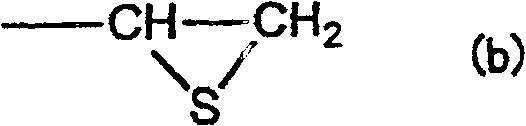Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
46results about How to "Suppress contrast drop" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
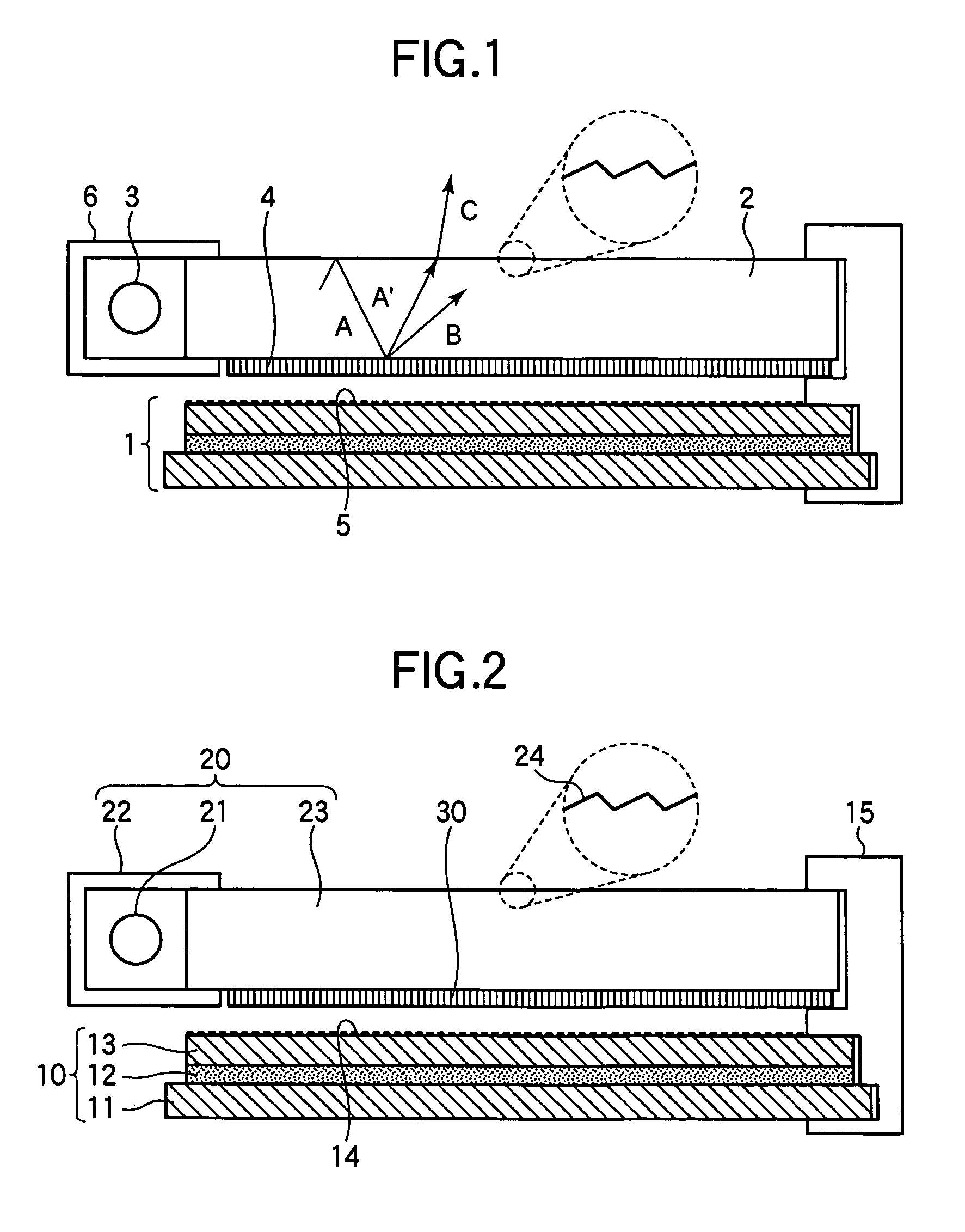
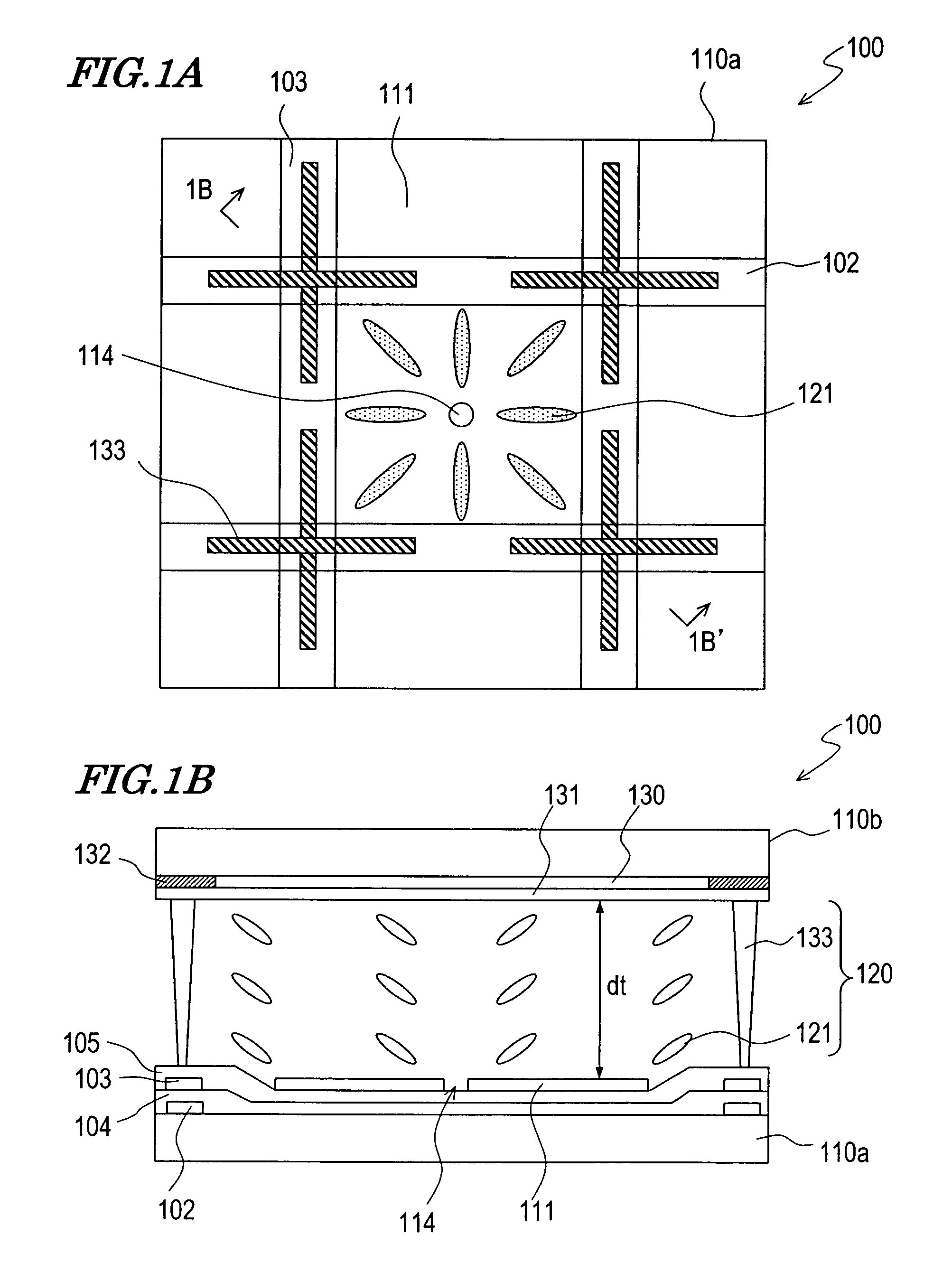
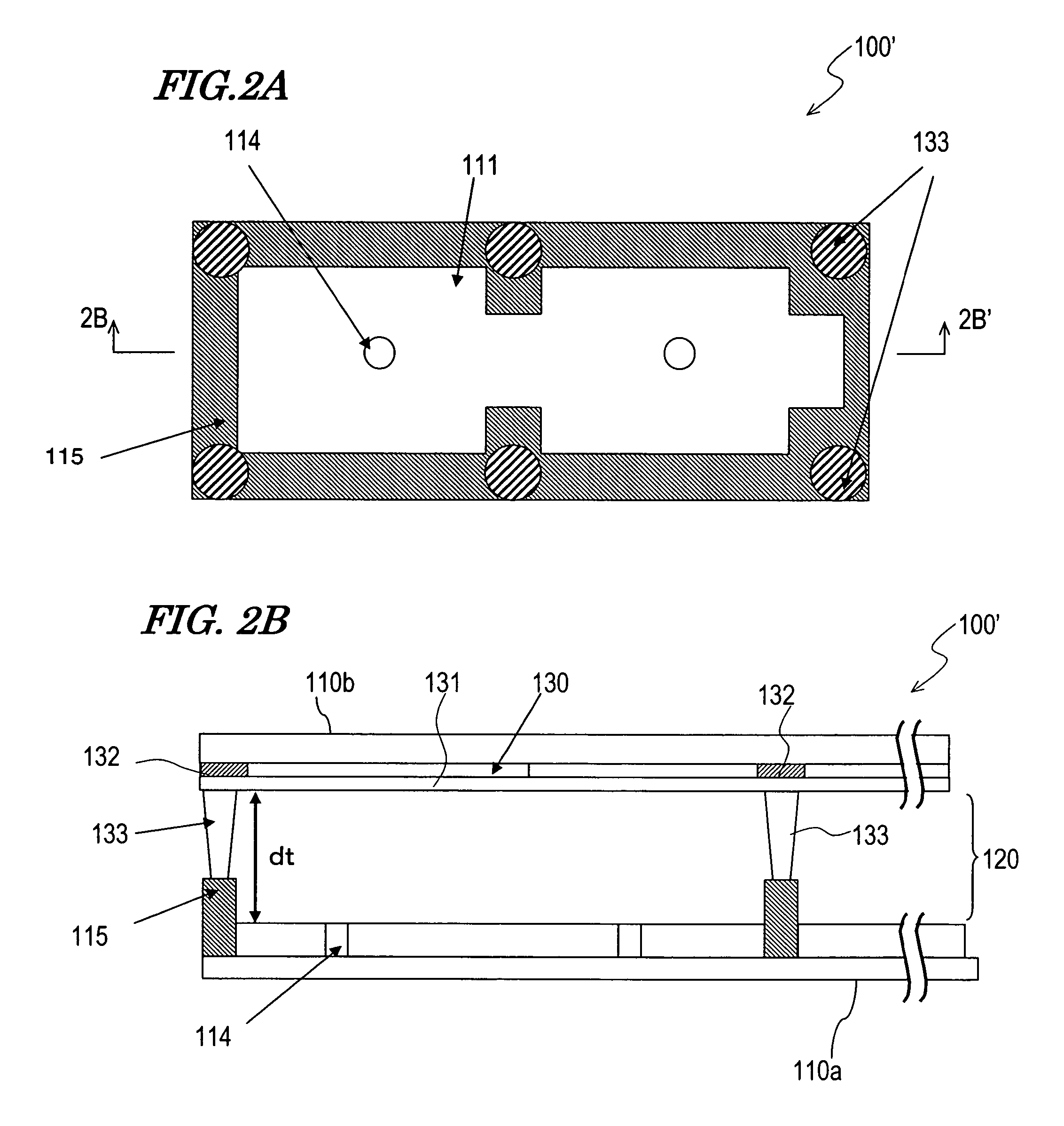
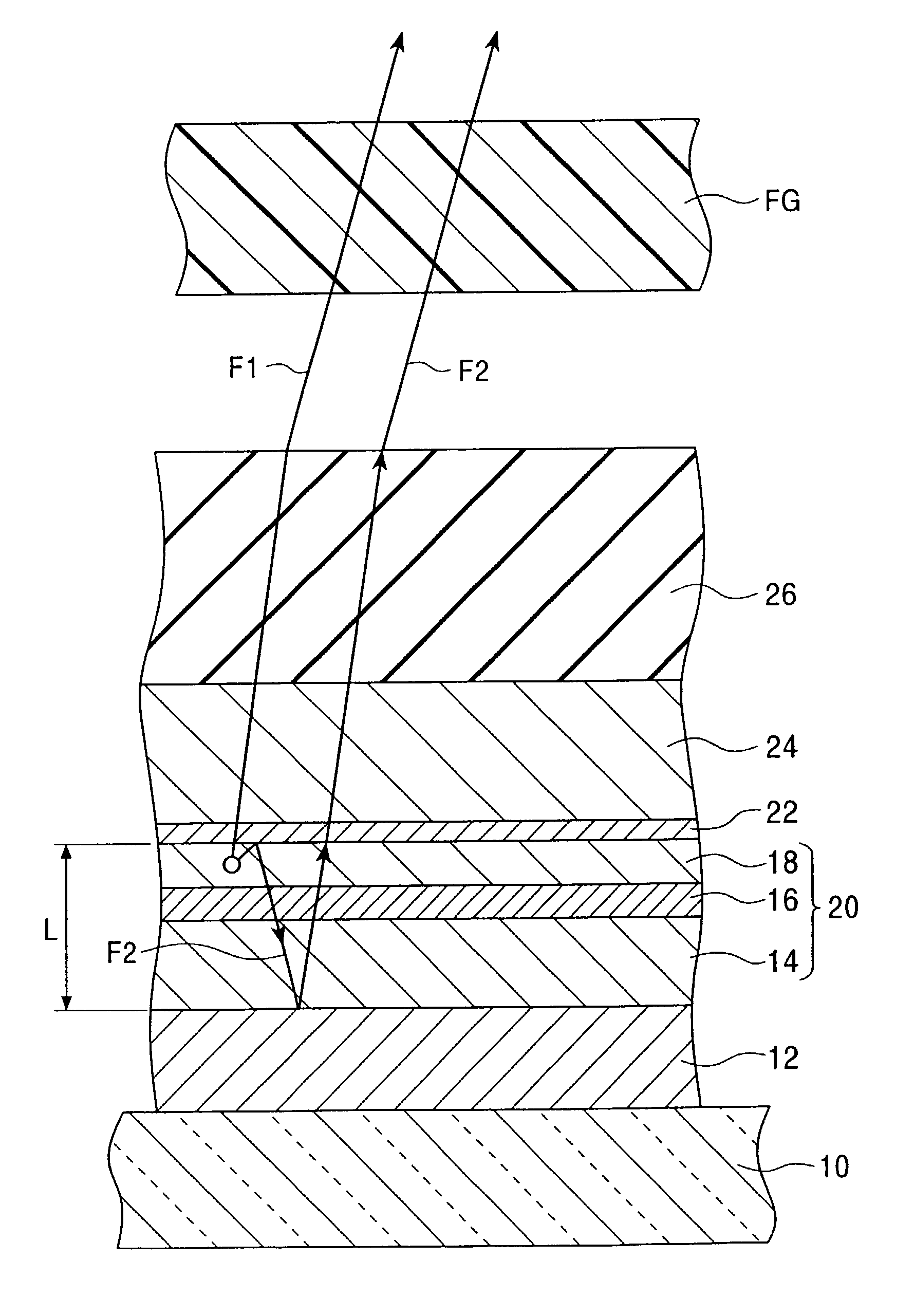
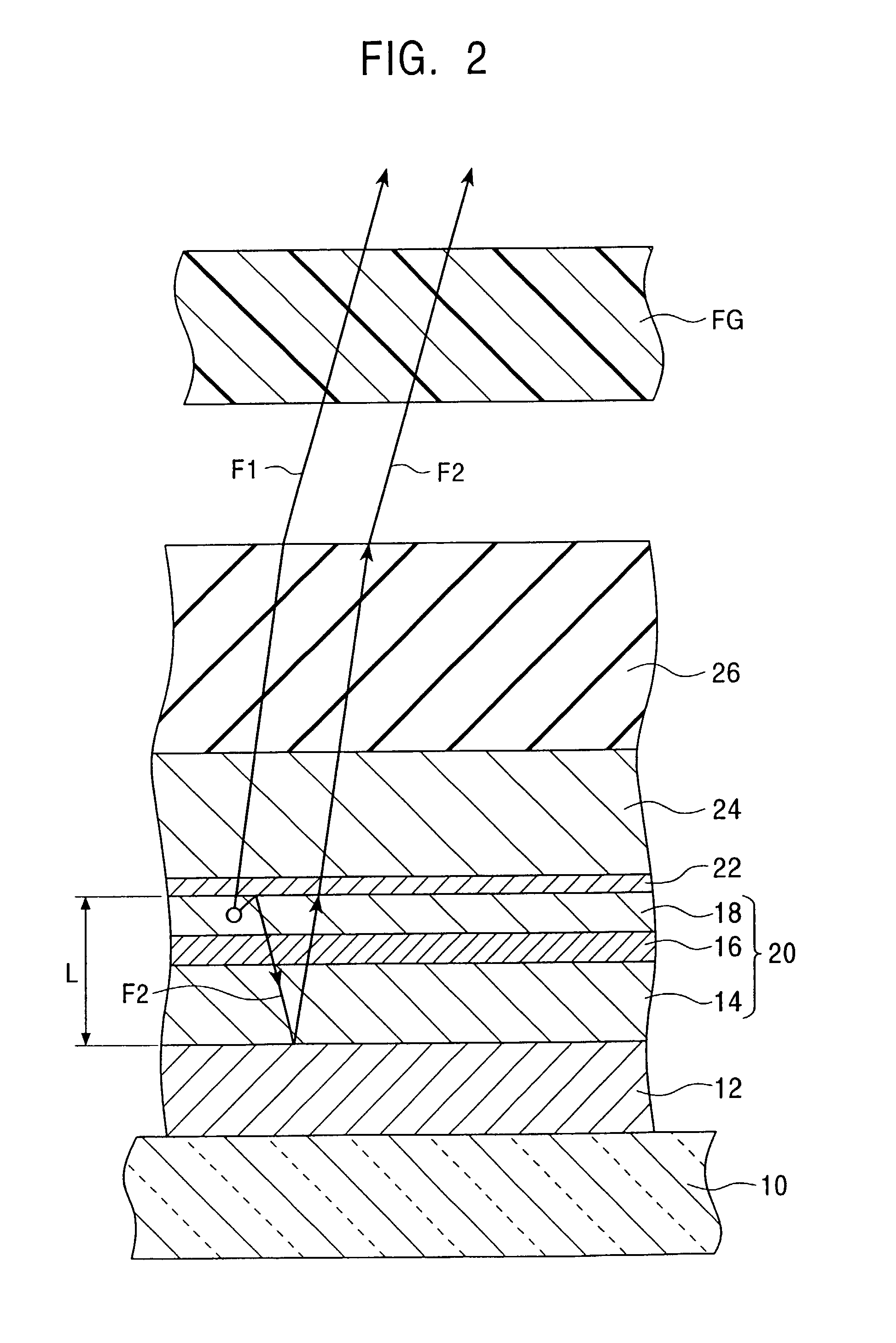
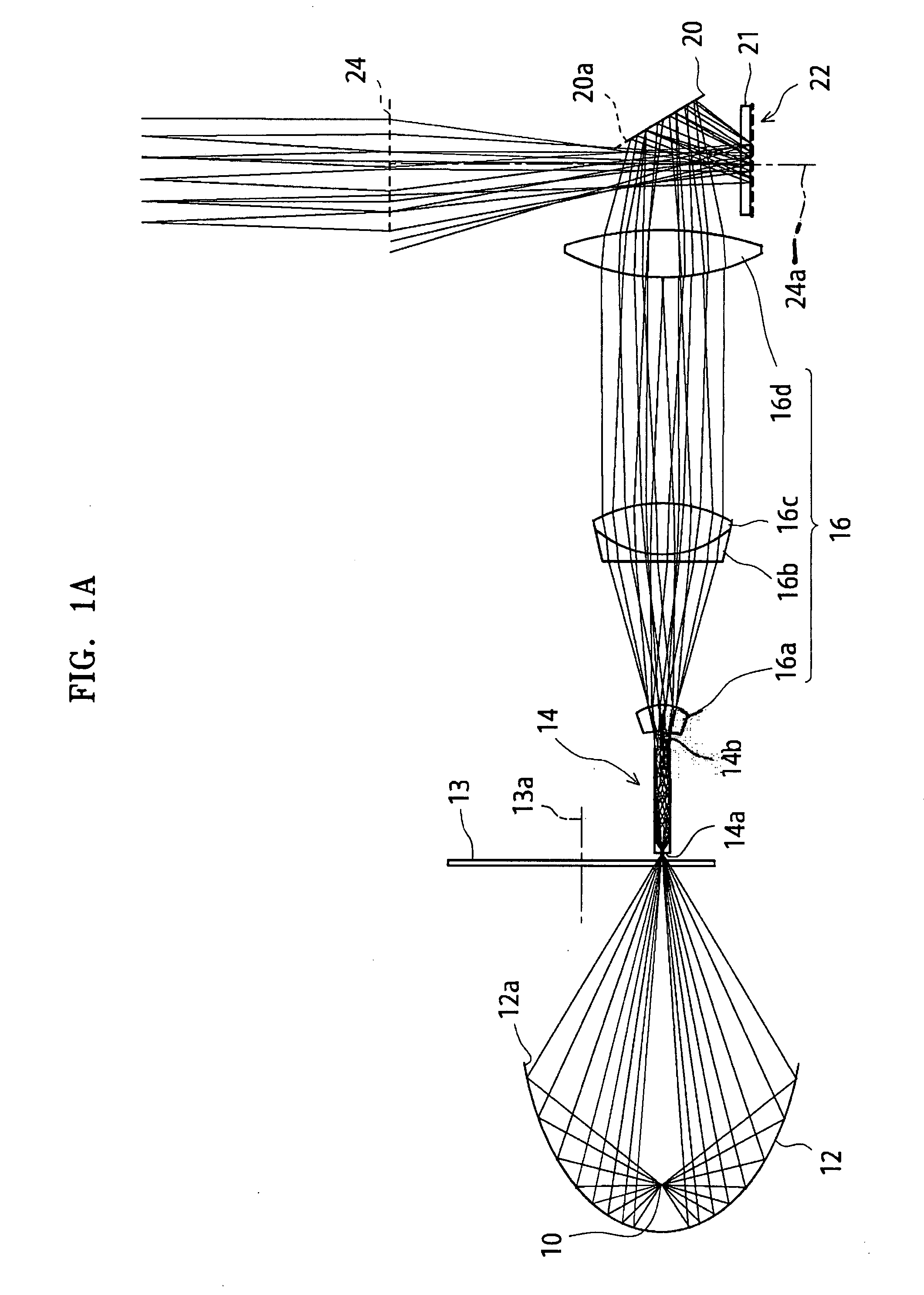
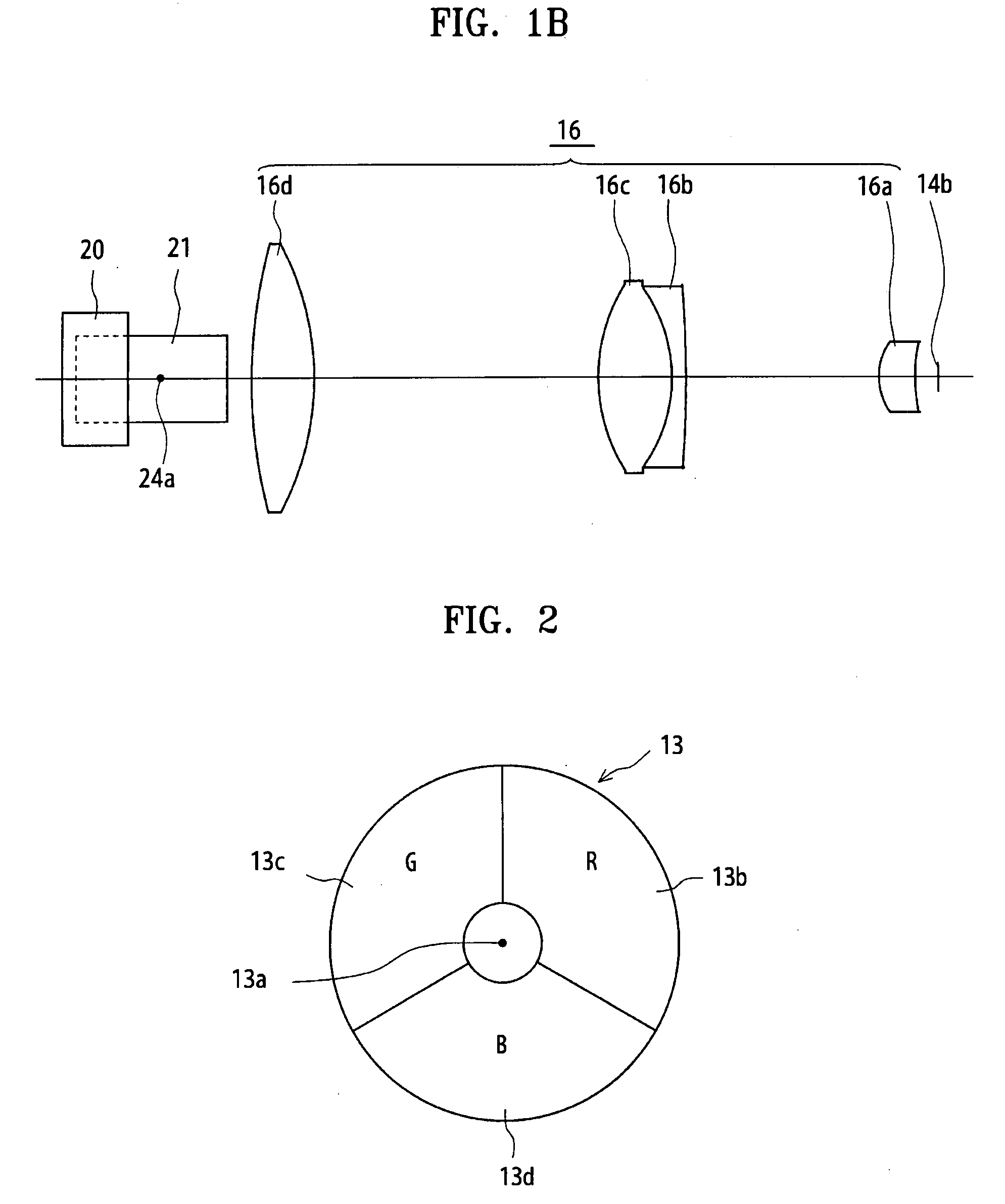
Reflection-type liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS7359011B2Suppress contrast dropQuality improvementOptical light guidesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayLight guide
To suppress a decrease in the contrast caused by the reflection on the interface to the air layer without decreasing the quality of display. A reflection-type liquid crystal display device includes a light guide plate having a polarizing element stuck or adhered thereto on the side facing a reflection-type liquid crystal display panel, a source of light arranged on an end surface side of the light guide plate, and the reflection-type liquid crystal display panel arranged maintaining a predetermined gap relative to the light guide plate, wherein a light-diffusing function is imparted to the surface of the reflection-type liquid crystal display panel on the side facing the light guide plate.
Owner:SHARP KK
Light guide plate, planar light source apparatus, display apparatus, and electronic device
ActiveUS20200049877A1Suppress uneven brightnessIncrease contrastMechanical apparatusElectric lightingLight guideLight beam
Provided is a light guide plate including: a diverging portion which is provided on an opposite side of a light exit surface from which light is emitted, the diverging portion causing a luminous flux emitted from a light emitting element to diverge; and a restricting portion which is provided, when a prescribed range from the light emitting element on the light exit surface is defined as an illuminated area illuminated by the light emitting element, in at least a periphery of the illuminated area on the light exit surface and which deflects or shields light traveling from inside toward outside of the illuminated area to restrict traveling, toward a side of the light exit surface, of light traveling toward the outside of the illuminated area.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
Liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20050200784A1Effective aperture ratioImprove contrast ratioPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsEngineeringVoltage
The liquid crystal display device of the present invention includes a first substrate, a second substrate and a vertically aligned liquid crystal layer interposed between the first and second substrate. The device has a plurality of pixels each including a first electrode formed on the first substrate, a second electrode formed on the second substrate, and the liquid crystal layer interposed between the first and second electrode, and a shading region provided around the pixels. A plurality of supports for defining the thickness of the liquid crystal layer are placed regularly on the surface of the first or second substrate facing the liquid crystal layer in the shading region. The liquid crystal layer forms at least one liquid crystal domain exhibiting axisymmetric alignment when at least a predetermined voltage is applied, and the tilt direction of liquid crystal molecules in the at least one liquid crystal domain is defined with inclined sides of the plurality of supports.
Owner:SHARP KK
Display panel and display device
InactiveCN102356348AImprove utilization efficiencySuppress contrast dropOptical filtersNon-linear opticsPhosphorRefractive index
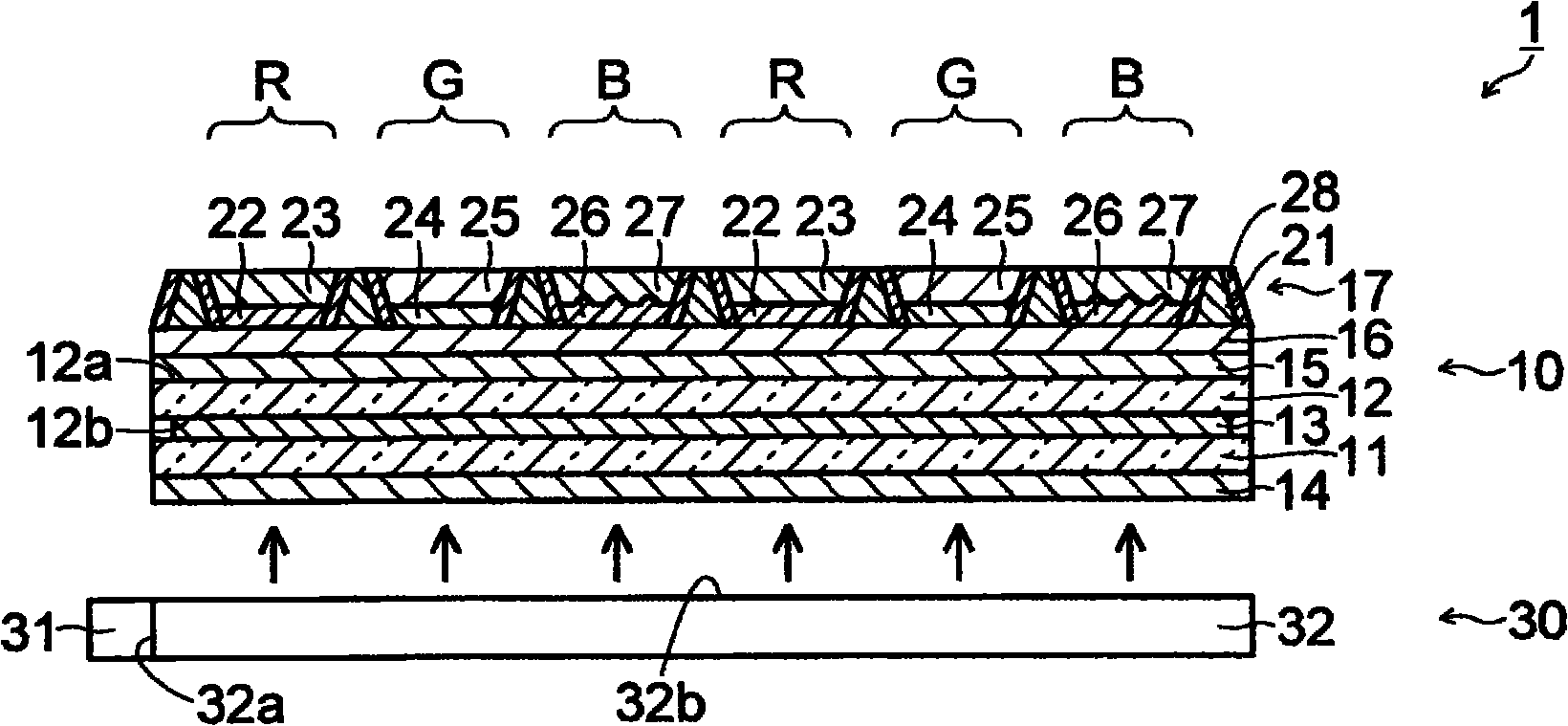
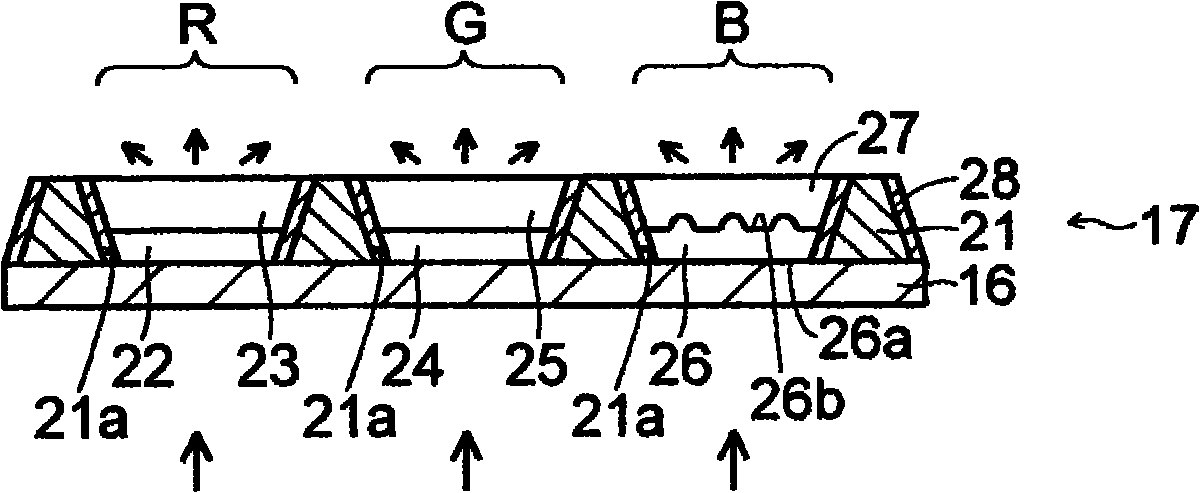
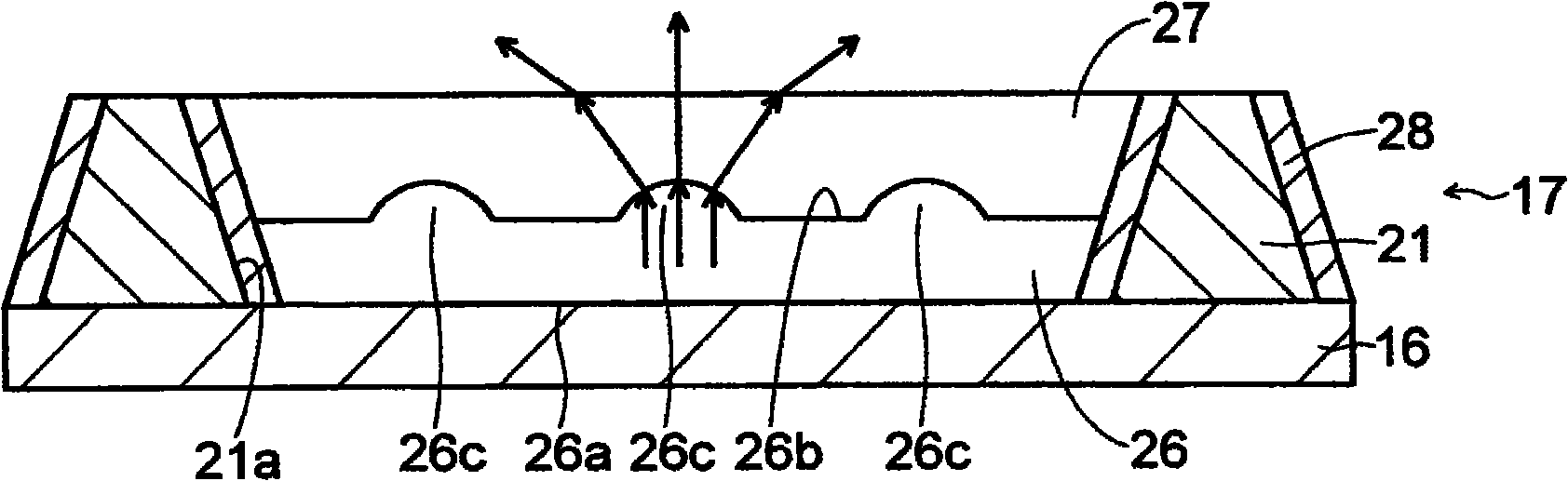
Disclosed is a liquid crystal display panel wherein the utilization efficiency of light can be improved, while suppressing deterioration of the contrast. Specifically, a color filter (17) of a liquid crystal display panel (10) comprises: a black matrix (21) which is provided with an opening (21a); a red phosphor layer (22) and a red filter layer (23) which are arranged within the opening (21a) in a red display region (R); a green phosphor layer (24) and a green filter layer (25) which are arranged within the opening (21a) in a green display region (G); and a transparent resin layer (26) and a blue filter layer (27) which are arranged within the opening (21a) in a blue display region (B). A light exit surface of the transparent resin layer (26) is provided with a plurality of projected portions (26c), and the transparent resin layer (26) has a refractive index different from that of the blue filter layer (27), which is in contact with the light exit surface. The transparent resin layer (26) is a light diffusion layer, and is capable of increasing the viewing angle of blue light.
Owner:SHARP KK
Liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS7391489B2Effective aperture ratioSuppress contrast dropPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsEngineeringVoltage
Owner:SHARP KK
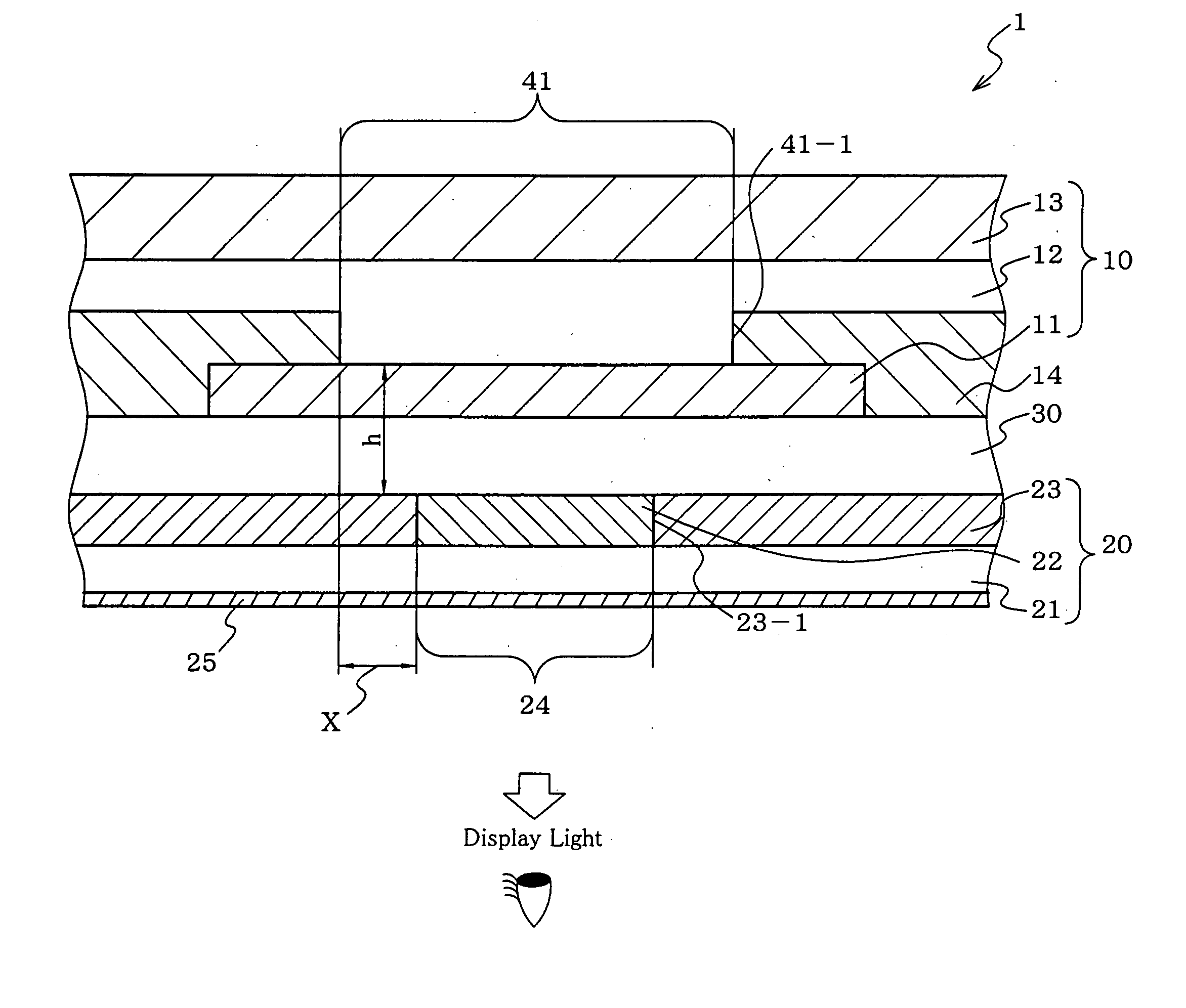
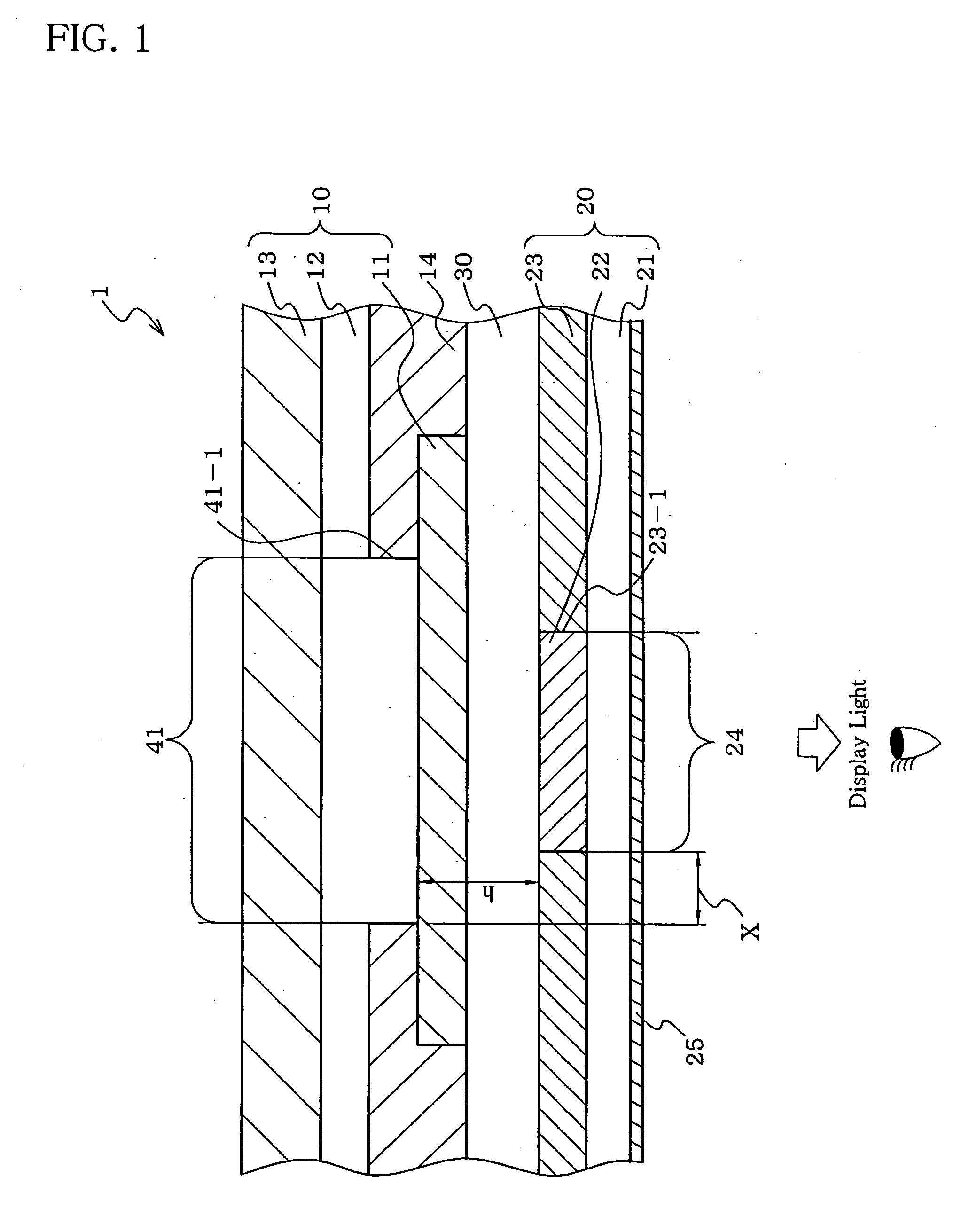
Organic electroluminescence display device
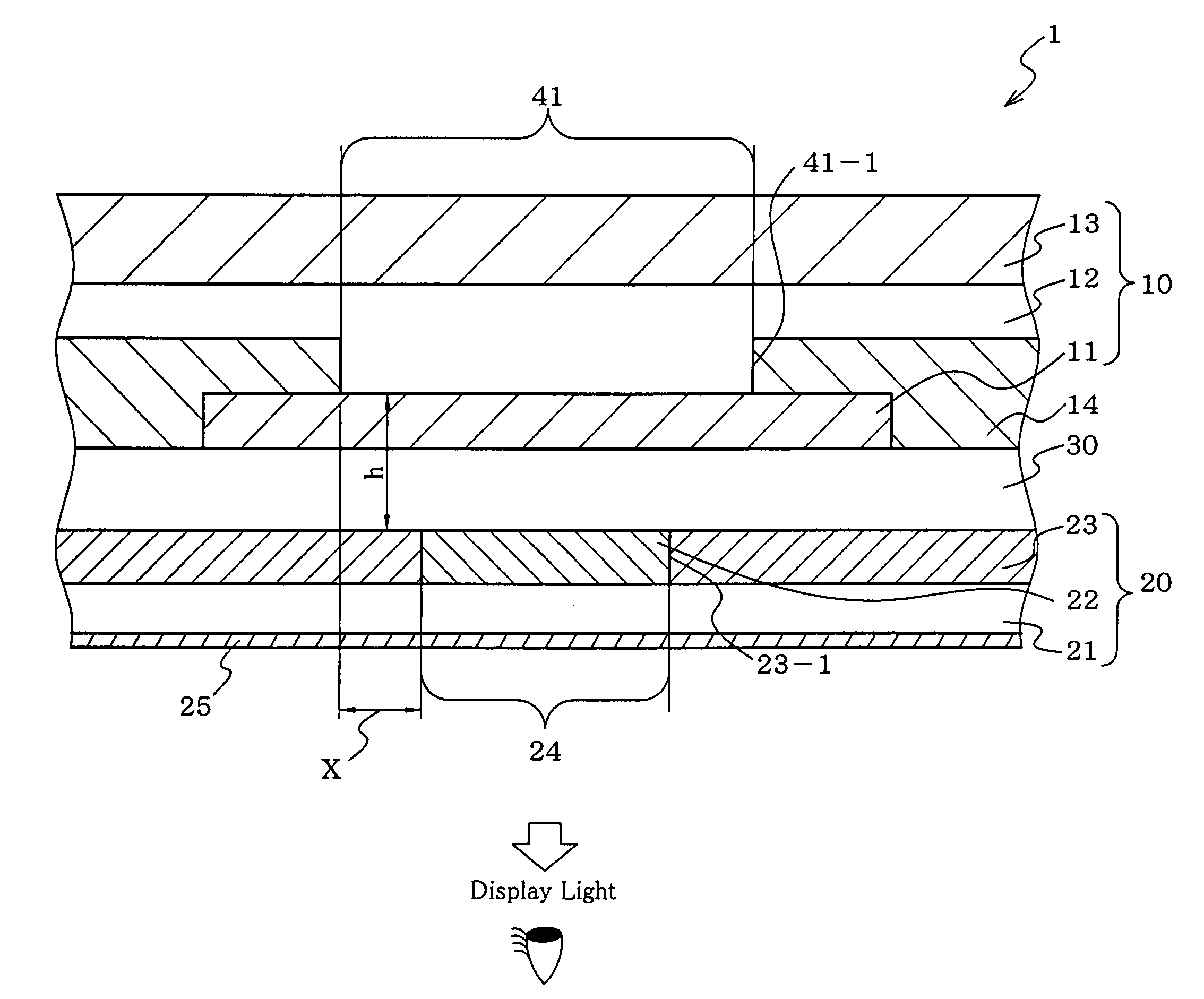
ActiveUS20070164662A1Increase contrastLight amountDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesOptoelectronicsOrganic electroluminescence
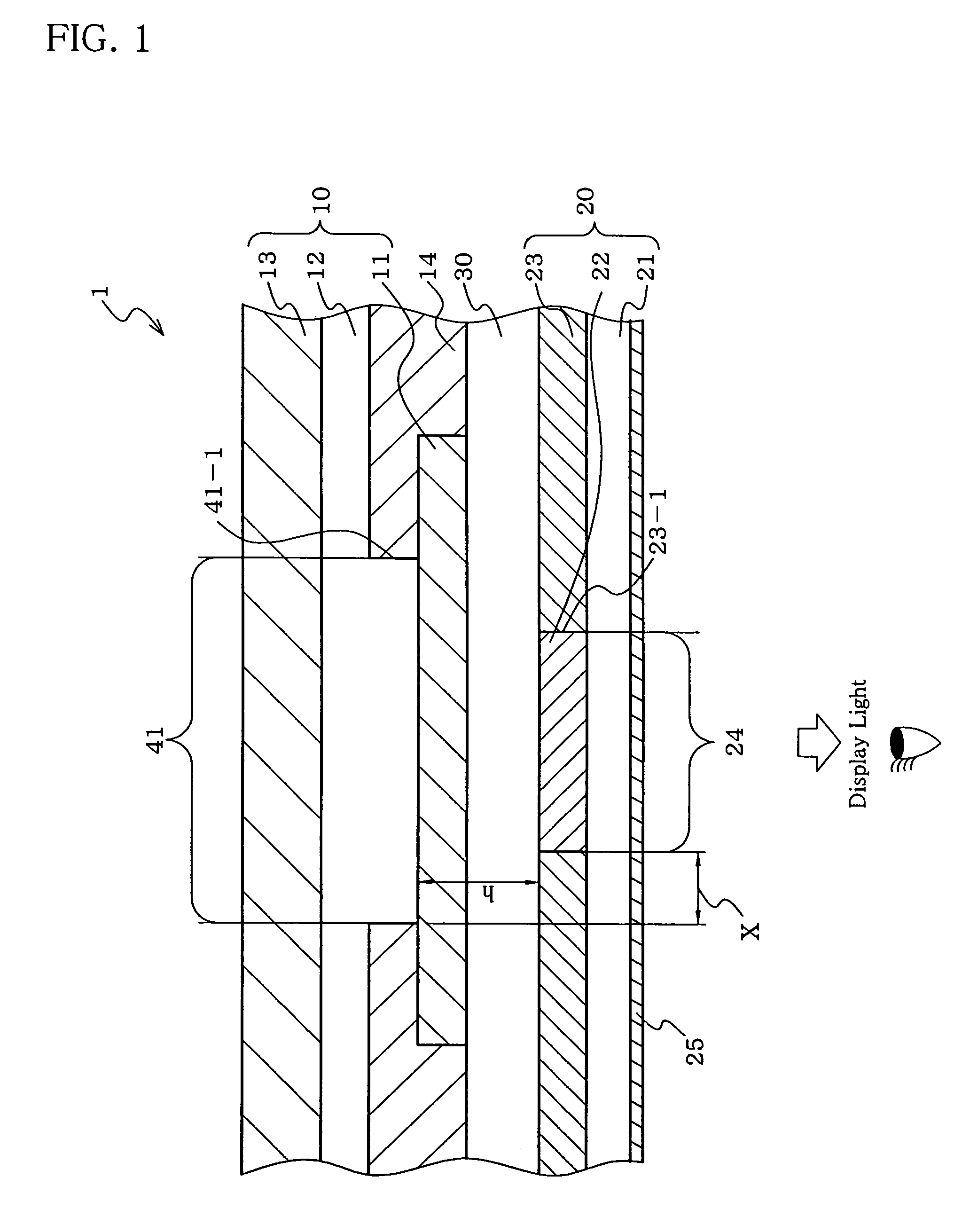
An organic electroluminescent display (1) including: an organic electroluminescent device (10), and a color converting member (20) including a shielding layer (23) and a shielding layer aperture region (24) including a color converting layer (22), edges (23-1) of the aperture region (24) being closer to the center of the aperture region (24) than edges (41-1) of an emission region (41) of the organic electroluminescent device (10).
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Substrate for electro-optical device, electro-optical device and electronic apparatus
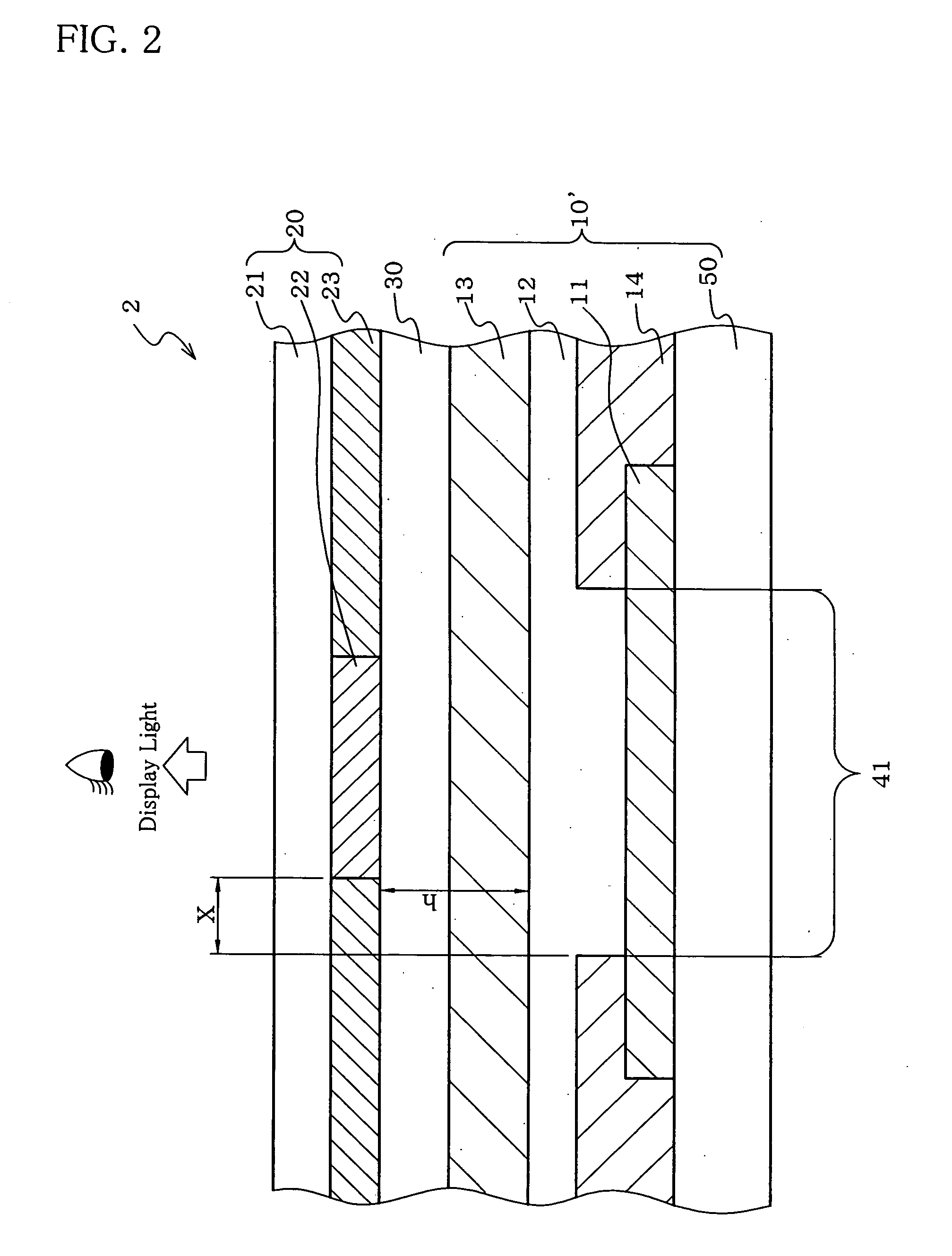
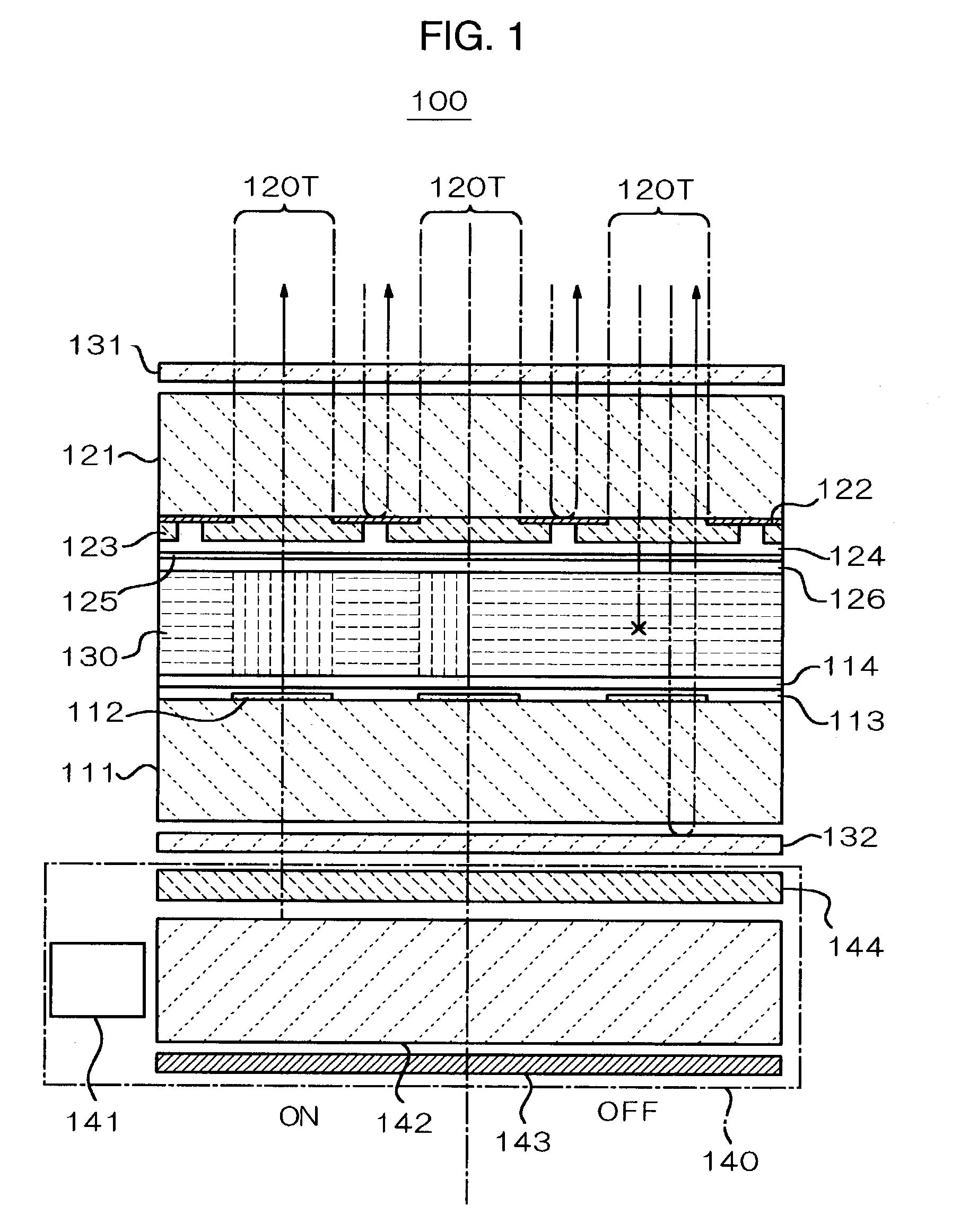
InactiveUS6958796B2Easy to useSuppress contrast dropMirrorsDischarge tube luminescnet screensReflective layerLiquid crystal
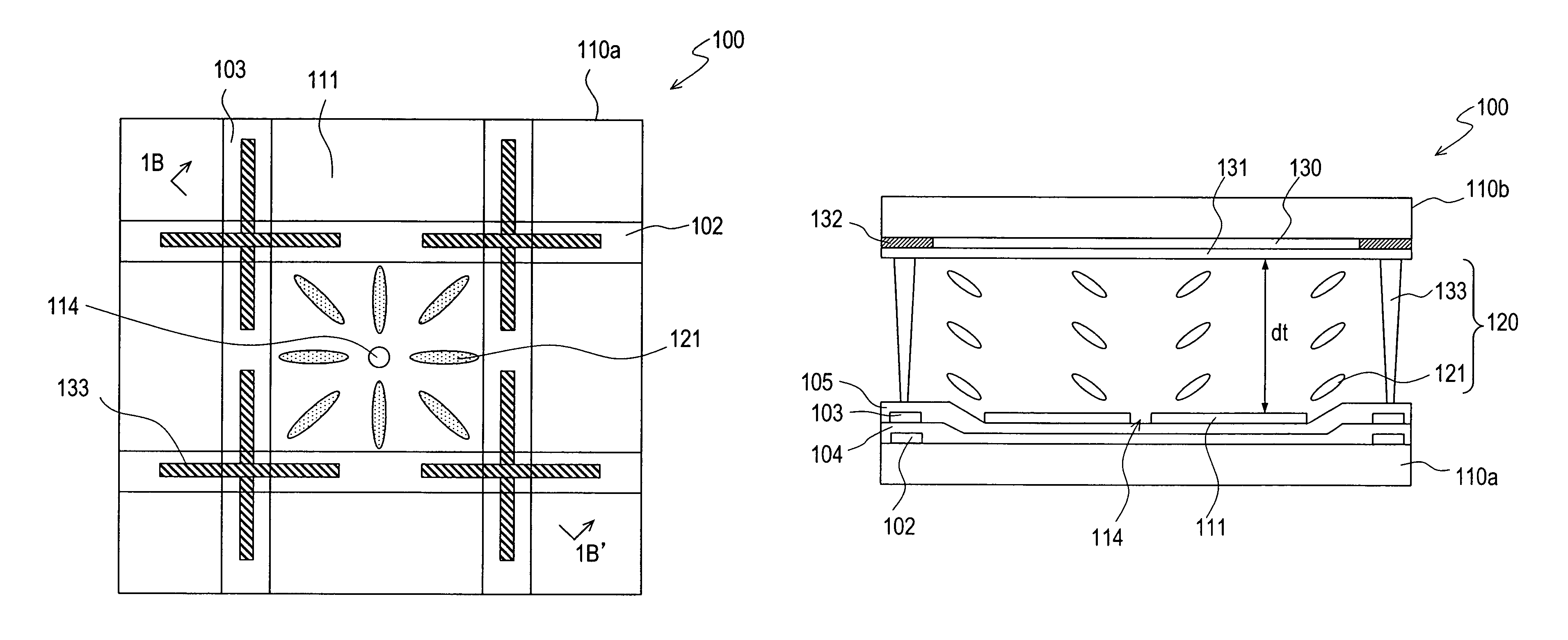
A substrate 121 has a reflecting layer 122 formed thereon, the reflecting layer 122 having a mirror surface on the substrate 121 side. When light is emitted from light transmitting regions 120T, a display mode is achieved in which a desired display mode is performed according to the state of the voltage applied to a liquid crystal 130. Also, when the voltage applied to the liquid crystal 130 is less than the threshold value, and a backlight 140 is turned off to substantially cut off light transmitted through all light-transmitting regions 120T, a mirror mode is set in which the entire surface is seen as a mirror surface by the mirror surface of the reflecting layer 122. Therefore, the display screen of the electro-optical device 100 can be used as a mirror.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
Intraocular lens
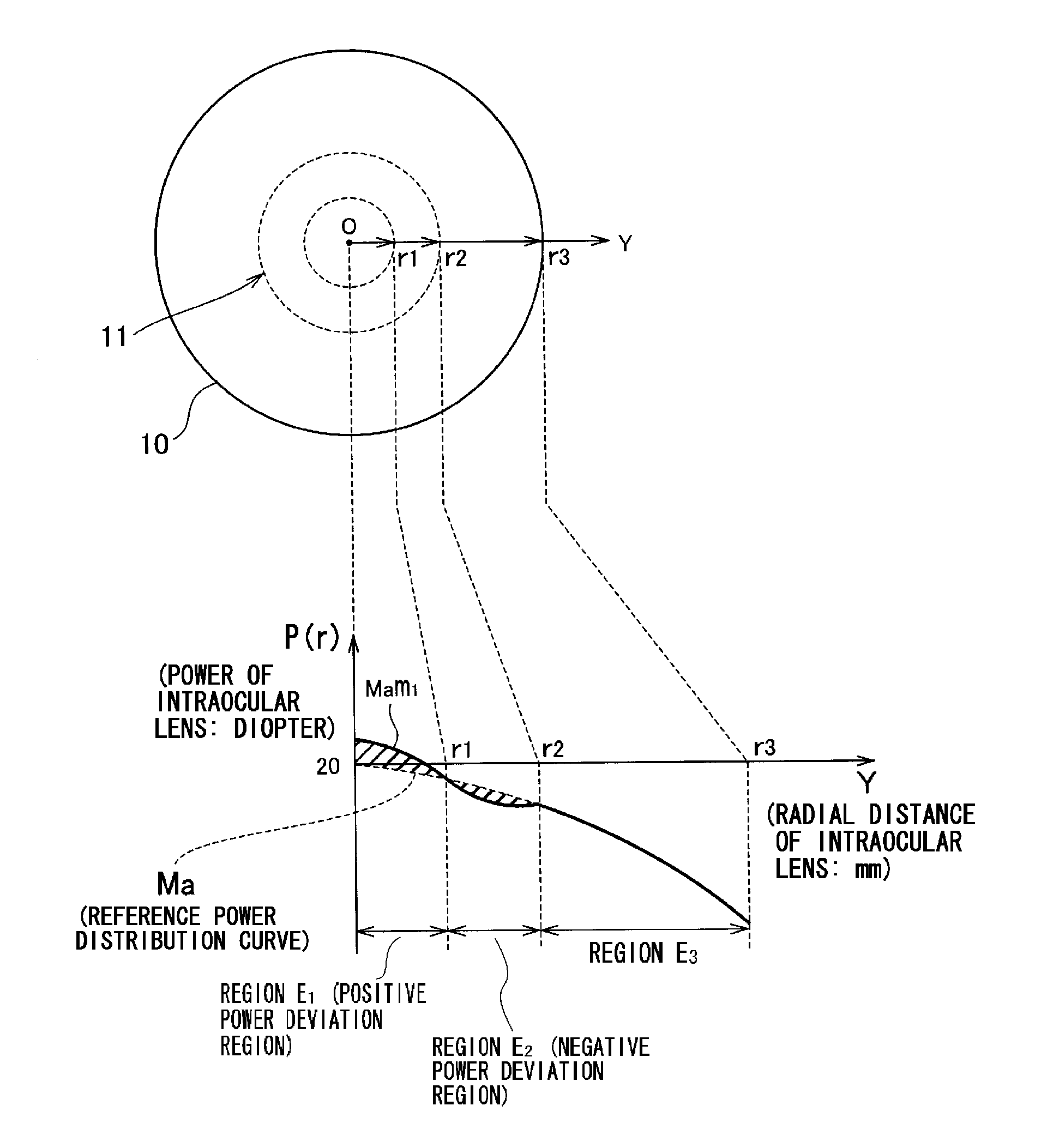
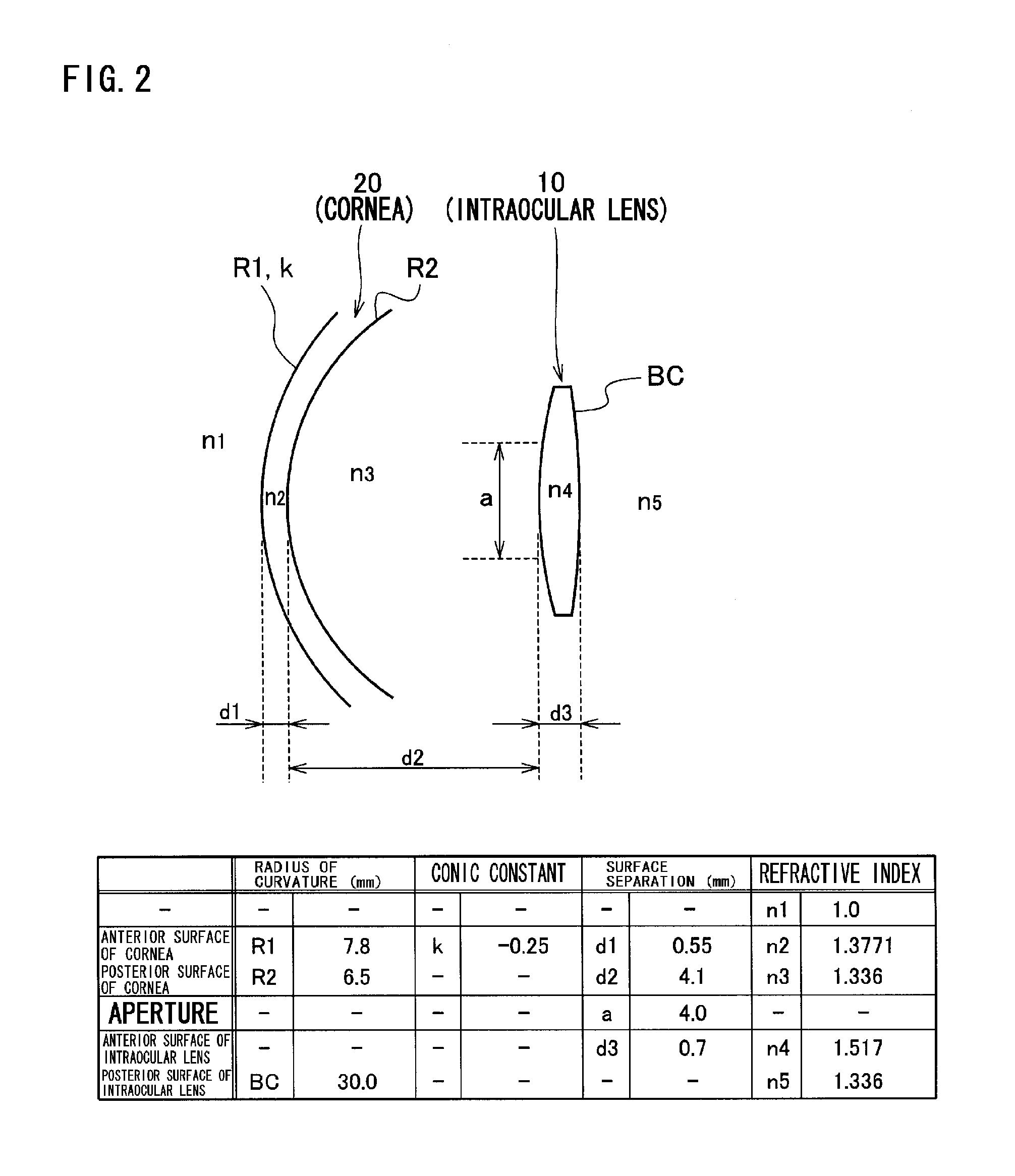
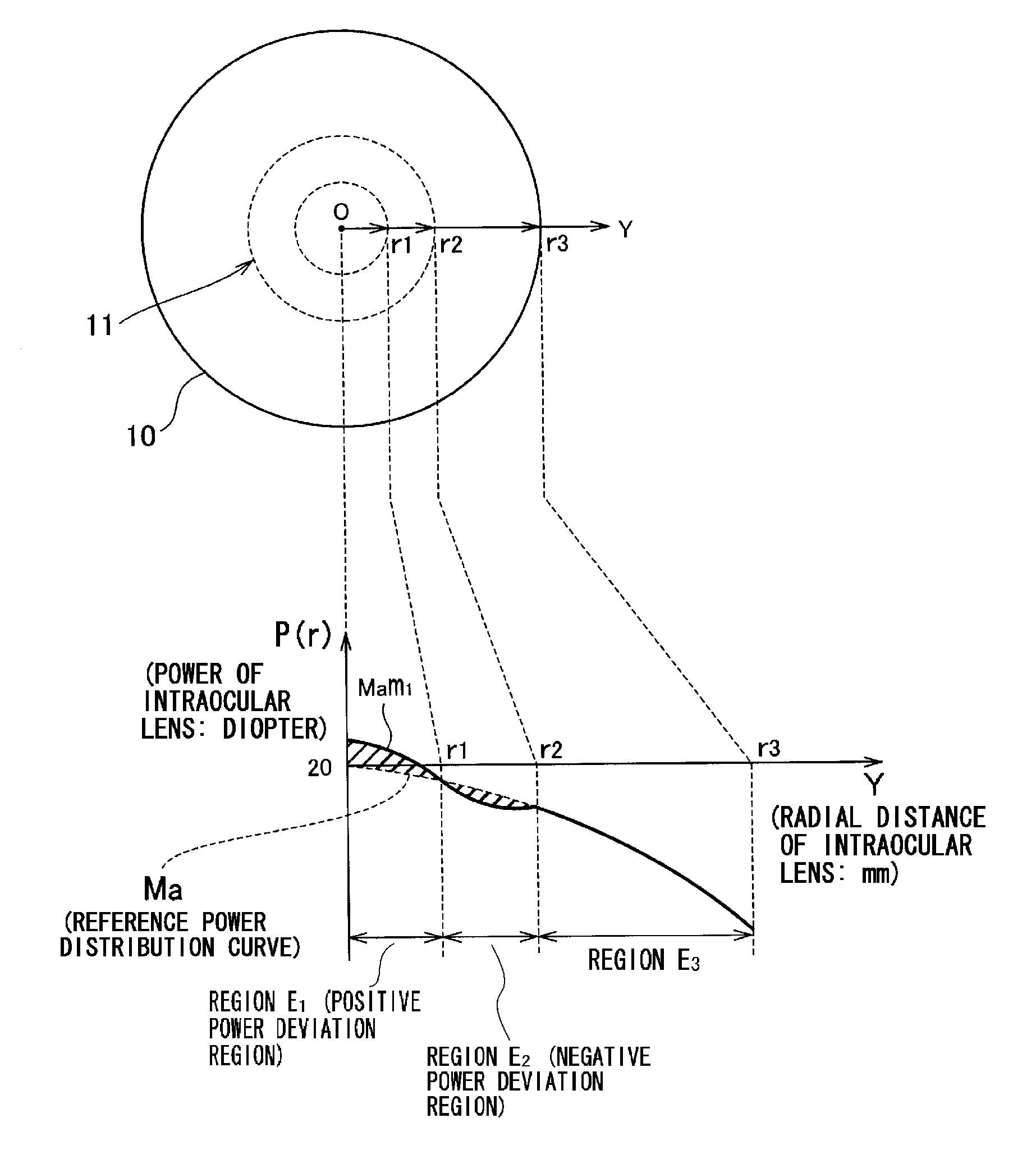
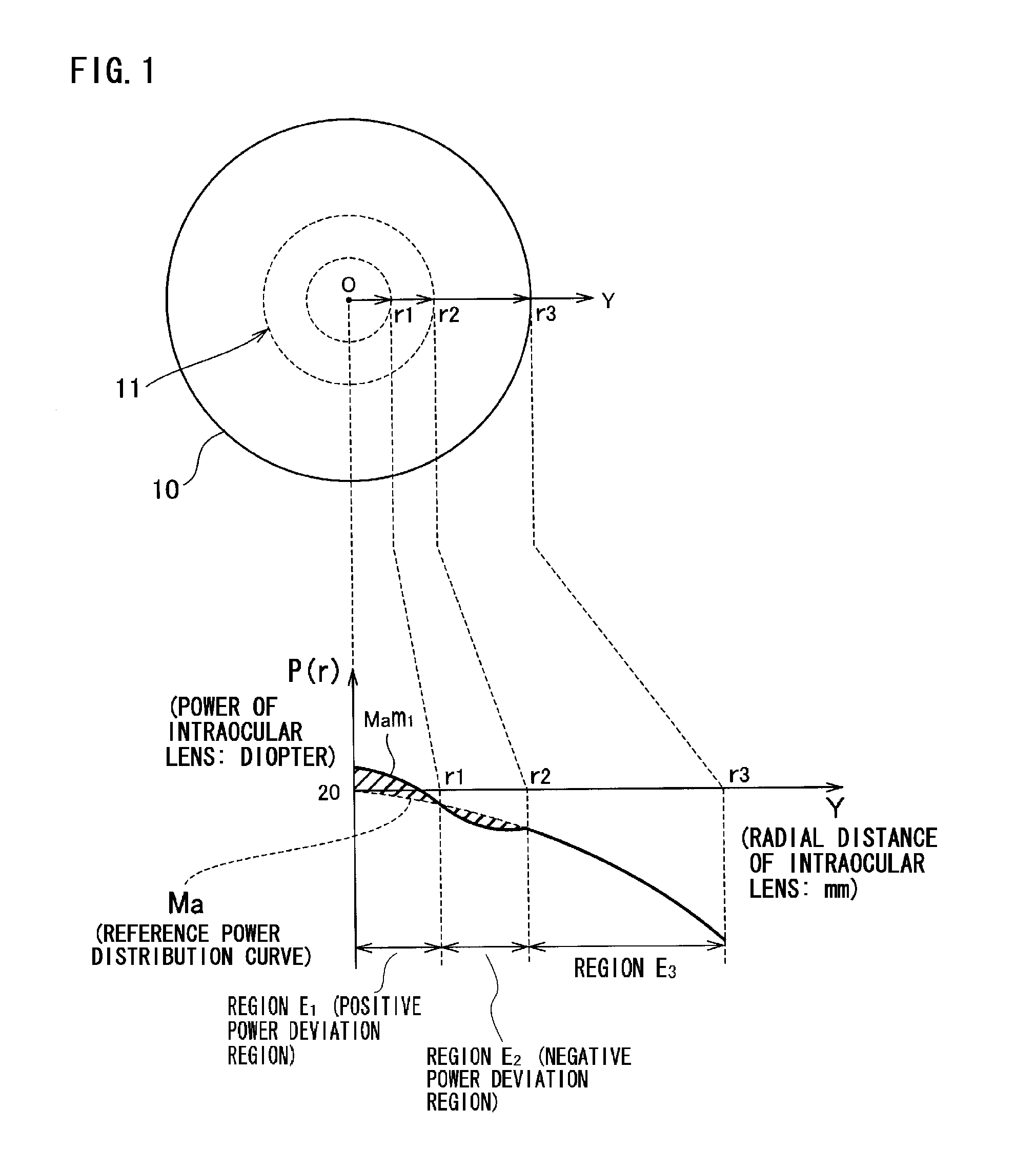
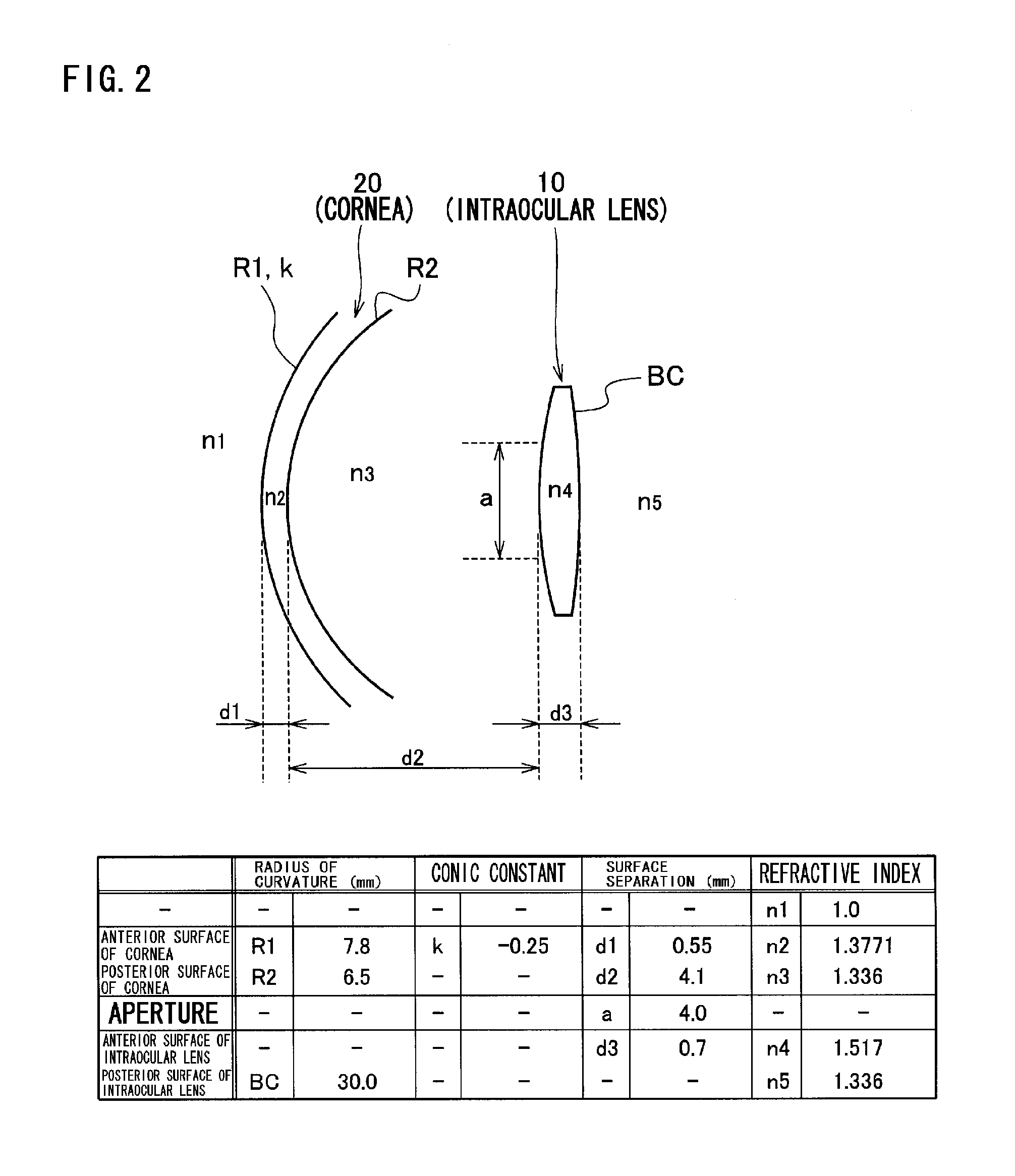
An intraocular lens in which deterioration in contrast is suppressed even when the optical axis of the intraocular lens is decentered from the optical axis of the eyeball when the intraocular lens is inserted into the eye while the advantage of a conventional aberration reduction type intraocular lens that the image is seen clearly is sustained by employing such a power distribution as respectively having at least one positive power deviation region (E1) having a power larger than that represented by the reference power distribution and at least one negative power deviation region (E2) having a power smaller than that represented by the reference power distribution in the central region of the intraocular lens assuming that a power distribution being set to cancel the spherical aberration of cornea when the intraocular lens is inserted into the eye is the reference power distribution.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Electro-optical device, method of driving electro-optical device, electronic apparatus, and projector
InactiveUS20130027446A1High voltageImprove trapping efficiencyCathode-ray tube indicatorsNon-linear opticsTrappingLow voltage
An electro-optical device of the invention includes a first substrate and a second substrate facing each other with an electro-optical medium sandwiched therebetween, a pixel region having a plurality of pixels, and an ion trap section having an electrode formed in a region outside of the pixel region. A trapping voltage applied to the electrode of the ion trap section varies in accordance with a calculated voltage value that is calculated from a driving voltage applied to the electro-optical medium in one or a plurality of the pixels serving as a reference. The trapping voltage is set relatively high when the calculated voltage value belongs to a relatively high voltage range, and the trapping voltage is set relatively low when the calculated voltage value belongs to a relatively low voltage range.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
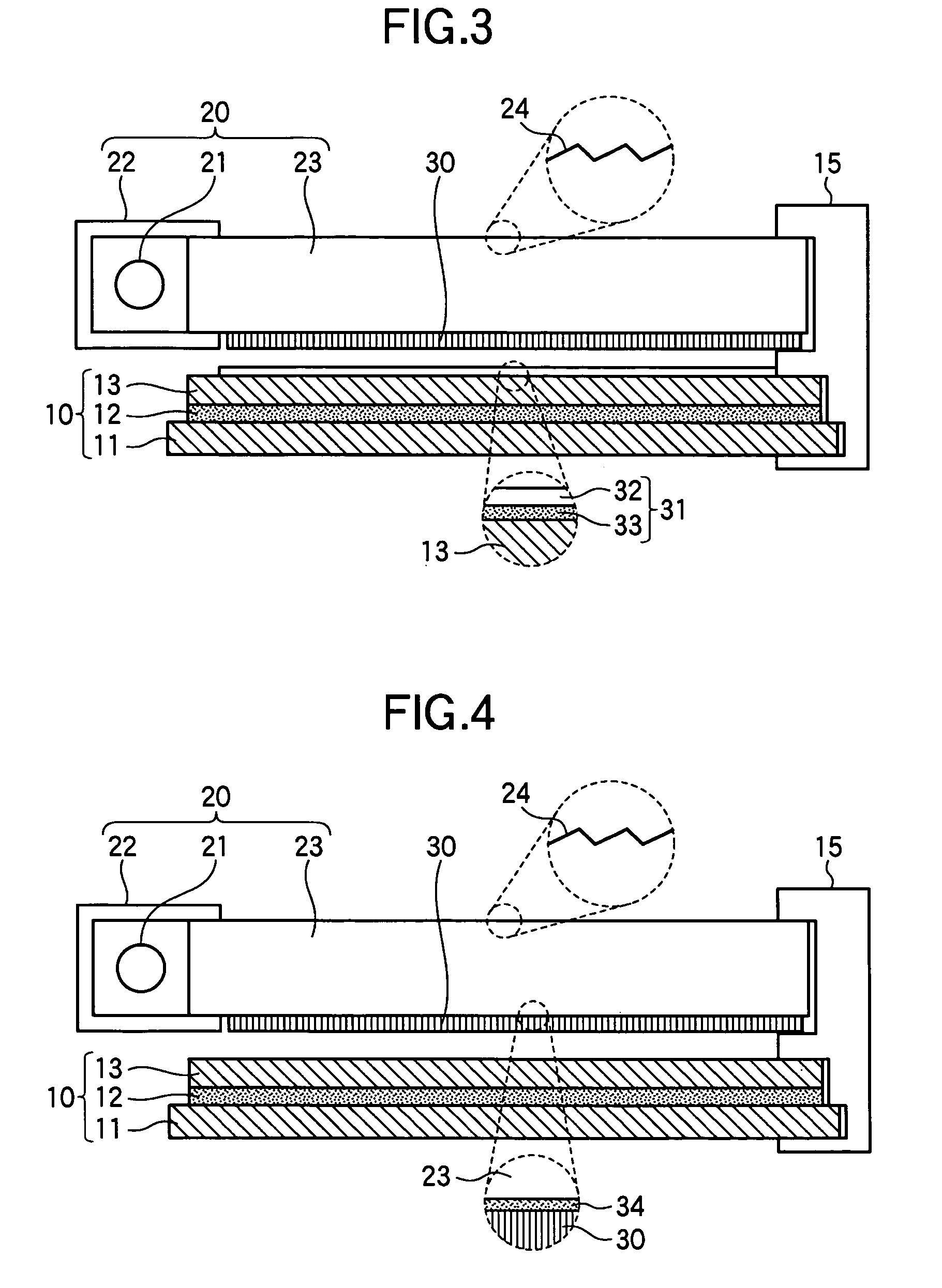
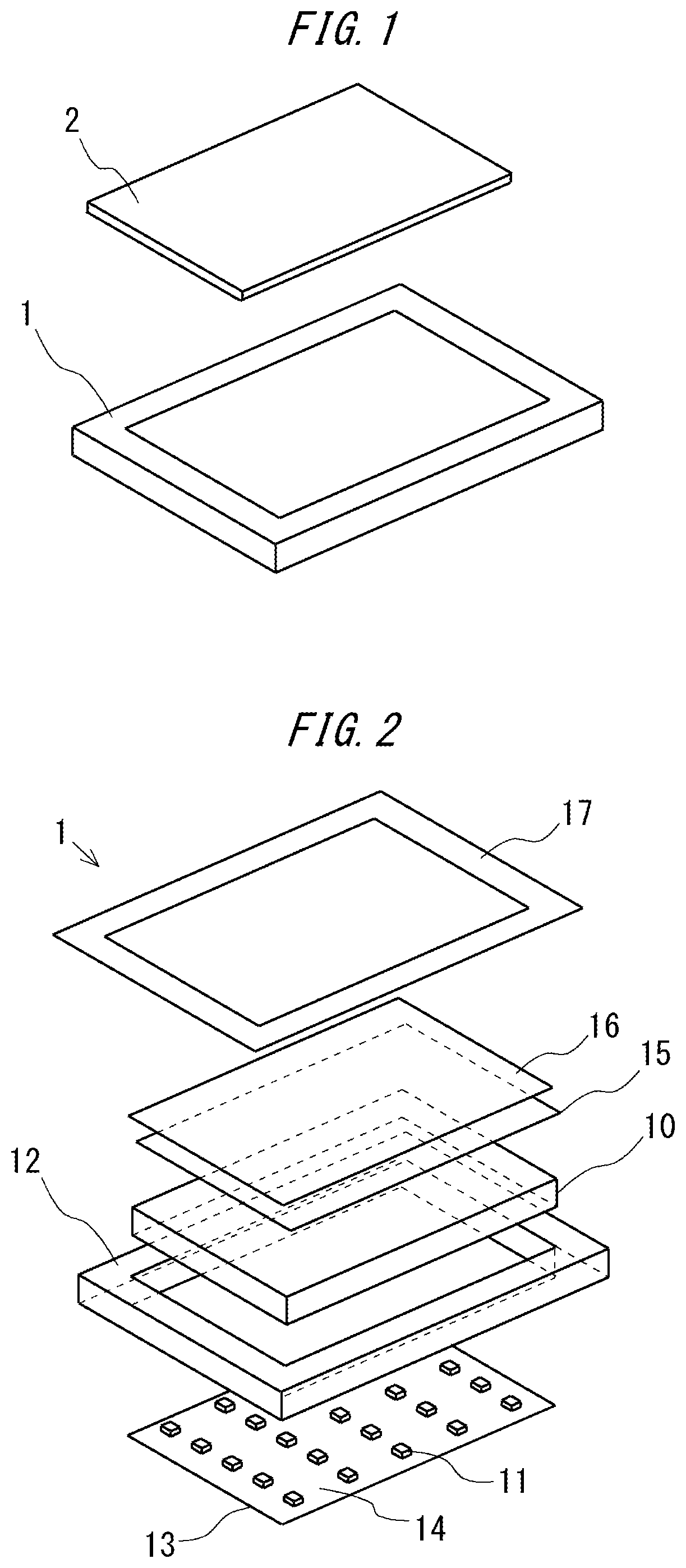
Method of manufacturing liquid crystal device and liquid crystal device
InactiveUS20100085514A1Suppress contrast dropPositional deviationSparking plugsSpark gaps adjustmentEngineeringPolarizer
A liquid crystal device includes a first substrate and a second substrate that are arranged so as to face each other, a liquid crystal layer that is pinched between the first substrate and the second substrate, one pair of polarizers that are arranged on both outer sides of the first substrate and the second substrate, a first optical element having a polarization separation function that is disposed in at least one spot of the first substrate, and a display area that contributes to display. The first optical element is arranged outside the display area.
Owner:138 EAST LCD ADVANCEMENTS LTD
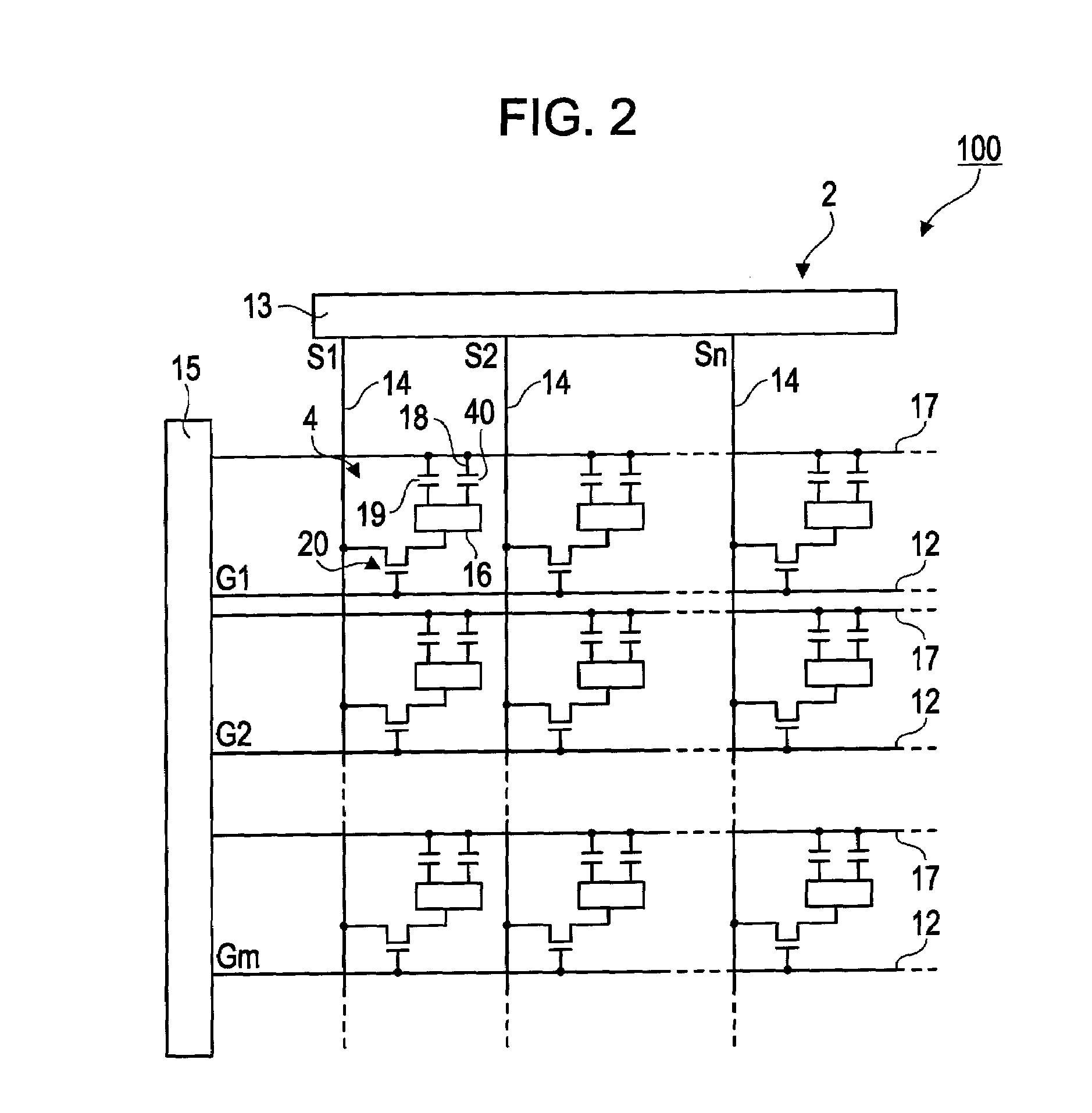
Method and apparatus for driving passive matrix liquid crystal
InactiveUS20060033692A1Reduce voltageReduce power consumptionStatic indicating devicesLow voltageChip size
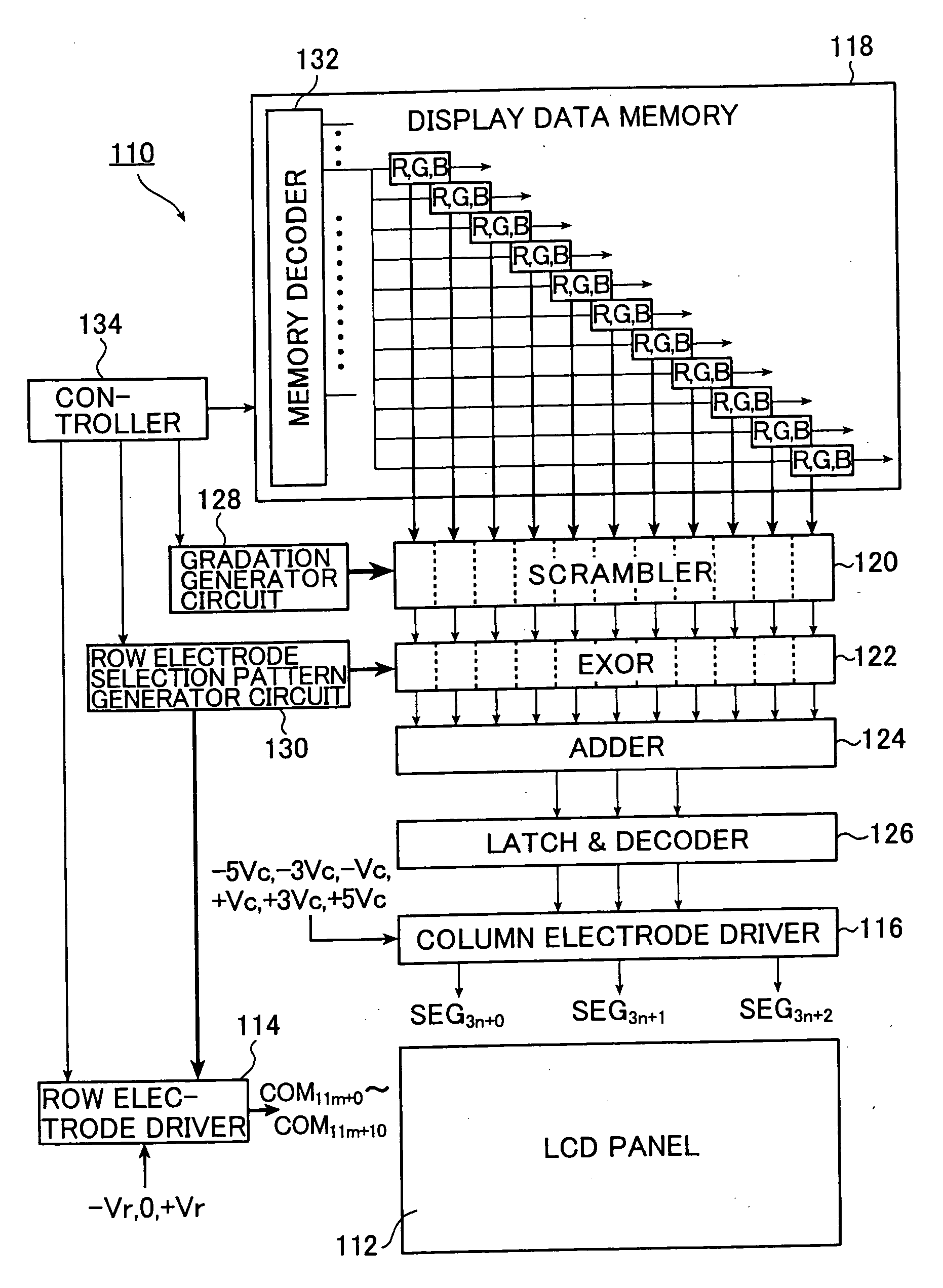
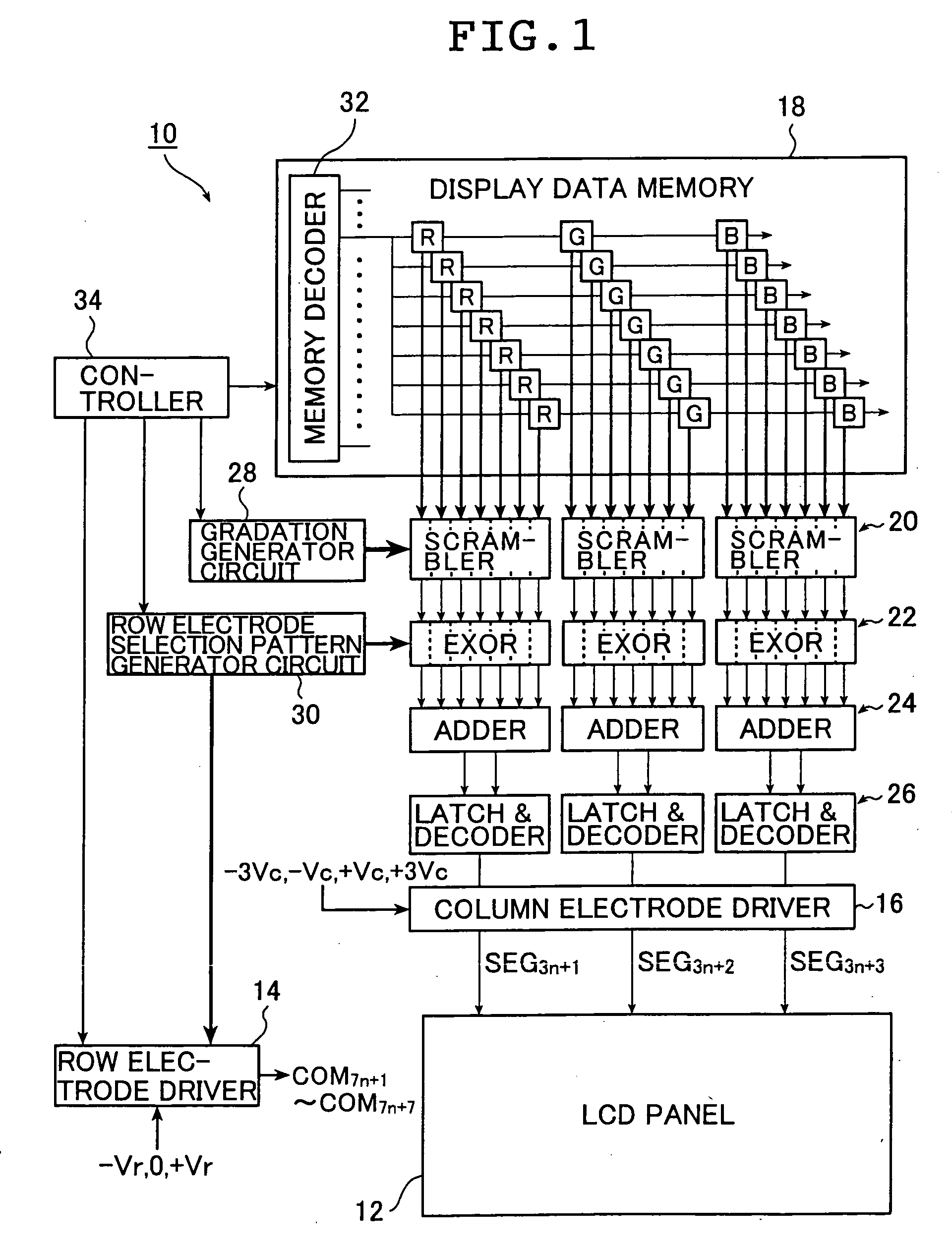
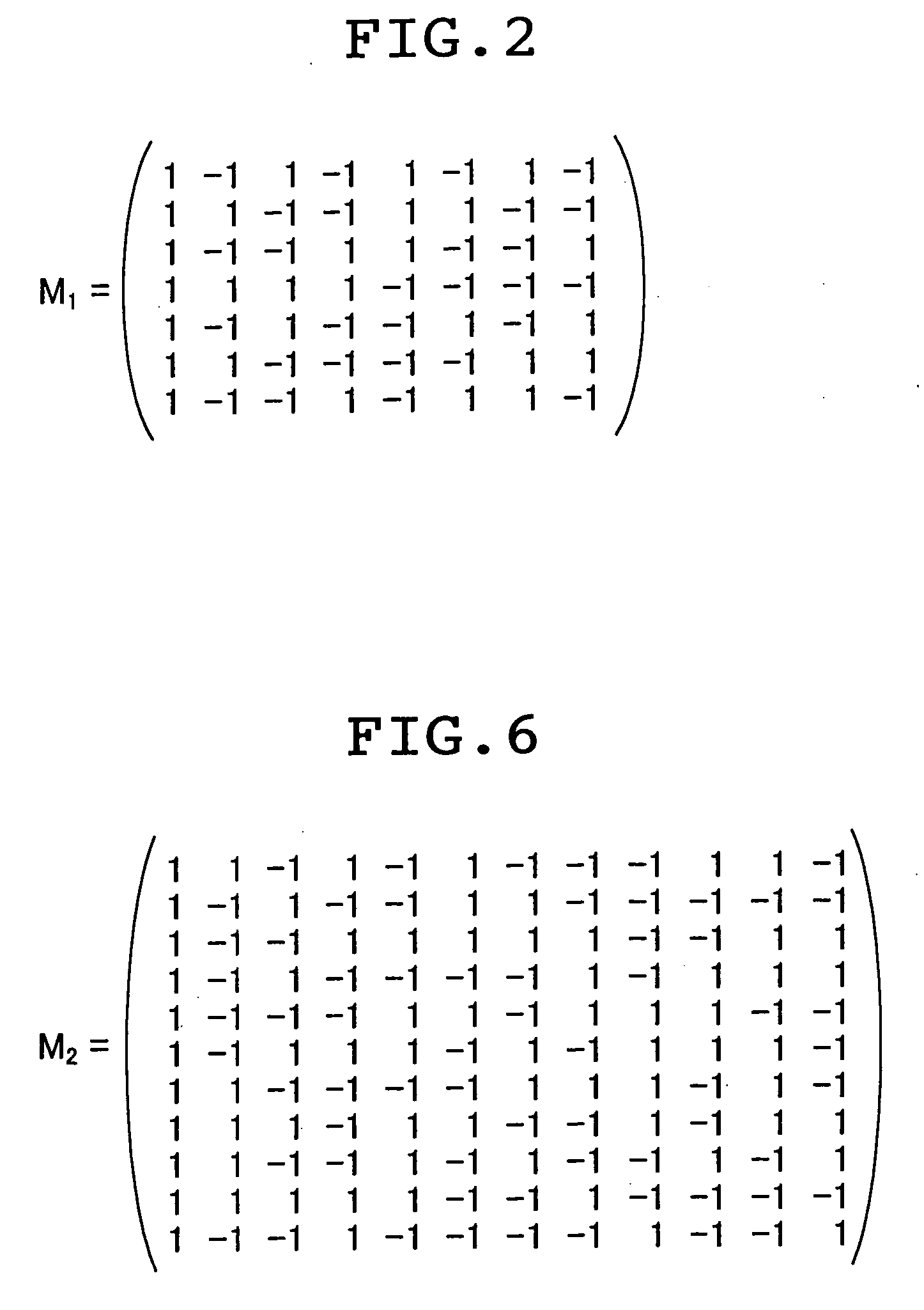
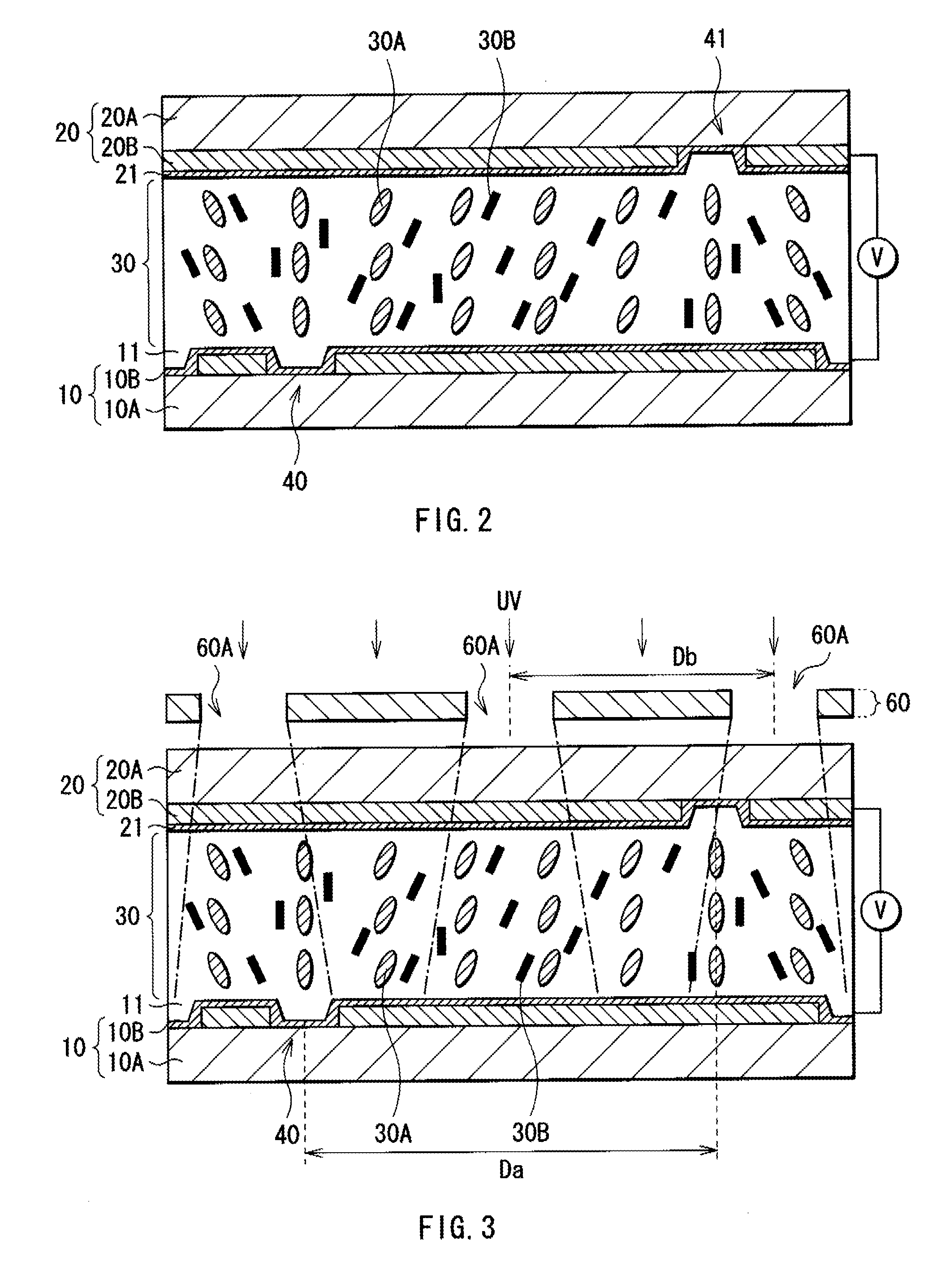
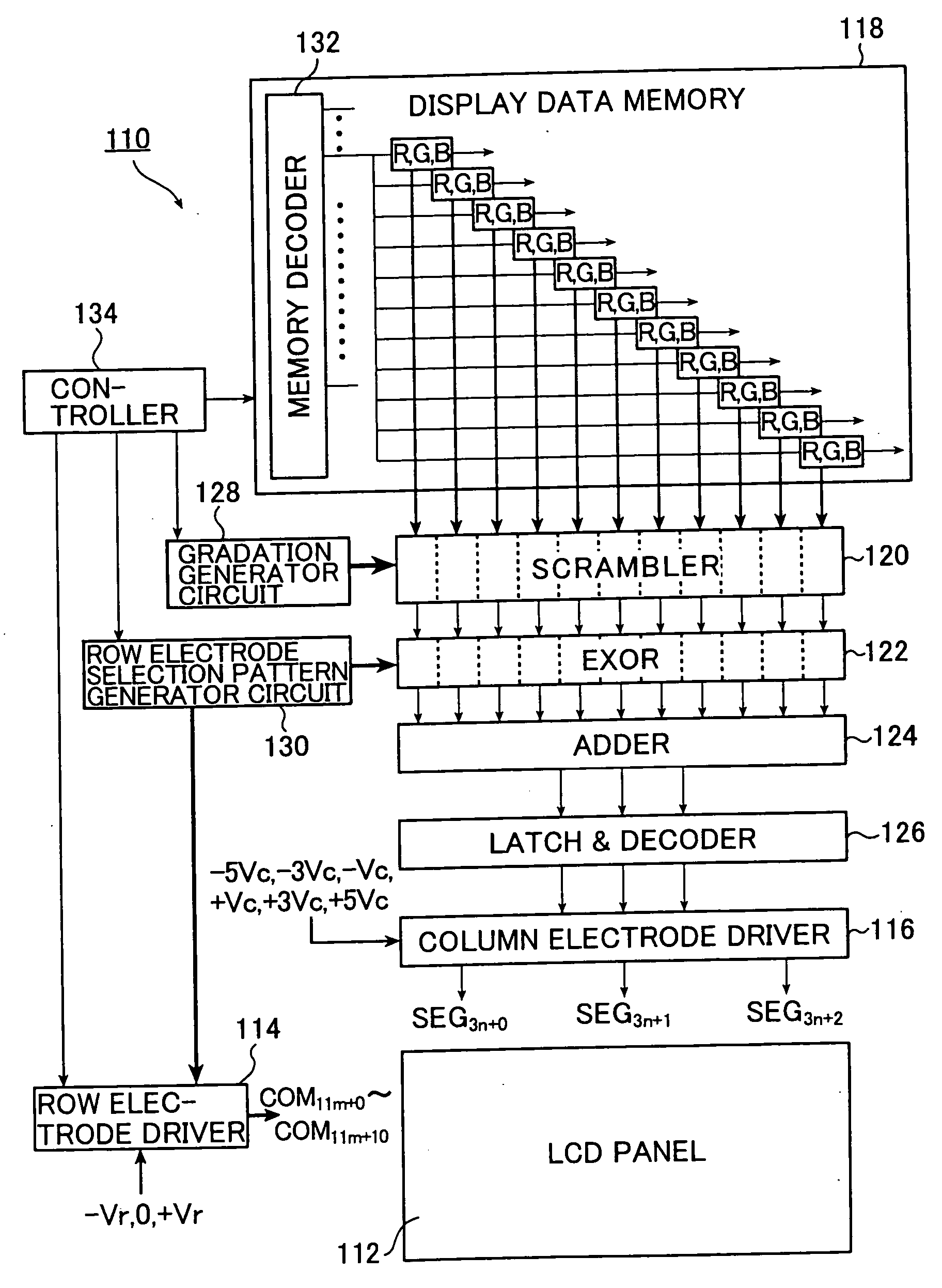
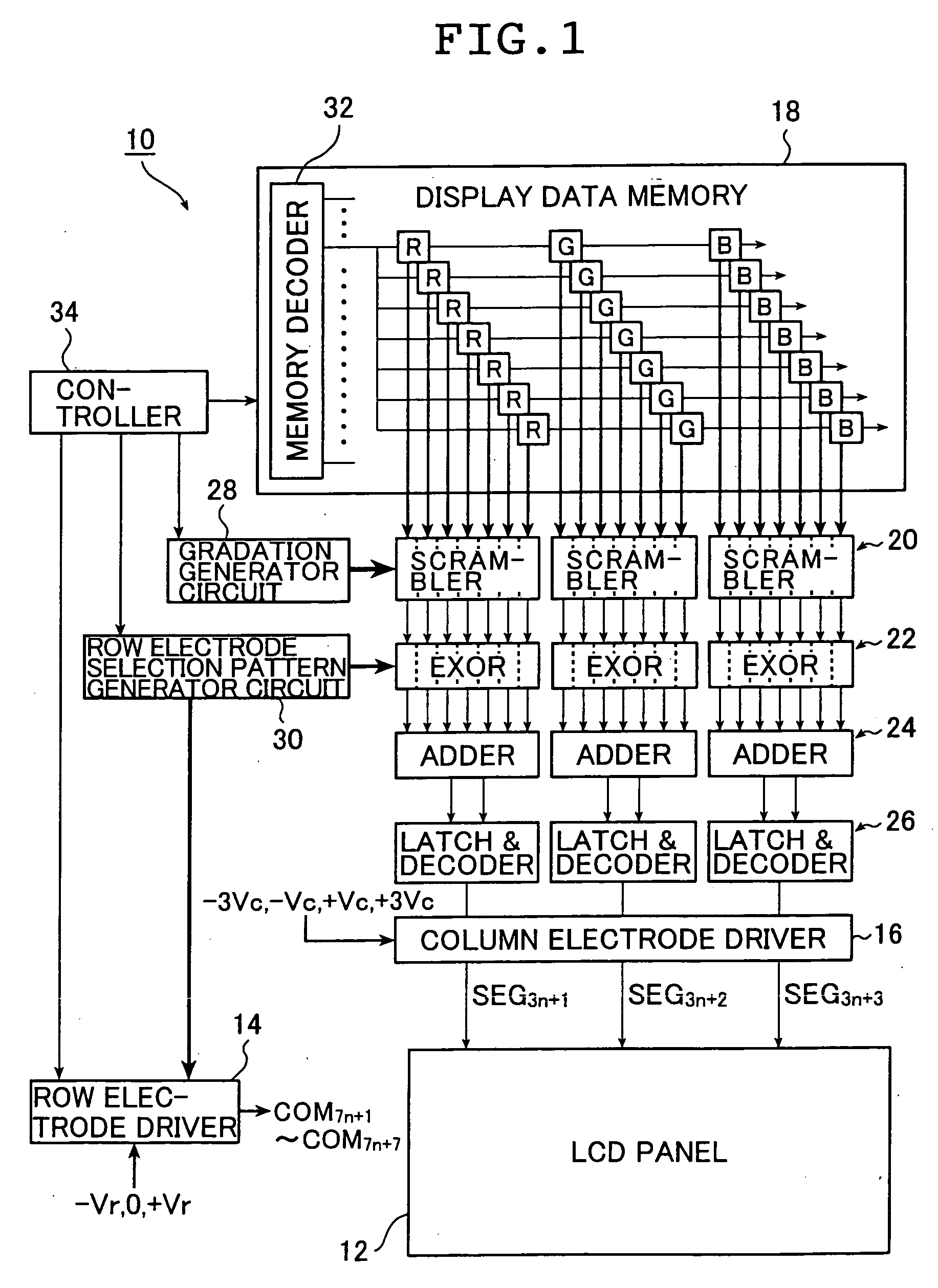
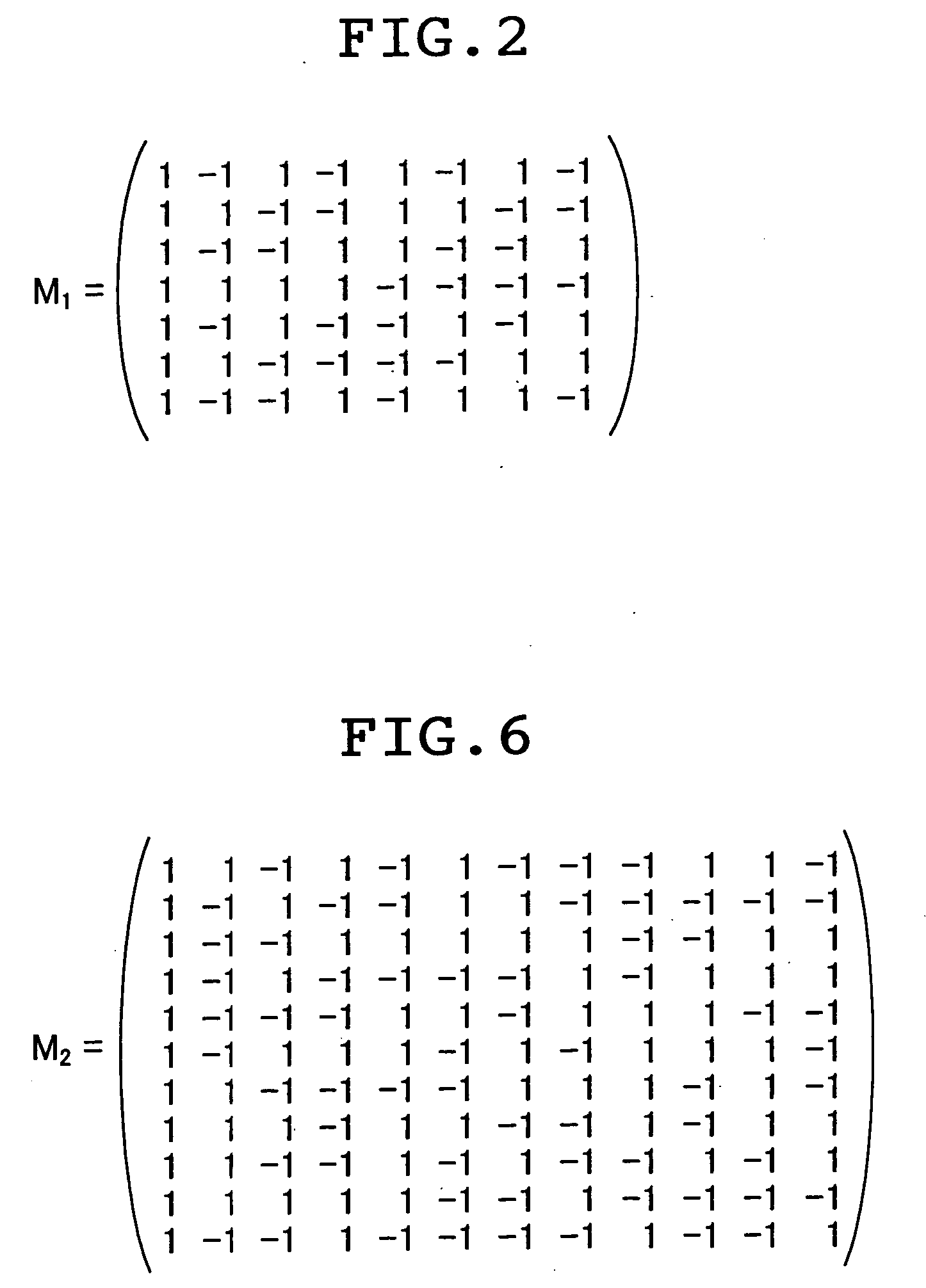
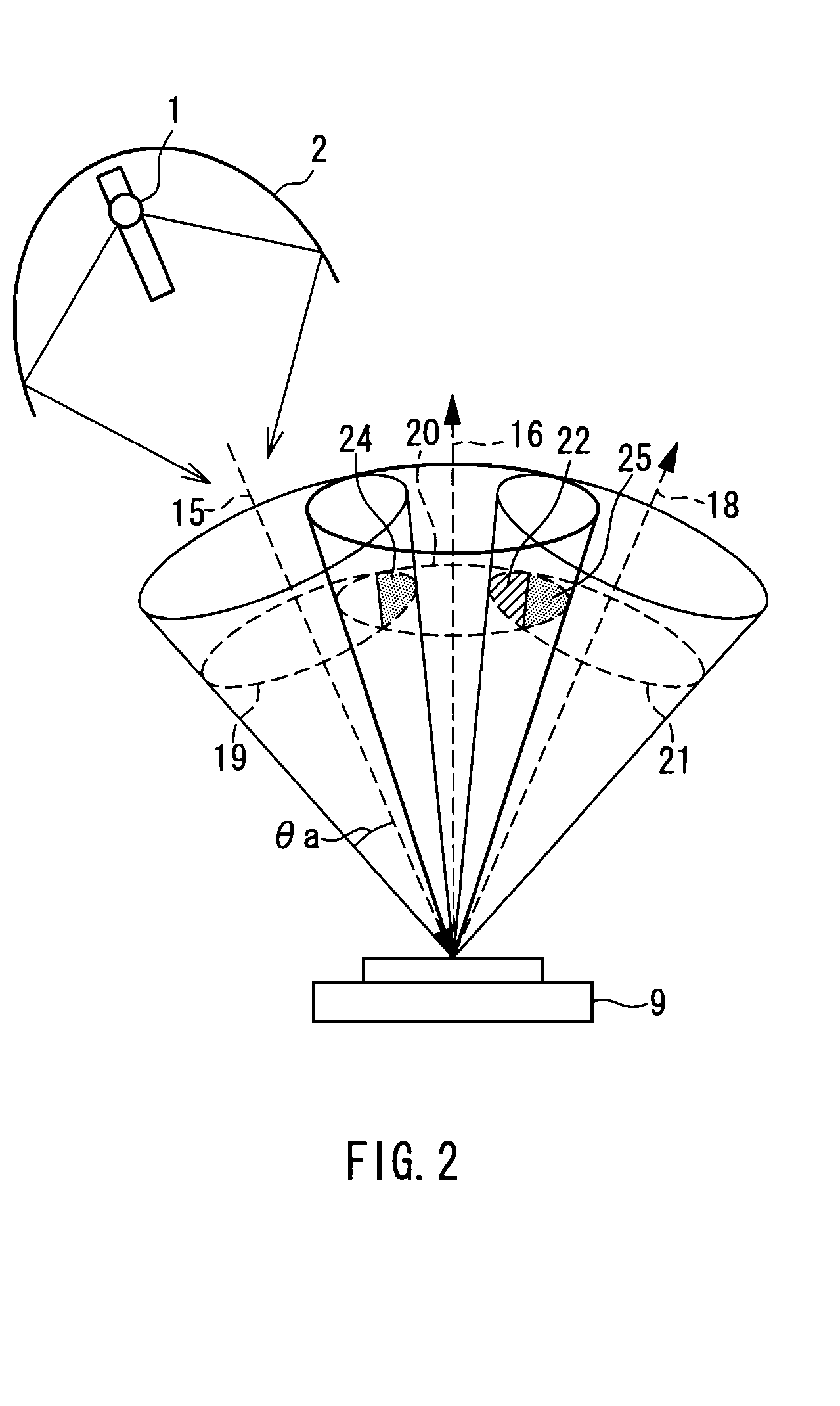
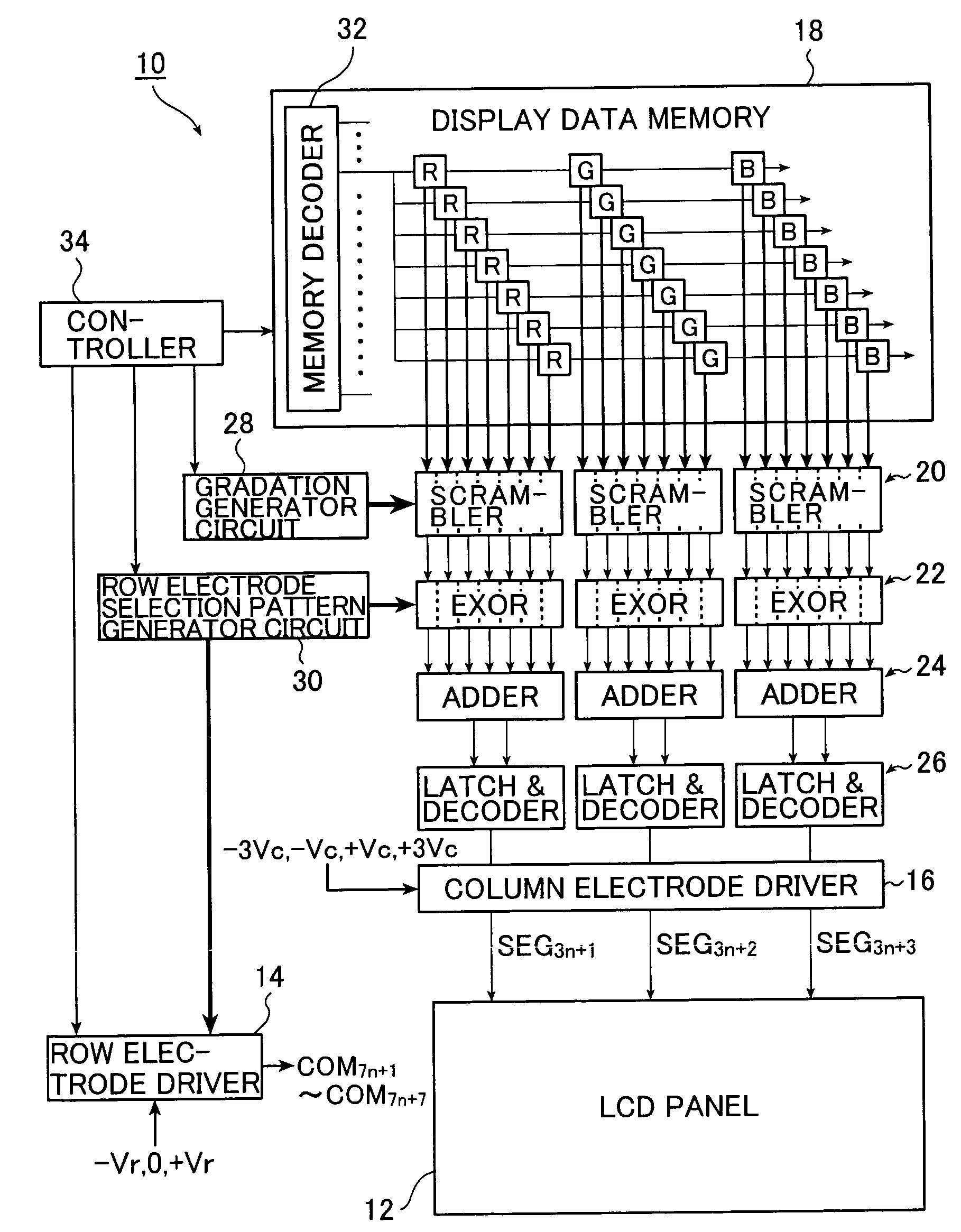
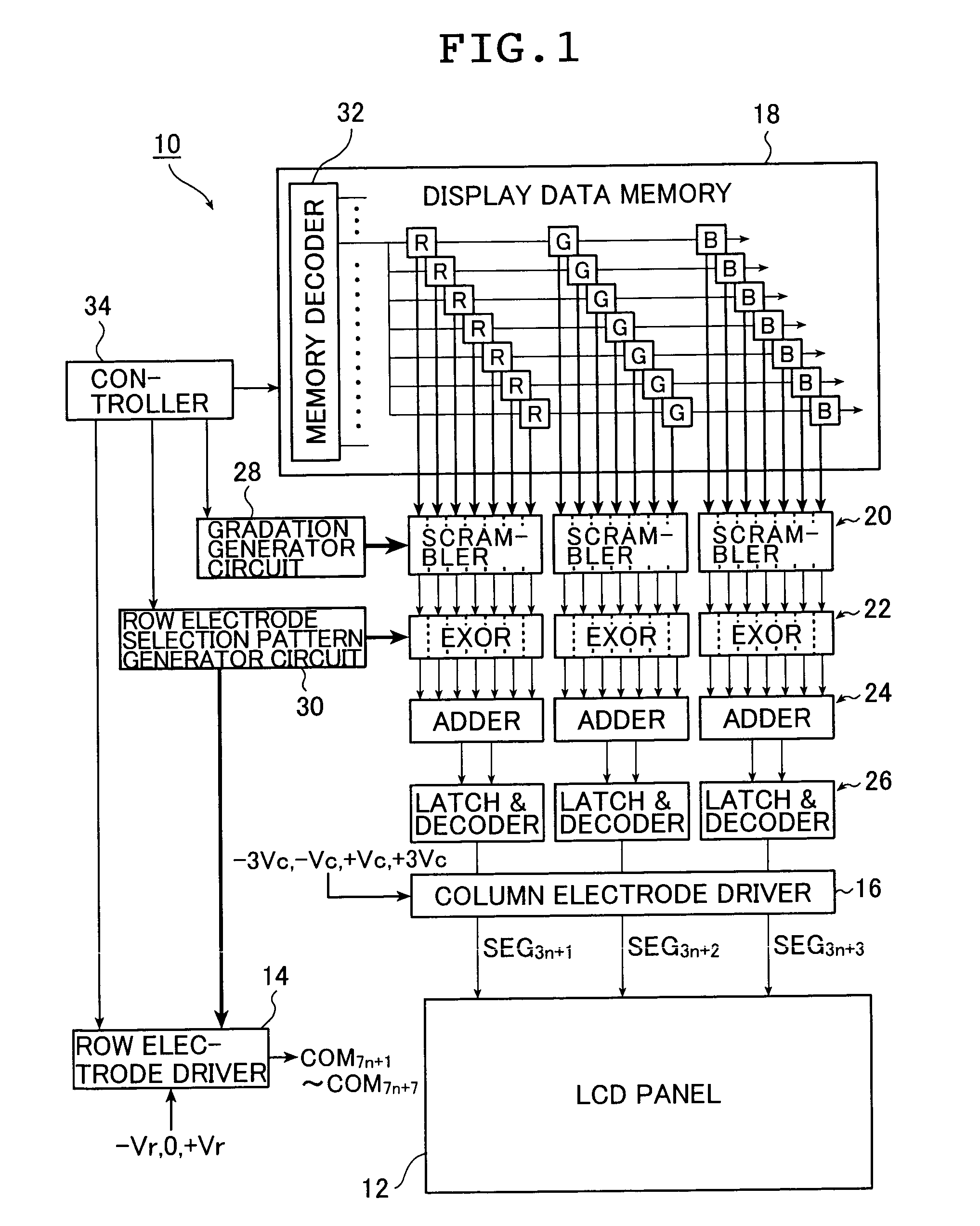
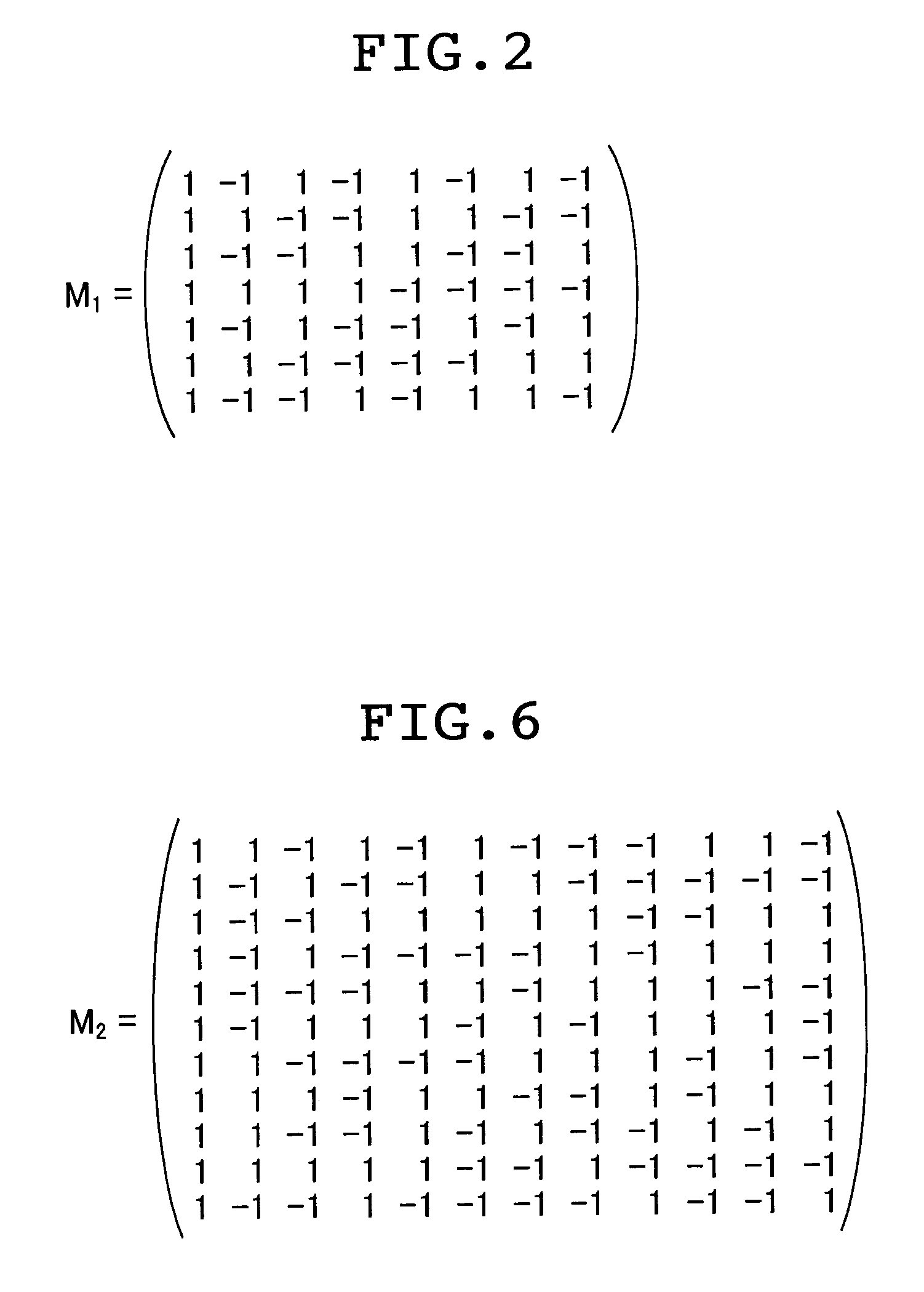
A method and an apparatus for driving passive matrix liquid crystal, comprising the steps of: simultaneously selecting Y row electrodes, where Y is an odd number of 7 and above; calculating an exclusive OR between a Y-bit row selection vector representing a selection pattern of the Y row electrodes and Y-bit ON / OFF display data representing a display pattern of column electrodes, for each corresponding bit; adding the exclusive ORs for each bit; when X=(Y+1) / 2, and a 1 / (X−1) voltage of the maximum voltage of the column electrodes is Vc, selecting a voltage level of the column electrodes from X voltage levels satisfying: [2×i−(X×1)]×Vc (i=an integer of 0 to (X−1)) in accordance with the result of the addition for driving. These method and apparatus prevent the frame response phenomenon of high-speed liquid crystal while realizing high-contrast display, low-voltage driving, low power consumption, and reduction in chip size.
Owner:KAWASAKI MICROELECTRONICS
Display unit
InactiveUS7045949B2Increase contrastSuppress contrast dropIncadescent screens/filtersDischarge tube luminescnet screensTransmittanceLength wave
A display unit has R, G, and B light-emitting pixels arranged in a predetermined sequence. The R pixels and the B pixels each have a G-light-absorbing filter at the image display side (light output side or external-light incident side) thereof. The G pixels have no filters. The R and B light-emitting pixels each have a composite structure including a reflective layer, an organic EL layer, and a translucent reflective layer. The translucent reflective layer and the reflective layer constitute an optical resonator that causes multiple interference of light. The transmittance of the G-light-absorbing filter is minimized at the G wavelength, at which the sensitivity of the naked eye is high, and maximized at the R and B wavelengths. Furthermore, the external light reflectance of each pixel is minimized at the G wavelength. This display unit significantly suppresses a decrease in contrast caused by external light without a decrease in luminance of an image.
Owner:SONY CORP
Reflection-type liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20080074591A1Increase contrastSuppress image blurOptical light guidesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayLight guide
To suppress a decrease in the contrast caused by the reflection on the interface to the air layer without decreasing the quality of display. A reflection-type liquid crystal display device includes a light guide plate having a polarizing element stuck or adhered thereto on the side facing a reflection-type liquid crystal display panel, a source of light arranged on an end surface side of the light guide plate, and the reflection-type liquid crystal display panel arranged maintaining a predetermined gap relative to the light guide plate, wherein a light-diffusing function is imparted to the surface of the reflection-type liquid crystal display panel on the side facing the light guide plate.
Owner:SHARP KK
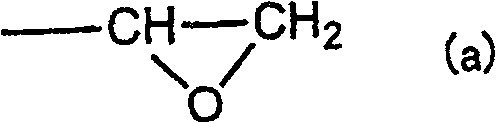
Liquid crystal alignment agent containing both polyamic acid ester and polyamic acid
ActiveCN103443697AReduce bumpsSuppress contrast dropCoatingsNon-linear opticsHydrogen atomOrganic group
Provided is a liquid crystal alignment agent which can reduce the surface nano-roughness of a liquid crystal alignment film and ensures improved liquid crystal alignment properties, improved electrical characteristics, and enhanced reliability. This liquid crystal alignment agent contains both a polyamic acid ester which comprises repeating units represented by formula (1) and a polyamic acid which comprises repeating units represented by formula (2), and is characterized in that at least 60 mol% of the divalent organic groups (Y1) of the polyamic acid ester and at least 60 mol% of the divalent organic groups (Y2) of the polyamic acid have the same structure. In the formulae, X1 and X2 are each independently a tetravalent organic group; Y1 and Y2 are each independently a divalent organic group; A1 and A2 are each independently a hydrogen atom, or optionally substituted, alkyl, alkenyl or alkynyl, each having 1 to 10 carbon atoms; and R1 is methyl.
Owner:NISSAN CHEM IND LTD
Intraocular lens
ActiveUS20090270984A1Suppressing deterioration in contrastDeterioration in contrast is suppressedIntraocular lensIntraocular lensOptical axis
An intraocular lens in which deterioration in contrast is suppressed even when the optical axis of the intraocular lens is decentred from the optical axis of the eyeball when the intraocular lens is inserted into the eye while the advantage of a conventional aberration reduction type intraocular lens that the image is seen clearly is sustained by employing such a power distribution as respectively having at least one positive power deviation region (E1) having a power larger than that represented by the reference power distribution and at least one negative power deviation region (E2) having a power smaller than that represented by the reference power distribution in the central region of the intraocular lens assuming that a power distribution being set to cancel the spherical aberration of cornea when the intraocular lens is inserted into the eye is the reference power distribution.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Liquid crystal display and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20080123037A1Improve response speedIncrease brightnessNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
A method of manufacturing a liquid crystal display includes the steps of forming pixel electrodes on inside surfaces of a couple of substrates facing each other, each of the pixel electrodes having gaps; sealing, between the couple of substrates with the pixel electrodes formed, a liquid crystal layer containing a light curing material; and exposing the liquid crystal layer through use of a light shielding film having a plurality of openings, under a voltage applied between a pair of pixel electrodes facing each other on the couple of substrates, where the gaps are alternately disposed to form a staggered arrangement between the pair of pixel electrodes and, spacing between adjacent openings of the light shielding film is smaller than spacing, in a substrate surface direction, between the gap of a pixel electrode on one substrate and the gap of a pixel electrode on the other substrate.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method and apparatus for driving passive matrix liquid crystal
InactiveUS20060033693A1Reduce voltageReduce power consumptionCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingLow voltageChip size
A method and an apparatus for driving passive matrix liquid crystal, comprising the steps of: simultaneously selecting Y row electrodes, where Y is an odd number of 7 and above; calculating an exclusive OR between a Y-bit row selection vector representing a selection pattern of the Y row electrodes and Y-bit ON / OFF display data representing a display pattern of column electrodes, for each corresponding bit; adding the exclusive ORs for each bit; when X=(Y+1) / 2, and a 1 / (X−1) voltage of the maximum voltage of the column electrodes is Vc, selecting a voltage level of the column electrodes from X voltage levels satisfying: [2×i−(X−1)]×Vc (i=an integer of 0 to (X−1)) in accordance with the result of the addition for driving. These method and apparatus prevent the frame response phenomenon of high-speed liquid crystal while realizing high-contrast display, low-voltage driving, low power consumption, and reduction in chip size.
Owner:KAWASAKI MICROELECTRONICS
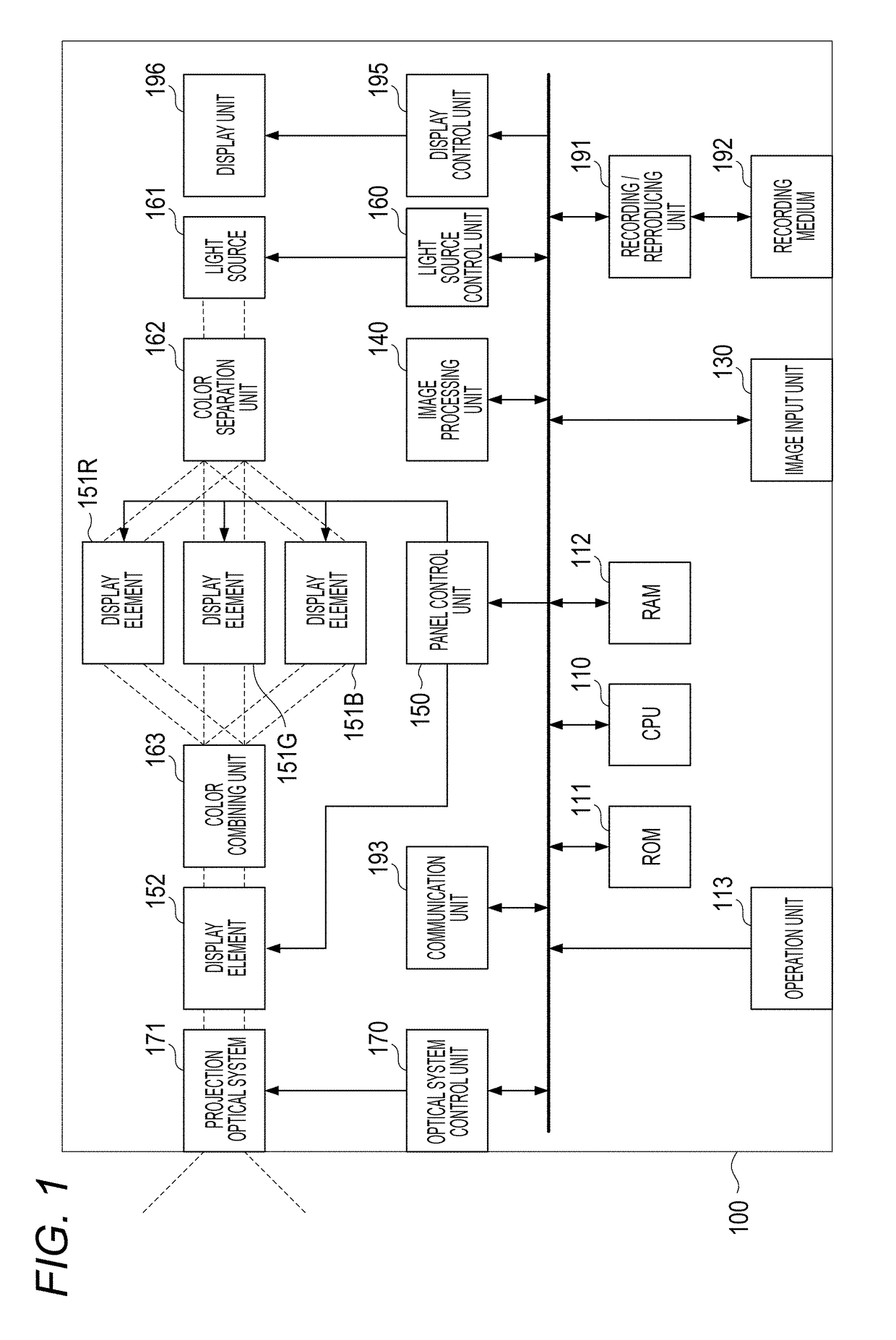
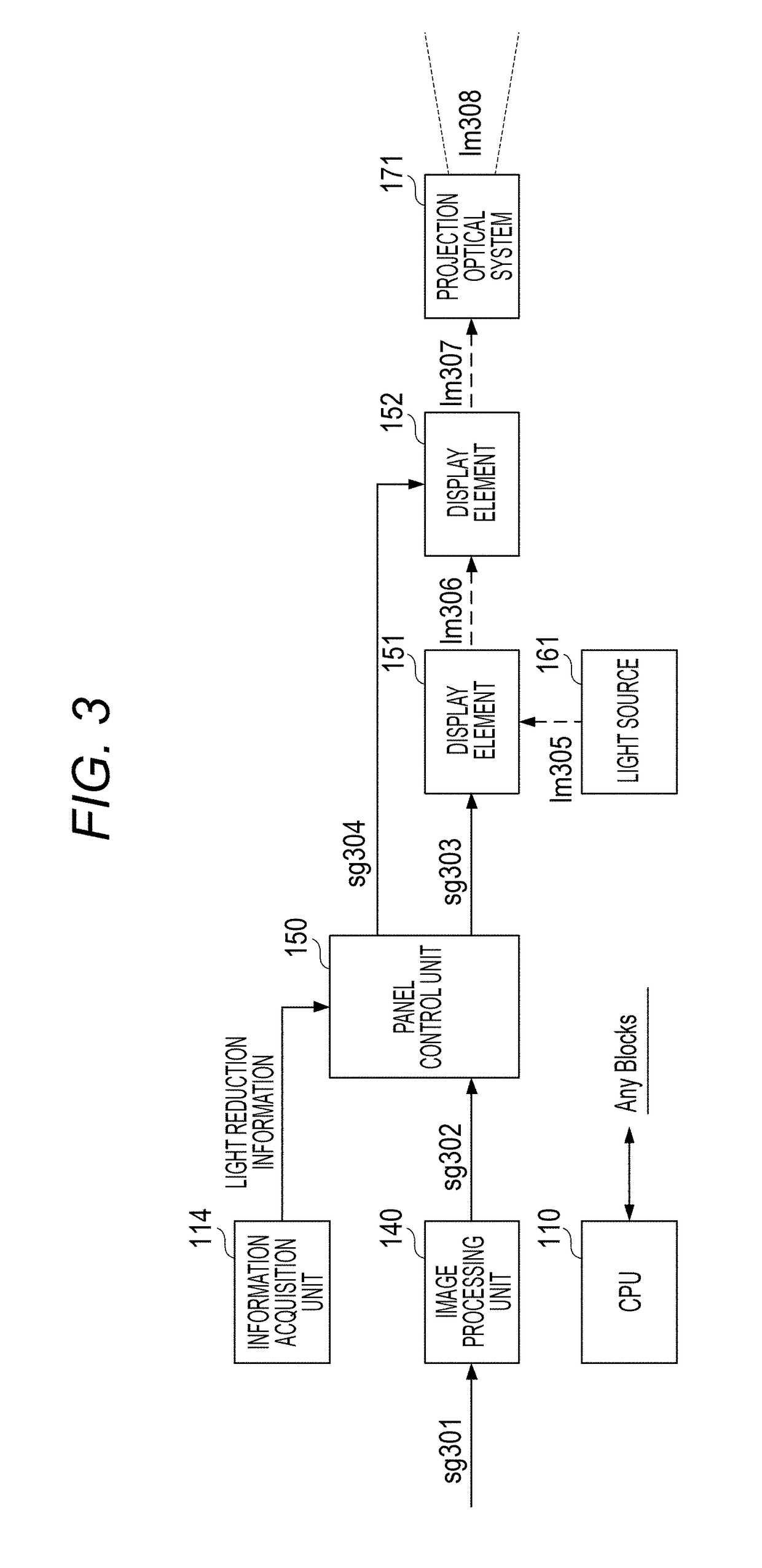
Projection apparatus, control method, and storage medium
ActiveUS20190052850A1Suppressing deterioration of contrastSuppress contrast dropPicture reproducers using projection devicesInformation controlData control
A projection apparatus that projects a projection image includes a first panel, a second panel, a projection optical system that projects light that has passed through the first panel and the second panel, an information acquisition unit that acquires light reduction information of a region which is a part of the projection image and overlaps with an image projected by another projection apparatus, and a panel control unit that controls the first panel based on data of the projection image and controls the second panel based on the light reduction information.
Owner:CANON KK
Organic electroluminescence display device
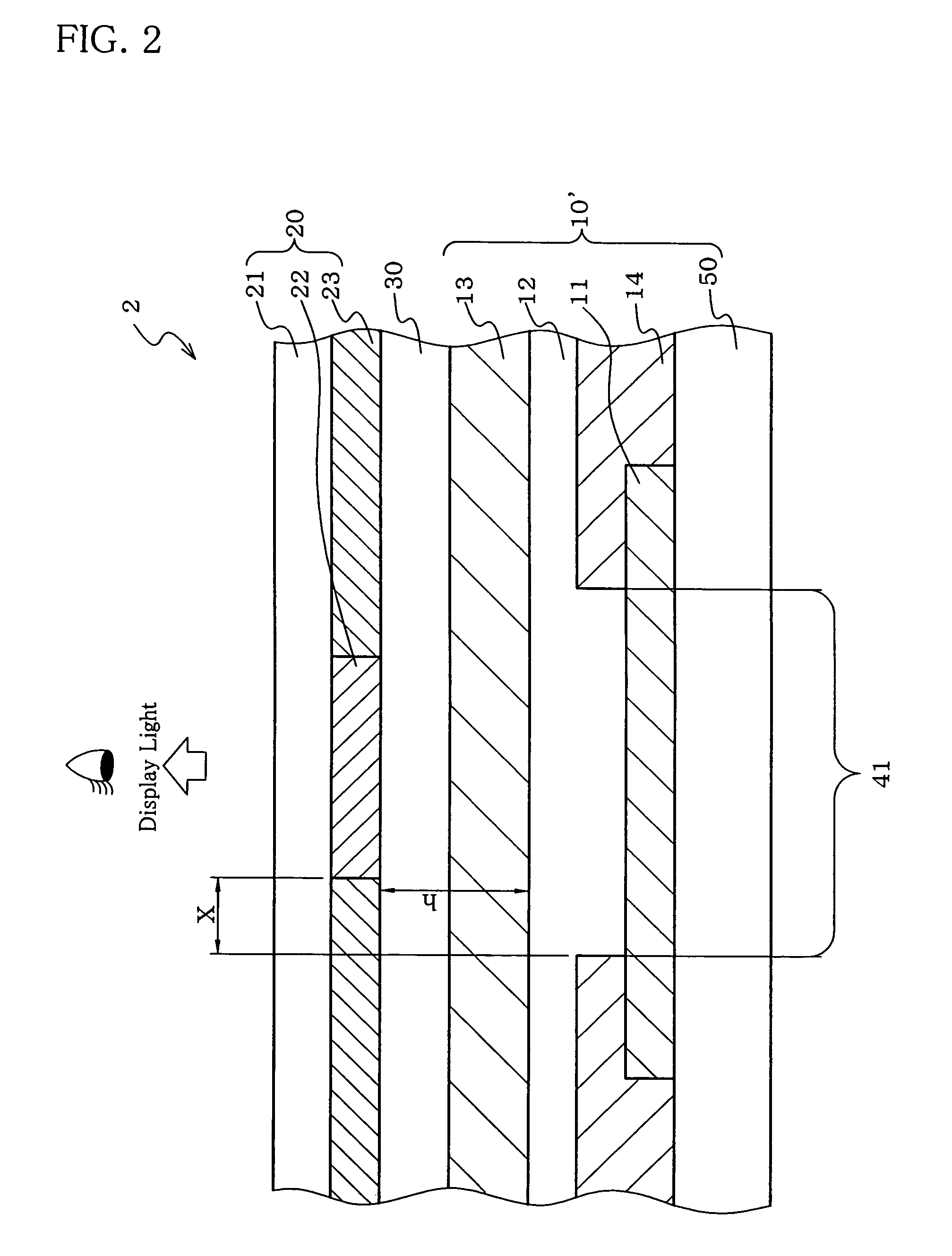
ActiveUS7550914B2Increase contrastLight amountDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesOptoelectronicsOrganic electroluminescence
An organic electroluminescent display (1) including: an organic electroluminescent device (10), and a color converting member (20) including a shielding layer (23) and a shielding layer aperture region (24) including a color converting layer (22), edges (23-1) of the aperture region (24) being closer to the center of the aperture region (24) than edges (41-1) of an emission region (41) of the organic electroluminescent device (10).
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Display device
ActiveUS20150008417A1Reduce light reflectionSuppress deterioration in contrastSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAcrylic resinDisplay device
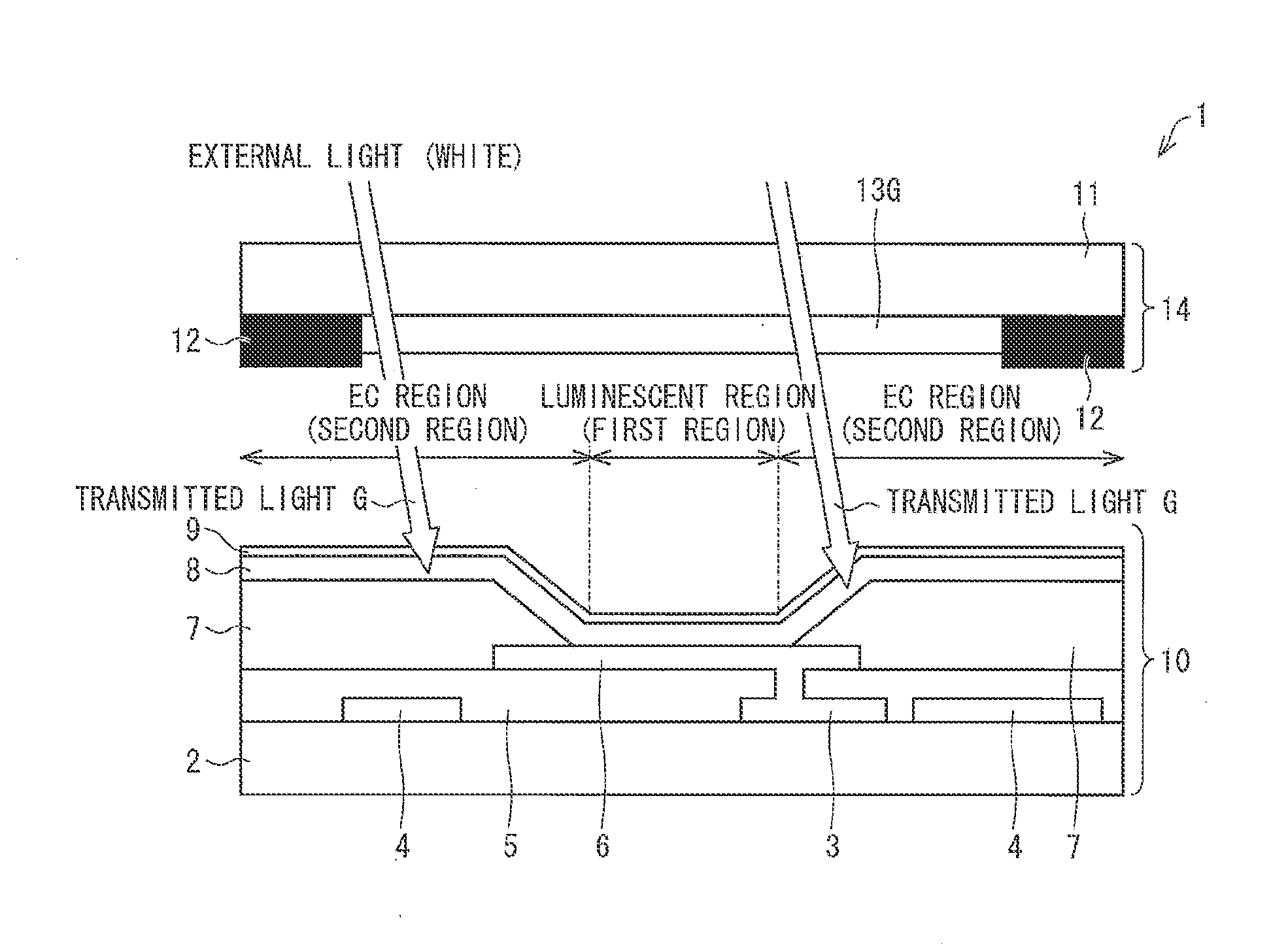
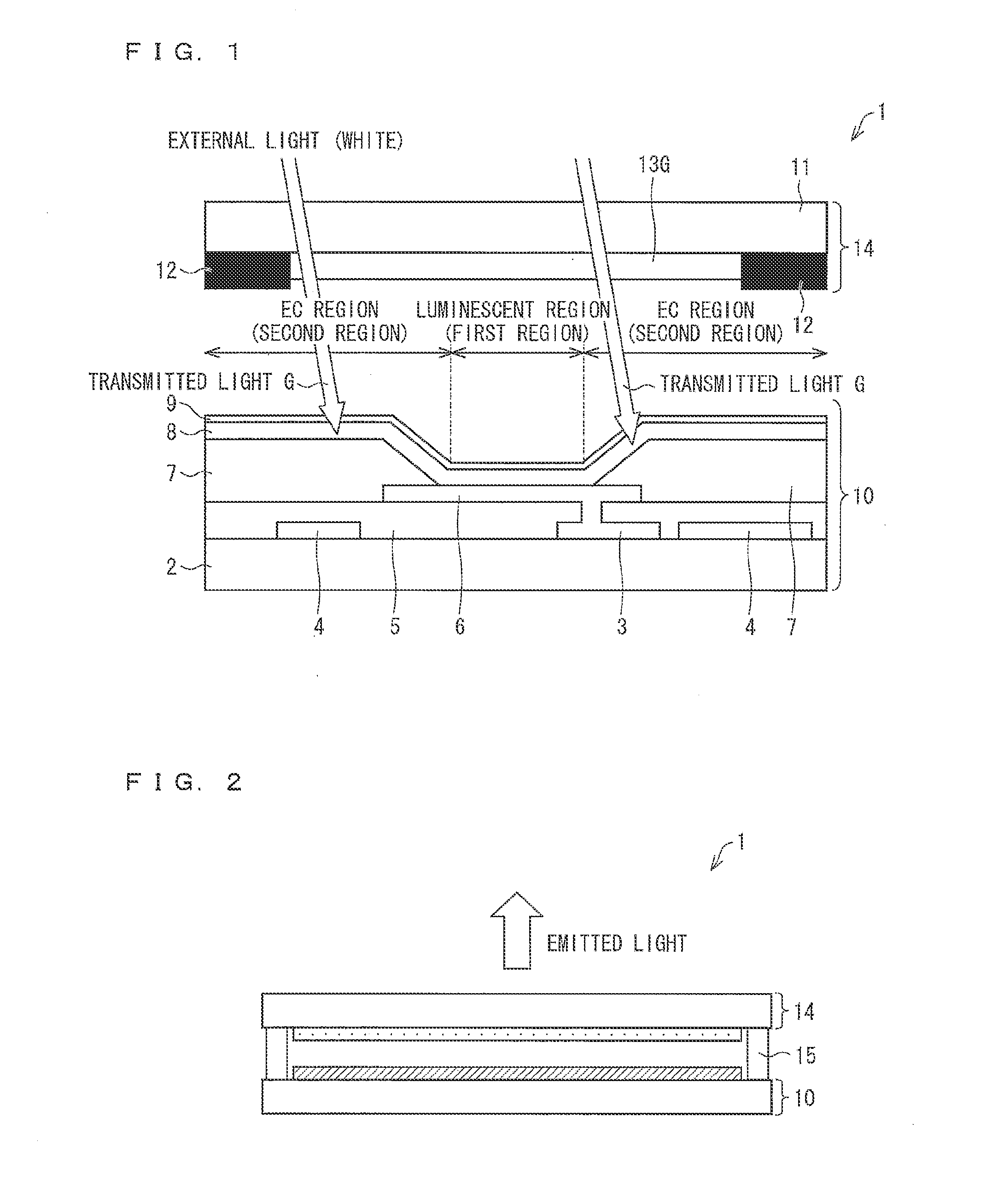
An EC region (second region) of an organic EL display device (1) has an optical interference layer which is a multilayer of (i) an edge cover (7) made from an acrylic resin having a lower refractive index, (ii) an organic layer (8), and (iii) a second electrode (9) which is a thin and semi-transparent film. Therefore, the organic EL display device (1) can suppress a deterioration in contrast without narrowing a display region, and can have a high reliability.
Owner:SHARP KK
Organic light-emitting device and organic display apparatus
ActiveUS20160190514A1Improve visibilityAvoid it happening againSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic light emitting deviceOrganic chemistry
A display panel includes an EL panel part, a CP panel part, and a resin layer. Light is extracted from a luminous part including an organic luminous layer in the EL panel part in a direction of an arrow. The CP panel part includes a circular polarizing film. The resin layer is formed to cover an upper surface of the EL panel part, has a layer thickness of 15 μm, and includes a resin part and a plurality of getter particles dispersed in the resin part. The getter particles are dispersed at a density at which the getter particles do not overlap one another in plan view.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Electro-optic device and electronic device
InactiveCN101162334ASuppression of aperture ratio dropSuppress contrast dropStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsElectronElectro-optics
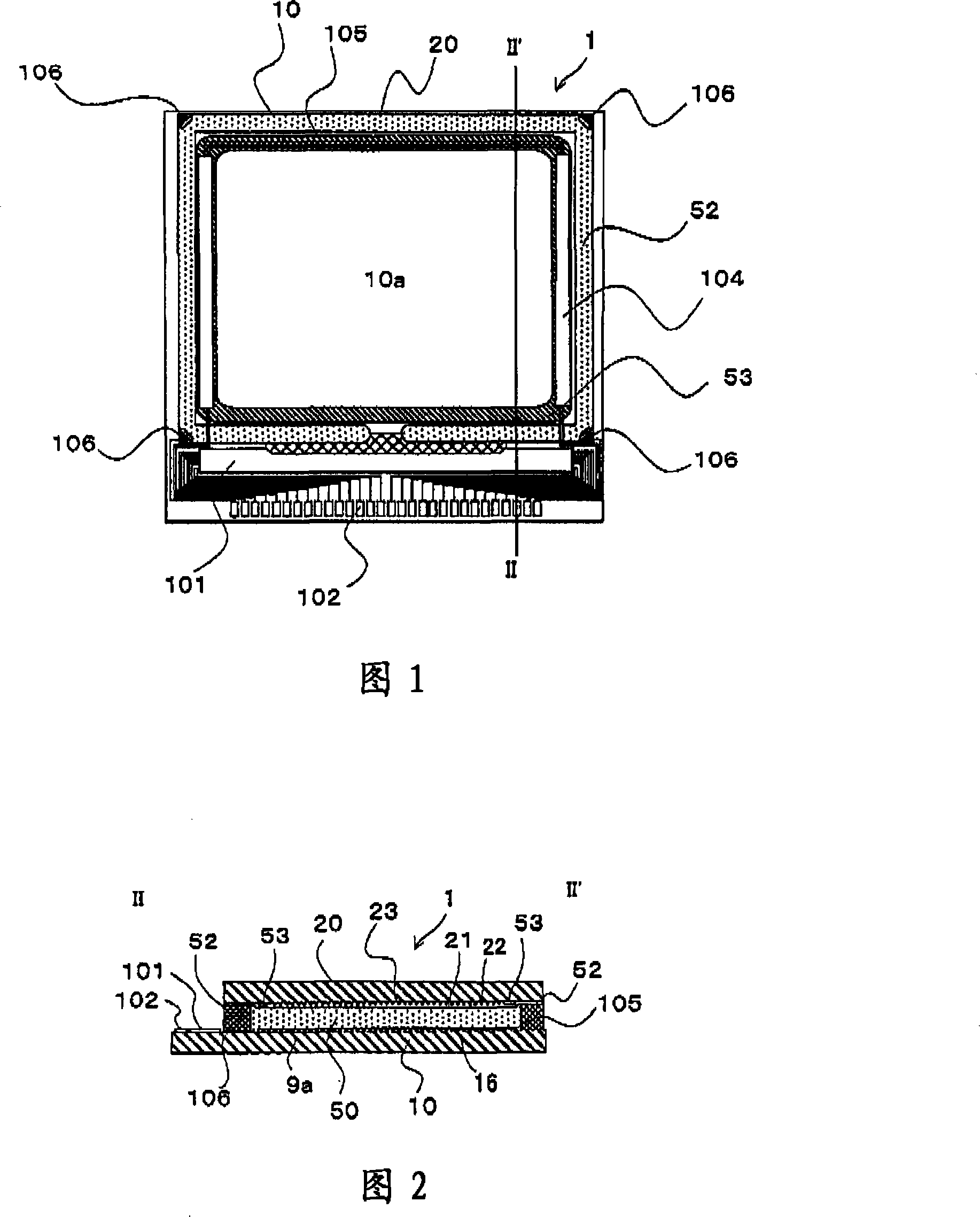
The present invention provides a photoelectric device and an electronic equipment, which are used for reducing the bad states of residual image and lag phenomenon and the like which are generated when the dynamic image is displayed. The external shape of the pixel electrode (9a1-1) is approximately rectangular, a first edge part (29a1) facing to the pixel electrode (9a1-1) in the four edge parts extends along the X direction of the accompanying diagram and a dent (501) is arranged at one part of the edge part. The external shape of the pixel electrode (9a2-1) is same to the pixel electrode (9a1-1) and is approximate rectangular, a second edge part (29a2) facing to the pixel electrode (9a1-1) in the four edge parts extends along the X direction of the accompanying diagram and a convex part (502) is arranged at one part of the edge part. The convex part (502) and the region (R) restricted by the dent (501) coincidently extend from the second edge part (29a2) to the first edge part (29a1).
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Projector
InactiveUS20100245689A1Reduce contrastSuppress contrast dropProjectorsColor television detailsOptoelectronicsOptical polarization
A projector includes: a light modulation device that changes the polarization state of incident light; and a polarization maintaining reflector provided along the outer edge of an effective pixel area in the light modulation device, the polarization maintaining reflector having a flat surface that reflects the incident light with its polarization state maintained.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Projection display device
InactiveUS20100118213A1Reduce lossesReduce contrastTelevision system detailsProjectorsOptoelectronicsPupil
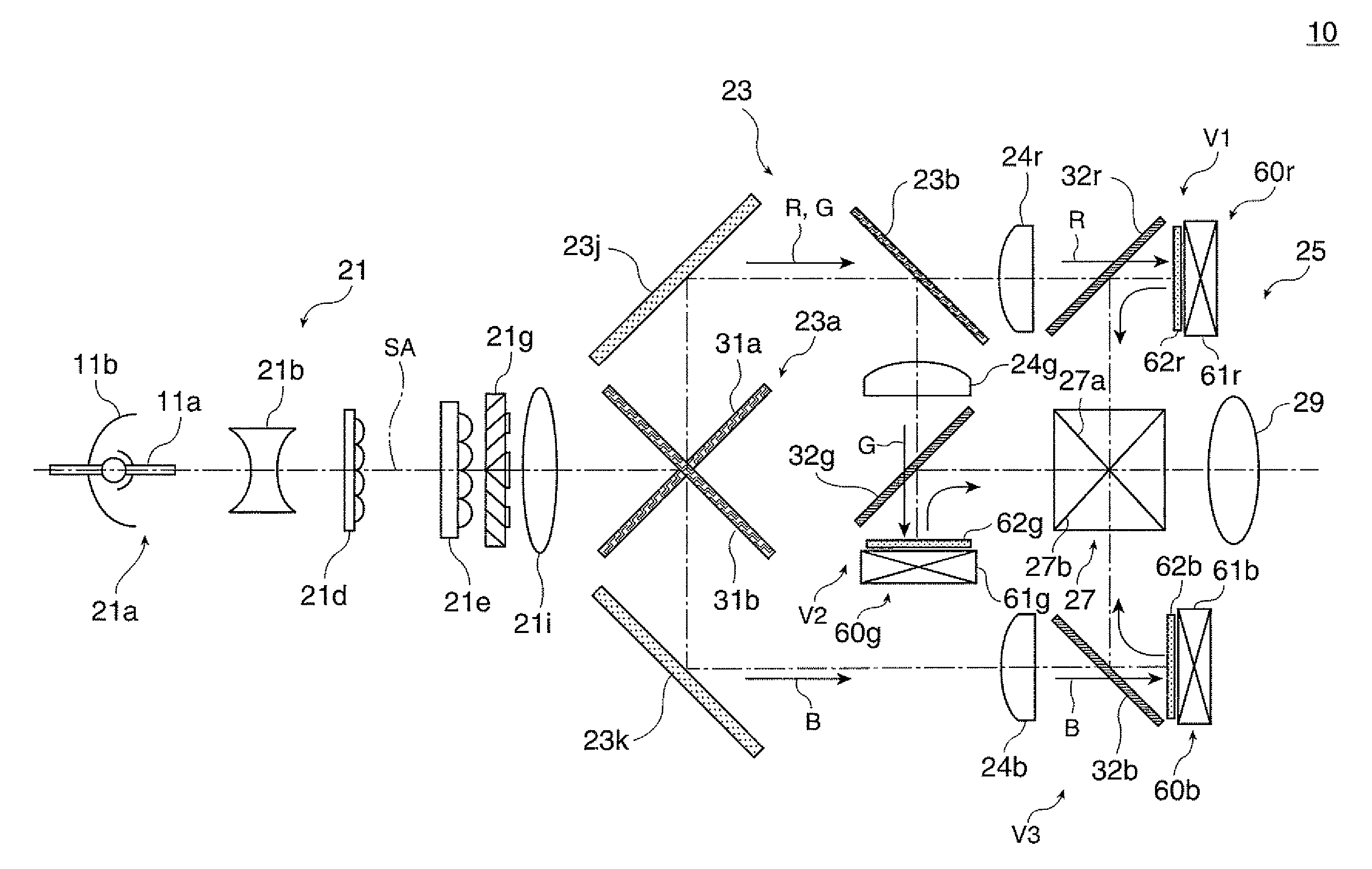
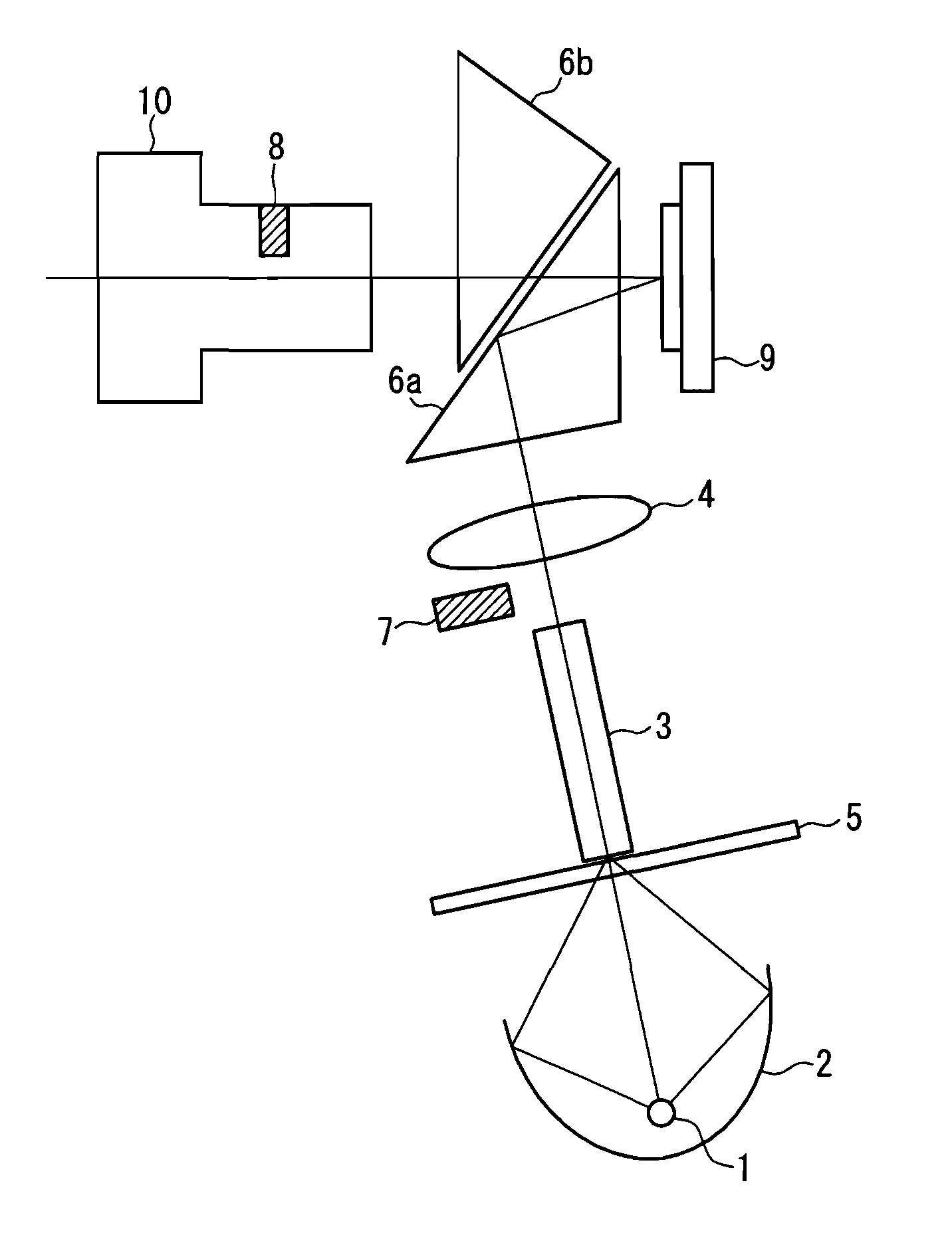
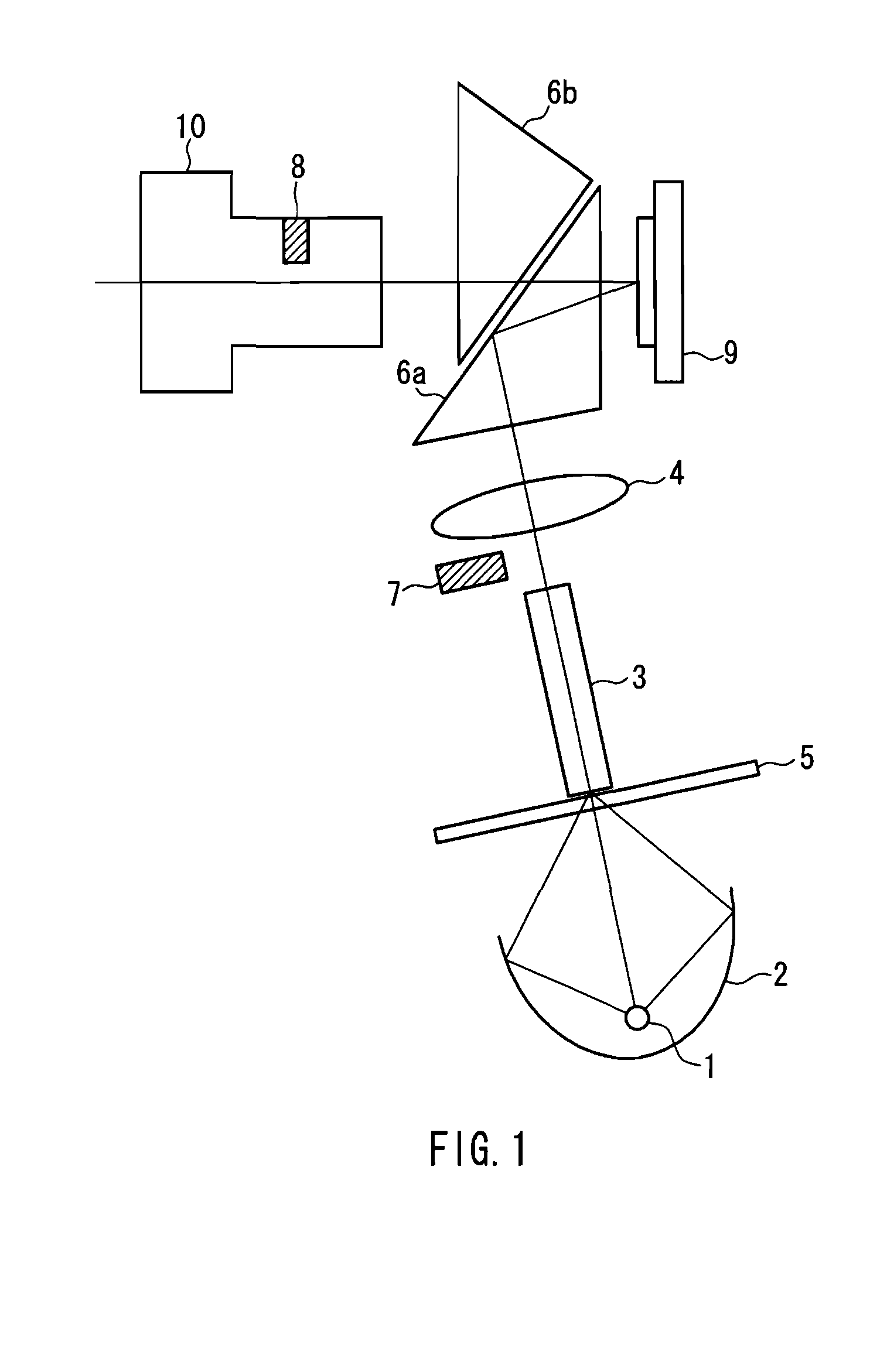
A device includes a light source 1, a reflection-type light valve 9 that controls a traveling direction of exiting light based on an input signal, an illumination optical system 2, 3, 4, 6a that focuses light from the light source on the reflection-type light valve as illumination light, a projection lens 10 that projects exiting light from the reflection-type light valve, a first diaphragm 7 provided at a position of a pupil of the illumination optical system so as to block a part of the light from the light source, and a second diaphragm 8 provided at a position of the pupil of the projection lens so as to block a part of the exiting light from the reflection-type light valve. A part of the illumination light reflected from a surface of the reflection-type light valve to be incident on a pupil of the projection lens as unnecessary light is blocked by a combination of the first diaphragm and the second diaphragm. The light shielding region of the first diaphragm corresponds to a divided region on an outer peripheral side between divided regions obtained by dividing the region of the pupil of the illumination optical system corresponding to the range of the unnecessary light by a line in a chord direction, and a light shielding region of the second diaphragm is shaped and arranged so as to correspond to the divided region on a center side. The unnecessary light incident on the projection lens is blocked efficiently, thereby achieving high brightness performance.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method and apparatus for driving passive matrix liquid crystal
InactiveUS7209129B2Improve the display effectReduce voltageCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingLow voltageChip size
A method and an apparatus for driving passive matrix liquid crystal, comprising the steps of: simultaneously selecting Y row electrodes, where Y is an odd number of 7 and above; calculating an exclusive OR between a Y-bit row selection vector representing a selection pattern of the Y row electrodes and Y-bit ON / OFF display data representing a display pattern of column electrodes, for each corresponding bit; adding the exclusive ORs for each bit; when X=(Y+1) / 2, and a 1 / (X−1) voltage of the maximum voltage of the column electrodes is Vc, selecting a voltage level of the column electrodes from X voltage levels satisfying:[2×i−(X−1)]×Vc (i=an integer of 0 to (X−1)) in accordance with the result of the addition for driving. These method and apparatus prevent the frame response phenomenon of high-speed liquid crystal while realizing high-contrast display, low-voltage driving, low power consumption, and reduction in chip size.
Owner:KAWASAKI MICROELECTRONICS
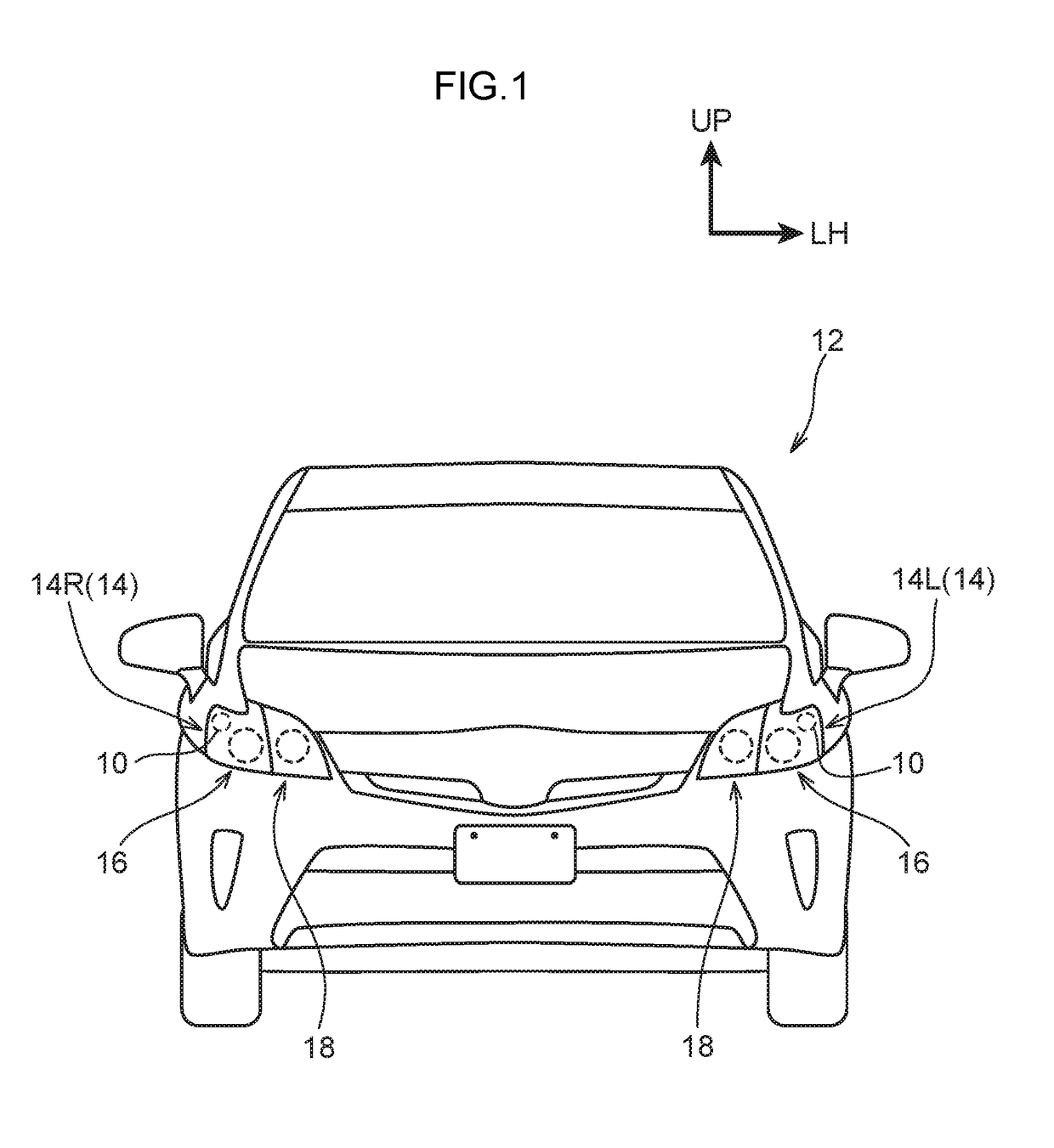
Illumination device for vehicle
ActiveUS20190070997A1Reduce contrastSuppress contrast dropVehicle headlampsOptical signallingOptoelectronicsLight source
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
Image display apparatus
InactiveUS20090040395A1Improve lighting efficiencySuppress degradation of contrastTelevision system detailsProjectorsOptical axisDisplay device
An image display apparatus is provided with a slim design and improved illumination efficiency and which is able to suppress degradation of contrast thereby eliminating ghosts. The image display apparatus includes: a light source; a condensing mirror which condenses light emitted from the light source and makes a virtual secondary light source; a light tunnel on which light passing through a color filter is incident; a relay lens system through which light exiting the light tunnel passes; a first mirror on which the light passing through the relay lens is directly or indirectly incident; a reflective display including a plurality of micromirrors arranged on a substrate in a matrix, on which the light reflected off the mirror is incident, wherein each micromirror is turned ON or OFF by individually changing the slope of the micromirrors and thus angles of reflection; and a projection lens which enlarges and projects light reflected from the micromirrors in the ON state, wherein the relay lens system and the first mirror are disposed opposite to each other with an optical axis of the projection lens interposed therebetween.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Microcapsule for electrophoretic display device, process for manufacturing the same and use thereof
InactiveCN100595662CSuppress contrast dropMicroballoon preparationNon-linear opticsHigh humidityElectrophoresis
An object of the present invention is to provide a microcapsule for an electrophoretic display device which can suppress reduction in later contrast even when the electrophoretic display device is allowed to stand under the high temperature and high humidity condition, favorably, under the high temperature and high humidity condition for a long time (e.g. under 60 DEG C., 90% RH for 24 hours). Asa means of achieving this object, a microcapsule according to the present invention for an electrophoretic display device comprises an electrophoretic fine particle and a solvent both of which are encapsulated in a shell, and is characterized in that an amount of an alkaline metal ion in the whole microcapsule is 150 ppm or smaller.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Light guide plate, planar light source apparatus, display apparatus, and electronic device
ActiveUS20210041617A1Suppress uneven brightnessSuppress contrast dropMechanical apparatusElectric lightingLight guideLight beam
To provide a technique for suppressing brightness non-uniformity of an area illuminated by a light source and also suppressing a decline in contrast between areas caused by incidence of a luminous flux of the area to another area. Provided is a light guide plate including: a diverging portion which is provided on an opposite side of a light exit surface from which light is emitted, the diverging portion causing a luminous flux emitted from a light emitting element to diverge; and a restricting portion which is provided, when a prescribed range from the light emitting element on the light exit surface is defined as an illuminated area illuminated by the light emitting element, in at least a periphery of the illuminated area on the light exit surface and which deflects or shields light traveling from inside toward outside of the illuminated area to restrict traveling, toward a side of the light exit surface, of light traveling toward the outside of the illuminated area.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
Display device
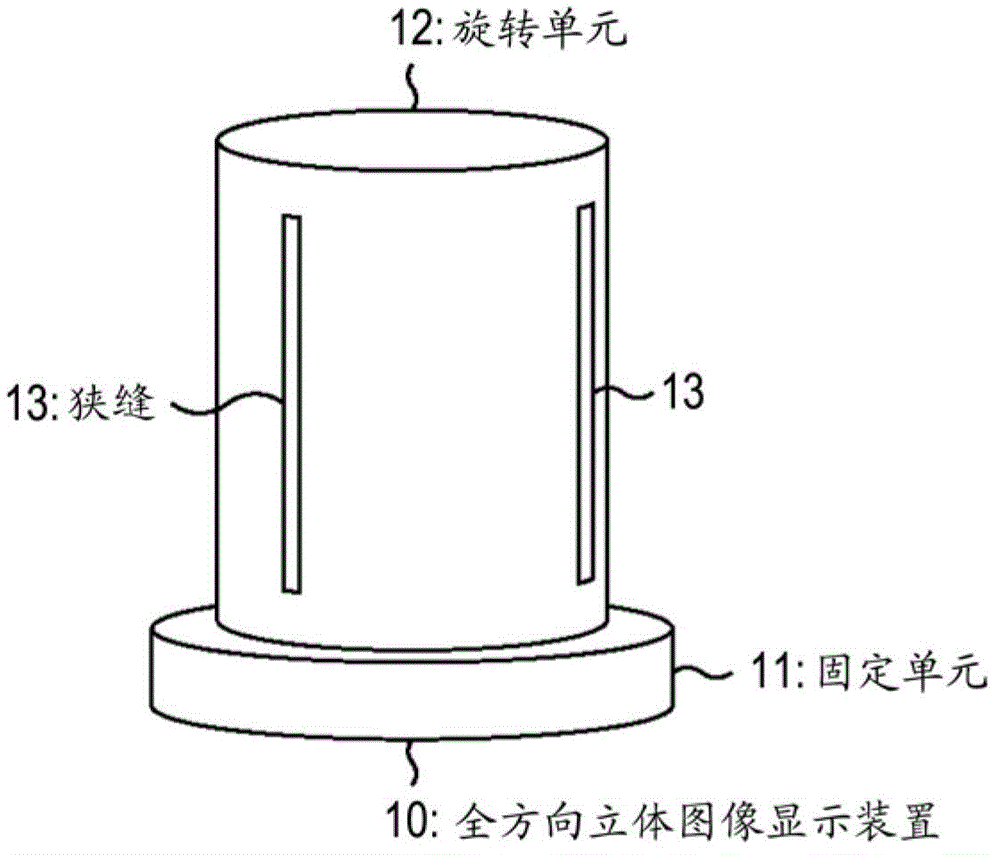
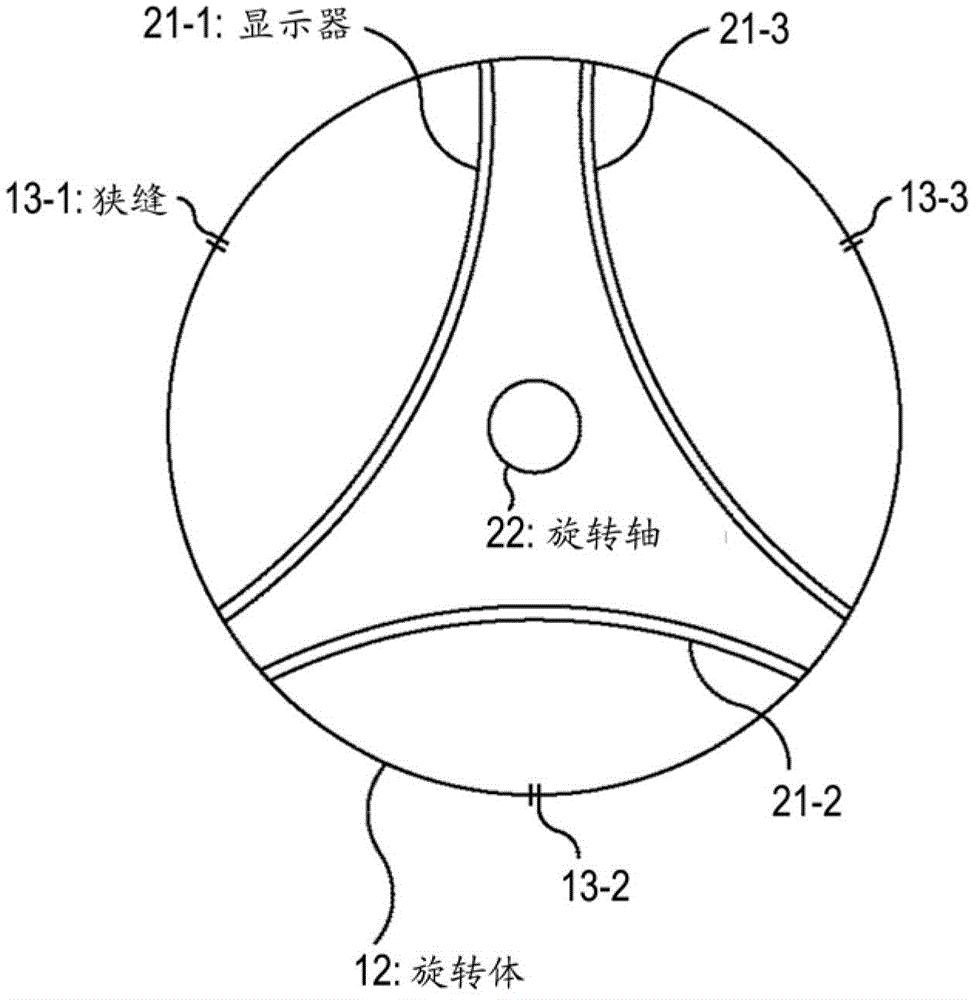
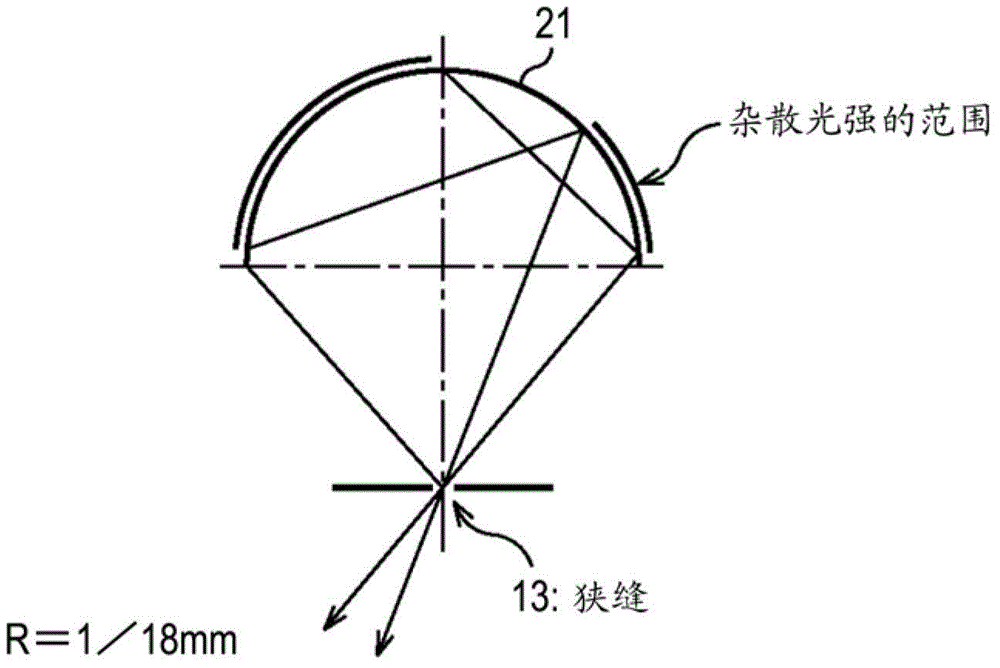
InactiveCN102866503AReduce contrastSuppress contrast dropStereoscopic photographySteroscopic systemsDisplay deviceSpecular reflection
Provided is a display device including a housing whose side surface has one or more slits, and a display that is mounted in the housing and has a substantially arc shape, wherein an image displayed on the display is visually recognized beyond the slit when the housing rotates, and a curvature of the display having the substantially arc shape is formed so that stray light resulting from a specular reflection does not occur.
Owner:SONY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com