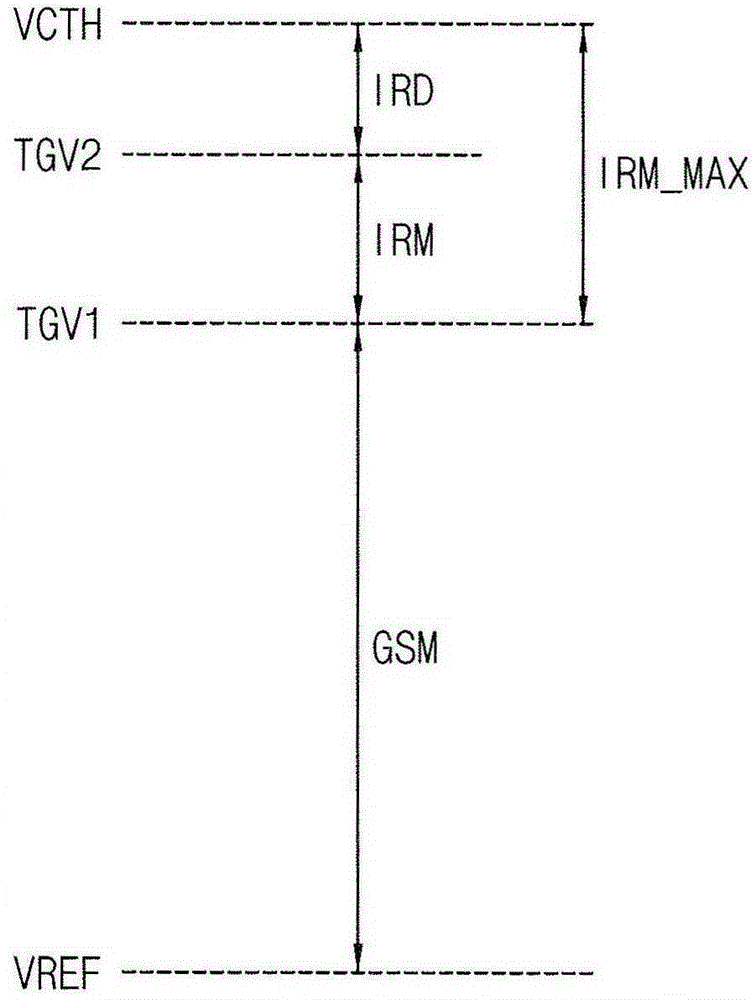
An electroluminescent display (10) and a method of driving the same are disclosed. In one aspect, the display includes a display panel (40) including a plurality of pixels (PX) configured to operate based on a first power supply voltage (ELVSS) having a negative voltage level. The display panel (40) is configured to generate at least one feedback voltage (VFB) corresponding to an ohmic drop (IRD) of the first power supply voltage (ELVSS). An analog-to-digital converter (50) is configured to generate at least one digital feedback signal (DG_VFB) based on the at least one feedback voltage (VFB). An adaptive voltage controller (20) is configured to generate a voltage control signal (DG_ELVSS) based on input image data (RGB_DATA), the at least one digital feedback signal (DG_VFB), a distribution of the input image data and the ohmic drop (IRD) of the first power supply voltage (ELVSS). A voltage converter (30) is configured to generate the first power supply voltage(ELVSS) based on an input voltage (VIN) and the voltage control signal (DG_ELVSS).
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Thin film transistor circuit, light emitting display apparatus, and driving method thereof
InactiveUS20110001747A1Suppress deterioration of display qualitySuppresses degradation of display qualityCathode-ray tube indicatorsElectric pulse generatorEngineeringElectric stress
In order to suppress an influence of an electrical stress on a TFT characteristic in use of a TFT, a light emitting display apparatus according to the present invention comprises organic EL devices and driving circuits for driving the organic EL devices. The driving circuit includes plural pixels each having a thin film transistor of which a threshold voltage reversibly changes due to the electrical stress applied between a gate terminal and a source terminal, and a voltage applying unit which sets gate potential of the thin film transistor higher than source potential. The voltage applying unit applies the electrical stress between the gate terminal and the source terminal at a time when the thin film transistor is not driven, so as to drive the thin film transistor in a region that the threshold voltage is saturated to the electrical stress.
Owner:CANON KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com