Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
56results about How to "Provide robustness" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
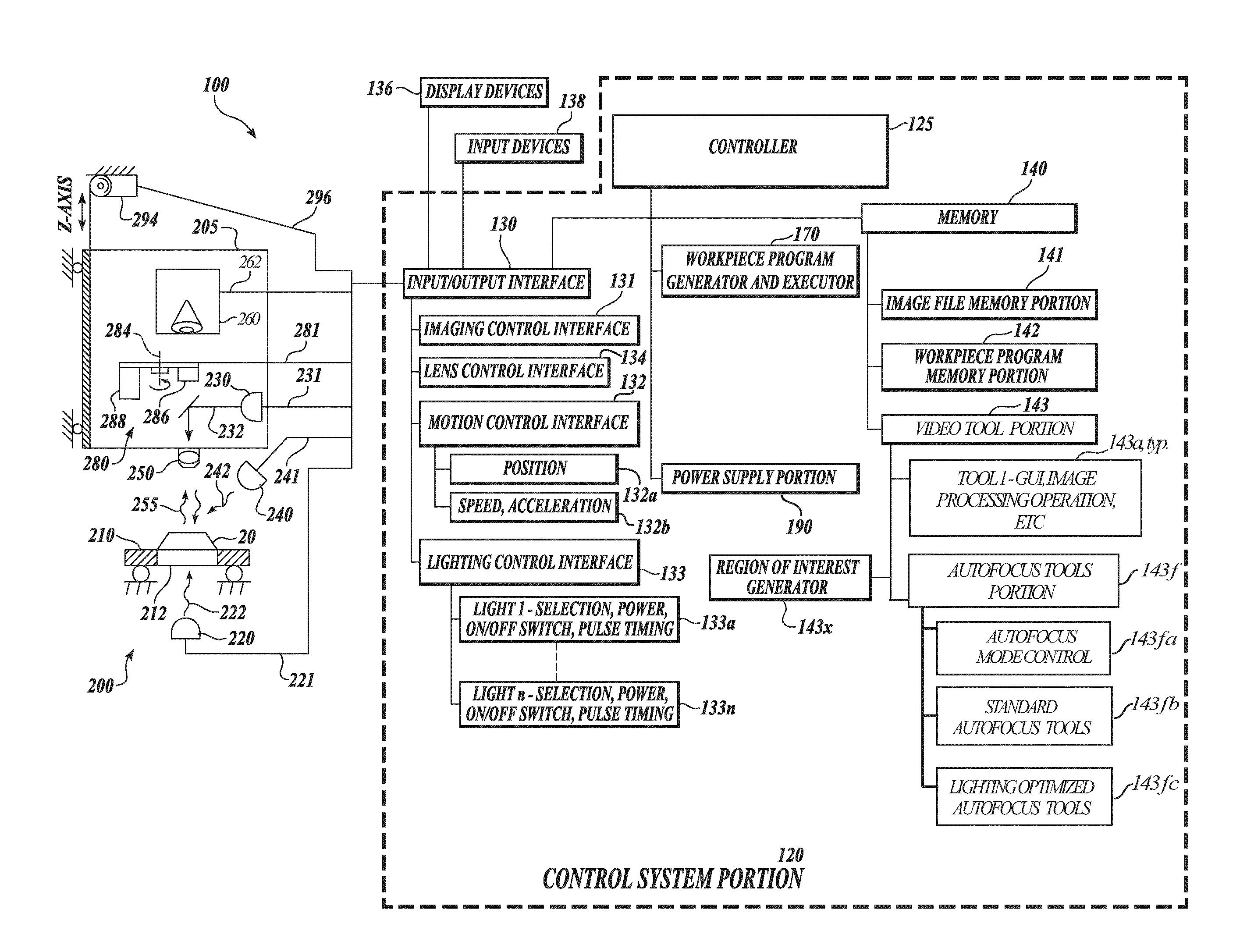
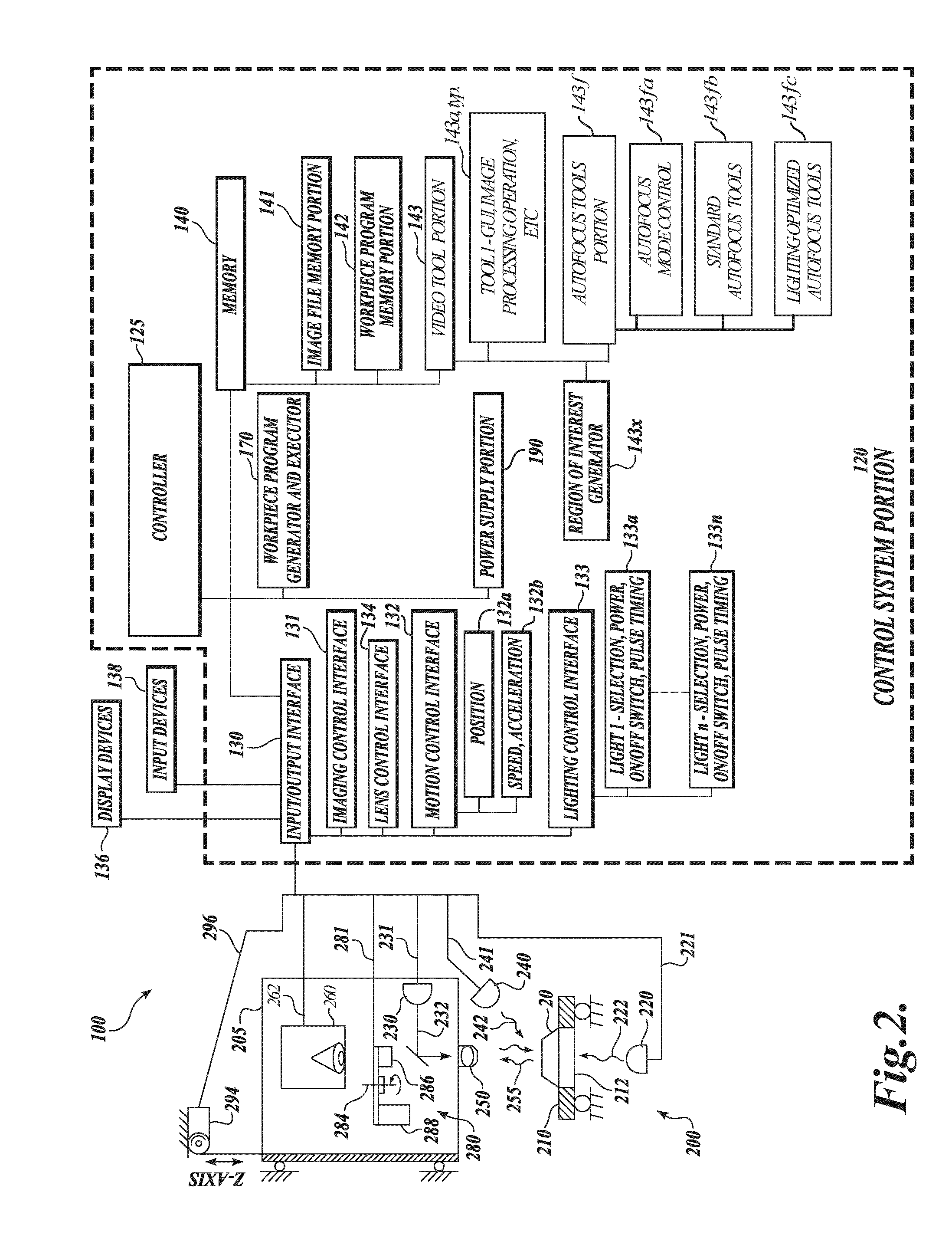
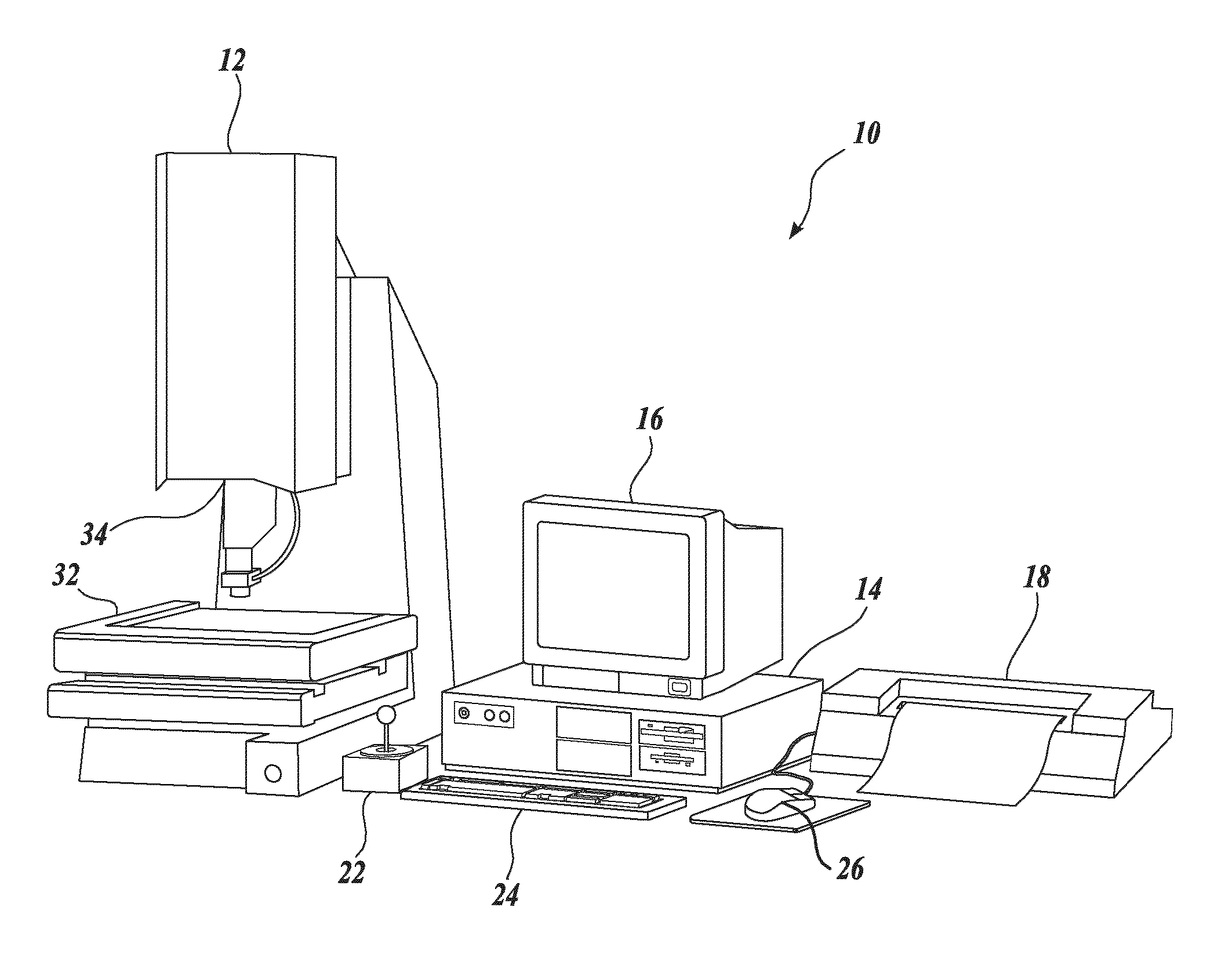
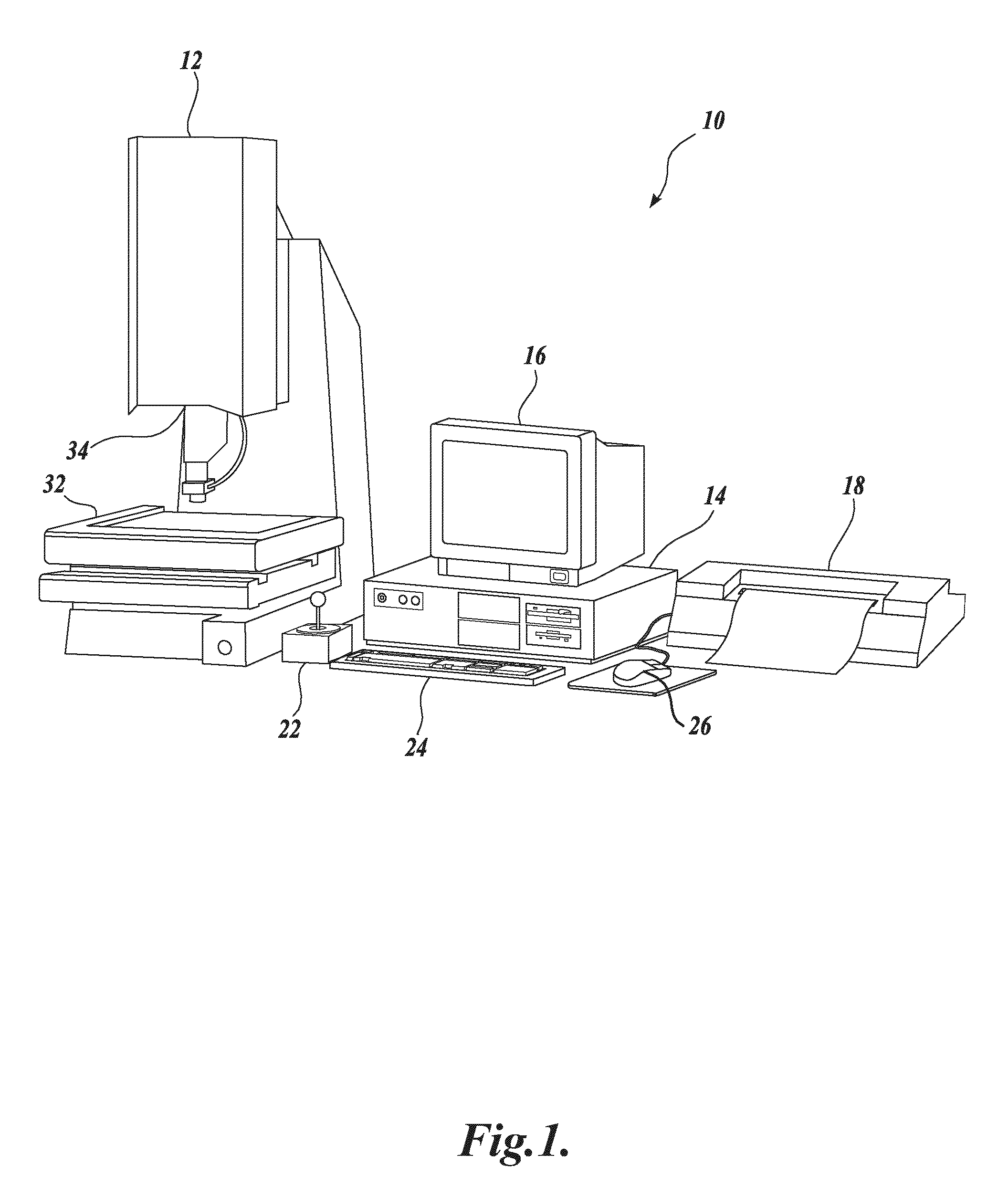
Autofocus video tool and method for precise dimensional inspection
ActiveUS8111905B2Reliable and robust determinationProvide accuracyMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)Radiology
A refined autofocus method provides optimized lighting between iterative autofocus operations, to reliably provide the best possible autofocus Z-height precision. The method includes a quantitative initial focus Z-height determination based on initial focus curve data from initial autofocus images acquired using initial light control parameters. Then, the camera is set at that initial focus Z-height such that well focused images are provided. Refined (optimized) light control parameters are then determined based on at least one respective image acquired using respective light control parameters at that Z-height, such that an image acquired using the refined light control parameters provides a near-optimum value for a contrast-related metric (e.g., a focus metric) at that Z-height. Then, refined autofocus images are acquired using the refined light control parameters and a refined precise Z-height is quantitatively determined base on the resulting focus curve.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
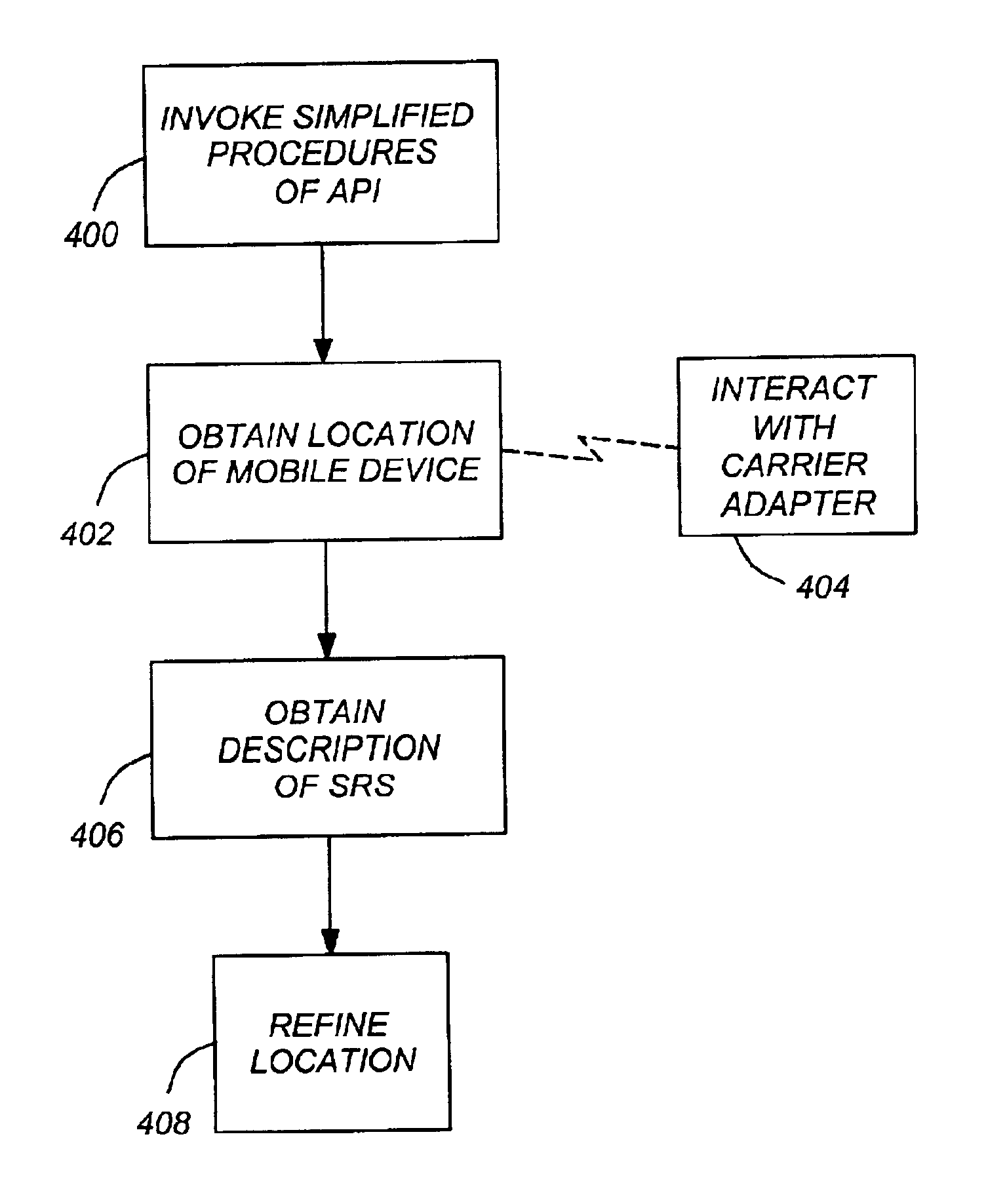
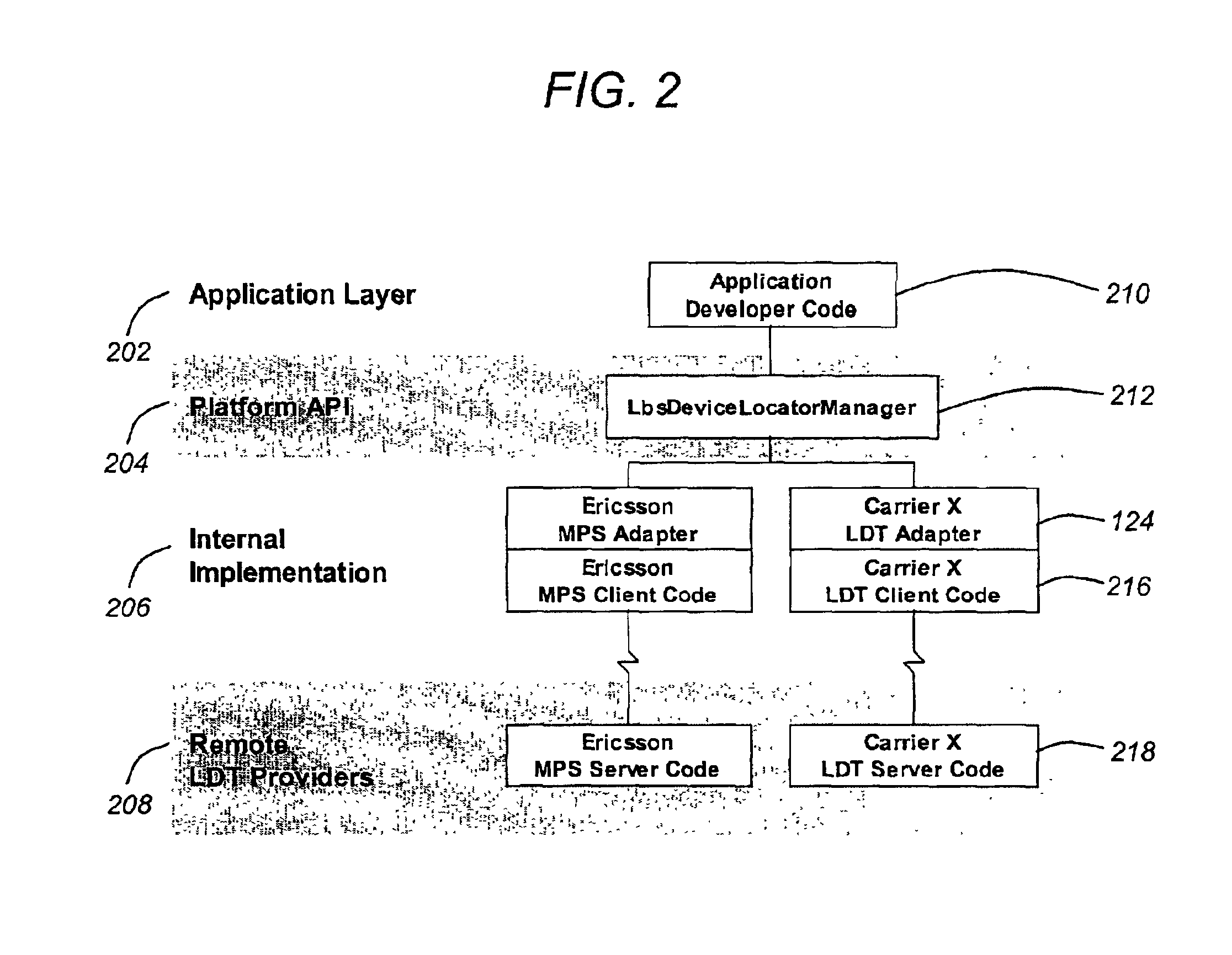
Mobile device locator adapter system for location based services
InactiveUS6963748B2Provide robustnessPosition fixationData switching by path configurationApplication programming interfacePosition dependent
One or more embodiments of the invention provide a method, apparatus, and article of manufacture for locating a mobile device. An application programming interface (API), executed by a computer, provides a plurality of simplified procedures that allow an application program executed by the computer to locate the mobile device. The application program invokes the simplified procedures of the API. The invoked procedures obtain a location of the mobile device given an identification of the mobile device and a description of a spatial reference system associated with the location. Additionally, the invoked procedures interact with specifics for a mobile positioning server of a carrier of the mobile device and with different methods of identifying the device as required by the carrier.
Owner:TELECOMM SYST INC
Autofocus video tool and method for precise dimensional inspection
ActiveUS20110103679A1Reliable and robust determinationProvide accuracyMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionAutofocusContrast ratio
A refined autofocus method provides optimized lighting between iterative autofocus operations, to reliably provide the best possible autofocus Z-height precision. The method includes a quantitative initial focus Z-height determination based on initial focus curve data from initial autofocus images acquired using initial light control parameters. Then, the camera is set at that initial focus Z-height such that well focused images are provided. Refined (optimized) light control parameters are then determined based on at least one respective image acquired using respective light control parameters at that Z-height, such that an image acquired using the refined light control parameters provides a near-optimum value for a contrast-related metric (e.g., a focus metric) at that Z-height. Then, refined autofocus images are acquired using the refined light control parameters and a refined precise Z-height is quantitatively determined base on the resulting focus curve.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
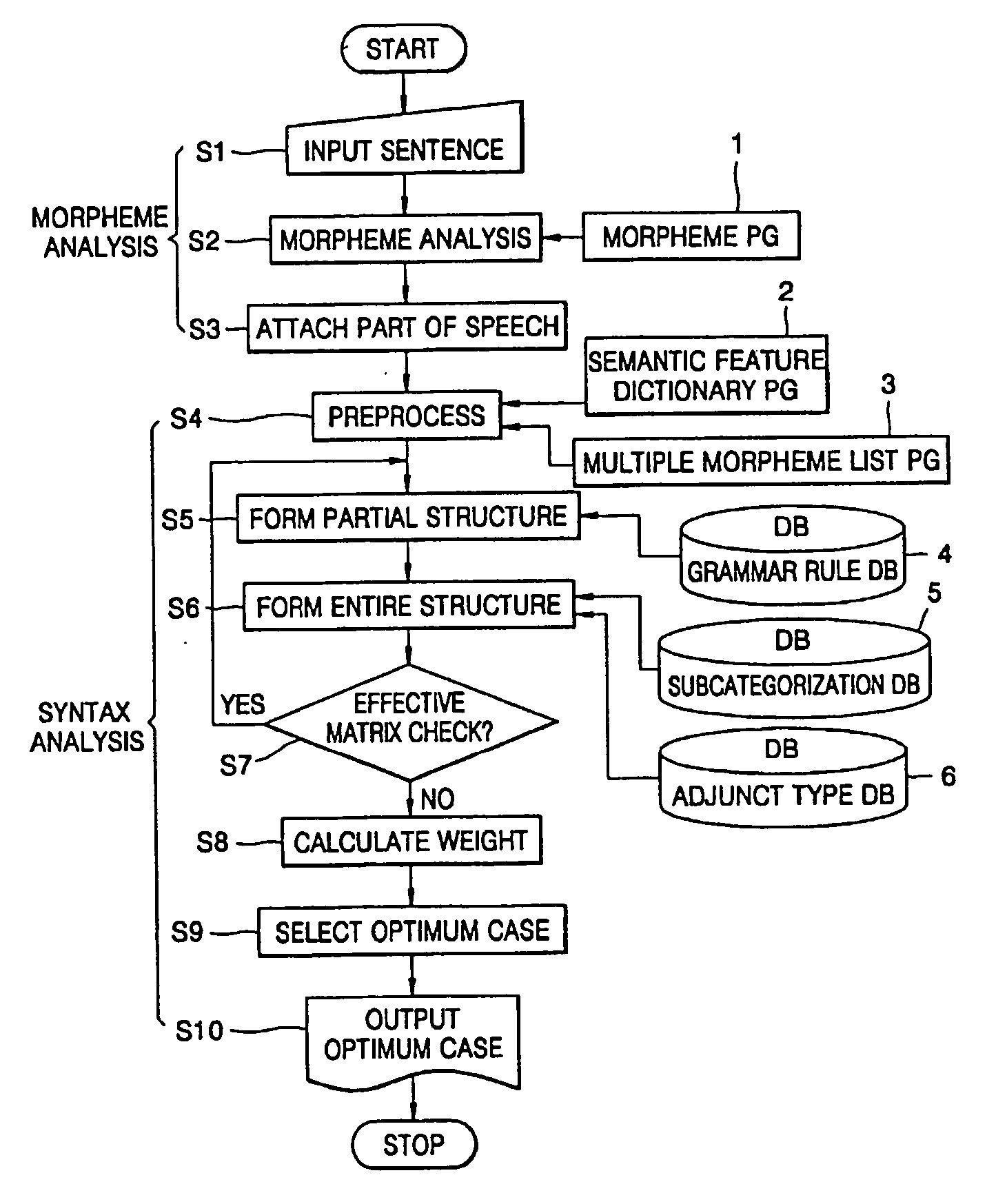
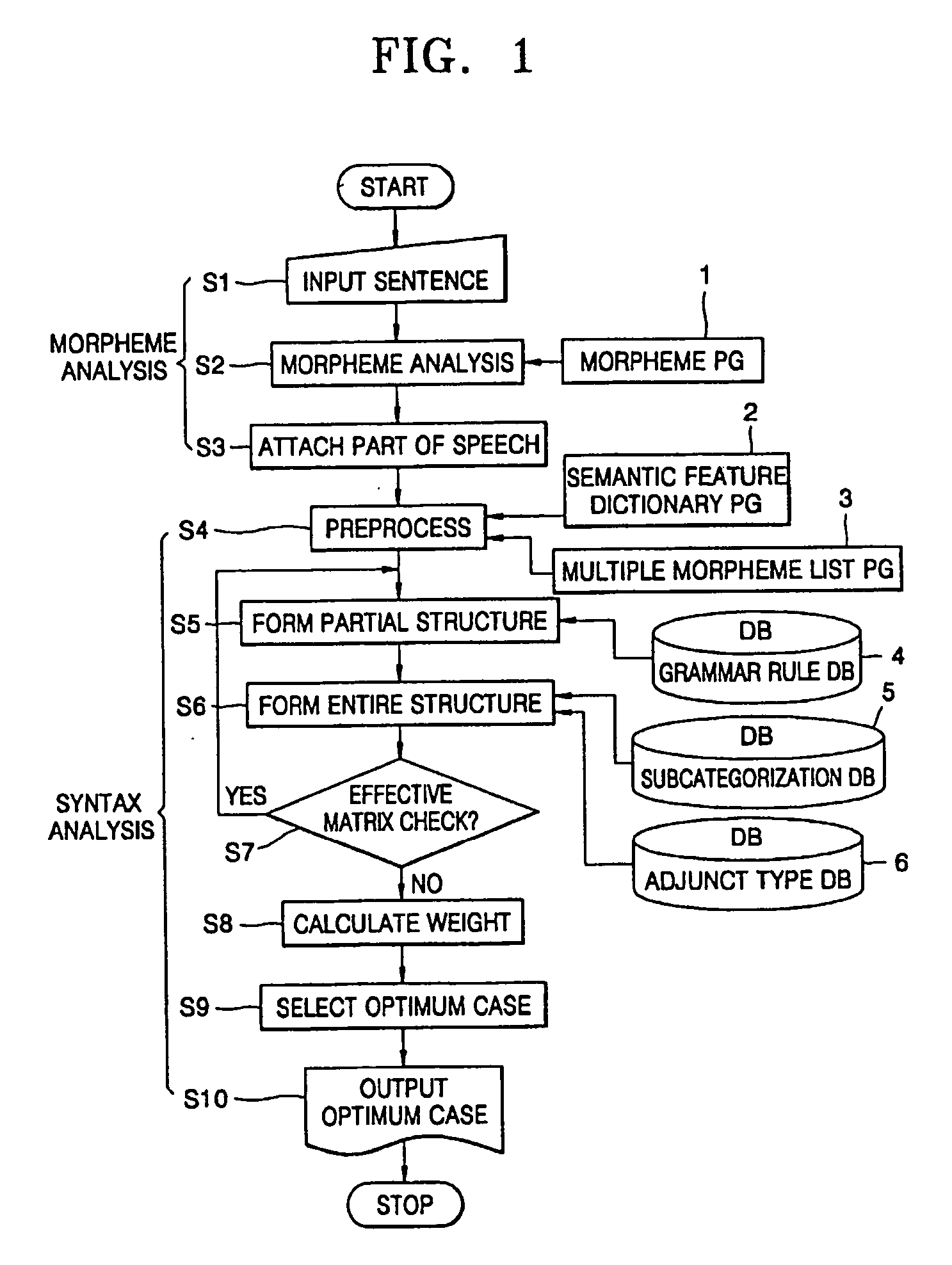
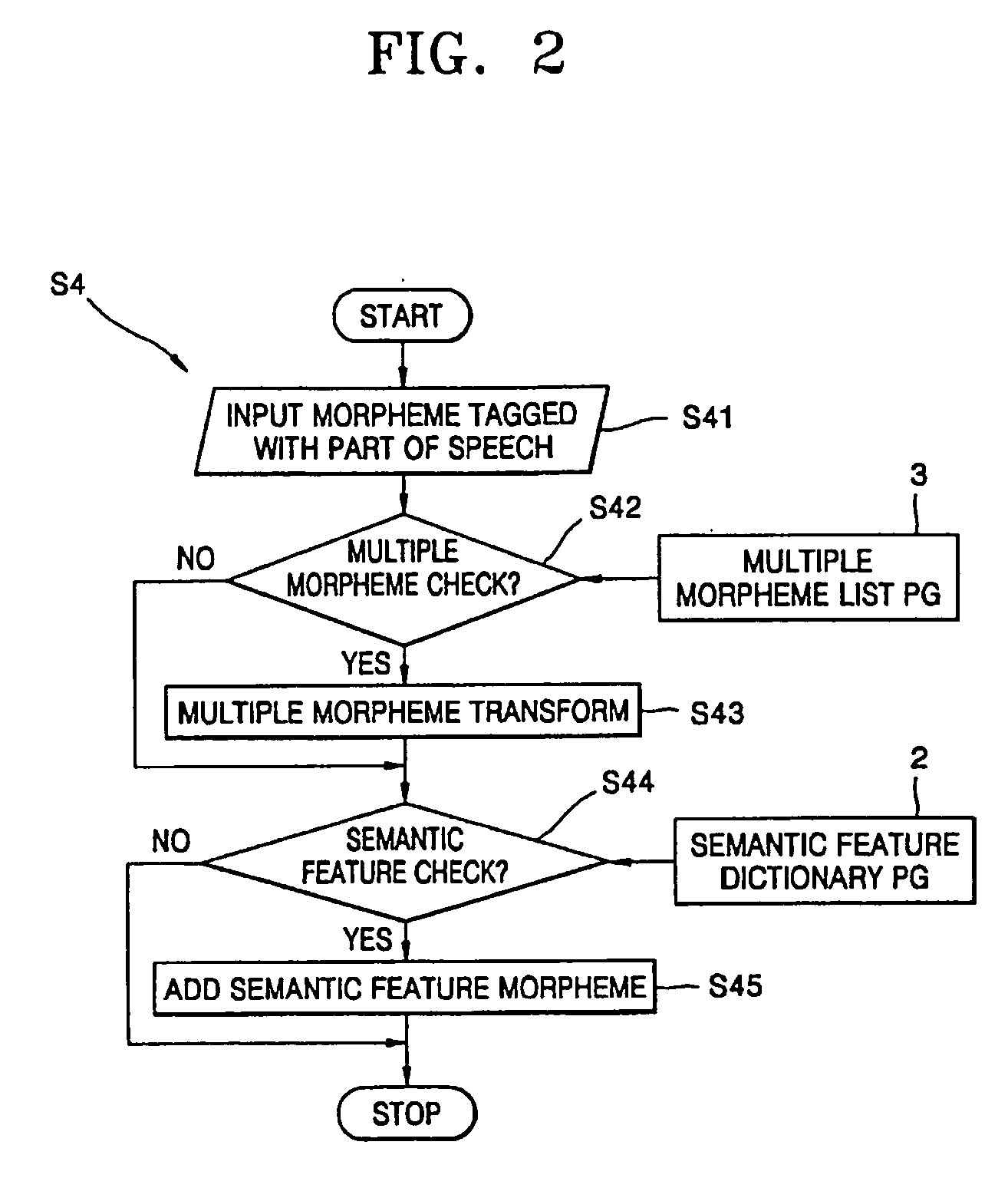
Method for sentence structure analysis based on mobile configuration concept and method for natural language search using of it
InactiveUS20070010990A1Analysis quicker and easyAccurate captureNatural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsStructure analysisAnalysis data
A method of syntax analysis based on a mobile configuration concept, and a natural language search method using the syntax analysis method, are provided. The syntax analysis method includes morpheme analysis and syntax analysis after establishing a morpheme dictionary program for analyzing morphemes of an input sentence, and a subcategorization database storing the details of subcategories belonging to heads, such as stems of words and word endings, of each component of a sentence such that the syntactic status of an inflective word ending is admitted based on the marker theory which regards both postpositions and endings as syntactic units, and combination relations between words can be grammatically defined as a whole. In the morpheme analysis, if a sentence desired to be analyzed is input, the contents of morphemes are analyzed in units of polymorphemes according to the morpheme dictionary program, and after selecting an analysis case of a morpheme appropriate to the input data among morpheme analysis data by polymorpheme, preprocessing is performed. In the syntax analysis, with the analyzed morphemes, partial structures of a sentence are first established according to grammatical roles stored in a grammar rule database, and then, by using the subcategorization database, the entire structure is established. Then, by calculating the weighted value of each structure, a most appropriate optimum case is determined and output. Accordingly, any scrambled sentence can be easily and quickly analyzed without any sophisticated parsing apparatus. Also, the grammatical relationships between expressions forming a sentence can be accurately captured such that information requested by a user is retrieved in the same manner as a human-being makes a decision, and accurate information can be provided.
Owner:WOO SOON JO
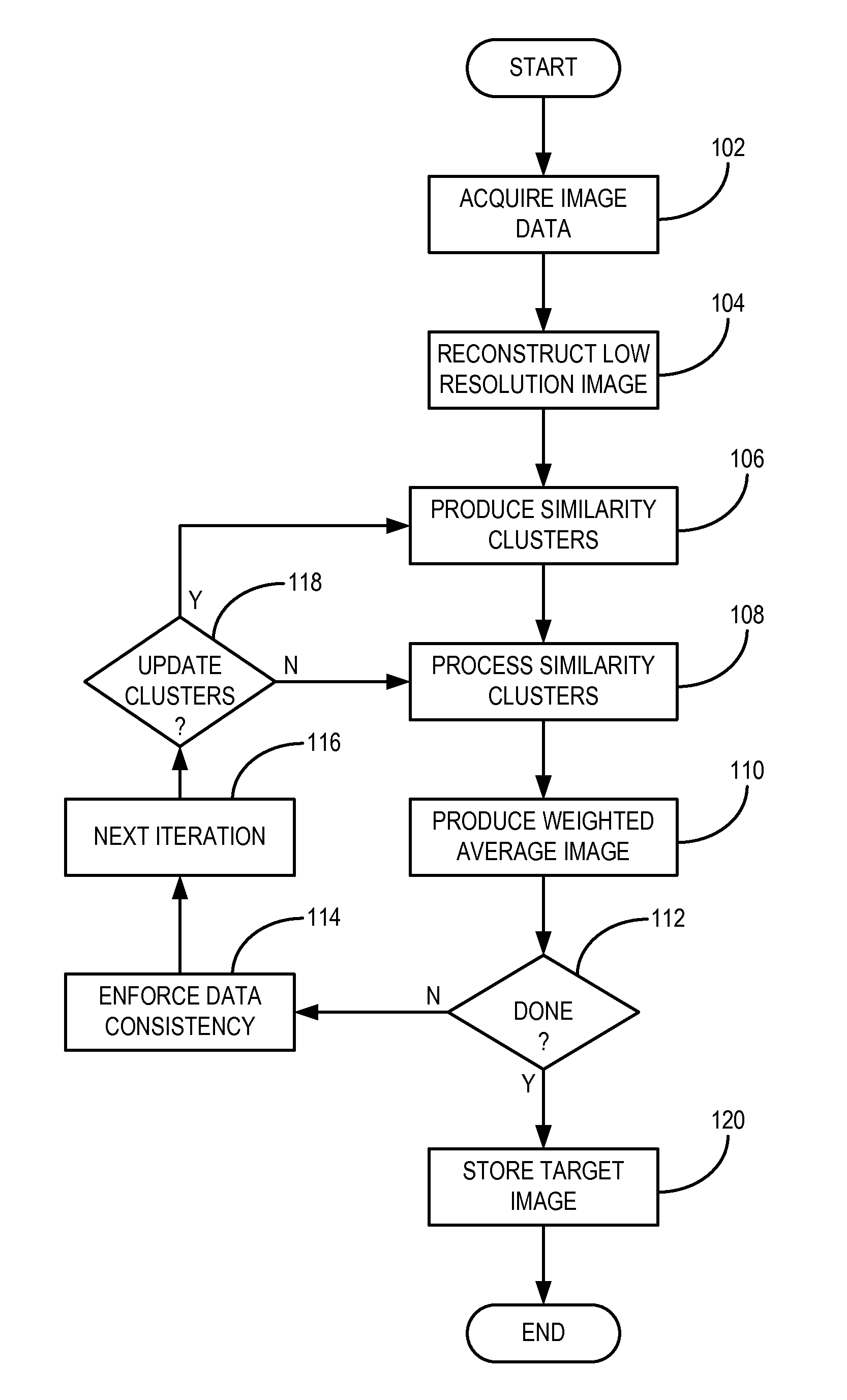
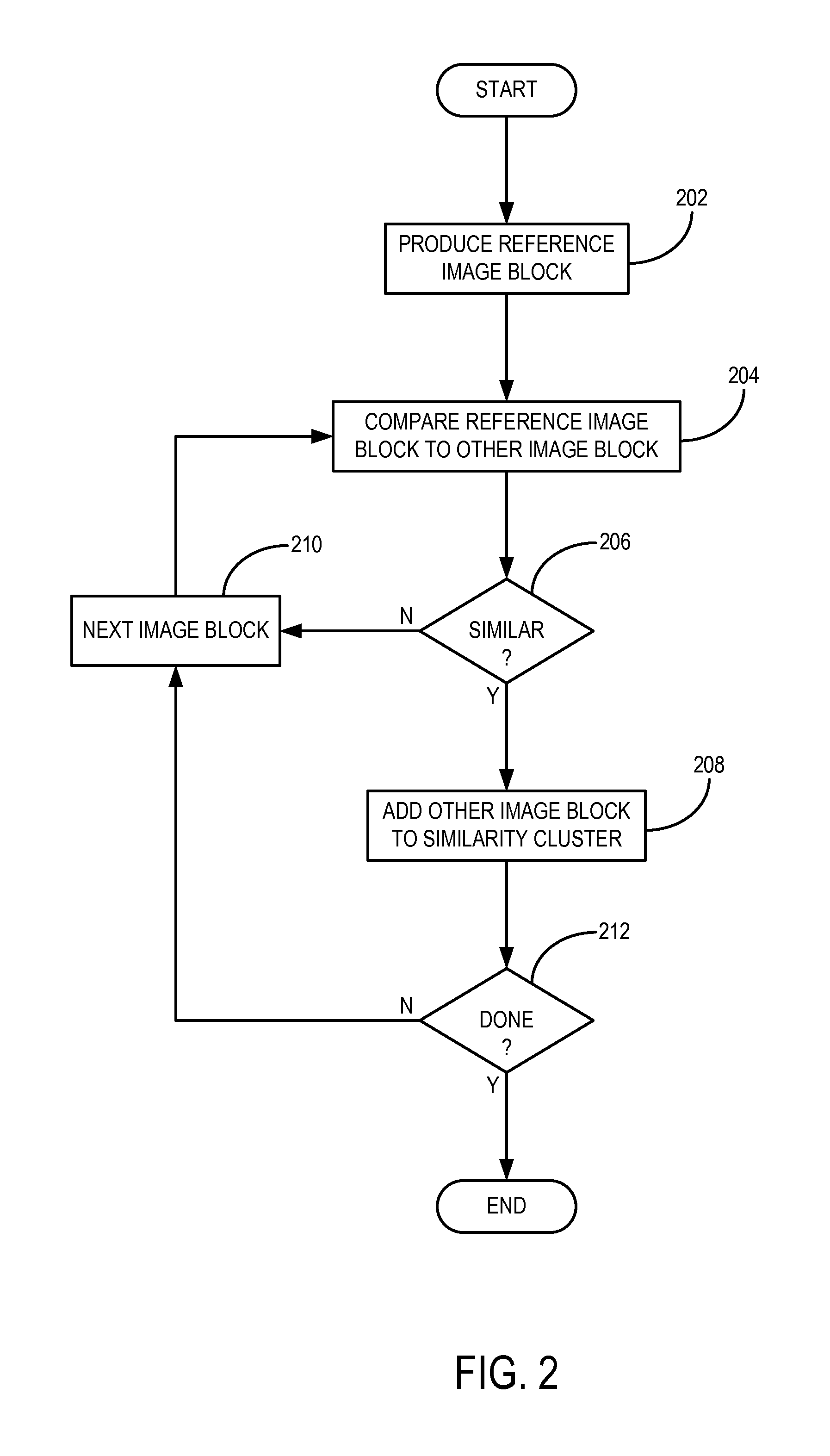
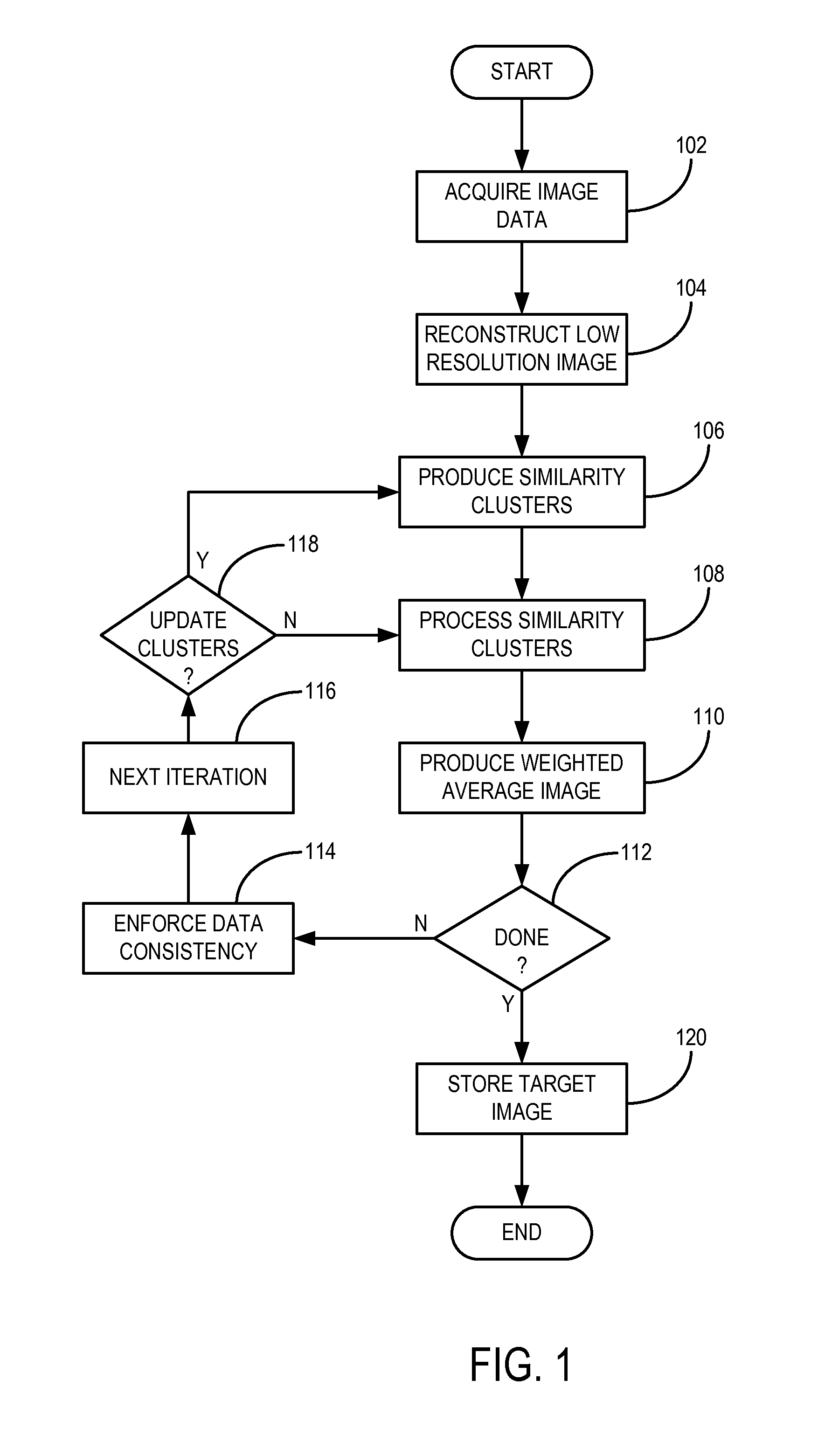
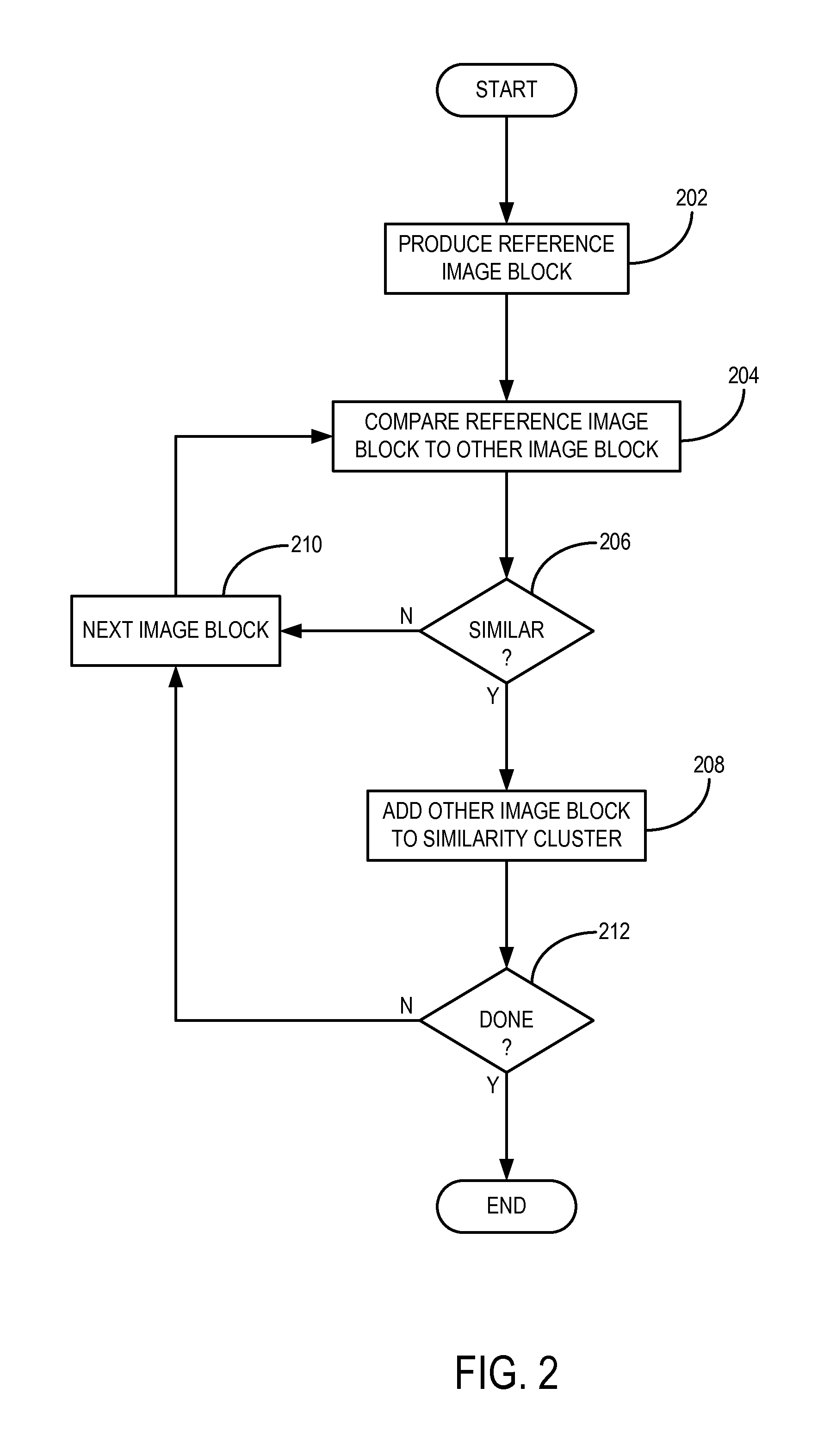
Method For Image Reconstruction Using Low-Dimensional-Structure Self-Learning and Thresholding
InactiveUS20120099774A1Improve reconstructionPromote reconstructionImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionImage resolutionPrincipal component pursuit
A method for reconstructing an image of a subject from undersampled image data that is acquired with an imaging system, such as a magnetic resonance imaging system or computed tomography system, is provided. From the acquired undersampled image data, an image of the subject is reconstructed and used to guide further image reconstruction. For example, a low resolution image is reconstructed from a portion of the undersampled image data, such as from a portion corresponding to the center of k-space when MRI is used. From this image, a number of similarity clusters are produced and processed. The processing may be by hard thresholding, Wiener filtering, principal component pursuit, or other similar techniques. These processed similarity clusters are then used to reconstruct a final, target image of the subject using, for example, a weighted average combination of the similarity clusters.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
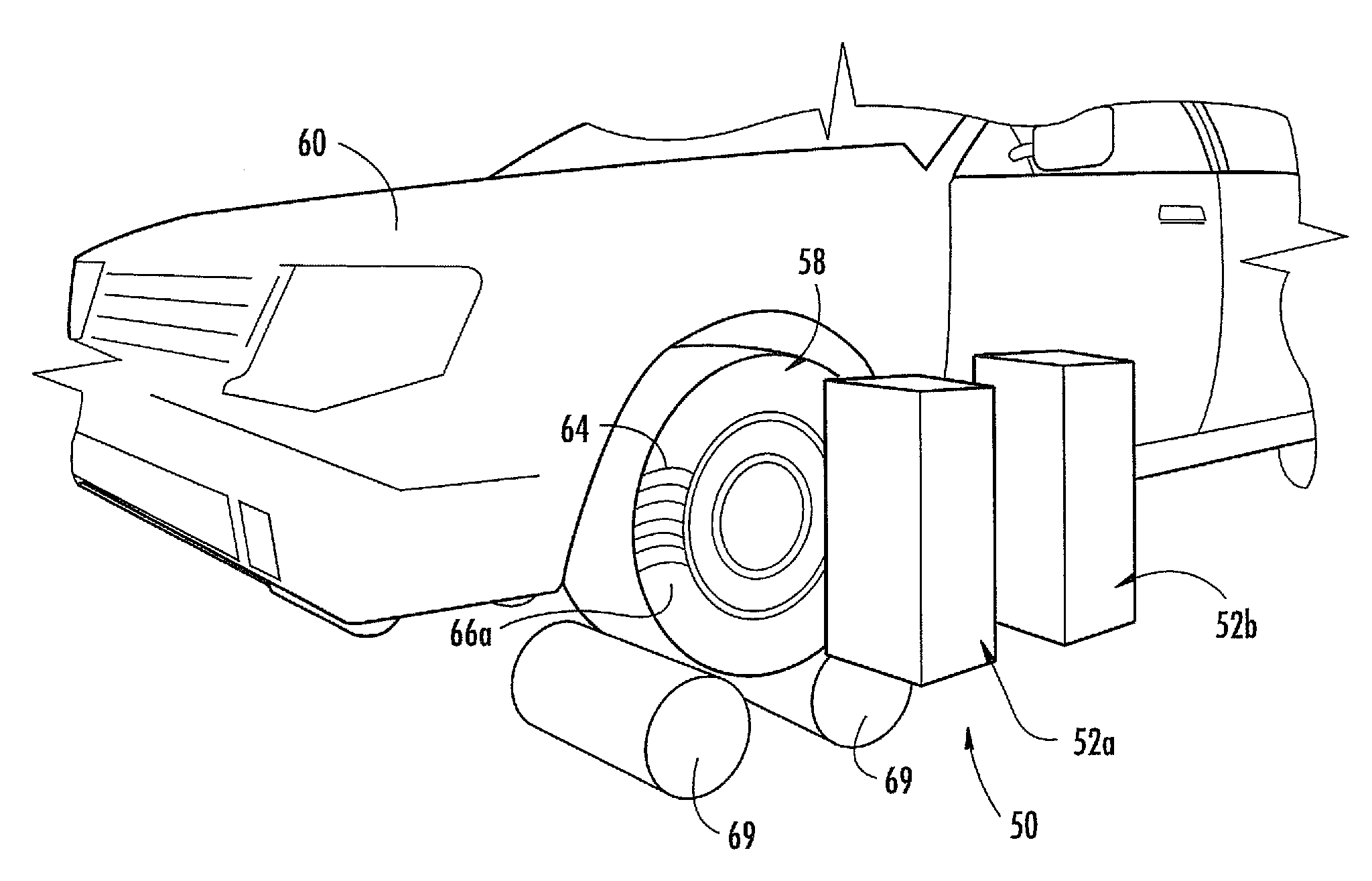
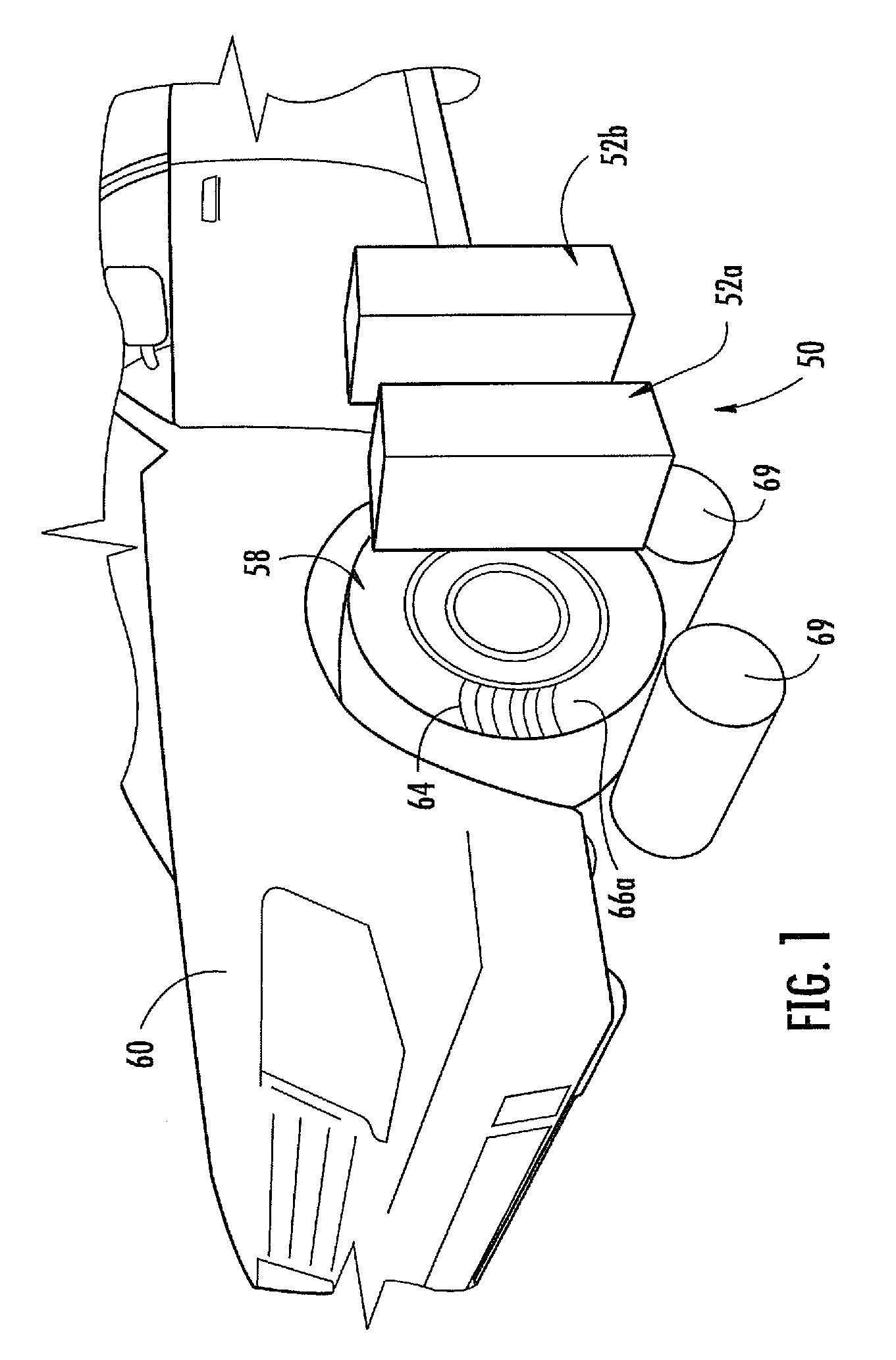
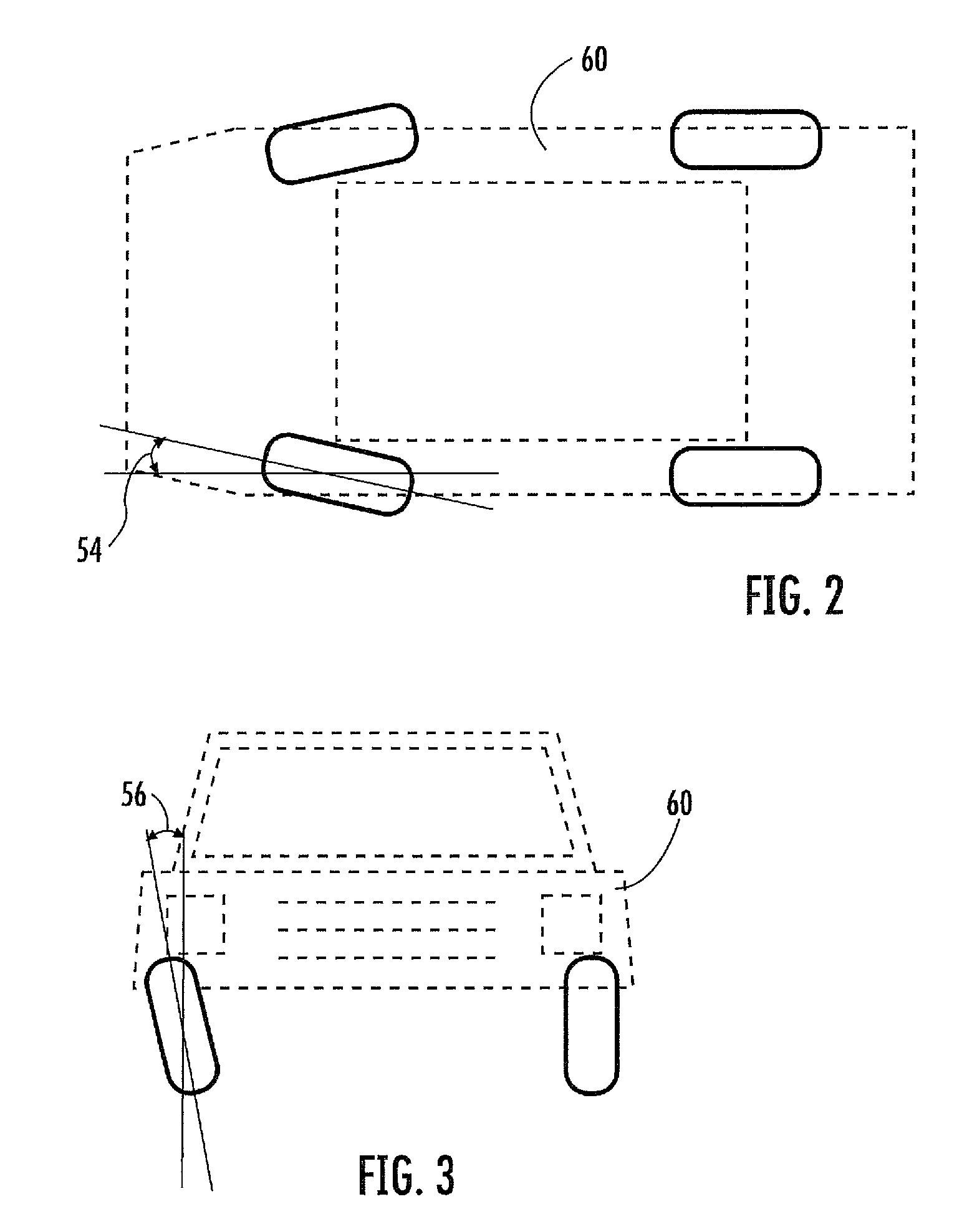
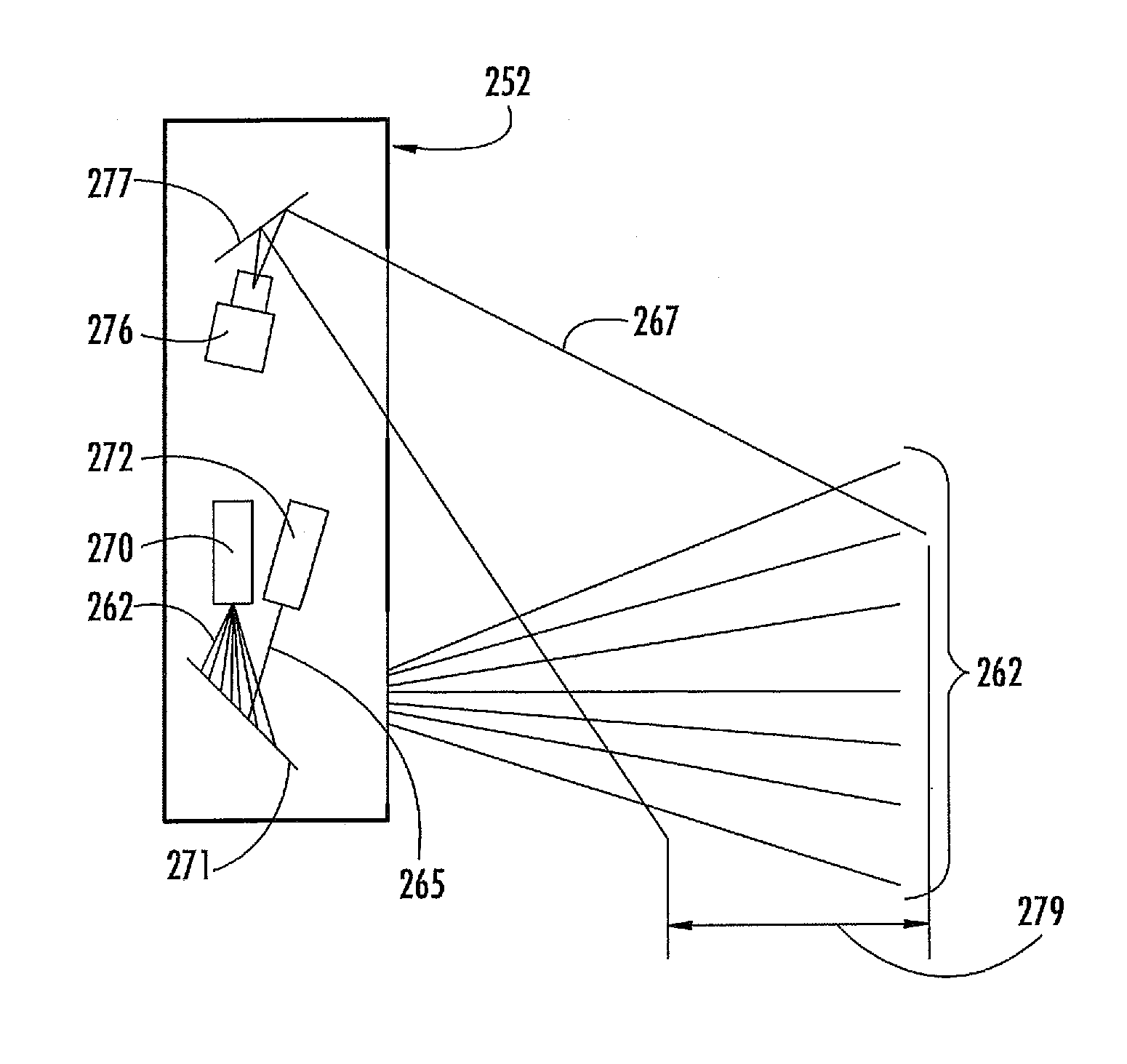
Non contact wheel alignment sensor and method
ActiveUS7864309B2Good precisionHigh sensitivityAngle measurementImage analysisEngineeringWheel alignment
Owner:VERHAERT NEW PROD & SERVICES +1
Non contact wheel alignment sensor and method
ActiveUS20080273194A1Good precisionHigh sensitivityAngle measurementImage analysisEngineeringWheel alignment
A sensor and method of determining the orientation of an object, such as the alignment characteristics of a tire and wheel assembly mounted on a vehicle, includes projecting a plurality of light planes from a first light projector onto a tire and wheel assembly to form a plurality of generally parallel illumination lines on a tire of the tire and wheel assembly, receiving a reflected image of at least some of the illumination lines with a photo electric device reflected from the tire at an angle relative to a projecting angle of the first light projector, and determining a plane defined by spatial coordinates from a selected point located on each illumination line imaged by the photo electric device, with the plane representing the orientation of the tire and wheel assembly.
Owner:VERHAERT NEW PROD & SERVICES +1
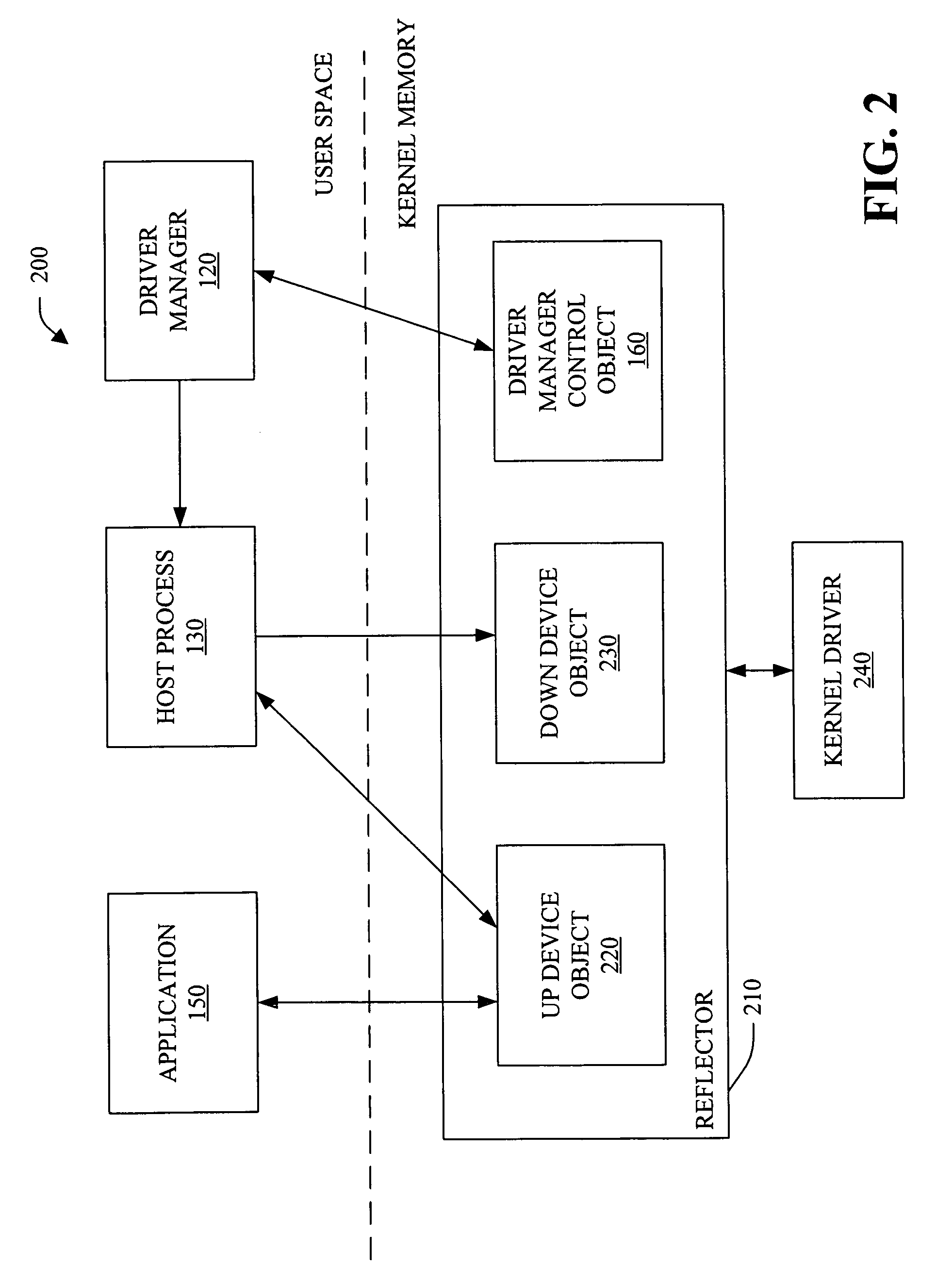
Protocol for communication with a user-mode device driver
InactiveUS7603484B2Low experience requirementReduce instabilityMultiprogramming arrangementsSpecific program execution arrangementsProgram managementOperational system
A user-mode device driver architecture is provided by the subject invention. The architecture includes a reflector, a driver manager and a host process which hosts and isolates one or more user-mode device driver(s). The user-mode device driver runs in the user-mode (UM) environment and has access to various UM services. The reflector resides in “kernel memory” (e.g., memory / resource(s) available to operating system) while the driver manager, host process and user mode device driver(s) are located in user space (e.g., memory / resource(s) available to user application(s)). The reflector provides a secure, stable communication path for application(s), the host process and / or user-mode device driver(s) to communicate with the operating system.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Multi-dimensional cardiac imaging
ActiveUS20120146641A1High scan accelerationImprove robustnessDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMissing dataMedicine
A 5-dimensional imaging method and system is provided to acquire and display the effect of dynamic physiologic changes (either spontaneous or induced) on cardiac function of a patient's heart to elucidate their effects on diastolic myocardial function. In a patient free-breathing magnetic resonance imaging study, 3-dimensional spatial information is encoded by a non-Cartesian 3-dimensional k-space readout trajectory and acquired concurrently with recordings of cardiac and respiratory cycles. The advantage of using non-Cartesian sampling in this invention compared to, for example, Cartesian sampling is higher scan acceleration, improved robustness to motion / flow effects (incoherent instead of coherent artifacts) and robustness to missing data points in k-space.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Event driven graph explorer for model-based testing of software
InactiveUS7302677B2Improve efficiencyImprove cost effectivenessError detection/correctionTransmissionGraphicsGraph traversal
A software testing system uses a graph traversal algorithm to explore a model simulating a software product in order to identify errors in the software product. The model employs a Petri's net construct for maintaining state and governing transitions. In particular, the model mediates between a test driver and the software product. The model-based approach is usable both to validate the design of the software and verify the implementation of that design. Using the Petri net model, the test space is bounded.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
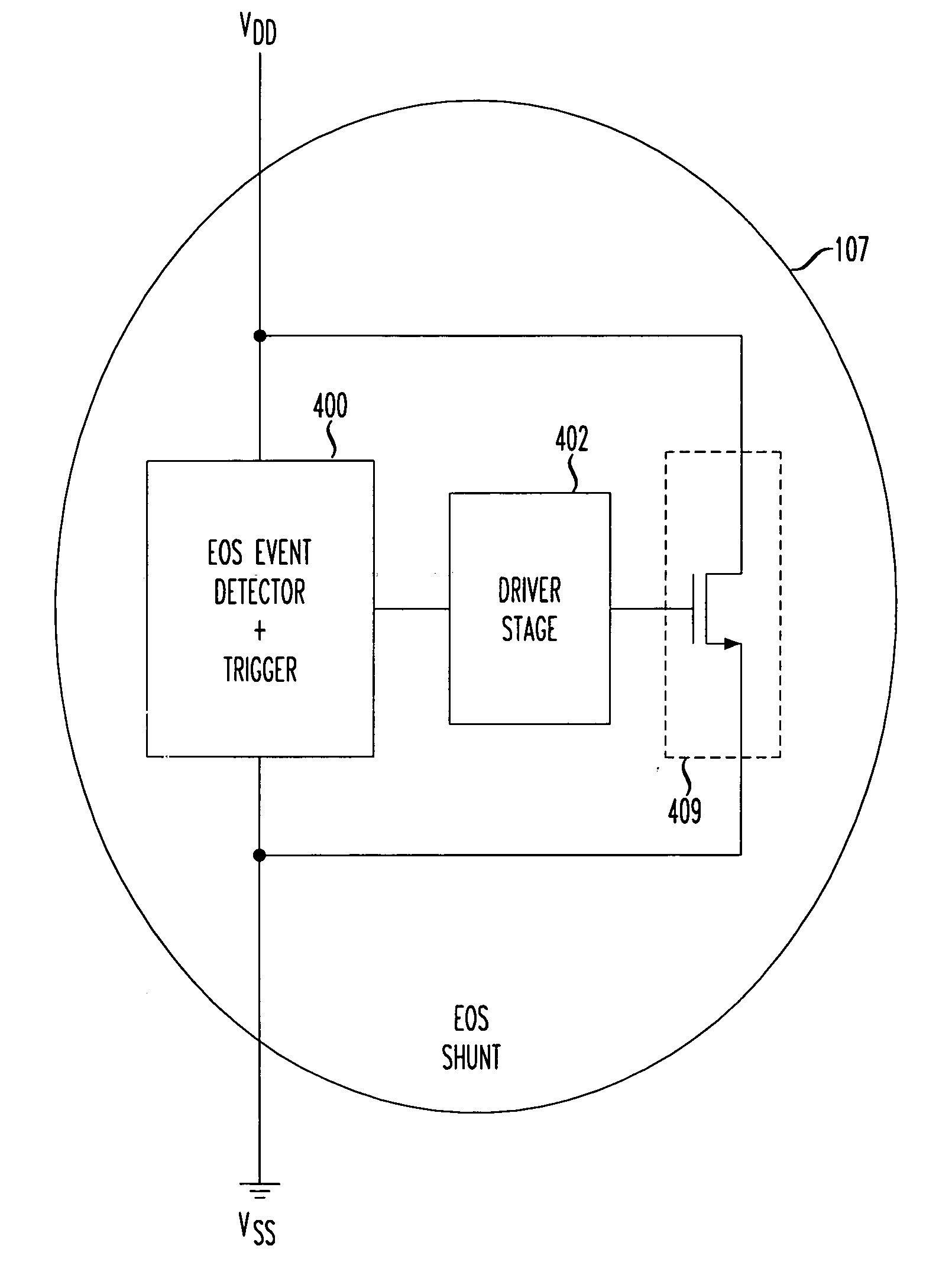
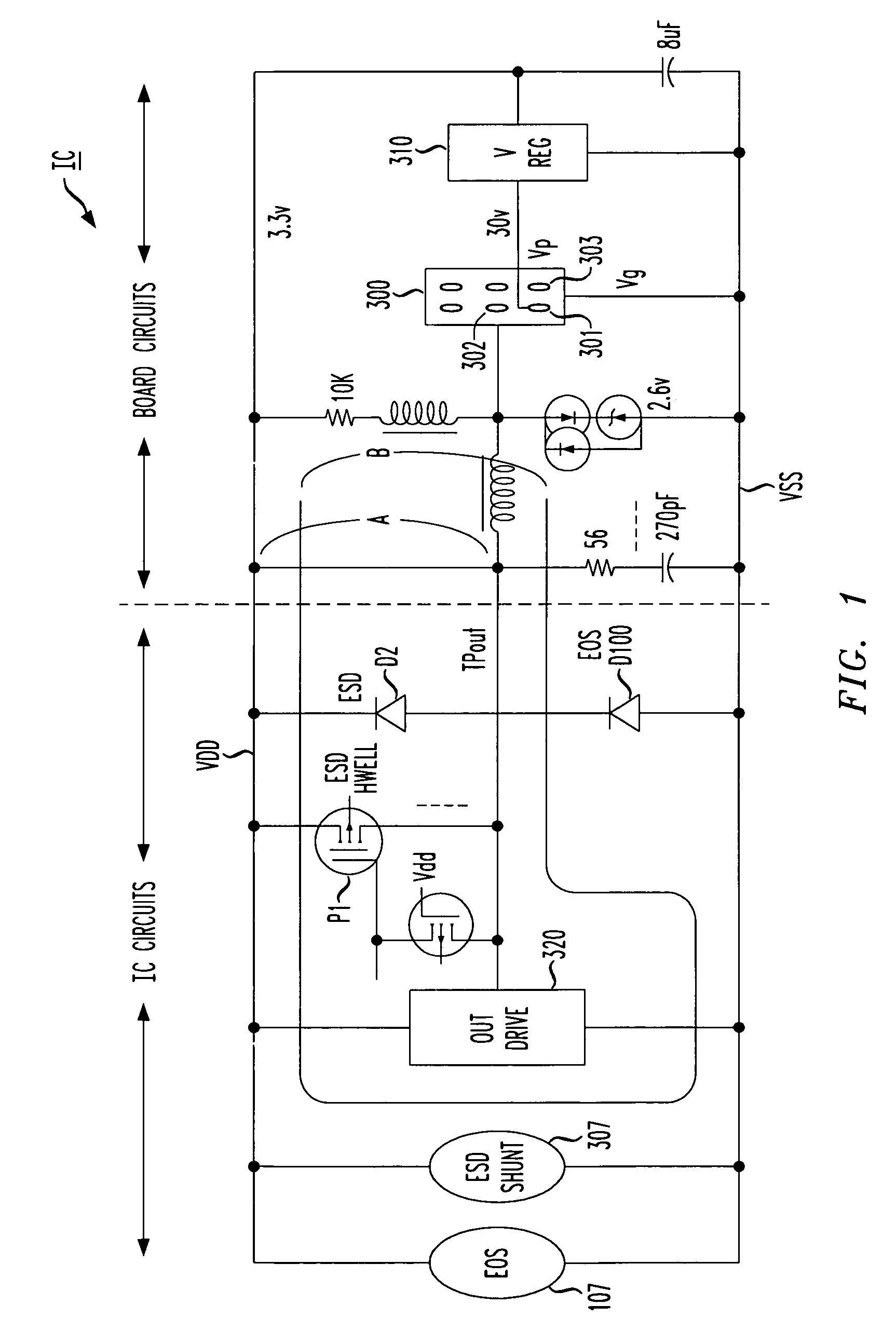
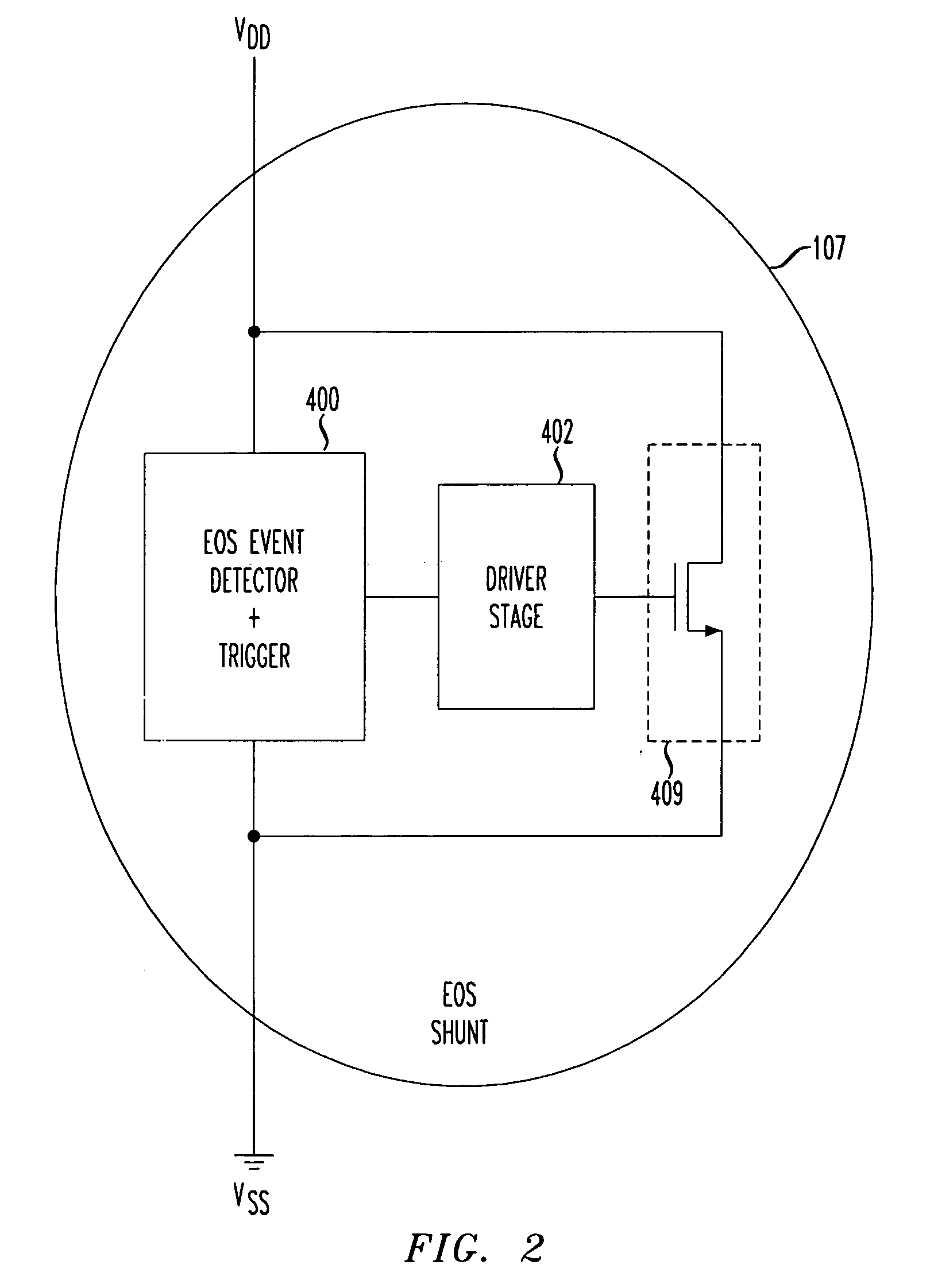
Electrical over stress robustness
InactiveUS20050225912A1Low resistanceProvide robustnessTransistorSolid-state devicesVoltInterface circuits
Protection is provided against electrical surges resulting from Electrical Over Stress conditions, e.g., when interfacing circuits with powered connections. An EOS shunt is activated for as long as the EOS condition exists. EOS protection using an EOS shunt in accordance with the principles of the present invention remains activated by a voltage threshold trigger as long as necessary. In a disclosed embodiment, an EOS shunt includes a voltage threshold detector that detects a voltage on a power bus with respect to a ground rail exceeding a predetermined amount, e.g., 5 volts in a device powered at 3.3 volts. During the EOS event, a path between power and ground comprising a transistor is turned on.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method to facilitate failure modes and effects analysis
ActiveUS20050138477A1Promote generationProvide robustnessProgramme controlError detection/correctionGraphicsGraphical user interface
A method and system to facilitate failure modes and effects analysis (FMEA) of one or more components of a system. The FMEA is indicated with the generation of an FMEA form. A graphical user interface provides a sequential order of completion for a number of steps. The steps are followed to generate graphical representations which are to be completed by an FMEA analyst and received by the graphical user interface to facilitate generating the FMEA form.
Owner:FORD MOTOR CO
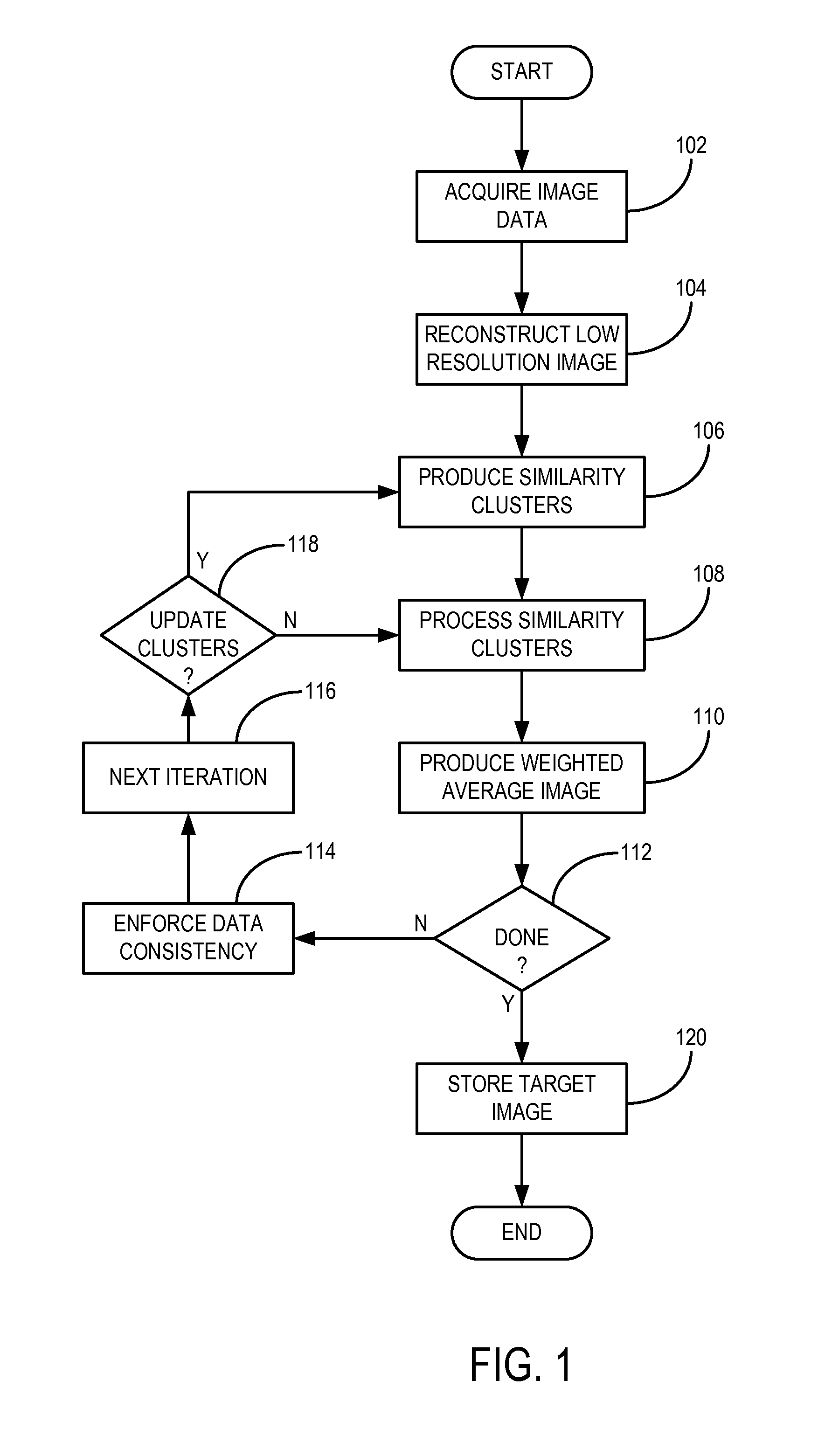
Method for image reconstruction using low-dimensional-structure self-learning and thresholding
InactiveUS8699773B2Promote reconstructionEliminate artifactsImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionPattern recognitionImage resolution
A method for reconstructing an image of a subject from undersampled image data that is acquired with an imaging system, such as a magnetic resonance imaging system or computed tomography system, is provided. From the acquired undersampled image data, an image of the subject is reconstructed and used to guide further image reconstruction. For example, a low resolution image is reconstructed from a portion of the undersampled image data, such as from a portion corresponding to the center of k-space when MRI is used. From this image, a number of similarity clusters are produced and processed. The processing may be by hard thresholding, Wiener filtering, principal component pursuit, or other similar techniques. These processed similarity clusters are then used to reconstruct a final, target image of the subject using, for example, a weighted average combination of the similarity clusters.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
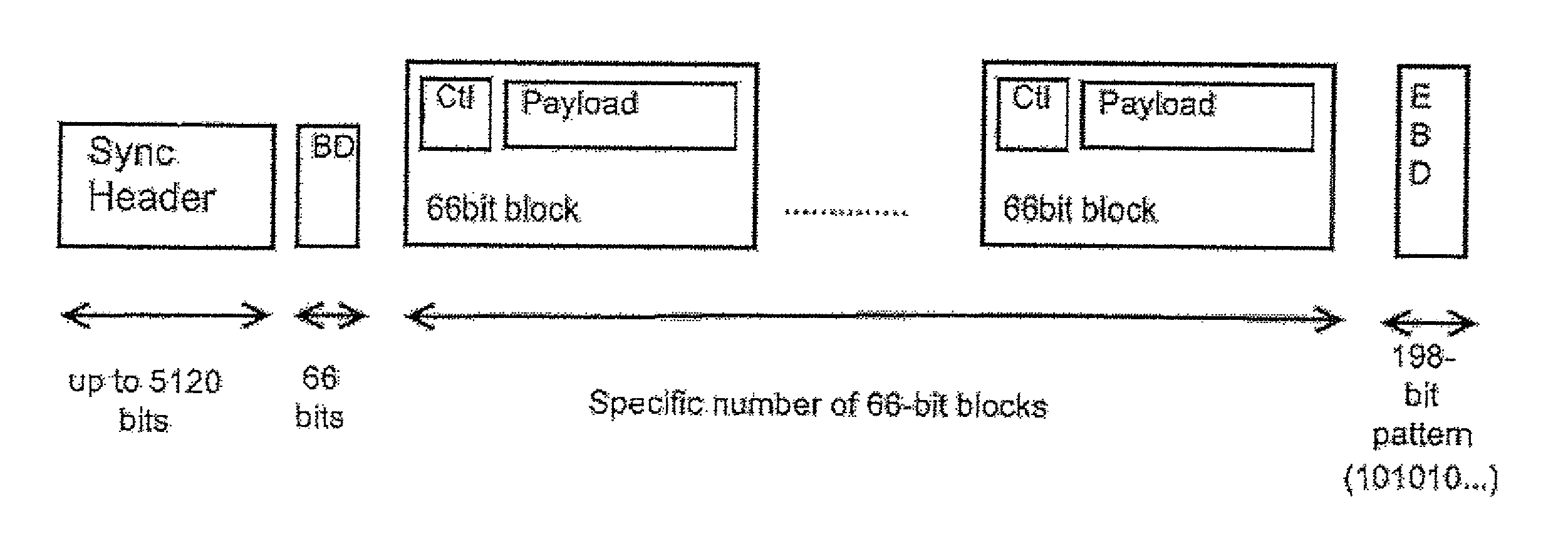
End-of-burst detection for upstream channel of a point-to-multipoint link
ActiveUS8102851B1Provide robustnessMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationTelecommunications linkCommunication link
A method of signaling and detecting end-of-transmission on a data communications link that uses scrambling comprises, by a transmitting node of the network, appending an end of burst delimiter (EBD) binary sequence to burst data and transmitting the burst data and the EBD over the communication link to a headend of the network. In a 10 G EPON using a 64B / 66B transmission code, the EBD is exemplarily a 198 bit pattern.
Owner:MICROSEMI ISRAEL STORAGE SOLUTIONS LTD
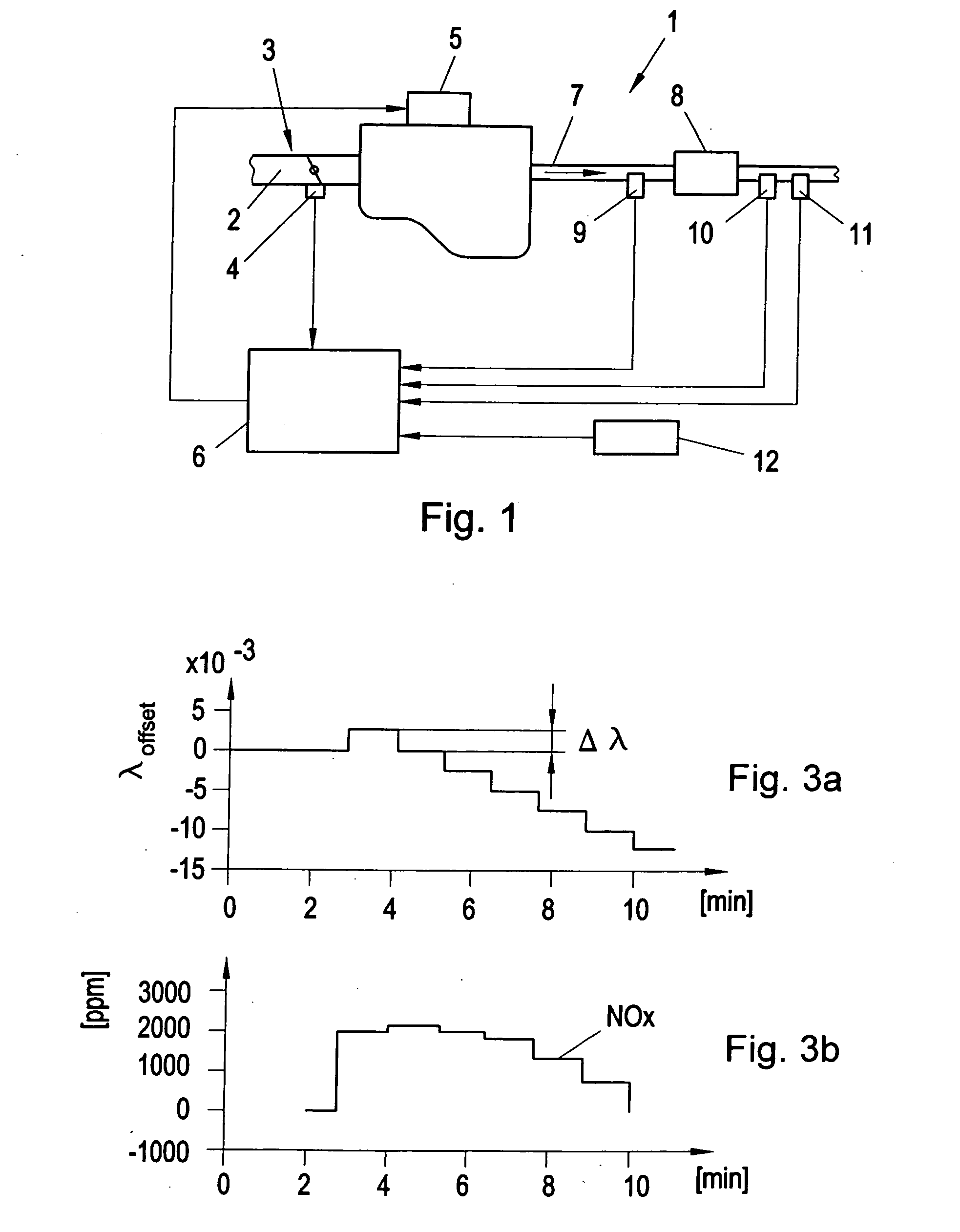
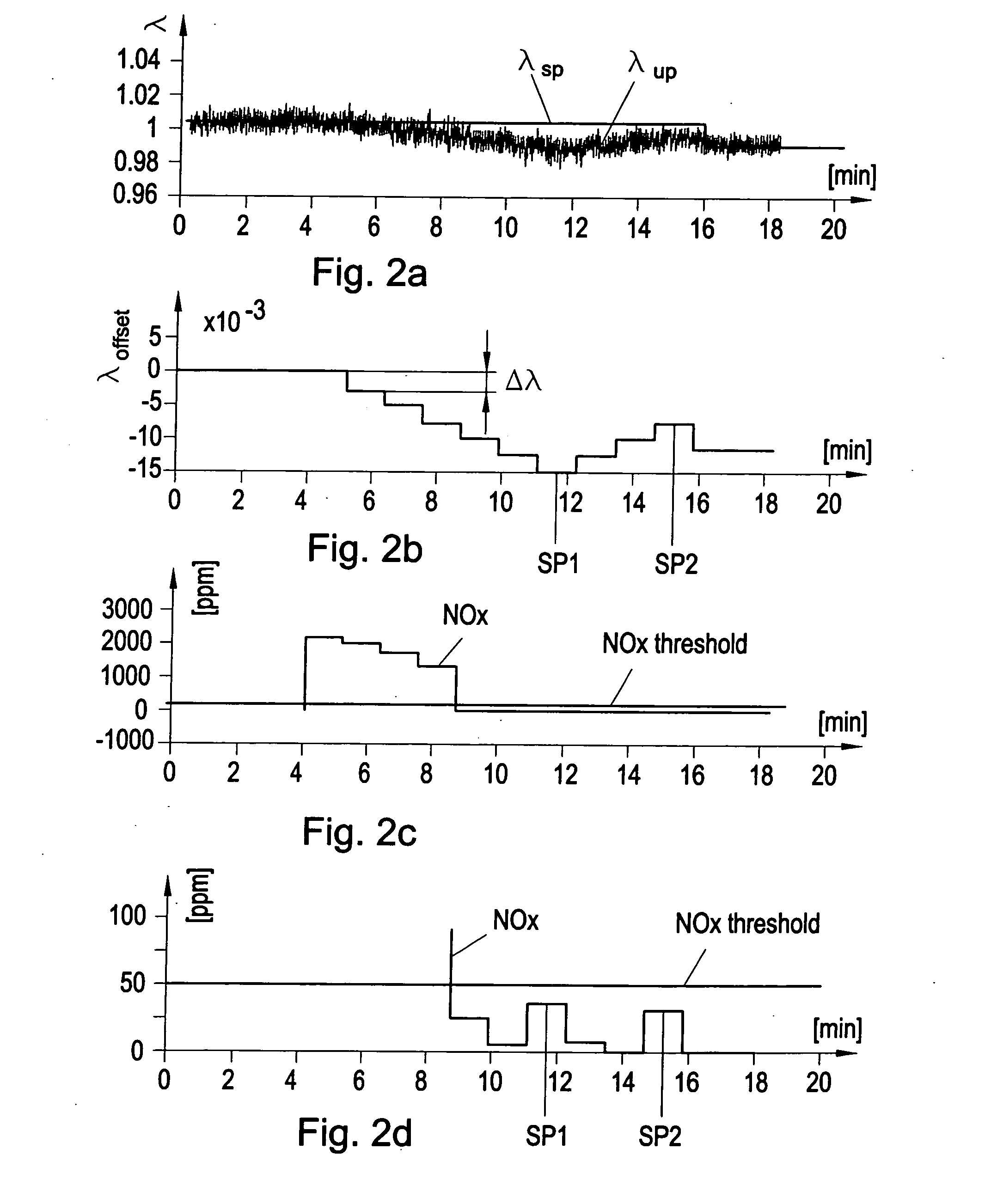
Air/Fuel Ratio Controller and Control Method
ActiveUS20130138326A1Provide robustnessSure easyElectrical controlDigital data processing detailsControl theory
An air / fuel ratio controller (6) and a method that uses an upstream control loop to maintain a given optimum air / fuel ratio (λopt), whereas the optimum air / fuel ratio (λopt) is determined in the controller (6) in an downstream control loop by adding incremental offset (Δλ) to the air / fuel ratio set-point (λSP) of an upstream control loop whilst monitoring a NOx sensor (10) output. The air / fuel ratio set-points (λSP) at two turning points (SP1, SP2) in the NOx sensor (10) output are used to calculate a new optimum air / fuel ratio set-point (λopt) as mean value of the air / fuel ratio set-points (λSP1, λSP2) at the turning points (SP1, SP2).
Owner:ALTRONIC
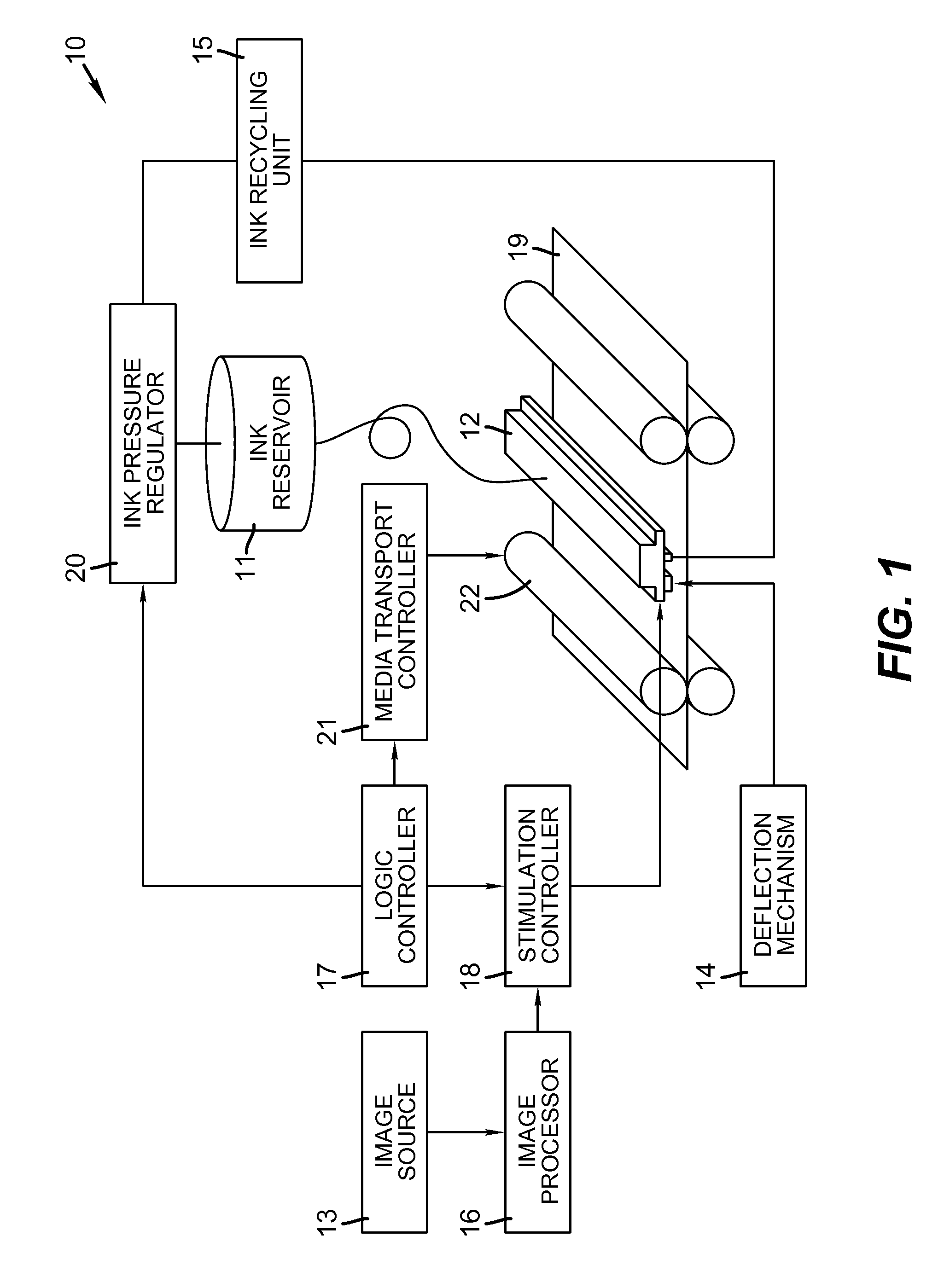
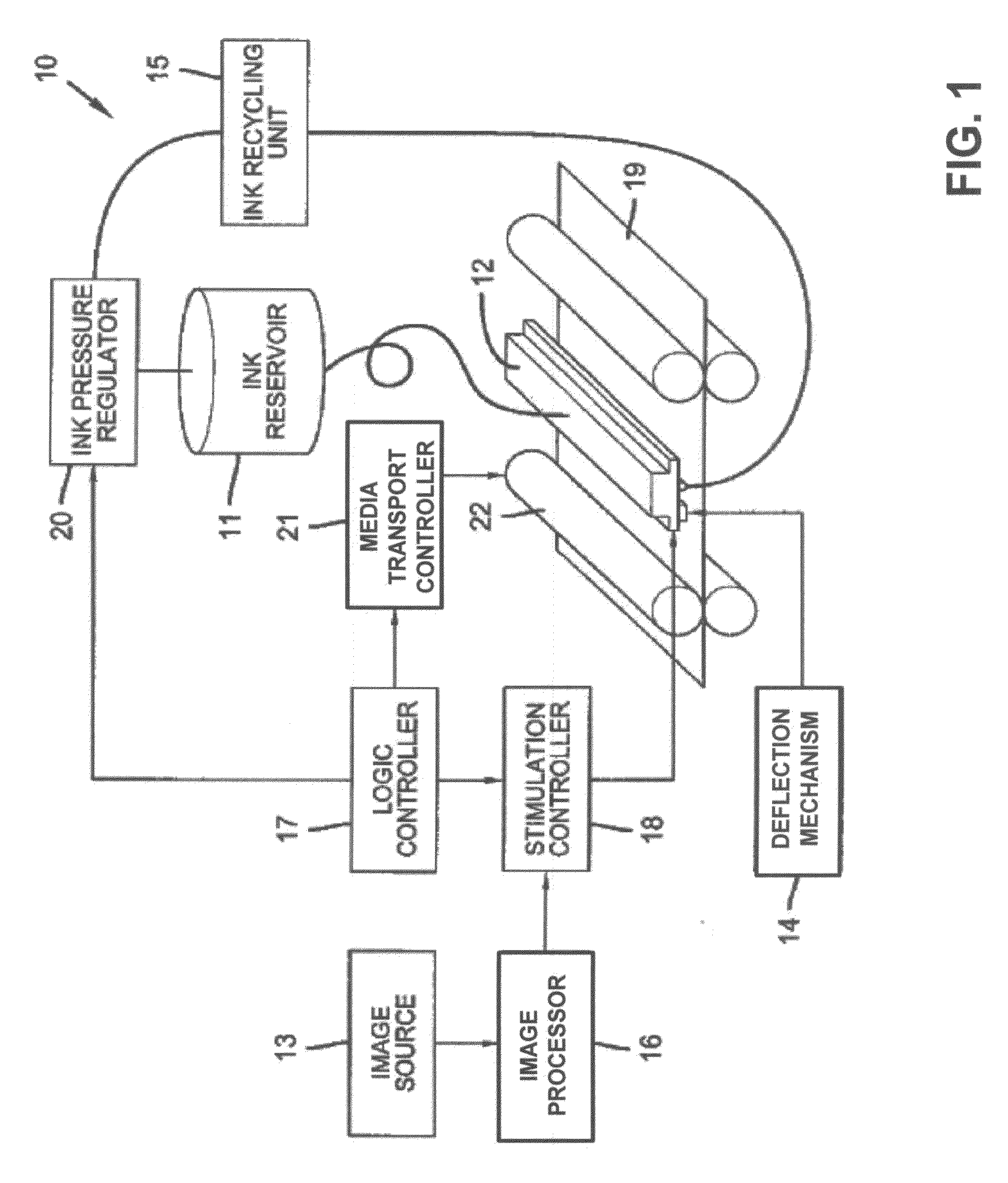
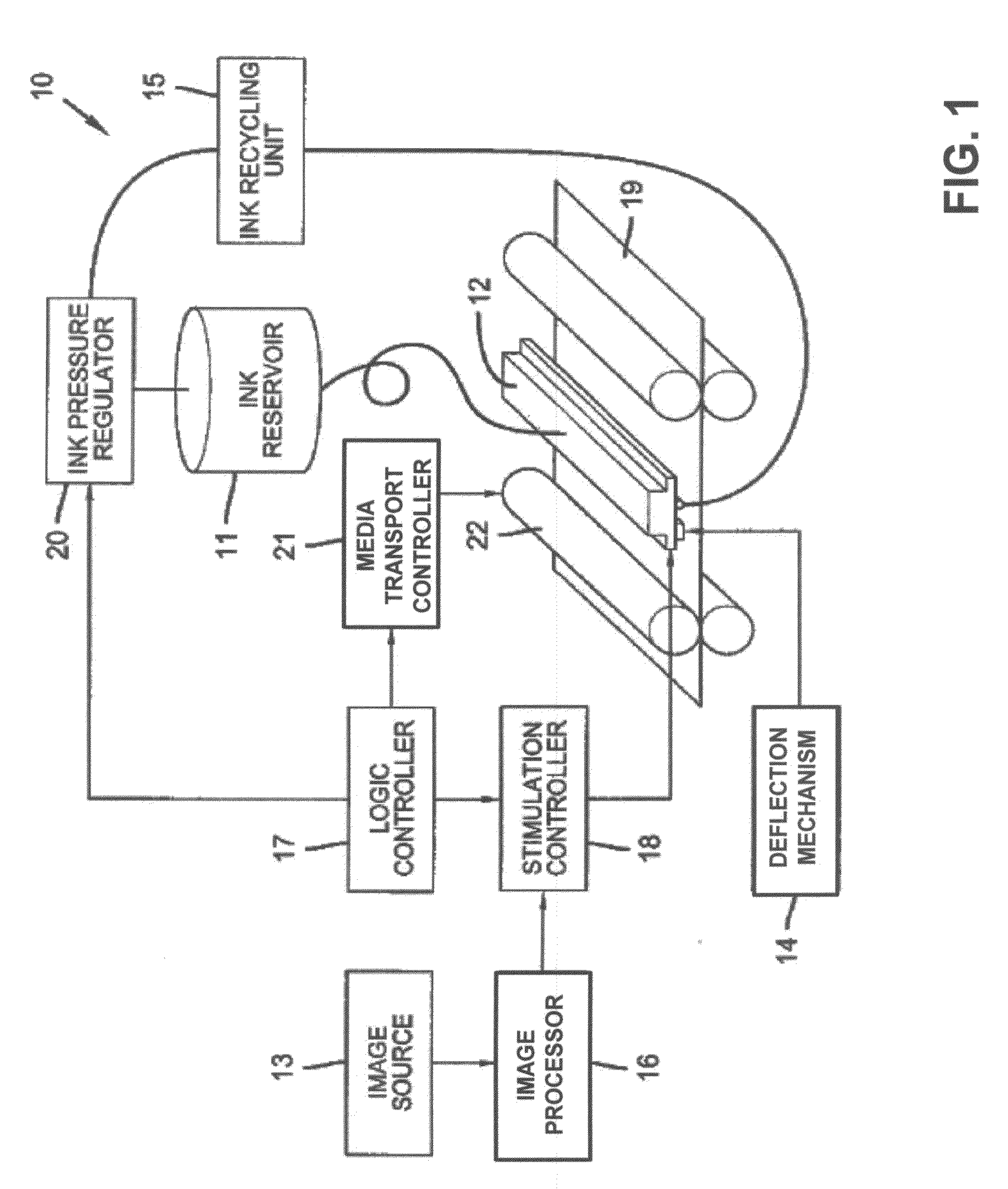
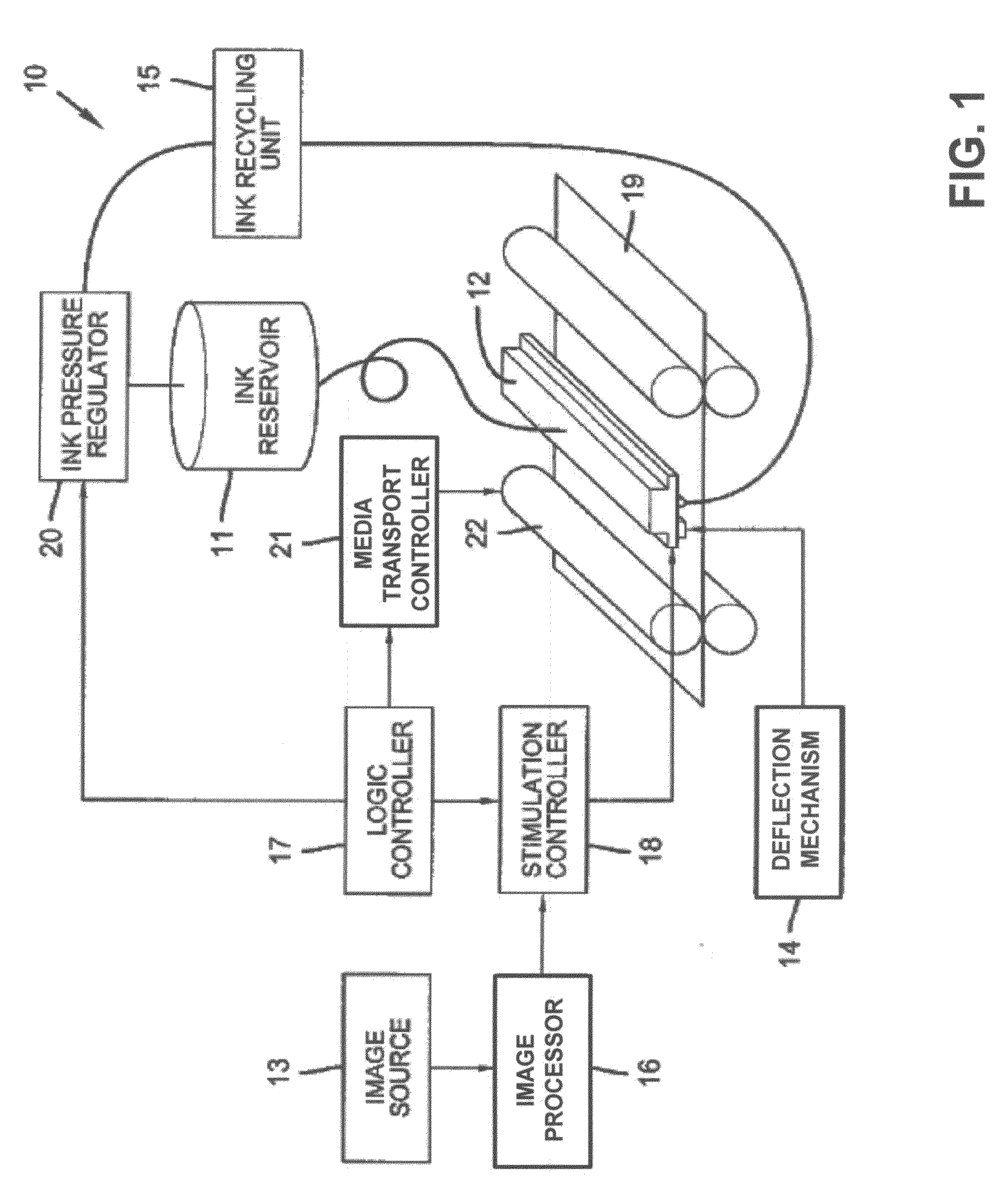
Liquid ejection system including drop velocity modulation
ActiveUS8657419B2Minimizing drop volume variation of dropQuality improvementPrintingLiquid jetSpray nozzle
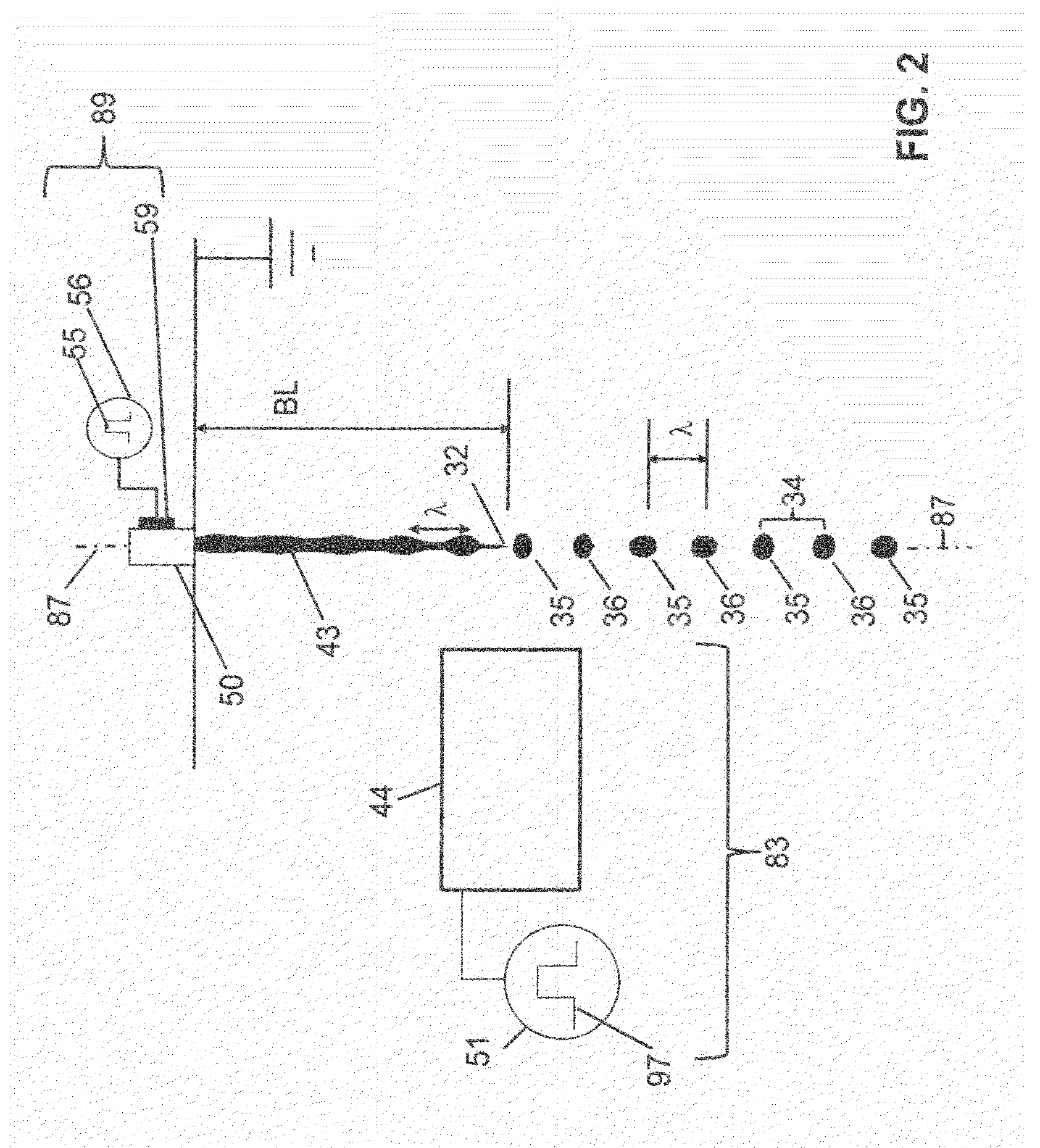
A continuous ejection system includes a chamber containing liquid under pressure sufficient to eject a liquid jet through a nozzle. A drop formation device modulates the jet causing portions to break into drop pairs including first and second drops separated in time on average by a drop pair period. A charging device includes a varying electrical potential source providing a waveform including first and second distinct voltage states and a period equal to the drop pair period. The charging device produces first and second charge states on first and second drops of the drop pair, respectively. A drop velocity modulation device varies a relative velocity of first and second drops of selected drop pairs causing first and second drops of selected drop pairs to form combined drops having a third charge state. A deflection device causes the first, second, and combined drops to travel along different paths.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
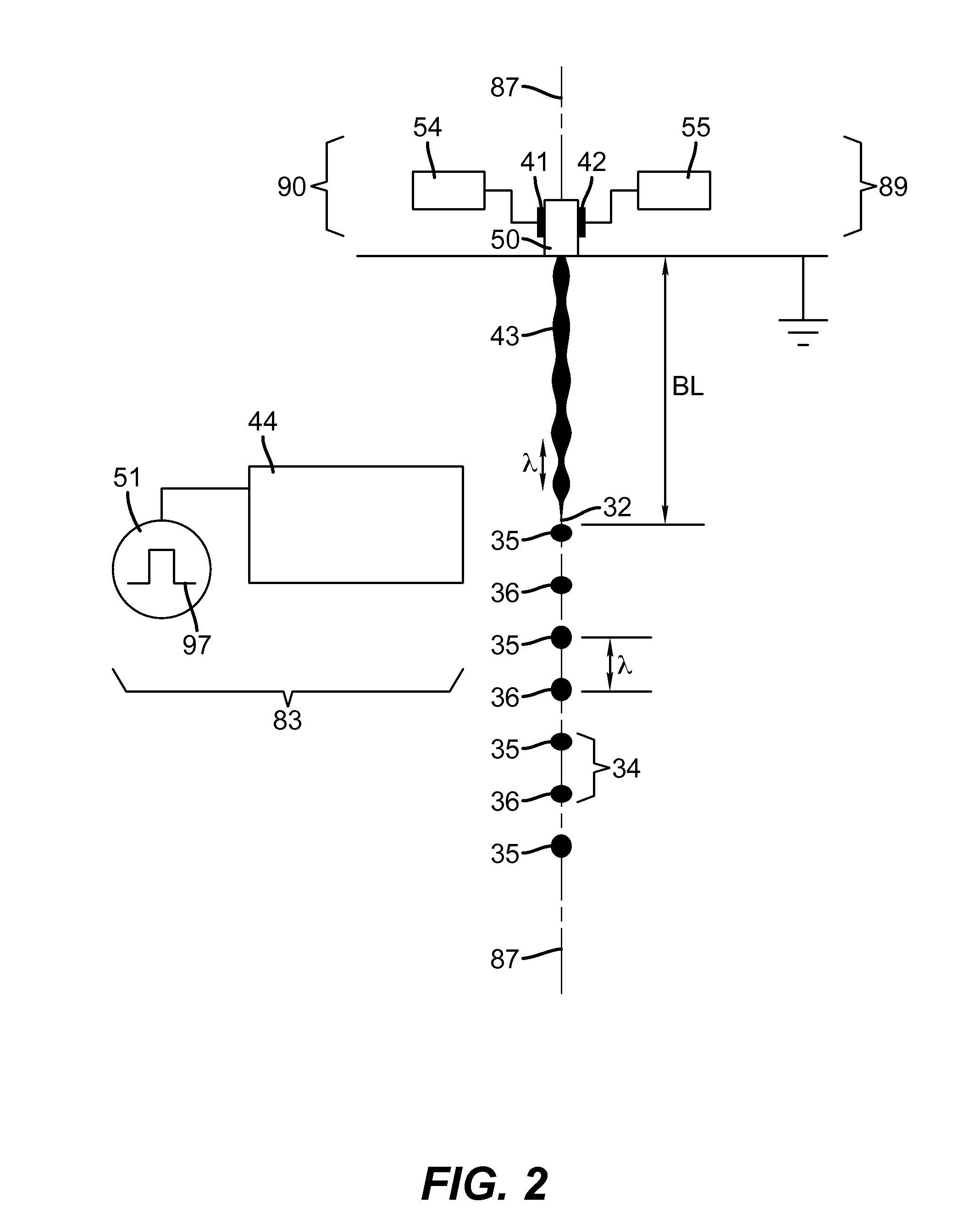
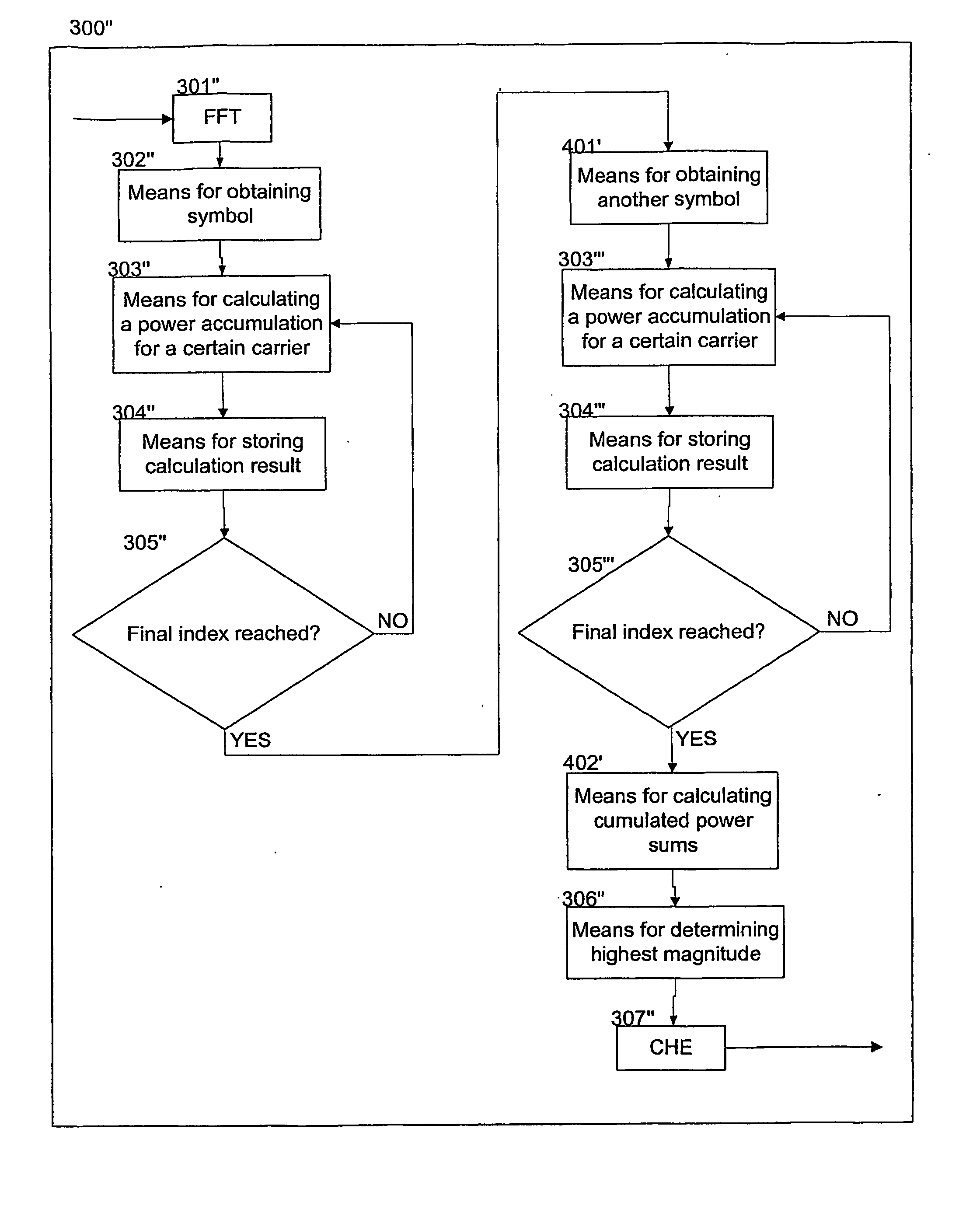
Method system and receiver for receiving a multi-carrier transmission
InactiveUS20070053281A1Cutting synchronizationEasy accessMulti-frequency code systemsOrthogonal multiplexCarrier signalMulti carrier
Mobile handheld terminals receiving DVB transmission require relatively low power consumption and TDM based transmission can be used to reduce power of the terminals. In order find pilot carrier position at least one symbol is accessed which is adapted to establish a correspondence pattern for pilot carriers in a matrix of the symbols. Carriers of the symbol are power accumulation summed within the matrix for determining a power accumulation sum maximum for indicating a pilot carrier position.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Communication system, article and method of configuring and establishing a connection therein
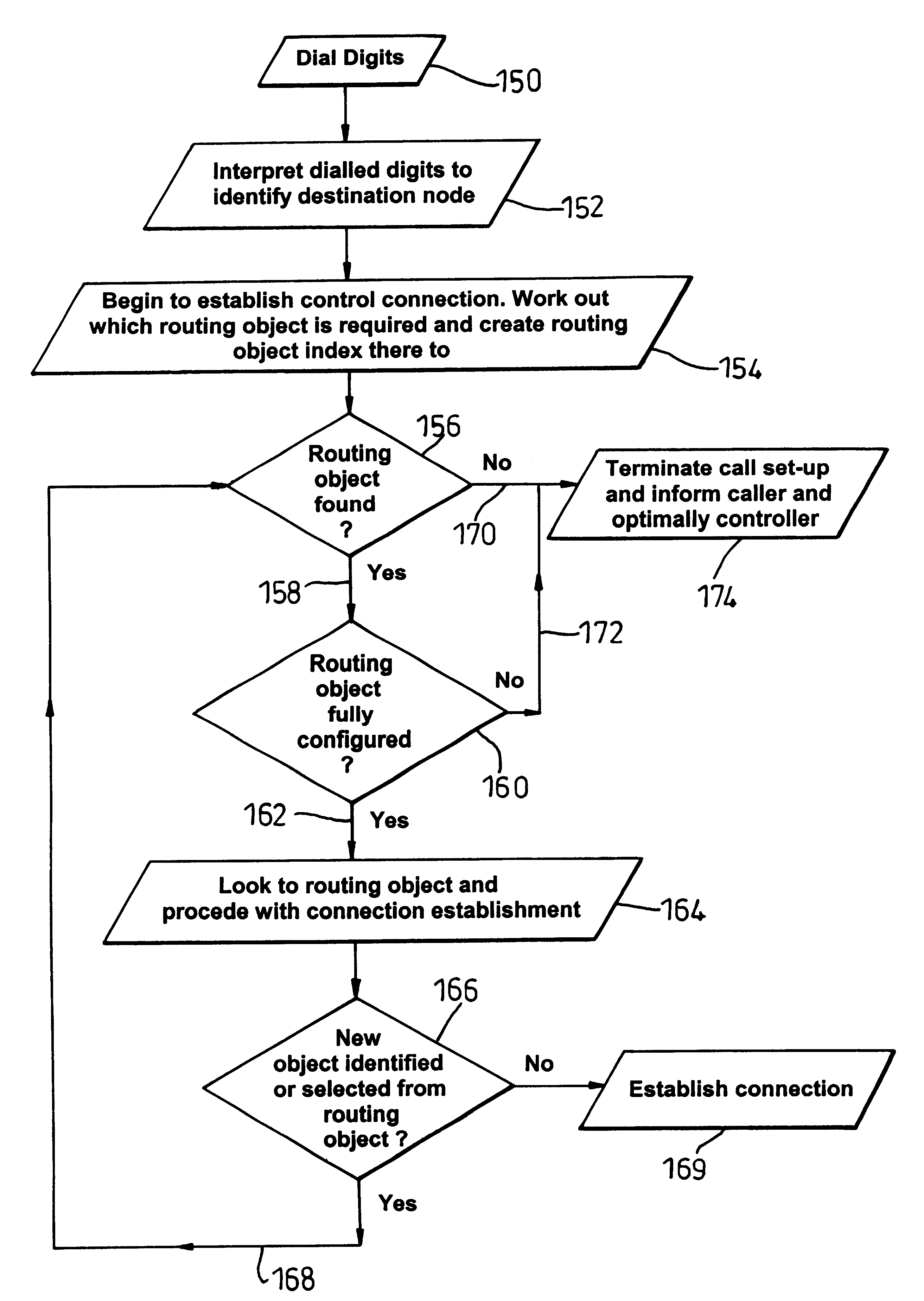
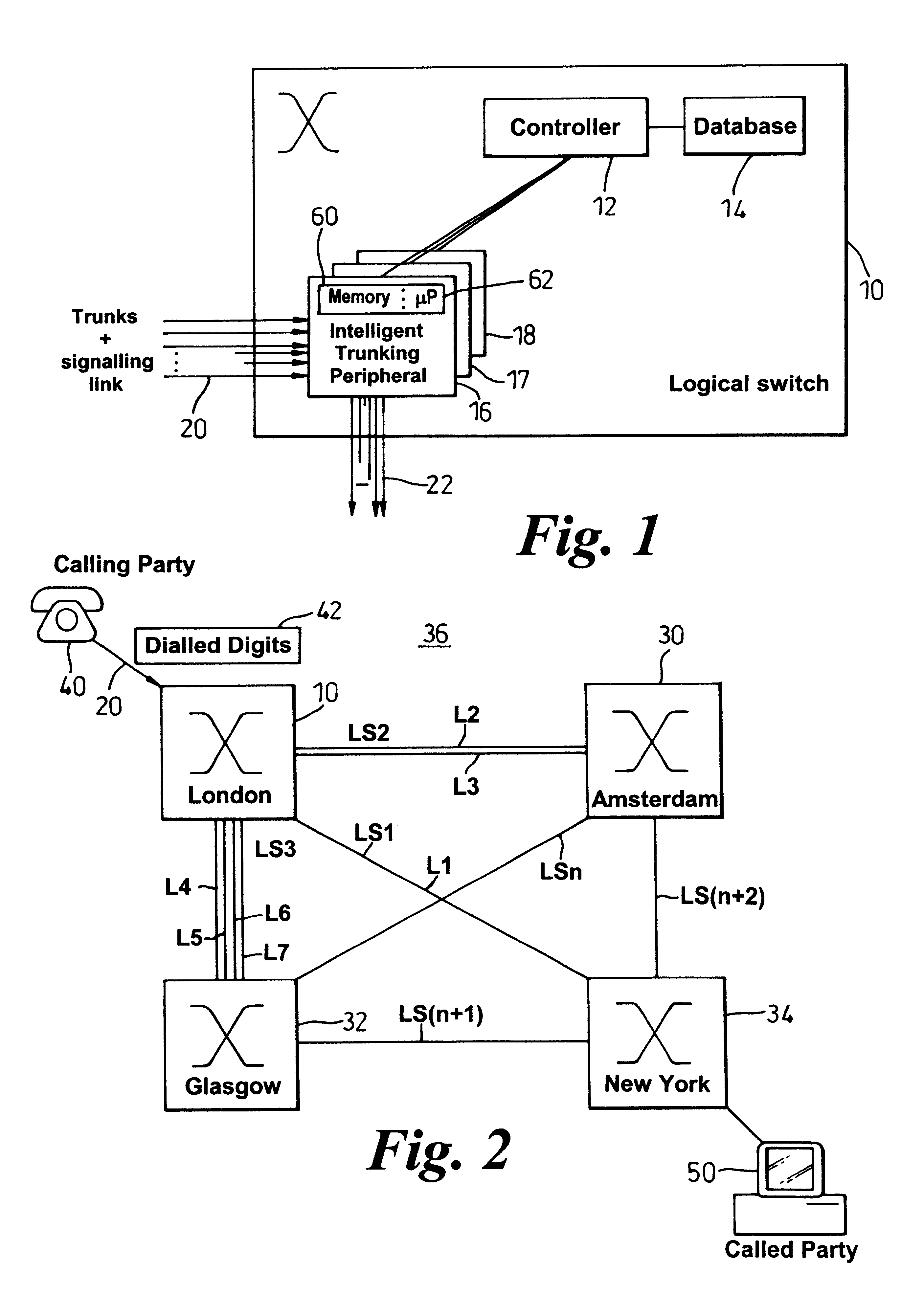
InactiveUS6449354B1Easy to handleRobustness in routingMultiplex system selection arrangementsInterconnection arrangementsCommunications systemSystem configuration
To avoid searching for objects that are not effectively configured and therefore to mitigate connectivity and system failure, an intermediate routing object index (100, 103) is created to each and every object in a system (36). In a telecommunications system, for example, an object is only operational at a node (10, 30-34), such as a switch, upon receipt of all necessary configuration messages (102) from an overall system controller (12) responsible for overseeing operation of the node (10, 30-34) and the set-up of a connection. The routing object index stores (103, 108) an indication of the receipt of the necessary configuration messages and so provides a direct indication of whether the object exists and whether it is effectively configured. Consequently, during a connection establishment process in which control information, such as dialled digits (42, 150), indicates a called party (50) and more especially its serving node (34), the system of the present invention initially creates (100) and then subsequently accesses (156) the routing object index before attempting to locate the associated object (164). Should the routing object index fail to provide verification (106, 172) of a fully configured object or if the routing object does not exist (170), the routing object index causes the system to indicate (174) that a connection is not presently possible. The routing object index can also provide a mechanism for tracking (114-118) system configuration at a node level.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
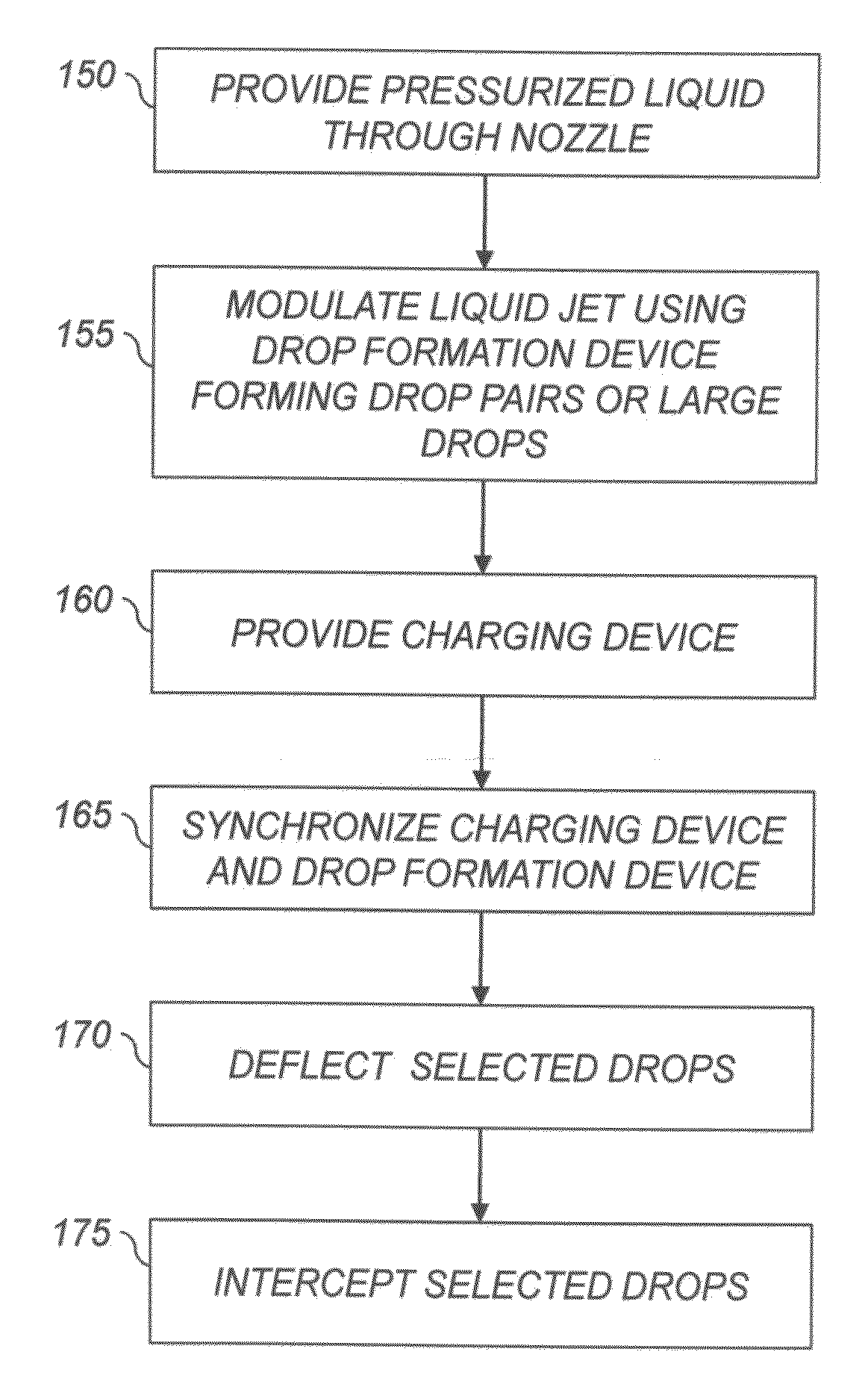
Liquid ejection method using drop velocity modulation
ActiveUS8469496B2Minimizing drop volume variation of dropQuality improvementPrintingLiquid jetEngineering
A liquid jet, ejected through a nozzle, is modulated using a drop formation device to cause the jet to form drop pairs, including first and second drops, traveling along a path separated in time on average by a drop pair period. A charging device, synchronized with the formation device, produces first and second charge states on the first and second drops, respectively, using a waveform including a period equal to the drop pair period and first and second distinct voltage states. A relative velocity of first and second drops from a selected drop pair is varied using a velocity modulation device to control whether the first and second drops of the selected drop pair form a combined drop having a third charge state. A deflection device causes the first, second, and combined drops having the first, second, and third charge states to travel along first, second, and third paths, respectively.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
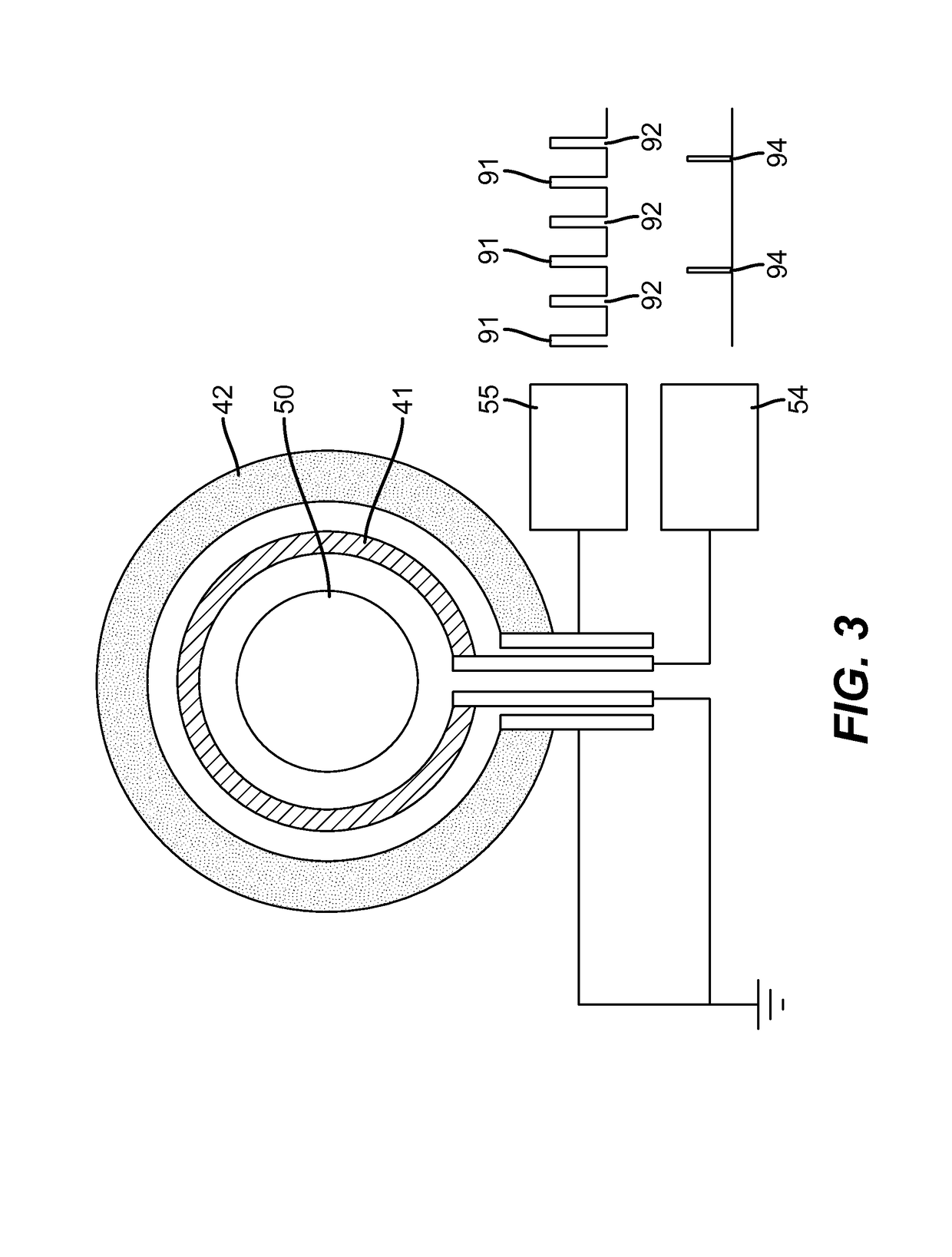
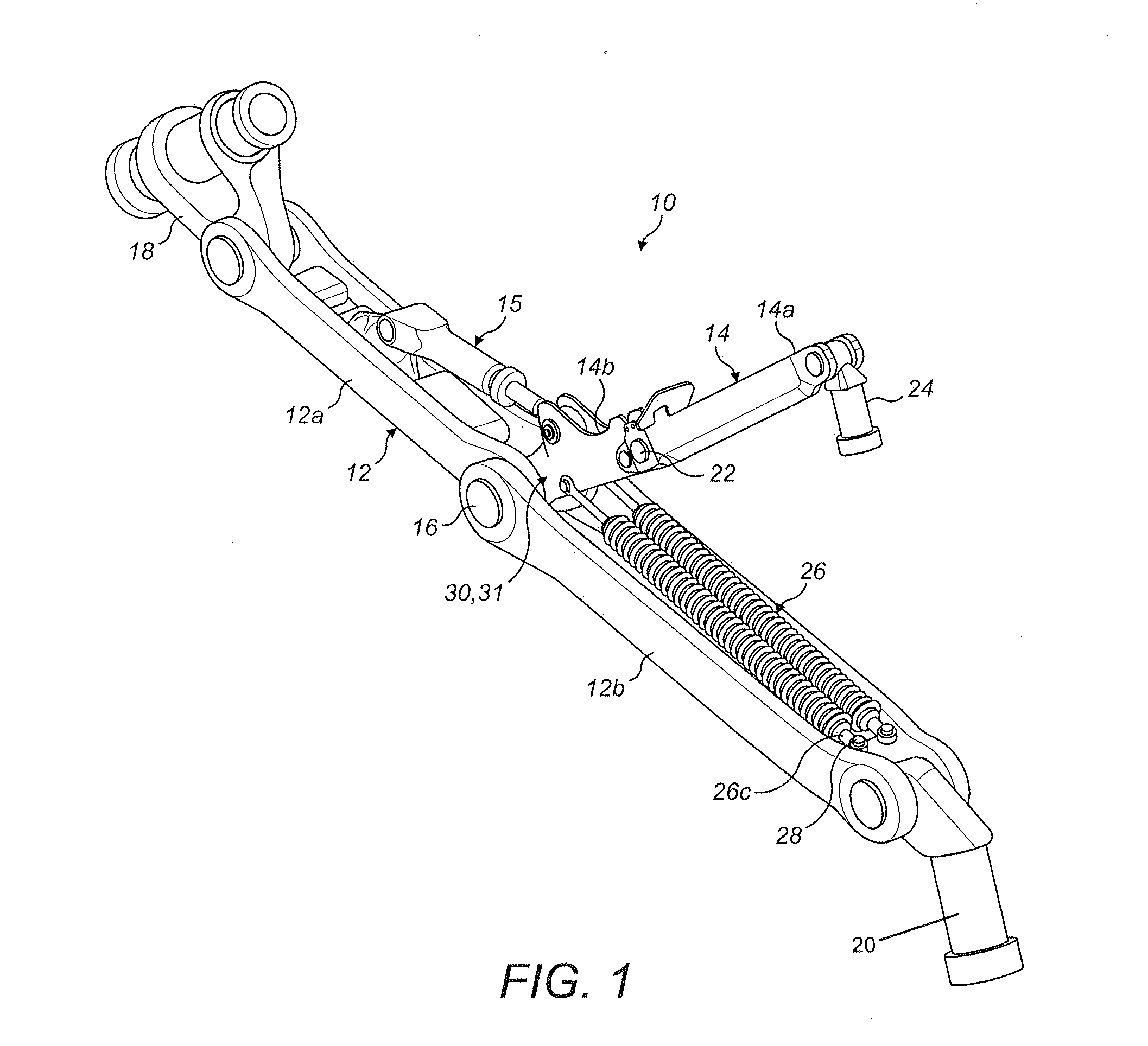
Aircraft spring assembly
ActiveUS20160347444A1Reduce the amplitudeLower Level RequirementsSpring motorHigh internal friction springsCouplingEngineering
An aircraft spring assembly having a spring, an end fitting including a spring engagement formation arranged to be mechanically coupled to an end region of the spring and a coupling formation for coupling the spring assembly to an aircraft anchor point. The coupling formation includes a load bearing surface via which loads from the anchor point can be transmitted into the spring assembly. The assembly further includes an integral damping member provided within the load path between the load bearing surface of the coupling formation and the end region of the spring.
Owner:MESSIER DOWTY
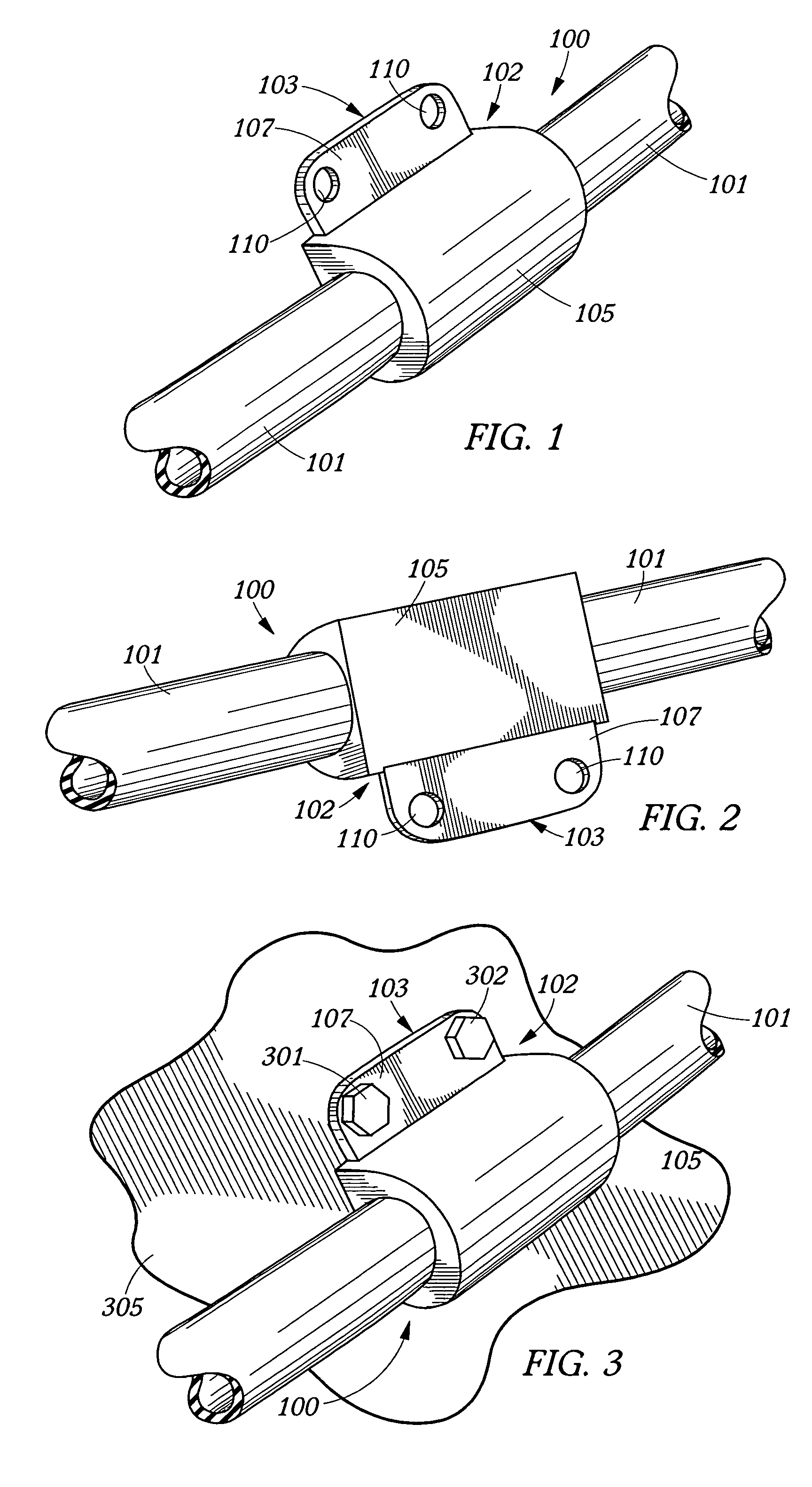
Hose and tubing assemblies and mounting systems and methods
ActiveUS20080011933A1Prevent abrasionLow skill-level procedurePipe supportsMining devicesBearing surfaceFastener
A hose assembly includes a length of hose and a bracket. The bracket includes a rigid insert and a resilient overmold encapsulating at least a portion of the insert and mechanically bonding with at least a portion of an exterior of the hose. A method to produce this assembly may employ thermoplastic injection molding and include the steps of associating the rigid insert with the length of hose and overmolding the rigid insert and a section of the length of hose associated with the rigid insert with the resilient material, thereby encapsulating a portion of the insert and mechanically bonding the resilient material with the section of the length of the hose. A portion of the rigid insert may extend from the bracket and provide amounting holes and a bearing surface for mounting fasteners.
Owner:THE GATES CORP
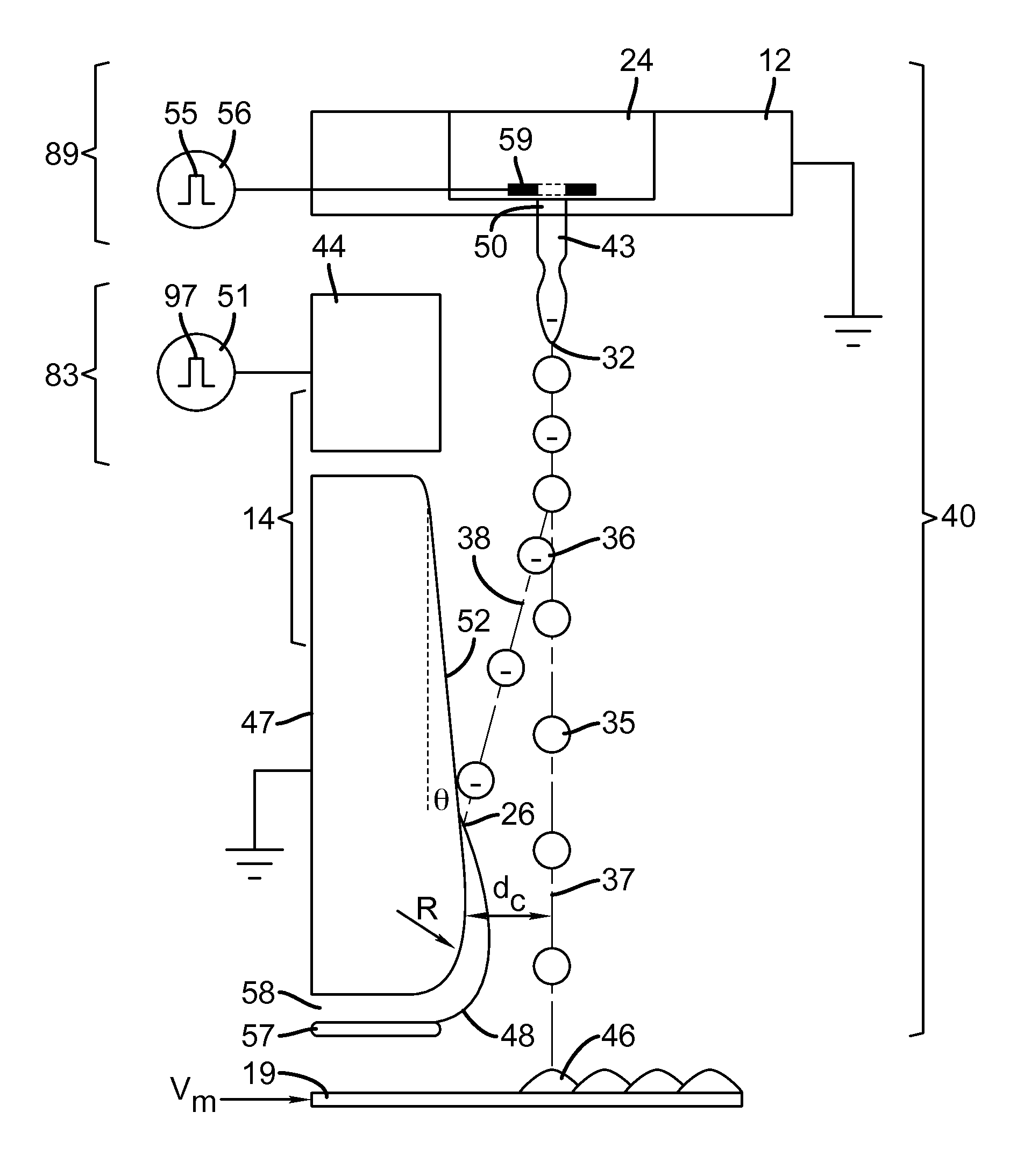
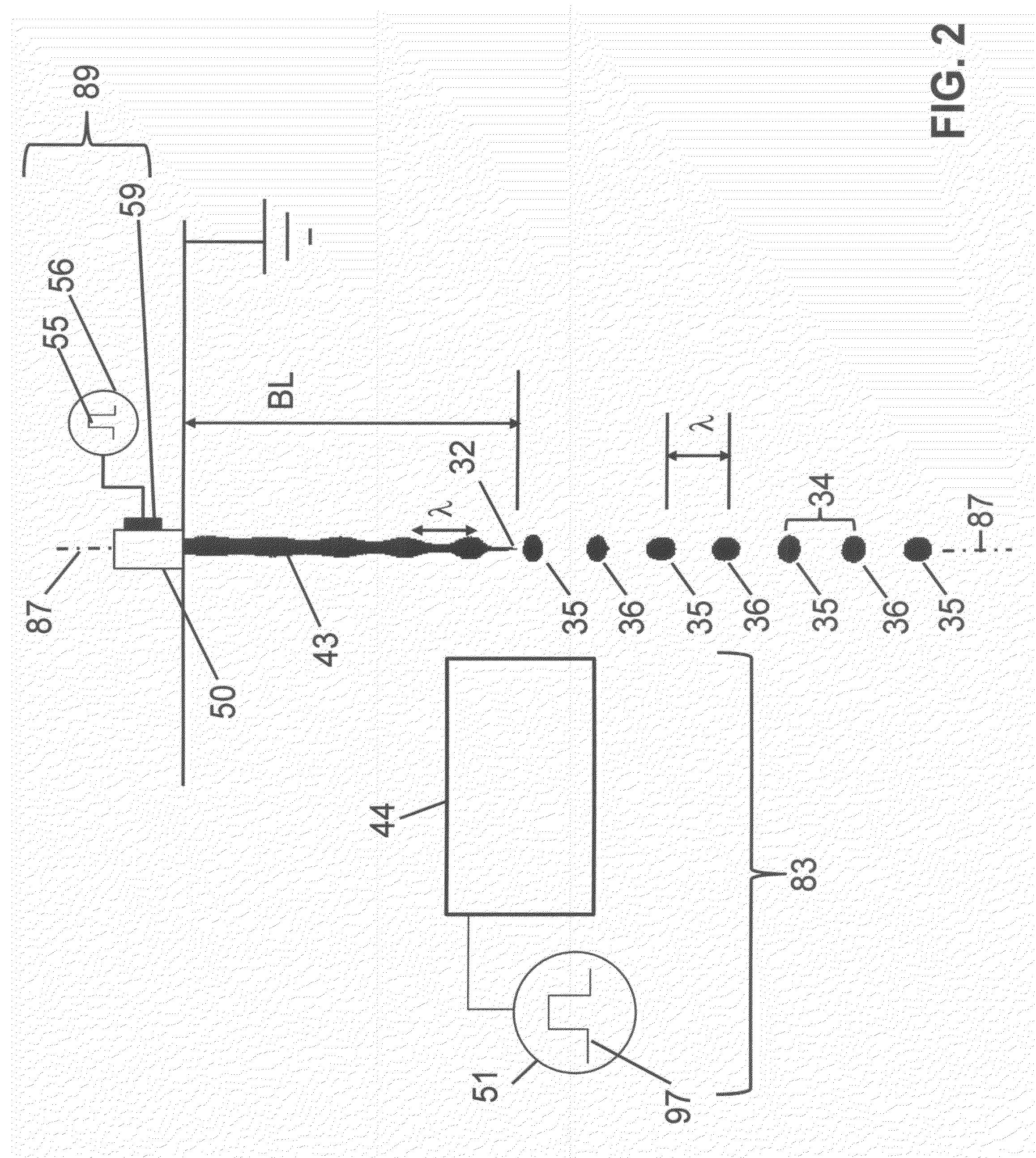
Liquid ejection using drop charge and mass
ActiveUS8465129B2Minimizing drop volume variation of dropQuality improvementPrintingLiquid jetMass ratio
A liquid ejection system ejects a liquid jet through a nozzle. A drop formation device modulates the jet causing portions to break off into drop pairs, including first and second drops, separated on average by a drop pair period, and modulates the jet to cause portions to break off into larger third drops separated on average by the same period. A charging device includes a varying electrical potential source providing a waveform including first and second distinct voltage states and a period equal to the drop formation period. The charging device and the formation device are synchronized to produce first, second, and third charge to mass ratios on the first, second, and third drops, respectively. A deflection device causes the first, second, and third drops to travel along first, second, and third paths, respectively. The first and third charge to mass ratios and paths are substantially the same.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
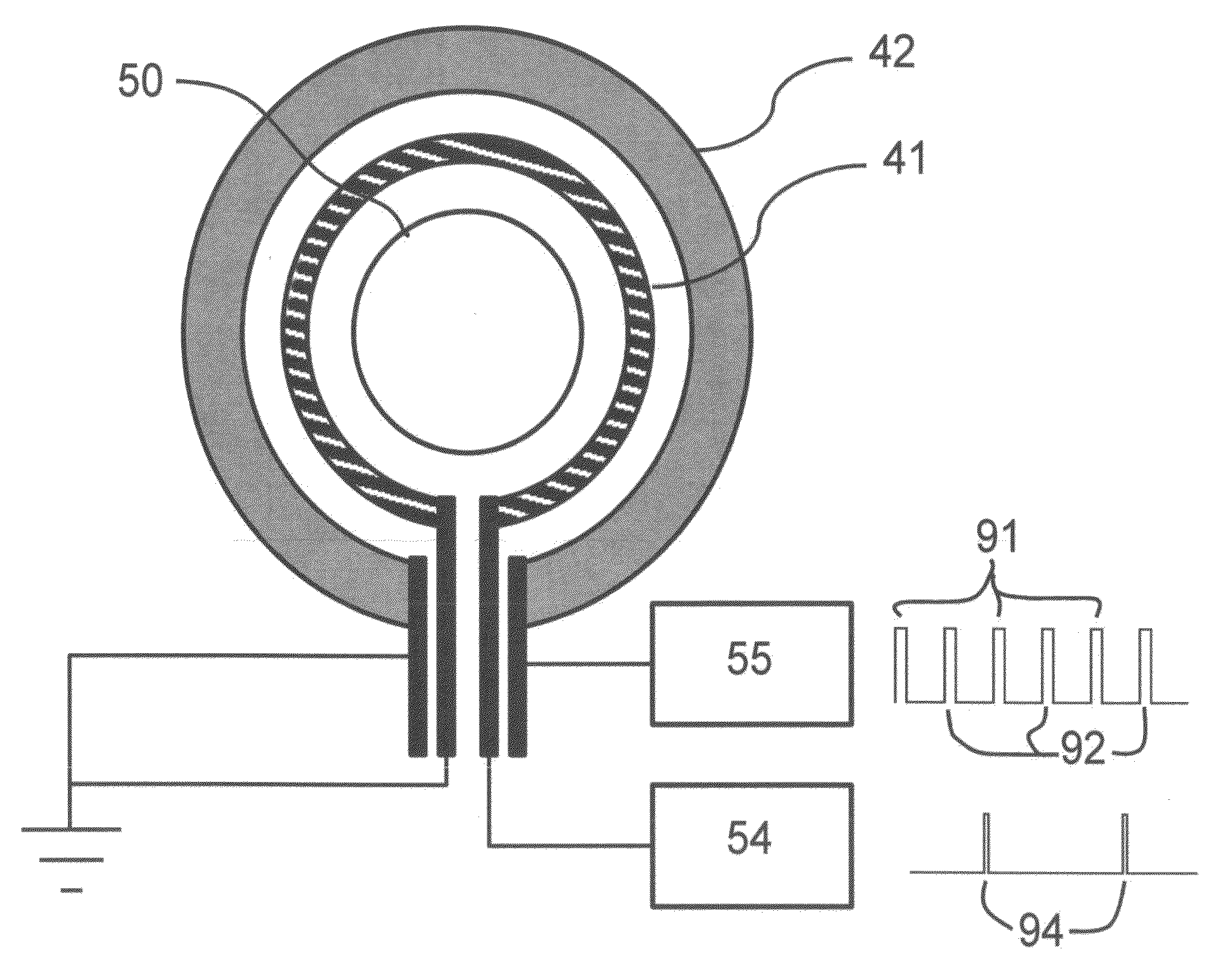
Ejecting liquid using drop charge and mass
ActiveUS8382259B2Minimizing drop volume variation of dropQuality improvementPrintingLiquid jetMass ratio
A liquid jet is modulated using a drop formation device to selectively cause portions of the liquid jet to break off into drop pairs and third drops traveling along a path. The third drop is larger than the drops of the drop pair. A charging device and the drop formation device are synchronized to produce a first charge to mass ratio on a first drop of the drop pair, produce a second charge to mass ratio on a second drop of the drop pair, and produce a third charge to mass ratio on the third drop. A deflection device causes the first drop having the first charge to mass ratio to travel along a first path, the second drop having the second charge to mass ratio to travel along a second path, and the third drop having a third charge to mass ratio to travel along a third path.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
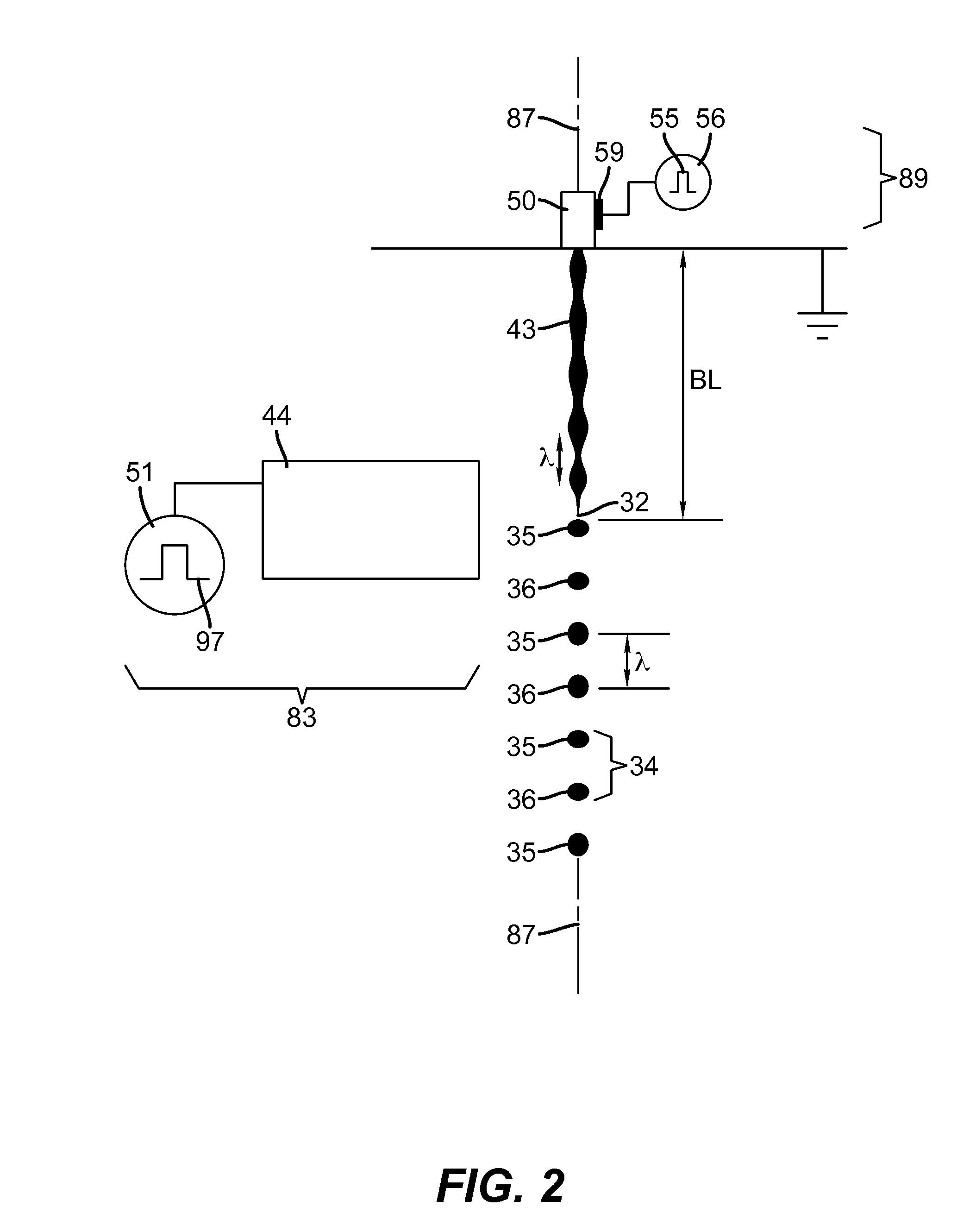
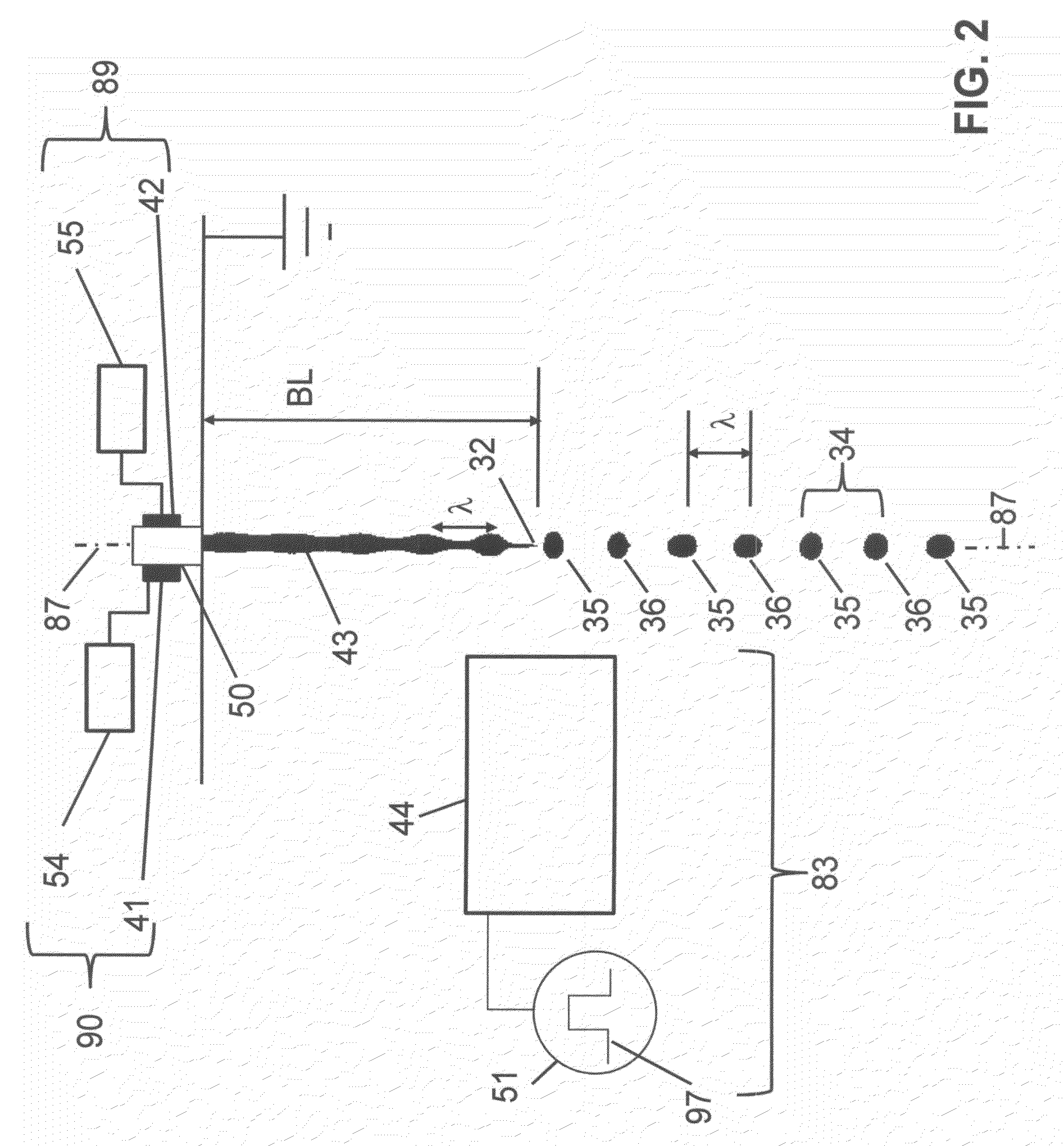
Liquid ejection method using drop velocity modulation
ActiveUS20120300001A1High resolutionMinimizing drop volume variation of dropPrintingLiquid jetElectric potential
A method of ejecting liquid drops includes providing liquid under pressure sufficient to eject a liquid jet through a nozzle of a liquid chamber. The liquid jet is modulated to cause portions of the liquid jet to break off into a series of drop pairs traveling along a path using a drop formation device. Each drop pair is separated in time on average by the drop pair period. Each drop pair includes a first drop and a second drop. A charging device is provided that includes a charge electrode associated with the liquid jet and a source of varying electrical potential between the charge electrode and the liquid jet. The source of varying electrical potential provides a waveform that includes a period that is equal to the drop pair period. The waveform also includes a first distinct voltage state and a second distinct voltage state. The charging device is synchronized with the drop formation device to produce a first charge state on the first drop and to produce a second charge state on the second drop. A relative velocity of a first drop and a second drop of a selected drop pair is varied using a drop velocity modulation device to control whether the first drop and the second drop of the selected drop pair combine with each other to form a combined drop. The combined drop has a third charge state. A deflection device is used to cause the first drop having the first charge state to travel along a first path, to cause the second drop having the second charge state to travel along a second path, and to cause the combined drop having the third charge state to travel along a third path.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Ejecting liquid using drop charge and mass
ActiveUS20120299999A1High resolutionMinimizing drop volume variation of dropPrintingLiquid jetMass ratio
A liquid jet is modulated using a drop formation device to selectively cause portions of the liquid jet to break off into drop pairs and third drops traveling along a path. The third drop is larger than the drops of the drop pair. A charging device and the drop formation device are synchronized to produce a first charge to mass ratio on a first drop of the drop pair, produce a second charge to mass ratio on a second drop of the drop pair, and produce a third charge to mass ratio on the third drop. A deflection device causes the first drop having the first charge to mass ratio to travel along a first path, the second drop having the second charge to mass ratio to travel along a second path, and the third drop having a third charge to mass ratio to travel along a third path.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Liquid ejection system including drop velocity modulation
ActiveUS20120300000A1High resolutionMinimizing drop volume variation of dropPrintingLiquid jetEngineering
A continuous liquid ejection system includes a liquid chamber in fluidic communication with a nozzle. The liquid chamber contains liquid under pressure sufficient to eject a liquid jet through the nozzle. A drop formation device is associated with the liquid jet and is actuatable to produce a modulation in the liquid jet that cause portions of the liquid jet to break off into a series of drop pairs traveling along a path. Each drop pair is separated in time on average by a drop pair period. Each drop pair includes a first drop and a second drop. A charging device includes a charge electrode associated with the liquid jet and a source of varying electrical potential between the charge electrode and the liquid jet. The source of varying electrical potential provides a waveform that includes a period that is equal to the drop pair period. The waveform also includes a first distinct voltage state and a second distinct voltage state. The charging device is synchronized with the drop formation device to produce a first charge state on the first drop and to produce a second charge state on the second drop. A drop velocity modulation device varies a relative velocity of a first drop and a second drop of a selected drop pair to control whether the first drop and the second drop of the selected drop pair combine with each other to form a combined drop. The combined drop has a third charge state. A deflection device causes the first drop having the first charge state to travel along a first path, causes the second drop having the second charge state to travel along a second path, and causes the combined drop having the third charge state to travel along a third path.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Hose and tubing assemblies and mounting systems and methods
ActiveUS8087425B2Low skill-level procedureReduce component complexityPipe supportsMining devicesEngineeringBearing surface
A hose assembly includes a length of hose and a bracket. The bracket includes a rigid insert and a resilient overmold encapsulating at least a portion of the insert and mechanically bonding with at least a portion of an exterior of the hose. A method to produce this assembly may employ thermoplastic injection molding and include the steps of associating the rigid insert with the length of hose and overmolding the rigid insert and a section of the length of hose associated with the rigid insert with the resilient material, thereby encapsulating a portion of the insert and mechanically bonding the resilient material with the section of the length of the hose. A portion of the rigid insert may extend from the bracket and provide amounting holes and a bearing surface for mounting fasteners.
Owner:THE GATES CORP
Method for manufacturing multi-fiber bundles
InactiveUS20150192739A1Easy to optimizeLow costGlass making apparatusSoldering apparatusFiber bundleEngineering
A method of manufacturing a multi-fiber bundle. The multi-fiber bundle includes a multi-fiber bundle neutral axis. The multi-fiber bundle includes at least three optical fibers. The at least three optical fibers includes respective optical fiber neutral axes. The at least three optical fibers are registered such that at least a portion, of the multi-fiber bundle neutral axis remains at a constant distance front at least a portion of the respective optical fiber neutral axes. The at least three optical fibers are coated with an optical fiber coating material. The at least three coated optical fibers are cured.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
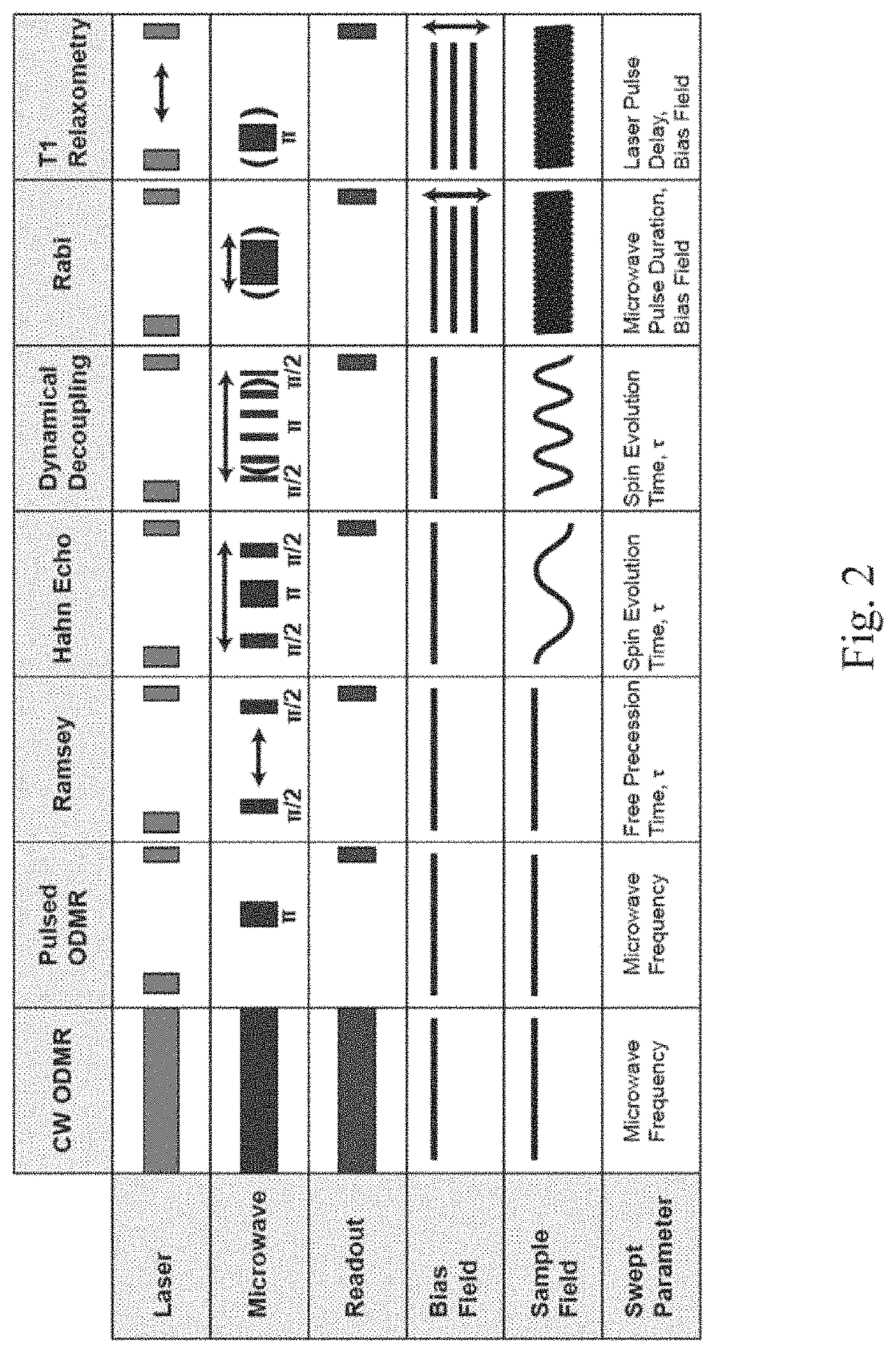
High-resolution magnetic field fingerprinting of integrated circuit activity with a quantum diamond microscope
ActiveUS20210239779A1Provide robustnessRobustness to external noiseMagnetic field offset compensationMagnetic property measurementsFluorescenceLight beam
Devices for determining a state of a magnetic field-generating article are provided. In various embodiments, a device comprises: a single crystal diamond having a plurality of NV centers, the single crystal diamond configured to be disposed adjacent to a magnetic field-generating article, and configured to generate a fluorescent signal in response to being illuminated by a light source; a coherent light source configured to generate a light beam directed at the single crystal diamond; a microwave (MW) radiation source configured to irradiate the single crystal diamond with a MW signal; a magnetic field source configured to apply a bias magnetic field to the single crystal diamond; a photosensor configured to collect the fluorescent signal generated by the single crystal diamond; and a computing node operatively coupled to each of the coherent light source, the MW radiation source, the magnetic field source, and the photosensor.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
Liquid ejection using drop charge and mass
ActiveUS20120299998A1High resolutionMinimizing drop volume variation of dropPrintingLiquid jetMass ratio
A continuous liquid ejection system includes a liquid chamber in fluidic communication with a nozzle. The liquid chamber contains liquid under pressure sufficient to eject a liquid jet through the nozzle. A drop formation device is associated with the liquid jet. The drop forming device is actuatable to produce a modulation in the liquid jet to selectively cause portions of the liquid jet to break off into one or more pairs of drops traveling along a path. Each drop pair is separated on average by a drop pair period. Each drop pair includes a first drop and a second drop. The drop formation device is also actuatable to produce a modulation in the liquid jet to selectively cause portions of the liquid jet to break of into one or more third drops traveling along the path separated on average by the same drop pair period. The third drop is larger than the first drop and the second drop. A charging device includes a charge electrode associated with the liquid jet and a source of varying electrical potential between the charge electrode and the liquid jet. The source of varying electrical potential provides a waveform that includes a period that is equal to the period of formation of the drop pairs or the third drops, the drop pair period. The waveform also includes a first distinct voltage state and a second distinct voltage state. The charging device and the drop formation device are synchronized to produce a first charge to mass ratio on the first drop of the drop pair, a second charge to mass ratio on the second drop of the drop pair, and a third charge to mass ratio on the third drop. The third charge to mass ratio is substantially the same as the first charge to mass ratio. A deflection device causes the first drop of the drop pair having the first charge to mass ratio to travel along a first path, and causes the second drop of the drop pair having the second charge to mass ratio to travel along a second path, and causes the third drop having a third charge to mass ratio to travel along a third path. The third path is substantially the same as the first path.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com