Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
39results about How to "Guaranteed maintenance space" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
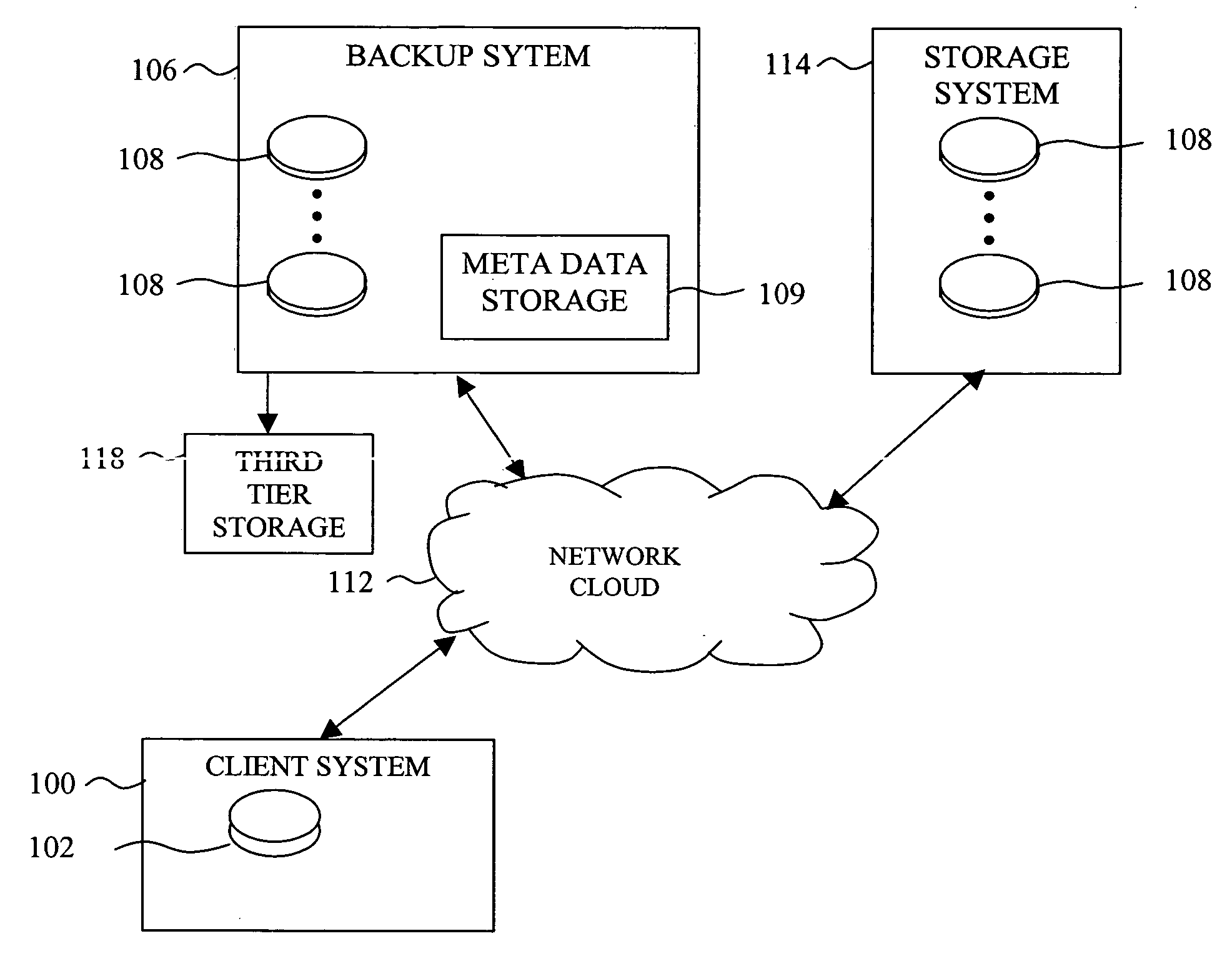
System and methods for efficiently managing incremental data backup revisions
InactiveUS20050246398A1Reduce loadIncreasing backup frequency of backupData processing applicationsError detection/correctionData elementEffective management
A system and methods for building an efficient incremental data backup system capable of managing high frequency backups sessions, and capable of efficiently expiring backup revisions and locating the useless data elements is disclosed. A reduced set of data elements that have a non-zero probability of becoming redundant when a backup revision expires is prepared while each backup revision is being processed by the backup system. The backup system also maintains data structures, which reduce the number of searches that should be performed for each such data element before it can be realized that the data element is exclusively needed to support the expired backup revision, and therefore could be removed from the second tier storage.
Owner:DATAMILLS
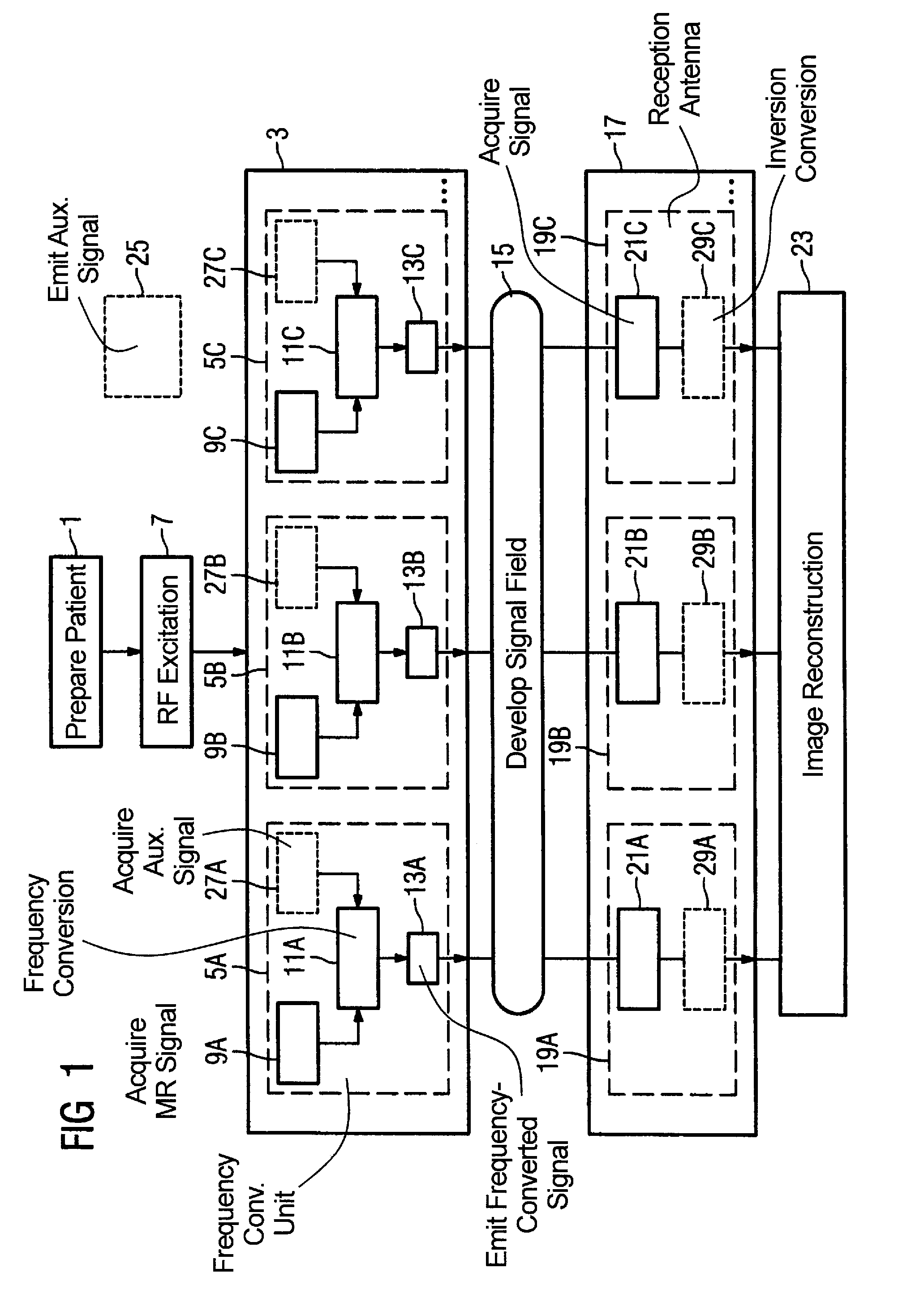
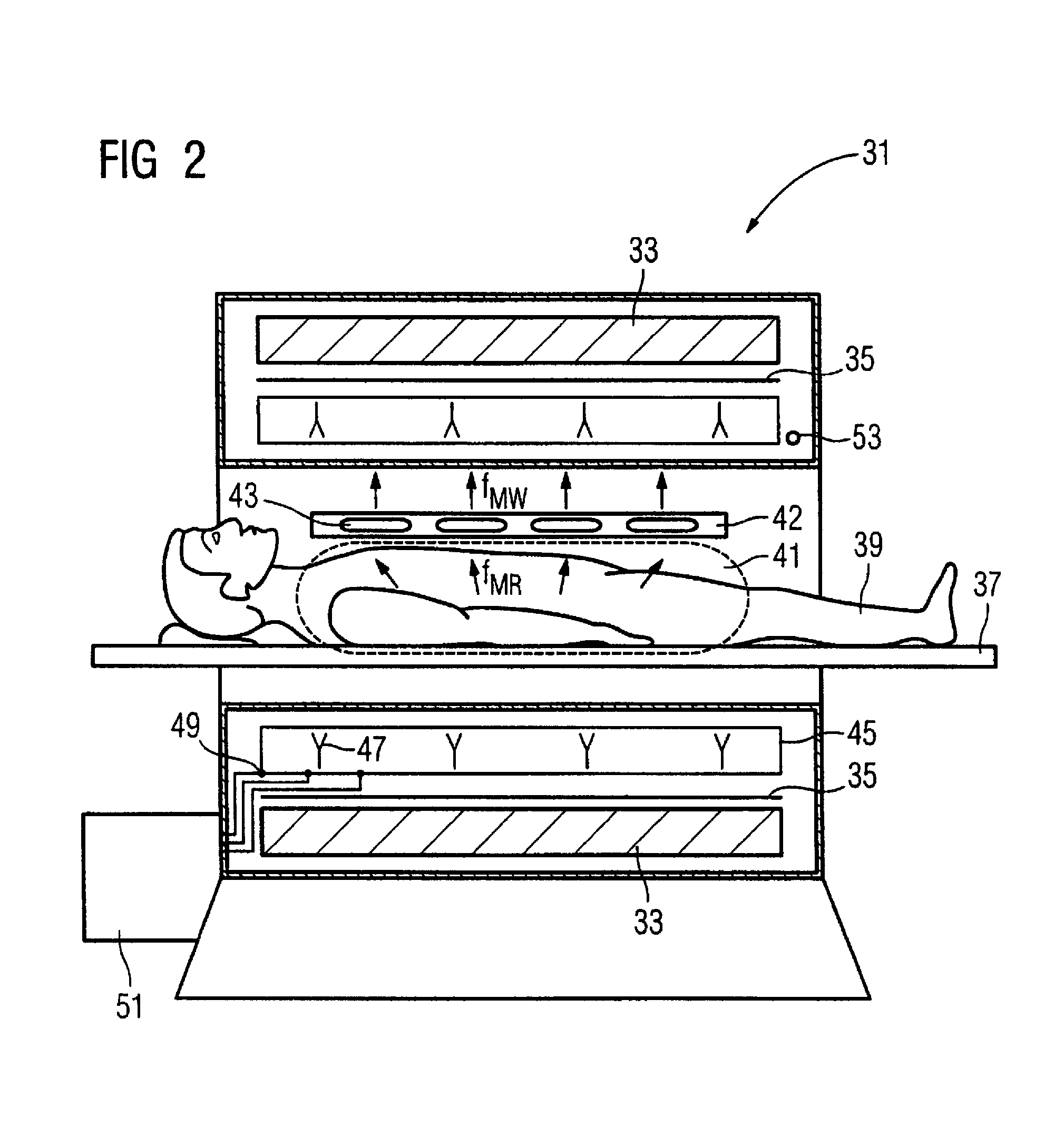
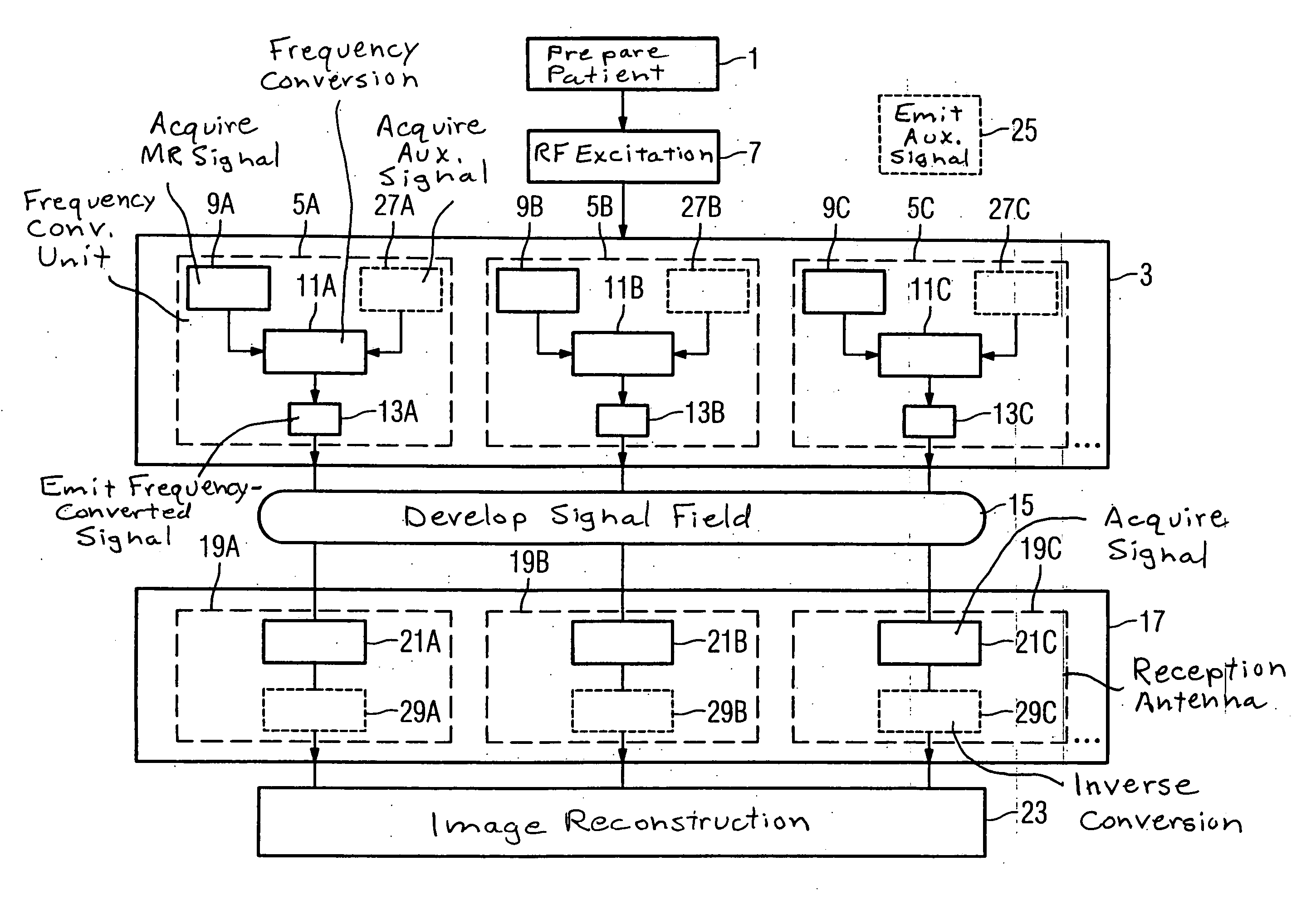
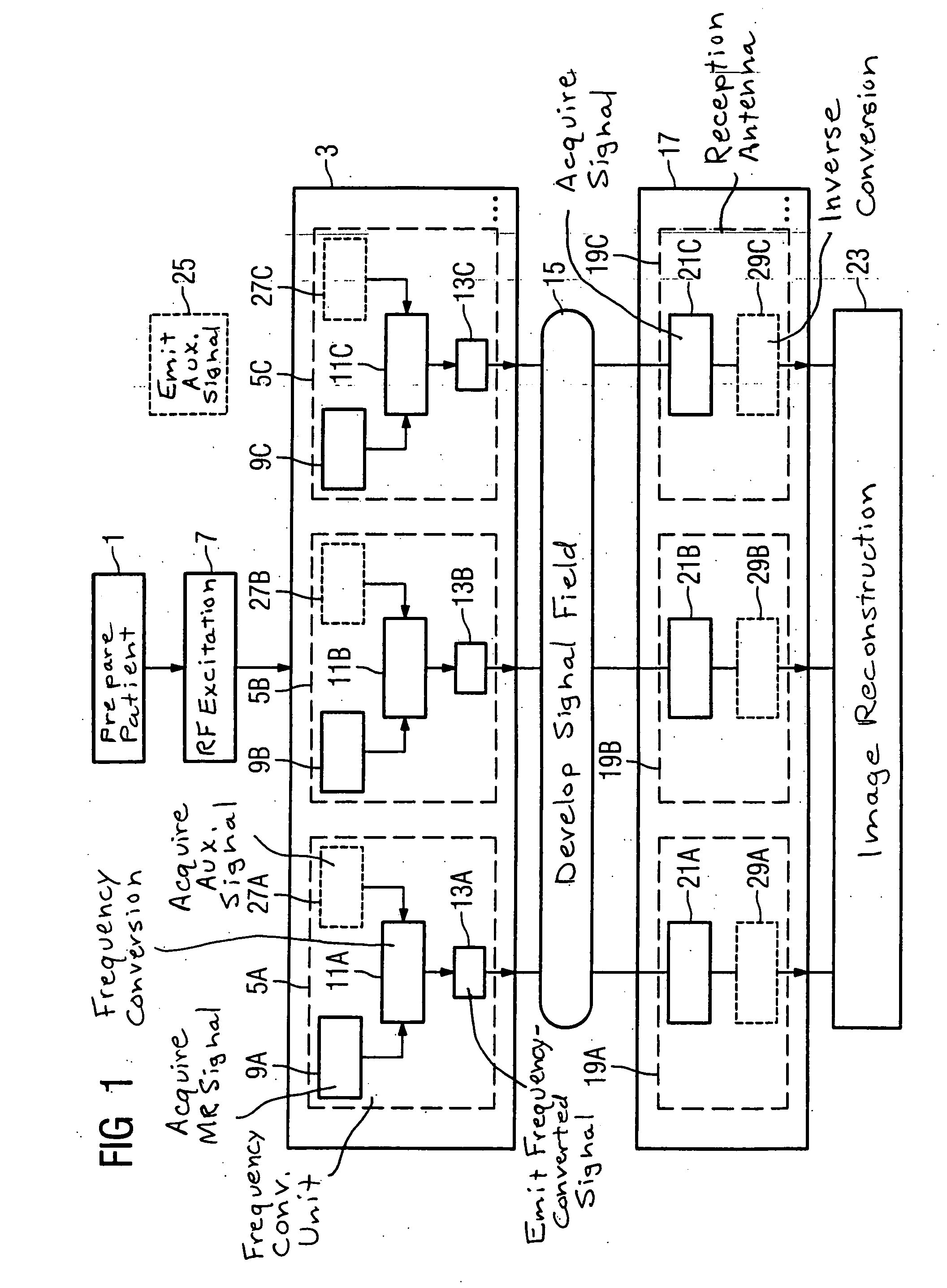
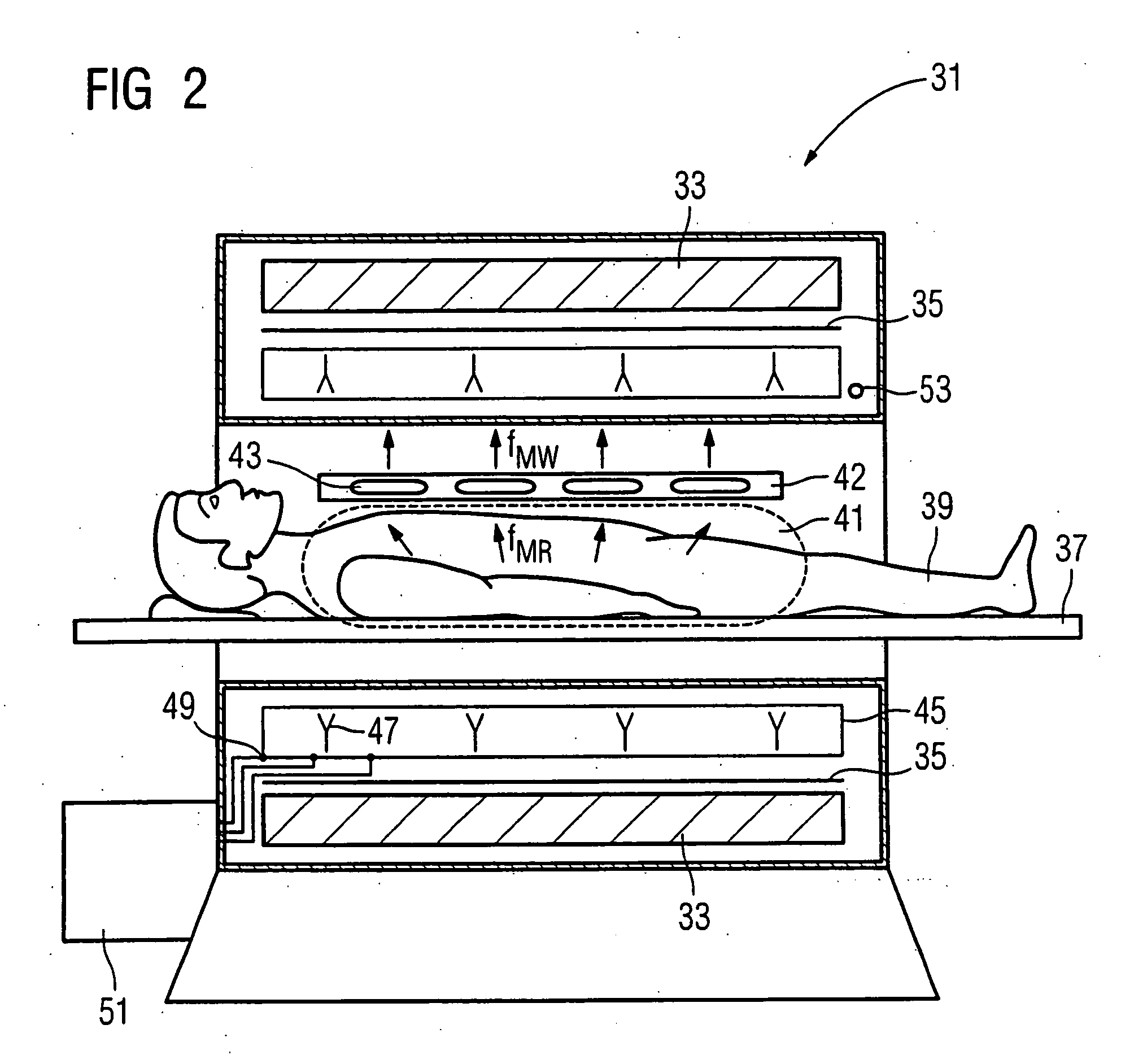
Method, examination apparatus and antenna array for magnetic resonance data acquisition
ActiveUS7417433B2Small power requirementRequired bandwidth is lessMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringFrequency conversionImage resolution
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
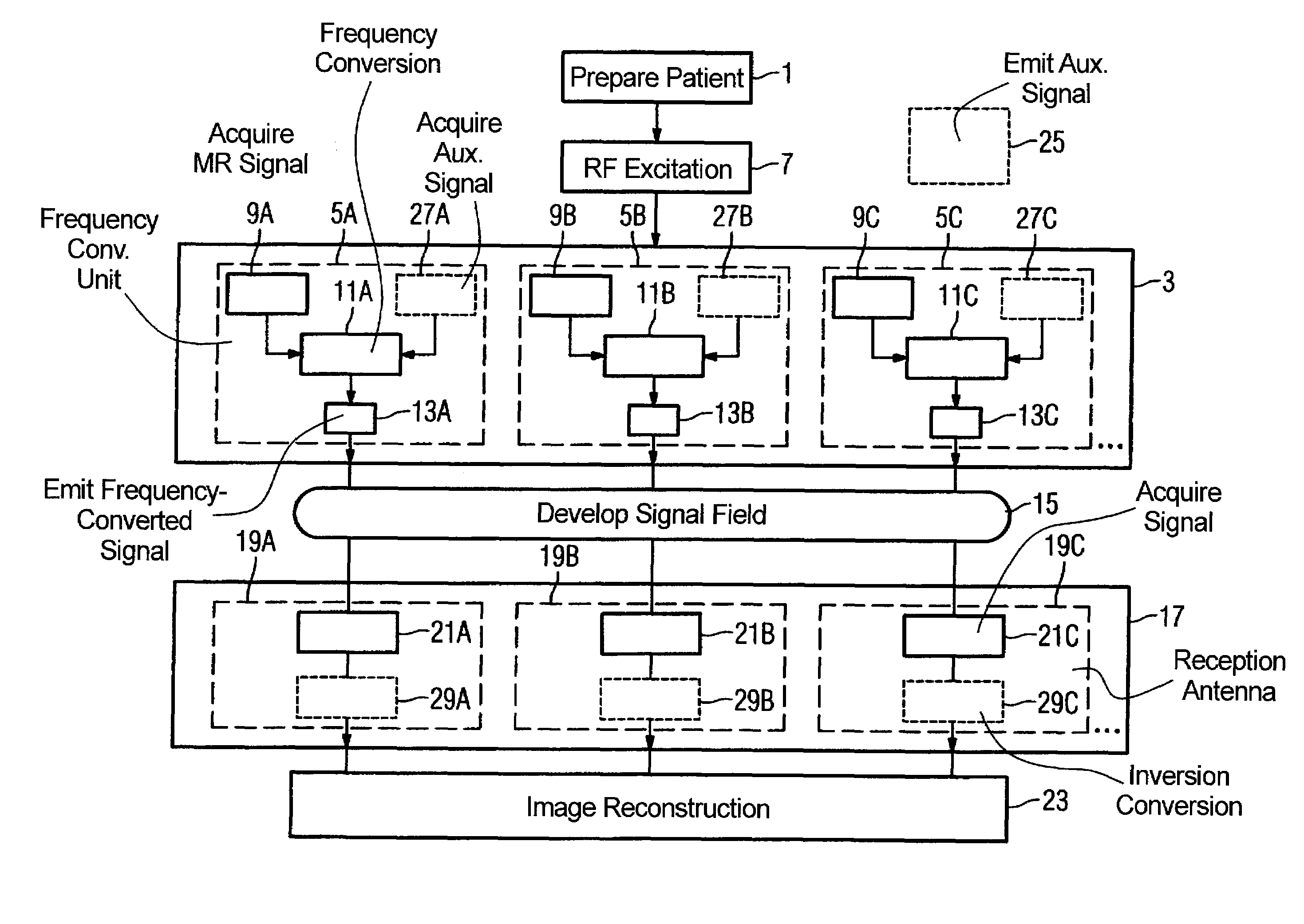
Method, examination apparatus and antenna array for magnetic resonance data acquisition
ActiveUS20070013376A1Reduce distractionsSmall power requirementMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringImage resolutionFrequency conversion
In a method for implementation of a magnetic resonance examination, and a magnetic resonance apparatus, and an array for acquisition of magnetic resonance signals, and a magnetic resonance signal at a magnetic resonance frequency are acquired from an examination region with an array of frequency conversion units after an RF excitation and are radiated as frequency-converted signals. The resulting signal field is acquired by a number of reception antennas of a second antenna array, which are arranged at different spatial positions and thus allow a spatial resolution of the frequency-converted signals. The acquired acquisition signals are used for image reconstruction.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
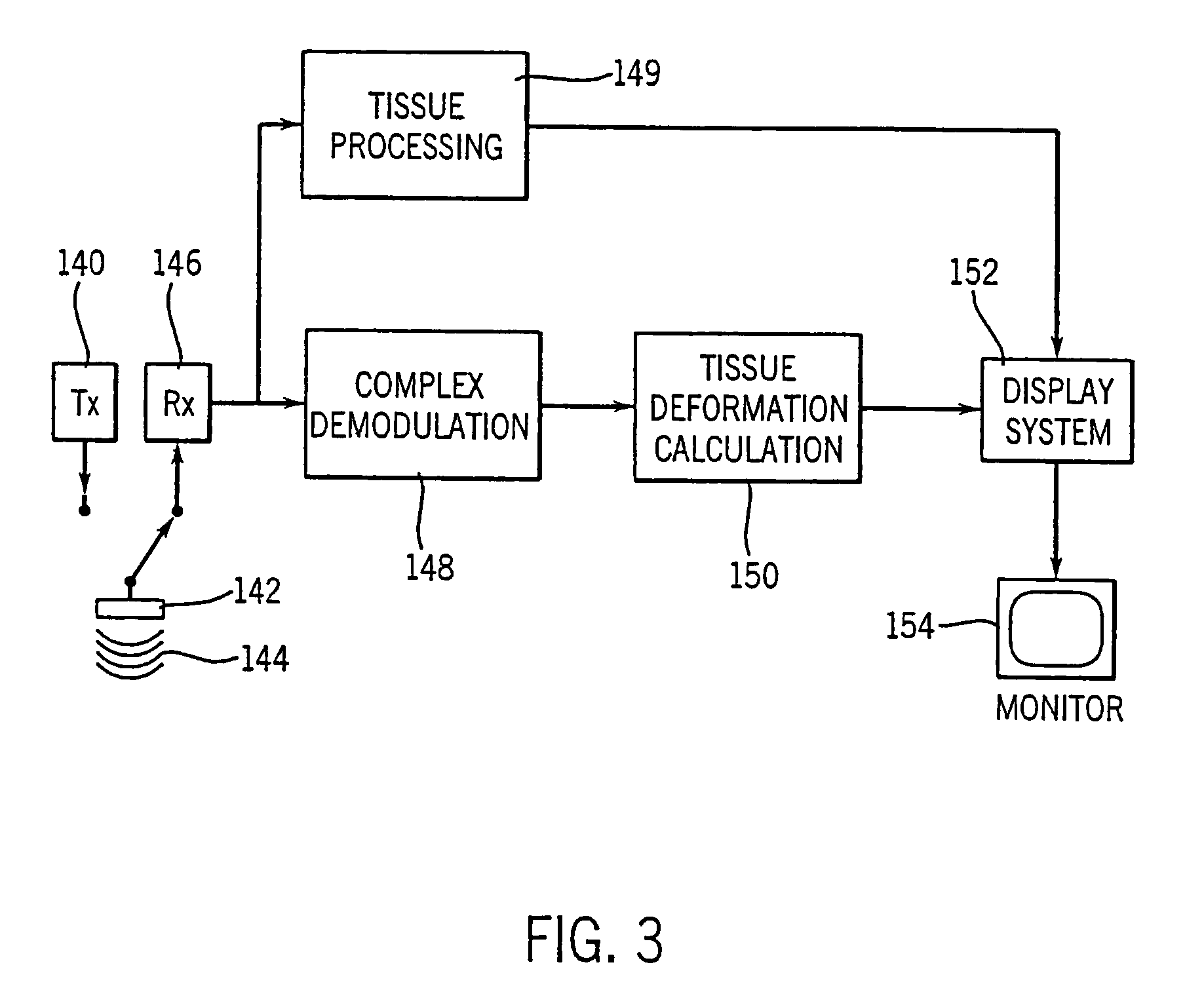
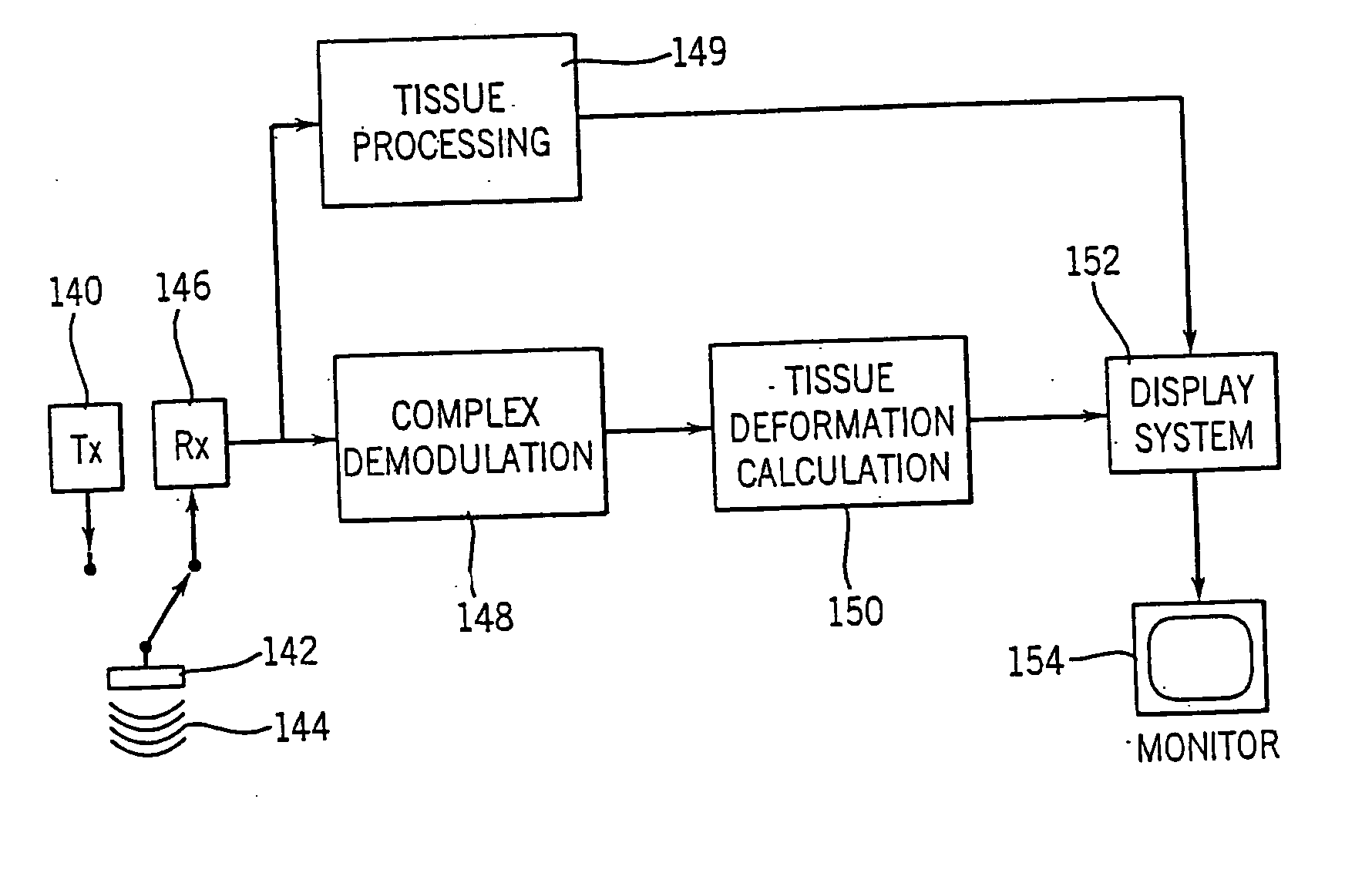
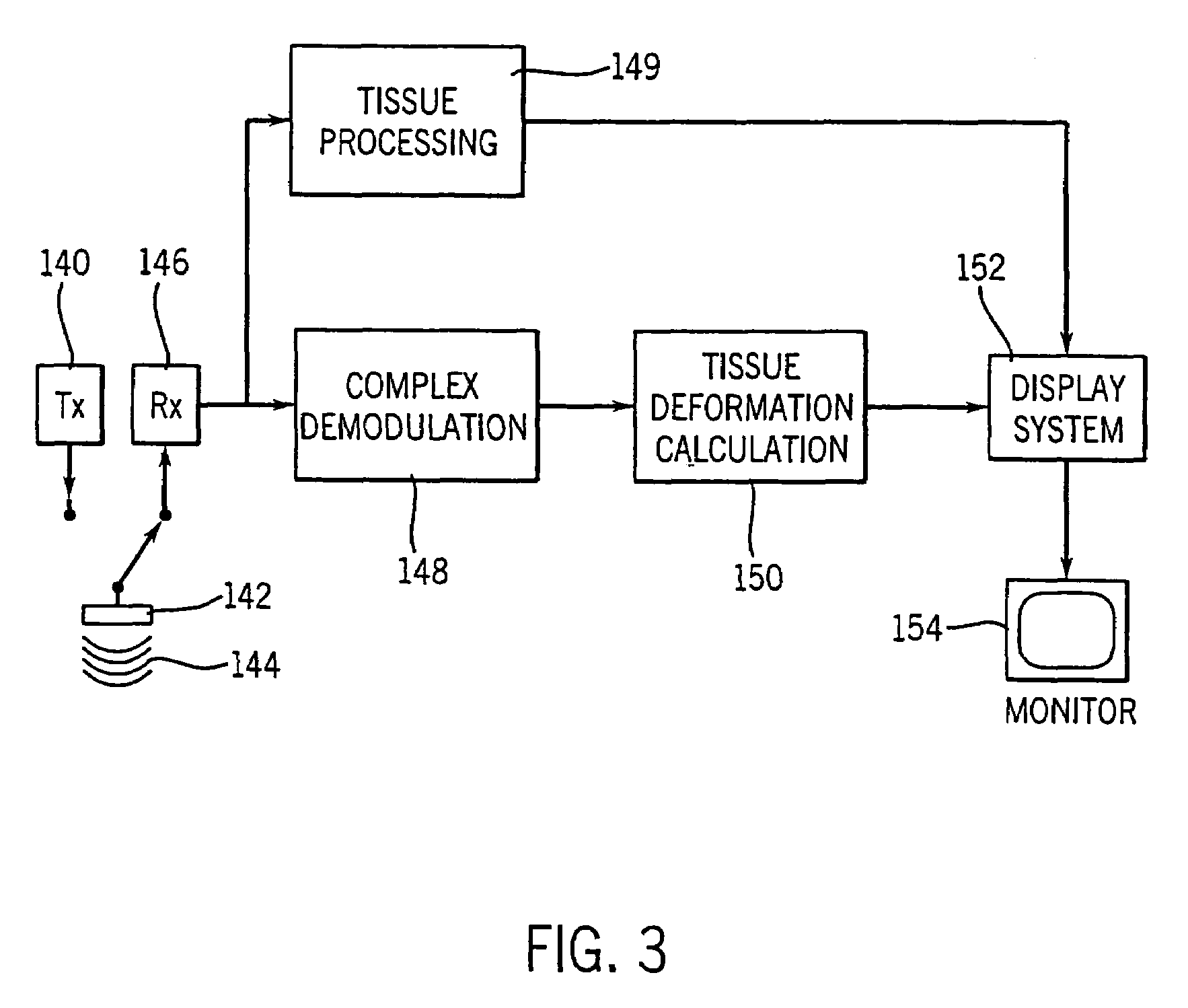
Method and apparatus for providing real-time calculation and display of tissue deformation in ultrasound imaging
InactiveUS7077807B2Reduce impactReduce aliasingElectrocardiographyOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasound imagingSonification
An ultrasound system and method for calculation and display of tissue deformation parameters are disclosed. A method to estimate a strain rate in any direction, not necessarily along the ultrasound beam, based on tissue velocity data from a small region of interest around a sample volume is disclosed. Quantitative tissue deformation parameters, such as tissue velocity, tissue velocity integrals, strain rate and / or strain, may be presented as functions of time and / or spatial position for applications such as stress echo. For example, strain rate or strain values for three different stress levels may be plotted together with respect to time over a cardiac cycle.
Owner:G E VINGMED ULTRASOUND
Method and apparatus for providing real-time calculation and display of tissue deformation in ultrasound imaging
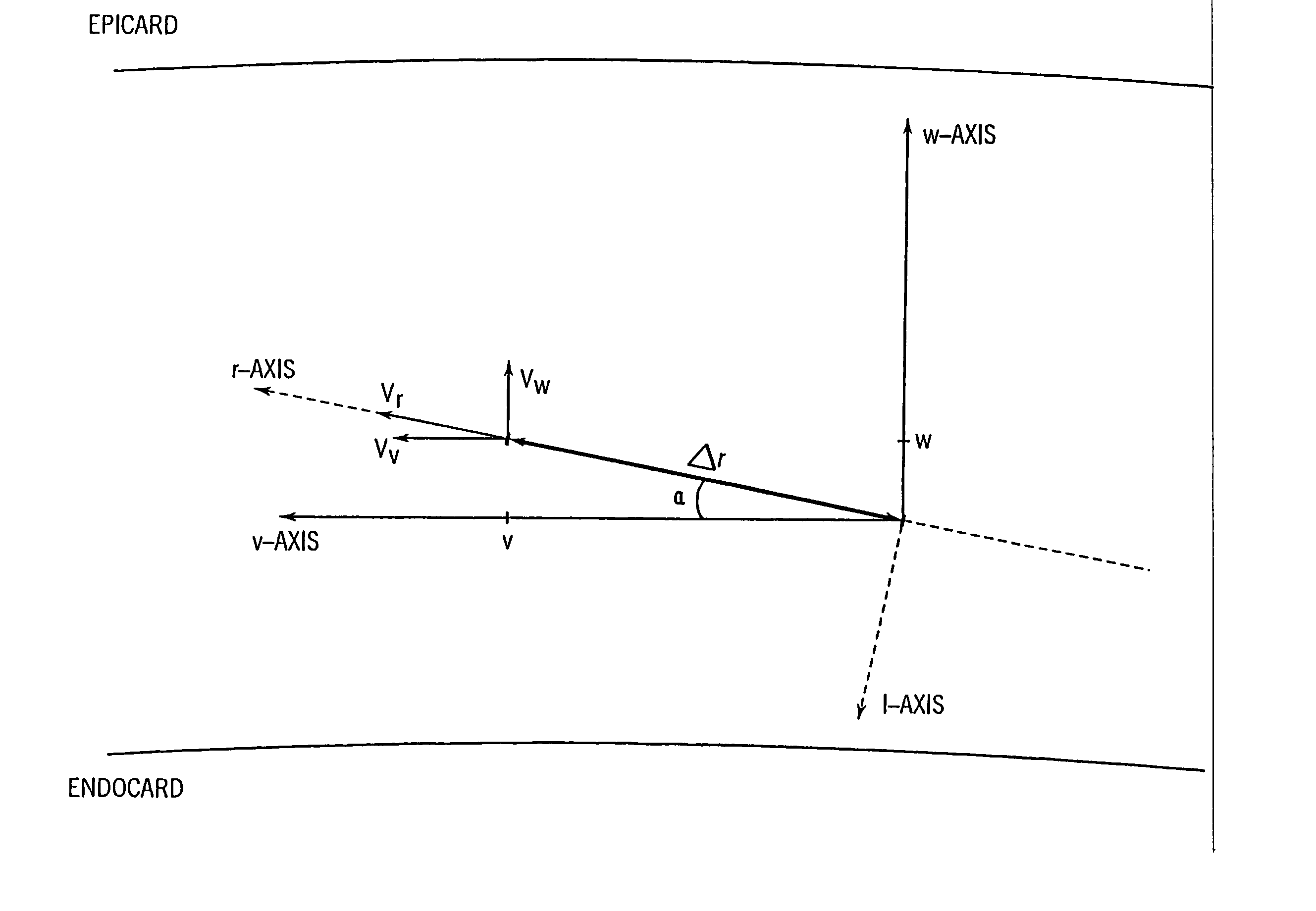
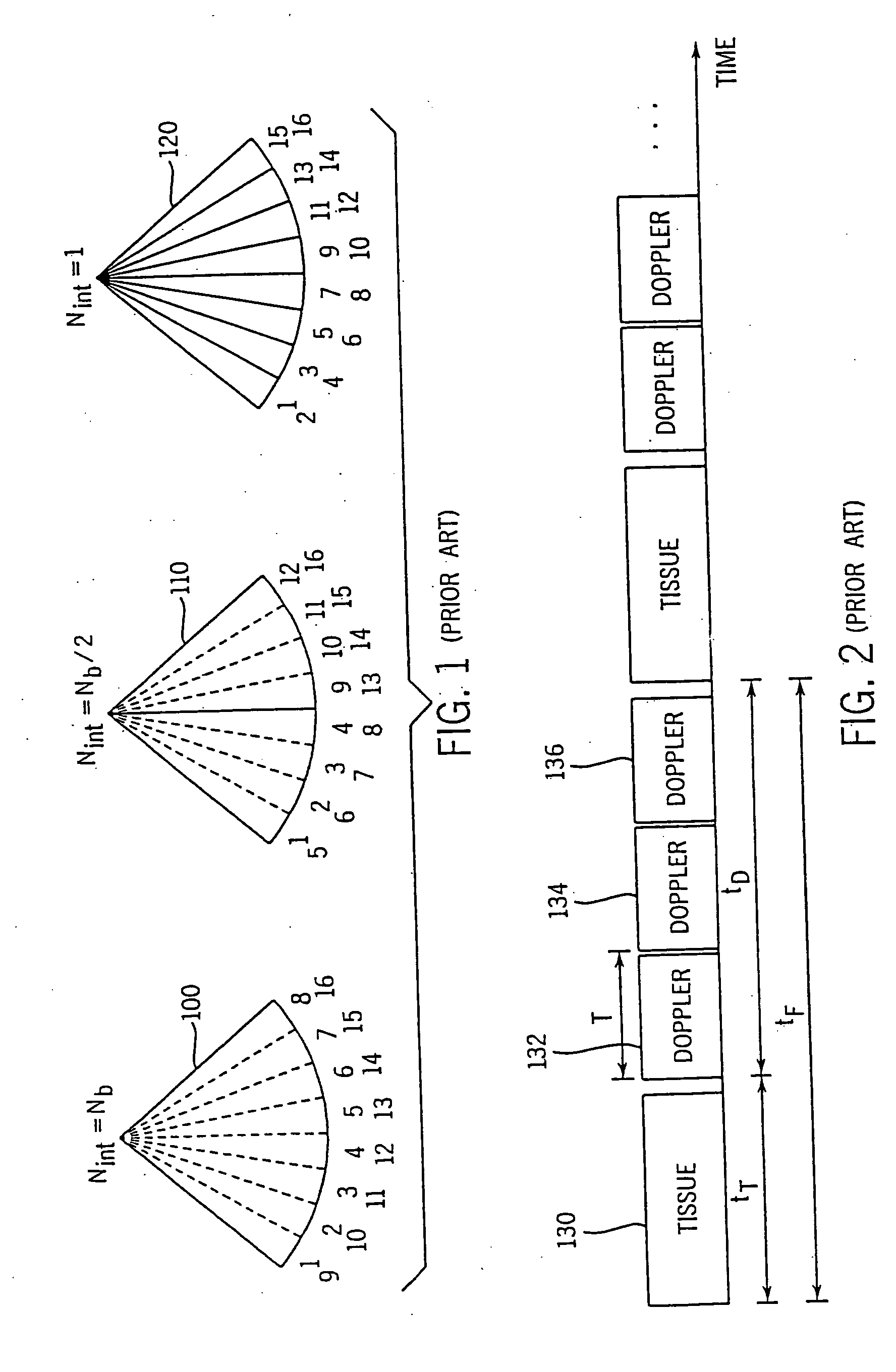
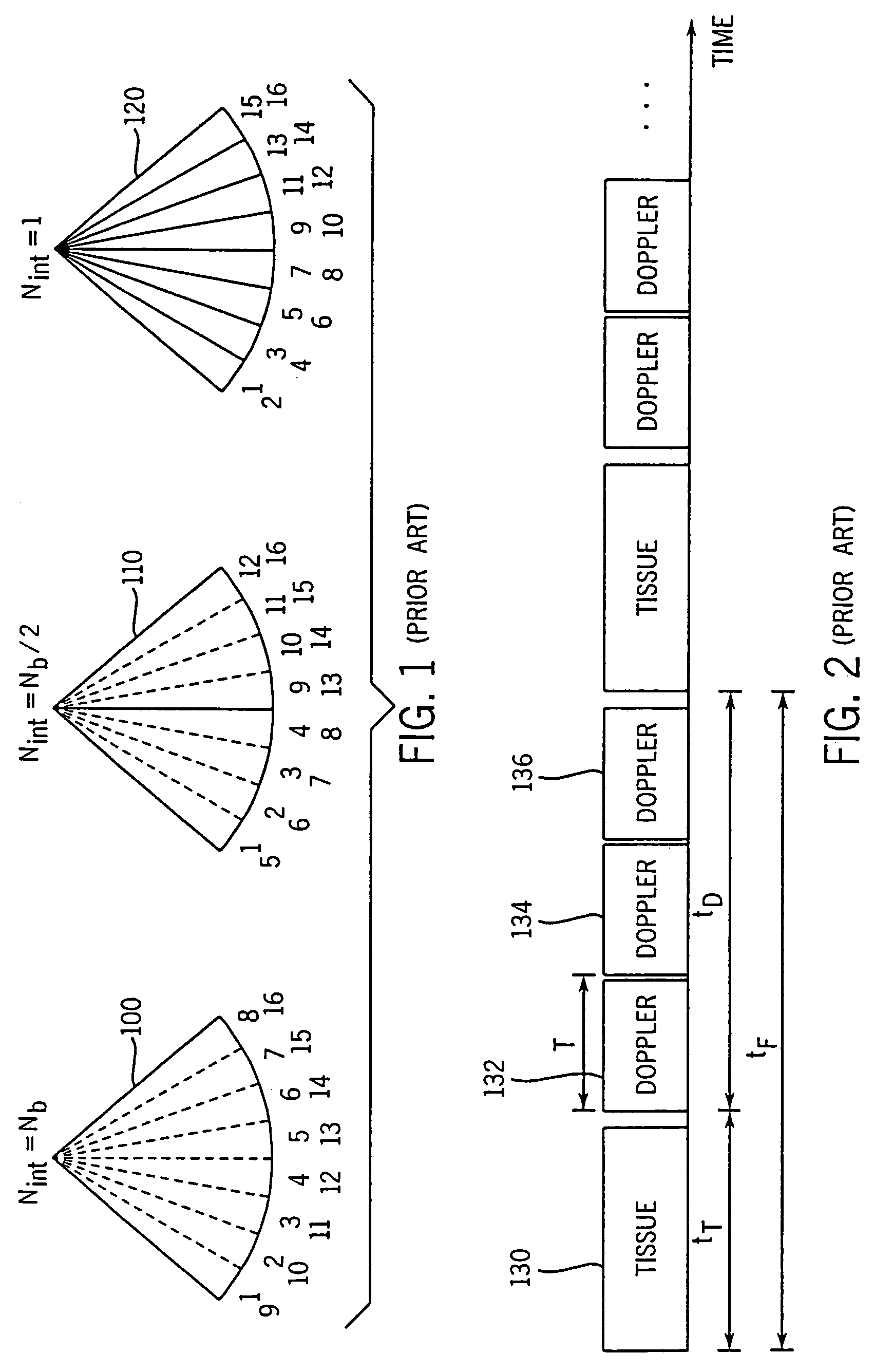
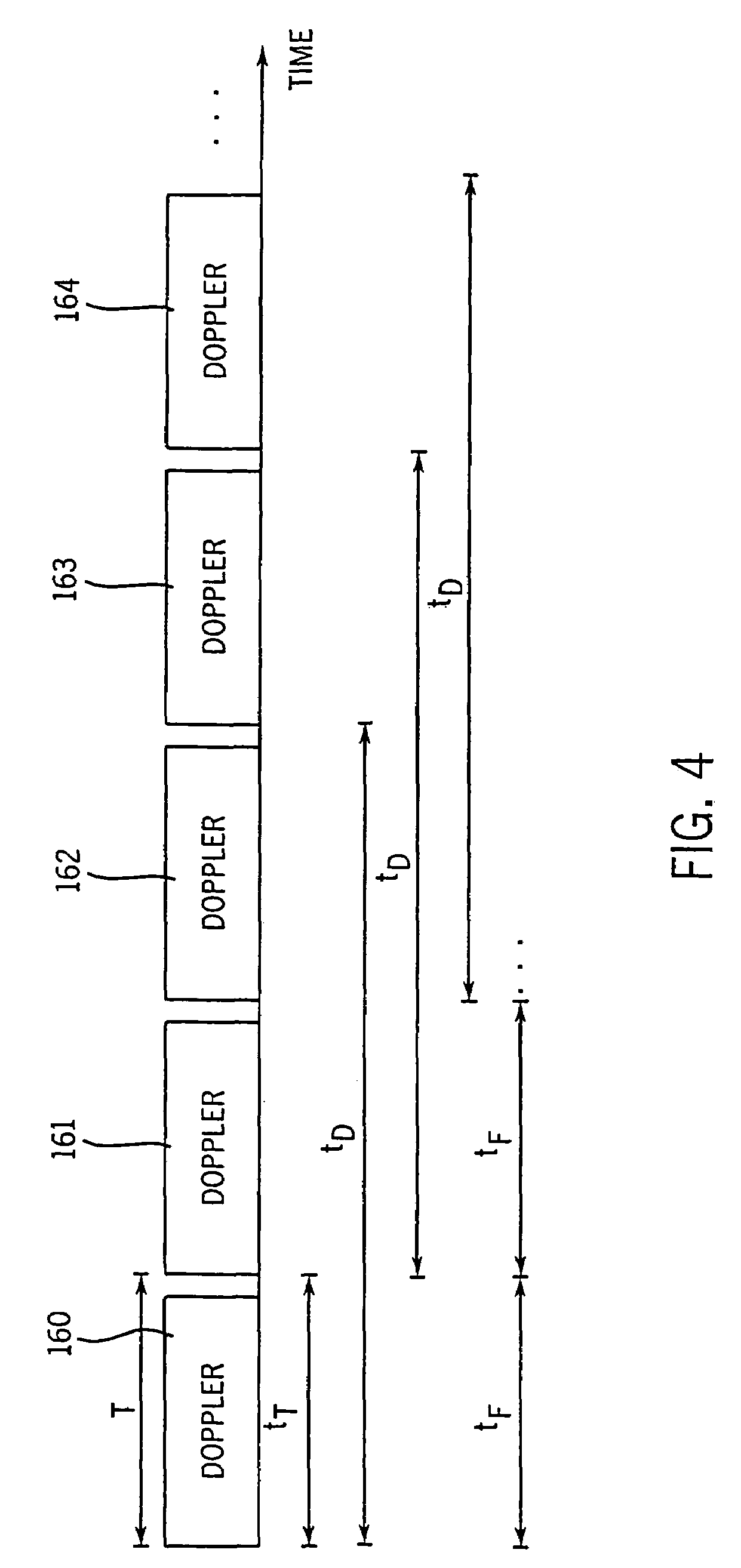
InactiveUS20050203390A1Reduce aliasingMaintain spatial resolutionElectrocardiographyOrgan movement/changes detectionRelative displacementImage resolution
An ultrasound system and method for calculation and display of tissue deformation parameters are disclosed. An ultrasound acquisition technique that allows a high frame rate in tissue velocity imaging or strain rate imaging is employed. With this acquisition technique the same ultrasound pulses are used for the tissue image and the Doppler based image. A sliding window technique is used for processing. The tissue deformation parameter strain is also determined by an accumulation of strain rate estimates for consecutive frames over an interval. The interval may be a triggered interval generated by, for example, an R-wave in an ECG trace. The strain calculation may be improved by moving the sample volume from which the strain rate is accumulated from frame-to-frame according to the relative displacement of the tissue within the original sample volume. The relative displacement of the tissue is determined by the instantaneous tissue velocity of the sample volume. An estimation of strain rate based upon a spatial derivative of tissue velocity is improved by adaptively varying the spatial offset, dr. The spatial offset, dr, can be maximized to cover the entire tissue segment (e.g., heart wall width) while still keeping both of the sample volumes at each end of the offset within the tissue segment. This may be accomplished by determining whether various parameters (e.g., grayscale value, absolute power estimate, magnitude of the autocorrelation function with unity temporal lag and / or magnitude of strain correlation) of the sample volumes within in the spatial offset are above a given threshold. Strain rate may be estimated using a generalized strain rate estimator that is based on a weighted sum of two-sample strain rate estimators with different spatial offsets. The weights are proportional to the magnitude of the strain rate correlation estimate for each spatial offset, and thus reduce the effect of noisy, i.e. poorly correlated, samples. An improved signal correlation estimator that uses a spatial lag in addition to the usual temporal lag is disclosed. The spatial lag is found from the tissue velocity. The improved signal correlation estimator can be utilized both in the estimation of strain rate and tissue velocity. Tissue velocity may be estimated in a manner that reduces aliasing while maintaining spatial resolution. Three copies of a received ultrasound signal are bandpass filtered at three center frequencies. The middle of the three center frequencies is centered at the second harmonic of the ultrasound signal. A reference tissue velocity is estimated from the two signals filtered at the outside center frequencies. The reference tissue velocity is used to choose a tissue velocity from a number of tissue velocities estimated from the signal centered at the second harmonic. A method to estimate the strain rate in any direction, not necessarily along the ultrasound beam, based on tissue velocity data from a small region of interest around a sample volume is disclosed. Quantitative tissue deformation parameters, such as tissue velocity, tissue velocity integrals, strain rate and / or strain, may be presented as functions of time and / or spatial position for applications such as stress echo. For example, strain rate or strain values for three different stress levels may be plotted together with respect to time over a cardiac cycle. Parameters which are derived from strain rate or strain velocity, such as peak systolic wall thickening percentage, may be plotted with respect to various stress levels,
Owner:G E VINGMED ULTRASOUND
Method and apparatus for providing real-time calculation and display of tissue deformation in ultrasound imaging
InactiveUS7261694B2Reduce impactReduce aliasingElectrocardiographyOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasound imagingSonification
An ultrasound system and method for calculation and display of tissue deformation parameters are disclosed. The tissue deformation parameter strain is determined by an accumulation of strain rate estimates for consecutive frames over an interval. The interval may be a triggered interval generated by, for example, an R-wave in an ECG trace. Three quantitative tissue deformation parameters, such as tissue velocity, tissue velocity integrals, strain rate and / or strain, may be presented as functions of time and / or spatial position for applications such as stress echo. For example, strain rate or strain values for three different stress levels may be plotted together with respect to time over a cardiac cycle. Parameters which are derived from strain rate or strain velocity, such as peak systolic wall thickening percentage, may be plotted with respect to various stress levels.
Owner:G E VINGMED ULTRASOUND
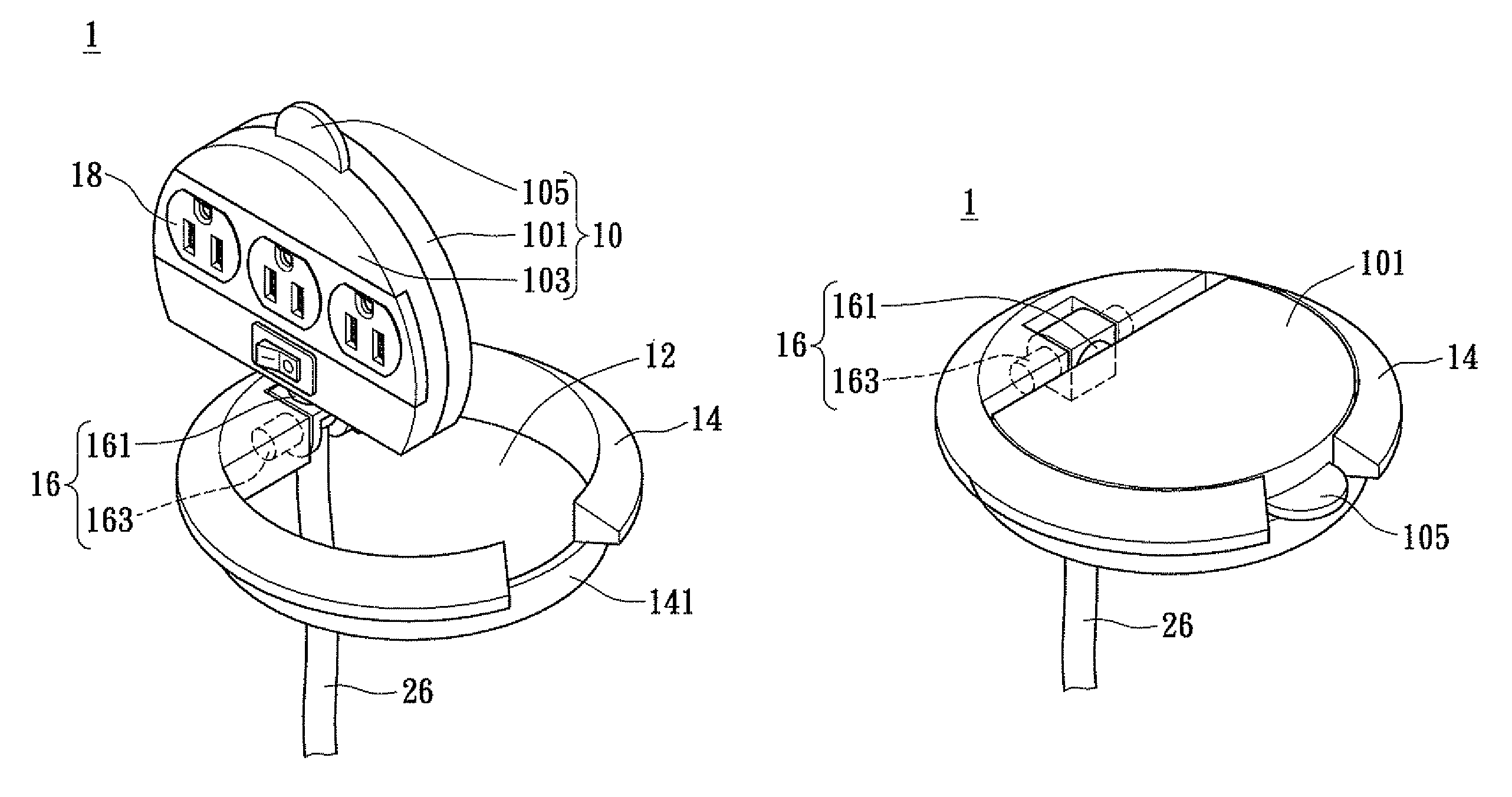
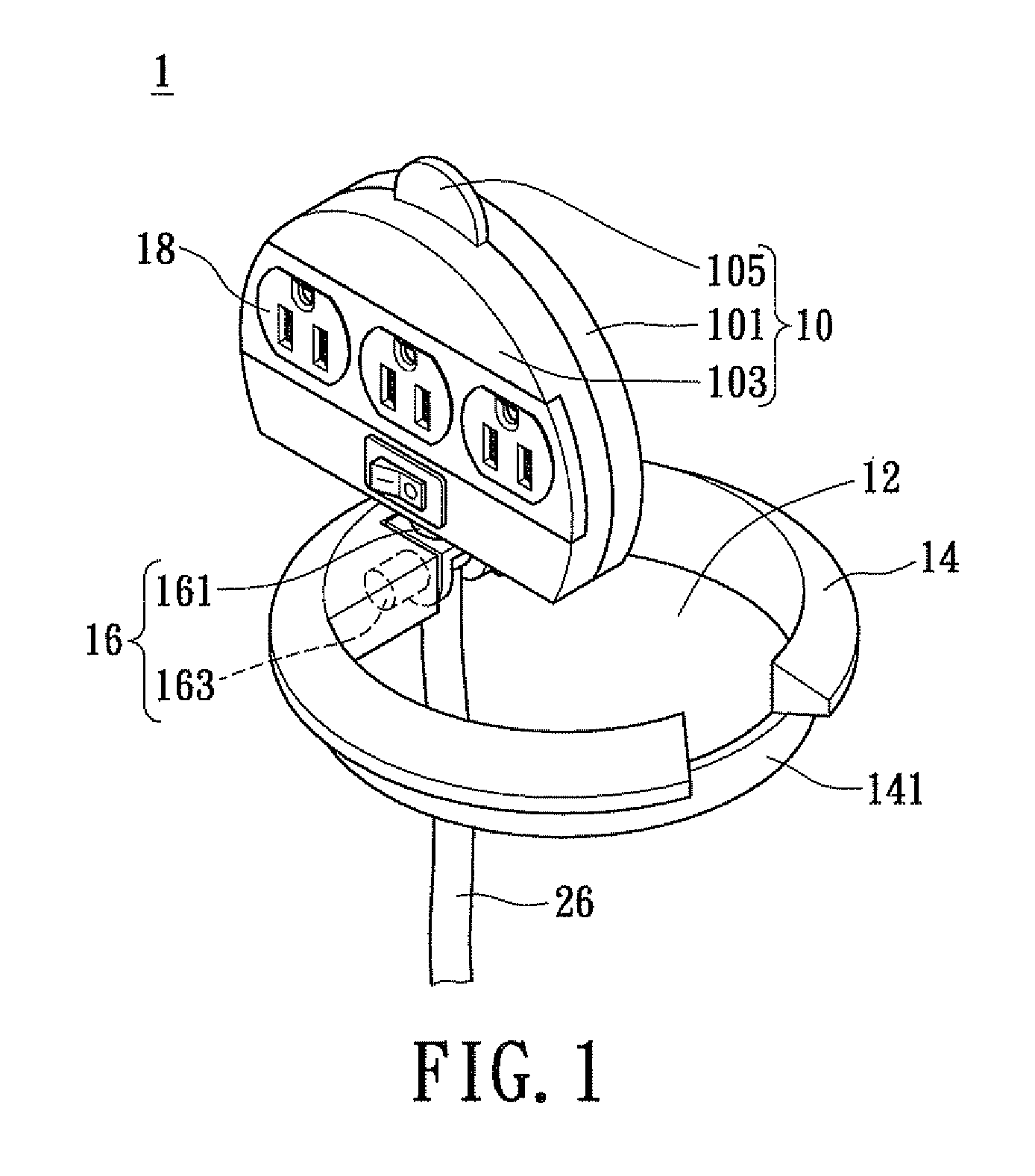
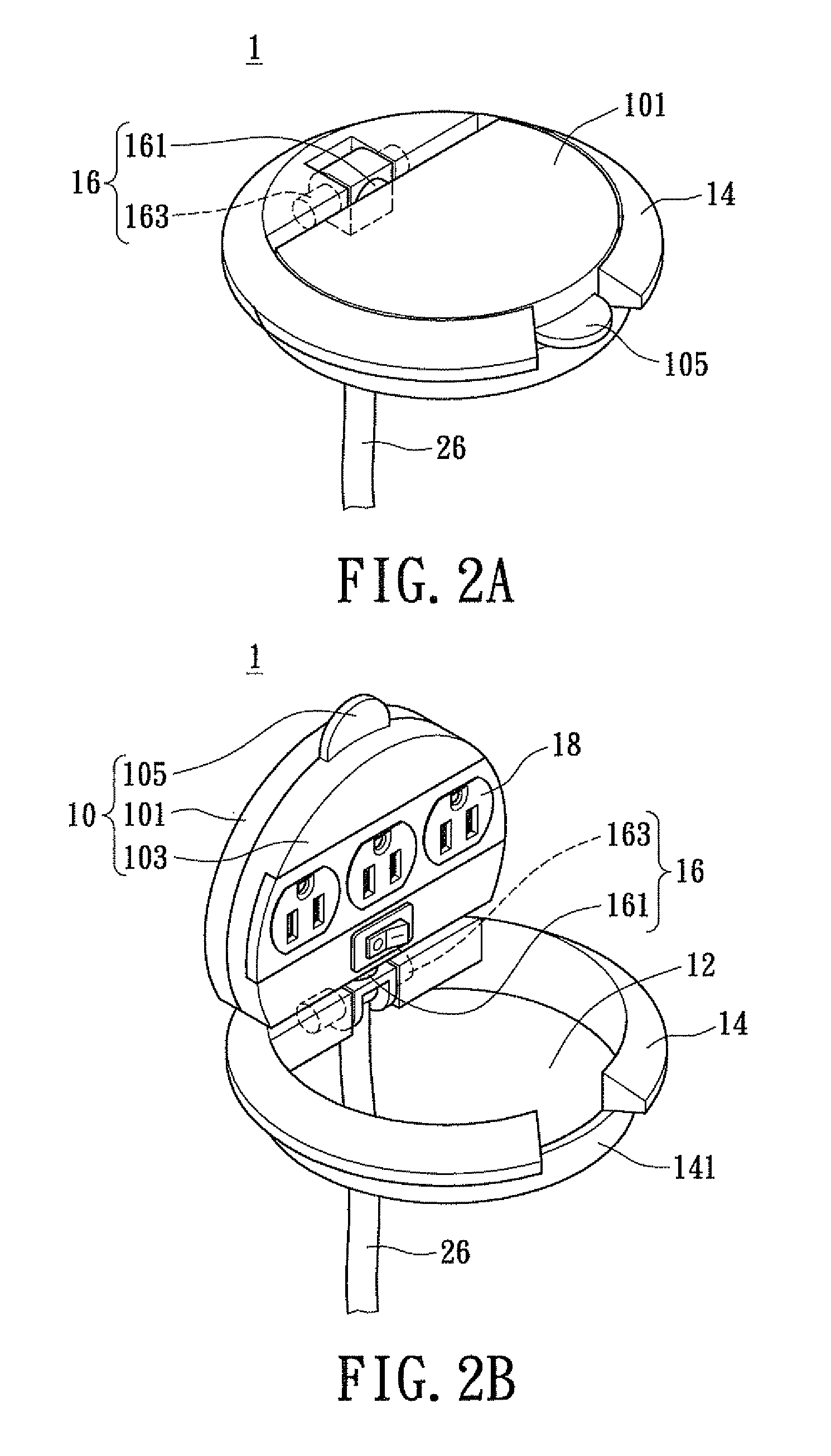
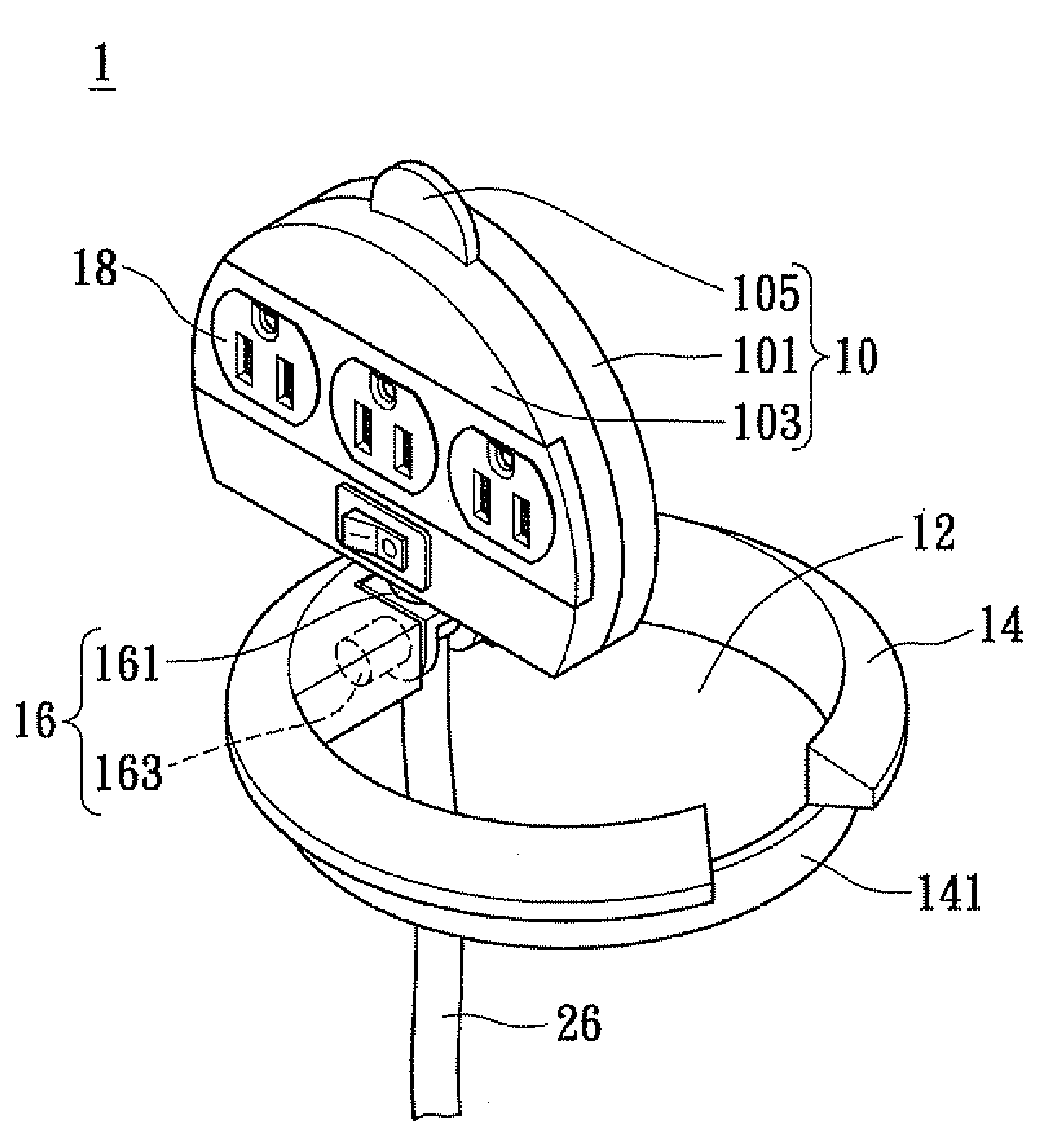
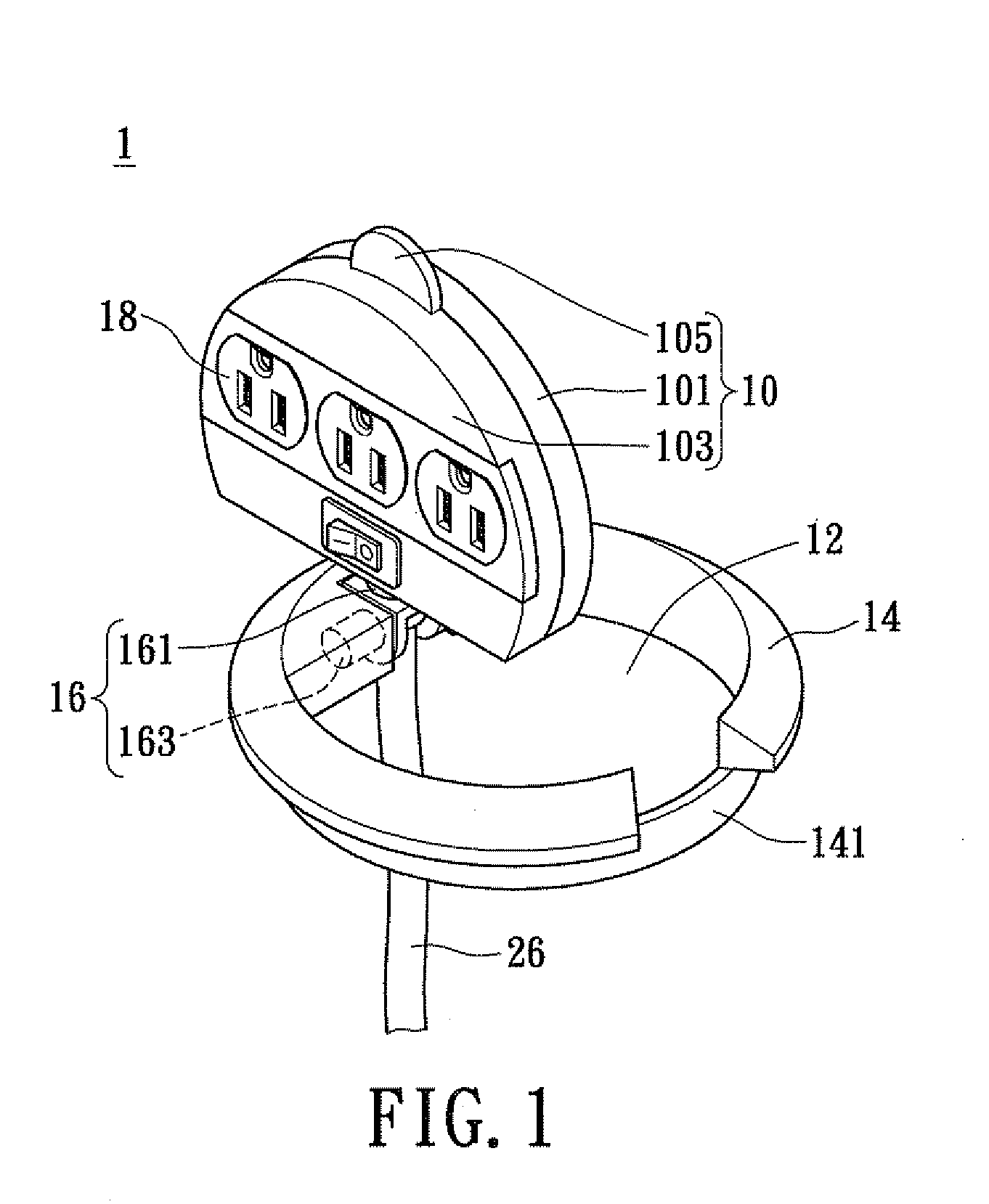
Rotatable and concealable electrical power receptacle
InactiveUS8007295B2Guaranteed maintenance spaceSimple structural designOffice tablesLive contact access preventionEngineeringMechanical engineering
Disclosed is a reversible and concealable electrical power receptacle, comprising: a main body, a shaft section, an accommodating section, and an electrical outlet assembly. The electrical outlet assembly is disposed on the main body; the accommodating section is for receiving the main body; the shaft section, comprises a first shaft member and a second shaft member. The second shaft member, being coupled to the main body and is perpendicular to the first shaft member, and the main body is rotatable with respect to the first and the second shaft members transversely respectively. Consequently, the main body is able to rotate transversely and perpendicularly with respect to the accommodating section in accordance with the rotational movements of the first shaft and the second shaft members, for resulting in an exposed state in use or a concealed state when not in use, thereby achieving effective space utilization.
Owner:POWERTECH INDAL
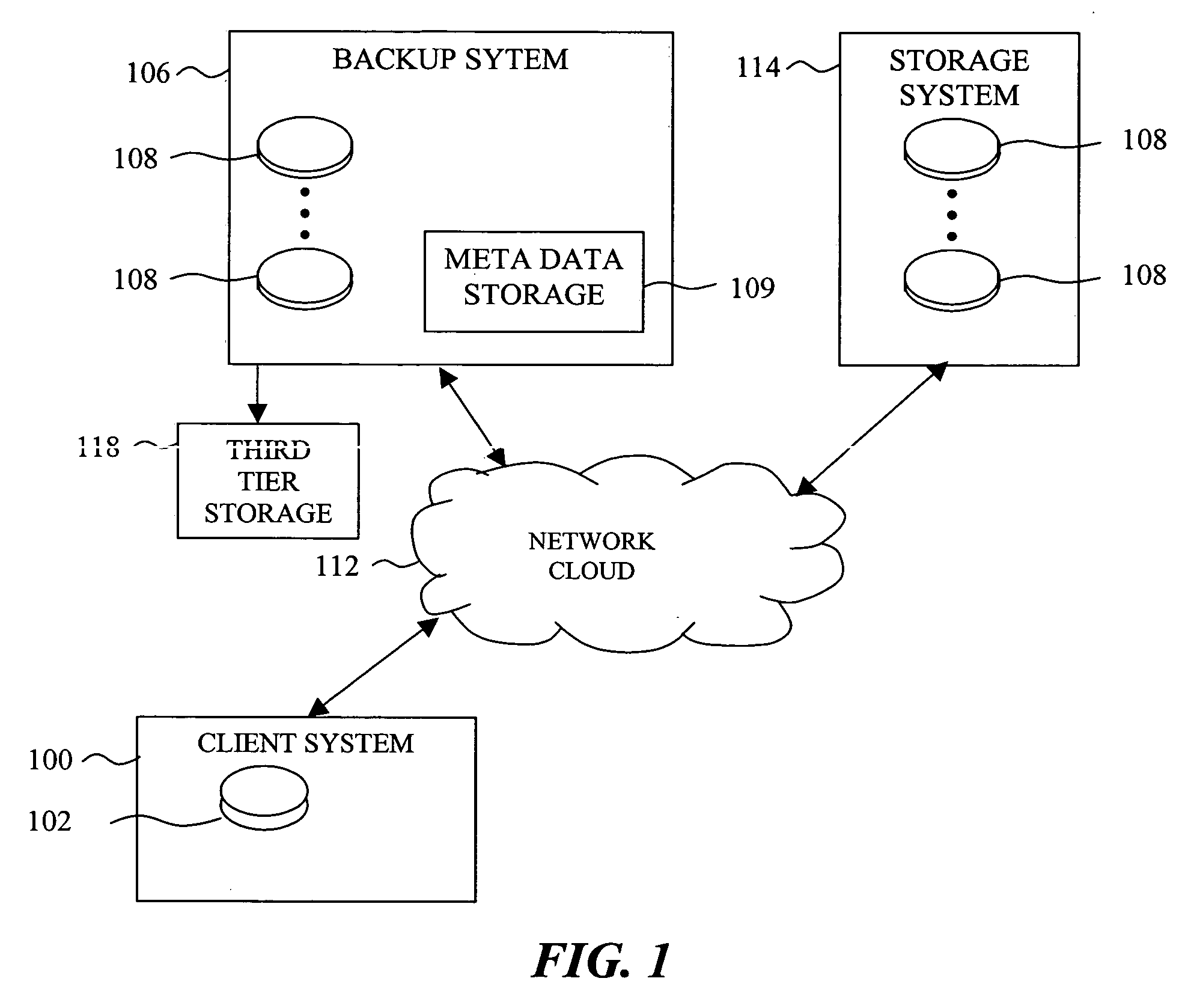
System and methods for efficiently managing incremental data backup revisions
InactiveUS7536424B2Efficient managementEfficient identificationData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsData elementData structure
A system and methods for building an efficient incremental data backup system capable of managing high frequency backups sessions, and capable of efficiently expiring backup revisions and locating the useless data elements is disclosed. A reduced set of data elements that have a non-zero probability of becoming redundant when a backup revision expires is prepared while each backup revision is being processed by the backup system. The backup system also maintains data structures, which reduce the number of searches that should be performed for each such data element before it can be realized that the data element is exclusively needed to support the expired backup revision, and therefore could be removed from the second tier storage.
Owner:DATAMILLS
Rotatable and concealable electrical power receptacle
ActiveUS20110177703A1Simple structural designReduce manufacturing costOffice tablesLive contact access preventionElectricityMechanical engineering
Disclosed is a reversible and concealable electrical power receptacle, comprising: a main body, a shaft section, an accommodating section, and an electrical outlet assembly. The electrical outlet assembly is disposed on the main body; the accommodating section is for receiving the main body; the shaft section, comprises a first shaft member and a second shaft member. The second shaft member, being coupled to the main body and is perpendicular to the first shaft member, and the main body is rotatable with respect to the first and the second shaft members transversely respectively. Consequently, the main body is able to rotate transversely and perpendicularly with respect to the accommodating section in accordance with the rotational movements of the first shaft and the second shaft members, for resulting in an exposed state in use or a concealed state when not in use, thereby achieving effective space utilization.
Owner:POWERTECH INDAL
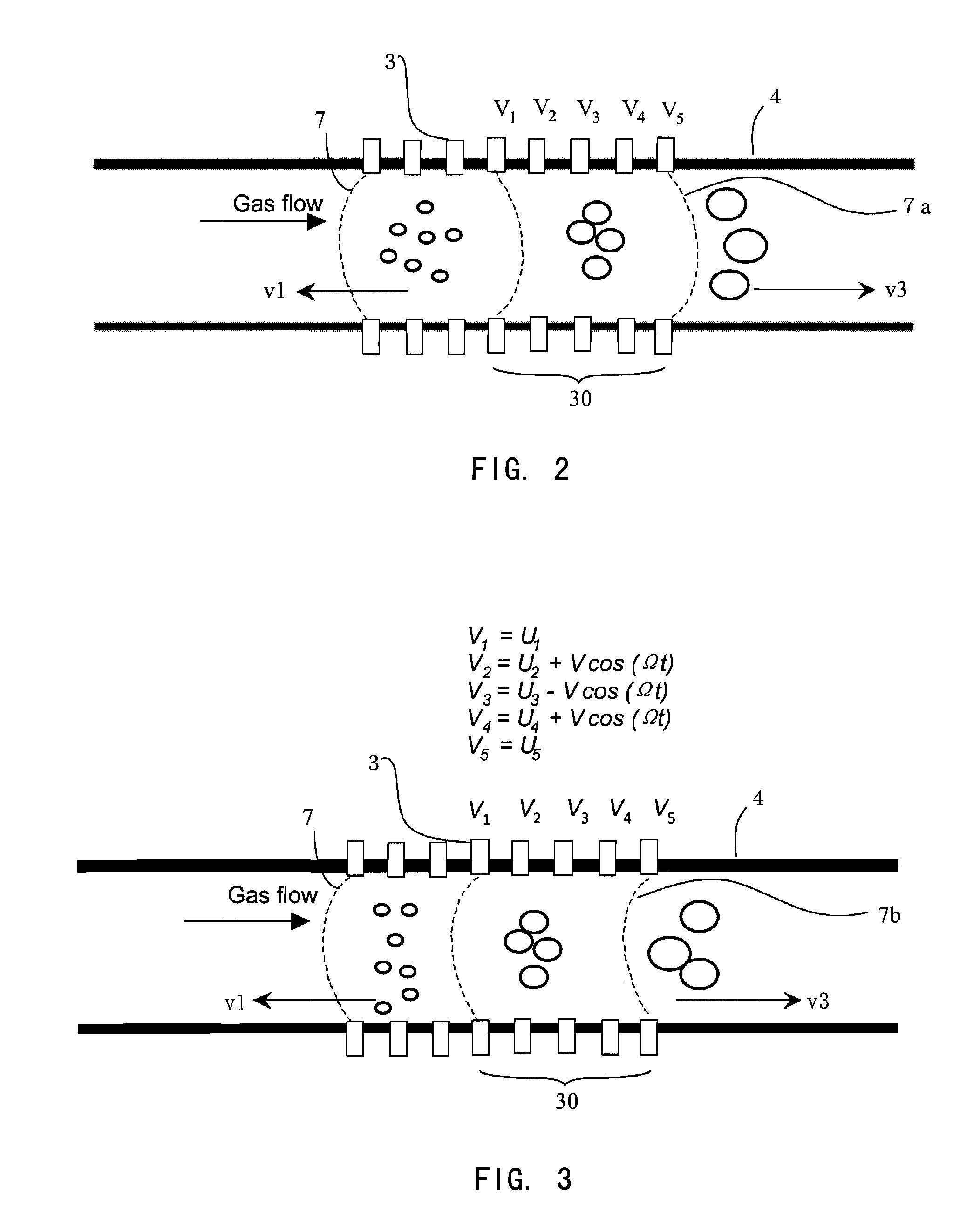
Device for separating, enriching and detecting ions
ActiveUS20110220790A1Increase ion enrichment timeImprove detection efficiencyTime-of-flight spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDynamic balanceMass analyzer
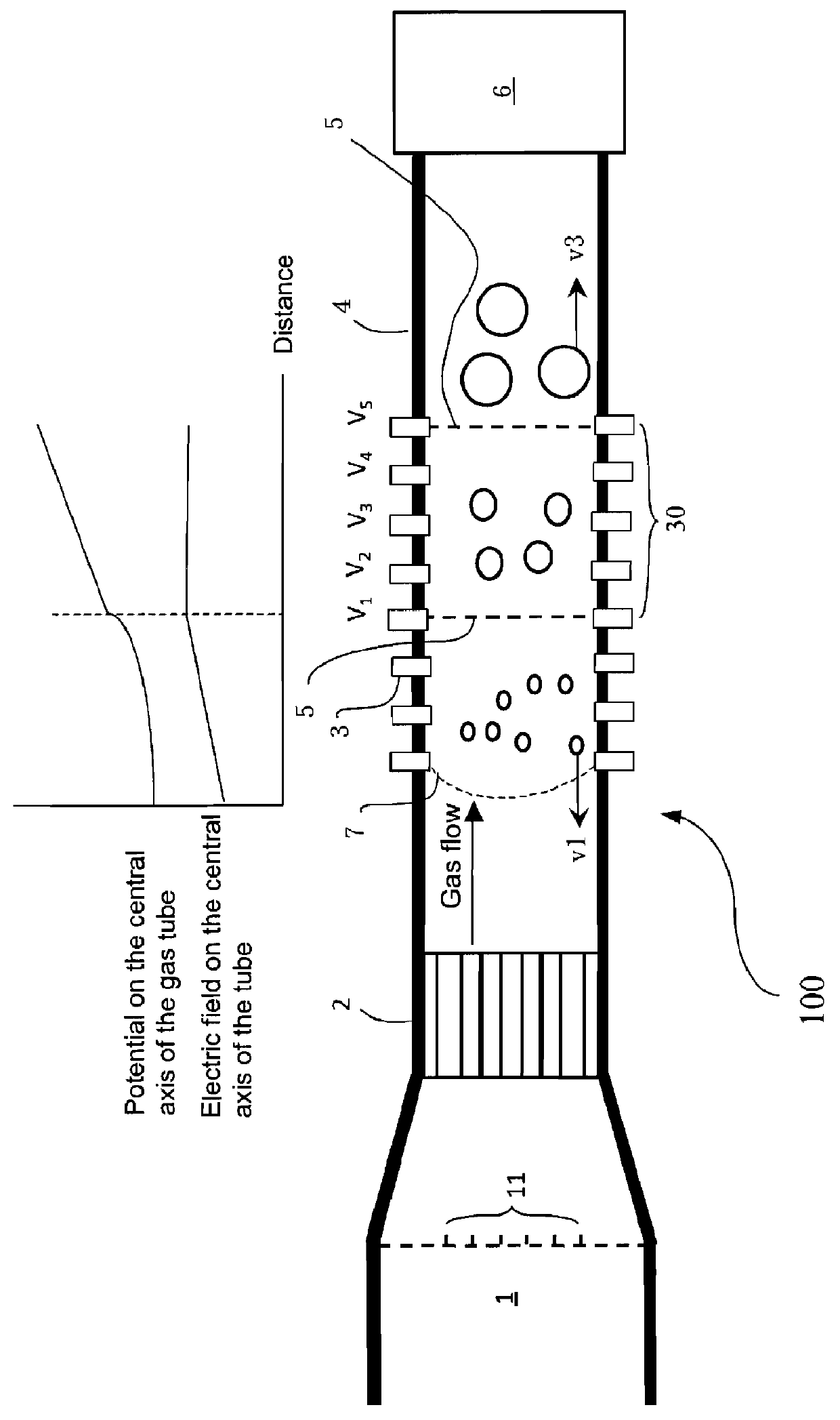
A device for separating, enriching and detecting ions comprises: a gas tube, in which a carrier gas flows at a uniform rate; an ion source; multiple electrodes provided in the gas tube and applied with electric voltages respectively, so that at least an electric field is produced along the axis of the gas tube; an ion detector; and an ion extraction channel, by which specific enriched ions will be guided across the side wall of the gas tube toward the ion detector and be analyzed. The device enriches ions utilizing the following characteristic: compound ions with specific ion mobility maintain a dynamic balance for a period of time in a flow field under the combination of a carrier gas and a suitable electrical field against the direction of the carrier gas. Simultaneously, multiple compound particles with different ion motilities can be separated and enriched at positions with different electrical field intensities in a flow field in the same manner. The device also comprises synchronously export latitudinally enriched ions at different positions in a flow field, and performs later mass analysis using a mass spectrometer.
Owner:SHIMADZU RES LAB SHANGHAI
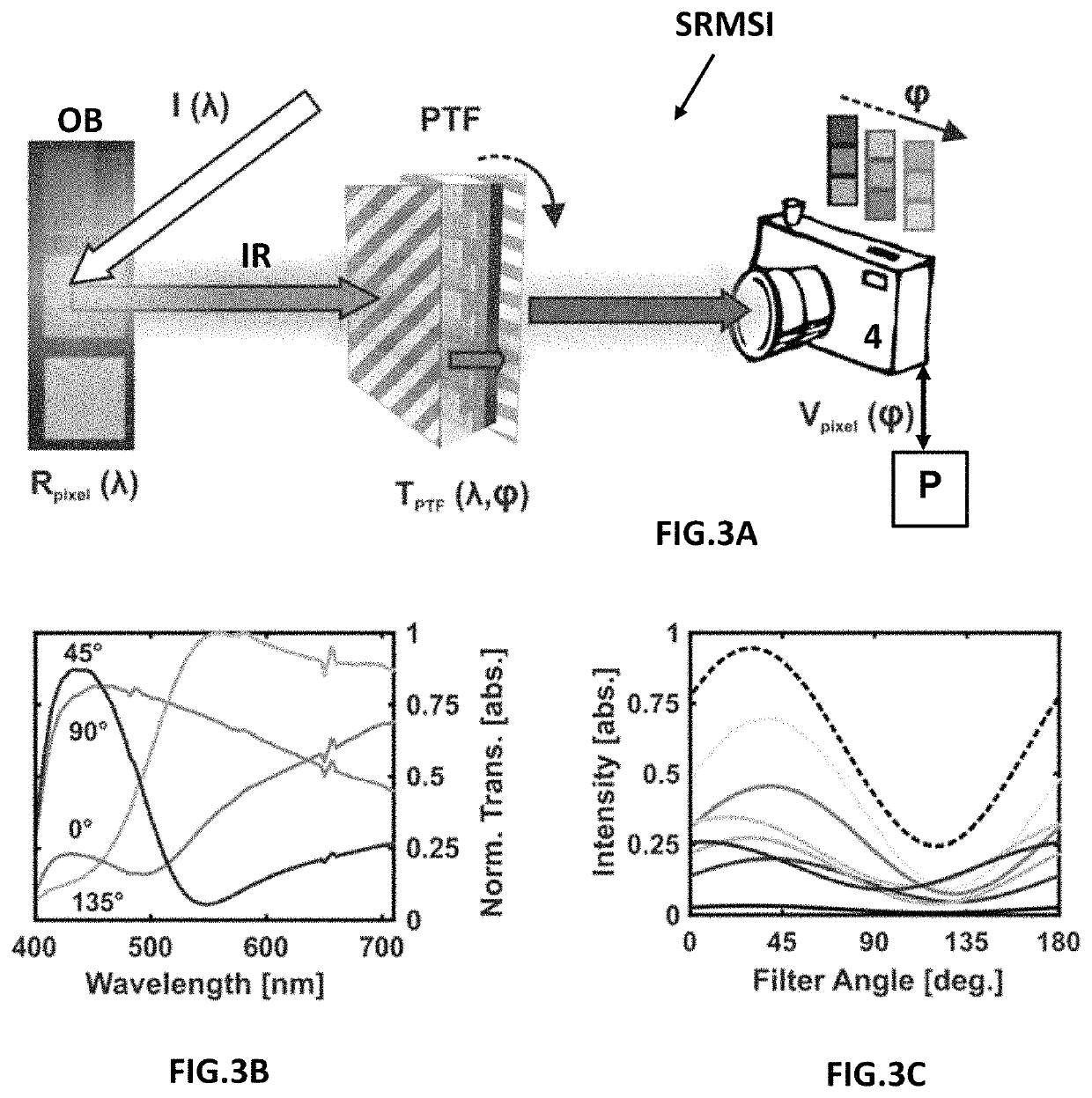
Multispectral or Hyperspectral Imaging and Imaging System Based on Birefringent Subwavelength Resonating Structure
ActiveUS20180107015A1Fabricate cost-efficientlyAngle stable transmissionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationPhysicsHyperspectral imaging
An angle-stable, miniaturized and integrate-able imaging system based on plasmon resonances or dielectric resonances for multispectral imaging maintaining full spatial resolution of the image sensor. Active tunability of the filter allows color recording, estimation of unknown spectra and determination of spectral singularities, for example laser lines, with the use of a conventional B / W camera. The system is characterized by high angular acceptance, cost-efficient fabrication and ease-of-use. This system can be used in conjunction with other commercial multispectral imaging systems such as RGB cameras to further enhance the spectral resolution. It can be adapted to different spectral ranges, depending on the application.
Owner:CSEM CENT SUISSE DELECTRONIQUE & DE MICROTECHNIQUE SA RECH & DEV
Rollover protection cab
InactiveUS20100147603A1Maintain normalWithstands weightVehicle seatsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementRolloverBuilding construction
Embodiments of the present invention generally relate to a rollover protection cab. In one embodiment, a rollover protection cab for a construction vehicle includes a structural frame defining cabin space for a vehicle operator. The structural frame is operable to substantially maintain the cabin space while withstanding a crushing load greater than or equal to twenty tons. The cab further includes a window; a door; a seat disposed in the cabin space; and controls for operating the vehicle disposed in the cabin space.
Owner:DAVIS DANIEL E
Image sensor and method of capturing an image
InactiveUS20130063622A1Lower spatial resolutionImprove dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImage sensorImage resolution
A better compromise between the dynamic range, the spatial resolution, the implementation outlay and the image quality is achieved if different subdivisions of the exposure interval into accumulation intervals are performed for different pixel sensors or pixels. In the event of more than one accumulation interval per exposure interval, the values detected in the accumulation intervals are summed to obtain the respective pixel value. Since the exposure effectively continues to take place for all pixels over the entire exposure interval, no impairment of the image quality arises, or no artifacts arise in image movements. All pixels undergo the same image blur on account of the movement. The additional hardware outlay compared with commercially available pixel sensors is either entirely non-existent or can be kept very small, depending on the implementation. Moreover, a reduction in the spatial resolution is not necessary since the pixels contribute equally to the image capturing.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
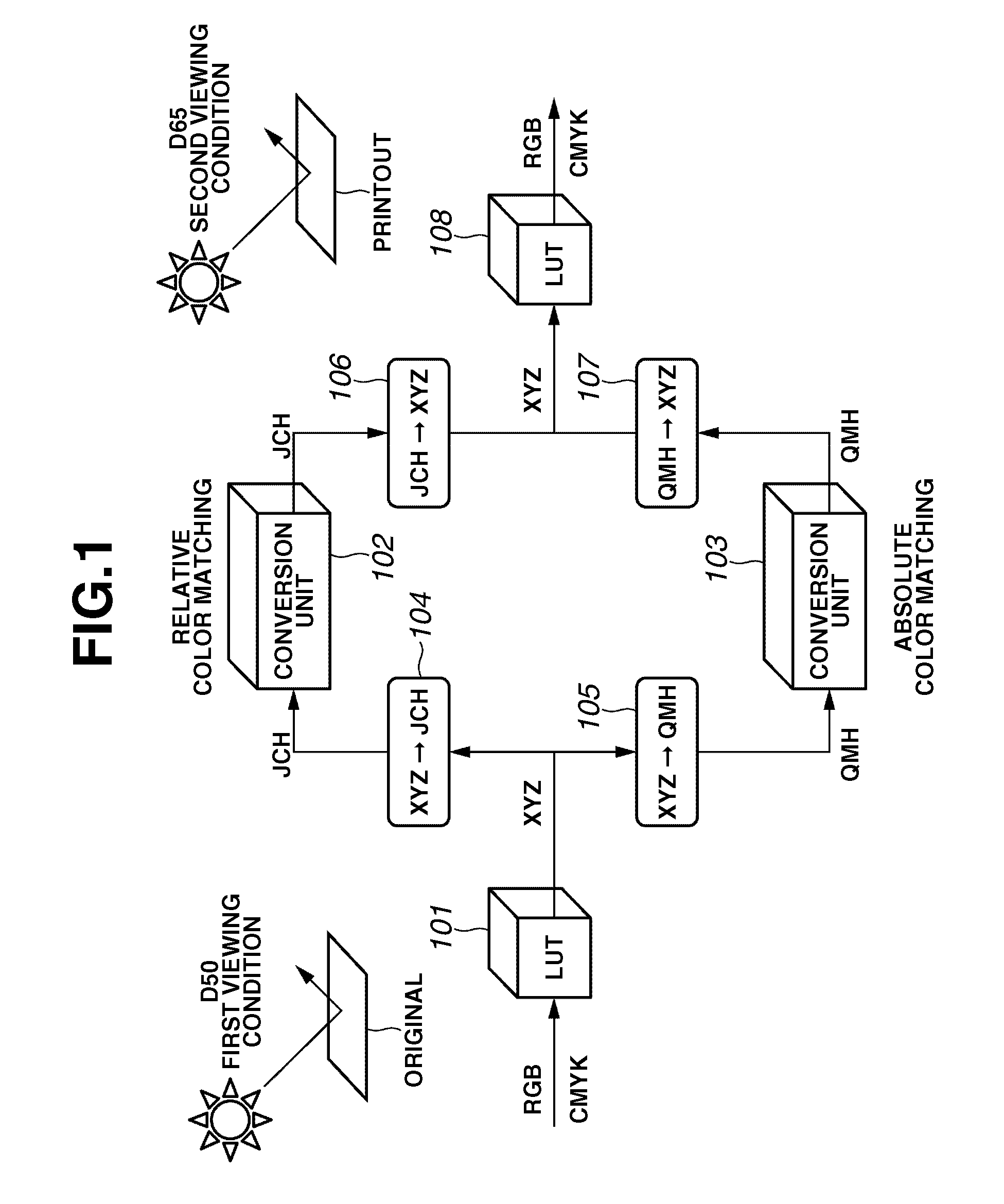
Color conversion apparatus and method
InactiveUS20070058184A1Improve accuracyHigh color reproductionDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsPattern recognitionColor transformation
A color conversion apparatus includes a plurality of color conversion units configured to perform color conversion using a conversion table with different algorithms, a weighting unit configured to set weightings applied to the plurality of color conversion units, and a mixing unit configured to mix a plurality of color conversion results obtained by the plurality of color conversion units using the weightings calculated by the weighting unit.
Owner:CANON KK
Differential phase-contrast imaging with improved sampling
InactiveUS9105369B2Improve spatial resolutionIncrease the areaImaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionSoft x rayDifferential phase
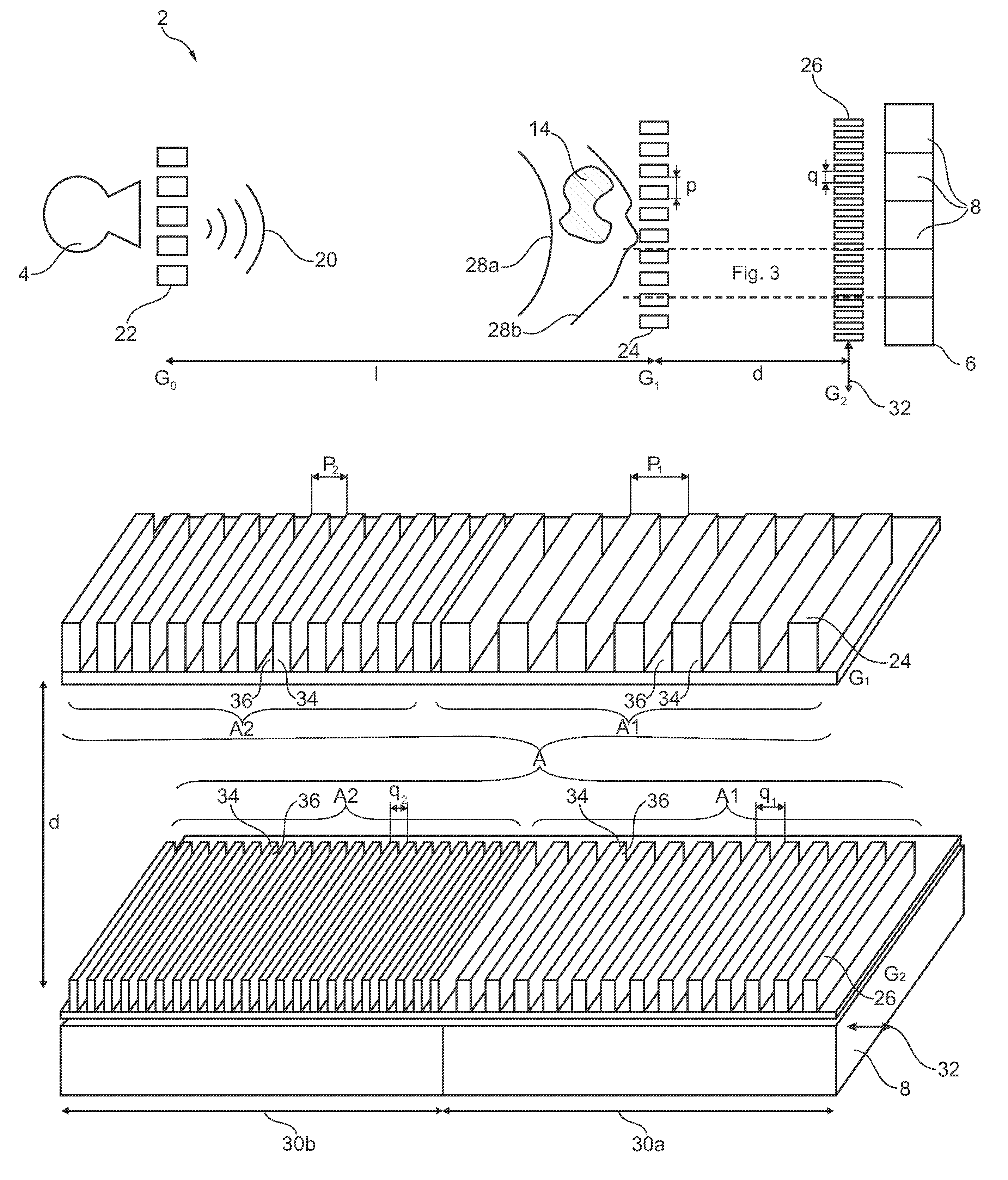
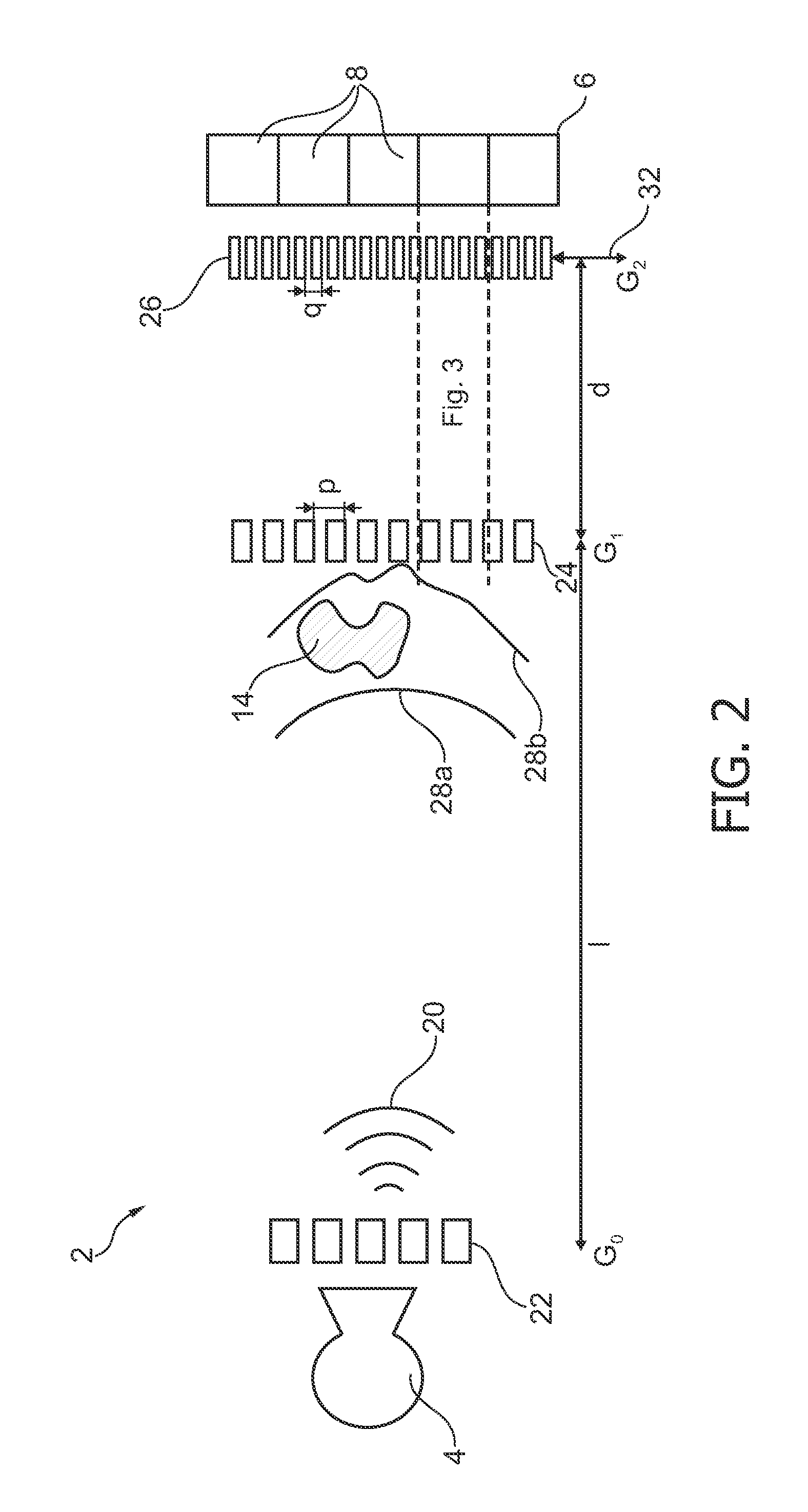
The present invention relates to differential phase-contrast imaging of an object. For increasing spatial resolution of an X-ray imaging system (2) the size of a detector pixel element (8) may be considered a limiting factor. Accordingly, it may be beneficial to increase the resolution of an apparatus (38) for phase-contrast imaging without further reducing the area of an individual pixel element (8). Accordingly, an apparatus (38) for phase-contrast imaging with improved sampling is provided, comprising an X-ray source (4), a first grating element G1 (24), a second grating element G2 (26) and an X-ray detector element (6) comprising a plurality of detector pixel elements (8), each detector pixel element (8) having a pixel area A. An object to be imagined (14) is arrangeable between the X-ray source (4) and the X-ray detector element (6). The first grating element G1 (24) as well as the second grating element G2 (26) are arrangeable between the X-ray source (4) and the X-ray detector element (6). The X-ray source (4), the first grating element G1 (24), the second grating element G2 (26) and the X-ray detector (6) are operatively coupled for acquisition of a phase-contrast image of the object (14). At least one of the first grating element G1 (24) and the second grating element G2 (26) comprise a first area A1 having a first grating pitch p1 and a second area A2 having a second grating pitch p2 different from the first grating pitch.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Differential phase-contrast imaging with improved sampling
ActiveUS20130170618A1Improve spatial resolutionIncreasing pixel areaImaging devicesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionDifferential phaseImage resolution
The present invention relates to differential phase-contrast imaging of an object. For increasing spatial resolution of an X-ray imaging system (2) the size of a detector pixel element (8) may be considered a limiting factor. Accordingly, it may be beneficial to increase the resolution of an apparatus (38) for phase-contrast imaging without further reducing the area of an individual pixel element (8). Accordingly, an apparatus (38) for phase-contrast imaging with improved sampling is provided, comprising an X-ray source (4), a first grating element G1 (24), a second grating element G2 (26) and an X-ray detector element (6) comprising a plurality of detector pixel elements (8), each detector pixel element (8) having a pixel area A. An object to be imagined (14) is arrangeable between the X-ray source (4) and the X-ray detector element (6). The first grating element G1 (24) as well as the second grating element G2 (26) are arrangeable between the X-ray source (4) and the X-ray detector element (6). The X-ray source (4), the first grating element G1 (24), the second grating element G2 (26) and the X-ray detector (6) are operatively coupled for acquisition of a phase-contrast image of the object (14). At least one of the first grating element G1 (24) and the second grating element G2 (26) comprise a first area A1 having a first grating pitch p1 and a second area A2 having a second grating pitch p2 different from the first grating pitch.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Differential pumping seal apparatus
InactiveUS7134668B2Maintain clean spaceEliminate disadvantageEngine sealsLinear bearingsMechanical engineeringEngineering
Owner:EBARA CORP
Rollover protection cab
InactiveUS8579363B2Guaranteed maintenance spaceWithstands weightVehicle seatsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementRolloverBuilding construction
Embodiments of the present invention generally relate to a rollover protection cab. In one embodiment, a rollover protection cab for a construction vehicle includes a structural frame defining cabin space for a vehicle operator. The structural frame is operable to substantially maintain the cabin space while withstanding a crushing load greater than or equal to twenty tons. The cab further includes a window; a door; a seat disposed in the cabin space; and controls for operating the vehicle disposed in the cabin space.
Owner:DAVIS DANIEL E
Device for separating, enriching and detecting ions
ActiveUS8384025B2High sensitivityExtension of timeStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersMotilityDynamic balance
Owner:SHIMADZU RES LAB SHANGHAI
RF amplifier control in parallel RF transmission based on power requirements
ActiveUS20150260808A1Low RF powerReduce power consumptionHigh frequency amplifiersRF amplifierResonanceAmplifier
The present invention relates to a magnetic resonance imaging MRI system (100) for acquiring magnetic resonance data from a target volume in a subject (101), the magnetic resonance imaging system (100) comprising: a plurality of excitation means (201) for generating a slice- / or slab-selective spatial radio frequency RF excitation magnetic field targeting slice / slab spatial variations in the target volume, and a controller (219) coupled to the plurality of excitation means (201), wherein the controller (219) is adapted for: determining a power level required by the plurality of excitation means (201) for generating the slice- / or slab-selective spatial RF excitation magnetic field, decomposing the slice- / or slab-selective spatial RF excitation magnetic field into respective RF excitation constituents of the plurality of excitation means (201), controlling each of the plurality of excitation means (201) to simultaneously generate the respective RF excitation constituent, using the determined power level for acquiring the magnetic resonance data.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Fast three dimensional t2 weighted balanced steady-state free precession imaging
InactiveUS20160313427A1Maintaining spatial resolutionHigh imagingMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsImage resolutionT2 weighted
A fast 3D T2-weighted imaging system and method is disclosed that uses balanced steady state free precession (bSSFP), variable flip angles, and an interleaved multi-shot spiral-out phase encode ordering strategy to acquire high resolution T2-weighted images quickly while maintaining spatial resolution.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Piezoelectric resonator unit, module component, and manufacturing method for same
ActiveUS20180167050A1Relieve pressureGuaranteed maintenance spaceImpedence networksEngineeringMechanical engineering
A piezoelectric resonator unit that includes a base, a piezoelectric resonator mounted on the base member, and a cover that is bonded to the base and that collectively forms an inner space that accommodates the piezoelectric resonator. The cover includes a top surface that faces the base with the piezoelectric resonator interposed therebetween, and a side wall that extends in a direction that intersects a main surface of the top surface. The piezoelectric resonator unit is designed so that the thickness of the top surface is larger than the thickness of the side wall.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
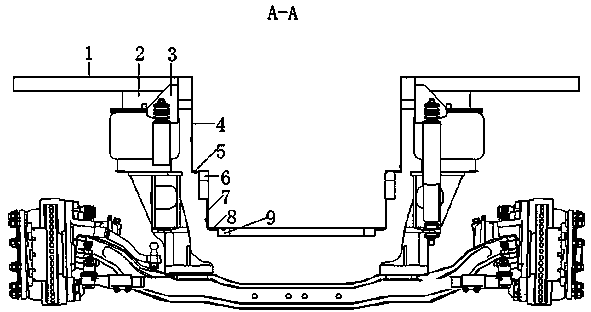
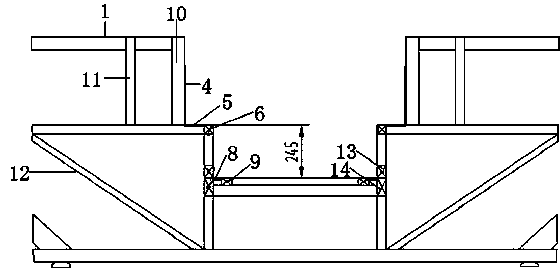
Fixing structure of front two-step bus air suspension
The invention relates to a fixing structure of a front two-step bus air suspension. The fixing structure of the front two-step bus air suspension comprises a wheel-guard assembly and a walkway assembly which are located above the air suspension. The wheel-guard assembly comprises a wheel-guard support, an upper wheel-guard seal plate and a wheel-guard vertical surface seal plate, wherein the wheel-guard support is fixedly arranged above a bus body frame, the upper wheel-guard seal plate is fixedly arranged above the wheel-guard support, and the wheel-guard vertical surface seal plate is fixedly arranged on the inner side of the wheel-guard support. The walkway assembly comprises a walkway support and a walkway seal plate, wherein the walkway support is fixedly arranged in the middle of the bus body frame, and the walkway seal plate is fixedly arranged above the walkway support. A support used for installing an air bag and a support used for installing a shock absorber are fixedly arranged below the wheel-guard support. A support used for installing a stabilization rod is fixedly arranged below the walkway support. The upper wheel-guard seal plate is provided with an assembly service port. The wheel-guard vertical surface seal plate is provided with a groove. The fixing structure of the front two-step bus air suspension is simple and reasonable in design, small in occupied space, and capable of not only enabling the heights of seats above a front wheel guard to meet the requirement for sitting comfort, but also enabling the width of a walkway to be suitable for increasing the speed of passengers getting on and off from the bus.
Owner:ANHUI ANKAI AUTOMOBILE
Color conversion apparatus and method
InactiveUS8111430B2Improve accuracyHigh color reproductionDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsColor transformationComputer graphics (images)
A color conversion apparatus includes a plurality of color conversion units configured to perform color conversion using a conversion table with different algorithms, a weighting unit configured to set weightings applied to the plurality of color conversion units, and a mixing unit configured to mix a plurality of color conversion results obtained by the plurality of color conversion units using the weightings calculated by the weighting unit.
Owner:CANON KK
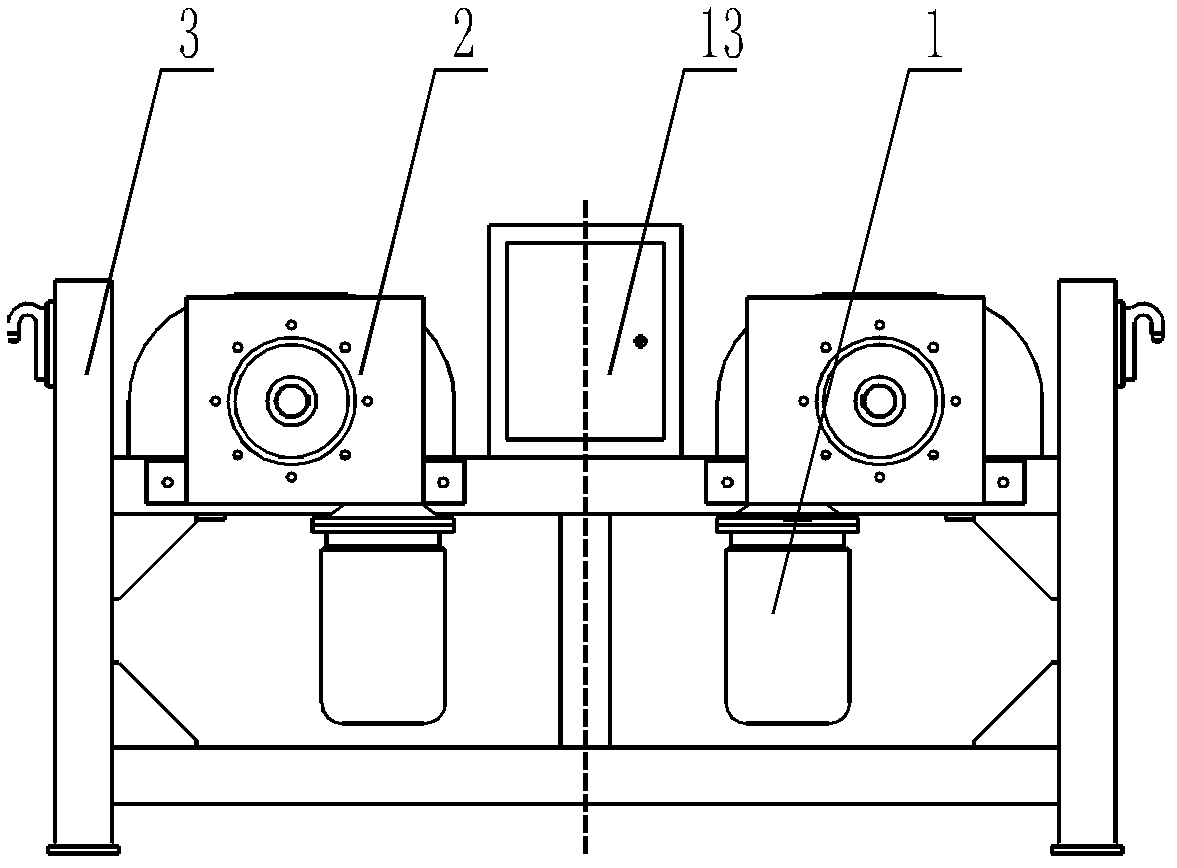
Automatic overturning device for maintenance operation of cylinder cover
The invention discloses an automatic overturning device for maintenance operation of a cylinder cover, which comprises a supporting base and at least one overturning mechanism. The overturning mechanism comprises an overturning support, two ends of the overturning support are installed on the supporting base through shafts, and the shaft on one side is connected with a worm gear reducer, a motor and a control box. At least one cylinder cover fixing portion is arranged on the overturning support, the cylinder cover fixing portion comprises a plurality of fixed screws and nuts, a valve fixing portion is arranged below the cylinder cover fixing portion, the valve fixing portion comprises a positioning support arranged below the cylinder cover fixing portion, a lifting lead screw penetrates through the positioning support through threads, the upper end of the lifting lead screw is connected with a supporting plate for fixing a valve, and a hand wheel is arranged at the lower end of the lifting lead screw. The automatic overturning device for the maintenance operation of the cylinder cover achieves overturning of a cylinder cover and fixation of the valve, reduces labor intensity, meets maintenance requirements, can overturn a plurality of cylinder covers, and improves working efficiency.
Owner:王本涛 +1
Configurable rotary security panel barrier
ActiveUS20150233140A1Simple to erectEasy to installFencingStructural engineeringMechanical engineering
Improved devices, systems and methods for deterring intruders are disclosed. The deterrent devices and systems may be attached to an upper portion of a vertical barrier or other structure. Embodiments of the invention include panels of a rigid material having a plurality of malleable elongate extensions capable of being configured into various arrangements, a panel support member for suspending the panels adjacent to a barrier, and system supports for attachment to the barrier and for supporting the panel support member. The panels are capable of rotating around the panel support member.
Owner:KELLY RORY
Configurable rotary security panel barrier
ActiveUS9334671B2Keep the distanceReduce frictionFencingStructural engineeringMechanical engineering
Improved devices, systems and methods for deterring intruders. The deterrent devices and systems may be attached to an upper portion of a vertical barrier or other structure. Embodiments of the invention include panels of a rigid material having a plurality of malleable elongate extensions capable of being configured into various arrangements, a panel support member for suspending the panels adjacent to a barrier, and system supports for attachment to the barrier and for supporting the panel support member. The panels are capable of rotating around the panel support member.
Owner:KELLY RORY
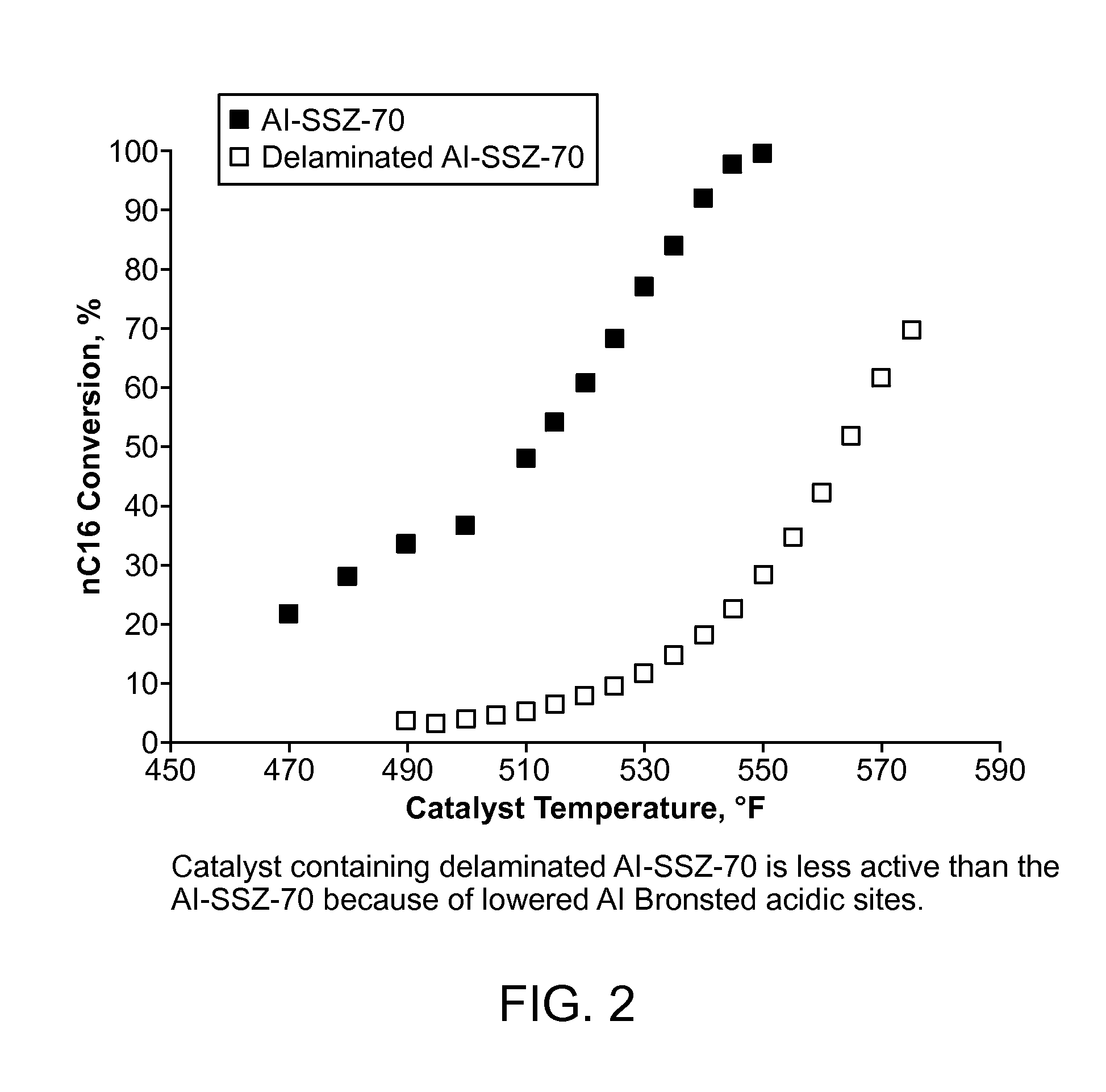
Hydroprocessing of hydrocarbons using delaminated zeolite supports as catalysts
InactiveUS20160115397A1Increased isomerizationElimination of mass transferHydrocarbon by isomerisationMolecular sieve catalystsZeoliteHydrocarbon
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Multispectral or hyperspectral imaging and imaging system based on birefringent subwavelength resonating structure
ActiveUS10642056B2Angle-stable transmissionSpatial resolutionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationDielectric resonanceMaterials science
Owner:CSEM CENT SUISSE DELECTRONIQUE & DE MICROTECHNIQUE SA RECH & DEV
A fixed structure of the front air suspension of a two-stage stepping bus
Owner:ANHUI ANKAI AUTOMOBILE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com