Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
119results about How to "Superfluous image" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
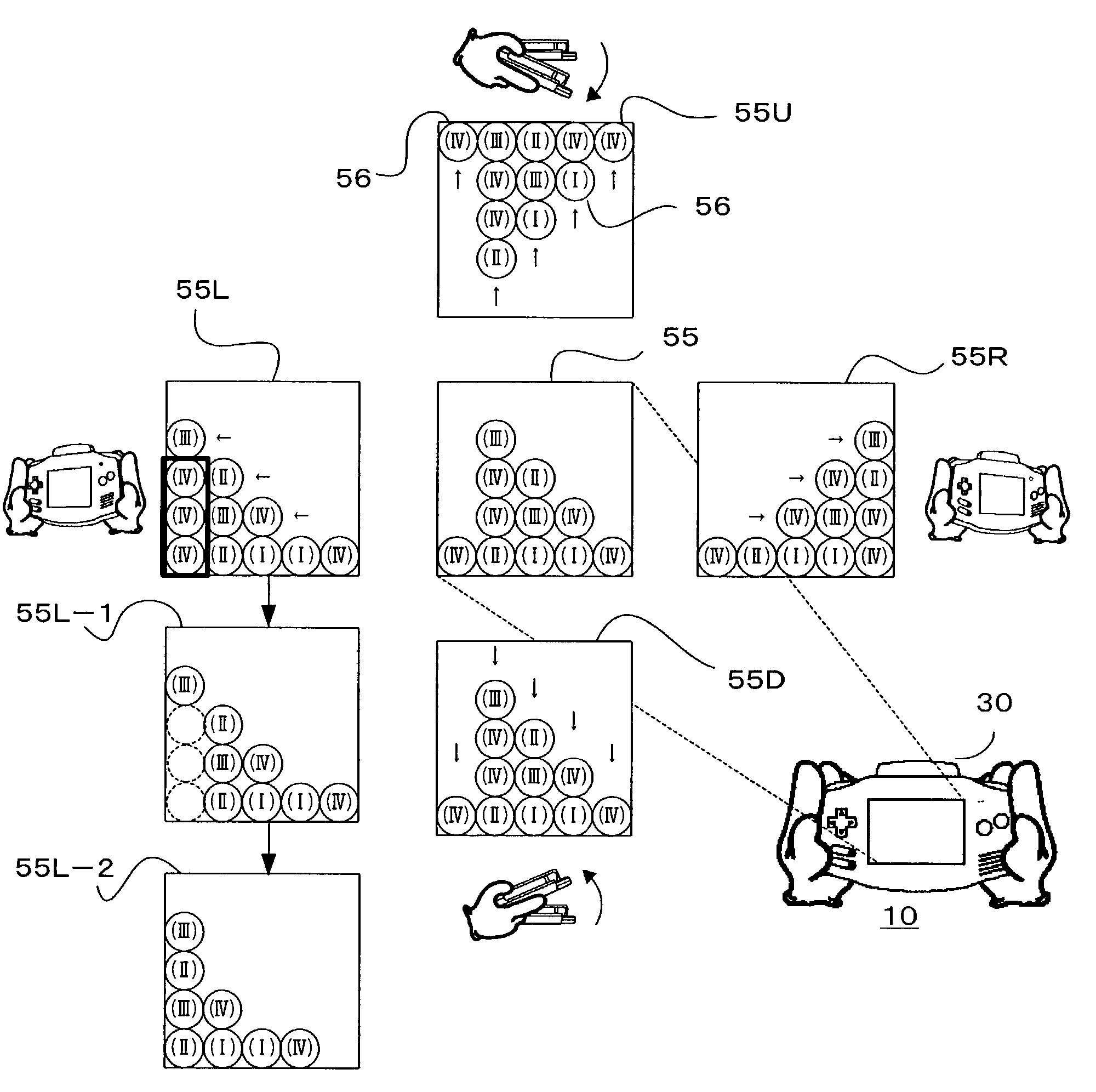
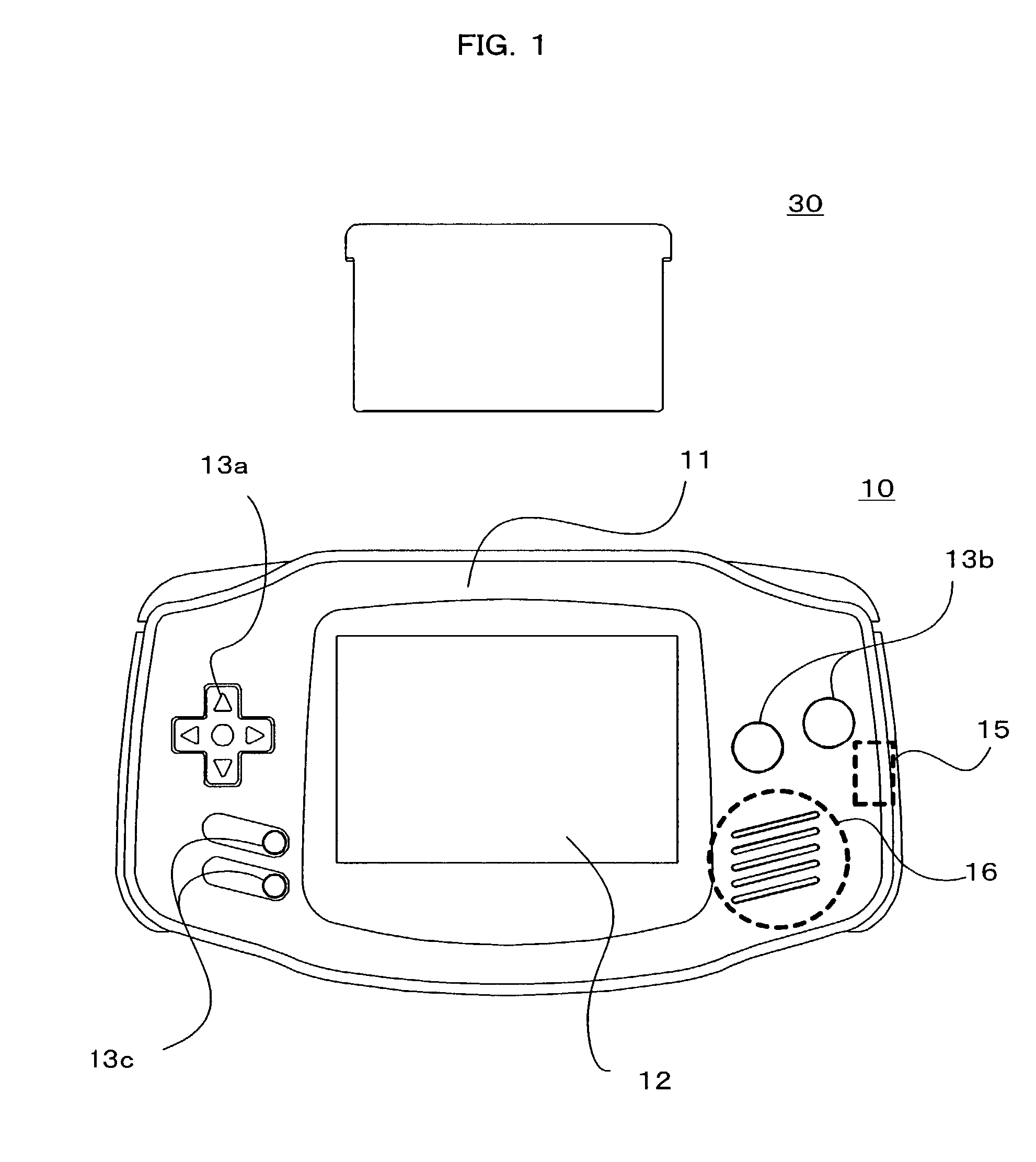
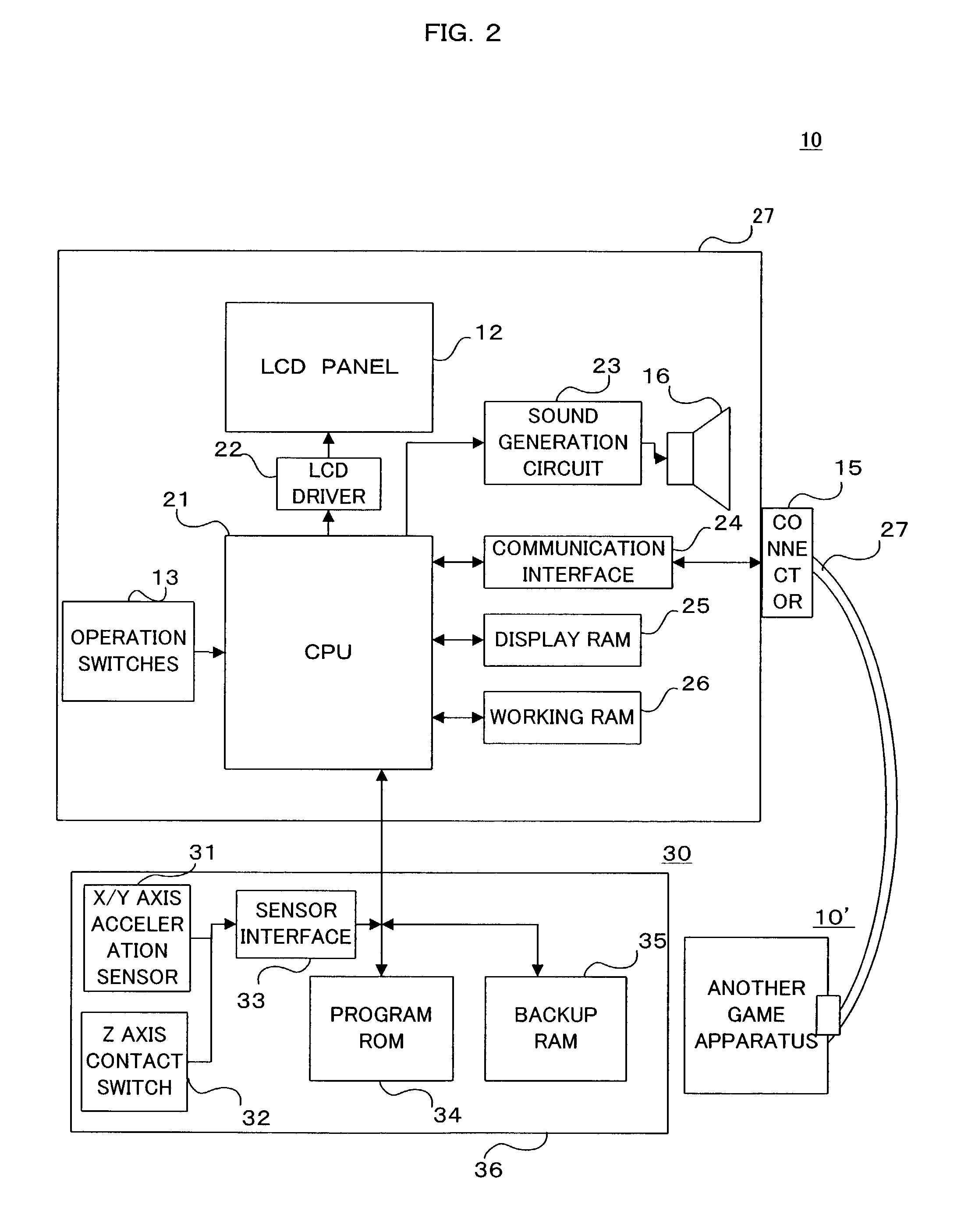
Game system, puzzle game program, and storage medium having program stored therein
ActiveUS7094147B2Superfluous imageProvide imageVideo gamesSpecial data processing applicationsStrategy makingMultimedia
Owner:NINTENDO CO LTD
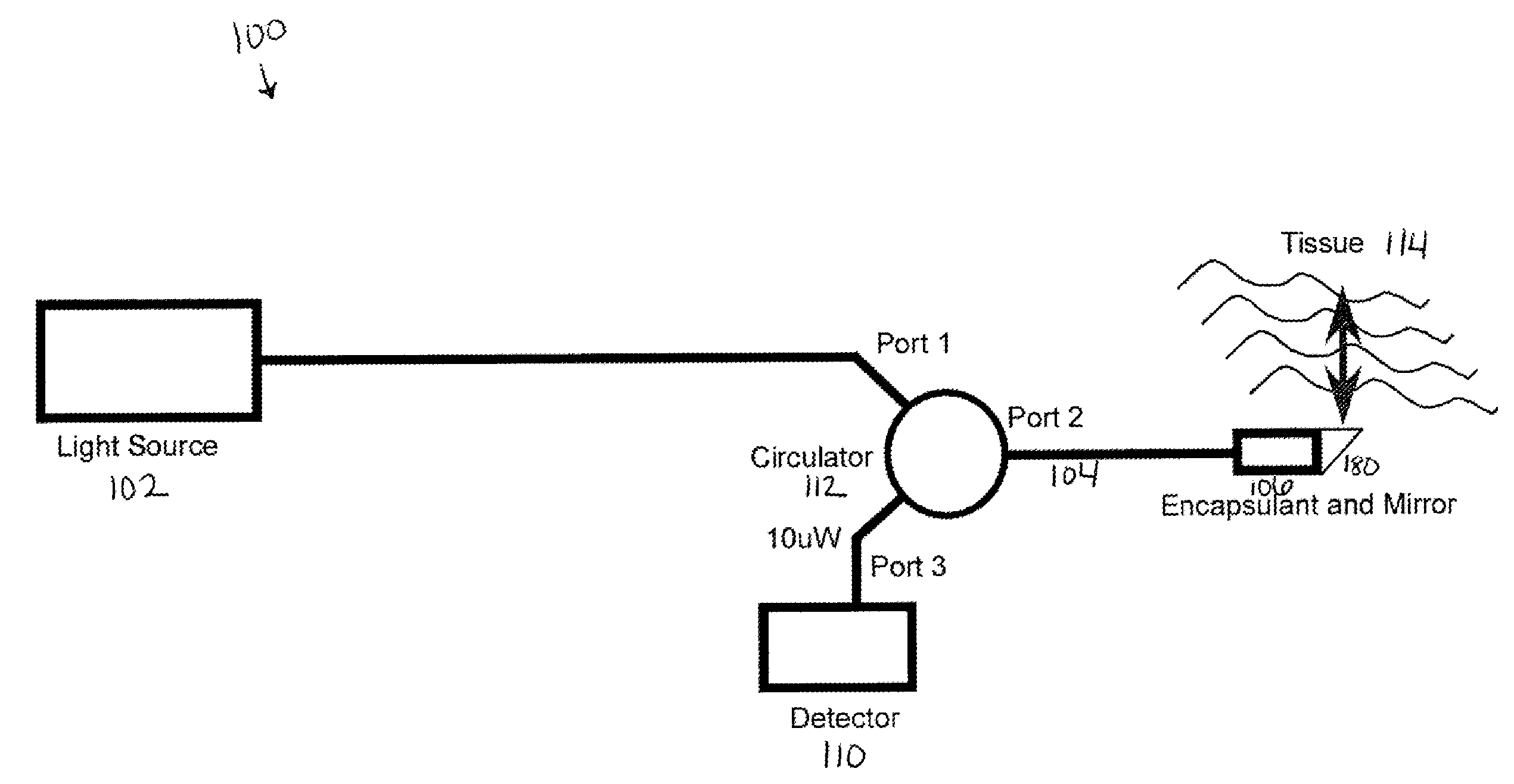
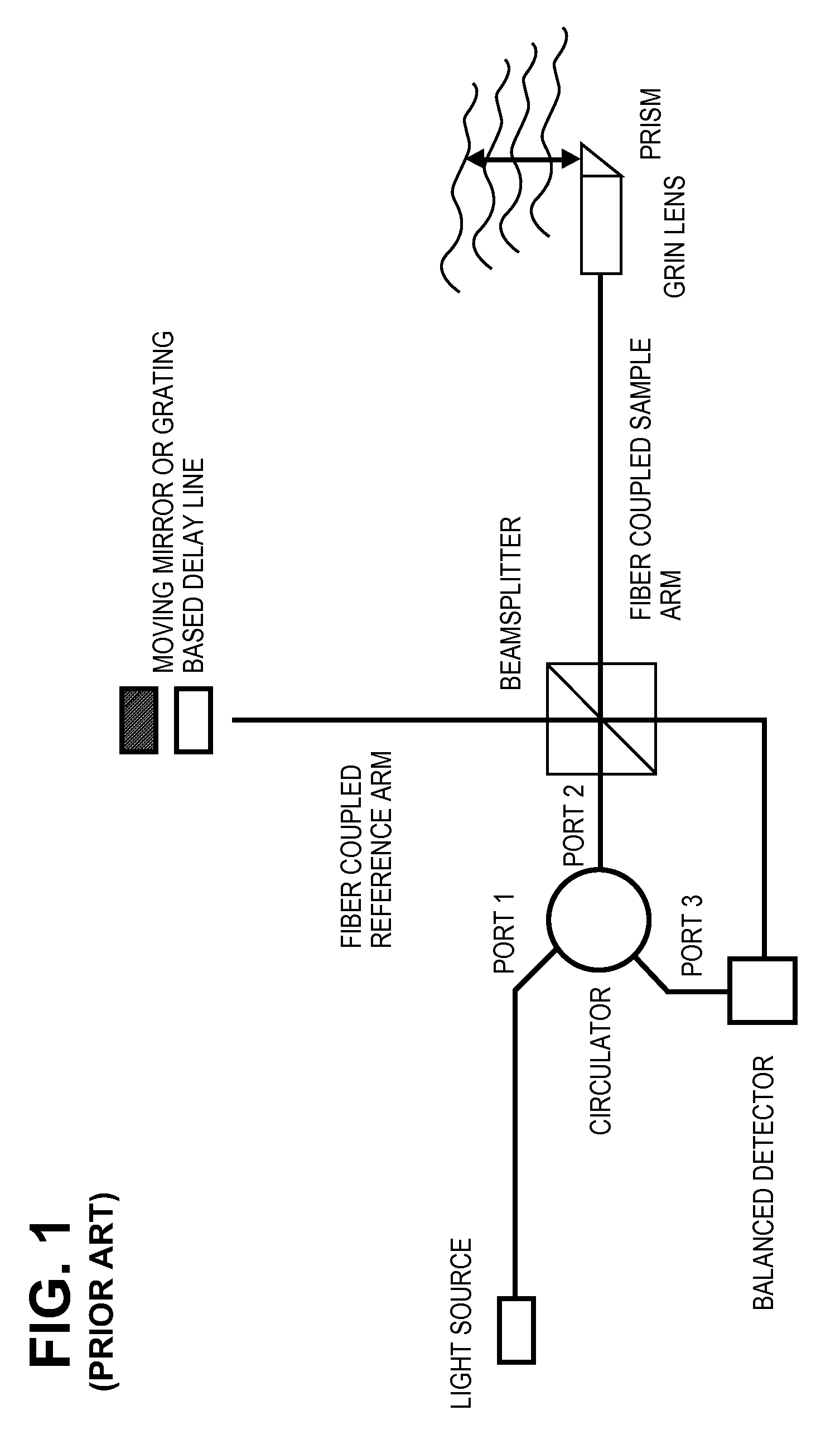
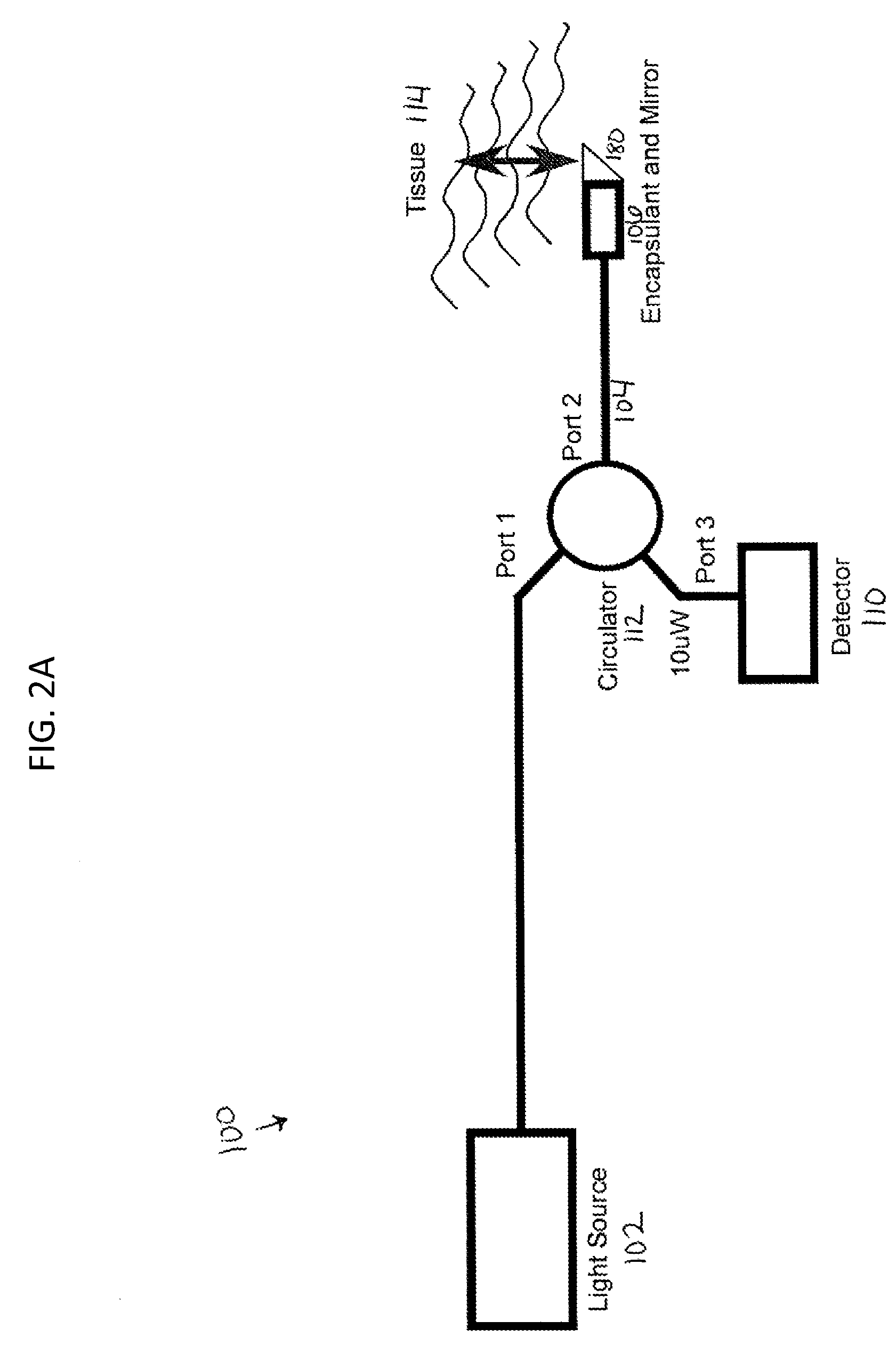
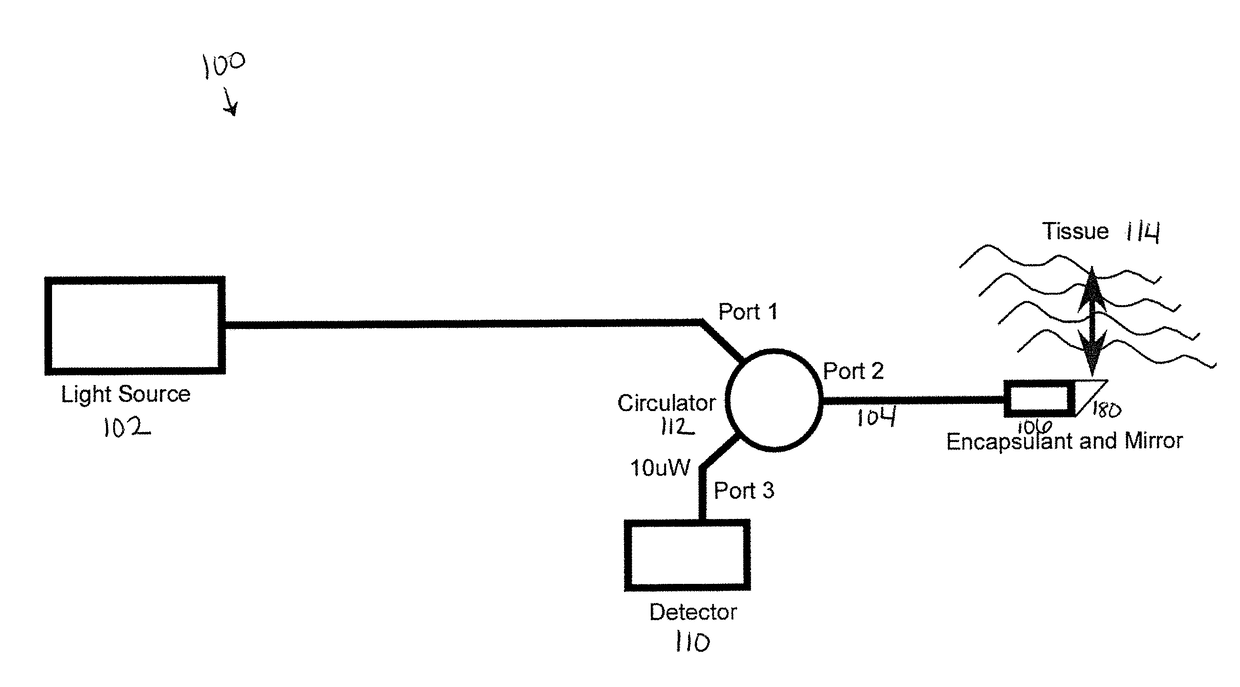
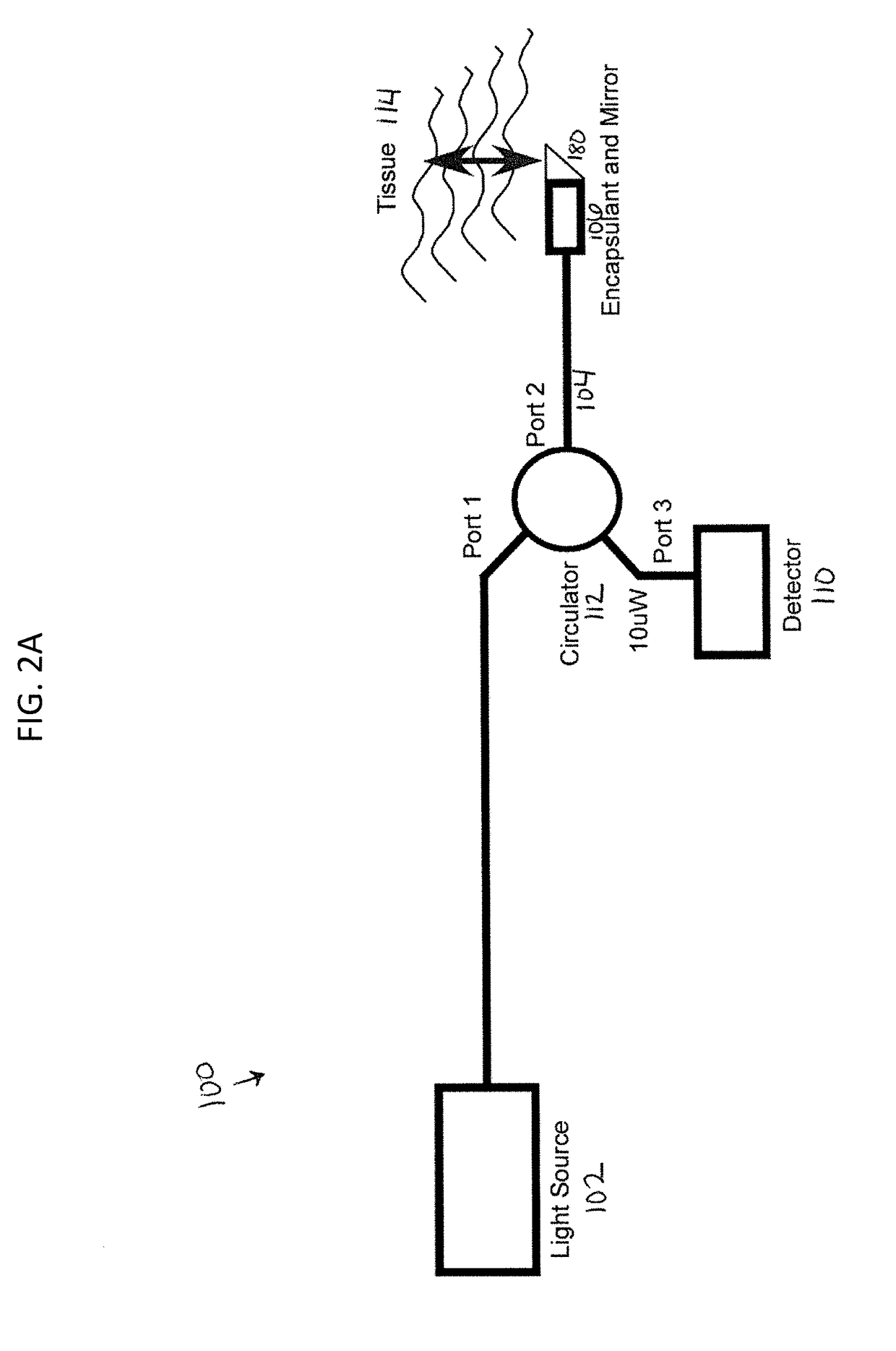
Optical coherence tomography for biological imaging
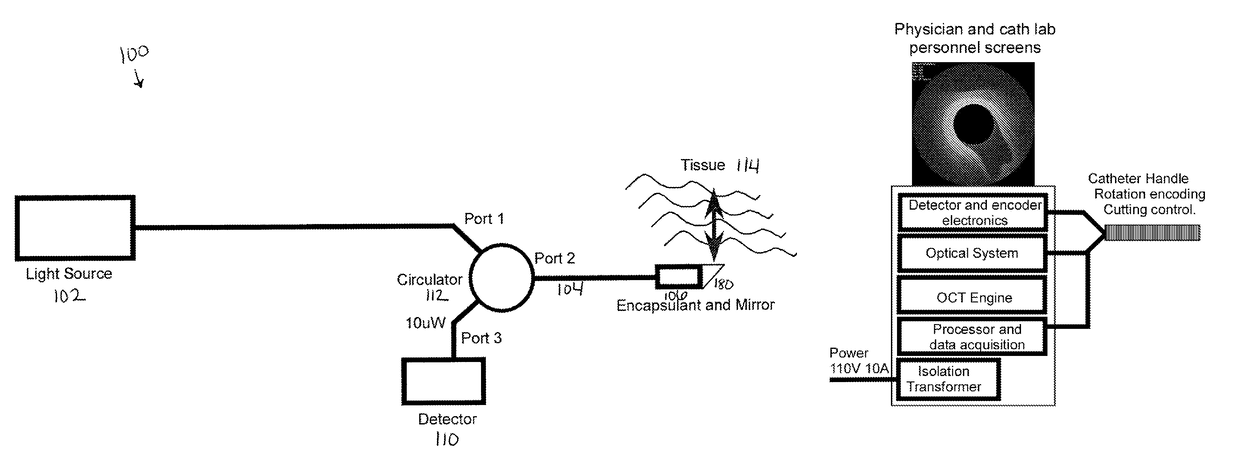
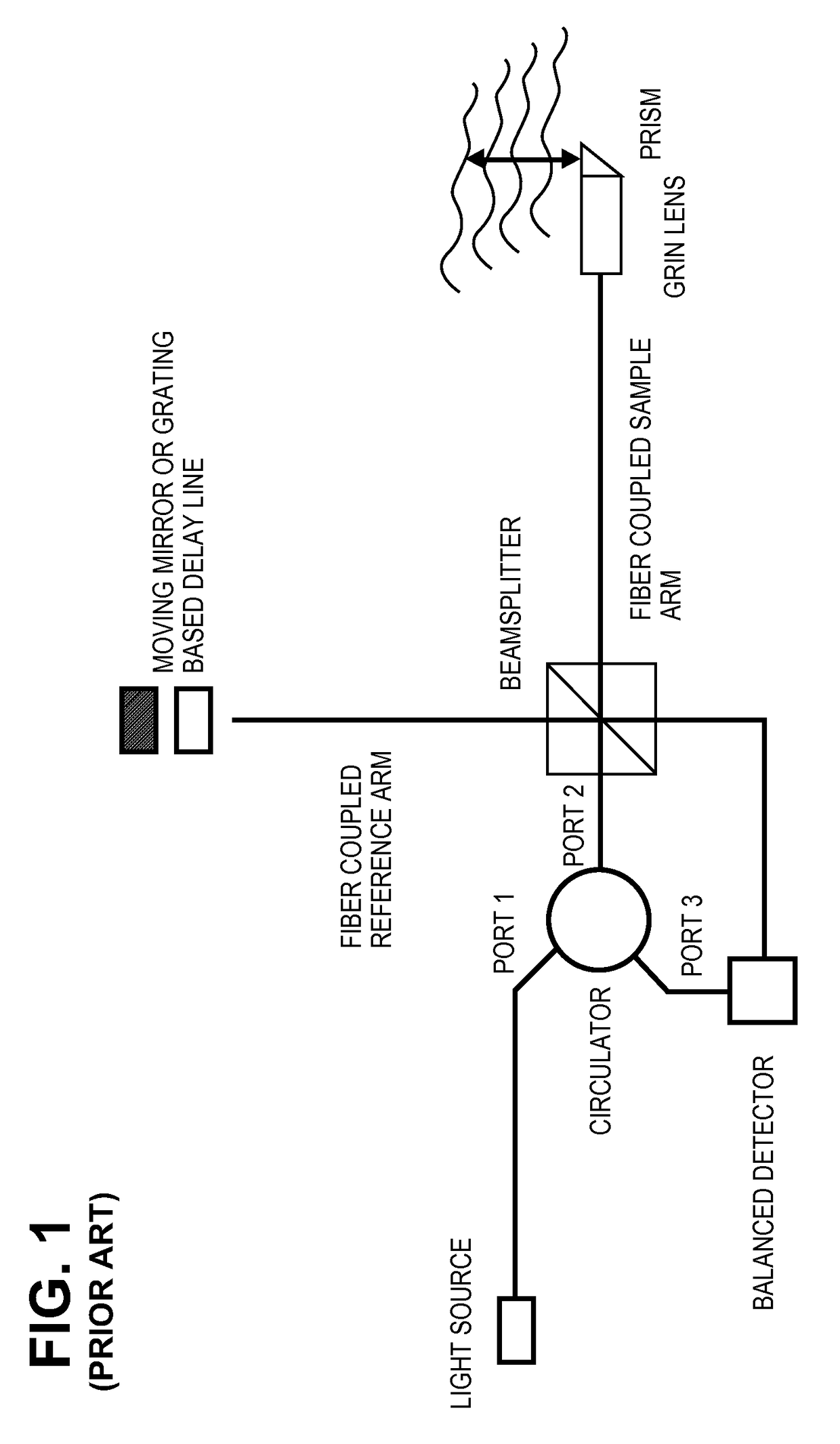
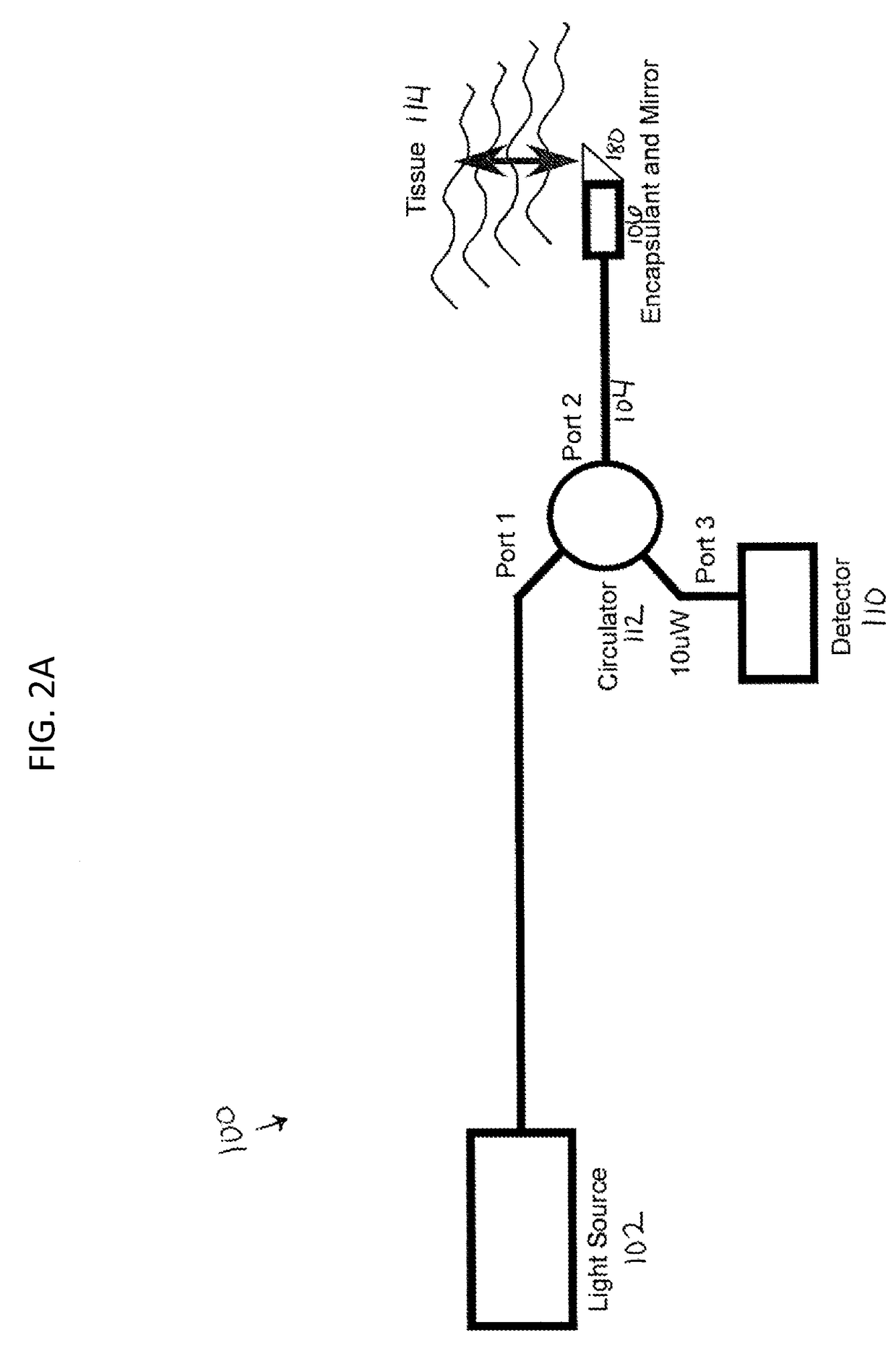
ActiveUS20100305452A1Shorten operation timeImprovement longCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringOptical radiationRefractive index
Described herein are catheters for use with Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) that include an optical fiber core having a first refractive index and an interface medium having a second refractive index, where the first and second refractive indexes are mismatched such that receiving electronics configured to receive optical radiation reflected from the reference interface and the target operate in a total noise range that is within 5 dB of the shot noise limit. These OCT catheters may include a silicon die mirror having a reflective coating that is embedded in the interface medium. The optical fiber can be fixed at just the distal end of the catheter, and may be managed within a handle that is attached to the proximal end of the catheter body, and is configured to allow rotation of the both catheter body and the optical fiber relative to the handle.
Owner:AVINGER
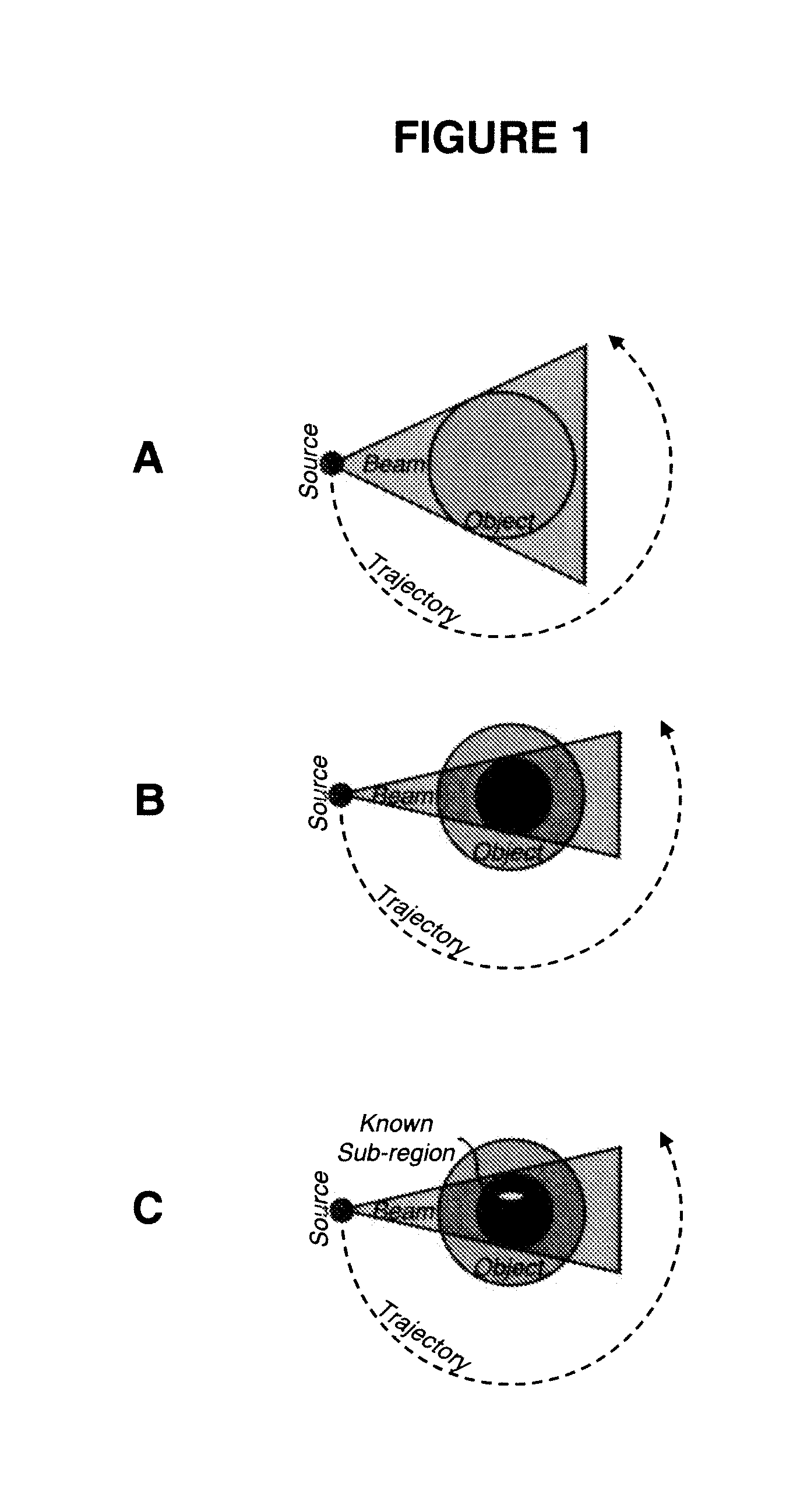
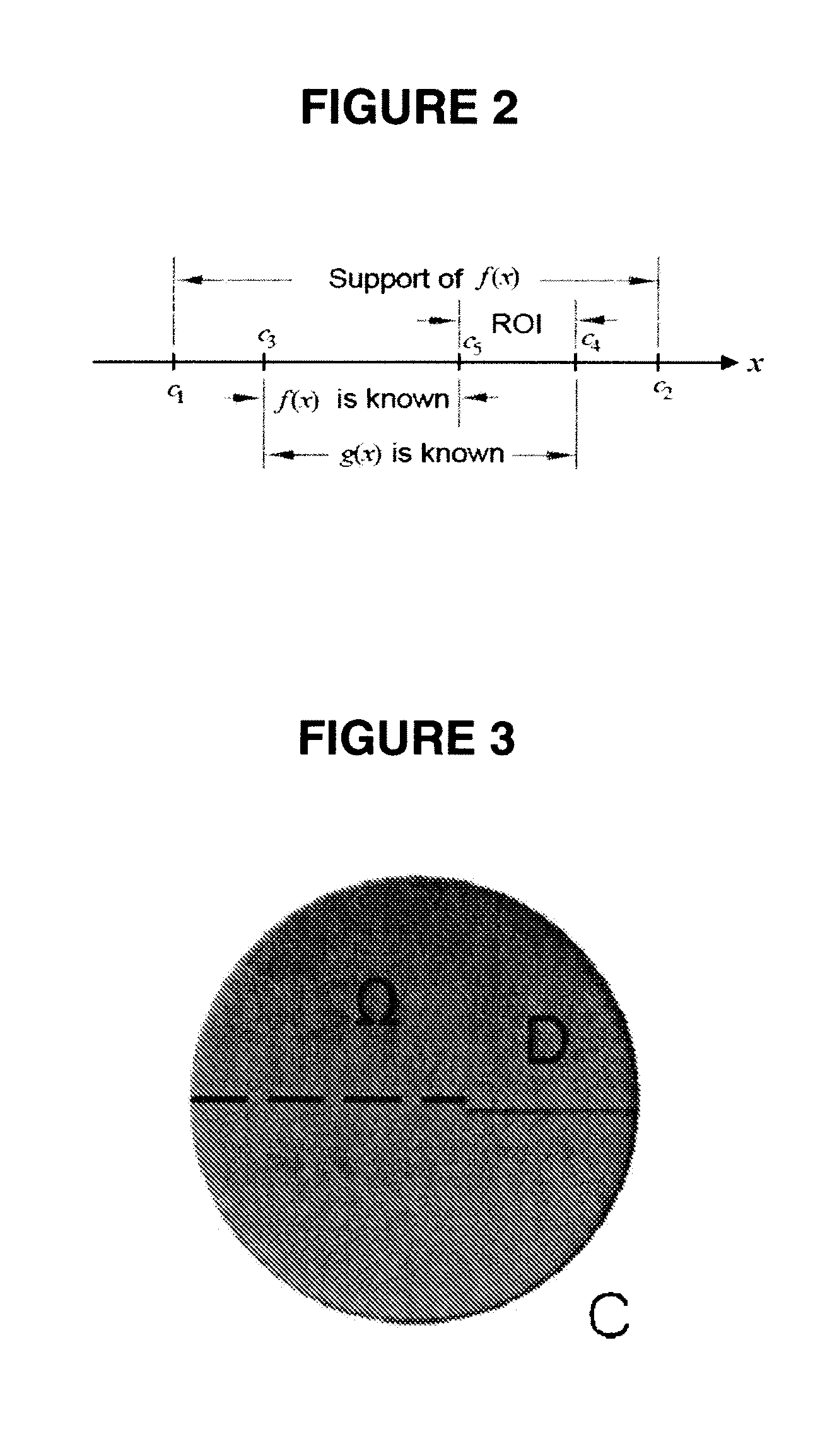
Interior Tomography and Instant Tomography by Reconstruction from Truncated Limited-Angle Projection Data
InactiveUS20090196393A1Faithful resolution of featureHigh spatial contrastReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAttenuation coefficientFractography
A system and method for tomographic image reconstruction using truncated limited-angle projection data that allows exact interior reconstruction (interior tomography) of a region of interest (ROI) based on the linear attenuation coefficient distribution of a subregion within the ROI, thereby improving image quality while reducing radiation dosage. In addition, the method includes parallel interior tomography using multiple sources beamed at multiple angles through an ROI and that enables higher temporal resolution.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND +1
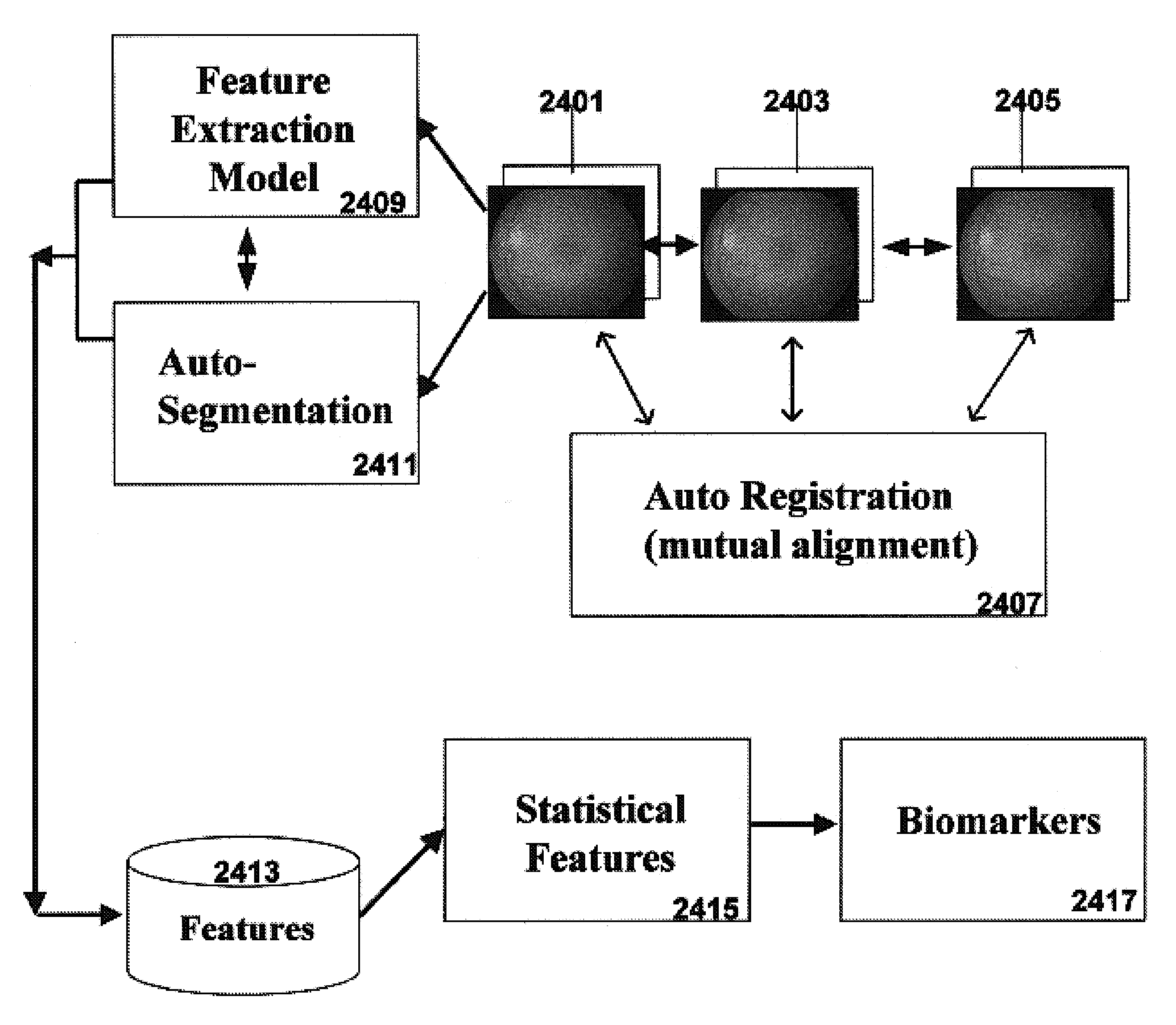
System and method for automation of morphological segmentation of bio-images
InactiveUS7668351B1Improve scoreShorten the timeImage enhancementImage analysisAutomatic segmentationFeature vector
Medical images are automatically segmented by customizing the morphological segmentation of features identified in the image based upon statistical analysis of the features within each region to be analyzed. The statistical description of the features, as reported through a feature vector, informs the system as to which input variables to select for further segmentation analysis for features residing within the region of the image analyzed. By customizing the automatic segmentation analysis to produce an enhanced image, features within the image are characterized more efficiently and precisely. False positive identification of lesions are minimized without sacrifice of true positive identifications.
Owner:KESTREL CORP
Display device
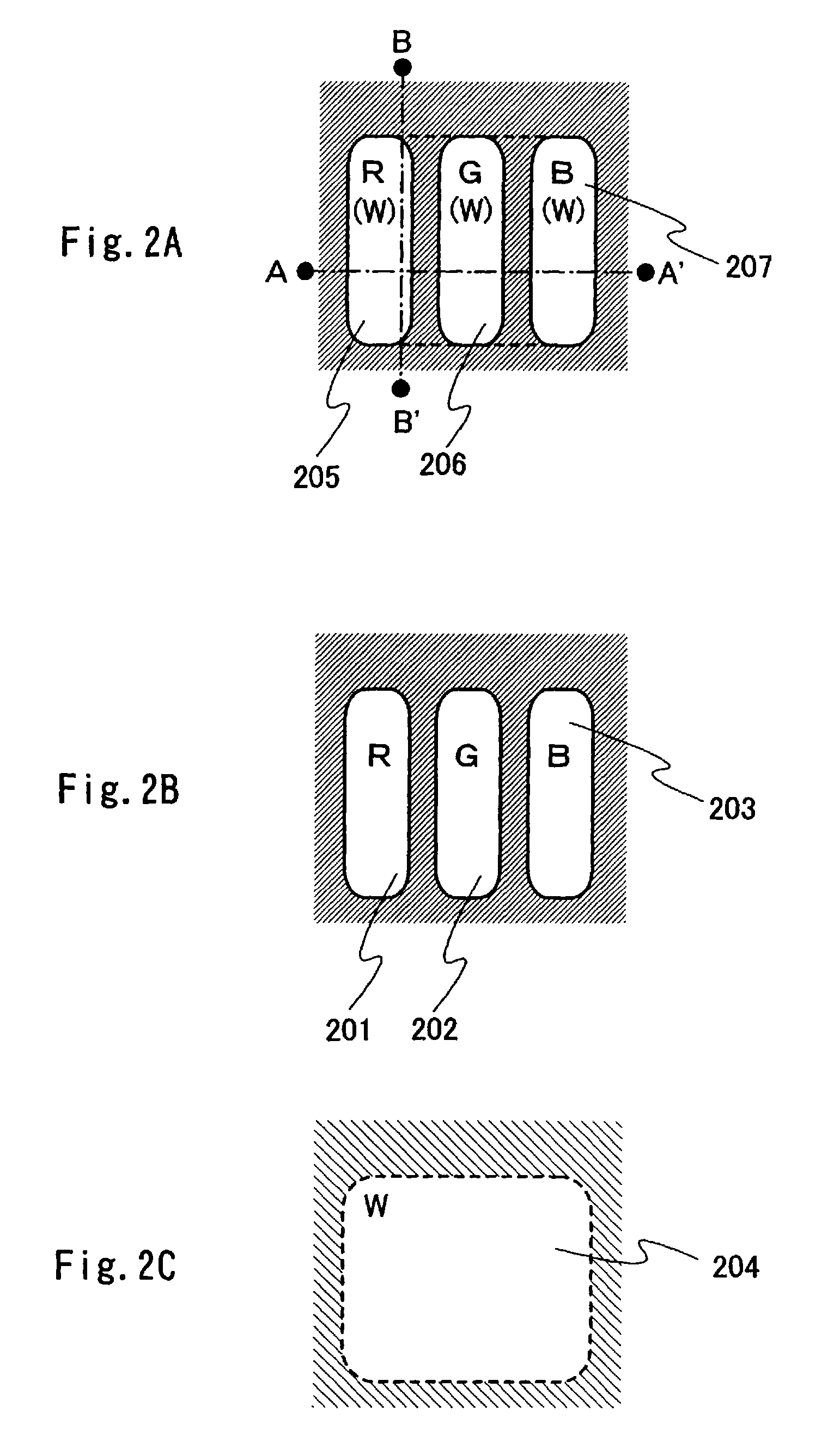
InactiveUS20060231842A1High chromaIncrease the number of colorsElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesImaging qualityDisplay device
To improve an image quality of an organic EL display by utilizing characteristics of a dual emission type organic light emitting element. A display device includes a first substrate over which a plurality of organic light emitting elements are provided and a second substrate over which an organic light emitting element is provided. The first and second substrates are facing each other. At least either the organic light emitting elements provided over the first substrate or the organic light emitting element provided over the second substrate emit / emits light toward both surfaces of the first or second substrate. Light emitting regions of the organic light emitting elements provided over the first substrate are overlapped with a light emitting region of the organic light emitting element provided over the second substrate as seen from the second substrate.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Single substrate camera device with CMOS image sensor
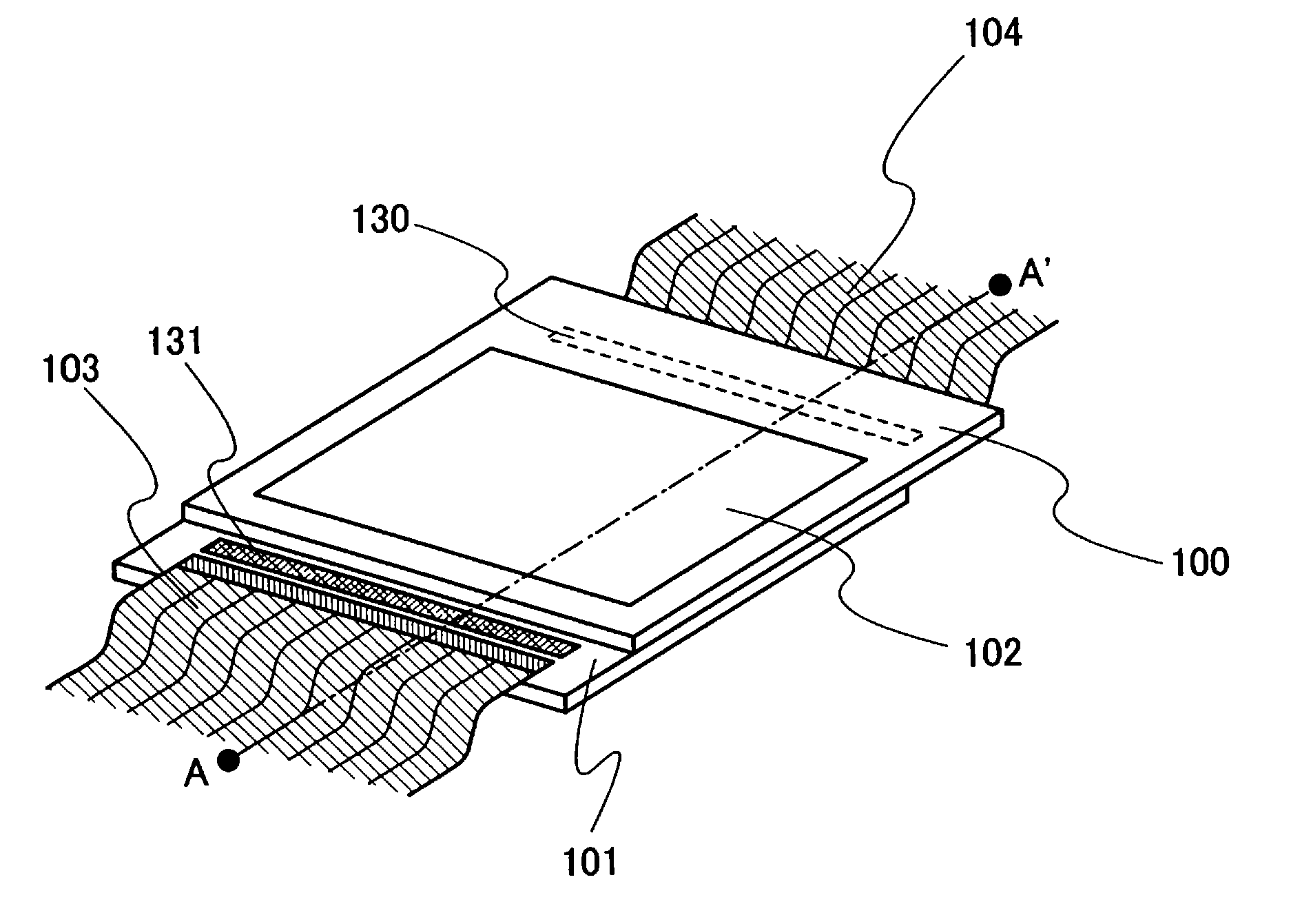
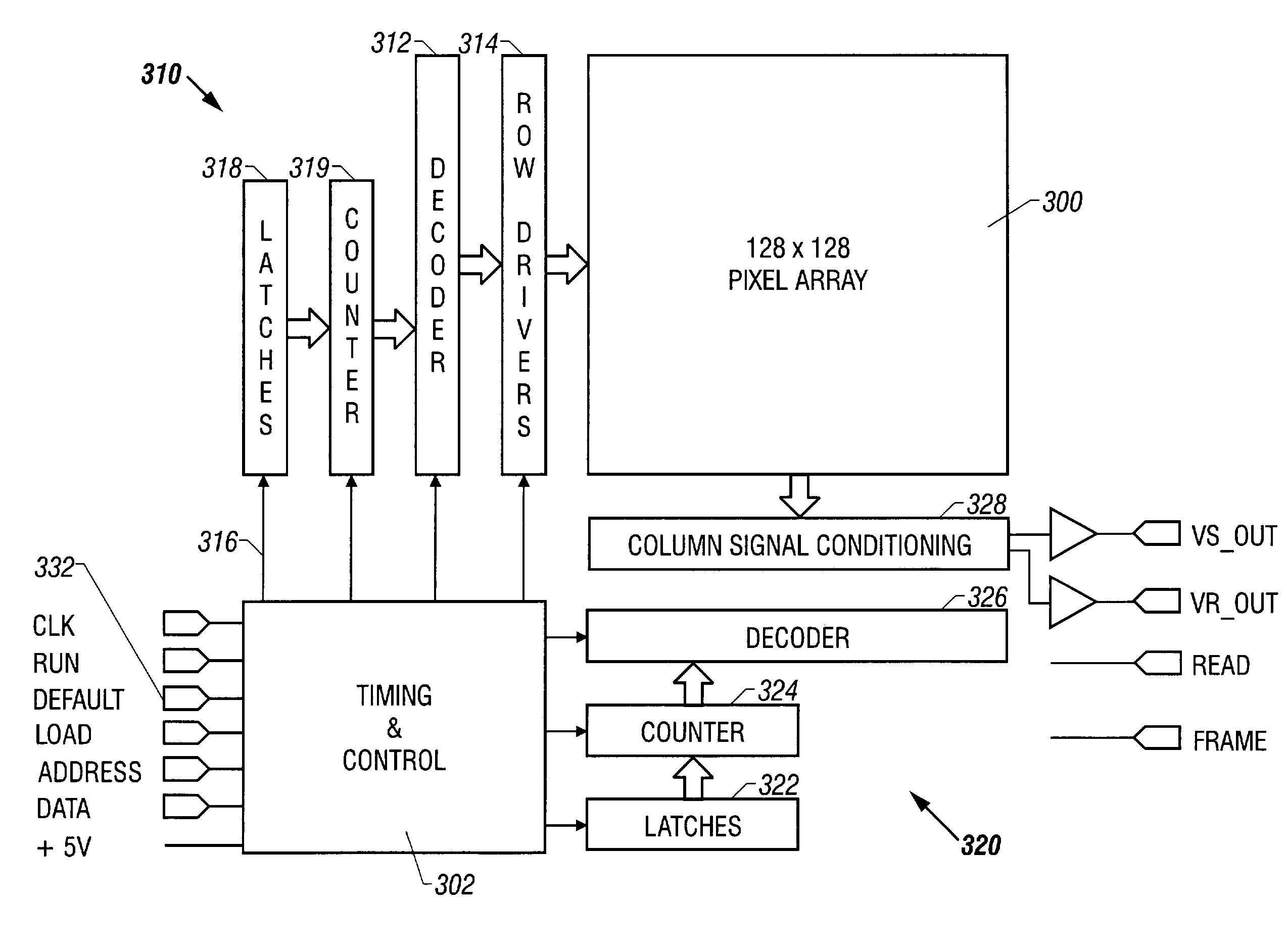
InactiveUS7369166B2Superfluous imageImprove fidelityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCMOSControl system
Single substrate device is formed to have an image acquisition device and a controller. The controller on the substrate controls the system operation.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
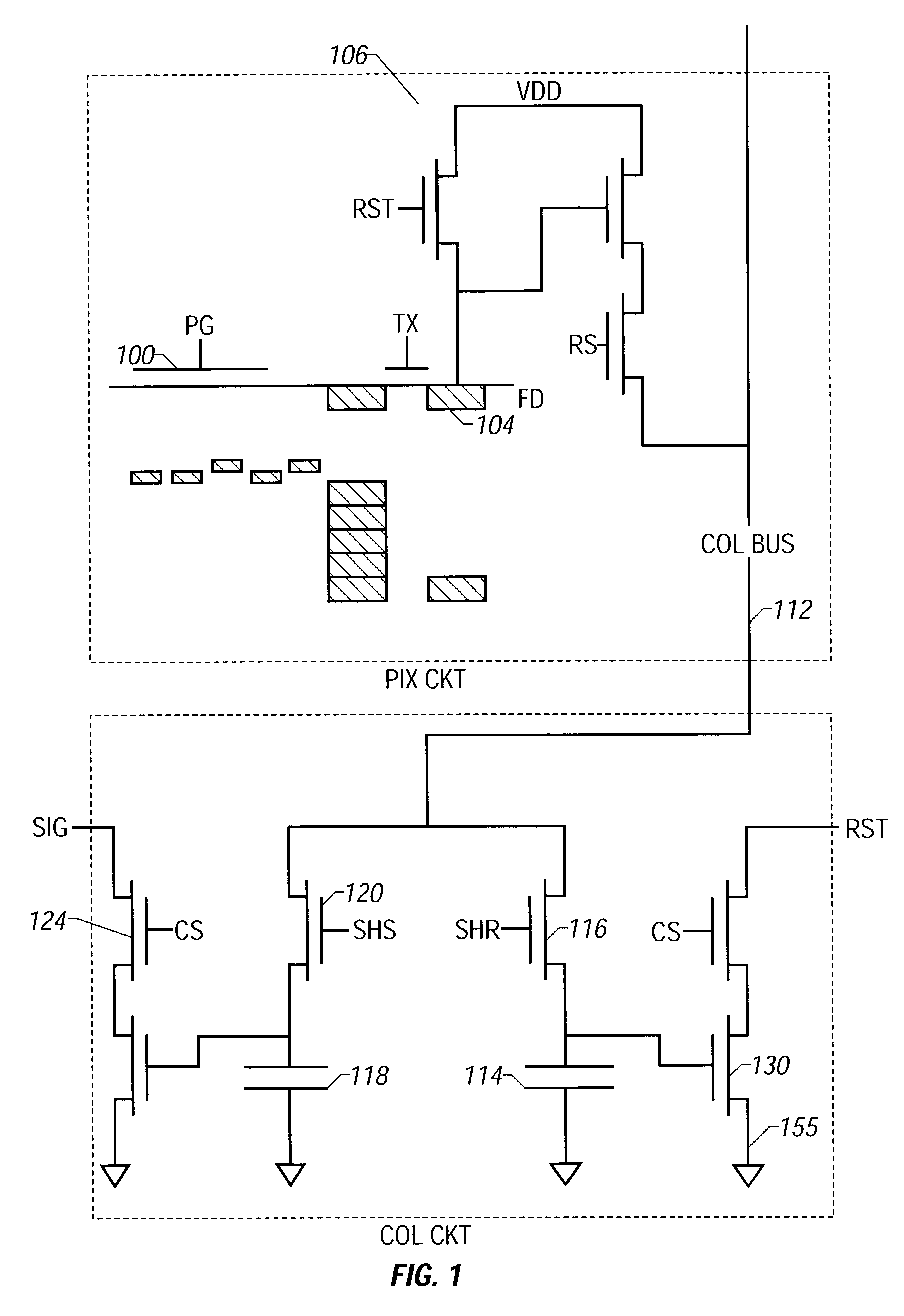
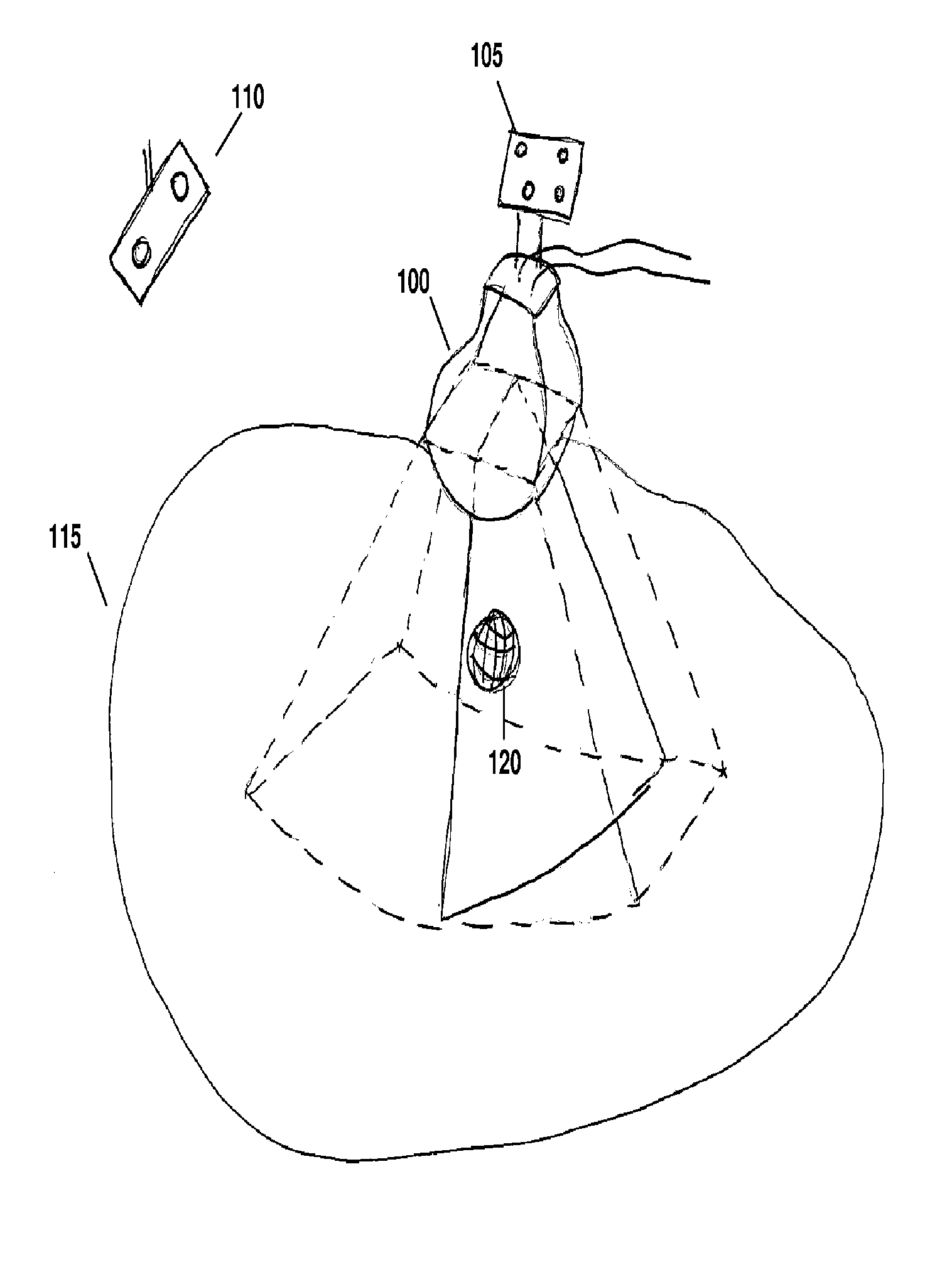
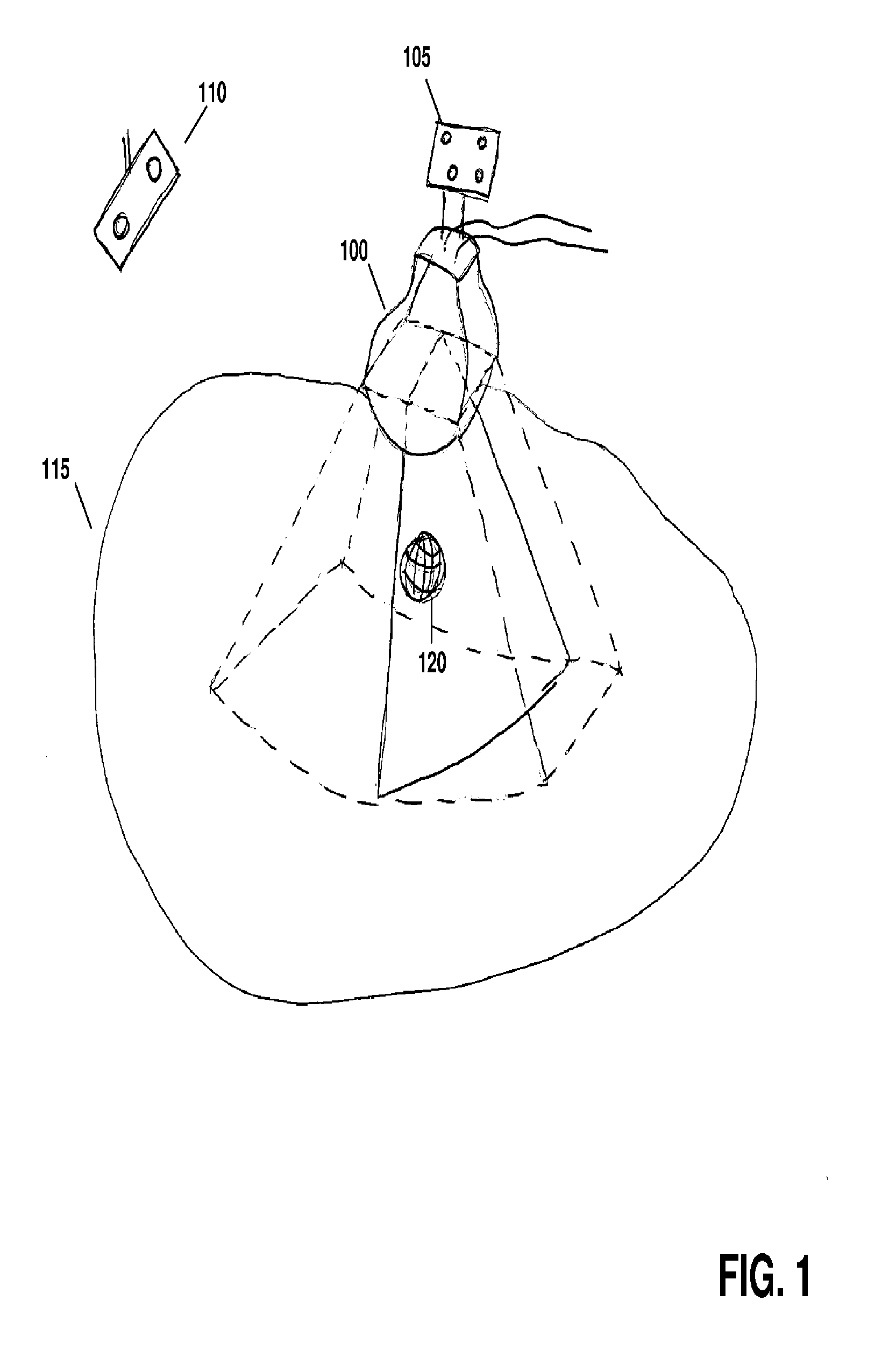
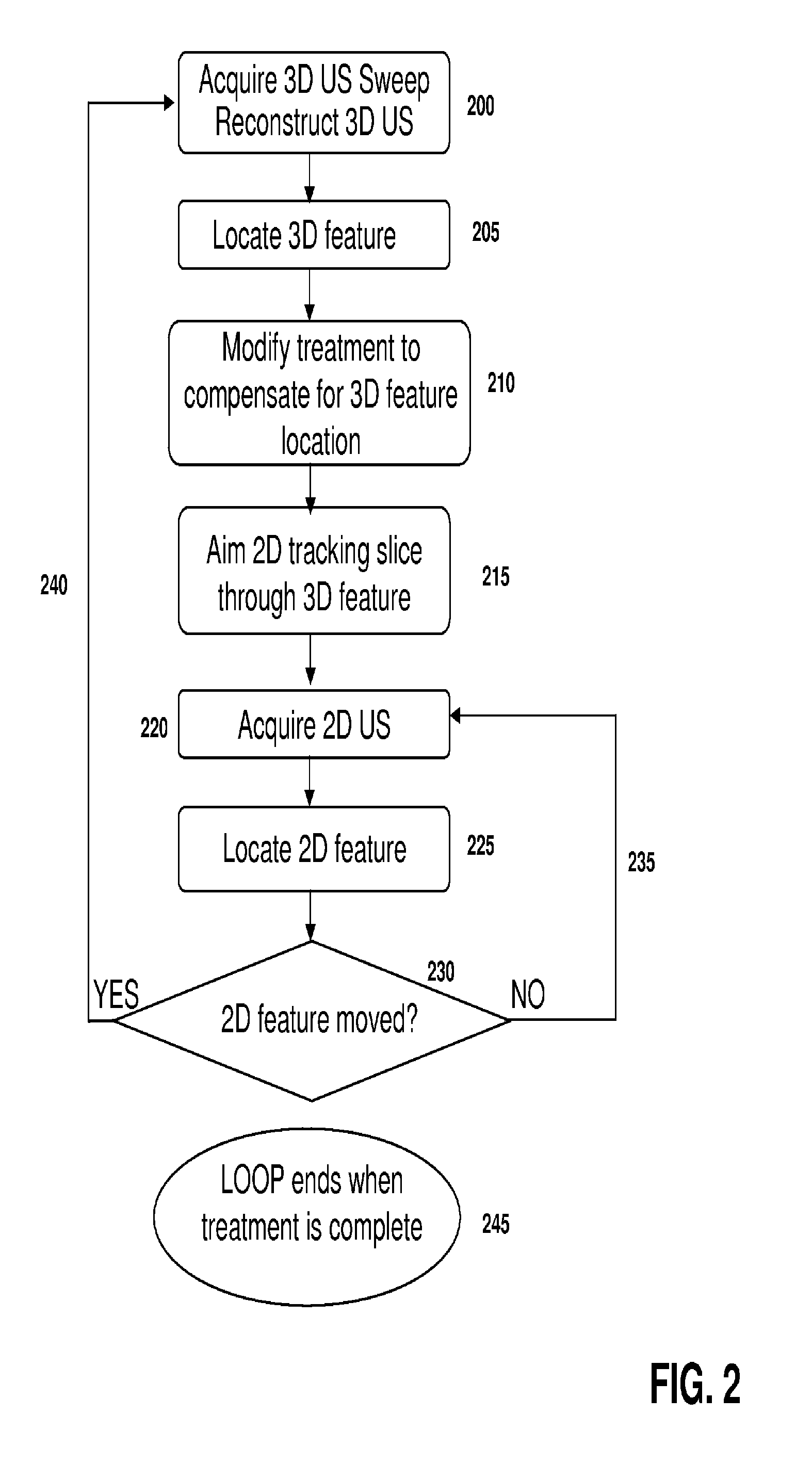
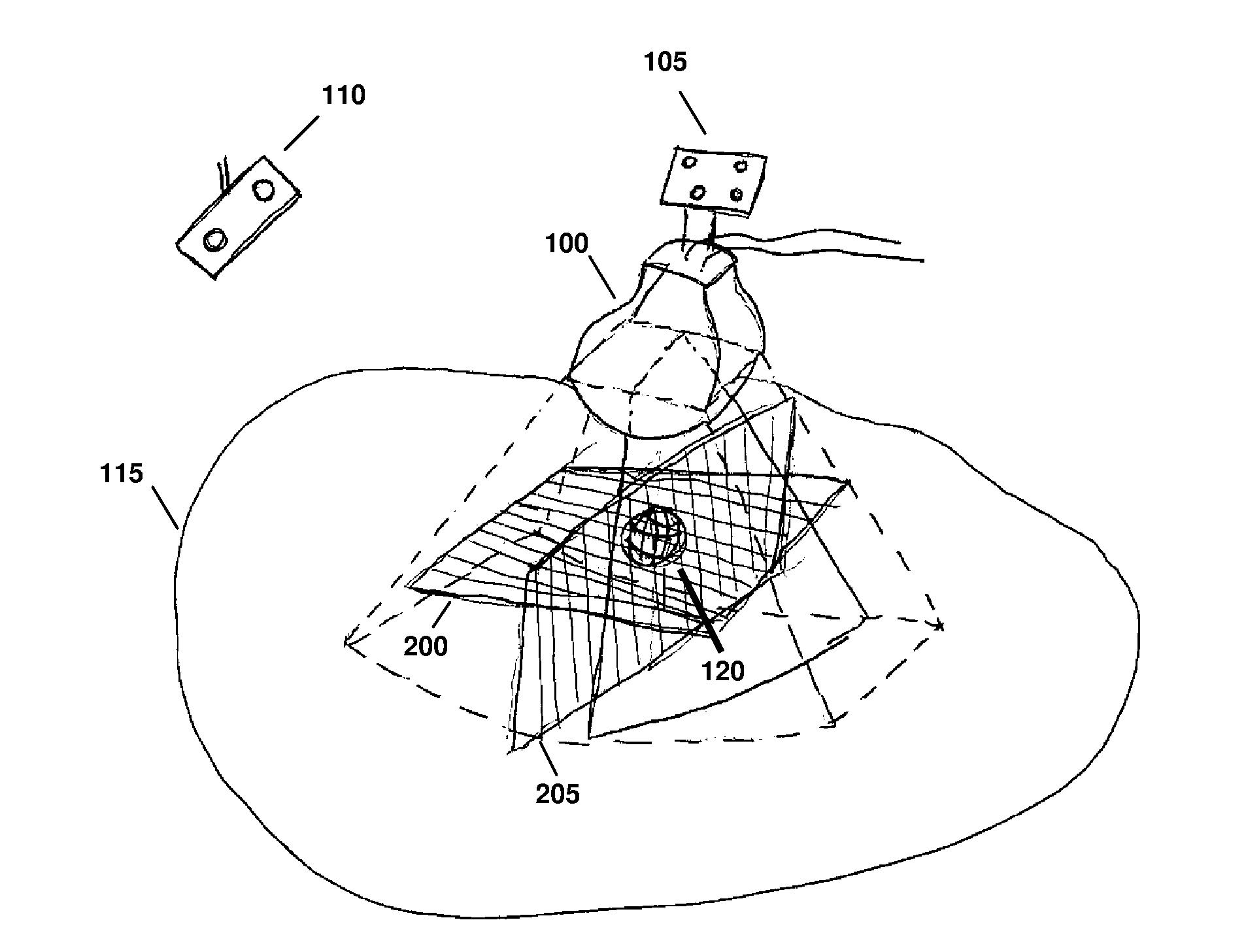
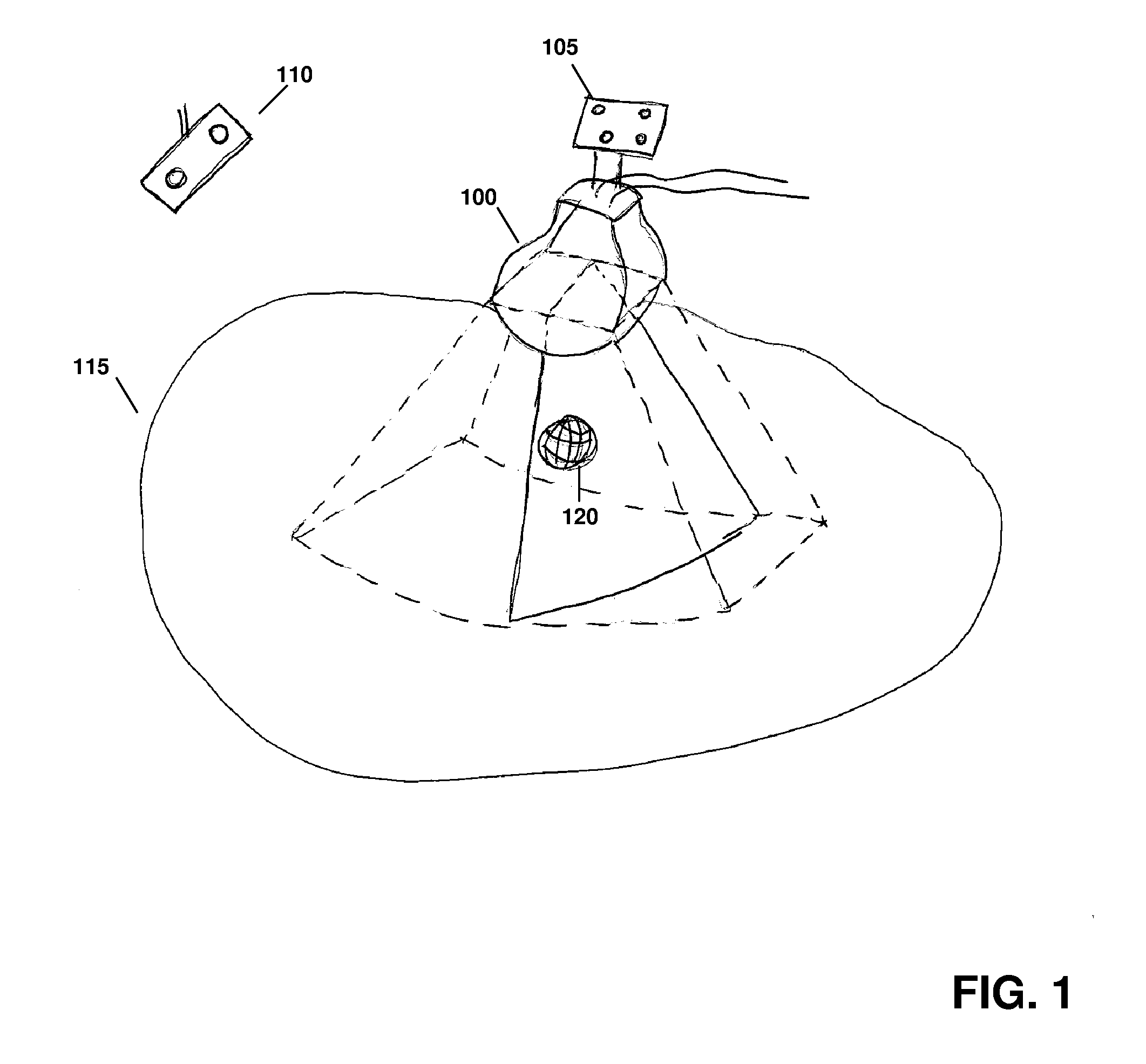
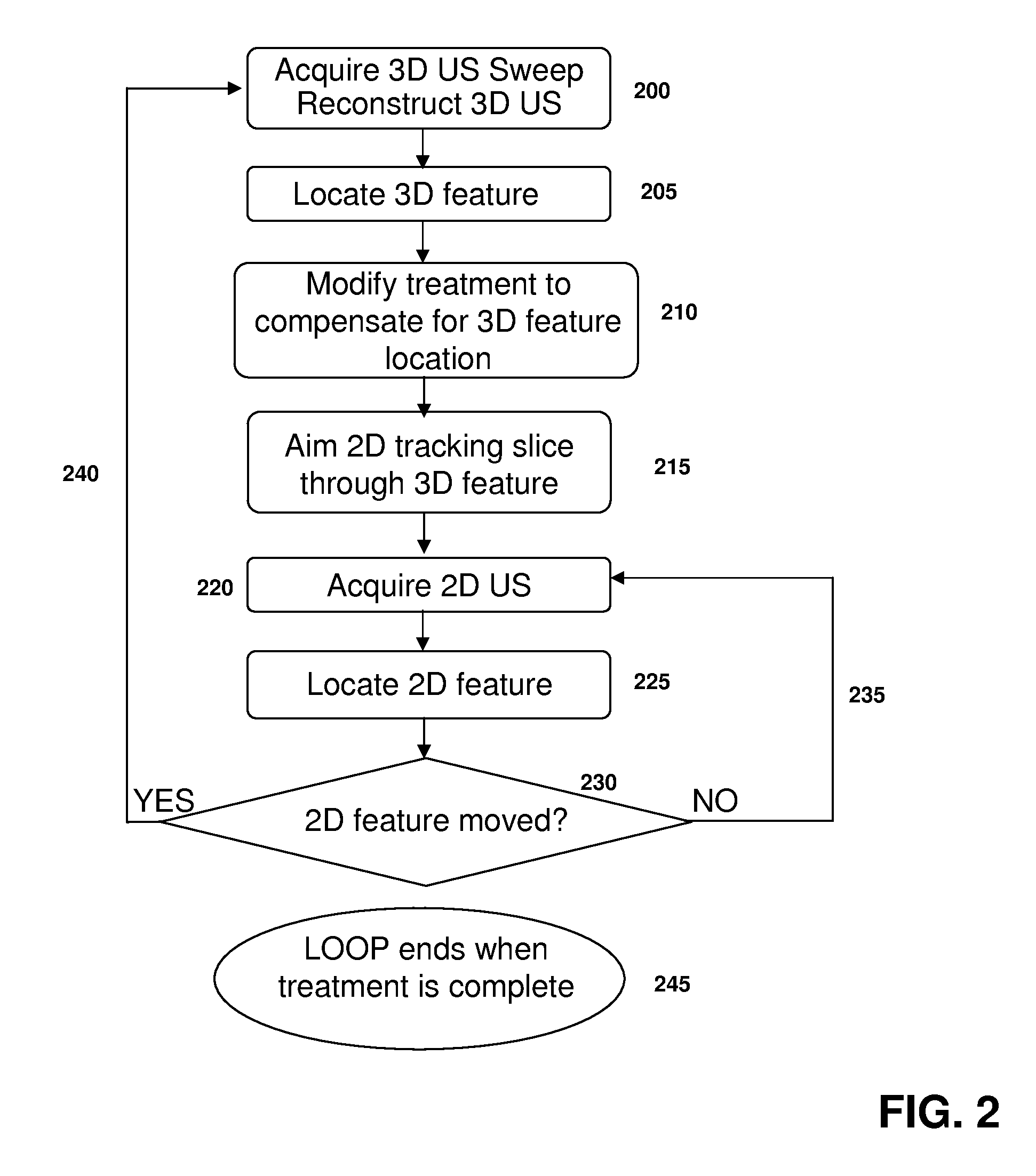
Feature Tracking Using Ultrasound
ActiveUS20120071758A1Reduce the burden onGood periodicityImage enhancementImage analysisSupporting systemSonification
Various implementations of the invention provide techniques and supporting systems that facilitate real-time or near-real-time ultrasound tracking for the purpose of calculating changes in anatomical features during a medical procedure. More specifically, anatomical features within a patient undergoing a medical procedure are tracked by obtaining temporally-distinct three dimensional ultrasound images that include the feature of interest and obtaining a targeted subset of ultrasound images focused on the feature. Based on the targeted subset of ultrasound images, a displacement of the feature is determined and image parameters used to obtain the targeted subset of ultrasound images are adjusted based on the displacement. This results in a time-based sequence of three dimensional images and targeted ultrasound images of the feature that identify changes in the position, size, location, and / or shape of the feature.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
Image display device
InactiveUS20100245345A1Enhanced stereoscopic effectImprove visual effectsSteroscopic systemsInput/output processes for data processingComputer graphics (images)Image transfer
An image display device 100 includes: a display unit 10 having an image screen 11 for displaying a two-dimensional image; an image transfer panel 20 located on a path of light left from the image screen 11; a floating image display unit 1 that displays, as a floating image, the light left from the image screen 11 in a space located on one side of the image transfer panel 20 opposite to the other side thereof facing the display unit 10; a direct-view image display unit 2 provided with a display unit 40 having an image screen 41 for displaying a two-dimensional image displayed on the image screen 41 as a direct view image. The image display device carries out:floating-image control that displays the floating image P2 such that the given object displayed as the floating image P2 is shifted in a specified first direction from the displayed position of the floating image P2 to the image screen 41; anddirect-view image control that executes a process associated with the given object during or after the shift of the given object, and displays, on the image screen 41, a two-dimensional image on which the executed process is reflected.
Owner:ASUKANET
Device and system for in vivo imaging
InactiveUS20060082648A1Quality improvementSuperfluous imageTelevision system detailsGastroscopesEngineeringIn vivo
The present invention provides a system and method for obtaining in vivo images. The system contains an imaging system and a transmitter for transmitting signals from a camera to a receiving system located outside a patient.
Owner:GIVEN IMAGING LTD
Display device
InactiveUS7714500B2High chromaIncrease the number of colorsDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesImaging qualityDisplay device
To improve an image quality of an organic EL display by utilizing characteristics of a dual emission type organic light emitting element. A display device includes a first substrate over which a plurality of organic light emitting elements are provided and a second substrate over which an organic light emitting element is provided. The first and second substrates are facing each other. At least either the organic light emitting elements provided over the first substrate or the organic light emitting element provided over the second substrate emit / emits light toward both surfaces of the first or second substrate. Light emitting regions of the organic light emitting elements provided over the first substrate are overlapped with a light emitting region of the organic light emitting element provided over the second substrate as seen from the second substrate.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Feature Tracking Using Ultrasound
InactiveUS20110172526A1Reduce the burden onGood periodicityImage enhancementImage analysisSupporting systemSonification
Various implementations of the invention provide techniques and supporting systems that facilitate real-time or near-real-time ultrasound tracking for the purpose of calculating changes in anatomical features during a medical procedure. More specifically, anatomical features within a patient undergoing a medical procedure are tracked by obtaining temporally-distinct three dimensional ultrasound images that include the feature of interest and obtaining a targeted subset of ultrasound images focused on the feature. Based on the targeted subset of ultrasound images, a displacement of the feature is determined and image parameters used to obtain the targeted subset of ultrasound images are adjusted based on the displacement. This results in a time-based sequence of three dimensional images and targeted ultrasound images of the feature that identify changes in the position, size, location, and / or shape of the feature.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
Blur Correction Device, Blur Correction Method, Electronic Apparatus Including Blur Correction Device, Image File And Image File Creating Apparatus
InactiveUS20080259170A1Avoid difficult choicesSmall amountImage enhancementTelevision system detailsThumbnail ImageCorrection method
Image files are rearranged according to the blurring amount obtained from each of blurring information pieces of the image files and displayed as thumbnail images. After several image files are selected from the displayed image files, the image information pieces of the selected image files are sequentially corrected.
Owner:XACTI CORP
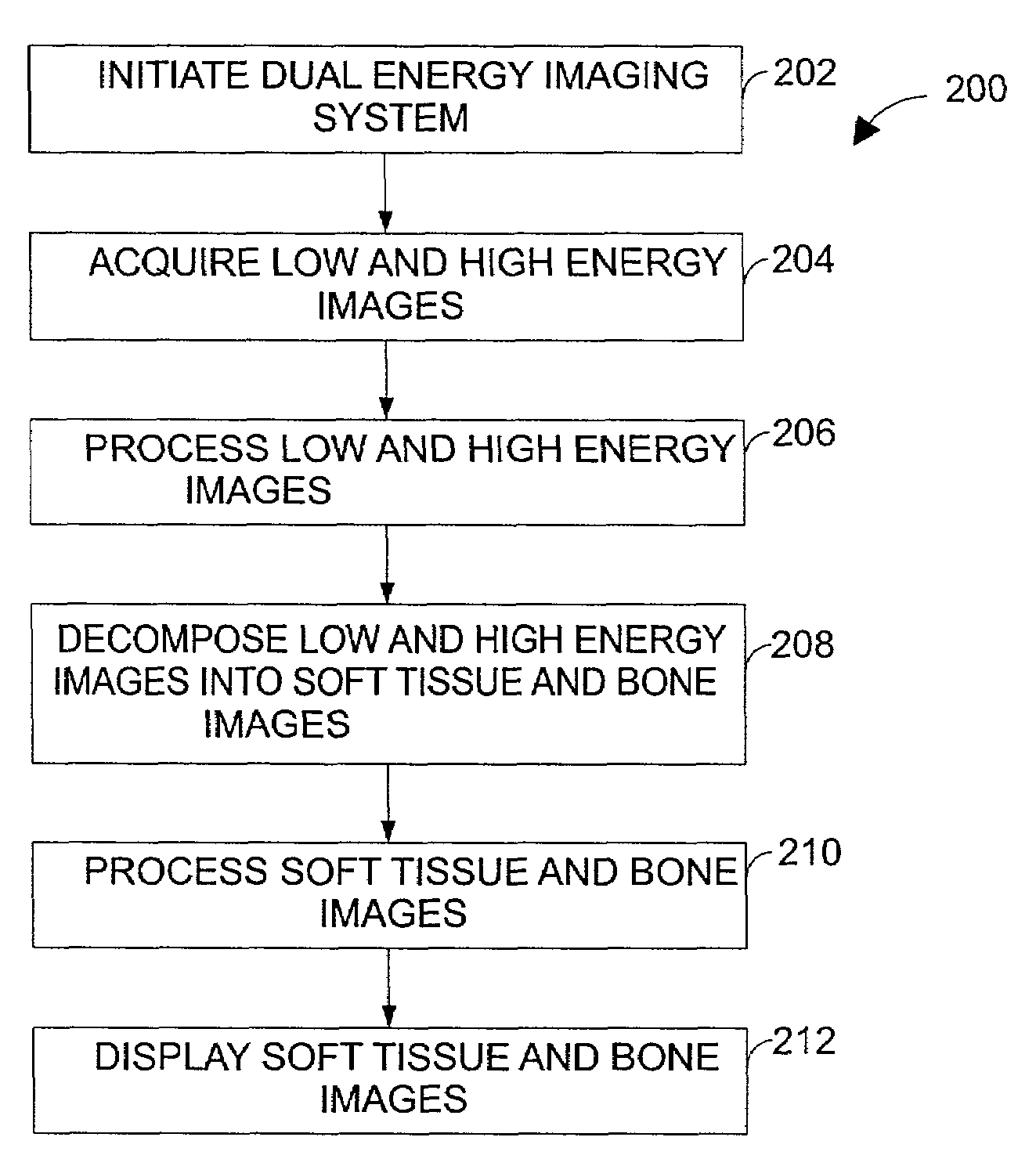
Automatic selection of the log-subtraction decomposition parameters for dual energy chest radiography
InactiveUS7068826B2Avoid problemsSuperfluous imageImage enhancementImage analysisFiltrationDecomposition
The present technique provides a variety of processing schemes for decomposing soft tissue and bone images more accurately from low and high-energy images acquired from an imaging system, such as a dual-energy digital radiography system using flat-panel technology. In particular, a parameter selection process is provided for automatically computing the decomposition parameters WS and WB to create soft tissue and bone images, respectively. The parameter selection process modifies a default decomposition parameter based on a variety of image and technique variables, such as intensity levels of the low and high-energy images, the patient size, and the collimator filtration setting. The parameter selection process avoids robustness problems associated with image-based algorithms, and the process may operate without any direct user interaction.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
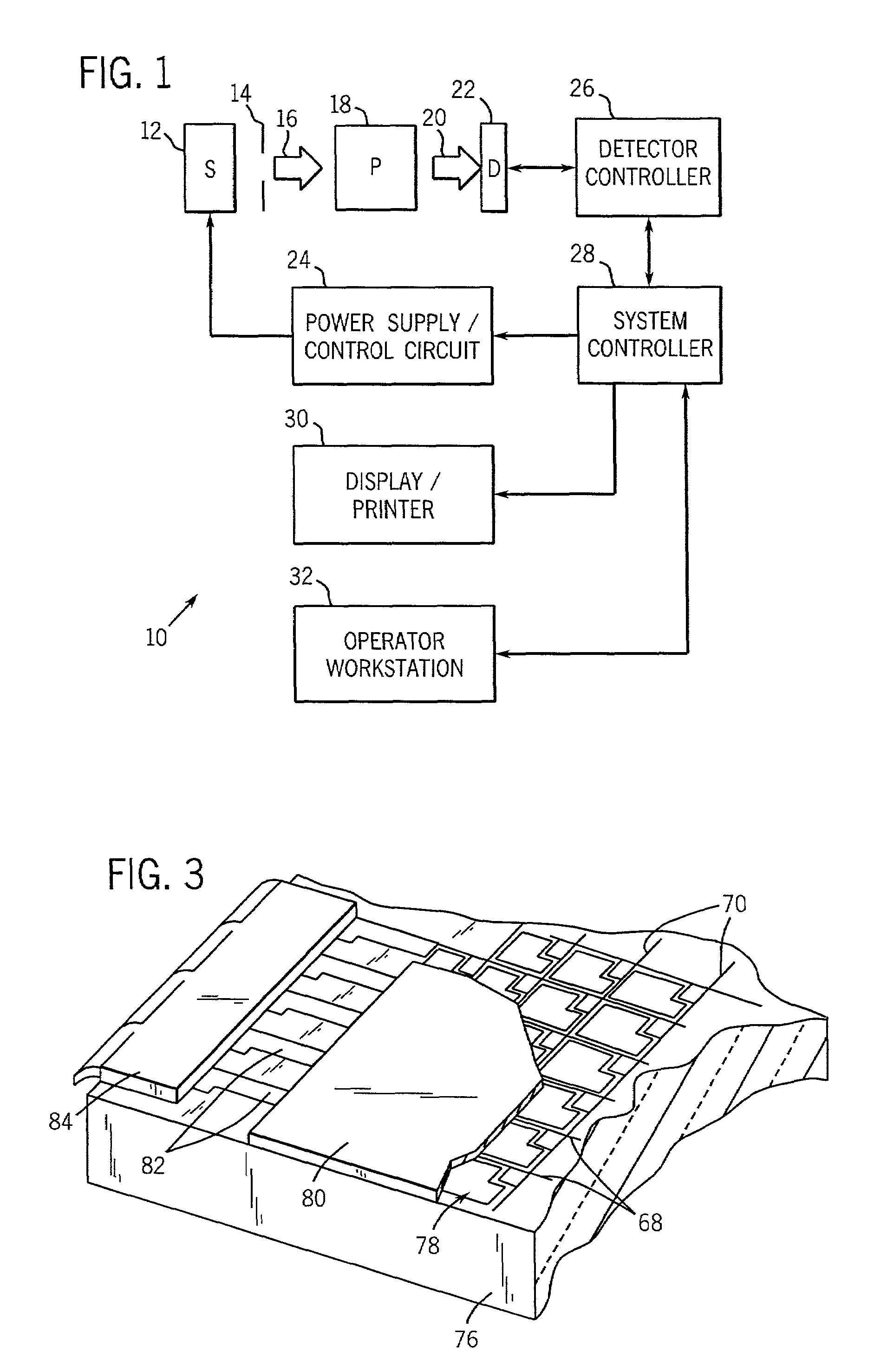
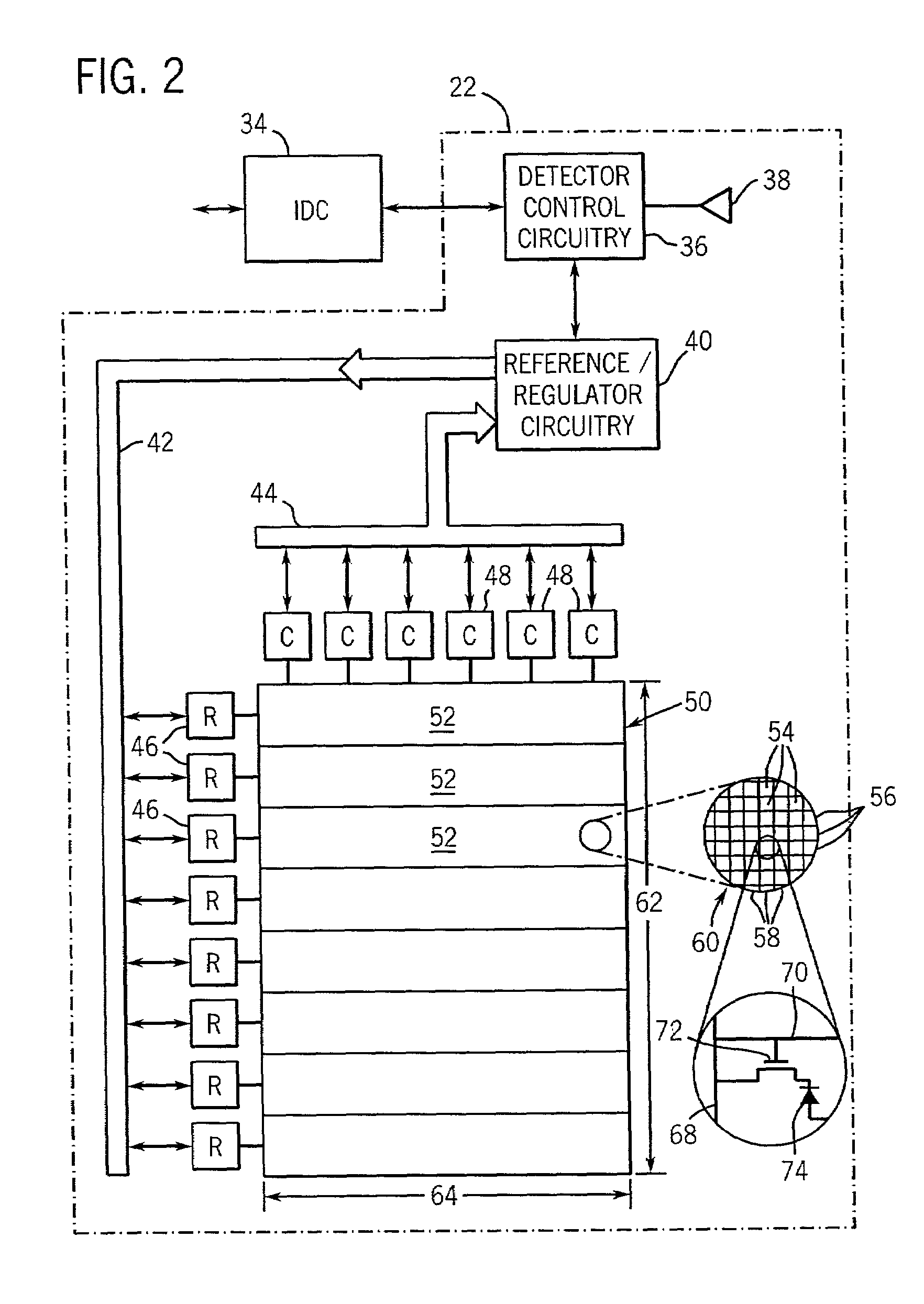
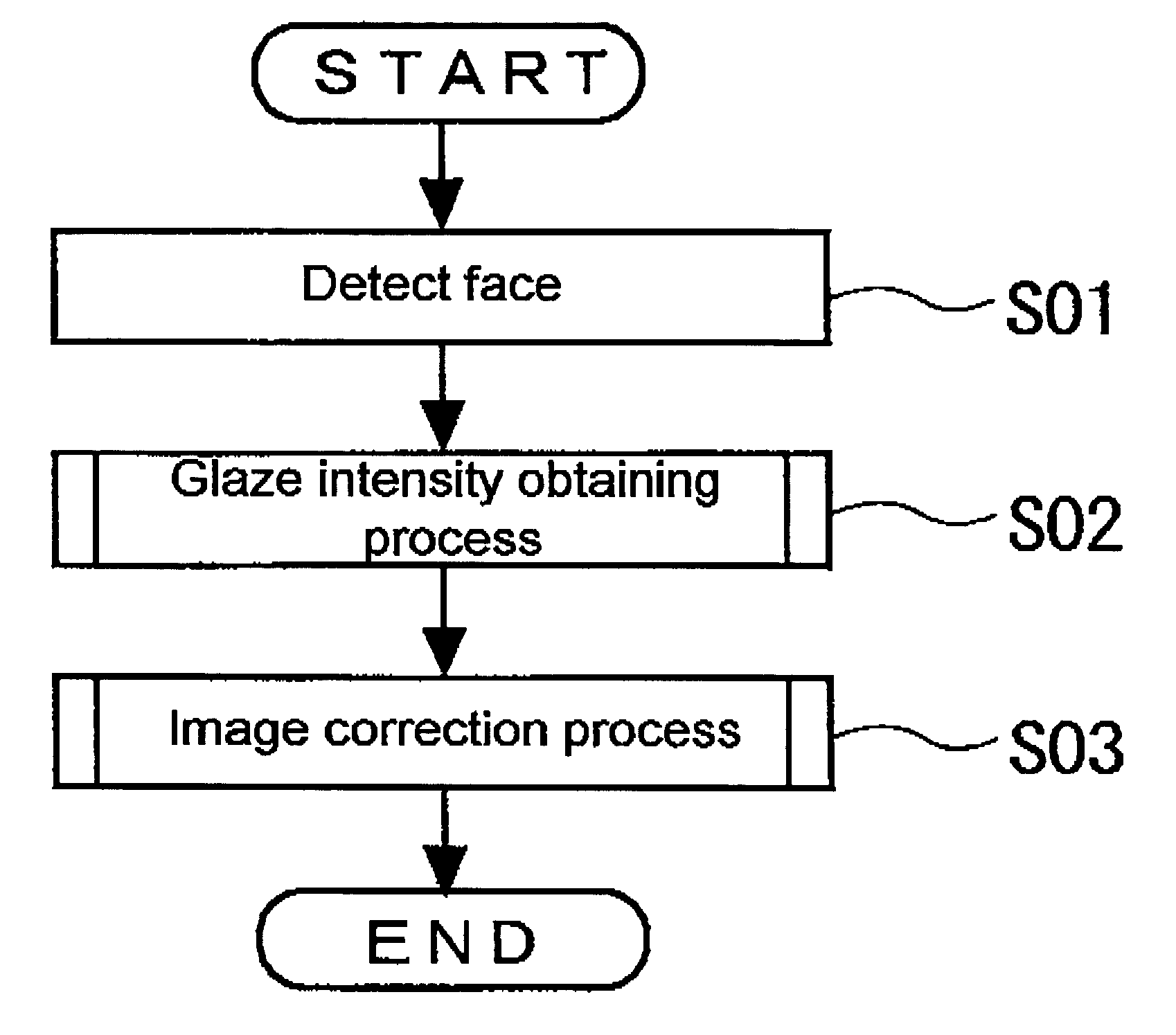
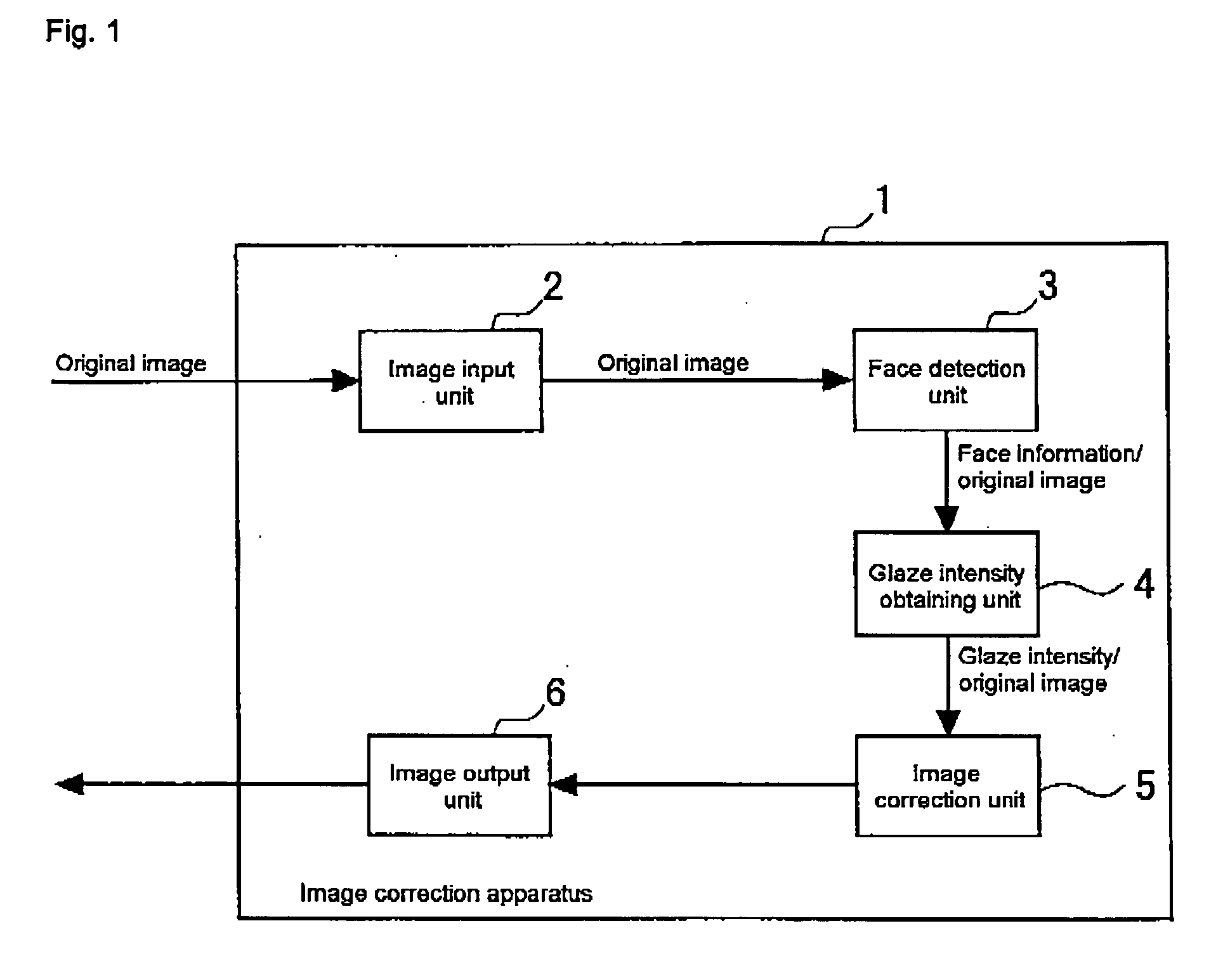
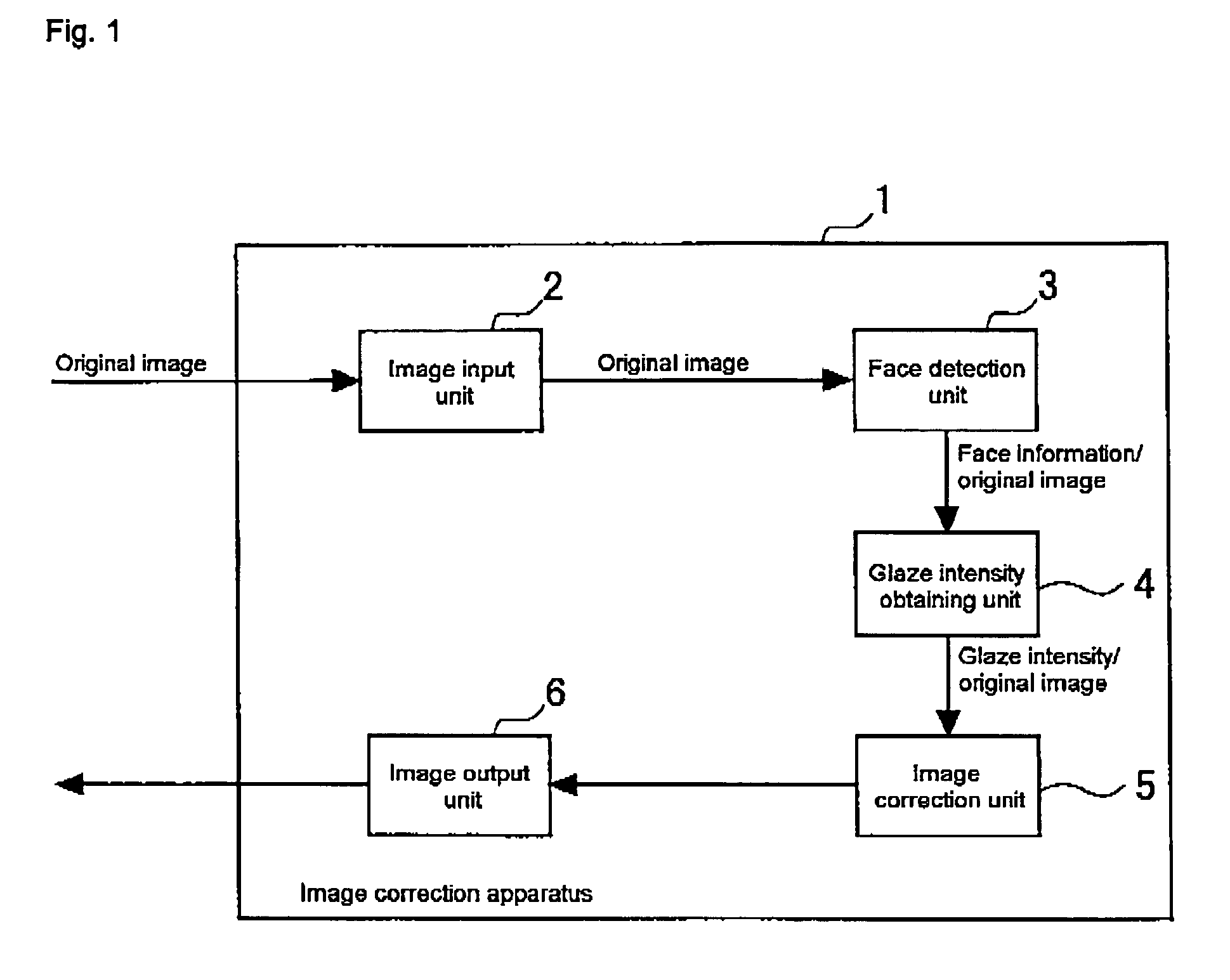
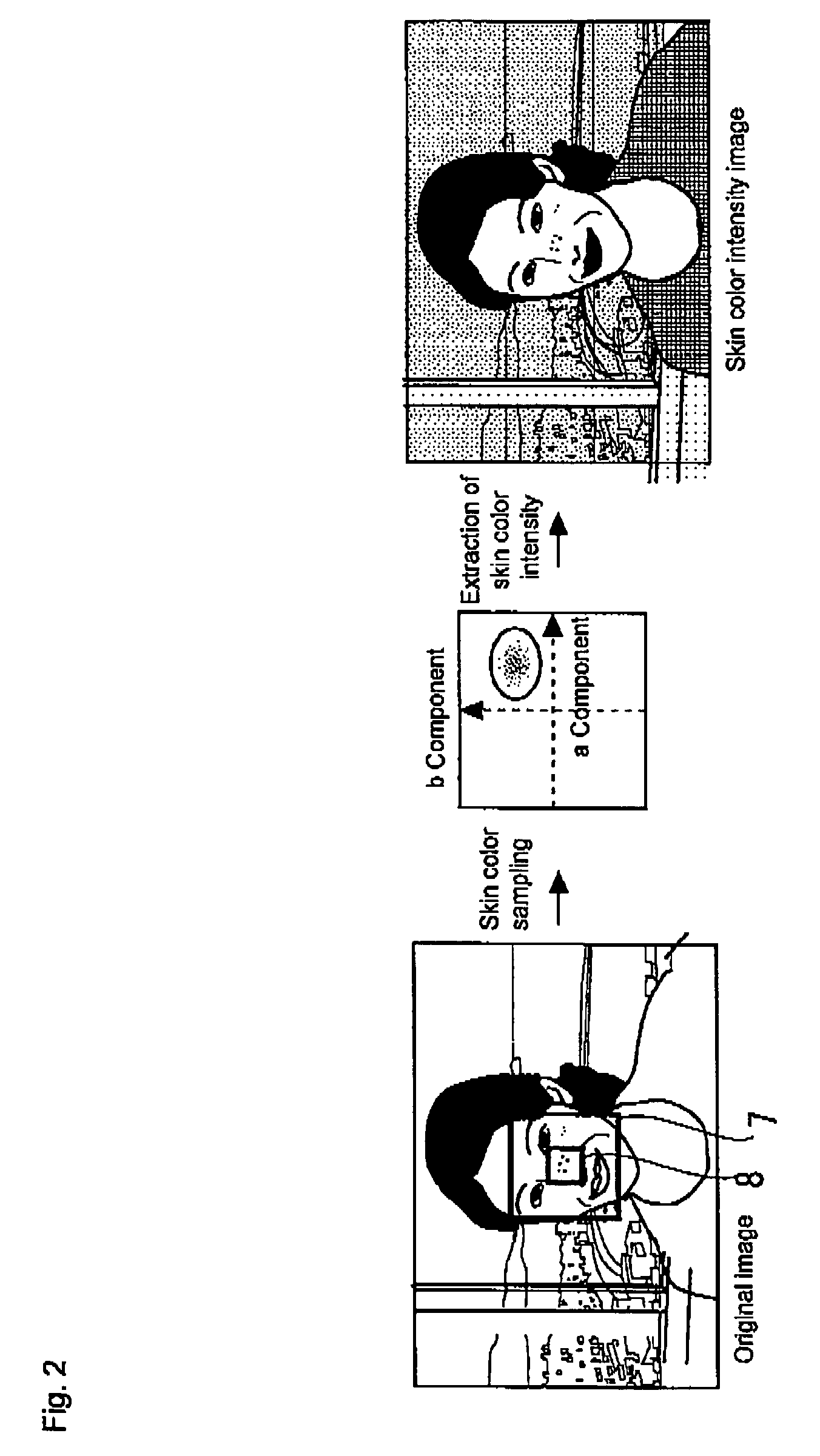
Image correction apparatus
ActiveUS20050271295A1Increase brightnessImage can be preventedImage enhancementImage analysisImage correctionComputer science
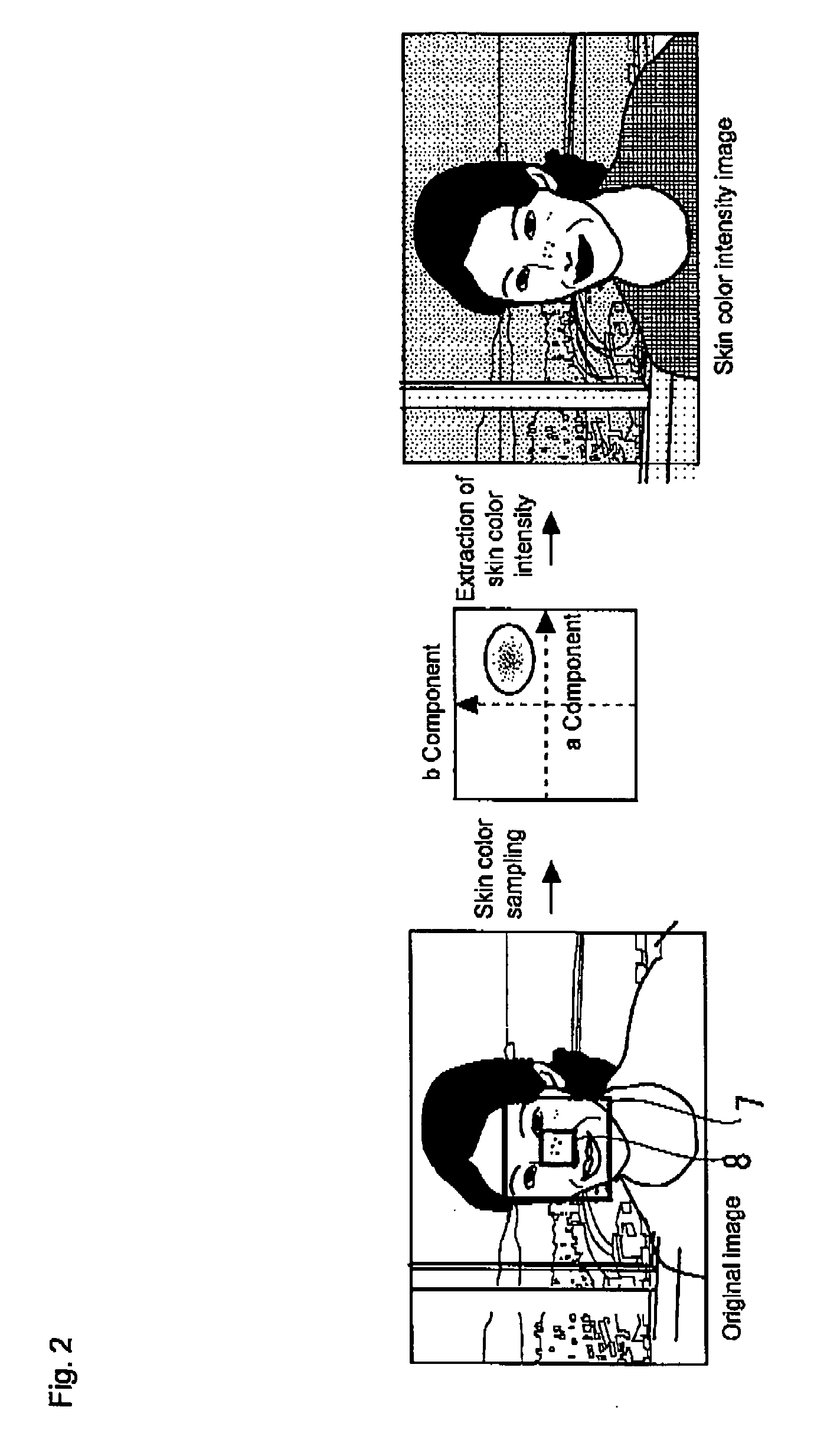
An object of the invention is to provide an apparatus which performs correction only to a high-brightness portion generated in a particular region, in which a decrease in brightness is necessary, and glaze is removed or reduced. A correction process in which the brightness or the lightness is decreased is simply performed to a pixel in which the brightness or the lightness is high, but a predetermined region (for example, face, eyes, and mouth) of a subject is detected and a degree of correction of each pixel is determined based on the detection result (a position and a color of the predetermined region). Therefore, the region in which the decrease in brightness is not necessary is maintained at high brightness, and the image correction is performed only to the region in which the decrease in brightness is necessary (for example, the region in which the glaze of a skin is generated).
Owner:ORMON CORP
Sweeping real-time single point fiber
InactiveUS6859203B2Increase computing speedSuperfluous imageImage enhancementImage analysisFiberVoxel
An imaging method for imaging a subject (18) including fibrous / anisotropic structures (102) includes acquiring three-dimensional image representations without and with a plurality of different diffusion weighting and directions. When a user (56) hovers a selection device over a voxel of the image, a fiber representation (54) is extracted in substantially real time. The representation is generated by following a direction of a major eigenvector e1 from voxel to voxel. A human-viewable display of the fiber representation is produced (210).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Systems for spectral multiplexing of source images to provide a composite image, for rendering the composite image, and for spectral demultiplexing the composite image, which achieve increased dynamic range in a recovered source image
InactiveUS7155068B2Maximum usable contrastImprove dynamic rangeCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsMultiplexingComputer graphics (images)
Methods and apparatus for spectrally-encoding plural source images and for providing the spectrally-encoded plural source images in a composite image, for rendering the composite image in a physical form, or for recovering at least one of the encoded source images from the rendered composite image such that the recovered source image is made distinguishable. The composite image is generated using an image-dependent dynamic range determination so as to provide a maximum usable contrast in a recovered source image.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Optical coherence tomography for biological imaging
ActiveUS9788790B2Shorten operation timeImprovements for long- and short-term outcomesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterOptical radiationBiological imaging
Described herein are catheters for use with Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) that include an optical fiber core having a first refractive index and an interface medium having a second refractive index, where the first and second refractive indexes are mismatched such that receiving electronics configured to receive optical radiation reflected from the reference interface and the target operate in a total noise range that is within 5dB of the shot noise limit. These OCT catheters may include a silicon die mirror having a reflective coating that is embedded in the interface medium. The optical fiber can be fixed at just the distal end of the catheter, and may be managed within a handle that is attached to the proximal end of the catheter body, and is configured to allow rotation of both the catheter body and the optical fiber relative to the handle.
Owner:AVINGER
Image correction apparatus
ActiveUS7539342B2Set become largeSuperfluous imageImage enhancementImage analysisImage correctionComputer science
Owner:ORMON CORP
Systems for spectral multiplexing of source images to provide a composite image, for rendering the composite image, and for spectral demultiplexing the composite image to obtain a normalized color image
InactiveUS7379588B2Avoid and reduce visual confusionMaximum usable contrastColor television with pulse code modulationCharacter and pattern recognitionColor imageRadiology
Methods and apparatus for spectrally-encoding plural source images and for providing the spectrally-encoded plural source images in a composite image, for rendering the composite image in a physical form, or for recovering a normalized version of an encoded source image from the rendered composite image such that the recovered source image is made distinguishable as a normalized color image.
Owner:XEROX CORP
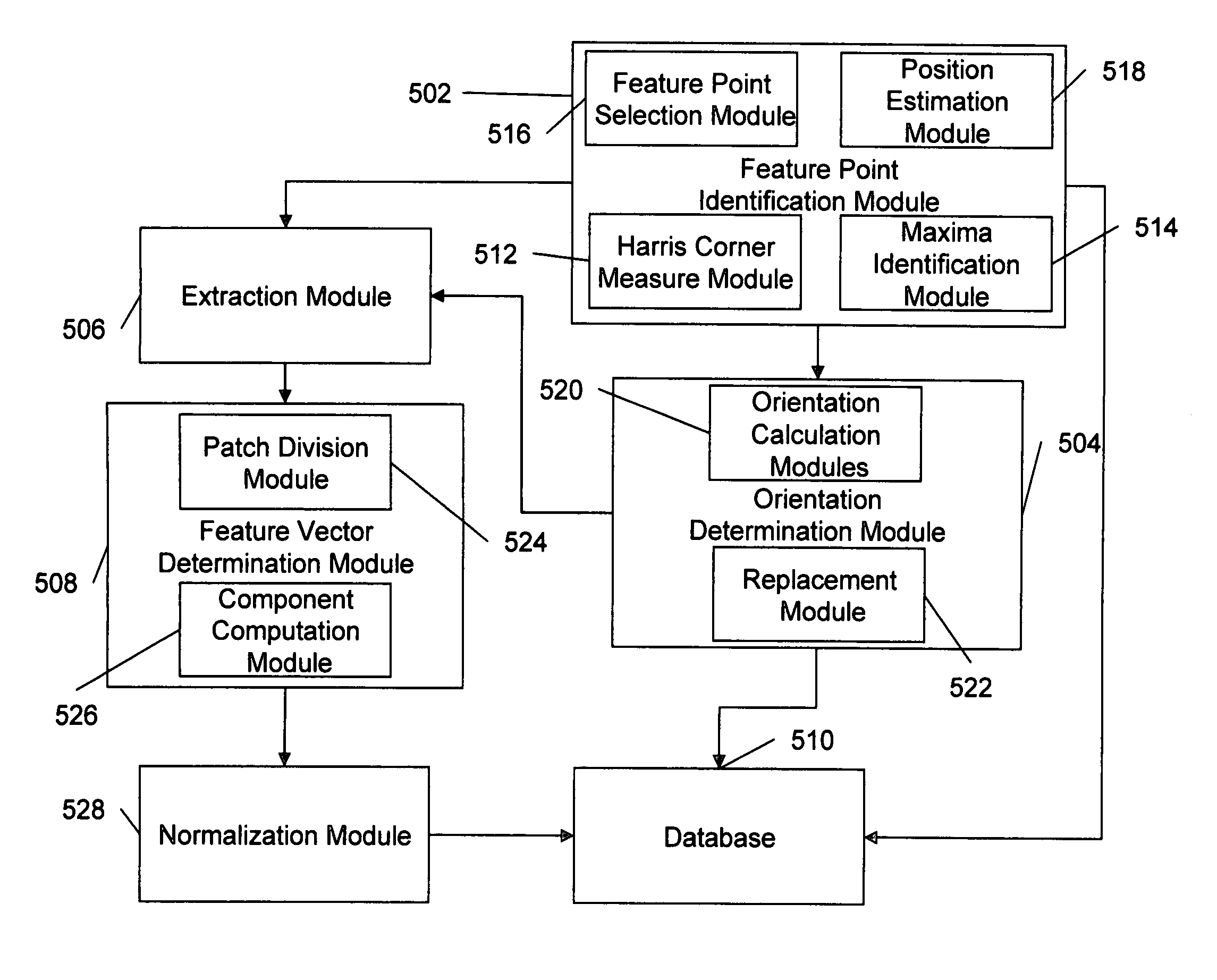
Method and system for representing image patches
ActiveUS8406507B2Improve representationSuperfluous imageCharacter and pattern recognitionImage codingFeature vectorScale space
A method, system and computer program product for representing an image is provided. The image that needs to be represented is represented in the form of a Gaussian pyramid which is a scale-space representation of the image and includes several pyramid images. The feature points in the pyramid images are identified and a specified number of feature points are selected. The orientations of the selected feature points are obtained by using a set of orientation calculating algorithms. A patch is extracted around the feature point in the pyramid images based on the orientations of the feature point and the sampling factor of the pyramid image. The boundary patches in the pyramid images are extracted by padding the pyramid images with extra pixels. The feature vectors of the extracted patches are defined. These feature vectors are normalized so that the components in the feature vectors are less than a threshold.
Owner:A9 COM INC
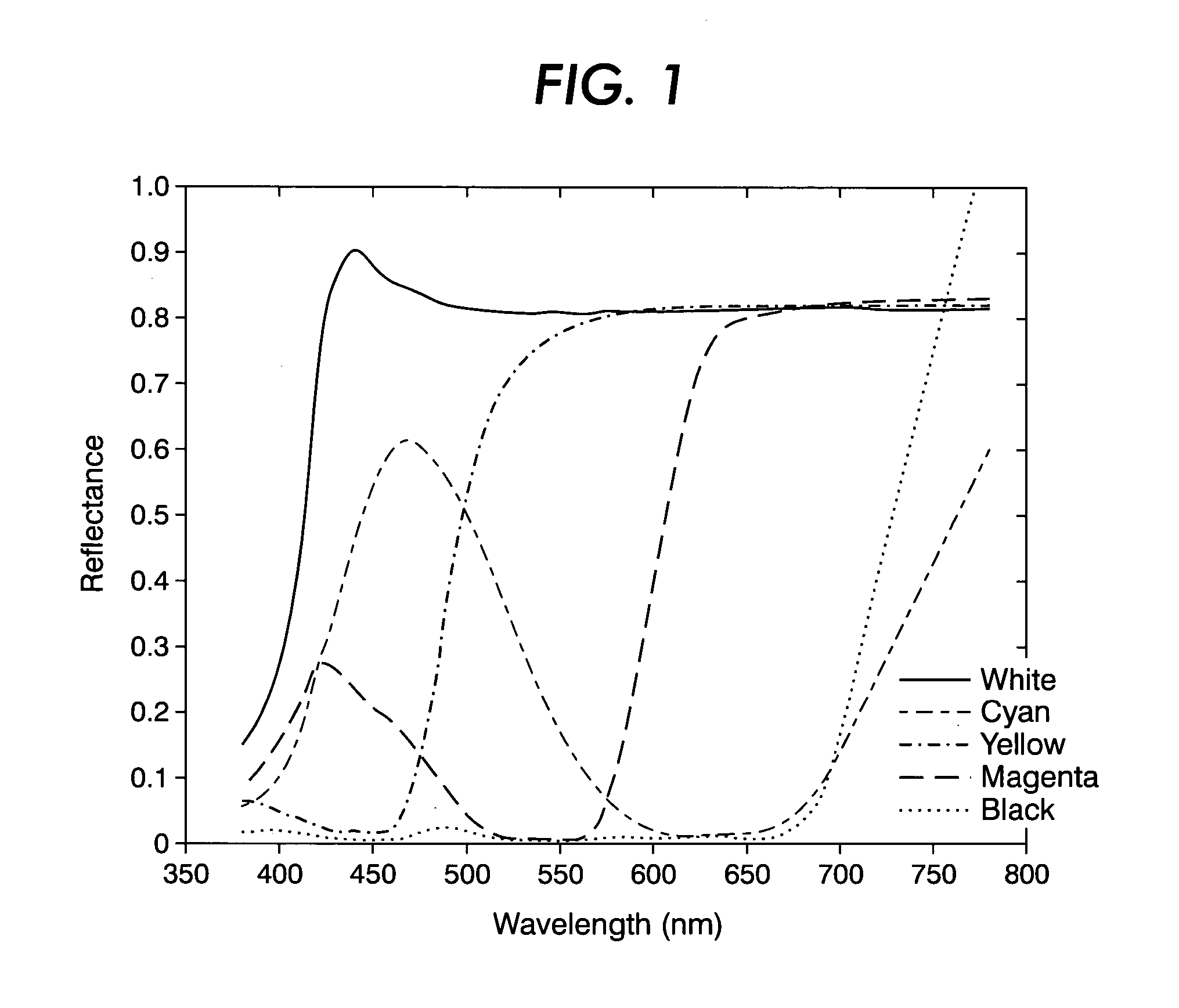
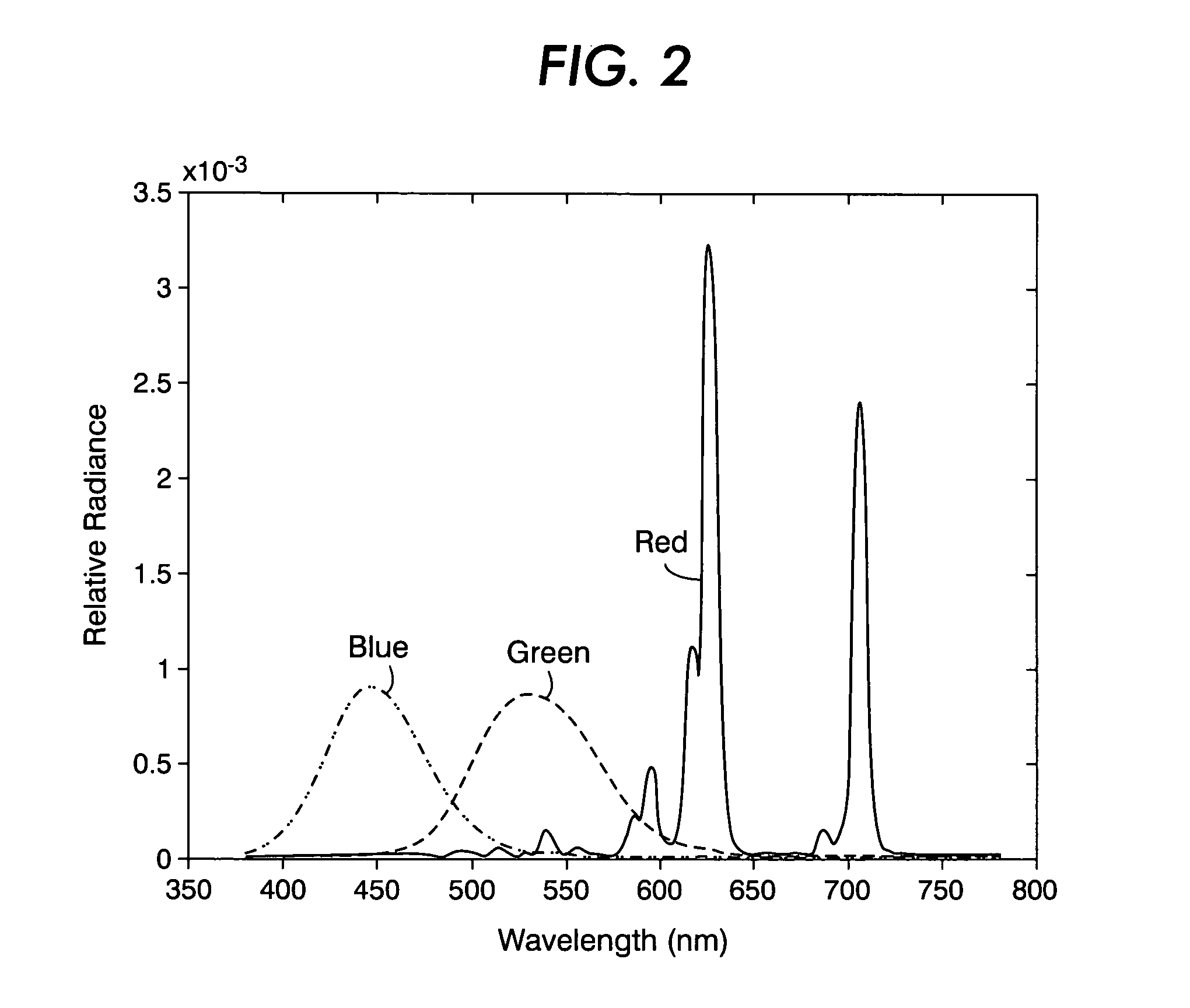
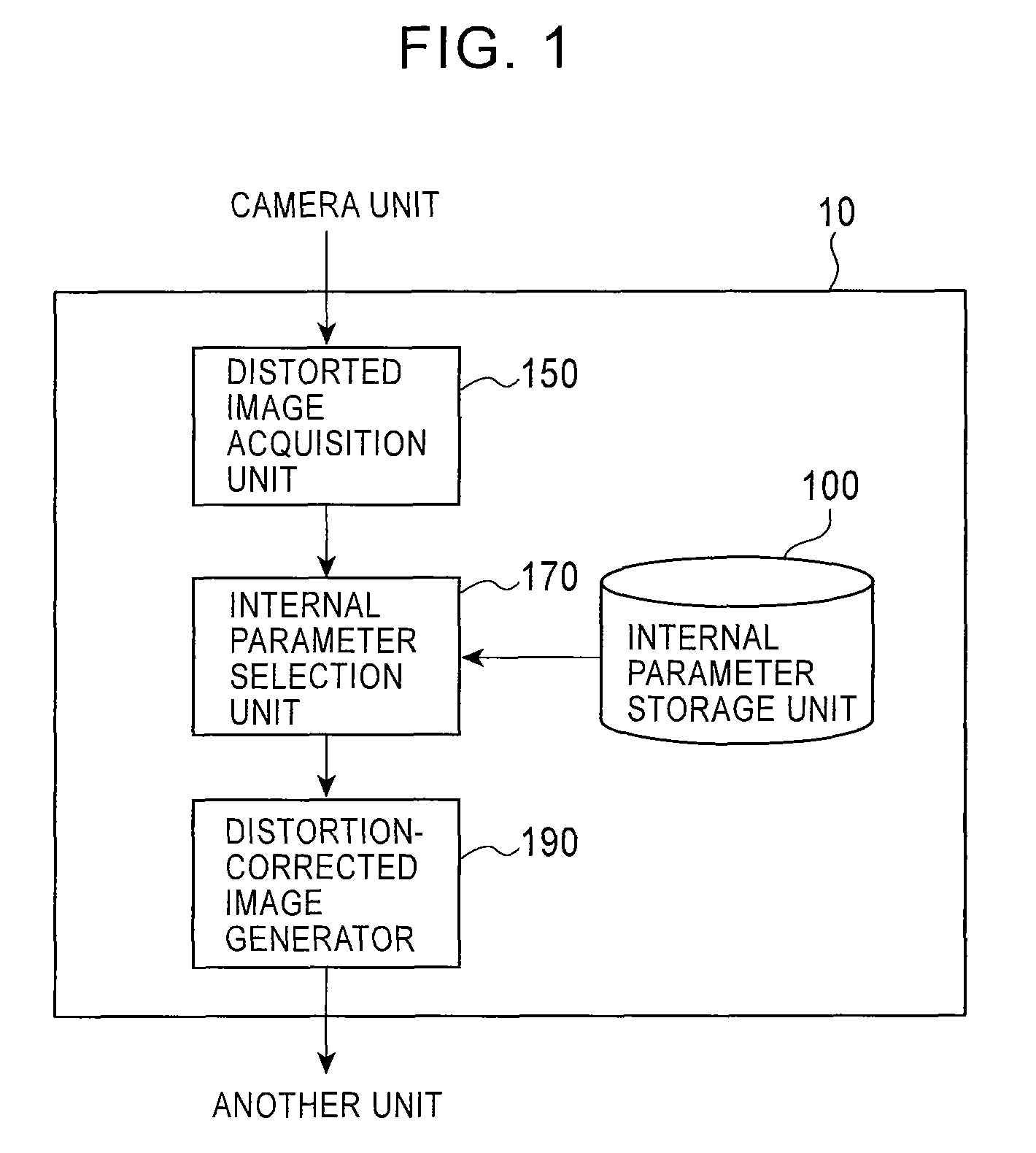
Distortion-corrected image generation unit and distortion-corrected image generation method
ActiveUS7965325B2Superfluous imageAccurate correctionImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPrincipal pointDistortion
Owner:ALPINE ELECTRONICS INC
Method and endoscopic device for examining or imaging an interior surface of a corporeal cavity
An auxiliary endoscopic imaging catheter is configured for insertion via a longitudinal working channel of an endoscopic. The endoscopic imaging catheter comprises a longitudinally extending tubular shaft having a proximal end, a distal end, and outer surface, and a longitudinal axis; one or more transparent or translucent elements positioned in the outer surface of the distal end of the shaft; and an imaging system comprising a reflector / refractor element and an imaging sensor, the imaging system being positioned interior of the distal end of the shaft. The reflector / refractor can be rotated or wobbled to obtain images of up to or over 360°. An illumination system is positioned on or in the distal end of the shaft, the illumination system being capable of illuminating a corporeal lumen or organ adjacent to the distal end.
Owner:NANAMED
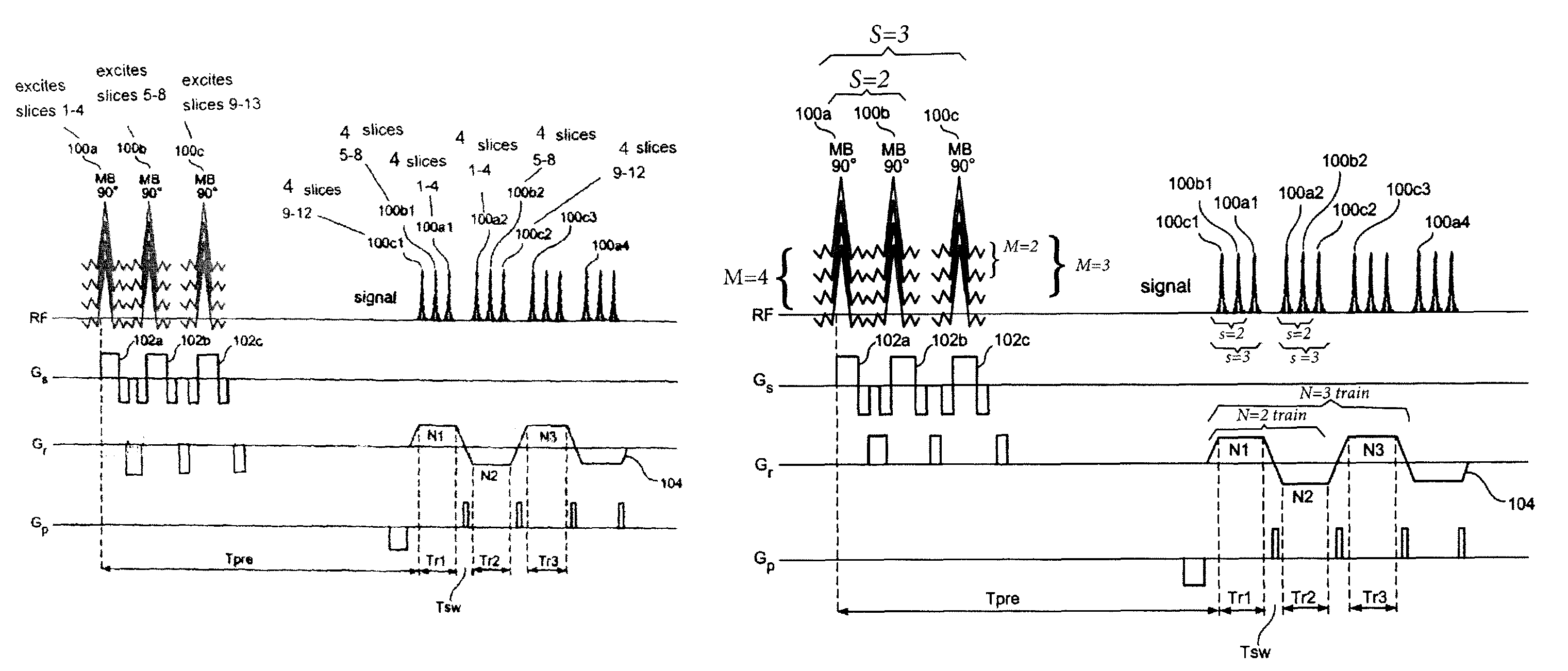
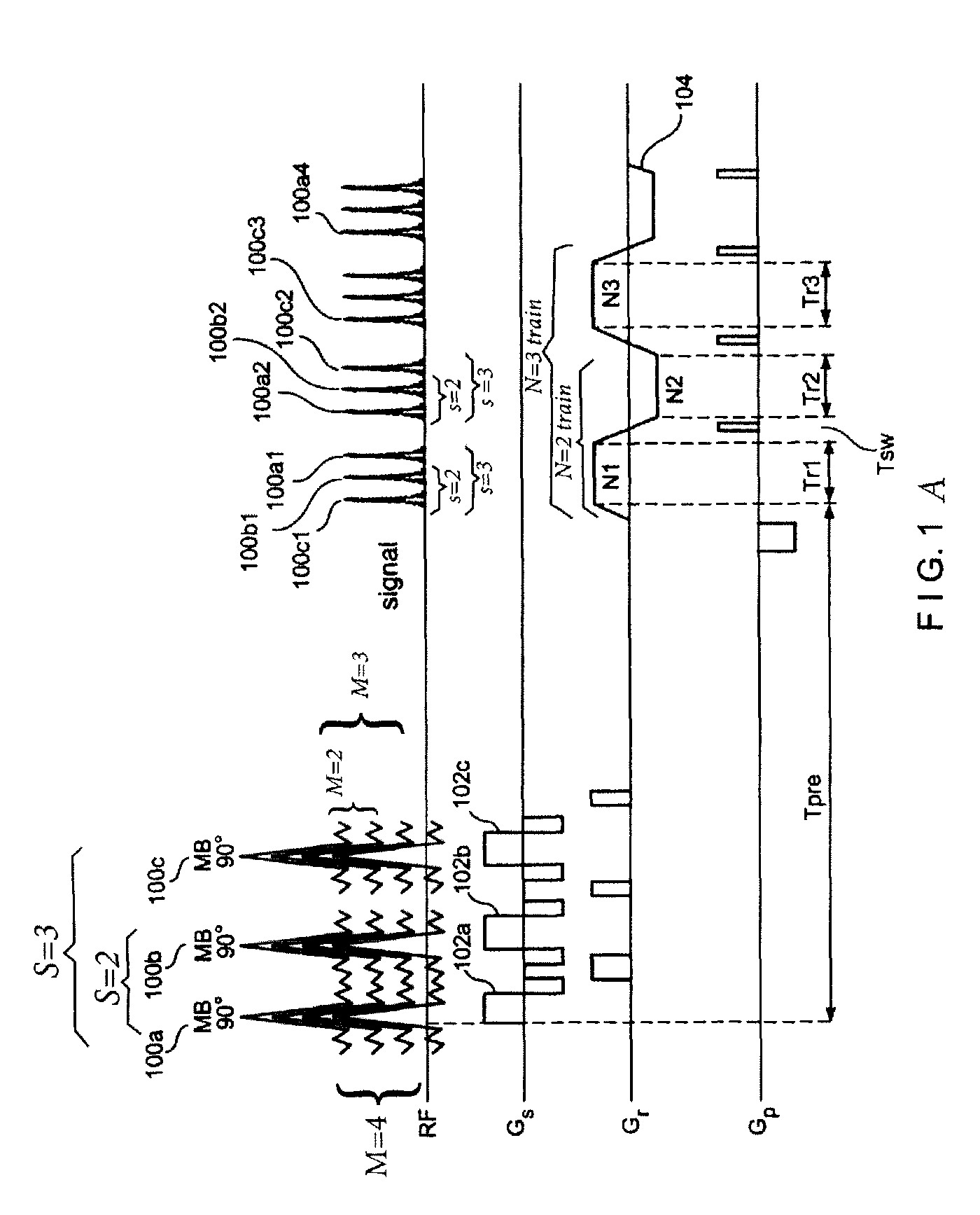
Multiplicative increase in MRI data acquisition with multi-band RF excitation pulses in a simultaneous image refocusing pulse sequence
ActiveUS8941381B2Reduce acquisition timeEffective imagingMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMultiplexingMulti band
Disclosed are methods and systems for carrying out super-multiplexed magnetic resonance imaging that entwines techniques previously used individually and independently of each other in Simultaneous Echo (or Imaging) Refocusing (SER or SIR) and Multi-Band (MB) excitation, in a single pulse sequence that provides a multiplication rather than summation of desirable effects while suppressing undesirable effects of each of the techniques that previously were used independently.
Owner:FEINBERG DAVID +1
Image processor
InactiveUS20050013485A1Effective balanceSuperfluous imageImage enhancementImage analysisColor imageImaging processing
In the image processing of color image, color image data are received, and the color image data are corrected to maximize an overlapping quantity of histograms of the image data on a plurality of colors. Alternatively, color image data are received, and histograms of a plurality of colors on the color image data are calculated. Then, color deviation of image is corrected to maximize an overlapping quantity of the histograms. Alternatively, color image data are received, and color fog is detected on the color image data and a color of the color fog is determined. Then, the image data of the color on which color fog is detected is decreased. Alternatively, color fog is detected in an input color image data; and a color of the detected color fog is displayed. Alternatively, color fog of input image is corrected first, and contrast on the image is corrected next.
Owner:MINOLTA CO LTD
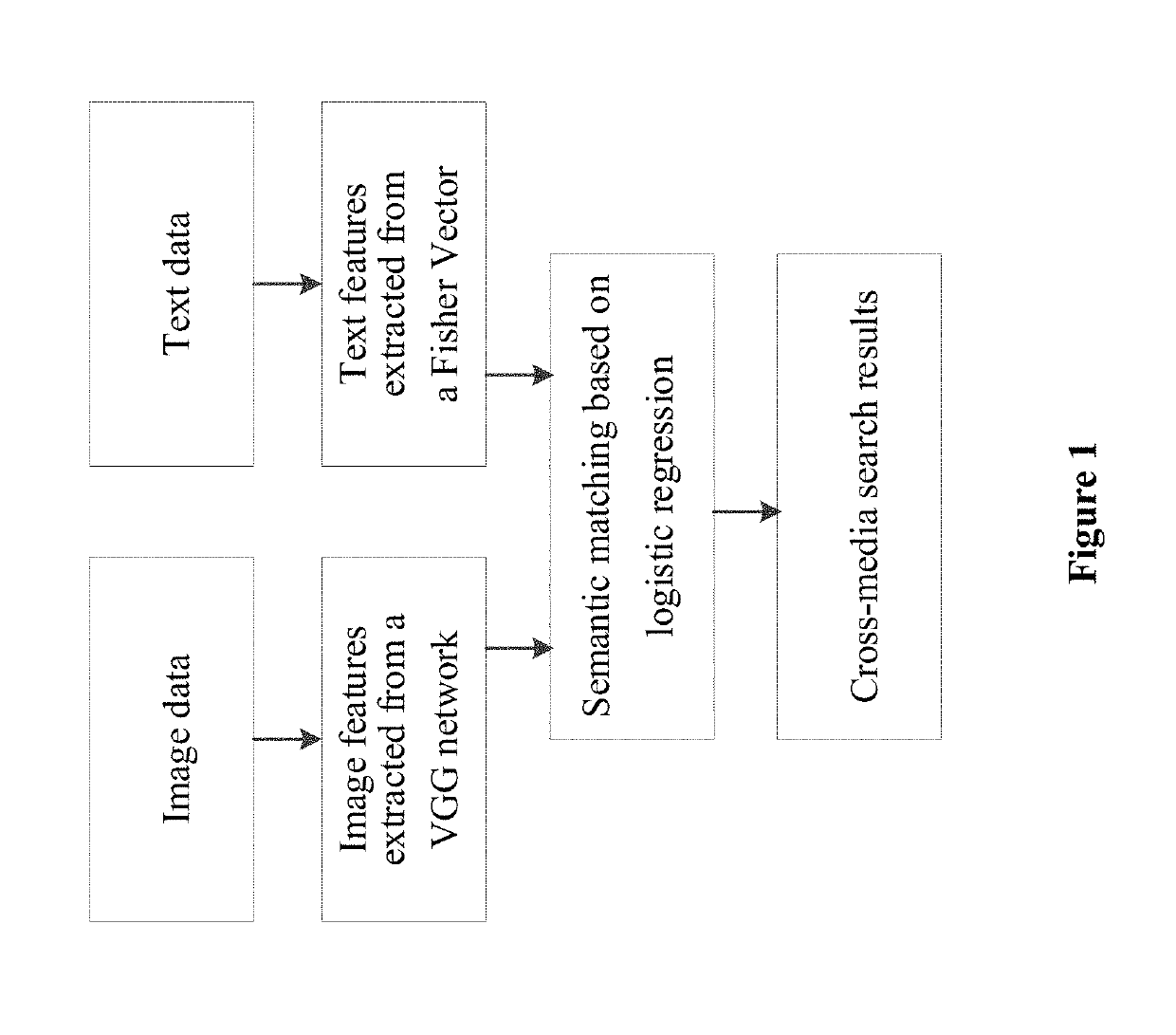
A cross-media search method
ActiveUS20190205393A1Improve efficiencyImprovement of computer computing performanceSemantic analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature extractionActivation function
A cross-media search method using a VGG convolutional neural network (VGG net) to extract image features. The 4096-dimensional feature of a seventh fully-connected layer (fc7) in the VGG net, after processing by a ReLU activation function, serves as image features. A Fisher Vector based on Word2vec is utilized to extract text features. Semantic matching is performed on heterogeneous images and the text features by means of logistic regression. A correlation between the two heterogeneous features, which are images and text, is found by means of semantic matching based on logistic regression, and thus cross-media search is achieved. The feature extraction method can effectively indicate deep semantics of image and text, improve cross-media search accuracy, and thus greatly improve the cross-media search effect.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Optical coherence tomography for biological imaging
ActiveUS20180049700A1Shorten operation timeImprovements for long- and short-term outcomesCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringOptical radiationBiological imaging
Described herein are catheters for use with Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) that include an optical fiber core having a first refractive index and an interface medium having a second refractive index, where the first and second refractive indexes are mismatched such that receiving electronics configured to receive optical radiation reflected from the reference interface and the target operate in a total noise range that is within 5 dB of the shot noise limit. These OCT catheters may include a silicon die mirror having a reflective coating that is embedded in the interface medium. The optical fiber can be fixed at just the distal end of the catheter, and may be managed within a handle that is attached to the proximal end of the catheter body, and is configured to allow rotation of the both catheter body and the optical fiber relative to the handle.
Owner:AVINGER
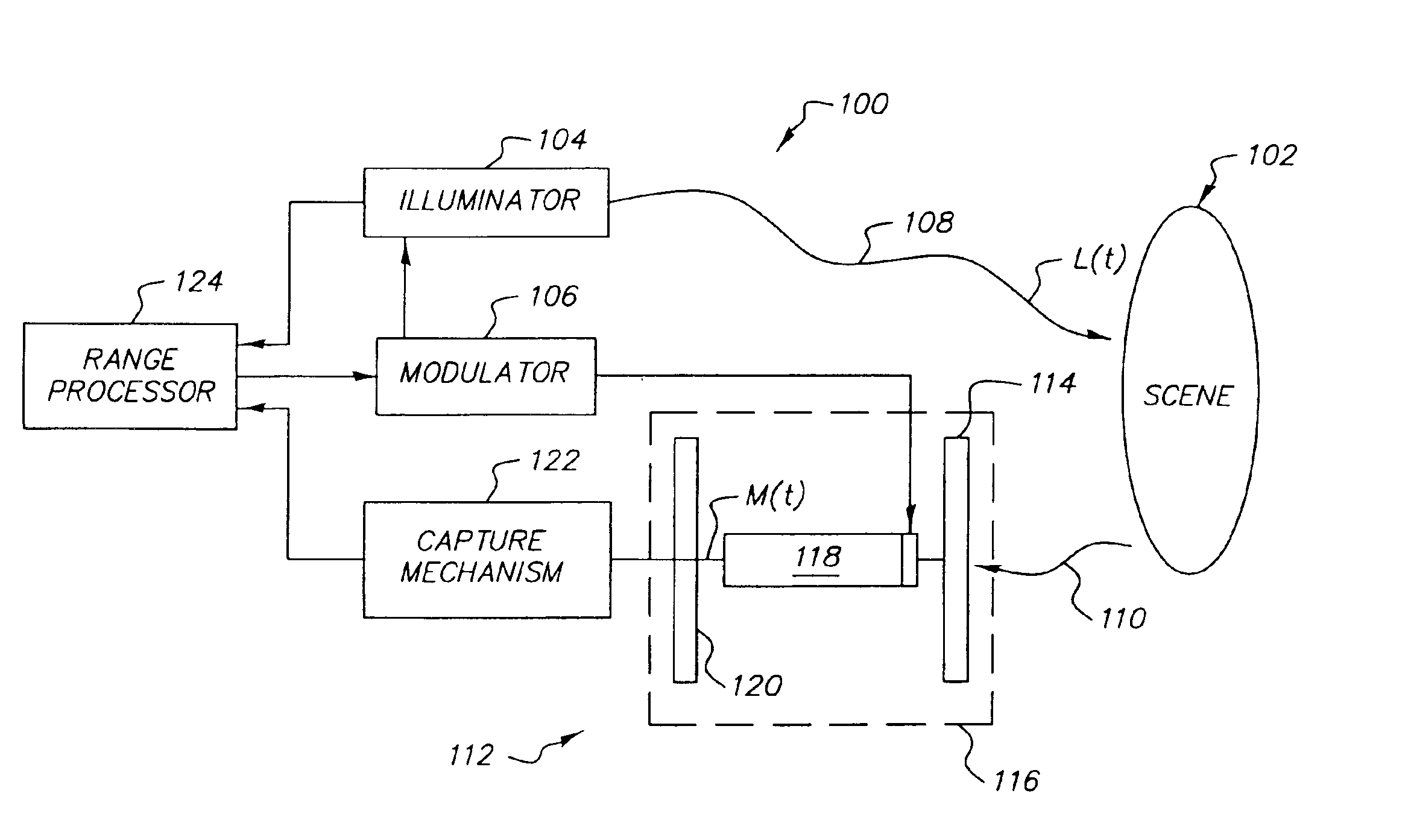
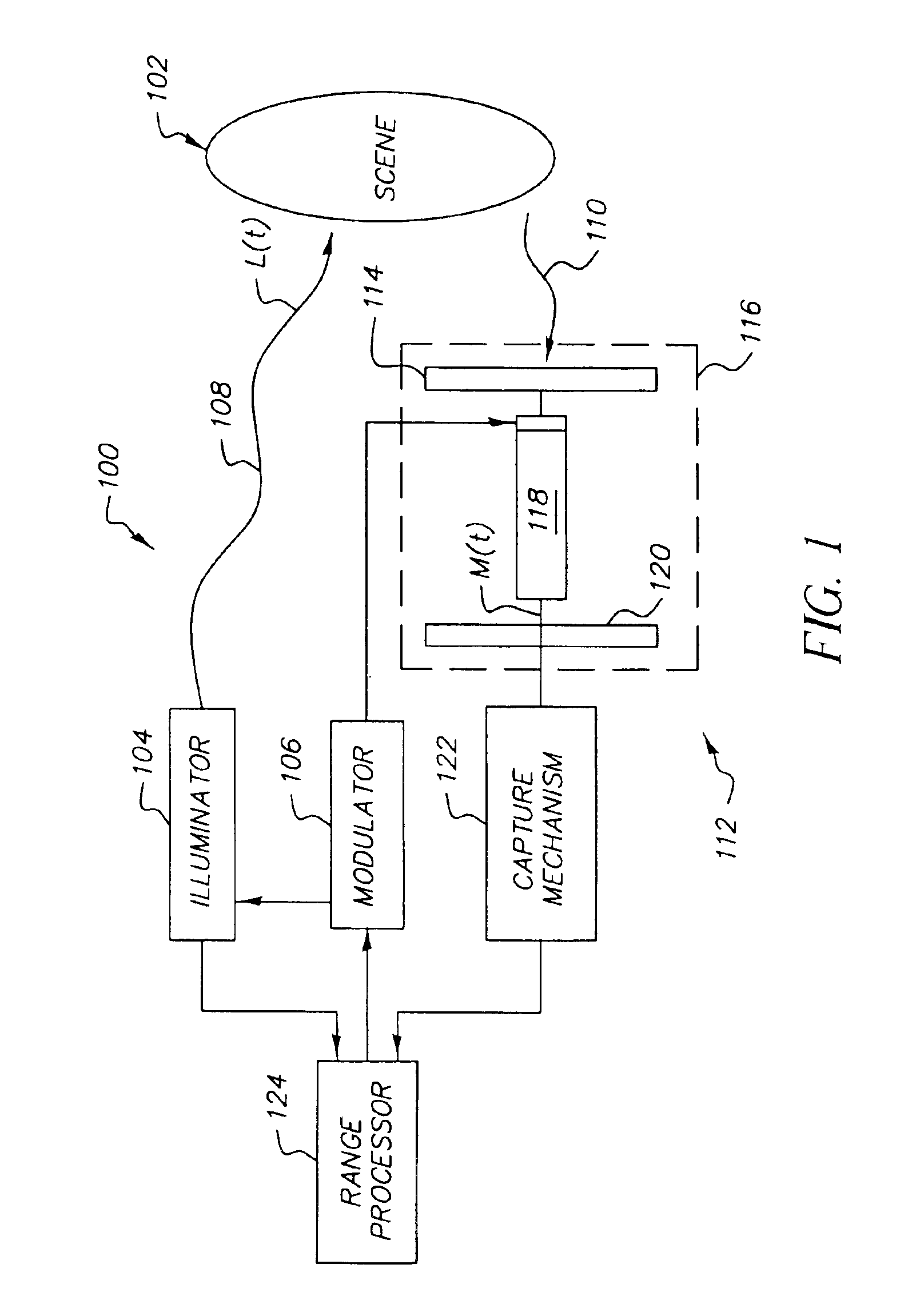
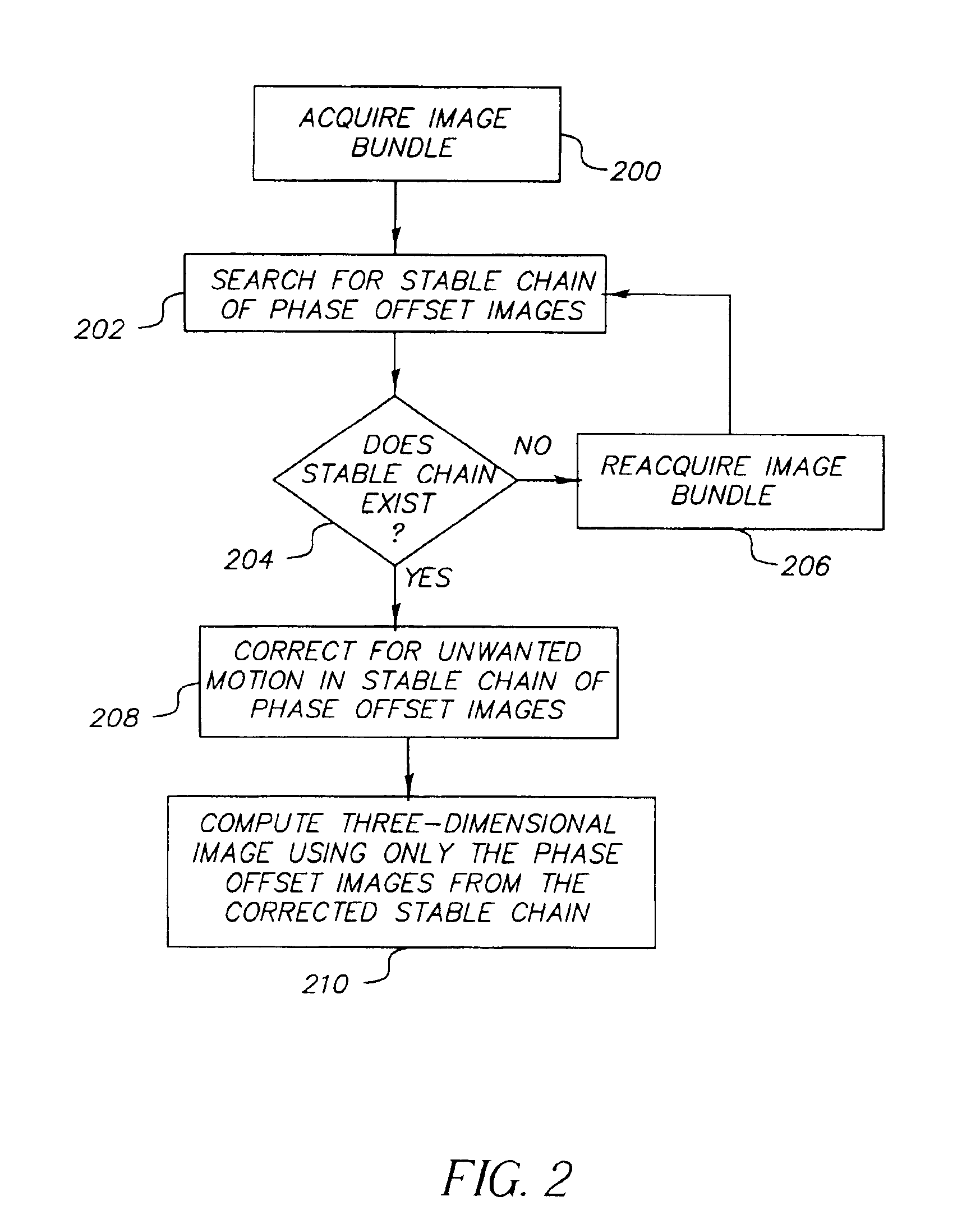
Stabilization of three-dimensional images in a scannerless range imaging system
ActiveUS6925195B2Small degreeUnwanted motionTelevision system detailsImage analysisThree-phaseImage motion
A method for generating a stabilized three-dimensional image from a scannerless range imaging system comprises the steps of acquiring a bundle of three or more phase offset images corresponding to modulated illumination reflected from a scene, whereby one or more of the phase offset images includes image motion relative to another phase offset image; searching for a stable chain of phase offset images in the image bundle, wherein a stable chain is a collection of images that is obtained by testing the phase offset images against a confidence measure that separates less severe correctable image motion from more severe image motion and then populating the stable chain only with those phase offset images that meet the confidence measure for correctable image motion; correcting for the image motion in the stable chain of images if a stable chain of at least three phase offset images is found to exist; and computing a stabilized three-dimensional image using the phase offset images from the stable chain of phase offset images.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
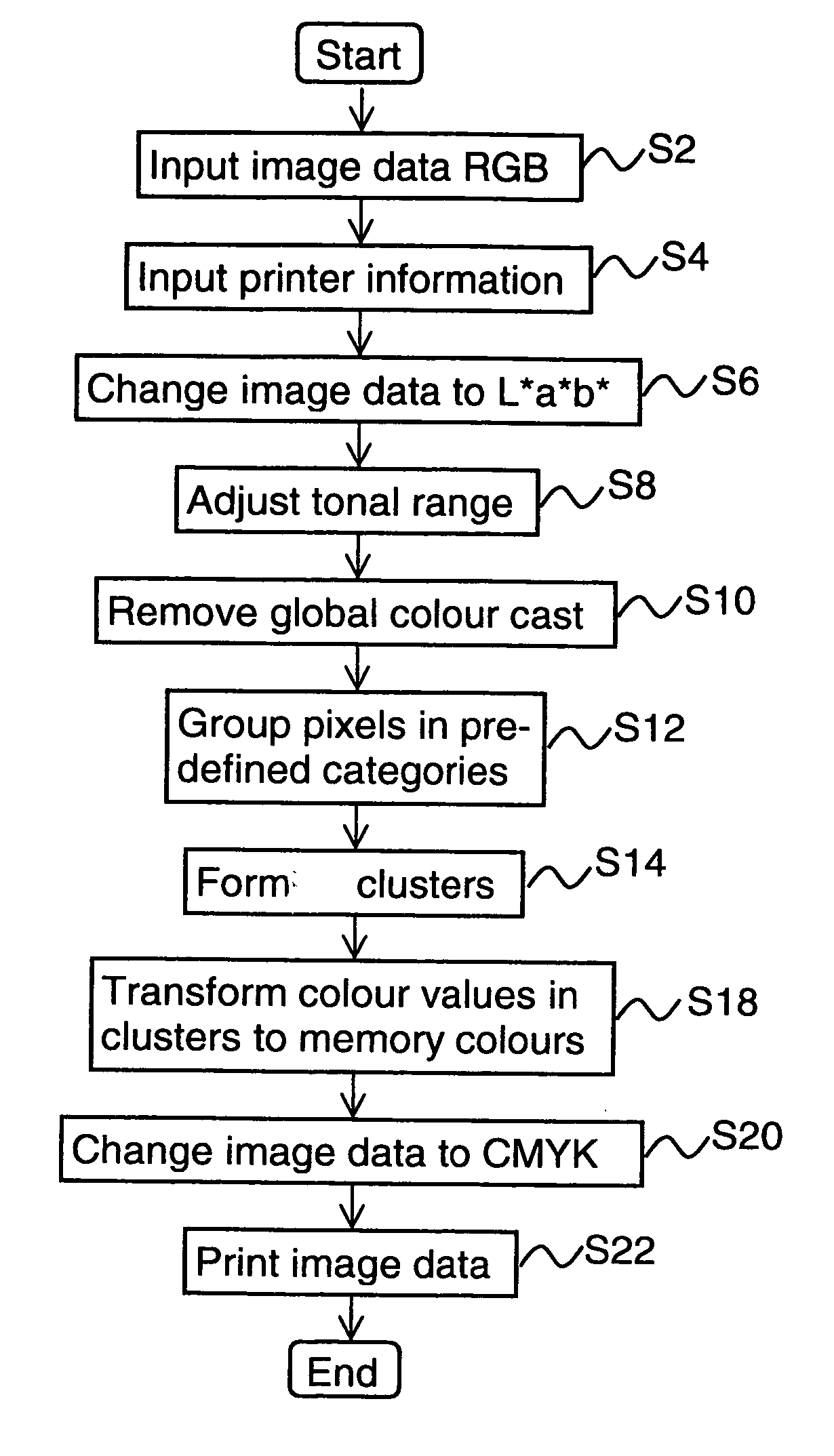
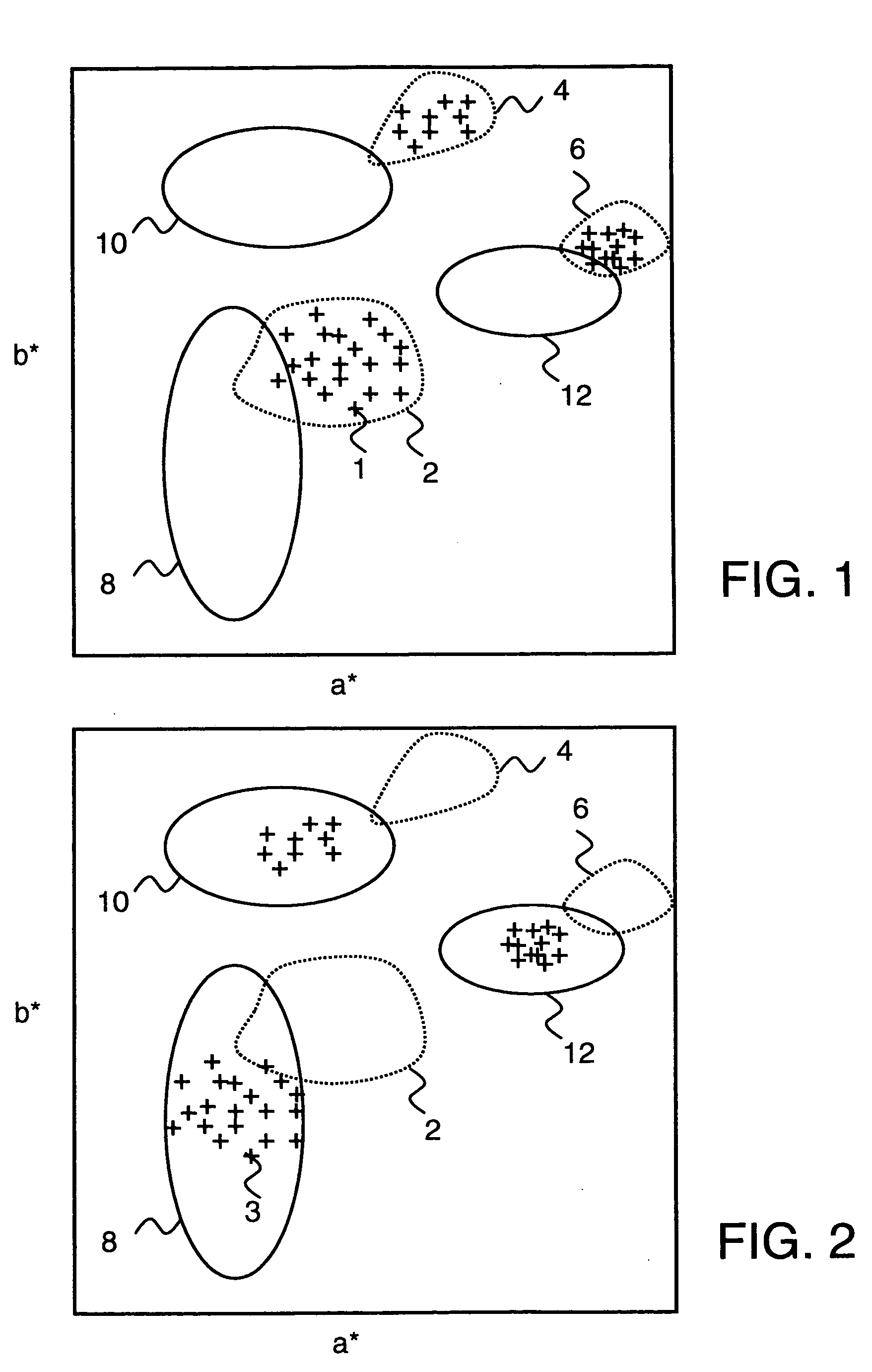
Method, apparatus and computer program for transforming digital colour images
InactiveUS20050259281A1Superfluous imageEfficiently formedImage enhancementOrganic active ingredientsImage formationColour image
A first digital colour image with pixels having colour values is transformed to a second digital colour image with pixels having transformed colour values, the colour values being defined in a selected colour space. Pixel clusters are formed for the first digital colour image whereby pixels of a pre-defined category are grouped into a particular cluster in the selected colour space. The colour values of the pixels in a particular cluster are transformed such that transformed colour values belong to a pre-defined area associated to the particular cluster in the selected colour space, the pre-defined area consisting of memory colours of the same pre-defined category. The second digital colour image can be rendered on a display screen or on a print medium.
Owner:OCE TECH
Digital camera having panning and/or tilting functionality, and an image rotating device for such a camera
InactiveUS7256834B1Faster and accurate panningFaster and accurate and tiltingTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensControl signal
A digital camera (300) has panning and / or tilting functionality and comprises: a camera housing (6) with an optical input (400), such as a lens or objective (8); an image capturing unit (500) for producing a digital image from light received through the optical input; and a controller (600). A first mirror (9) is mounted externally to the camera housing (6). An image rotating device (200) receives an angular displacement control signal from the controller (600) and rotates the first mirror at an angle with respect to the optical input (400, 8) of the camera housing (6).
Owner:AXIS
Method and System for Analog/Digital Image Simplification and Stylization
ActiveUS20140307978A1Good image structureMore imageImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImage captureImage structure
A computer program product includes instructions for a processor to perform a method of improving image structure and coherence, and / or for simplification / stylization. The method includes inputting the image, by: scanning the image; image capture using a camera; and / or image creation using a computer. Multi-channel images are converted into a single-channel grayscale image, which is separated into a first image component—the high spatial frequencies, and a second component image—the low spatial frequencies. The first and second component images are each formed by filtering to remove frequencies outside of respective upper and lower threshold frequencies. A gain multiplier is applied to the filtered first and second component images to control detail amplification. The first and second component images are each blurred at the respective upper and lower threshold frequencies. An improved stylized composite image results by subtracting the gain multiplied first component image from the gain multiplied second component image.
Owner:BALESTRIERI JOHN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com