Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
112results about How to "Help accuracy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
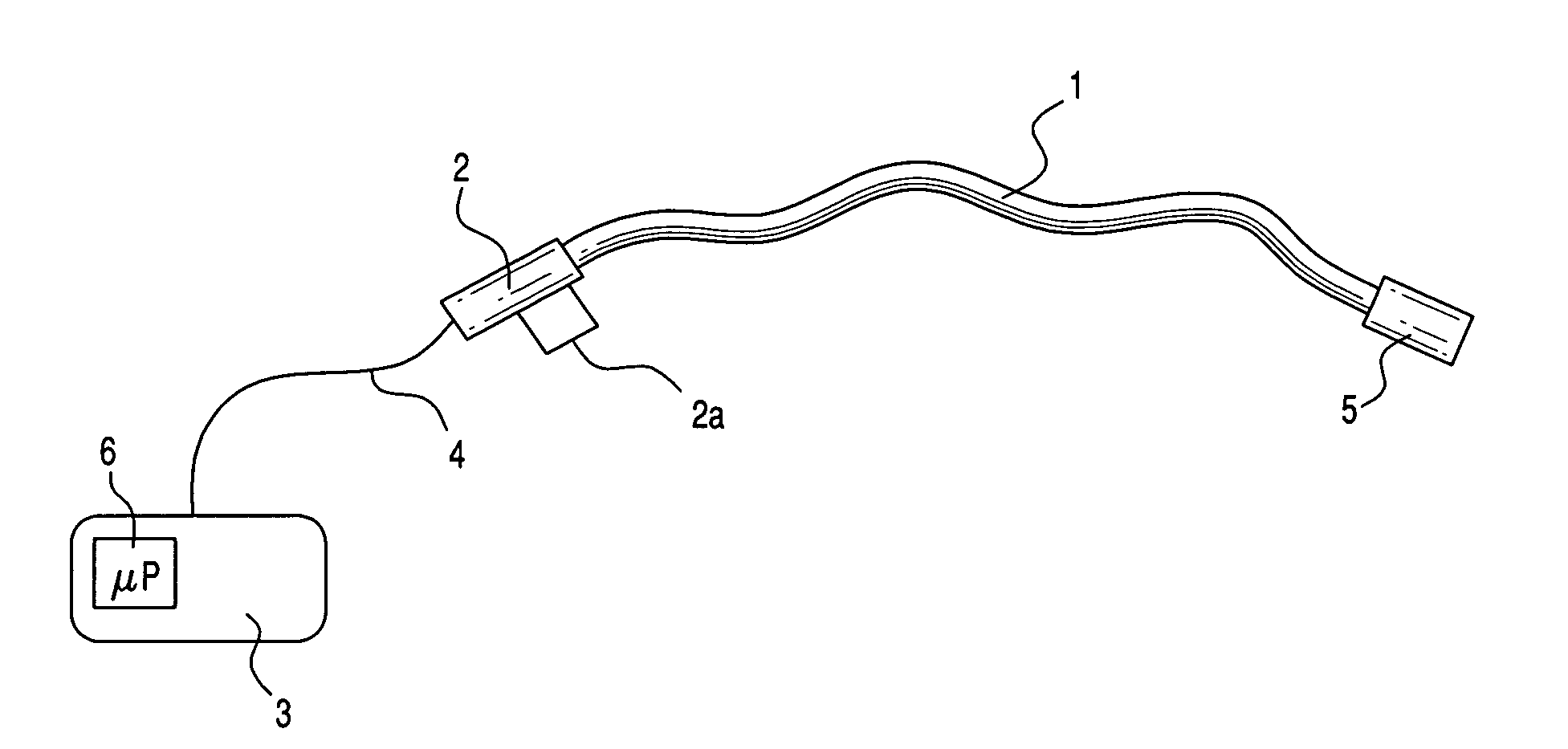
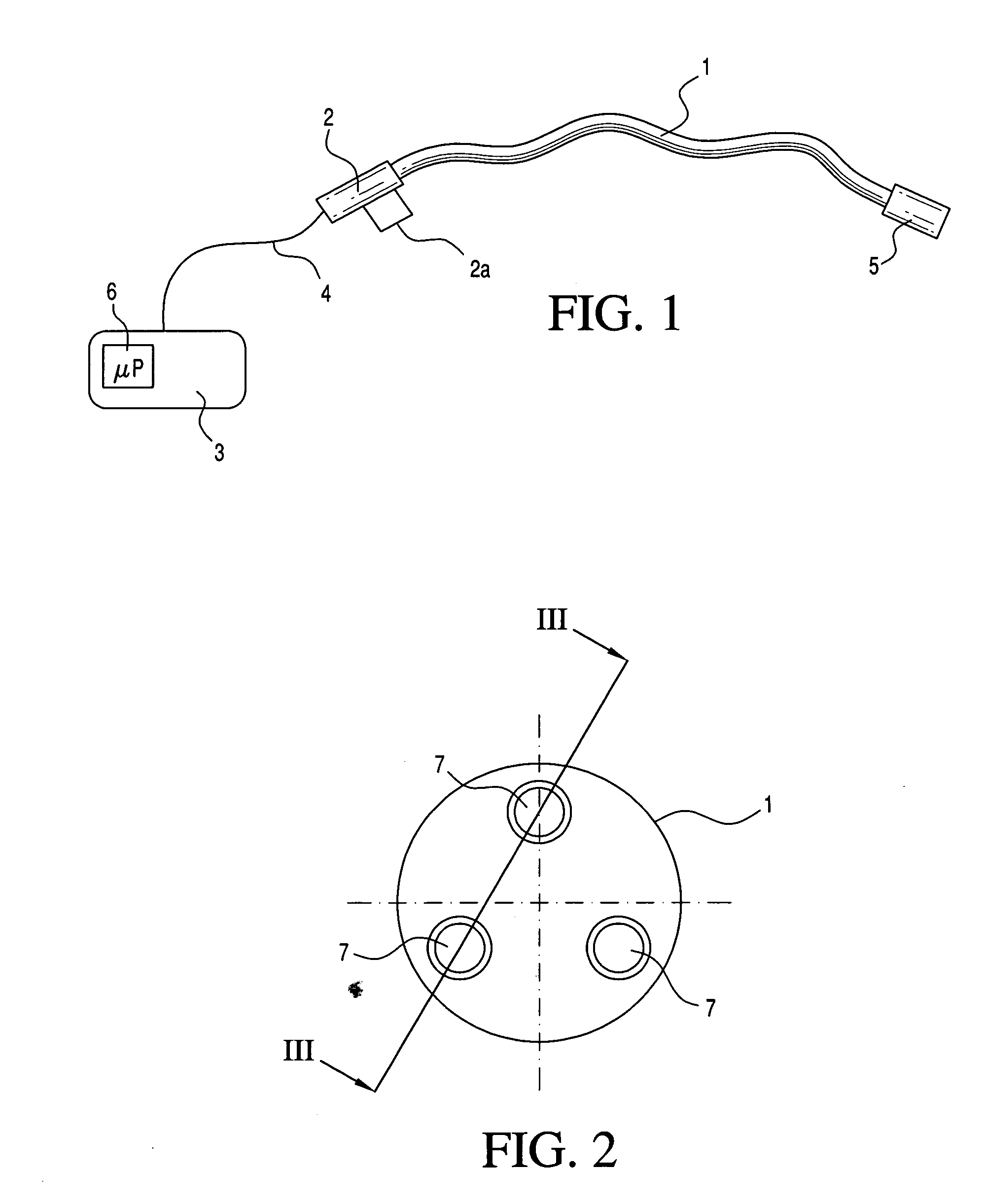
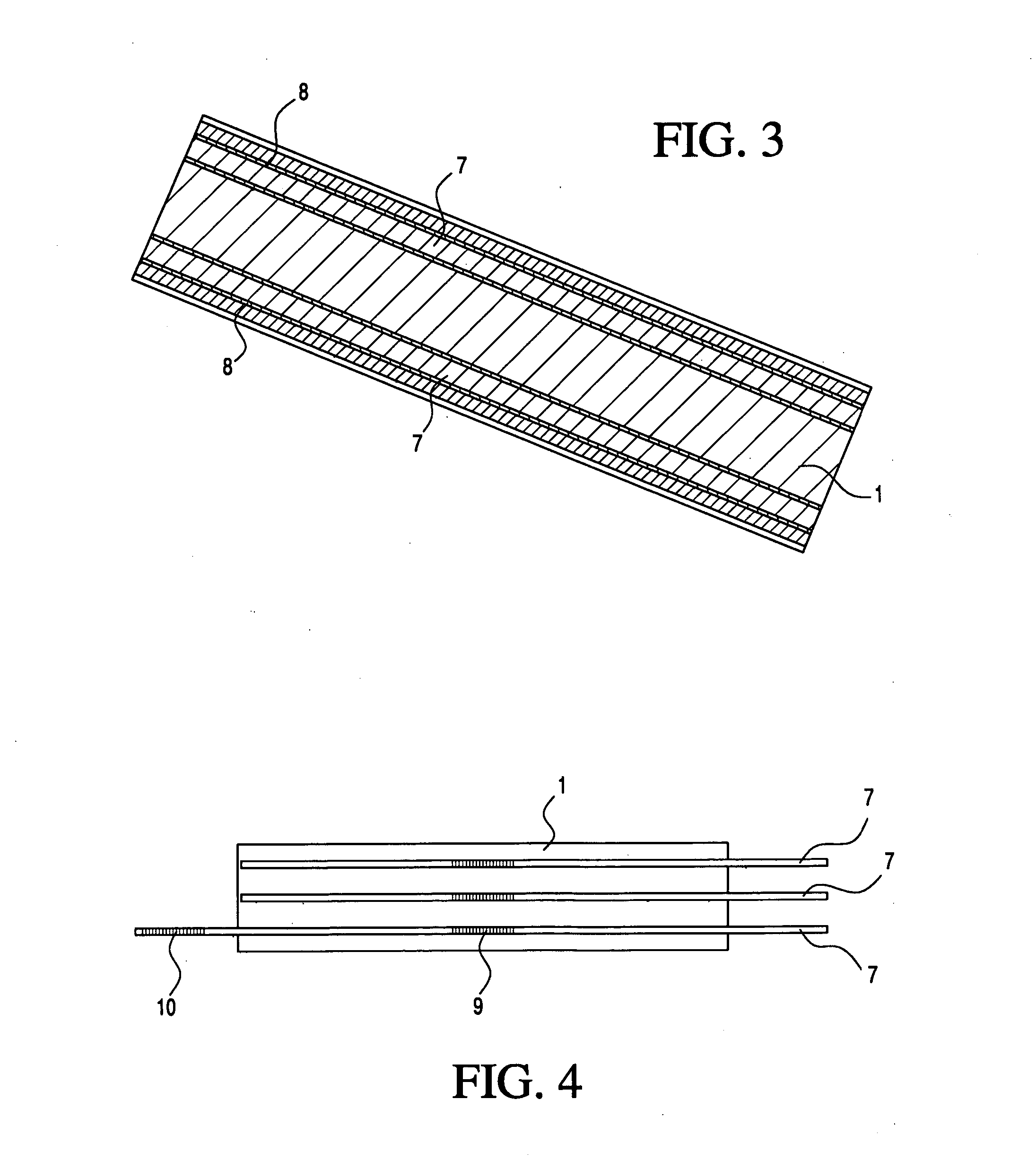
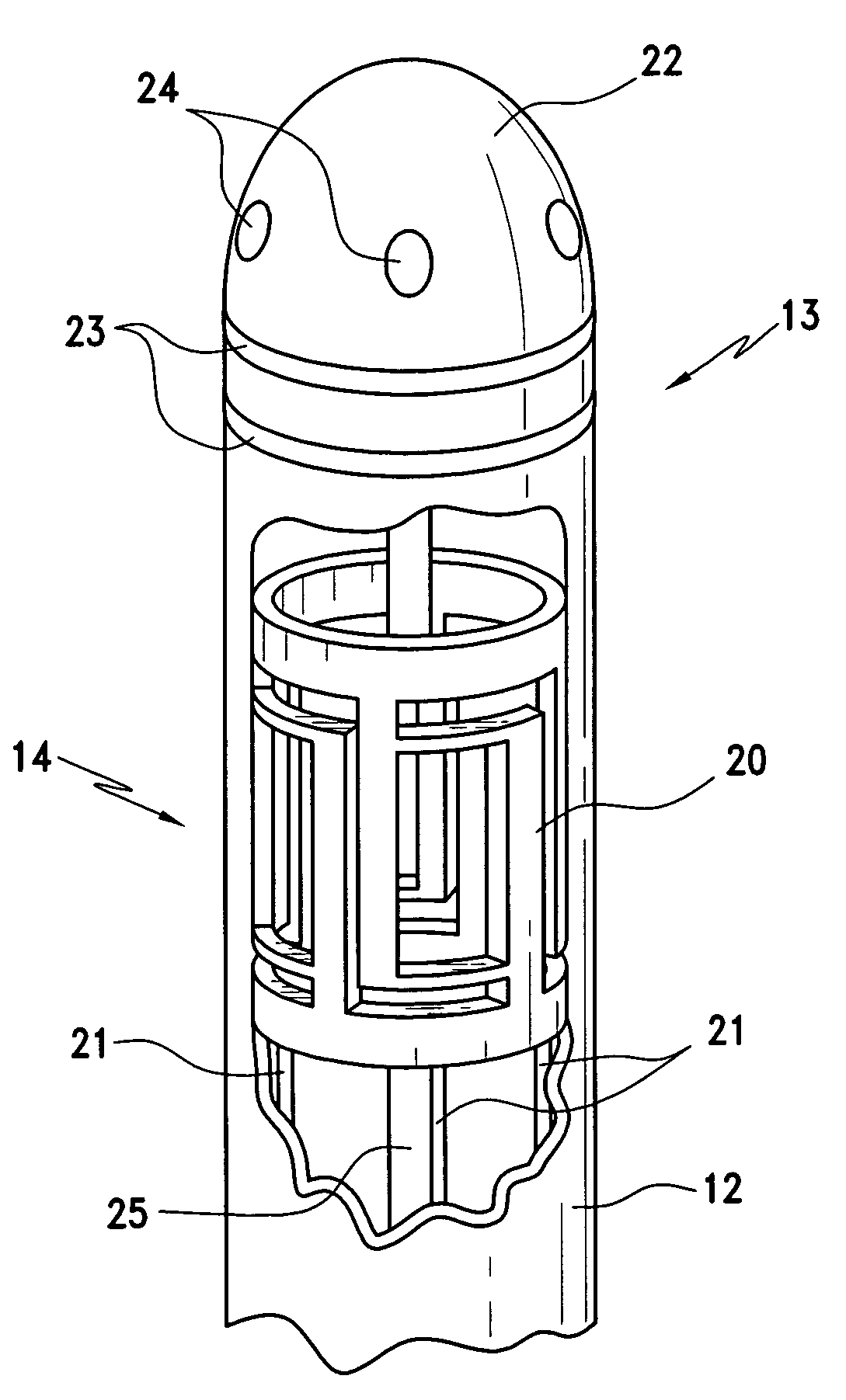
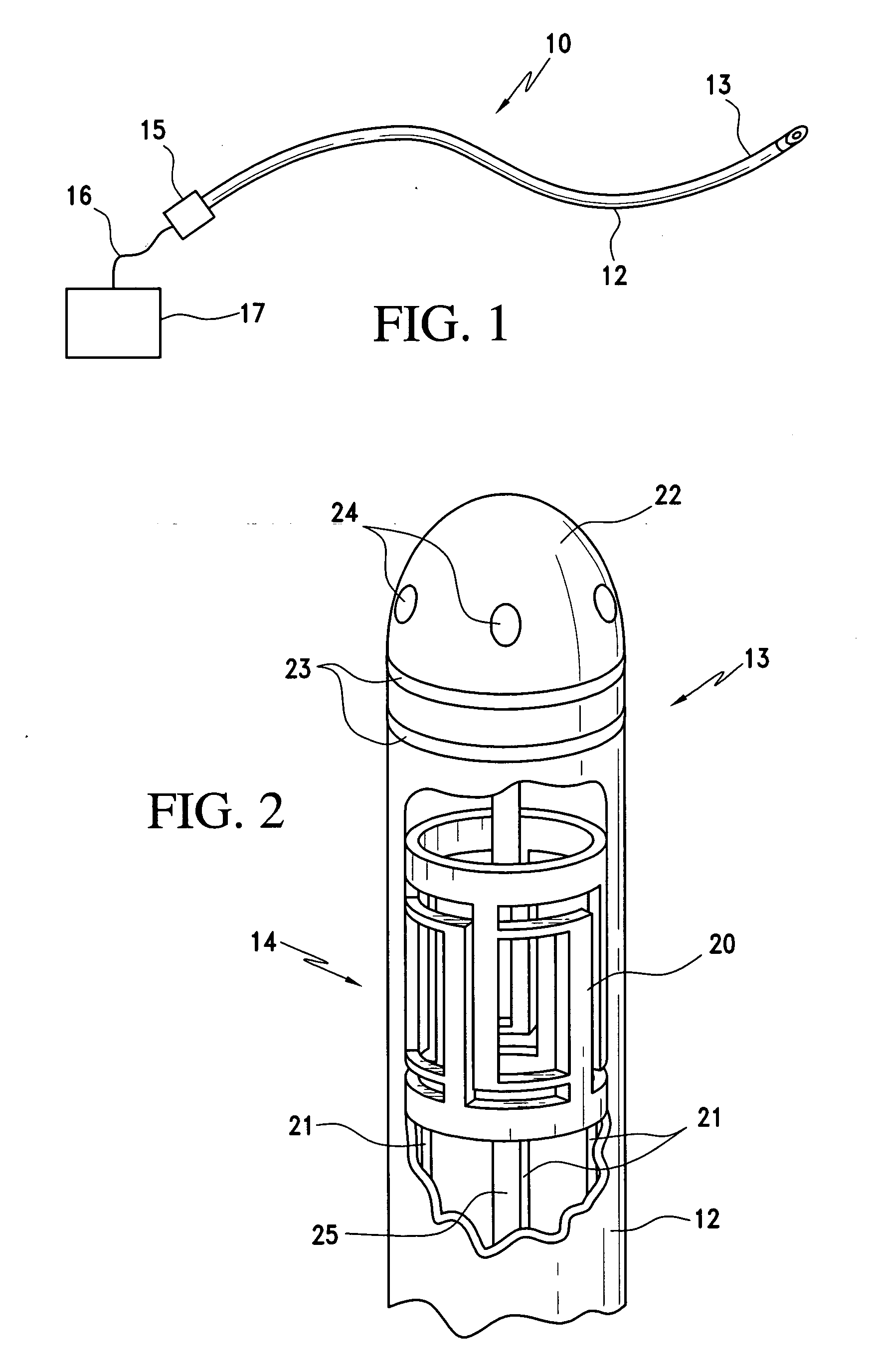
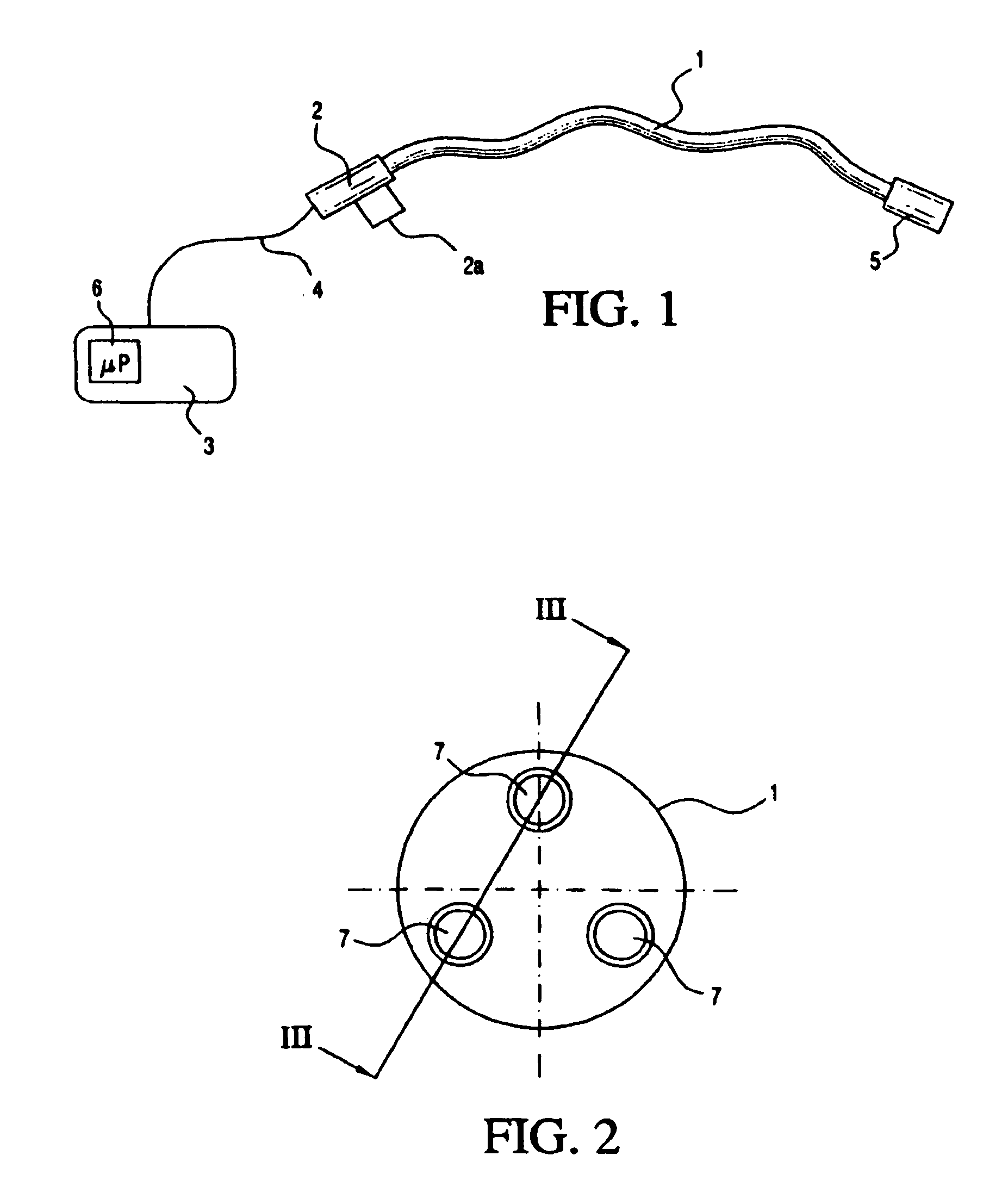
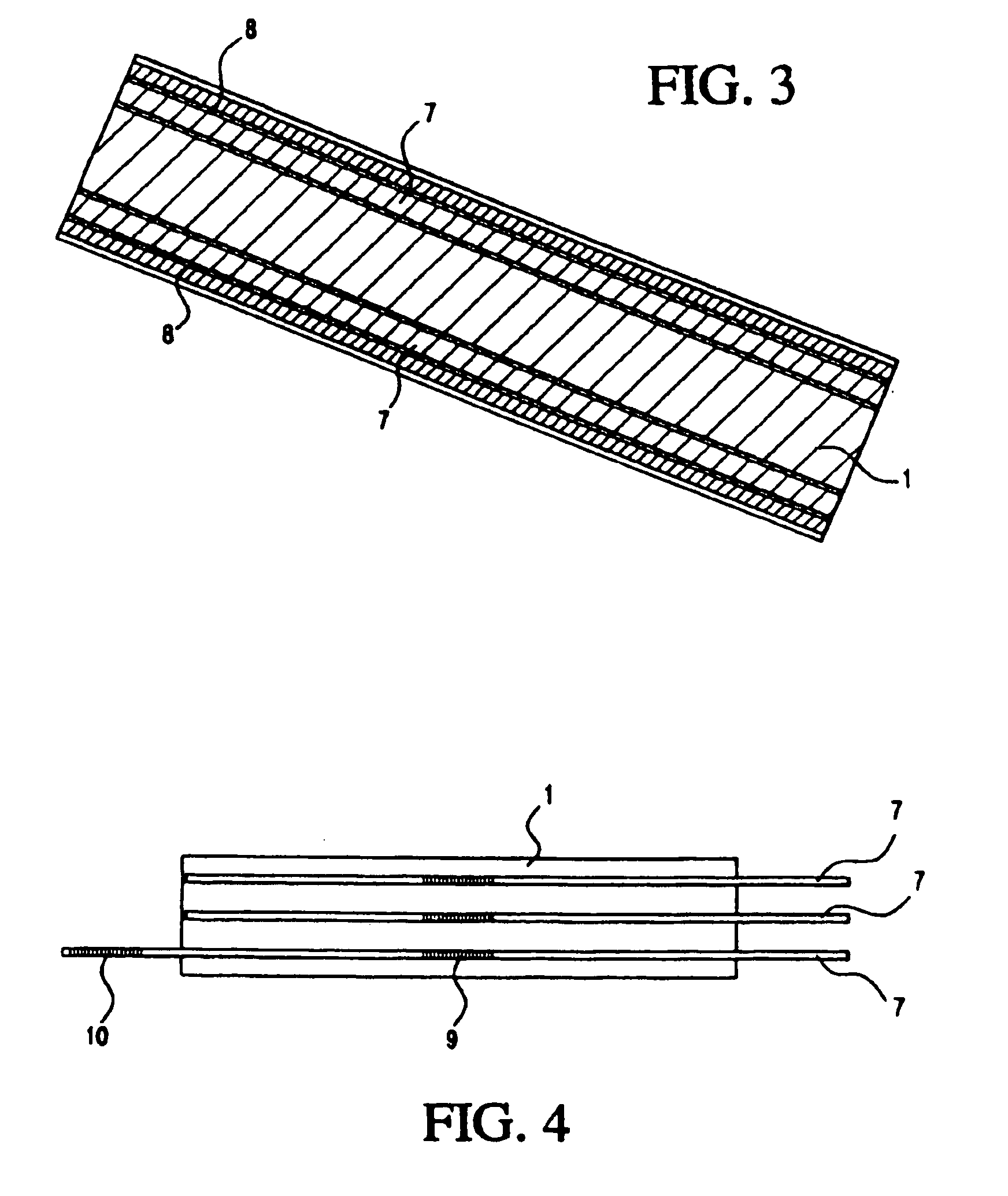
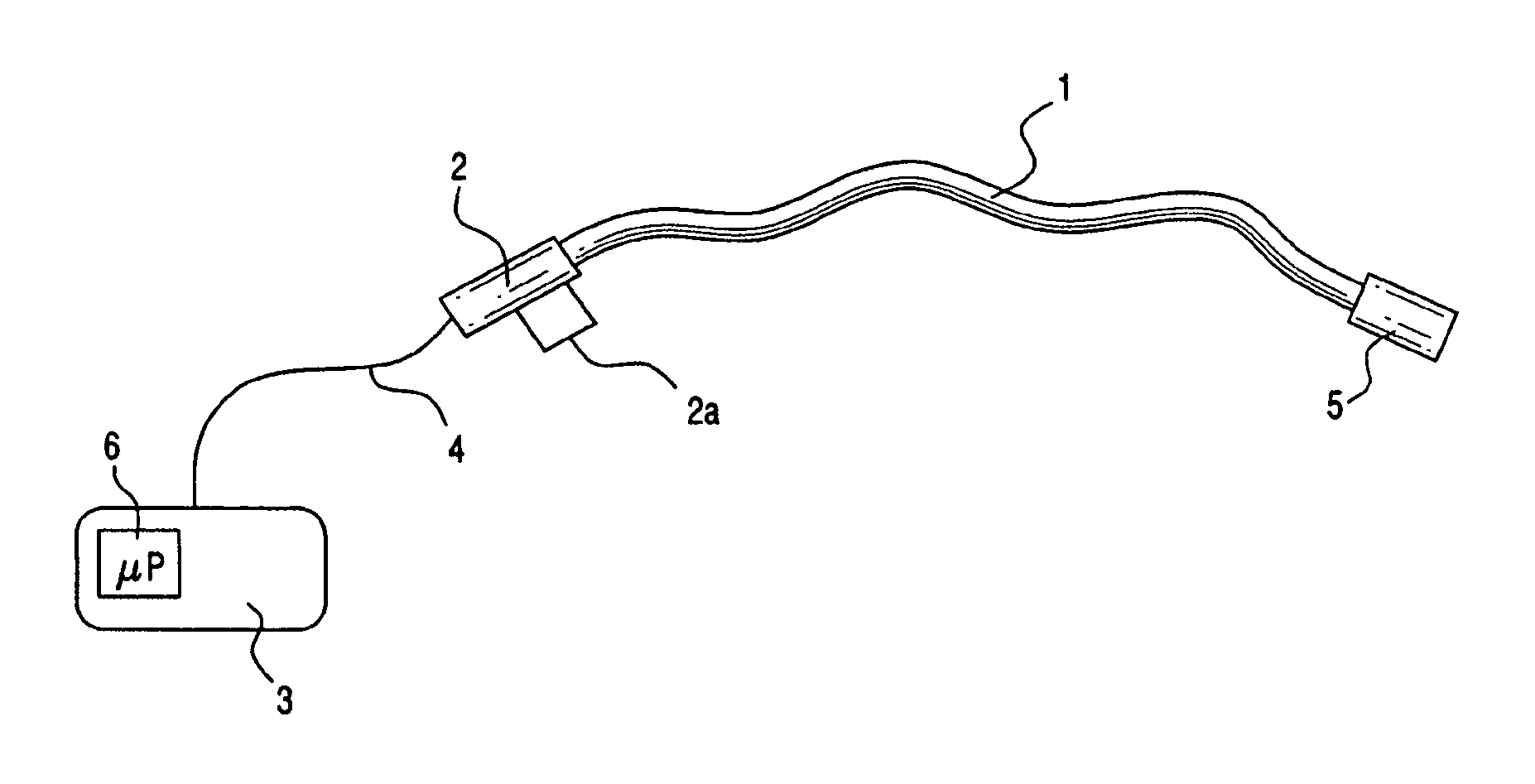
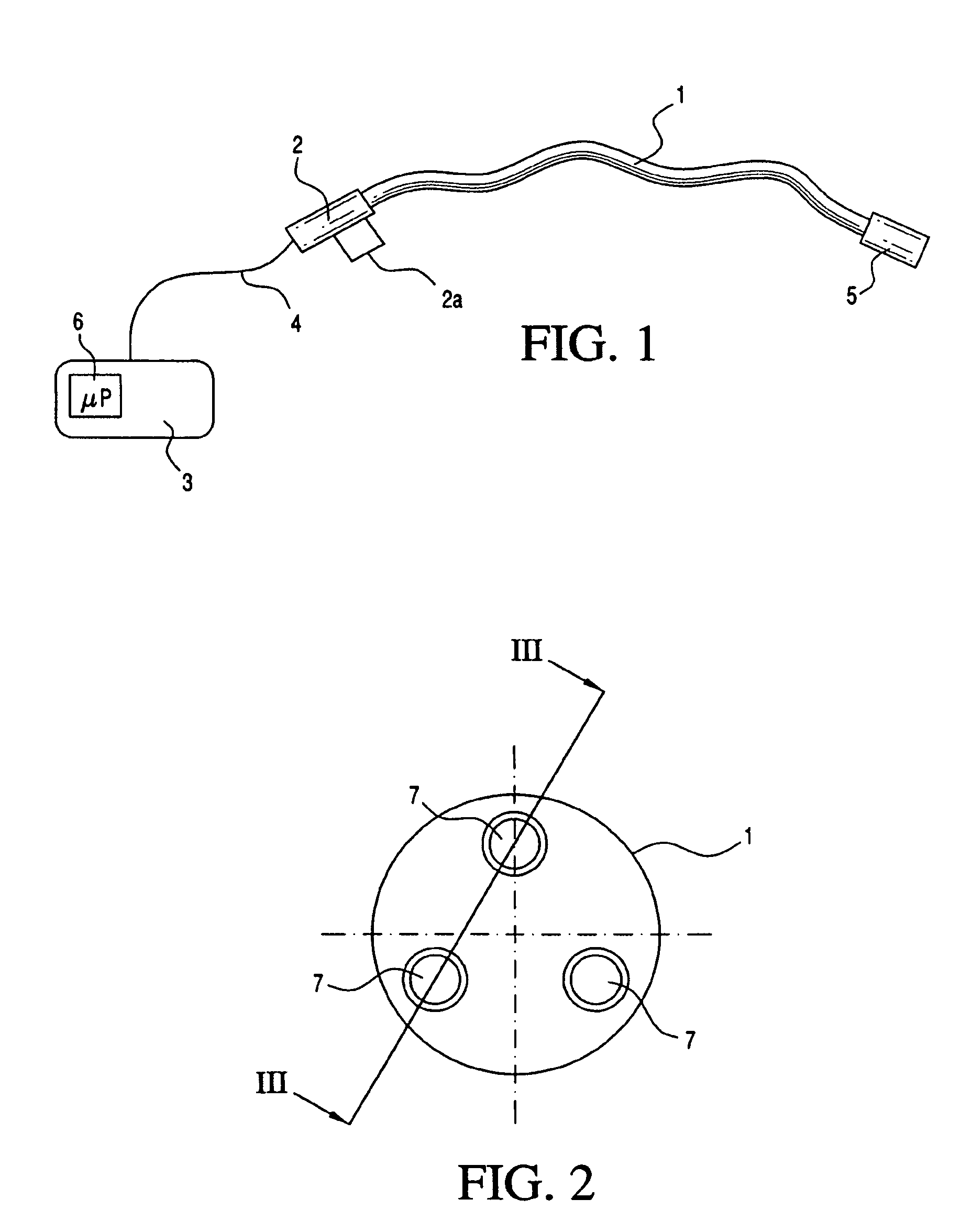
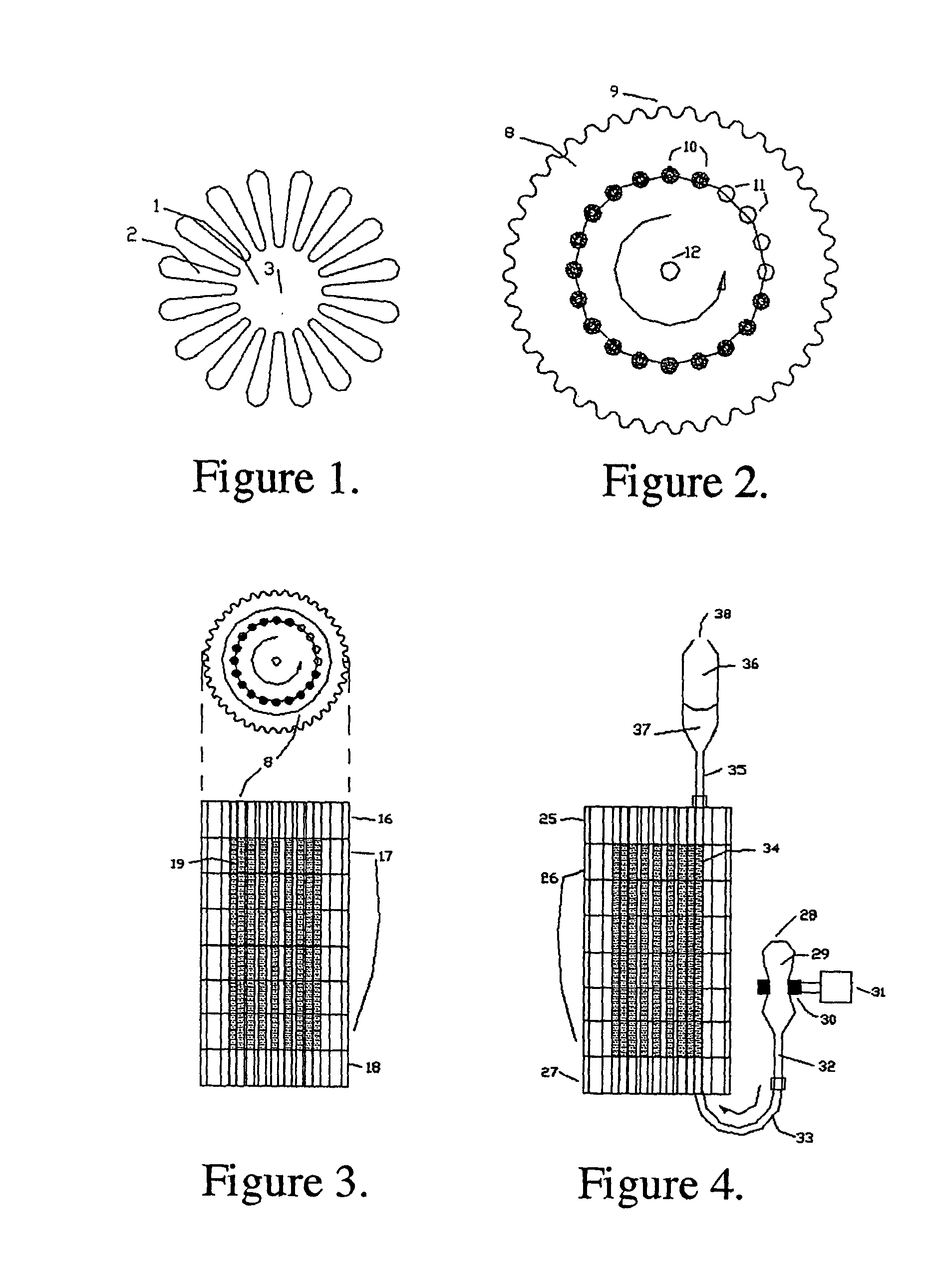
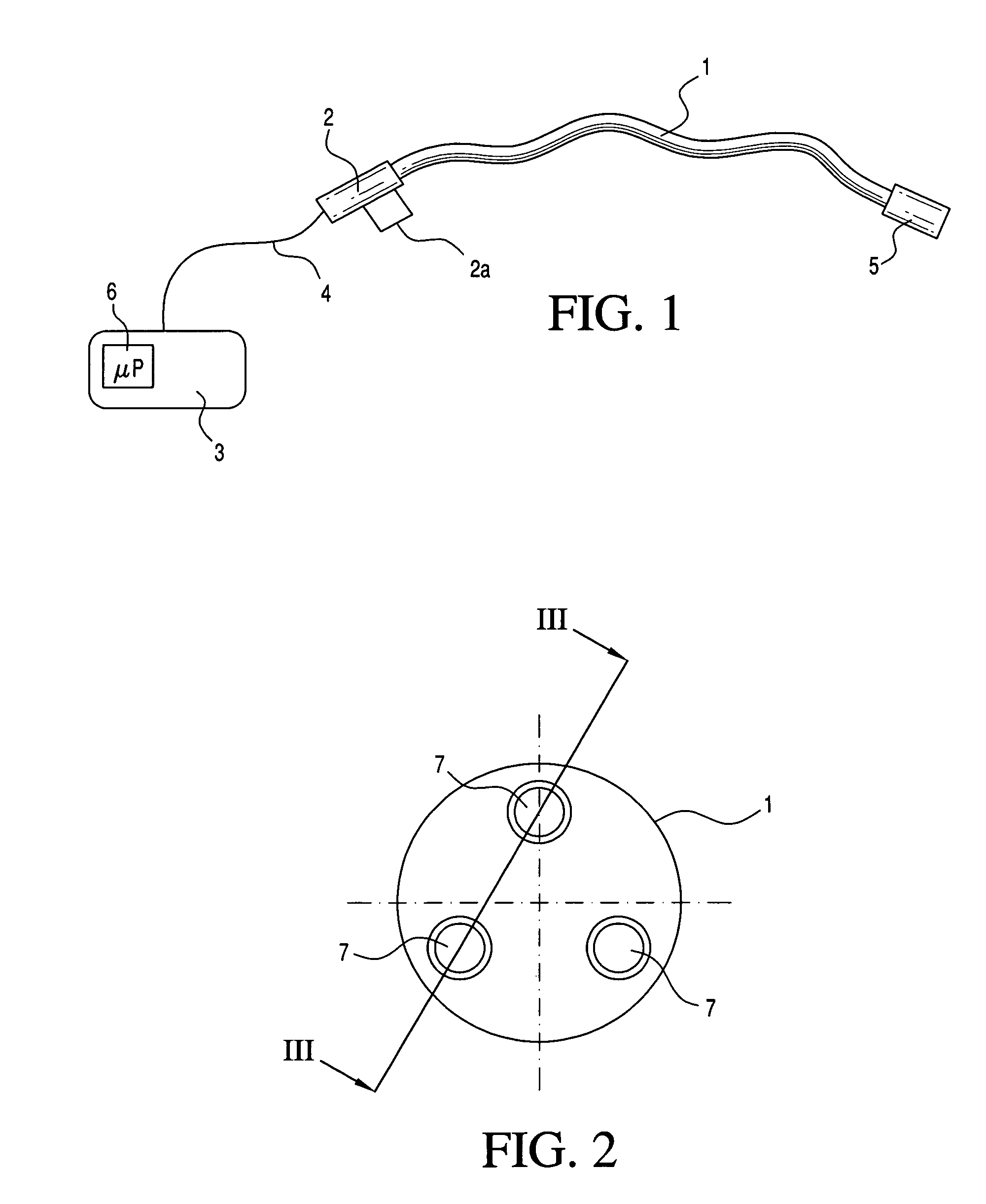
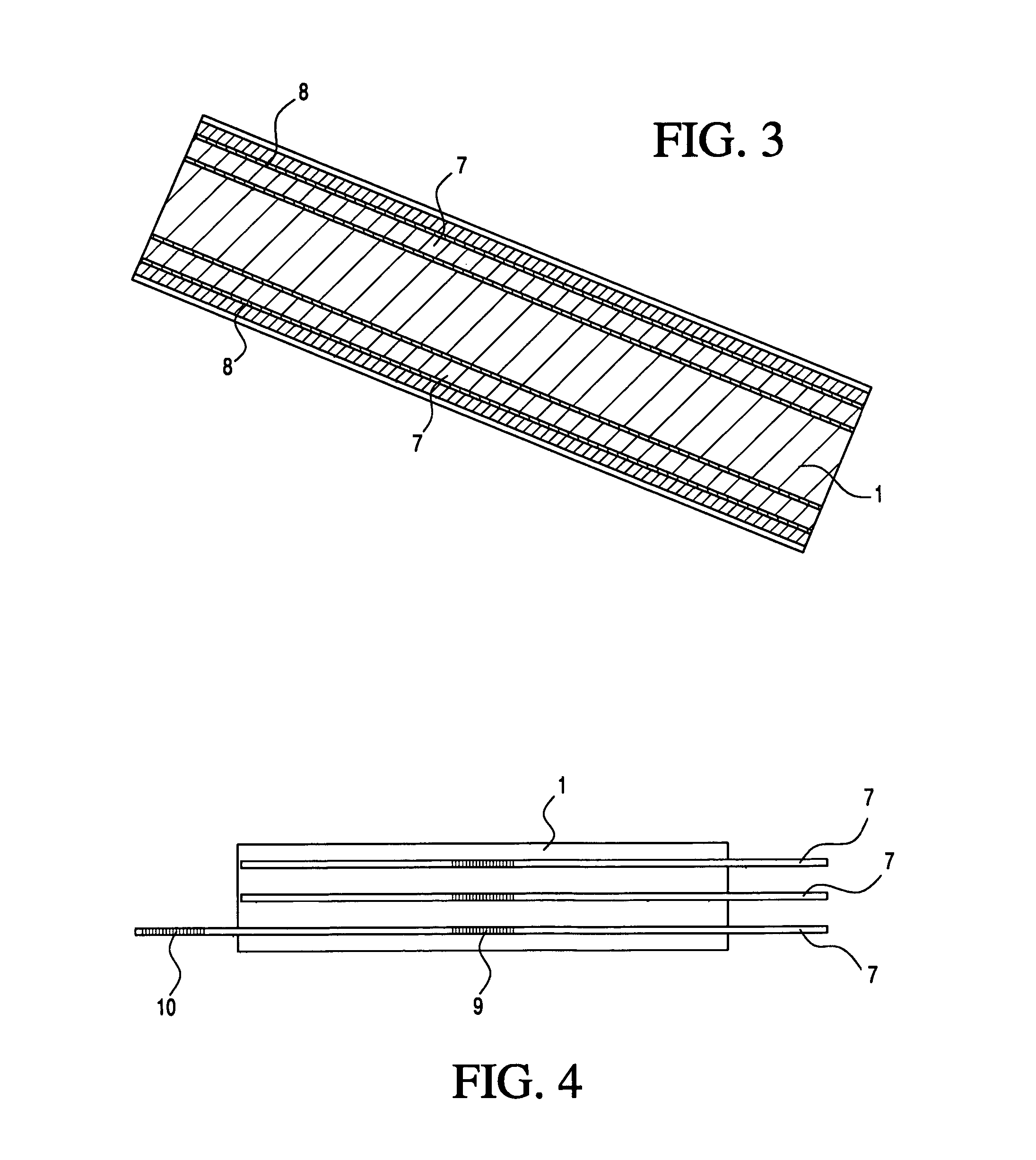
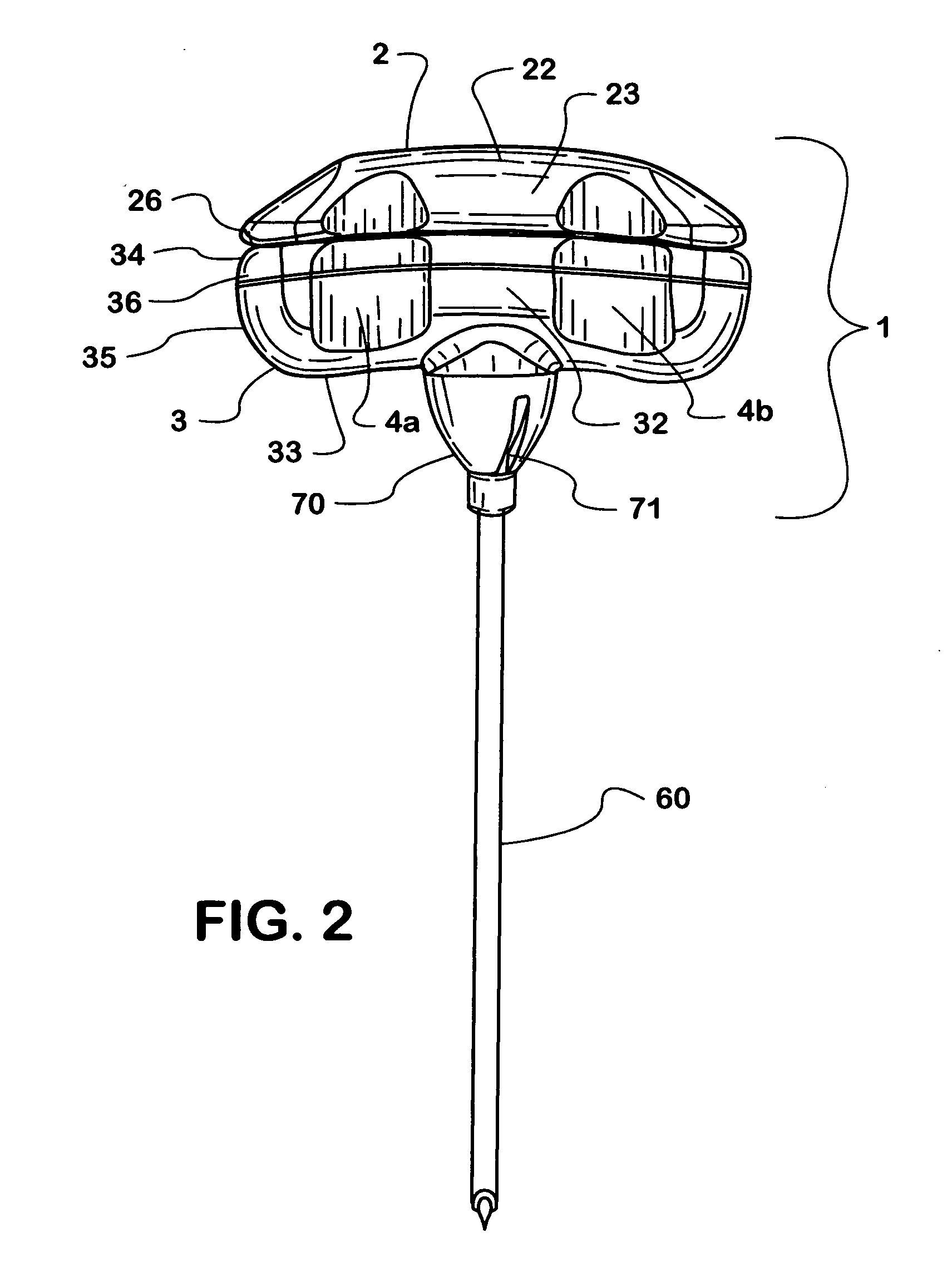
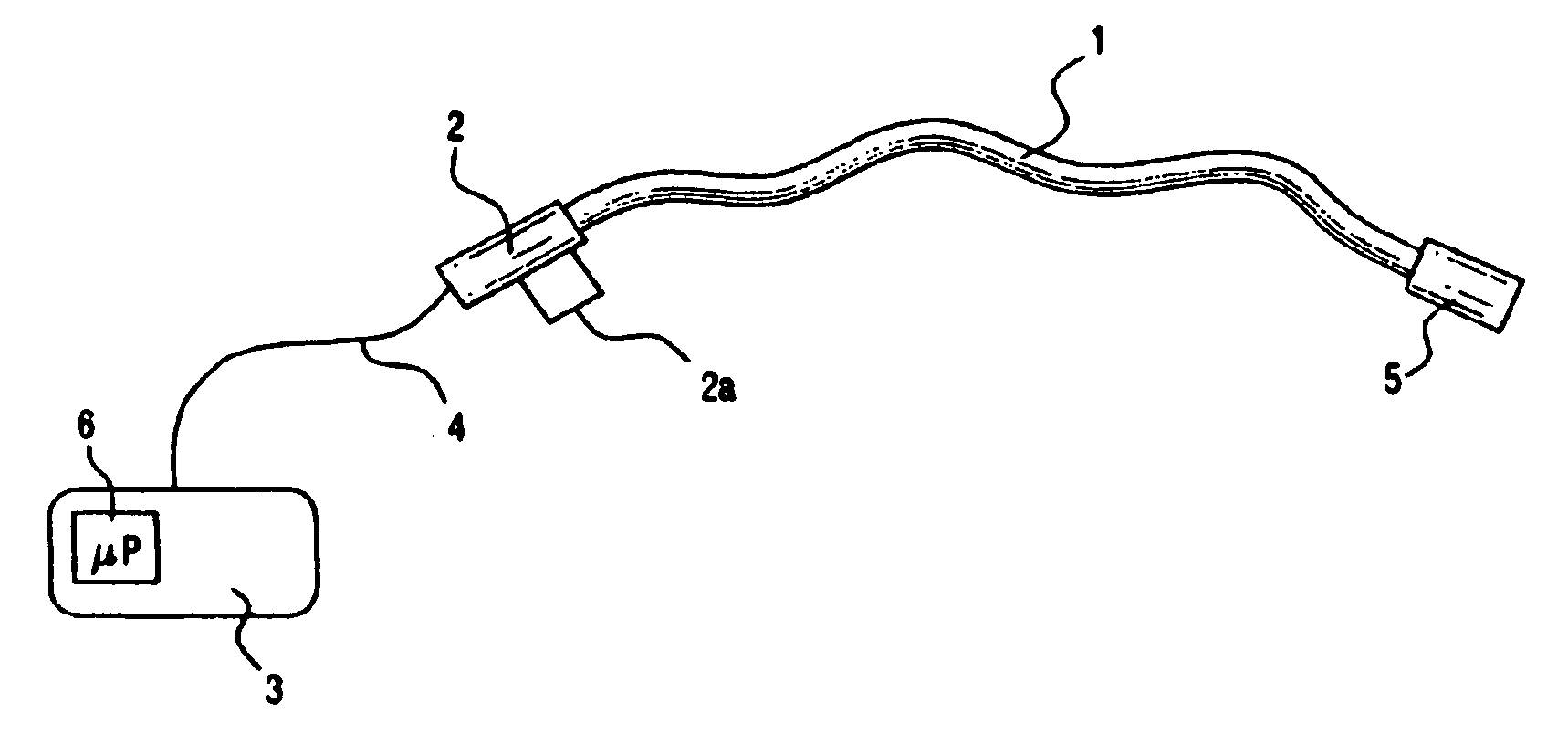
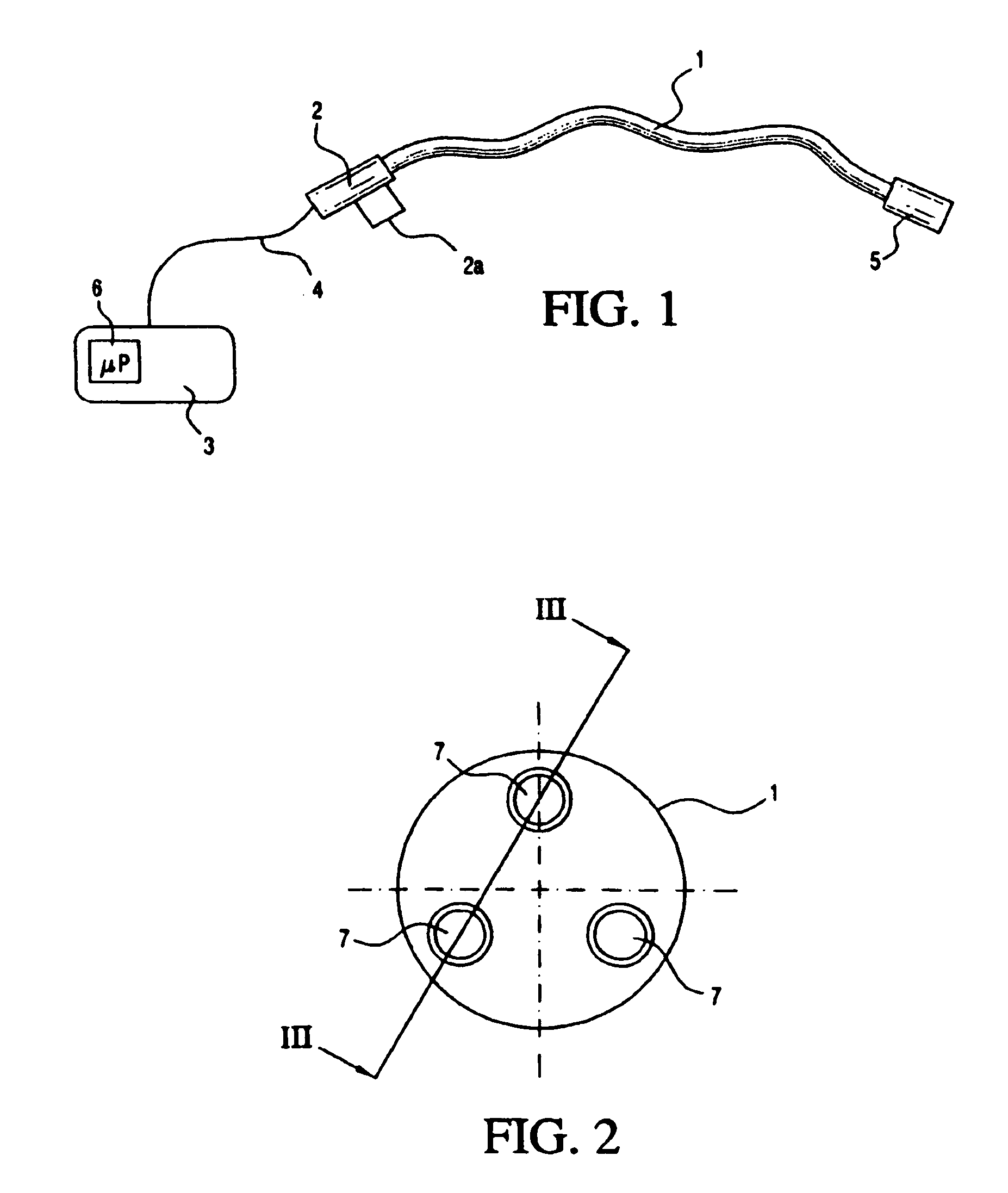
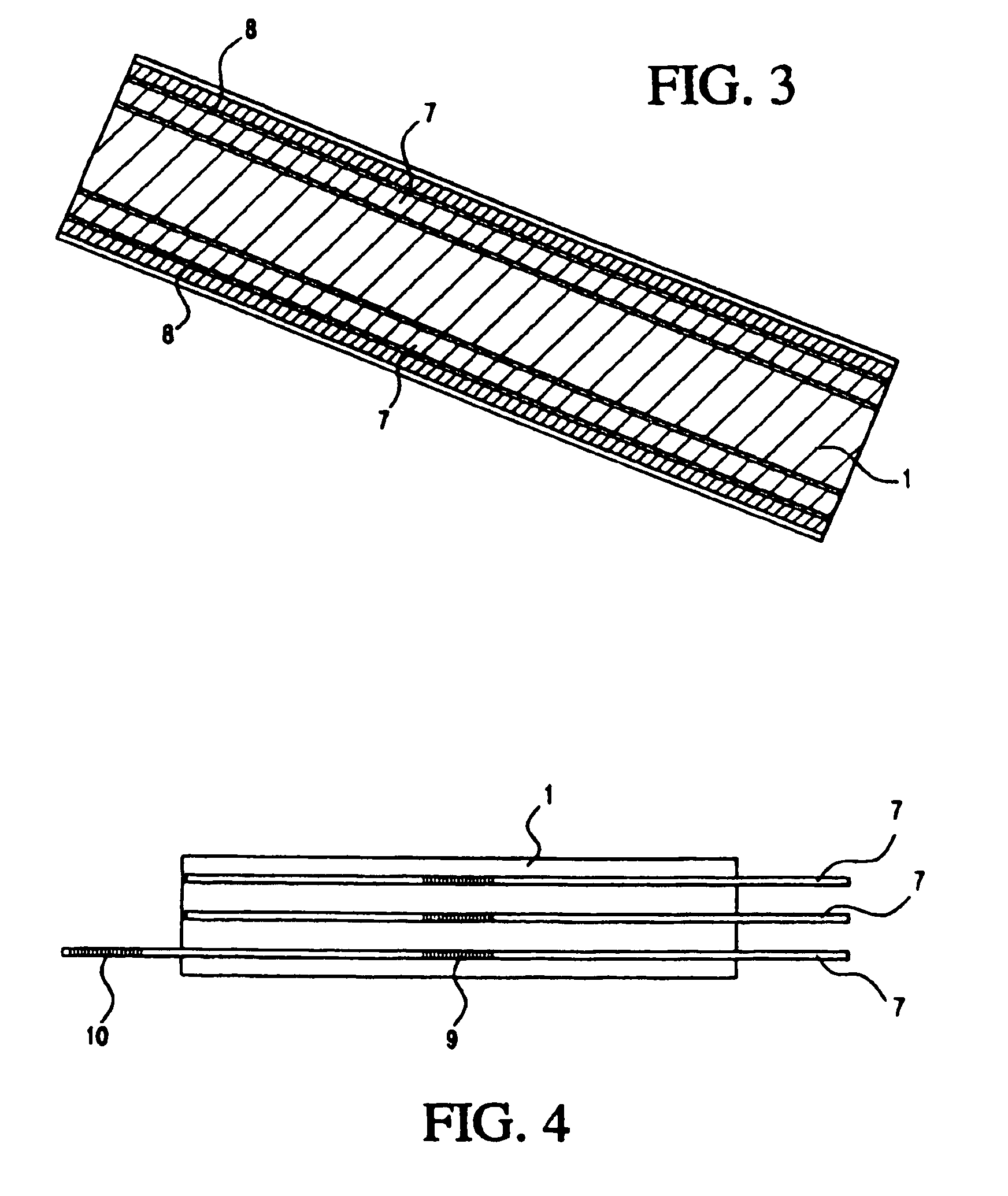
Medical apparatus system having optical fiber load sensing capability
ActiveUS20060200049A1Facilitate speedHelp accuracyStrain gaugePerson identificationRobotic systemsProcess logic
Apparatus is provided for diagnosing or treating an organ or vessel, wherein a deformable body having at least two optical fiber sensors disposed in a distal extremity thereof is coupled to processing logic programmed to compute a multi-dimensional force vector responsive to detected changes in the optical characteristics of the optical fiber sensors arising from deflection of the distal extremity resulting from contact with the tissue of the wall of the organ or vessel. The force vector may be used to facilitate manipulation of the deformable body either directly or automatically using a robotic system.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL INT HLDG SARL
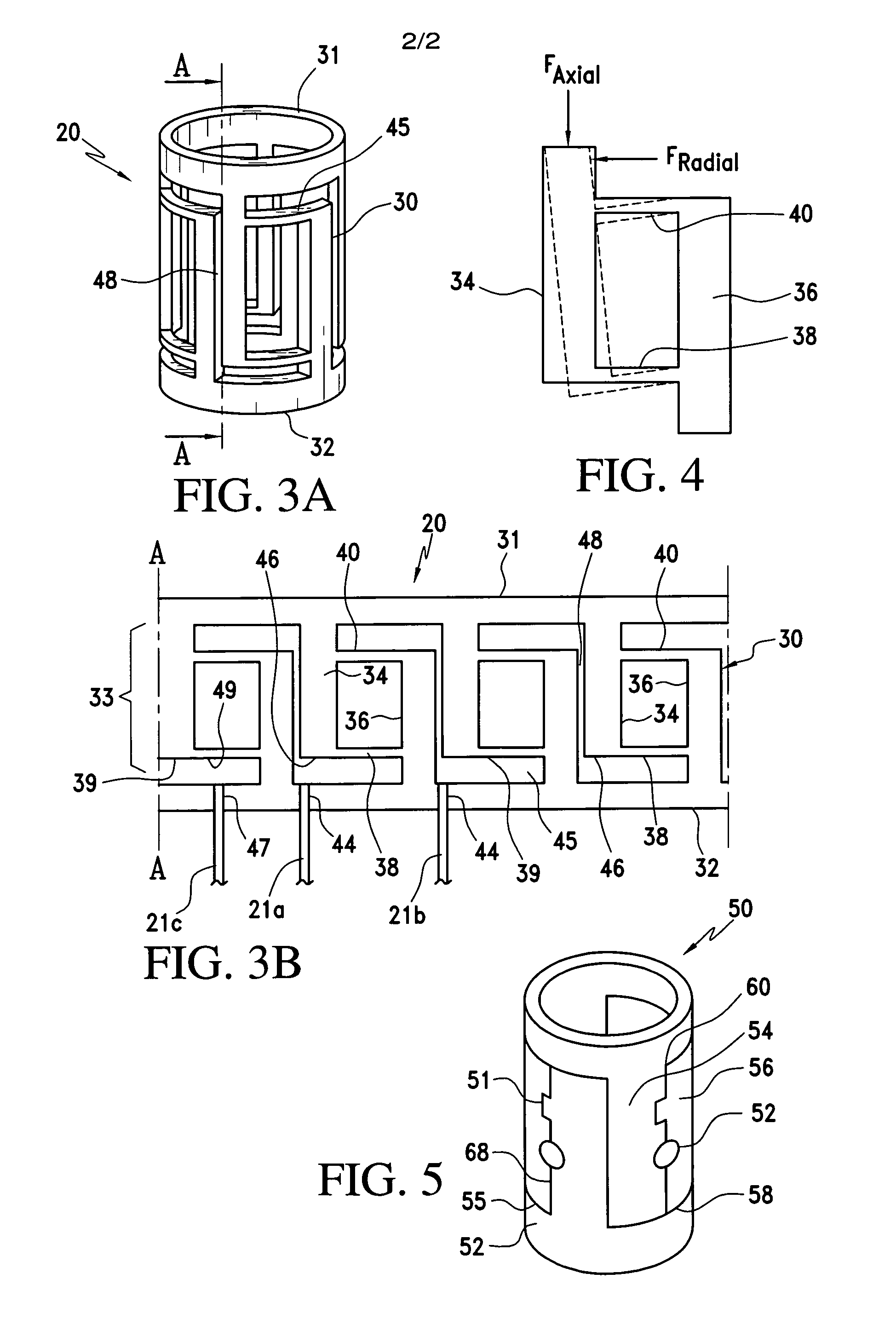
Catheter having tri-axial force sensor
ActiveUS20080009750A1Plenty of spaceFacilitate speedElectrocardiographySurgical instrument detailsAxial forceContact force
A catheter for diagnosis or treatment of a vessel or organ is provided in which a flexible elongated body includes a tri-axial force sensor formed of a housing and a plurality of optical fibers associated with the housing that measure changes in the intensity of light reflected from the lateral surfaces of the housing resulting from deformation caused by forces applied to a distal extremity of the housing. A controller receives an output of the optical fibers and computes a multi-dimensional force vector corresponding to the contact force.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL INT HLDG SARL
Medical apparatus system having optical fiber load sensing capability
ActiveUS20070060847A1Reduces sensor artifactReduction factorStrain gaugePerson identificationLoad sensingEngineering
Apparatus is provided for diagnosing or treating an organ or vessel, wherein a device having at least two optical fiber sensors disposed in a distal extremity thereof is coupled to processing logic programmed to compute a multi-dimensional force vector responsive to detected changes in the optical characteristics of the optical fiber sensors arising from deflection of the distal extremity resulting from contact with the tissue of the wall of the organ or vessel. The force vector may be used to facilitate manipulation of the catheter either directly or automatically using a robotic system.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL INT HLDG SARL
Skills database management system and method
InactiveUS6266659B1Help accuracyImprove efficiencyDigital data processing detailsRelational databasesRelational databaseManagement system
A computer-based on-line skills / résumé management system, the system has: (a) a relational database having a plurality of fields wherein a portion of the fields are arranged in a hierarchical relationship; (b) database population mechanism for populating the database with information, the population mechanism interfacing with a first user and prompting the first user for information for at least a portion of the fields arranged in the hierarchical relationship; (c) query generation mechanism for interfacing with a second user and prompting the second user to select a combination of the fields in the hierarchical relationship to form at least a portion of a query for searching the database; (d) search mechanism operatively connected to database for applying the query to the relational database; and (e) output mechanism for providing the second user with results of the search.
Owner:MEC MANAGEMENT LLC +1
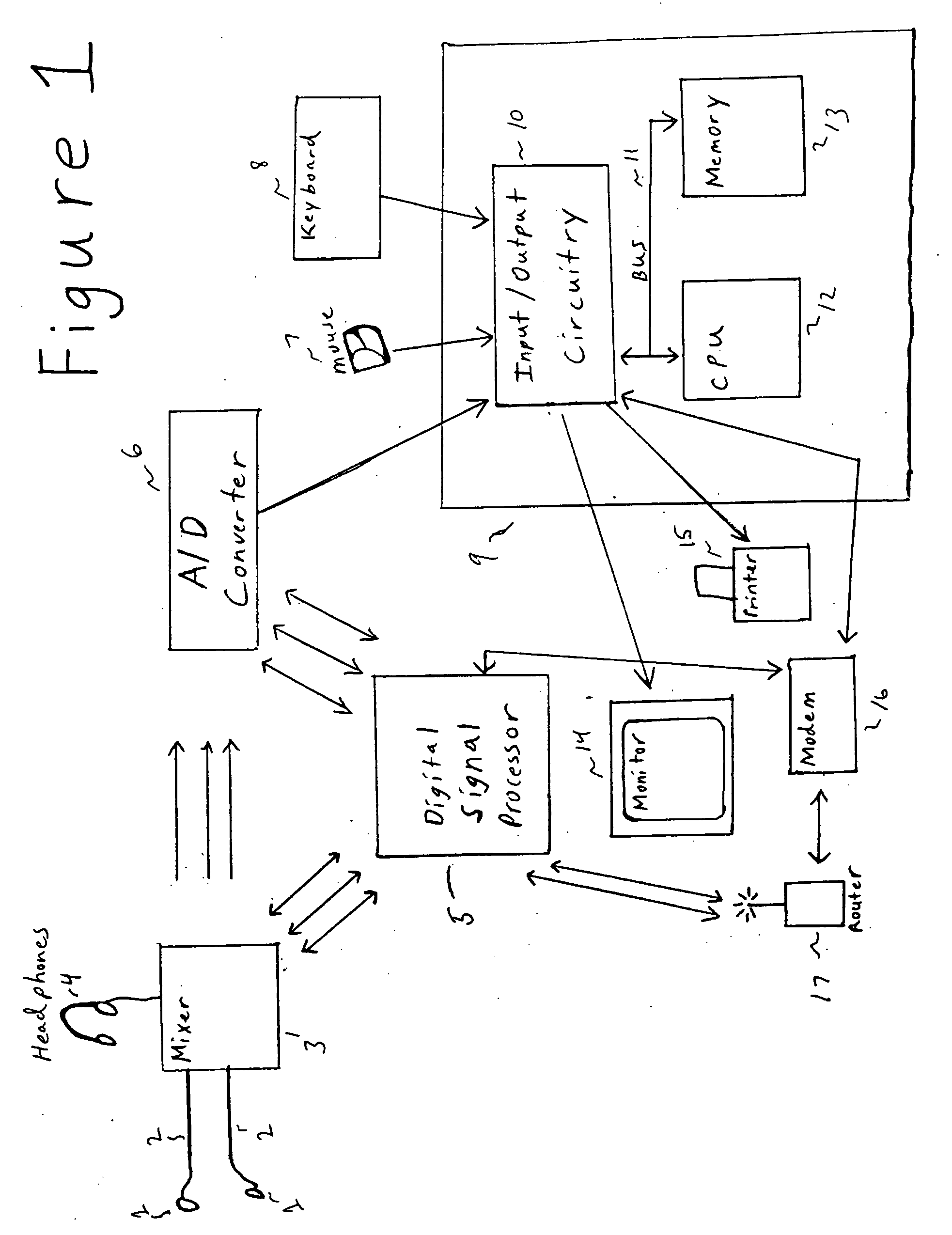
System and method for acquisition and analysis of physiological auditory signals
ActiveUS20070282174A1Improve clinical efficiencyImprove clinical outcomesStethoscopeDiagnostic recording/measuringGraphicsDigital signal processing
A diagnostic system for collecting, processing, recording and analyzing sounds associated with the physiologic activities of various human organs. The system includes a plurality of transducers placed on the body surface at the operator's discretion. The microphones are coupled to analogue / digital signal processing circuitry for enhancement of the desired signal and exclusion of ambient noise. An A / D converter digitizes the incoming data and transmits data, which is divided into a multitude of discrete blocks, received over very finite intervals of time, to a computer workstation and moved through an analysis program sequentially. The program is displayed as a series of icons which depict operations that the program performs and which allow the operator to reprogram the system at any time. The data is finally displayed in graphical format and stored in memory as the program processes each block sequentially.
Owner:AUDIO EVOLUTION DIAGNOSTICS INC
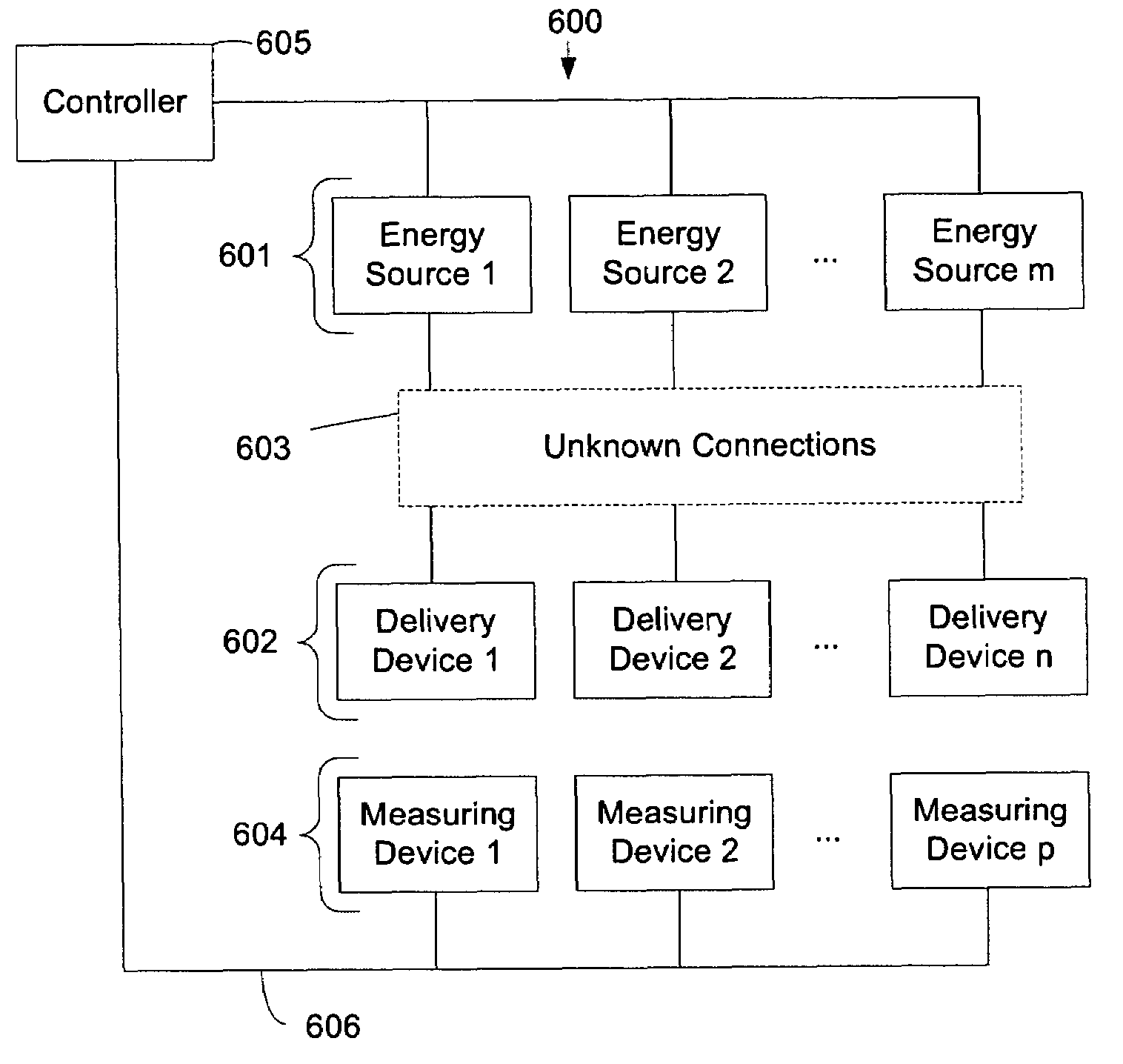
Determining connections of multiple energy sources and energy delivery devices
ActiveUS7163536B2Improve abilitiesHigh strengthSurgical instruments for heatingTherapeutic coolingMeasurement deviceProcess engineering
A method and system are disclosed for the mapping of energy delivery devices to energy sources. Energy capable of affecting a measurable property of the system is delivered through the energy delivery devices from the energy sources. A change in a property when the energy is delivered is measured using measuring devices that are associated in a known way with the energy delivery devices. A profile of the change is compared to a profile of the energy output in order to determine which energy sources produce an output capable of affecting the property measurable by each measuring device and, because of the association between measuring devices and energy delivery devices, each energy delivery device.
Owner:AVANOS MEDICAL SALES LLC
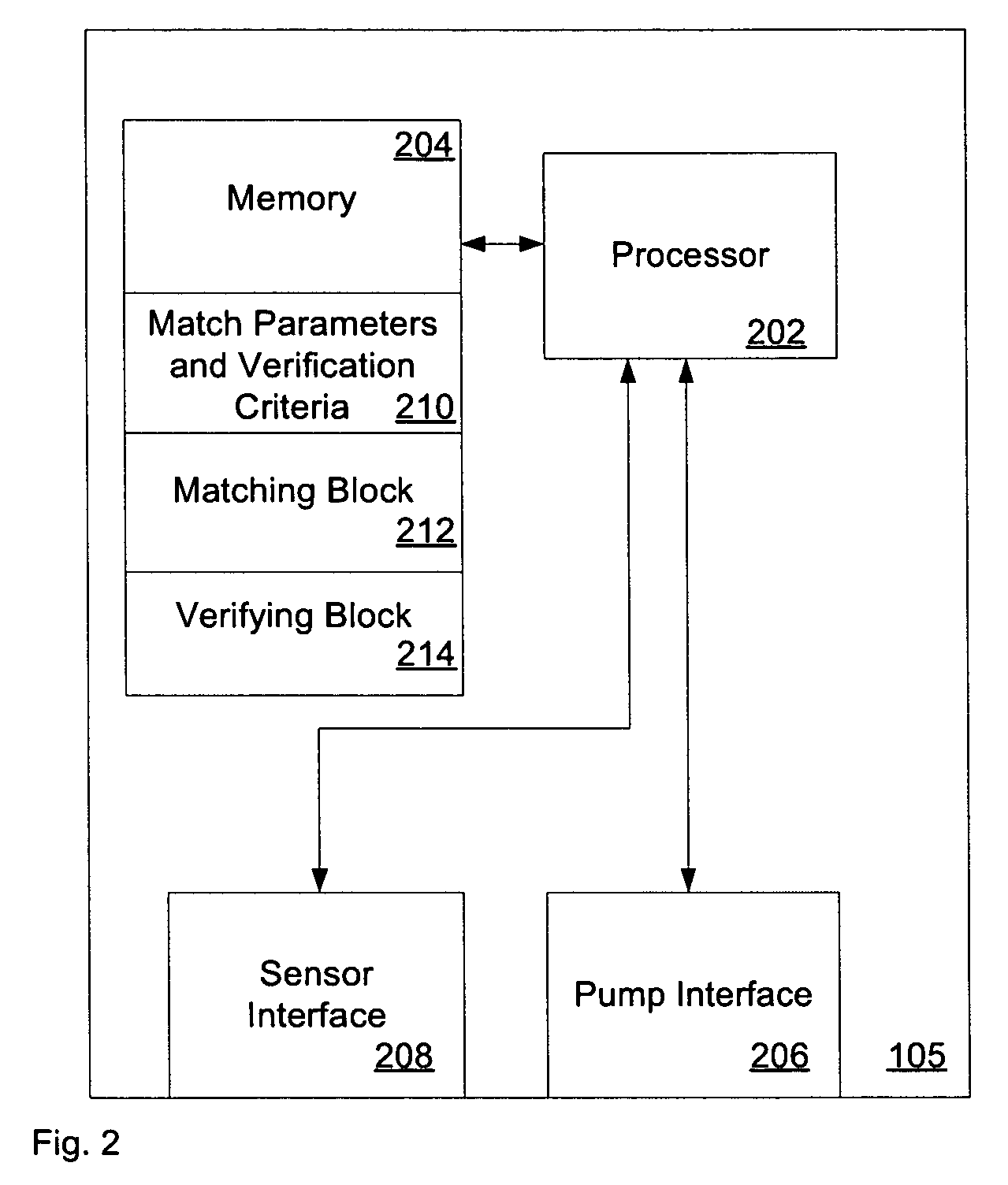
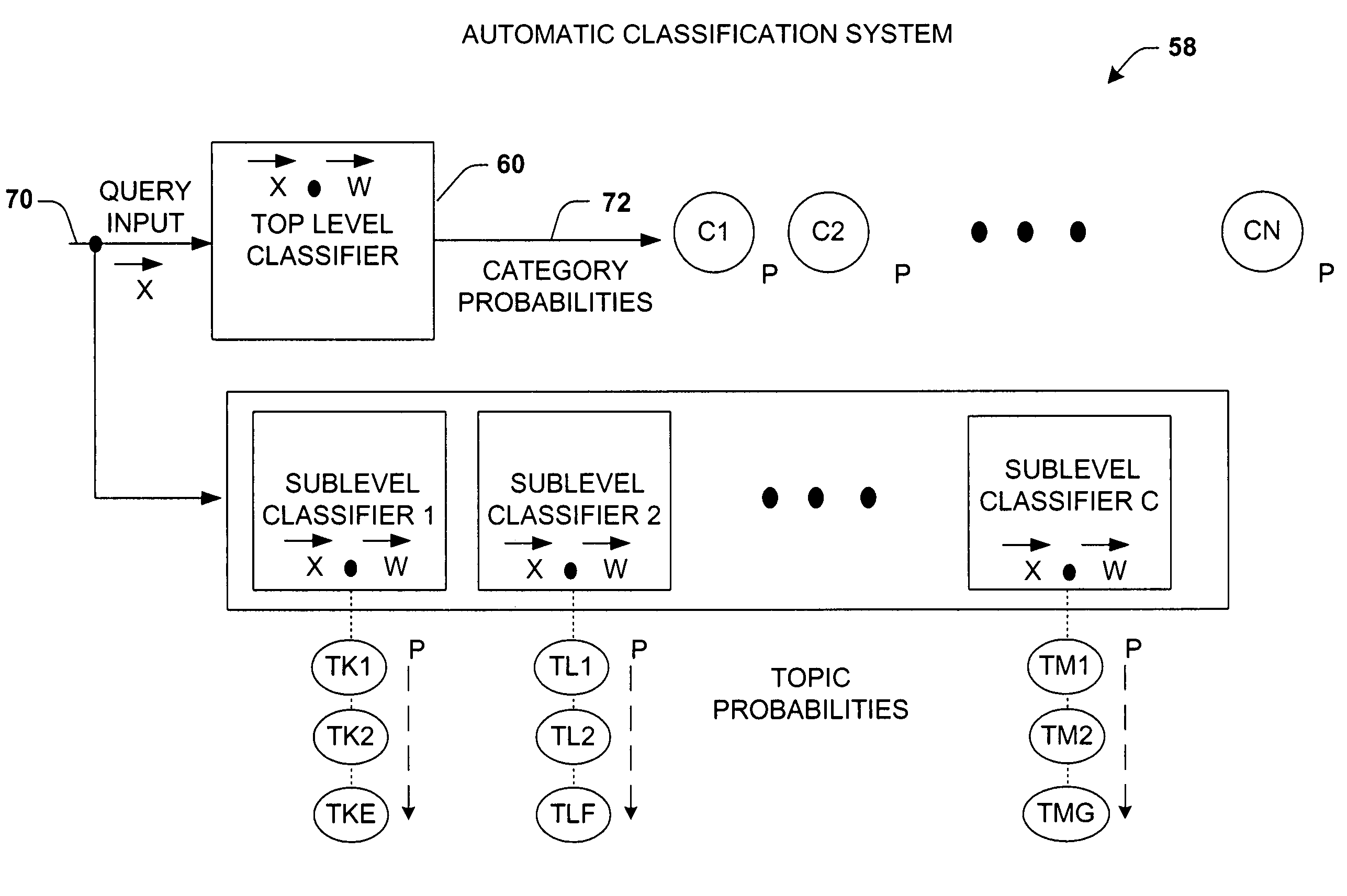
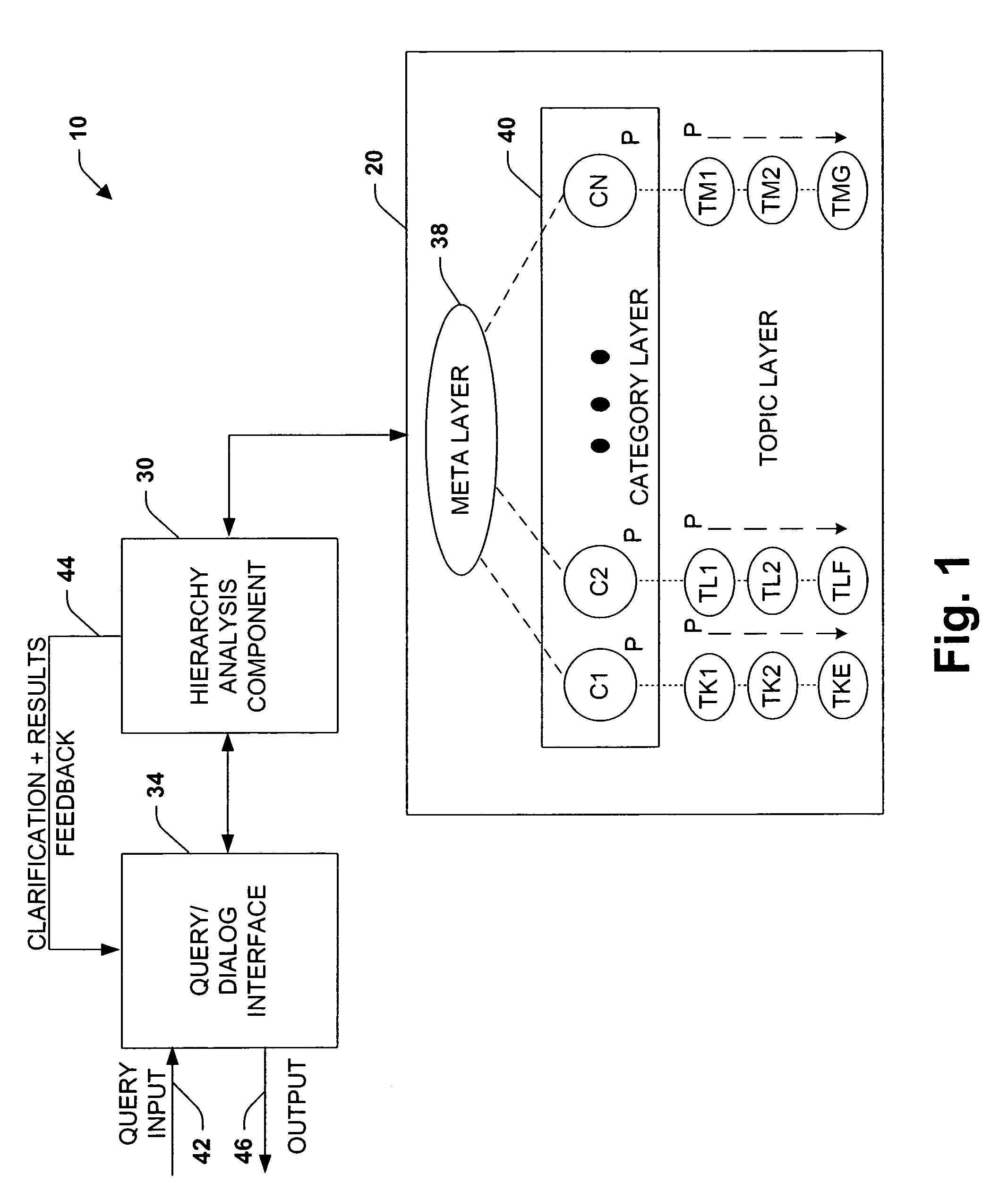
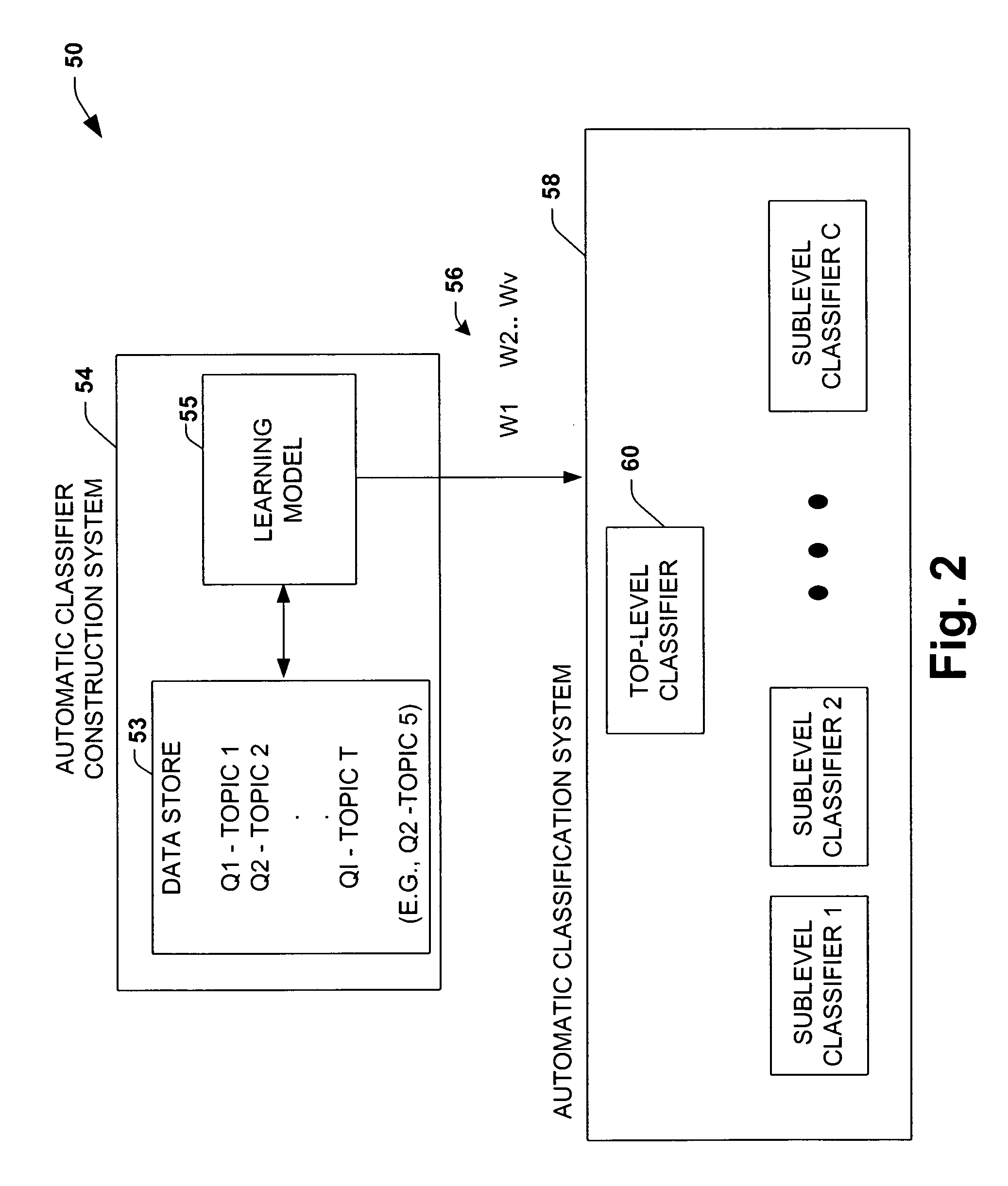
System, representation, and method providing multilevel information retrieval with clarification dialog
InactiveUS7089226B1Facilitates informationFacilitate speed and accuracyData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsStratified analysisDialog box
An information retrieval system, including a learning and real-time classification methodology, is provided in accordance with the present invention. The system includes a hierarchal analysis component that receives a query and processes probabilities associated with N categories, each category having one or more topics, wherein N is an integer. An interactive component drives clarification dialog that is derived from the query and the probabilities associated with the N categories and the one or more topics. The clarification dialog, driven by a rule-based policy, a decision-theoretic analysis considering the costs of dialog to focus the results versus the costs of browsing larger lists, or combinations of rules and decision-theoretic analysis is employed when valuable to determine at least one category of the N categories to facilitate retrieval of at least one of the topics.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
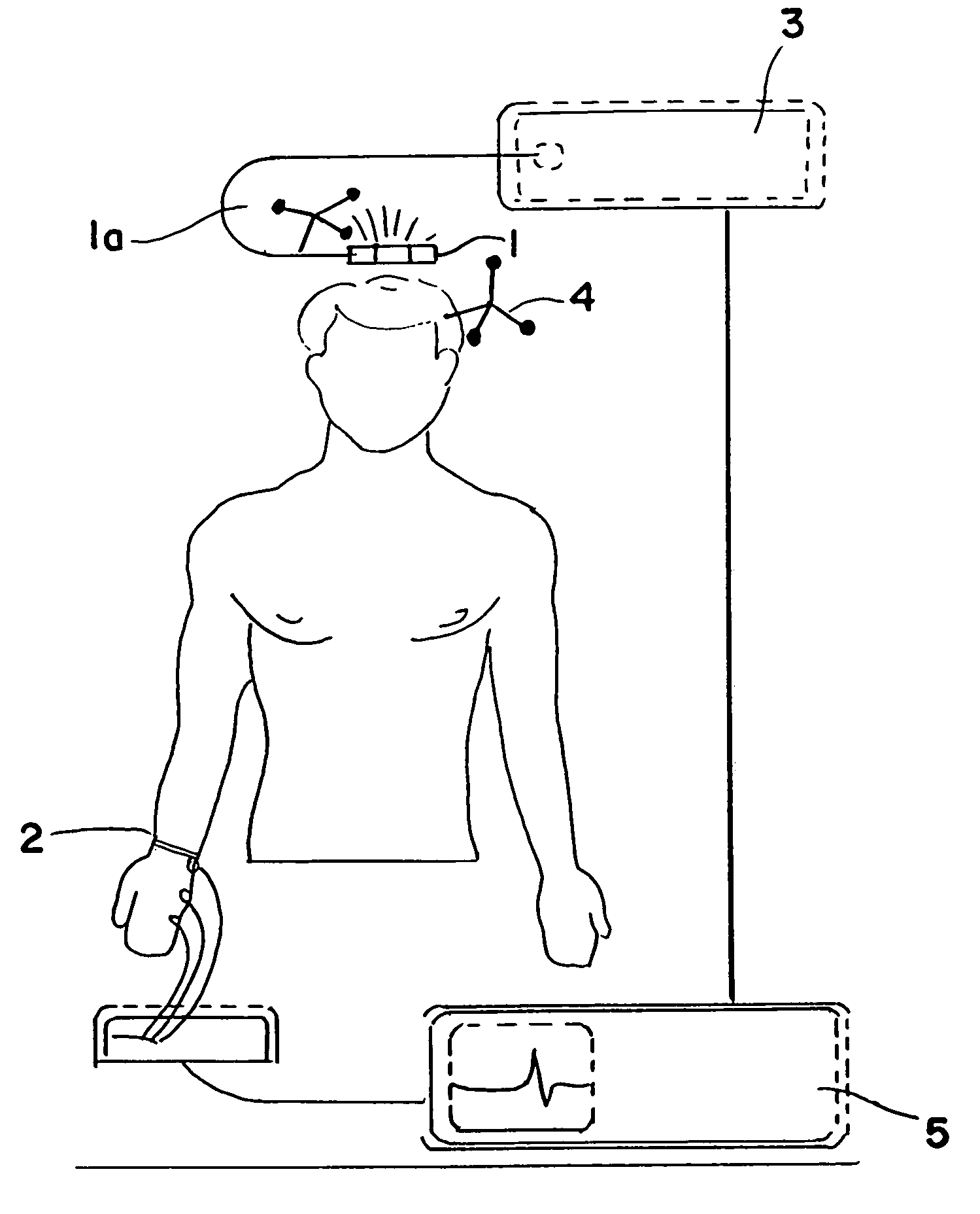
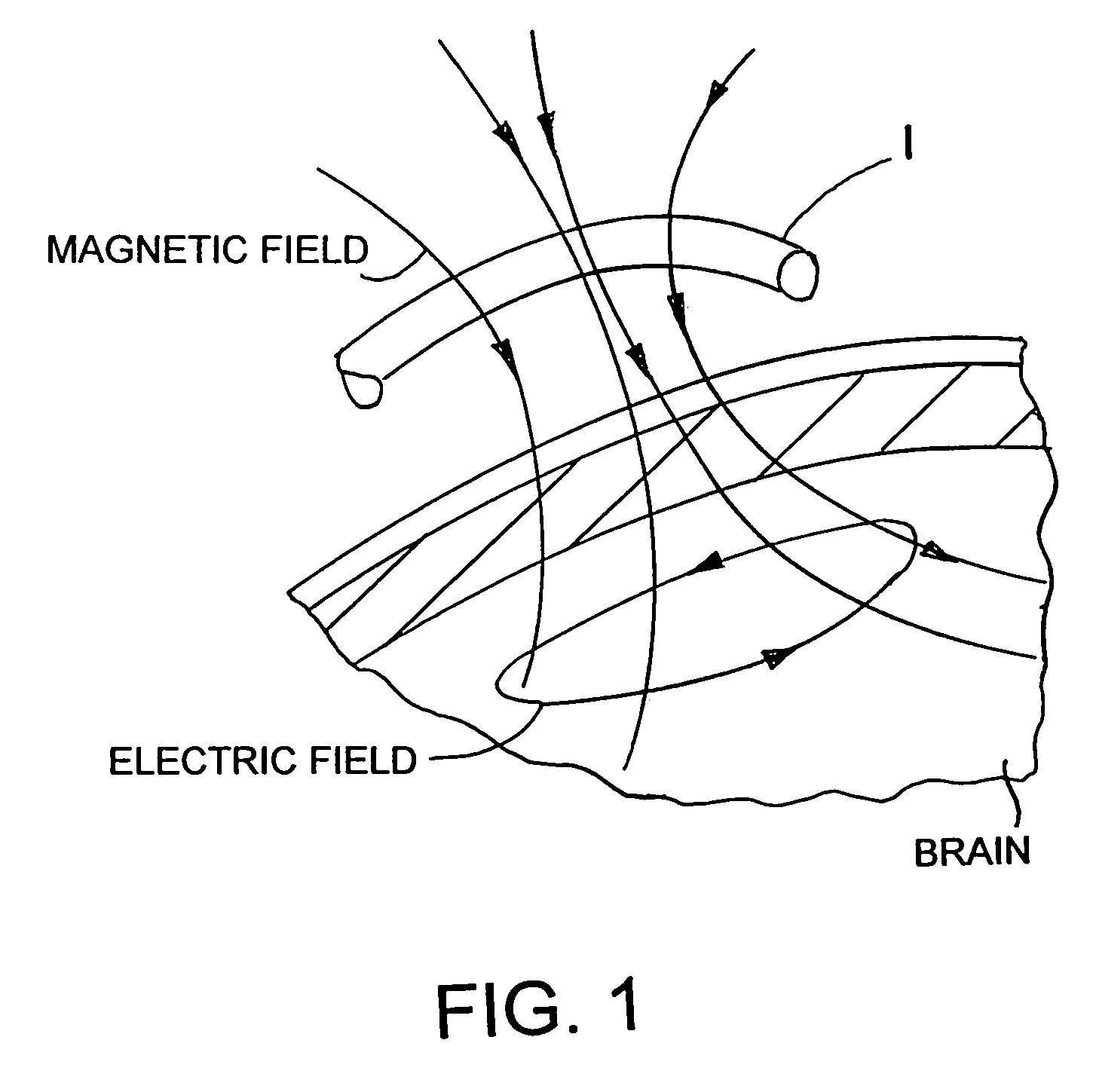
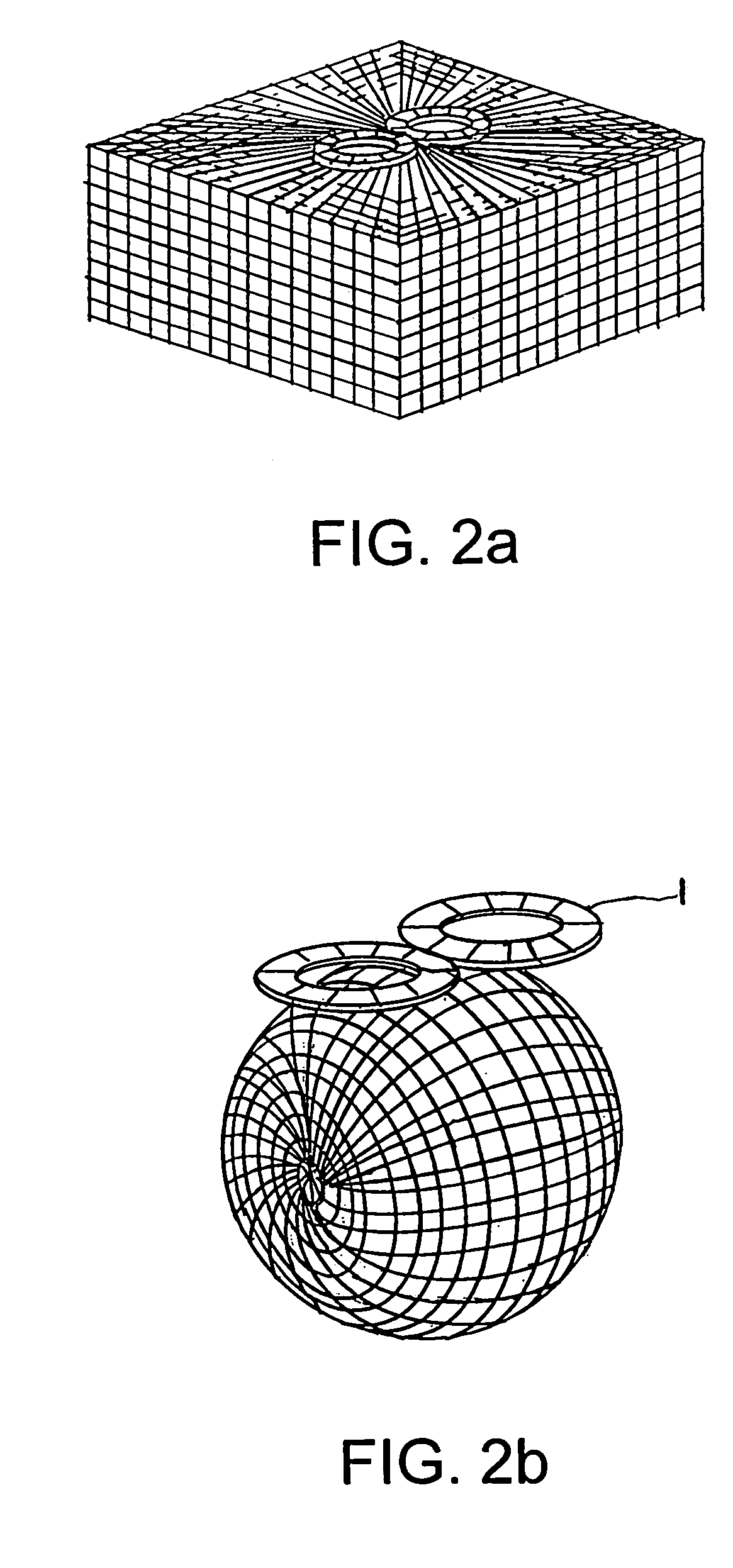
Method and device for transcranial magnetic stimulation
InactiveUS7008370B2Stimulating areaBroaden applicationElectroencephalographyElectrotherapyPower flowSpatial structure
The invention relates to a method for stimulating specific areas of a brain using an induction device, comprising the following steps: recording the spatial structure of the head, in particular the brain; generating a simulation model of the induction device; and arranging the induction device relative to the head such that a specific area of the brain determined by means of the simulation model of the induction device is stimulated by a current flowing in the induction device, as well as to a method for stimulating specific areas of a brain using an induction device, comprising the following steps: recording the spatial structure of the head, in particular the brain; generating a simulation model of the head; and arranging the induction device relative to the head such that a specific area of the brain determined by means of the simulation model of the head is stimulated by a current flowing in the induction device, as well as to a device for stimulating specific areas of a brain using an induction device connected to a marker.
Owner:BRAINLAB
Medical apparatus system having optical fiber load sensing
ActiveUS20110087112A1Reduces sensor artifactReduction factorStrain gaugeCatheterProcess logicOptical property
Apparatus is provided for diagnosing or treating an organ or vessel, wherein a device having at optical fiber contact force sensors disposed in a distal extremity thereof and a deflection mechanism configured to deflect the elongate body at a location proximal of the distal extremity. The optical fiber contact force sensors are configured to be coupled to processing logic programmed which computes a force vector responsive to detected changes in the optical characteristics of the optical fiber contact force sensors arising from deflection of the distal extremity resulting from contact with the tissue of the wall of the organ or vessel.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL INT HLDG SARL
Medical apparatus system having optical fiber load sensing capability
ActiveUS8075498B2Facilitate speedHelp accuracyStrain gaugePerson identificationLoad sensingEngineering
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL INT HLDG SARL
Securing an augment to a prosthetic implant component
InactiveUS6896702B2Improve securityEasy selectionJoint implantsKnee jointsTibiaProsthesis Implantation
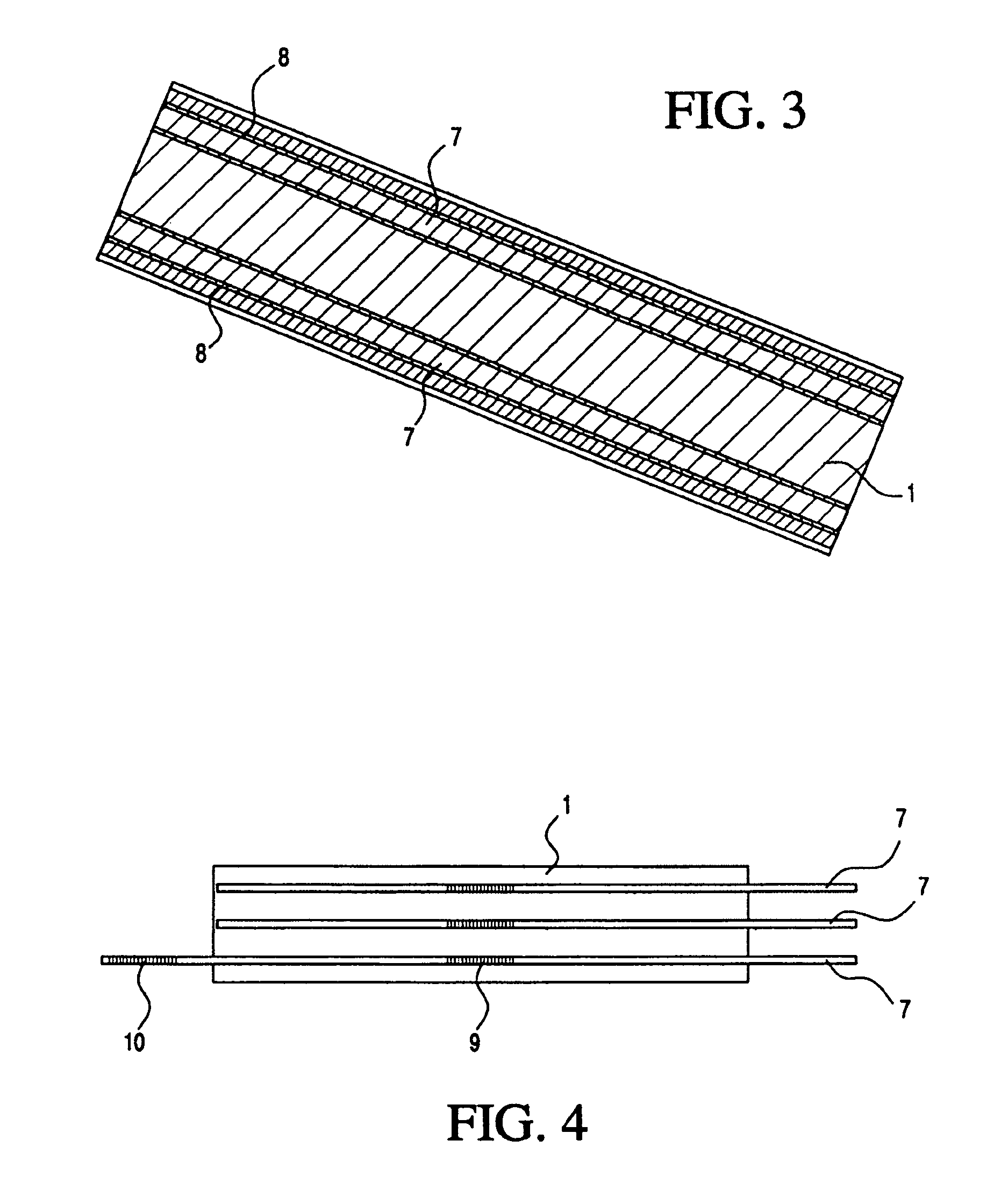
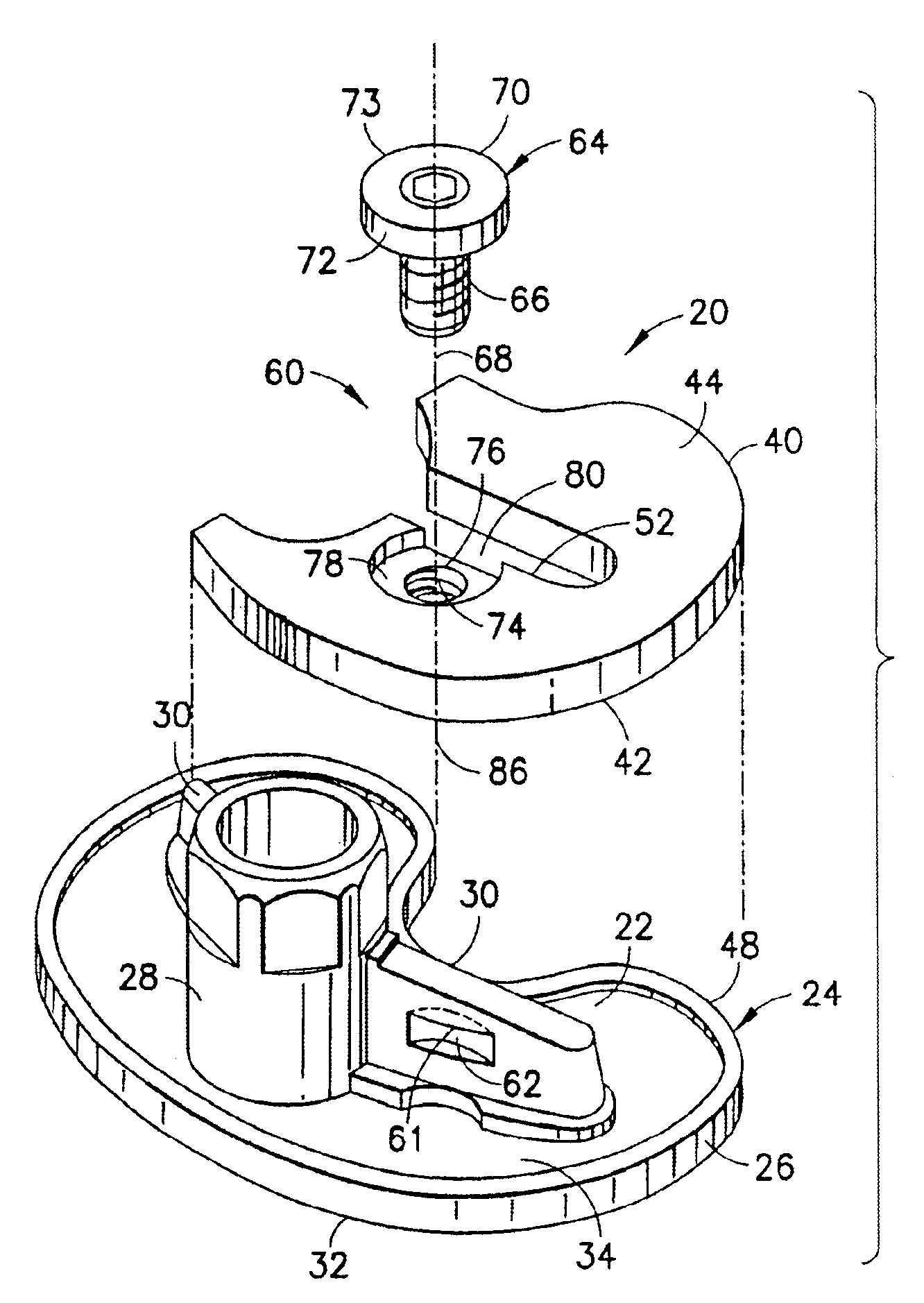
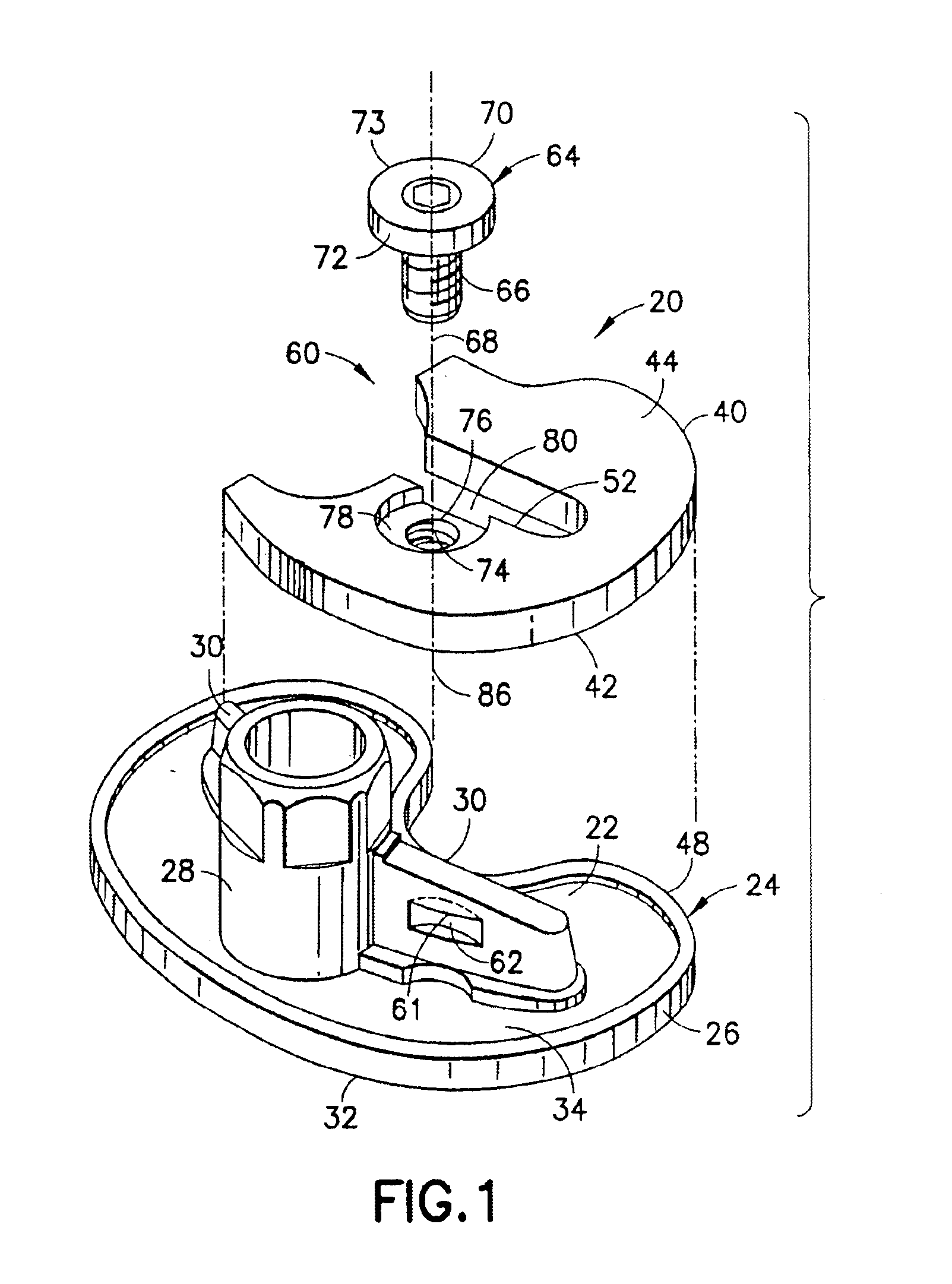
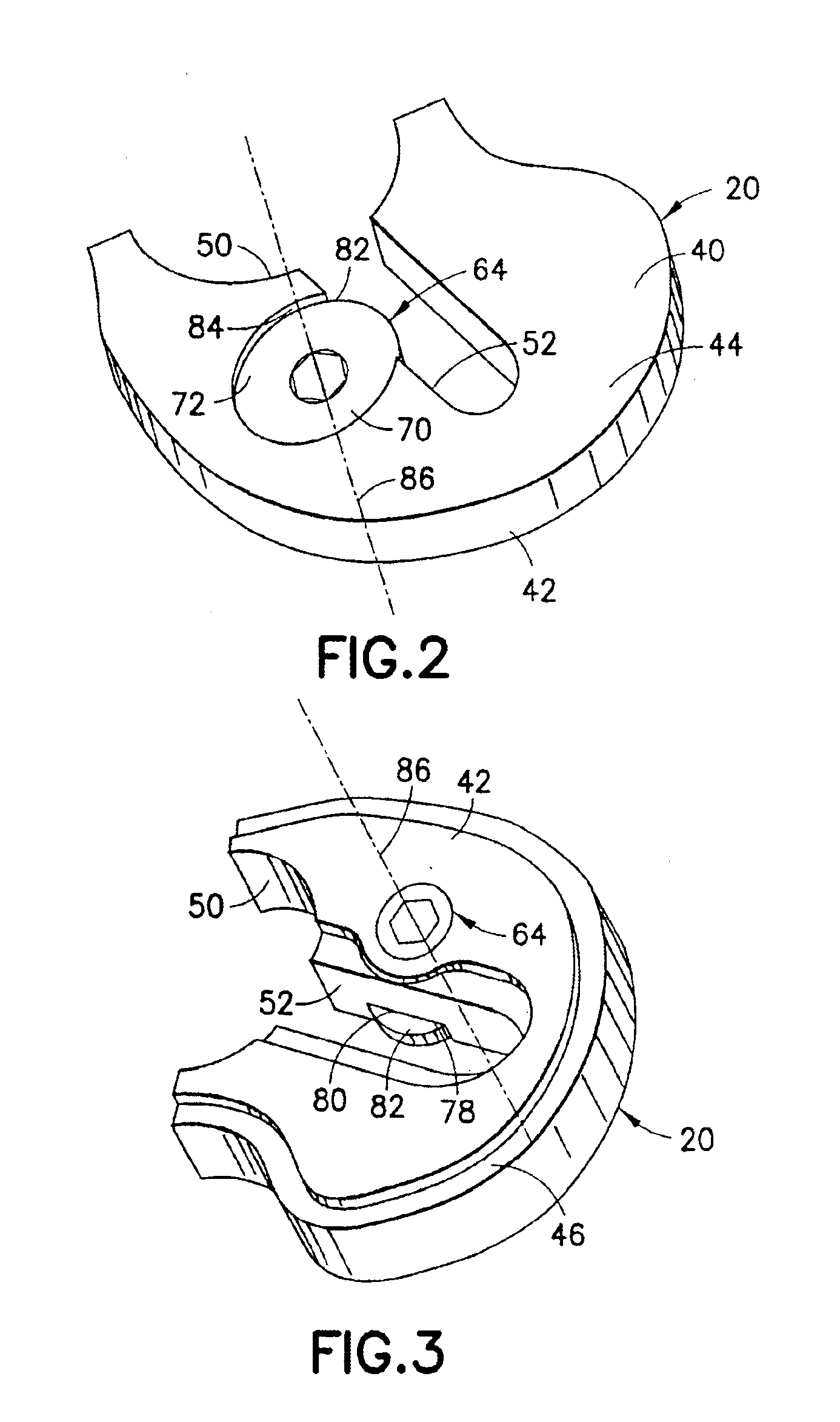
A selected augment, shown as a tibial augment, is secured at an augmentation location on a prosthetic implant component, shown as a tibial implant component, by a securing element assembled with the body of the augment for displacement relative to the augment body to selectively engage an abutment located on a depending structure of the implant component, adjacent the augmentation location, so as to establish a securing force between the securing element and the depending structure for urging the augment against the implant component, and thereby secure the augment to the implant component at the augmentation location. In the tibial augment, a distal surface includes surface portions extending in anterior-posterior directions and oriented essentially normal to medial-lateral directions.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
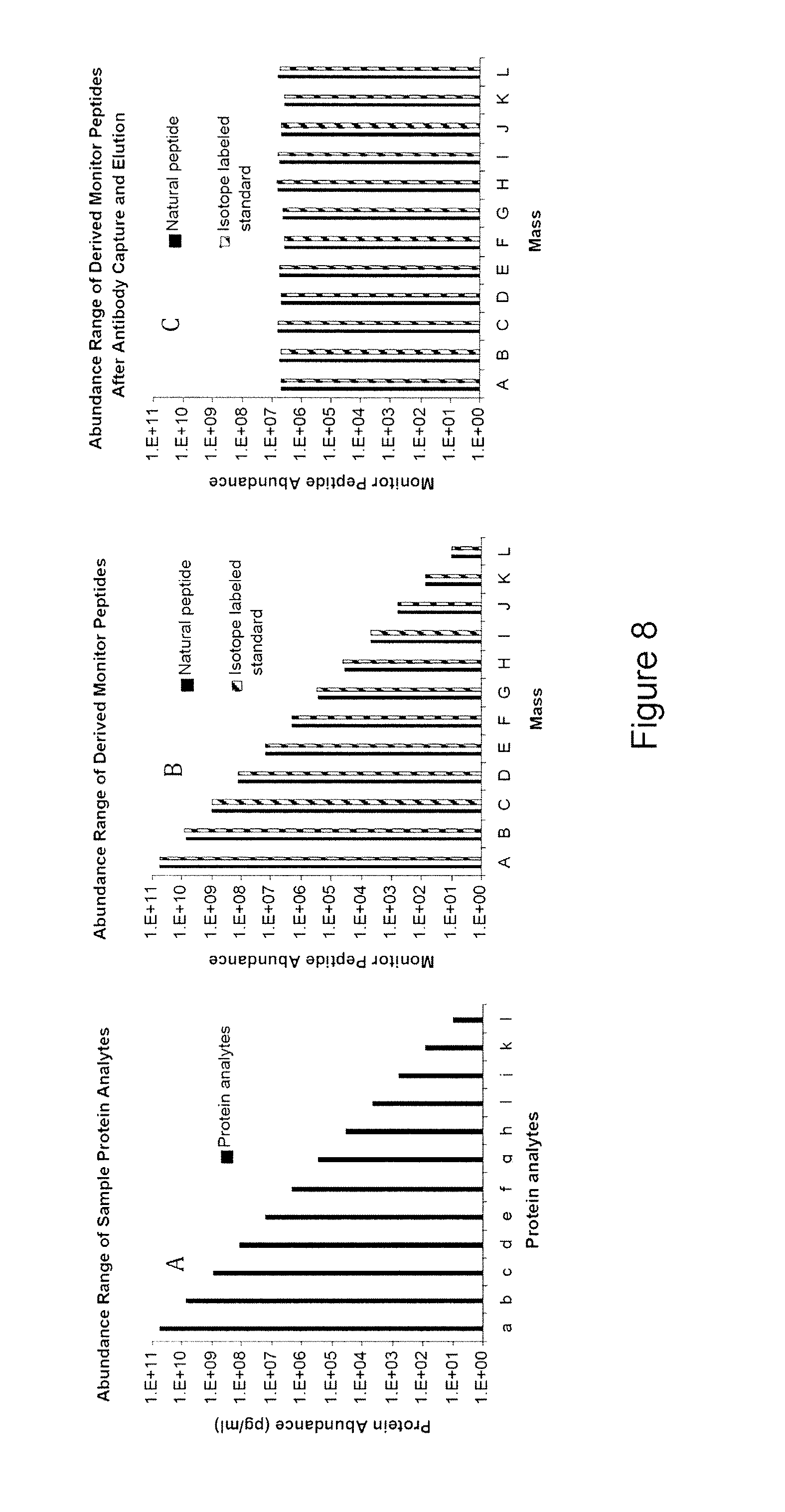
High sensitivity quantitation of peptides by mass spectrometry
InactiveUS7632686B2Reduce complexityOverwhelm resolutionSamplingComponent separationChemical structureProtein target
The instant invention provides an economical flow-through method for determining amount of target proteins in a sample. An antibody preparation (whether polyclonal or monoclonal, or any equivalent specific binding agent) is used to capture and thus enrich a specific monitor peptide (a specific peptide fragment of a protein to be quantitated in a proteolytic digest of a complex protein sample) and an internal standard peptide (the same chemical structure but including stable isotope labels). Upon elution into a suitable mass spectrometer, the natural (sample derived) and internal standard (isotope labeled) peptides are quantitated, and their measured abundance ratio used to calculate the abundance of the monitor peptide, and its parent protein, in the initial sample.
Owner:ANDERSON FORSCHUNG GROUP
Medical apparatus system having optical fiber load sensing capability
ActiveUS8182433B2Facilitate speedHelp accuracyStrain gaugePerson identificationRobotic systemsProcess logic
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL INT HLDG SARL
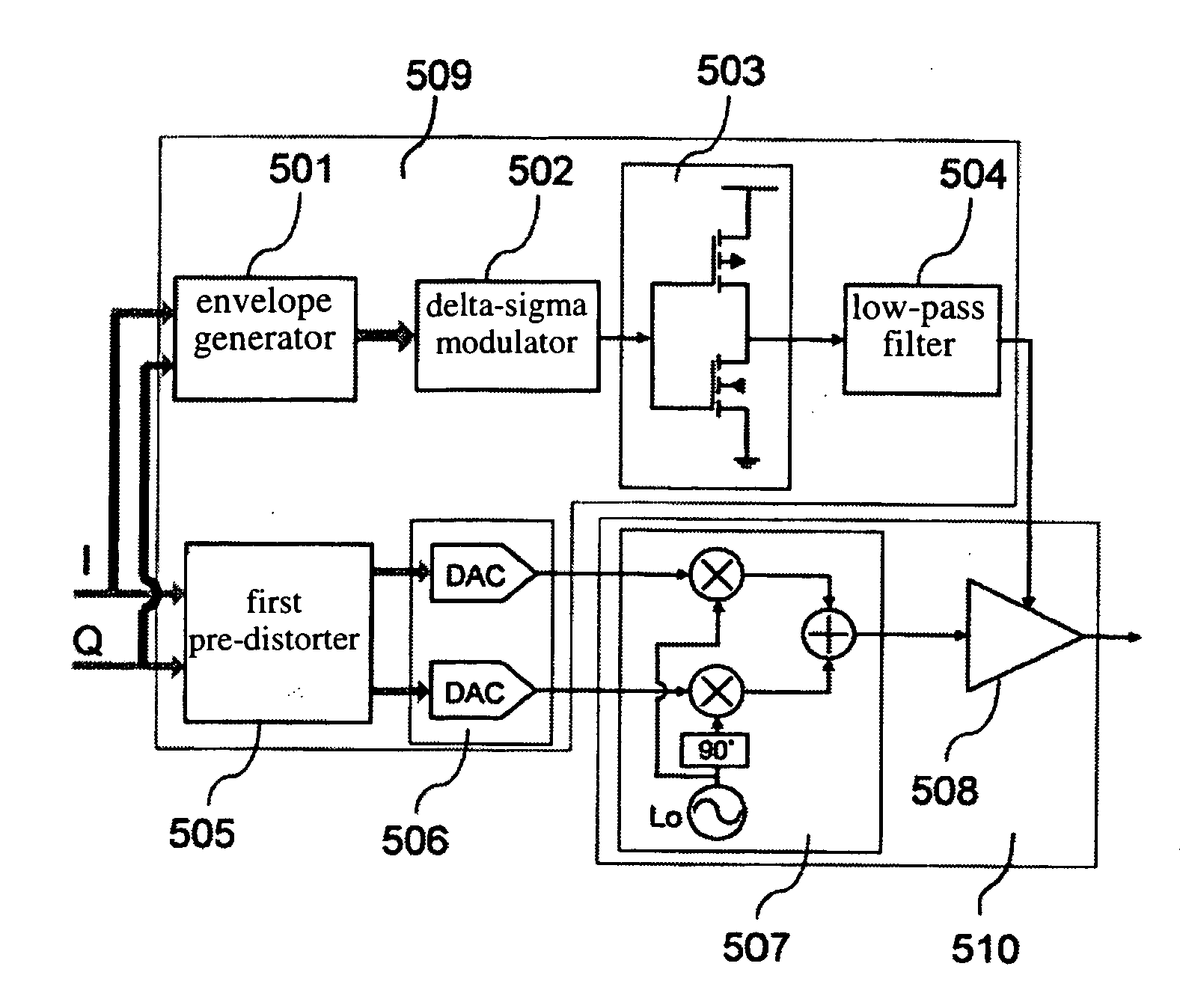
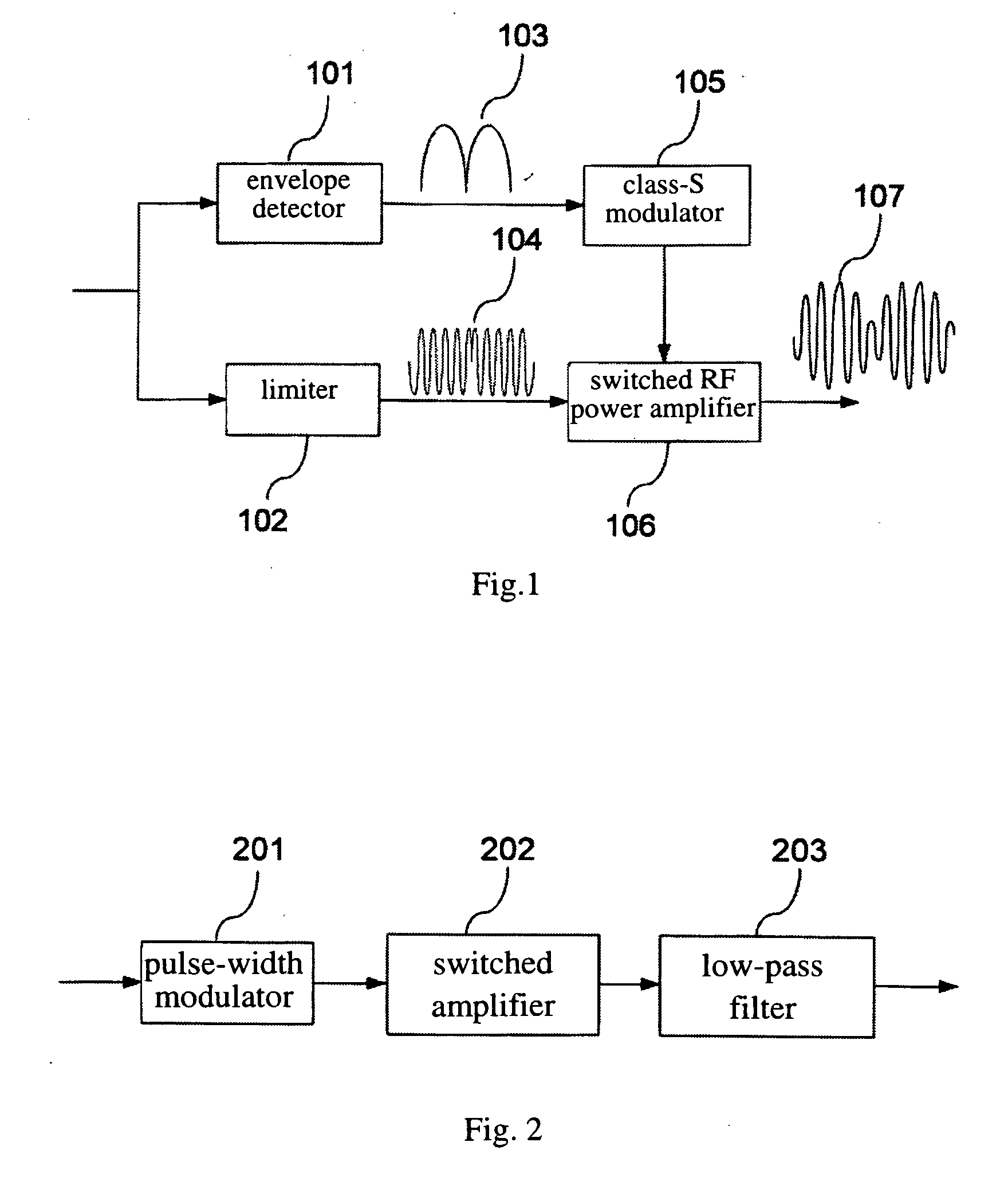
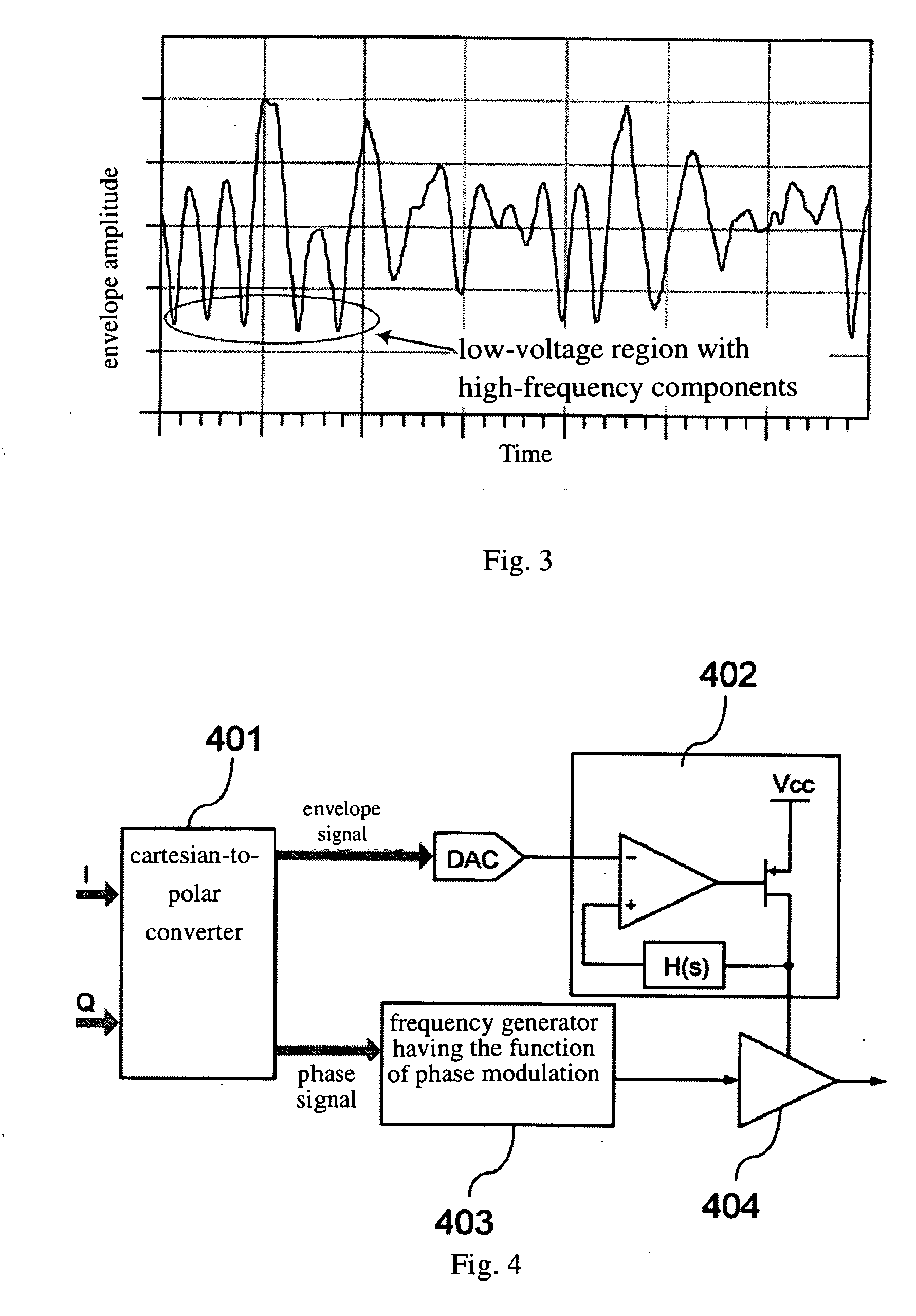
Microwave transmitter and the method for increasing envelope bandwidth
InactiveUS20070018718A1Low efficiencyPower flexibleAmplifier detailsDc amplifiers with modulator-demodulatorCarrier signalEngineering
The microwave transmitter of the present invention can perform two-terminal dynamic modulation with respect to the voltage supply terminal and the RF input terminal of a RF power amplifier. The microwave transmitter of the present invention comprises a first modulator and a second modulator. The first modulator uses the baseband digital delta-sigma modulation technique to process the envelope signal and outputs this signal to the voltage supply terminal of the RF power amplifier as a supply voltage. The second modulator uses the baseband digital pre-distortion technique to process the IQ-modulated carrier and outputs this signal to the RF input terminal of the RF power amplifier as a RF input signal. Thereby, the RF power amplifier can highly efficiently reconstruct the power-amplified RF modulated carrier without distortion at the RF output terminal. In addition, the baseband digital processing techniques used in the two modulators make the microwave transmitter of the present invention suitable for multi-mode operation.
Owner:NAT SUN YAT SEN UNIV +1
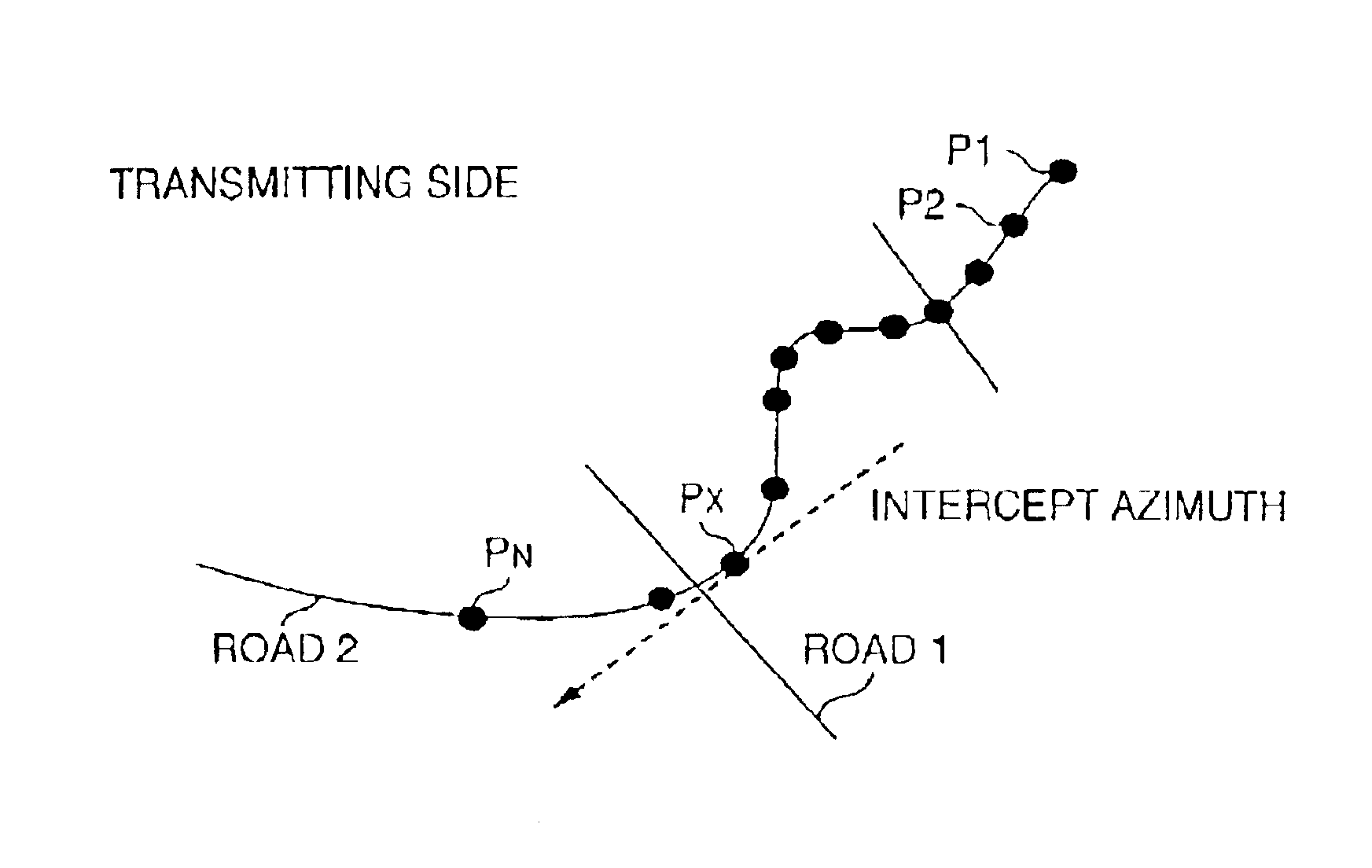
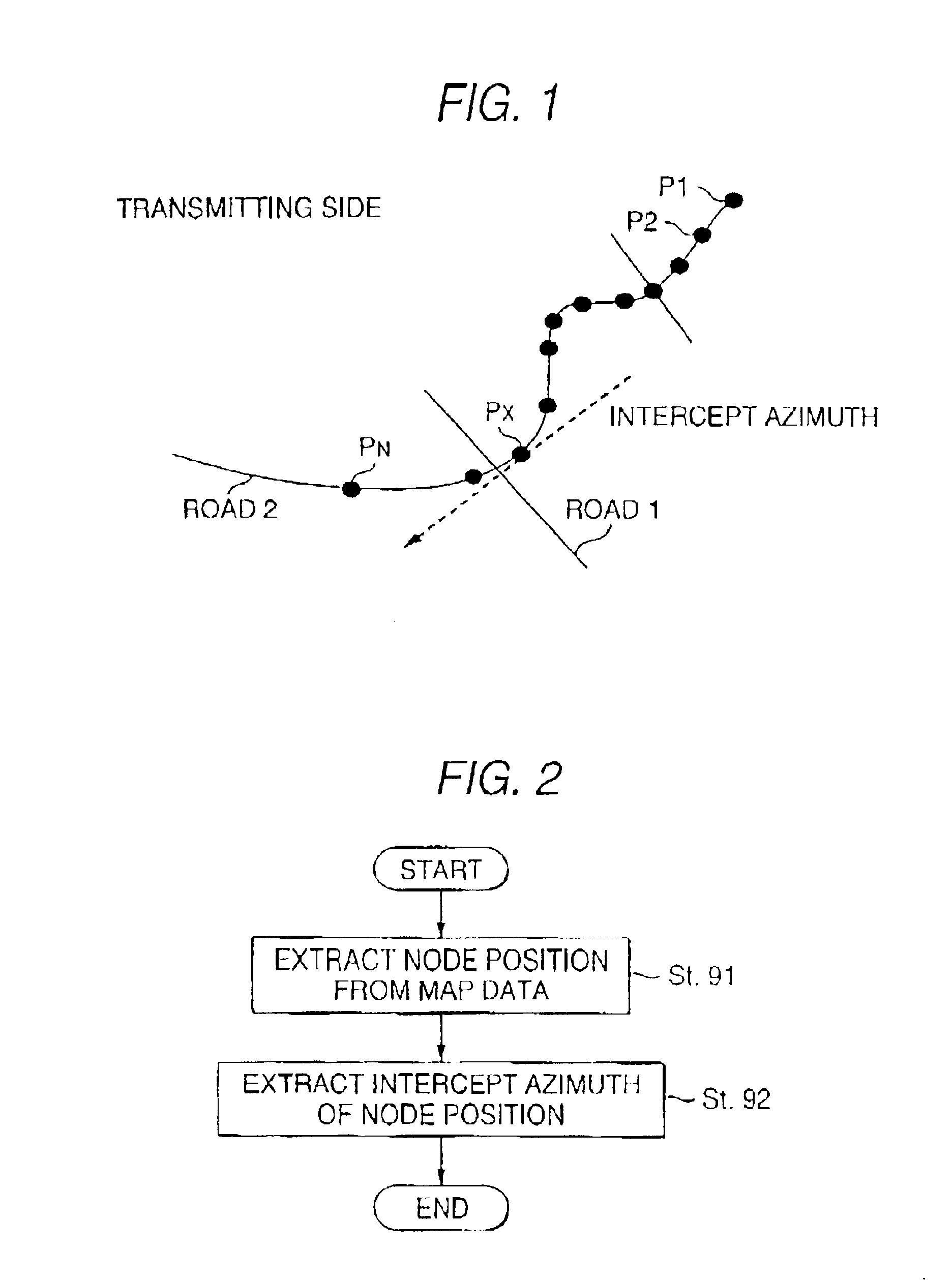
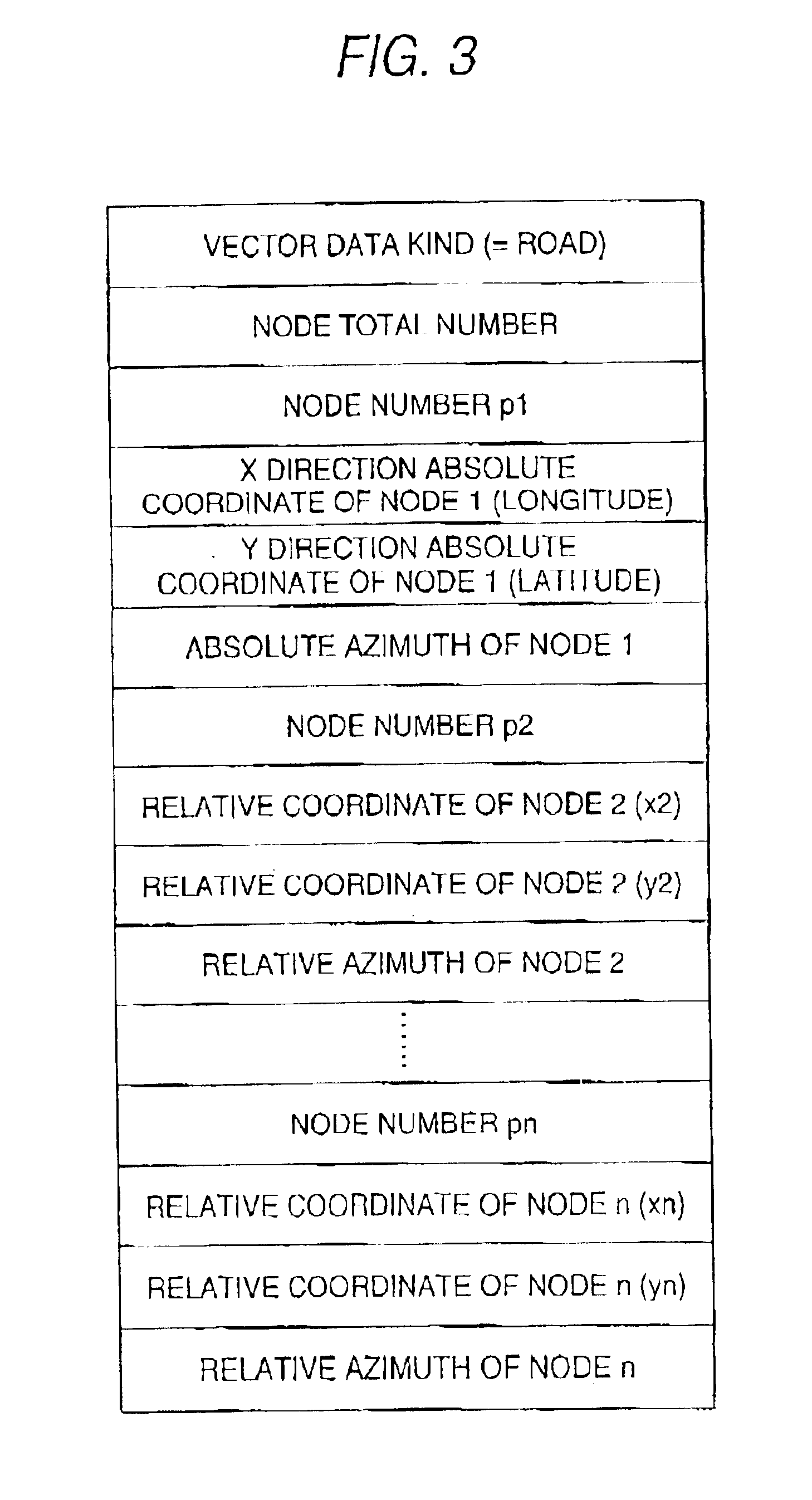
Method for transmitting information on position on digital map and device used for the same
InactiveUS6931319B2Improve matching efficiencyEfficiently and accurately be transmittedInstruments for road network navigationDetection of traffic movementComputer scienceMap matching
A method of transmitting position information of a digital map capable of transmitting a position on a digital map efficiently and accurately in which a transmitting side transmits position information including coordinate series information for specifying a vector shape on a digital map and a receiving side execute map matching by the coordinate series information to the thereby identify the vector shape on the digital map, the coordinate series information is transmitted by adding azimuth information of a coordinate point included in the information thereto. By transmitting shape data by adding the azimuth information thereto, accuracy of matching can be promoted and necessary time for matching can be shortened.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
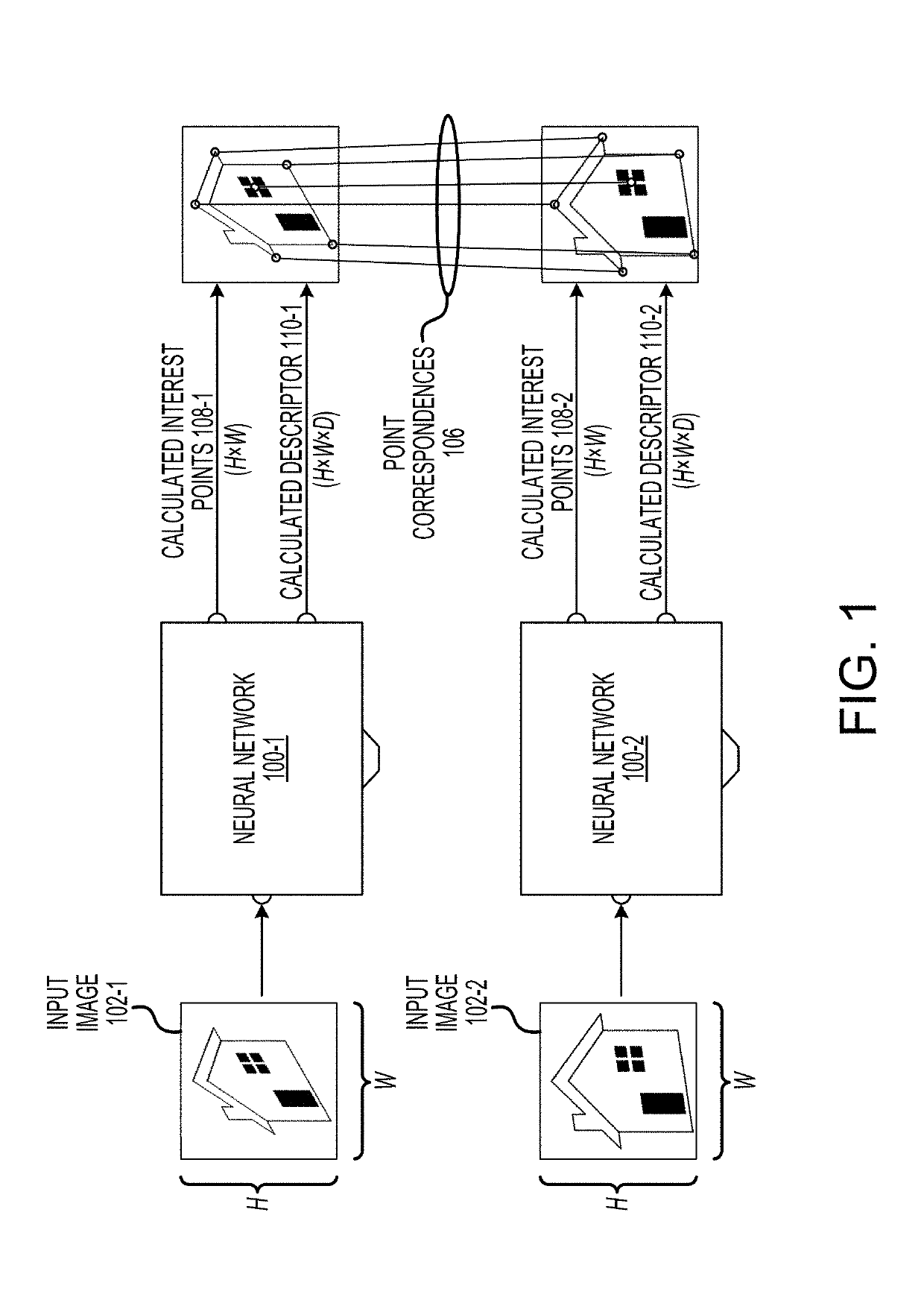
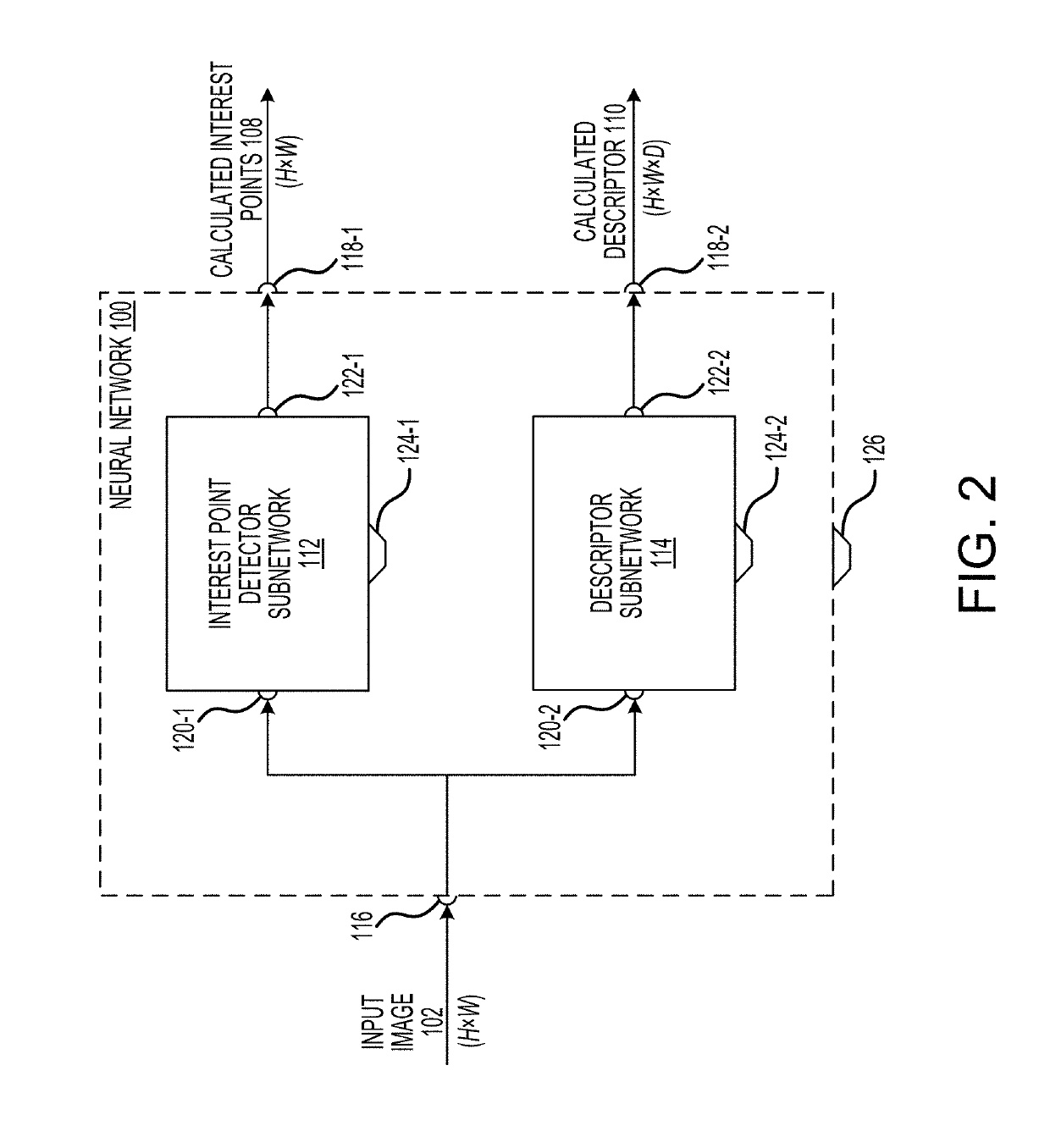
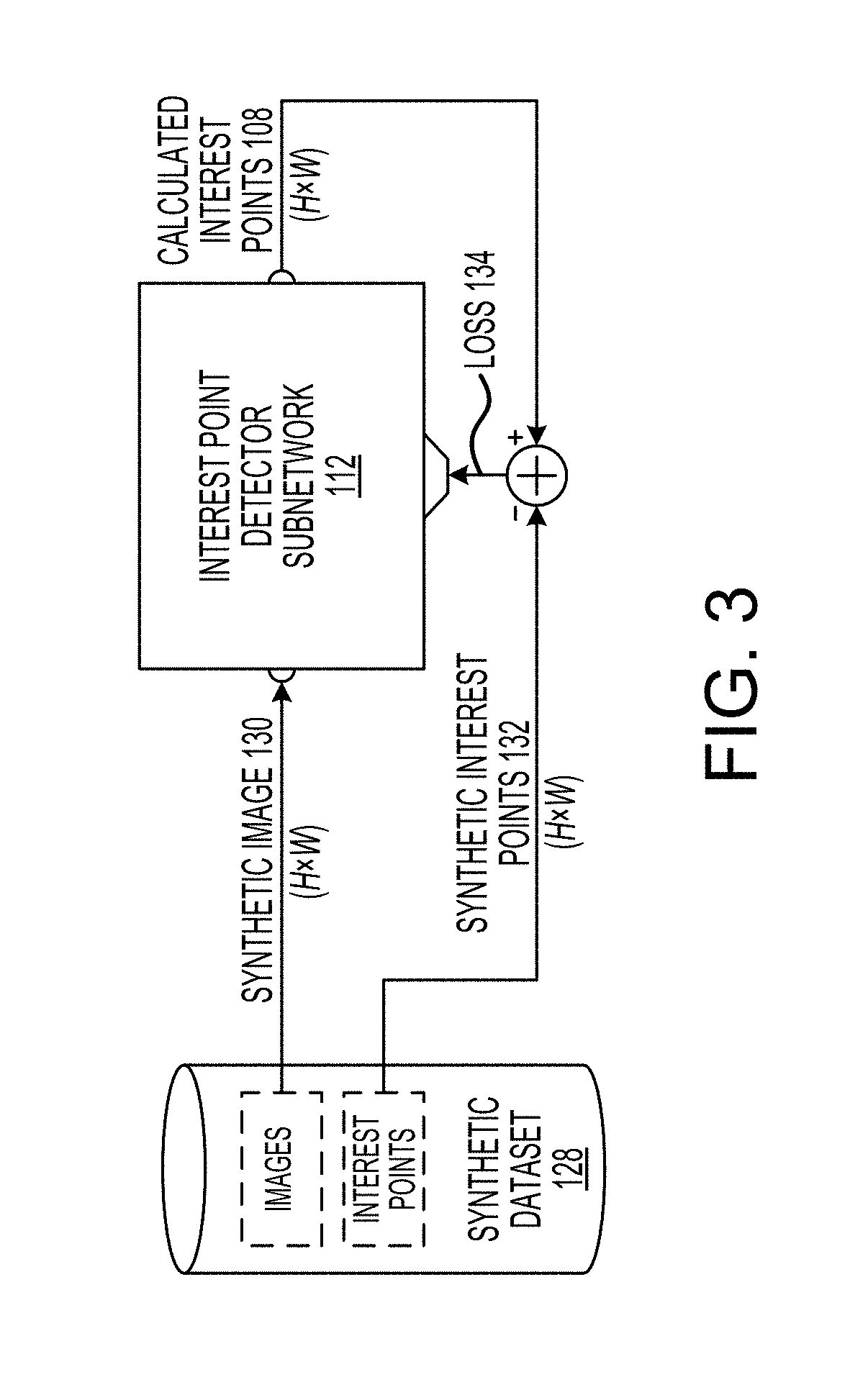
Fully convolutional interest point detection and description via homographic adaptation
ActiveUS20190147341A1Boosting interest point detection accuracyReadily apparentImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionEyepiece
Systems, devices, and methods for training a neural network and performing image interest point detection and description using the neural network. The neural network may include an interest point detector subnetwork and a descriptor subnetwork. An optical device may include at least one camera for capturing a first image and a second image. A first set of interest points and a first descriptor may be calculated using the neural network based on the first image, and a second set of interest points and a second descriptor may be calculated using the neural network based on the second image. A homography between the first image and the second image may be determined based on the first and second sets of interest points and the first and second descriptors. The optical device may adjust virtual image light being projected onto an eyepiece based on the homography.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP
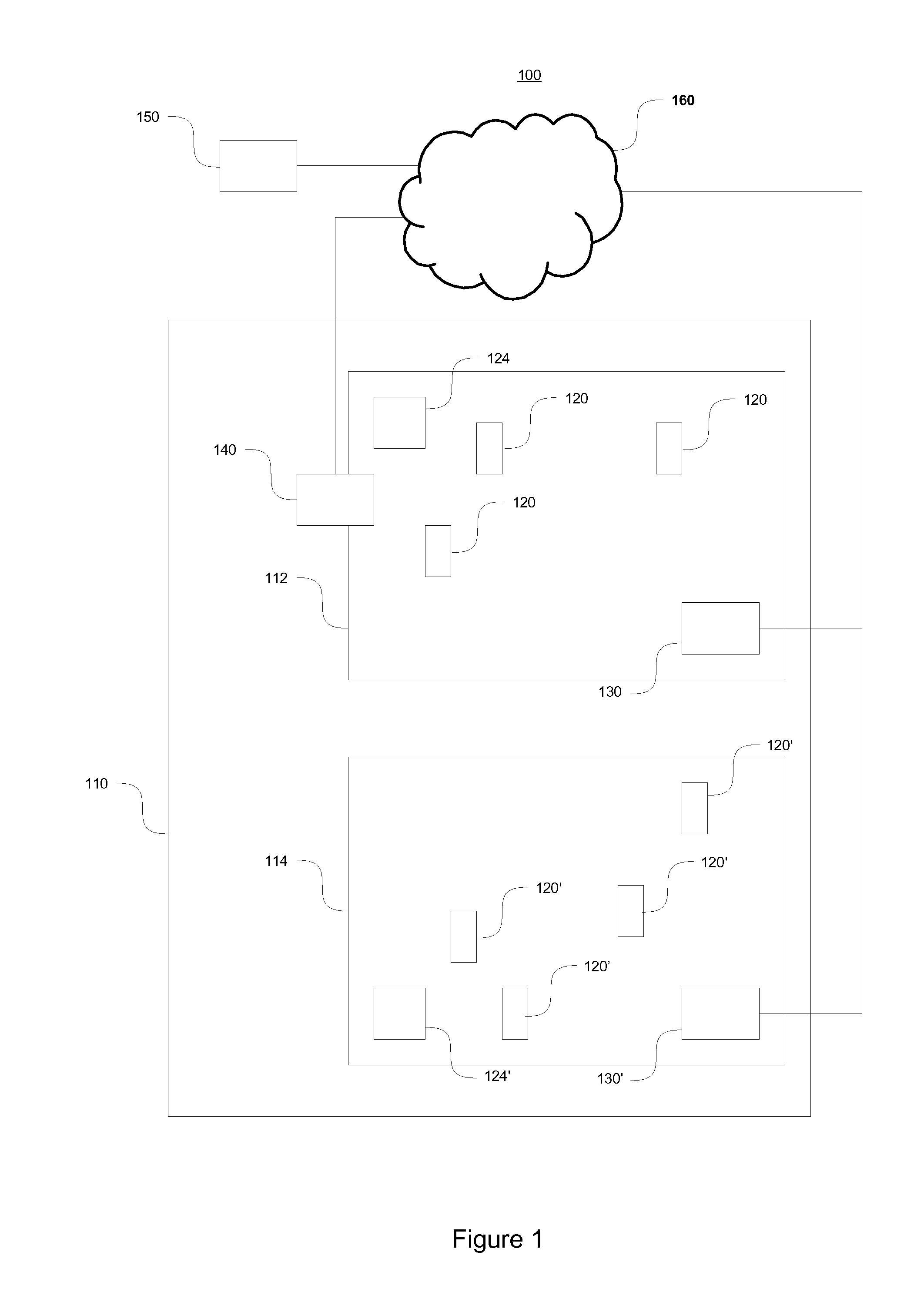
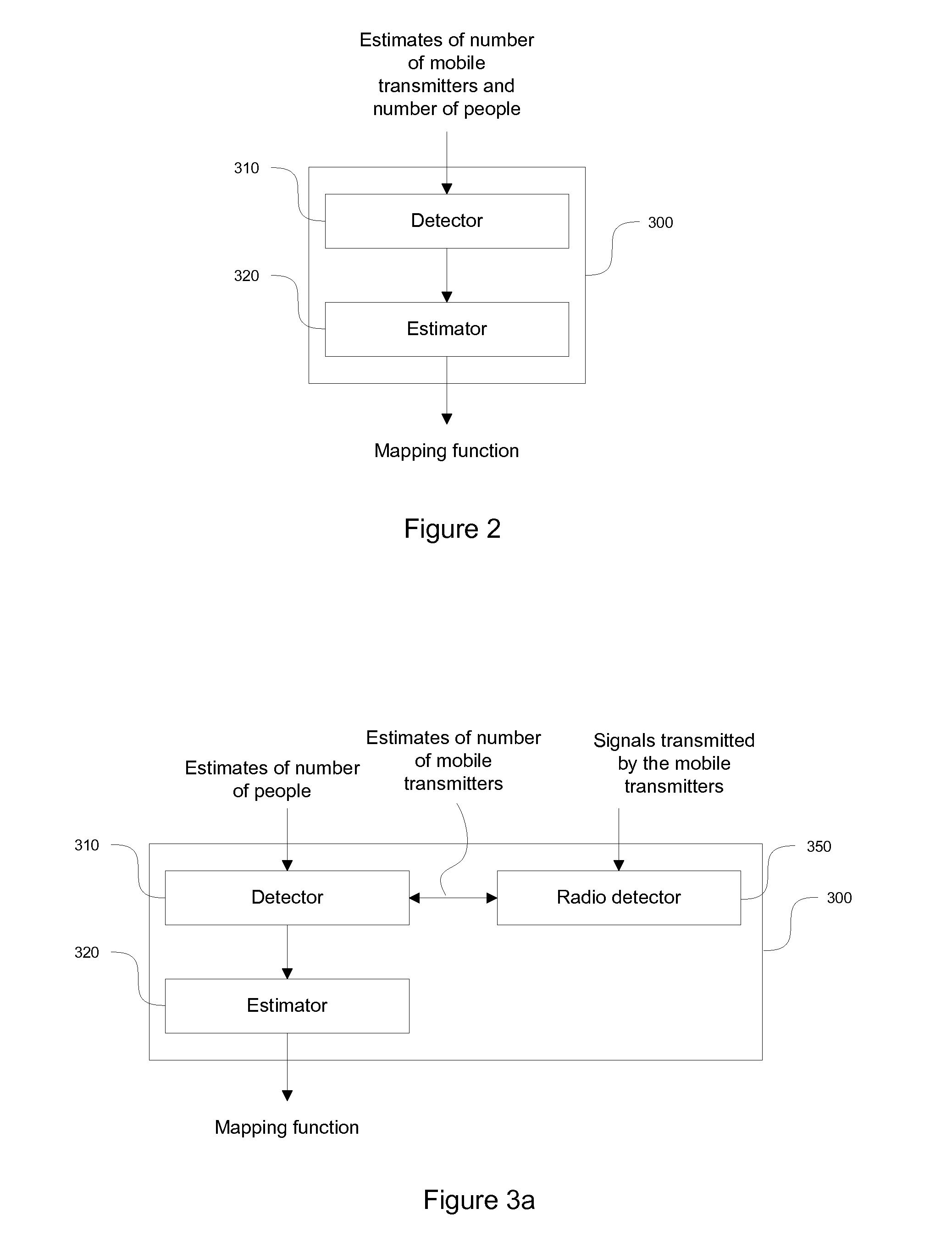
A method, an apparatus and a system for estimating a number of people in a location
InactiveUS20150334523A1Facilitate improved accuracyHelp accuracyIndividual entry/exit registersWireless commuication servicesTransmitterComputer program
An apparatus, method, system and computer program for estimating a number of people within a location. The estimation includes obtaining a plurality of estimates of the number of mobile transmitters and respective estimates of the number of people within a first location during a first period of time, and determining a mapping function providing a mapping between an estimate of the number of mobile transmitters at a location and an estimate of the number of people at the location on basis of the plurality of estimates of the number of mobile transmitters and the respective plurality of estimates of the number of people for determination of a second estimate of the number of people within a second location during a second period of time on basis of a second estimate of the number of mobile transmitters obtained at the second location during the second period of time.
Owner:INNORANGE
Water wand
InactiveUS20010042797A1Uniform and gentle patternWater wand more gentleDust removalFire preventionEngineeringSingle line
A hand-held, portable dispensing device (i.e. a wand) is described for dispensing a curtain spray pattern of liquid which includes an elongated tubular body having an open end and a closed end. The open end can be connected to a flexible hose or the like for supplying pressurized liquid to the tubular body which has a plurality of spaced openings along its length on one side. The spacing of the discharge openings is determined by the diameter of the openings, and the ratio of the total area of the openings to the inside diameter of the tubular body is in a defined range. The openings can be in a single line or in a plurality of rows, for example, An adjustable control valve and a quick connect coupler can also be included.
Owner:SHRIGLEY ROSS P
Method for sequencing using branching fraction of incorporatable nucleotides
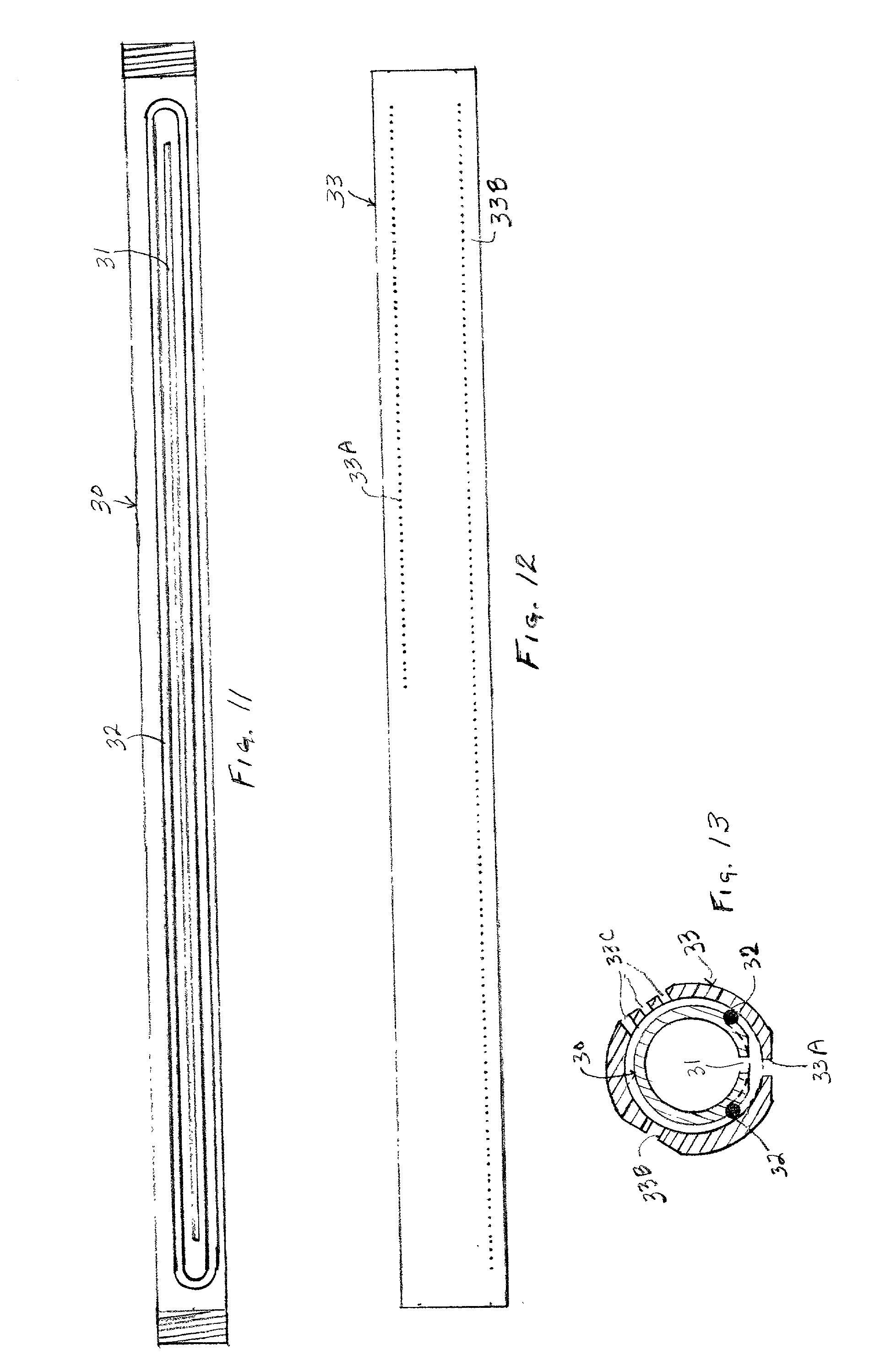
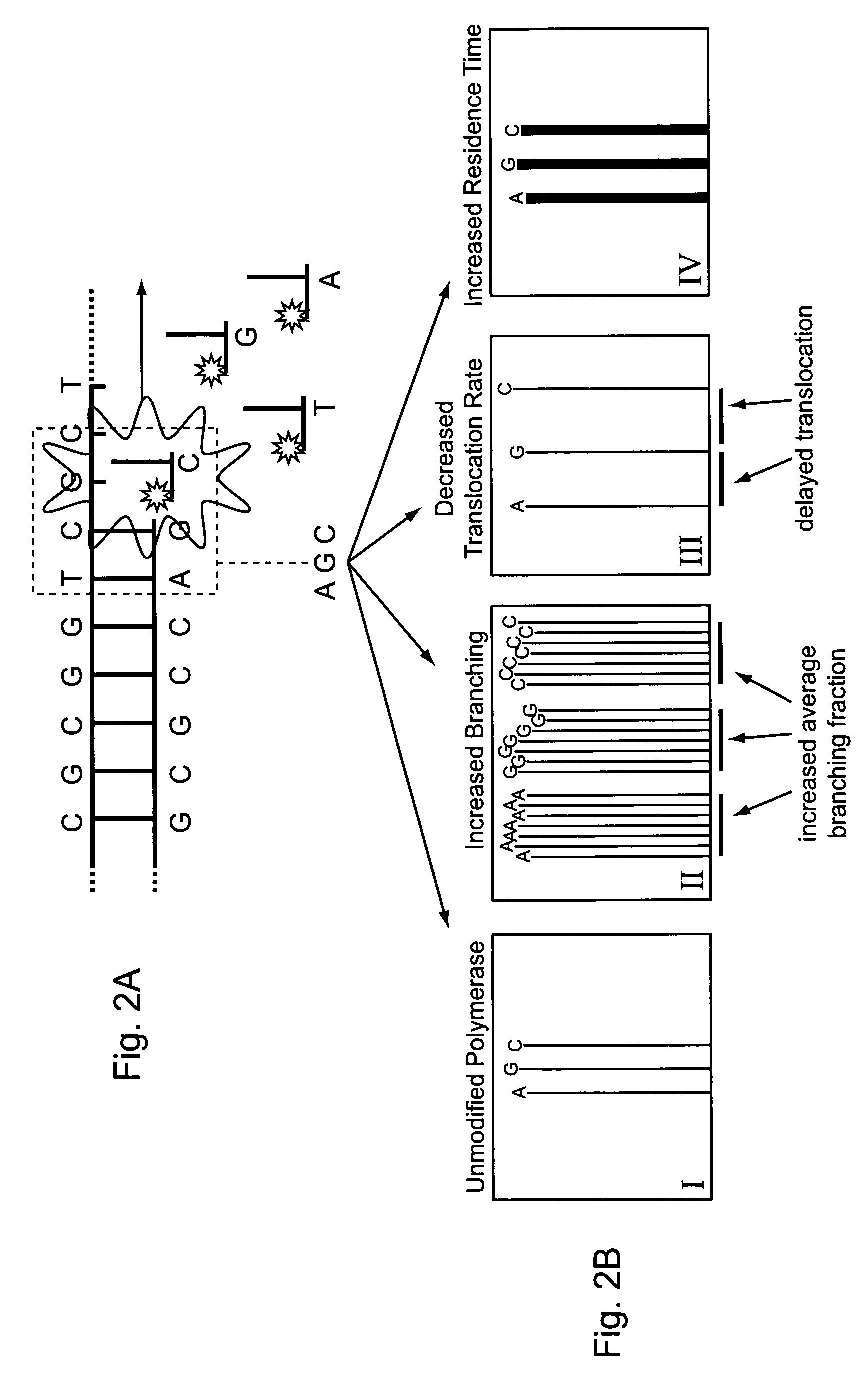
ActiveUS8530164B2Easy to identifyIncrease) the branching rate of a polymerization reactionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleotidePolymerase L
Provided are methods for enhanced sequencing of nucleic acid templates. Also provided are reaction conditions that increase branching fractions during polymerization reactions. Also provided are compositions comprising modified recombinant polymerases that exhibit branching fractions that are higher than the branching fractions of the polymerases from which they were derived. Provided are compositions comprising modified recombinant polymerases that exhibit delayed translocation relative to the polymerases from which they were derived. Also provided are compositions comprising modified recombinant polymerases that exhibit increased nucleotide or nucleotide analog residence time at an active site of the polymerase. Provided are methods for generating polymerases with the aforementioned phenotypes and methods of using such polymerases to sequence a DNA template or make a DNA. Also provided are methods and nucleic acid sequencing systems for determining which labeled nucleotide is incorporated at a site during a template-dependent polymerization reaction.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Method for scanning projective capacitive touch panel
InactiveUS20110175847A1Reduce the differenceScanning accuracy can be promotedTransmission systemsInput/output processes for data processingCurrent voltageVoltage reference
The present invention relates to a method for scanning a projective capacitive touch panel. The method includes the following steps: scanning the mutual capacitance that are divided into at least two groups by applying different frequency excitation signals to different mutual capacitance groups, wherein a frequency of a excitation signal applied to a mutual capacitance group with greater RC constant is lower than that of a excitation signal applied to a mutual capacitance group with smaller RC constant; obtaining a first current voltage of each mutual capacitance; comparing the first current voltage with a first reference voltage to obtain candidate mutual capacitance whose first current voltage exceed the first reference voltage by a first threshold value; scanning the candidate mutual capacitance by applying a low frequency excitation signal; obtaining a second current voltage of each candidate mutual capacitance; comparing the second current voltage of each candidate mutual capacitance with a corresponding second reference voltage to obtain touched mutual capacitance whose second current voltage exceed the corresponding second reference voltage by a second threshold value.
Owner:TPK TOUCH SOLUTIONS (XIAMEN) INC +1
Accessory device for nail and staple guns
InactiveUS6631836B2Eliminate impact damageEasy to useStapling toolsNailing toolsStaple gunTongue and groove
An accessory device for fastener-driving tools such as nail and staple guns is provided. The device serves as a positioning guide for the tool and is designed to provide sufficient spacing and orientation between the fastener-driving tool and the target construction material. The device can be integrated into the body of the fastener-driving tool, manufactured as an attachment or manufactured as a separate tool. It prevents impact marring at the visible surface of the construction material by redirecting the force of the blow to a non-visible surface on the assembled construction material. Furthermore it increases speed and ease of movement for the user by serving as a guide for stability and ease of alignment. The device changes the impact point between the driving tool and the construction material, broadens the area of impact and protects the top edge of a tongue and groove construction material from impact damage.< / PTEXT>
Owner:DICKHAUT JOHN
Lift mechanism for plunge routers
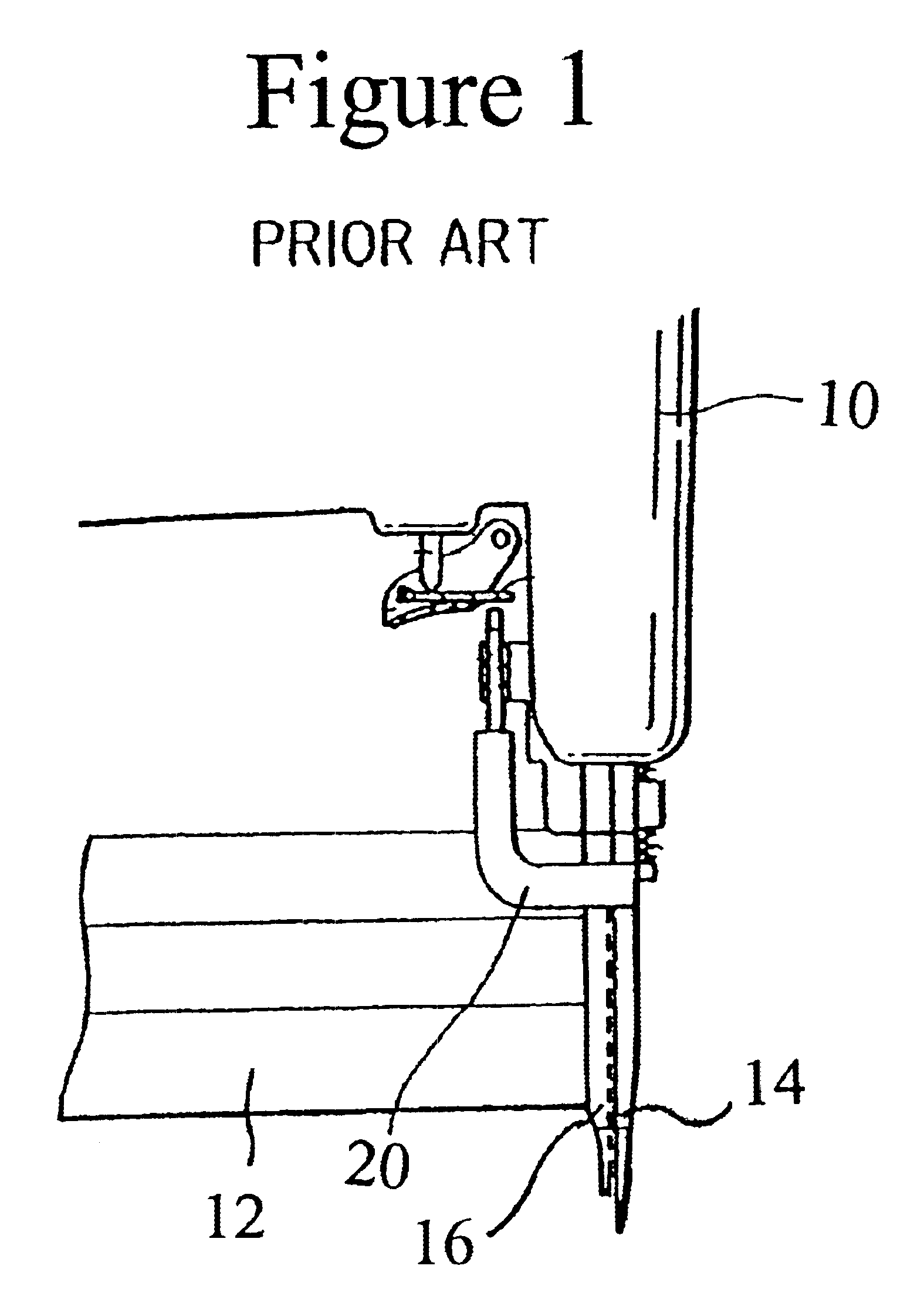
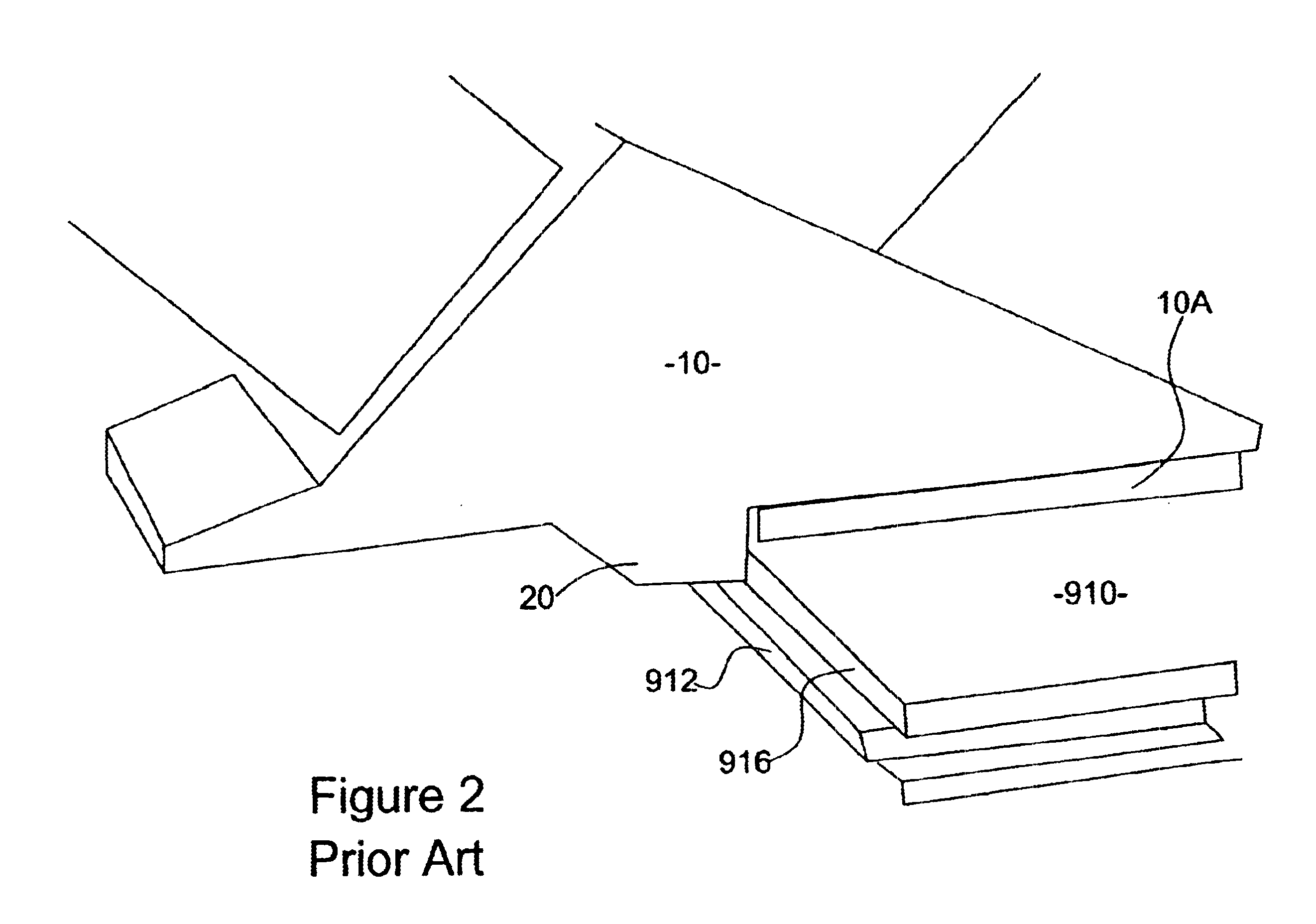
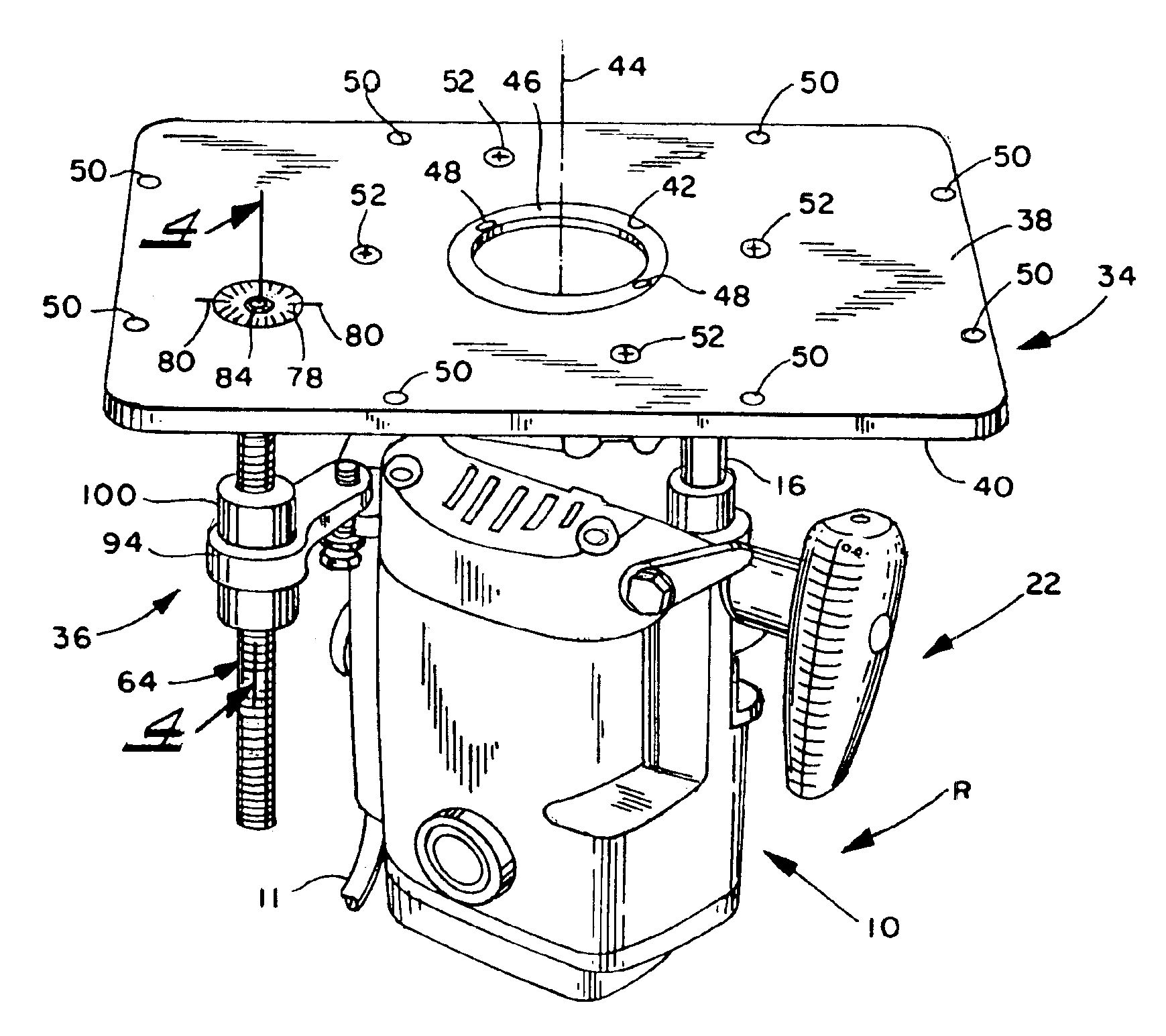
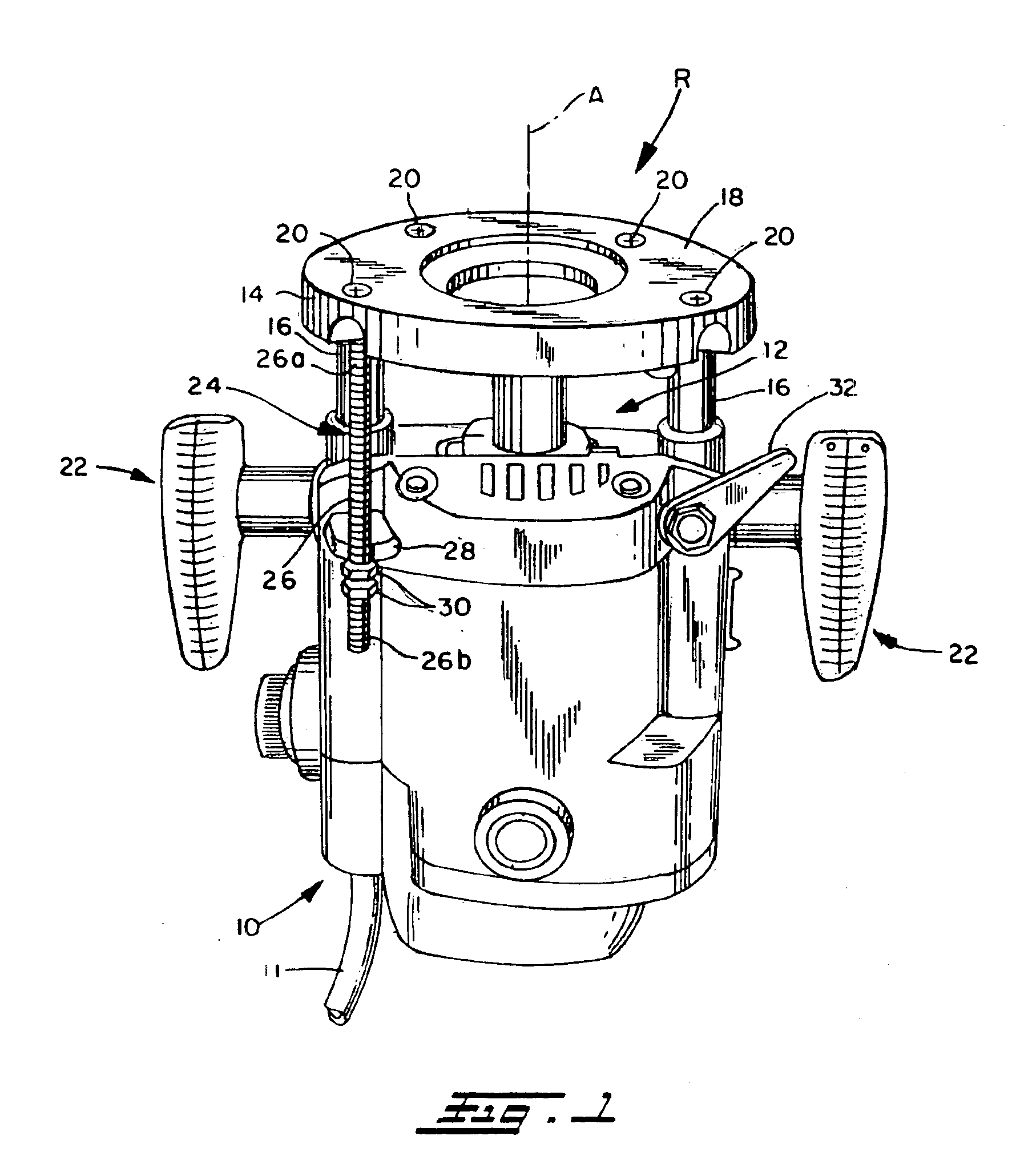
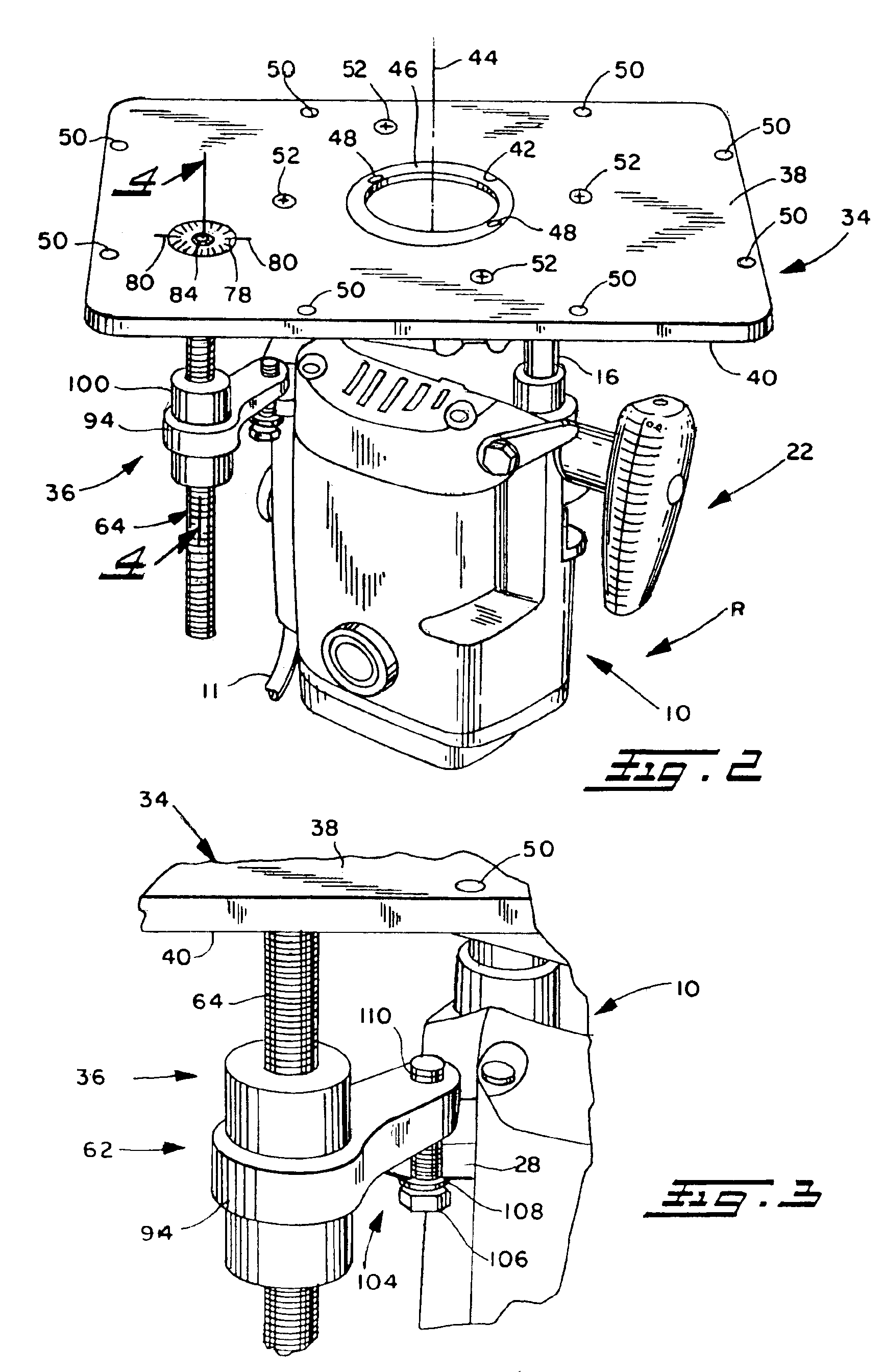
InactiveUS6948892B2Optimization mechanismEliminating any awkwardnessMilling cuttersMulti-purpose machinesMechanical engineering
A lift mechanism for a plunge router mounted on the underside of a router table comprises an adjusting screw extending vertically beneath the table and being rotatable relative to the table from the top side thereof, and a lift arm threadedly engaged with the screw and having an end spaced from the screw and interconnected with the router, whereby rotation of the screw displaces the router relative to the table.
Owner:WOODPECKERS LLC
Systems and methods for rate control in video coding using joint machine learning and game theory
ActiveUS20180139450A1Improve smoothnessImprove performanceDigital video signal modificationAlgorithmBit allocation
Systems and methods which provide a joint machine learning and game theory modeling (MLGT) framework for video coding rate control (RC) are described. A machine learning based R-D model classification scheme may be provided to facilitate improved R-D model prediction accuracy and a mixed R-D model based game theory approach may be implemented to facilitate improved RC performance. For example, embodiments may provide inter frame Coding Tree Units (CTUs) level bit allocation and RC optimization in HEVC. Embodiments provide for the CTUs being classified into a plurality of categories, such as by using a support vector machine (SVM) based multi-classification scheme. An iterative solution search method may be implemented for the mixed R-D models based bit allocation method. Embodiments may additionally or alternatively refine the intra frame QP determination and the adaptive bit ratios among frames to facilitate improving the coding quality smoothness.
Owner:CITY UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Gripper having sensor for detecting displacement
ActiveUS20080101895A1Facilitating improved accuracyHelp accuracyProgramme controlComputer controlInductorEngineering
A gripper assembly includes at least one movable gripper jaw and a sensor member coupled for movement with the at least one gripper jaw. The sensor member includes a slot. A sensor is located at least partially within the slot and includes at least one inductor for inductively detecting a proximity of the sensor member.
Owner:NORGREN AUTOMATION SOLUTIONS
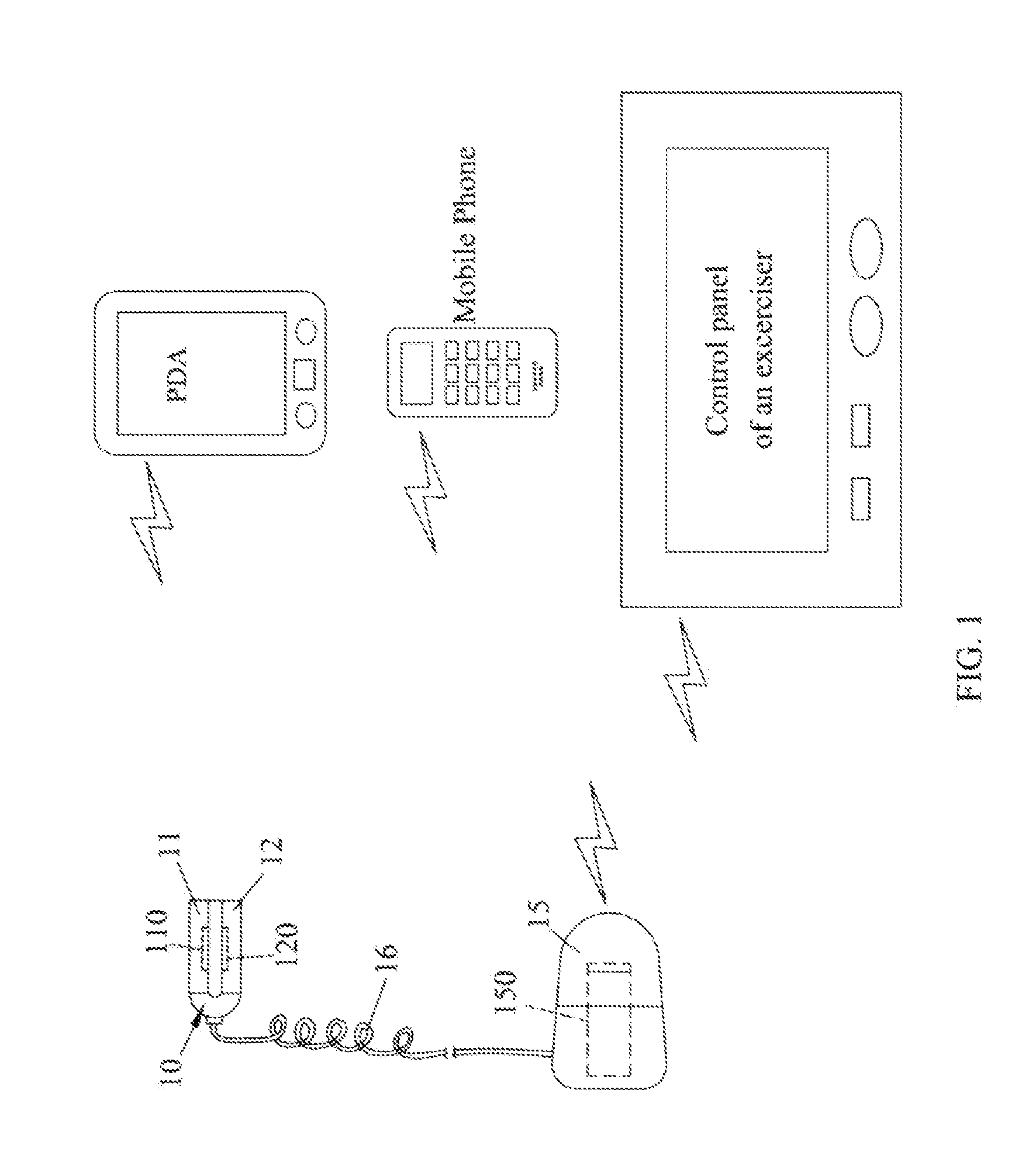
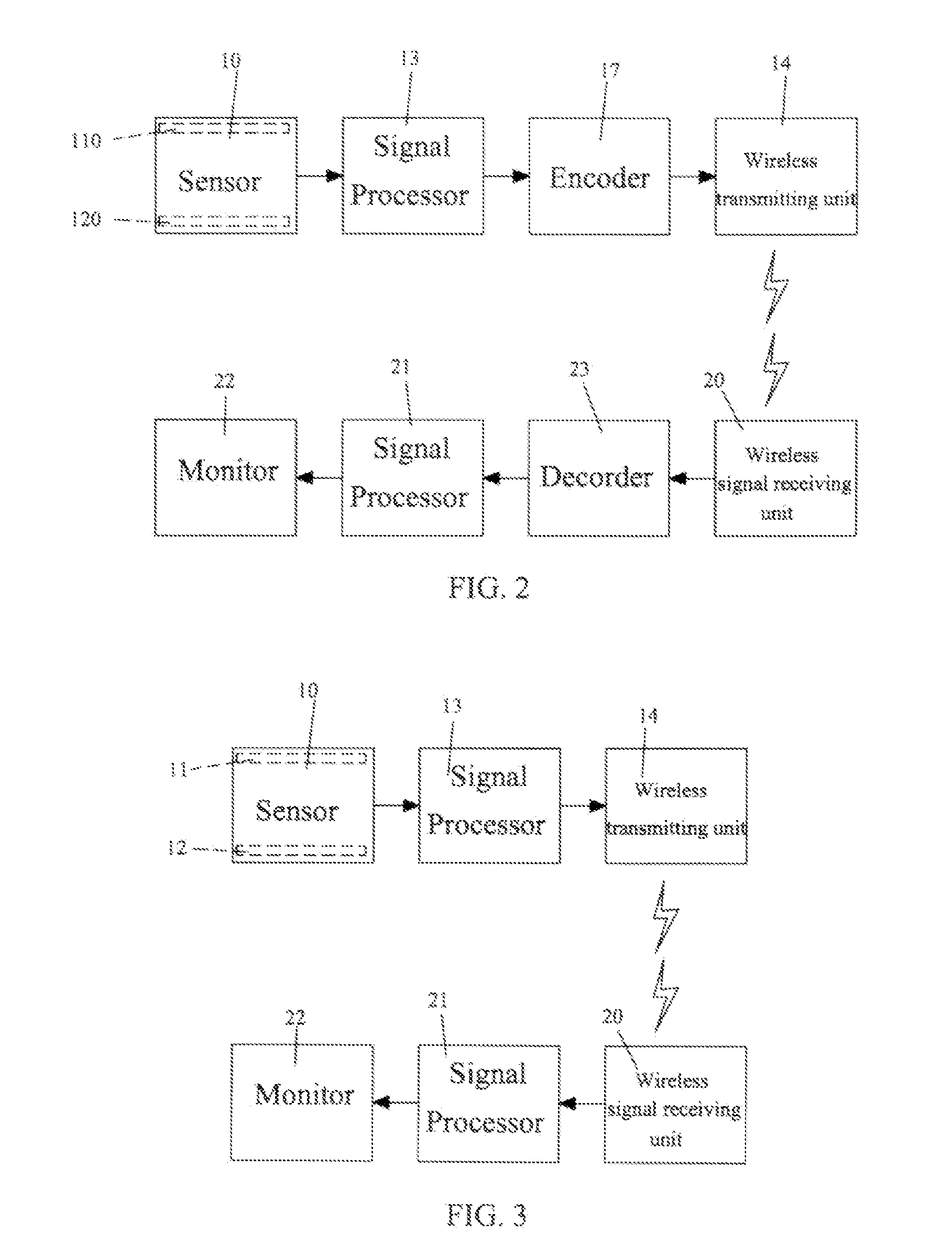
Wireless Ear-Clips Heart Rate Monitor
InactiveUS20070219457A1Detection accuracy can be promotedImprove ease of useSensorsTelemetric patient monitoringWireless transmissionPulse rate
This invention relates to a wireless ear-clips heart rate monitor comprising a sensor unit of ear-clips type that detects a user's heart rate, a signal-processing unit that receives and processes the signal generated from the sensor unit, and a wireless signal-transmitting unit that receives the signals from the signal-processing unit and then transmits the signals out. The sensor unit detects frequency of change of blood density to derive heart rate, with the features of precision and efficiency on the detection of heart rate, cooperating with the technique of wireless transmission, the purpose of promoting accuracy of detection and improving convenience of using is attained.
Owner:LO CHIU HSIANG
Biopsy device handle assembly
InactiveUS20050267383A1Enhancing comfort and maneuverability and precisionHelp accuracySurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsOuter CannulaBiopsy device
The invention described herein relates to a handle assembly for biopsy devices which comprise an outer cannula and stylet component structure. The handle assembly permits securing and removal of the inner stylet from the inside of the outer cannula by virtue of separating top and bottom portions of the handle, and at the same time enhances the comfort and maneuverability of the entire device during its use. In particular, the invention provides a biopsy device comprising a handle assembly, said handle assembly comprising at least two separable handle components together forming a generally elongated arcuate handle having concave arcuate indentations located on the side of the handle.
Owner:GROENKE GREGORY C +1
Apparatus for acquiring and processing of physiological auditory signals
ActiveUS8920343B2Accurate assessmentEasy diagnosisStethoscopeDiagnostic recording/measuringGraphicsDigital signal processing
A diagnostic system for collecting, processing, recording and analyzing sounds associated with the physiologic activities of various human organs. The system includes a plurality of transducers placed on the body surface at the operator's discretion. The transducers are coupled to analog / digital signal processing circuitry for enhancement of the desired signal and exclusion of ambient noise. An A / D converter digitizes the incoming data and transmits data, which is divided into a multitude of discrete blocks, received over very finite intervals of time, to a computer workstation and moved through an analysis program sequentially. The program is displayed as a series of icons which depict operations that the program performs and which allow the operator to reprogram the system at any time. The data is finally displayed in graphical format and stored in memory as the program processes each block sequentially.
Owner:AUDIO EVOLUTION DIAGNOSTICS INC
Medical apparatus system having optical fiber load sensing capability
ActiveUS8894589B2Facilitate speedHelp accuracyStrain gaugePerson identificationProcess logicOptical property
Apparatus is provided for diagnosing or treating an organ or vessel, wherein a device having at optical fiber contact force sensors disposed in a distal extremity thereof and a deflection mechanism configured to deflect the elongate body at a location proximal of the distal extremity. The optical fiber contact force sensors are configured to be coupled to processing logic programmed which computes a force vector responsive to detected changes in the optical characteristics of the optical fiber contact force sensors arising from deflection of the distal extremity resulting from contact with the tissue of the wall of the organ or vessel.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL INT HLDG SARL
Queuing system
ActiveUS20170098337A1Easy to manageImprove efficiencyReservationsChecking apparatusData access controlMedia access control
A technique for controlling access to one or more attractions is achieved using a number of access keys, each being issued to one or more users. An electronic queue management part manages a virtual queue in respect of each attraction and receives electronic requests for attraction access, each request relating to an access key and being for the users associated with it to access a particular attraction. Receipt of each request causes the respective users to be added to a corresponding virtual queue. A time at which each group of users reaches the front of the virtual queue and can access the attraction is determined. The users access the attractions by presenting an access key to an access control part, in communication with the electronic queue management part. Only a user presenting an access key at the correct time for accessing the attraction is allowed access to the attraction.
Owner:ACCESSO TECH GRP
Volume charge density measuring system
InactiveUS6586950B1Minimize chargeImprove linearityResistance/reactance/impedenceVoltage/current isolationCapacitanceElectrical conductor
A capacitive sensor is shielded against external electric fields to maximize measurement accuracy. The sensor may include two coaxial, tubular conductors with a chamber between them into which a material sample to be measured is introduced. A measurement circuit connected to the sensor may include a reference oscillator that oscillates at a constant frequency and a test oscillator that oscillates at a frequency responsive to sensor capacitance. The circuit may display a value responsive to the difference between the test and reference frequencies. The circuit may also reverse the polarity of the signal applied to the sensor to minimize charge buildup, a phase-locked loop frequency measuring circuit, a temperature compensating circuit, and a non-linearity compensating circuit. The indicating circuit that displays a representation of the measured capacitance may display a continuous-scale or proportional representation or may display a binary or "go-nogo" representation. An alternative sensor of the system includes coaxial, finned inner and outer conductors that intermesh to maximize capacitive surface area. Another alternative sensor includes two parallel, plate-like conductors. The sensor system may be used to measure volume charge density of a fluid or parameters responsive to changes in volume charge density, such as flow velocity.
Owner:JOFRACH L L C
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com