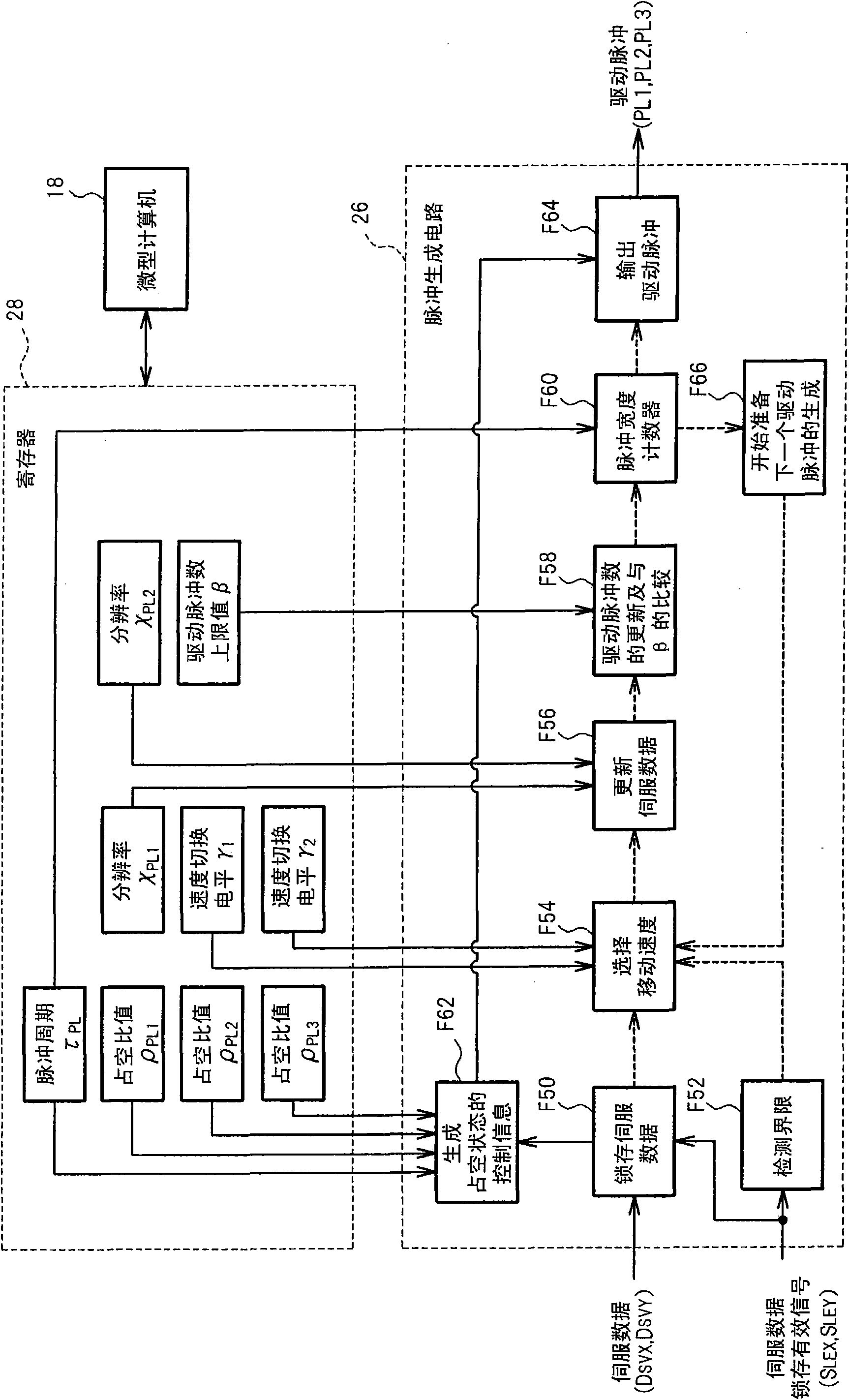
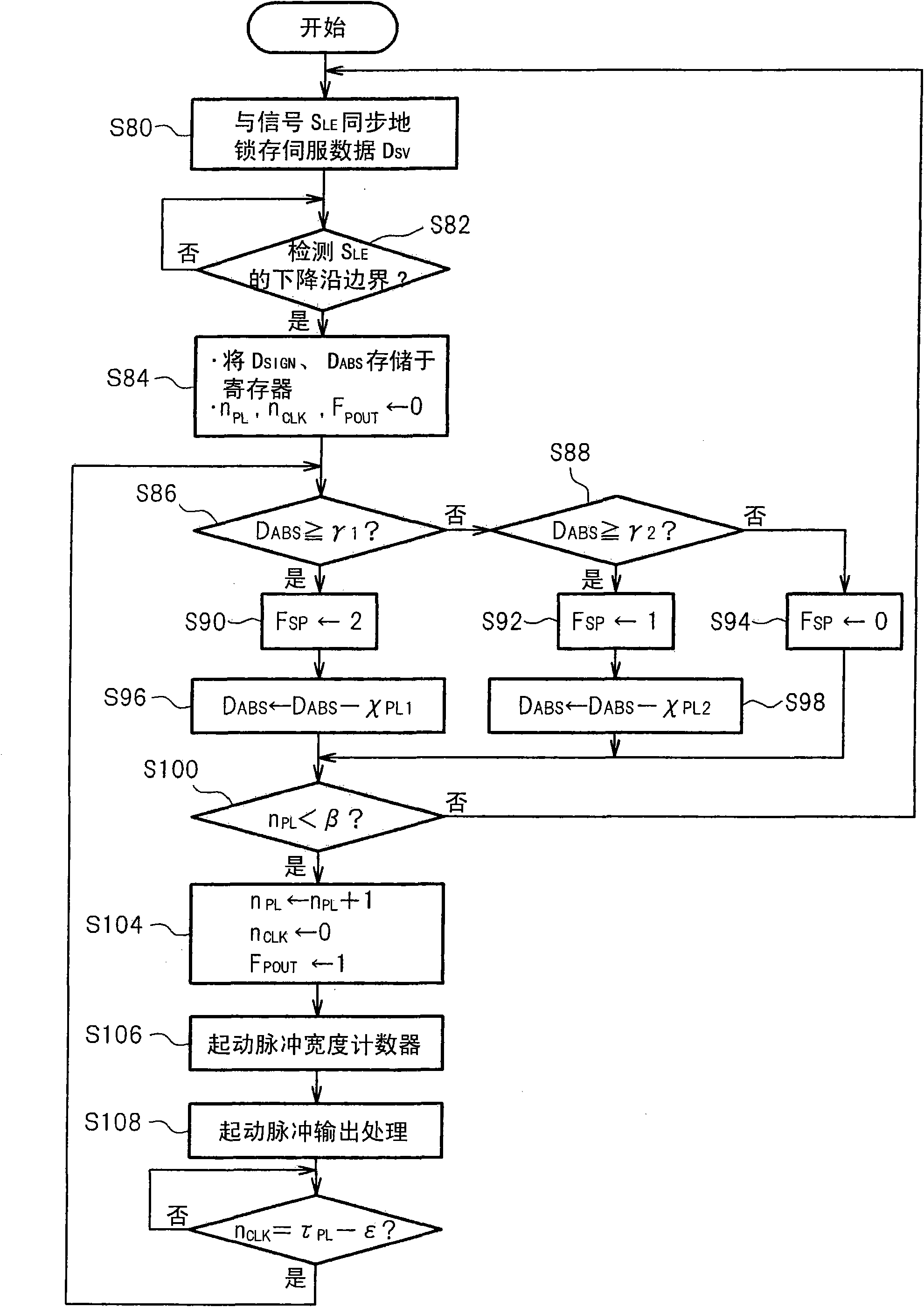
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
53results about How to "Suppress abnormal noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
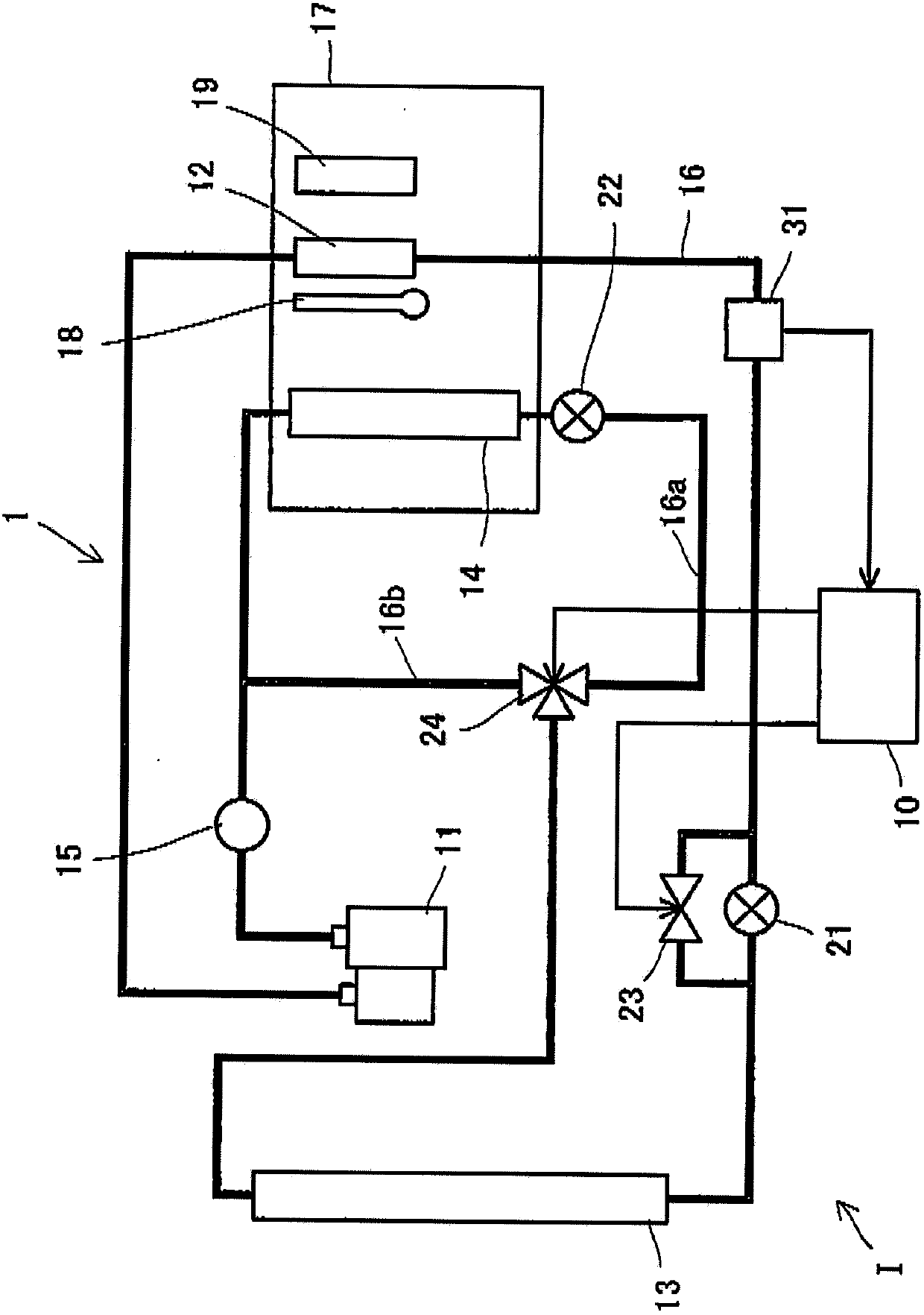
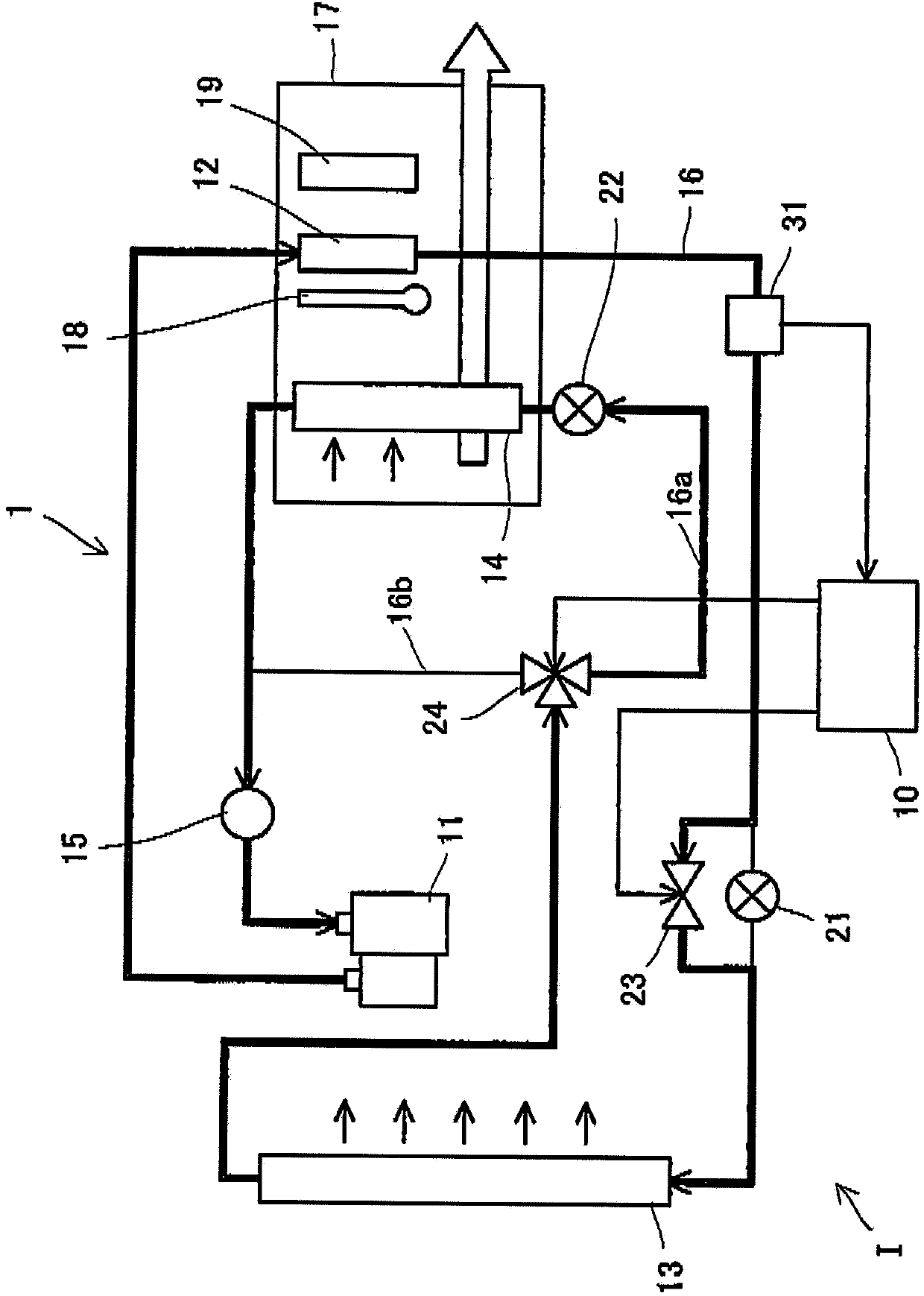
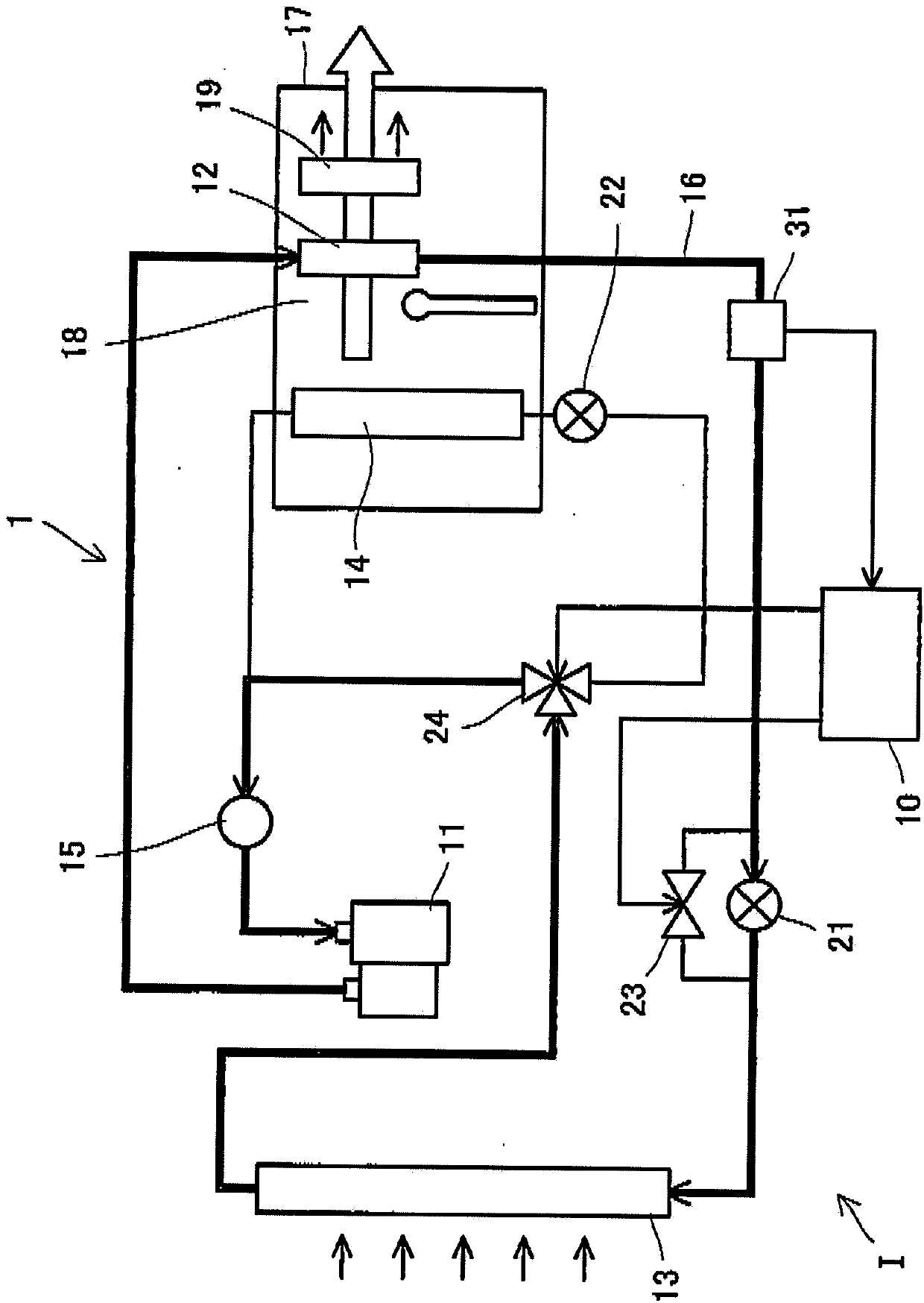
Vehicle air conditioner
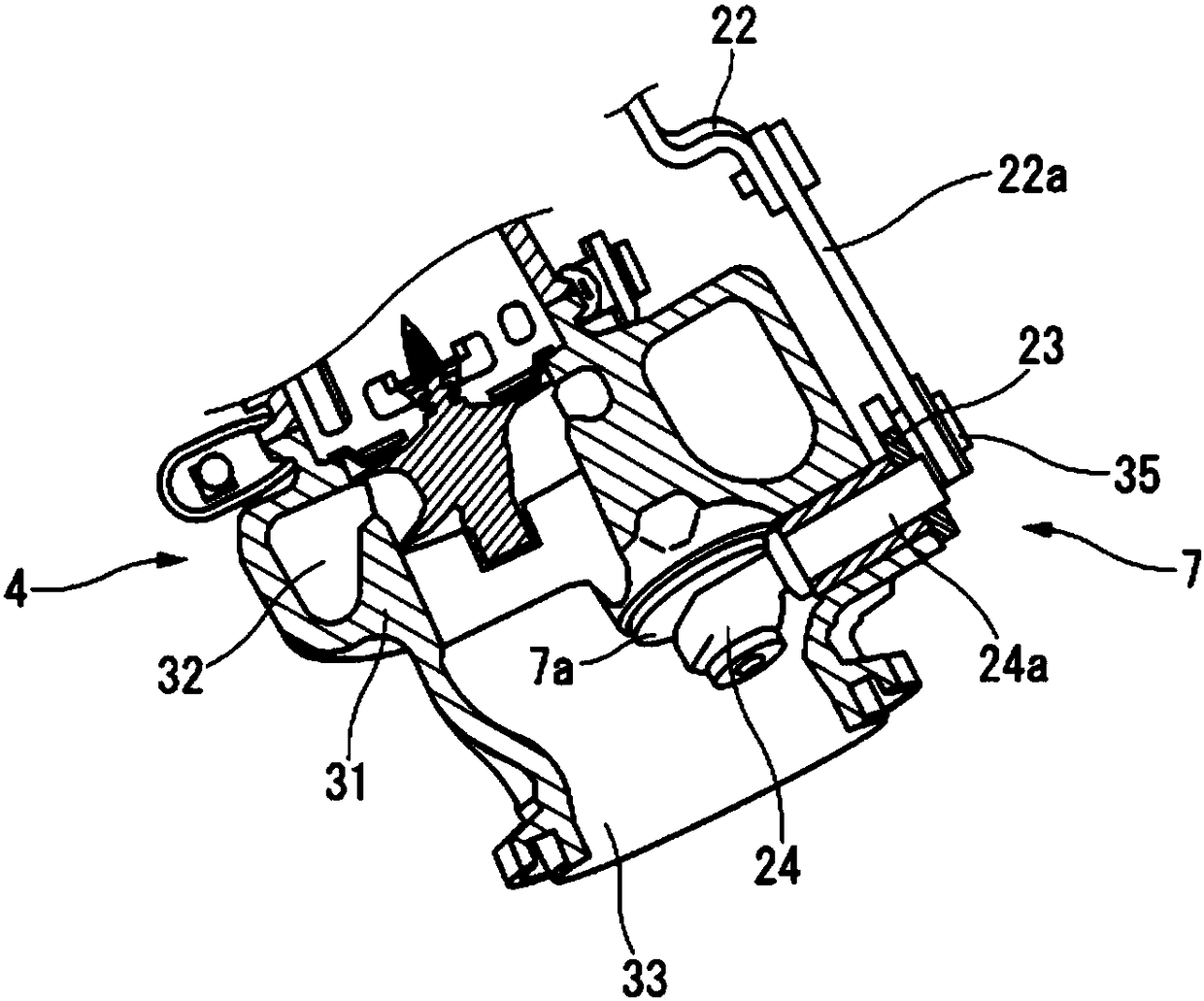
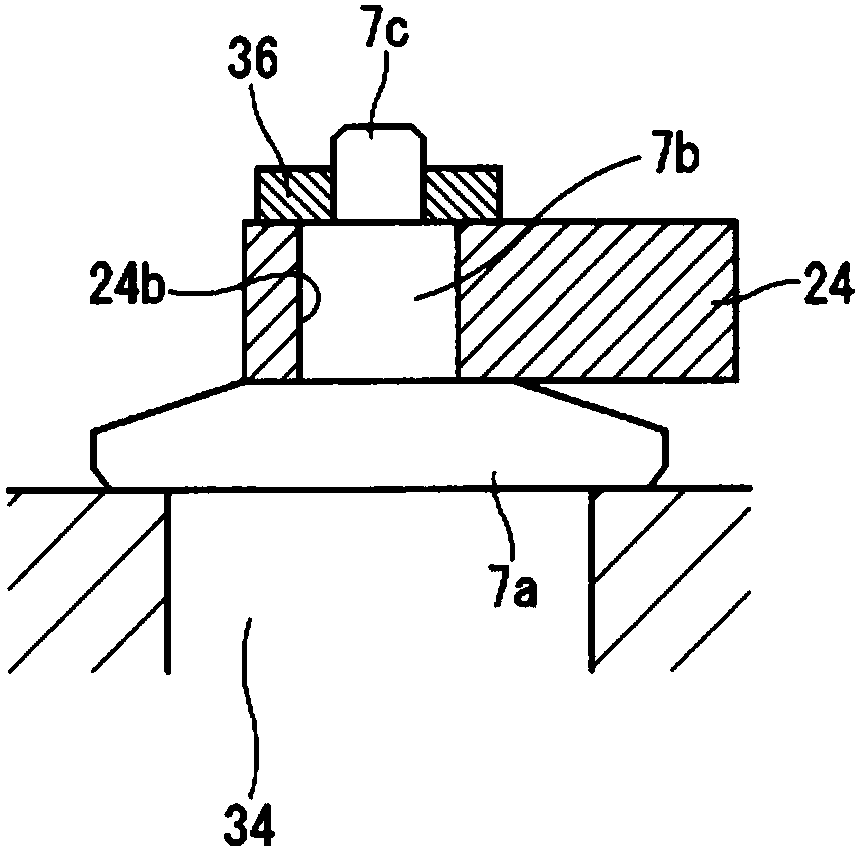
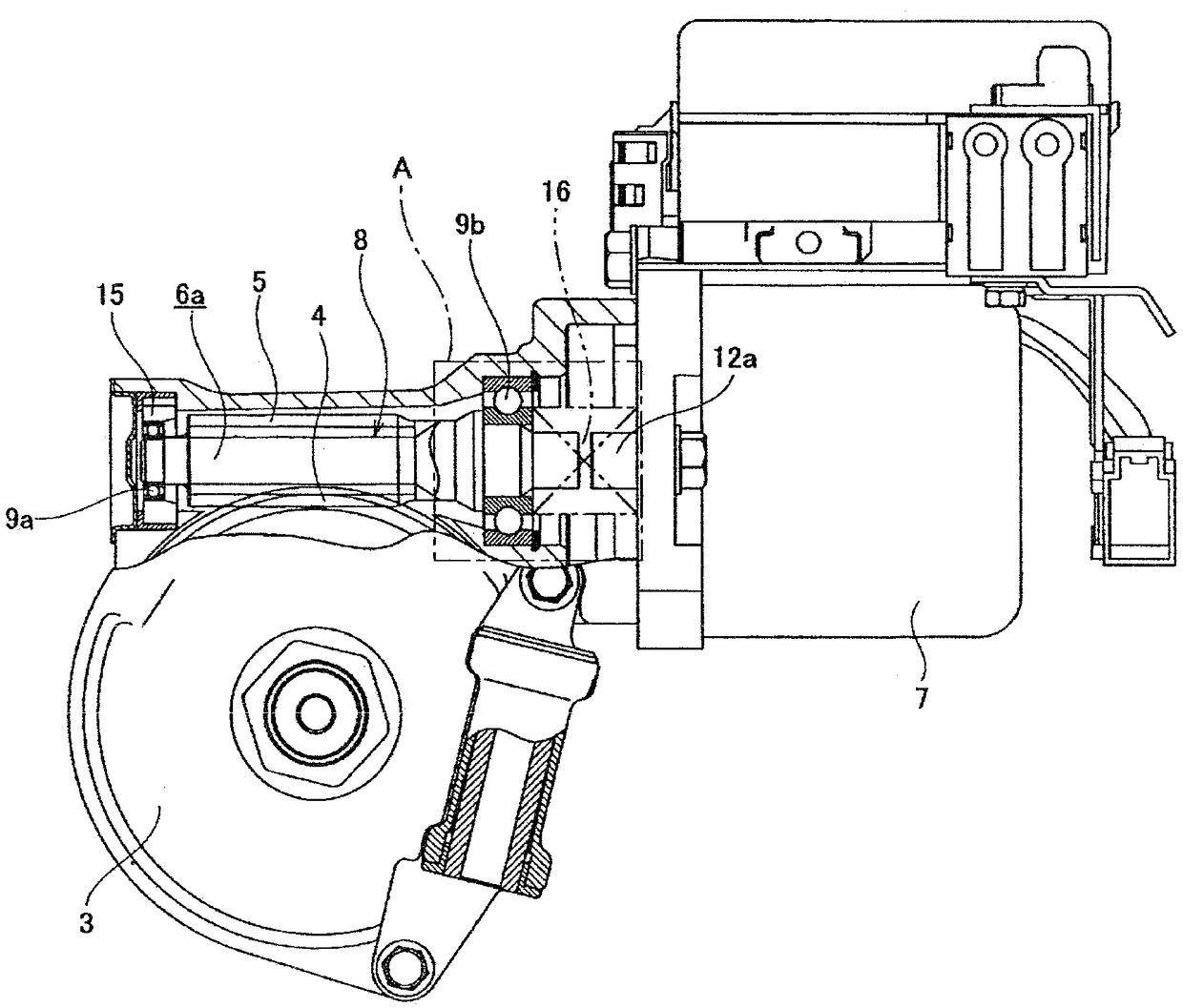
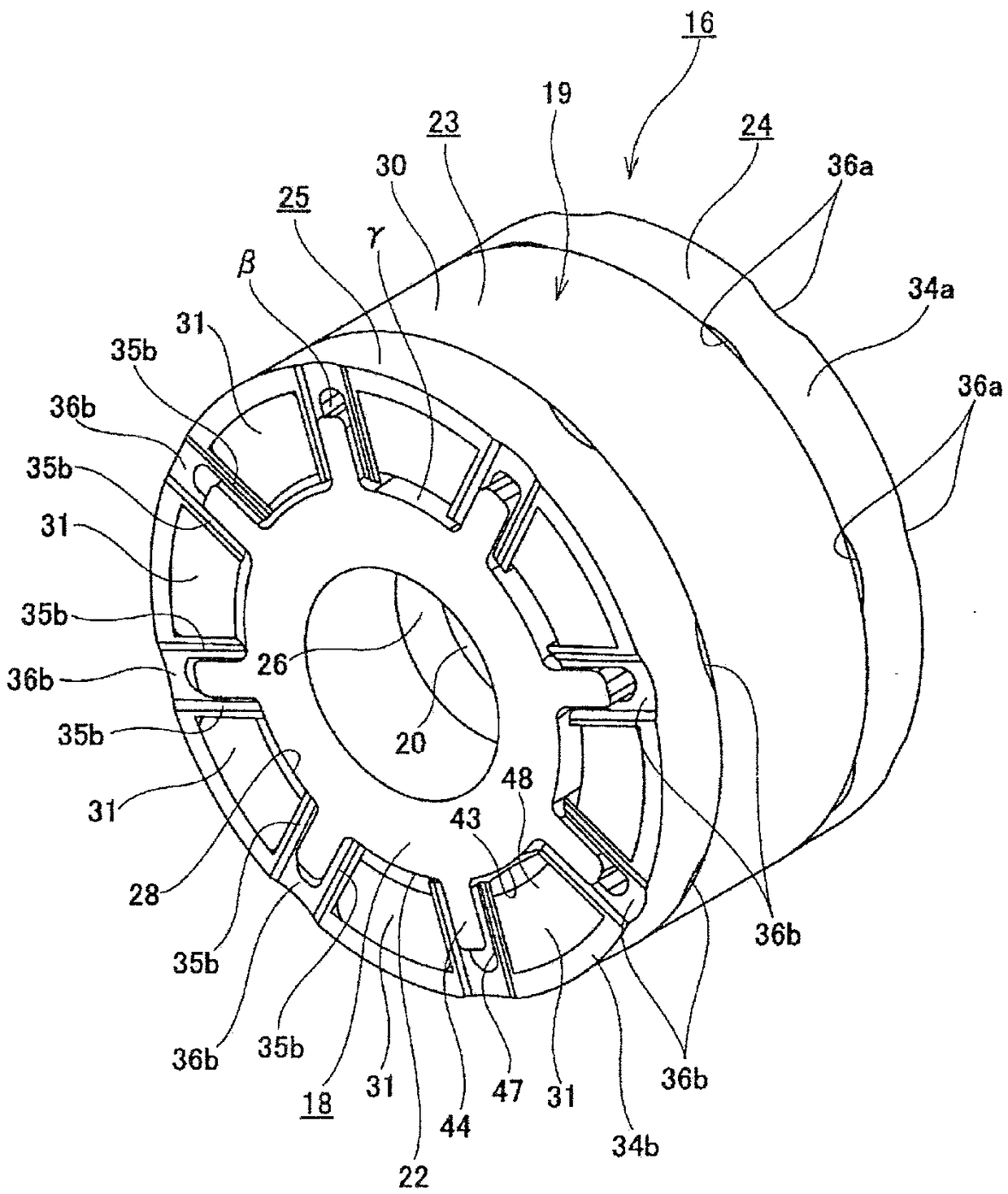
InactiveCN103786547ASuppress abnormal noiseAir-treating devicesVehicle heating/cooling devicesEngineeringOperation mode
A vehicle air conditioner, which can suppress the occurrence of an abnormal noise when switching the operation mode of air conditioning, is provided. The vehicle air conditioner comprises compression means for compressing a heating medium, pressure reducing means for reducing the pressure of the heating medium, a heat exchanger for performing heat exchange between the heating medium and air, a flow passage having a heating path and a cooling path, a flow passage selector valve for changing the path in the flow passage, and a control unit for allowing the flow passage selector valve to act in accordance with an air conditioning operation mode. If a switching instruction on the air conditioning operation mode is inputted, the control unit stops the compression means and also defers the action of the flow passage selector valve until a predetermined time elapses or until a pressure difference between the paths becomes a predetermined value or less.
Owner:MITSUBISHI MOTORS CORP
Motor control device and electric power steering device
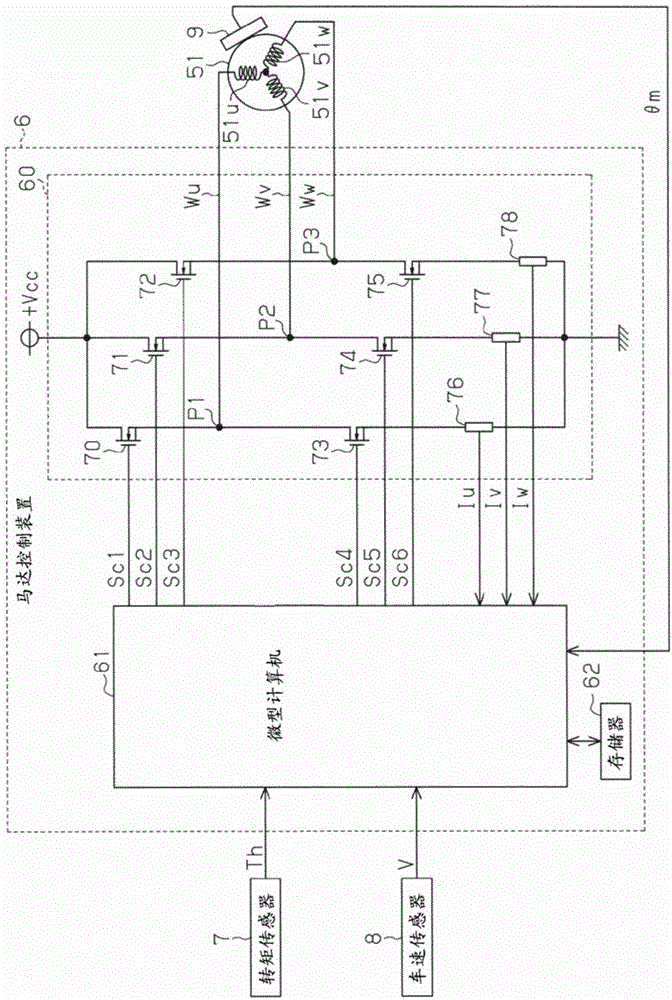
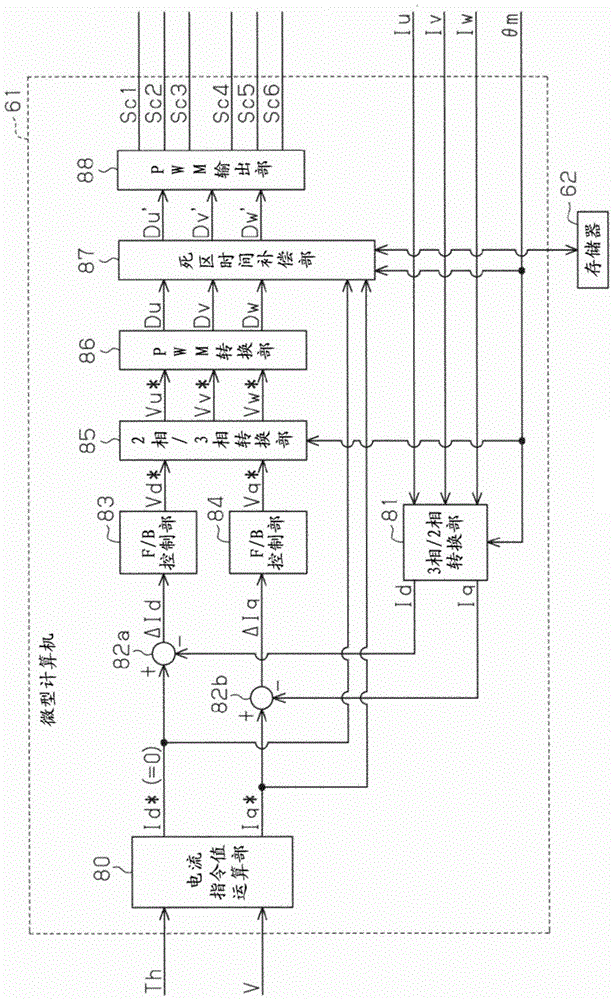
ActiveCN104901601ASuppress abnormal noiseSuppress discomfortSpeed controllerVector control systemsMicrocomputerElectric power steering
A motor control device includes a motor drive circuit and a microcomputer that controls the drive circuit. The microcomputer generates a control signal on the basis of duty command values Du, Dv, and Dw to control the drive circuit. The microcomputer includes a dead time compensation section 87 that corrects the duty command values Du, Dv, and Dw on the basis of dead time compensation values Ddu, Ddv, and Ddw. The dead time compensation section 87 includes a basic compensation value computation section 92 that computes a basic compensation value Dd as a fundamental value of the dead time compensation values Ddu, Ddv, and Ddw, and a filter section 93 that performs a filtering process corresponding to a low-pass filter on the basic compensation value Dd. The dead time compensation section 87 sets the dead time compensation values Ddu, Ddv, and Ddw on the basis of an output value ± from the filter section 93.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Control gear of automatic gearbox
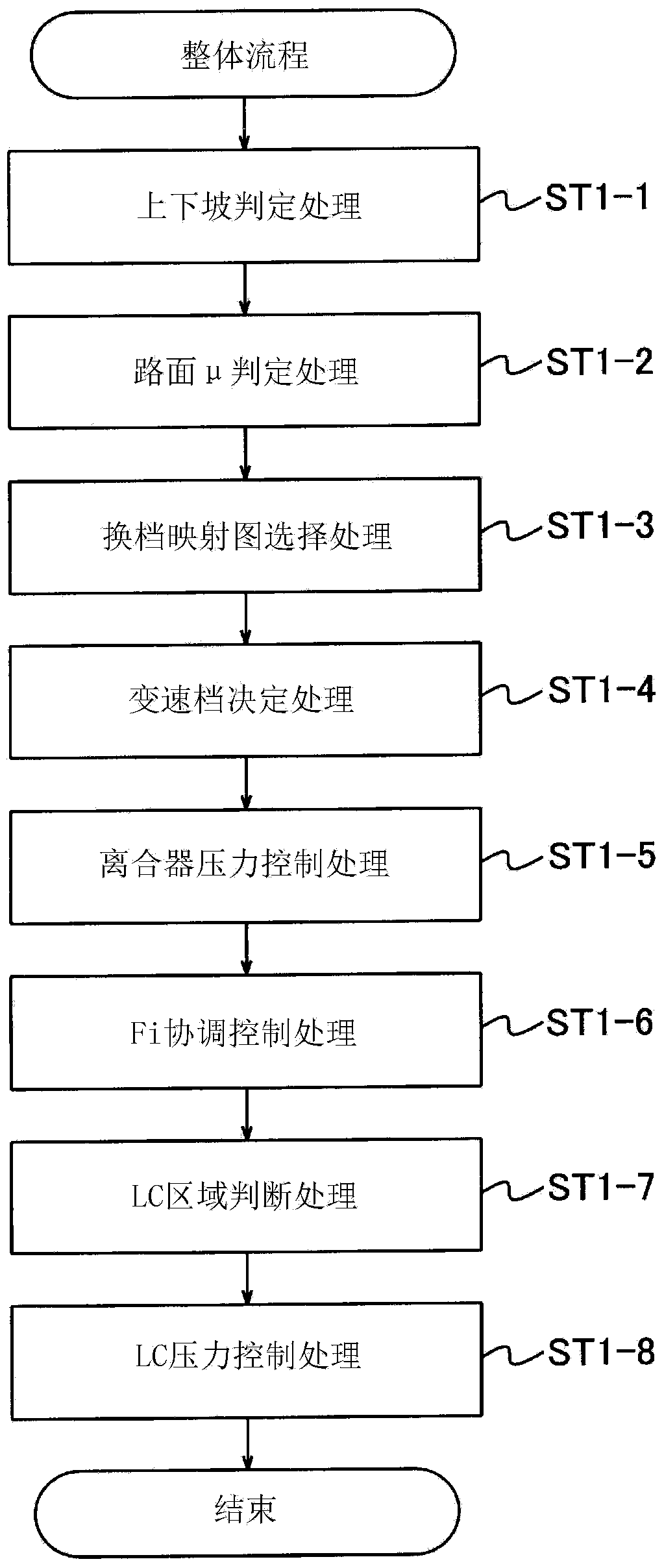
ActiveCN103542086APrevent slippingLarge amount of bondingGearing controlFluid gearingsAutomatic transmissionTimer
The invention provides a control device of automatic gearbox, which can be used in an oil pressure control of lock-up clutch during speed change, thereby preventing oil pressure reduction caused by speed change prepration pressure, and appropriately adjusting oil pressure in required area for the lock-up clutch, and not only inhibiting slipping of the lock-up clutch, but also preventing generation of abnormal noise. When the oil pressure instruction of the lock-up clutch is sent, whether the speed change instruction for a speed change mechanism is sent is judged; if the speed change instruction is sent, summing of adjusting oil pressures (PA) for the control oil pressure (P) for the lock-up mechanism is carried out. Moreover, a timer (TM) is set used from summing the adjusting oil pressures (PA) to the end. The timer (TM) is set as that the adjusting oil pressures (PA) are summed after the speed change signals are connected and the ending is before the speed change mechanism begins to change speed.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Vehicle seat slide device
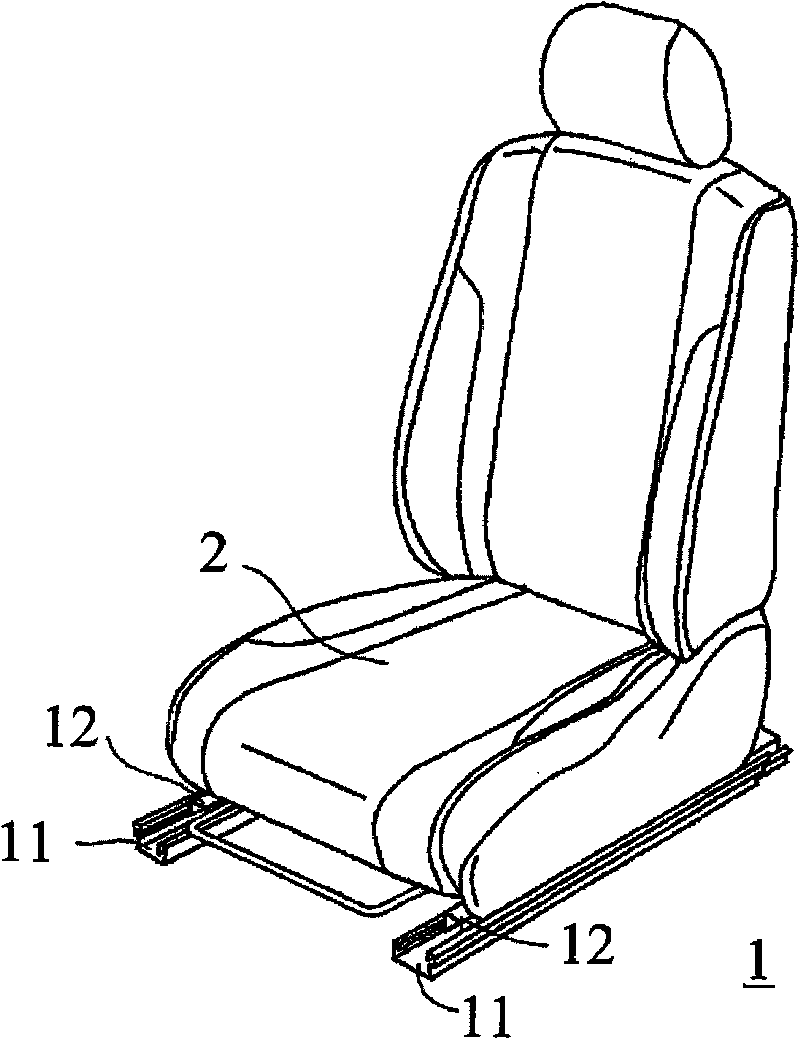
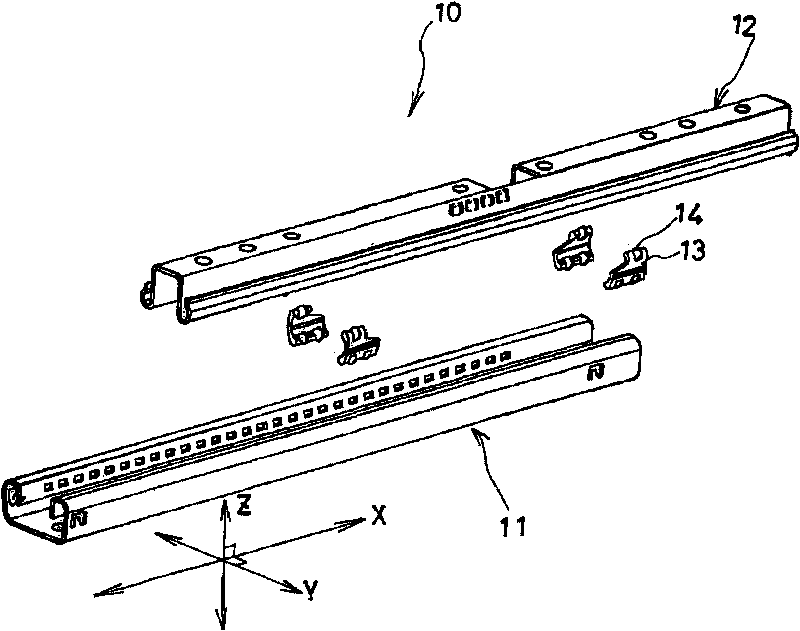
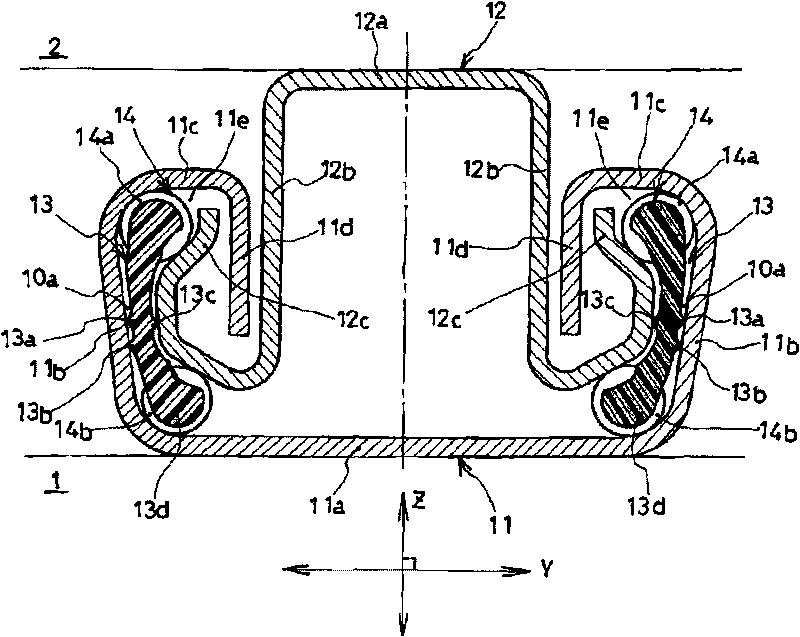
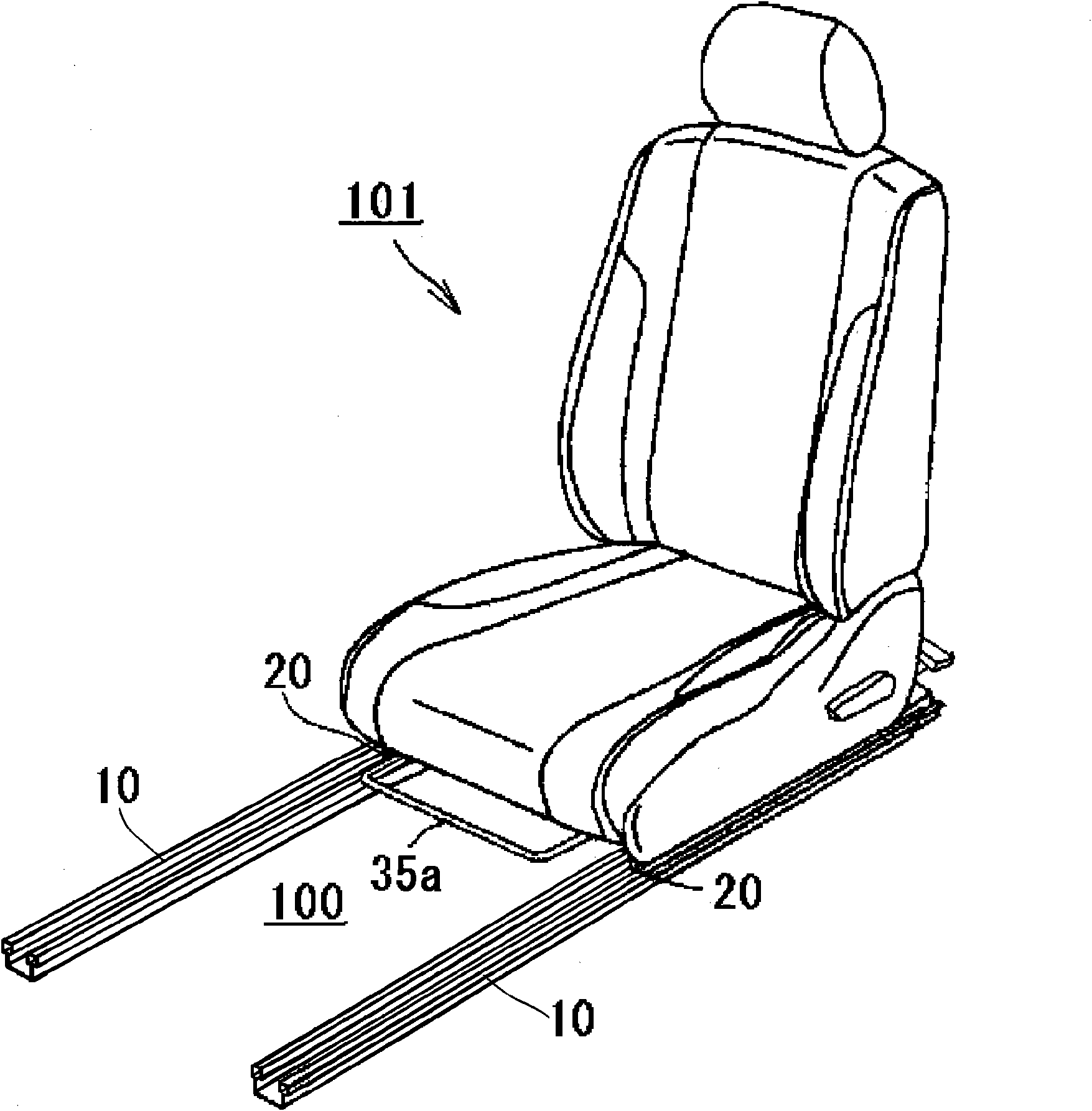
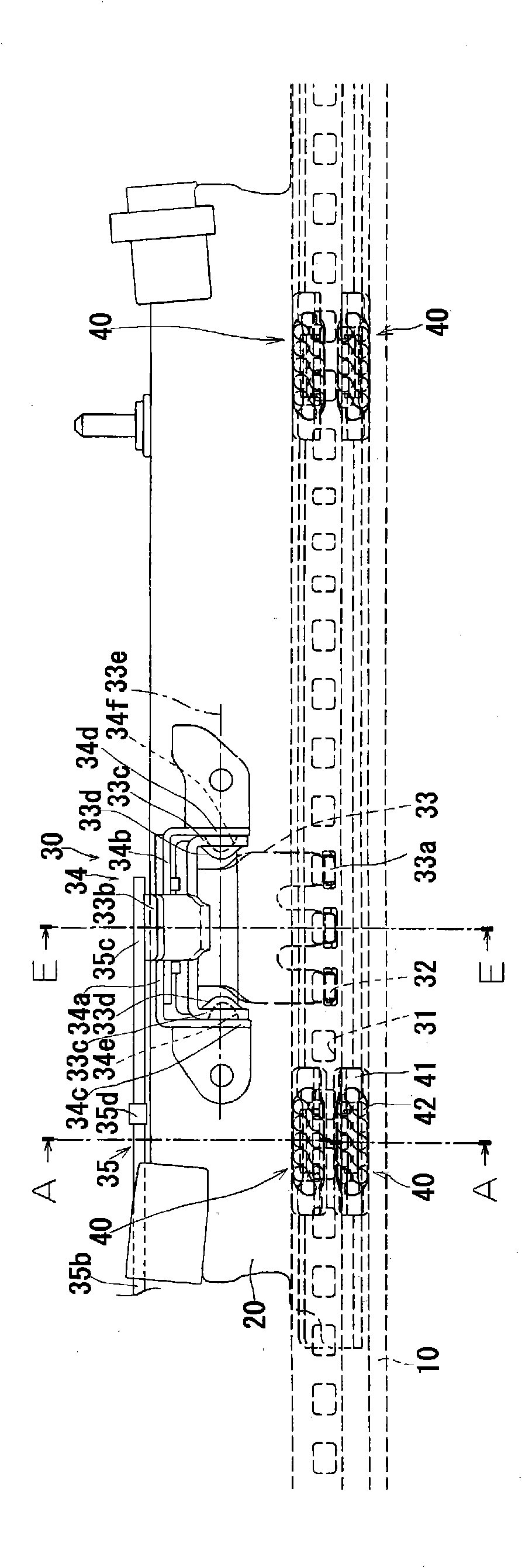
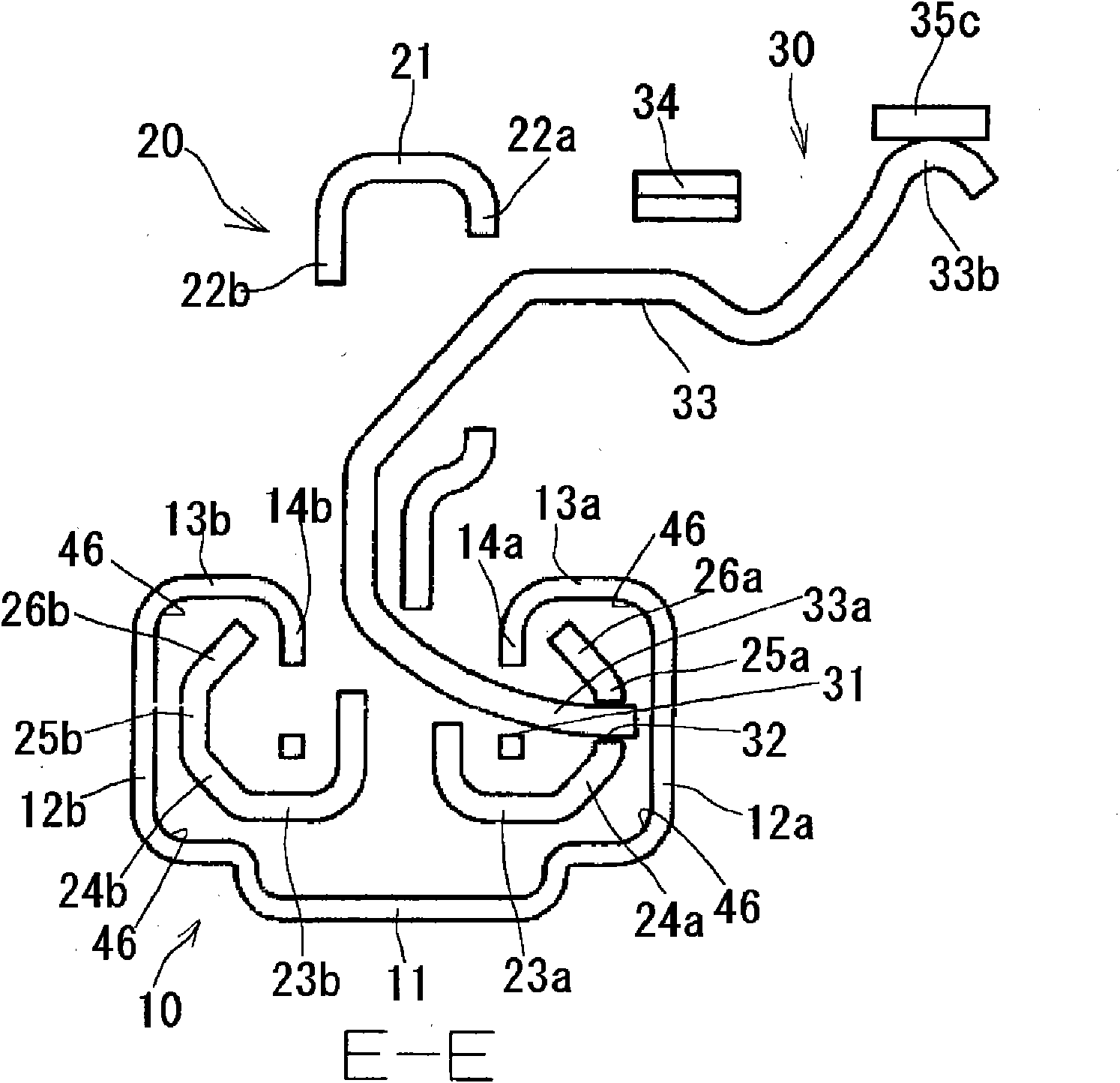
InactiveCN101707903AControllable contact areaSuppress abnormal noiseLinear bearingsBearing componentsEngineeringSteel ball
Noise occurring when an upper rail is slid on a lower rail with retainers in contact with either or both of the rails is suppressed. A vehicle seat slide device (10) has the lower rail (11), the upper rail (12), the retainers (13) disposed between both rails (11, 12), and rolling elements (steel balls) rollably supported by the retainers (13) and rolling while being in contact with both rails (11, 12). Each retainer (13) has a retainer body (13d) and projections (13a, 13b, 13c) projecting from the retainer body (13d). The projections (13a, 13b, 13c) are formed of a resin material integrally with the retainer body (13d). Because of the projections (13a, 13b, 13c) formed on the retainer (13), when the retainers (13) make contact with both rails (11, 12), the projections (13a, 13b, 13c) invariably make contact with both rails (11, 12).
Owner:AISIN SEIKI KK
Shaft coupling mechanism for electric power steering device
InactiveCN106662162AAvoid Radial CollisionsSuppress abnormal noiseYielding couplingElectrical steeringElectric power steeringCoupling
A shaft coupling mechanism (1) for an electric power steering device comprises a coupling base (3) coupled to a rotating shaft (2), a coupling base (5) coupled to a rotating shaft (4), a rotation transmission member (8) arranged between the rotating shaft (2) and the rotating shaft (4) via the coupling bases (3, 5) and composed of a pair of rigid rotation transmission members (6, 7) for transmitting rotation in an R direction centered about the axial center (O) of the rotating shaft (2) to the rotating shaft (4), an elastic member (9) arranged between the rotation transmission members (6, 7), superimposed over the rotation transmission members (6, 7) in the axial direction, and linked to the rotation transmission members (6, 7), and a linking means (10) for linking the pair of rotation transmission members (6, 7) together.
Owner:OILES CORP
Pillar trim structure
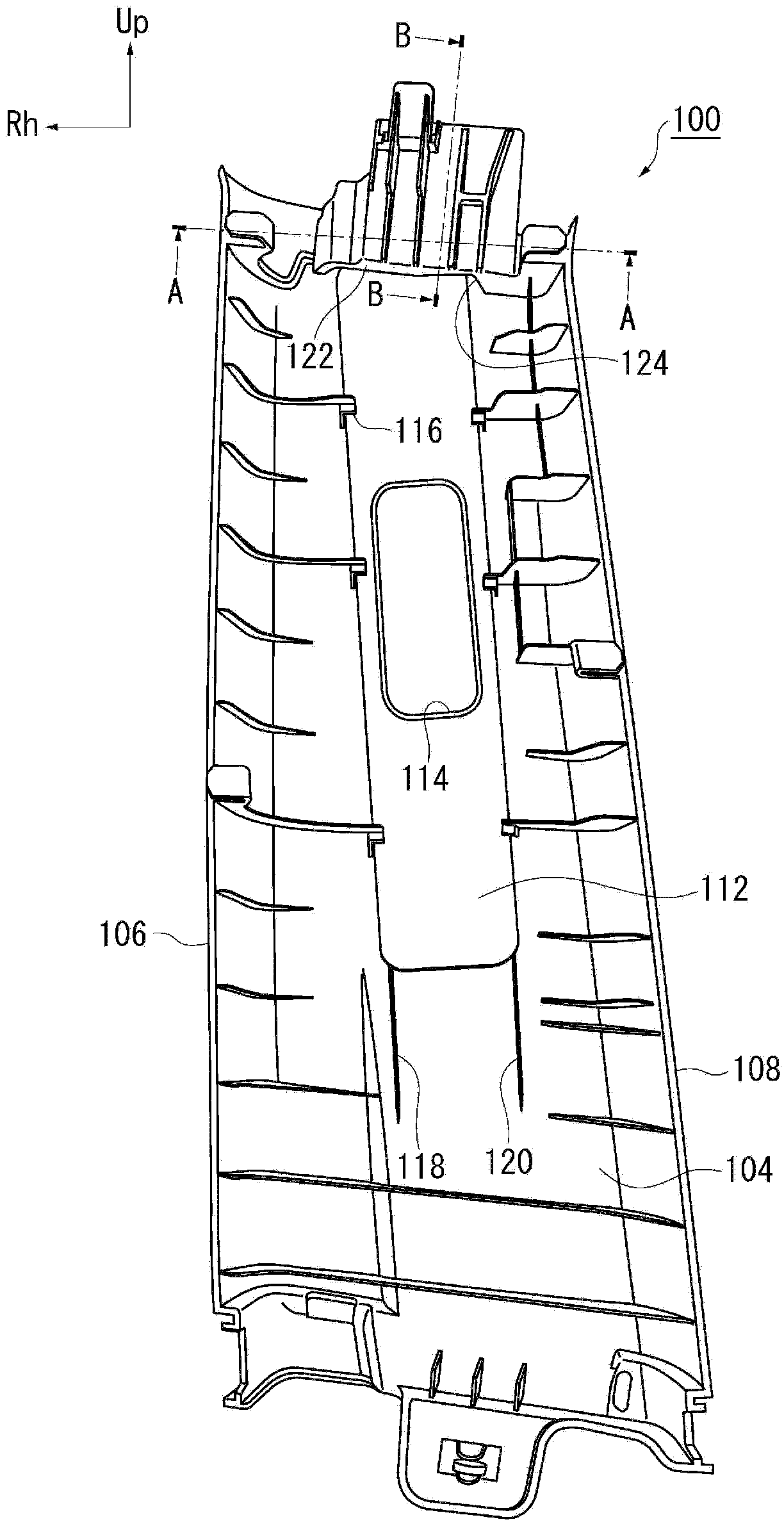
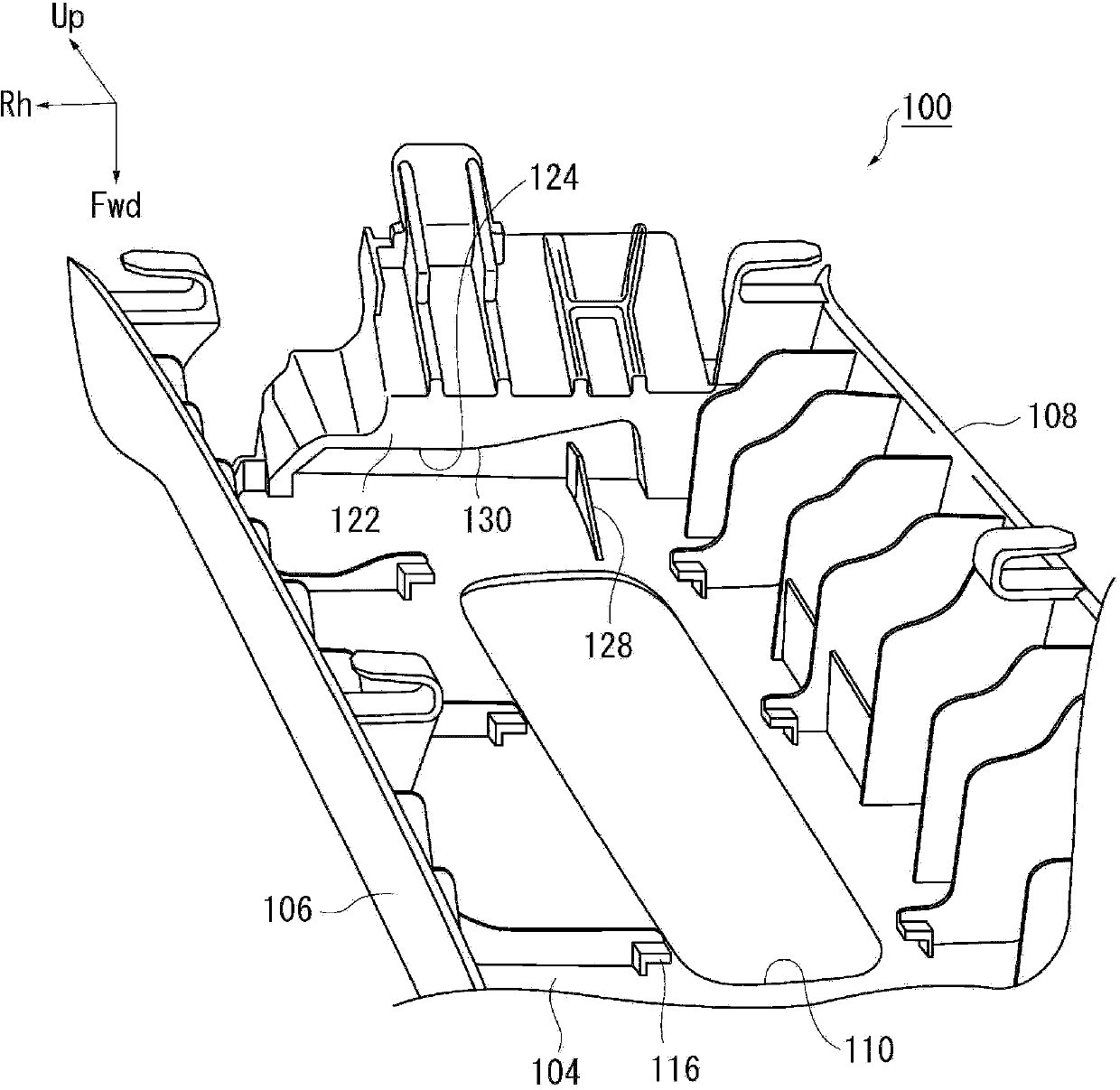
InactiveCN103419724ASuppress abnormal noiseAvoid interferenceSuperstructure subunitsVehicle safety beltsStructural engineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:SUZUKI MOTOR CORP
Bearing device for wheel
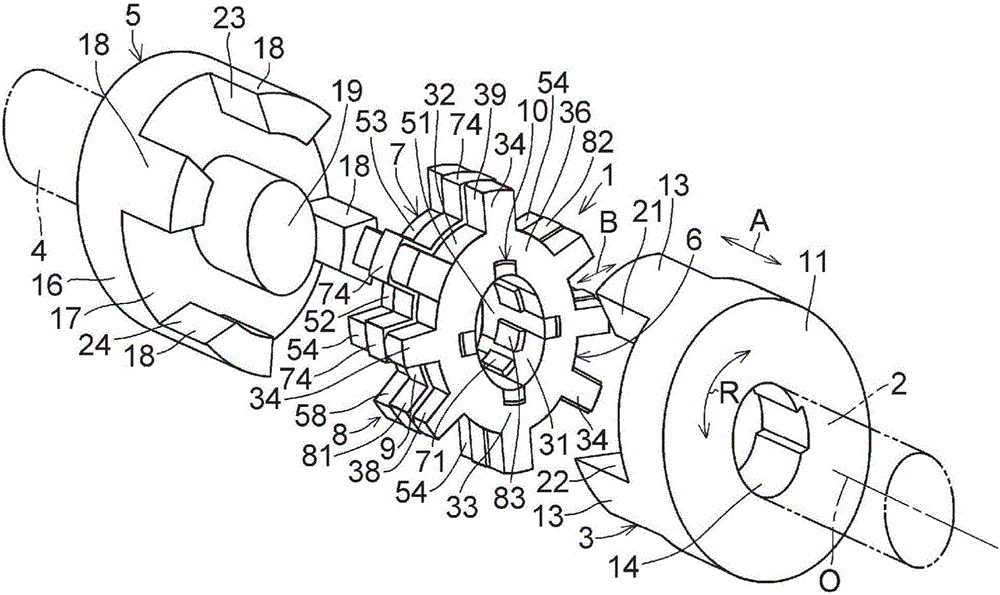
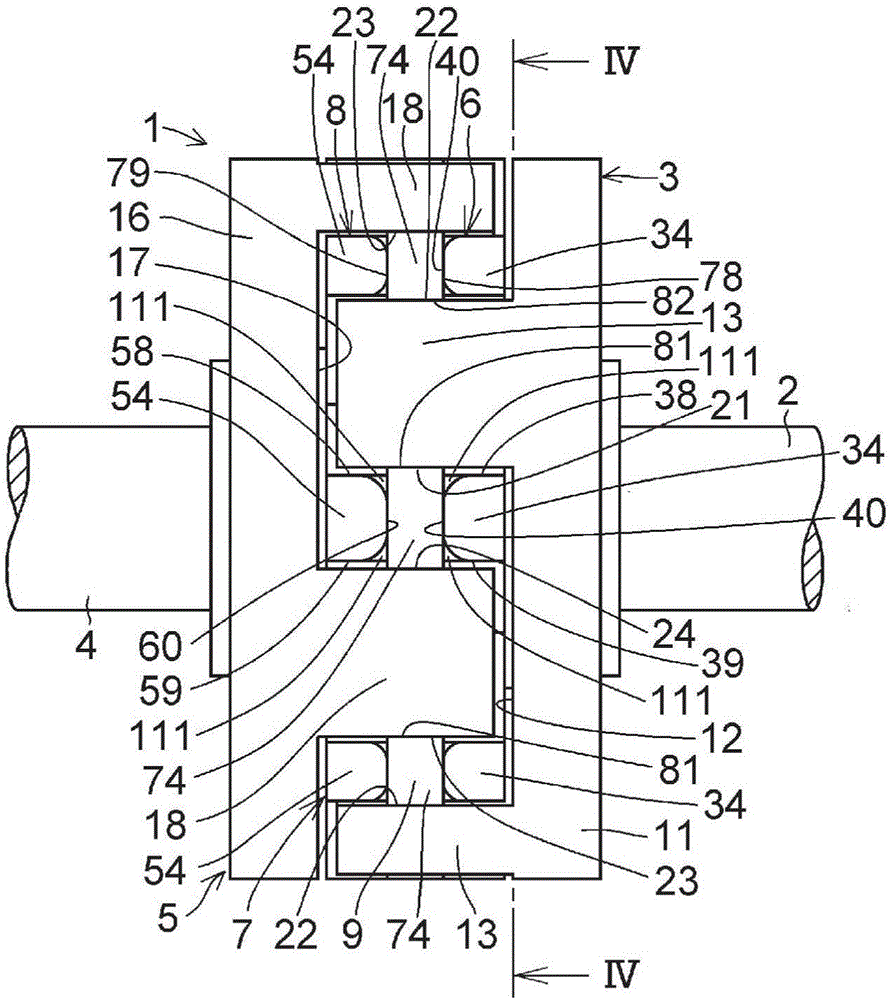
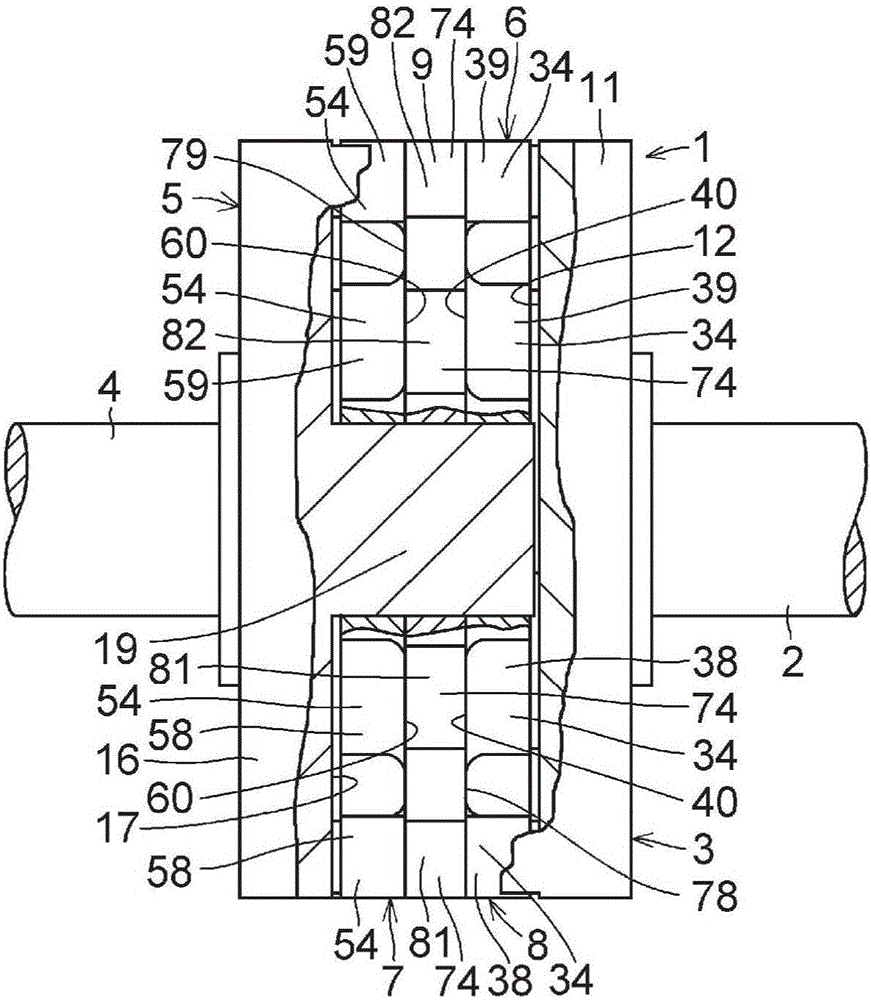
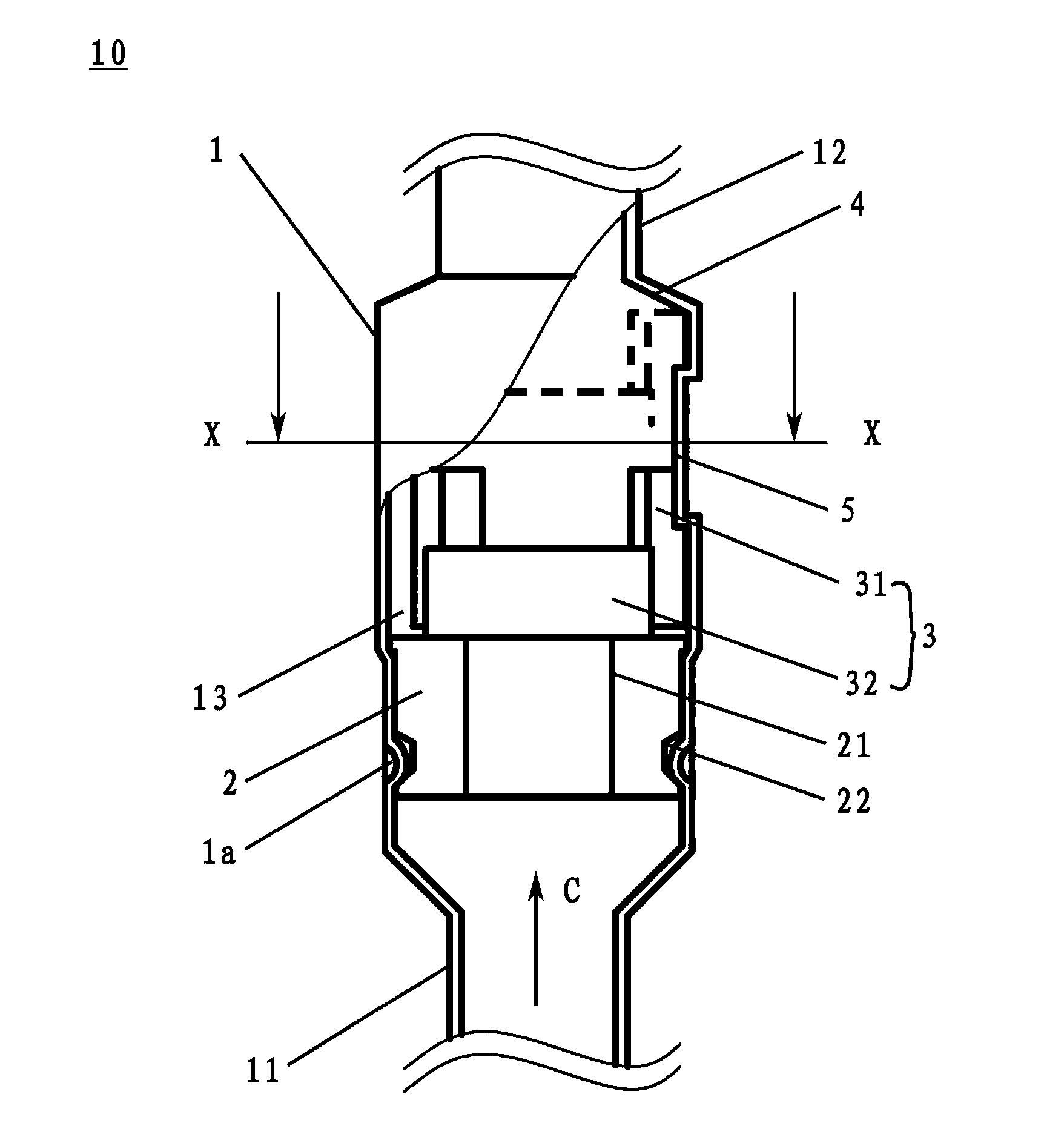
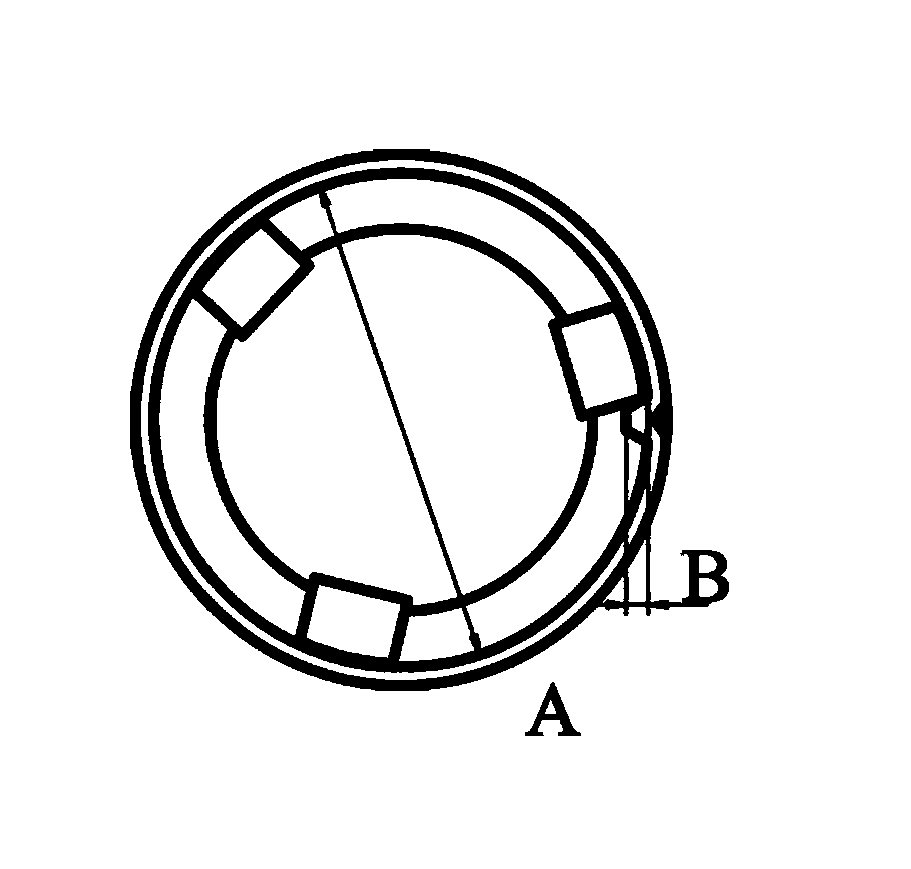
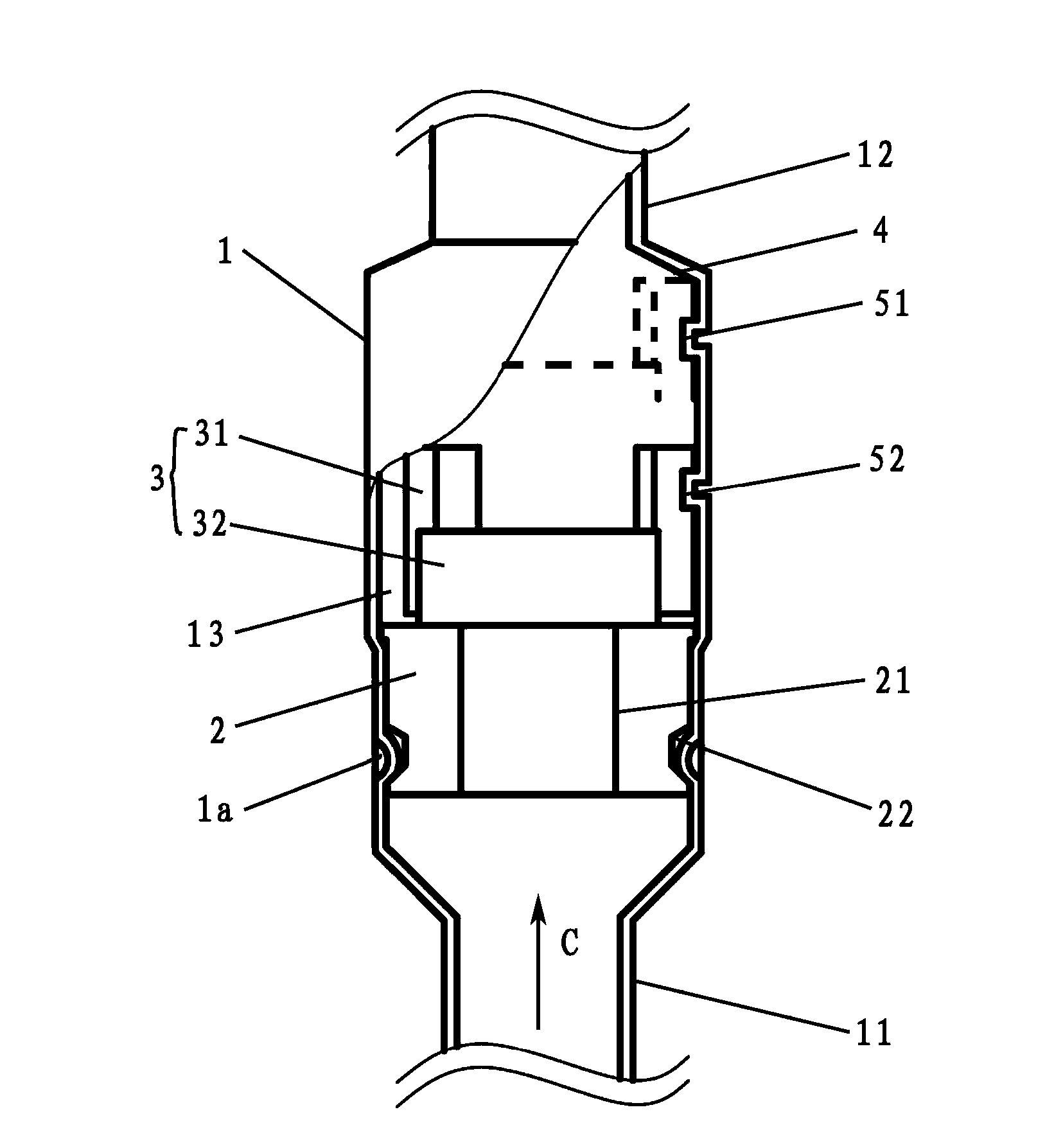
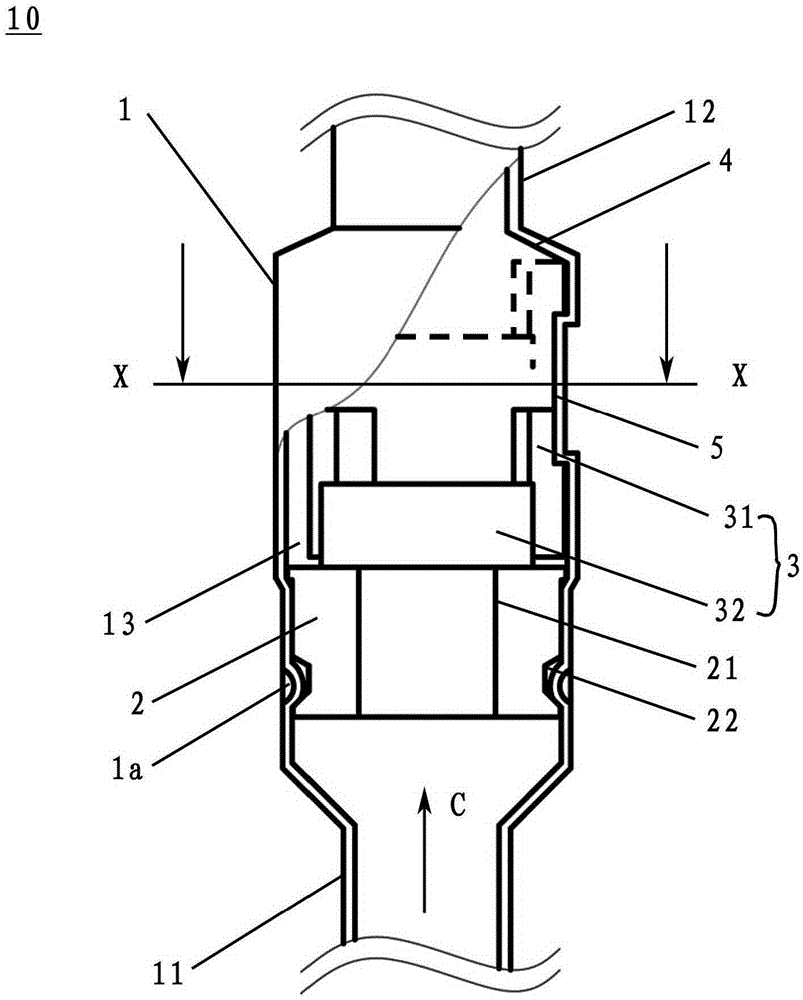
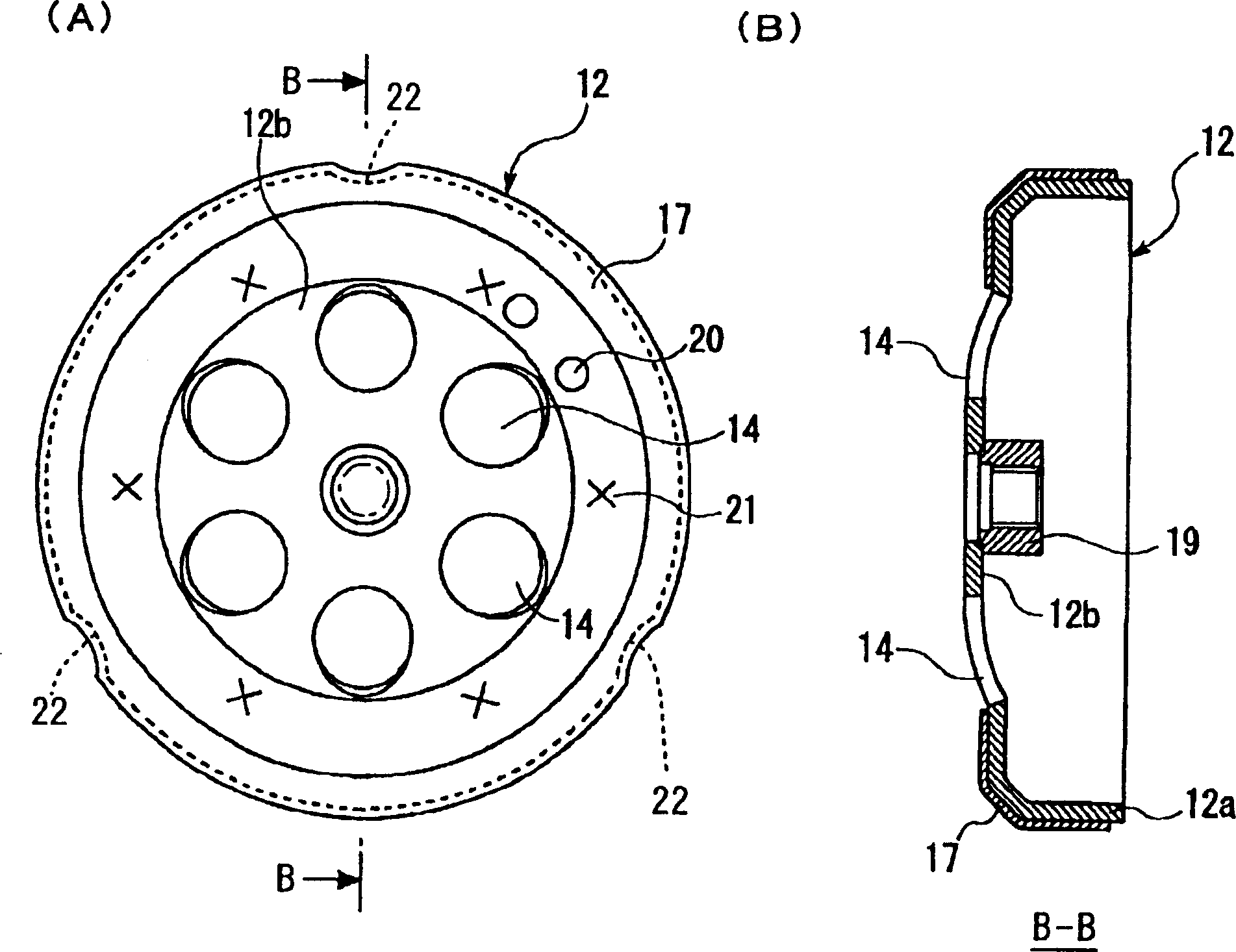
InactiveCN101641225ADoes not generate abnormal noiseHigh strengthRolling contact bearingsAxle unitsKnuckleEngineering
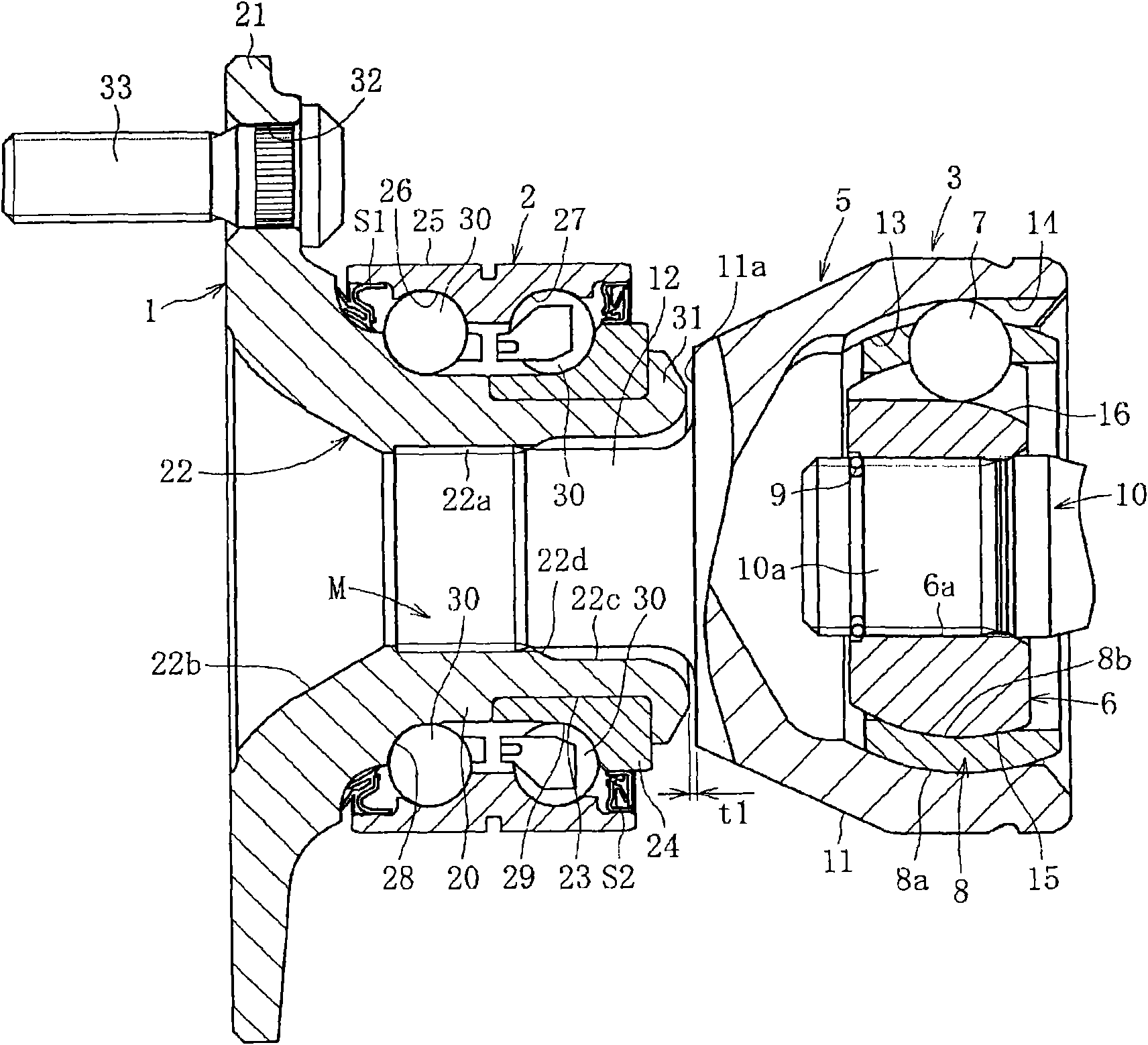
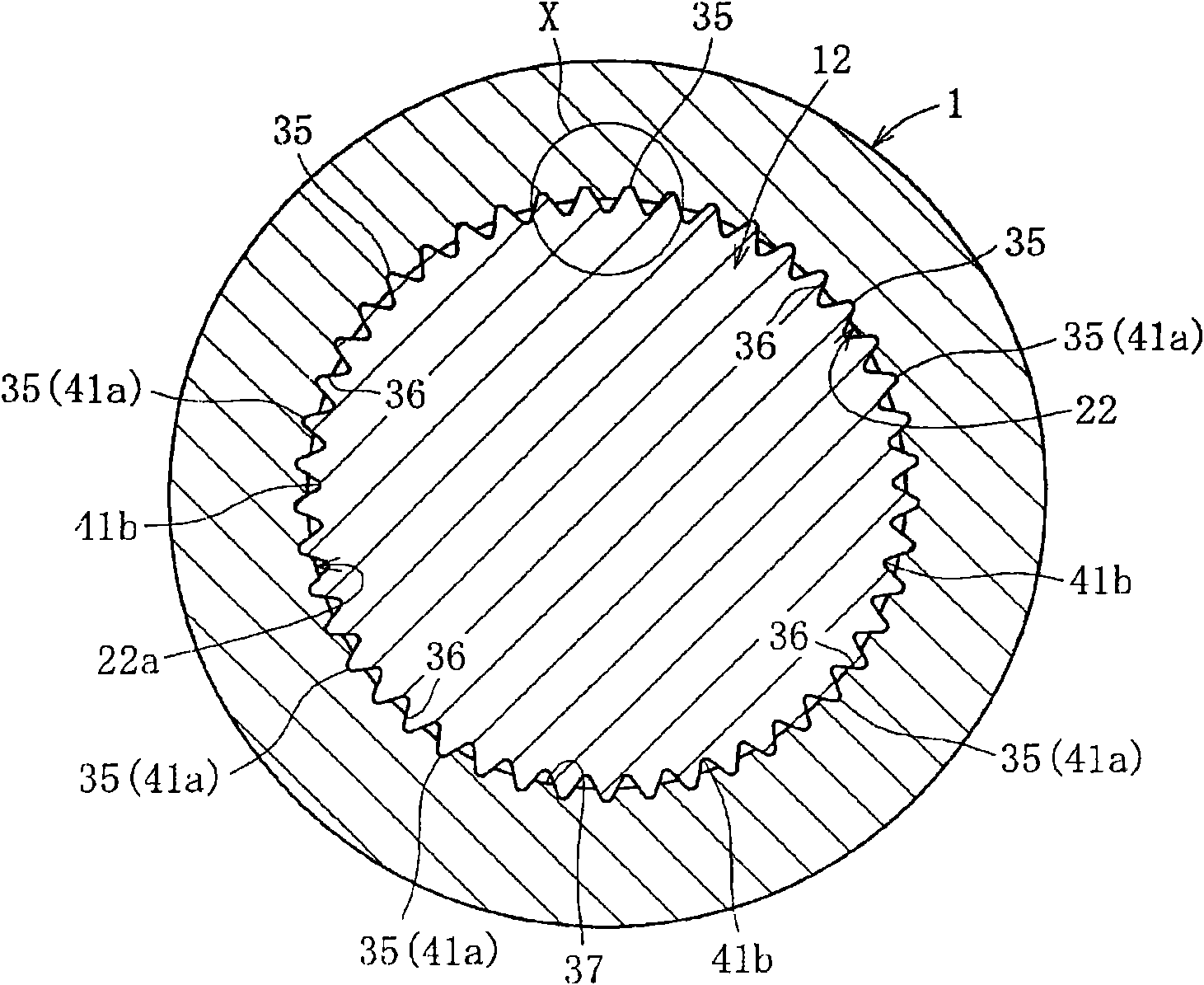
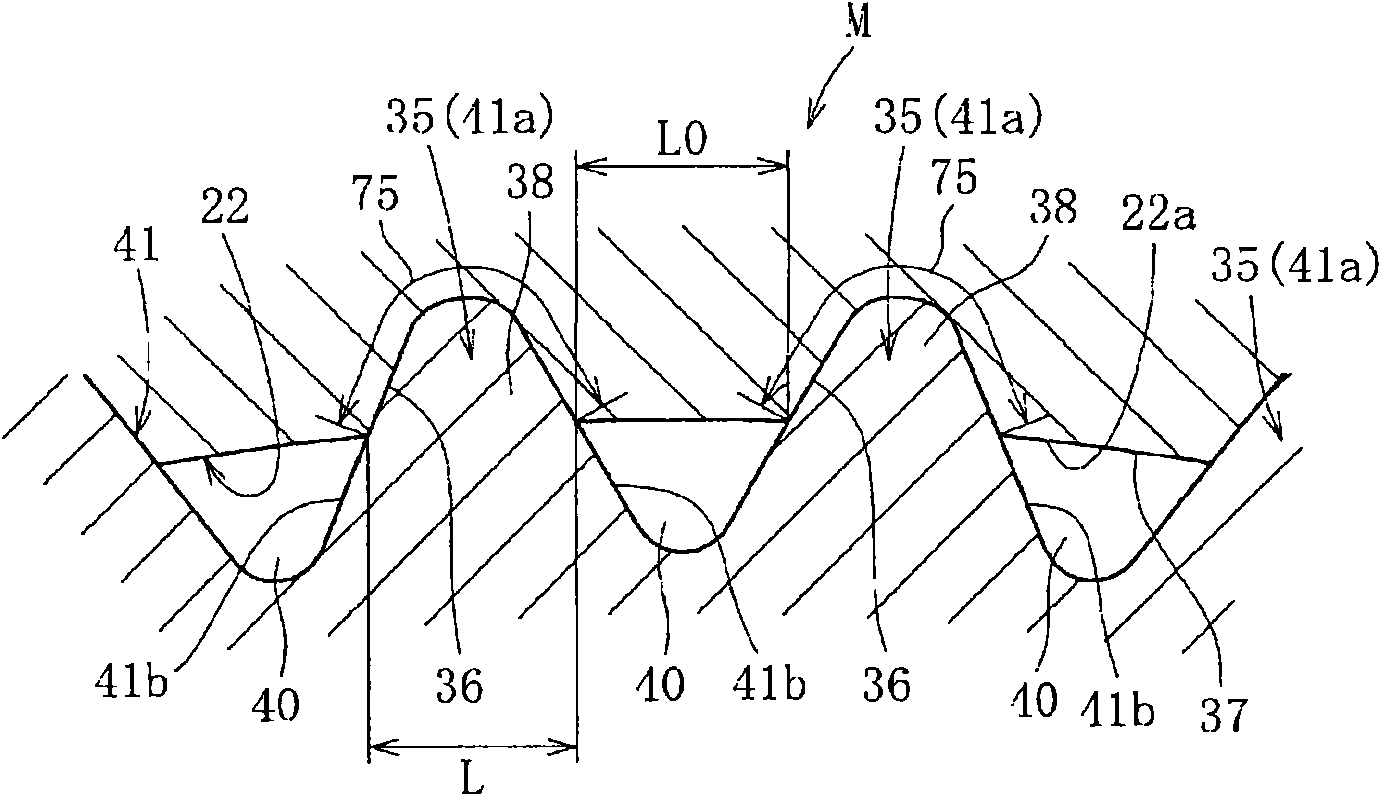
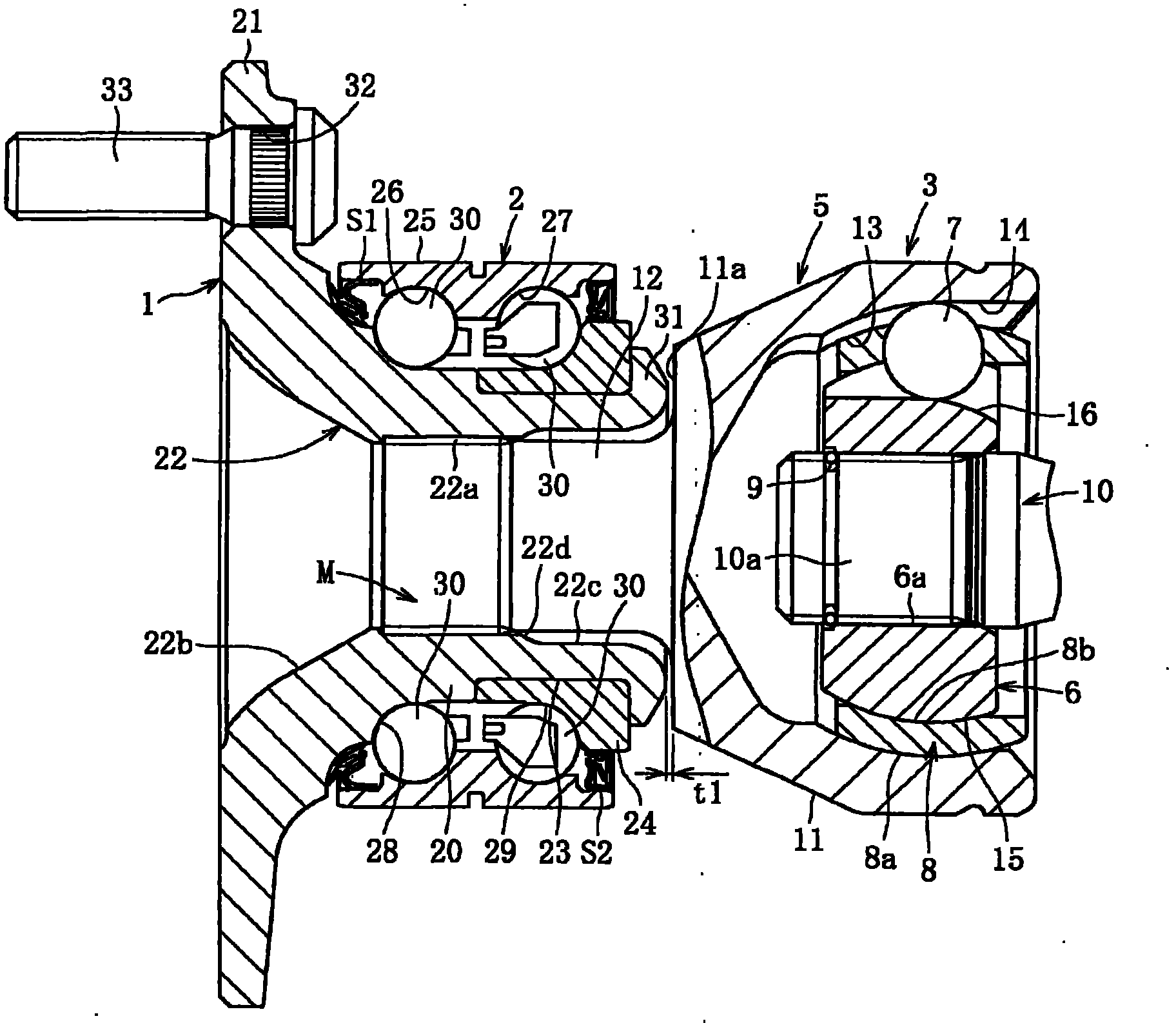
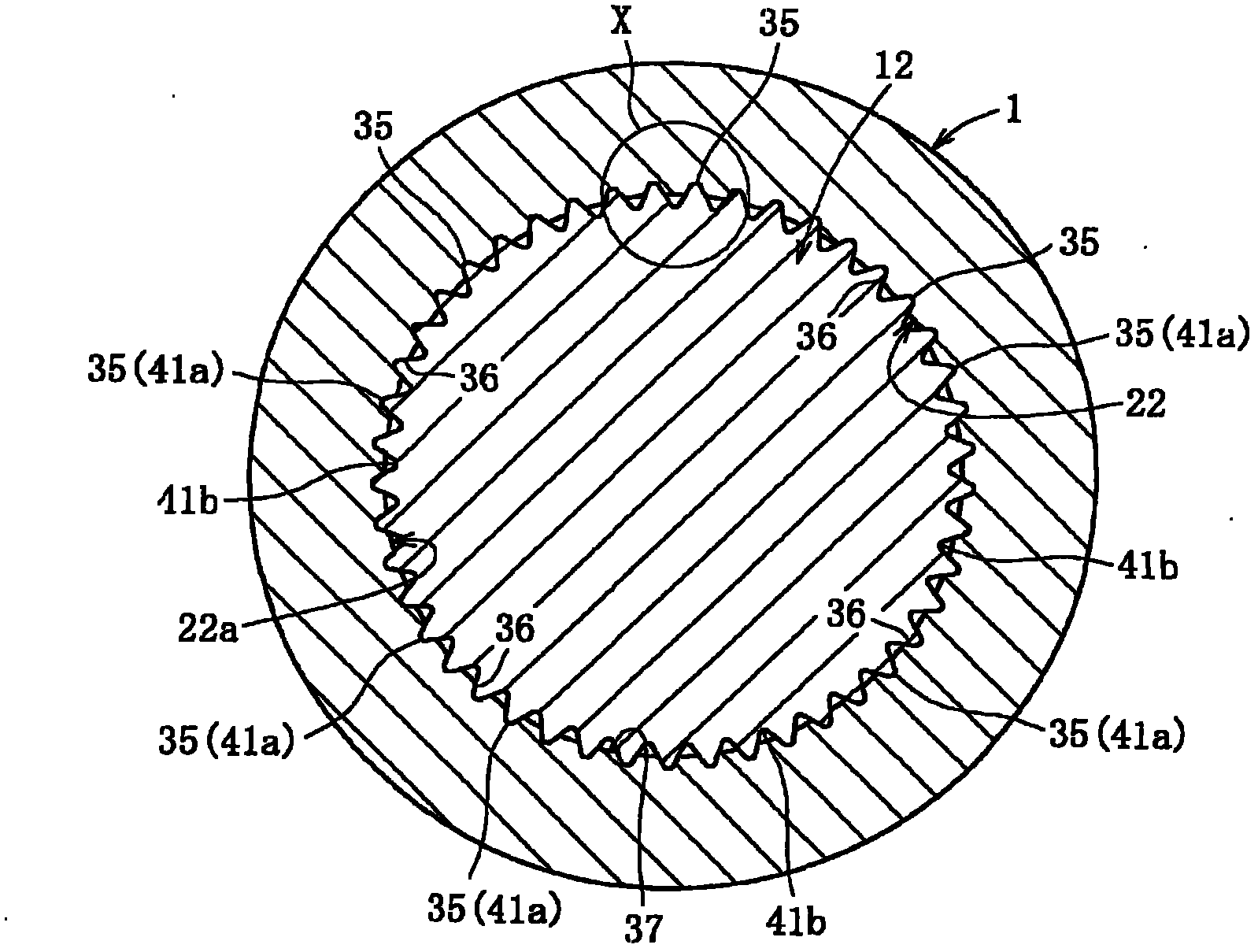
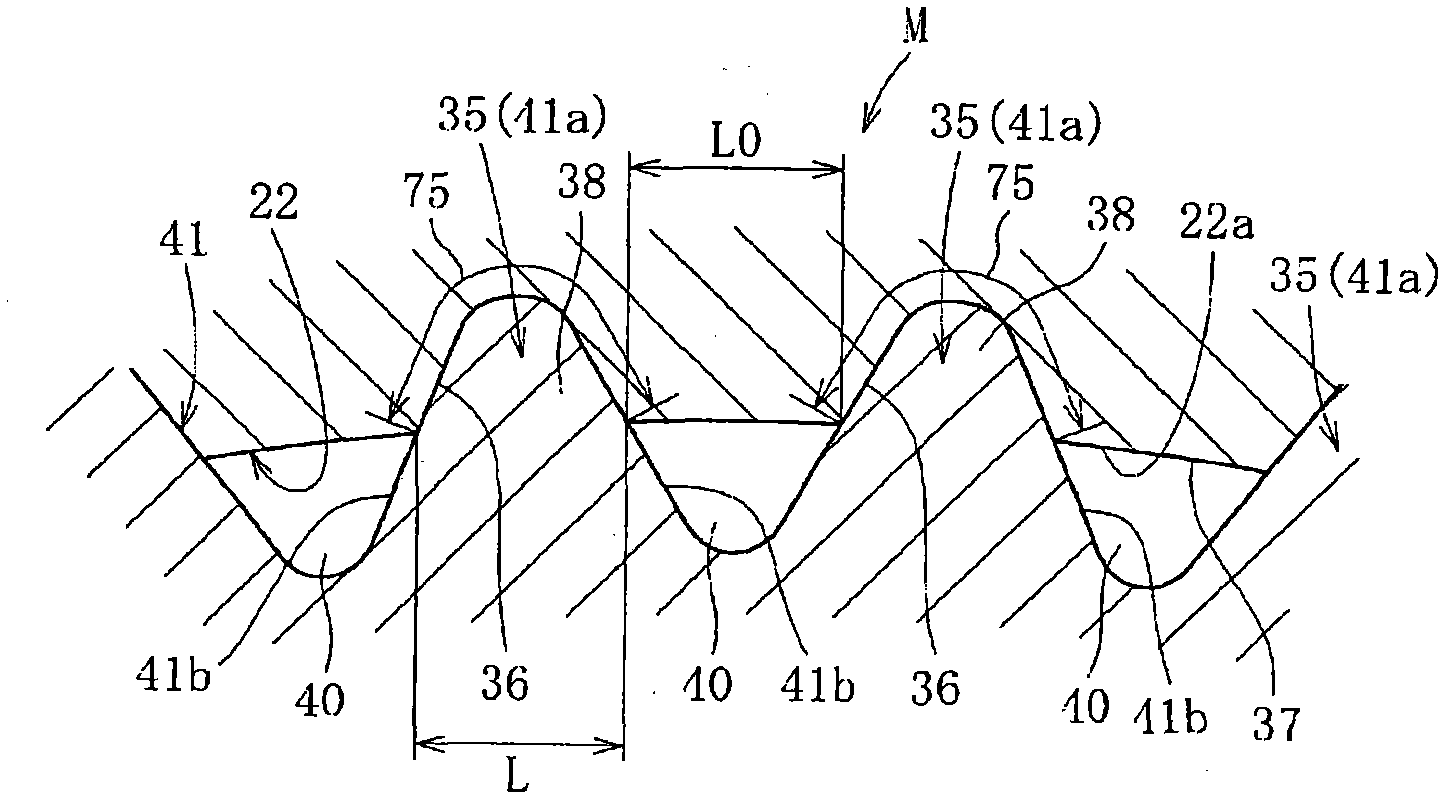
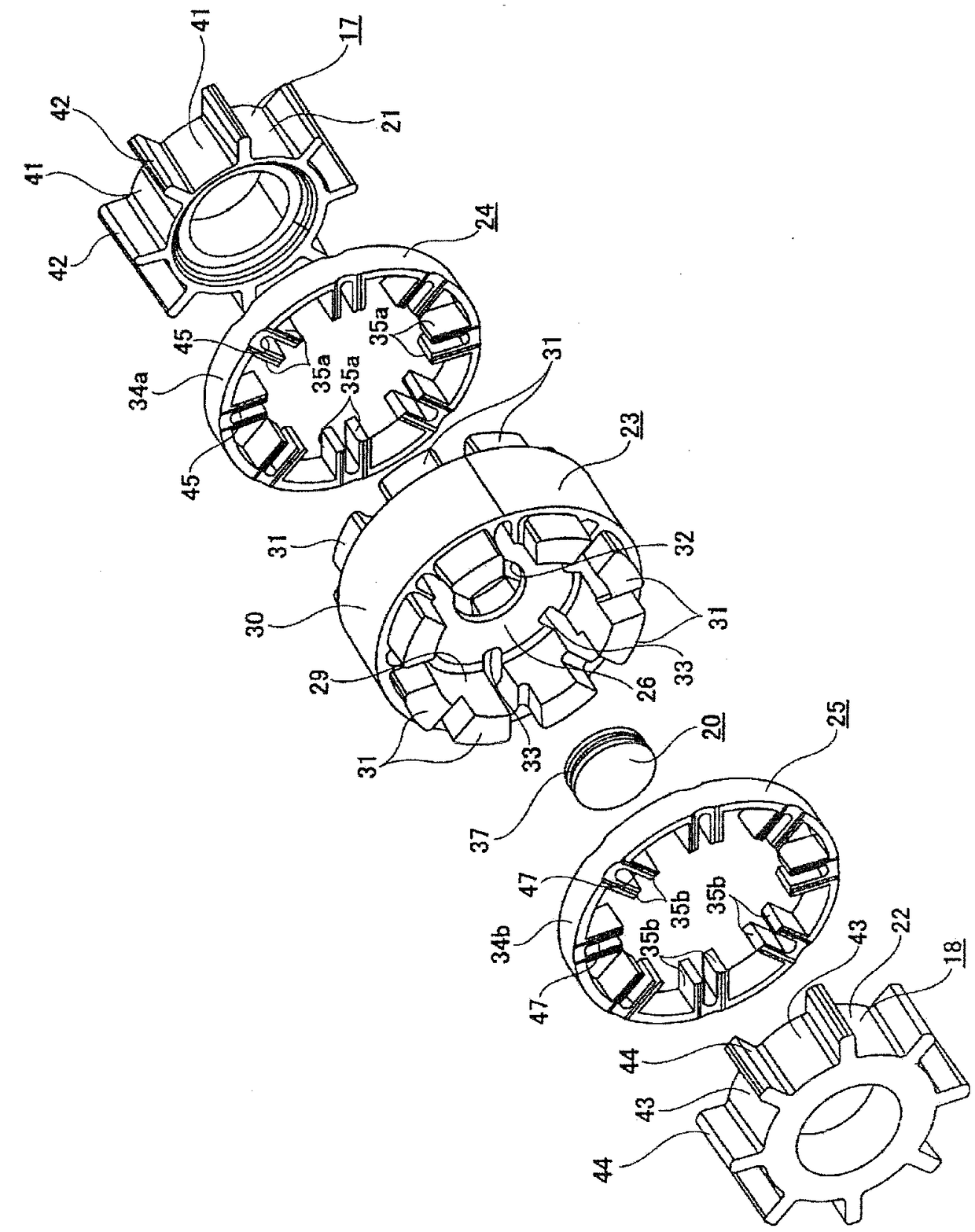
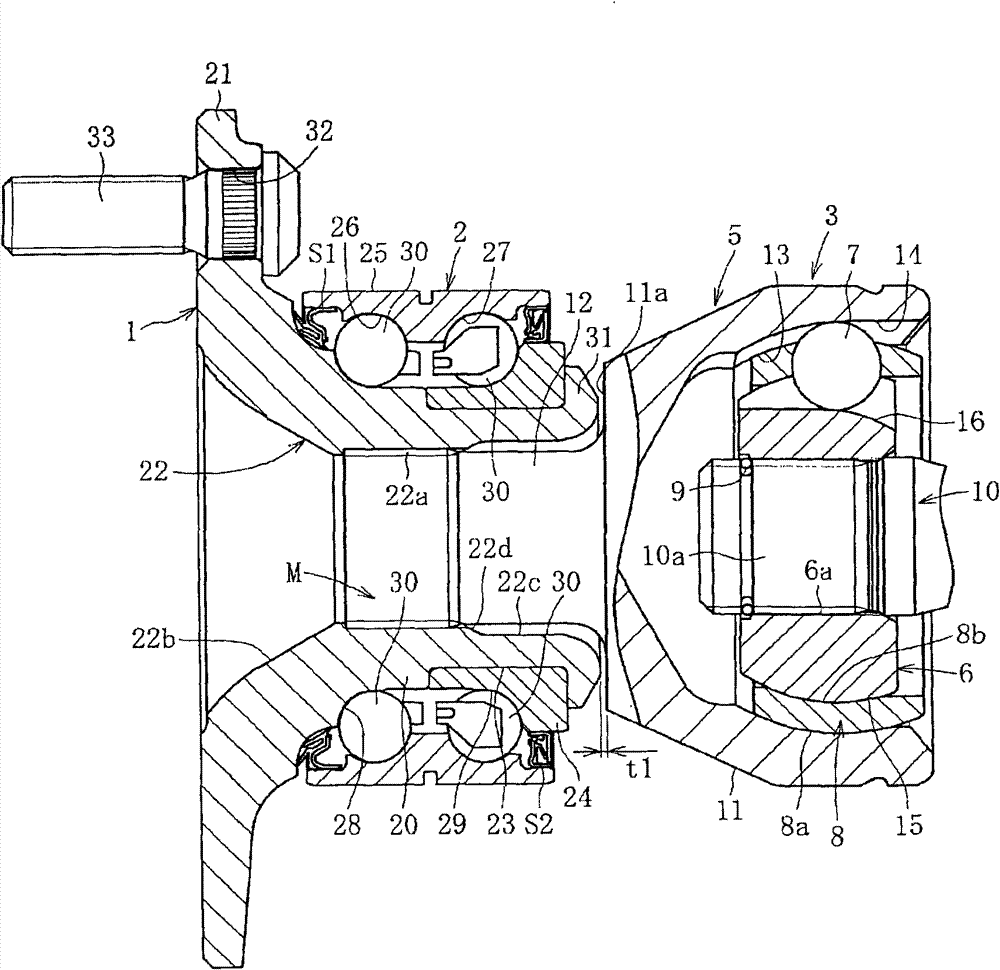
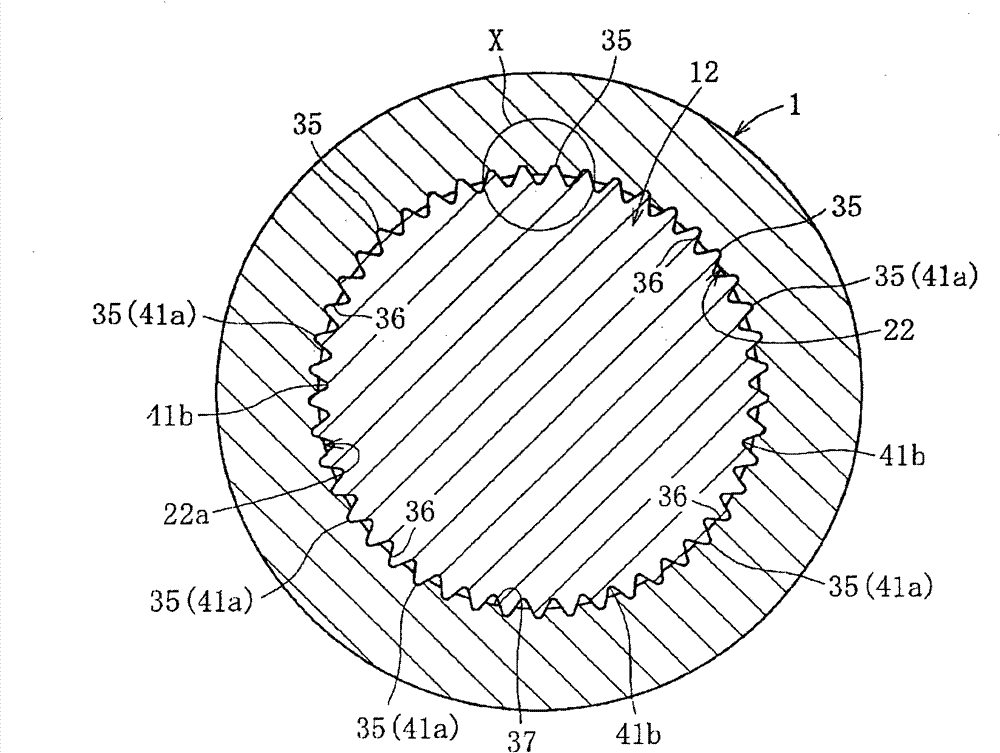
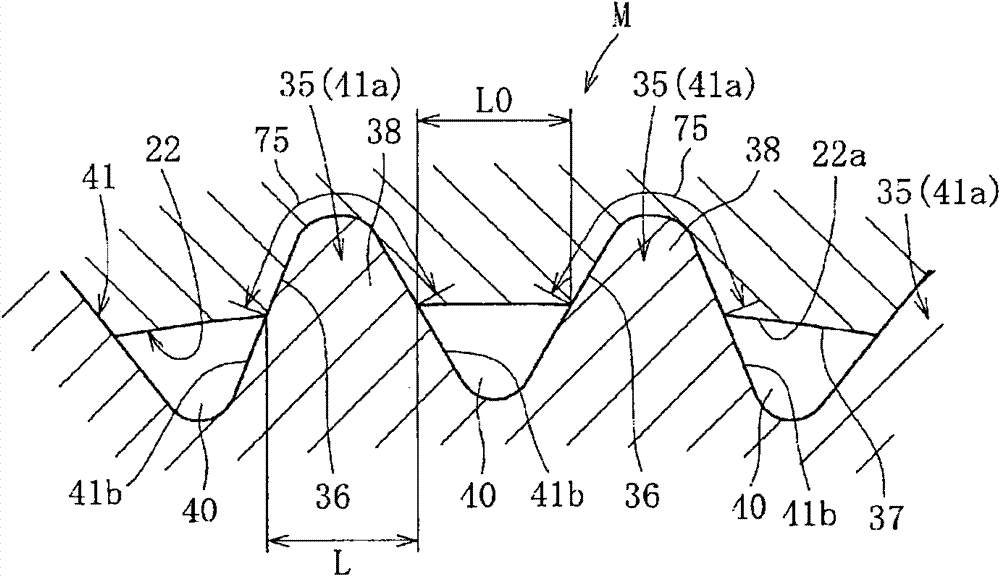
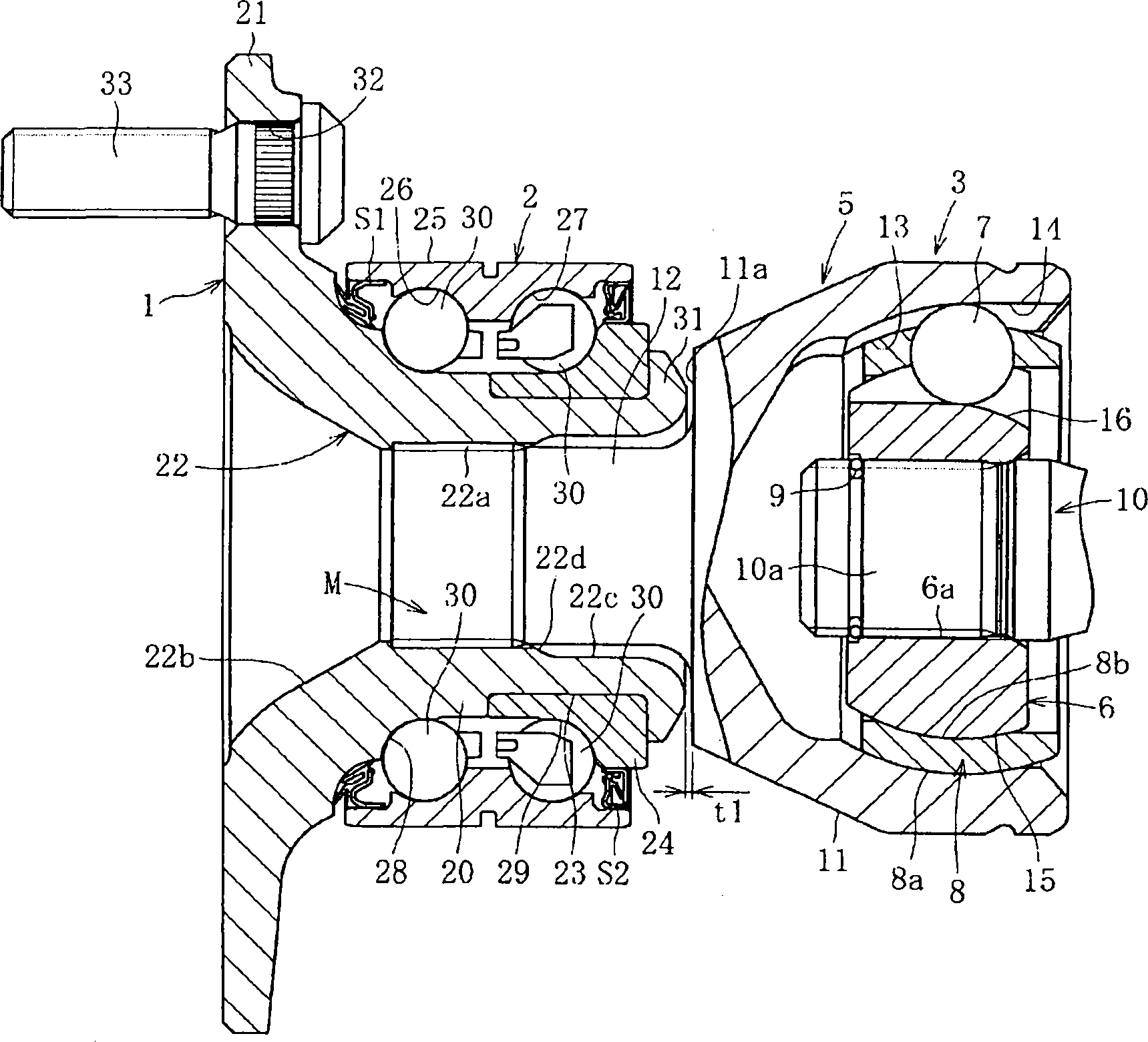
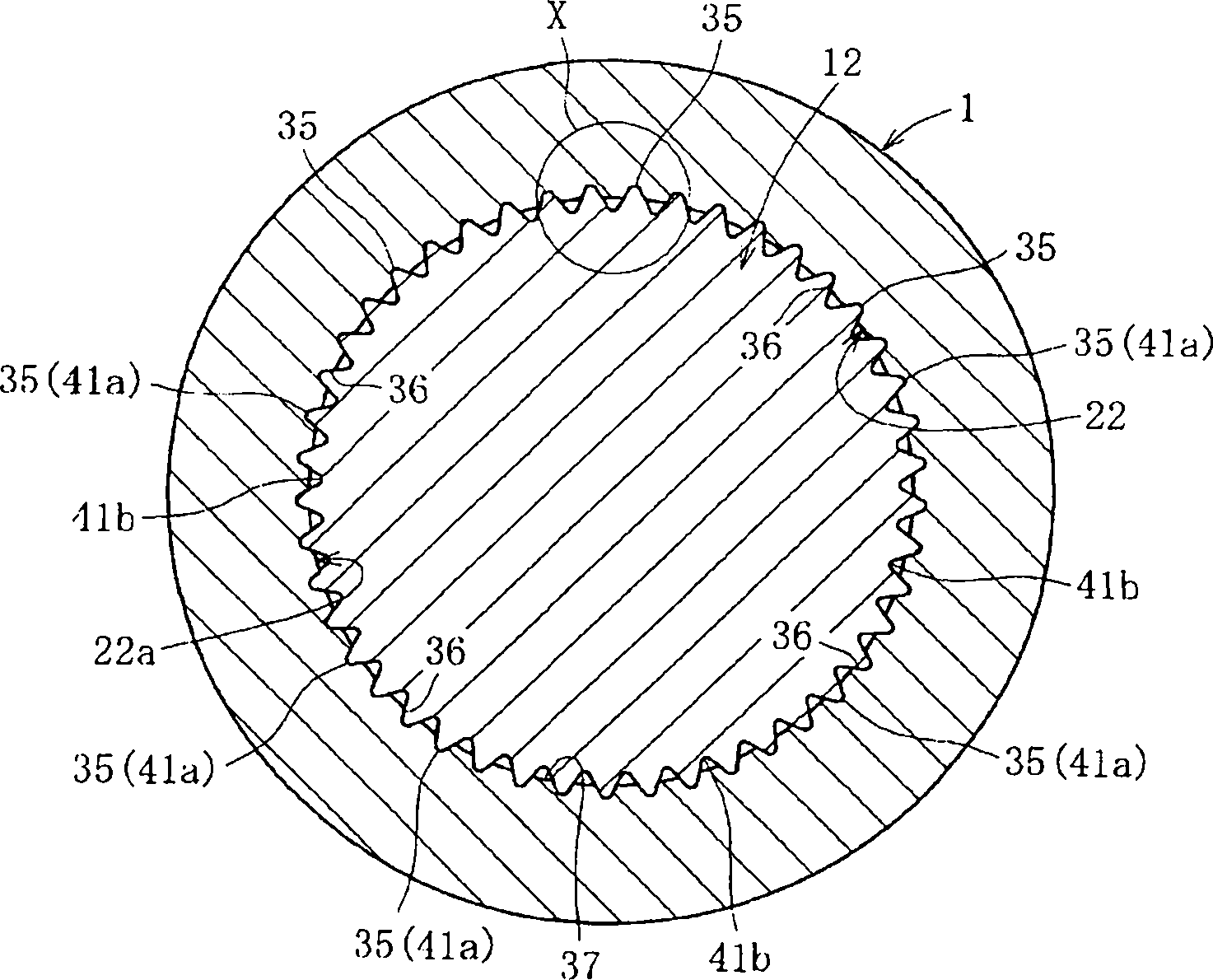
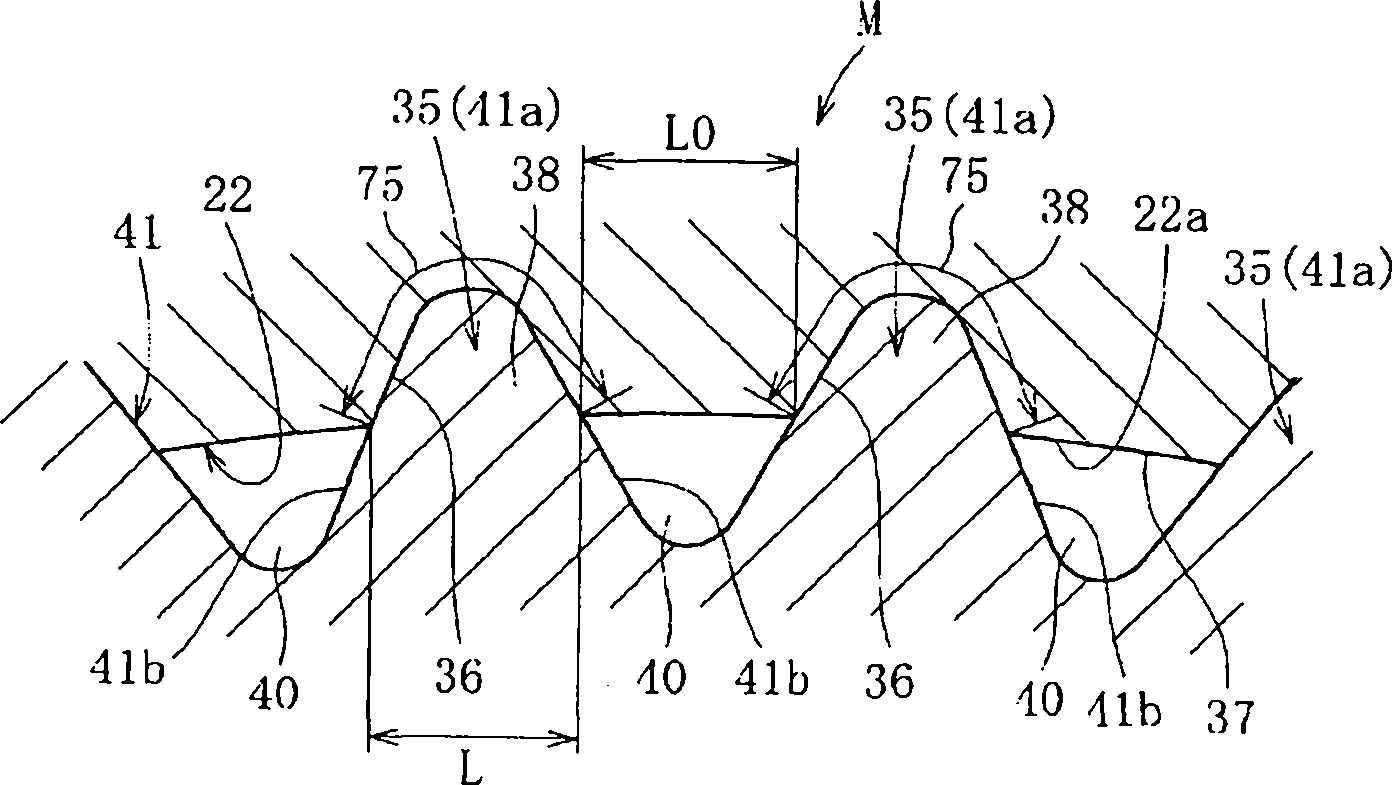
A bearing device for a wheel, in which circumferential play is suppressed, which facilitates connection between a hub ring and an outer coupling member, in which a reduction in NVH characteristics due to play at a joint between the hub ring and the constant velocity universal joint and by play between a bearing outer member and a knuckle is prevented, and which performs highly accurate transmission of rotational torque. The bearing device has a groove-ridge fitting structure (M) by which the hub ring (1) and a shaft section (12) of the outer coupling member of the constant velocity universal joint (3) are integrated together, and the shaft section (12) is fitted in a hole (22) of the hub ring (1). In the groove-ridge fitting structure (M), ridges (35) on the outer diameter surface of the shaft section (12) and grooves (36) in the inner diameter surface (37) of the hub ring (1) are fitted to each other in a fitting contact portion (38), and the ridges (35) and the grooves (36) are in intimate contact with each other in the entire fitting contact portion (38).
Owner:NTN CORP
Bearing device for wheel
InactiveCN102152711AStable deliveryHigh strengthYielding couplingRolling contact bearingsUniversal jointTorque transmission
Provided is a bearing device for a wheel that can realize prevention of a backlash in a circumferential direction and is excellent in workability of connection of a hub wheel and an outer joint member of a constant velocity universal joint. Further, provided is a bearing device for a wheel that can prevent deterioration in NVH characteristics, which is caused by the backlash occurring in a joint section between the hub wheel and the constant velocity universal joint or between an outer member and a knuckle, and can perform rotation torque transmission with high accuracy. The bearing device includes a recess-projection fitting structure (M) in which the hub wheel (1) and a shaft section (12), which is fitted in a hole (22) of the hub wheel (1) of the outer joint member of the constant velocity universal joint (3) are unitized together. In the recess-projection fitting structure (M), entire fitting regions among projections (35) on the outer surface of the shaft section (12) of the outer joint member and recesses (36), which fit on the projections, are brought into intimate contact with each other.
Owner:NTN CORP
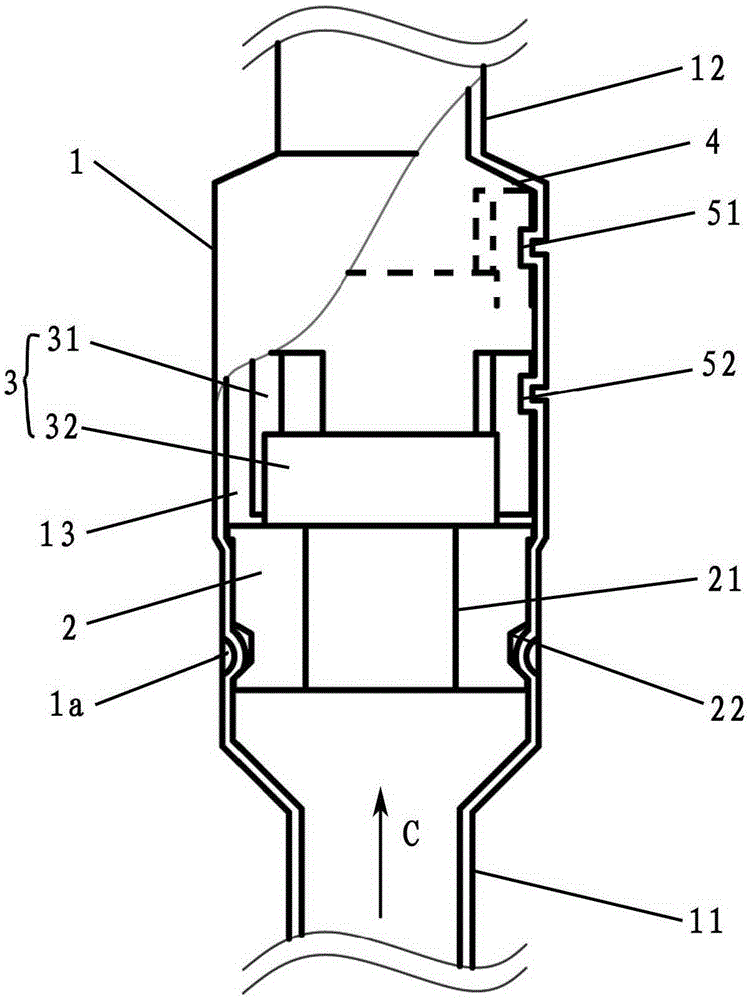
Evaporated fuel processing device
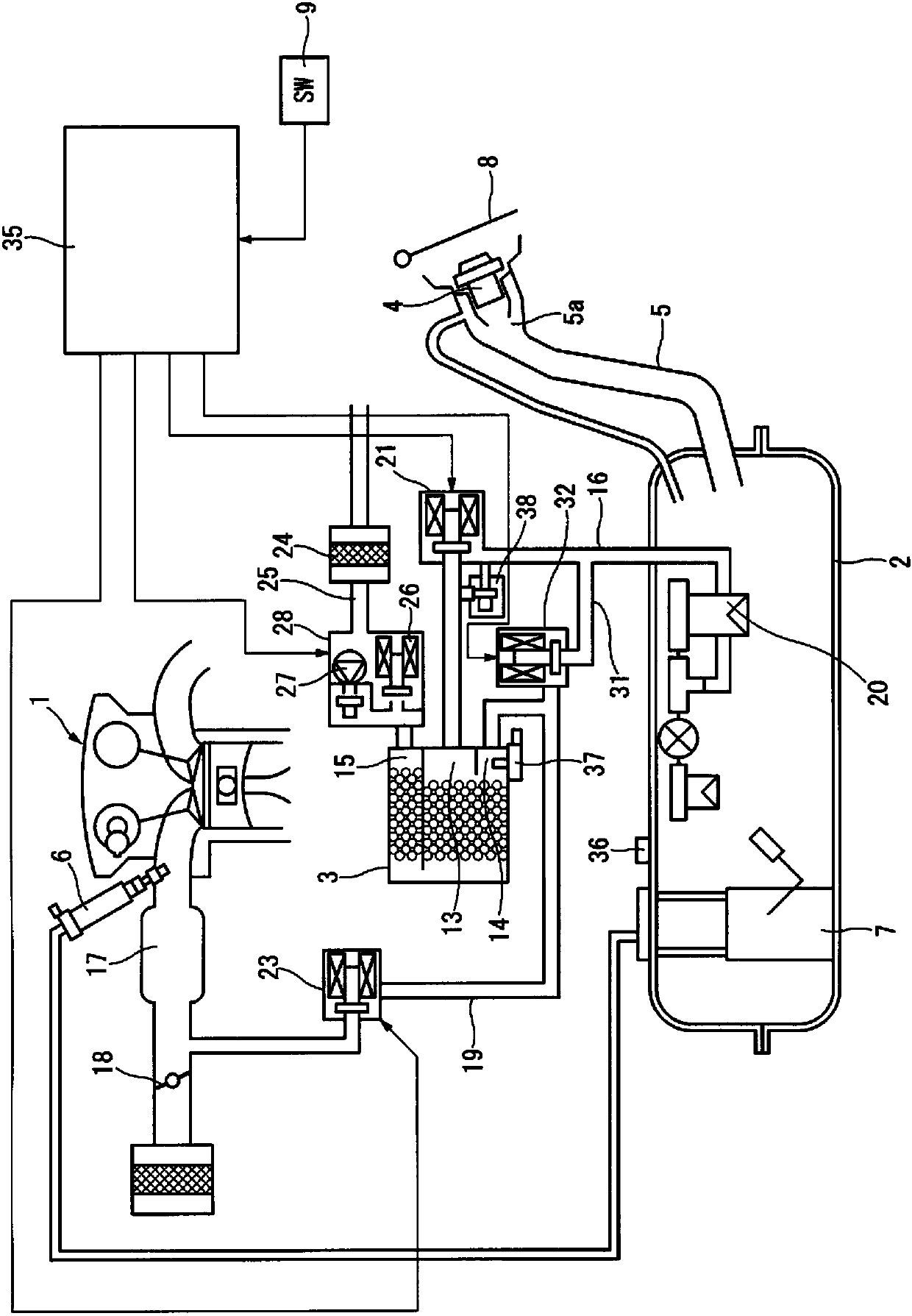
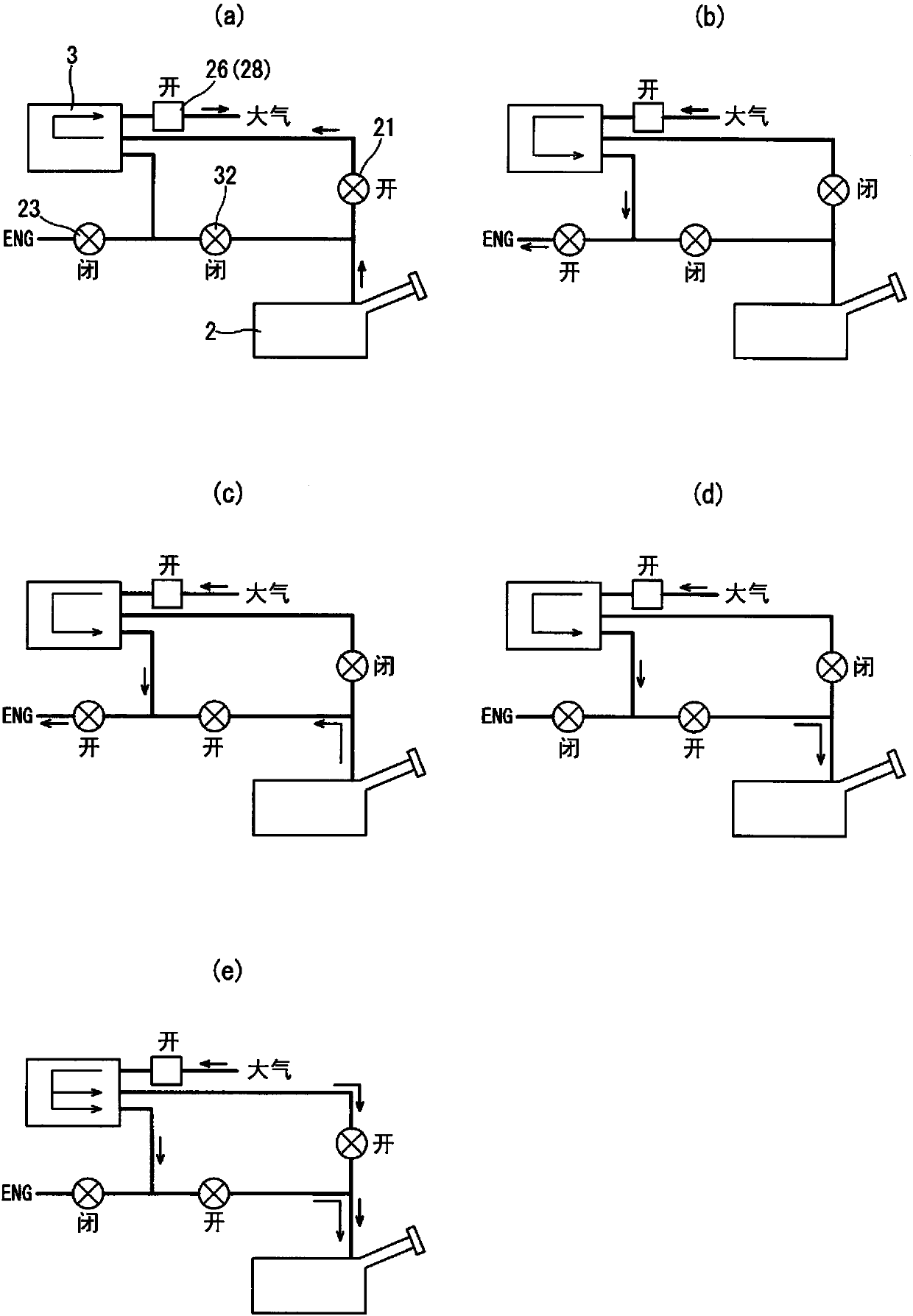
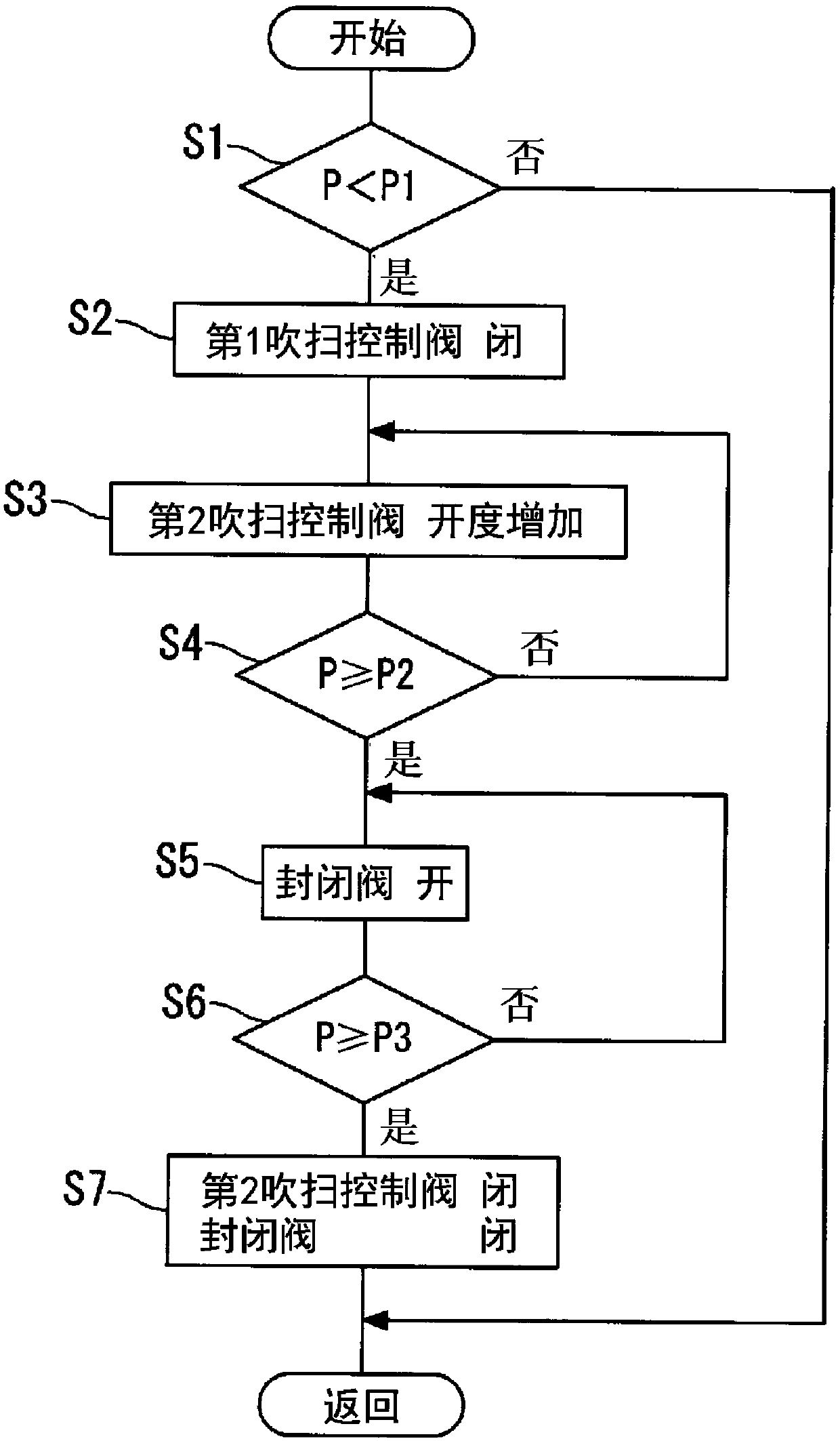
ActiveCN107735562AImport smoothSuppress abnormal noiseNon-fuel substance addition to fuelFuel injection apparatusFuel tankBlocked valves
The invention discloses an evaporated fuel processing device. This evaporated fuel processing device is provided with: an evaporated fuel passage (16) through which a fuel tank (2) and a canister (3)communicate with each other; a blocking valve (21) opening / closing the evaporated fuel passage (16); a purge passage (19) through which the canister (3) and an intake passage (17) of an internal combustion engine (1) communicate with each other; a first purge control valve (23) opening / closing the purge passage (19); a tank opening passage (31) through which an upstream side position from the first purge control valve (23) in the purge passage (19) and the fuel tank (2) communicate with each other; and a second purge control valve (32) opening / closing the tank opening passage (31). When a negative pressure is formed in the fuel tank (2), the second purge control valve (32) is opened, thereby introducing atmospheric pressure through the canister (3).
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Outdoor unit for air conditioner
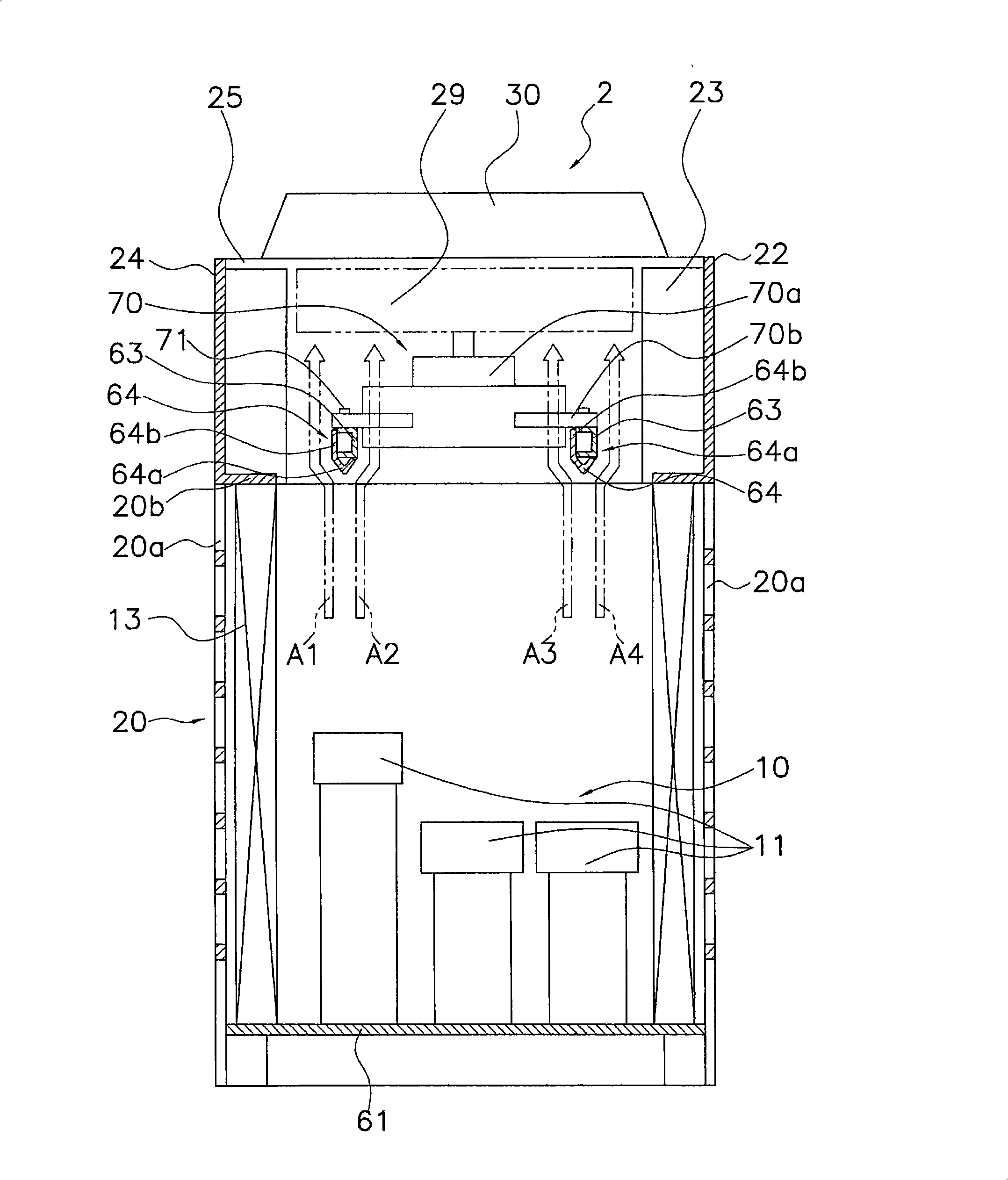
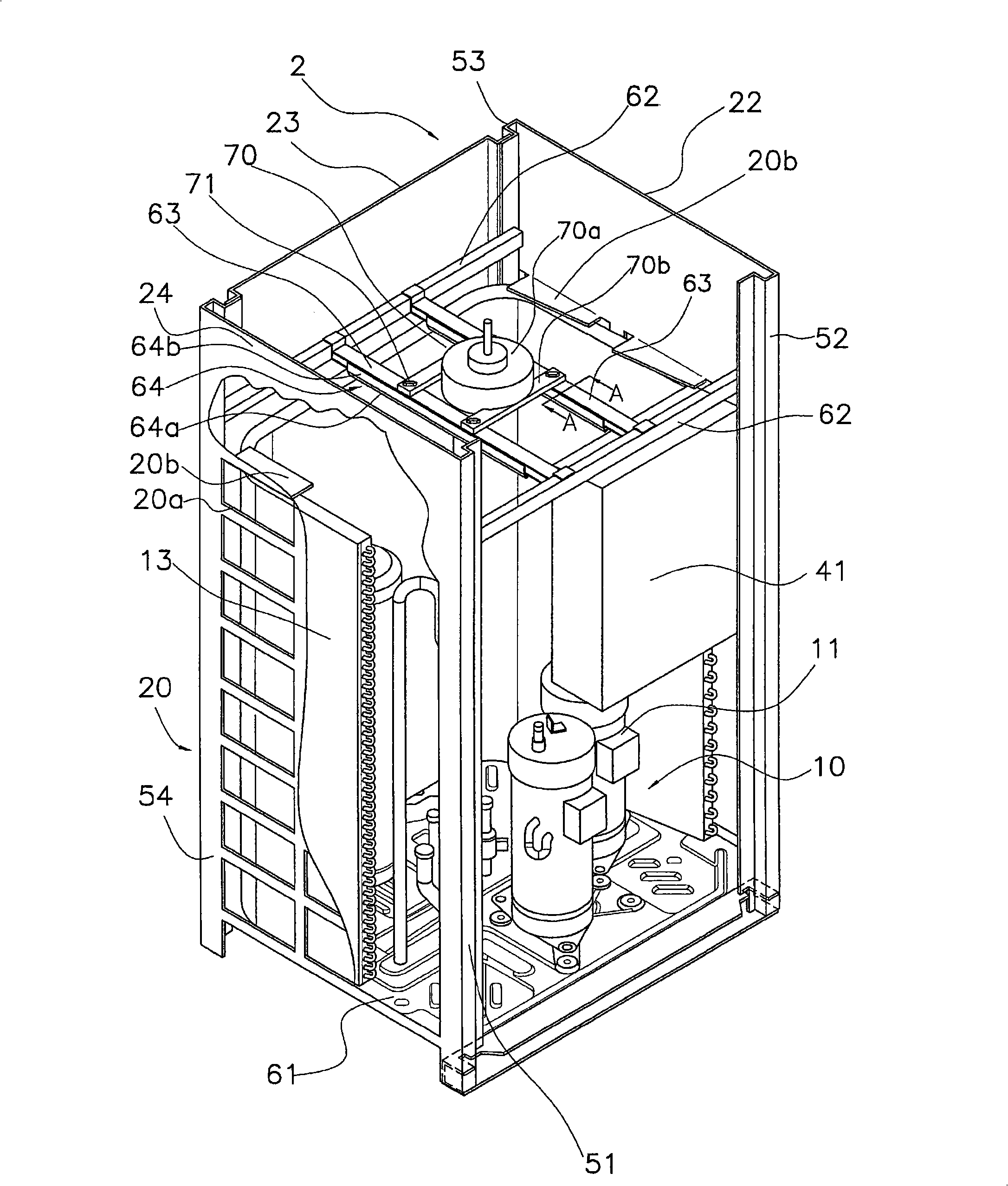
InactiveCN101292119AReduce resistanceReduce wind shearLighting and heating apparatusAir conditioning systemsEngineeringRefrigerant
An outdoor unit of an air conditioner in which a wind whistling sound and a vibration noise due to airflow are reduced is provided. The outdoor unit includes an outdoor heat exchanger (13), a fan (29), a motor (70) for driving the fan (29), and a motor support table (63) for supporting the motor (70). The fan (29) blows air to the outdoor heat exchanger (13) and promotes heat exchange between refrigerant and air. The motor support table (63) is provided with a rectifying member (64), and the rectifying member (64) deflects air flowing toward the motor support table (63) in a predetermined direction.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
Apparatus for controlling internal combustion engine provided with turbocharger
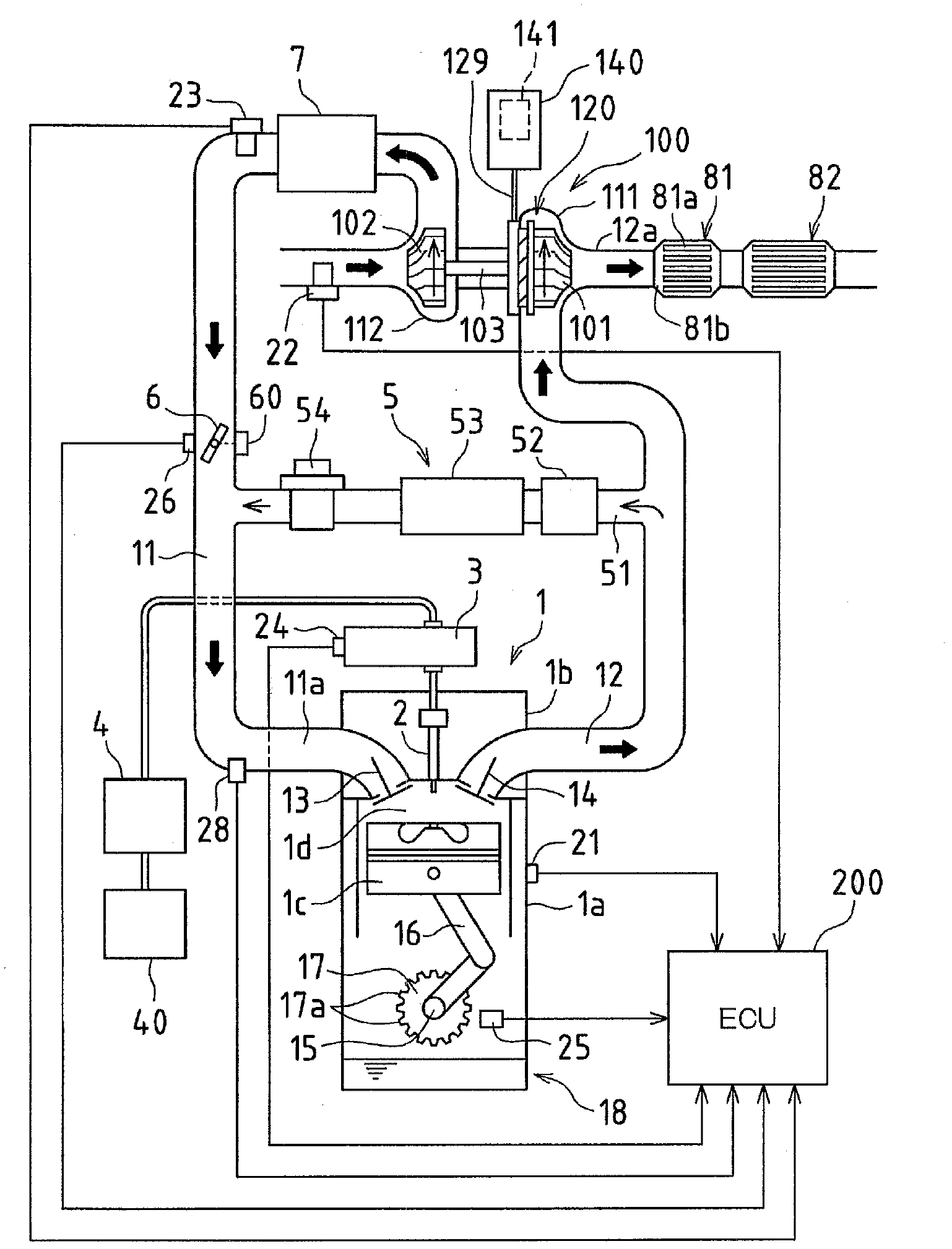
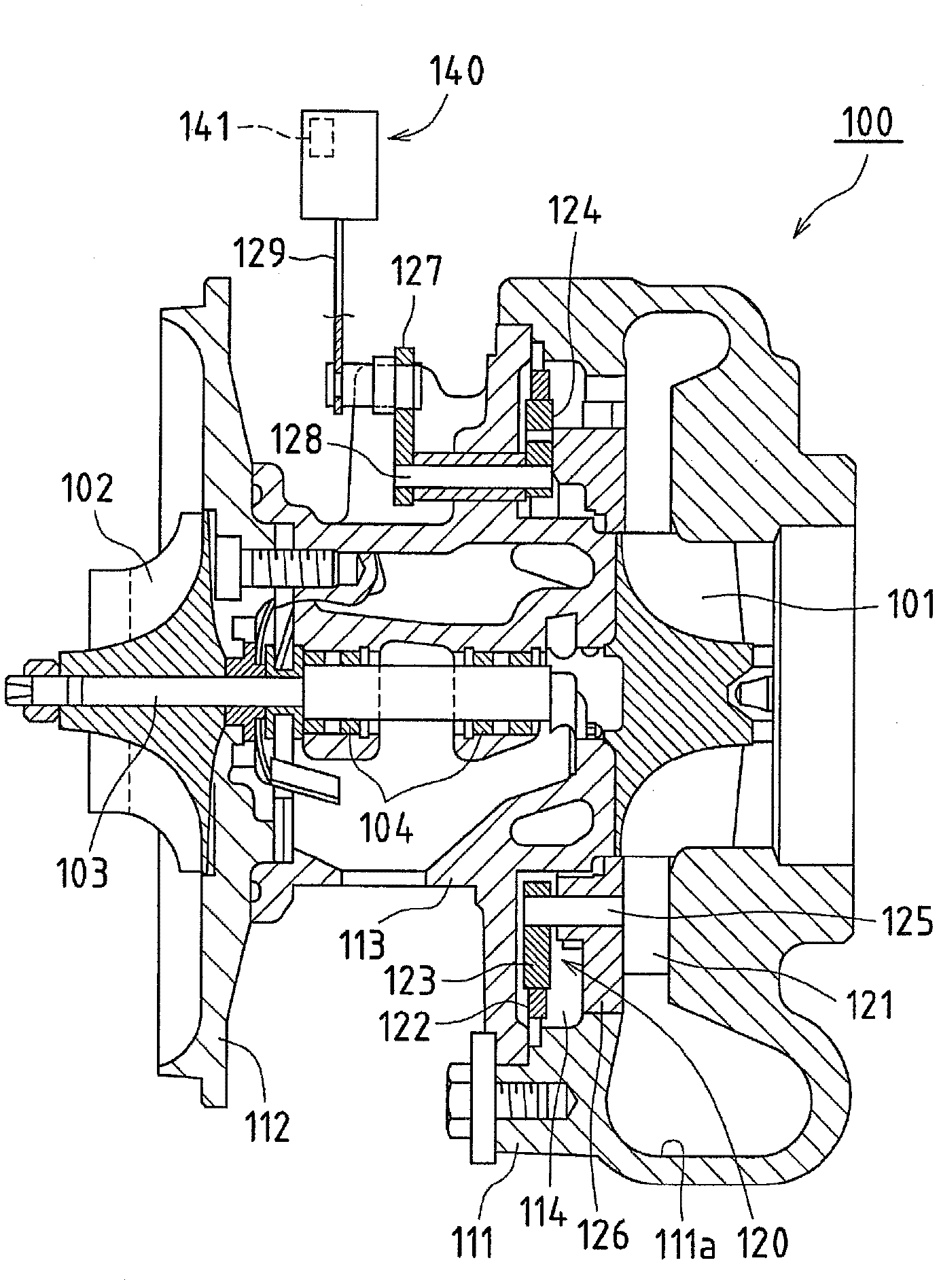
InactiveCN103221656ASuppress abnormal noiseElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelExhaust gasForced induction
The present invention enables an exhaust gas to quickly pass through a spatial resonance region in an exhaust gas passage space ranging from a turbine housing to a catalyst, by increasing the flow velocity (VN passing flow velocity) of the exhaust gas passing through a nozzle vane when the exhaust gas reaches the spatial resonance region at the time of acceleration in an internal combustion engine provided with a variable nozzle vane turbocharger. When the exhaust gas reaches the spatial resonance region at the time of deceleration, the VN passing flow velocity is decreased to enable the exhaust gas to quickly pass through the spatial resonance region. By this control, it is possible to reduce the time during which the frequency of pressure pulsation generated at the rear end of the nozzle vane is amplified in the spatial resonance region. It is also possible to suppress the generation of abnormal noise caused by the pressure pulsation.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
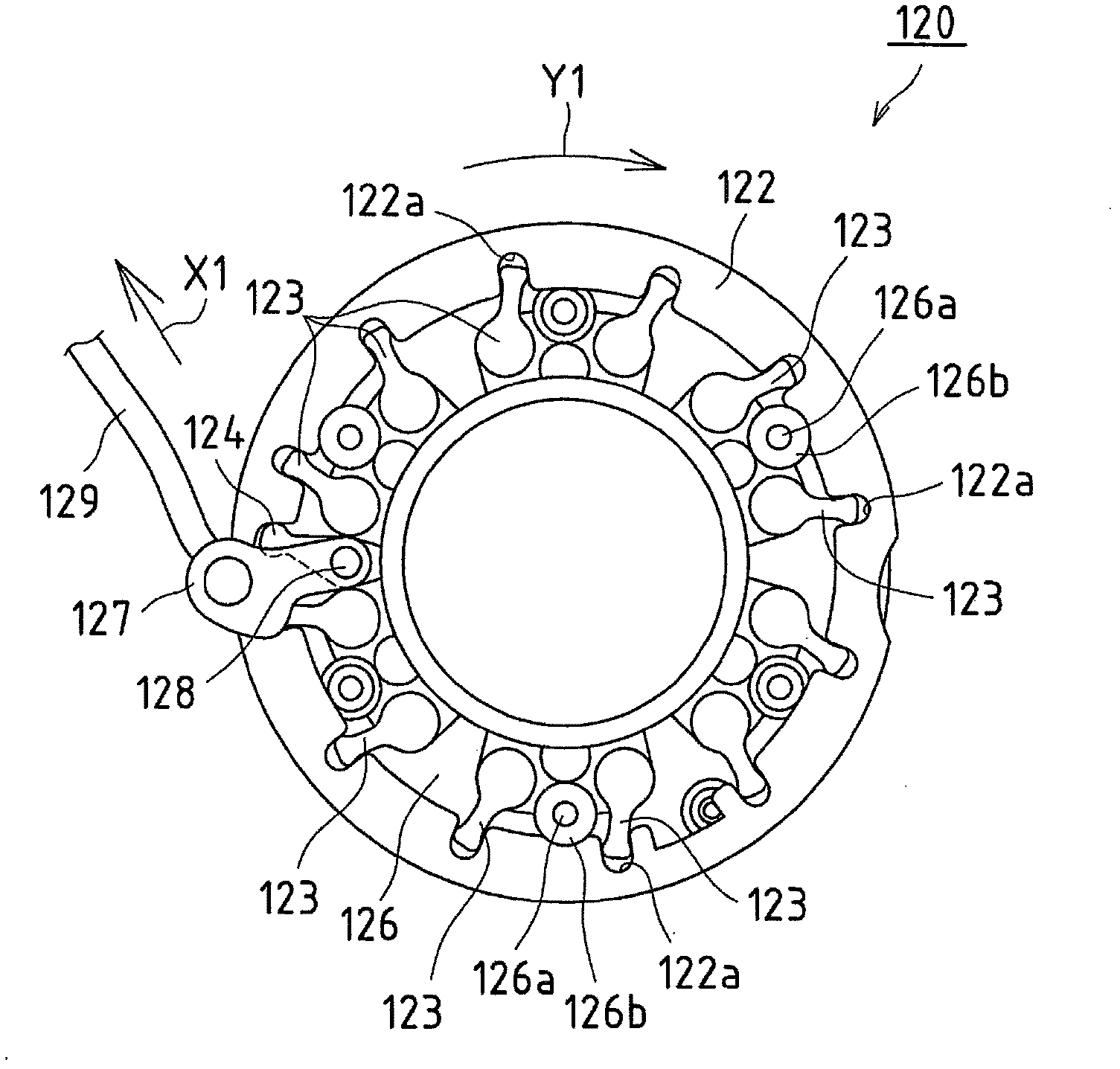
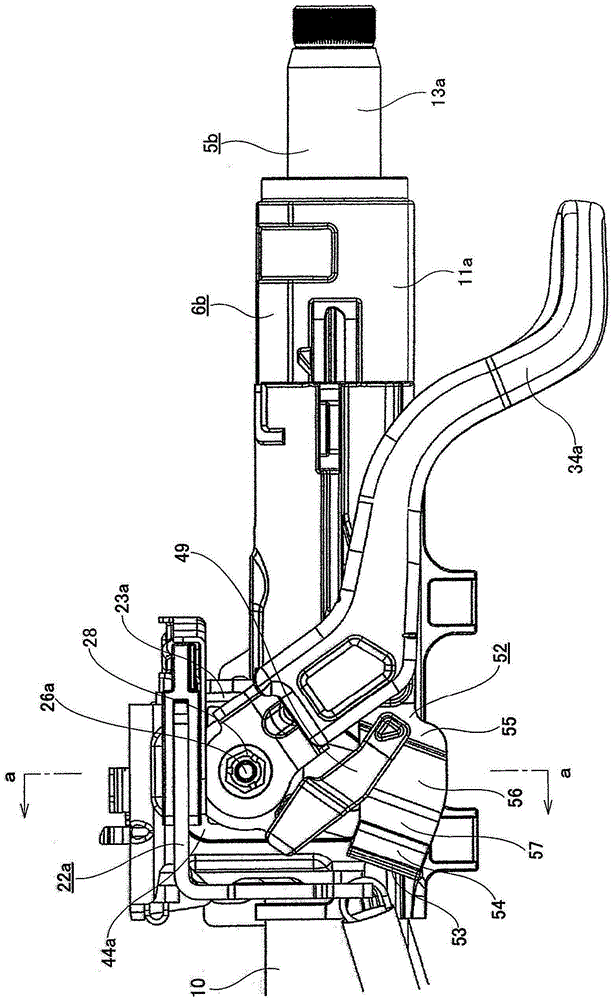
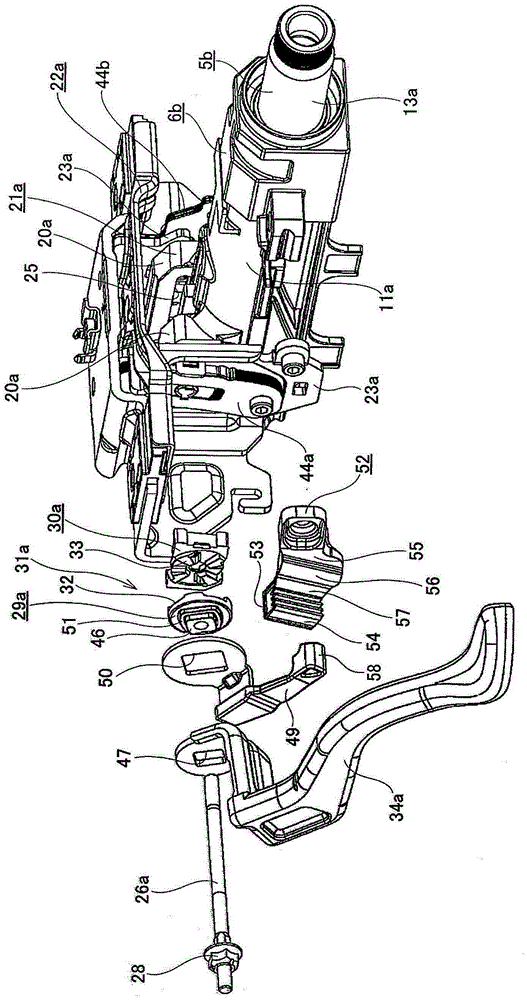
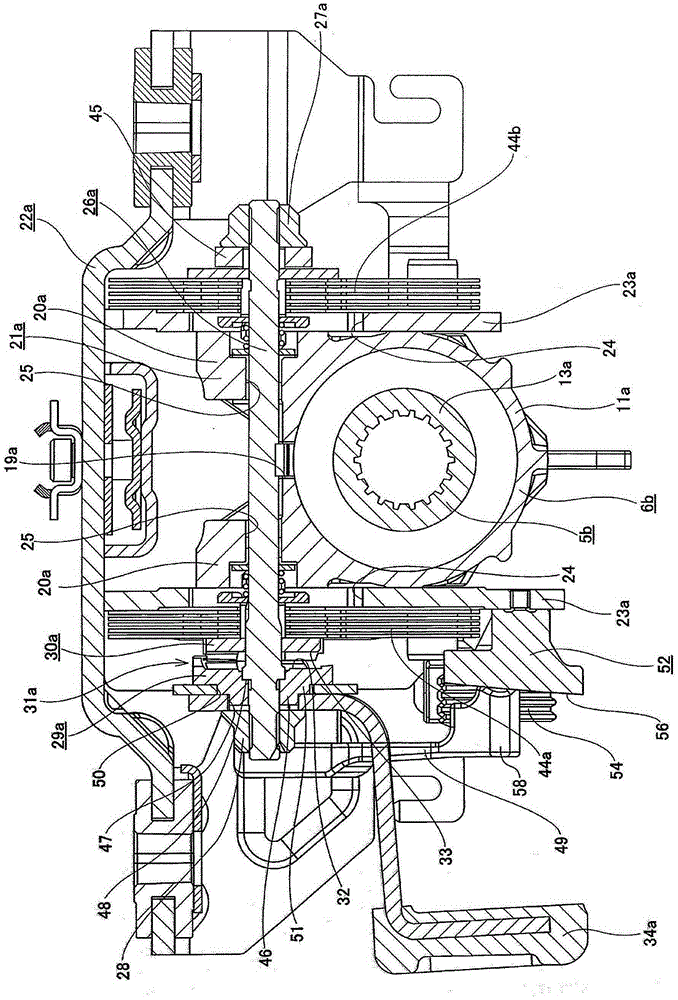
Position adjusting-type steering device
In the present invention, fixed to a base end part of an adjustment lever (34a) is a sub-arm (49) that rotates with the adjustment lever (34a). A reception-side member (52) is fixed to the outer surface of one support plate part (23a) of a support bracket (22a), and a buffer member (54) made of an elastic material is fixed to the reception-side member (52). In a case where the adjustment lever (34a) is rotated in a specific direction, prior to the step parts of both driving side and driven side cam surfaces (32, 33) making contact with each other, the tip end part of the sub-arm (49) makes contact with the buffer member (54). Due to this configuration, in a case where the adjustment lever (34a) is caused to rotate in a specific direction (the direction in which the axial direction dimensions of a cam device (31a) are reduced) so as to adjust the position of a steering wheel, the generation of unpleasant noise that accompanies the coming into contact of the step parts present on both the driving side and driven side cam surfaces (32, 33) can be prevented.
Owner:NSK LTD
Check valve
ActiveCN103383012AGuaranteed lifePrevent rotationCheck valvesValve members for absorbing fluid energyEngineeringCheck valve
The invention provides a check valve which comprises a valve seat component, a valve main body of a limiting part, a circular plate part, a plurality of guide parts protruding from the periphery of the circular plate part and a valve body capable of moving between the valve seat component and the limiting part and losing the valve due to dead weight, wherein fluid passages are formed in the periphery of the circular plate part by gaps between the adjacent guide parts; on the moving range part of the valve main body corresponding to the valve body, convex parts protruding from the inner side of the valve main body are arranged; the condition that the valve body rotates due to the rotation component of the fluid cannot happen in the check valve.
Owner:SAGINOMIYA SEISAKUSHO INC
check valve
ActiveCN103383012BGuaranteed lifePrevent rotationCheck valvesValve members for absorbing fluid energyEngineeringCheck valve
Owner:SAGINOMIYA SEISAKUSHO INC
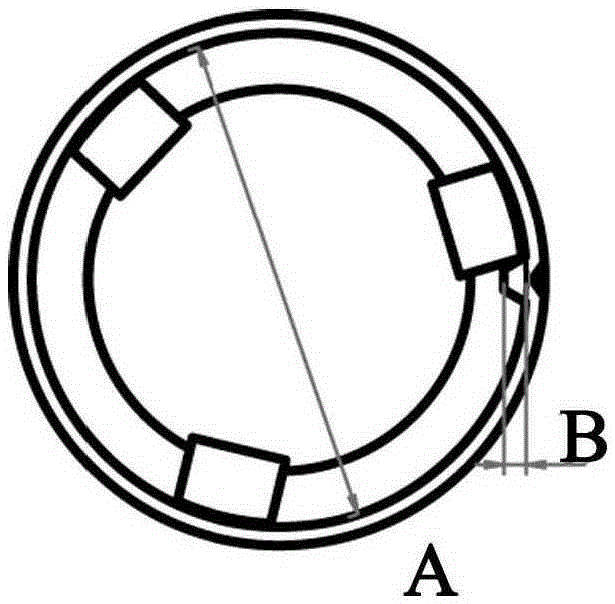
Centrifugal type clutch and its assembly method
ActiveCN1737396ASuppression of radial displacementAvoid unusual noiseAutomatic clutchesVibration controlEngineering
The present invention provides a centrifugal clutch capable of preveting vibration of a cluth housing and effectively preventing ccurrence of abnormal sound. This centrifugal clutch is composed of the clutch housing 12 composed of a circular cylindrical part 12a whose inner face becomes a slide-contact face and a bottom plate part 12b covering one end part of the circular cylindrical part, a rotary shaft which has the same axis as the circular cylindrical part of the clutch housing and to which rotation force is transmitted by the clutch housing, a centrifugal shoe for connecting with the clutch housing 12 or disconnecting from it by rotating around the rotary shaft and coming into contact with or leaving the slide-contact face, and a vibration control cover 17 put on an outer side of the circular cylindrical part. The clutch housing 12 and the vibration control cover 17 have contact parts 30, 40 coming into contact mutually, a non-contact part 50 not in contact, and positioning marks 14, 22 for positioning the clutch housing 12 and the vibration control cover 17 at predetermined relative positions for preventing occurrence of abnormal sound.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Slide device for vehicle
InactiveCN102105326AEliminate loosenessSmooth circulationLinear bearingsMovable seatsMechanical engineering
A slide device for a vehicle, wherein the slide device has a long stroke for adjustment in which a second rail can be adjusted so as to be smoothly movable without play in the front-rear direction along a first rail. In the slide device for a vehicle, rolling elements (42) are annularly arranged in a mounting section (43) mounted on the second rail (20). When the second rail (20) slides on the first rail (10), the rolling elements (42) are always in contact with an operation surface (46) of the first rail (10) and with an operation surface (47) of the mounting section (43), and as a result, play in the top-bottom and left-right directions of the second rail (20) relative to the first rail (10) is eliminated. Also, because the rolling elements (42) roll and circulate in the mounting section (43), the second rail (20) smoothly moves in the front-rear direction along the first rail (10).
Owner:AISIN SEIKI KK
Electrically powered suspension system
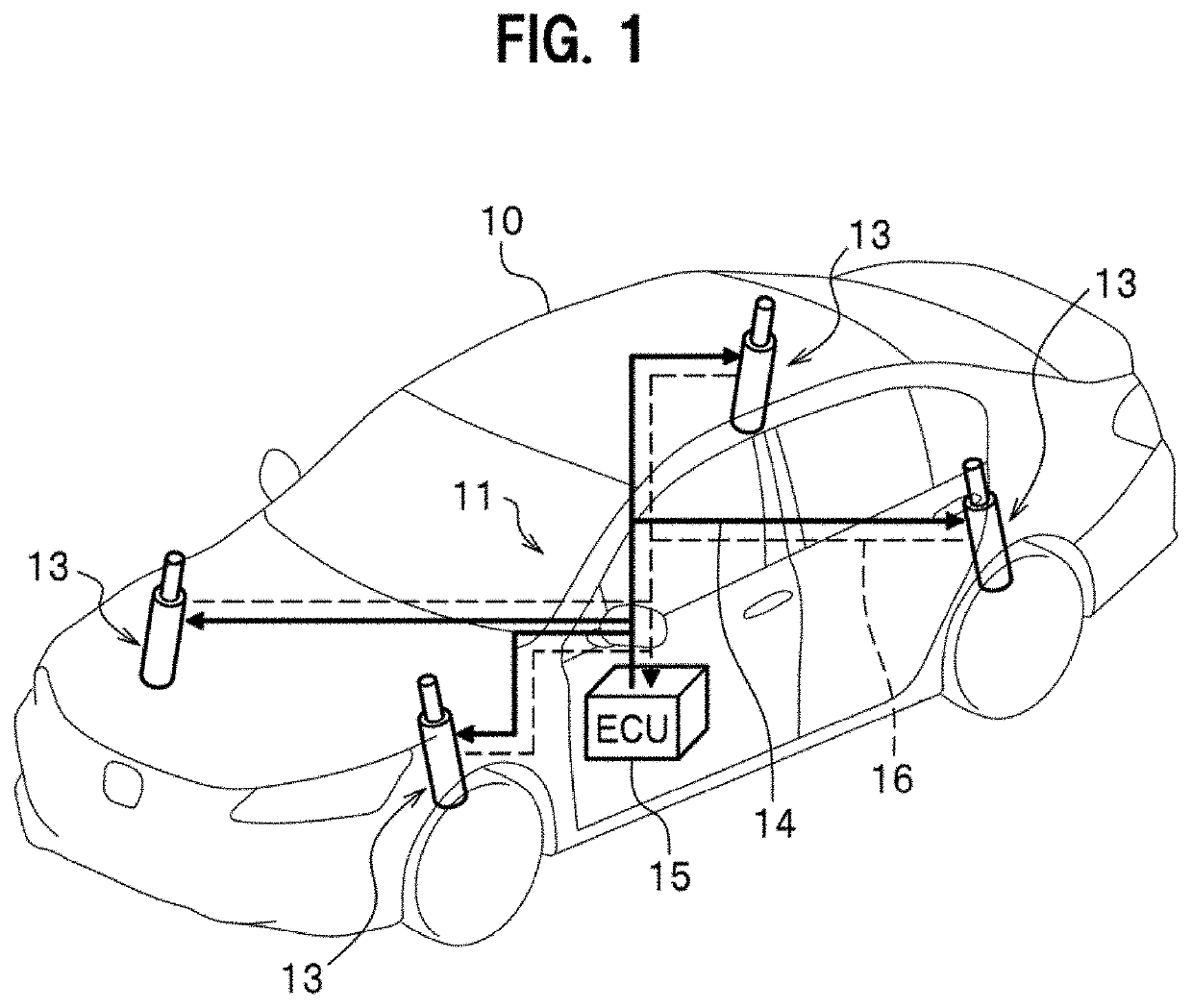
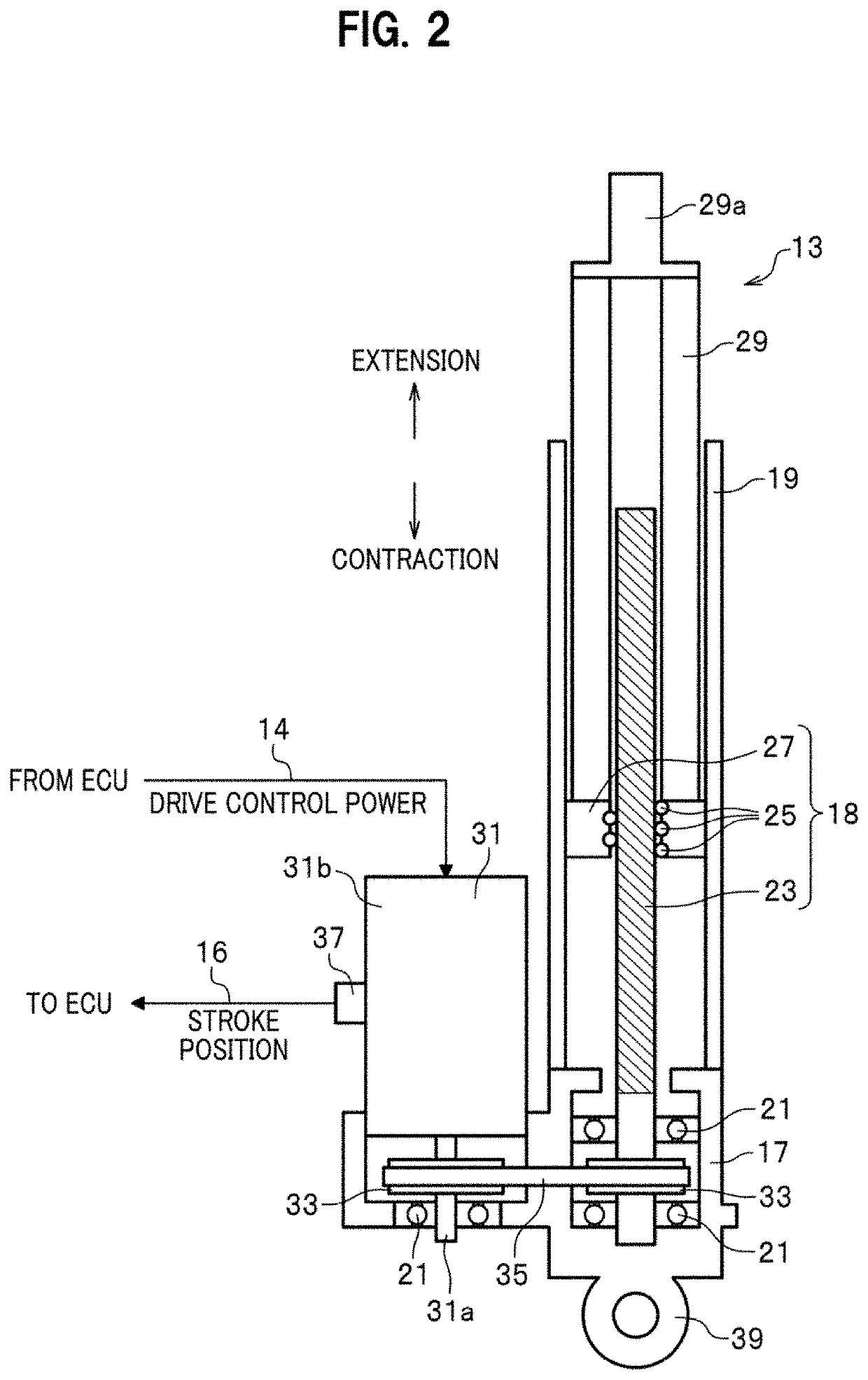
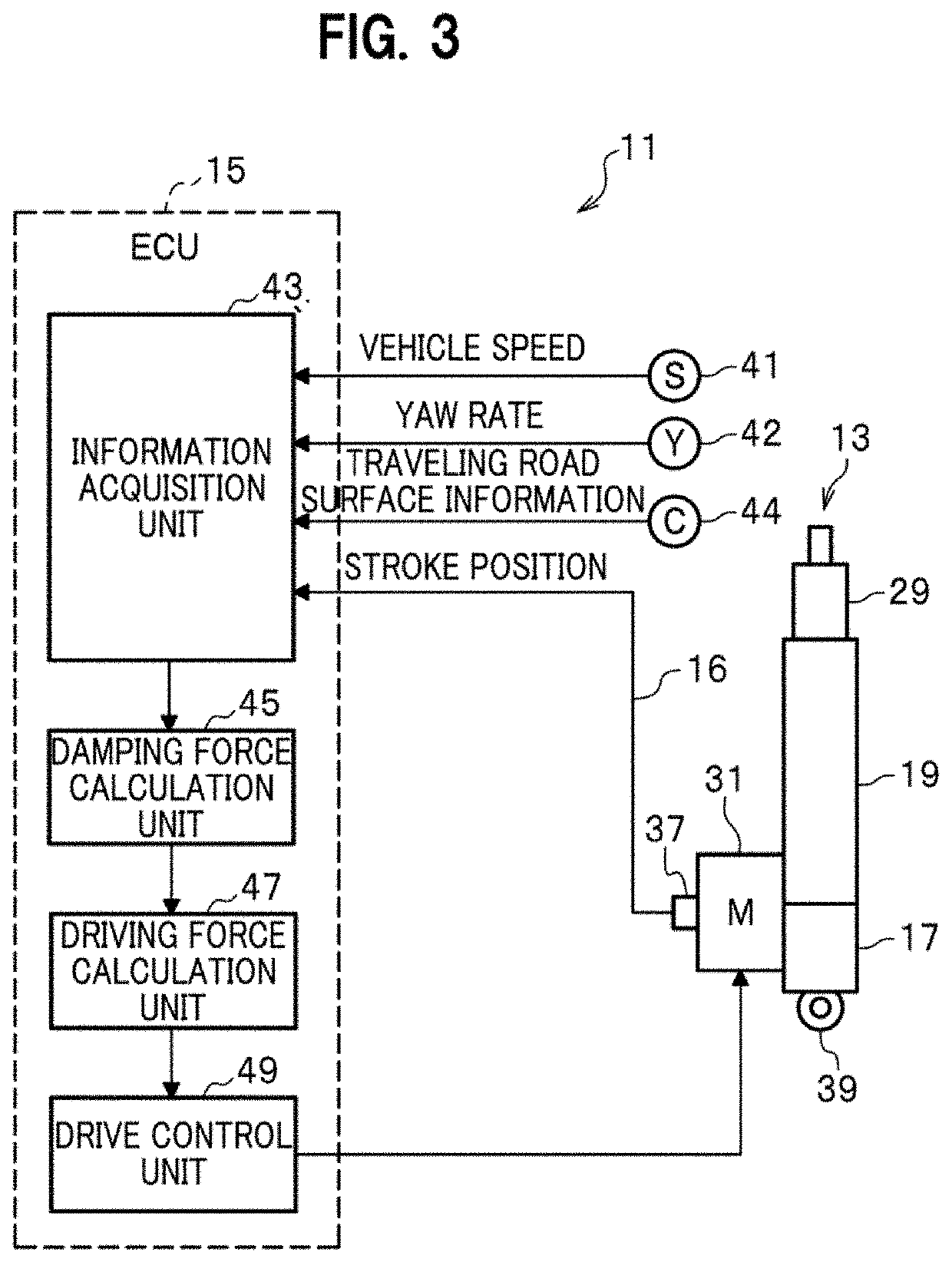
ActiveUS20200331316A1Suppress abnormal noiseResilient suspensionsVehicle springsControl cellEngineering
An electrically powered suspension system includes: an electromagnetic actuator; an information acquisition unit configured to acquire time-series information related to stroke position of the electromagnetic actuator, information on stroke velocity, and an amount of change in stroke of the electromagnetic actuator and information on a stroke direction based on the time-series information; a damping force calculation unit configured to calculate target damping force based on the information on the stroke velocity; and a drive control unit configured to control driving of the electromagnetic actuator using target driving force obtained based on the target damping force. The damping force calculation unit calculates equivalent friction compensation force based on the amount of change in the stroke and the information on the stroke direction, and corrects the target damping force based on the calculated equivalent friction compensation force. The equivalent friction compensation force has elastic force component and dynamic friction force component.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Drive apparatus, drive method, and optical device
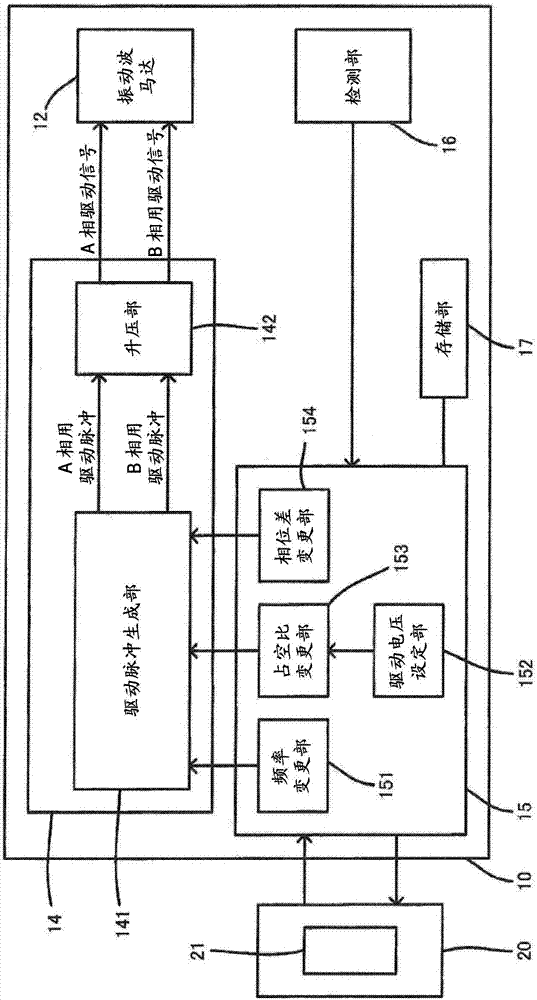
ActiveCN104272159ASuppress abnormal noiseReduce power consumptionTelevision system detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesDuty cycleControl theory
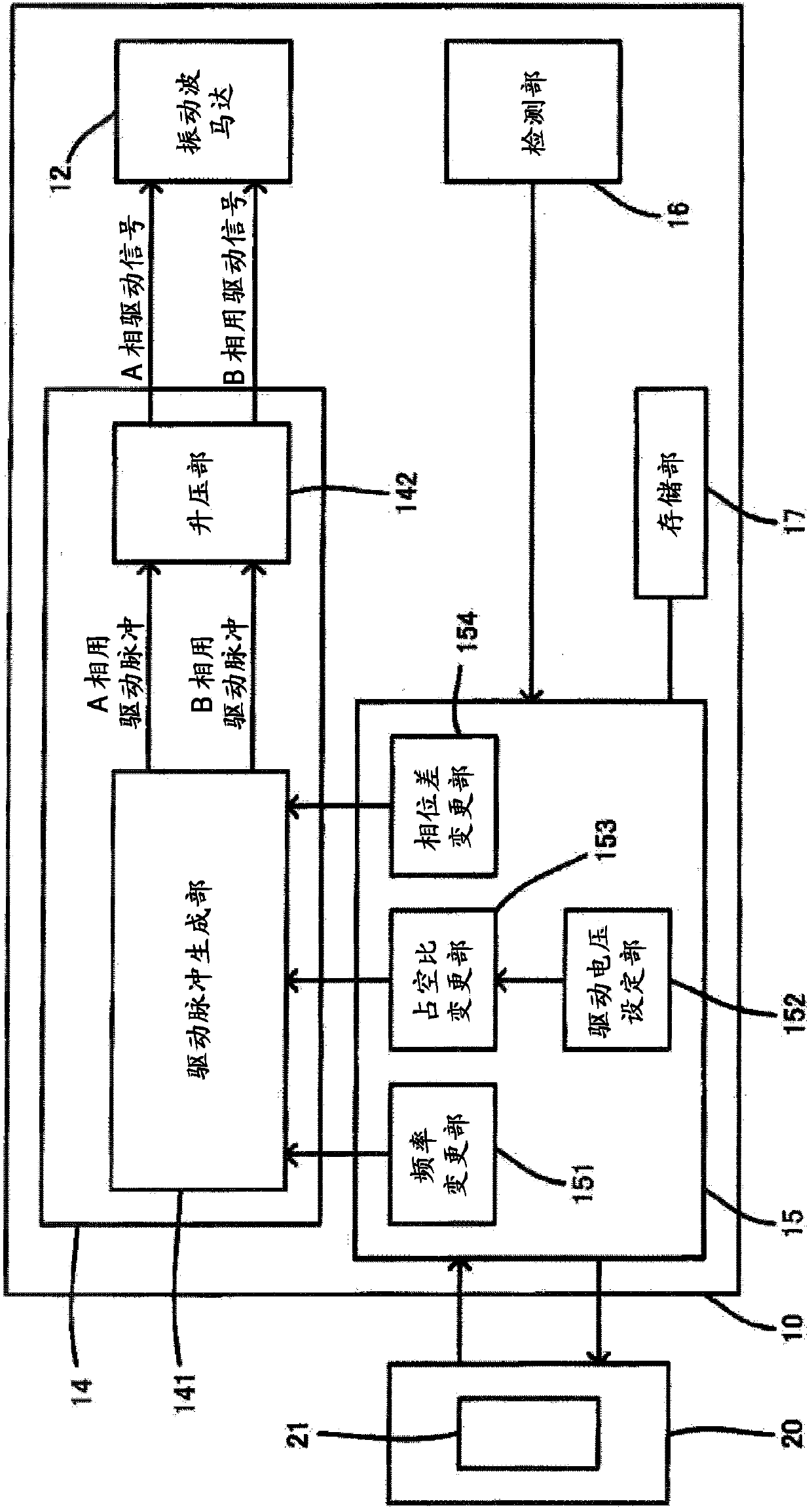
Noise produced during phase-difference changes is minimized without decreasing the responsiveness of a vibration-wave motor. A lens-side MCU (15) for a lens barrel (10) controls a drive apparatus (14) that applies a drive voltage to the vibration-wave motor (12) by outputting an A-phase drive signal and a B-phase drive signal thereto. The lens-side MCU (15) uses, for example, a drive-voltage setting unit (152) and a duty-cycle change unit (153) to change the drive voltage. Also, the lens-side MCU (15) is provided with a phase-difference change unit (154) that changes the phase difference between the A-phase drive signal and the B-phase drive signal. When driving the vibration-wave motor (12), the lens-side MCU (15) changes the drive voltage to V reg , and when the phase-difference change unit (154) is changing the aforementioned phase difference, the drive voltage is changed to V 1 , V 1 being greater than zero and less than V reg .
Owner:NIKON CORP
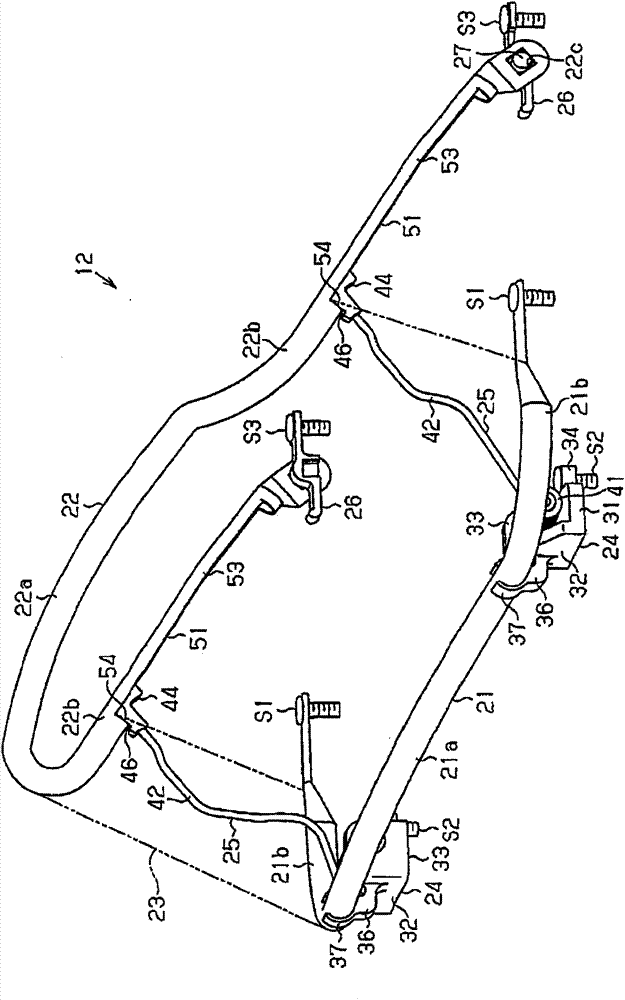
Deflector apparatus for vehicle
A deflector apparatus for a vehicle (12) includes a fixed frame (21), a movable frame (22) positioned at an upper side of the fixed frame and being rotatable between a raised position and a retracted position, a mesh member (23) connected to the fixed frame and the movable frame and brought to a raised state and a retracted state, and a spring member. The spring member includes a sliding portion (44) fitted to a guide groove (51) formed at the movable frame and slidably making contact with the guide groove to transmit a biasing force of the spring member in a state where the movable frame is rotating. The spring member further includes an engagement portion (46) engaging with the movable frame when the movable frame is in the raised position. The movable frame is configured to be maintained at the raised position by the engagement with the engagement portion of the spring member.
Owner:AISIN SEIKI KK
Drive Apparatus, Drive Method, And Optical Device
ActiveCN107040160ASuppress abnormal noiseReduce power consumptionPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesProjector focusing arrangementPhase differenceDuty cycle
Noise produced during phase-difference changes is minimized without decreasing the responsiveness of a vibration-wave motor. A lens-side MCU (15) for a lens barrel (10) controls a drive apparatus (14) that applies a drive voltage to the vibration-wave motor (12) by outputting an A-phase drive signal and a B-phase drive signal thereto. The lens-side MCU (15) uses, for example, a drive-voltage setting unit (152) and a duty-cycle change unit (153) to change the drive voltage. Also, the lens-side MCU (15) is provided with a phase-difference change unit (154) that changes the phase difference between the A-phase drive signal and the B-phase drive signal. When driving the vibration-wave motor (12), the lens-side MCU (15) changes the drive voltage to Vreg, and when the phase-difference change unit (154) is changing the aforementioned phase difference, the drive voltage is changed to V1, V1 being greater than zero and less than Vreg.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Electromagnetic converter
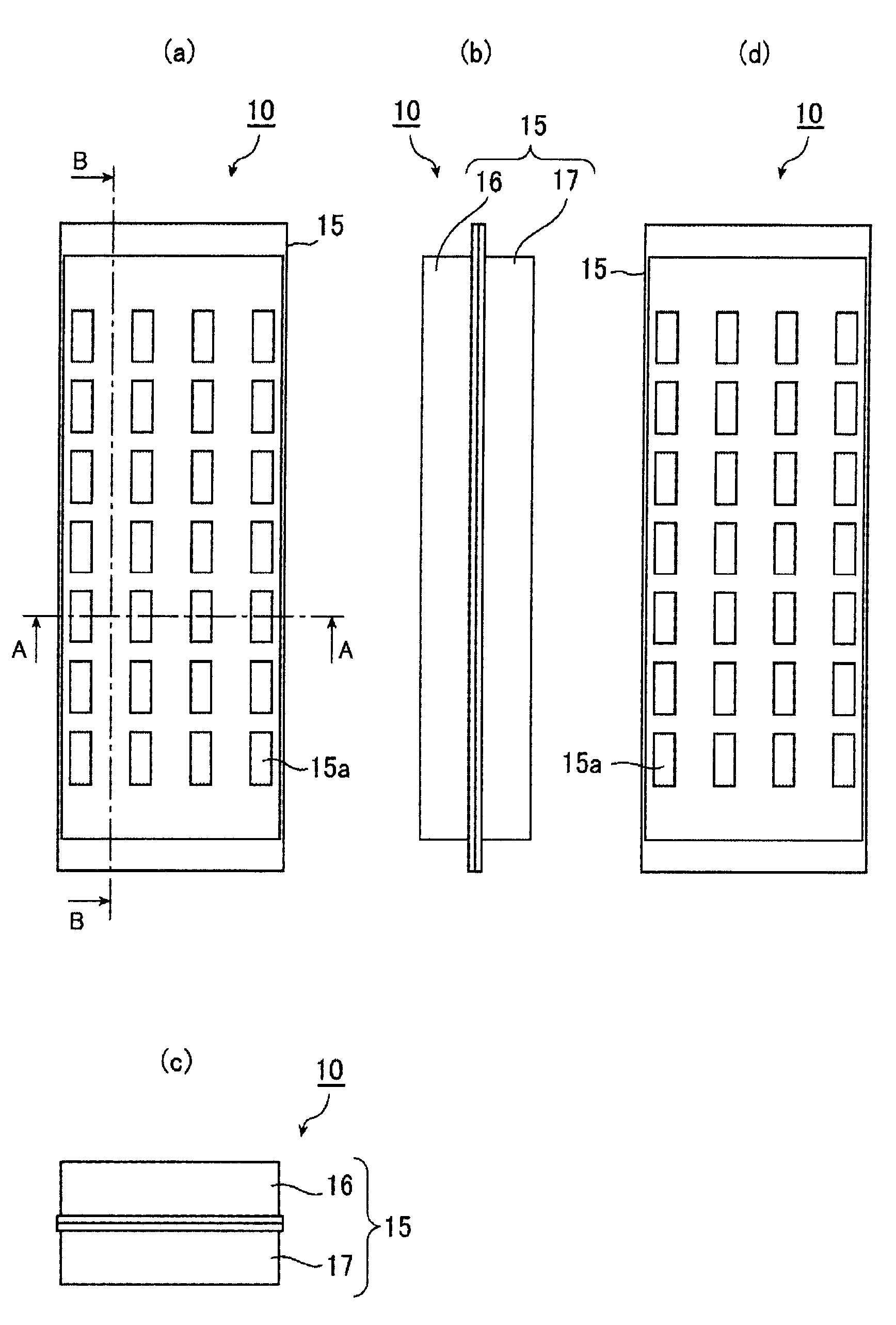
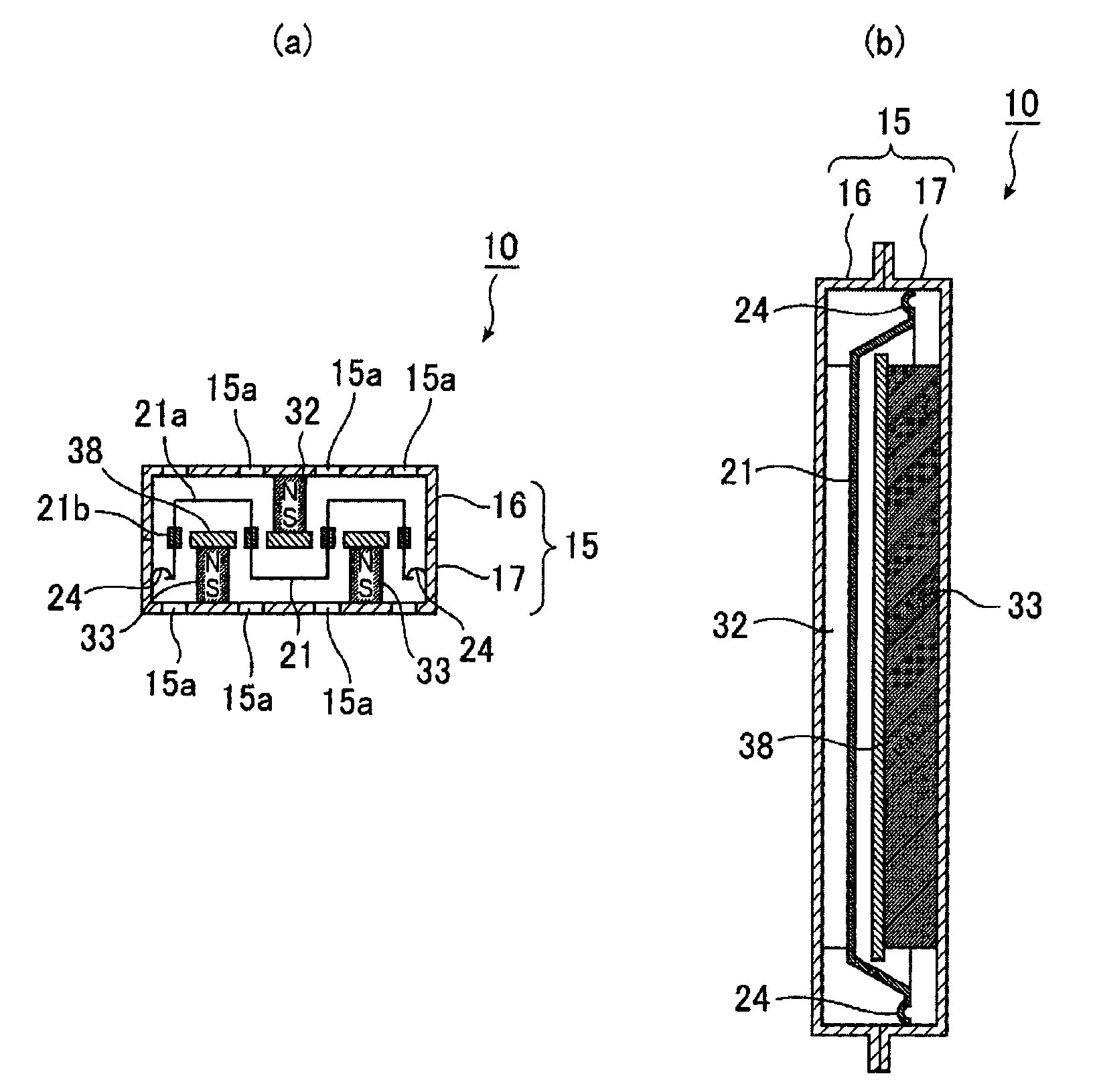
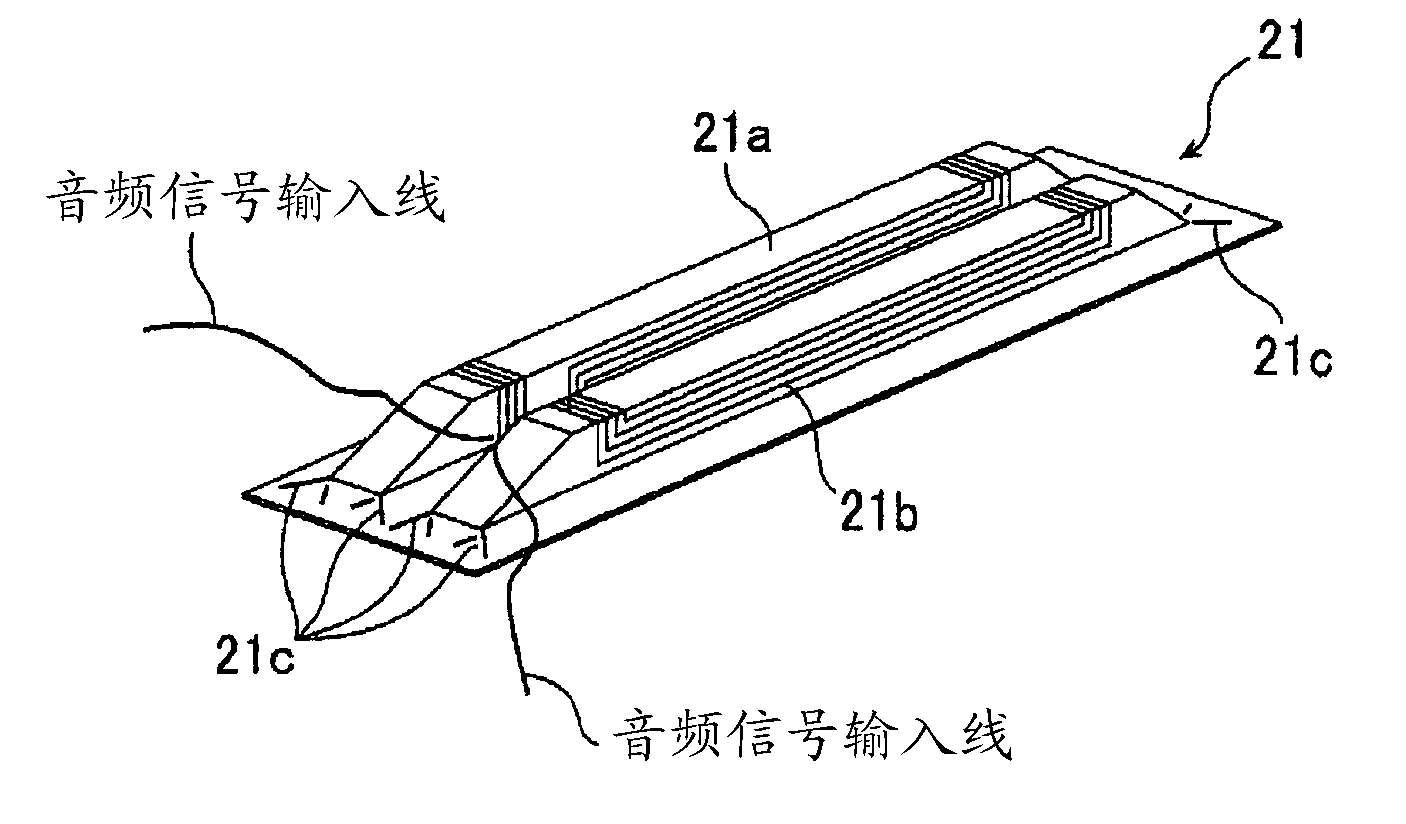
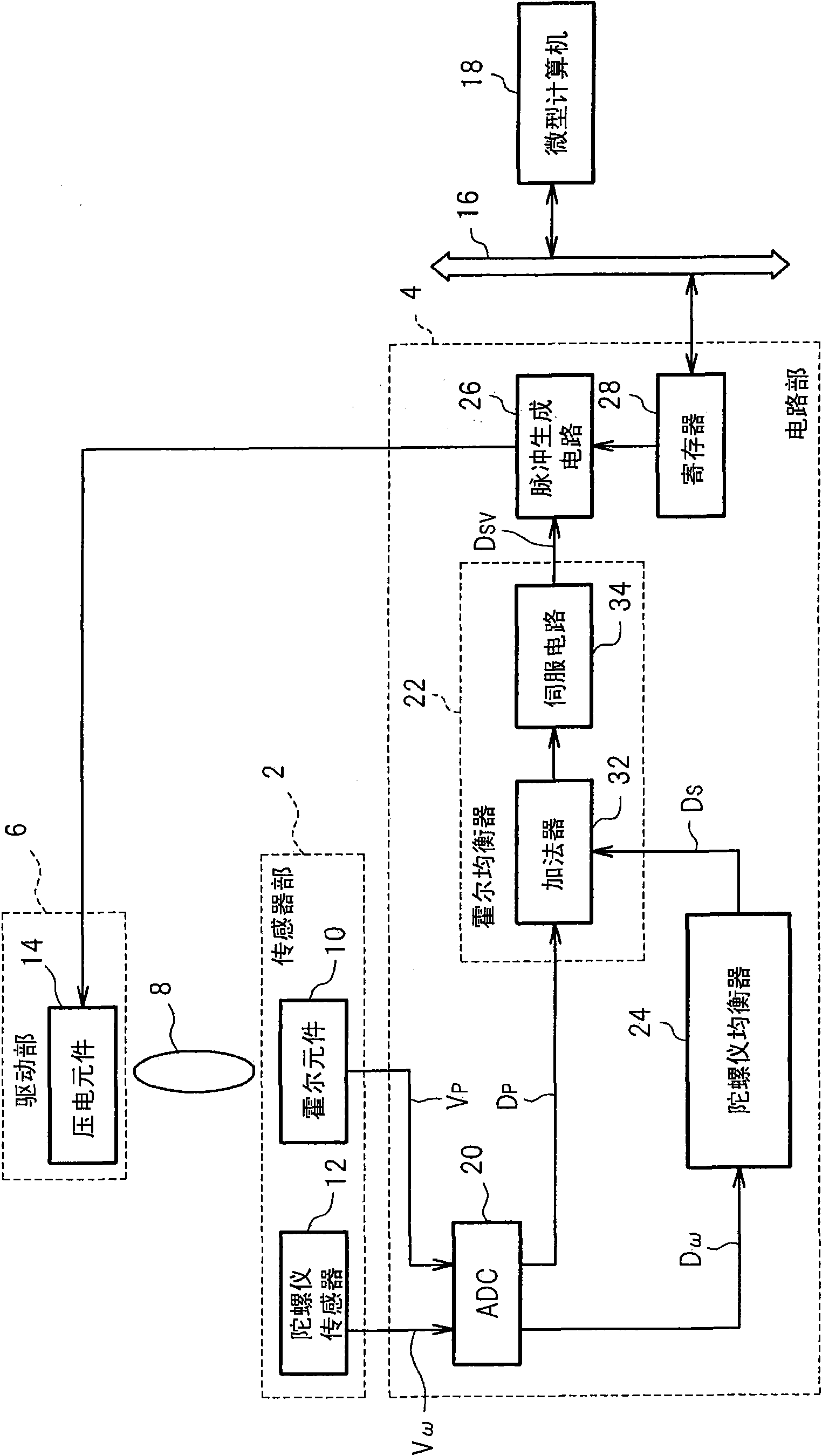
ActiveCN102067629AImprove rigiditySuppress abnormal noisePolymeric diaphragmsMetallic diaphragmsSolid structureMagnetic flux
A hollow inner section is formed when a pair of frames (16, 17) are combined, and a plate (38) which concentrates a magnetic flux is arranged on permanent magnets (32, 33) arranged inside the pair of frames (16, 17). In a diaphragm (21), a coil pattern (21b) which receives the magnetic flux from the plate (38) is formed on the vibrating film (21a), and the vibrating film (21a) having uniform thickness is formed as an uneven solid structure.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC ENG CO LTD
Method for driving piezoelectric actuator, piezoelectric-actuator control circuit, and image-stabilization control circuit
InactiveCN101873085ASimple structureSuppress abnormal noisePrintersPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectricityPiezoelectric actuators
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD +2
Power transmission belt and belt drive system with the same
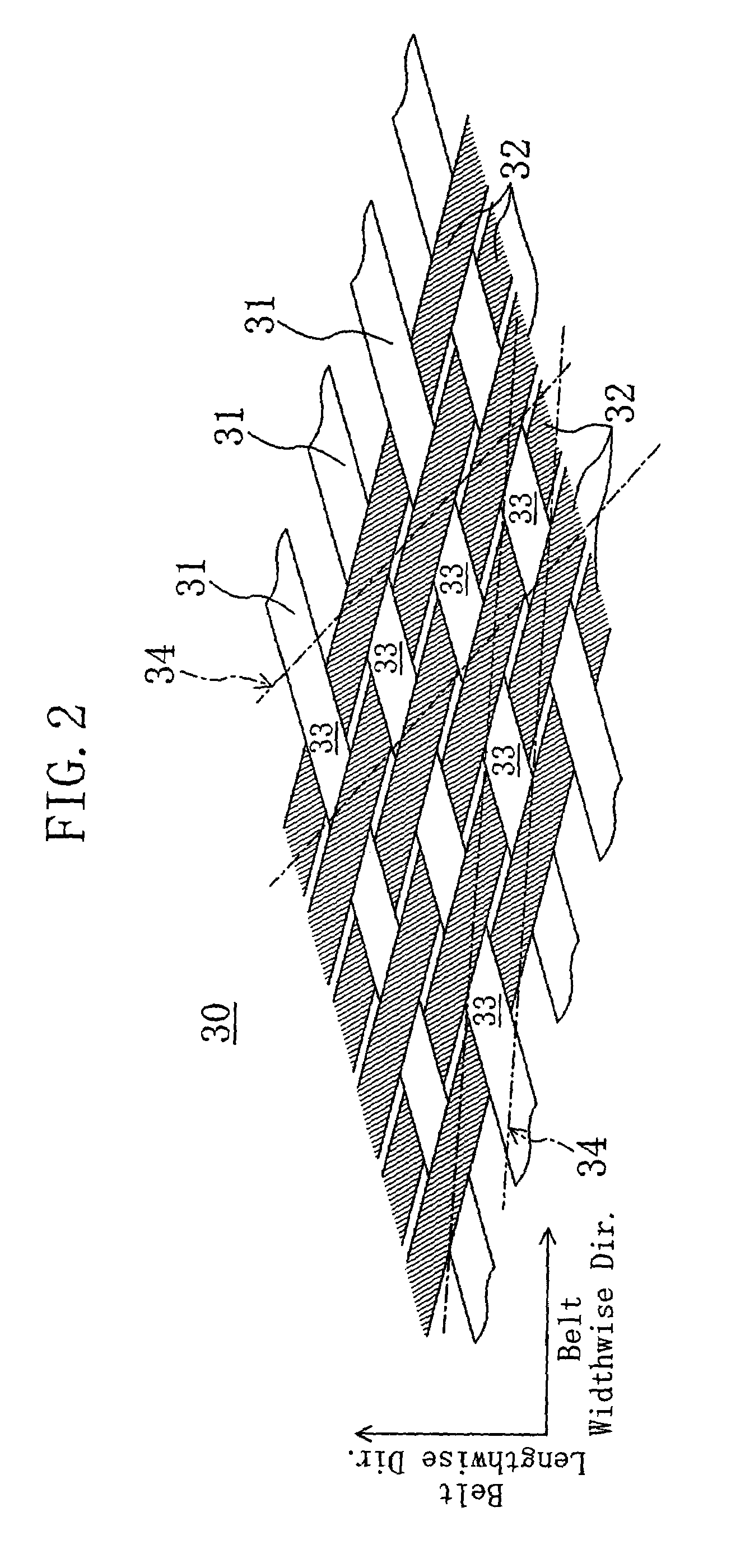
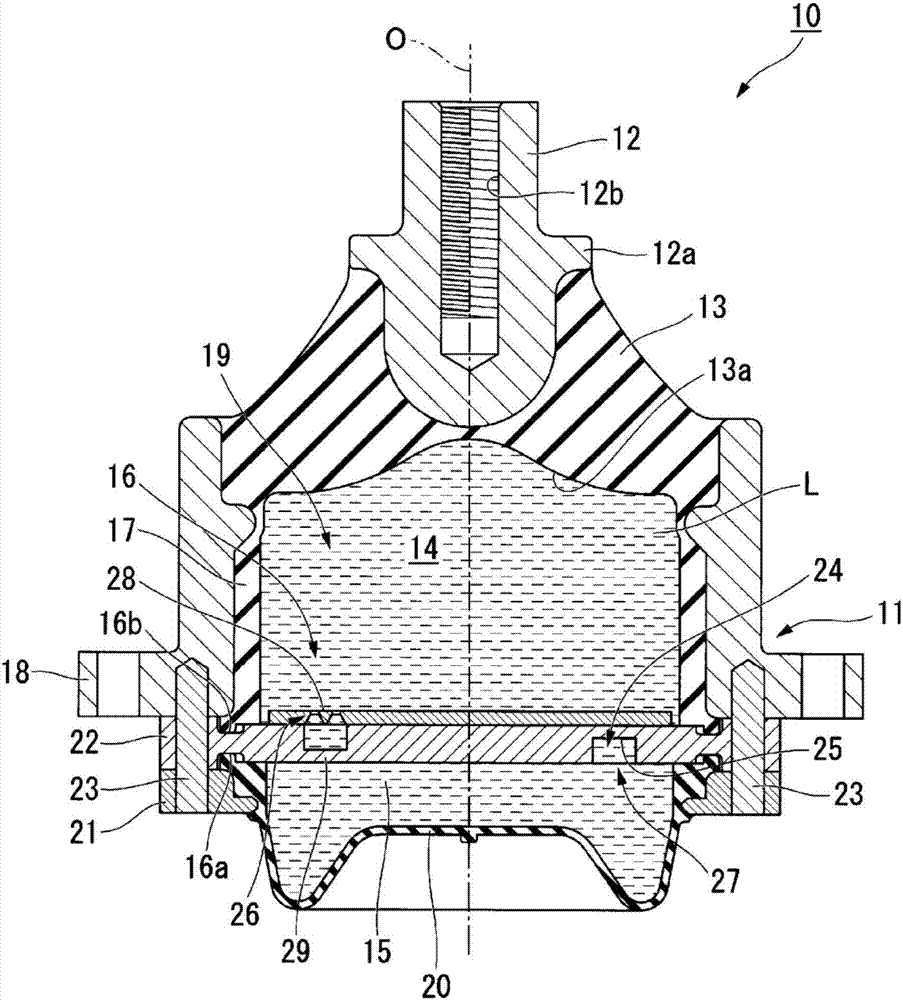
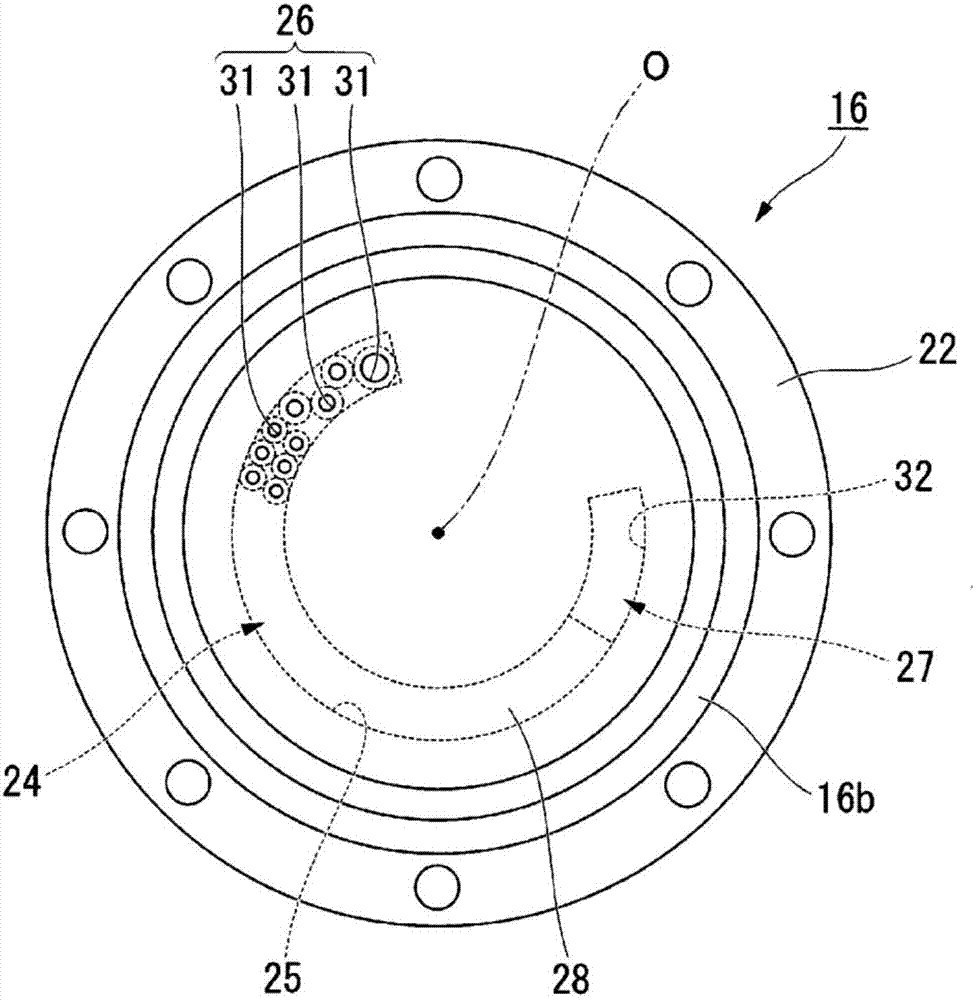
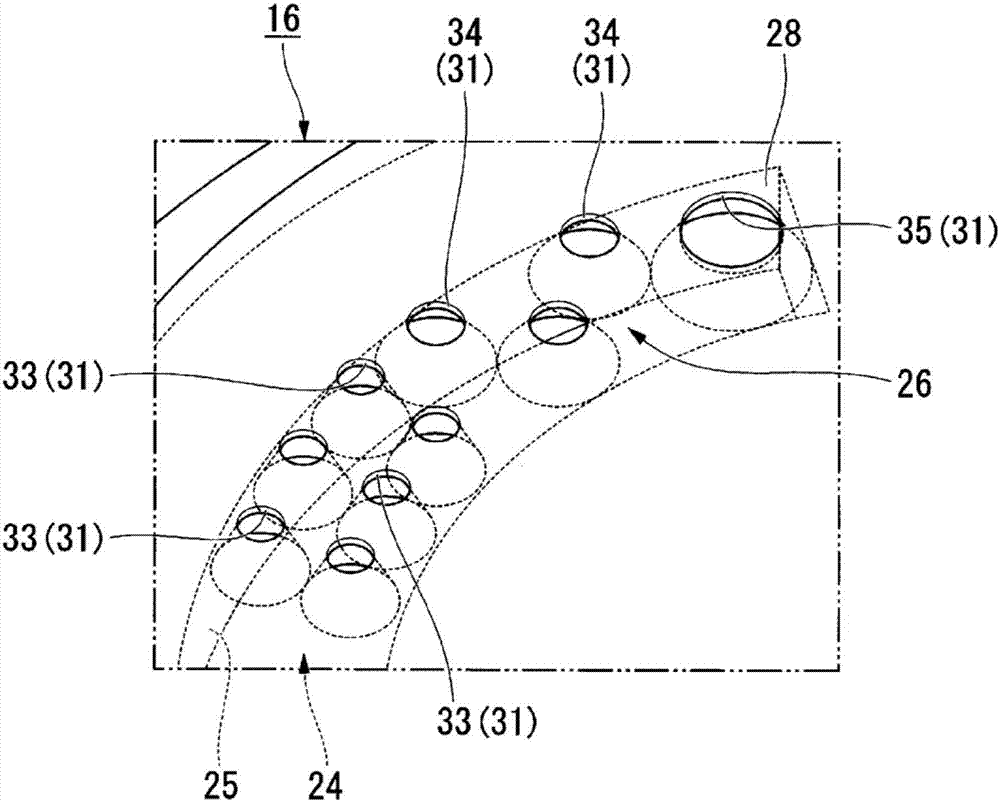
InactiveUS7052425B2Suppress abnormal noiseSuppresses the generation of abnormal noiseV-beltsRopes and cables for vehicles/pulleyYarnEngineering
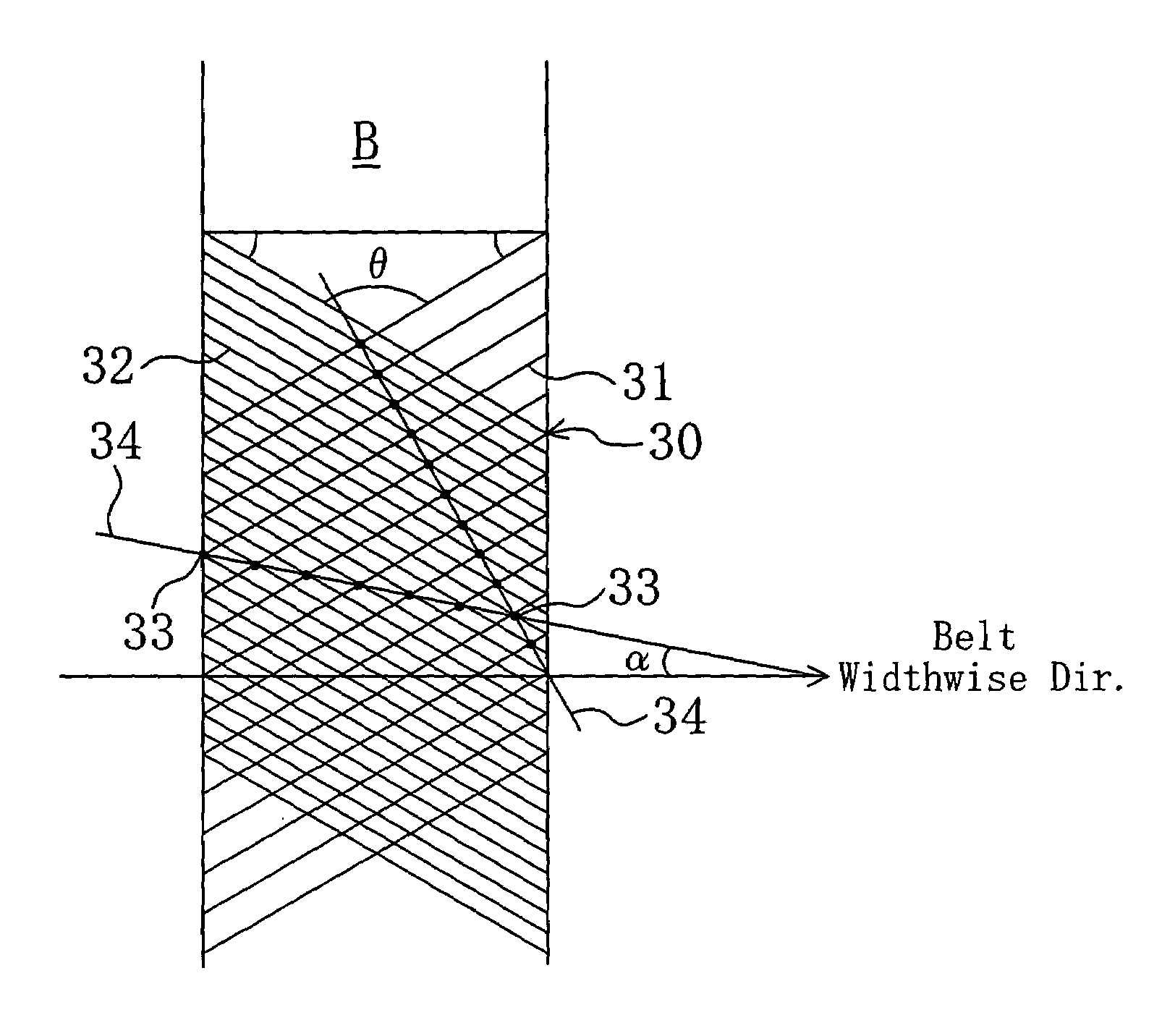
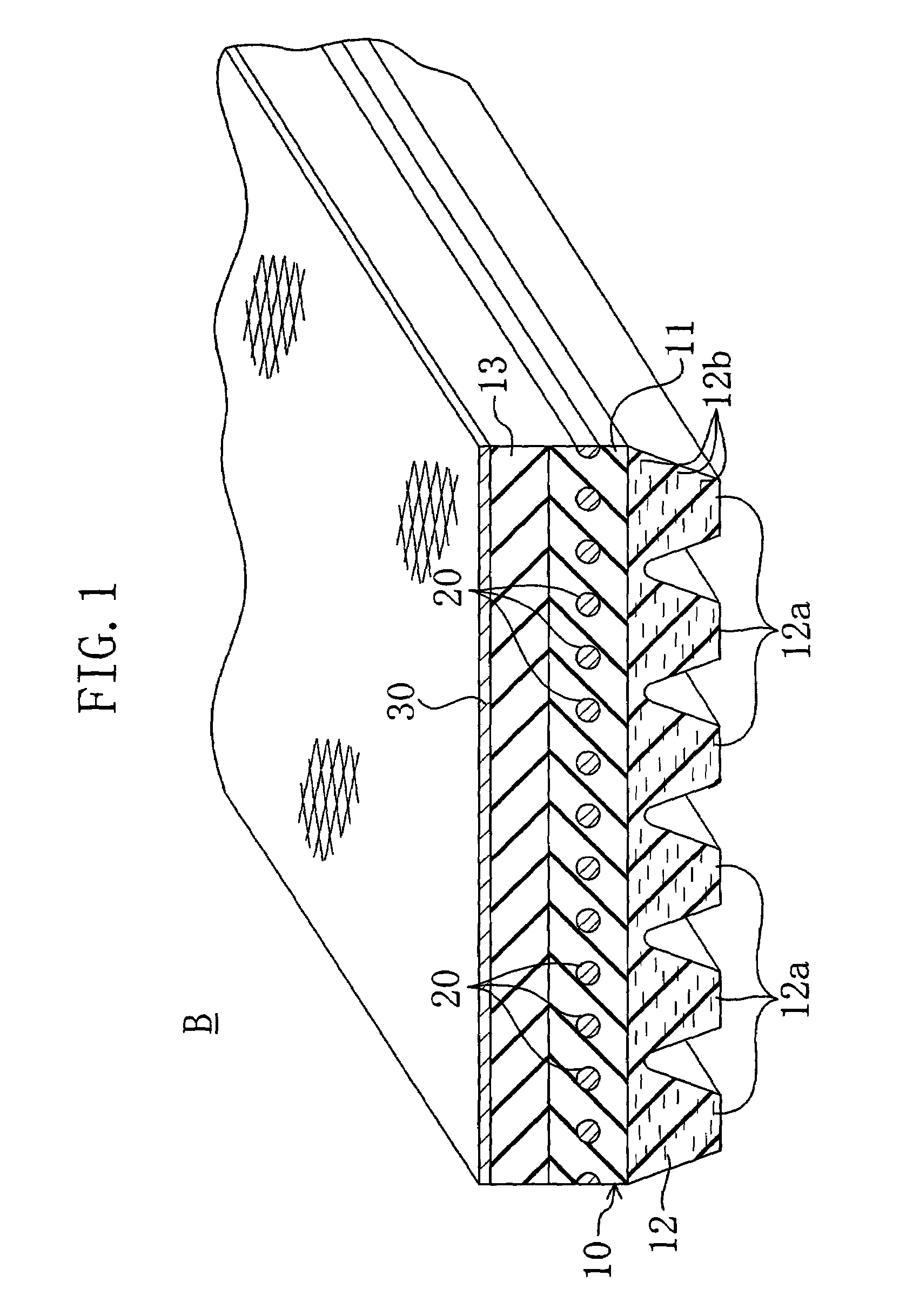
A power transmission belt is formed so that the back face side of a belt body is covered with a reinforced fabric woven with warps and wefts. In the reinforced fabric, the direction of warps and the direction of wefts make equal angles with the belt widthwise direction, and each of two directions of consecutive yarn intersections of the warps and wefts formed to stand out from the belt surface makes a certain angle with the belt widthwise direction.
Owner:BANDO CHEM IND LTD
Vibration-damping device
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
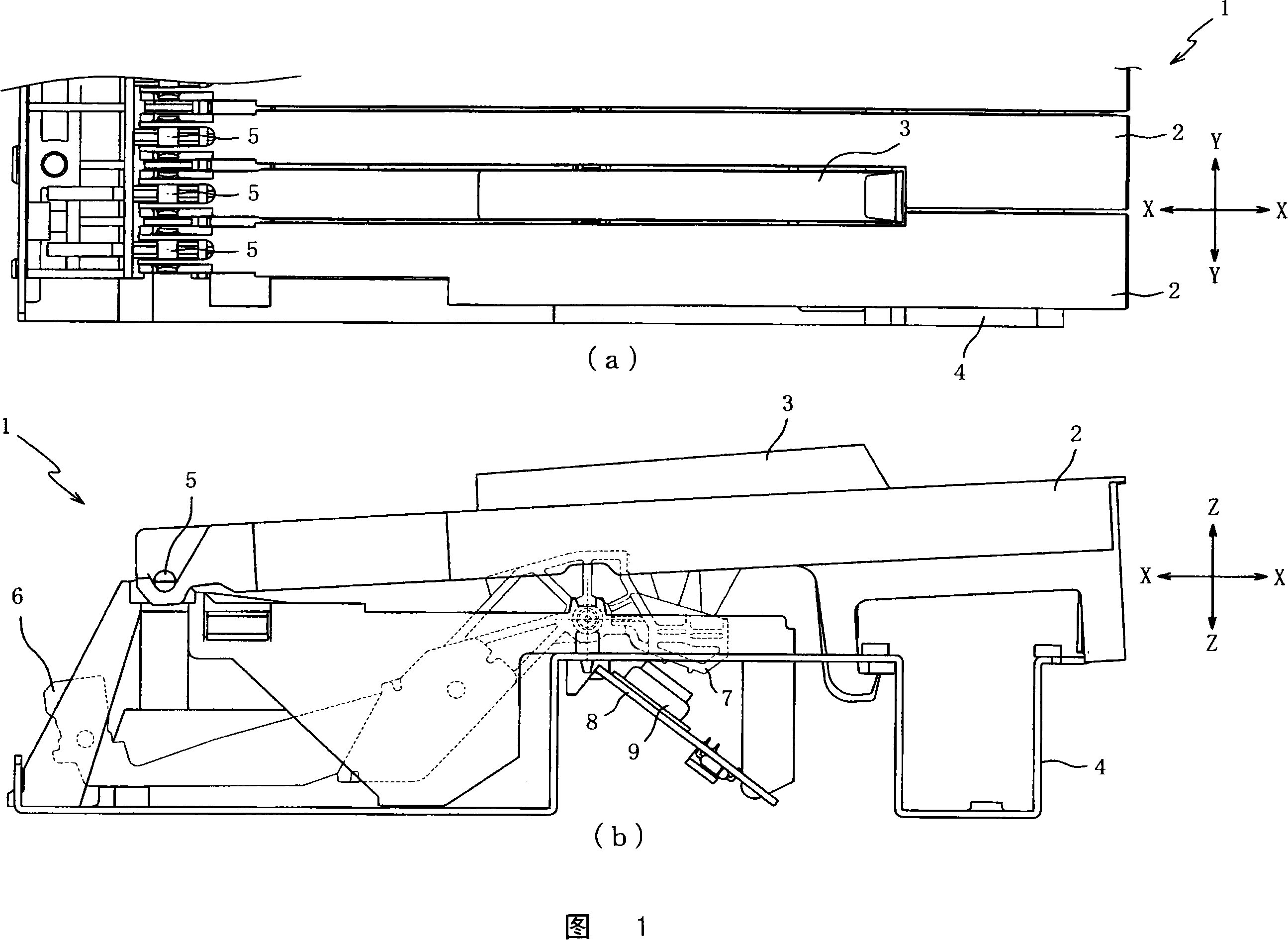
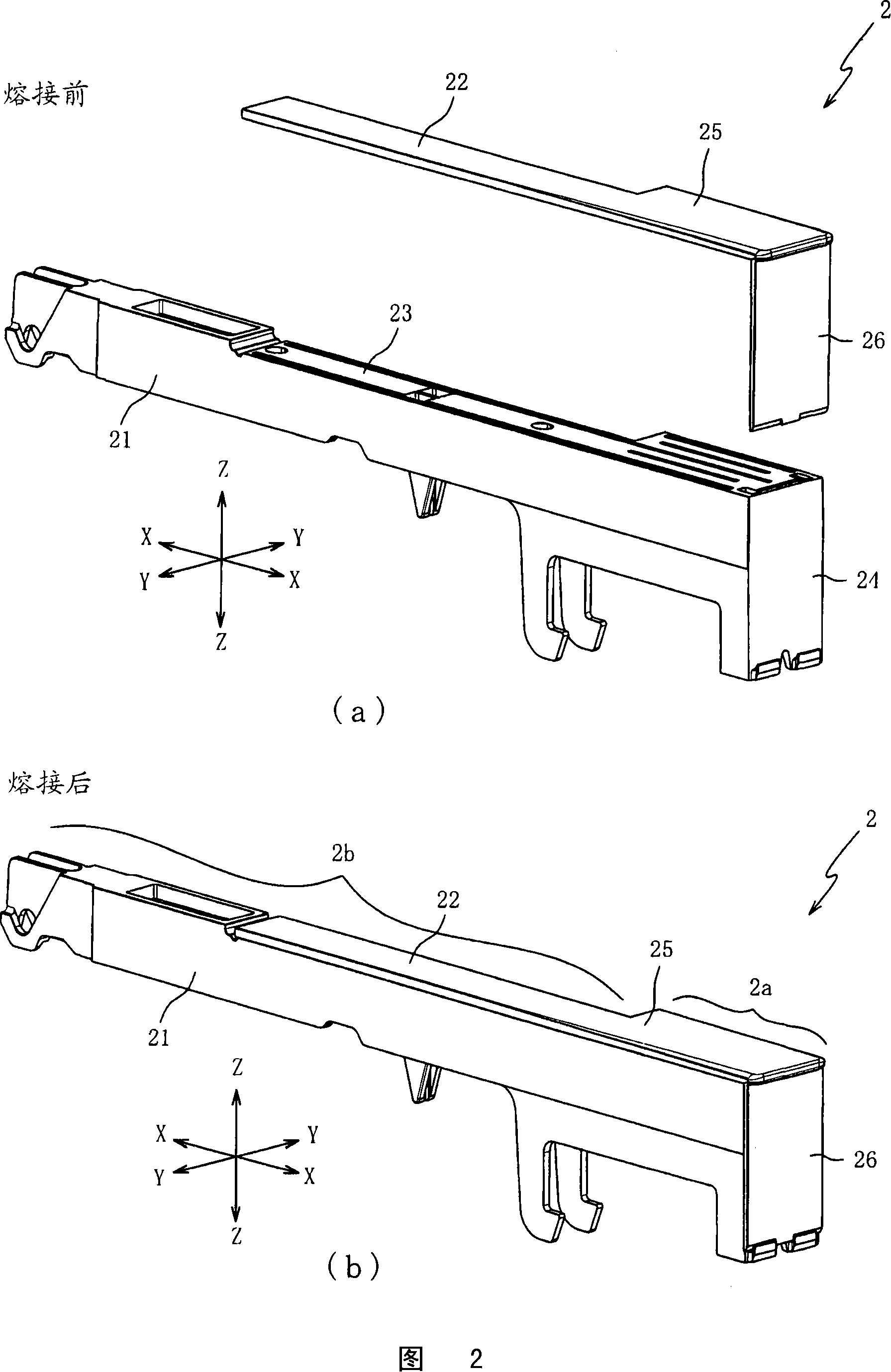
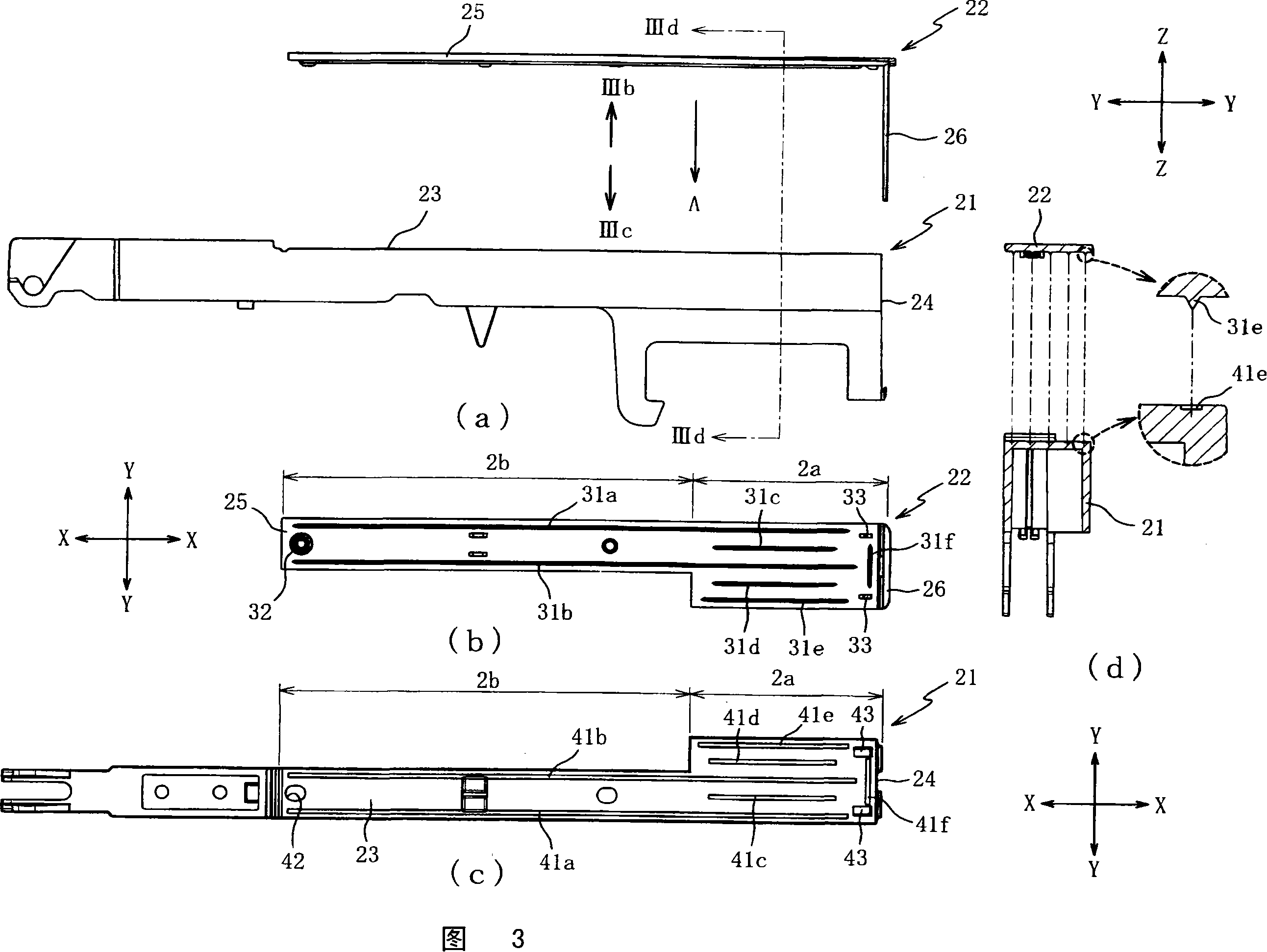
Keyboard device
InactiveCN101154374AGood sweat absorptionHigh strengthStringed musical instrumentsWind musical instrumentsAdhesiveEngineering
The present invention provides a keyboard device, capable of fixing matrix part and plate part hard and reducing abnormity noise generated by key-press. The matrix part (21) is burned together with the plate part through supersonic welding, so as to fix each other hard compared to the condition of connecting through adhesive. Thus, it is able to restrain the matrix part (21) peeling off from the plate part (22) even though executants press key with high power or during a long time. Moreover, as to noses (31a to 31f) of the plate part (22), the occupied ratio of the noses relative to key-press part (2a) is more than that of the noses (31a, 31b) relative to a slightness part (2b), thus the welding connection of the key-press part (2a) is tighter. There is no clearance between the matrix part (21) and the plate part (22), so the key-press part (2a) can restrain the abnormity noise due to key-press.
Owner:ROLAND CORP
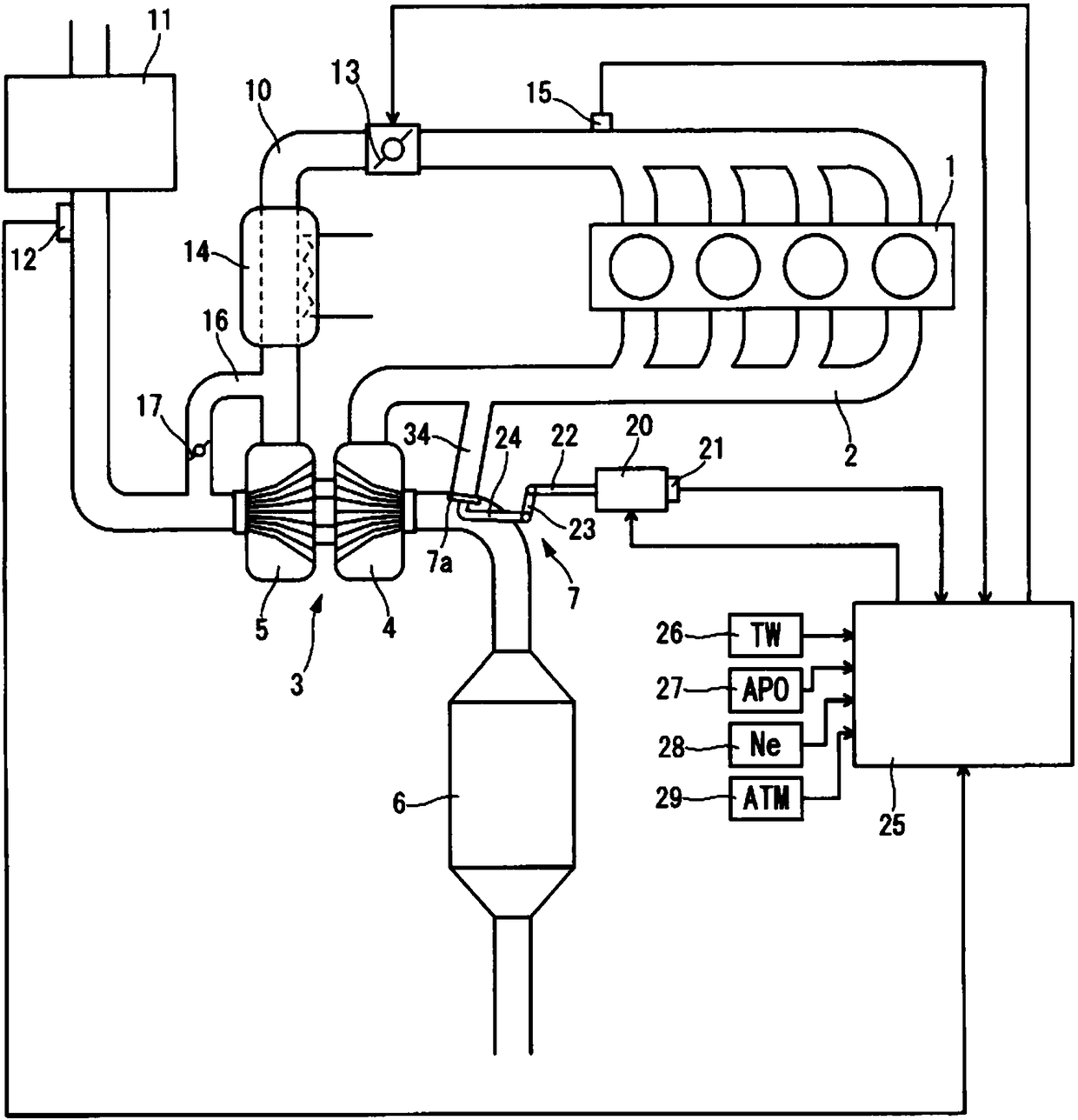
Waste gate valve control method and control device
ActiveCN108463620ASuppress abnormal noiseElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesPtru catalystTurbocharger
A waste gate valve (7) of a turbocharger (3) is fully open during idling after warm-up is complete in order to reduce exhaust resistance, and during cool-down idling when a cooling water temperature (TW) is below a threshold value (TW1), the waste gate valve (7) is open-loop controlled to an intermediate opening degree that is smaller than fully open. The ignition time is delayed for catalyst warm-up. When the cooling water temperature (TW) reaches (t3) the threshold value (TW1), the opening degree of the waste gate valve (7) is set to fully open. When the accelerator opening degree (APO) becomes large (t4) before warm-up is complete, control of the opening degree is released.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Joint for torque transmission, and electric power steering device
InactiveCN108779808ASuppress abnormal noiseYielding couplingToothed gearingsElectric power steeringTorque transmission
Owner:NSK LTD
Bearing device for wheel
InactiveCN101641225BImprove qualityPrevent creepRolling contact bearingsAxle unitsUniversal jointEngineering
A bearing device for a wheel, in which circumferential play is suppressed, which facilitates connection between a hub ring and an outer coupling member, in which a reduction in NVH characteristics dueto play at a joint between the hub ring and the constant velocity universal joint and by play between a bearing outer member and a knuckle is prevented, and which performs highly accurate transmission of rotational torque. The bearing device has a groove-ridge fitting structure (M) by which the hub ring (1) and a shaft section (12) of the outer coupling member of the constant velocity universal joint (3) are integrated together, and the shaft section (12) is fitted in a hole (22) of the hub ring (1). In the groove-ridge fitting structure (M), ridges (35) on the outer diameter surface of the shaft section (12) and grooves (36) in the inner diameter surface (37) of the hub ring (1) are fitted to each other in a fitting contact portion (38), and the ridges (35) and the grooves (36) are in intimate contact with each other in the entire fitting contact portion (38).
Owner:NTN CORP
Bearing device for wheel
InactiveCN102152711BImprove qualityPrevent creepYielding couplingRolling contact bearingsUniversal jointTorque transmission
Owner:NTN CORP
Power transmission mechanism and multi-shaft drive device
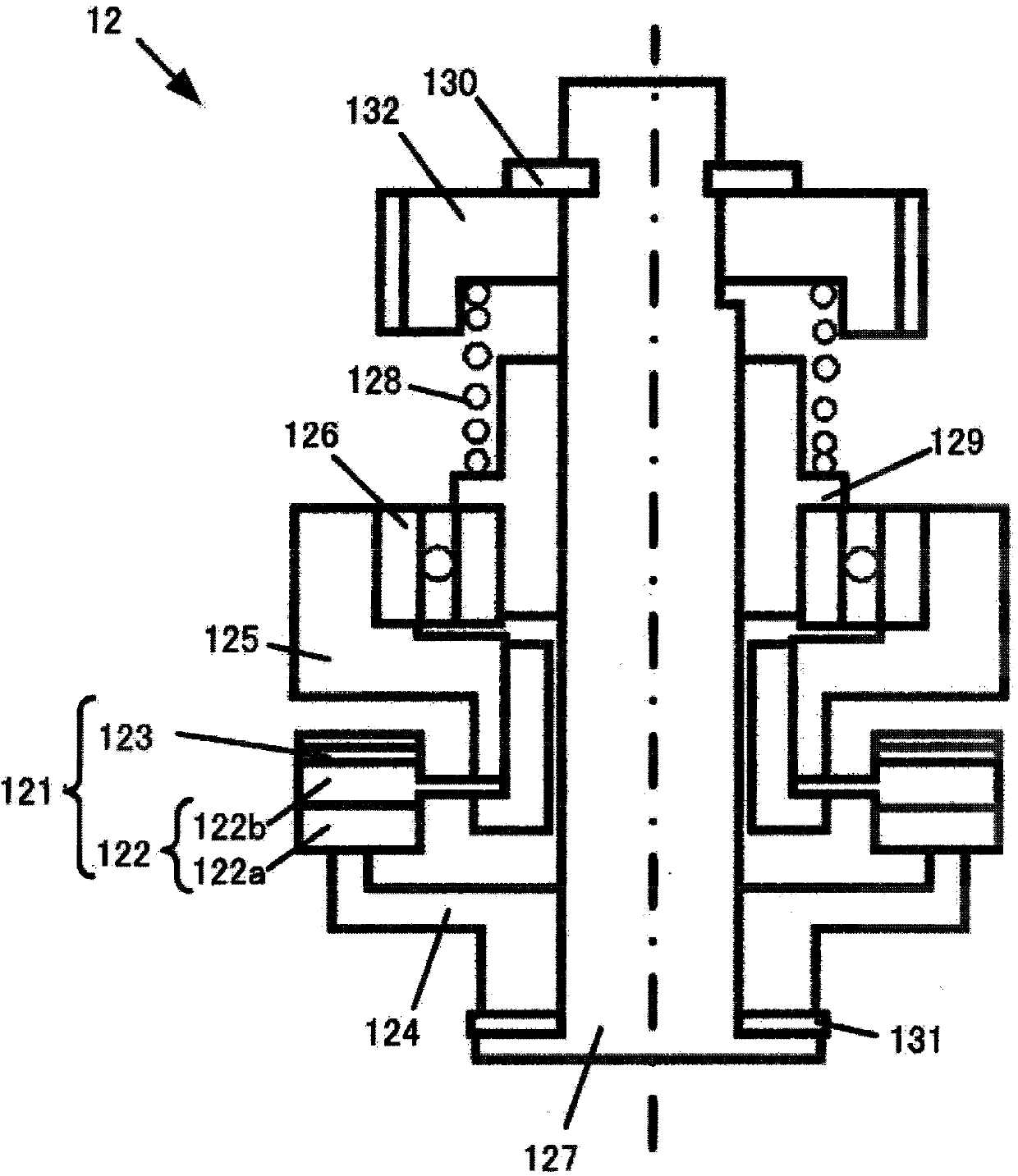
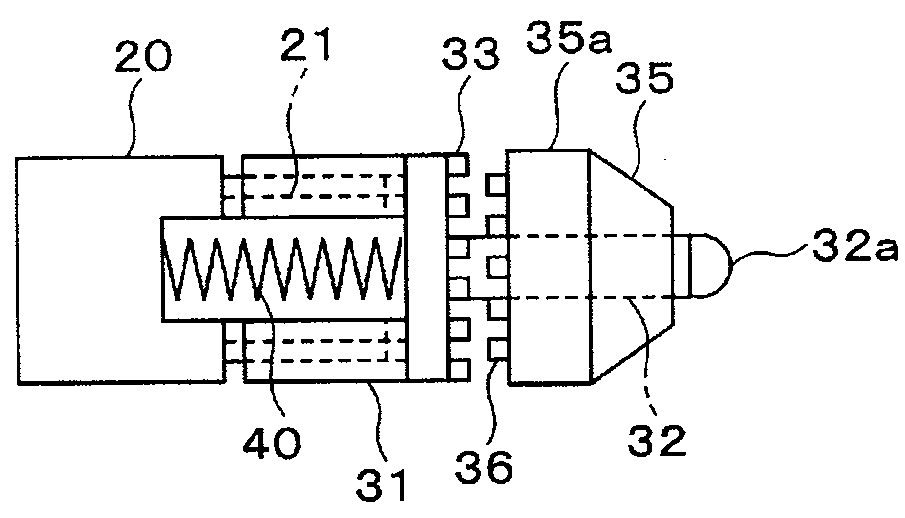
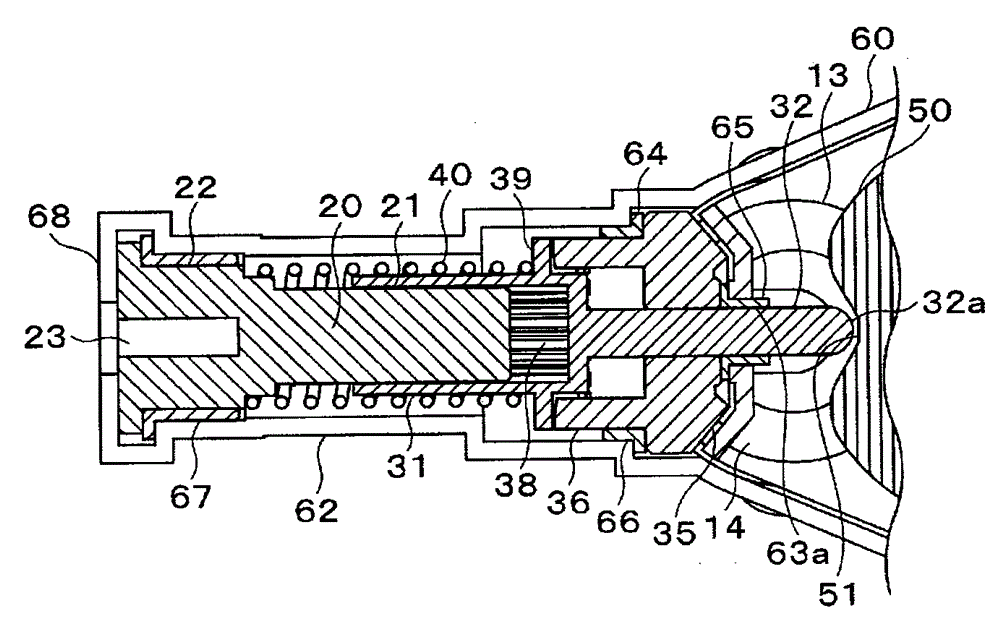
Force of used spring can be weak, wear amount of power transmission member (gear or the like) can be reduced, and generation of strange noises can inhibited. When the dial cam 50 is rotated and the recess 51 of the outer peripheral surface 52 faces the front end portion 32a of the pin 32 of the connection shaft 31, the connection shaft 31, which is biased by the force of the coil spring 40, is connected to the bevel gear 35, which engages with the bevel gear 14 and is rotated, via the clutch teeth 33 and 36. Thus, the connection shaft 31 is rotated, and the output shaft 20 is rotated together with the connection shaft 31. That is, the power of the motor 10 is transmitted to the output shaft 20. Since the coil spring 40 is used for connecting the connection shaft 31 to the bevel gear 35, the force of the coil spring 40 can be reduced.
Owner:NHK SPRING CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com