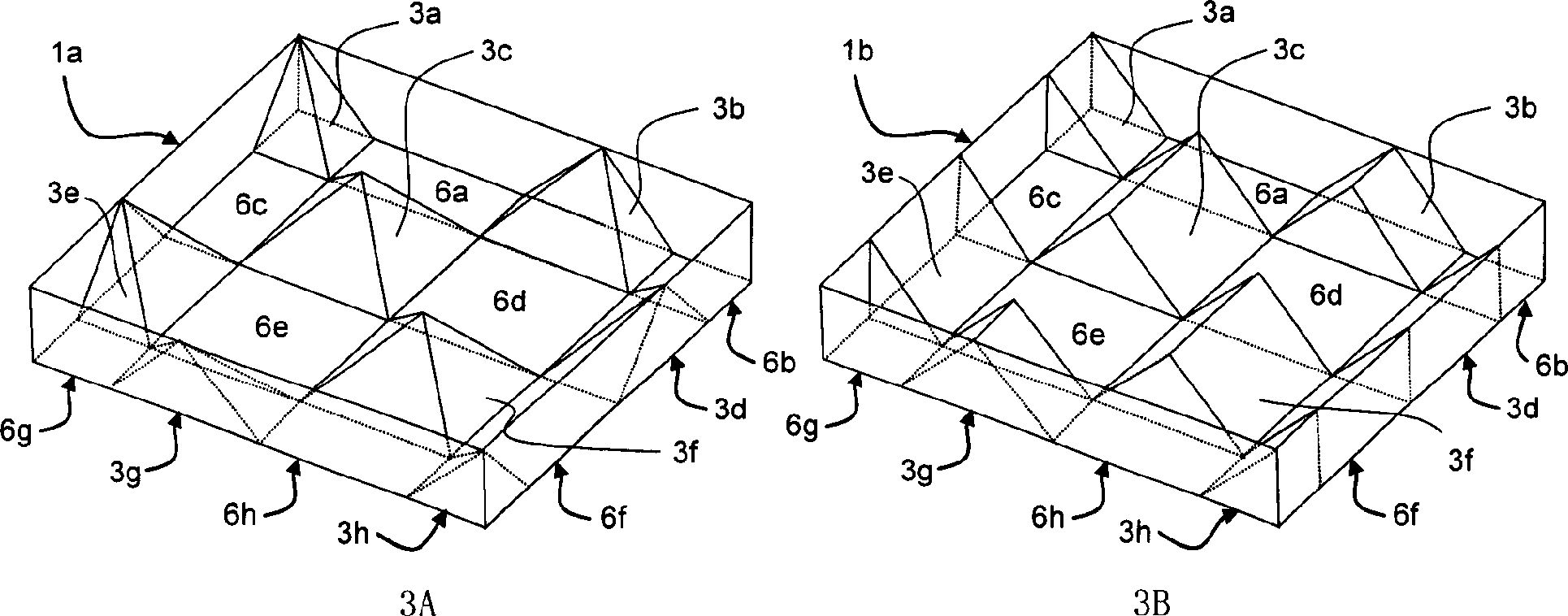
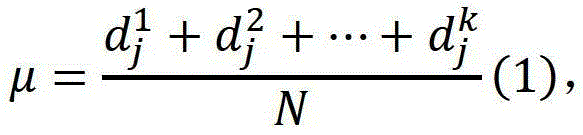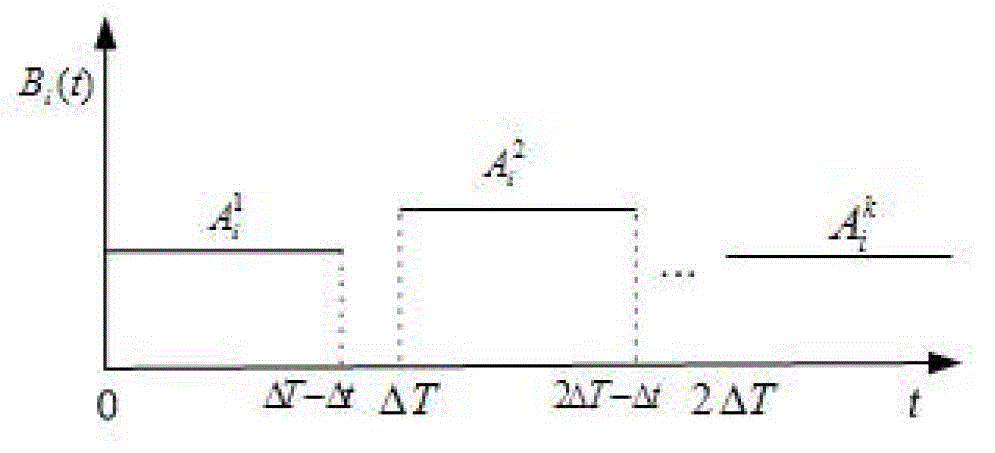Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
97results about How to "Lower energy bills" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
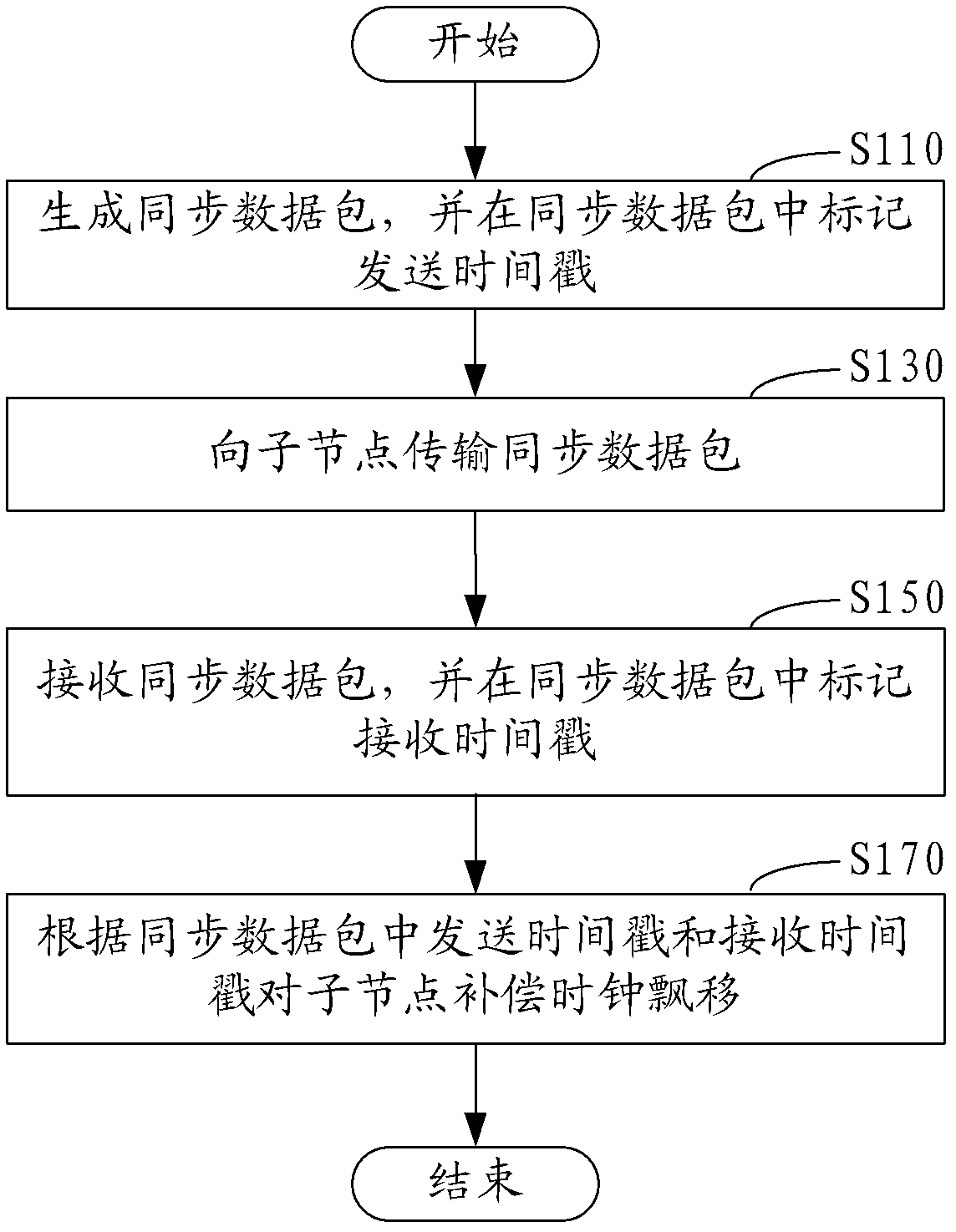
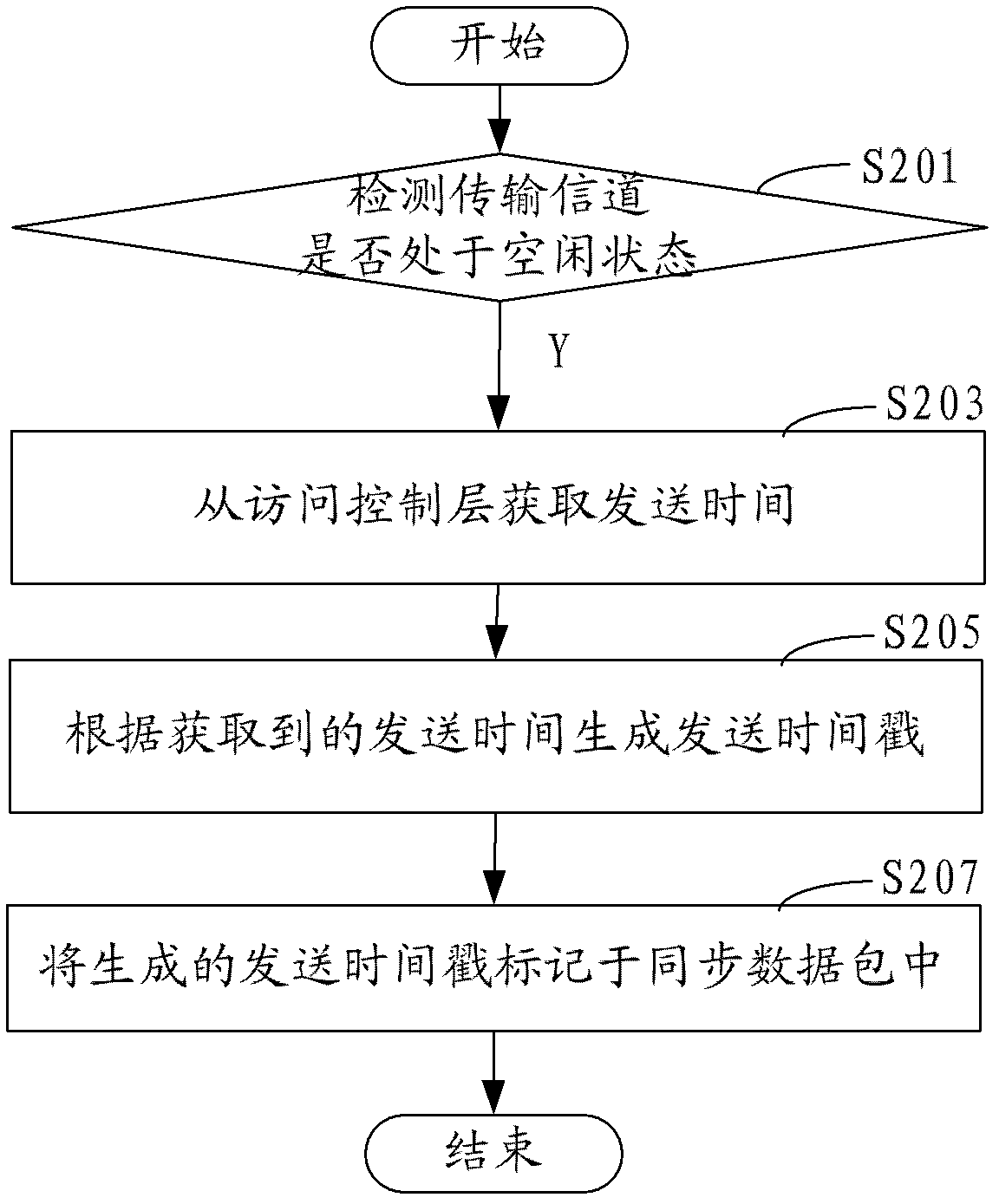
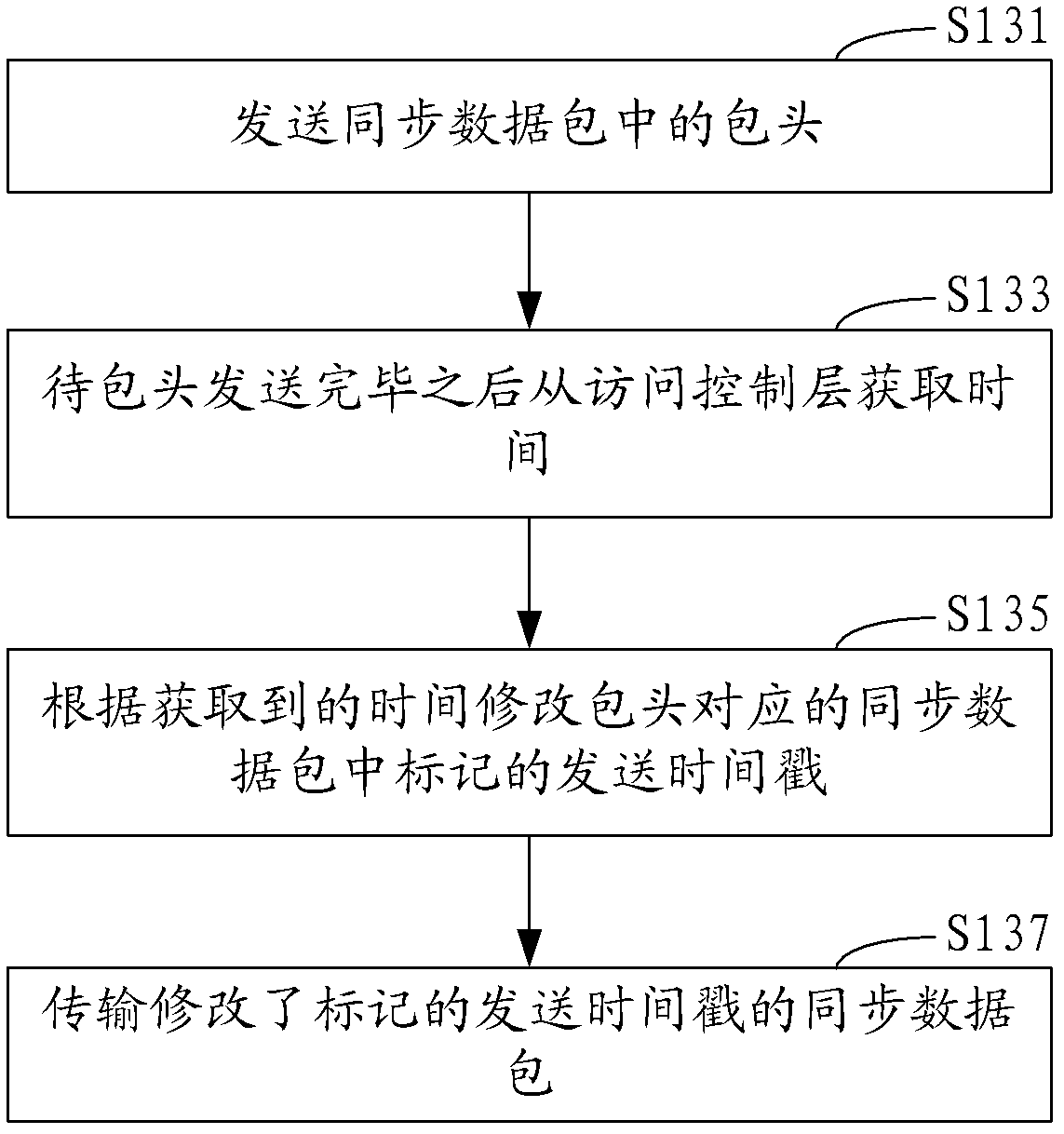
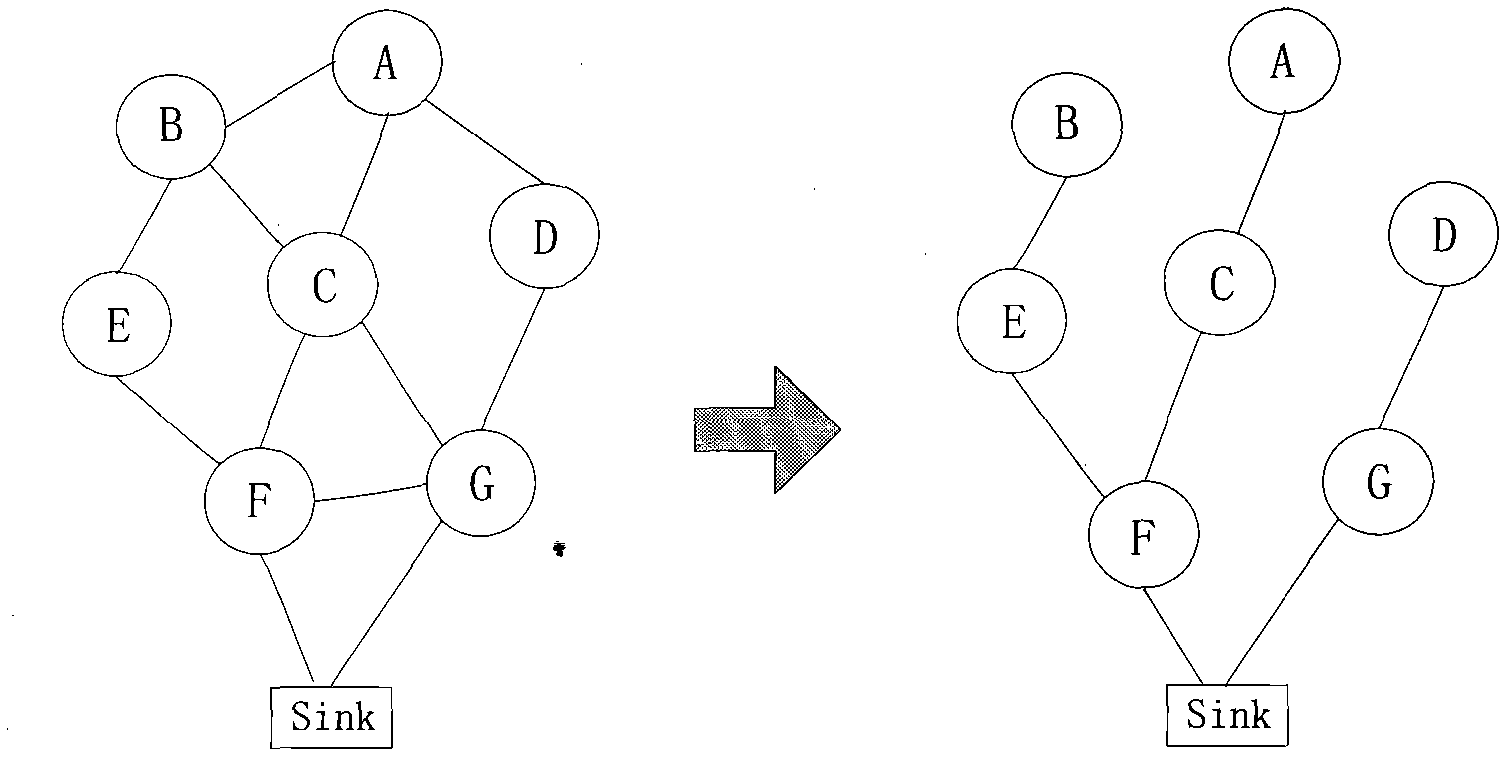
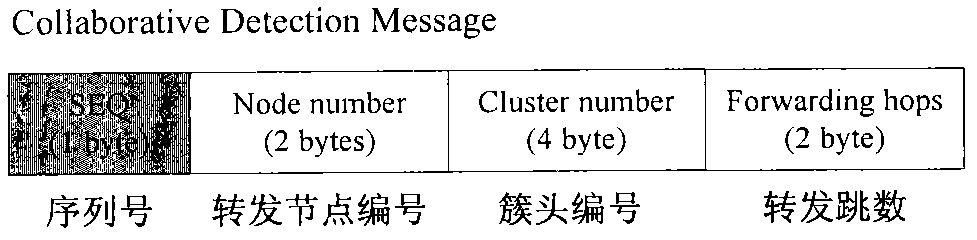
Time synchronization method and system for wireless sensor network
ActiveCN102355319AReduce consumptionAvoid consumptionSynchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexData synchronizationClock drift
The invention discloses a time synchronization method for a wireless sensor network. The method comprises the following steps of: generating a synchronous data packet, and marking a transmission timestamp in the synchronous data packet; transmitting the synchronous data packet to a child node; receiving the synchronous data packet, and marking a receiving timestamp in the synchronous data packet; and compensating for the clock drift of the child node according to the transmission timestamp and the receiving timestamp in the synchronous data packet. By the time synchronization method and the time synchronization system for the wireless sensor network, clock drift compensation between a parent node and the child node is realized only by transmitting the synchronous data packet to the child node to realize regional time synchronization in a region formed by the parent node and the child node, and compared with conventional all-network time synchronization, the regional time synchronization reduces network energy consumption and also can avoid the energy consumption caused by crosstalk interference as much as possible.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
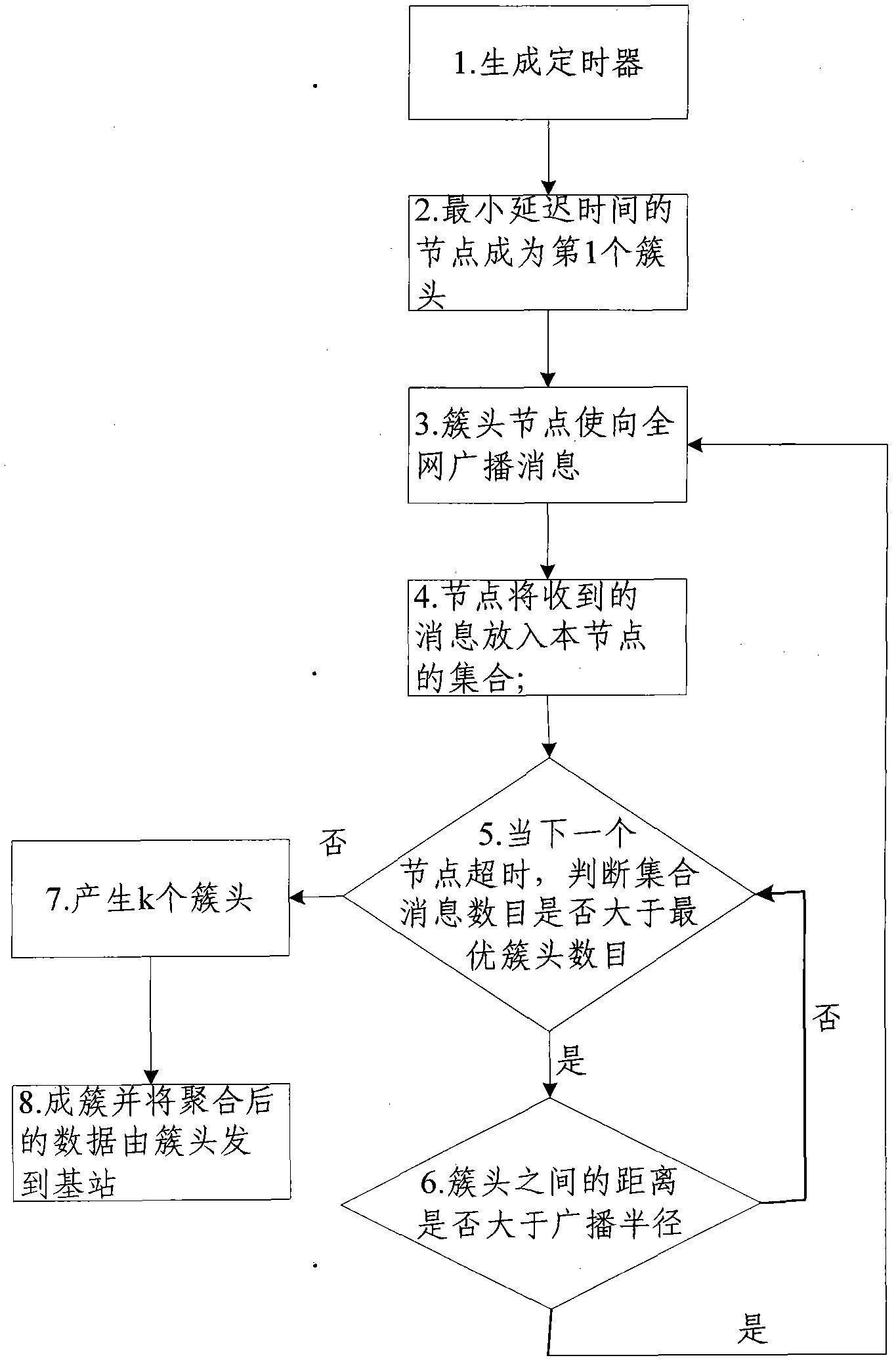
Distributed multi-jump energy-saving communication method in wireless sensor network
ActiveCN102026331AAvoid confictLower energy billsPower managementEnergy efficient ICTWireless sensor networkingEnergy consumption
The invention relates to a method for carrying out distributed multi-jump energy-saving communication in a wireless sensor network. In a process of cluster head selection, a node with large energy is preferentially used as a cluster head, and cluster heads with the same energy can not collide in a process of cluster head competition, thereby the cluster heads are uniformly distributed. In a process of transmitting data to a base station from the cluster heads, the cluster heads uniformly distributed in the network constitute a route tree, and the quantity of cluster head nodes directly communicating with the base station is reduced in the mode of multi-jump transmission, thereby energy consumption is further reduced. Simultaneously, the method also limits the shortest transmitting distance of a multi-jump route, lowers the circuit consumption of a middle node, reduces the transmission times of multi-jump data, saves the energy consumption of the network, weakens the hot problems in the network, saves network energy, keeps network load balanced and prolongs the life cycle of the network.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Static material stirrer
A static material mixer is composed of one or more mixing structures with mountain-like projected parts. The cross-section of the external surface of said mixing structure is circle or polygon. Its inside has two or more mountain-like projected parts and discharge outlets, which are alternatively arranged. The mountain-like projected parts and discharge outlets between adjacent mixing structures are staggered. It can cut, mixing and move the materials and can make collision between material and the mixer or material, resulting in high mixing effect.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
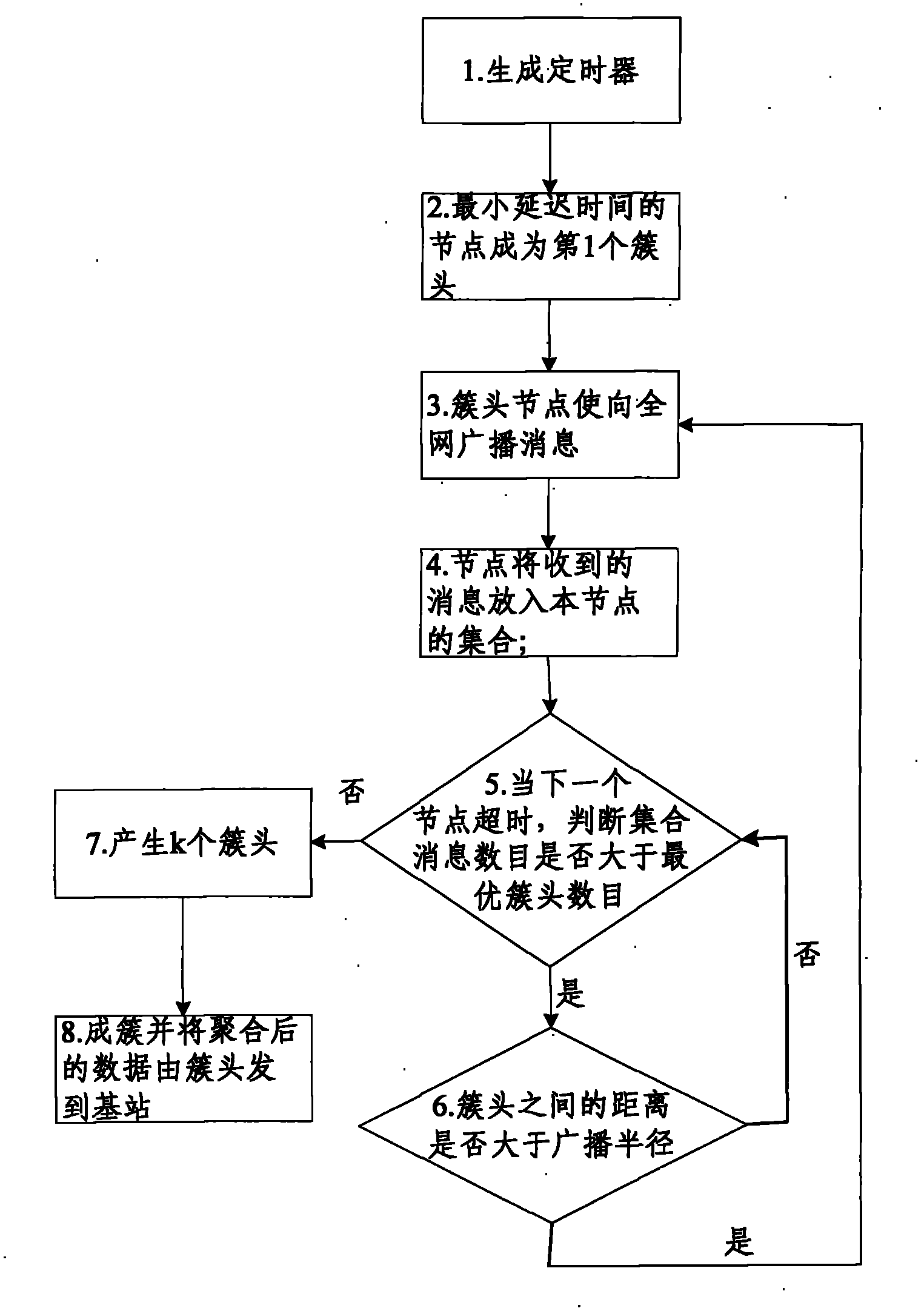
Effective key management method and its operation method for sensor network with clustering structure
InactiveCN101155024AShorten the life cycleLower energy billsKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageComputer hardwareCluster systems
The present invention discloses a method for managing the key of the sensor network with a clustering structure, each node can adopt different types of secret key encryption to the different information, at the same time the different secret key pair storing mode is corresponding arranged, the different types of secret key encryption are stored respectively aiming at the base station, cluster head node and cluster member node. Aiming at the key managing method the invention discloses a low-power consumption self-adapting cluster system namely the method for running the LEACH route system basing on the cluster. The invention has the advantages of reducing the storing space of the node and the communication energy, satisfying the low-power consumption requirement and guaranteeing the network safe capacity, perfecting the network, and effectively avoiding the illegally interception of the node number and data.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Signal energy synchronous transmission relay transmission method in physical layer safety communication
ActiveCN105245269ALower energy billsExtend network lifePower managementRadio transmissionNetwork serviceVIT signals
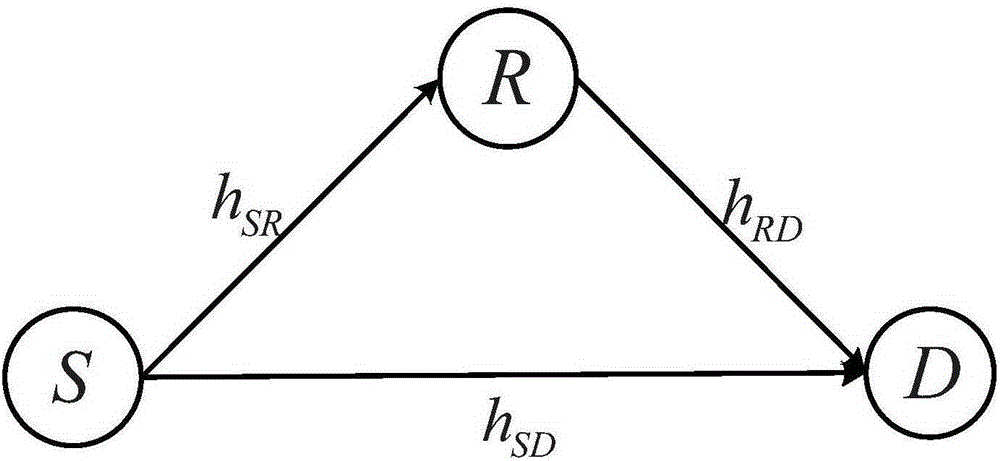
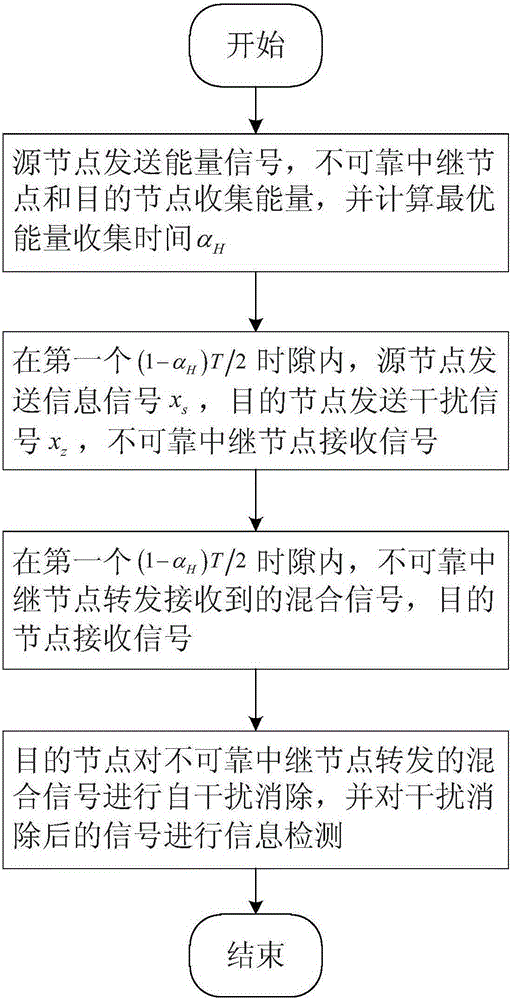
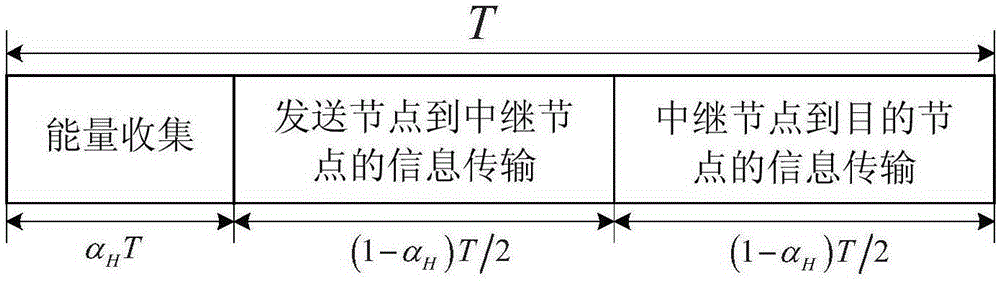
The invention discloses a signal energy synchronous transmission relay transmission method in physical layer safety communication. The method comprises the following implementation steps that: 1) a source node transmits an energy signal and calculates an optimal energy collection time scale alpha<H>, and an unreliable relay node and a destination node collect energy; 2) in a first (1-alpha<H>)T / 2 time slot, the source node transmits an information signal x<s>, the destination node transits an interference signal x<z>, and the unreliable relay node receives the signals; 3) in a second (1-alpha<H>)T / 2 time slot, the unreliable relay node forwards the received mixed signals, and the destination node receives the signals; 4) the destination node performs adaptive interference cancellation for the mixed signals forwarded by the unreliable relay node, and performs information detection on the signals of which interference is cancelled. The method provided by the invention can effectively prolong network service life of a relay network, and has low implementation complexity and high transmission safety, thus, the method can be used for a physical layer safety relay collaborative communication system.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
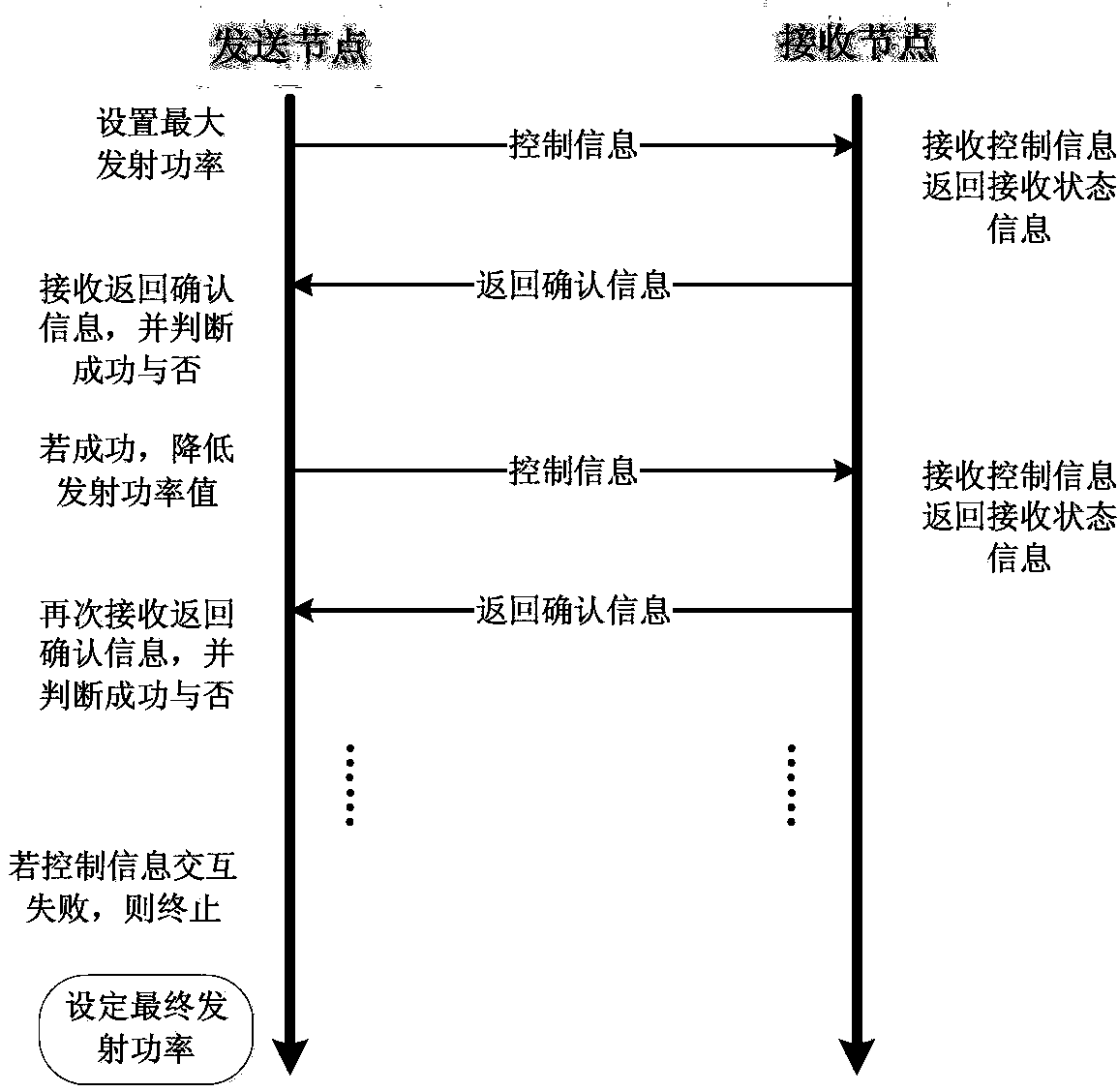
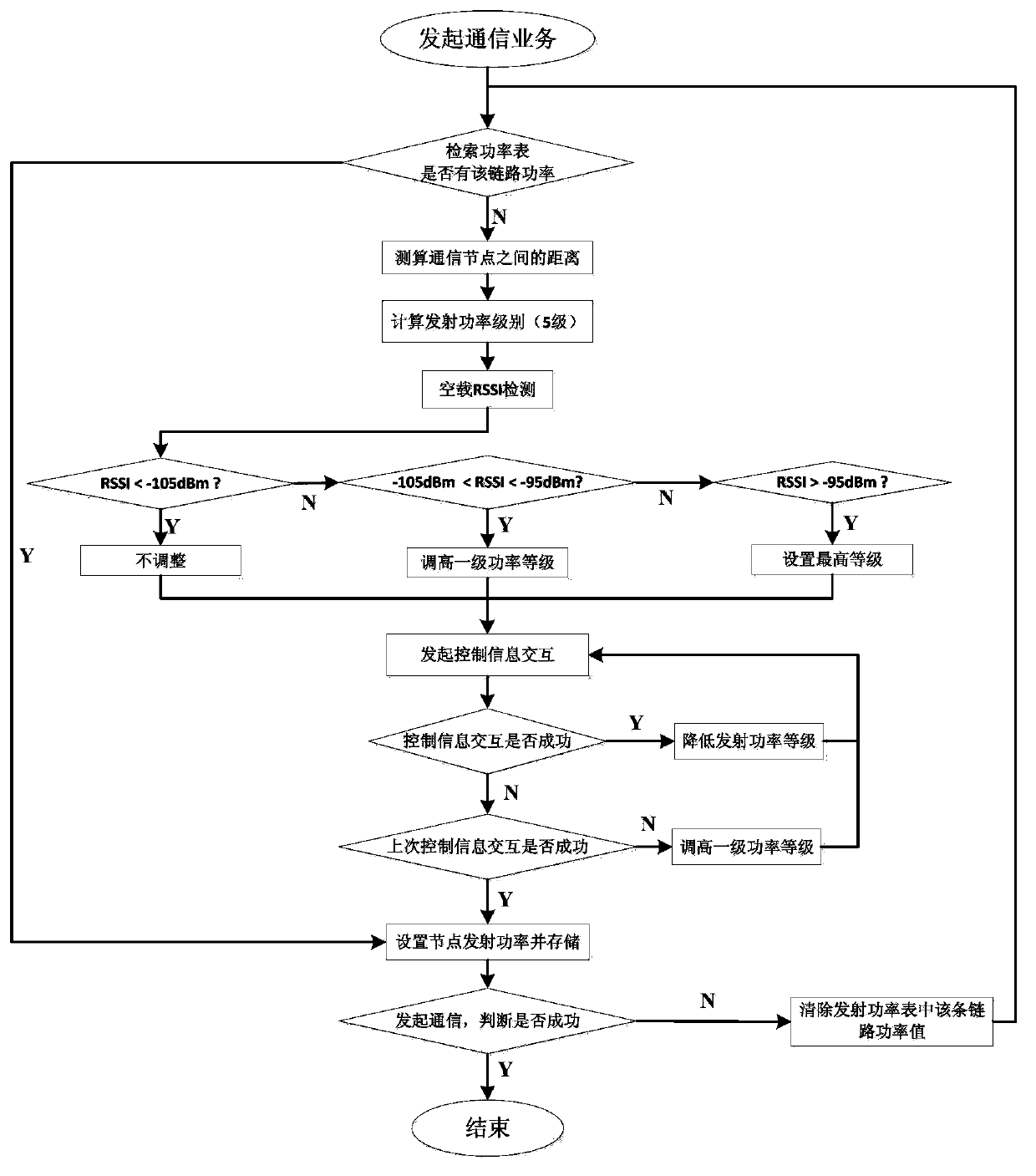
Method for configuring multilevel transmitting power in wireless sensor network
ActiveCN103379608ANarrow selectionReduce the number of interactionsEnergy efficient ICTPower managementTelecommunications linkTransmitted power
The invention discloses a method for configuring multilevel transmitting power in the wireless sensor network. When a communication service is initially initiated by a sending node to a receiving node in the wireless sensor network, the theoretical communication distance between the two communication nodes is measured and calculated by the sending node. Theoretical transmitting power needed by the nodes is calculated, the stages of the transmitting power are initially selected, and each transmitting power stage is provided with a plurality of transmitting power values. The node no-load received signal strength instruction namely RSSI detection is sent out, and the needed transmitting power stages are dynamically adjusted. The minimum effective transmitting power value is determined from the selected transmitting power stages based on the exploratory transmitting power control method. The transmitting power values determined based on the power setting method are stored, and the transmitting power is set to initiate the communication service. The two nodes initiate the communication service again to directly acquire the stored transmitting power, and if the communication is failed, the stored transmitting power values are eliminated, and the method for configuring the multilevel transmitting power is launched again to set the transmitting power value suitable for a communication link.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
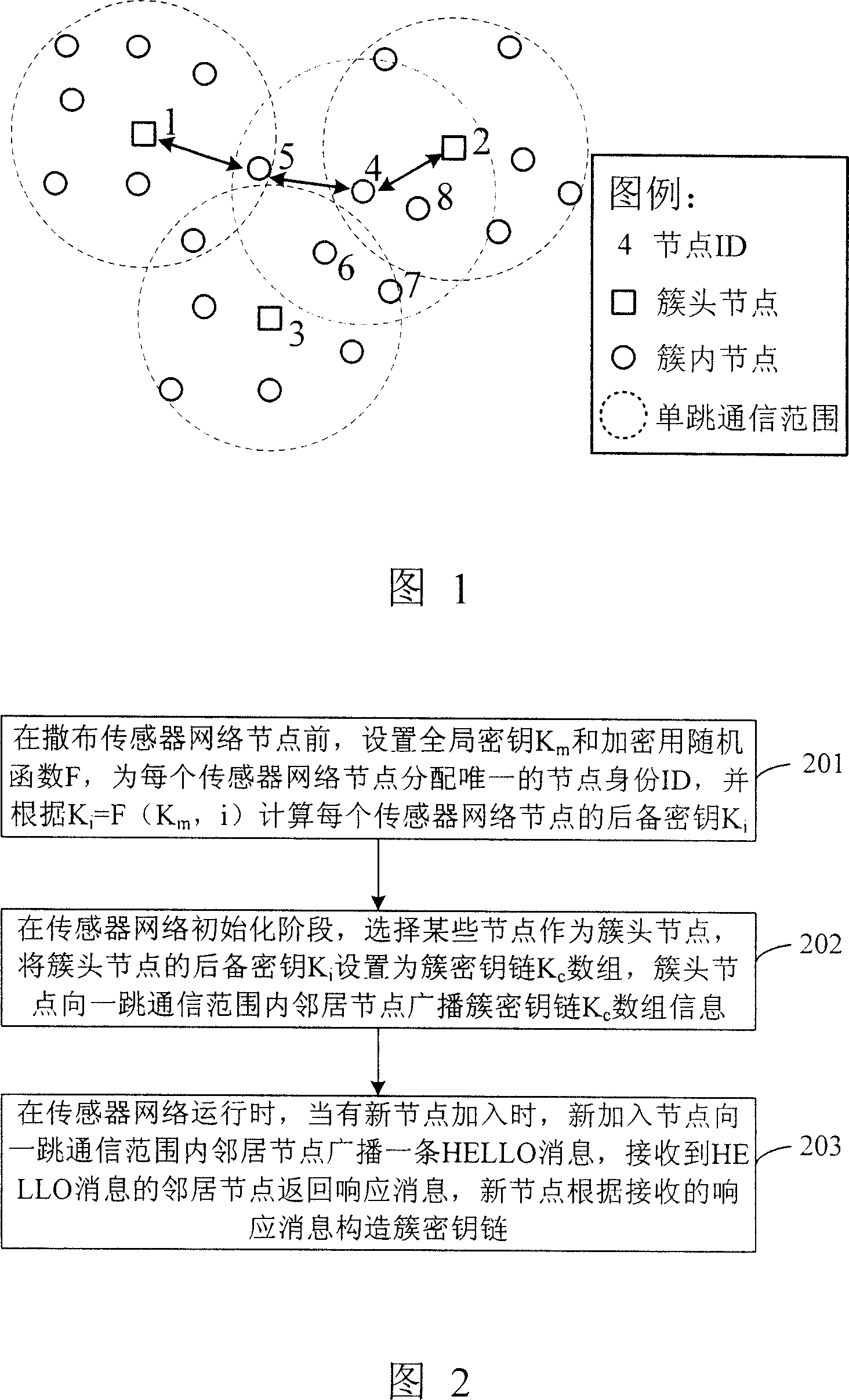
Allocation and management method of the secrete key in the sensor network
InactiveCN1996833AEnable secure communicationPrevent eavesdroppingKey distribution for secure communicationData switching by path configurationData setArray data structure
This invention discloses one method to align and manage in sensor network, which comprises the following steps: a, before distributing sensor network points to set whole key Km and coded random function F for each point with only identification and to compute point backup key Kid; b, in sensor initiating phase, establishing sensor network by cluster structure as cluster code key data set; c, in sensor operation, when there is new points, adding new communication range of HELLO information.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
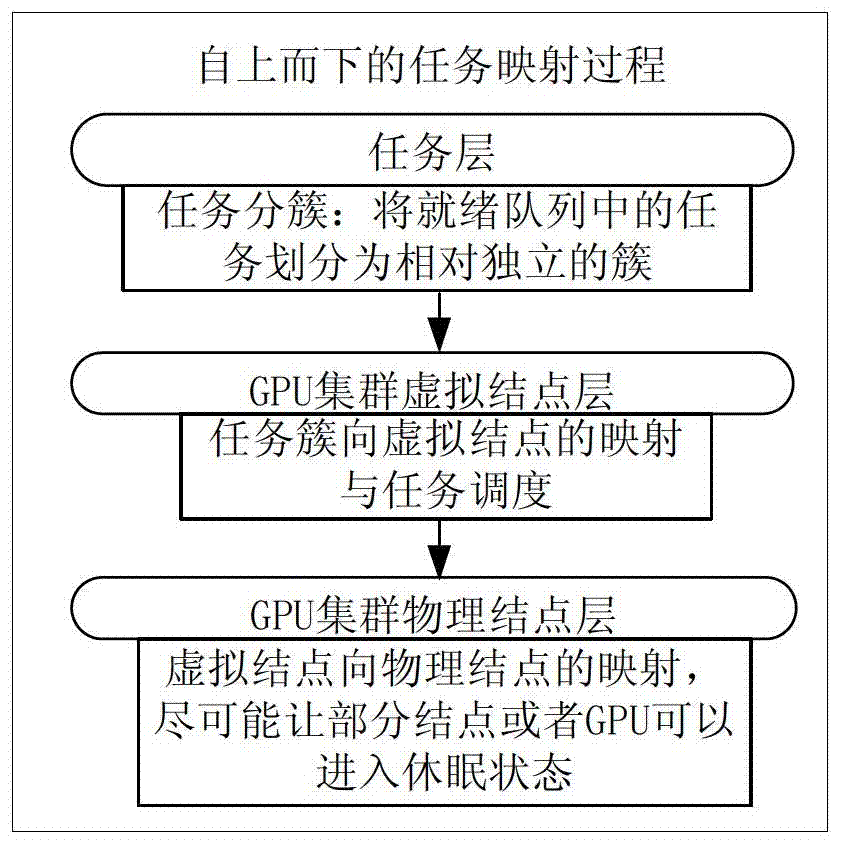
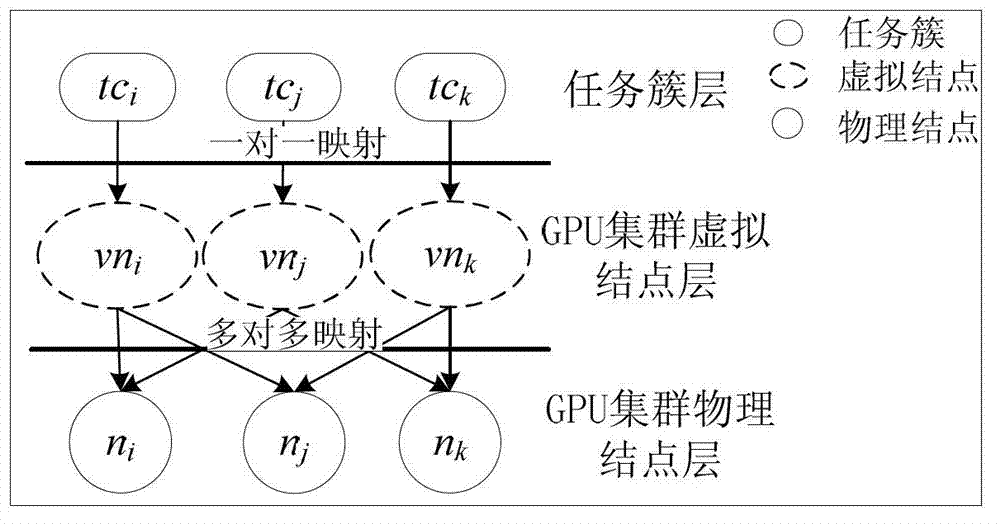
Budget power guidance-based high-energy-efficiency GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) cluster system scheduling algorithm
ActiveCN102819460AContinuous energy saving effectGood energy saving effectEnergy efficient ICTResource allocationHigh energyCluster systems
The invention discloses a budget power guidance-based high-energy-efficiency GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) cluster system scheduling algorithm, which comprises the following steps of: decomposing all tasks to be scheduled into basic tasks; dividing all the basic tasks into a plurality of independent task clusters; generating virtual nodes according to the task clusters to form one-to-one mapping relation between the task clusters and the virtual nodes; and finally performing many-to-many mapping on the virtual nodes to physical nodes to meet the requirement of dynamically allocating a proper processor to the tasks in the task clusters for execution of the tasks. According to the budget power guidance-based high-energy-efficiency GPU cluster system scheduling algorithm, the energy efficiency of a GPU cluster system can be effectively increased, so that an obvious energy-saving effect can be realized in the long term.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
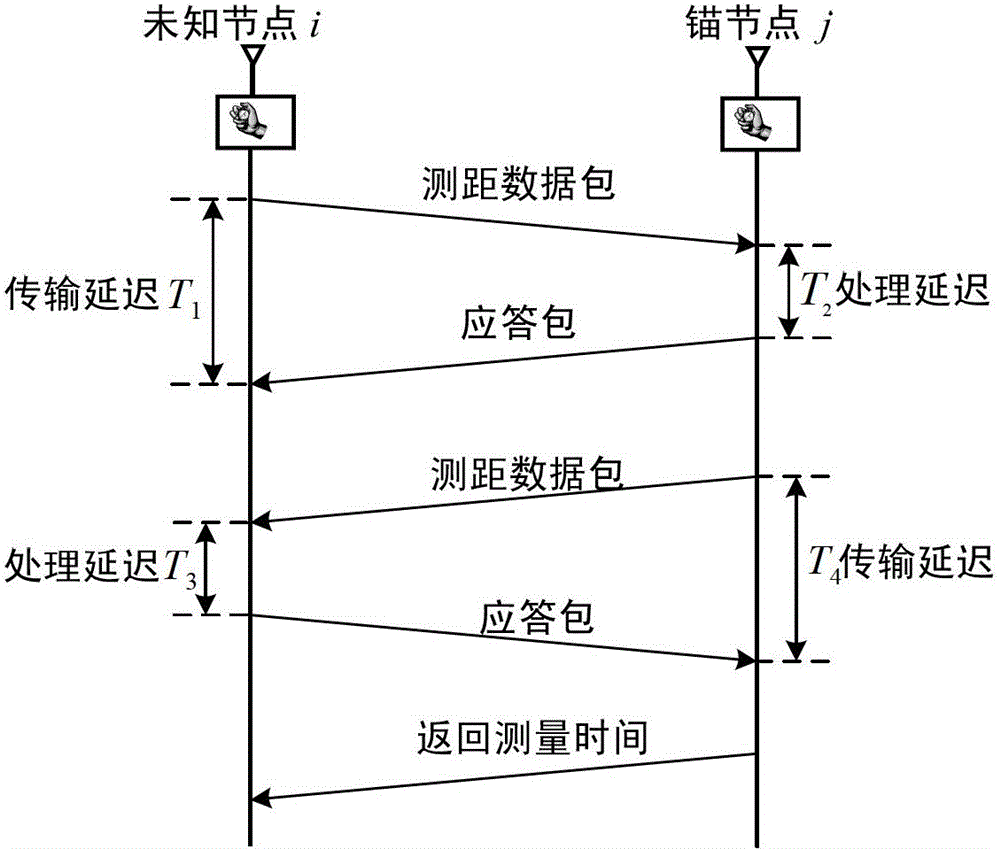
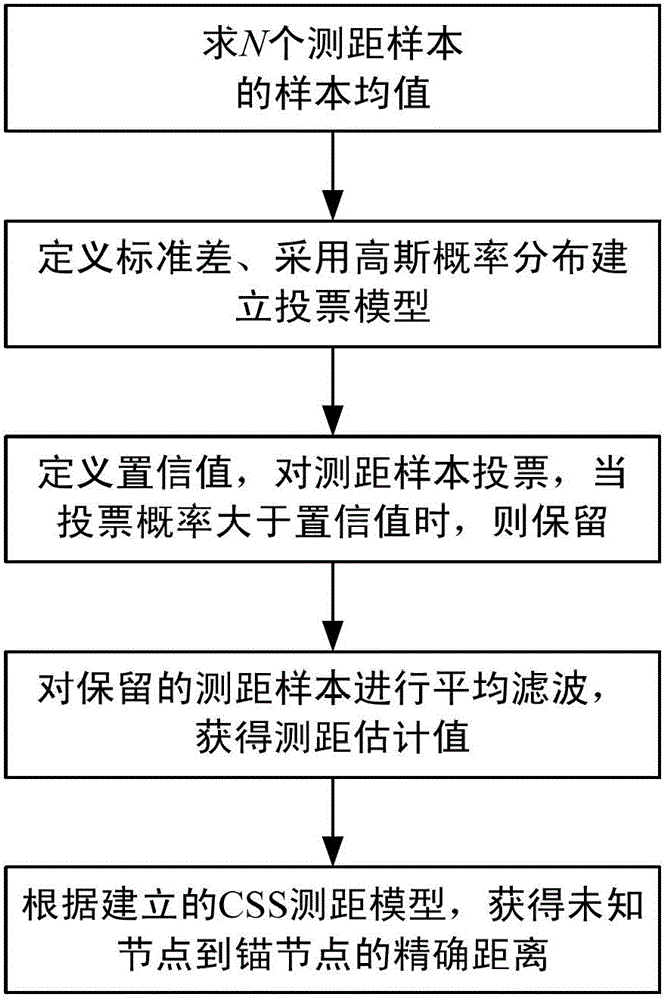
Positioning method of node in wireless sensor network
ActiveCN103152824AReduce the impact of rangingImprove ranging accuracyWireless communicationRectangular coordinatesFilter algorithm
The invention discloses a positioning method of a node in a wireless sensor network. The positioning method comprises the following steps of: establishing a rectangular coordinate system to obtain position coordinates of each anchor node in each wireless sensor network; enabling a node to be positioned to acquire ID (Identification) and position coordinates of all the anchor nodes as well as hop counts of the node to be positioned and the corresponding anchor node in the wireless sensor network through a distance vector exchange agreement, and establishing a corresponding anchor node information list for the node to be positioned; inquiring a self anchor node information list by the node to be positioned; when the number of the anchor nodes is more than or equal to 3 in a 1 hop range, carrying out ranging by using the node to be positioned to acquire a ranging sample between the node to be positioned and each anchor node; and processing the ranging sample by using a voting average combined filtering algorithm to establish a CSS (Chirp Spread Spectrum) ranging mode to acquire accurate ranging information between the node to be positioned and each anchor node.
Owner:THE 28TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
Low-energy consumption sleeping monitoring method synchronous relative to time of wireless sensor network
InactiveCN102083183AReduce energy consumptionReduce synchronization overheadPower managementEnergy efficient ICTClock driftWireless mesh network
The invention relates to a low-energy consumption sleeping monitoring method synchronous relative to time of a wireless sensor network. The traditional method is high in energy consumption. The method in the invention comprises the following steps: in the stage of creating a relative synchronization table at a new node, broadcasting addition request network packets by the new node firstly to obtain synchronizing information of a neighbourhood node; then estimating clock skew, and linearly fitting multigroup of synchronization information of the neighbourhood node to estimate clock drift; and finally saving the sleeping period of the neighbourhood node, the estimated clock skew and the clock drift into the relative synchronization table; and in the stage of prediction and transmission of data packets of the node, realizing relative synchronization with a target node by the node according to the created relative synchronization table, then predicting the waking time at the next time according to the sleeping period of the node, setting a transmission timer, and finally transmitting data packets by a short permeable when the transmission timer is triggered. According to the invention, the energy overhead for sending the data packets by the node can be saved, and the idle time of a transmitting node is reduced, and the sleeping time of the transmitting node is increased.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Safe positioning method of wireless sensor network
ActiveCN102123389AResist Wormhole AttacksDefense against distance spoofing attacksEnergy efficient ICTNetwork topologiesWireless sensor networkBase station
The invention relates to a safe positioning method of a wireless sensor network, comprising three stages, namely a doubtful node recognition stage, a malicious node isolation stage and a node position safety calculation stage, wherein in the doubtful node recognition stage, anchor nodes are cooperated mutually, broadcast information packets in a hopping communication range, detect doubtful nodes according to whether the information packets are abnormal, and record ID (identification) information of corresponding doubtful nodes; in the malicious node isolation stage, the anchor nodes report the ID information of the doubtful nodes to a base station which is carried out safety level area division on the wireless sensor network and isolated malicious nodes; and in the node position safety calculation stage, as for the main anchor node and the auxiliary anchor nodes in areas with higher safety level preferably, the calculation of sensor nodes is finished by a passive positioning algorithmbased on time difference. In the safe positioning method, the malicious nodes are effectively detected and isolated, the influence of the malicious attack to the positioning process is reduced, the positioning accuracy is improved, the energy consumption for positioning is saved and the life cycle of the network is prolonged.
Owner:CHANGZHOU ANKONG ELECTRICAL INFORMATION TECH
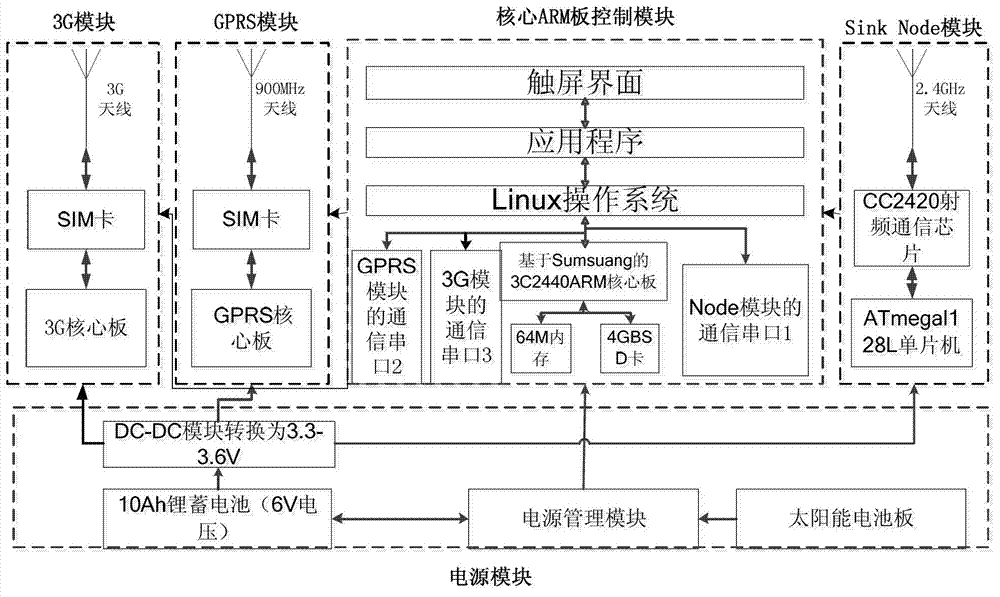
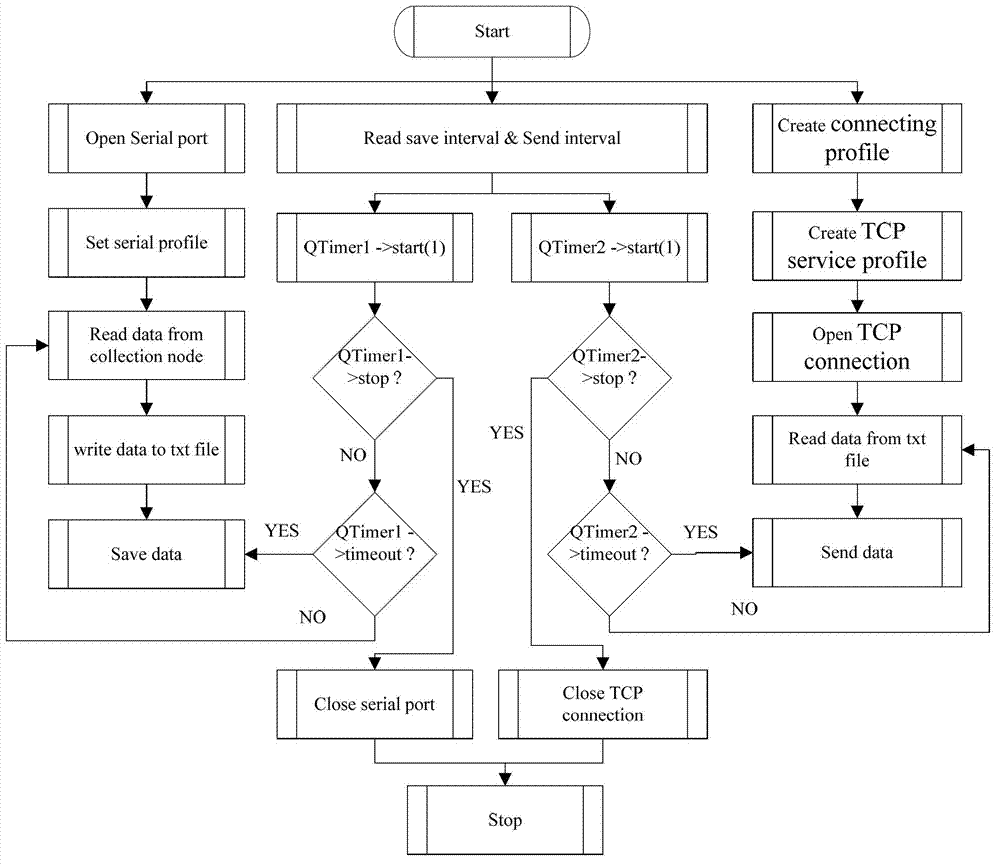
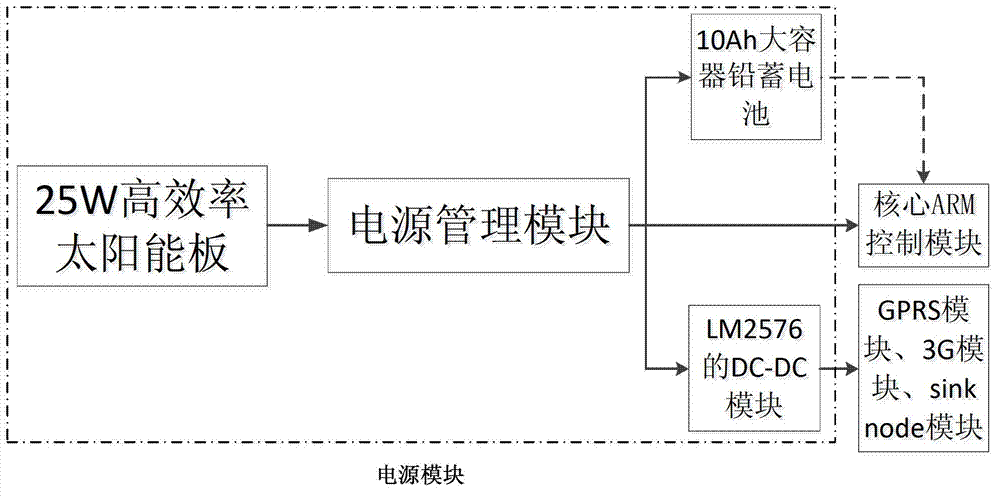
Internet of Things gateway for perceiving wild environment and data transmission method thereof
InactiveCN102932964AImprove robustnessImprove reliabilityNetwork topologiesGeneral Packet Radio ServiceSensing data
The invention discloses an Internet of Things gateway for perceiving wild environment and a data transmission method thereof. The gateway comprises a SinkNode module, a core advanced RISC machines (ARM) control module, a general packet radio service (GPRS) module, a third generation telecommunication (3G) module and a power supply module, the SinkNode module, the GPRS module, the 3G module are respectively connected with the core ARM control module, and the power supply module is connected with other modules. The method includes that node acquisition data of a monitored region is sent to the SinkNode module, the SinkNode module sends the data to the core ARM control module, the data is classified and sent to the GPRS module and the 3G module by the core ARM control module, the GPRS module sends sensing data to a remote server, and the 3G module sends image data to the remote server. The gateway uploads the perception data of the wild environment to a data base of the remote server through the GPRS network and 3G network on the Internet of Things gateway, so that a monitoring center can real-timely receive the data and can further process the data in the data base of the remote server, and the data remote supervision by the monitoring center is achieved.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
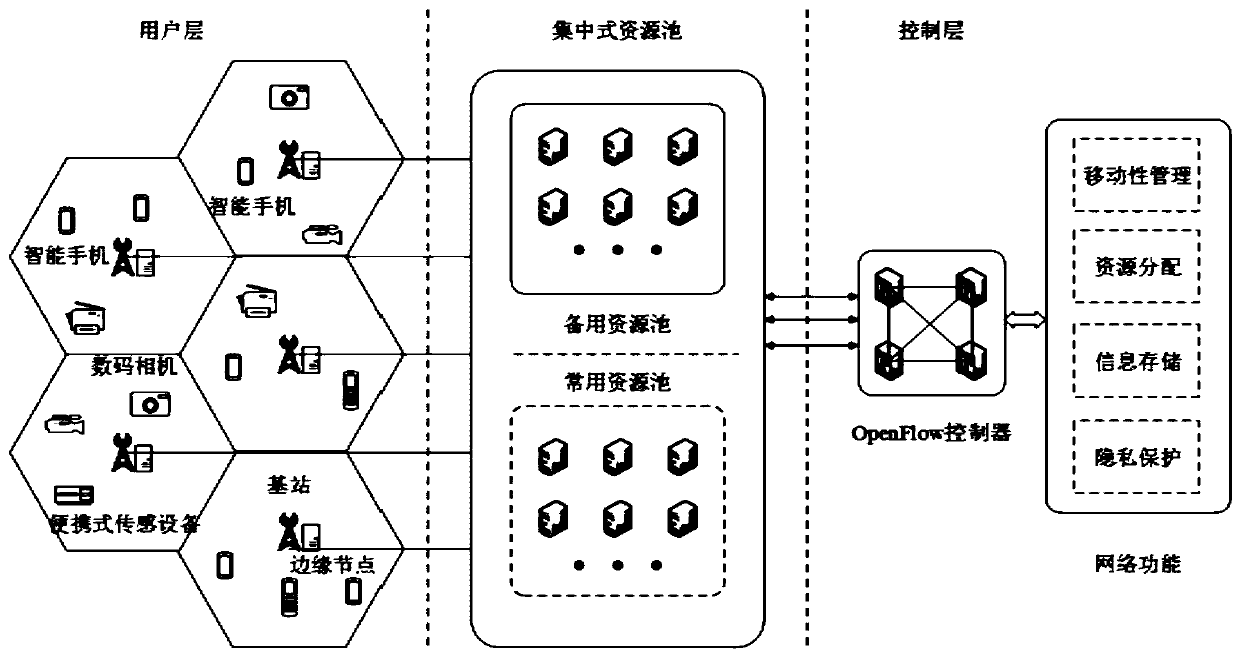
Software-defined edge computing system oriented to Internet of Things and resource allocation method
ActiveCN109981753ATransponder communication to realize the forwarding of user dataRealize forwardingNetwork traffic/resource managementData switching networksResource poolQuality of service
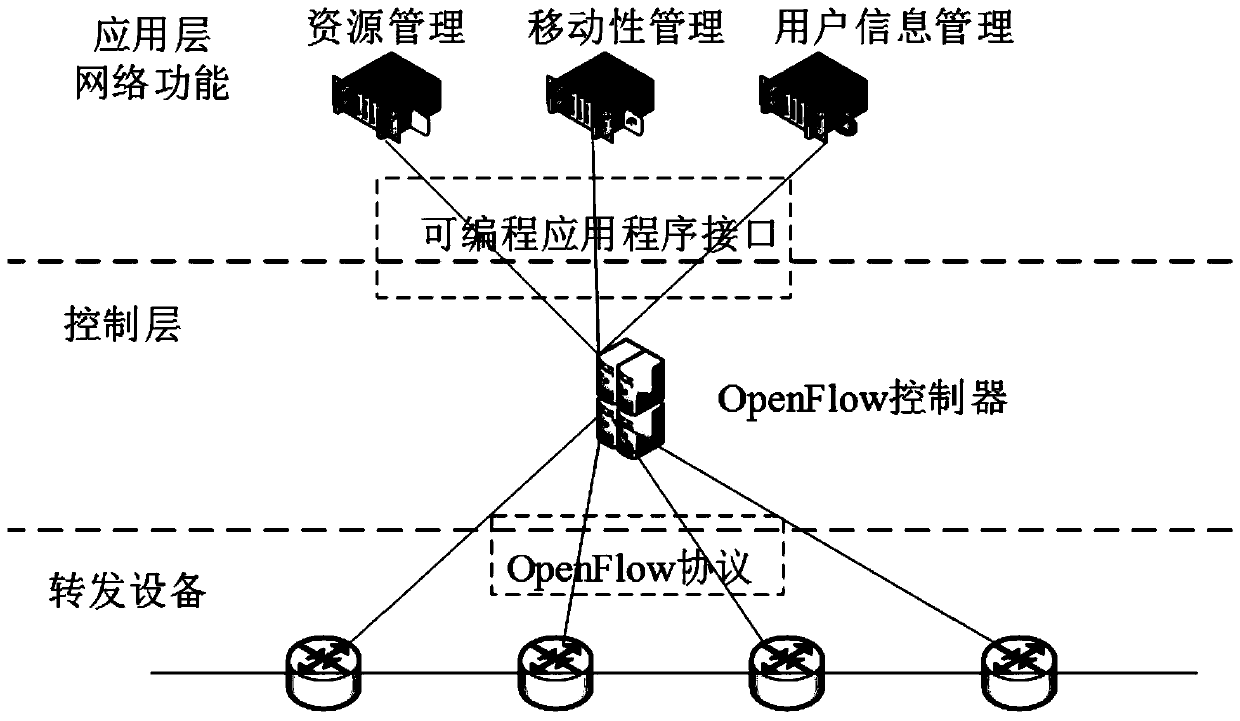
The invention discloses a software-defined edge computing system oriented to Internet of Things and a resource allocation method, and the system comprises multi-access base station equipment deployedin a cellular manner, an edge node EN with data processing and computing functions is deployed at each base station, and meanwhile, the EN is connected to a centralized computing resource pool througha high-speed optical fiber. A software defined network and network function virtualization concept is introduced, a data level and a control level are separated, and a network function is decoupled from hardware equipment. An OpenFlow controller is adopted to realize centralized control, mobile management, data processing and resource distribution functions are executed upwards through a programmable application program interface, and the OpenFlow controller is communicated with a transponder downwards through an OpenFlow interface to realize forwarding of user data. Different characteristicsof the Internet of Things terminal user are considered, and the Stackelberg game is applied to the distribution process of computing resources of the Internet of Things terminal user, so that the resource utilization rate is improved to the maximum extent on the premise of ensuring the service quality of the user, and the requirements of more different types of users are met.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
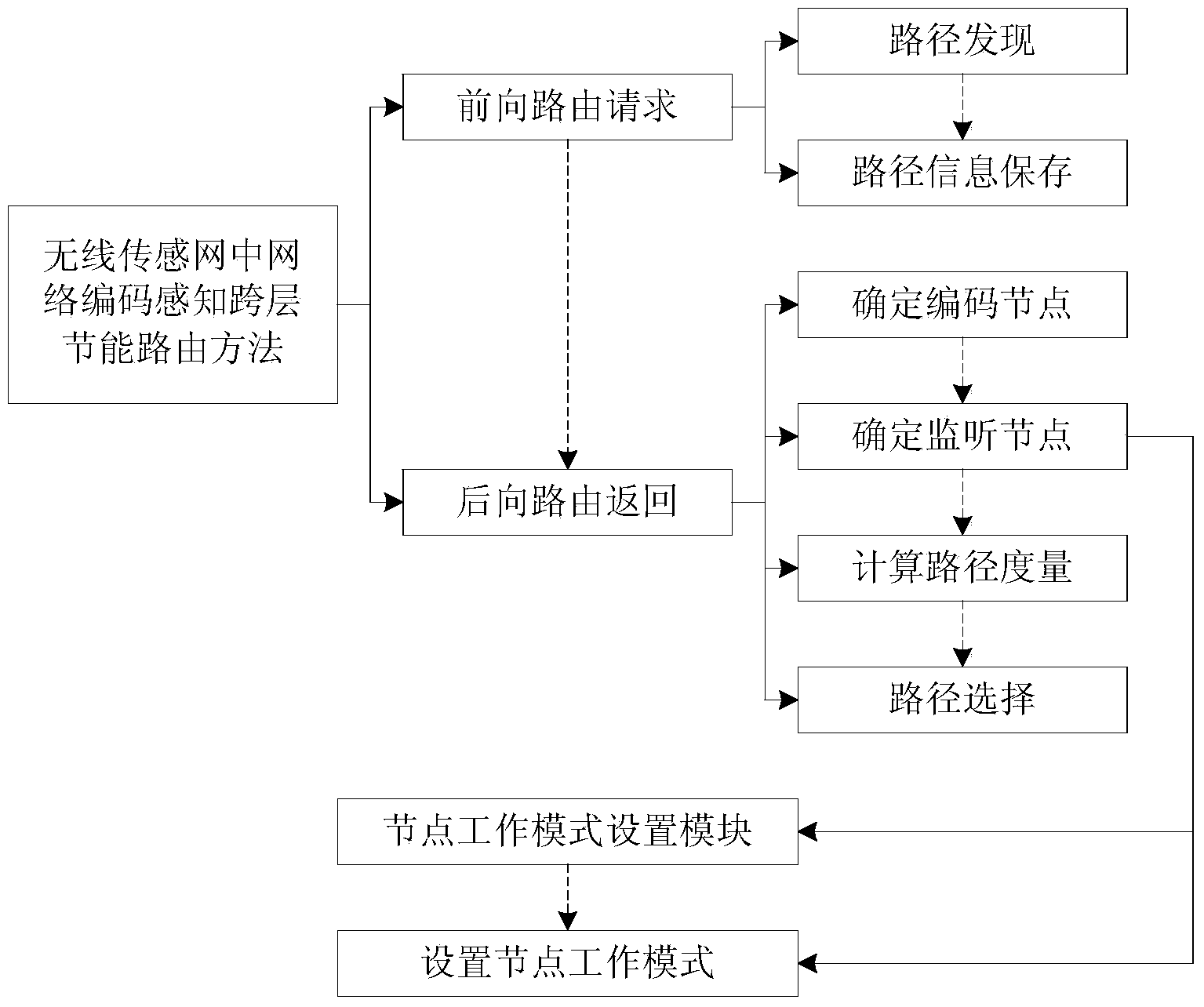
Method for network code sensing cross-layer energy-saving routing in wireless sensor network
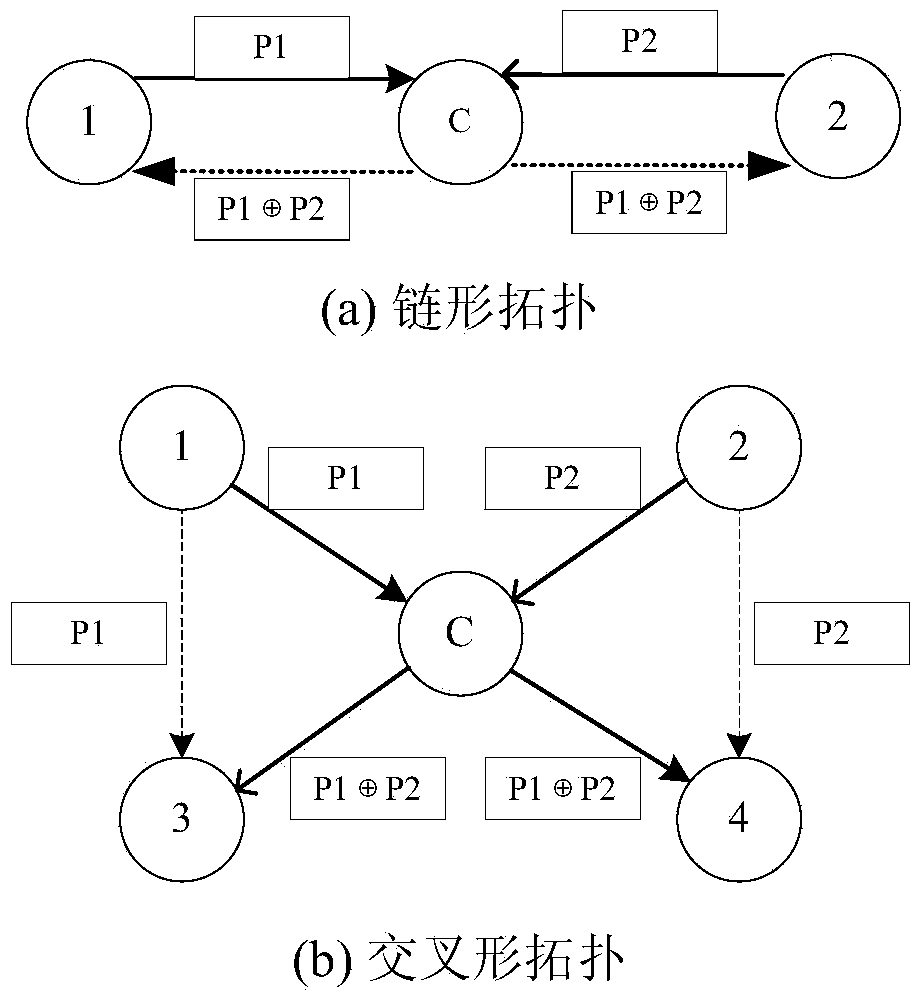
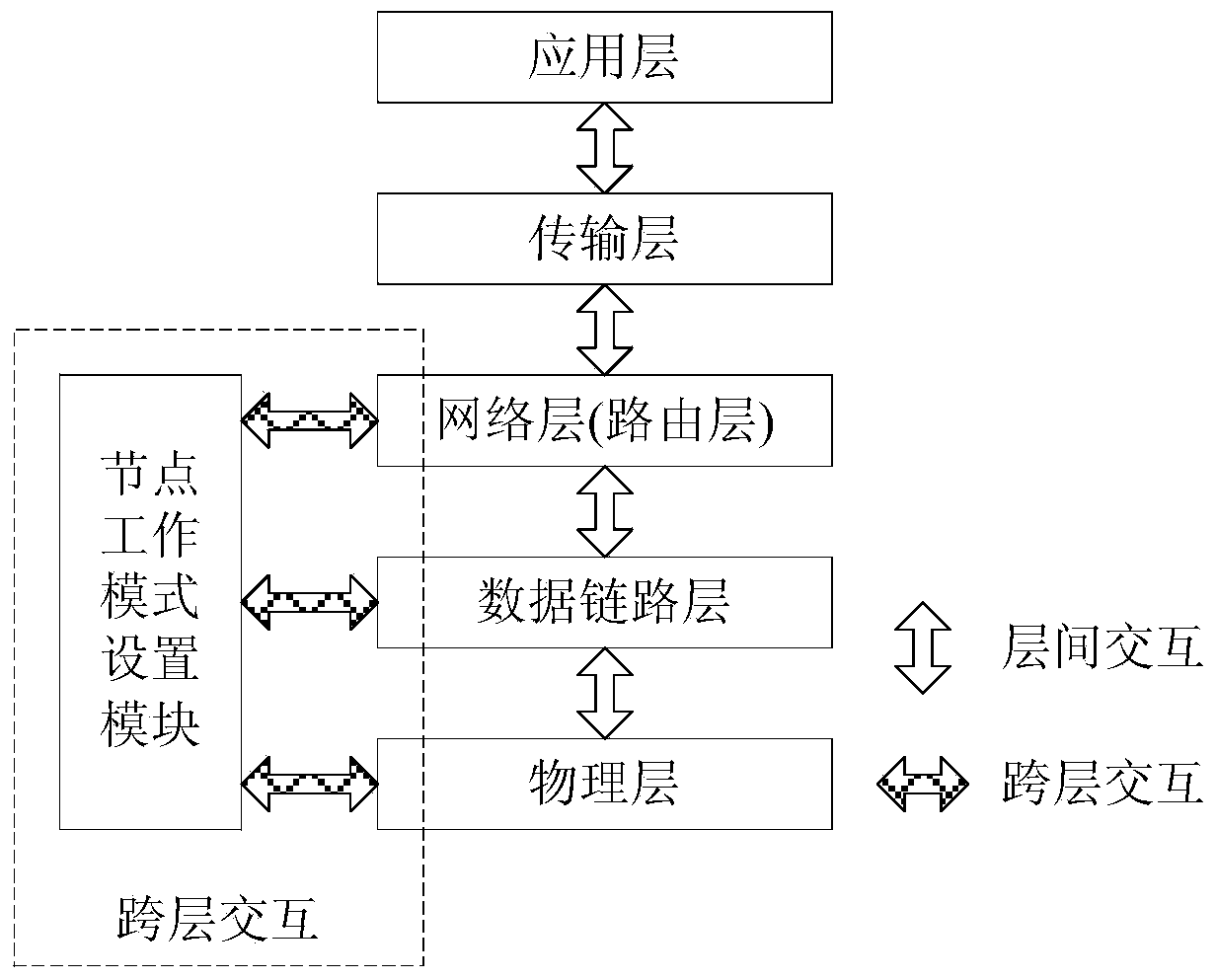
ActiveCN103458487AReduce the number of transfersImprove data transfer efficiencyPower managementHigh level techniquesMobile wireless sensor networkNetwork code
The invention discloses a method for network code sensing cross-layer energy-saving routing in a wireless sensor network. The method for network code sensing cross-layer energy-saving routing in the wireless sensor network mainly comprises the steps that (1) inter-flow network coding is used to reduce the frequency of data transmission and energy consumption, (2) a cross-layer mechanism among a network layer, a data link layer and a physical layer is used to determine monitoring nodes in a network, then a large amount of energy consumption, used for unnecessary monitoring, of nodes is reduced, the lifetime of the nodes is prolonged, and therefore the lifetime of the network is prolonged. According to the method for network code sensing cross-layer energy-saving routing in the wireless sensor network, the cross-layer mechanism is used for network code sensing routing, the number of the monitoring nodes is greatly reduced by means of the cross-layer mechanism on the premise that the inter-flow network coding is used to reduce the frequency of data transmission and the energy consumption, unnecessary energy consumption of a large number of nodes for monitoring in existing network code sensing routing is eliminated, therefore, energy consumption of sensing nodes in the wireless sensor network is reduced, and the network lifetime of the sensor network is prolonged.
Owner:YANCHENG INST OF TECH
Vehicle position privacy protection method of vehicular ad hoc network
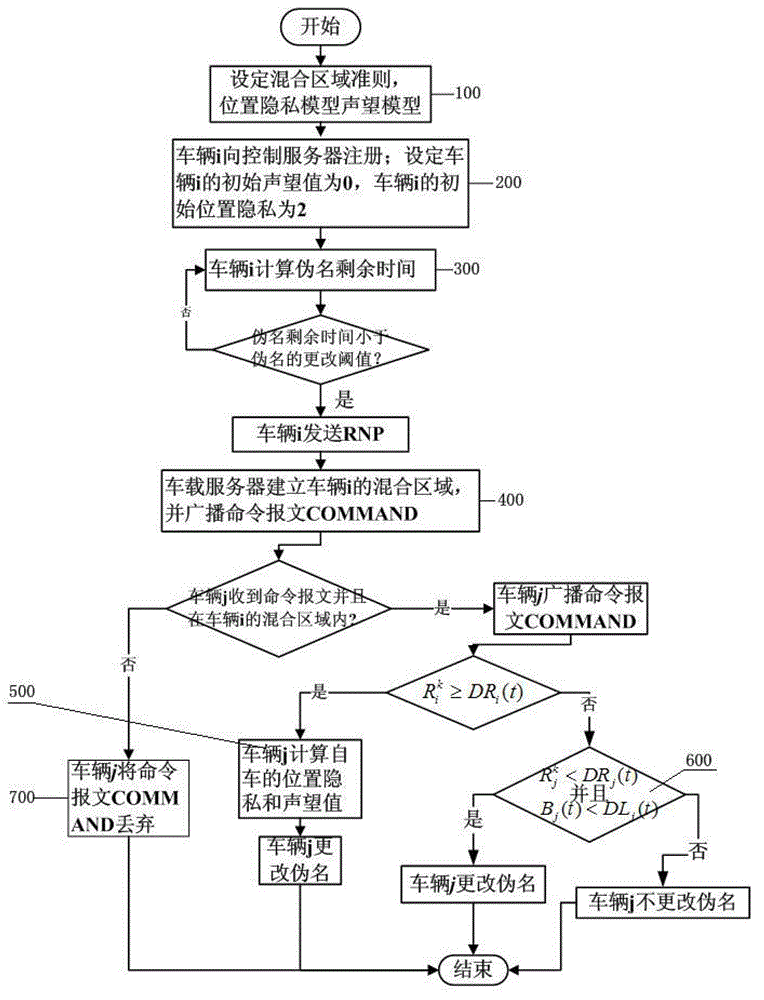
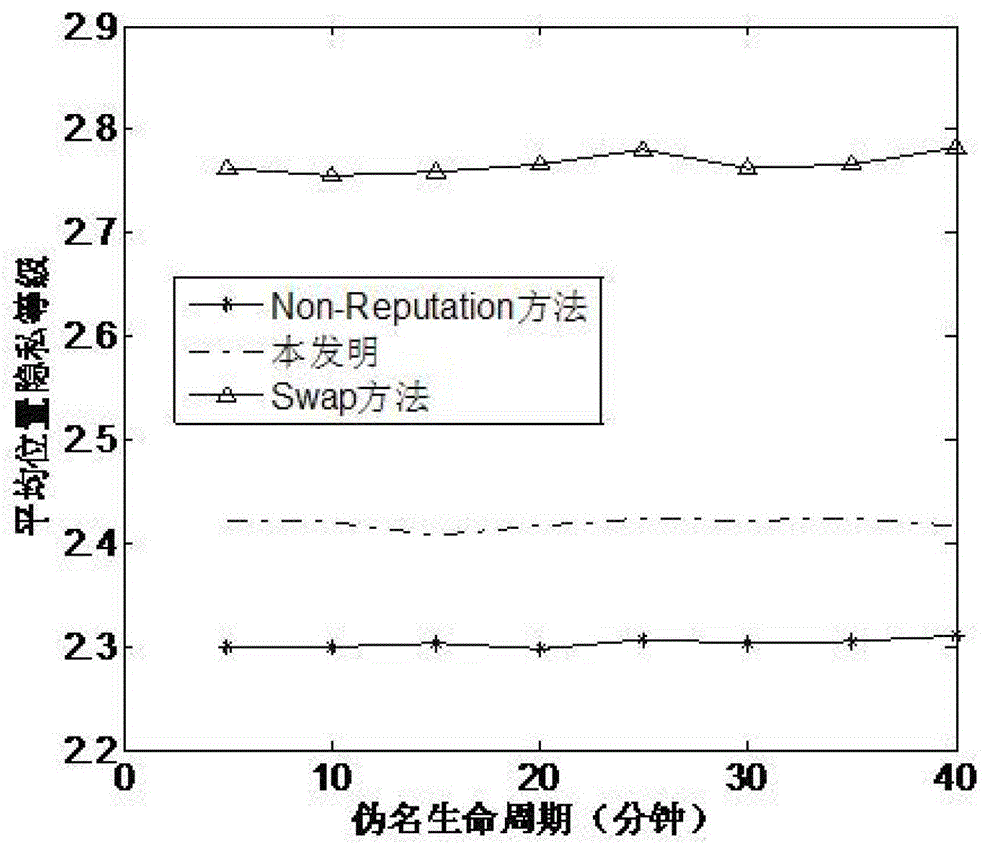
InactiveCN103338444AHigh location privacy and securityLower energy billsParticular environment based servicesNetwork topologiesPrivacy protectionWireless network
The invention discloses a vehicle position privacy protection method of a vehicular ad hoc network. The method comprises the following steps: a privacy model is first set to assess a current position privacy of different vehicles so as to reflect a reputation module and a mix-zone criterion of a cooperation degree of the current vehicle; any one vehicle in the vehicular ad hoc network determines whether to cooperate and change a pseudo name to protect a vehicle i according to a current reputation value of the vehicle i sending a pseudo name request and based on a judgment whether the one vehicle is within a mix-zone of the vehicle i; and the reputation value of the one vehicle can be dynamically adjusted according to the current position privacy of the one vehicle and pseudo name residual time. The method of the invention can meet the requirement of protecting the current position of the vehicle and can substantially reduce the energy cost; and the method has the advantages that more vehicles are involved in the pseudo name change and the safety of the position privacy of the vehicular wireless network is greater.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
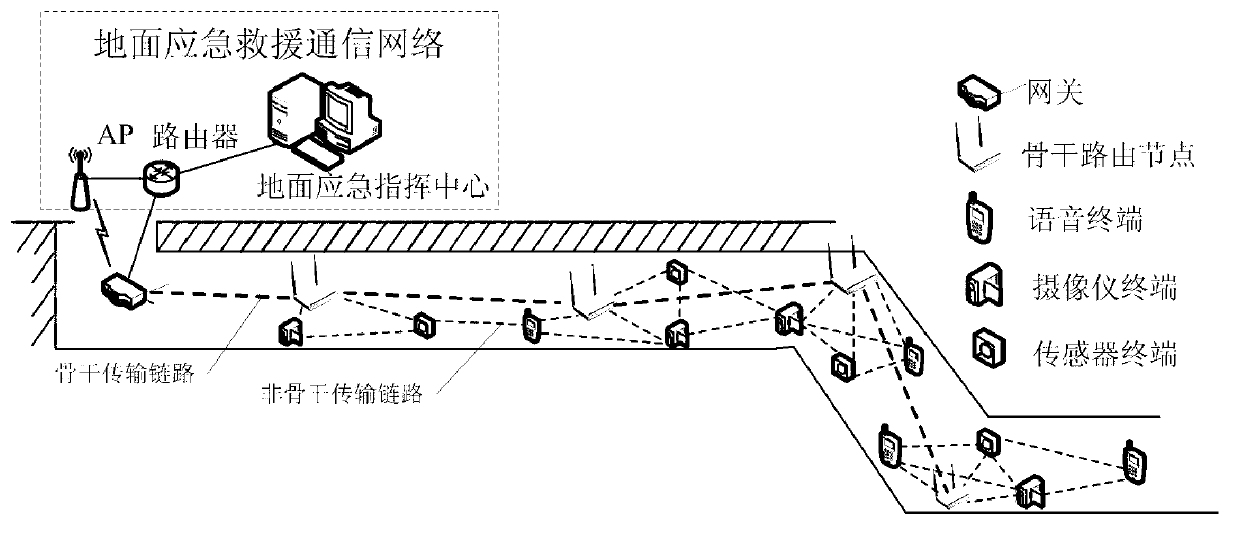
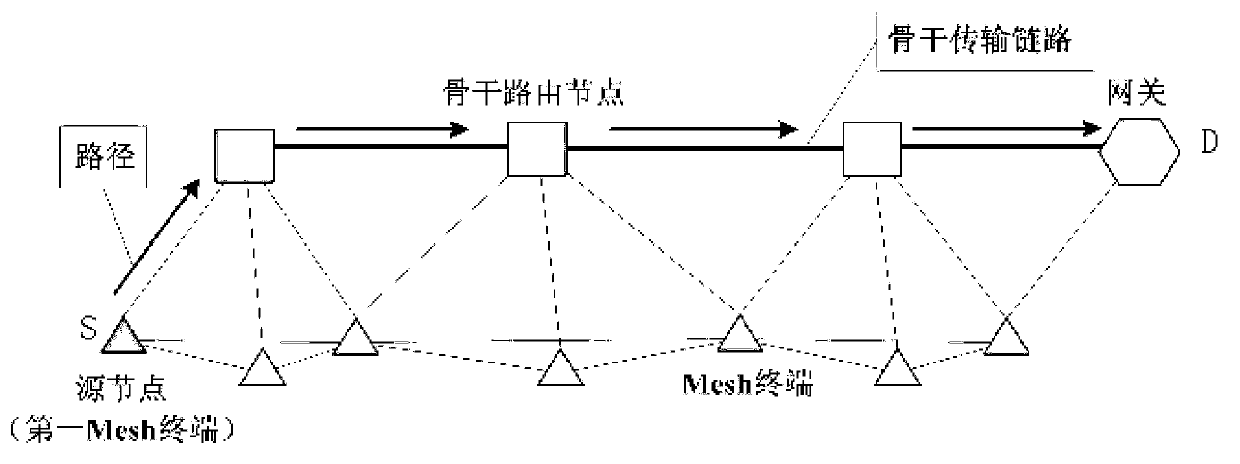
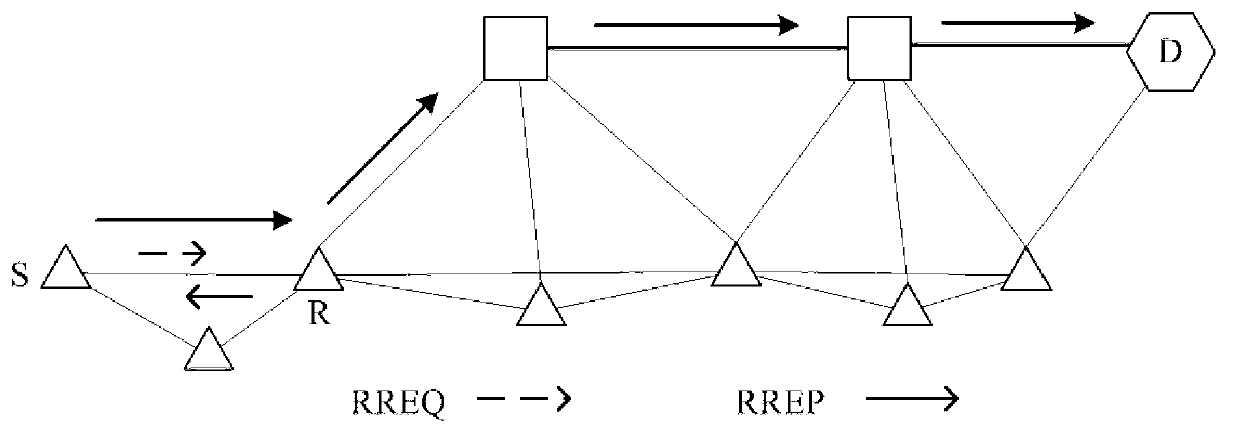
Energy saving routing algorithm of composite structure mine emergency rescue wireless mesh network
ActiveCN103108374AReduce the use effectNarrow downEnergy efficient ICTHigh level techniquesWireless mesh networkEmergency rescue
The invention discloses an energy saving routing algorithm of a composite structure mine emergency rescue wireless mesh network. The algorithm includes the following steps: step 1, node type information is set up; step 2: communication states of Mesh wireless terminals are divided into three types, namely, an 'interior' state, an 'edge' state and a 'repair' state; step 3, each Mesh terminal node maintains one Mesh backbone routing node list; and step 4, if the first Mesh terminal is found to be in the 'interior' state, the neighbor backbone routing nodes nearest to a gateway are selected to set up a route to the gateway directly according to information of the Mesh backbone routing node lists.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Energy-saving sensor data collection method based on cross layer safe compression
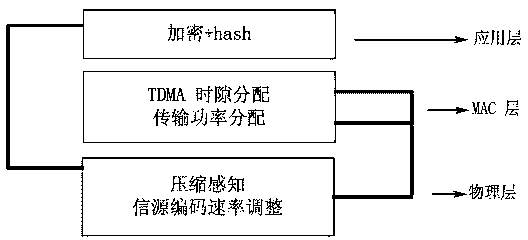
ActiveCN103763696AEnsure safetyImprove data securityPower managementSecurity arrangementSource encodingHigh energy
The invention discloses an energy-saving sensor data collection method based on cross layer safe compression. High energy efficiency and safety are achieved by means of the CS cross layer safe compression method. The method comprises a CS-based safe compression method and a cross layer combined optimization method. According to the CS-based safe compression method, encryption and integrity checking is combined with compressed sensing, and safety and low redundancy rate of data are ensured; cross layer combined optimization relates to the source encoding rate, transmission power and TDMA time slot assignment of a physical layer and a MAC layer, and energy minimization is achieved by means of the nonlinearity convex optimization algorithm. The energy-saving sensor data collection method based on cross layer safe compression achieves higher data safety, optimized energy efficiency, smaller transmission information amount, and smaller system complexity.
Owner:江苏数一科技服务有限公司
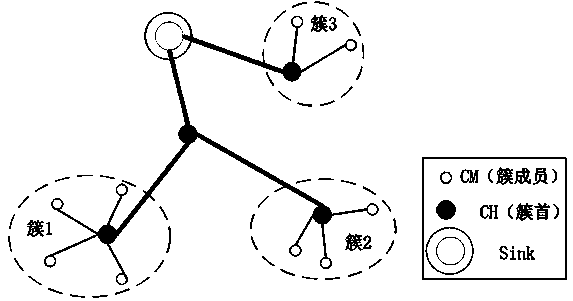
Gradient based energy-efficient uneven clustering data forwarding method
ActiveCN104080144ABalanced energy consumptionEven consumptionPower managementHigh level techniquesClustered dataWireless sensor networking
The invention discloses a gradient based energy-efficient uneven clustering data forwarding strategy designing method in the wireless sensor network. In a conventional data forwarding strategy based on an even clustering technology, the problem of unbalanced energy consumption is caused by multi-hop routing realized by a backbone network constituted by cluster-head nodes, that is, the network is partitioned and the network survival time is shortened due to the fact that the cluster-head node close to a base station forwards mass data, is excessively loaded, untimely consumes the energy and loses efficacy. Therefore, a clustering mechanism is operated on a gradient model, and data forwarding is completed through uneven clustering and dynamic selection based on node energy, the number of non-cluster-head nodes and low-gradient key nodes in the opposite positions of the nodes so as to improve the energy efficiency of inter-cluster communication. According to the designing method provided by the invention, the energy overhead of the network is reduced while the energy consumption among the nodes can be balanced, so that the utilization rate of network resources is improved, and the network survival time is maximized.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Threshold adaptation energy detection method
InactiveCN102324992AImprove the level of intelligenceImprove adaptabilityTransmission monitoringData transmissionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
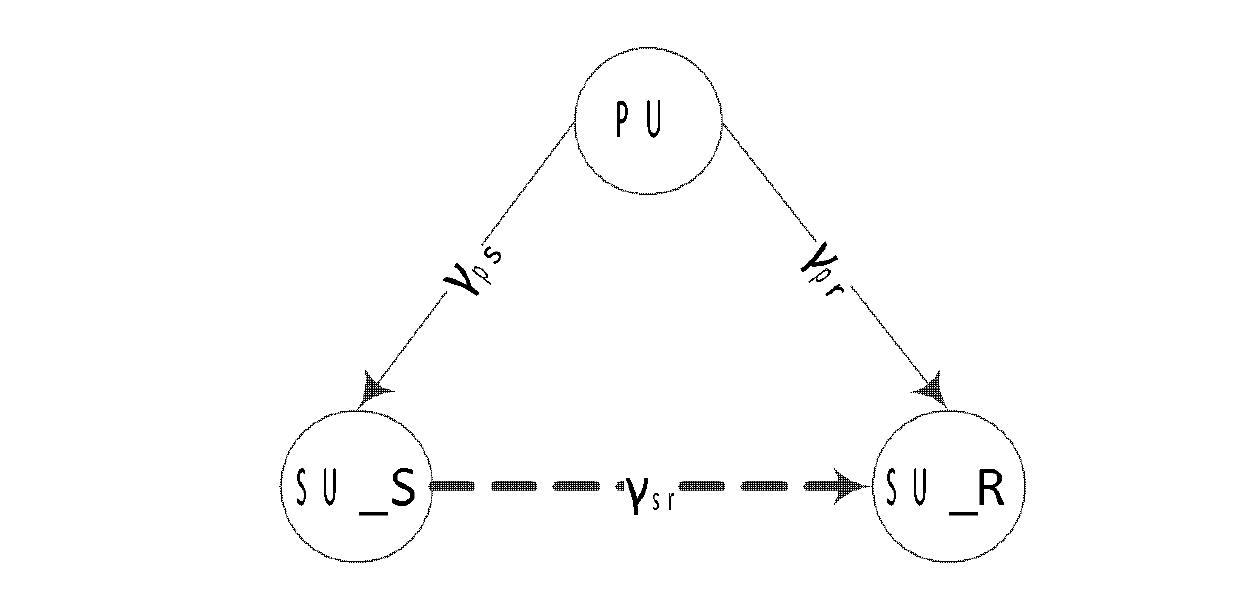
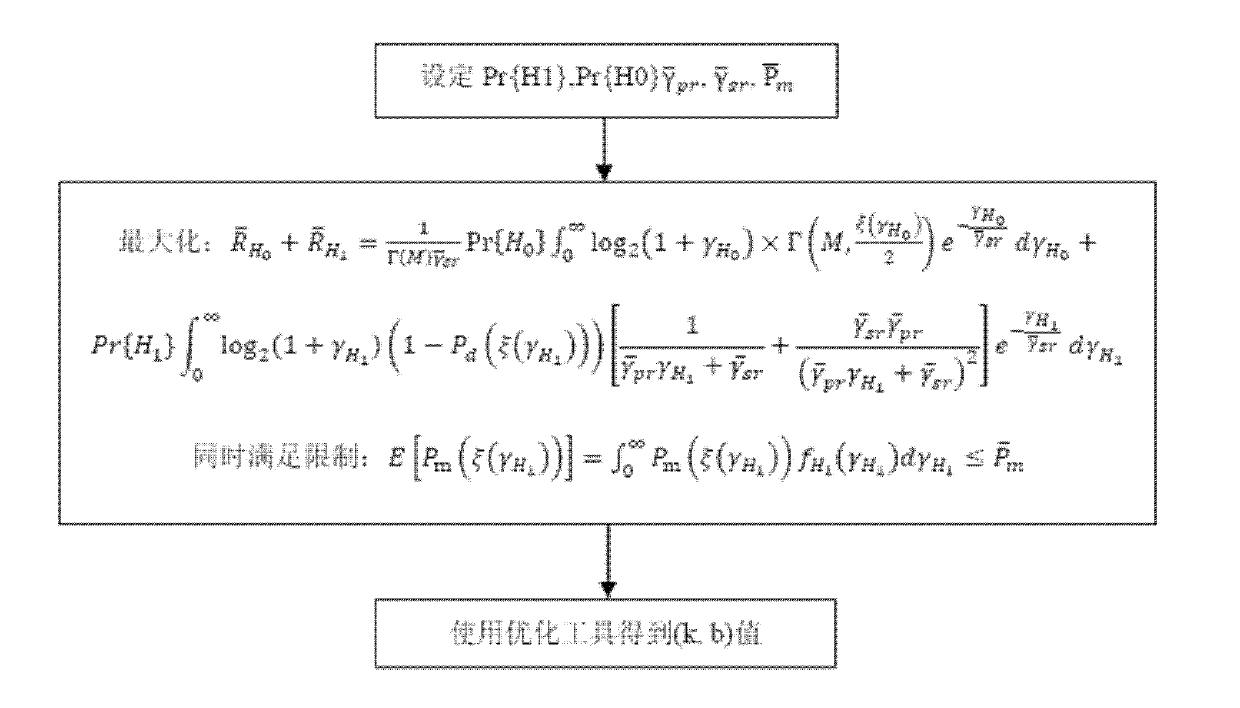
The invention discloses a threshold adaptation energy detection method. In the energy detection method, a parameter computing scheme for an offline energy judgment threshold decision function and an online energy judgment threshold judgment scheme are sequentially realized. In the threshold adaptation energy detection method provided by the invention, the energy judgment threshold decision function is offline established, a value of an energy judgment threshold is dynamically regulated according to different signal to noise ratios, and online judgment is performed, so the intellectualization level of a cognitive radio user is improved, false alarm probability Pf(xi) is decreased to maximize the average data transmission rate of a secondary user (SU), energy overhead required in a running process is decreased, and an average value of false dismissal probability Pm(xi) is limited within a preset probability threshold range to avoid excessive interference in a primary user (PU).
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Energy-efficient identity authentication method in multi-level clustering wireless sensor network
ActiveCN102612035AKeep your identity safeAvoid the authentication processEnergy efficient ICTNetwork topologiesMobile wireless sensor networkWireless mesh network
The invention provides an energy-efficient identity authentication method in a multi-level clustering wireless sensor network, which belongs to the technical field of computer networks. According to the method disclosed by the invention, a symmetric encryption algorithm is taken as the basis, a base station is used for transferring identity information, and all the nodes only need to be subjected to double-way identity authentication with cluster head nodes according to the characteristics of the multi-level clustering wireless sensor network, so that the unnecessary authentication process is avoided. According to the energy-efficient identity authentication method disclosed by the invention, the energy-efficient whole-network necessary identity authentication can be realized in the multi-level clustering wireless sensor network, and identity safety of the nodes of the whole network can be ensured at minimum energy cost.
Owner:福建汇智数字通达科技有限公司
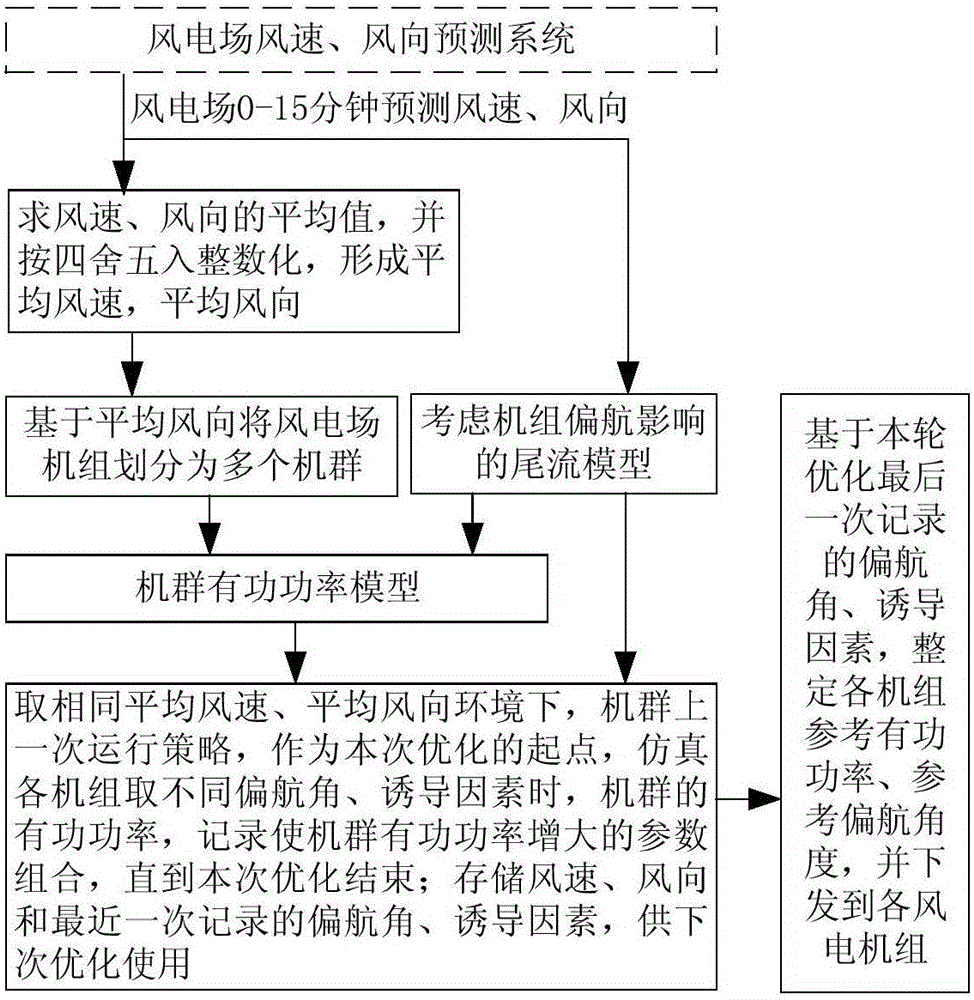
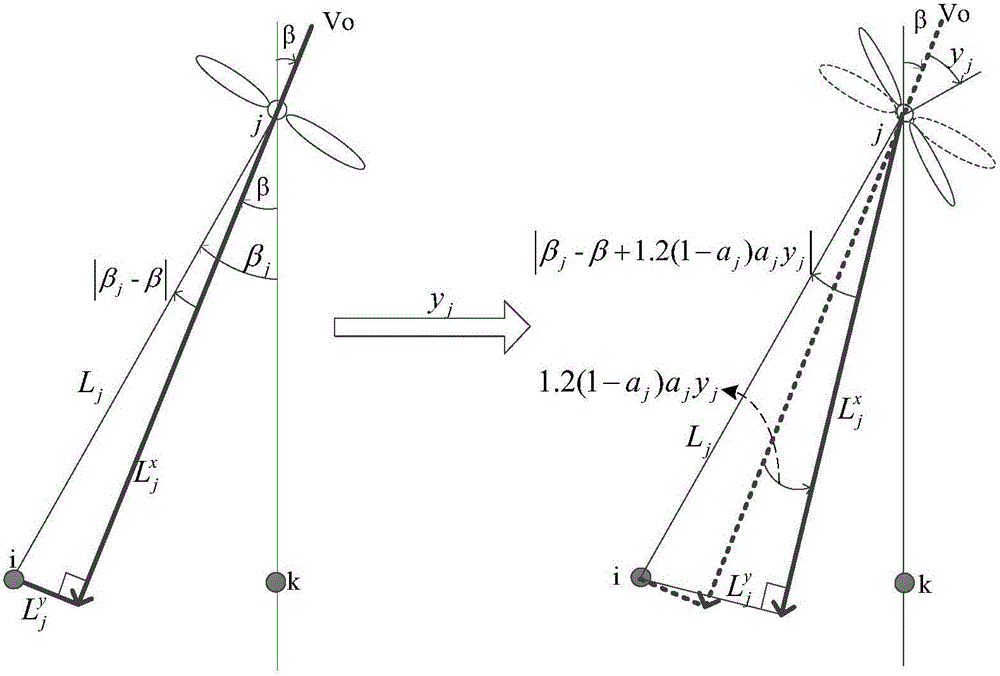
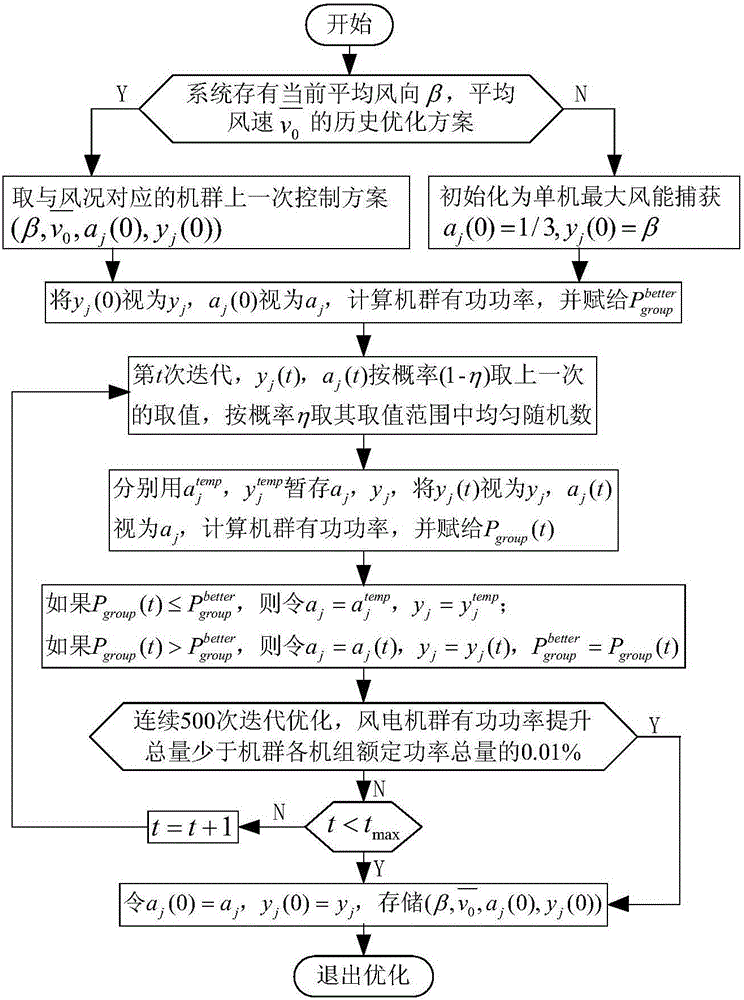
Wind power plant synergy method with yawing and active power integrated cooperation among units
The invention discloses a wind power plant synergy method with yawing and active power integrated cooperation among units, and the method comprises the steps: firstly dividing a wind power plant into a plurality of machine groups according to an averaged wind direction; secondly building a wake flow model and a machine group active power model; thirdly a former operation strategy of the machine groups under the same wind condition as a starting point of optimization at this time, simulating the active power of each machine group at different yawing angles and inducing factors, recording a parameter combination which enables the active power of the machine groups to be increased till the optimization is finished, and storing the wind speed, the wind direction, the latest recorded yawing angle and the inducing factor for the next optimization; finally setting the optimization result as the reference active powers and yawing angles of the machine groups, and transmitting the optimization result to each machine group. The method provided by the invention is smaller in calculation amount, can effectively inherit a historical optimization result, and can achieve the optimization control at lower cost. The yawing angle is dispatched for one time in one control period, and the method achieves the wind power plant active power optimization with the yawing and active power integrated cooperation at lower cost.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV +1
Method for implementing wireless sensor network query, and data return method
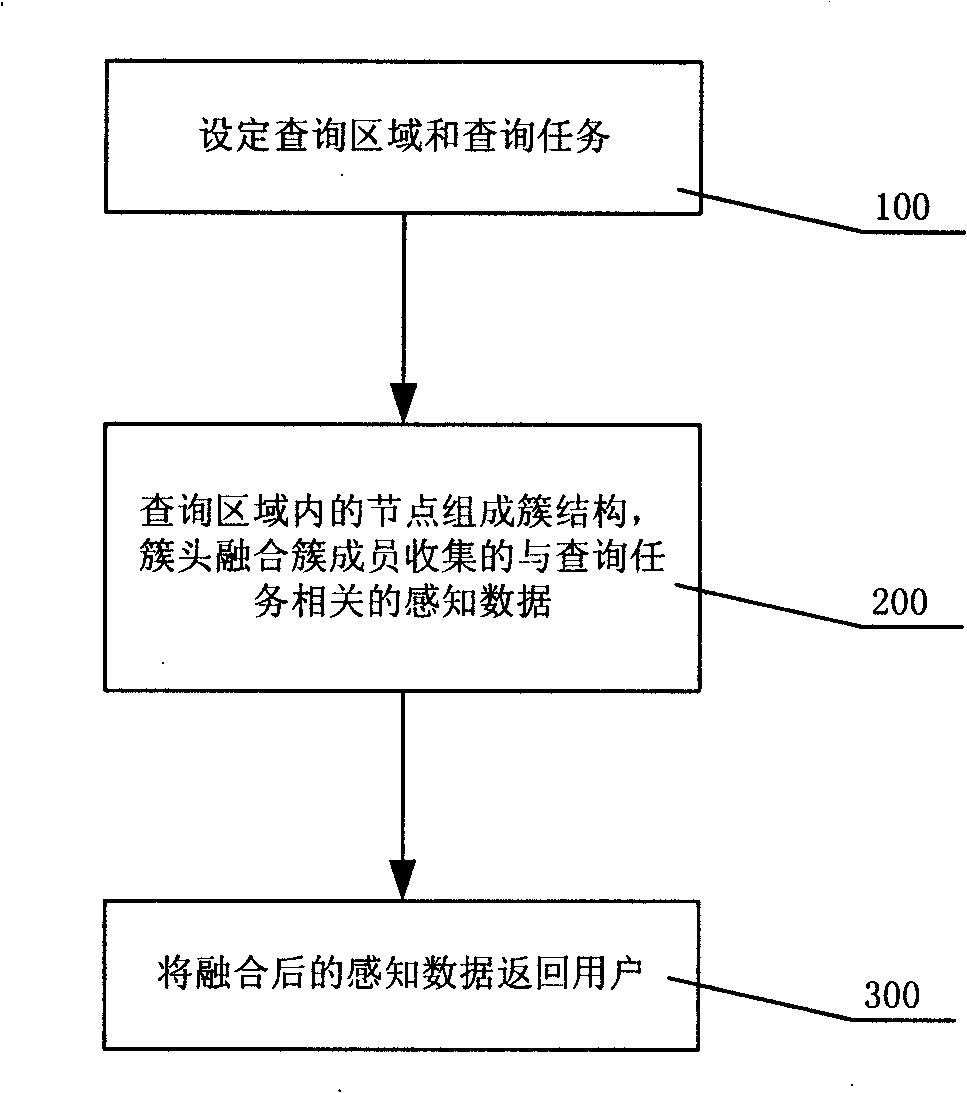
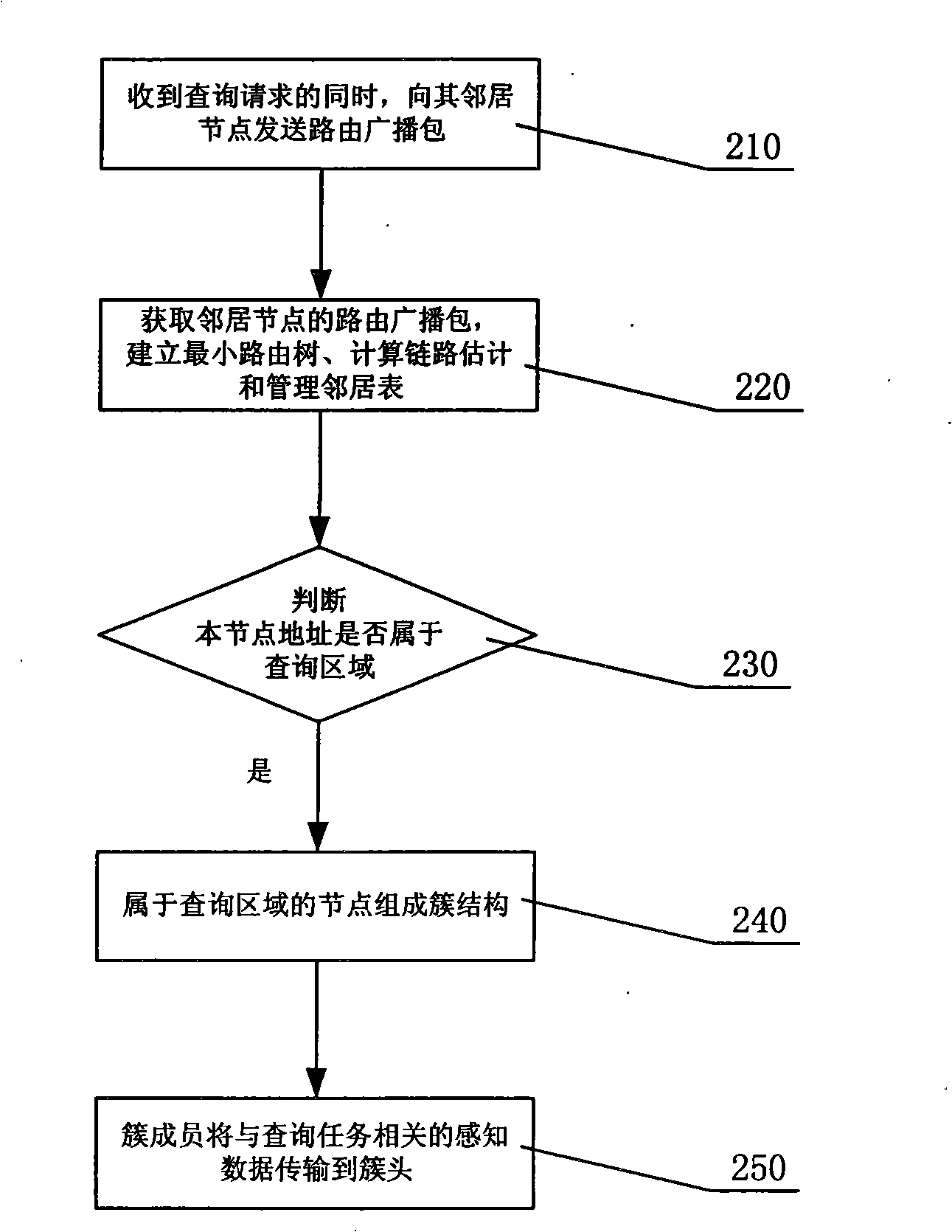
ActiveCN101321184ALower energy billsAvoid it happening againData switching networksControl signalWireless sensor networking
The invention discloses a method of implementing wireless sensor network query and a method of transmitting data back, wherein the method of network query includes the following steps: a node in the sensor network receives the query request set by the user, the query request at least includes a query area and a query task; the nodes in the query area form a cluster structure, the cluster head of the cluster structure inosculates the sensitive data which are collected by the cluster members and correspond to the query task; the inosculated sensitive data are returned to the user. The expenditure of the control signals in the total network range can be reduced by adopting the method.
Owner:汉摩尼(江苏)光电科技有限公司
Wireless chain-type transmission system
InactiveCN103916939AReduce transmission delayFacilitate timely transmissionPower managementNetwork topologiesData packWireless sensor networking
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Parallel decoding method and system for multi-tag signals in backscattering protocol
ActiveCN107944316AReduced manpower and material resourcesReduce energy consumptionNear-field in RFIDHigh level techniquesDecoding methodsComputer science
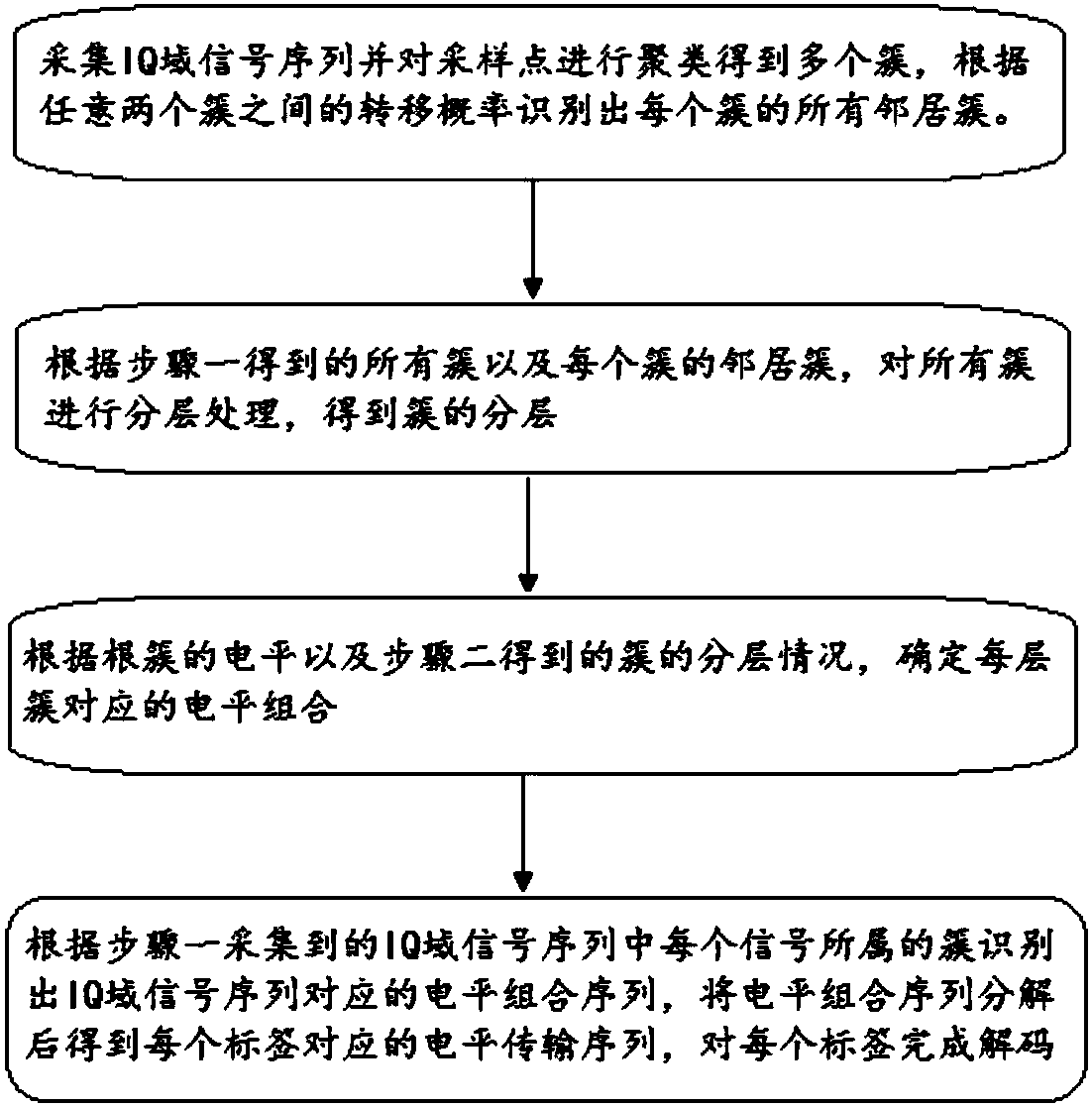
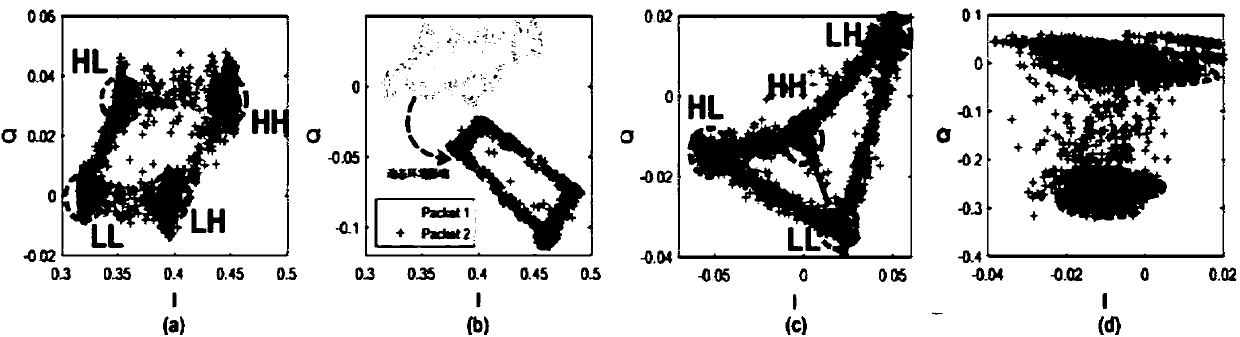
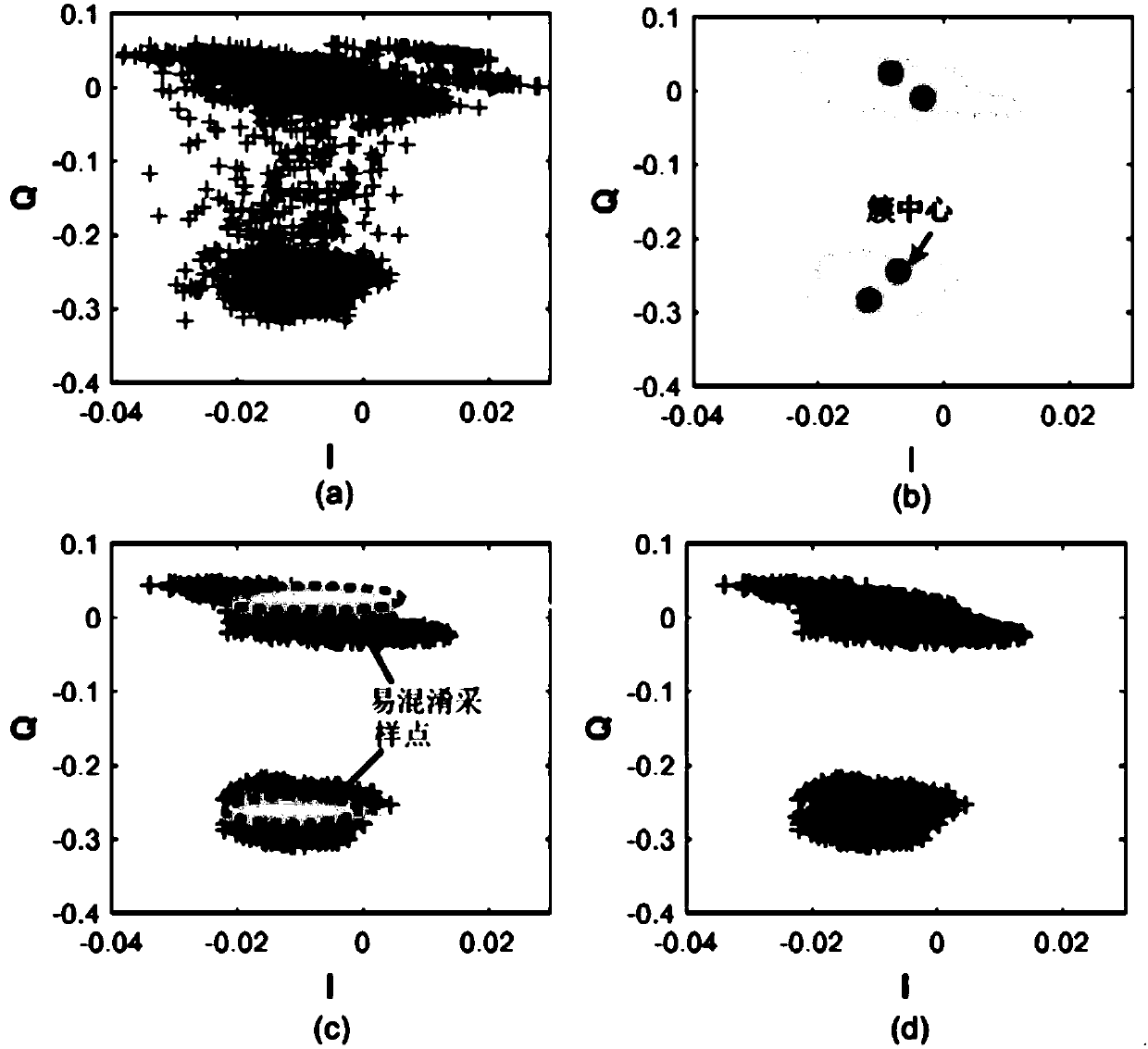
The invention discloses a parallel decoding method and a parallel decoding system for multi-tag signals in a backscattering protocol. The parallel decoding method comprises the steps of: acquiring anIQ domain signal sequence and clustering sampling points to obtain a plurality of clusters, and identifying all neighbor clusters of each cluster according to a transition probability between arbitrary two clusters; acquiring layers of the clusters according to all the acquired clusters and all the neighbor clusters of each cluster; determining level combinations corresponding to each layer of theclusters; and identifying a level combination sequence corresponding to the IQ domain signal sequence according to a cluster to which each signal belongs, decomposing the level combination sequence to obtain a level transmission sequence corresponding to each tag, and completing the decoding of each tag. The parallel decoding method and the parallel decoding system realize the decoding of a plurality of collision tags in a dynamic environment, and are very suitable for a highly dynamic and highly unstable backward scattering system in practical application. Since the parallel decoding methodand the parallel decoding system do not depend on stability of signals, the tag side does not need to make any changes, thereby reducing energy consumption of the tag side and improving the reliability and robustness of the algorithm.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
Energy optimized safe routing method
InactiveCN101478751ATimely updateImprove securityEnergy efficient ICTNetwork topologiesDistribution methodCluster based
An energy optimizing secure routing method provides a secure routing protocol based on low consumption cluster head election algorithm, directed towards solving the security threatening problem faced by cluster-based routing protocol and the problem that cluster head election algorithm consumes too much energy. The protocol adopts mutual cooperation to obtain the total of the nodes participating election currently in the cluster election process, and can correctly calculate the threshold value of the currently-produced cluster nodes, which allows the probability of producing optimal cluster number to be largest and the allows the network energy consumption to be optimal. The invention adopts a preset shared key pair distribution method and raises the security of routing effectively. At the same time of optimizing energy, the new protocol raises the security of routing and prolongs network lifetime.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
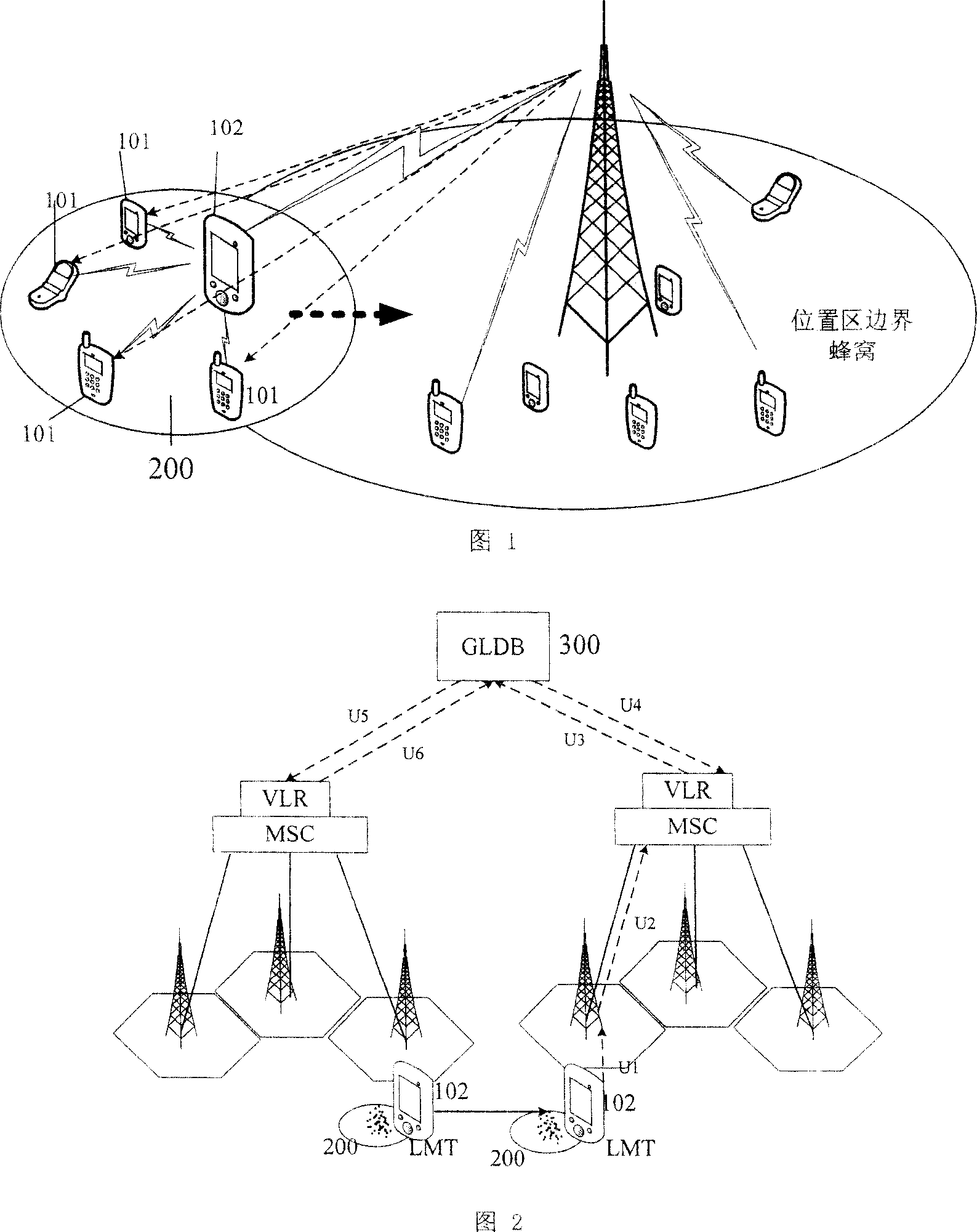
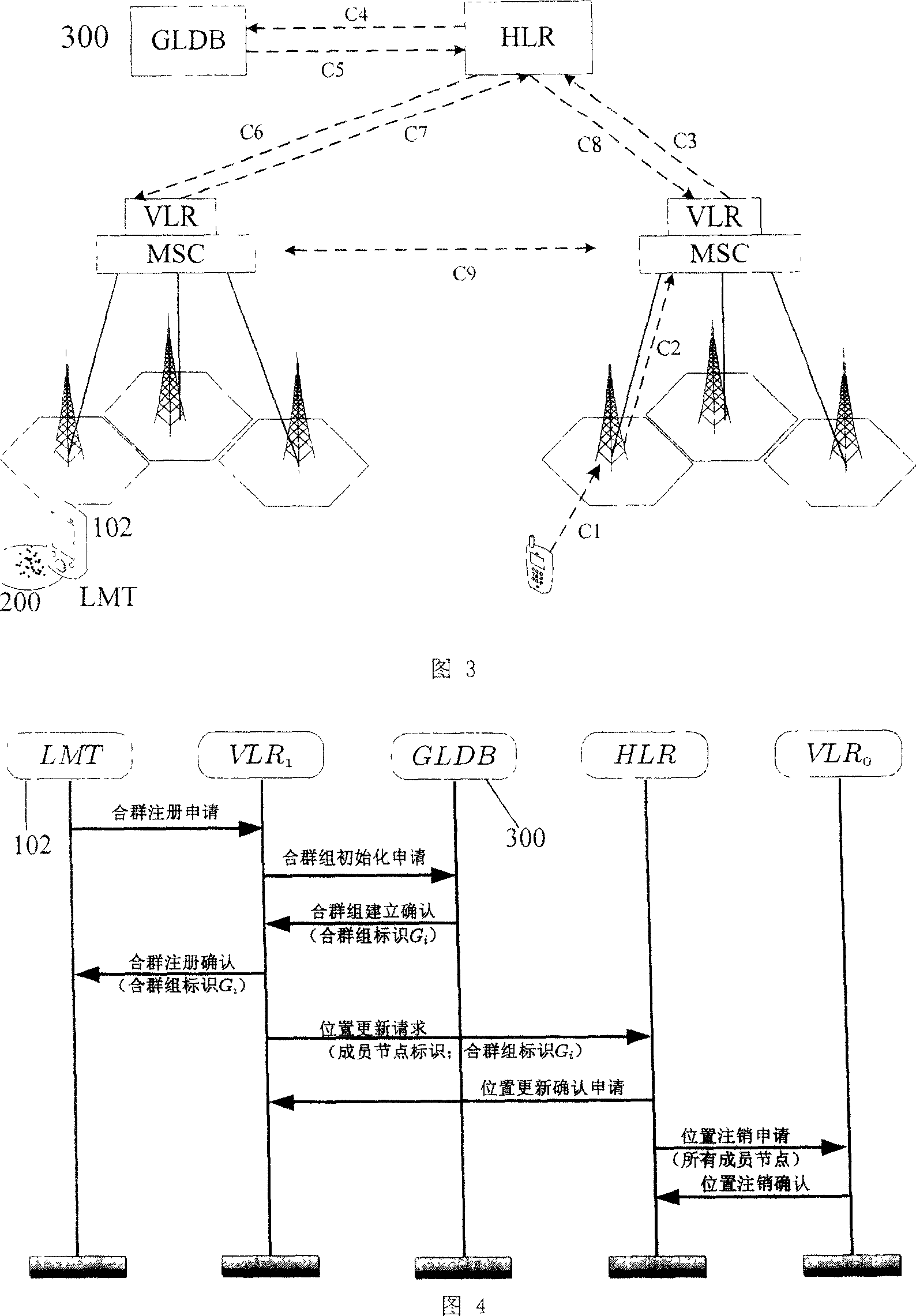
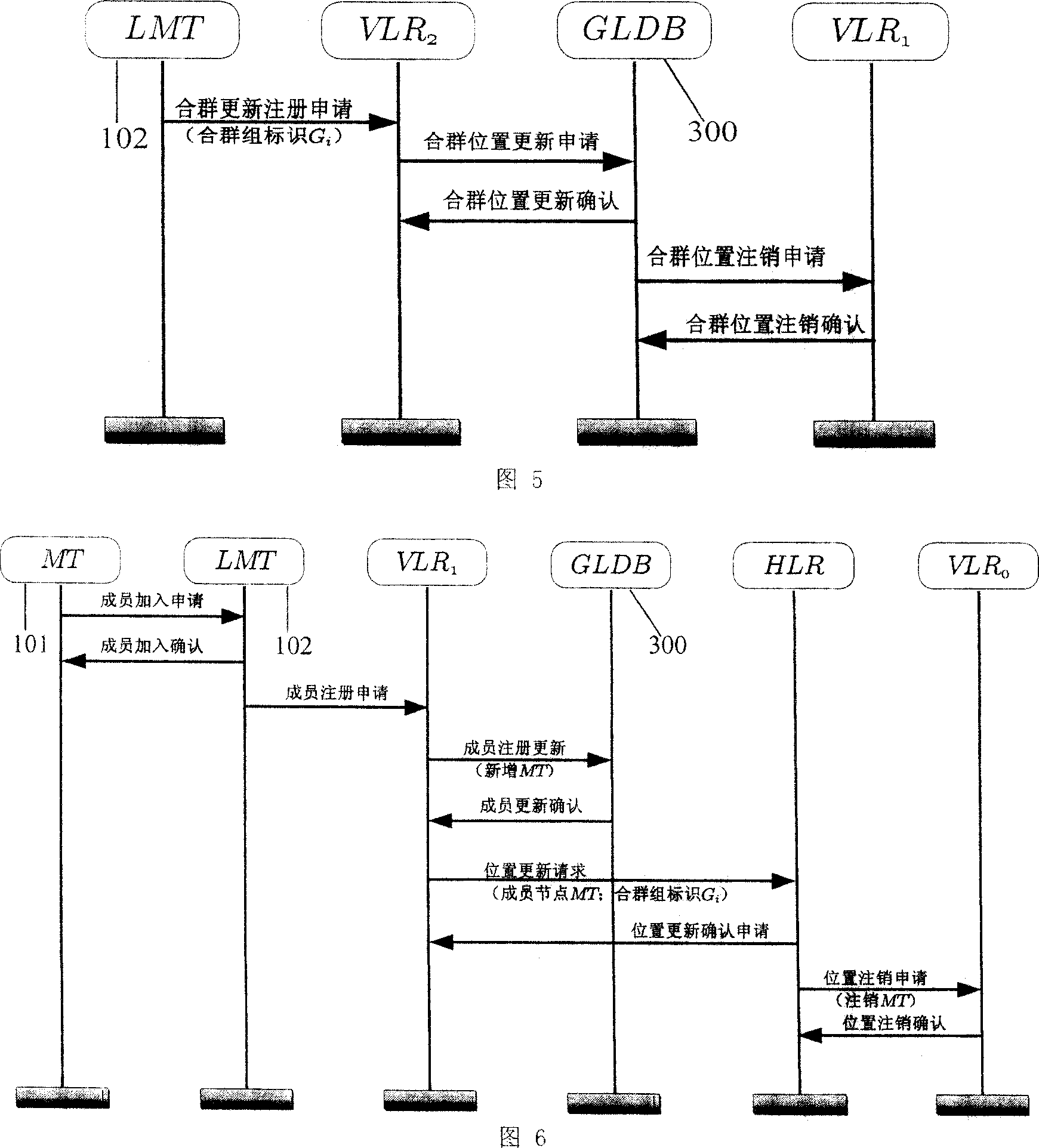
Block position managing method based on mixed mobile network
InactiveCN101001414ASave bandwidth resourcesSave frequency resourcesEnergy efficient ICTTelephonic communicationNetwork communicationMobile station
This invention discloses a block position management method based on the next generation mixed mobile network communication divided into two modes of horizontal and vertical communications, which takes several mobile stations close to each other and with the same moving trend in the mobile communication network as a grouped set to be managed unifiedly including: 1, a new mixed communication mode: vertical and horizontal, 2, four kinds of new network elements: multiple radio mobile terminals, a grouped set, a group head and a blocked position database, 3, the blocked position renewing method: setting up a grouped set, which is registered initially, renewing the members and renewing the grouped set, 4, a related call transfer method.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
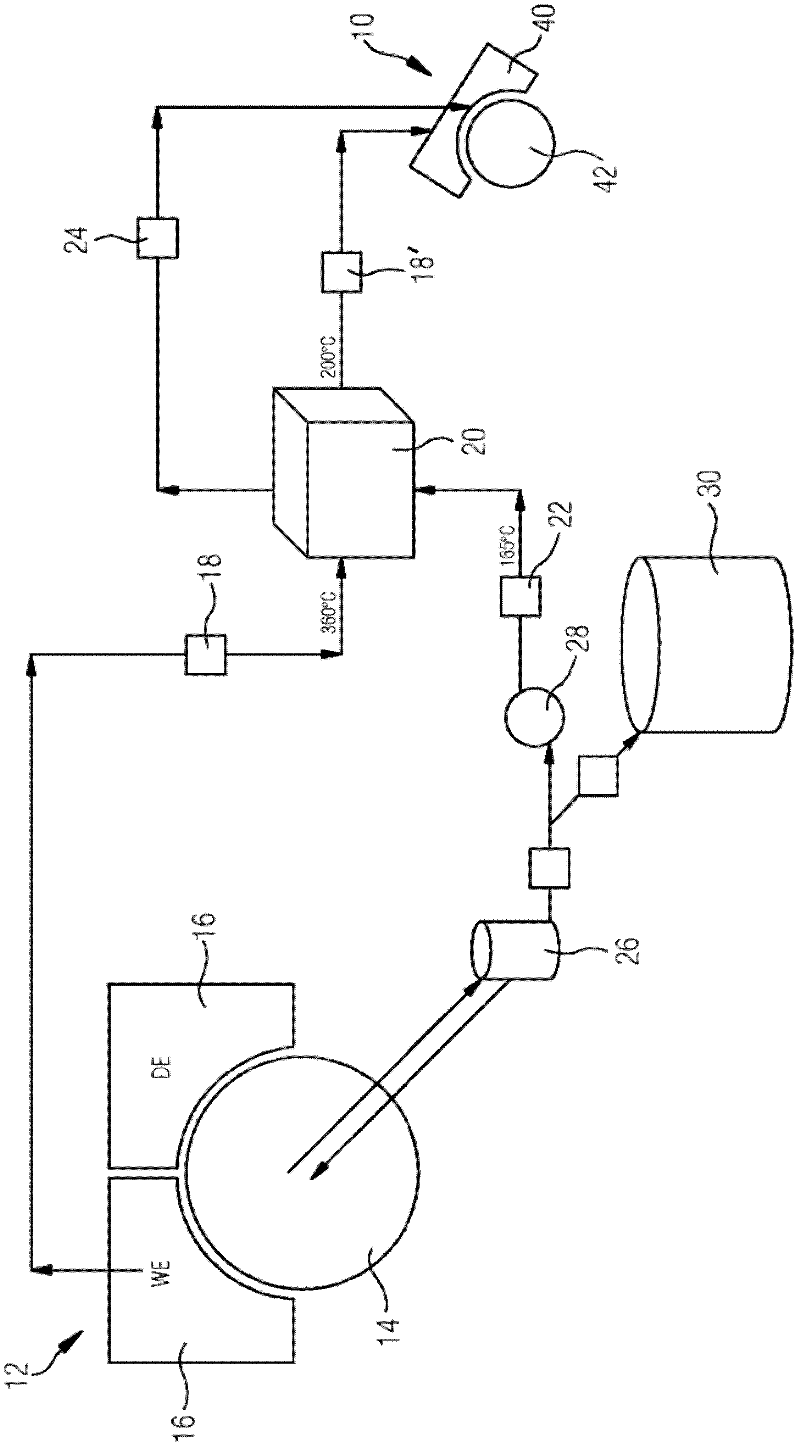
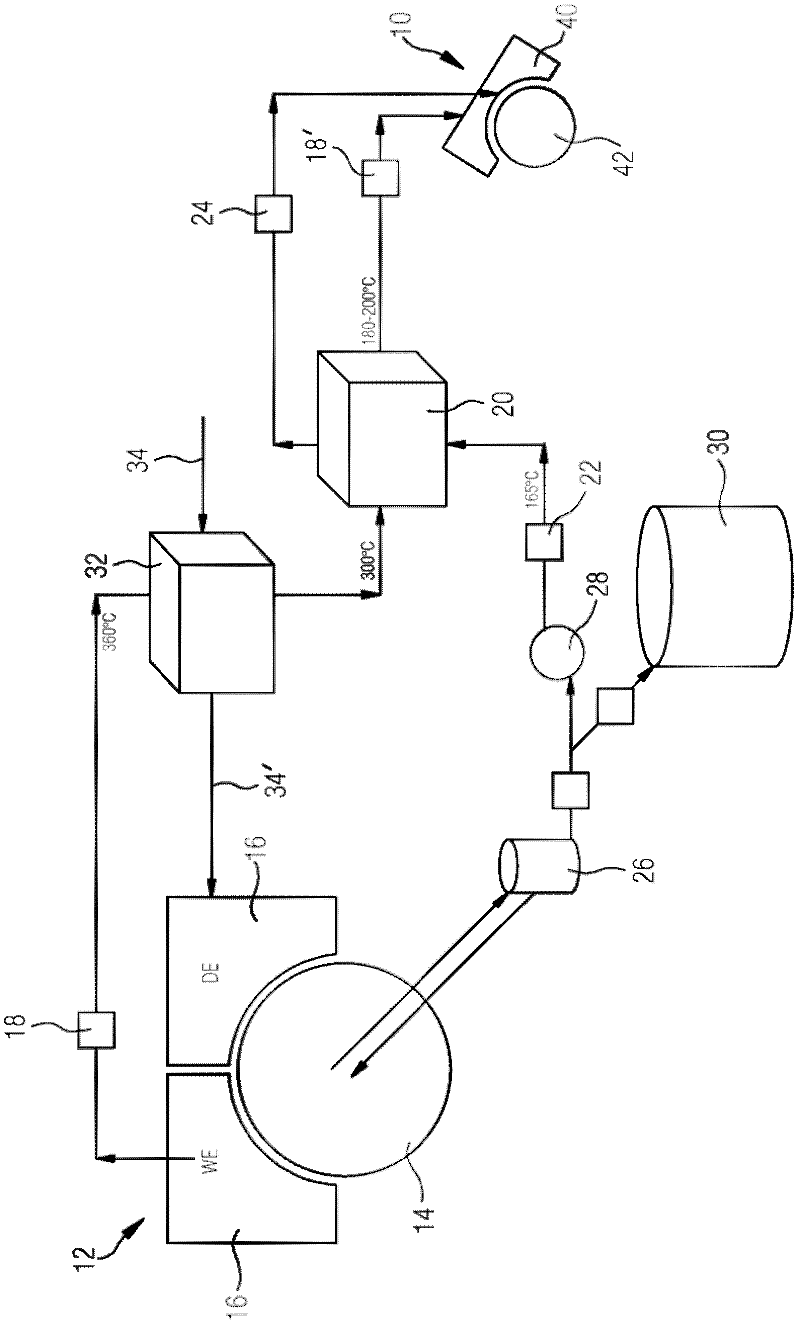
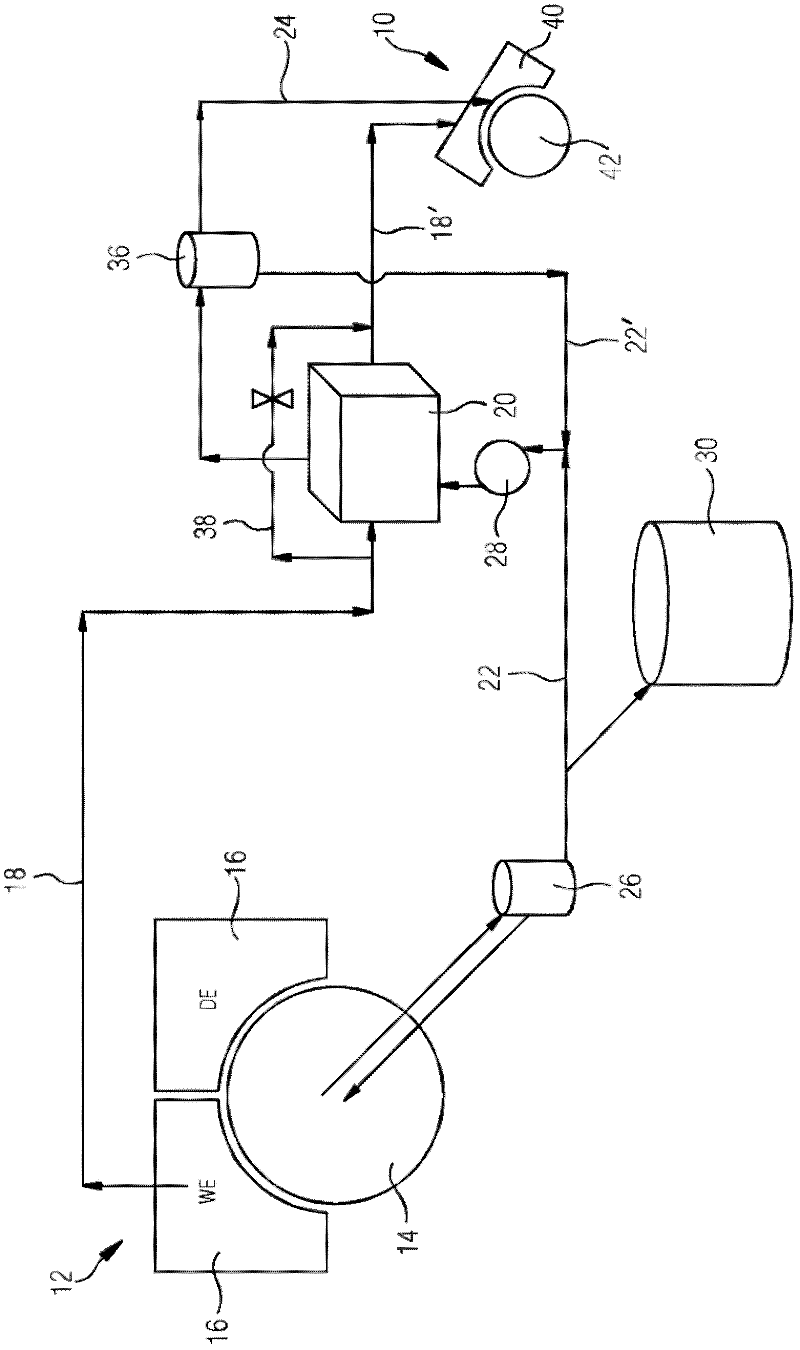
Method and device for drying a fibrous web
InactiveCN102317540AReduce consumptionLower energy billsDryer sectionPress sectionFresh waterEngineering
The invention relates to a method and to a device for drying a fibrous web, wherein the traveling fibrous web is acted upon by steam and hot, moist air in the region of a preceding drying zone (10) and is then fed to the preceding drying zone (10) of a downstream drying zone (12) comprising a drying cylinder (14) and a hood (16) allocated thereto. Hot air (18) is taken out of the hood (16) allocated to the drying cylinder (14) of the downstream drying zone (12). To create at least a portion of the steam for the preceding drying zone (10), condensate and / or fresh water occurring in the drying cylinder (14) of the downstream drying zone (12) is heated by the hot air (18) taken out of the hood (16) by means of a first heat exchanger (20). Alternatively or additionally for creating at least a portion of the hot, moist air for the preceding drying zone (10), the hot air (18) taken out of the hood (16) guided through the first heat exchanger (20) is fed to the preceding drying zone (10).
Owner:VOITH PATENT GMBH
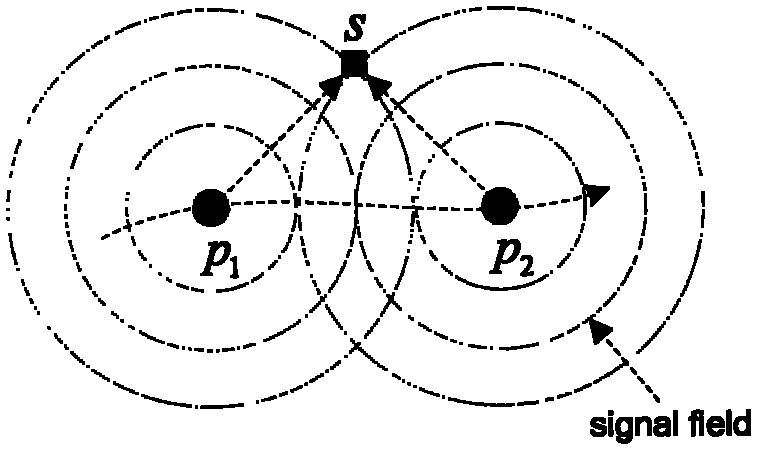
Correlation-based multi-sensor collaborative target detection method
InactiveCN102781032AEffective control quantityLower energy billsNetwork topologiesSensor nodeSearch and rescue
The invention discloses a correlation-based multi-sensor collaborative target detection method. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps that sensor nodes measure signals in a monitoring area independently; when the measured value of a certain sensor node exceeds a preset threshold, triggering to generate a dynamic detection cluster; member nodes in the cluster transmit a detection value sequence in a period of time to a cluster head node to form a detection matrix; and the cluster head node calculates the correlation measure among detection vectors in the detection matrix, and judges the existence of a target according to a calculation result. The target detection method provided by the invention is a measured value-based fusion detection method; a single sensor node does not need to perform local judgment; the influence on the judgment result caused by noises can be inhibited effectively; and the detection result has high accuracy. The method can be used in the aspects such as anti-intrusion alarm, people search and rescue under sudden disasters and traffic control in important places and areas.
Owner:NAVAL AERONAUTICAL & ASTRONAUTICAL UNIV PLA
Method and device for settling device address collision in UWB system
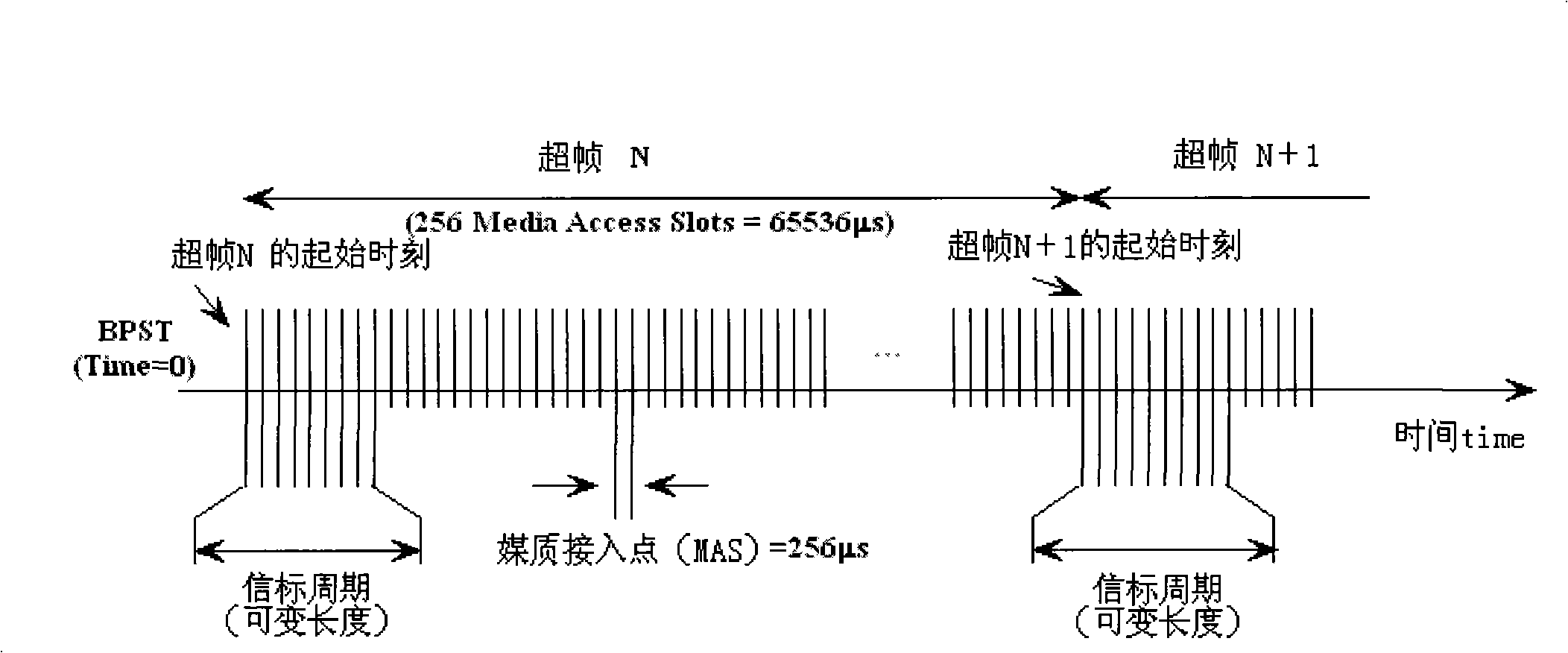
InactiveCN101345669ALower energy billsData switching by path configurationComputer scienceOperating system
An embodiment of the invention provides an implement method of solving device address conflict in a UWB system, particularly when the device address conflict happens, one of the device is selected to perform address redistribution, while the other device keeps available address unchangeable. According to the embodiment of the technical scheme in the invention, only one of the device is performed with address redistribution in the two devices with device address conflict, while the other device keeps the address unchangable, thereby reducing probability of the conflict device to select the same address to conflict; meanwhile, energy cost is saved since the other device has no address redistribution.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Topology control method of underwater wireless sensor network based on non-cooperative game
ActiveCN103987102ALower energy billsUniform energyPower managementEnergy efficient ICTTopology controlEnergy cost
The invention provides a topology control method of an underwater wireless sensor network based on a non-cooperative game. The method comprises the steps that based on a cooperative evolutionary theory, three behavior characteristics of nodes are analyzed first, after the behavior characteristics of the nodes are formulized, the forwarding strategy of the nodes is made combining with the energy information of the nodes, and the node with the high forwarding probability is chosen to conduct data forwarding. The topology method of the underwater wireless sensor network based on the non-cooperative game can reduce the energy cost of the nodes, balance the energy of the network nodes, prolong the life cycle of the entire network, and be suitable for the underwater wireless sensor network with limited node energy.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com