Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
31results about How to "Improve MTF" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
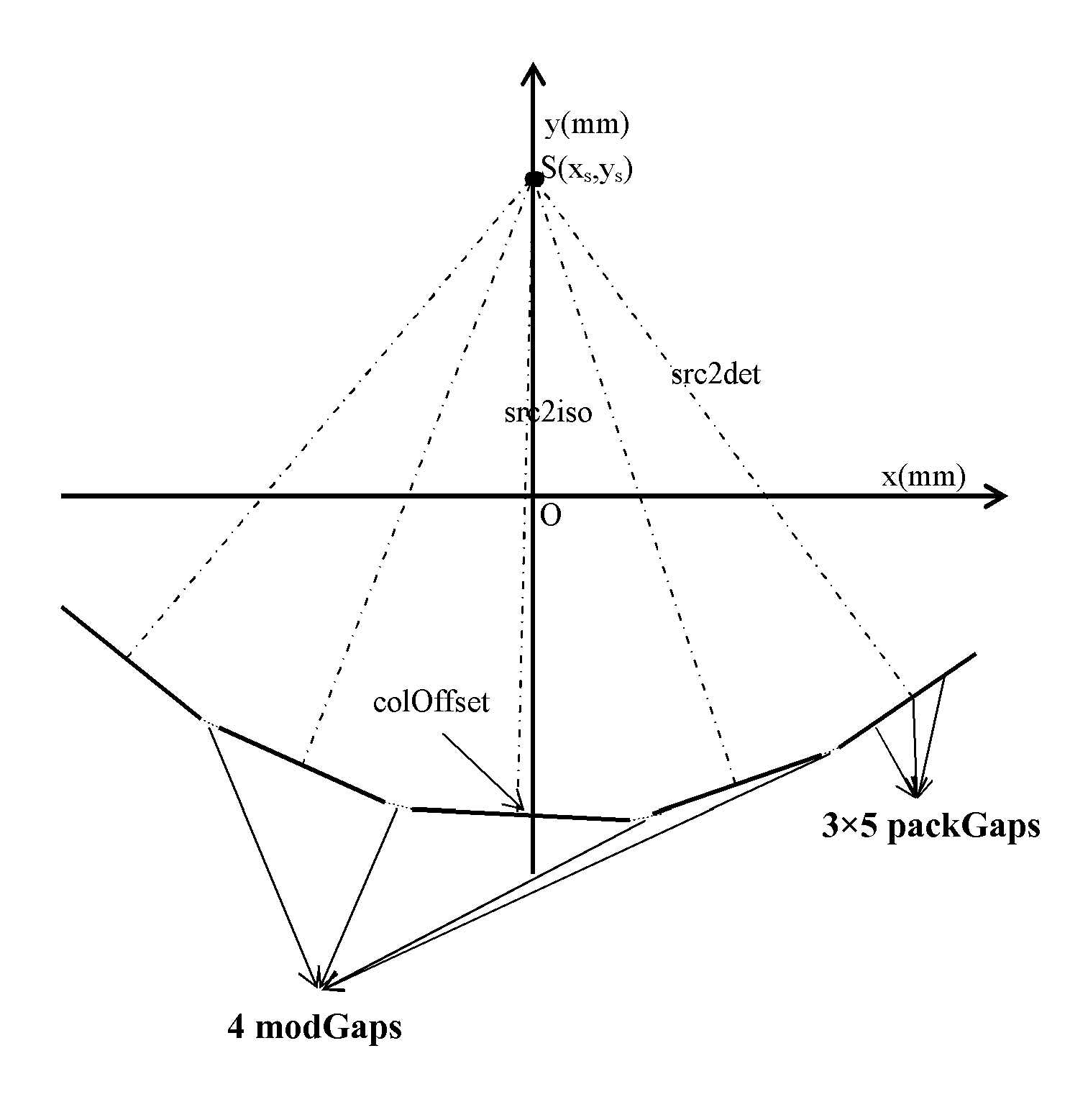
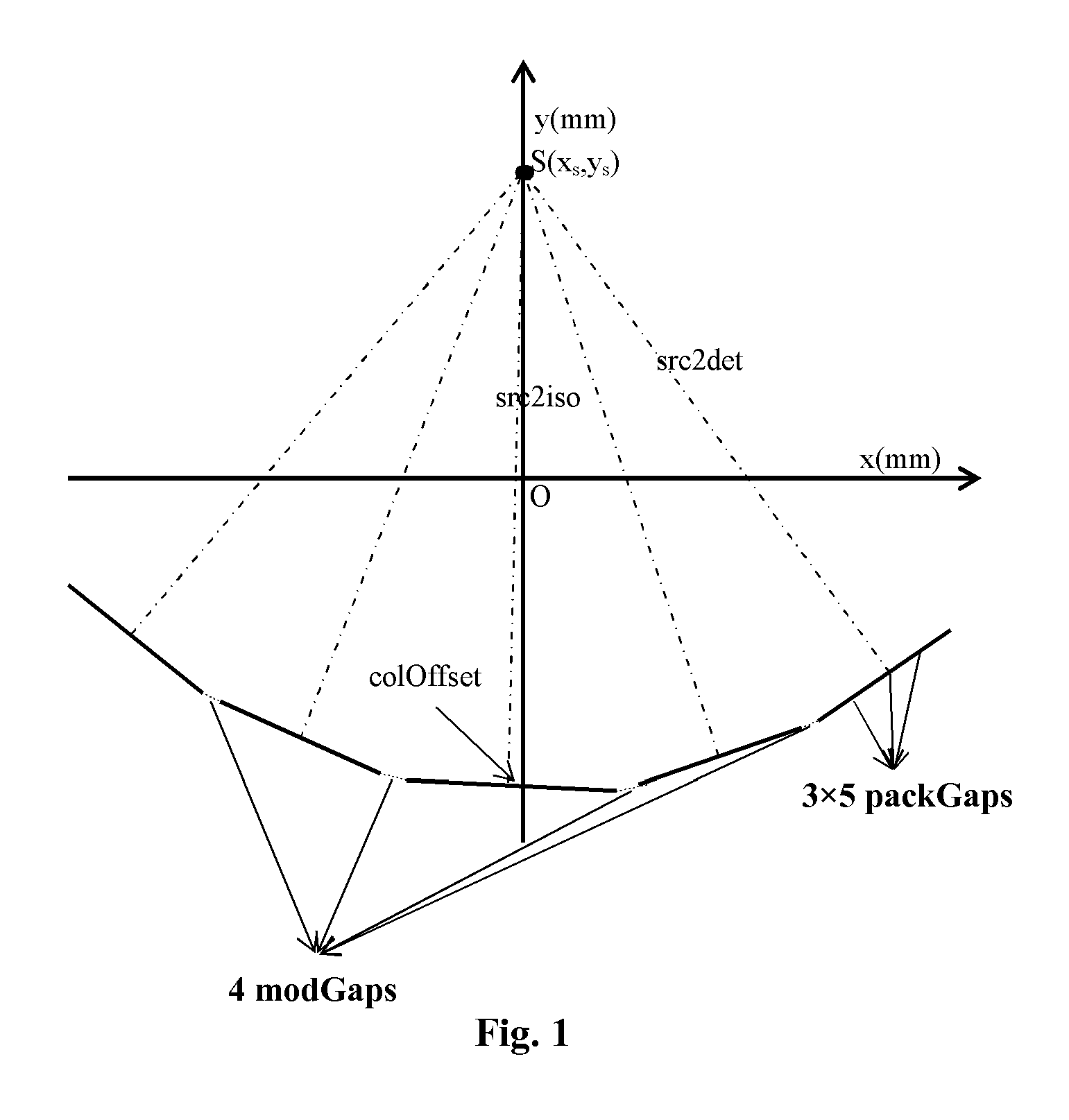
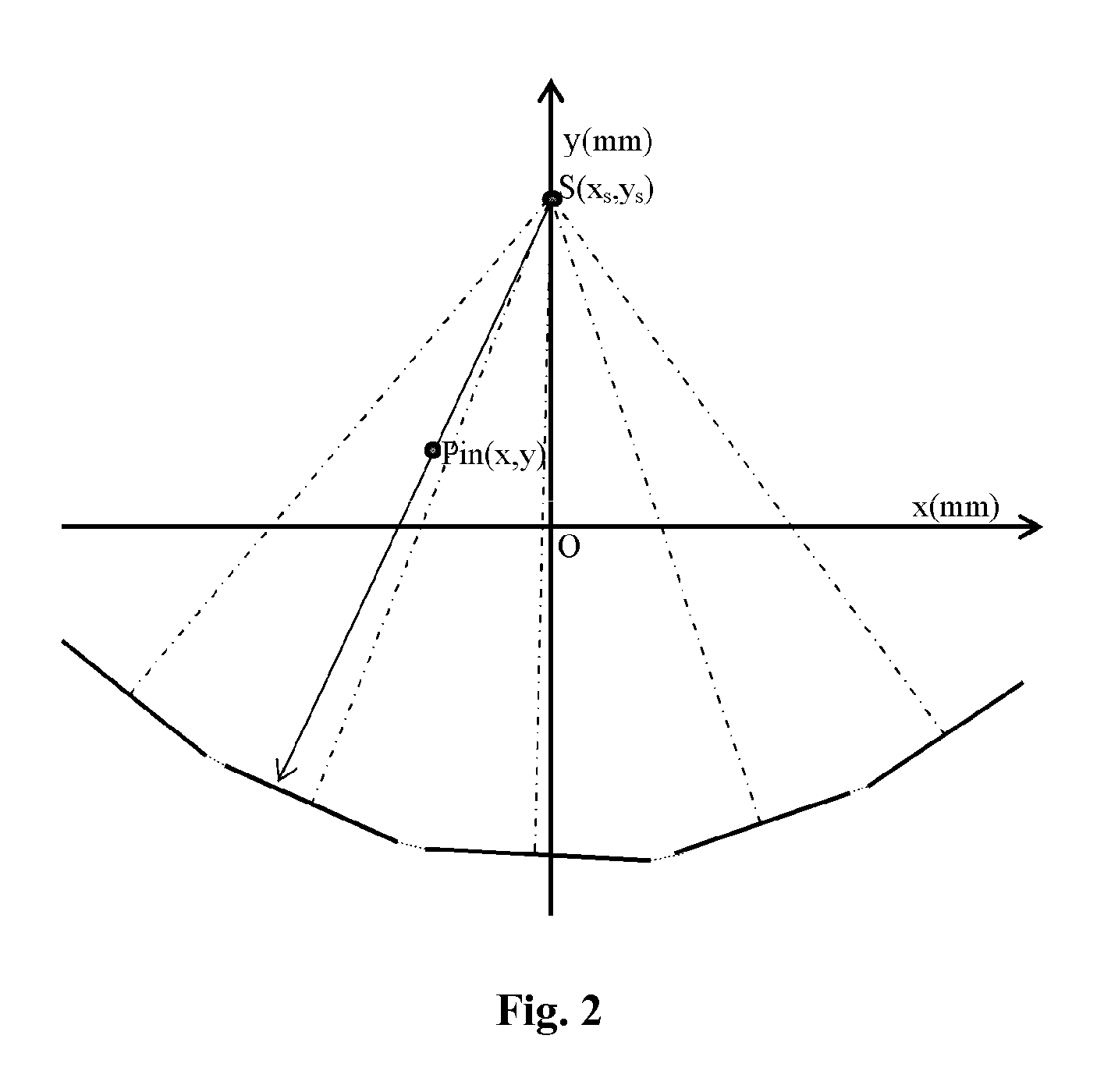
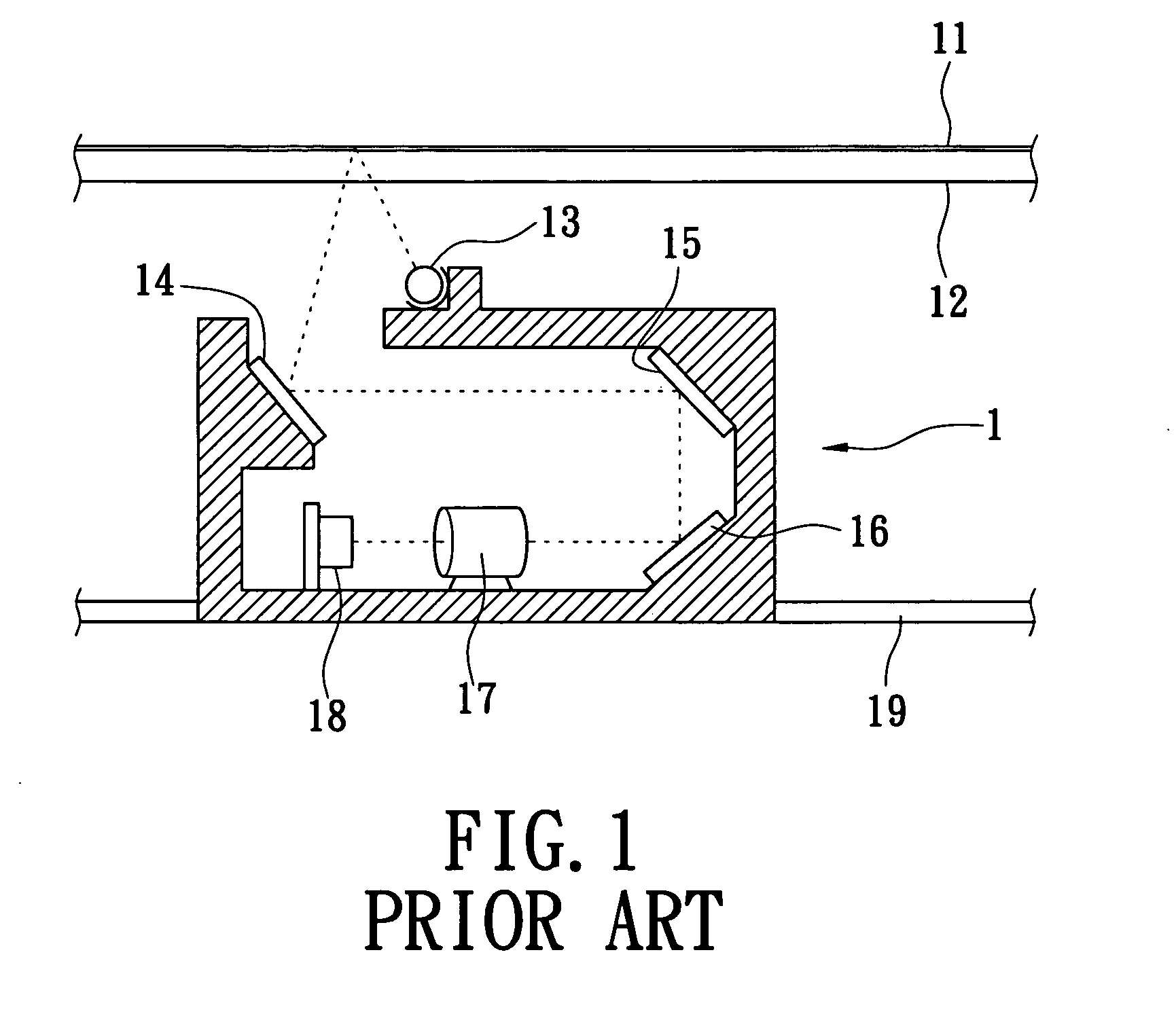
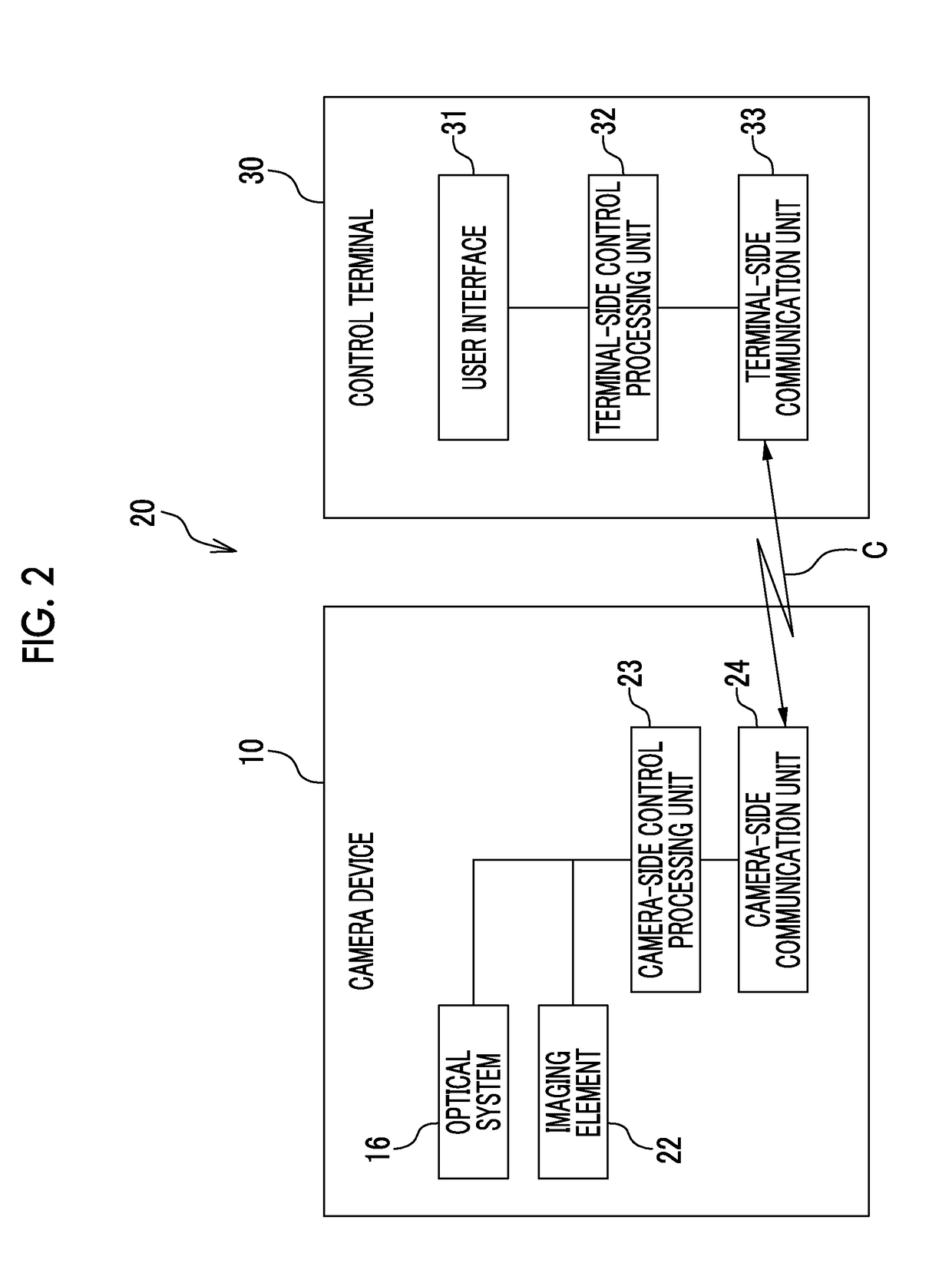
Geometry calibration algorithm for large flat module detector CT scanner
ActiveUS9398890B2The process is simple and effectiveSmall sizeComputerised tomographsTomographyCt scannersComputer science
A method for geometric calibration of a CT scanner, including, for each row of at least one row of detector cells, establishing a complete geometric description of the CT scanner, including at least one unknown geometric parameter, establishing a description of a forward projection function using the complete geometric description, acquiring actual projection coordinates of a calibration phantom placed in a scanning field of view (SFOV) on a current row of detector cells and corresponding to a plurality of angles, acquiring calculated projection coordinates of the calibration phantom on the current row of detector cells and corresponding to the plurality of angles using the description of the forward projection function, and acquiring a calibrated value for the at least one unknown geometric parameter by evaluating the at least one unknown geometric parameter based on the acquired actual projection coordinates and calculated projection coordinates via a nonlinear least square fitting algorithm.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
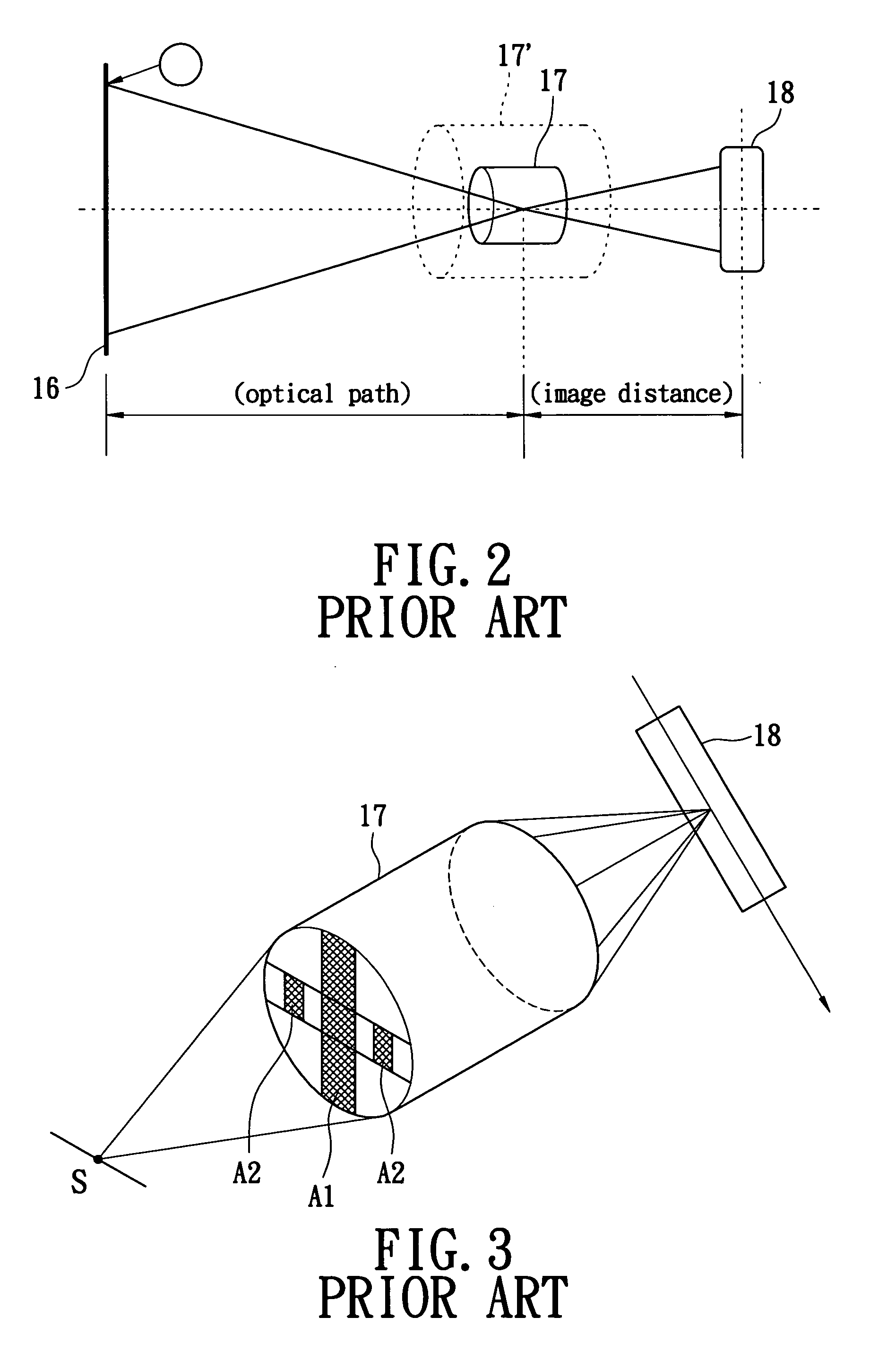
Large-visual-field off-axis reflection zooming optical system
InactiveCN104977705AAchieve clear imagingMiniaturizationOptical elementsVisual field lossImaging quality
The invention belongs to the technical field of aerospace detection and identification imaging optics, and provides a large-visual-field off-axis reflection zooming optical system. The optical system adopts a coaxial off-aperture and off-visual-field off-axis structure mode and is composed of a first negative reflecting mirror, a second positive reflecting mirror, a third positive reflecting mirror, a detector and a diaphragm. The diaphragm is arranged on the first negative reflecting mirror. The first main reflecting mirror 1 adopts a quadric surface with negative focal power to act as a front fixing group; the second positive quadric surface reflecting mirror acts as a zooming group to realize an objective of zooming; and the third reflecting mirror acts as a compensation group so that the large-visual-field zooming optical system with stable image surface can be obtained. According to the optical system with the structural type, three times of zooming of focal length of 25mm-75mm can be realized, the visual field can be 6.7-19 degrees, and the modulation transfer function (MTF) of each zooming position is greater than 0.3@50lp / mm so that imaging quality is quite high.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
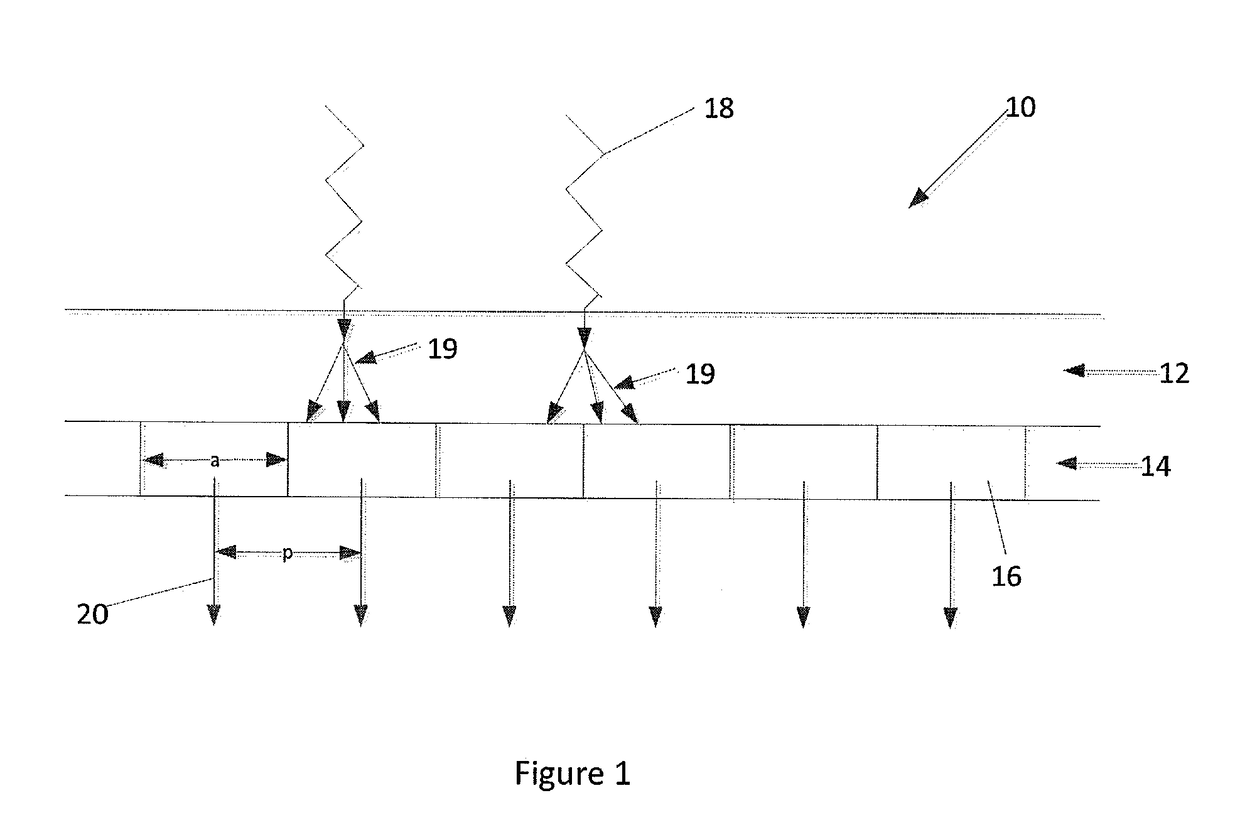
Method and apparatus for improved detective quantum efficiency in an X-ray detector
ActiveUS10182194B2Improve efficiencyFunction increaseTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDetective quantum efficiencyX-ray
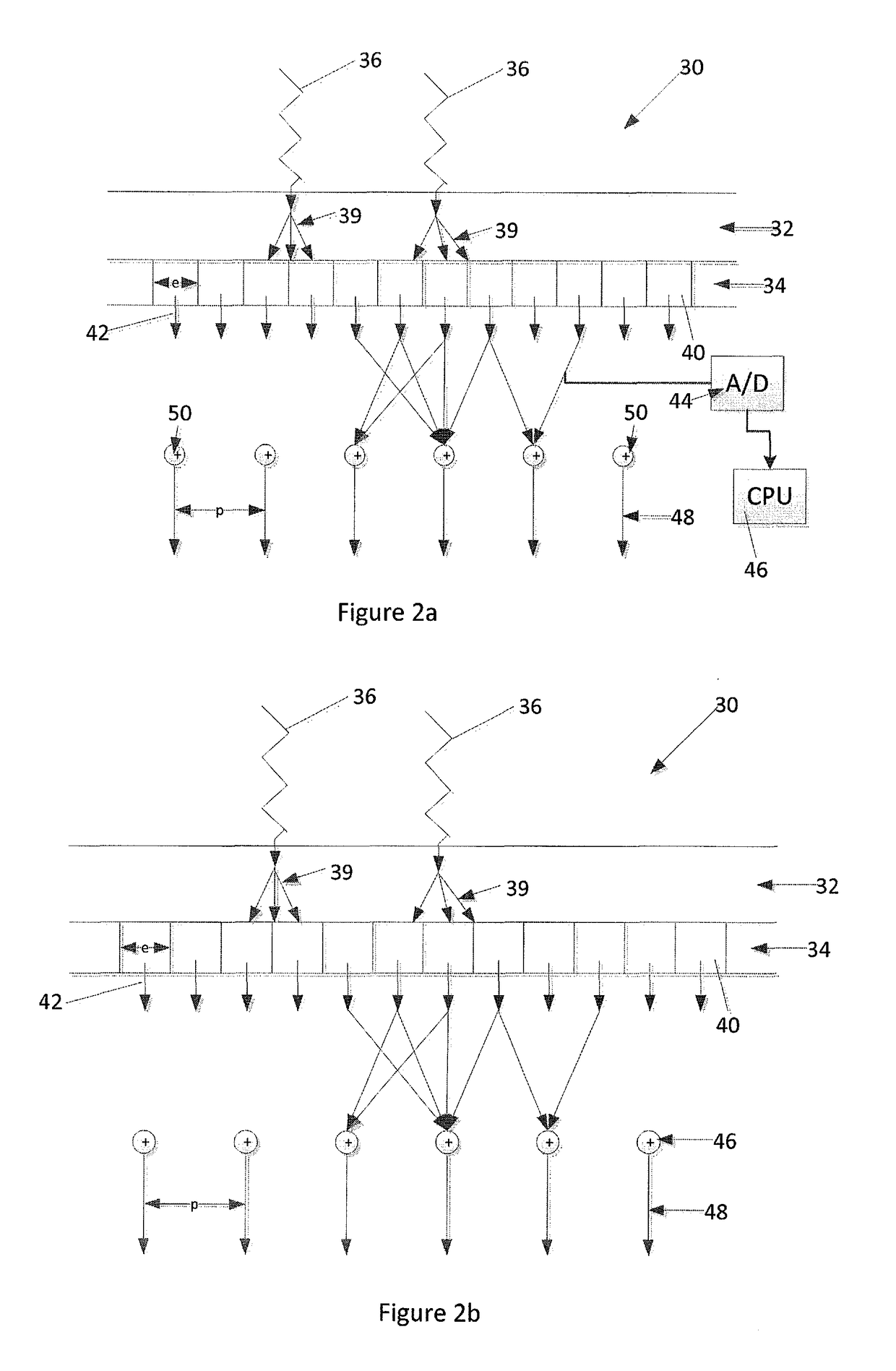
The disclosure is directed at a method and apparatus for improving method and apparatus for improved modulation transfer function and detective quantum efficiency of X-ray detectors. The method and apparatus include digitizing microelement outputs obtained by micro sensor elements and the generating pixel outputs from these digitized microelement outputs. Each pixel output is the sum of a plurality of weighting factored microelement outputs.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO
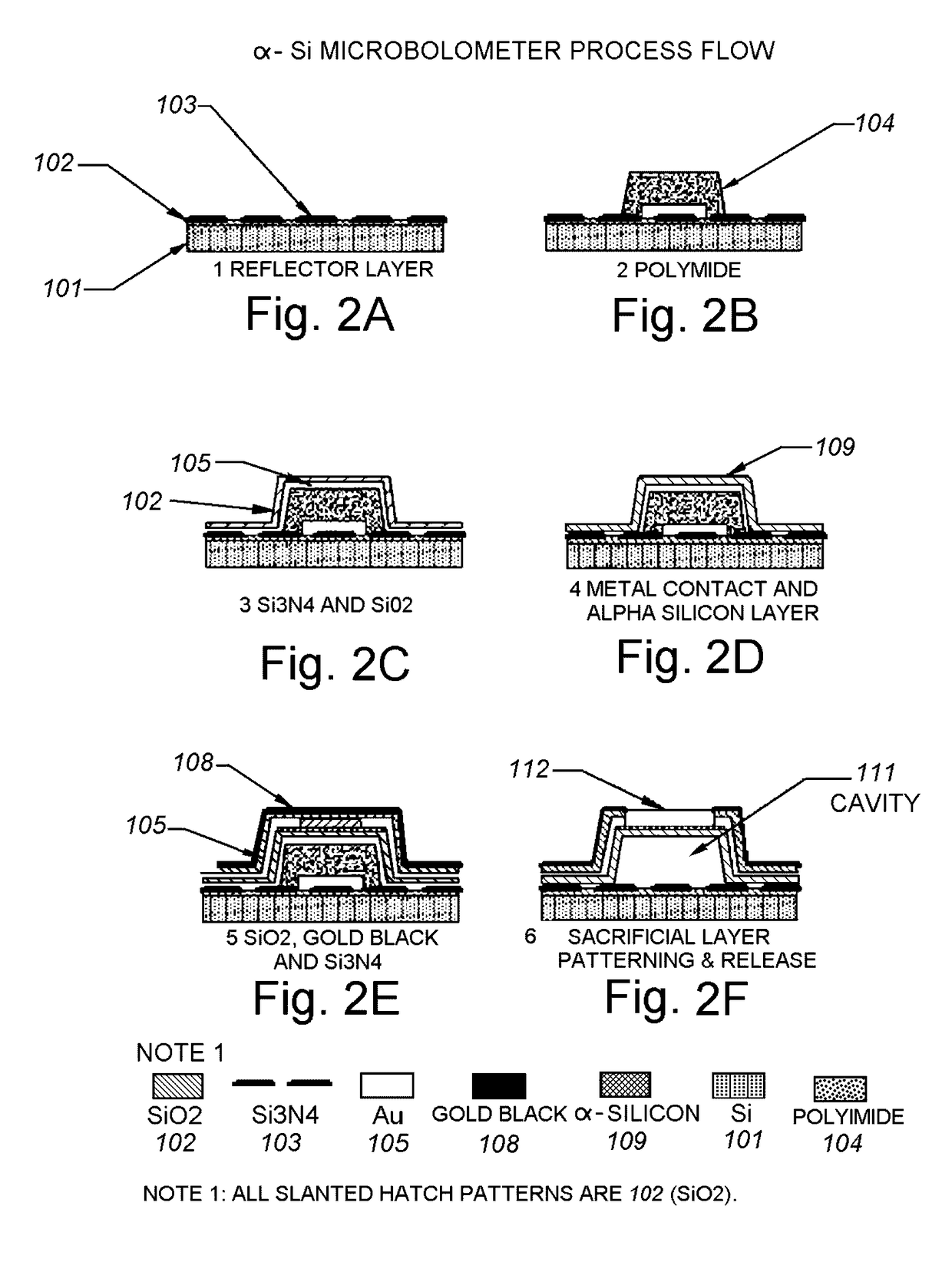
Infrared radiation detectors using carbon nanotubes-silicon vanadium oxide and or amorphous silicon nanoparticles-CNT nanocomposites and methods of constructing the same
ActiveUS9677946B1High sensitivityIncrease transferPyrometry using electric radation detectorsSemiconductor devicesNanometreCarbon nanotube
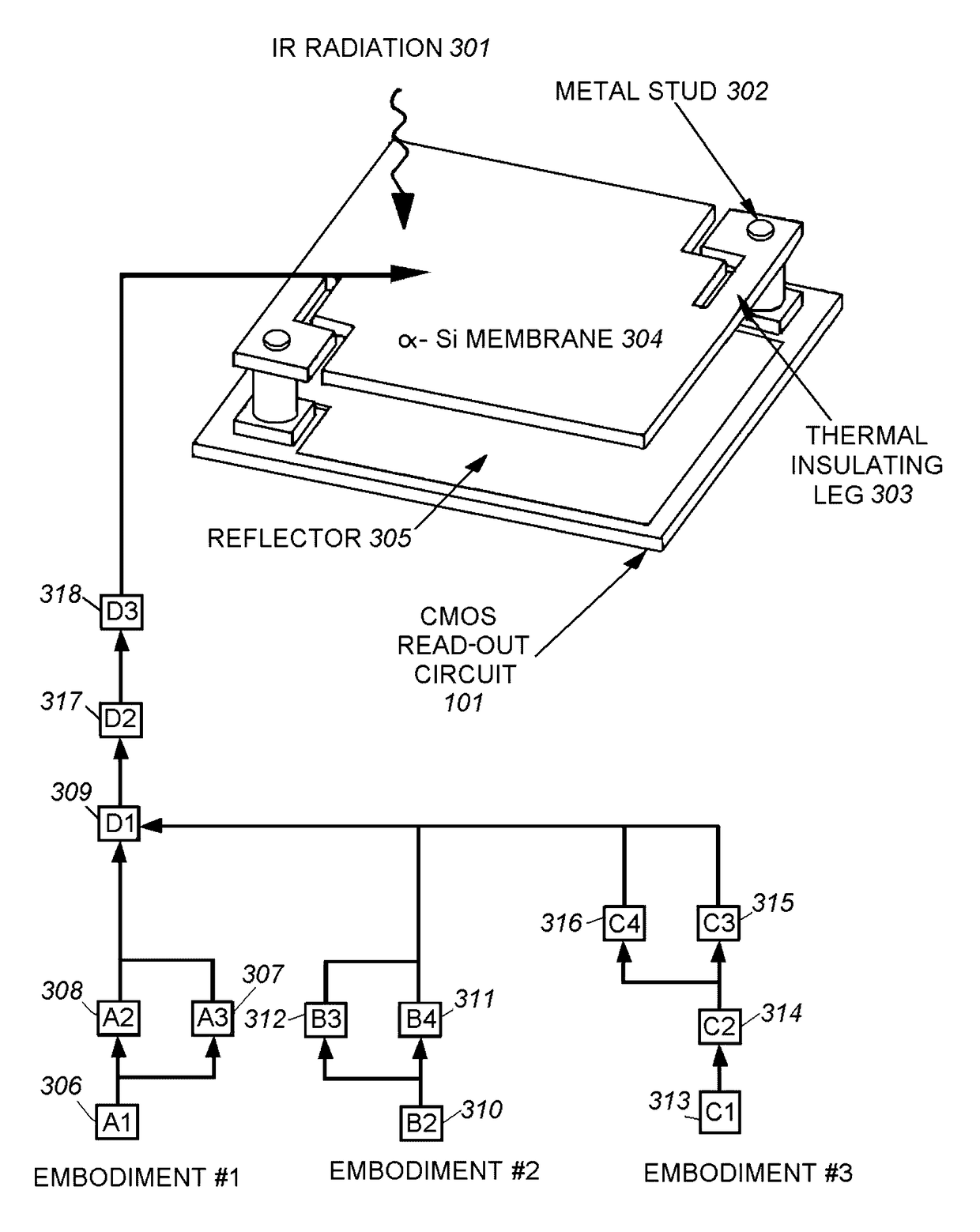
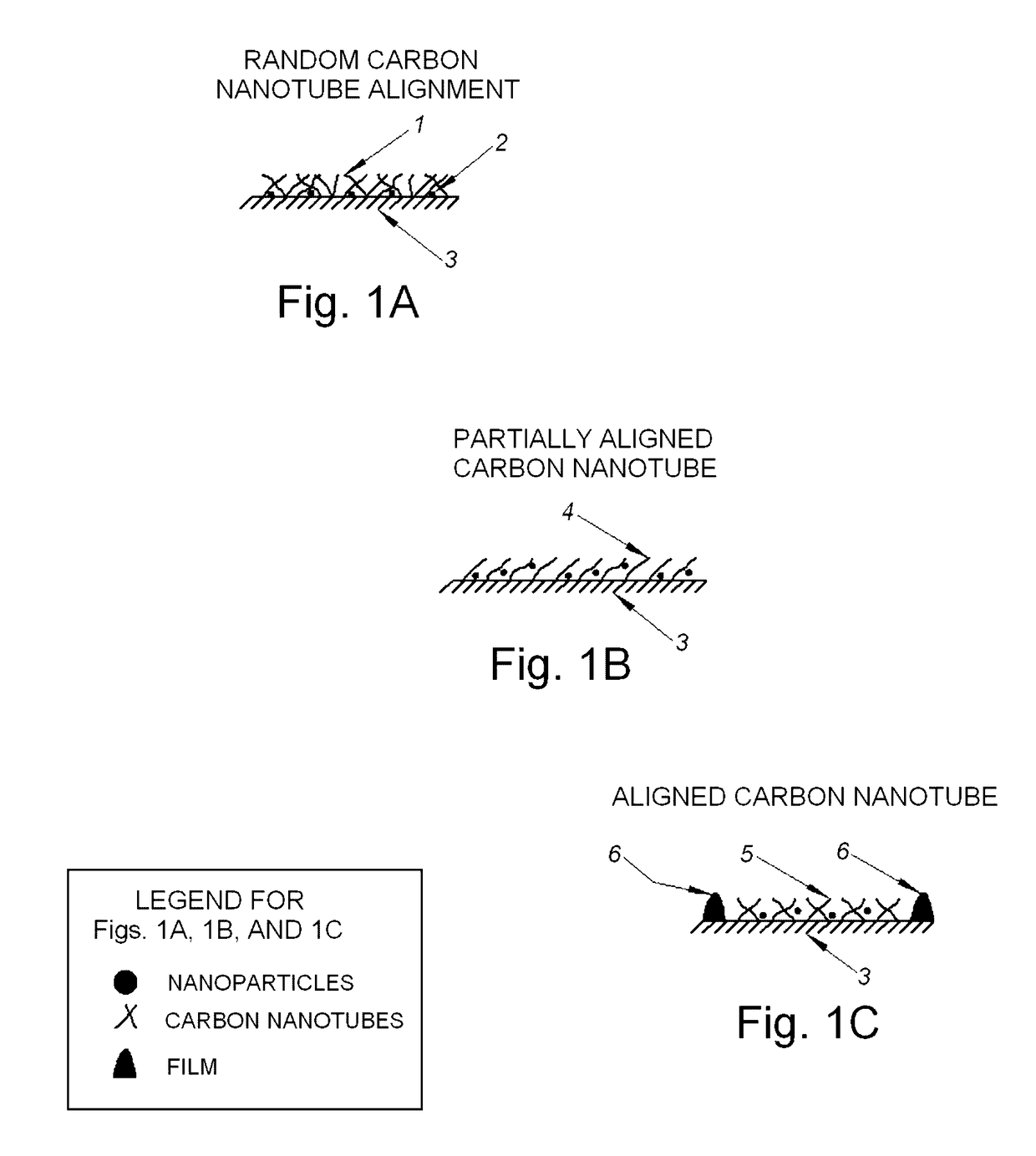
The present disclosure relates to microbolometer structures having top layers of amorphous silicon or vanadium oxide. In some examples, combinations of carbon nanotubes, nanoparticles, and / or thin films can be deposited atop the existing top layer of amorphous silicon or top layer of vanadium oxide of a microbolometer structure. Such configurations can increase the sensitivity of the microbolometers to less than 4 mK, less than 2 mK, and in some examples less than 1 mK.
Owner:MAGNOLIA OPTICAL TECH
Radiological image detection apparatus and method of manufacturing the same
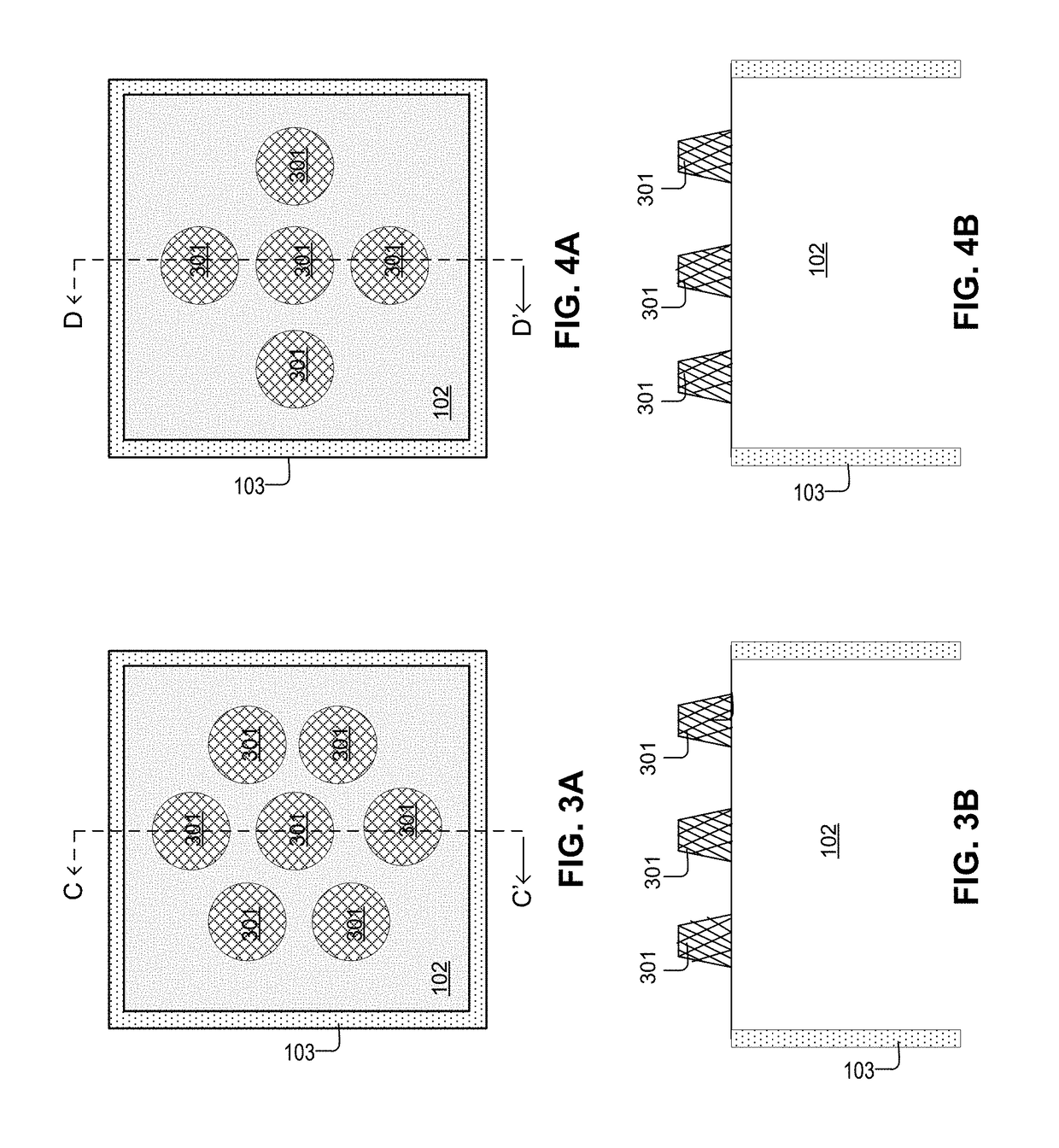
InactiveUS20120205543A1Increase volumeImprove MTFSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A radiological image detection apparatus includes: a first scintillator and a second scintillator that emit fluorescent lights in response to irradiation of radiation; and a first photodetector and a second photodetector that detect the fluorescent lights; in which the first photodetector, the first scintillator, the second photodetector, and the second scintillator are arranged in order from a radiation incident side, and a high activator density region in which an activator density is relatively higher than an average activator density in a concerned scintillator is provided to at least one of the first scintillator located in vicinity of the first photodetector and the second scintillator located in vicinity of the second photodetector.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Radiological image detection apparatus and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS8525121B2Increase volumeImprove MTFSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A radiological image detection apparatus, includes: two scintillators that convert irradiated radiation into lights; and a photodetector arranged between two scintillators, that detects the lights converted by two scintillators as an electric signal; in which: an activator density in the scintillator arranged at least on a radiation incident side out of two scintillators in vicinity of the photodetector is relatively higher than an activator density in the scintillator on an opposite side to a photodetector side.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
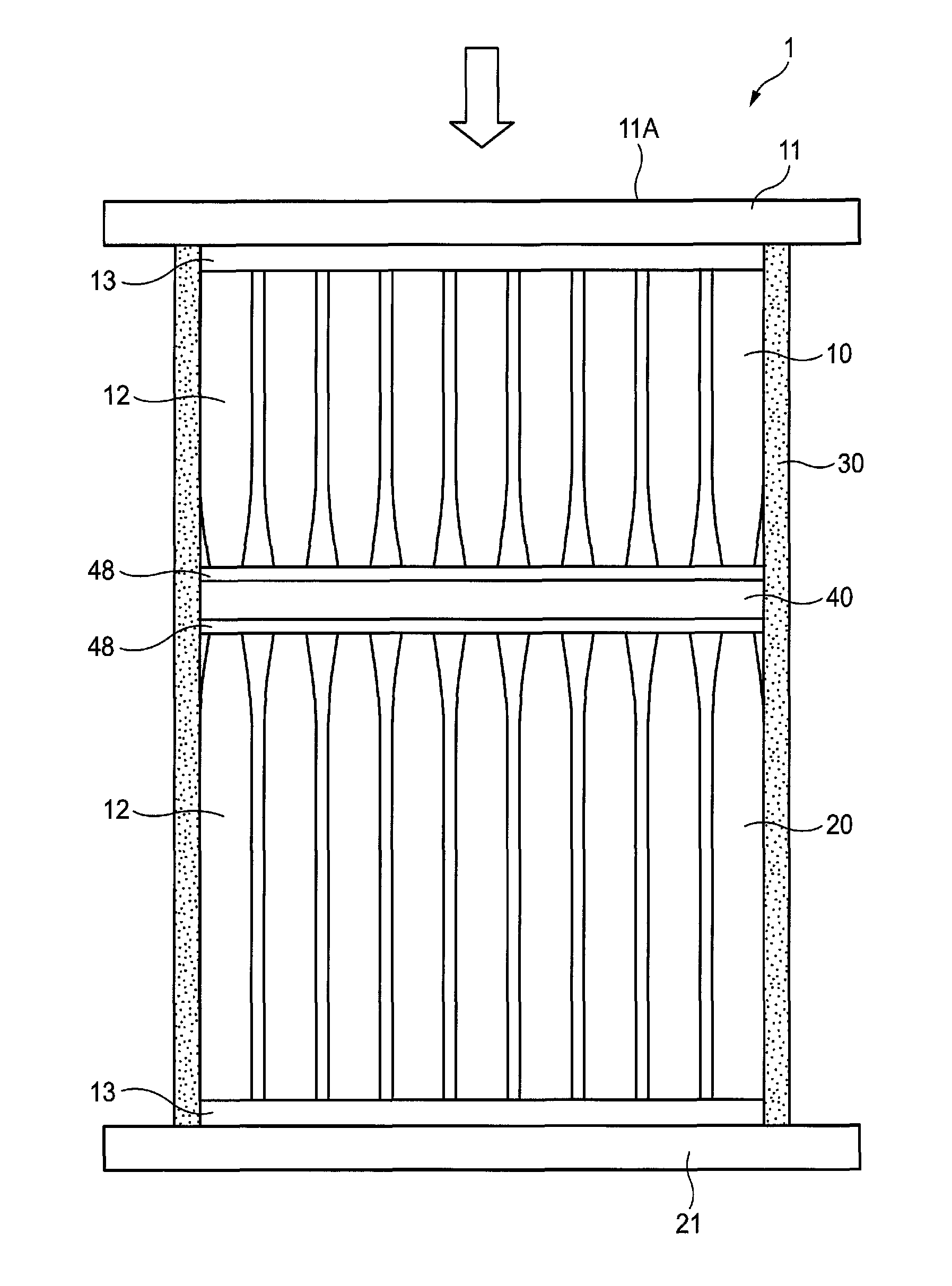
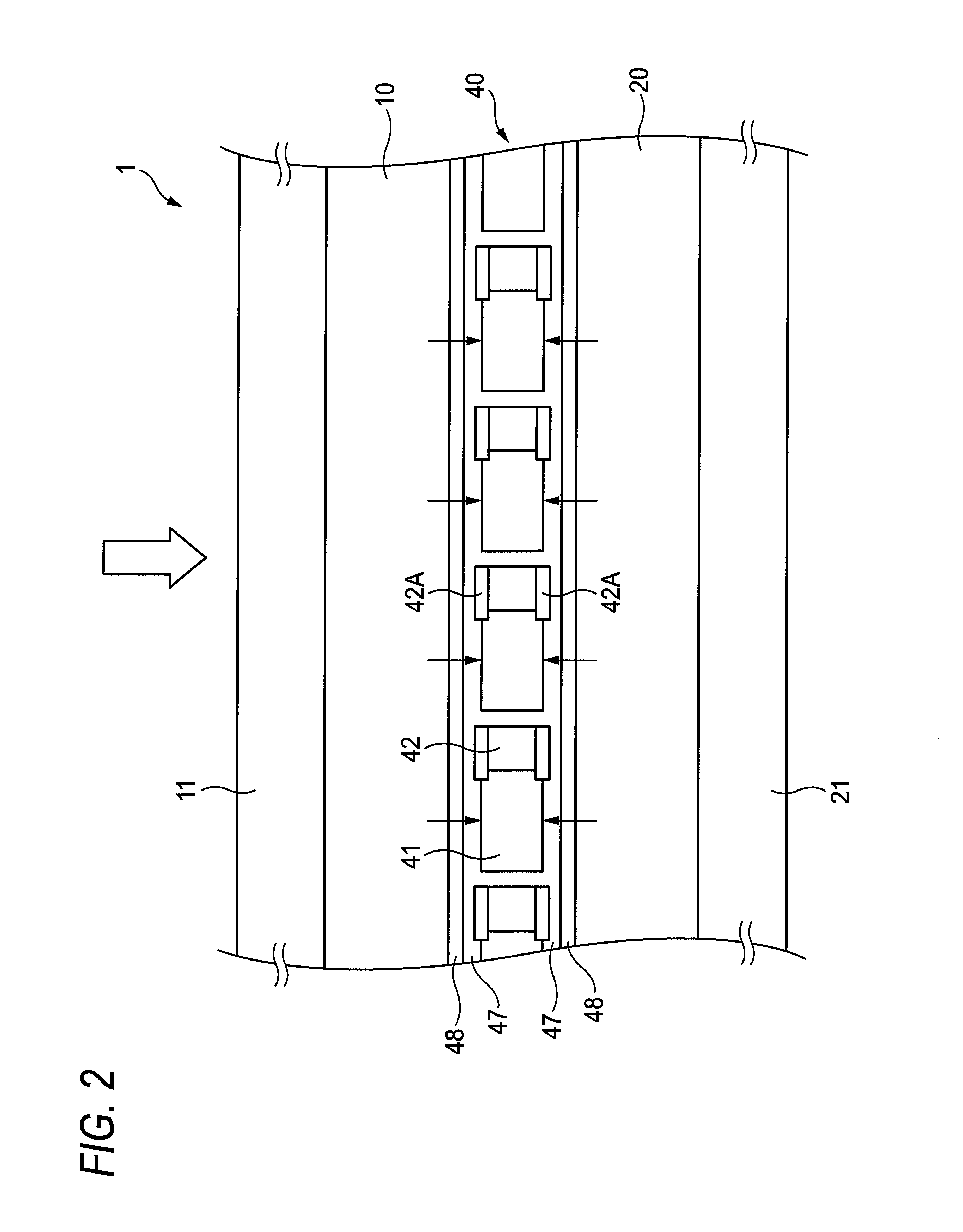
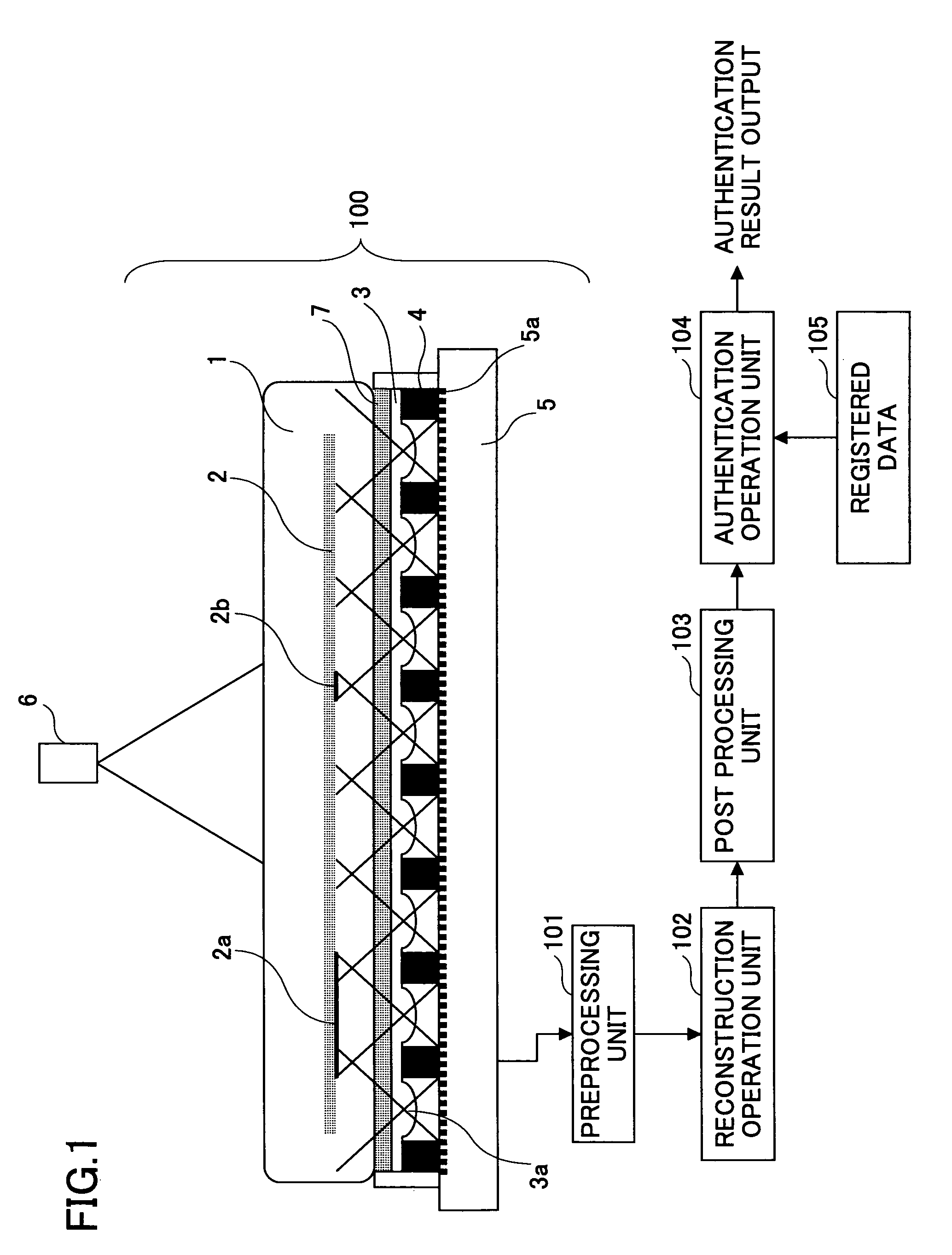
Image input apparatus, image input method, personal authentication apparatus, and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS8085312B2Lower Level RequirementsReduce variationTelevision system detailsDiagnostics using lightElectric forcePositive power
An image input apparatus that inputs an image of an object residing within a living body is disclosed. The image input apparatus includes a light source that irradiates near infrared light on the living body, a lens array arranged at a position facing the living body and including plural lenses each having a face with zero or negative power arranged at a side facing the living body and a face with positive power arranged at a side facing an image surface, an imaging unit arranged at the image surface side of the lens array that forms a compound-eye image corresponding to a collection of ommatidium images formed by the lenses of the lens array, and a reconstruction unit that reconstructs a single image from the compound-eye image using a parallax between the ommatidium images. The reconstructed single image is input as the image of the object.
Owner:RICOH KK
Optical system of attitude sensor
ActiveCN101762871ASmall sizeUniform speckleNavigation by astronomical meansOptical elementsFlat glassFull field
The invention discloses an optical system of an attitude sensor. A diaphragm of the optical system is arranged on the first surface of the quartz window plate glass of the optical system, which is beneficial to reducing the size of the optical system and eliminating parasitic light; and the optical system can simultaneously realize large field, large aperture and achromatism by utilizing four common optical materials and effectively shorten the size of the optical system by using a plurality of osculant positive and negative lenses to correct aberration. By adopting the layout mode, the optical system has higher MTF (modulation transfer function) while ensuring relatively uniform full field defocused spots, thereby being capable of giving consideration to both the optical imaging of a star sensor and the imaging of the optical sensor with high resolution requirements.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Wavelet MTF compensation method based on optimal core shape
InactiveCN102044068AImprove on-orbit dynamic MTFInformation losslessImage enhancementSatellite remote sensingDigital image
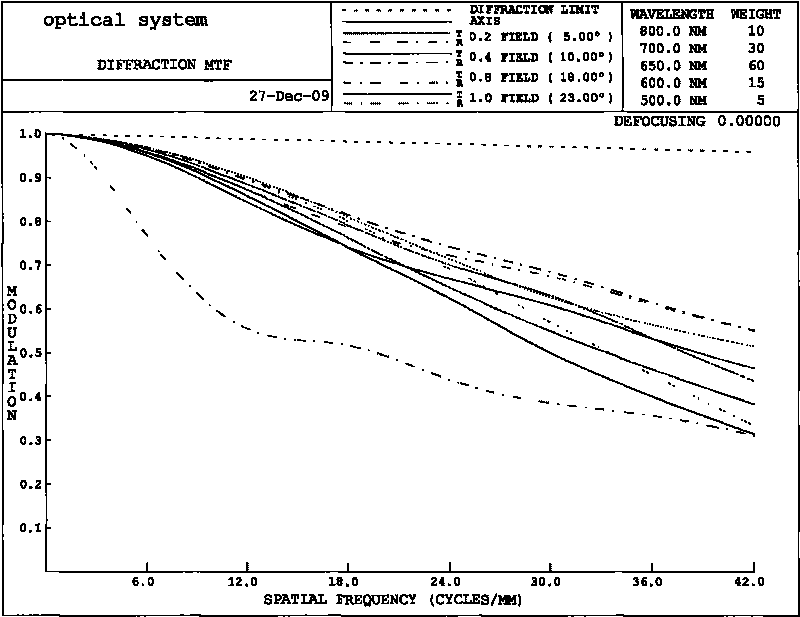
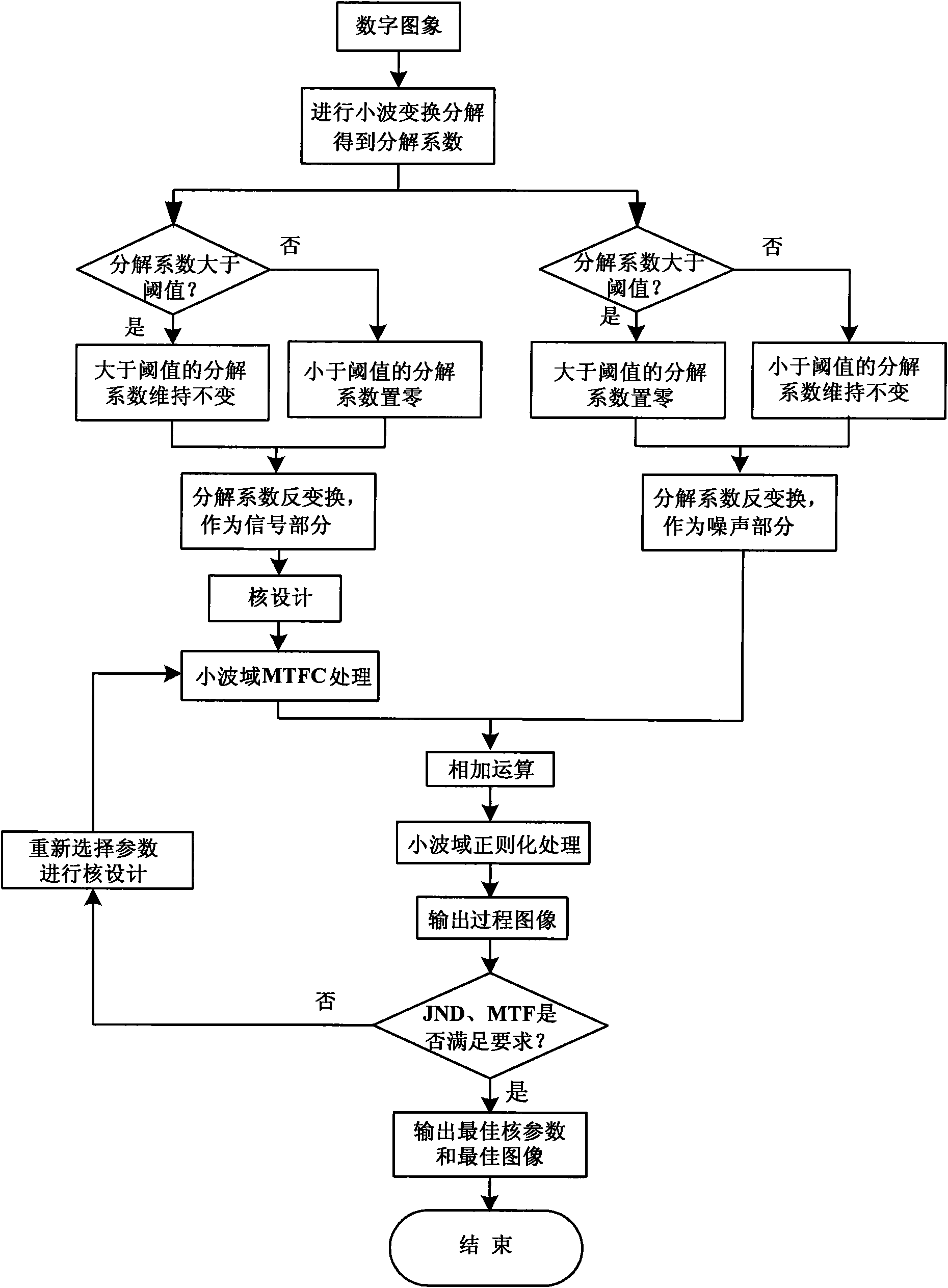
The invention discloses a wavelet modulation transfer function (MTF) compensation method based on the optimal core shape, and can be applied to a ground processing system for satellite remote sensing images. The method comprises the following steps of: according to priori knowledge of noise of an imaging system, inputting a threshold value, and partially separating input digital image signals and noise in a wavelet domain; inputting parameters a and b for initial core design, performing wavelet domain modulation transfer function compensation (MTFC) processing on the signal part, adding with the noise part, performing wavelet domain normalizatioin processing and outputting process images; continuously regulating the parameters a and b, generating different cores and corresponding different process images, and measuring corresponding just noticeable difference (JND) and MTF through the process images; and recording the parameters a and b which meet the requirement, and using the parameters a and b as the optimal core parameters of the imaging system. The invention can improve the MTF for the imaging system with low ontrack dynamic MTF, improve the quality grade of the images, and improve system performance.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
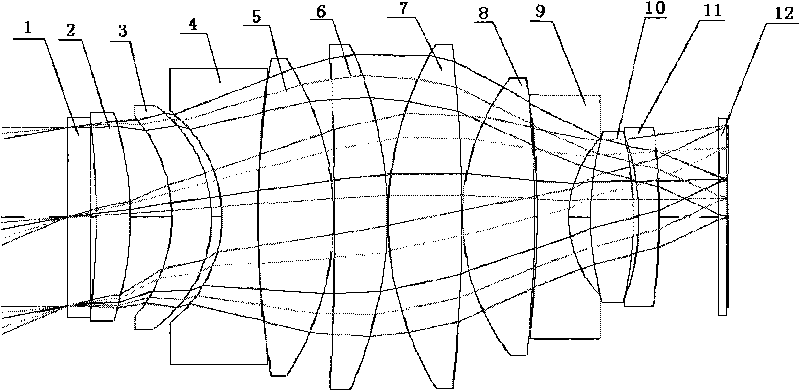
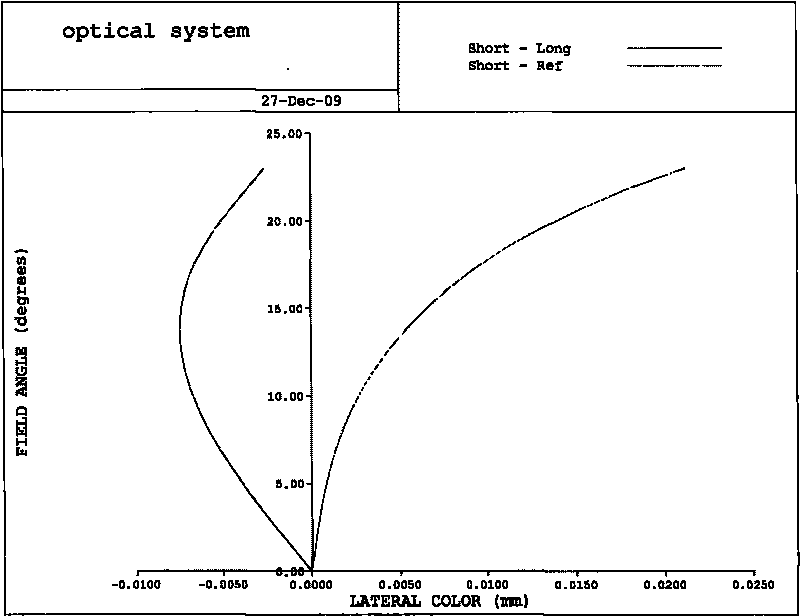
Low-distortion and large-relative-aperture wide-angle TOP optical lens, and manufacturing method thereof
PendingCN109541786ASmall optical distortionMeet the needs of low distortionOptical elementsCamera lensLow distortion
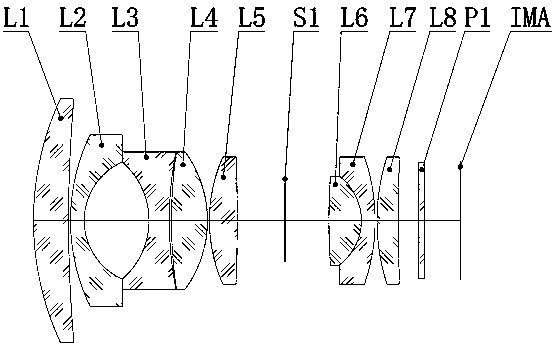
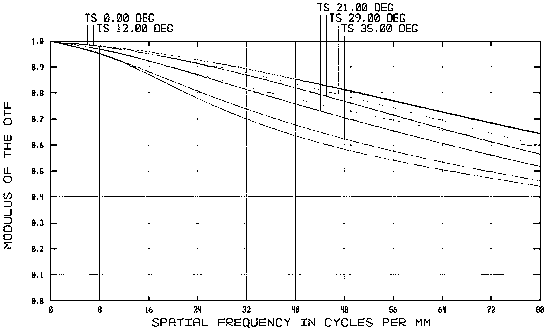
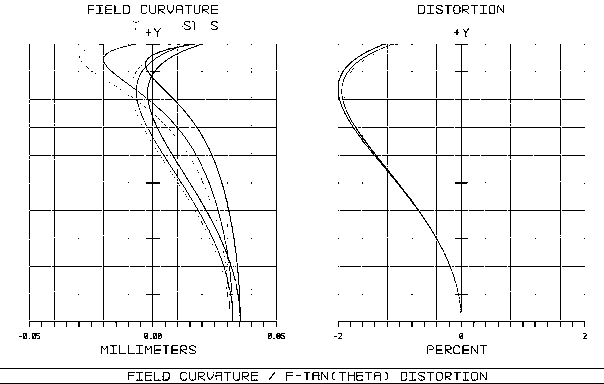
The invention relates to a low-distortion and large-relative-aperture wide-angle TOP optical lens, and a manufacturing method thereof. A TOP optical lens system comprises eight glass spherical lens, wherein a first positive-focal-power meniscus lens L1, a second negative-focal-power meniscus lens L2, a third negative-focal-power biconcave lens L3, a fourth positive-focal-power biconcave lens L4, afifth positive-focal-power biconcave lens L5, an aperture diaphragm S1, a glued lens formed by a sixth positive-focal-power biconcave lens L6 and a seventh negative-focal-power meniscus lens L7, andan eighth positive-focal-power meniscus lens L8 are sequentially arranged from an object plane to an image plane; and a parallel glass plate P1 is located in front of the image plane IMA. The TOP optical lens system has the advantages of larger field angle, extremely low optical distortion and large relative aperture, and light source power requirements can be reduced; and the lens can be used with a 1-megapixel TOF chip.
Owner:FUJIAN FORECAM OPTICS CO LTD
CMOS image sensor having enhanced near infrared quantum efficiency and modulation transfer function
ActiveUS20190019832A1High sensitivityAvoid crosstalkTransistorTelevision system detailsSemiconductor materialsNir light
An image sensor comprises a semiconductor material having an illuminated surface and a non-illuminated surface; a photodiode formed in the semiconductor material extending from the illuminated surface to receive an incident light through the illuminated surface, wherein the received incident light generates charges in the photodiode; a transfer gate electrically coupled to the photodiode to transfer the generated charges from the photodiode in response to a transfer signal; a floating diffusion electrically coupled to the transfer gate to receive the transferred charges from the photodiode; and a near infrared (NIR) quantum efficiency (QE) and modulation transfer function(MTF) enhancement structure. The NIR QE and MTF enhancement structure comprises: a NIR QE enhancement sub-structure comprising at least one NIR QE enhancement elements within a photosensitive region of the photodiode, wherein the NIR QE enhancement sub-structure is configured to modify the incident light at the illuminated surface of the semiconductor material by at least one of diffraction, deflection and reflection, to redistribute the incident light within the photodiode to improve optical sensitivity, including NIR light sensitivity, of the image sensor; and a MTF enhancement sub-structure disposed on the non-illuminated surface of the semiconductor material, facing toward the NIR QE enhancement sub-structure, wherein the MTF enhancement structure has a geometry corresponding to the NIR QE enhancement sub-structure, to ensure the incident light is still within the photodiode after redistribution.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
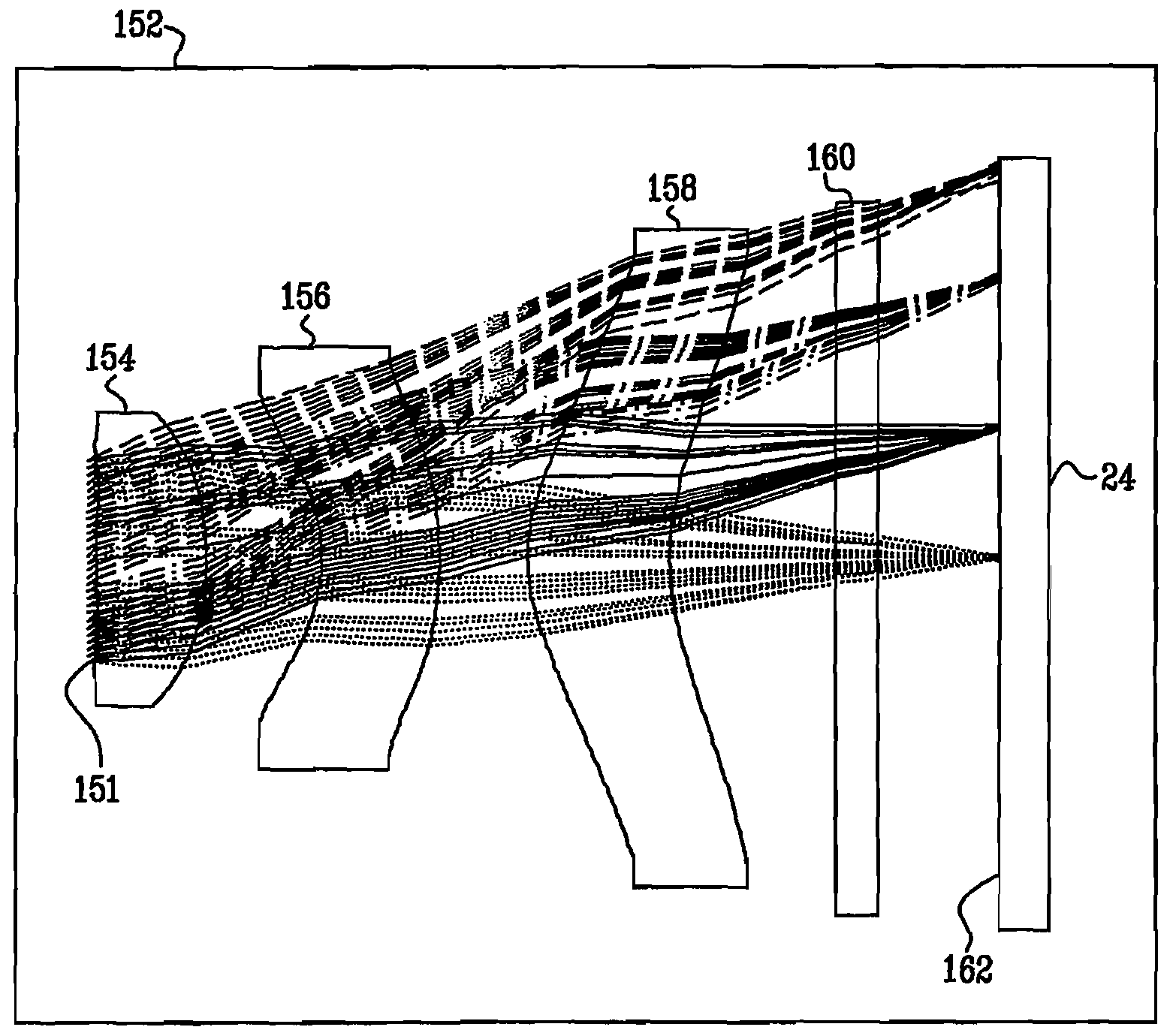
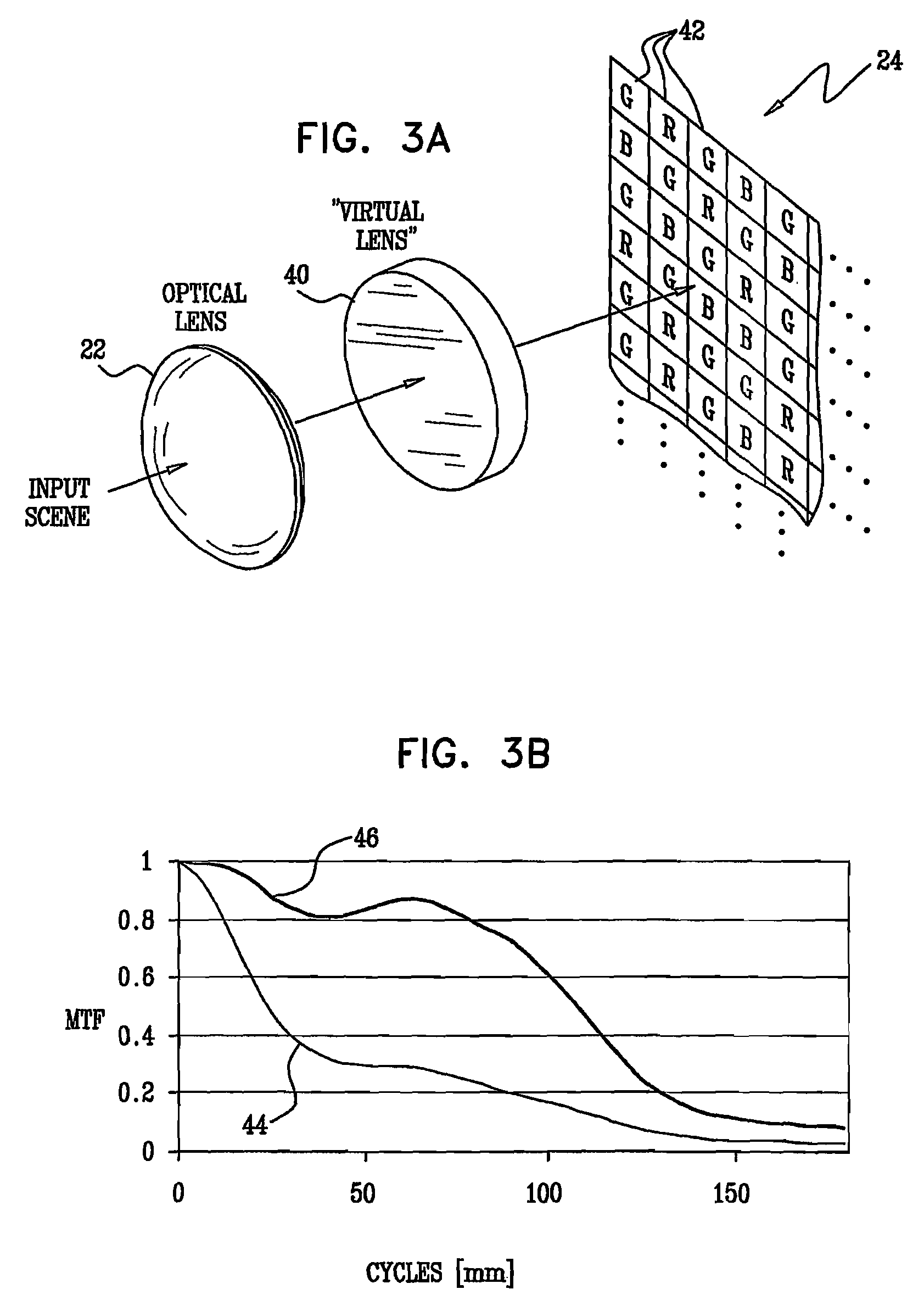
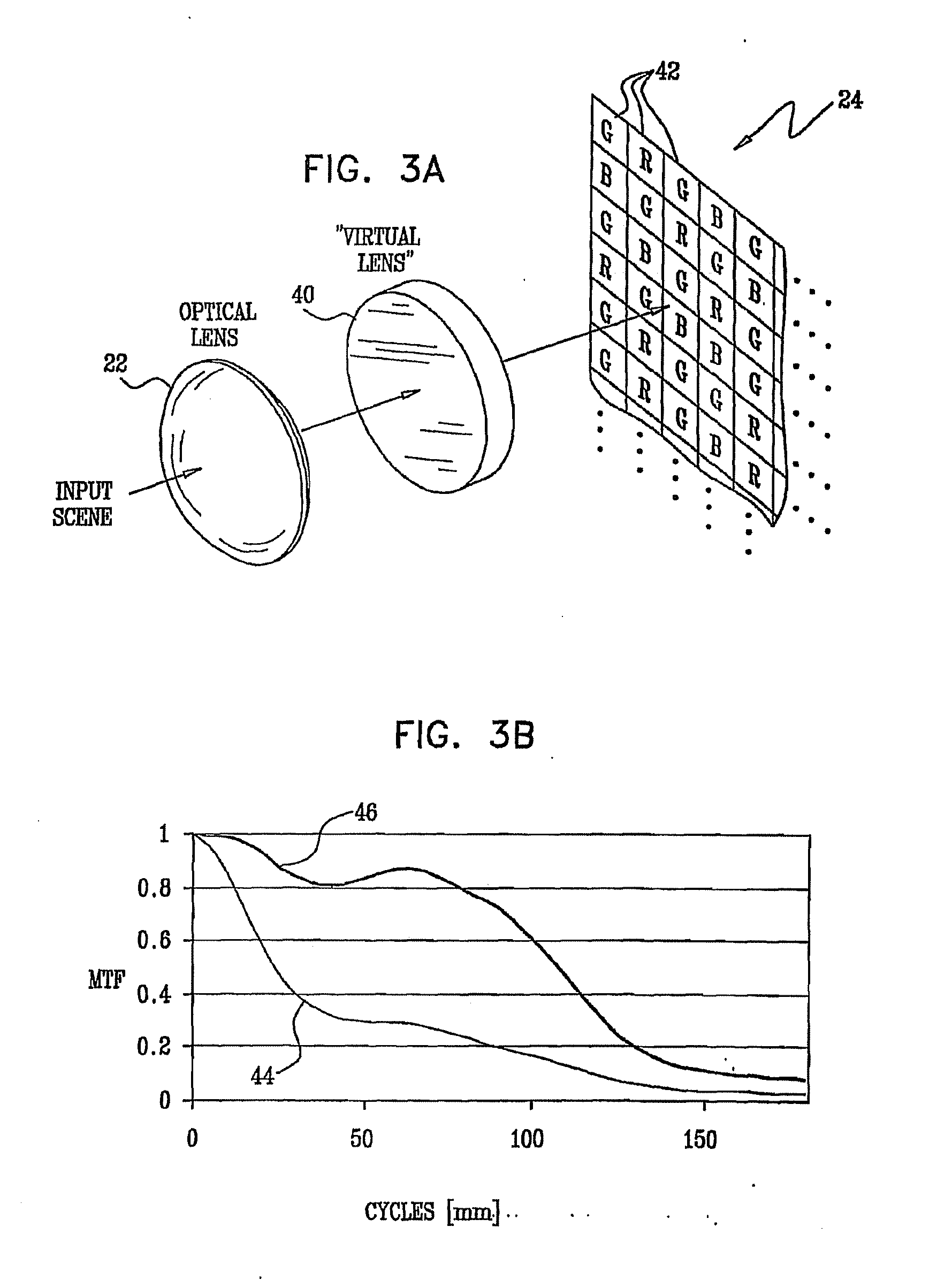
Optics for an extended depth of field
An optical imaging assembly (22) having cylindrical symmetry, comprising a plurality of lenses having surfaces with curvatures and spacings between the surfaces, such that an optical image formed by the plurality of lenses has a defocus aberration coefficient greater than 0.1 at a focal plane of the assembly.
Owner:NANCHANG O FILM OPTICAL ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Optics For An Extended Depth of Field
InactiveUS20130116981A1Improve MTFAdd depthTelevision system detailsComputer aided designDepth of fieldExtended depth of focus
An optical imaging assembly having cylindrical symmetry, comprising a plurality of lenses having surfaces with curvatures and spacings between the surfaces, such that an optical image formed by the plurality of lenses has a defocus aberration coefficient greater than 0.1 at a focal plane of the assembly.
Owner:NANCHANG O FILM OPTICAL ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
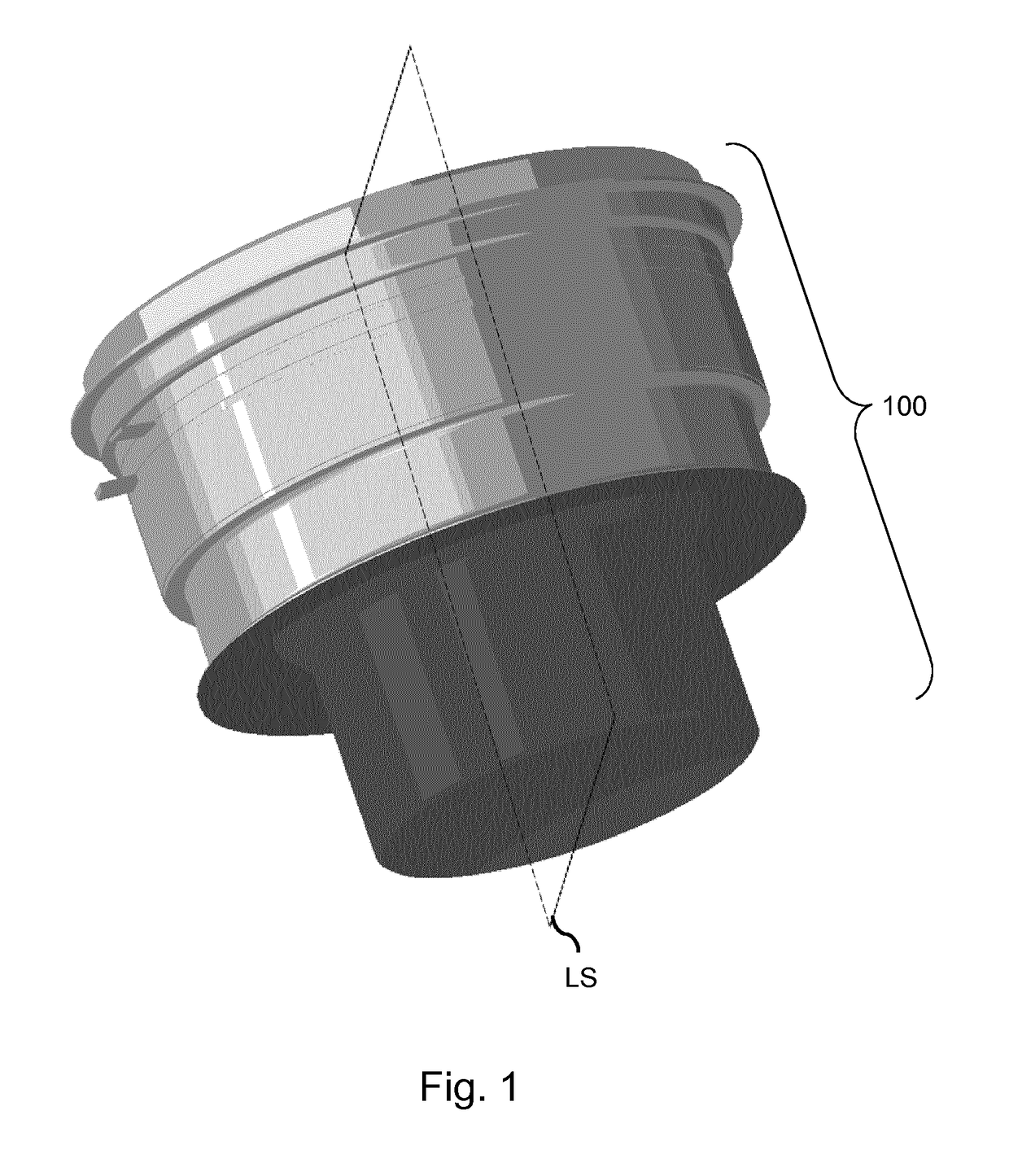
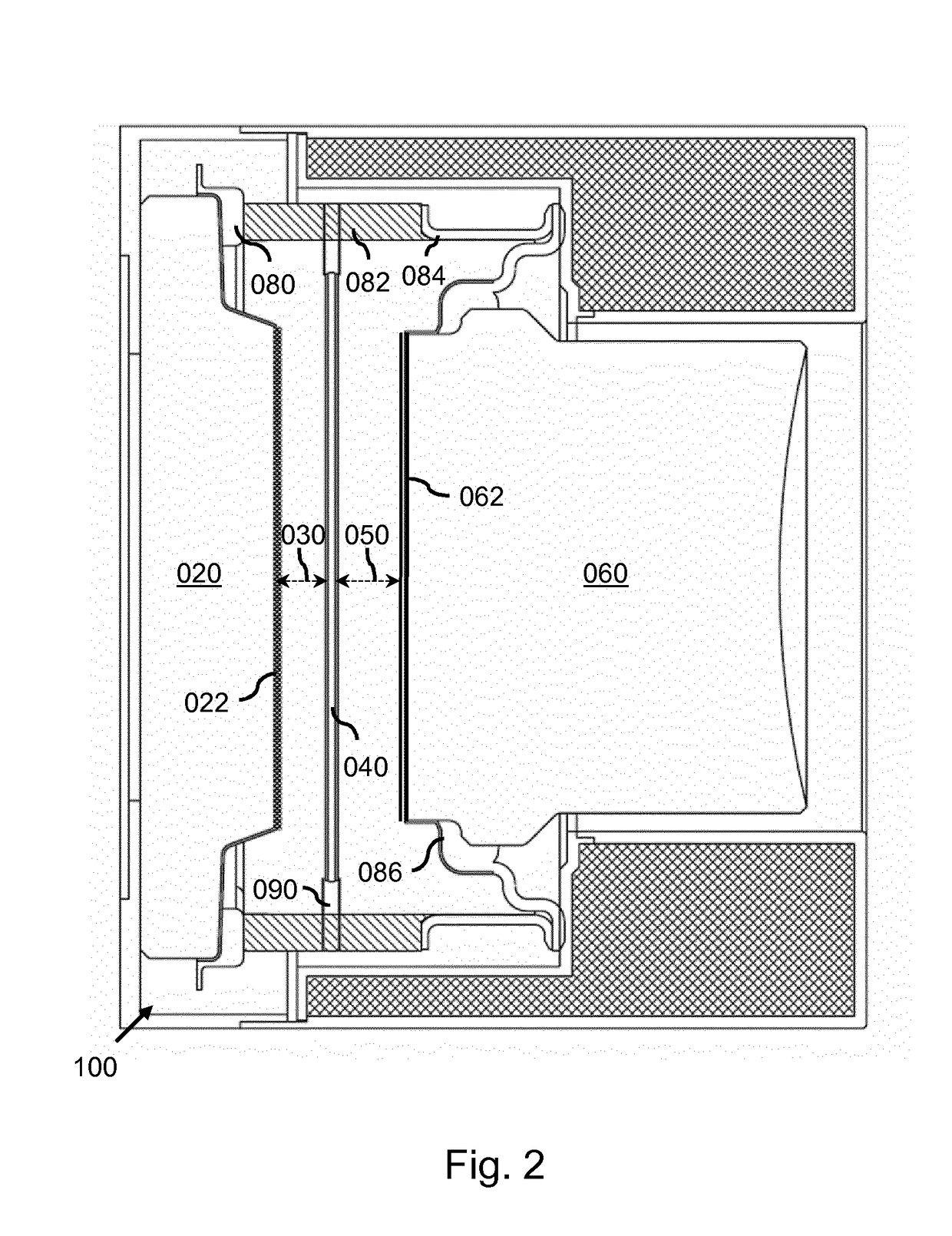
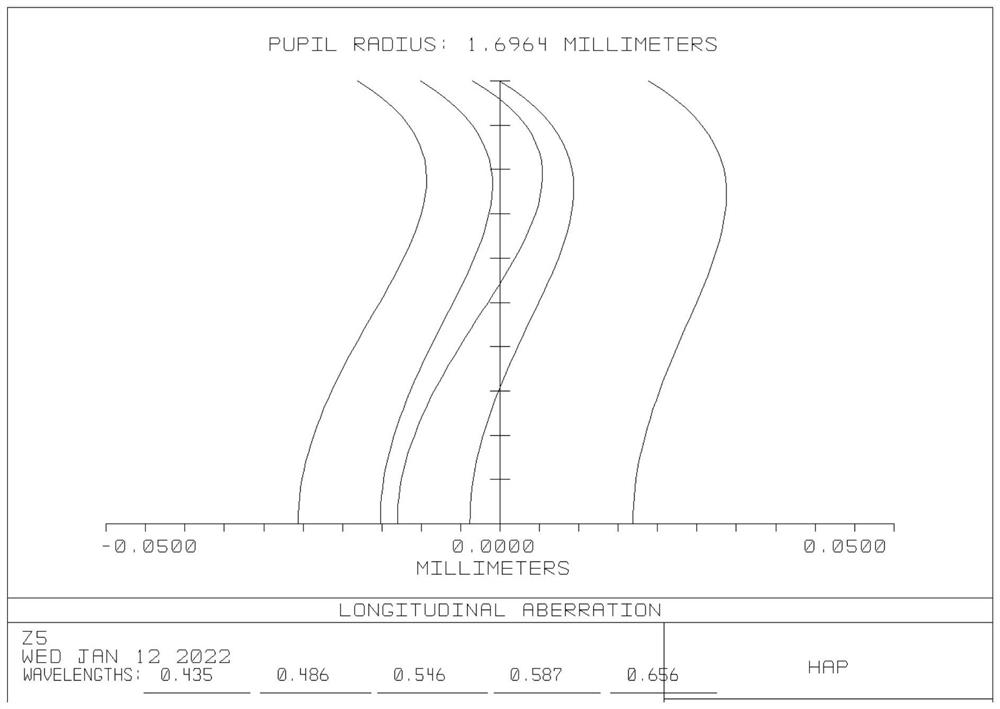
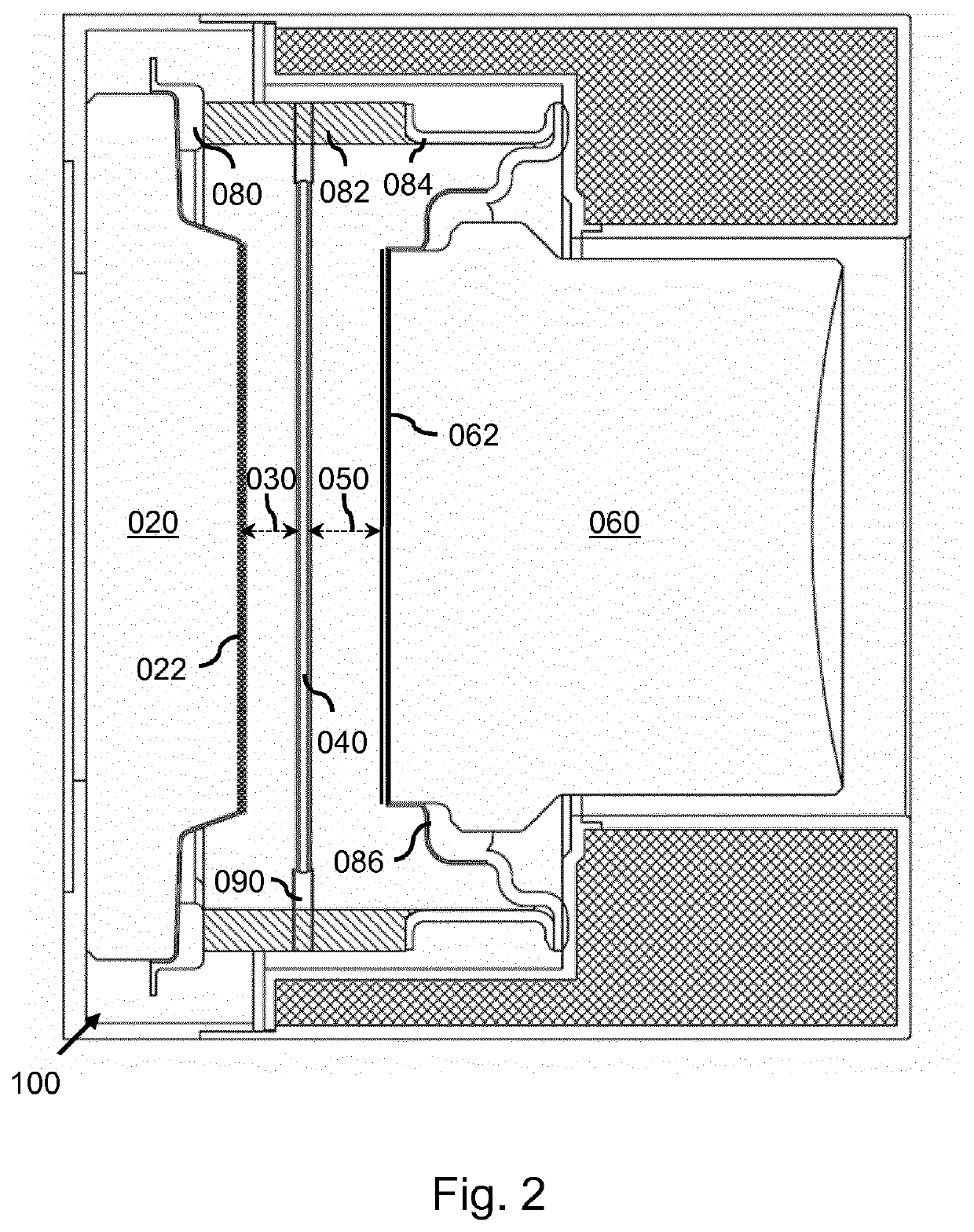
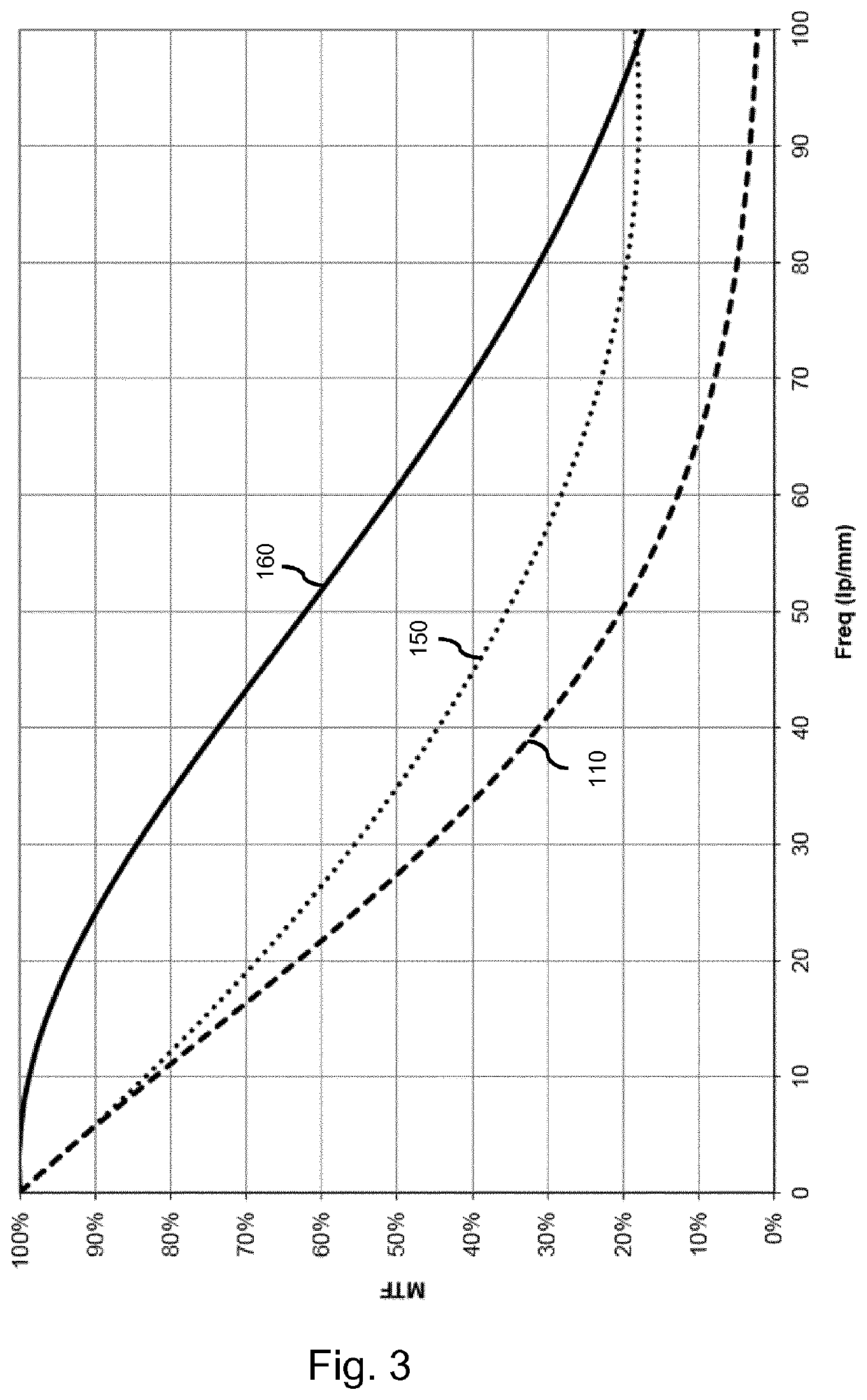
Image intensifier for night vision device
ActiveUS20190019646A1Improve image qualityReduced MTFTelescopesMutiple dynode arrangementsCharge carrierCrystal structure
An image intensifier is provided in which a thin film (090) is arranged between an output surface of the electron multiplier (040) and the phosphorous screen. The thin film is a semi-conductor or insulator with a crystalline structure comprising a band gap equal or larger than 1 eV, wherein the crystalline structure has a carrier diffusion length equal or larger than 50% of the thickness of the thin film. In addition, the thin film has an anode directed surface which has a negative electron affinity. By way of provisioning a thin film of the above type in the image intensifier, an improvement in mean transfer function of the overall image intensifier is obtained.
Owner:PHOTONIS NETHERLANDS
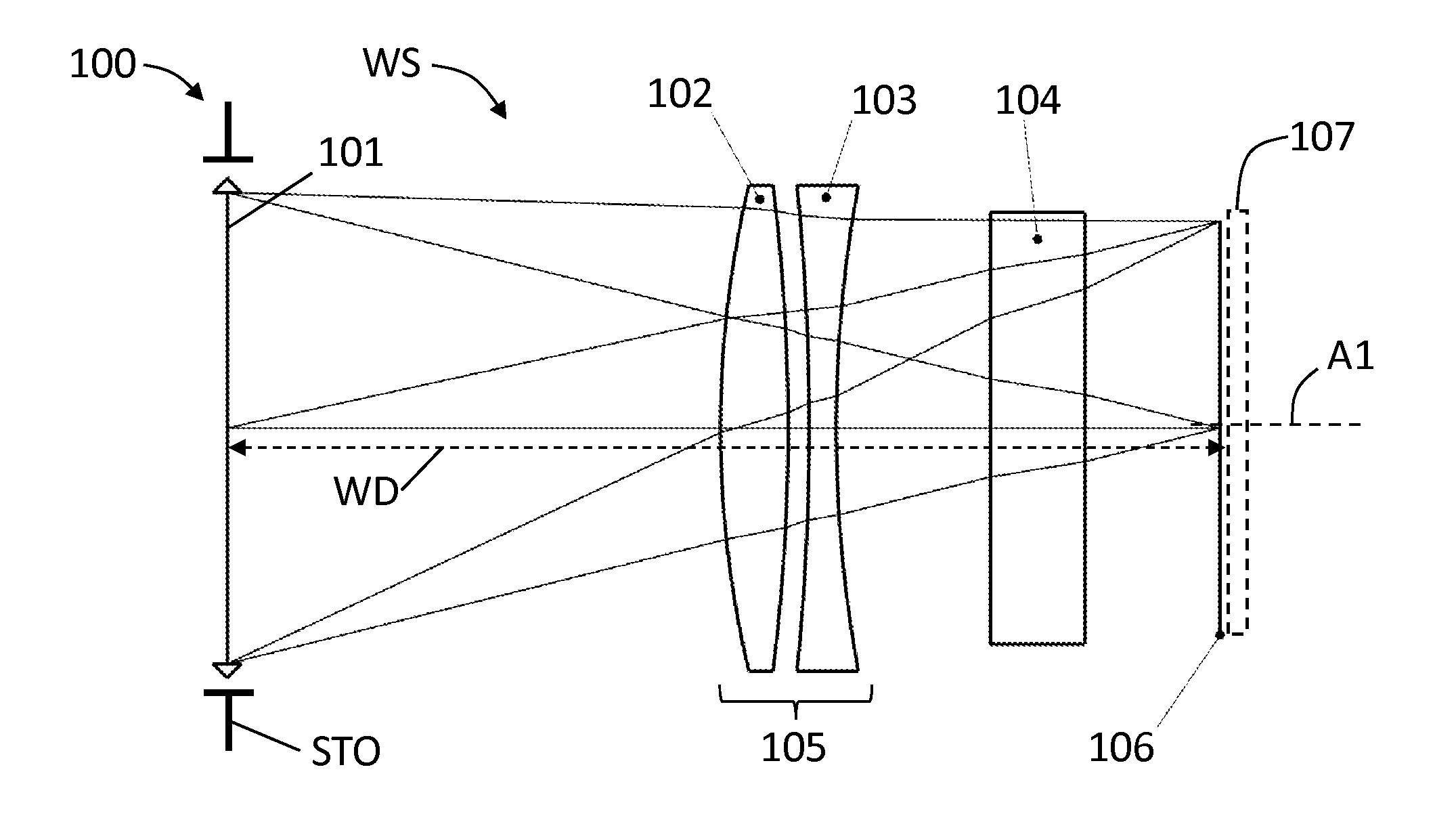
Corrective optical systems and methods
InactiveUS20140085532A1Reduce aberrationSmall permissible working distanceTelevision system detailsColor television detailsParallel platePhysics
A corrective optical system for an imaging optical system is disclosed, wherein the imaging optical system has an objective having a working space, and whose imaging performance is not corrected for one or more plane parallel plates located in the working space. The corrector optical system resides in the working space between the one or more plane parallel plates and objective and serves to reduce the aberrations introduced by the one or more plane parallel plates. The corrector optical system enables objectives originally designed for film to be used with digital cameras.
Owner:CALDWELL PHOTOGRAPHIC
Optics for an extended depth of field
InactiveUS8294999B2Improve MTFAdd depthTelevision system detailsMountingsDepth of fieldOptical image
An optical imaging assembly having cylindrical symmetry, comprising a plurality of lenses having surfaces with curvatures and spacings between the surfaces, such that an optical image formed by the plurality of lenses has a defocus aberration coefficient greater than 0.1 at a focal plane of the assembly.
Owner:NANCHANG O FILM OPTICAL ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Flat type light condensing device
InactiveUS20050162759A1Reduce extra spaceReduce unwanted intermixingMountingsCondensersOptoelectronicsLightness
A flat type light condensing device used in an optical path device includes a hollow frame whose two ends have rectangular openings and a plurality of lenses arranged in the frame. The flat type light condensing lens is used in a scanner to reduce the occupied space in an optical path device and also facilitate the design. Moreover, only data of a single line are captured to reduce unwanted intermixing of data from other lines for enhancing the MTF of the scanner and further letting the brightness be more uniform when imaging.
Owner:TECO IMAGE SYST
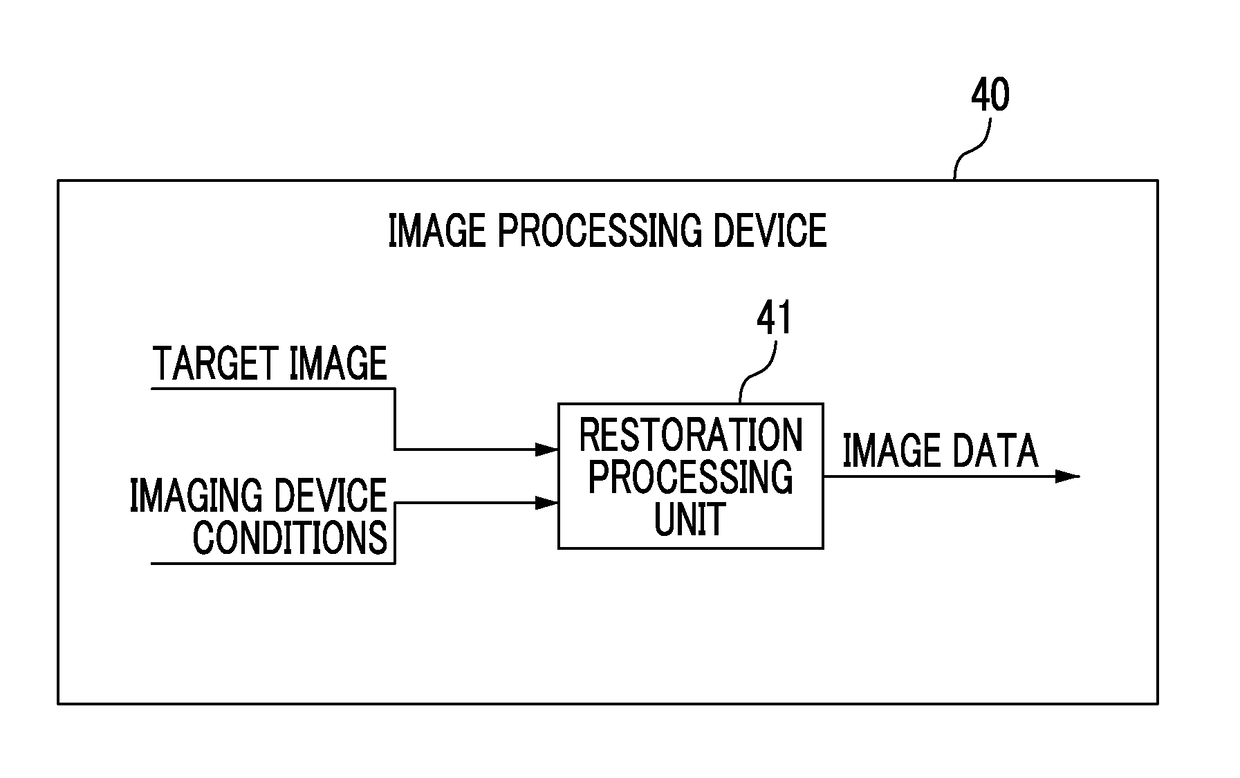
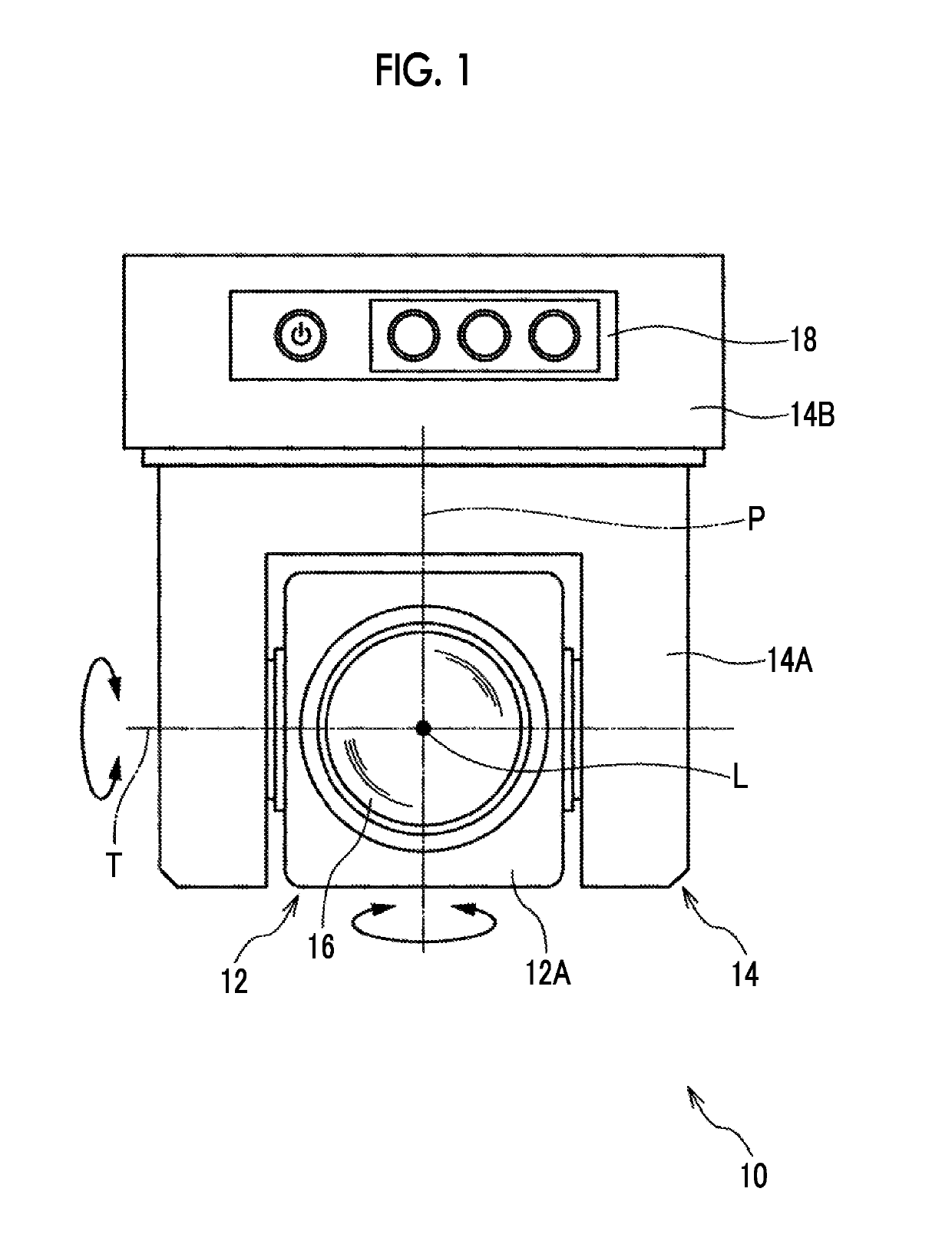
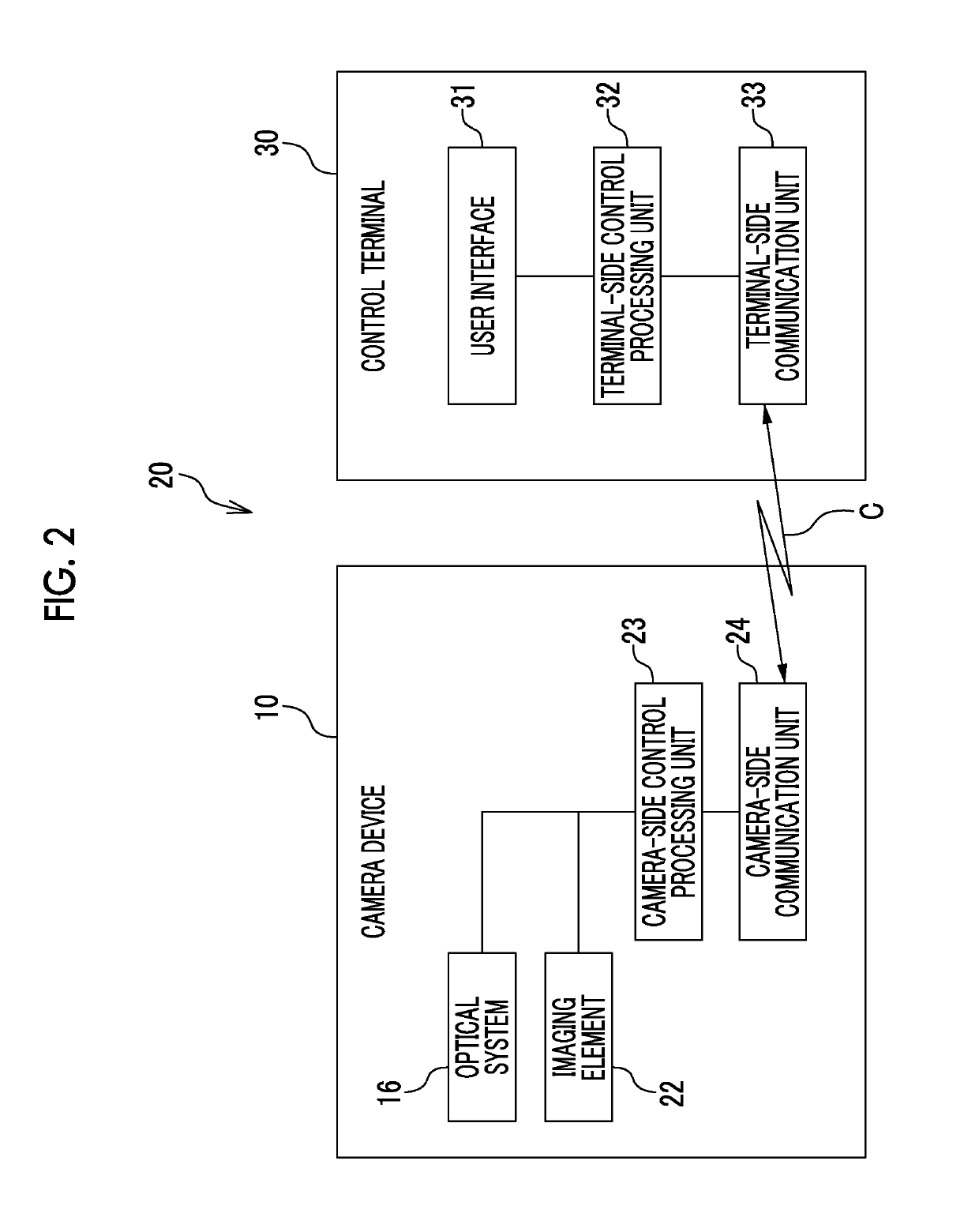
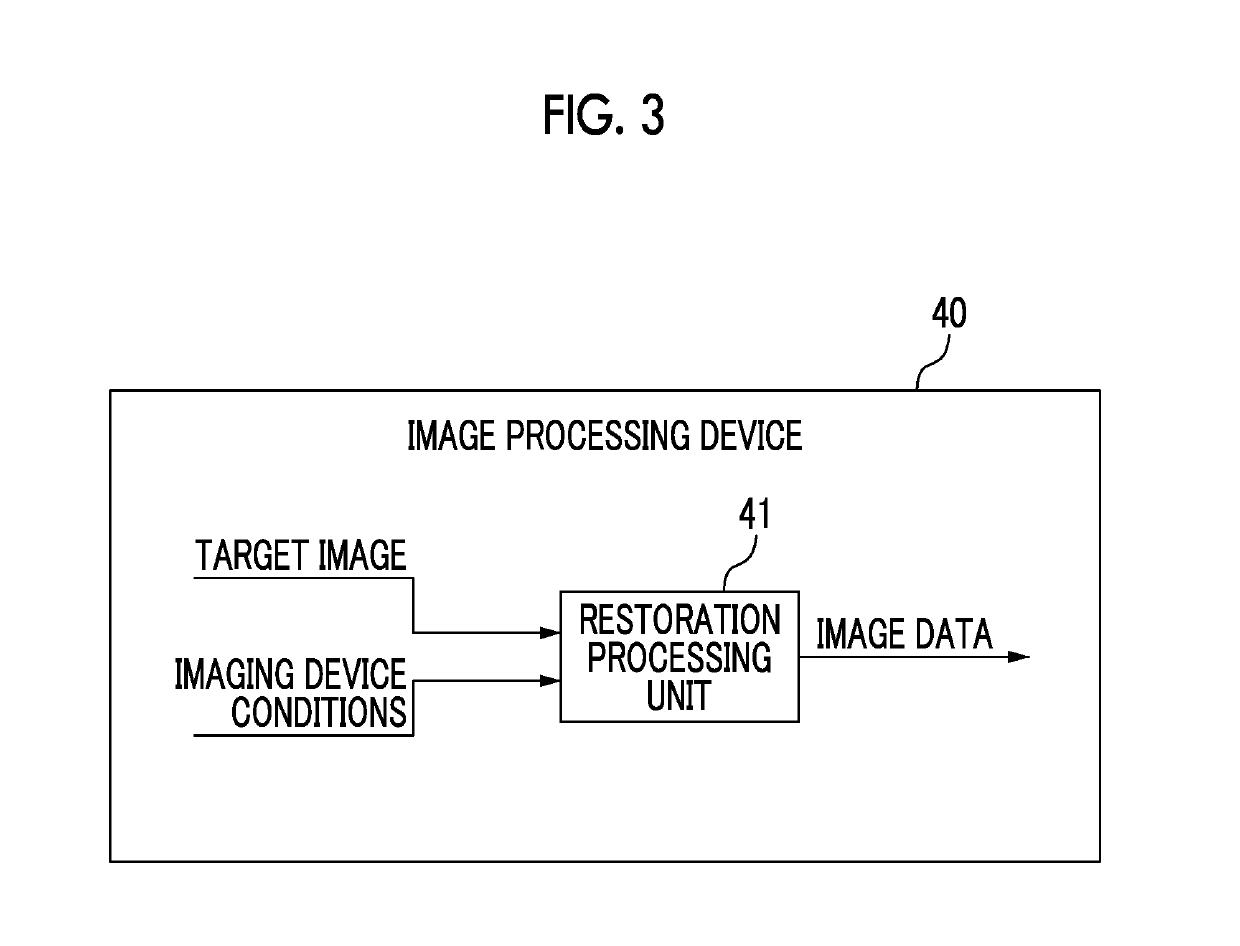
Imaging device, image processing device, image processing method, program, and recording medium
ActiveUS20180047139A1Quality of target can be improvedImprove balanceImage enhancementClosed circuit television systemsImaging processingDiagonal
A restoration processing unit performs a restoration process based on an optical transfer function of an optical system for a target image. The entire angle of view of the optical system is greater than 90 degrees. A light amount evaluation region of the optical system is a region in which a distance from the center of an image formation plane is not less than 80% of half of the length of a diagonal line of an imaging surface of an imaging element. When a first evaluation wavelength is used, the ratio of the amount of light in the light amount evaluation region to the amount of light in a region of the optical system corresponding to the center of the image formation plane is not less than 25%. When a second evaluation wavelength is used, the value of the MTF of the optical system acquired at half of the Nyquist frequency of the imaging element is not less than 15%.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method and apparatus for improved detective quantum efficiency in an x-ray detector
ActiveUS20170244910A1Improve MTFRemoving and reducing noise aliasingTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDetective quantum efficiencyX-ray
The disclosure is directed at a method and apparatus for improving method and apparatus for improved modulation transfer function and detective quantum efficiency of X-ray detectors. The method and apparatus include digitizing microelement outputs obtained by micro sensor elements and the generating pixel outputs from these digitized microelement outputs. Each pixel output is the sum of a plurality of weighting factored microelement outputs.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WATERLOO
CMOS image sensor having enhanced near infrared quantum efficiency and modulation transfer function
ActiveUS10224364B2High sensitivityAvoid crosstalkTransistorTelevision system detailsSemiconductor materialsNir light
An image sensor comprises a semiconductor material having an illuminated surface and a non-illuminated surface; a photodiode formed in the semiconductor material extending from the illuminated surface to receive an incident light through the illuminated surface, wherein the received incident light generates charges in the photodiode; a transfer gate electrically coupled to the photodiode to transfer the generated charges from the photodiode in response to a transfer signal; a floating diffusion electrically coupled to the transfer gate to receive the transferred charges from the photodiode; and a near infrared (NIR) quantum efficiency (QE) and modulation transfer function(MTF) enhancement structure. The NIR QE and MTF enhancement structure comprises: a NIR QE enhancement sub-structure comprising at least one NIR QE enhancement elements within a photosensitive region of the photodiode, wherein the NIR QE enhancement sub-structure is configured to modify the incident light at the illuminated surface of the semiconductor material by at least one of diffraction, deflection and reflection, to redistribute the incident light within the photodiode to improve optical sensitivity, including NIR light sensitivity, of the image sensor; and a MTF enhancement sub-structure disposed on the non-illuminated surface of the semiconductor material, facing toward the NIR QE enhancement sub-structure, wherein the MTF enhancement structure has a geometry corresponding to the NIR QE enhancement sub-structure, to ensure the incident light is still within the photodiode after redistribution.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
Optics for an extended depth of field
InactiveUS20100296179A1Improve MTFAdd depthTelevision system detailsTelescopesDepth of fieldOptical image
An optical imaging assembly having cylindrical symmetry, comprising a plurality of lenses having surfaces with curvatures and spacings between the surfaces, such that an optical image formed by the plurality of lenses has a defocus aberration coefficient greater than 0.1 at a focal plane of the assembly.
Owner:NANCHANG O FILM OPTICAL ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
A Method for Obtaining Optimal Parameters of Phase Mask Applied in Wavefront Coding System
The invention relates to a phase mask plate optimal parameter acquisition method applied to a wavefront coding system. The method comprises the following steps that (1) three optimization objectives expected to be achieved are established, wherein the three optimization objectives expected to be achieved are OTF defocusing invariability, MTF defocusing invariability and PTF defocusing invariability; (2) Fisher information is calculated according to a defocused MTF, a defocused PTF and a defocused OTF respectively; (3) an objective function is established through weighting according to the Fisher information corresponding to the three objectives to be optimized; (4) a phase mask plate optimal parameter is acquired according to the objective function established in the step (3). The phase mask plate optimal parameter acquisition method is applied to the wavefront coding system, and the stability of the defocused PTF of the system can be improved through the method.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV +1
Single-degree-of-freedom self-adaptive balance assembling mechanism
ActiveCN108227234ACounteract gravityGuaranteed image qualityOptical elementsPull forceSingle degree of freedom
The invention discloses a single-degree-of-freedom self-adaptive balance assembling mechanism which comprises a precision platform, a self-adaptive balancing device, a rope, a bracket and a position adjusting device, wherein a reflector and the bracket are arranged on the precision platform and are leveled based on the precision platform; the self-adaptive balancing device is connected to a supporting piece of the reflector; and the position adjusting device is arranged on the bracket through the rope and is connected to the self-adaptive balancing device, and the tension applied to the rope by the position adjusting device is equal to the sum of the gravities of the supporting piece of the reflector and that of the self-adaptive balancing device. The single-degree-of-freedom self-adaptivebalance assembling mechanism disclosed by the invention can eliminate influence on the shape of the reflector when the supporting piece of the reflector is assembled.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Weighted sampling method and a weight factor optimization method oriented to large-area-array small-pixel component
PendingCN113612947AImprove image qualityImprove MTFTelevision system detailsColor television detailsAlgorithmImaging quality
The invention relates to a weighted sampling method and a weight factor optimization method oriented to a large-area-array small-pixel component, based on a large-area-array small-pixel imaging device and compared with a traditional multi-pixel combination method, different weights are set for different sub-pixels, the different sub-pixels are subjected to weighted combination, and meanwhile, in order to solve the problem of weight factor setting, the weight factor of the pixel is set as a variable, an optimization objective function of the weight factor is constructed, and optimization design is performed on the weight factor. The advantages of a small-pixel imaging device are fully explored, the SNR and the MTF of the imaging system can be comprehensively considered, and better imaging quality is obtained.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
Optical system of attitude sensor
ActiveCN101762871BSmall sizeUniform speckleNavigation by astronomical meansOptical elementsFlat glassFull field
The invention discloses an optical system of an attitude sensor. A diaphragm of the optical system is arranged on the first surface of the quartz window plate glass of the optical system, which is beneficial to reducing the size of the optical system and eliminating parasitic light; and the optical system can simultaneously realize large field, large aperture and achromatism by utilizing four common optical materials and effectively shorten the size of the optical system by using a plurality of osculant positive and negative lenses to correct aberration. By adopting the layout mode, the optical system has higher MTF (modulation transfer function) while ensuring relatively uniform full field defocused spots, thereby being capable of giving consideration to both the optical imaging of a star sensor and the imaging of the optical sensor with high resolution requirements.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
A Single Degree of Freedom Self-adaptive Balance Assembly Mechanism
ActiveCN108227234BCounteract gravityGuaranteed image qualityOptical elementsSingle degree of freedomSelf adaptive
The invention discloses a single-degree-of-freedom self-adaptive balance assembly mechanism. The single-degree-of-freedom adaptive balance assembly mechanism includes: a precision platform, an adaptive balance device, a string, a bracket, and a position adjustment device; the mirror and the bracket are all arranged on the precision platform, and the The precision platform is a reference leveling; the self-adaptive balance device is connected to the support of the mirror; the position adjustment device is arranged on the support through the string, and the position adjustment device is connected to the The self-adaptive balancing device is connected, and the pulling force exerted by the position adjusting device on the string is equal to the sum of the gravitational force of the supporting member of the reflector and the self-adapting balancing device. The single-degree-of-freedom self-adaptive balance assembling mechanism provided by the invention can eliminate the influence of the support member of the reflector on the surface shape of the reflector during assembly.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Phase mask plate optimal parameter acquisition method applied to wavefront coding system
The invention relates to a phase mask plate optimal parameter acquisition method applied to a wavefront coding system. The method comprises the following steps that (1) three optimization objectives expected to be achieved are established, wherein the three optimization objectives expected to be achieved are OTF defocusing invariability, MTF defocusing invariability and PTF defocusing invariability; (2) Fisher information is calculated according to a defocused MTF, a defocused PTF and a defocused OTF respectively; (3) an objective function is established through weighting according to the Fisher information corresponding to the three objectives to be optimized; (4) a phase mask plate optimal parameter is acquired according to the objective function established in the step (3). The phase mask plate optimal parameter acquisition method is applied to the wavefront coding system, and the stability of the defocused PTF of the system can be improved through the method.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV +1
Ultra-wide-angle large-aperture aspheric lens
PendingCN114578528AHigh resolutionIncrease the angle of incidenceOptical elementsImage resolutionAspheric lens
The invention relates to an ultra-wide-angle large-aperture aspherical lens, which comprises a first lens group, an iris diaphragm and a second lens group which are sequentially arranged along a light incidence direction, wherein the first lens group has a fixed positive focal power position; the second lens group has a movable positive focal power position; and the focal length value f1 of the first lens group and the focal length value f2 of the second lens group satisfy 1.5 < f1 / f2 < 2. Therefore, the lens has the advantages of large aperture, small total length, small distortion, high resolution and close-range focusing.
Owner:ZHUHAI CHUANFU OPTICAL TECH
Image intensifier for night vision device
ActiveUS10886095B2Improve image qualityReduced MTFTelescopesMutiple dynode arrangementsElectron multiplicationElectron multiplier
An image intensifier is provided in which a thin film (090) is arranged between an output surface of the electron multiplier (040) and the phosphorous screen. The thin film is a semi-conductor or insulator with a crystalline structure comprising a band gap equal or larger than 1 eV, wherein the crystalline structure has a carrier diffusion length equal or larger than 50% of the thickness of the thin film. In addition, the thin film has an anode directed surface which has a negative electron affinity. By way of provisioning a thin film of the above type in the image intensifier, an improvement in mean transfer function of the overall image intensifier is obtained.
Owner:PHOTONIS NETHERLANDS
Imaging device, image processing device, image processing method, program, and recording medium
ActiveUS10269101B2Improve low signal-to-noise ratioIncrease valueImage enhancementClosed circuit television systemsDiagonalImage formation
A restoration processing unit performs a restoration process based on an optical transfer function of an optical system for a target image. The entire angle of view of the optical system is greater than 90 degrees. A light amount evaluation region of the optical system is a region in which a distance from the center of an image formation plane is not less than 80% of half of the length of a diagonal line of an imaging surface of an imaging element. When a first evaluation wavelength is used, the ratio of the amount of light in the light amount evaluation region to the amount of light in a region of the optical system corresponding to the center of the image formation plane is not less than 25%. When a second evaluation wavelength is used, the value of the MTF of the optical system acquired at half of the Nyquist frequency of the imaging element is not less than 15%.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com